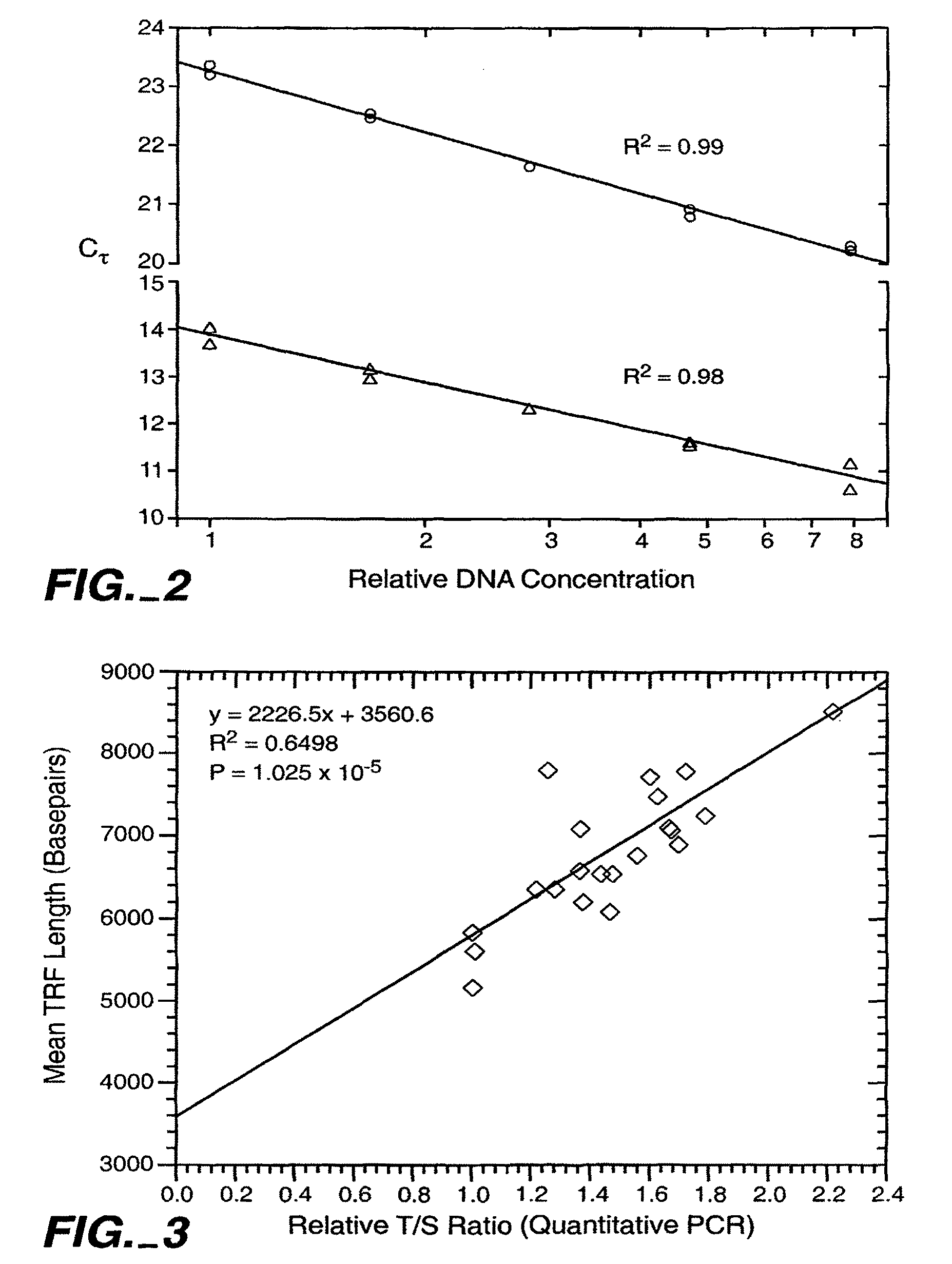
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Repetitive Regions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automated repetitive array microstructure defect inspection
InactiveUS7065239B2Eliminating and minimizing impactImage enhancementImage analysisMicro fabricationDisplay device
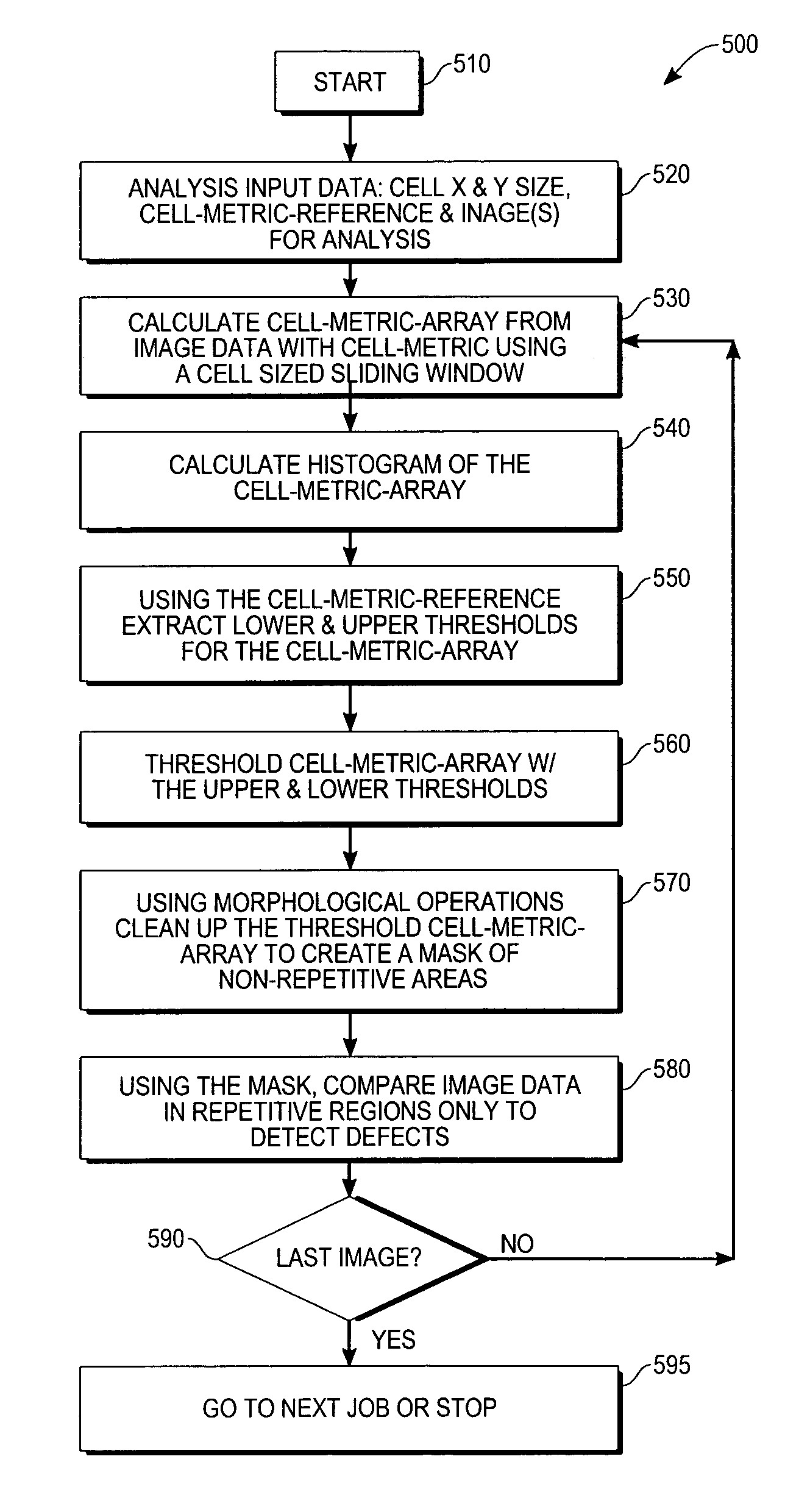
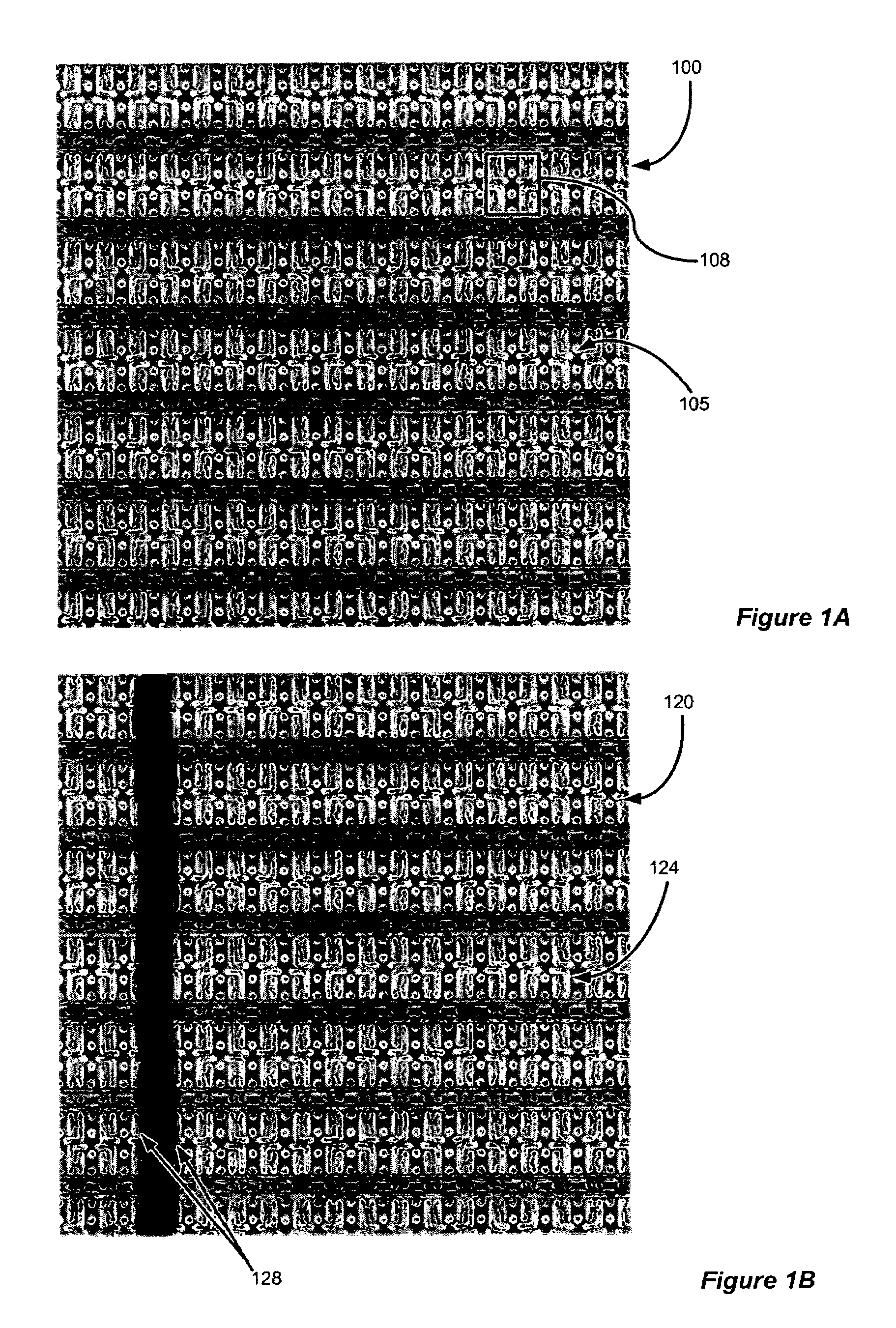
A method and system for defect inspection of microfabricated structures such as semiconductor wafers, masks or reticles for micro-fabrication, flat panel displays, micro-electro-mechanical (MEMs) having repetitive array regions such as memories or pixels. In one embodiment a method of inspection of microfabricated structures includes the steps of acquiring contrast data or images from the microfabricated structures, analyzing automatically the contrast data or images to find repetitive regions of the contrast data and comparing the repetitive regions of the contrast data with reference data to detect defects in the microfabricated structures. In the analyzing step, a cell-metric such as the range, or mean or other statistical or mathematical measure of the contrast data is used to find the repetitive regions. Image or contrast data acquisition can be performed with an optical, e-beam or other microscope suited for microfabricated structures.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reducing non-target nucleic acid dependent amplifications: amplifying repetitive nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20100151477A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRepetitive Regions
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method for melting curve analysis of repetitive PCR products
InactiveUS6664064B1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probePolynucleotide
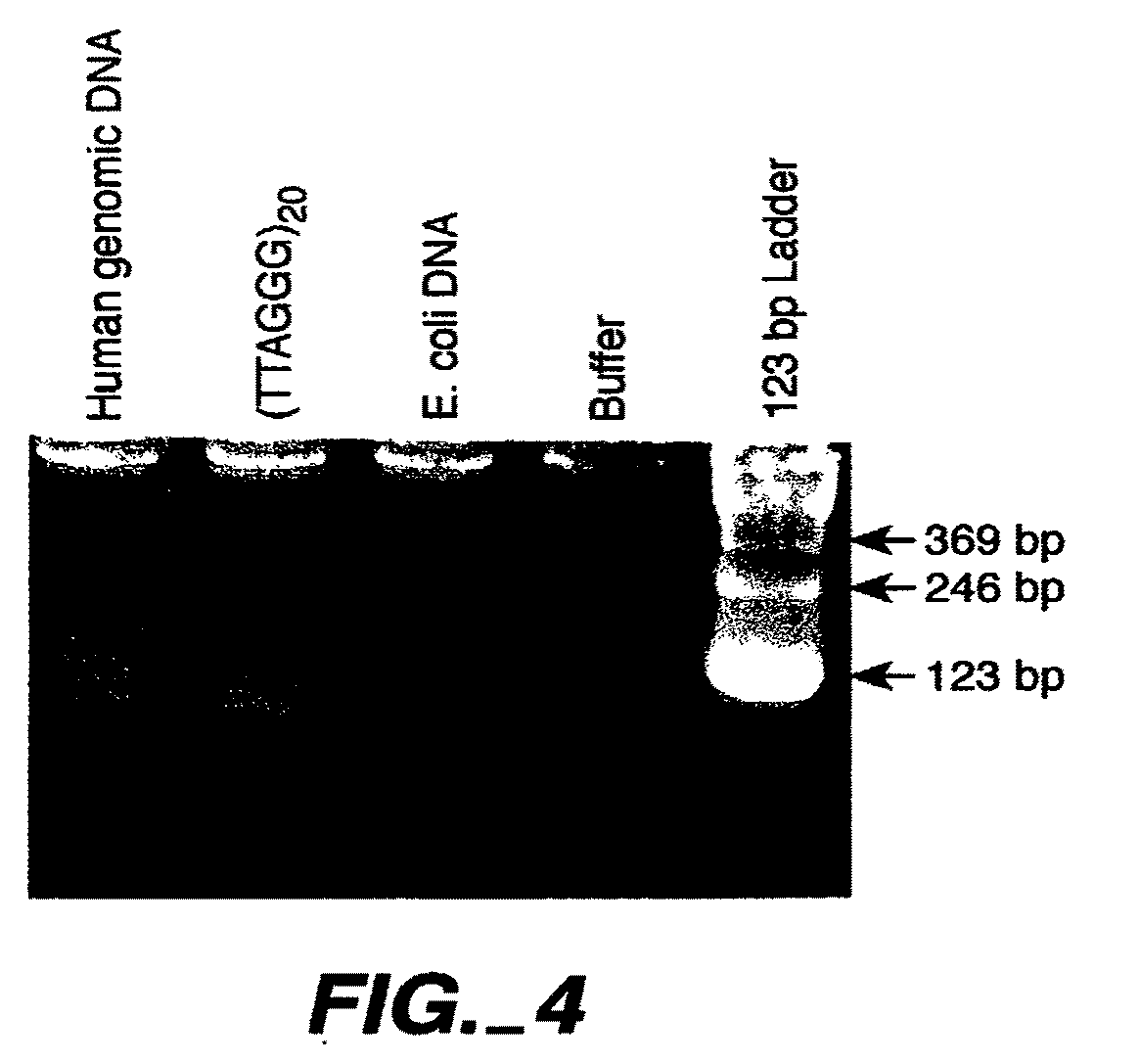
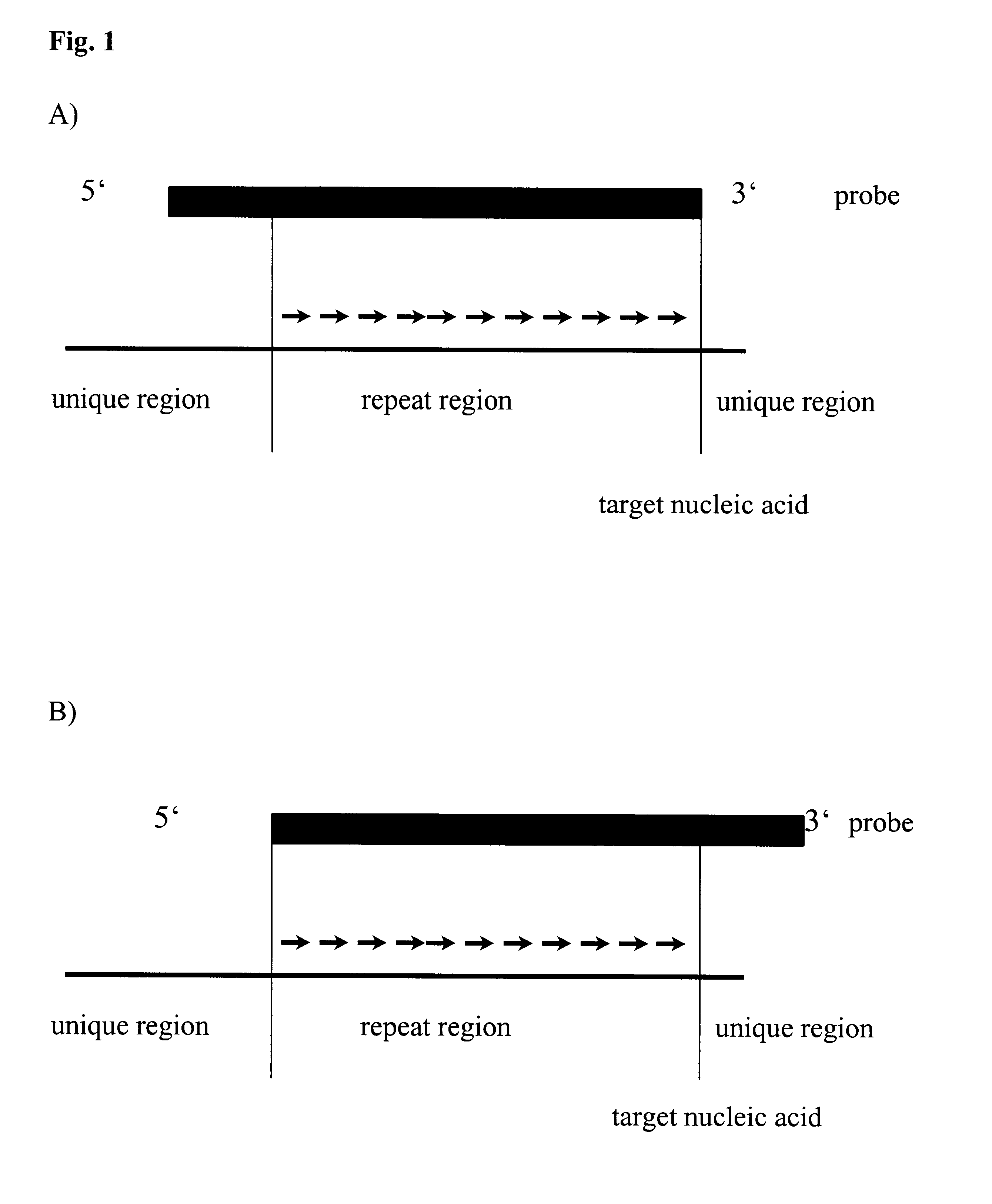
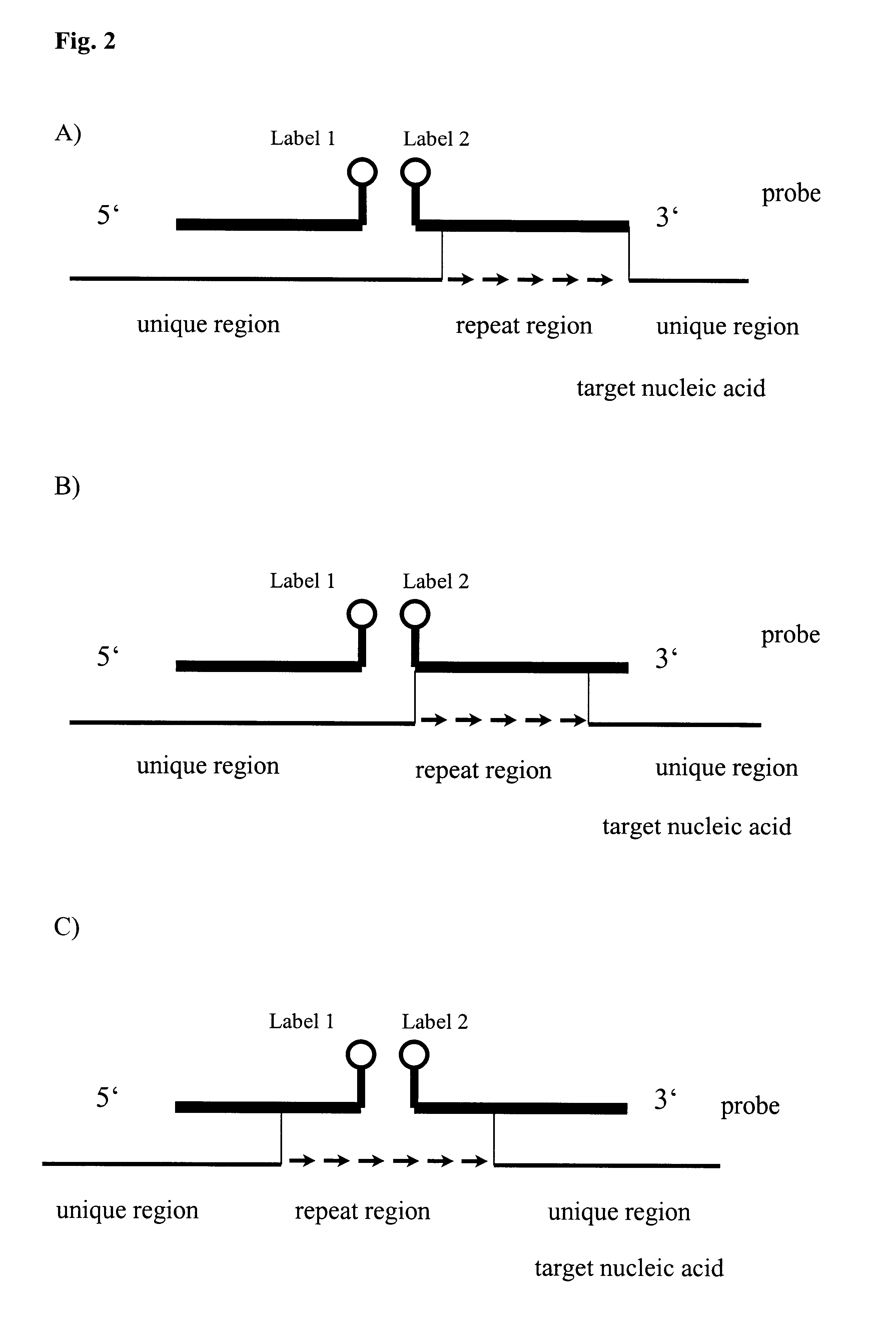
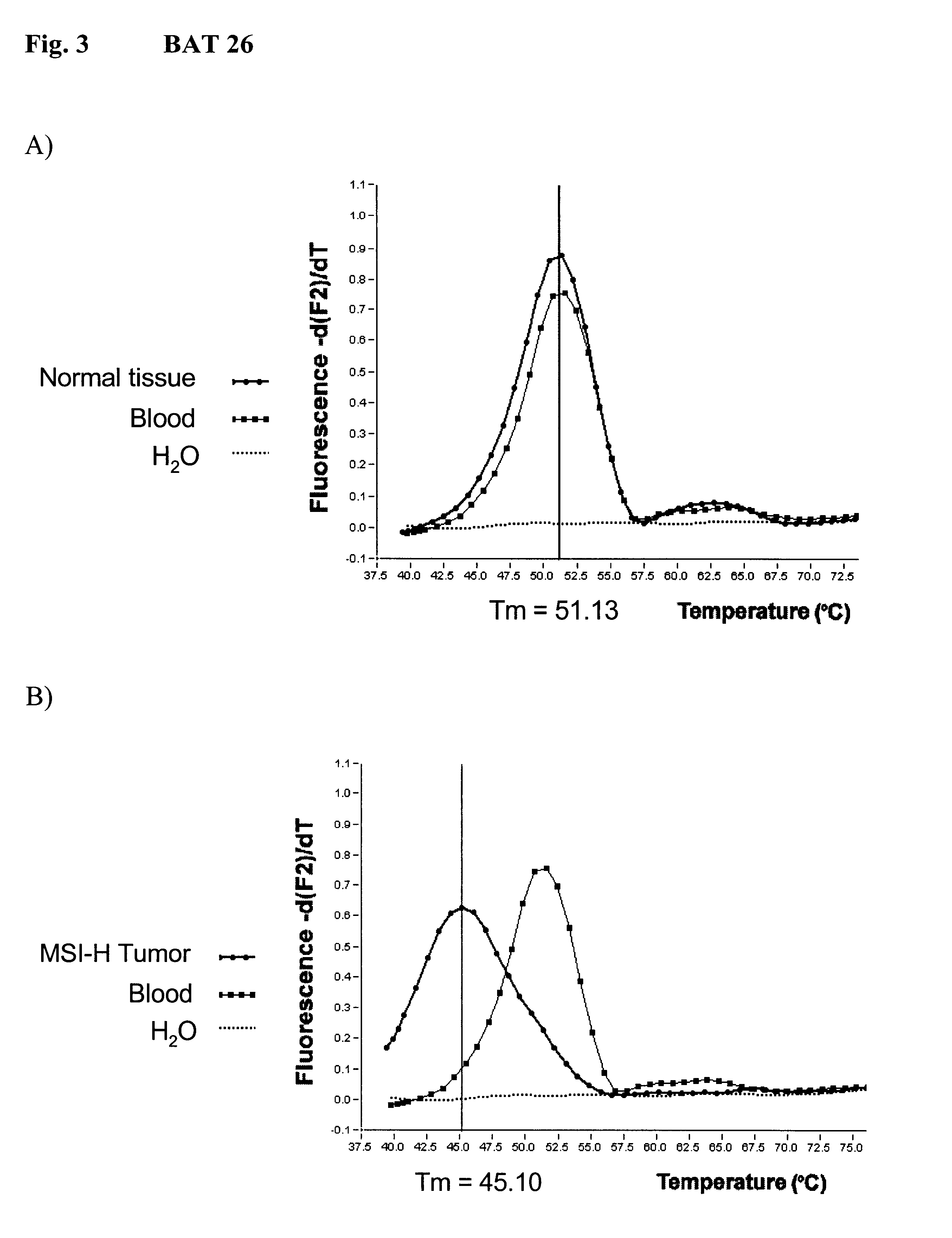
The invention relates to method, wherein the number of repeat sequences which are present in a sample is detemined by means of melting temperature analysis. More precisely, the invention relates to a method for analysis of a target nucleic acid consisting of repetitive and non repetitive sequences comprising (i) hybridization of at least one polynucleotide hybridization probe comprising a first segment which is complementary to a non repetitive region and a second segment which is compementary to an adjacent repetitive region, said second segment consisting of a defined number of repeats and (ii) determination of the melting point temperature of the hybrid which has been formed between the target nucleic acid and the at least one hybridization probe.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Reducing non-target nucleic acid dependent amplifications: amplifying repetitive nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS7695904B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingRepetitive Regions
