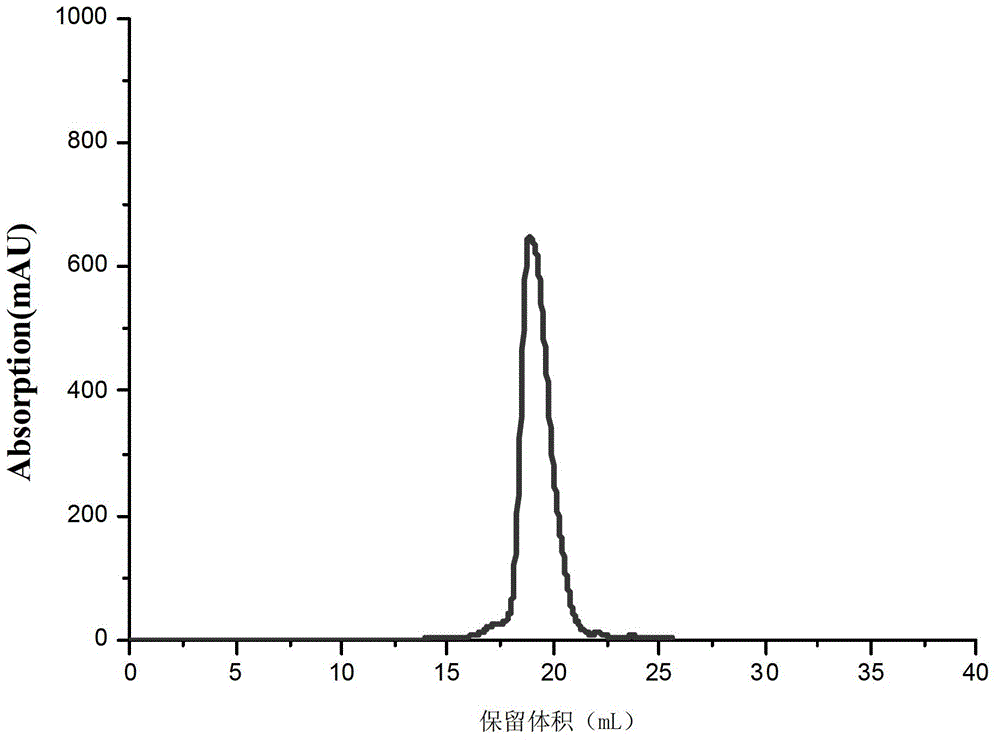
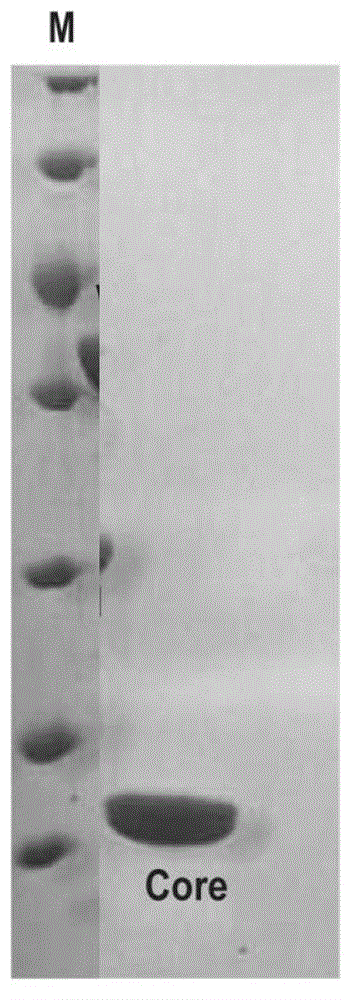
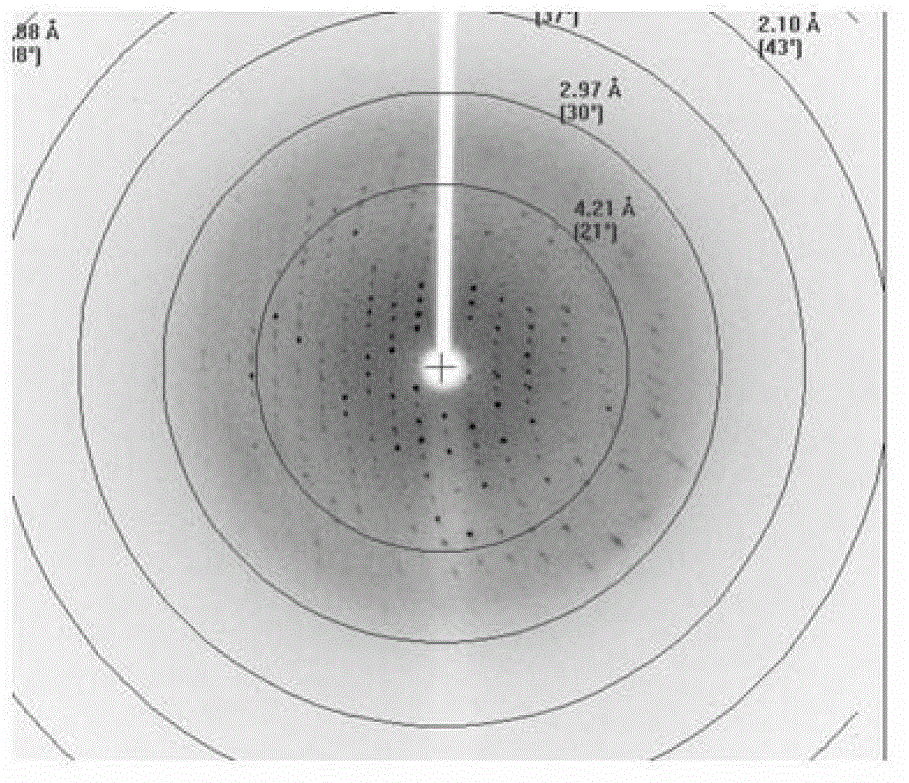
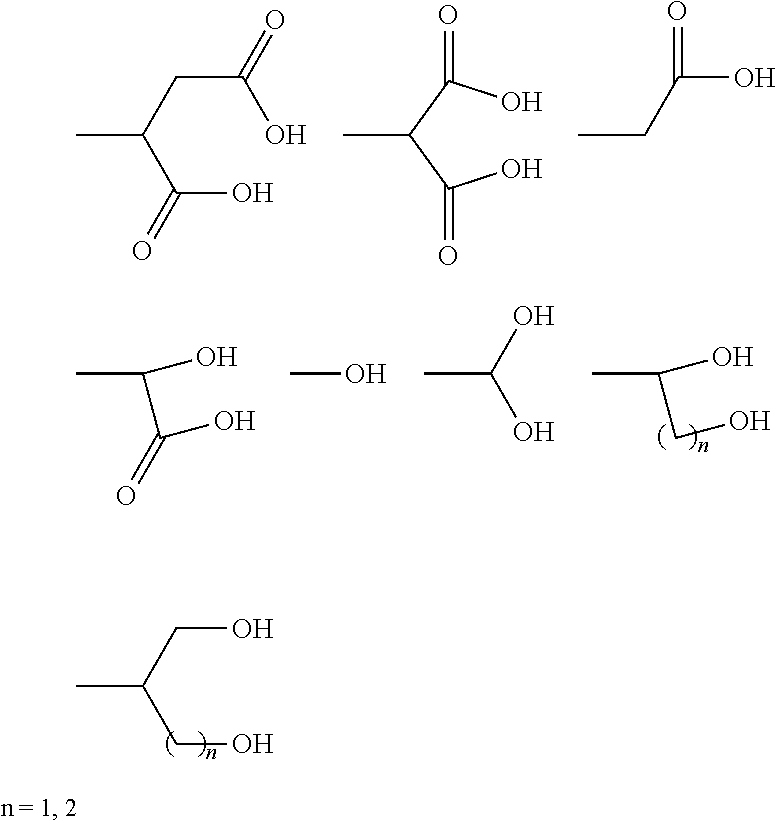
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Dna binding activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The DNA binding activity of Fos and Jun is regulated in vitro by a post-translational mechanism involving reduction-oxidation. Redox regulation occurs through a conserved cysteine residue located in the DNA binding domain of Fos and Jun.
Compositions and methods for identifying and testing TGF- beta pathway agonists and antagonists
InactiveUS6046165ASimple and sensitiveEasy to separateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsAgonist
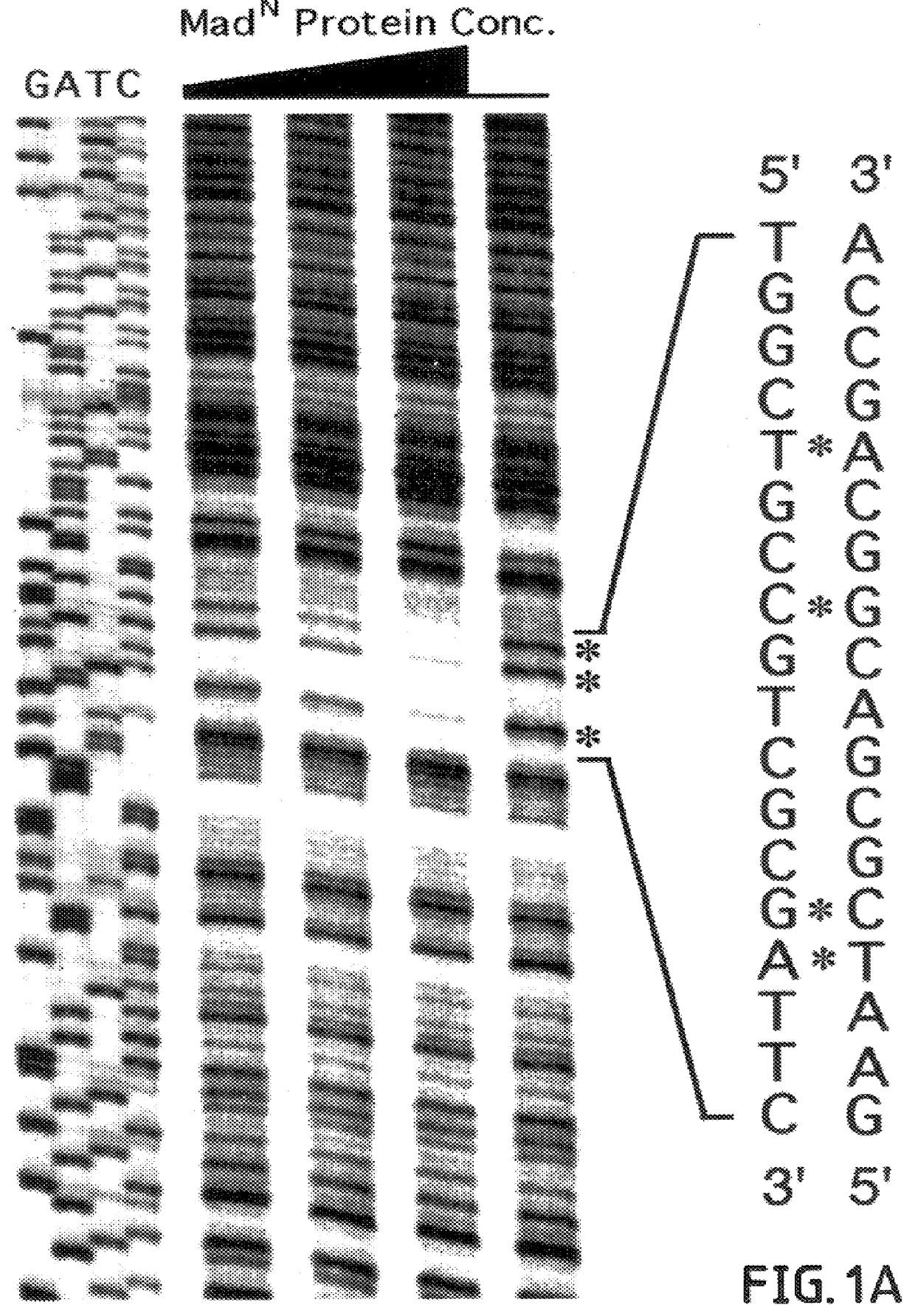
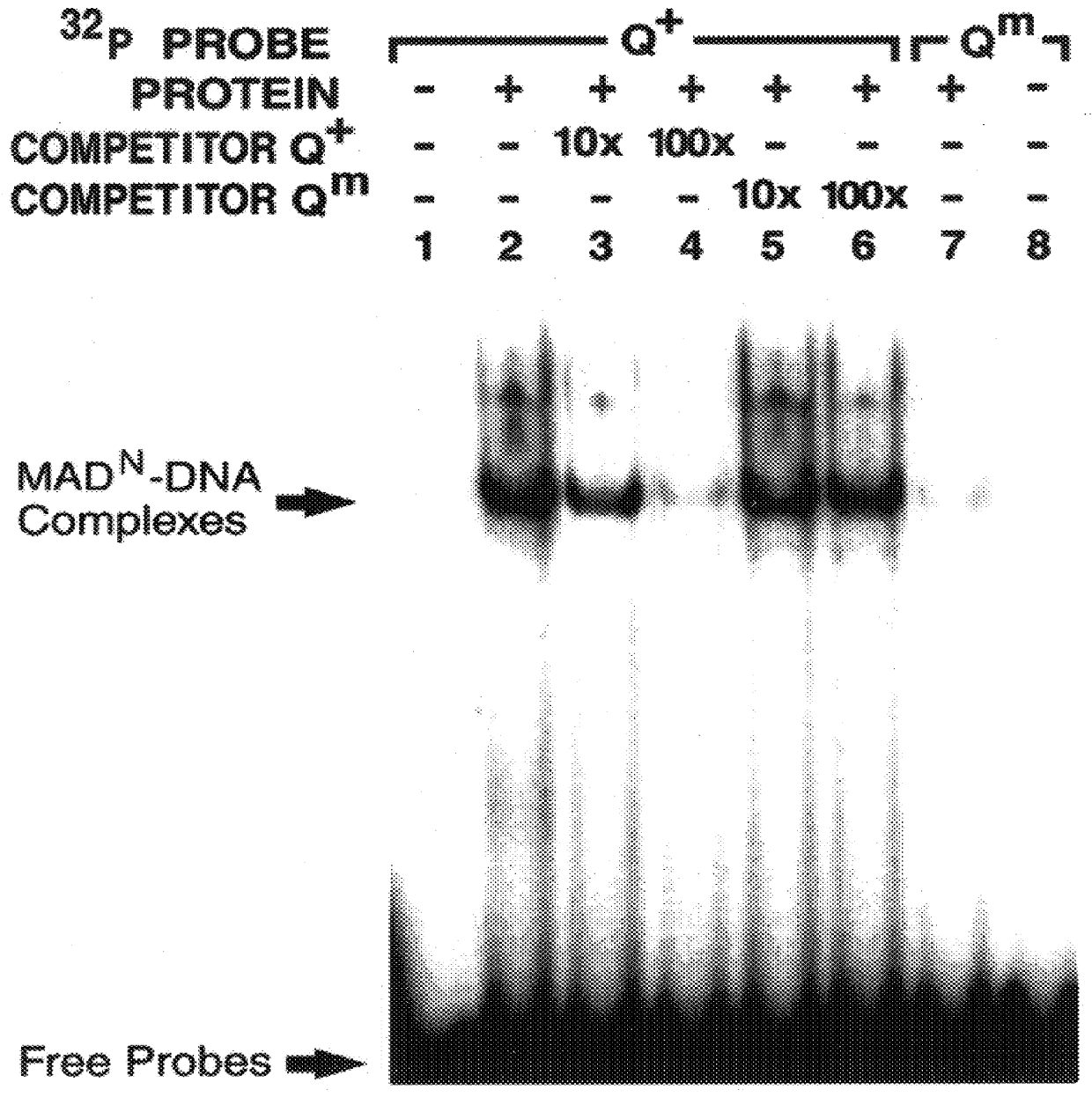
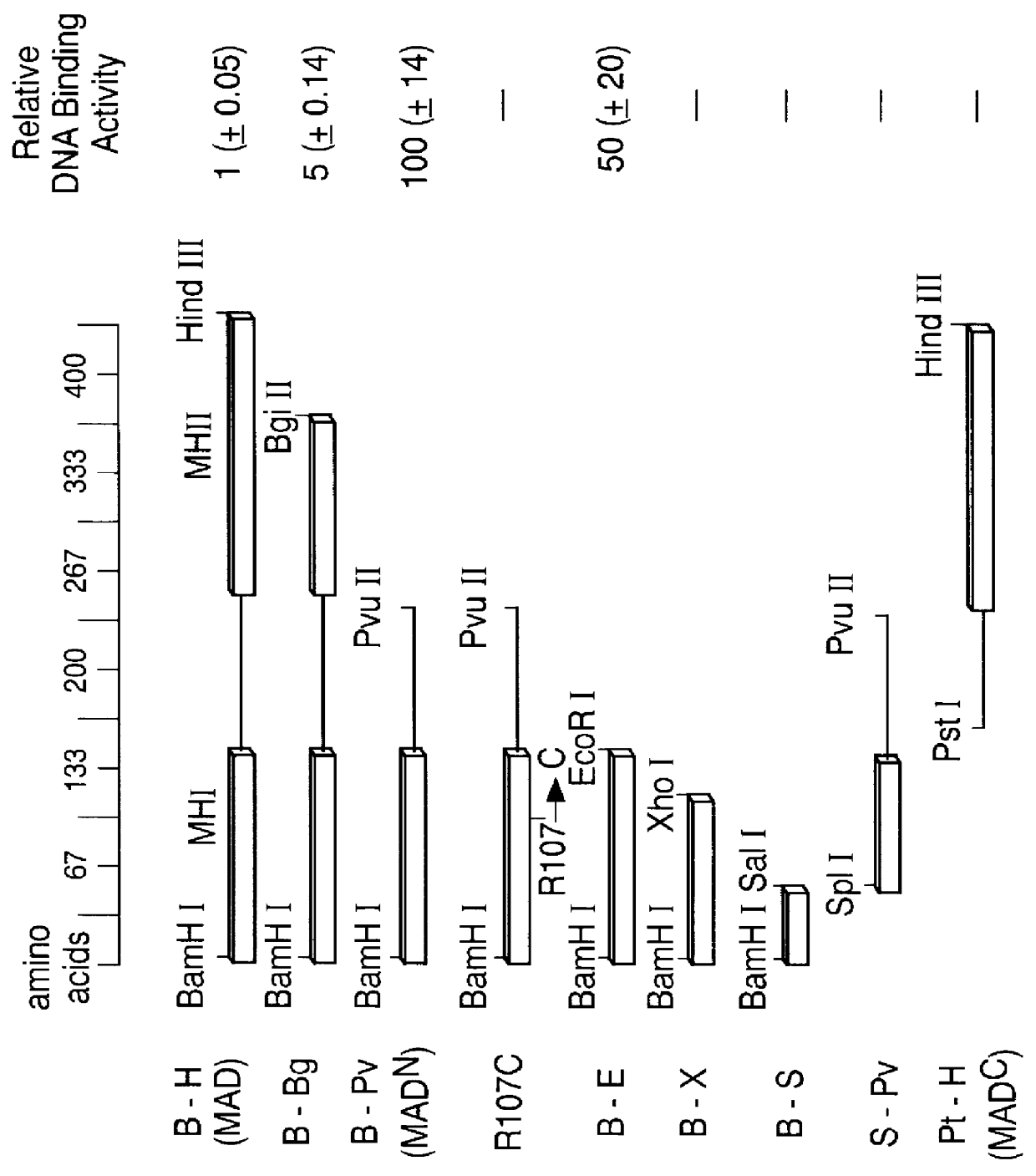
The invention provides compositions and methods of identifying and testing TGF- beta pathway agonists and antagonists, and in particular compositions comprising Mothers against DPP (MAD) proteins and related Smad polypeptides which exhibit sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. The invention also provides a novel DNA sequence (SEQ ID NO:19); (SEQ ID NO:20); (SEQ ID NO:21) that is bound with high affinity by Drosophila MAD protein. This protein is useful for identifying compounds that will enhance or interfere with MAD protein-DNA binding.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Evolution of talens
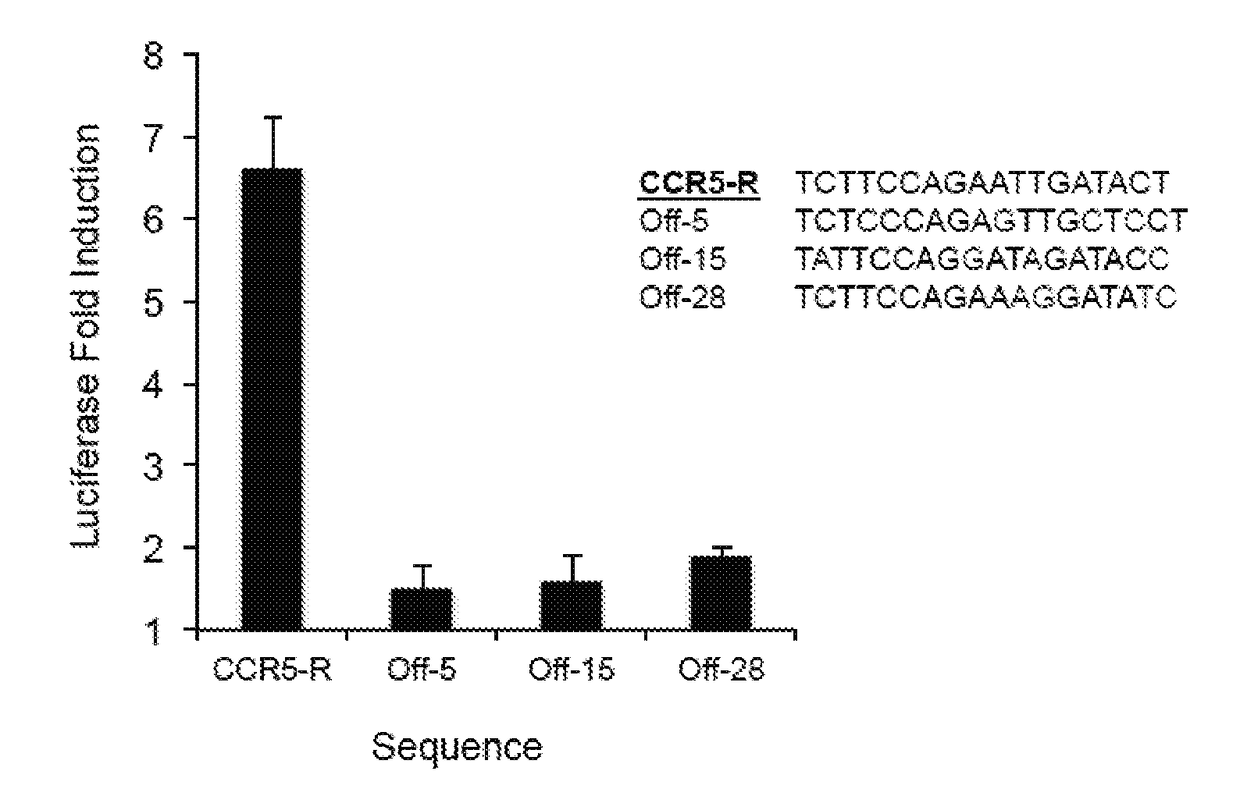
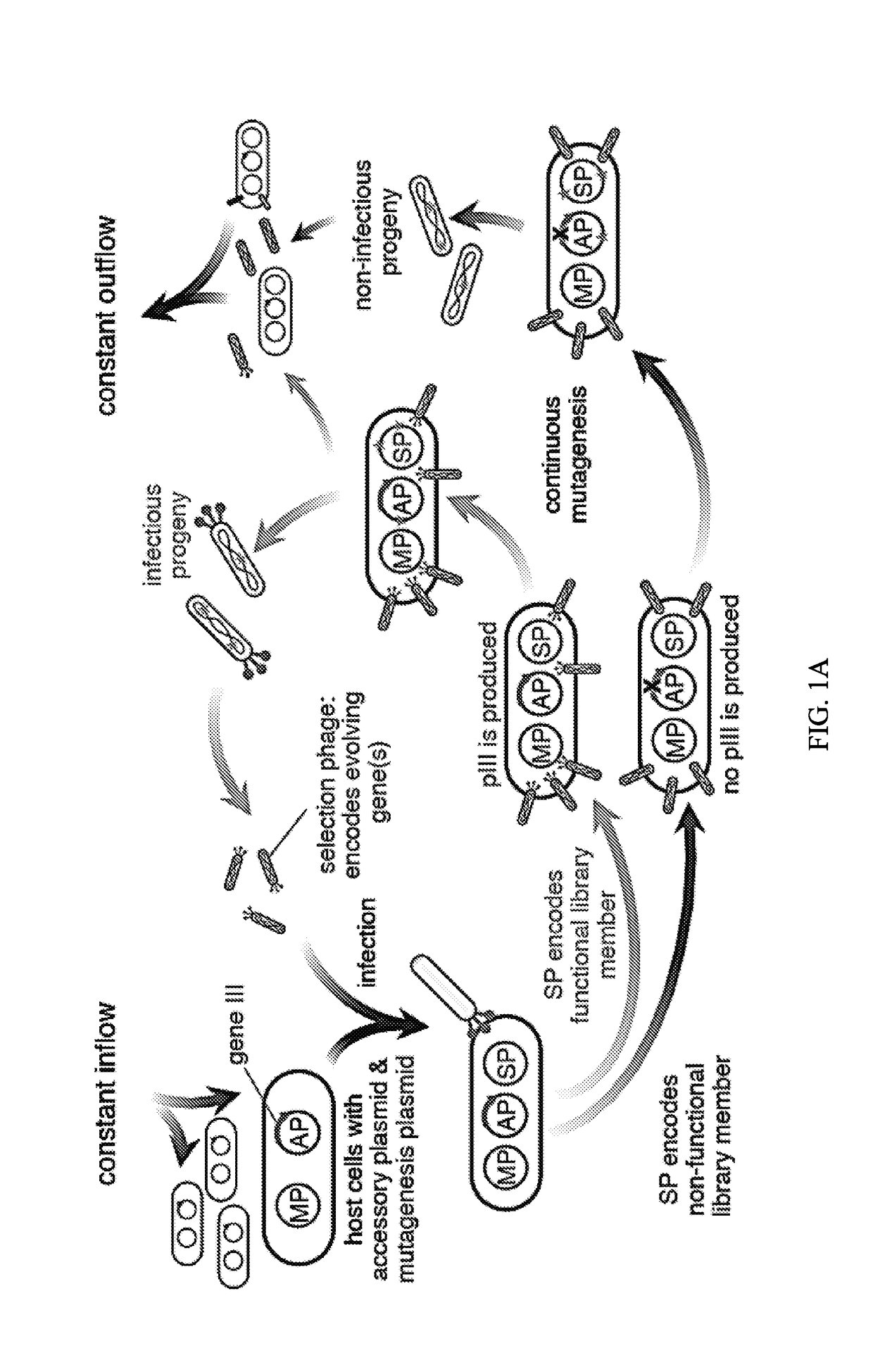
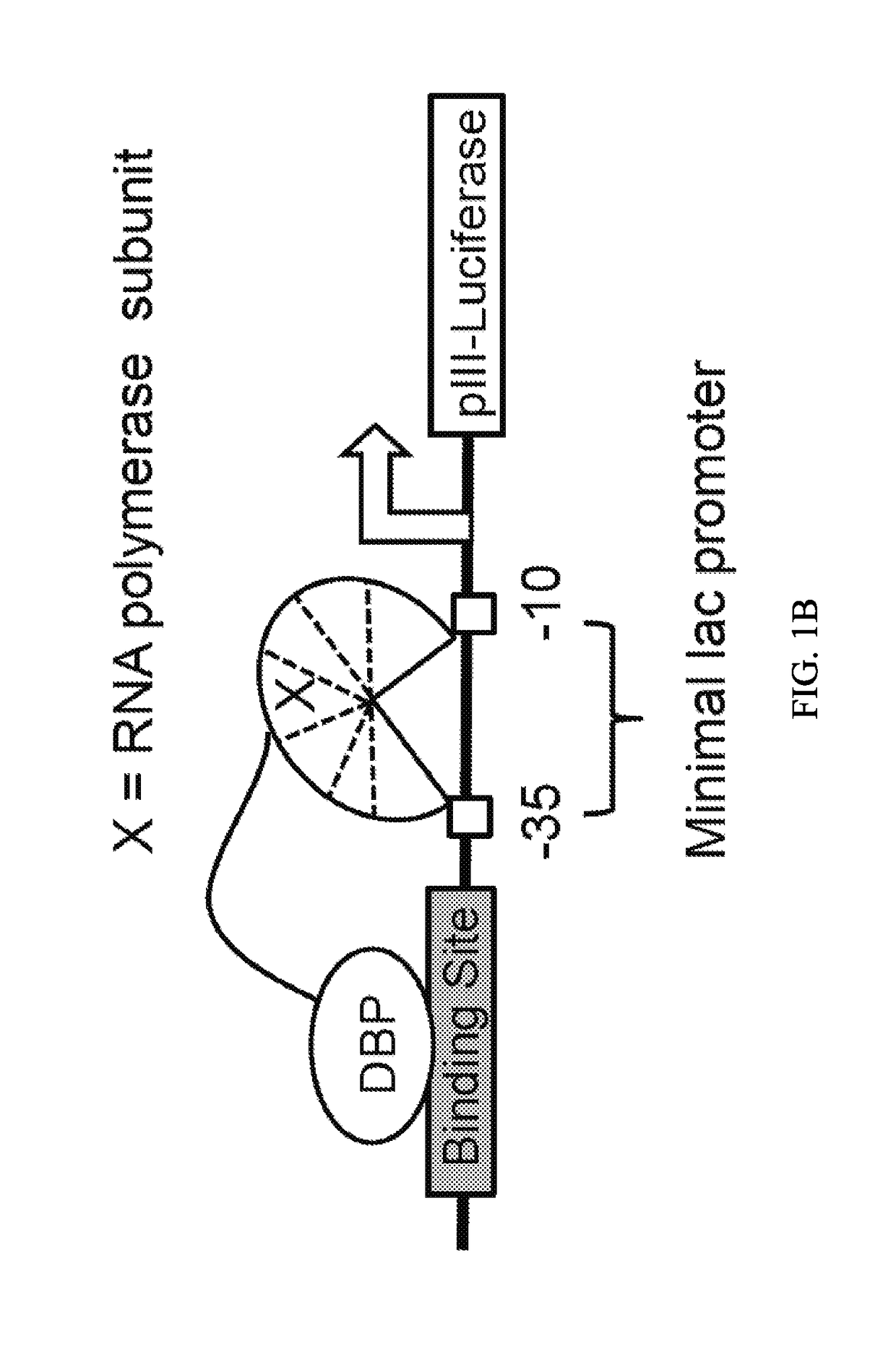
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Argonaute protein mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110229799APromote enrichmentReduce lossesFusion with RNA-binding domainNucleotide librariesTernary complexMutant
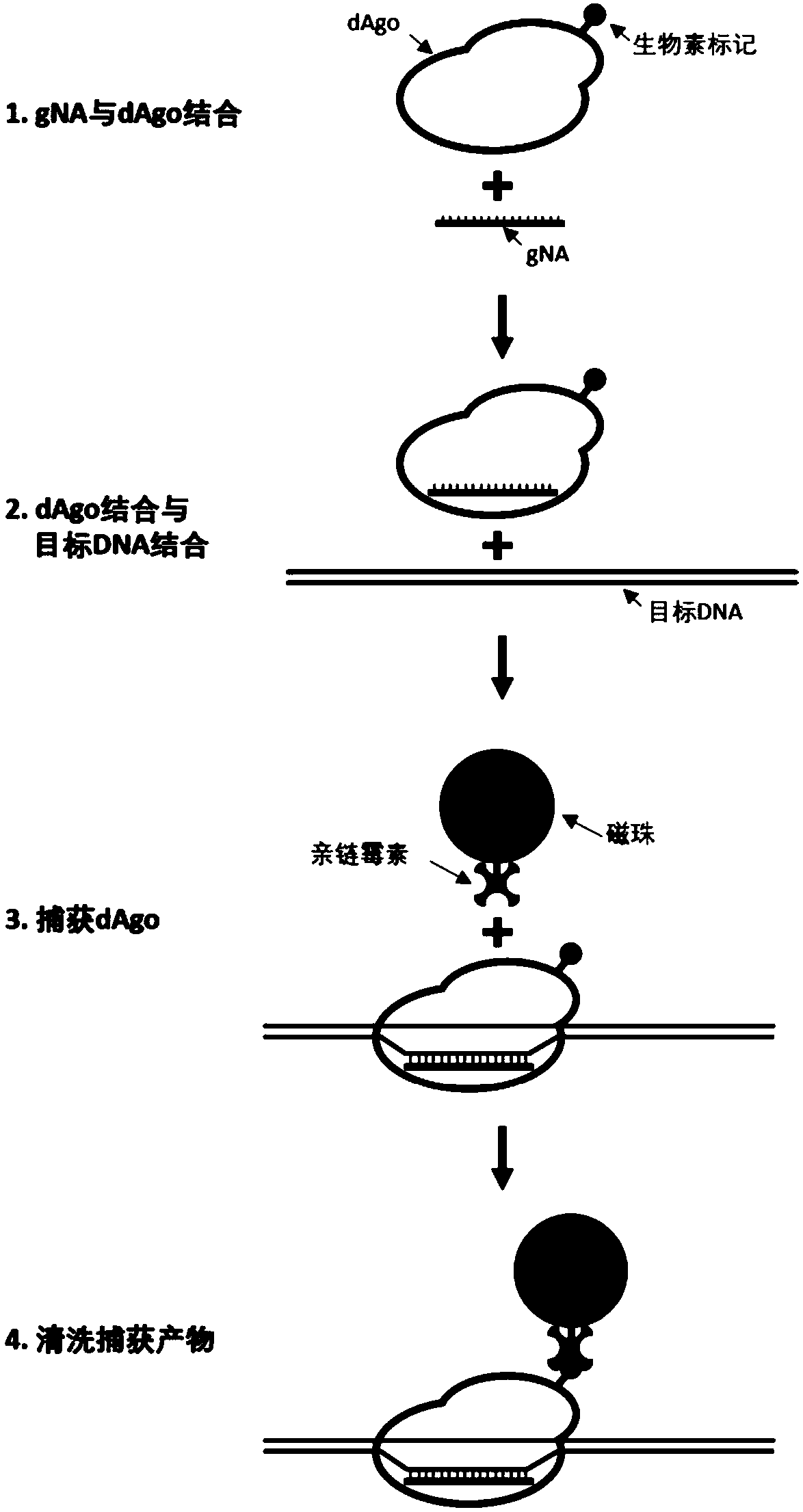
The present invention relates to an Argonaute protein mutant which lacks DNA cleavage activity, but has DNA binding activity. The mutation of the mutant is located in a PIWI domain. The invention alsorelates to application of the protein mutant particularly in the enrichment of target DNA and in the construction of a sequencing library. Therefore, the present invention also relates to a method for enriching the target DNA. The method