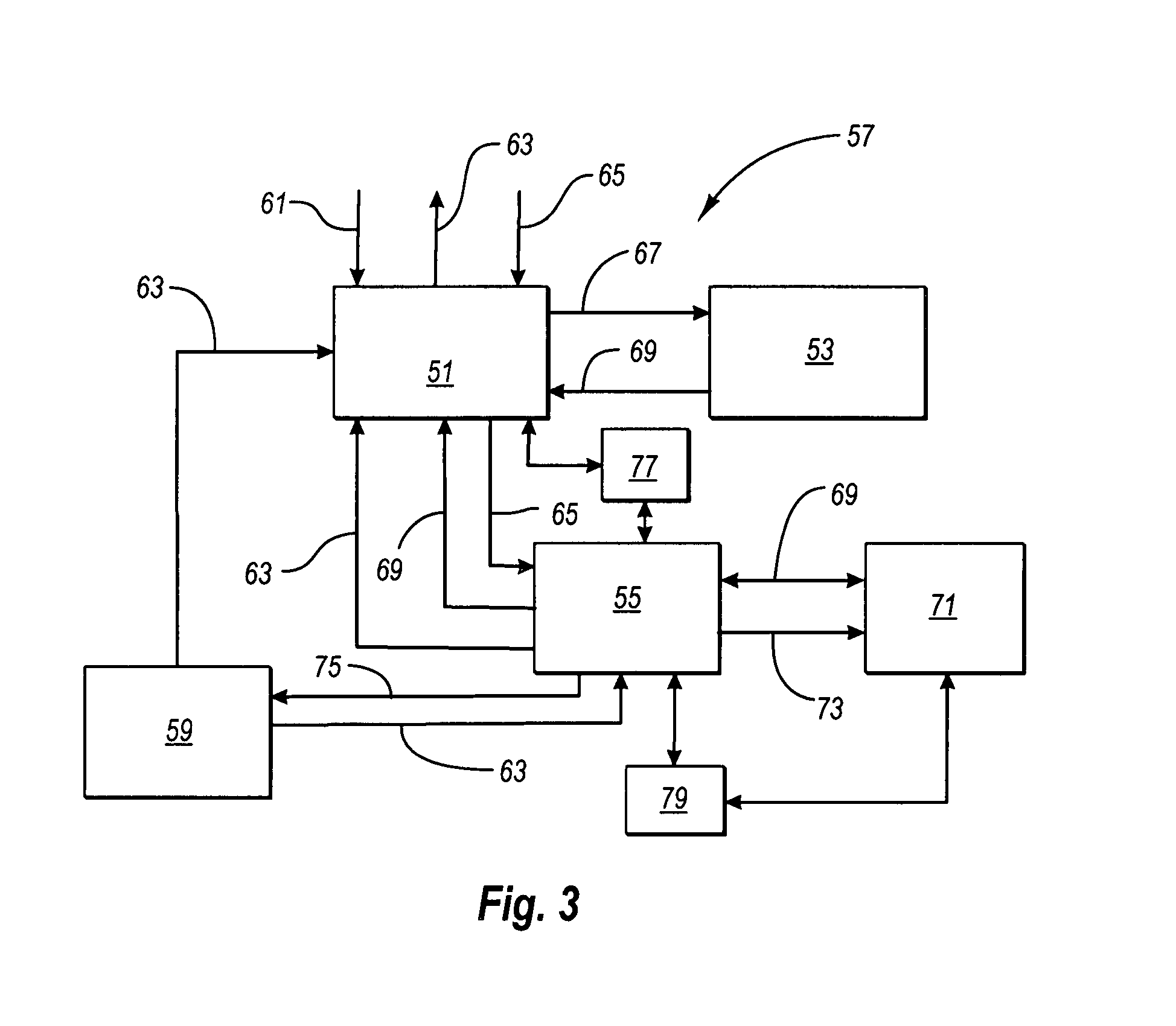
Patents
Literature
136 results about "Transaction Code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
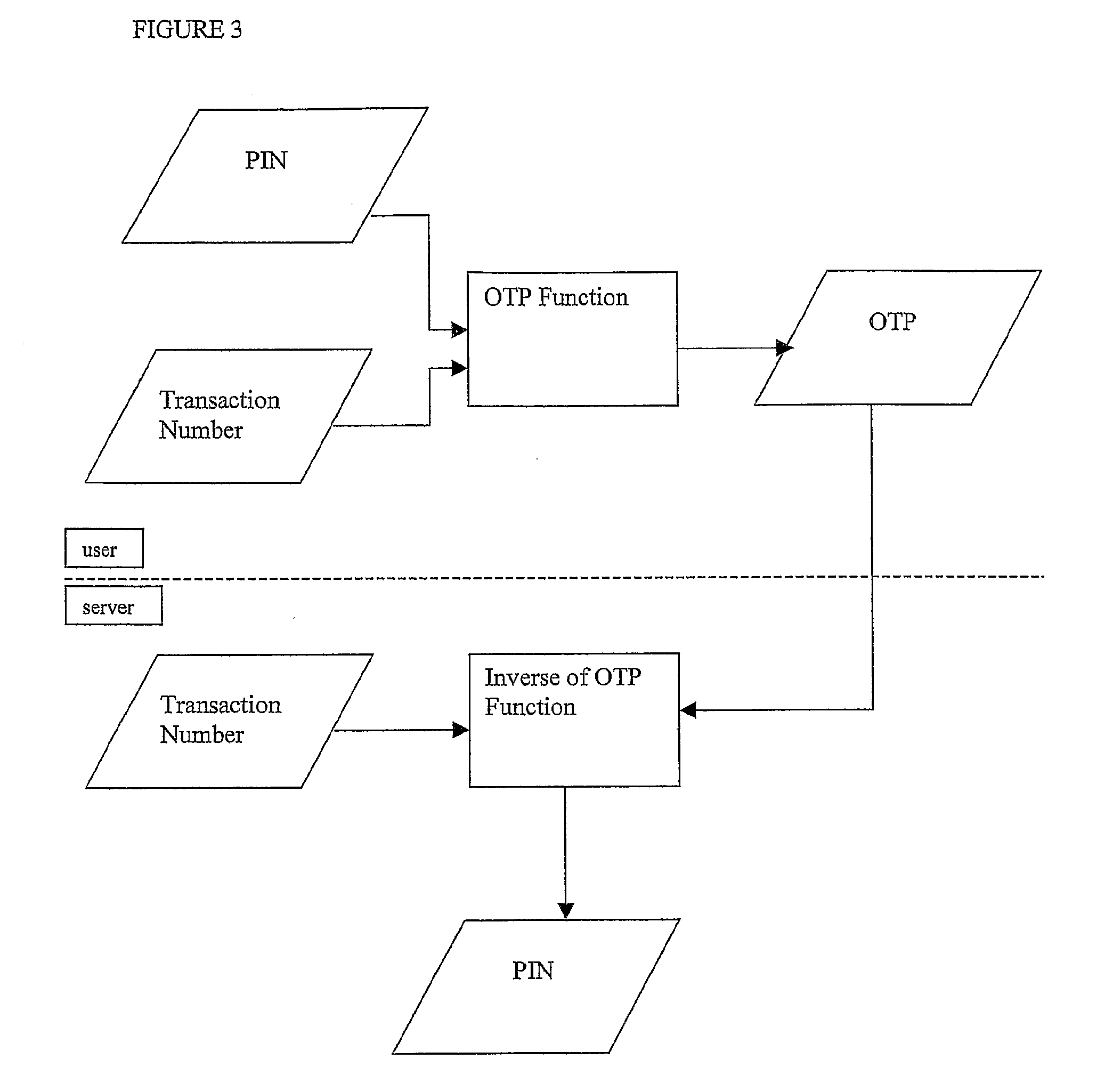
A transaction code (or t-code) consists of letters, numbers, or both, and is entered in the command field at the top of the SAP screen. Each function in SAP ERP has an SAP transaction code associated with it.
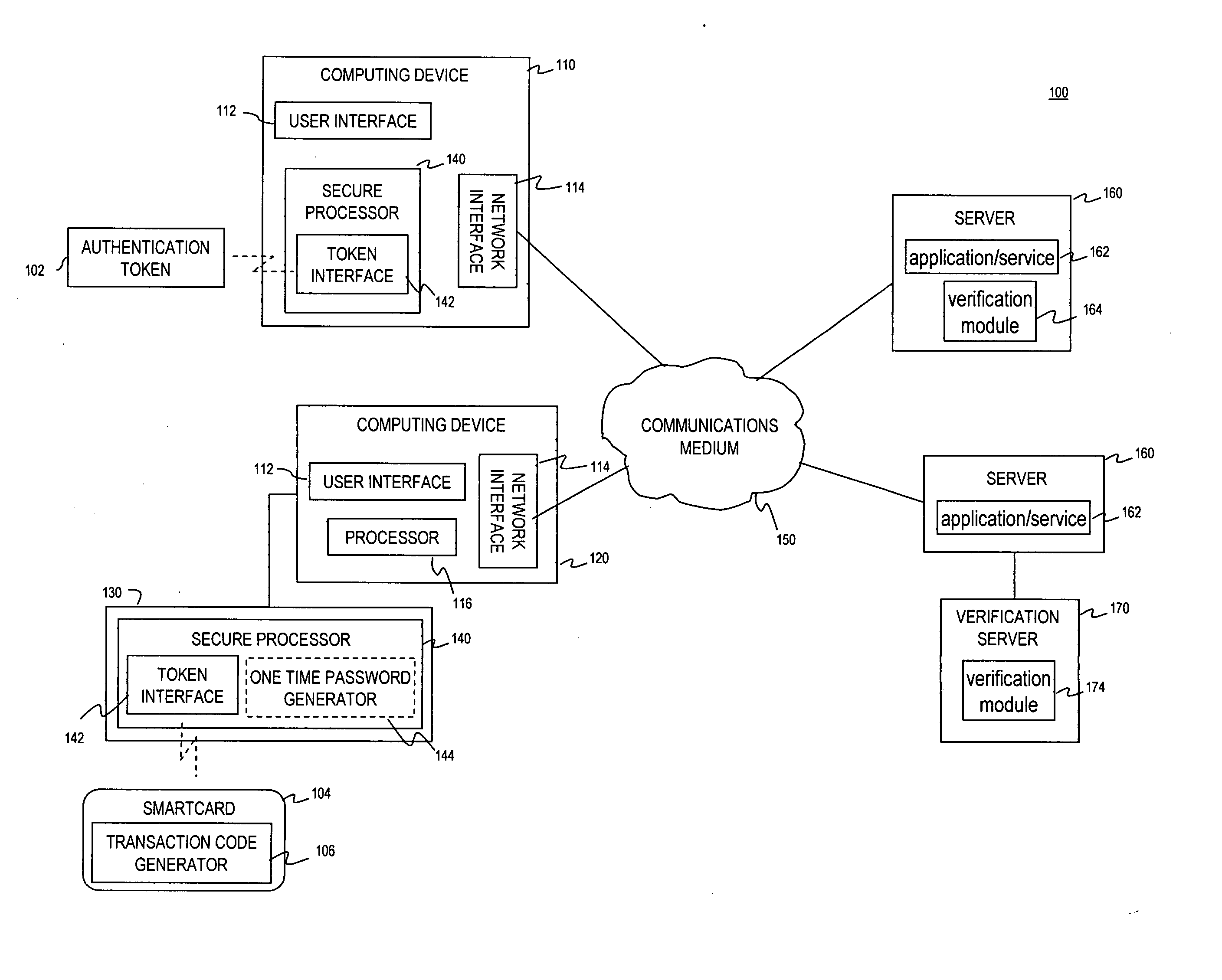
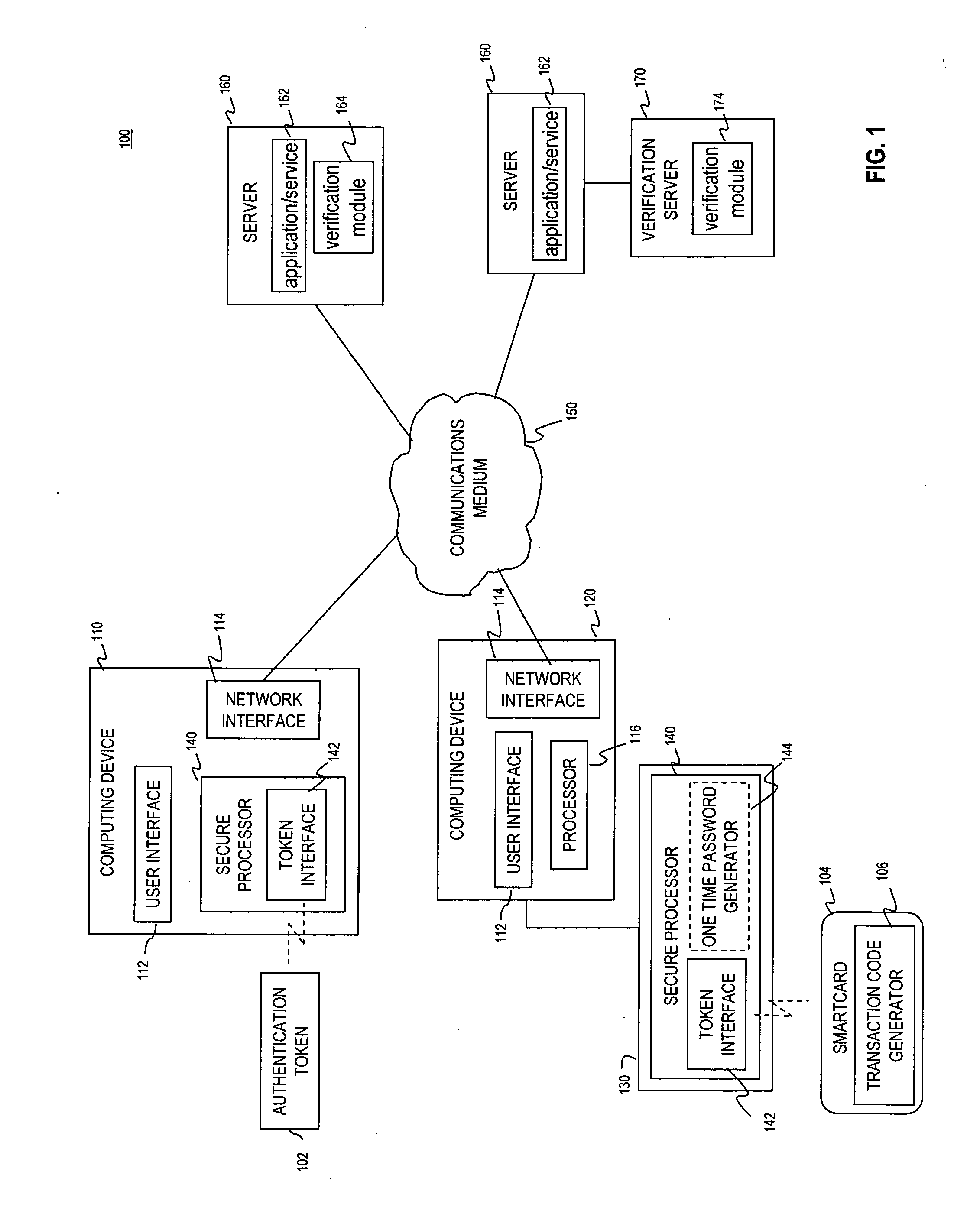
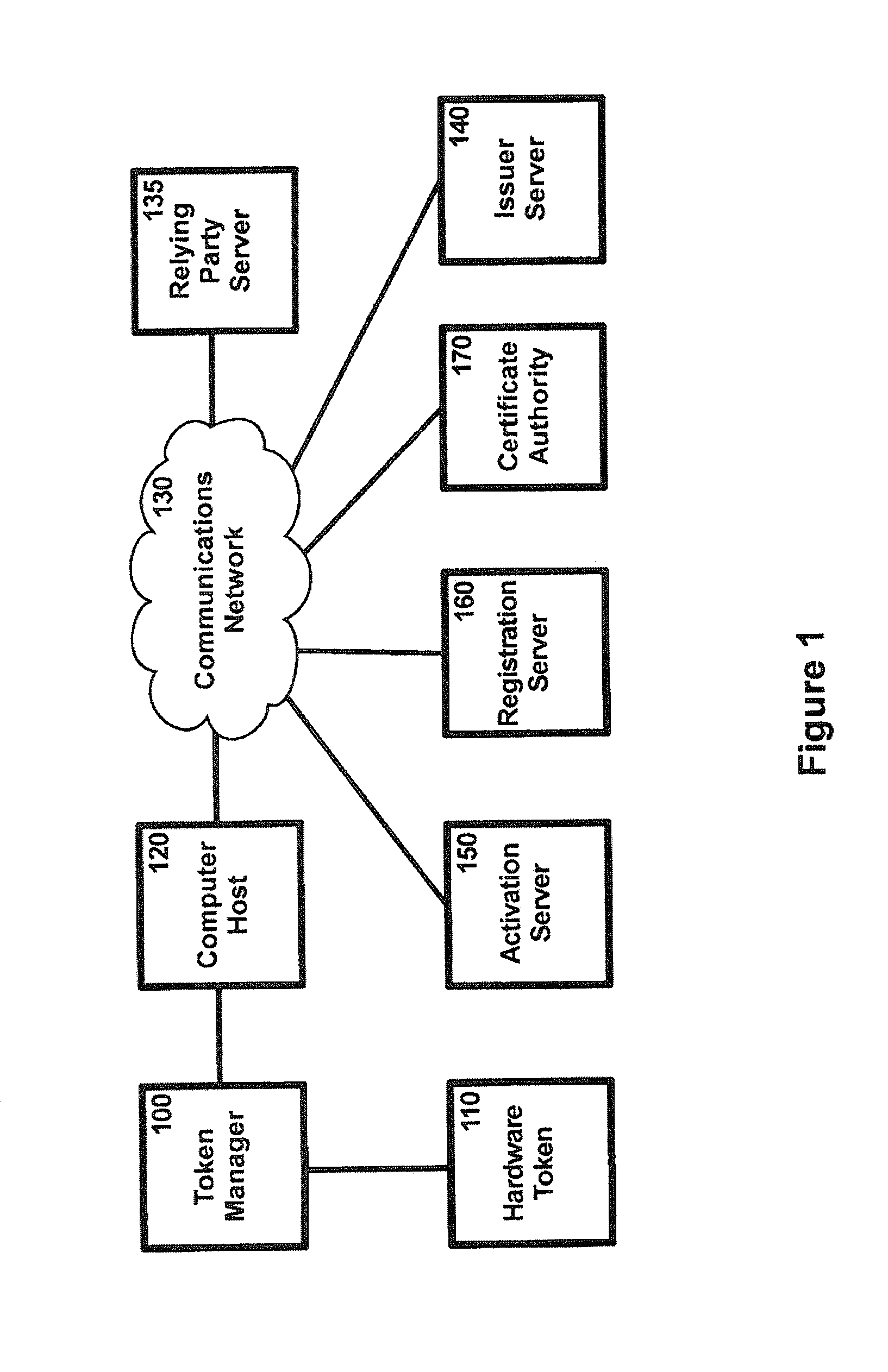
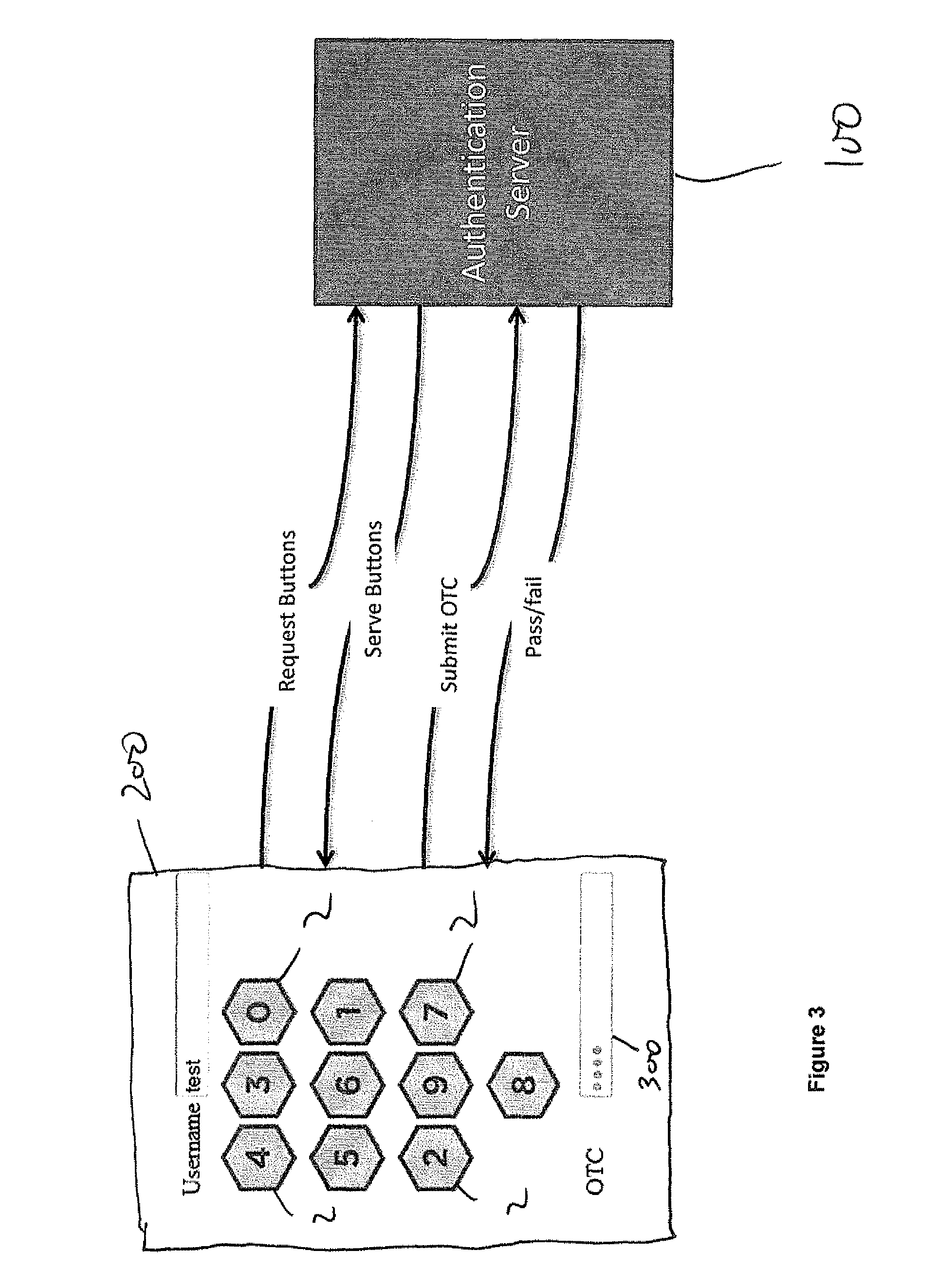
Multi-factor authentication using a smartcard
ActiveUS20070118745A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationThe Internet
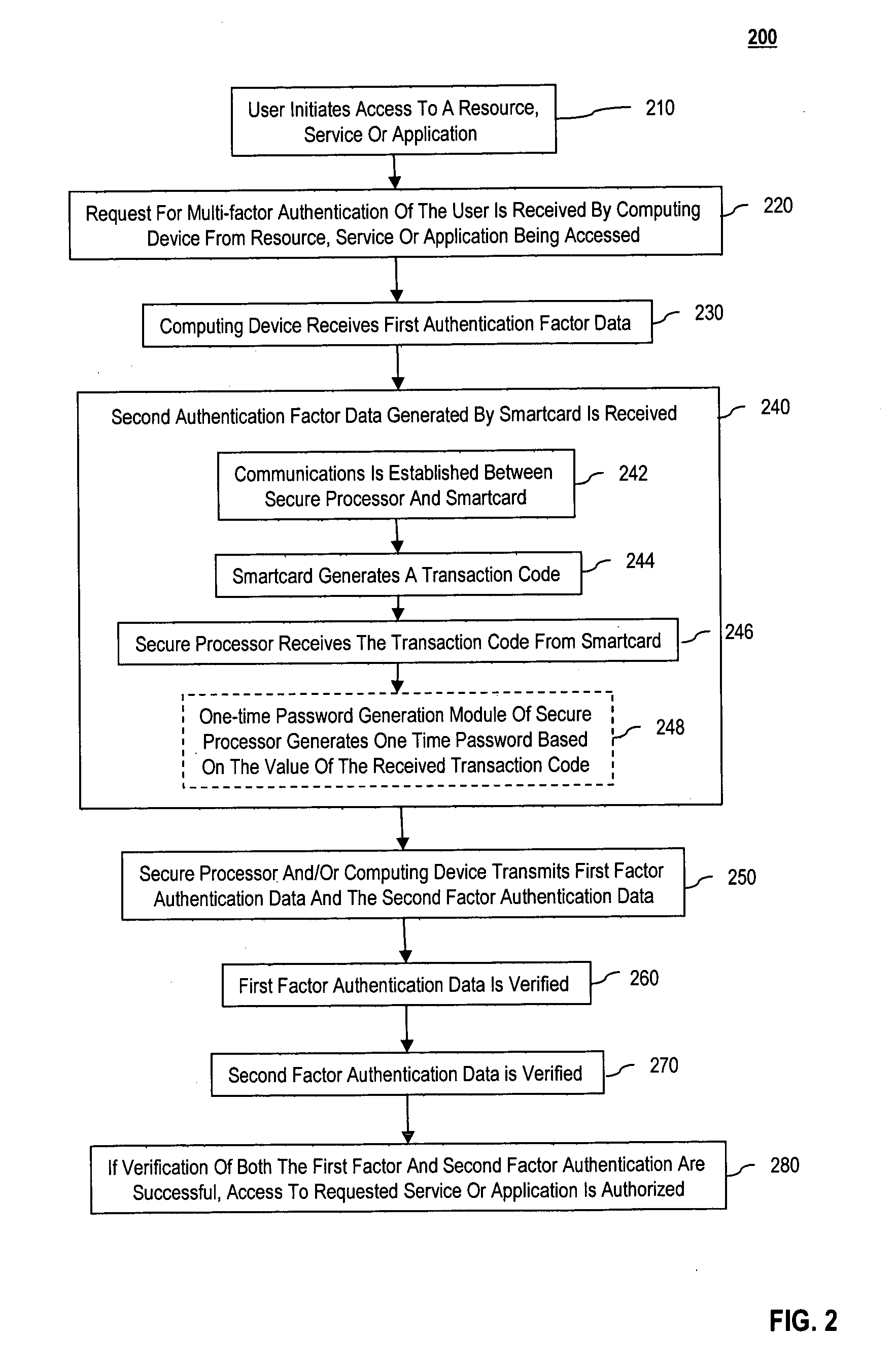
Methods and systems are provided for non-cryptographic capabilities of a token such as a smartcard to be used as an additional authentication factor when multi-factor authentication is required. Smartcards are configured to generate a transaction code each time a transaction is attempted by the smartcard. The transaction code is dynamic, changing with each transaction, and therefore is used as a one-time password. When a user attempts to access a service or application requiring at least two authentication factors, a secure processor is used to read transaction code from the smartcard. The secure processor establishes a secure communication with the remote computer hosting the service or application. The transaction code can then be encrypted prior to transmission over the public Internet, providing an additional layer of security.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Device, method and system for authorizing transactions
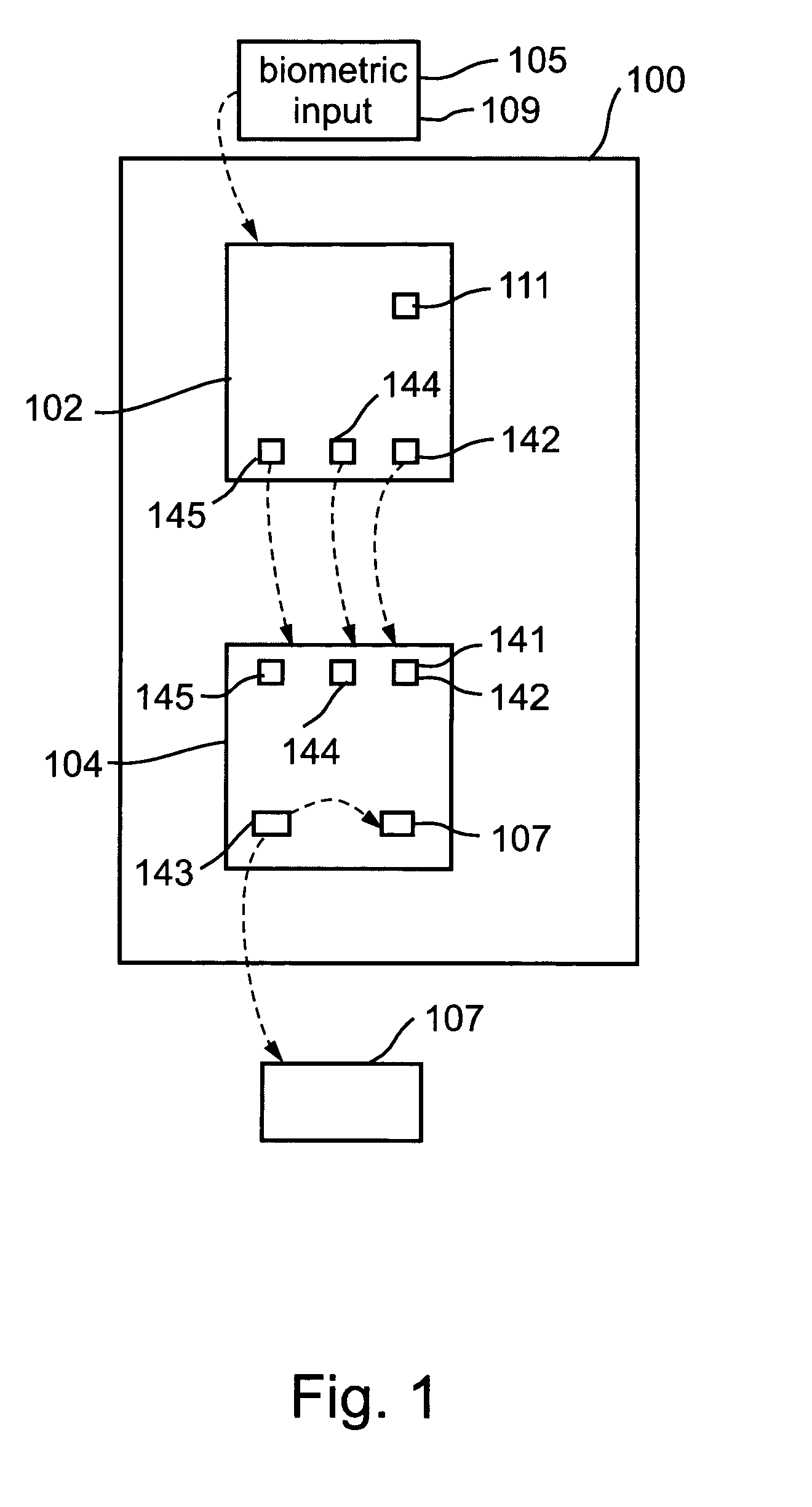
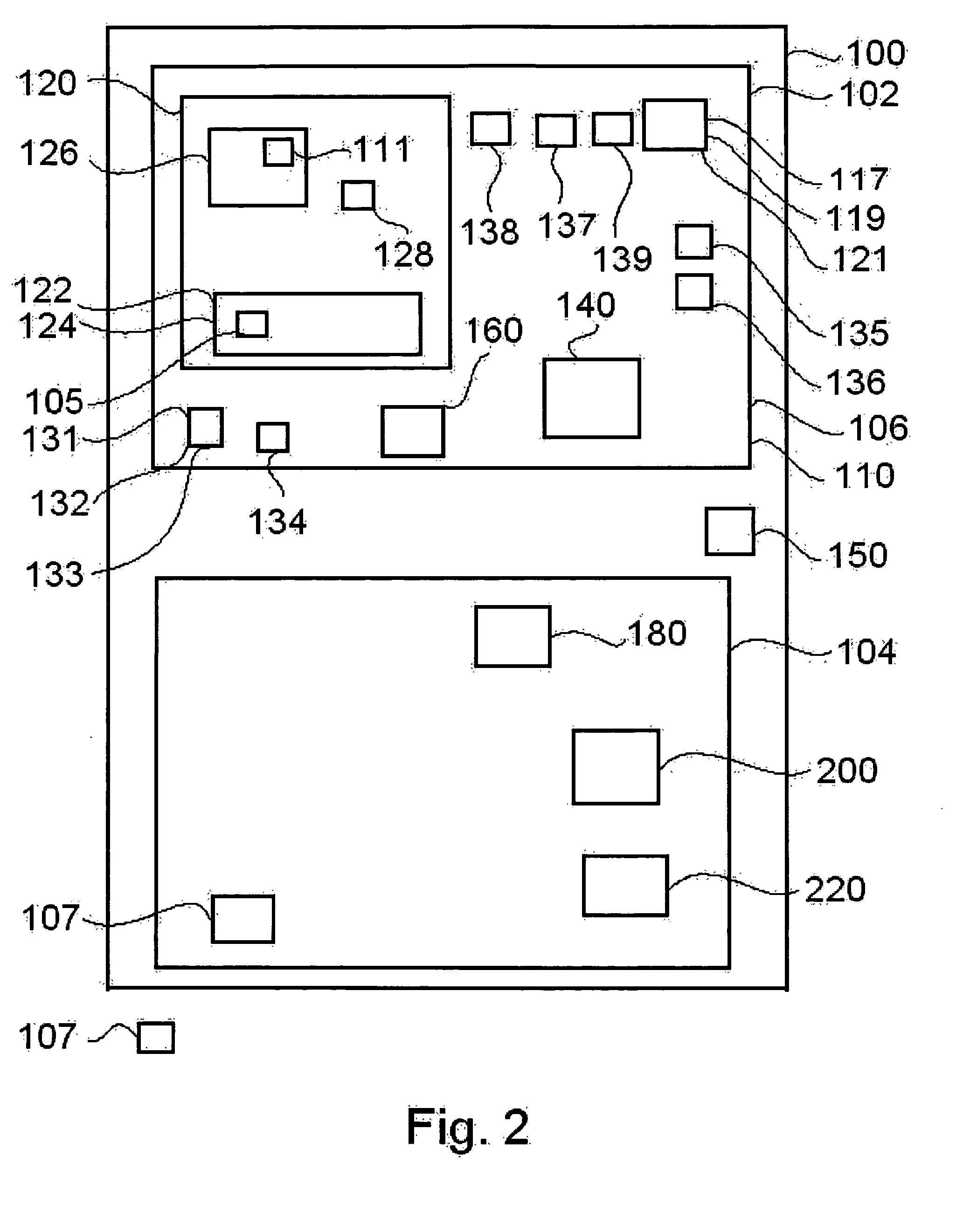
A system, device, and method for authorizing transactions of a plurality of applications. The system comprises a plurality of application servers operable to authorize transactions of applications and a plurality of user devices. Each transaction authorization is dependent upon receipt, by the authorizing server, of a transmitted code verified by the server as being an appropriate transaction code for the selected application. Each user device is operable to verify the identity of a user by comparing real-time biometric input from the user with data derived from biometric input provided by the user during device initialization. Each user device is further operable to select an application from among a plurality of applications and to emit a non-repeating non-guessable transaction code appropriate for the selected application. Emission of the transaction code is dependent upon biometric verification, by the user device, of the user's identity.
