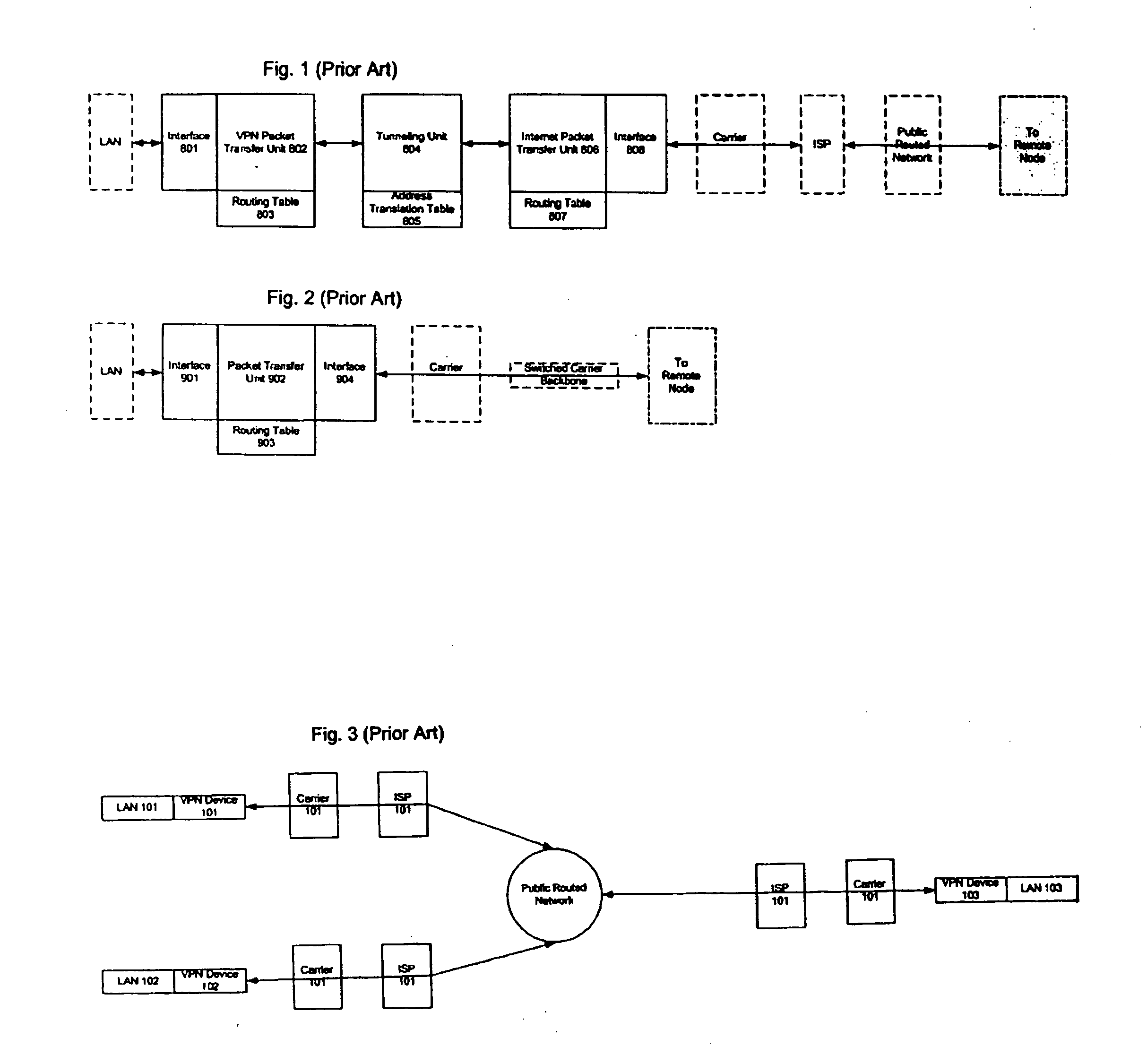
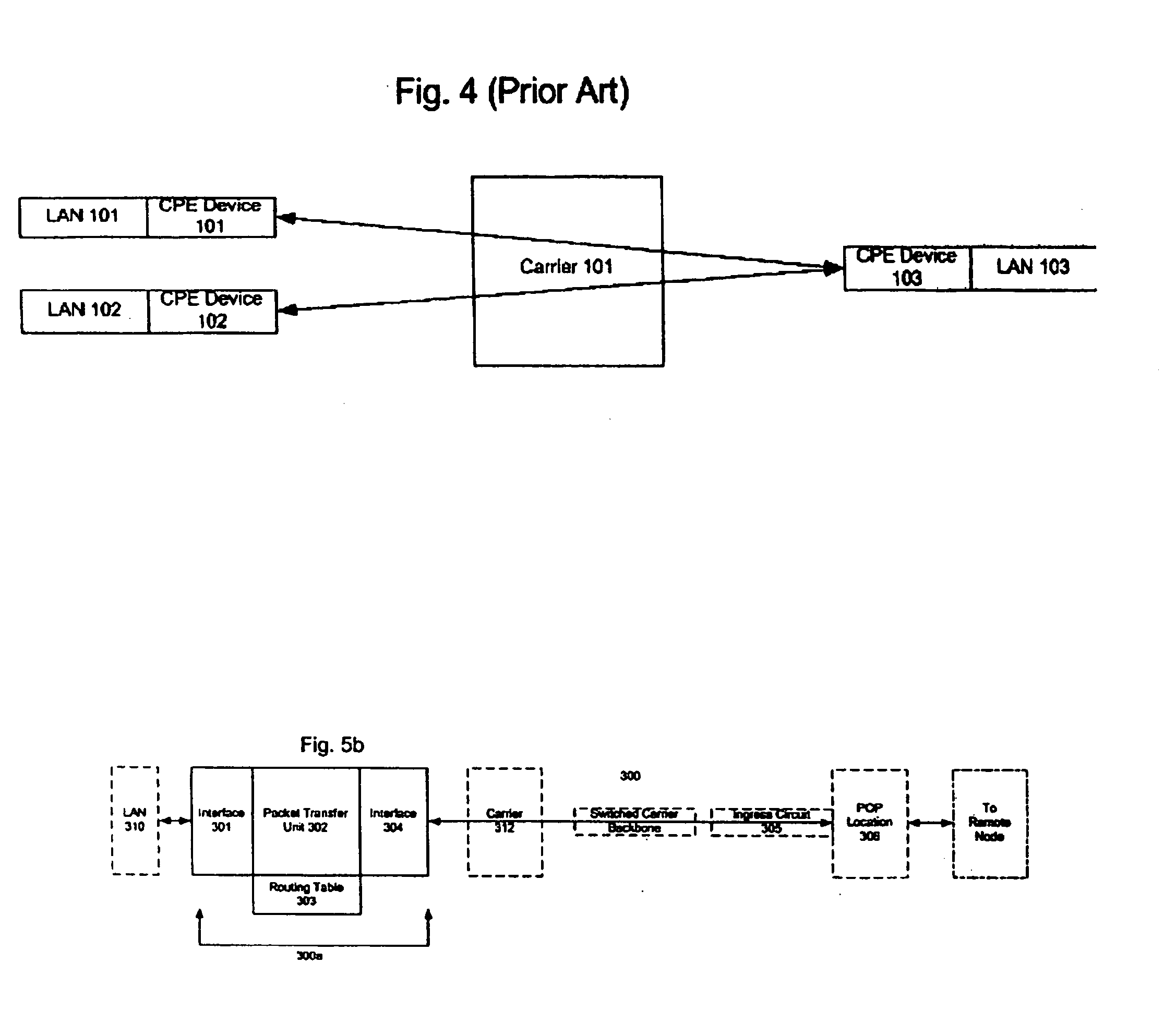
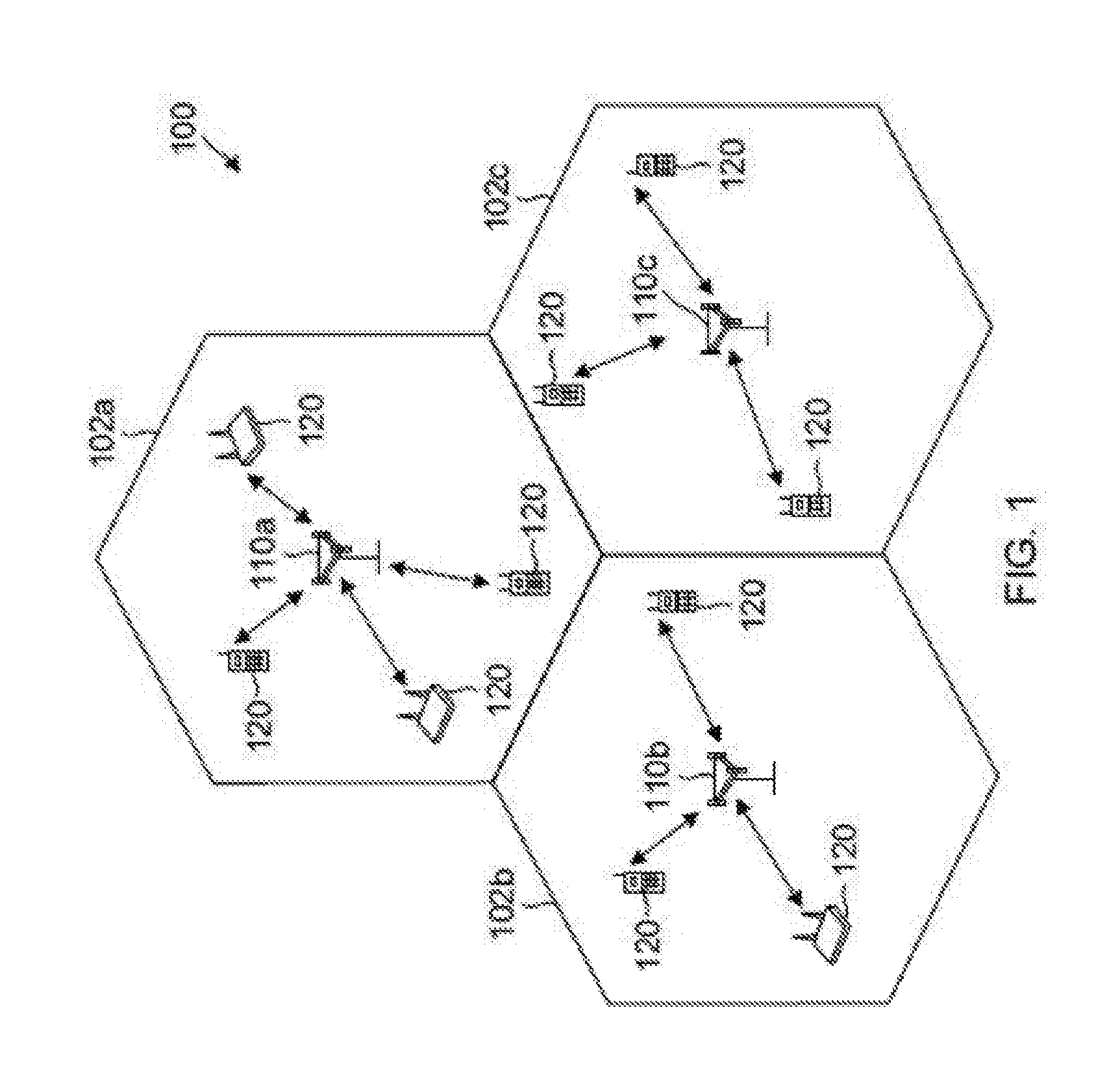
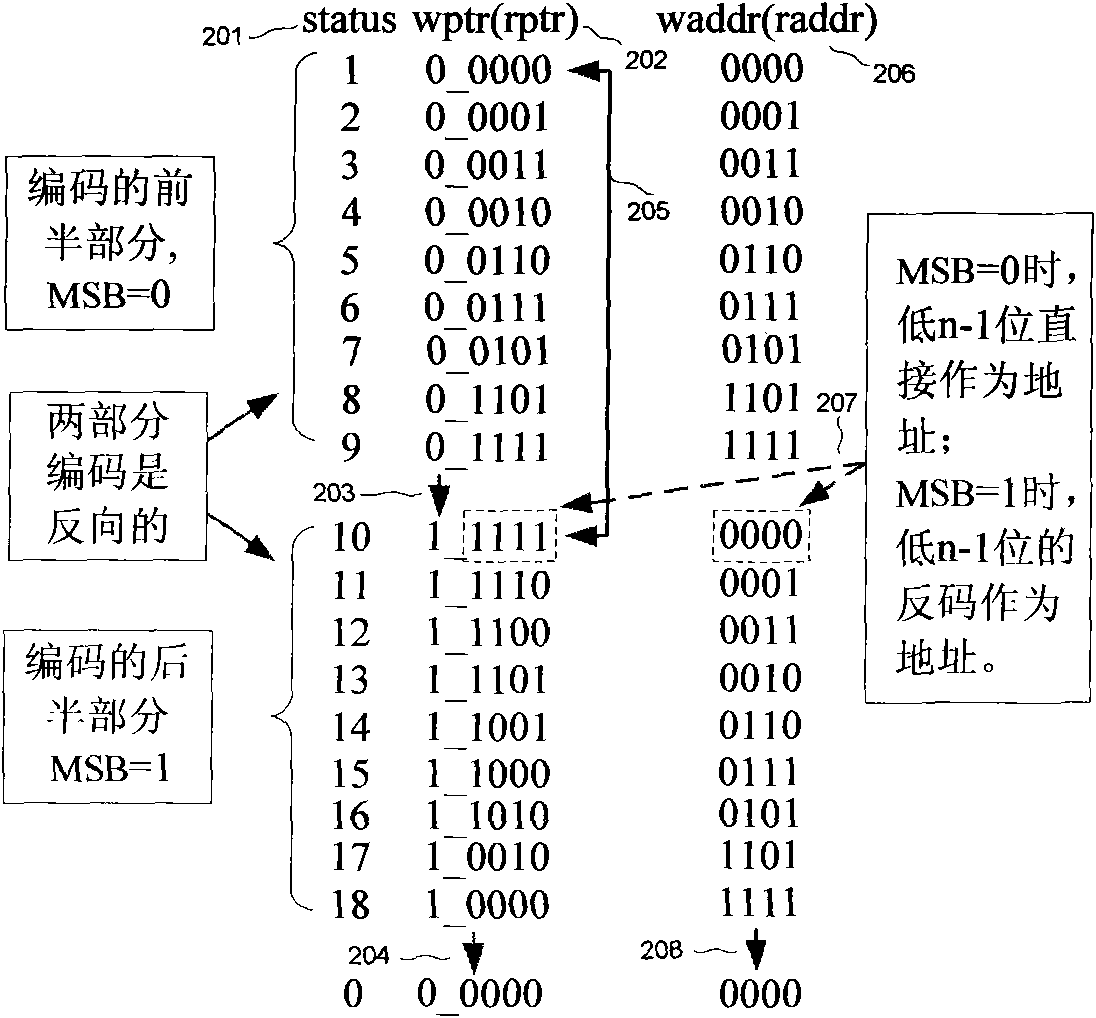Patents
Literature
72 results about "Data latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In business intelligence (BI), data latency is how long it takes for a business user to retrieve source data from a data warehouse or business intelligence dashboard. In order for a business to be agile and quickly respond to changing market conditions, the business' IT department needs to reduce data latency and provide business users with access to real-time and near-time operational data.
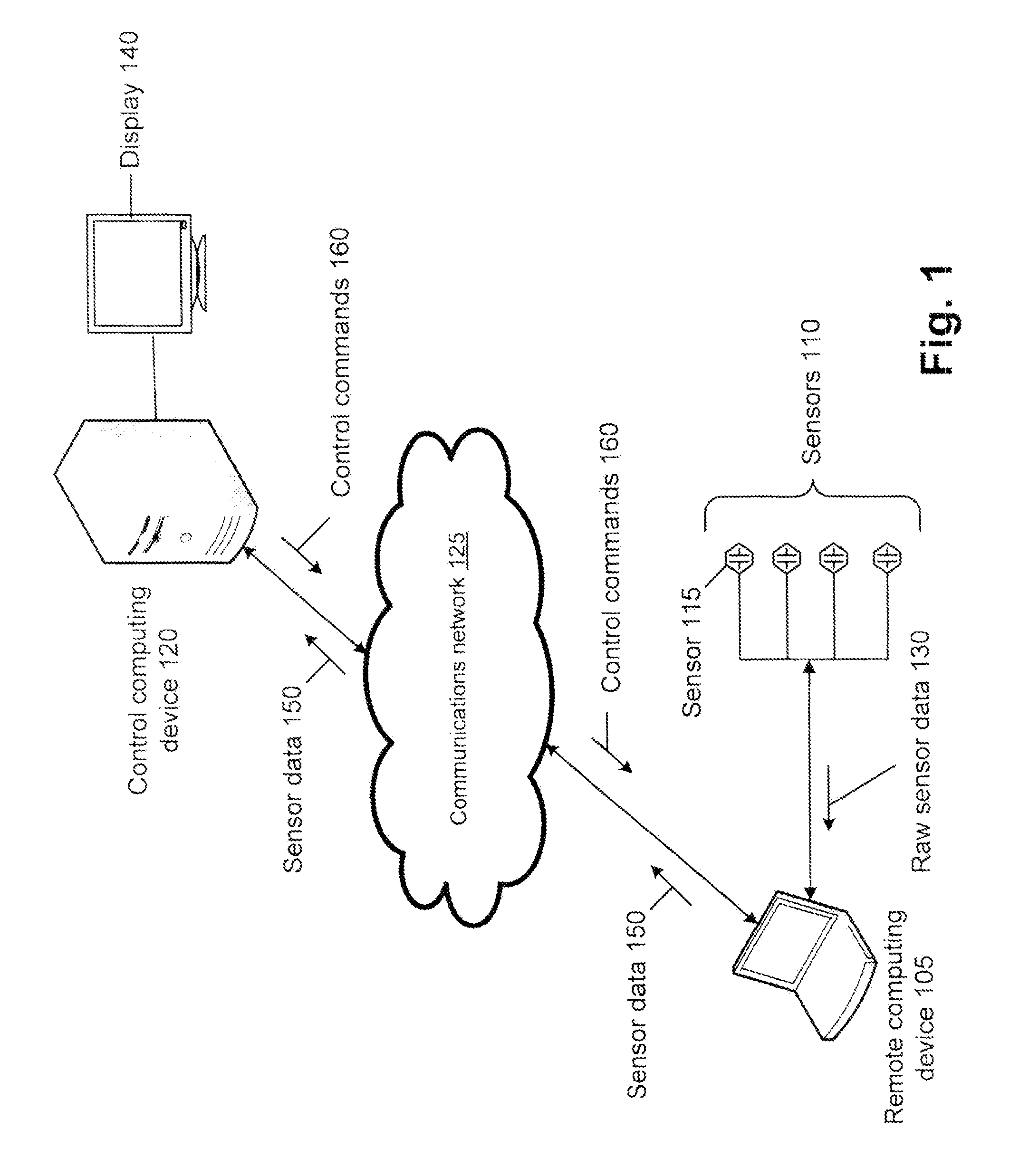
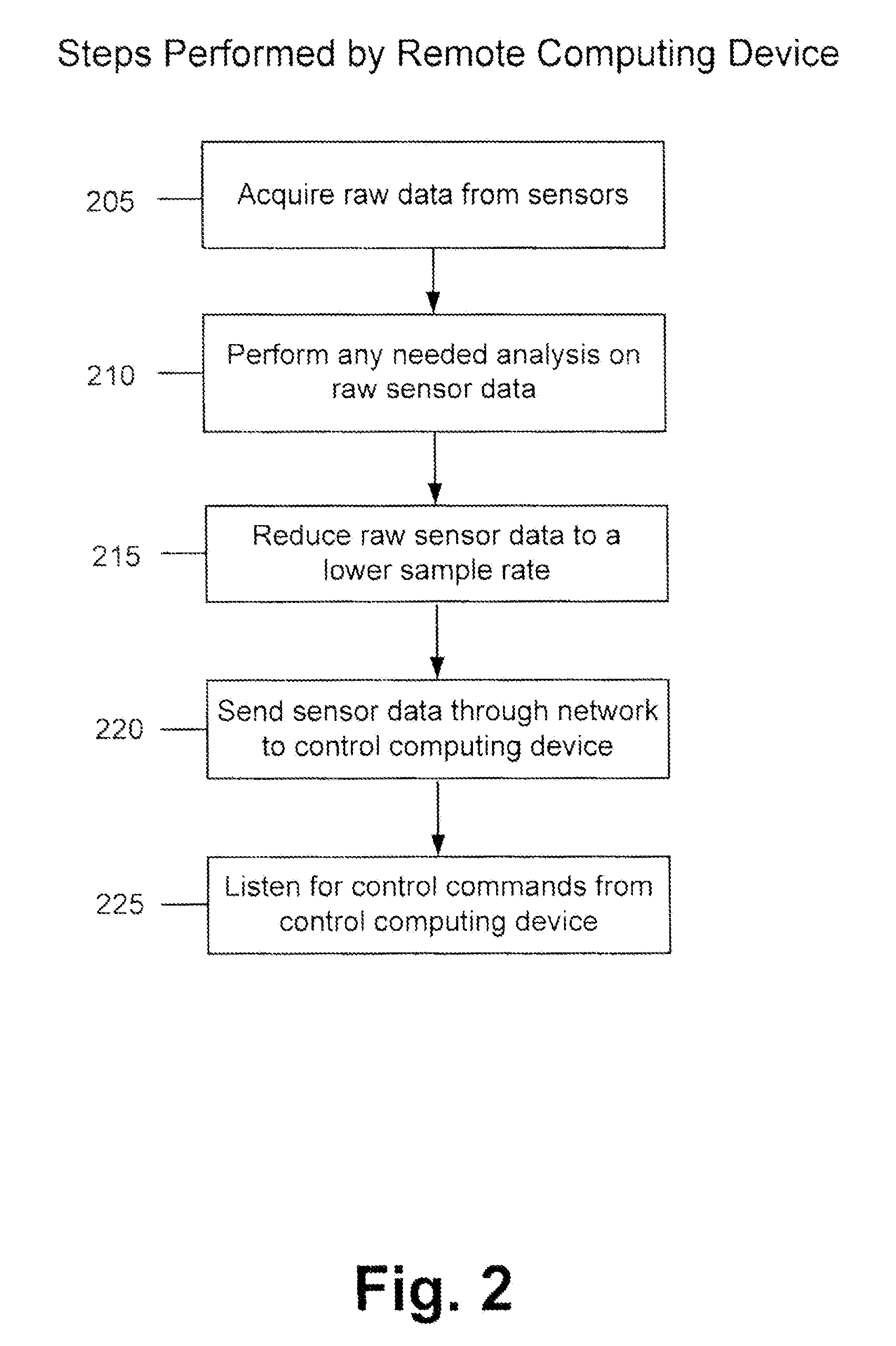
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission of sensor data with latency controls
ActiveUS20100278086A1High bandwidthData latency is minimizedNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAutomatic controlThroughput
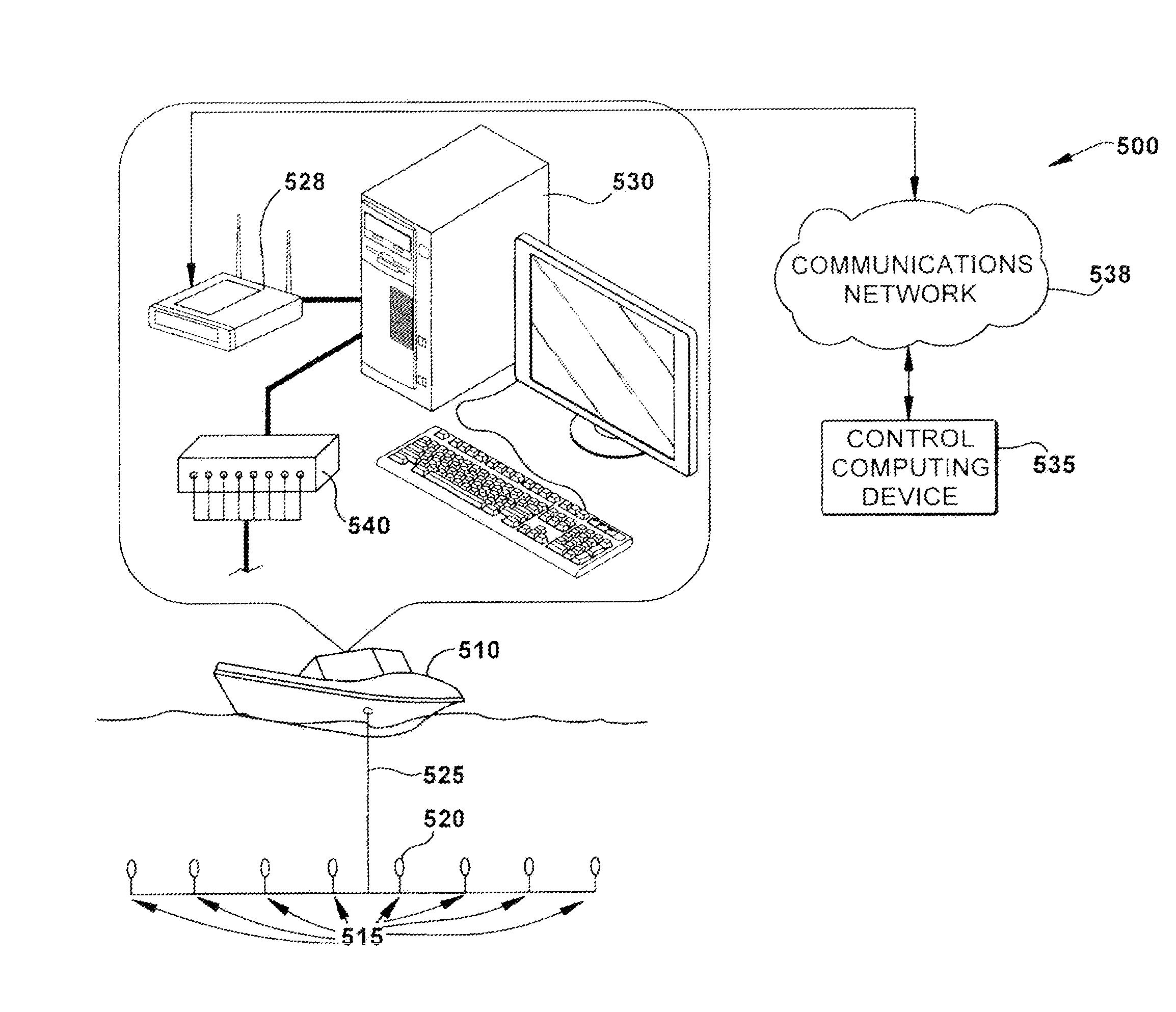
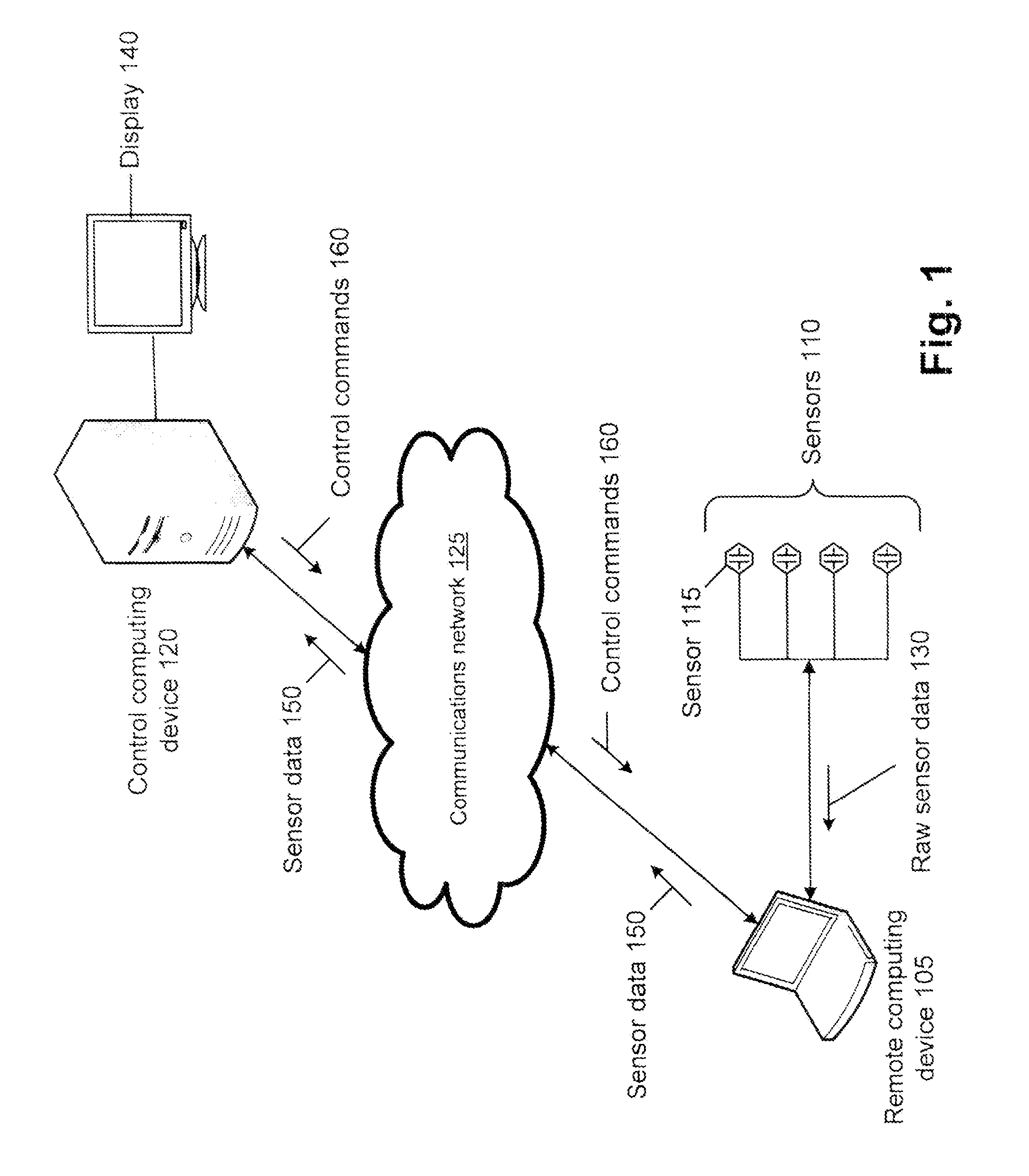
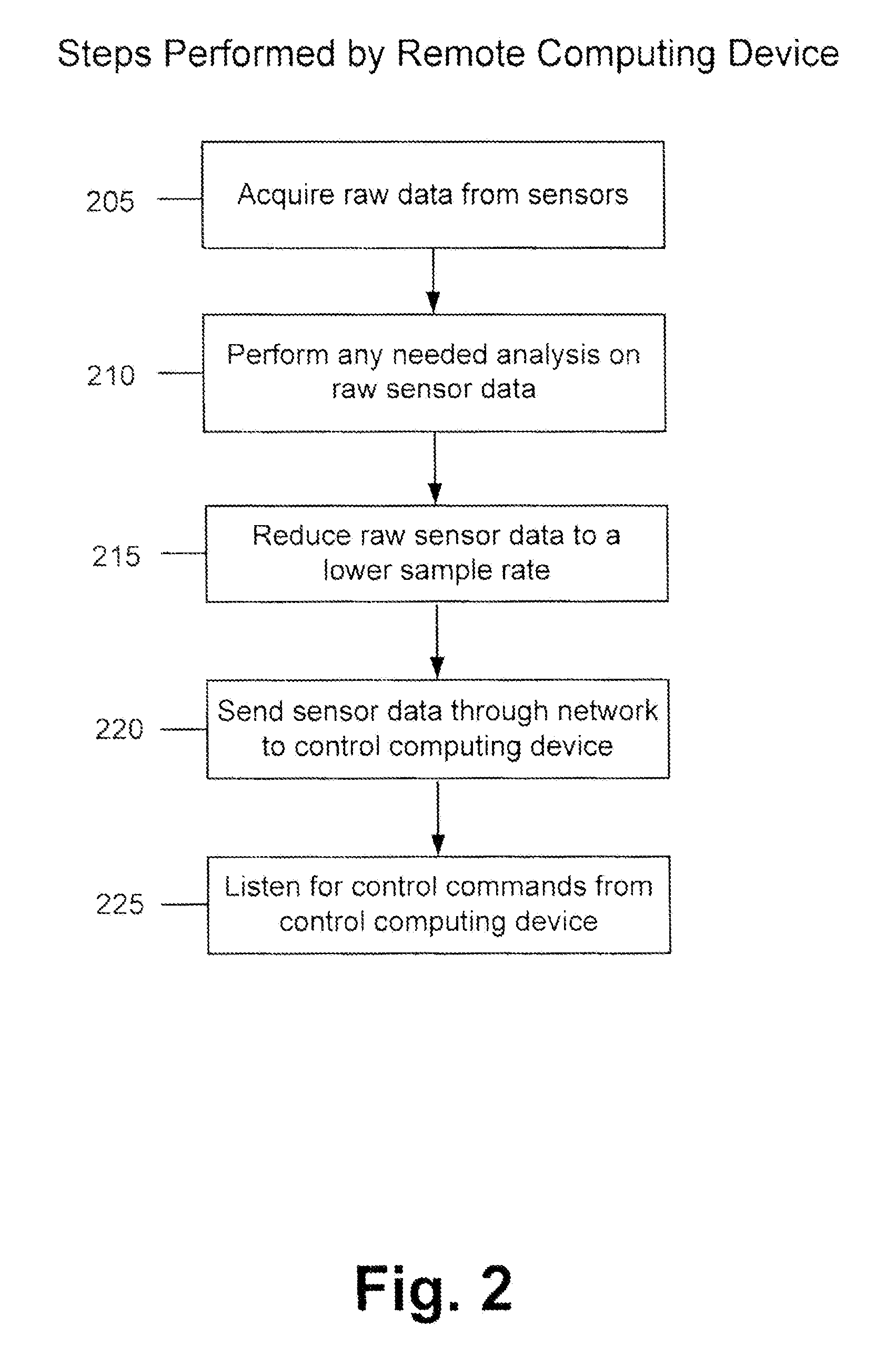
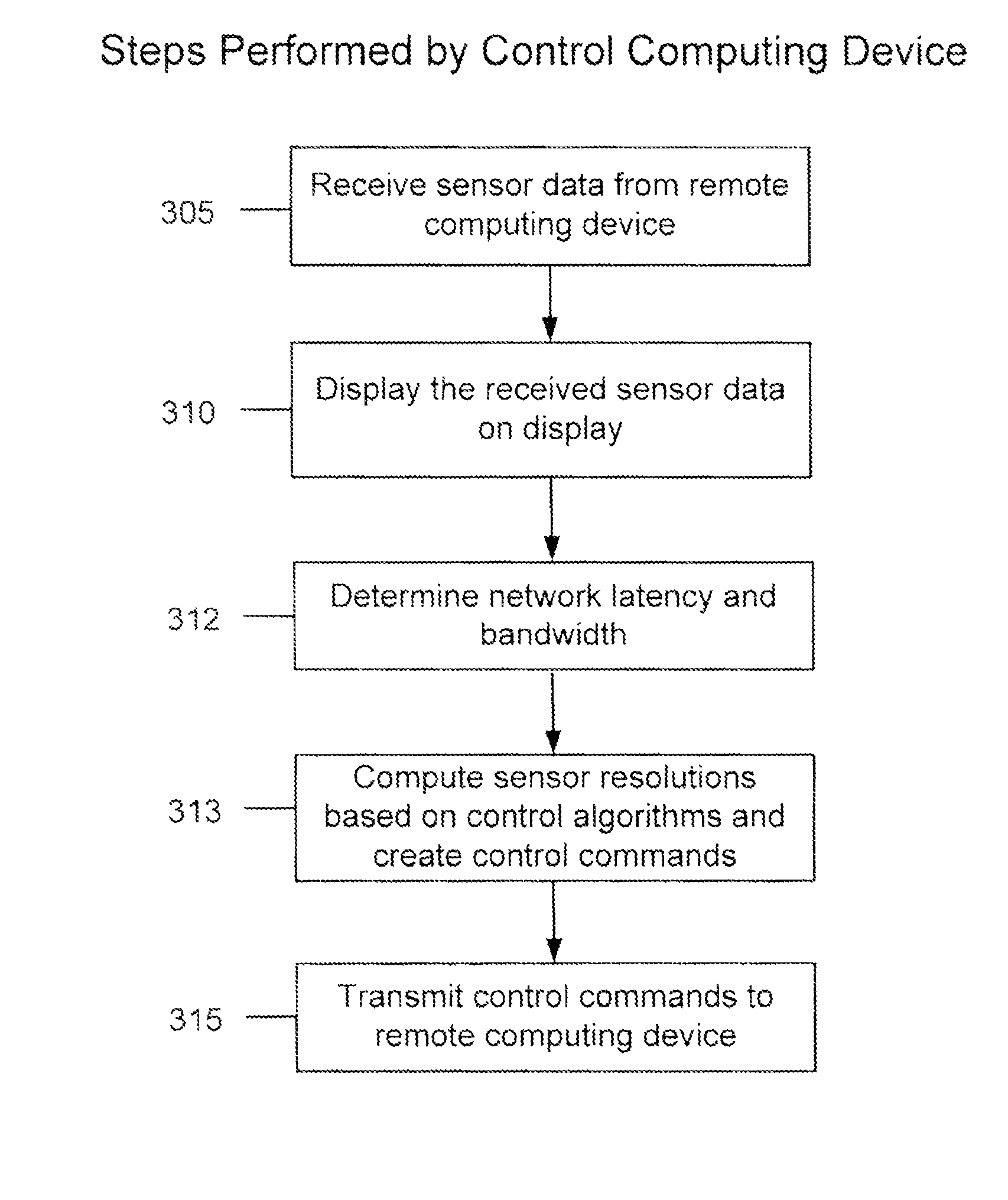
Disclosed is a method and apparatus to continuously transmit high bandwidth, real-time data, on a communications network (e.g., wired, wireless, and a combination of wired and wireless segments). A control computing device uses user or application requirements to dynamically adjust the throughput of the system to match the bandwidth of the communications network being used, so that data latency is minimized. An operator can visualize the instantaneous characteristic of the link and, if necessary, make a tradeoff between the latency and resolution of the data to help maintain the real-time nature of the system and better utilize the available network resources. Automated control strategies have also been implemented into the system to enable dynamic adjustments of the system throughput to minimize latency while maximizing data resolution. Several applications have been cited in which latency minimization techniques can be employed for enhanced dynamic performance.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
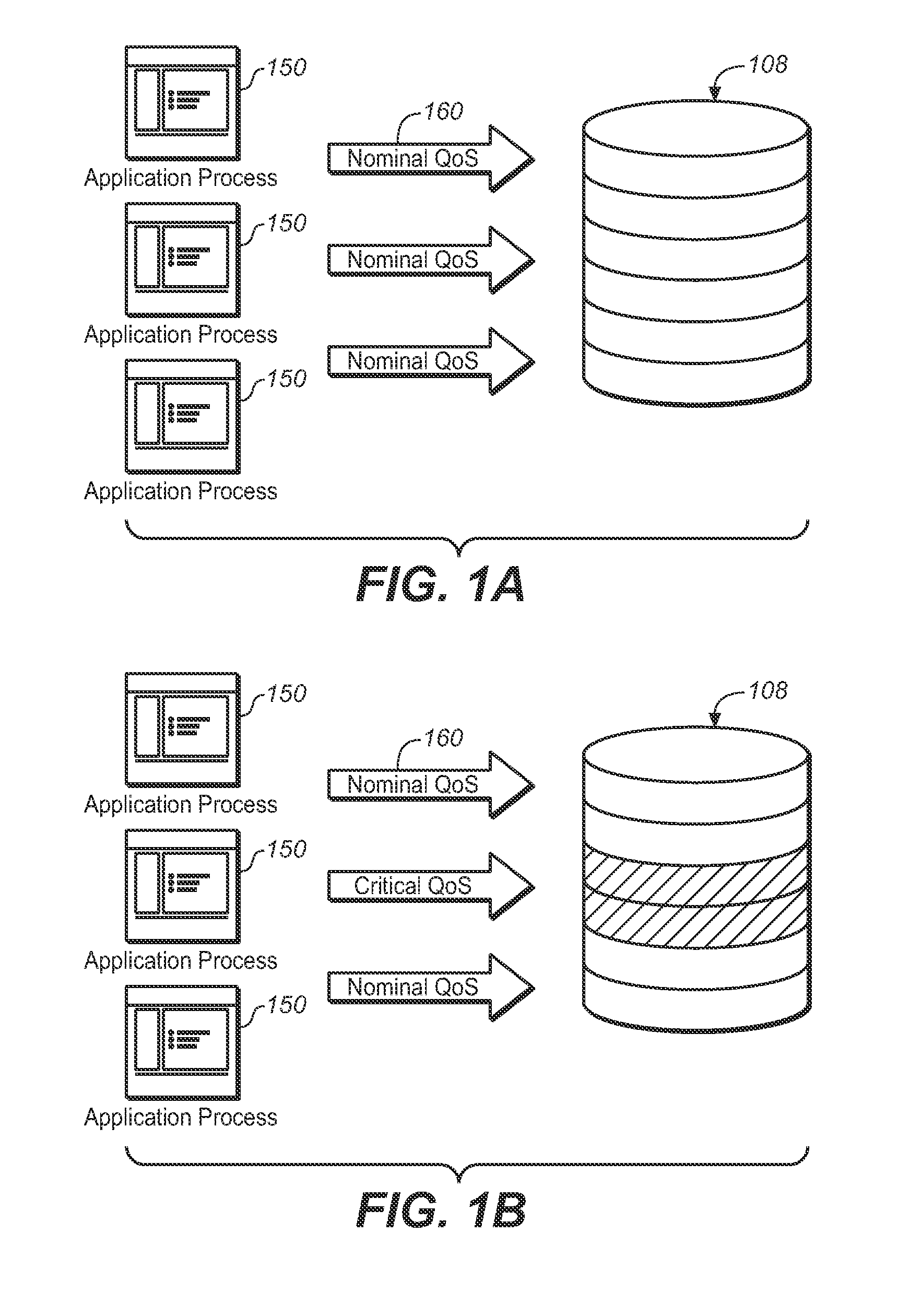
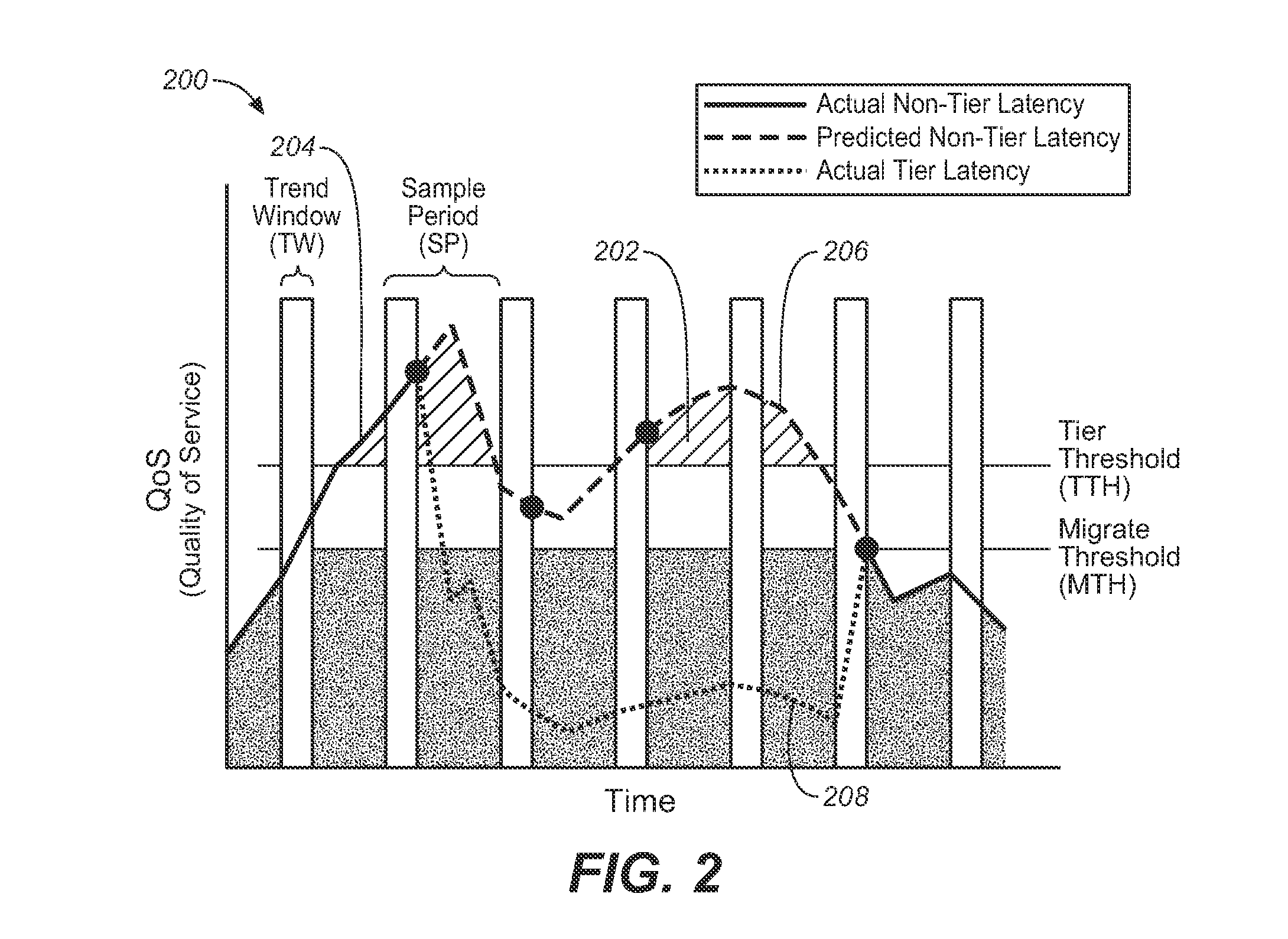
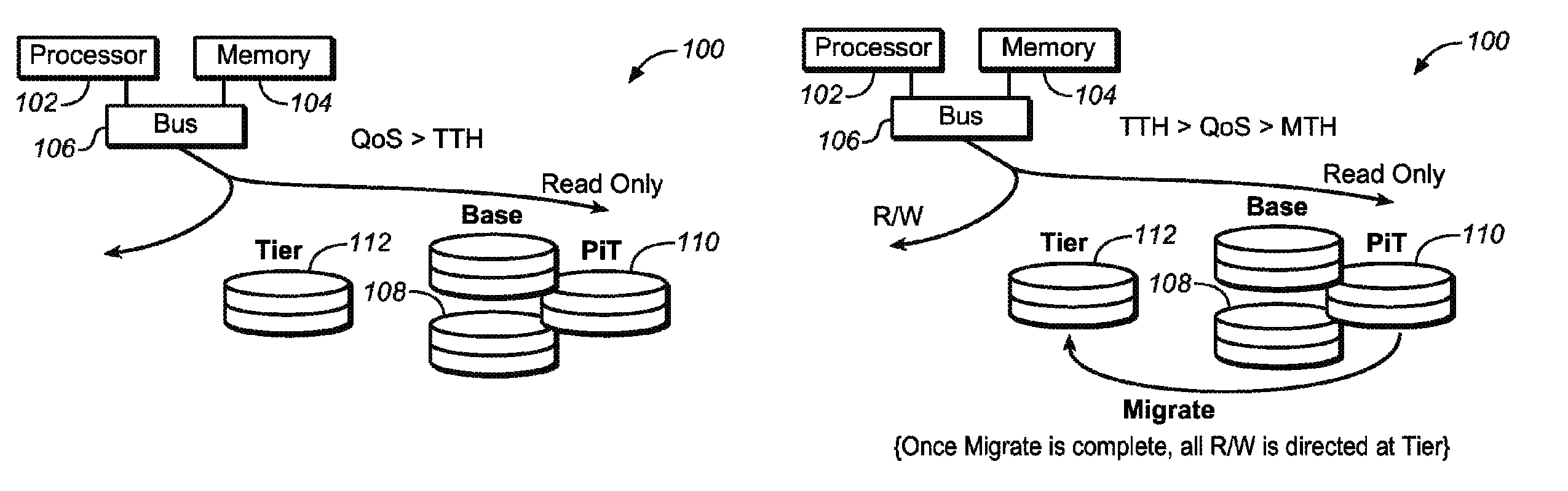
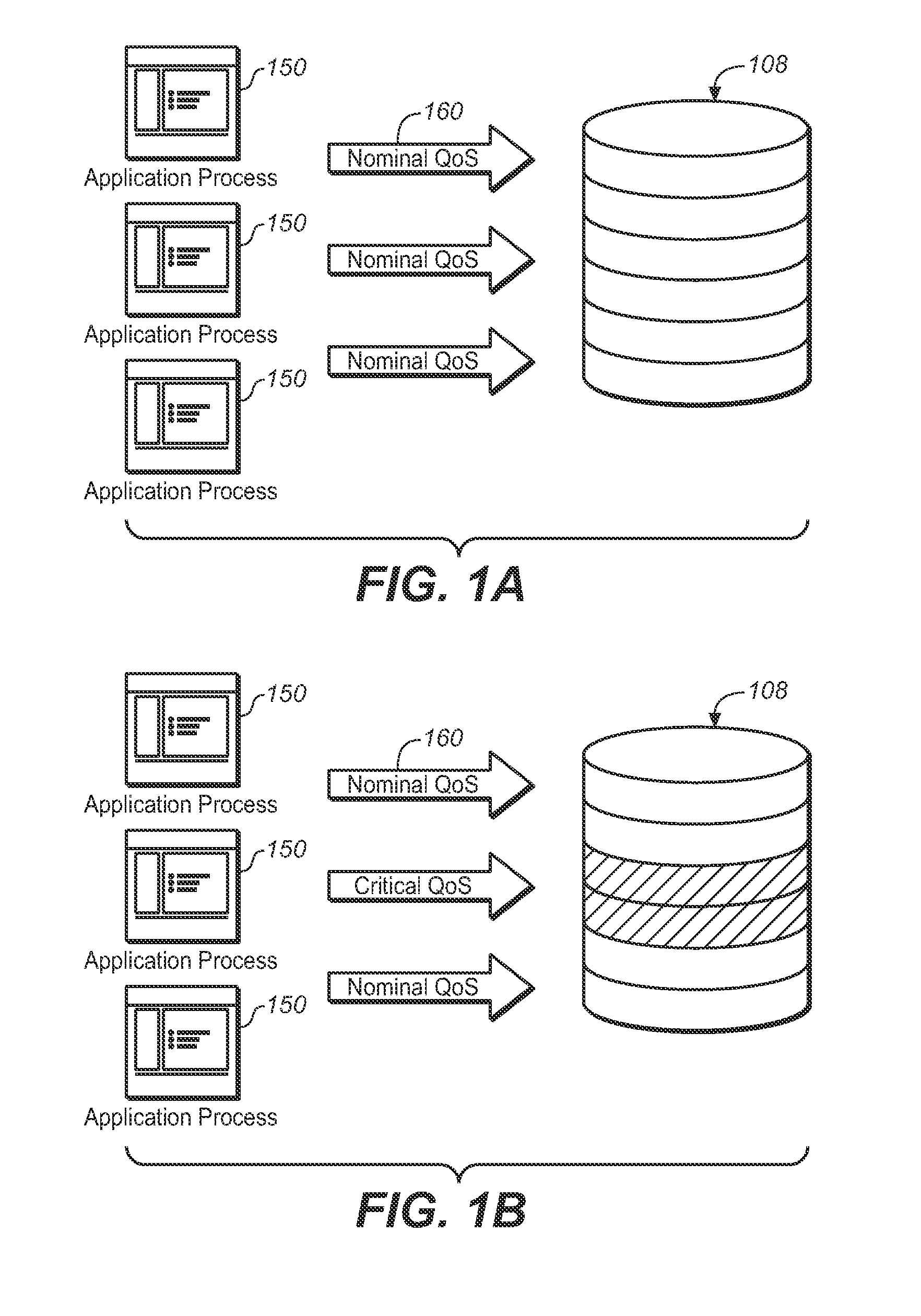
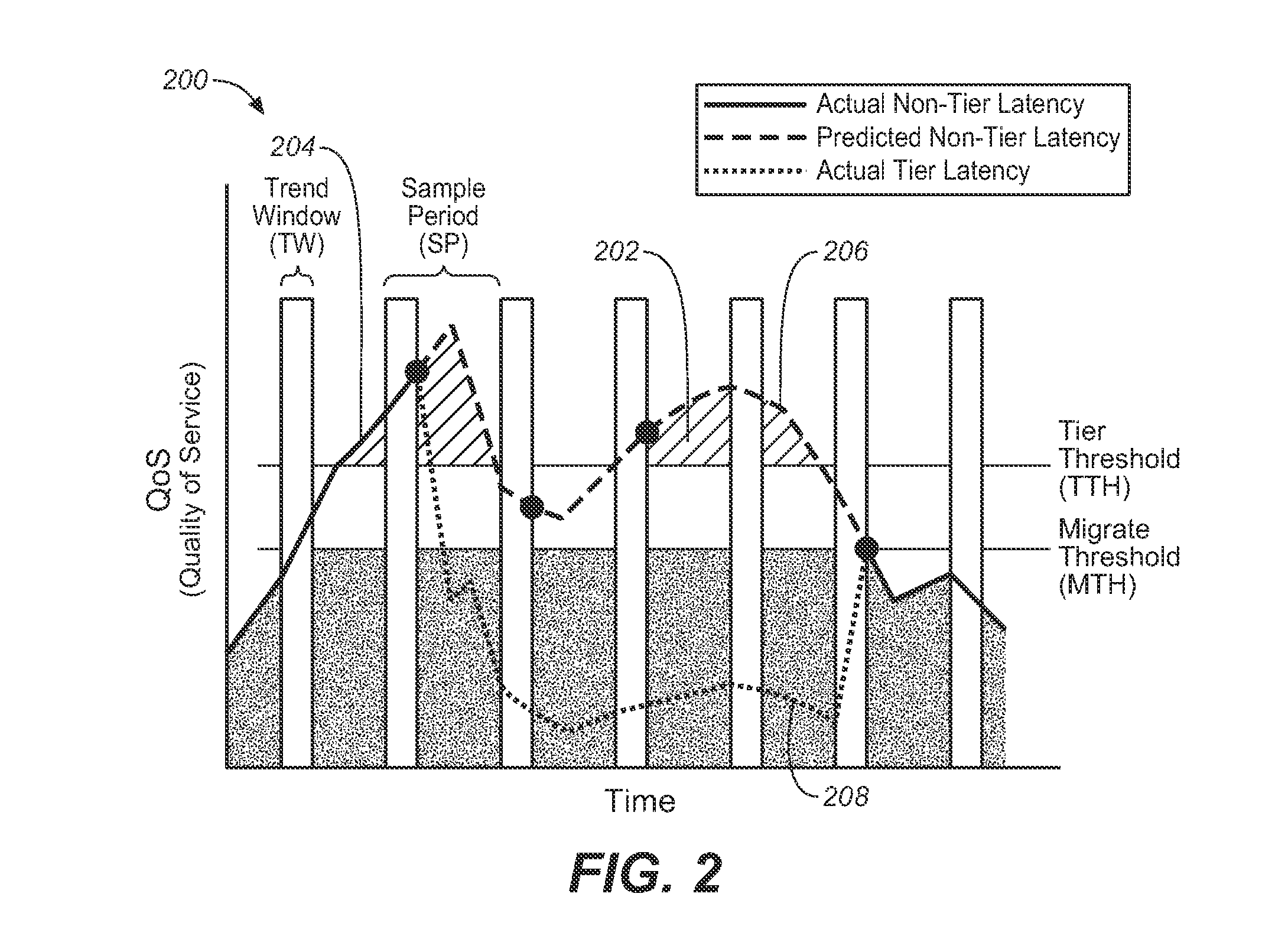
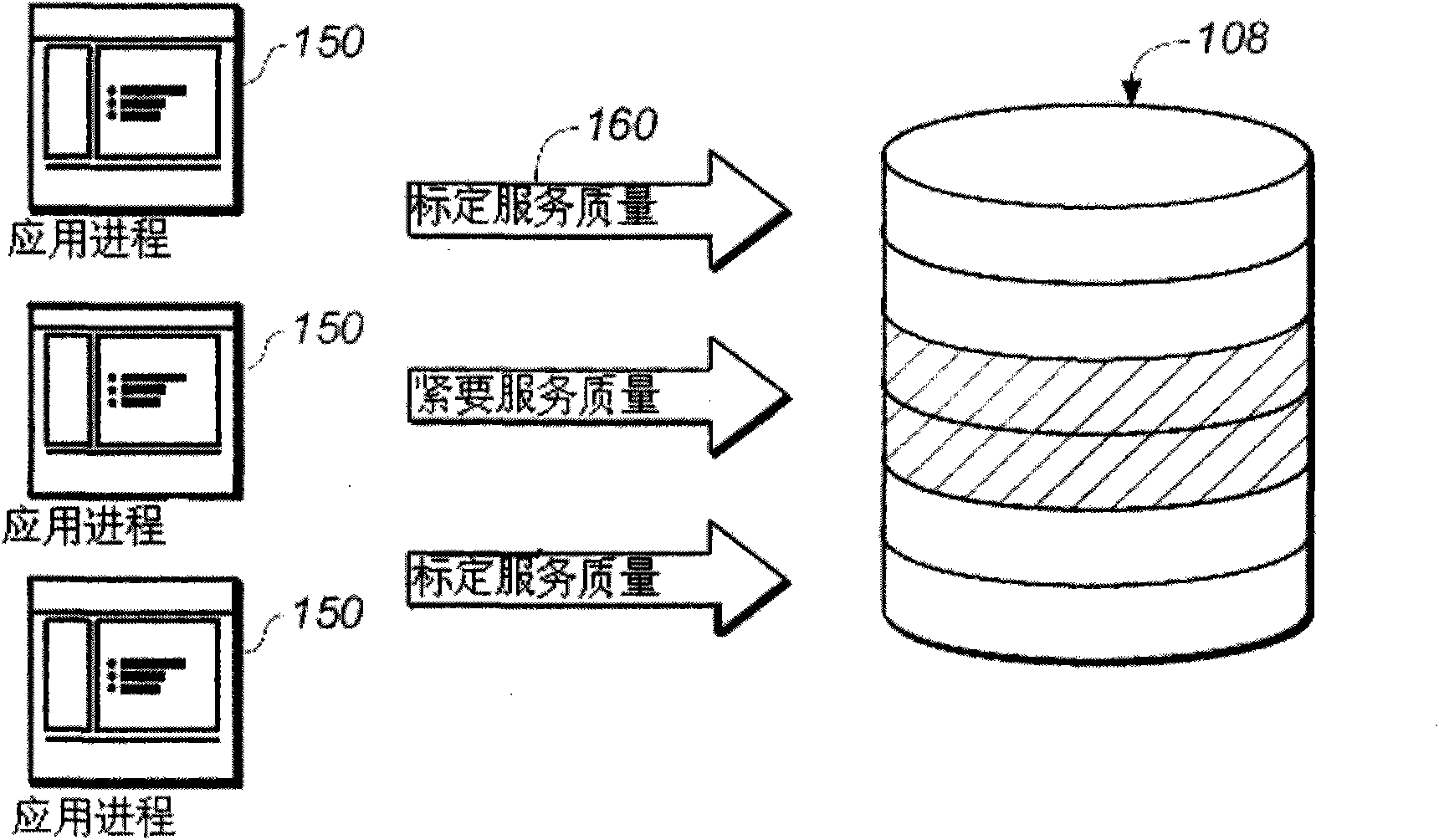
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR QoS-BASED STORAGE TIERING AND MIGRATION TECHNIQUE
InactiveUS20110197027A1Provide quality of serviceSacrificing all of its material advantageError detection/correctionMemory systemsQuality of serviceData latency
The present invention is directed to a method for providing Quality Of Service (QoS)-based storage tiering and migration in a storage system. The method allows for configurable application data latency thresholds to be set on a per user basis and / or a per application basis so that a storage tiering mechanism and / or a storage migrating mechanism may be triggered for moving application data to a different class of storage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
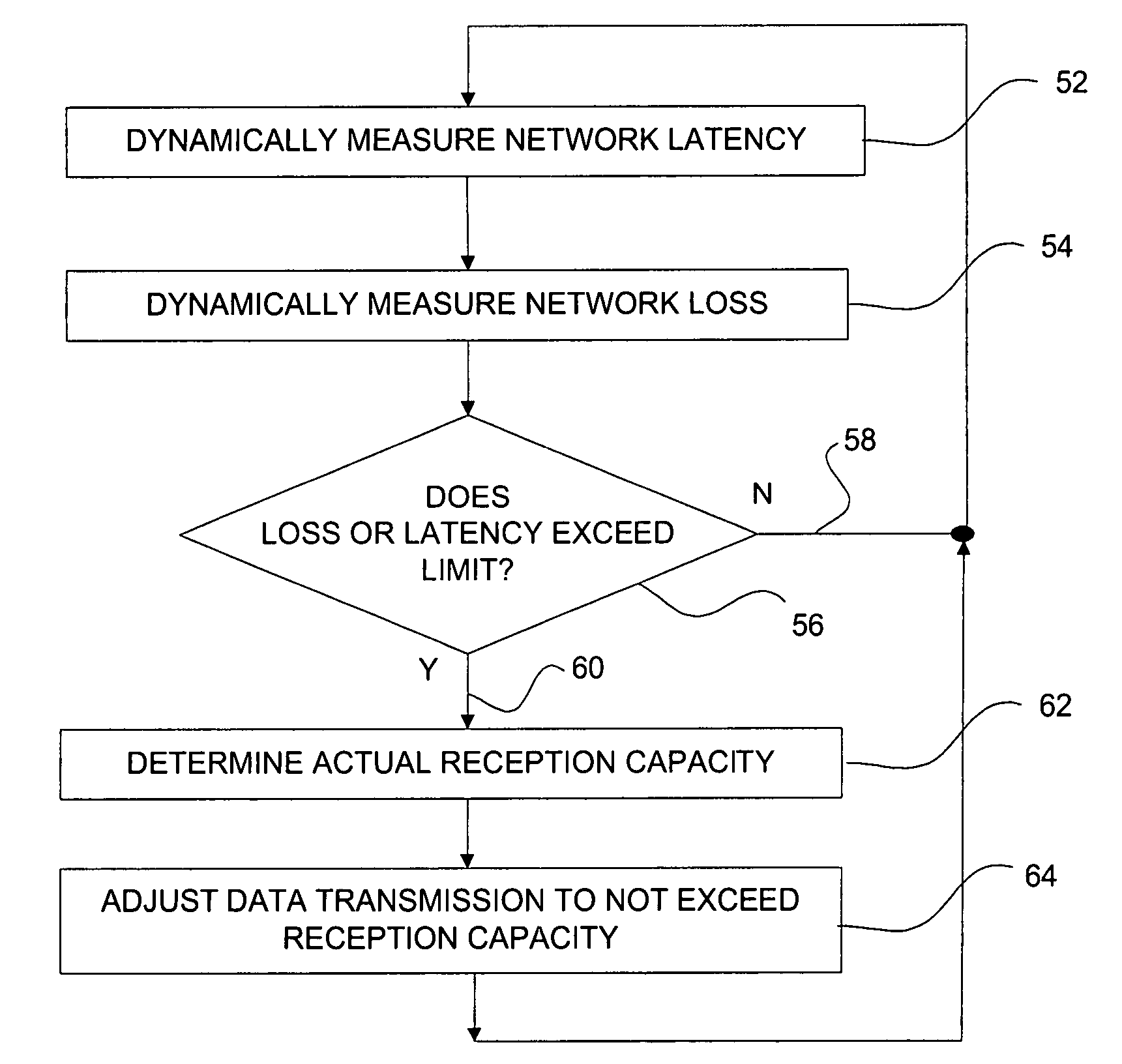