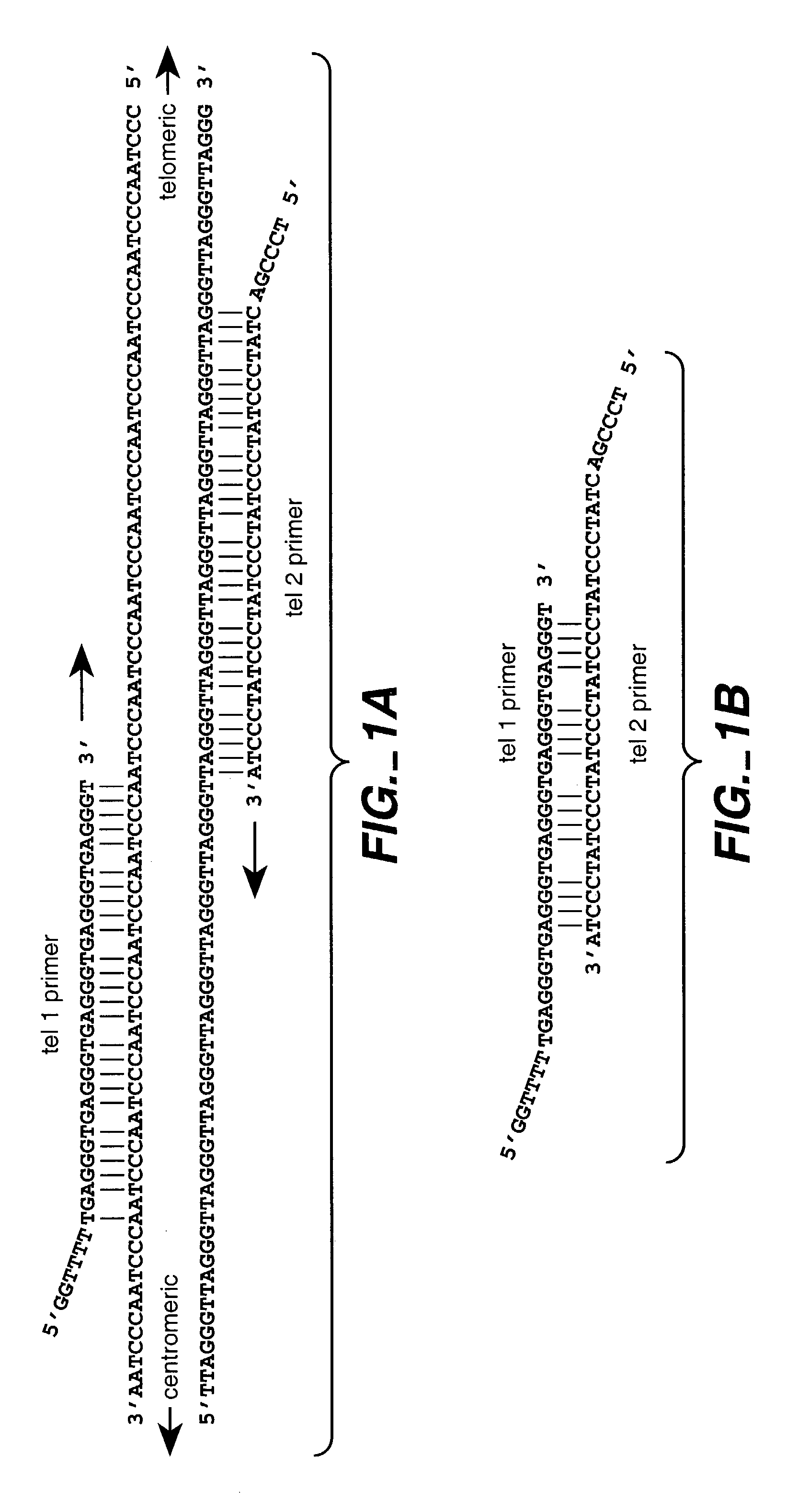
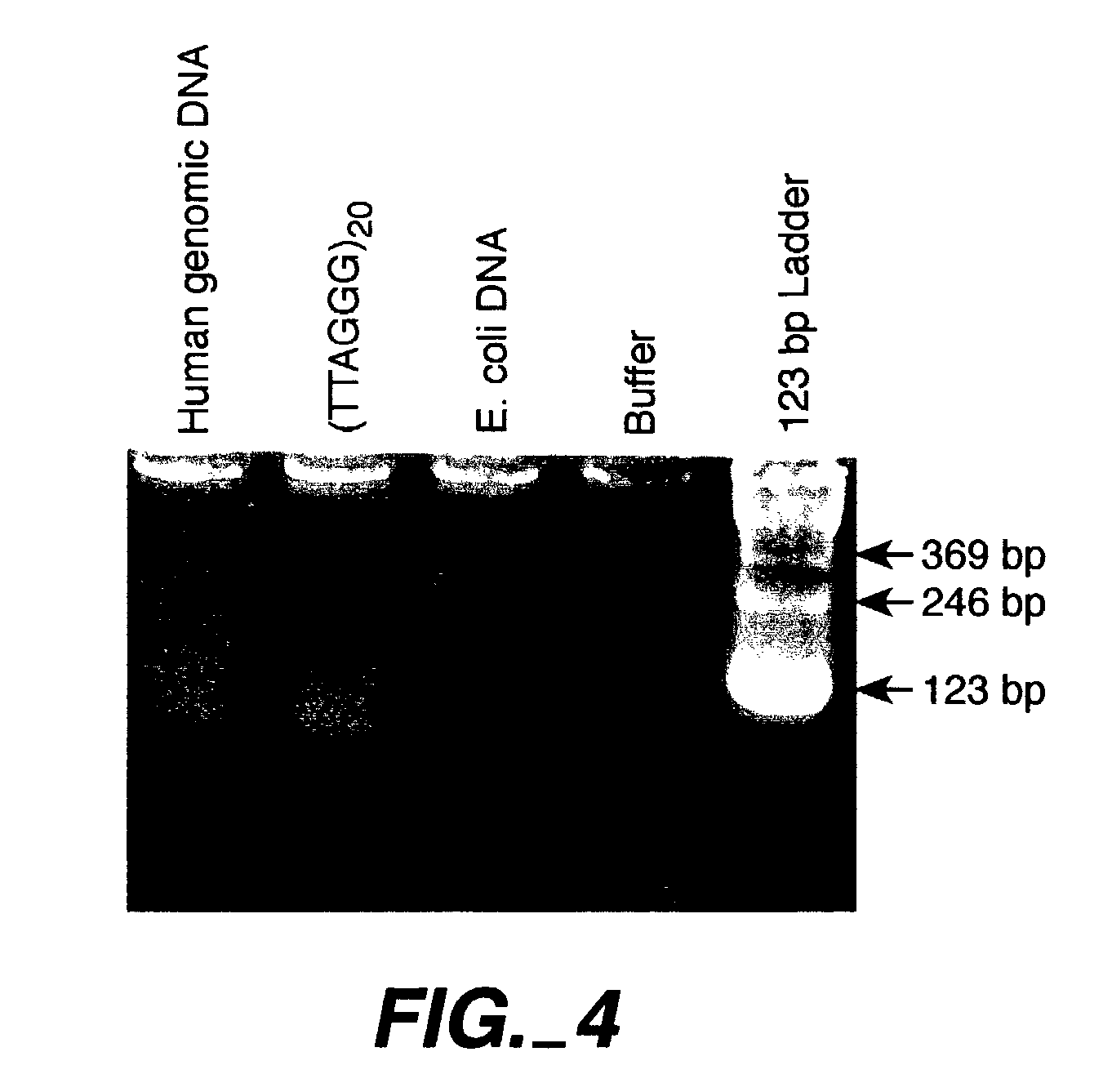
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for amplifying target nucleic acids using nucleic acid primers designed to limit non-target nucleic acid dependent priming events. The present invention permits amplifying and quantitating the number of repetitive units in a repetitive region, such as the number of telomere repetitive units.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
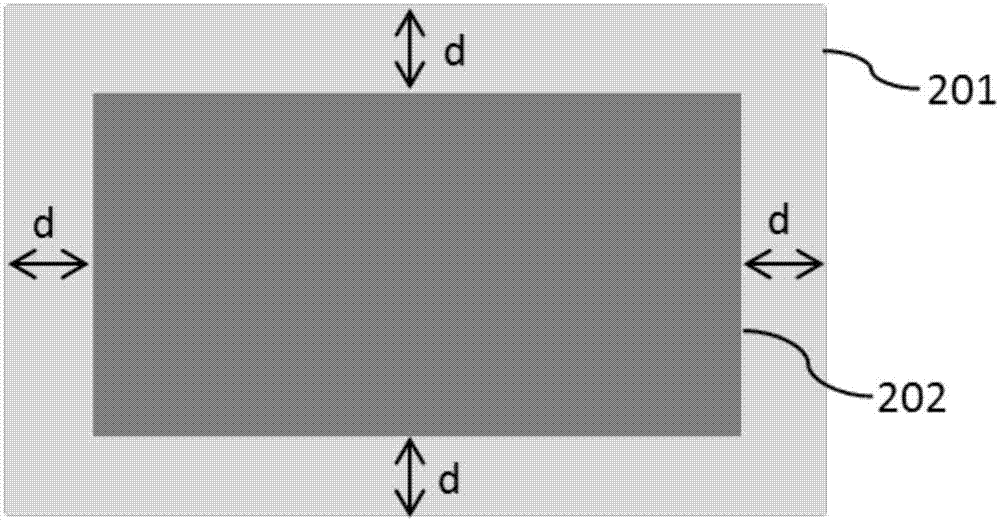
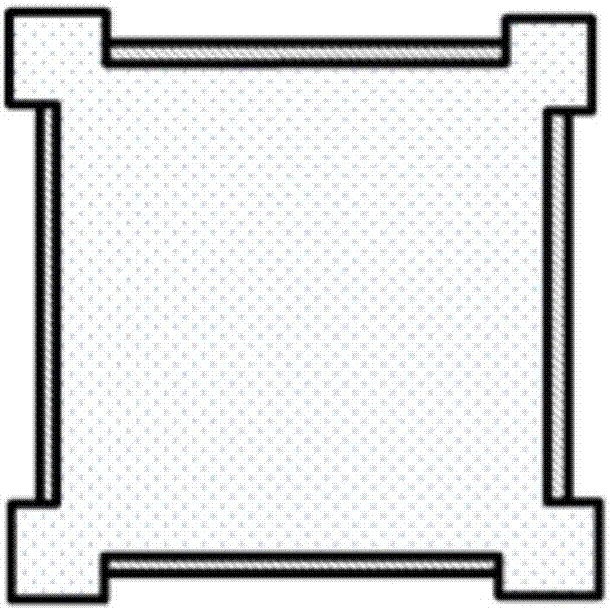
Method and system for evaluating an object
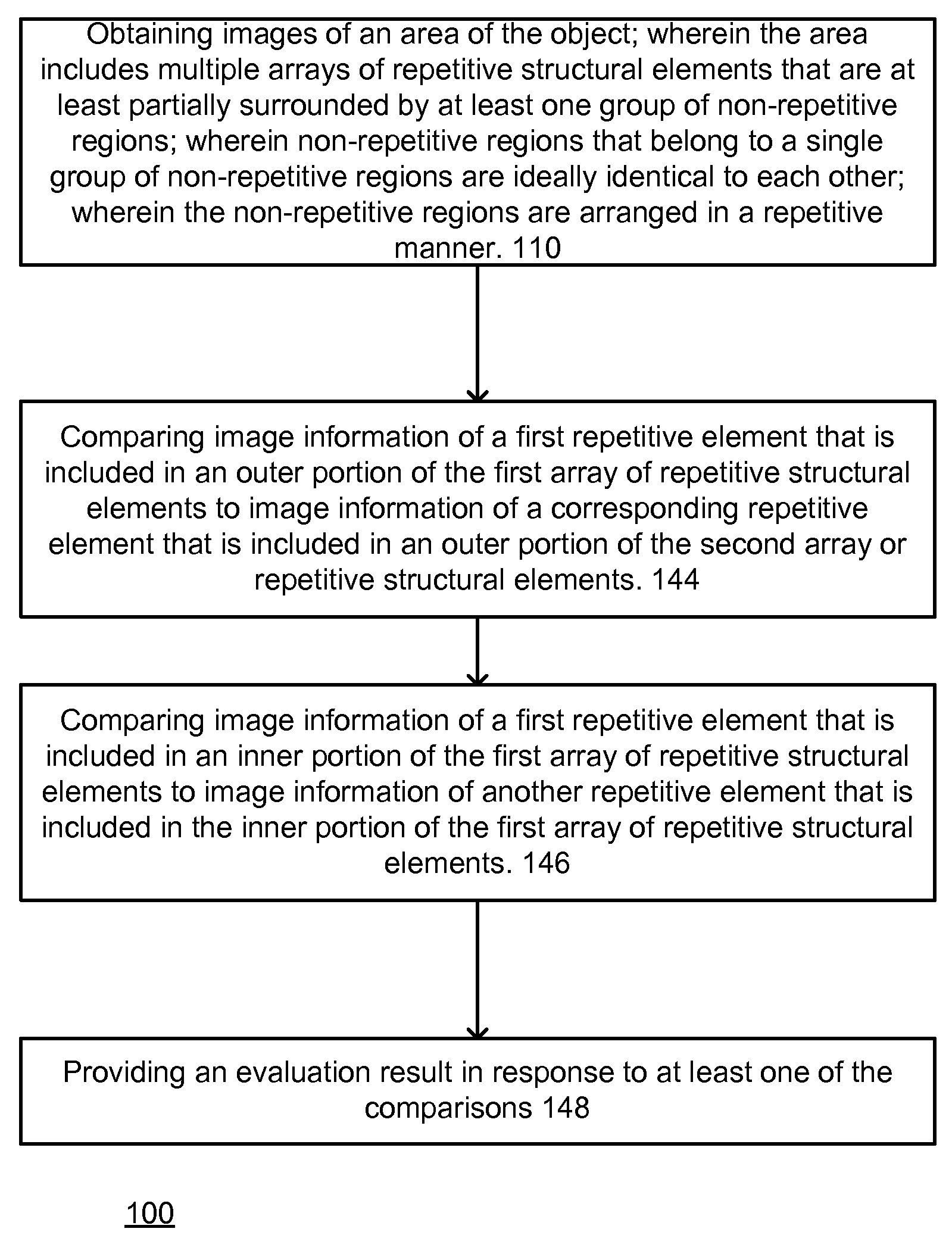
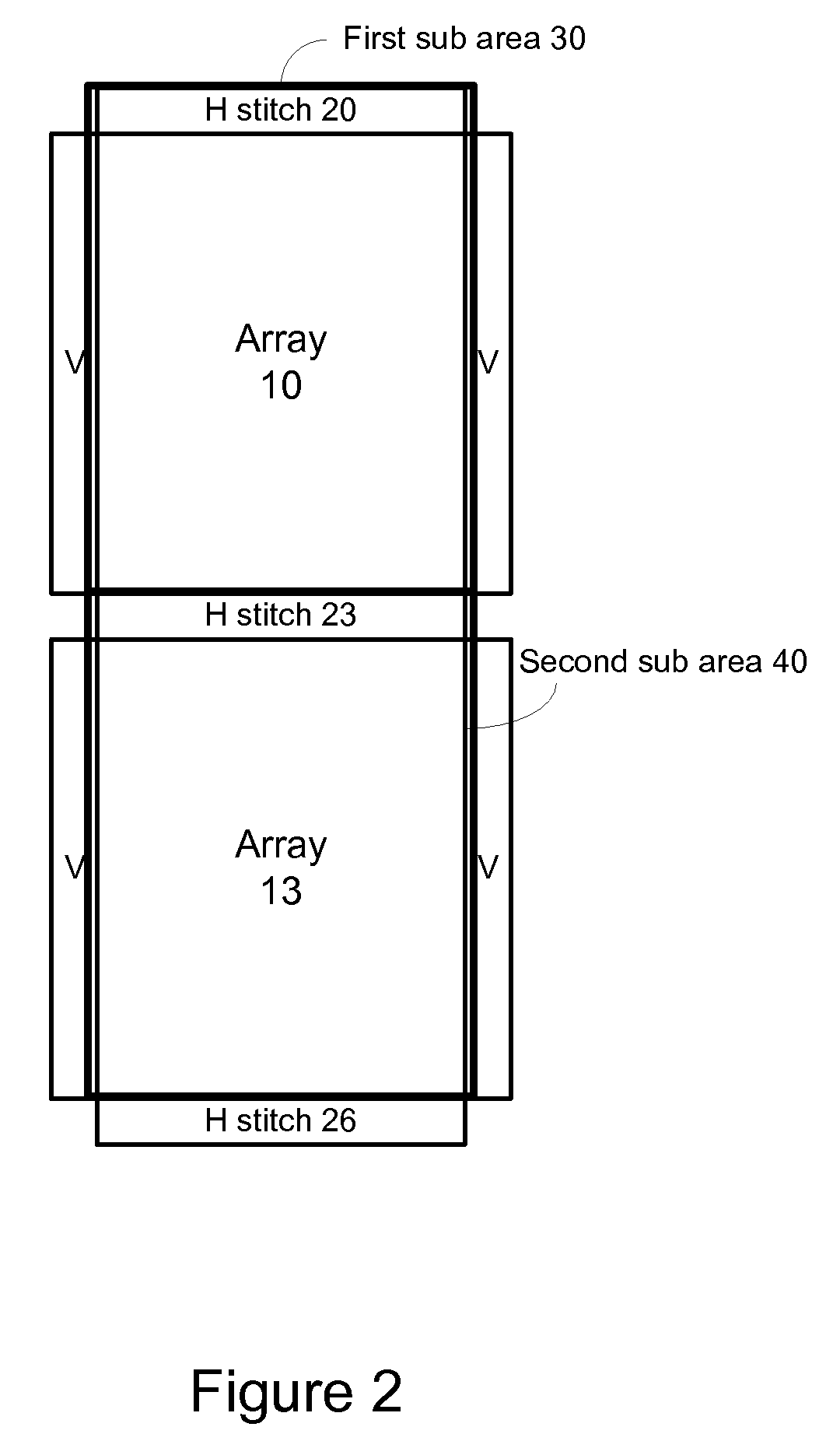
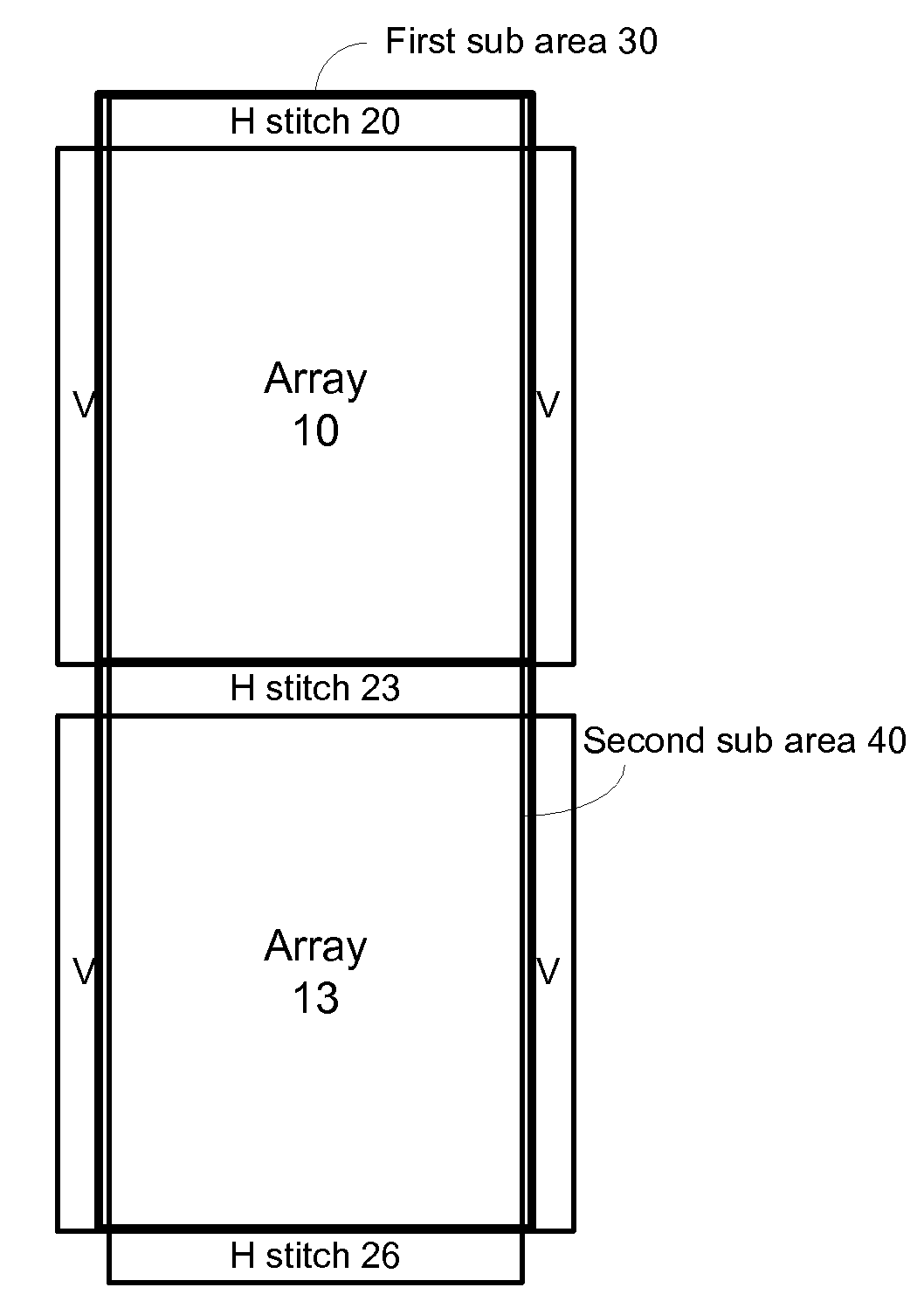
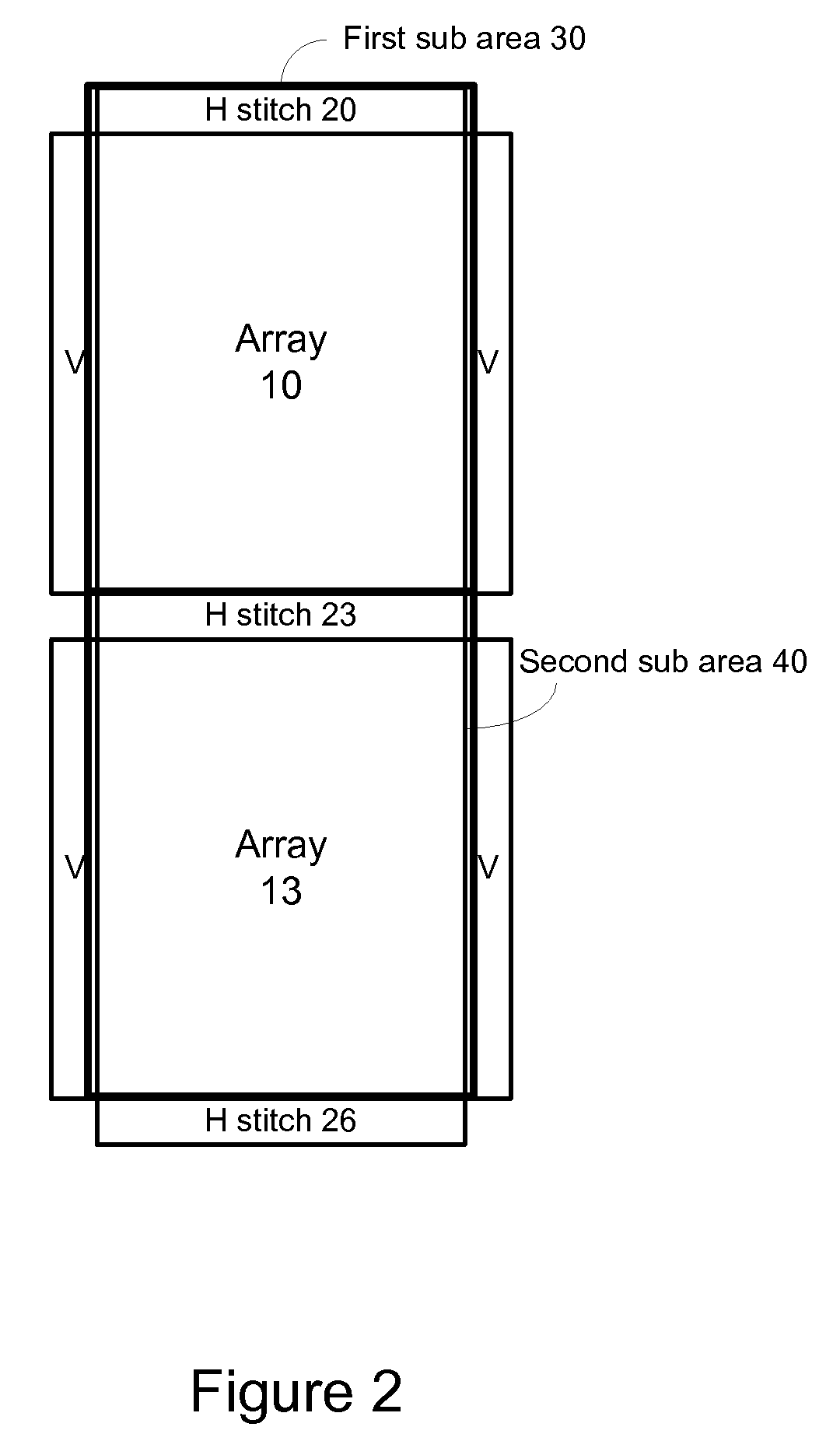
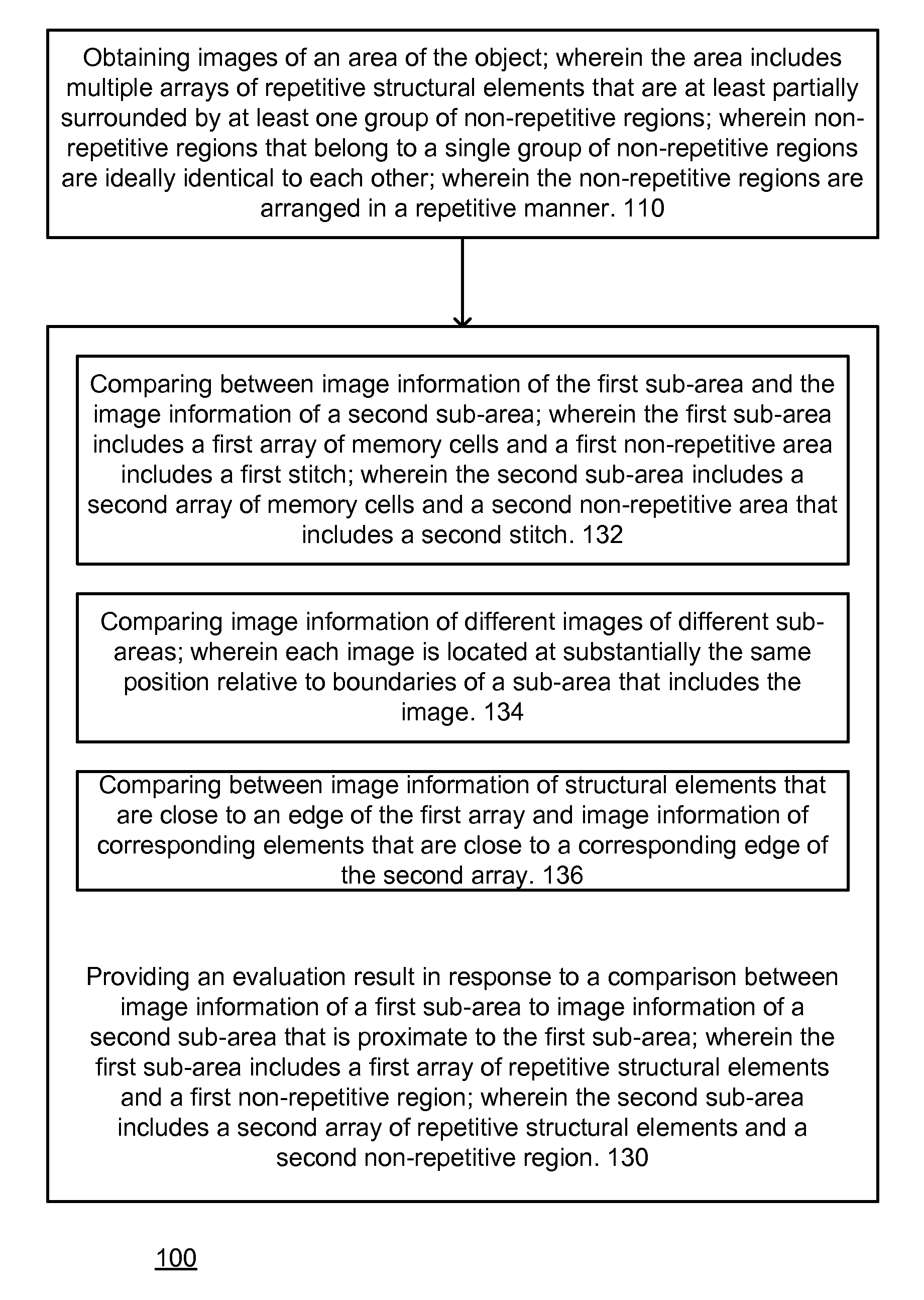
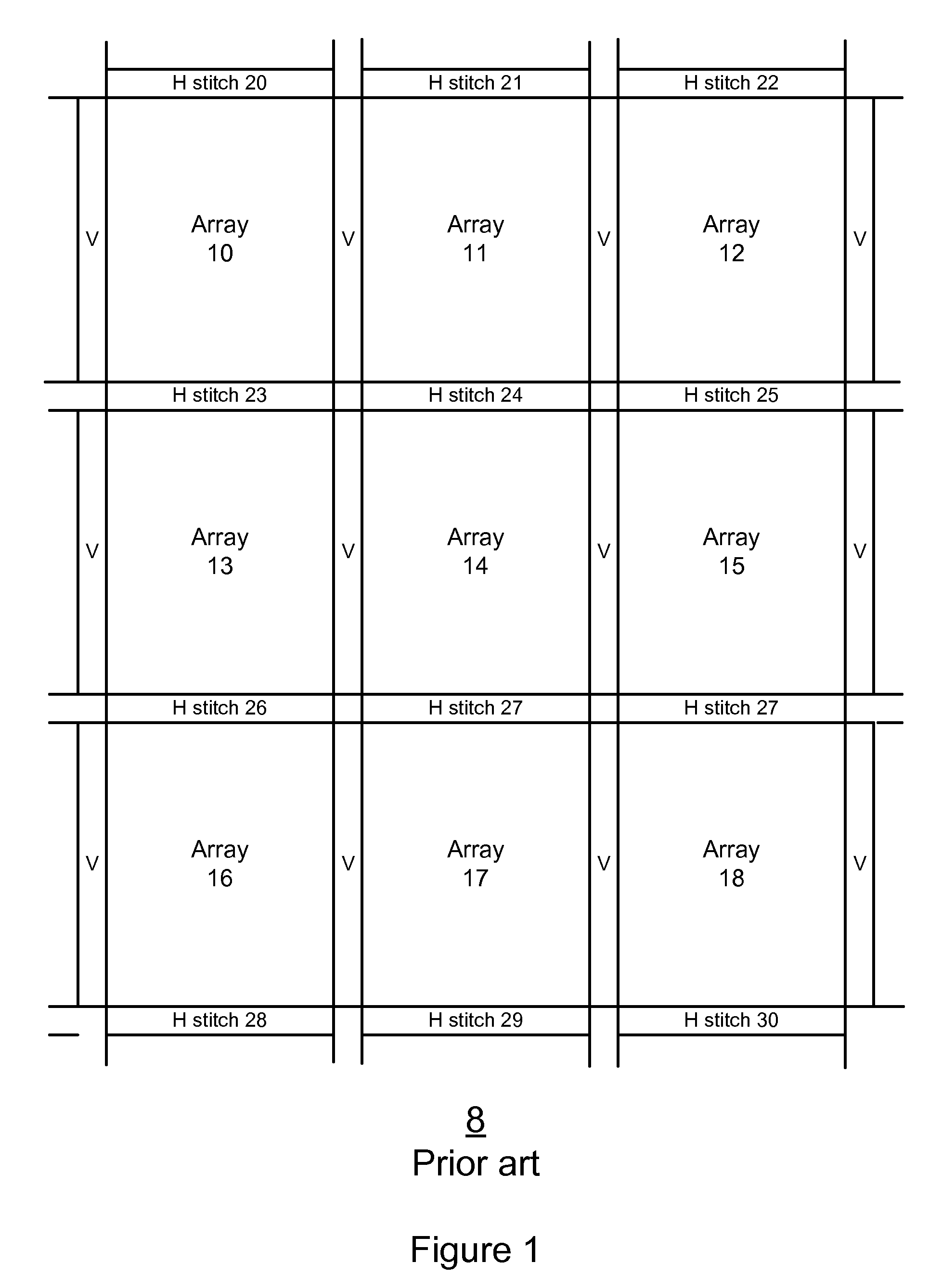
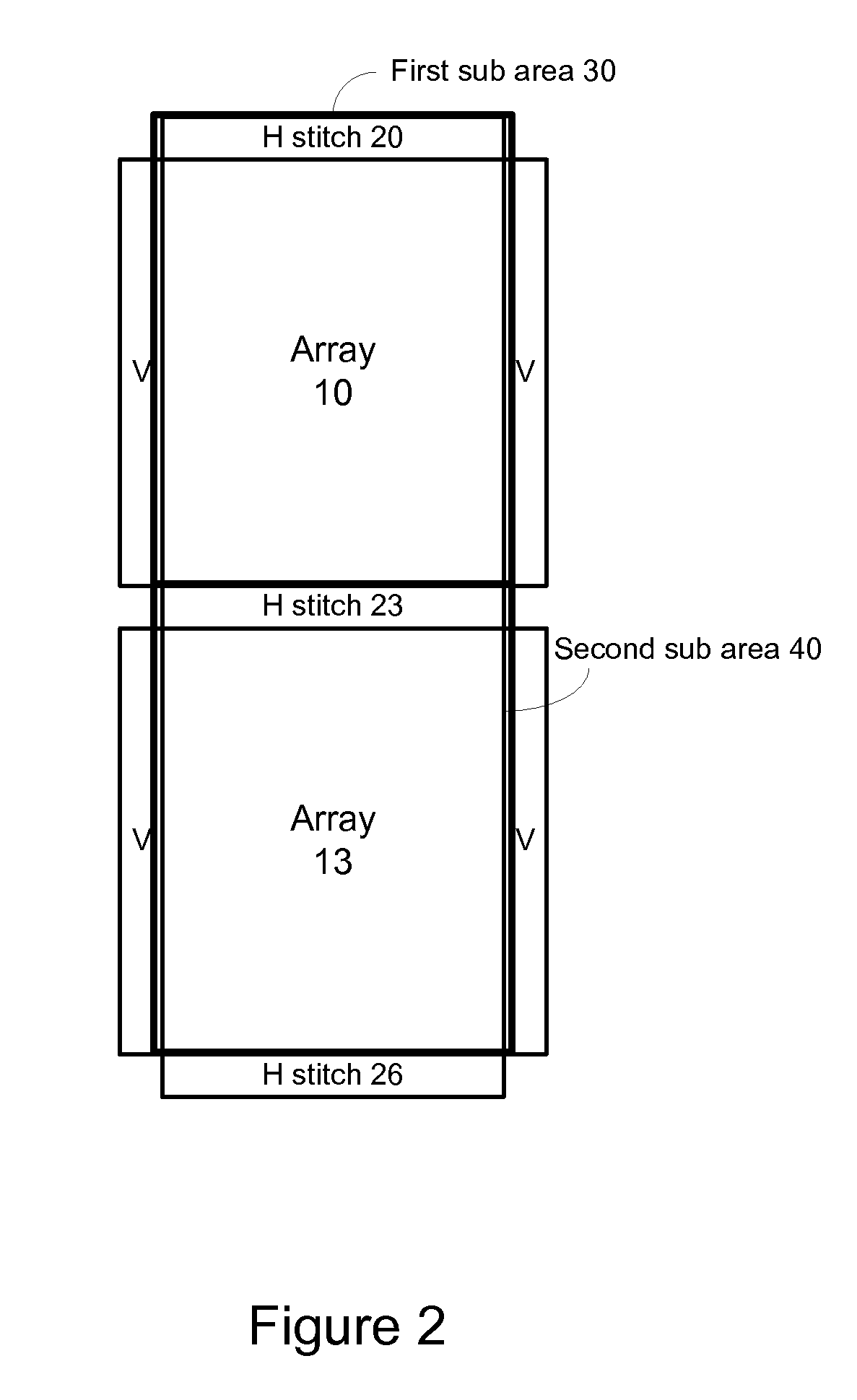
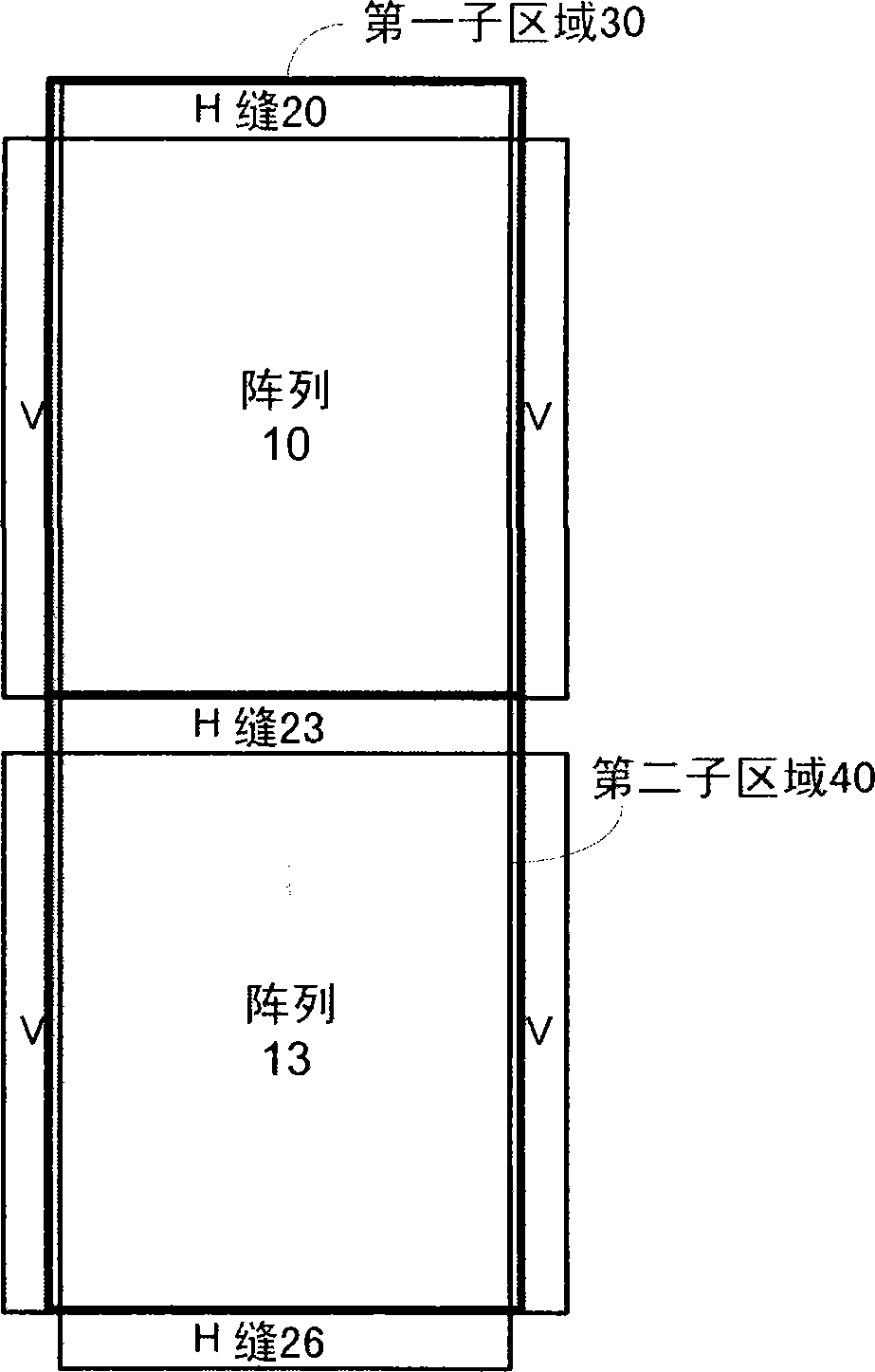
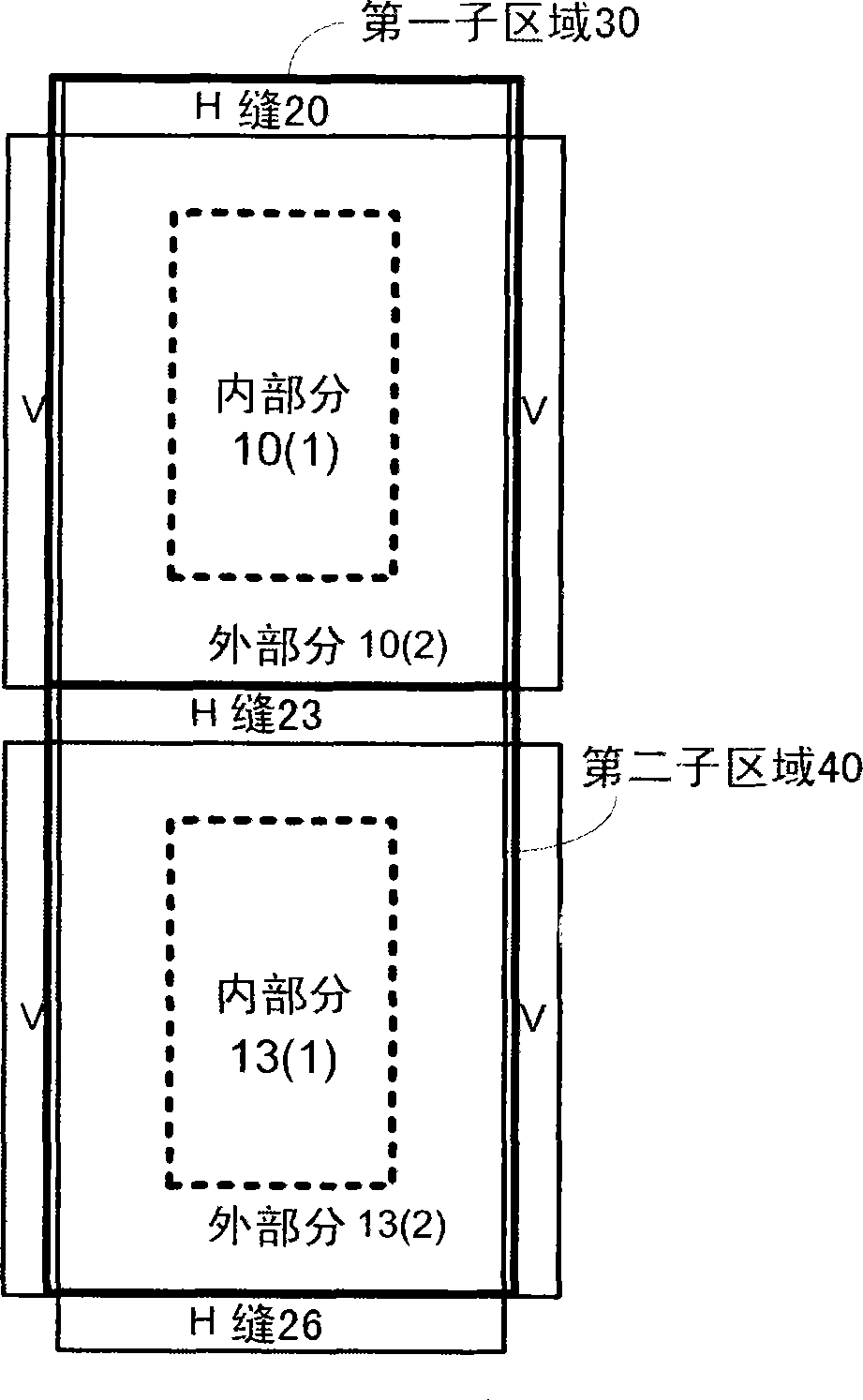
A method, system aid a computer program product for evaluating a object; the method includes: (i) obtaining an image of an area of the object; wherein the area comprises multiple arrays of repetitive structural elements that are at least partially surrounded by at least one group of non-repetitive regions; wherein non-repetitive regions that belong to a single group of non-repetitive regions are ideally identical to each other; wherein the non-repetitive regions are arranged in a repetitive manner; and (ii) providing an evaluation result in response to a comparison between image information of a first sub-area to image information of a second sub-area that is proximate to the first sub-area; wherein the first sub-area comprises a first array of repetitive structural elements and a first non-repetitive region; wherein the second sub-area comprises a second array of repetitive structural elements and a second non-repetitive region.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Reducing non-target nucleic acid dependent amplifications: amplifying repetitive nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS8048631B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for amplifying target nucleic acids using nucleic acid primers designed to limit non-target nucleic acid dependent priming events. The present invention permits amplifying and quantitating the number of repetitive units in a repetitive region, such as the number of telomere repetitive units.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
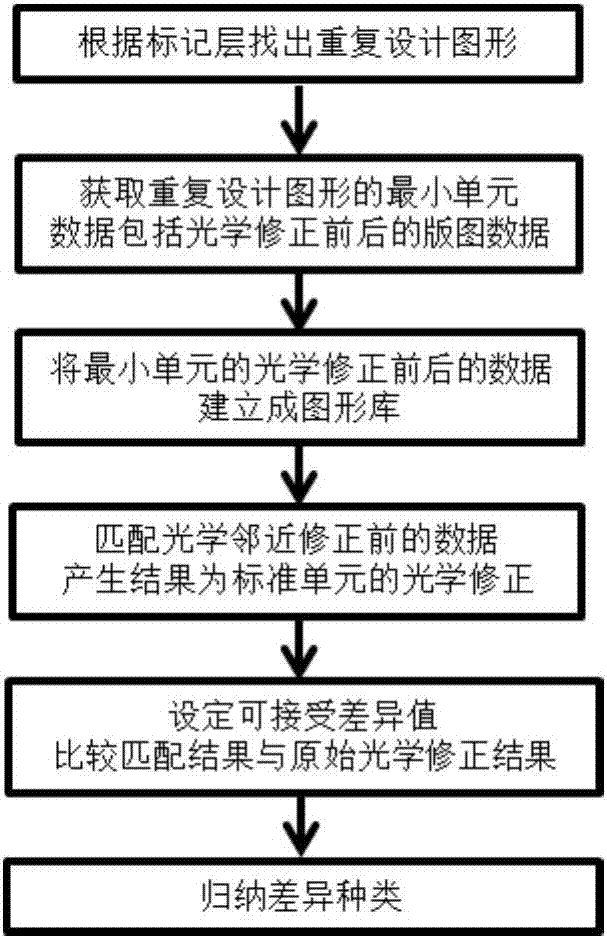
Checking method for optical proximity effect correction consistency of layout repetitive units
ActiveCN106980719AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsRepetitive Regions
