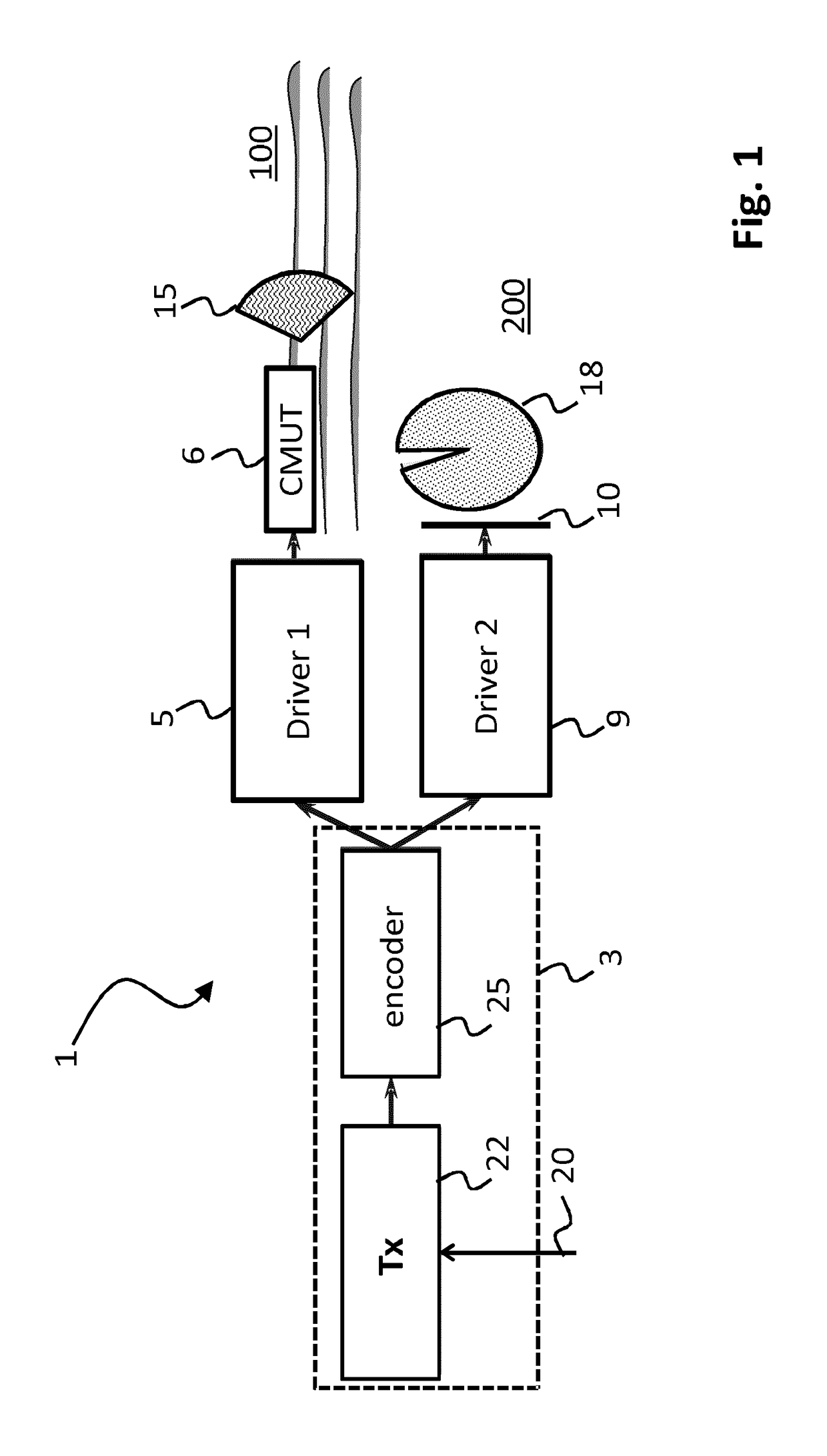
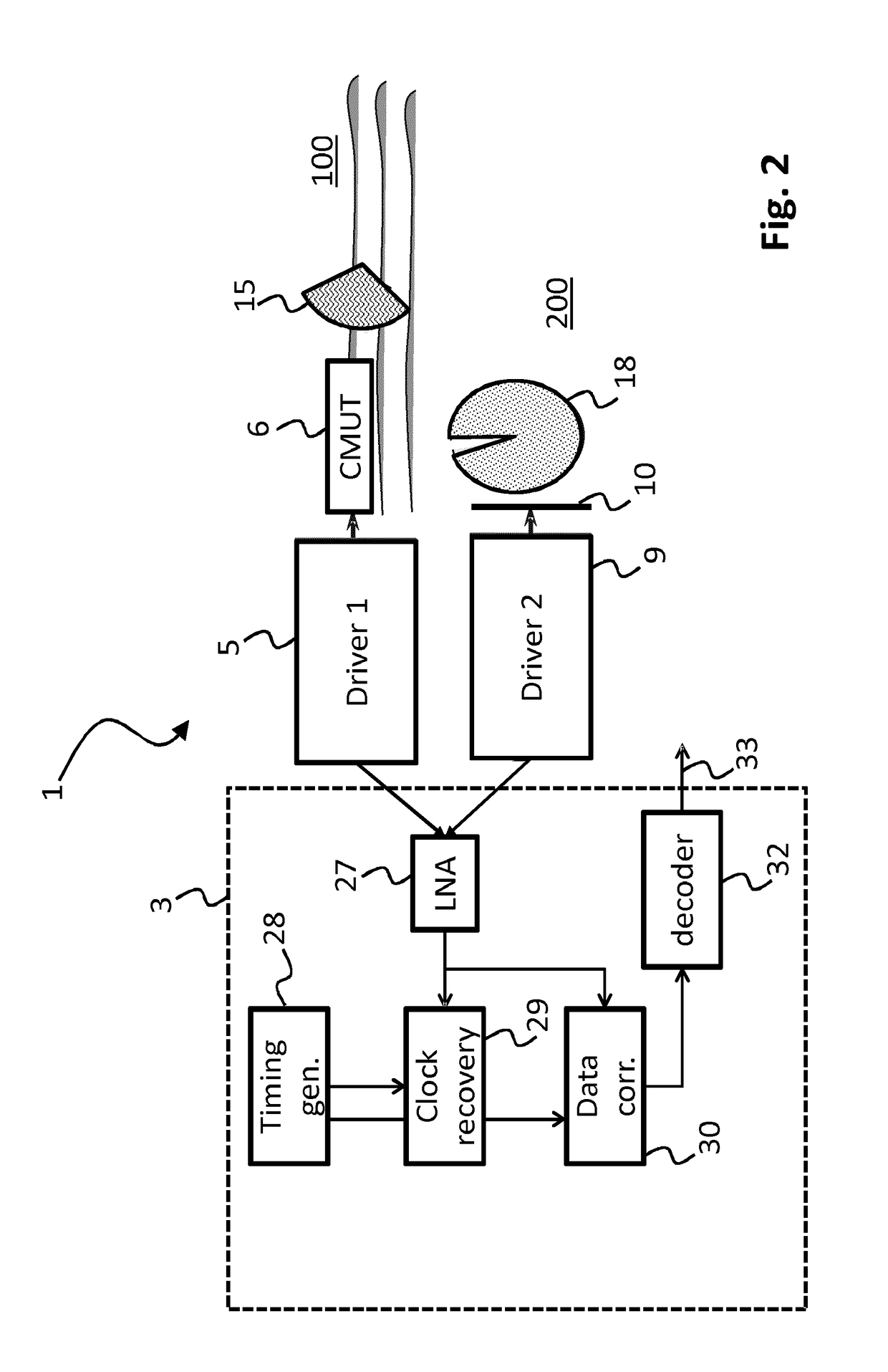
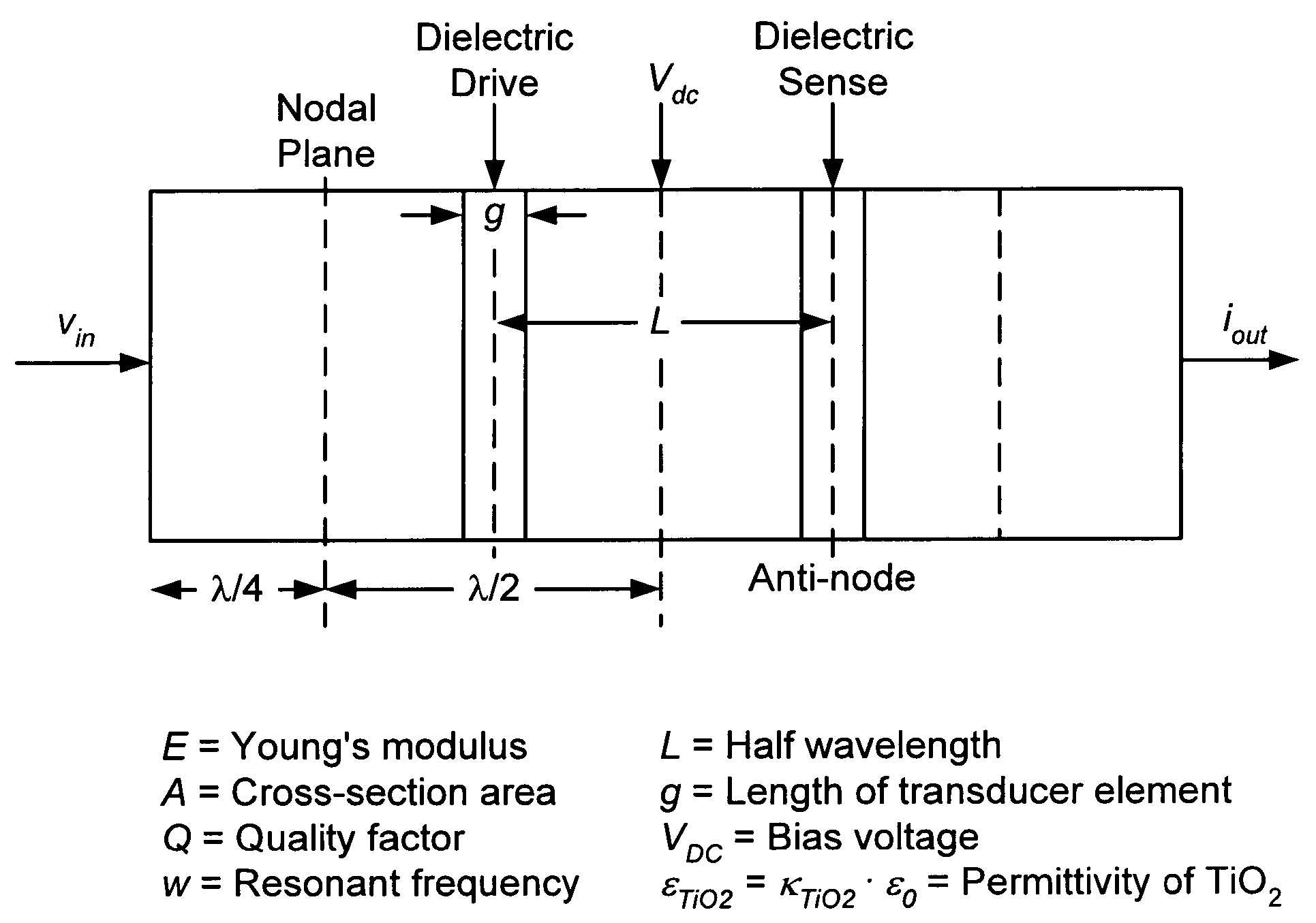
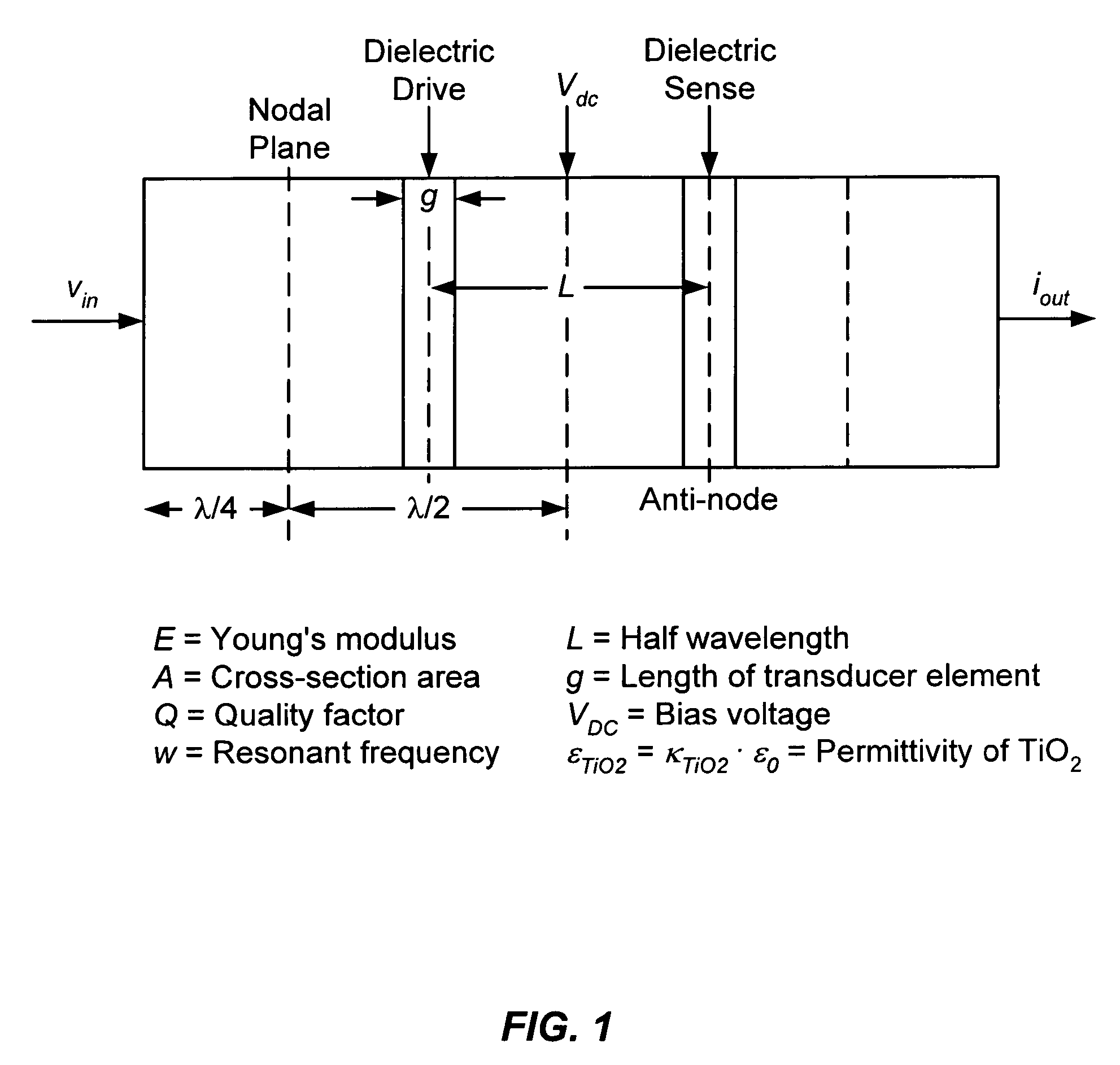
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Electrostatic transducer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
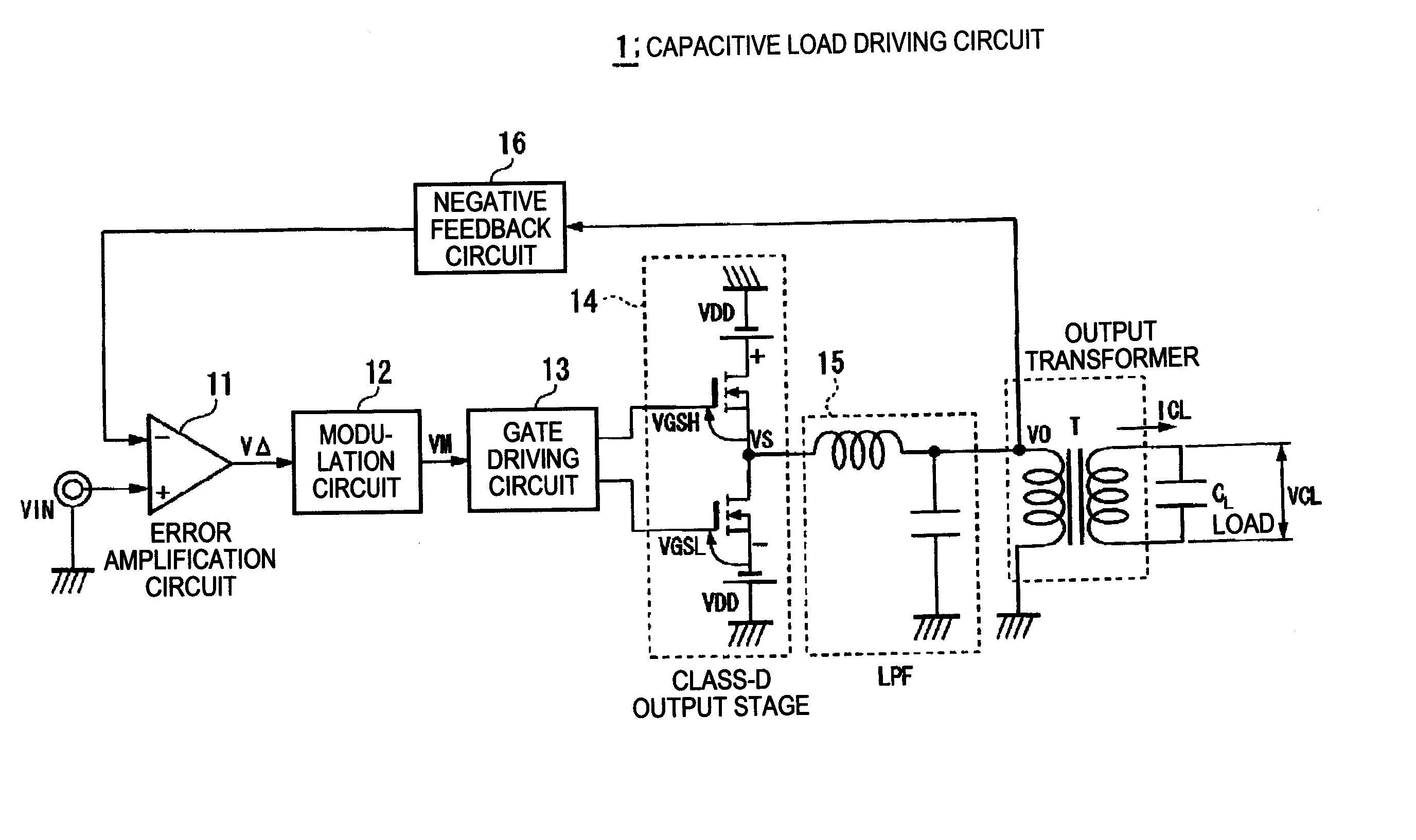
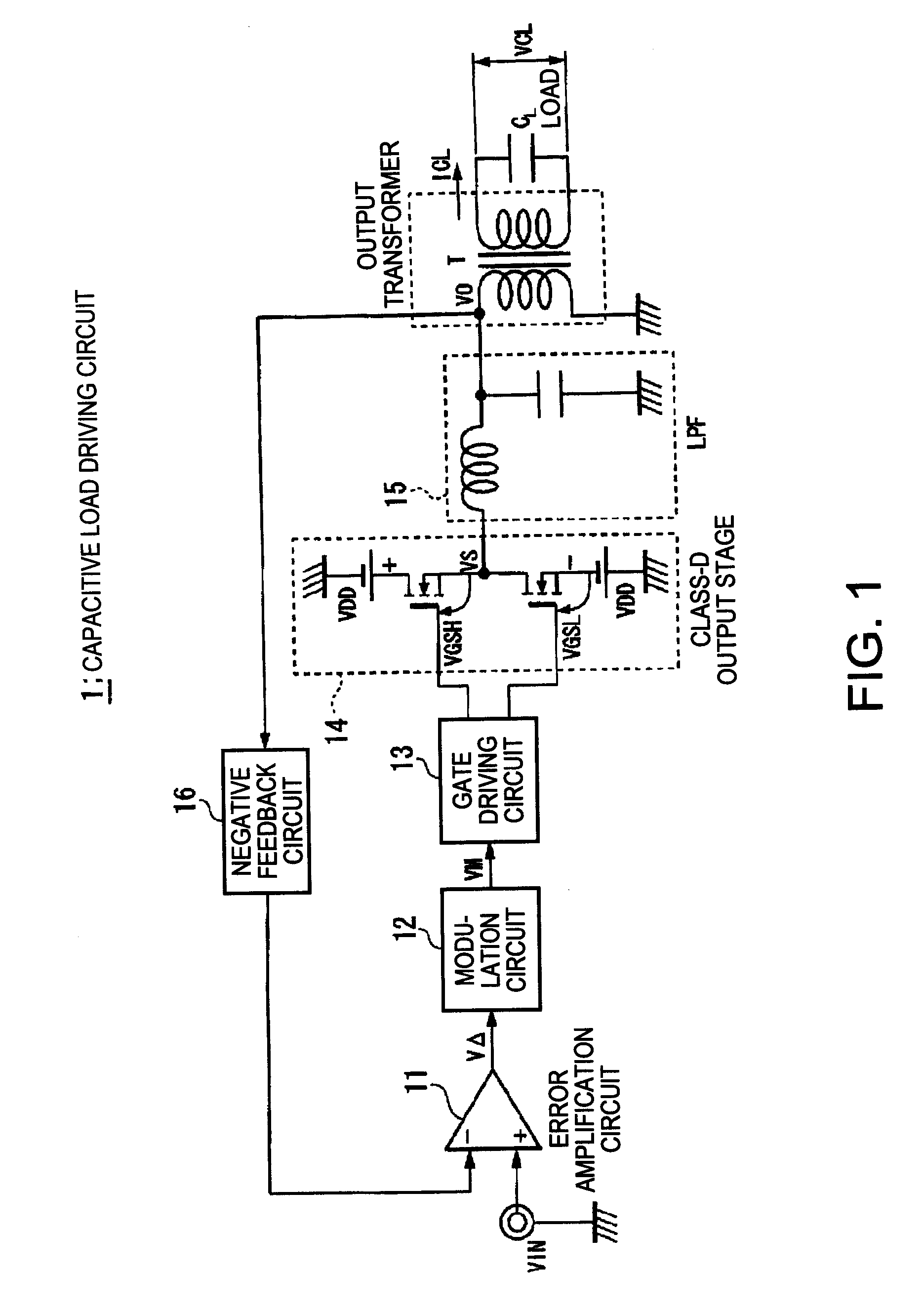
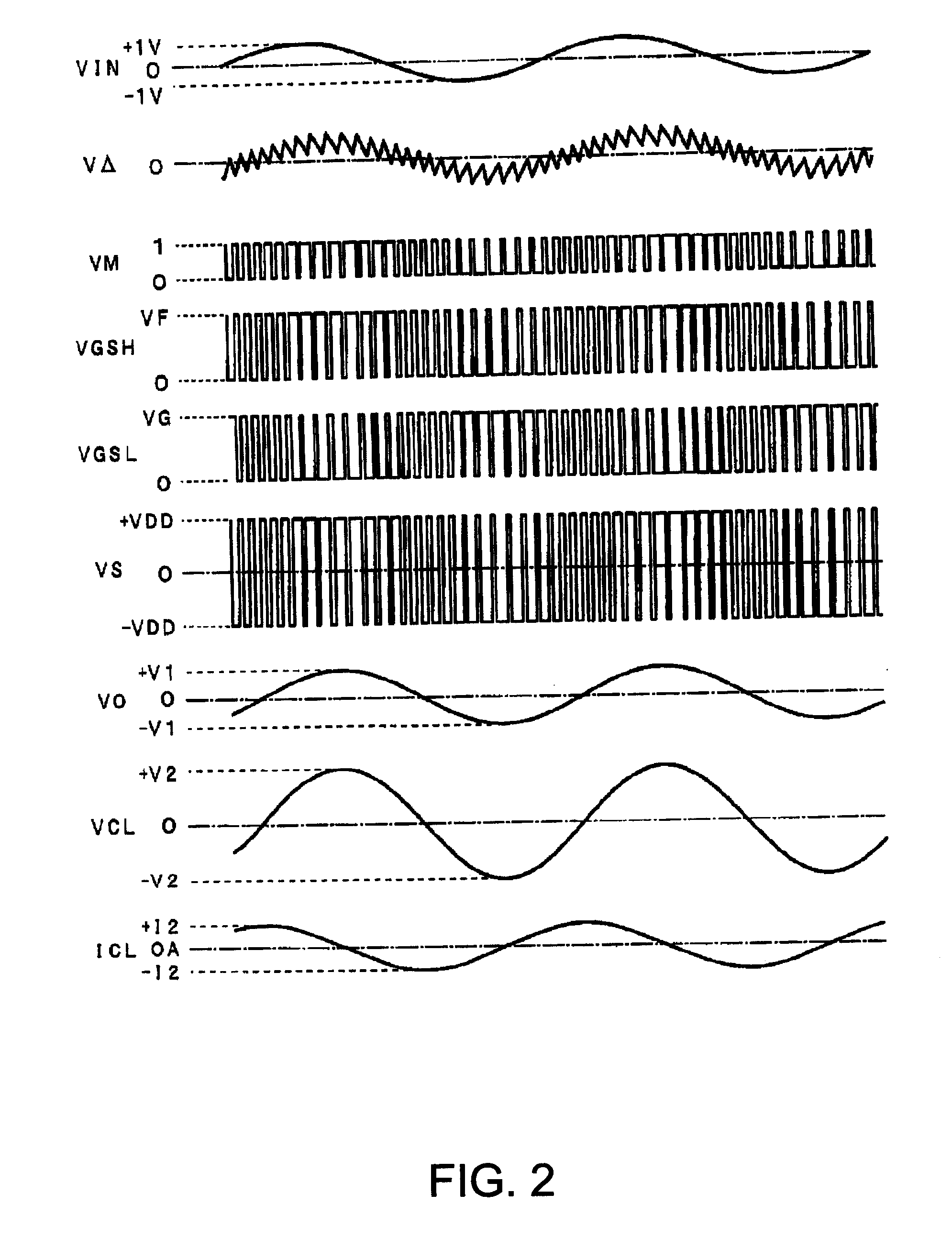
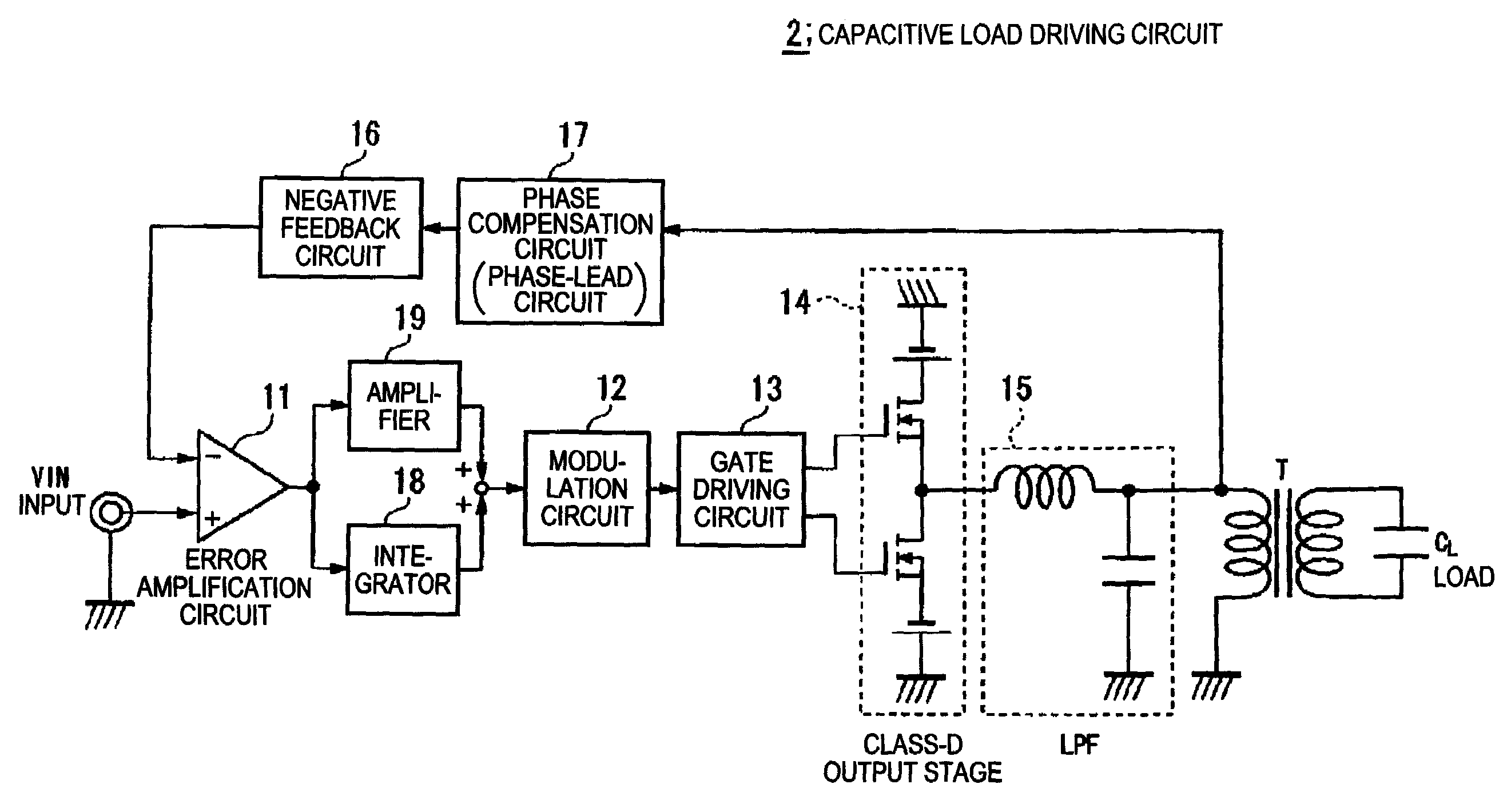
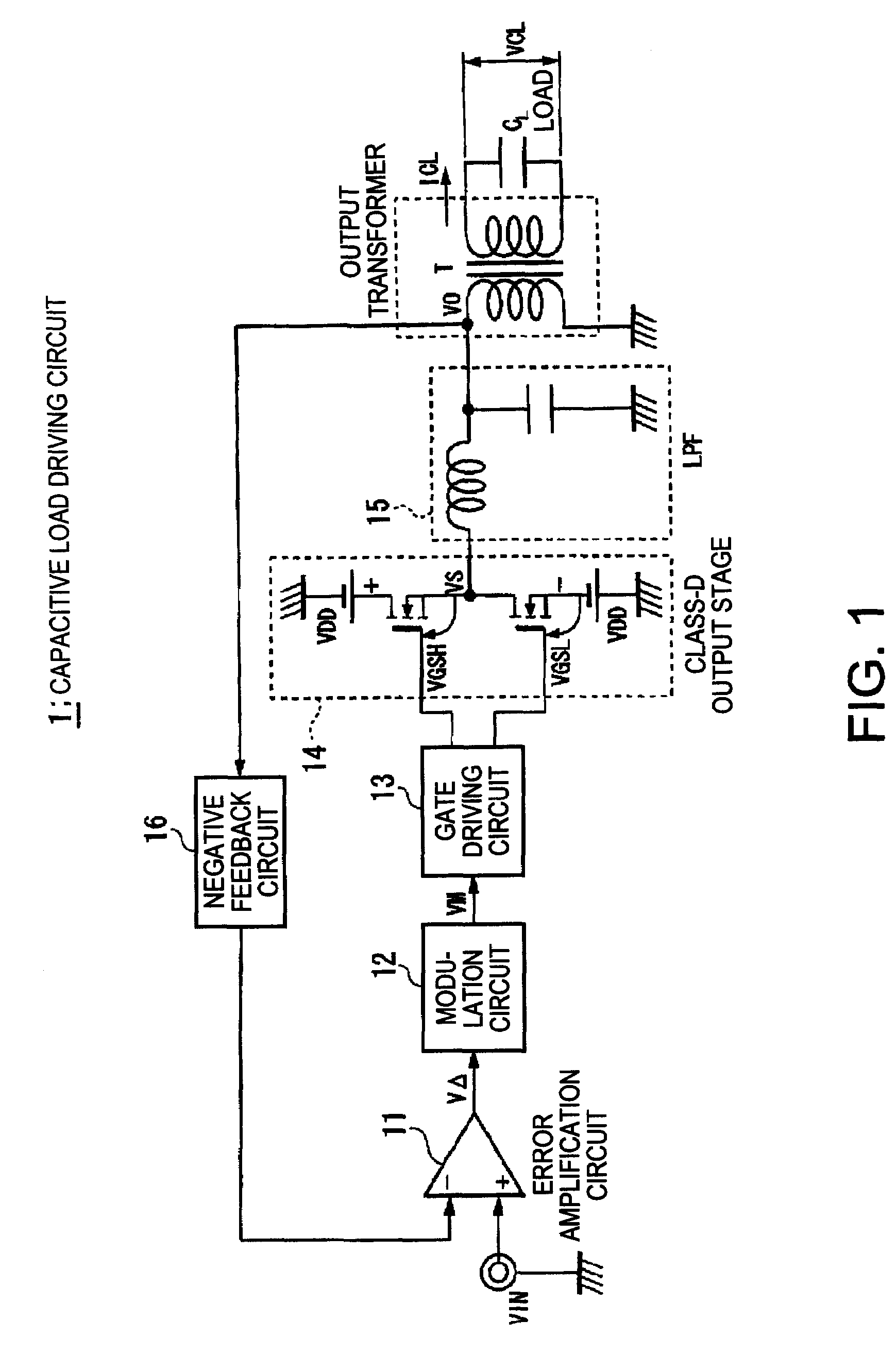
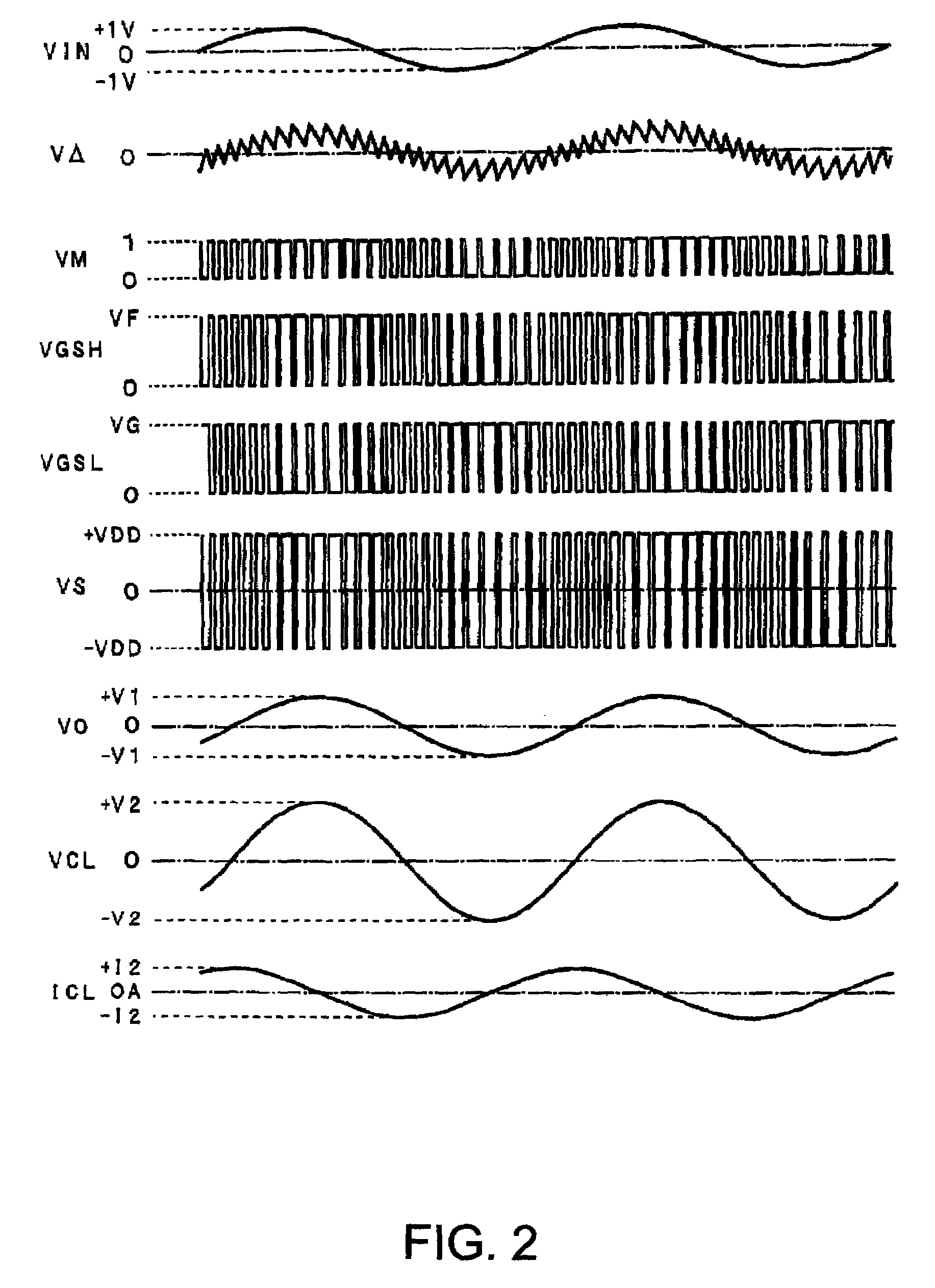
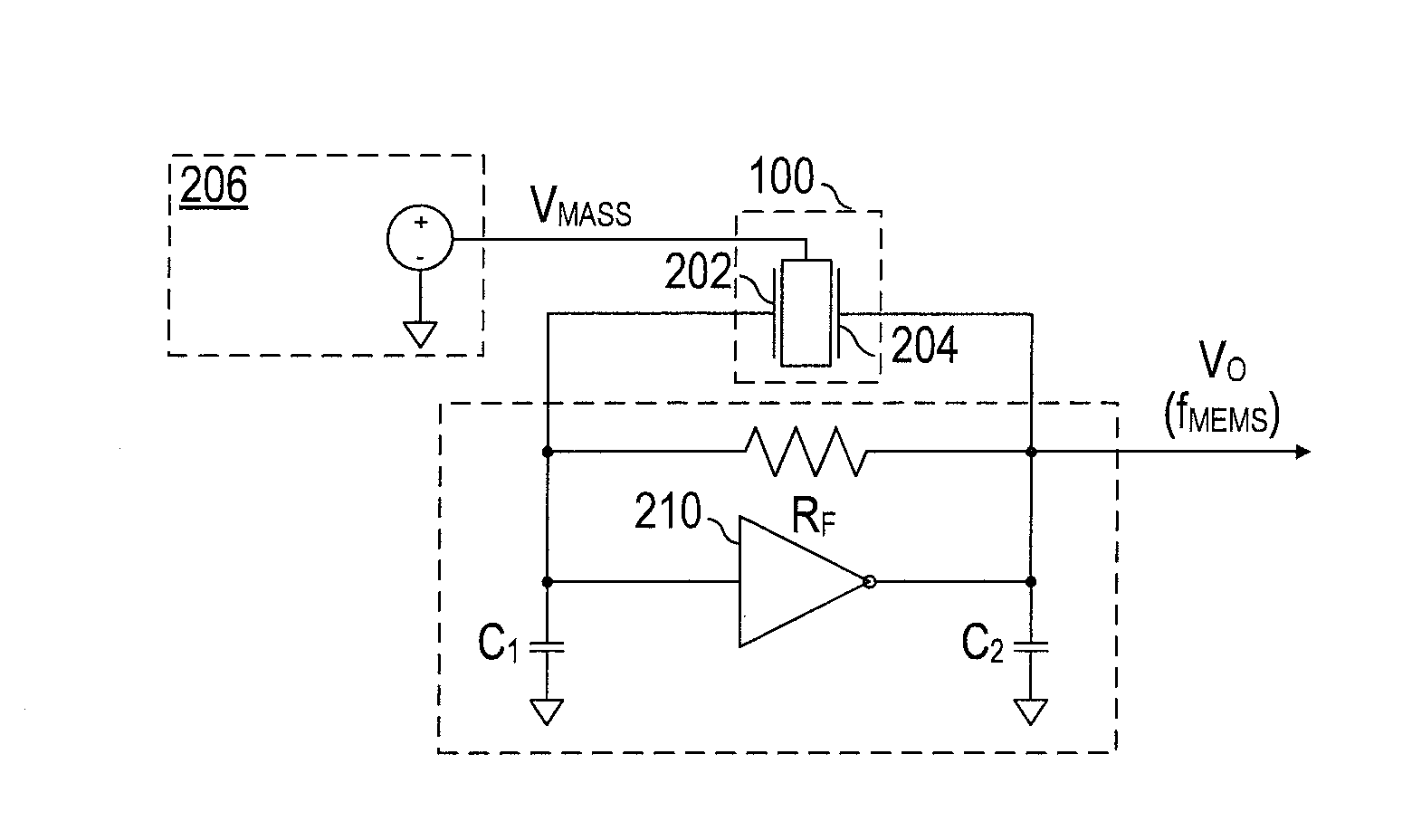
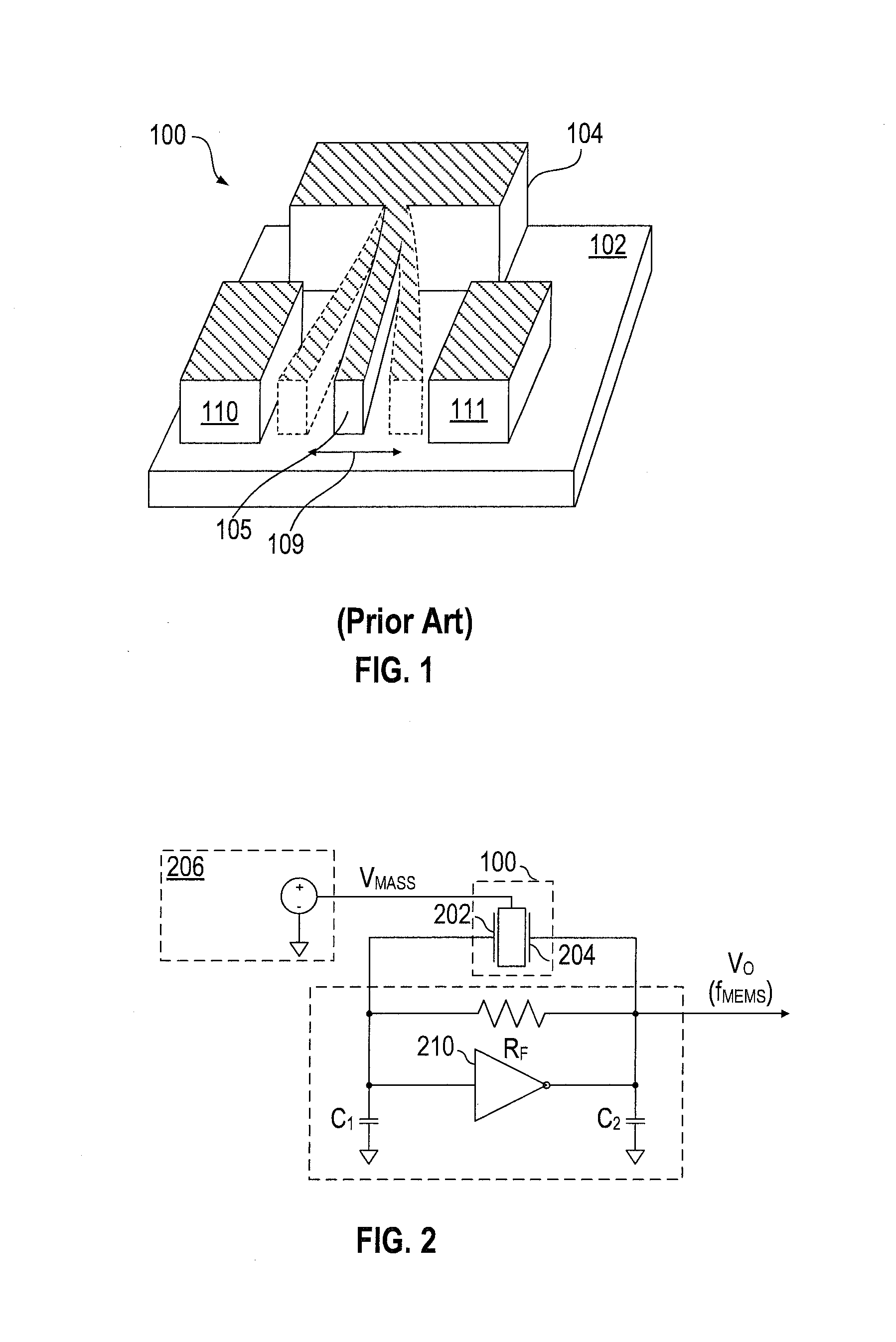
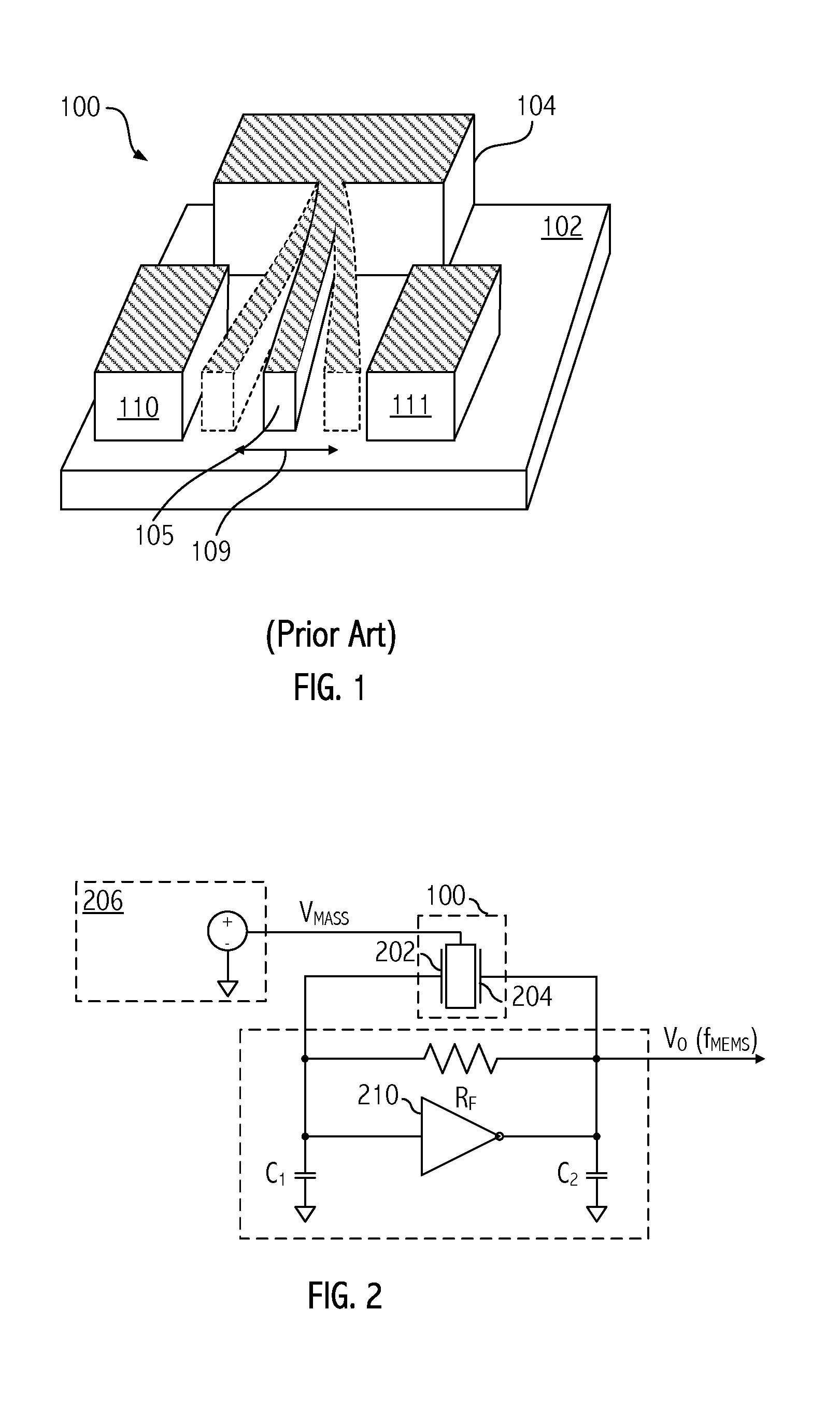
Capacitive load driving circuit, electrostatic transducer, method of setting circuit constant, ultrasonic speaker, display device, and directional acoustic system
InactiveUS20070124620A1Reduce lossImproved sound presenceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceOutput transformer
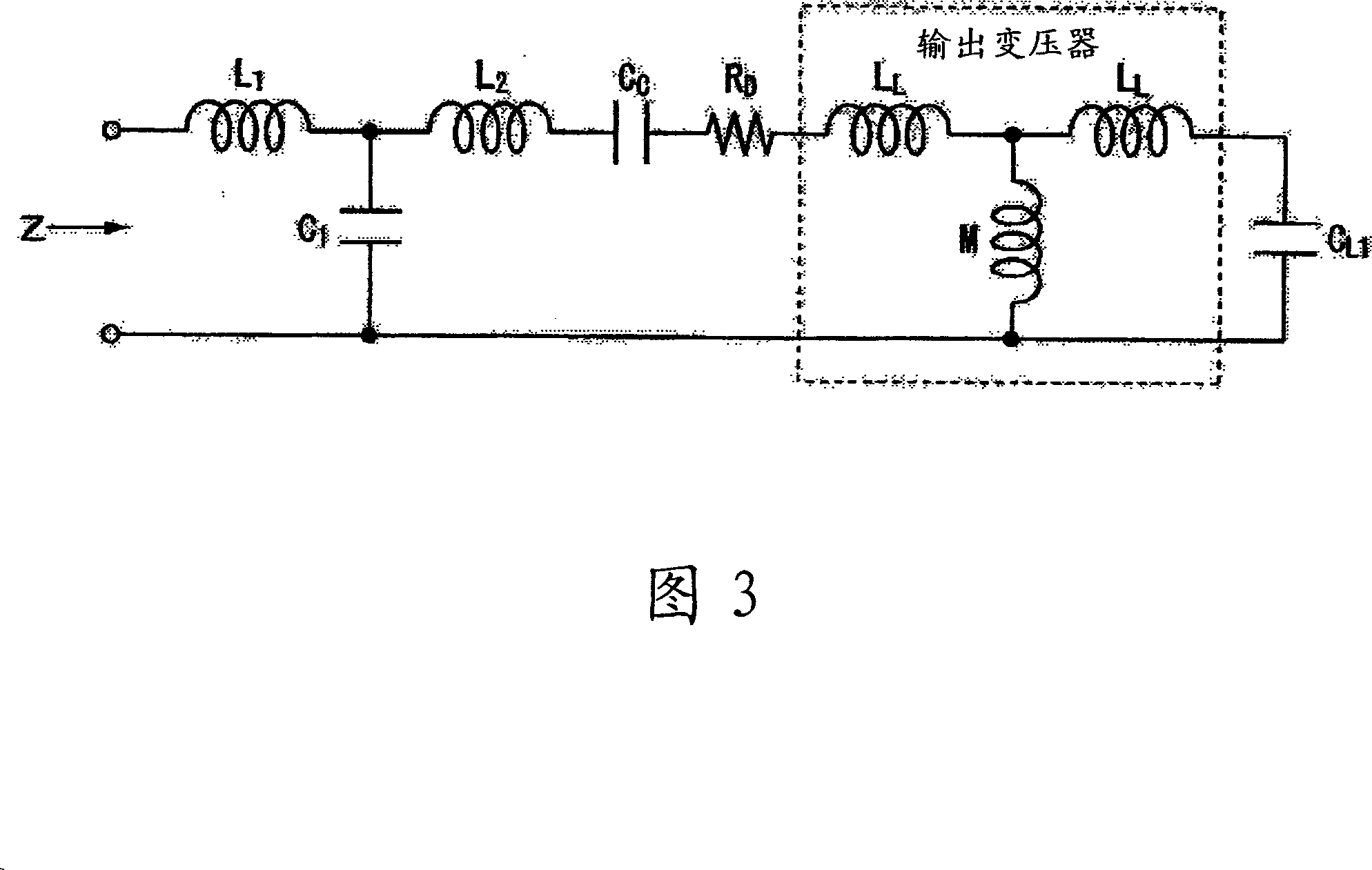
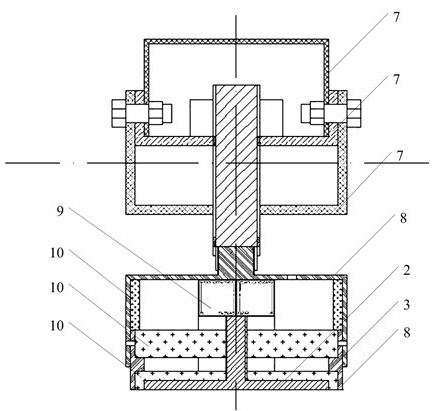
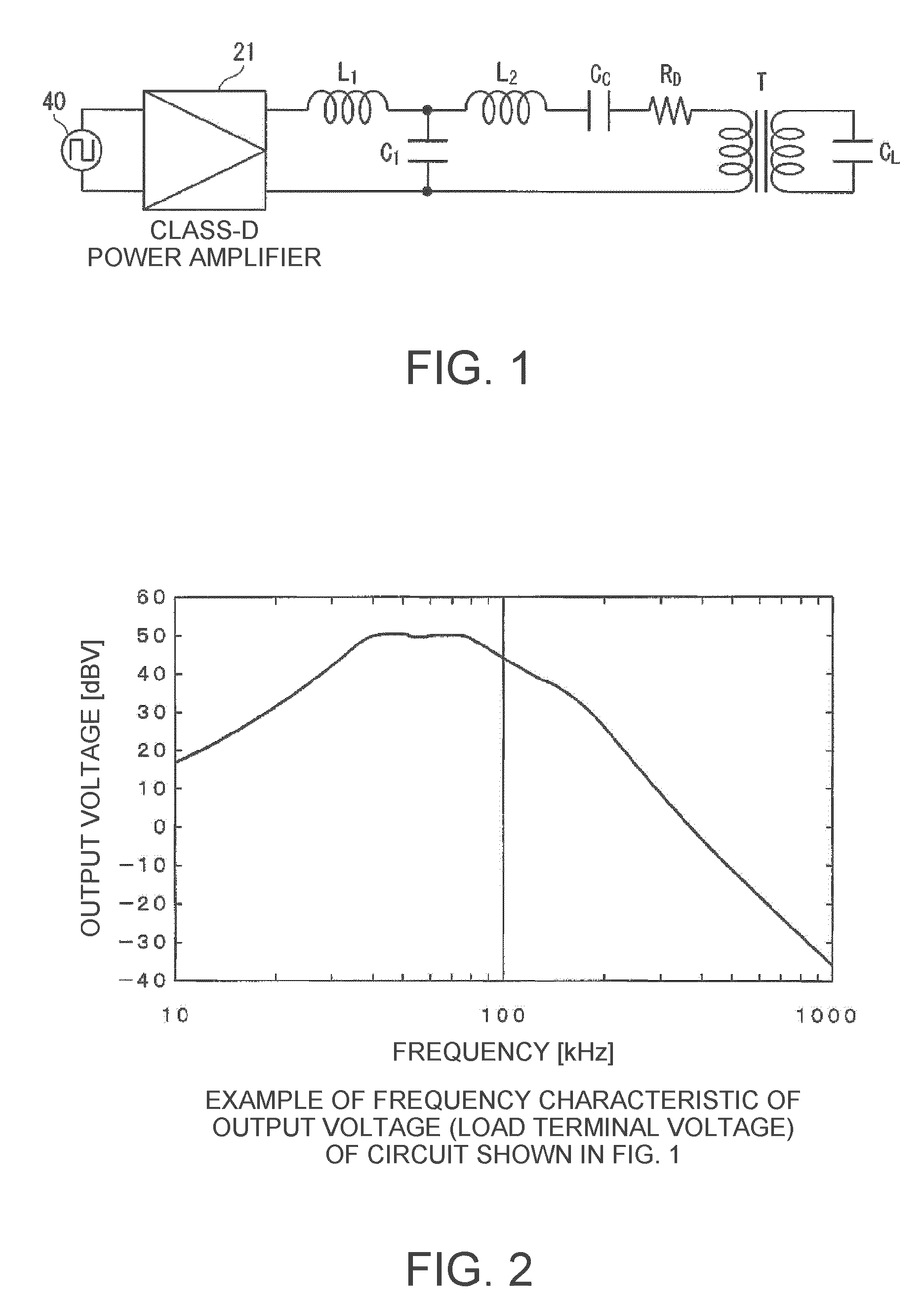
A capacitive load driving circuit includes an error amplification circuit that amplifies a difference between an external input signal provided to one input terminal and a negative feedback signal provided from the following negative feed back circuit to the other input terminal; a modulation circuit that pulse-modulates the signal outputted from the error amplification circuit; a power switching circuit that switches between a power supply voltage and a ground potential or between a positive power supply voltage and a negative power supply voltage; a gate driving circuit that generates a gate driving signal for switching-controlling a switching element configuring the power switching circuit, from a modulated signal outputted from the modulation circuit; a low-pass filter that is connected to an output side of the power switching circuit and removes switching carrier components included in an output signal of the power switching circuit; an output transformer that boosts an output signal of the low-pass filter and has a primary winding connected to an output terminal of the low-pass filter; a capacitive load that is connected in parallel with a secondary winding of the output transformer; and a negative feedback circuit that performs a negative feedback from the output terminal of the low-pass filter to an input side of the error amplification circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electrostatic loudspeaker capable of dispersing sound both horizontally and vertically
ActiveUS20070242844A1Improved dispersion of soundIncreased angular dispersion of soundElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEffect lightEngineering
Owner:LUMINOS INDS
Internal electrostatic transduction structures for bulk-mode micromechanical resonators
InactiveUS20060017523A1High dielectric constantMotional impedance is decreasedImpedence networksCMOSClassical mechanics
