Patents
Literature
42 results about "Grafting procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
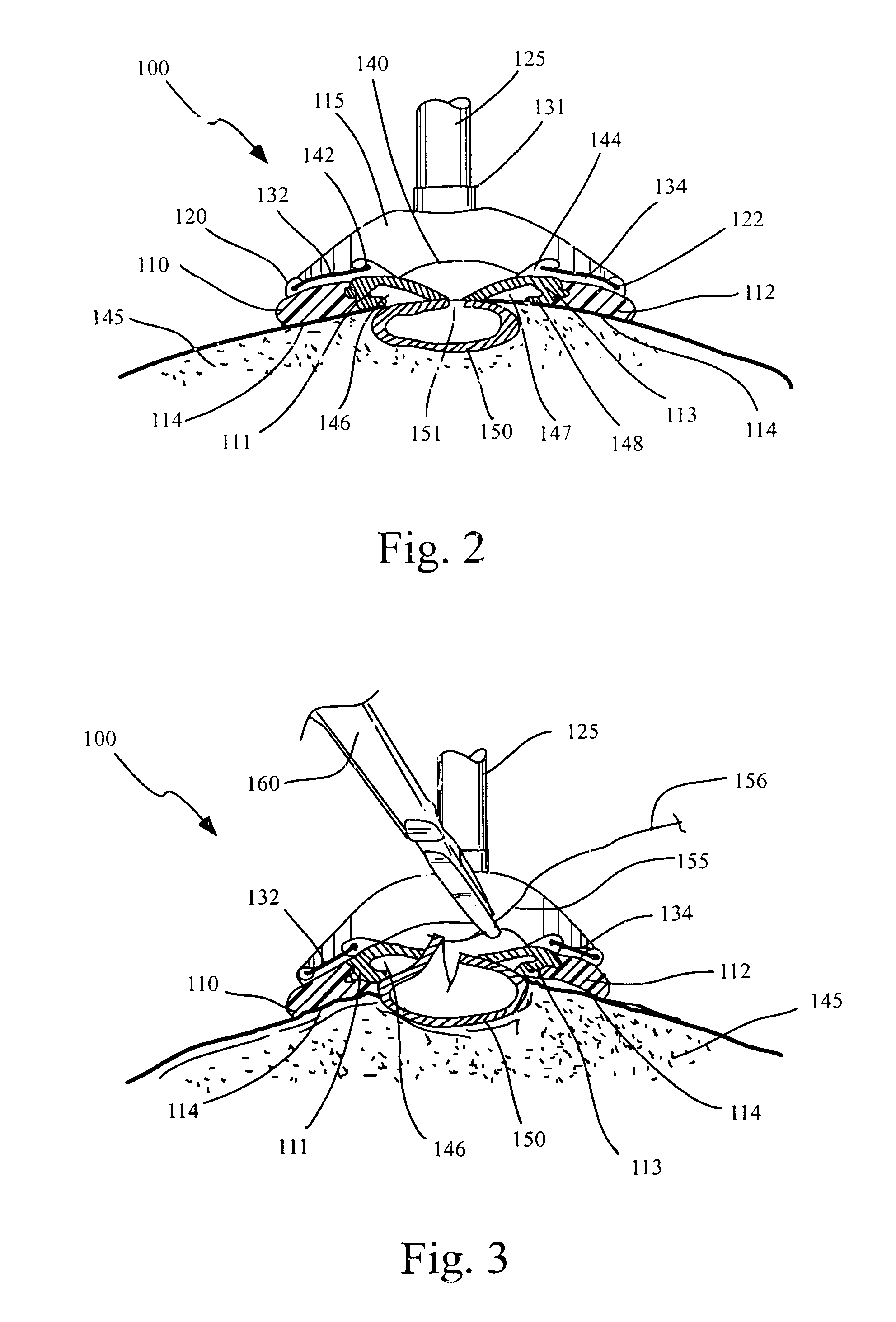
Endoscopic beating-heart stabilizer and vessel occlusion fastener
InactiveUS7250028B2Physiological motion of stabilizedAvoid relative motionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgical operationSurgical department
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method and system for performing closed-chest bypass
InactiveUS6869437B1Addressing slow performancePromote recoverySurgical staplesWound clampsMeasurement deviceThoracic cavity
A coronary artery bypass graft procedure is performed through one or more openings made in the patient to create a point of entry to the thoracic cavity. A vein measurement device measures the distance between the proximal and distal anastomotic sites for each graft. A proximal anastomosis tool splits to release a graft vessel after deploying an anastomosis device at the proximal anastomosis site. The tool may be articulated. An integrated stabilizer stabilizes one or more tools relative to the surface of the beating heart at a distal anastomotic site. A distal anastomotic tool may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and connects one end of the graft vessel to a target vessel. An epicardial dissector may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and dissects the epicardium from the target vessel at a distal anastomotic site, as needed.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Tissue stabilizer having an articulating lift element
InactiveUS7326177B2Easy to operateEasy to demonstrateSurgical pincettesProsthesisSurgical operationCoronary Artery Bypasses
Devices and methods are disclosed for stabilizing tissue within a patient's body during a surgical operation to provide a relatively motionless surgical field, such as during a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The devices include tissue stabilizers which engage and provide stabilization to a targeted area of tissue and further have the ability to engage and manipulate some portion of tissue within or adjacent the targeted area to improve the surgical presentation of that portion of tissue. The tissue stabilizer typically has one or more stabilizer feet which have a first foot portion configured to provide stabilization to the targeted tissue and a second foot portion moveable relative to the first foot portion for manipulating a portion of tissue to improve the surgical presentation.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
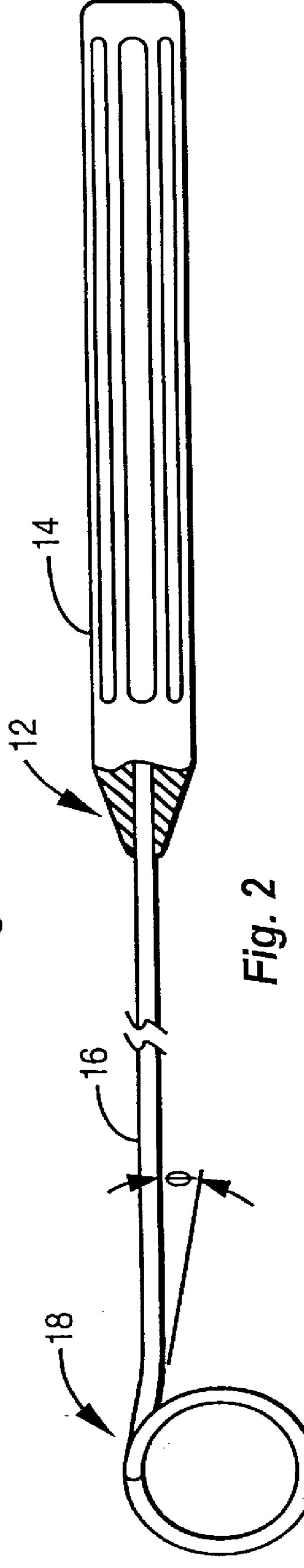
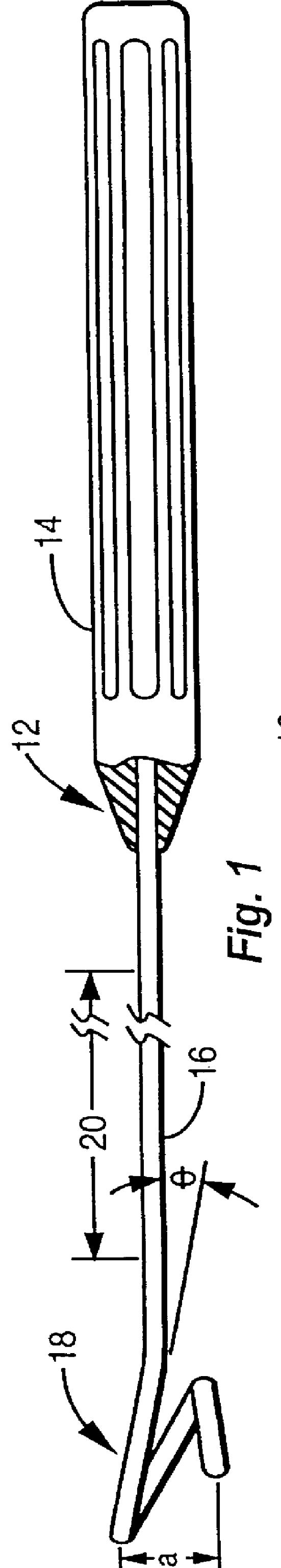
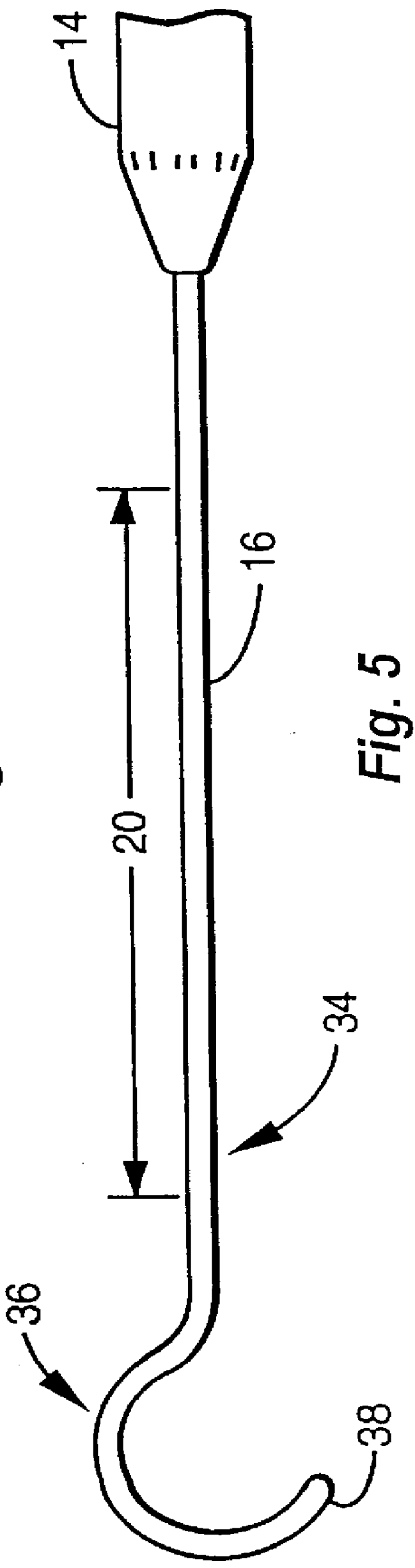
Surgical instrument for facilitating the detachment of an artery and the like
InactiveUS6110190AReduce in quantityGreat of motionCannulasSurgical instruments for heatingVisibilityMammary artery
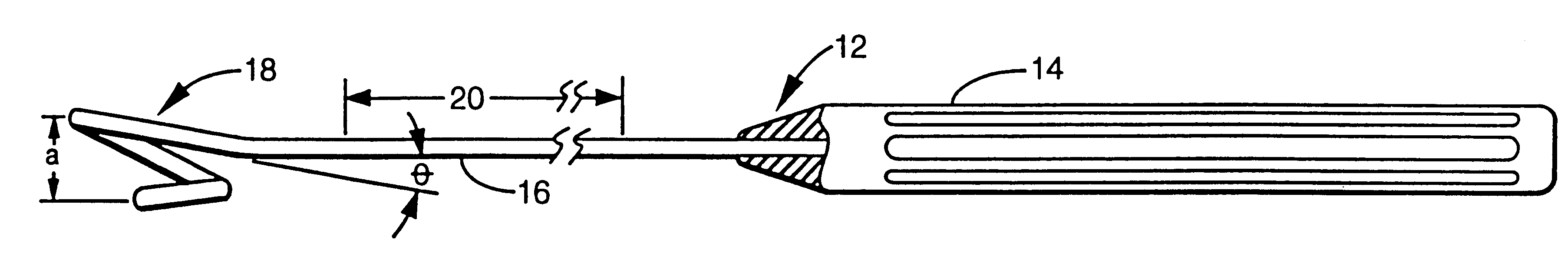
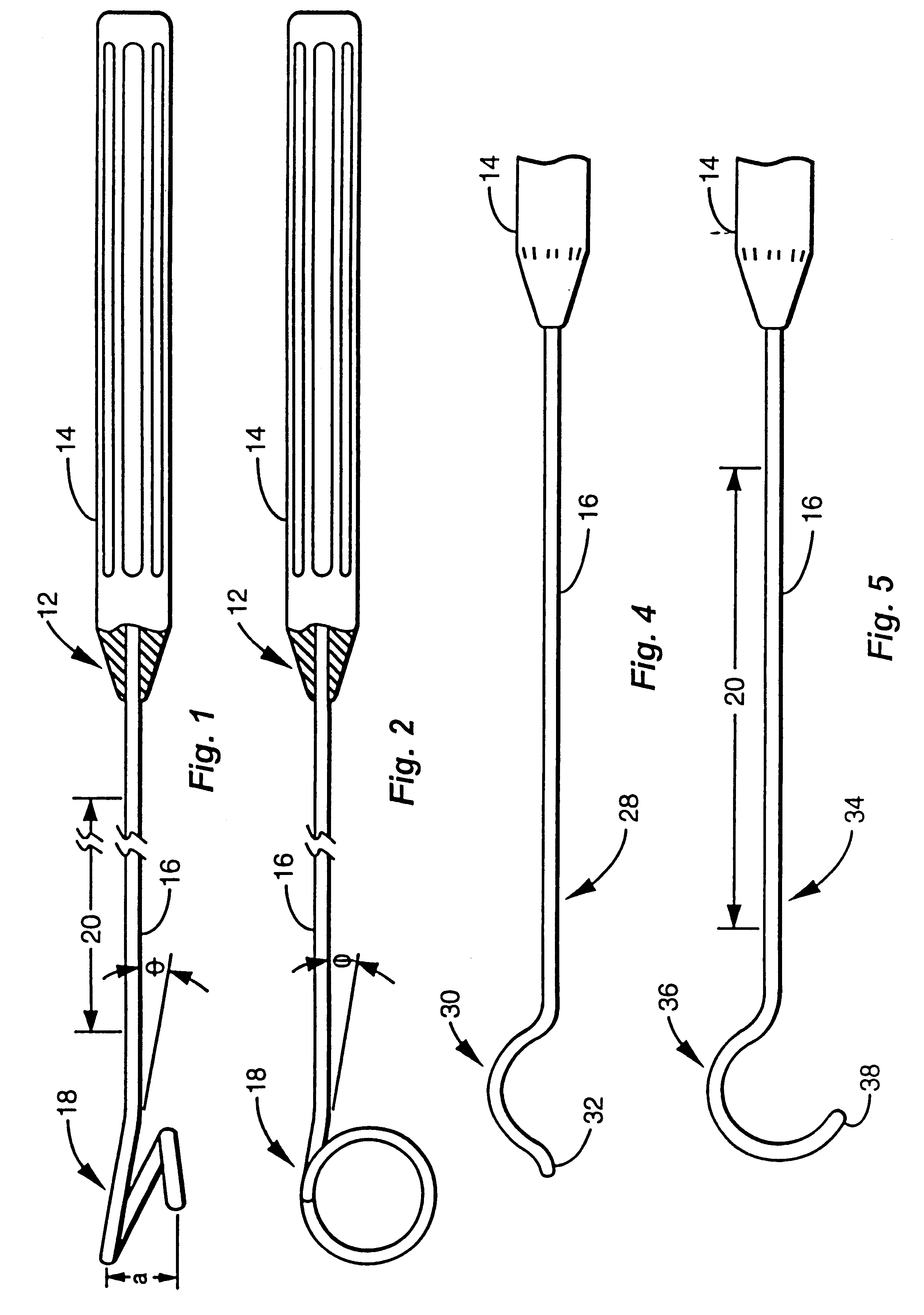
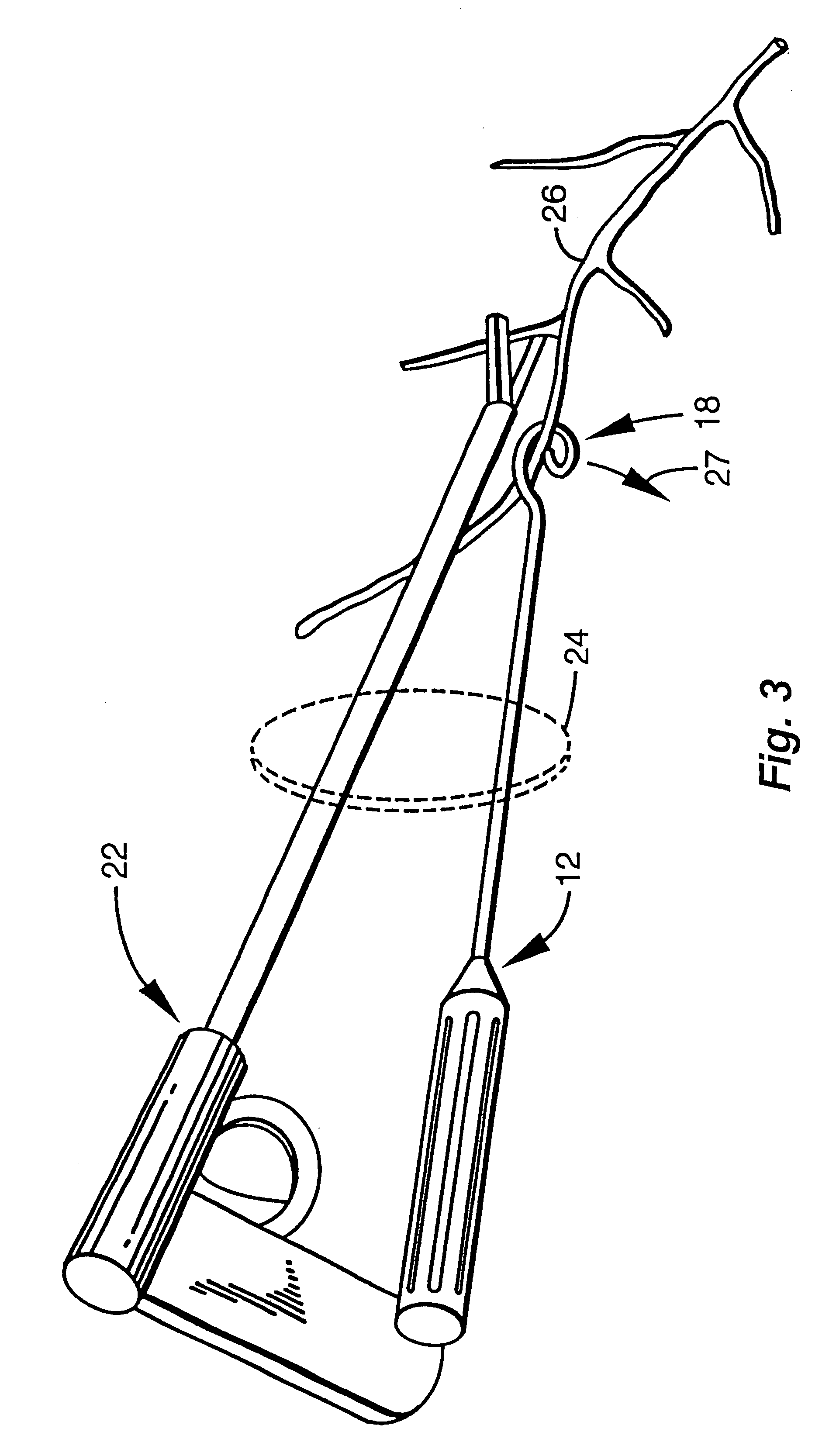
A surgical instrument is configured to aid in performing a procedure of detaching an internal mammary artery (IMA) and the like, from the connecting tissues and side branch vessels which surround the artery in its native location, wherein the detaching procedure is preliminary to the performing of a coronary artery bypass grafting procedure and wherein the IMA is detached via a minimally invasive thoracotomy. To this end, an elongated slender rod includes a handle at its proximal end and an artery engaging loop, arc, fork configuration, or hook at its distal working end. Embodiments may incorporate electrosurgical capability or electrical insulation. A surgeon thus has means for harvesting an intact and undamaged graft vessel from its native location through a minimally invasive incision with enhanced speed, visibility, and freedom of motion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Method and system for preparing soft tissue for grafting, enhancing grafting results, and grafting autologous fat to soft tissue such as the breast
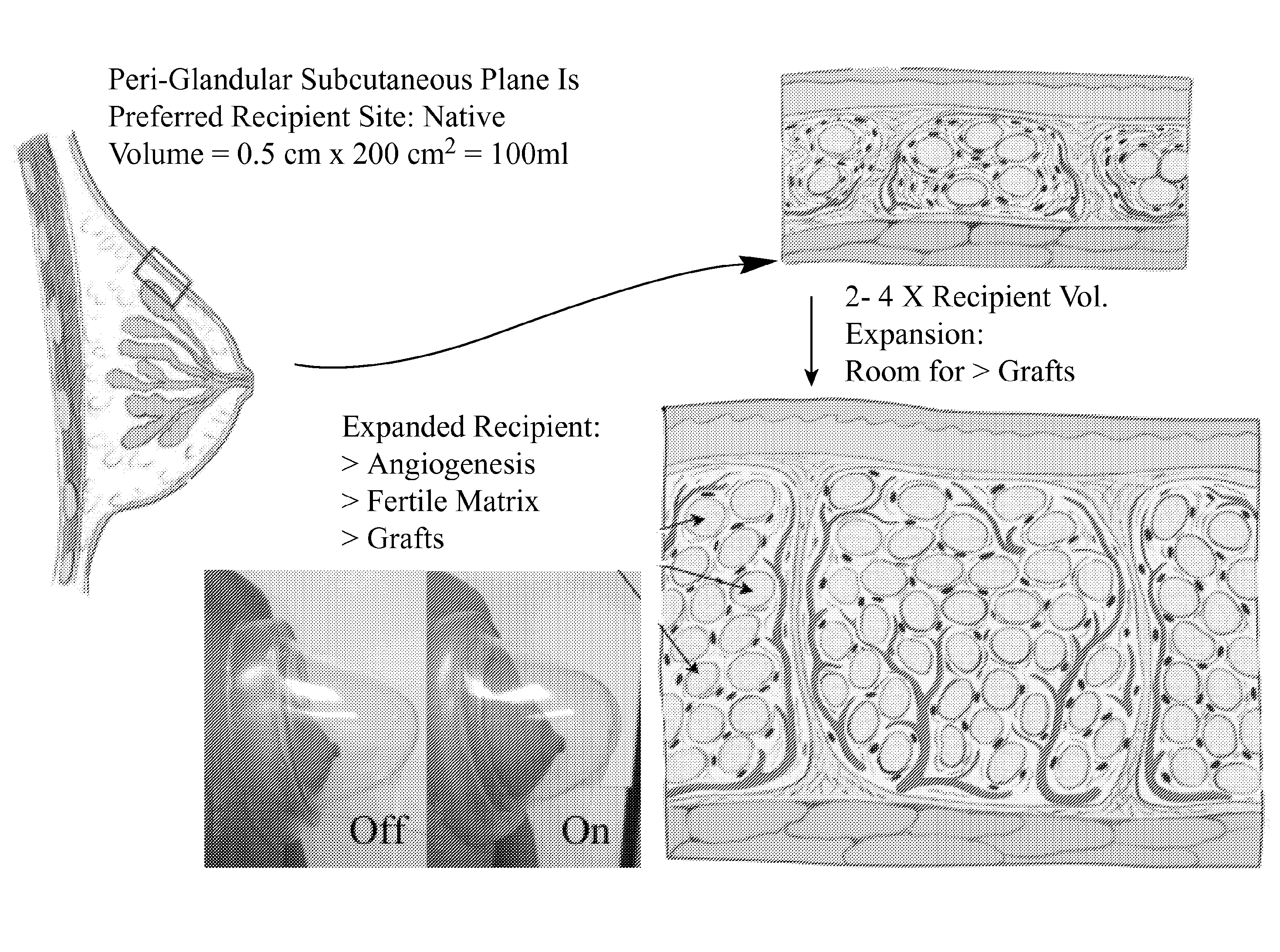
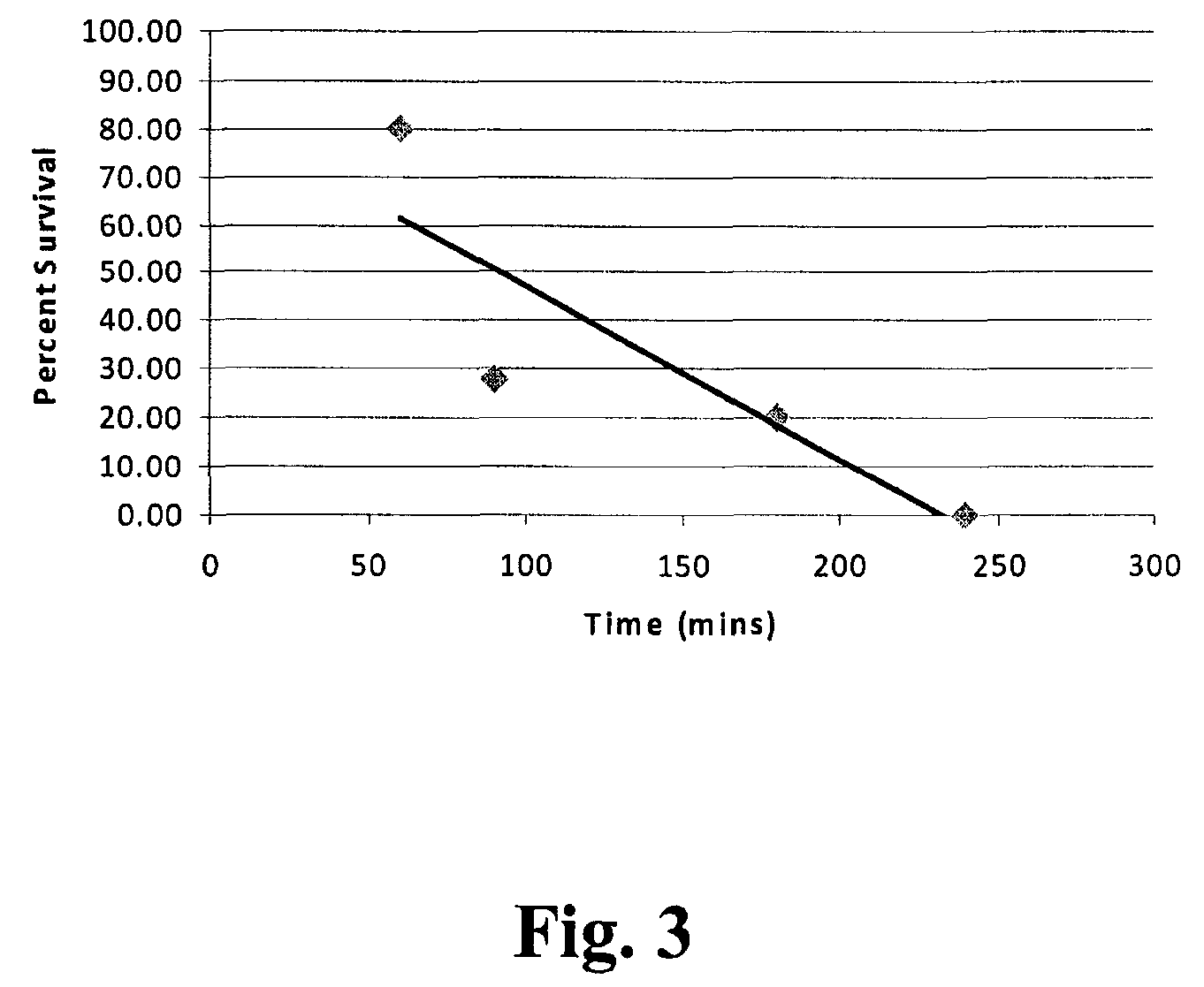
A method is disclosed for preparing a soft tissue site, and augmenting the soft tissue site, such as the breast(s) of a subject through use of devices that exert a distractive force on the breast(s) and grafting of autologous fat tissue such as domes with sealing rims for surrounding each of the breasts and a regulated pump. The method for preparing the soft tissue site, and enhancing fat graft results, entails application of the distracting force to the targeted soft tissue site for several weeks prior to the graft procedure. A related aspect of the invention includes following the preparation steps by transfer of fat from other areas of the subject to the subject's breast(s), and then reapplication of the distractive force to the breast(s) that received the autologous fat graft. Alternatively, fat from genetically related sources may be used, and the fat may be further processed prior to injection. Substantial breast augmentation, high rates of graft survival and negligible graft necrosis (data demonstrating 80% survival and only 20% necrosis is presented) or calcification result from the practice of these methods.
Owner:KHOURI ROGER K
Method and system for preparing soft tissue for grafting, enhancing grafting results, and grafting autologous fat and adipocyte derived stem cells to soft tissue such as the breast and other tissue defects
ActiveUS20090312746A1Reduce the possibilityEliminate fatMammary implantsDiagnosticsHigh rateFat grafting
A method is disclosed for preparing a soft tissue site, and augmenting the soft tissue site, such as the breast(s), scar, depression, or other defect, of a subject through use of devices that exert a distractive force on the breast(s) and grafting of autologous fat tissue such as domes with sealing rims for surrounding each of the soft tissue site and a regulated pump. The method for preparing the soft tissue site, and enhancing fat graft results, entails application of the distracting force to the targeted soft tissue site at least intermittently for some period of time and preferably several weeks prior to the graft procedure. A related aspect of the invention includes following the preparation steps by transfer of fat from other areas of the subject to the subject's soft tissue site, and then reapplication of the distractive force to the soft tissue site that received the autologous fat graft. Alternatively, fat from genetically related sources may be used, and the fat may be further processed prior to injection. Substantial soft tissue augmentation, high rates of graft survival and negligible graft necrosis (data demonstrating 80% survival and only 20% necrosis is presented) or calcification result from the practice of these methods.
