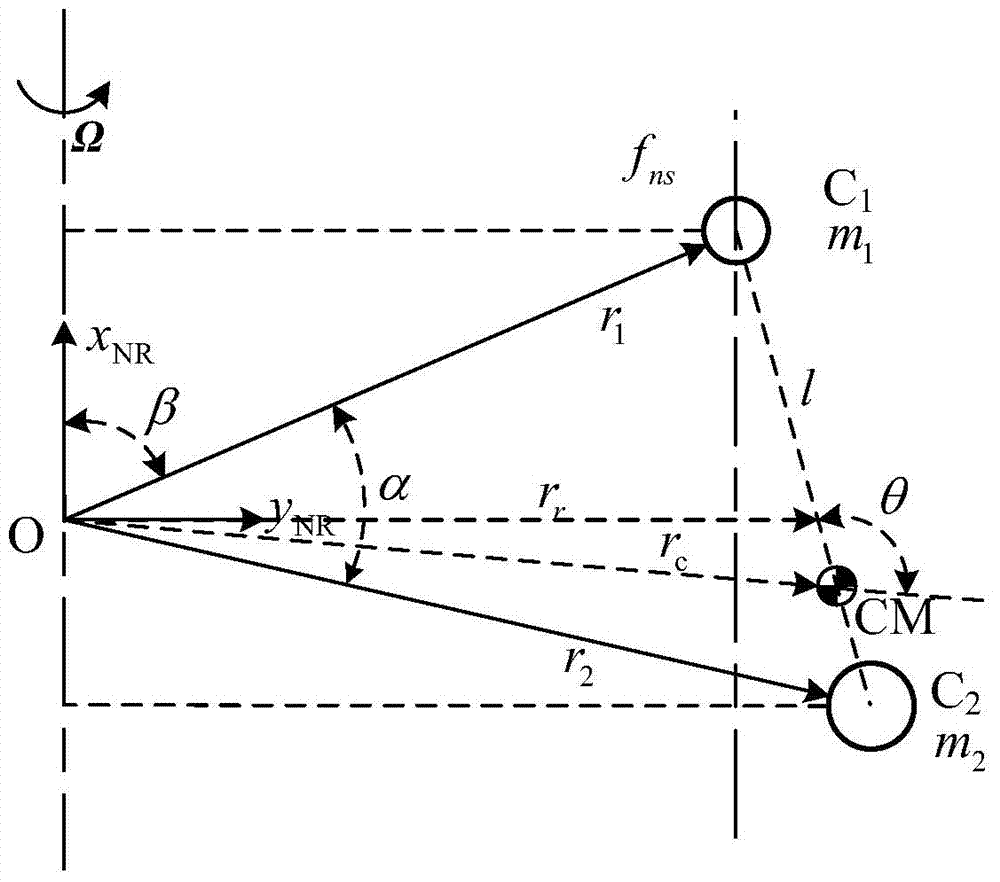
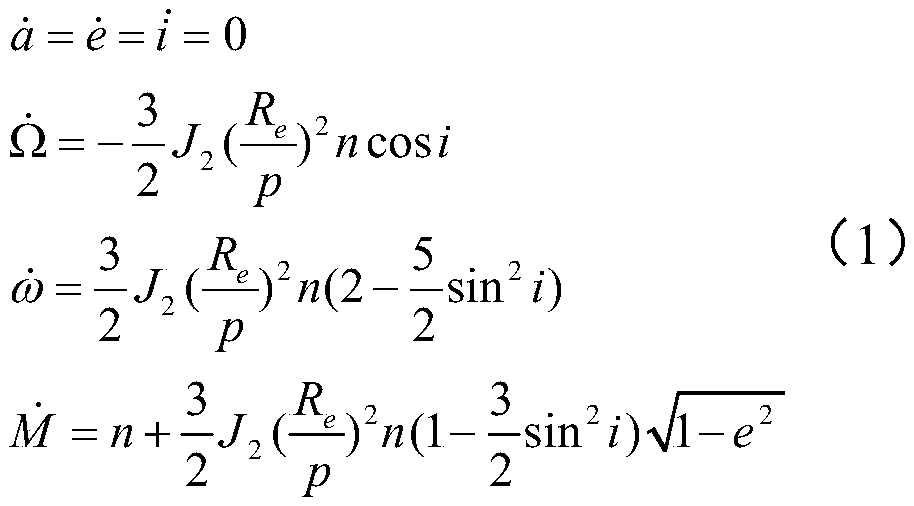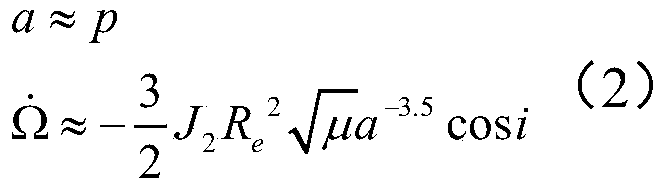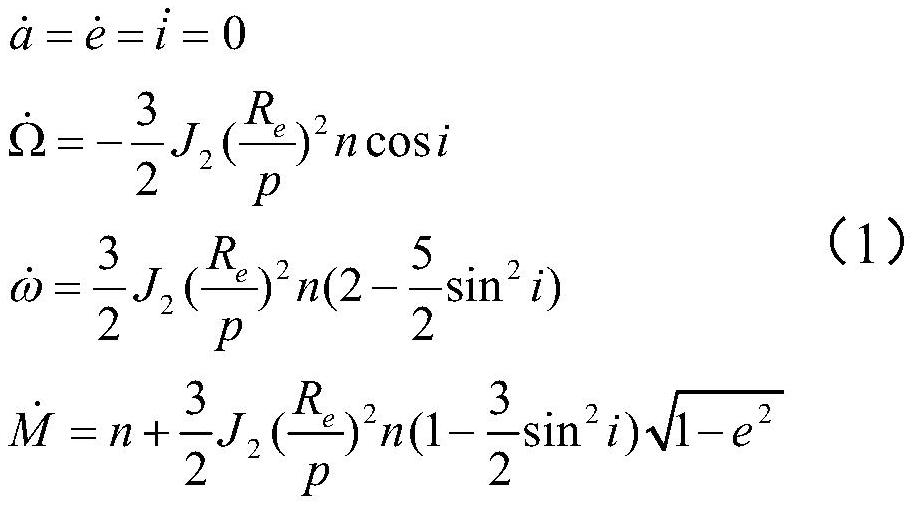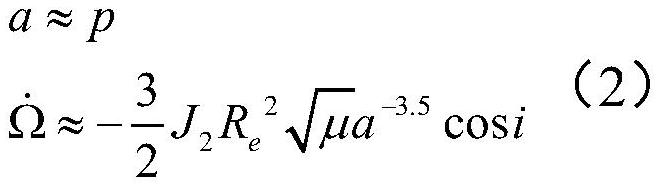Patents
Literature
52 results about "Orbit+Face" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
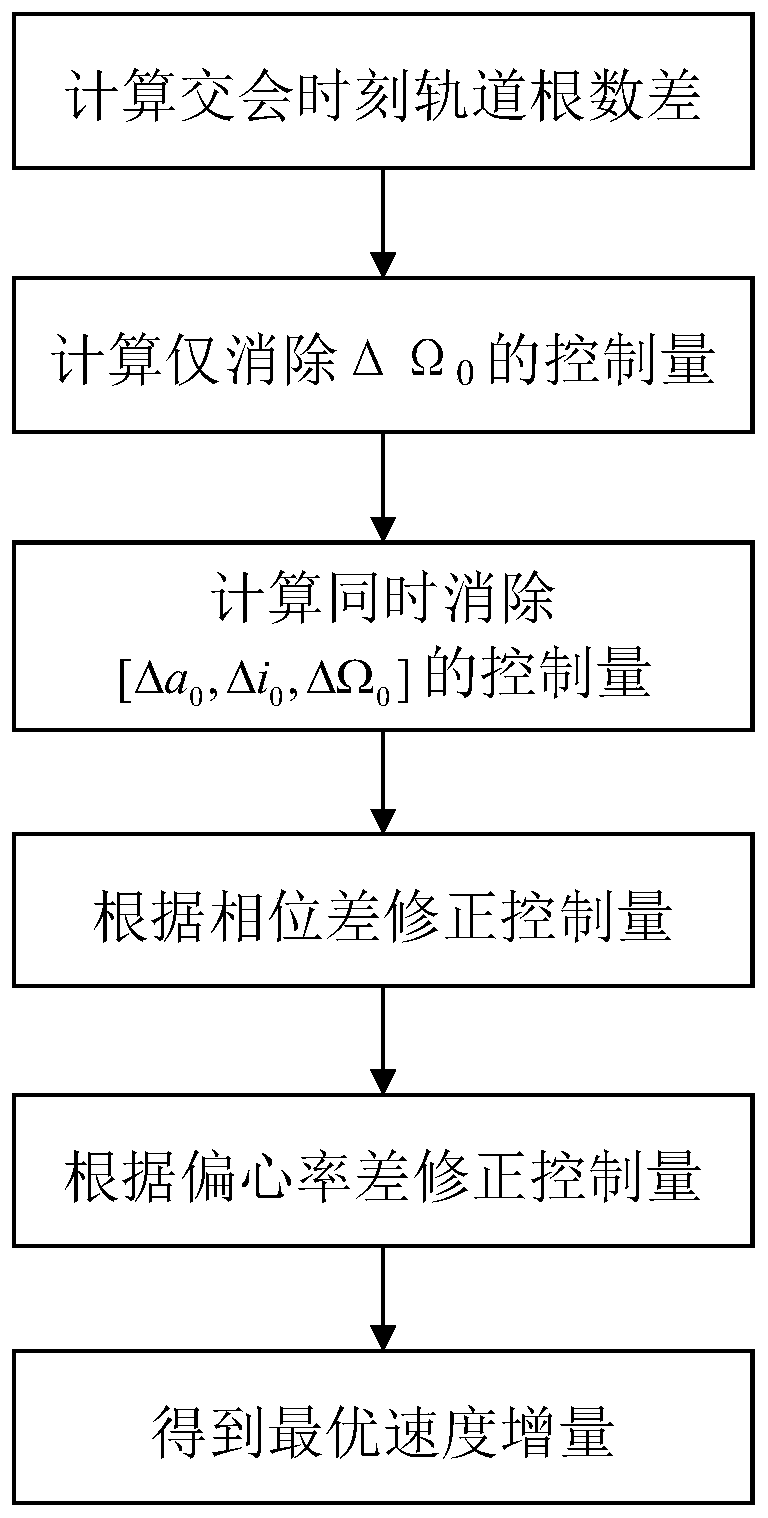
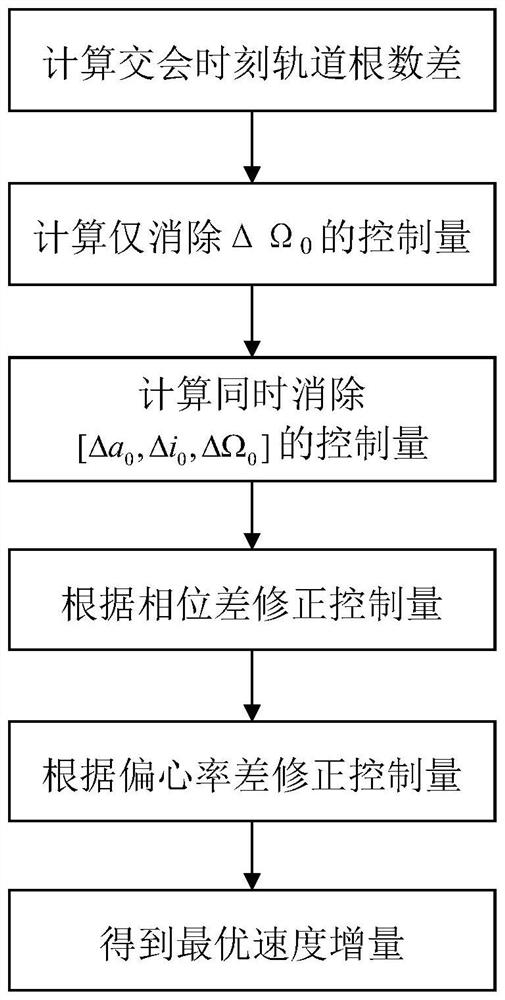
Method for rapidly estimating long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation
ActiveCN110789739ADecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeSimulation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly estimating a long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation. The method includes the steps of calculating the orbital element difference of a non-maneuvering spacecraft and a target at the rendezvous moment, calculating an optimal control amount when only the ascending node ascensional difference is eliminated, substituting the optimal control amount as the initial value into a control amount optimizing model for eliminating the semi-major axis, dip angle and ascending node ascensional difference at the same time to obtain a new optimal control amount, modifying the control amount according to the phase difference in an orbital plane, modifying the control amount according to the eccentricity ratio vector difference,and finally obtaining the estimated optimal rendezvous speed increment. The method realizes the purpose of rapidly estimating the optimal rendezvous speed increment when precise solution is not neededand is high in estimating precision and suitable for the situations with large initial ascending node ascensional difference from a target orbit and small element differences from other orbits.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
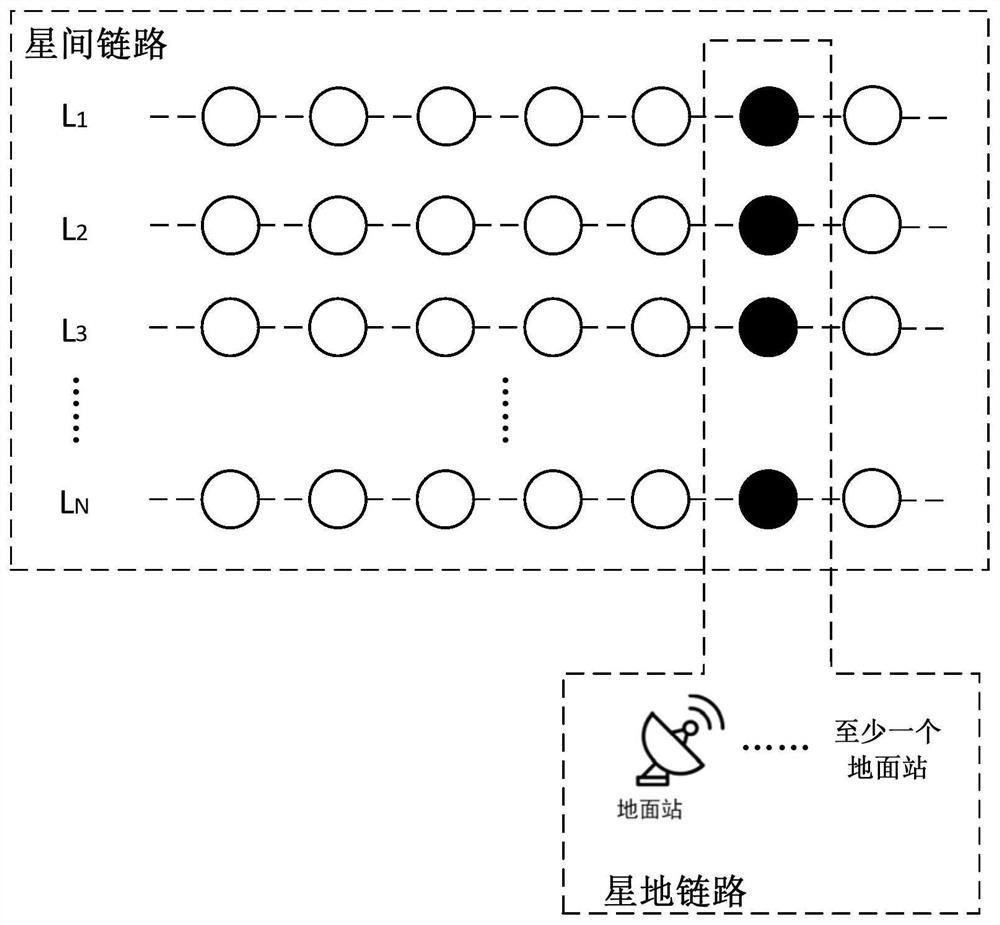
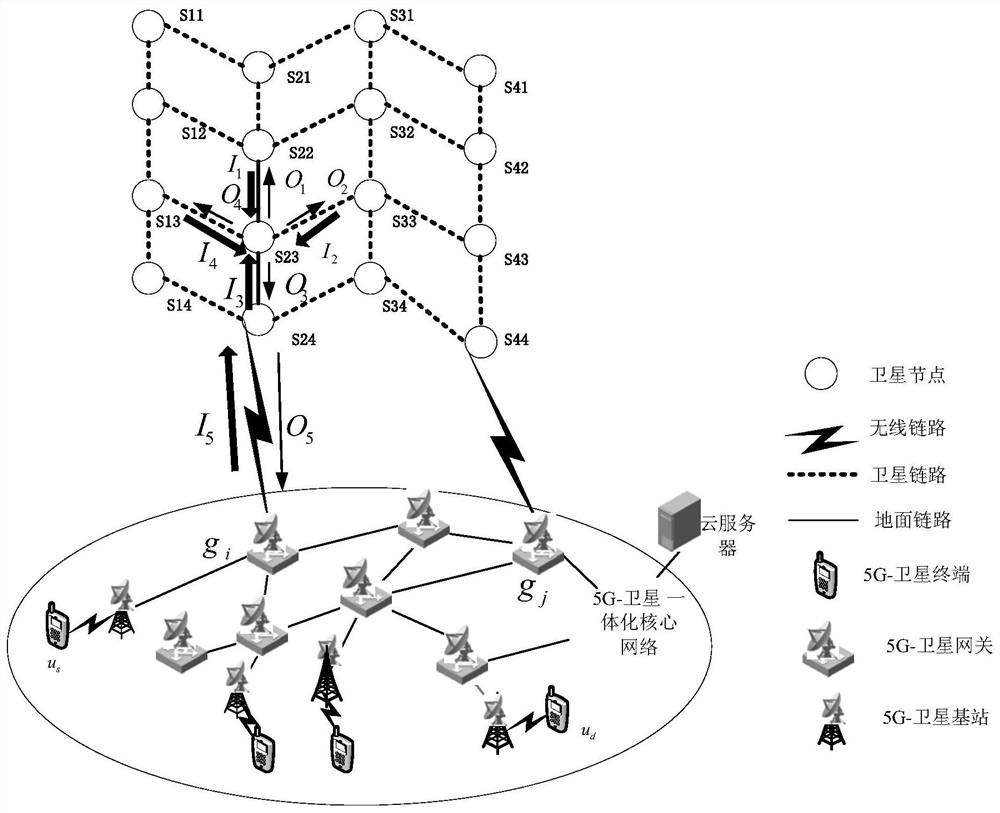
Measurement, operation and control system and method for low-orbit satellite constellation
The invention relates to a satellite positioning technology, and discloses a measurement, operation and control system and method for a low-orbit satellite constellation. The measurement, operation and control system comprises N common-orbit inter-satellite links corresponding to N orbital planes, each common-orbit inter-satellite link is used for data transmission between node satellites of the corresponding orbital plane, and N is larger than or equal to 2; and the system further comprises a satellite-ground link which is used for specifying the node satellites running to the intersection ofthe N orbital planes in each common-orbit inter-satellite link as hub satellites, and each common-orbit inter-satellite link performs data transmission with at least one ground station arranged nearthe latitude of the intersection of the N orbital planes through the hub satellites. According to the embodiment of the invention, while the low-orbit satellite constellation measurement, operation and control requirements are met, the technical complexity of the satellite is reduced, the cost of the satellite and the ground station is reduced, and the engineering feasibility of real-time measurement, operation and control of the low-orbit satellite constellation is improved.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
Co-location construction method for satellite queue
InactiveCN104714554ASolve resource problemsSolve conflictsPosition/course control in three dimensionsGeostationary orbitOrbit+Face
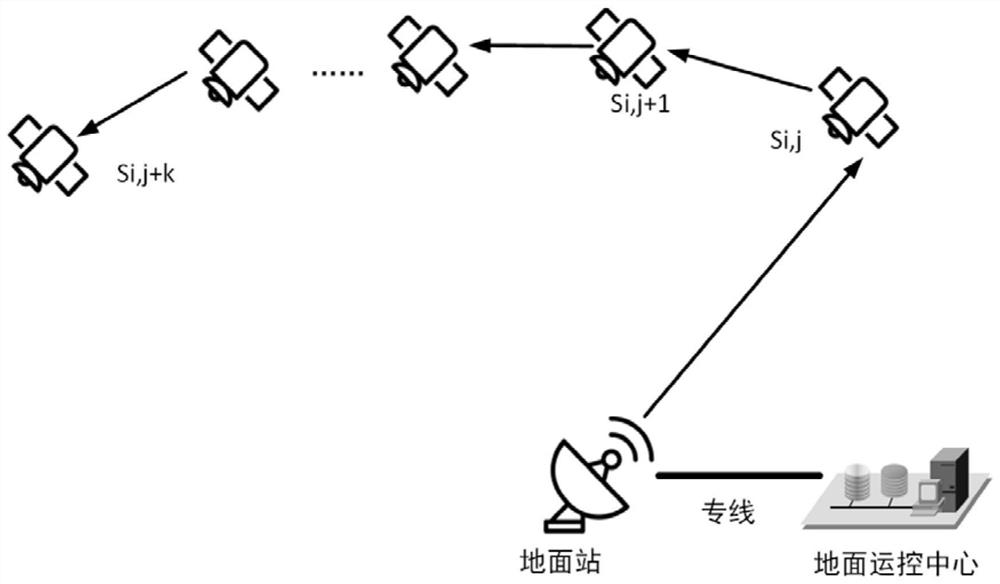
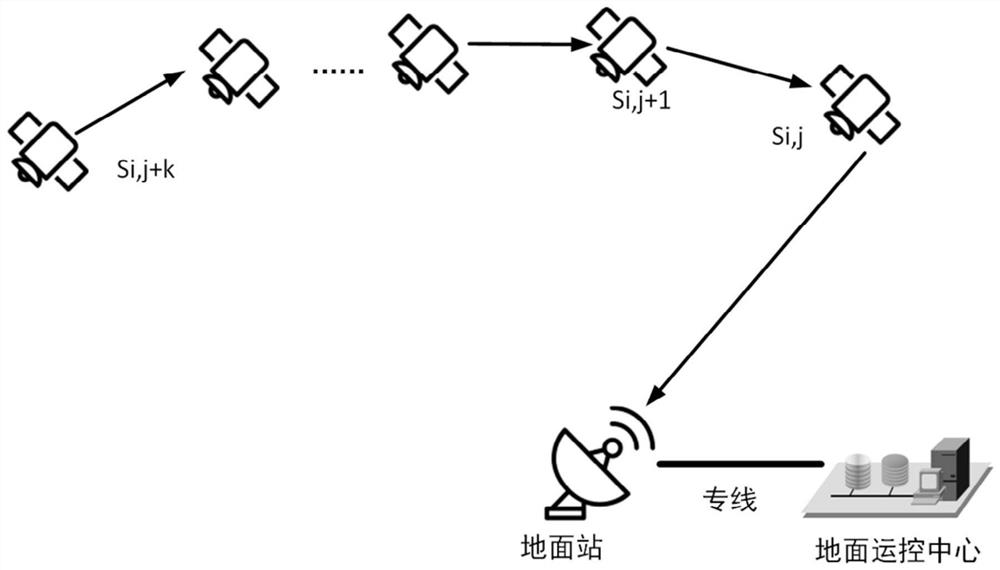
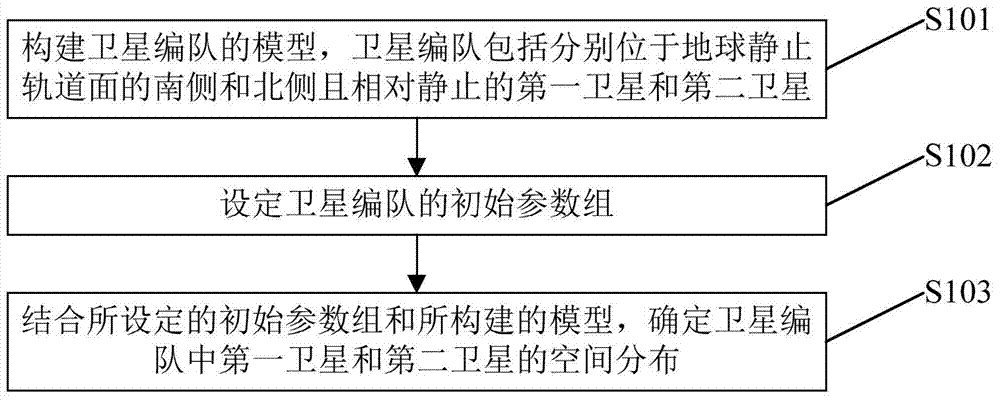
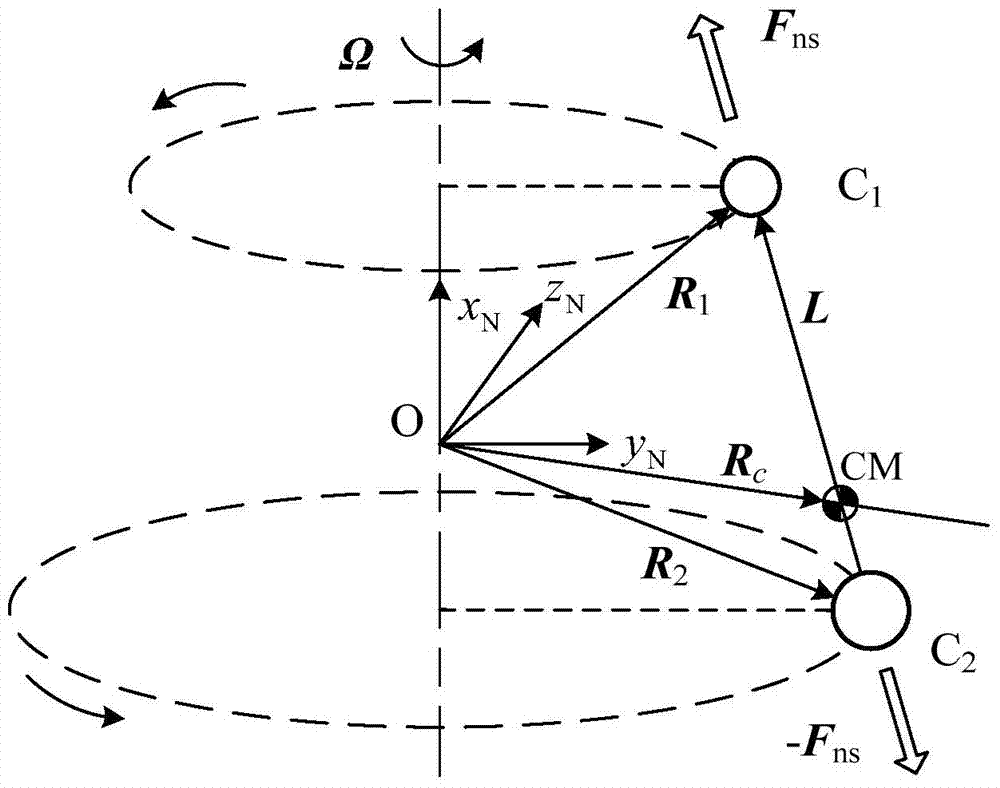
The invention discloses a co-location construction method for a satellite queue, and belongs to the technical field of satellite queues. The satellite queue comprises a first satellite and a second satellite, so that the technical problem about how to increase the number of the satellites capable of being contained by an earth stationary orbit is solved. The co-location construction method for the satellite queue includes the steps that a satellite queue model is established, and the satellite queue comprises the first satellite and the second satellite which are located on the south side and the north side of the earth stationary orbit face respectively and are relatively stationary; an initial parameter set of the satellite queue is set; combined with the set initial parameter set and the established model, the spatial distribution of the first satellite and the second satellite in the satellite queue is determined.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Space target orbit association method