An electrostatic transducer for micromechanical resonators, in which the electrode gaps are filled with a dielectric material having a much higher permittivity than air. This internal electrostatic transducer has several advantages over both air-gap electrostatic and piezoelectric transduction; including lower motional impedance, compatibility with advanced scaled CMOS device technology, and extended dynamic range. In one aspect, in order to minimize energy losses, the dielectric material has an acoustic velocity which is matched to that of the resonator material. Internal electrostatic transduction can be adapted to excite and detect either vertical modes (perpendicular to the substrate) or lateral modes (in the plane of the substrate). Its increased transduction efficiency is of particular importance for reducing the motional resistance of the latter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
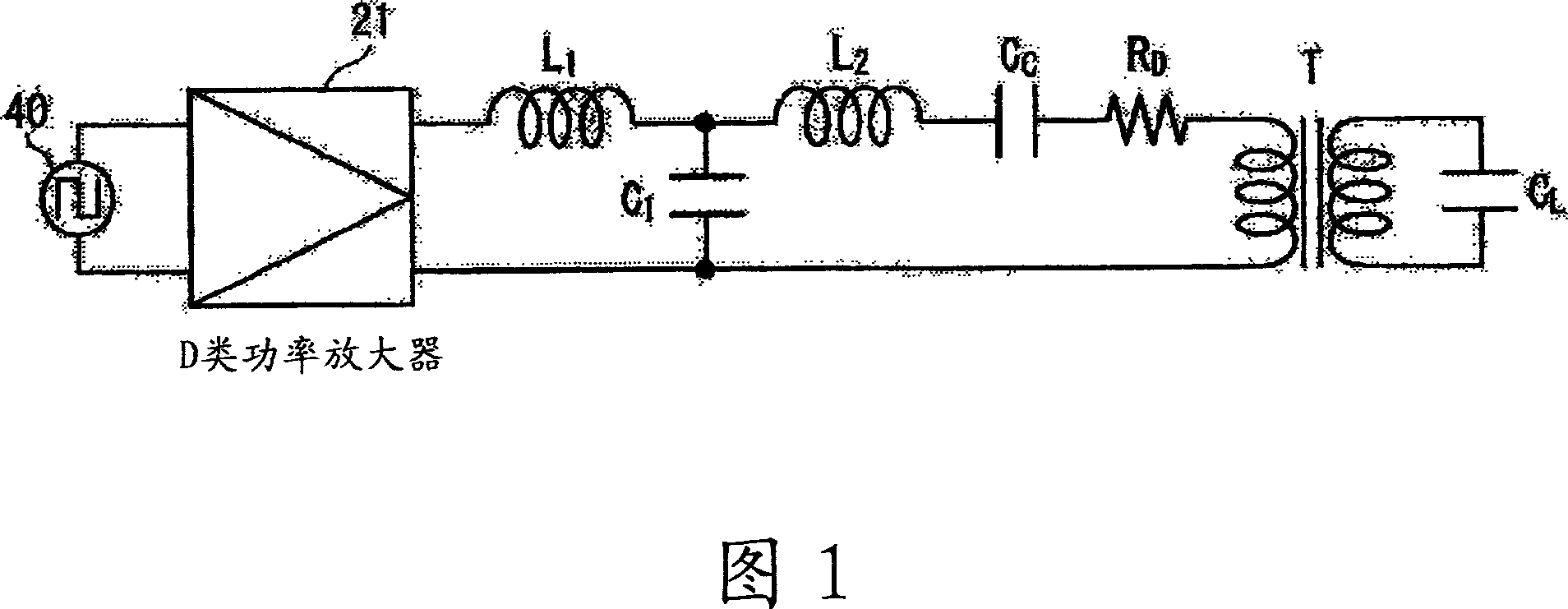
Electrostatic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, driving circuit of capacitive load, method of setting circuit constant, display device, and directional sound system
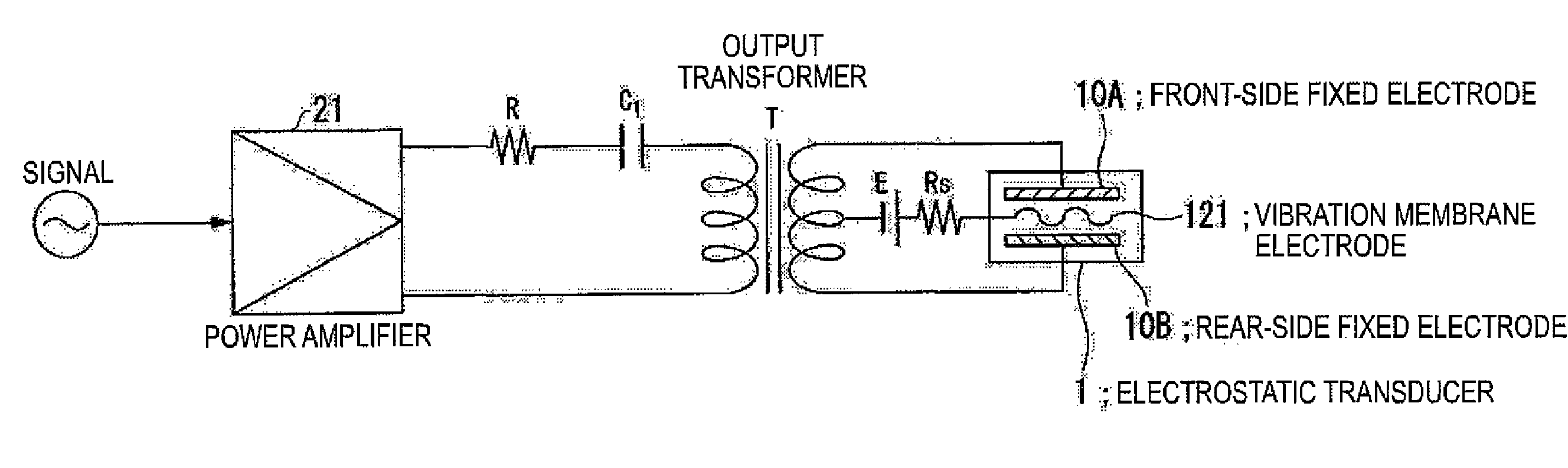
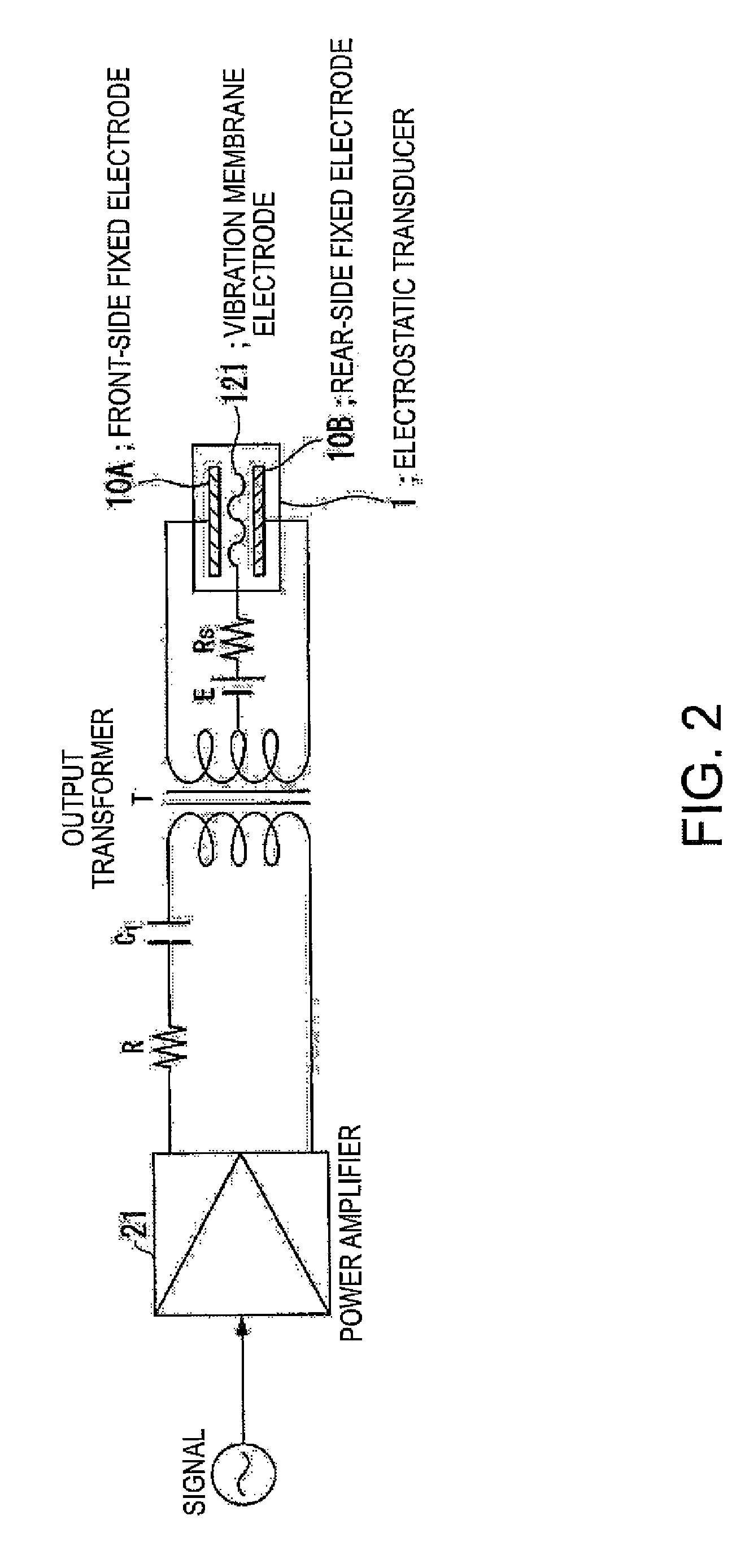
InactiveUS20070121970A1Reduce lossSufficient sound pressurePiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersCapacitanceOutput transformer
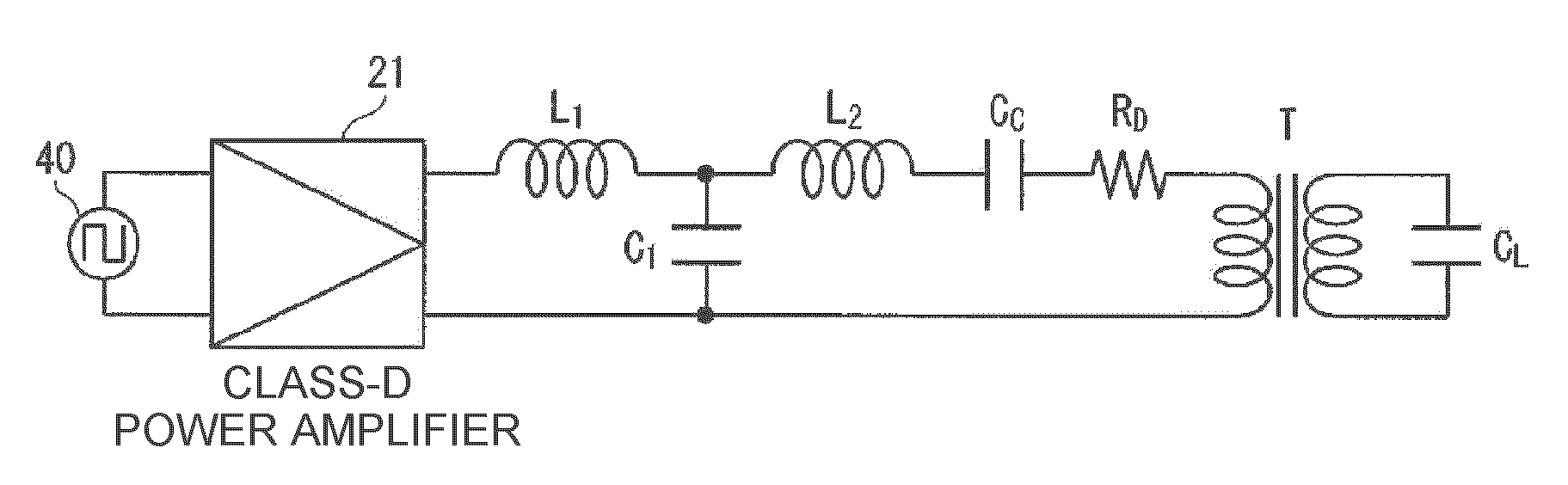
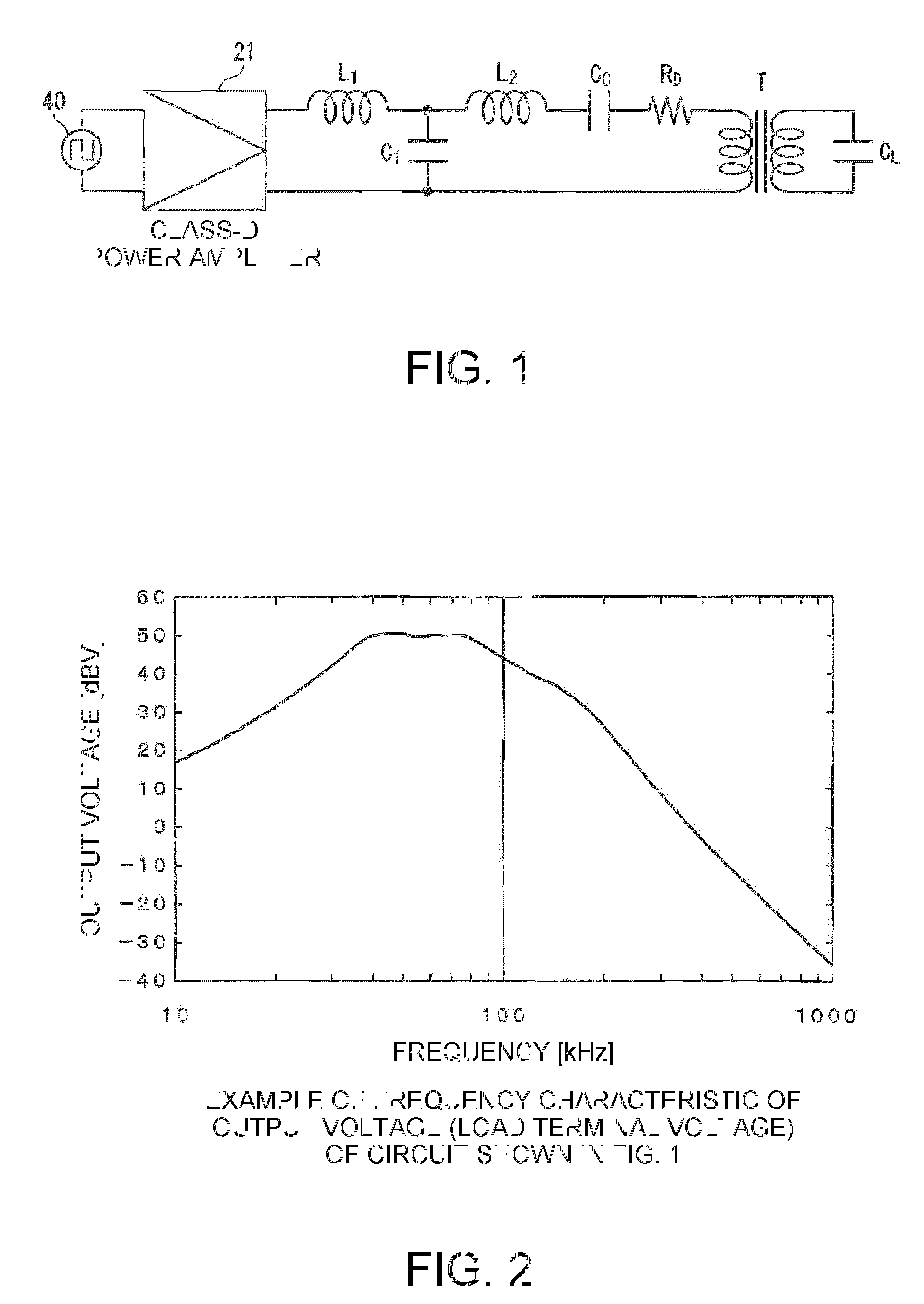
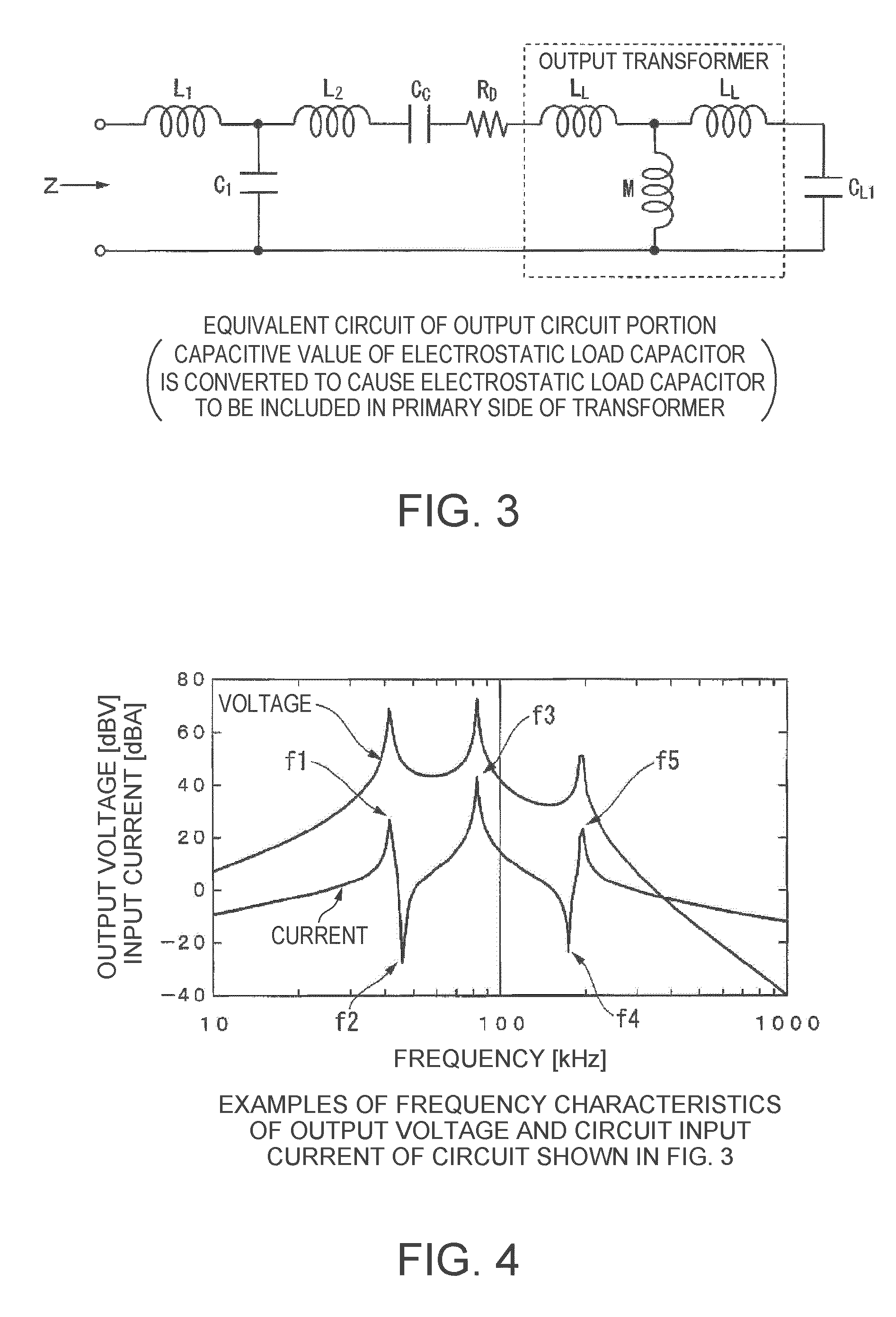
An electrostatic transducer includes: a class-D power amplifier that amplifies an input signal; and a low pass filter that has a plurality of pairs of inductors and capacitors, is connected to an output side of the class-D power amplifier, and serves to eliminate switching carrier components included in an output of the class-D power amplifier. An electrostatic load capacitor of the electrostatic transducer serving as a driving load is disposed at a capacitor, which is closest to the output side of the class-D power amplifier, of circuit elements forming the low pass filter, an electrostatic coupling capacitor and an output transformer are interposed between the electrostatic load capacitor of the electrostatic transducer and an inductor closest to the output side of the class-D power amplifier of the low pass filter, and a damping resistor is connected in series to a primary coil of the output transformer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transducer assembly
ActiveUS8345898B2Electrostatic transducer microphonesFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringElectrostatic transducer
A transducer assembly includes a first electroacoustic transducer and a second electroacoustic transducer. The first and the second electrostatic transducers include an electrode and a counter electrode. An inner circumference of an outer diaphragm section lying within an outer circumference forms the counter electrode of the first electroacoustic transducer. An inner diaphragm section that lies within the inner circumference of the outer diaphragm section forms the counter electrode of the second electroacoustic transducer.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
High-temperature electrostatic transducers and fabrication method