comprises the steps of: (a) designing a leader sequence for a specific sequence in the target DNA; (b) combining the mutant, the leader sequence and the target DNA according to the present invention to obtain a mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex; (c) capturing the mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex through a capture medium; and (d) isolating the target DNA from the captured mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex to obtain enriched target DNA.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
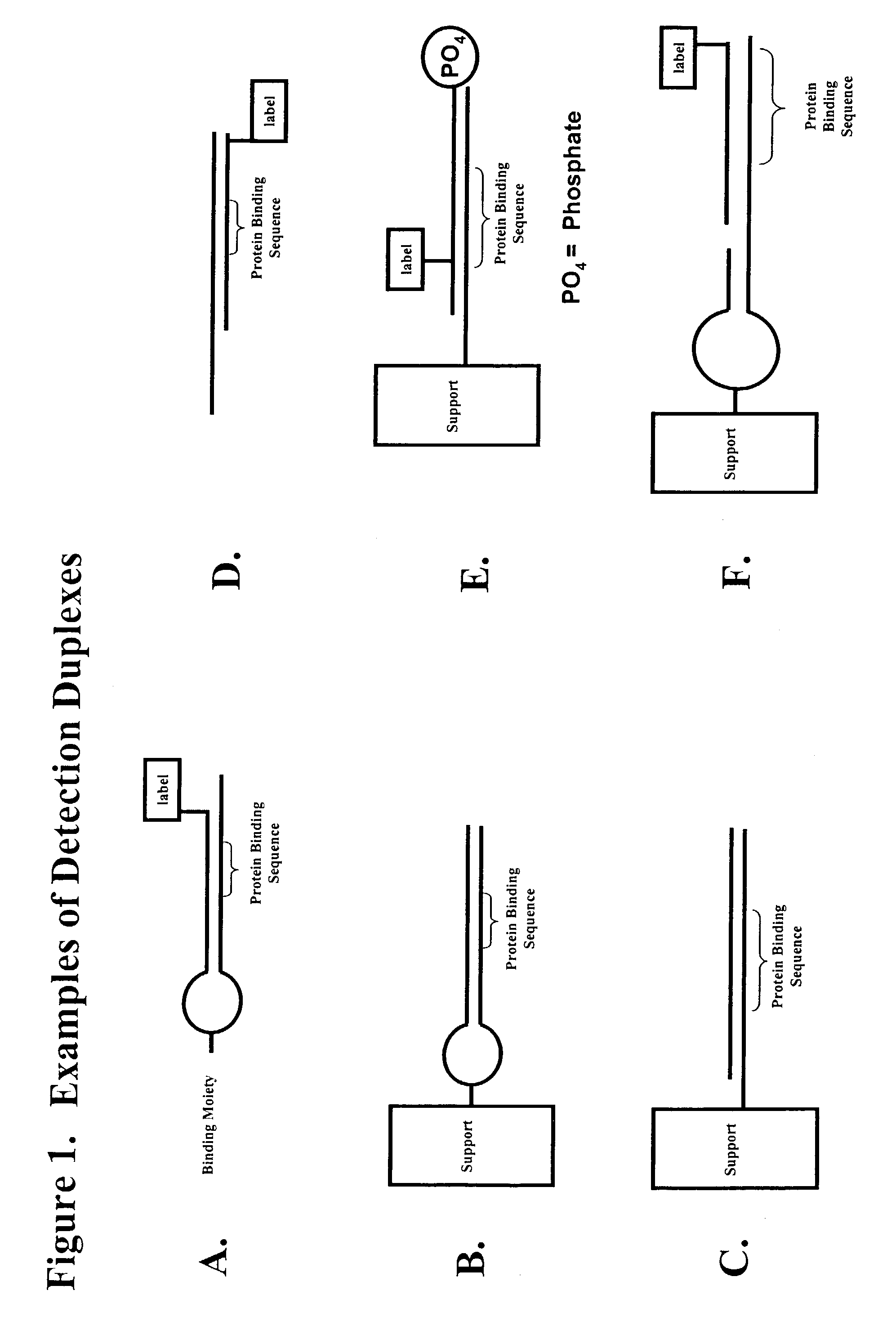
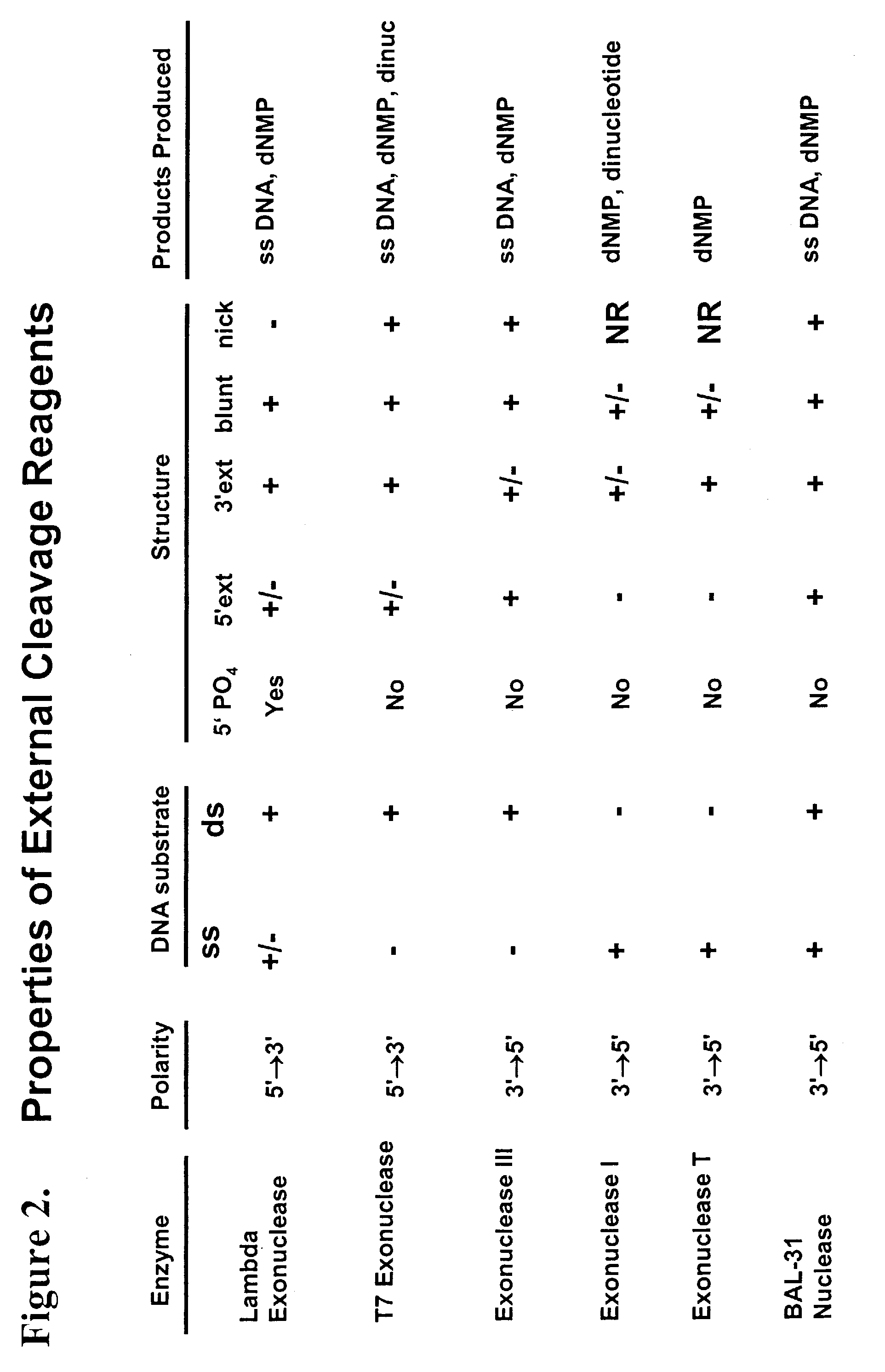
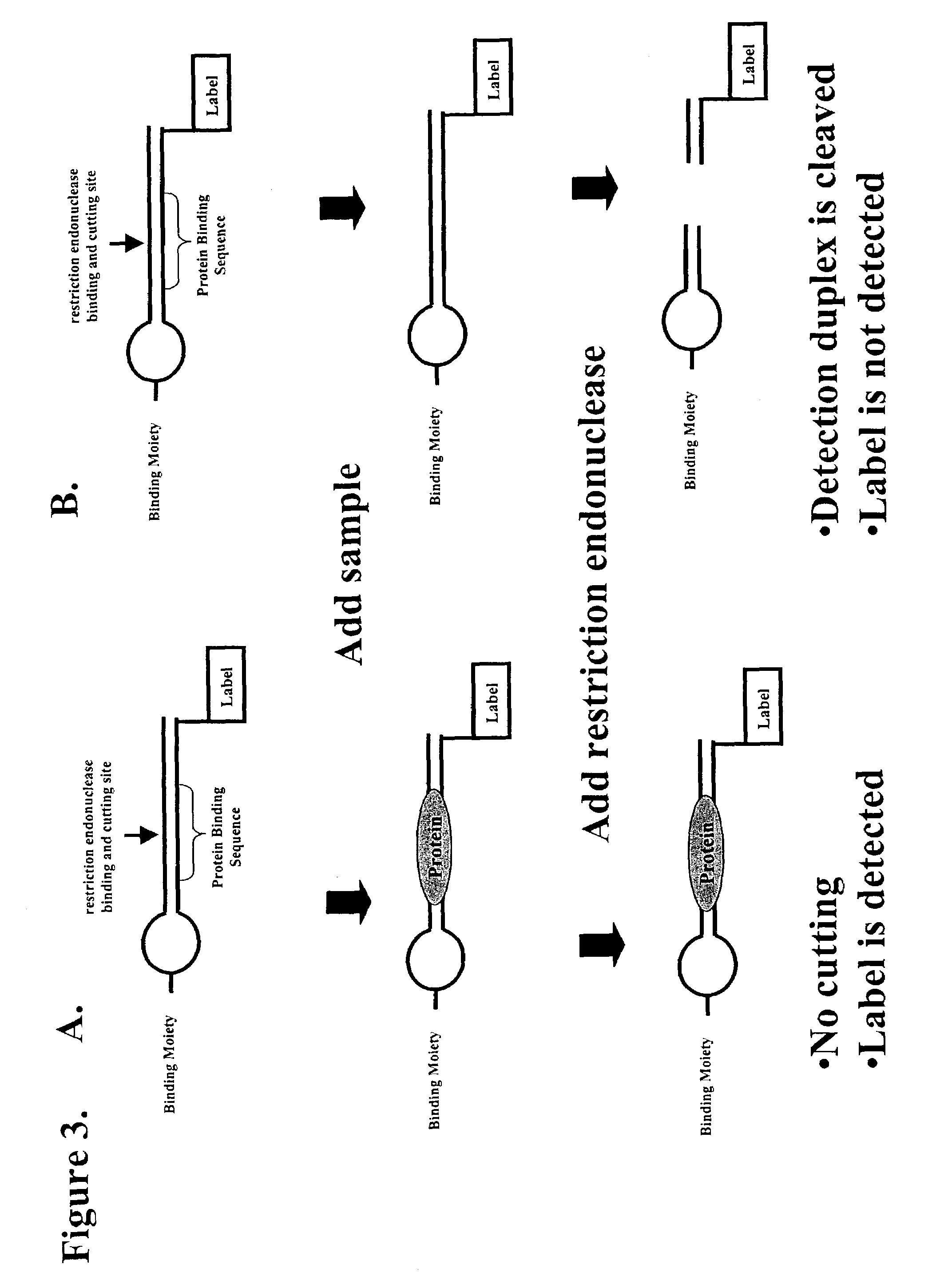
Multiplex method of detecting sequence-specific DNA binding proteins using detection duplexes comprising unmodified nucleic acid sequences as capture tags
InactiveUS7122317B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSingle sampleSequence-Specific DNA Binding Protein
Compositions and methods are provided for detecting and measuring DNA-binding proteins. The compositions and methods permit the simultaneous or near-simultaneous detection of multiple DNA-binding proteins in a multiplex or array format, and can be used to generate profiles of DNA binding activity by proteins, specifically, transcription factors. Multiple protein-DNA binding events in a single sample may be detected and quantitated in a high-throughput format.
Owner:MARLIGEN BIOSCI
1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors
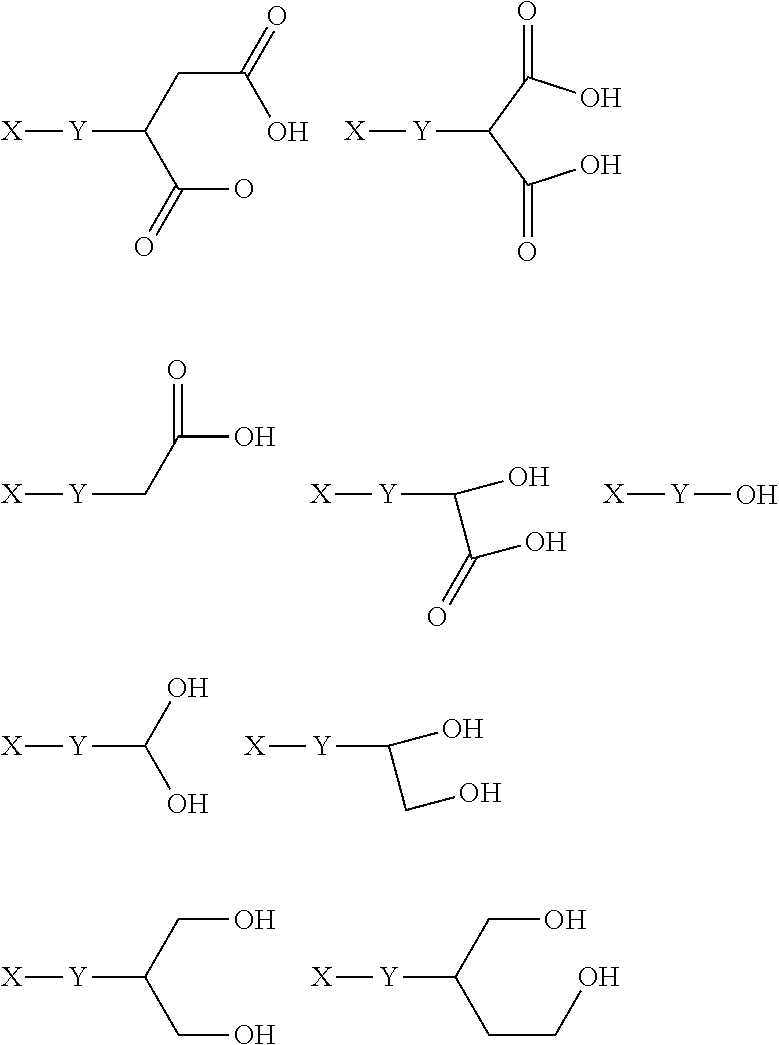
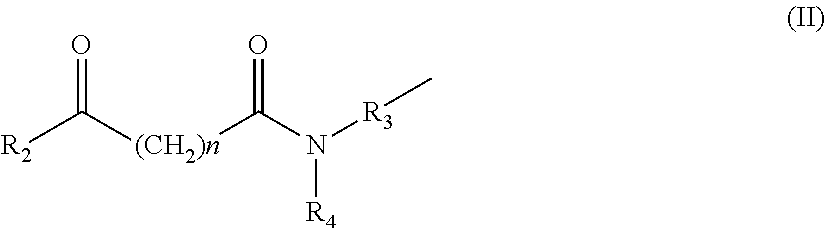
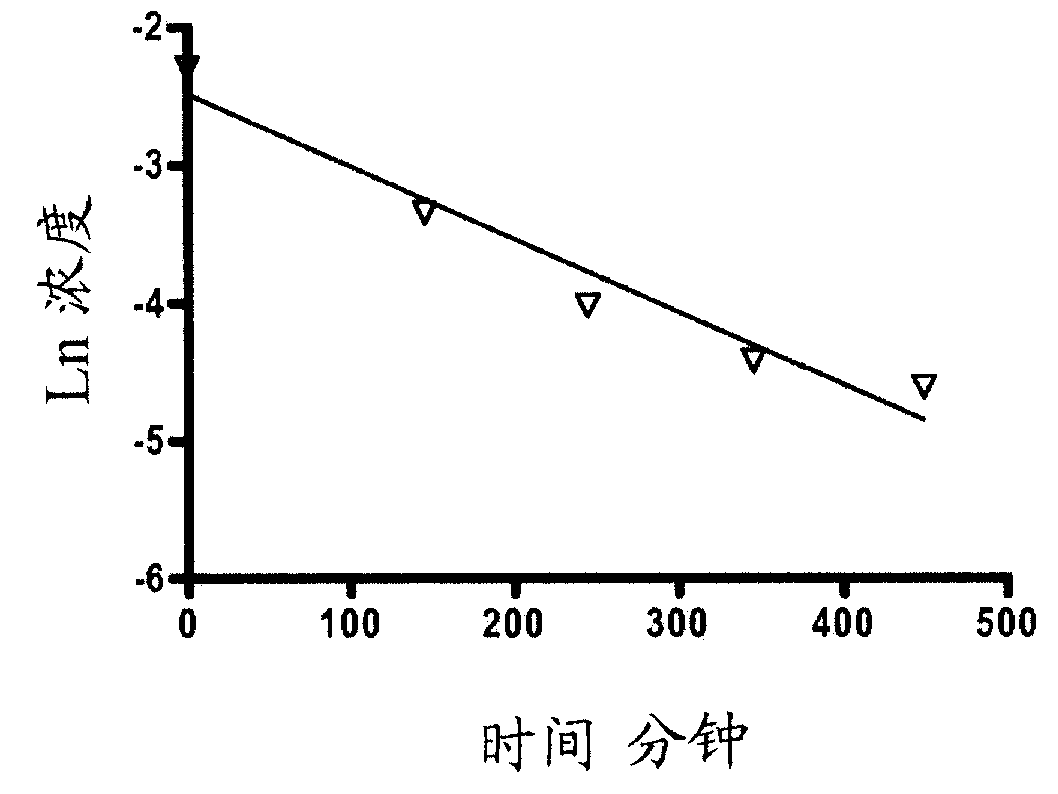
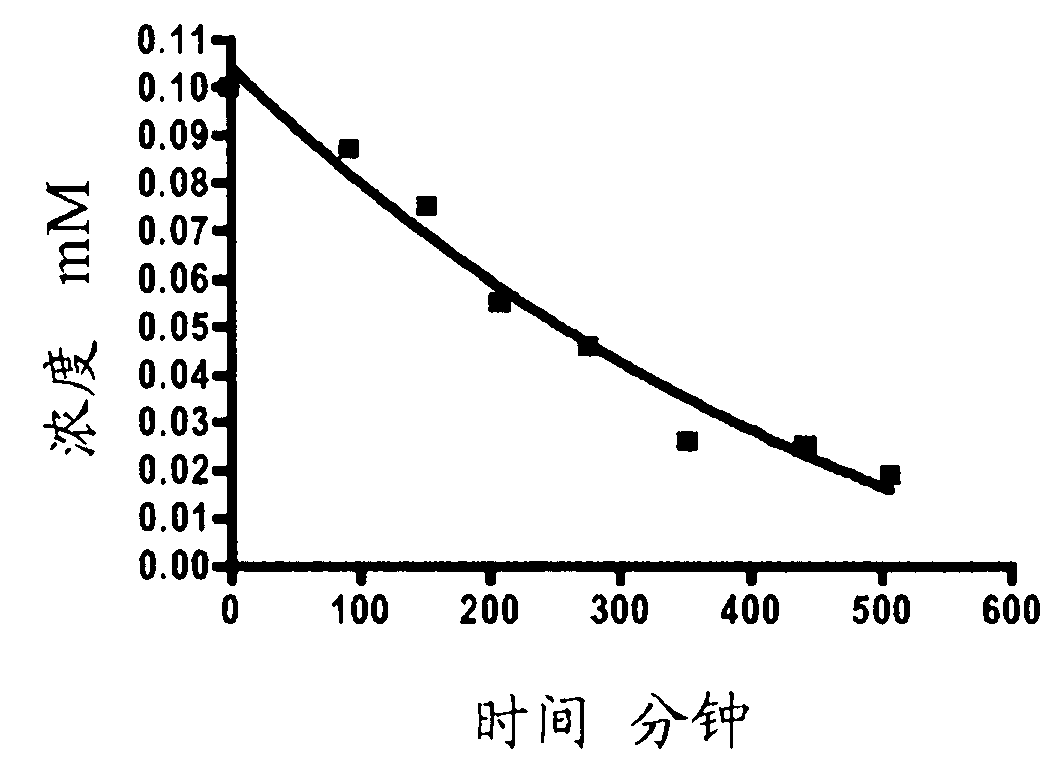
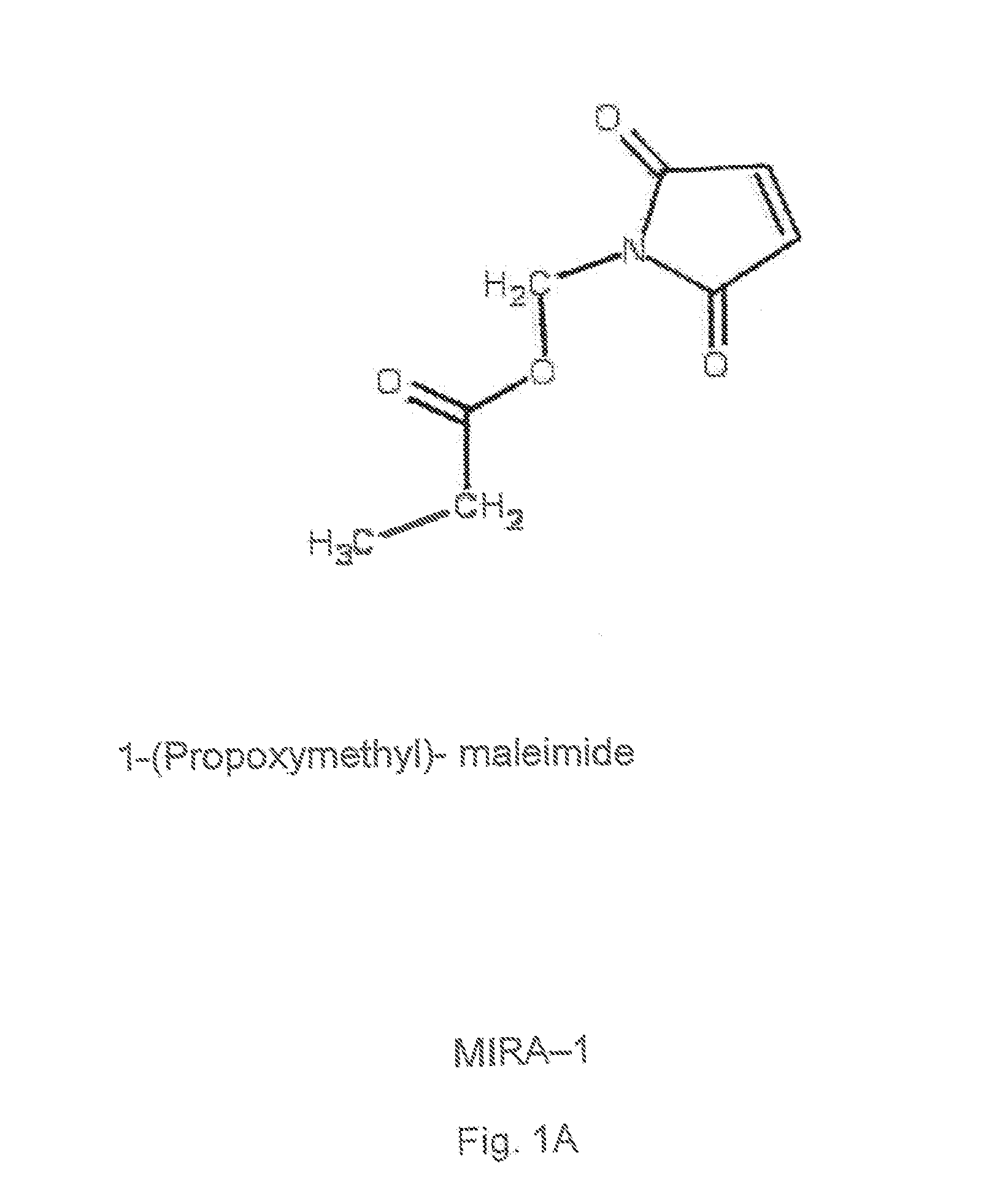
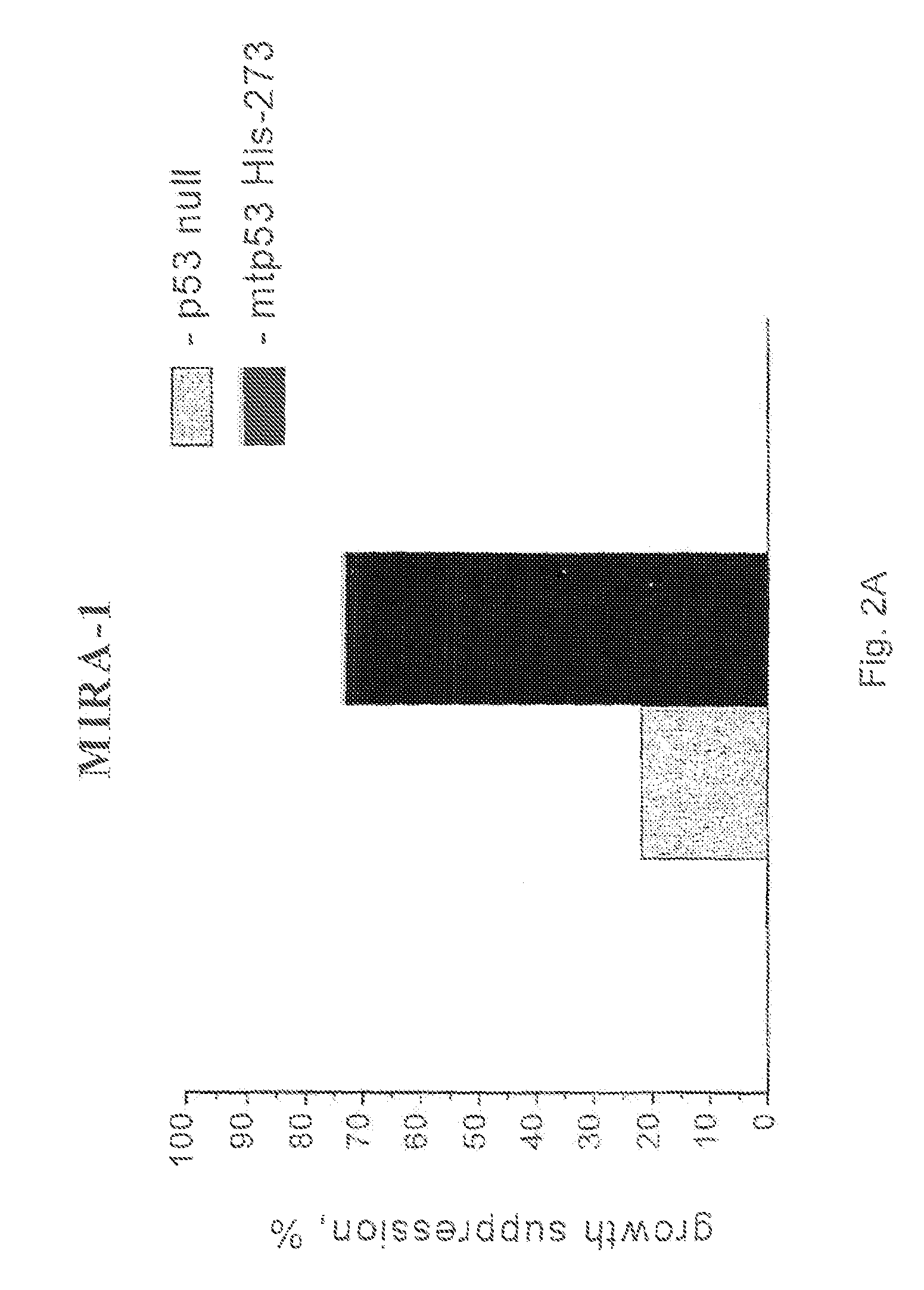
The present invention provides novel compounds, corresponding to formulae I and II, respectively, which are able to reactivate the apoptosis-inducing function of mutant p53 proteins. This reactivation is provided by restoration of sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcriptional transactivation function to mutant p53 proteins, and modulation of the conformation-dependent epitopes of the p53 protein. Accordingly, the substances according to the invention will be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of patients suffering from various types of tumors.