Owner:KHOURI ROGER
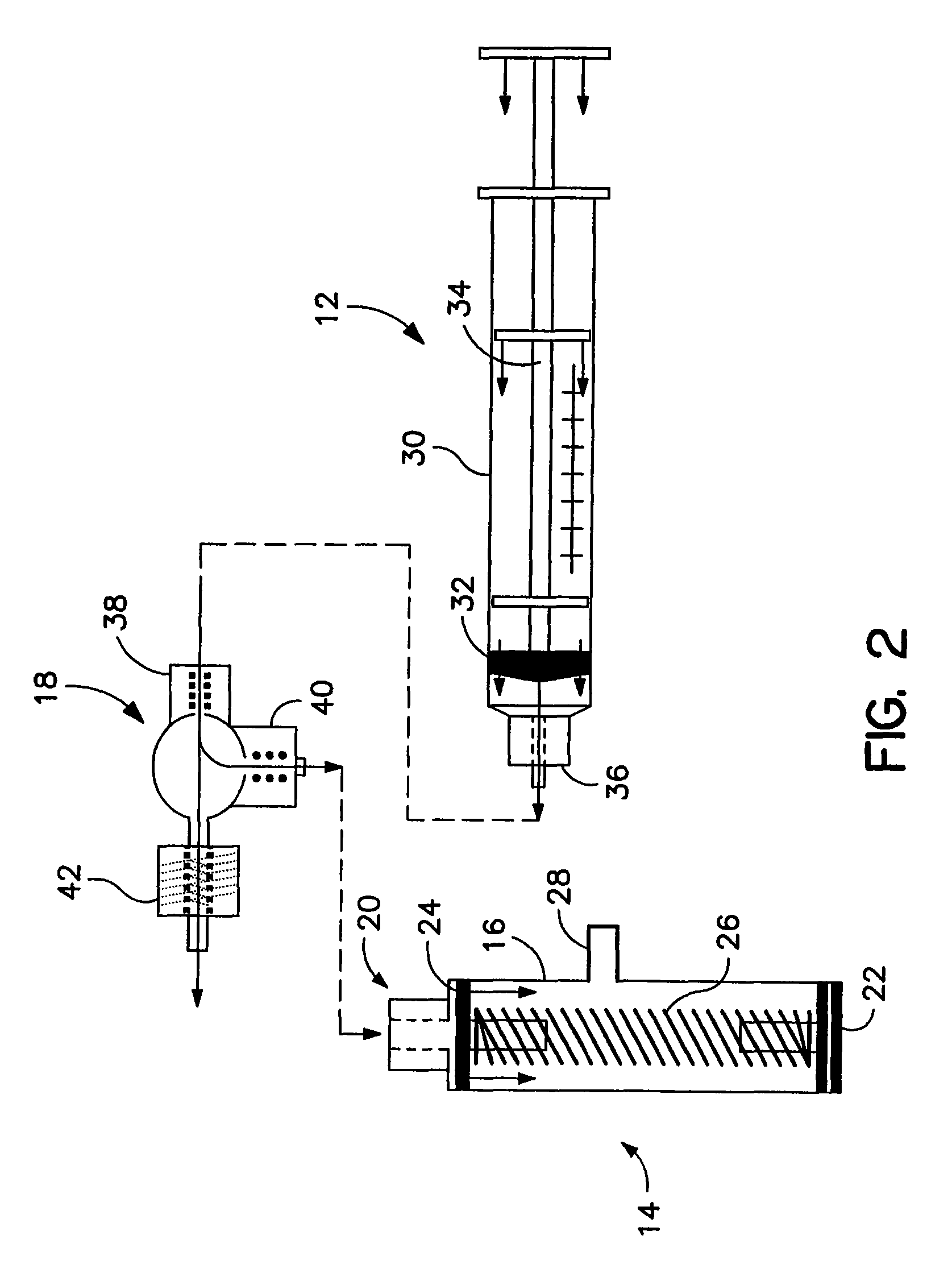
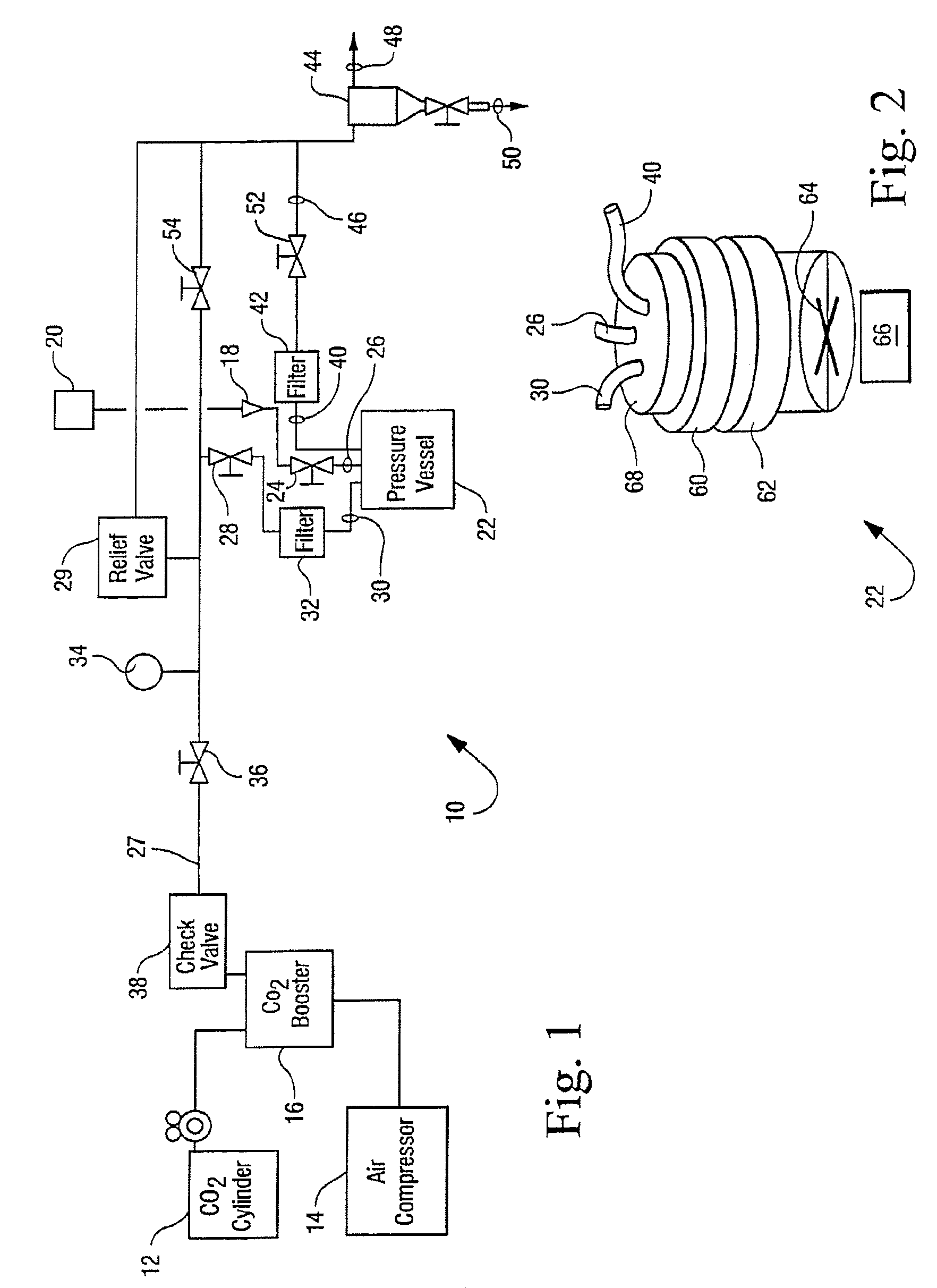
Method and apparatus for regulating pressure during medical procedures
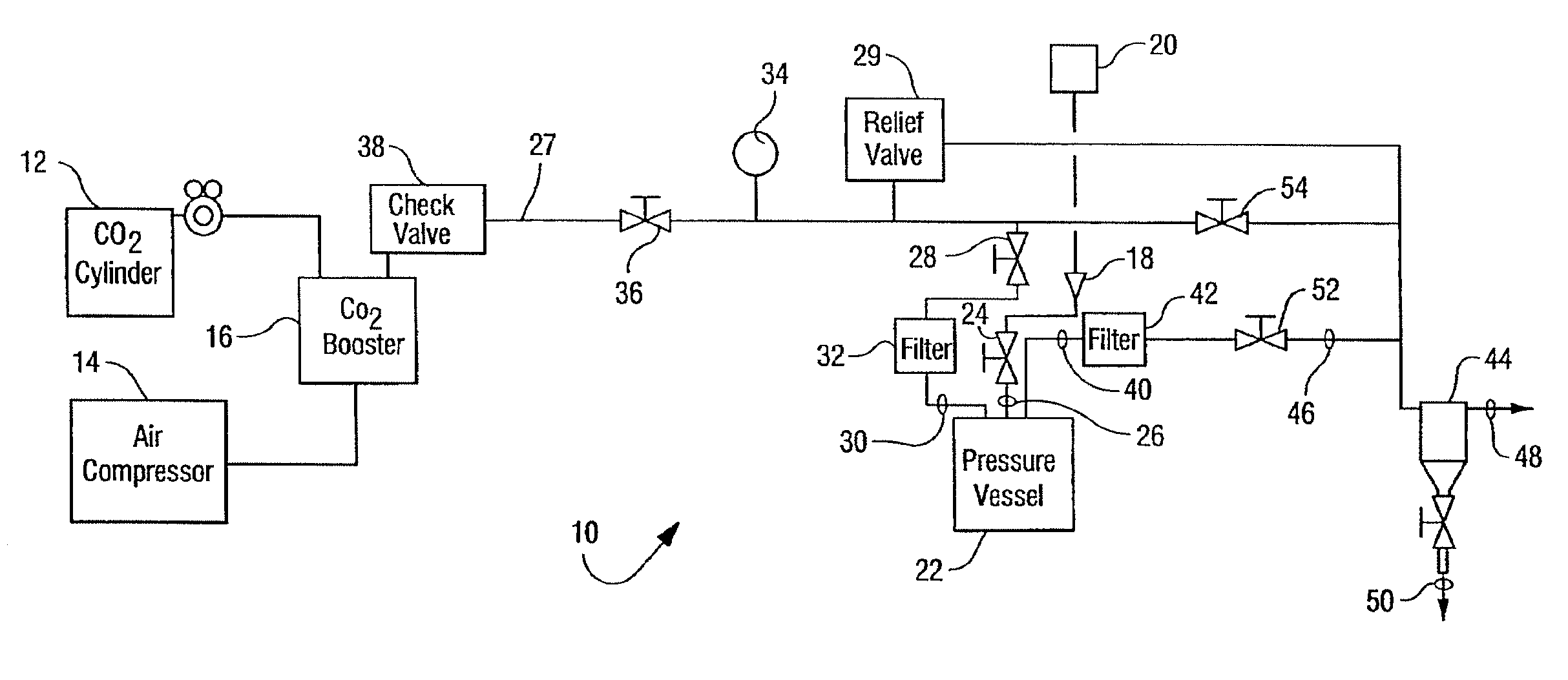
A method and apparatus are provided for regulating pressure applied during a medical procedure, including an inelastic housing enclosing an inner volume, a housing having a first and second end; an aperture in the housing, the aperture for coupling to an element for applying a pressure during a medical procedure, the element having an inner volume communicated with the inner volume of the housing; and a pressure-operated valve coupled to the housing for providing access to the inner volume of the housing when pressure in the housing is above a threshold, whereby the valve releases pressure from within the inner volume of the housing. The method and apparatus are particularly useful in preparation of conduits such as veins and arteries during grafting procedures.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
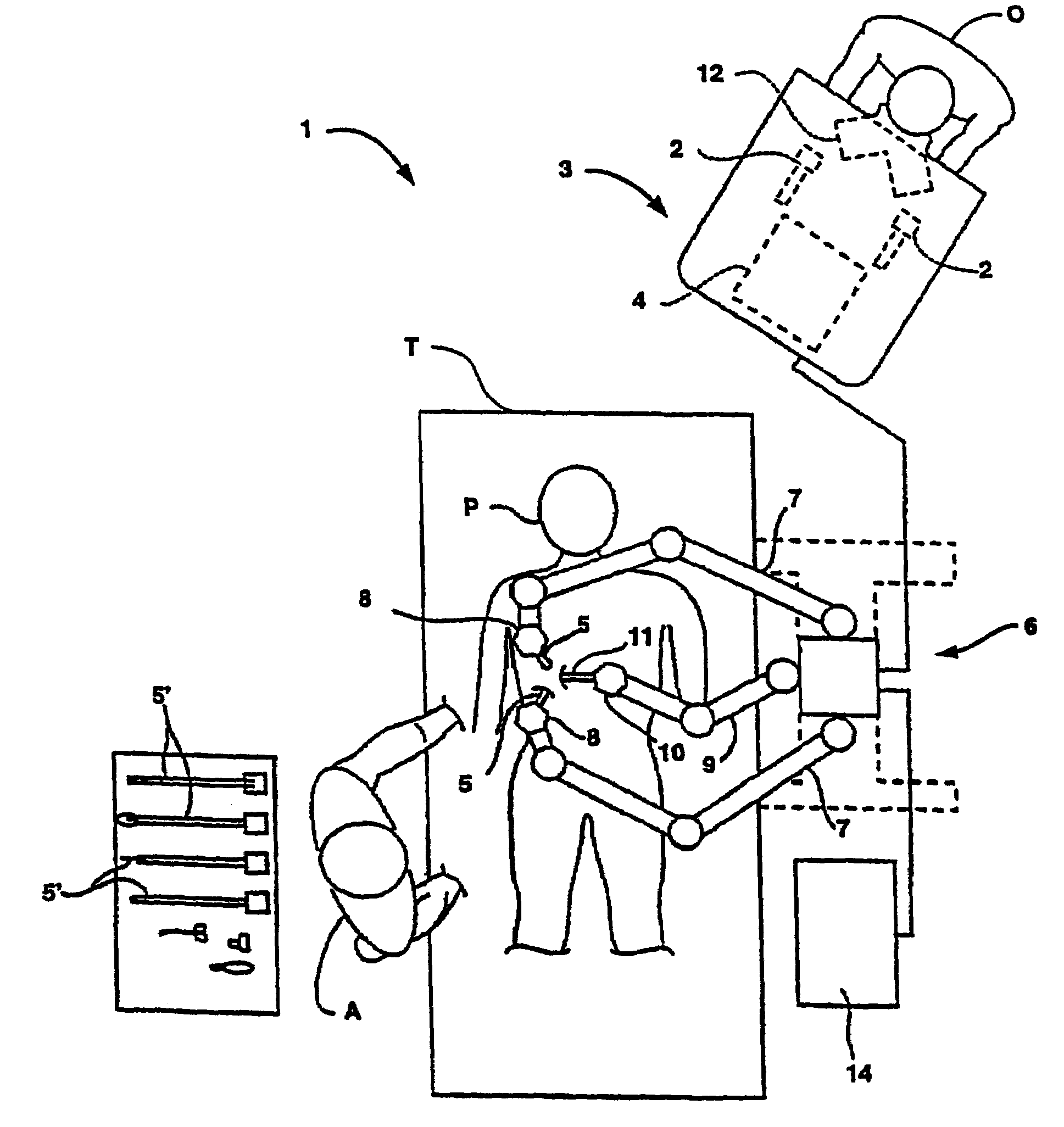
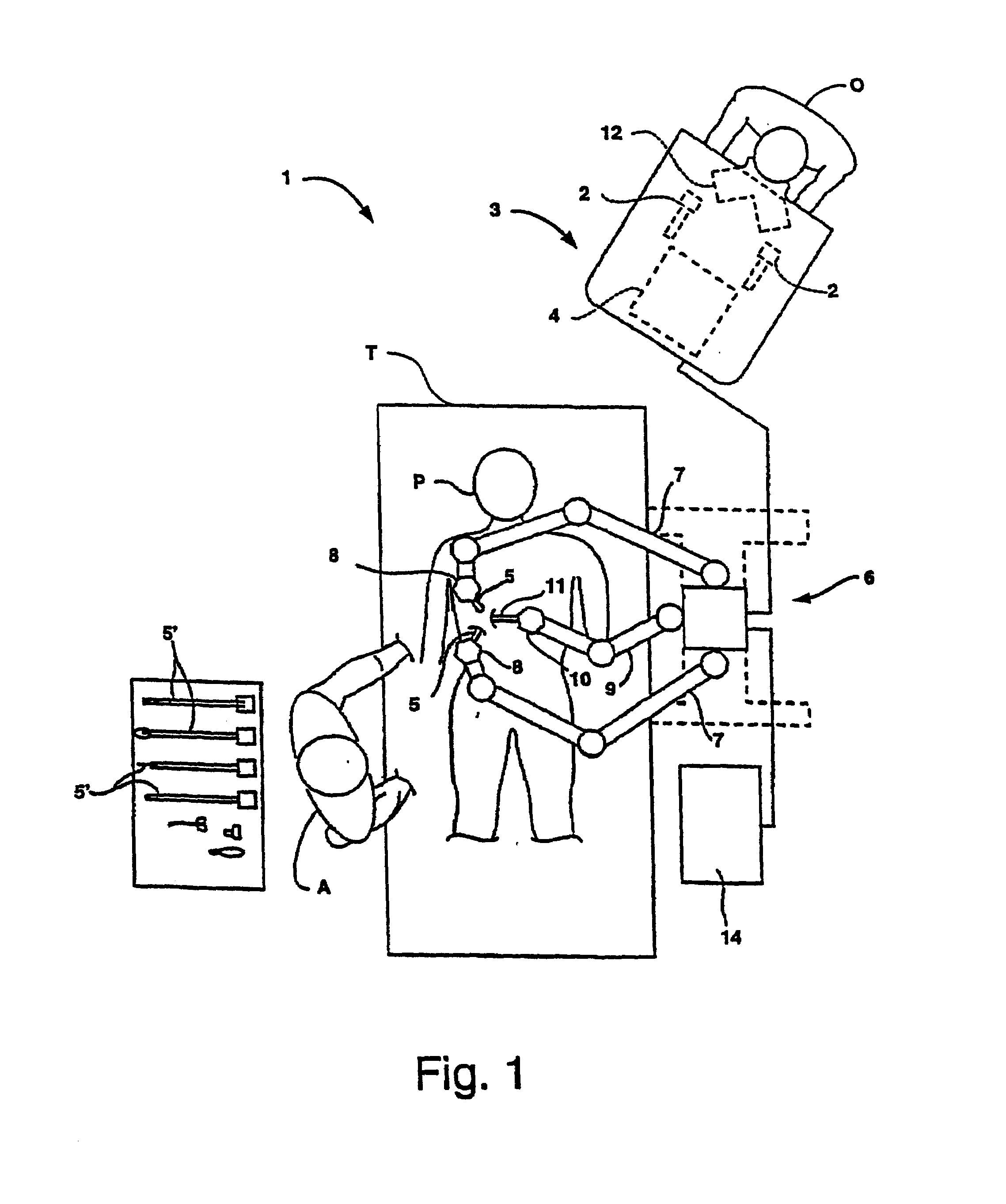
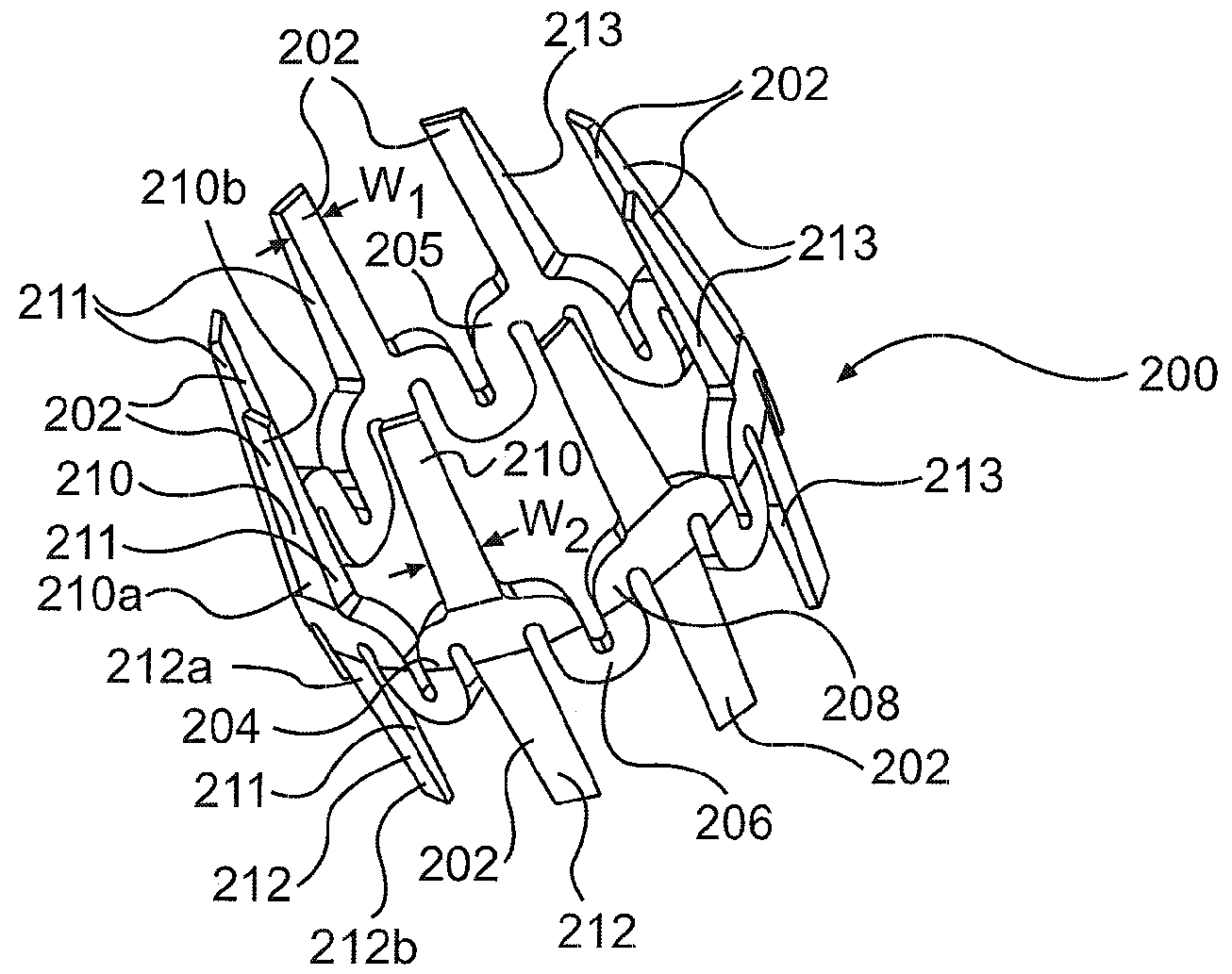
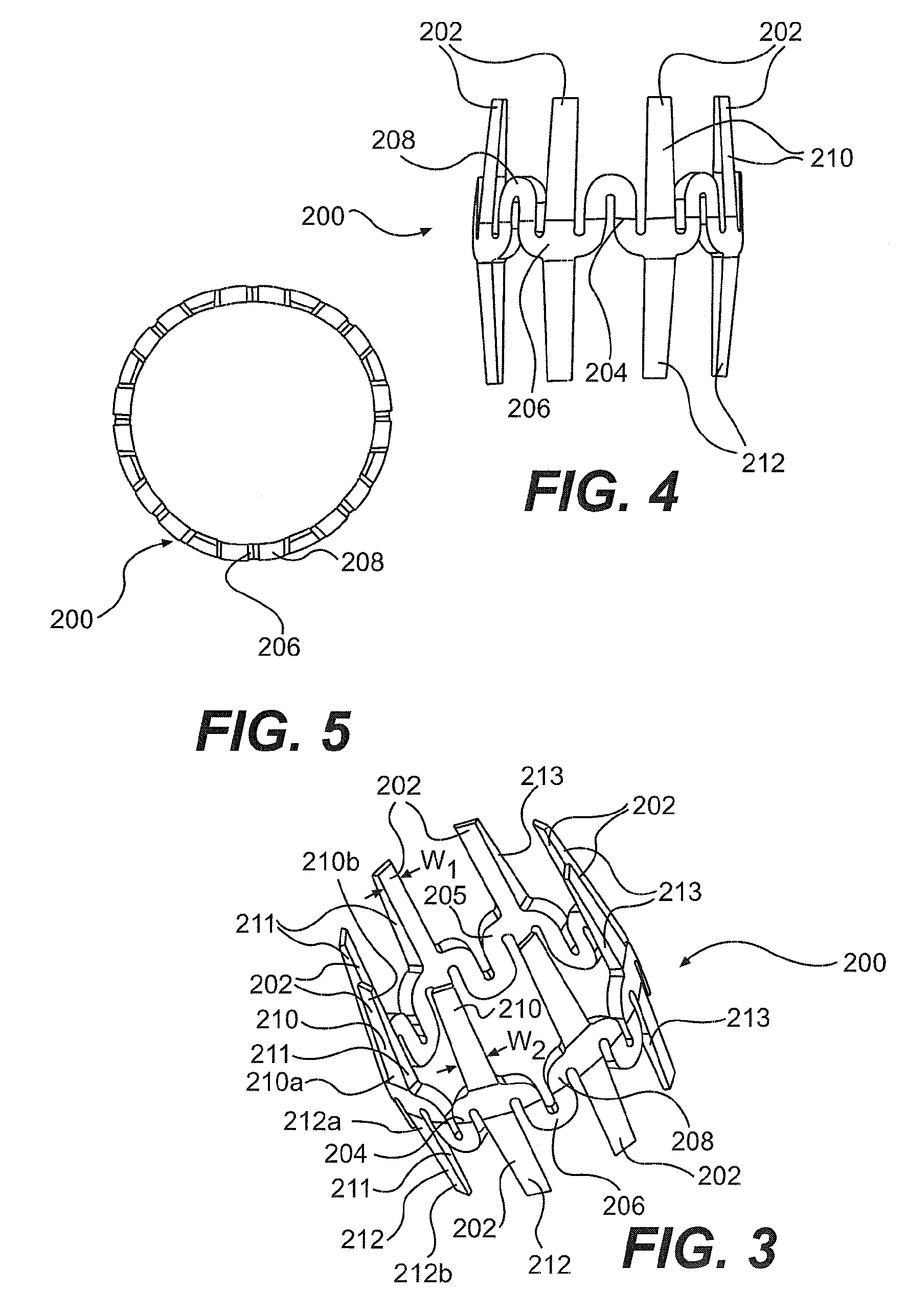
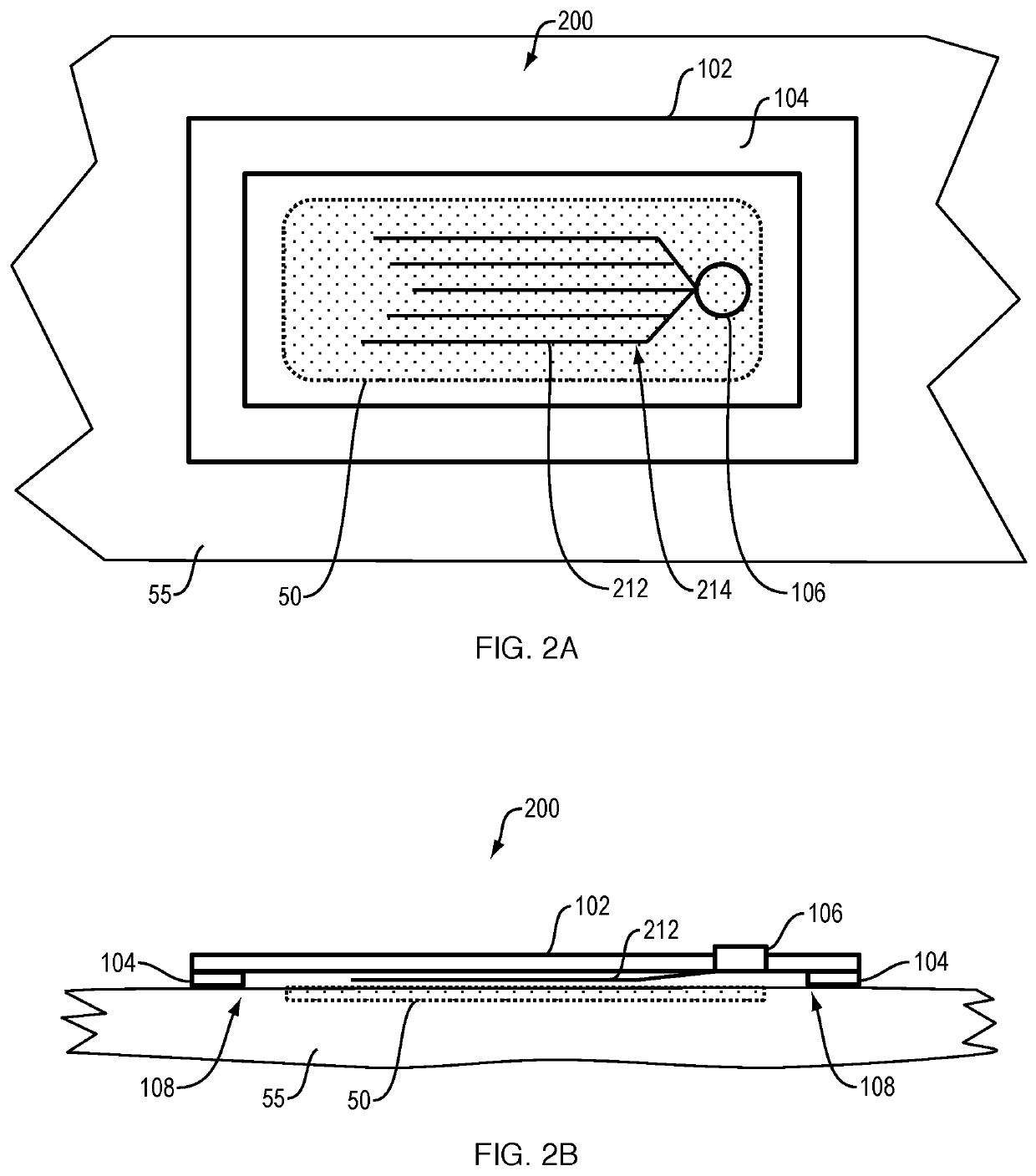
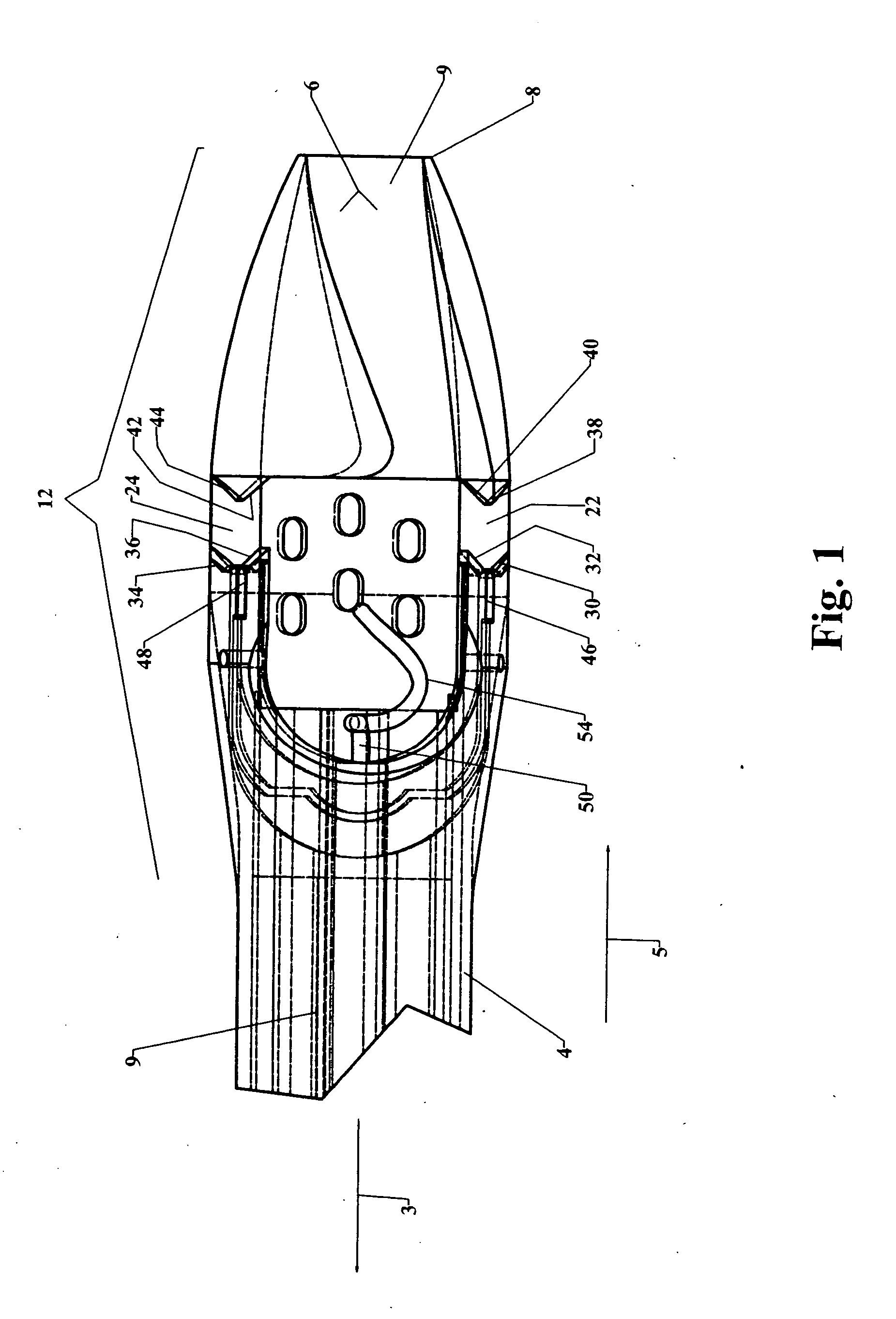
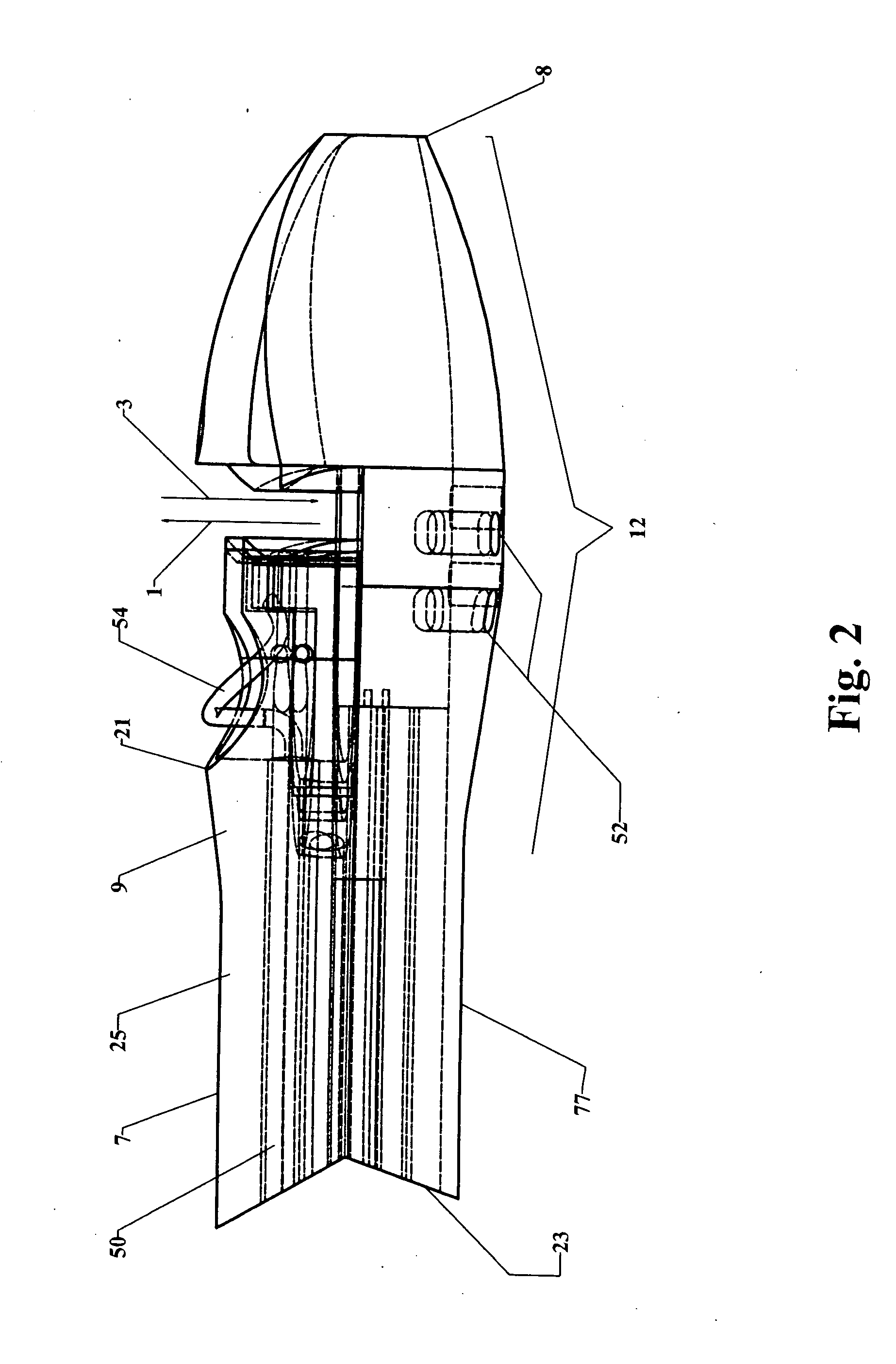
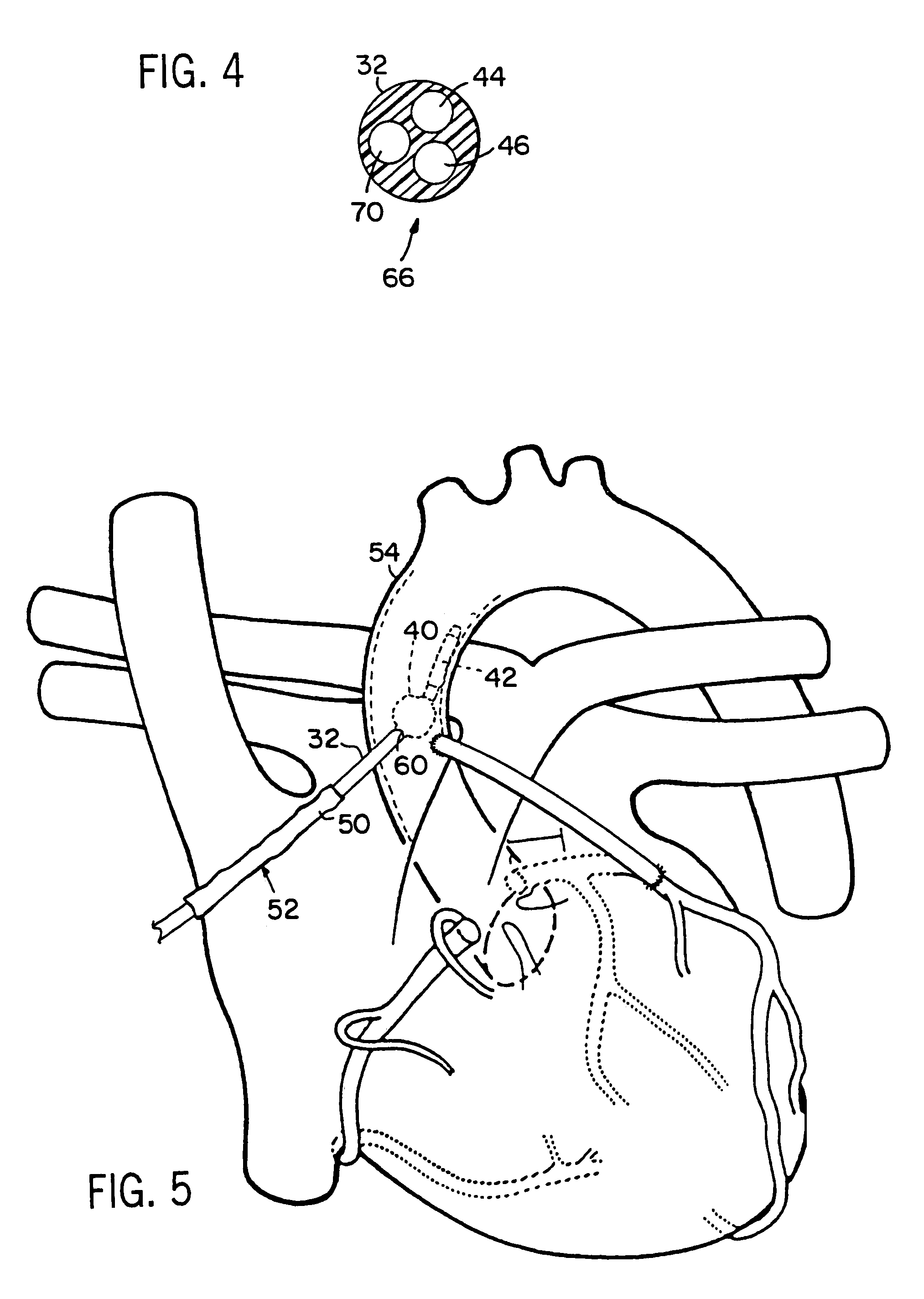
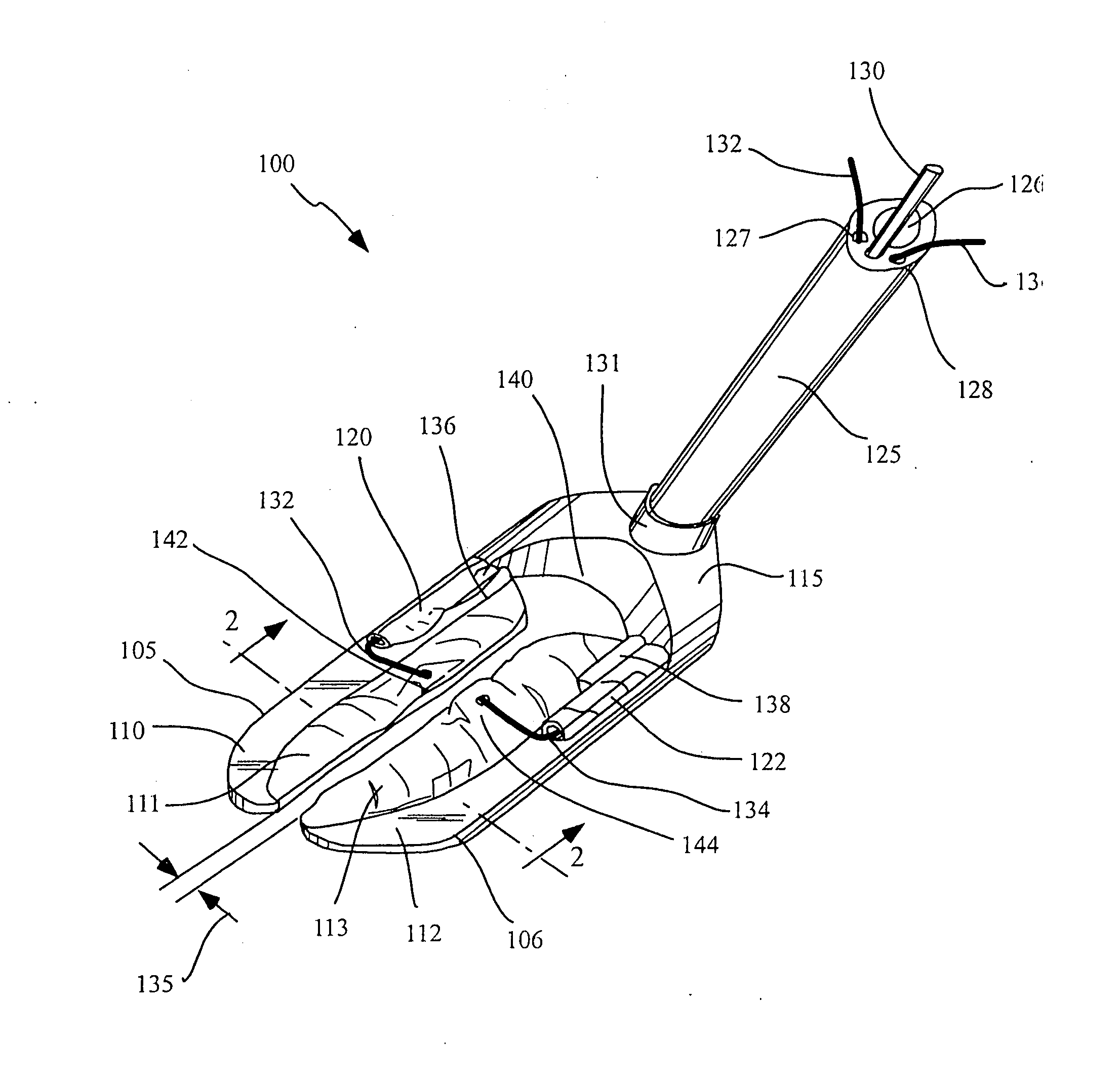
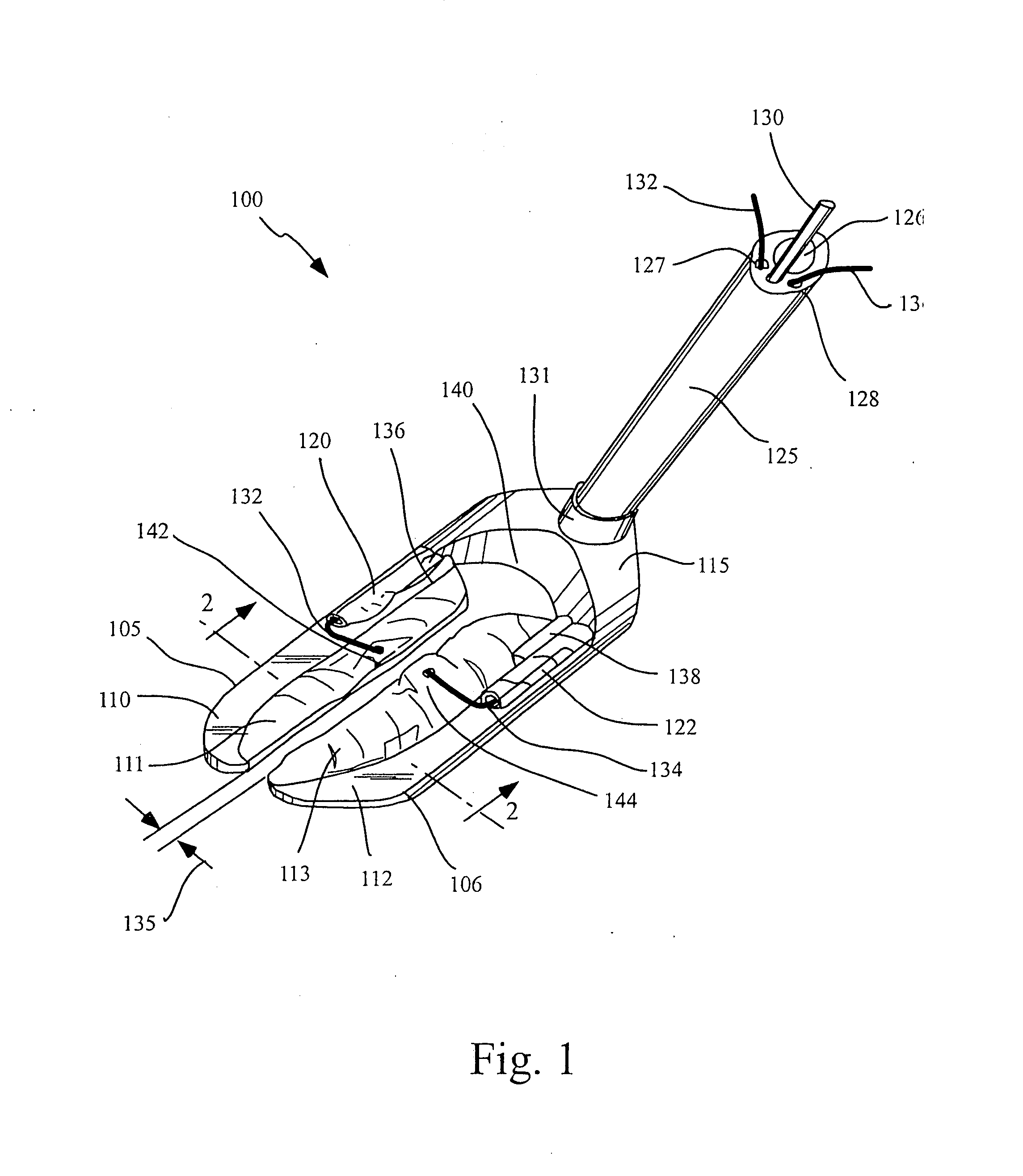
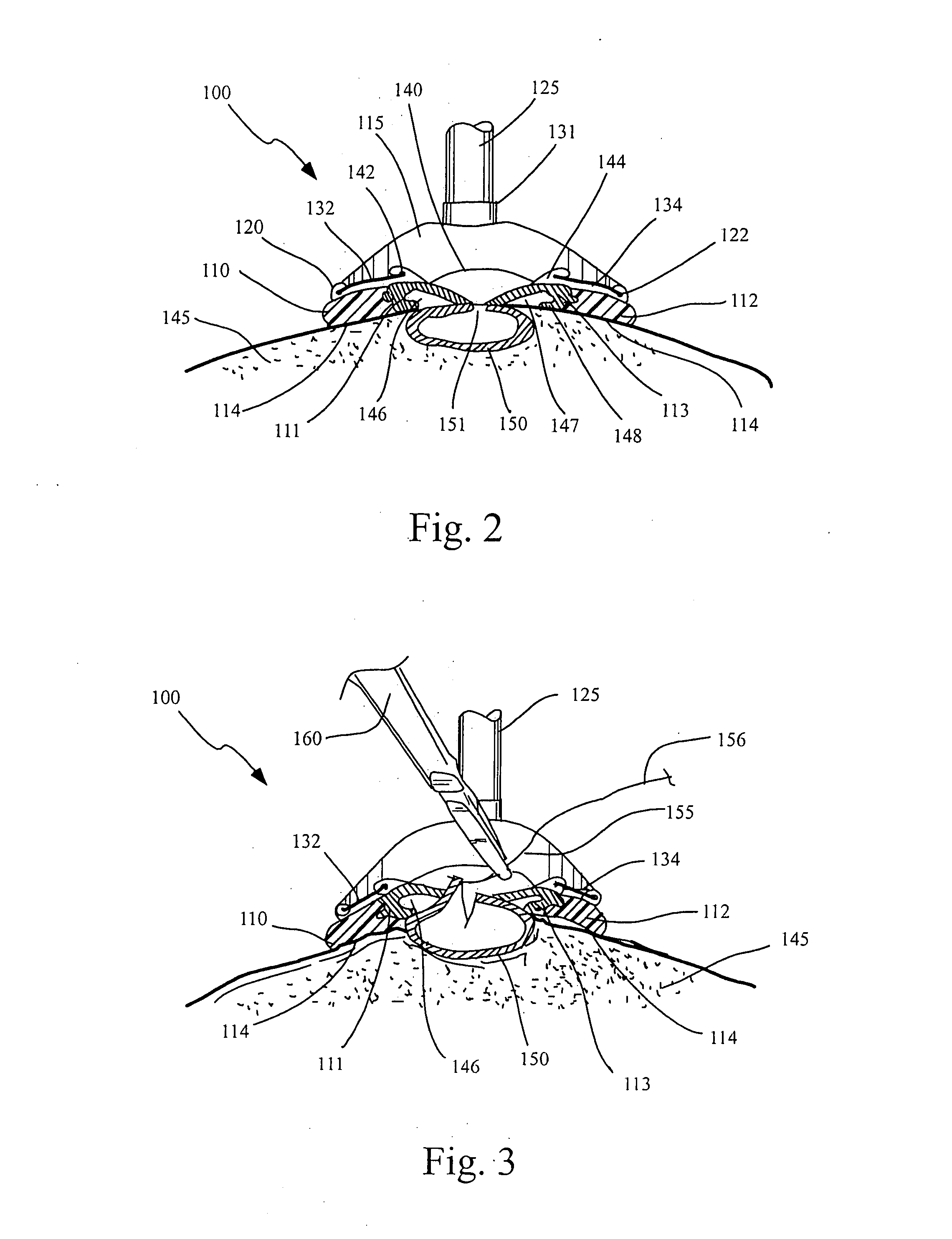
Endoscopic beating-heart stabilizer and vessel occlusion fastener
ActiveUS20070208223A1Smooth motionAvoid relative motionSuture equipmentsEndoscopesSurgical operationTarget tissue
Devices, systems and methods related to endoscopic surgery, particularly related to robotic surgical operations, provide a tissue stabilizer for endoscopically stabilizing a target tissue within a patent's body. For stabilizing a beating heart during a closed-chest coronary artery bypass grafting procedure, a stabilizer is inserted through an endoscopic cannula and provides sufficient surface area to contact the heart and effectively stabilize the target tissue area. The stabilizer can straddle a blood vessel, such as a coronary artery, which is targeted for an anastomosis. Vessel occlusion fasteners may occlude the target blood vessel prior to the anastomosis procedure.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
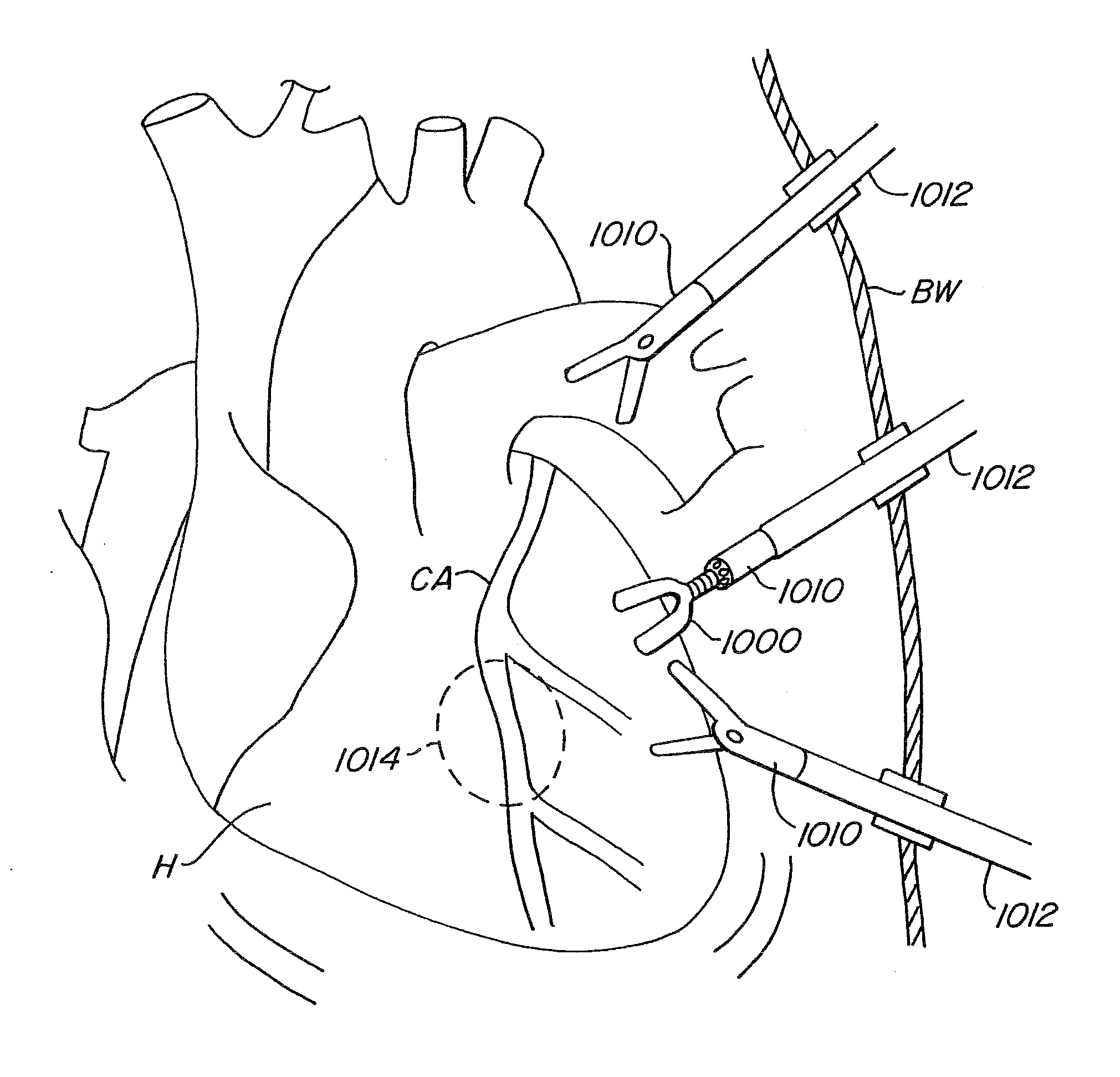
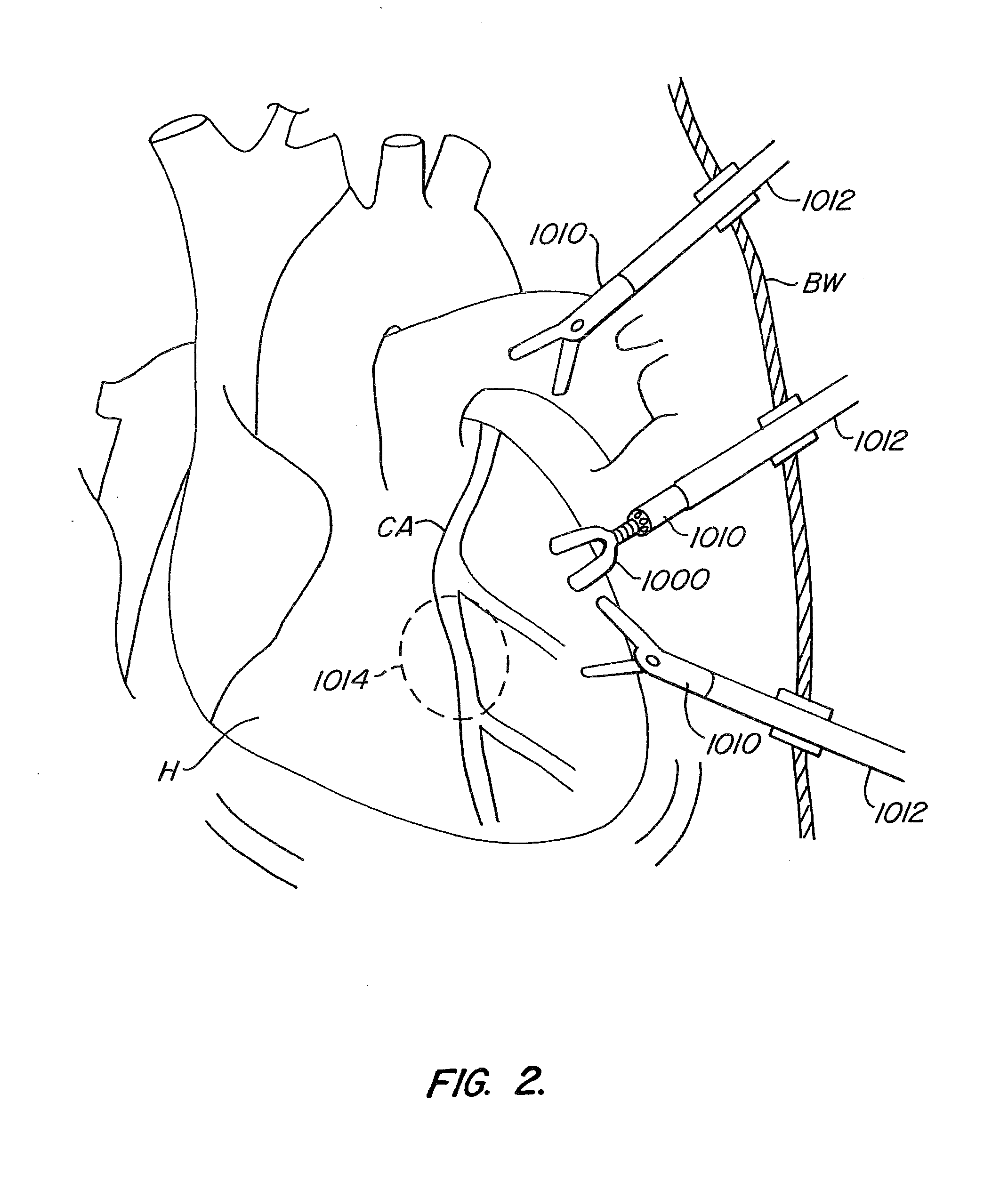
Method for performing a vascular anastomosis
InactiveUS20090112304A1Quickly and reliably performingDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsThoracic structureVascular anastomosis
Owner:INNOVATIVE INTERVENTIONAL TECH
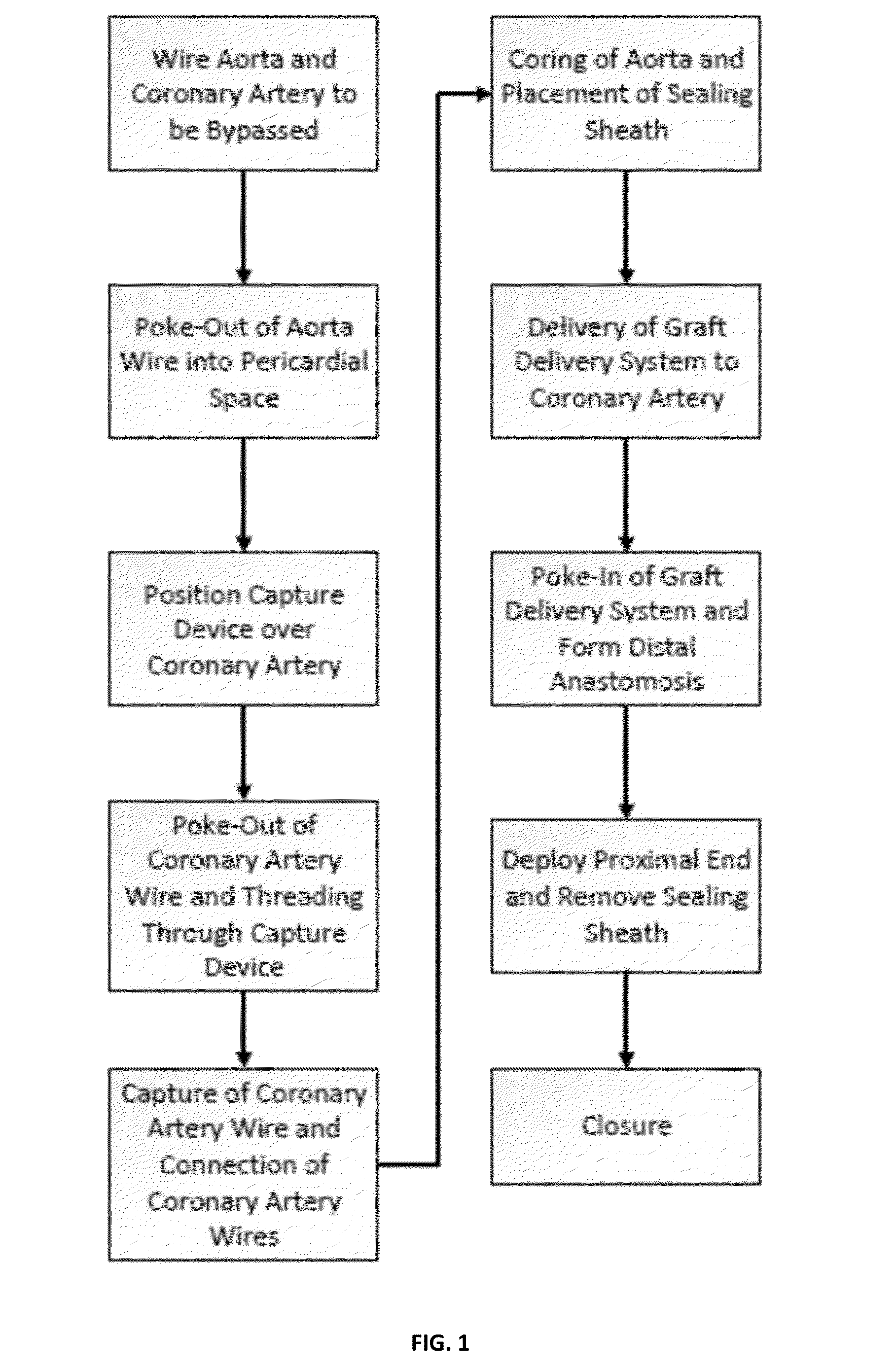
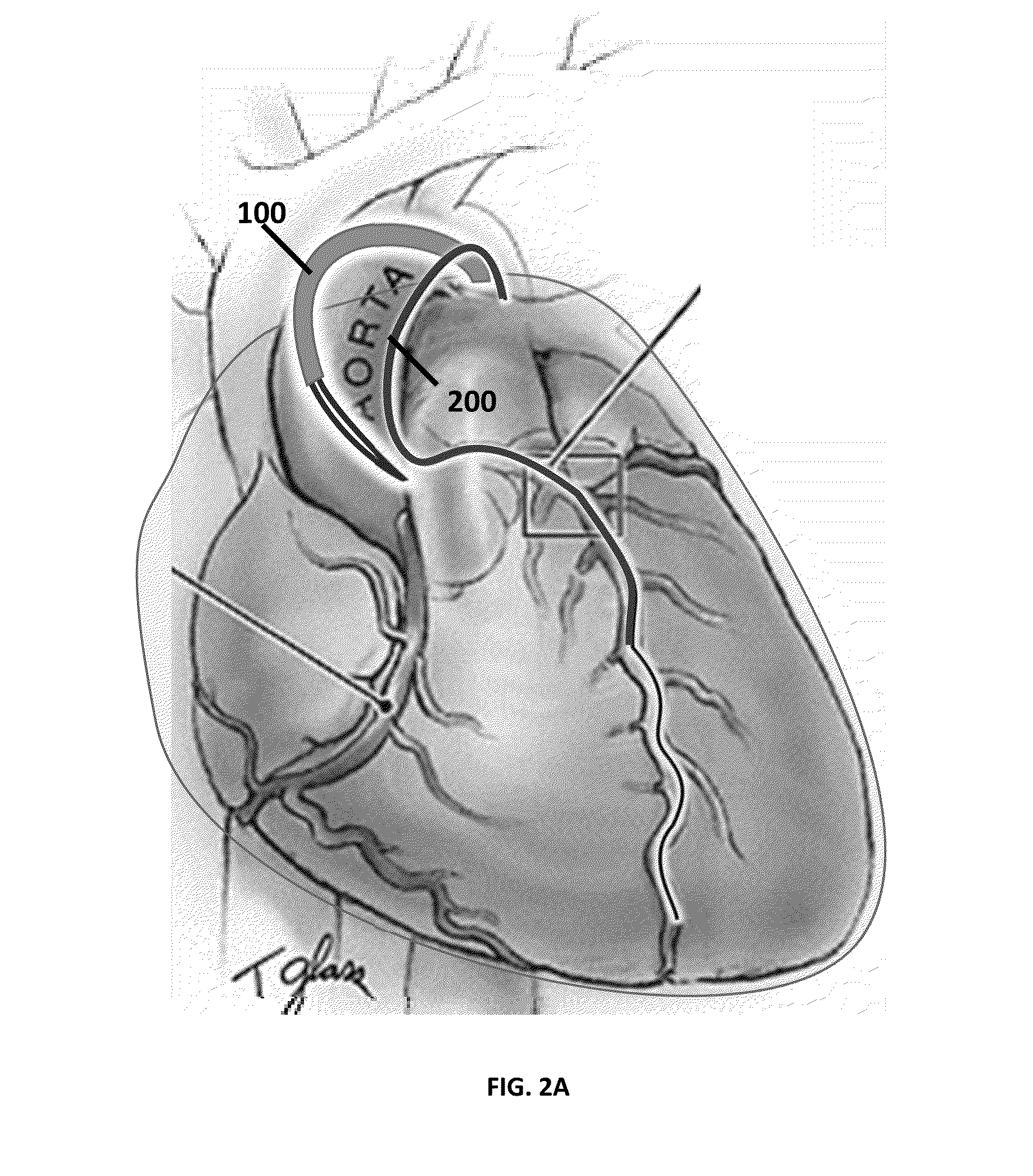
Methods and devices for minimally invasive transcatheter coronary artery bypass grafting