InactiveUS20090140357A1Television system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic sensorElectrostatic transducer
A high temperature micromachined ultrasonic transducer (HTCMUT) is provided. The HTCMUT includes a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate having a doped first silicon layer, a doped second silicon layer, and a first insulating layer disposed between the first and second silicon layers. A cavity is disposed in the first silicon layer, where a cross section of the cavity includes a horizontal cavity portion on top of vertical cavity portions disposed at each end of the horizontal cavity portion, and the vertical cavity portion spans from the first insulating layer through the first silicon layer, such that a portion of the first silicon layer is isolated by the first insulating layer and the cavity. A membrane layer is disposed on the first silicon layer top surface, and spans across the cavity. A bottom electrode is disposed on the bottom of the second silicon layer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
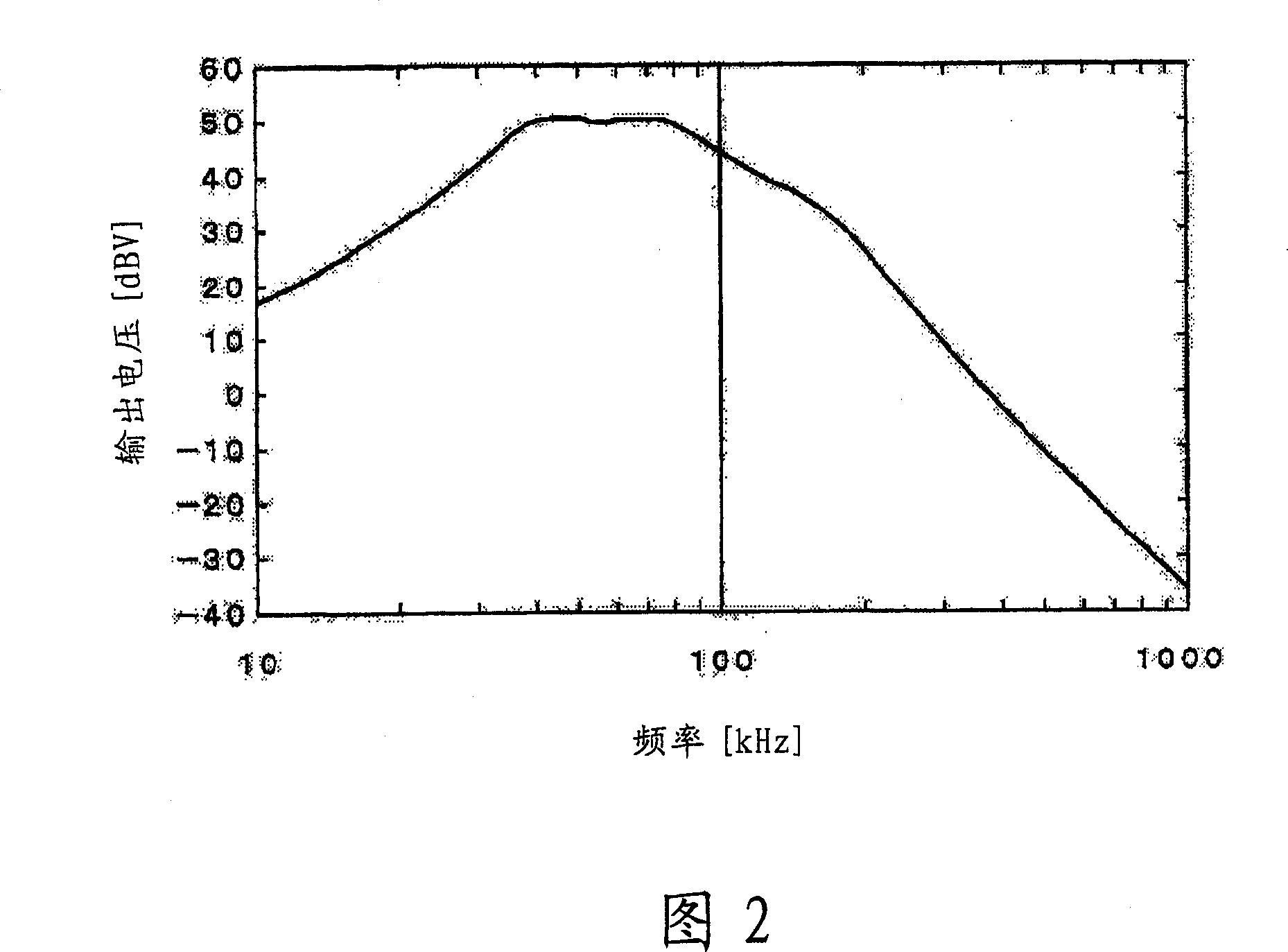
Electrostatic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, driving circuit of capacitive load
InactiveCN1972530AFlat Output Frequency CharacteristicsPower amplifiersProjectorsCapacitanceOutput transformer
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transducer assembly
ActiveUS20090214062A1Electrostatic transducer microphonesFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsElectrostatic transducerEngineering
A transducer assembly includes a first electroacoustic transducer and a second electroacoustic transducer. The first and the second electrostatic transducers include an electrode and a counter electrode. An inner circumference of an outer diaphragm section lying within an outer circumference forms the counter electrode of the first electroacoustic transducer. An inner diaphragm section that lies within the inner circumference of the outer diaphragm section forms the counter electrode of the second electroacoustic transducer.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Capacitive load driving circuit, electrostatic transducer, method of setting circuit constant, ultrasonic speaker, display device, and directional acoustic system
InactiveUS7461281B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsOutput transformerNegative feedback
A capacitive load driving circuit includes an error amplification circuit that amplifies a difference between an external input signal provided to one input terminal and a negative feedback signal provided from the negative feedback circuit to another input terminal; a modulation circuit; a power switching circuit; a gate driving circuit; a low-pass filter connected to an output side of the power switching circuit and that removes switching carrier components included in an output signal of the power switching circuit; an output transformer that boosts an output signal of the low-pass filter and has a primary winding connected to an output terminal of the filter; a capacitive load that is connected in parallel with a secondary winding of the output transformer; and the negative feedback circuit performs a negative feedback from the output terminal of the low-pass filter to an input side of the error amplification circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