Network communications bandwidth control
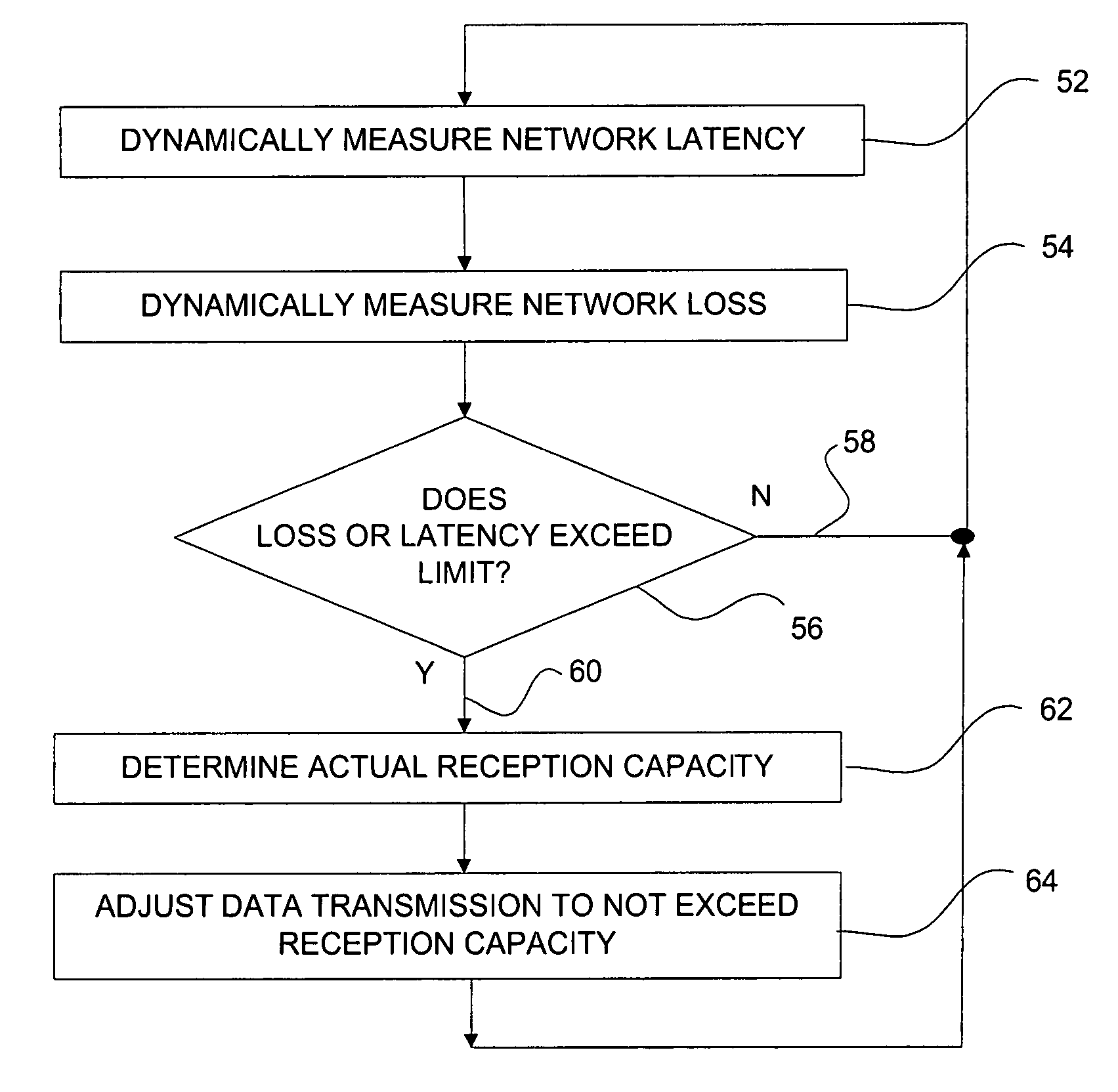
ActiveUS20050232151A1Reduce probabilitySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPacket lossReal-time data
A method for controlling real time data communications over a packet based network comprises steps of dynamically measuring data packet loss between a receiver and a sender on the network, dynamically measuring data latency between the sender and receiver, and comparing the dynamically measured data packet loss to a loss limit and comparing the dynamically measured data latency to a latency limit. If one or both of the loss limit or the latency limit is exceeded, then the method may include reducing the rate of data transmission from the sender.
Owner:IOCOM UK LTD
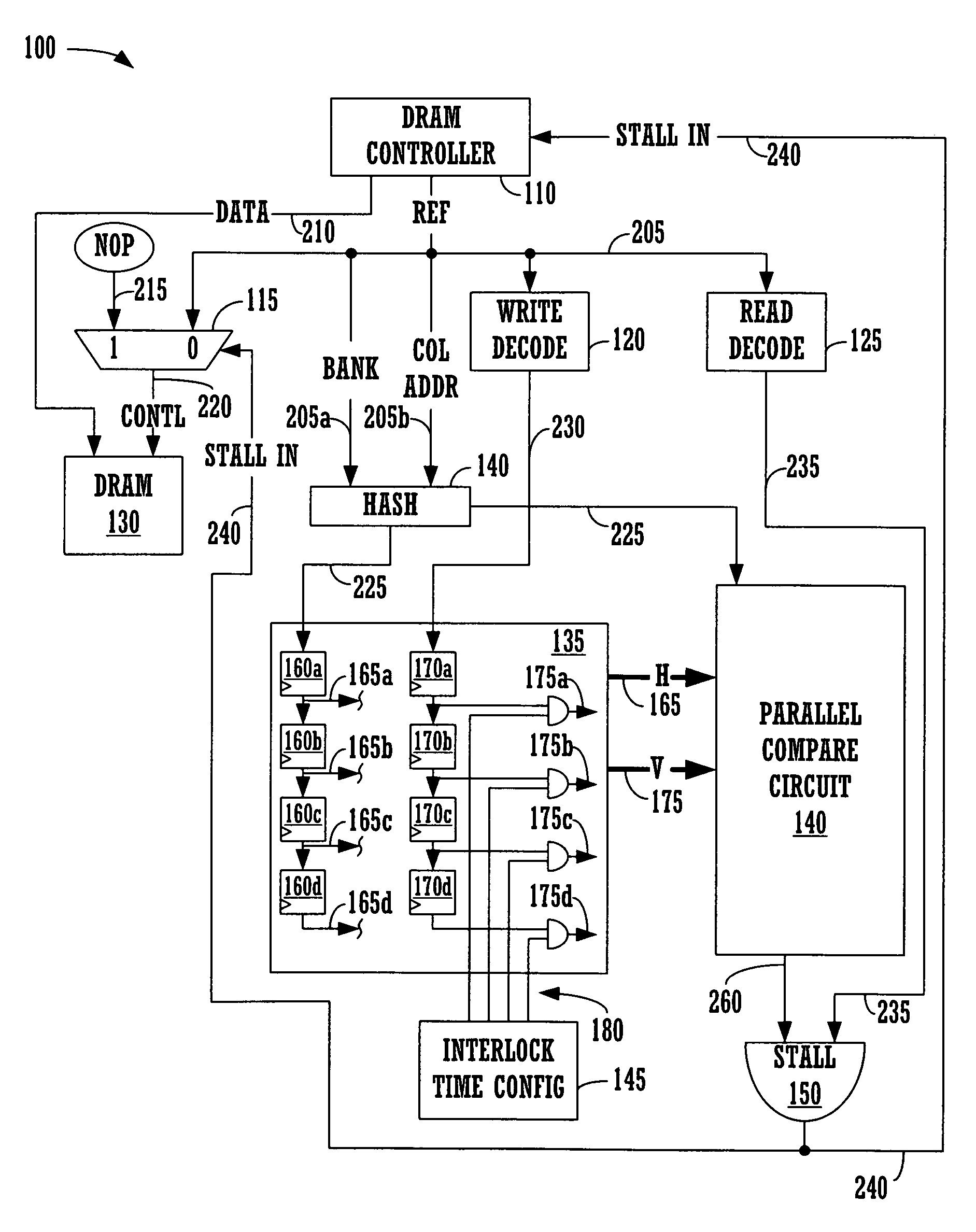
Method and system for efficiently executing reads after writes in a memory employing delayed write data
A method and system for efficiently executing reads after writes in a memory. The system includes a memory controller and a memory core interfacing with the memory controller. The memory operates with a read data latency and a similar write data latency, and the memory immediately processes a read in a read-after-write situation. The system further includes a control circuit for controlling the memory and detecting an address collision between the read and a previously issued write and, in response thereto, stalling the memory by delaying issuance of the read to the memory until after the previously issued write completes.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
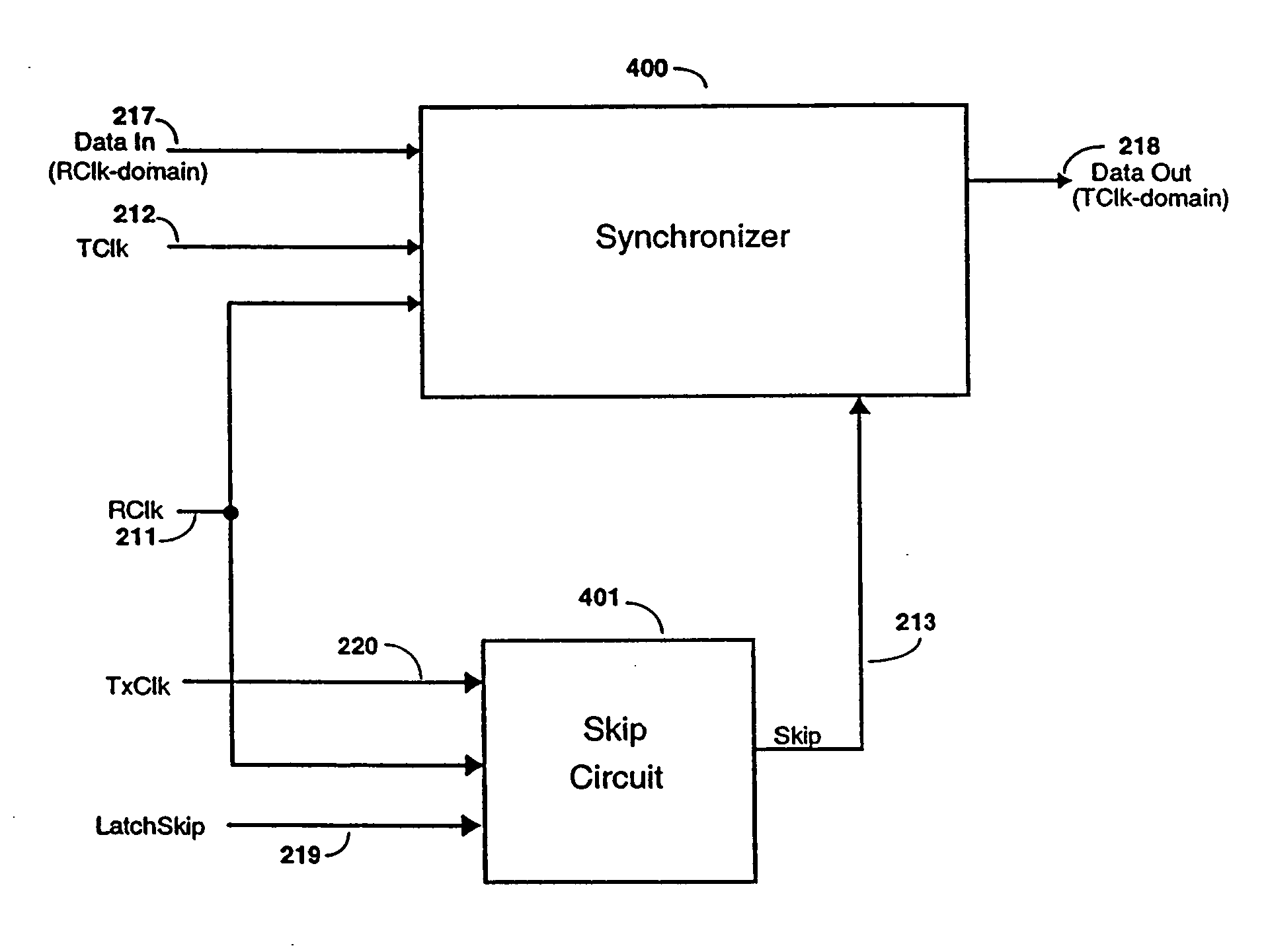
Method and apparatus for fail-safe resynchronization with minimum latency
InactiveUS20060022724A1Guaranteed uptimeMinimizes shiftingSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlData latencyVoltage shift
Owner:RAMBUS INC
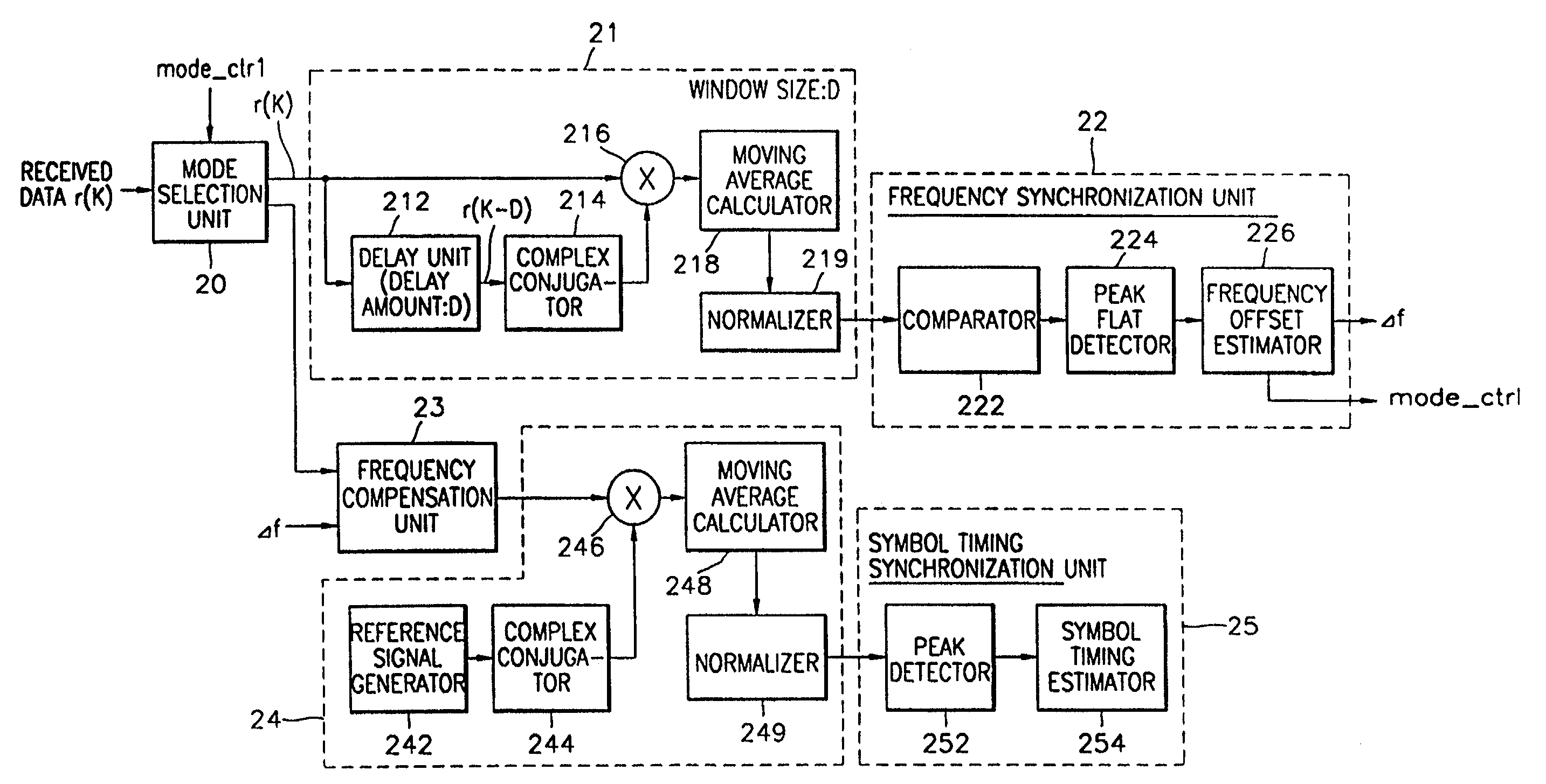
Apparatus and method for achieving symbol timing and frequency synchronization to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing signal
InactiveUS7058151B1Accurate frequency synchronizationAccurate symbol timingCarrier regulationTime-division multiplexFlat detectorPeak value
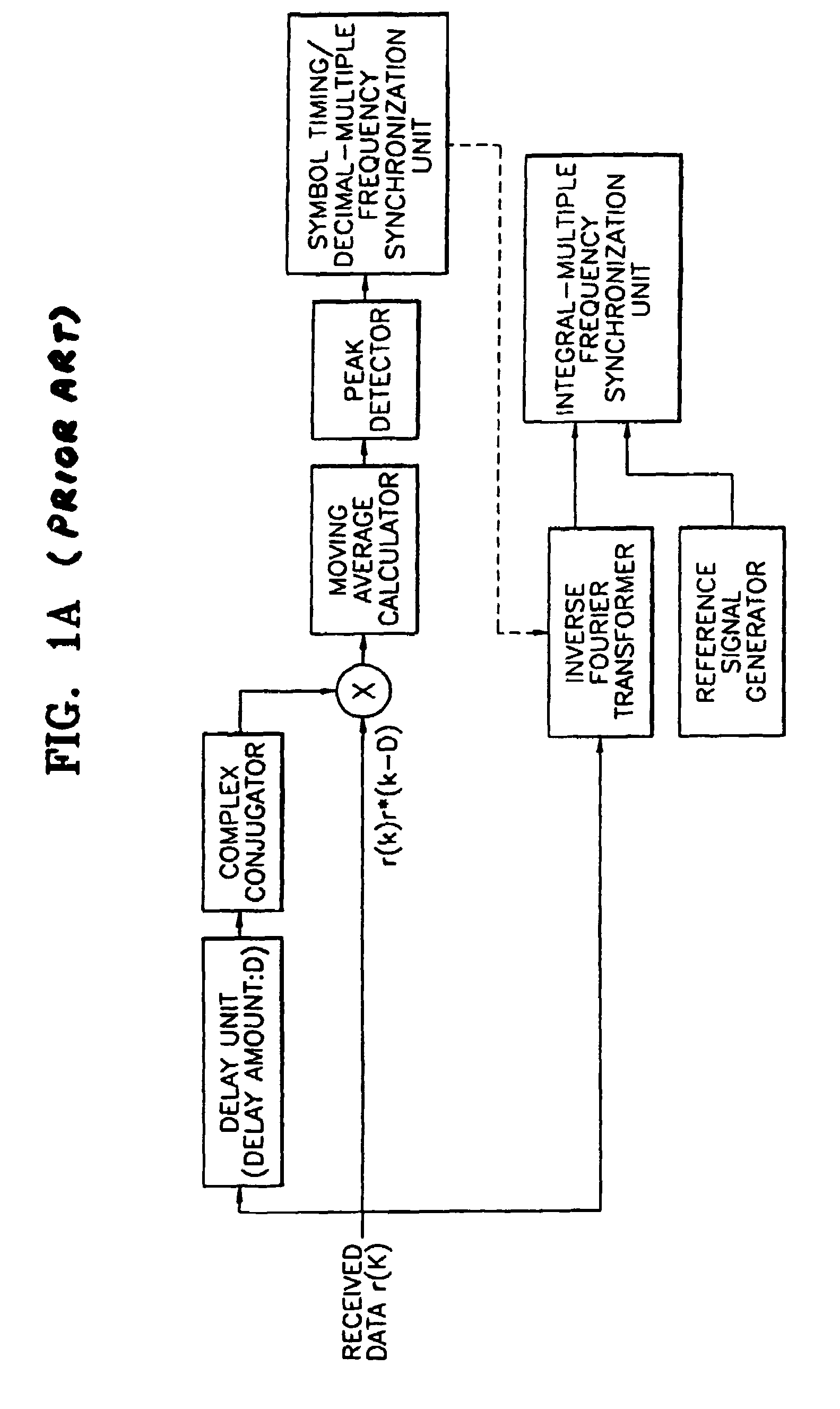
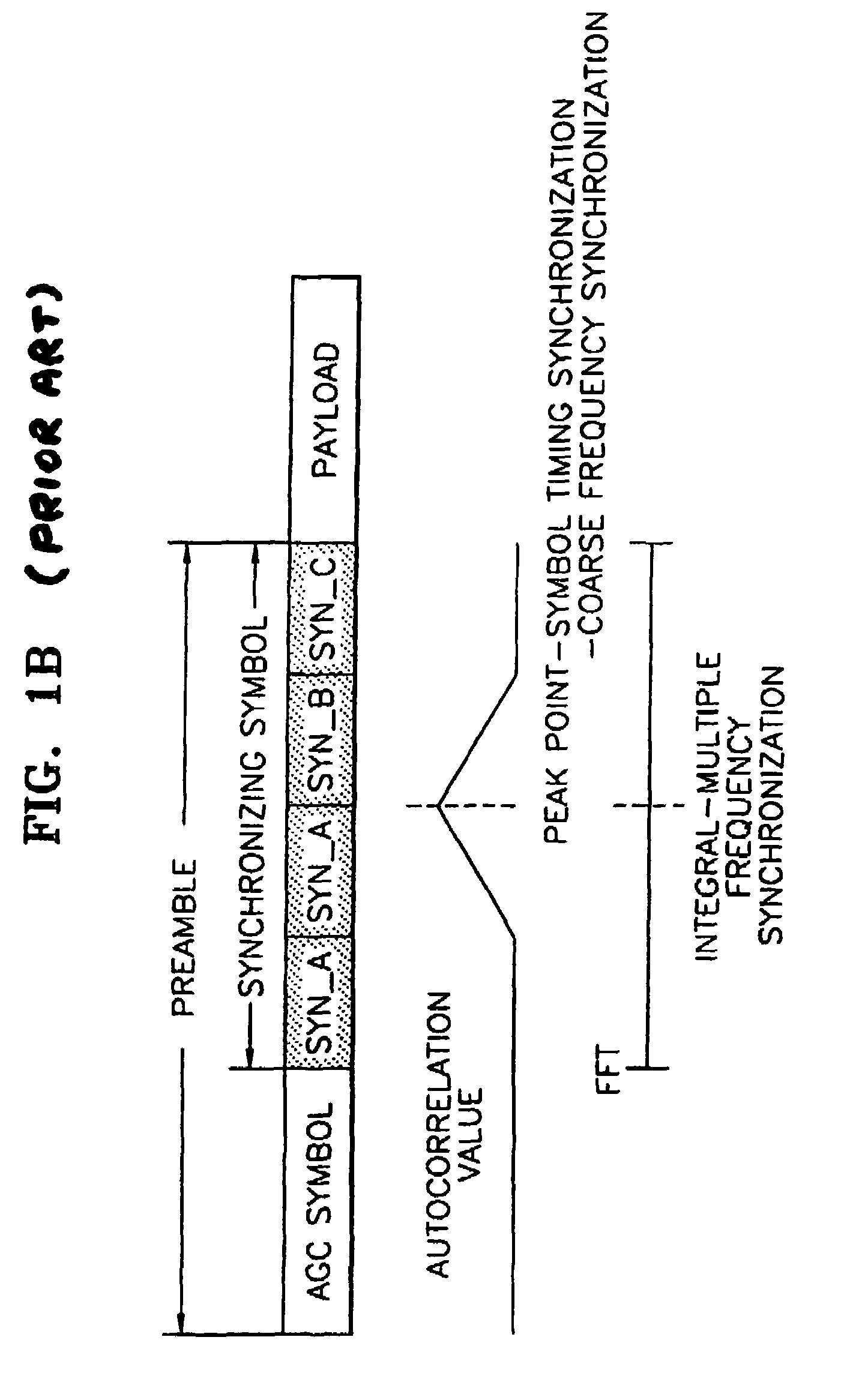
A frequency and symbol timing synchronization apparatus for orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) signals, and a method performed by the apparatus are provided. This apparatus includes an autocorrelation unit, a comparator, a peak flat detector, a frequency offset estimator, a frequency offset compensation unit, a cross correlation unit and a symbol timing synchronization unit. The autocorrelation unit receives data including a synchronizing symbol made up of at least three identical synchronizing signals, delays the received data by a predetermined delay amount, performs autocorrelation between the received data and the delayed data, normalizes an autocorrelated value, and outputs a normalized autocorrelated value. The comparator compares the normalized autocorrelated value with a predetermined threshold value. The peak flat detector detects as a flat section a section where the normalized