Systems and methods for performing transcatheter coronary artery bypass grafting procedures are provided. The methods generally involve passing the graft from the aorta to the coronary artery through the pericardial space. The systems include poke-out wires, a coring device, and devices for forming anastomoses at the proximal and distal ends of a vascular graft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
Post-Operative Hybrid Dressing To Optimize Skin-Grafting Procedures In Reconstructive Surgery
A device and associated method for treating a skin graft donor site includes a sheet having dimensions to cover the skin graft donor site and an area of skin surrounding the skin graft donor site. An adhesive is provided that has properties of adhering to the skin and the sheet in a manner that forms a liquid impermeable boundary surrounding the skin graft donor site. A port is integrated with the sheet that enables a suction force to be applied therethrough to produce a negative pressure between the sheet and skin graft donor site to manage fluid produced by the skin graft donor site.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method for performing a coronary artery bypass graft procedure
InactiveUS20050203551A1Quickly and reliably performingDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsThoracic structureCoronary Artery Bypasses
A method for performing a coronary artery bypass graft procedure on a patient to connect a bypass vessel to a target vessel includes the steps of creating an opening in the patient that communicates with the thoracic cavity of the patient; providing a bypass vessel having a lumen and at least one free end; passing the free end of the bypass vessel from the thoracic cavity through the opening to a position outside the body of the patient; attaching a connector to the free end of bypass vessel while the free end of the bypass vessel is outside the body of the patient; passing the free end of the bypass vessel from the position outside the body of the patient through the opening and into the thoracic cavity; and connecting the free end of the bypass vessel to a target vessel with the connector.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Surgical instrument for facilitating the detachment of an artery and the like
InactiveUS6280455B1Minimal bleedingReducing eliminating needCannulasSurgical instruments for heatingVisibilityMammary artery