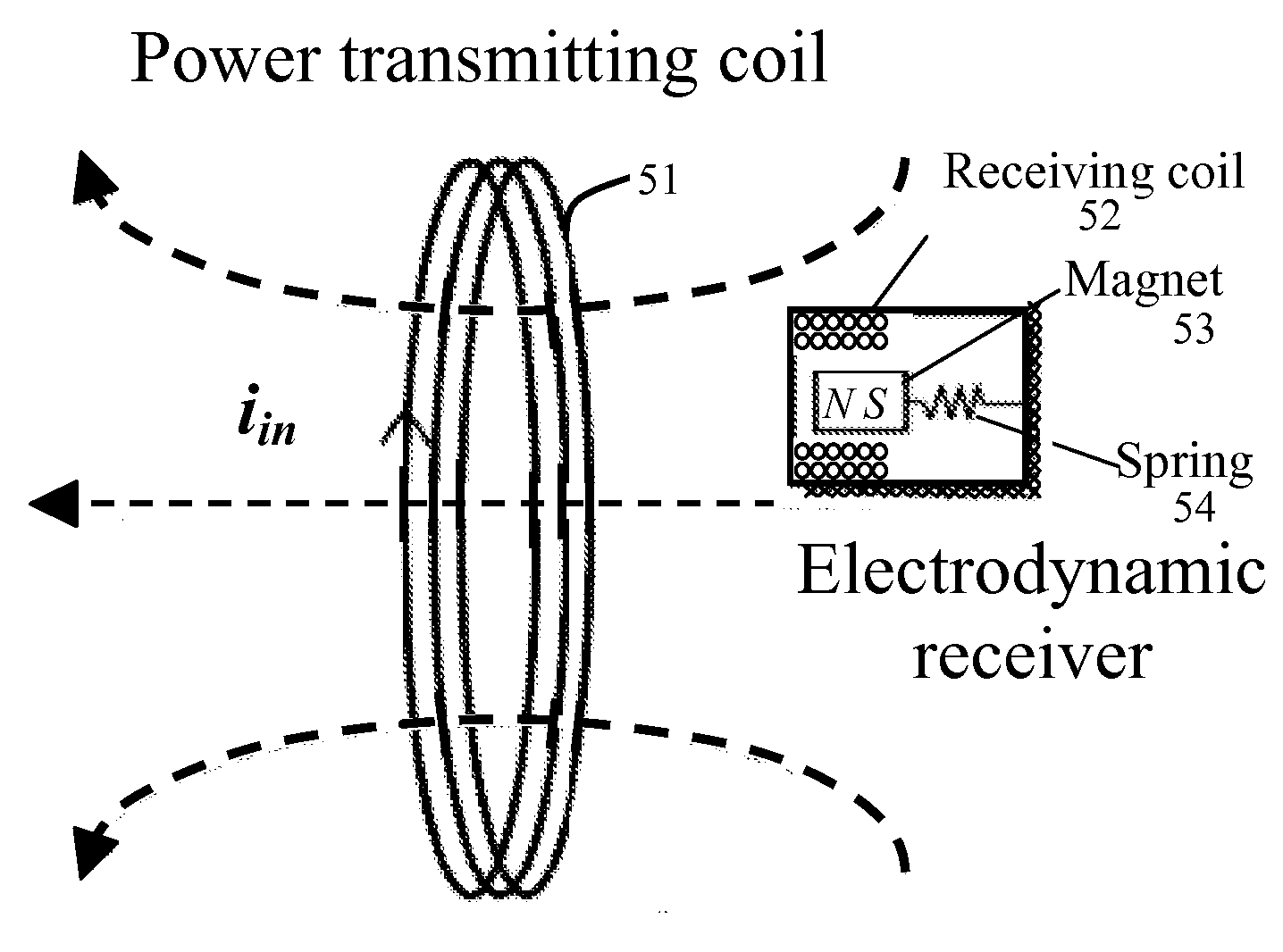
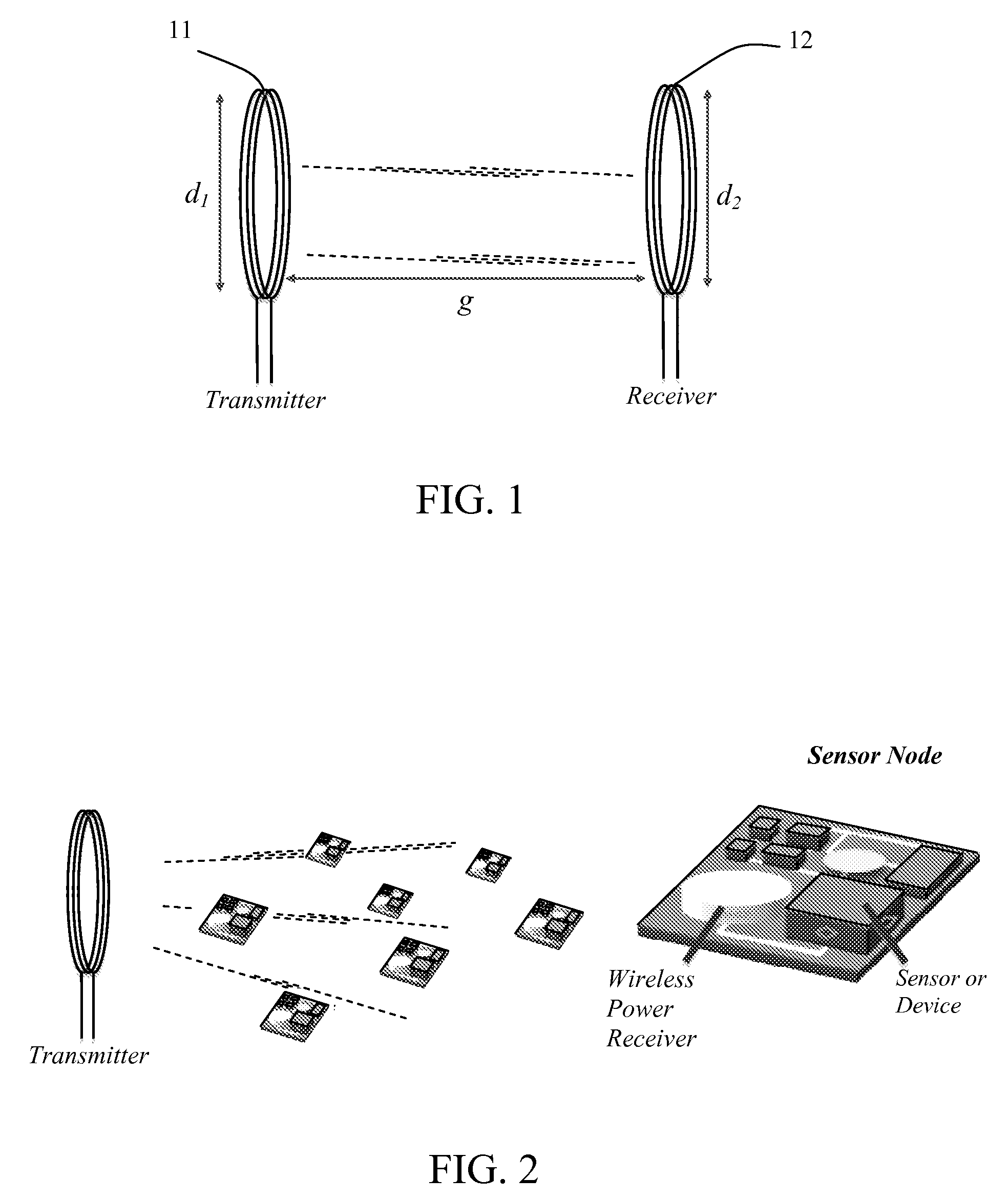
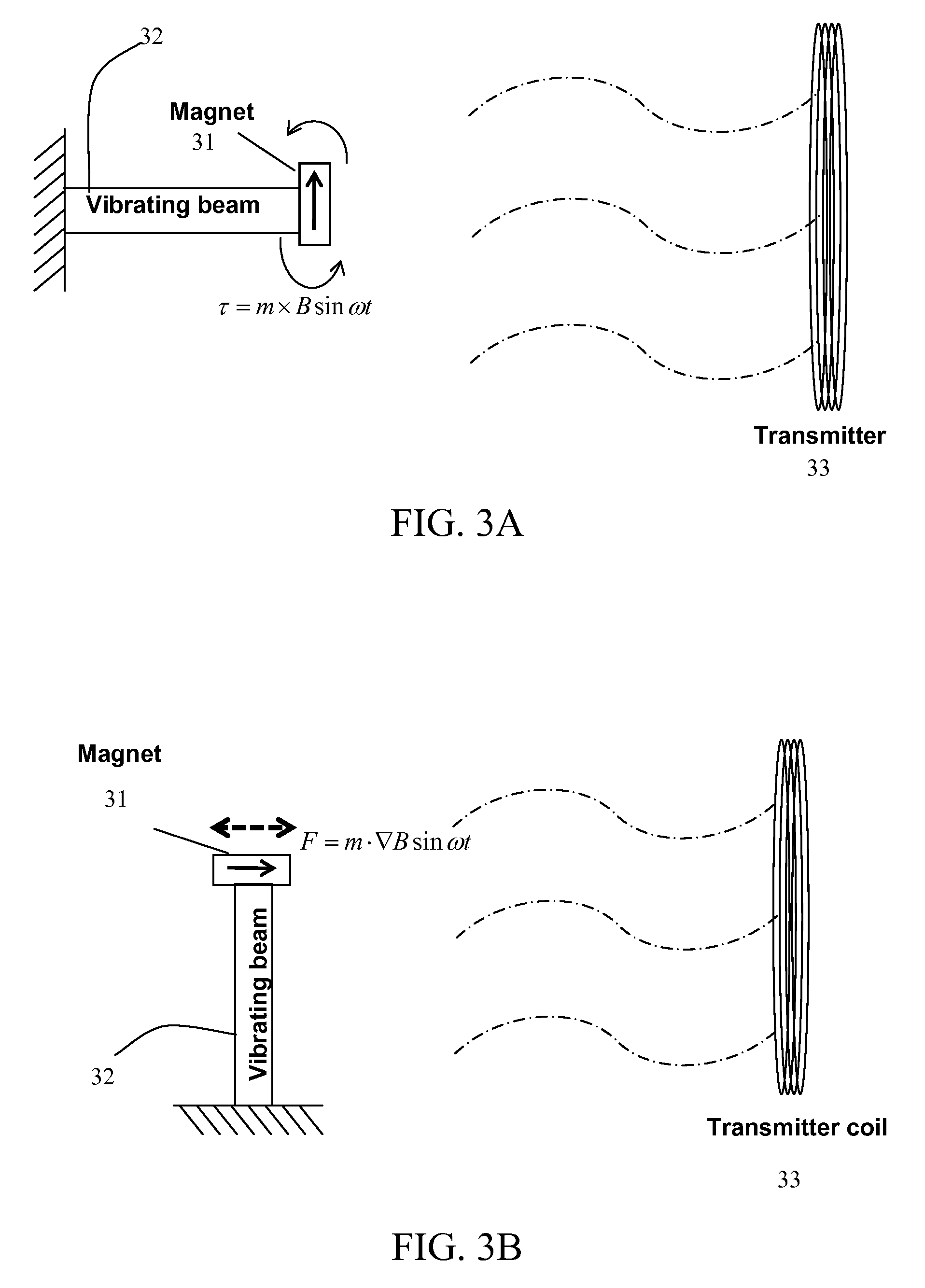
Wireless power transfer via electrodynamic coupling
ActiveUS20130241309A1Reduce exposureElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersElectric forceEnergy harvester
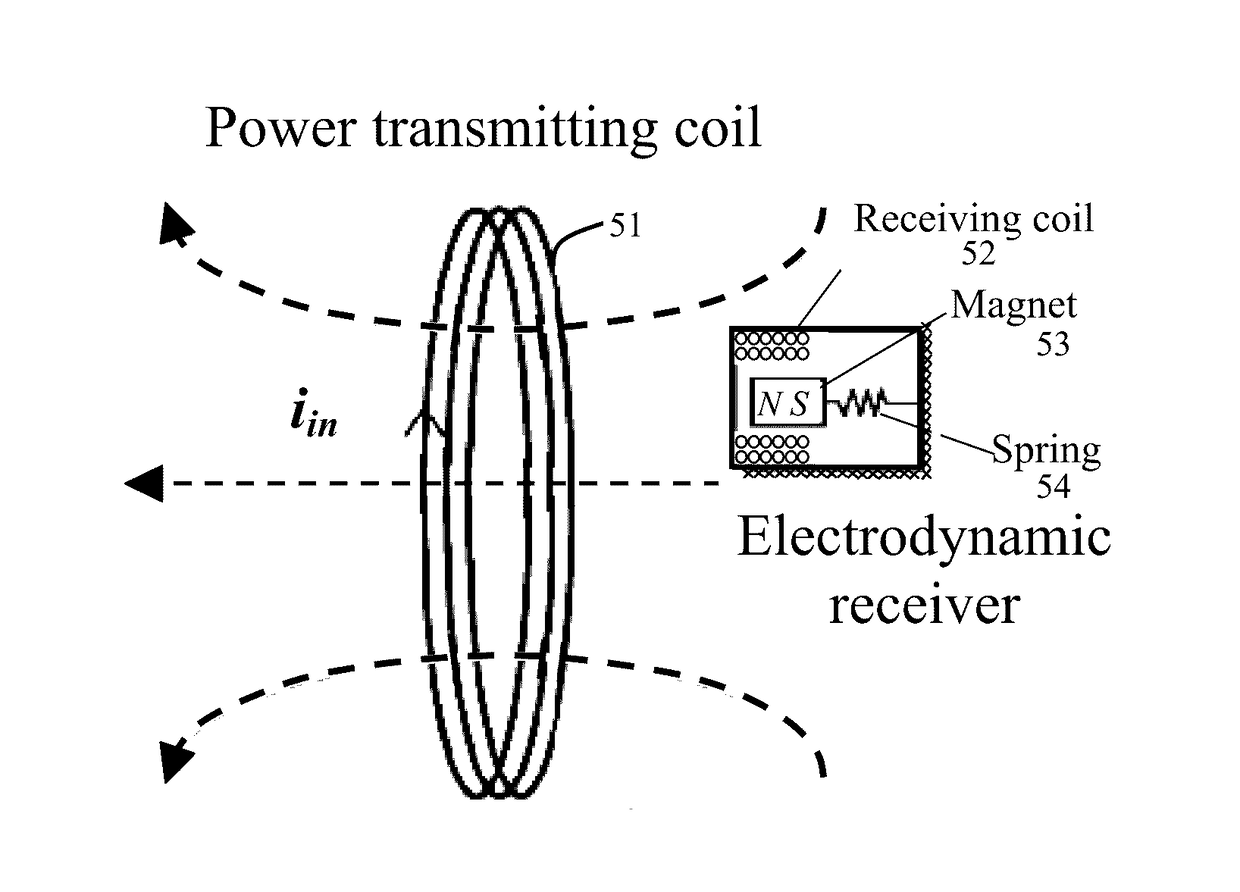
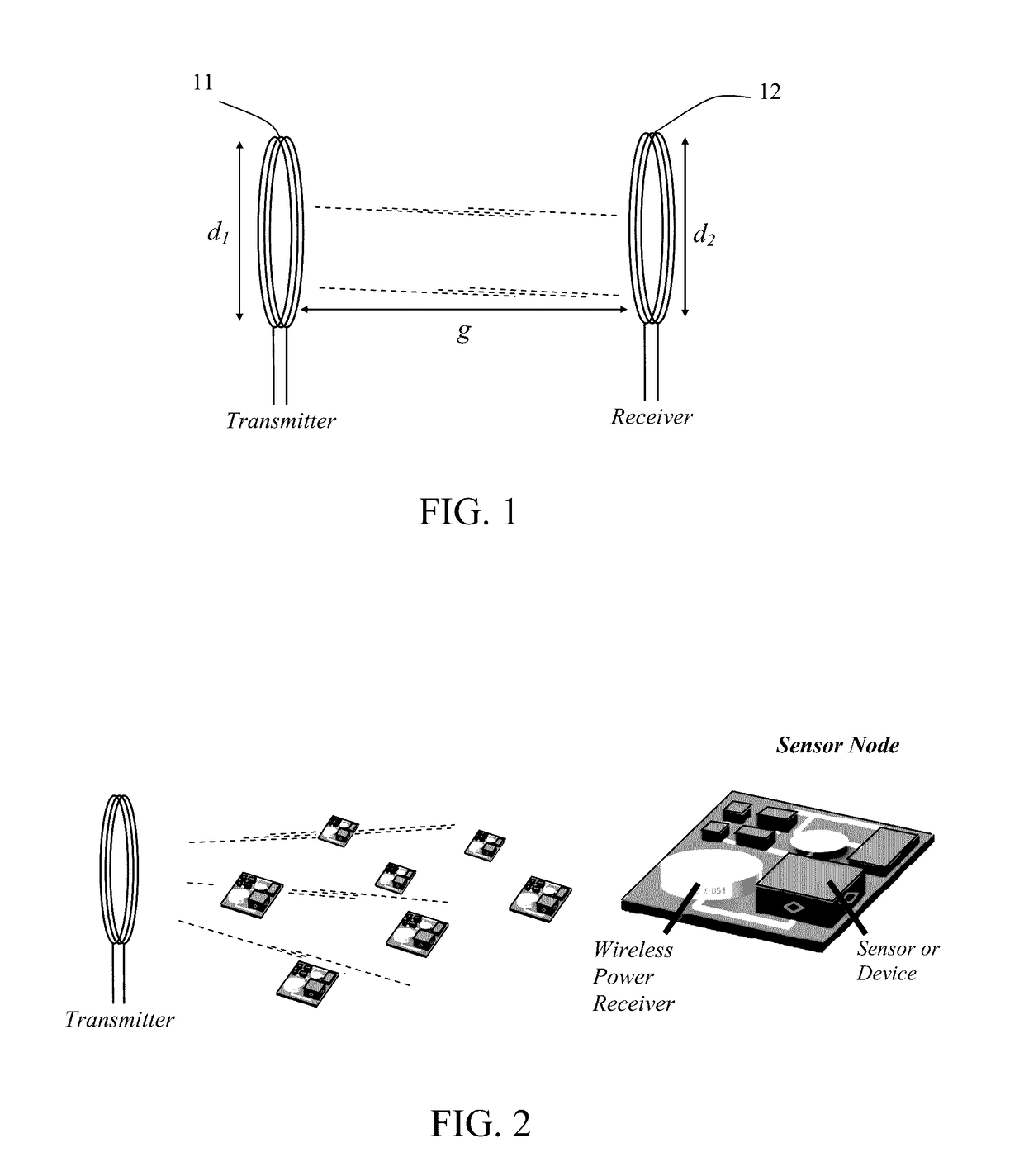
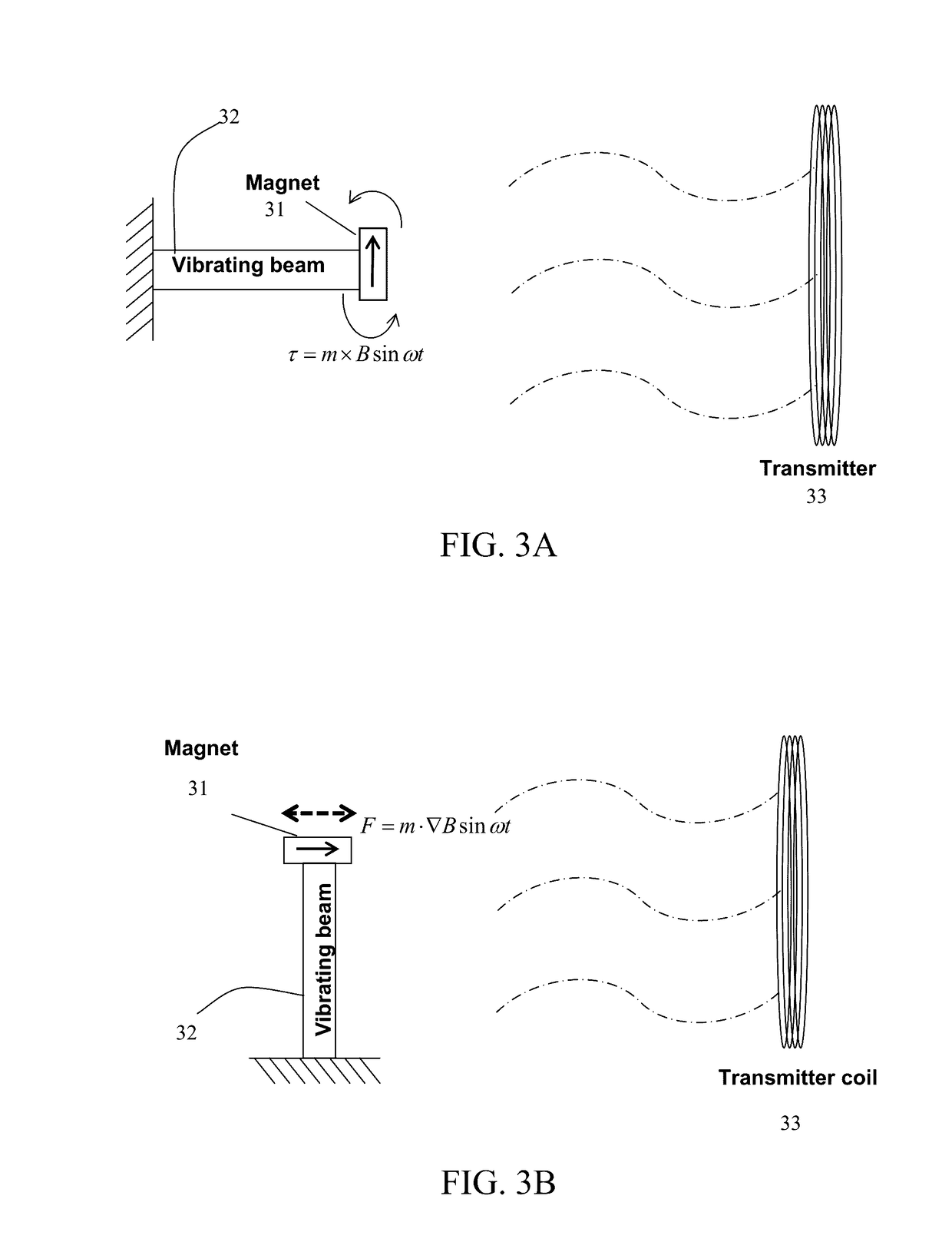
Wireless power transmission (WPT) systems are provided. According to an embodiment, the WPT system uses one or more power transmitting coils and a receiver for electromagnetically coupled wireless power transfer. The electrodynamic receiver can be in the form of an electrodynamic transducer where a magnet is allowed to oscillate near a receiving coil to induce a voltage in the receiving coil, a piezoelectric transducer where the magnet causes a vibrating structure with a piezoelectric layer to move, an electrostatic transducer where movement of the magnet causes a capacitor plate to move, or a combination thereof. An alternating magnetic field from the transmitting coil(s) excites the magnet in the receiver into mechanical resonance. The vibrating magnet then functions similar to an energy harvester to induce voltage / current on an internal coil, piezoelectric material, or variable capacitor. Embodiments utilize magnetic coupling and electromechanical resonance for safe, spatially distributed, low-frequency power delivery to portable devices.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
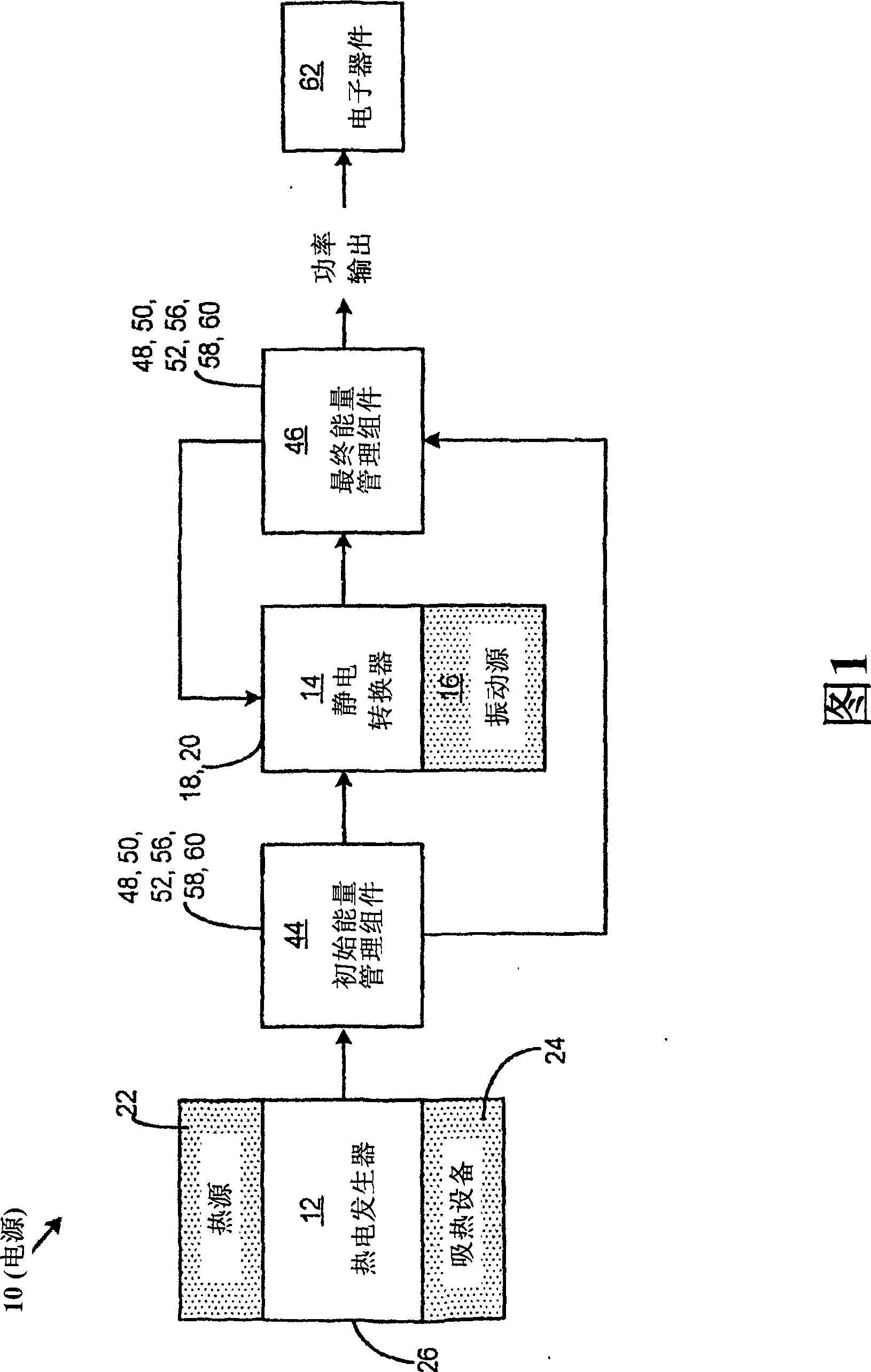
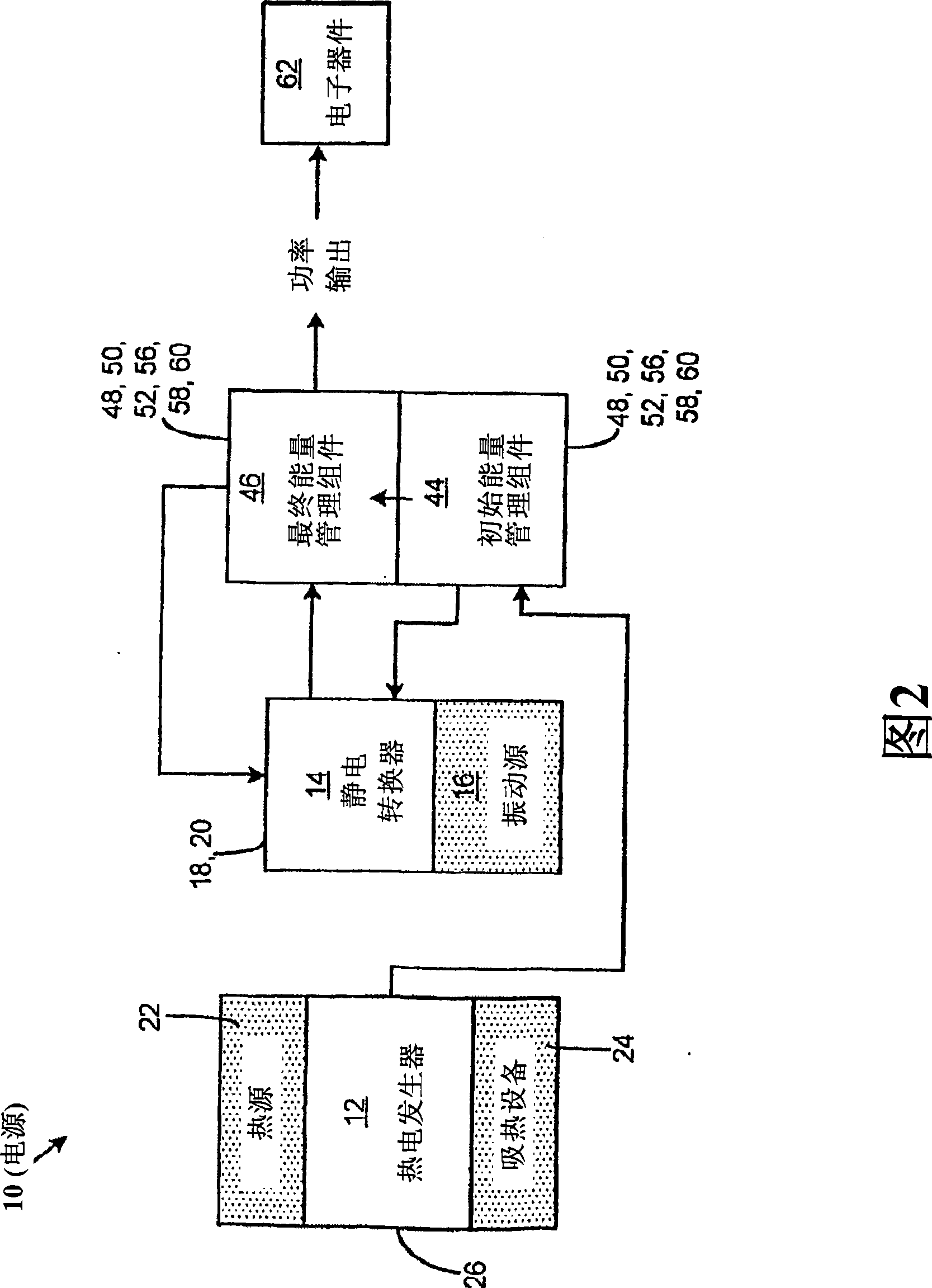
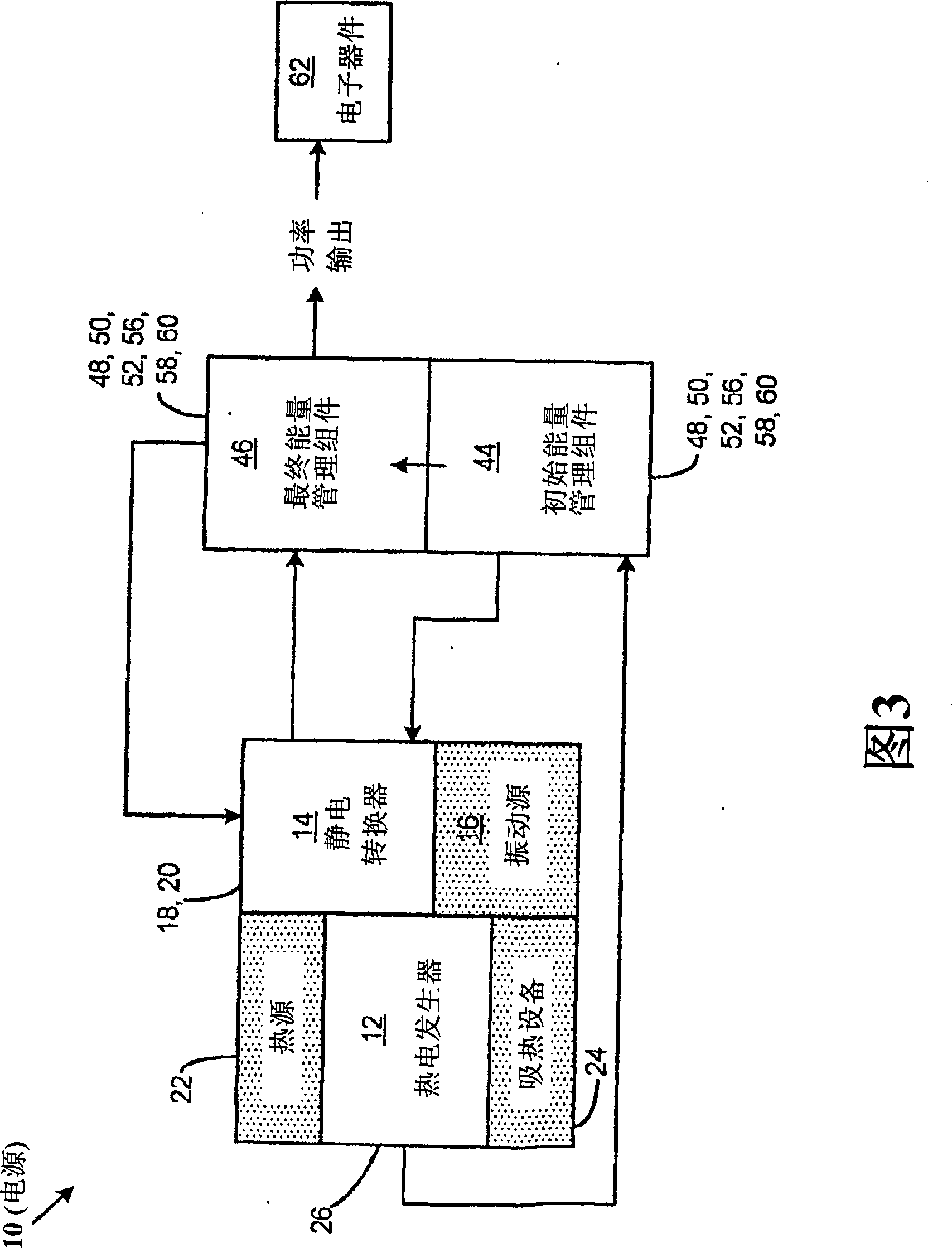
Thermoelectric generator with micro-electrostatic energy converter
InactiveCN101454914AThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSecondary cellsElectricityActivation energy
A power supply comprises a thermoelectric generator, an initial energy management assembly, an electrostatic converter and a final energy management assembly. The thermoelectric generator is adapted to generate an electrical activation energy with sufficiently high voltage in response to a temperature gradient acting across the thermoelectric generator. The initial energy management assembly is connected to the thermoelectric generator and is adapted to receive and condition the electrical activation energy produced by the thermoelectric generator. The electrostatic converter is connected to the initial energy management assembly and is activatable by the electrical activation energy received therefrom and is configured to generate electrical energy in response to vibrational energy acting thereupon. The final energy management assembly is connected to the electrostatic converter and is adapted to condition the electrical energy produced thereby.