Owner:HOFI EYAL
Authentication system and method
InactiveUS20100180328A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationProgramming languageUser device
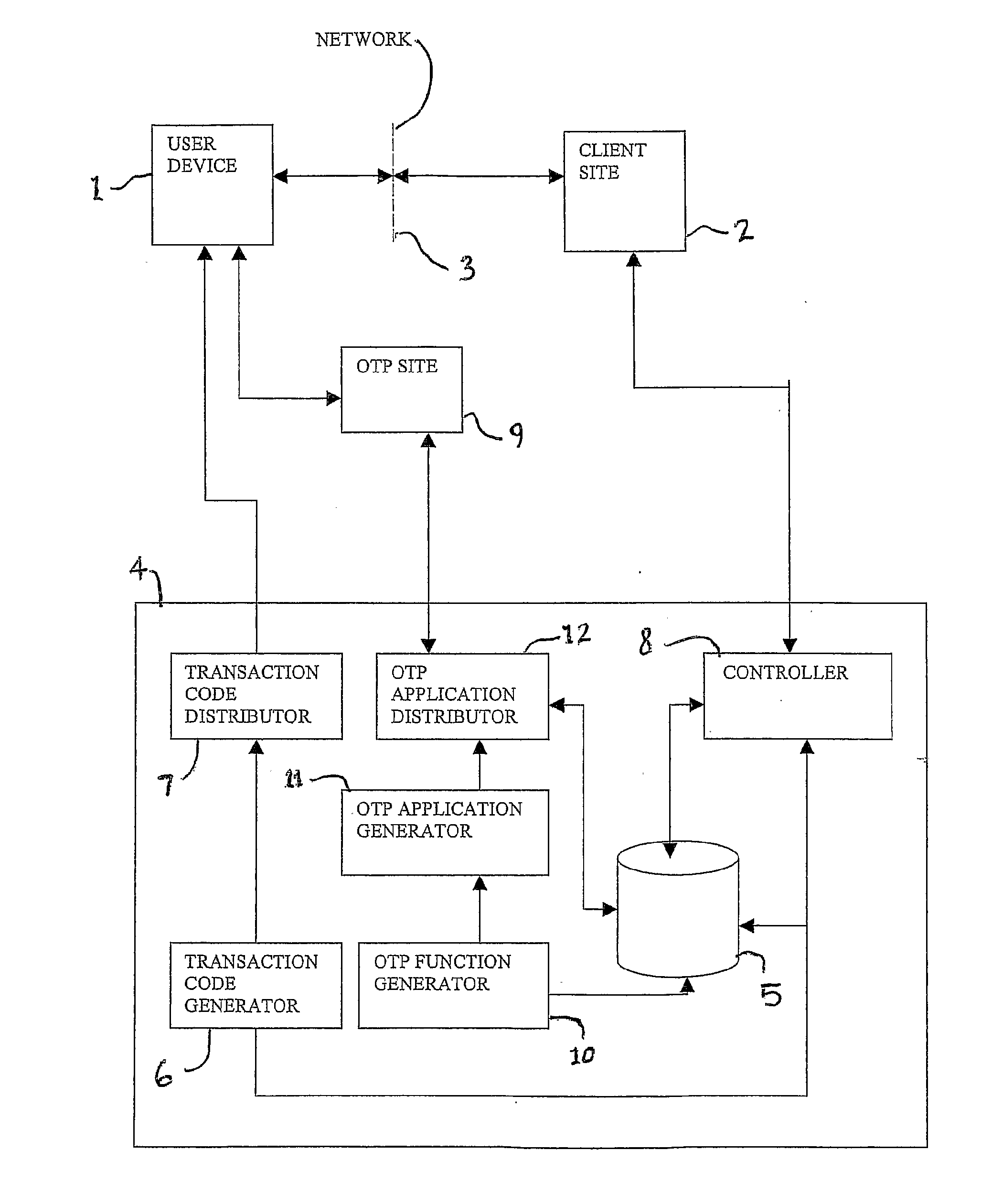
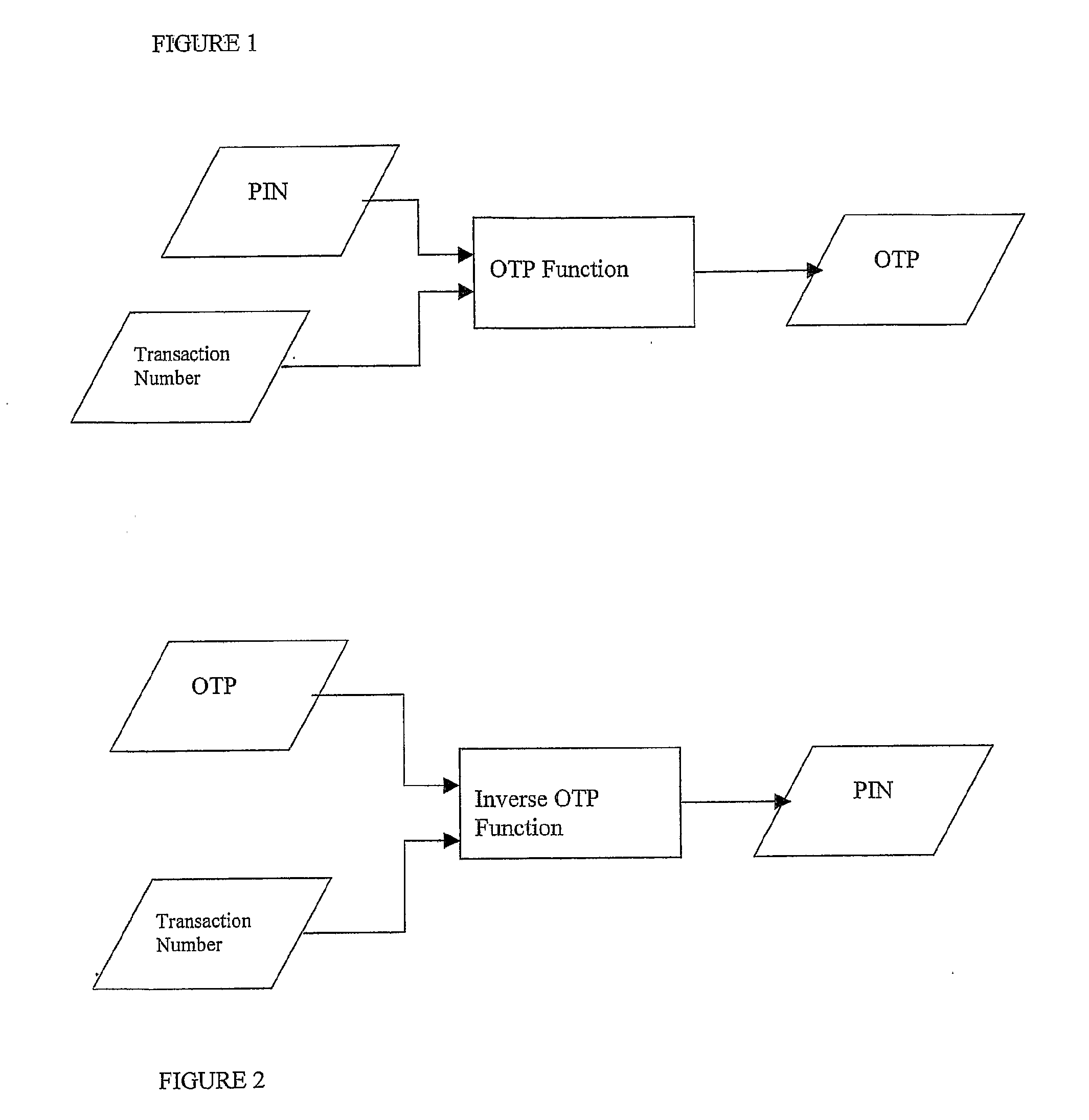
An authentication system and method axe provided, the method comprising, storing a user identification code associated with said user, generating a plurality of functions for producing a pass code based on at least one input by a user, said at least one input comprising said user identification code, storing at least one function and associating said function with a user, generating an application adapted to implement said at least one function on the user device, supplying the application to said user device, generating a transaction code associated with said transaction and supplying the transaction code to said application; and receiving a pass code for said transaction from the user device and authenticating the transaction on the basis of the received pass code, the function associated with said user, the user identification code and the transaction code associated with said transaction.
Owner:MINTED PEAS TECH
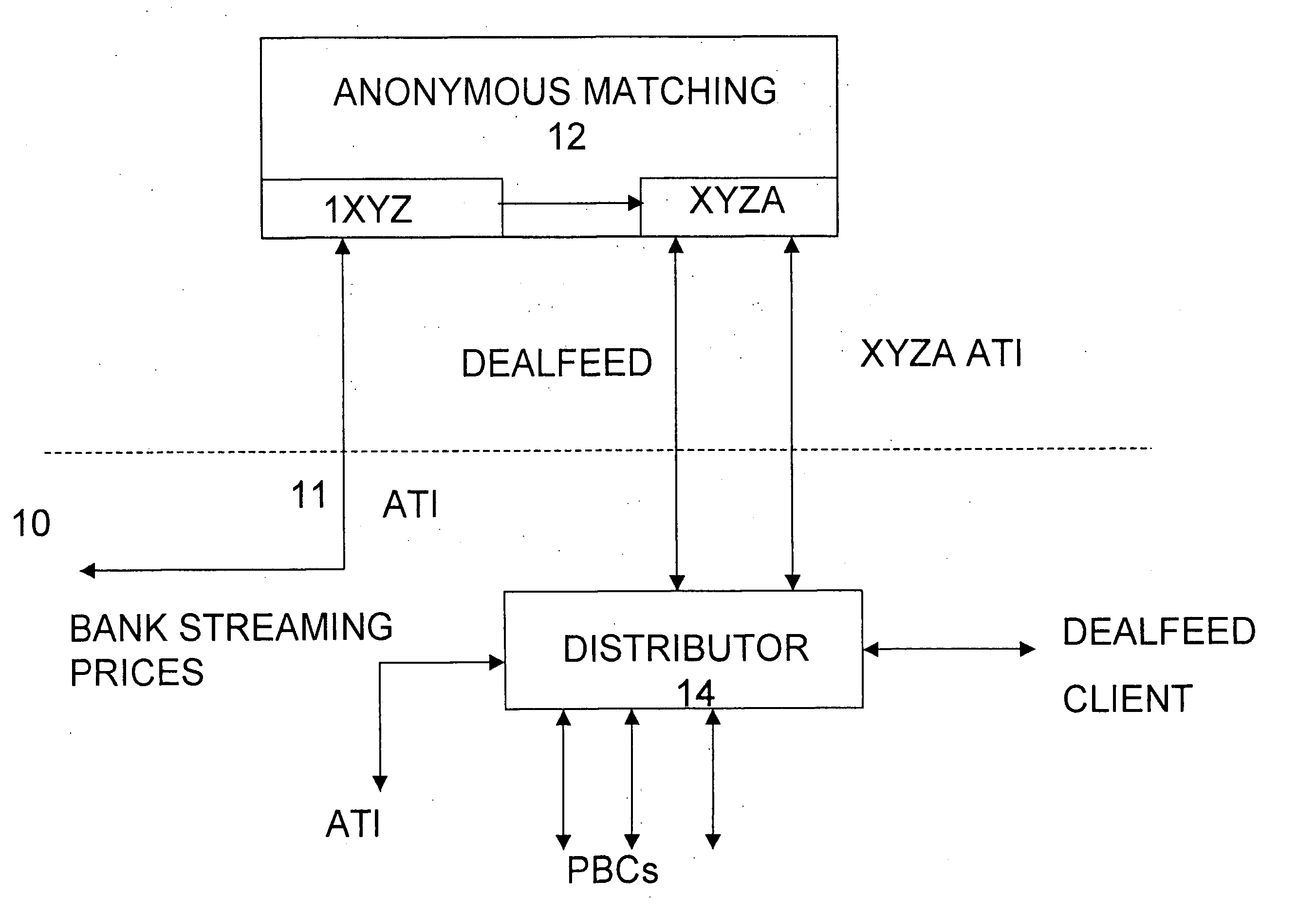
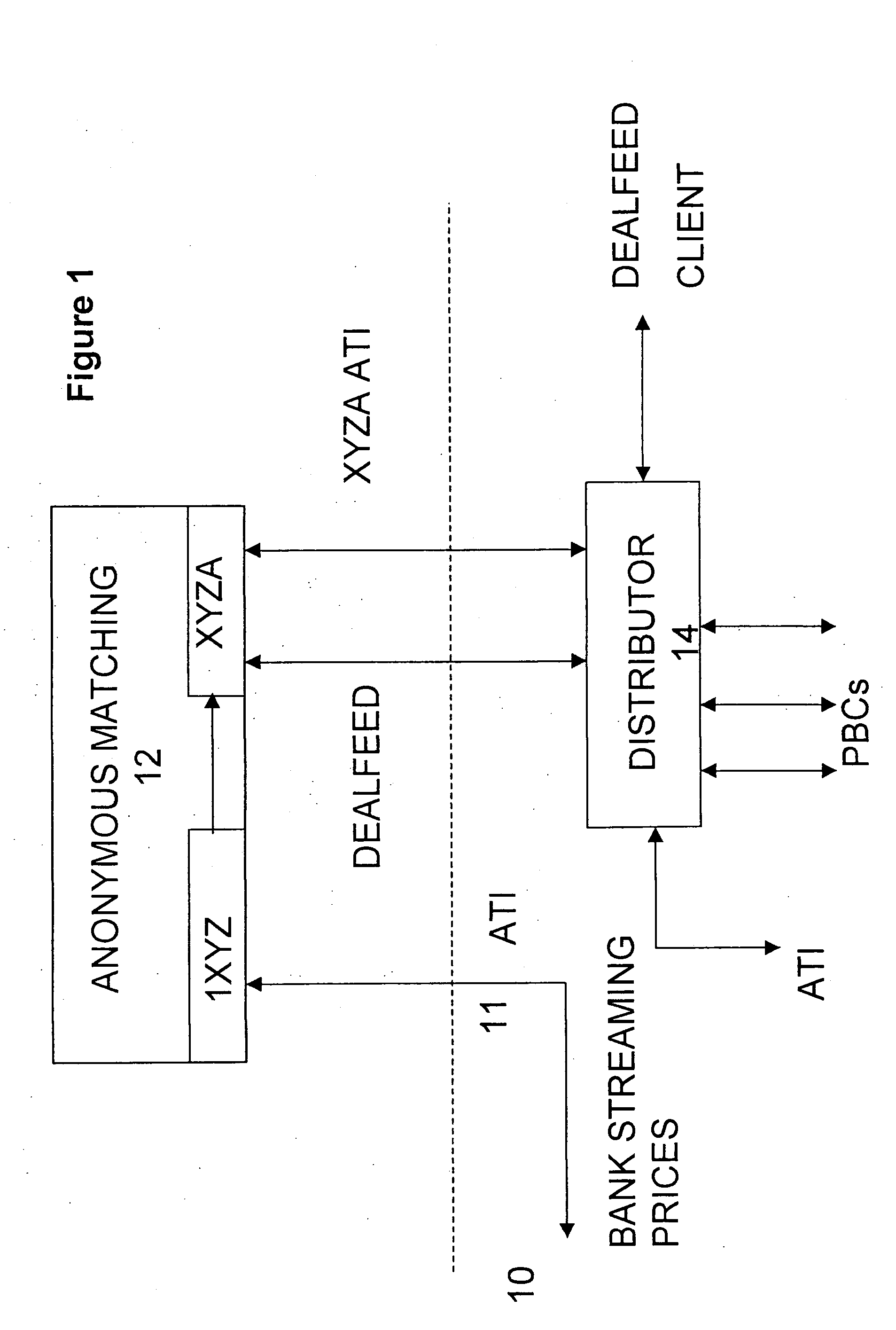
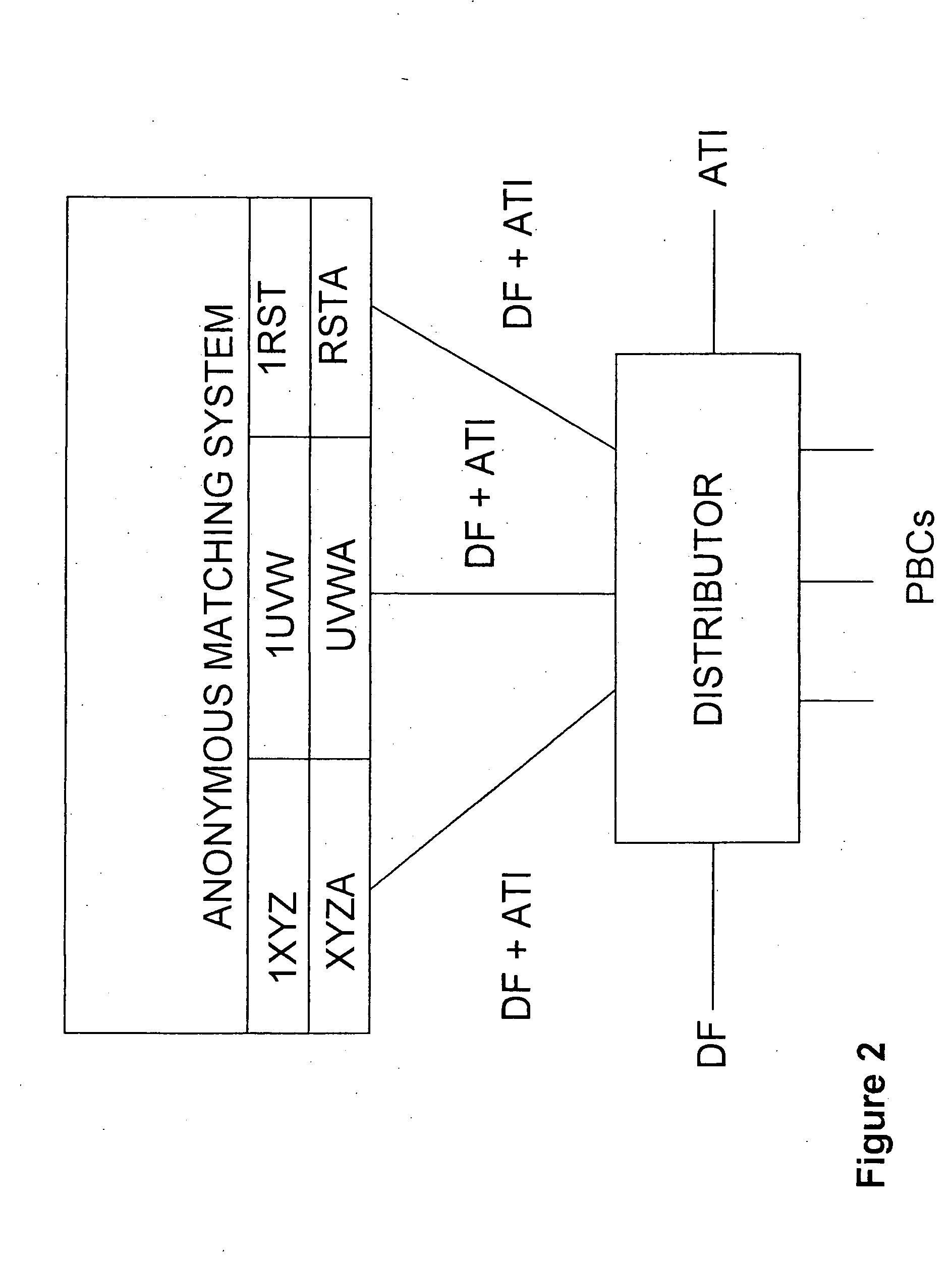
Automated trading system
An anonymous trading system is configured to receive a price stream from a bank or other institution. The price stream is converted into a quote stream and input into the trading system via an automated trading interface. The quote stream has its own deal code. The deal code credit limits are set so that the only parties that have credit with the deal code are other deal codes of the same institution. At least one of these deal codes represents a prime broker bank and prime broker customers therefore have access to the institution's price stream to the exclusion of other parties trading on the system. A distributor distributes the quotes from the trading system to the prime broker customers' traders, to prime broker customer automated trading interfaces, and to prime broker customer deal feed systems for logging of deal tickets and communication of those deal tickets to back office systems.