A surgical instrument is configured to aid in performing a procedure of detaching an internal mammary artery (IMA) and the like, from the connecting tissues and side branch vessels which surround the artery in its native location, wherein the detaching procedure is preliminary to the performing of a coronary artery bypass grafting procedure and wherein the IMA is detached via a minimally invasive thoracotomy. To this end, an elongated slender rod includes a handle at its proximal end and an artery engaging loop, arc, fork configuration, or hook at its distal working end. Embodiments may incorporate electrosurgical capability or electrical insulation. A surgeon thus has means for harvesting an intact and undamaged graft vessel from its native location through a minimally invasive incision with enhanced speed, visibility, and freedom of motion.
Owner:LASALLE CAROL +1
Combined use of an alkaline earth metal compound and a sterilizing agent to maintain osteoinduction properties of a demineralized bone matrix
A method is disclosed that produces allografts from matrices typically containing demineralized bone matrix (DBM) powder, demineralized bone matrix gel, demineralized bone matrix paste, bone cement, cancellous bone, or cortical bone and mixtures thereof. The matrices are sterilized utilizing supercritical CO2 in the presence of a sterilizing additive and an entrainer such as an alkaline earth metal compound, preferably CaCO3. The resultant allograft materials have a reduced rate of rejection when used in allograft procedures including, bone, cartilage, tendon, and ligament grafting procedures.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
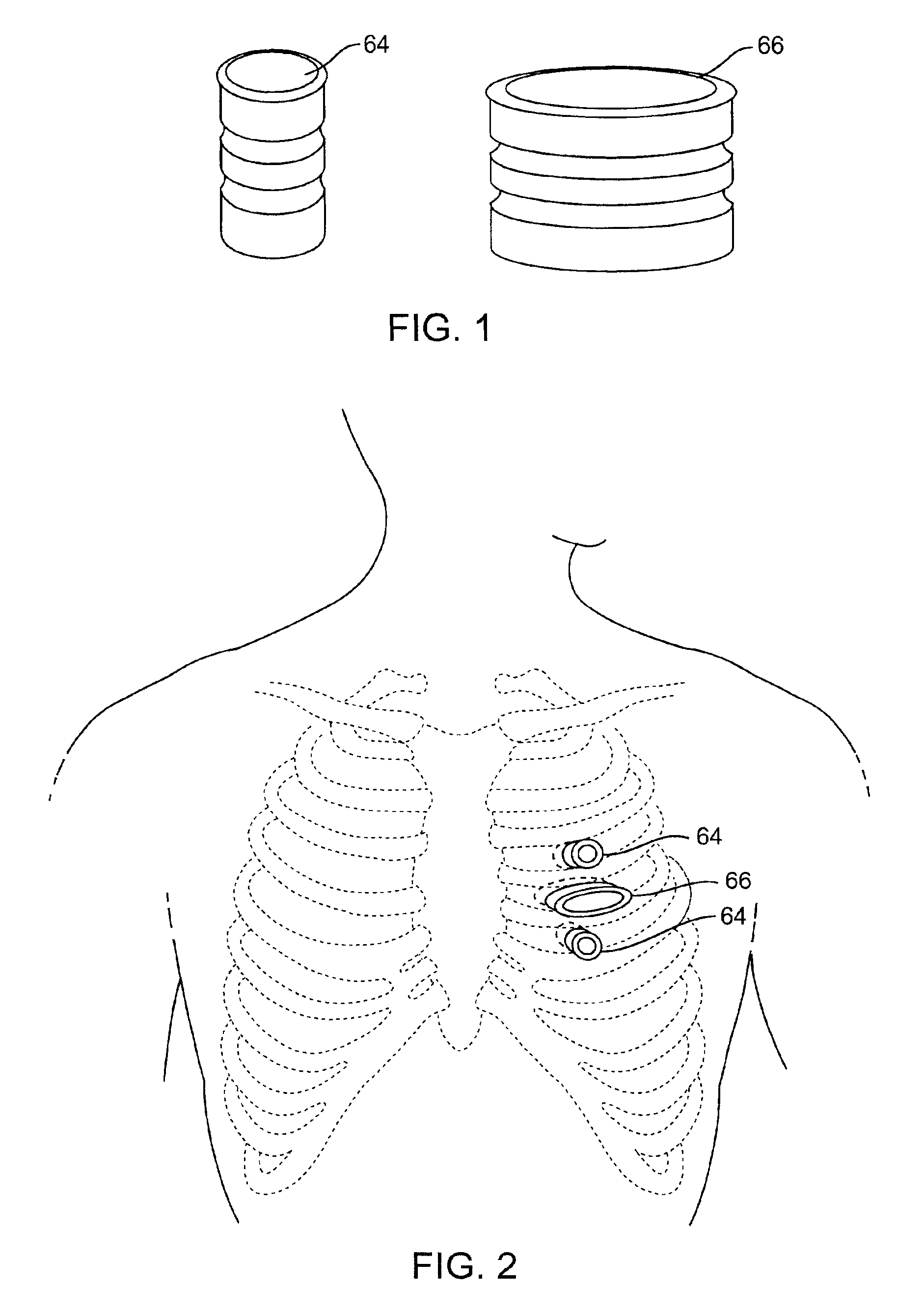
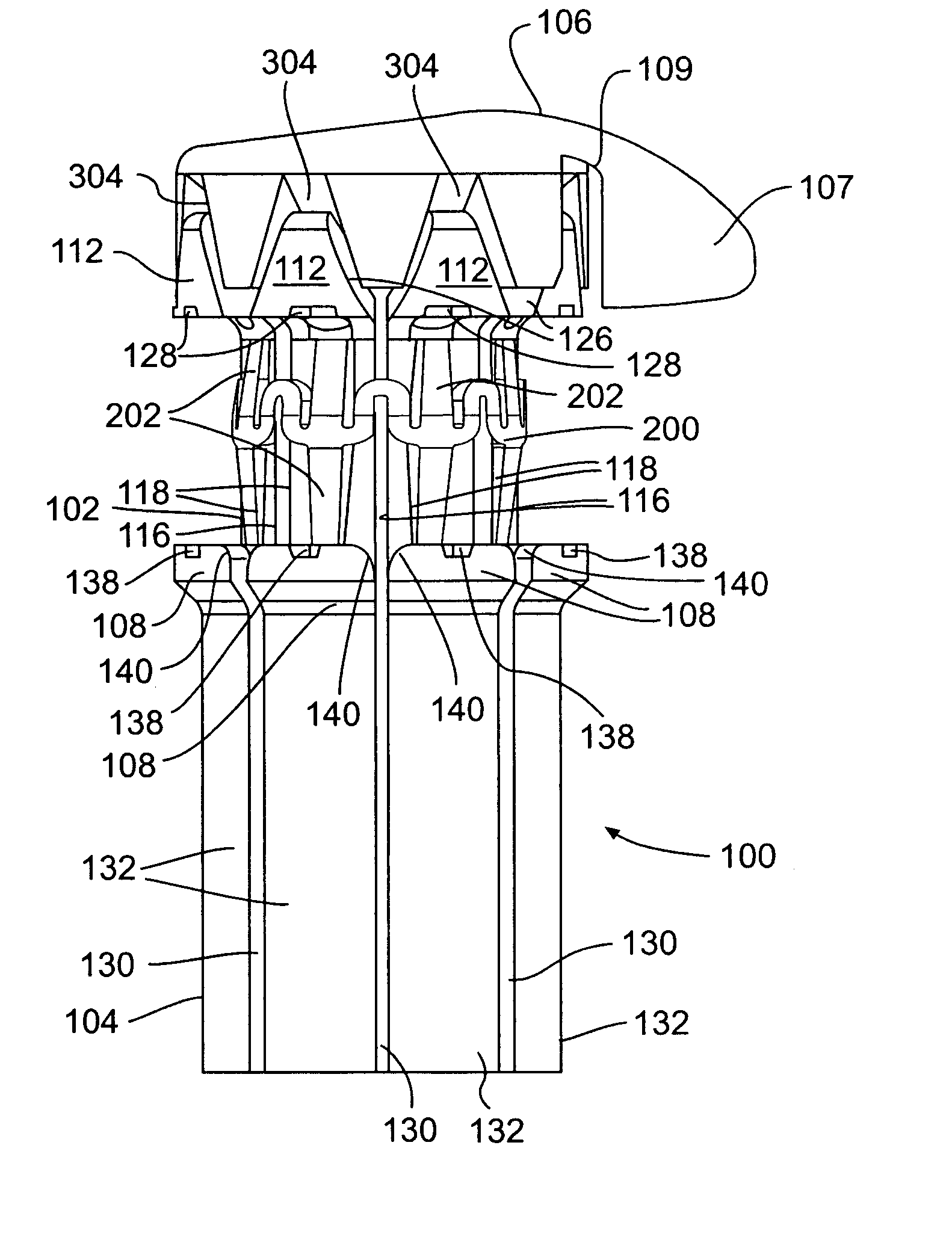
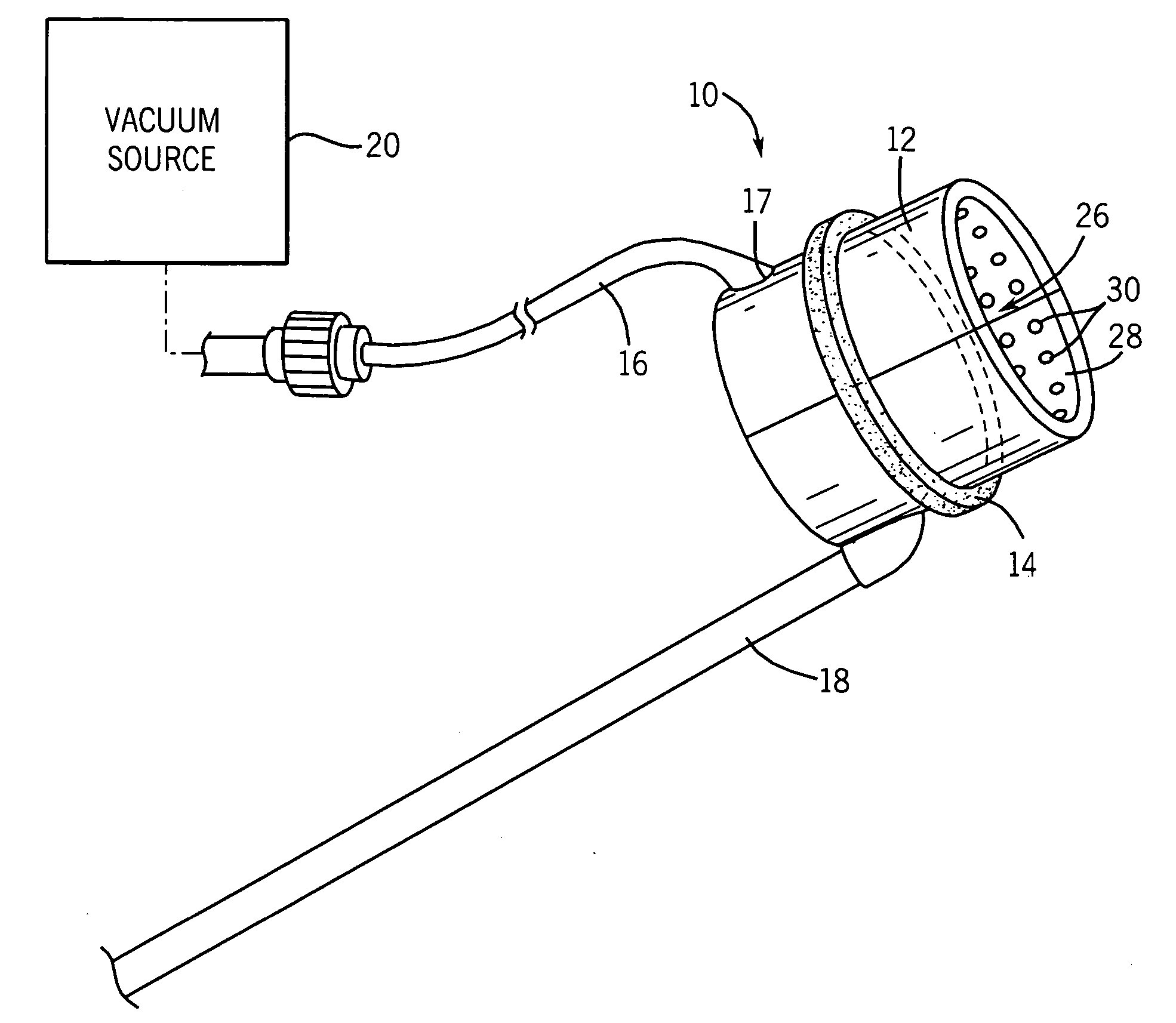
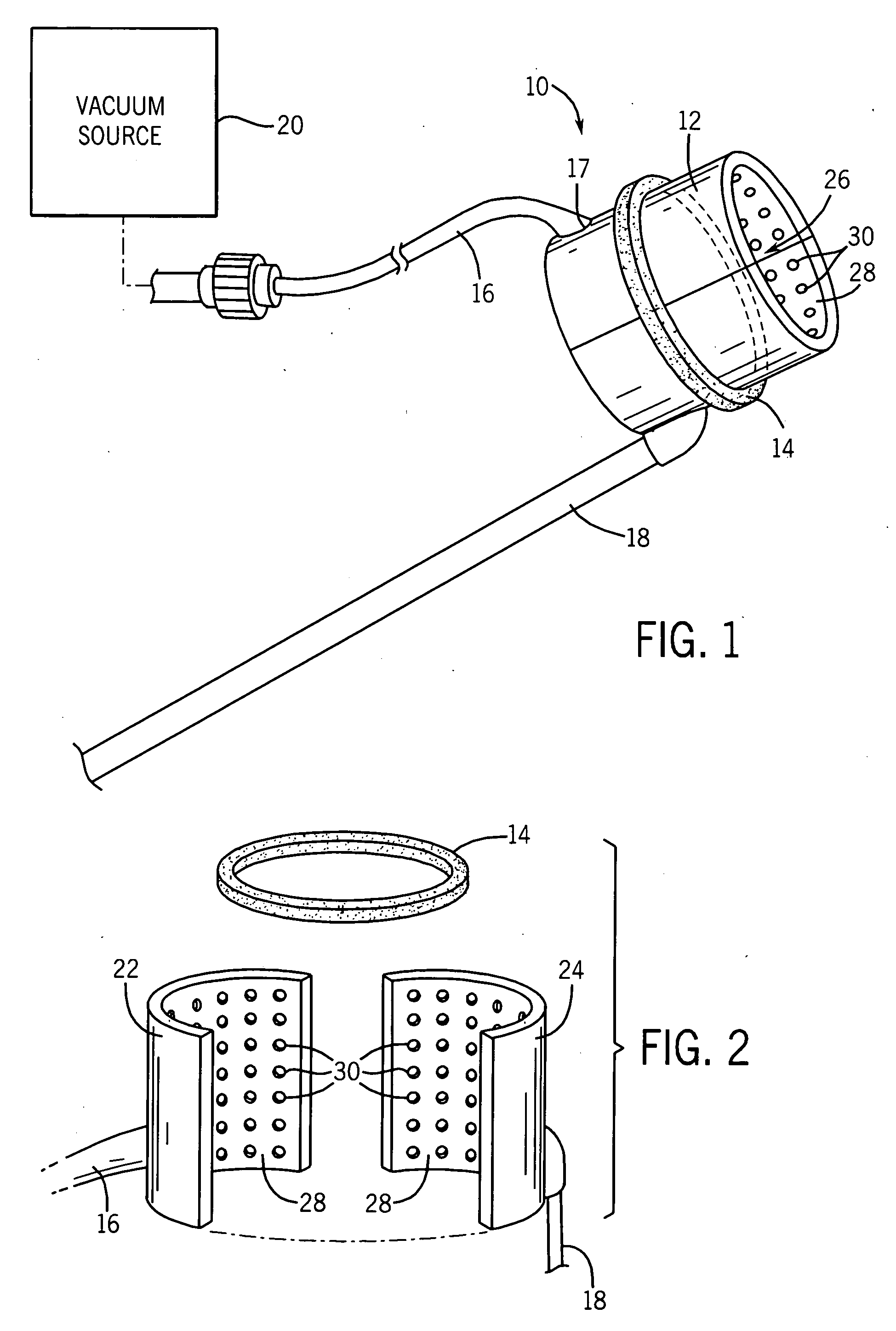
Blood vessel holding and positioning system
A device used to hold and position a blood vessel in the performance of a coronary artery bypass graft procedure includes a handle and an attachment head coupled to the handle. The attachment head has a collar adapted to substantially encircle the blood vessel and having a number of suction apertures. A vacuum port is adapted to be coupled to a vacuum source and communicates a suction to the suction apertures to hold the blood vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for grafting red plum and peach
The invention relates to the field of red plum grafting technology, and particularly to a method for grafting a red plum and a peach. The method comprises processing a red plum and a peach, choosing the red plum as a scion and the peach as a stock, inserting the red plum in the peach, and processing through a resistance nutrient solution during the grafting procedure. The grafting portion can be high in resistance to prevent the grafting portion from pathology, the cultivated variety is high in resistance, the cost for plum tree variety cultivation can be reduced, so the cost during plantation can be reduced, and the profit and economic value can be raised. The method for grafting a red plum and a peach is simple in operation, the raw material for preparing a resistance nutrient solution can be easily obtained, and a preparation method thereof is simple.
