Patents
Literature
221 results about "MD5" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Although MD5 was initially designed to be used as a cryptographic hash function, it has been found to suffer from extensive vulnerabilities. It can still be used as a checksum to verify data integrity, but only against unintentional corruption. It remains suitable for other non-cryptographic purposes, for example for determining the partition for a particular key in a partitioned database.
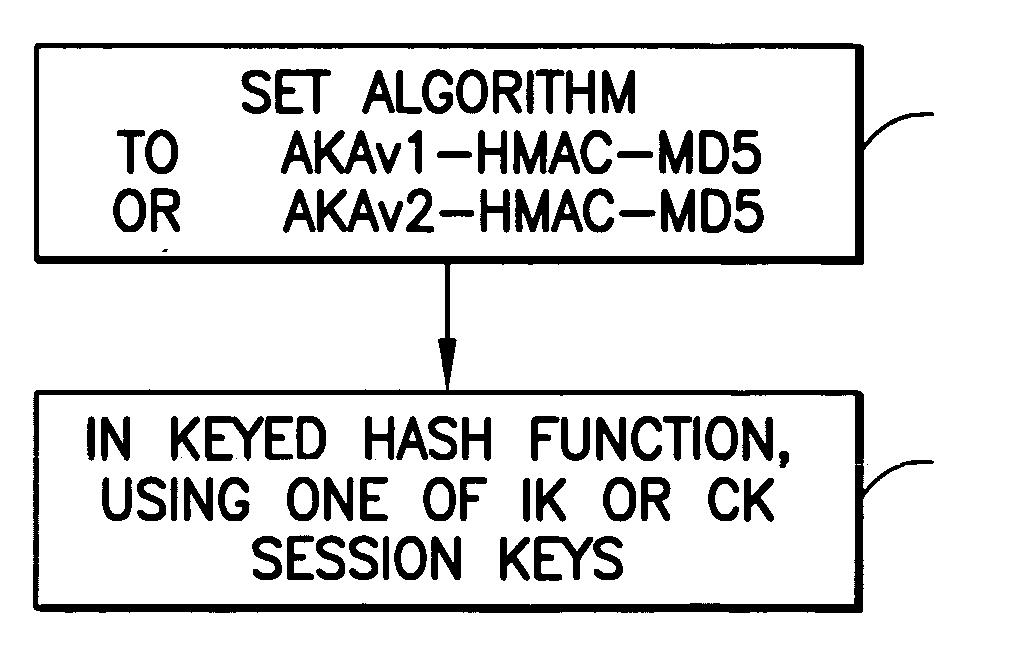
Method of protecting digest authentication and key agreement (AKA) against man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack
ActiveUS20050044365A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsHash functionCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and system to discourage a MITM attacker in a data communications system that includes client and a server. The method includes, in a Digest Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) challenge sent to the client from the server, setting an “algorithm” field to ‘algorithm=“AKAv1-HMAC-MD5”’ for directing the client to use the HMAC-MD5 keyed hash function when producing Digest credentials; and using at least one of an AKA Integrity Key (IK) or an AKA Cipher Key (CK) in the keyed hash function.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
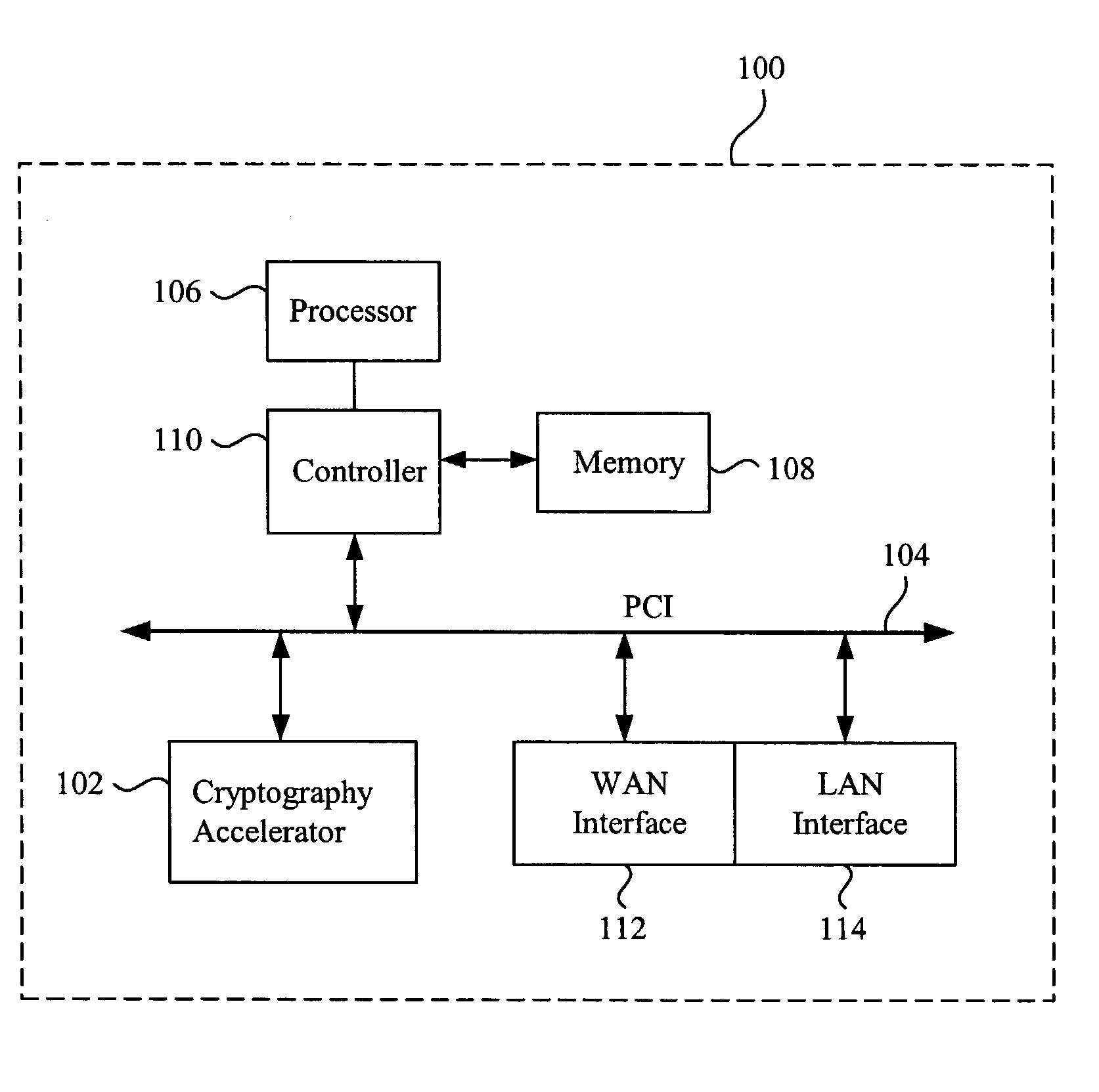
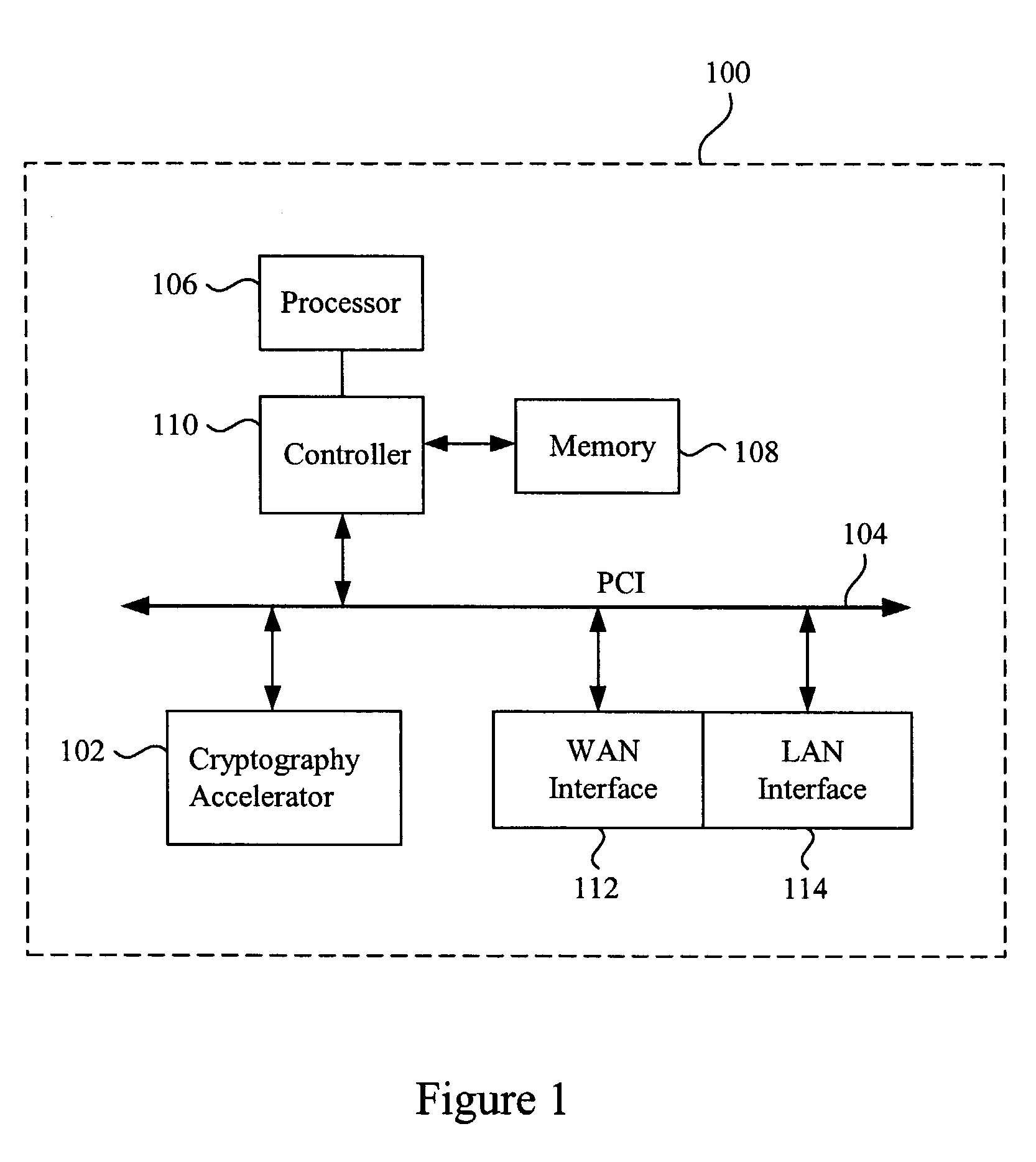
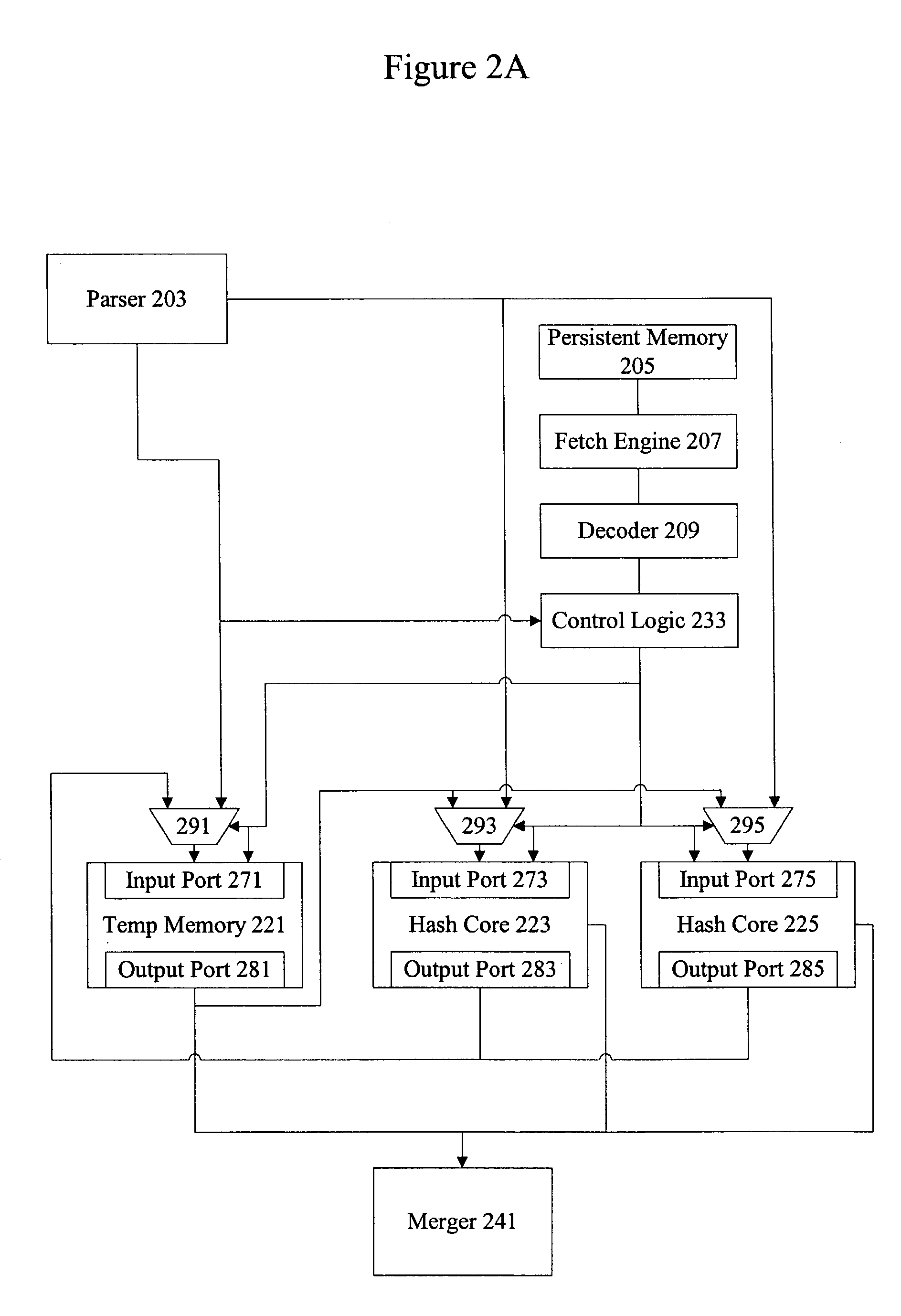
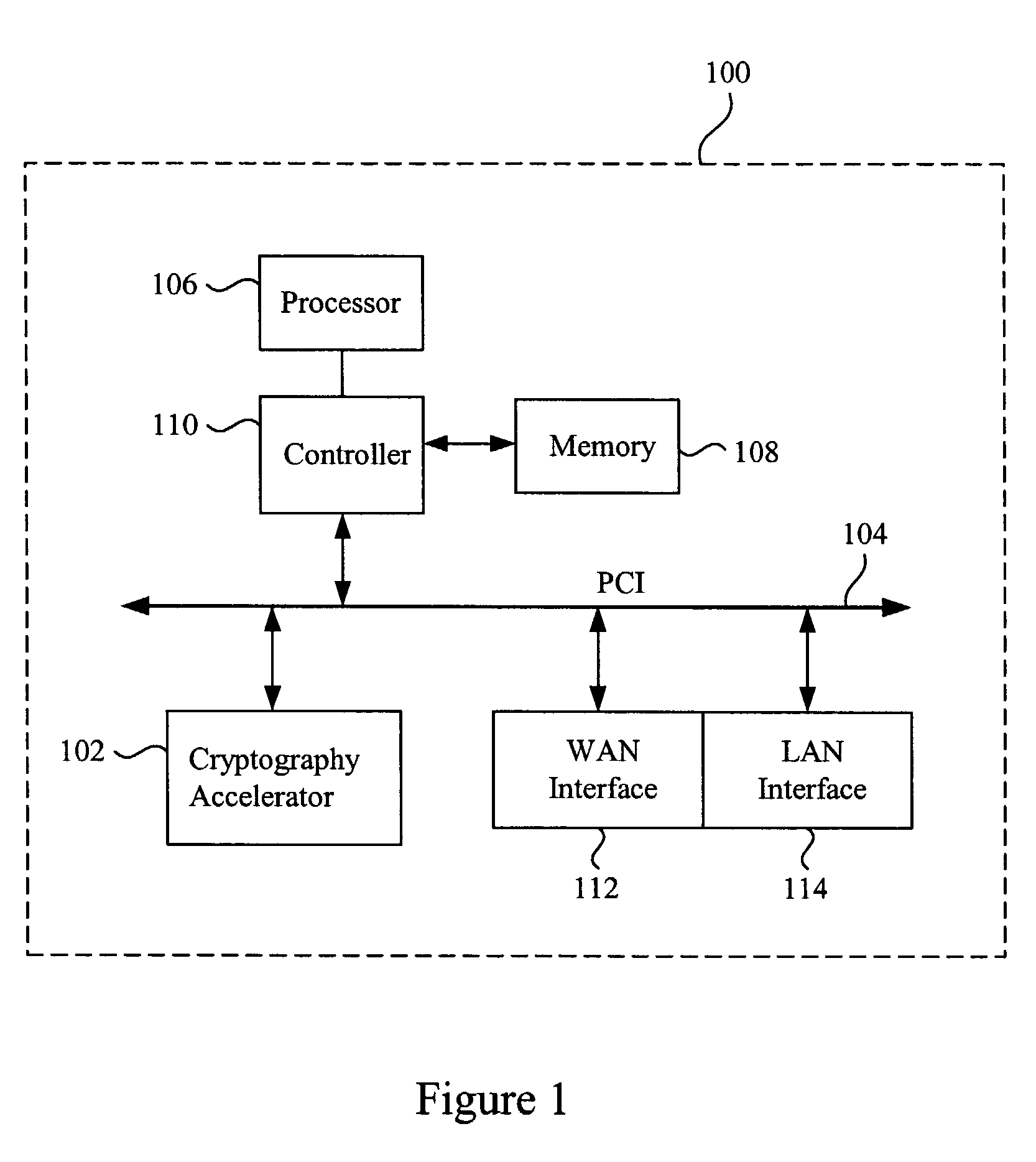
Methods and apparatus for performing hash operations in a cryptography accelerator