The invention provides a checking method for optical proximity effect correction consistency of layout repetitive units. According to the method, first, a graphic library containing original design layers corresponding to all datum graphs and layers obtained after the original design layers are corrected by the optical proximity effect is established; second, xor operation is performed on the original design layers corresponding to all the datum graphs in the graphic library, the layer obtained after the original design layer corresponding to the datum graph which is completely and successfully matched with each region of original design of a layout is corrected by the optical proximity effect and the layers obtained after the original design layers corresponding to all the datum graphs in the graphic library are corrected by the optical proximity effect, and differences and corresponding difference values are obtained; and last, the differences with the difference values greater than an acceptable difference value are classified to reduce difference types. In this way, ten millions of differences can be reduced into several or tens of differences, and the accuracy and efficiency of correction consistency checking work in a repetitive region of layout design correction work are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Fluorescence in situ hybridization probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109161542AReduce pairingReduce non-specific reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHybridization probeFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence in situ hybridization probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the fluorescence in situ hybridization probe provided by the invention and the fluorescence in situ hybridization probe prepared with the preparation method are specifically designed for non-repetitive regions of a genome, and can reduce non-specificreactions and reduce the background interference; the constructed probe is a single-stranded DNA, and compared with traditional double-stranded probes such as BAC or PCR products, the probe providedby the invention can reduce the pairing of the probe with itself and increase the efficiency of hybridization; and the constructed single-stranded DNA probe is small in fragments, and can combine withtargeted sequences more quickly and reduce hybridization time.
Owner:广州简册生物技术有限公司
Primer composition for lysosomal disease gene screening and kit using the same
InactiveCN104131094AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNPC1GLB1
The invention provides a primer composition for lysosomal disease gene screening and a kit using the same. The primer composition comprises multiple primer sequences respectively aiming at non-repetitive regions of IDUA, ARSB, MAN2B1, ST3GAL5, SMPD1, CTNS, MFSD8, IDS, GUSB, GBA, ARSA, GNPTAB, SLC17A5, CLN8, SGSH, HYAL1, PSAP, GNPTAG, PPT1, CTSD, NAGLU, FUCA1, GLB1, SUMF1, MCOLN1, TPP1, HGSNAT, NAGA, GM2A, GALC, LIPA, CLN3, GALNS, NEU1, HEXA, GLA, NPC1, CLN5, MANBA, HEXB, ASAH1, NPC2 and CLN6 genes.