Owner:DIGITAL ANGEL CORP
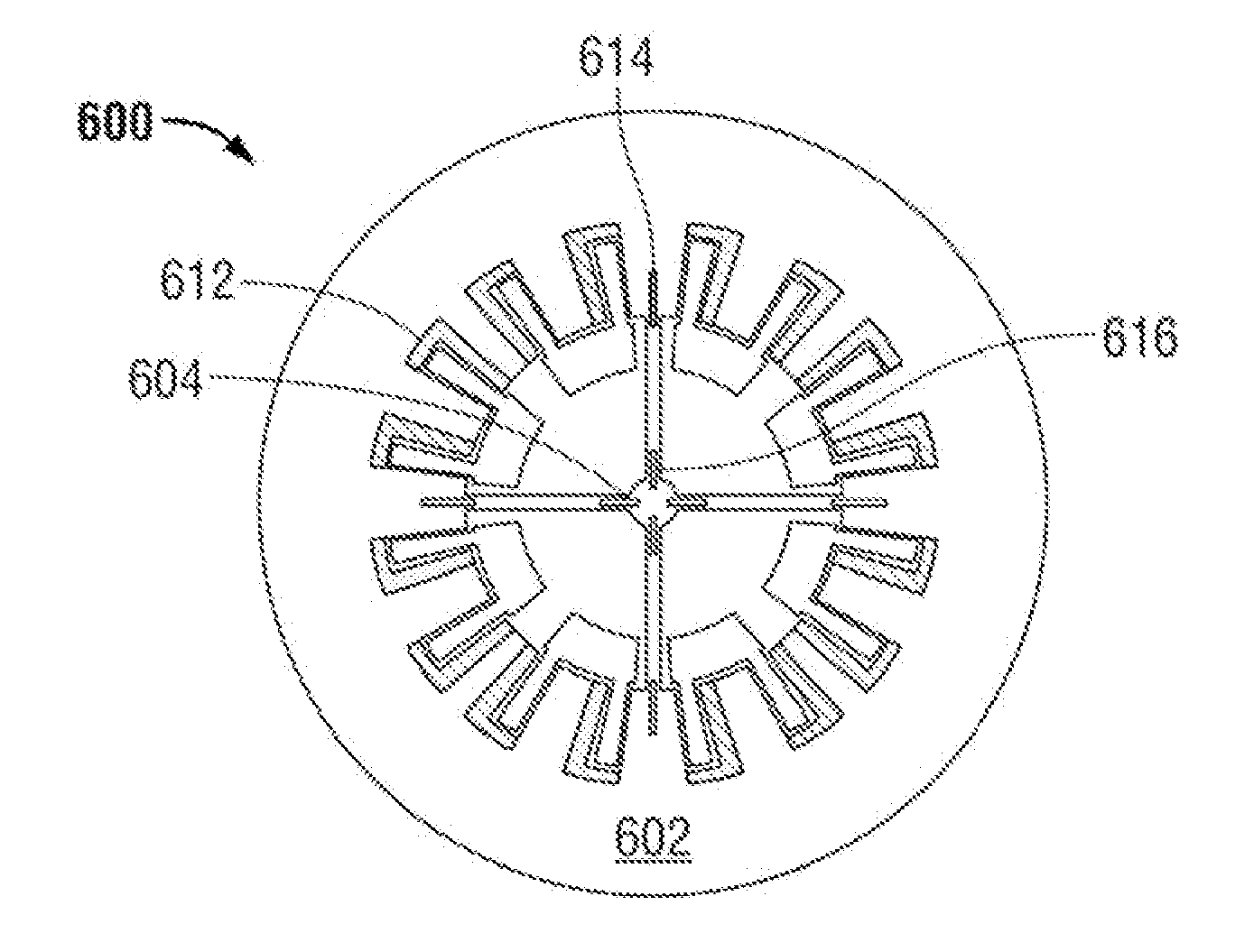
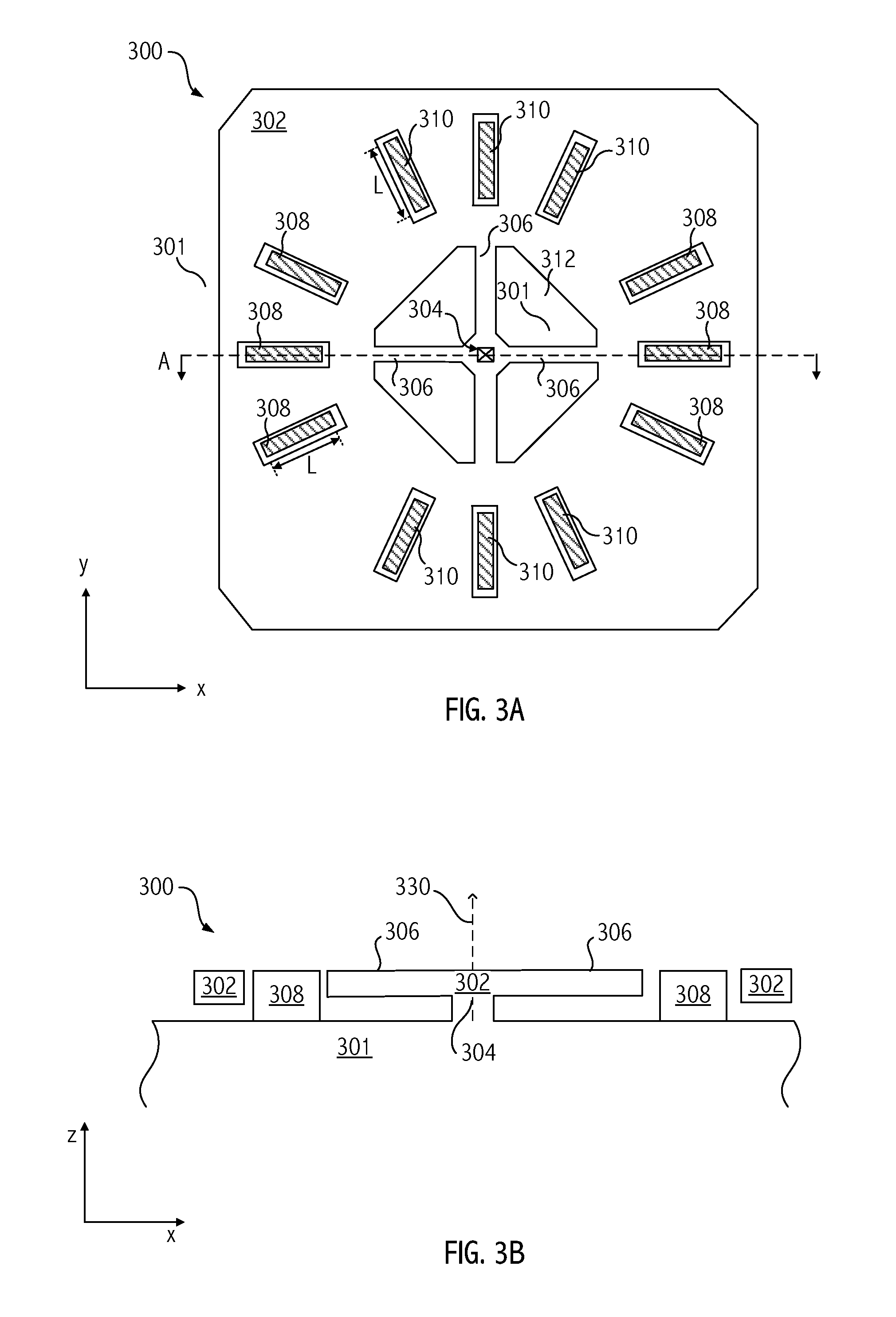
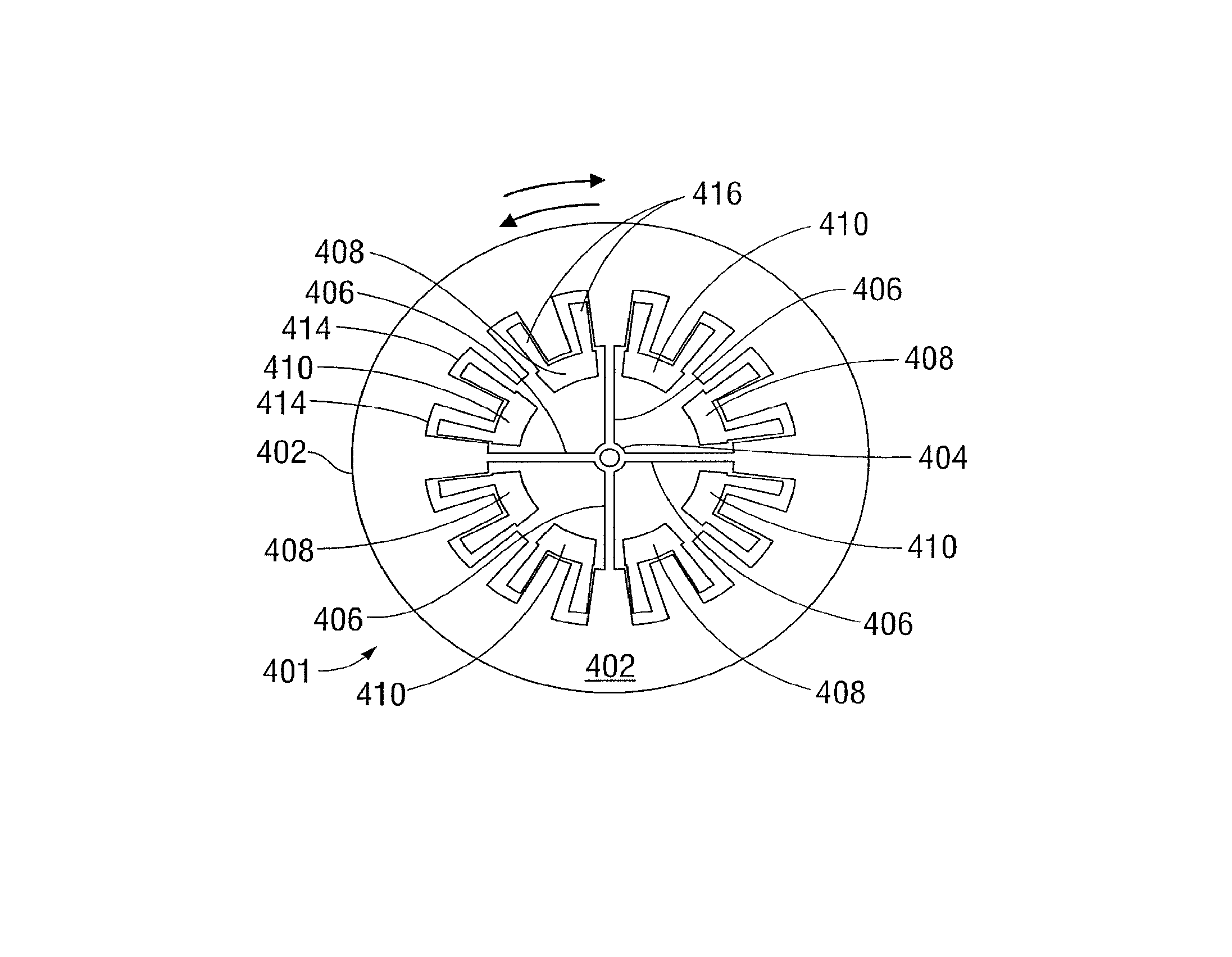
Rotational MEMS resonator for oscillator applications
An apparatus includes a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) device. The MEMS device includes a resonator suspended from a substrate, an anchor disposed at a center of the resonator, a plurality of suspended beams radiating between the anchor and the resonator, a plurality of first electrodes disposed about the anchor, and a plurality of second electrodes disposed about the anchor. The plurality of first electrodes and the resonator form a first electrostatic transducer. The plurality of second electrodes and the resonator form a second electrostatic transducer. The first electrostatic transducer and the second electrostatic transducer are configured to sustain rotational vibrations of the resonator at a predetermined frequency about an axis through the center of the resonator and orthogonal to a plane of the substrate in response to a signal on the first electrode.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
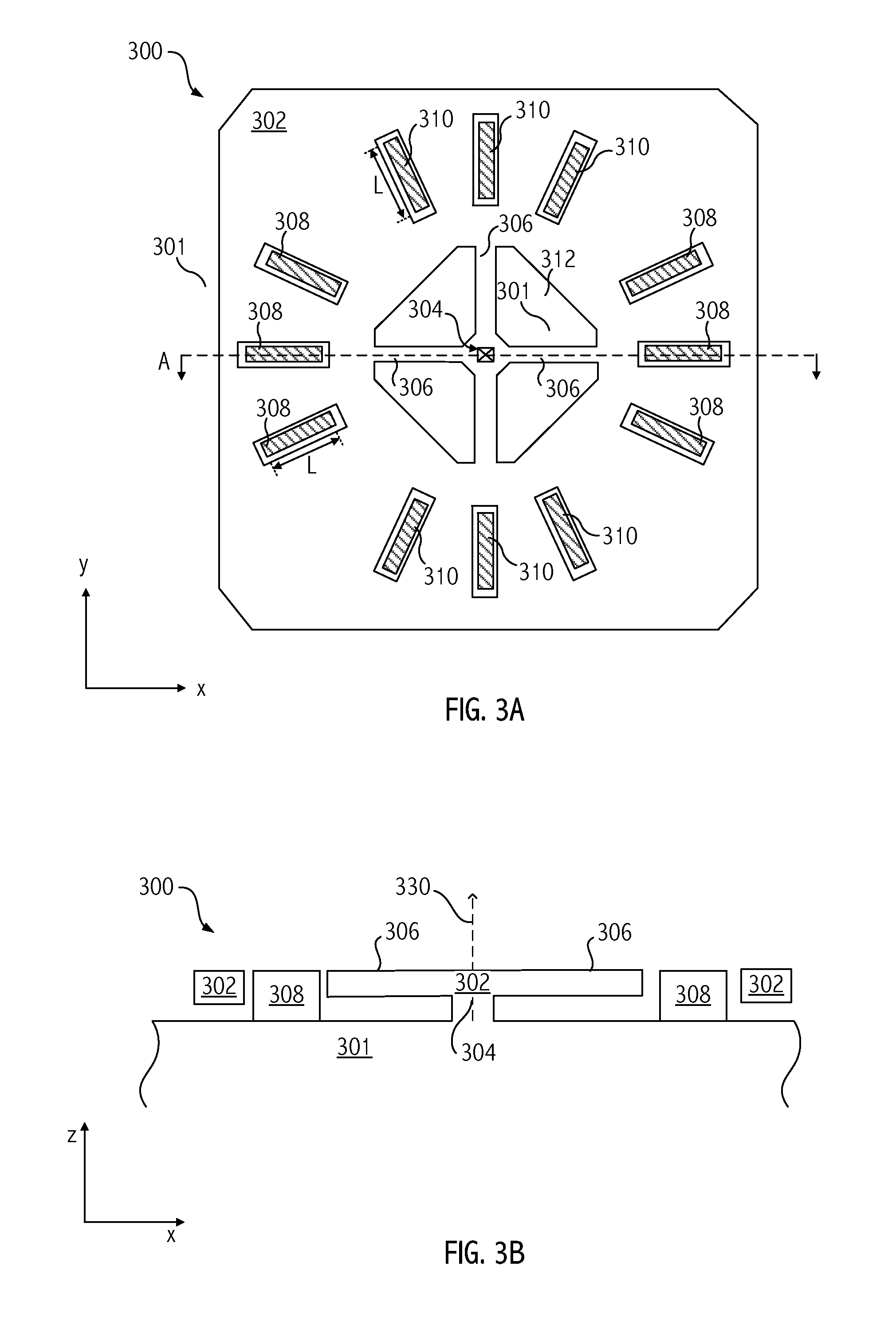
Suspended passive element for MEMS devices
InactiveUS20140361844A1Reduces and eliminates transferMultiple-port networksElectrical transducersCouplingEngineering
A technique decouples a MEMS device from sources of strain by forming a MEMS structure with suspended electrodes that are mechanically anchored in a manner that reduces or eliminates transfer of strain from the substrate into the structure, or transfers strain to electrodes and body so that a transducer is strain-tolerant. The technique includes using an electrically insulating material embedded in a conductive structural material for mechanical coupling and electrical isolation. An apparatus includes a MEMS device including a first electrode and a second electrode, and a body suspended from a substrate of the MEMS device. The body and the first electrode form a first electrostatic transducer. The body and the second electrode form a second electrostatic transducer. The apparatus includes a suspended passive element mechanically coupled to the body and electrically isolated from the body.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
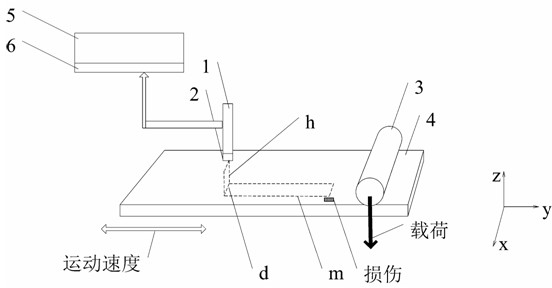
Electrostatic induction based metal surface contact damage on-line monitoring system and monitoring method
InactiveCN102520052AImprove securityIncreased impact on securityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringSignal monitoring
The invention discloses an electrostatic induction based metal surface contact damage on-line monitoring system and a monitoring method. The system provided by the invention contains an electrostatic transducer, a signal acquisition and processing analysis system and an auxiliary part, wherein the electrostatic transducer is composed of an electrostatic induction head, a shielding cover, an insulation part and a charge amplifying circuit; the signal acquisition and processing analysis system is composed of a computer, a signal processing program and a signal conditioning acquisition hardware; and the auxiliary part contains a sensor mounting rack. The system can be utilized to monitor metal surface contact damage on line, determine whether there is contact damage on the metal surface and determine the degree of the damage. The monitoring system and the method belong to the field of direct monitoring of damaged surface and can replace commonly-used monitoring systems and methods by secondary influence parameters such as vibration signal monitoring, temperature monitoring and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electrostatic transducer, ultrasonic speaker, driving circuit of capacitive load, method of setting circuit constant, display device, and directional sound system
InactiveUS8041059B2Reduce lossesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersOutput transformerLow-pass filter
An electrostatic transducer includes: a class-D power amplifier that amplifies an input signal; and a low pass filter that has a plurality of pairs of inductors and capacitors, is connected to an output side of the class-D power amplifier, and serves to eliminate switching carrier components included in an output of the class-D power amplifier. An electrostatic load capacitor of the electrostatic transducer serving as a driving load is disposed at a capacitor, which is closest to the output side of the class-D power amplifier, of circuit elements forming the low pass filter, an electrostatic coupling capacitor and an output transformer are interposed between the electrostatic load capacitor of the electrostatic transducer and an inductor closest to the output side of the class-D power amplifier of the low pass filter, and a damping resistor is connected in series to a primary coil of the output transformer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
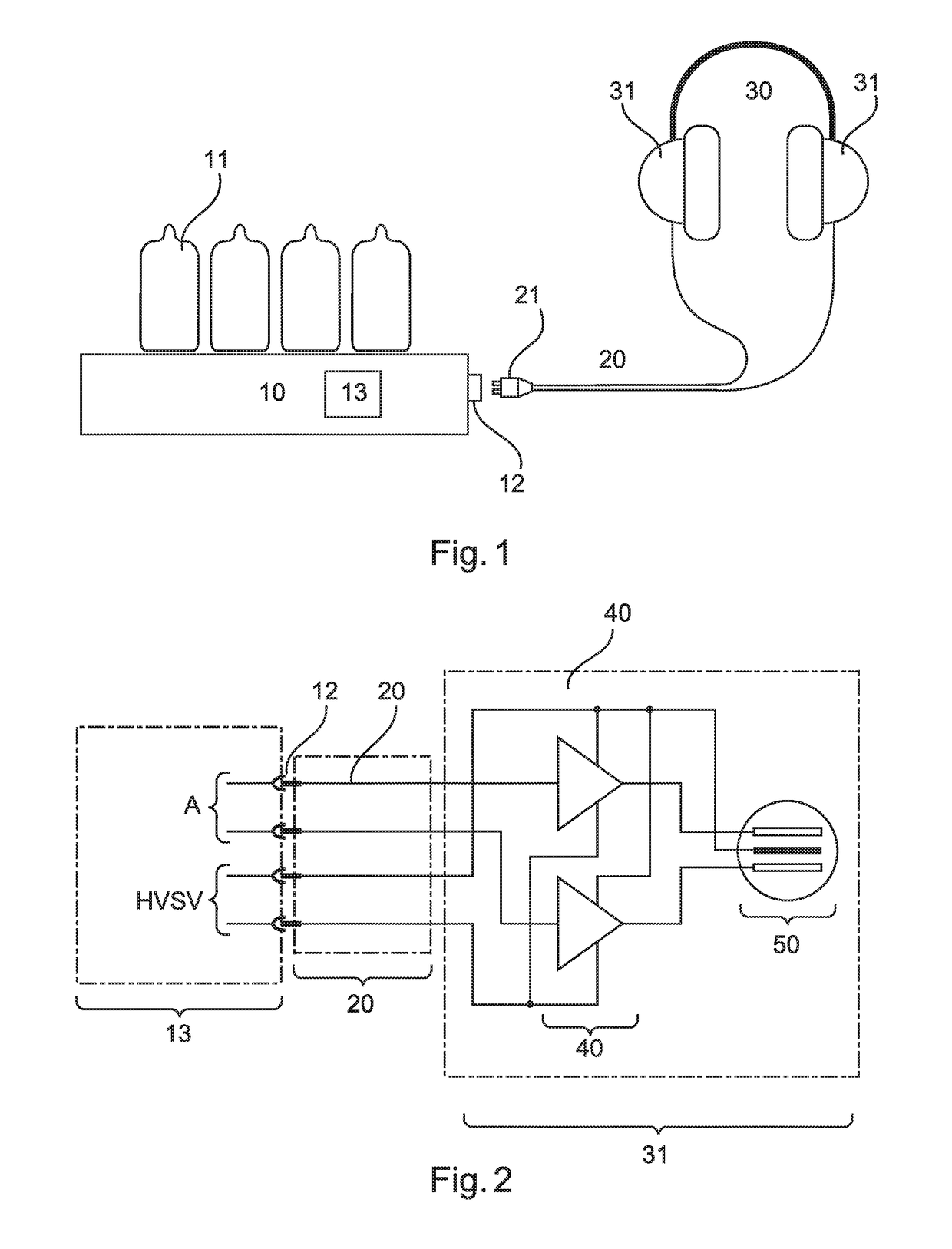
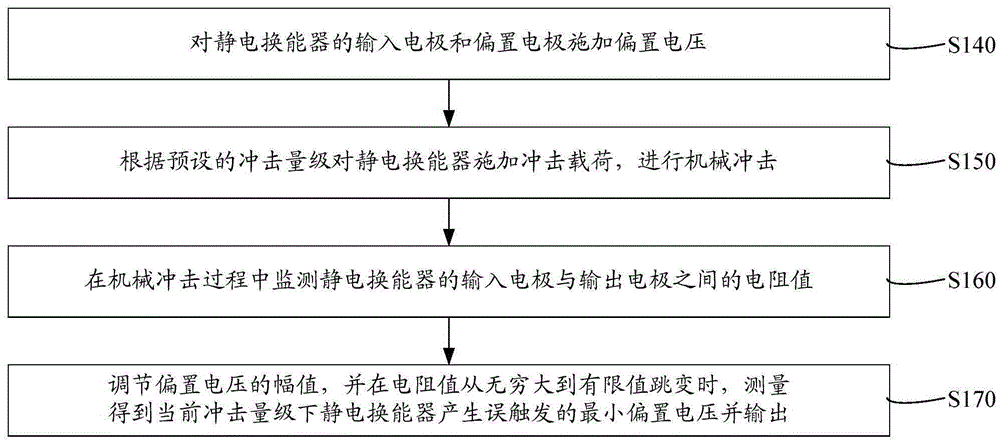
Headphone unit
ActiveUS10178465B2Reduce signal distortionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierPush pull
A headphone unit comprising a headphone, a headphone pre-amplifier for pre-amplification of an audio signal to be reproduced, and a cable between the headphone pre-amplifier and the headphone. The headphone has two symmetrically designed electrostatic transducers in the push-pull mode of operation. The pre-amplifier is adapted to output an audio signal to be reproduced by way of a first amplifier stage as a voltage-amplified audio signal at an output. The headphone has second amplifier stages which are in the form of high-voltage amplifier stages which are supplied by way of the cable with a pre-amplified audio signal to be reproduced and a high-voltage supply.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
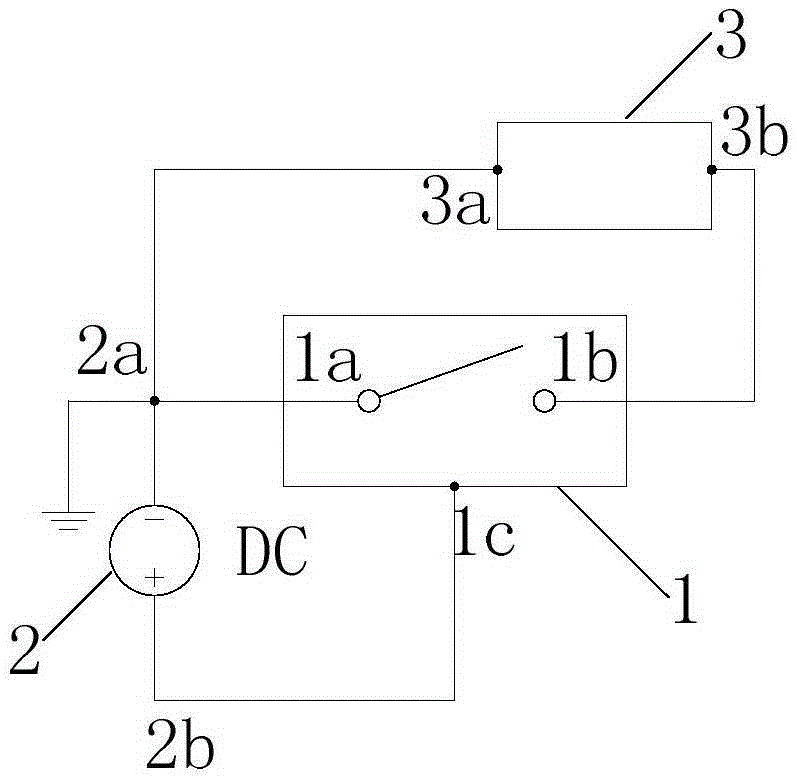
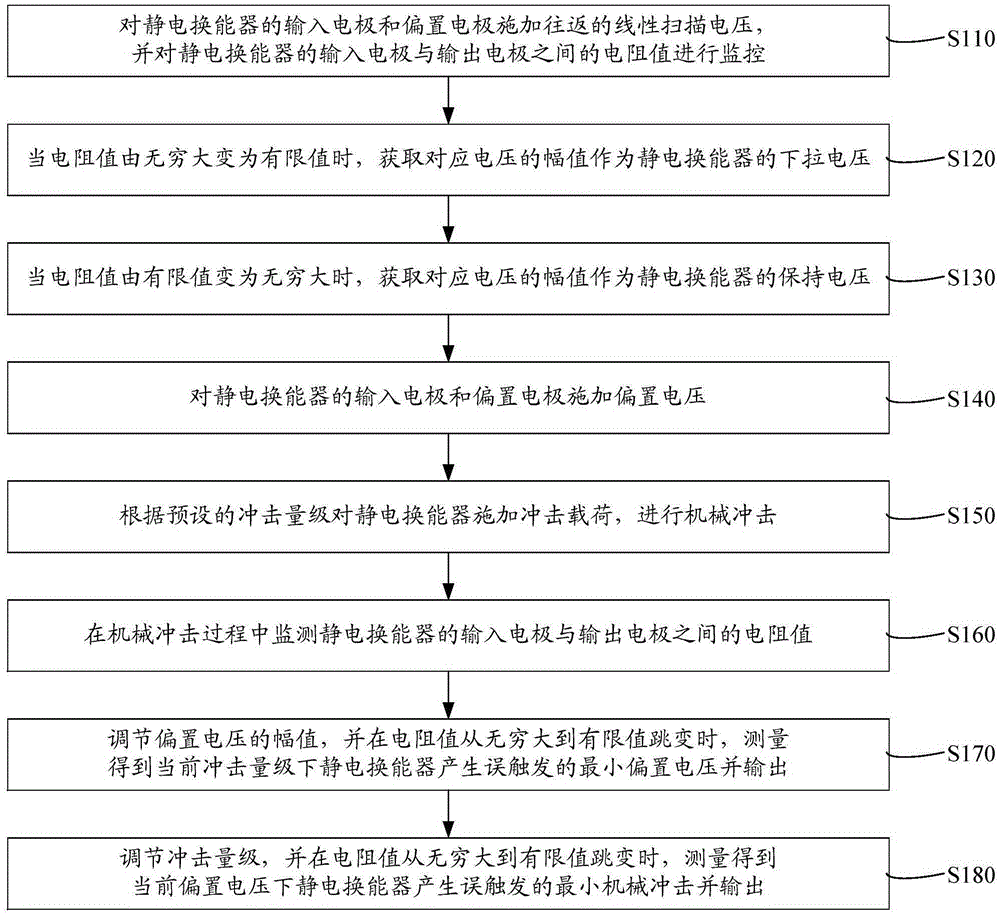
Electrostatic transducer reliability analysis method and system
ActiveCN105403799AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityEnvironmental/reliability testsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
The invention relates to an electrostatic transducer reliability analysis method and a system. The analysis method comprises steps of imposing bias voltage on an input electrode and a bias electrode of an electrostatic transducer; imposing impulse load on the electrostatic transducer according to the preset impact magnitude and carrying out mechanical impact; monitoring the resistance value between an input electrode and an output electrode of the electrostatic transducer during the mechanical impact; and adjusting the amplitude of the bias voltage and when the resistance value jumps from infinity to the limit value, obtaining and outputting the minimal bias voltage of false triggering the electrostatic transducer via measurement in the current impact magnitude. Thus, it is achieved that in a certain mechanical impact condition, the minimal bias voltage of false triggering caused by down drawing of a movable flat plate can be obtained; the shock resistance design of the electrostatic transducer and prediction and prevention for false contact actions caused by the mechanical impact and static electric power coupling can be obtained; and stability and reliability of the electrostatic transducer are improved.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
Wireless power transfer via electrodynamic coupling
ActiveUS20170155287A1Reduce exposureCircuit arrangementsVehicular energy storageElectric power transmissionEnergy harvester
Wireless power transmission (WPT) systems are provided. According to an embodiment, the WPT system uses one or more power transmitting coils and a receiver for electromagnetically coupled wireless power transfer. The electrodynamic receiver can be in the form of an electrodynamic transducer where a magnet is allowed to oscillate near a receiving coil to induce a voltage in the receiving coil, a piezoelectric transducer where the magnet causes a vibrating structure with a piezoelectric layer to move, an electrostatic transducer where movement of the magnet causes a capacitor plate to move, or a combination thereof. An alternating magnetic field from the transmitting coil(s) excites the magnet in the receiver into mechanical resonance. The vibrating magnet then functions similar to an energy harvester to induce voltage / current on an internal coil, piezoelectric material, or variable capacitor. Embodiments utilize magnetic coupling and electromechanical resonance for safe, spatially distributed, low-frequency power delivery to portable devices.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Communication device and system for performing data communication using a human or animal body as transmission medium
InactiveUS20170244495A1Avoid accumulationImprove signal-to-noise ratioPower managementTransmissionTransceiverUser device
The invention is directed at a communication device for performing data communication using a human or animal body as transmission medium. The communication device comprises a transceiver unit comprising at least one of a transmitter and a receiver. The communication device also comprises an electrostatic transducer for enabling data communication via a surface of the body with one or more user devices in touch with or located near (i.e. in close proximity, e.g. within a range of 0-10 mm therefrom) the body. The communication device further comprises an ultrasonic transducer for enabling data communication through the body using ultrasonic waves. Both the electrostatic transducer and the ultrasonic transducer are capacitive type transducers connected to and operated via the transceiver unit.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Internal electrostatic transduction structures for bulk-mode micromechanical resonators
InactiveUS7522019B2High dielectric constantReduce resistanceImpedence networksCMOSClassical mechanics
An electrostatic transducer for micromechanical resonators, in which the electrode gaps are filled with a dielectric material having a much higher permittivity than air. This internal electrostatic transducer has several advantages over both air-gap electrostatic and piezoelectric transduction; including lower motional impedance, compatibility with advanced scaled CMOS device technology, and extended dynamic range. In one aspect, in order to minimize energy losses, the dielectric material has an acoustic velocity which is matched to that of the resonator material. Internal electrostatic transduction can be adapted to excite and detect either vertical modes (perpendicular to the substrate) or lateral modes (in the plane of the substrate). Its increased transduction efficiency is of particular importance for reducing the motional resistance of the latter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrostatic loudspeaker capable of dispersing sound both horizontally and vertically
ActiveUS8184832B2Good dispersionImprove efficiencyElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringHigh pressure
An acoustic transducer, specifically an electrostatic loudspeaker (ESL) providing curvature in two directions for improved dispersion of sound waves. The compound curvature also provides a virtual focus of the propagated sound waves for accurate reproduction of musical program material recorded with standard single-point microphones. The highly directional nature of high frequency sound waves requires that a flat or cylindrical electrostatic transducer must be physically tall to allow a listener to either recline or stand. The two-axis curved structure enables a compact form of ESL to be realized, including bookshelf type loudspeakers whereas all known commercial units are comparable in height to that of a human listener. The individual curved ESL panels can also be readily combined to create larger transducer assemblies including omni-directional units. A preferred stator panel hole-geometry is included for improved high voltage operation of coated perforated metal stator panels, and methods of forming the metal panel are described. The artistic nature of the two-dimensionally curved electrostatic transducer also lends itself to other non-traditional forms such as integration into lighting fixtures and other such architectural uses.