Owner:NEX GRP PLC
System and method of improved recording of medical transactions
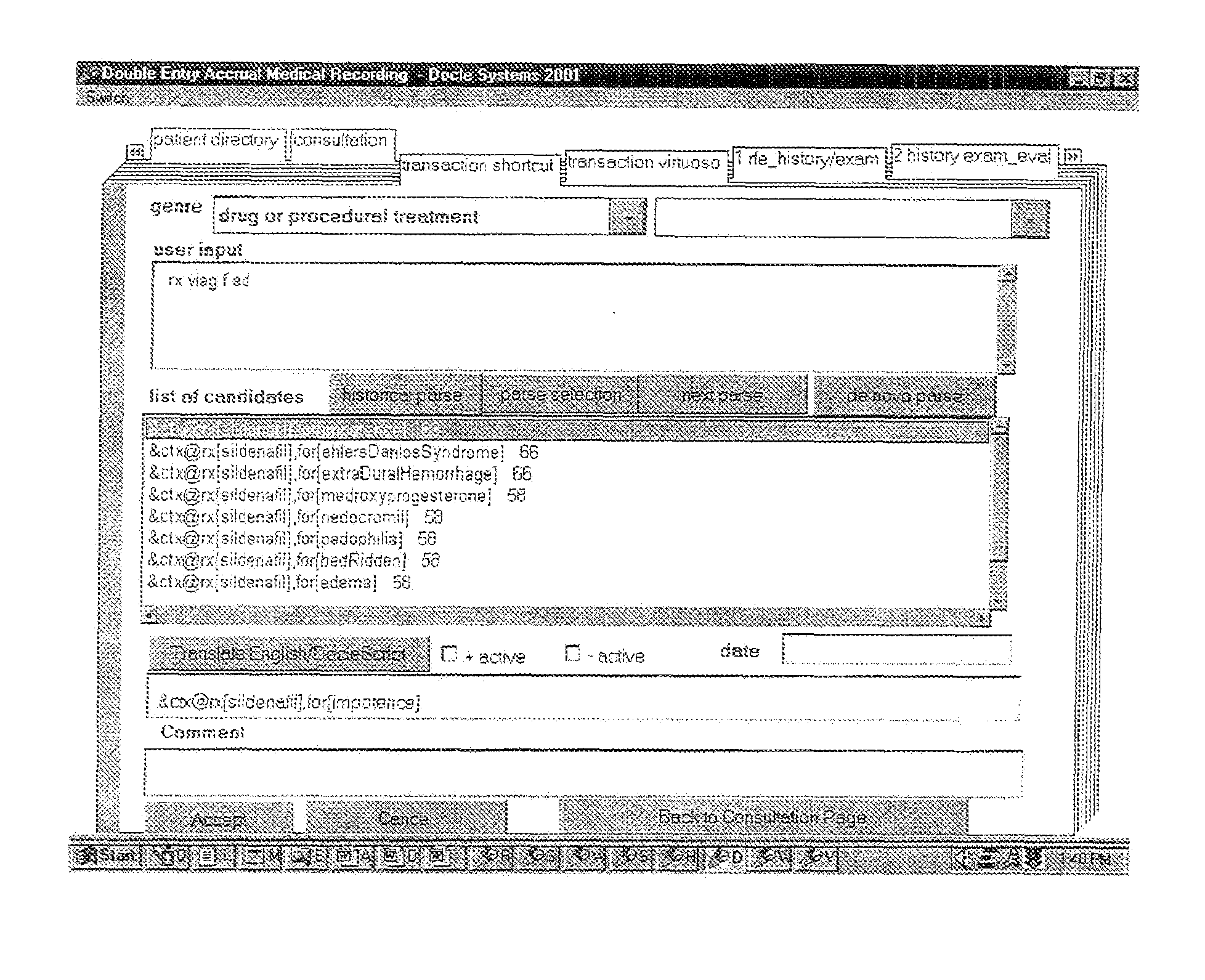
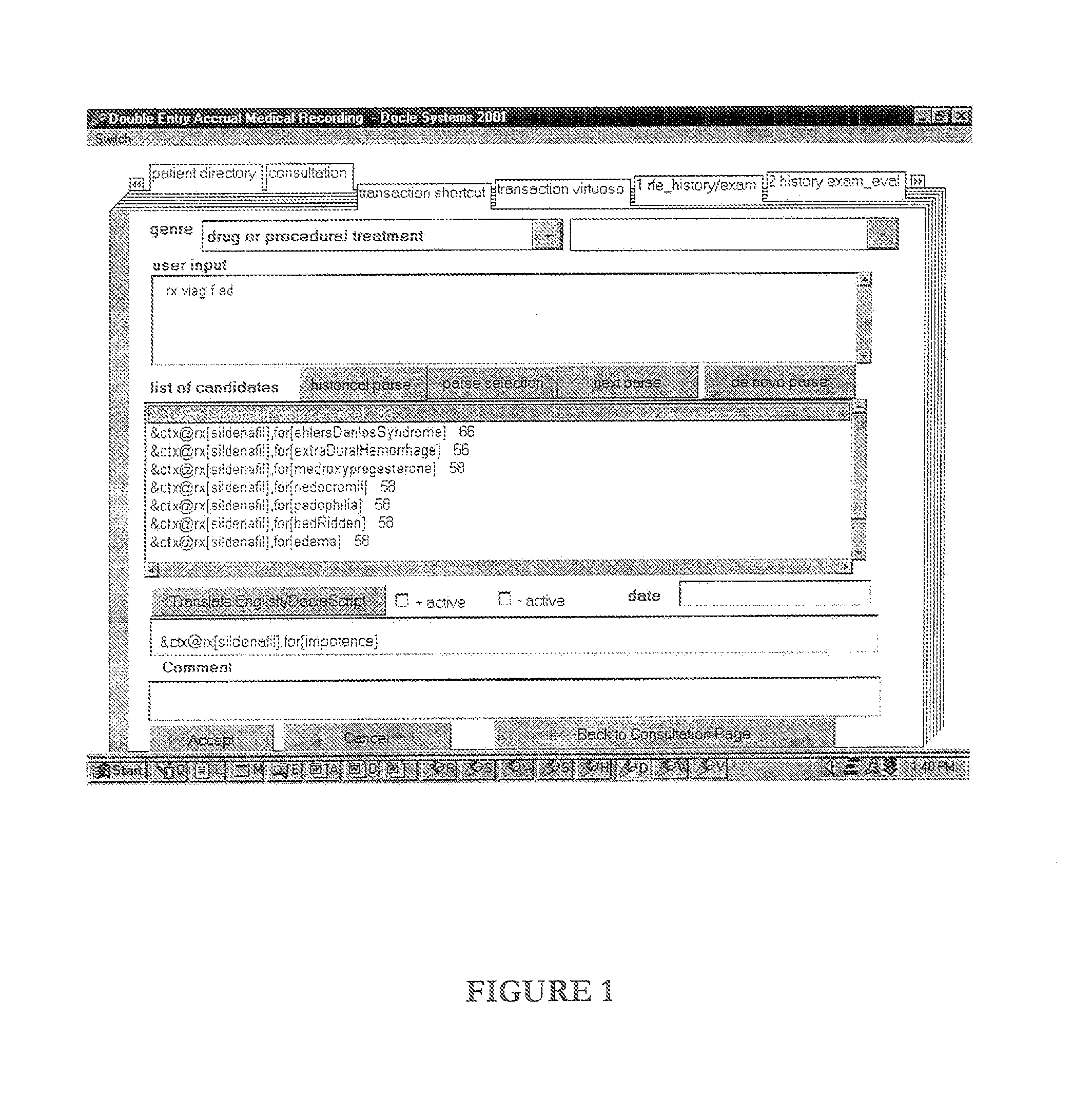
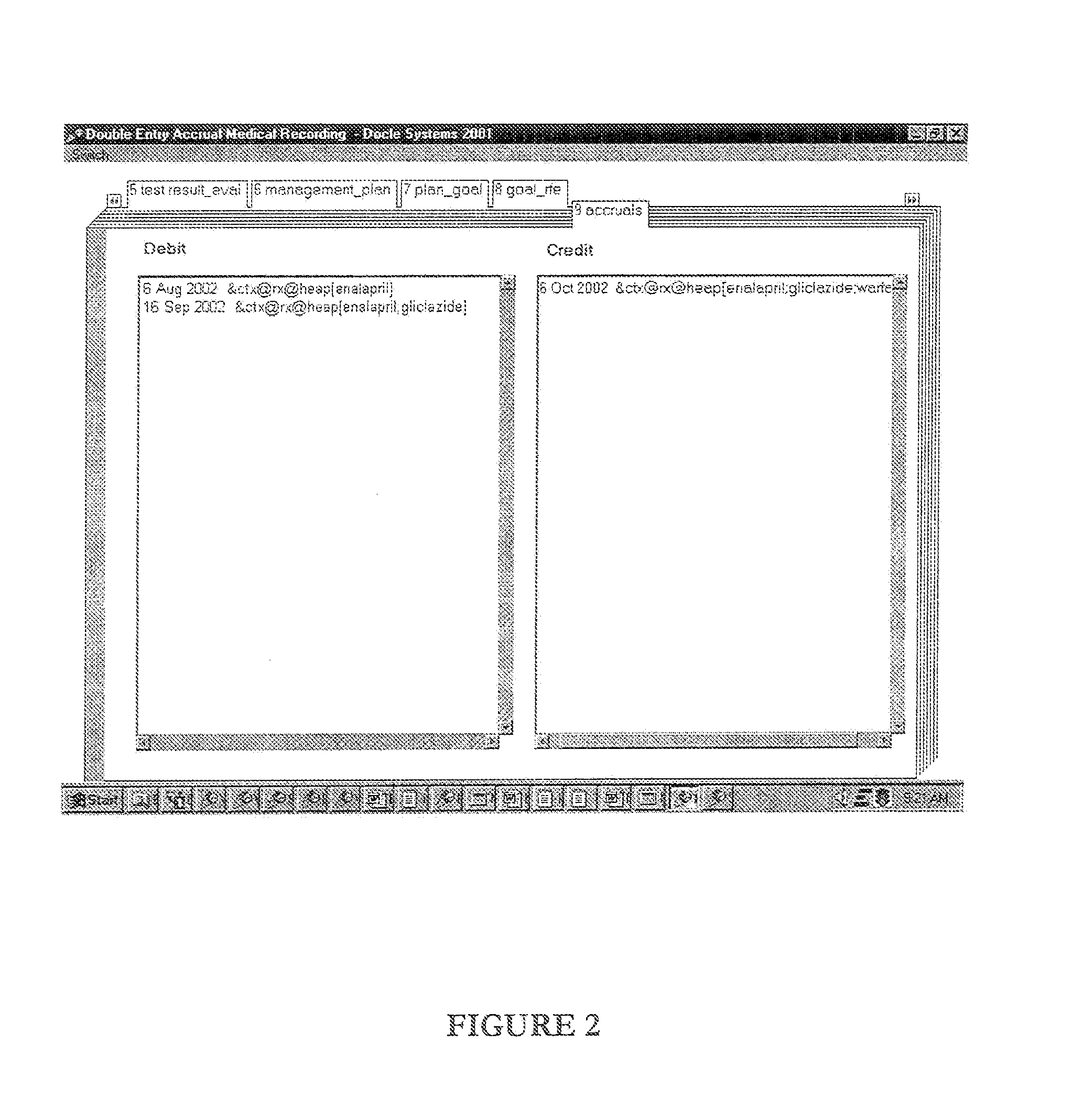
This invention relates to the field of patient health care. In particular, it relates to medical informatics, and to systems and methods for recording medical transactions. A system for recording medical transactions is disclosed, the system comprising distinct and multi-linguistic representation layers, allowing the de novo composition and construction of medical transaction codes; including a user interface including means for inputting medical transactions in a semiotic form one, the semiotic form one input being a free form-type, abbreviation-oriented natural language textual input, a transaction parser-coder configured to parse said semiotic form one input and to convert it into coded medical transactions in a semiotic form two output, the transaction codes composed and constructed de novo, the semiotic form two output embodying high level machine-parseable computer language statements comprehensible to a high certainty level by human users, means for evoking a display of system reflection in the form of coded medical transactions in said semiotic form two and system-rated confidence levels representing the match between a code and correspondence with perceived user intent, means for receiving user selection input for verifying a selected coded medical transaction, and a transaction mapper configured to convert a semiotic form two input into a semiotic form three transaction by mapping the selected coded transaction into data row in a relational database to render the transaction data amenable to structured query language processing. There is further disclosed a computer-based method for the management of medical transactions, including storing each medical transaction as a transaction code in a data row in a database table, each transaction code including a genre key relating to the nature of the transaction, and including providing storage ledgers for each genre, such that each transaction can be retrieved and displayed as an entry in a storage ledger in accordance with its genre key. This allows medical transactions to be treated akin to accounting transactions, signifying credits and debits in defined transaction ledgers.
Owner:OON YEONG K
System and methods for online authentication
ActiveUS20110307949A1Authentication is convenientDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideAuthorization
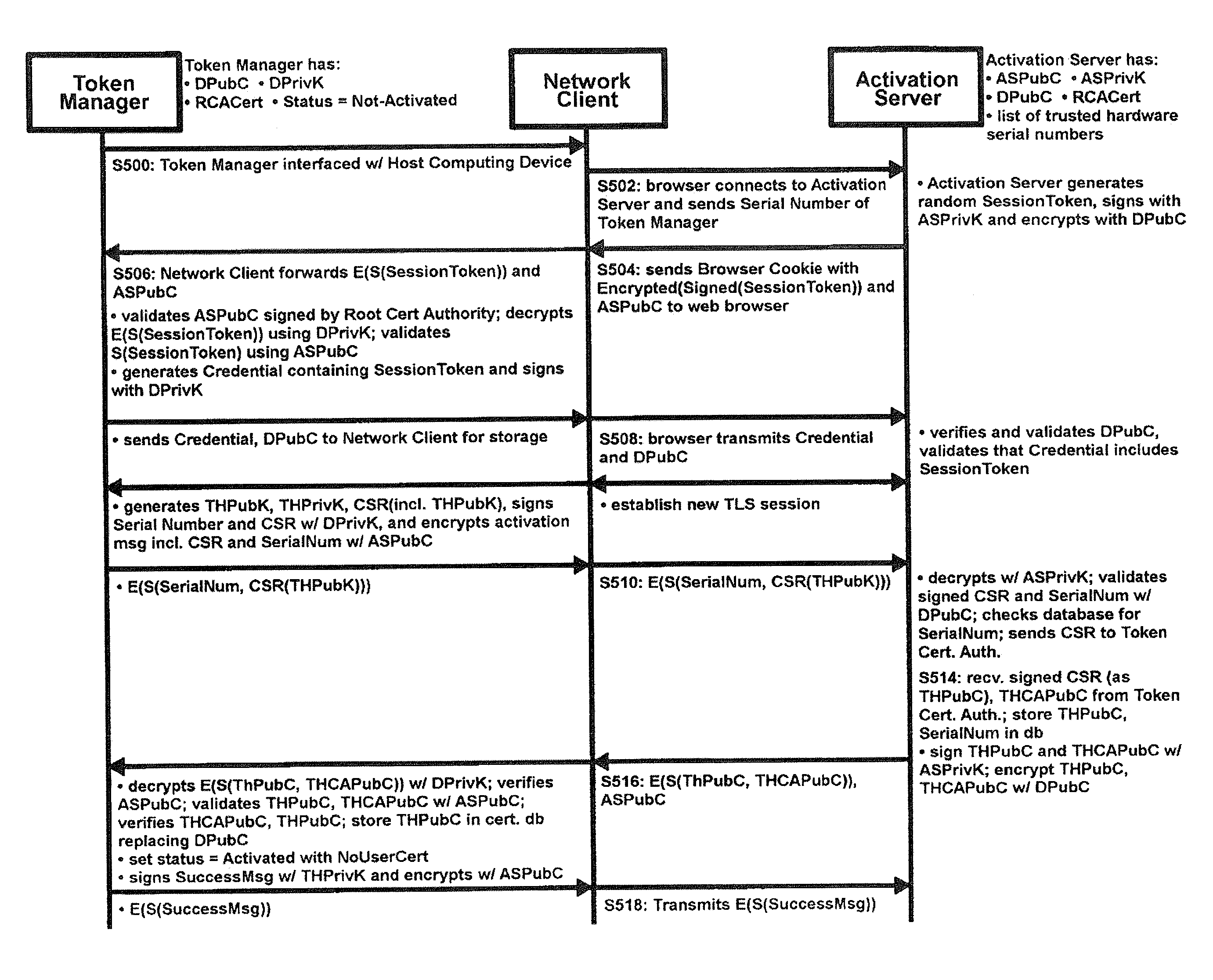
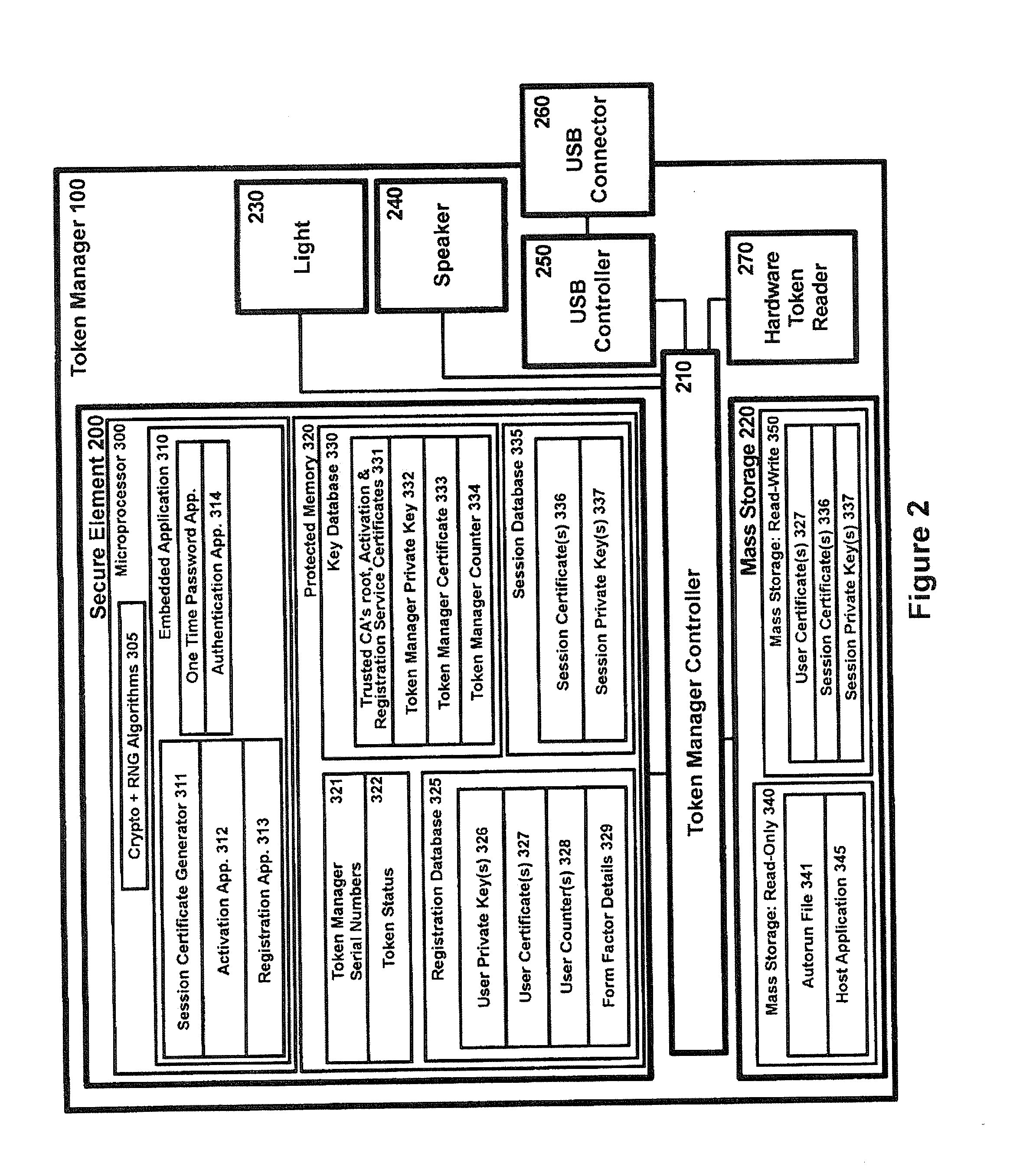
A method of authenticating a network client to a relying party computer via a computer server comprises the computer server receiving a transaction code from a token manager via a first communications channel. The network client is configured to communicate with a token manager which is configured to communicate with a hardware token interfaced therewith. The network client is also configured to communicate with the relying party computer and the computer server. The computer server also receives a transaction pointer from the relying party computer via a second communications channel that is distinct from the first communications channel. Preferably, the transaction pointer is unpredictable by the computer server. The computer server transmits an authorization signal to the relying party computer in accordance with a correlation between the transaction code and the transaction pointer. The authorization signal facilitates authentication of the network client to the relying party computer.
Owner:SECUREKEY TECH
Methods and apparatus for brokering a transaction
InactiveUS20140372319A1Improve immunityWithout risk of fraudFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsInternet privacySecret code
Methods of brokering a transaction between a first party and a second party with a trusted transaction server (TTS) and apparatus therefor. In an aspect, the method includes receiving at the TTS a request for a brokered transaction from the first party over a first communication channel and authenticating the identity of the first party with the TTS. The TTS stores a transaction code with at least some transaction details received from the first party. The TTS receives a message containing the transaction code from the second party over a second communication channel and matches the transaction code with the stored transaction details. The TTS sends a request for authorization for brokering the transaction to the second party. The TTS then authenticates the identity of the second party by way of a secret code and brokers the transaction.