Owner:封志纯
Method and system for evaluating an object
A method, system and a computer program product for evaluating a object; the method includes: (i) obtaining an image of an area of the object; wherein the area comprises multiple arrays of repetitive structural elements that are at least partially surrounded by at least one group of non-repetitive regions; wherein non-repetitive regions that belong to a single group of non-repetitive regions are ideally identical to each other; wherein the non-repetitive regions are arranged in a repetitive manner; and (ii) providing an evaluation result in response to a comparison between image information of a first sub-area to image information of a second sub-area that is proximate to the first sub-area; wherein the first sub-area comprises a first array of repetitive structural elements and a first non-repetitive region; wherein the second sub-area comprises a second array of repetitive structural elements and a second non-repetitive region.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Sequence assembly method
InactiveUS20170132361A1Sequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsRepetitive RegionsComputer science
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
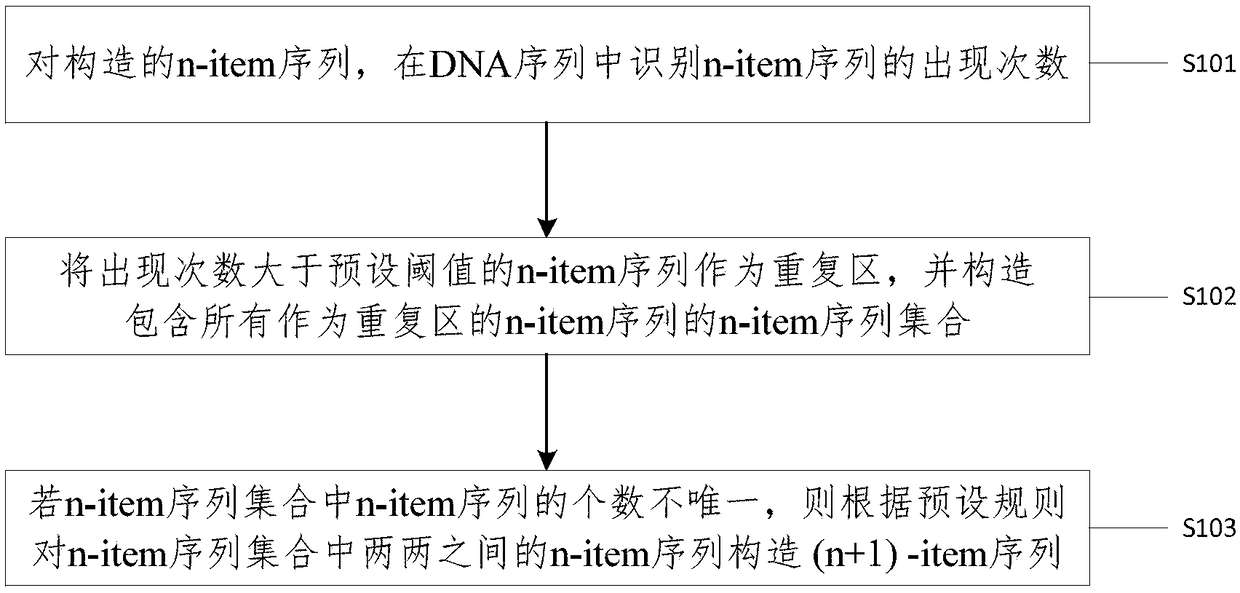
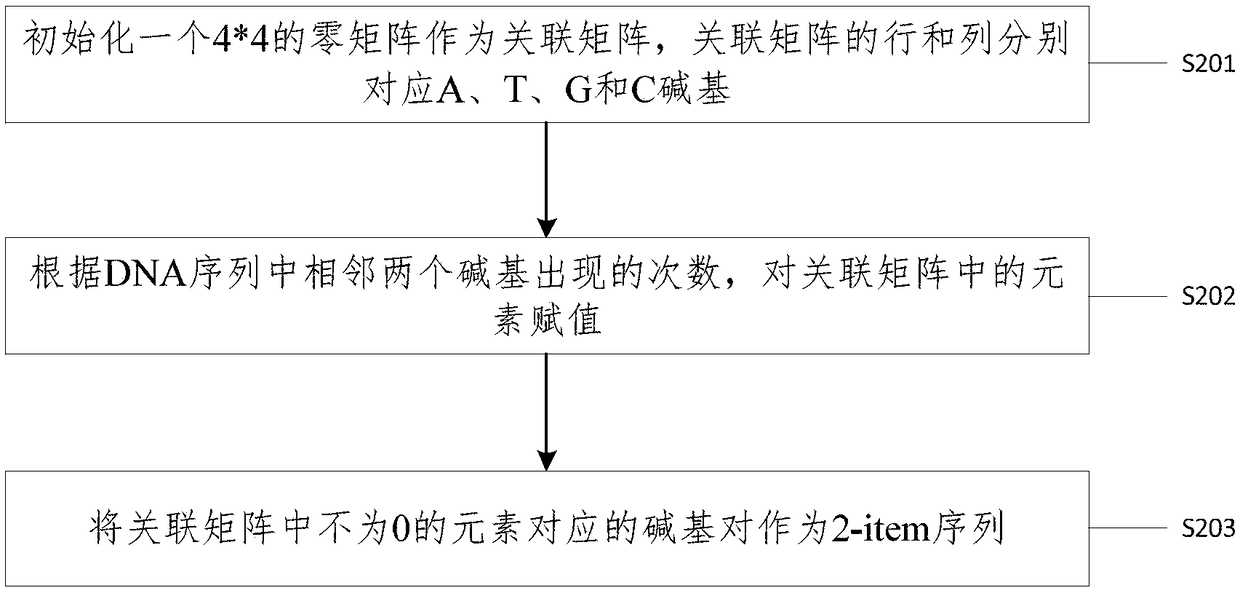
Method and device for identifying repetitive regions in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences
InactiveCN108763868AImprove recognition efficiencyRecognized object reductionSpecial data processing applicationsRepetitive RegionsDNA
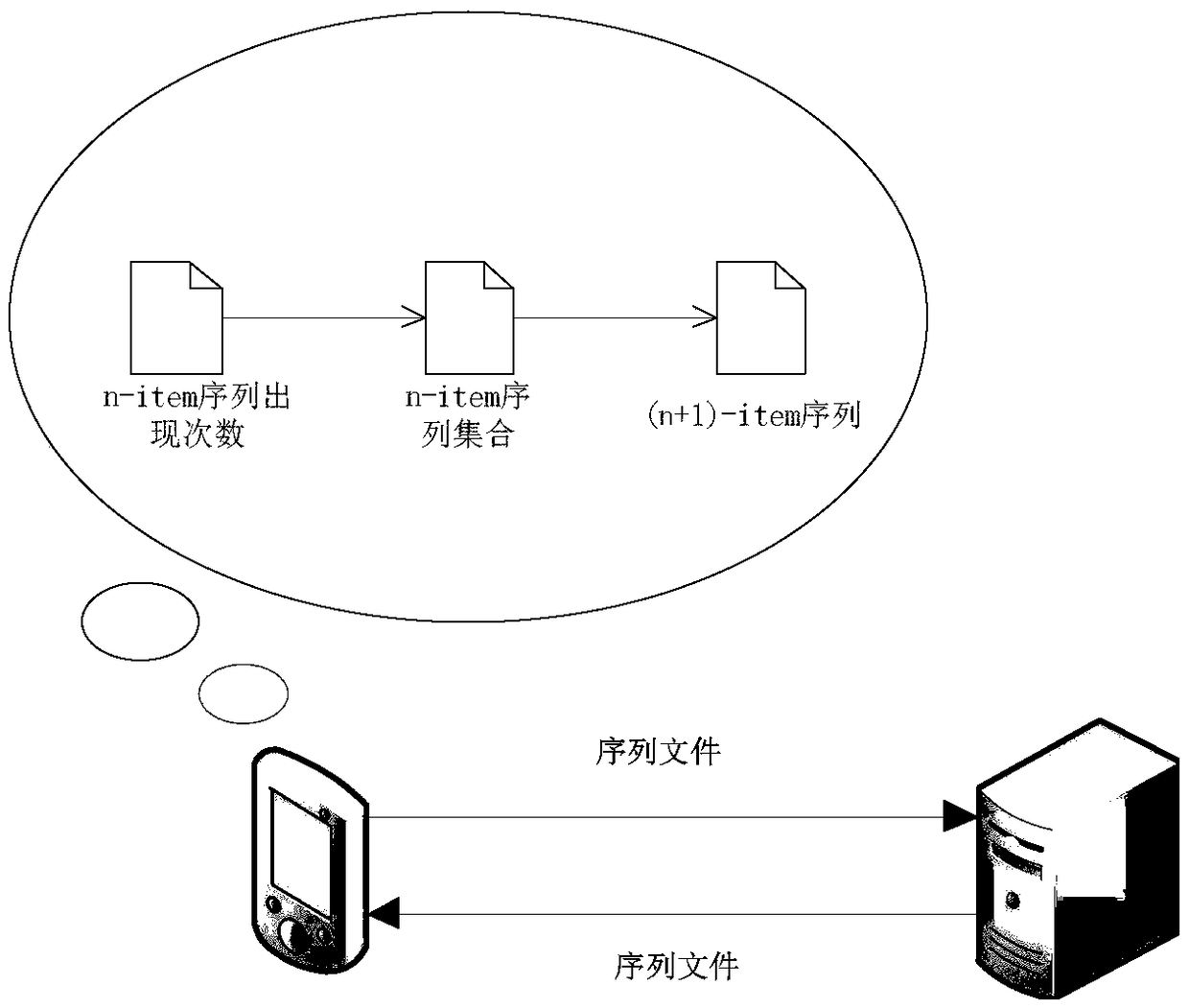
The invention provides a method and device for identifying repetitive regions in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences. The method comprises the steps of: identifying occurrence number of constructedn-item sequences in the DNA sequences; taking the n-item sequences with the occurrence number greater than a preset threshold as the repetitive regions and constructing a n-item sequence set of all the n-item sequences serving as the repetitive regions; and if the number of the n-item sequences in the n-item sequence set is not unique, constructing (n+1)-item sequences between two n-item sequencesin the n-item sequence set according to a preset rule. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the embodiment of the invention has the advantages that only the constructed DNA subsequences are needed to be identified, so that identified objects are greatly reduced; the process of obtaining the repetitive regions can also be obtained by counting the occurrence number in the identification process, so that the identifying efficiency is further improved; and longer DNA subsequences are constructed from the repetitive regions through the preset rule with no need for firstly combiningthe repetitive regions with single bases and traversing the entire DNA sequence one by one, so that the identifying efficiency of the genomic repetitive regions can be greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for detecting and typing repeat number of short tandem repeat sequence
ActiveCN113362892AThe test result is accurateImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsGeneticsTyping methods
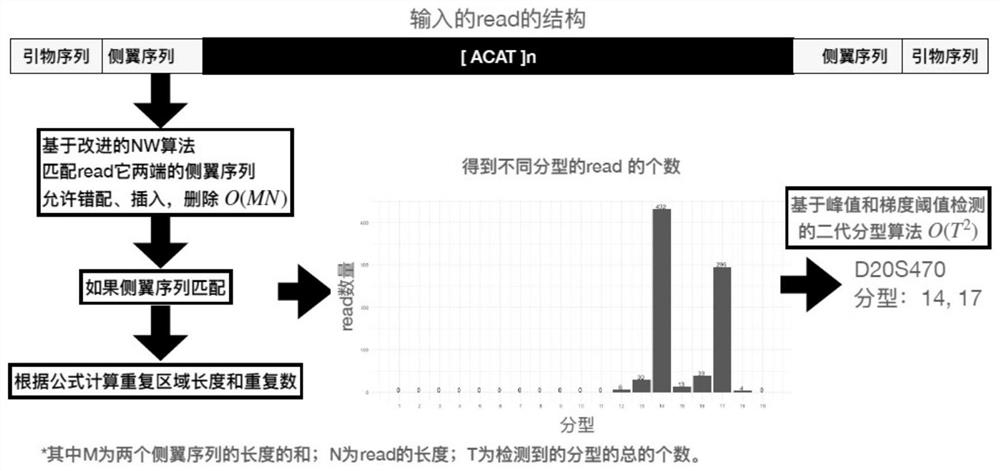
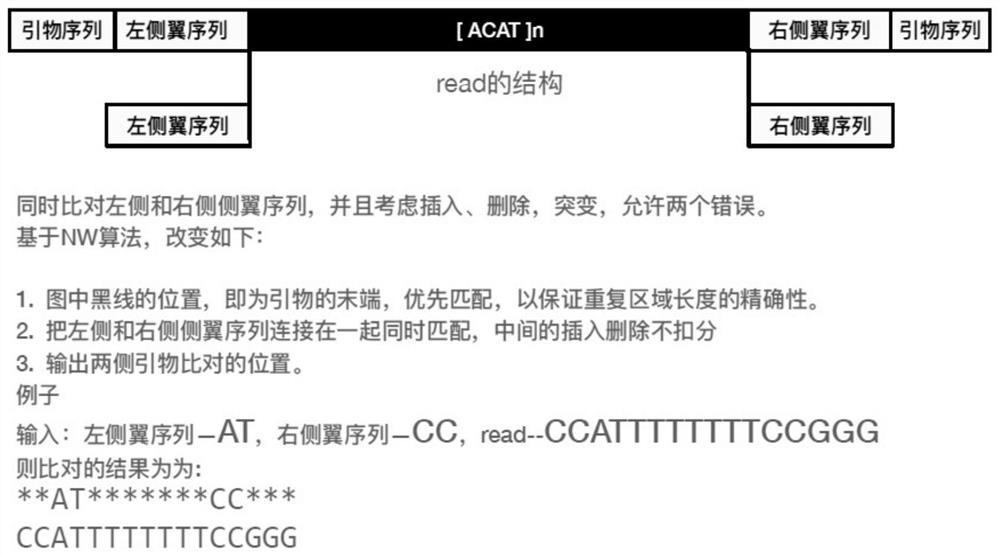
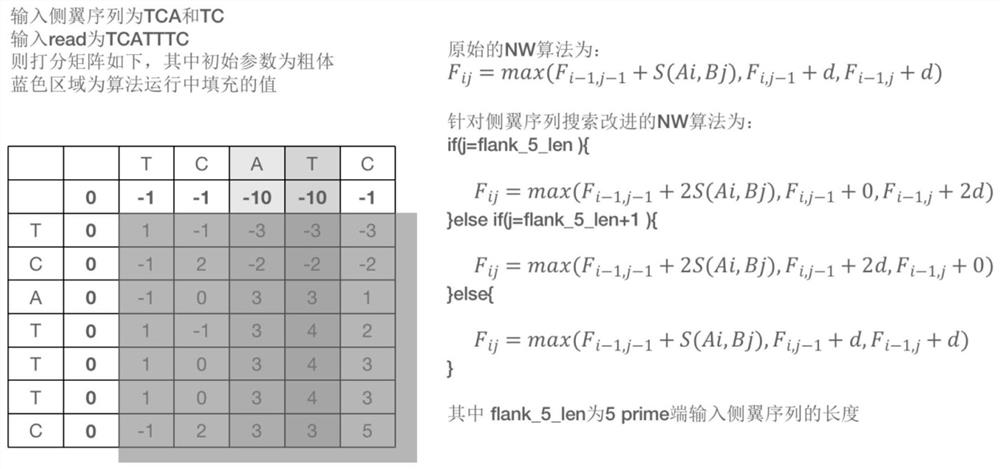
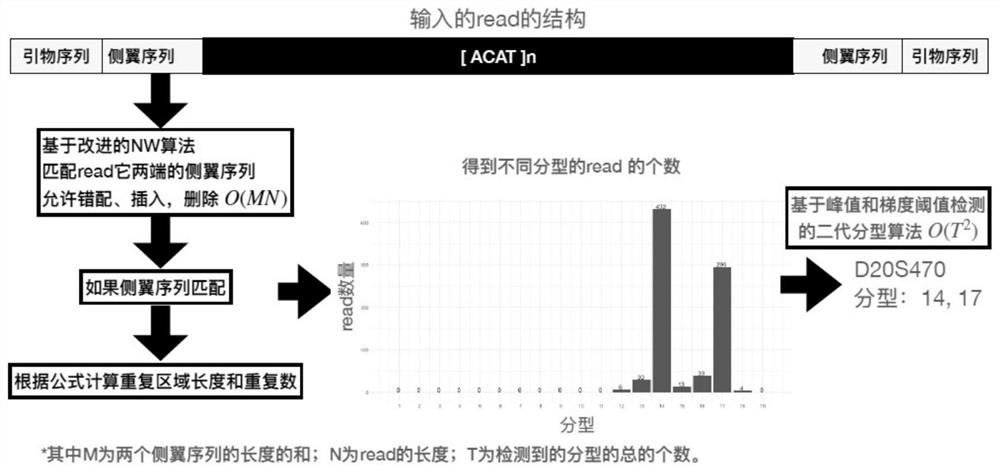
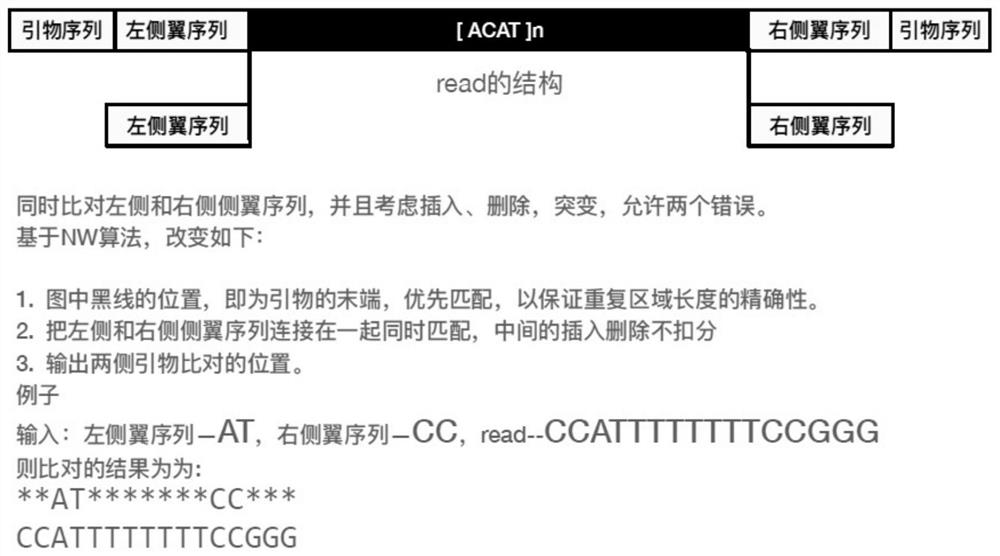
The invention relates to the field of information analysis of sequencing data, and particularly provides a method for detecting and typing the repetition number of a short tandem repeat sequence based on next-generation sequencing. According to the detection method, two flanking sequences can be compared at the same time across a middle repeated region, and mismatching, insertion and deletion of the flanking sequences are considered at the same time; the typing method is an STR typing method for performing dynamic threshold setting by combining repetition number difference based on detection of an effective peak value, and can be applied to detection of repetition numbers of different next-generation sequencing platforms.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Probe set for detecting amplification level of HER2 gene and application of probe set
PendingCN112795649AHigh-resolutionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideFluorophore
The invention relates to the technical field of gene detection, in particular to a probe set for detecting the amplification level of the HER2 gene and application of the probe set. The probe set is prepared from a nucleotide sequence shown in a specification table 1. In a non-repetitive region of the HER2 gene, a plurality of oligonucleotide libraries with different lengths are adopted, and on the basis of using as few probes as possible, the resolution of the probe is increased; and a PCR doping method is also adopted in the preparation process to ensure that the product contains more fluorophores. The probe set is used for detecting the amplification level of the HER2 gene, FISH hybridization of a paraffin tissue sample can be completed within 30 minutes, sensitivity is high, specificity is strong, a hybridization background is clean, and a signal-to-noise ratio is low.
Owner:WUHAN YZY MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Method and system for evaluating an object
A method, system and a computer program product for evaluating a object; the method includes: (i) obtaining an image of an area of the object; wherein the area comprises multiple arrays of repetitive structural elements that are at least partially surrounded by at least one group of non-repetitive regions; wherein non-repetitive regions that belong to a single group of non-repetitive regions are ideally identical to each other; wherein the non-repetitive regions are arranged in a repetitive manner; and(ii) providing an evaluation result in response to a comparison between image information of a first sub-area to image information of a second sub-area that is proximate to the first sub-area; wherein the first sub-area comprises a first array of repetitive structural elements and a first non-repetitive region; wherein the second subarea comprises a second array of repetitive structural elements and a second non-repetitive region.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
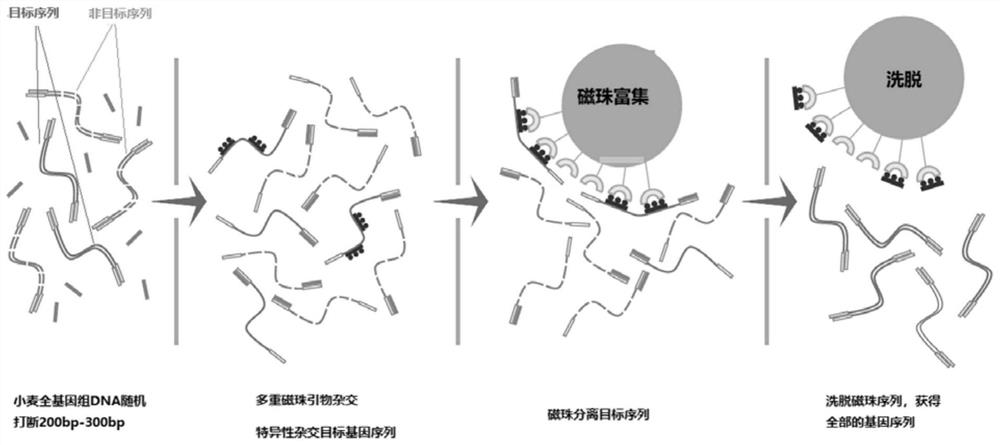
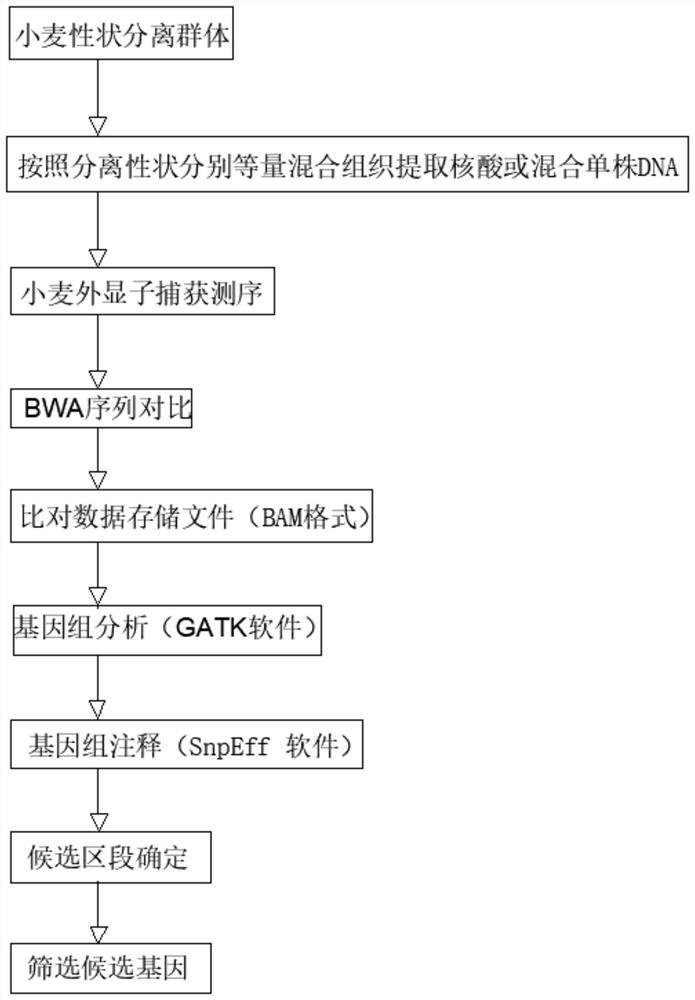
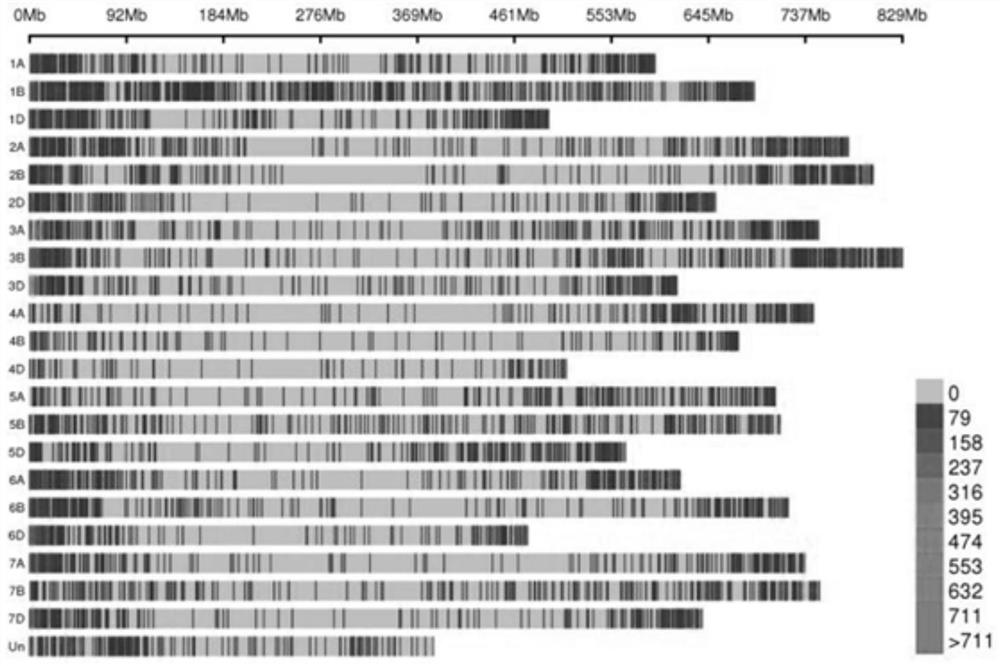
Probe design method and positioning method for wheat exon sequencing gene positioning
The invention relates to the technical field of wheat functional gene localization, in particular to a probe design method for wheat exon sequencing gene localization, which comprises the following steps of: sequencing through a high-throughput sequencing platform to obtain transcriptome data, comparing and analyzing the transcriptome data with a comparison reference genome, splicing and combining transcripts, and performing ORF prediction; and deleting the sequence of the repeated region, and performing high-density probe synthesis on the screened sequence to obtain the probe. The gene localization method comprises the following steps: breaking wheat DNA into fragments, hybridizing the broken wheat DNA with the high-density probe, enriching magnetic beads, eluting the liquid, and carrying out high-throughput sequencing, variation detection and statistical localization. The invention solves the problem of high gene positioning cost caused by huge wheat genome in the prior art, and by designing the superhigh-density multiple primer probe, sequencing is only carried out on the gene exon sequence, and the sequencing cost is reduced by 80% under the condition of the same gene sequencing depth.
