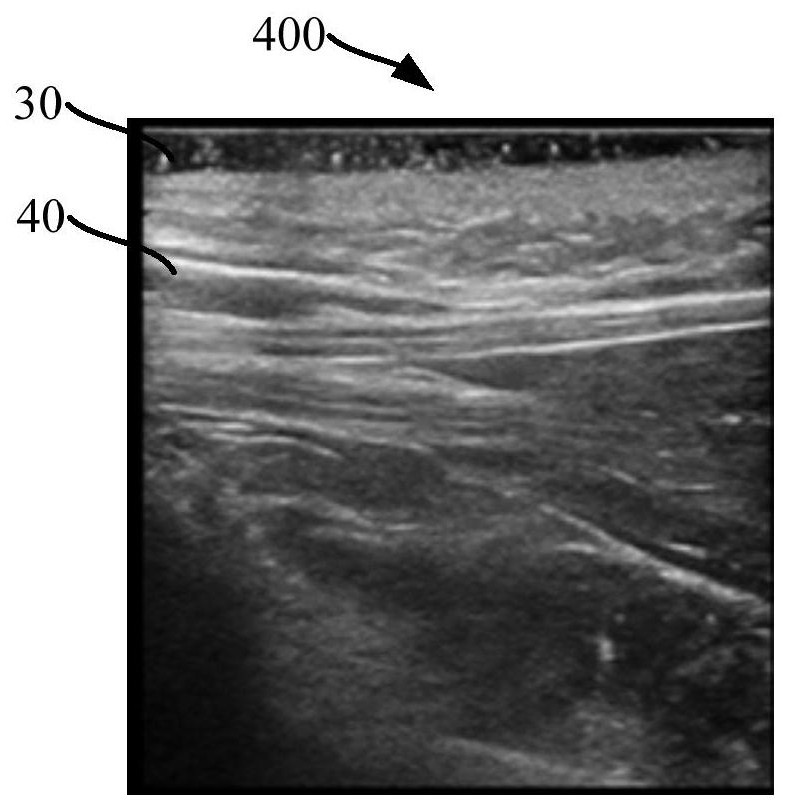
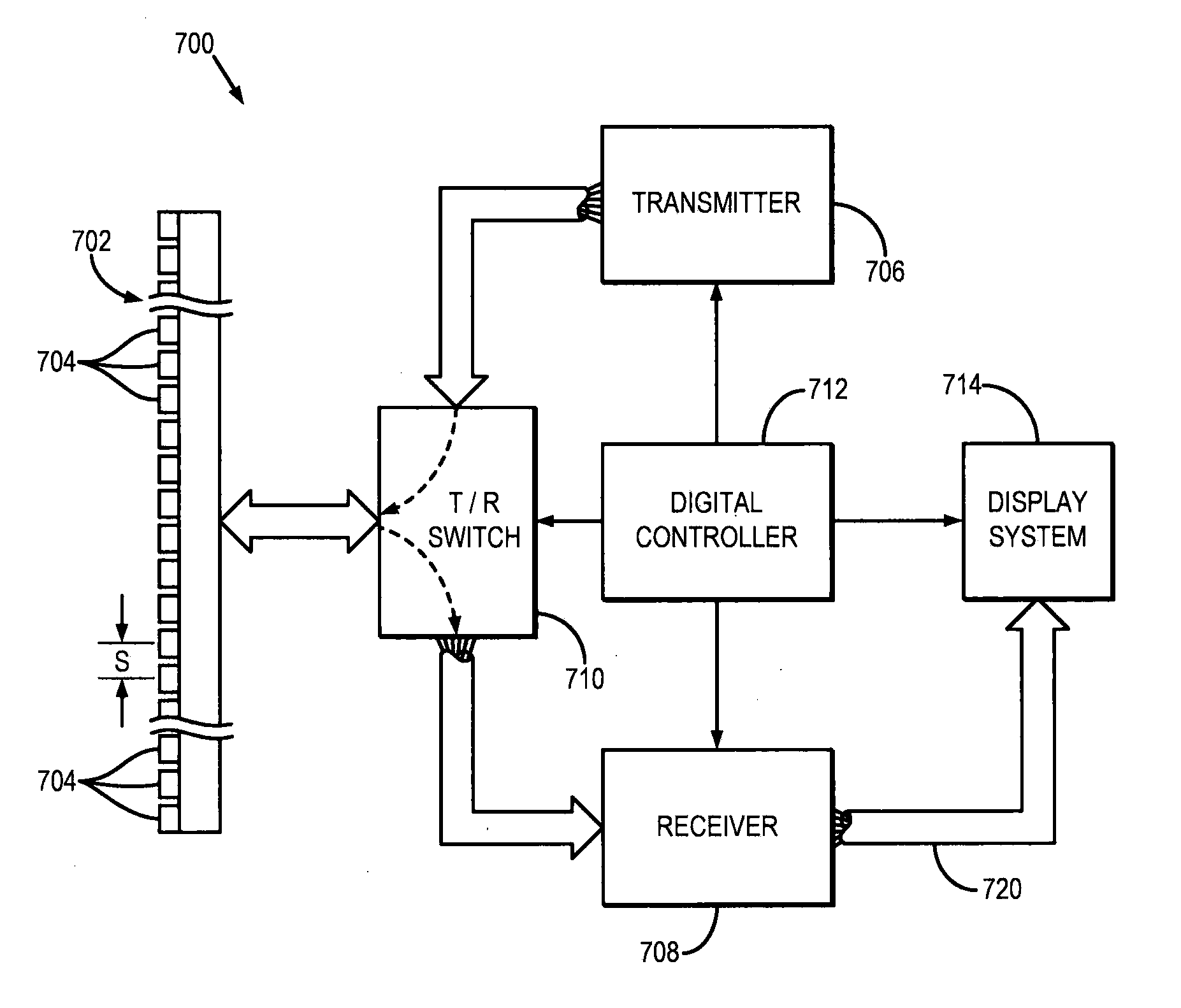
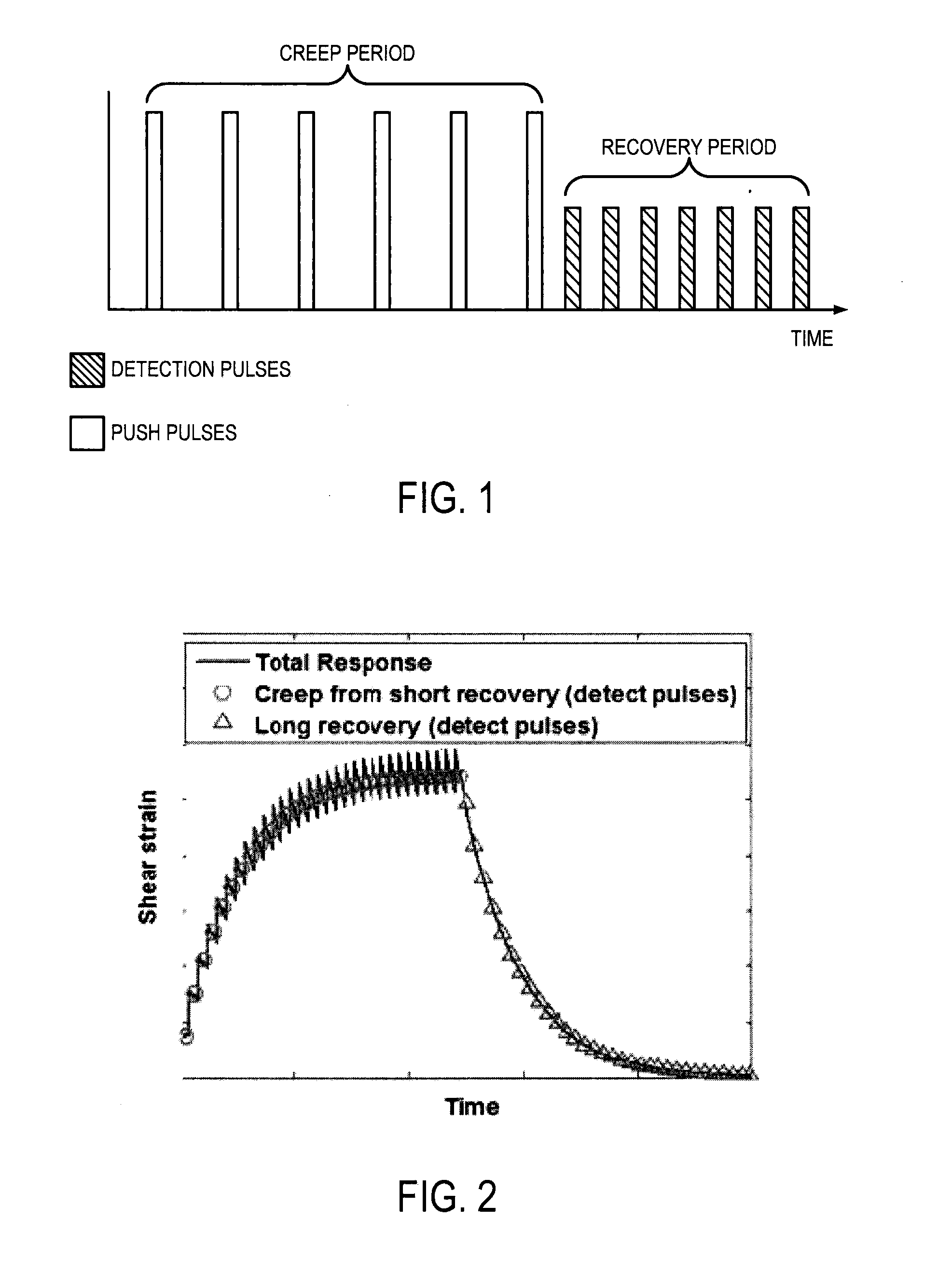
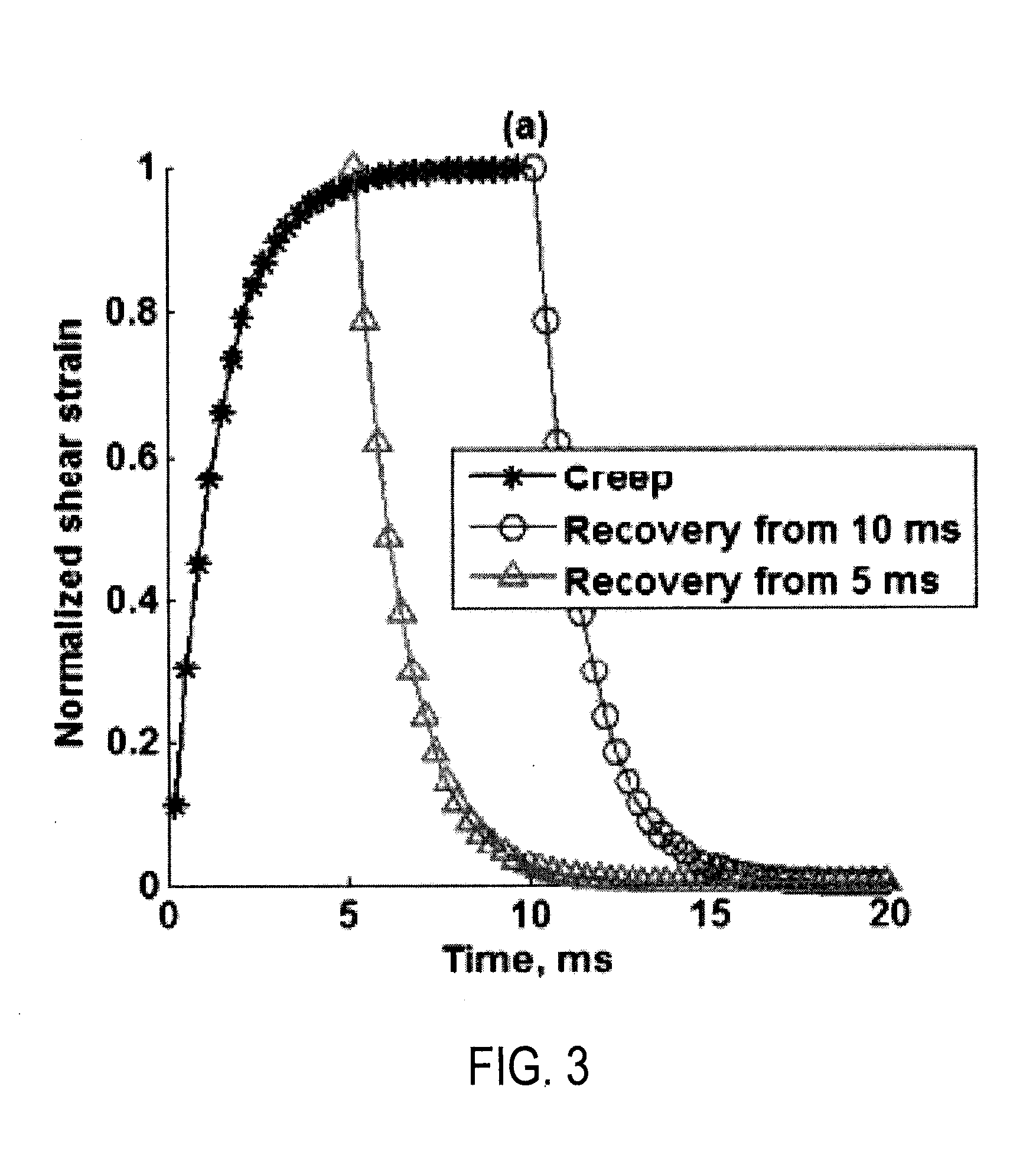
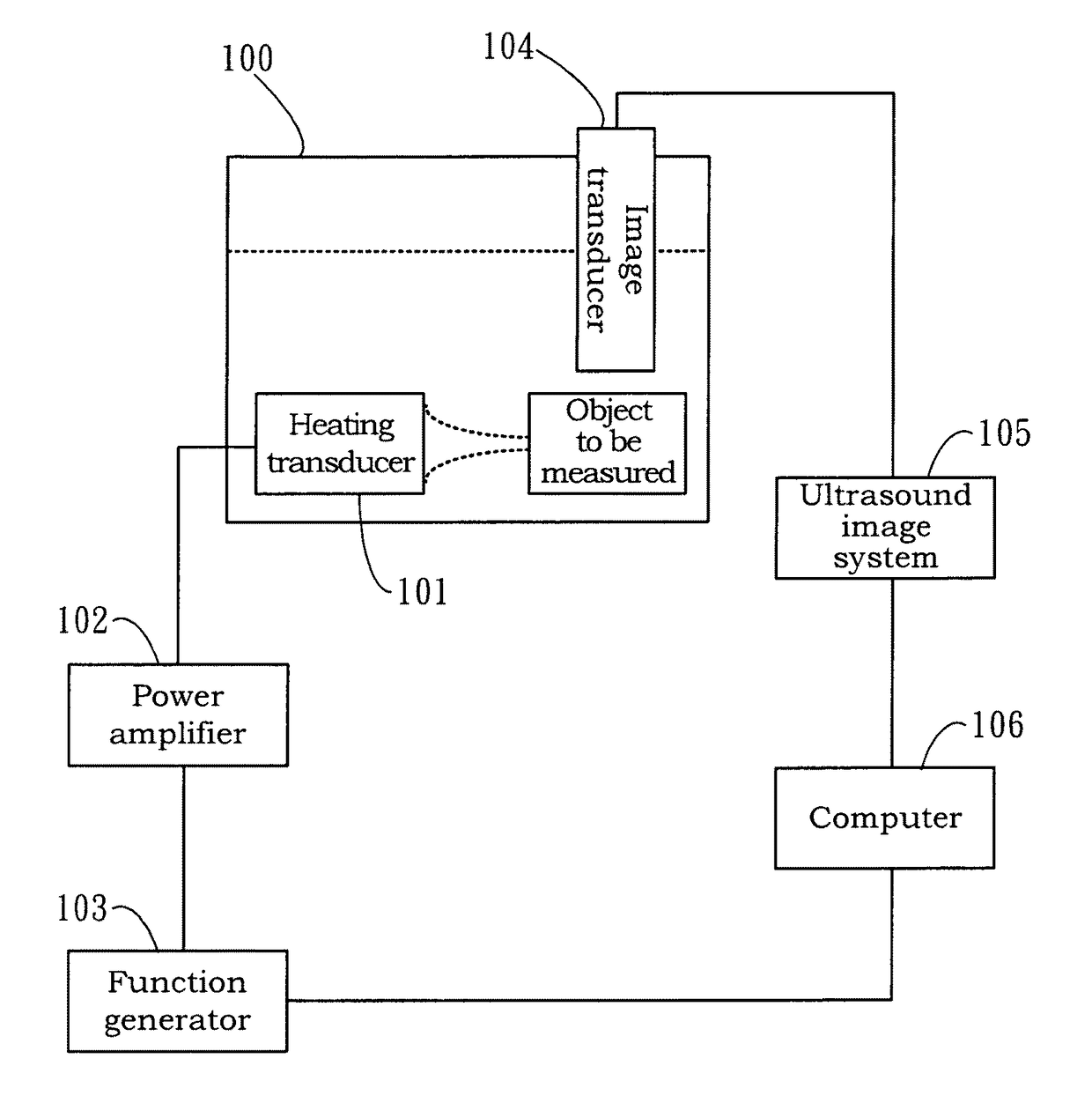
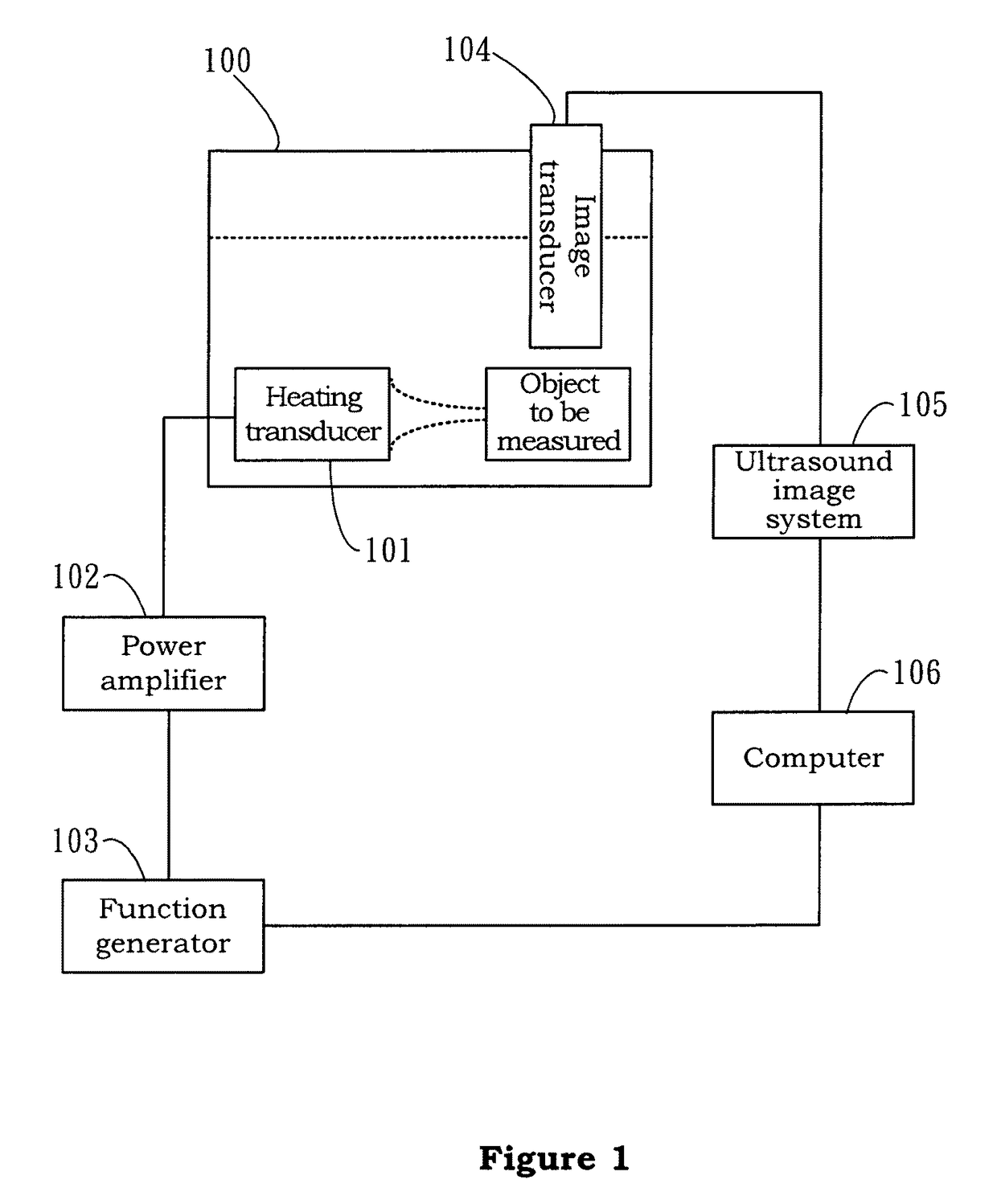
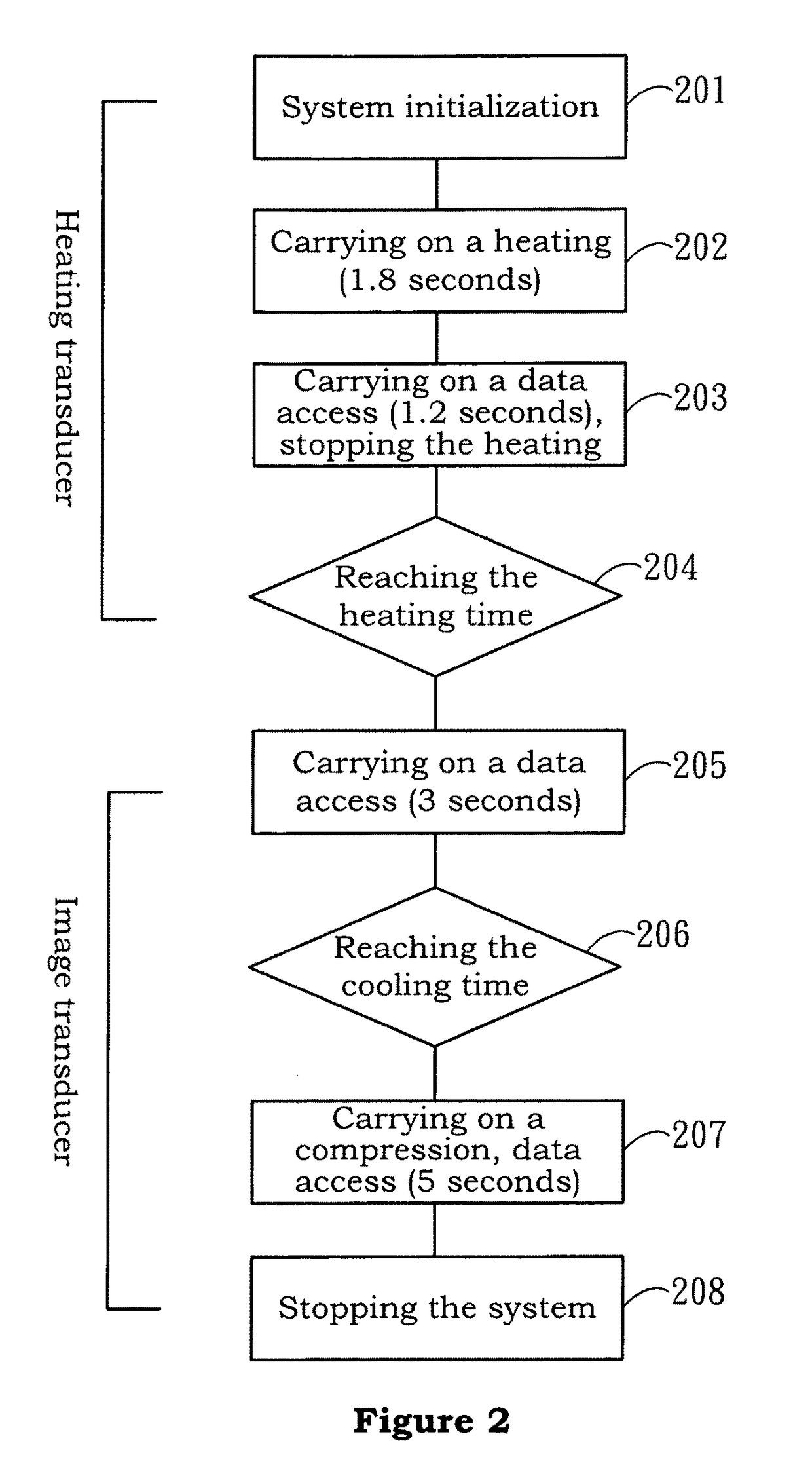
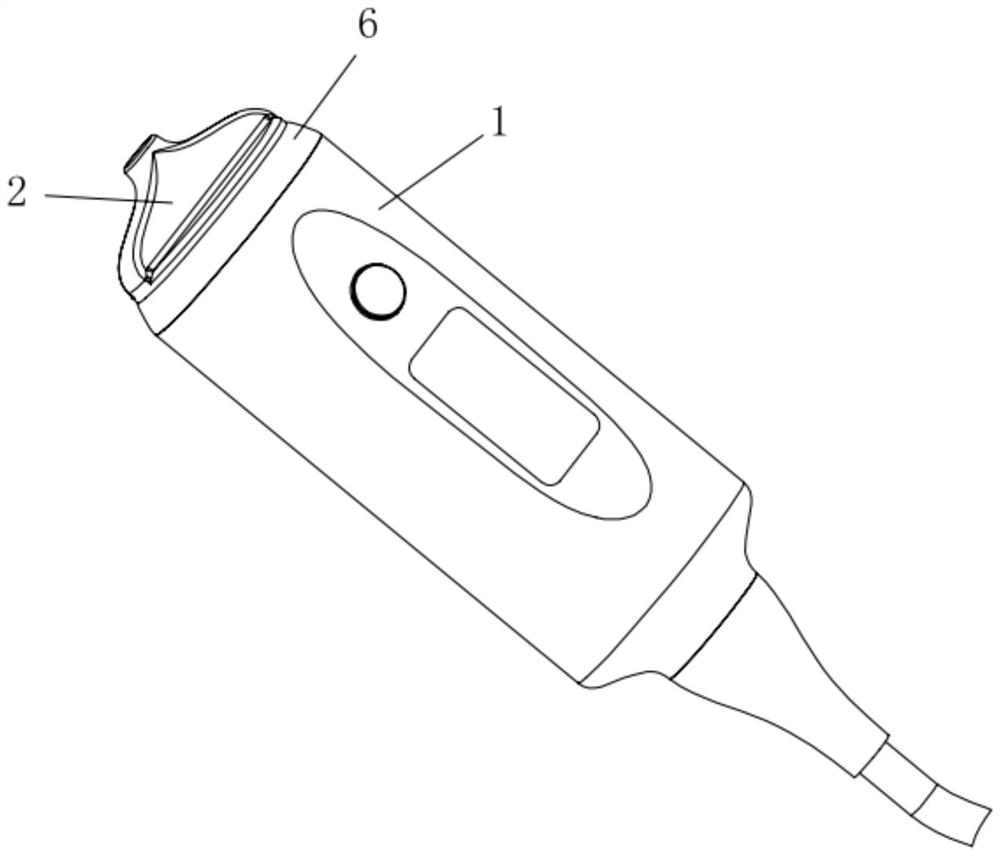
Patents
Literature
99 results about "Arfi elastography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
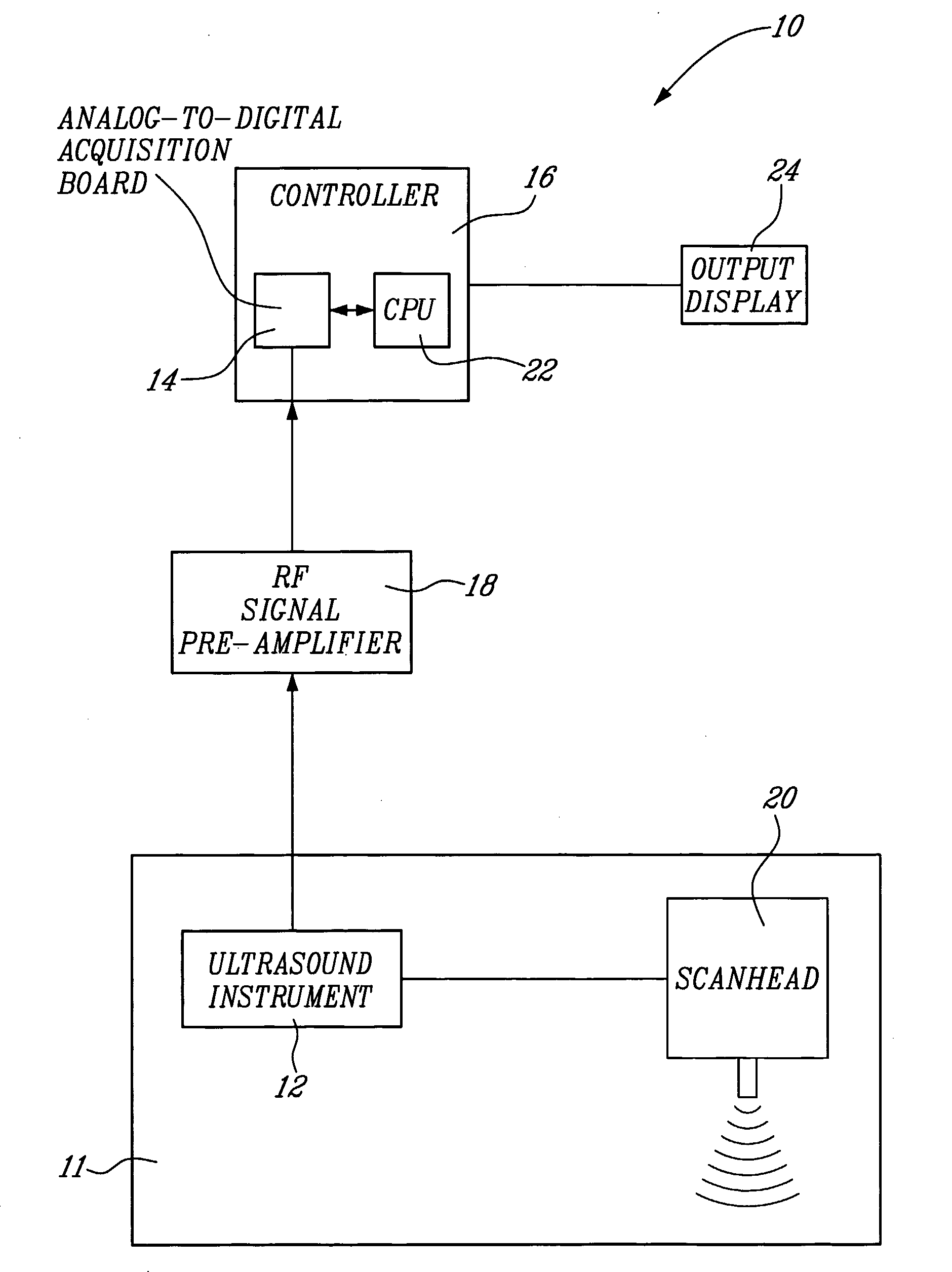
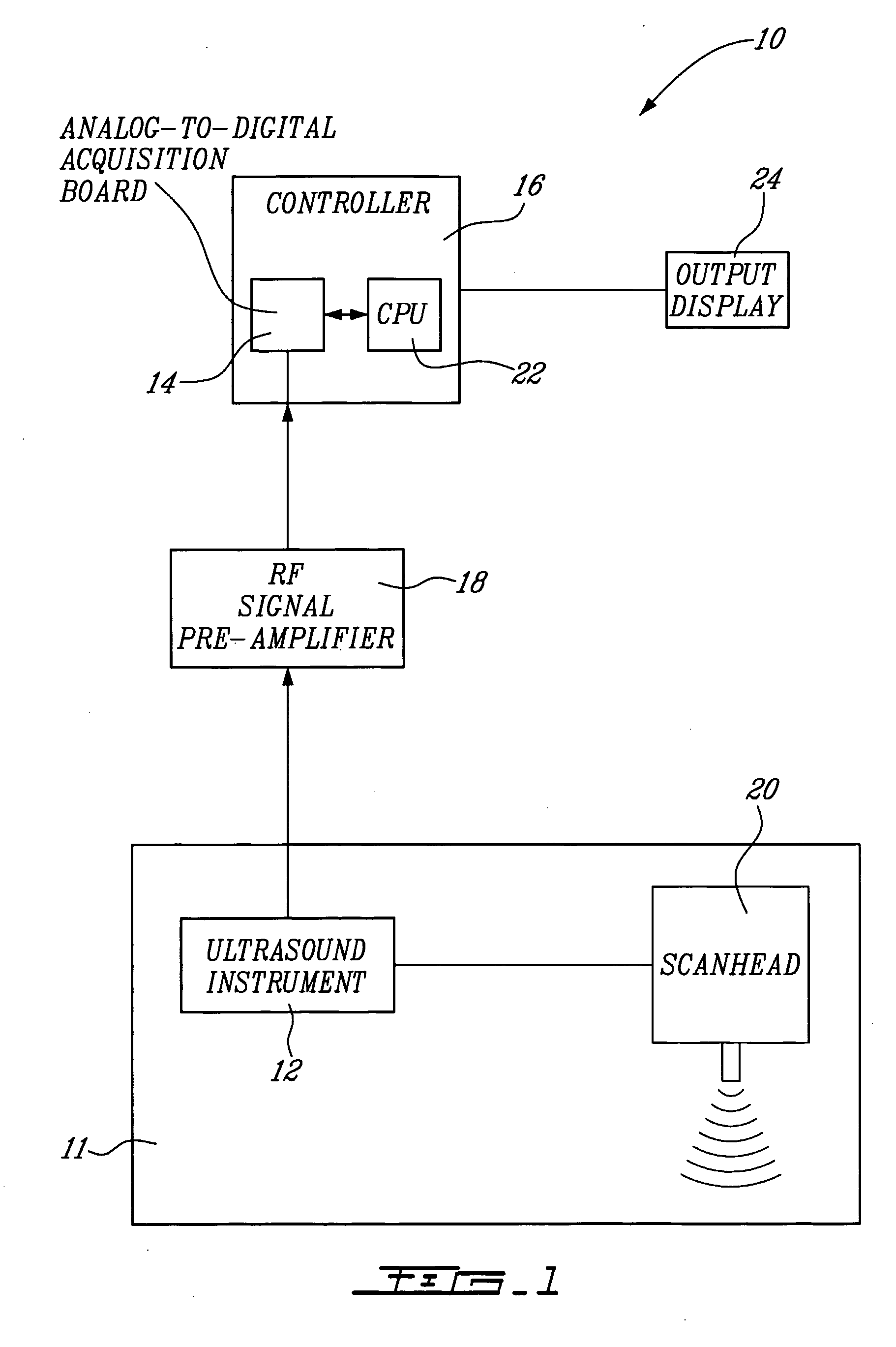
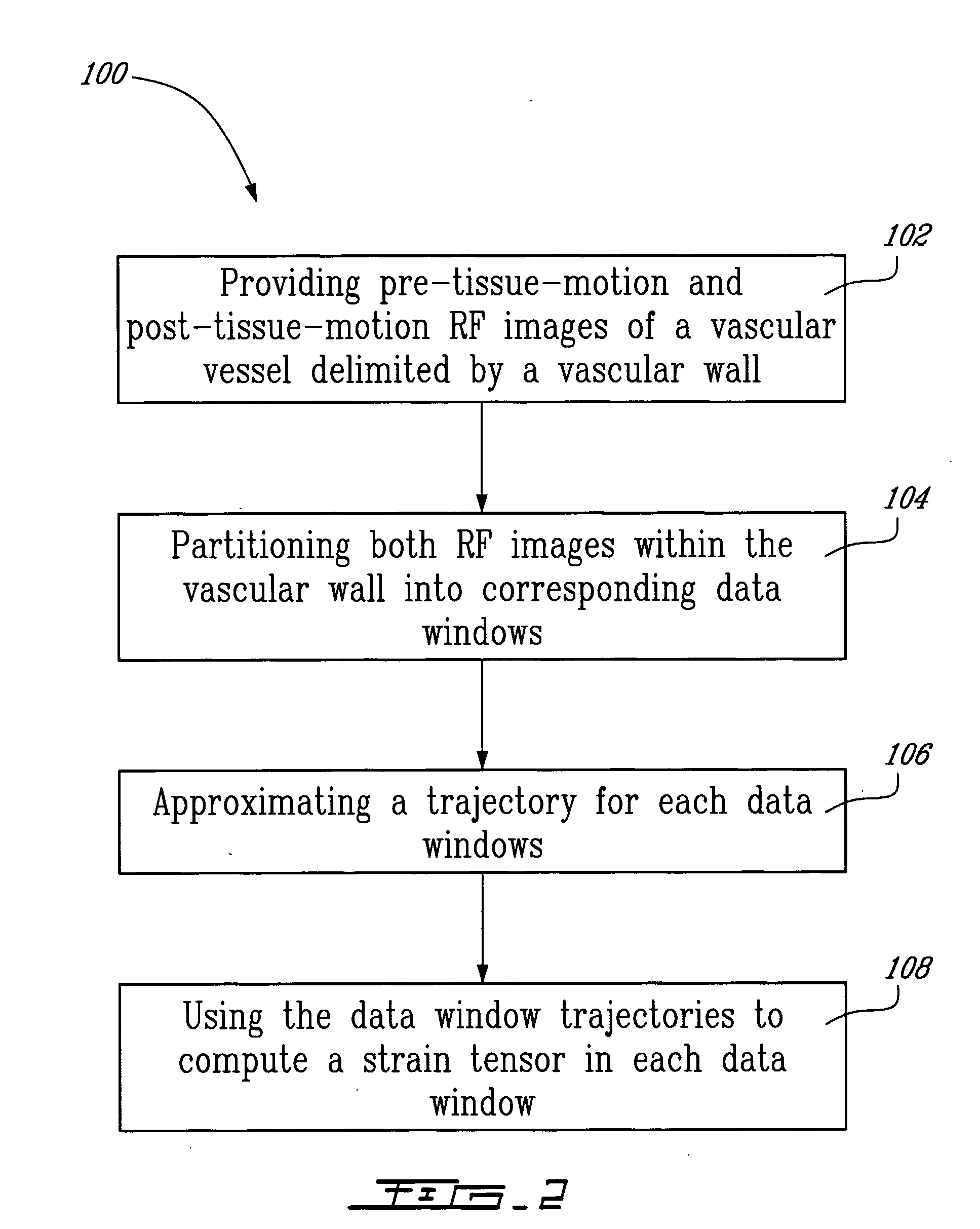
Method And System For Vascular Elastography
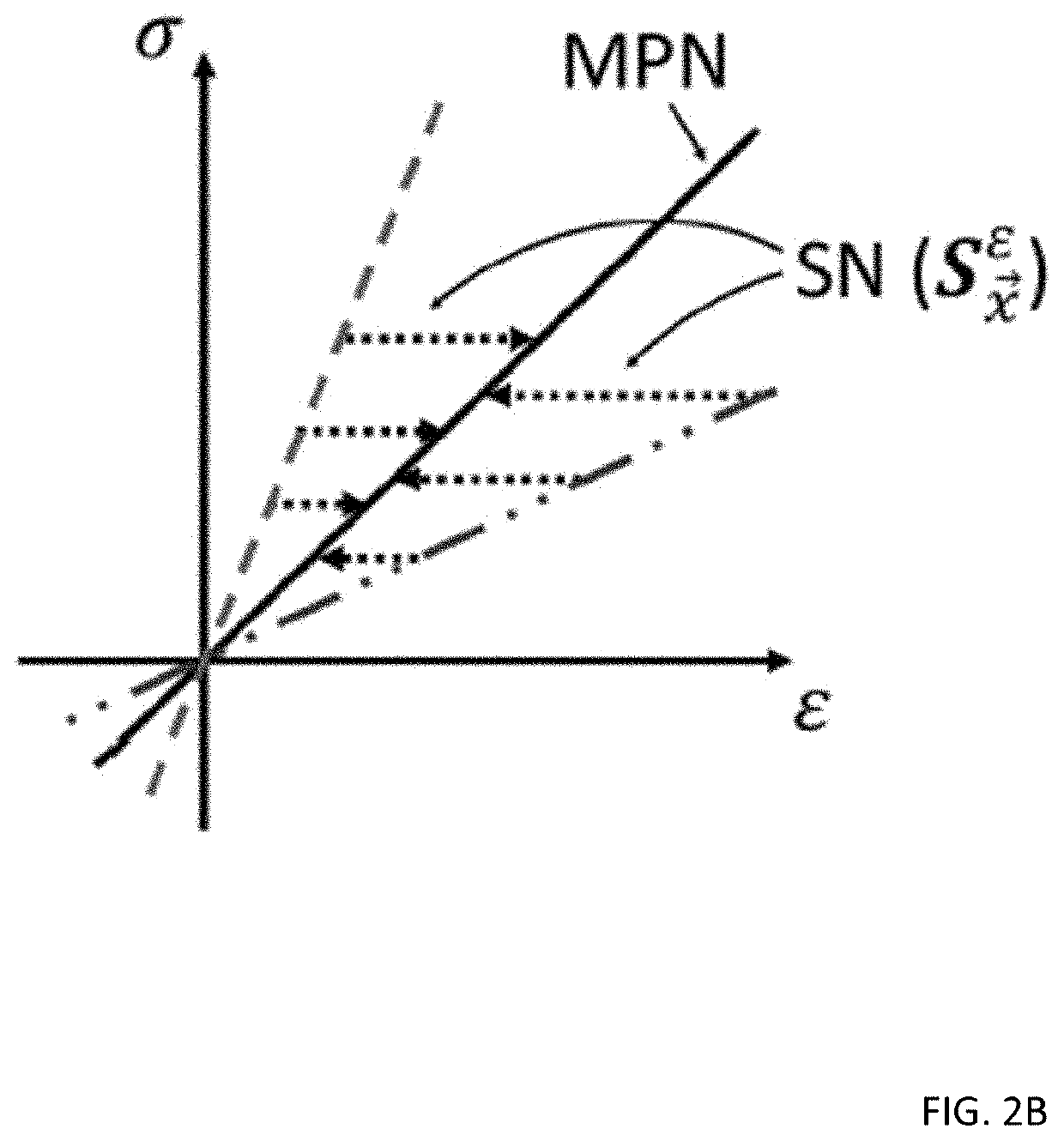
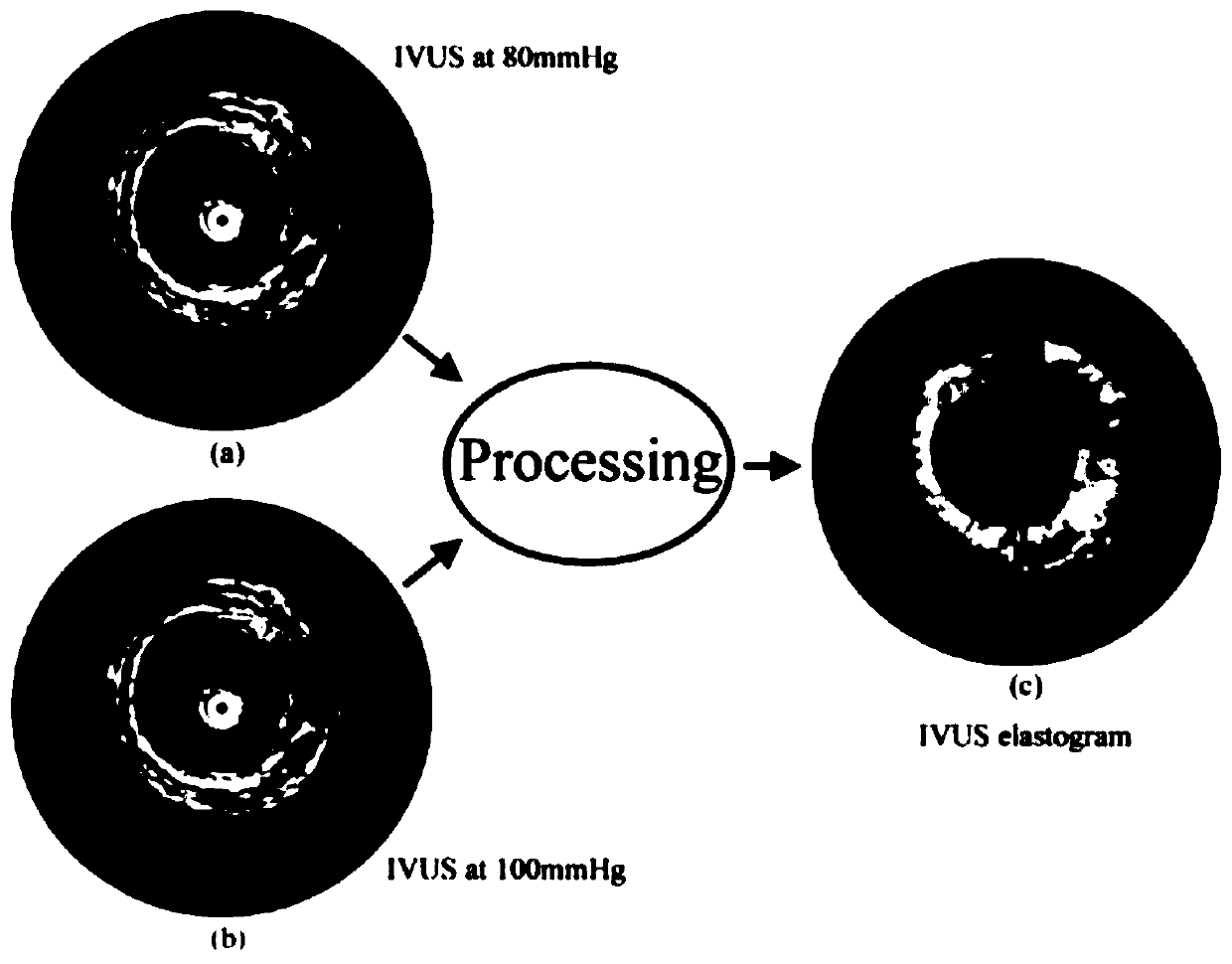
The method for vascular elastography comprises: i) obtaining a sequence of radio-frequency (RF) images including pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images in digital form of a vessel delimited by a vascular wall; the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images being representative of first and second time-delayed configuration, of the whole vessel; ii) partitioning both the pre-tissue-motion and post-tissue-motion images within the vascular wall into corresponding data windows; approximating a trajectory between the pre- and post-tissue-motion for corresponding data windows; and using the trajectory for each data window to compute the full strain tensor in each data window, which allow determining the Von Mises coefficient. The method can be adapted for non-invasive vascular elastography (NIVE), for non-invasive vascular micro-elastography (MicroNIVE) on small vessels, and for endovascular elastography (EVE).
Owner:UNIV JOSEPH FOURIER +1
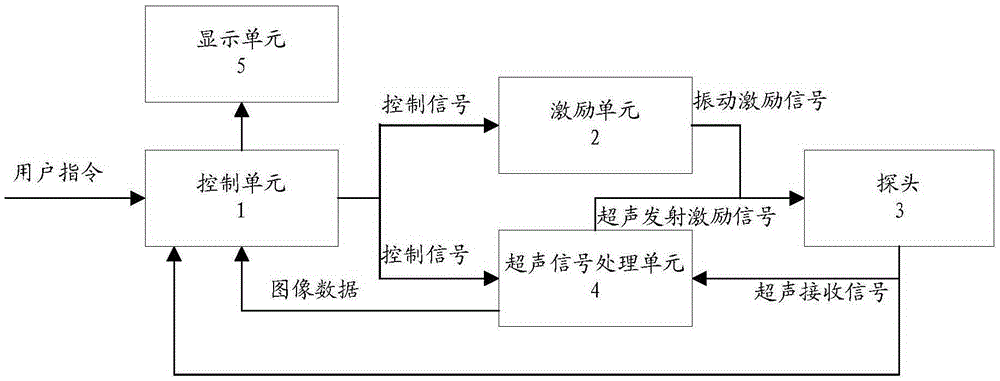
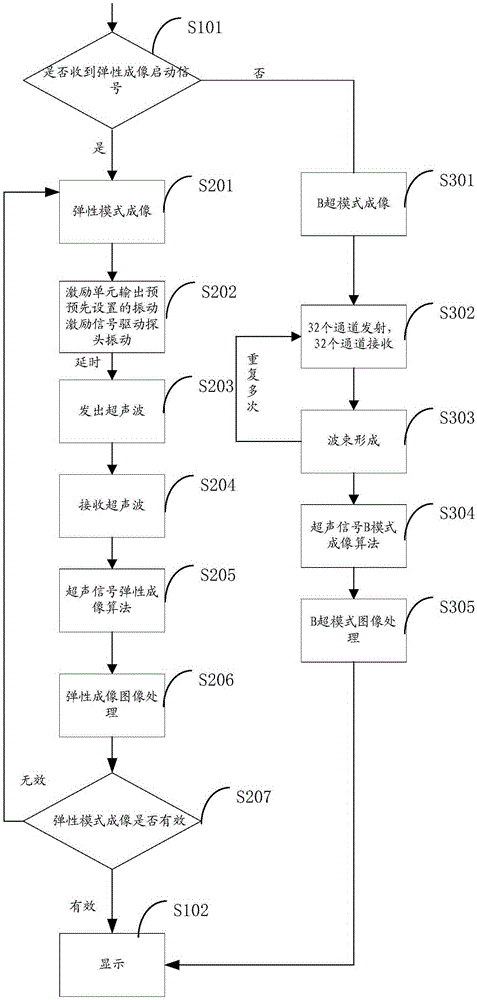
Ultrasonic elastic imaging system and method
ActiveCN105395218ASolve the problem of inaccurate positioning of transient elastographyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorControl signal
The invention relates to an ultrasonic elastic imaging system and method. The ultrasonic elastic imaging system comprises a control unit, an exciting unit, a probe and an ultrasonic signal processing unit. The probe comprises an ultrasonic sensor array, a vibration exciter and a pressure sensor. The control unit selects a work mode according to a received user instruction