Owner:LUMINOS INDS
Electrostatic transducer loudspeaker
InactiveUS8755539B2Semiconductor electrostatic transducersAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransformerResonance
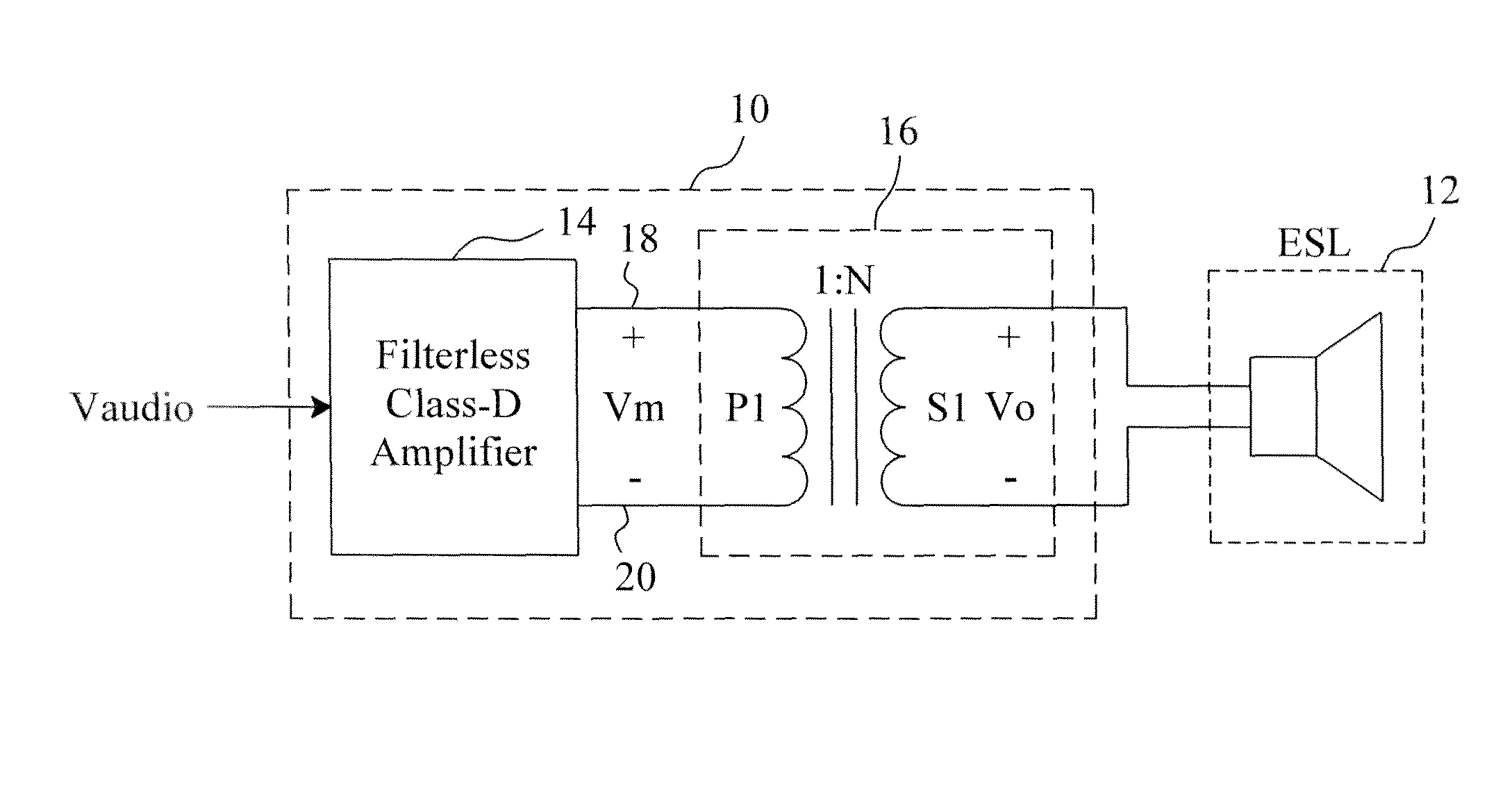
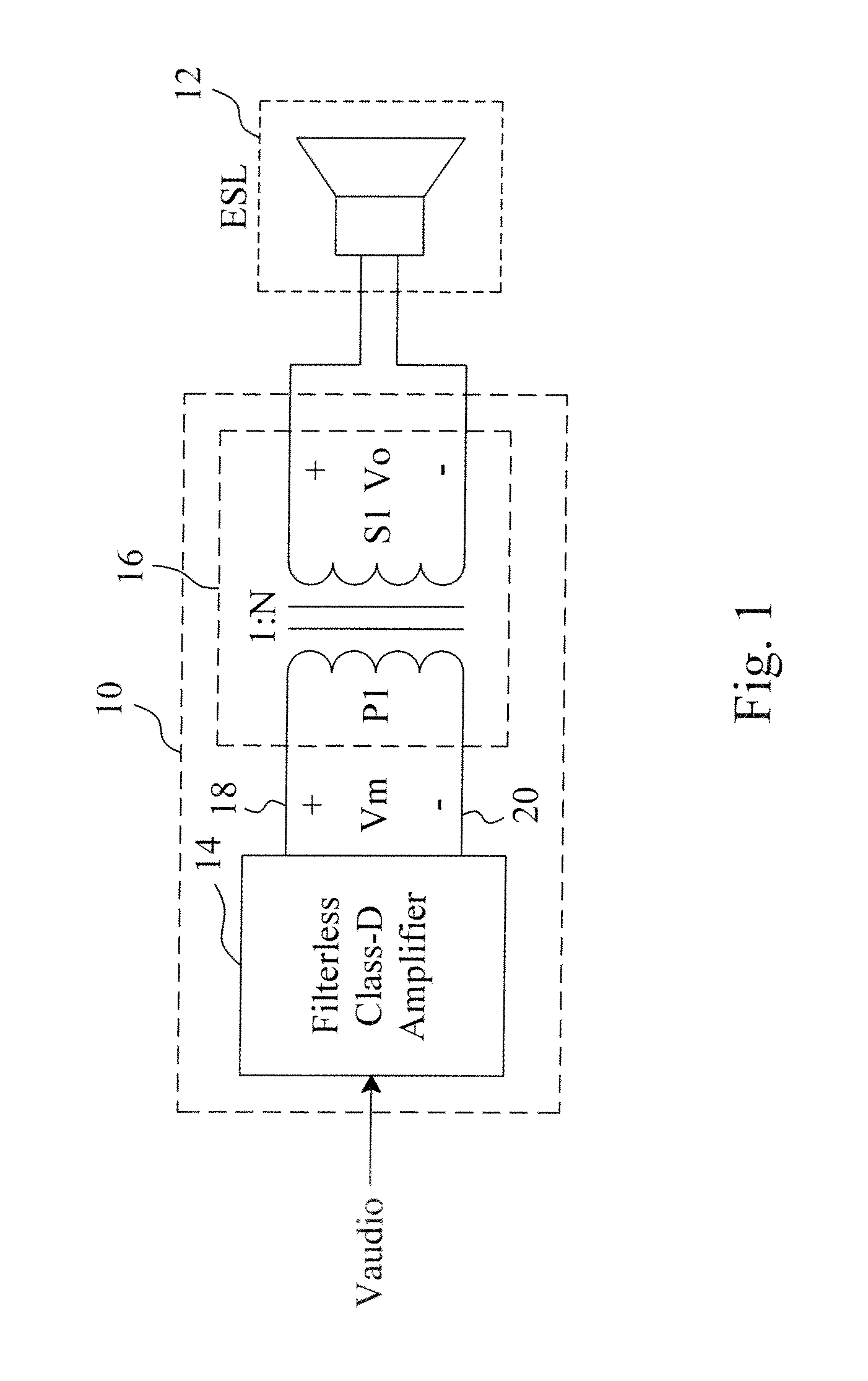
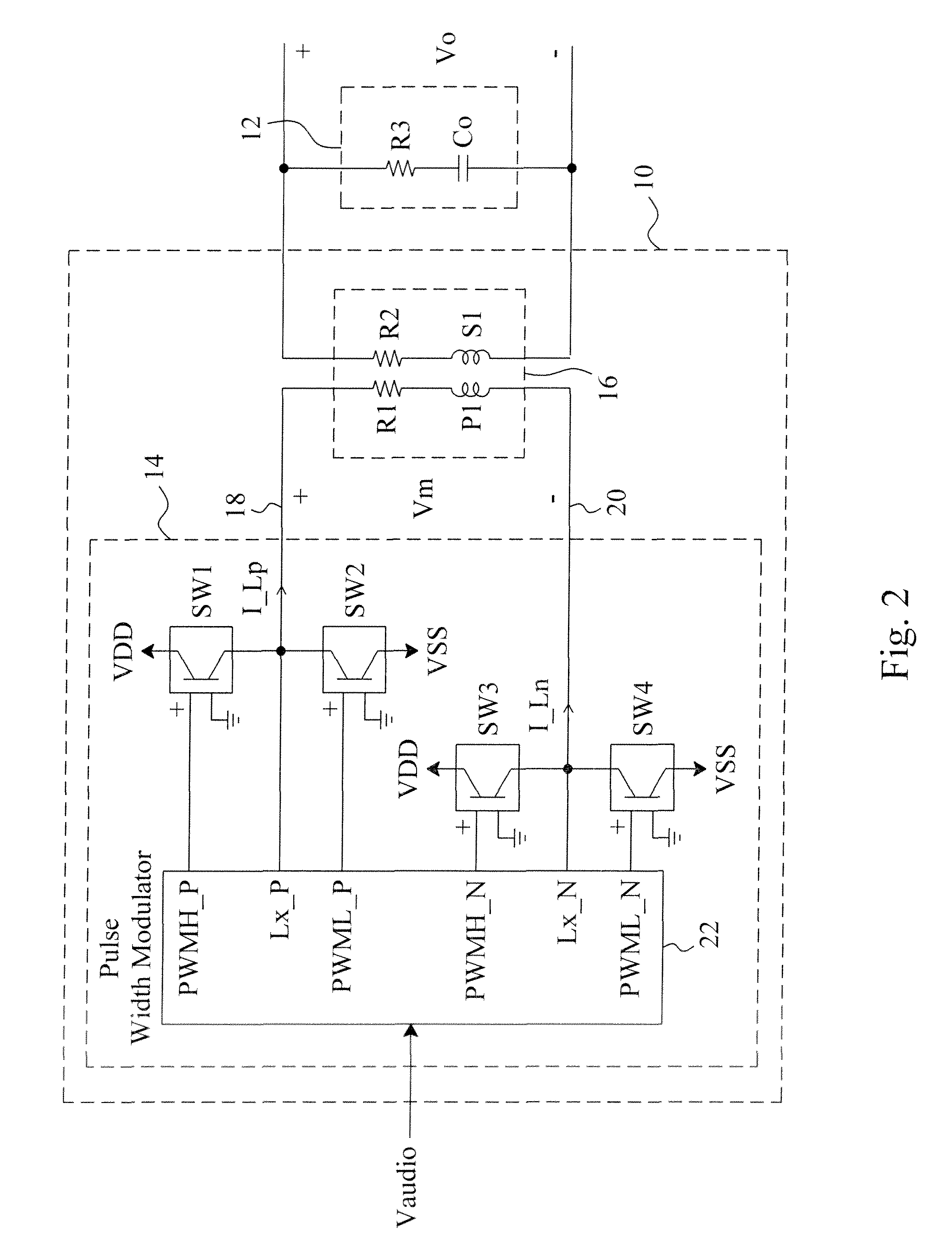
An electrostatic transducer loudspeaker includes a filterless class-D amplifier to modulate an audio input signal to generate a modulated signal containing a PWM switching carrier component, and a transformer directly connected at an output side of the filterless class-D amplifier and directly connected at an input side of an electrostatic transducer, whereby the equivalent capacitance of the electrostatic transducer and the equivalent inductance of the transformer establish a resonance circuit to demodulate the modulated signal to generate an AC voltage to drive the electrostatic transducer.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Improved electrostatic transducer
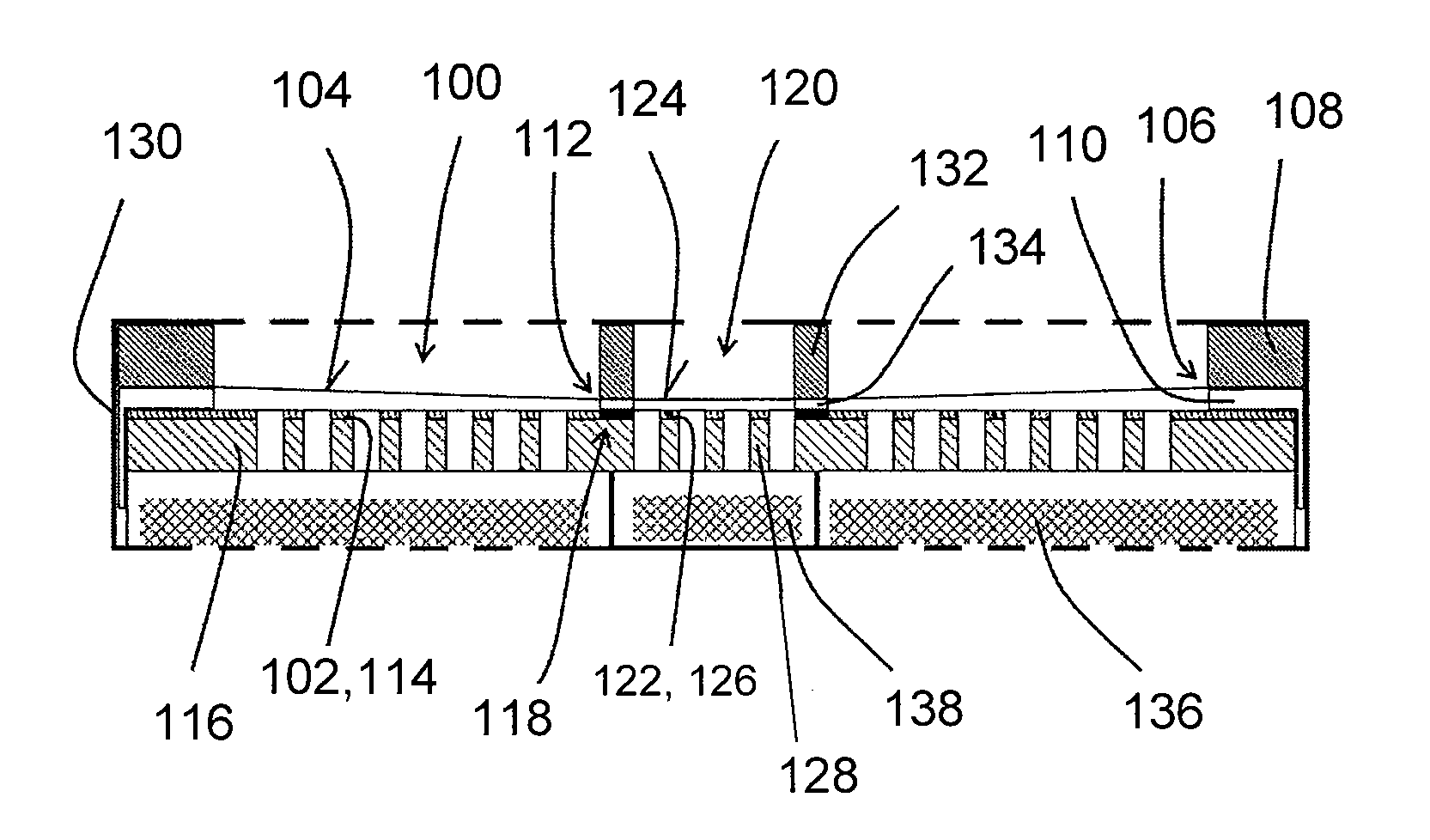
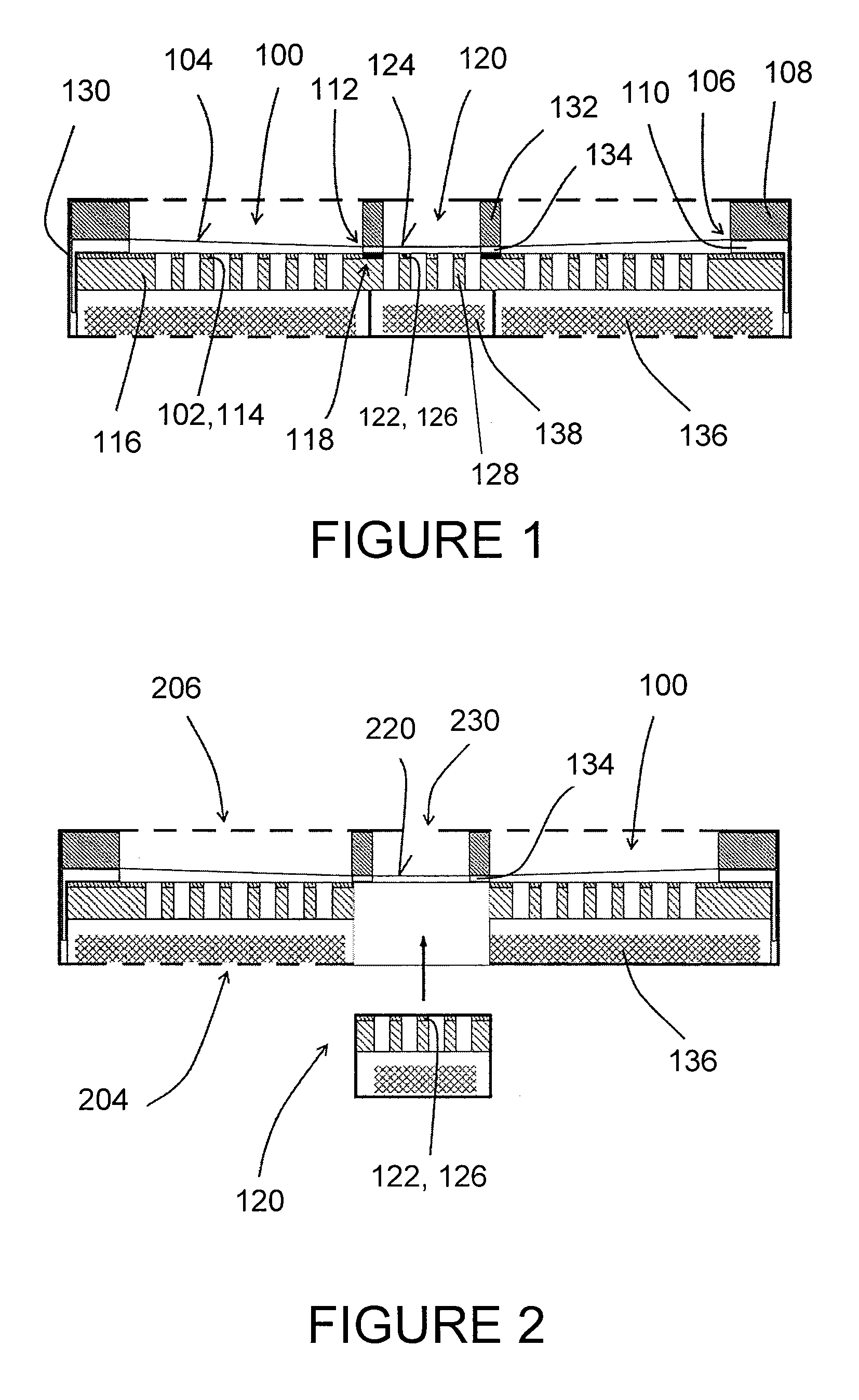
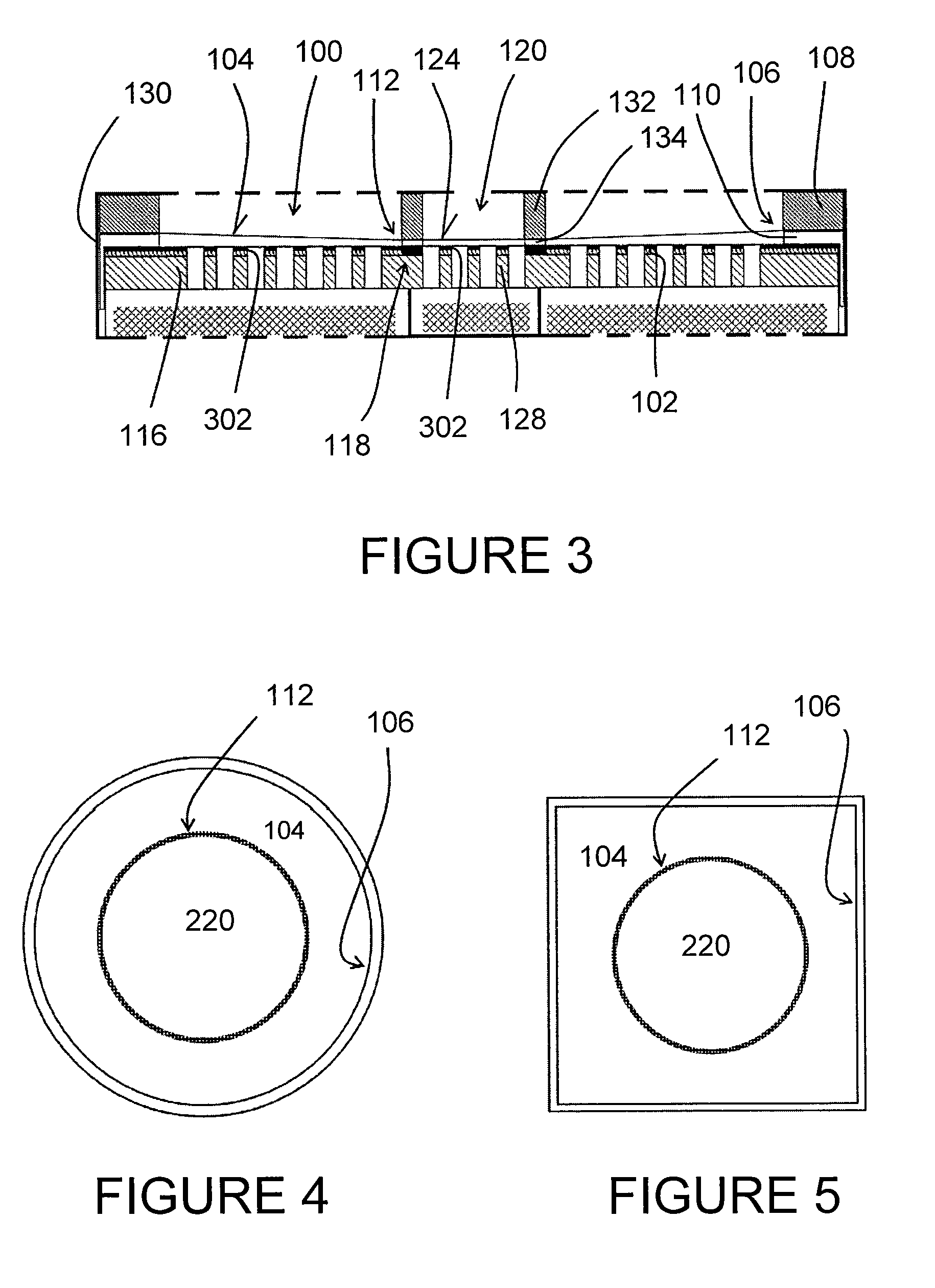
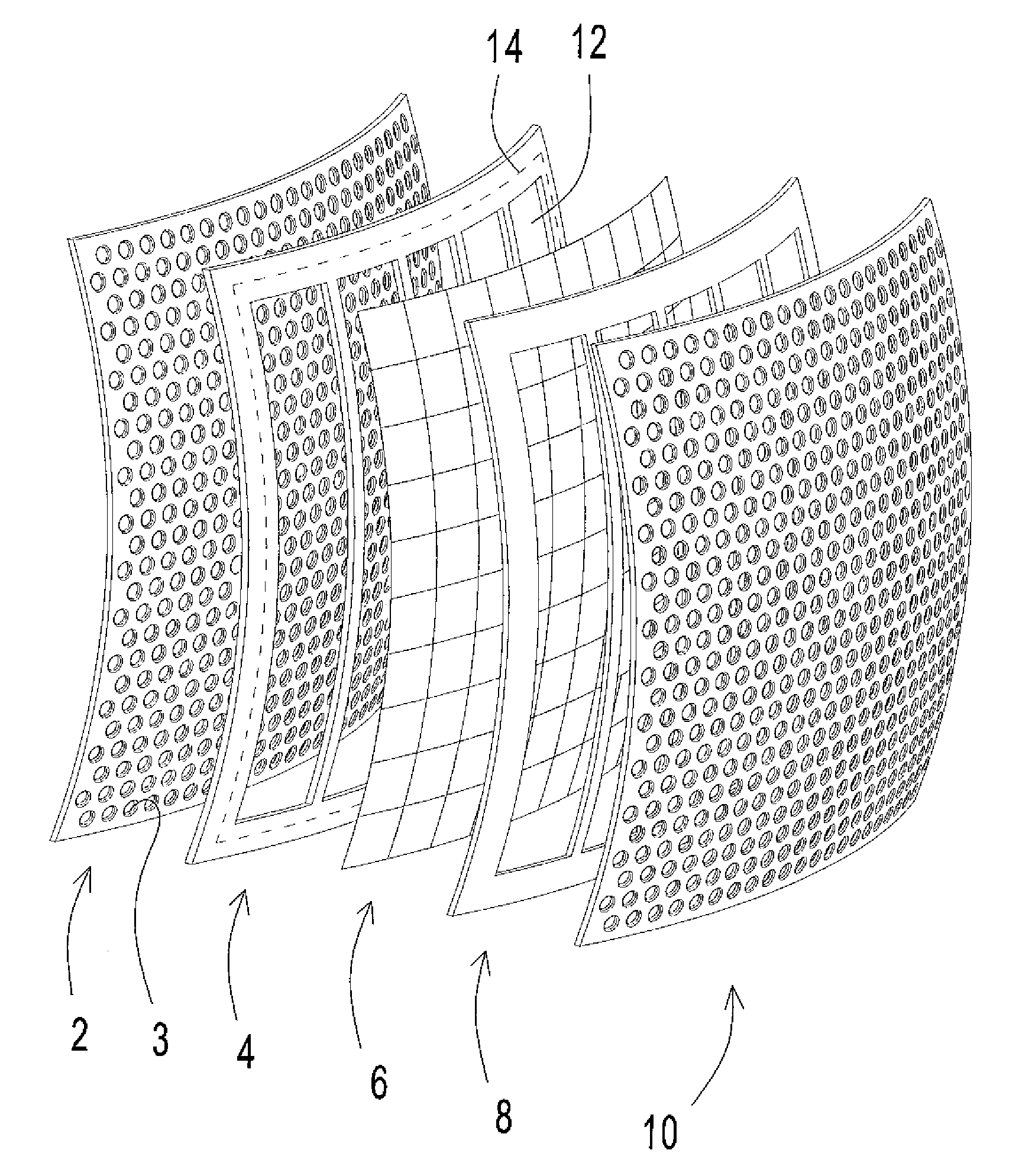
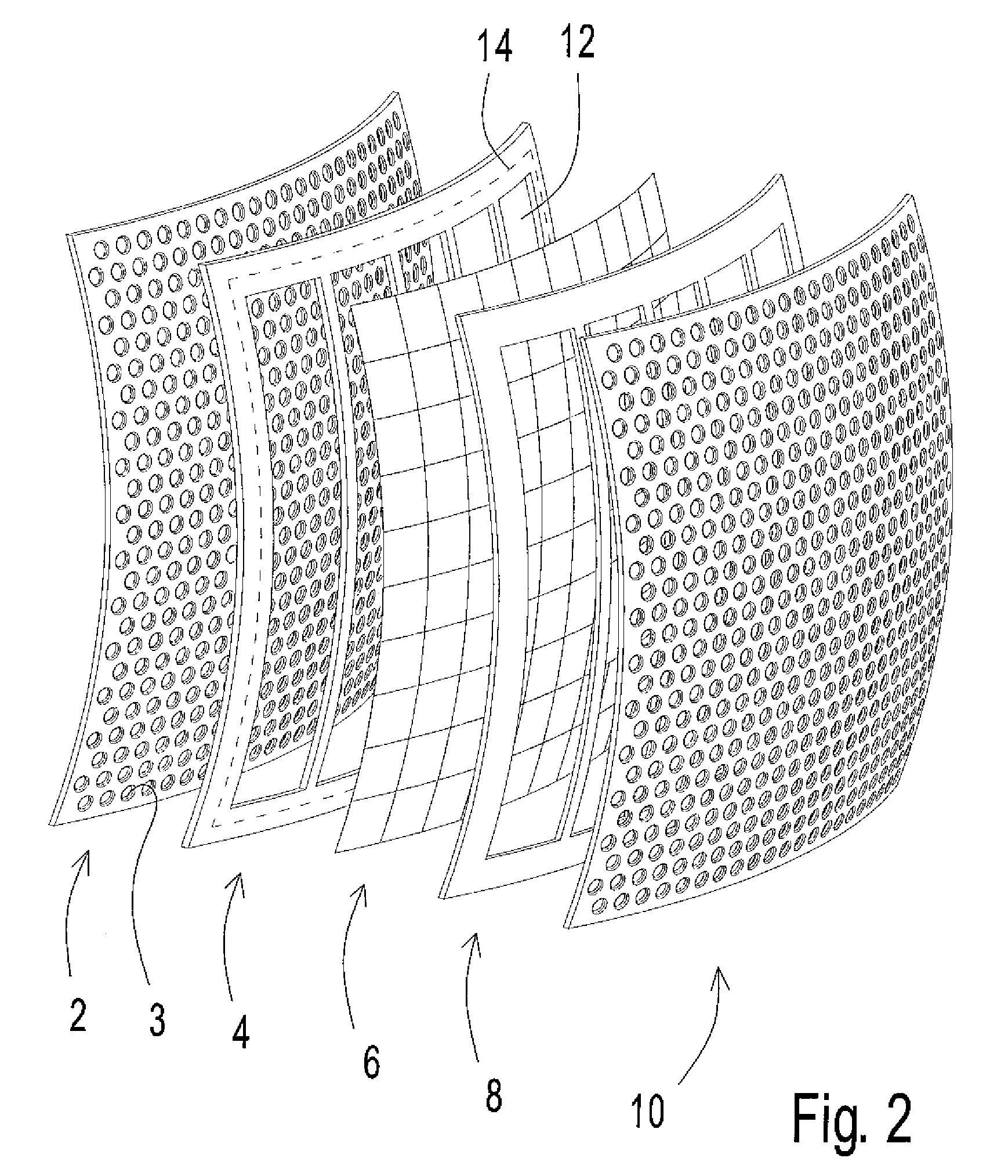
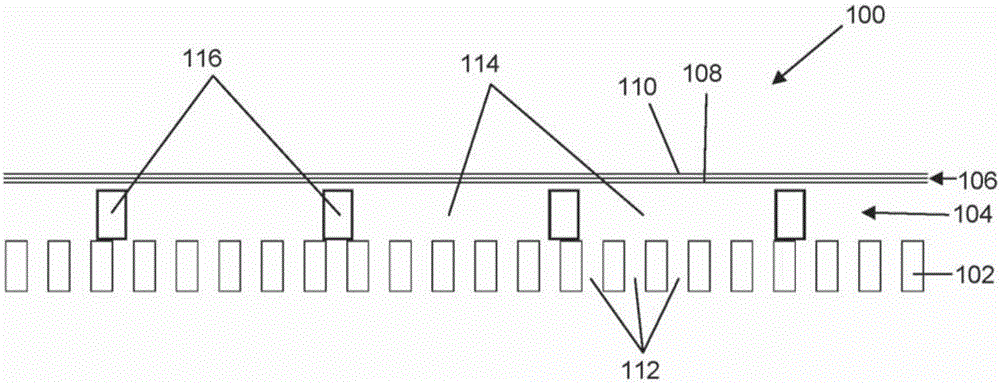
ActiveCN106165449AImprove qualityImprove acoustic performanceMicrophonesLoudspeakersElectrostatic transducerBiomedical engineering
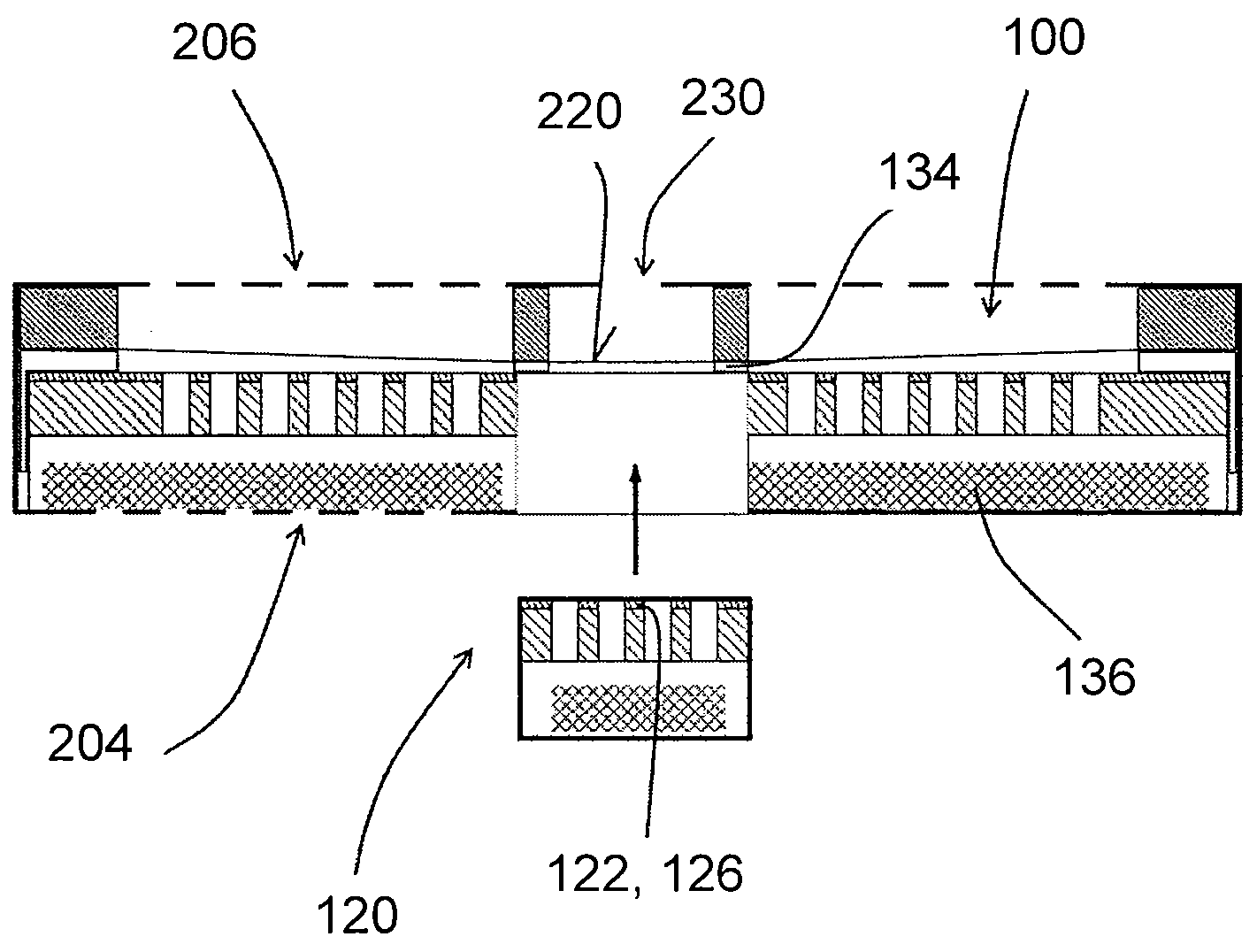
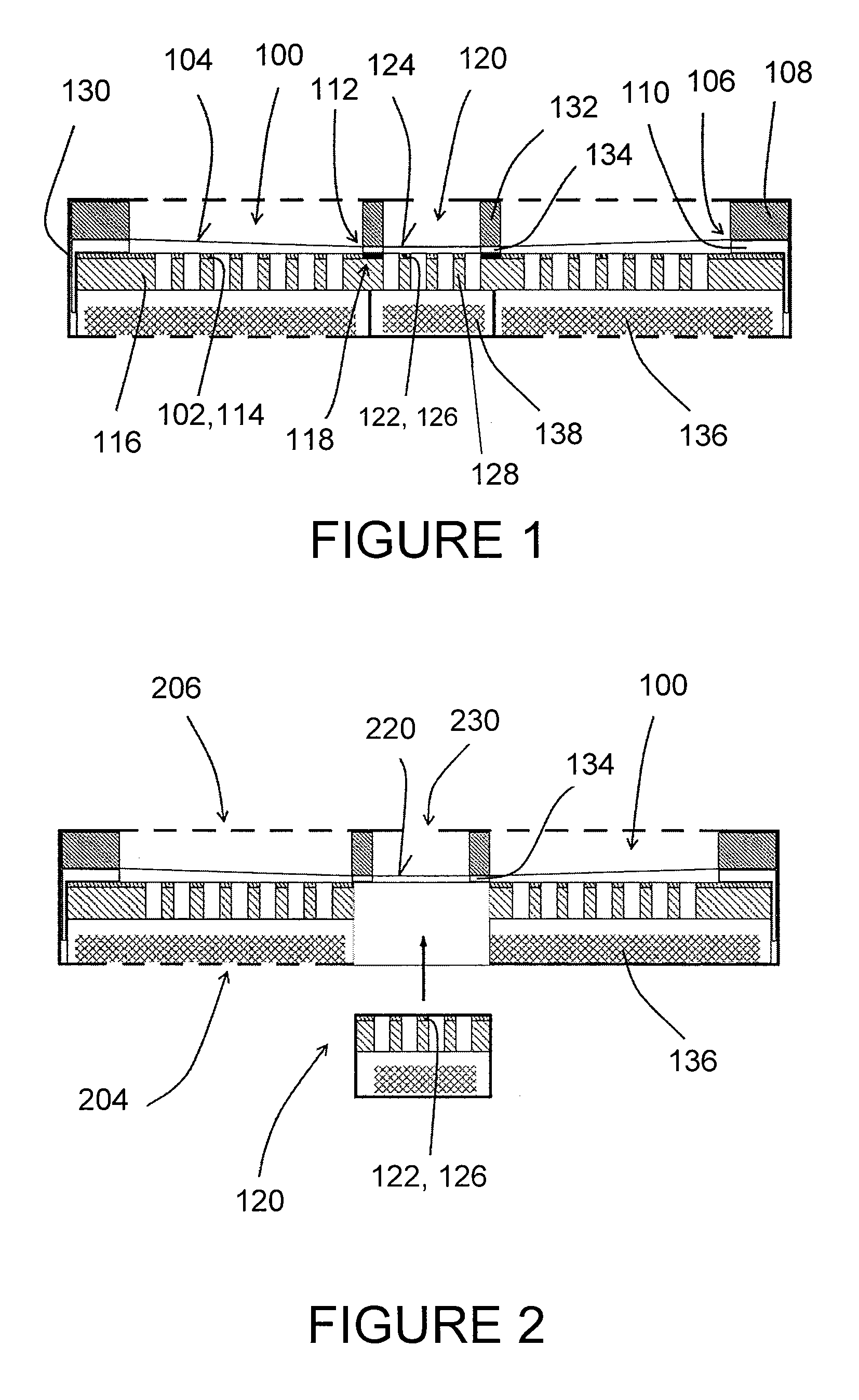
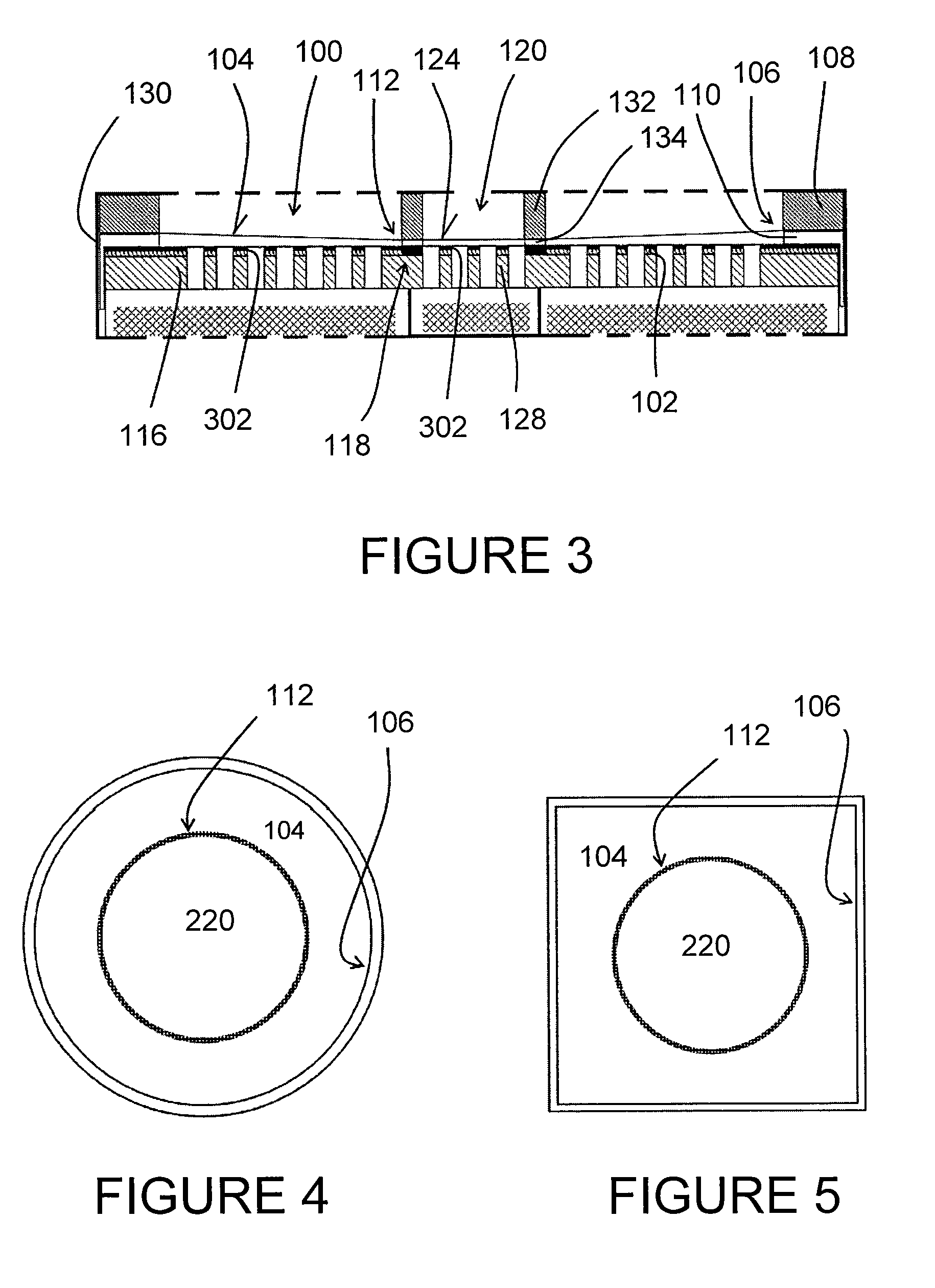
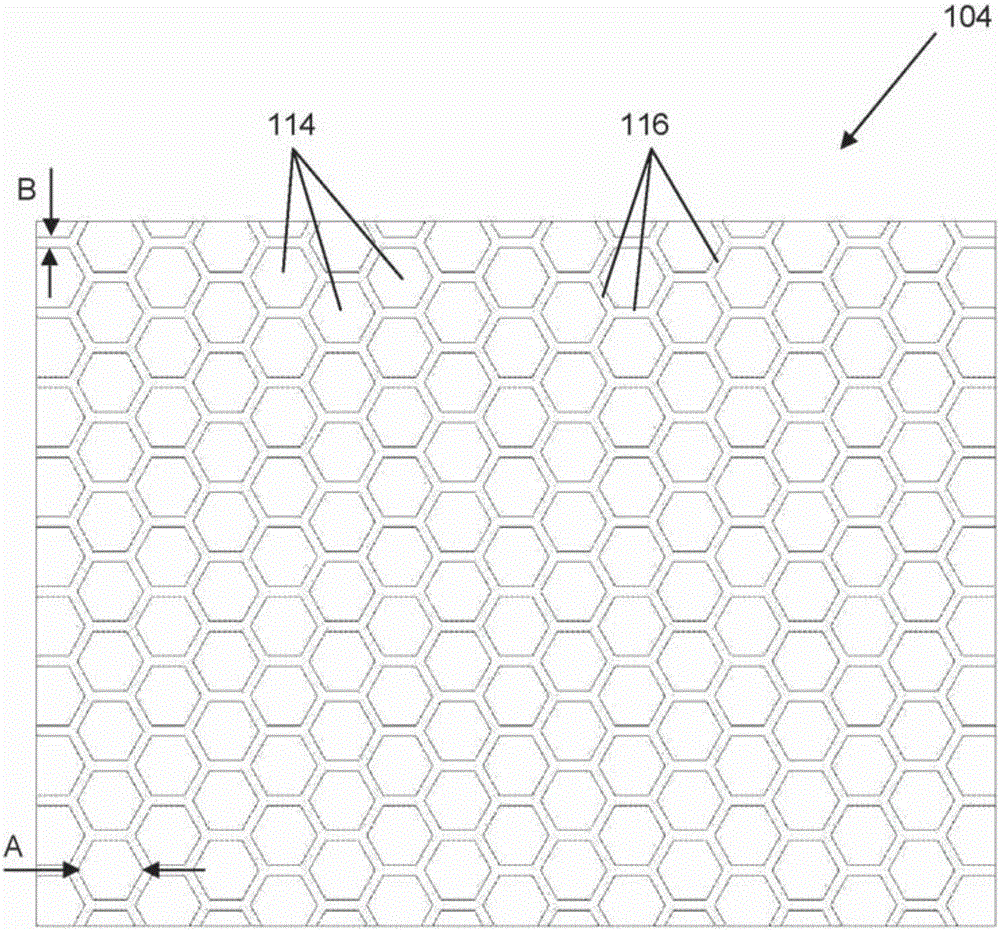
An electrostatic transducer (100) comprises an electrically conductive backplane member (102) having an array of through apertures (112); a spacer member (104) disposed over the backplane member (102), the spacer member (104) having an array of holes (114) therethrough, the holes (114) each having a maximum lateral dimension less than twice a minimum lateral dimension; and a flexible electrically conductive membrane (106) disposed over the spacer member (104). The transducer (100) is arranged in use to apply an electrical potential which gives rise to an attractive electrostatic force between the backplane member (102) and the membrane (106) thereby moving portions of the membrane (106) spanning said holes in the spacer member (104) towards said backplane member (102).