Owner:成都天成未来科技有限公司
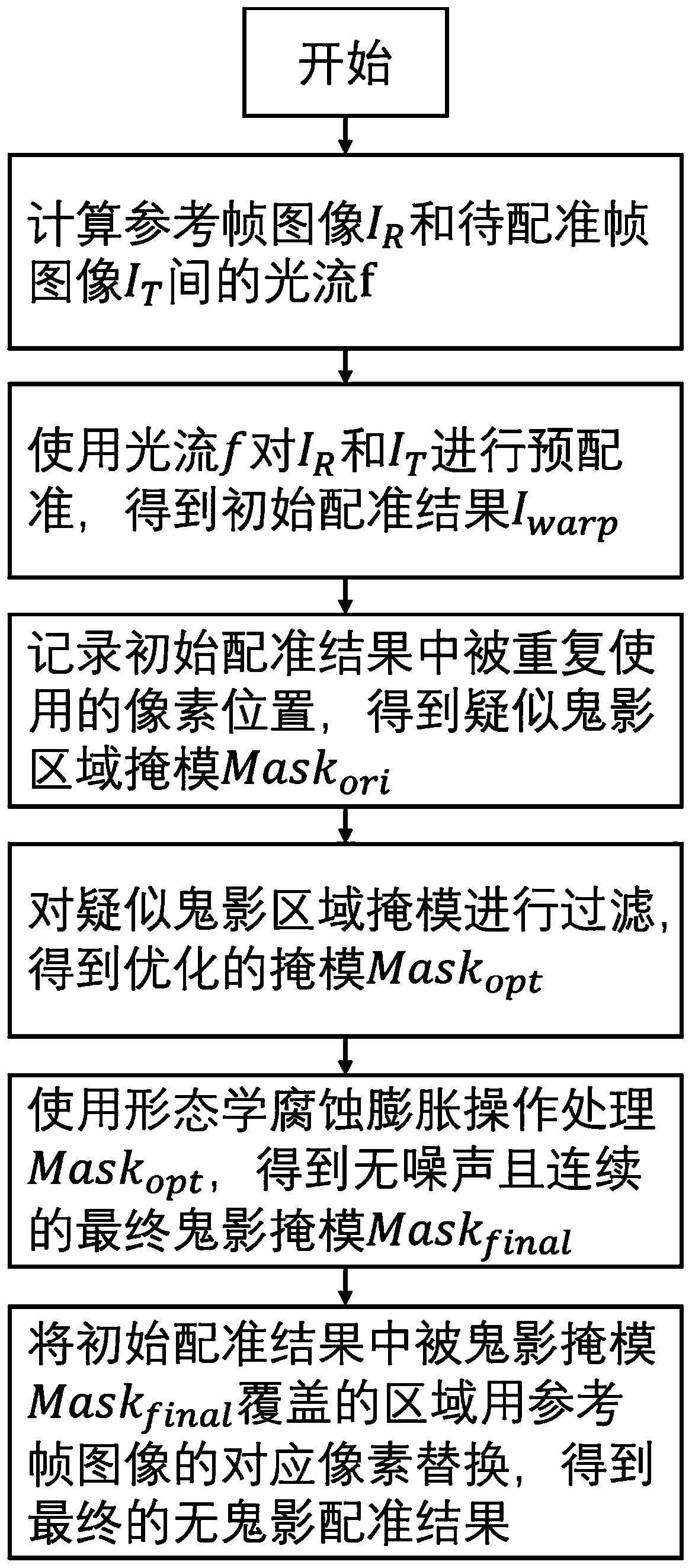
Image registration ghost elimination method based on optical flow mapping repetitive region detection
ActiveCN110619652AReduce time complexityImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOptical flowTime complexity
The invention discloses an image registration ghost elimination method based on optical flow mapping repetitive region detection. The method comprises the following steps: pre-registering two images by using an optical flow between a reference frame image and a frame image to be registered; recording the corresponding position of each pixel in the image to be registered in the pre-registration result; taking a corresponding position of a pixel which is used for multiple times in the image to be registered in the pre-registration result as a suspected ghost position; and removing the pixel mostsimilar to the reference frame image from the plurality of candidate ghost image pixels, determining the rest pixels as ghosts, and finally, replacing the pre-registration result by using the corresponding pixel of the reference frame image at the detected ghost position, thereby obtaining a ghost-free image registration result. The method is high in precision and high in efficiency, can effectively remove the ghosting without increasing the time complexity of the registration algorithm, and is a practical method and means capable of realizing image registration and ghosting removal in an actual camera imaging system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
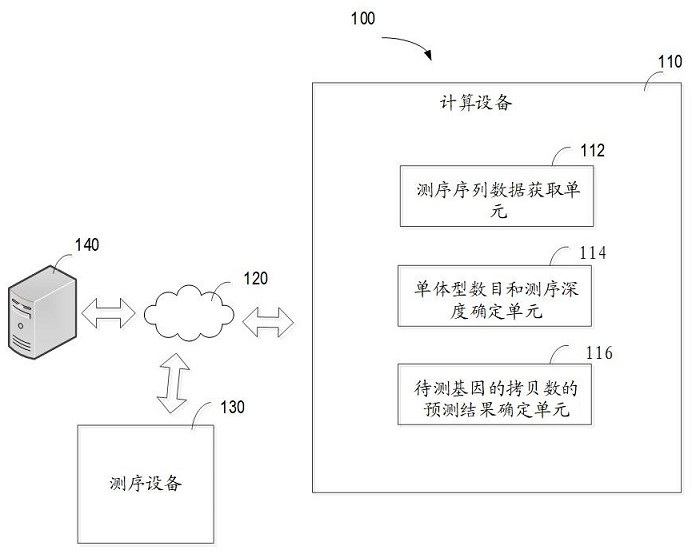
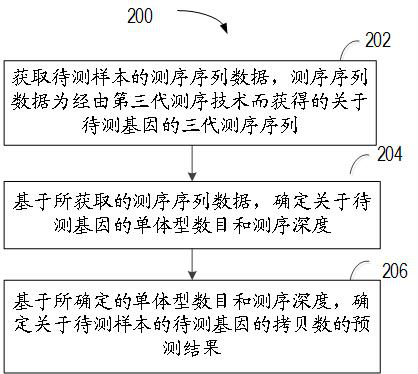
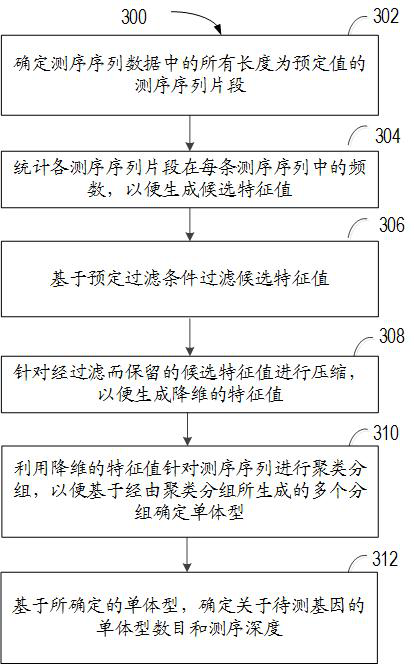
Method for predicting copy number of gene to be detected, computing device and storage medium
The invention relates to a method for predicting the copy number of a gene to be detected, computing equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sequencing sequence data of a to-be-detected sample, wherein the sequencing sequence data is a third-generation sequencing sequence about a to-be-detected gene obtained by a third-generation sequencing technology; based on the obtained sequencing sequence data, determining the haplotype number and the sequencing depth of the to-be-detected gene; and based on the determined haplotype number and the sequencing depth, determining a prediction result of the copy number of the to-be-detected gene of the to-be-detected sample. According to the method, the gene copy number can be accurately determined aiming at repeated regions or highly homologous genes at low cost.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Primer, kit and analysis method for ADTKD gene mutation detection
PendingCN113403388AReduce testing costsReduce waiting time for detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence analysisGenome sequence analysis