autocorrelated value is equal to or greater than the threshold value. The frequency offset estimator estimates a frequency offset within the flat section to obtain a frequency offset value. The frequency offset compensation unit compensates for the frequency offset of a received signal using the frequency offset value. The cross correlation unit performs cross correlation using a frequency offset-compensated signal and a reference signal, and normalizes the cross-correlated value to output a normalized cross-correlated value. The symbol timing synchronization unit detects a point where the cross-correlated value is maximum, and performs symbol timing estimation, thereby performing symbol timing synchronization. In the symbol timing and frequency synchronization apparatus and method, accurate frequency synchronization can be achieved because a large sample error can be allowed. Also, a symbol timing error can be reduced since symbol timing synchronization is achieved using a frequency offset-compensated signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
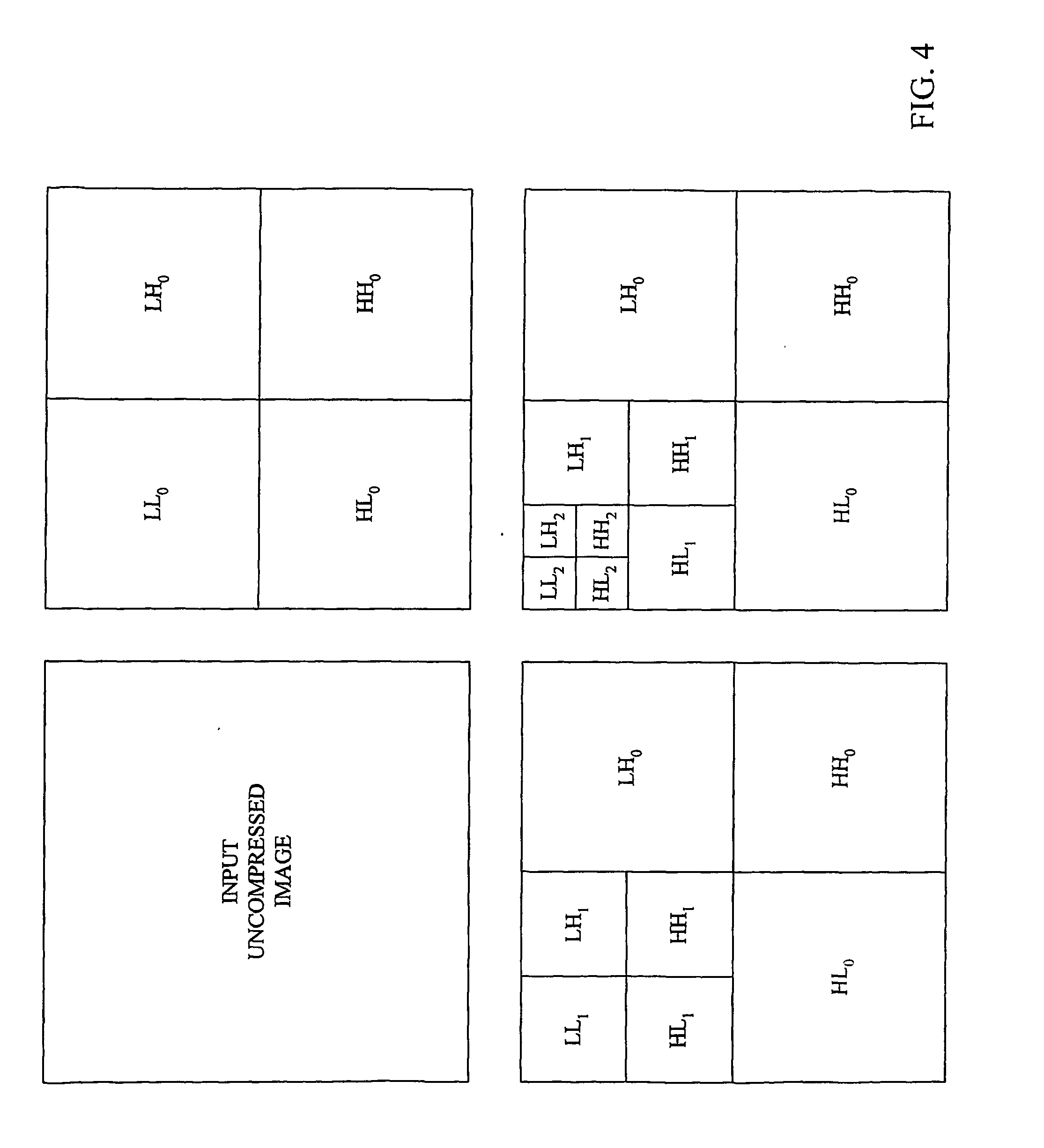
Fast codec with high compression ratio and minimum required resources
ActiveUS20060053004A1Adapt quicklyPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisData compressionProbability estimation
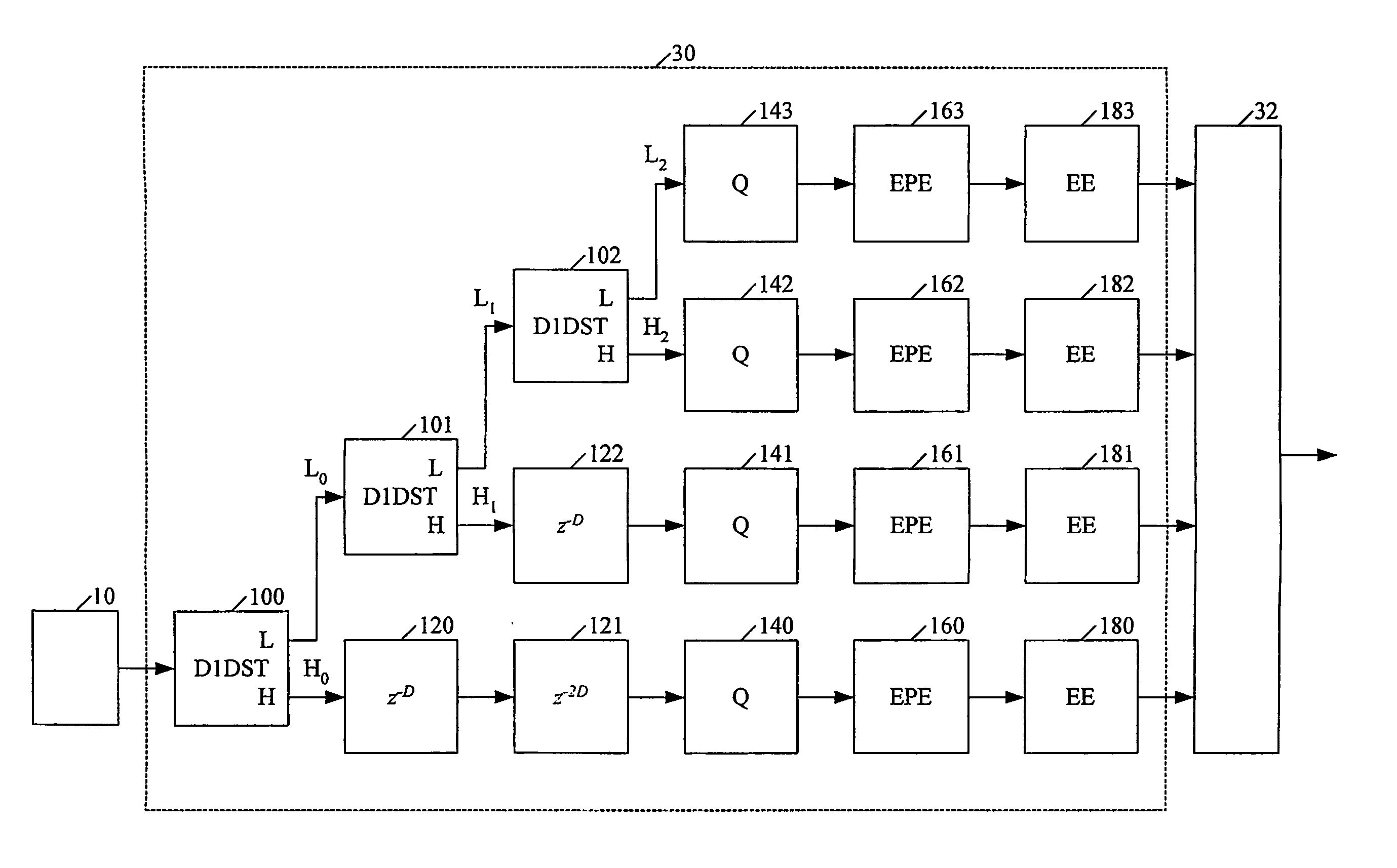
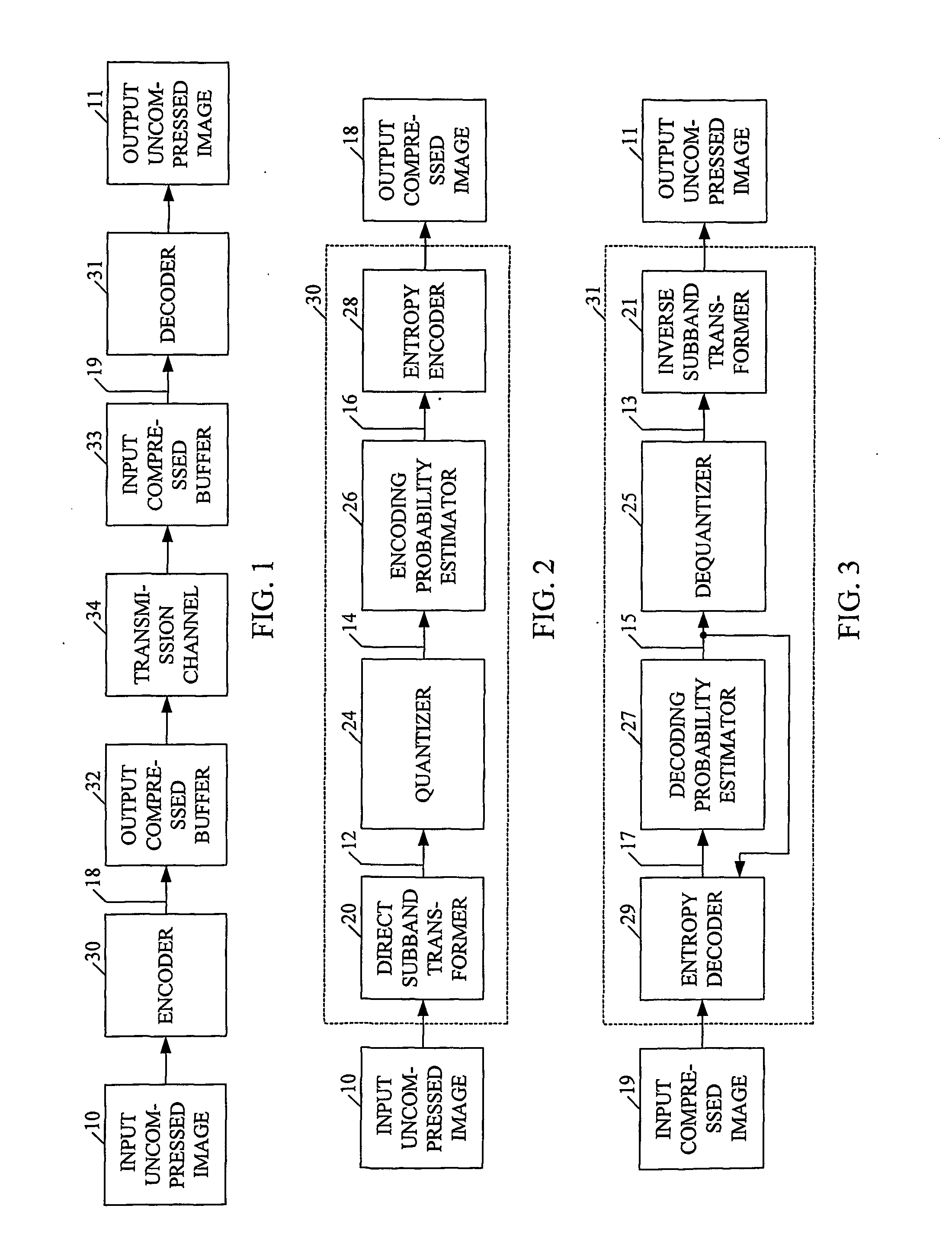
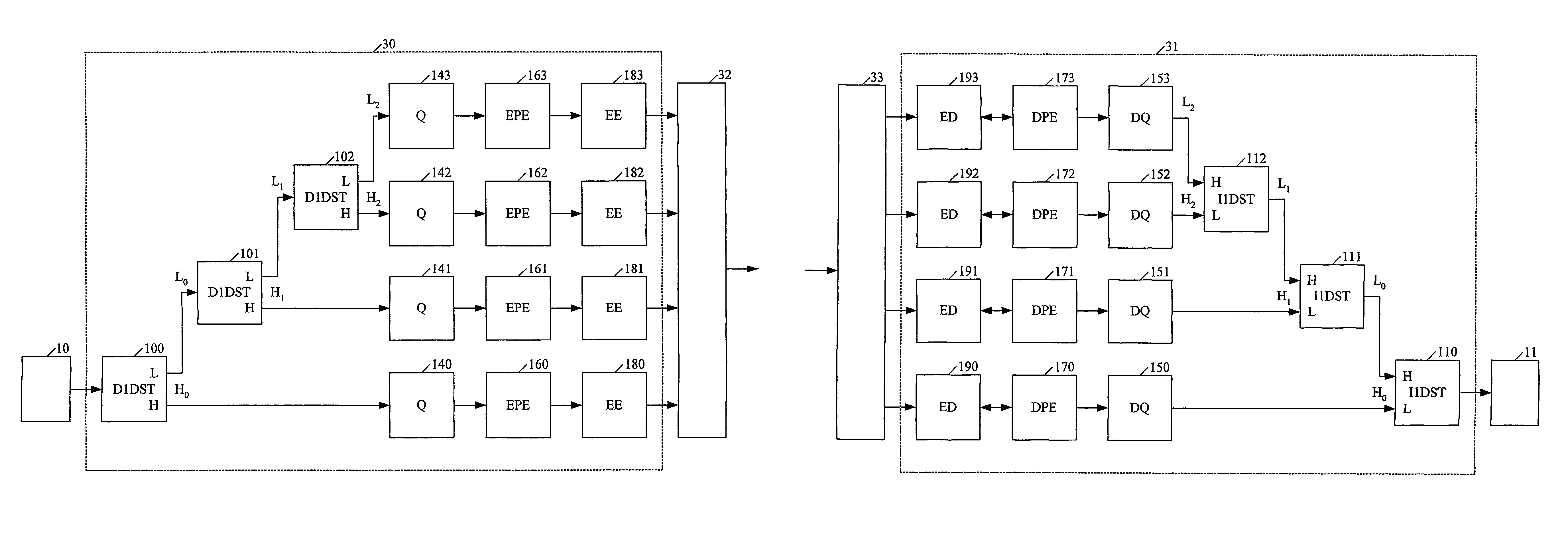
This invention provides a novel single-pass and multi-pass synchronized encoder and decoder, performing order(s) of magnitude faster data compression and decompression, at any compression ratio with the higher or the same perceived and measured decompressed image quality in comparison with the best state-of-the-art compression methods, using order(s) of magnitude less system resources (processor complexity, memory size, consumed power, bus bandwith, data latency). These features are achieved using novel direct and inverse non-stationary filters for the recusive octave direct and inverse subband transformation, novel simple context modeling and symbol probability estimation using a minimum number of histograms with the fast adaptation for the sign and the magnitude of the transformation coefficients, a novel accelerated range coder without division operations, and a novel synchronisation of the compressed data.
Owner:CEPERKOVIC VLADIMIR +3
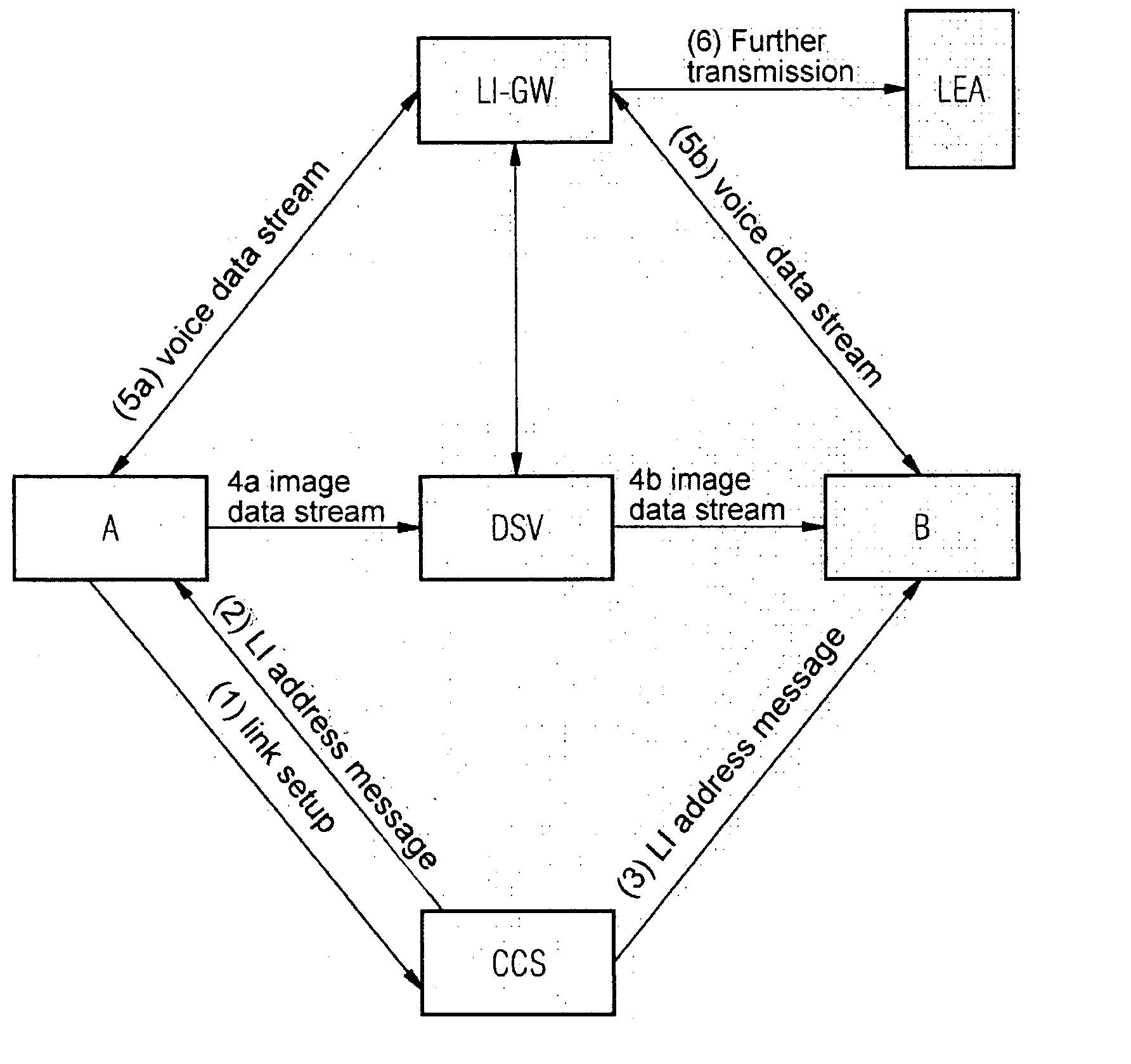
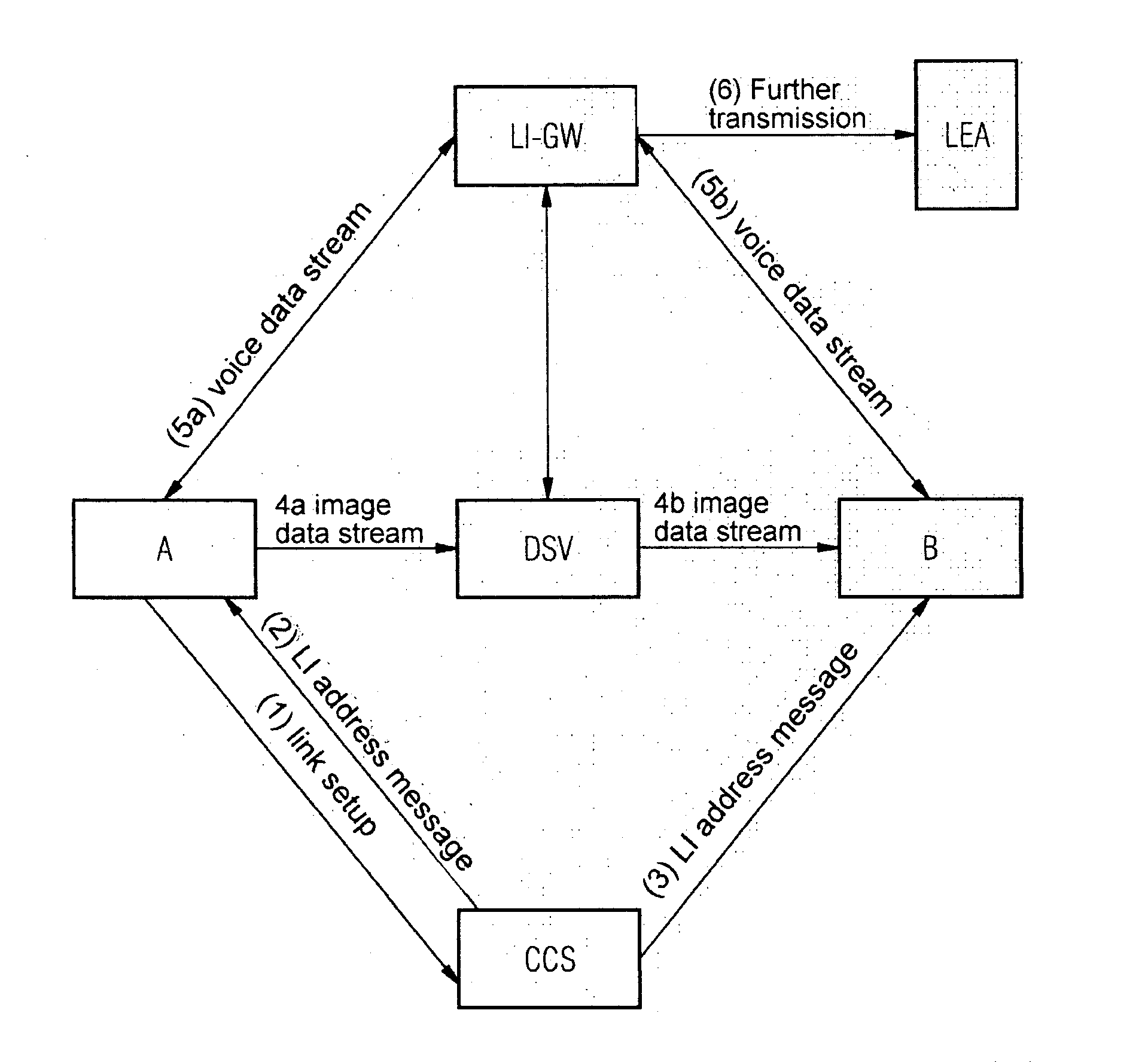
Device For Tapping Useful Data From Multimedia Links In A Packet Network
InactiveUS20080095146A1Active connectionTelevision systemsAutomatic exchangesLawful interceptionData latency
In one aspect, a device for lawful interception of multimedia links in a packet network, over which voice data and image data are transmitted separately is provided. The device includes a receiver unit that receives a image data from a transmit device, and a delay unit that routes the received image data with a delay to a receive device.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
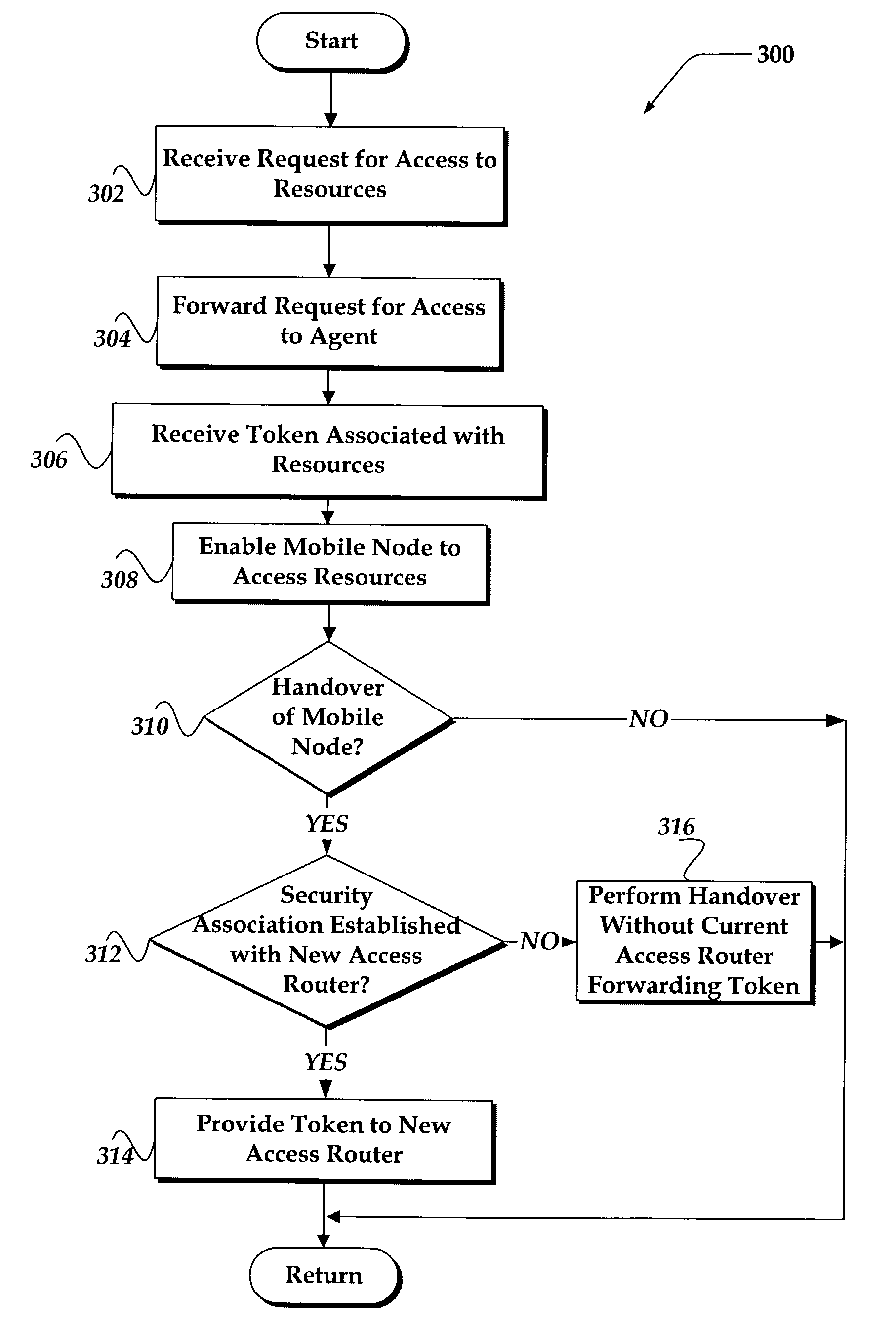
System and method for resource authorizations during handovers
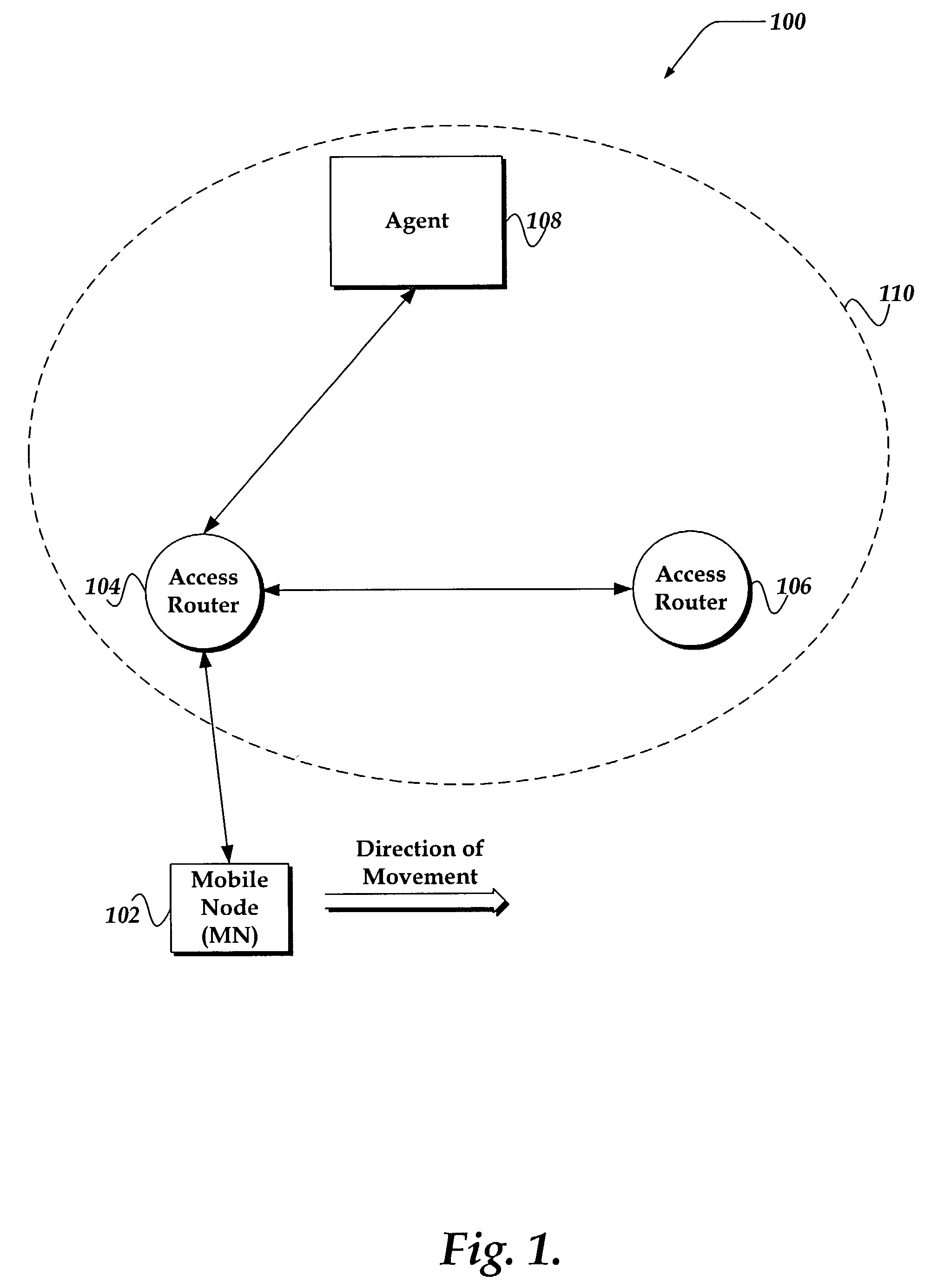