The invention discloses a space target orbit association method. For an unknown space target tracked by using an autonomous search mode, orbit information and a cataloged space target are associated,whether the cataloged target and a to-be-identified target are the same target (the same target), whether the cataloged target and the to-be-identified target operate (are coplanar) in the same orbitplane and whether the cataloged target and the to-be-identified target operate (are on the same orbit) are identified, and the confidence is calculated. Whether the two targets are the same target ornot can be associated, whether the two targets run in the same track surface or run on the same track or not can be associated for two sets of track information which are not the same target, and thetrack association result confidence can be calculated.
Owner:中国人民解放军32035部队
Energy transformation demonstration apparatus
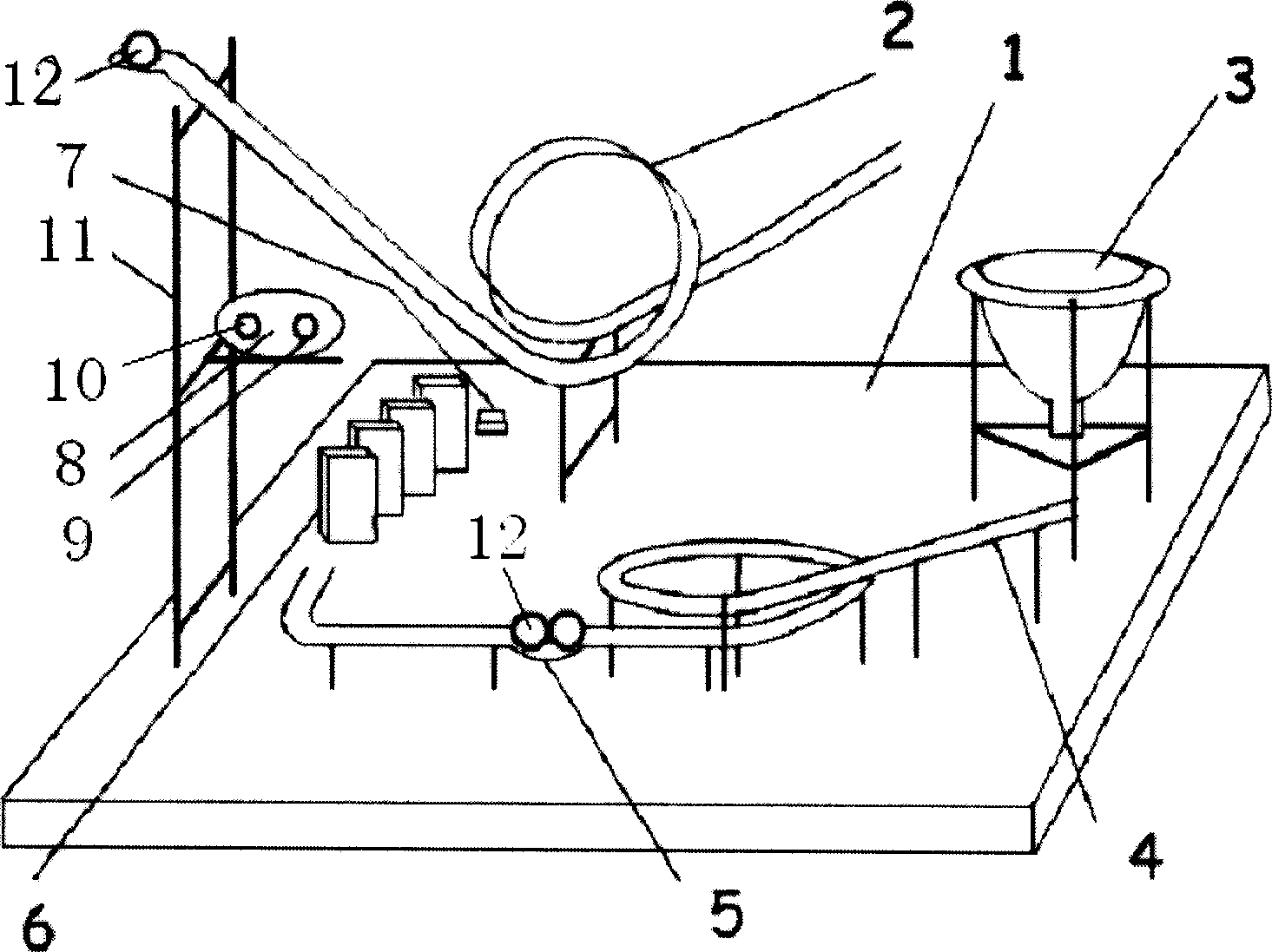
The invention discloses an energy-conversion demonstration device, which consists of installing an entrance point locating on the maximum point of the said device and an exit end below the said entrance point on the circular orbit of the vertical plane, in which the said exit end is tangent with the outer circumference of the analog planet orbit and the iron shot from the exit end can drop in along the tangential direction of the outer circumference of analog planet orbit; the exit end of the analog planet orbit faces the entrance point of the circular orbit of the plane and the entrance point forms an oblique angle with the plane, and the exit end of the circular orbit of the plane binds with a collision orbit placed with two steel balls close to each other; the exit end of the collision orbit is placed with dominoes which can be hit by steel balls from the exit end and an acousto-optic alteration switch which can be hit by dominoes to start and stop is placed on the last domino. The device can demonstrate mutual conversion relation among various energies of objects very vividly and visually.
Owner:上海市嘉定区第二中学
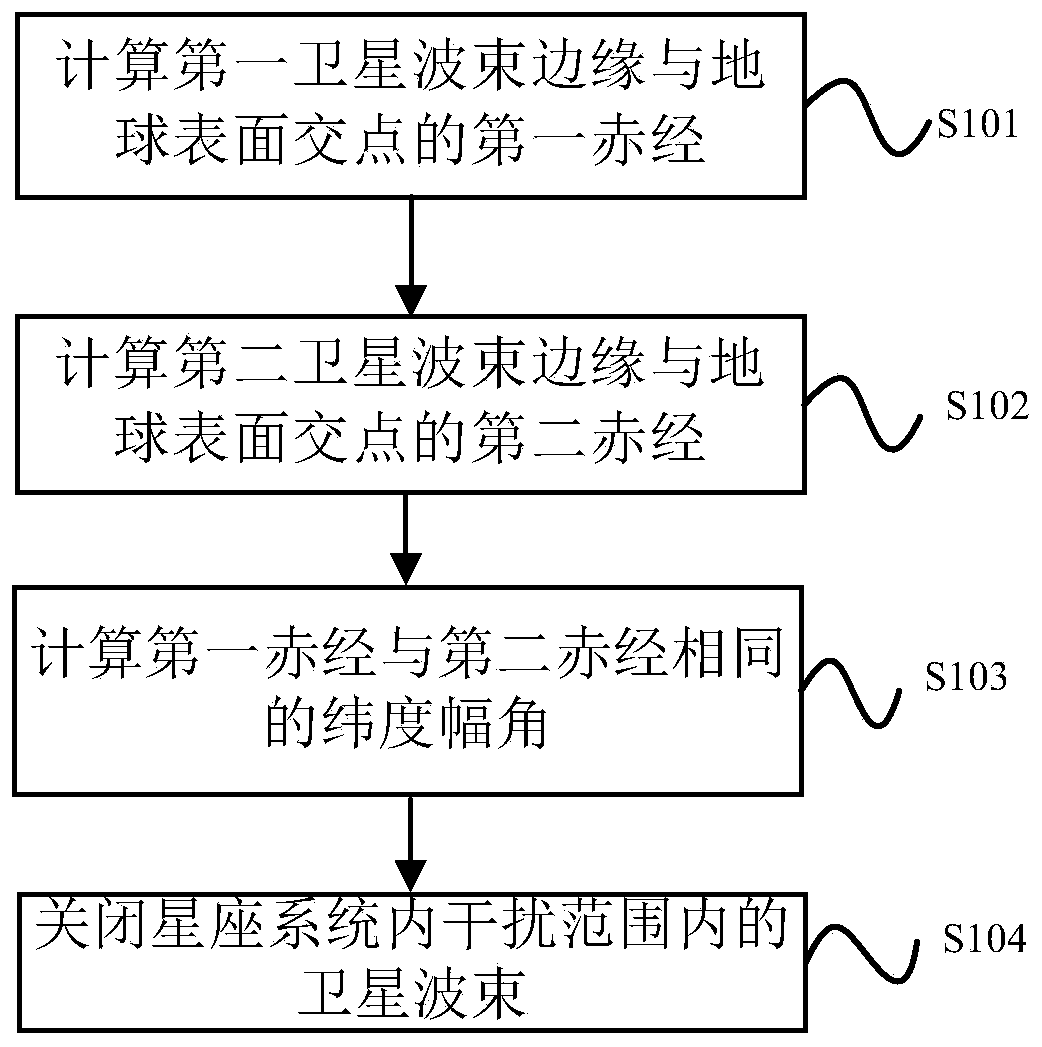
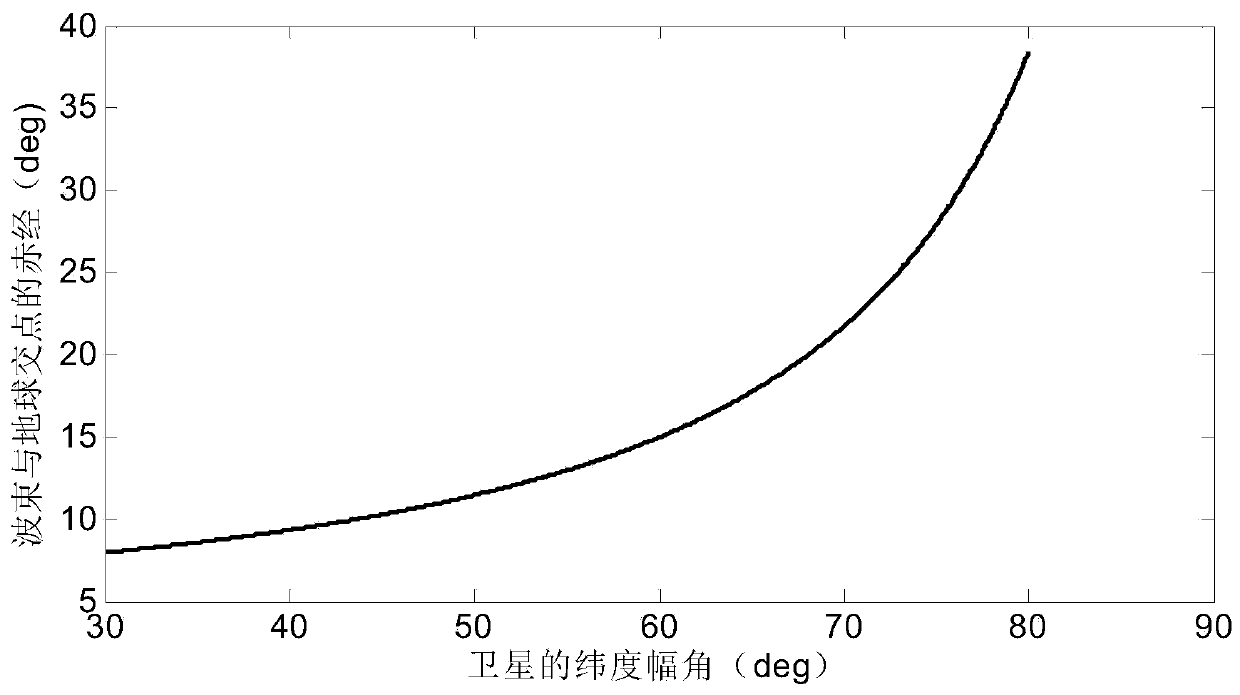
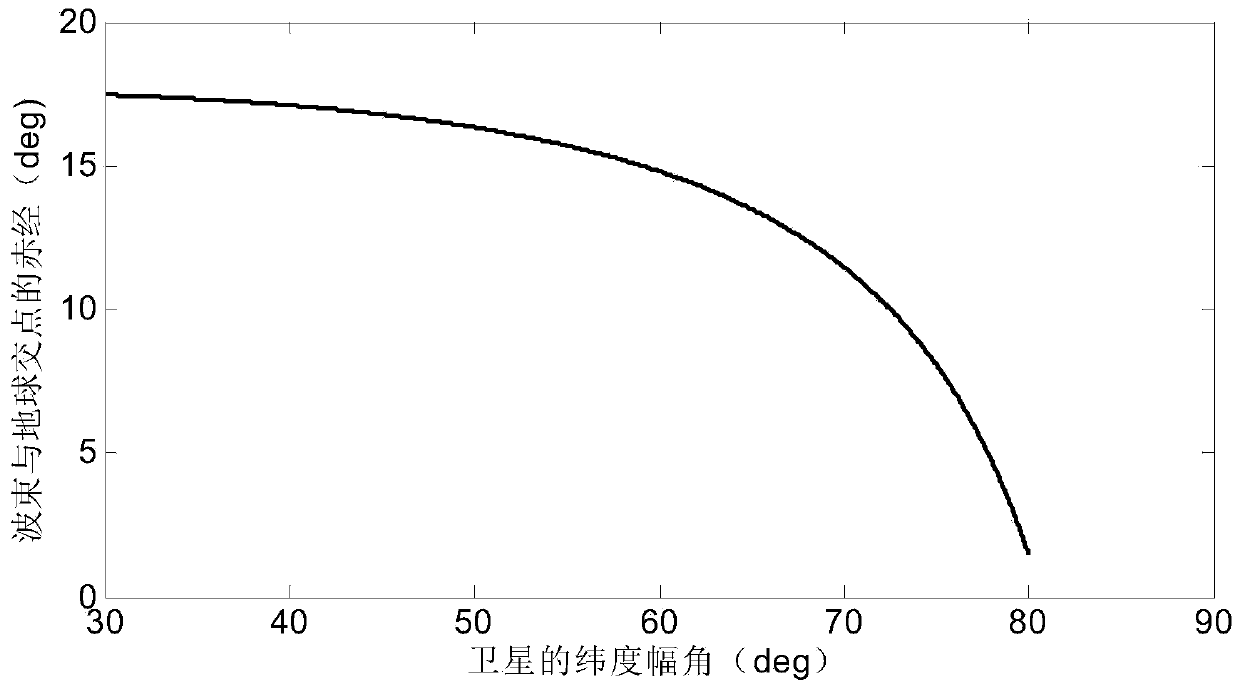
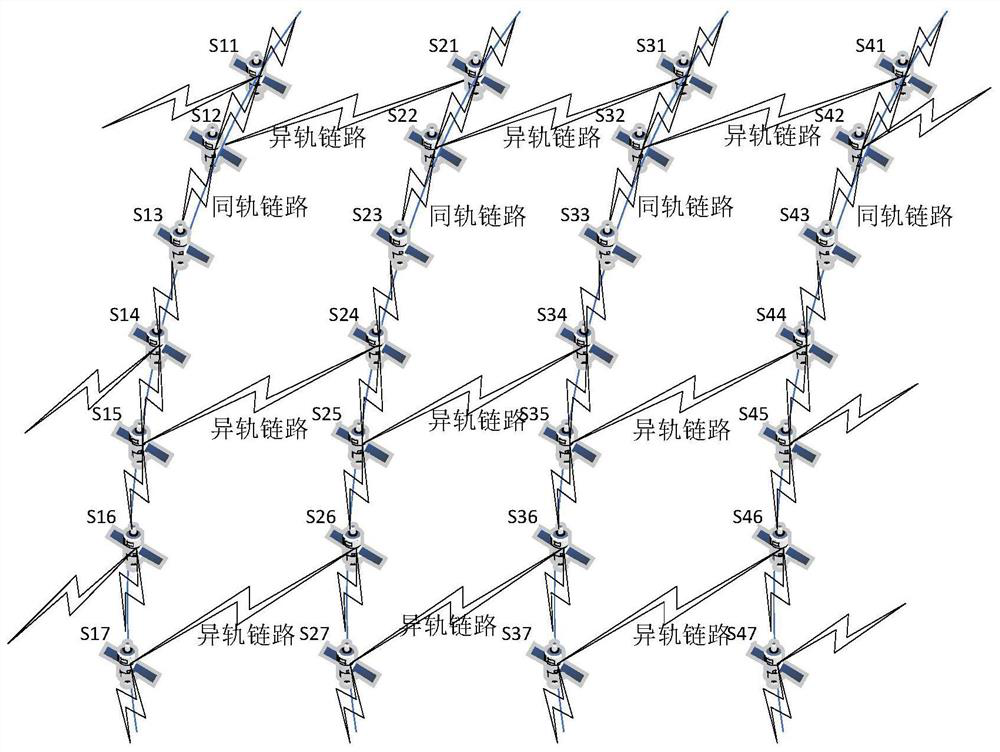
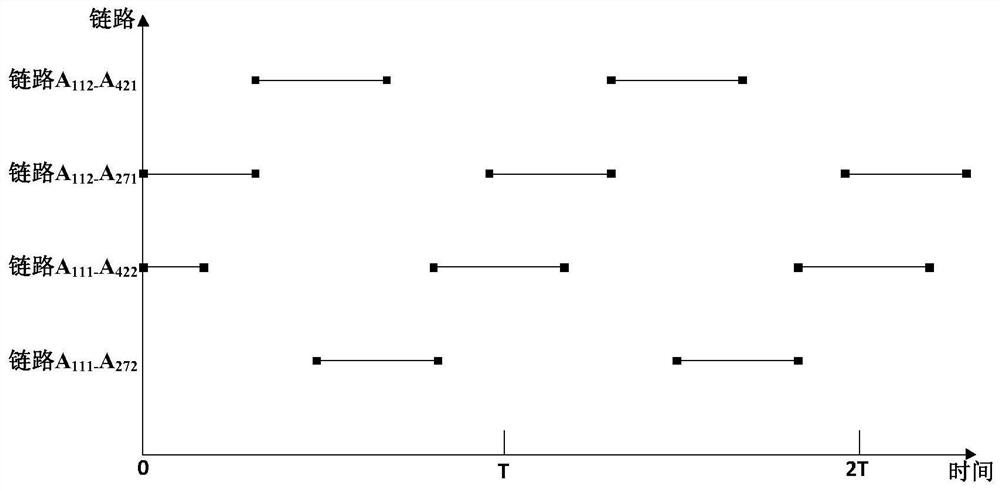
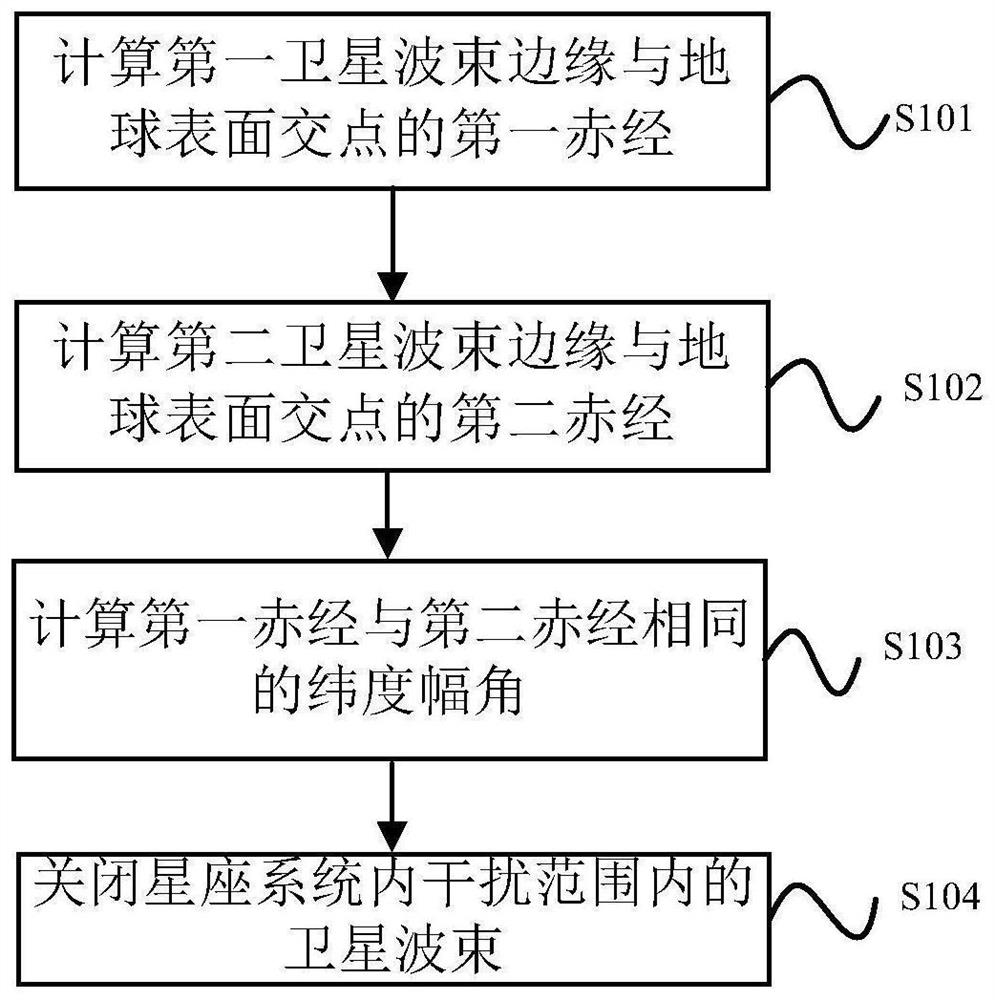
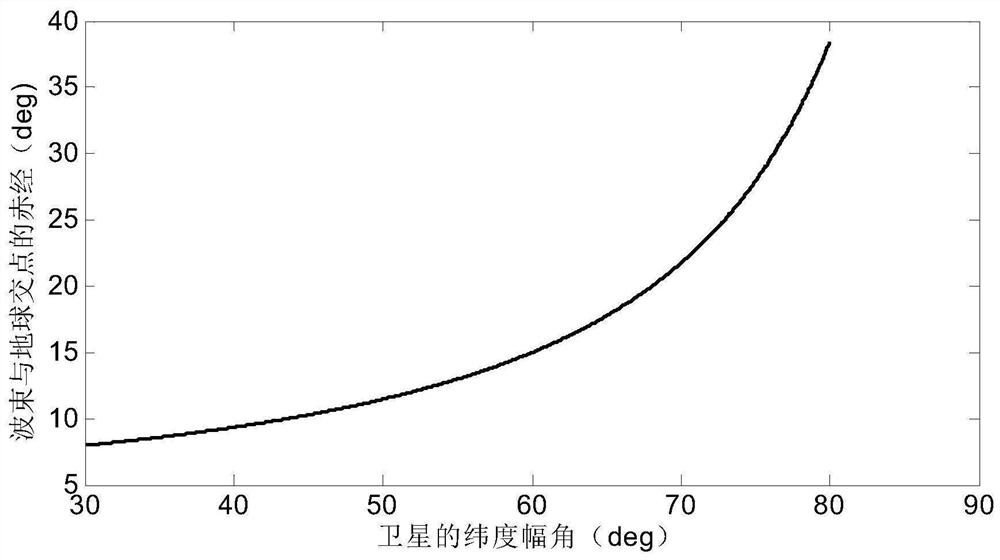
Internal frequency interference suppression method for a low-orbit constellation system
The invention discloses an internal frequency interference suppression method for a low-orbit constellation system. The low-orbit constellation system comprises satellites running on at least three orbital planes, each orbital plane comprises at least one satellite, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the first right ascension of the intersection point of the beam edge of a first satellite and the earth surface, wherein the first satellite is any satellite in any one of the at least three orbital planes; calculating a second right ascension of an intersection point of a beam edge of a second satellite and the earth surface, the second satellite being a satellite spaced apart from the first satellite by a distance of two orbital planes, and the second satellite and the first satellite having the same latitude argument; and calculating the same latitude argument uc of the first right ascension and the second right ascension, and determining the satellite beam shutdown range according to the calculated latitude argument uc. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention effectively suppresses the internal frequency interference of the low-orbitconstellation system on the premise of realizing the full coverage of the constellation system in the high-latitude area on the ground beams.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