and converts the user instruction into a control signal. The exciting unit receives the controls signal and outputs a vibration exciting signal; the vibration exciter receives the vibration exciting signal and drives the probe to make periodical mechanical vibration; the ultrasonic signal processing unit receives the control signal, transmits and receives ultrasonic waves through the ultrasonic sensor array and performs signal processing on the received ultrasonic waves, and a processing result is sent to the control unit. An instantaneous elastic imaging probe and a B ultrasonic mode probe are combined. The B ultrasonic mode probe has the effects of transmitting and receiving ultrasounds and meanwhile has the function of vibrating an exciting source. Seamless switching of elastic imaging measurement and B ultrasonic mode measurement is achieved through the relevant imaging process and the relevant imaging algorithm. The problem that ultrasonic elastic imaging in the prior art is not accurate is solved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
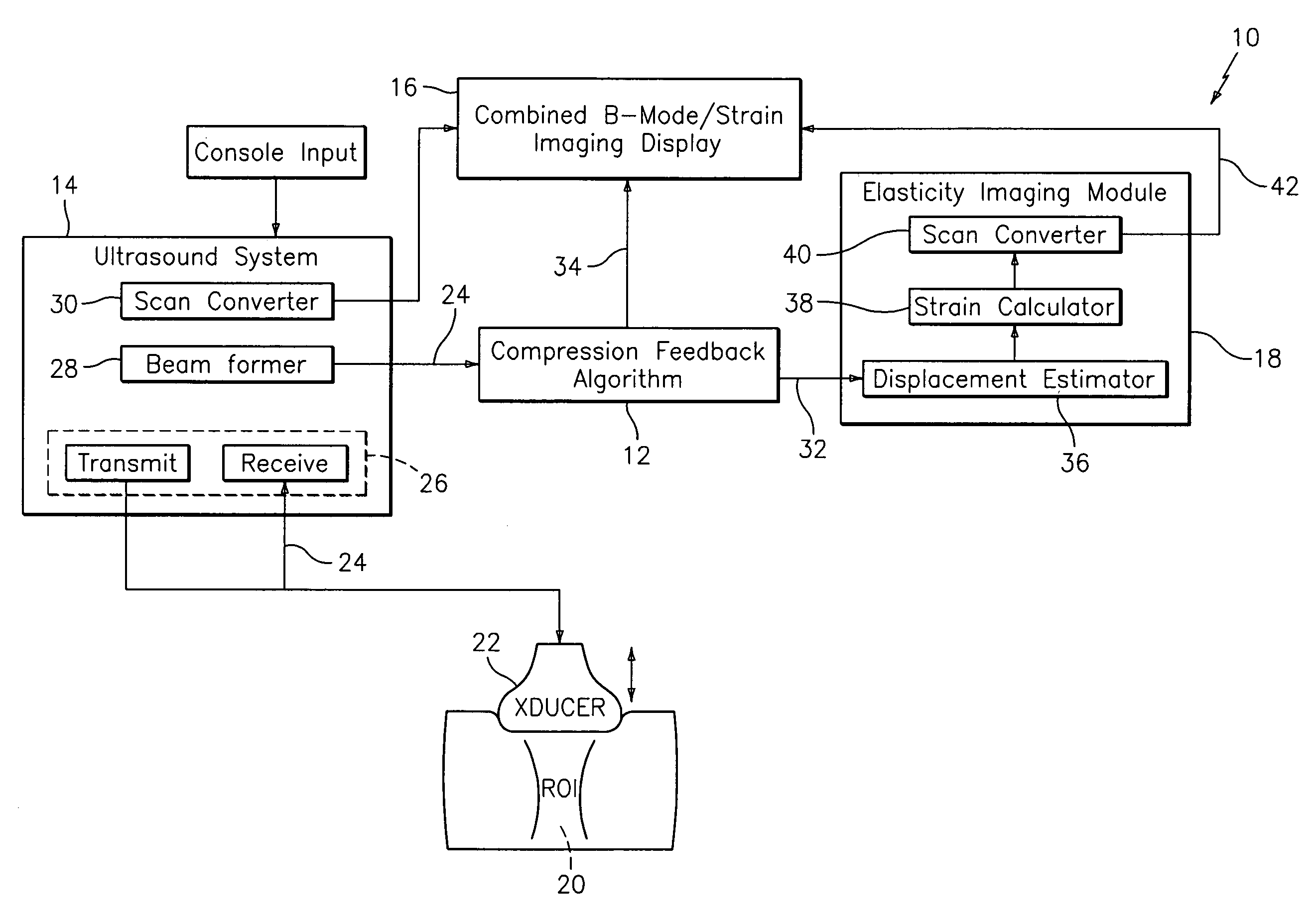
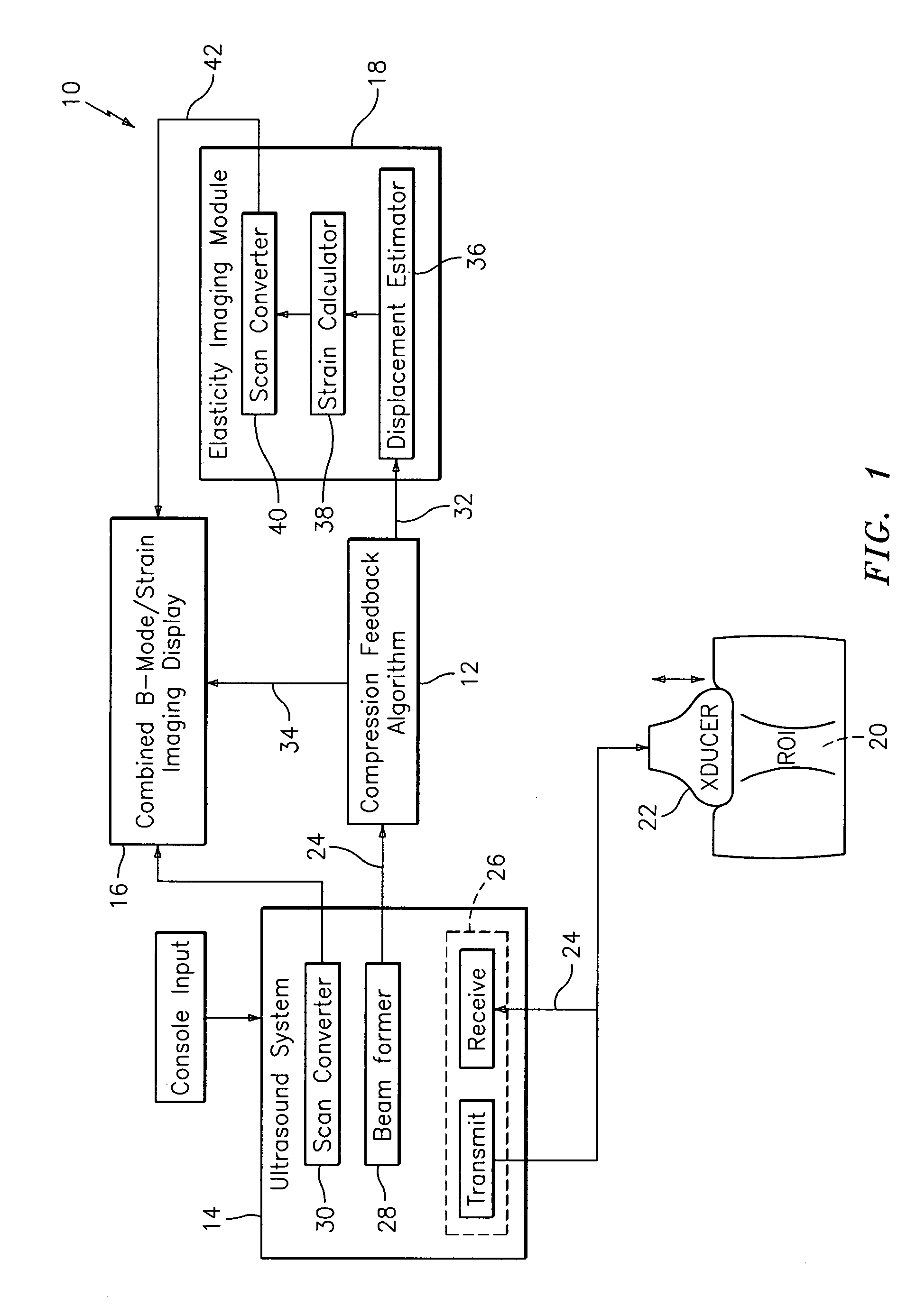
Method and apparatus for elasticity imaging
InactiveUS7223241B2Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingElastography
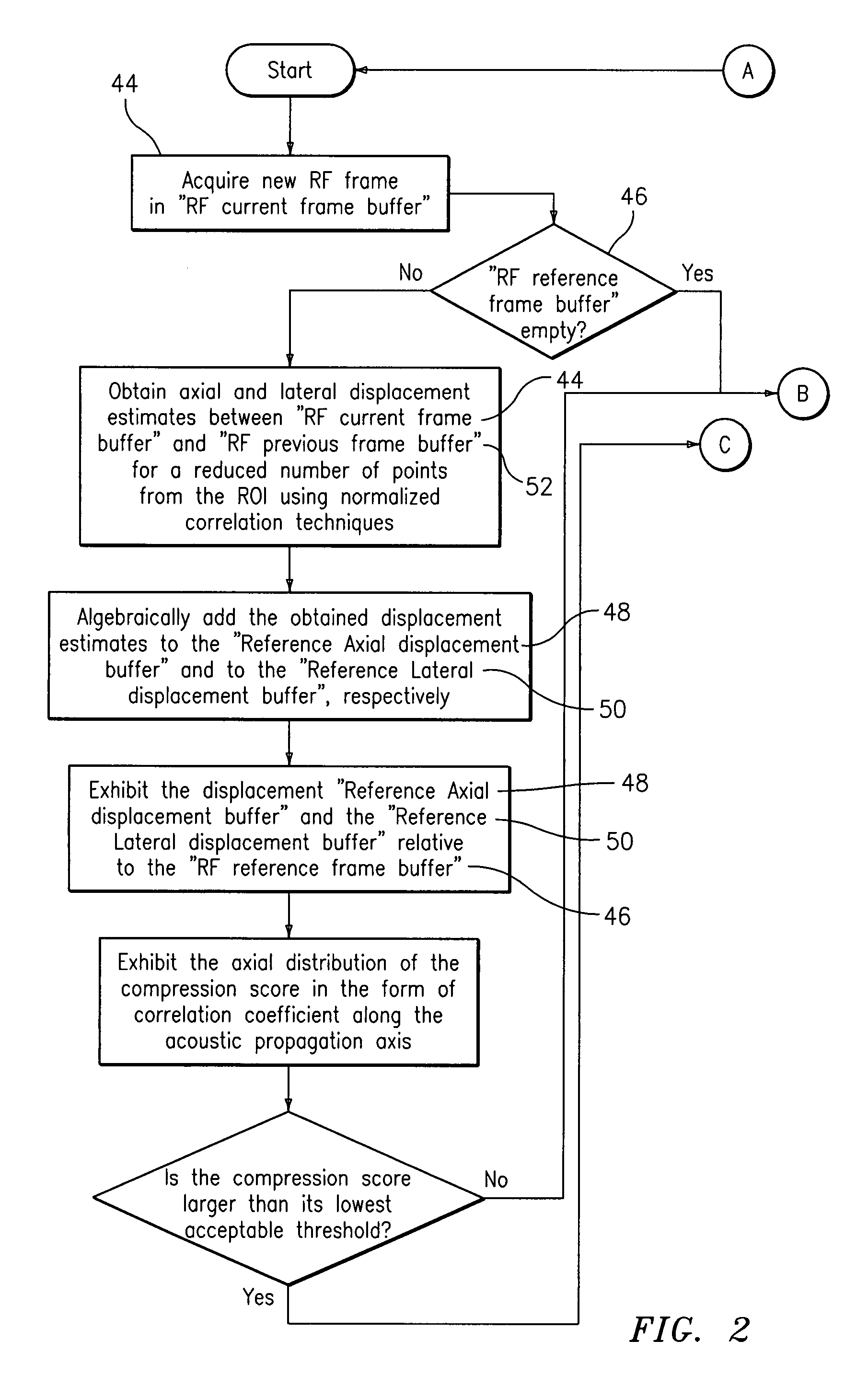
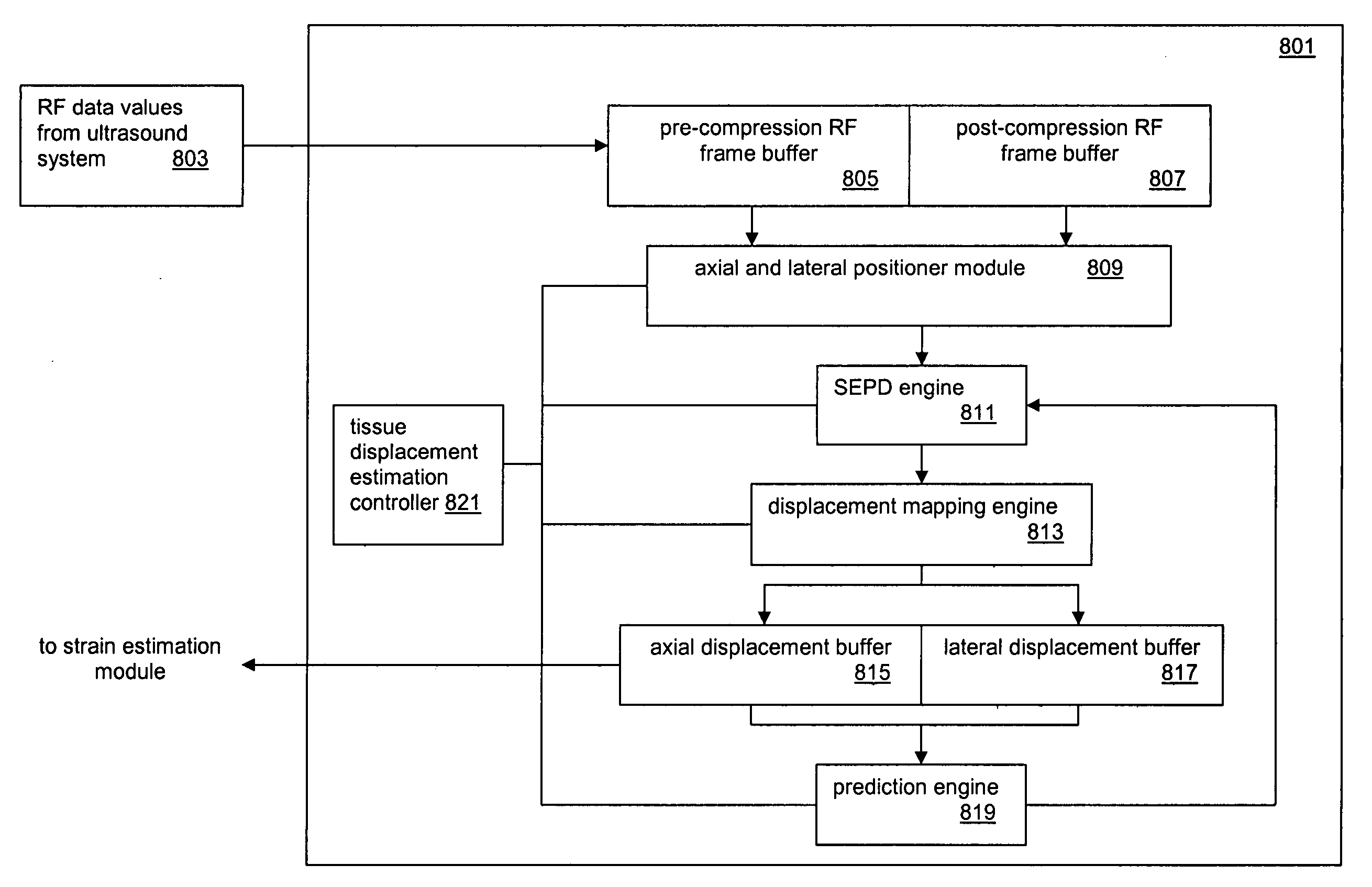
A computational efficient algorithm for compression analysis of free-hand static elasticity imaging performed using medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment offers tissue compression quality and quantity feedback to the operator. The algorithm includes a criterion for automatic selection of the most advantageous pre- and post-compression frame pairs delivering elasticity images of optimal dynamic ranges (DR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The use of the algorithm in real time eases operator training and reduces significantly the amount of artifact in the elasticity images while lowering the computational burden.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Bandpass sampling for elastography
ActiveUS8668647B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsConventional medicineDiagnostic ultrasound
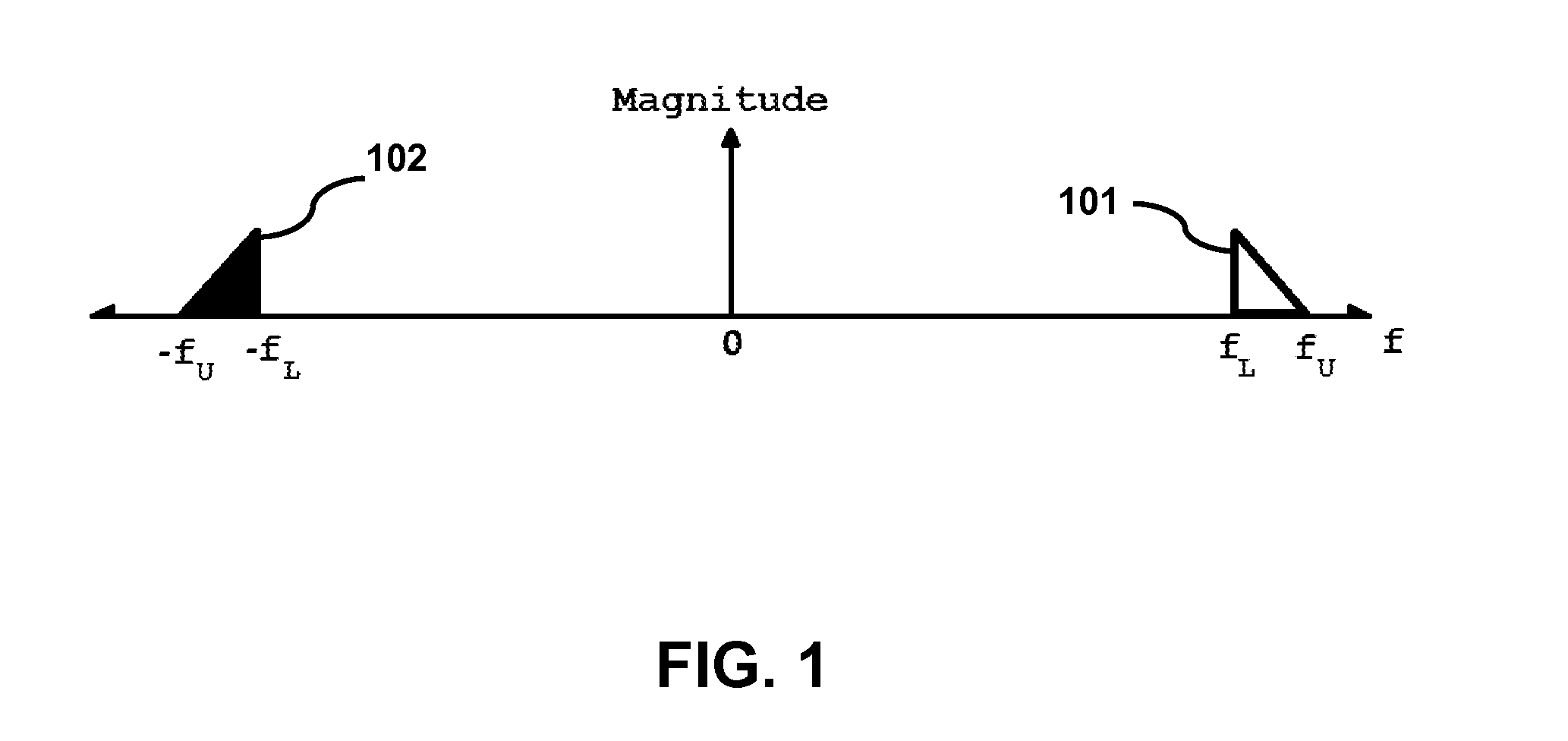
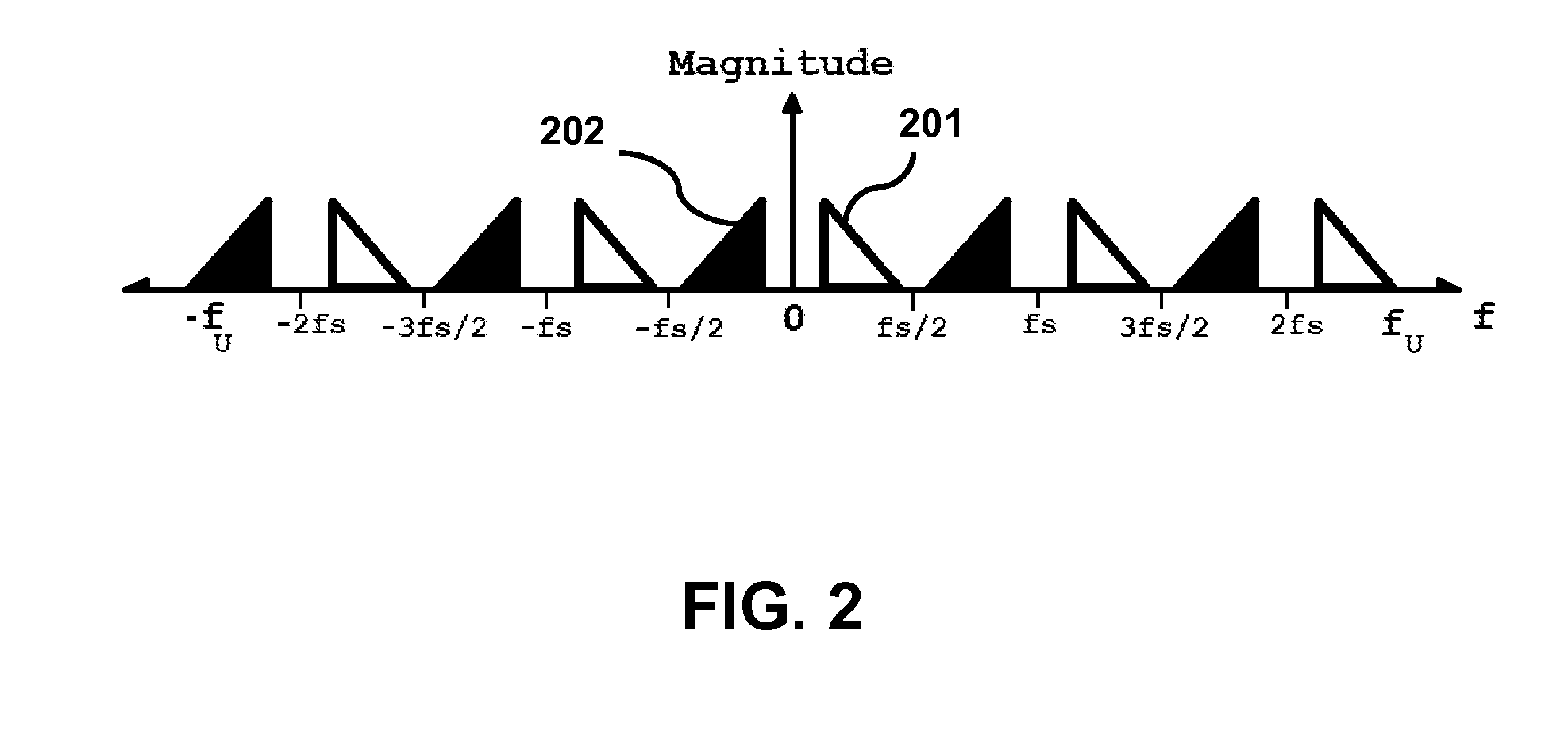