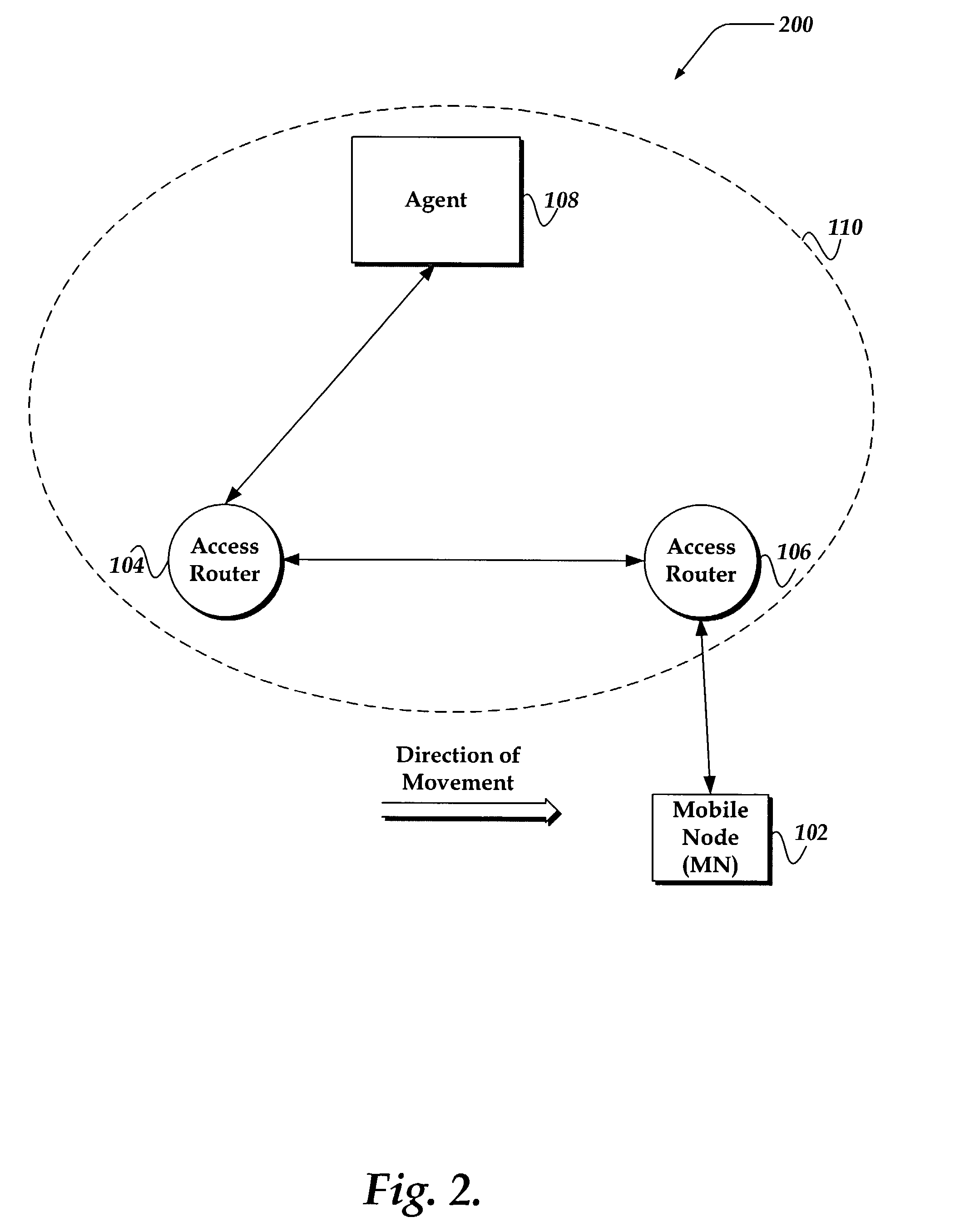
InactiveUS7130286B2Network traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsAccess networkData field
A system and method is provided that enables the transfer of policy resource tokens (PRT) in the process of a handover of a mobile node in a wireless network. The system includes a granting agent that grants the PRT to a first access router to enable the mobile node to access network resources. In one embodiment, in the process of handing over the mobile node, the first access router provides the PRT to the second access router, thereby reducing data latency, and a disruption for an application executing on the mobile node. In another embodiment, the mobile node provides the PRT to the second access router after connectivity is established. A PRT data structure also is provided that includes a data field of profile types. A profile type describes context authorization information for granting access to a network resource.
Owner:RPX CORP
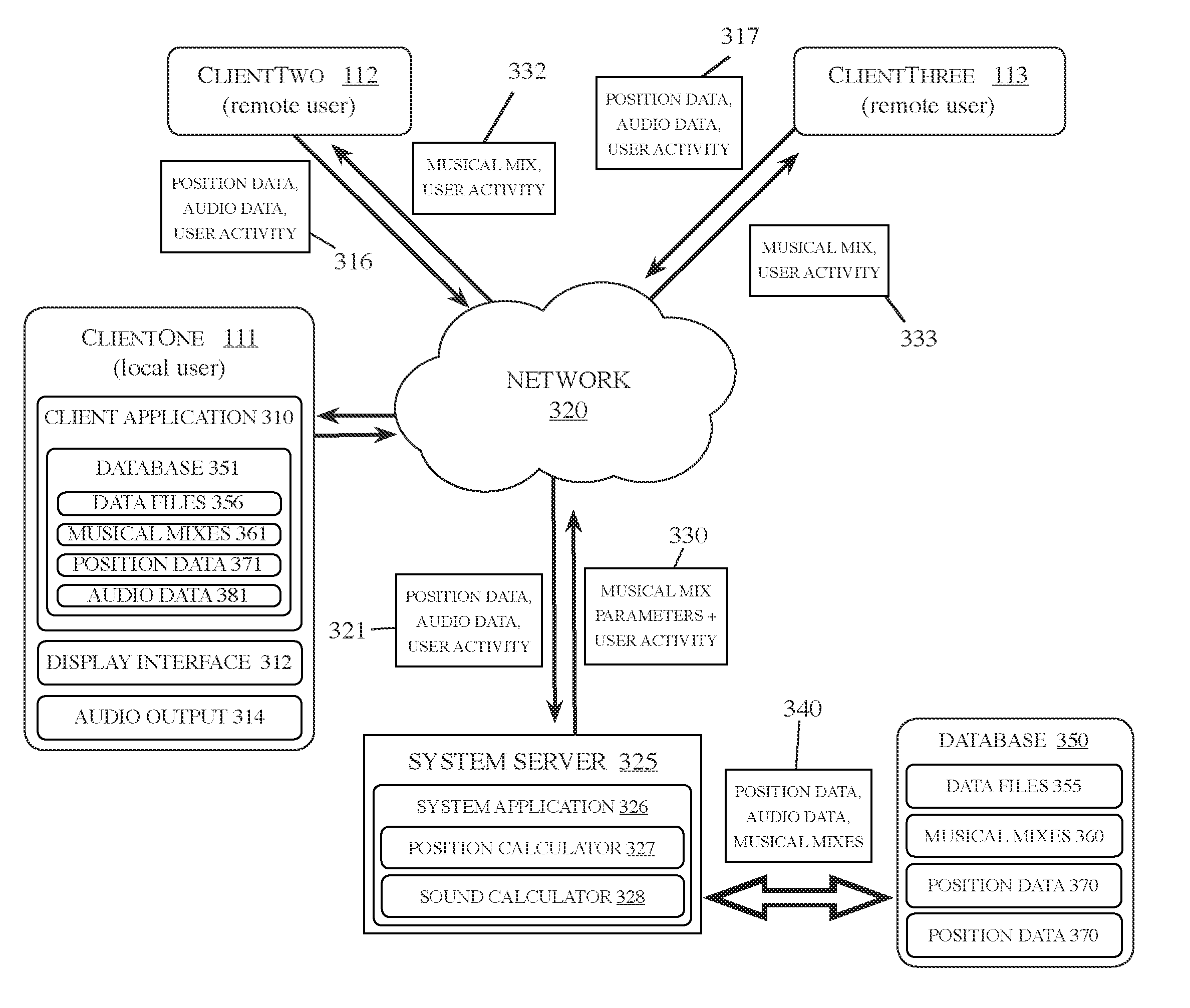
System and method for musical collaboration in virtual space
A system and method for musical collaboration in virtual space is described. This method is based on the exchange of data relating to position, direction and selection of musical sounds and effects, which are then combined by a software application for each user. The musical sampler overcomes latency of data over the network by ensuring that all loops and samples begin on predetermined temporal divisions of a composition. The data is temporarily stored as a data file and can be later retrieved for playback or conversion into a digital audio file.
Owner:PODSCAPE HLDG
Network communications bandwidth control
ActiveUS7701884B2Reduce probabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationReal-time dataPacket loss
A method for controlling real time data communications over a packet based network comprises steps of dynamically measuring data packet loss between a receiver and a sender on the network, dynamically measuring data latency between the sender and receiver, and comparing the dynamically measured data packet loss to a loss limit and comparing the dynamically measured data latency to a latency limit. If one or both of the loss limit or the latency limit is exceeded, then the method may include reducing the rate of data transmission from the sender.
Owner:IOCOM UK LTD
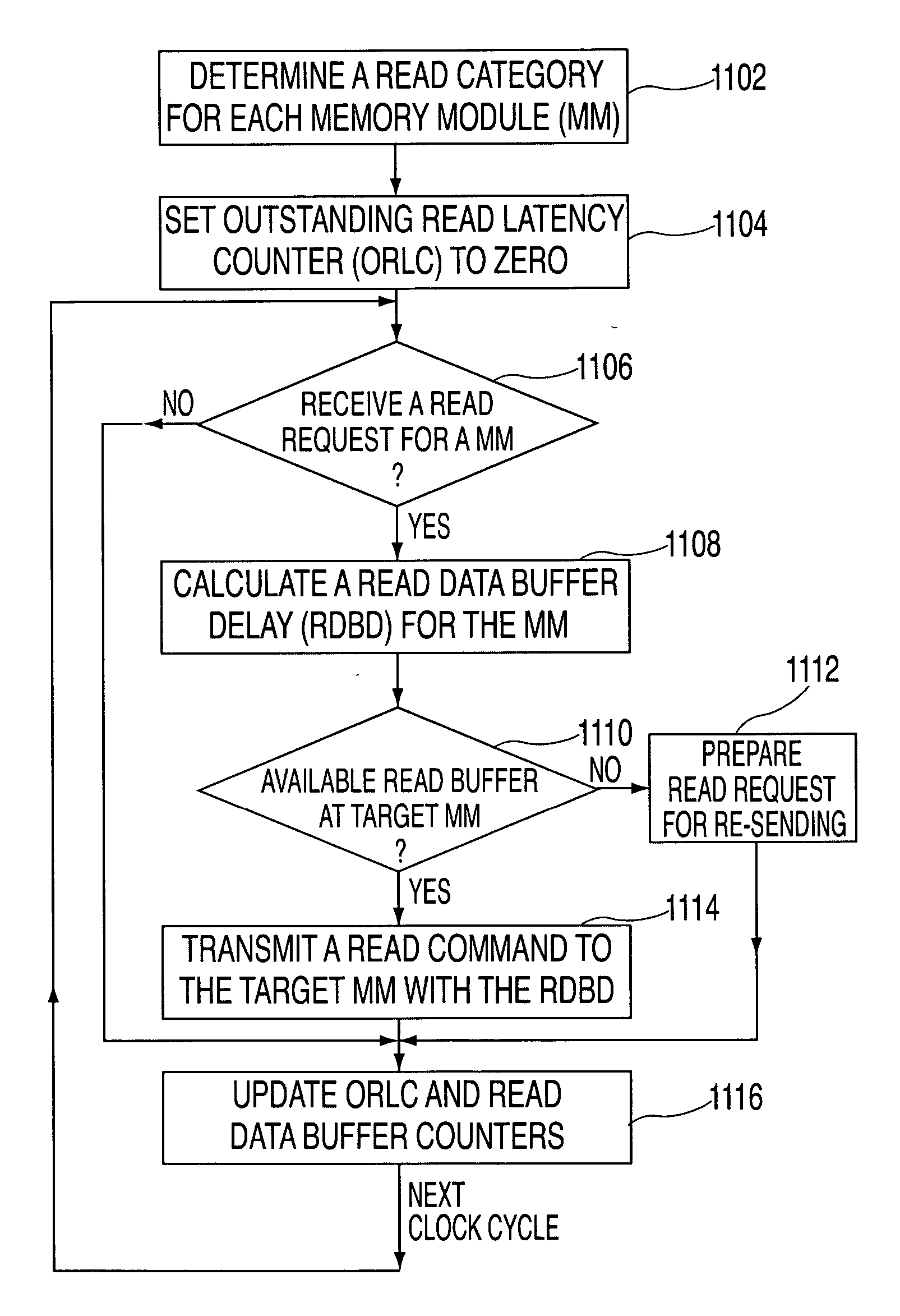
System, method and storage medium for a memory subsystem with positional read data latency
A memory subsystem with positional read data latency that includes a cascaded interconnect system with one or more memory modules, a memory controller and one or more memory busses. The memory controller includes instructions for providing positional read data latency. The memory modules and the memory controller are interconnected by a packetized multi-transfer interface via the memory busses.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for communicating and isolating packetized data through a plurality of last-mile carriers to form a multi-node intranet
InactiveUS20060203820A1Reduce needEliminate needData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsPrivate networkCarrier signal