Owner:APREA THERAPEUTICS AB
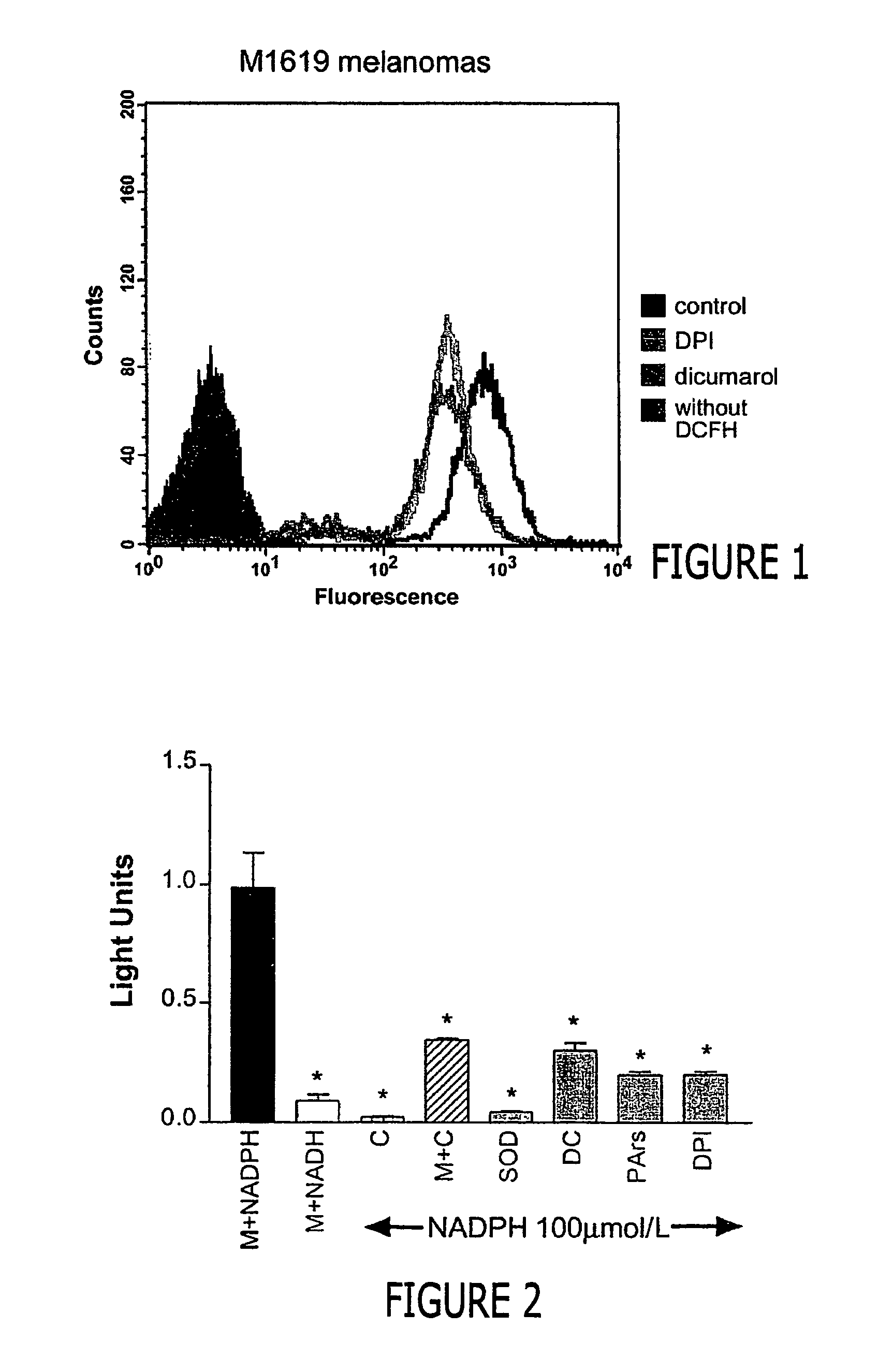
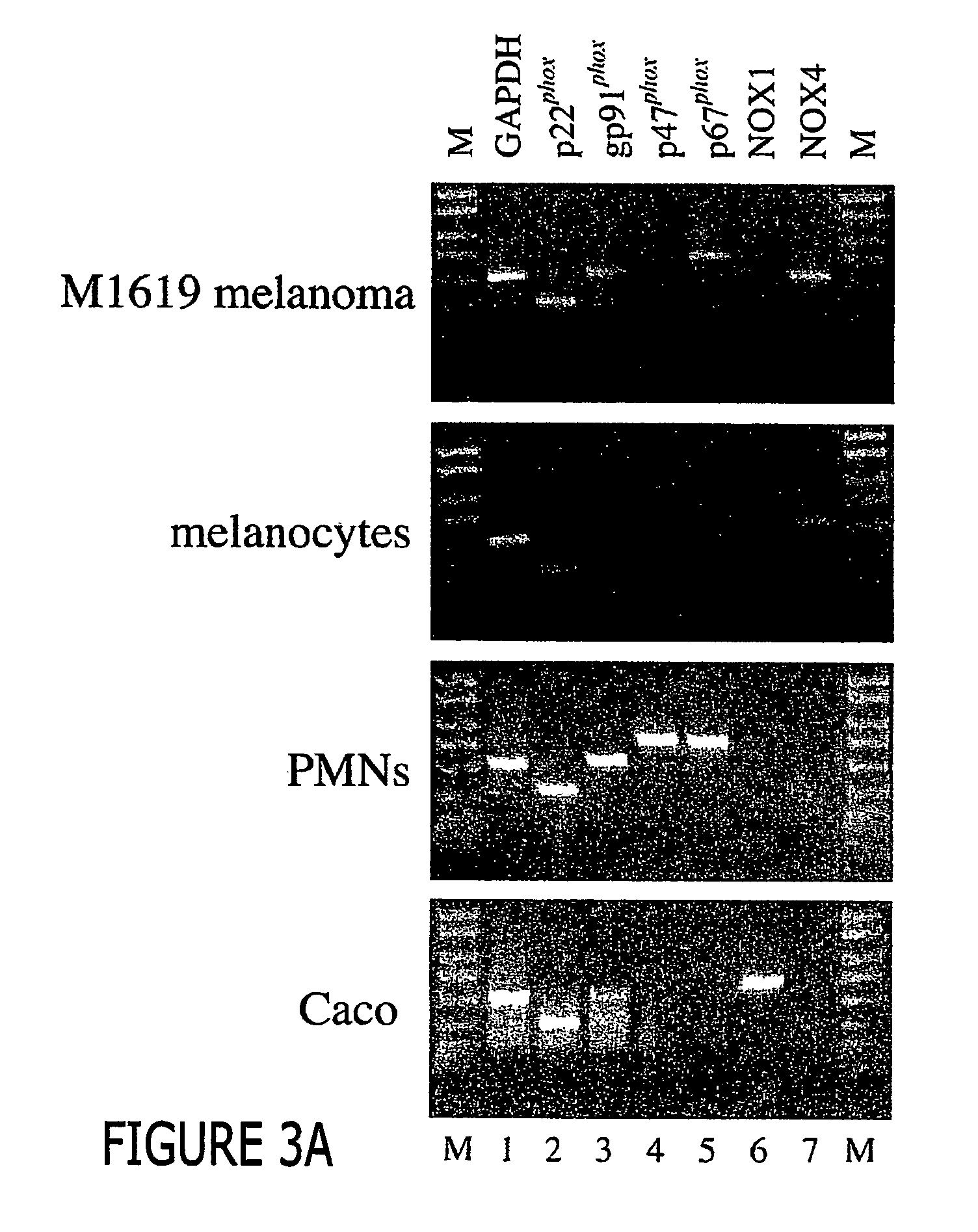
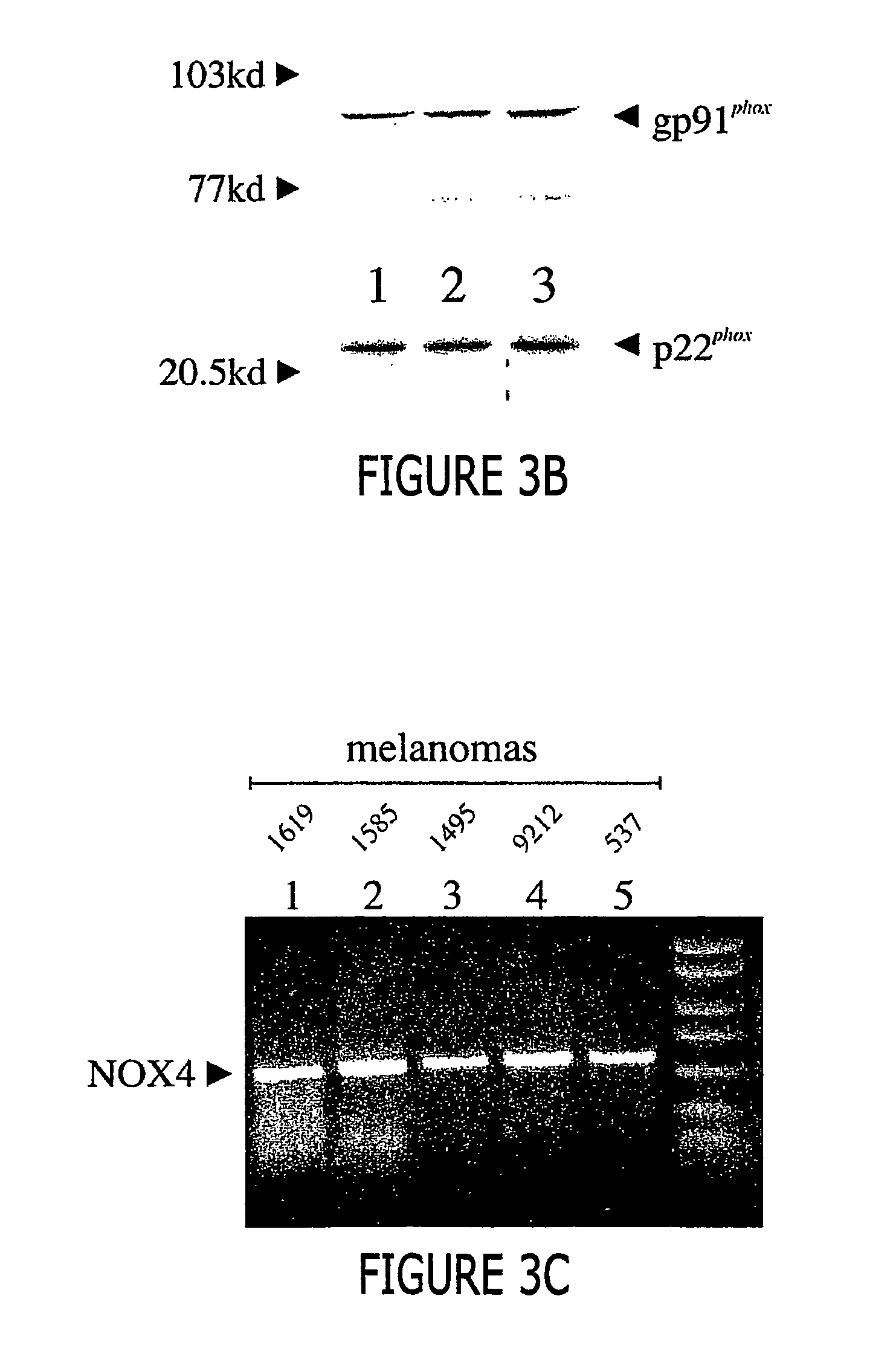
Regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase growth and transcription in melanoma cells
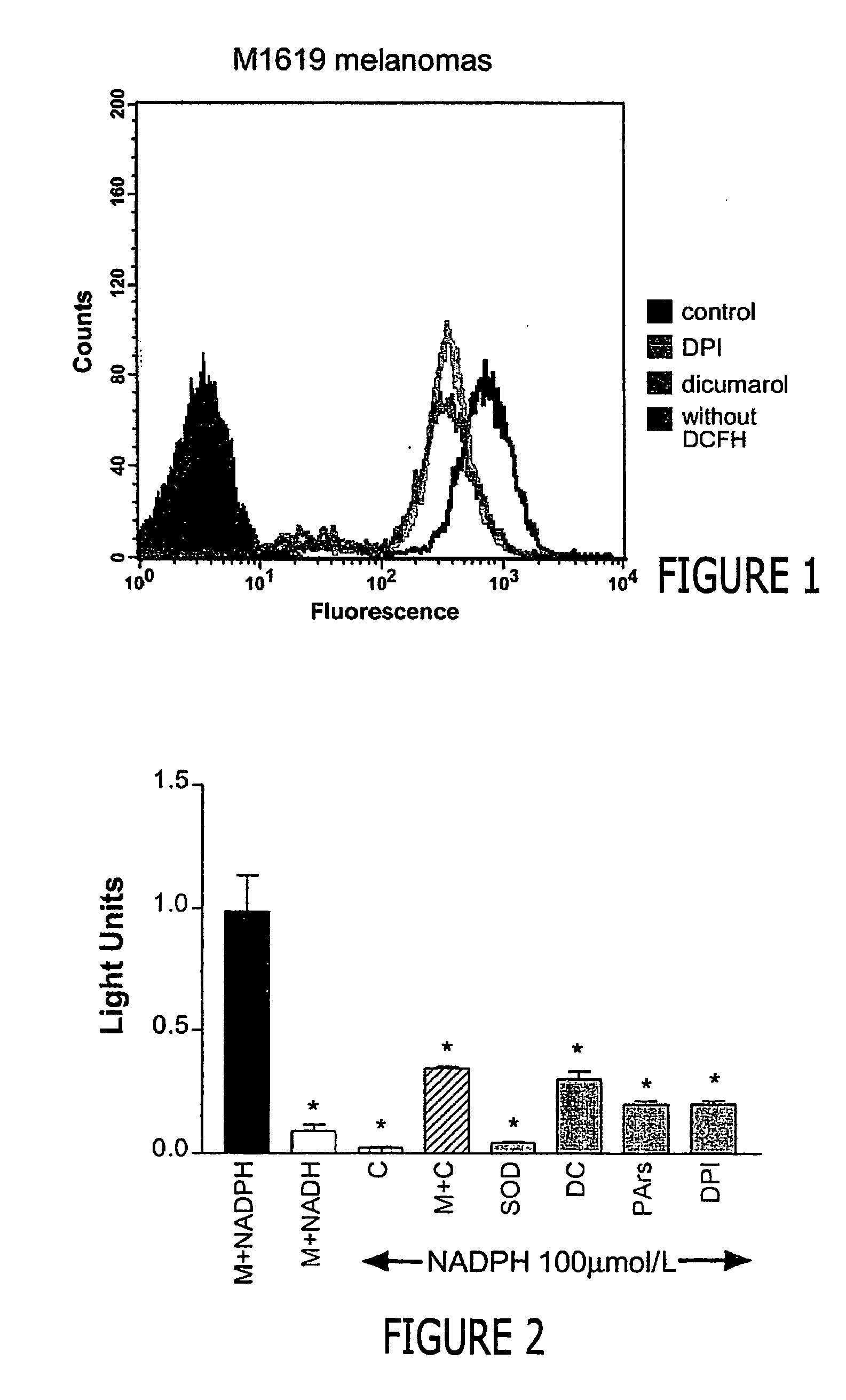
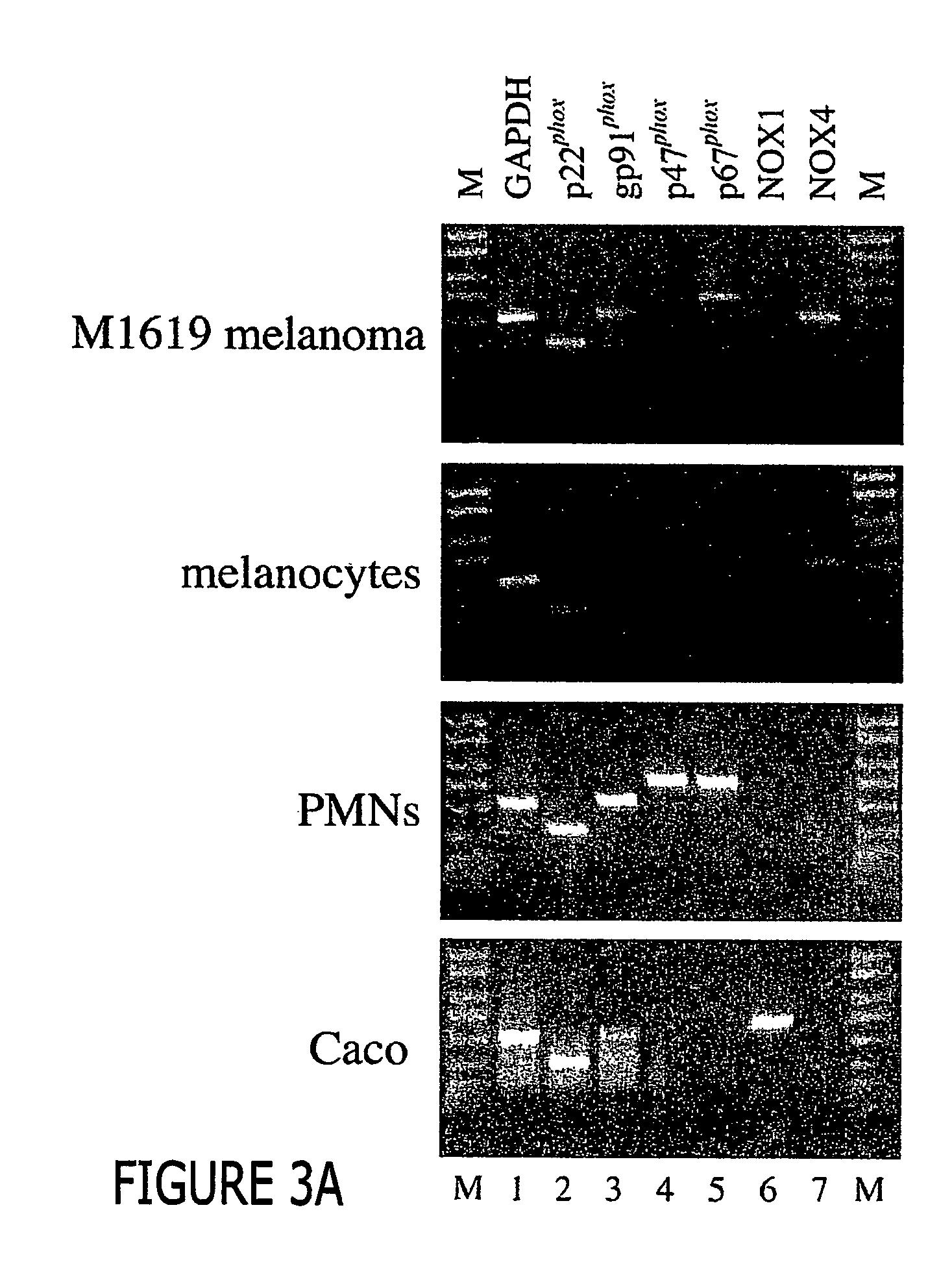
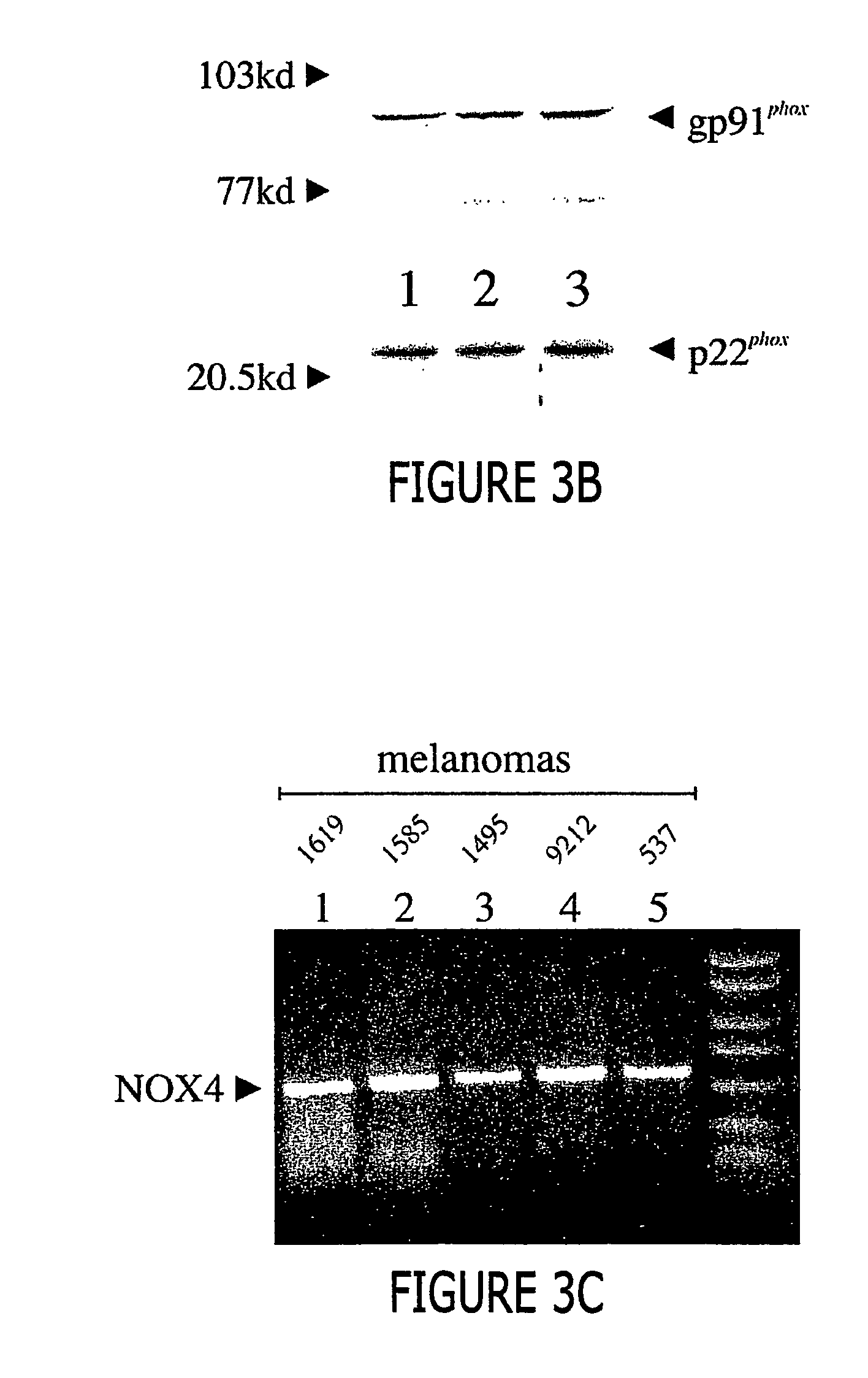
Malignant melanoma cells spontaneously generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) that promote constitutive activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB). Although antioxidants and inhibitors of NAD(P)H oxidases significantly reduce constitutive NF-kB activation and suppress cell proliferation, the nature of the enzyme responsible for ROS production in melanoma cells has not been determined. To address this issue, we now have characterized the source of ROS production in melanoma cells. ROS are generated by isolated, cytosol-free melanoma plasma membranes, with inhibition by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors. The p22phox, gp91phox and p67phox components of the human phagocyte NAD(P)H oxidase, and the 91phox homolog NOX4 were demon-strated in melanomas by RT-PCR and sequencing, and protein product for both p22phox and gp91phox were detected in cell membranes by immunoassay. Normal human epidermal melanocytes expressed only p22phox and NOX4. Melanoma proliferation was reduced by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors and by transfection of antisense but not sense oligonucleotides for p22phox and NOX4. Also, the flavoprotein inhibitor diphenylene iodonium inhibited constitutive DNA binding of nuclear protein to the NF-kB and cyclic-AMP response element consensus oligonucleotides, without affecting DNA binding activity to AP-1 or OCT-1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Targeting diazo prodrugs for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases
Provided herein are compounds, compositions and methods for decreasing NFkB DNA-binding activity in a patient comprising administering of a therapeutically effective amount of a compound or composition of the application to the patient to reduce, alleviate or treat various gastrointestinal diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
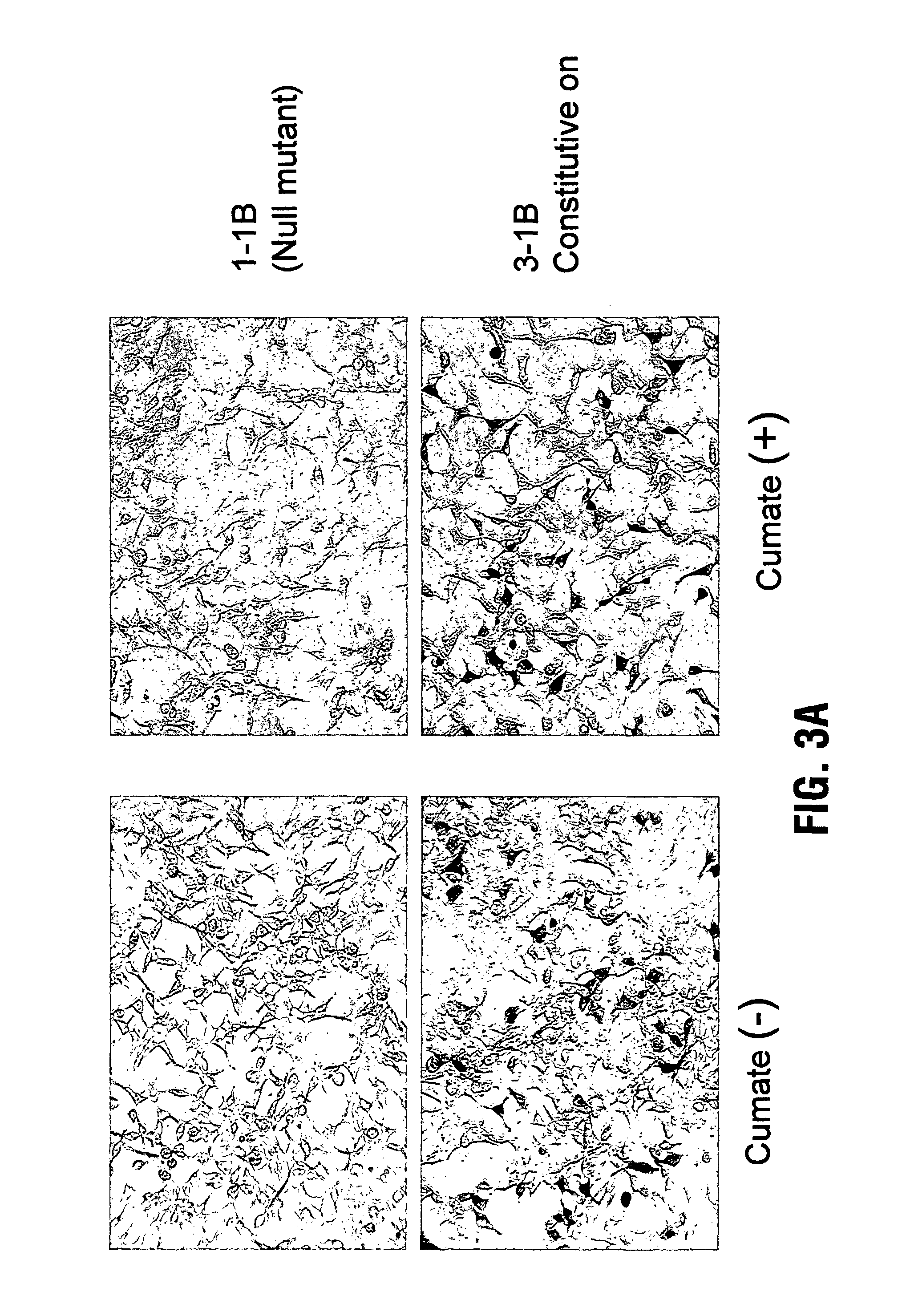
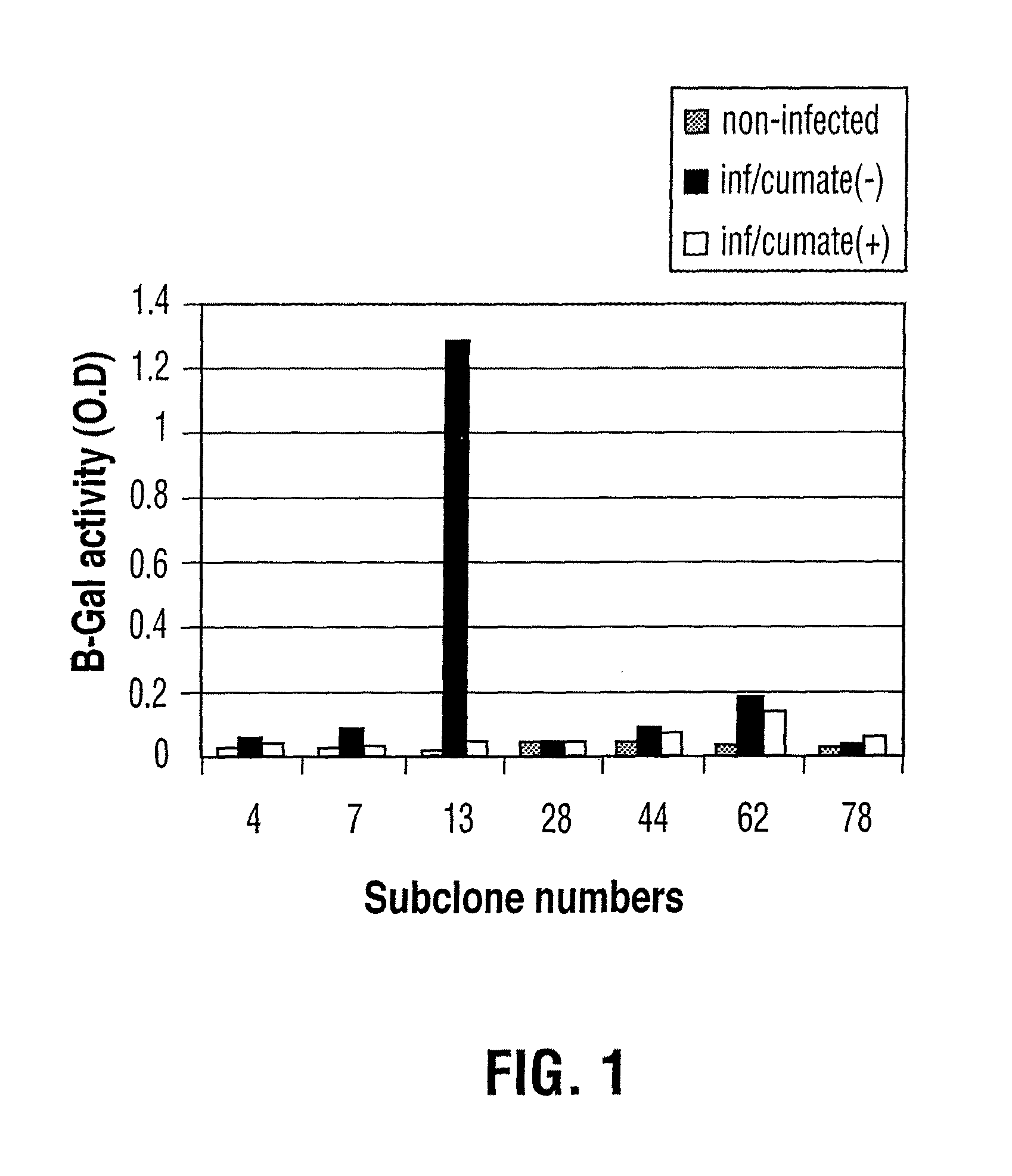
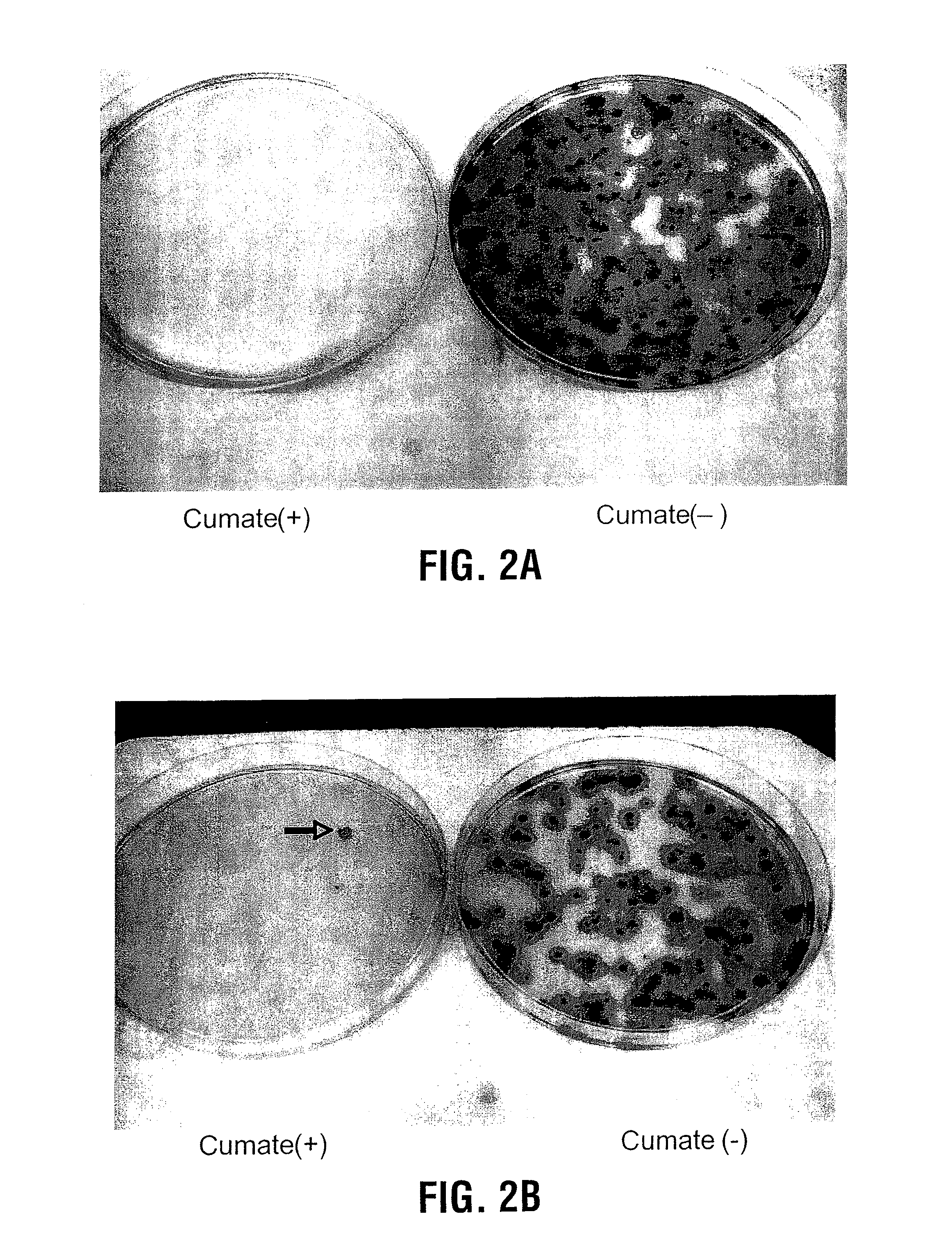
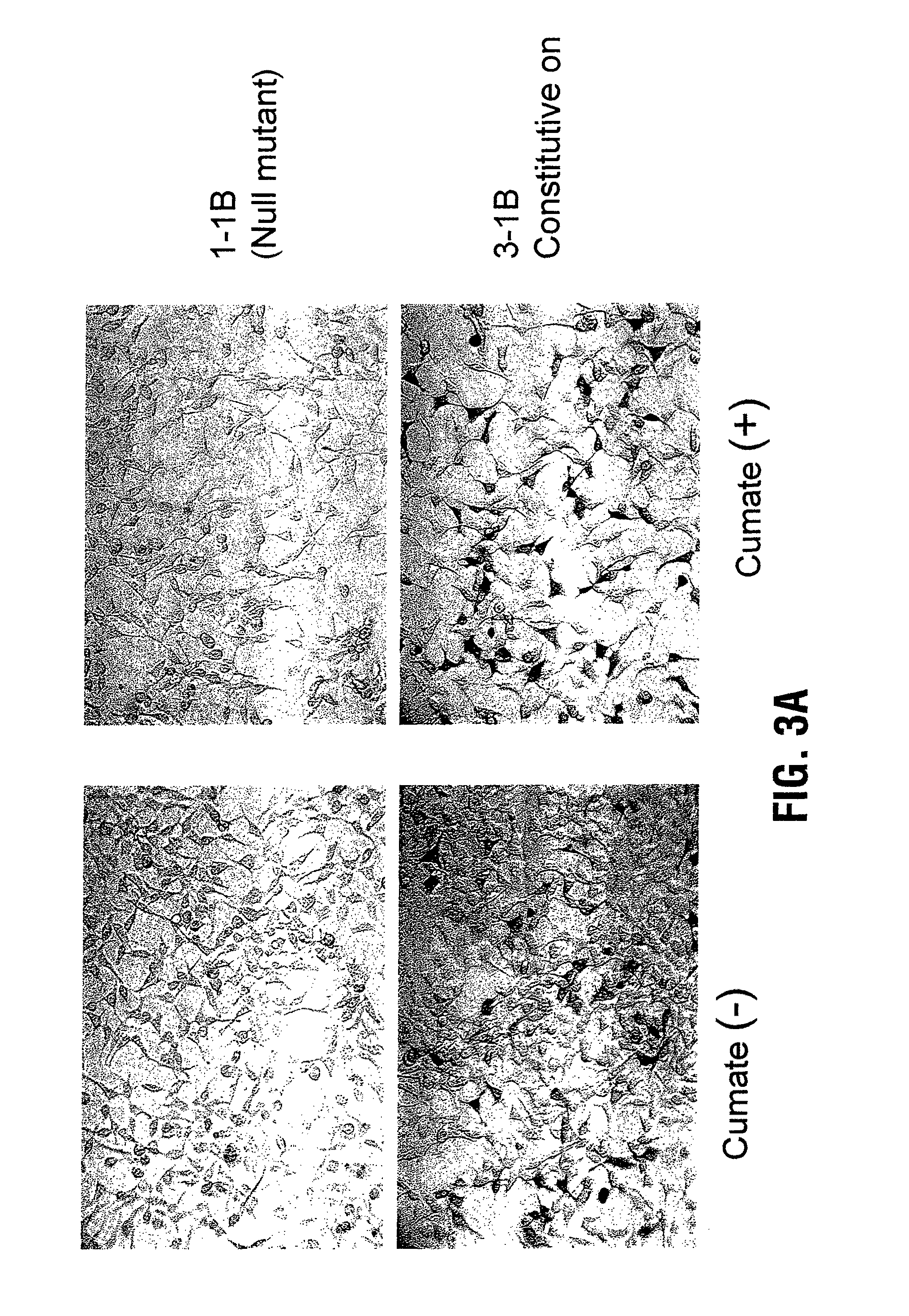
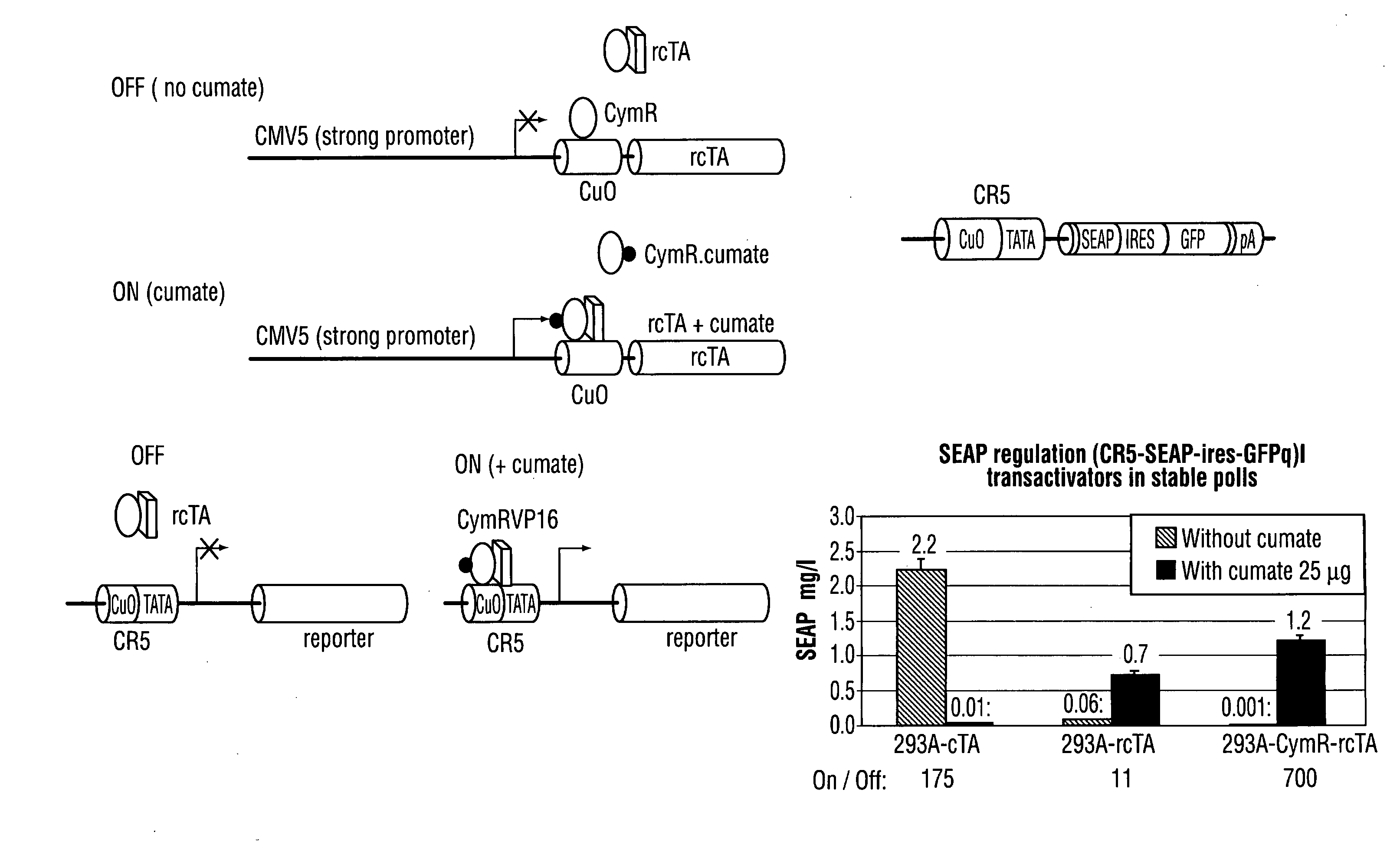
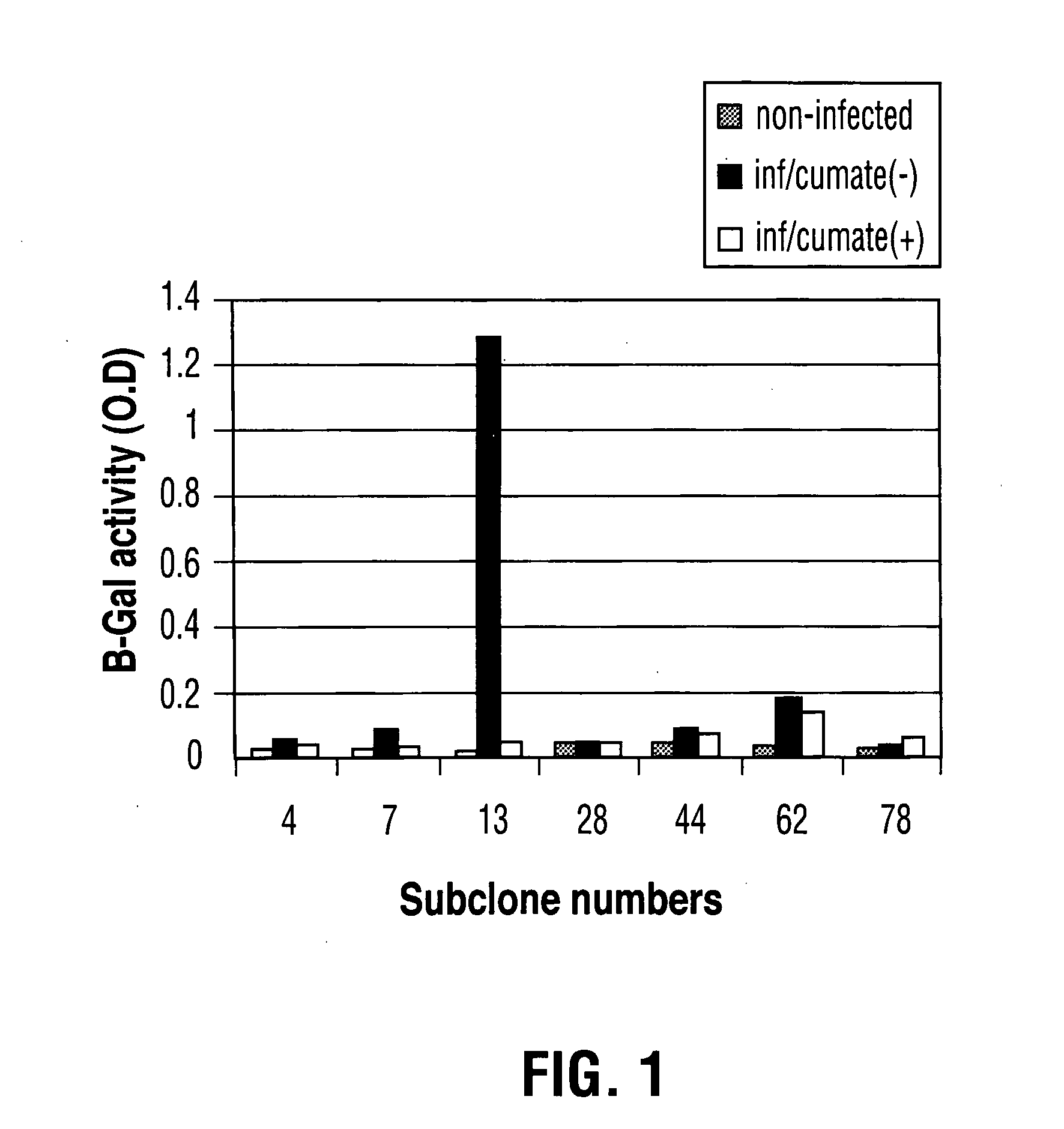
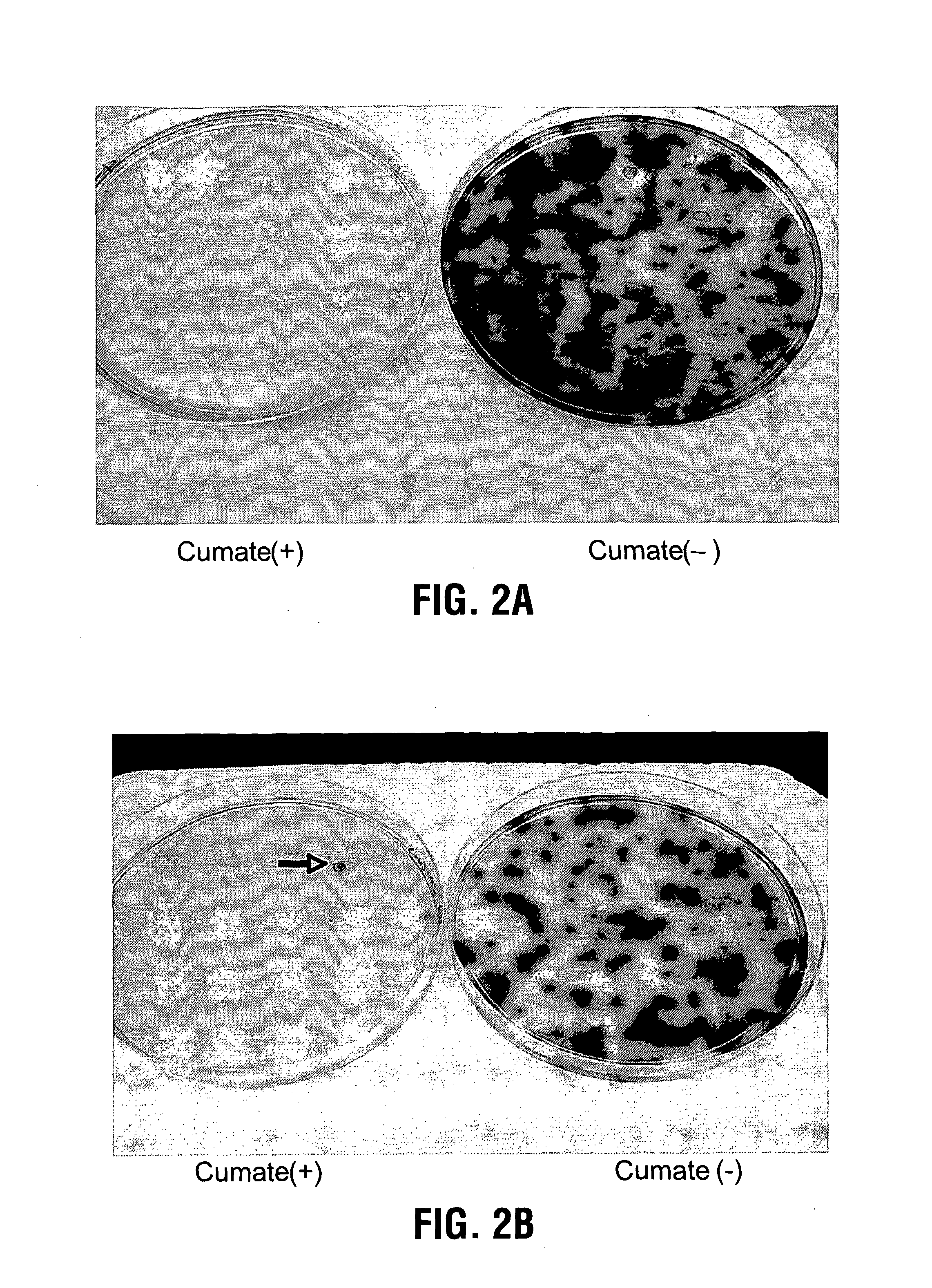
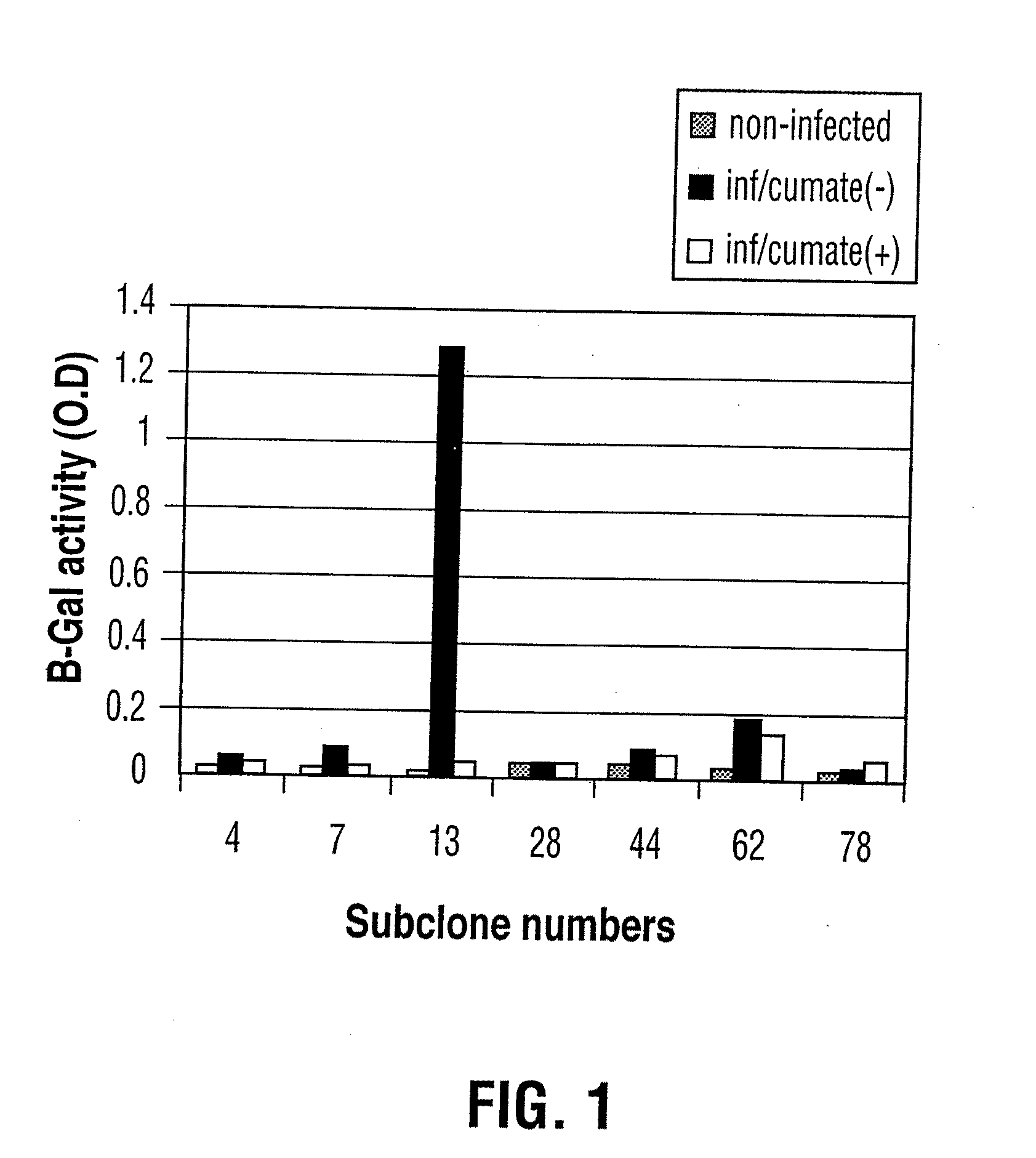
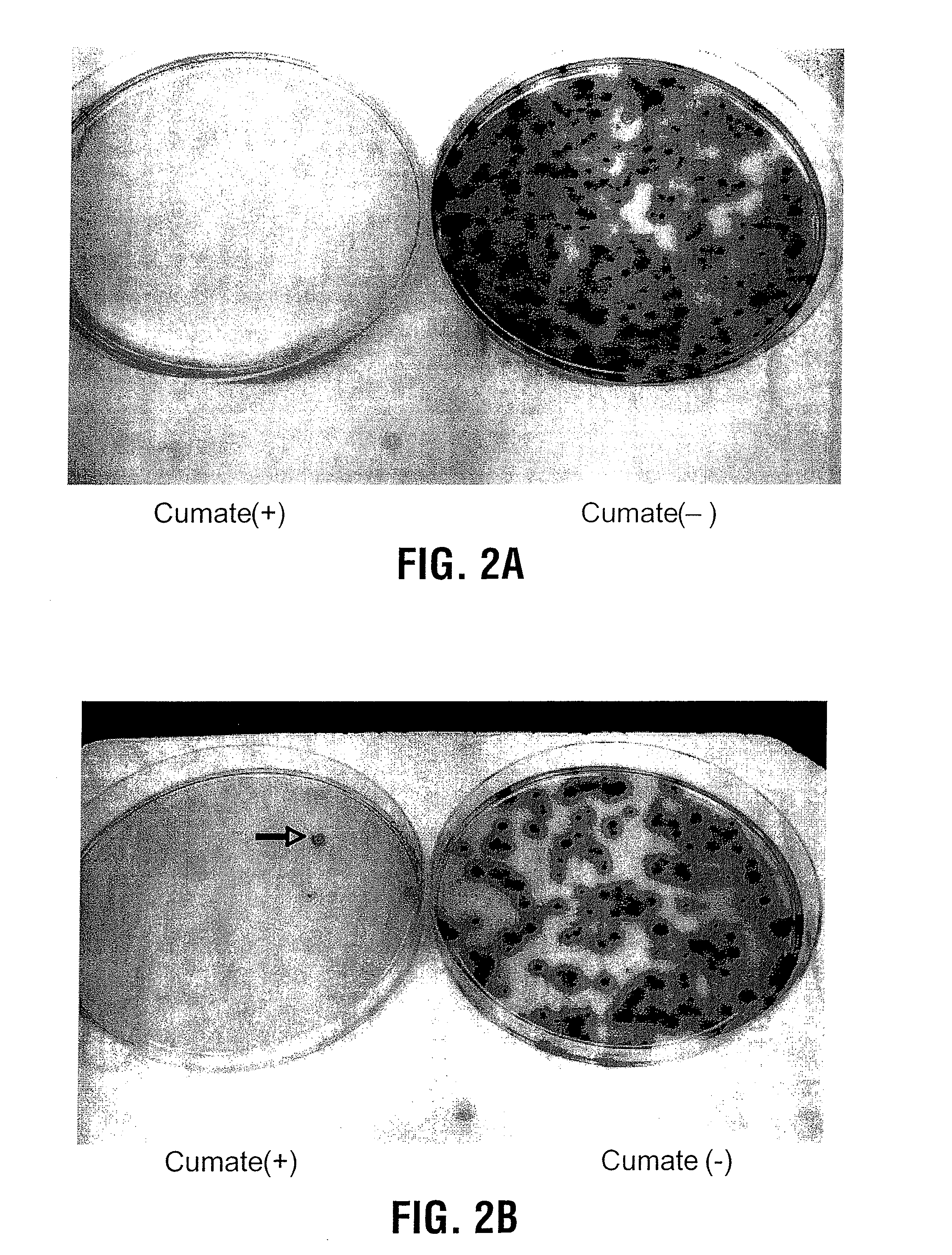
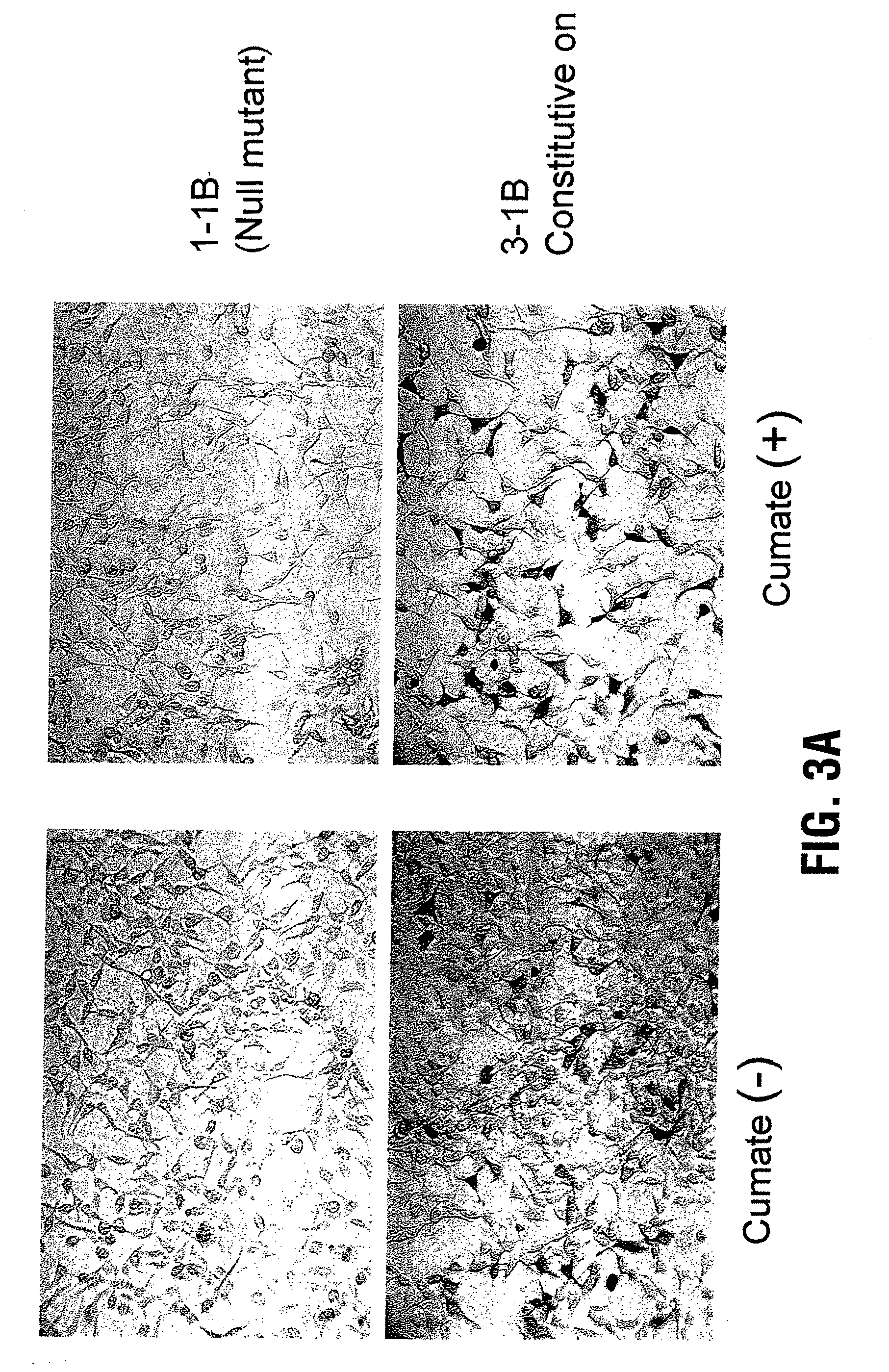
Reverse cumate repressor mutant
Recently, the development of inducible expression systems has involved exploitation of the p-cym operon from Pseudomonas putida. Disclosed herein are novel expression systems and components thereof, which involve the development of CymR variants with reverse DNA binding activity, such that they exhibit increased affinity for DNA in a presence rather than an absence of an effector molecule such as cumene or an equivalent thereof. Also disclosed are the CymR variants, fusion proteins incorporating such variants, and their use in the control and expression of polynucleotides.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Reverse cumate repressor mutant