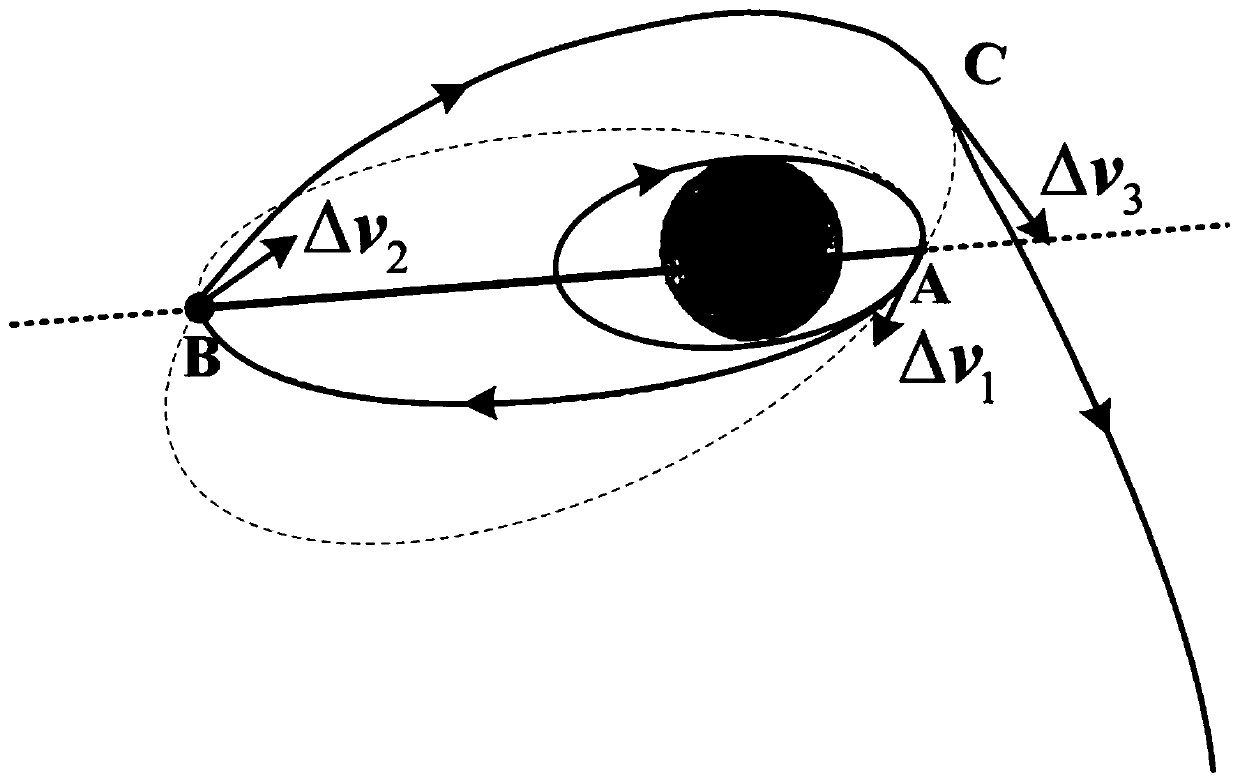
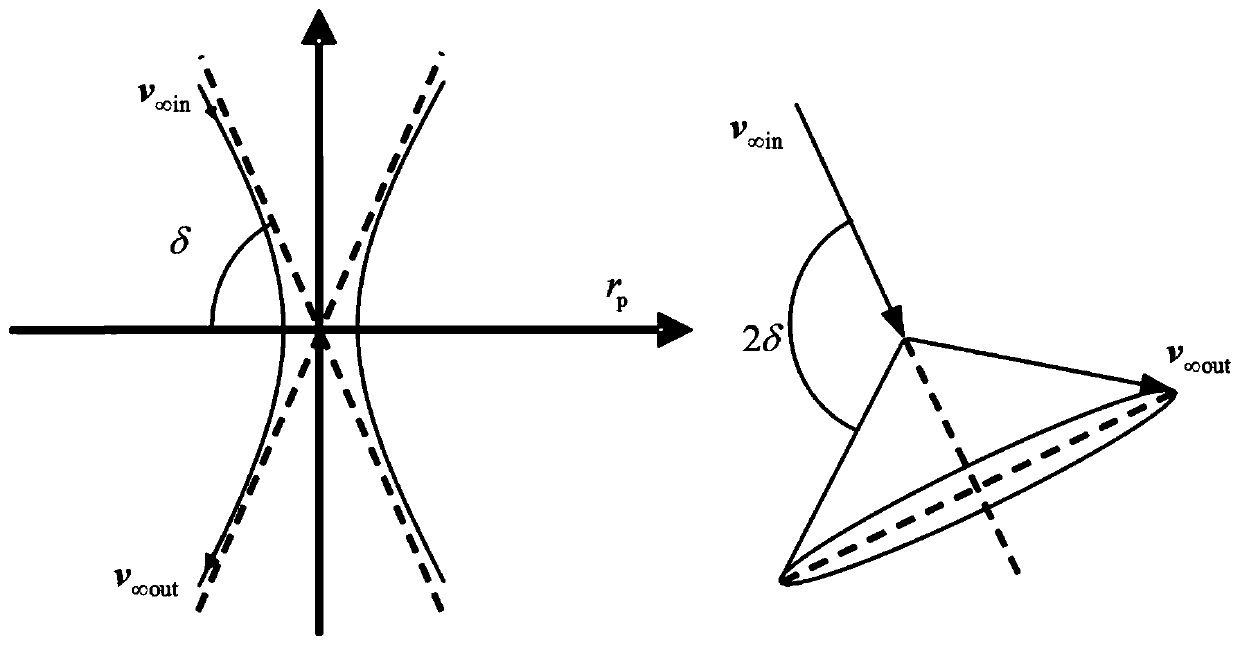
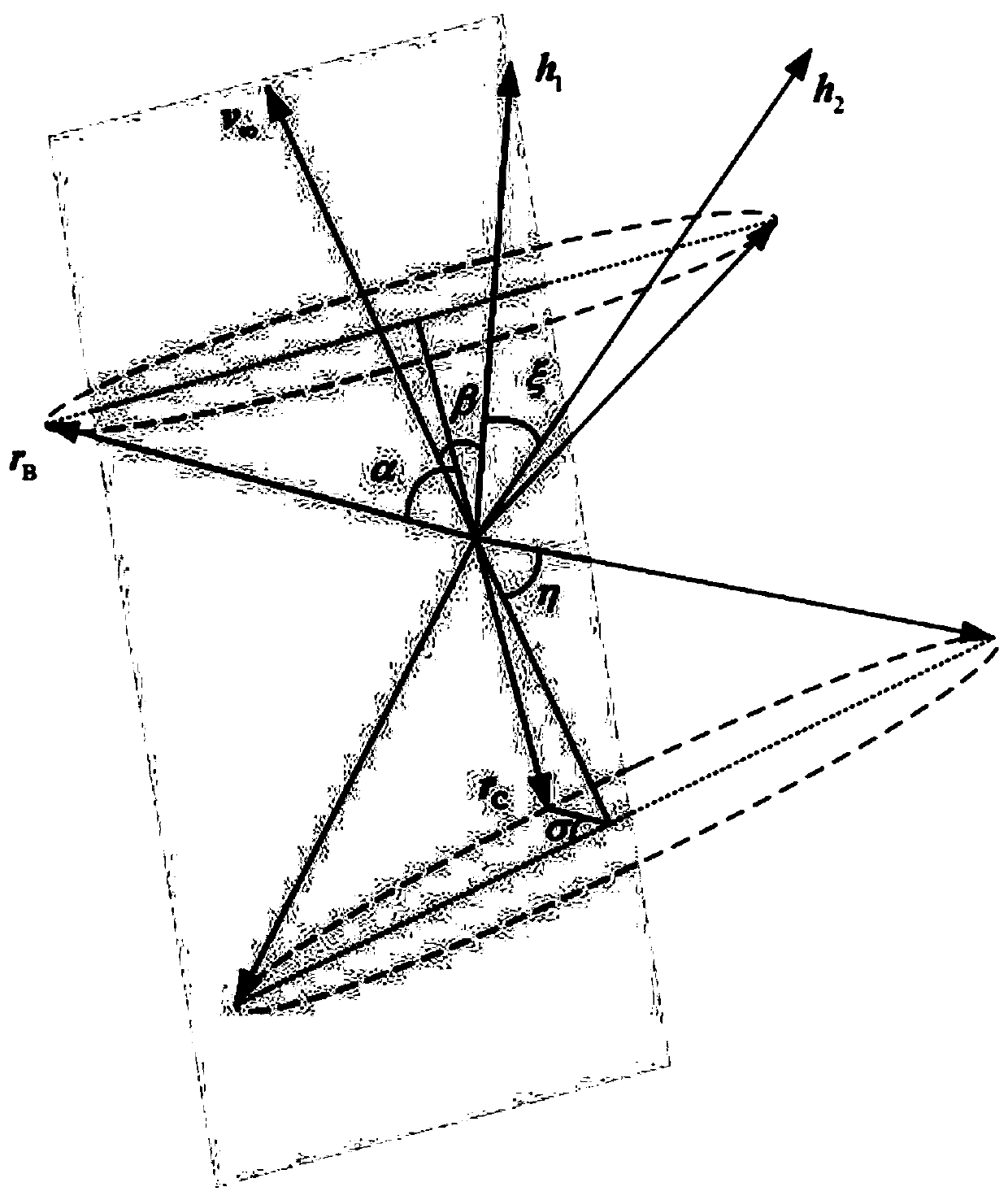
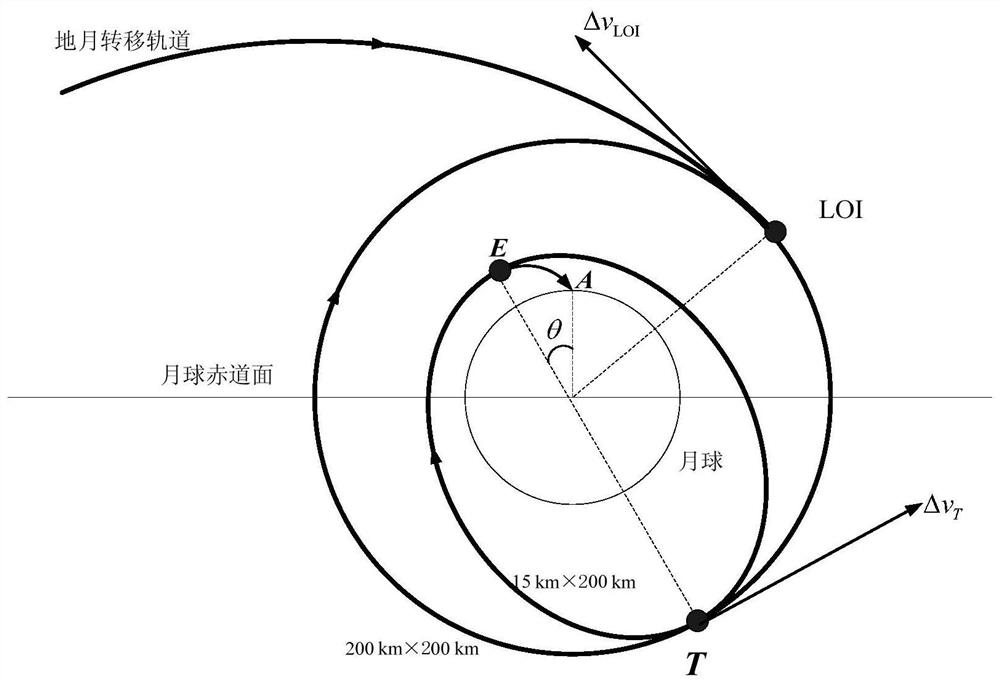
Month-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method
ActiveCN110704952AFast and efficient preliminary approximation analysisIntuitive and concise preliminary approximate analysisGeometric CADDelta-vEngineering
The invention discloses a moon-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method, which comprises the following steps: A, obtaining a normal unit vector h1 of a lunar orbit plane, a normal unit vector h2 of a lunar escape orbit plane and positions rA, rB and rC for applying three pulses by taking a moon center as an original point; B, obtaining a conical surface S1 with the lunar escape orbit aiming v infinity out as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S1 is eta; C, enabling the plane where v infinity out and h1 are located to serve as the datum plane, setting the rotating angle sigma of rC around the straight line where v infinity out is located, and determining rC and a lunar escape orbit plane; D, obtaining a conical surface S2 with the straight line where rC is located as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S2 is alpha; E, obtaining the included angle beta between h1 and v infinity out and the different-plane differencexi between the lunar orbit and the lunar escape orbit; F, solving the sizes delta v1, delta v2 and delta v3 of the three pulses; G, solving a total speed increment delta v; and H, changing the independent variable influencing the delta v to obtain a change rule of the delta v. According to the method, the spatial geometrical relationship is utilized, and preliminary approximate analysis can be rapidly, effectively, visually and simply carried out on the speed increment required by the three-pulse maneuvering process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
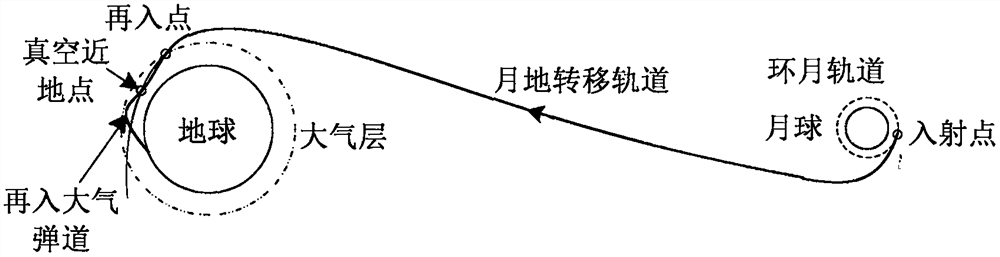
Method and device for determining moon-earth transfer orbit
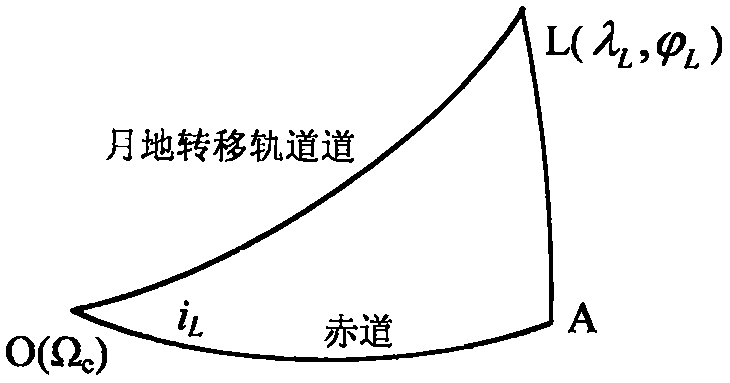
PendingCN113310496ASimplify the solution processImprove computing efficiencyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAtmospheric layerOrbital inclination
The invention discloses a method and device for determining a moon-earth transfer orbit. The method comprises the steps of according to the approximate reentry time of a detector reentering a preset reentry point of the earth atmosphere from the moon, a preset orbit inclination angle when the detector arrives at the preset reentry point, the latitude and longitude of a drop point, and the moon-earth transfer time of the detector, determining a reentry time initial value of a preset reentry point; determining a moon-earth transfer orbit number of the preset reentry point, and determining a moon-earth transfer orbit under a two-body model according to the reentry time initial value and the moon-earth transfer orbit number; correcting the moon-earth transfer orbit under the two-body model to obtain a target moon-earth transfer orbit under the high-precision model; according to a preset intersection line strategy corresponding to a moon-earth transfer orbit and a moon-surrounding orbit, correcting a perilune height and a lunar section moon-earth transfer inclination angle in the target moon-earth transfer orbit under the high-precision model; and when the corrected lunar section moon-earth transfer inclination angle enables the perilune of the moon-earth transfer orbit to be in the lunar orbit plane, determining moon-earth incidence control parameters.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CONTROL CENT
Constellation design method