ActiveUS20030185391A1User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareCryptographic accelerator
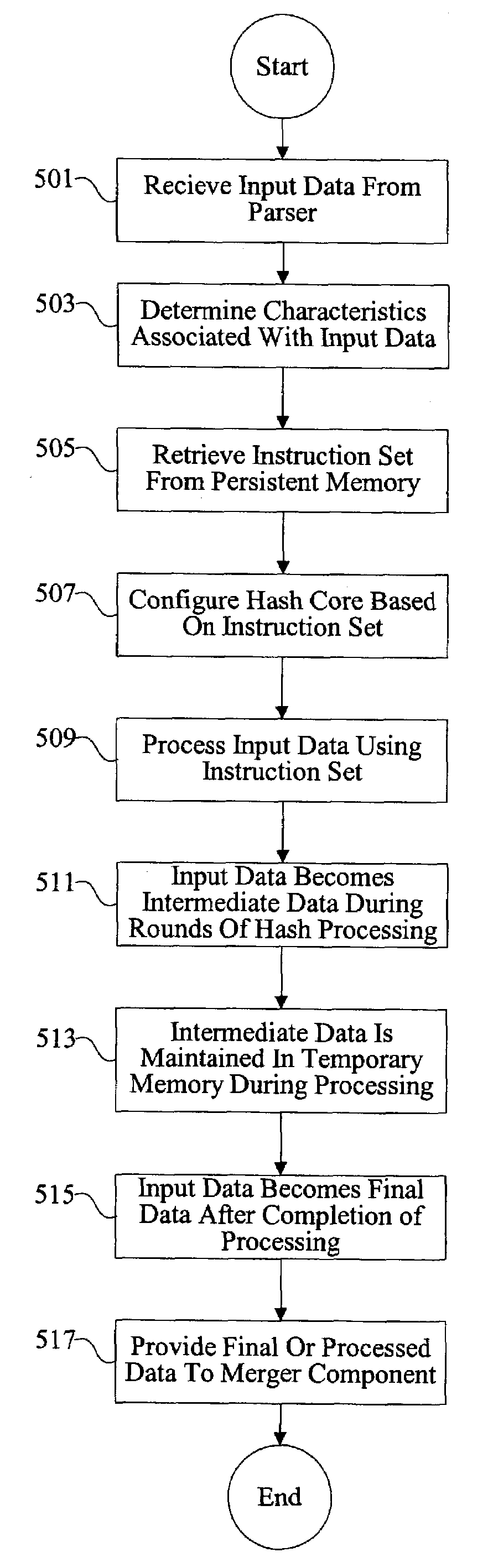
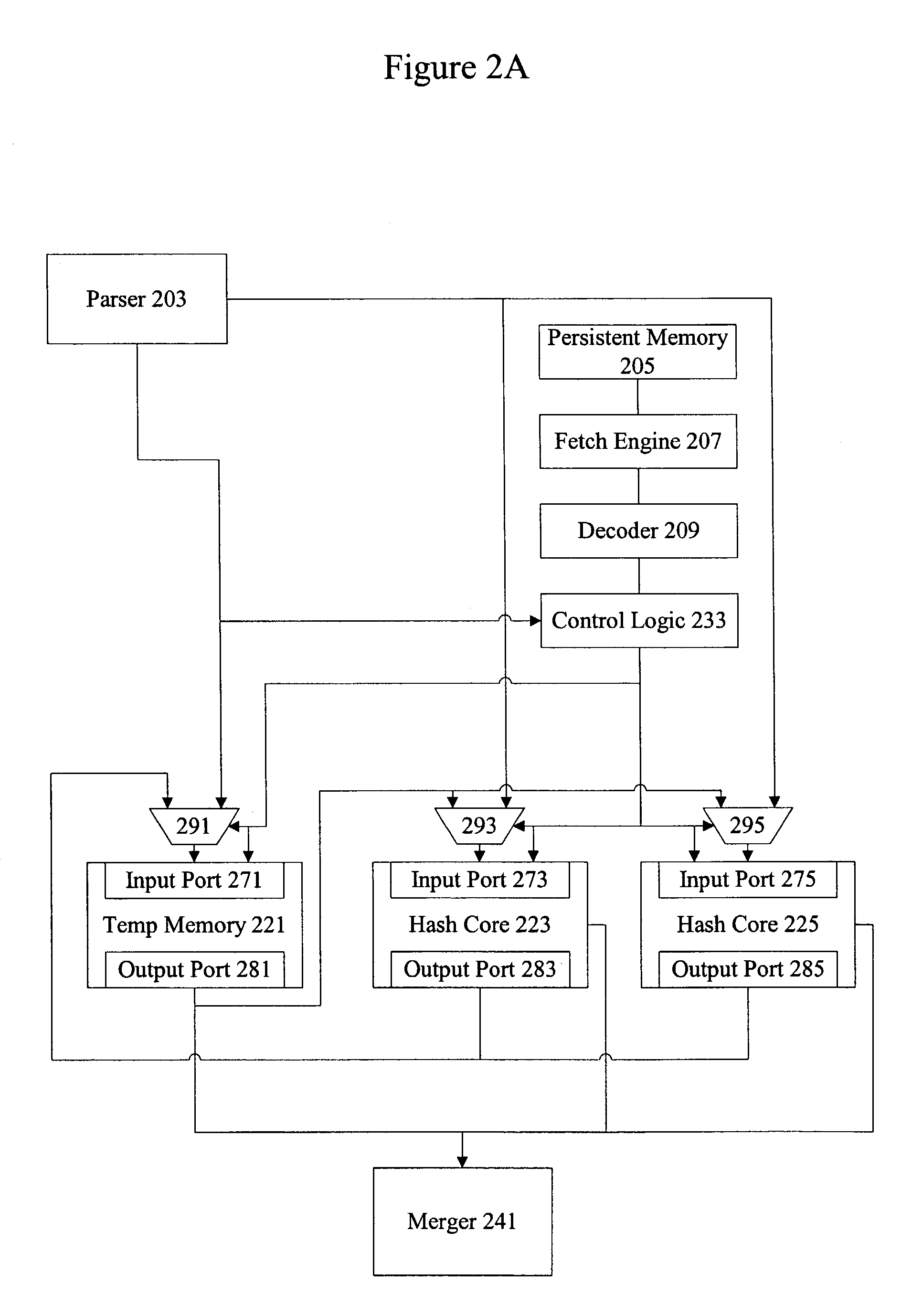
Methods and apparatus are provided for implementing a cryptography accelerator for performing operations such as hash operations. The cryptography accelerator recognizes characteristics associated with input data and retrieves an instruction set for processing the input data. The instruction set is used to configure or control components such as MD5 and SHA-1 hash cores, XOR components, memory, etc. By providing a cryptography accelerator with access to multiple instruction sets, a variety of hash operations can be performed in a configurable cryptographic accelerator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
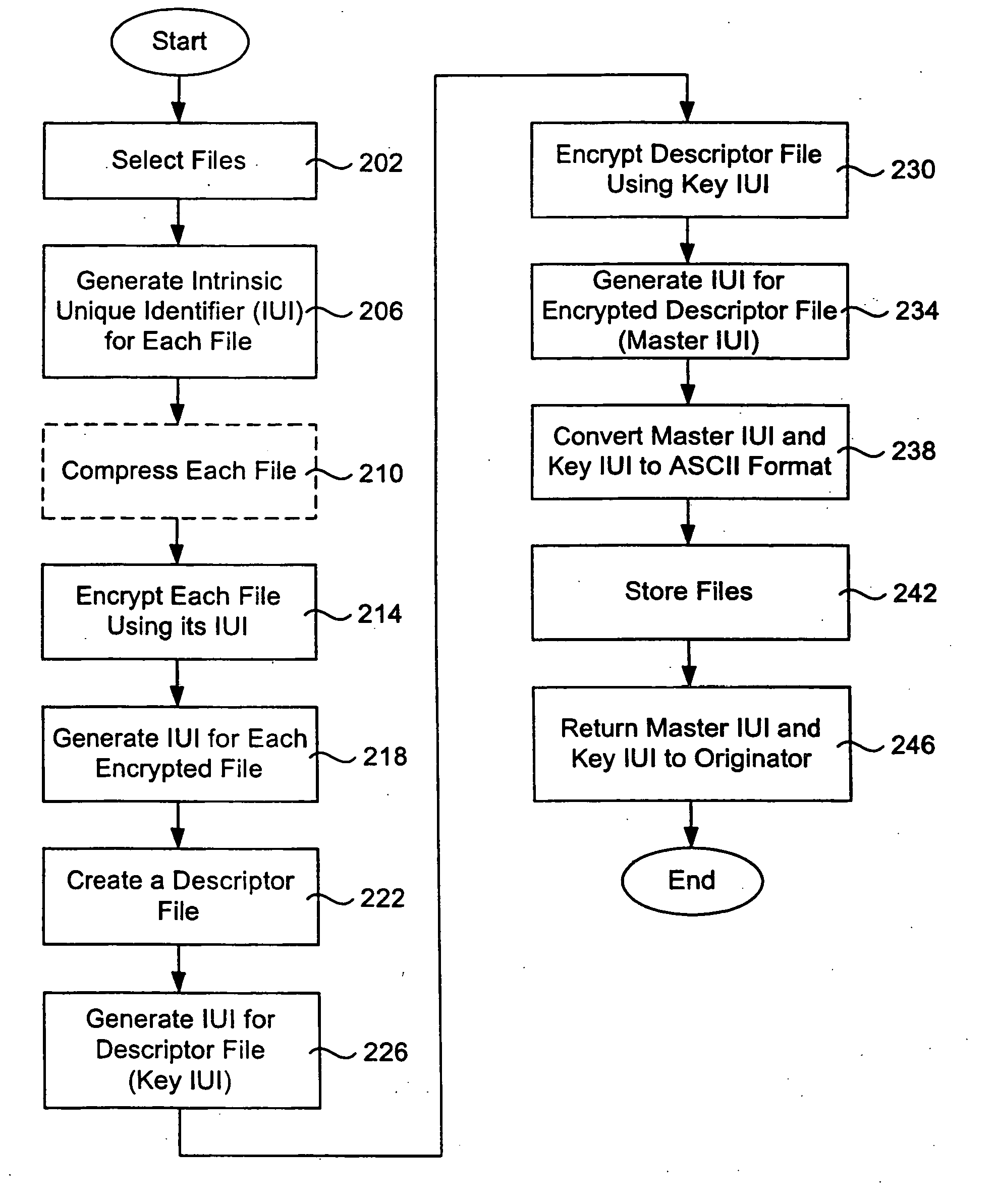
System and method for secure storage, transfer and retrieval of content addressable information
InactiveUS20050172123A1Safe storageSafe transferData processing applicationsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePlaintext
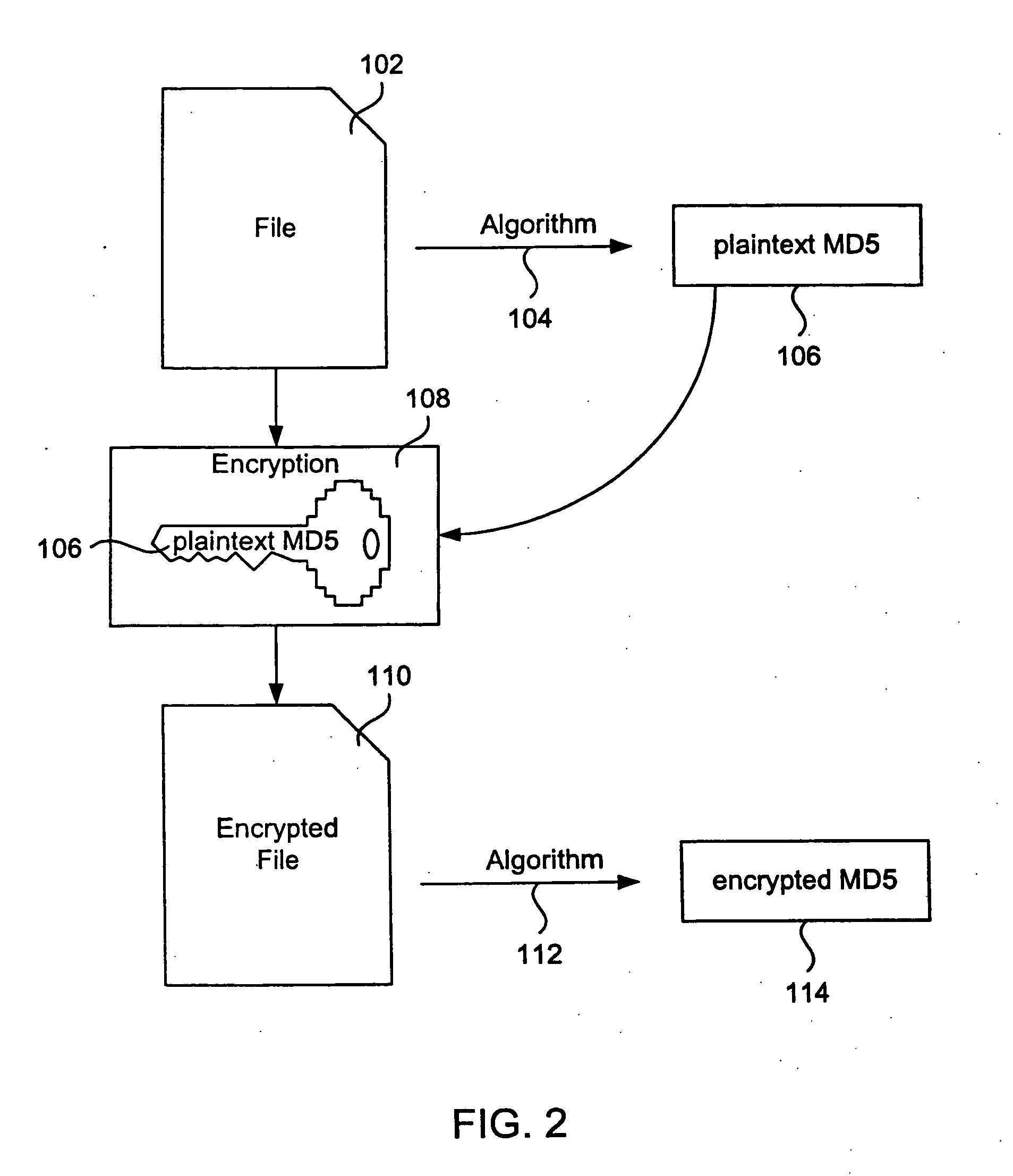
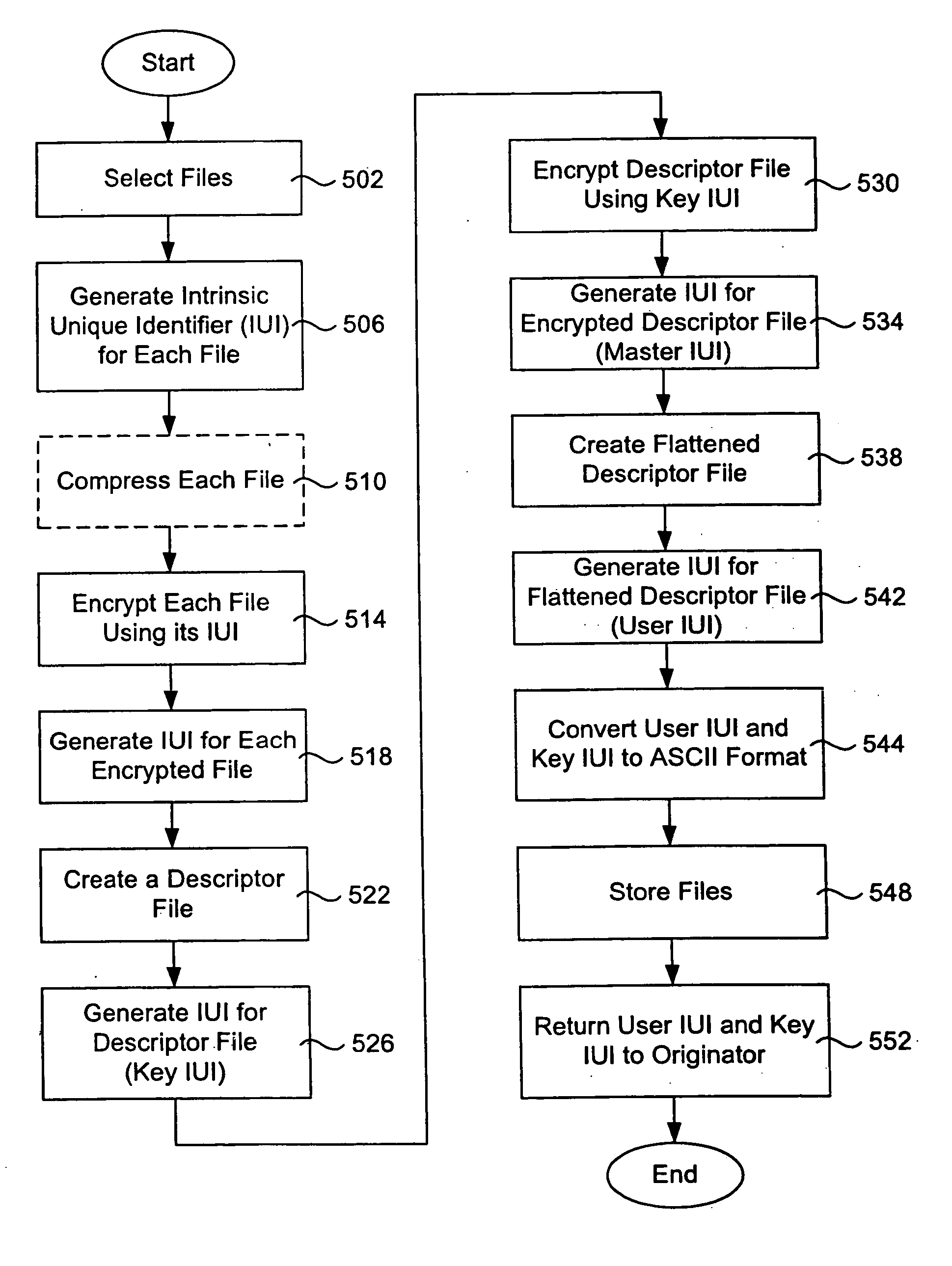
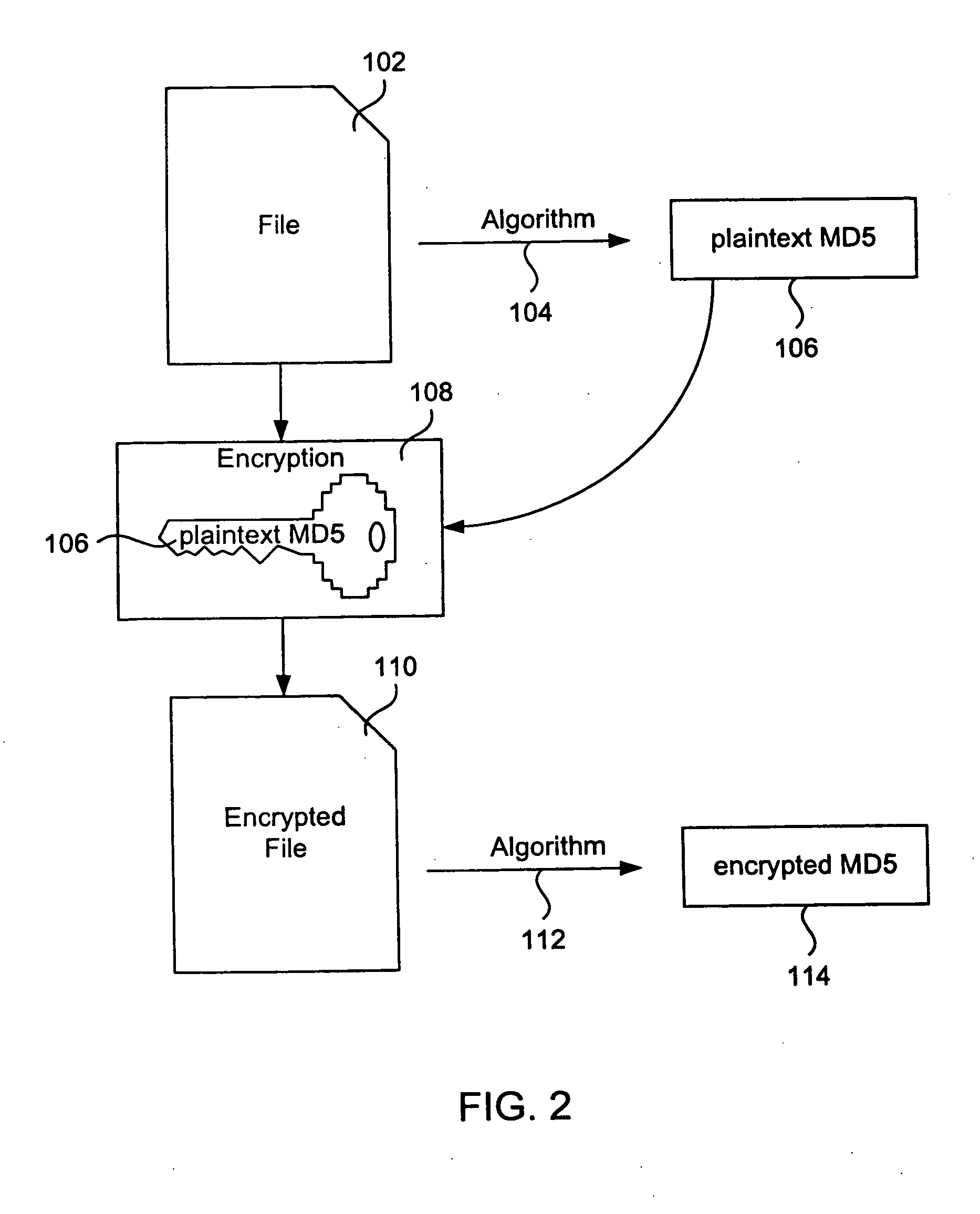
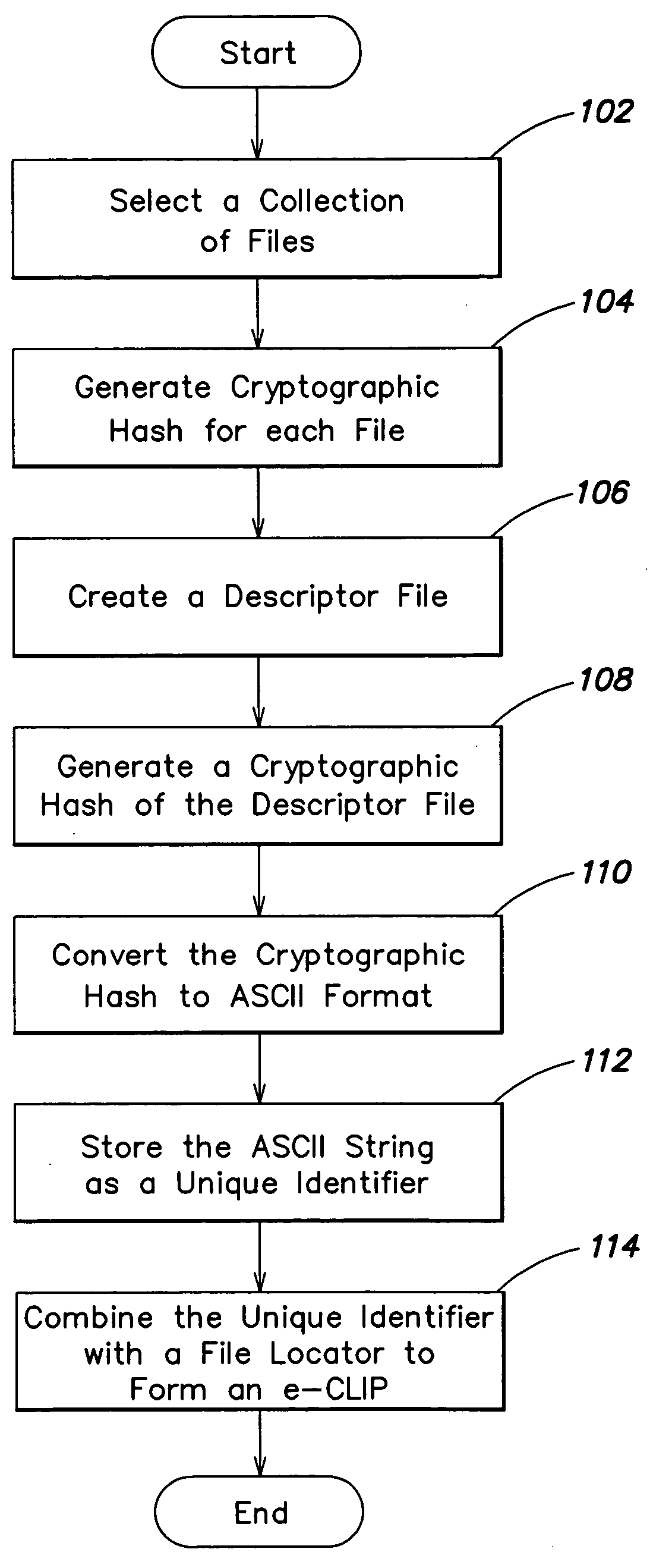
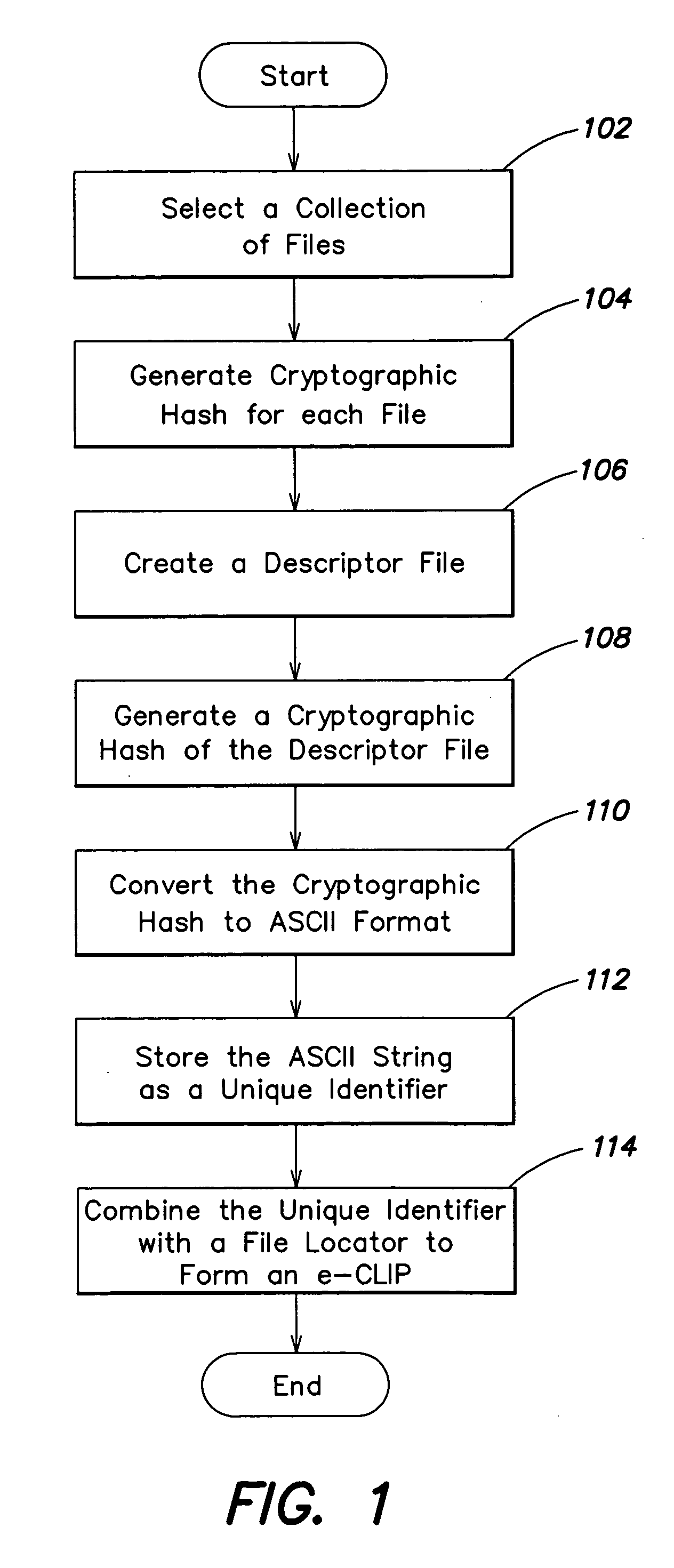
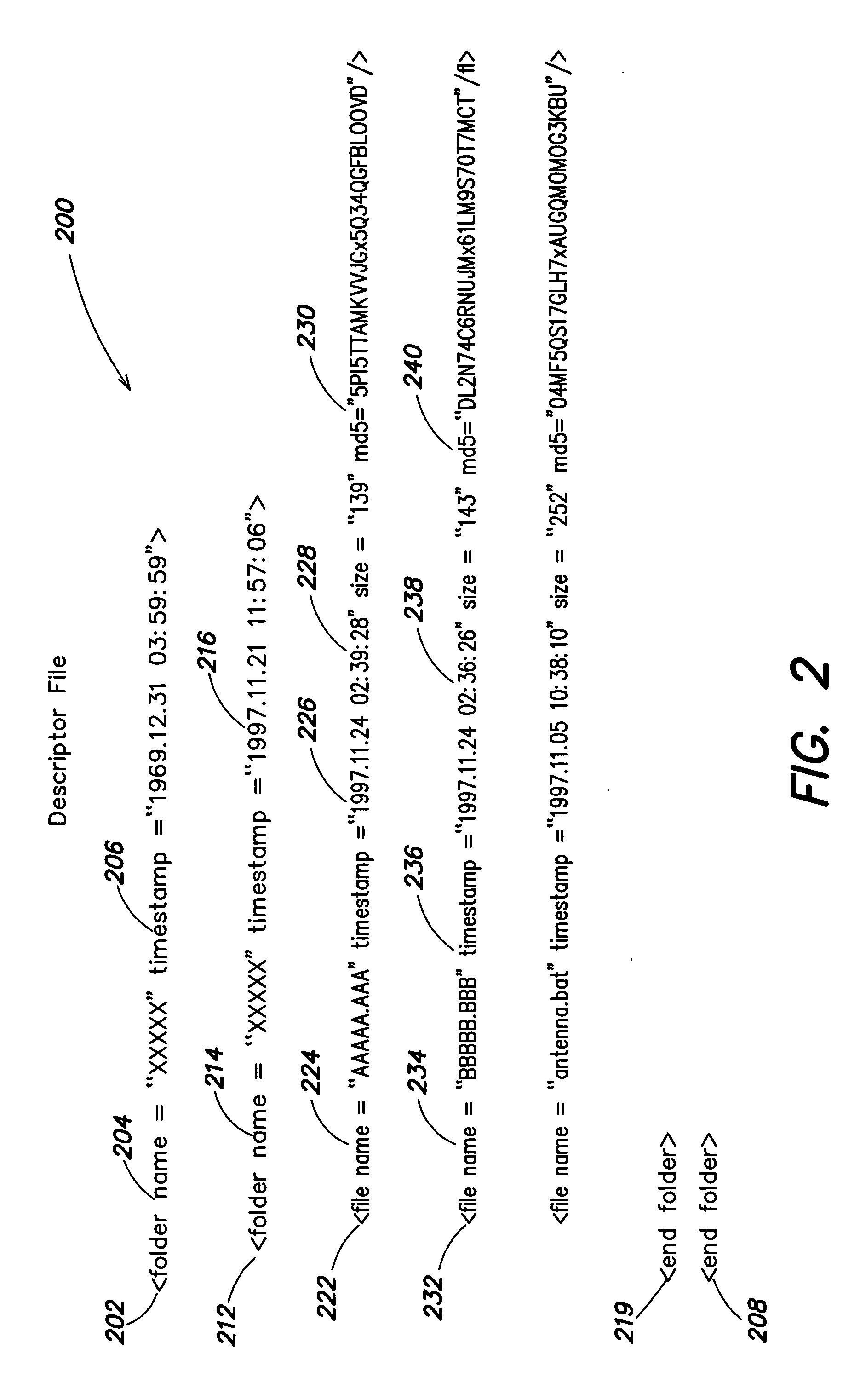
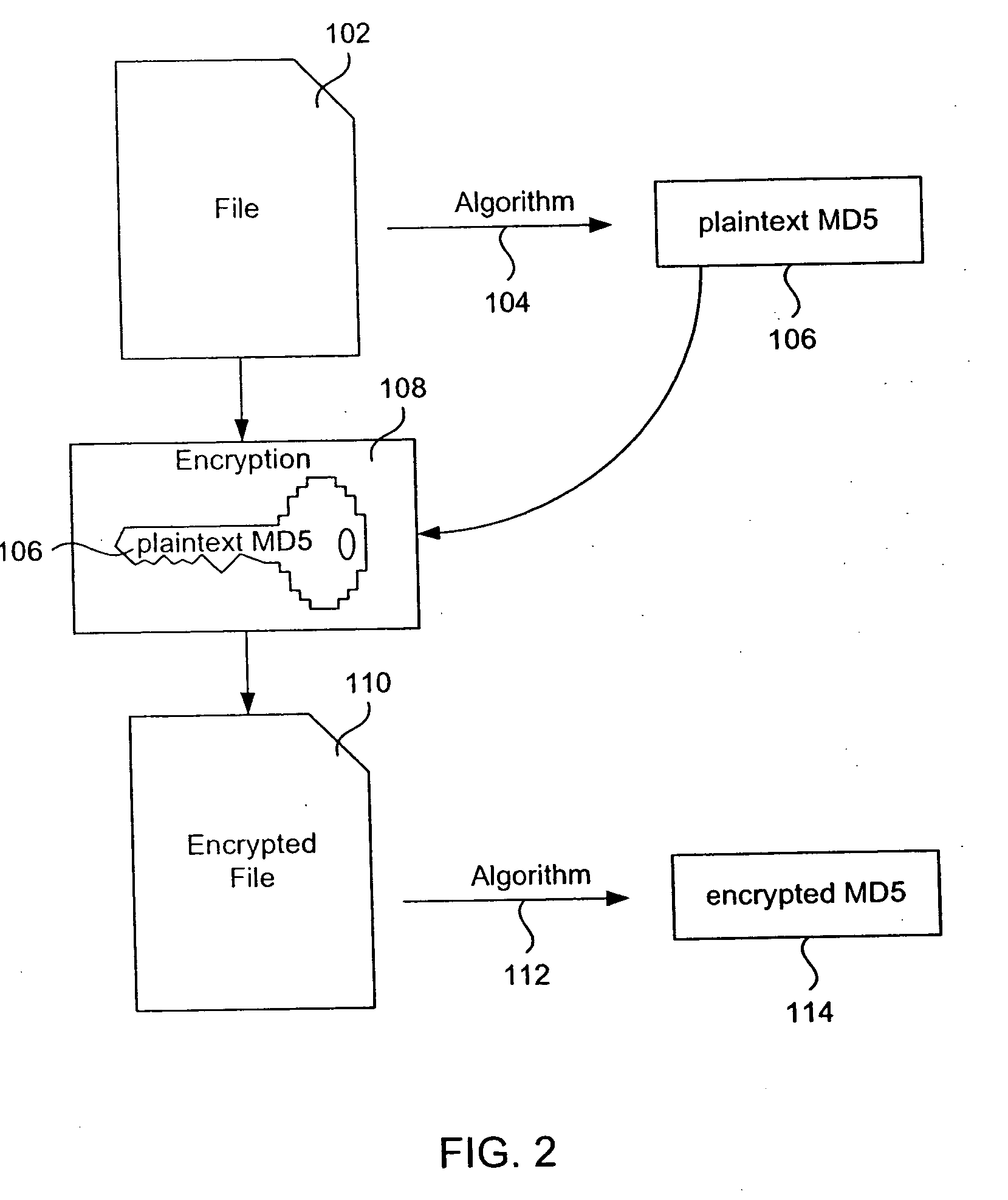
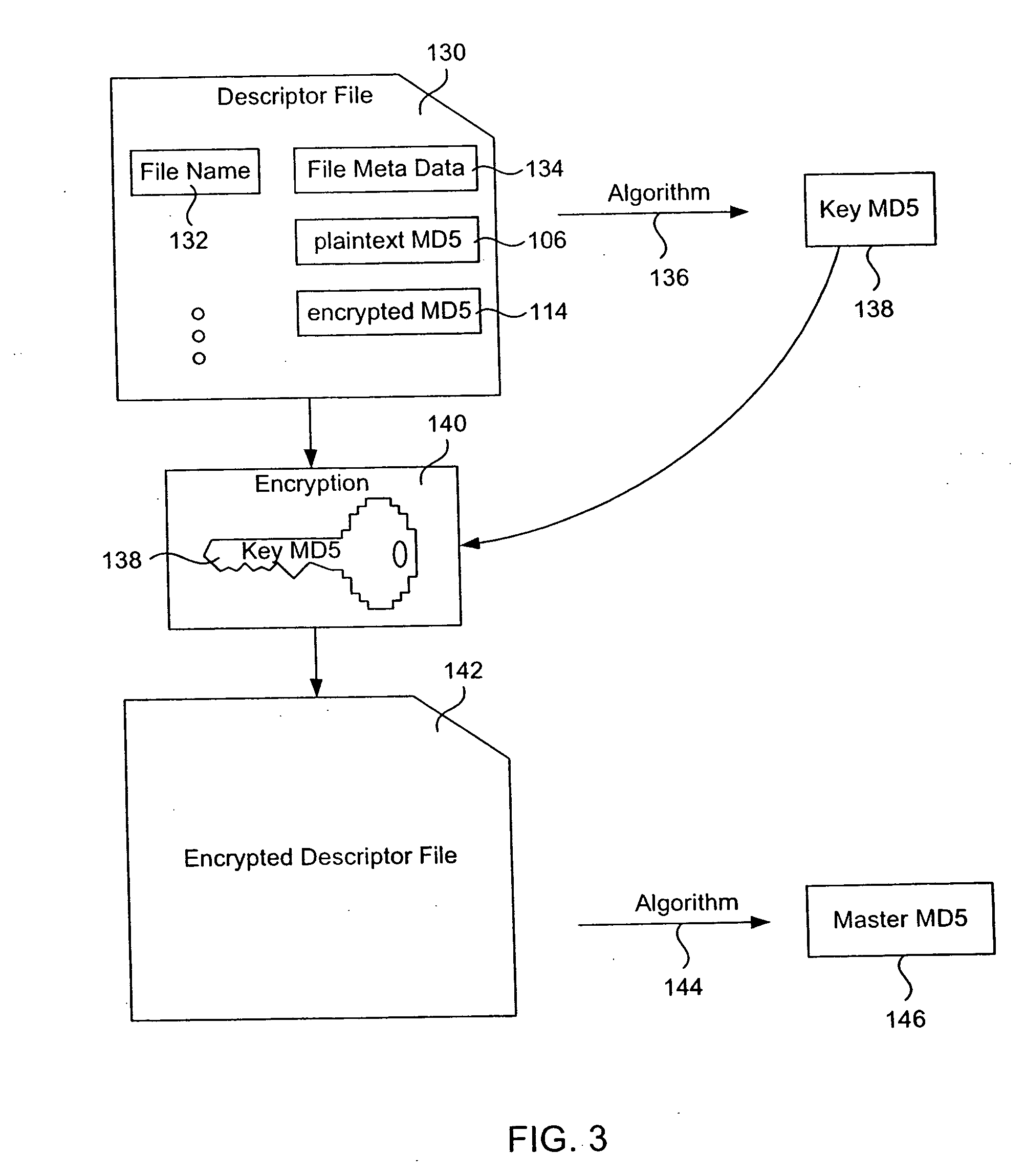
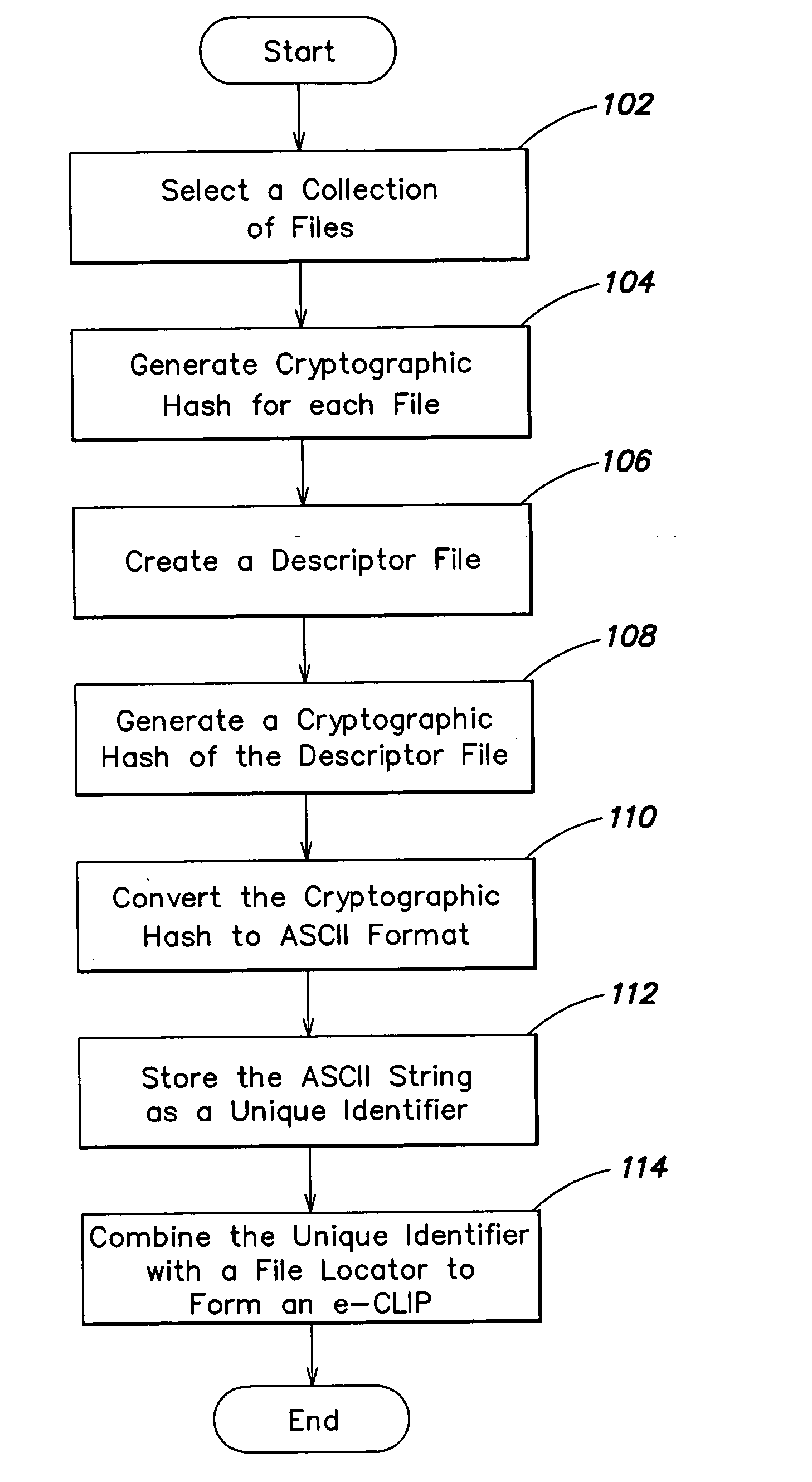
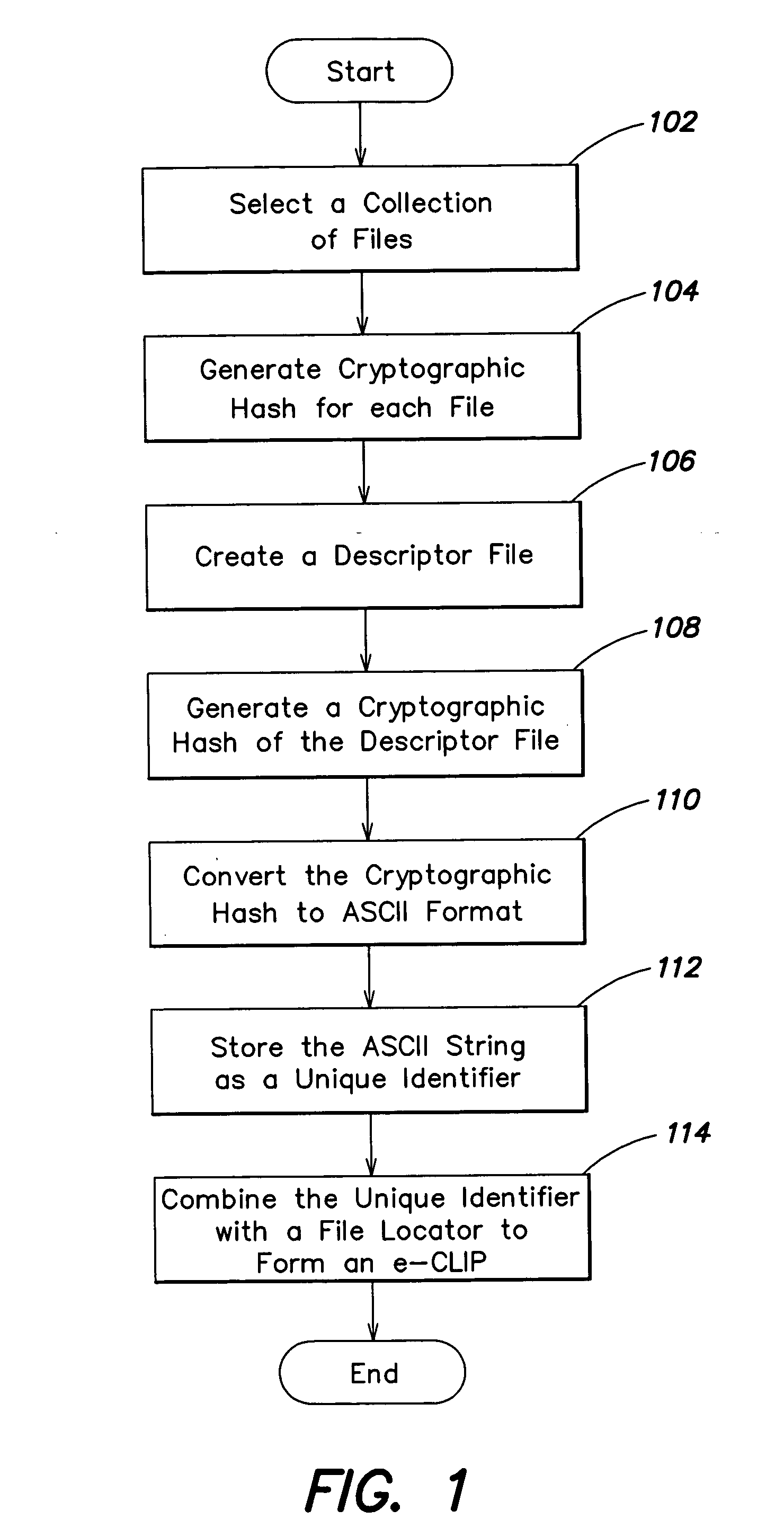
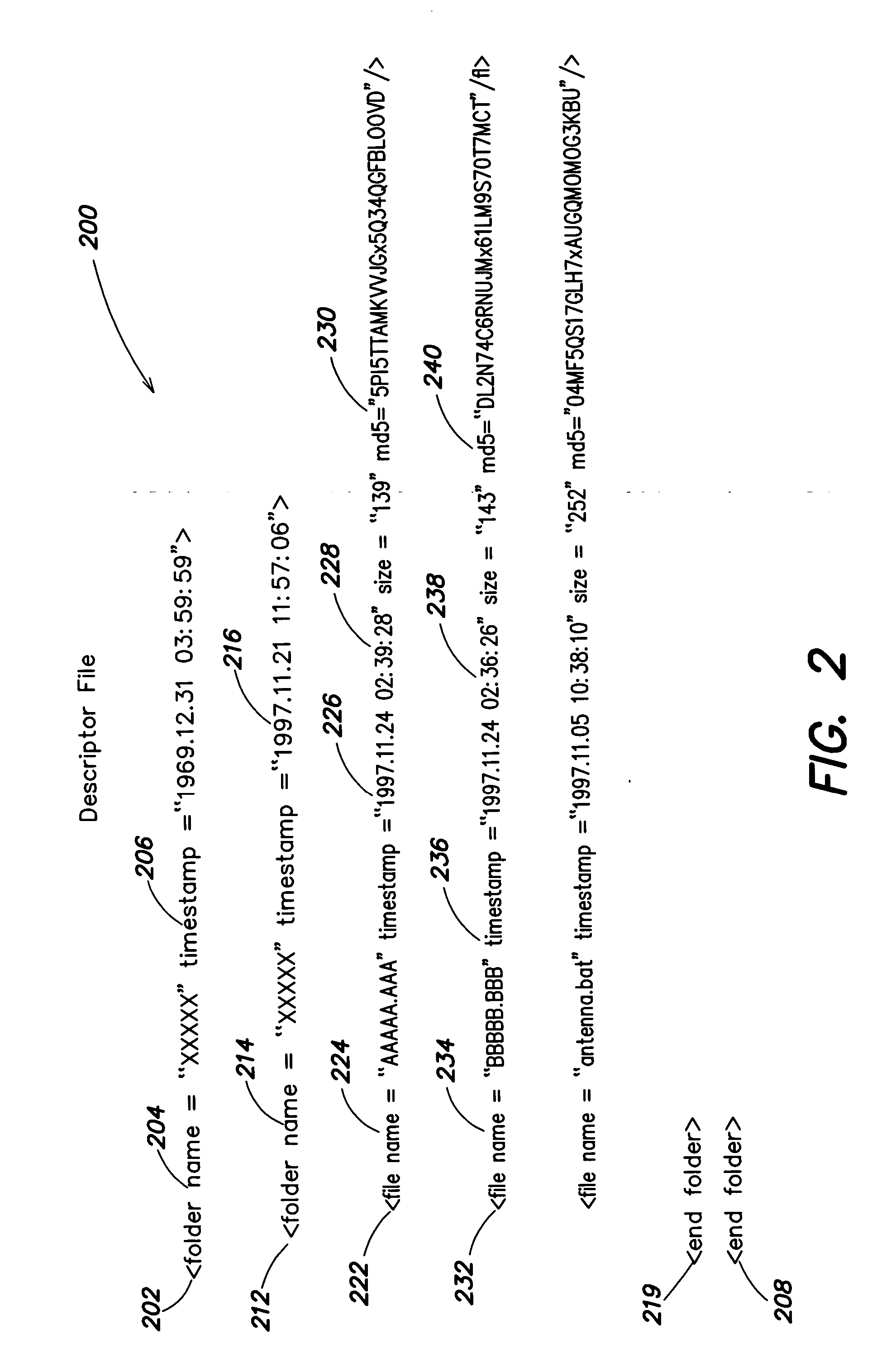
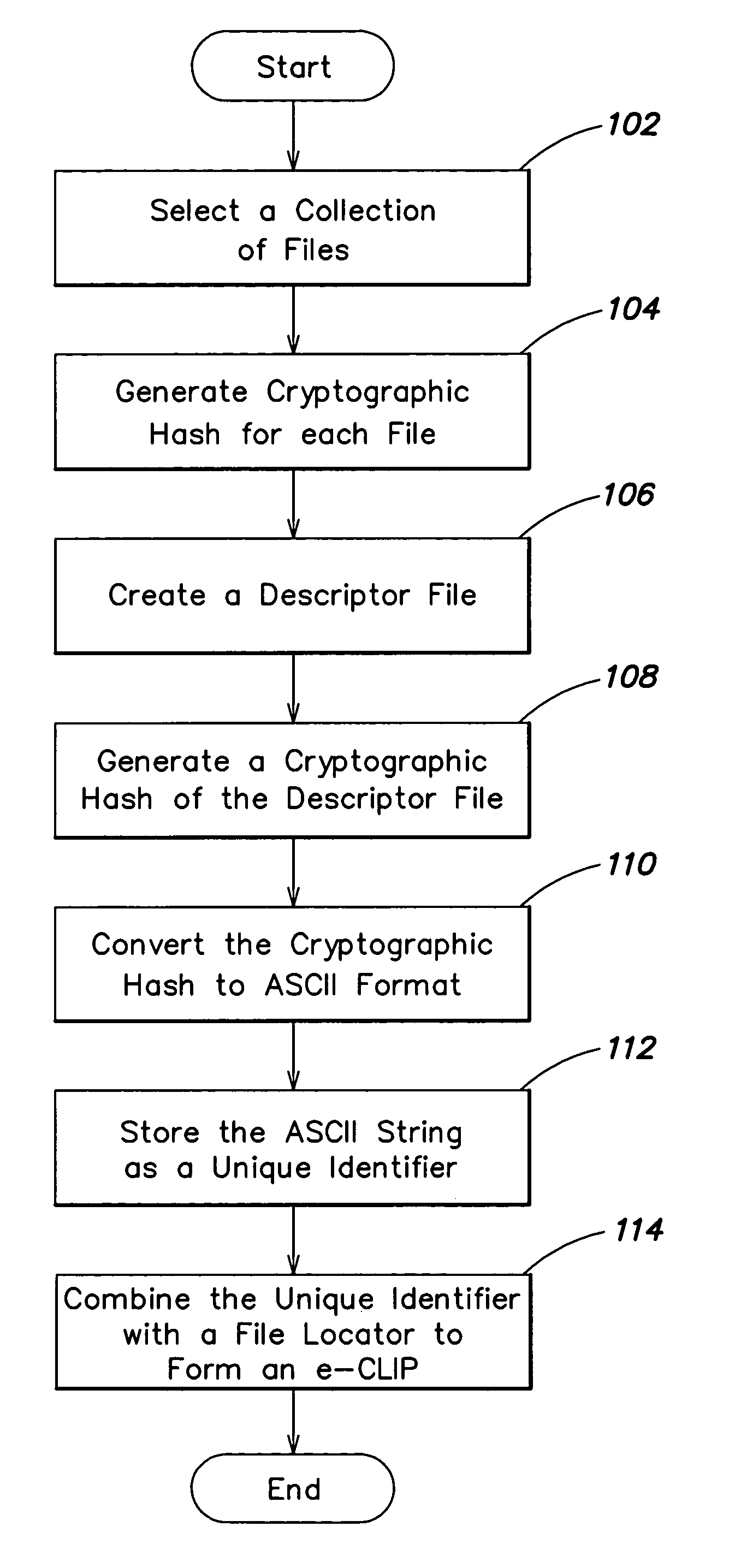