The characterization of tissue viscoelastic properties requires the measurement of tissue displacements over a region of interest at frequencies that exceed significantly the frame rates of conventional medical imaging devices. The present invention involves using bandpass sampling to track high-frequency tissue displacements. With this approach, high frequency signals limited to a frequency bandwidth can be sampled and reconstructed without aliasing at a sampling frequency that is lower than the Nyquist rate. With bandpass sampling, it is feasible to use conventional beam-forming on diagnostic ultrasound machines to perform high frequency dynamic elastography. The method is simple to implement as it does not require beam interleaving, additional hardware or synchronization and can be applied to magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA IND LIAISON OFFICE
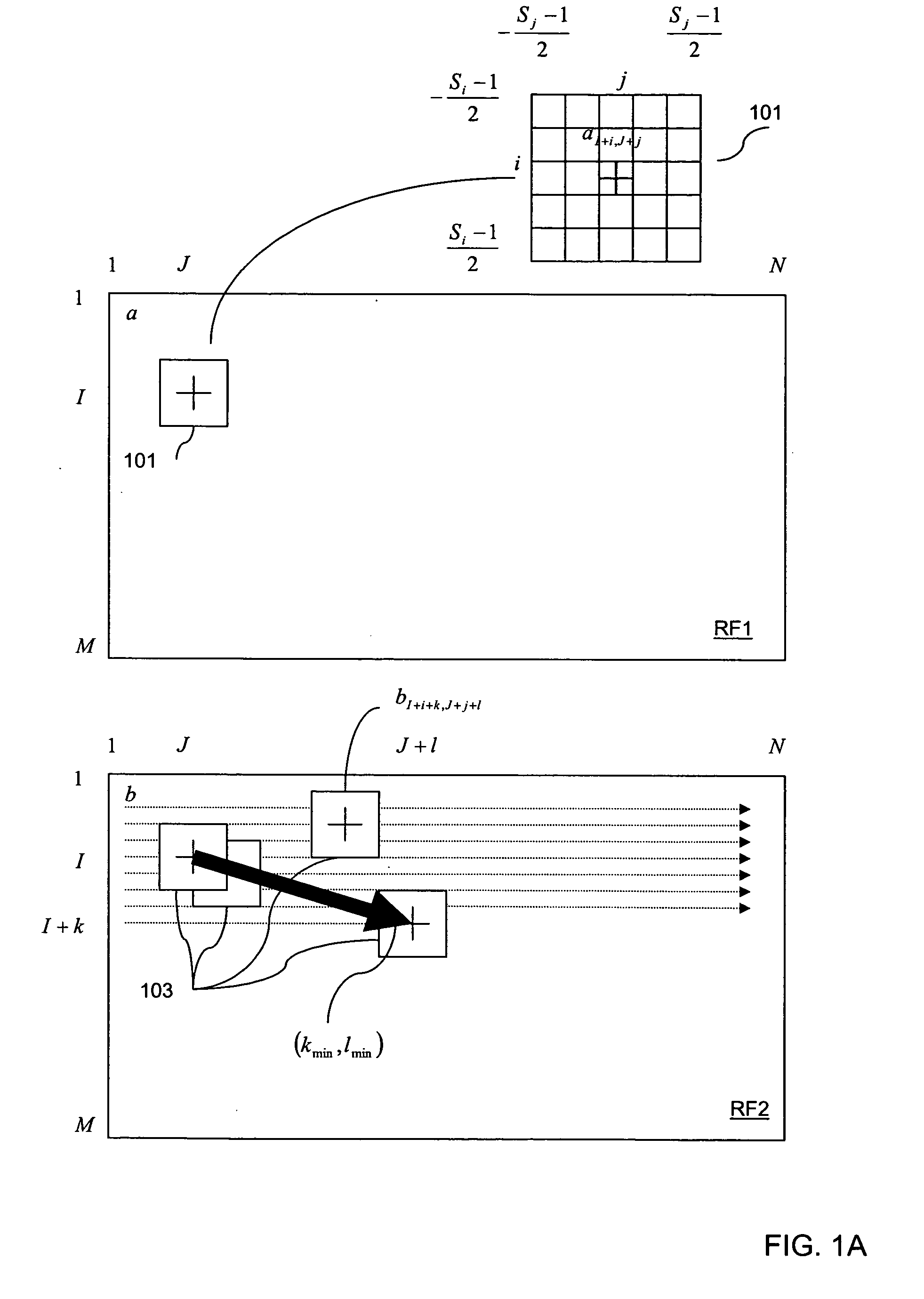
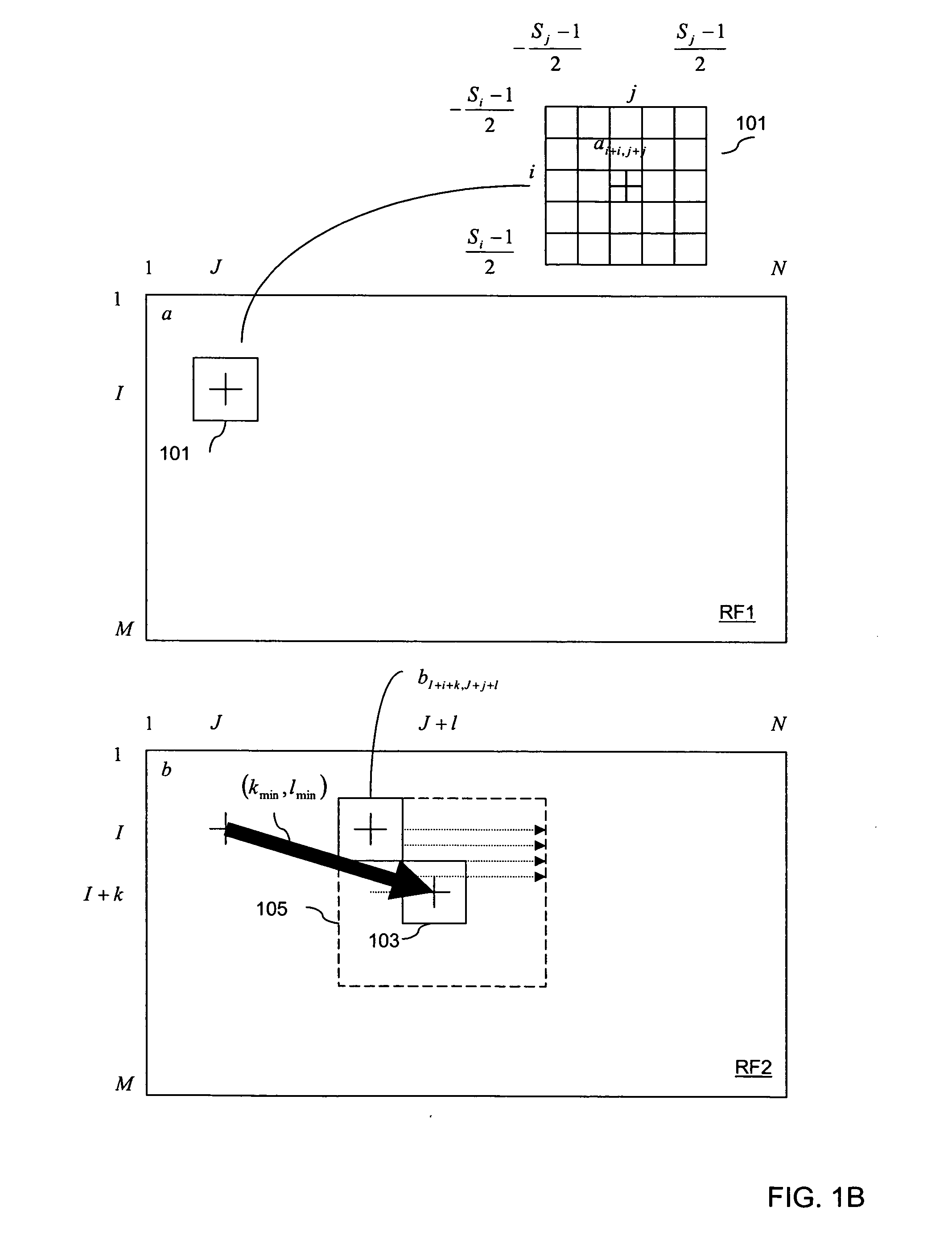
Optimal block searching algorithm for tissue displacement estimation in elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20080144902A1Efficient processingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisElastographySonification
Disclosed is a method and system that efficiently compares data from two ultrasound images and derives a tissue displacement map for real-time diagnostic imaging applications.
Owner:ALOKA CO LTD
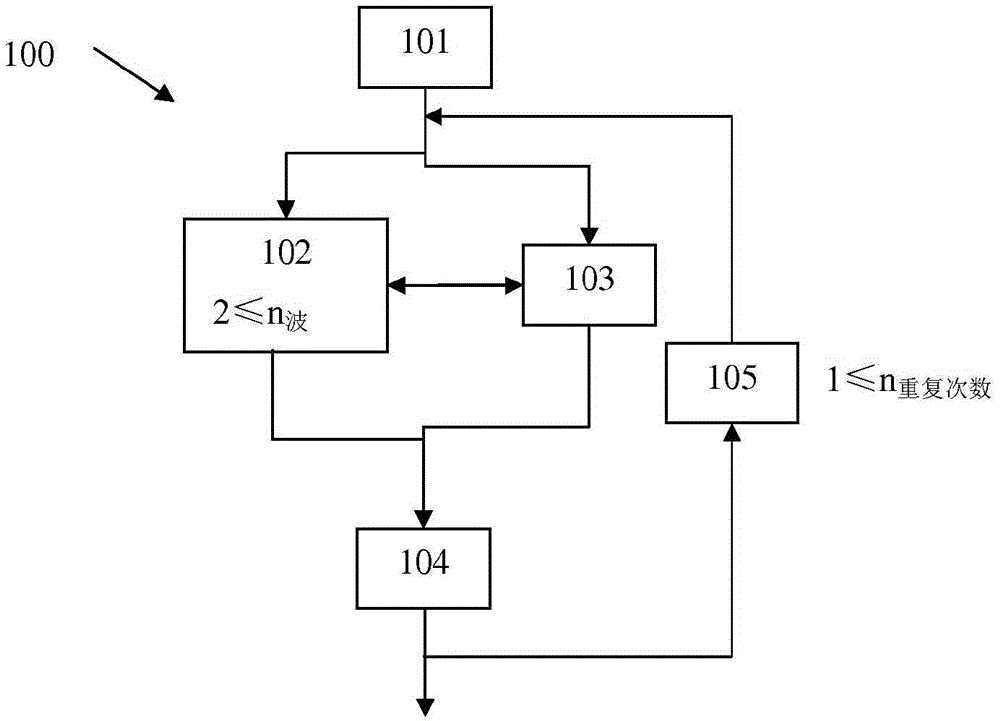
Multipulse elastography method
ActiveCN104380134AWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionAcousticsBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a multipulse elastography method (100) for quantitatively measuring at least one mechanical property of a viscoelastic medium having an ultrasonic signal after ultrasonic illumination, said method (100) comprising the following steps: defining (101) the characteristics of at least two mechanical pulses; generating (102) said at least two mechanical pulses in a viscoelastic medium; monitoring (103) the propagation, in said viscoelastic medium, of the at least two shearing waves from said at least two mechanical pulses by means of the transmission and acquisition of ultrasonic signals; and calculating (104) at least one mechanical property of said viscoelastic medium by means of said acquisitions of said ultrasonic signals.