The invention discloses a constellation design method, and the method comprises the steps: determining the area of an observed fixed region, and determining a corresponding circular coverage region when a single satellite covers the observed fixed region according to the area; determining a view field angle or a beam angle of the observed fixed region according to a preset view field pointing constraint condition, and calculating the orbit height of the single satellite according to the circular coverage region and the view field angle or the beam angle; determining the number of satellites required for covering one latitude zone region, an orbit inclination angle and a difference value of true near-point angles of two adjacent satellites in the same orbit plane according to the circular coverage region, and determining the number of orbit planes according to the number of satellites; and calculating the number of satellites in the same orbital plane according to the difference, calculating the total number of satellites according to the number of orbital planes and the number of satellites in the same orbital plane, and designing a satellite constellation. The technical problem that in the prior art, constellations are not suitable for serving ground fixed areas and observing fixed areas in celestial spheres is solved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
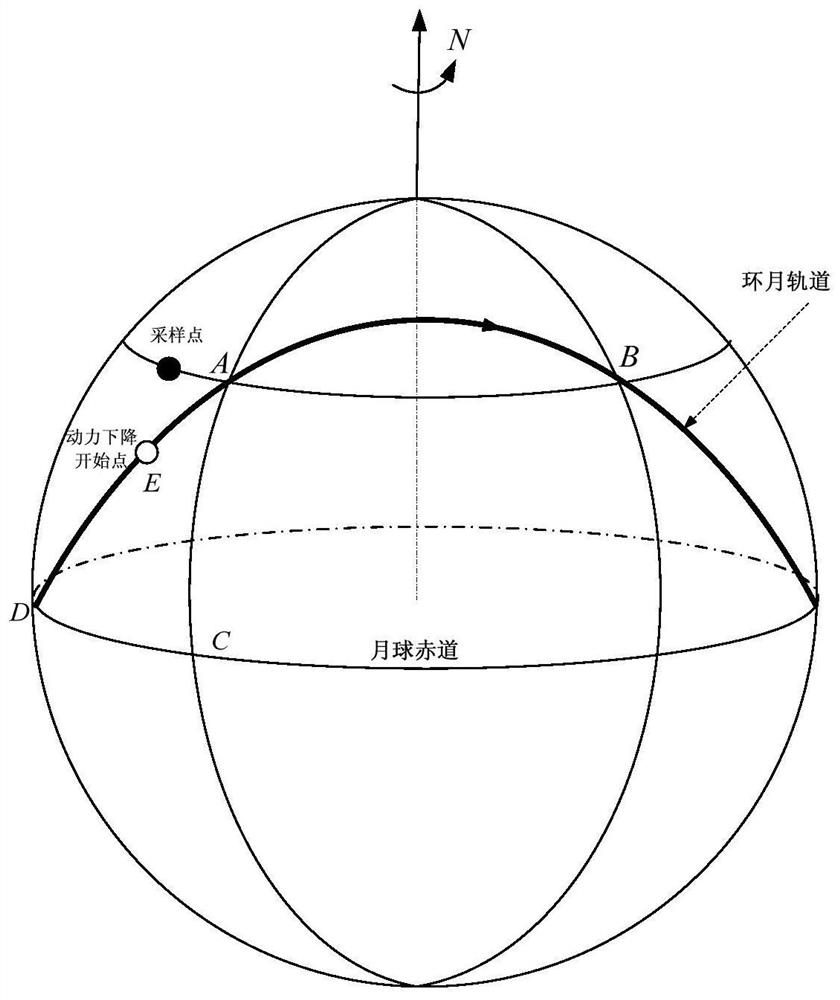
Method for designing fixed-point landing orbit in lunar sampling return task
PendingCN113311854AMinimize Correction Velocity IncrementFixed-point landinghigh-precisionAttitude controlClassical mechanicsLongitude
The invention discloses a method for designing a fixed-point landing orbit in a lunar sampling return task, which comprises the steps of aiming at the longitude of a predetermined lunar surface drop point by introducing an orbit surface normal speed increment component in a near-moon braking maneuver in combination with the optimization of a near-moon inclination angle of an earth-moon transfer section of the lunar sampling return task, aiming at the latitude of the predetermined lunar surface drop point and the height of a power drop starting point through a lunar orbit drop and orbit transfer latitude argument and an orbit plane internal speed increment component, and enabling the lunar surface drop point to be located in a target orbit plane at a predetermined lunar surface rising moment; and furthermore, eliminating the longitudinal voyage error by introducing a lunar orbit descending speed increment normal component to correct the longitude of the drop point and adjusting the power descending moment. According to the method, the problem that the correction speed increment of the moon orbit rendezvous and docking orbit surface is large due to the fact that the influence of orbit design on subsequent moon orbit rendezvous and docking is not considered in the existing fixed-point landing technology is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
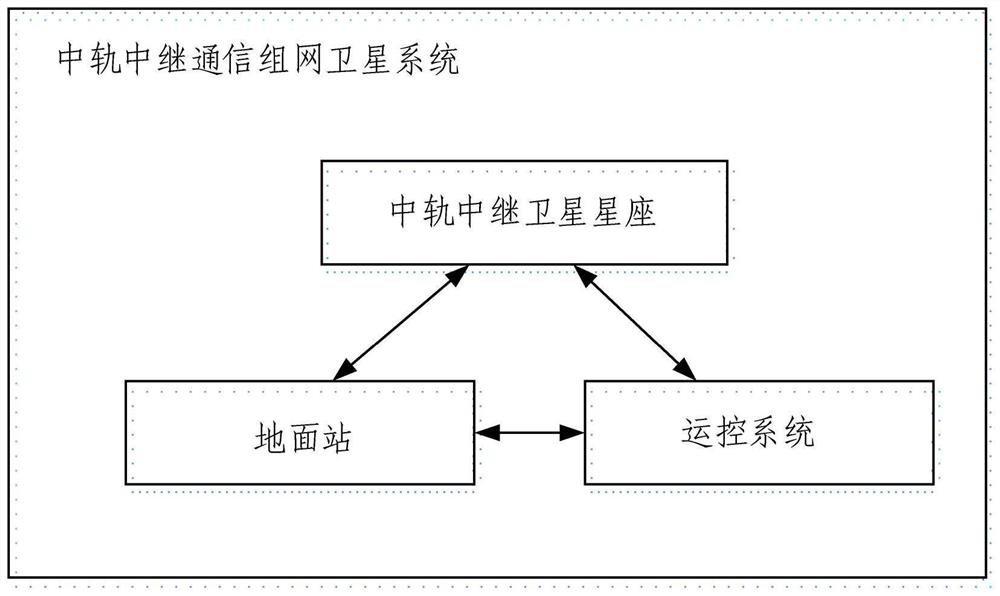
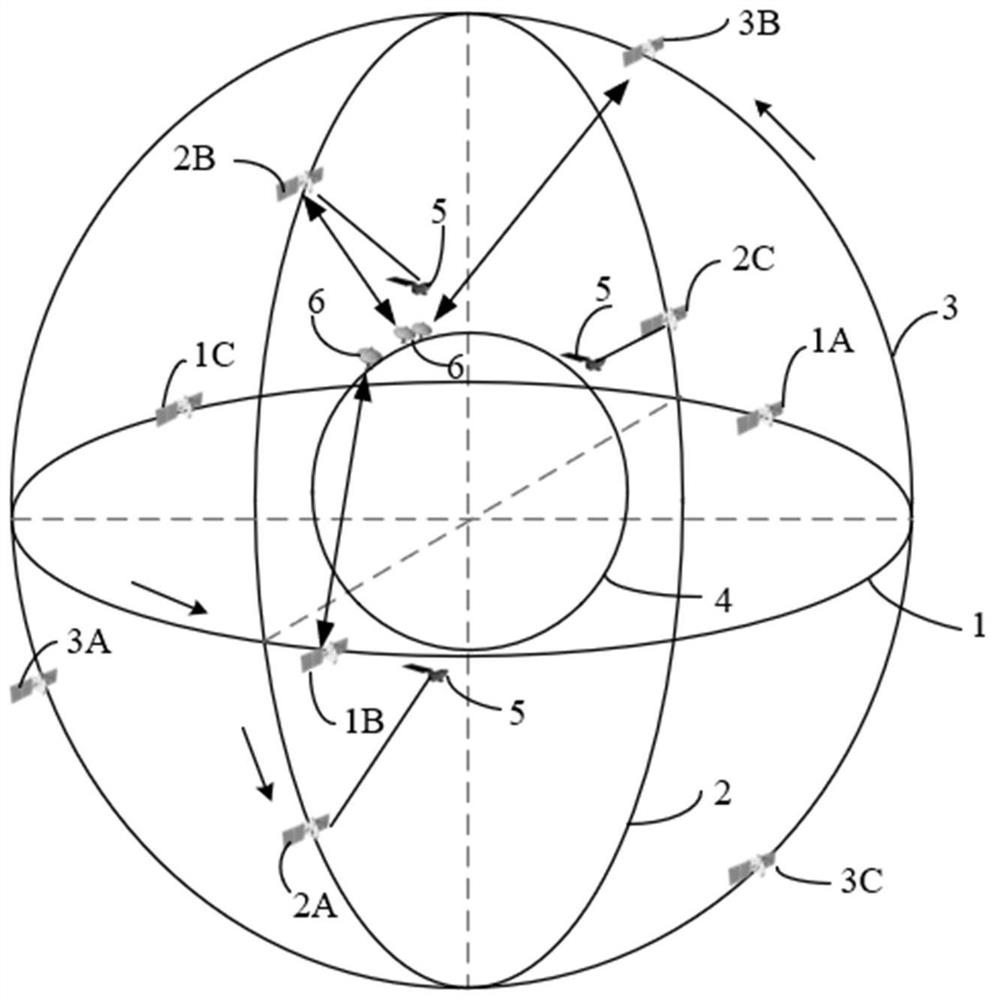
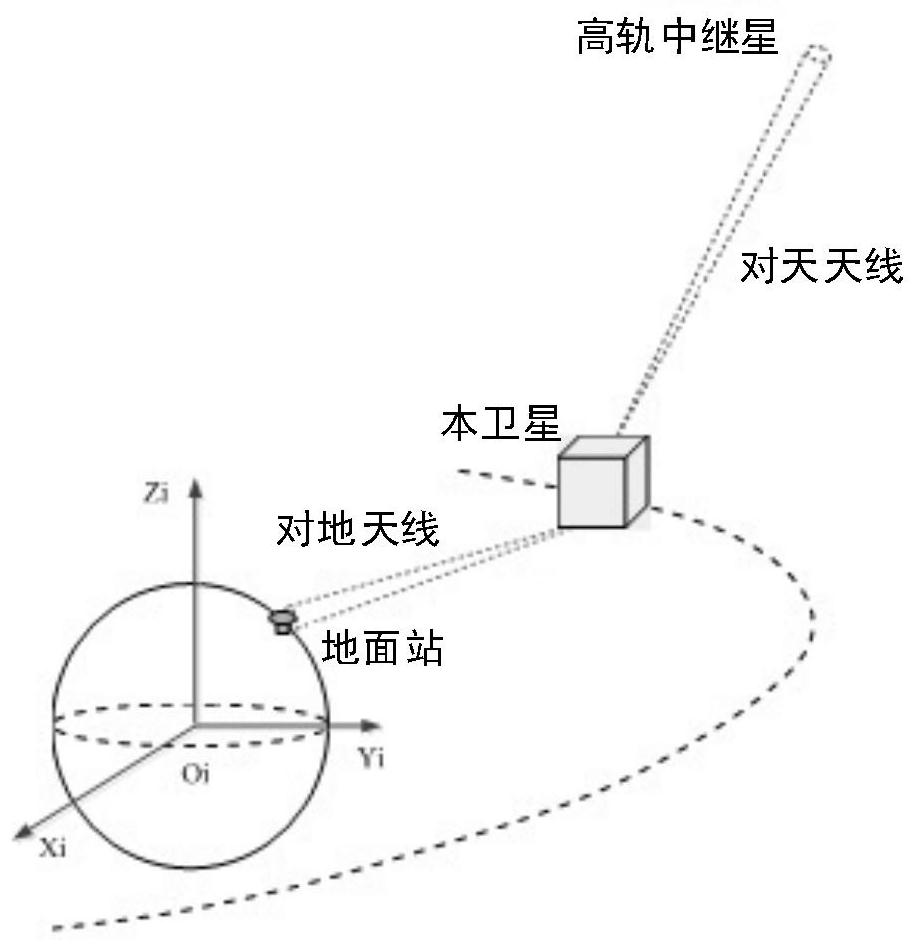
Medium-orbit relay communication networking satellite system and communication method
PendingCN114513246AImprove real timeIncrease coverageSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionGround stationReal-time communication
The invention provides a medium-orbit relay communication networking satellite system and a communication method. The system at least comprises a medium-orbit relay satellite constellation, a ground station and an operation control system, the medium orbit relay satellite constellation comprises nine relay satellites on three orbit planes, the three relay satellites on each orbit plane are uniformly distributed, and the included angle between the three relay satellites and the earth center connecting line is 120 degrees; the three orbital planes are perpendicular to one another, one orbital plane is an equator orbital plane, and the other two orbital planes are polar orbital planes; every two relay satellites in the same orbit plane communicate with each other through an inter-satellite laser link, the relay satellites communicate with a ground station through a satellite-ground microwave link, and the relay satellites are both located in a medium orbit range. The satellite system provided by the invention can provide corresponding access services for a plurality of low-orbit spacecrafts with different data rates and different orbits; a high-real-time, high-coverage and multi-user space-based measurement and control and data transmission system is established without depending on an overseas satellite ground station, and the 100% global coverage real-time communication capability is achieved.