ActiveUS7935788B2High expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas putidaWild type
Recently, the development of inducible expression systems has involved exploitation of the p-cym operon from Pseudomonas putida. Disclosed herein are novel expression systems and components thereof, which involve the development of a CymR variant with reverse DNA binding activity, such that they exhibit increased affinity for DNA in a presence rather than an absence of an effector molecule such as cumene or an equivalent thereof. Also disclosed are the CymR variant, fusion proteins incorporating such a variant, and its use in the control and expression of polynucleotides. The CymR variant comprises a 142Glu to 142Gly single point mutation of wild type CymR.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Expression System, Components Thereof and Methods of Use
Recently, the development of inducible expression systems has involved exploitation of the p-cym operon from Pseudomonas putido. Disclosed herein are novel expression systems and components thereof, which involve the development of CymR variants with reverse DNA binding activity, such that they exhibit increased affinity for DNA in a presence rather than an absence of an effector molecule such as cumene or an equivalent thereof. Also disclosed are the CymR variants, fusion proteins incorporating such variants, and their use in the control and expression of polynucleotides.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
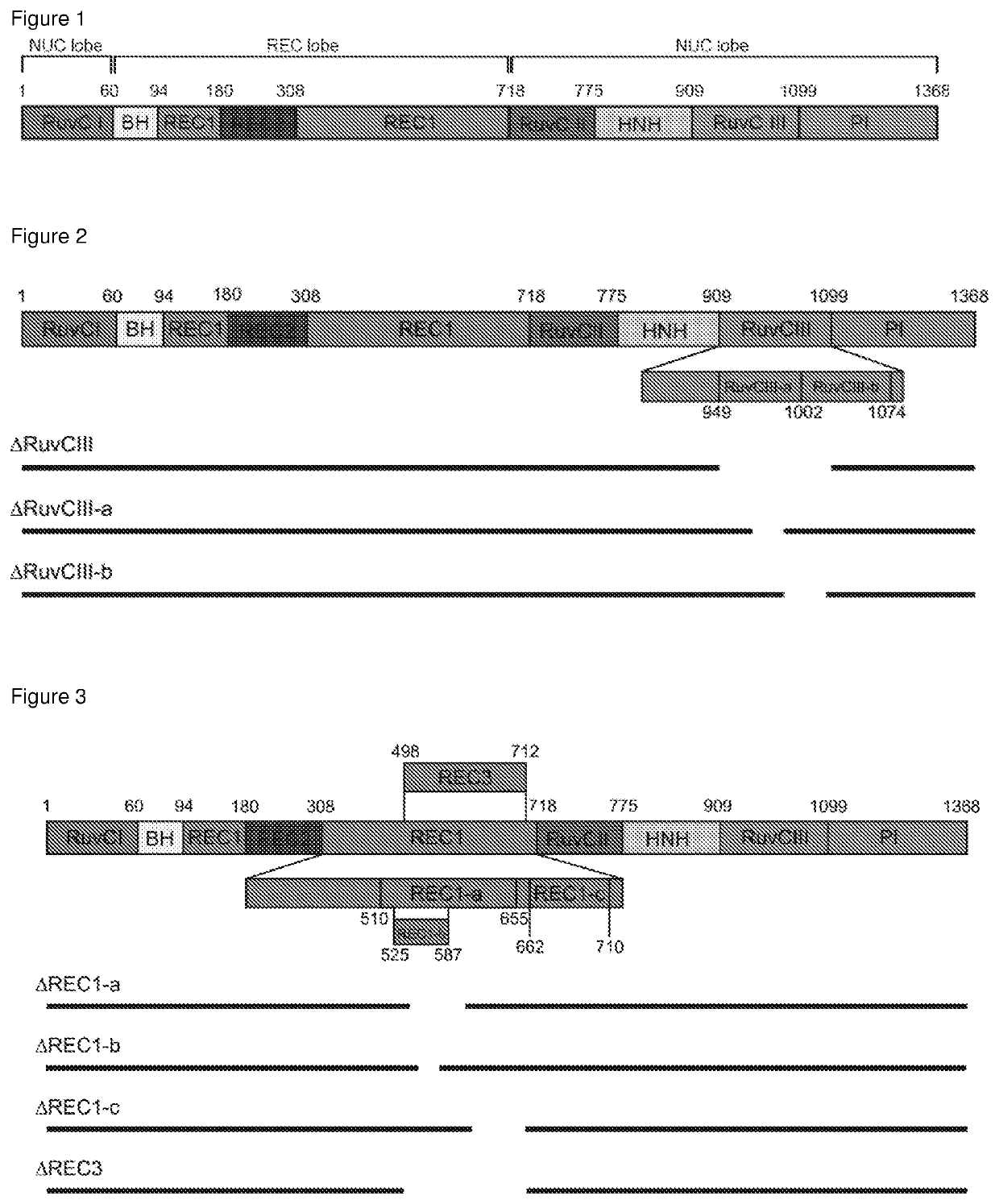
Truncated crispr-cas proteins for DNA targeting
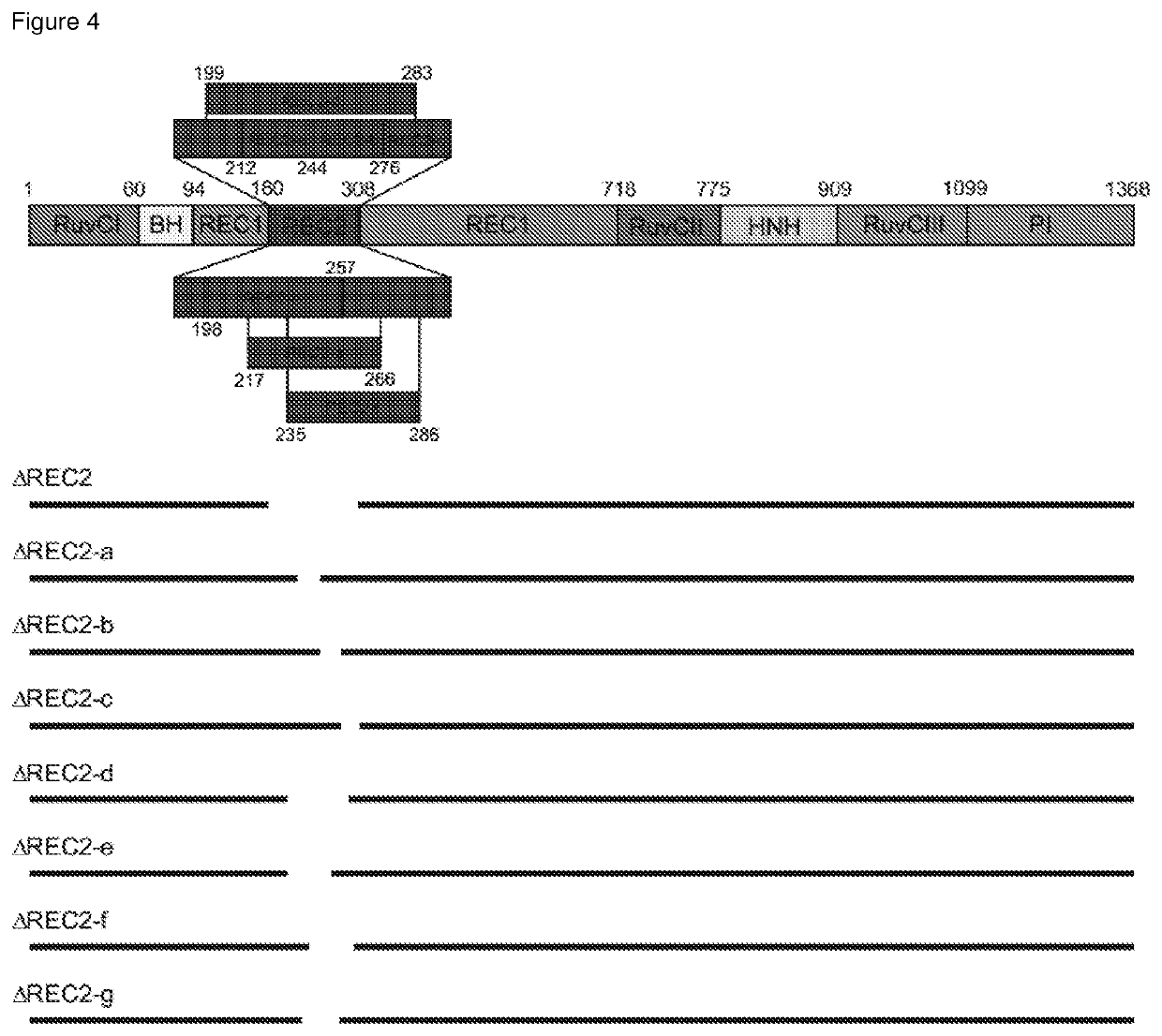
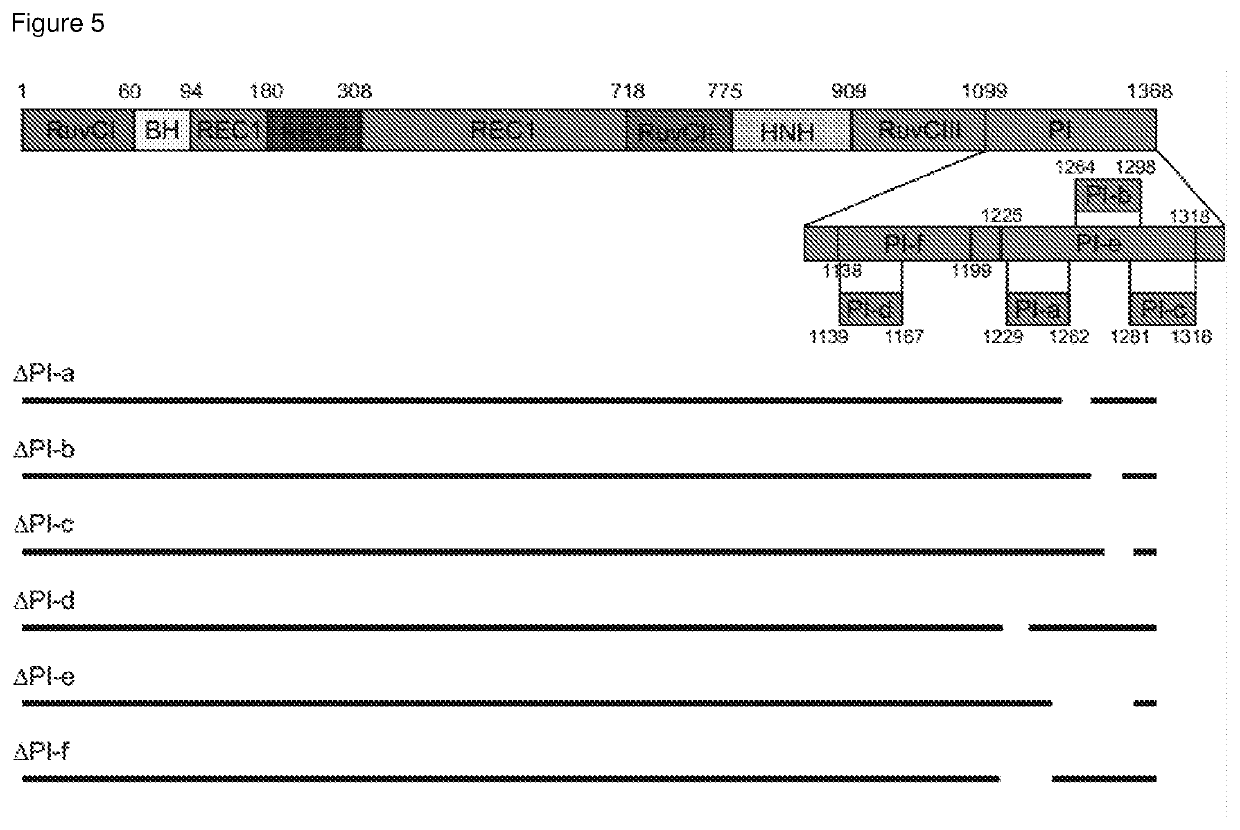
The present invention relates to a polypeptide comprising at least one at least one deletion selected from the group consisting of ΔHNH (Δ775-909), ARuvCIII-b (Δ1002-1074), AREC1-a (Δ510-655), AREC1-b (Δ525-587), AREC1-c (Δ662-710), AREC2 (Δ180-308), AREC2-a (Δ212-244), AREC2-b (Δ244-276), AREC2-c (Δ276-308), AREC2-d (Δ199-283), AREC2-e (Δ198-257), AREC2-f (Δ235-286), AREC2-g (Δ217-266), AREC3 (Δ498-712) and combinations thereof, wherein the position numbering is in accordance with SEQ ID NO: 1 encoding for S. pyogenes Cas9, and wherein the polypeptide has CRISPR-Cas DNA-binding activity. The polypeptide may further comprises a missense mutations selected from G12R, T13K, T13R, N14K, N497K, T657K, T657R, N767K, T770K, T770R, Q920K, Q920R, S1109R, D1135K, D1135R, S1338R and combinations thereof. Also claimed are nucleic acid molecules encoding for said polypeptides, compositions and method of site-directed engineering of a target DNA thereof.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Chromatin imaging method and chromatin imaging system based on Type I-F CRISPR/Cas
ActiveCN111849978AOptimization and liveness detectionDouble-stranded DNA binding activityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNADouble strandMammalian expression
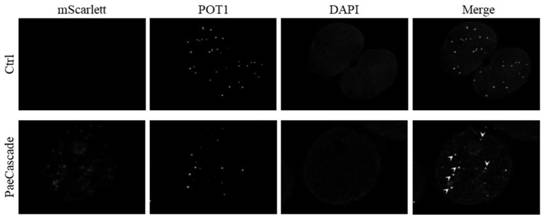