Owner:安顺市西秀区春实绿化苗木有限公司
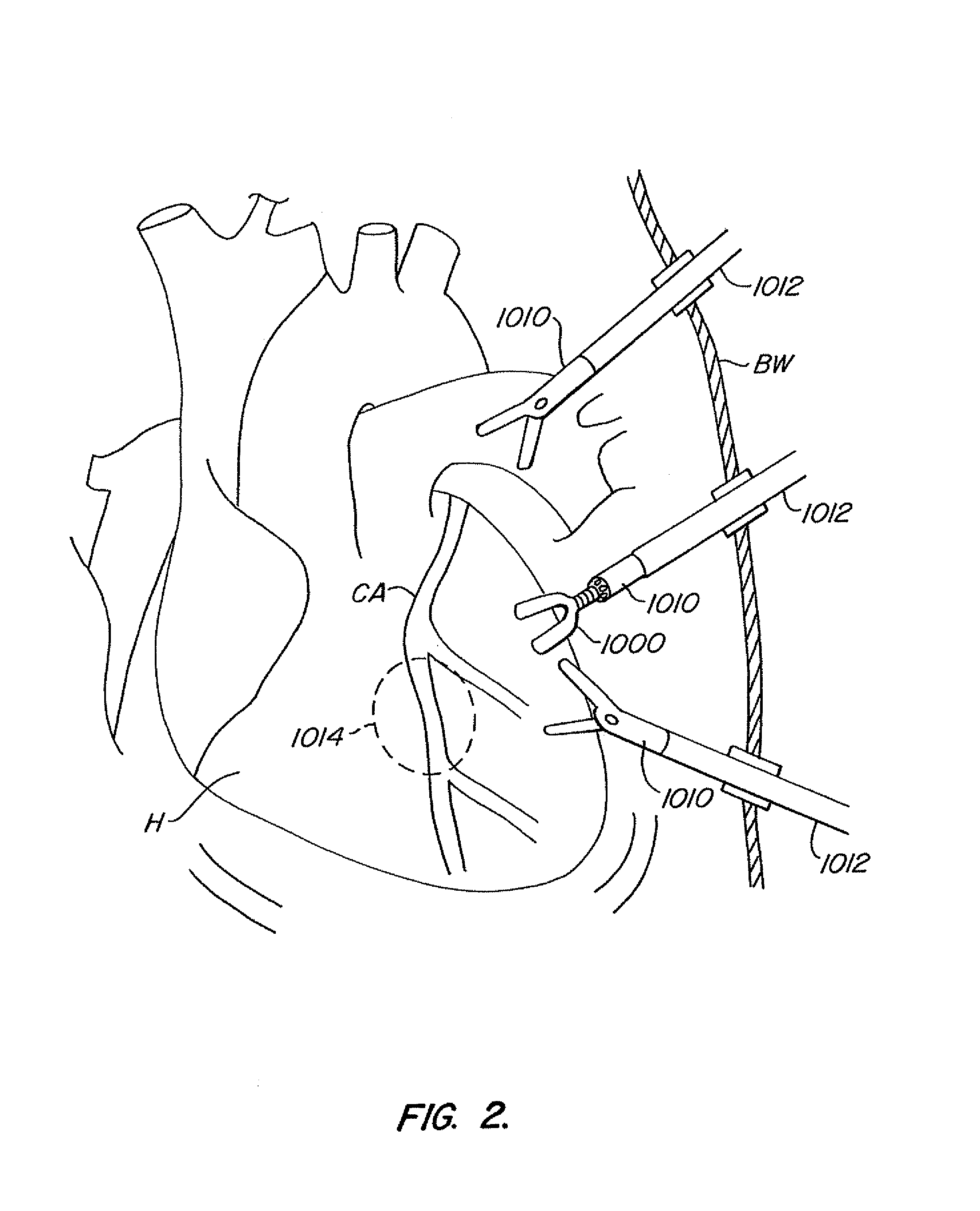
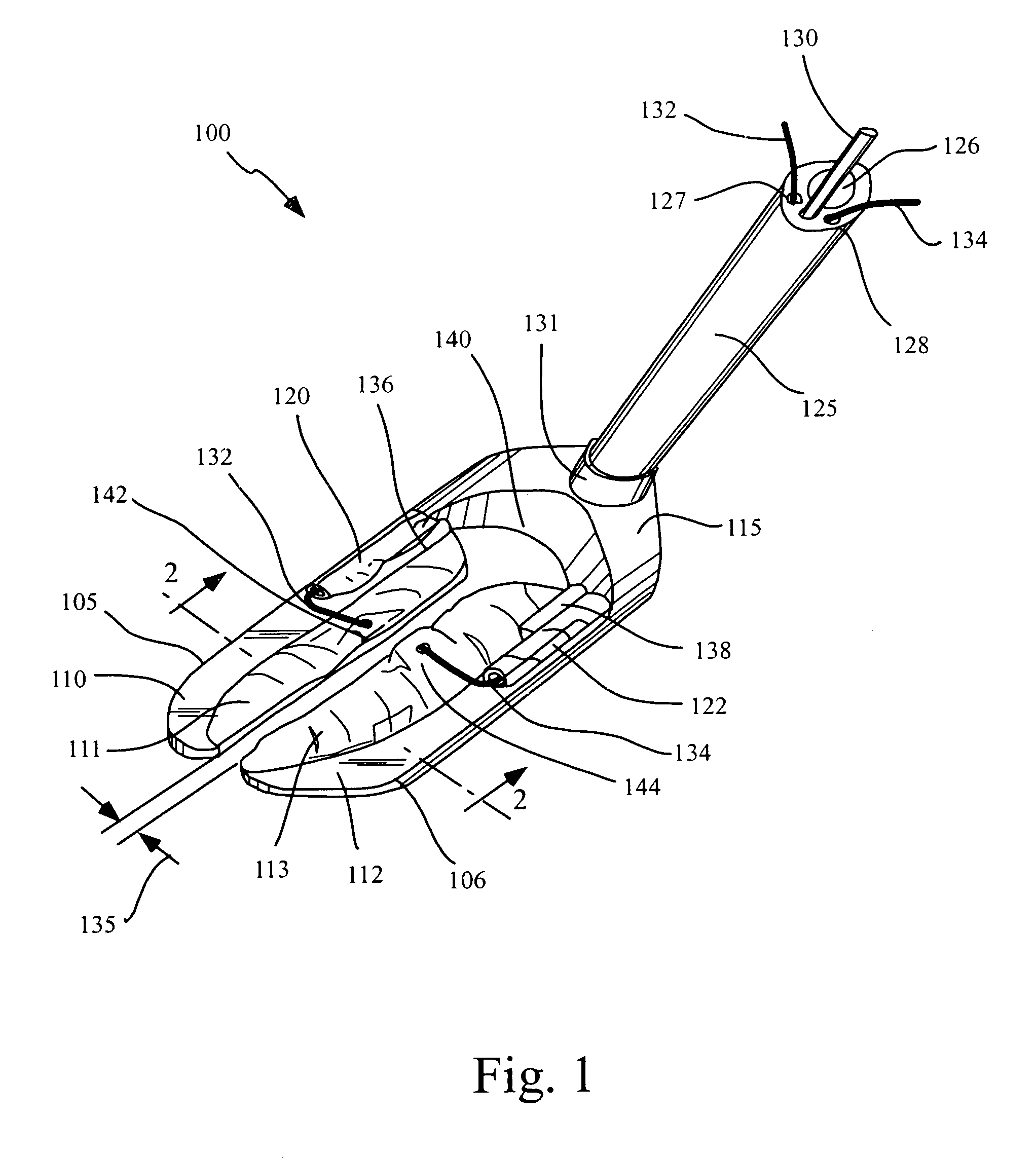
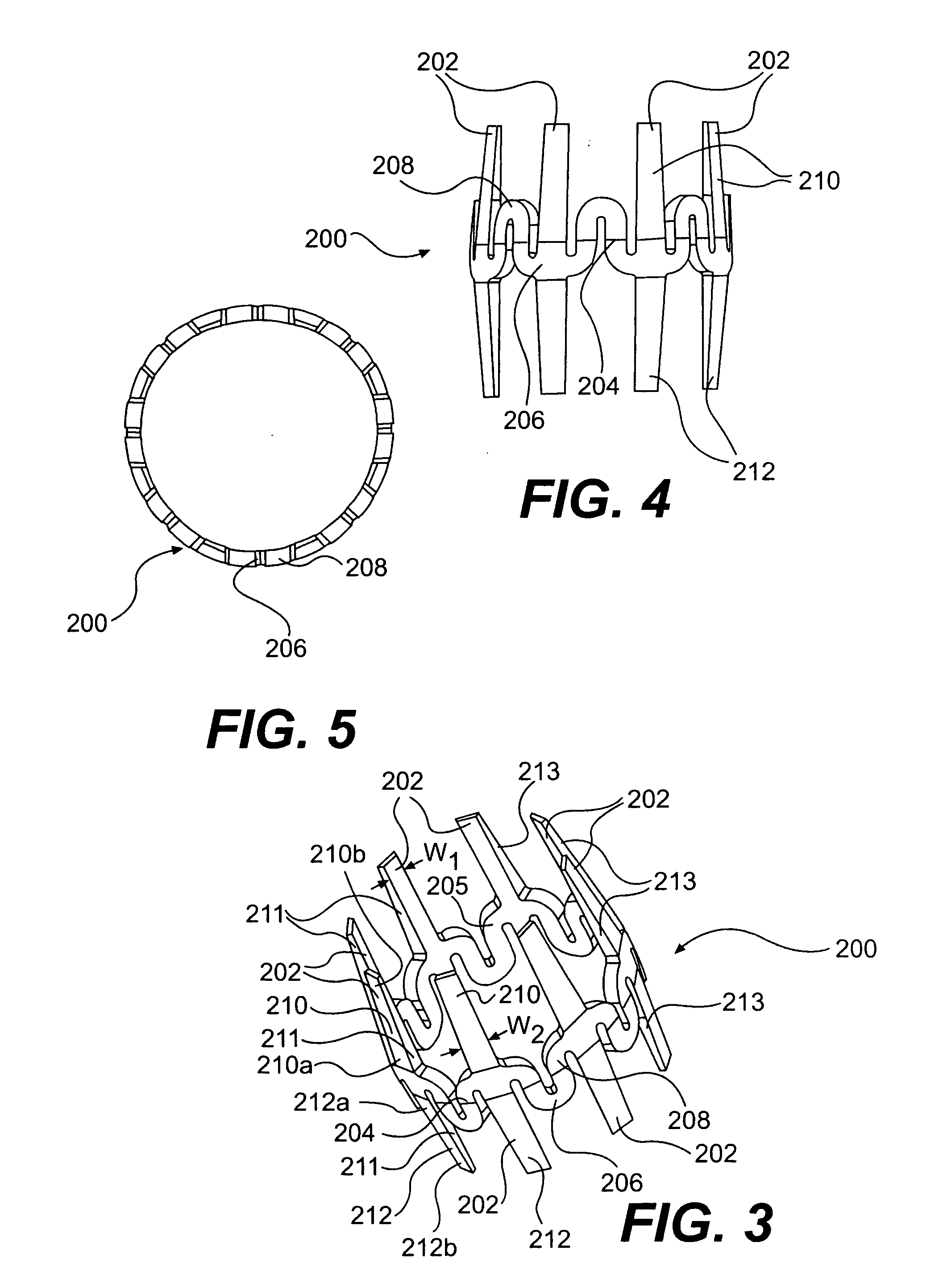
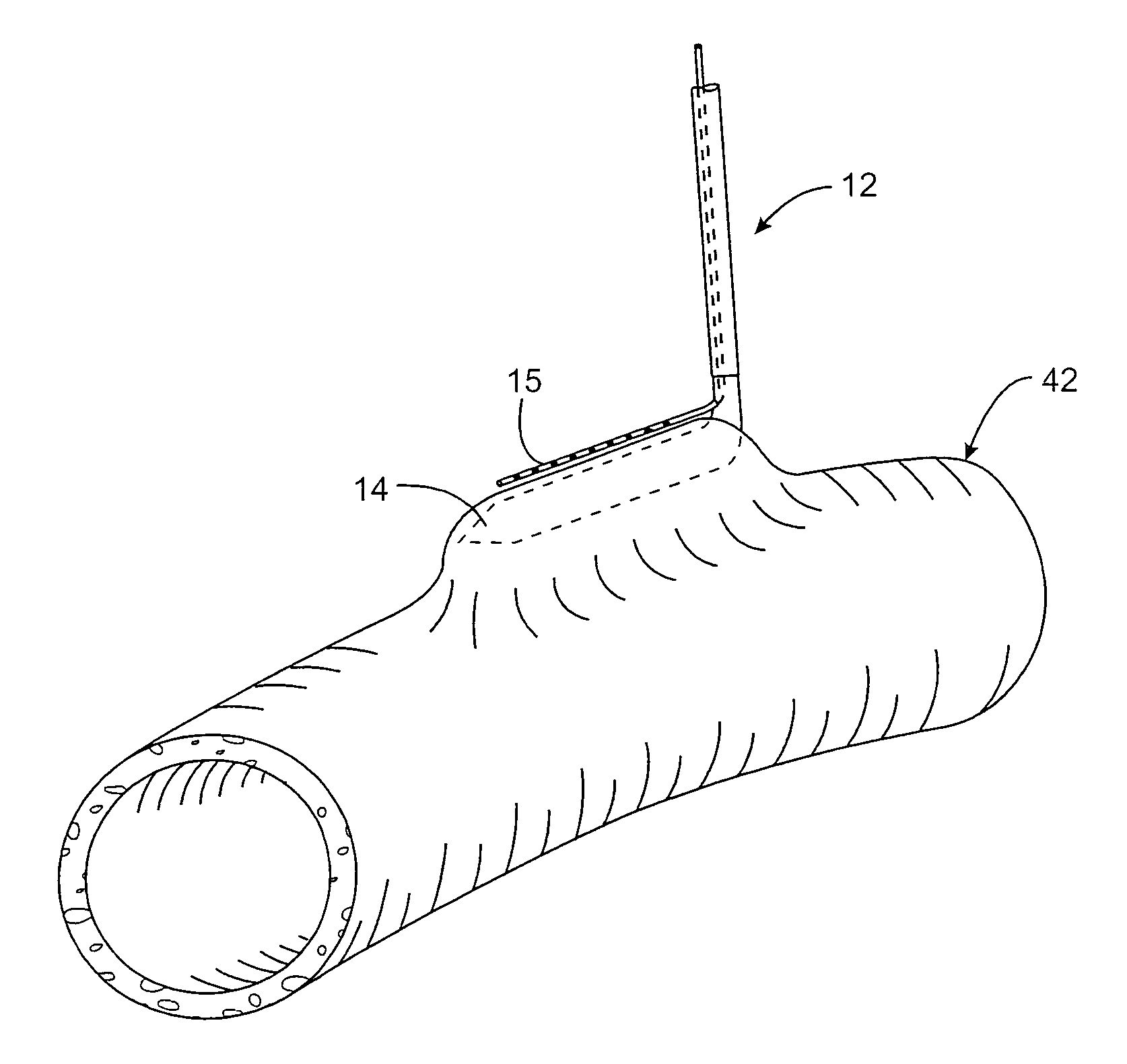
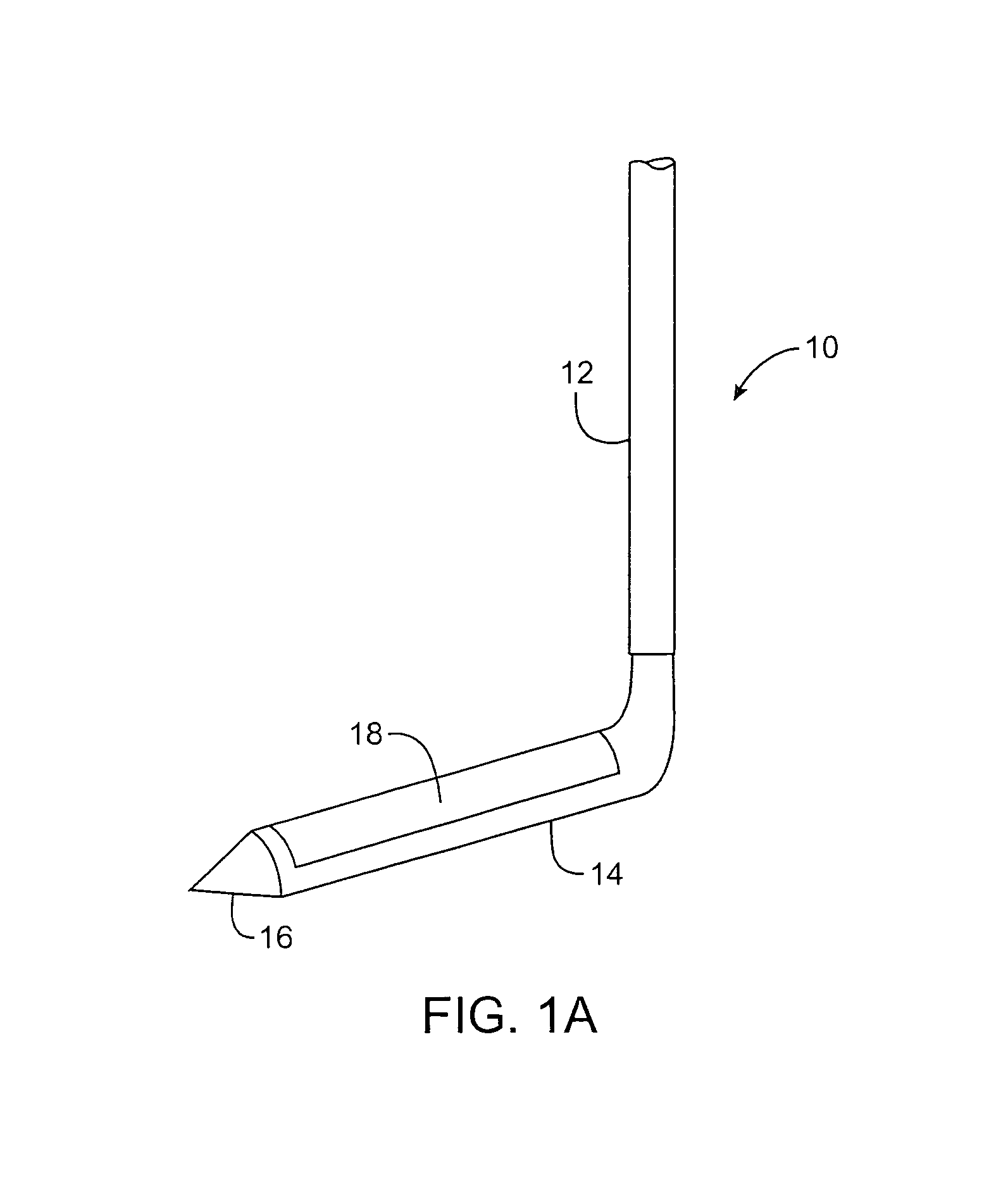
Device and method for isolating a surgical site
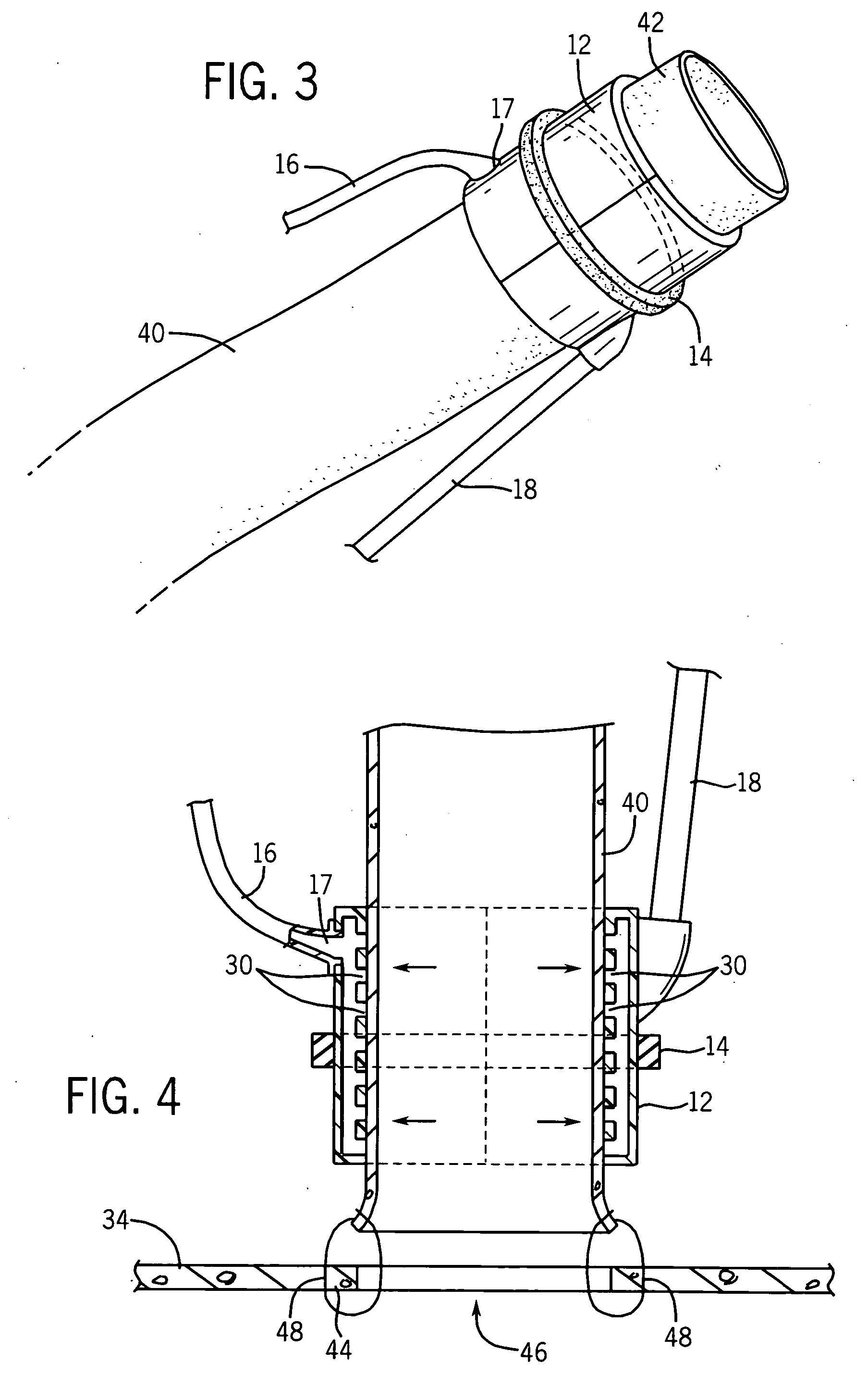
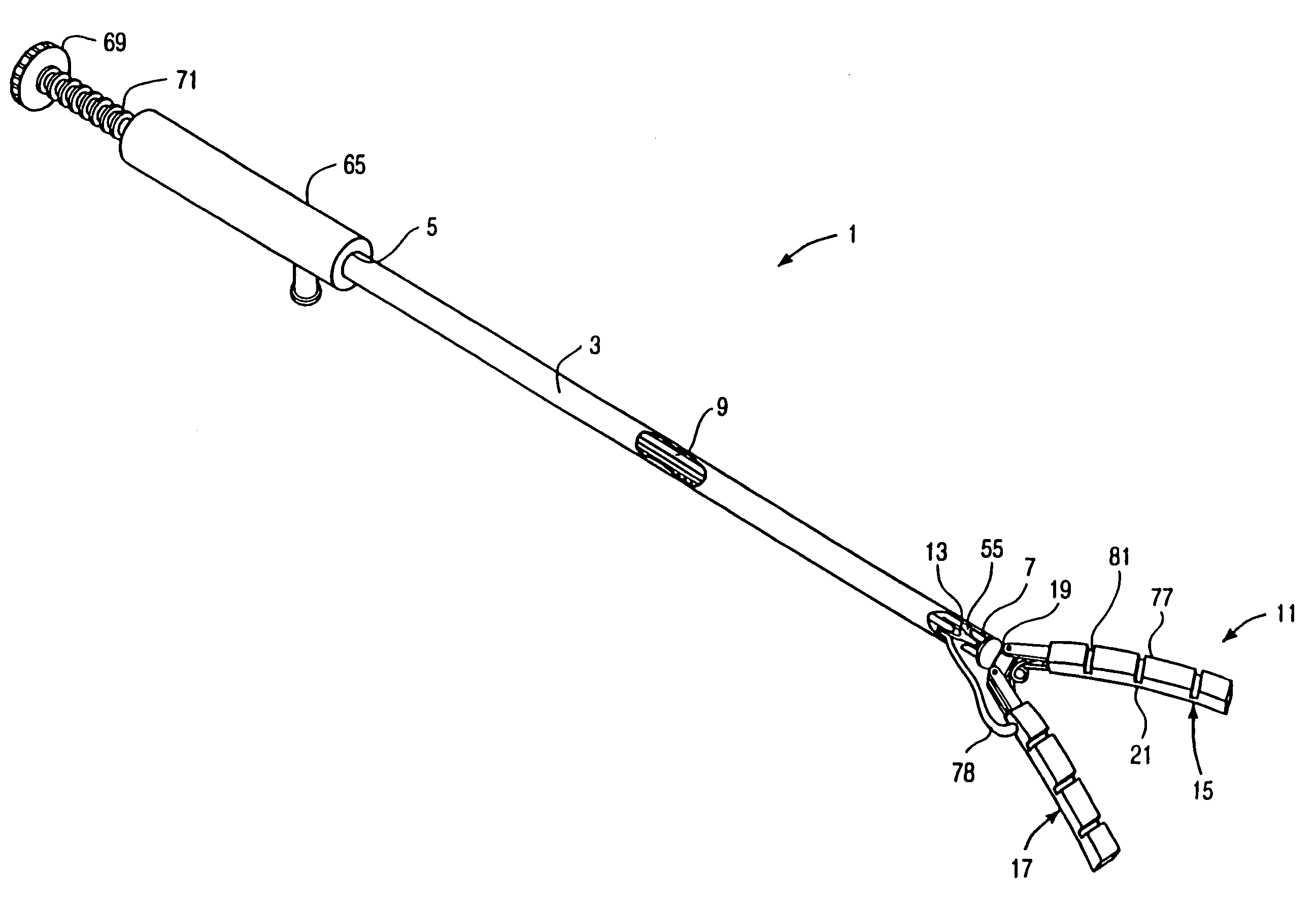
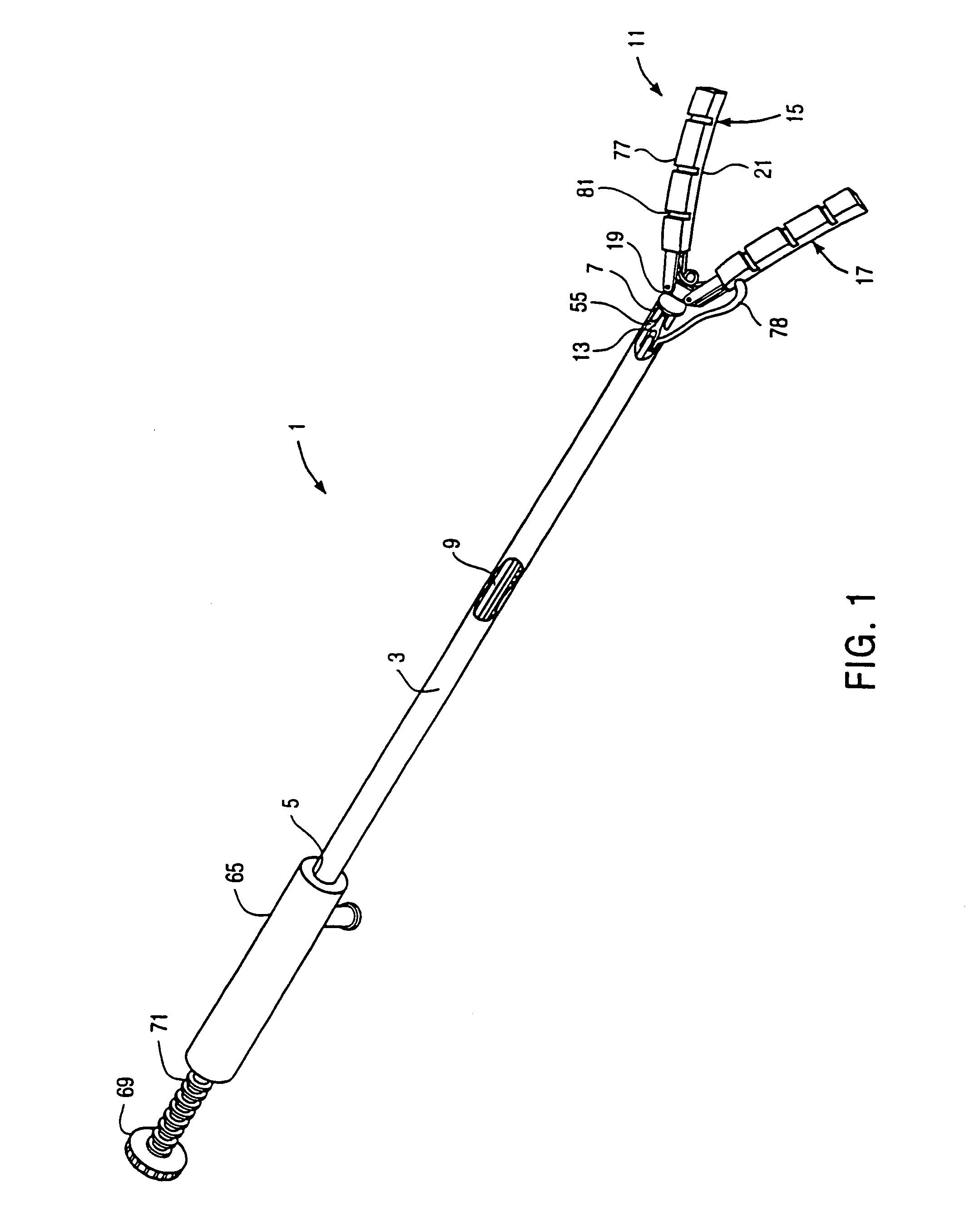
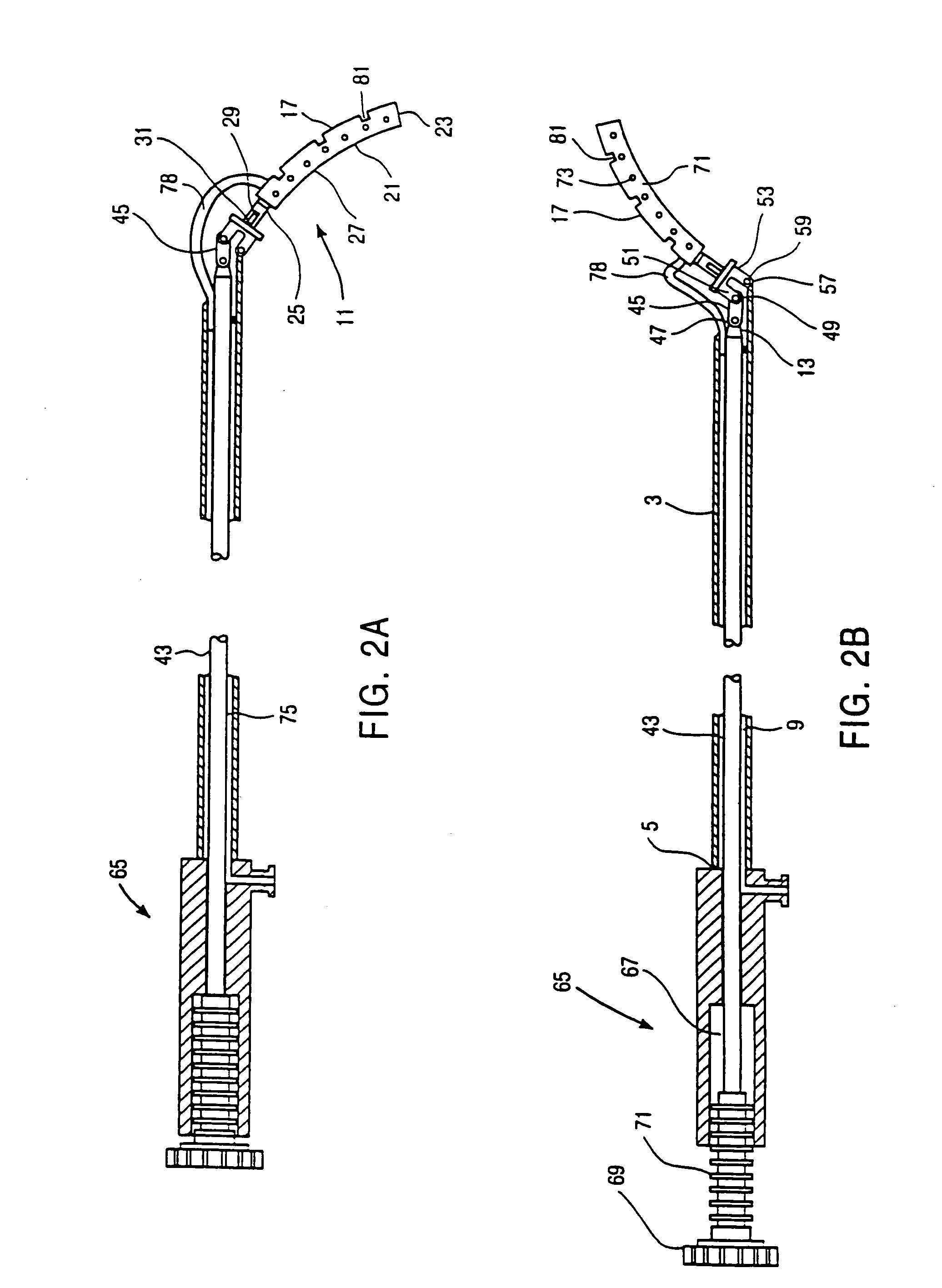
InactiveUS7025722B2Clear away blood and debrisAvoid flowSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTransverse axisMammary artery
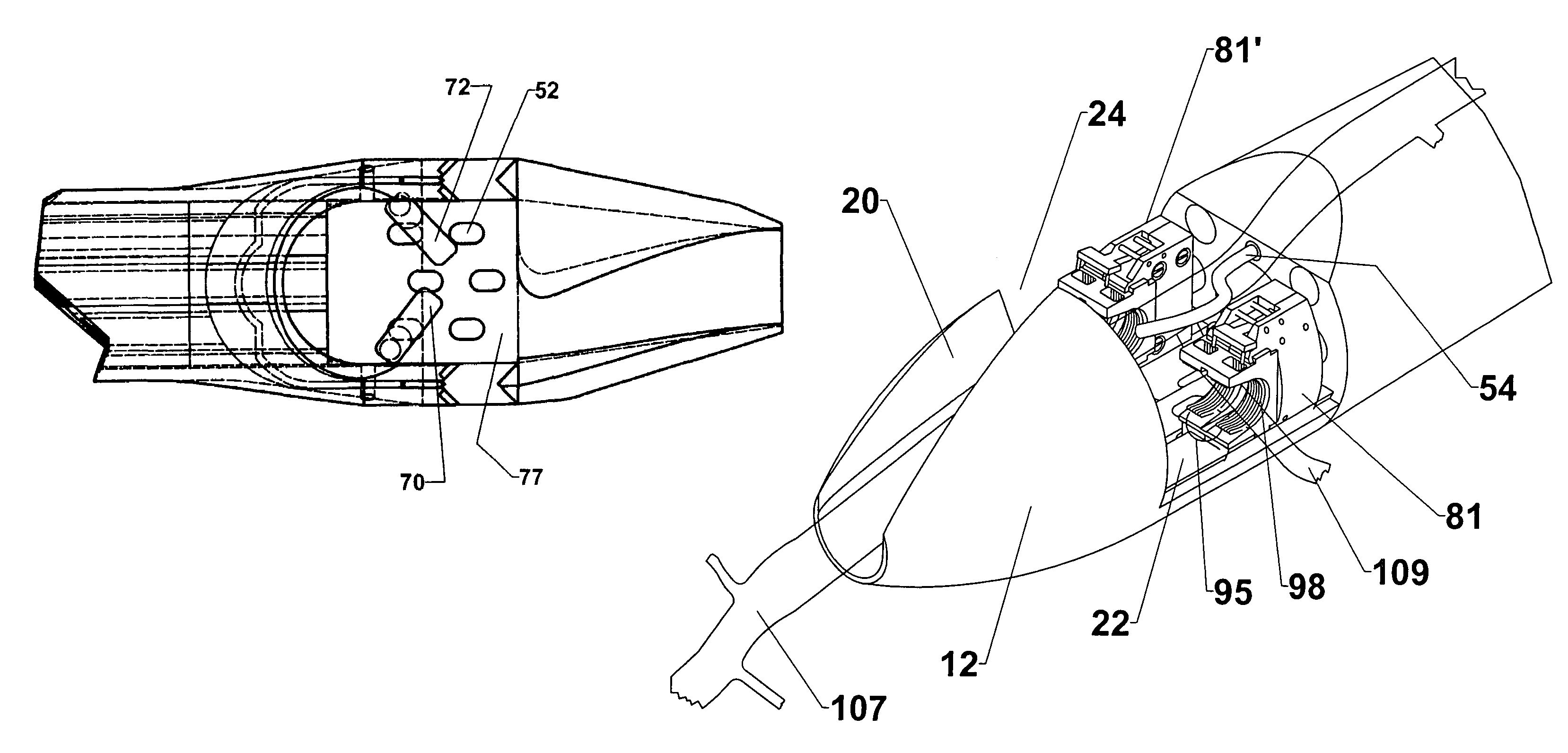
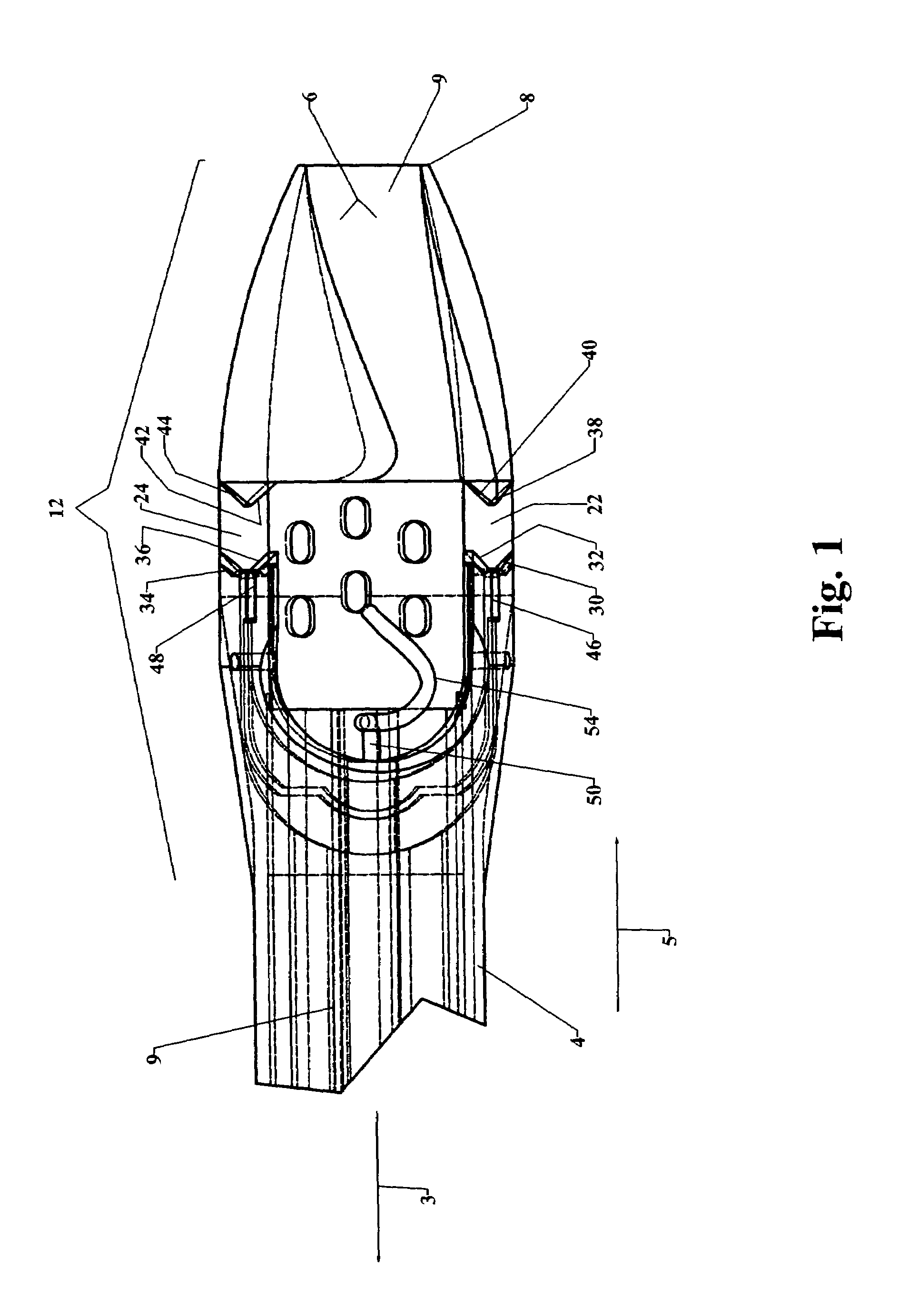
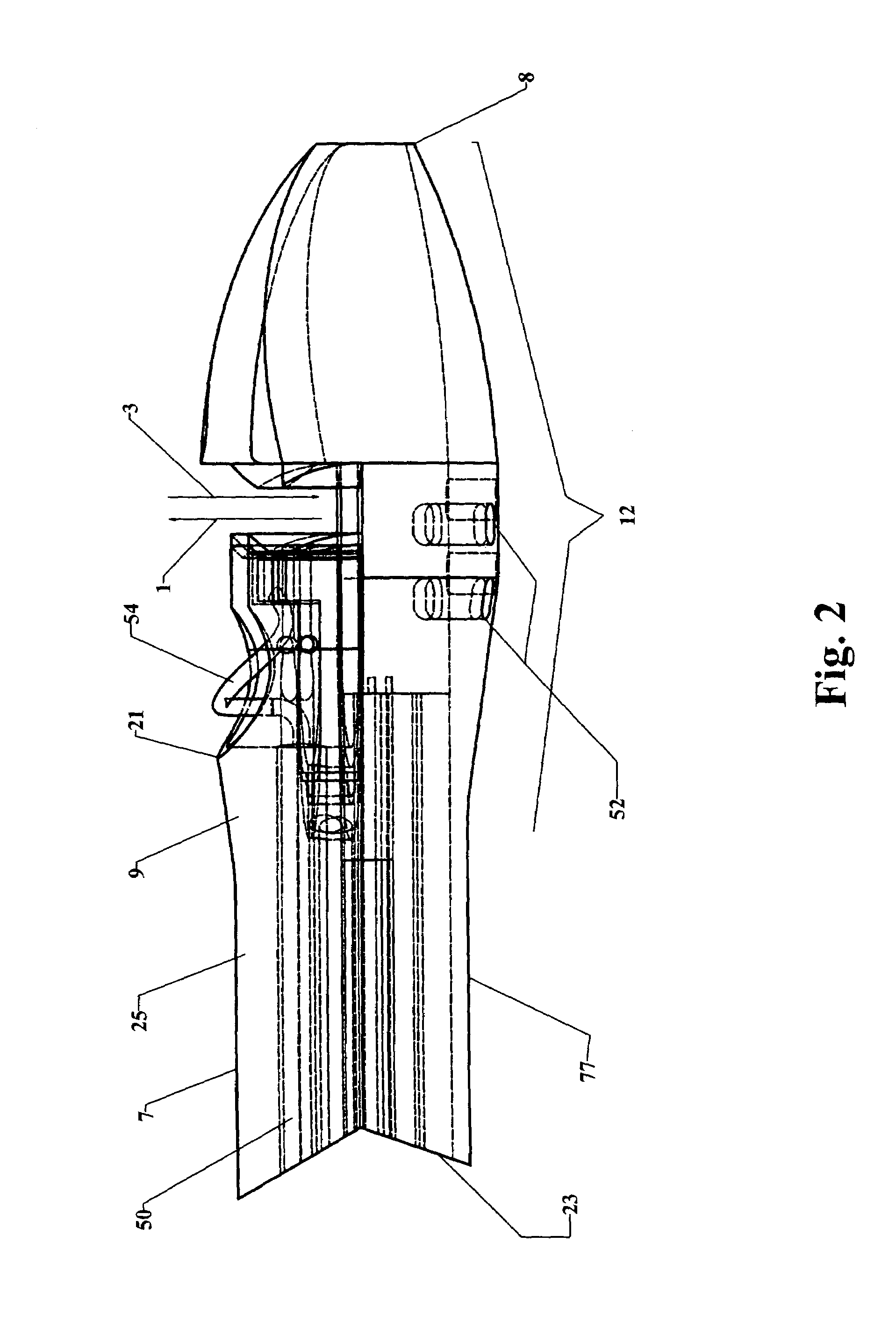
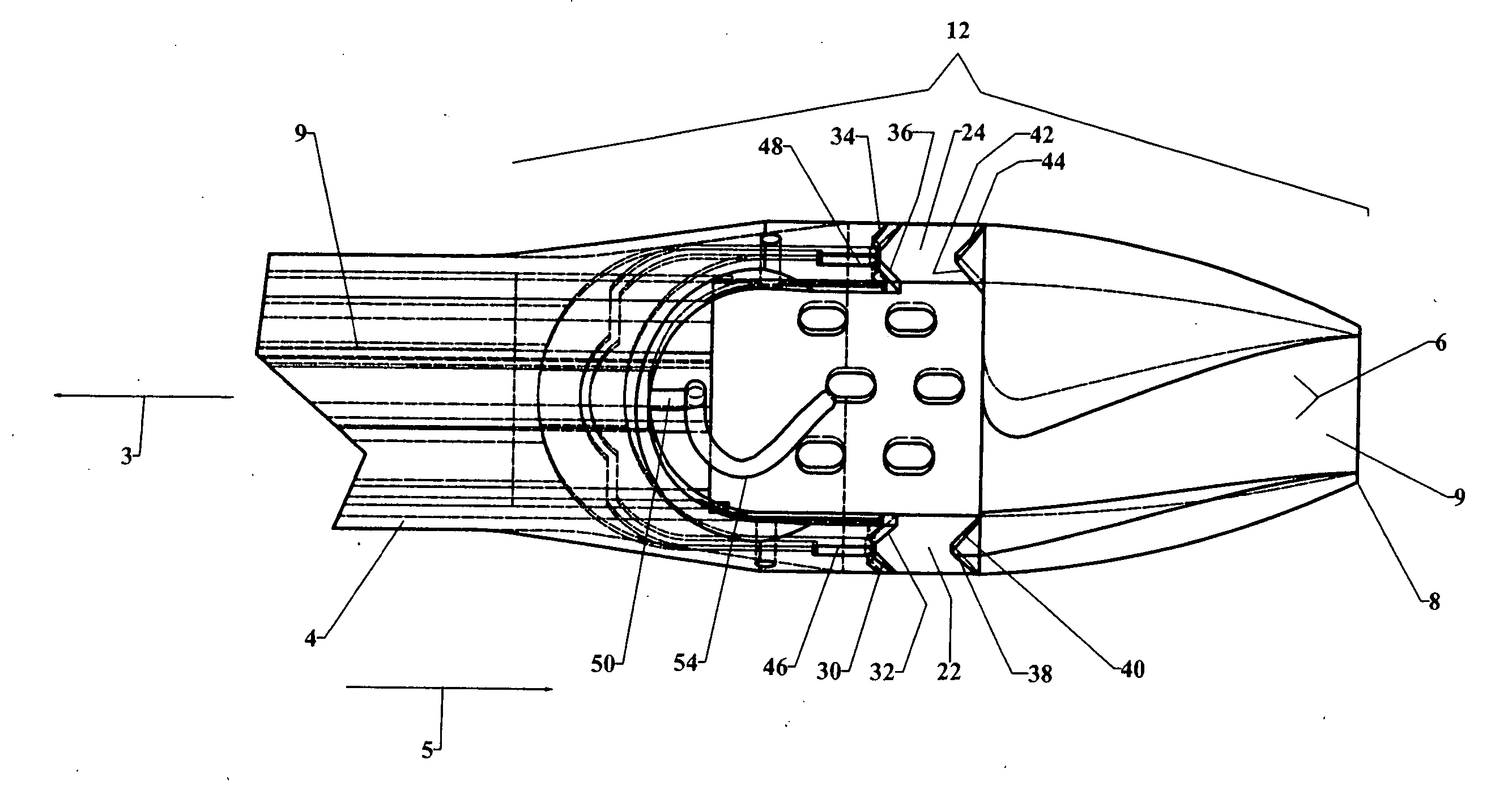
The invention provides a system and method for performing less-invasive surgical procedures within a body cavity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a system and method for isolating a surgical site such as an anastomosis between an internal mammary artery and a coronary artery in a thoracoscopic coronary artery bypass grafting procedure. The system comprises a foot (11) pivotally coupled to the distal end of a shaft (3) by a linkage (13). The foot has first and second engaging portions (15, 17) with contact surfaces for engaging a tissue surface. The engaging portions are movable between an open position, where the contact surfaces are separated by a gap, and a collapsed position, where the foot is configured for delivery through the percutaneous penetration. An actuator, at the proximal end of the shaft, can be rotated to pivot the foot about a transverse axis so that the contact surfaces are oriented generally parallel to the surgical site to apply pressure to the tissue structure on both sides of the surgical site.
Owner:HEARTPORT
Heatless blood vessel harvesting device
InactiveUS7309342B2Enhance and diminish and productionEnhance and diminish releaseCannulasEndoscopesVeinVascular endothelium
A method and device are disclosed directed at harvesting of vessels, such as arteries and veins, especially as required in vessel grafting procedures. The device and method discloses a cannula-like device that provides, identification, capture, manipulation, hemostasis and cleavage of branch vessels from the harvested vessel without need for further devices. In certain preferred embodiments of the disclosed method and device, the disclosed harvesting device achieves branch vessel cleavage and hemostasis without the use of heat producing means such as cautery. In addition, certain embodiments utilize a clip / coil magazine technology so as to enable severance and hemostasis of multiple branch vessels without need for removal of the device from the surgical site. Further embodiments disclose the incorporation and use of irrigants containing CO2, as well as other agents capable of stimulate release of nitric oxide from vascular endothelium are applied to subject vessels so as to enhance the viability of vessels to be harvested as graft material.