Owner:北京天路砺成科技发展中心(有限合伙)
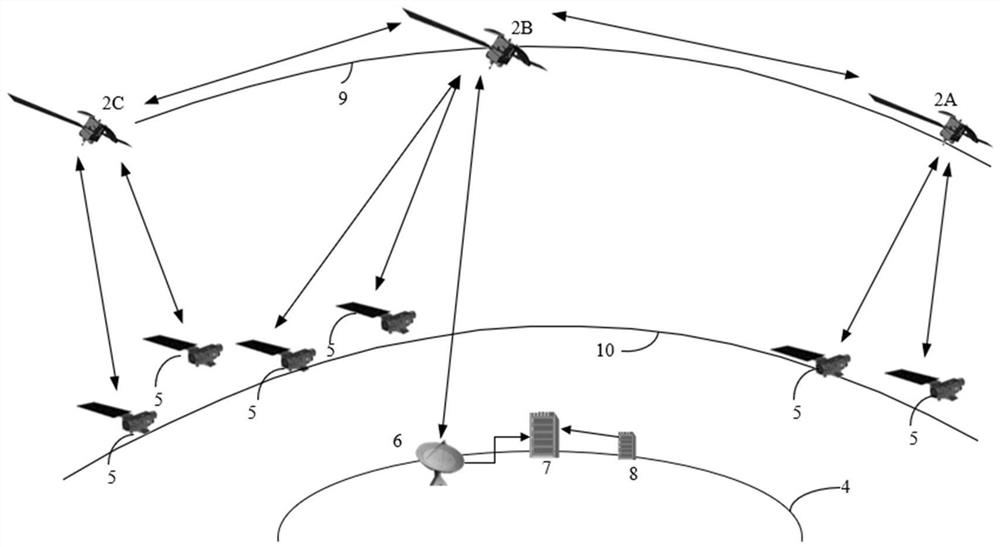
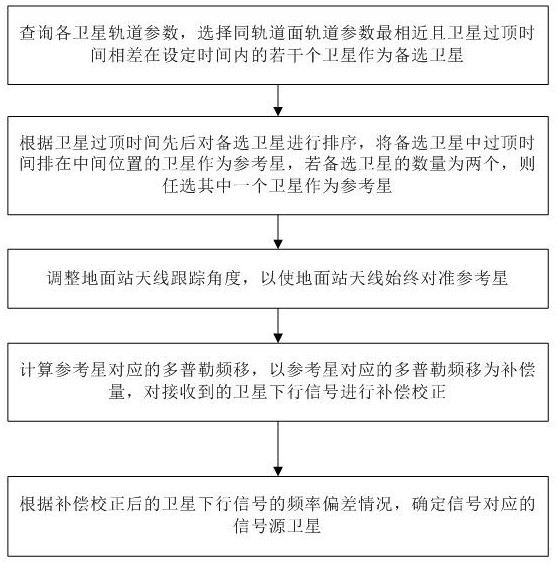
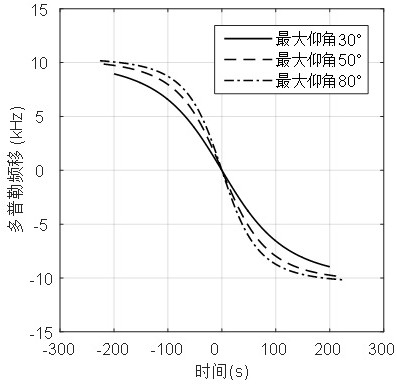
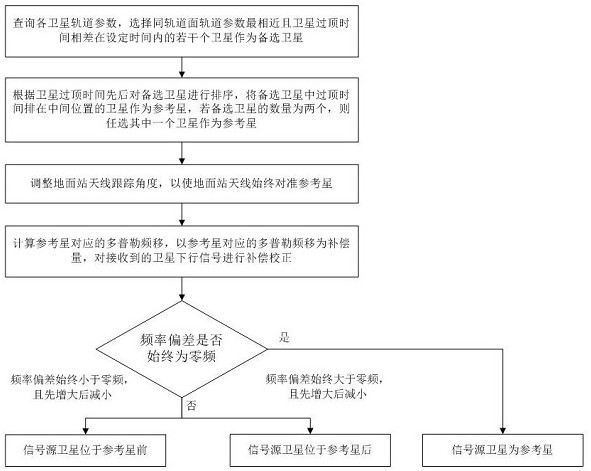
Satellite determination method and device based on Doppler effect
ActiveCN112269198AThe implementation process is simpleSimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingOrbital planeGround station
The invention discloses a satellite determination method and device based on a Doppler effect. The method comprises the steps of selecting a plurality of satellites which are most similar to orbital parameters of an orbital plane and have satellite topping time difference within set time as alternative satellites; sorting the alternative satellites according to the satellite topping time, and taking the satellite of which the topping time is ranked in the middle as a reference satellite; adjusting the tracking angle of a ground station antenna to always align the antenna with the reference satellite; calculating the Doppler frequency shift corresponding to the reference satellite, and carrying out compensation correction on the received satellite downlink signal by taking the Doppler frequency shift as a compensation amount; and determining a signal source satellite corresponding to the signal according to the frequency deviation condition of the compensated and corrected satellite downlink signal. According to the satellite determination method and device based on the Doppler effect, the signal source satellite corresponding to the signal can be determined when the received satellite signal cannot be analyzed on the ground or the satellite signal does not contain the real-time position information of the satellite, the implementation process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
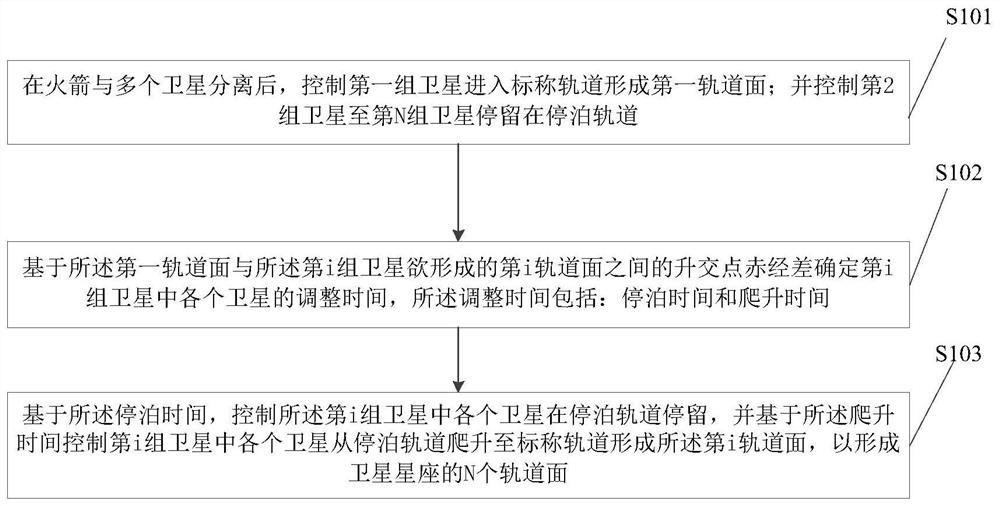
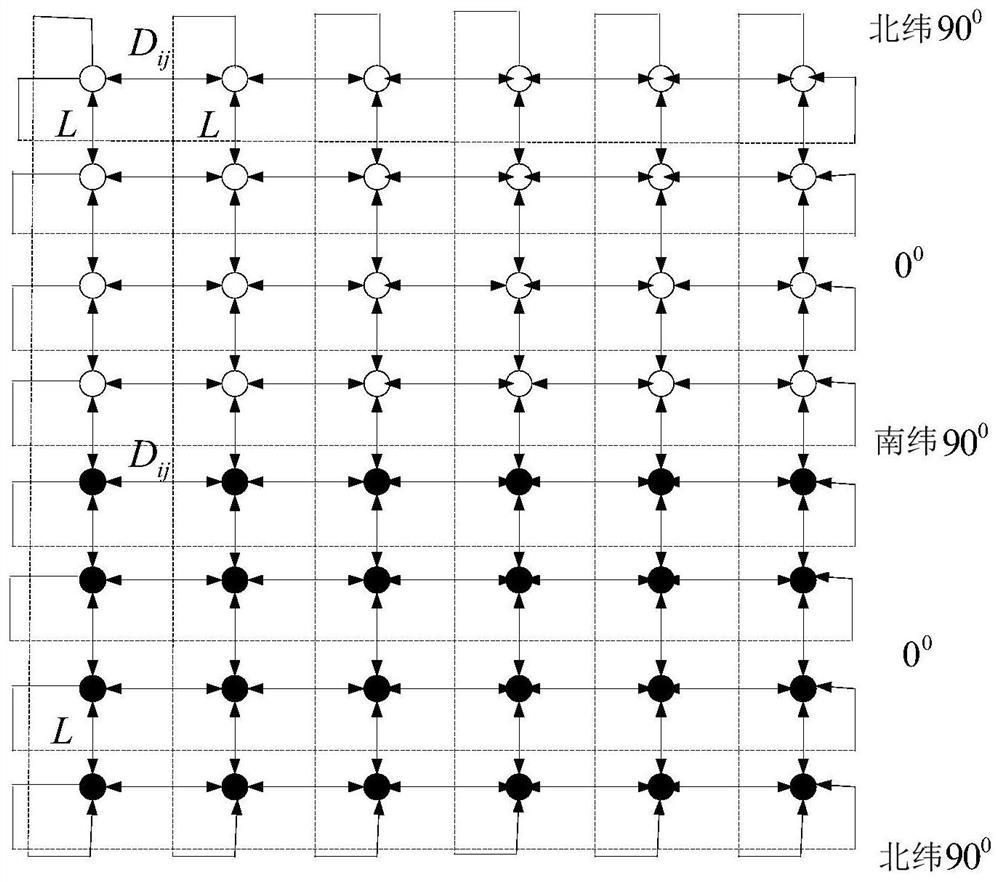
Large-scale low-orbit satellite constellation deployment method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113525719AImplement the deployment methodShorten the durationArtificial satellitesHigh level techniquesOrbital planeSatellite constellation
The invention provides a large-scale low-orbit satellite constellation deployment method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of controlling a first group of satellites to enter a nominal orbit to form a first orbit surface after a rocket is separated from a plurality of satellites, controlling the second group of satellites to the Nth group of satellites to stay in a parking orbit, wherein the multiple satellites are divided into N groups, and the height of the nominal orbit is larger than that of the parking orbit, determining the adjustment time of each satellite in the ith group of satellites based on the right ascension difference of the ascending node between the first orbital plane and the ith orbital plane to be formed by the ith group of satellites, wherein the adjustment time comprises the parking time and the climbing time, and based on the parking time, controlling each satellite in the ith group of satellites to stay in a parking orbit, and based on the climbing time, controlling each satellite in the ith group of satellites to climb to a nominal orbit from the parking orbit to form the ith orbit surface so as to form a satellite constellation.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
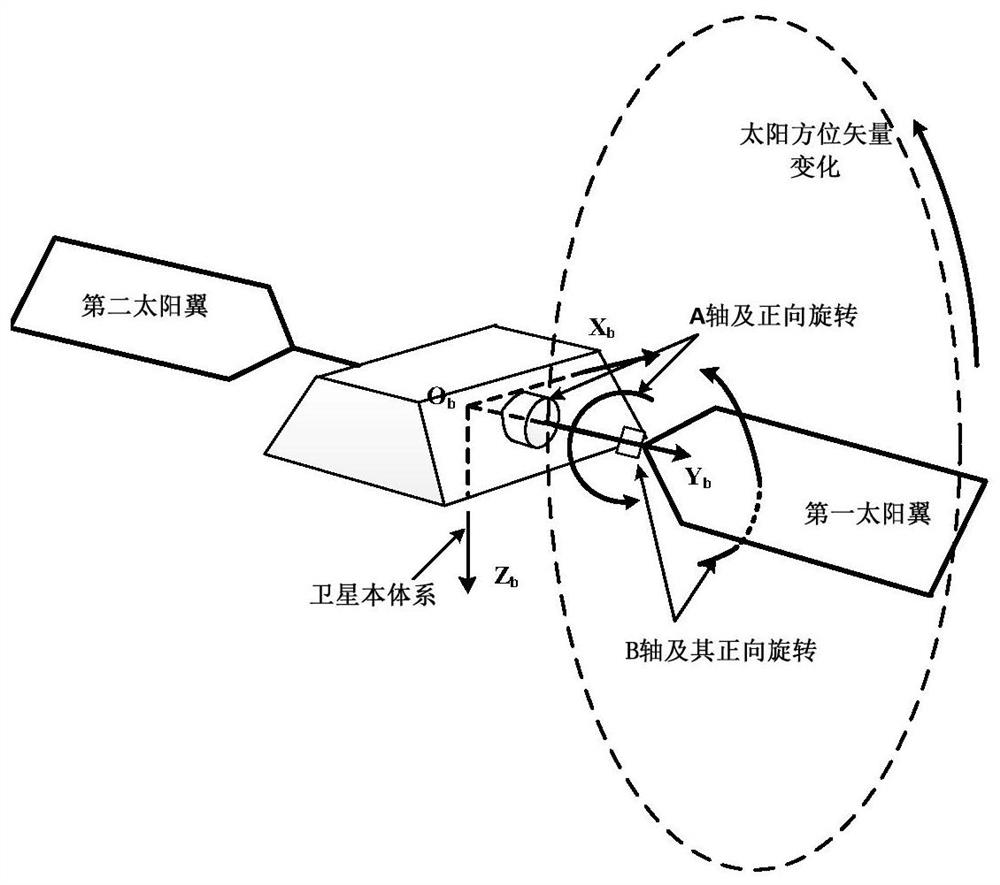
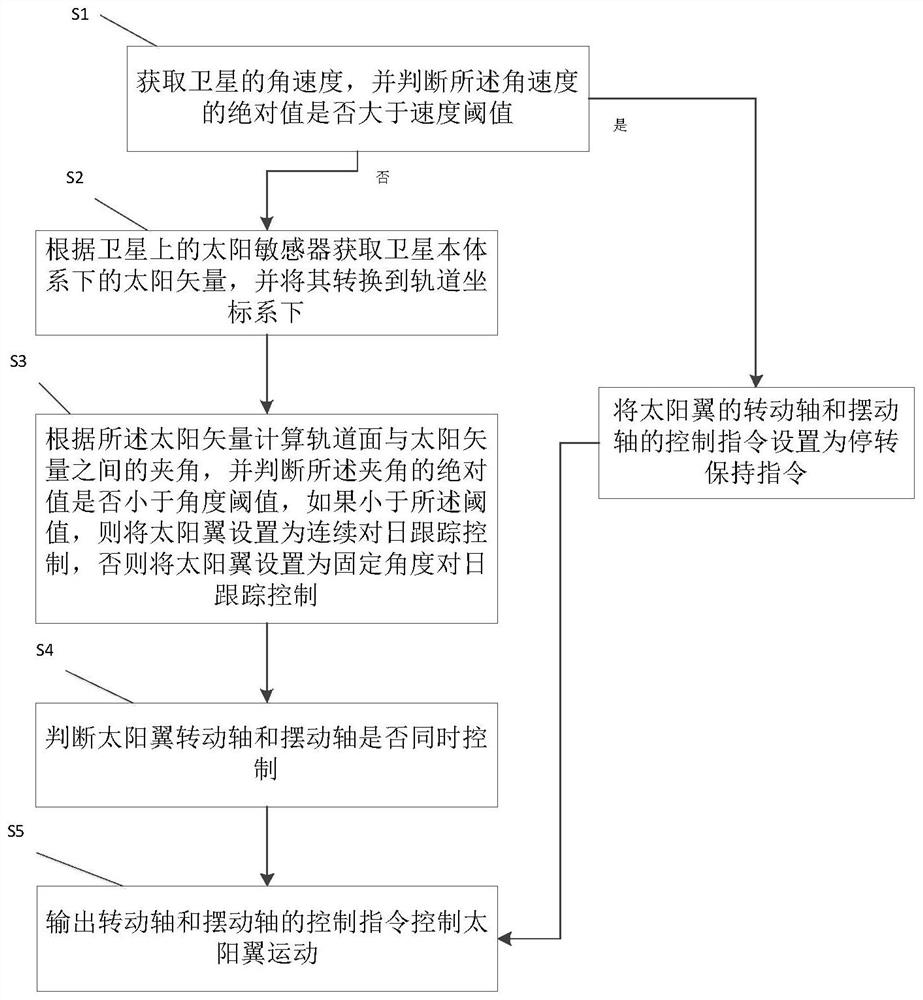
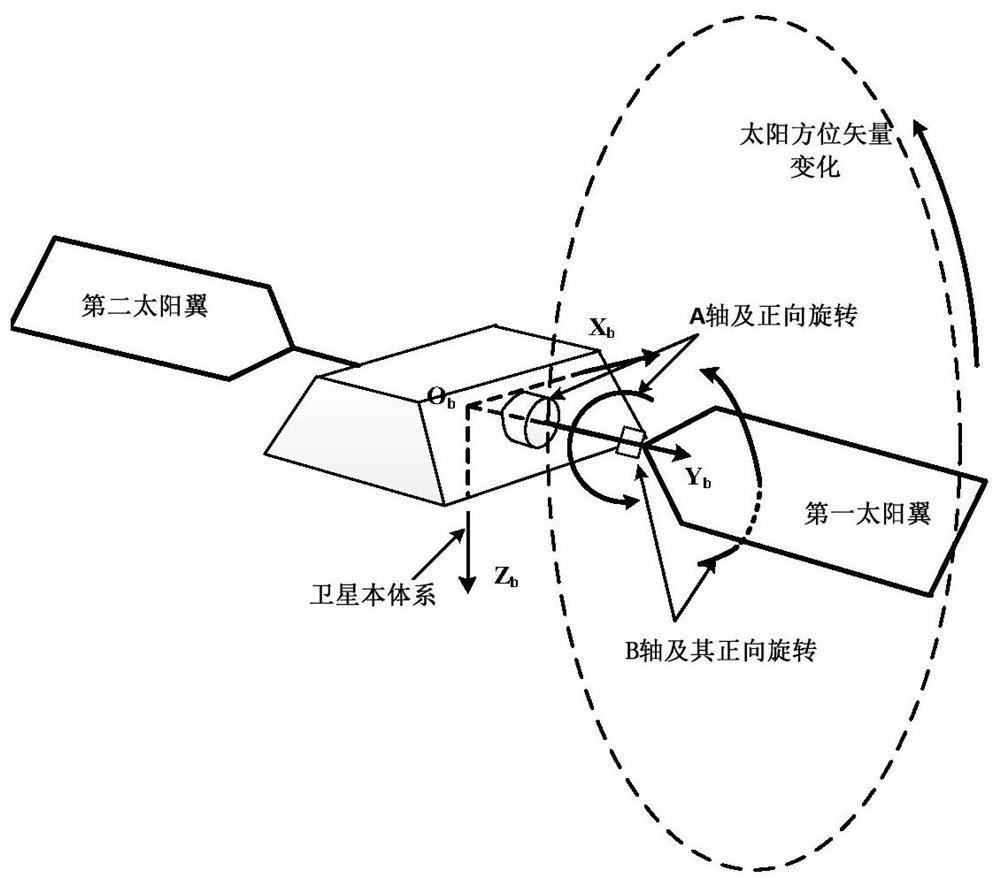
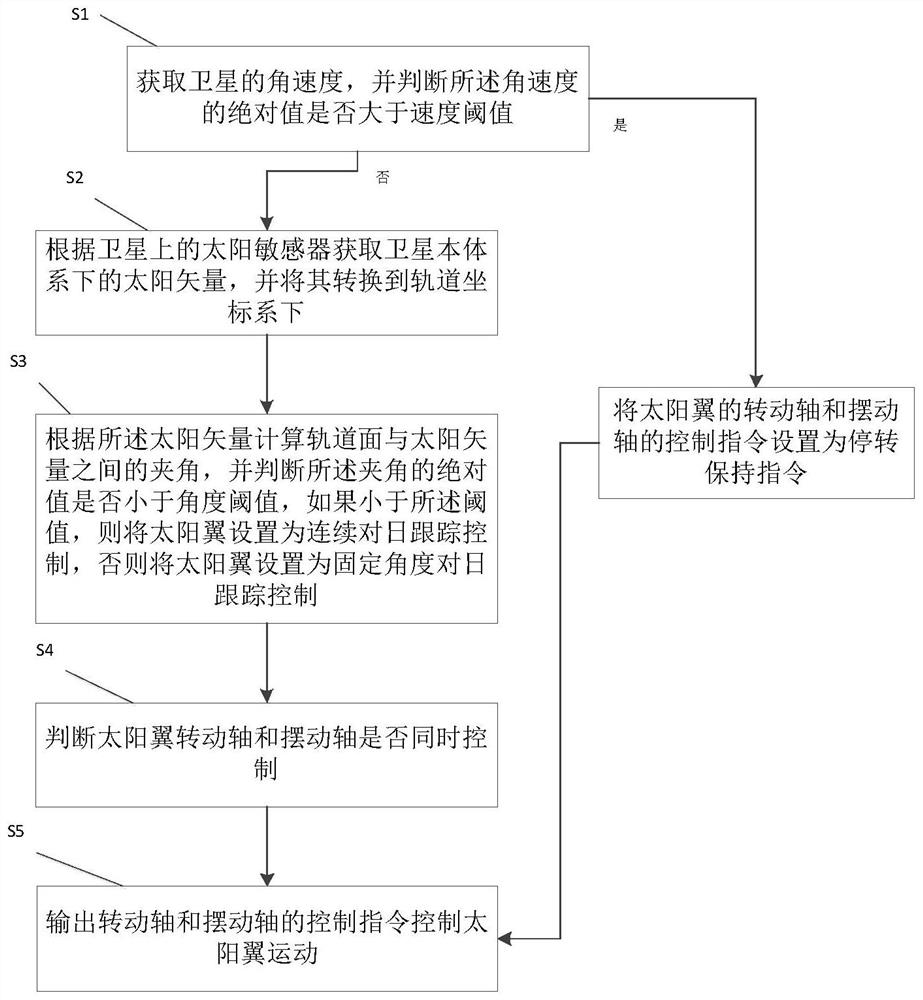
Low-orbit satellite two-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method
ActiveCN112937919AImprove work efficiencyReduce management costsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsOrbital planeClassical mechanics
The embodiment of the invention discloses a low-orbit satellite two-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method, which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring the angular velocity of a satellite, judging whether the absolute value of the angular velocity is greater than a velocity threshold value, if yes, setting a control instruction of a rotating shaft and a swinging shaft of a solar wing as a stalling keeping instruction, and then performing S5, otherwise, performing S2; S2, acquiring a sun vector in a satellite body system, and converting the sun vector into an orbital coordinate system; S3, calculating an included angle between the orbital plane and the sun vector, judging whether the absolute value of the included angle is smaller than an angle threshold value or not, if so, setting the solar wing as continuous sun tracking control, and otherwise, setting the solar wing as fixed-angle sun tracking control; S4, judging whether the rotating shaft and the swinging shaft of the solar wing are controlled at the same time, if yes, executing S5, and otherwise, adjusting the instruction of the rotating shaft; and S5, outputting control instructions of the rotating shaft and the swinging shaft to control the solar wing to move.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
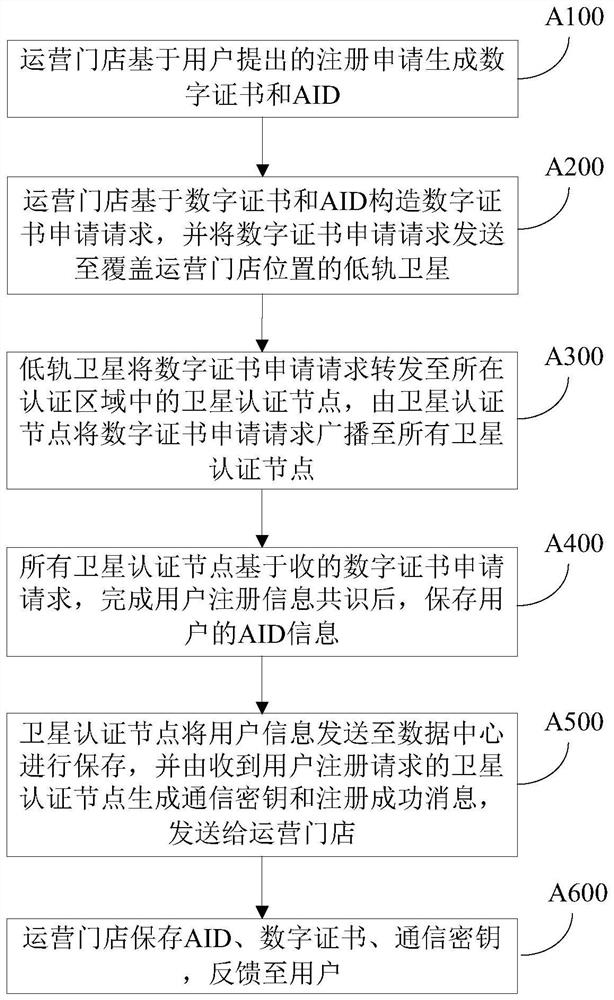
Distributed user authentication system and authentication method suitable for low earth orbit satellite network
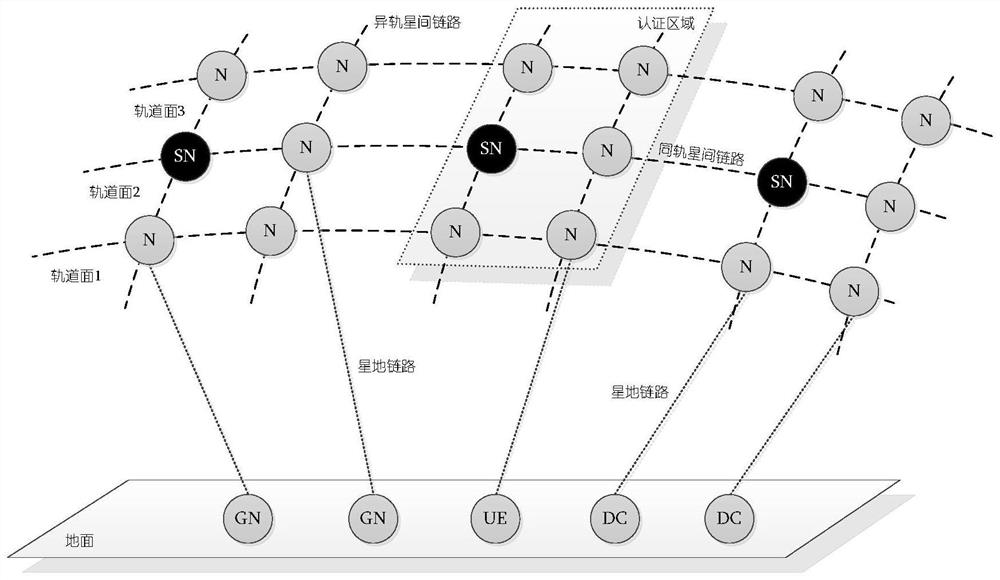
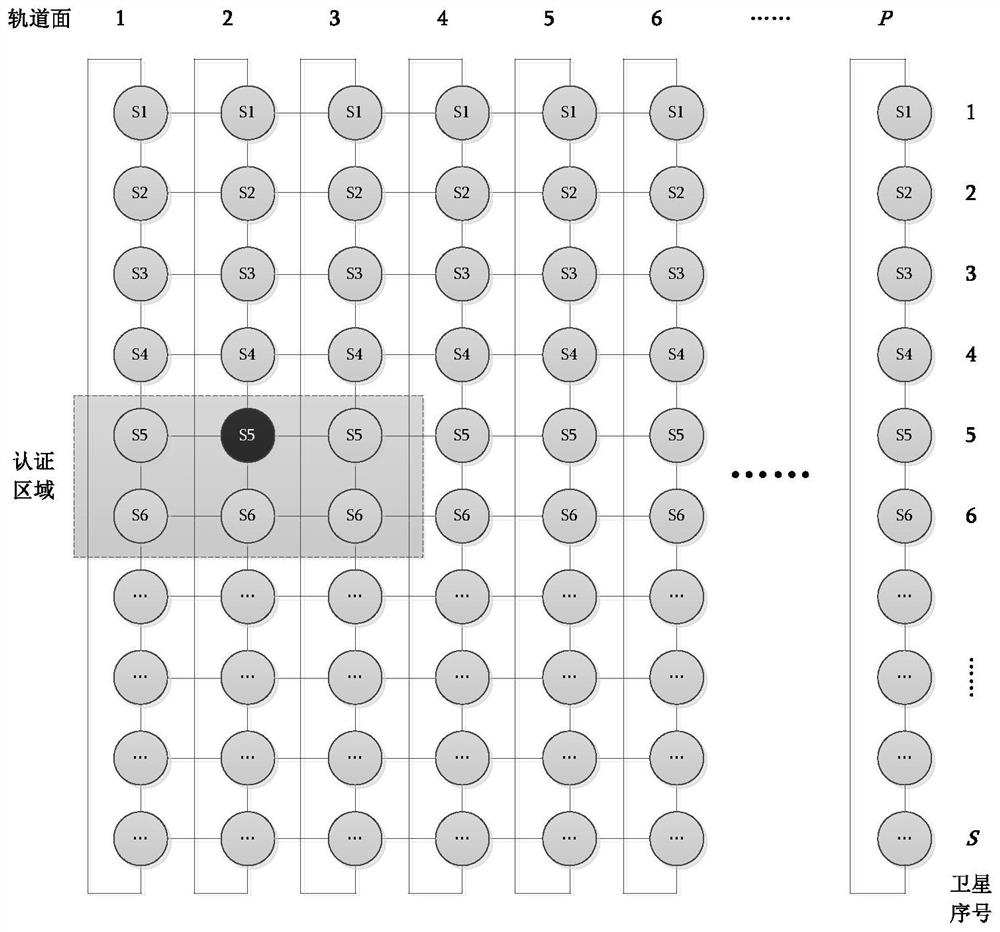
PendingCN114466359AImprove securityBreak down barriers of trustNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionUser authenticationLow earth orbit
The invention provides a distributed user authentication system suitable for a low-orbit satellite network, an authentication method and an authentication system, the system comprises a space-based subsystem and a ground subsystem, the space-based subsystem comprises a plurality of low-orbit satellites, the plurality of low-orbit satellites are distributed on a plurality of orbit planes, each orbit plane is provided with a plurality of low-orbit satellites, and the plurality of low-orbit satellites are distributed on the ground subsystem. The adjacent satellites on the same orbit and the adjacent low-orbit satellites on the adjacent orbit surfaces are in communication connection through inter-satellite links; the ground subsystem is in communication connection with the space-based subsystem, the ground subsystem comprises a user machine, an operation store and a data center, and the user machine is provided with an authentication client program for a user to log in; the operation store is used for providing registration service; the data center is used for storing legal user information; wherein a plurality of low-orbit satellites in the space-based subsystem are divided into a plurality of authentication areas which are not overlapped with one another according to a preset arrangement mode, and each authentication area is provided with a satellite authentication node used for user registration and login for authentication.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECH OF CETC