The invention discloses a chromatin imaging system based on a Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system. According to the present invention, the Cascade compound, such as the PaeCascade compound, belonging to the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system is firstly researched and displayed, and can be effectively used for chromatin imaging; meanwhile, a Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system is subjected to mammal expression system optimization, the system is enabled to have efficient double-stranded DNA binding activity in mammalian cells, and fluorescent molecule is subjected to fusion expression to optimized Cascade subunit so as to successfully construct chromatin imaging system; the application of the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system in chromatin imaging of mammalian cells becomes possible, and a necessary tool is provided for chromatin imaging based on the Type I-F CRISPR / Cas system.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Regulation of NAD(p)h oxidase growth and transcription in melanoma cells
Malignant melanoma cells spontaneously generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) that promote constitutive activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB). Although antioxidants and inhibitors of NAD(P)H oxidases significantly reduce constitutive NF-kB activation and suppress cell proliferation, the nature of the enzyme responsible for ROS production in melanoma cells has not been determined. To address this issue, we now have characterized the source of ROS production in melanoma cells. ROS are generated by isolated, cytosol-free melanoma plasma membranes, with inhibition by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors. The p22phox, gp91phox and p67phox components of the human phagocyte NAD(P)H oxidase, and the 91phox homolog NOX4 were demonstrated in melanomas by RT-PCR and sequencing, and protein product for both p22phox and gp91phox were detected in cell membranes by immunoassay. Normal human epidermal melanocytes expressed only p22phox and NOX4. Melanoma proliferation was reduced by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors and by transfection of antisense but not sense oligonucleotides for p22phox and NOX4. Also, the flavoprotein inhibitor diphenylene iodonium inhibited constitutive DNA binding of nuclear protein to the NF-kB and cyclic-AMP response element consensus oligonucleotides, without affecting DNA binding activity to AP-1 or OCT-1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Use of low molecular weight compounds for preparing a medicament useful in treating mutant p53 mediated diseases
The present invention provides novel compounds, corresponding to formulae I and II, respectively, which are able to reactivate the apoptosis-inducing function of mutant p53 proteins. This reactivation is provided by restoration of sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcriptional transactivation function to mutant p53 proteins, and modulation of the conformation-dependent epitopes of the p53 protein. Accordingly, the substances according to the invention will be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of patients suffering from various types of tumours.