Owner:GENOVESI MARK +1
Heatless blood vessel harvesting device
InactiveUS20050070940A1Improve visualizationPrecise positioningCannulasEndoscopesVeinVascular endothelium
A method and device are disclosed directed at harvesting of vessels, such as arteries and veins, especially as required in vessel grafting procedures. The device and method discloses a cannula-like device that provides, identification, capture, manipulation, hemostasis and cleavage of branch vessels from the harvested vessel without need for further devices. In certain preferred embodiments of the disclosed method and device, the disclosed harvesting device achieves branch vessel cleavage and hemostasis without the use of heat producing means such as cautery. In addition, certain embodiments utilize a clip / coil magazine technology so as to enable severance and hemostasis of multiple branch vessels without need for removal of the device from the surgical site. Further embodiments disclose the incorporation and use of irrigants containing CO2, as well as other agents capable of stimulate release of nitric oxide from vascular endothelium are applied to subject vessels so as to enhance the viability of vessels to be harvested as graft material.
Owner:GENOVESI MARK +1
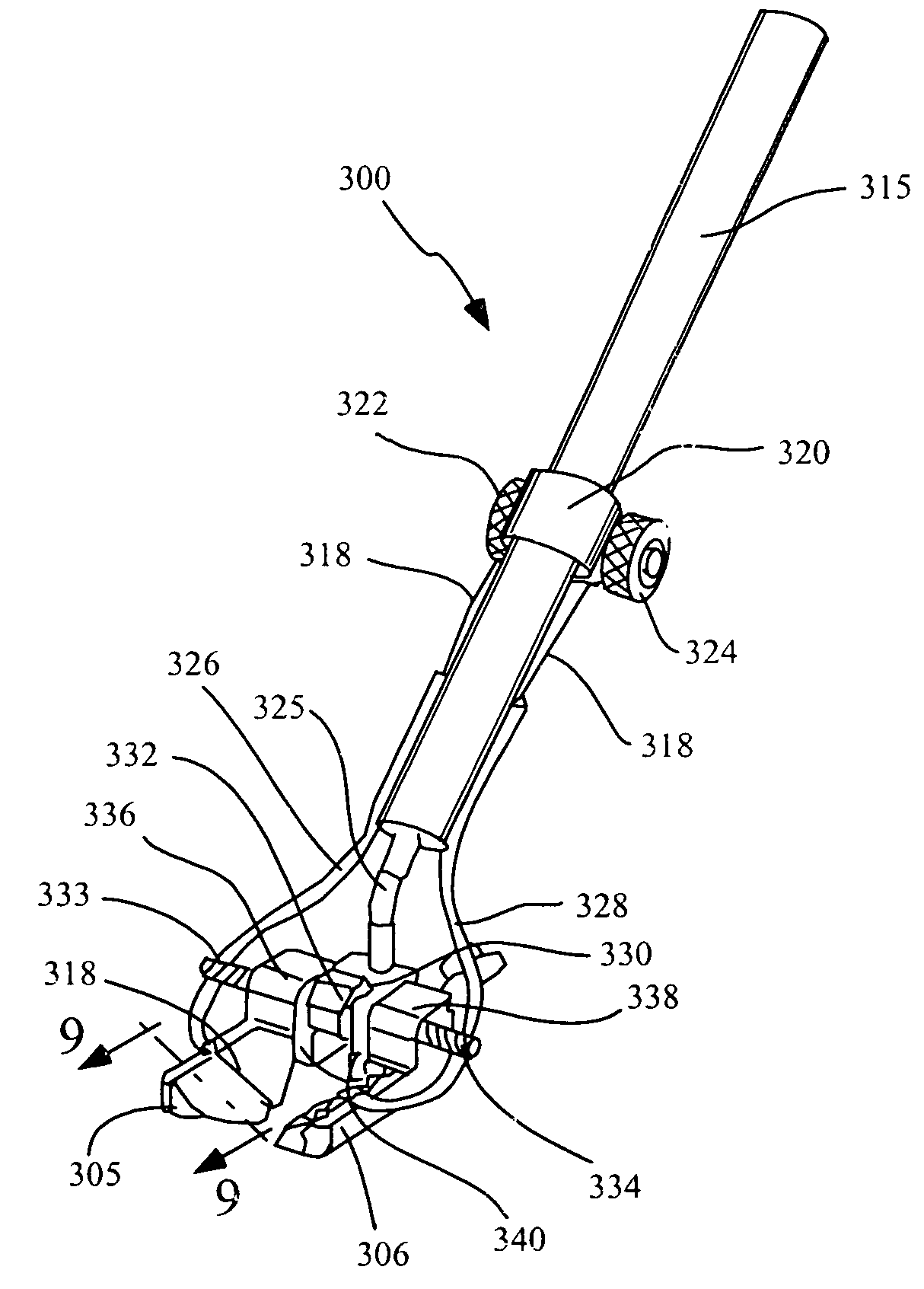
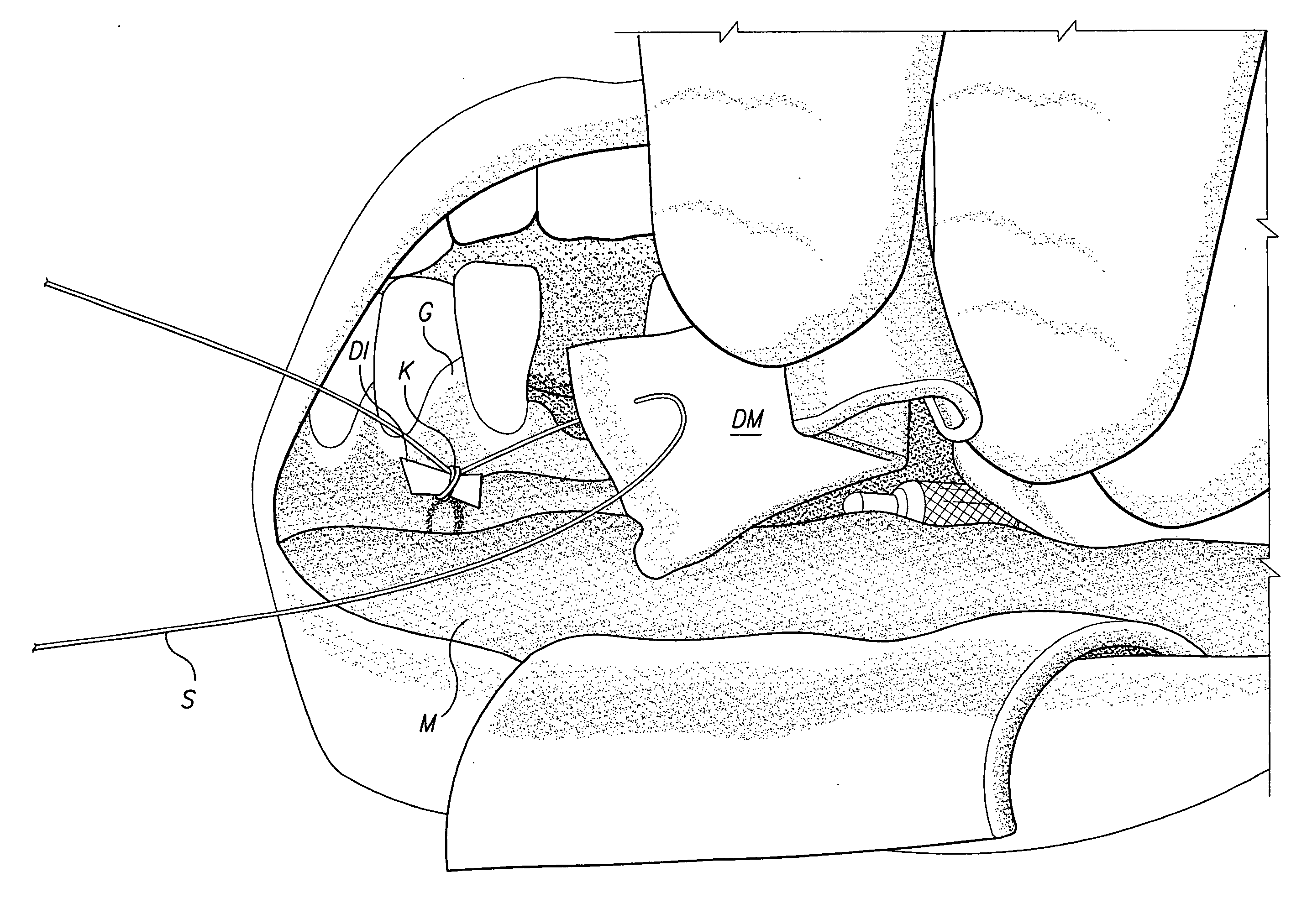
Tissue bonding system and method for controlling a tissue site during anastomosis
A method and system for performing anastomosis uses an anvil to control and support a tissue site during an anastomosis procedure involving tissue bonding techniques such as tissue welding and adhesive tissue bonding. The anvil is particularly useful for supporting a wall of a coronary artery during attachment of a graft vessel in a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The anvil is inserted into a pressurized or unpressurized target vessel and is pulled against an inner wall of the target vessel causing tenting of the thin tissue of the vessel wall. A graft vessel is then advanced to the anastomosis site and an end of the graft vessel is positioned adjacent an exterior of the target vessel. When tissue welding is used, a graft vessel fixture is positioned over the tissue surfaces to be welded in order to clamp the graft and target vessel tissue together. The tissue contacting surfaces of the anvil and / or graft vessel fixture are provided with one or more energy applying surfaces. Energy in the form of RF power, laser energy or ultrasonic energy is then applied to the compressed graft and target vessel tissue to weld the vessels together. When adhesive bonding is used, the adhesive may be applied to mating surfaces of the graft and / or target vessels either before or after the vessels are brought into contact. After tissue bonding is complete, an incision is formed in the wall of the target vessel to allow blood flow between the target vessel and the graft vessel. The incision may be made with an electro-cautery cutting device.