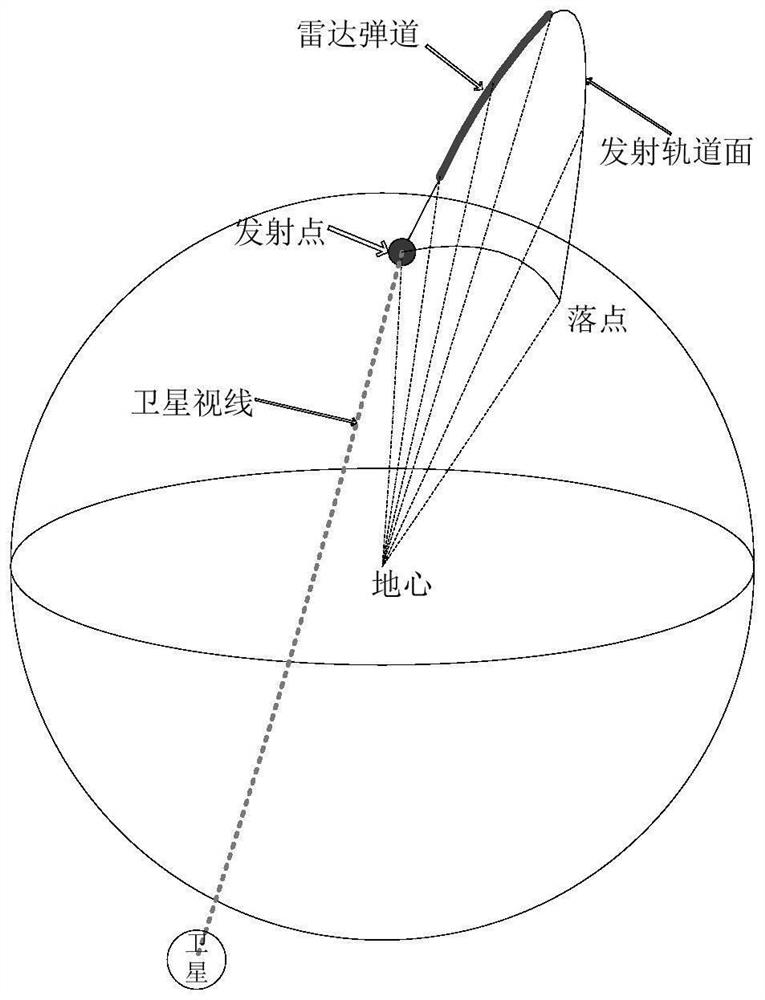
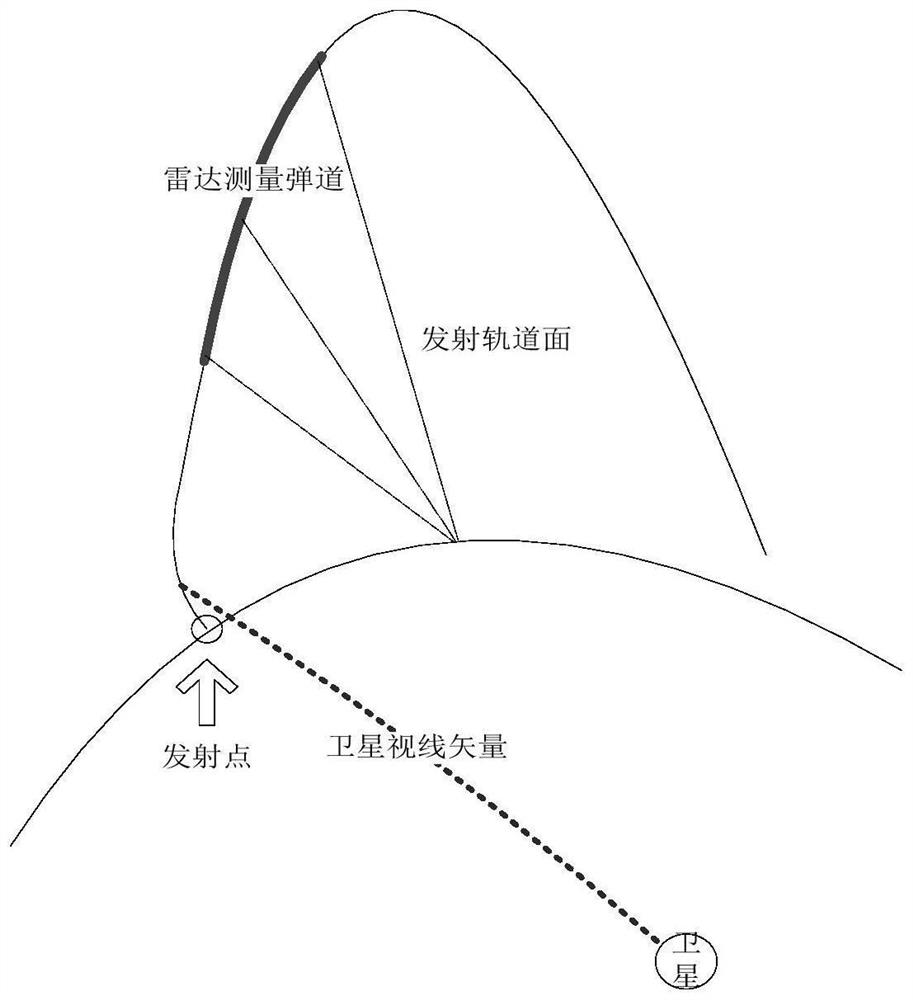
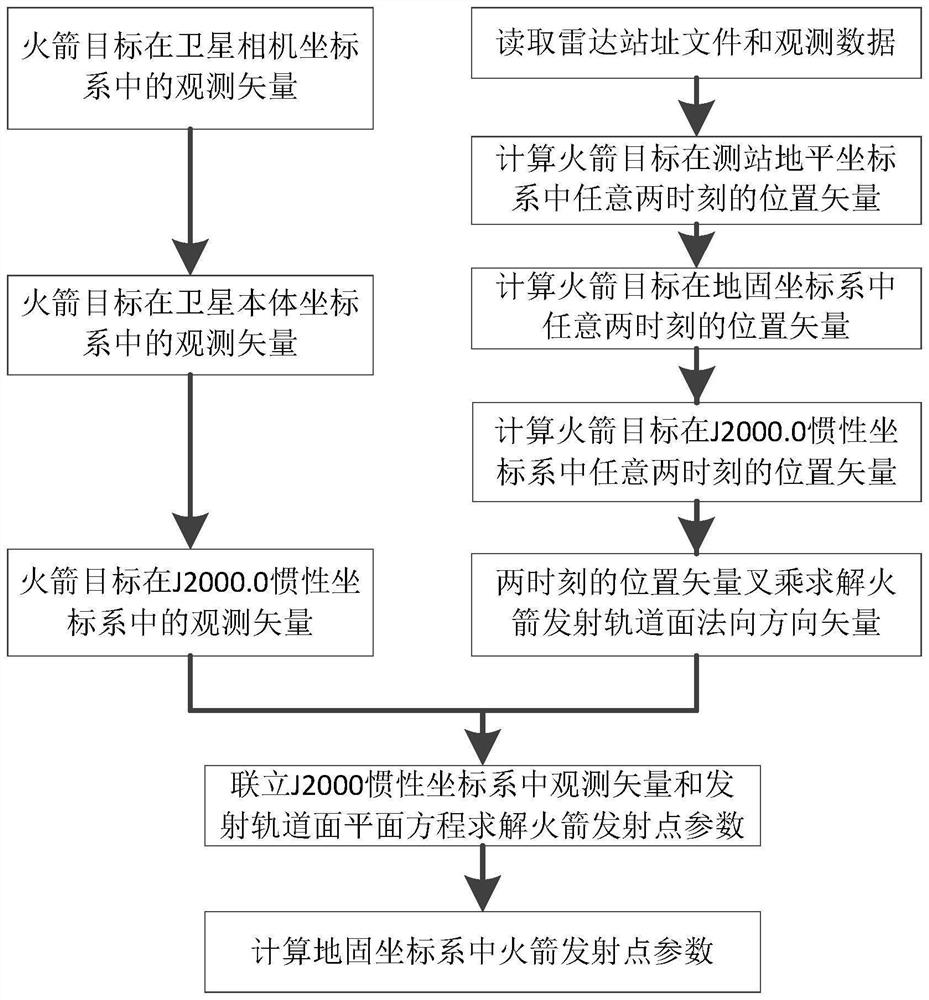
Backtracking calculation method for rocket launching point parameters
PendingCN114063054ADisplay accuracyShow validityRocket launchersNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSkyRocket launch
The invention discloses a backtracking calculation method for rocket launching point parameters, which comprises the following steps of: 1, calculating an observation vector from a satellite to a rocket target in a J2000 inertial coordinate system through rocket target data observed by the satellite; 2, calculating a linear equation of an observation vector in a J2000.0 inertial coordinate system; 3, calculating a position vector of the rocket target in the earth-fixed coordinate system by using radar external measurement data; 4, calculating a plane equation of a launching orbit plane in the J2000.0 inertial coordinate system; 5, calculating the coordinates of a rocket launching point by combining the plane equation of the launching orbit plane and the linear equation of the observation vector; and 6, calculating latitude and longitude parameters of a rocket launching point in the earth-fixed coordinate system. According to the backtracking calculation method for the rocket launching point parameters, accuracy and effectiveness are shown for measuring the active section of a rocket in a sky-ground non-cooperative mode and rapidly determining the launching point parameter calculation in a high-precision mode.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
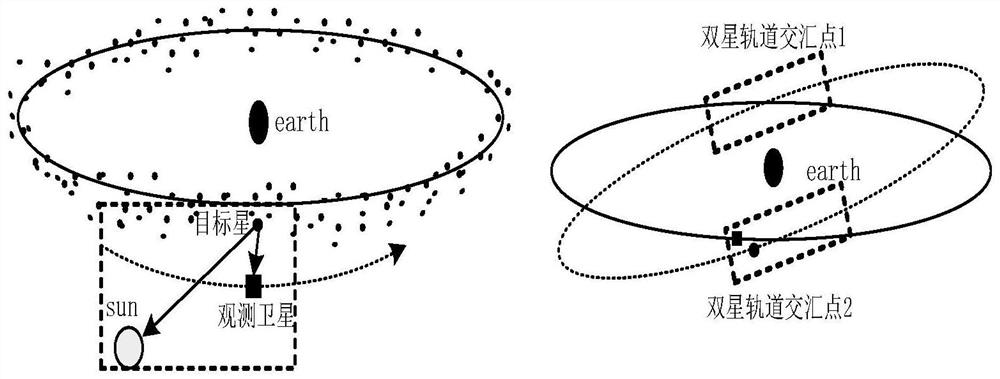
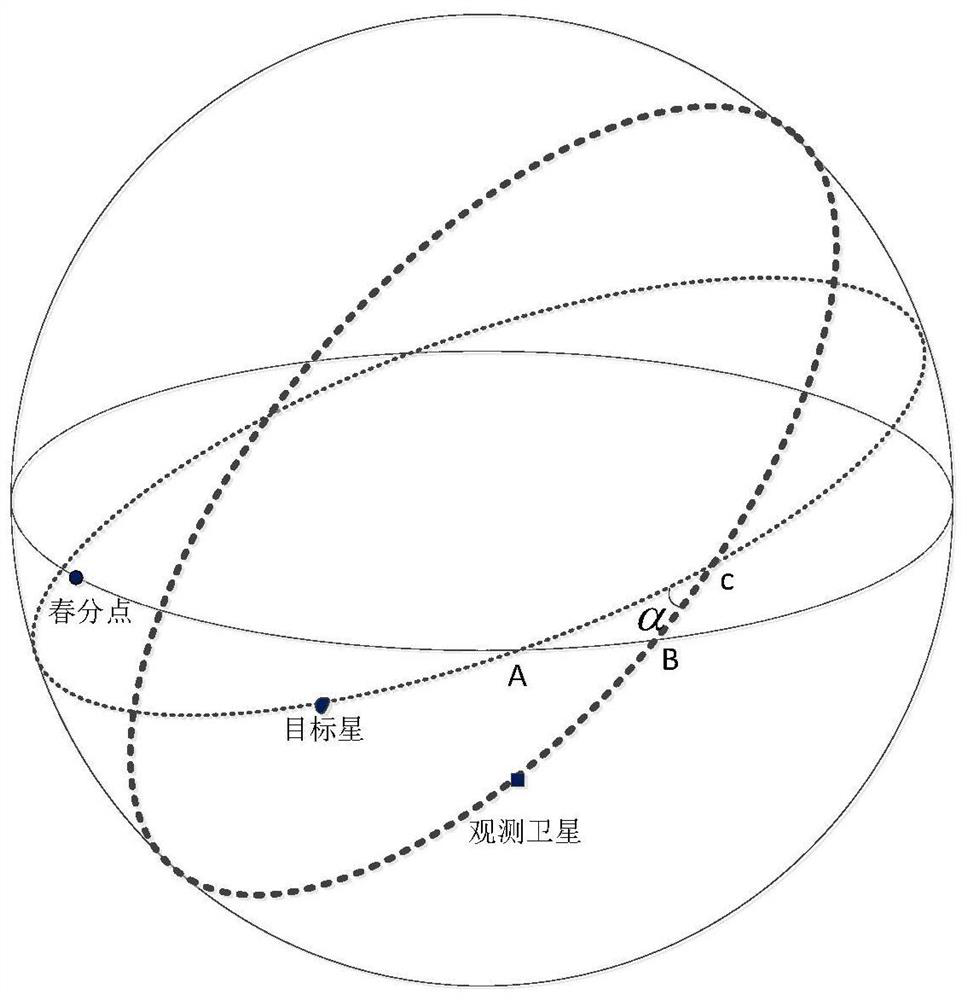
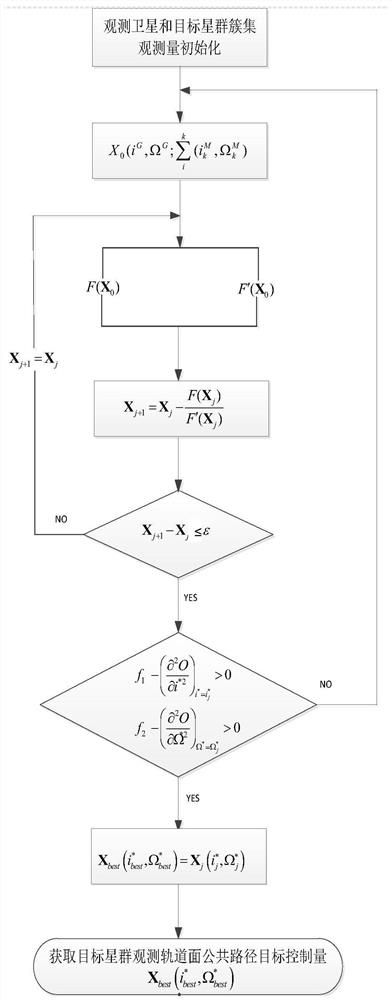
Synchronous orbit star group multi-target observation orbit plane common path design method
PendingCN114880779AAvoid controlReduce consumptionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSynchronous orbitSingle star
The invention relates to a synchronous orbit star group multi-target observation orbit plane common path design method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring orbit ephemeris of n target stars of a synchronous orbit star group and an initial orbit ephemeris of an observation satellite; establishing an observation orbital plane common path model of the observation satellite, and forming an objective function model formula of the observation orbital plane common path of the observation satellite through a plurality of observed quantities; establishing a preset iterative algorithm model, and traversing and solving extreme points of the objective function model; setting a threshold value epsilon (1) of a preset iterative algorithm model; and when the extreme point of the objective function model formula is less than or equal to a threshold value epsilon, operation is stopped, and the optimal common path of the observation orbit surface is obtained. According to the embodiment of the invention, one-time orbital plane control is adopted, and an invariable observation plane public path is established, so that node single-satellite multi-batch orbital plane control is avoided while the maximum effective observation of the observation target is met, and the fuel consumption is greatly saved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
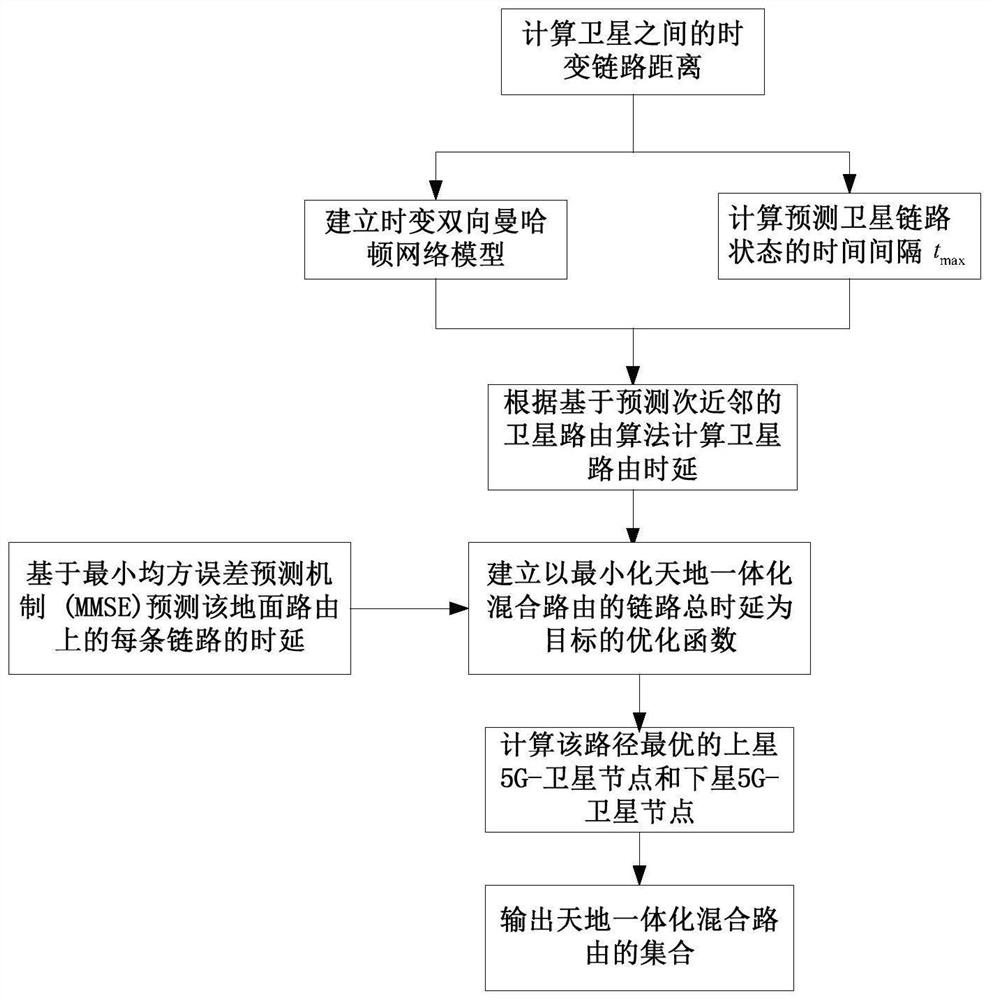
A Hybrid Routing Method for Sky-Ground Integration
ActiveCN110505153BPrevent lossExtended forecast rangeRadio transmissionData switching networksTelecommunicationsHybrid routing
The invention provides a space-ground integrated hybrid routing method, including calculating the link distance between satellites in the orbital plane and based on the time-varying link distance between orbital satellites, establishing a time-varying two-way Manhattan satellite network model; The queue delay between the satellite and the neighbor satellite node and the queue delay between the satellite-ground link with the ground node; calculate the time interval that does not affect the network routing performance, and predict the link transmission time between the neighbor node and the second nearest neighbor node within the time interval Delay and queue delay; according to the satellite routing algorithm based on predicting the next nearest neighbor, calculate the link delay of satellite network routing; when the source terminal communicates with the destination terminal, based on the minimum mean square error prediction mechanism, predict each link on the ground route The queue delay of the route; under the 5G-satellite integrated architecture, the goal is to minimize the total link delay of the space-ground integrated hybrid route, and select the optimal path for the on-satellite 5G-satellite node and the off-satellite 5G-satellite node , to get the set of integrated hybrid routes of heaven and earth.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A Fast Estimation Method of Optimal Velocity Increment for Long-term Orbital Rendezvous under j2 Perturbation
ActiveCN110789739BDecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeClassical mechanics
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
A control method for a low-orbit satellite with two degrees of freedom for solar wings
ActiveCN112937919BImprove work efficiencyReduce management costsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsAngular velocitySatellite system