The invention relates to a primer, a kit and an analysis method for ADTKD gene mutation detection. The technical scheme provided by the invention comprises the steps of PCR primer design, replacement magnetic bead, enzyme and applicable system design and the like. Through optimized screening of a series of reagents, gene mutation detection of different samples, different types and the like is realized. According to the method, gene segments of five genes are targeted, the sequencing length ranges from 1.6 kbp to 3 kbp, the genes do not need to reach a short segment of about 300 bp, a targeted full-length sequence is directly obtained, and meanwhile through cyclic consistent sequence analysis, the detection accuracy of mutation and indel is higher. Especially for the MUC1 gene, the method overcomes the defect that the WES cannot accurately splice and compare the repetitive regions of the gene, can obtain an accurate circulating consistent sequence, visually identifies the number of the repetitive regions and mutation sites, and solves the problem that the WES cannot detect the mutation of the gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
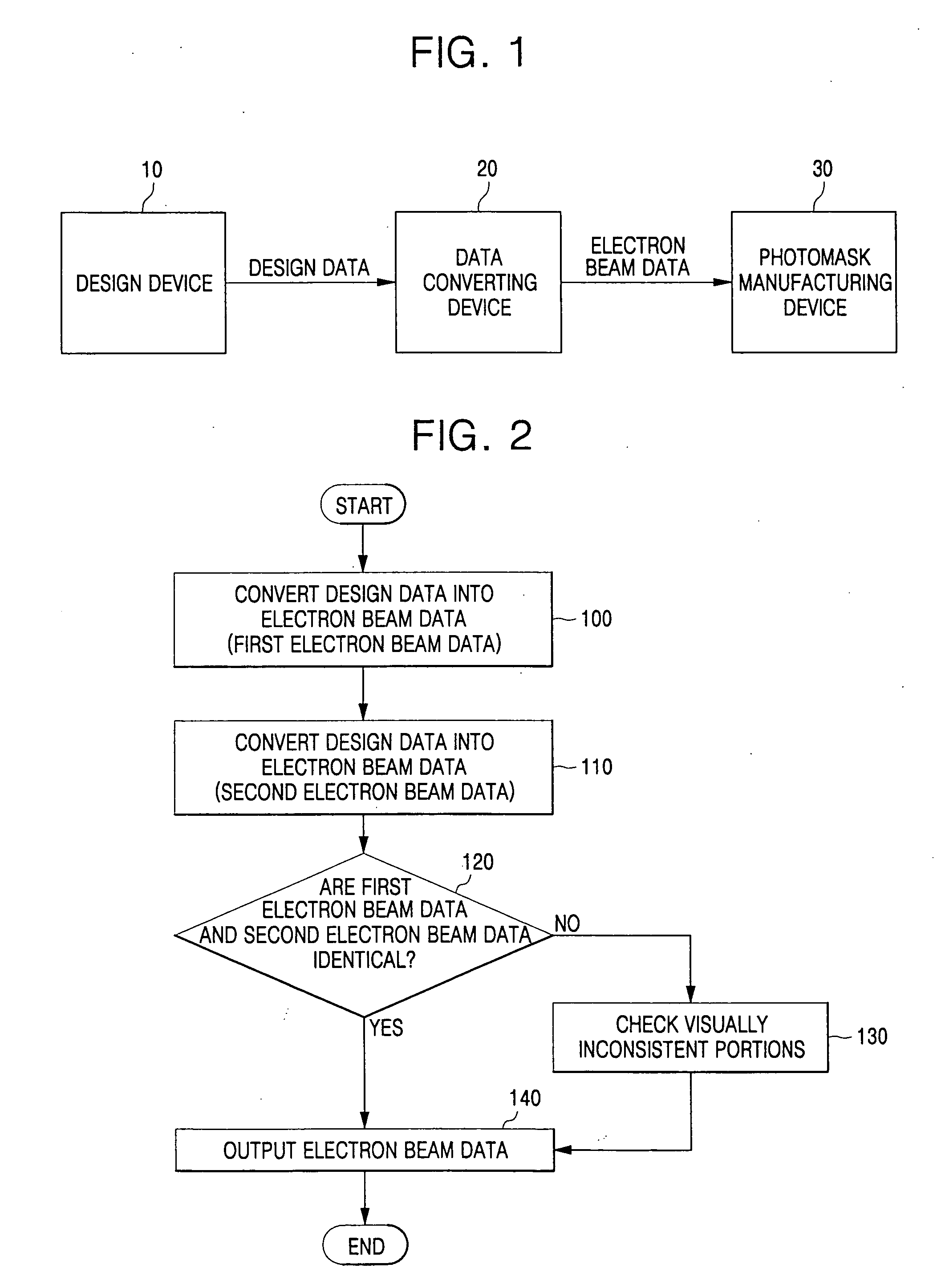
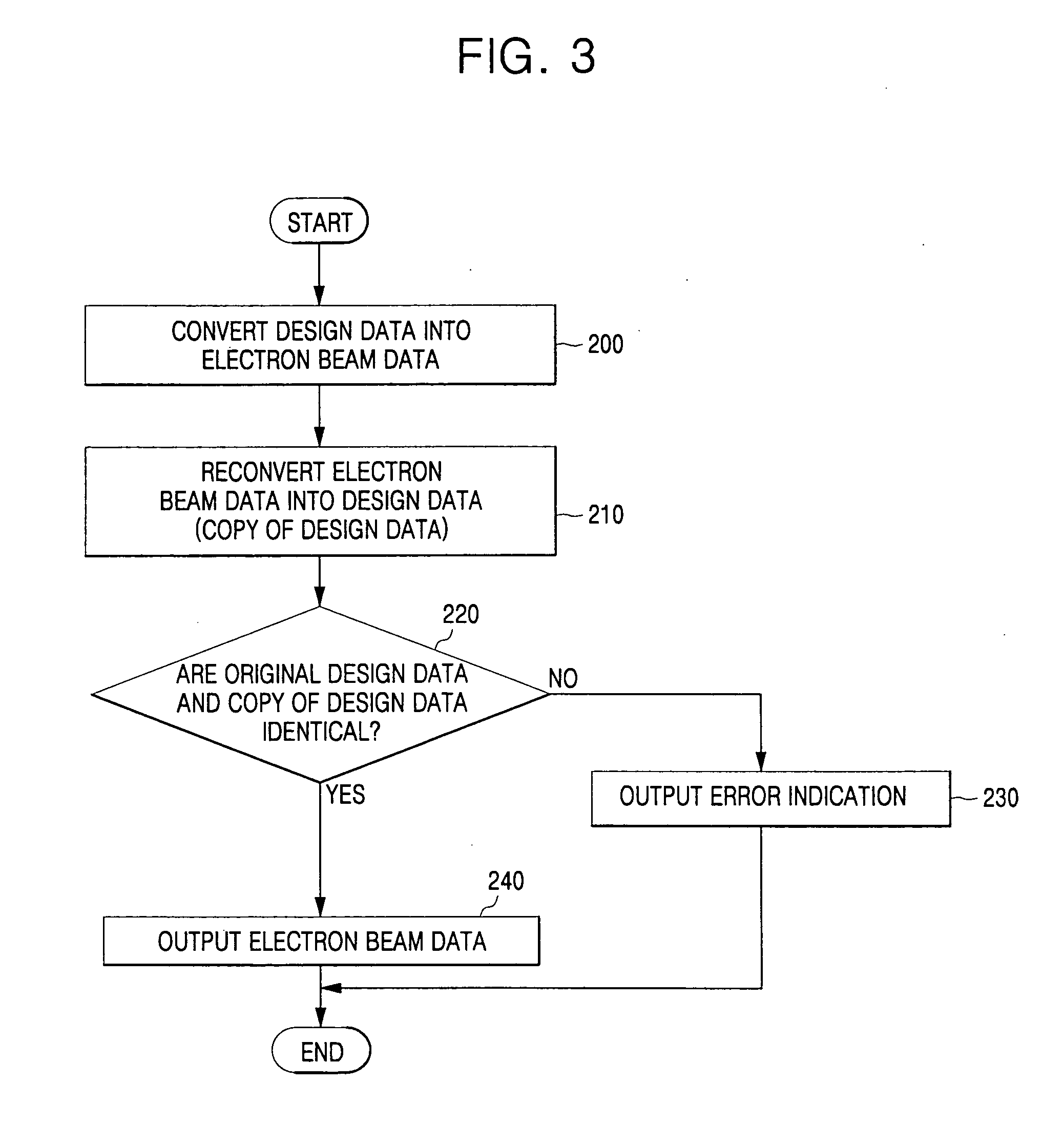
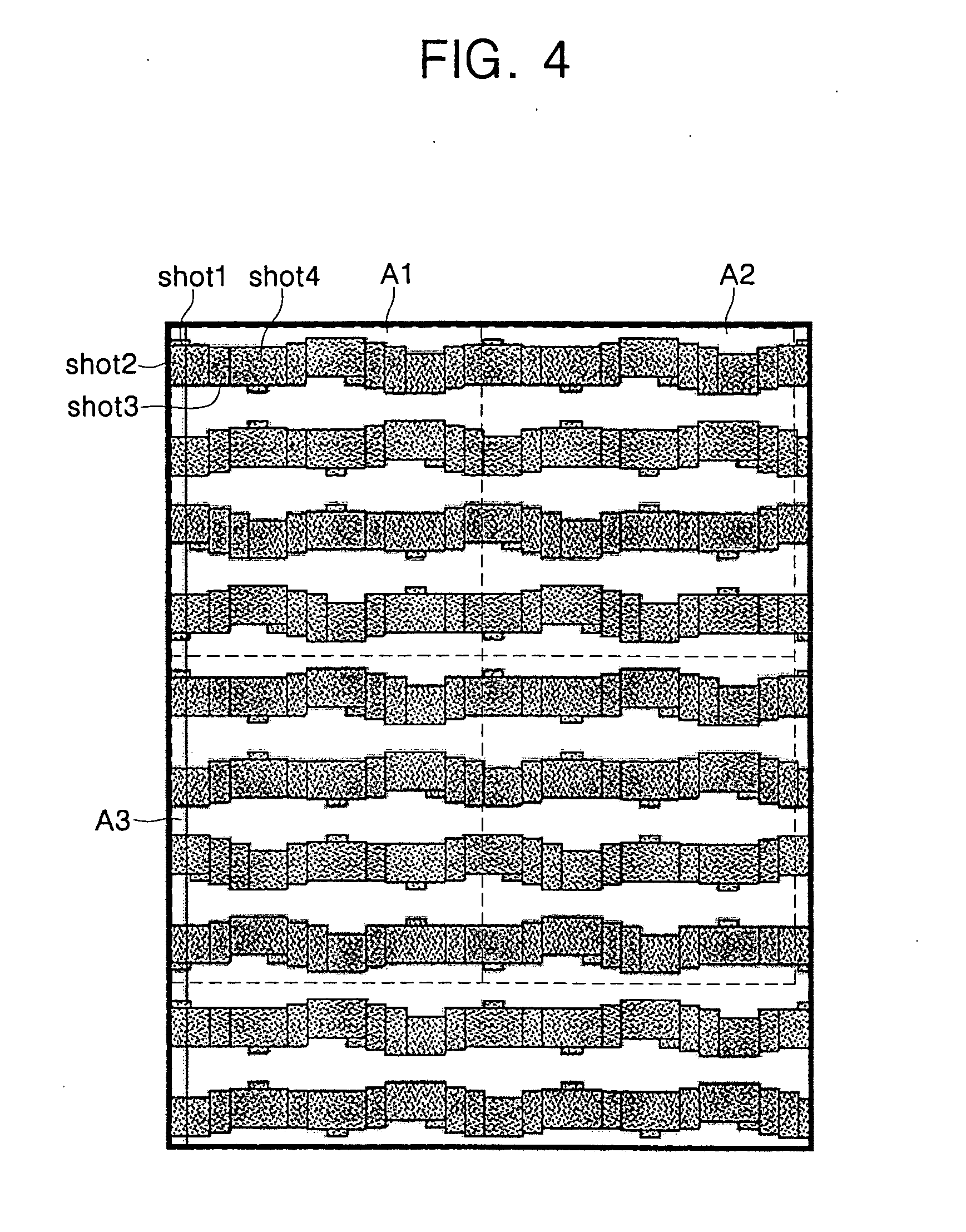
Method of verifying electron beam data
InactiveUS20060093961A1Electric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRepetitive RegionsElectron
A method of verifying electron beam data used to produce a photomask comprises dividing design data for the photomask into a plurality of repetitive regions, sequentially converting the sequential regions into electron beam data, and determining whether electron beam data corresponding to a current repetitive region is substantially identical to electron beam data corresponding to a previous repetitive region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
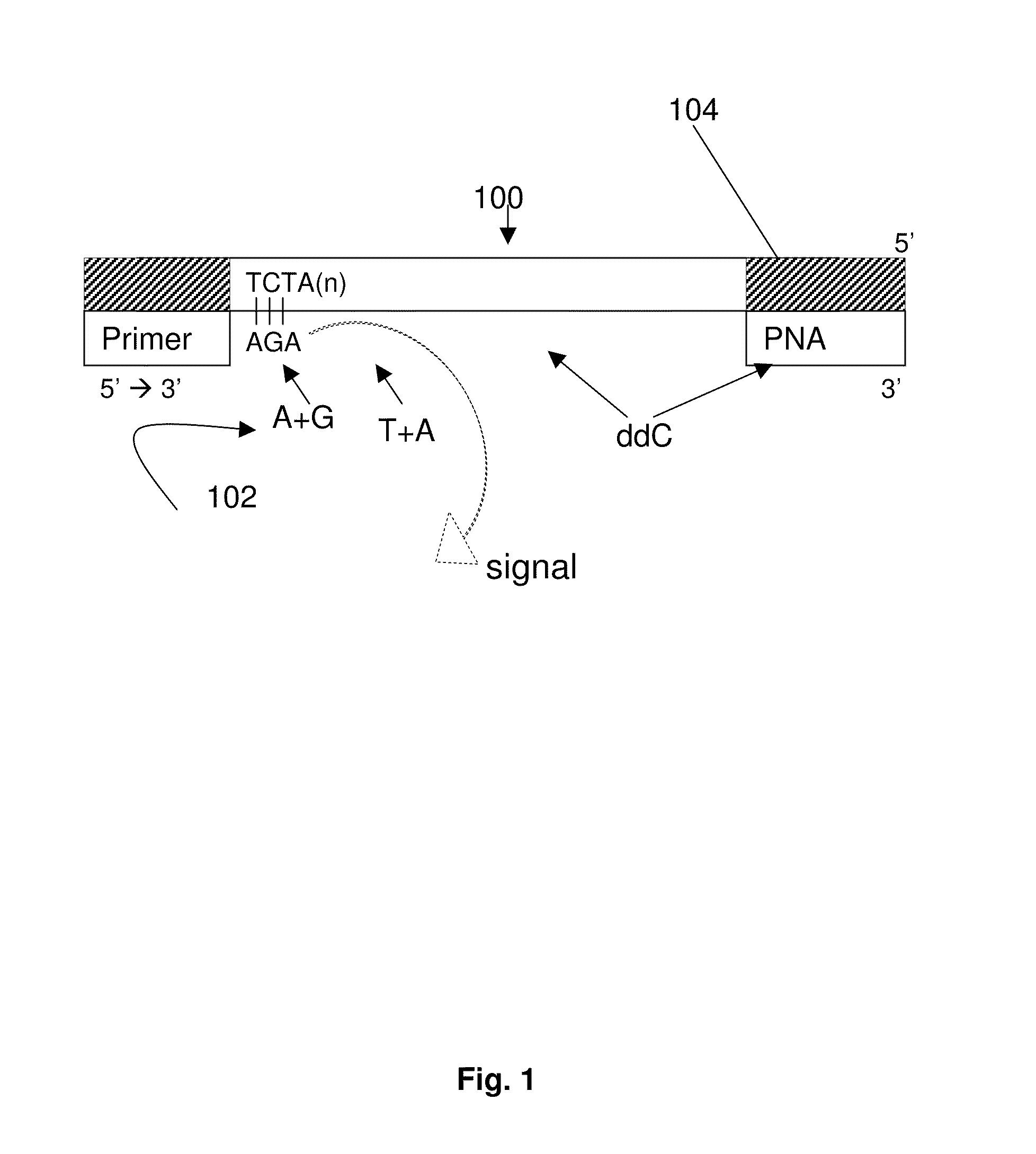
DNA template tailoring using PNA and modified nucleotides
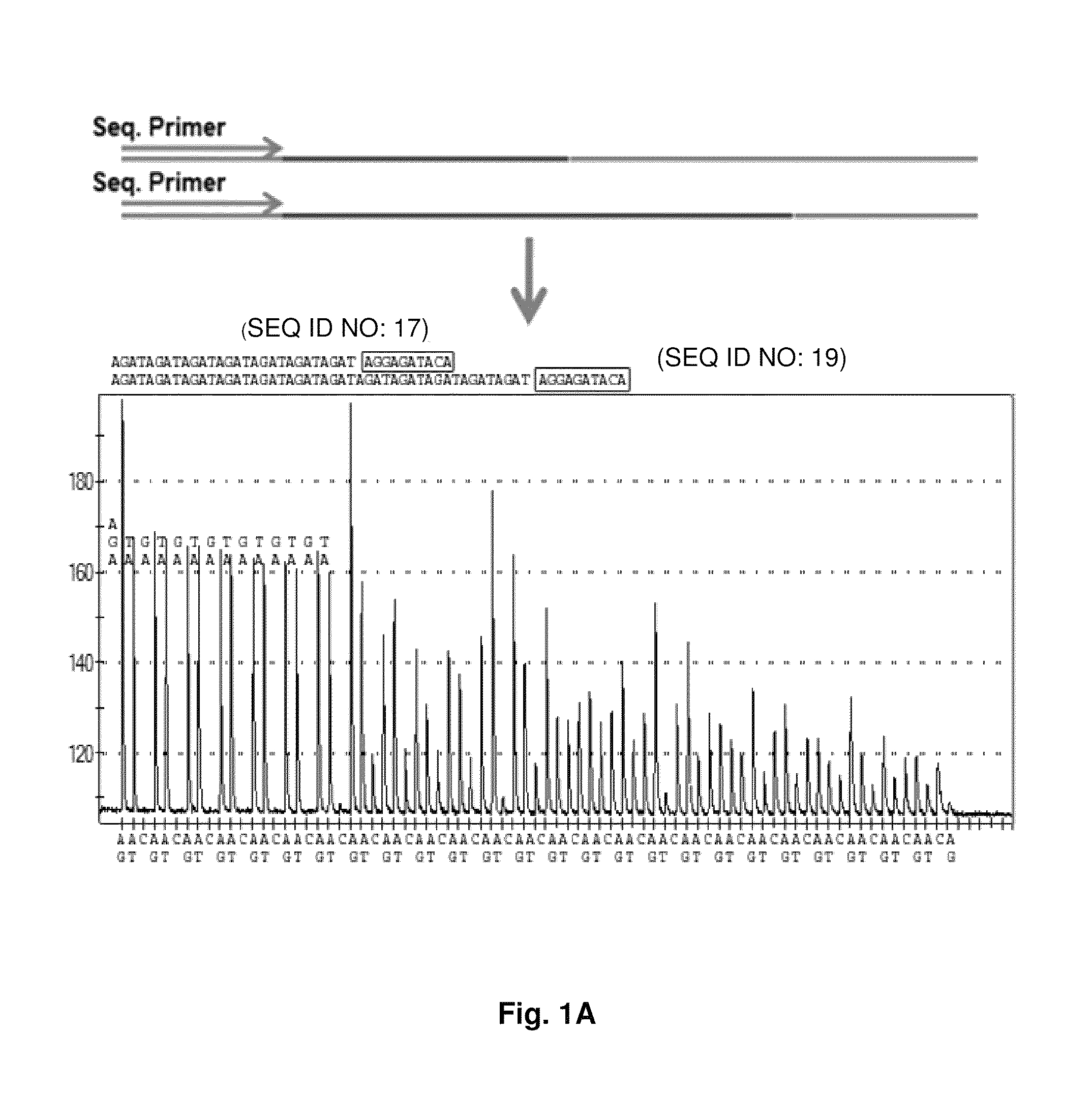
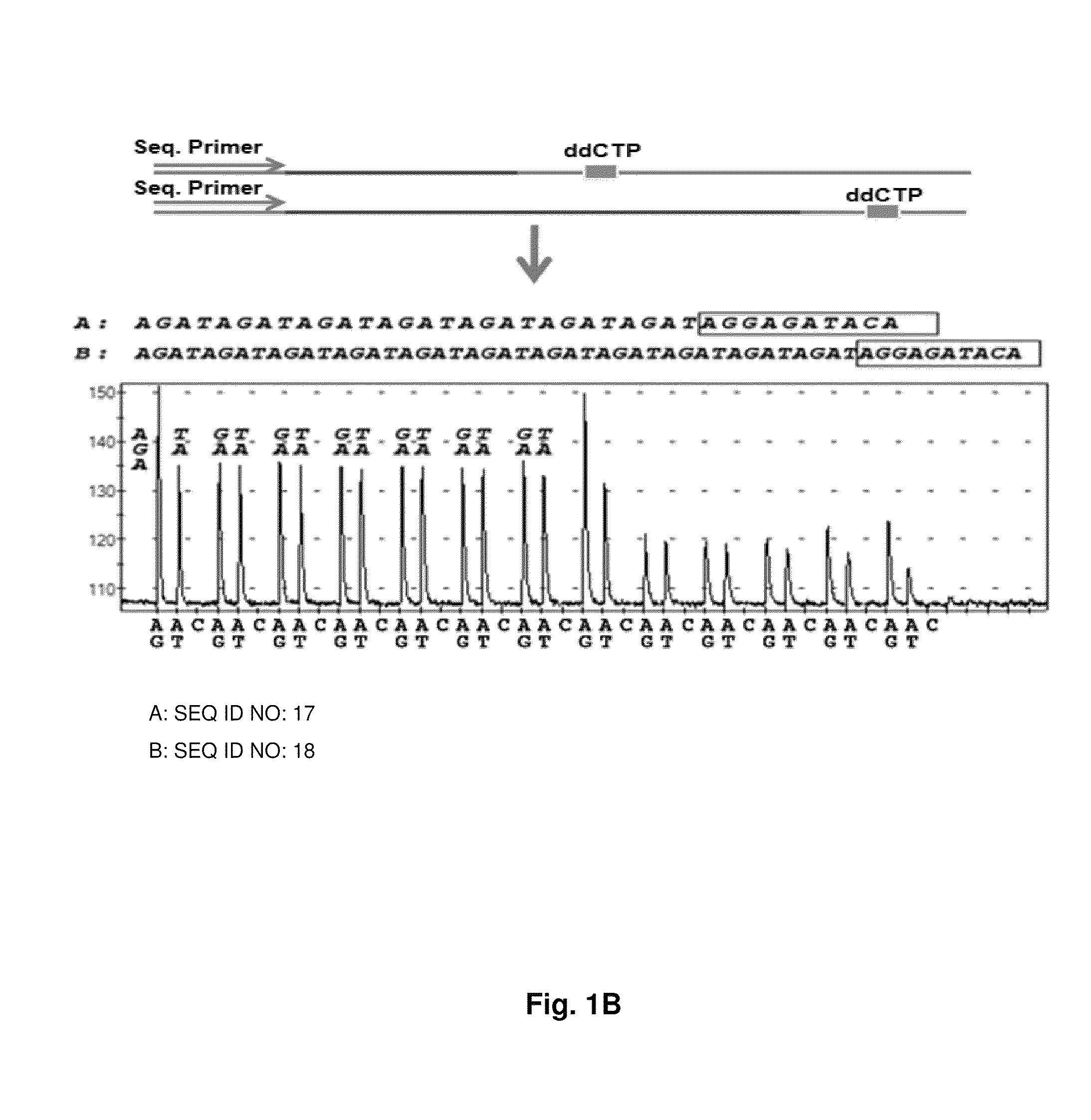
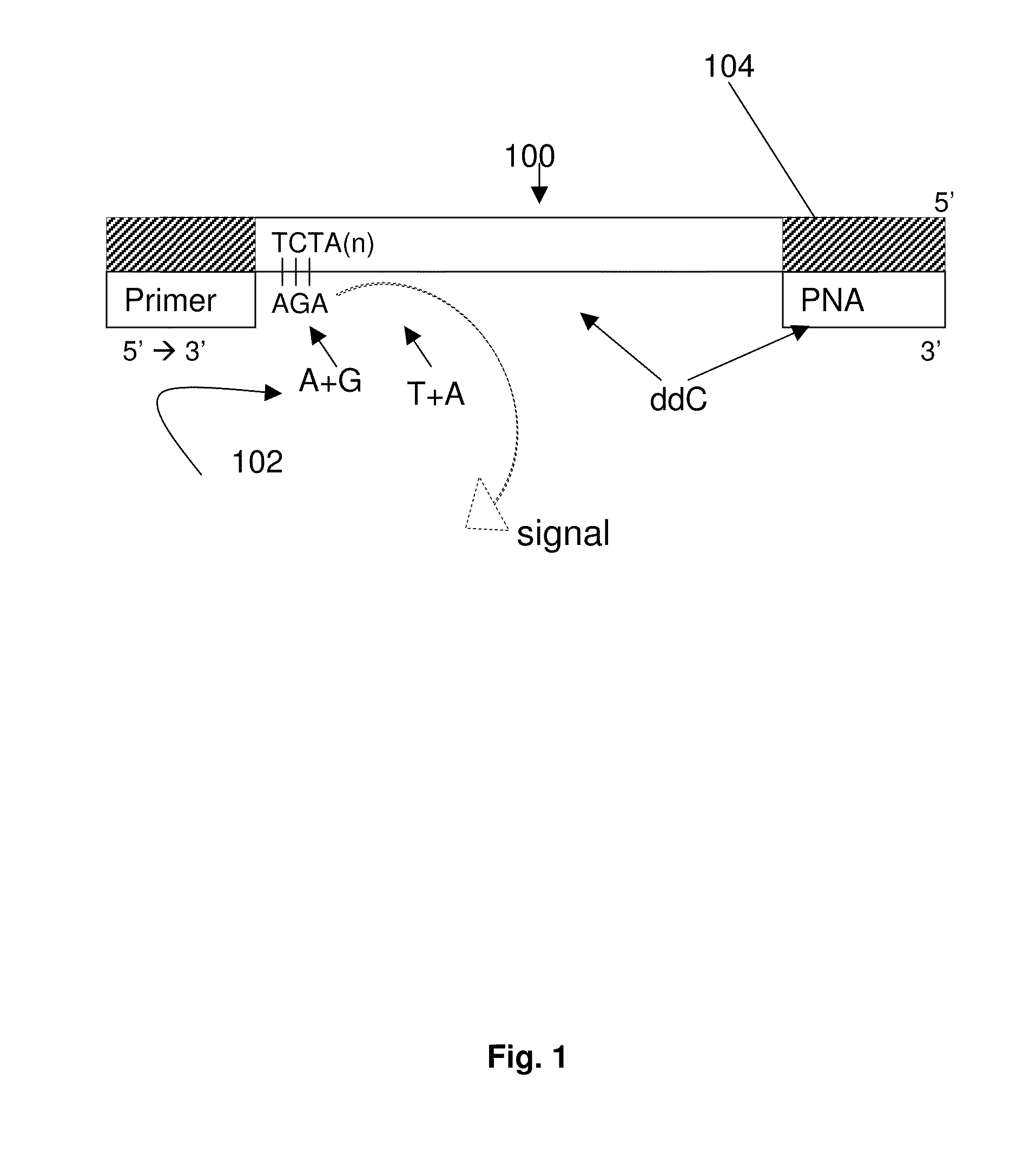
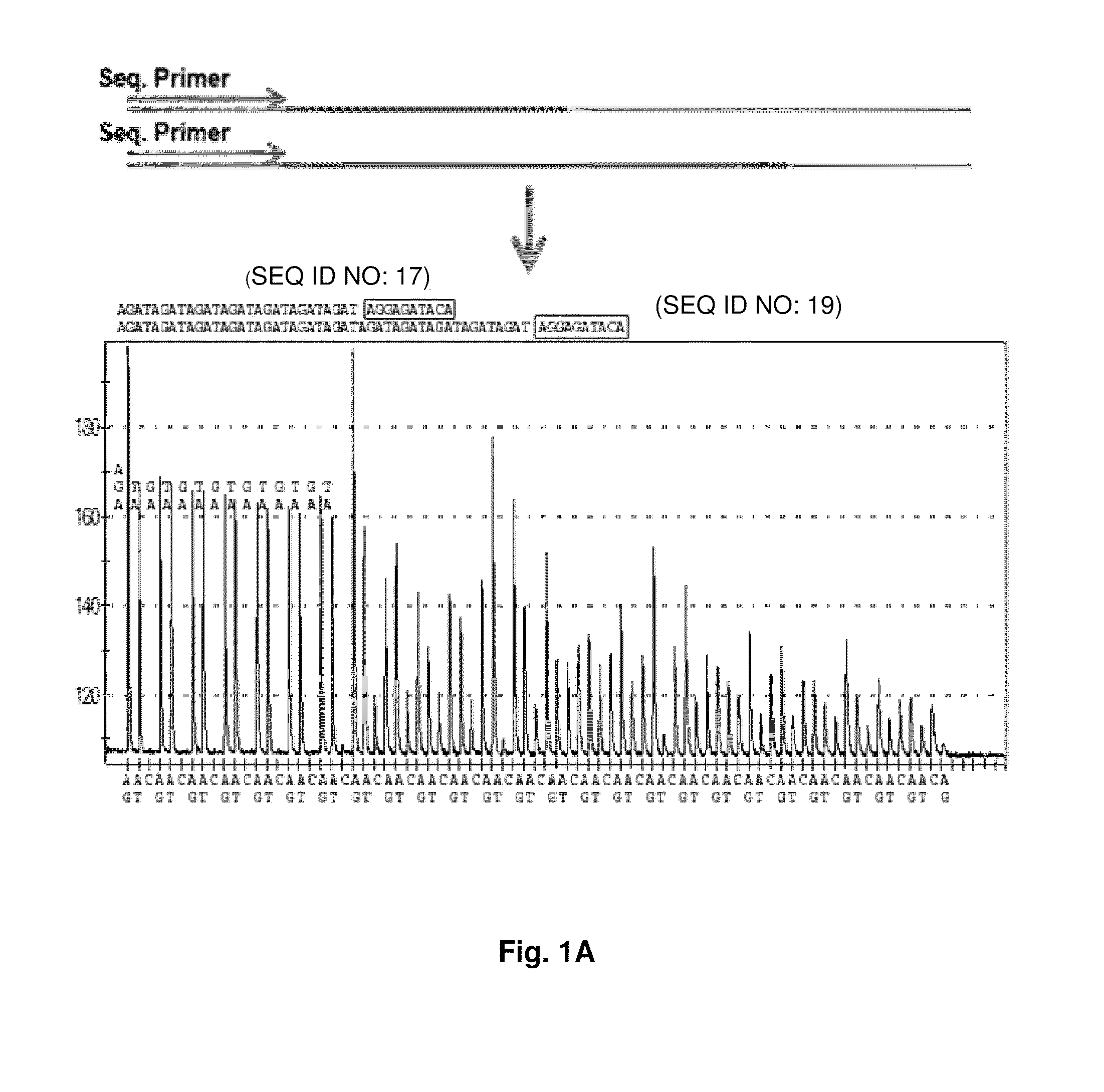
ActiveUS9187782B2Reliable and rapid and information-rich and cost-effective approachQuick measurementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
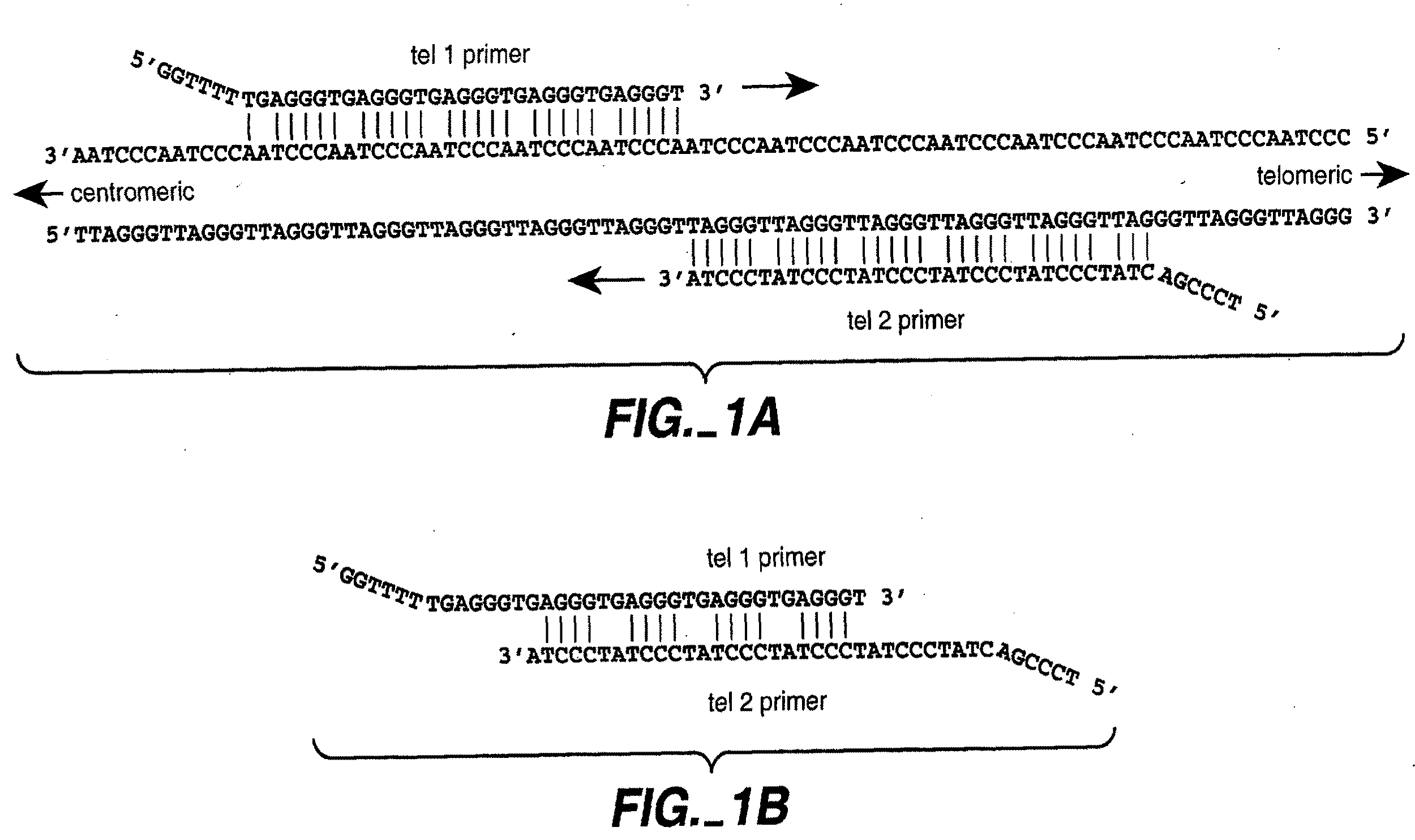
Disclosed is a method whereby a repetitive nucleic acid sequence, such as a short tandem repeat (STR), may be characterized as to its length. Pyrosequencing is used to sequence an STR repetitive region to measure the length of STRs in a rapid manner. A combinatorial approach is disclosed for the addition of multiple nucleotides (e.g., two mononucleotides) at a time by the polymerase, which reduces the sample analysis time by half. In addition, modified nucleic acids, such as peptide nucleic acids, are used as blocking probe to stop polymerization on the flanking region which makes it possible to use pyrosequencing for DNA length measurement both in the case of homozygous or heterozygous samples for varying repeat patterns of different markers. Further, dideoxynucleotides are added to stop polymerization in the flanking region of the STR.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