Owner:WOLOVITZ LIONEL
Distribution, recognition and accountability system for intellectual and copy written properties in digital media's
InactiveUS6947909B1Increase market shareIncrease dominanceComputer security arrangementsCommerceIntellectual propertyE-commerce
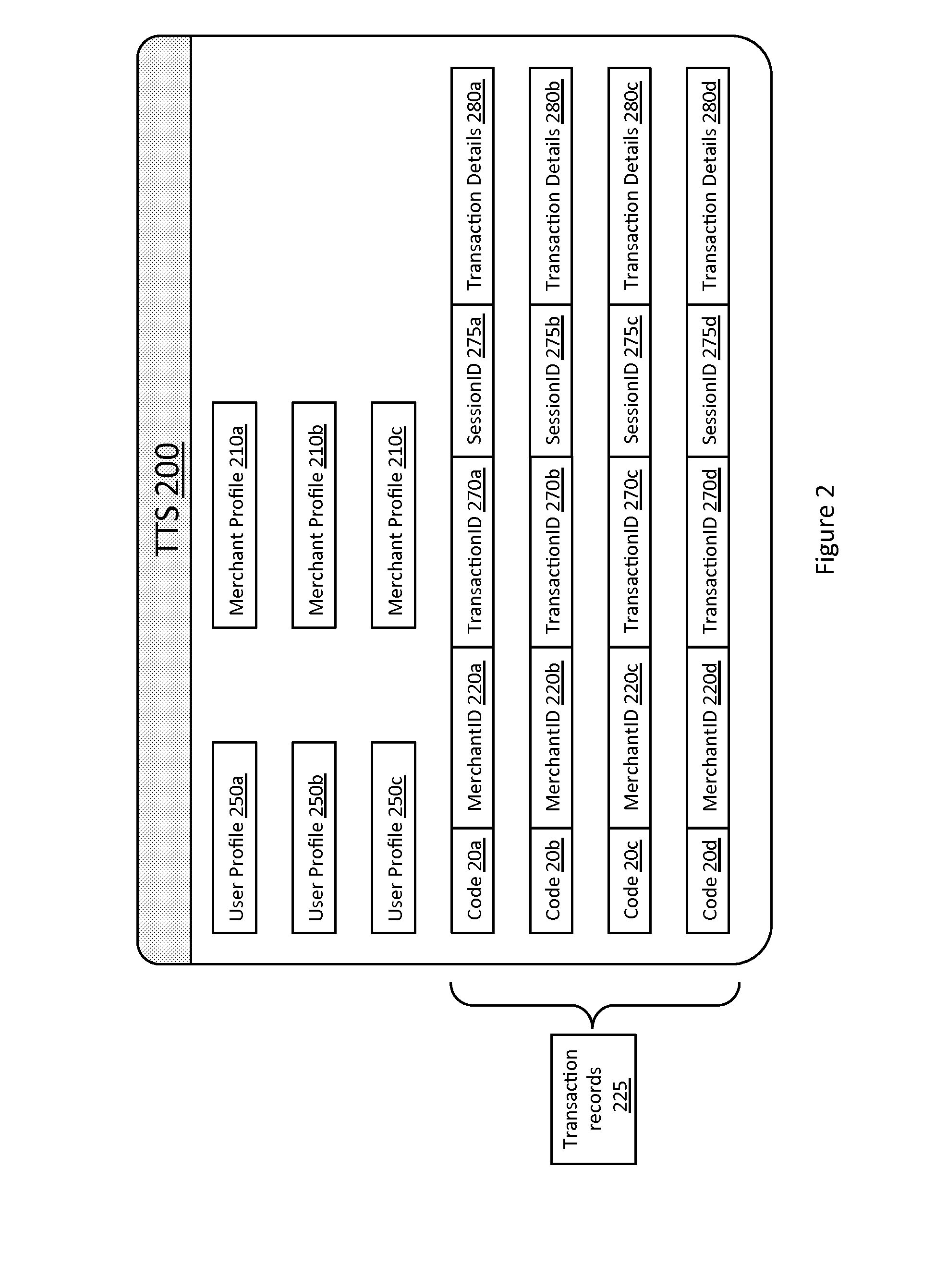
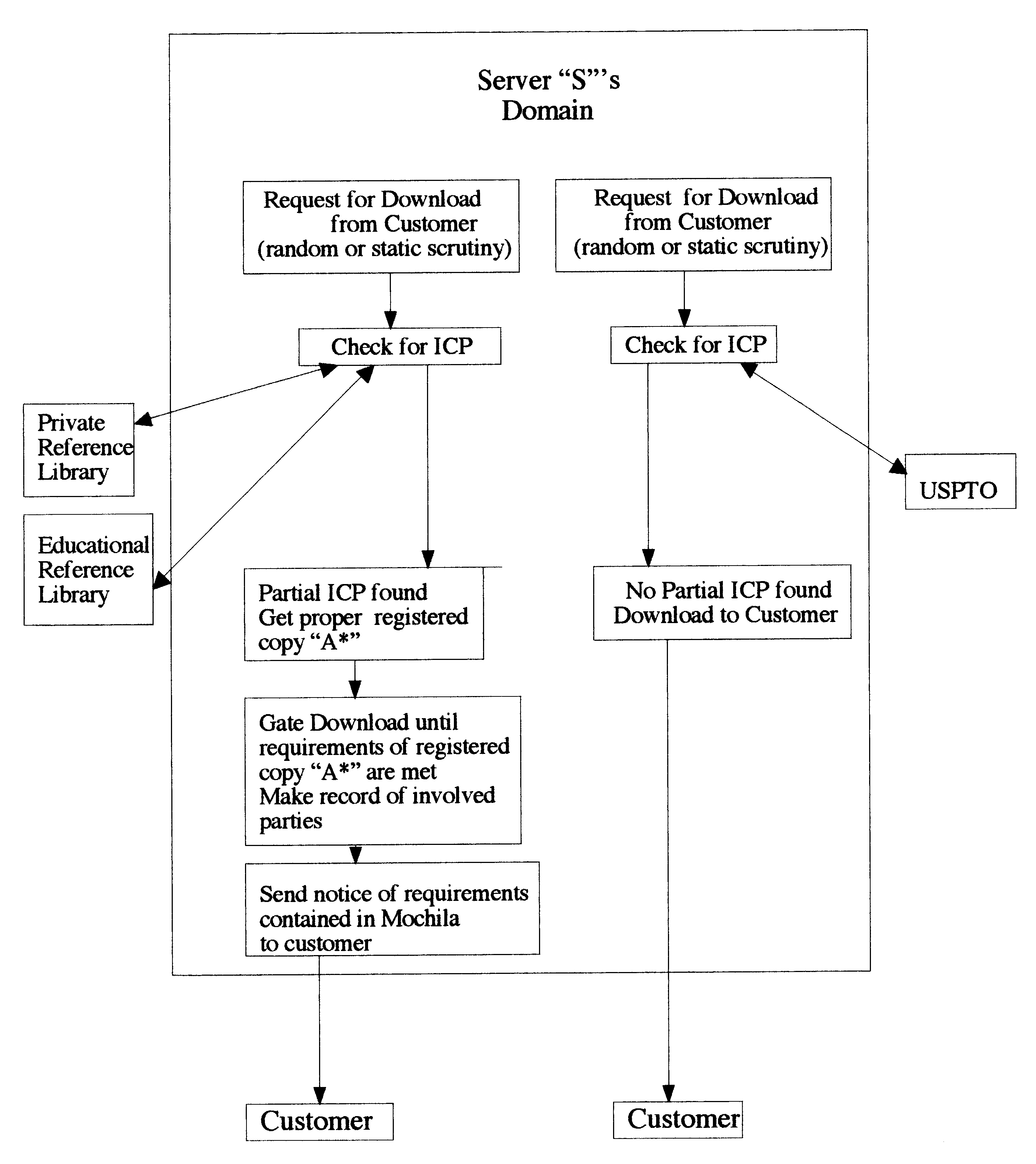
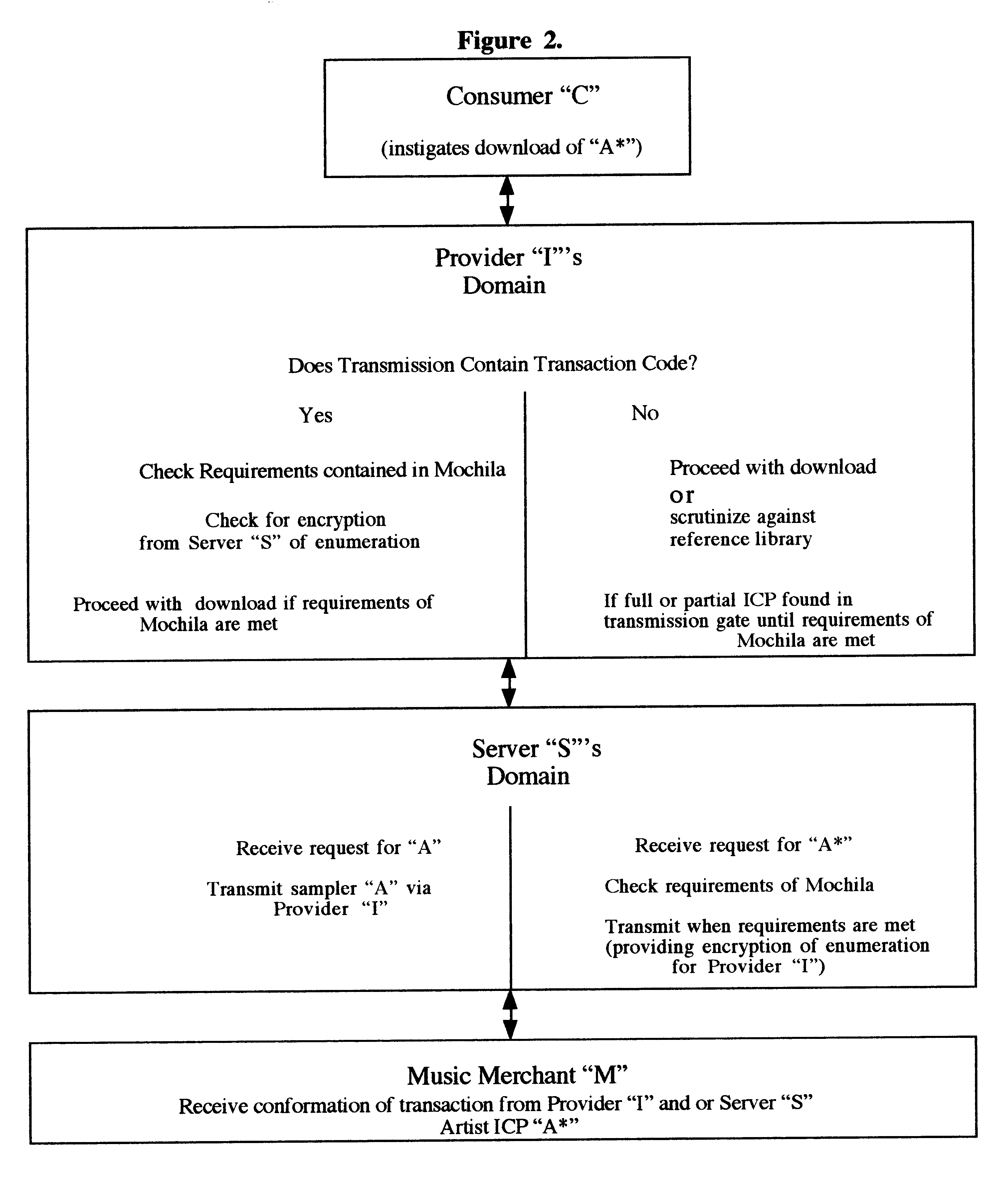
A method for distribution, recognition and accountability for Intellectual and Copy written Properties in digital media's by associating a Transaction Code Identifier or Designator and further bundled information which distinguishes digital files as Intellectual or Copy written Property, and therefore unique and bound to restrictions with regard to transfer, ownership, proliferation and electronic commerce. The employment of said transaction code identifier further promotes novel distribution scenarios for electronic commerce. Further delineated is the role of network providers and servers in promoting the interests of owners of Intellectual and Copy written Property in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:HOKE JR CLARE L
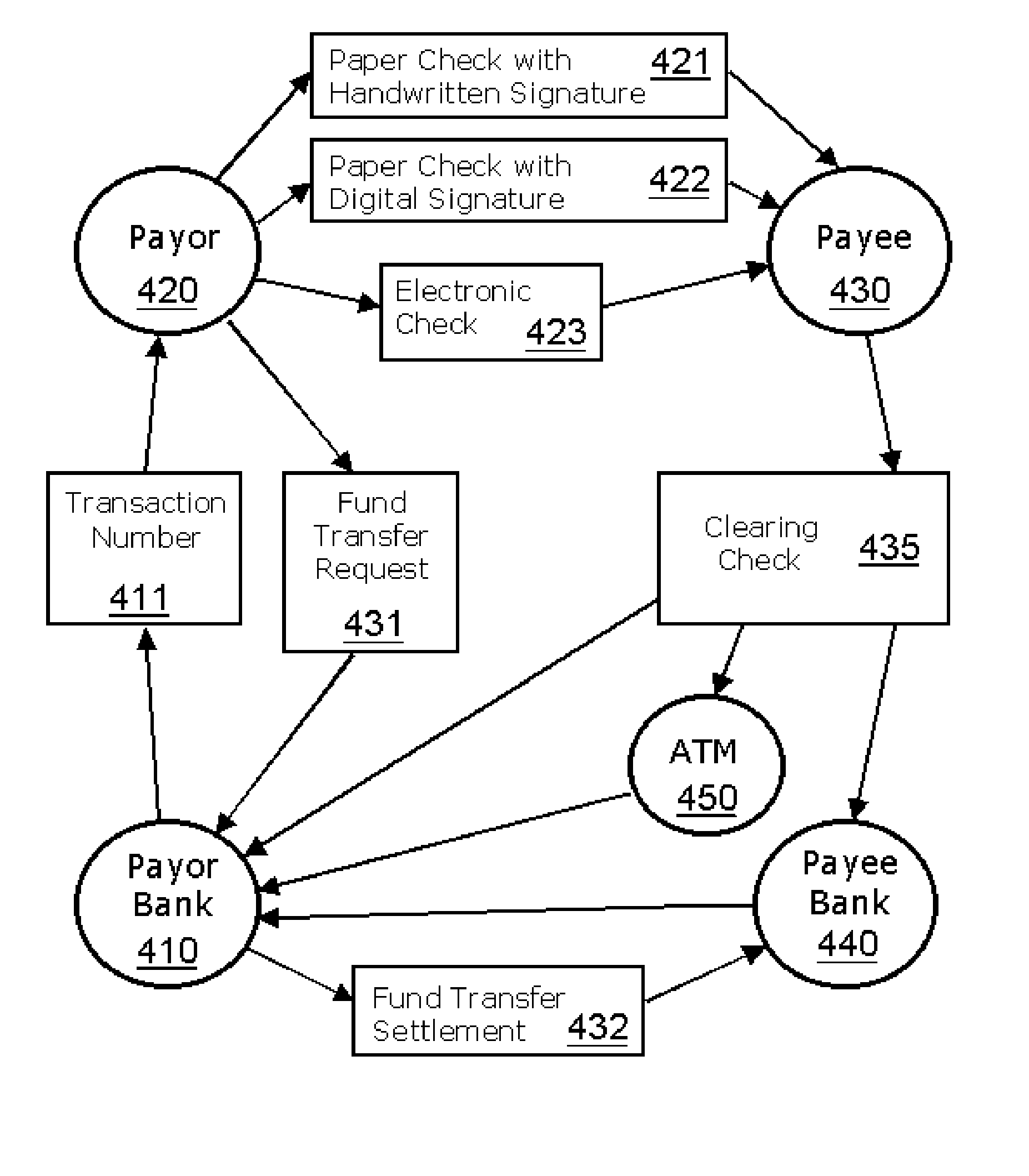
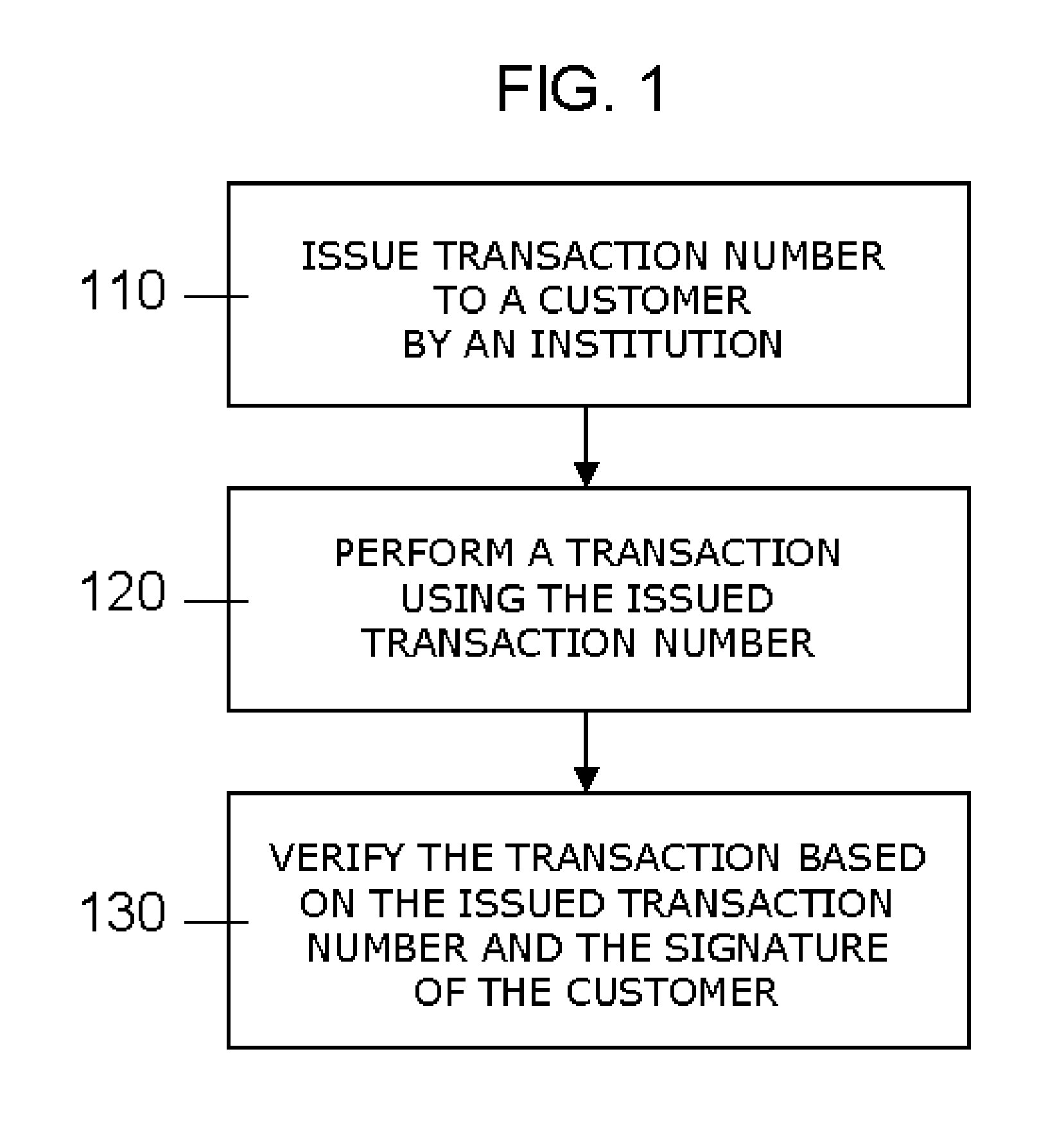
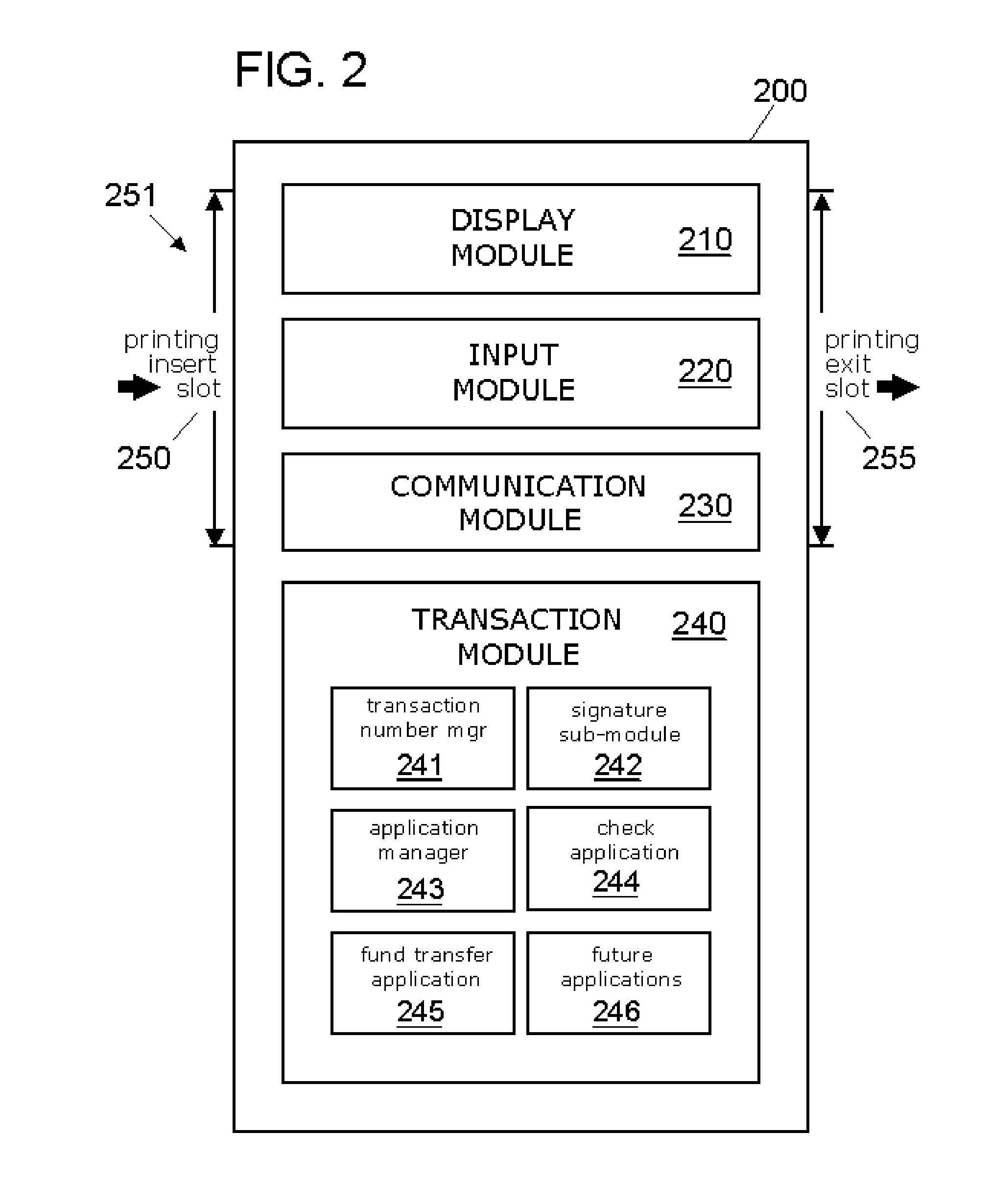
Transaction Method and System Using an Issued Transaction Number for Verification of a Transaction
A system and method for performing transactions using transaction codes is described. An issuer apparatus issues transaction codes which are unique for particular types of transactions to a customer and stores the issued transaction codes in a database. A transaction apparatus selects a transaction code from the issued transaction codes and associates the transaction code with a document to perform a transaction. The transaction apparatus then performs the transaction using the document with the associated transaction code. A verification means of the issuer apparatus verifies the transaction by performing a comparison between the issued transaction code stored in the database and the transaction code associated with the document. The issuer apparatus modifies the transaction code in the database after positive verification of the transaction.
Owner:SUISA DANIEL
Device group partitions and settlement platform
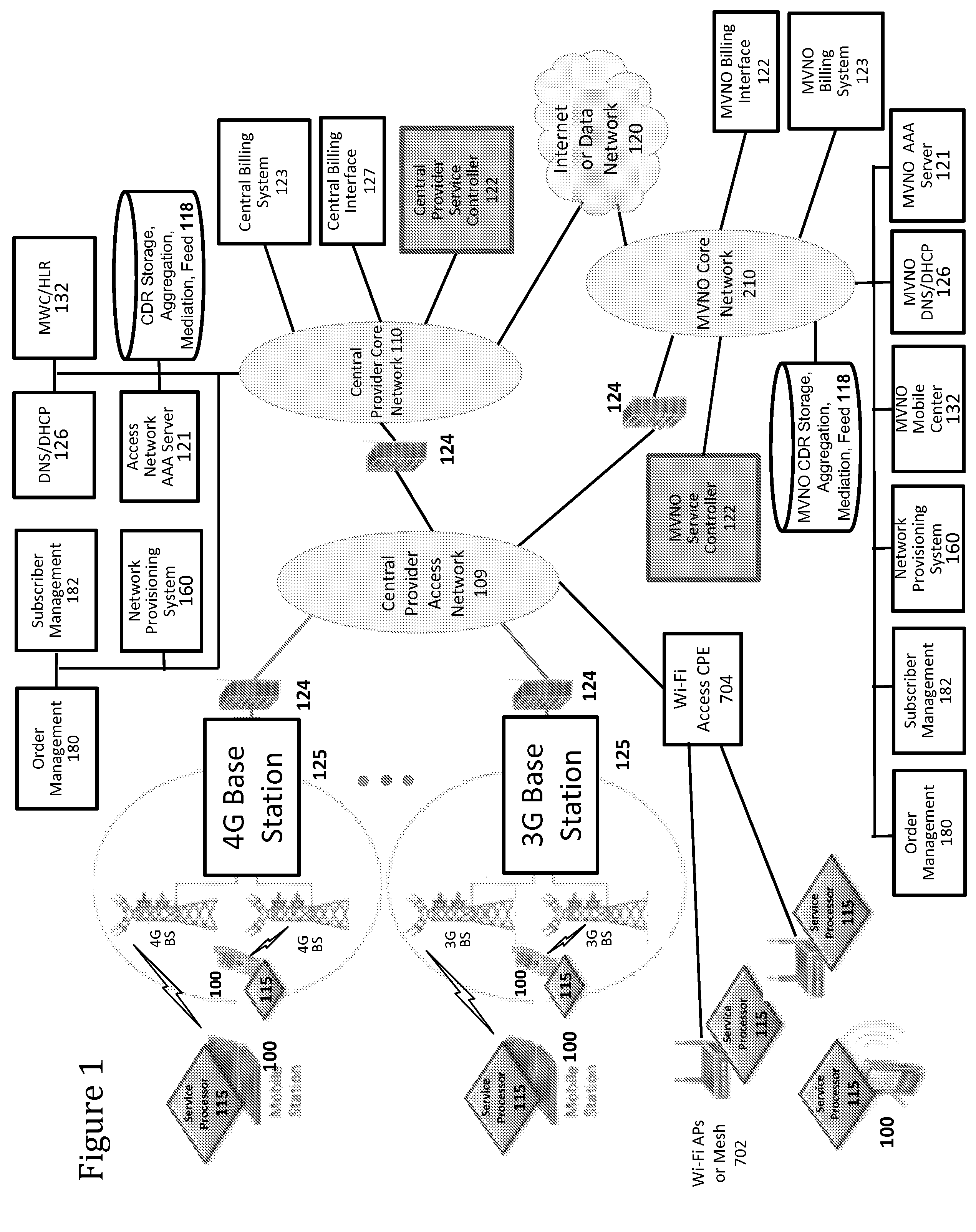
ActiveUS20100197267A1Complete banking machinesAccounting/billing servicesService controlService usage
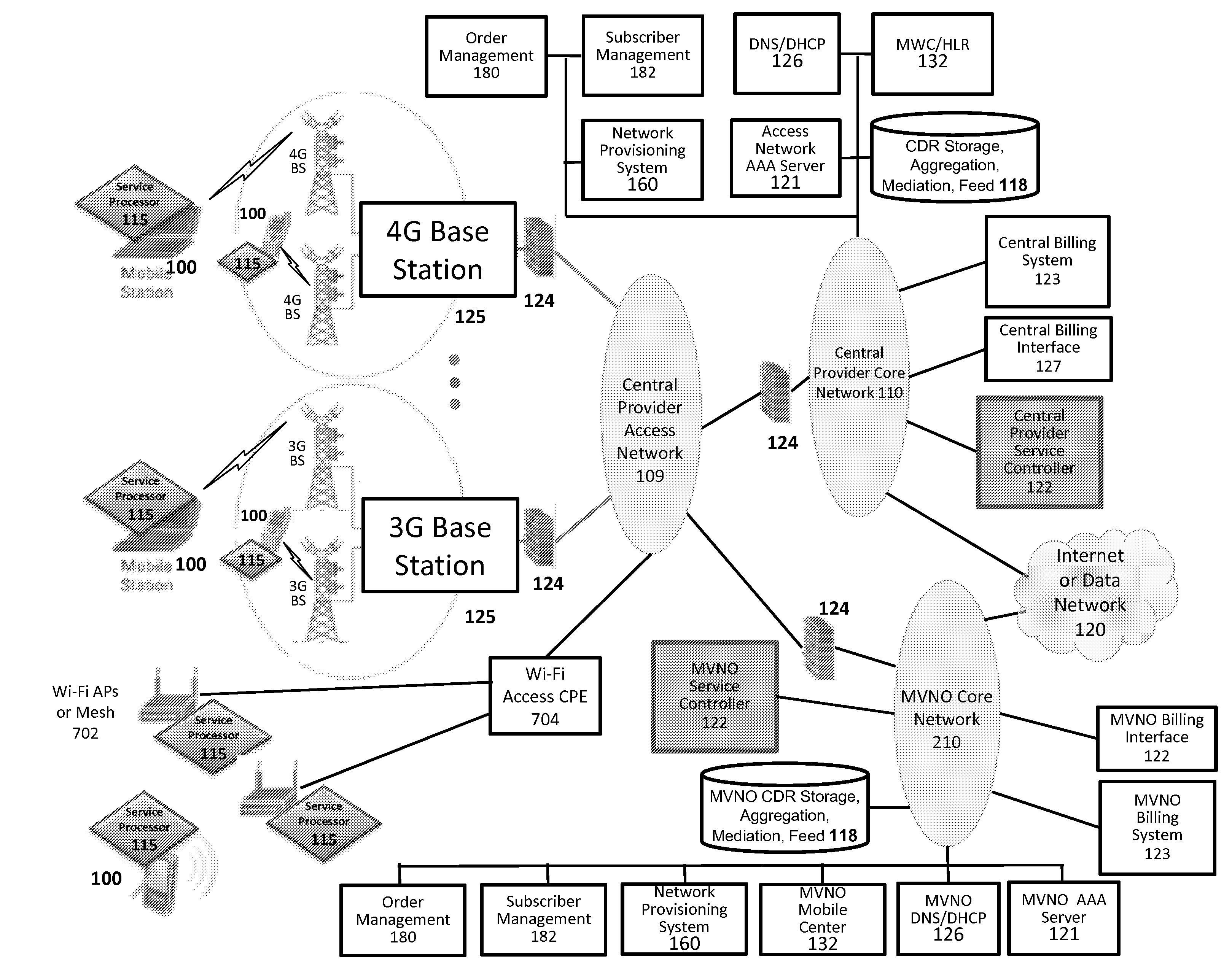
Device group partitions and a settlement platform are provided. In some embodiments, device group partitions (e.g., partitions of devices based on associated device groups) are provided. In some embodiments, a settlement platform service is provided. In some embodiments, a settlement platform service is provided for partitioned devices. In some embodiments, collecting device generated service usage information for one or more devices in wireless communication on a wireless network; and aggregating the device generated service usage information for a settlement platform for the one or more devices in wireless communication on the wireless network is provided. In some embodiments, a settlement platform implements a service billing allocation and / or a service / transactional revenue share among one or more partners. In some embodiments, service usage information includes micro-CDRs, which are used for CDR mediation or reconciliation that provides for service usage accounting on any device activity that is desired. In some embodiments, each device activity that is desired to be associated with a billing event is assigned a micro-CDR transaction code, and a service processor of the device is programmed to account for that activity associated with that transaction code. In some embodiments, a service processor executing on a wireless communications device periodically reports (e.g., during each heartbeat or based on any other periodic, push, and / or pull communication technique(s)) micro-CDR usage measures to, for example, a service controller or some other network element for CDR mediation or reconciliation.