Owner:AESCULAP AG +1
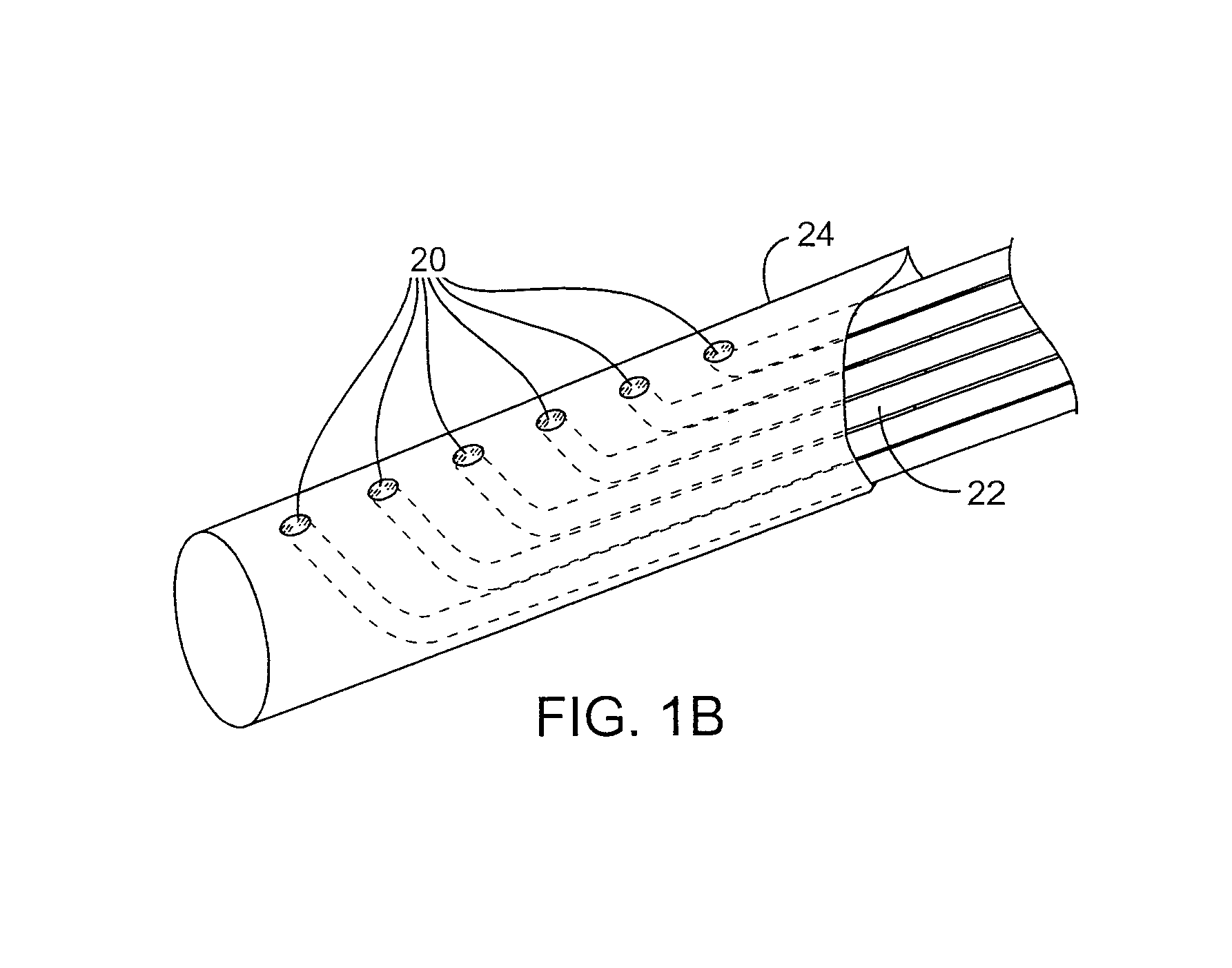
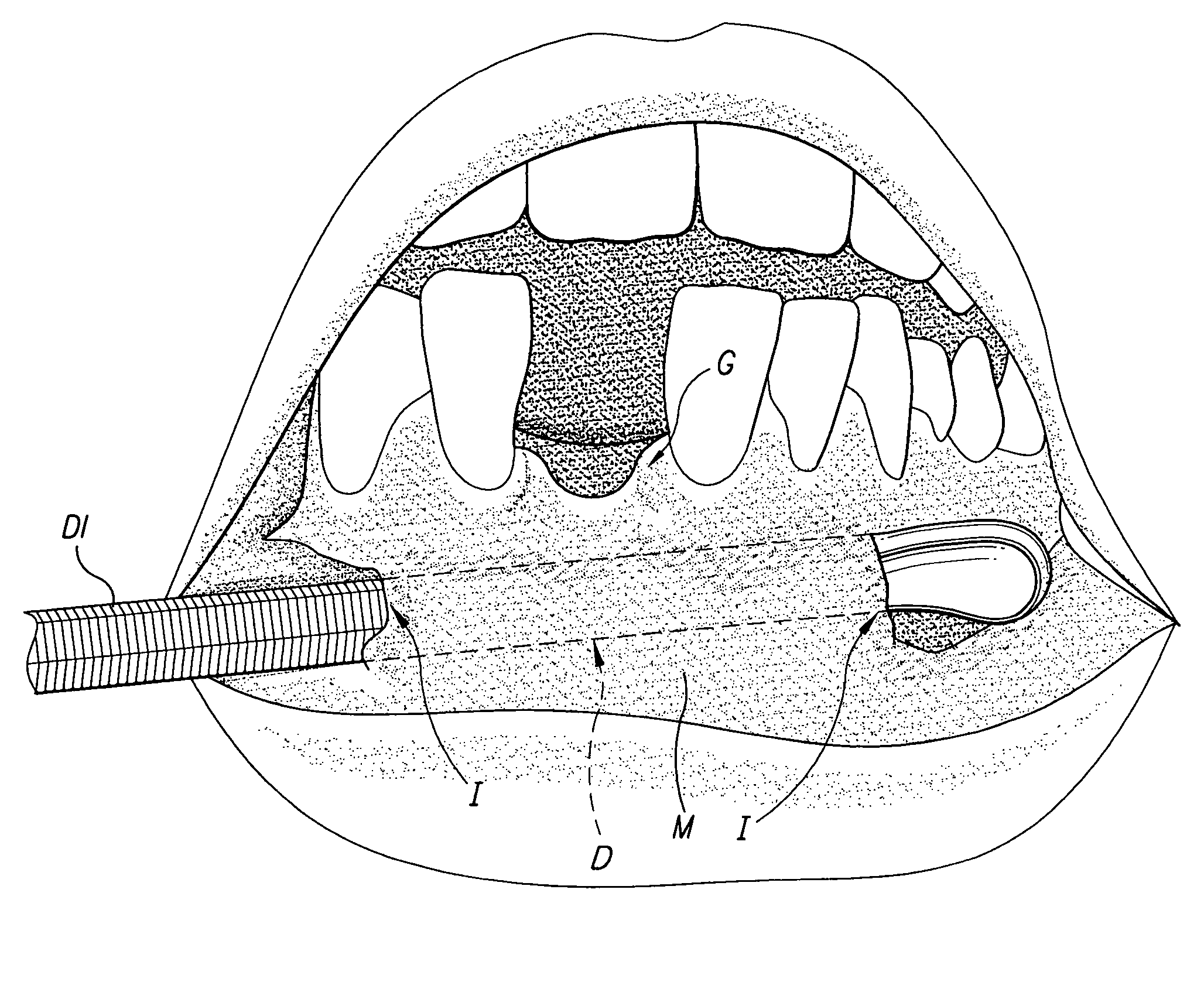
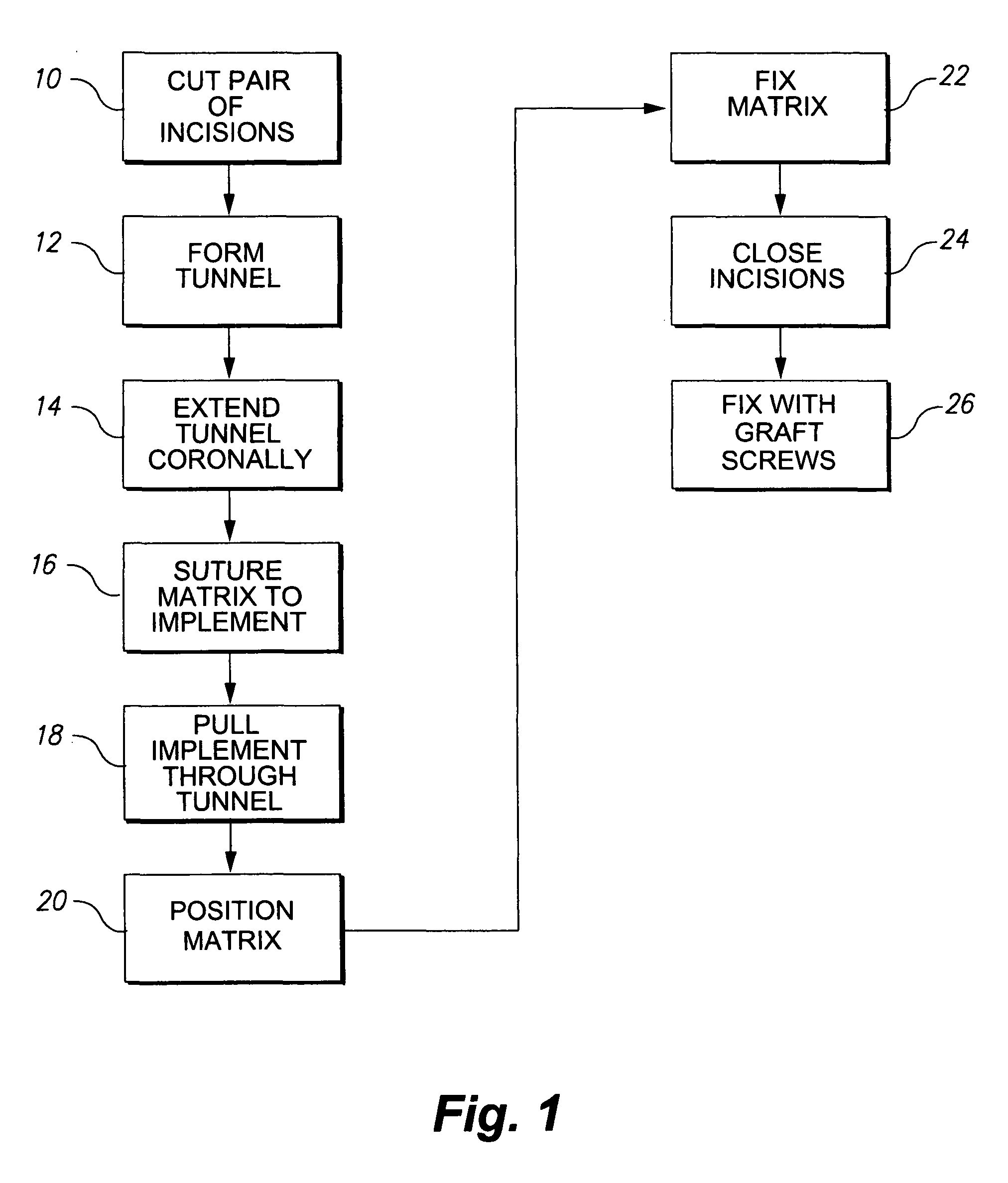
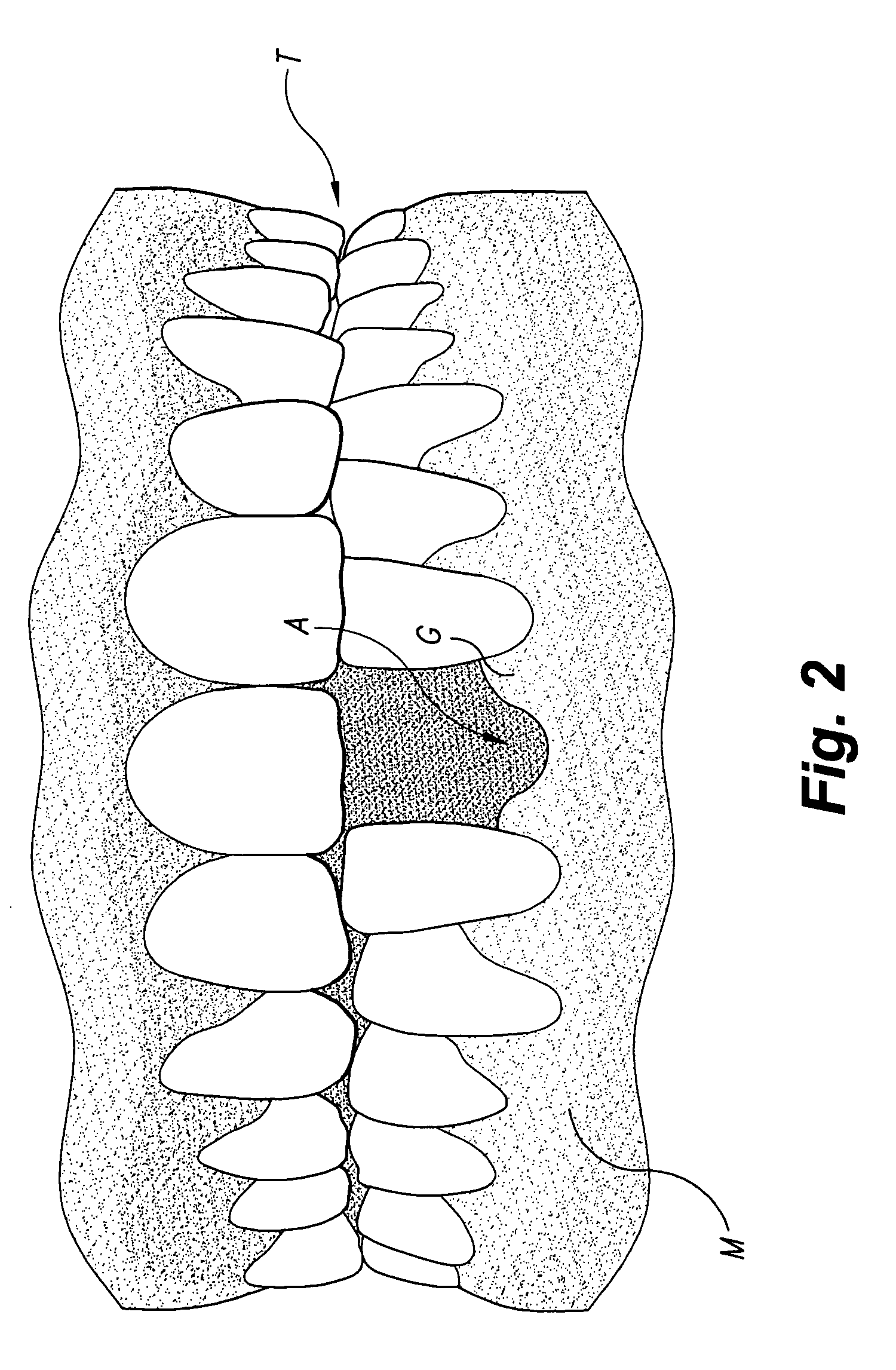
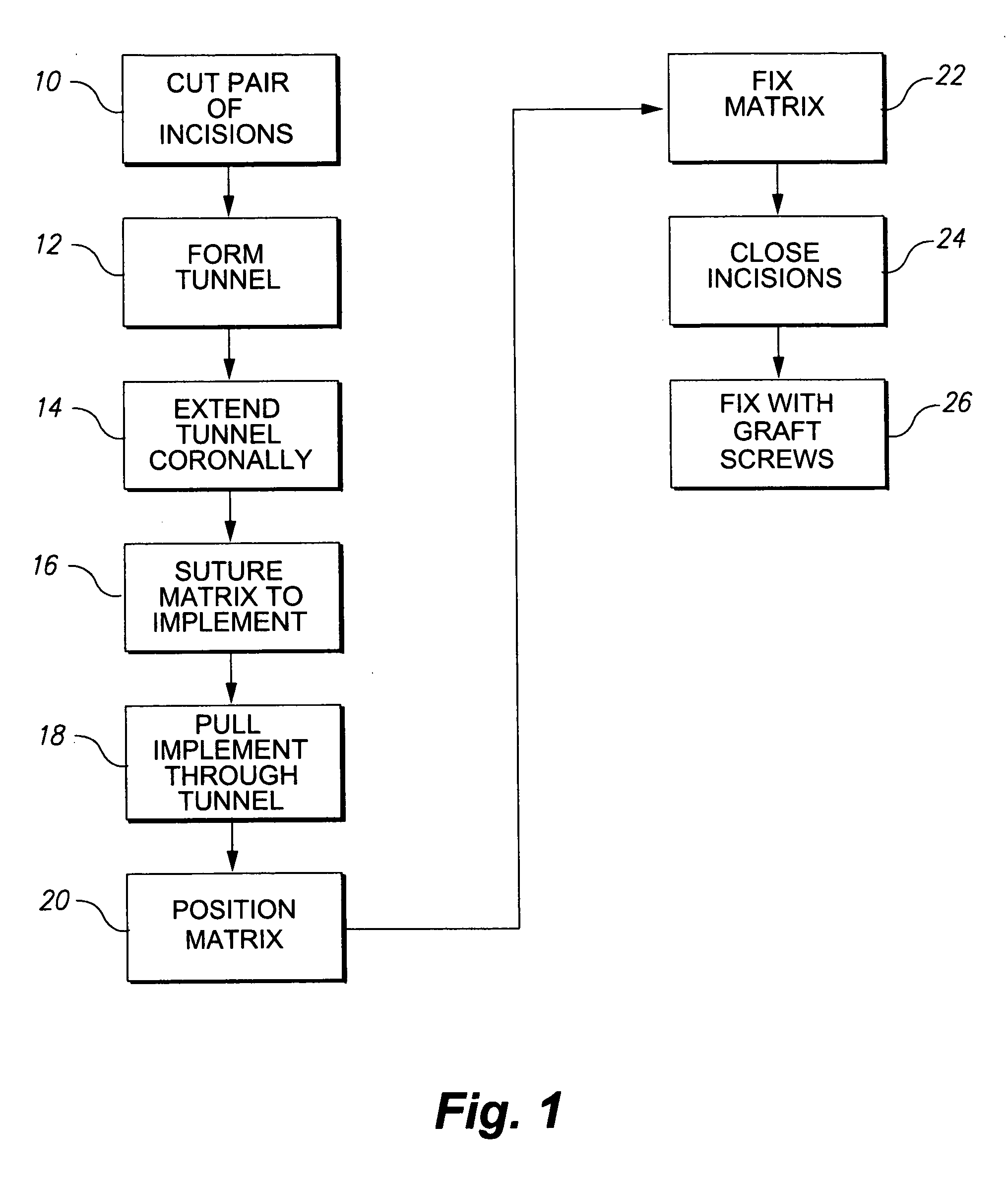
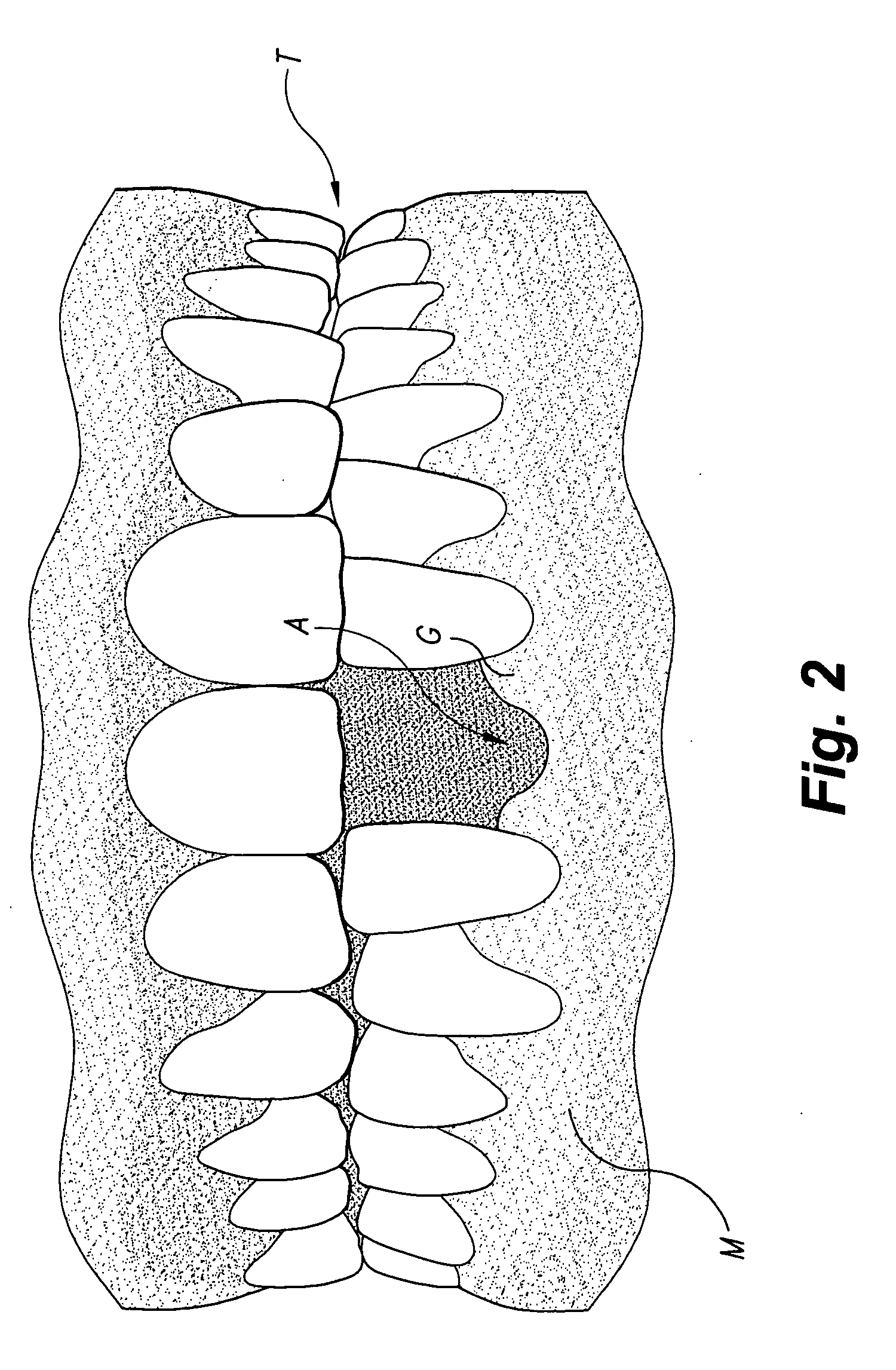
Tunneling method for dental block grafting
The tunneling method for dental block grafting is surgical method for increasing the thickness of the soft tissue of the mouth prior to performing block grafting procedures for dental implants. The method includes cutting a pair of incisions in the mucosa. A tunnel is formed through the mucosa which extends between, and connects, the pair of incisions. The tunnel is then extended coronally to undermine tissue covering the recipient site. An acellular dermal matrix is then sutured to an exposed end of a dental implement pulled through the tunnel to position the acellular dermal matrix within the tunnel. The acellular dermal matrix is then positioned over the recipient site using a periosteal elevator, and the acellular dermal matrix is fixed coronally by suspension sutures. The pair of incisions are closed with interrupted sutures, and a block graft is fixed to the recipient site by a pair of titanium screws.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
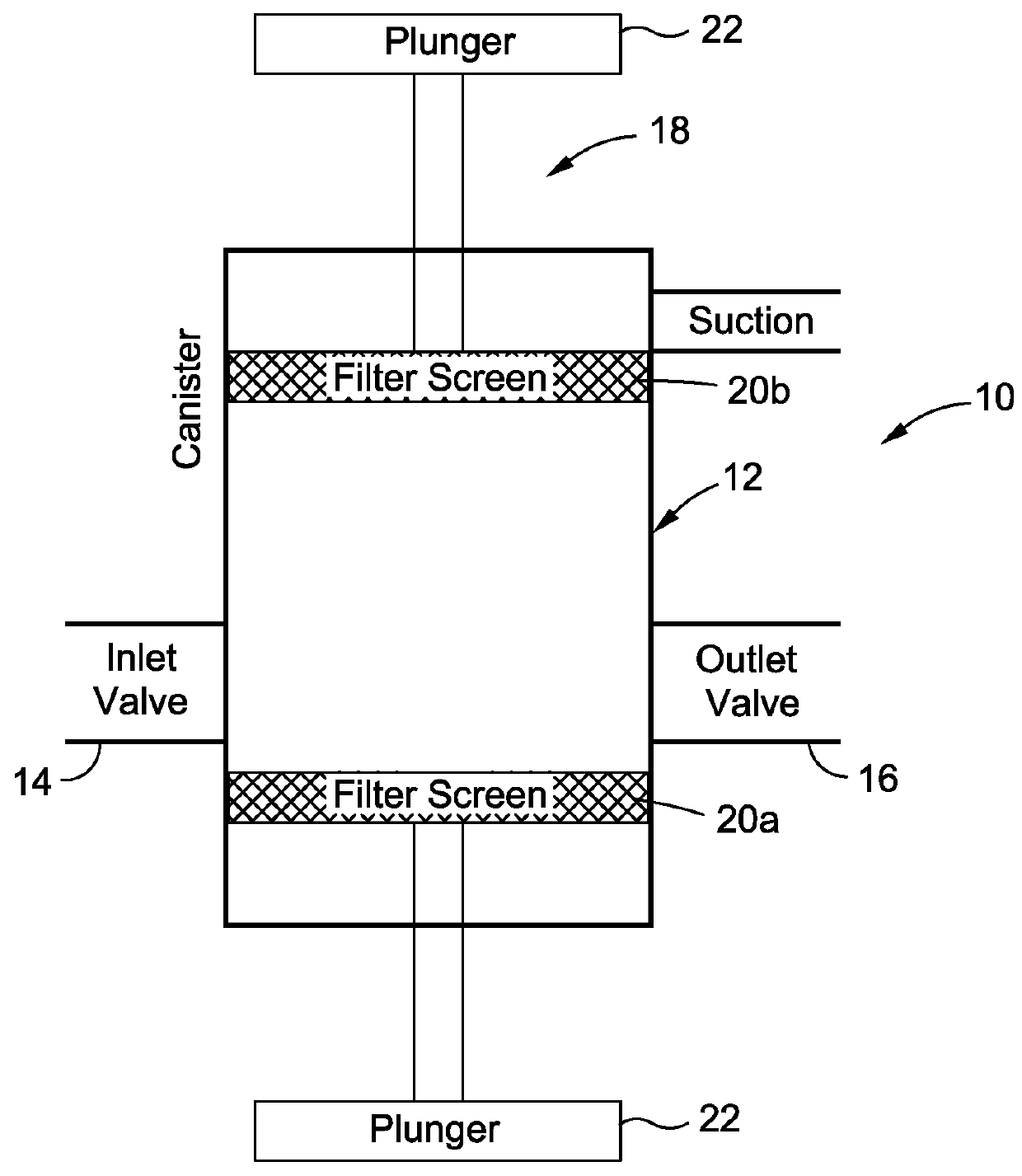
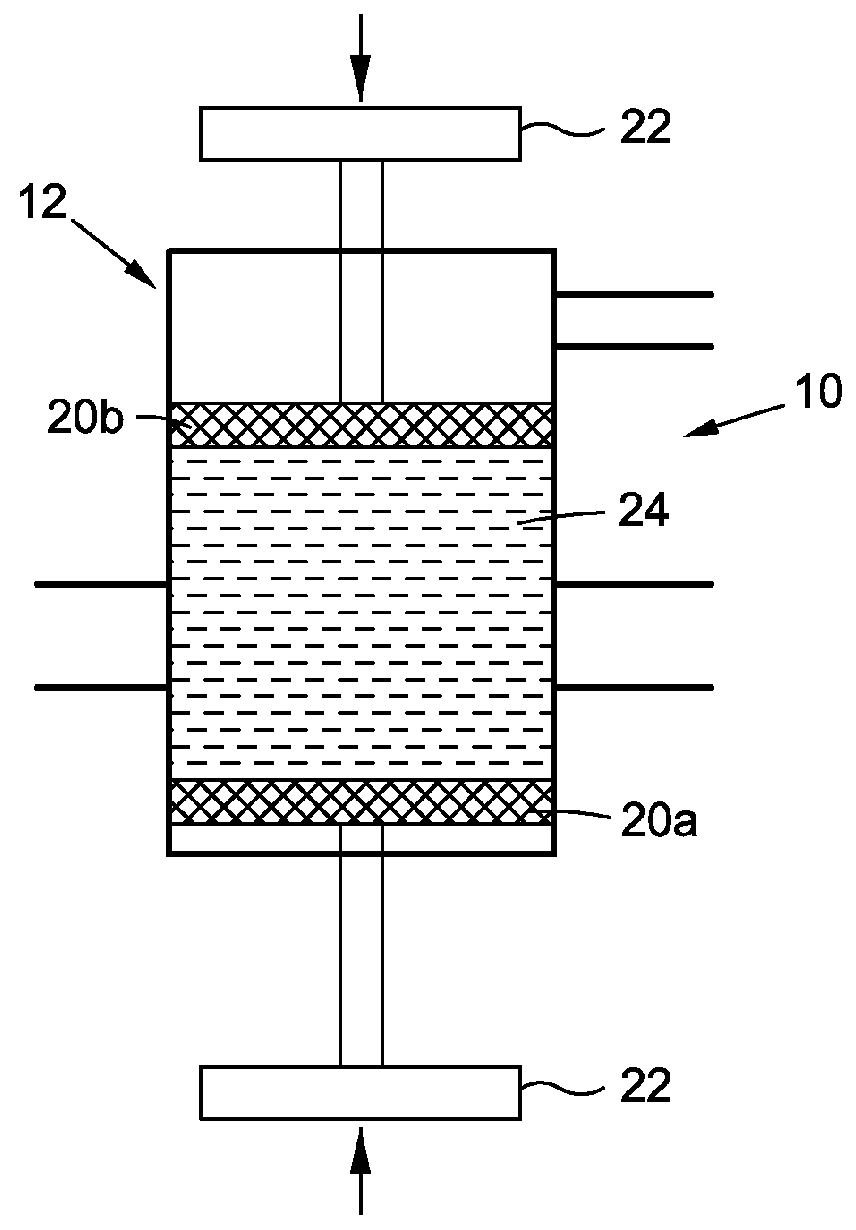
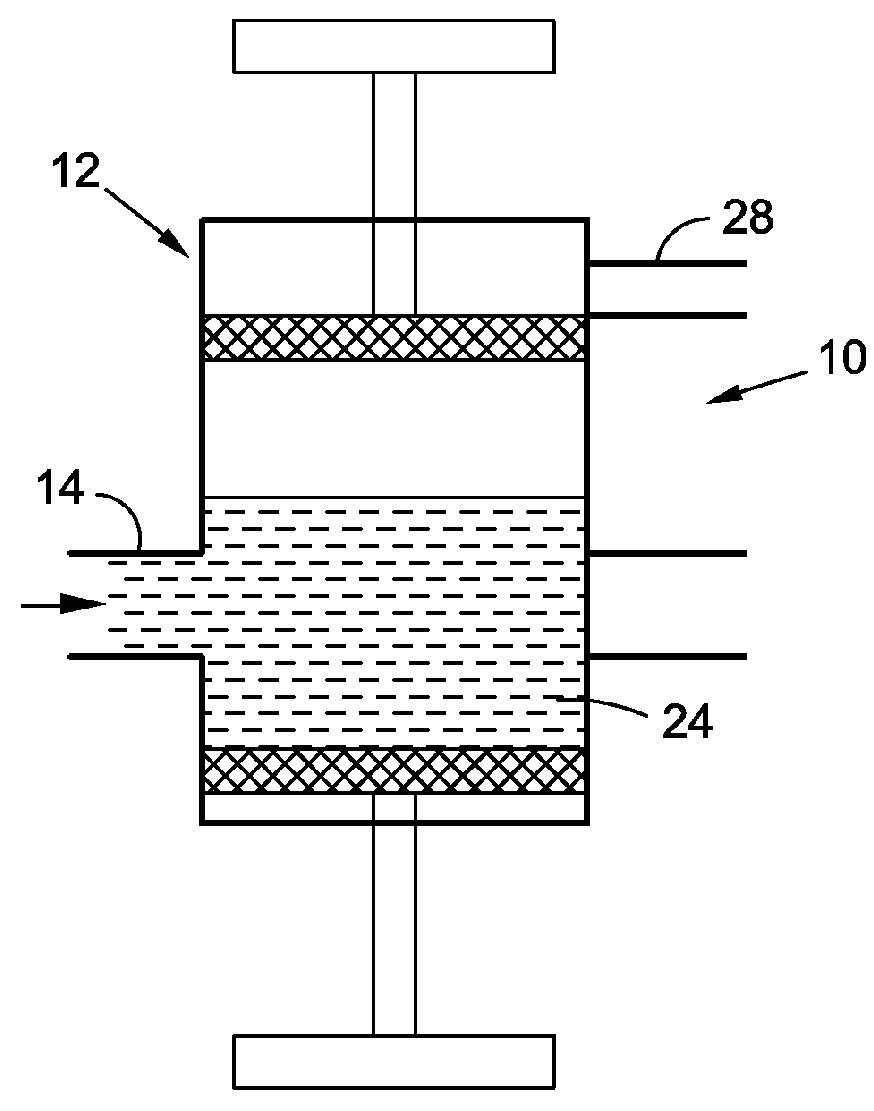
Fat processing system
ActiveUS9248384B2Liquid suspension thickening by filtrationMedical devicesCellular componentFat grafting
Methods and devices for treating lipoaspirate for use in fat grafting procedures are provided and generally include a canister for containing lipoaspirate, a separation mechanism structured to separate both oils and other materials from cellular components of lipoaspirate contained in the canister. The separation mechanism includes filters having different filtering capacities, for example, different pore sizes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
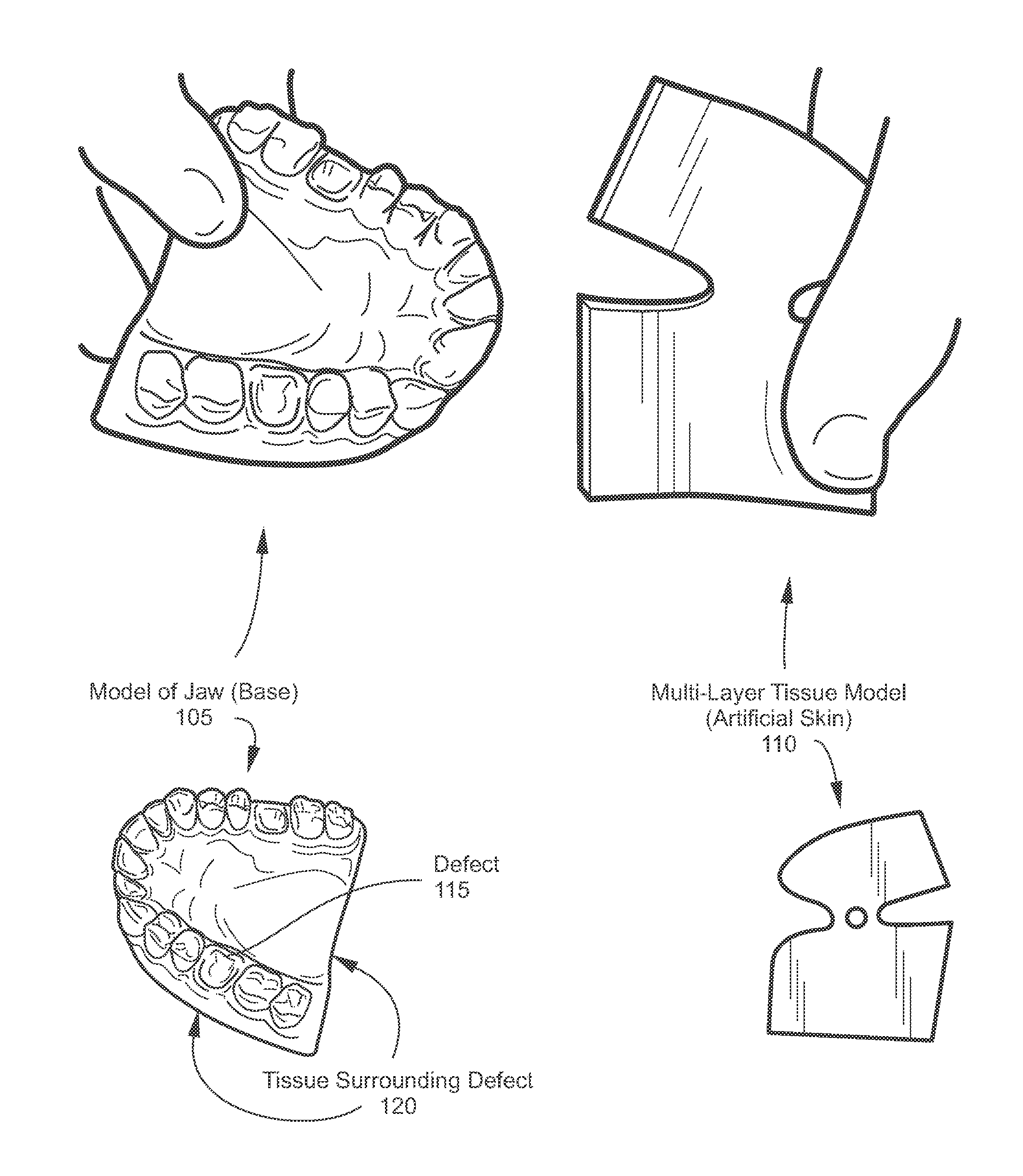
Bone augmentation training system
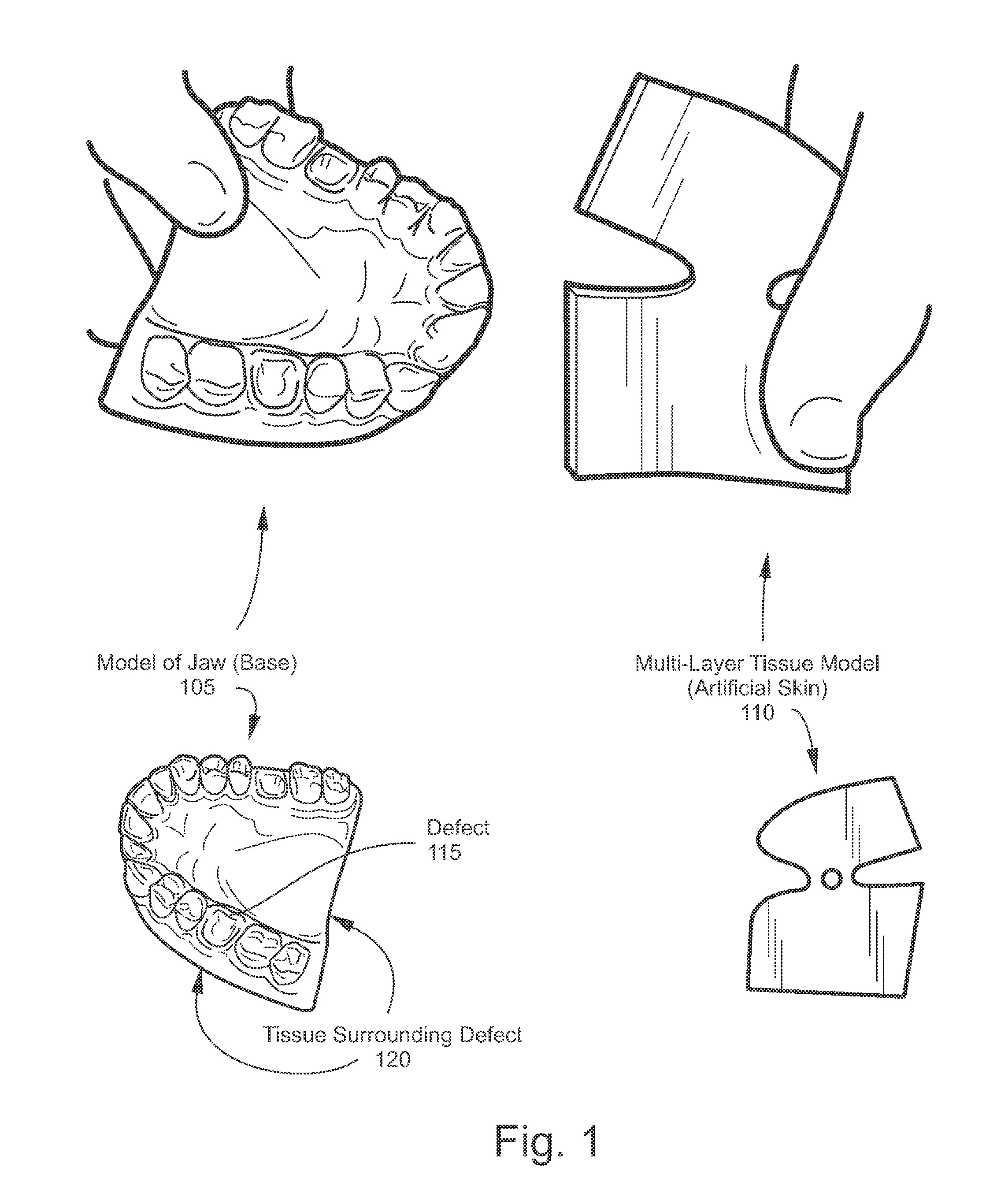
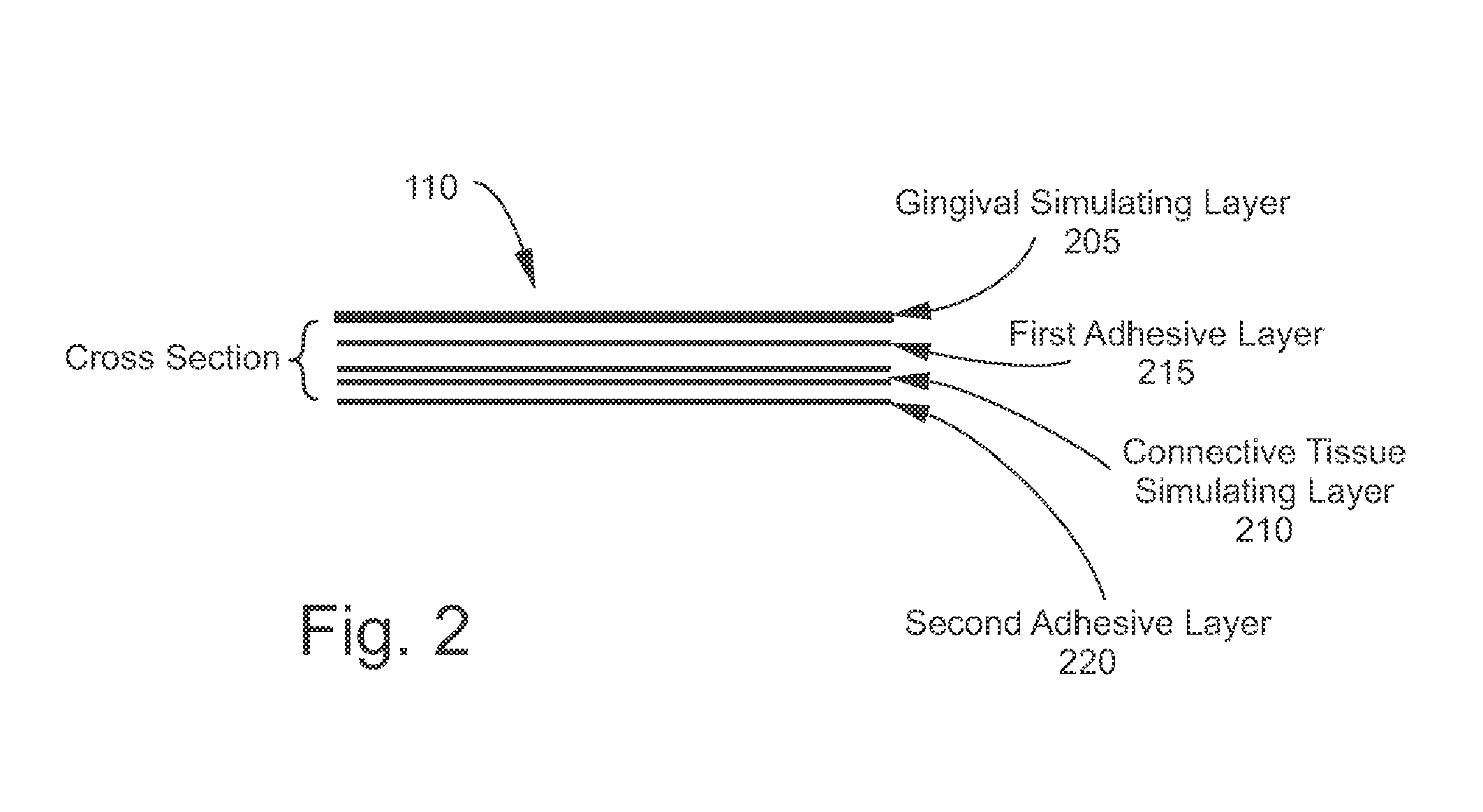
ActiveUS8641422B2Practical and efficientElasticityEducational modelsConnective tissueGraft procedure
The disclosed apparatuses, methods, and systems provide for simulations of real-life bone graft procedures. One embodiment is a model that includes a base in the shape of at least a portion of a maxillary or mandibular dental arch, and includes a defect on its surface. The model also includes a multi-layer tissue model configured to overlay at least a portion of the base in a covering relationship with the defect and surrounding tissue. The multi-layer tissue model includes a gingival simulating layer, connective tissue simulating layer, and two adhesive layers. The first of the two adhesive layers connects the connective tissue simulating layer to the gingival simulating layer, and the second adhesive layer, affixed to the connective tissue simulating layer opposite the first layer, is configured to adhere the multi-layer tissue model to the base. The multi-layer tissue model also includes a removable backing covering the second adhesive layer.
Owner:FRANCAVILLA VINCENT
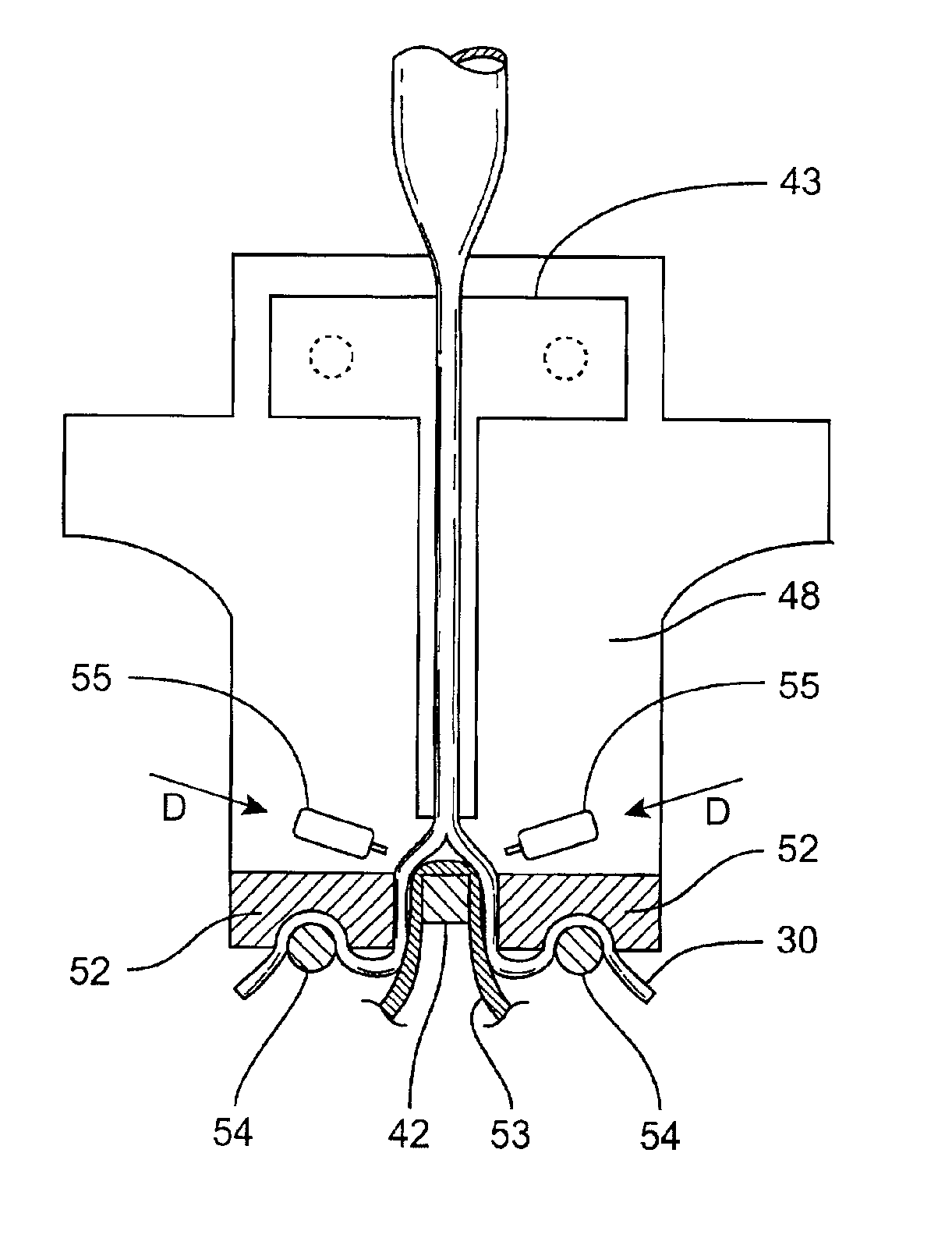
Intravascular balloon occlusion device and method for using the same
InactiveUS6966903B2Overcome problemsKeeping the surgical field clearStentsBalloon catheterCoronary arteriesCoronary Artery Bypasses
An intravascular balloon occlusion device according to the invention is shown. The device is ideally suited for use in a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The device includes a body having at least one selectively inflated balloon provided on the distal end thereof. Preferably, the body is a closed end body so that fluid can only flow from the proximal end of the body into the balloon. In use, the distal end of the body and the balloon are inserted into an aperture provided in the aorta. The balloon is inflated and then the device is retracted until the balloon seats against the incision or aperture in the aorta, thereby effectively sealing the aperture from the blood flow through the aorta, but not occluding blood flow through the body of the aorta itself. Next, the graft vessel is telescopically positioned on the occlusion device and mounted to the aorta. Once the vessel is secured thereto, the balloon is deflated and then the occlusion device is retracted from both the aorta and the graft vessel. Finally, the second end of the graft vessel is mounted to the appropriate coronary artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Heatless blood vessel harvesting device
InactiveUS20080097145A1Enhance and diminish and productionEnhance and diminish releaseCannulasDiagnosticsVeinVascular endothelium