Owner:ECHOSENS SA
Acquisition control for elasticity ultrasound imaging
InactiveCN104939869AImage analysisSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUltrasound imagingImage resolution
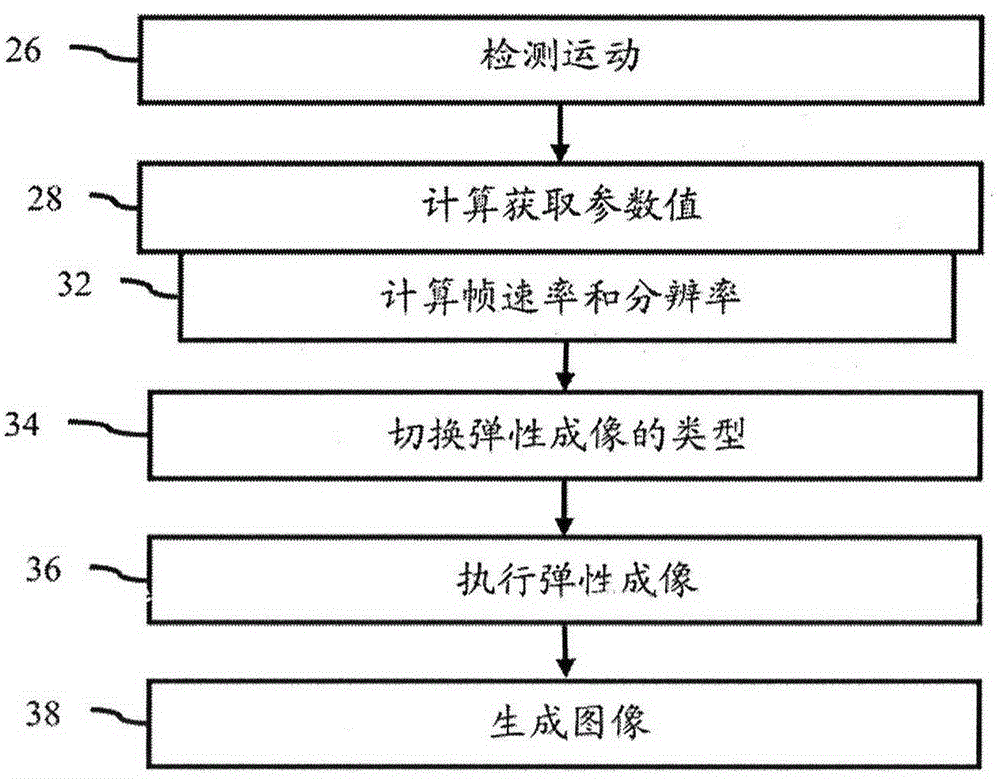
Acquisition settings for elasticity imaging are controlled (28) based on detected motion (26). Rather than rely solely on user settings, one or more acquisition parameters are automatically set (28) based on the detected motion (26). For example, the settings provide for a more rapid frame rate with less resolution in elasticity imaging for times associated with greater motion and for less rapid frame rate with greater resolution for times associated with lesser motion.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
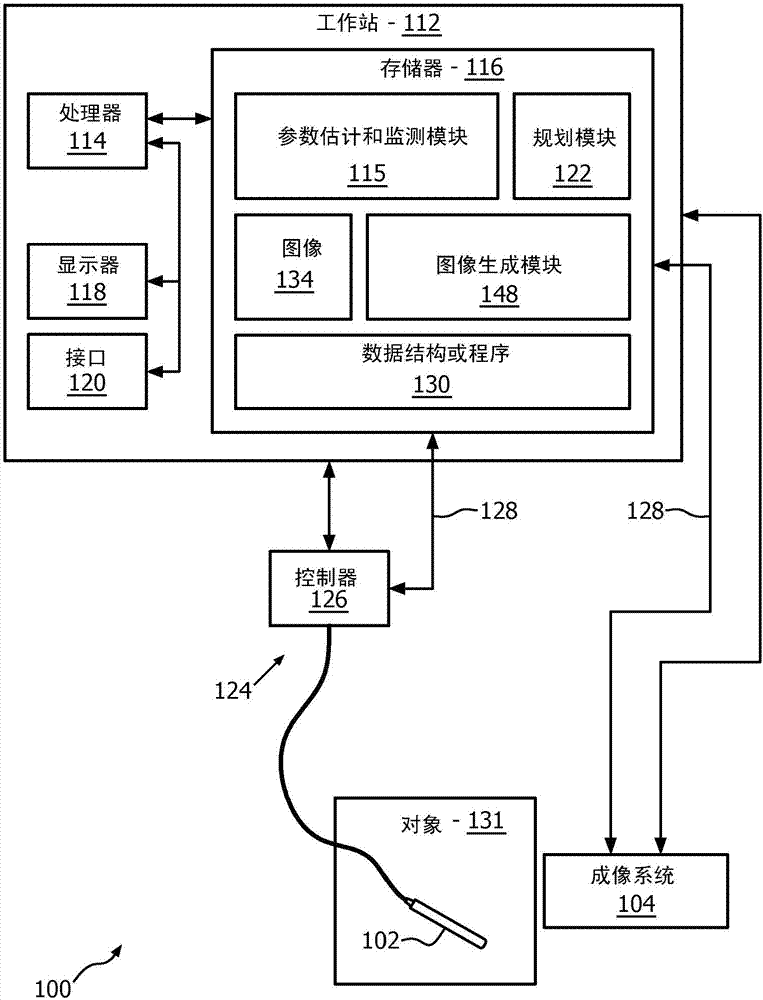
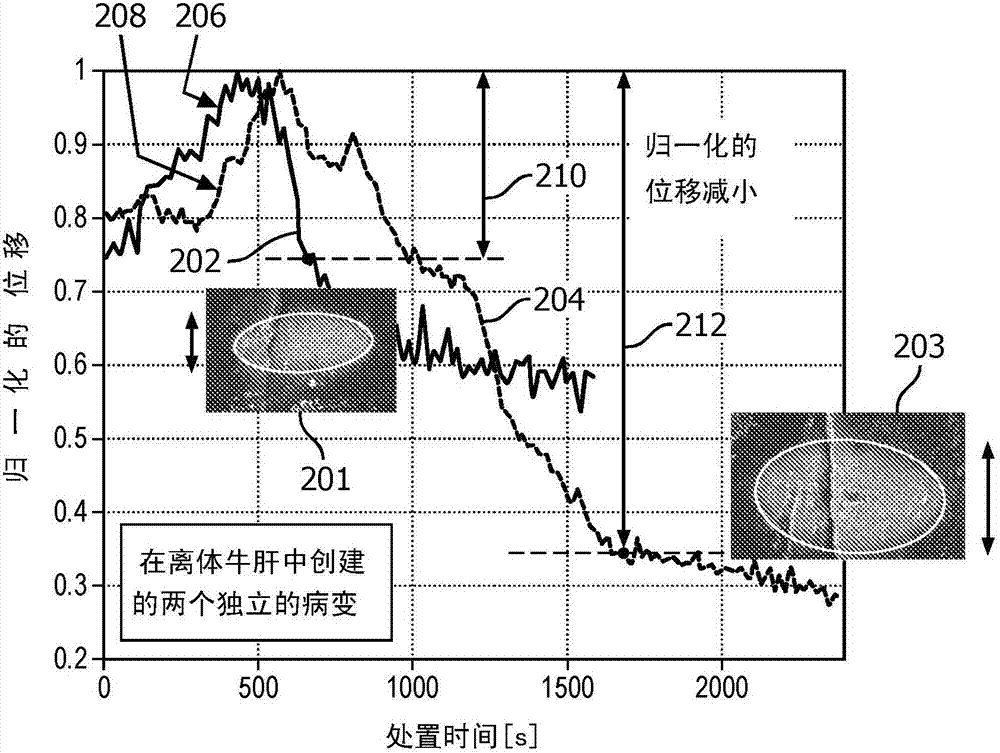
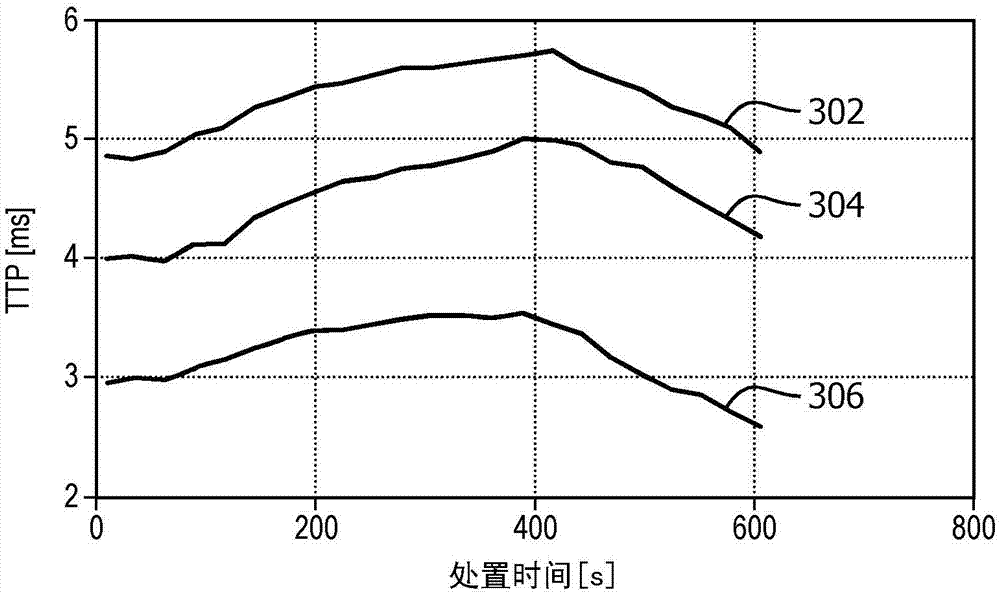
System and method for adaptive ablation and therapy based on elastography monitoring
A system for performing ablation includes an ablation device (102) configured to ablate tissue in accordance with control parameters and configured to make measurements during the ablation process. An imaging system (104) is configured to measure an elastographic related parameter to monitor ablation progress. A parameter estimation and monitoring module (115) is configured to receive the measurements from the ablation device and / or the elastographic related parameter to provide feedback to adaptively adjust imaging parameters of the imaging device at different times during an ablation process.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for producing elastic image and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
A method of generating an elastography image includes transmitting unfocused push signals comprising a plurality of ultrasound signals to an object in different directions; transmitting a detection ultrasound signal to the object in which a shear wave is generated by the unfocused push signals; receiving a response signal in response to the detection ultrasound signal from the object; and generating the elastography image of the object based on the response signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
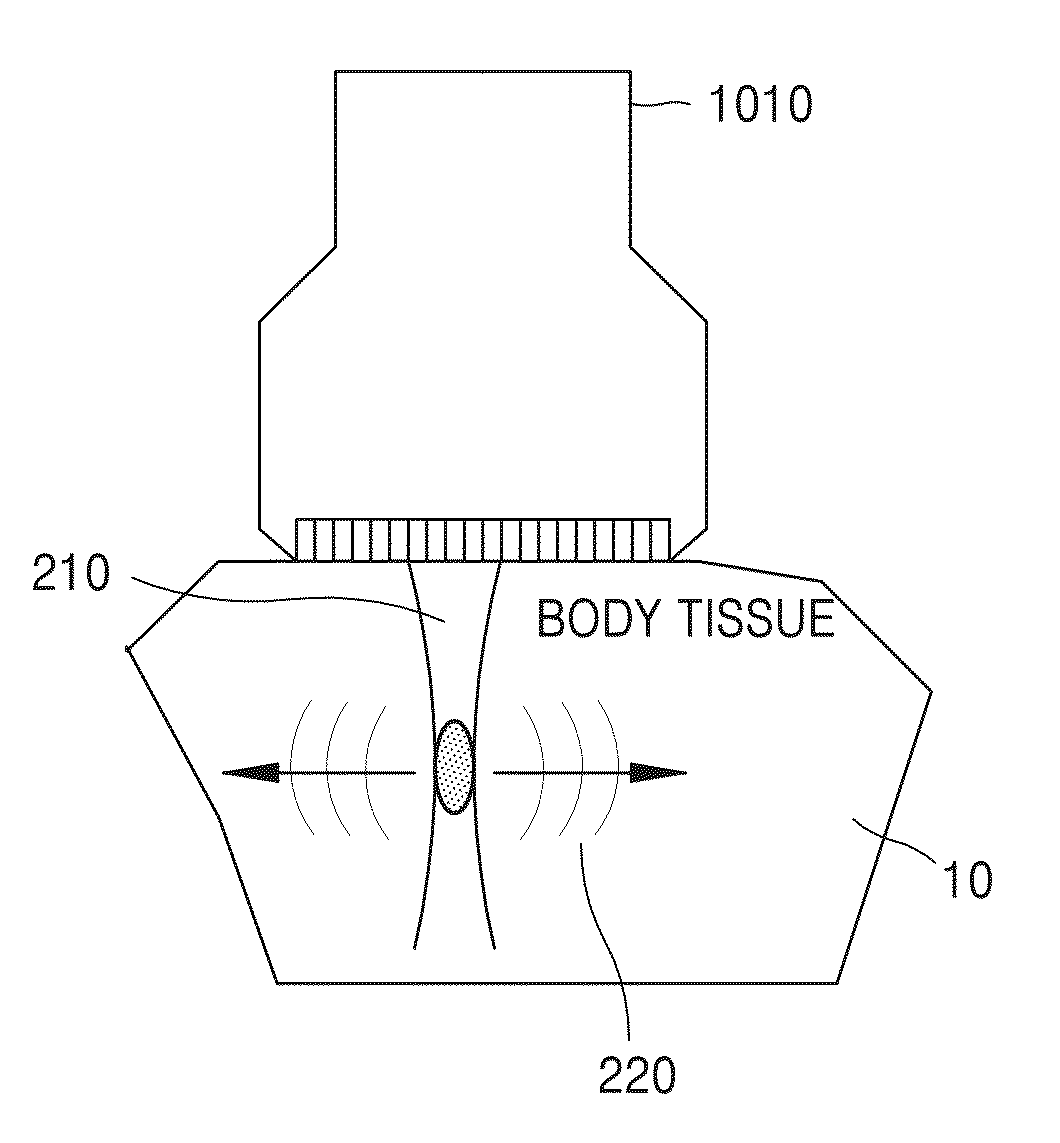
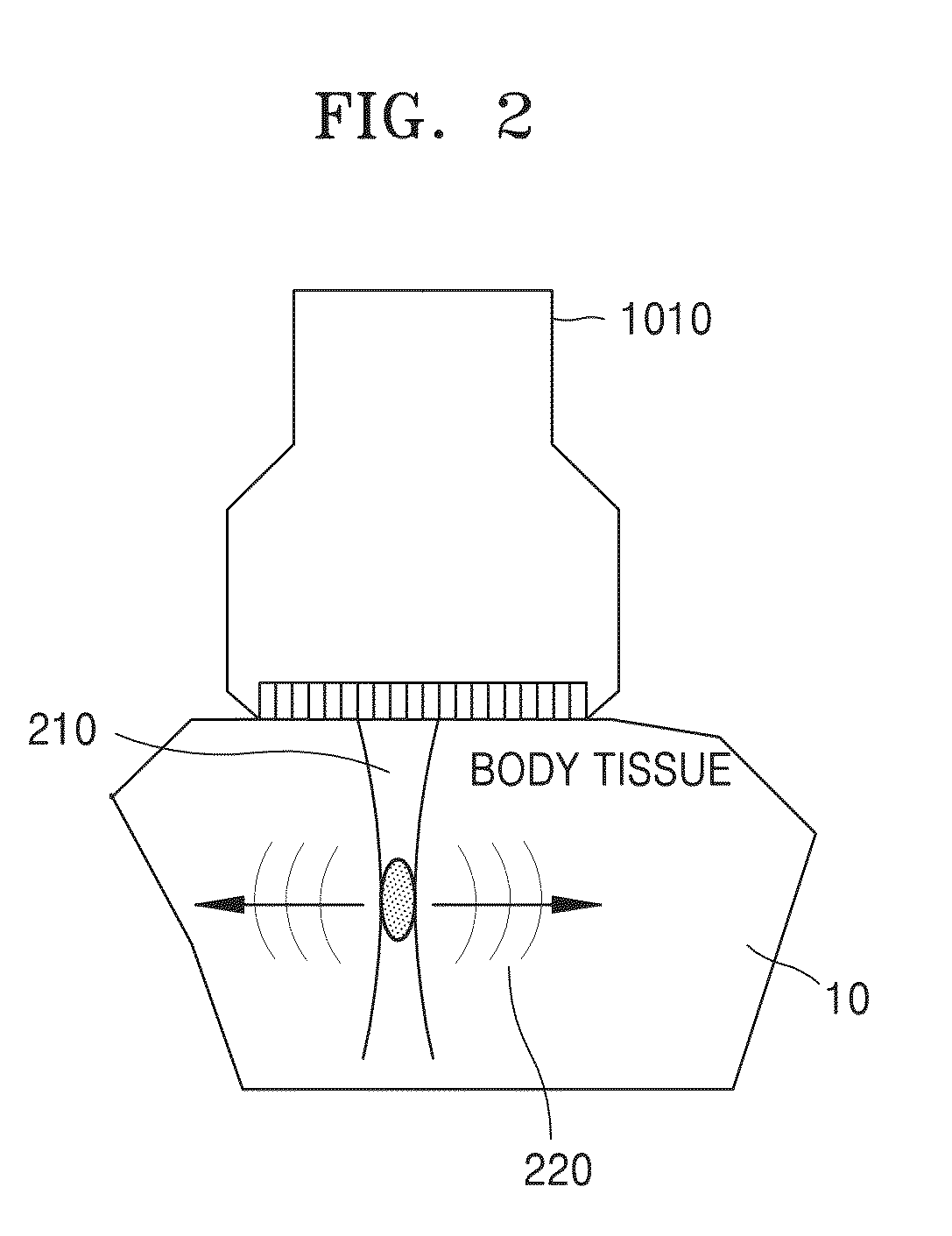
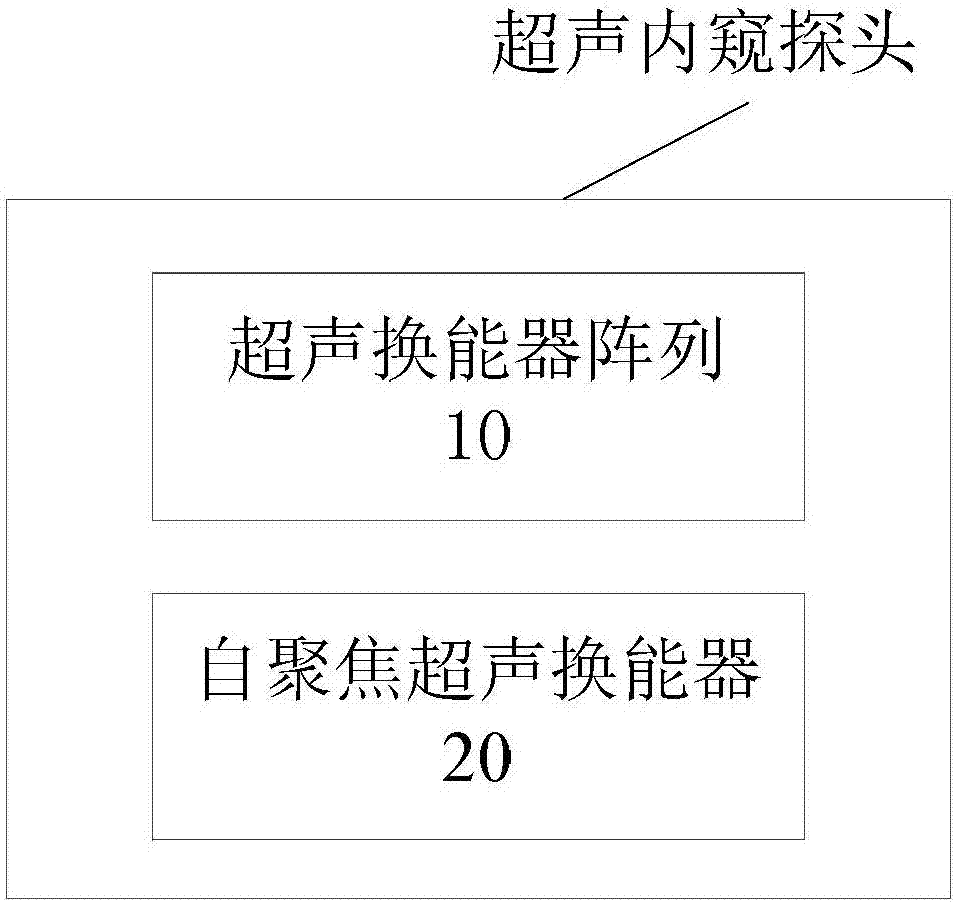
Ultrasonic peeping probe and elastic imaging system and method
PendingCN107260216ARelieve painSimple and fast operationOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an ultrasonic peeping probe and an elastic imaging system and method. The ultrasonic peeping probe comprises an ultrasonic transducer array including multiple ultrasonic transducers for transmitting ultrasonic waves and receiving ultrasonic echoes, reflected by the biological tissue to be detected of ultrasonic waves, and a self-focused ultrasonic transducer for producing focused ultrasonic wave beams, wherein the focused ultrasonic wave beams produce an acoustic radiation force acting on the biological tissue to be detected. The ultrasonic peeping probe produces the focused ultrasonic wave beams through the self-focused ultrasonic transducer, acts on the biological tissue to be detected through the acoustic radiation force of the focused ultrasonic wave beams and accordingly makes the biological tissue to be detected deform. Accordingly, the ultrasonic echo signals of the biological tissue before and after compression are obtained by adopting the ultrasonic peeping probe without the external force exerted by an operator, the operating process is simple and convenient without external mechanical devices, and the system cost is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOKE ULTRA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
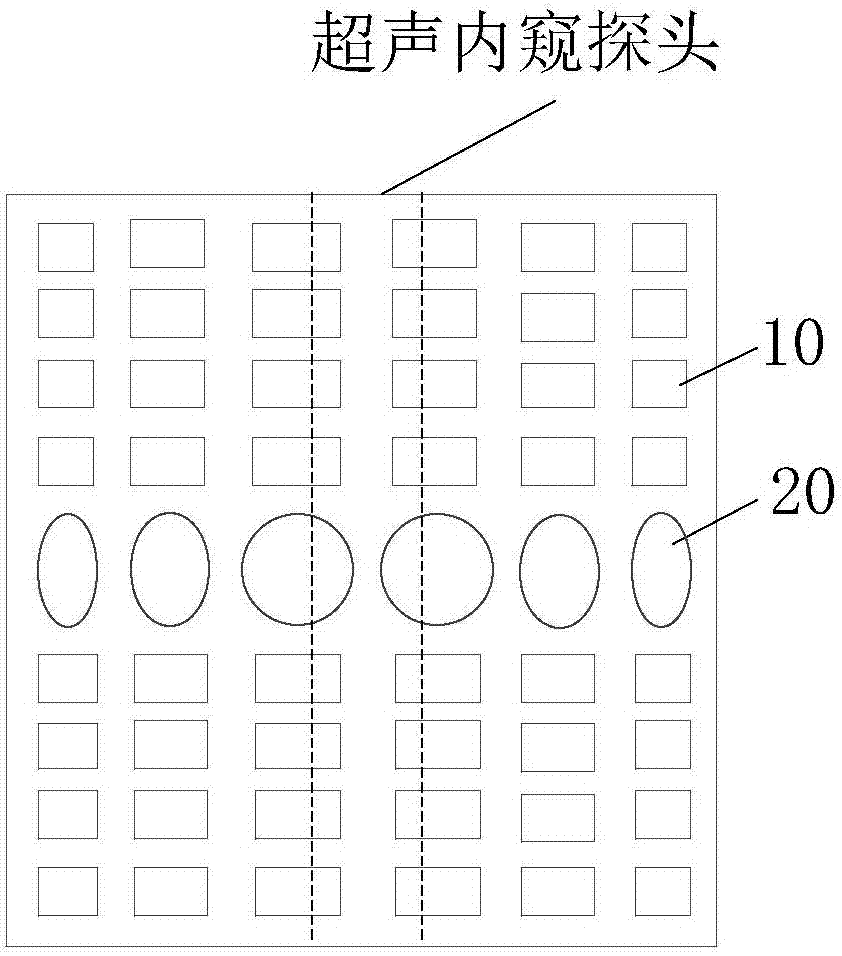
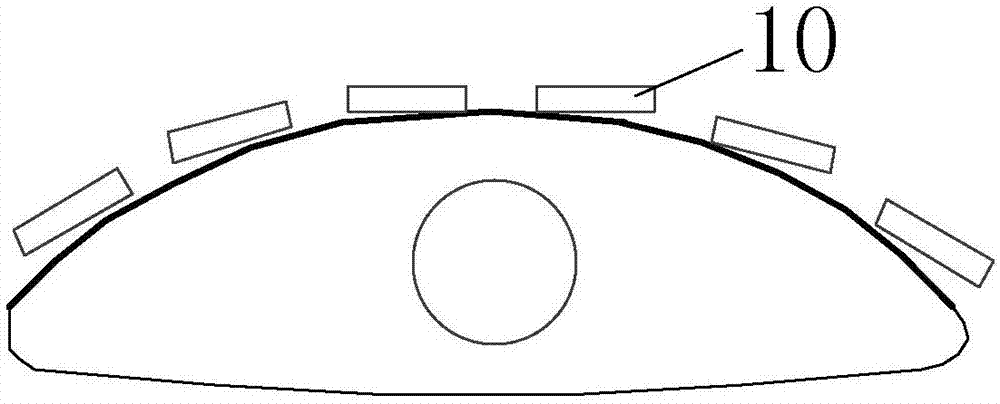
Ultrasonic elastography cornea detection method, device and system and storage medium
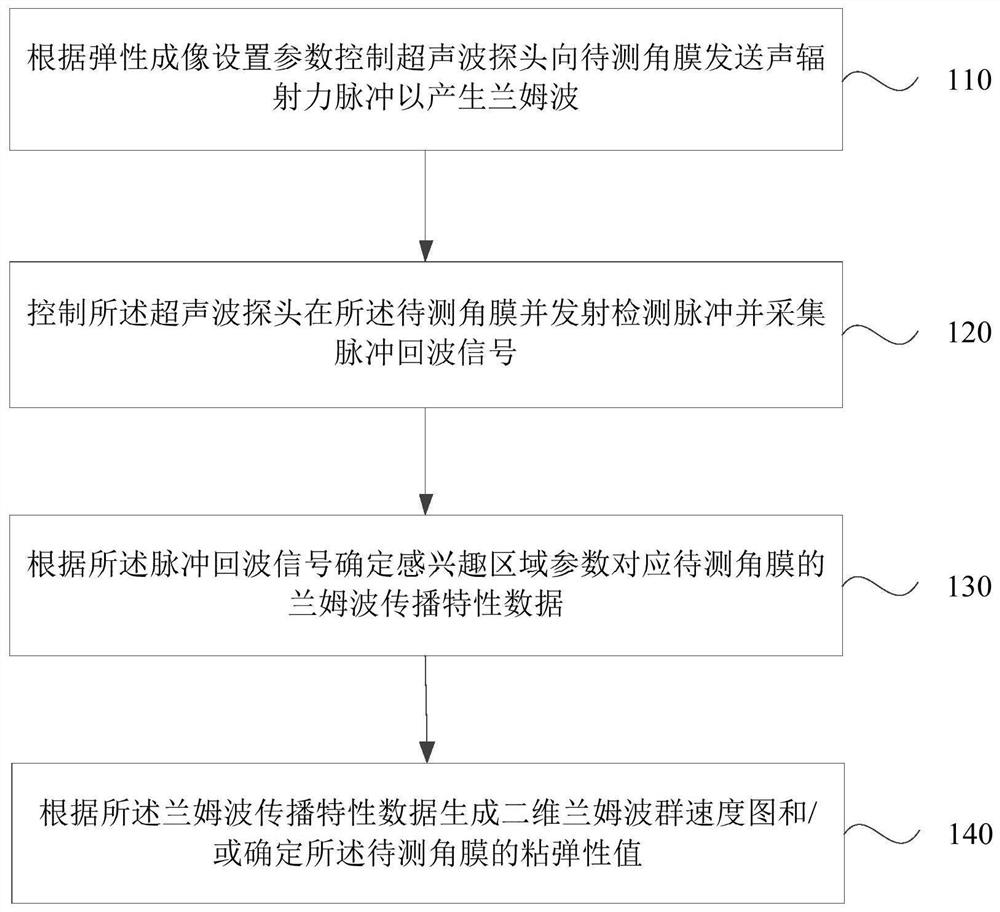
ActiveCN112022215AAchieve clinical diagnosisImprove accuracySustainable transportationInfrasonic diagnosticsControl ultrasoundEcho signal
The invention discloses an ultrasonic elastography cornea detection method, device and system and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of controlling an ultrasonic probe to send an acoustic radiation force pulse to a to-be-detected cornea according to an elastography setting parameter, so as to generate a lamb wave, wherein the ultrasonic probe at least comprises two channel array elements; controlling the ultrasonic probe to be in the cornea to be detected, transmitting a detection pulse and acquiring a pulse echo signal; determining lamb wave propagation characteristic data of the cornea to be measured corresponding to the region-of-interest parameter according to the pulse echo signal; and generating a two-dimensional lamb wave group velocity diagram and / or determining the viscoelasticity value of the cornea to be measured according to the lamb wave propagation characteristic data. According to the embodiment of the invention, the ultrasonic probes of the multichannel array elements excite the cornea to obtain the propagation characteristics of the lamb waves, and the biomechanical characteristics of the cornea are determined according to the propagation characteristics of the lamb waves in the cornea, so that the clinical detection of the cornea is realized, the resolution of detection imaging is improved, and the accuracy of a detection result is enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