Owner:APREA THERAPEUTICS AB
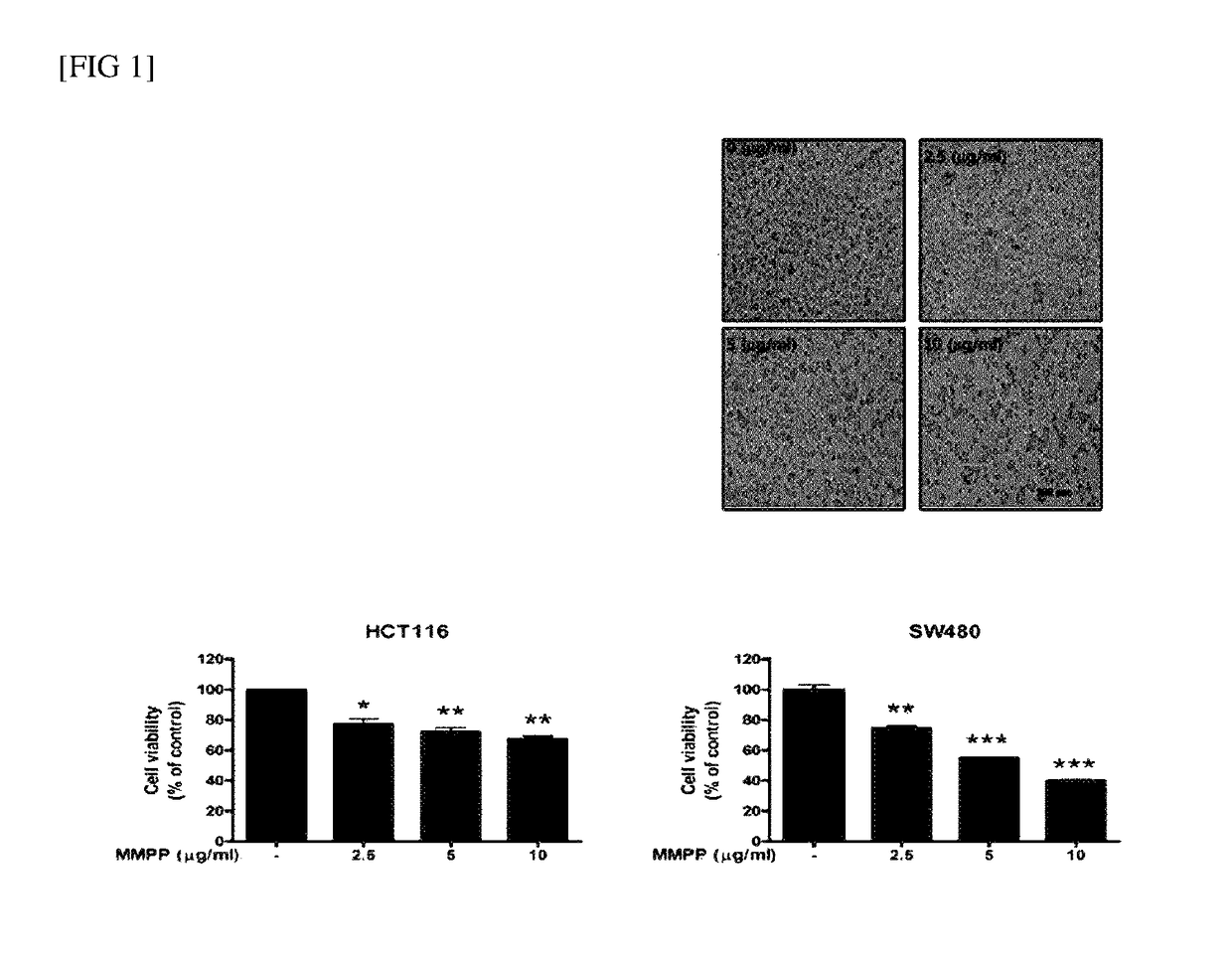
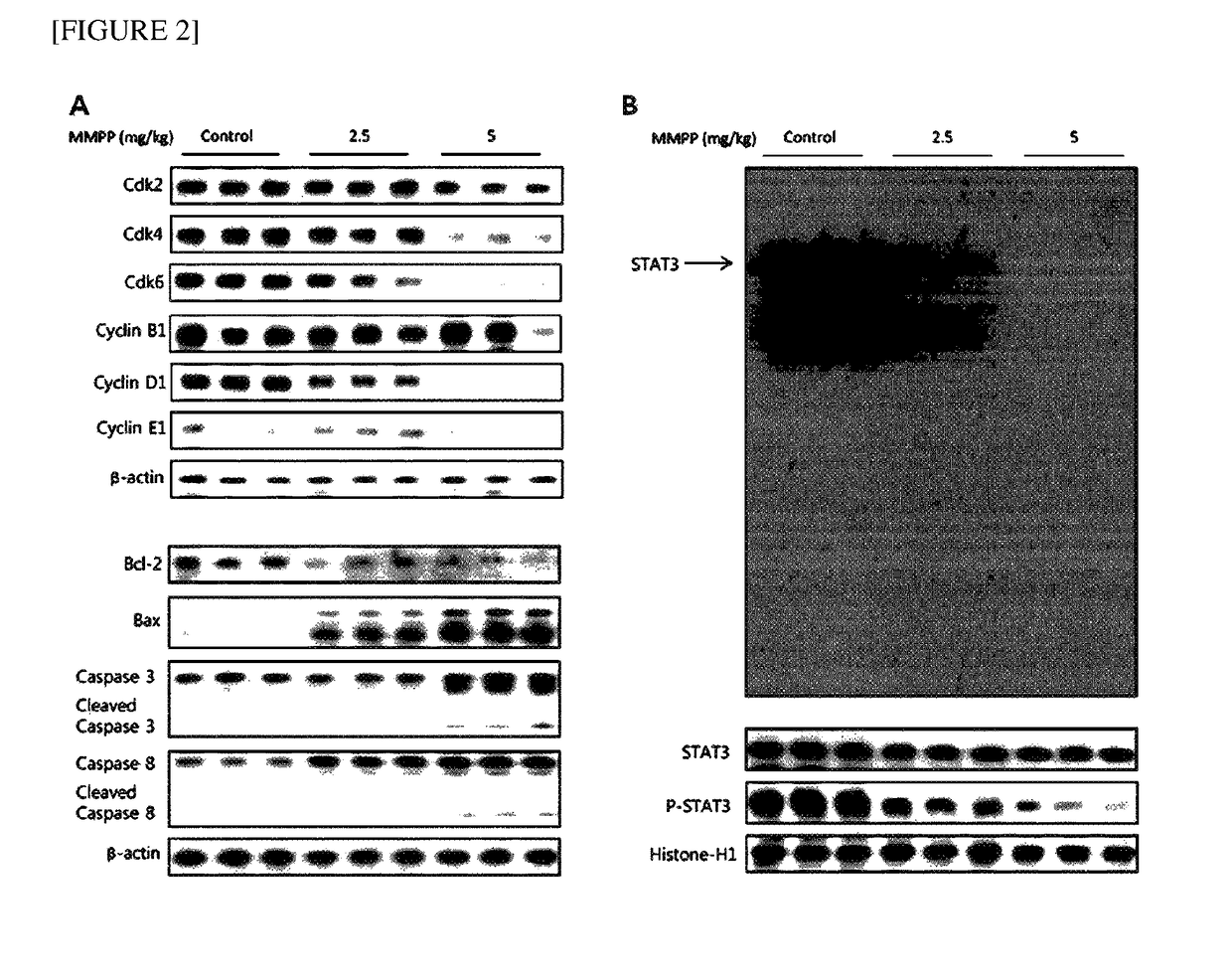
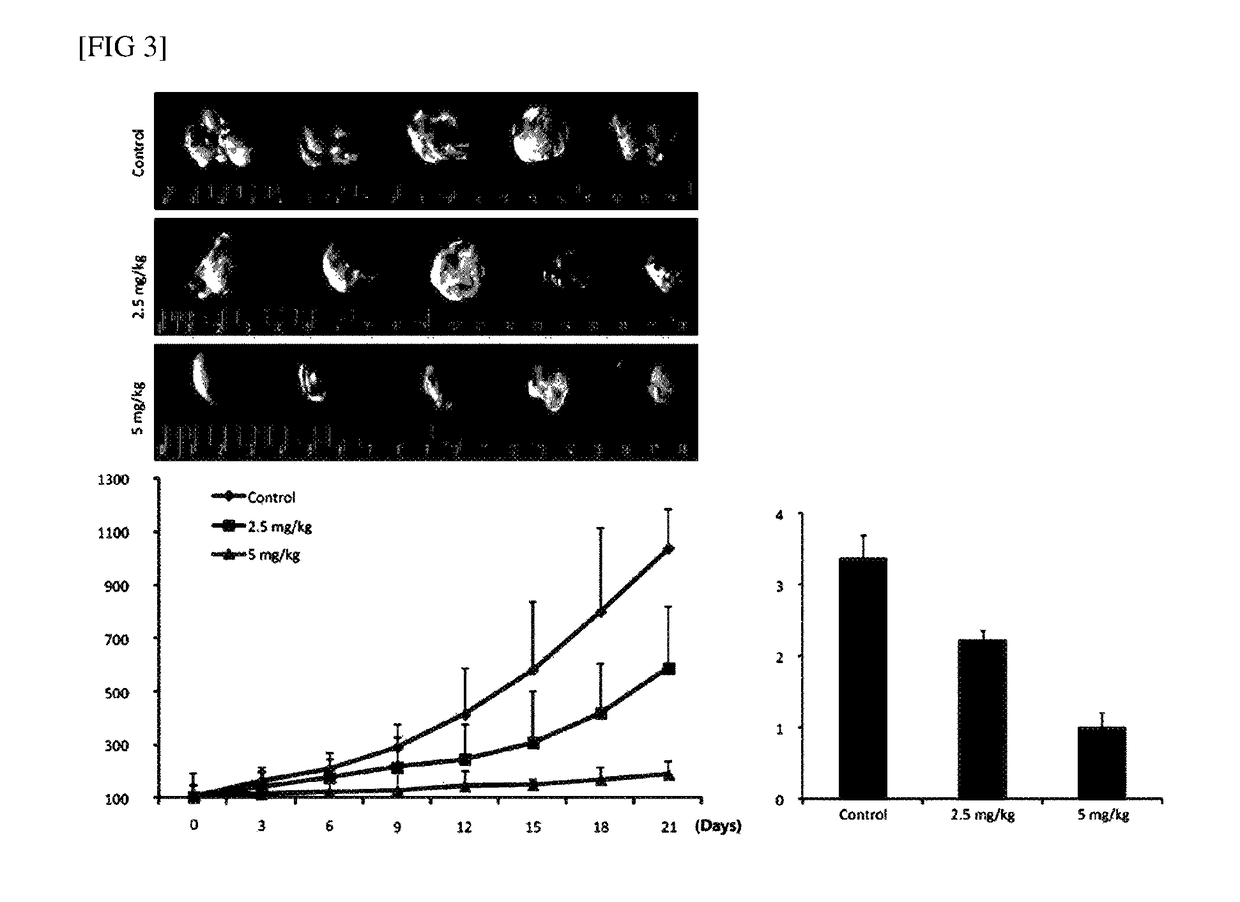
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer including 2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-1-en-1-yl)phenol as active ingredient
ActiveUS20180133168A1Growth inhibitionInhibit expressionHydroxy compound active ingredientsEther/acetal active ingredientsCancer cellApoptosis
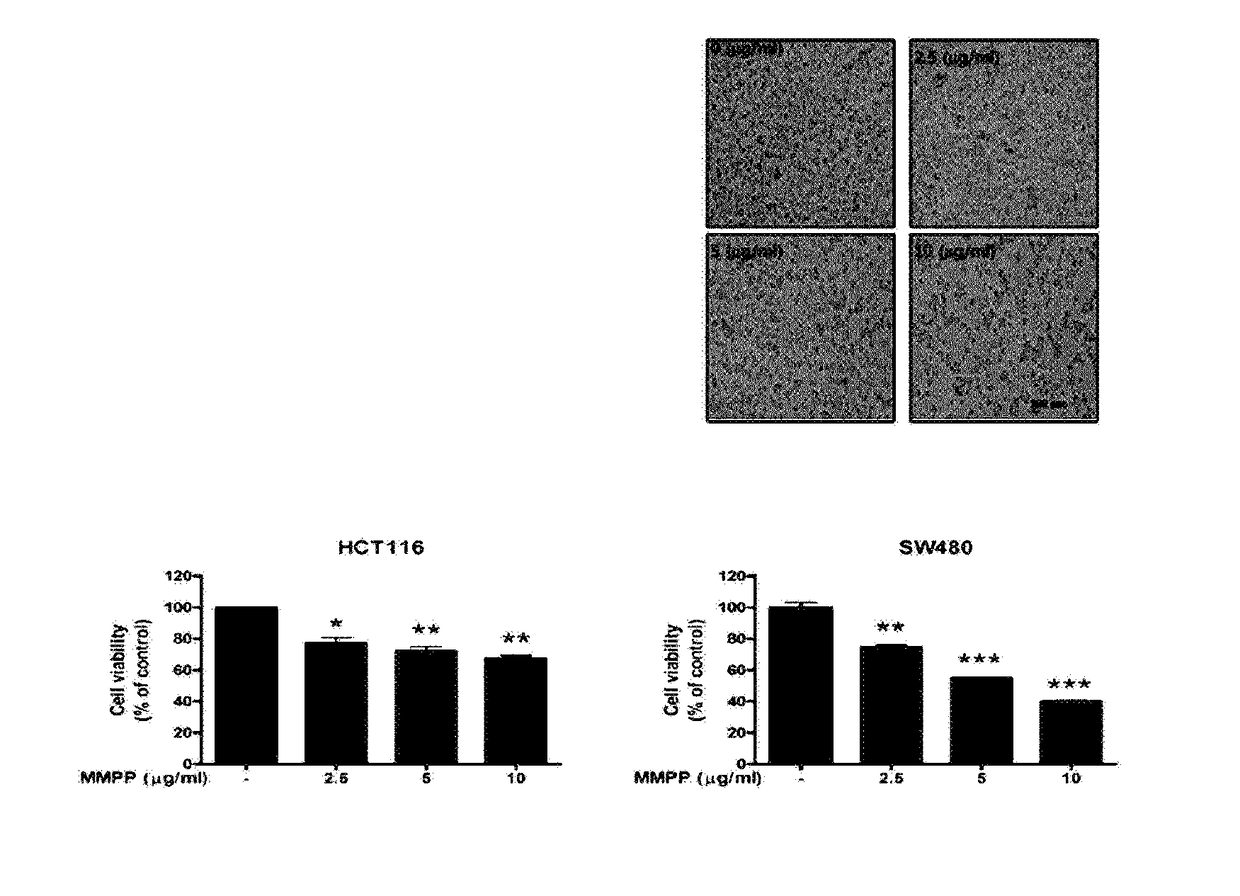
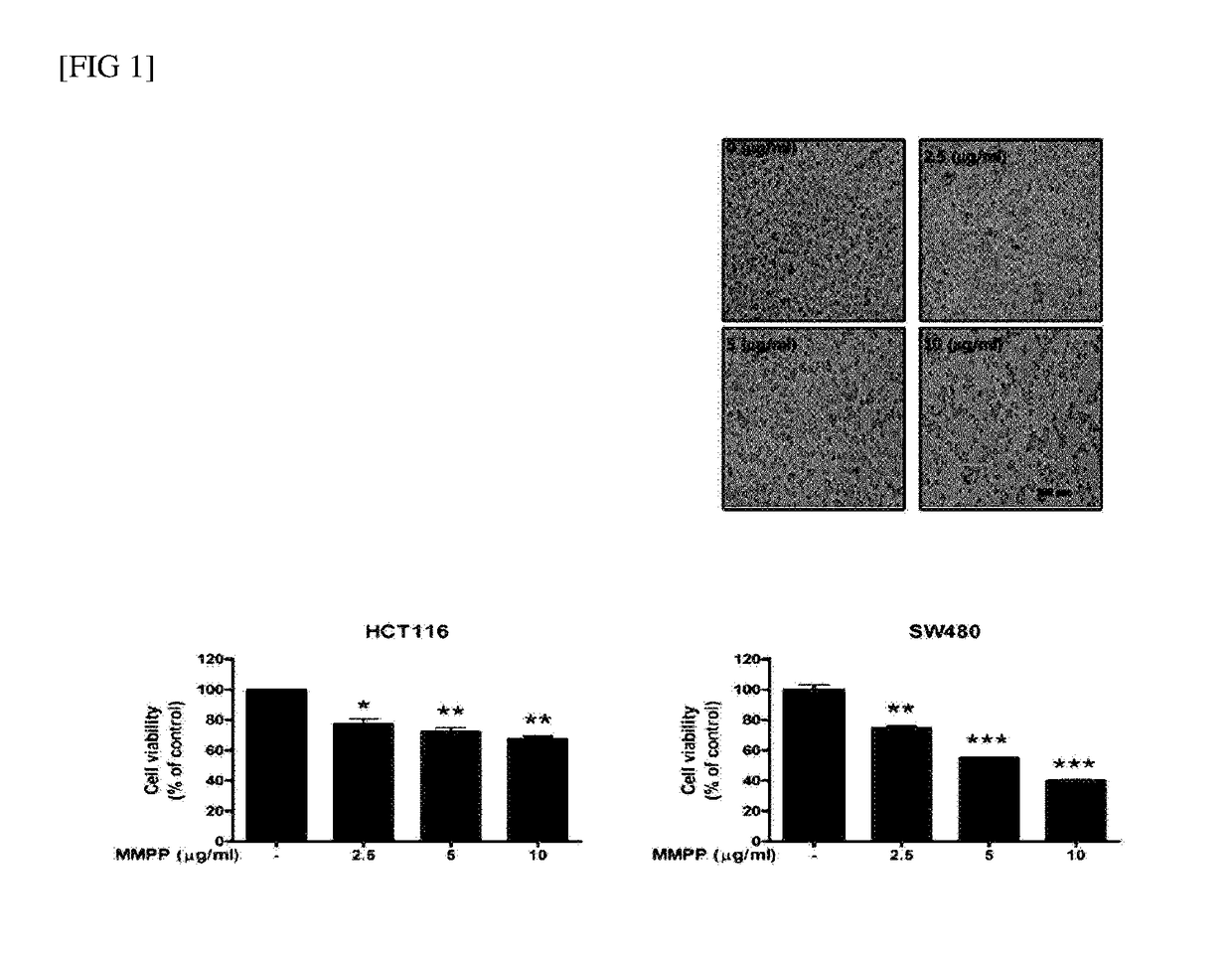
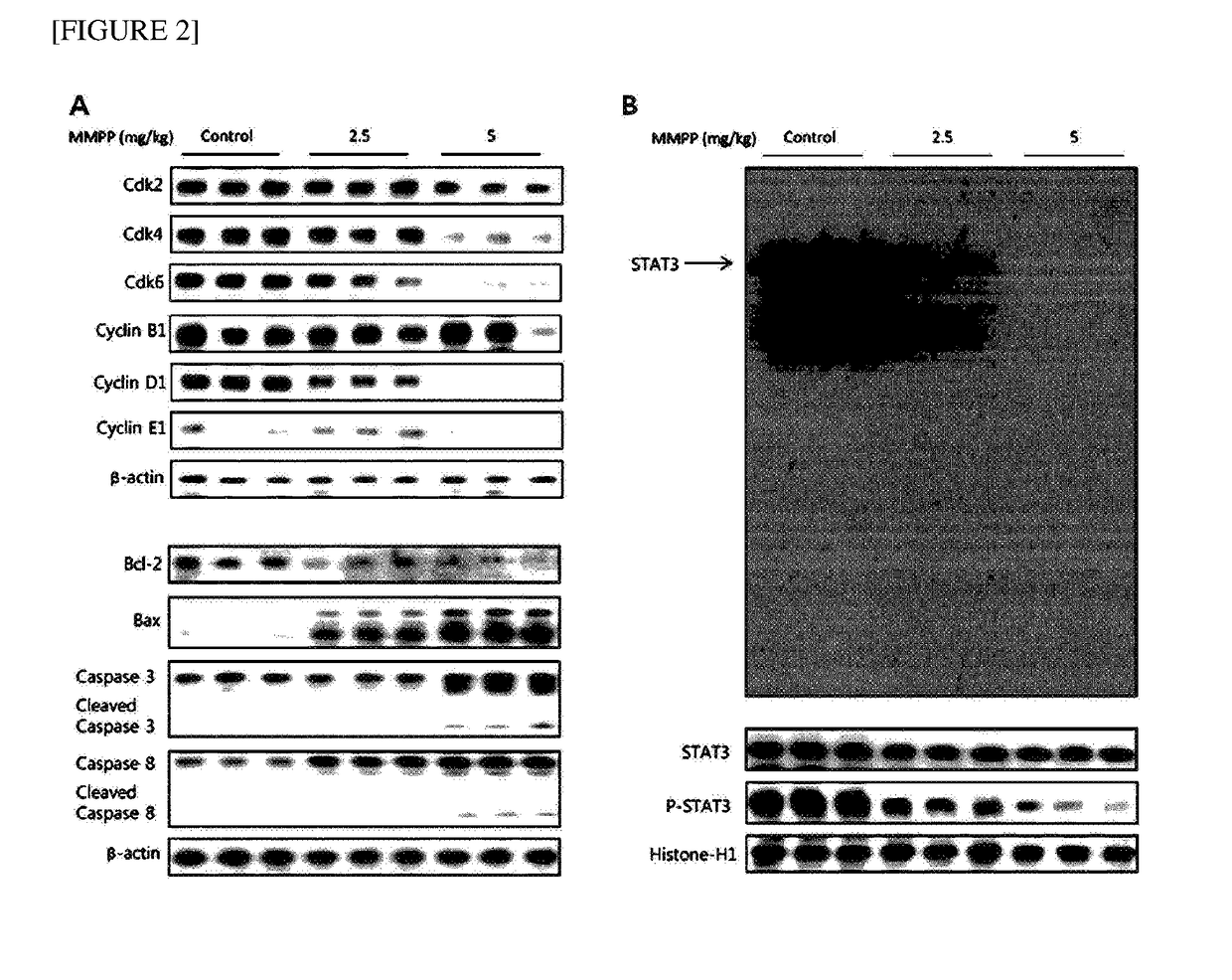
The present disclosure relates to an anticancer use of a novel compound, i.e., 2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propyl-1-en-1-yl)phenol. The compound of the present disclosure effectively inhibits the growth of cancer cells and tumors in vitro and in a xenograft animal model. The compound of the present disclosure illustrates an anticancer activity by inhibiting a DNA binding activity of transcription factor STAT 3 in cancer cells, inducing apoptosis of cancer cells, and reducing the expression of a cell cycle regulatory protein. The compound of the present disclosure can be developed as an active ingredient of a strong anticancer drug.
Owner:CHUNGBUK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Epigenetic regulatory complex for control of gene expression
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
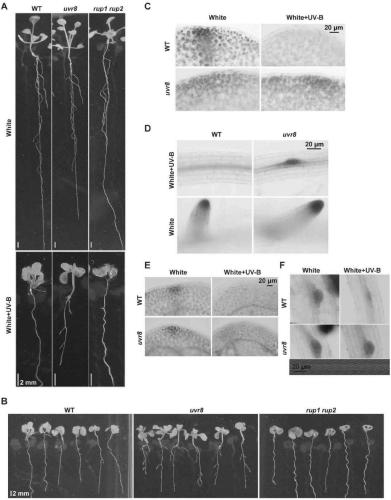
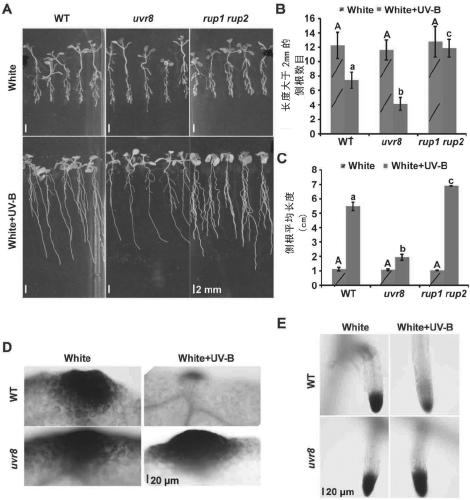
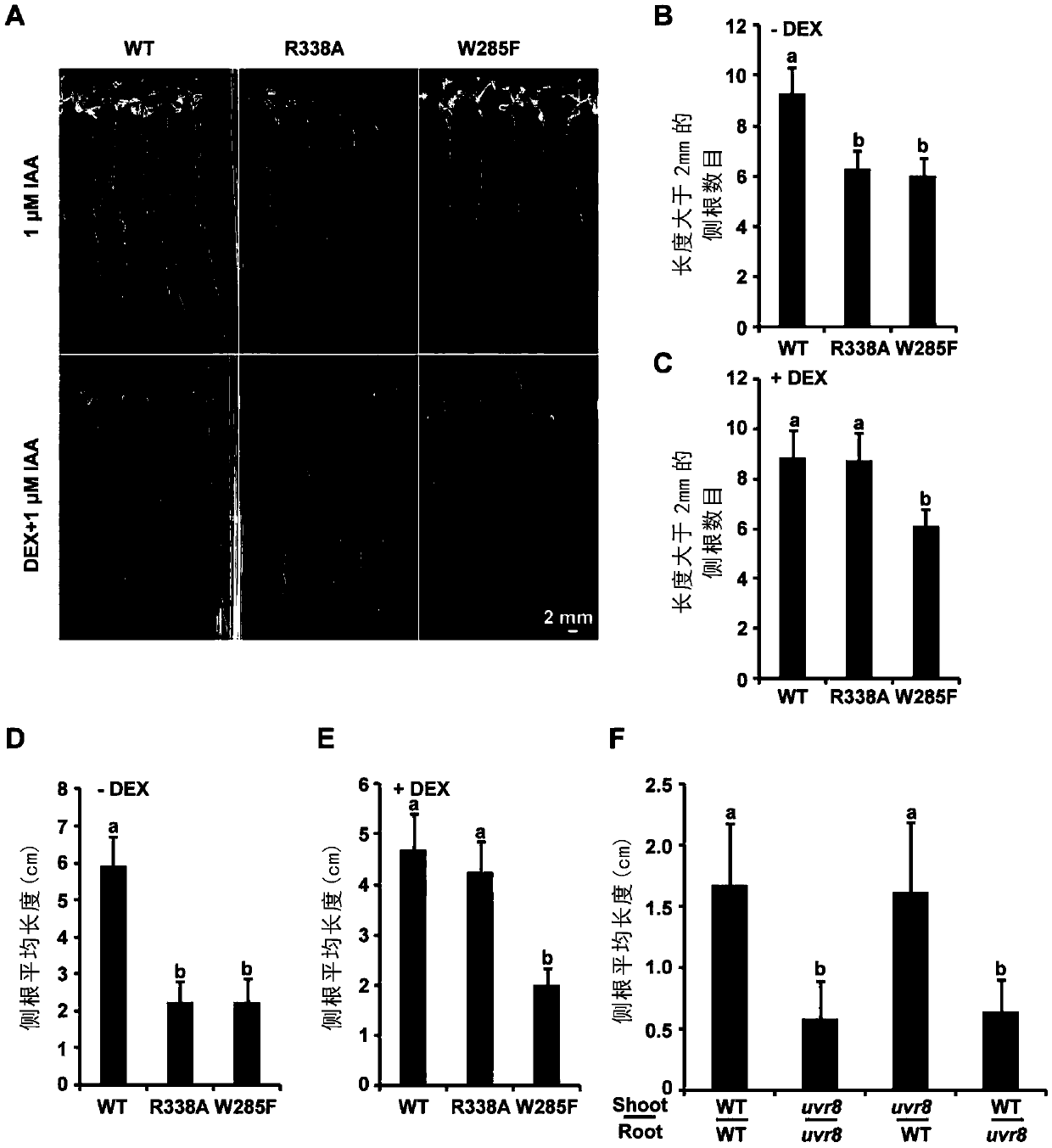
Method for controlling growth and development of plant roots by mutually combining MYB and UVR8 in UV-B dependent form
The invention relates to a method for controlling the growth and development of plant roots by mutually combining MYB and UVR8 in a UV-B dependent form and an application based the method. The invention discloses a method for controlling the growth and development of the plant roots and particularly lateral roots by controlling, by UV-B, photomorphogenesis and stress response by virtue of UVR8 andinhibiting an auxin signal by virtue of UVR8. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses two transcription factors MYB73 and MYB77 interacting with UVR8 in the UV-B dependent form, UV-B induces UVR8to interact with MYB73 / MYB77 to inhibit the DNA binding activity of MYB73 / MYB77, and thus, the auxin signal is controlled to control the growth of the plant roots and particularly the lateral roots. The technical solution provided by the invention is not only helpful to study how plants adapt to the environment better, but also provides a novel tool for photogenetics.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
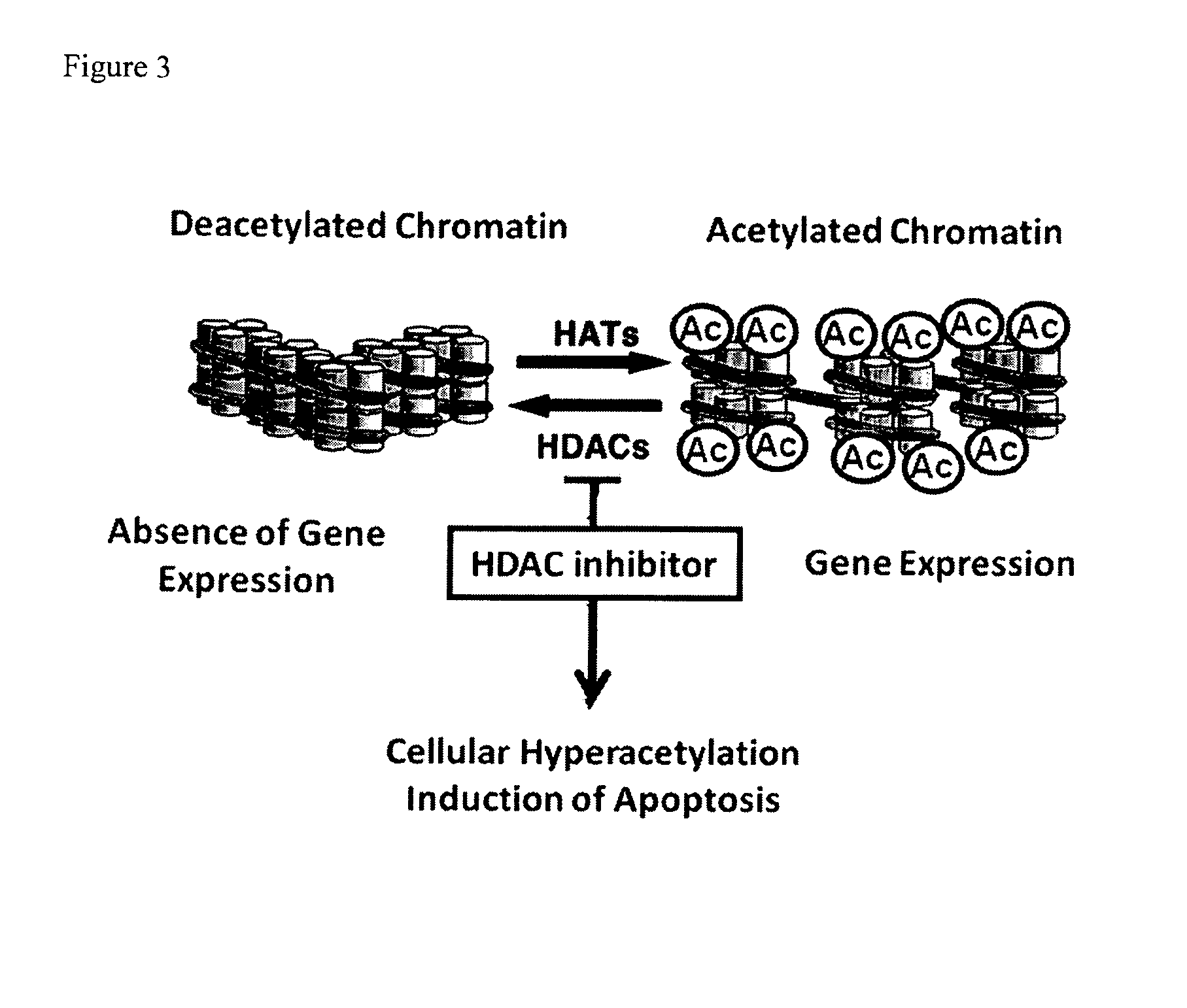
Metal complexes having dual histone deacetylase inhibitory and DNA-binding activity
InactiveUS20120190874A1High anticancer activityHigh selectivityPlatinum organic compoundsMetallocenesIn vivoEnzyme
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Expression system, components thereof and methods of use
ActiveUS20090176275A1High expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas putidaWild type
Recently, the development of inducible expression systems has involved exploitation of the p-cym operon from Pseudomonas putida. Disclosed herein are novel expression systems and components thereof, which involve the development of a CymR variant with reverse DNA binding activity, such that they exhibit increased affinity for DNA in a presence rather than an absence of an effector molecule such as cumene or an equivalent thereof. Also disclosed are the CymR variant, fusion proteins incorporating such a variant, and its use in the control and expression of polynucleotides. The CymR variant comprises a 142Glu to 142Gly single point mutation of wild type CymR.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer including 2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-1-en-1-yl)phenol as active ingredient
ActiveUS10166203B2Growth inhibitionInhibit expressionHydroxy compound active ingredientsEther/acetal active ingredientsCancer cellApoptosis
The present disclosure relates to an anticancer use of a novel compound, i.e., 2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propyl-1-en-1-yl)phenol. The compound of the present disclosure effectively inhibits the growth of cancer cells and tumors in vitro and in a xenograft animal model. The compound of the present disclosure illustrates an anticancer activity by inhibiting a DNA binding activity of transcription factor STAT 3 in cancer cells, inducing apoptosis of cancer cells, and reducing the expression of a cell cycle regulatory protein. The compound of the present disclosure can be developed as an active ingredient of a strong anticancer drug.