Owner:WARWICK AUDIO TECH LTD
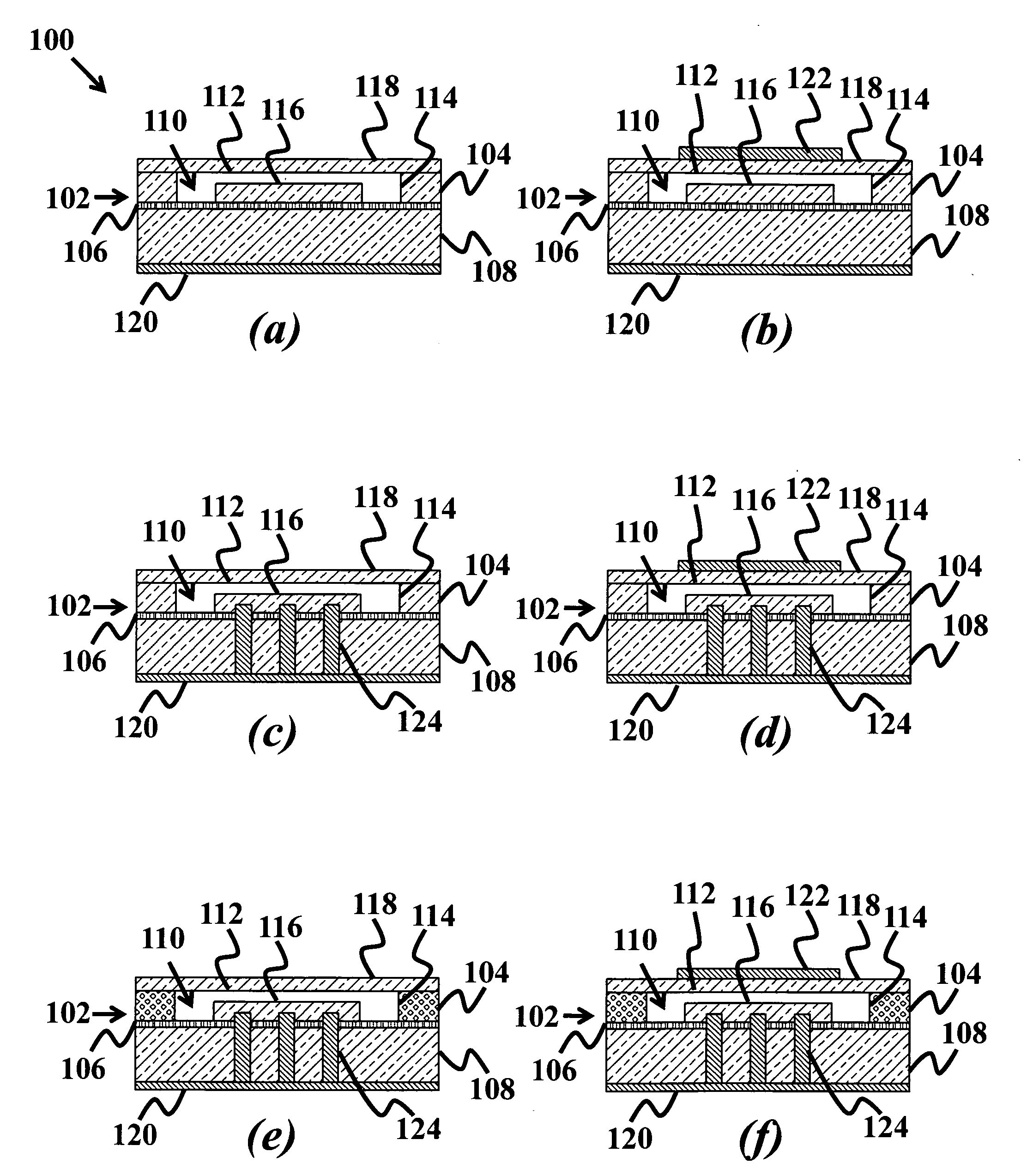
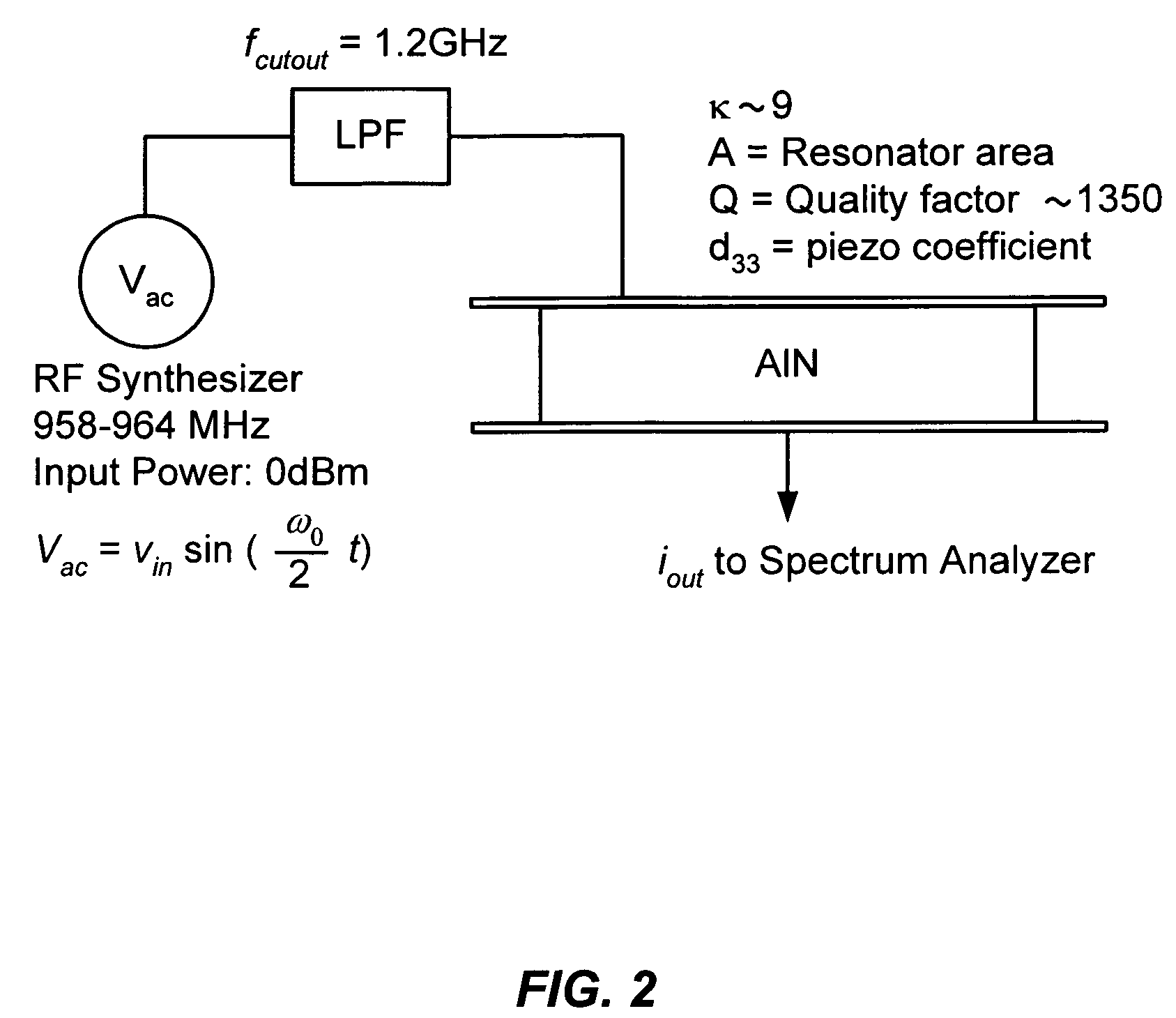
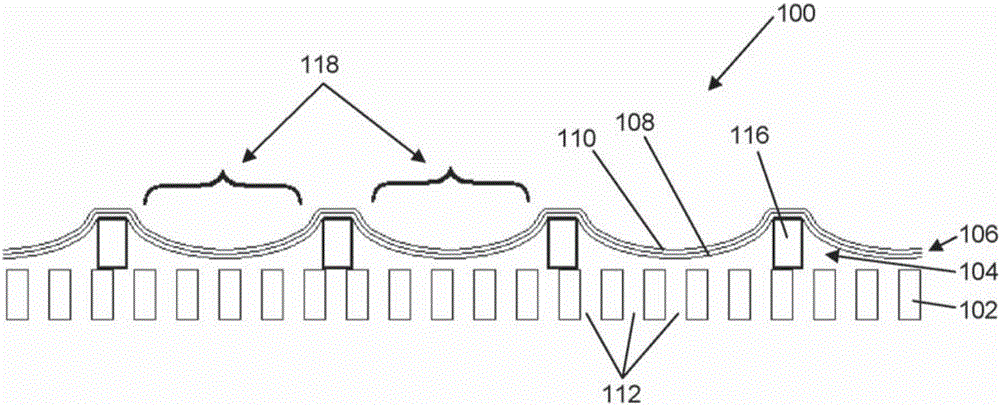
Electrostatic transducer
An electrostatic transducer comprises an electrically conductive first layer (1), a flexible insulating second layer (25) disposed over the first layer, and a flexible electrically conductive third layer (26) disposed over the second layer. Between the first and the second layers are provided spacers (24) and between the second and the third layers are provided spacers (27). The spacers may be provided by strips of adhesive or by bonding the layers together by welding, for example. The first layer (1) is provided with an array of through apertures (5) each having an inlet (6) facing the second layer (2) and an outlet (7). In response to signals applied to the first and third layers, the second and third layers have portions which are displaced towards the outlets of the apertures by electrostatic forces. The apertures (5) may have conducting walls and the walls may converge.
Owner:WARWICK AUDIO TECH LTD
Rotational MEMS resonator for oscillator applications
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
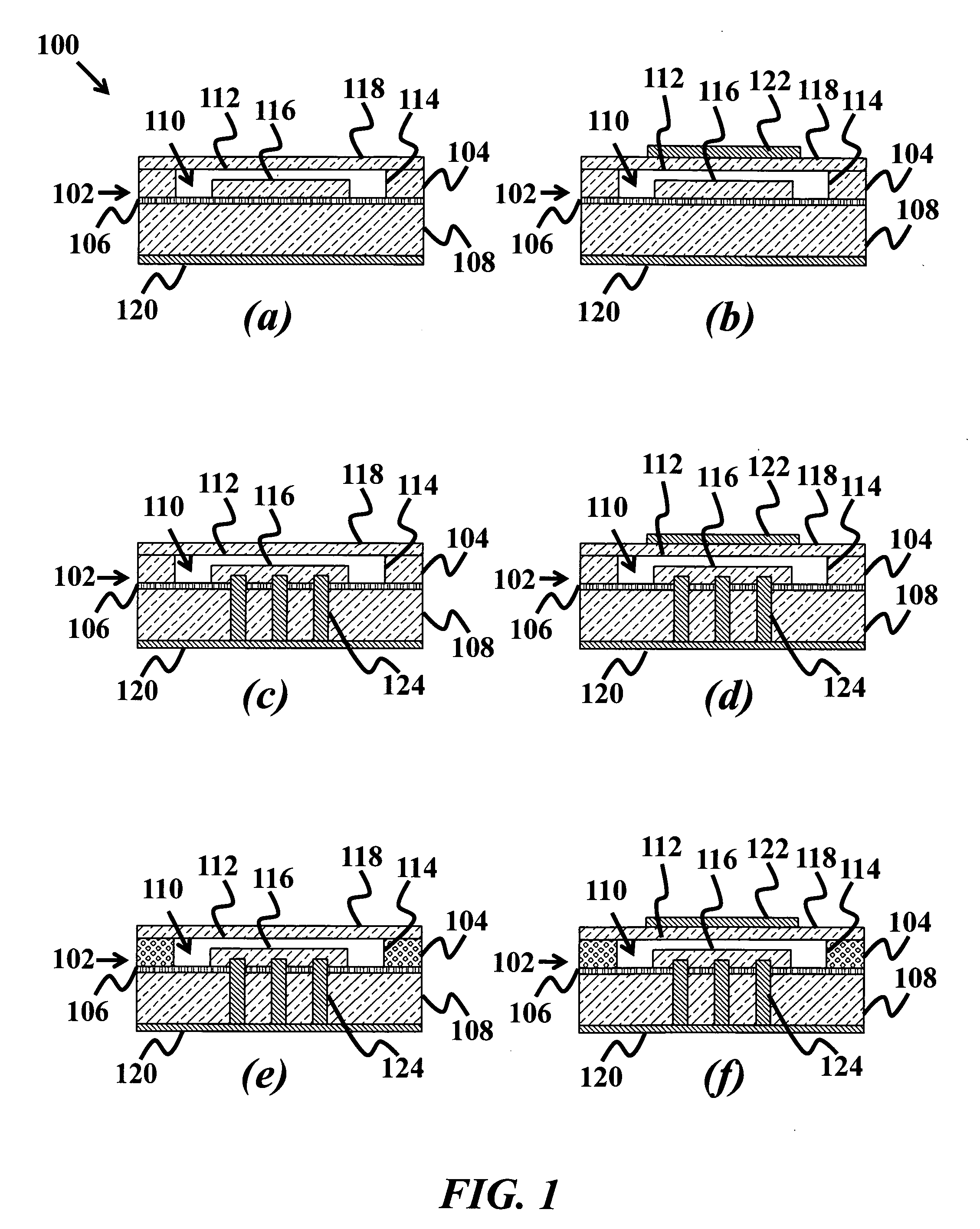
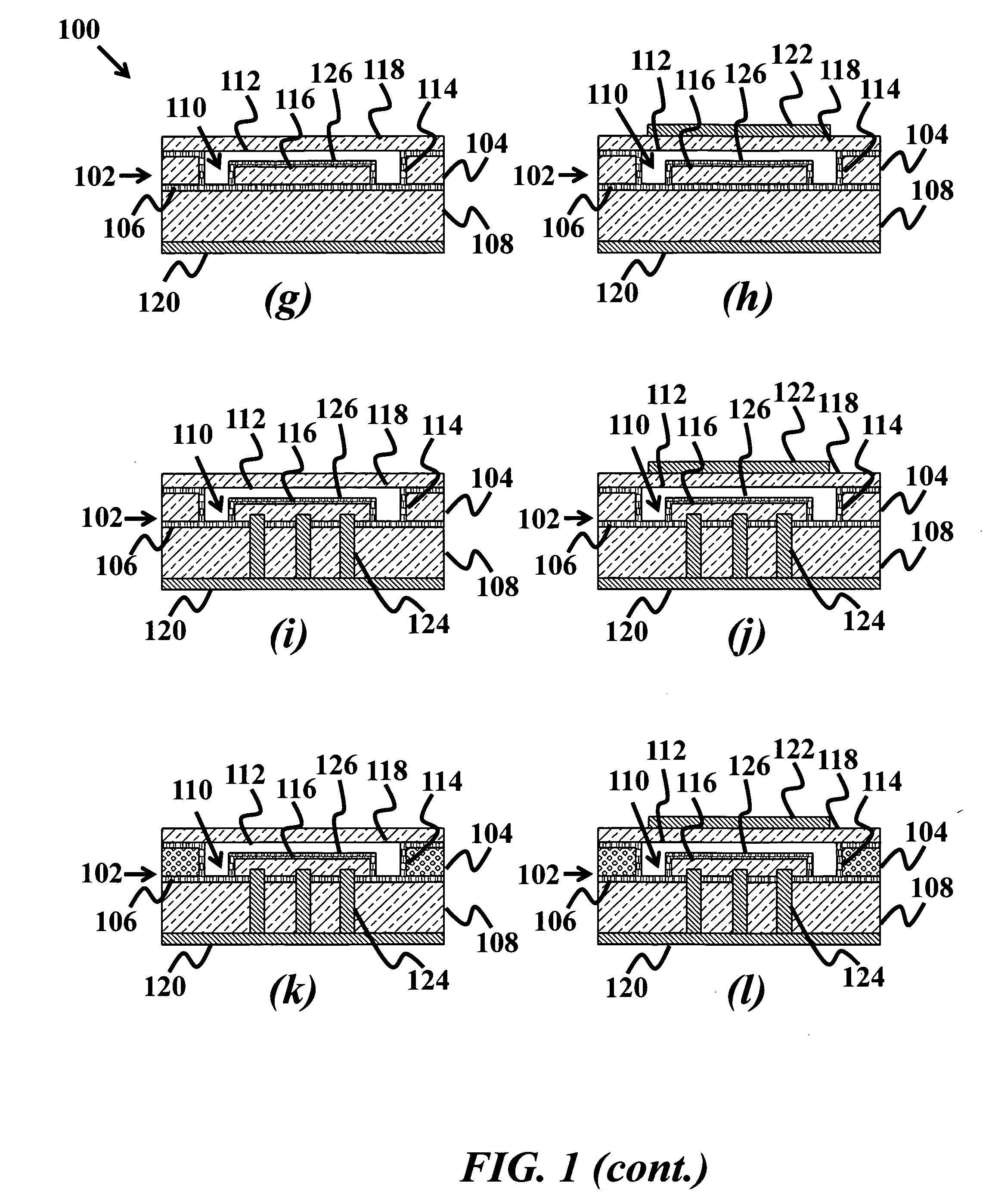
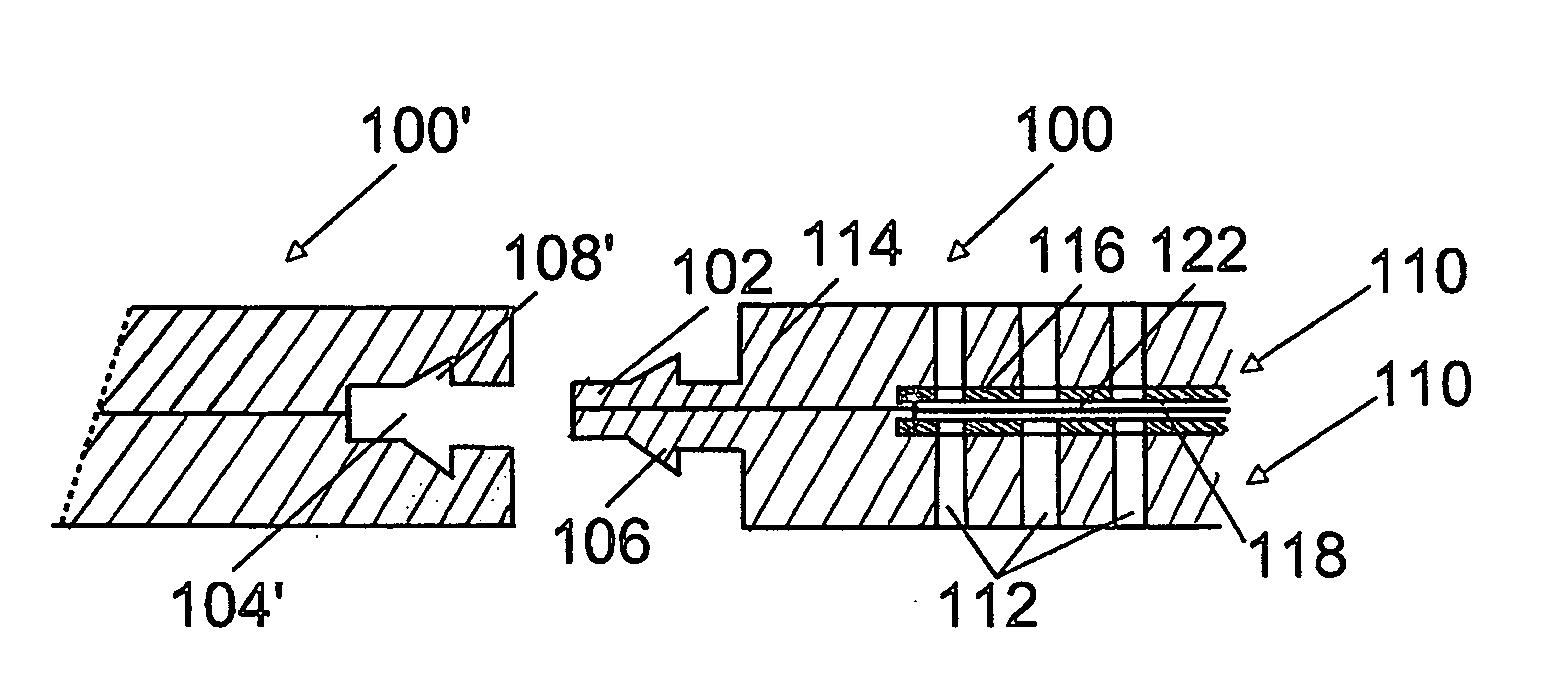
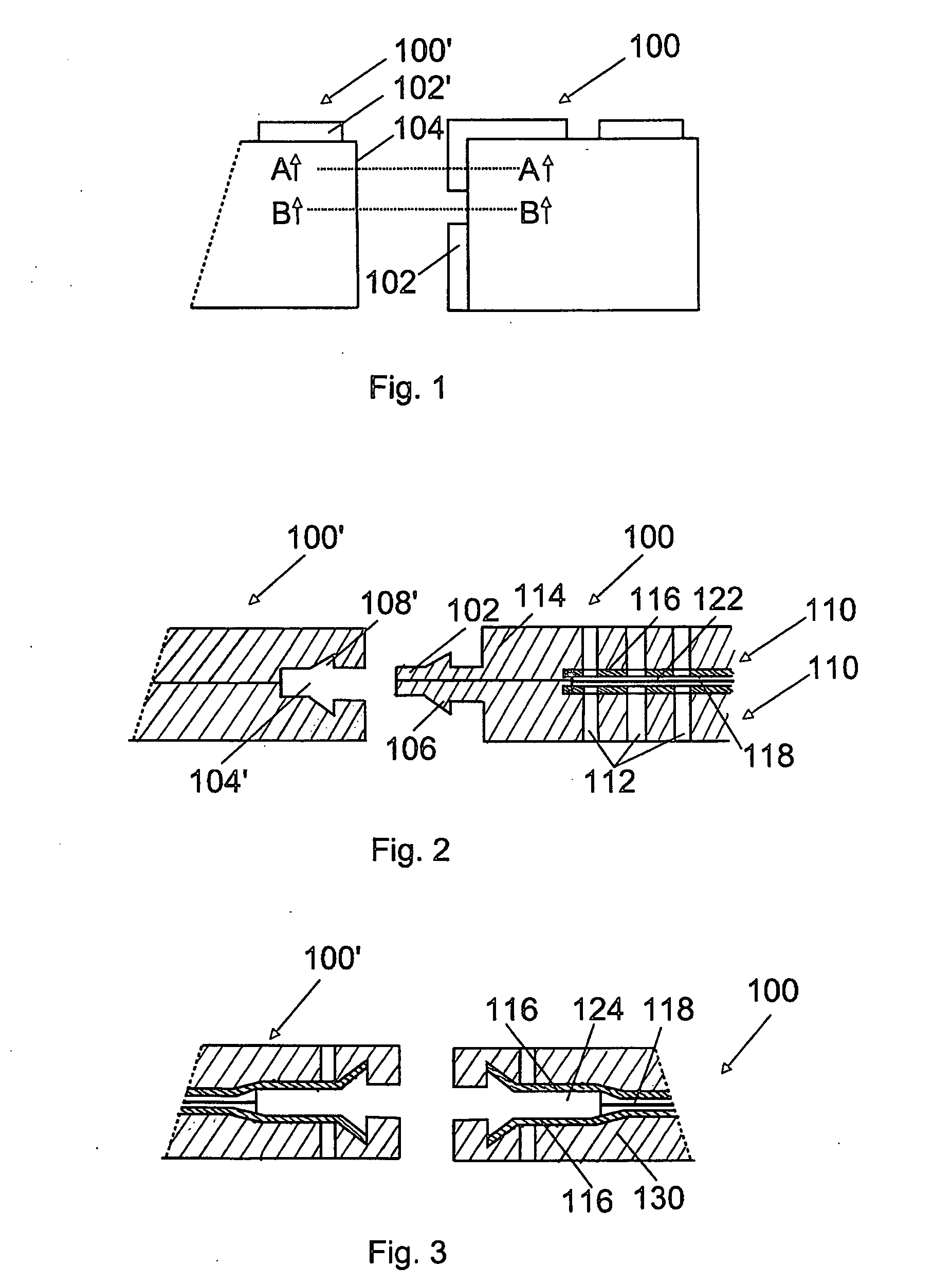
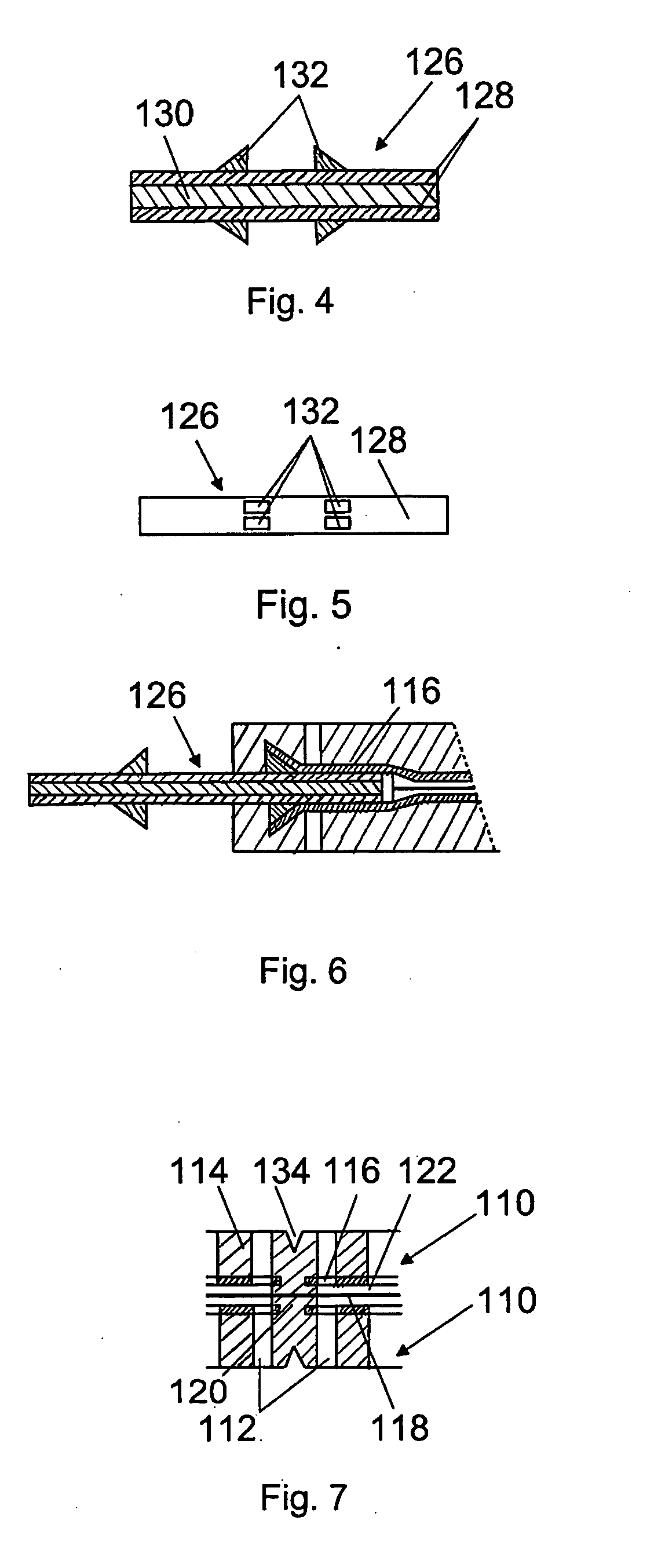
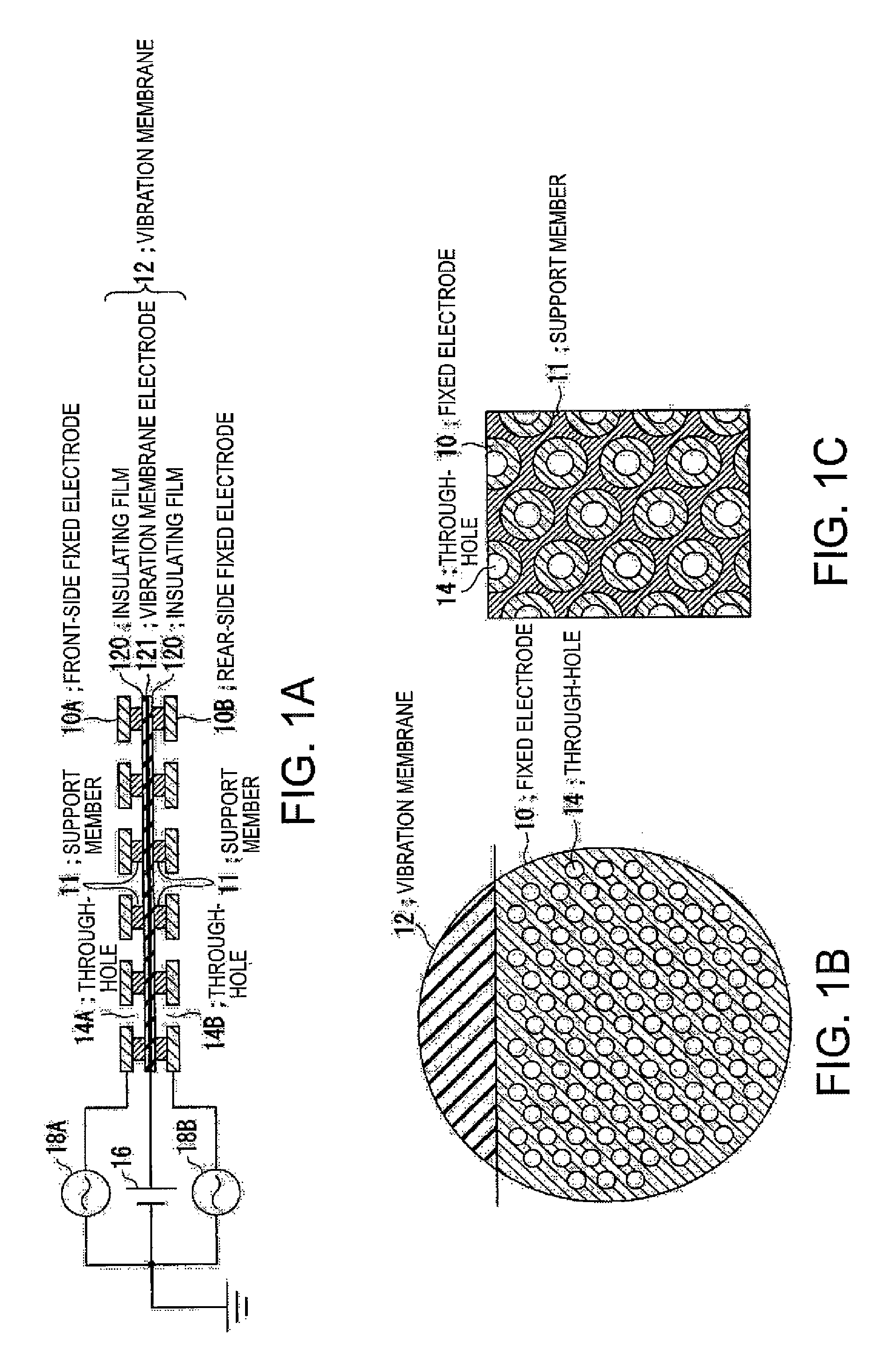
Electrostatic transducer, method for connecting the same and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060245607A1Fast and simple to manufactureBulky assemblyCircuit lead arrangements/reliefElectrostatic transducersEngineeringElectrostatic transducer
An electrostatic transducer, a method for connecting the same and a manufacturing method. The electrostatic transducer comprises at least one stator, which comprises an insulating layer and a conducting layer, and a film element which is arranged to vibrate in response to voltage supplied to it and which is provided in such a manner that an air gap is formed between the conducting layer and the film element. The electrostatic transducer also comprises at least one fastening edge arranged on the outer edge of the electrostatic transducer, the fastening edge being arranged to be fastened to a fastening element of a second electrostatic transducer.