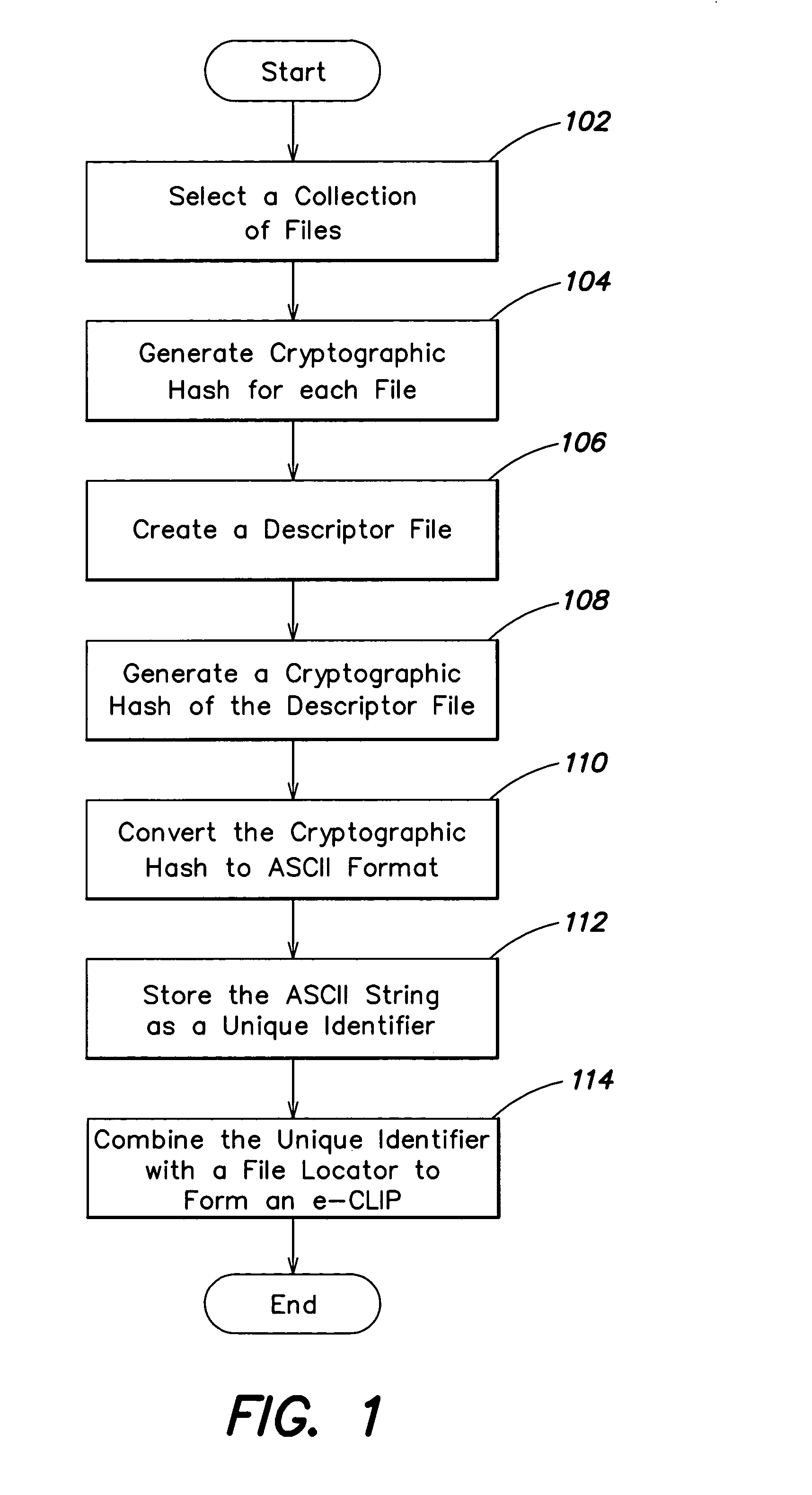
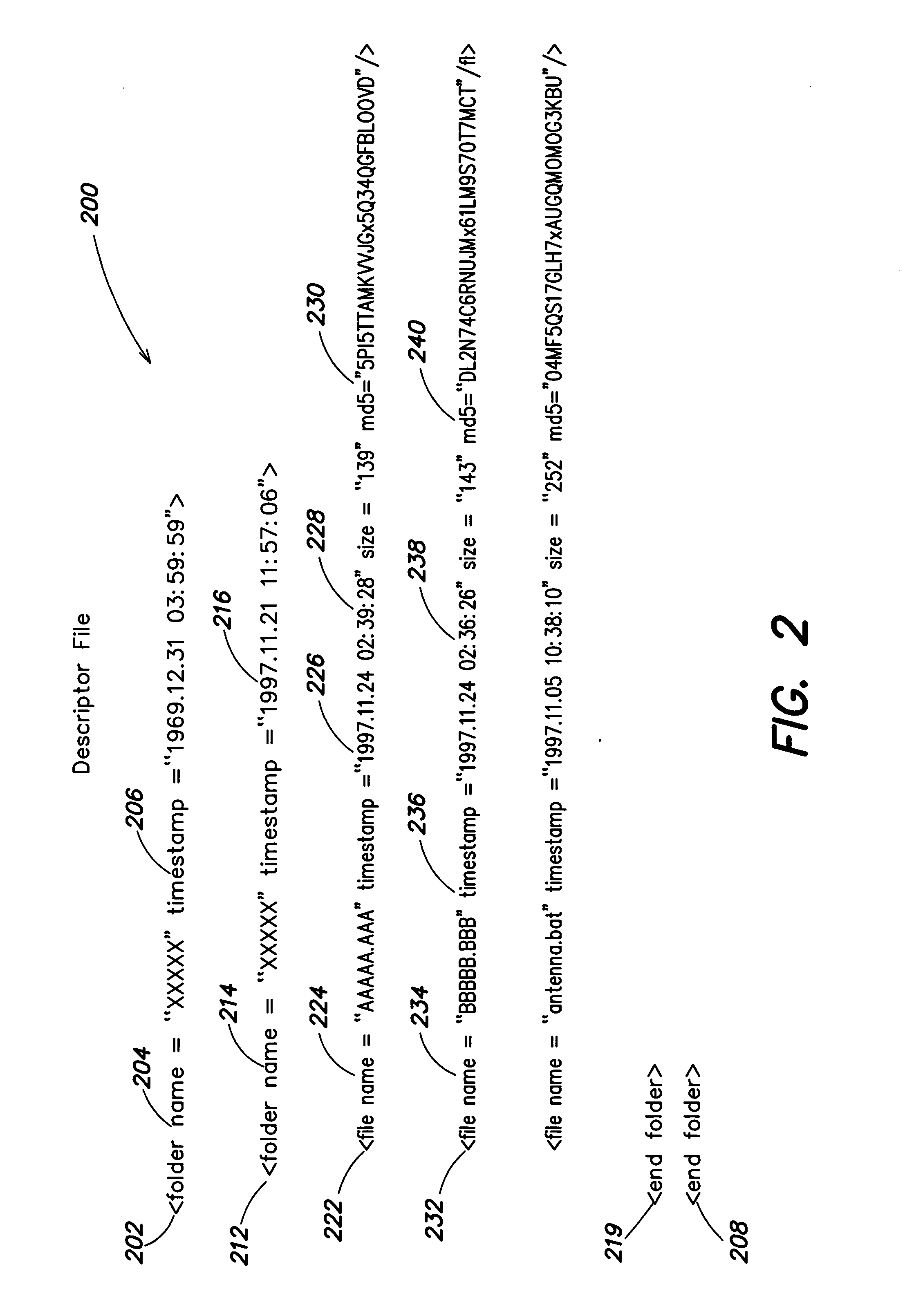
An algorithm (such as the MD5 hash function) is applied to a file to produce an intrinsic unique identifier (IUI) for the file (or message digest). The file is encrypted using its IUI as the key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is then applied to the encrypted file to produce an IUI for the encrypted file. The encrypted file is safely stored or transferred within a network and is uniquely identifiable by its IUI. The encrypted file is decrypted using the IUI of the plaintext file as the key. The IUI serves as both a key to decrypt the file and also as verification that the integrity of the plaintext file has not been compromised. IUIs for any number of such encrypted files may be assembled into a descriptor file that includes meta data for each file, the IUI of the plaintext file and the IUI of the encrypted file. An algorithm is applied to the descriptor file to produce an IUI for the descriptor file. The plaintext descriptor file is then encrypted using the descriptor file IUI as a key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is applied to the encrypted descriptor file to produce an IUI for the encrypted descriptor file. The IUI of the encrypted descriptor file is a location-independent identifier to locate the encrypted descriptor file. A flattened descriptor file includes the IUIs of encrypted data files and the IUI of the encrypted descriptor file. An algorithm is applied to the flattened descriptor file to produce its own IUI.