A method and device are disclosed directed at harvesting of vessels, such as arteries and veins, especially as required in vessel grafting procedures. The device and method discloses a cannula-like device that provides, identification, capture, manipulation, hemostasis and cleavage of branch vessels from the harvested vessel without need for further devices. In certain preferred embodiments of the disclosed method and device, the disclosed harvesting device achieves branch vessel cleavage and hemostasis without the use of heat producing means such as cautery. In addition, certain embodiments utilize a clip / coil magazine technology so as to enable severance and hemostasis of multiple branch vessels without need for removal of the device from the surgical site. Further embodiments disclose the incorporation and use of irrigants containing CO2, as well as other agents capable of stimulate release of nitric oxide from vascular endothelium are applied to subject vessels so as to enhance the viability of vessels to be harvested as graft material.
Owner:GENOVESI MARK +1
Tissue stabilizer having an articulating lift element
InactiveUS20080064919A1Easy to operateFine surfaceSurgical pincettesProsthesisSurgical operationCoronary Artery Bypasses
Devices and methods are disclosed for stabilizing tissue within a patient's body during a surgical operation to provide a relatively motionless surgical field, such as during a coronary artery bypass graft procedure. The devices include tissue stabilizers which engage and provide stabilization to a targeted area of tissue and further have the ability to engage and manipulate some portion of tissue within or adjacent the targeted area to improve the surgical presentation of that portion of tissue. The tissue stabilizer typically has one or more stabilizer feet which have a first foot portion configured to provide stabilization to the targeted tissue and a second foot portion moveable relative to the first foot portion for manipulating a portion of tissue to improve the surgical presentation.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Tunneling method for dental block grafting
The tunneling method for dental block grafting is surgical method for increasing the thickness of the soft tissue of the mouth prior to performing block grafting procedures for dental implants. The method includes cutting a pair of incisions in the mucosa. A tunnel is formed through the mucosa which extends between, and connects, the pair of incisions. The tunnel is then extended coronally to undermine tissue covering the recipient site. An acellular dermal matrix is then sutured to an exposed end of a dental implement pulled through the tunnel to position the acellular dermal matrix within the tunnel. The acellular dermal matrix is then positioned over the recipient site using a periosteal elevator, and the acellular dermal matrix is fixed coronally by suspension sutures. The pair of incisions are closed with interrupted sutures, and a block graft is fixed to the recipient site by a pair of titanium screws.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Bone Graft Substitute Containing a Temporary Contrast Agent and a Method of Generating Such and A Method of Use Thereof
A bone graft substitute for use in orthopedic bone grafting procedures comprising a radiolucent bone graft substitute combined with a temporary radiopaque agent. Methods of making and using the composition are also disclosed. Bone graft substitutes have become an effective means of regenerating bone in orthopedic procedures where bone loss results from surgically created defects or traumatic injury to the bone. Bone graft substitutes include mineral-based materials such as hydroxyapatite, calcium phosphates, and calcium phosphosilicates as well as allograft-derived materials and xenograft-derived materials such as collagen-based matrices and demineralized bone matrices.
Owner:BACTERIN INT
System and method for planning and executing autologous bone grafting procedures
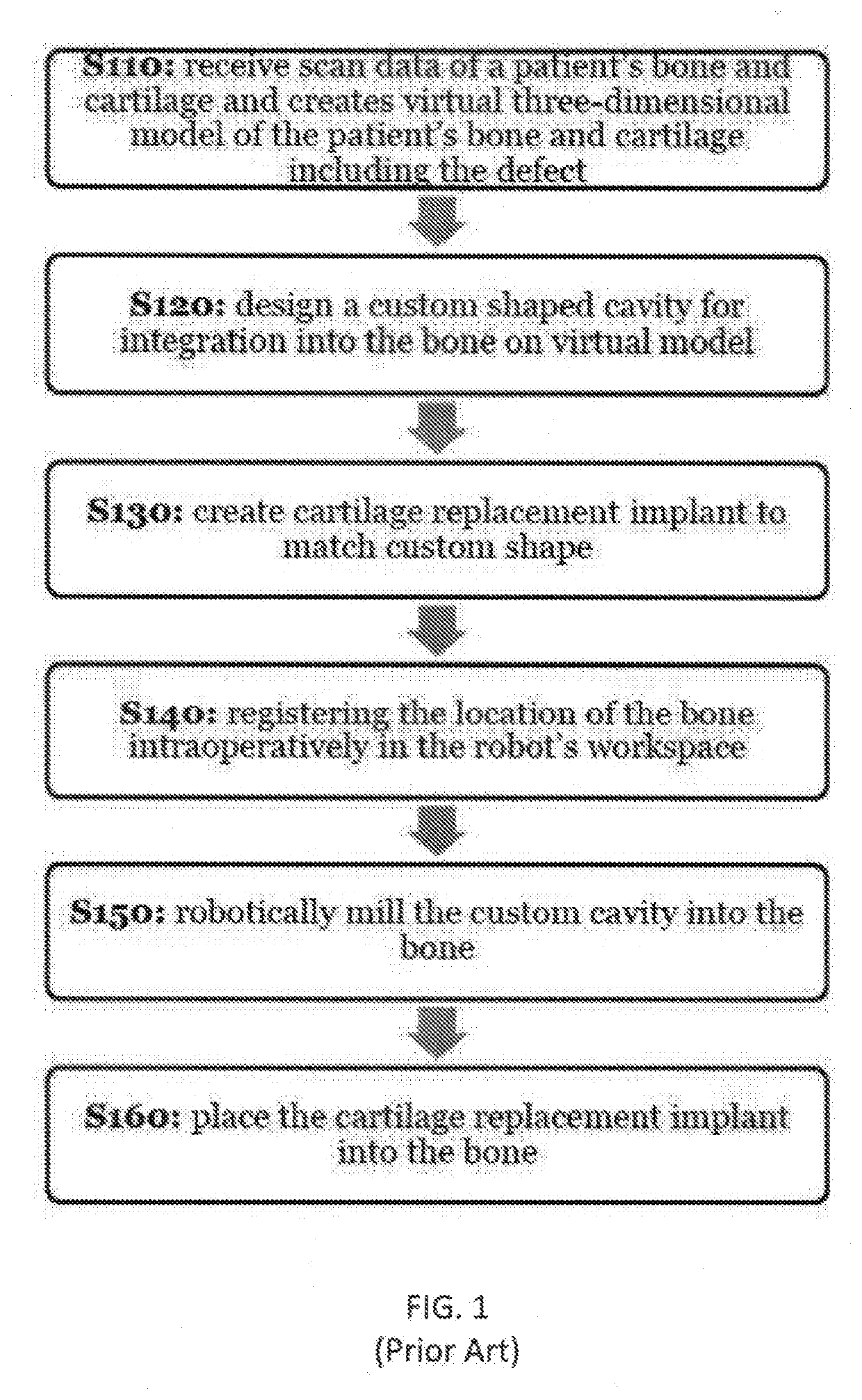
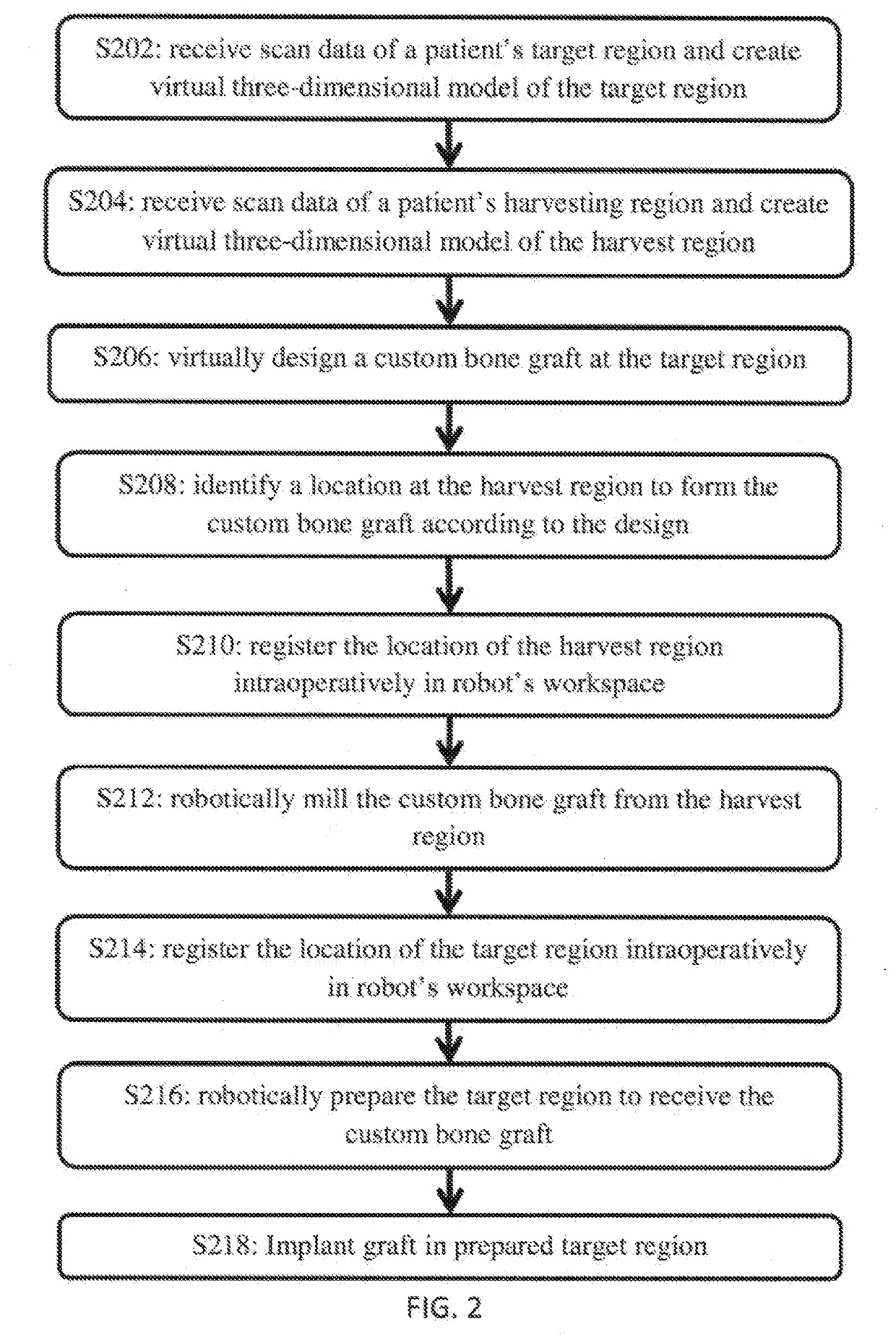
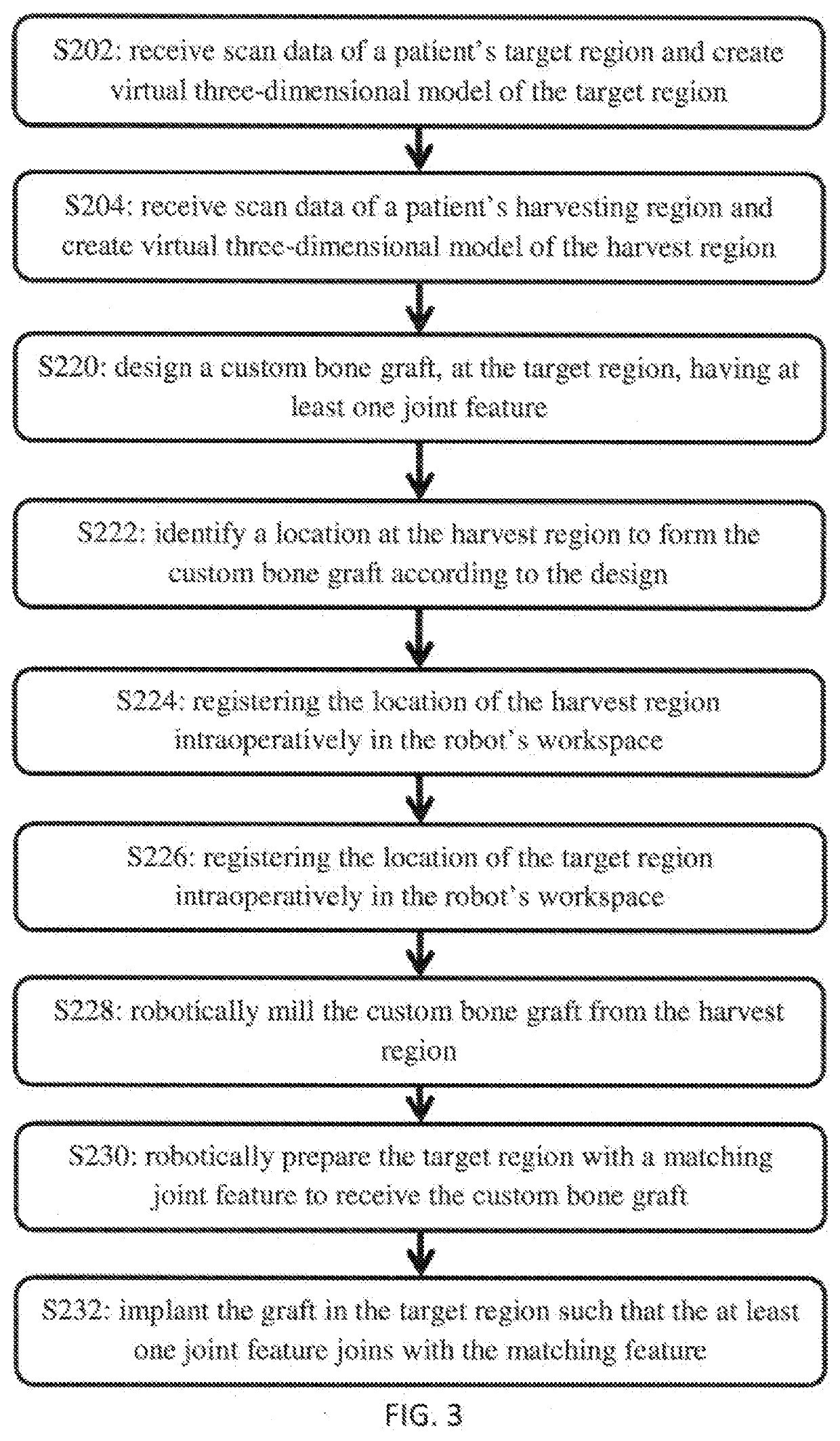
InactiveUS20200121391A1Surgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingGraft procedureBone grafting
A method for planning a bone grafting procedure includes the collection of imaging scan data of the target region and of a harvest region as a source for a bone graft complementary to the target region. Virtual bone model and harvest regions are generated. A computer processor determines at least one parameter for a bone graft model complementary to the target region. A location at the harvest region for the bone graft is identified based on the bone graft model. The location of the harvest region is registered to a first computer-assist device and the bone graft is harvested. The target region is registered to the first computer-assist device or another device. The cutting characteristics for the target region are communicated to the first computer-assist device or the other device to receive the bone graft. A surgical system for performing the computerized method is also provided.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Fgf-18 in graft transplantation and tissue engineering procedures
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com