The invention provides a system and method for transporting packetized data between remote geographic locations in a multi facilities-based carrier and multi-last mile access environment to form a multi-node intranet. The purpose of the invention is to implement a secure, private data service using disparate facilities-based carriers for last-mile connectivity to achieve cost reduction compared to single-carrier, private line or switched or routed private solutions. This is done by providing a system for increased data latency predictability, increased average data latency reduction, and end-to-end data prioritization compared to virtual private networking services utilizing tunneling protocols or public infrastructures for data switching or routing.
Owner:COLUCCIO MARC
Method, system and device for adjusting data volume
ActiveCN101969669ALower latencyAvoid congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityData latency
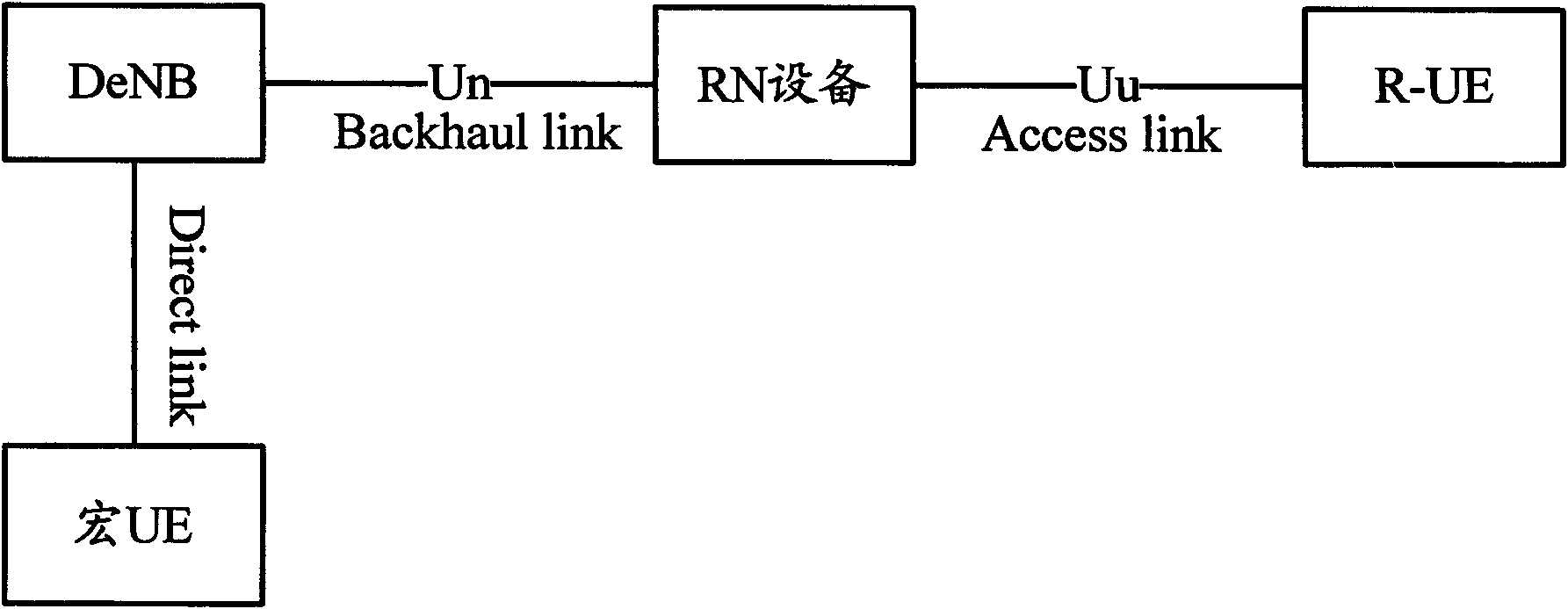
The embodiment of the invention relates to the wireless communication technology, in particular to a method, system and device for adjusting data volume, aiming to solve the problem of the prior art that after the relay-node (RN) is introduced in a long term evolution-advanced (LTE-A) system, DeNB is difficult to control downlink data volume so that the congestion of the downlink data of the RN device and the delay of the downlink data of R-UE are easy to cause. The method of the embodiment of the invention comprises the following steps: the RN device determines traffic scheduling parameter according to the volume of the downlink cache data; the RN device sends the traffic scheduling parameter to a base station and requests the base station to adjust the data volume of the downlink backhaul link according to the traffic scheduling parameter. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, the delay of the downlink data can be reduced and the efficiency of data transmission and the system performance can be increased.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Fast codec with high compression ratio and minimum required resources
ActiveUS8306340B2Adapt quicklyPulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisData compressionProbability estimation
This invention provides a novel single-pass and multi-pass synchronized encoder and decoder, performing order(s) of magnitude faster data compression and decompression, at any compression ratio with the higher or the same perceived and measured decompressed image quality in comparison with the best state-of-the-art compression methods, using order(s) of magnitude less system resources (processor complexity, memory size, consumed power, bus bandwith, data latency). These features are achieved using novel direct and inverse non-stationary filters for the recusive octave direct and inverse subband transformation, novel simple context modeling and symbol probability estimation using a minimum number of histograms with the fast adaptation for the sign and the magnitude of the transformation coefficients, a novel accelerated range coder without division operations, and a novel synchronisation of the compressed data.