Owner:EMC CORP
System and method for secure storage, transfer and retrieval of content addressable information
InactiveUS20050172124A1Safe storageSafe transferData processing applicationsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash functionTheoretical computer science
An algorithm (such as the MD5 hash function) is applied to a file to produce an intrinsic unique identifier (IUI) for the file (or message digest). The file is encrypted using its IUI as the key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is then applied to the encrypted file to produce an IUI for the encrypted file. The encrypted file is safely stored or transferred within a network and is uniquely identifiable by its IUI. The encrypted file is decrypted using the IUI of the plaintext file as the key. The IUI serves as both a key to decrypt the file and also as verification that the integrity of the plaintext file has not been compromised. IUIs for any number of such encrypted files may be assembled into a descriptor file that includes meta data for each file, the IUI of the plaintext file and the IUI of the encrypted file. An algorithm is applied to the descriptor file to produce an IUI for the descriptor file. The plaintext descriptor file is then encrypted using the descriptor file IUI as a key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is applied to the encrypted descriptor file to produce an IUI for the encrypted descriptor file. The IUI of the encrypted descriptor file is a location-independent identifier to locate the encrypted descriptor file. A flattened descriptor file includes the IUIs of encrypted data files and the IUI of the encrypted descriptor file. An algorithm is applied to the flattened descriptor file to produce its own IUI.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for reducing memory requirements of firmware
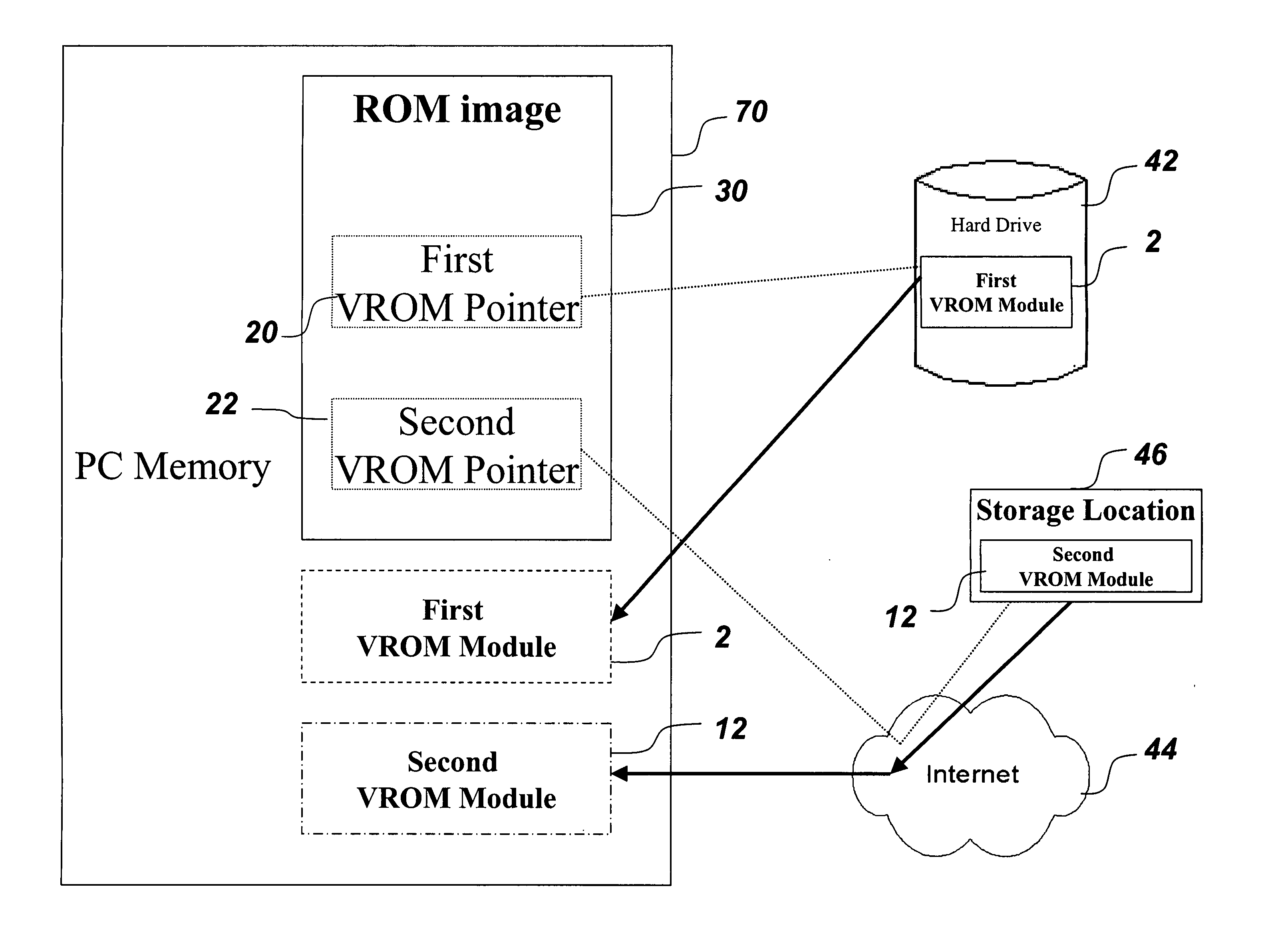
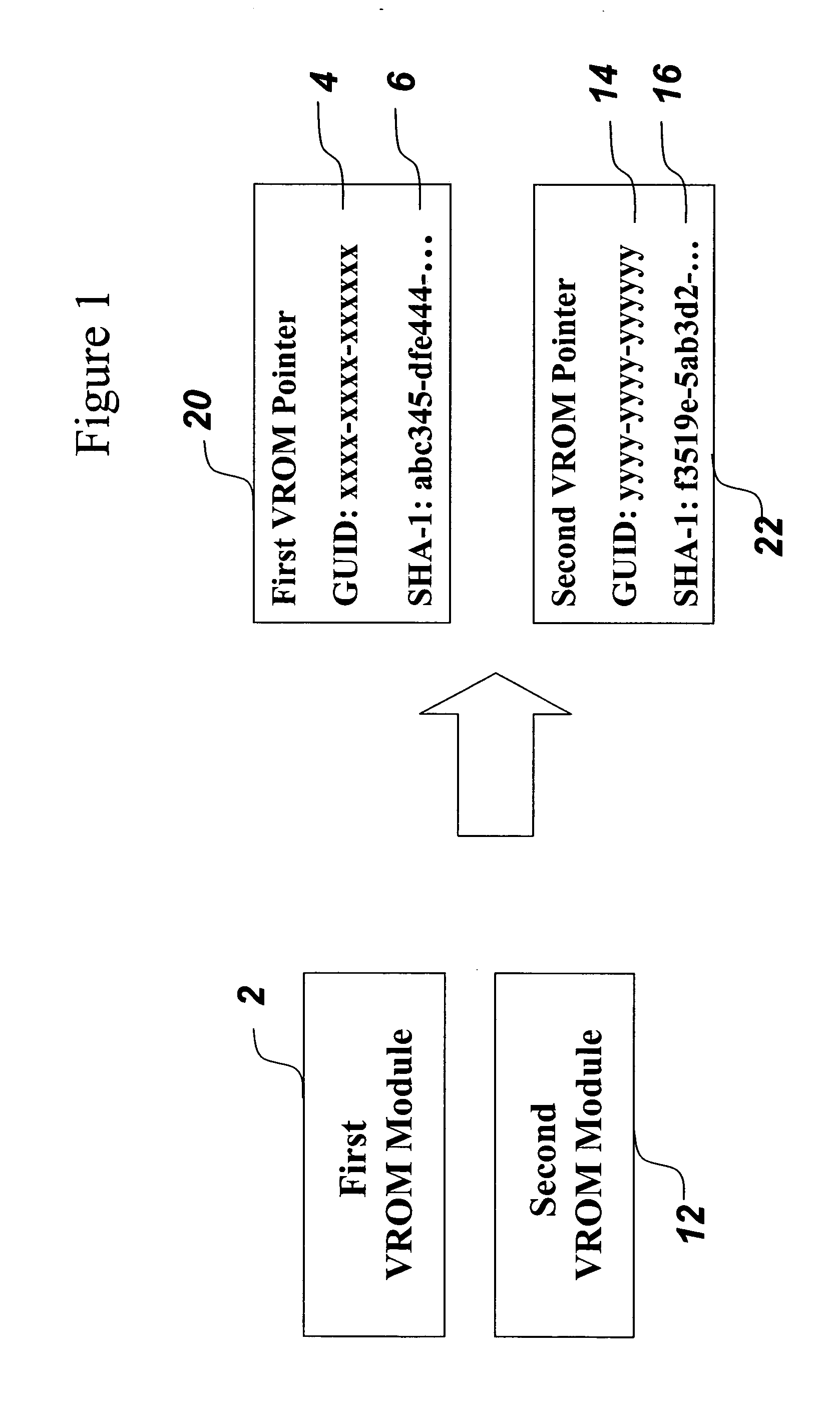
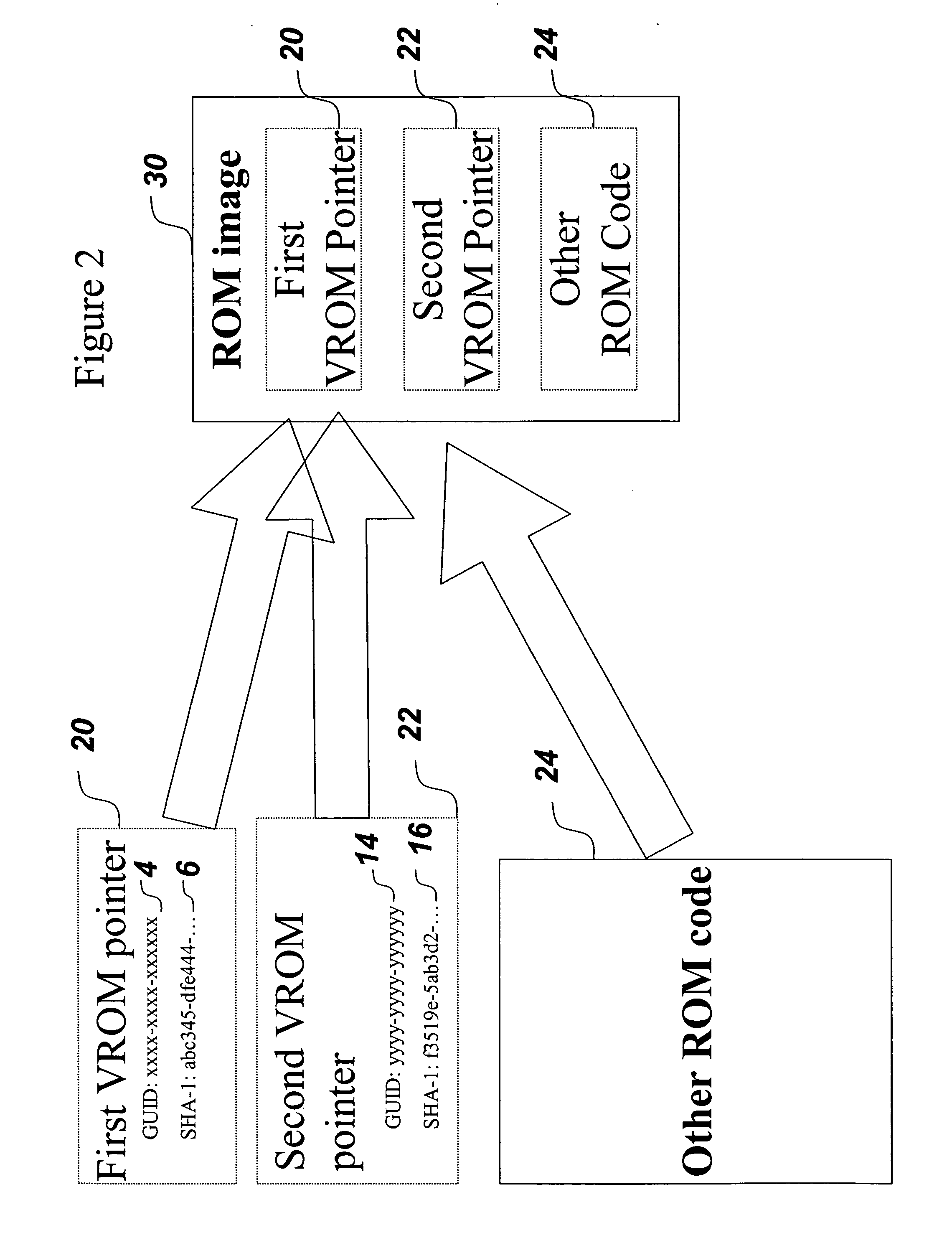
ActiveUS20060174055A1Reduce memory requirementsUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsUnique identifierMD5
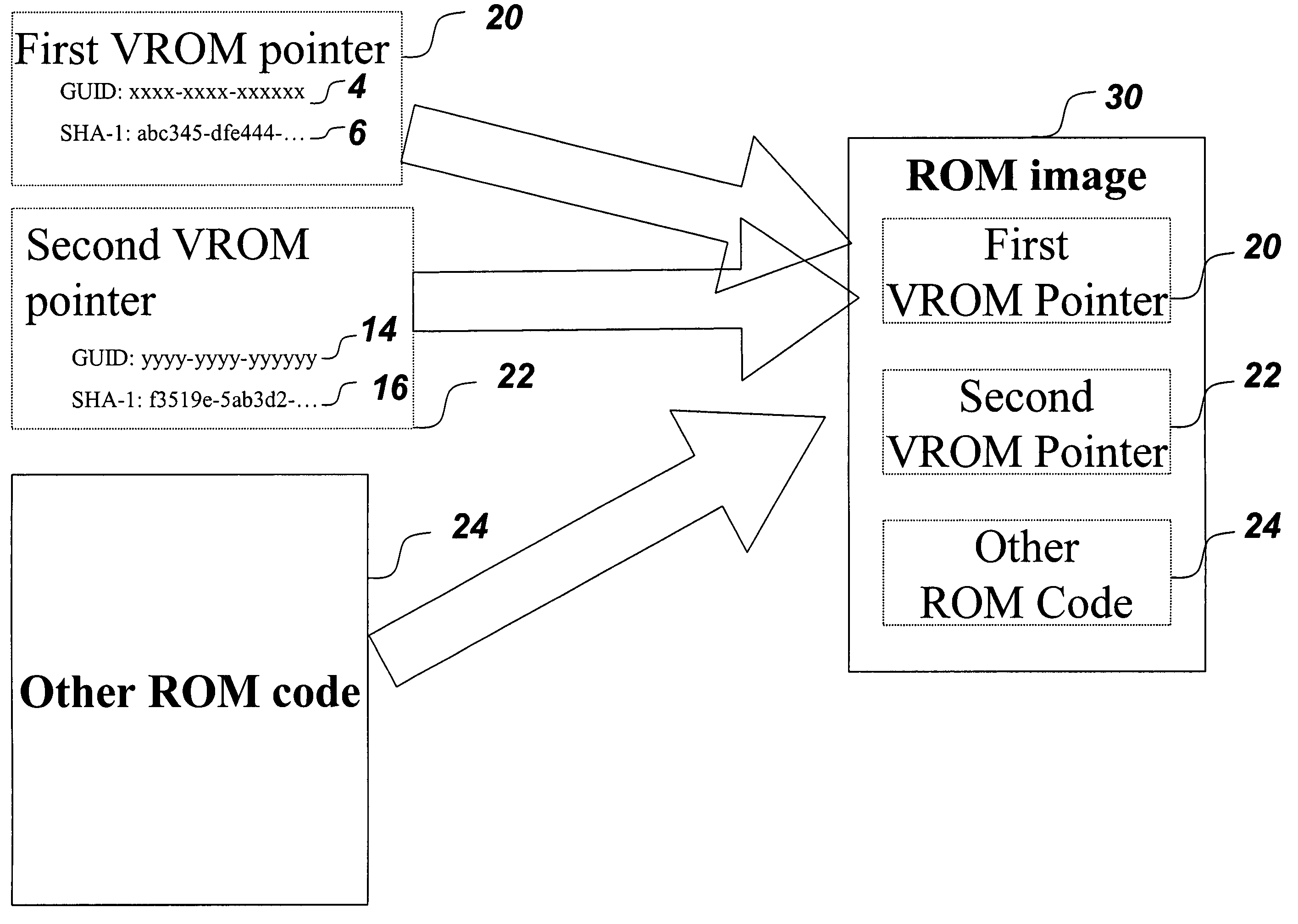
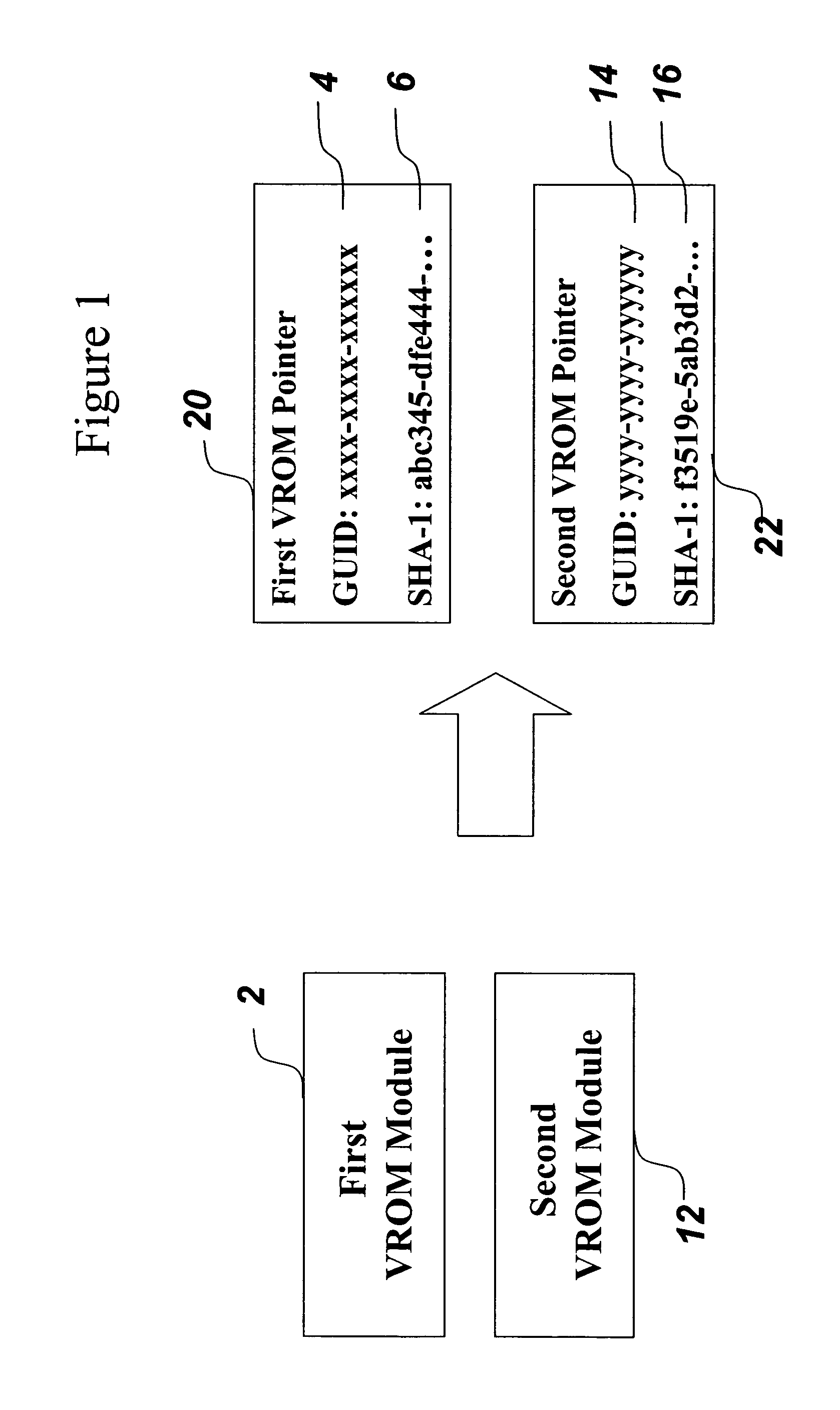
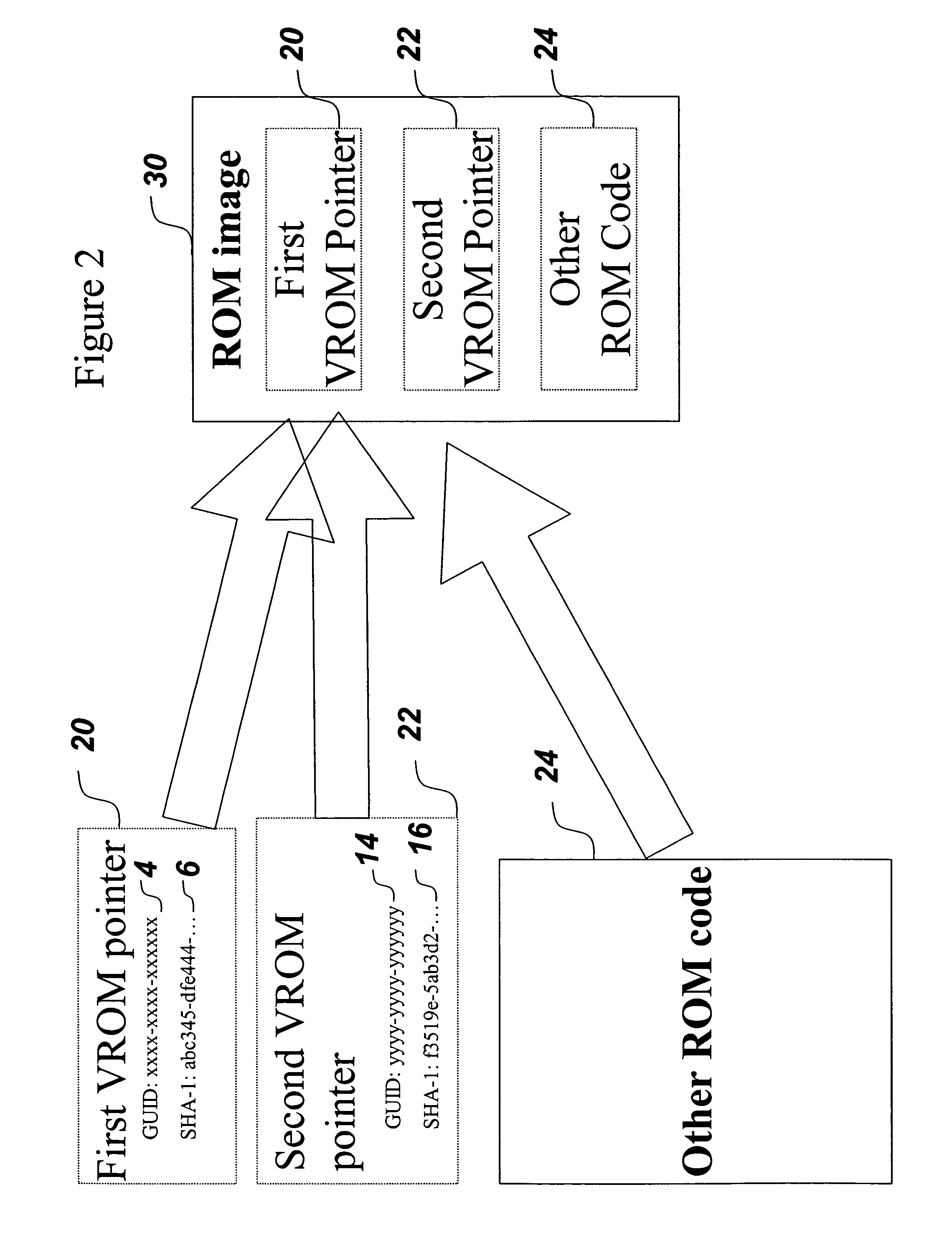
A mechanism for making increased amounts of firmware available to a computer pre-boot is discussed. To increase the amount of firmware available pre-boot, a design decision is made during the build process as to which segments of the firmware need to be placed on the ROM part and which segments of the firmware can be located elsewhere. The segments of the firmware that are stored remotely from the ROM are referred to as “virtual ROM modules”. Each of the virtual ROM modules is assigned a generated unique identifier, and a “message digest” is constructed for each module using an algorithm such as MD5 or SHA-1. In the software build of the ROM image, the message digest-unique identifier pair created for each Virtual ROM module is used as a logical pointer for the virtual module. Additionally, a search path variable is placed into the ROM image in non-volatile storage. The search path provides for one or more locations in which to look for the Virtual ROM modules, and may be updated at a later point in time.
Owner:INSYDE SOFTWARE
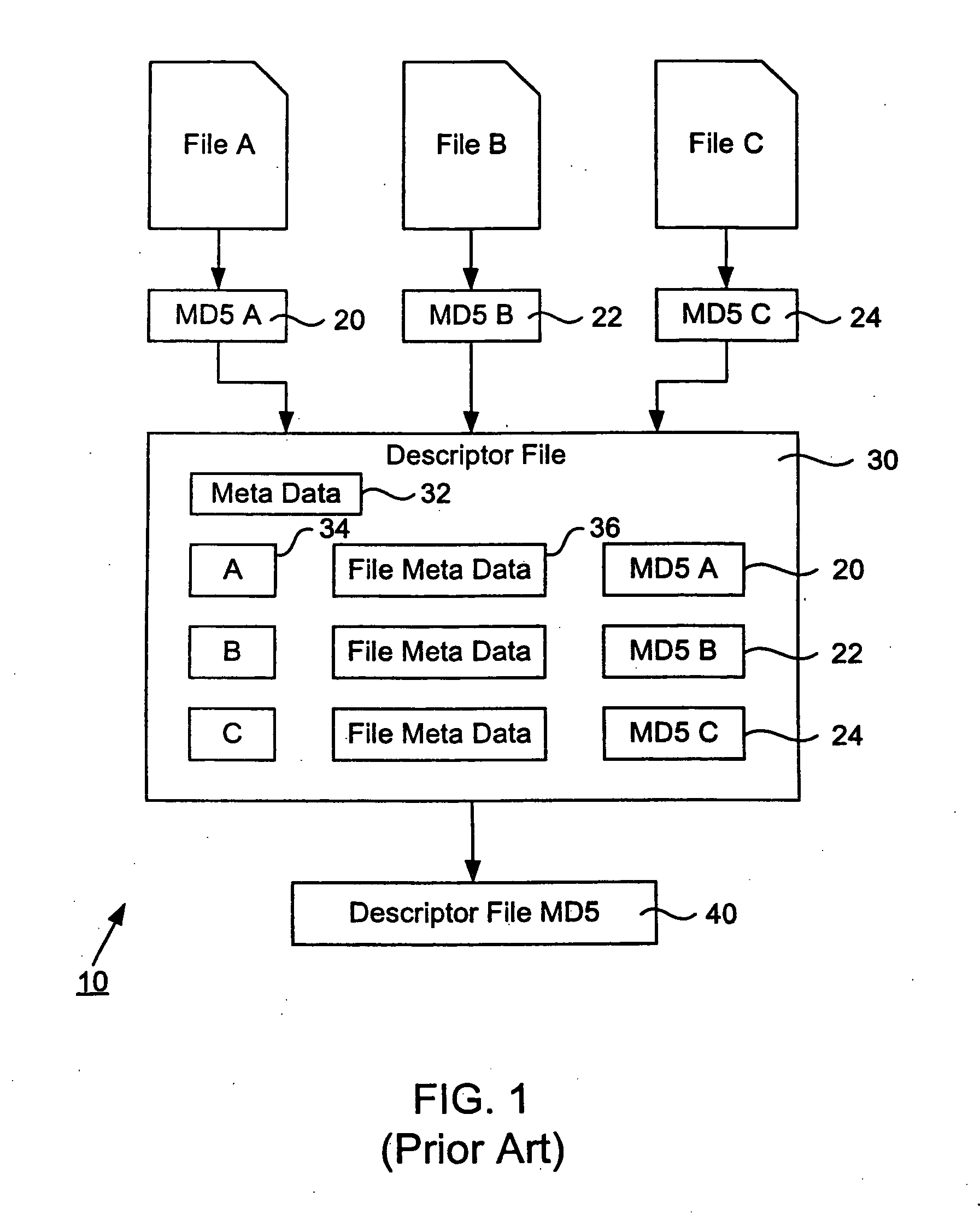
Content addressable information encapsulation, representation, and transfer
InactiveUS20050044417A1Simple structureSpecial service provision for substationDigital data processing detailsCryptographic hash functionMD5
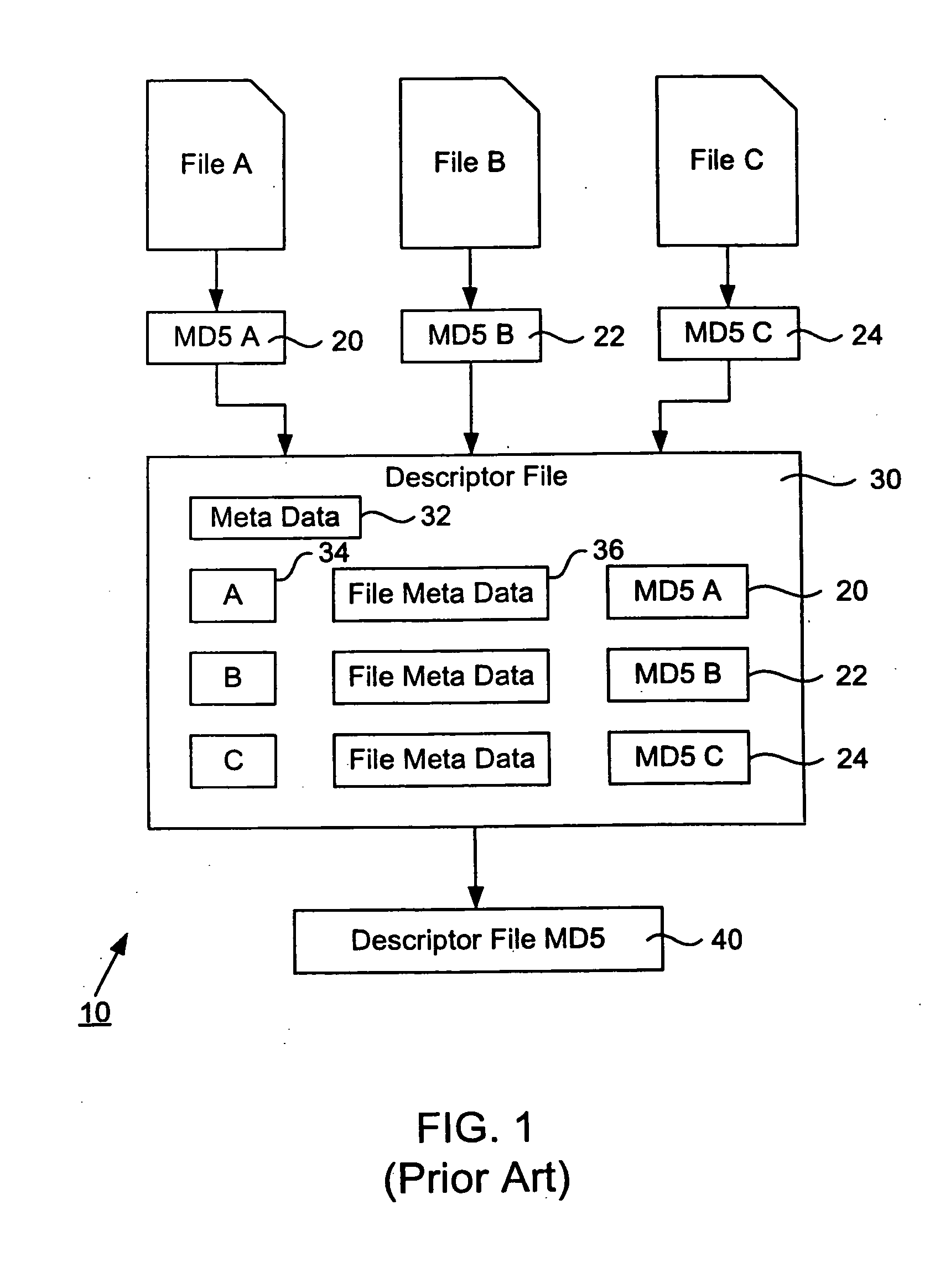
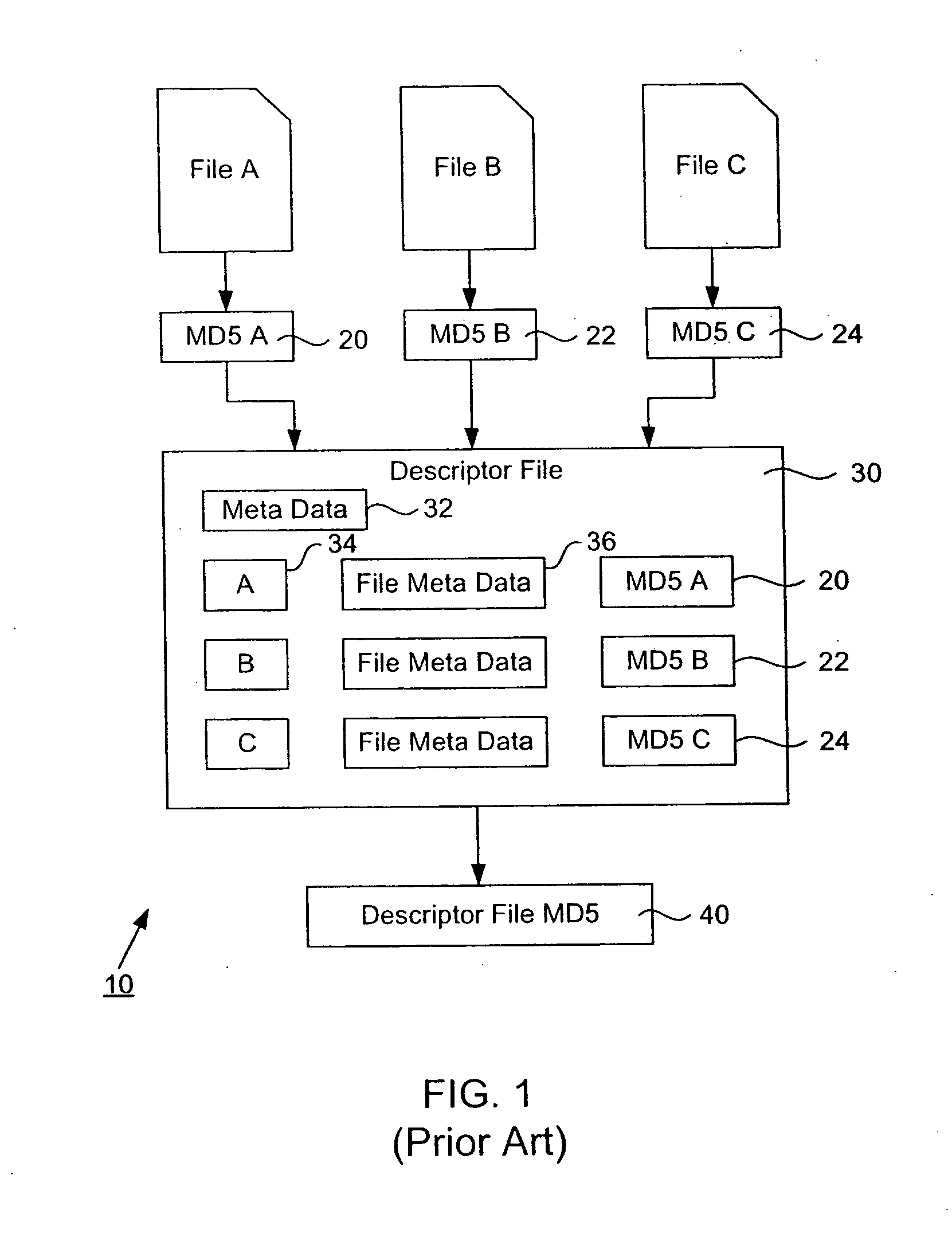
Representing a number of assets on an originating computer begins with selecting the assets to be represented. Cryptographic hash asset identifiers are generated; each of the asset identifiers is computed using the contents of a particular asset. The asset identifier is a content-based or content-addressable asset name for the asset and is location independent. An asset list is generated that includes the asset identifiers computed from the assets. A cryptographic hash asset list identifier is generated that is computed from the asset list. The asset list identifier is stored for later retrieval. The assets selected are also stored for safekeeping either locally or on a computer network. In the event of loss of the files from the originating computer, the asset list identifier is retrieved. Using the asset list identifier, the original asset list is found and retrieved from its safe location. The asset identifiers from the retrieved asset list are used to find and retrieve the individual assets from their backup locations. The assets are verified by recomputing the cryptographic hash asset identifier for each asset retrieved and comparing it to the asset identifier from the asset list. The MD5 algorithm is used for the cryptographic hash function. Assets are retrieved using a multicast protocol. A series of importer programs searches for assets to retrieve in progressively more remote locations. Assets are retrieved whole or in segments.
Owner:EMC CORP
System and method for secure storage, transfer and retrieval of content addressable information
InactiveUS20050223224A1Safely stored and transferredProvide securityData processing applicationsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwarePlaintext
An algorithm (such as the MD5 hash function) is applied to a file to produce an intrinsic unique identifier (IUI) for the file (or message digest). The file is encrypted using its IUI as the key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is then applied to the encrypted file to produce an IUI for the encrypted file. The encrypted file is safely stored or transferred within a network and is uniquely identifiable by its IUI. The encrypted file is decrypted using the IUI of the plaintext file as the key. The IUI serves as both a key to decrypt the file and also as verification that the integrity of the plaintext file has not been compromised. IUIs for any number of such encrypted files may be assembled into a descriptor file that includes meta data for each file, the IUI of the plaintext file and the IUI of the encrypted file. An algorithm is applied to the descriptor file to produce an IUI for the descriptor file. The plaintext descriptor file is then encrypted using the descriptor file IUI as a key for the encryption algorithm. An algorithm is applied to the encrypted descriptor file to produce an IUI for the encrypted descriptor file. The IUI of the encrypted descriptor file is a location-independent identifier to locate the encrypted descriptor file. A flattened descriptor file includes the IUIs of encrypted data files and the IUI of the encrypted descriptor file. An algorithm is applied to the flattened descriptor file to produce its own IUI.