Owner:CHUNGBUK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Pharmaceutical composition inhibiting interaction between MZF-1 and Elk-1
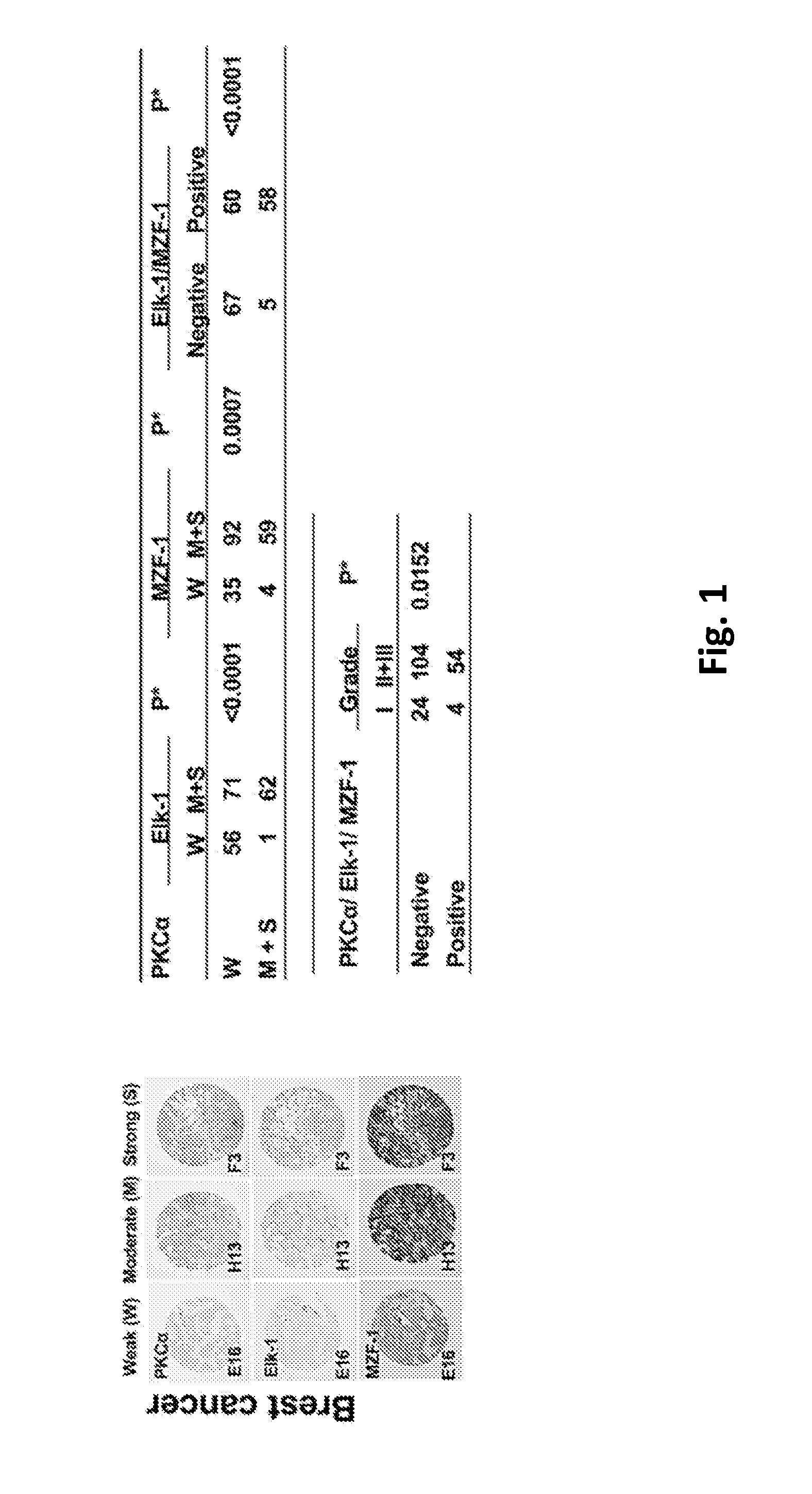
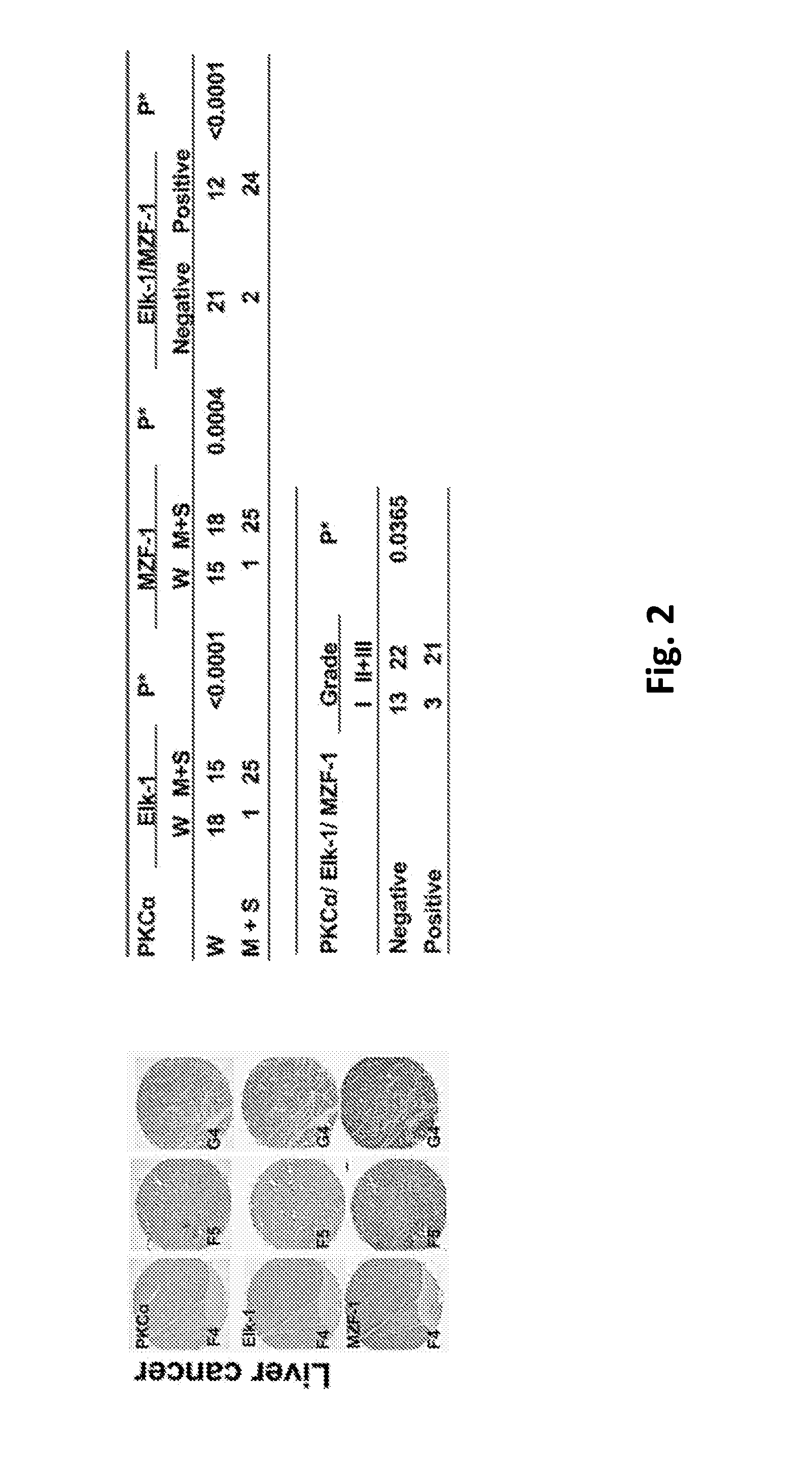
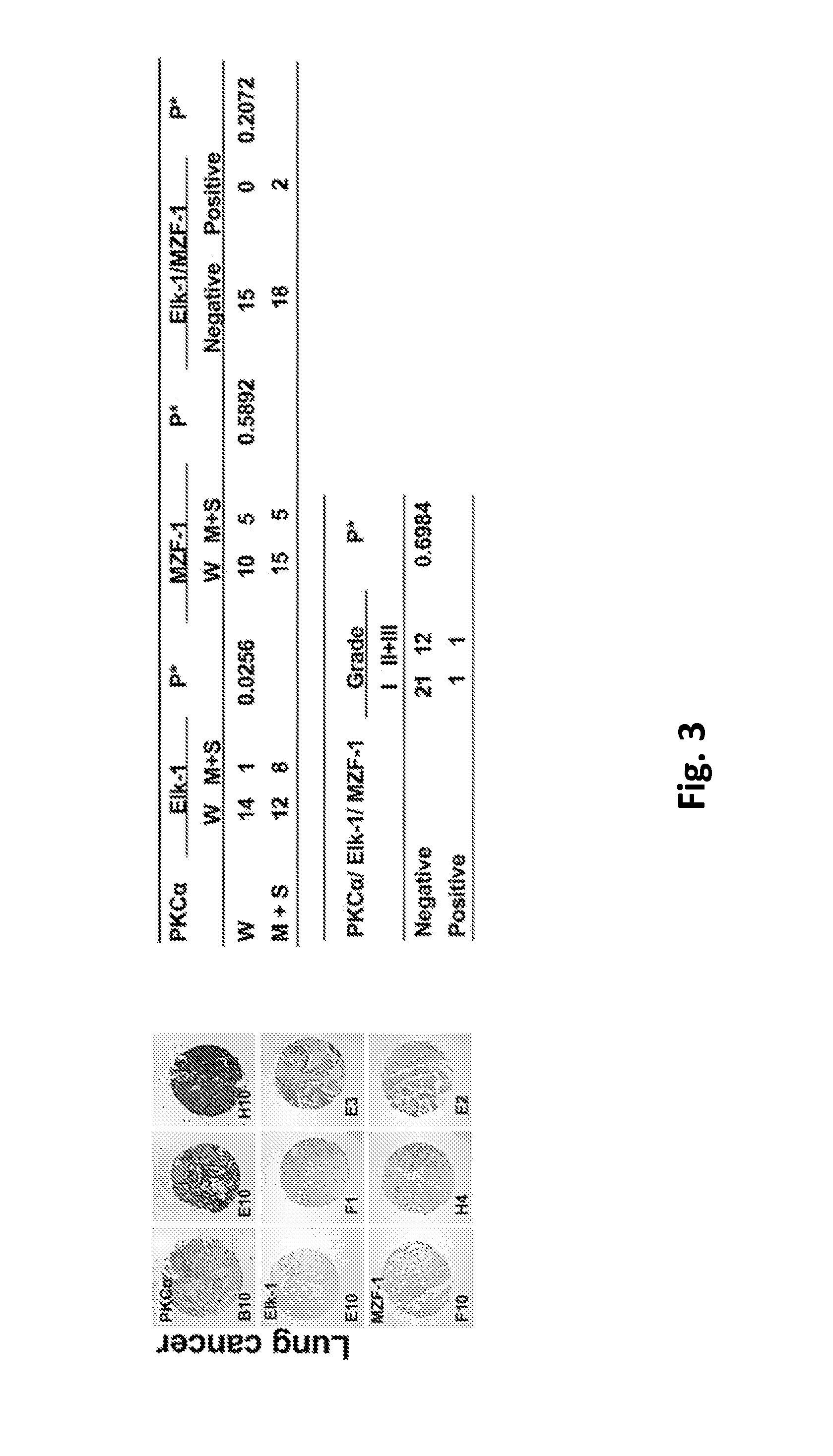
InactiveUS20160362463A1Reduce tumor volumePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DegradationsCancer cell
This invention discloses a peptide, which inhibits the interaction between of MZF-1 and Elk-1 and further inhibits cancers. Both myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF-1) and Ets-like protein-1 (Elk-1) expressions correlate to PKCα expression in cancer cells. Furthermore, it is the interaction between the acidic domain of MZF-1 and the heparin-binding domain of Elk-1 which facilitated their heterodimeric complex formation before their binding to the PKCα promoter. Blocking the formation of the heterodimer changed Elk-1 nuclear localization, MZF-1 protein degradation, their DNA-binding activities, and subsequently the expression of PKCα in cancer cells. Thus, migration, tumorigenicity, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition potential of cancer cells decreased, suggesting that the Elk-1 / MZF-1 heterodimer is considered as a mediator of PKCα in TNBC cell malignancy. The obtained data also suggest that the next therapeutic strategy in the treatment of cancer will come from the blocking of Elk-1 / MZF-1 interaction through the saturation of Elk-1 or MZF-1 binding domains, such as through the application of cell-penetrating HIV transactivating regulatory protein-fused peptides.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Benzoquinone derivatives for the treatment of bladder cancer
PendingUS20220249421A1Inhibits redox functionInhibit tumor cell growthPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsTumor reductionTherapeutic effect
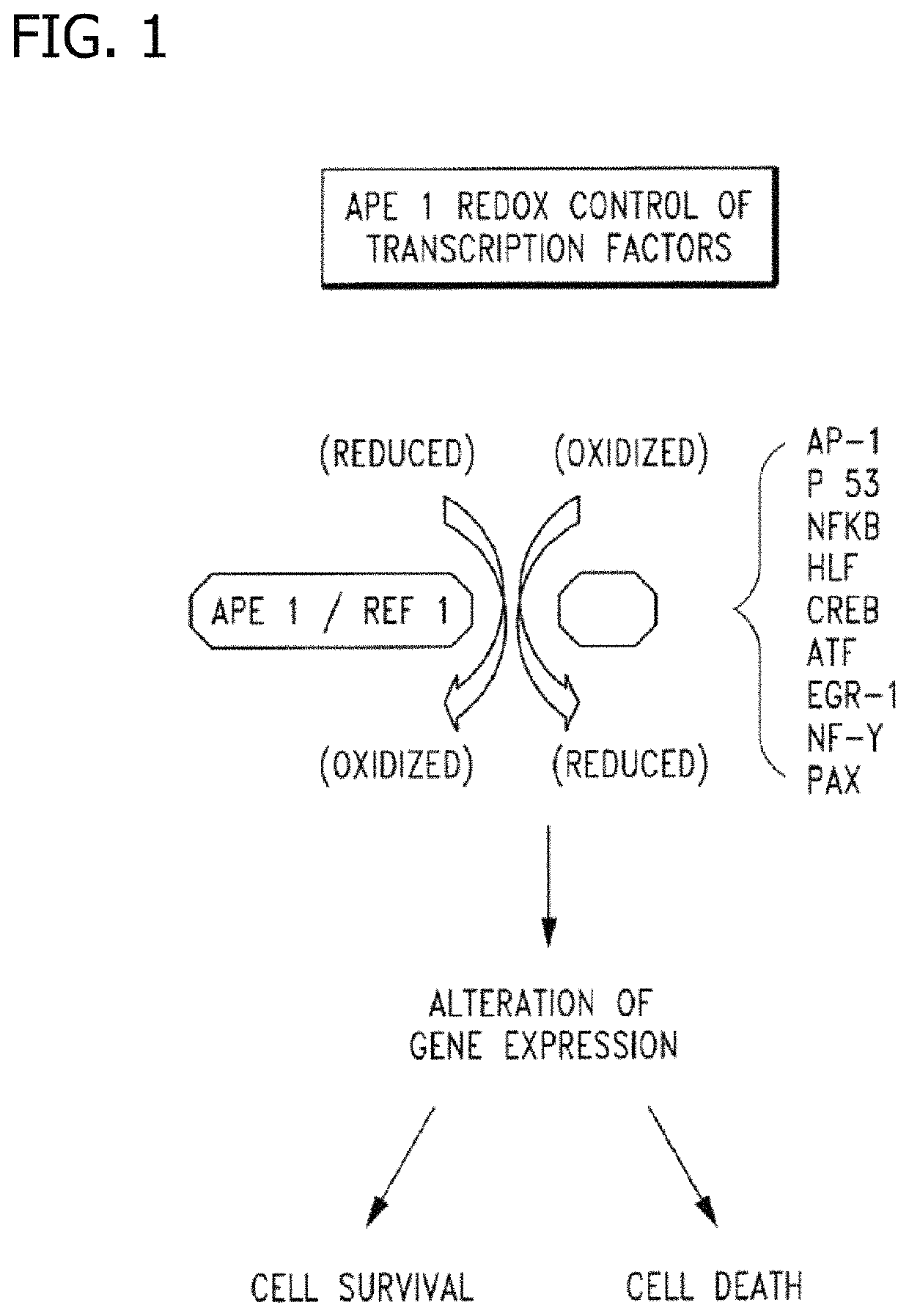
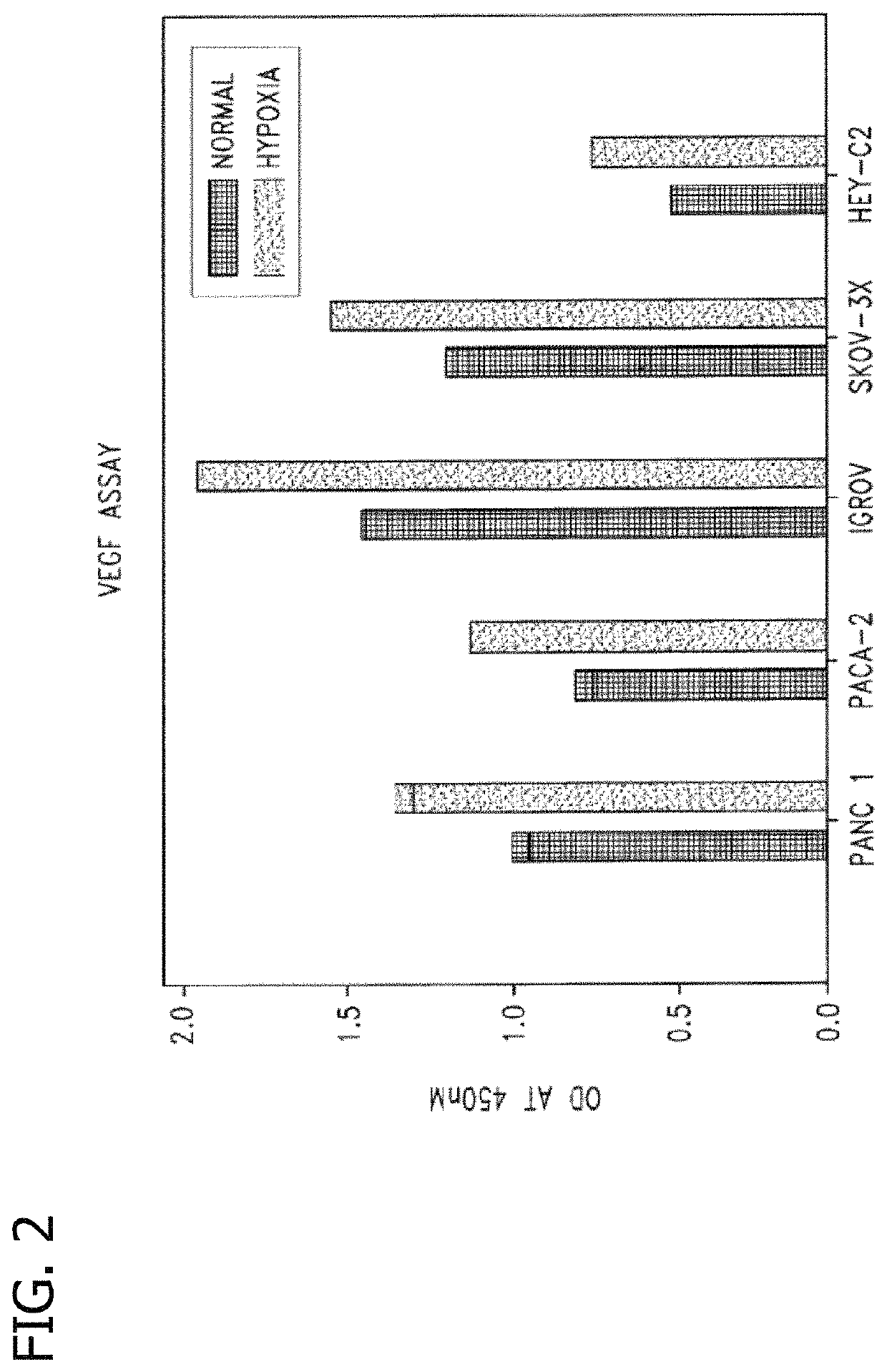
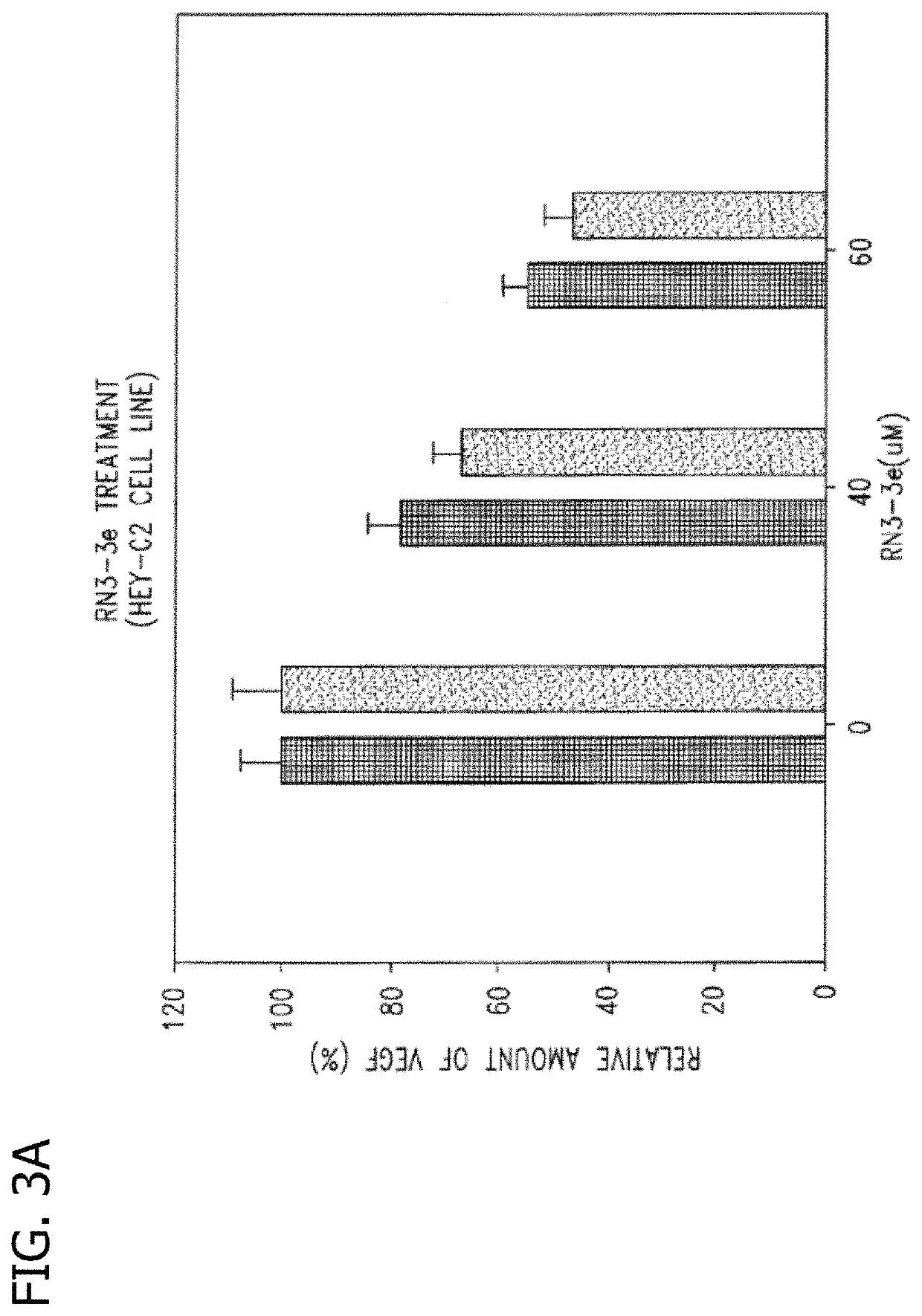
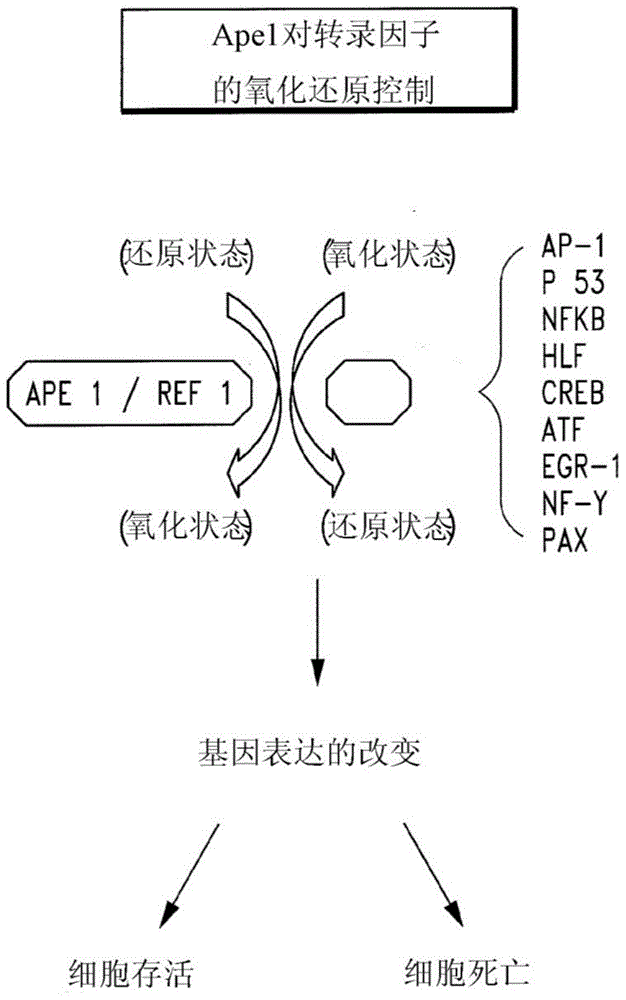
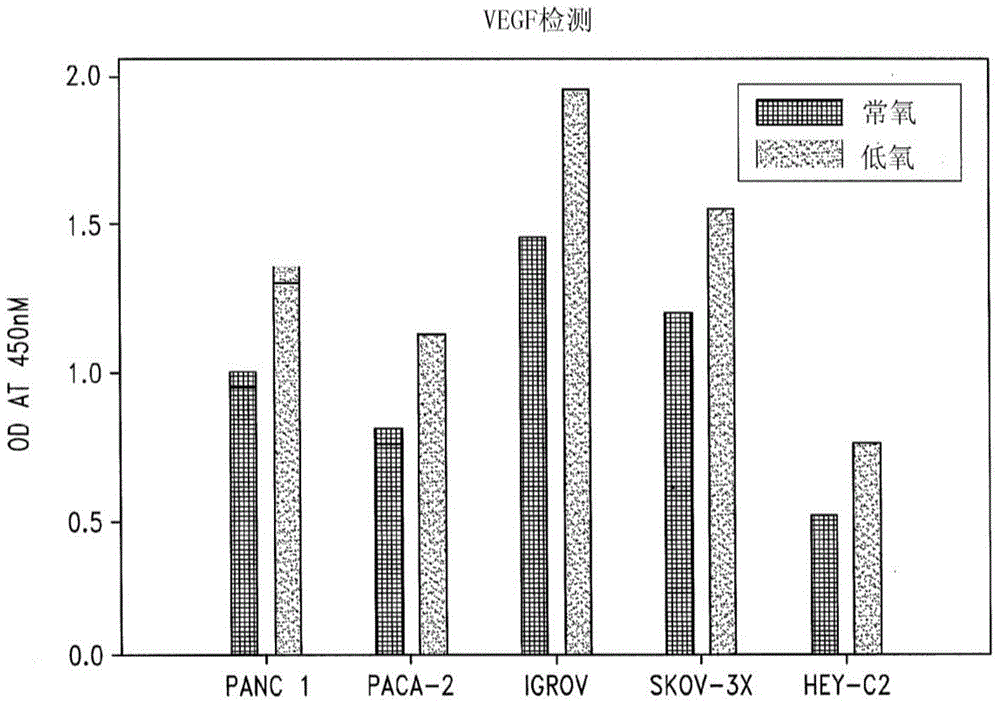
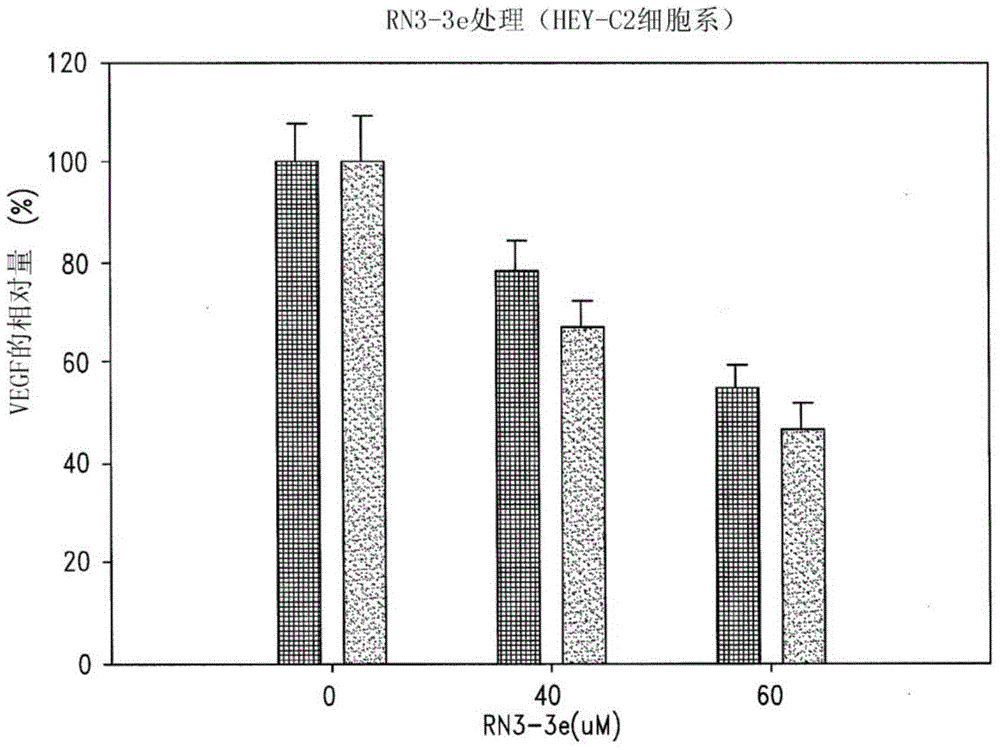
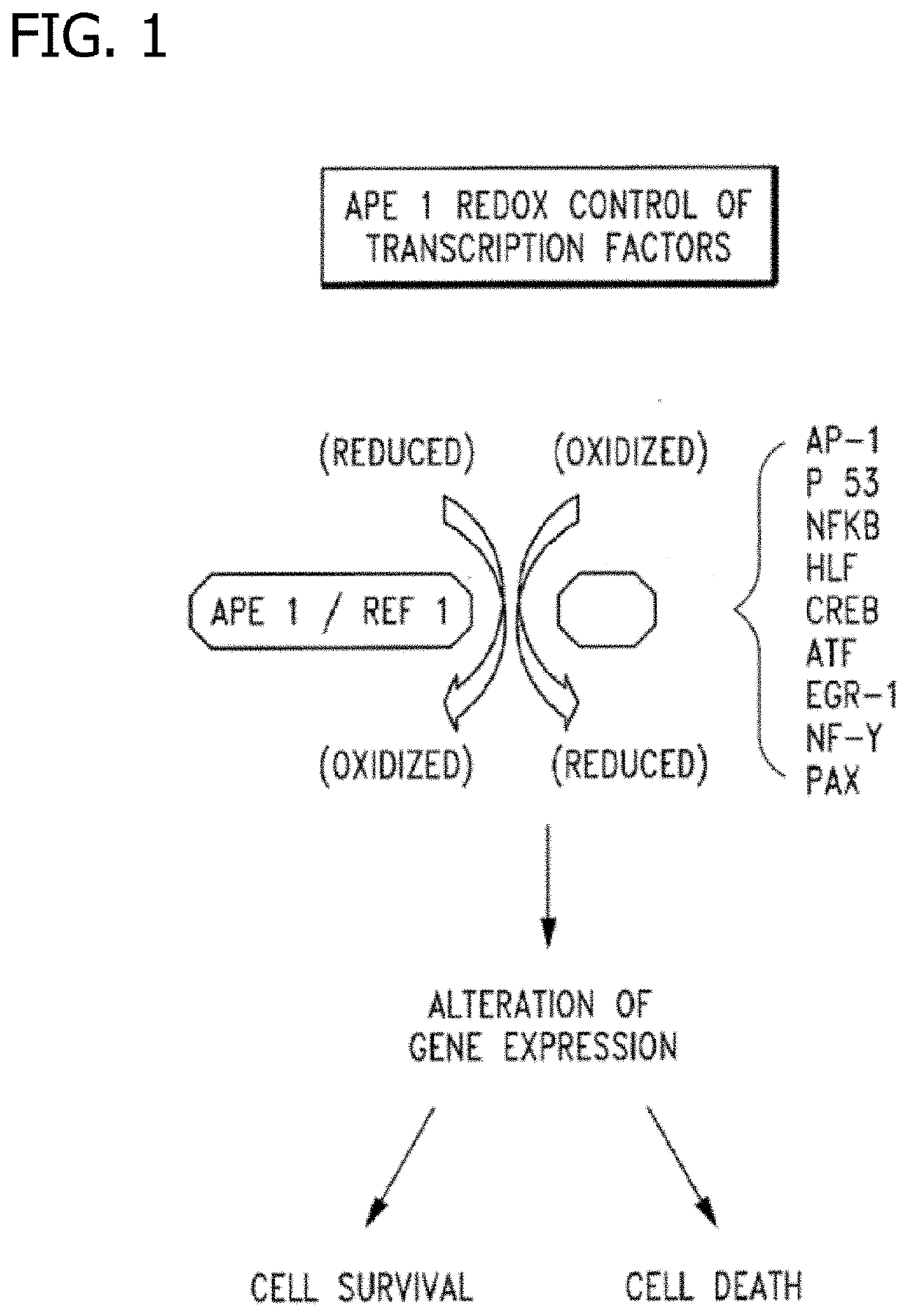
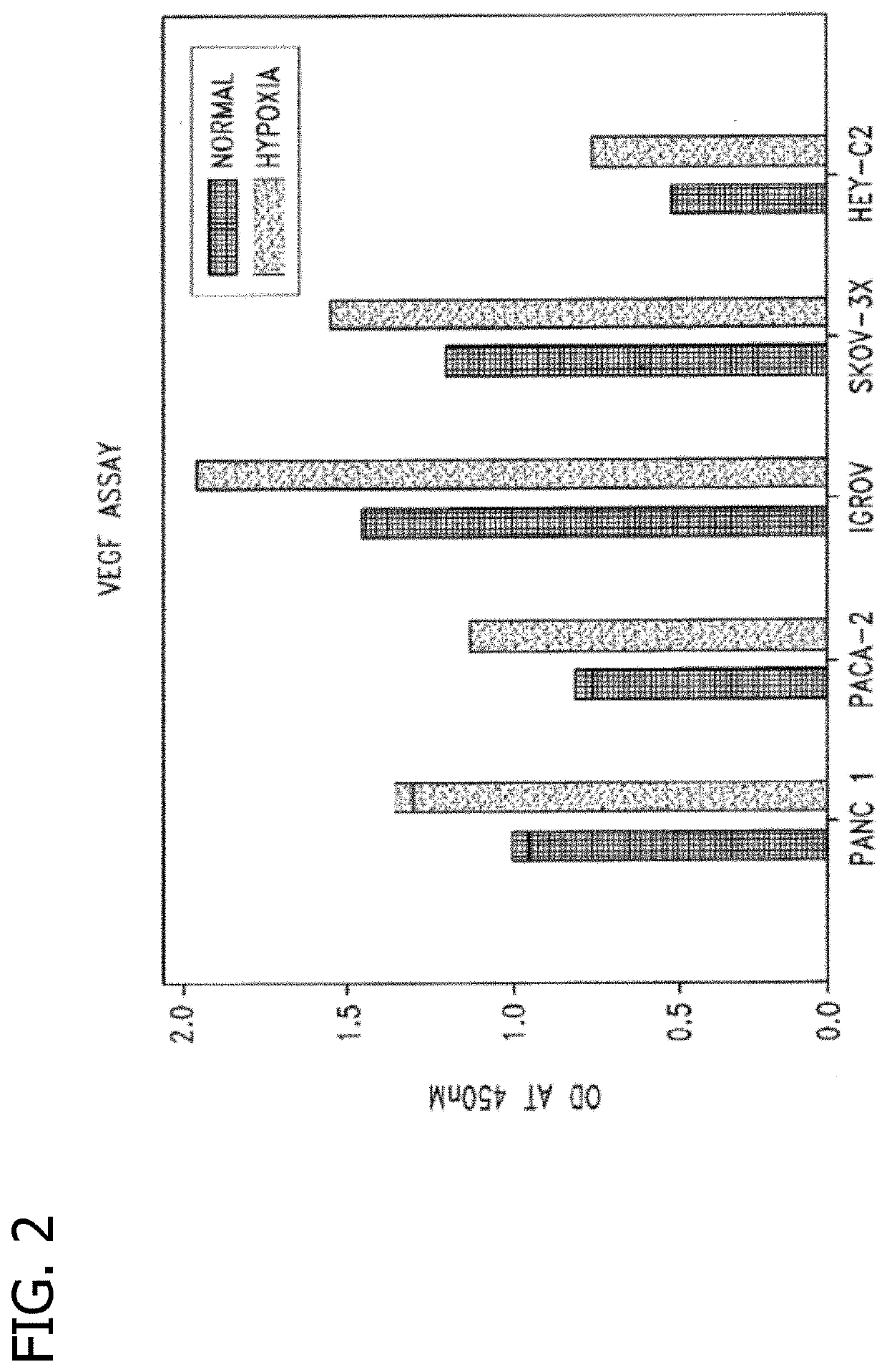
Disclosed are novel methods for the therapeutic treatment of cancer and angiogenesis. The enzyme Ape1 / Ref-1, via its redox function, enhances the DNA binding activity of transcription factors that are associated with the progression of cancer. The present disclosure describes the use of agents to selectively inhibit the redox function of Ape1 / Ref-1 and thereby reduce tumor cell growth, survival, migration and metastasis. In addition, Ape1 / Ref-1 inhibitory activity is shown to augment the therapeutic effects of other therapeutics and protect normal cells against toxicity. Further, Ape1 / Ref-1 inhibition is shown to decrease angiogenesis, for use in the treatment of cancer as well other pathologic conditions of which altered angiogenesis is a component.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives
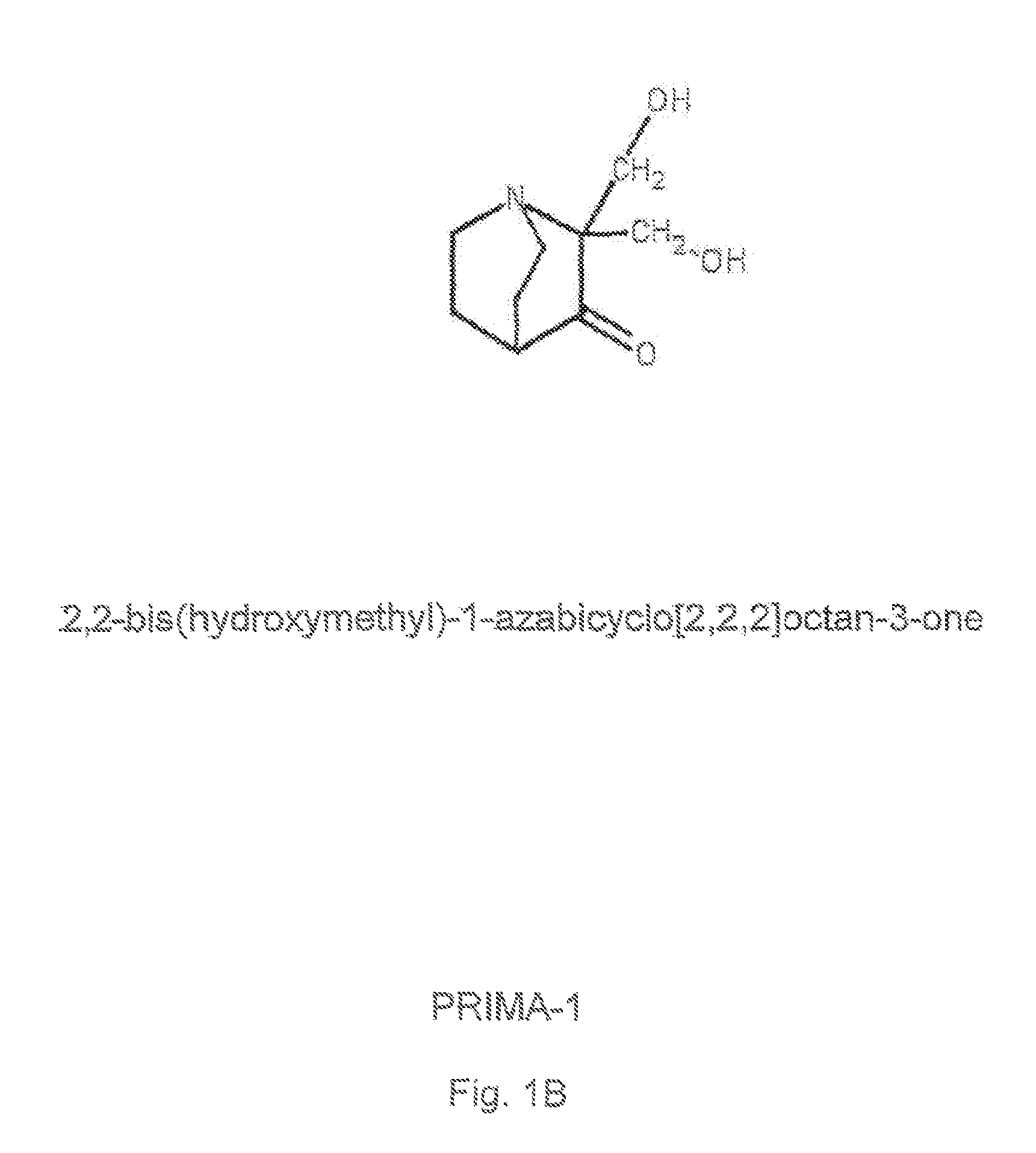
The present invention provides novel compounds, corresponding to formulae I and II, respectively, which are able to reactivate the apoptosis-inducing function of mutant p53 proteins. This reactivation is provided by restoration of sequence-specific DNA-binding activity and transcriptional transactivation function to mutant p53 proteins, and modulation of the conformation-dependent epitopes of the p53 protein. Accordingly, the substances according to the invention will be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of patients suffering from various types of tumors.
Owner:APREA THERAPEUTICS AB
Benzoquinone derivative E3330 in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of bladder cancer
ActiveUS11331294B2Hydroxy compound active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor reductionTherapeutic effect
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Heat-resistant DNA ligase with high reactivity
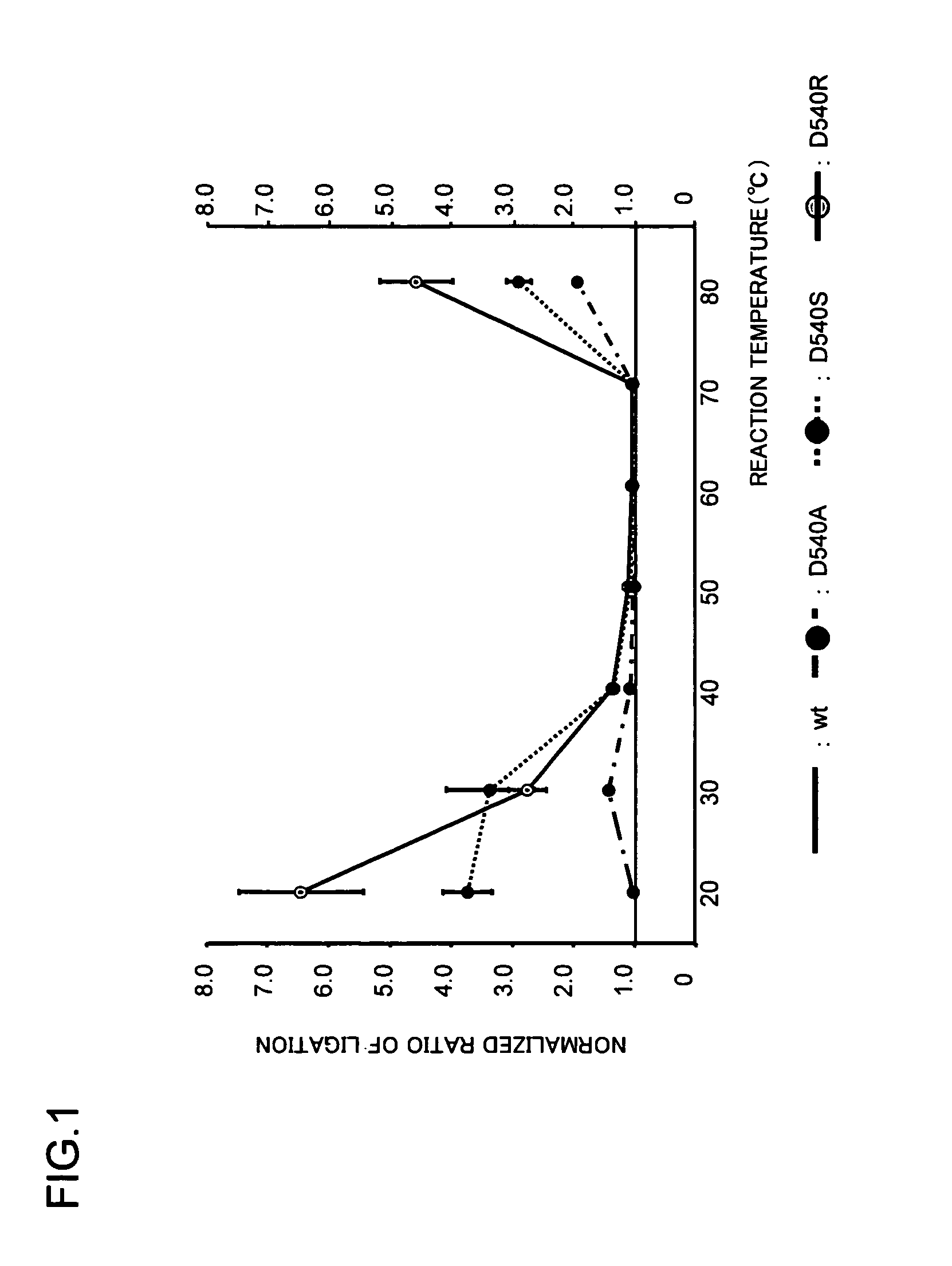
Thermostable DNA ligases with enhanced DNA binding activity and reaction activity are obtained. These modified thermostable DNA ligases having enhanced DNA binding activity compared to the wild type can be obtained by substituting a negatively charged amino acid (for example, the amino acid corresponding to the aspartic acid at position 540 of SEQ ID NO: 1) present at the N-terminal side of the C-terminal helix moiety of thermostable DNA ligases from thermophilic bacteria, hyperthermophilic bacteria, thermophilic archaea, or hyperthermophilic archaea, with a non-negatively charged amino acid (for example, alanine, serine, arginine, or lysine).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Benzoquinone derivative E3330 in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer and angiogenesis
Disclosed are novel methods for the therapeutic treatment of cancer and angiogenesis. The enzyme Apel / Ref-1, via its redox function, enhances the DNA binding activity of transcription factors that are associated with the progression of cancer. The present invention describes the use of agents to selectively inhibit the redox function of Apel / Ref-1 and thereby reduce tumor cell growth, survival, migration and metastasis. In addition, Apel / Ref-1 inhibitory activity is shown to augment the therapeutic effects of other therapeutics and protect normal cells against toxicity. Further, Apel / Ref-1 inhibition is shown to decrease angiogenesis, for use in the treatment of cancer as well other pathologic conditions of which altered angiogenesis is a component.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
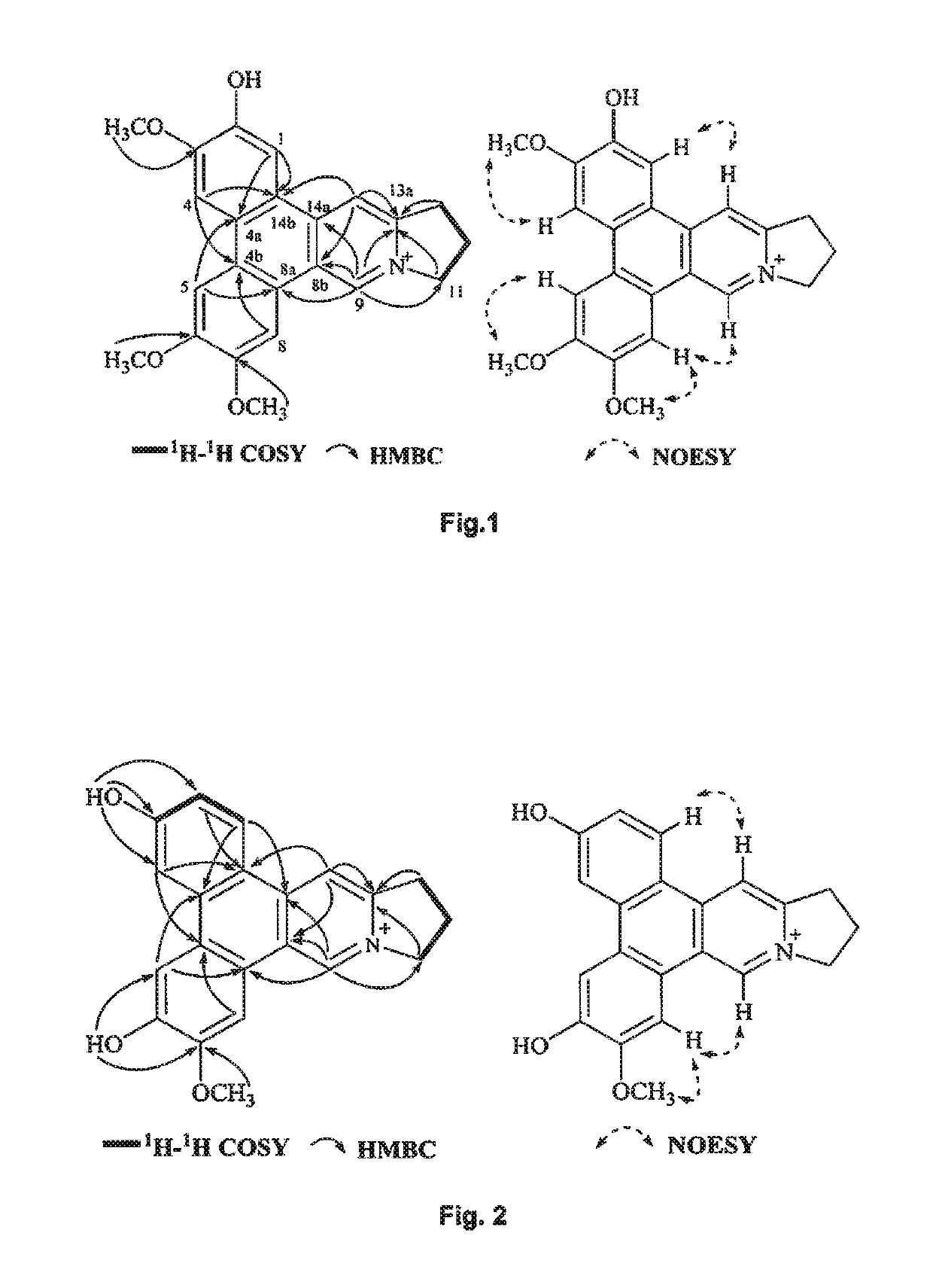