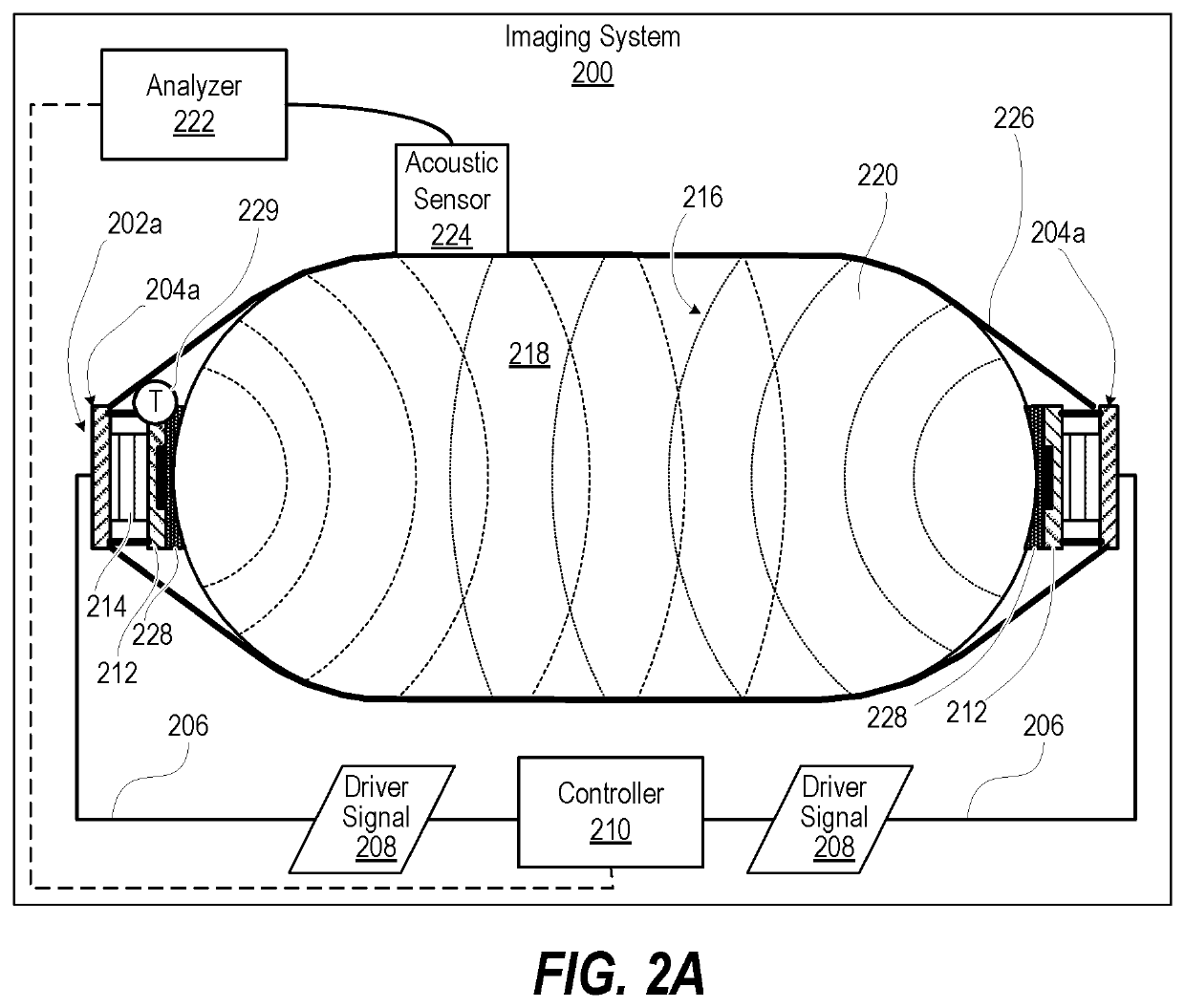
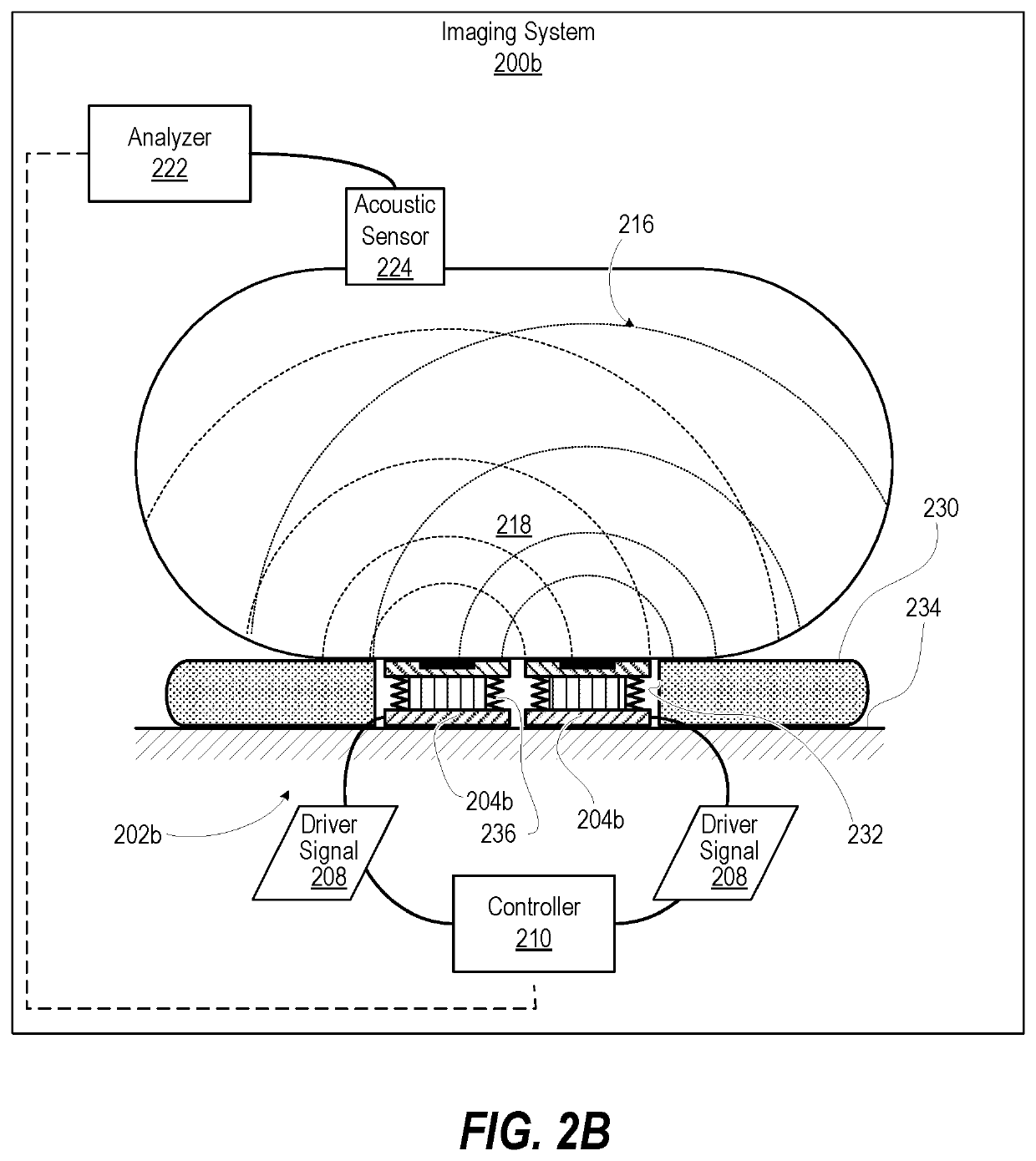
Systems and methods for elastographic and viscoelastographic imaging
PendingUS20210018606A1Desired effectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationWave fieldAcoustics
A High Definition ViscoElastography (HDVE) inertial driver apparatus of an imaging system and method includes one or more HDVE inertial driver devices. Each HDVE inertial driver device has: (i) a driver interface that enables receiving a driver signal from a controller; (ii) a resonating surface; and (iii) an inertial driver communicatively coupled to the driver interface and mechanically coupled to the resonating surface to independently generate a resonating displacement of the resonating surface. A support member of the HDVE inertial driver apparatus positions the two or more HDVE inertial driver devices into acoustic contact with a body to produce a shear wave field through a volume of tissue within the body or a material within an object.
Owner:ELASTANCE IMAGING LLC
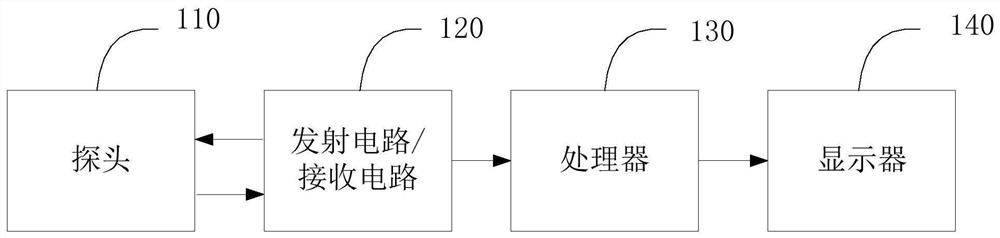
Wireless palm size color ultrasound instrument
InactiveCN107361789AExpand the range of detection objectsFast imagingInfrasonic diagnosticsSonic diagnosticsRapid imagingData connection
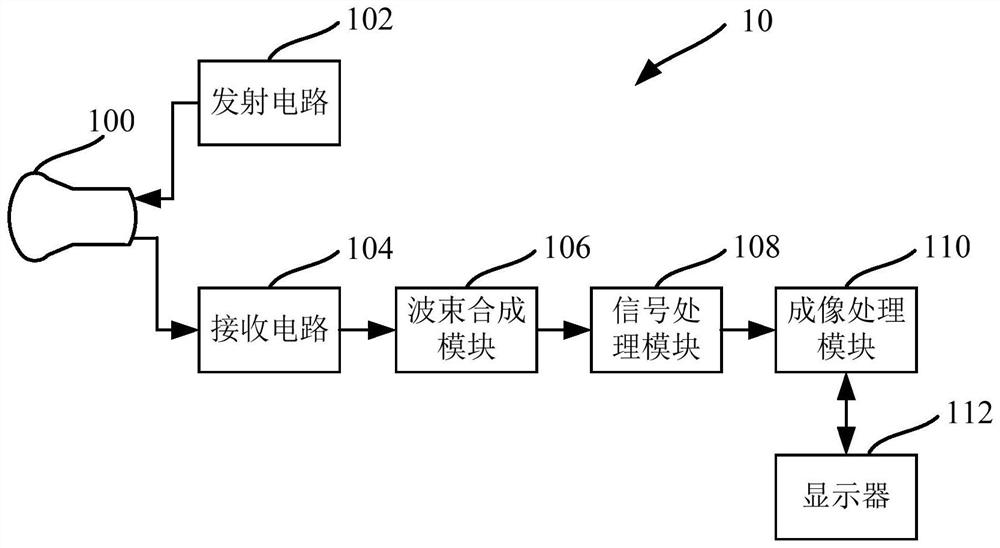
The invention discloses and provides a wireless palm size color ultrasound instrument, and belongs to the field of medical apparatuses and instruments. The instrument can transmit real-time imaging signals through wireless signals and is clear in imaging, rapid in imaging, precise in imaging and wide in detecting object range on the basis of the instantaneous elasticity imaging technology. The wireless palm size color ultrasound instrument comprises a body and a replaceable probe arranged on the top of the body in a matched mode. An ultrasonic transmitting module and an ultrasonic echo collecting module are arranged inside the replaceable probe. A probe data connecting module, an elastic imaging processing module, a data imaging module and a wireless transmission module which are electrically and sequentially connected inside the body. The probe data connecting module is electrically connected with the ultrasonic echo collecting module. The wireless transmission module is connected with an external displayer through a wireless signal.
Owner:ZHUHAI WELLHOME MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Hydraulic ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging
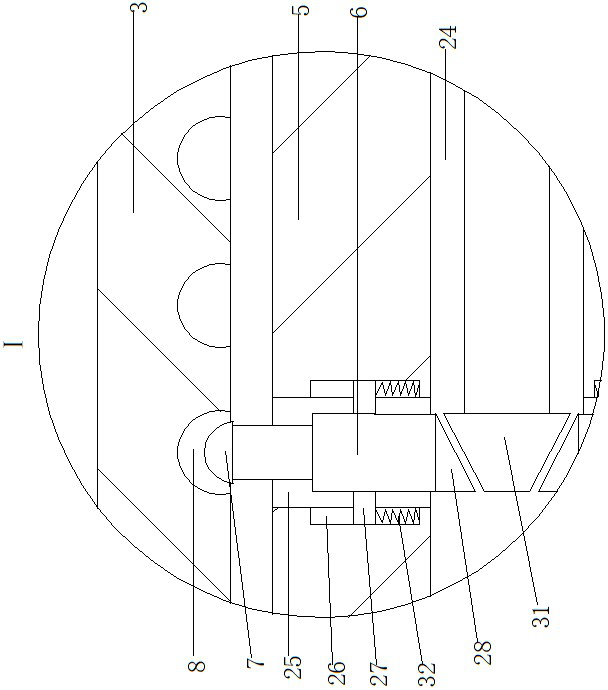
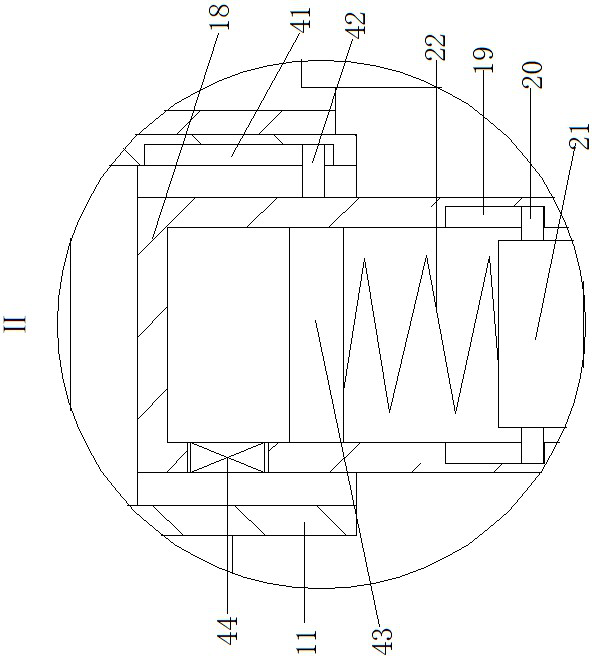
ActiveCN111772672AAchieve the effect of elastographyAffect clarityOrgan movement/changes detectionWater resource assessmentReciprocating motionUltrasound probe
The invention provides a hydraulic ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging. The hydraulic ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging comprises an installing seat, wherein the installing seat is providedwith a vertical upright post through a rotating device; a first cylinder body is arranged on the upright post; the right end of the first cylinder body is provided with an opening; a first piston block is arranged in the first cylinder body in a cooperative way; a first rod body is fixedly arranged at the right side wall of the first piston block; vertical elastic telescopic rods are symmetricallyarranged at the upper and lower side walls of the first rod body; and a hemispheroid is arranged on each of the elastic telescopic rods. The ultrasonic probe is controlled to press the human body formany times through a reciprocating ascending and descending device; meanwhile, the reciprocating ascending and descending device does vertical reciprocating movement for a certain number of times, and then, the ultrasonic probe can be pushed to move a certain distance to detect the next region of the human body; in addition, in the moving process, the ultrasonic probe is enabled to be always in contact with the body surface of a patient; and in addition, through the cooperation of the elastic telescopic rod, the hemispheroids and arc-shaped grooves, the counting effect is achieved on the number of the vertical reciprocating movement times of the ultrasonic probe, so that the downwards pressing number of the ultrasonic probe in each time is identical, and the influence of the elasticity imaging result on the judgment of doctors is avoided.
Owner:文静
Shear wave elasticity imaging method, ultrasonic imaging system and computer readable storage medium
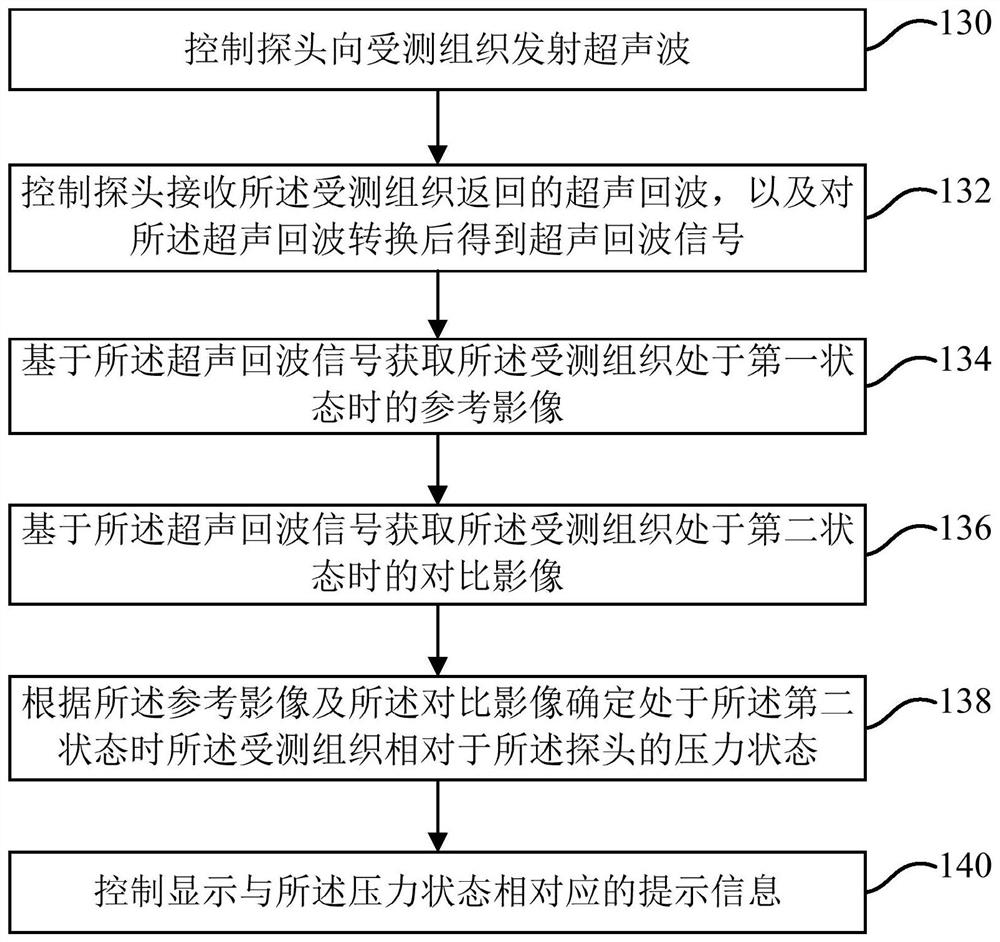
PendingCN112386276AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingRadiology
The embodiment of the application discloses a shear wave elasticity imaging method and system and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: controlling a probe to transmit ultrasonic waves to tested tissue; receiving an ultrasonic echo returned by the tested tissue, and controlling the probe to convert the ultrasonic echo to obtain an ultrasonic echo signal; acquiring a reference image of the tested tissue when the tested tissue is in the first state based on the ultrasonic echo signal; acquiring a comparison image of the tested tissue when the tested tissueis in a second state based on the ultrasonic echo signal in a shear wave imaging mode; determining the pressure state of the tested tissue relative to the probe when the tested tissue is in the second state according to the reference image and the comparison image; and controlling display of prompt information corresponding to the pressure state. According to the shear wave elasticity imaging method, the ultrasonic imaging system and the computer readable storage medium, the pressure state between the probe and the tested tissue is determined through the ultrasonic image, and the corresponding prompt information is output, so that a user can conveniently determine the accuracy of the obtained elasticity information of the tested tissue according to the prompt information.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for acoustic radiation force creep-recovery and shear wave propagation elasticity imaging
ActiveUS20160135788A1Wave based measurement systemsHealth-index calculationShear wavesRadiation force
A model-independent method for producing a viscoelastic tissue property metric using ultrasound is provided. A mechanical stress, such as an acoustic force, is applied to a tissue during a creep period using an ultrasound system to generate a creep response. Tissue displacement resulting from the applied acoustic force is measured during a recovery period following the creep period. From the tissue displacement measurements, a relative complex modulus is extracted, and a loss tangent is calculated based on extracted complex modulus. Using the calculated loss tangent, viscoelastic tissue property metrics may be calculated.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
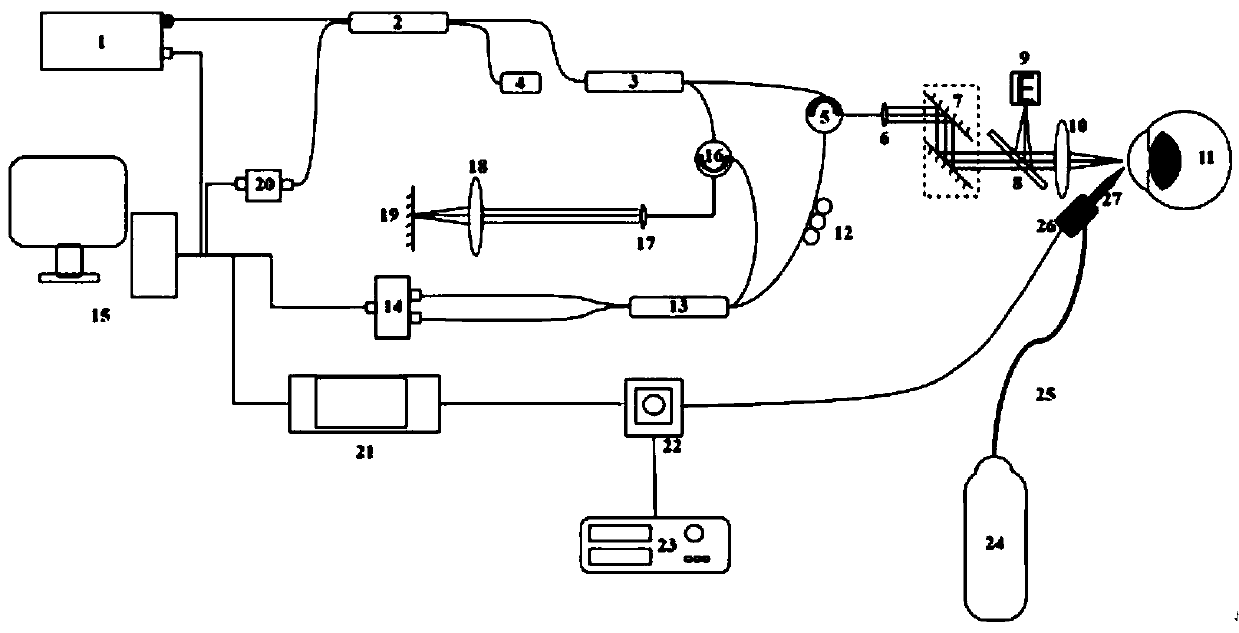
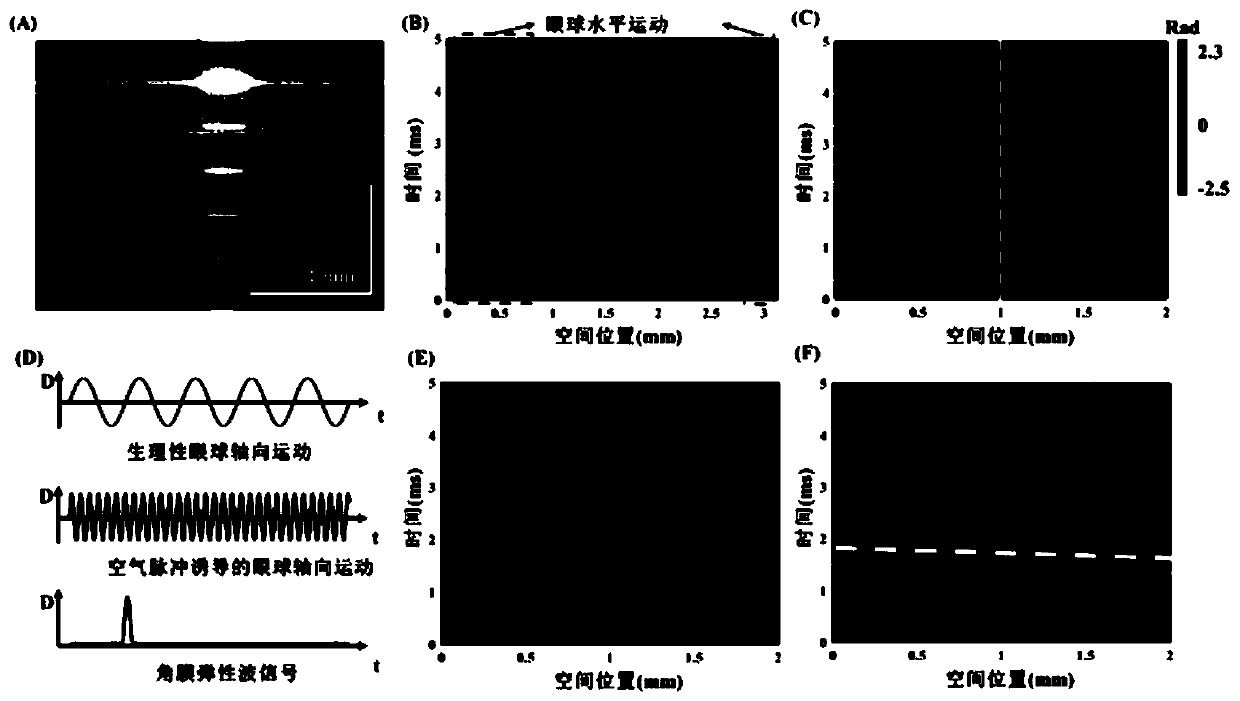
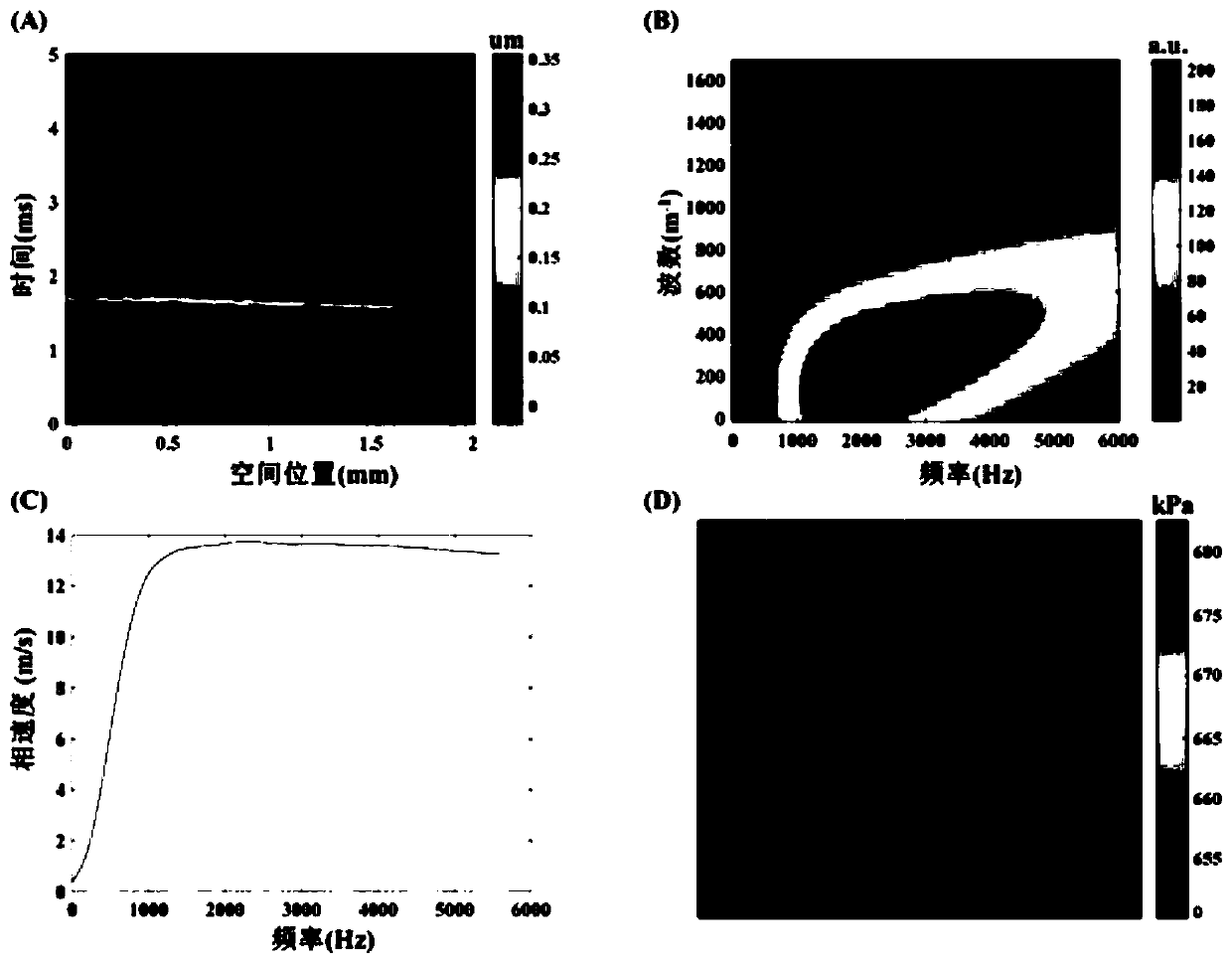
Method for measuring elasticity modulus of in-vivo human cornea based on jet-propelled optical coherence elasticity imaging technology
The invention discloses a method for measuring the elasticity modulus of an in-vivo human cornea based on a jet-propelled optical coherence elasticity imaging technology. Doppler images of different cross sections of an in-vivo corneal tissue are acquired by using an optical coherence tomography (OCE) technology; elastic wave information in the cornea tissue is extracted through a human eye eyeball movement artifact correction algorithm; and the elasticity modulus of the cornea tissue is estimated according to a lamb wave model. Therefore, a problem that in-vivo human cornea elasticity imagingis difficult to realize through the existing OCE is solved.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
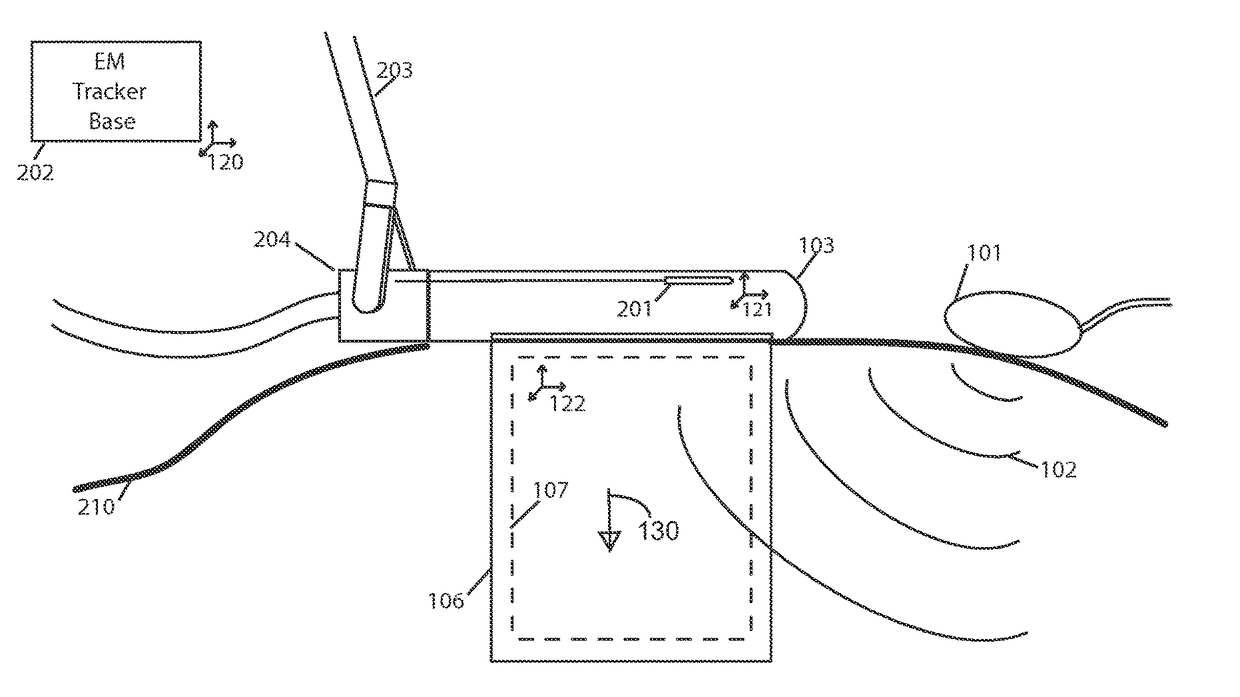
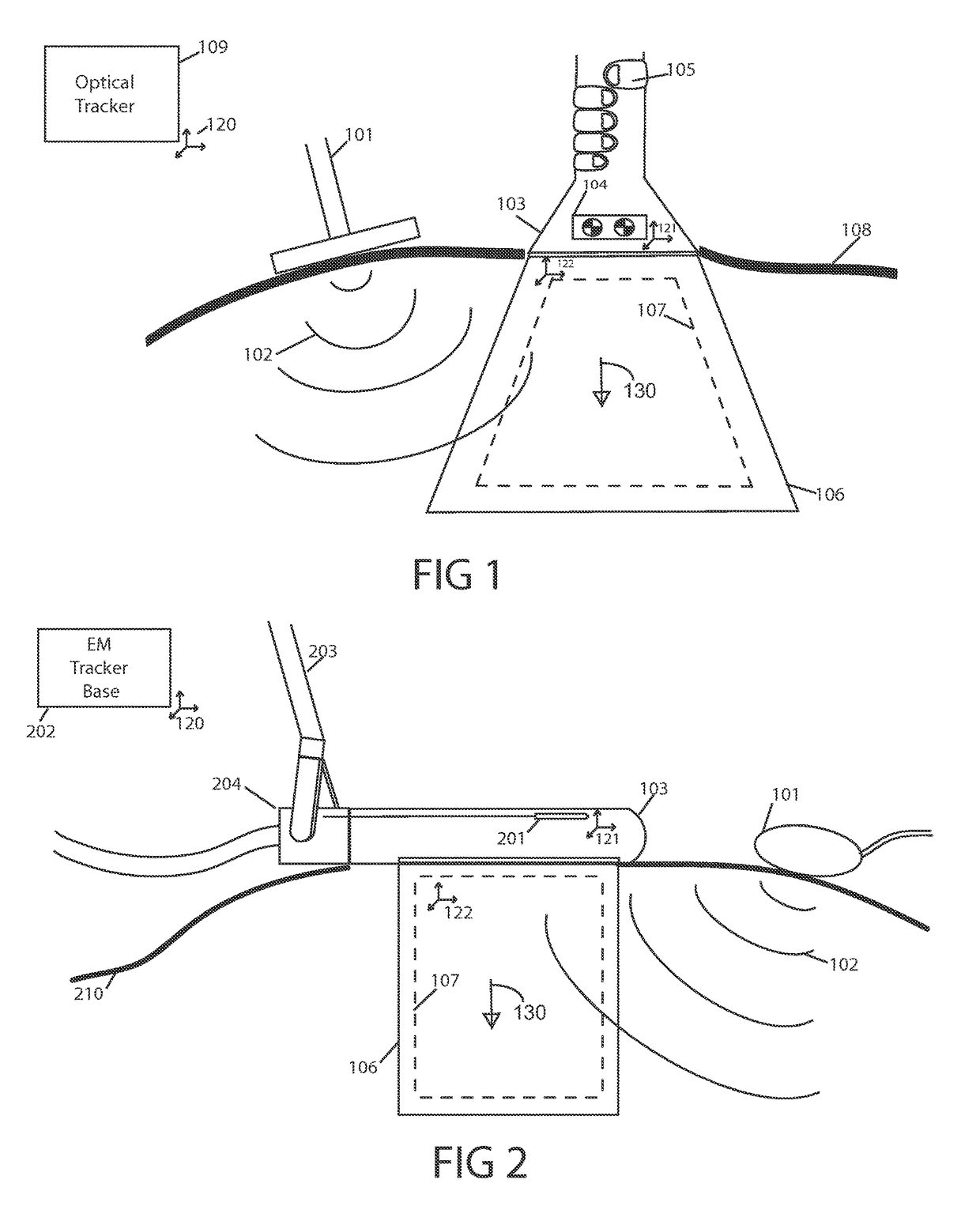
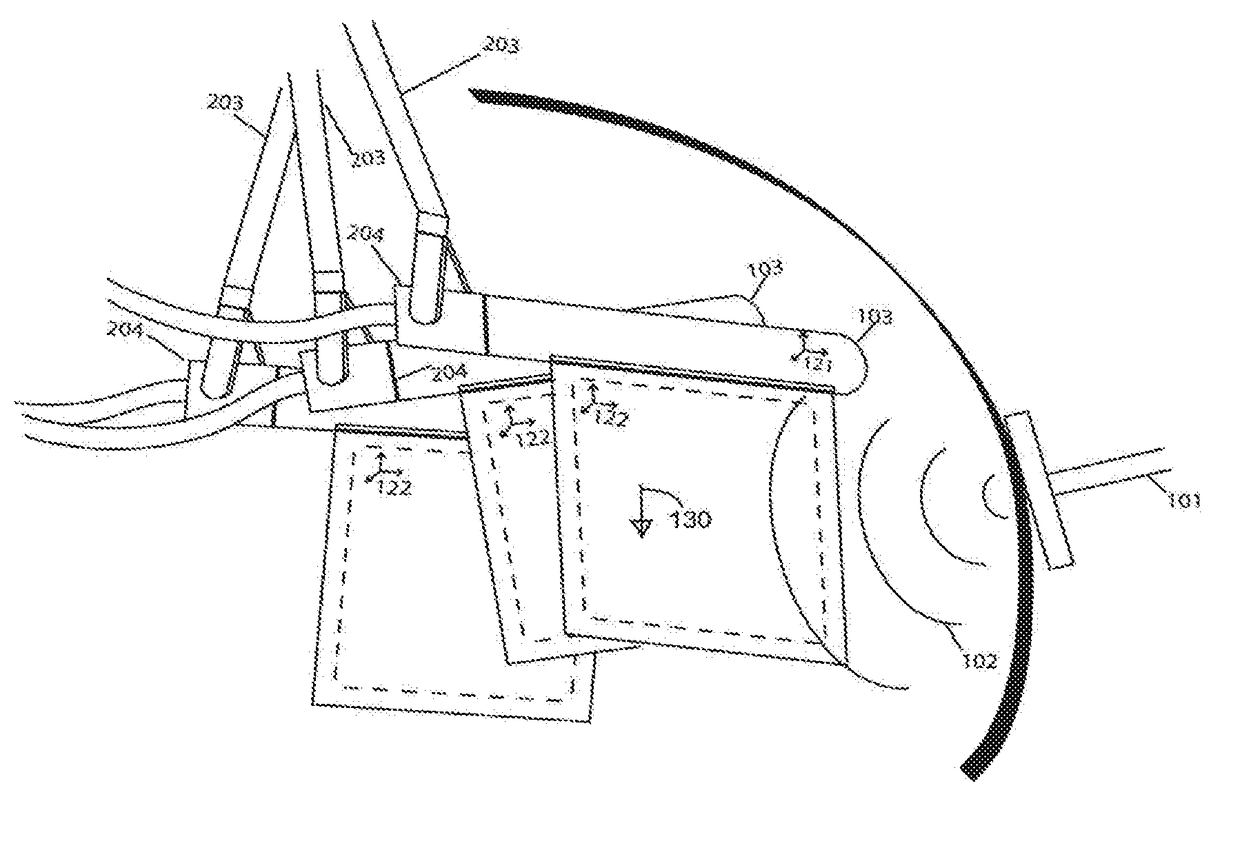
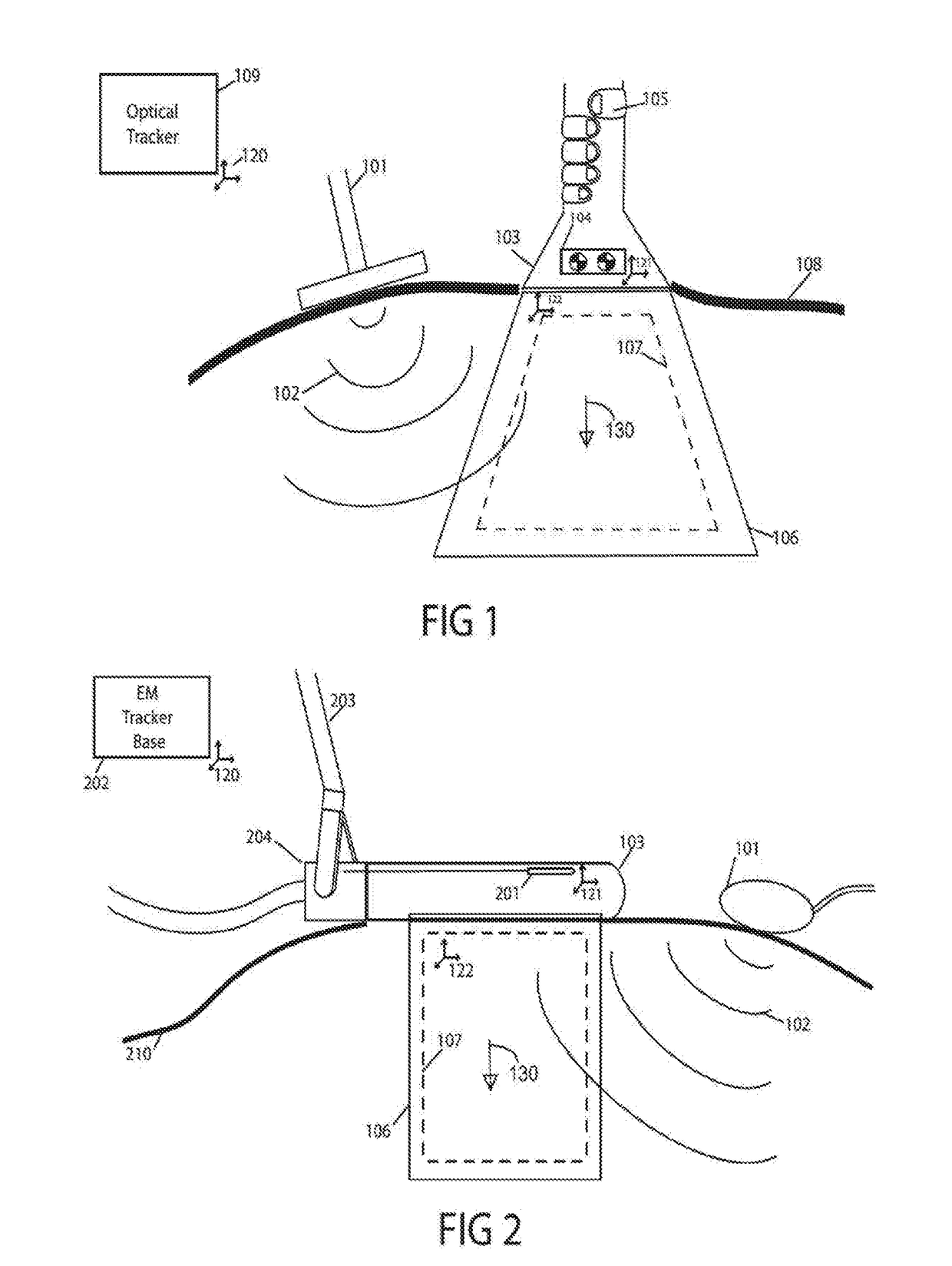
Quantitative elastography with tracked 2D ultrasound transducers
A method is described for acquiring 3D quantitative ultrasound elastography volumes. In one embodiment, the method comprises using a 2D ultrasound transducer to scan a volume of tissue through which shear waves are created using an external vibration source, the synchronized measurement of tissue motion within the plane of the ultrasound transducer with the measurement of the transducer location in space, the reconstruction of tissue displacements in time and space over a volume from this synchronized measurement, and the computation of one or several mechanical properties of tissue from this volumetric measurement of displacements. The tissue motion in the plane of the transducer may be measured at a high effective frame rate in the axial direction of the transducer, or in the axial and lateral directions of the transducer. The tissue displacements over the measured volume may be interpolated over a regular grid in order to make the computation of mechanical properties easier.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
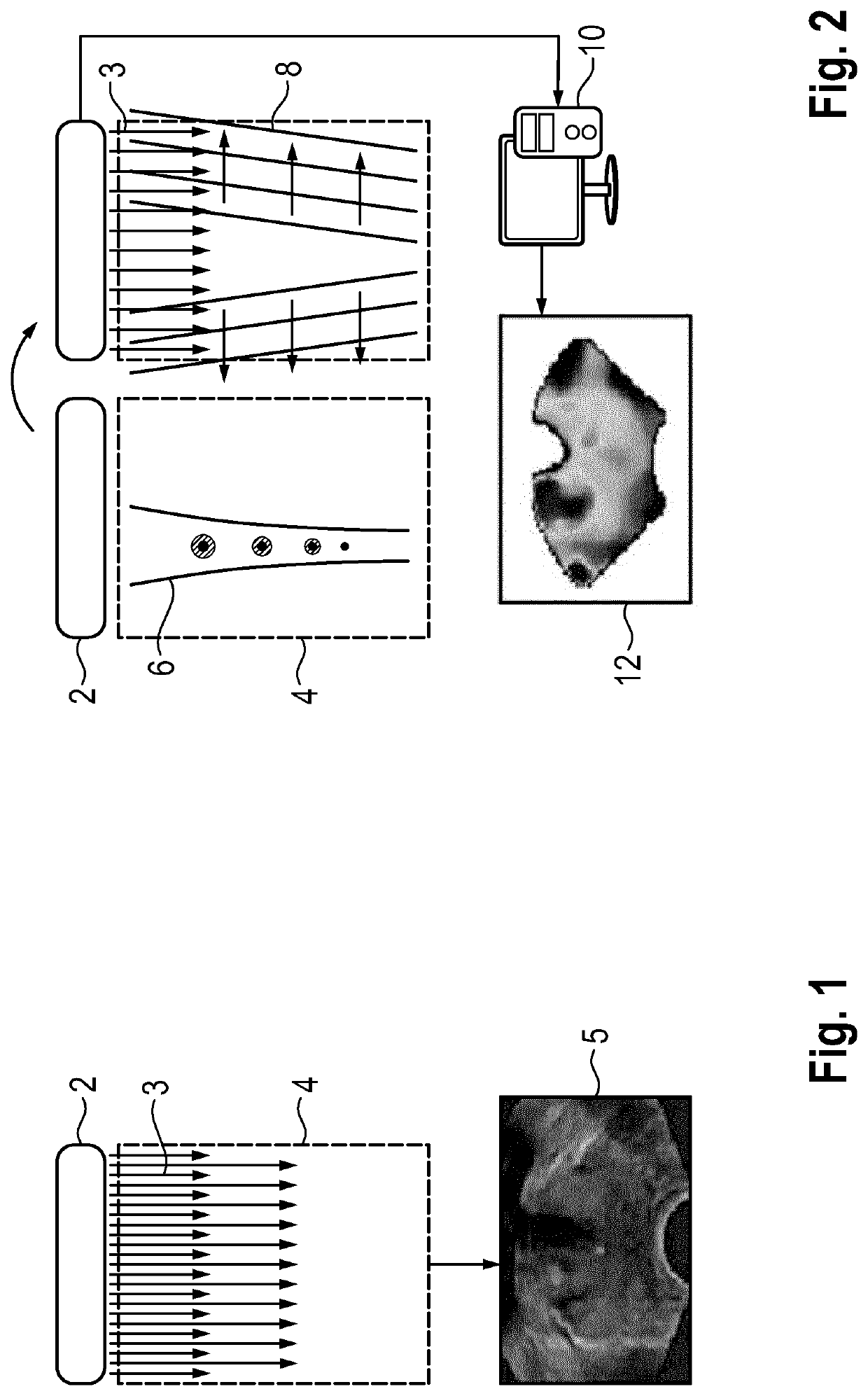
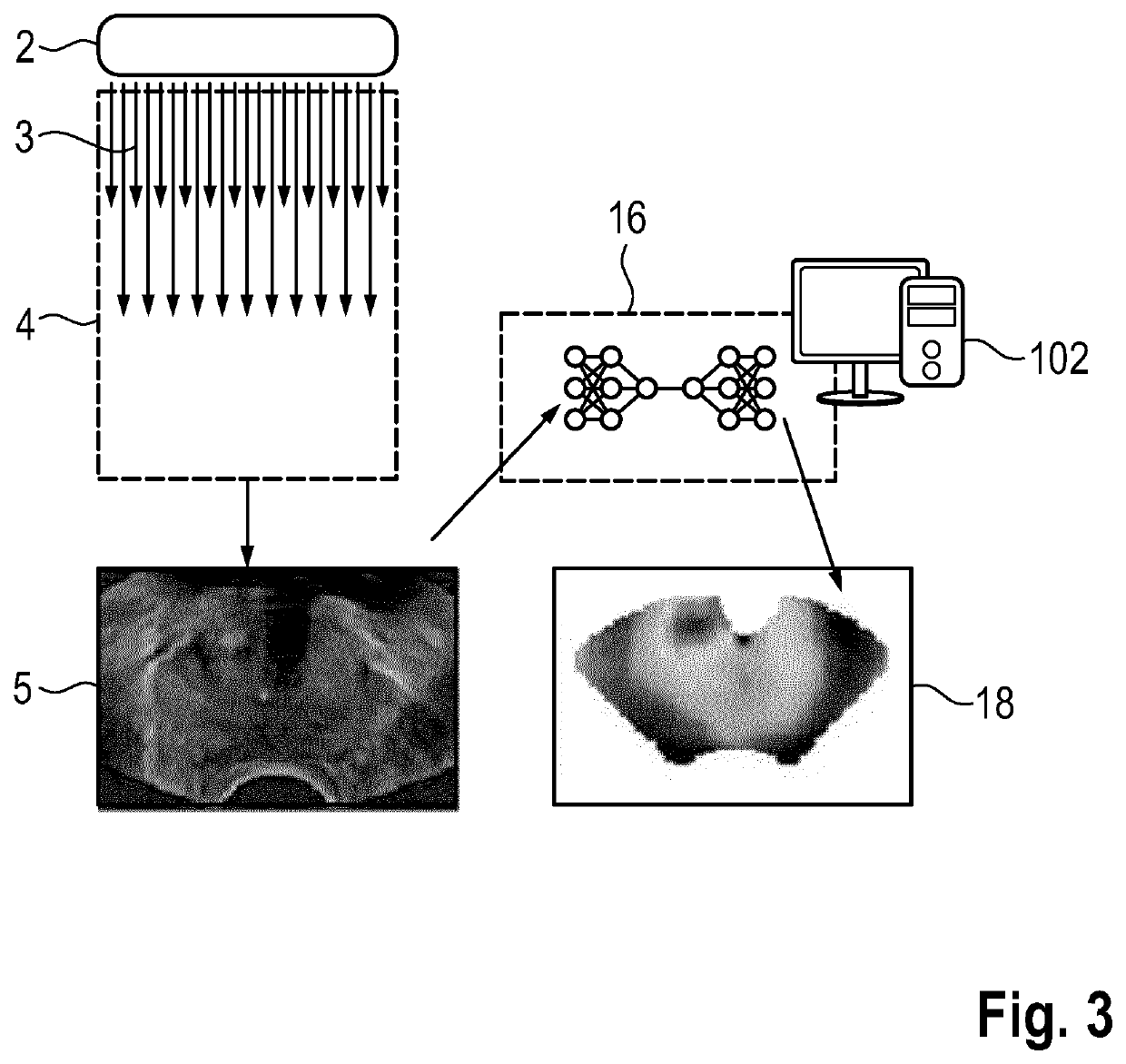
Method and system for generating a synthetic elastrography image
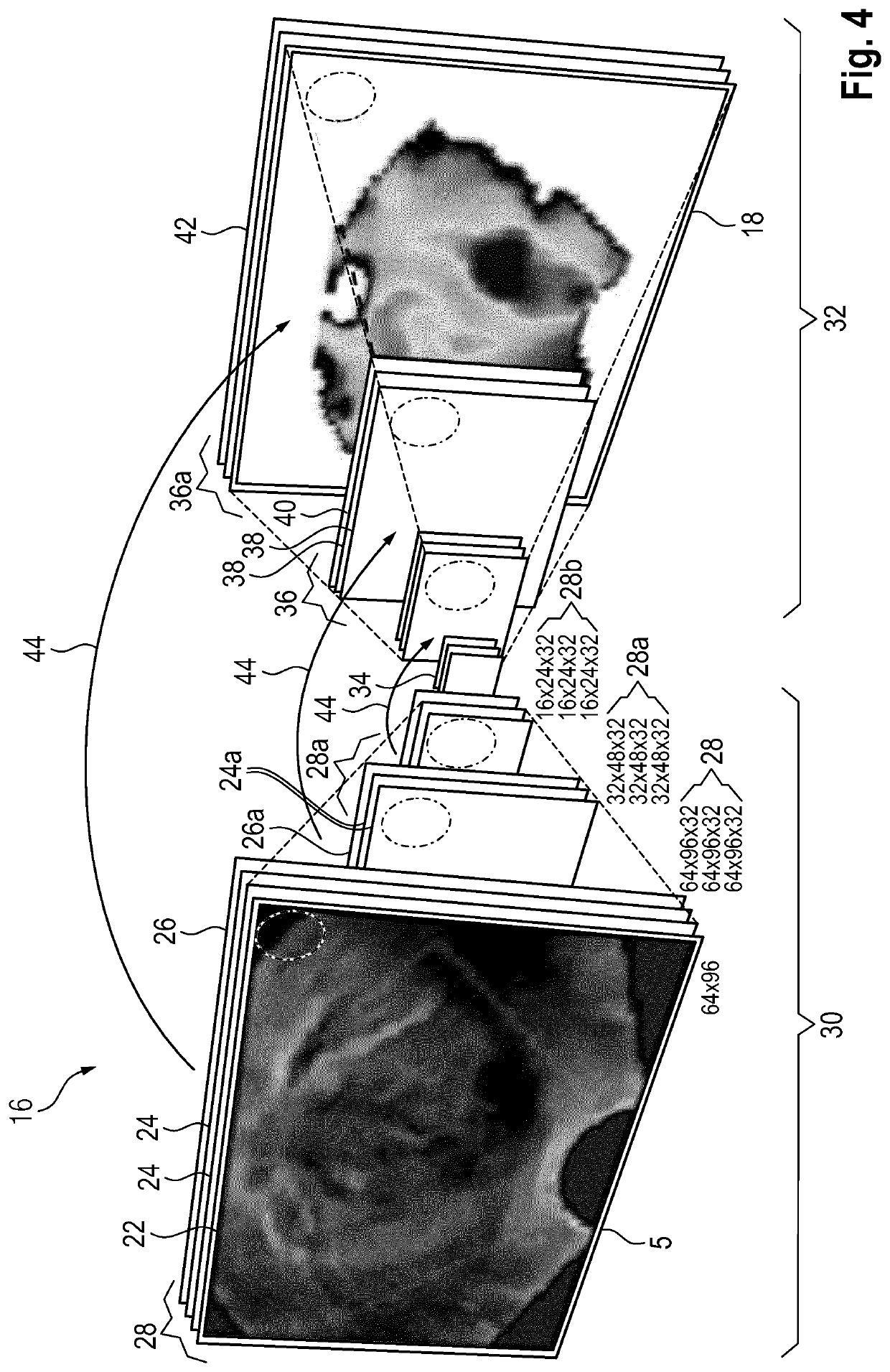
PendingUS20220361848A1Robust synthesisReduce computing costImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionEngineeringComputer science
The invention relates to a method for generating a synthetic elastography image (18), the method comprising the steps of (a) receiving a B-mode ultrasound image (5) of a region of interest; (b) generating a synthetic elastography image (18) of the region of interest by applying a trained artificial neural network (16) to the B-mode ultrasound image (5). The invention also relates to a method for training an artificial neural network (16)5 useful in generating synthetic elastography images, and a related computer program and system.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ultrasonic detection probe