Owner:EMC CORP +1
Methods and apparatus for performing hash operations in a cryptography accelerator
ActiveUS7400722B2User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareCryptographic accelerator
Methods and apparatus are provided for implementing a cryptography accelerator for performing operations such as hash operations. The cryptography accelerator recognizes characteristics associated with input data and retrieves an instruction set for processing the input data. The instruction set is used to configure or control components such as MD5 and SHA-1 hash cores, XOR components, memory, etc. By providing a cryptography accelerator with access to multiple instruction sets, a variety of hash operations can be performed in a configurable cryptographic accelerator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
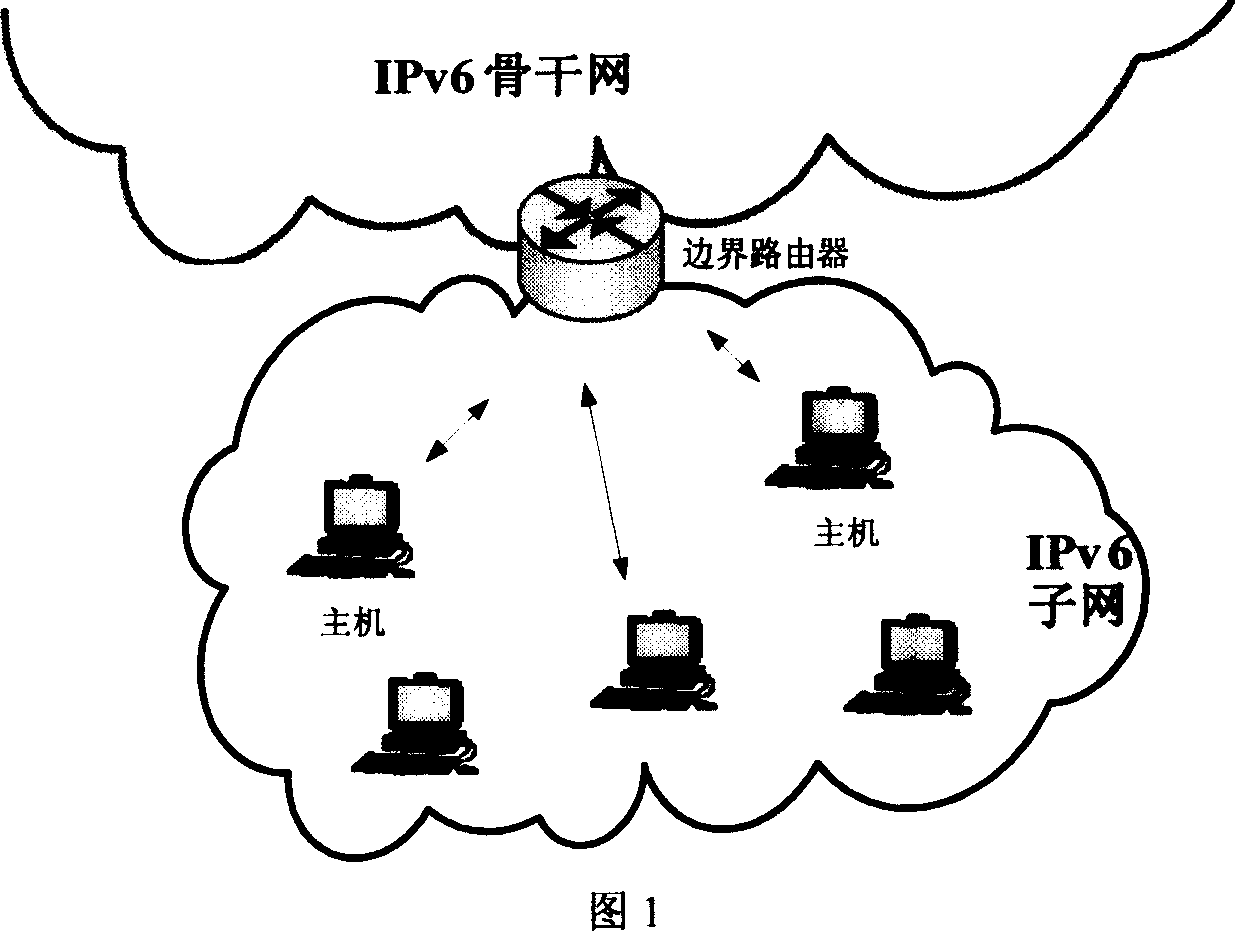
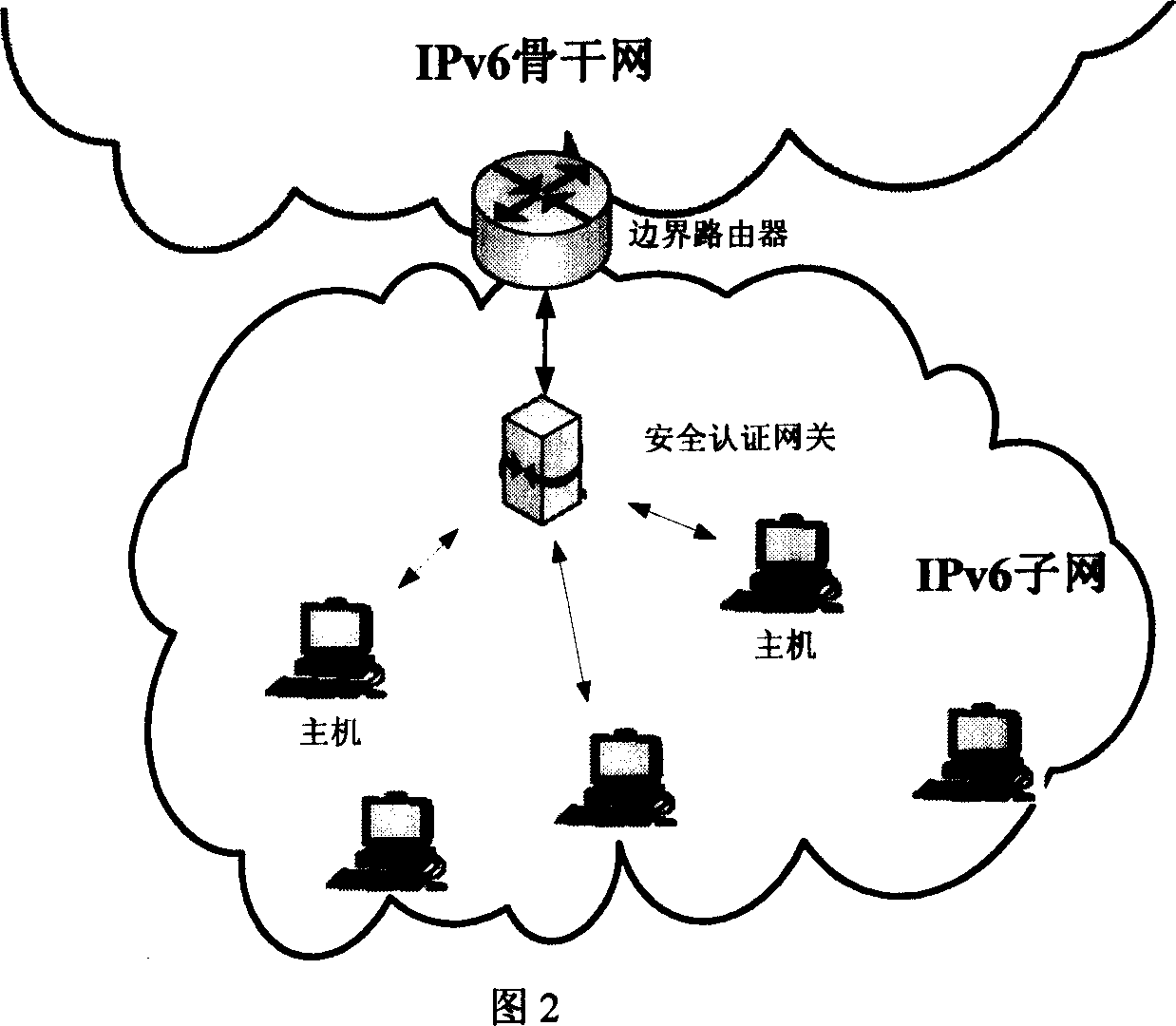
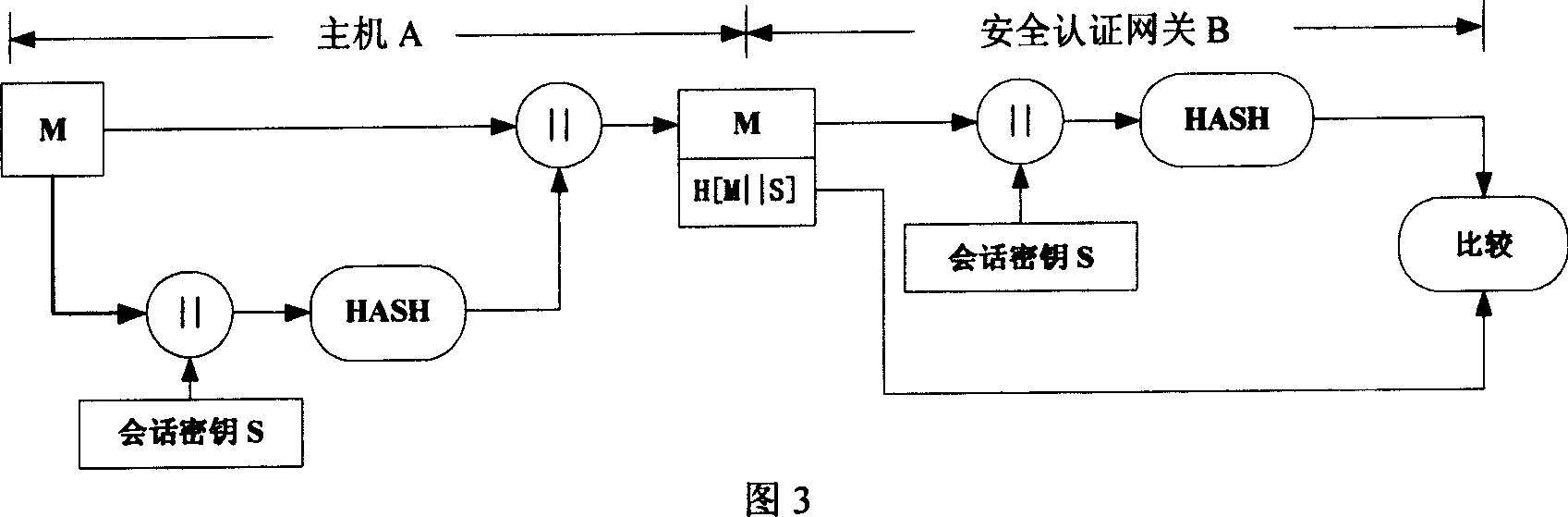
Method for preventing forgery of source address based on signature authentication inside IPv6 sub network
ActiveCN1921488AImprove efficiencyImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksMD5Secure authentication
The invention relates to a method for avoiding false source address based on sign identification in IPv6 sub network. Wherein, the invention is characterized in that: the user host sends one report to external network, which carries one sign formed by application information summary function MD5 or SHA1 as conversation key, source address, target address, and report serial number; the safety identification gateway at the inlet of edge route of IPv6 sub network checks the report sign, to confirm its source address is true; at the same time, the gateway judges if its serial number is increased in the life of conversation key to judge if it is replay report. The invention can effectively avoid false source address, while it supports increase setting.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
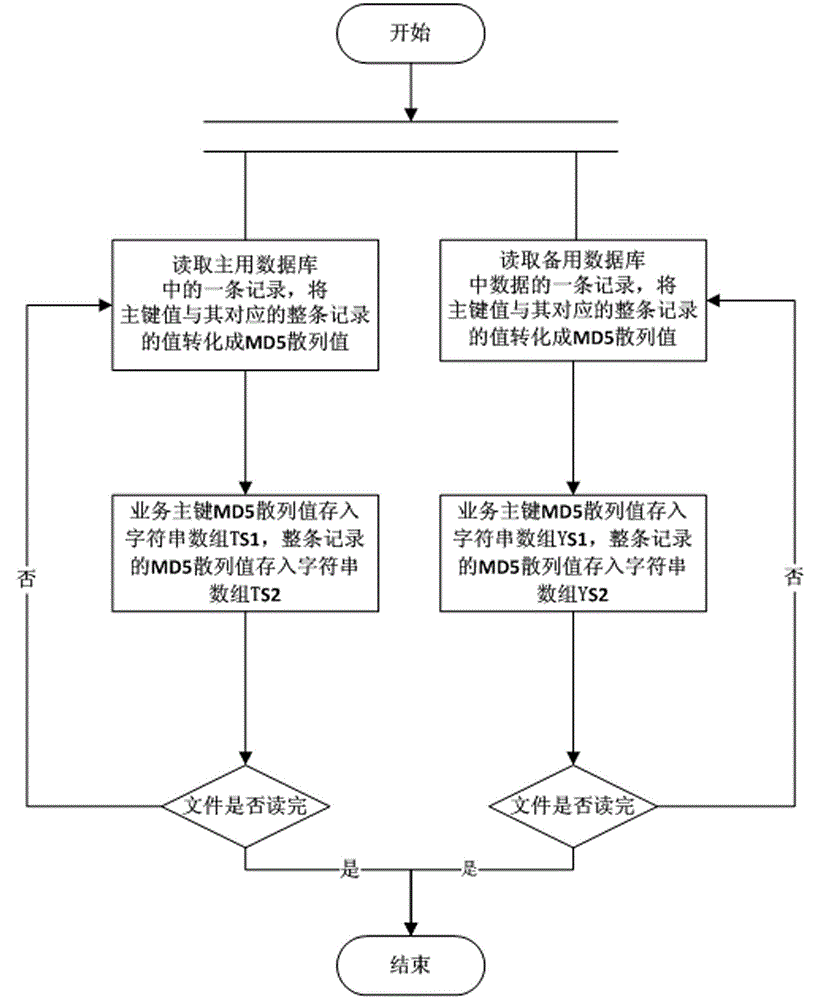
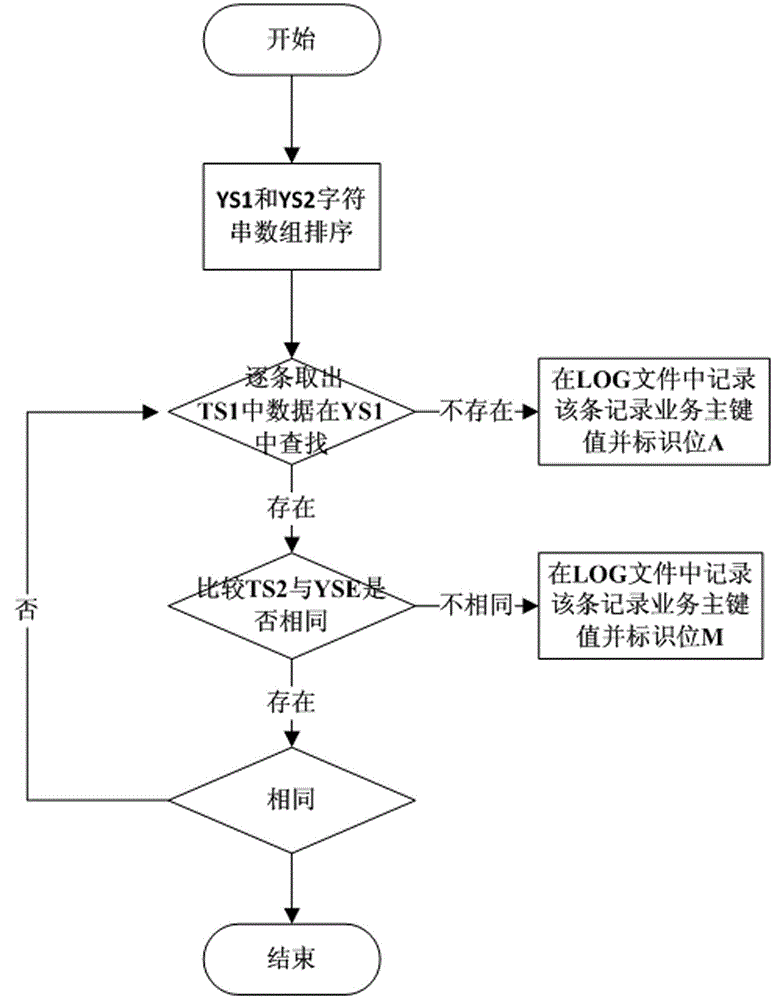
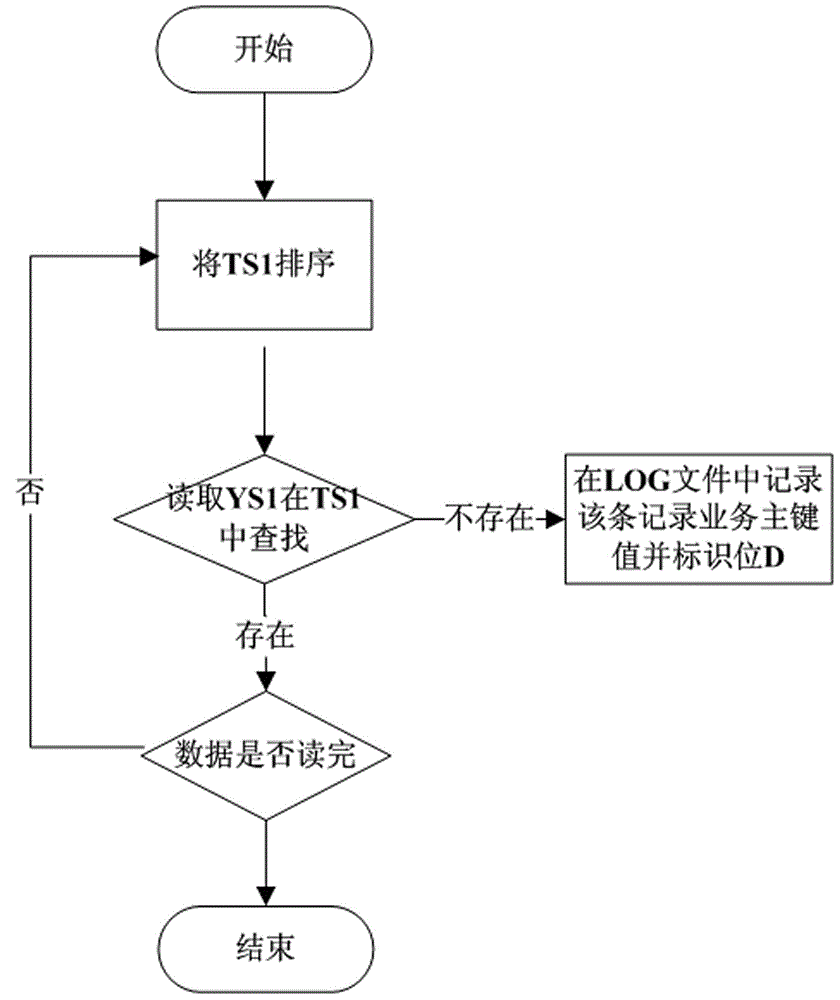
Method and system for verification of consistency of backup data of host database and backup database
ActiveCN104021132AImprove the efficiency of consistency check backupGood for security auditSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionMD5Engineering
A method for verification of consistency of backup data of a host database and a backup database comprises the steps of (1) reading the data of the host database and the backup database, and hashing the data in the host database and the backup database one by one by means of the MD5 informative abstract algorithm; (2) comparing the MD5 hashed value of the data in the host database with the MD5 hashed value of the data in the backup database by means of the quick search algorithm, and generating a comparison result LOG file by means of the labeling method; (3) acquiring corresponding service data in the host database according to the comparison result LOG file, and updating the service data to the comparison result LOG file; (4) achieving incremental backup of the backup database and updating of a backup operation LOG sheet of the backup database simultaneously according to the LOG file. According to the method, by conducting MD5 hashing on the host database and the backup database and comparing the two MD5 hashed values by means of the binary quick search algorithm, verification efficiency is improved, and mass backup data consistency verification efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU IMAN TECH DEV +1
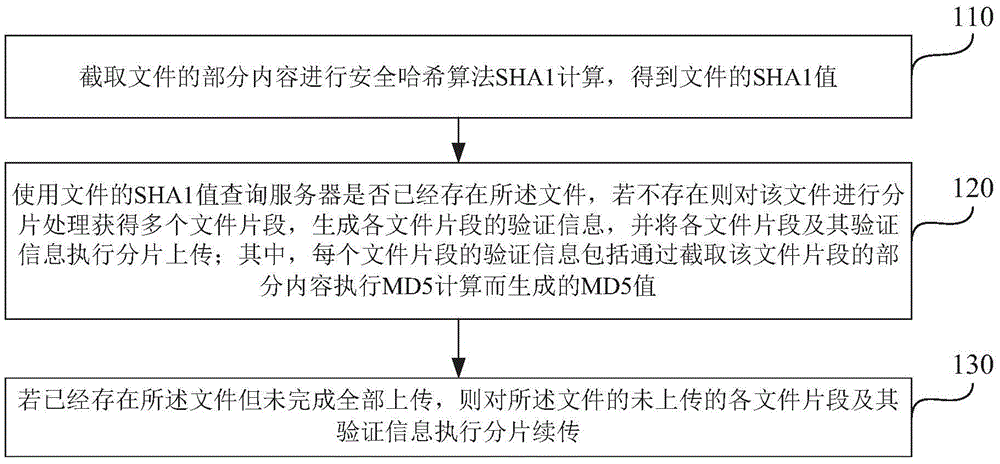
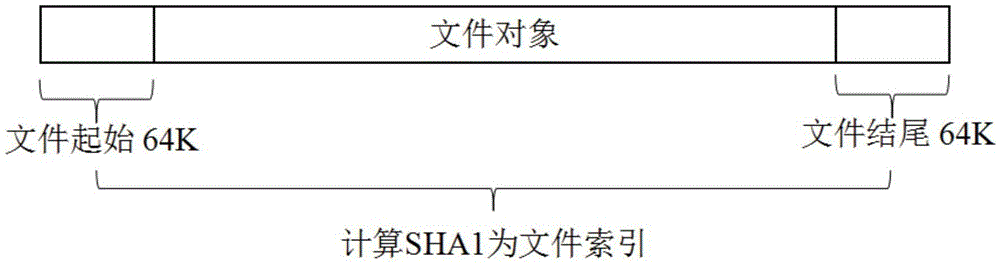
Big file uploading and continuous uploading method and device for browser or server
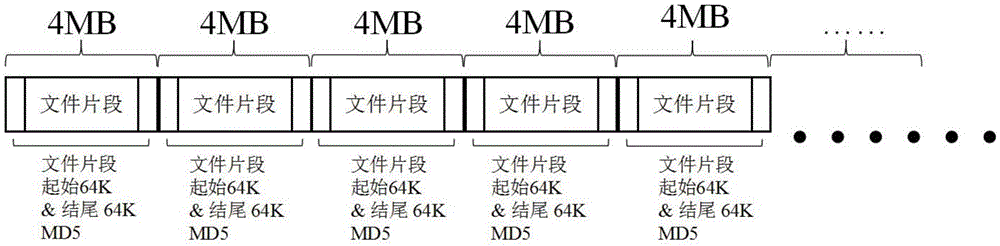
InactiveCN105635324AReduce development costsReduce operating proceduresTransmissionSecure Hash AlgorithmFragment processing
The invention provides a big file uploading and continuous uploading method and device for a browser or a server. The big file uploading and continuous uploading method for the browser comprises the following steps: capturing a part of content of a file and carrying out secure Hash algorithm SHA1 calculation to obtain an SHA1 value of the file; searching the server to judge whether the server has the file according to the SHA1 value of the file; if not, carrying out fragment processing on the file to obtain a plurality of file fragments, generating verification information of each file fragment, and carrying out fragment uploading on each file fragment and the verification information thereof, wherein the verification information of each file fragment comprises an MD5 value generated by carrying out MD5 calculation on a part of captured content of the file fragment; and if the server has the file but the file is not uploaded completely, carrying out fragment uploading on each un-uploaded file fragment of the file and the verification information thereof. SHA1 and MD5 sampling modes are optimized, and performance is improved.