DNA template tailoring using pna and modified nucleotides
ActiveUS20110207118A1Reliable and rapid and information-rich and cost-effective approachShorten analysis timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
Disclosed is a method whereby a repetitive nucleic acid sequence, such as a short tandem repeat (STR), may be characterized as to its length. Pyrosequencing is used to sequence an STR repetitive region to measure the length of STRs in a rapid manner. A combinatorial approach is disclosed for the addition of multiple nucleotides (e.g., two mononucleotides) at a time by the polymerase, which reduces the sample analysis time by half. In addition, modified nucleic acids, such as peptide nucleic acids, are used as blocking probe to stop polymerization on the flanking region which makes it possible to use pyrosequencing for DNA length measurement both in the case of homozygous or heterozygous samples for varying repeat patterns of different markers. Further, dideoxynucleotides are added to stop polymerization in the flanking region of the STR.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
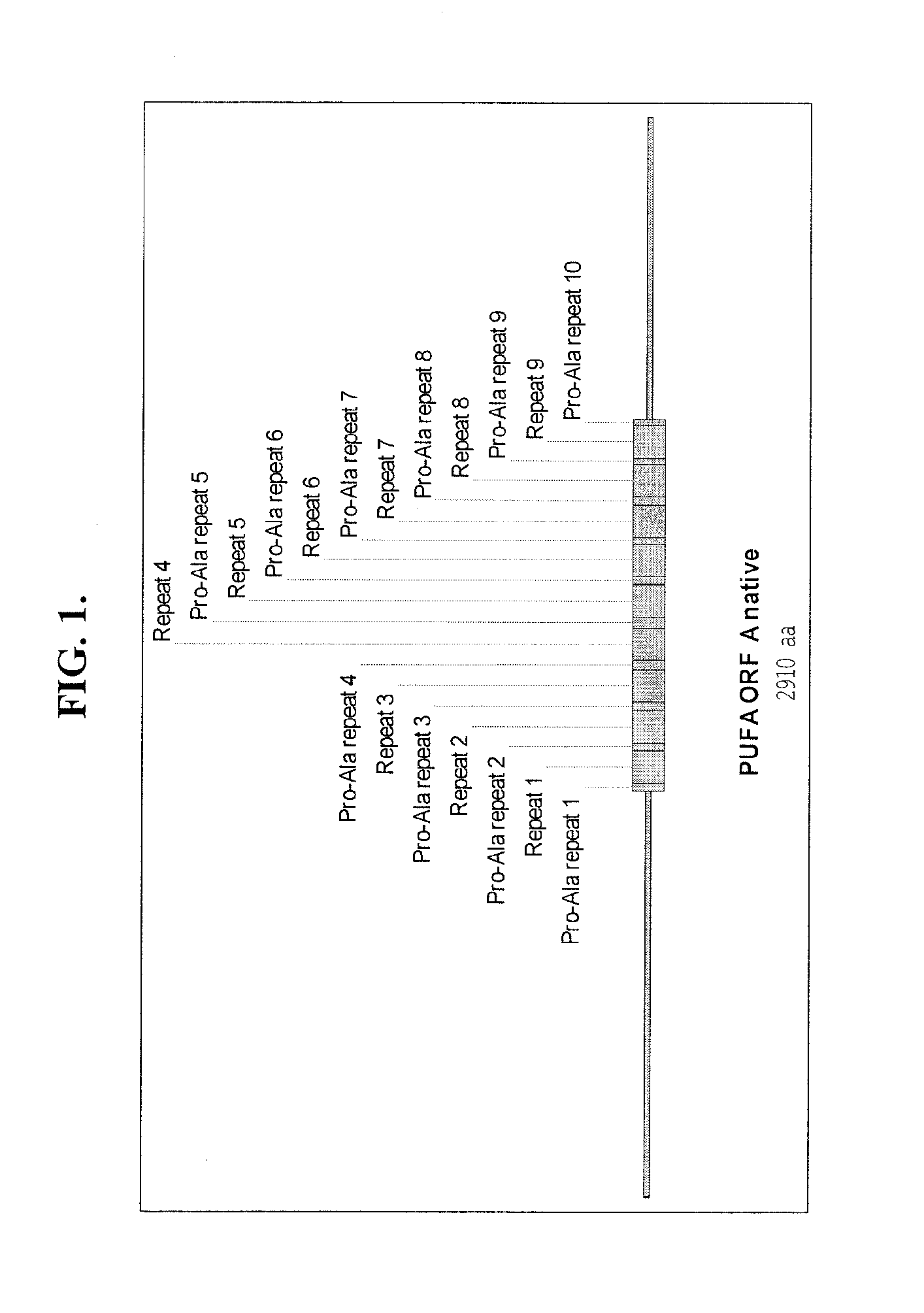
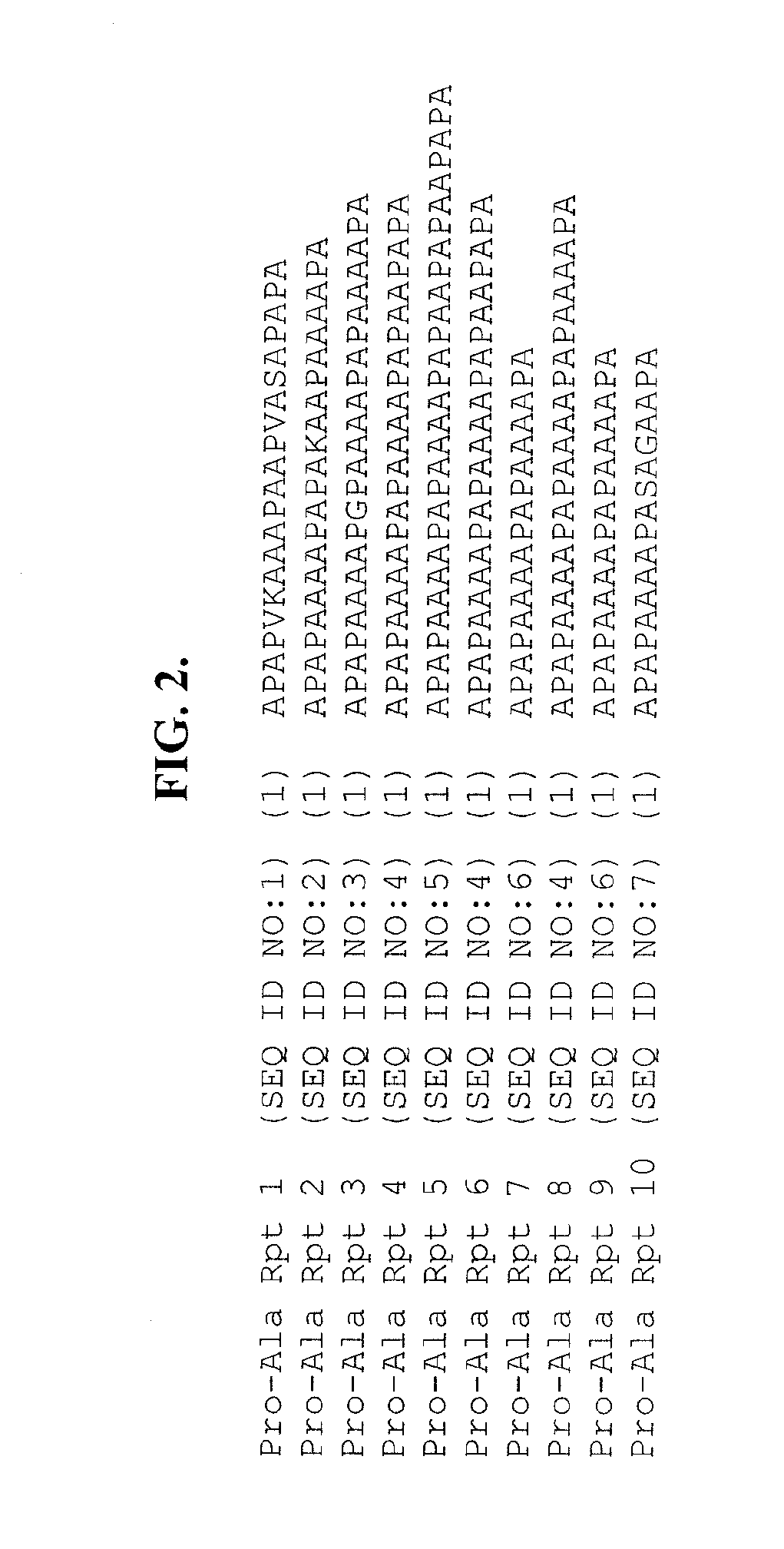
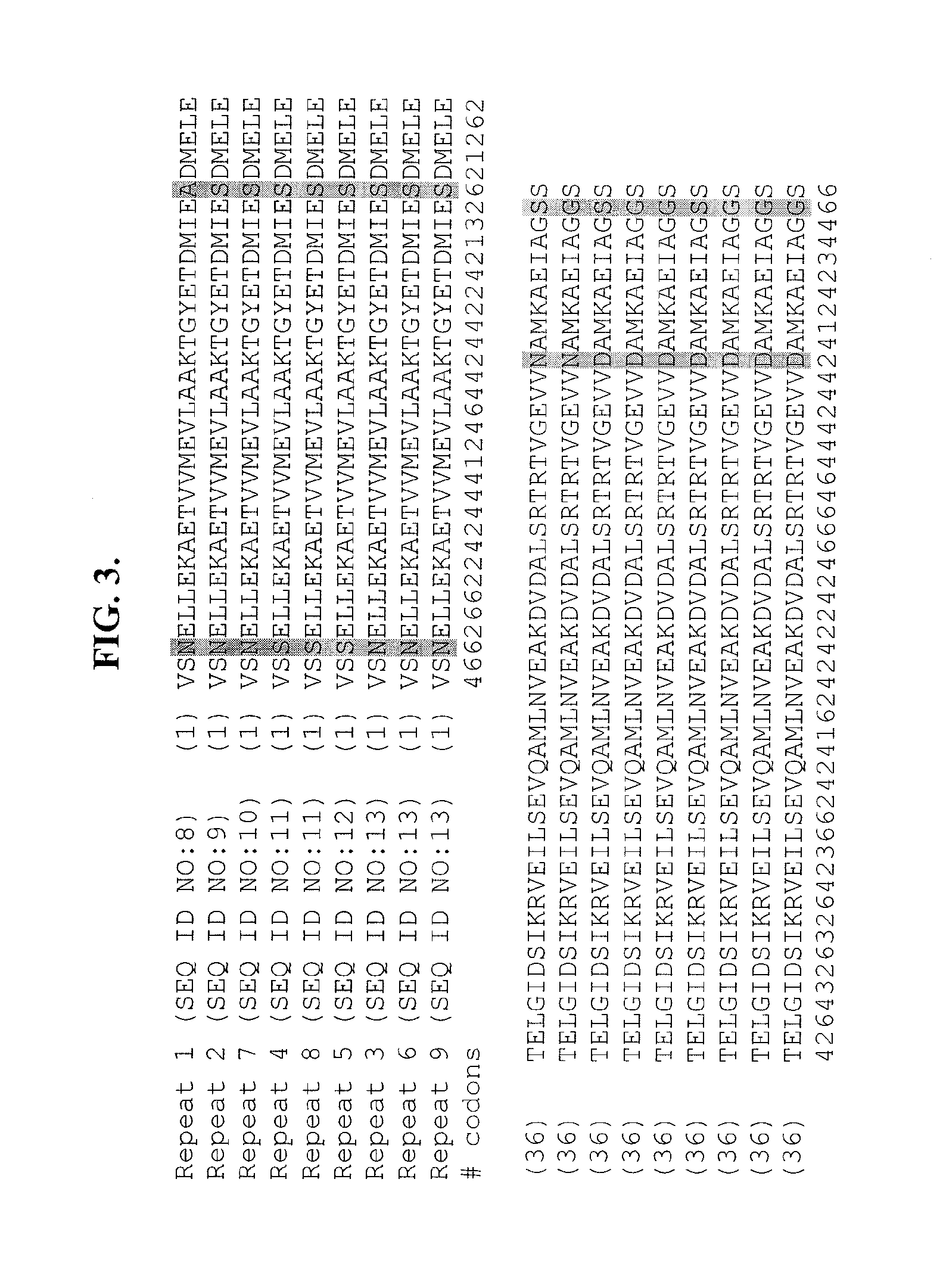
Process for designing diverged, codon-optimized large repeated DNA sequences
ActiveUS20150175672A1Assure codonAssure sequence diversitySugar derivativesUnicellular algaeRepetitive RegionsAmino acid
This disclosure concerns methods for the design of synthetic nucleic acid sequences that encode polypeptide amino acid repeat regions. This disclosure also concerns the use of such sequences to express a polypeptide of interest that comprises amino acid repeat regions, and organisms comprising such sequences.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Methods and compositions for assaying repetitive sequences
PendingUS20210087628A1Facilitate qPCR-basedMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesGenetics
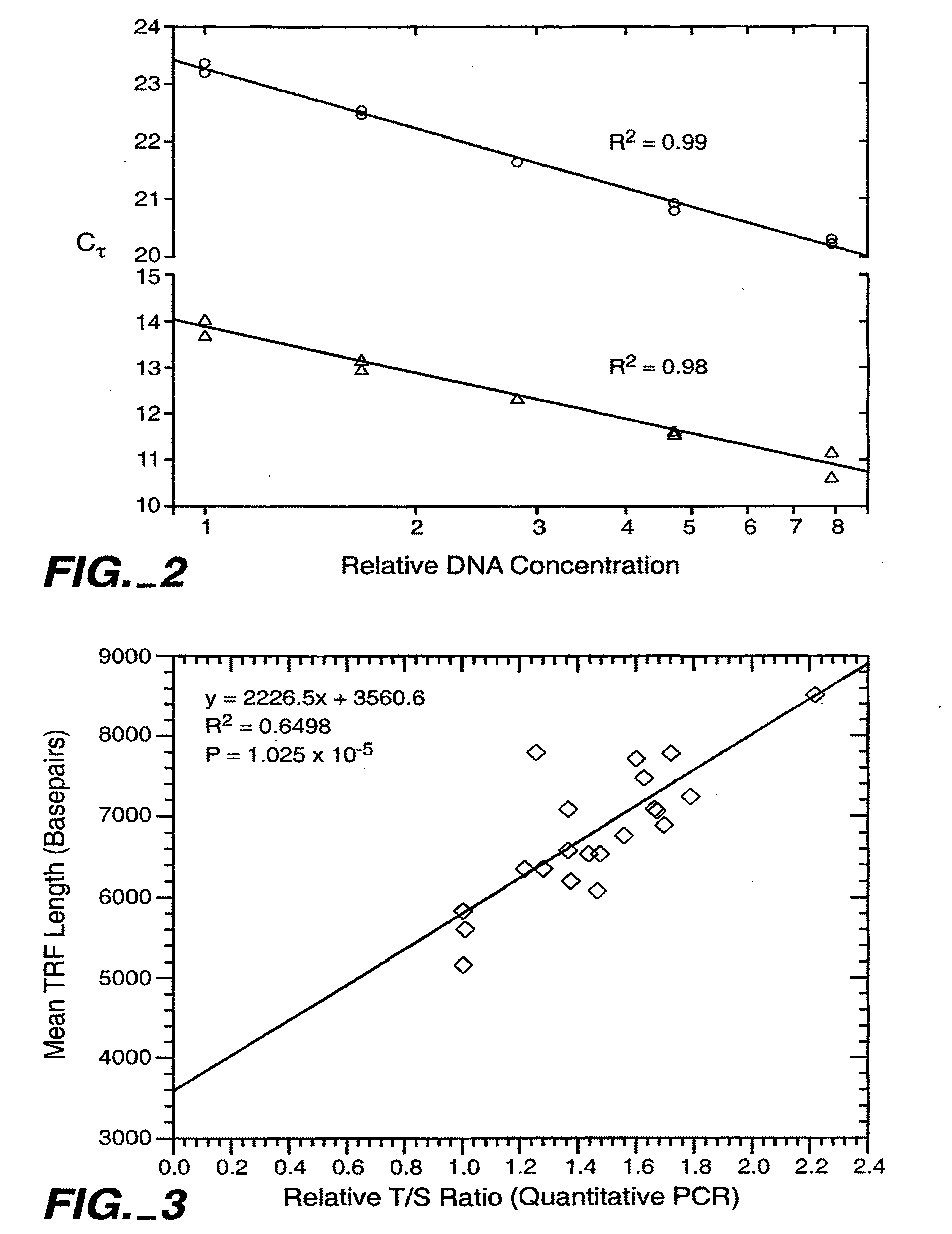
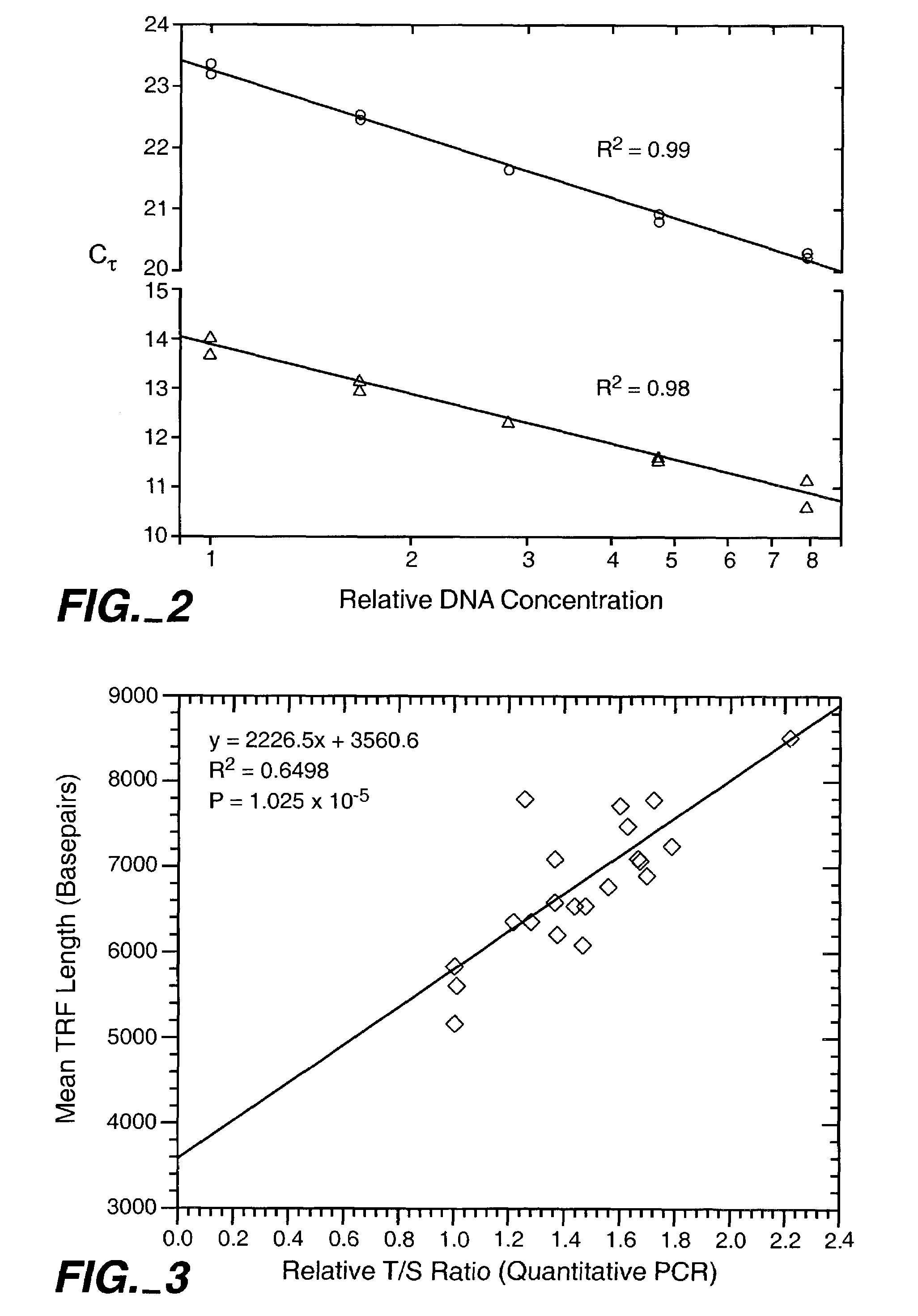
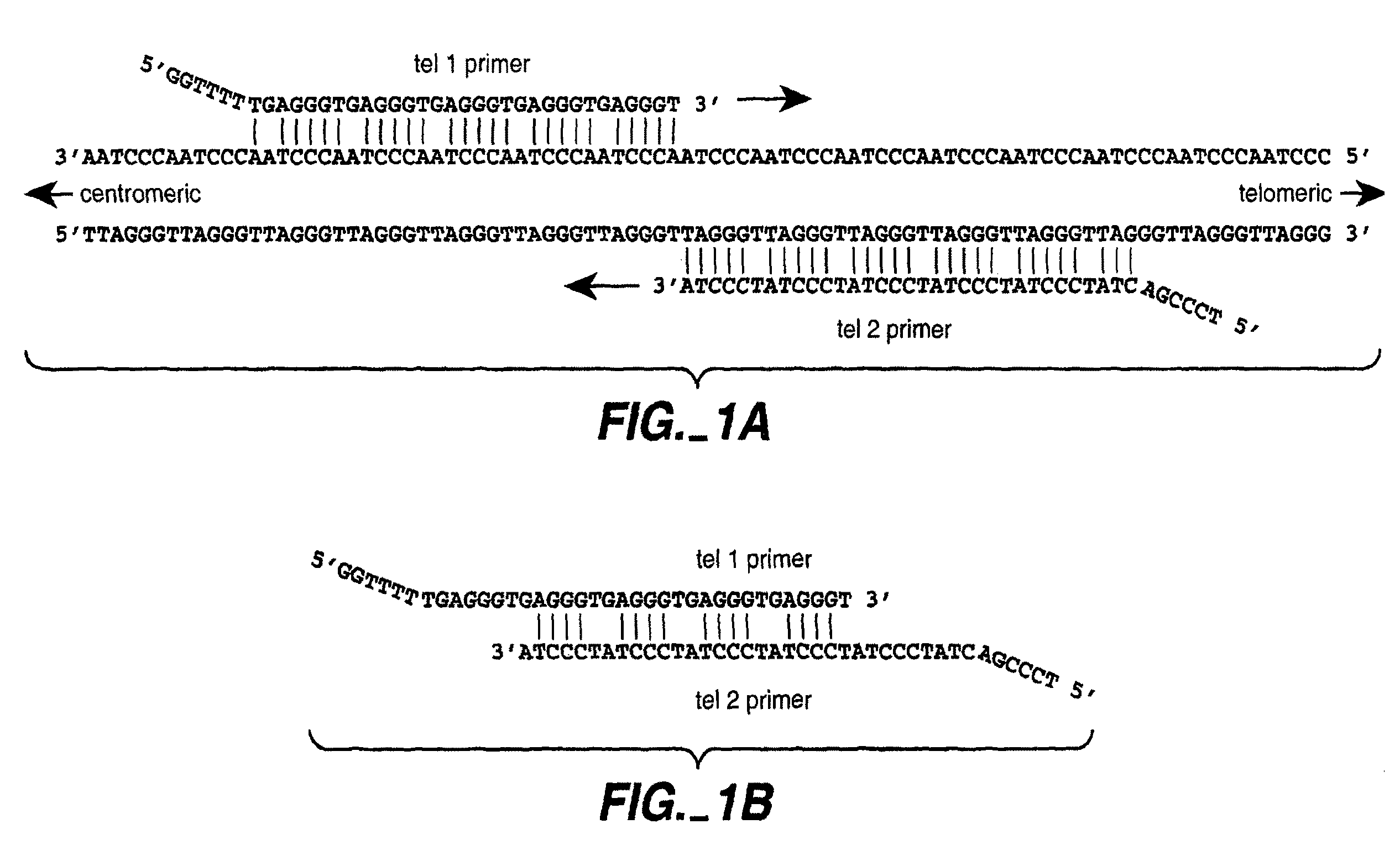
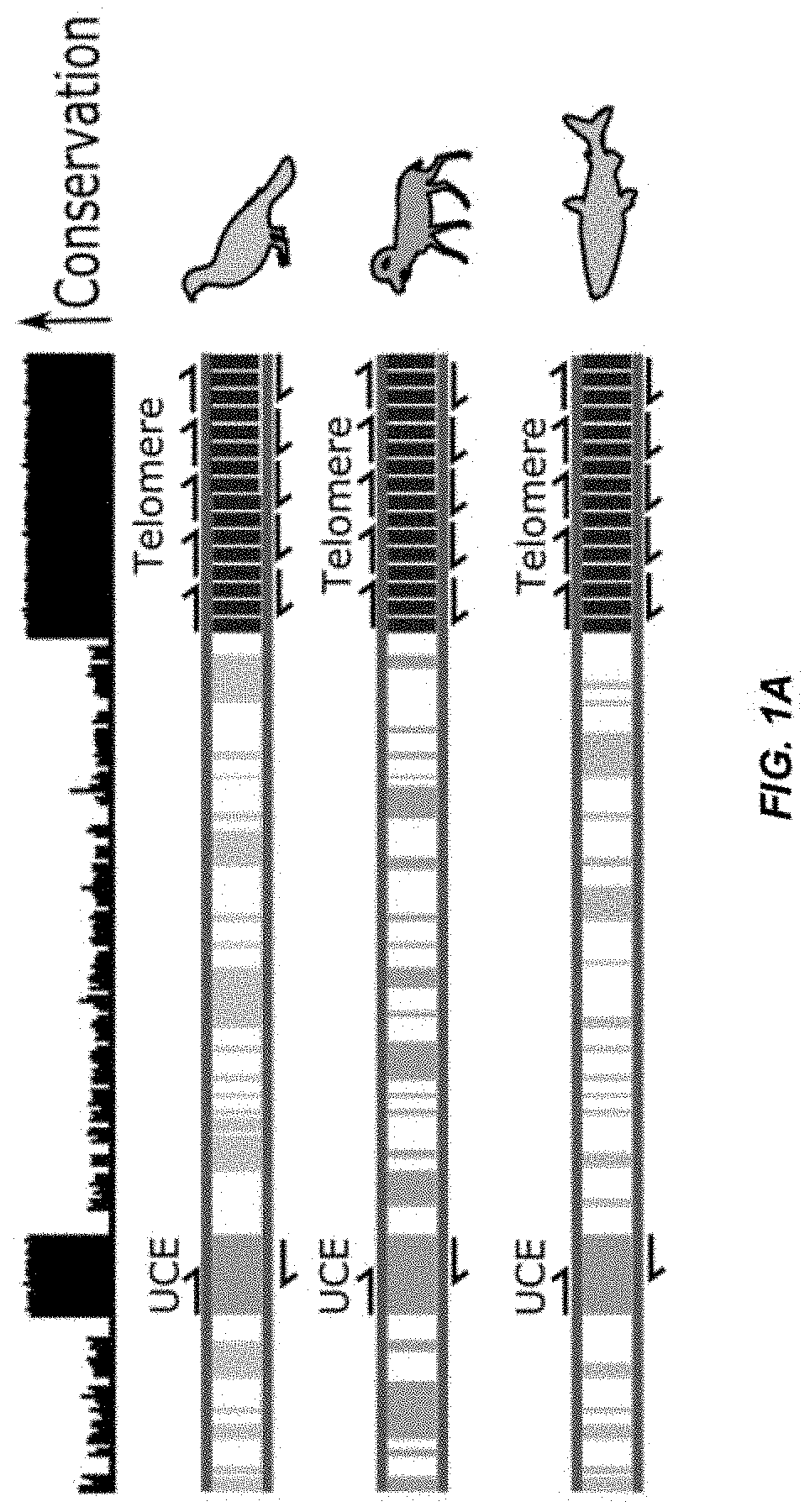
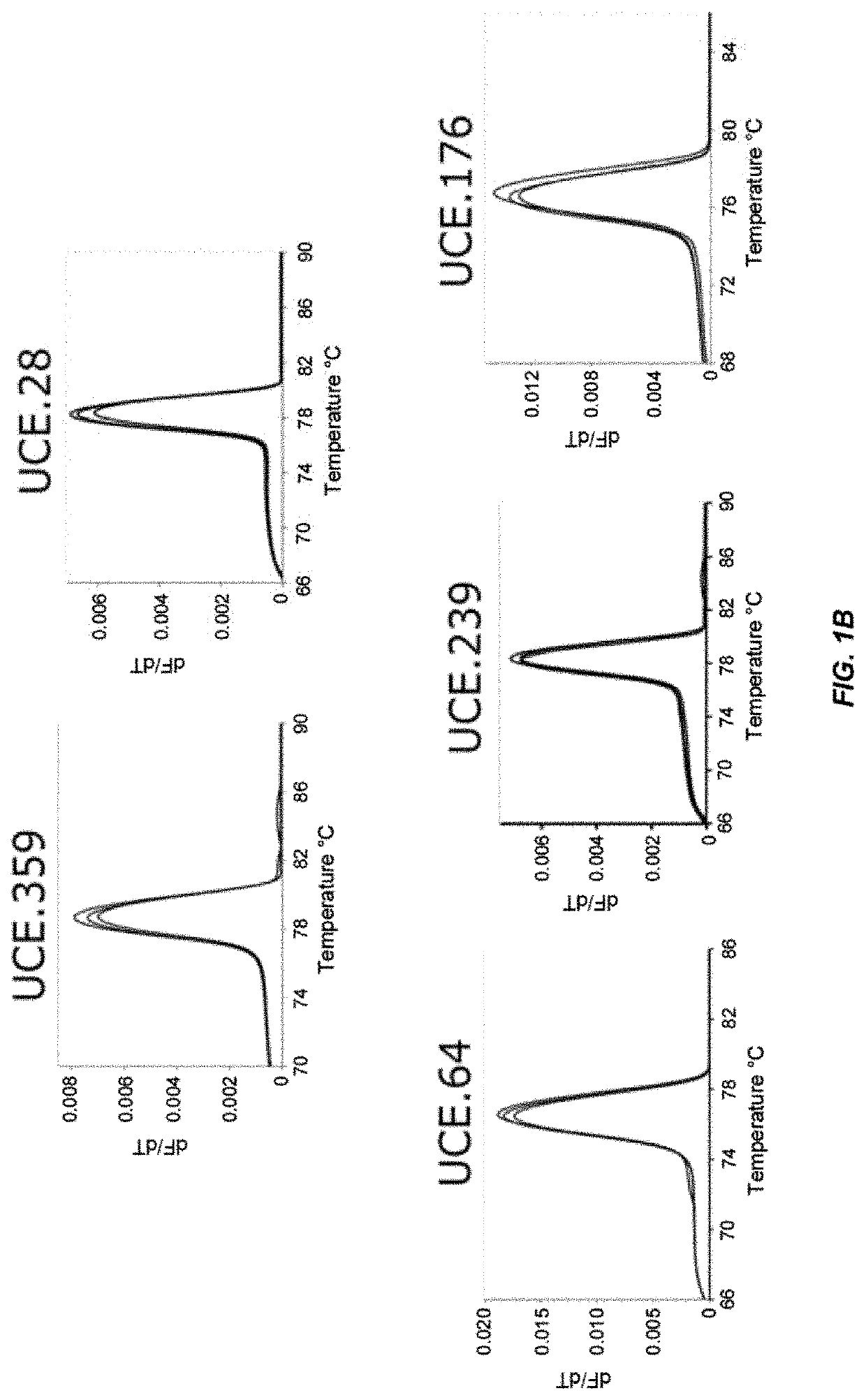
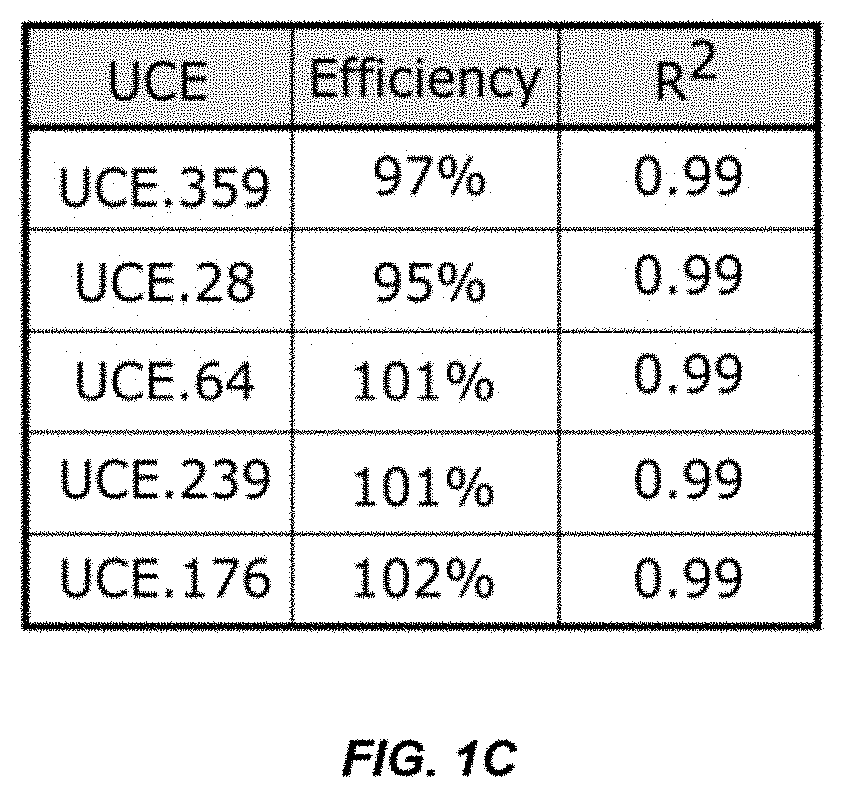
Disclosed herein are methods of determining telomere length using universal reference primers. The reference primer pairs efficiently and reproducibly amplify genomic DNA in any vertebrate species. Kits for determining the length of telomeres or others repetitive regions in a sample are also provided.