Owner:CEPERKOVIC VLADIMIR +3
Adaptive bandwidth utilization for telemetered data
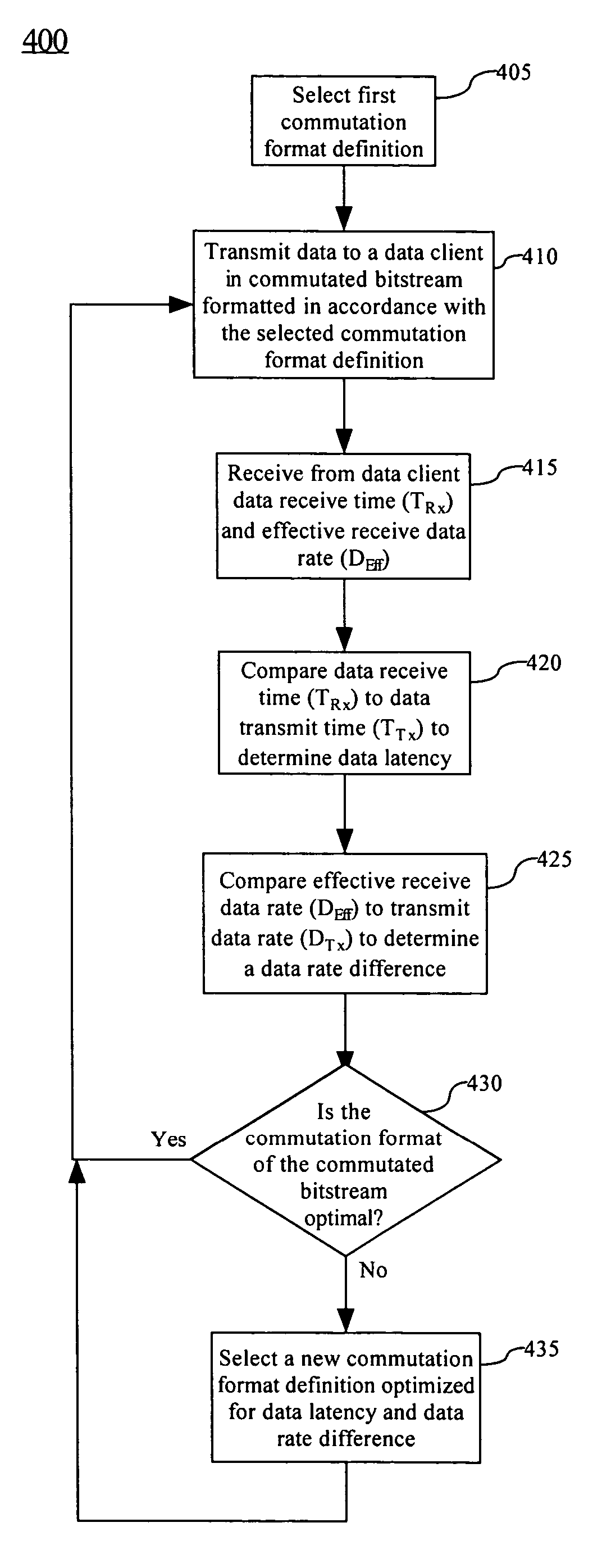
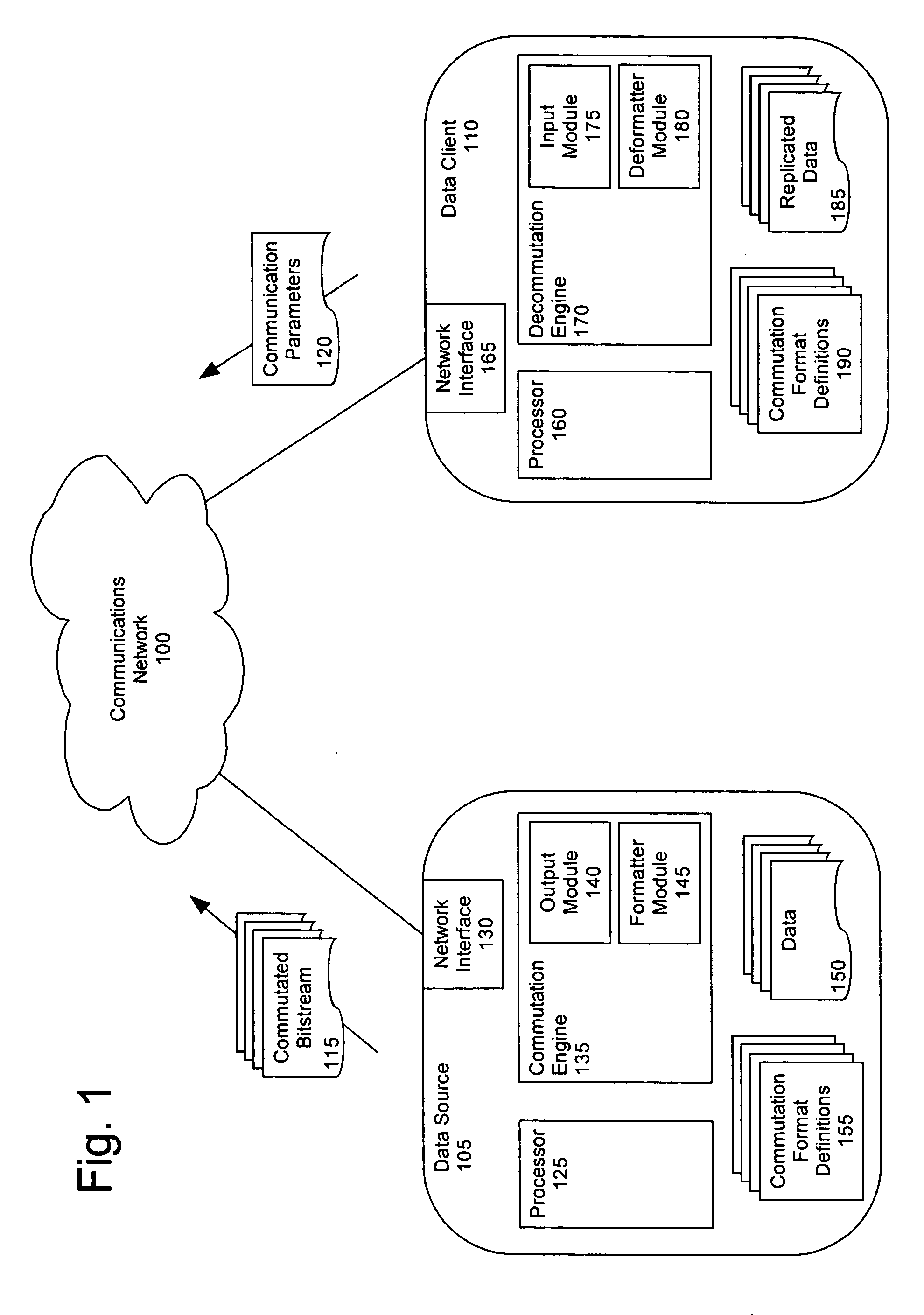
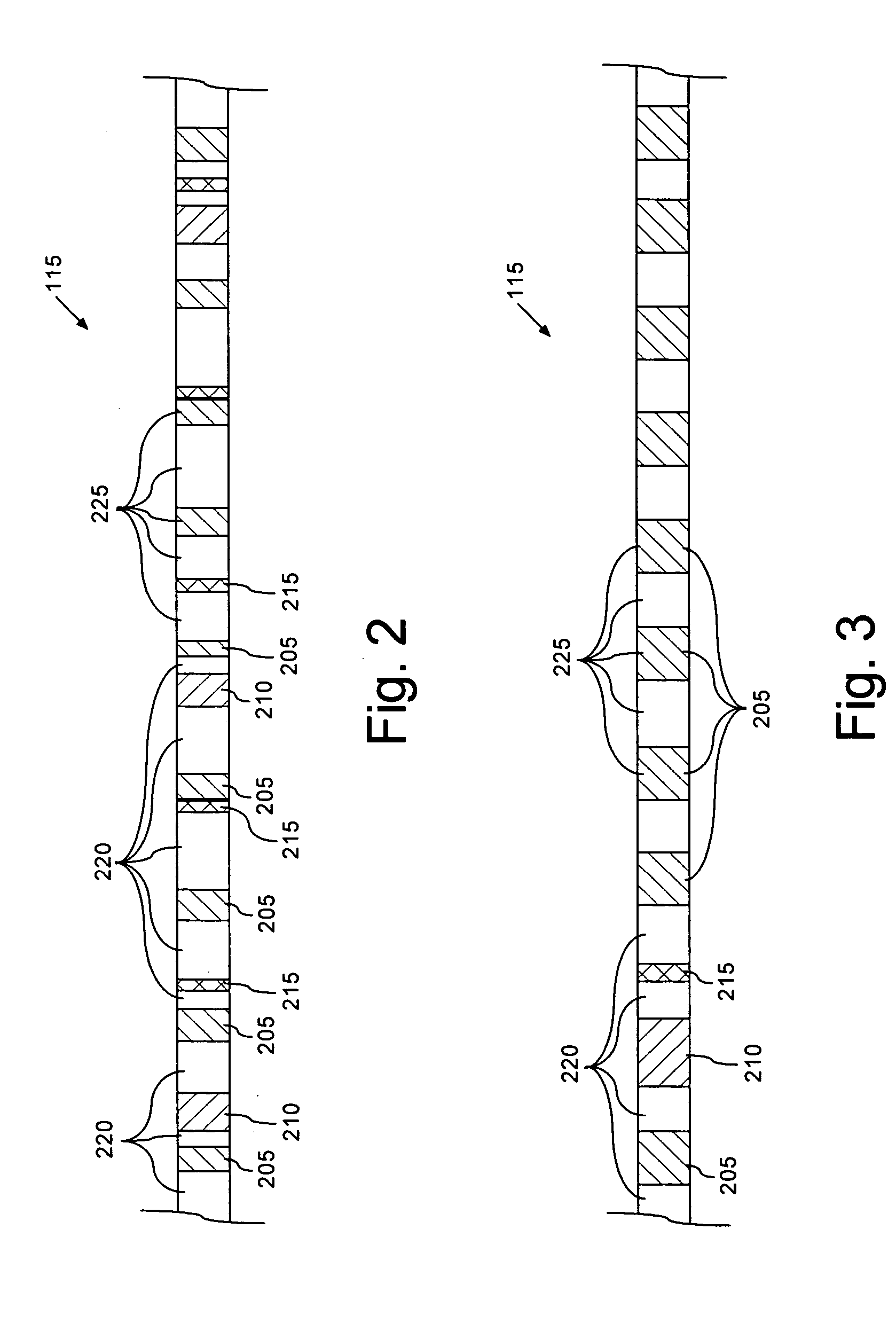
A method (400) for optimizing bandwidth utilization in a communications network (100). The communications network can include a data source (105) and a data client (110). Responsive to a measurement of at least one communication parameter (120) of a commutated bitstream (115) which is transmitted to the client, the data source can change a commutation format of the commutated bitstream. The communication parameters can include a data receive time (TRx), a data latency and / or an effective receive data rate (DEff) of the commutated bitstream. The communication parameters can be transmitted to the data source as telemetry. The change of commutation format can occur in an open systems interconnection (OSI) layer such as a session layer and / or a transport layer.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Pilot reconfiguration and retransmission in wireless networks
ActiveUS20160352481A1Transmission path divisionSignal allocationTelecommunicationsWireless mesh network
Adaptive signaling (e.g., pilot signaling, control signaling, or data signaling) is disclosed in which resources allocated to one or more symbols are allowed to vary to more closely match channel conditions and data latency requirements. In one embodiment, a method includes determining that low-latency data is available to transmit during a first transmission time interval (TTI) and informing a mobile station that the low-latency data will be transmitted during one slot reserved for a symbol in the first TTI. The low-latency data may be transmitted during the first time slot in the first TTI and the symbol (originally scheduled symbols) may be transmitted during a second time slot.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
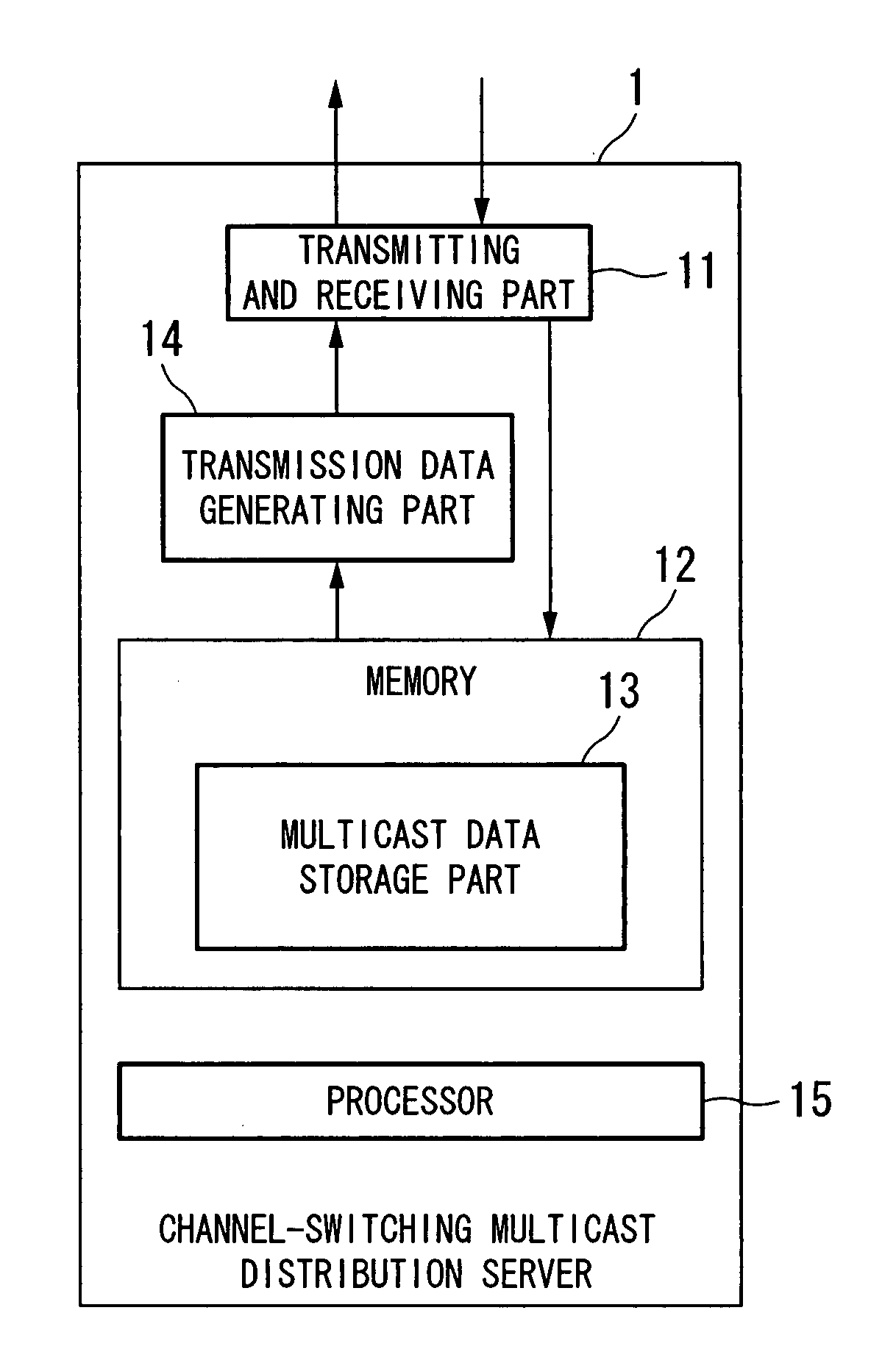
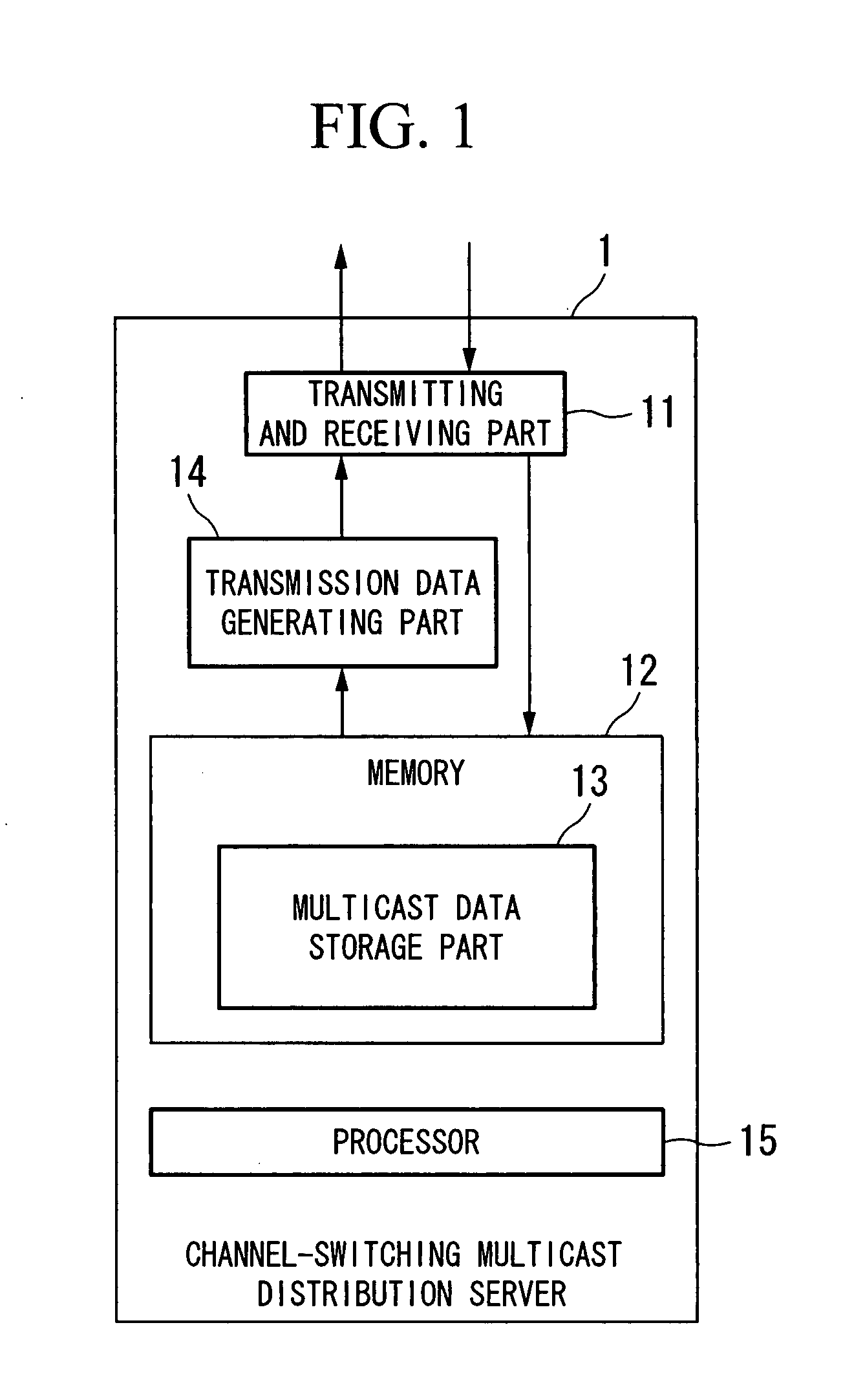
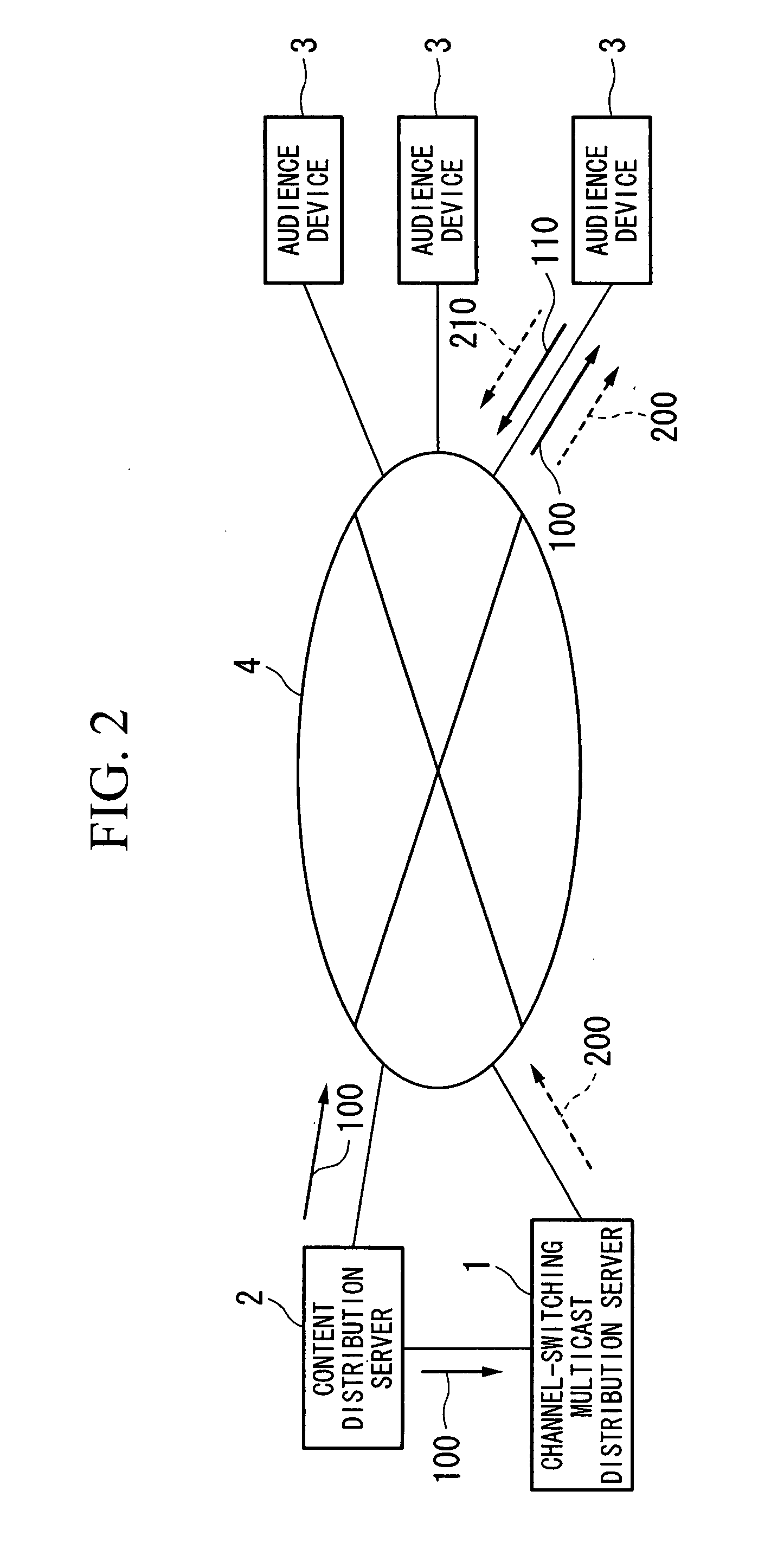
Channel-switching multicast distribution apparatus and method, and multicast reception apparatus
InactiveUS20080013563A1Reduce loadSimplify the communication processTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionData latencyMulticast
A channel-switching multicast distribution apparatus in a system for providing channels by multicast. The apparatus includes a device for receiving multicast data of a first multicast group for a first channel; a device for storing the received multicast data; a delaying device for reading the stored multicast data, and delaying the data by a predetermined time; and a transmission device for transmitting the delayed data through a second multicast group for performing channel switching so as to select the first channel. Instead of the delaying device and the transmission device, a data rearranging device for reading the stored multicast data, and rearranging the data so as to change the order of packets thereof; and a transmission device for transmitting the rearranged data through a second multicast group for performing channel switching so as to select the first channel may be provided.
Owner:KDDI CORP
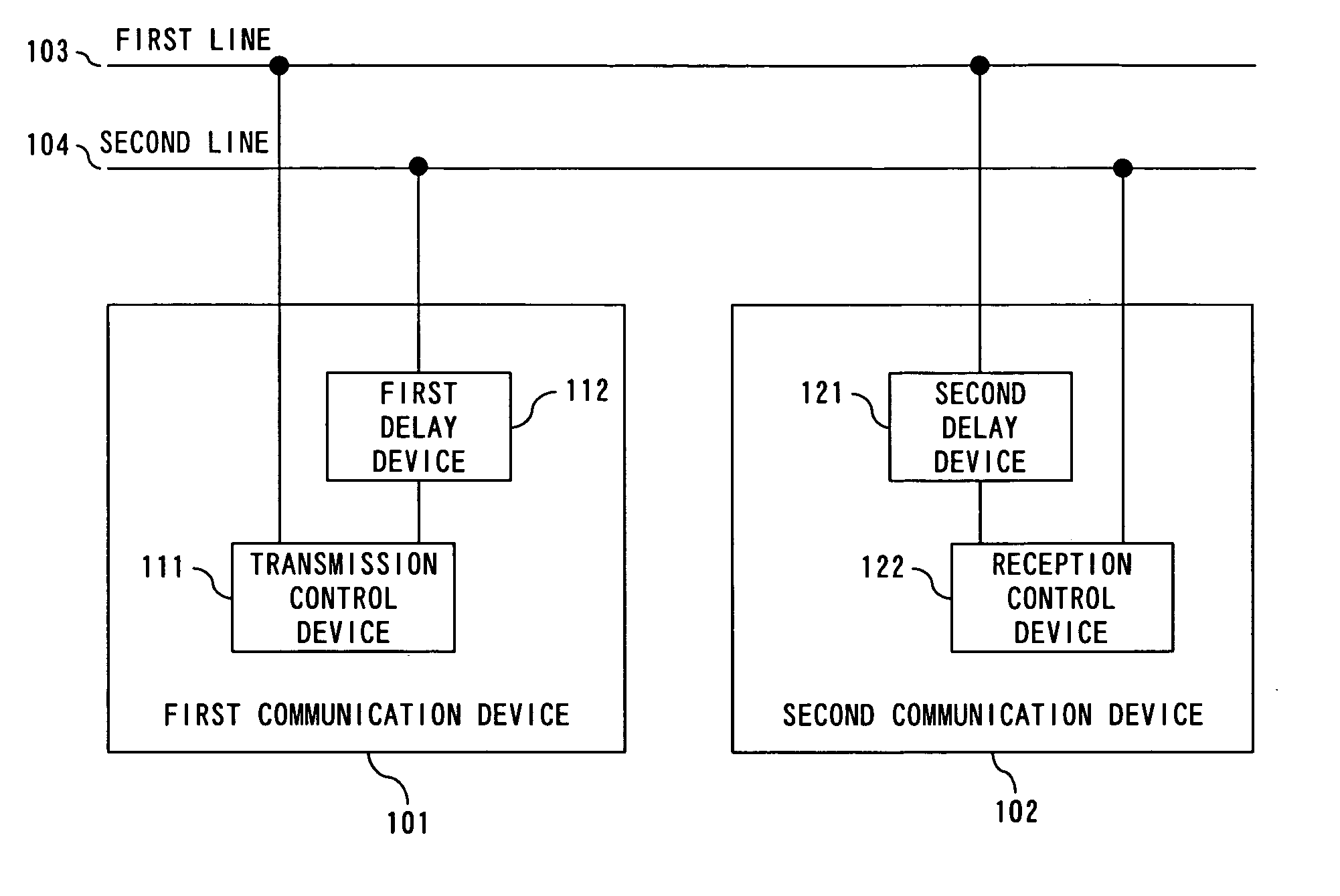
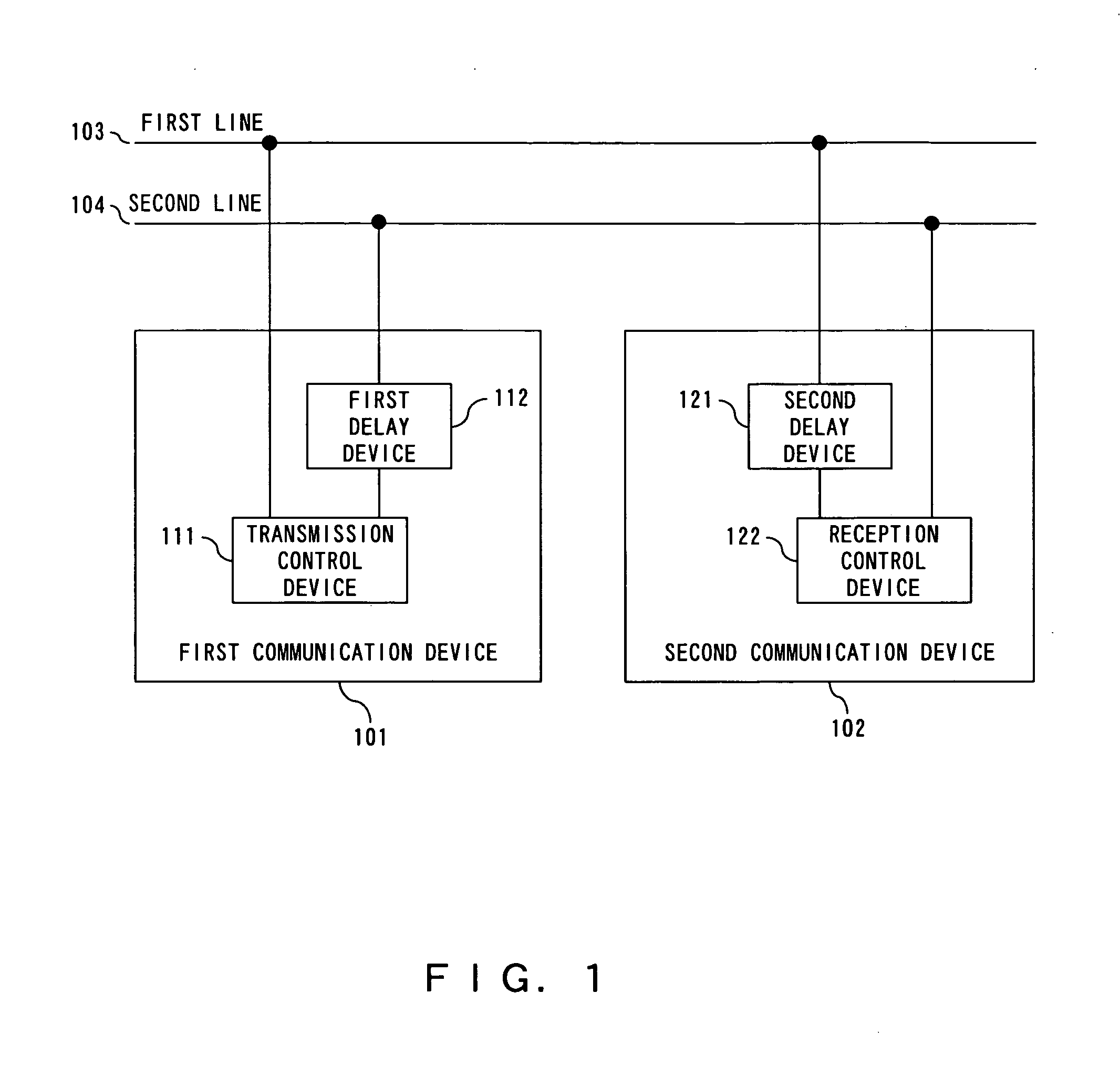
Communication device for performing redundant data communication
InactiveUS20080002571A1Short timeNormal dataError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemData latency
In a communication system for transmitting / receiving redundant data between a first communication device and a second communication device, using first and second lines, the first communication device transmits first transmitting data to the first line, and also delays the first transmitting data by a prescribed time and transmits the delayed transmitting data to the second line as second transmitting data. The second communication device delays first receiving data inputted from the first line by the prescribed time and generates the delayed receiving data, and selects one of the second receiving data inputted from the second line and the delayed receiving data.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
System and method for QoS-based storage tiering and migration technique
InactiveUS8230192B2Sacrificing all of its material advantageError detection/correctionMemory systemsQuality of serviceData latency
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method of determining data latency over a network
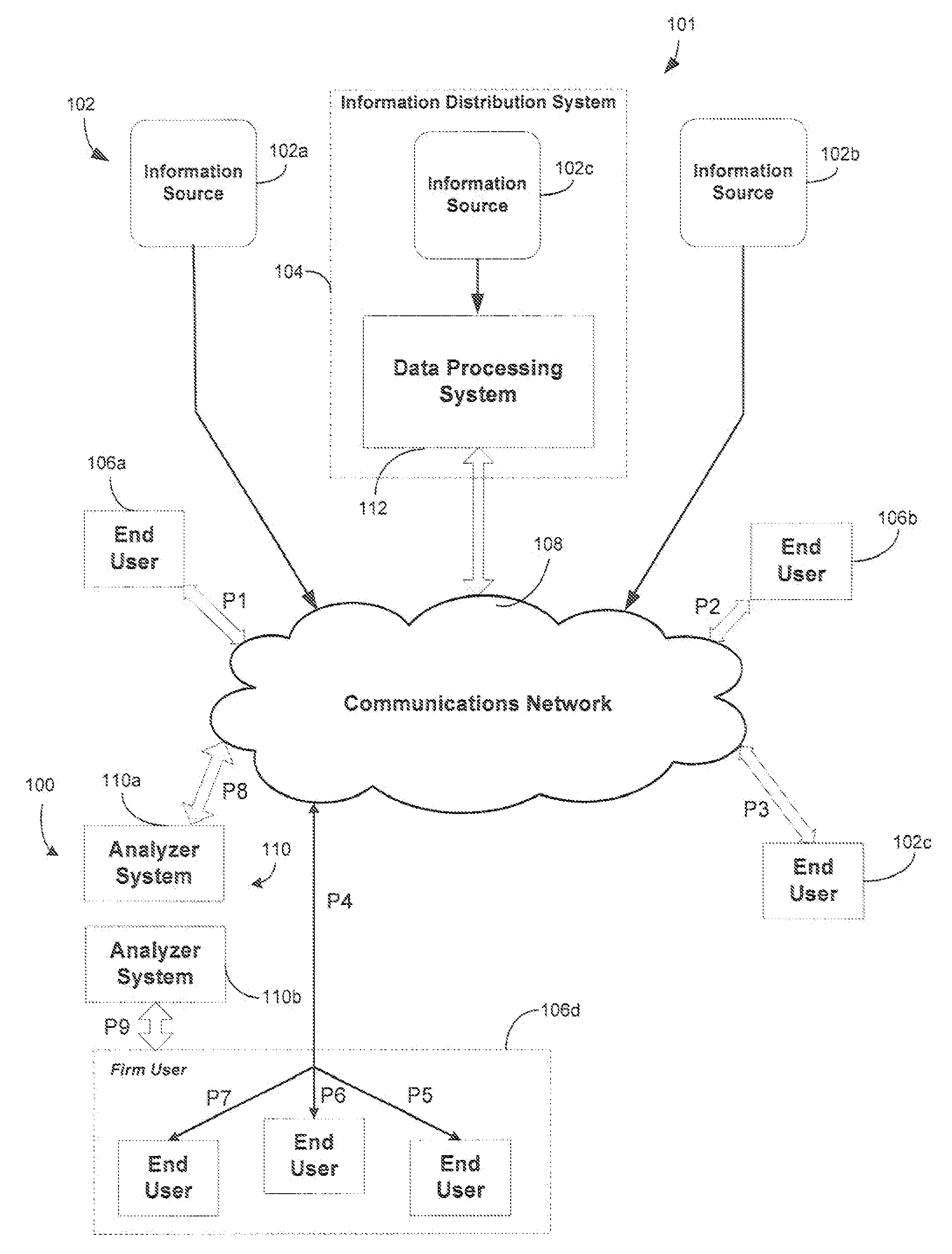
A system and method of determining data latency in a network is provided. A first data sample of application level data (e.g., financial data) is provided from a data stream received at a first network point. A second data sample of application level data (e.g., financial data) is also provided from a data stream received at a second network point, where the data streams in the first and second network points include common data and the first and second data samples include common data. A correlation between common data, in the first and second data samples is determined and a time difference between the correlated common data in the first and second data samples is then calculated.