PendingCN114271855AReduce transmissionSmall attenuationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsTransducerEngineering
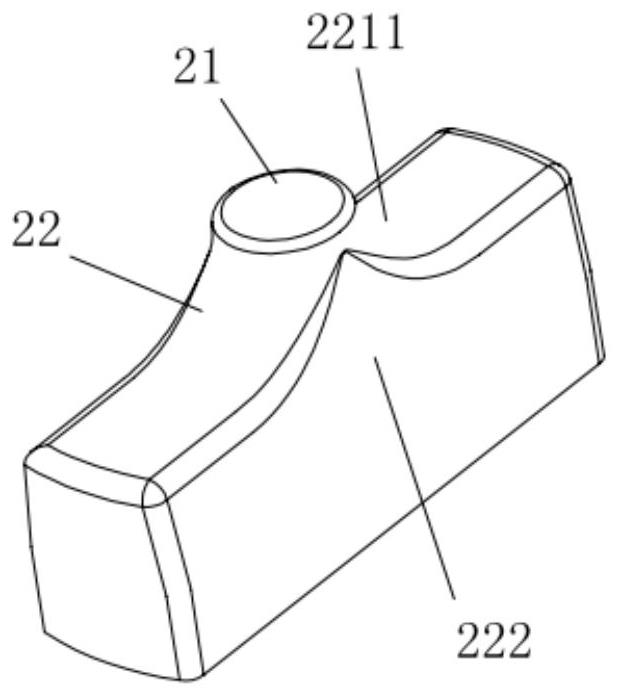
The invention discloses an ultrasonic detection probe. The ultrasonic detection probe comprises a shell; an ultrasonic transducer; the sound transmission structure is arranged at the front end of the ultrasonic transducer; the driving assembly is arranged in the shell, and the driving assembly is used for driving the sound transmission structure; wherein the sound transmission structure is provided with a first cavity, and a sound transmission medium is arranged in the first cavity. When the driving assembly drives the sound transmission structure to vibrate, shear waves are generated in the detection target, and more ultrasonic signals emitted by the ultrasonic transducer can be propagated in the sound transmission medium through the sound transmission medium in the sound transmission structure, so that propagation in the sound transmission structure is reduced, attenuation of the ultrasonic signals can be reduced, and the detection accuracy is improved. And thus, the elasticity imaging detection quality is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGYUEYILIAO TECH CO LTD
High-intensity focused ultrasound thermal ablation apparatus having integrated temperature estimation and elastography for thermal lesion determination and the method thereof
ActiveUS9643030B2Improve performanceIncrease elasticityUltrasound therapyHealth-index calculationExAblateRadiology
The invention disclosed a high-intensity focused ultrasound thermal ablation apparatus having integrated temperature estimation and elastography for thermal lesion determination and the method thereof, using the different power to burn by the same focused ultrasound transducer, and then using the apparatus to measure the temperature and elasticity estimating by the relevant analysis method.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Ultrasonic probe
PendingCN114098821AIncrease the areaRelieve stressOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic sensorTransducer
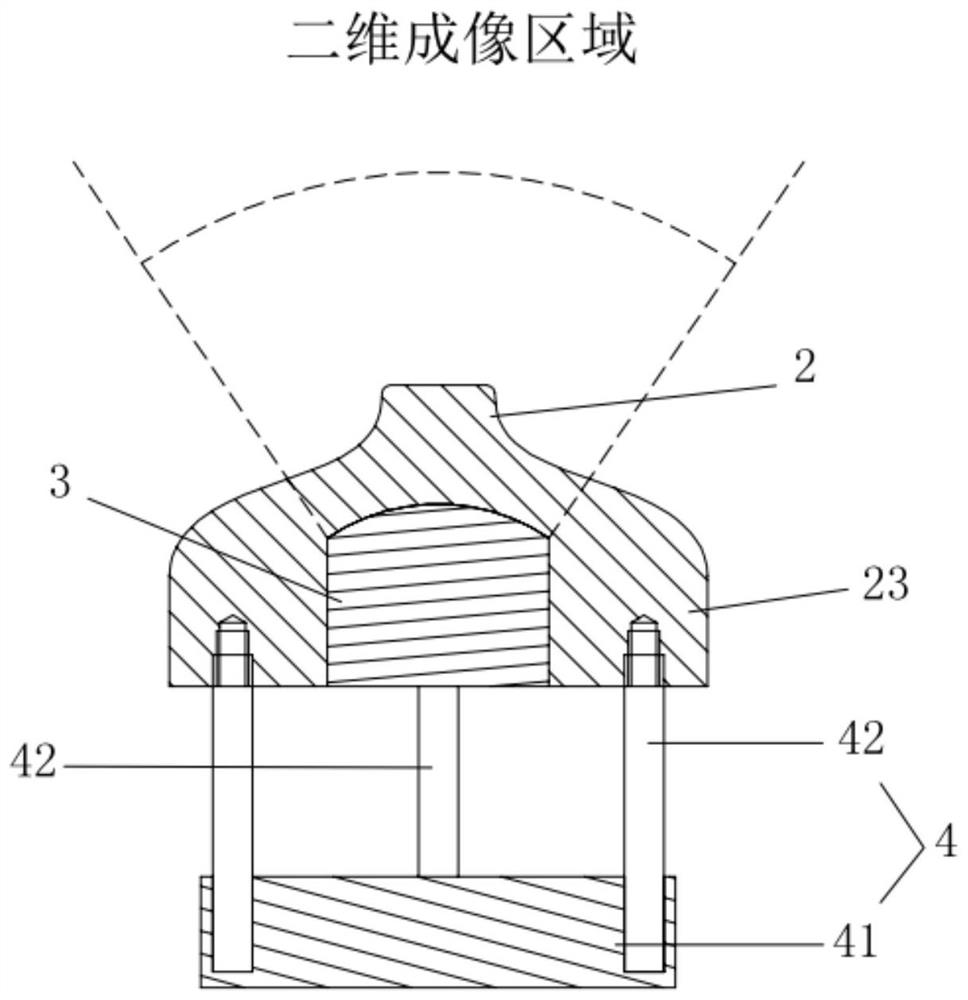
The invention discloses an ultrasonic probe. The ultrasonic probe comprises a shell; an ultrasonic transducer; a convex part is arranged at the top of the sound transmission structure, and the sound transmission structure is arranged at the front end of the ultrasonic transducer; the driving assembly is arranged in the shell and is used for driving the sound transmission structure; and the curved surface structure extends from the end face of the convex part to the edge of the sound transmission structure, first curved surfaces are formed on the left side and the right side of the convex part, each first curved surface comprises a concave curved surface section, and the concave curved surface sections extend downwards along the left side and the right side of the end face of the convex part. According to the invention, the two-dimensional imaging effect can be improved while high-quality instantaneous elastography detection is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGYUEYILIAO TECH CO LTD
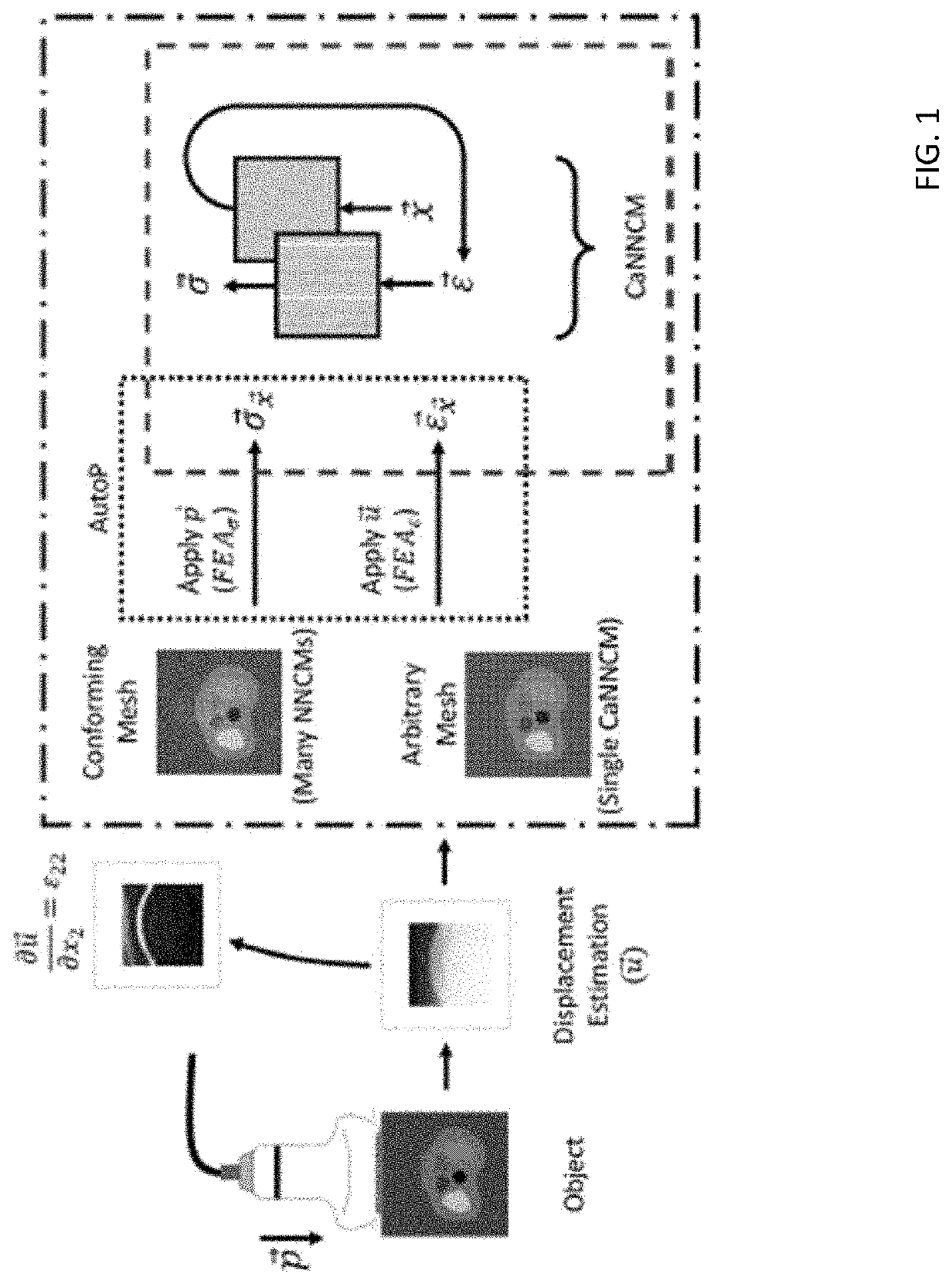
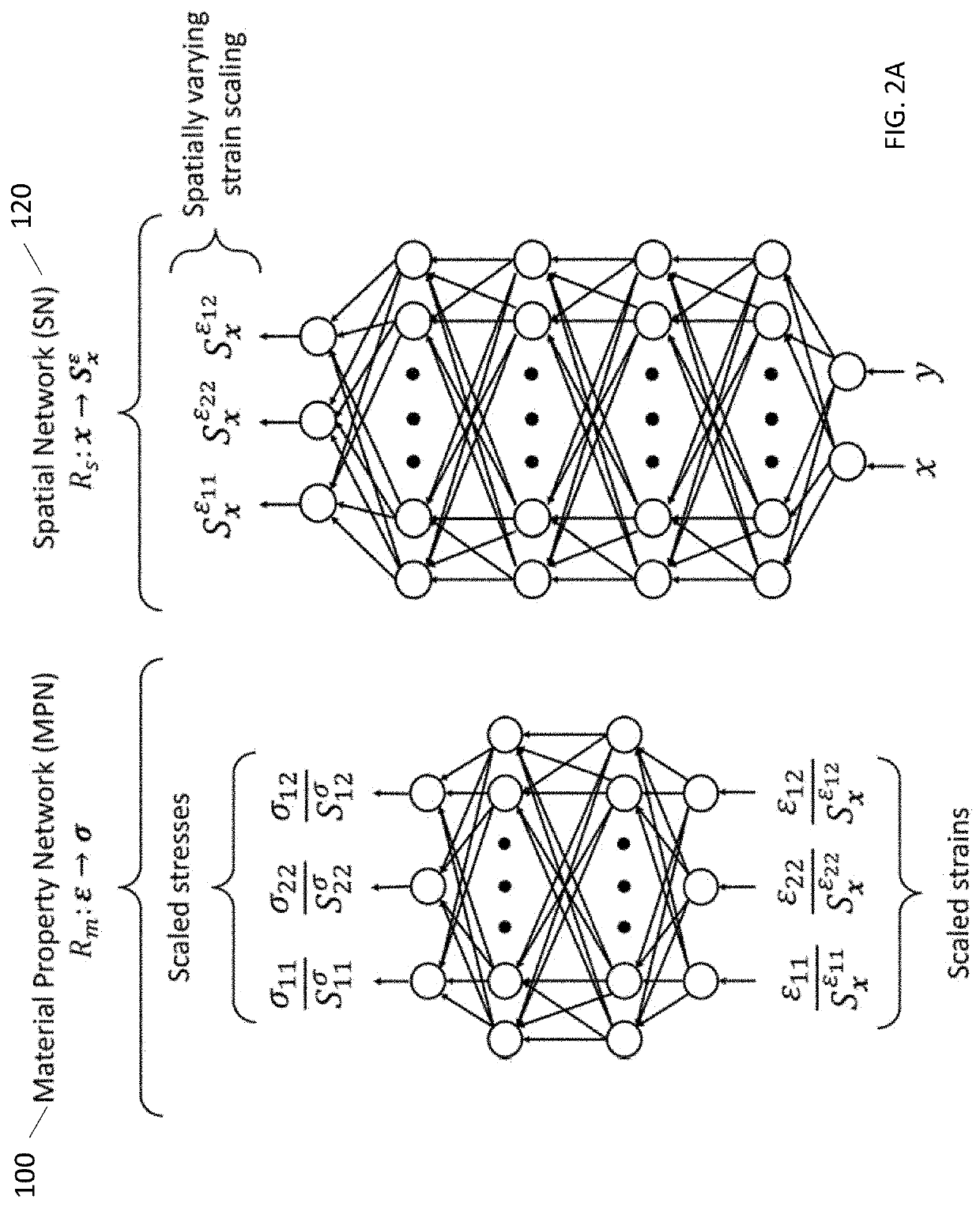
Data-Driven Elasticity Imaging
Systems and methods are provided for employing informational models trained using the Autoprogressive Algorithm to learn the mechanical behavior and internal structure of biological materials using a sparse sampling of force and displacement measurements. Forces are applied to the biological material and the force and displacement are measured and applied to the AutoP algorithm. Additionally, a coordinate based scaling factor is applied to the measured displacement.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
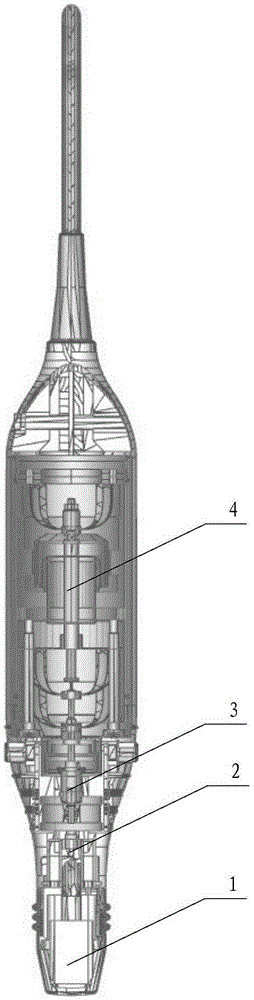
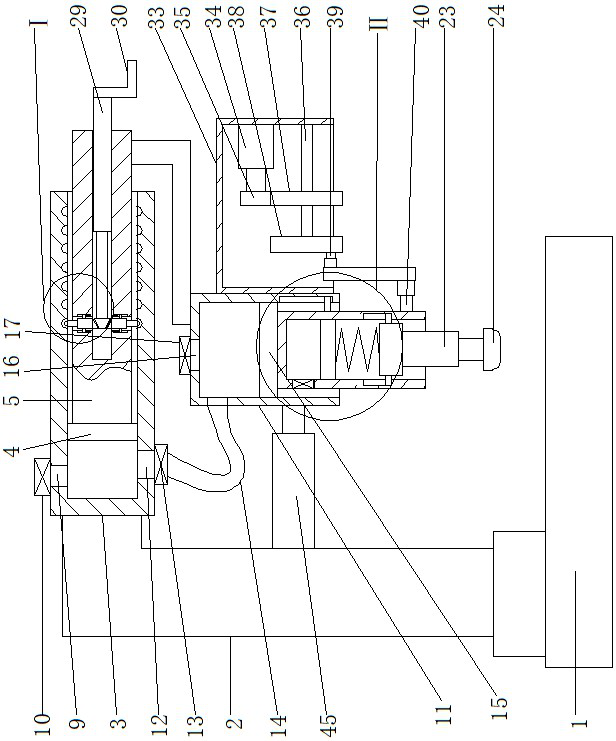
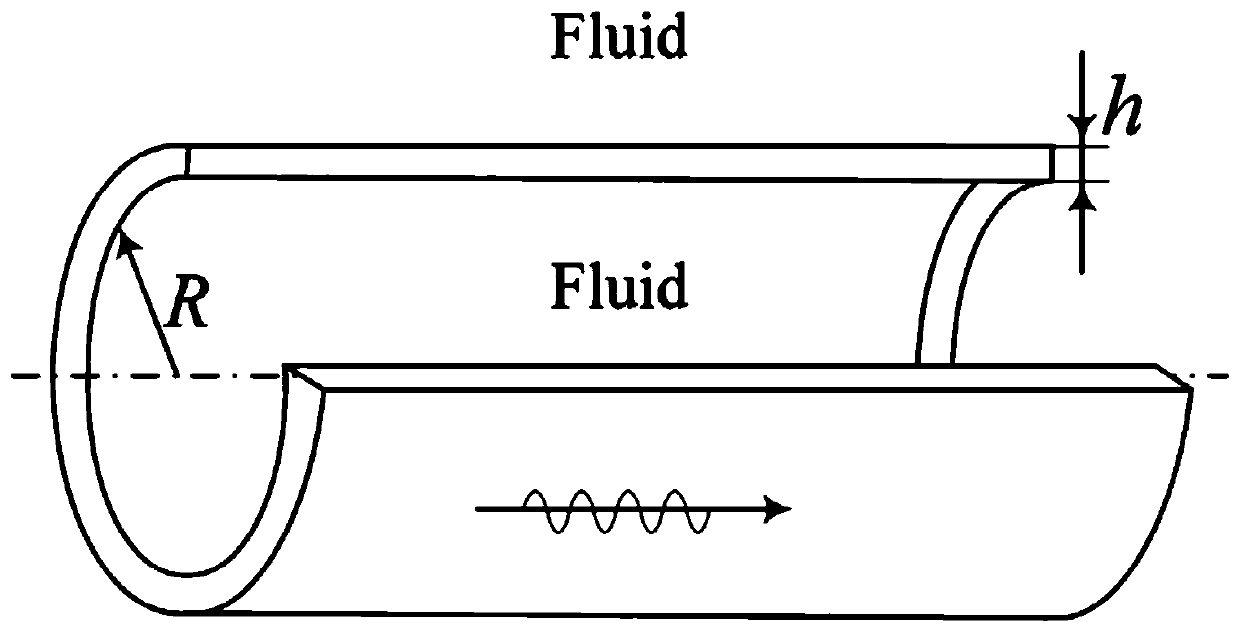
Device and method for measuring the viscoelastic properties of a viscoelastic medium
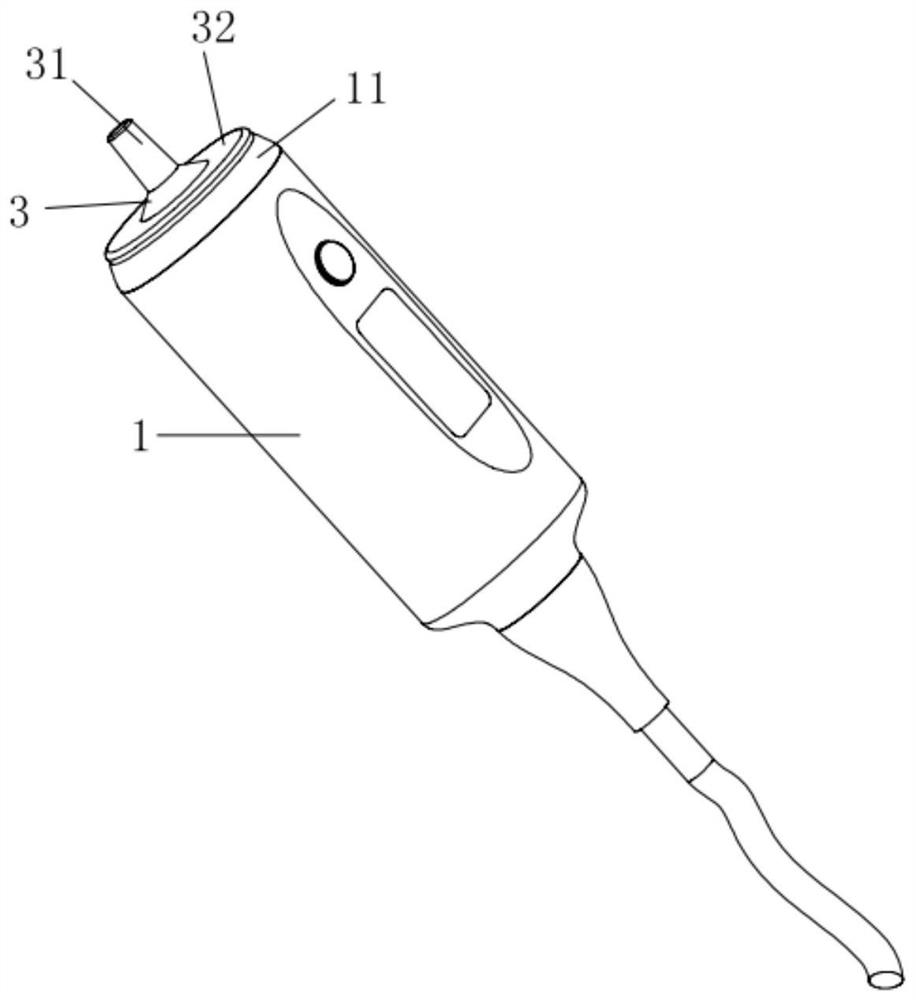
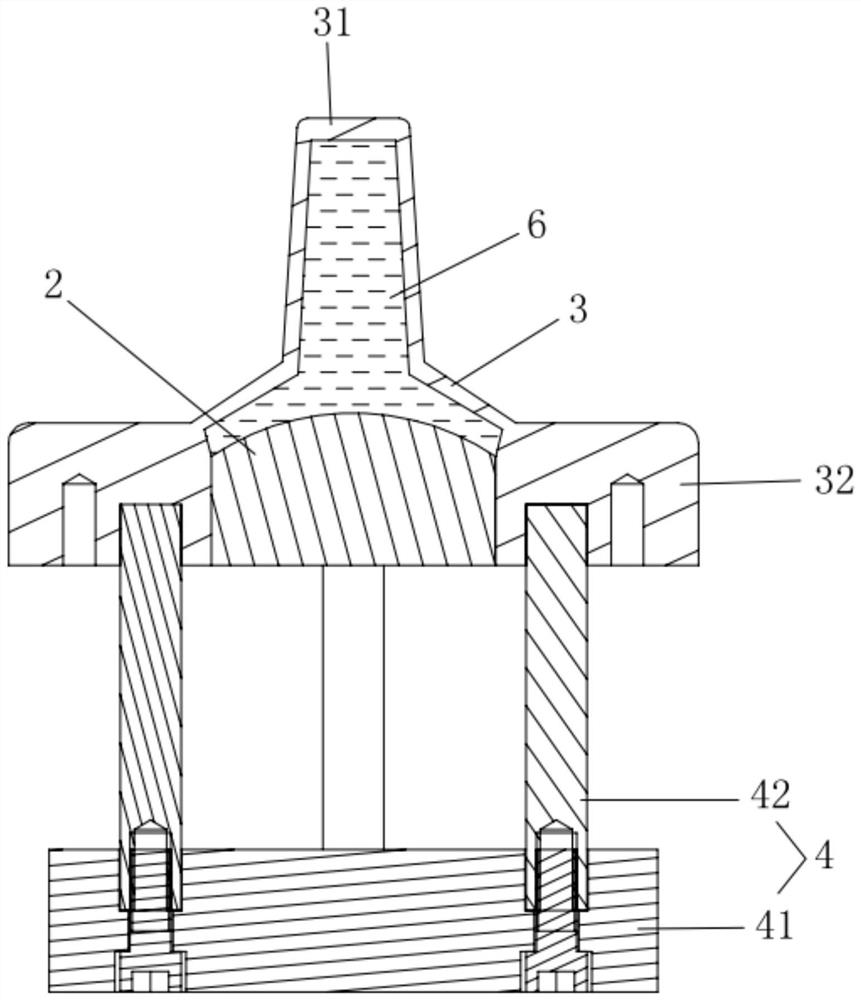
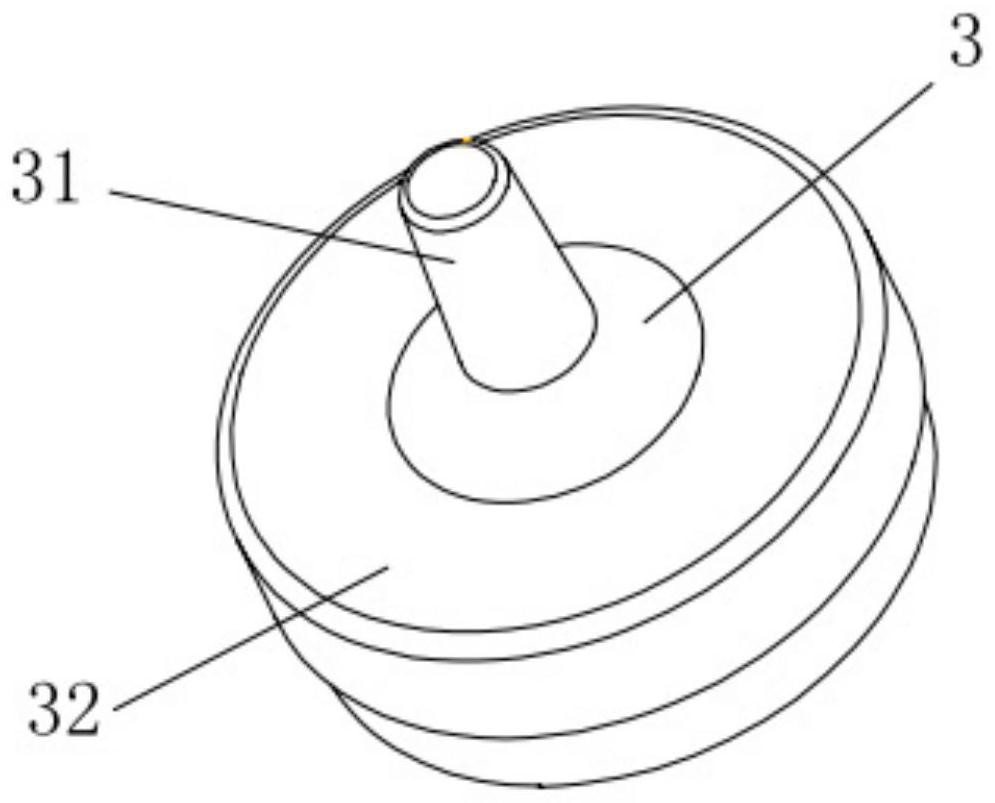
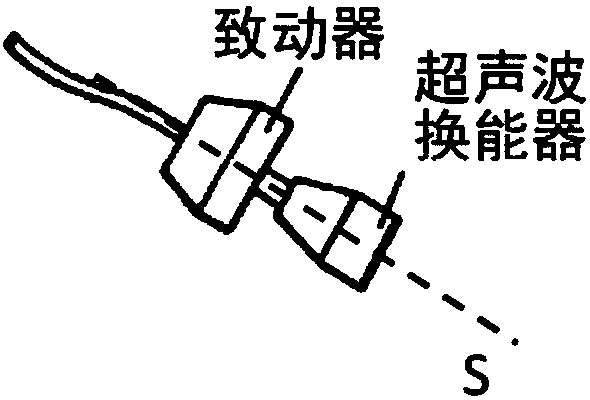
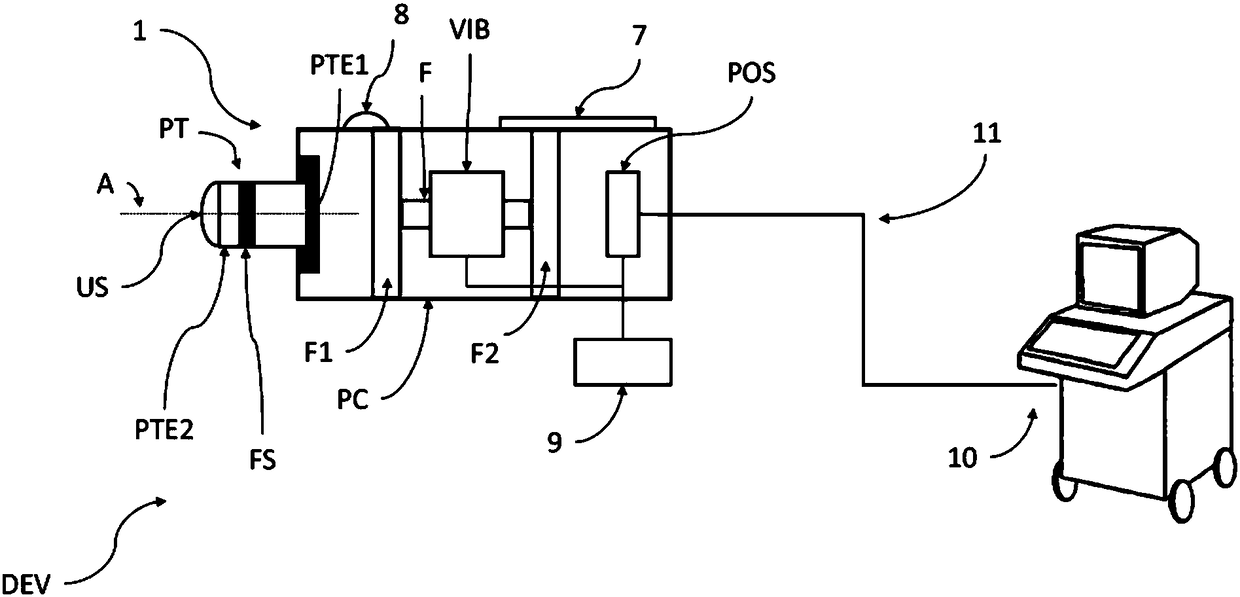
ActiveCN108652667AMotion monitoringOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTransducerSignal generator
The invention relates to a device (DEV) and a method for measuring the viscoelastic properties of a viscoelastic medium, and the medium has ultrasonic signals after receiving ultrasonic wave pulses. The device comprises: at least one probe (1) for elastography, comprising at least one ultrasonic transducer (2) constructed and arranged to transmit and receive ultrasonic signals, a movable tip (3) constructed and arranged to be embedded in the end of the ultrasonic transducer (2), and an electric actuator (4) constructed and configured to cause displacement of the movable tip (3). The device (DEV) comprises a signal generator (9) that emits a contact completion signal when the transducer (2) of the ultrasonic probe (1) contacts the viscoelastic medium to be measured.