Owner:HEADWATER RES LLC
System and method for supporting multiple alternative methods for executing transactions
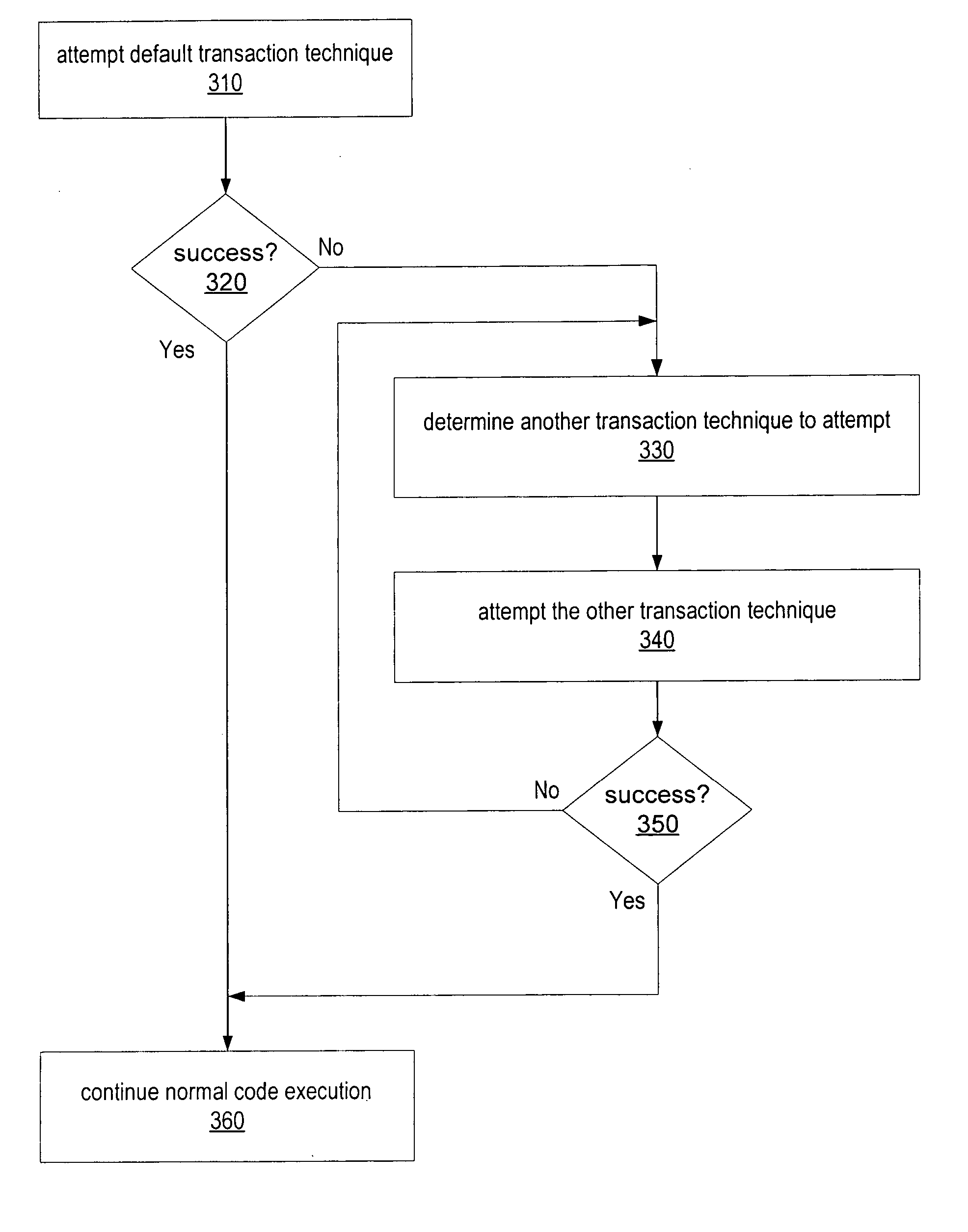
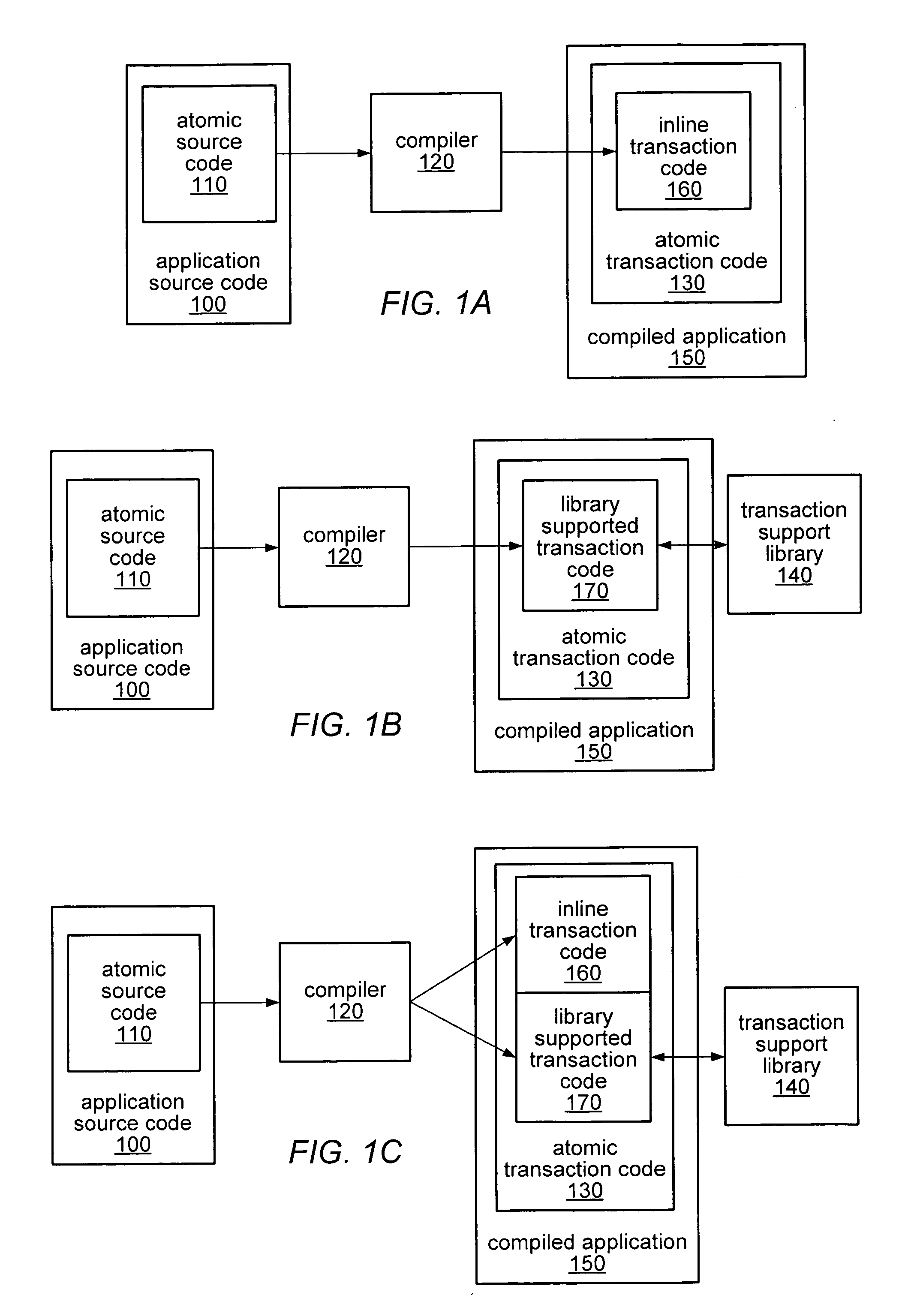
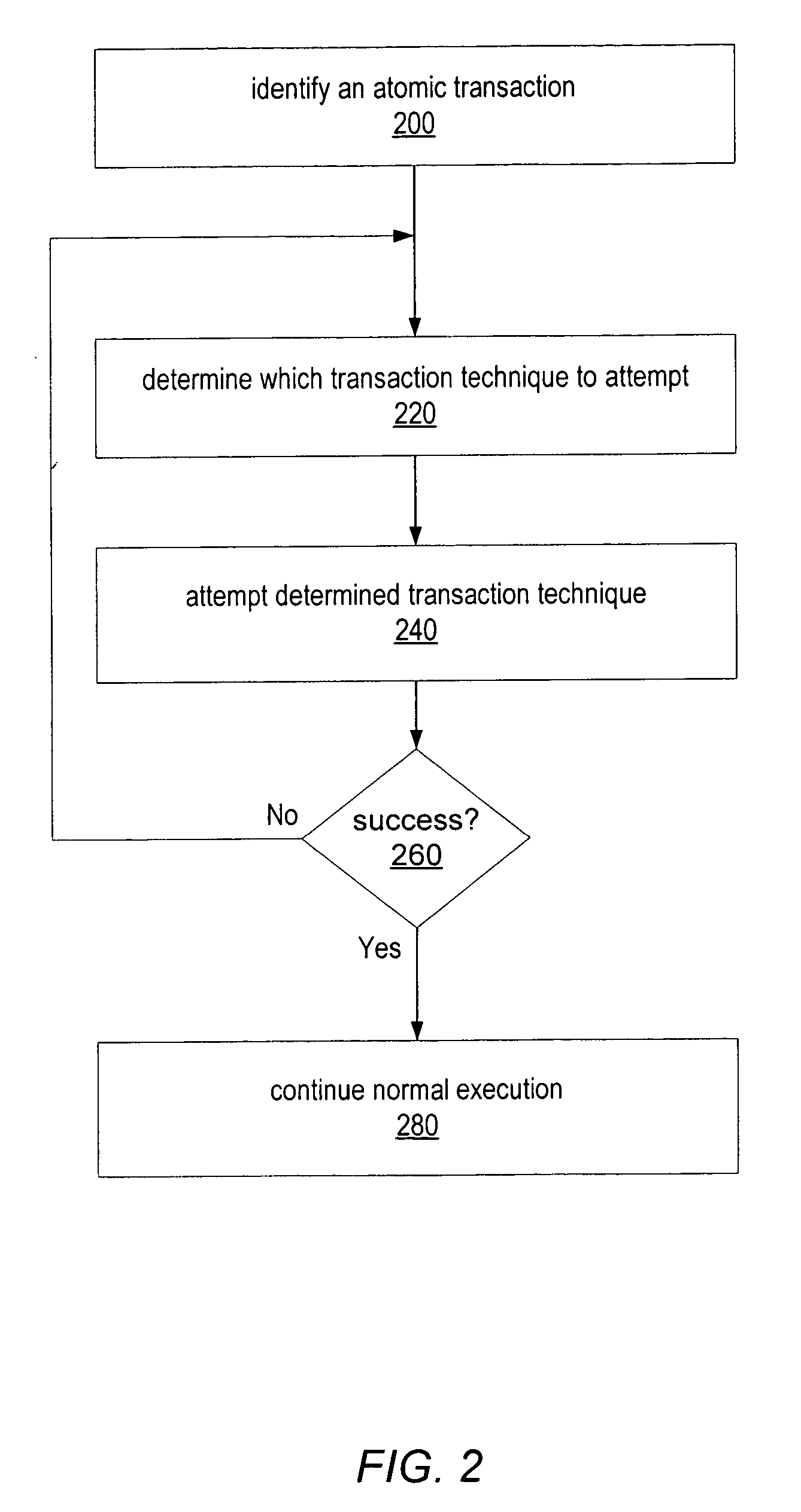
ActiveUS20070055960A1Ensure correct executionReduce difficultyError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsTransactional memoryAlternative methods
Transaction code written by the programmer may be translated, replaced or transformed into a code that is configured to implement transactions according to any of various techniques. A compiler may replace programmer written transaction code into code allowing multiple compatible transaction implementation techniques to be used in the same program, and at the same time. A programmer may write transaction code once using familiar coding styles, but the transaction to be effected according to one of a number of compatible alternative implementation techniques. The compiler may enable the implementation of multiple, alternative transactional memory schemes. The particular technique implemented for each transaction may not be decided until runtime. At runtime, any of the various implemented techniques may be used to effect the transaction and if a first technique fails or is inappropriate for a particular transaction, one or more other techniques may be attempted.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and software for processing containers having tools with associated transmitters
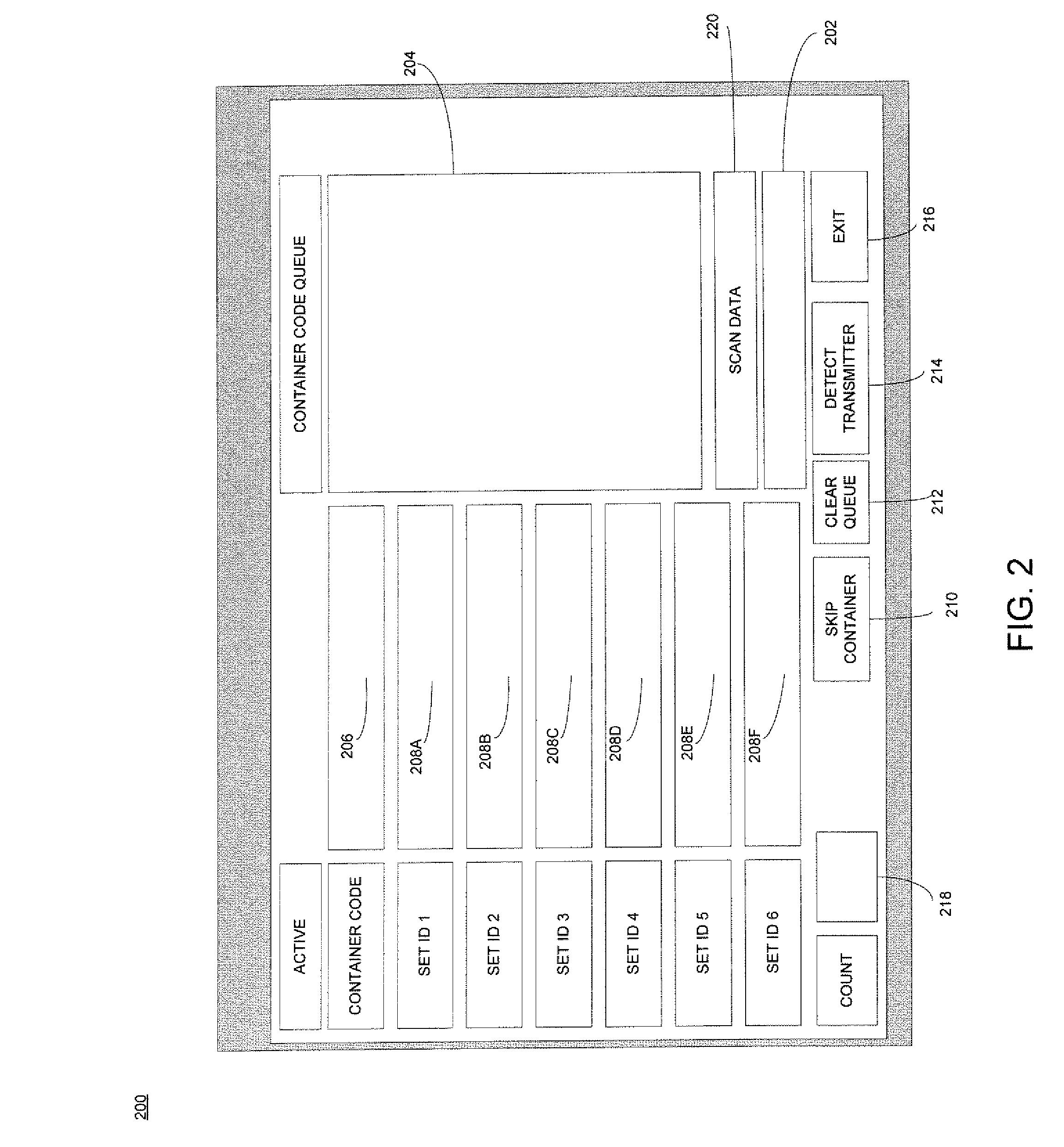
InactiveUS20070239289A1Easy to manageSimple processComputer controlSimulator controlComputer hardwareTransmitter
A software method may include receiving scan data from a device after the device retrieves a readable code from a container, the container having at least one transmitter contained therein, processing the scan data to generate a container code based on the readable code, receiving a signal from the at least one transmitter, the signal including identification information, generating a transaction code based on the container code and the identification information, and instructing the device to transmit the transaction code to a processing device.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
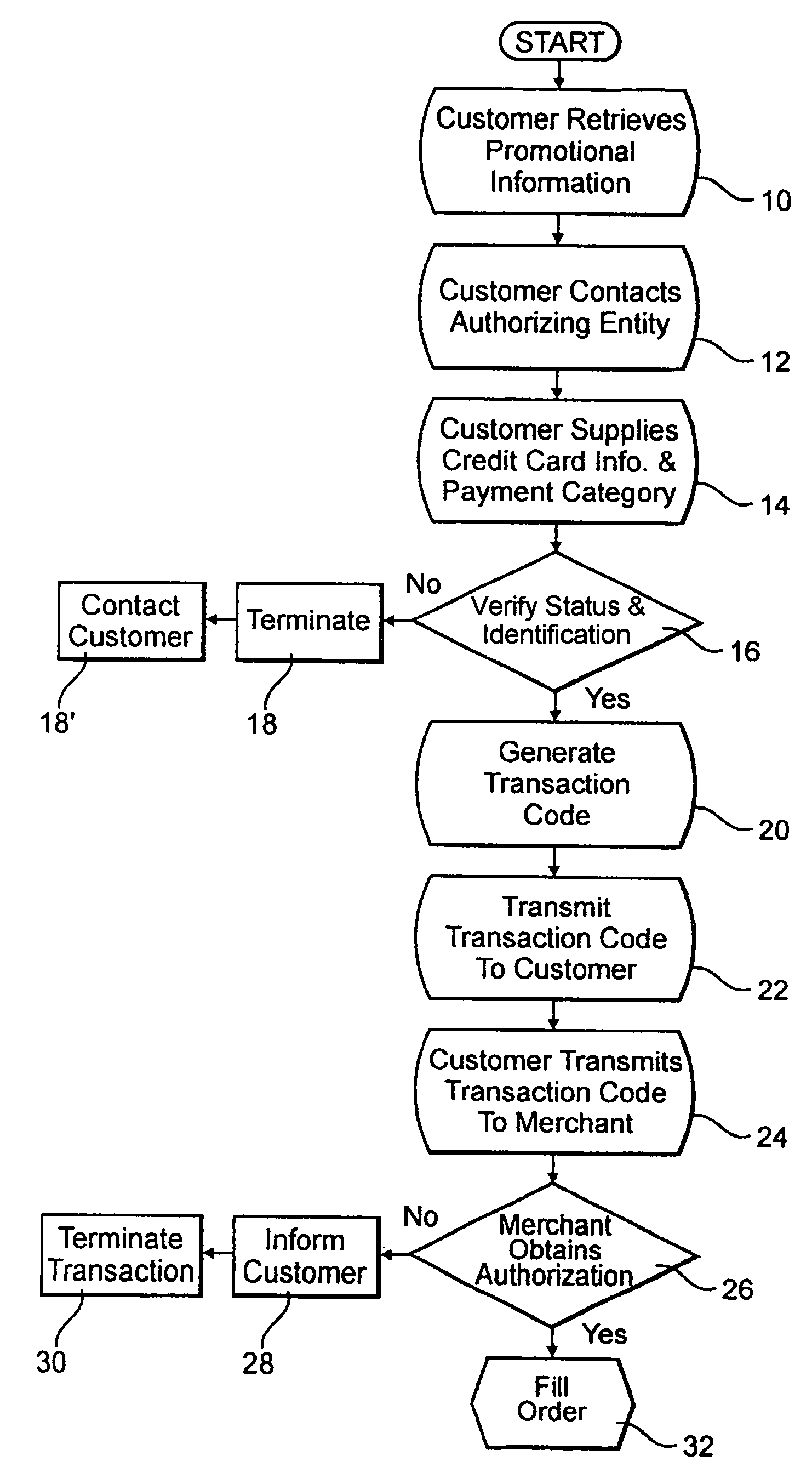
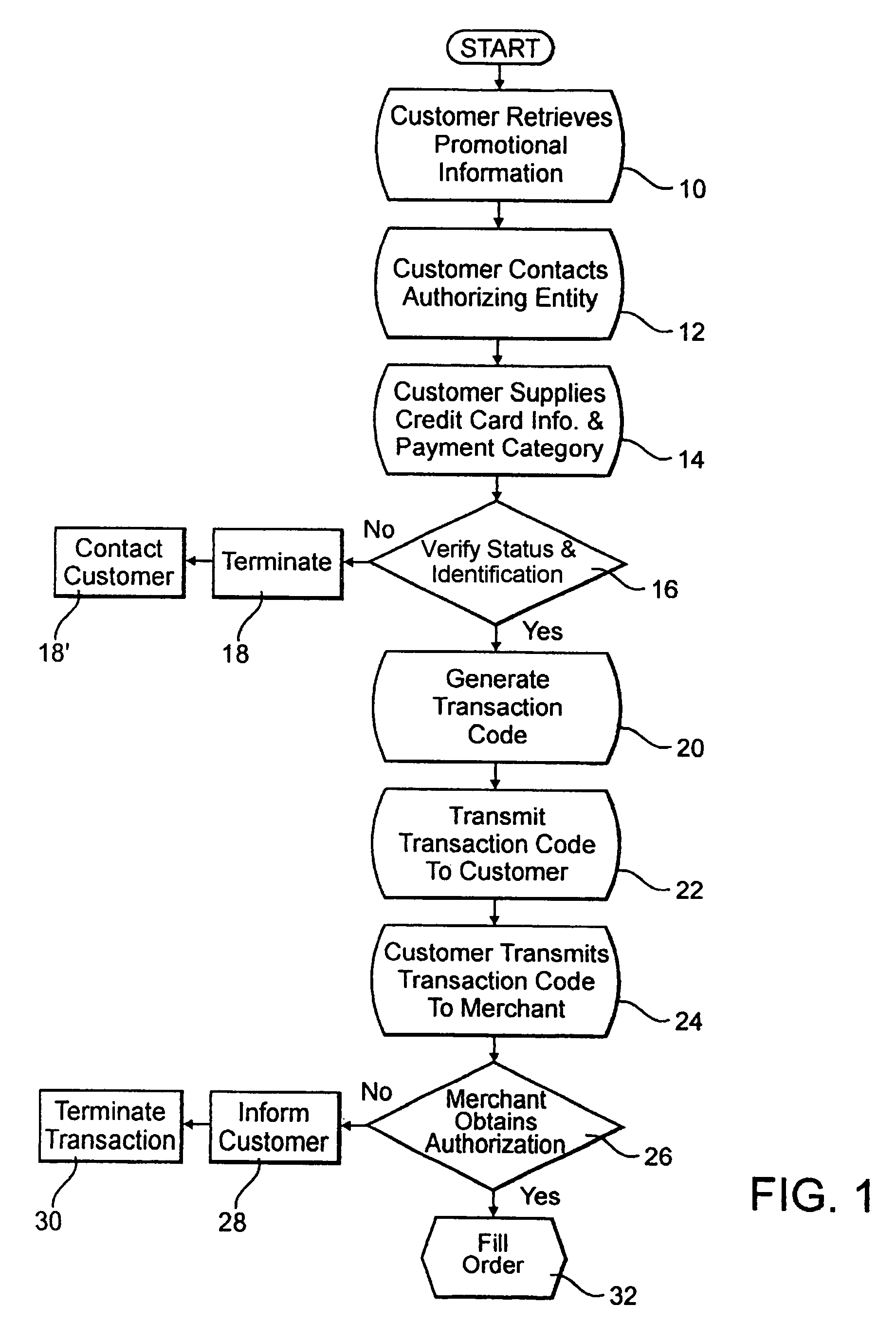
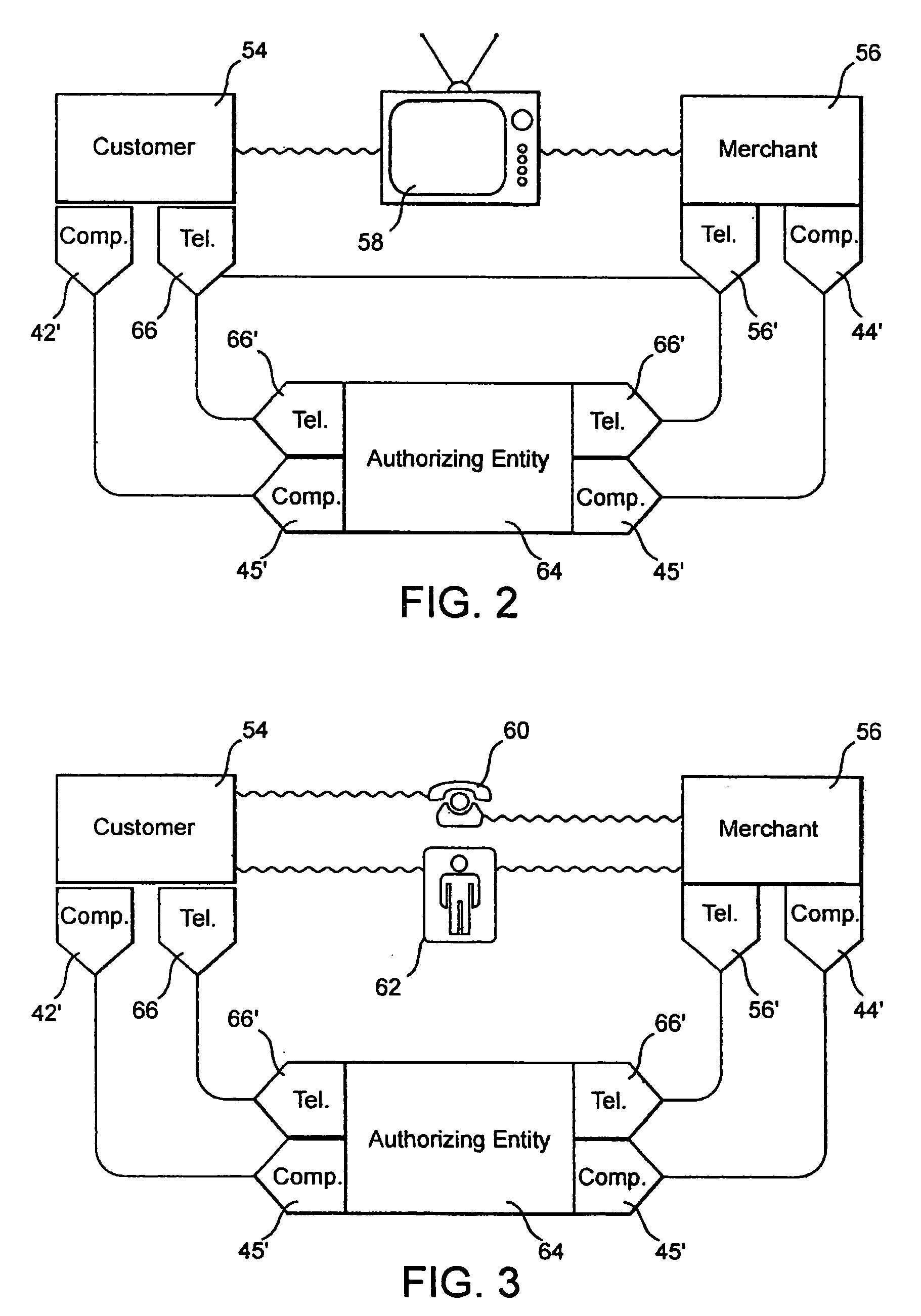
System and method for performing secure credit card purchases
A method and system of performing secure credit card purchases in the context of a remote commercial transaction, such as over the telephone, wherein only the customer, once generally deciding upon a product or service to be purchased, communicates with a custodial authorizing entity, such as a credit card company or issuing bank wherein such entity has previous knowledge of the credit card number as well as custodial control of other account parameters such as interest rate, payment history, available credit limit etc. The customer supplies the custodial authorizing entity with the account identification data such as the credit card number and a requested one of a possible plurality of predetermined payment categories which define the dollar amount for the purchase and specific, predetermined time parameters within which authorization by the custodial authorizing entity will remain in effect. The custodial authorizing entity then generates a transaction code which is communicated exclusively to the customer wherein the customer in turn communicates only the transaction code to the merchant instead of a credit card number. The transaction code is indicative of merchant identification, credit card account identification and a designated one of the plurality of predetermined payment categories.