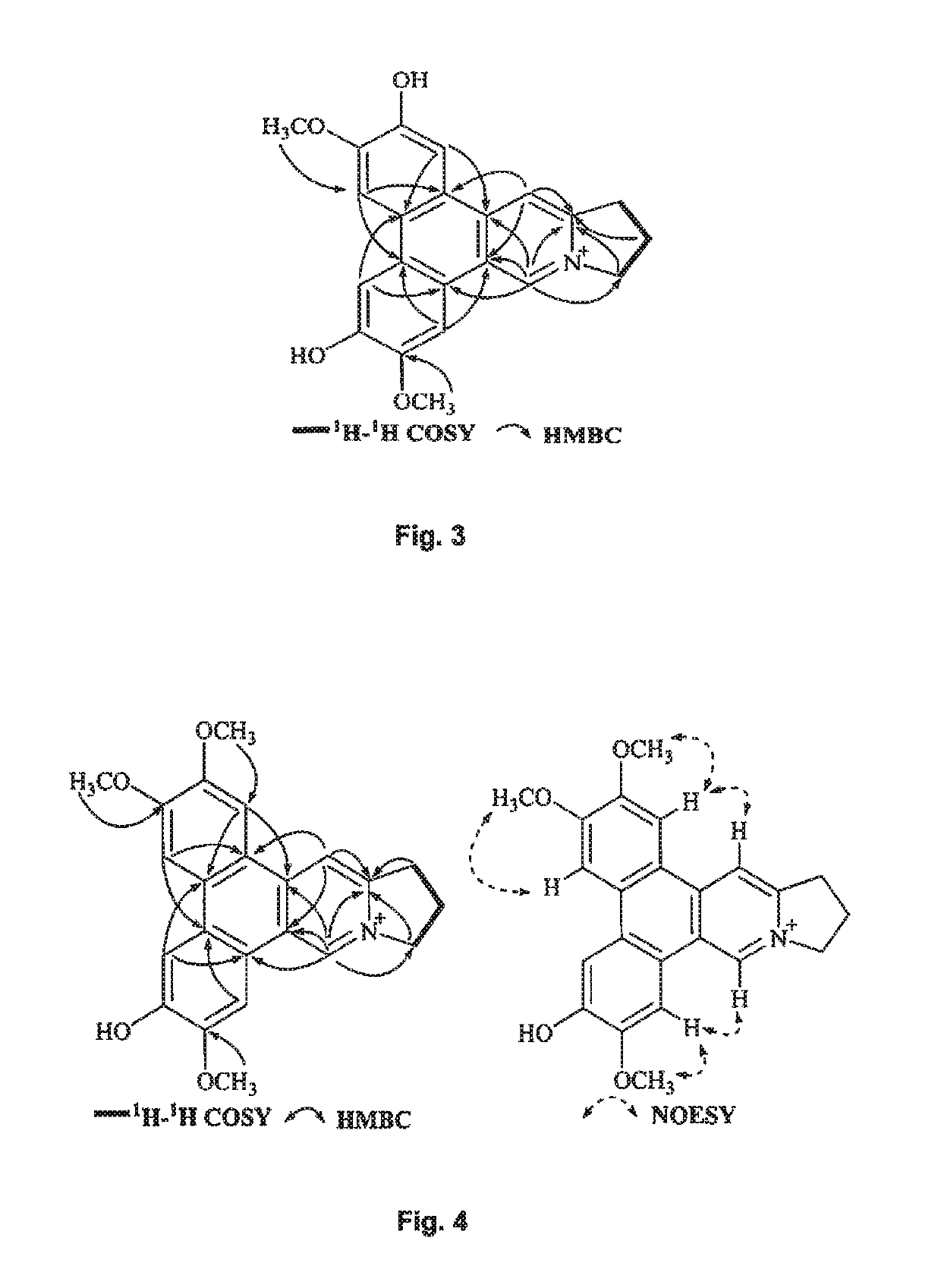
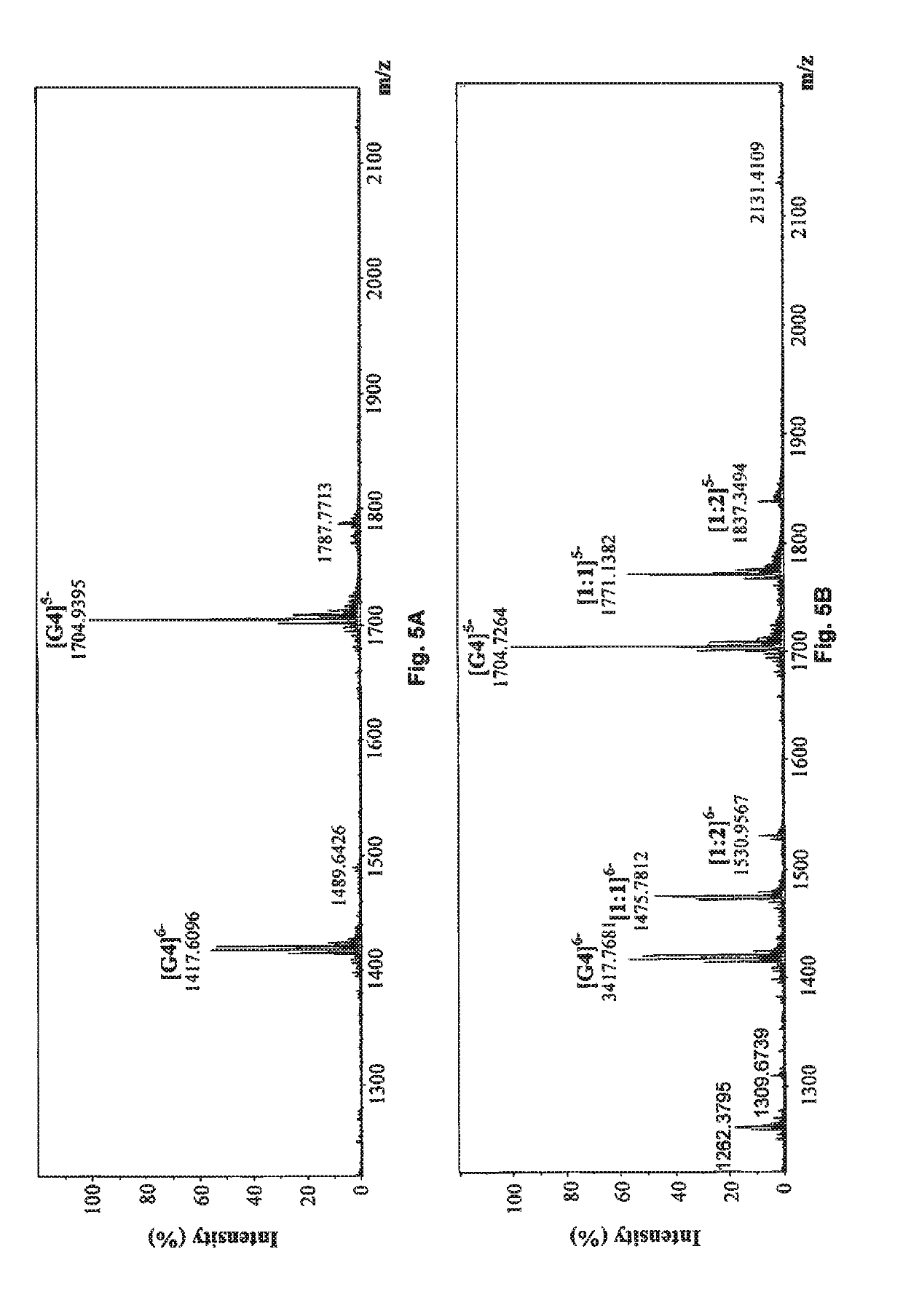
Method of isolating quaternary phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids with G-quaduplex DNA binding activity from Tylophra atrofolliculata, compositions comprising them and their medical use
ActiveUS10278966B2Potent inhibitory effects on telomerase activityEffective combinationOrganic active ingredientsPlant ingredientsTelomeraseAlkaloid
A method of isolating at least one phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid, in particular with telomerase inhibitory activity, from Tylophora atrofolliculata is used to isolate and obtain for example about six to eight phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids, including at least four new phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids which have not been previously isolated. Experimental tests confirmed an exceptional telomerase inhibitory activity of the phenanthroindolizidine alkaloids isolated. A pharmaceutical composition includes at least one phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid and at least one pharmaceutical tolerable excipient. Still further, a method of treating a subject suffering from cancer includes administering at least one phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid isolated from Tylophora atrofolliculata. Also, a method of treating a subject suffering from cancer includes administering to the subject at least one phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid having certain formula.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Core structural domain of VirB protein, and coding genes and applications thereof
The invention discloses a core structural domain of VirB protein, and coding genes and applications thereof. The invention provides VirB core segments or fusion proteins containing the VirB core segments; the VirB core segments are described as (a) or (b). (a) a protein composed of amino acid residues from the 22nd site to the 143rd site in the sequence table sequence No.1; (b) proteins which are derived from the proteins of (a), wherein one or a plurality of amino acid residues are substituted and / or lost and / or added, and the proteins of (b) possess DNA binding activity. The invention also discloses the applications of the VirB core segments or the fusion proteins in preparation of products used for binding with DNA, and in preparation of products used for identifying DNA. The invention provides the core structural domain of VirB protein, and operating principles of VirB protein are revealed at the molecular level, so that accurate and all-around structural biology information is provided for the design of structure oriented drugs.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Core structural domain of VirB protein, and coding genes and applications thereof
The invention discloses a core structural domain of VirB protein, and coding genes and applications thereof. The invention provides VirB core segments or fusion proteins containing the VirB core segments; the VirB core segments are described as (a) or (b). (a) a protein composed of amino acid residues from the 22nd site to the 143rd site in the sequence table sequence No.1; (b) proteins which are derived from the proteins of (a), wherein one or a plurality of amino acid residues are substituted and / or lost and / or added, and the proteins of (b) possess DNA binding activity. The invention also discloses the applications of the VirB core segments or the fusion proteins in preparation of products used for binding with DNA, and in preparation of products used for identifying DNA. The invention provides the core structural domain of VirB protein, and operating principles of VirB protein are revealed at the molecular level, so that accurate and all-around structural biology information is provided for the design of structure oriented drugs.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Metal complexes having dual histone deacetylase inhibitory and DNA-binding activity
InactiveUS8901337B2High anticancer activityHigh selectivityPlatinum organic compoundsMetallocenesCounterionIn vivo
Compounds comprising a metal complex having the structure [X—Y—Z-Mn+]p+.B are disclosed in which X is a histone deacetylase inhibitor, Mn+ is a DNA-binding heavy metal ion, Y is an aliphatic or aromatic spacer or is absent, and Z is a mono- or bi-dentate or chelating donor linker, or a bridging linker, P+ designates the charge on the complex ion, which may be positive, negative or absent and B is a counterion or is absent. The linker Z is labile and its metal complex X—Y—Z-Mn+ is capable of being hydrolysed in-vivo. The compounds find application in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00001.png)
![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00002.png)
![1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one derivatives and maleimide derivatives and their use for treating cancer tumors](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/42082f5c-c7d0-421d-b391-520197caf426/US06921765-20050726-D00003.png)
![1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives 1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5921c5c8-c218-46e6-ad43-34b6ccc20af6/US20050090540A1-20050428-D00001.png)
![1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives 1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5921c5c8-c218-46e6-ad43-34b6ccc20af6/US20050090540A1-20050428-D00002.png)
![1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives 1-Azabicyclo [2,2,2] octan-3-one derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5921c5c8-c218-46e6-ad43-34b6ccc20af6/US20050090540A1-20050428-D00003.png)