Owner:ECHOSENS SA
Muscle ultrasonic elastography optimization method and system
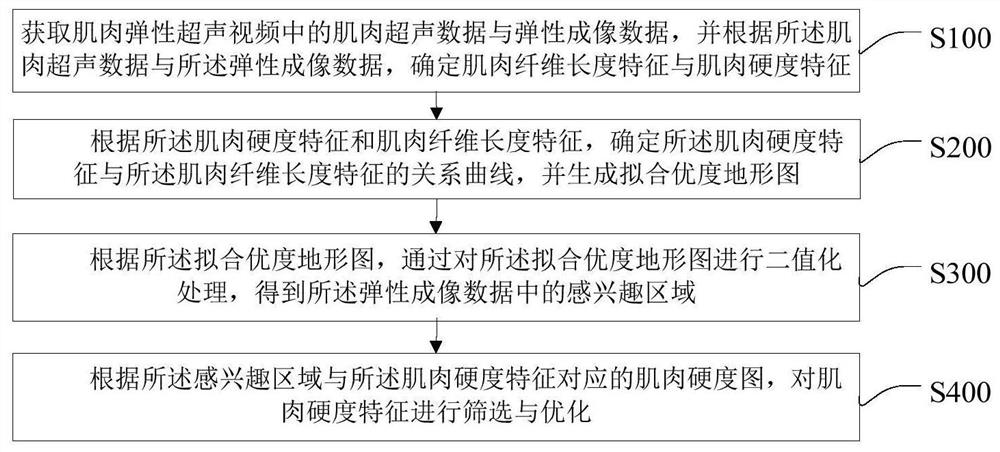
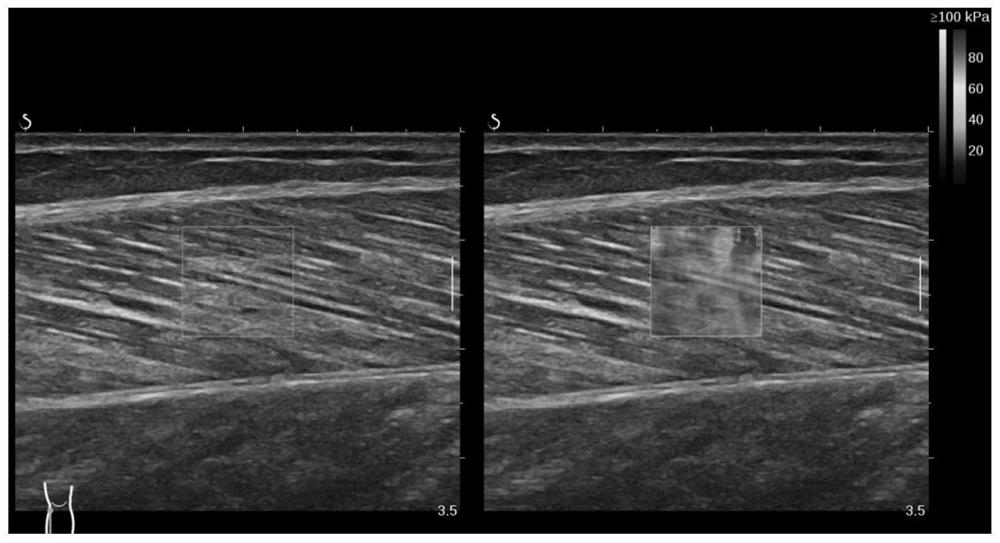
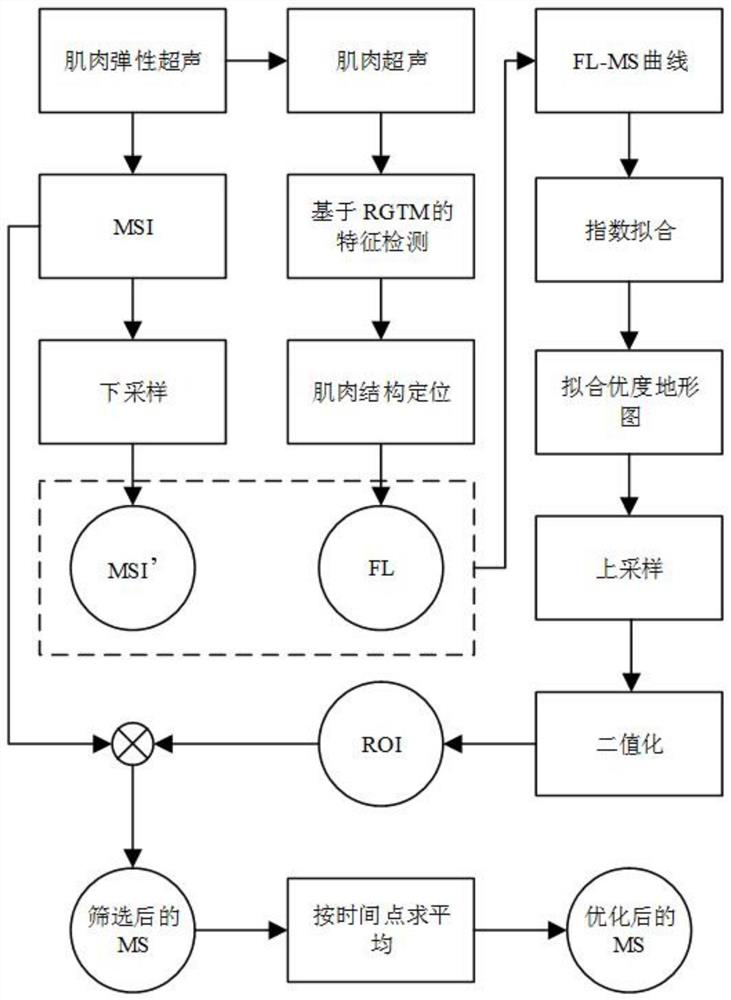
PendingCN112674791AEliminate noise interferenceReduce Spatial InhomogeneityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsTopographic mapBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a muscle ultrasonic elastography optimization method and system. The method comprises the steps as follows: obtaining elastography data and muscle ultrasonic data in a muscle elasticity ultrasonic video, and determining muscle hardness characteristics and muscle fiber length characteristics according to the elastography data and the muscle ultrasonic data; according to the muscle hardness characteristics and the muscle fiber length characteristics, determining a relation curve of the muscle hardness characteristics and the muscle fiber length characteristics, and generating a goodness-of-fit topographic map; according to the goodness-of-fit topographic map, performing binarization processing on the goodness-of-fit topographic map to obtain a region of interest in the elastography data; and screening and optimizing the muscle hardness characteristics according to a muscle hardness diagram corresponding to the region of interest and the muscle hardness characteristics. According to the muscle ultrasonic elastography optimization method and system, physiological characteristics of muscles subjected to ultrasonic elastography can be fully utilized, the region of interest of muscle ultrasonic elastography is automatically selected, and therefore, noise interference in the muscle ultrasonic elastography is eliminated.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Vascular guided wave elastography method and system based on machine learning
ActiveCN109567872BHigh measurement accuracyImprove scalabilityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsElement analysisFinite element software
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultrasonic imaging method and system
PendingCN112773403AEasy to operateImprove accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingRadiology
An ultrasonic imaging method comprises the following steps of emitting an ultrasonic wave to interested target tissue in a contrast imaging manner, and receiving an echo signal, to obtain contrast images of the interested target tissue within a period of time; determining a reference section in each contrast image, and meanwhile acquiring a tissue structure image corresponding to the reference section; emitting the ultrasonic wave to the interested target tissue to obtain current tissue structure images; matching the current tissue structure images with the tissue structure images corresponding to the reference sections, and determining to-be-examined section of current tissue structure images meeting the predetermined condition; emitting the ultrasonic wave to the interested target tissue in an elasticity imaging manner, to obtain an elasticity image of the interested target tissue on each to-be-examined section; and at least simultaneously displaying the contrast images of the reference sections and the elasticity images on the to-be-examined sections. Contrast imaging and elasticity imaging are carried out on a same section and the contrast images and the elasticity images are displayed at the same time, so that the operation process of a user is simplified, and the examination result is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
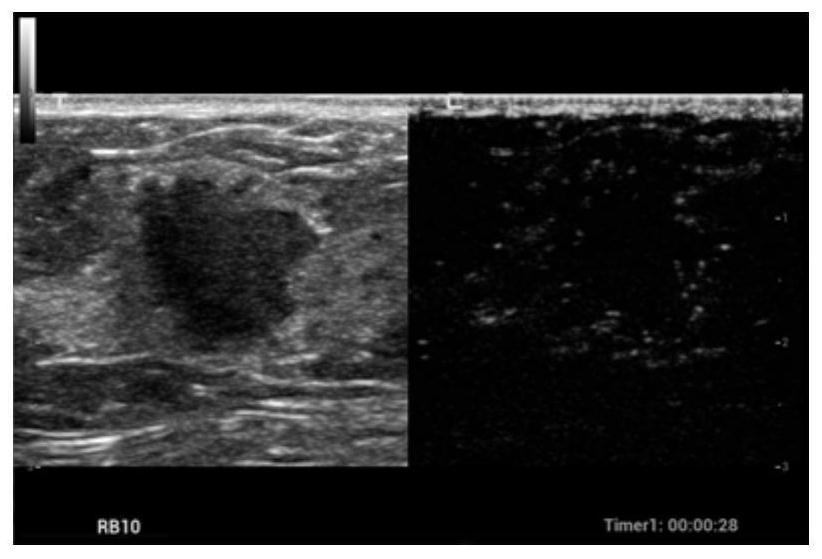
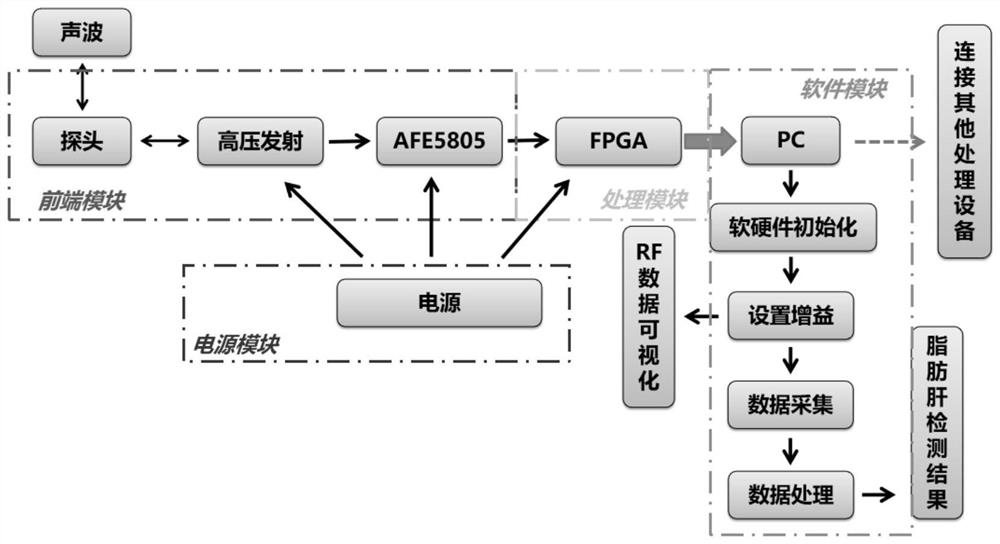
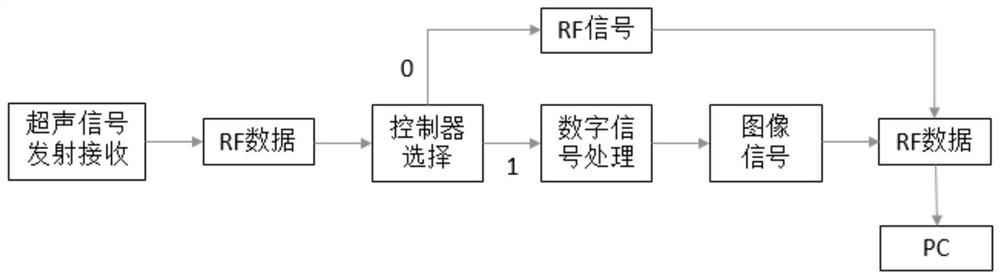
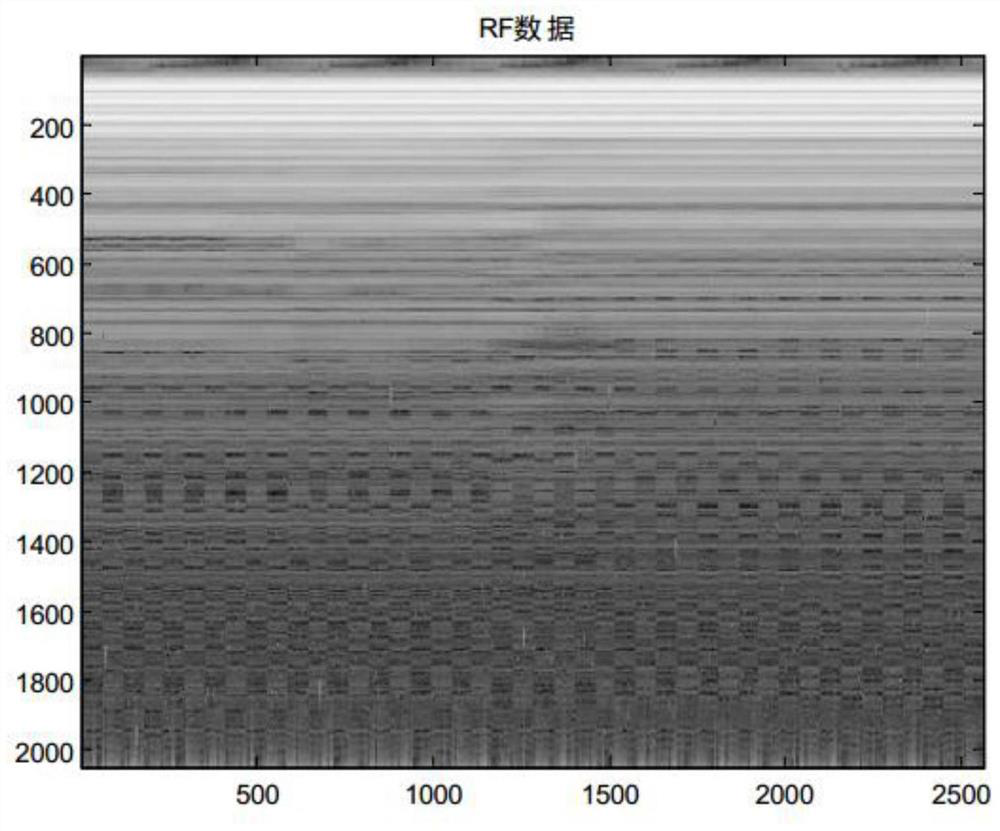
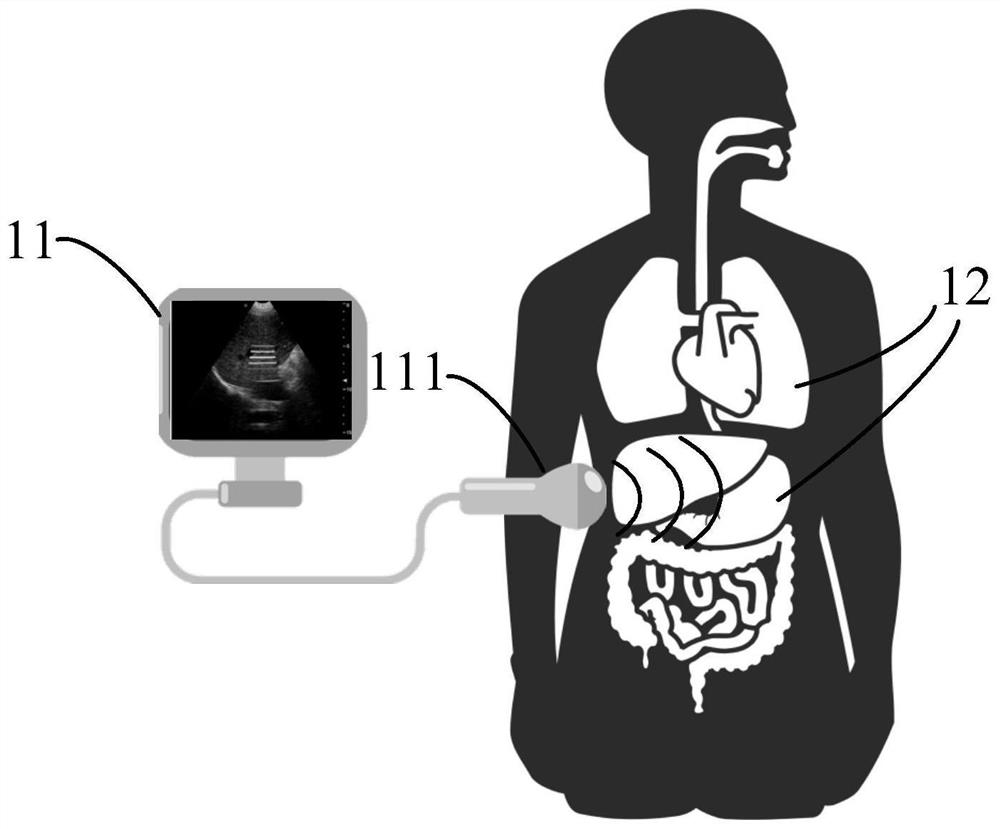
Portable fatty liver detection device based on ultrasound and data processing method thereof
PendingCN113662587AReduce transmit powerReduce complexityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsFatty liverMedical equipment
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, and particularly relates to a portable fatty liver detection device based on ultrasound and a data processing method thereof. Aiming at the difficulty in miniaturization and portability of an ultrasonic-based fatty liver detection device in the prior art, the invention provides a data processing method of the portable fatty liver detection device based on ultrasound, and the method comprises the following steps: enabling an ultrasonic probe to emit ultrasonic waves with at least two frequencies and receive ultrasonic echo data; performing beam forming on the ultrasonic echo data to obtain ultrasonic RF data; and finally, according to an instruction of a user, outputting the ultrasonic RF data, or performing post-processing on the ultrasonic RF data in the portable fatty liver detection device. The invention further provides a portable fatty liver detection device which is simple in structure, low in power and small in size. Under the condition that the requirement for the chip structure is extremely low, portable equipment can detect the fatty liver by obtaining an ultrasonic attenuation coefficient or an elastic imaging result and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICINE SCI
Quantitative elastography with tracked 2d ultrasound transducers
A method is described for acquiring 3D quantitative ultrasound elastography volumes. A 2D ultrasound transducer scans a volume of tissue through which shear waves are created using an external vibration source, the synchronized measurement of tissue motion within the plane of the ultrasound transducer with the measurement of the transducer location in space, the reconstruction of tissue displacements and / or tissue velocities in time and space over a volume from this synchronized measurement, and the computation of one or several mechanical properties of tissue from this volumetric measurement of displacements. The tissue motion in the plane of the transducer may be measured at a high effective frame rate in the axial direction of the transducer, or in the axial and lateral directions of the transducer. The tissue displacements and / or tissue velocities over the measured volume may be interpolated over a regular grid in order to facilitate computation of mechanical properties.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
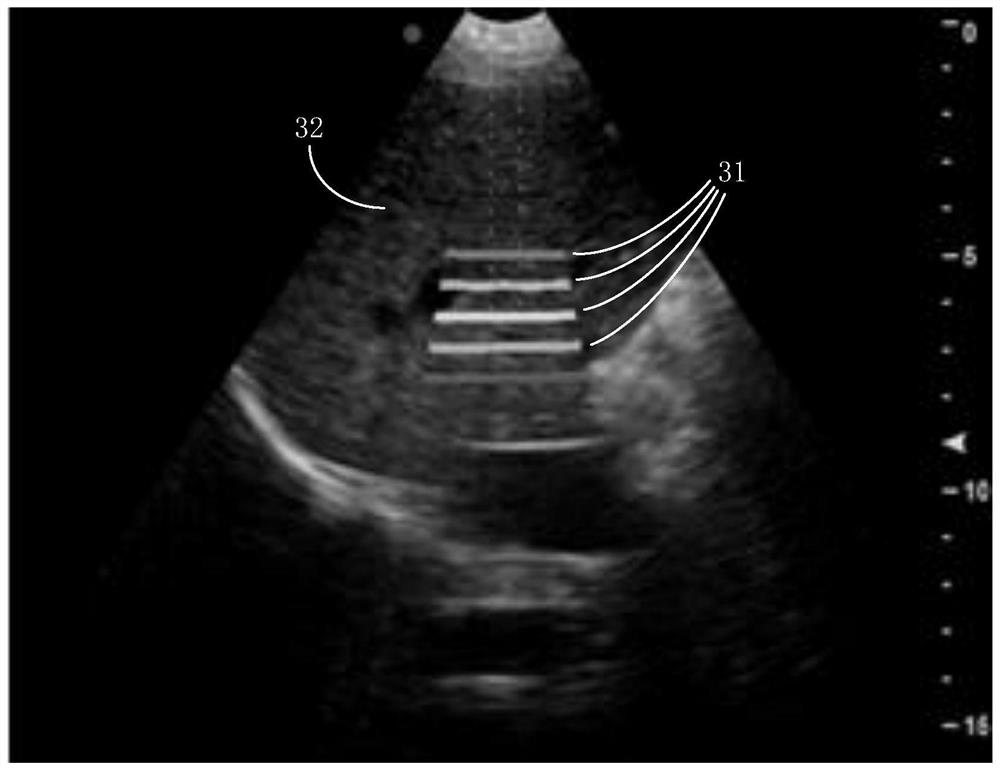
Elastic imaging method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113081038AImprove accuracyRapid quality control test resultsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHuman bodySignal quality
The embodiment of the invention provides an elastic imaging method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: applying vibration excitation to a to-be-detected tissue, and carrying out the ultrasonic detection, thereby obtaining an ultrasonic echo signal; according to the ultrasonic echo signal, an ultrasonic detection image and an elasticity detection image are generated, and the elasticity detection image is used for representing tissue elasticity detection information and the signal quality of the ultrasonic detection signal at the corresponding moment; according to the position relation between the test region corresponding to the ultrasonic detection image and the test region corresponding to the elasticity detection image, the ultrasonic detection image and the elasticity detection image are displayed in an overlapped mode, and after the ultrasonic detection image is generated, the elasticity detection image is displayed on the ultrasonic detection image in an overlapped mode. The imaging quality of the ultrasonic detection image is represented by using the elastic detection image, so that an operator can quickly control the quality of the detection result, the influence caused by the reasons such as poor test position and breath of the detected human body is eliminated, the ultrasonic imaging quality is improved, and the accuracy of the detection result is improved.
Owner:WUXI HISKY MEDICAL TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com