Owner:DAGOSTINO JOHN
Test script generating method and test script generating device applied in financial field
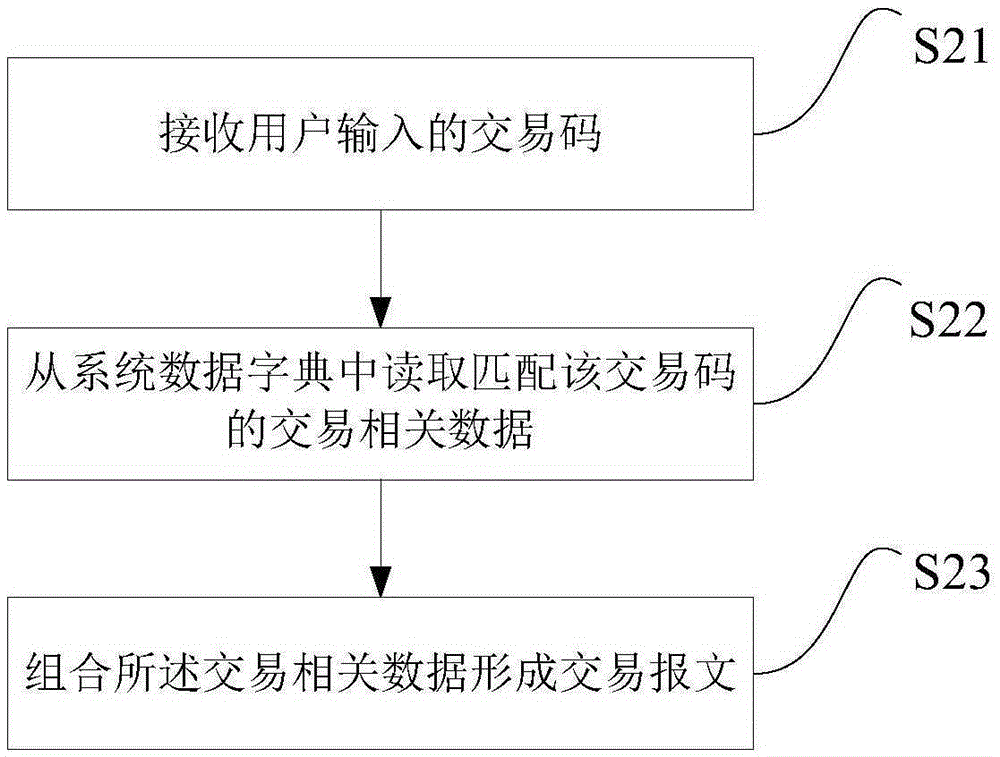
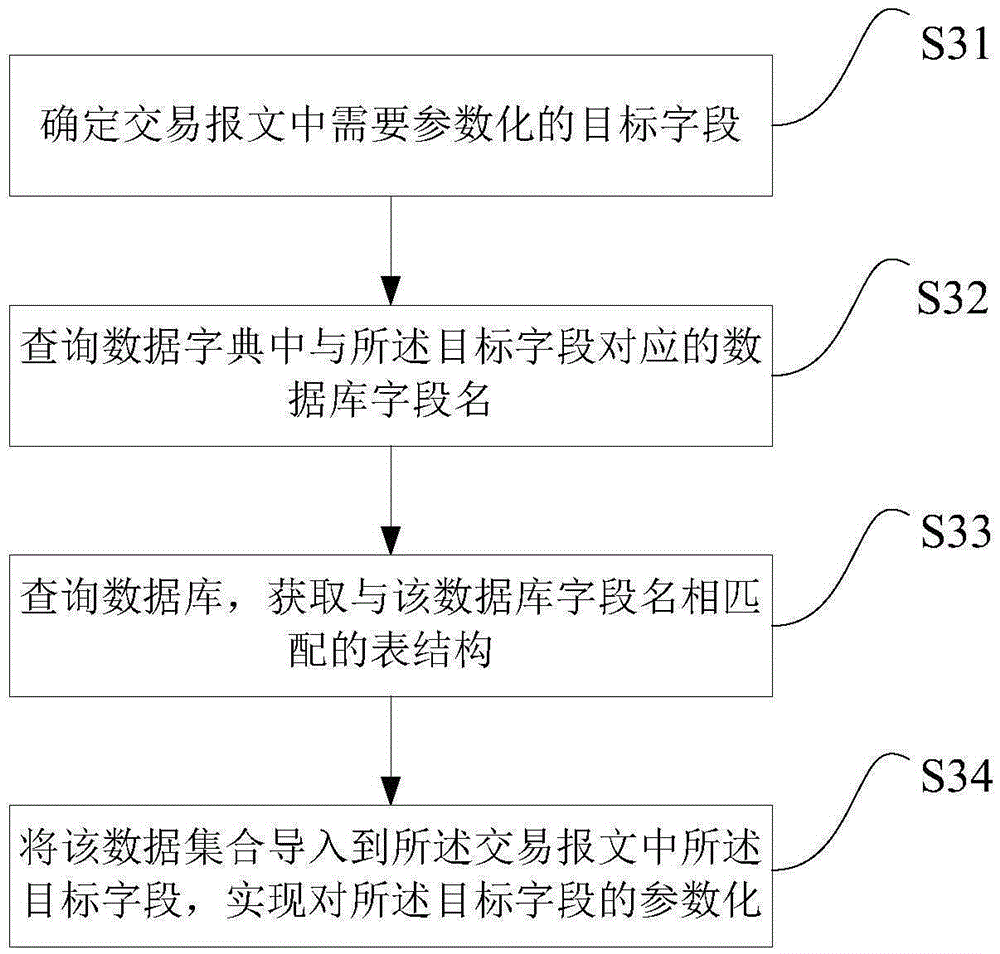
ActiveCN105279090AImprove reliabilityReduce error rateSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware development processTest script
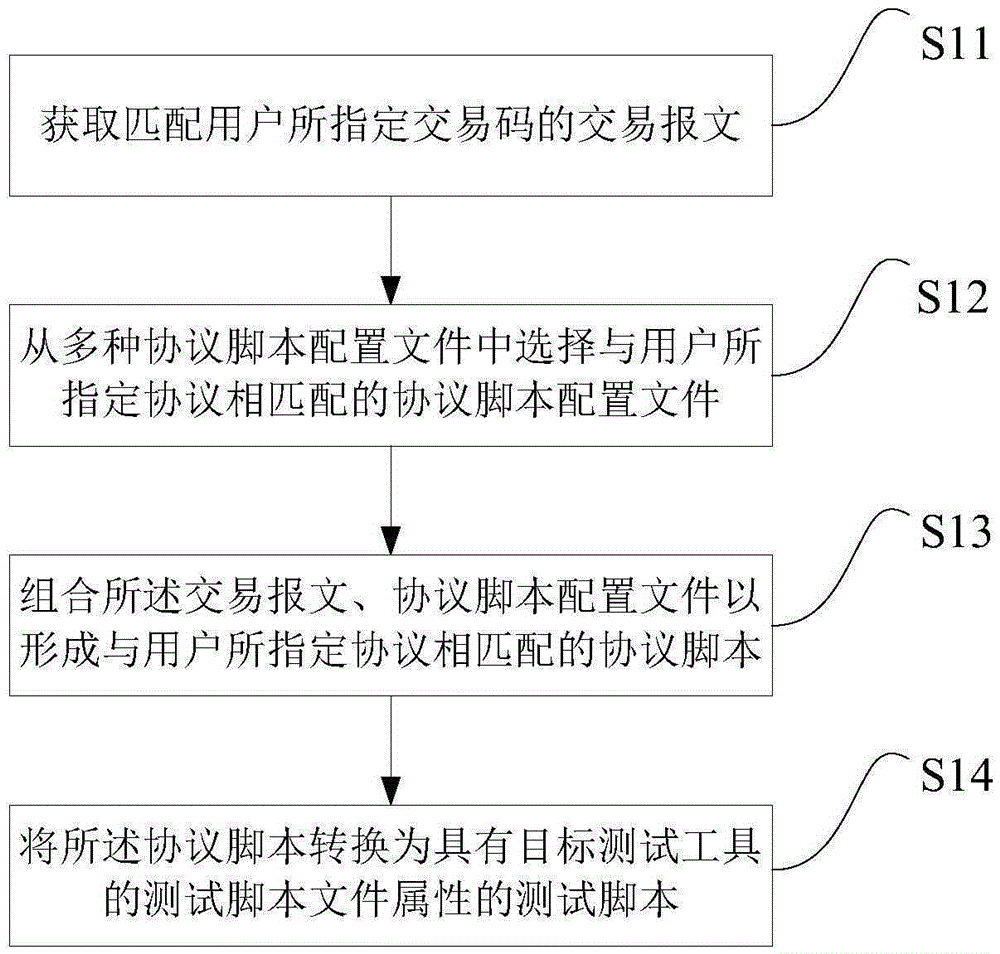
An embodiment of the invention discloses a test script generating method and a test script generating device applied in a financial field. The test script generating method comprises the steps of acquiring a transaction message which matches a transaction code that is assigned by a user, wherein the message is formed through combining transaction related data which correspond with the transaction code in a data dictionary, and the transaction related data are used for describing a role and a content for finishing the transaction that is assigned by the transaction code; selecting a protocol script configuration file which matches a protocol that is assigned by the user from a plurality of protocol script configuration files; combining the transaction message with the protocol script configuration file for forming a protocol script which matches the protocol that is assigned by the user; and converting the protocol script to the test script with the test script file attribute of a target test tool. The test script generating method and the test script generating device provided by the embodiment of the invention can reduce man participation, thereby reducing dependence degree to professional skills of testing personnel and shortening a script development process.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
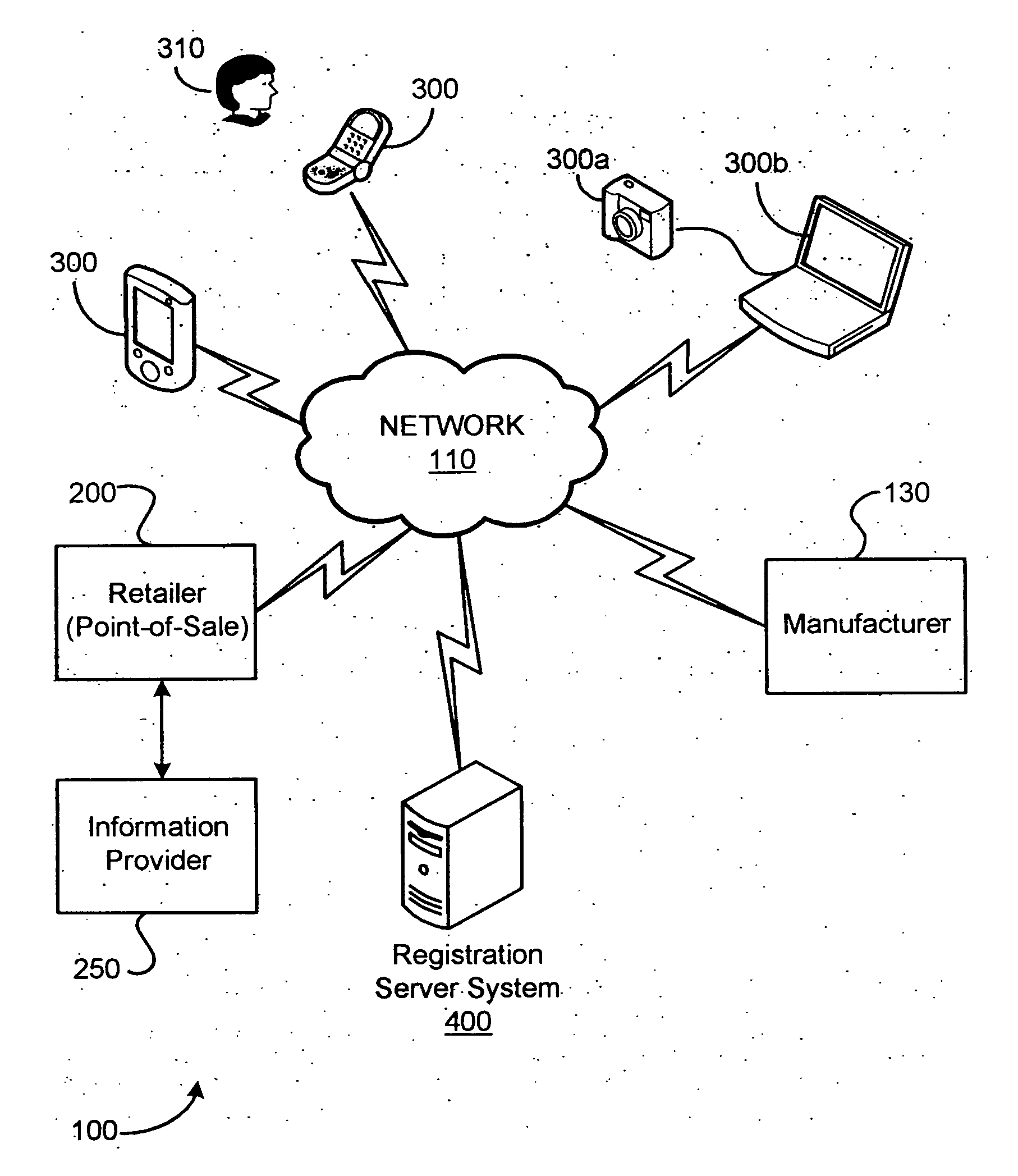
System and method for registration of an electronic device
InactiveUS20070221726A1Visual presentationBuying/selling/leasing transactionsComputer hardwareDevice Identifiers
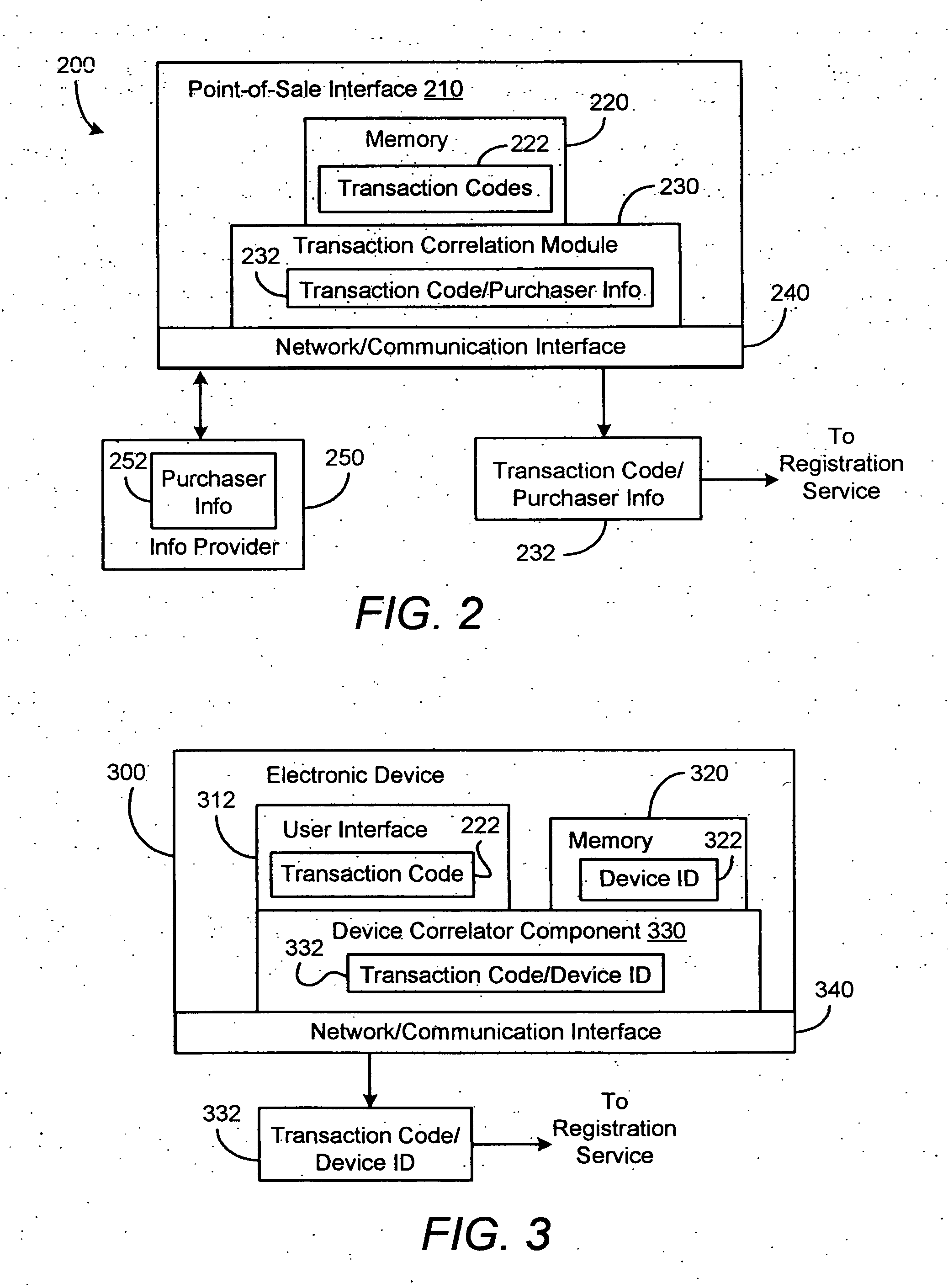
A method for registering an electronic device includes receiving from a point-of-sale interface a transaction code and purchaser information associated with a purchase of an electronic device. While the transaction code is associated with the purchase of the electronic device, it does not uniquely identify the electronic device purchased. The method also includes receiving from the electronic device the transaction code and a device identifier that uniquely identifies the electronic device. The purchaser information and the device identifier are associated via the transaction code for registering the electronic device.
Owner:SCENERA MOBILE TEHNOLOGIES LLC
Method for implementing secured electronic charging
InactiveCN101308557ASimple and fast operationImprove securityPayment architectureProgramming languagePayment
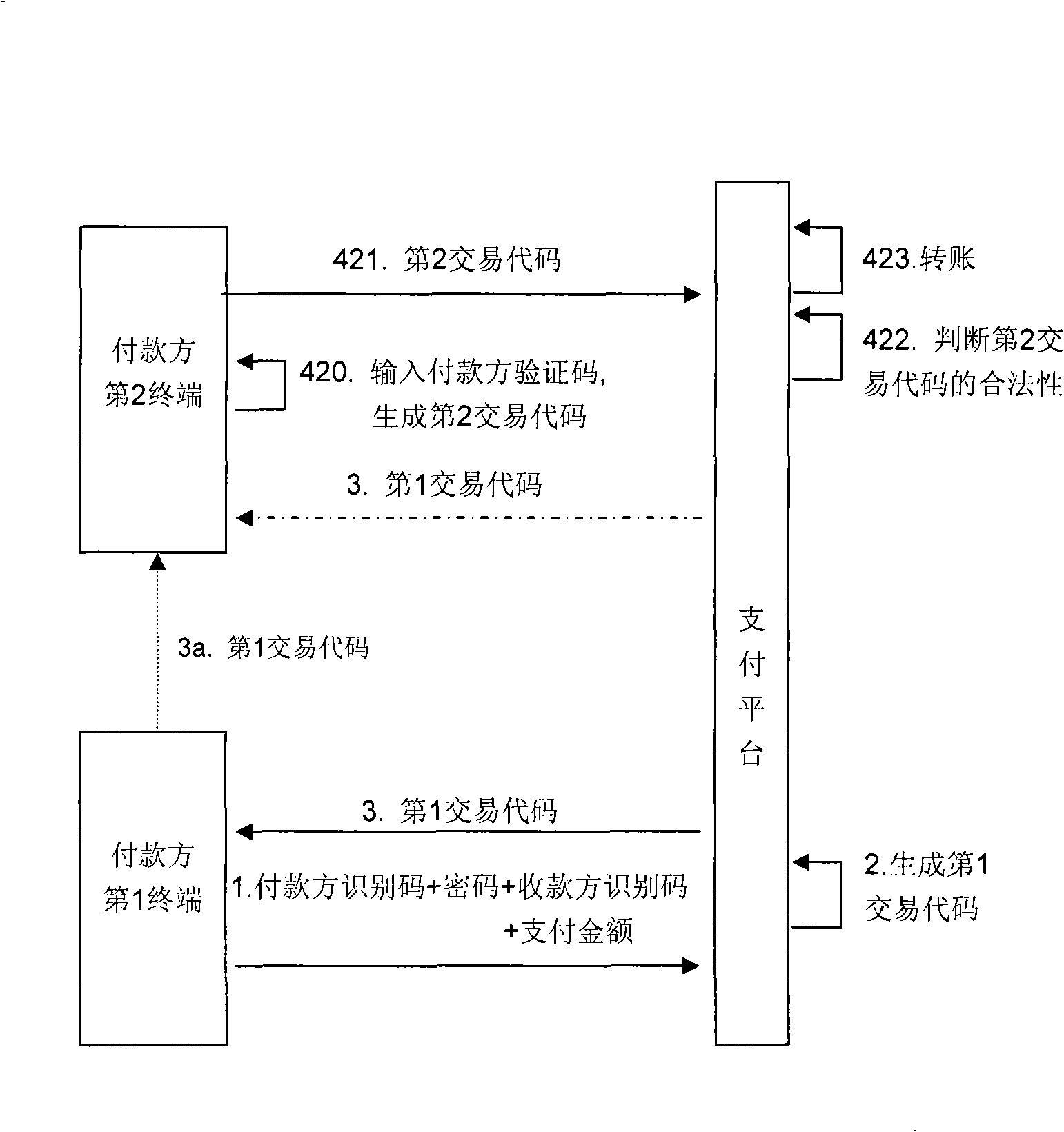
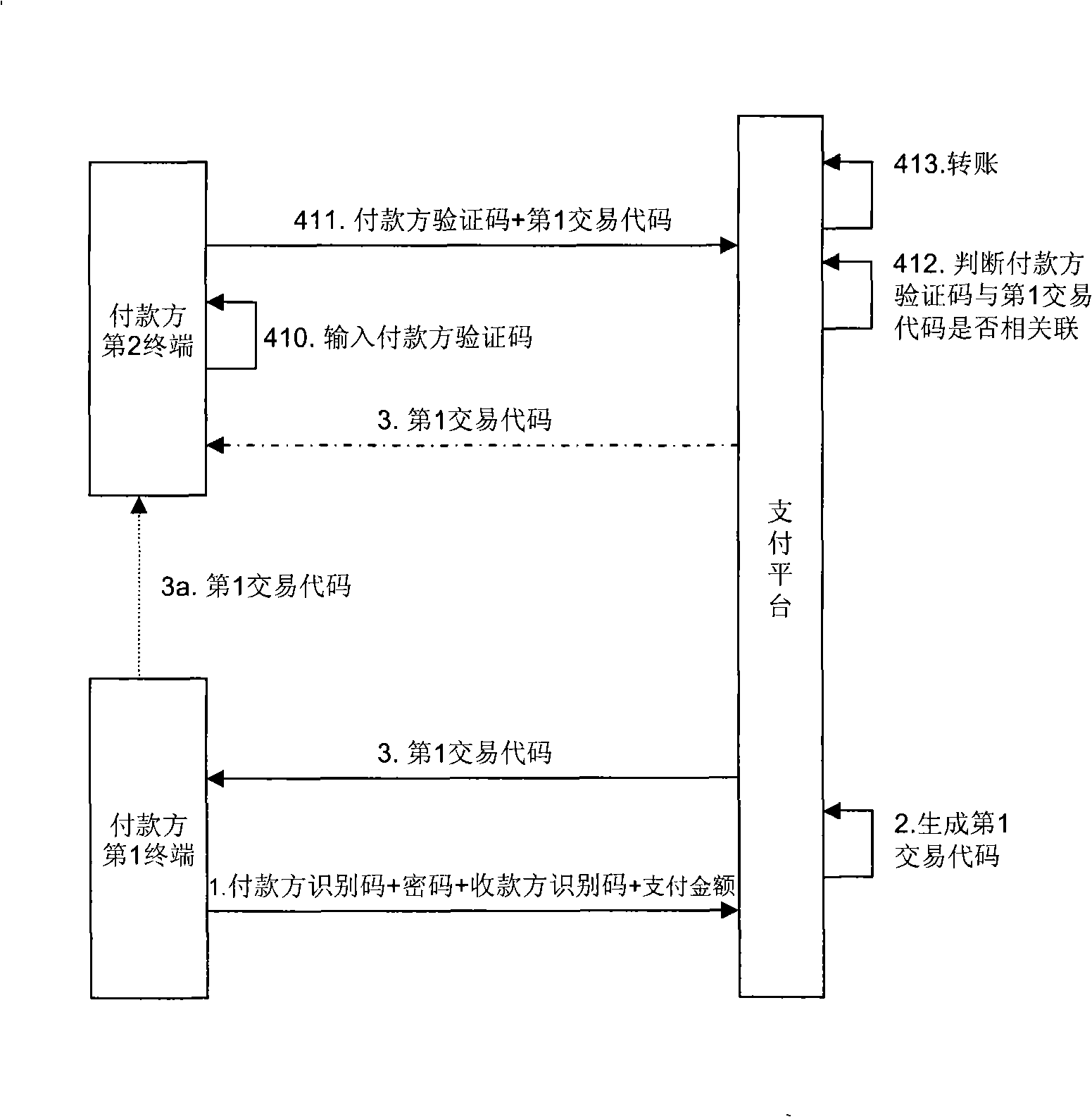
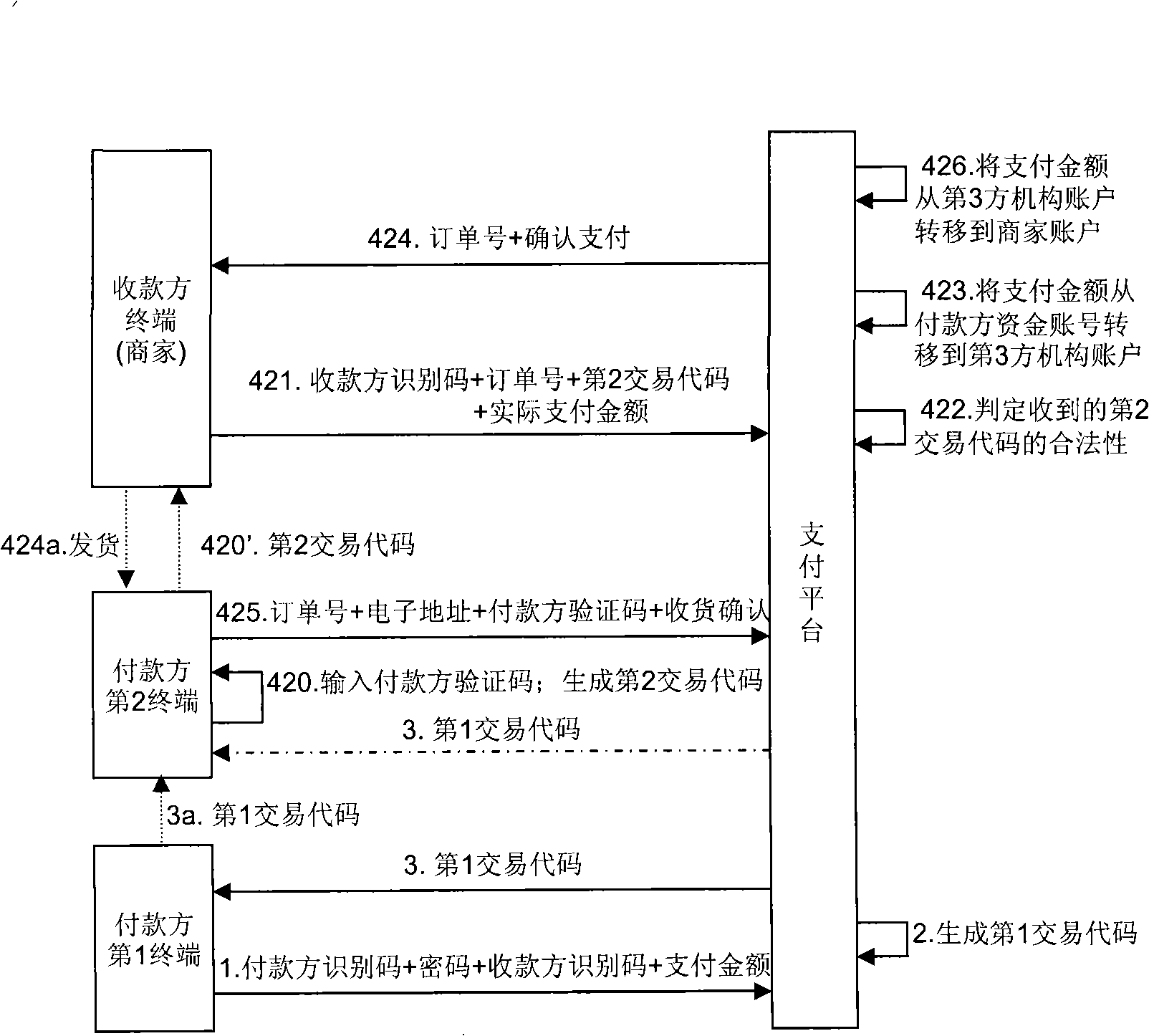
The invention provides a method for realizing secure electronic payment. First of all, after the user information of the payer is received and identified in a payment platform and verified, the payment platform generates a first transaction code for the payment; then, the payment platform sends the first transaction code to the payer terminal; finally, the payer uses a payer verification code and the first transaction code to approve the transaction, or the payer uses a second transaction code to approve the transaction, wherein, the second transaction code is generated by the payer verification code and the first transaction code through operation. The method can be widely used in the e-commerce field.
Owner:祁勇
Payment apparatus and method
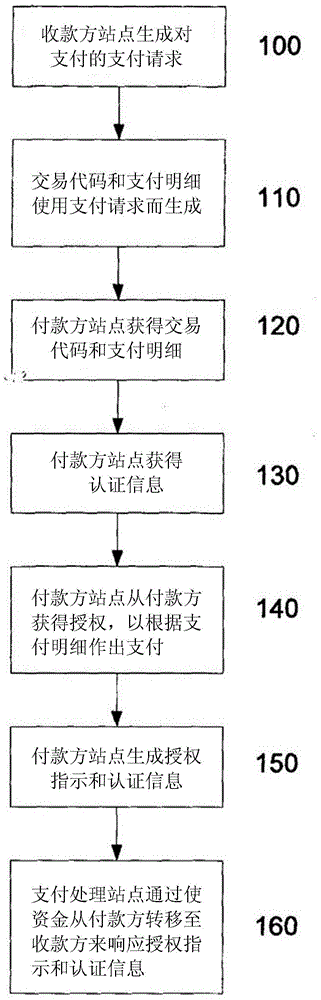
A method for performing a payment from a payer to a payee, wherein the method includes receiving a payment request for the payment, the payment request being generated in response to the payee requesting funds from the payer; generating a transaction code and payment details using the payment request, the transaction code being obtained by the payer; receiving the transaction code from the payer; and, in response to receiving the transaction code, providing at least some of the payment details to the payer including a payment amount and an indication of the payee, thereby allowing the payer to authorise the payment.
Owner:IP PAYOVATION
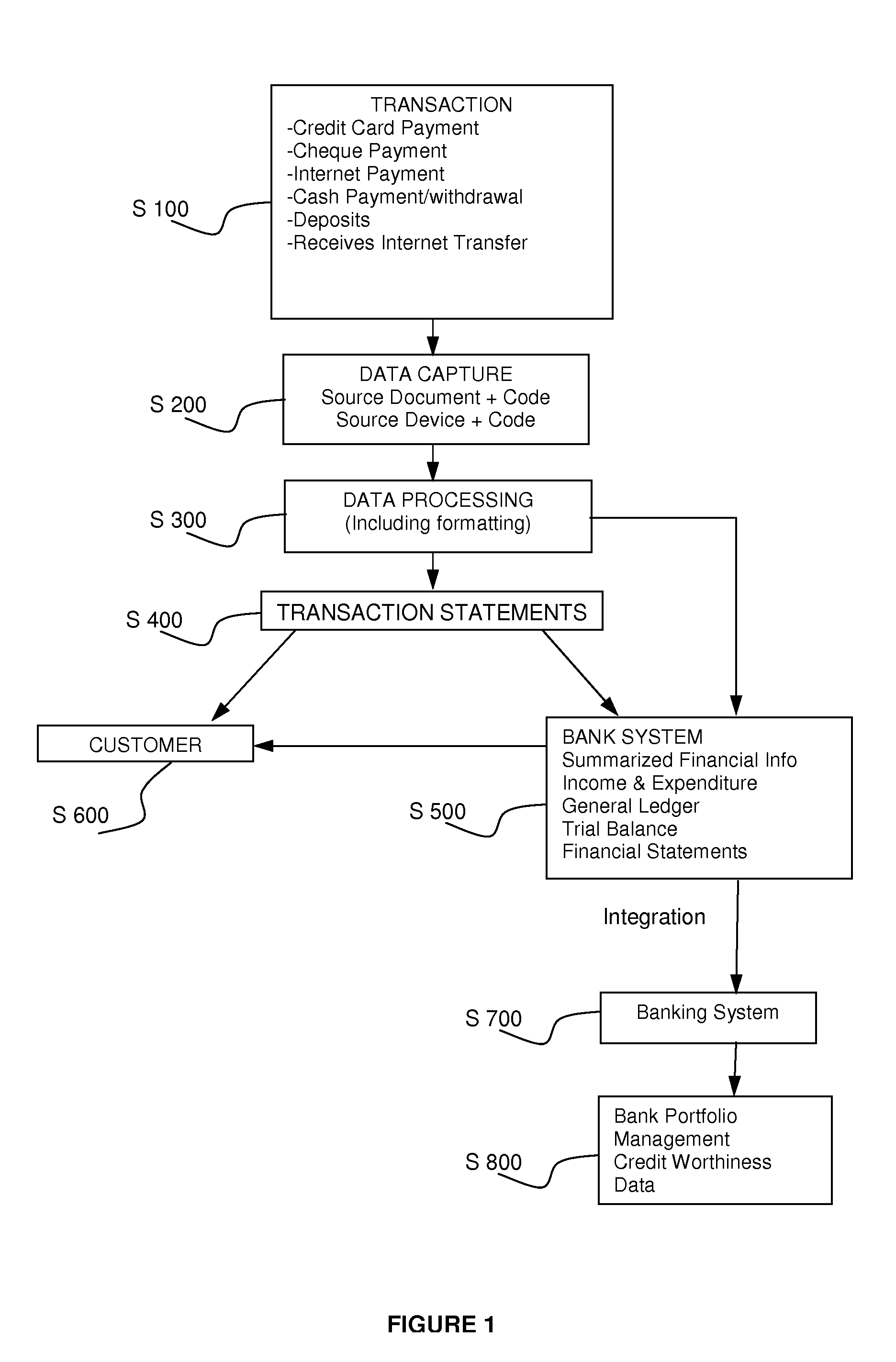
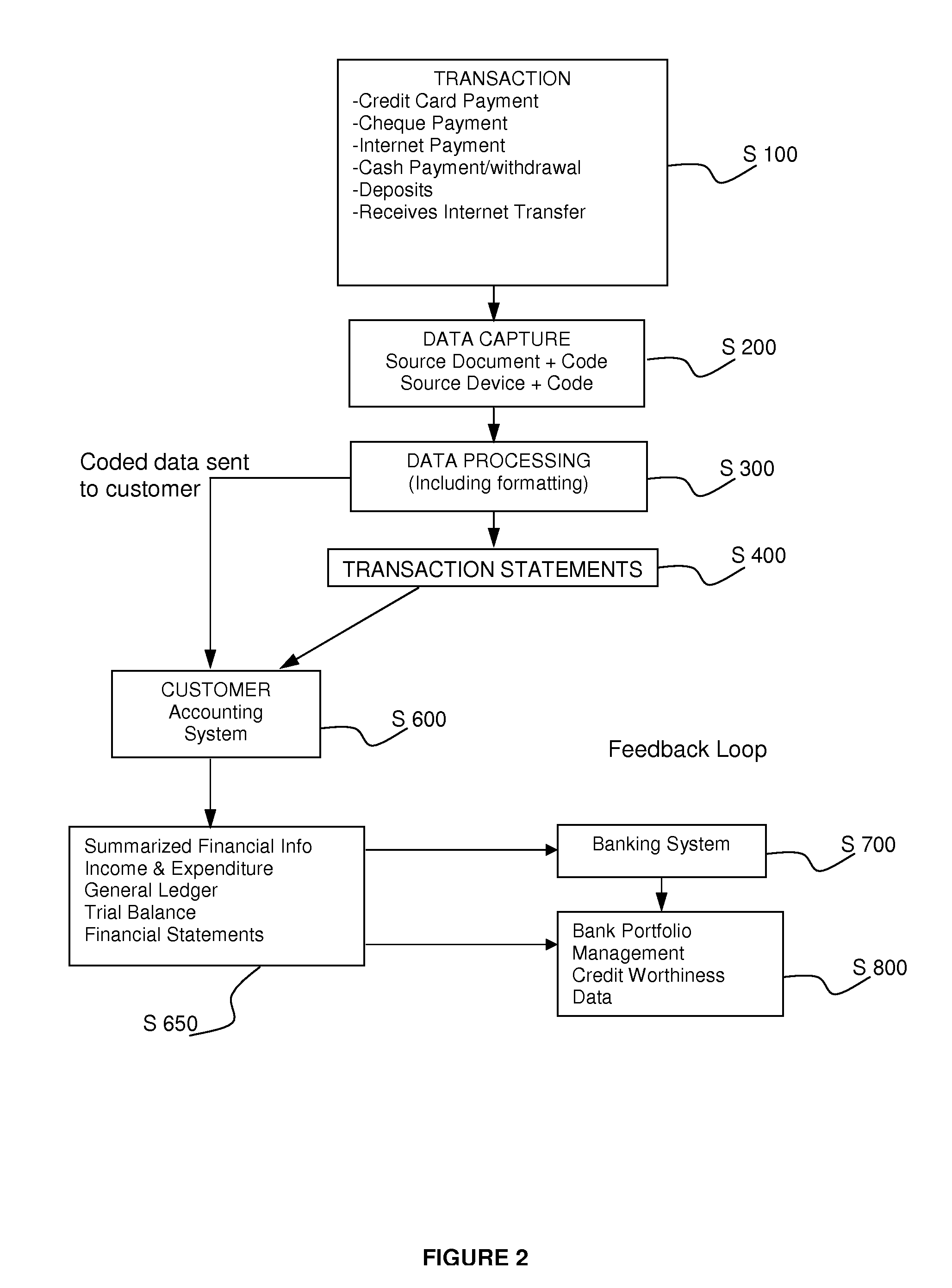
Accounting Process
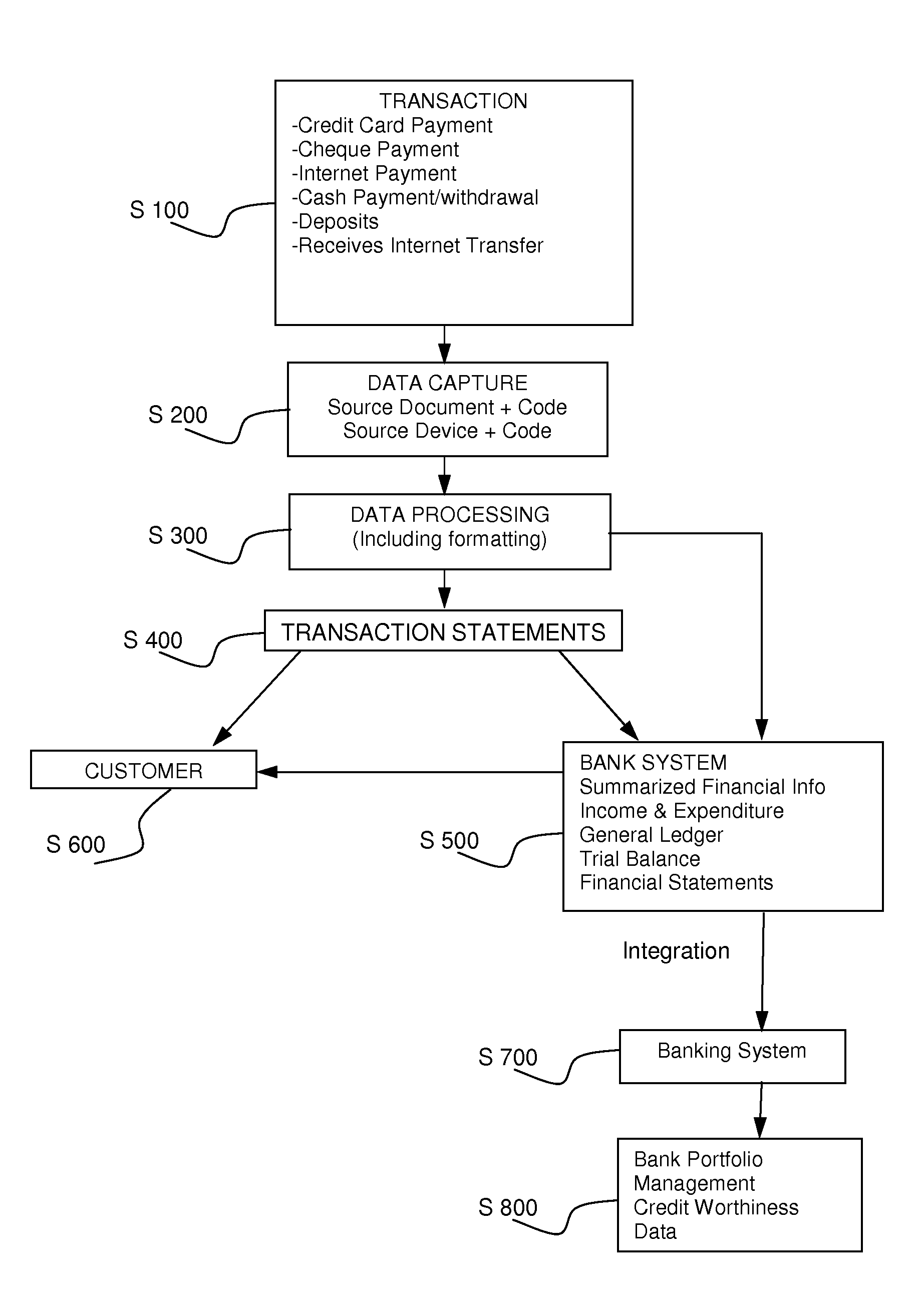
InactiveUS20080262949A1Avoid repetitionEfficient managementComplete banking machinesFinanceTransaction dataDatabase
A computerized accounting process and system capturing customer transaction data, creating transaction codes or references at the time of the transaction and generating accounting reports for the customer.