One embodiment of the present invention discloses a low-orbit satellite dual-degree-of-freedom solar wing control method, including: S1: Acquiring the angular velocity of the satellite, and judging whether the absolute value of the angular velocity is greater than a speed threshold, and if greater, the solar wing's S5 is performed after the control commands of the rotation axis and the swing axis are set to stop and maintain the command, otherwise S2 is performed; S2: obtain the sun vector under the satellite body system, and convert it to the orbital coordinate system; S3: calculate the orbital plane and the sun vector The angle between the vectors, and judge whether the absolute value of the angle is less than the angle threshold, if less, set the solar wing to continuous sun tracking control, otherwise set it to a fixed angle sun tracking control; S4: judge the sun Whether the wing rotation axis and the swing axis are controlled at the same time, if they are controlled at the same time, go to S5, otherwise adjust the command of the rotation axis; S5: output the control commands of the rotation axis and swing axis to control the movement of the solar wing.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
Thermal layer atmospheric density prediction method and system based on distributed sensing units
ActiveCN111259310AHigh precision requirementsBreak through the defect that the space cannot be expandedComplex mathematical operationsICT adaptationOrbital planeData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of atmospheric density sensing methods and space physics, and particularly relates to a hot layer atmospheric density prediction method based on distributed orbit atmospheric sensing units, which comprises the following steps: obtaining P distributed orbit atmospheric sensing units; in combination with an energy dissipation rate or semi-major axis attenuation, calculating an atmospheric density correction ratio of a track surface thermal layer where each distributed track atmospheric sensing unit is located; periodically and dynamically selecting the multiple space targets are uniformly distributed in the P distributed orbit atmosphere sensing units at different places; in all P distributed track atmosphere sensing units, calculating the atmospheric density of the space point of the space target on the corresponding orbital plane every 2-30 seconds; periodically acquiring a full-space atmospheric density data set {rhoO} within 3-24 hours; calculating a spherical harmonic coefficient, calculating the corrected inflection point temperature and escape layer temperature to form a thermal layer atmospheric density correction model, and obtaining the dynamically corrected thermal layer atmospheric density by using the correction model to predict the atmospheric density of any position in the future space.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
A constellation design method for spectrum coexistence between LEO constellation systems
ActiveCN110198184BSpectrum coexistenceNatural isolation angleRadio transmissionOrbital planeOrbital inclination
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
Autonomous safety control method for space optical relative measurement equipment
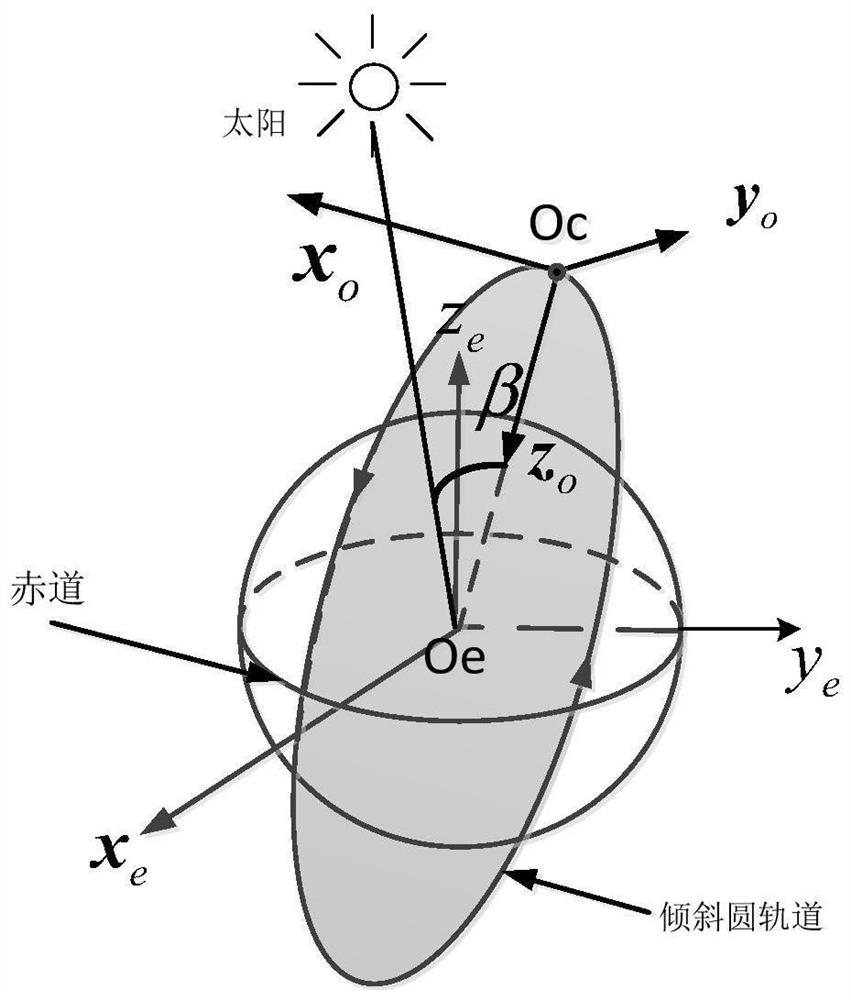
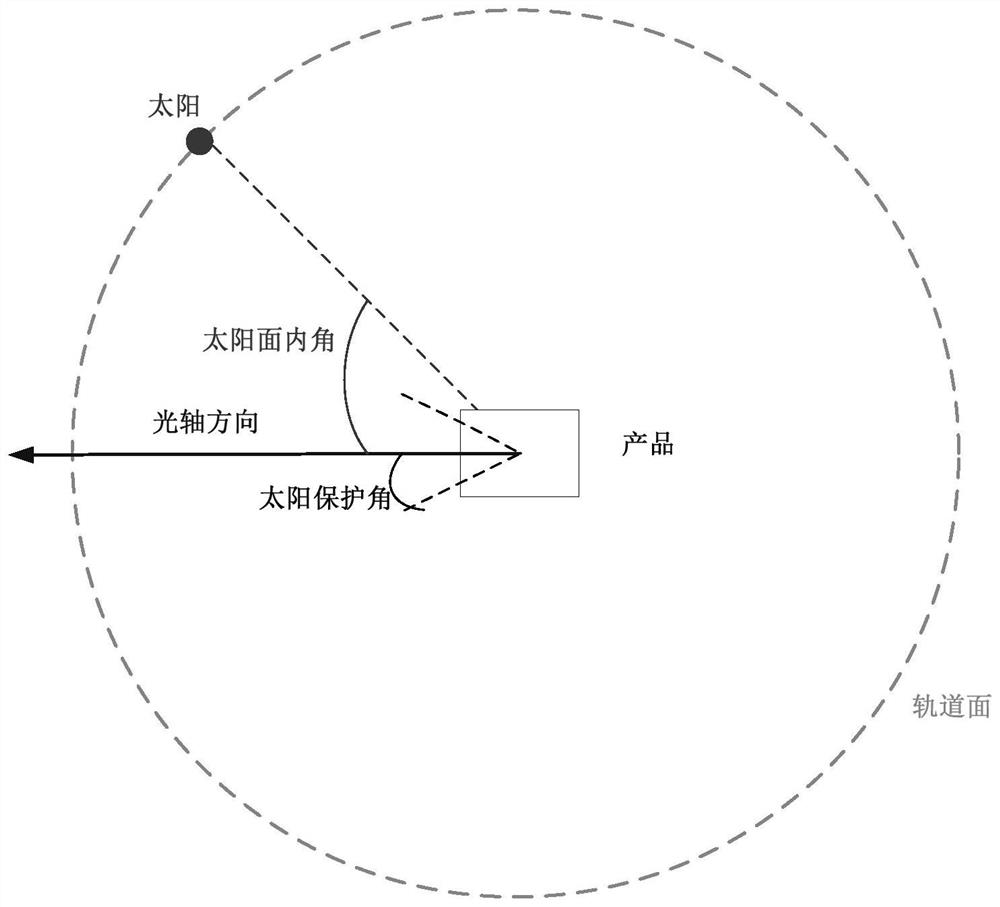
ActiveCN111988529ASatisfy the safety work requirements of on-orbit operationThe principle of the method is clearTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAngle of incidenceSpace optics
The invention discloses an autonomous safety control method for space optical relative measurement equipment. The method comprises the steps: S1, determining the relative position of the sun on an operation orbit plane of space optical relative measurement equipment, and representing the relative position through a sun plane interior angle; S2, calculating an included angle between the optical axis of the space optics relative measurement equipment and the solar plane interior angle in the S1, and representing the included angle as a solar incident angle; and S3, executing a corresponding modestate according to a size relationship between the solar incident angle and the solar protection angle threshold of the space optics relative measurement equipment. The method has the advantages thatthe relation among the solar surface interior angle, the solar incident angle and the solar protection angle threshold value is reasonably utilized, the on-orbit operation safety work requirement ofthe space relative measurement equipment is met, the method is clear in principle, convenient to implement and suitable for on-orbit work, and the work safety of the space relative measurement equipment can be guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Engineering Design Methodology of Navigation Satellite Constellation
ActiveCN105335541BImprove compatibilityBest interoperabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSatellite orbitSatellite constellation
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
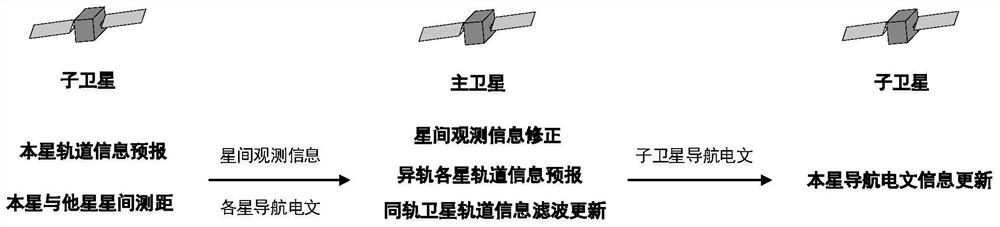
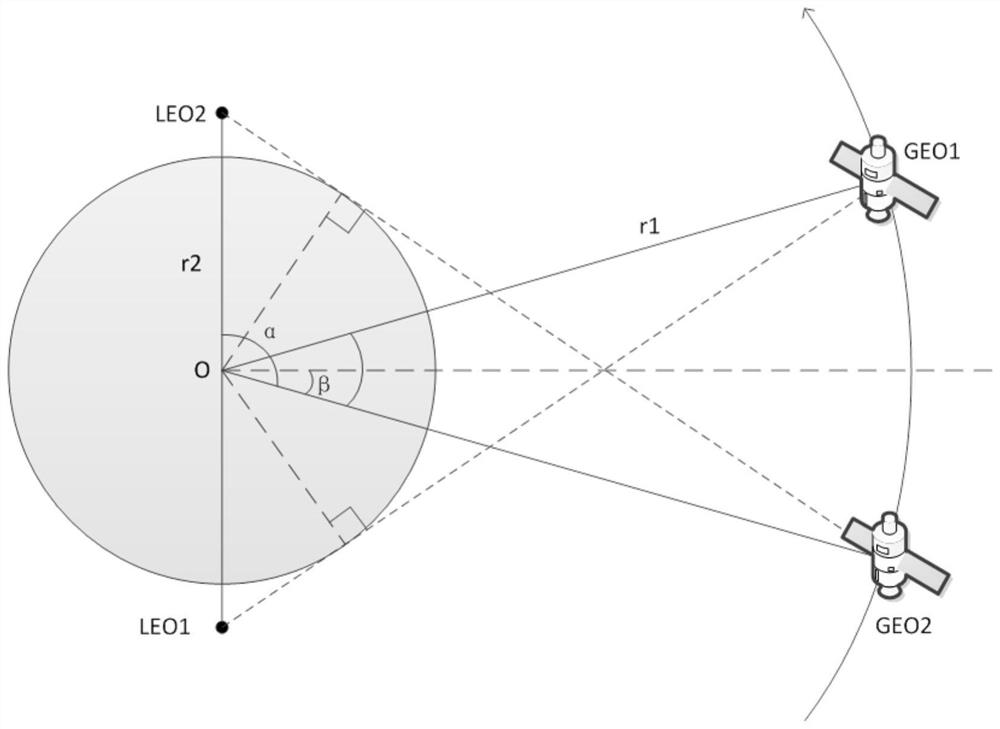
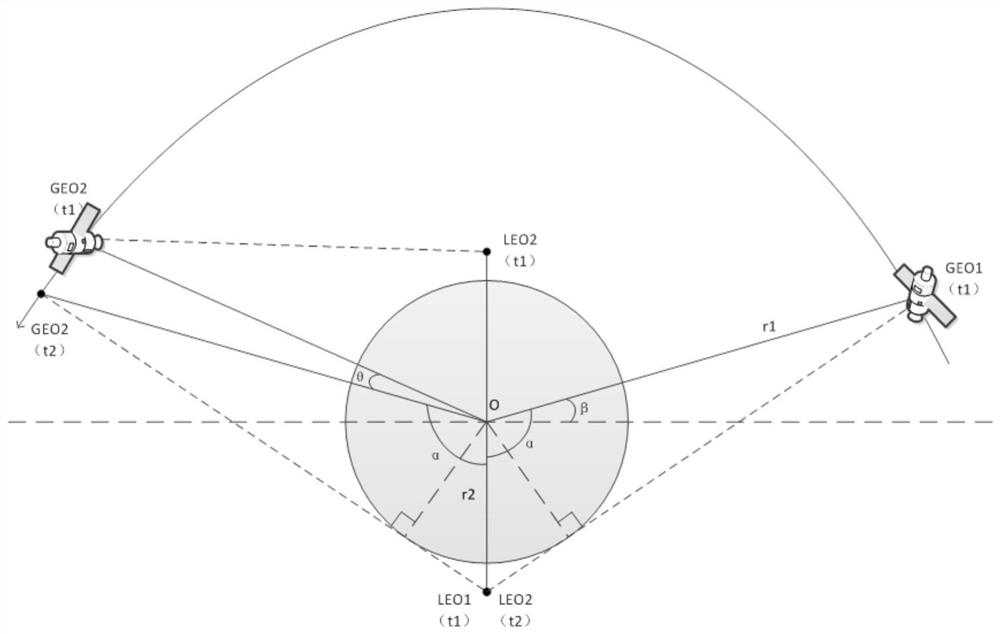
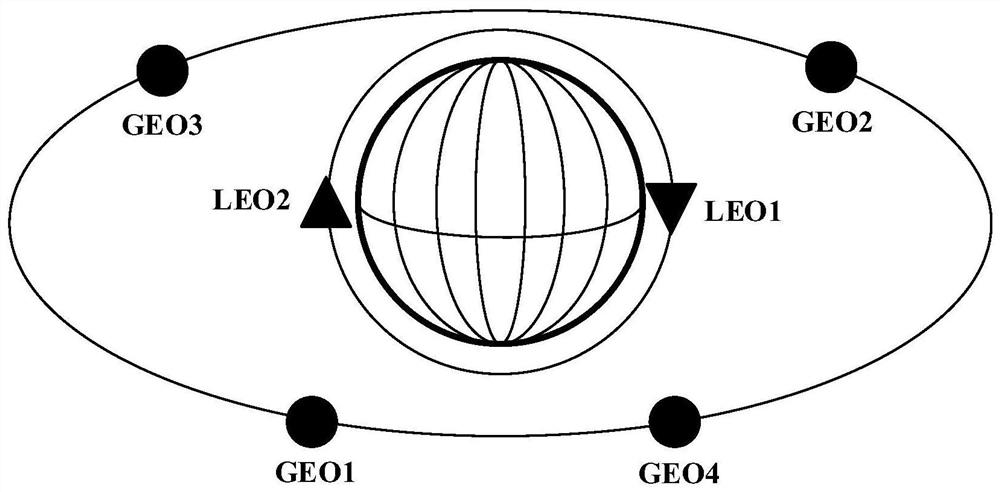
Constellation co-orbital satellite autonomous navigation method and navigation system
The invention provides an autonomous navigation method and a navigation system for satellites in the same orbital plane of a constellation. The obtained two-way ranging information is centrally processed to obtain the navigation information of each satellite in the orbital plane; each sub-satellite uses the Ka inter-satellite link to realize the inter-satellite ranging between the local satellite and other satellites, and the sub-satellites switch the phase of the Ka antenna phased array. Realize switching with surrounding satellites to establish chain ranging, and obtain the inter-satellite ranging information between the local satellite and the satellites on the same orbit, as well as the inter-satellite ranging information between the local satellite and the satellites on the different orbit; The laser terminal uses a laser link to establish a link with two adjacent satellites in the same orbit to realize high-speed data communication between satellites in the same orbit; each sub-satellite in the same orbit transmits information to the main satellite, and the main satellite uses the co-orbit area. The centralized navigation algorithm realizes the precise orbit determination of each satellite in the orbit plane.