Owner:SINA COM TECH (CHINA) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for removing call ticket repeat
InactiveCN101442731AEasy to handleImprove efficiencyAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationExtensibilityMD5
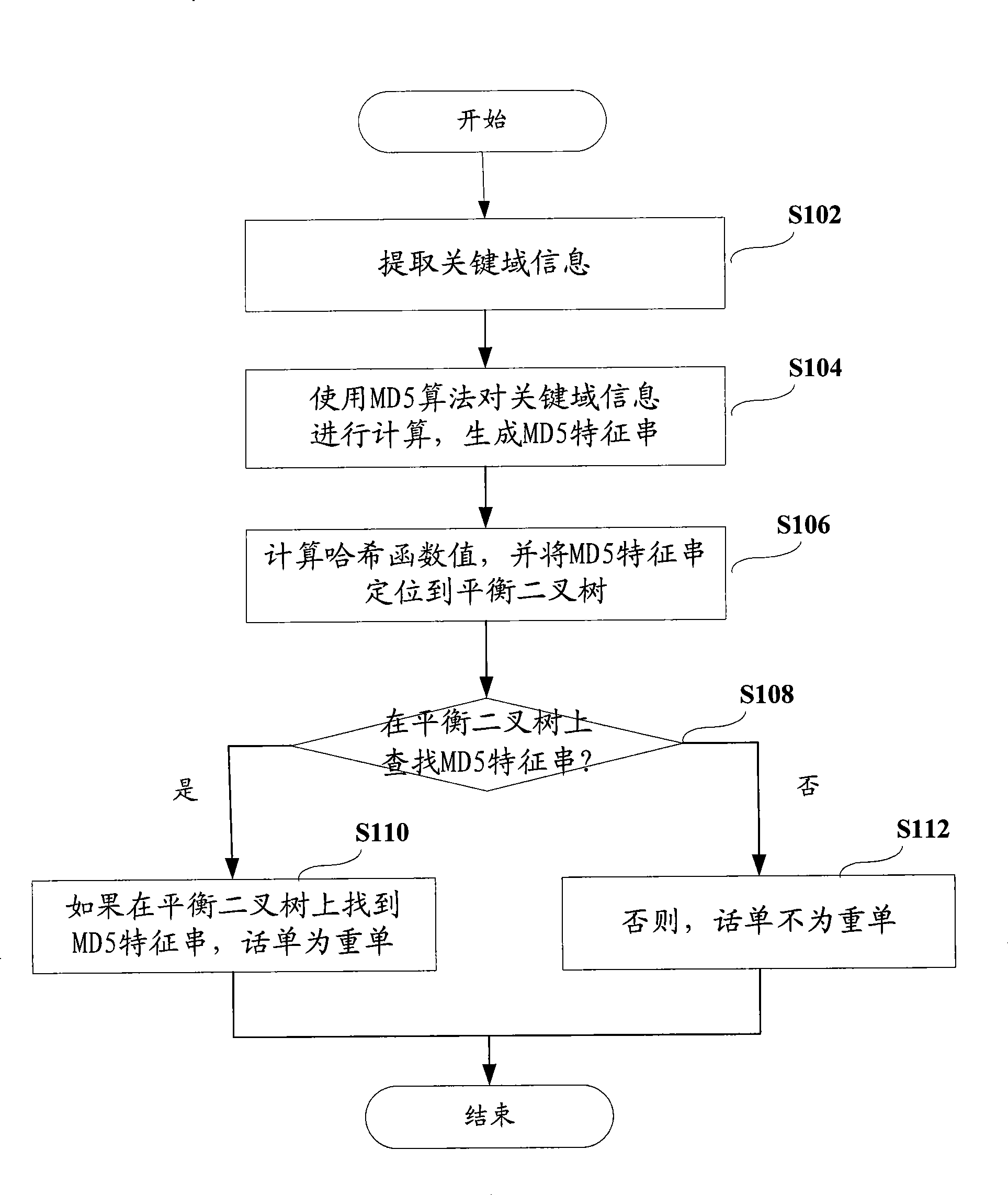
The invention discloses a repetition deleting method and device for ticket, mainly applied in communication charging field and comprising following steps: extracting key domain information from ticket; computing the key domain information using MD5 algorithm, generating MD5 characteristic string; comparing the MD5 characteristic string with that corresponding to normal ticket stored in index file; if finding same MD5 characteristic string, then the ticket is duplicate, then deleting, or keeping the MD5 characteristic string the ticket corresponds to index file and confirming the ticket as normal ticket. In the invention, MD5 characteristic string of index file is stored in hash table whose conflict is solved through chained list or balanced binary tree. The invention integrates advantage of hash table, balanced binary tree and MD5 algorithm, implements effective processing for arbitrary service and ticket of arbitrary type, then unique repetition deleting index is formed and length of index is unique, which promotes repetition deleting efficiency and expandability, largely saves memory space.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP ANHUI
Content addressable information encapsulation, representation, and transfer
InactiveUS20050010794A1Simple structureCompact formSpecial service provision for substationData processing applicationsCryptographic hash functionMD5
Representing a number of assets on an originating computer begins with selecting the assets to be represented. Cryptographic hash asset identifiers are generated; each of the asset identifiers is computed using the contents of a particular asset. The asset identifier is a content-based or content-addressable asset name for the asset and is location independent. An asset list is generated that includes the asset identifiers computed from the assets. A cryptographic hash asset list identifier is generated that is computed from the asset list. The asset list identifier is stored for later retrieval. The assets selected are also stored for safekeeping either locally or on a computer network. In the event of loss of the files from the originating computer, the asset list identifier is retrieved. Using the asset list identifier, the original asset list is found and retrieved from its safe location. The asset identifiers from the retrieved asset list are used to find and retrieve the individual assets from their backup locations. The assets are verified by recomputing the cryptographic hash asset identifier for each asset retrieved and comparing it to the asset identifier from the asset list. The MD5 algorithm is used for the cryptographic hash function. Assets are retrieved using a multicast protocol. A series of importer programs searches for assets to retrieve in progressively more remote locations. Assets are retrieved whole or in segments.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Automatic software updating method and system
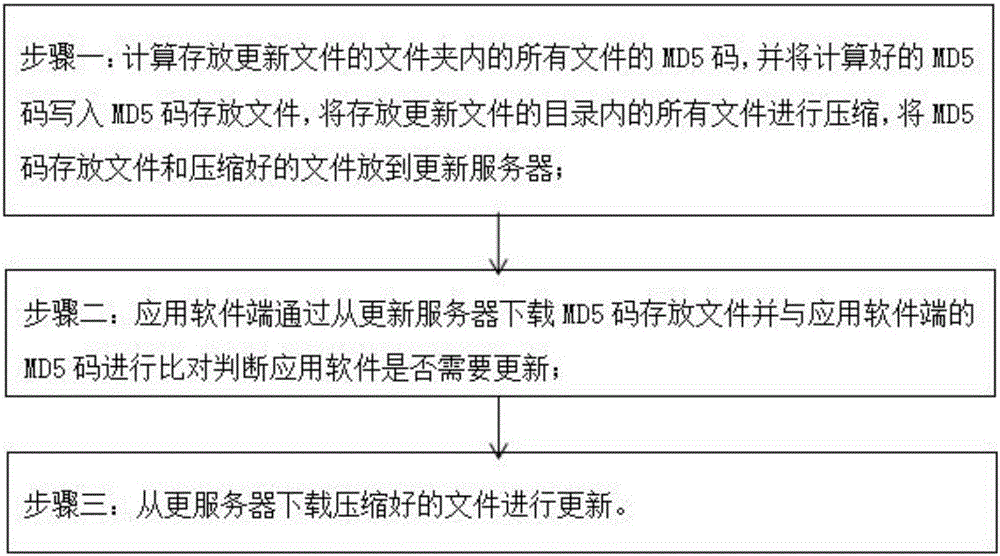
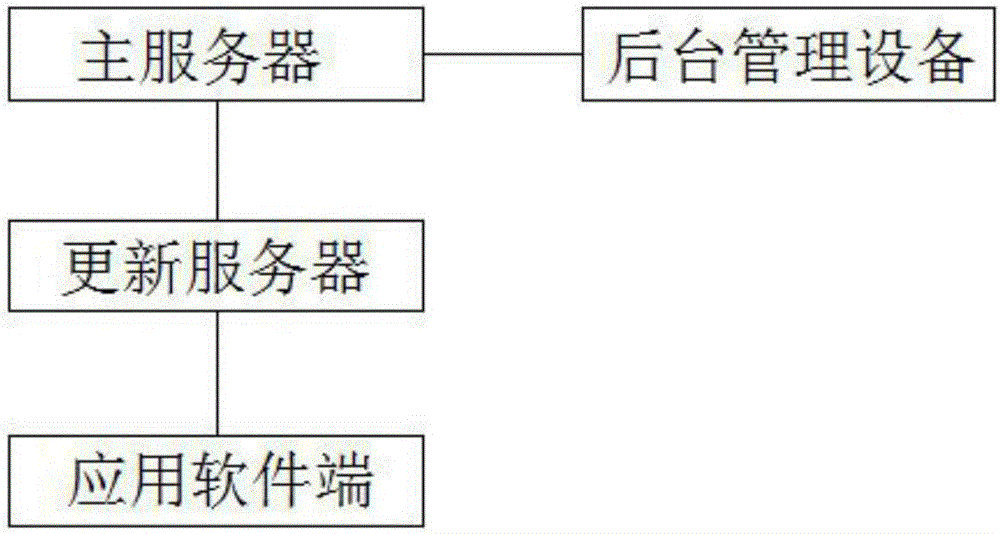
InactiveCN106095500ASave resourcesShorten update timeProgram loading/initiatingSoftware deploymentSoftware updateApplication software
The invention provides an automatic software updating method and system. The method comprises the following steps that 1, MD5 codes of all files inside a file folder for storing updating files are calculated, the calculated MD5 codes are written into an MD5 code storing file, and all files inside a catalog for storing the updating files are compressed, and the MD5 code storing file and the compressed files are stored into an updating server; 2, an application software terminal downloads the MD5 code storing file from the updating server and compares the MD5 code storing file with MD5 codes of the application software terminal, and whether the application software needs to be updated or not is judged; 3, the compressed file downloaded from the updating server is updated. The automatic software updating system comprises a main server, a background management device, an updating server and an application software terminal. The software updating speed is high, resources are saved, and workloads and cost of application, updating and maintenance of a client side can be reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGWEI TECH SOFTWARE SYST
Encryption and decryption system based on medium security protection of IPTV platform
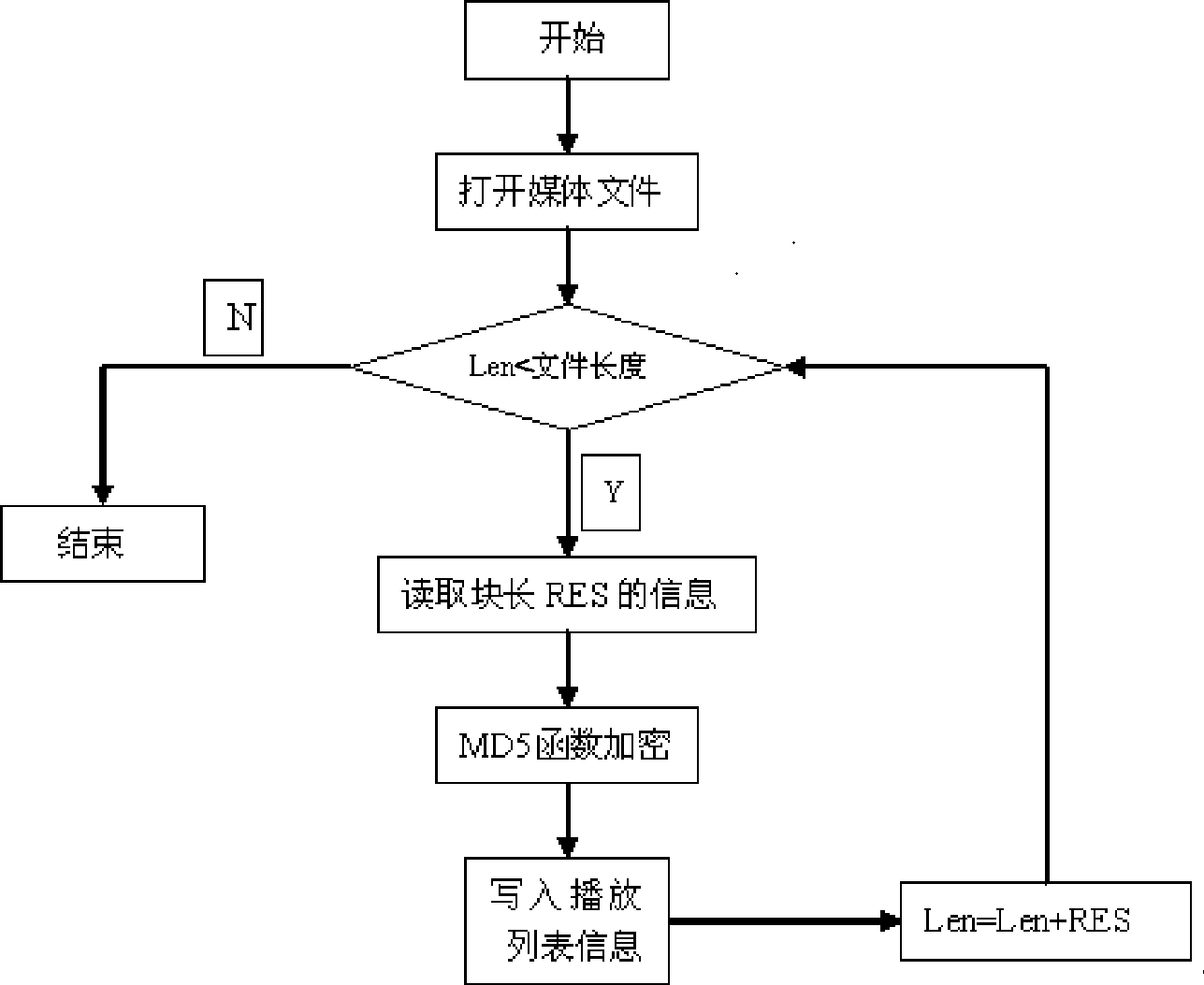
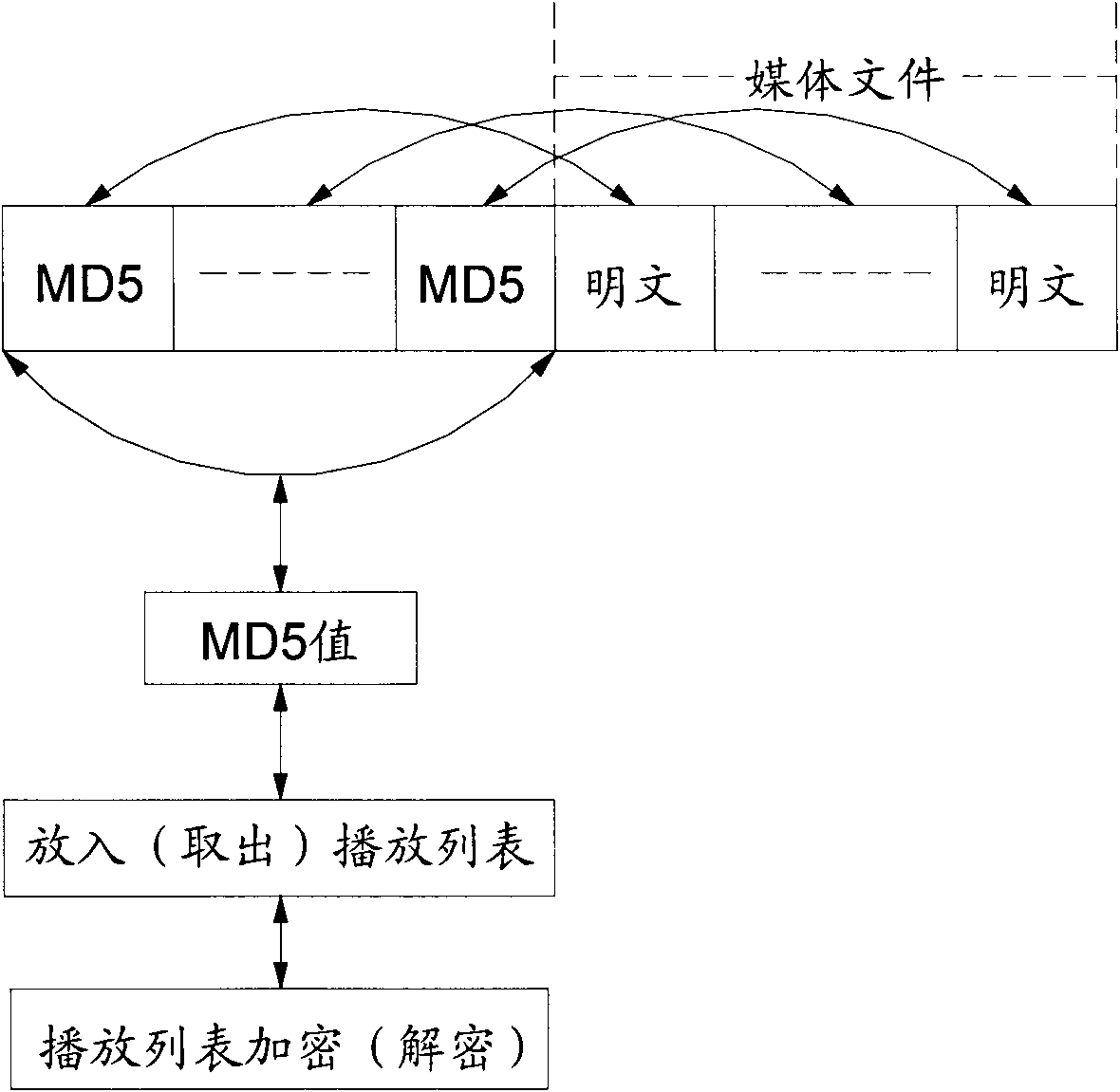
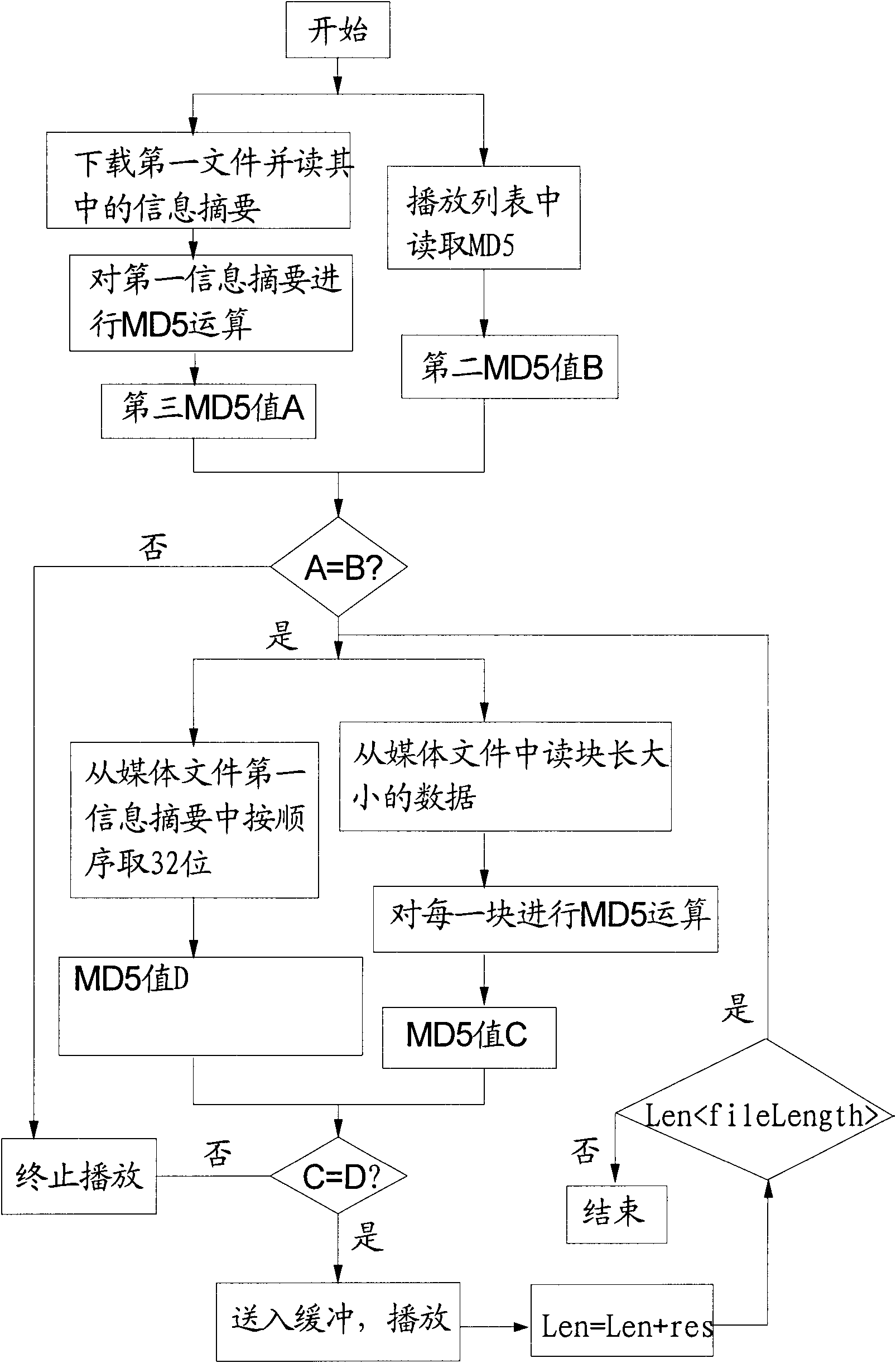
InactiveCN101521818AEnsure safetyStrengthen security managementKey distribution for secure communicationPulse modulation television signal transmissionMD5Value of information
The invention discloses an encryption and decryption system based on the medium security protection of an IPTV platform. On a platform end in the method, each sub-block of a media file is firstly carried out with MD5 operation, then a section of information is combined by the MD5 values obtained from the sub-blocks, the information is carried out with MD5 operation again, an obtained result is placed in a playlist, and finally, the playlist is encrypted. On a terminal, firstly, the playlist is decrypted, MD5 values of information abstracts of the media file, which are obtained from the playlist, are compared with the MD5 of information abstracts combined by all the sub-blocks of an operation file; if the two MD5 values are not identical, the play is prohibited; if the two MD5 values are identical, the MD5 of each sub-block is compared, if identical, the information is placed in a buffer area to by played; and if else, the play is stopped. The method has high speed and high safety factor.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for preventing in-car terminal from being detached
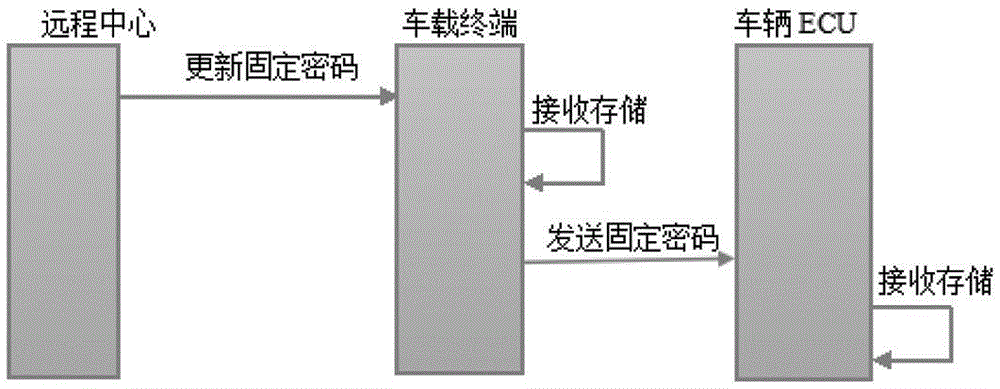
InactiveCN105245406AImplement the encryption functionImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksIn vehiclePassword
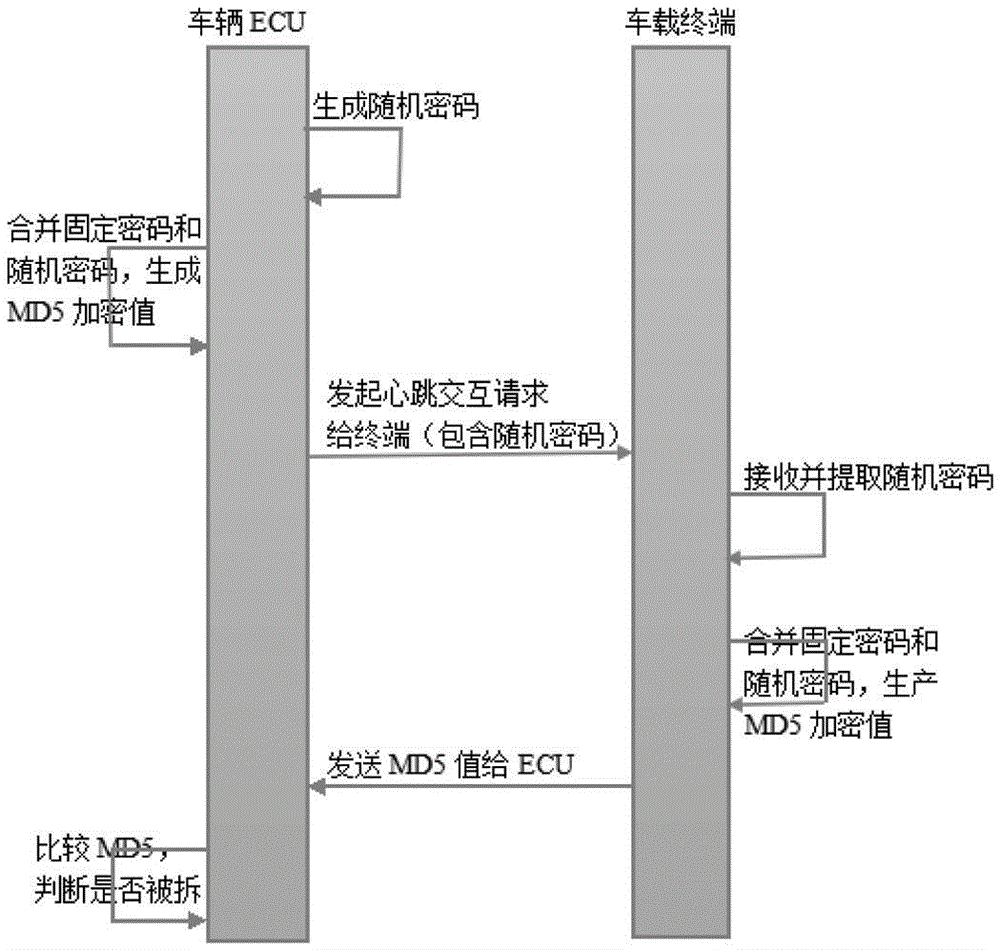
The invention relates to an anti-detachment technology field, in particular to a method for preventing an in-car terminal from being detached. The method includes: 1) stipulating a fixed password between the in-car terminal and a vehicle ECU; 2) generating a random password R by the vehicle ECU, joining the fixed password of the vehicle ECU with the random password R, generating an MD5 encrypted value which is a dynamic password A, sending a heartbeat interactive request to the in-car terminal by the vehicle ECU through a CAN bus, wherein a frame of the heartbeat interactive request contains the random password R; 3) after a CAN transceiver of the in-car terminal receives the heartbeat interactive request of the vehicle ECU, extracting the random password R, joining the fixed password of the in-car terminal with the random password R by the in-car terminal, generating an MD5 encrypted value which is a dynamic password B, and sending the dynamic password B to the vehicle ECU through the CAN transceiver, wherein the dynamic password B is used as a heartbeat frame; 4) after the vehicle ECU receives the heartbeat frame, comparing the dynamic password A with the dynamic password B, and if the dynamic password A coincides with the dynamic password B, determining that the in-car terminal is normal, otherwise determining that the in-car terminal is detached. The method has a characteristic of high safety.
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
Content addressable information encapsulation, representation, and transfer
InactiveUS20050187902A1Simple structureSpecial service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalCryptographic hash functionMD5
Representing a number of assets on an originating computer begins with selecting the assets to be represented. Cryptographic hash asset identifiers are generated; each of the asset identifiers is computed using the contents of a particular asset. The asset identifier is a content-based or content-addressable asset name for the asset and is location independent. An asset list is generated that includes the asset identifiers computed from the assets. A cryptographic hash asset list identifier is generated that is computed from the asset list. The asset list identifier is stored for later retrieval. The assets selected are also stored for safekeeping either locally or on a computer network. In the event of loss of the files from the originating computer, the asset list identifier is retrieved. Using the asset list identifier, the original asset list is found and retrieved from its safe location. The asset identifiers from the retrieved asset list are used to find and retrieve the individual assets from their backup locations. The assets are verified by recomputing the cryptographic hash asset identifier for each asset retrieved and comparing it to the asset identifier from the asset list. The MD5 algorithm is used for the cryptographic hash function. Assets are retrieved using a multicast protocol. A series of importer programs searches for assets to retrieve in progressively more remote locations. Assets are retrieved whole or in segments.