Owner:BOISE STATE UNIVERSITY
Method and system for evaluating object
InactiveCN101566585BOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSpecial data processing applicationsStructuring elementRepetitive Regions
The invention provides a method, a system and a computer program product for evaluating objects. The method for evaluating objects comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the image of a region ofan object, wherein the region comprises repetitive structure elements of a plurality of arrays which are at least partly surrounded by at least a group of non-repetitive regions, the non-repetitive r egions belonging to the single group of non-repetitive region are ideally identical, and the non-repetitive regions are arranged in a repetitive mode; (2) and responding to the comparison between the image information of a first sub-region and the image information of a second sub-region close to the first sub-region to provide an evaluation result, wherein the first sub-region comprises repetitive structure elements of a first array and a first non-repetitive region, and the second sub-region comprises repetitive structure elements of a second array and a second non-repetitive region.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Isolated antibodies to a secretory membrane protein
InactiveUS7235640B2Altered morphologicallyInhibit cell proliferationMovable measuring chambersBone-inducing factorCell membraneADAMTS Proteins
Three genes encoding secretory membrane proteins have been successfully isolated from an osteoblast-like cell line by a method for specifically cloning secretory membrane proteins. One of these genes encodes a novel receptor protein. The protein has only the extracellular region, binds to the cell membrane via a GPI anchor, and carries therein a cysteine-rich, repetitive region commonly conserved in the TNF receptor super family. Overexpression of this protein in osteoblast-like cell line cells suppresses cell proliferation, changes cell morphology, and increases alkaline phosphatase activity, which is one of markers for differentiation of osteoblasts.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Novel secretory membrane protein
InactiveUS20020128435A1Inhibit cell proliferationAltered morphologicallyNGF/TNF-superfamilyTissue cultureCell membraneADAMTS Proteins
Three genes encoding secretory membrane proteins have been successfully isolated from an osteoblast-like cell line by a method for specifically cloning secretory membrane proteins. One of these genes encodes a novel receptor protein. The protein has only the extracellular region, binds to the cell membrane via a GPI anchor, and carries therein a cysteine-rich, repetitive region commonly conserved in the TNF receptor super family. Overexpression of this protein in osteoblast-like cell line cells suppresses cell proliferation, changes cell morphology, and increases alkaline phosphatase activity, which is one of markers for differentiation of osteoblasts.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for detecting and typing repeat number of short tandem repeat sequence
ActiveCN113724783AThe test result is accurateImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsGeneticsTyping methods
The invention relates to the field of information analysis of sequencing data, and particularly provides a method for detecting and typing the repetition number of a short tandem repeat sequence based on next-generation sequencing. According to the detection method, two flanking sequences can be compared at the same time across a middle repeated region, and mismatching, insertion and deletion of the flanking sequences are considered at the same time; the typing method is an STR typing method for performing dynamic threshold setting by combining repetition number difference based on detection of an effective peak value, and can be applied to detection of repetition numbers of different next-generation sequencing platforms.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
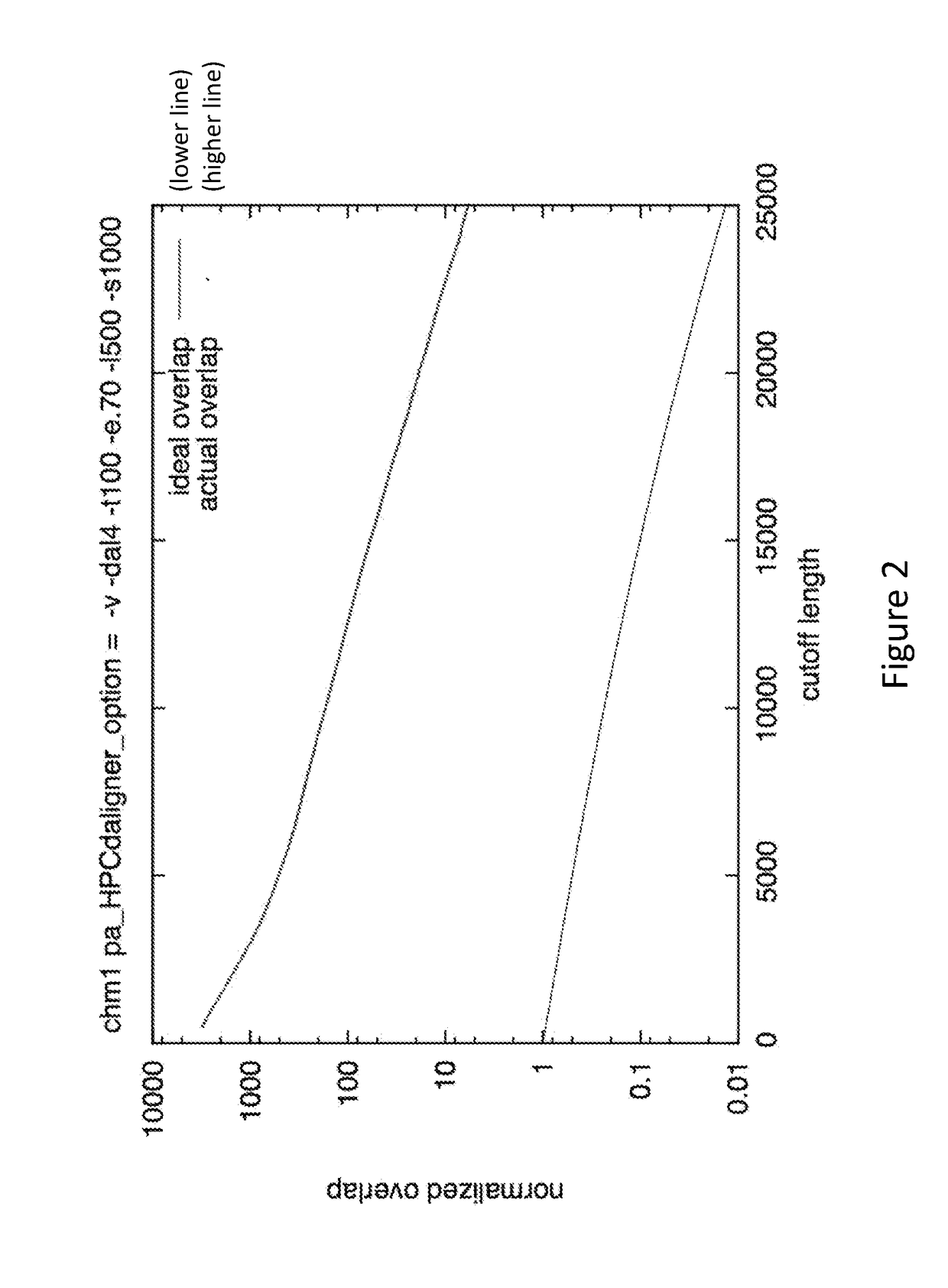
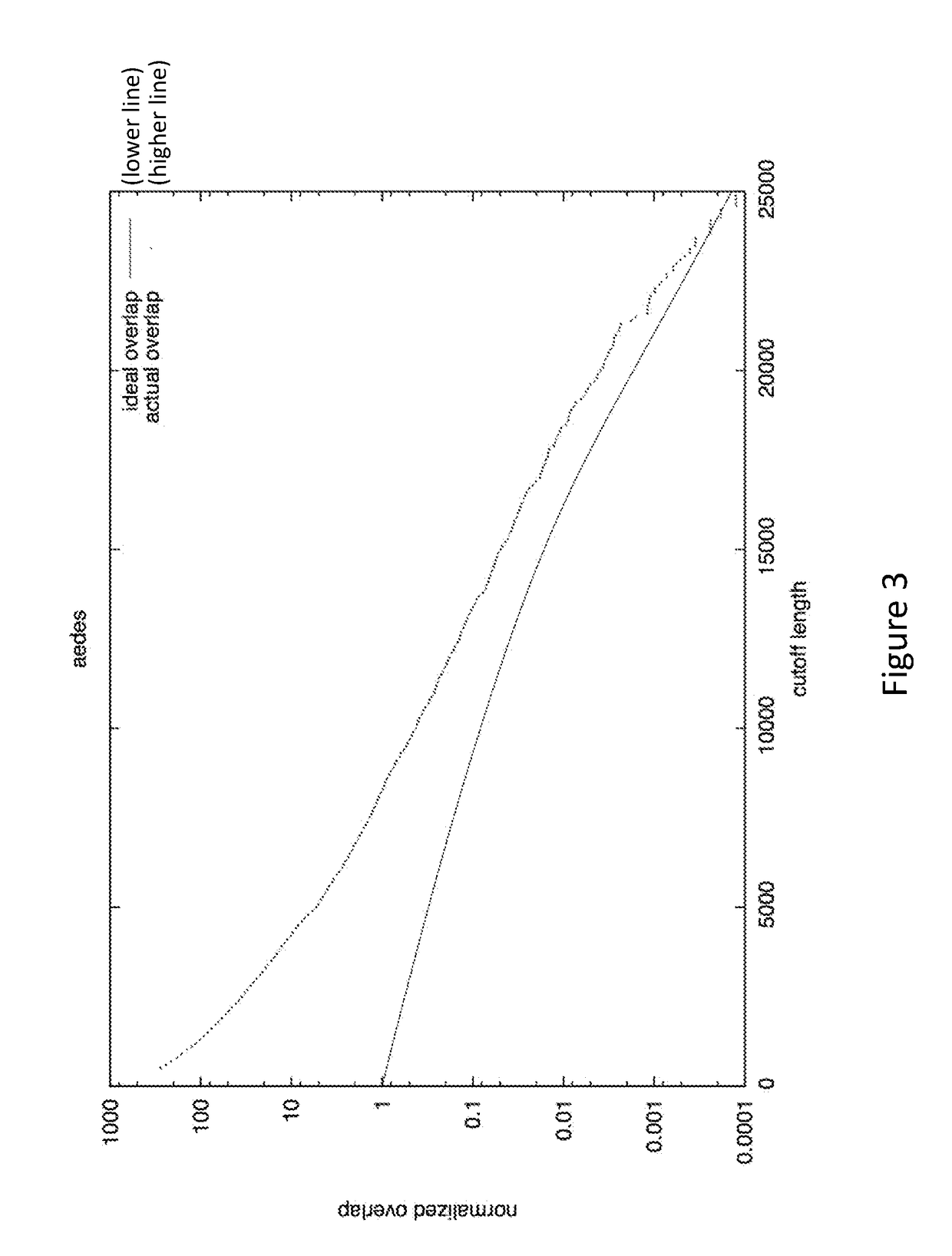
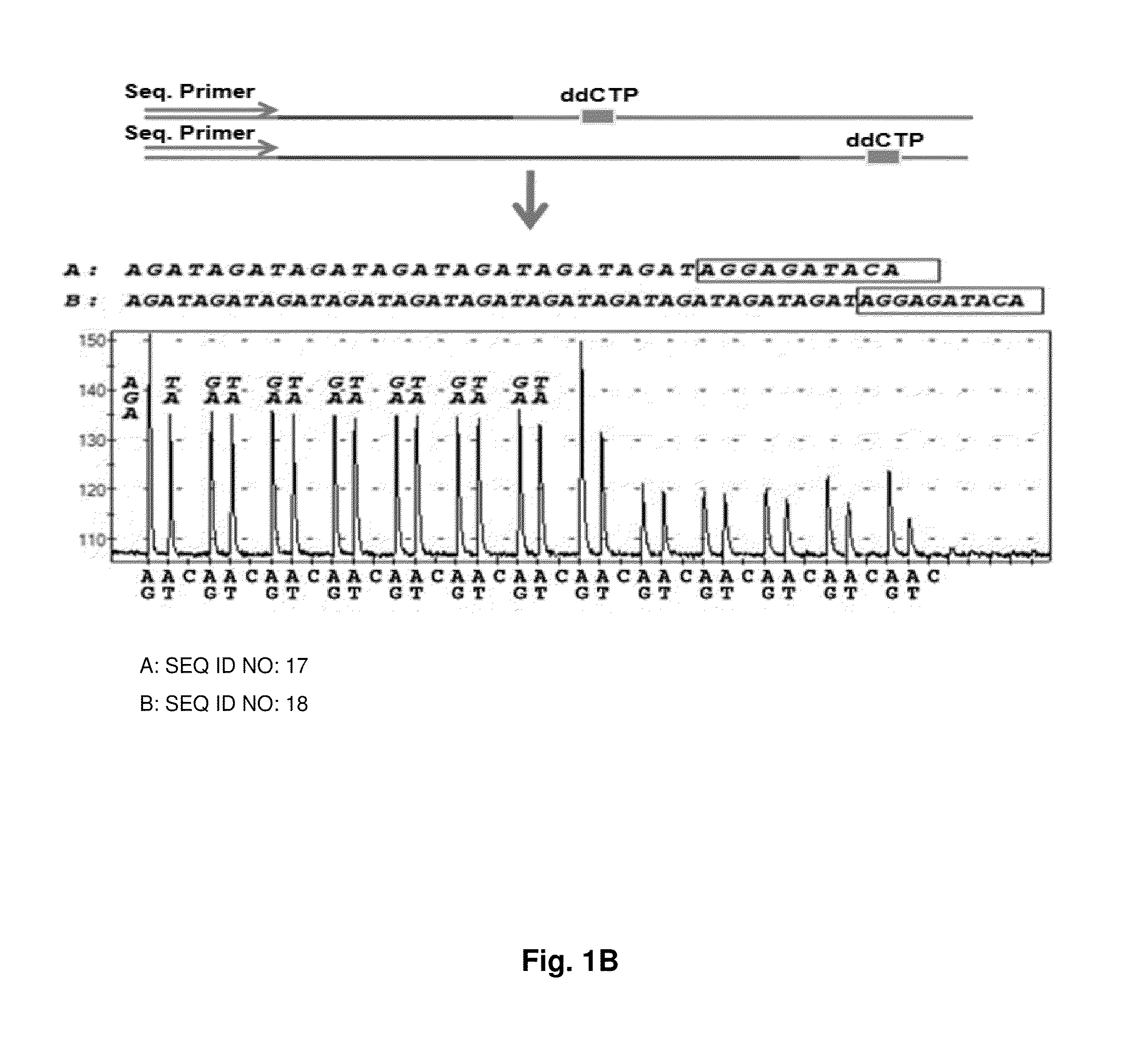
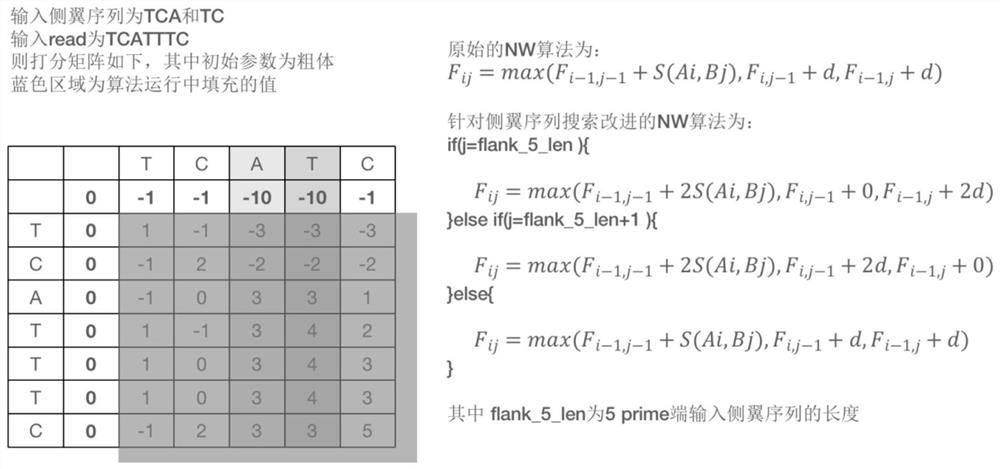
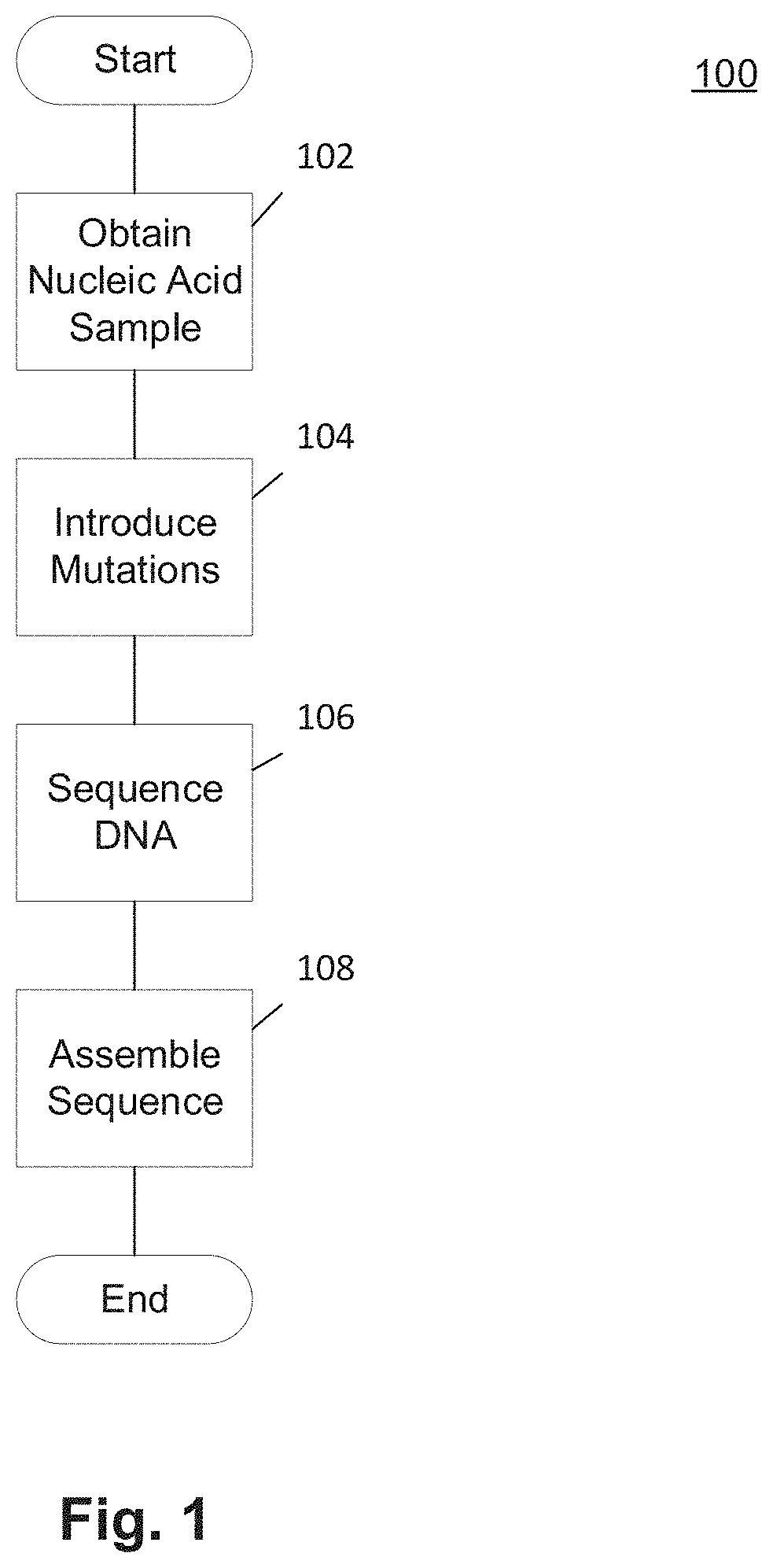
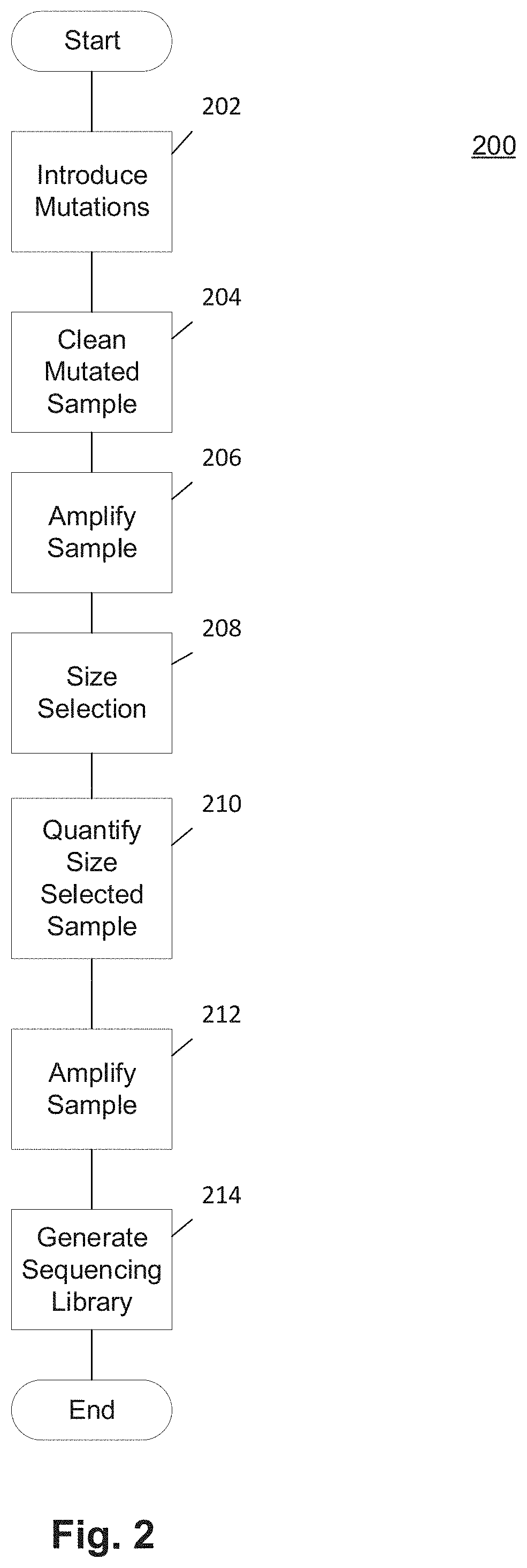
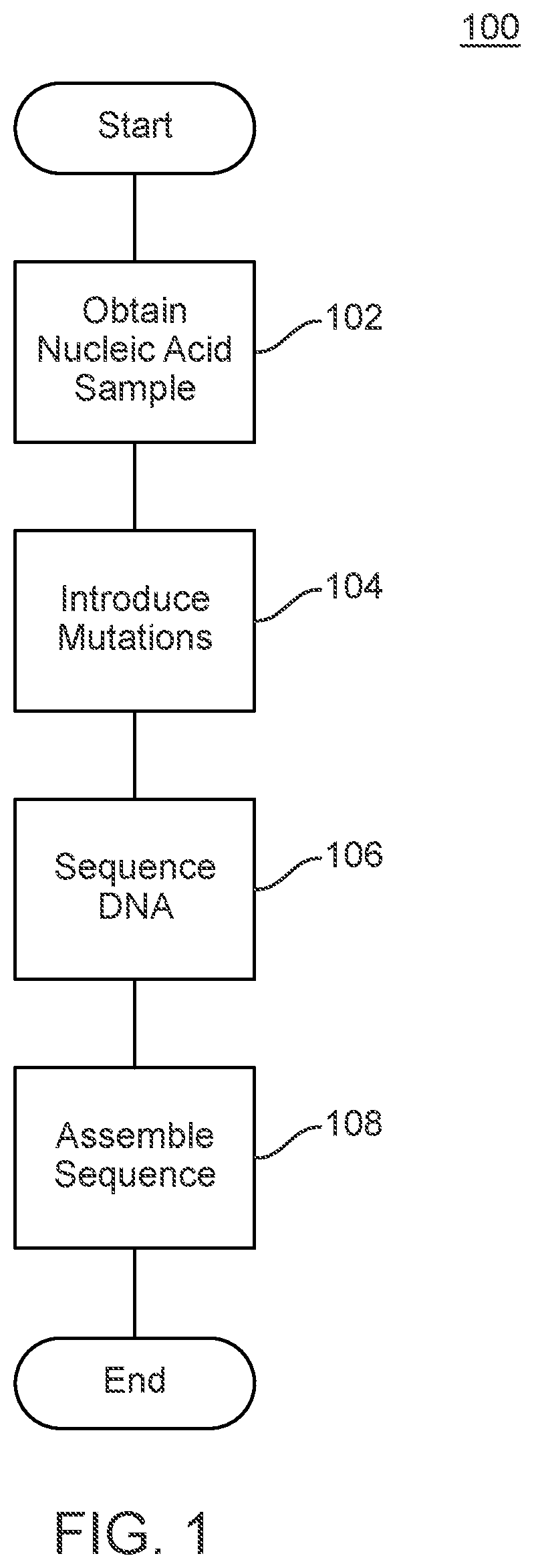
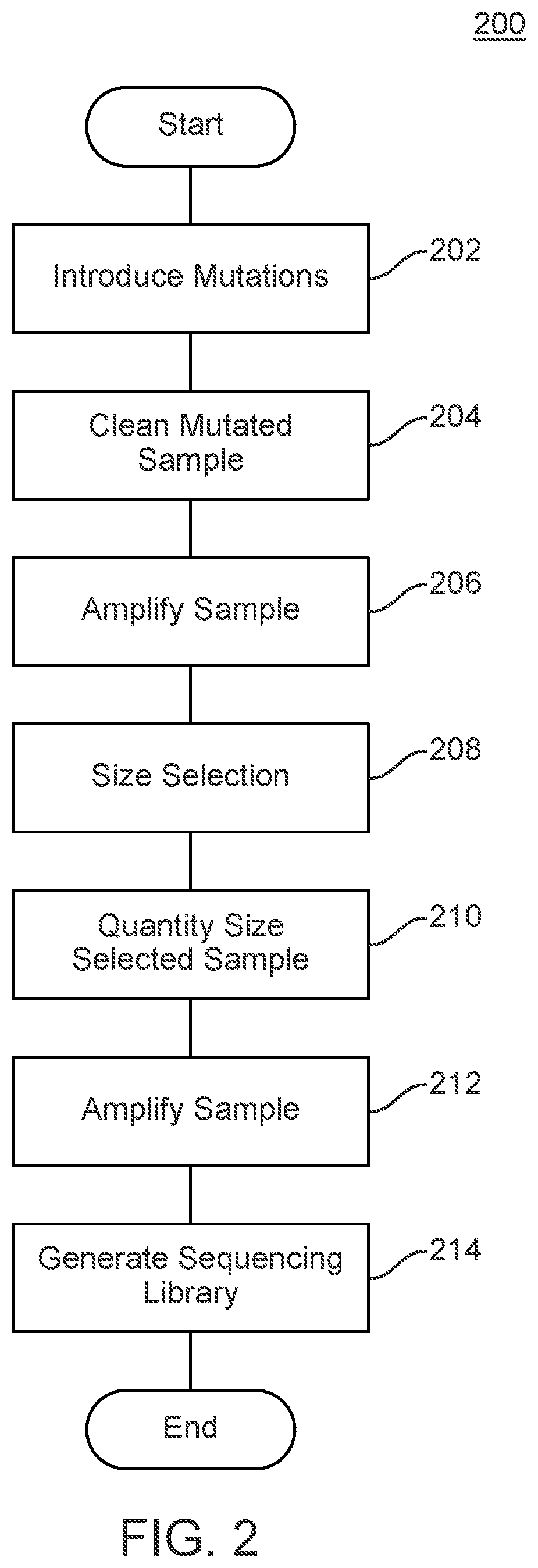
Methods and Uses of Introducing Mutations into Genetic Material for Genome Assembly
ActiveUS20200140848A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenetic MaterialsNucleic acid sequencing
Methods of sequencing and assembling a nucleic acid sequence from a nucleic acid sample containing repetitive or low-information regions, which are typically difficult to sequence and / or assemble are provided. The methods of sequencing and assembling introduce mutations into the sample to increase sequence diversity between various repetitive regions present in the nucleic acid sample. This sequence diversity allows various segments to assemble independently of different, but similar sequences present in the nucleic acid sample.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and uses of introducing mutations into genetic material for genome assembly
ActiveUS11155806B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenetic MaterialsNucleic acid sequencing
Methods of sequencing and assembling a nucleic acid sequence from a nucleic acid sample containing repetitive or low-information regions, which are typically difficult to sequence and / or assemble are provided. The methods of sequencing and assembling introduce mutations into the sample to increase sequence diversity between various repetitive regions present in the nucleic acid sample. This sequence diversity allows various segments to assemble independently of different, but similar sequences present in the nucleic acid sample.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com