Owner:QWILL
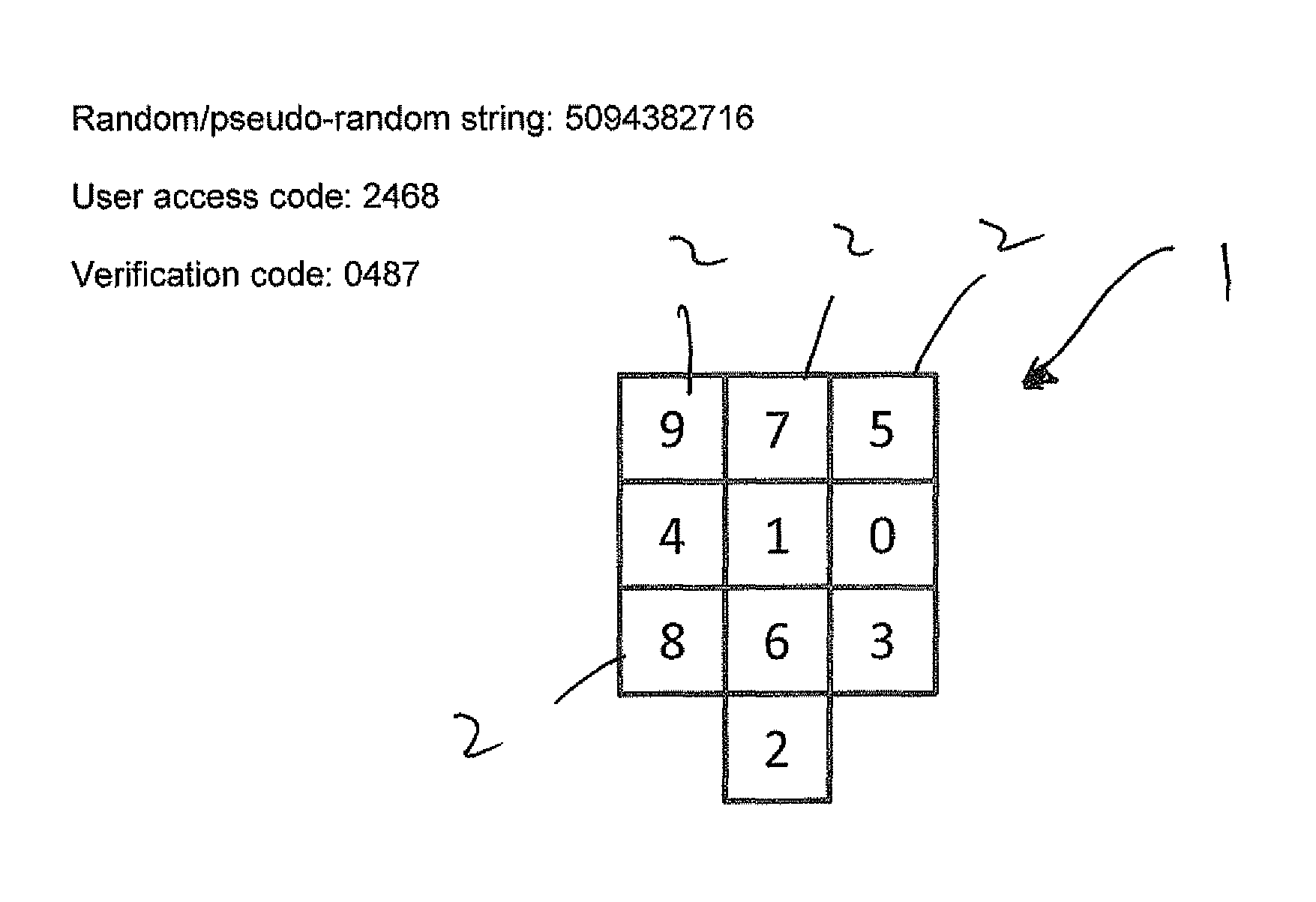
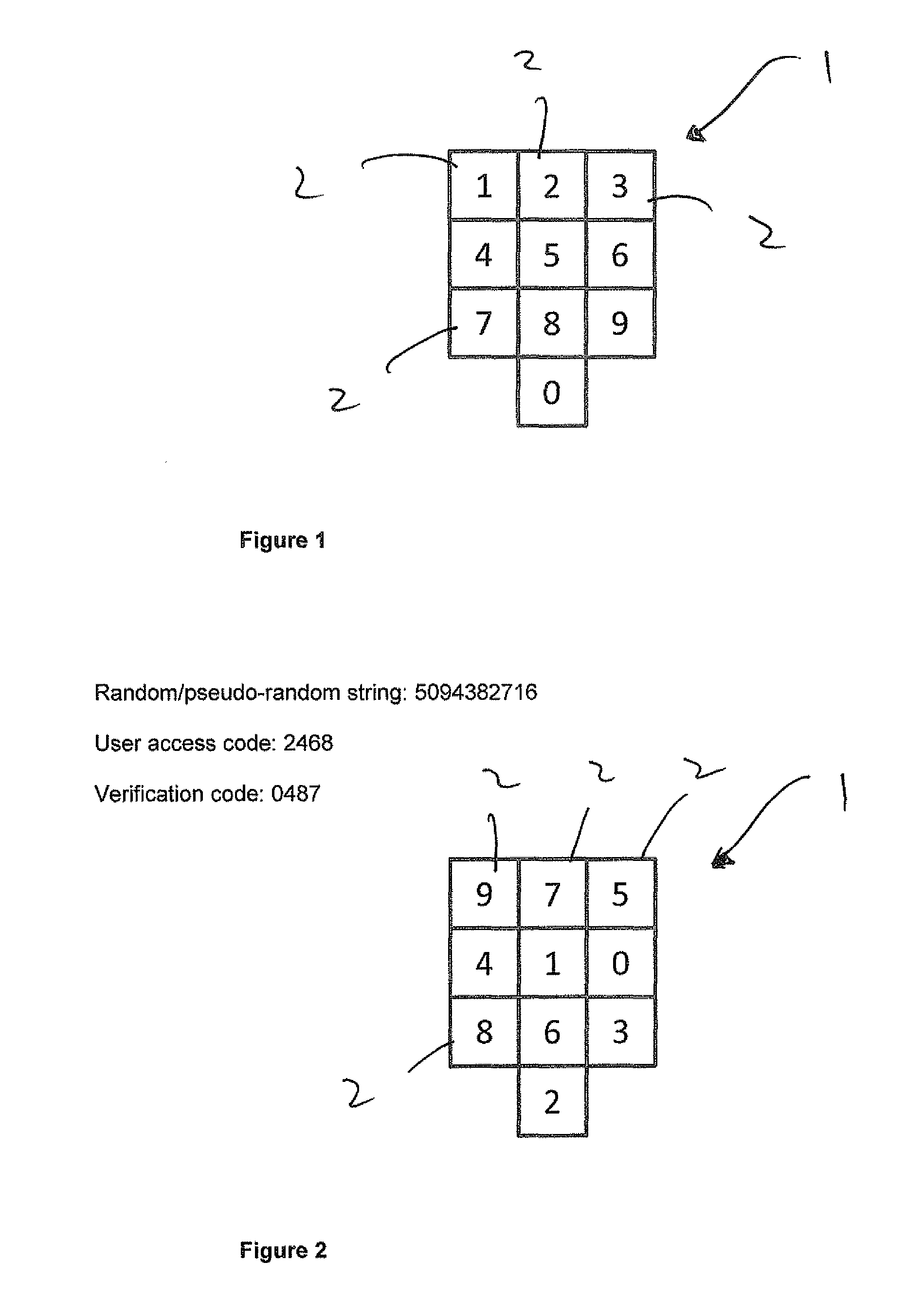
Method and system for secure user identification
ActiveUS20150134526A1Process safetyReduce riskAcutation objectsFinanceComputerized systemDisplay device
There is disclosed a method and system for verifying an identity of a user to a computer system. The user is assigned a user access code in the form of an invariant string of integers from 0 to 9, with length no greater than ten. The user access code is stored in the computer system; the computer system generates a ten-digit random or pseudo-random non-repeating string of the integers 0 to 9, the string having 1st to 10th positions each with a unique integer and having respective positional values 1 to 10; and the computer system performs a predetermined algorithm to combine the user access code and the random or pseudo-random string, thereby to determine a one-time verification code in the form of a string of the same length as the user access code. The computer system also generates 1st to 10th cells, the cells having respective locational values 1 to 10; populates the cells with the integers of the non-repeating string such that the locational value of each cell corresponds to the integer it contains combined with the random or pseudo-random string using the same predetermined algorithm as used previously; and displays the cells on a display. A user uses an input device of the computer system to select, in order, the cells on the display that contain the integers constituting the user access code. Each act of selection returns the locational value of the selected cell, thereby to generate a one-time transaction code comprising a string of integers from 0 to 9 having the same length as the user access code. The computer system then compares the verification code with the one-time transaction code and makes a successful identity verification if the verification code matches the one-time transaction code.
Owner:SWIVEL SECURE LTD
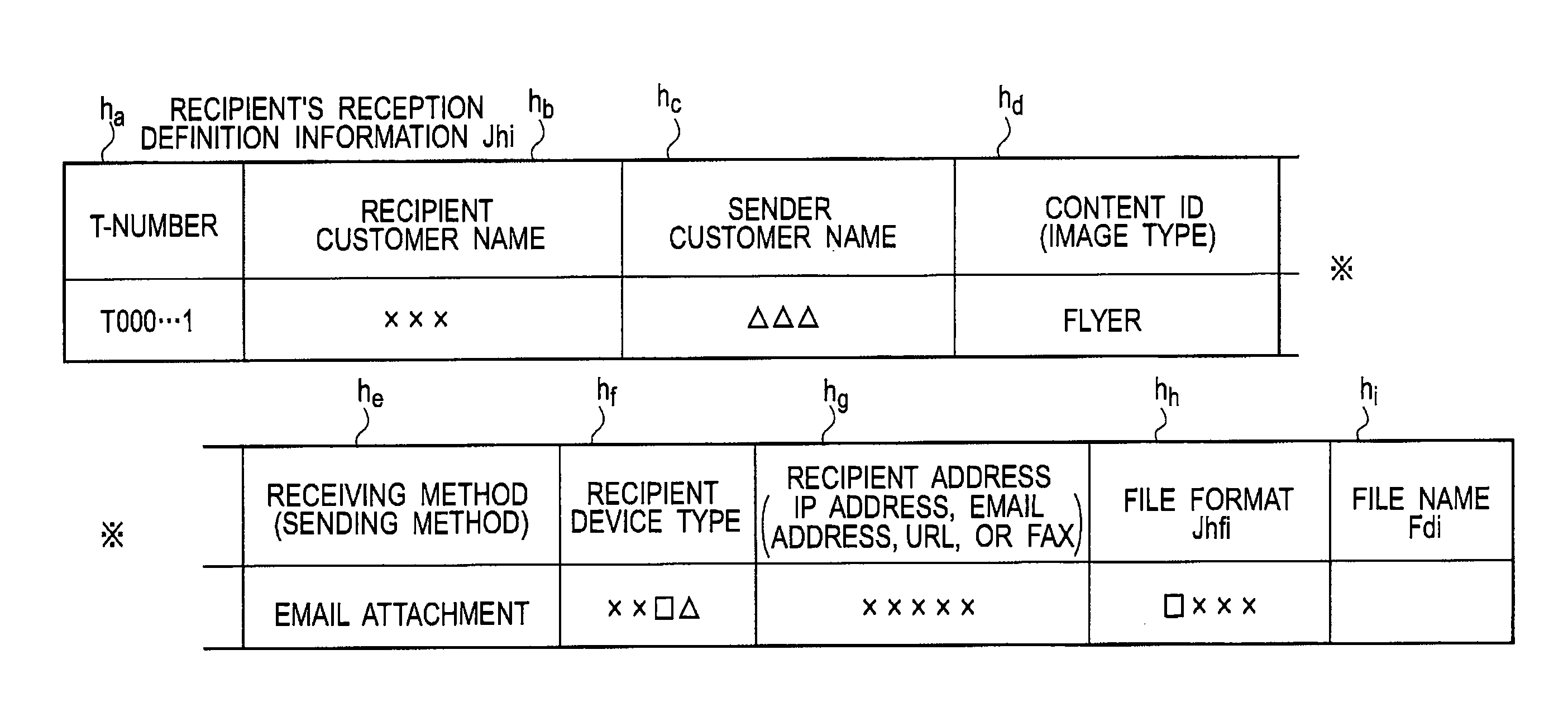
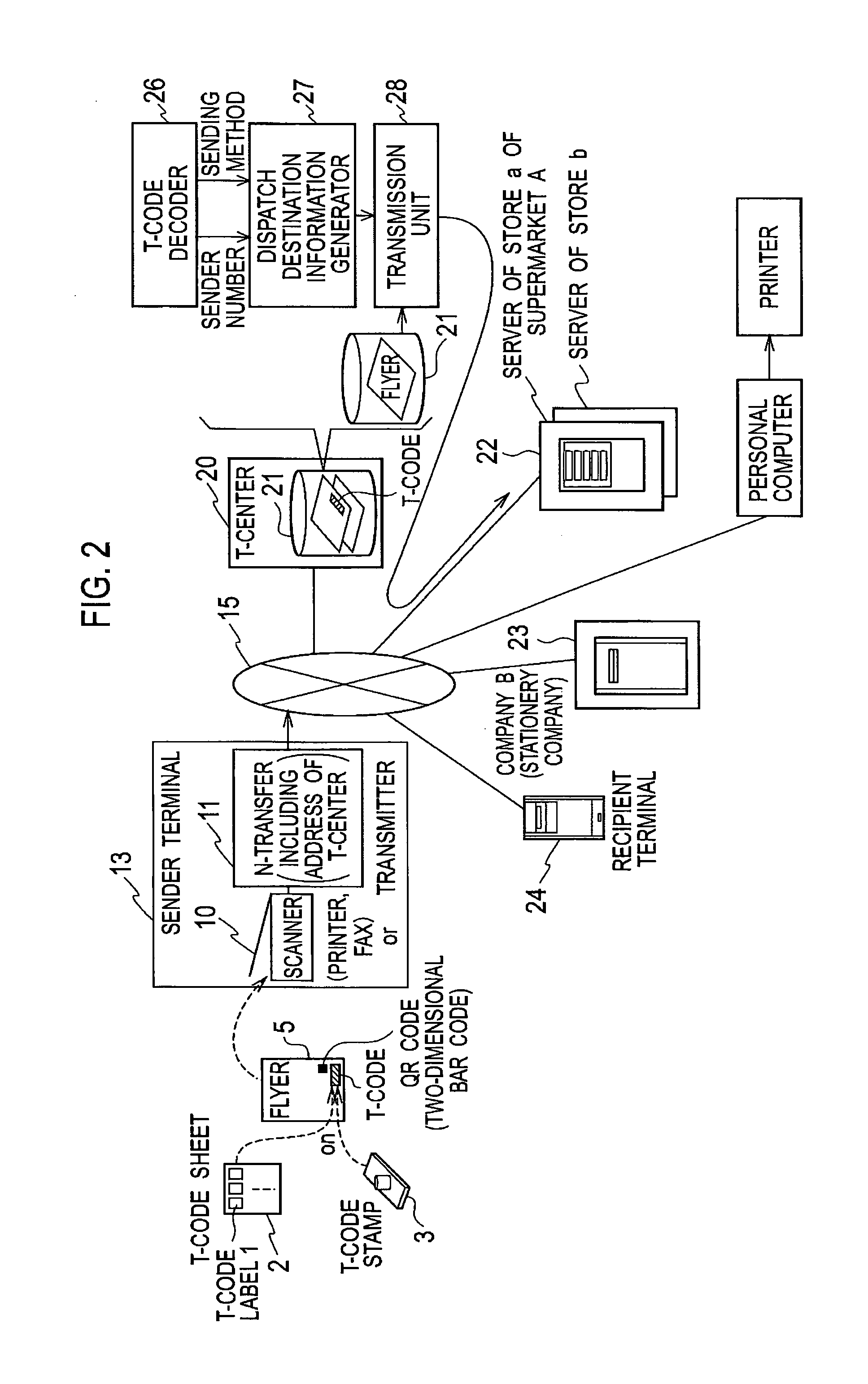
Sender-side content transmission method and information transmission system
InactiveUS20140222948A1Multiple digital computer combinationsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsInformation transmissionOrder form
The user side is provided with a scanner and a transmitter, the T-center side is provided with a T-code decoder and a dispatch information generator, the user side transmits T-code-inserted image data, while the T-center generates order information (sender name, recipient name, sending method, address (recipient, sender), T-code-inserted image data, URL of supermarket, etc.) from the user, based on the decoding result of the image data, and the order information (simply dispatch information) is transmitted to supermarket via a communication network.
Owner:DYNAMIC LAB CORP
On-site payment system and method implemented based on identity authentication token
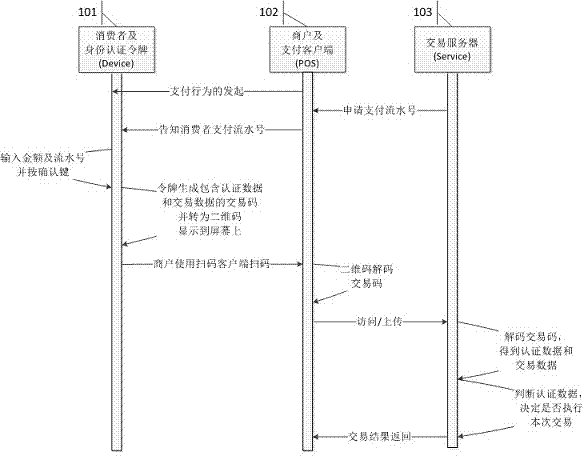
InactiveCN103886460AReduce hardware costsImprove payment experienceUser identity/authority verificationPoint-of-sale network systemsKey pressingLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses an on-site payment system and method implemented based on an identity authentication token. The on-site payment system comprises identity authentication token hardware, a commercial tenant client program and a transaction server. During an on-site transaction, a consumer inputs amount of money and other information through keys on an identity authentication token and presses down an enter key, and a sequence of transaction codes are calculated according to a secret key, an algorithm and required parameters set in the token and are converted into two-dimension codes to be displayed on a liquid crystal display screen; a commercial tenant scans the two-dimension codes with terminals such as a mobile phone where a payment client program is installed, and transaction codes obtained after the two-dimension codes are decoded are uploaded to a transaction server; the transaction server receives the transaction codes, and transaction data and authentication data are obtained through analysis; whether the transaction data are legal and valid or not can be recognized according to the authentication data, and corresponding transaction operations such as account transfer are executed if the transaction data are valid. According to the on-site payment system and method implemented based on the identity authentication token, transaction safety is ensured through the identity authentication token, the transaction data are transmitted through the two-dimension codes, the commercial tenant can scan the two-dimension codes with the mobile phone, the complexity of the cash-free transaction mode is reduced, user experience is improved, and the transaction cost is reduced.