Owner:CARPENTIER PAUL R +2
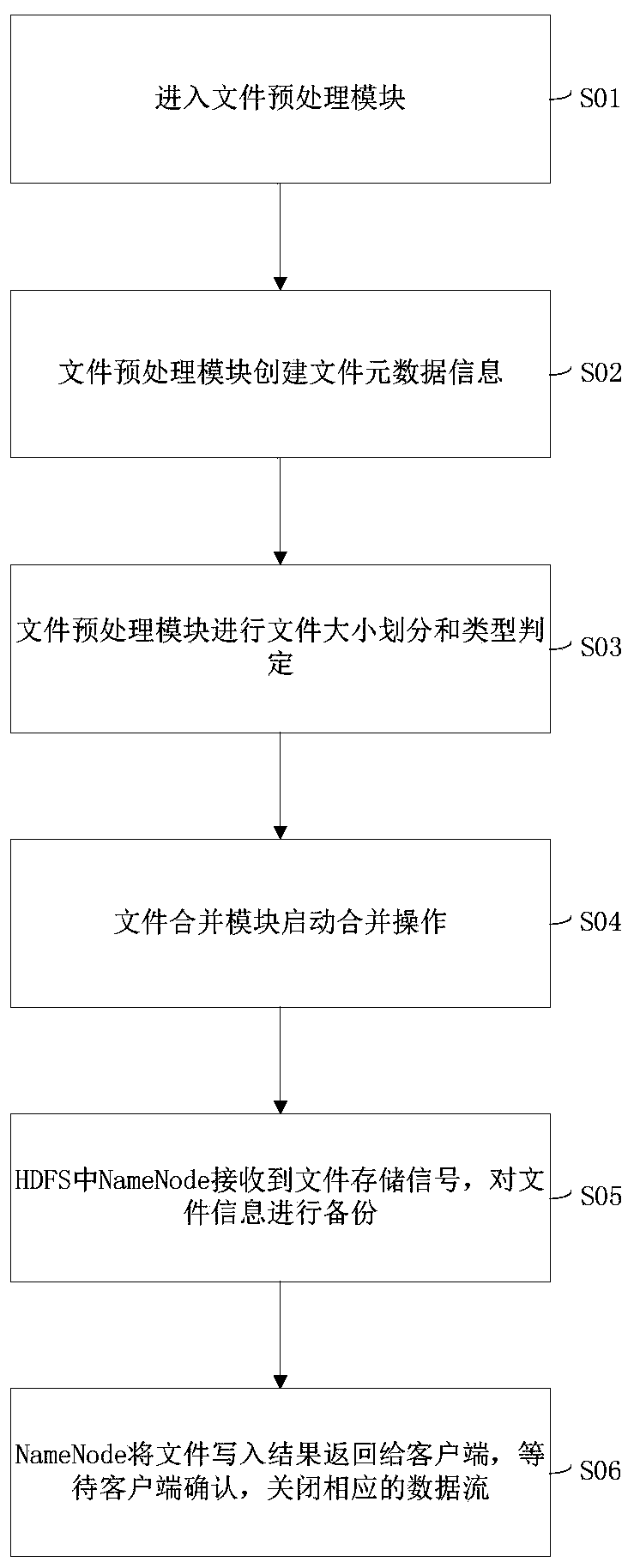
High-performance file storage and management system based on HDFS
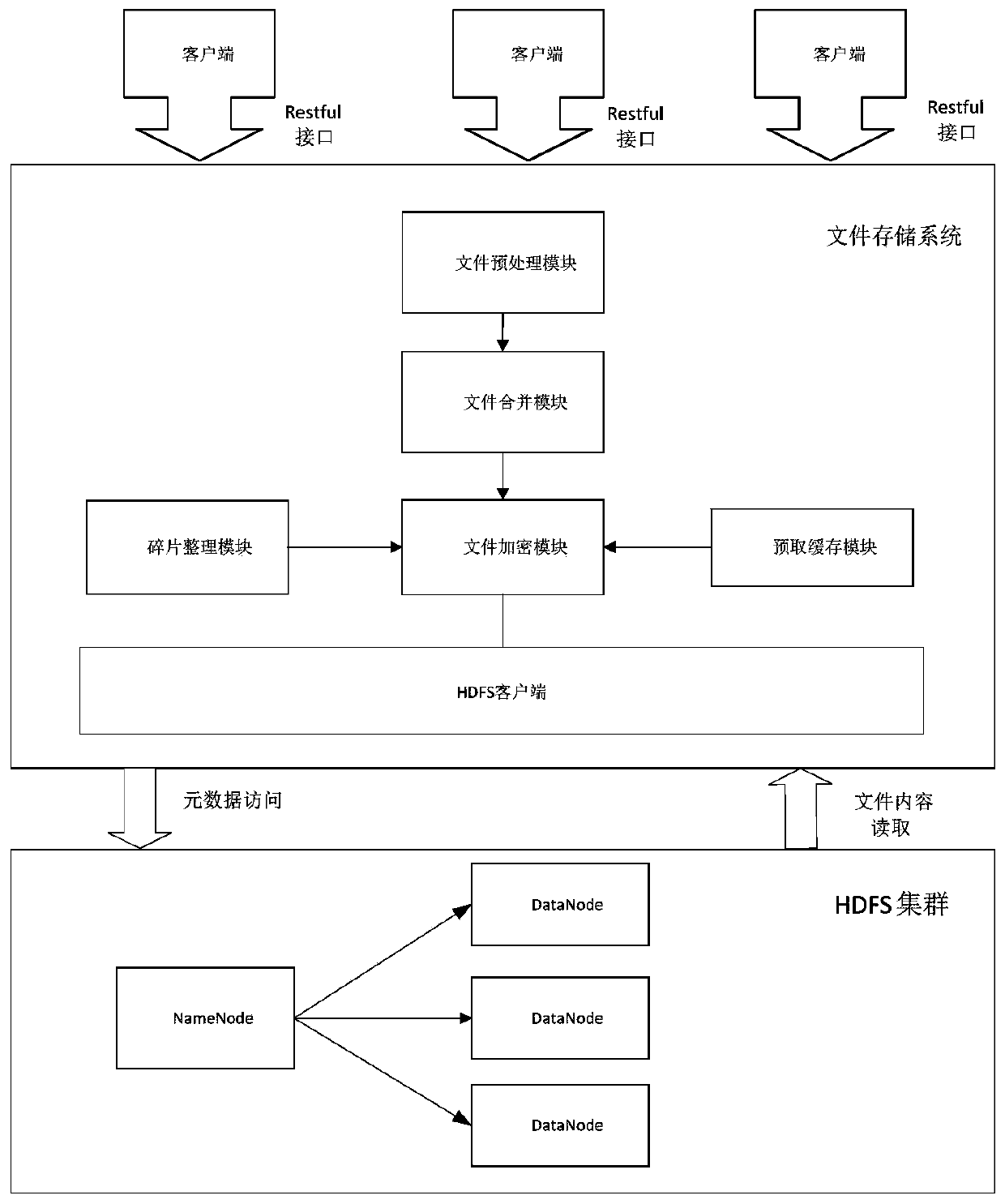
PendingCN110647497AImprove retrieval efficiencyAvoid wastingFile system administrationSpecial data processing applicationsShardDistributed File System
The invention provides a high-performance file storage and management system based on an HDFS. A file preprocessing module and a file merging module are provided for overcoming the defect that an HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System) supports small file storage, a pre-fetching cache module is provided for improving the file reading efficiency, a fragmentation module is provided for improving the overall space utilization rate, and a data encryption module is provided for protecting private files of a user. The invention provides a universal small file merging strategy and an HDFS client optimization scheme, and combines the advantages of an HAR file archiving method and a MapFile method so as to be suitable for any type of files. Specifically, the system optimizes a small file merging strategy and provides a defragmentation mechanism which is easy to update so as to improve the space utilization rate of an HDFS cluster. Meanwhile, a hotspot file strategy based on frequency statistics improves the reading speed of data, and improves the safety of a user account and a private file based on MD5 login encryption and AES file encryption.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
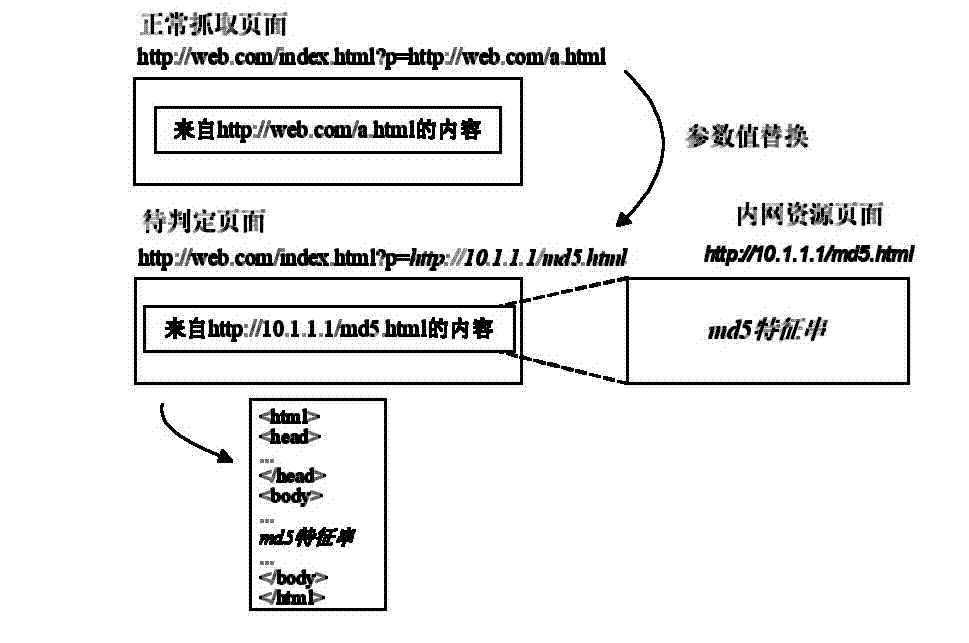
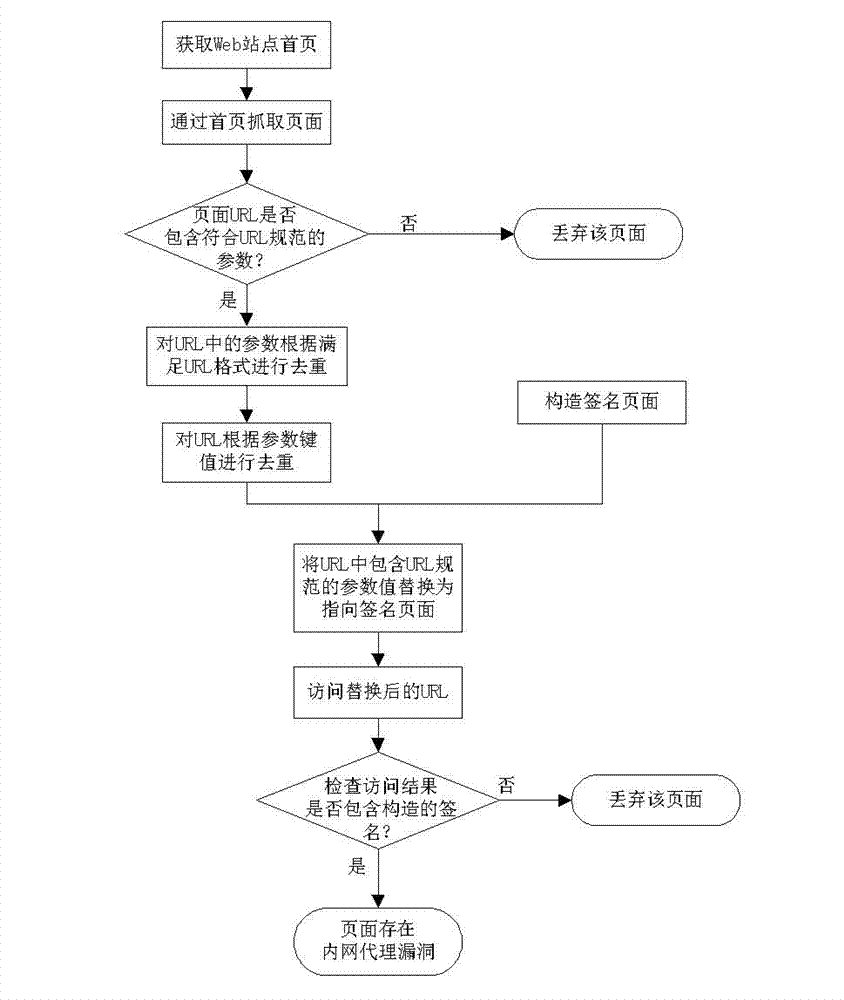
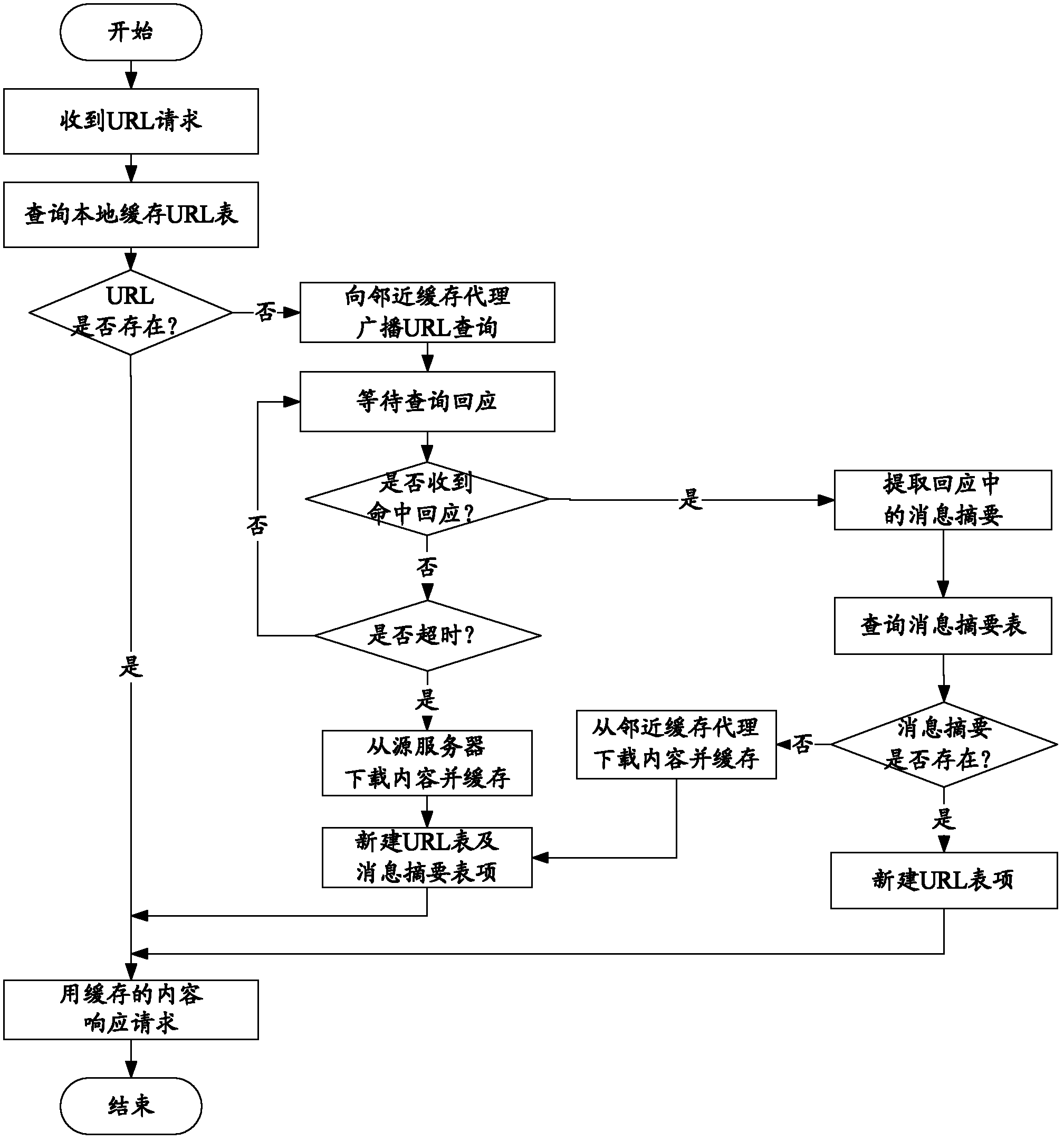
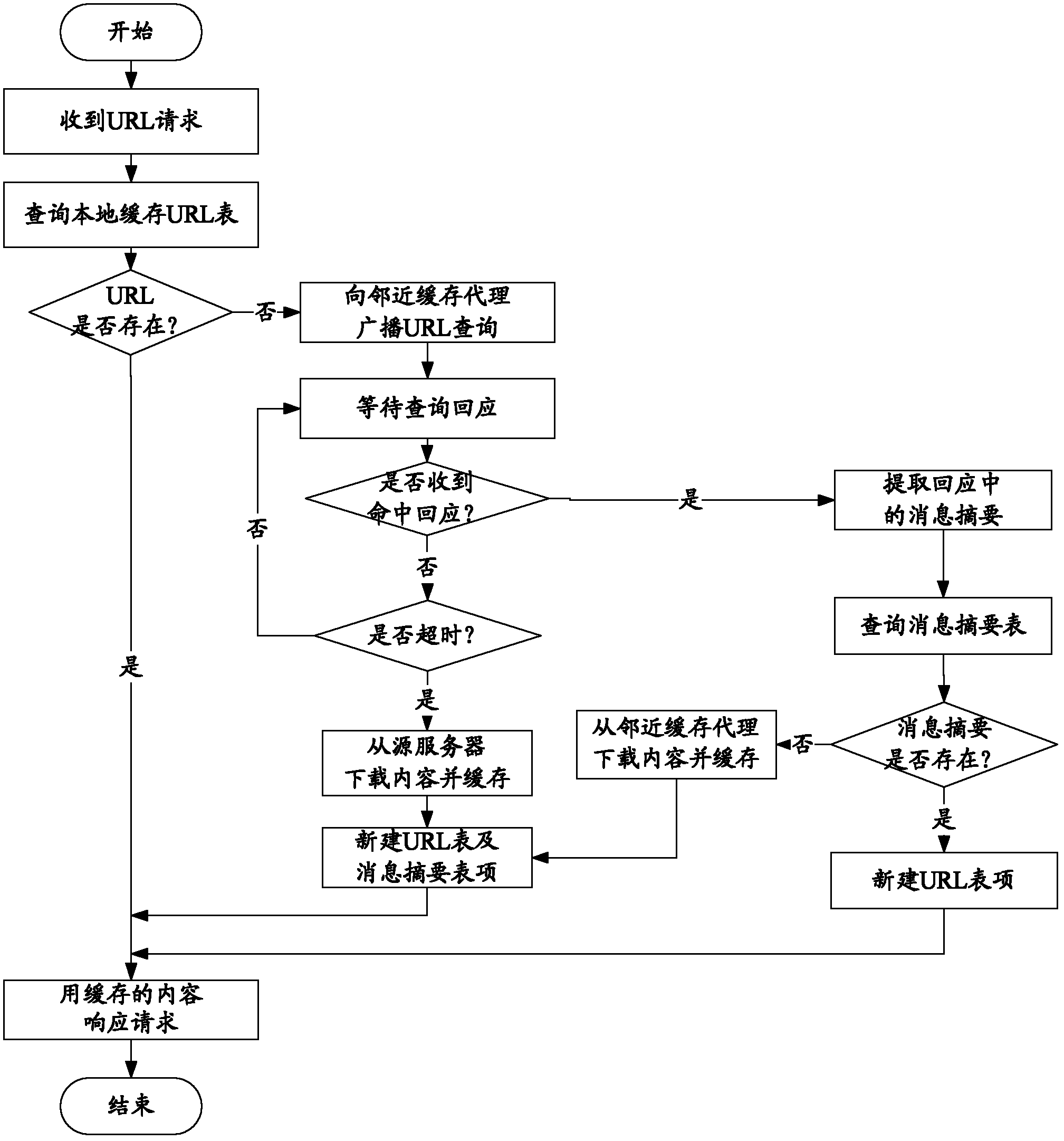
Method for discovering Web intranet agent bugs
The invention discloses a method for discovering Web intranet agent bugs. Capture of intranet network pages is achieved and uniformed resource locators (URLs) of all pages are obtained through a network crawler technology; then filtering is performed twice to screen URLs possibly existing intranet agent bugs out based on UPL specifications and characteristics of parameter values; feature pages containing a section of message algorithm digest 5 (MD5) strings are constructed in a Web intranet; and for each filtered URL, original parameter content containing the URL is replaced with the URLs of the feature pages, the URLs after the replacement are requested, if request responses contain the MD5 strings in the feature pages, the intranet agent bugs exist in the page URLs, and otherwise, the intranet agent bugs do not exist in the page URLs. The defects in the artificial method are overcome by using the programmed intranet agent detection method, the intranet agent bugs in Web service can be discovered effectively and comprehensively, and the safety of the Web can be improved.
Owner:周耕辉
Anti-crawler data query method and device as well as client and server
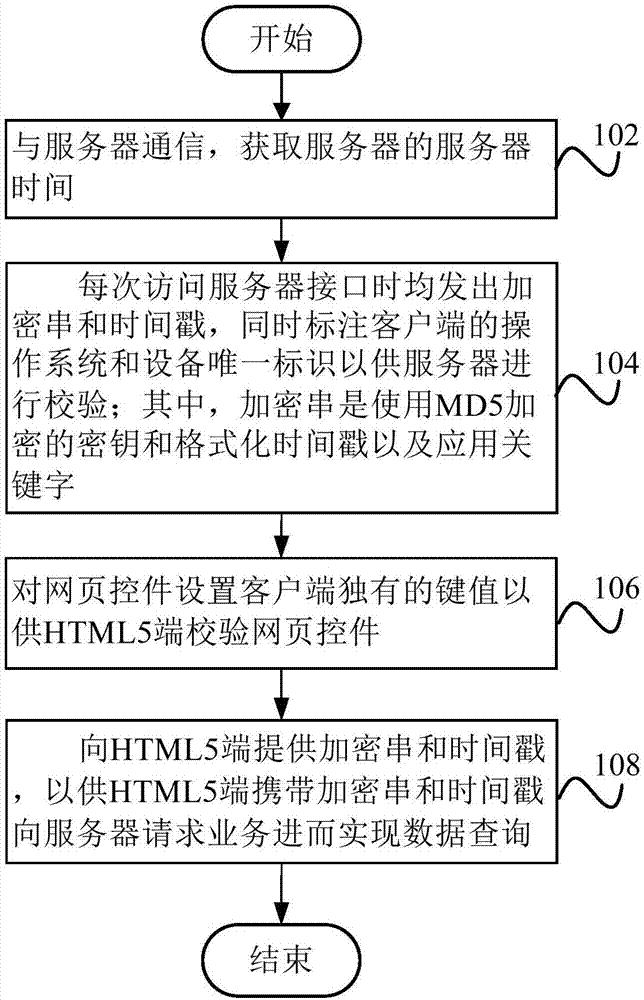
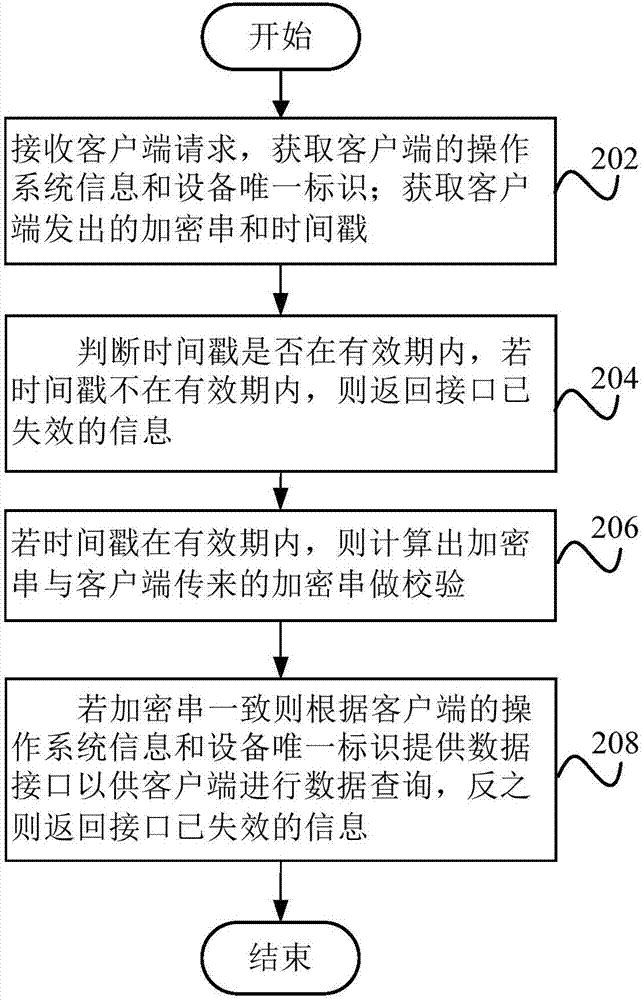
InactiveCN107483563AIncrease the difficultyRelieve pressureWeb data indexingTransmissionHTML5Internet communication
The invention provides an anti-crawler data query method and device as well as a client and a server, relating to the field of internet communication technology. The anti-crawler data query method is applied to the client, and comprises the following steps: communicating with the server to obtain the service time of the server; issuing an encryption string and a timestamp when accessing a server interface each time, and simultaneously marking an operation system and a unique equipment identifier of the client for the server to perform verification, wherein the encryption string is a key, a formatted timestamp and application keywords that are encrypted by using MD5; setting a unique key value of the client to a web page control for an HTML5 end to verify the web page control; and supplying the encryption string and the timestamp to the HTML5 end to ensure that the HTML5 end carries the encryption string and the timestamp to request services from the server to further achieve data query. Thereby, non-login users can query data freely, the phenomenon that a large amount of data is crawled by abnormal users can also be prevented, the pressure of operation and maintenance layers can be reduced, and junk data of interface layers can be reduced.
Owner:九次方大数据信息集团有限公司
Encryption method of playlist and media task of networking information release system
ActiveCN101615411ALittle effect on playbackFulfil requirementsRecord information storageRecording signal processingMD5Computer terminal
The invention relates to an encryption method of a playlist and a media task of a networking information release system. The encryption method comprises the following steps of: carrying out blocking to media files according to the specified size of the blocks, then carrying out MD5 operation to each block of the media files, combining the obtained MD5 values of each block into a section of information, carrying out MD5 operation again to the section of information, putting the final MD5 values into the playlist, and finally carrying out encryption to the playlist; on a terminal, firstly carrying out decryption to the playlist, comparing whether the MD5 values of information abstracts of media files obtained from the playlist are same with the MD5 of the information abstracts formed by all the blocks in the files, if not, prohibiting playing; if so, starting to compare whether the MD5 of each block is same, if so, putting the section of information into a buffer zone to wait for playing; and if no, ending the playing. For small files, the step of blocking can be saved. The encryption method has the advantages of ensuring legal playing of the media resources on the terminal, but having no influence on playing effect of videos.
Owner:FUJIAN STAR NET COMM
System and method for reducing memory requirements of firmware
ActiveUS7603562B2Reduce memory requirementsUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsMD5Unique identifier
A mechanism for making increased amounts of firmware available to a computer pre-boot is discussed. To increase the amount of firmware available pre-boot, a design decision is made during the build process as to which segments of the firmware need to be placed on the ROM part and which segments of the firmware can be located elsewhere. The segments of the firmware that are stored remotely from the ROM are referred to as “virtual ROM modules”. Each of the virtual ROM modules is assigned a generated unique identifier, and a “message digest” is constructed for each module using an algorithm such as MD5 or SHA-1. In the software build of the ROM image, the message digest-unique identifier pair created for each Virtual ROM module is used as a logical pointer for the virtual module. Additionally, a search path variable is placed into the ROM image in non-volatile storage. The search path provides for one or more locations in which to look for the Virtual ROM modules, and may be updated at a later point in time.
Owner:INSYDE SOFTWARE CORP
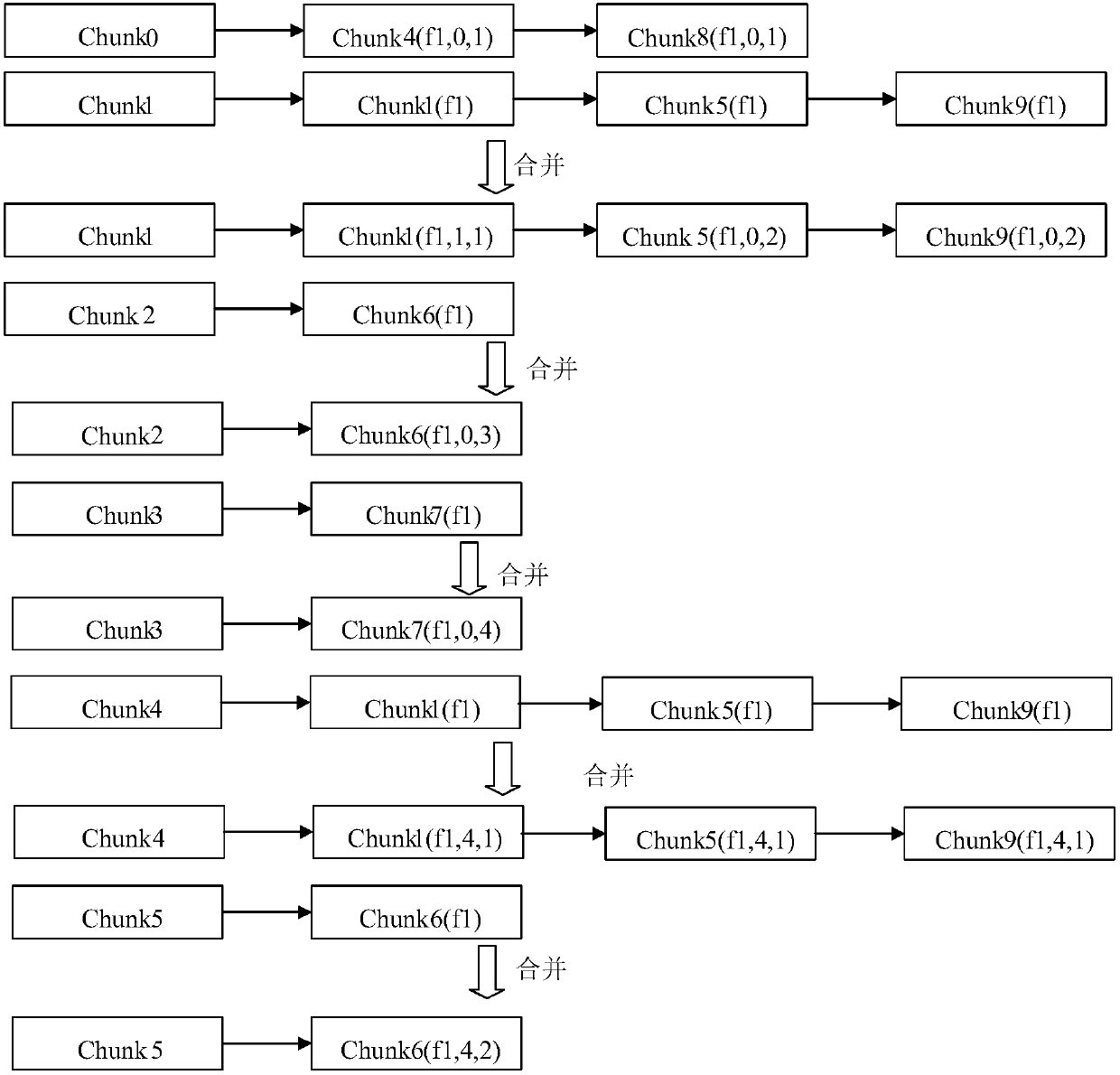
Method for carrying out combined detection on source code file cloning adjacency lists
InactiveCN107066262ARealize massive detectionSoftware engineeringSoftware testing/debuggingSource code fileDistributed index
The invention relates to a method for carrying out combined detection on source code file cloning adjacency lists. For an engineering project file, a fingerprint Chunk is constructed by using MD5 and a fingerprint library is established by taking the file as a unit and by taking scanning carried out on each line and fixed line number of codes as a granularity. The fingerprint library is stored in a MySQL database, and a detection algorithm is carried out by taking an ID of an open source project where a fingerprint is located and a Hash value of the Chunk as indexes so that detection of 0 to 3 clone classes can be performed. Namely, the invention discloses a scheme and algorithm for carrying out combined detection on source code file cloning adjacency lists on the basis of distributed indexes. According to the algorithm, cloned code files can be detected under the conditions that the time complexity is O (nm) and the space complexity is O (nm), so as to realize mass detection.
Owner:苏州棱镜七彩信息科技有限公司
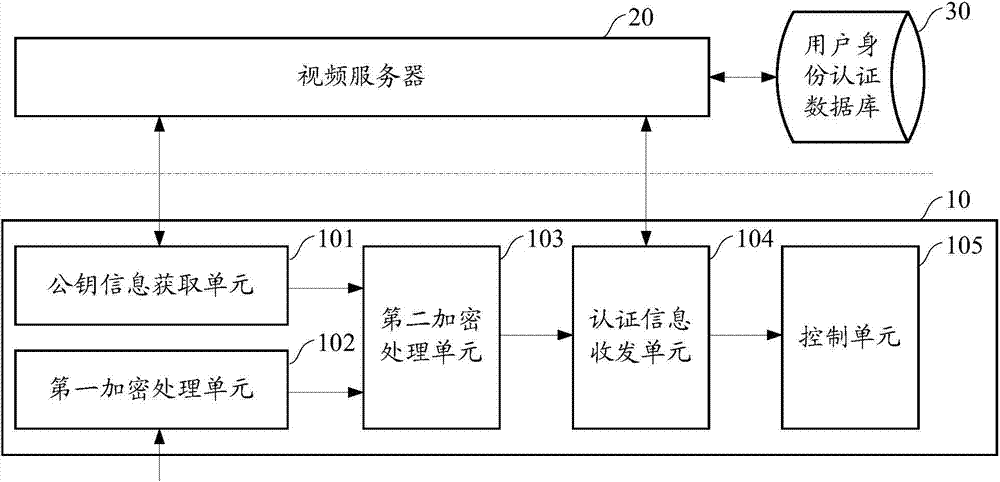
User authentication realizing method, device and system thereof for multimedia data transmission
InactiveCN104754571AAvoid the problem of low security caused by easy leakageEnsure safetySecurity arrangementSecuring communicationThird partyMD5
The present invention discloses a user authentication realizing method, device and system thereof for multimedia data transmission. In the method disclosed by the present invention, MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm 5) encryption is performed on the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) of a mobile terminal (such as a mobile phone); the encryption result of the MD5 encryption is used for the identity authentication of the mobile terminal; and in addition, in order to avoid the problem of low security caused by easy leakage of information in the process of multimedia data transmission, on the side of the mobile terminal, a public key on a video server side is adopted for encrypting identity authentication information, thereby ensuring that effective identity verification information cannot be obtained even if the identity authentication information is stolen by a malicious third party. Thus, the security of user information is guaranteed.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZTE NETVIEW TECH
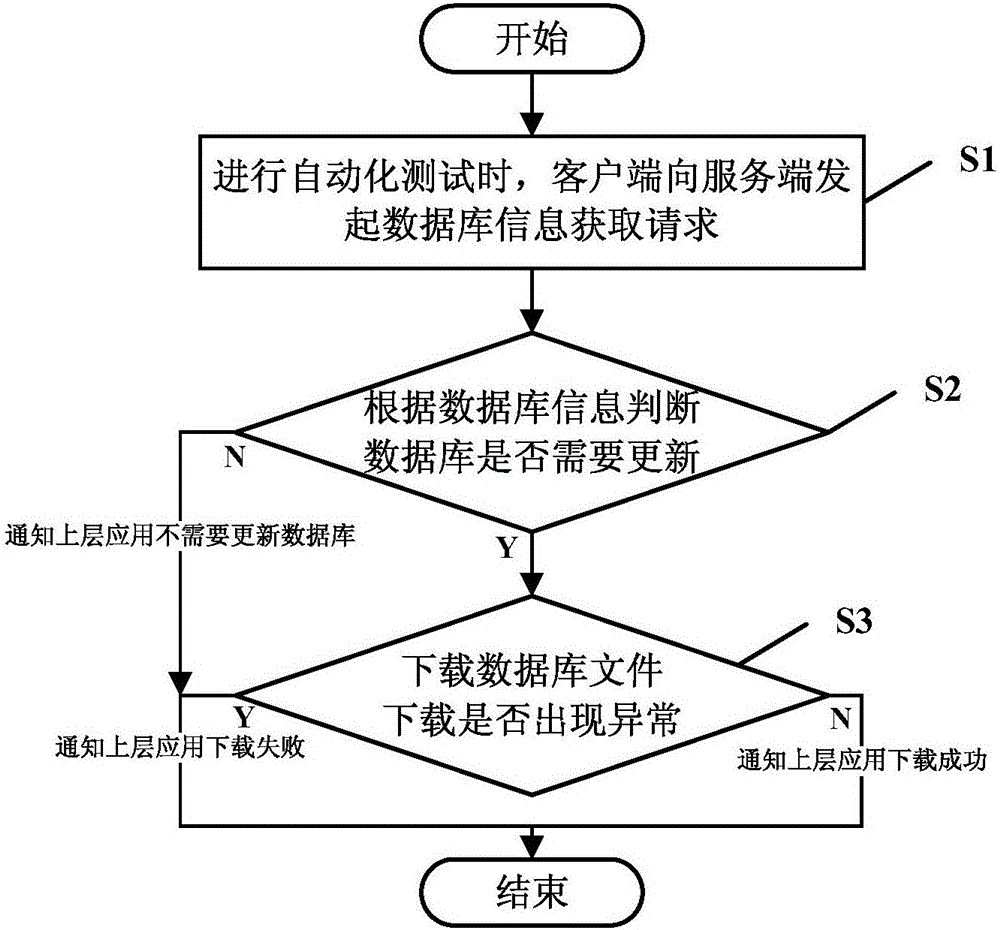
Method and system for synchronizing databases of client side and server side during automated testing
ActiveCN106502883AReduce trafficImprove download speedDatabase distribution/replicationSoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyDatabase file
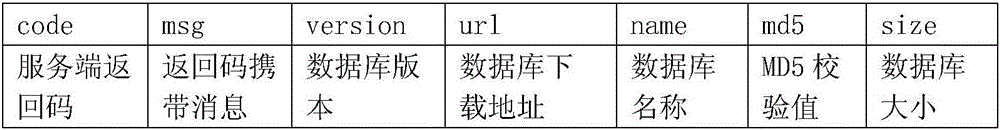
The invention discloses a method and a system for synchronizing databases of a client side and a server side during automated testing, and relates to the field of automated testing of application programs. The method comprises the following steps: when an application program is subjected to automated testing on the client side, the client side initiates a database information acquisition request to the server side; the client side acquires and analyzes the database information returned by the server side, splices database version acquired through analysis, database document size and database name form a character string, performs MD5 check on the character string and generates a local MD5 check code; and when the local MD5 check code is equal to an MD5 check value and the value of the database version acquired through analysis is more than the value of the local database version of the client side, the client side downloads the database document on the server side according to the database downloading address. According to the method and the system, the testing efficiency of the automated testing can be improved and the testing cost can be reduced; and the method and the system are very convenient for people to use and suitable for popularization.