Owner:PANPHONICS OY
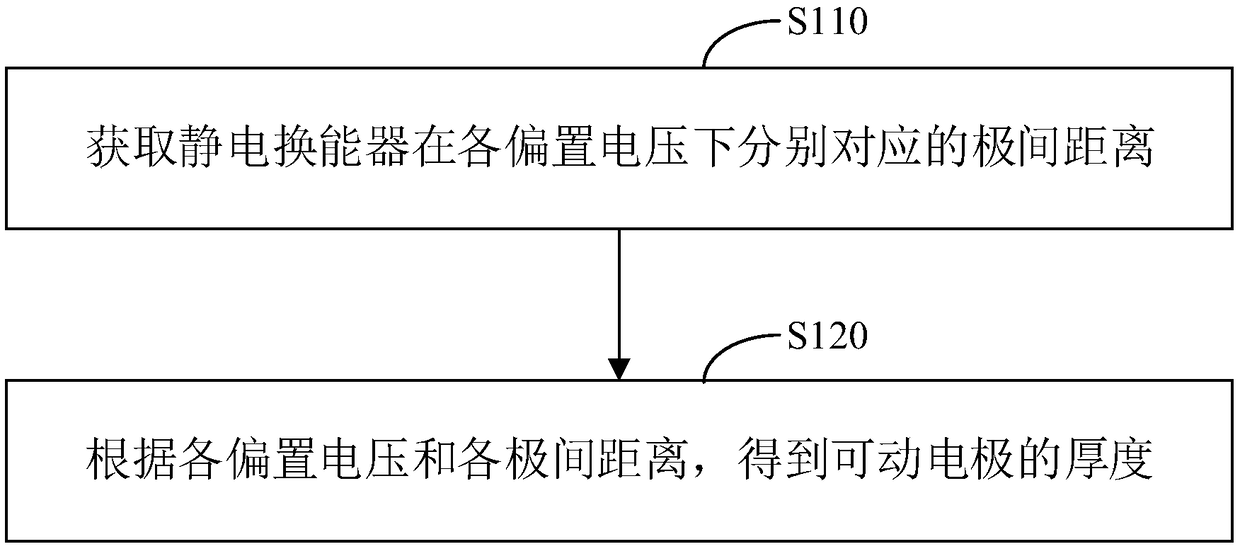
Method, device and system for measuring thickness of parallel movable electrode
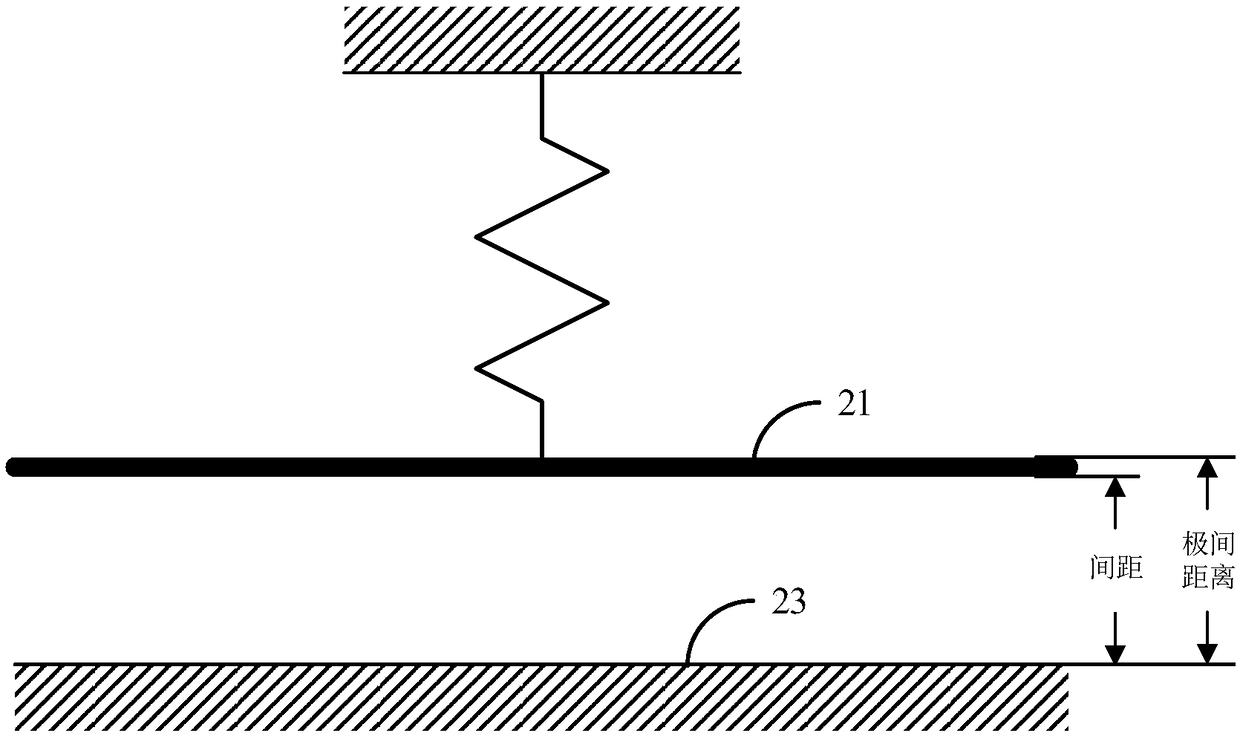
ActiveCN109489605AHigh precisionAvoid errorsUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsElectrostatic transducer
The invention relates to a method, device and system for measuring the thickness of a parallel movable electrode. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the inter-electrode distance ofan electrostatic transducer respectively corresponding to each bias voltage, wherein the inter-electrode distance is the distance from a first end face of the movable electrode of the electrostatic transducer to a first end face of the fixed electrode; the first end face of the movable electrode is arranged far away from the fixed electrode; the first end face of the fixed electrode is arranged close to the movable electrode; the thickness of the movable electrode is obtained according to each bias voltage and each inter-electrode distance, therefore, the relationship among the bias voltage,the inter-electrode distance and the thickness of the movable electrode is established by a method for measuring the thickness of the parallel movable electrode, the error caused by direct instrumentmeasurement is avoided, and the precision of measuring the thickness of the movable electrode of the electrostatic transducer with a parallel structure is improved, so that good support is provided for analyzing the performance of the electrostatic transducer.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS PROD RELIABILITY & ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING RES INST THE FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MIITCEPREI LAB
Electrostatic mutual inductor
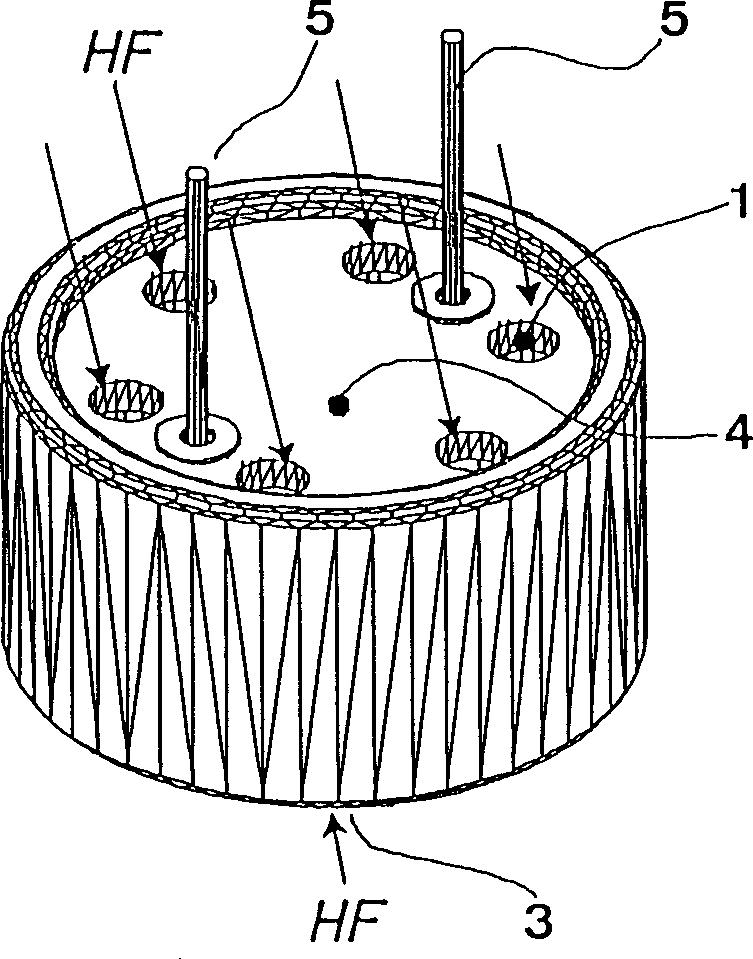
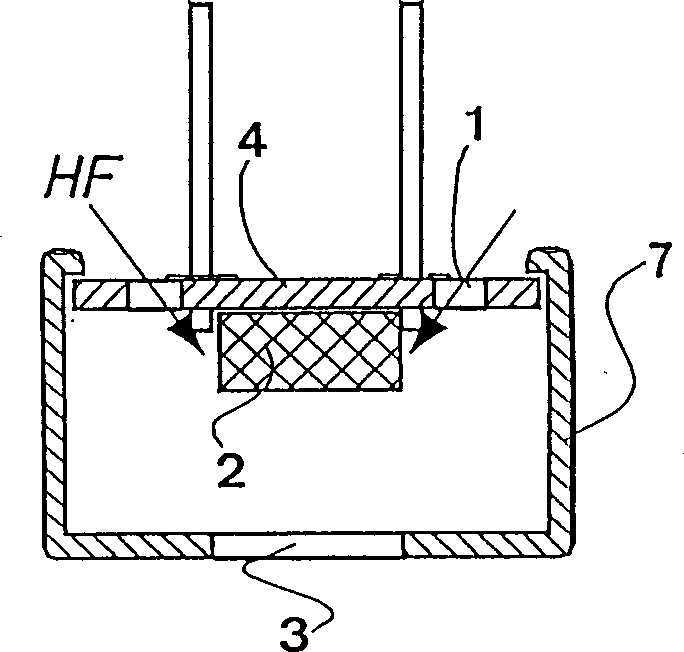
InactiveCN1349368AIncrease distanceReduce the degree of impactElectrets selectrostatic transducerElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersElectronic systemsInductor
An electrostatic transducer of small size, particularly having a diameter of 2-30 mm, is provided with a metal housing or electrically conductive housing having at least one front sound entry opening and a print arranged on a rear side of the housing, wherein the print substantially closes off the housing and has at least one rear sound entry opening, and wherein an electronic system is arranged on the inner side of the print. The at least one rear sound entry opening is formed at the periphery of the print.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Electrostatic transducer, driving circuit of capacitive load, method for setting circuit constant, ultrasonic speaker, display device and directional acoustic system
InactiveUS7899197B2Reduce total powerReduce lossProjectorsRecord information storageCapacitanceOutput transformer
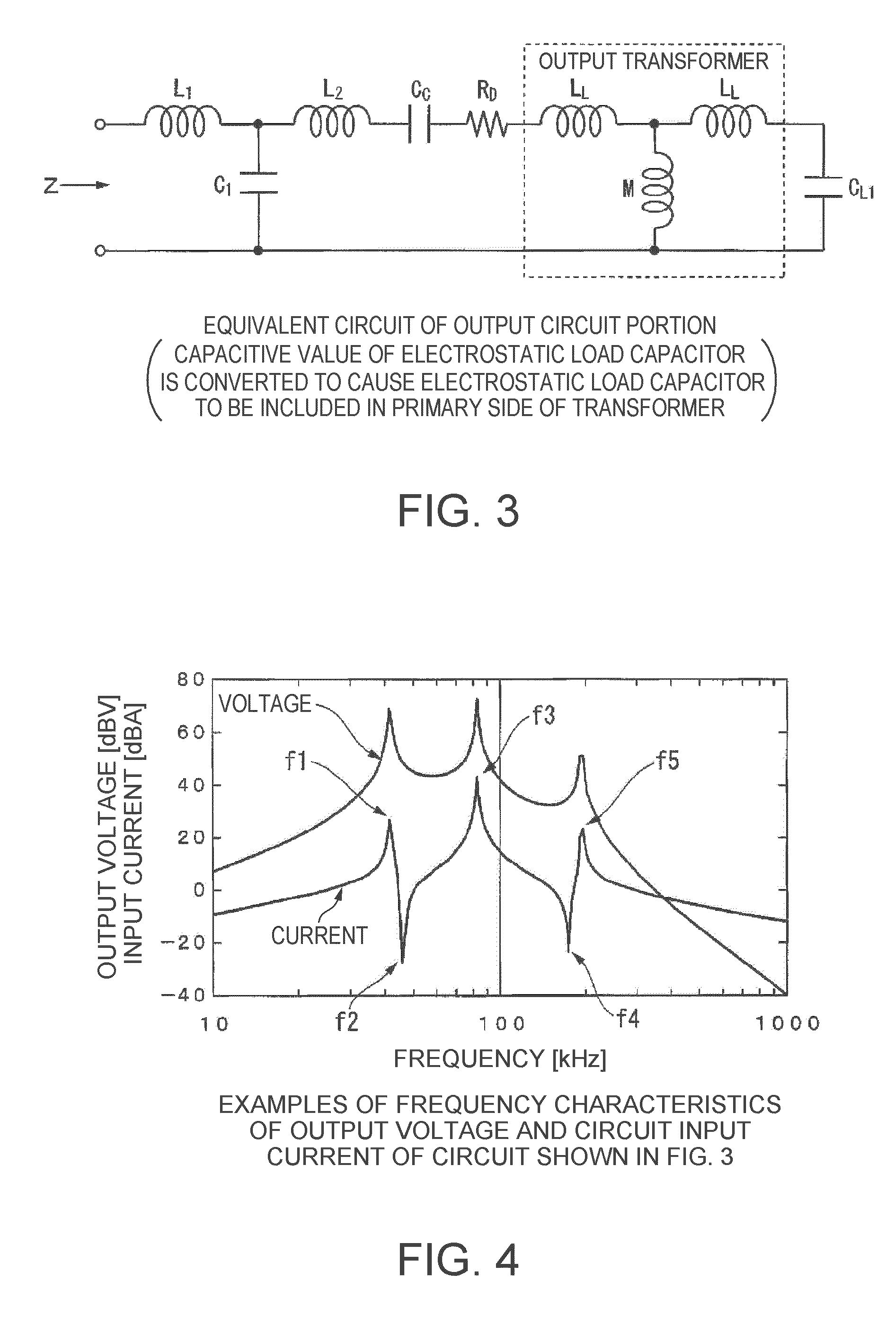
Provided is an electrostatic transducer which is driven by a boosted driving signal by boosting a modulated signal obtained by modulating a carrier wave with an acoustic signal in an audio frequency band, the transducer including: an output transformer T which connects the electrostatic transducer to a secondary side winding thereof in parallel and boosts the modulated signal; and a resistor R and a coupling capacitance C1 connected in series to a primary side winding of the output transformer T, wherein a circuit constant of a primary side circuit of the output transformer T including a serial circuit of the resistor R and the coupling capacitance C1 and a circuit constant of a secondary side circuit of the output transformer including a self-inductance L2 and a load capacitance CL of the secondary side winding of the output transformer T are set such that a resonance frequency f0 of a circuit formed by the self-inductance L2 of the secondary side winding of the output transformer T and the load capacitance CL(F) of the electrostatic transducer is matched or approximately matched to a carrier wave frequency fc of the electrostatic transducer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electrostatic transducer
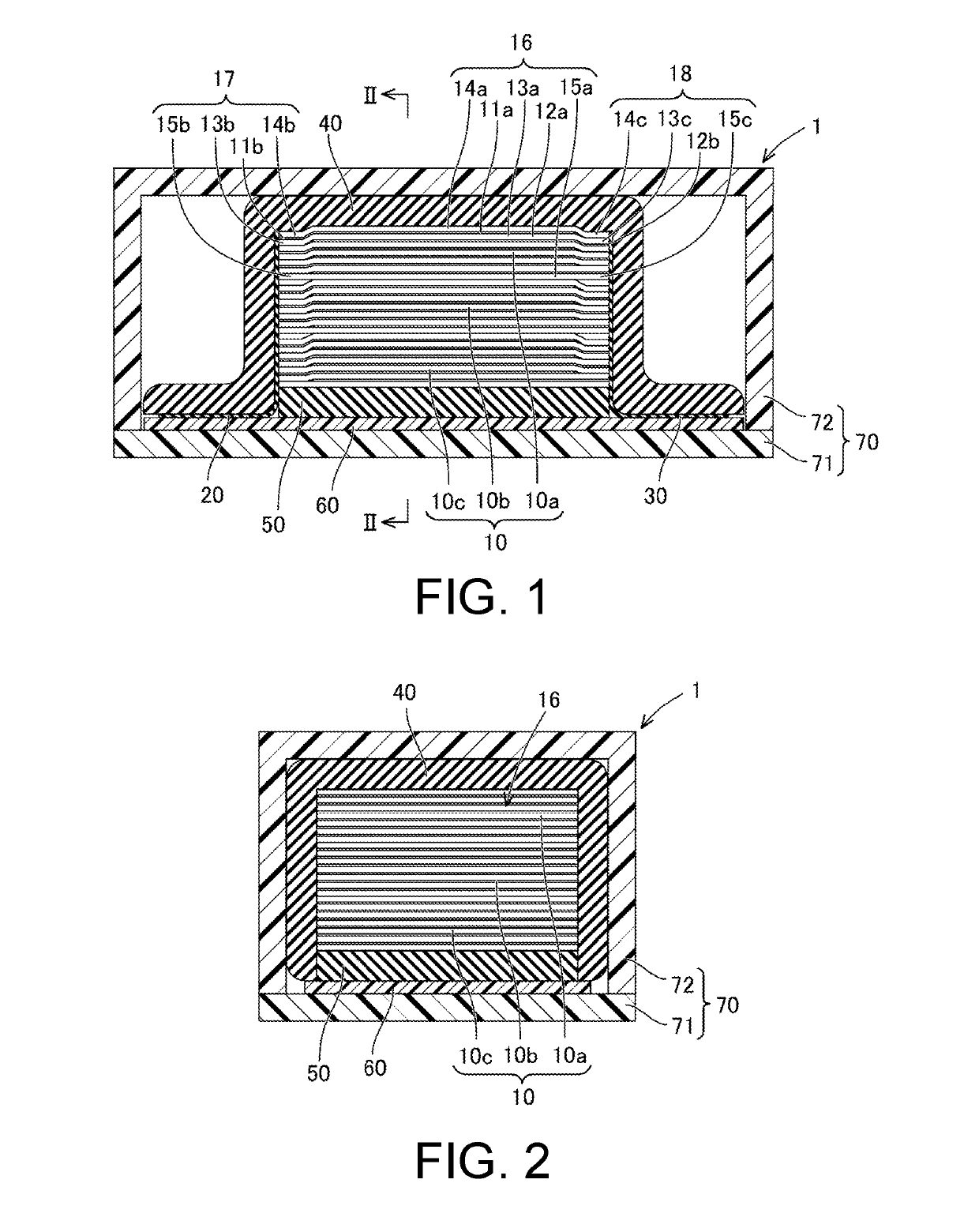
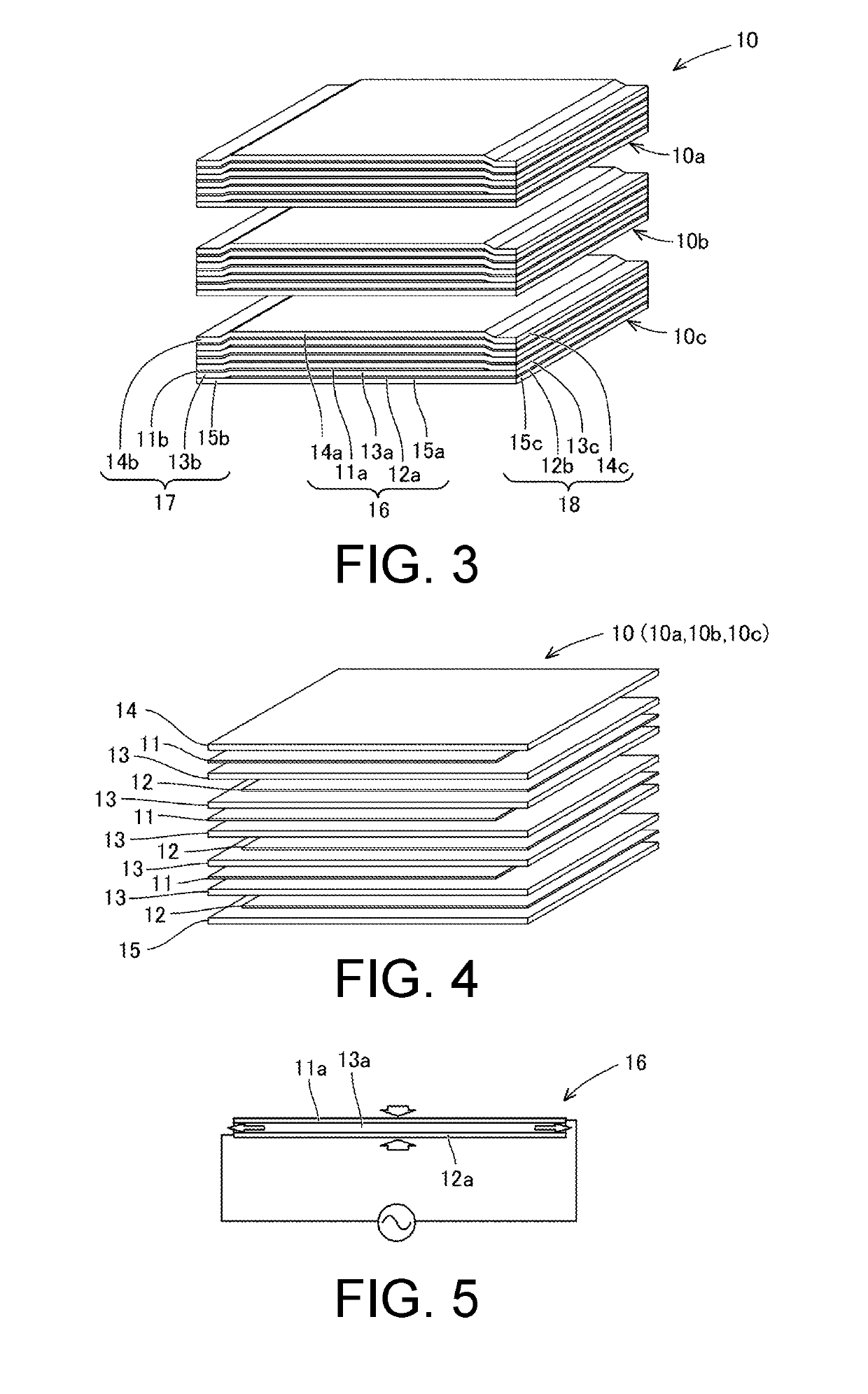
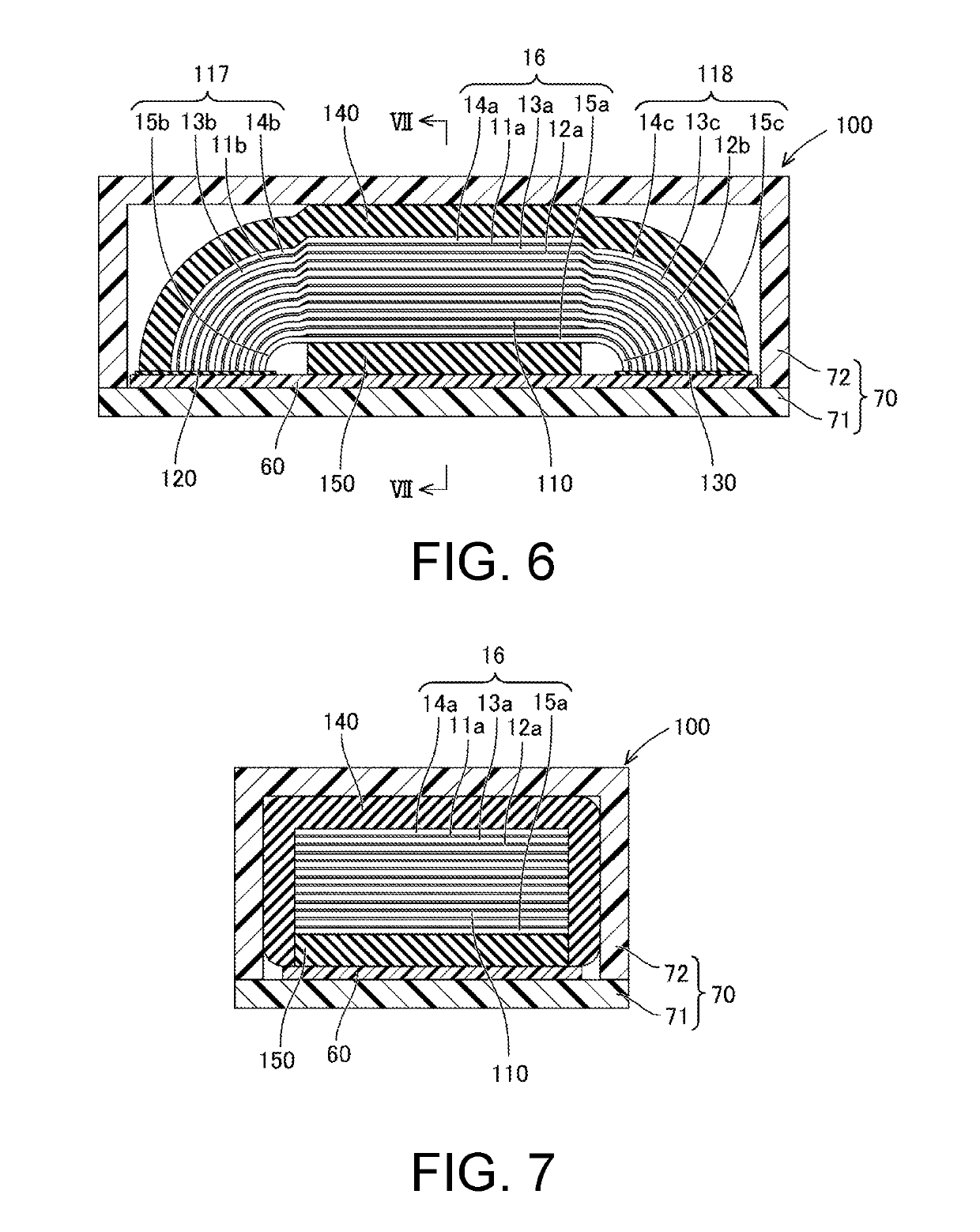
InactiveUS20190181327A1Suppress generationIncreased durabilityElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersElectrostatic transducer microphonesCapacitanceElectrostatic transducer
Provided is an electrostatic transducer which is small in size and has a large electrostatic capacitance, while having a durable constituent part of a conduction path, said constituent part being connected to an electrode. This electrostatic transducer is provided with a plurality of first electrode sheets, a plurality of second electrode sheets and a plurality of dielectric sheets. Each one of the plurality of first electrode sheets is provided with a first counter electrode part and a first terminal electrode part. Each one of the plurality of second electrode sheets is provided with a second counter electrode part and a second terminal electrode part. Each one of the plurality of dielectric sheets is provided with a dielectric main body, a first extending part that is interposed between a plurality of first terminal electrode parts, and a second extending part that is interposed between a plurality of second terminal electrode parts.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com