Owner:BLOOMBER FINANCE LP +1
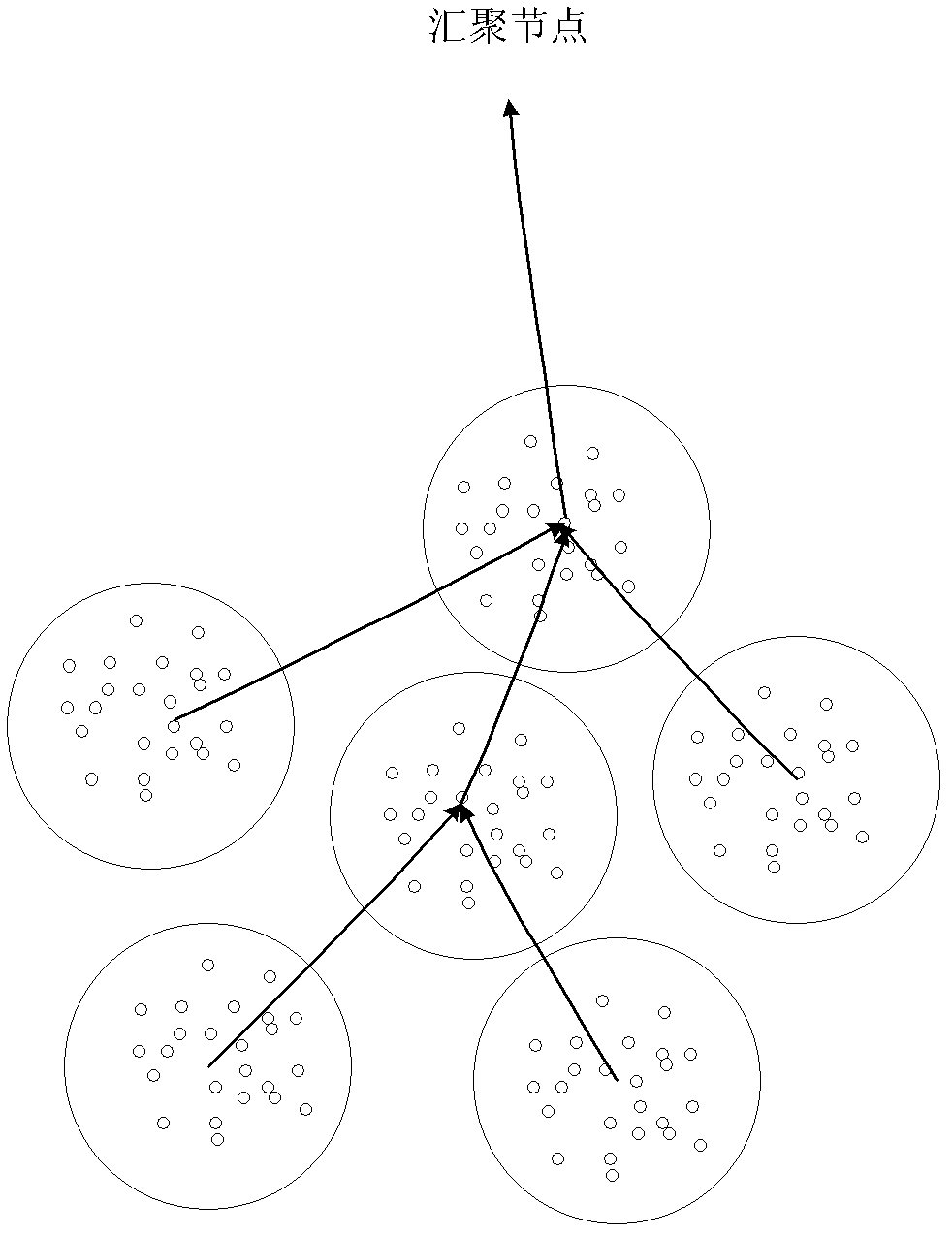
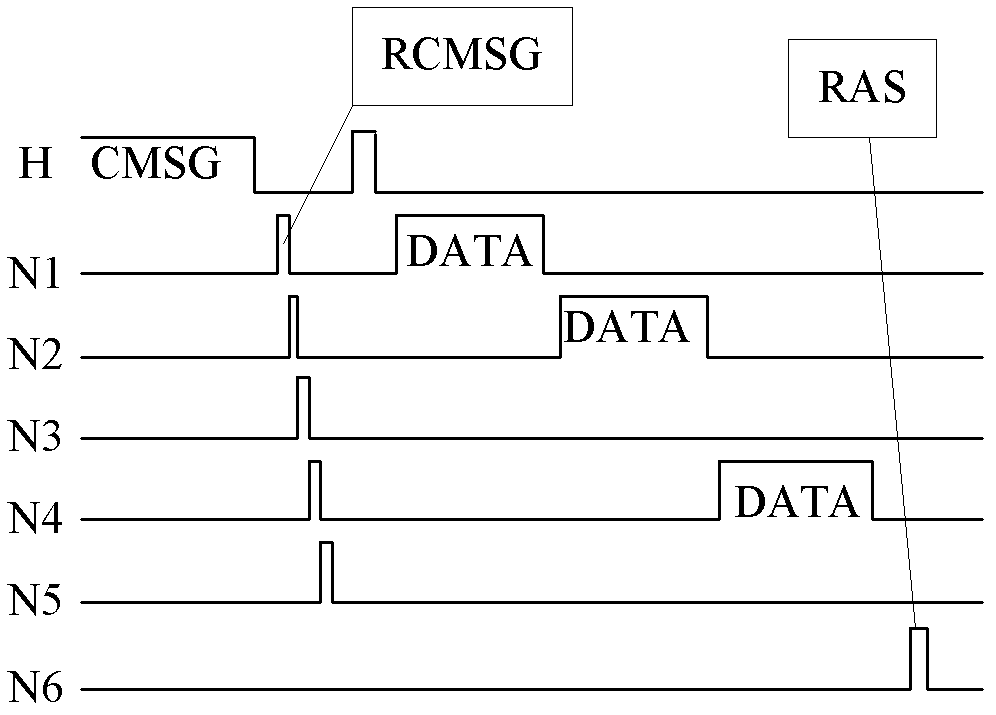
Low-latency data aggregation algorithm
InactiveCN102497440ANetwork topologiesData switching networksClear to sendTime division multiple access
The invention provides a data aggregation algorithm in a wireless sensor network, belonging to the field of wireless sensor networks. The method is suitable for hierarchical networks with a topology structure. The algorithm has the following beneficial effects: through a dynamic time division multiple access (TDMA) mechanism in a cluster, a cluster head data cache mechanism in a cluster head grouping and forwarding mechanism, a cluster head path selection algorithm and a cluster head data forwarding low-latency request to send / clear to send (RTS / CTS) mechanism, the transmission congestion of the network can be relieved, conflicts and collision in transmission can be reduced and the transmission efficiency of the wireless channels is improved; and compared with the traditional data aggregation mechanisms, the low-latency data aggregation mechanism can reduce the data latency from acquisition to transmission to convergent nodes on the basis that the data aggregation efficiency is ensured.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Storage function method and apparatus in a passive optical network
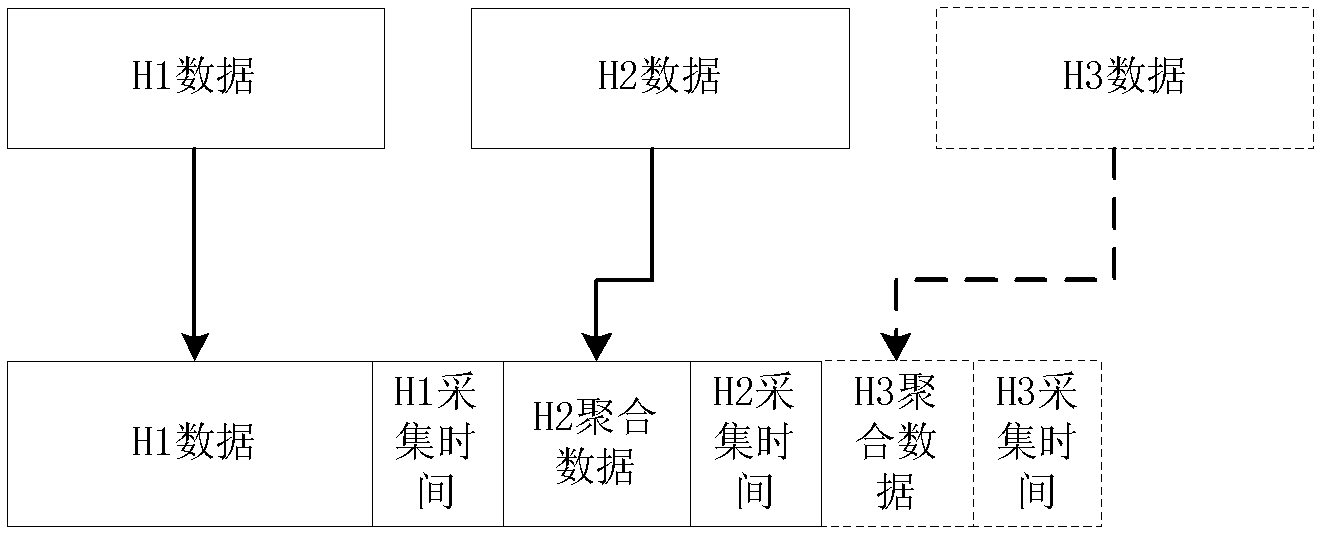
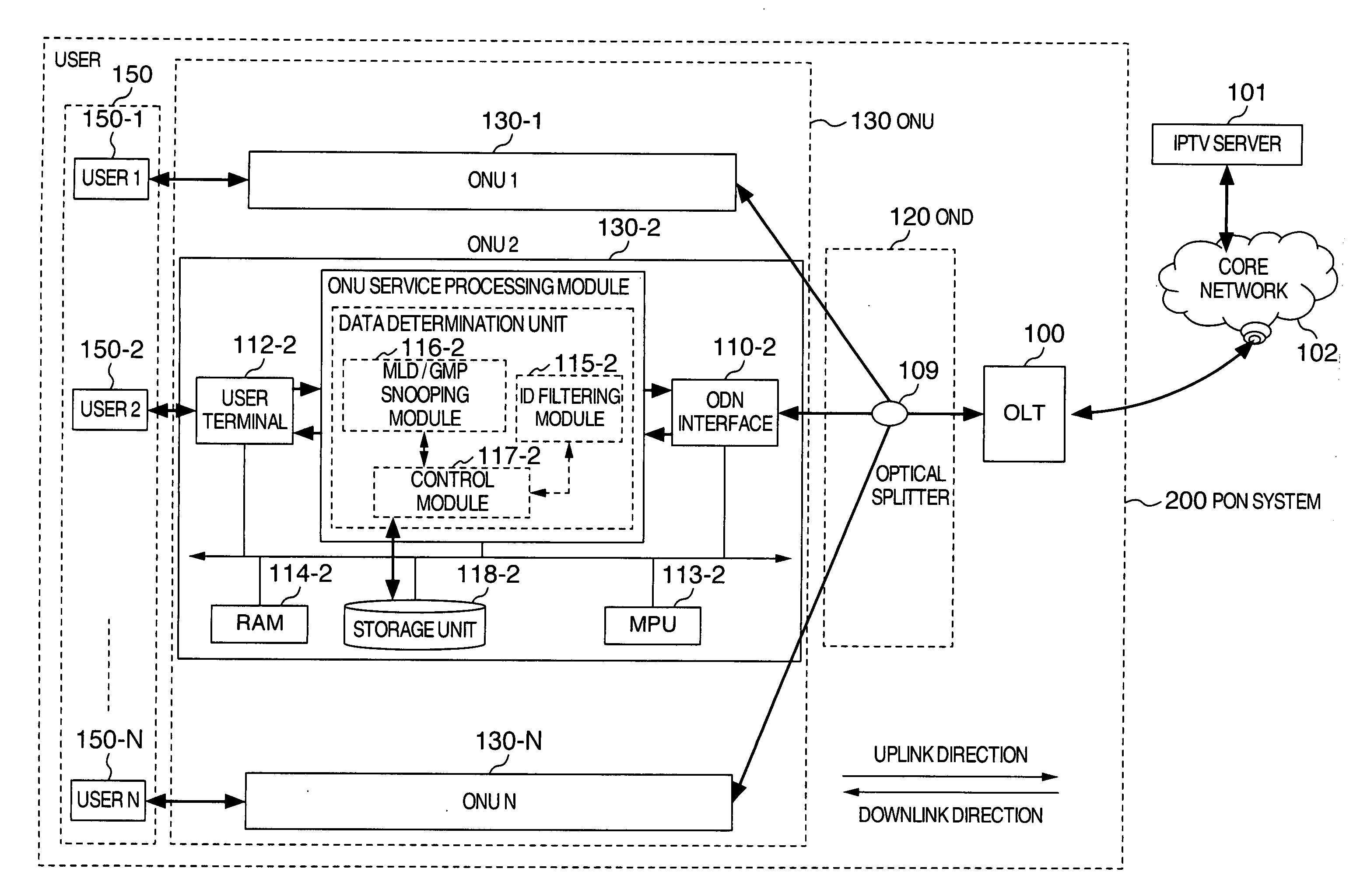
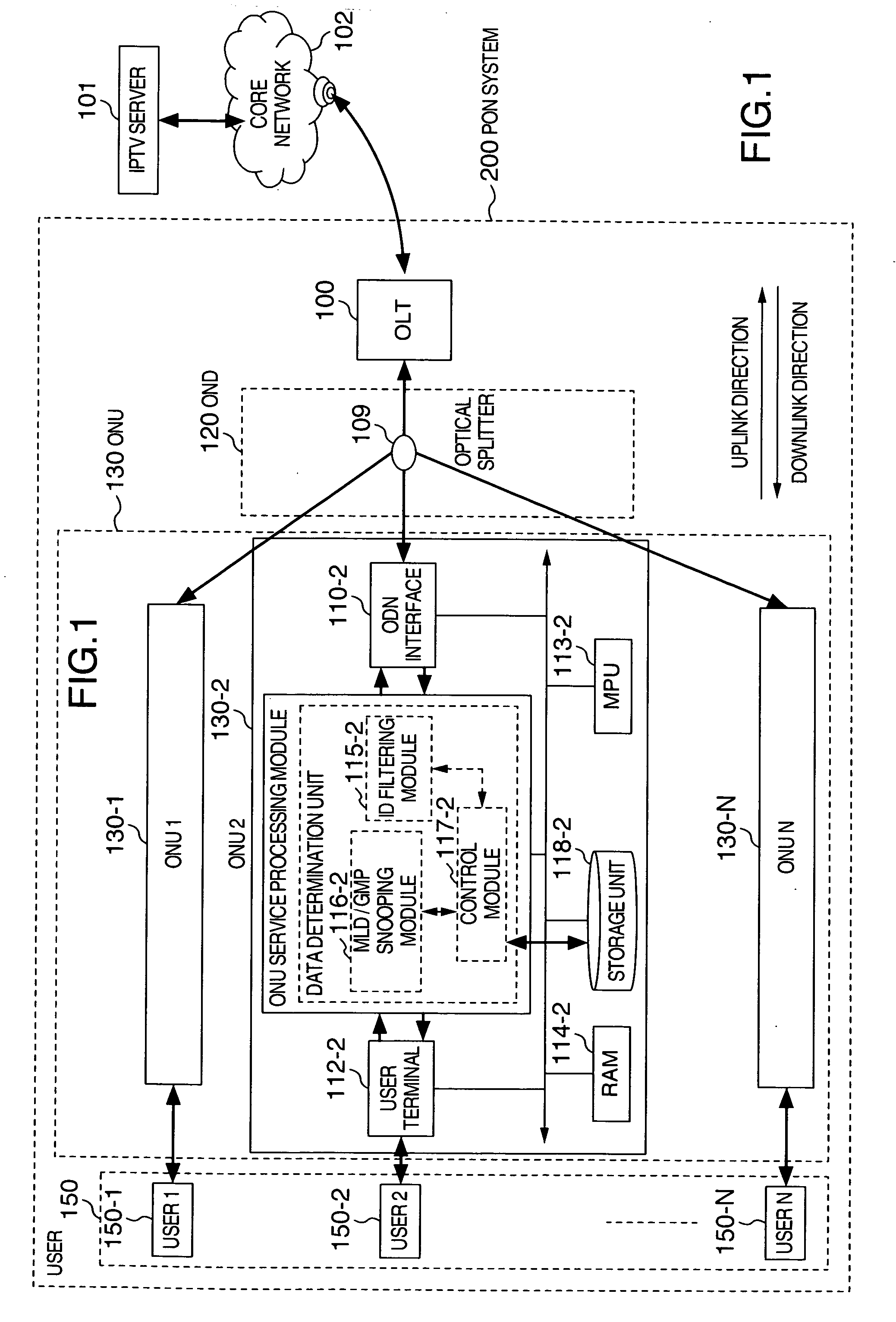
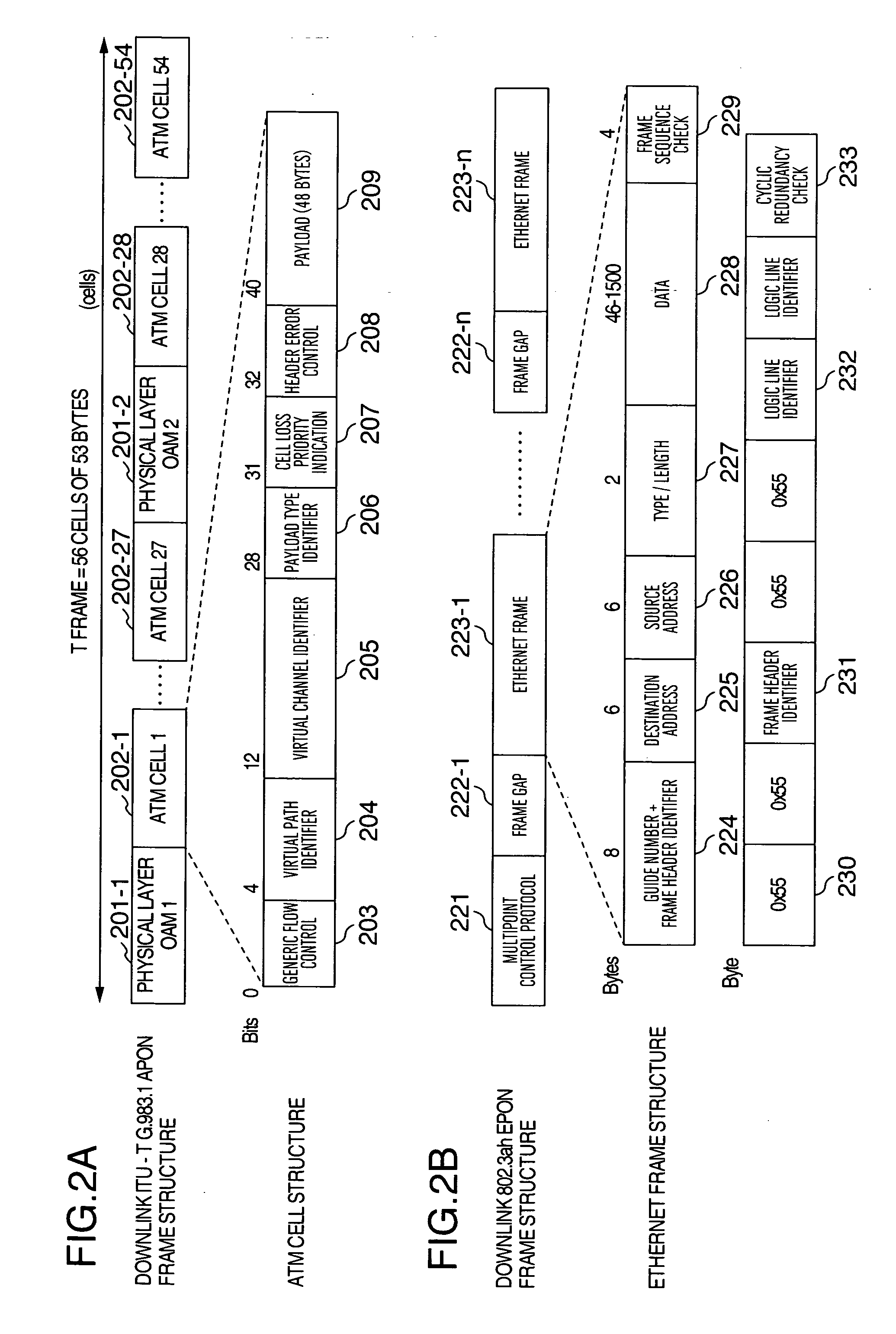
InactiveUS20070230471A1Increase profitReduce congestionTelevision system detailsStar/tree networksData storeCore network
A method and an apparatus for implementing a storage function in a passive optical network (PON) system. On the basis of a LINK ID held by the data, data requiring storage, e.g. data making exclusive use of a wide bandwidth such as audiovisual data and large-volume data packages, are determined among all the data sent to an optical network unit. These data requiring storage are stored in a storage device installed in the optical network unit. In case the user requests data stored in the storage device, the stored data are transferred directly to the user, without any need to request and send these data for the second time via an IPTV server and the core network. It is possible to avoid duplicate transfers of data, and in particular to avoid duplicate transfers of data making exclusive use of a comparatively wide bandwidth such as audiovisual data and large-volume data packages, to improve the utilization factor of the downlink bandwidth, and to reduce flow congestion and data delays.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Asynchronous FIFO memory design with power of which the depth is not 2
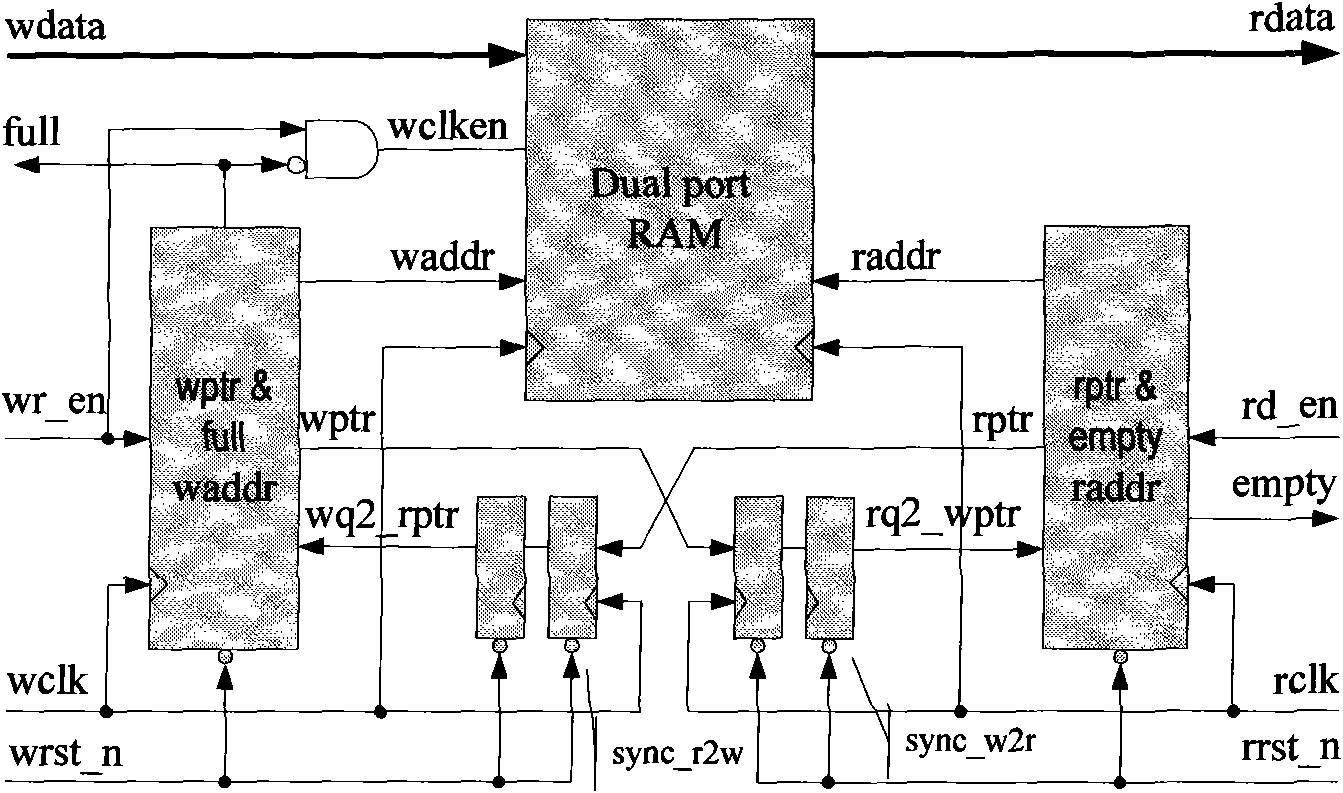
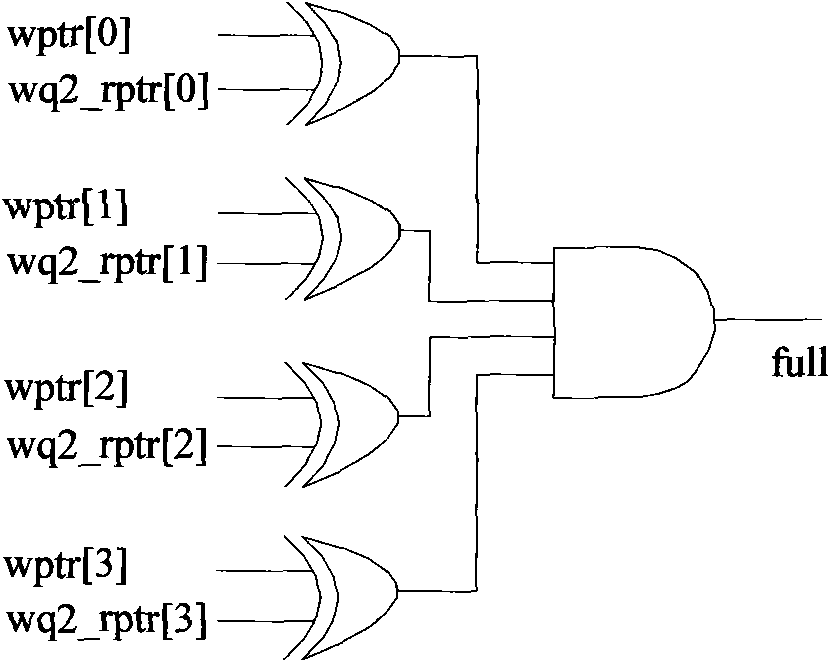
InactiveCN101930350AAvoid conversionSimple structureSpecial data processing applicationsData conversionMostly TrueData latency
The invention relates to an asynchronous FIFO memory design with power of which the depth is not 2, belonging to the field of integrated circuits, and being used for solving the problem of quick transfer of data among different clock domains. Data transfer among asynchronous clock domains is generally realized by adopting an asynchronous FIFO memory. Because the asynchronous FIFO generally adopts a Gray code design mode, the designed FIFO depth is 2n as required. Under most conditions, the actually required depth can not happen to be 2n, thus the design requirement not only increases the area and power consumption, but also due to the FIFO working mode, redundant memory depth is bound to cause the increase of data output latency. The invention proposes the design clew for realizing asynchronous FIFO by constructing a single step cyclic code, so that the designed depth is no longer a designated value, thereby not only saving the area and power consumption of a chip, but also reducing the data latency.