Owner:WUHAN DOUYU NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Mobile terminal position track monitoring system and method based on block chain
InactiveCN110210250AGuaranteed data privacyImprove monitoring efficiencyDigital data protectionMonitoring systemMD5
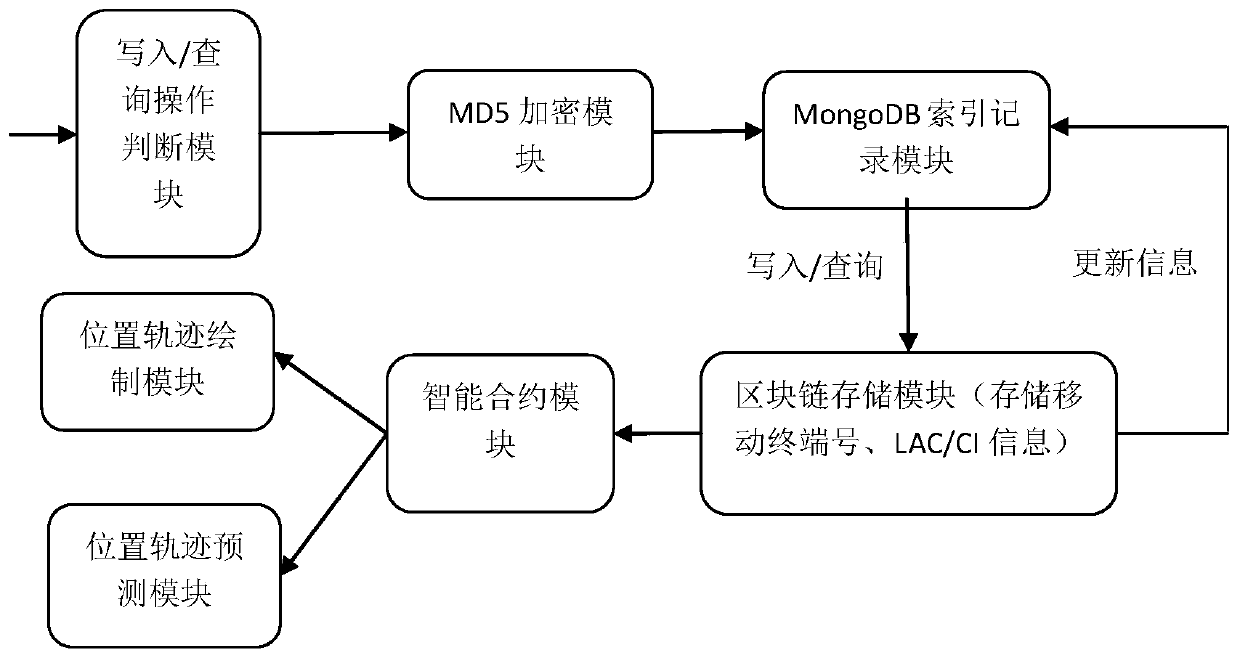
The invention particularly relates to a mobile terminal position track monitoring system and method based on a block chain. The mobile terminal position track monitoring system based on a block chaincomprises a write-in / query operation judgment module, an MD5 encryption module, a MongoDB index recording module, a block chain storage module, an intelligent contract module, a position track drawingmodule and a position track prediction module, wherein the write-in / query operation judgment module is connected to the block chain storage module through the MD5 encryption module and the MongoDB index recording module in sequence, and the block chain storage module is connected to the position track drawing module and the position track prediction module through the intelligent contract module.The method has the advantages that the LAC / CI data generated when the user uses the communication service is accessed based on the block chain technology, the key information such as the number of the mobile terminal of the user is encrypted by combining the MD5 message digest algorithm, and the user position track monitoring efficiency is improved on the premise that the privacy of the user datais effectively guaranteed.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
Portable elevator safety performance monitoring system based on CAN bus
ActiveCN106672724ASpeed up the testing processGuarantee authenticityElevatorsBus networksNoise detectionStructure of Management Information
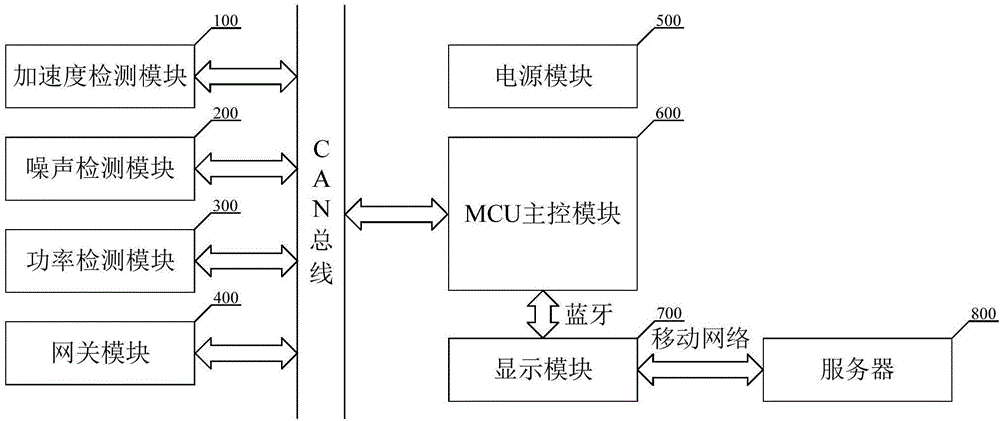
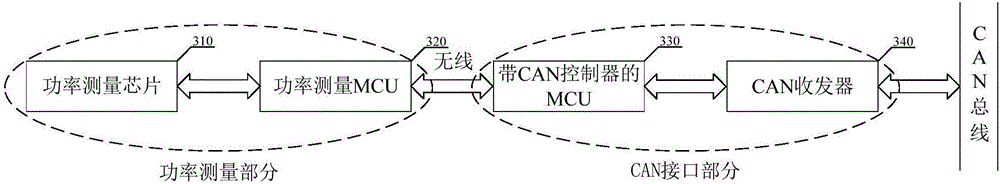
The invention discloses a portable elevator safety performance monitoring system based on a CAN bus. The system comprises an acceleration detection module, a noise detection module, a power detection module, a man-machine interaction module, an MCU master control module, a gateway module, a power supply module and other parts, wherein all the functional modules are provided with CAN bus interfaces; through CAN bus configuration, the functional modules can be configured according to the requirement of a field test and realize plug and play, and the structure of the detection system is more reliable and flexible; a CAN communication protocol is set up, and detection results are encrypted with MD5, so that the authenticity and traceability of information are ensured; and a remote server can supervise schedules of maintenance personnel and allocate tasks in real time, and thus is conductive to quickening the elevator detection process and improving the efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Acceleration method of financial element matching
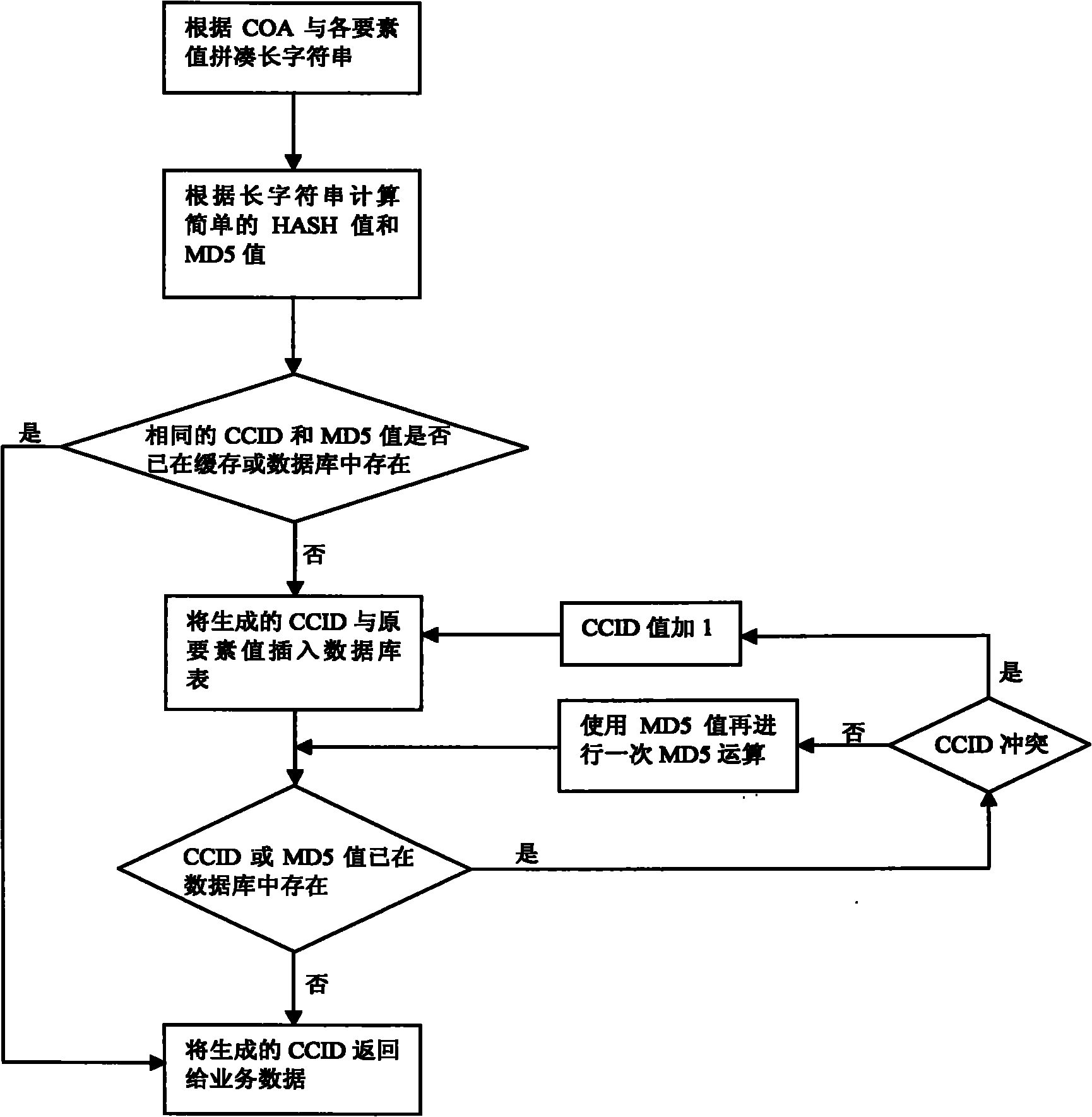
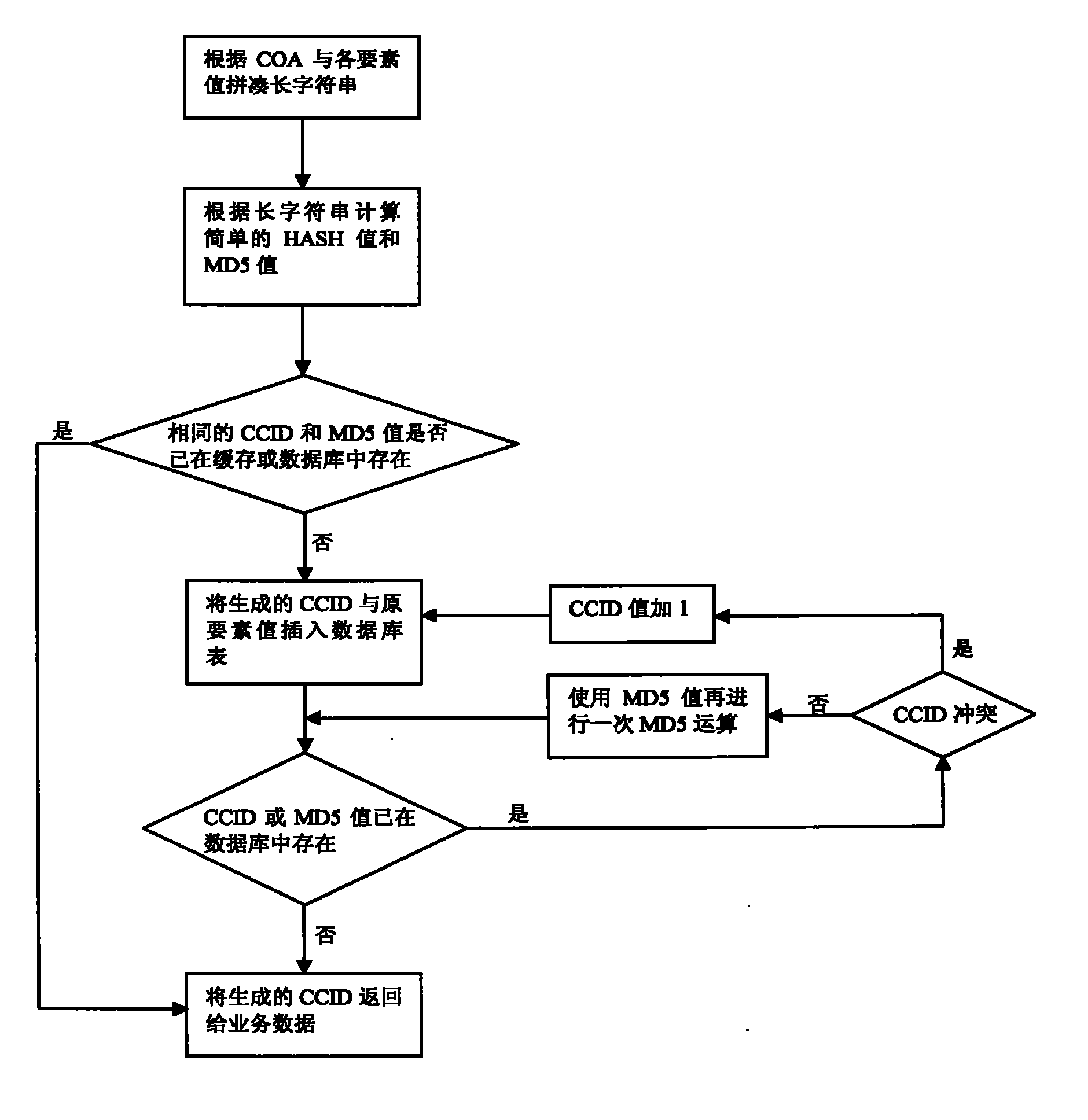
ActiveCN101916262AImprove securityUniqueness guaranteedFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmMD5
The invention relates to a data processing method, in particular to an acceleration method of financial element matching. The method comprises the following steps of: splicing into a long character string according to the multidimensional account structure COA and all element values, calculating a simple HASH value used as specific data CCID for element configuration by a simple integer HASH algorithm, and calculating an MD5 value by an MD5 algorithm; combining the simple integer HASH algorithm with the MD5 algorithm to obtain element configuration data CCID which not only meets the requirements of sufficient short main key and convenient query and indexing, but also ensures the uniqueness of CCID record through the association of CCID field and MD5 field. Compared with the prior art, the invention has no need of assembling SQL (Structured Query Language) containing a plurality of elements for element matching any more, the matching speed is increased, and mass account keeping operations are supported, and the safety of data is greatly improved.
Owner:北京用友政务软件股份有限公司
Apparatus to Implement Dual Hash Algorithm
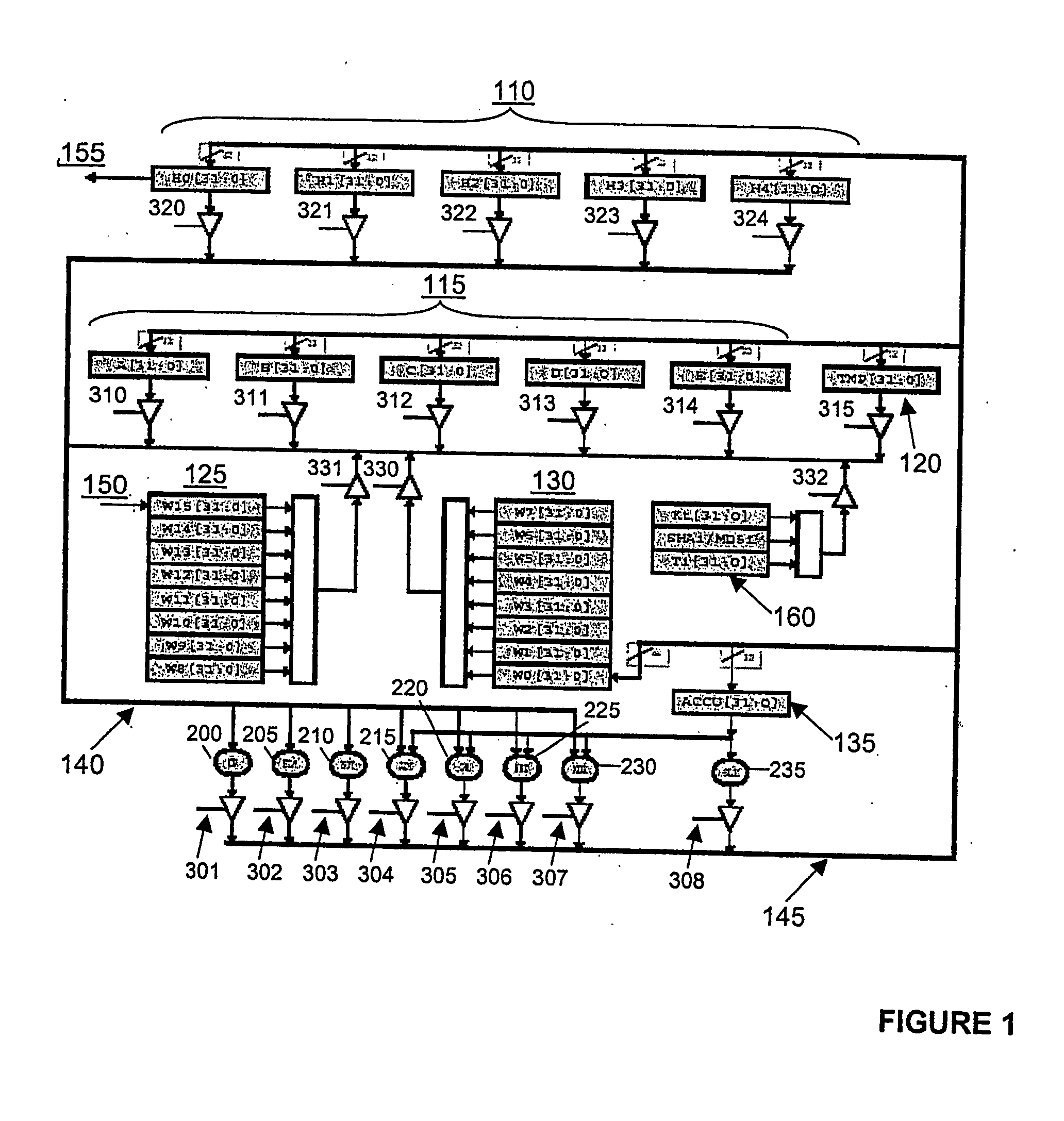
InactiveUS20080123841A1Easy to processEffective calculationReliability increasing modificationsUser identity/authority verificationAlgorithmProcessor register
An apparatus arranged to accept digital data as an input and to process the data according to one of either the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-1) or Message Digest (MD5) algorithm to produce a fixed length output word. The apparatus includes a plurality of rotational registers for storing data, one of the registers arranged to receive the input data, and data stores for initialization of some of the plurality of registers according to whether the SHA-1 or MD5 algorithm is used. The data stores include fixed data relating to SHA-1 and MD5 operation. Also included is a plurality of dedicated combinatorial logic circuits arranged to perform logic operations on data stored in selected ones of the plurality of registers.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Cache method for content identification based on message digests
InactiveCN102523299AEfficient use ofIncrease profitTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsTraffic capacityParallel computing
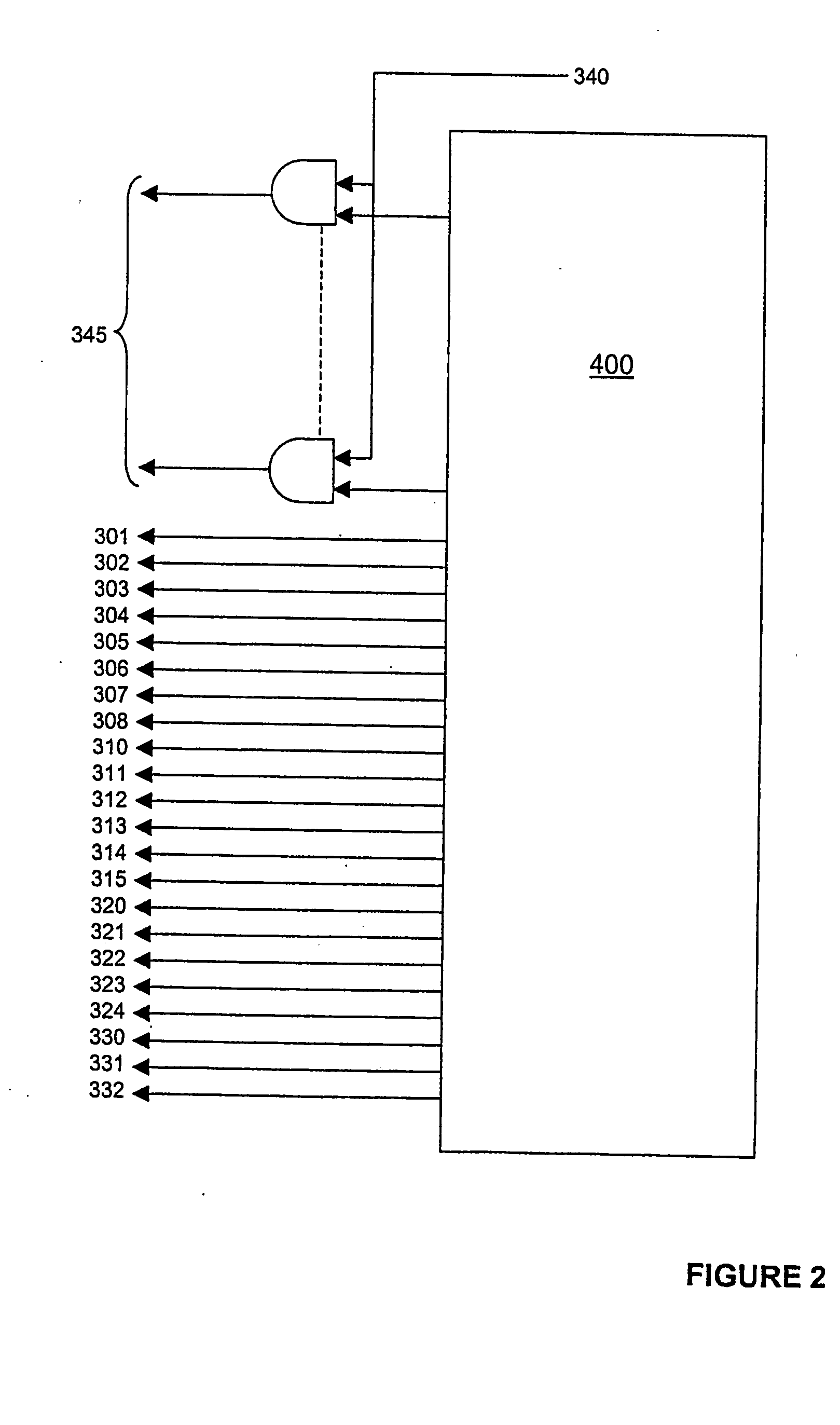
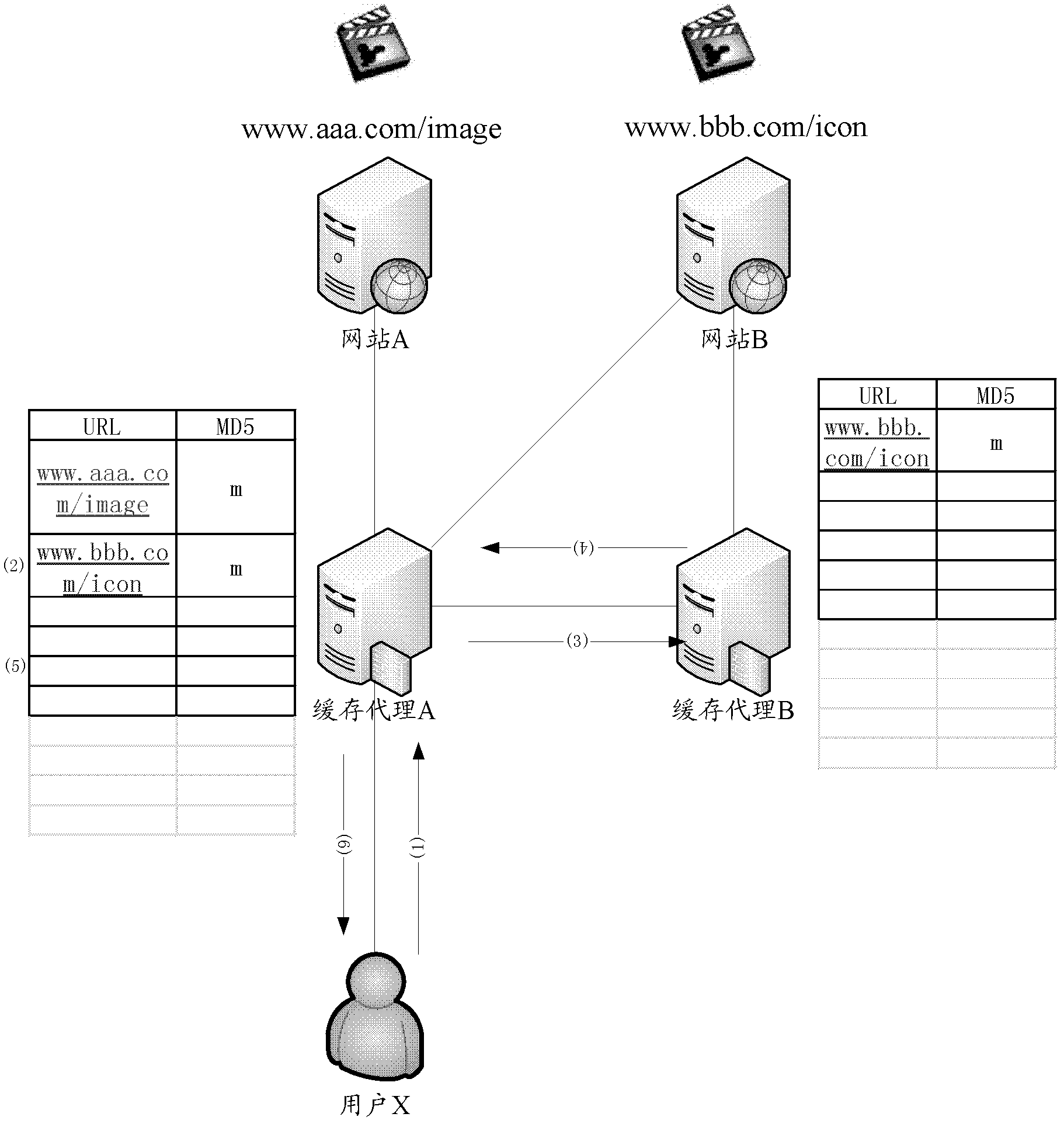
A cache method for content identification based on message digests includes steps of performing hash computation of contents by utilizing MD5 (message digest 5) of the fifth edition of the message digest algorithm, acquiring message digests of the contents and then utilizing the message digests namely the hash values of the contents to identify each independent content in cache so as to substitute for an identification method utilizing uniform resource locator (URL) to identify the contents between original cache proxies, separating content information from the URL and then inquiring and transmitting the contents by the aid of identification. The cache method utilizing cache coordination control strategies based on the identification method separates the content information from the URL, so that cache information quantity of cache space is increased, and cache utilization rate is increased while communication flows among various caches is reduced evidently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com