Owner:上海中科辰新卫星技术有限公司
GEO and LEO mixed constellation and design method thereof
ActiveCN112019258AAlleviate the problem of data landingReduce switching frequencySatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsOrbital inclination
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
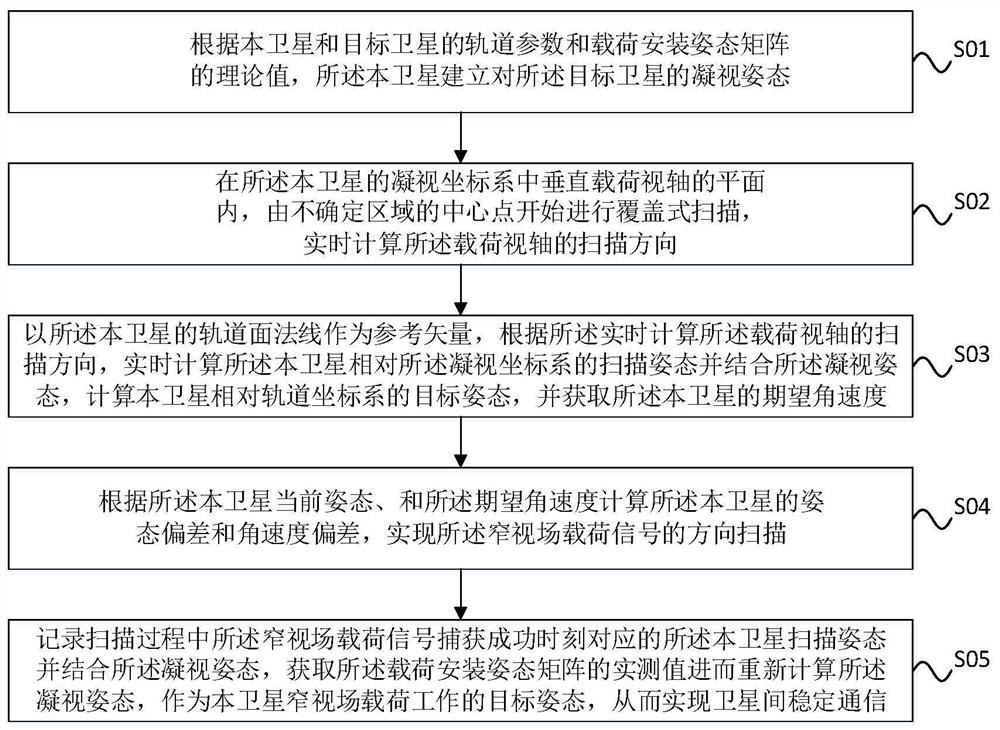
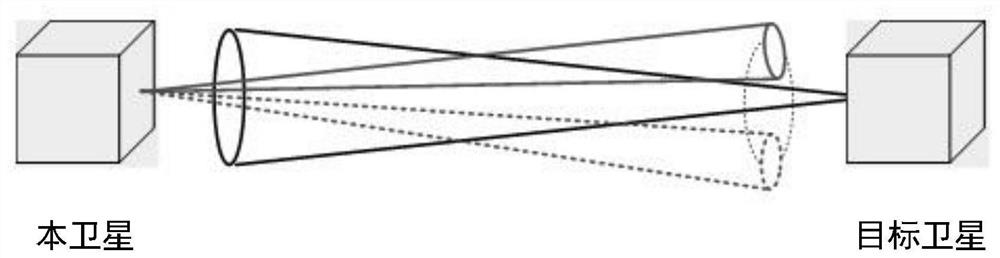
Method for realizing narrow-view-field load pointing calibration by satellite attitude maneuver assistance
The invention discloses a method for realizing narrow view field load pointing calibration by satellite attitude maneuver assistance. The method comprises the following steps that a target staring attitude is established according to orbit parameters of a local satellite and a target satellite and a theoretical value of a load installation matrix; in a vertical load visual axis plane in a satellite staring coordinate system, an Archimedes spiral is calculated from a central point, and the scanning direction of a load visual axis is planned in real time; a scanning attitude of a satellite relative to a staring coordinate system in real time is calculated according to a load visual axis direction planned by a spiral line by taking an orbital plane normal as a reference vector, a target attitude of the satellite relative to an orbital coordinate system is calculated in combination with the staring attitude, and an expected angular velocity of the satellite is obtained; the deviation of the attitude and the angular velocity is calculated according to the current attitude and the angular velocity of the satellite so as to realize spiral line scanning in the load signal direction; after the two parties capture the signals, the current attitude is recorded, the actual measurement value of the installation matrix corresponding to the load is calculated in combination with the theoretical attitude, and normal communication of the narrow-view-field load can be realized without spiral scanning again.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
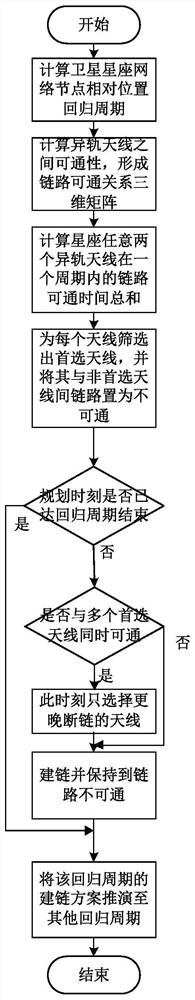
Satellite constellation network different orbit link planning method
ActiveCN113840294AReduce switching timesRealize autonomous planningRadio transmissionNetwork planningTelecommunicationsNetwork management
The invention discloses a satellite constellation network different orbit link planning method, which can obtain a different orbit link establishment planning scheme with relatively stable network topology and efficient network management. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a regression period of a relative position relation of nodes of the satellite constellation network according to the orbit height, obtaining a link connectivity relation between antennas used for different orbit links in one regression period, and forming a link connectivity relation three-dimensional Boolean matrix; traversing all antennas which can be used for different-orbit link establishment, respectively selecting an antenna which has the longest sum of available time of a link with the antenna in a regression period from two adjacent orbit surfaces, and setting the available relation between the antenna and a non-preferred antenna to be non-available; and traversing each moment and each antenna of the regression period, selecting a different-track idle antenna from the link connectable relation three-dimensional Boolean matrix according to a longest continuous link establishment time algorithm for each antenna to establish a link with the antenna, and deducing a link establishment scheme of the regression period to other periods to obtain a final network topology plan.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Method and device for suppressing internal frequency interference in low-orbit constellation system
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
A method for adjusting orbit attitude coupling for deorbit delivery of low-orbit space debris with geomagnetic energy storage
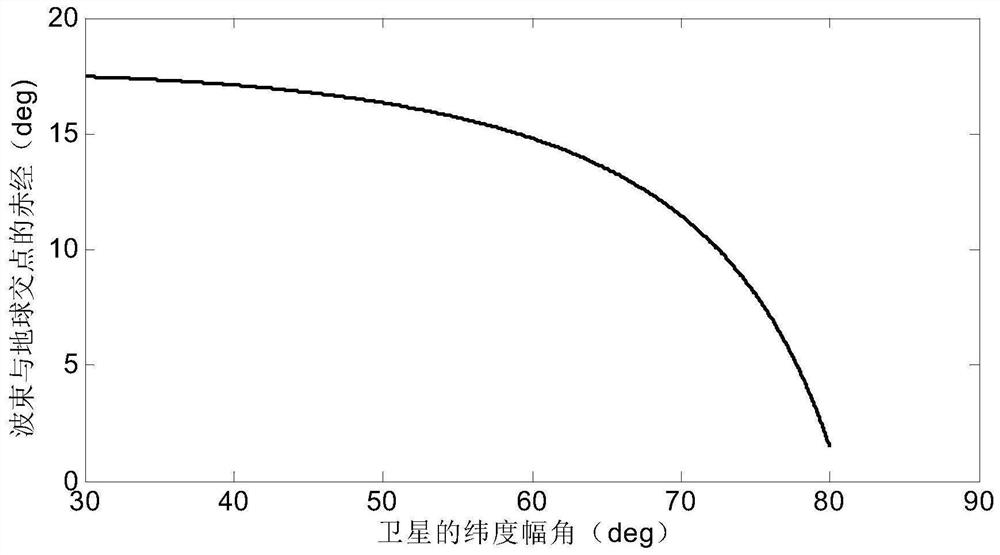
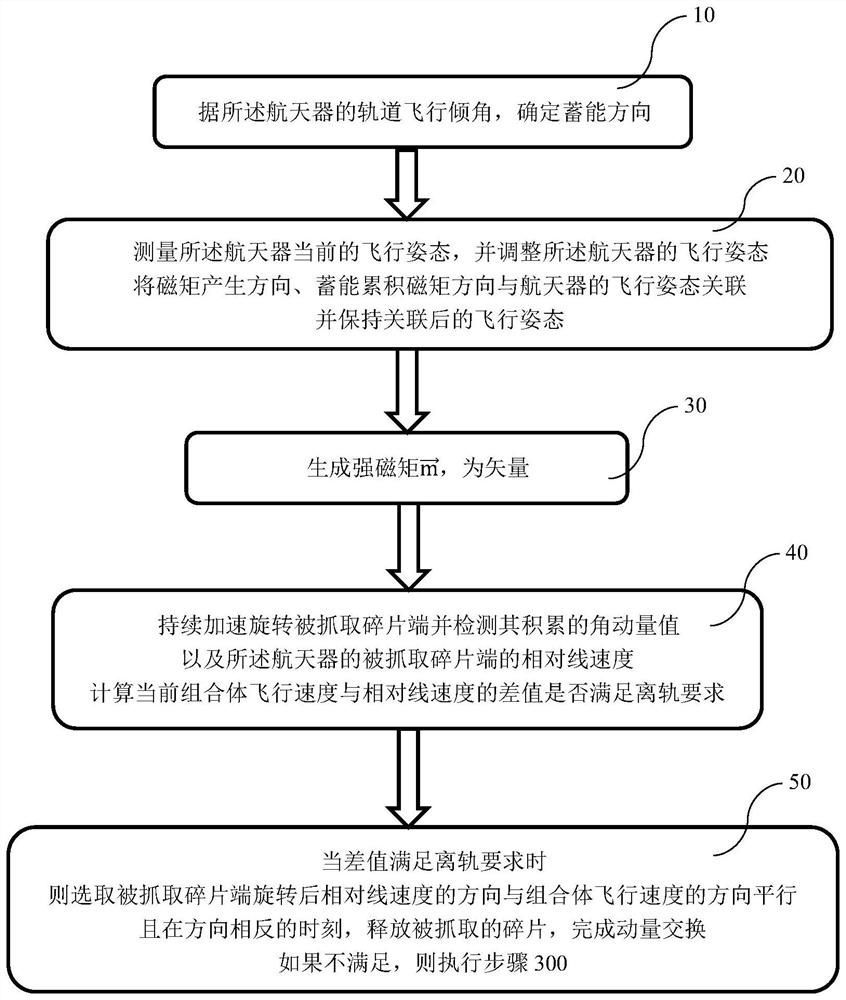
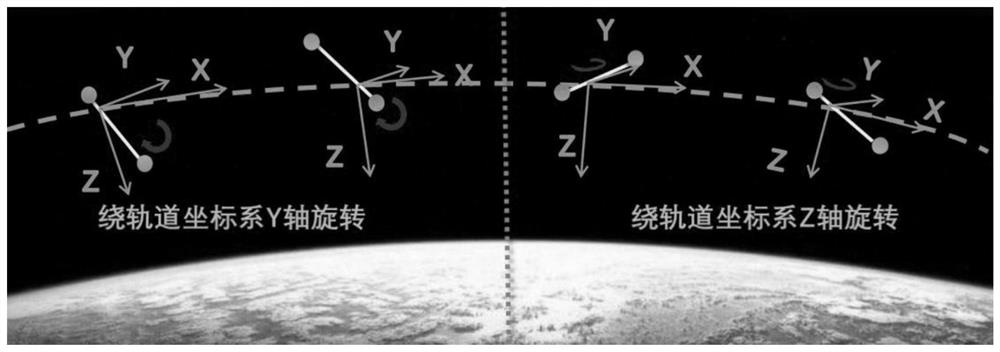
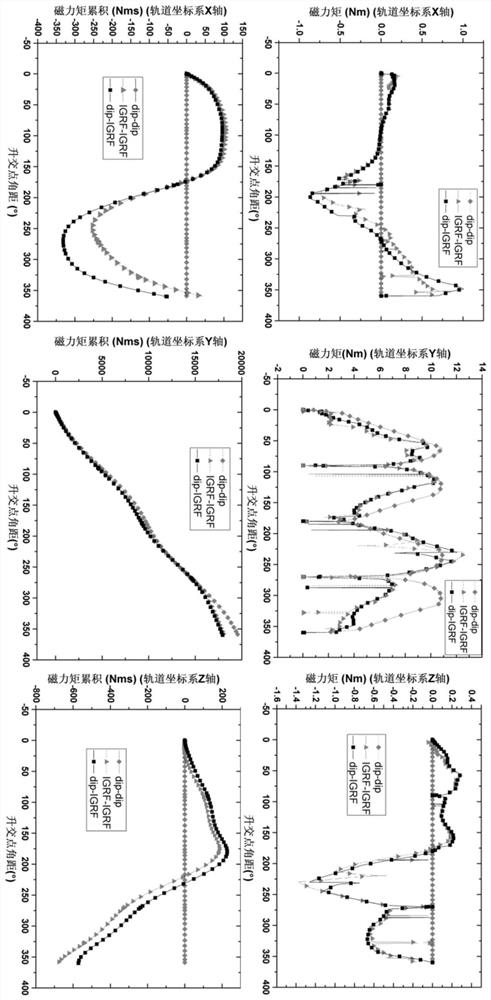
ActiveCN110510154BImprove efficiencyImprove economyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusOrbital planeOrbital period
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a geomagnetic energy storage low orbit space debris off-orbit delivery orbit attitude coupling adjustment method, which includes the following steps: Step 100, decomposing the entire geomagnetic energy storage low orbit period into energy gathering arcs and energy releasing arcs section, and configure the momentum wheel energy-absorbing device on the three axes of the spacecraft; step 200, respectively determine the energy-gathering arc section and the energy-discharging arc section when the spacecraft performs energy storage and accumulation around the y-axis of the orbital plane and the z-axis of the orbital plane; Step 300, after determining the energy-gathering arc segment, for the energy storage targets of different orbital coordinate systems Y-axis or Z-axis, complete the de-orbiting operation of space debris based on the geomagnetic energy storage low-orbit space debris de-orbiting control method; Step 400, After the energy release arc is determined, the three-axis momentum wheel energy absorbing device of the spacecraft is unloaded through the generated magnetic moment.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com