Owner:MAANSHAN LONGXUN TECH
System and method for qos-based storage tiering and migration technique
InactiveCN102147709AInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionQuality of serviceData latency
The present invention relates to a system and method for QoS-based storage tiering and migration technique. The method allows for configurable application data latency thresholds to be set on a per user basis and / or a per application basis so that a storage tiering mechanism and / or a storage migrating mechanism may be triggered for moving application data to a different class of storage.
Owner:LSI CORP
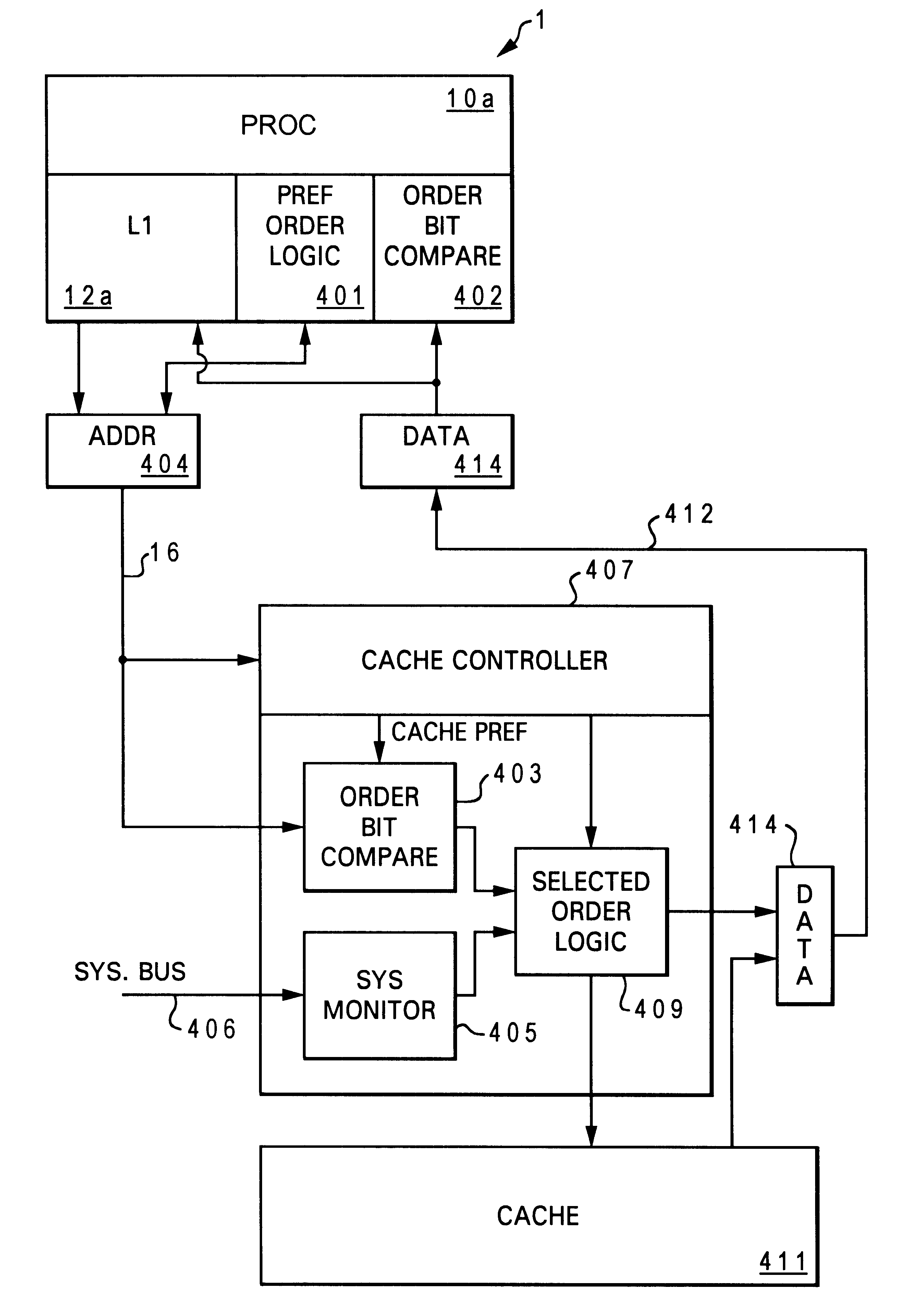
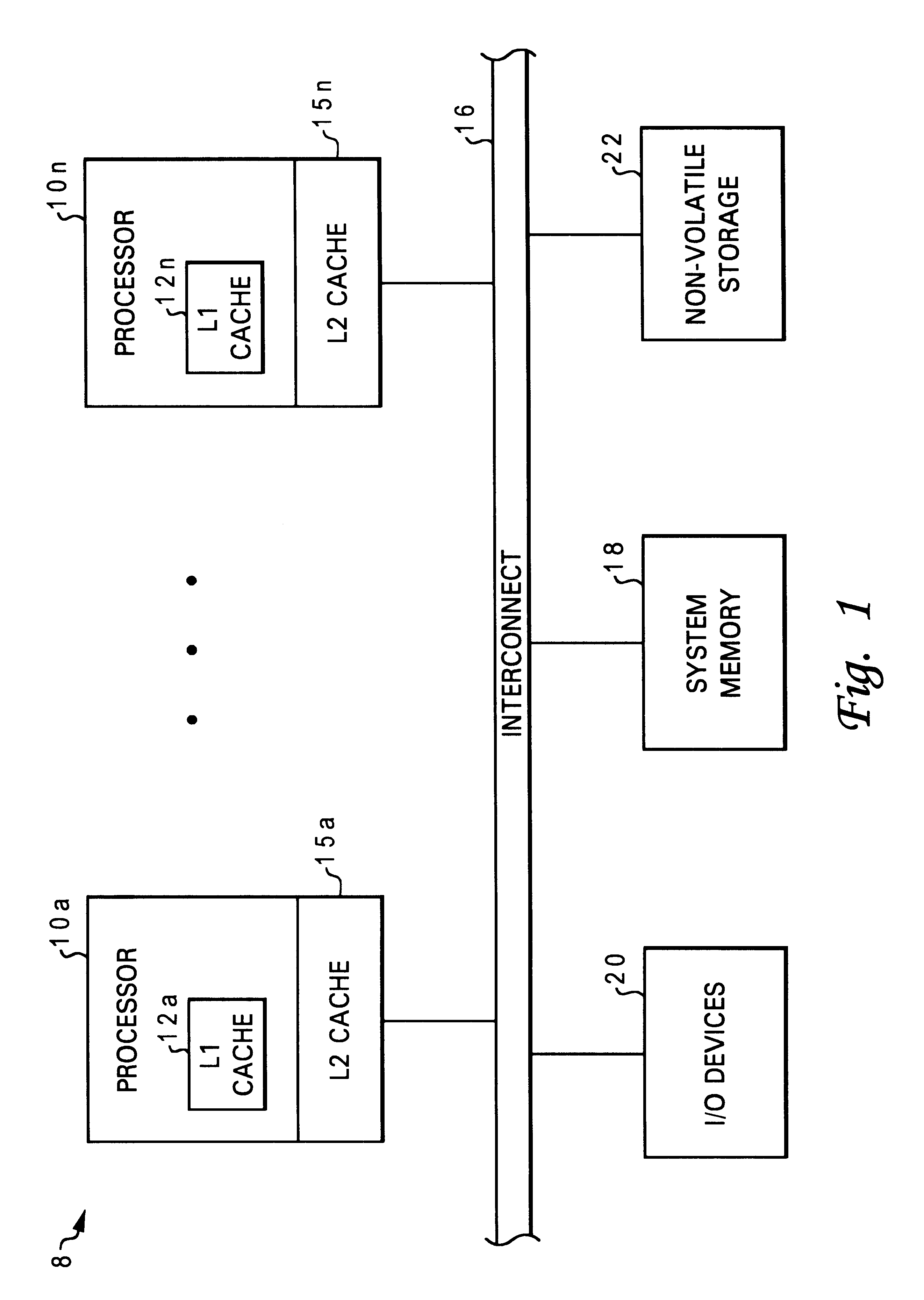
System bus read data transfers with bus utilization based data ordering
InactiveUS6535957B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationNext instruction address formationData processing systemData latency
A method for selecting an order of data transmittal based on system bus utilization of a data processing system. The method comprises the steps of coupling system components to a processor within the data processing system to effectuate data transfer, dynamically determining based on current system bus loading, an order in which to retrieve and transmit data from the system component to the processor, and informing the processor of the order selected by issuing to the data bus a plurality of selected order bits concurrent with the transmittal of the data, wherein the selected order bit alerts the processor of the order and the data is transmitted in that order. In a preferred embodiment, the system component is a cache and a system monitor monitors the system bus usage / loading. When a read request appears at the cache, the modified cache controller preference order logic or a preference order logic component determines the order to transmit the data wherein the order is selected to substantially optimize data bandwidth when the system bus usage is high and selected to substantially optimize data latency when system bus usage is low.
Owner:IBM CORP
Flow control mechanism
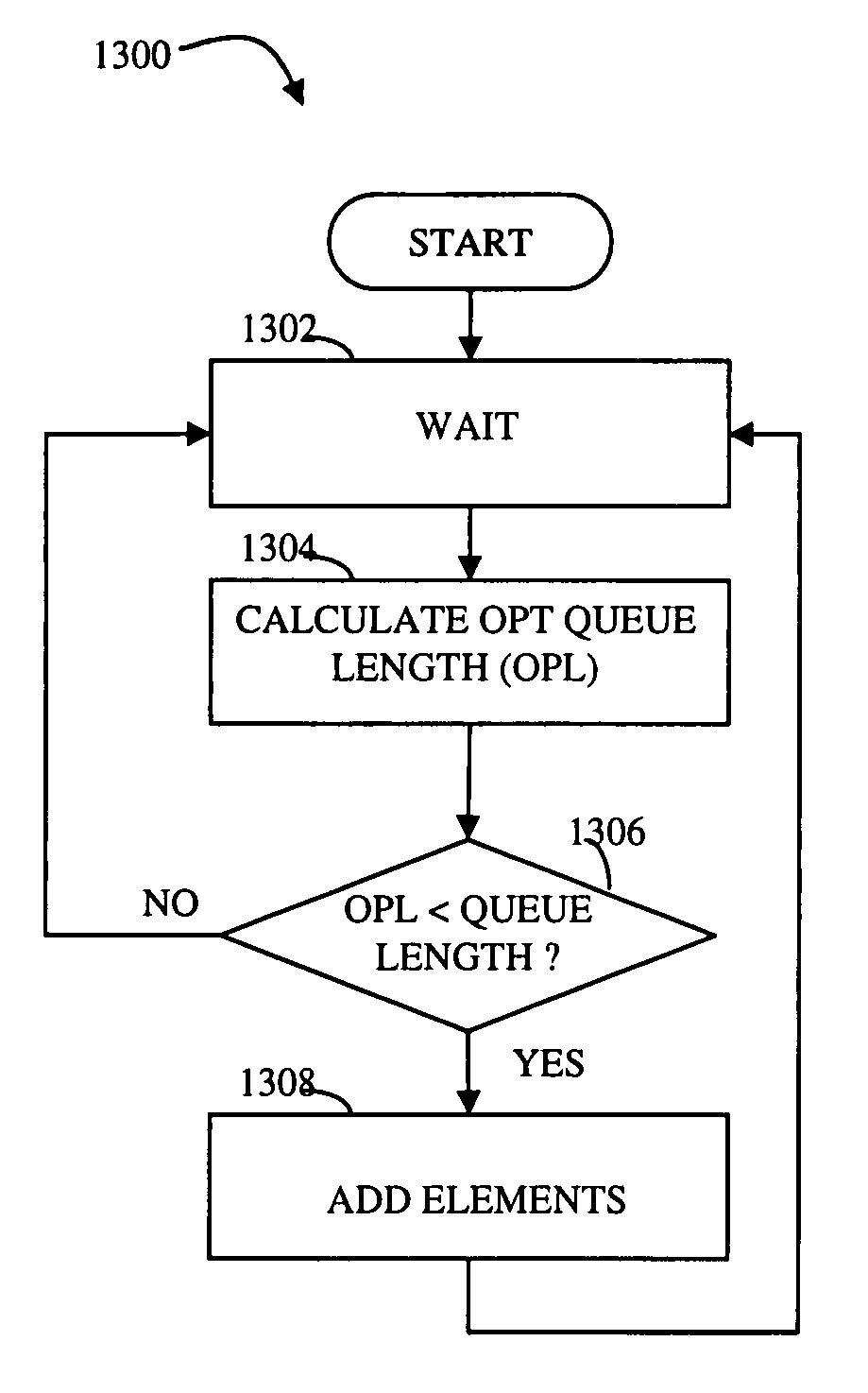
ActiveUS7730237B1Extended latencyConstant gainMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData latencyData element
Transferring data elements from a source to a destination includes providing a transmission queue at the source, where data elements in the transmission queue are transferred from the source to the destination, determining an optimal length for the transmission queue, where the optimal queue length is inversely proportional data latency time at the destination, and, if the optimal length is greater than an instantaneous length of the transmission queue, adding data elements to the transmission queue. Adding data elements may include adding a number of elements corresponding to a difference between the optimal length and the instantaneous length of the transmission queue. Determining optimal length may include dividing a constant by the data latency time at the destination. Transferring data elements may also include providing a network between the source and the destination.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Radio integrated circuit
InactiveUS20060182188A1Increase ratingsError preventionModulated-carrier systemsData latencyField data
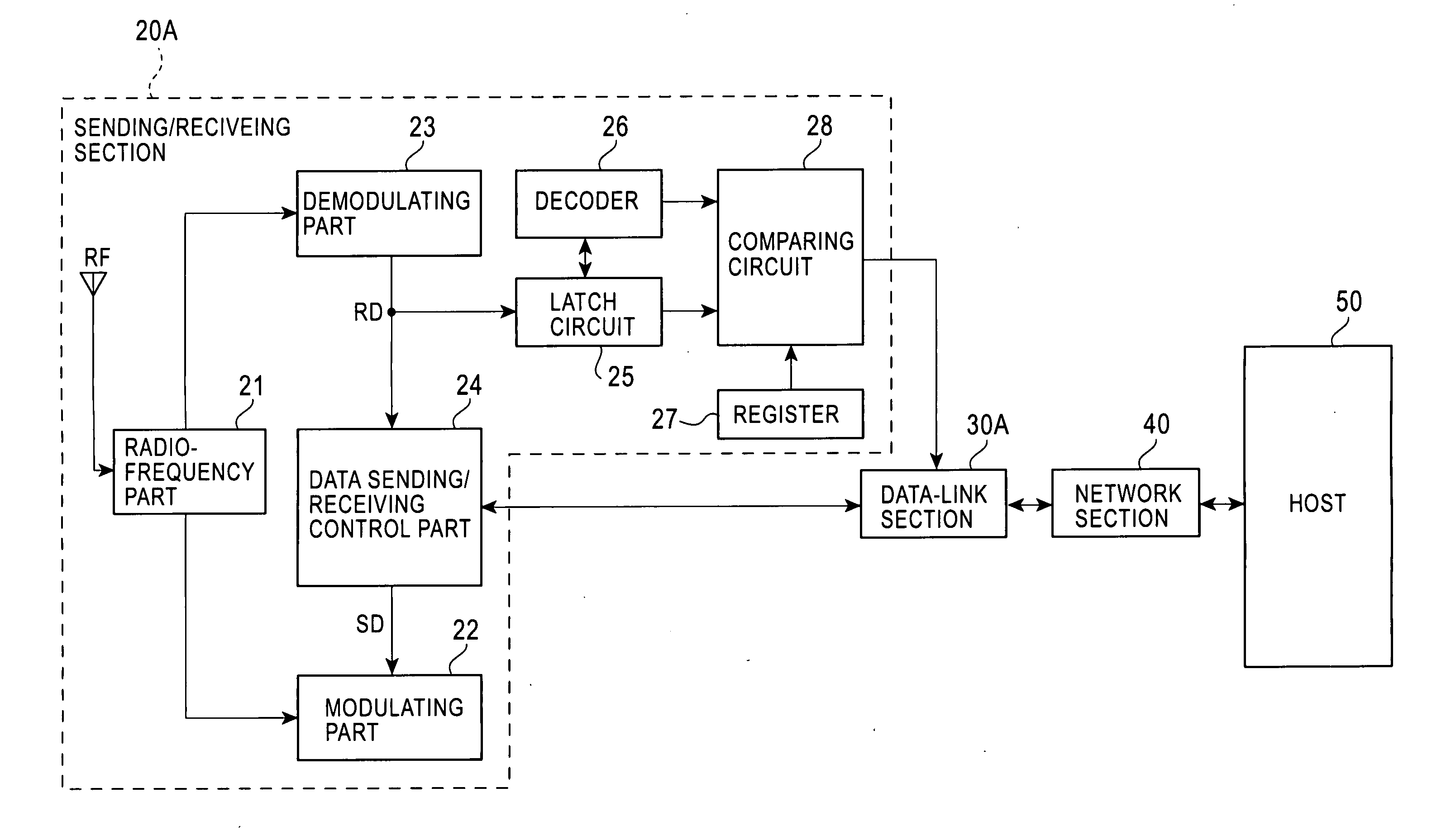
A radio LSI is provided that is not to cause a delay in sending acknowledgement data. A latch circuit provided in a sending / receiving section latches frame control information out of data being received. A decoder decodes the frame control information to decode a data length and structure of an address field. Furthermore, a latch circuit latches the address-field data of the reception data according to the decoded address-field information. A comparing circuit compares a content of a register entered with an address of the opposite-of-communication completely prepared data to be sent, with a source address of the data being received, to determine a setting / resetting of frame pending in acknowledgement data. A content of the determination is sent to a data-link section. This provides information required for acknowledgement data before completely receiving data, thus eliminating the possibility to cause a delay in sending acknowledgement data.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission of sensor data with latency controls
ActiveUS8462681B2High bandwidthData latency is minimizedNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAutomatic controlThroughput
Disclosed is a method and apparatus to continuously transmit high bandwidth, real-time data, on a communications network (e.g., wired, wireless, and a combination of wired and wireless segments). A control computing device uses user or application requirements to dynamically adjust the throughput of the system to match the bandwidth of the communications network being used, so that data latency is minimized. An operator can visualize the instantaneous characteristic of the link and, if necessary, make a tradeoff between the latency and resolution of the data to help maintain the real-time nature of the system and better utilize the available network resources. Automated control strategies have also been implemented into the system to enable dynamic adjustments of the system throughput to minimize latency while maximizing data resolution. Several applications have been cited in which latency minimization techniques can be employed for enhanced dynamic performance.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
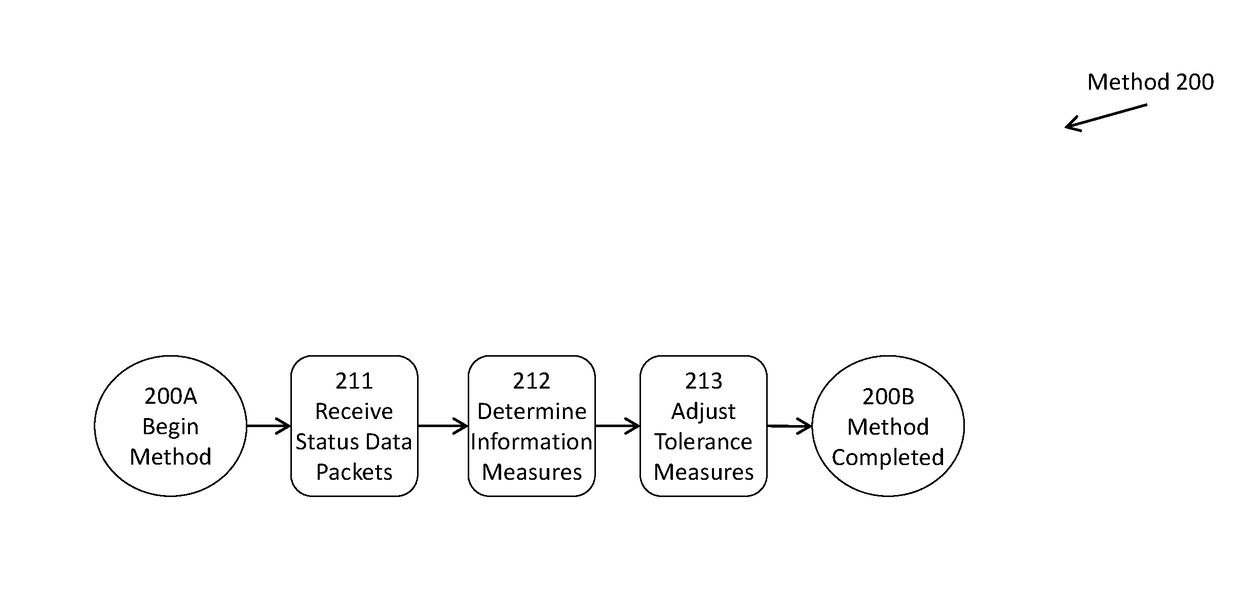
Enhanched flow processing
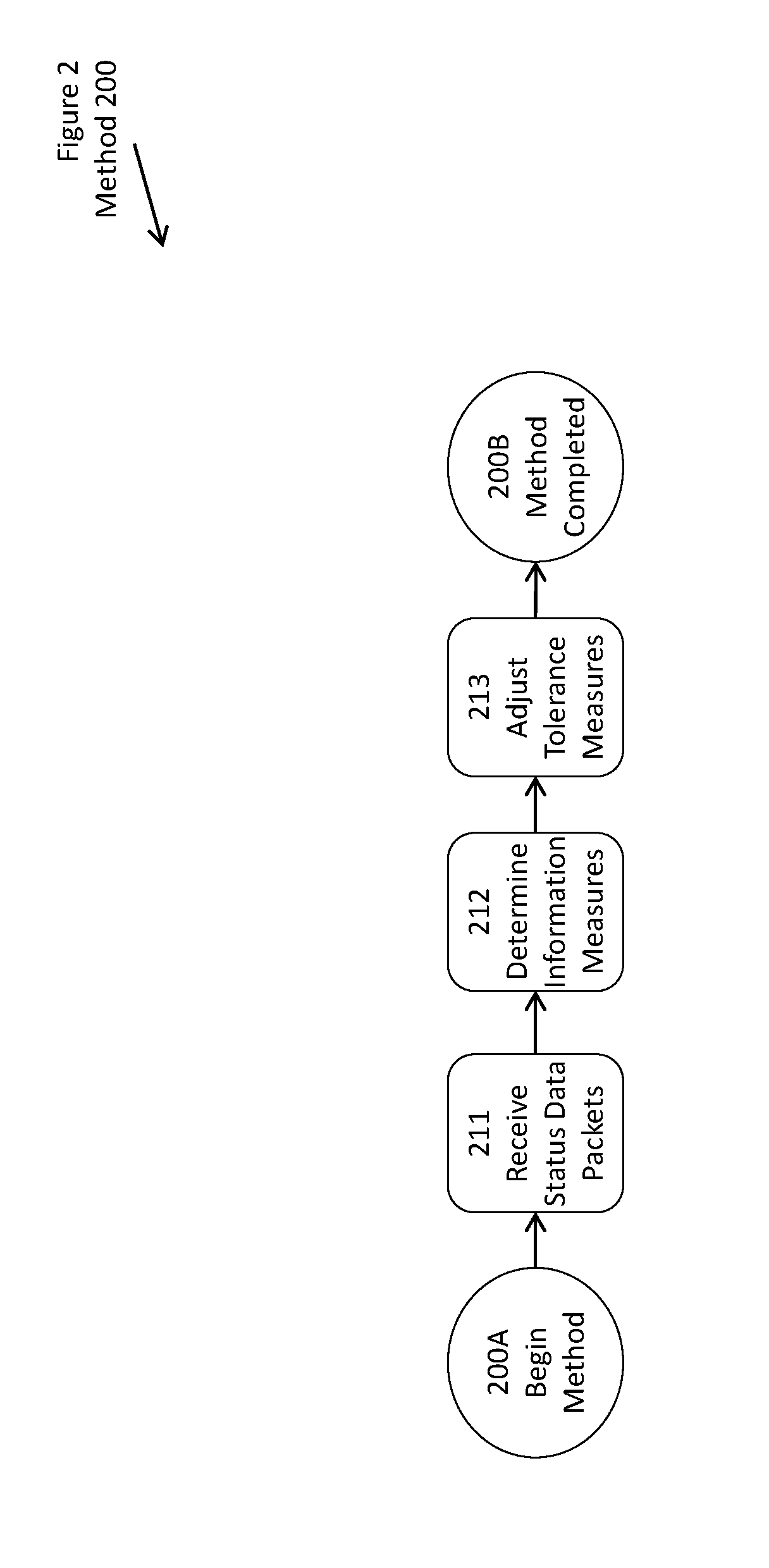
ActiveUS9935858B1Accurately reportReduce amount of considerationData switching networksData latencyNetwork monitoring
A network monitoring device responds to a network status data (whether “pushed” from the network device or “pulled” from the network device), maintaining a buffer of saved status data. The status data is reordered, manipulated, and presented to users in order. The monitoring device can thus report an accurate momentary report of the status of the network environment. When status data is delayed too long, the monitoring device can discard it, or reduce its weighted consideration. The monitoring device adjusts its wait for status data, either as an average or individually per device, attempting to balance accuracy and latency. The monitoring device also records of how much status data it is required to process, in response to the amount it can process reliably, and maintains a sampling rate for status data, somewhere between evaluating all of the status data, and evaluating only a small portion of the status data, when capable, attempting to balance the degree of sampling, against both error and latency.
Owner:VIRTUAL INSTR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com