Owner:徐永君
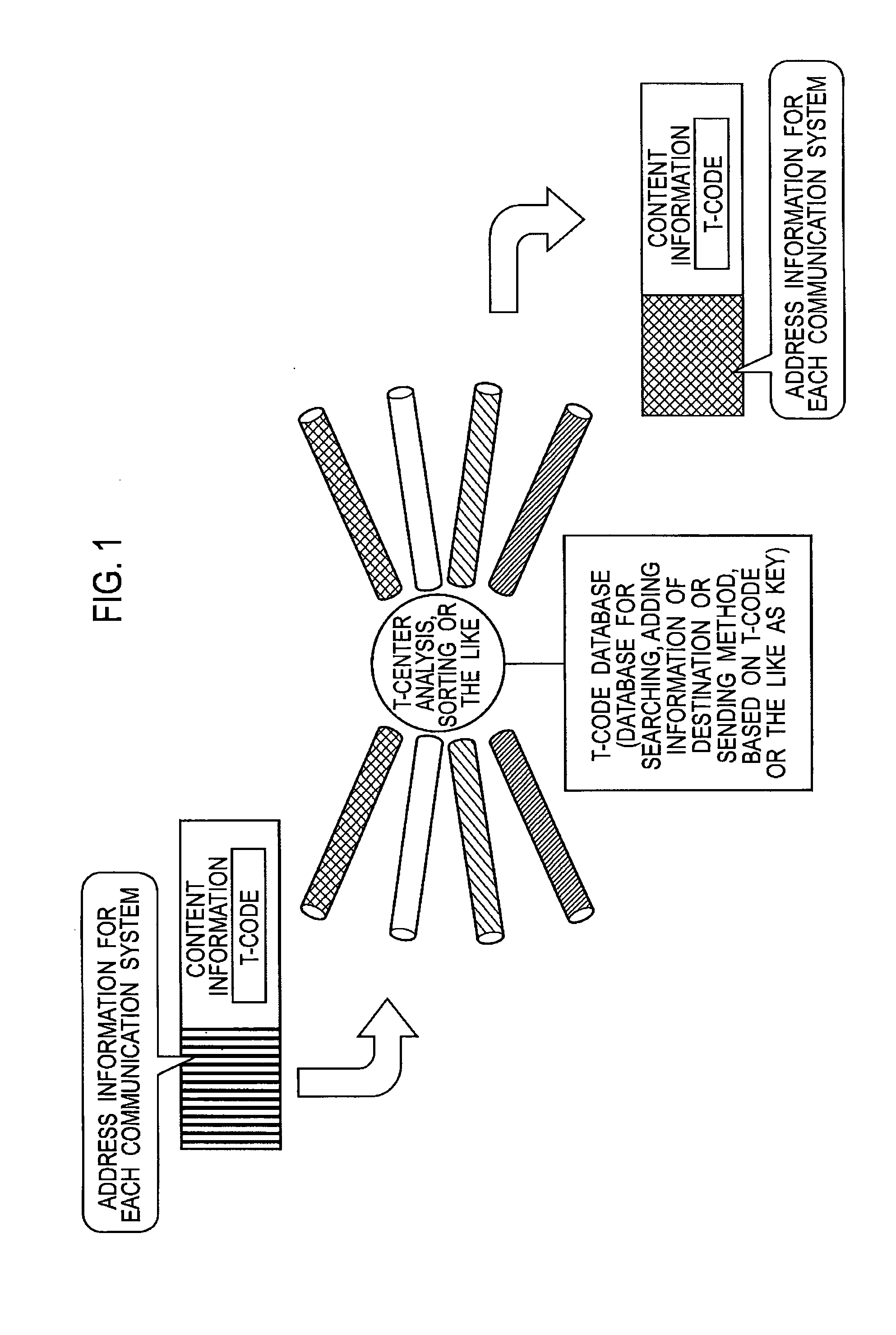
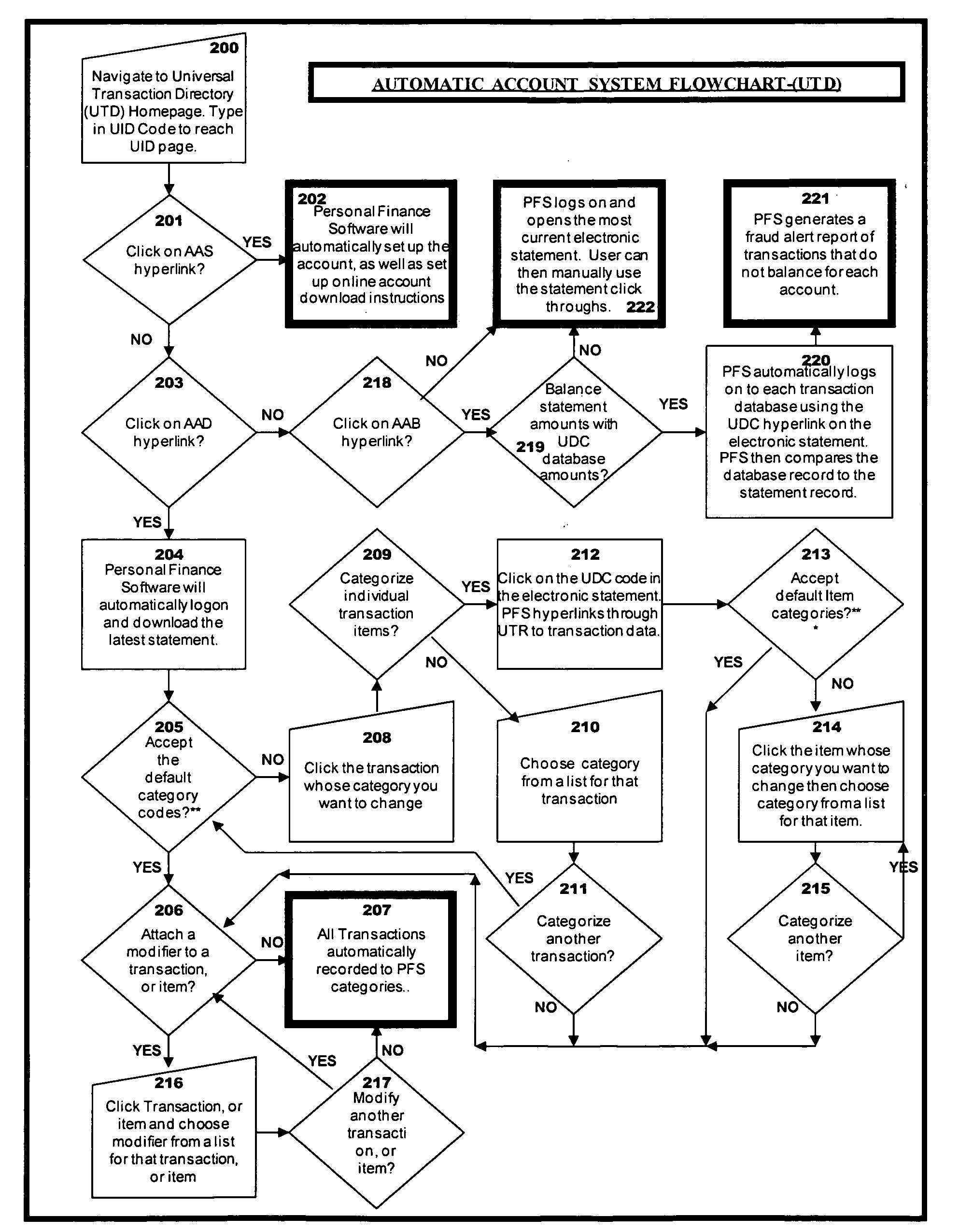
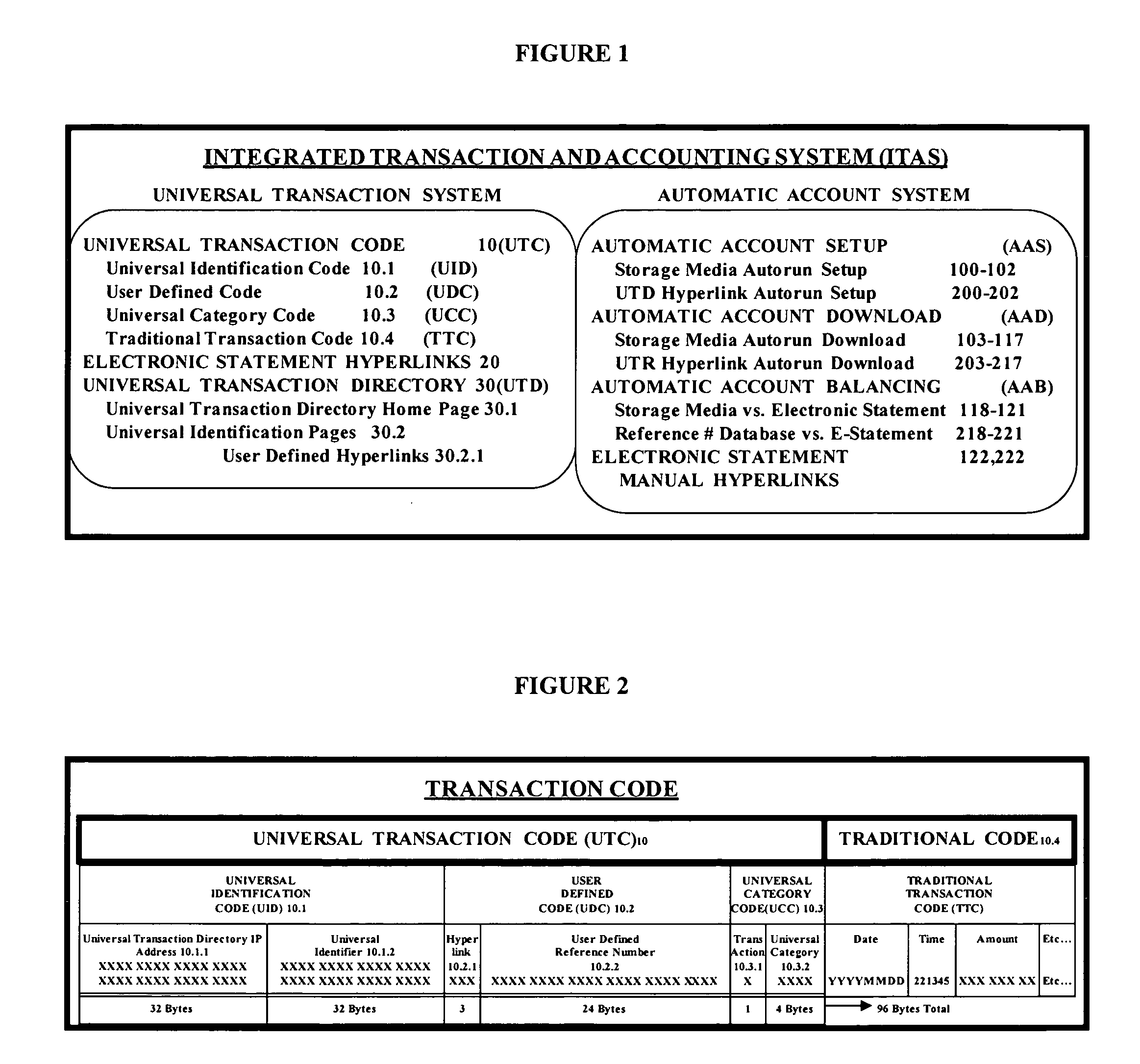
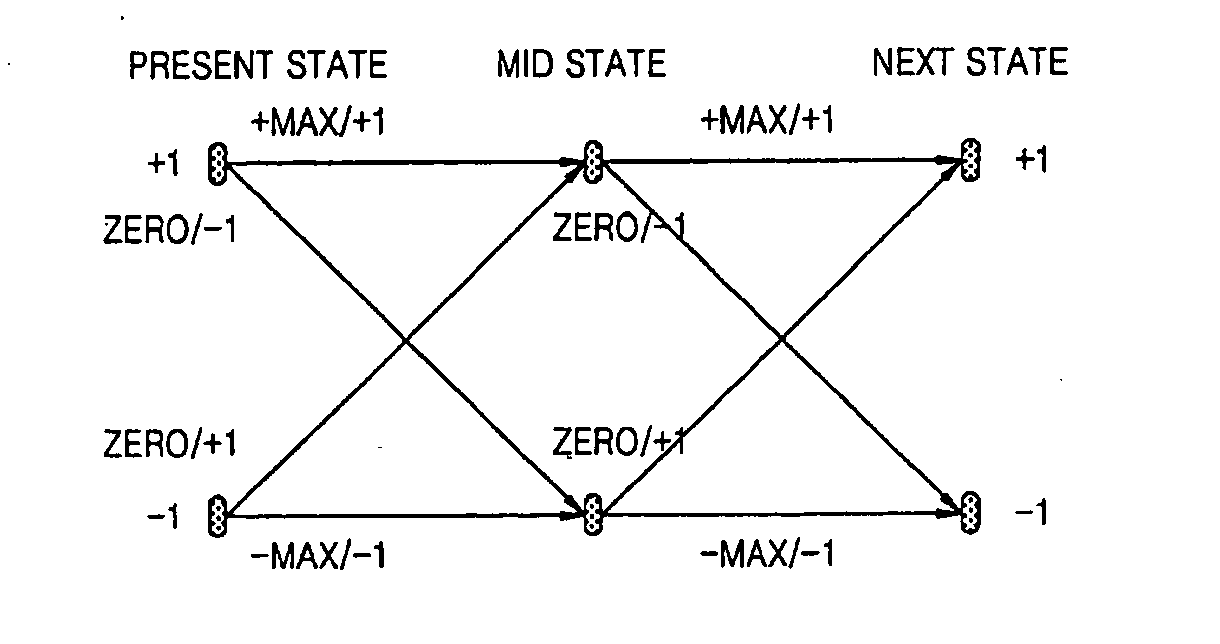
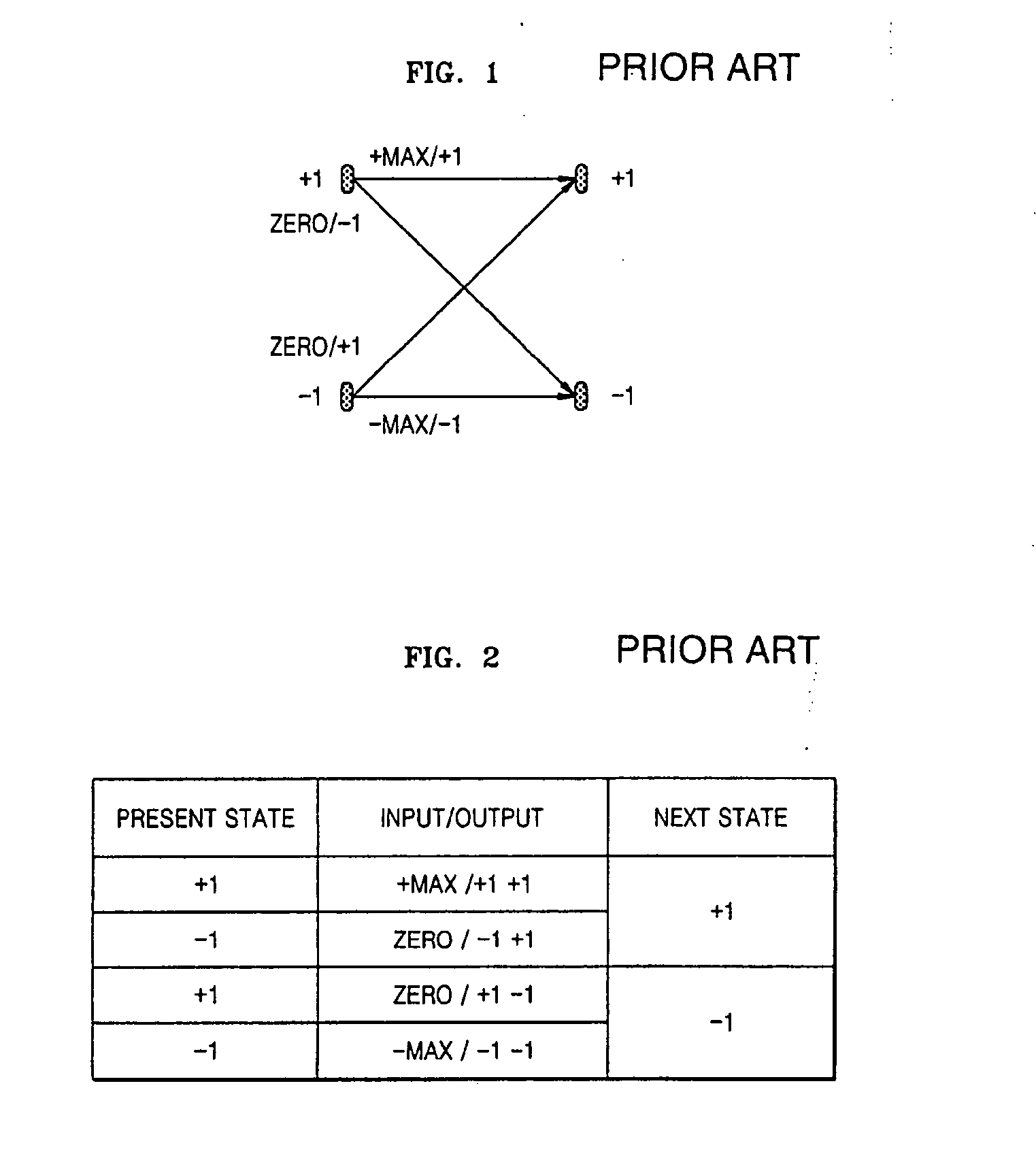
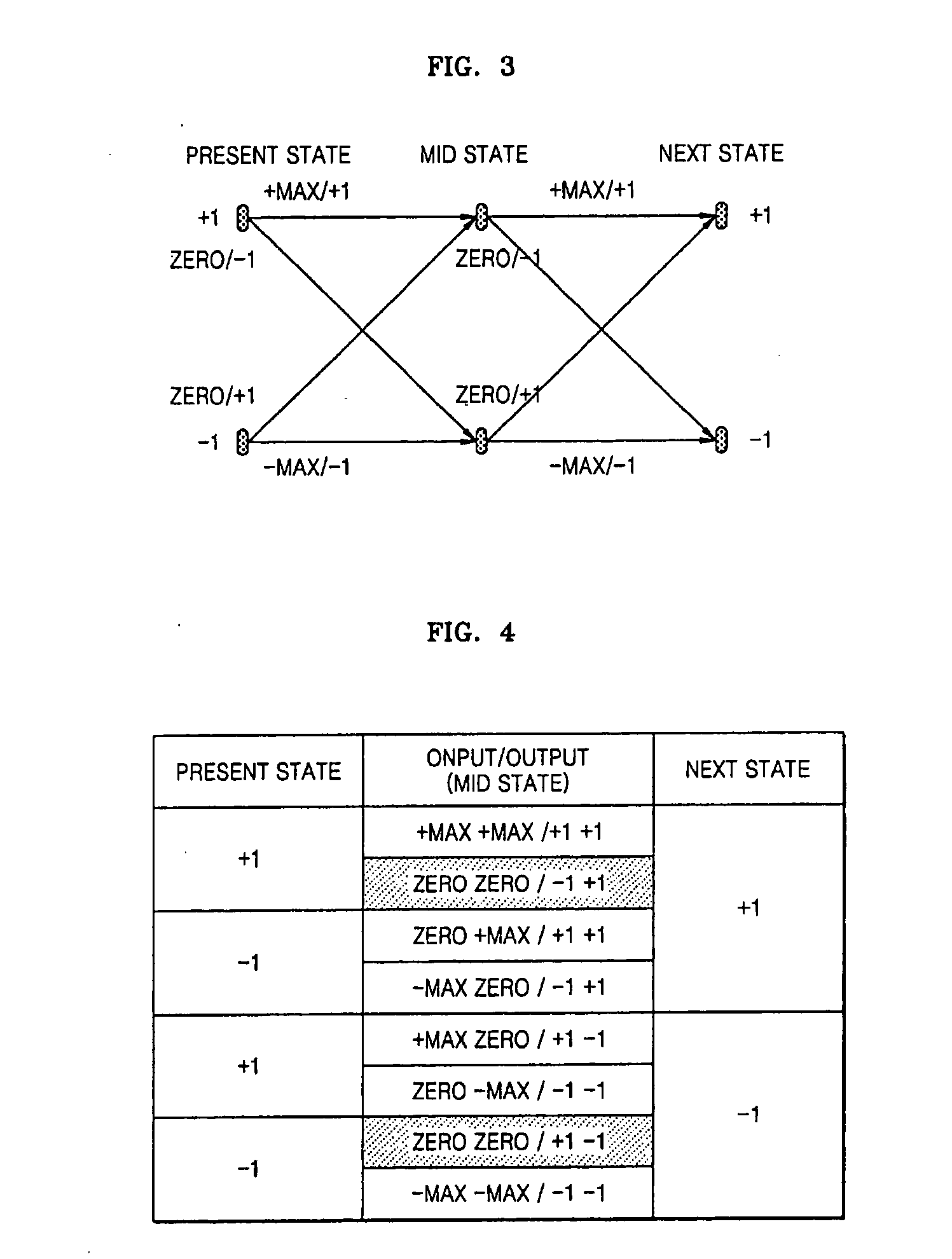
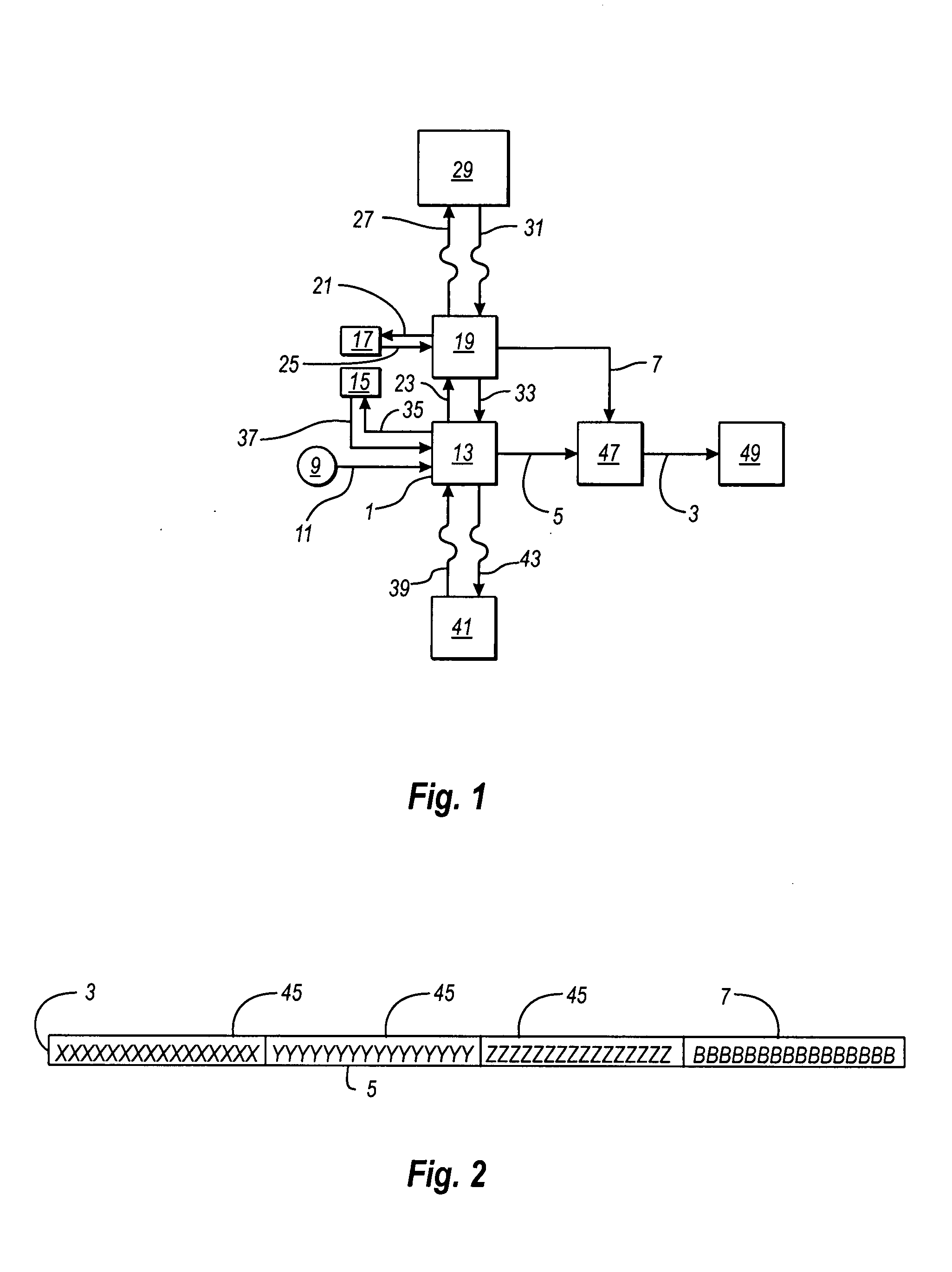
Universal transaction code (UTD) used to standardize the method of capturing, storing, and retrieving transaction data
A new standardized Universal Transaction Code (10), as well as a standard Universal Transaction Directory (30). These two core components form the foundation of an Integrated Transaction and Accounting System (FIG. 1). This system will provide the framework to enable several disparate; identification methods, transaction accounting methods, transaction receipt methods, transaction storage methods, and website access methods to work together providing a synergistic effect. The benefits for the consumer are: simple, nearly automatic, personal finance tracking, as well as standardized transaction record and website access. An automatic way of tracking finances will increase a consumer's awareness of his or her spending practices thereby exposing and highlighting frivolous spending. The benefits for industry are: vastly increased efficiency and profit margins by reducing the dependence on outdated paper based methods, virtual elimination of “no receipt” fraudulent returns, and knowledgeable consumers focused on reducing frivolous purchases while increasing wealth building practices.
Owner:VAN BEEK SCOTT DALE
Viterbi detection apparatus and method therefor
InactiveUS20050066259A1Good for high speed operationRun at high speedData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer scienceBase Number
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
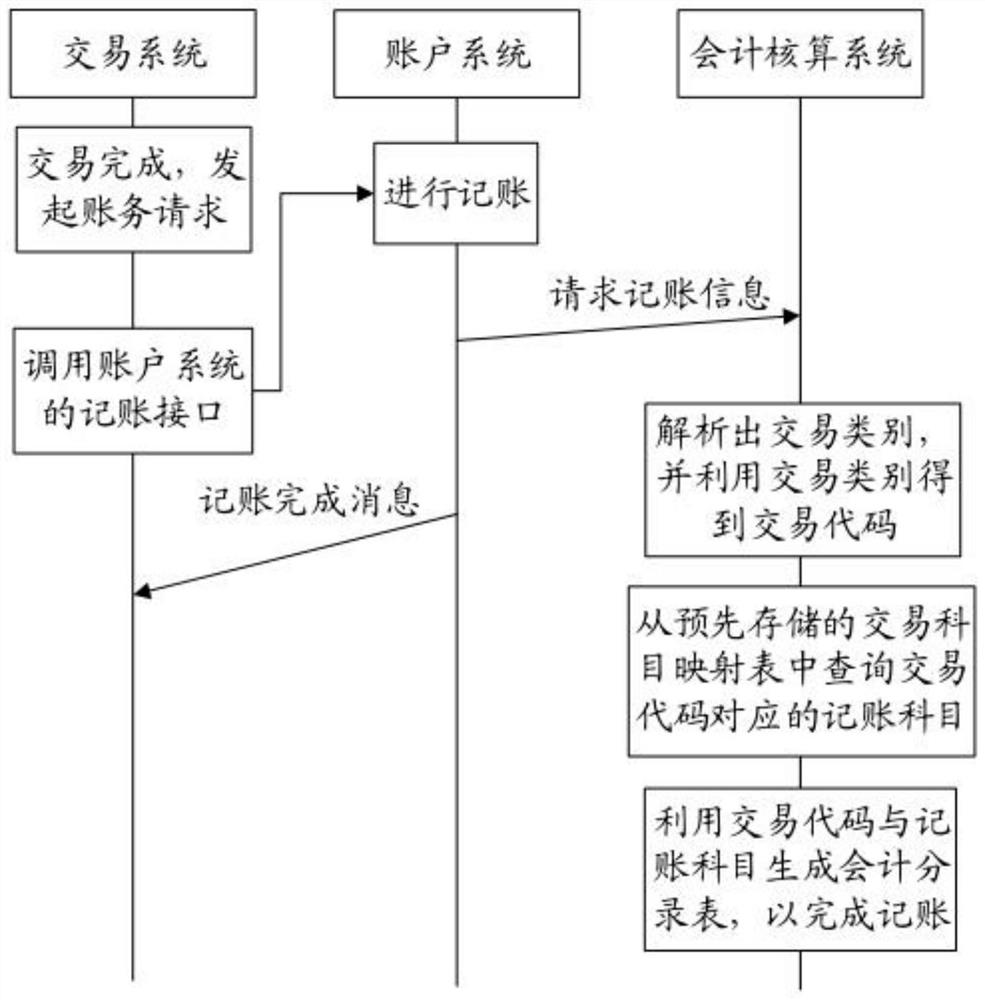
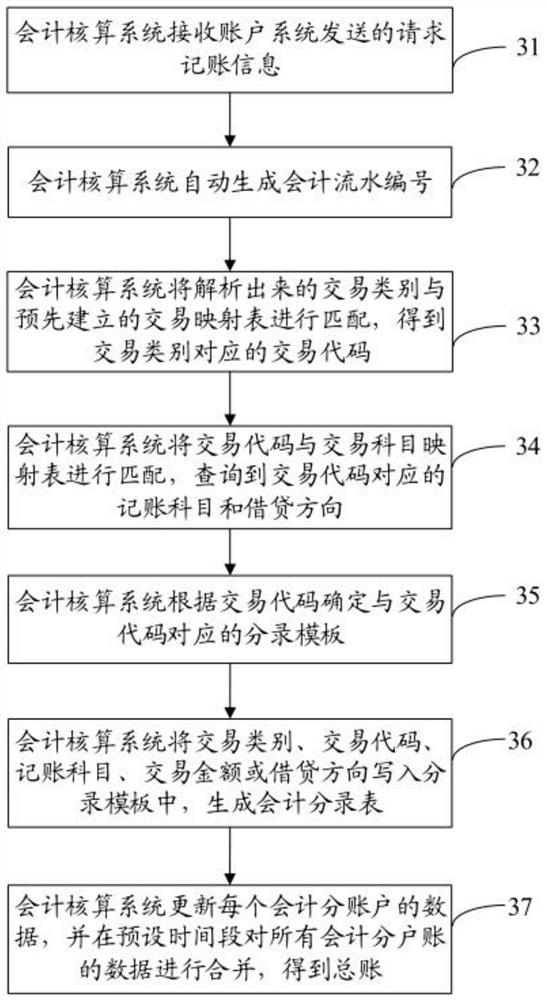
Accounting method, accounting system, account system and payment system
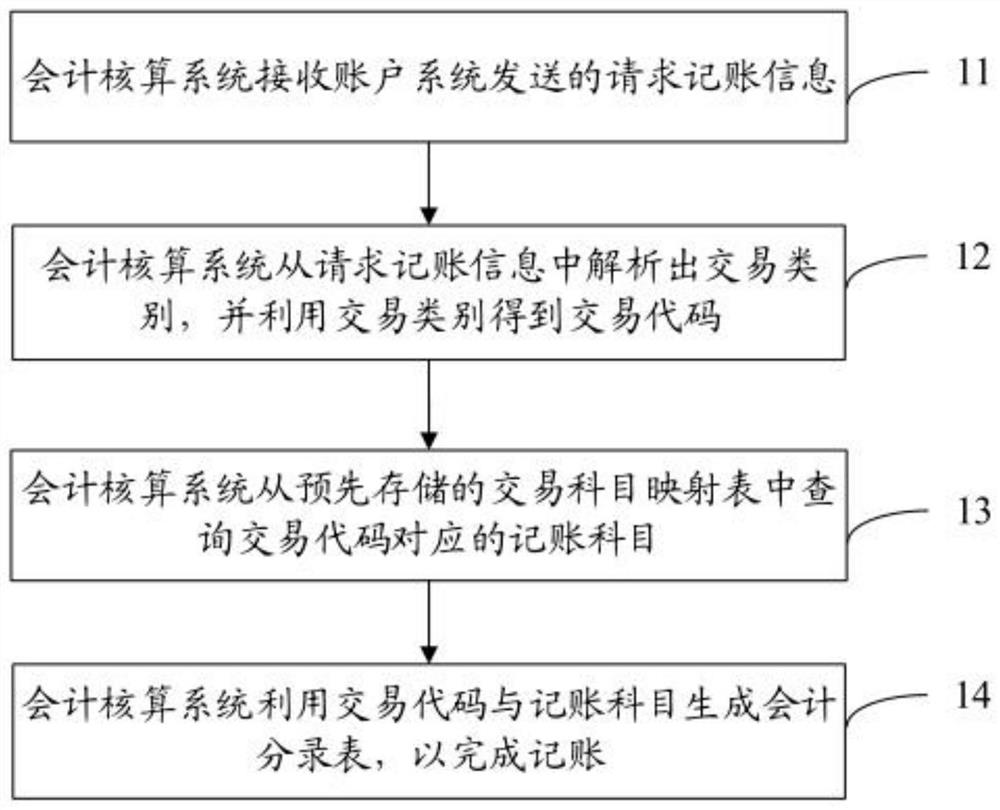
ActiveCN111699486ASolve accounting problemsFlexible response to system complexityFinancePayment architectureFinancial transactionAccounting method
The invention discloses an accounting method, an accounting system, an account system, a payment system and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps that the accounting system receives request accounting information sent by the account system, and the request accounting information comprises an accounting request, a transaction type or a transaction amount; the accounting system analyzes a transaction category from the request accounting information and obtains a transaction code by using the transaction category, and the transaction code is a serial number of the transaction category; the accounting system queries an accounting subject corresponding to the transaction code from a pre-stored transaction subject mapping table, and the transaction subject mapping table comprisesat least one transaction code and an accounting subject corresponding to the transaction code; and the accounting system generates an accounting entry table by using the transaction code and the accounting subject so as to complete accounting. Through the above mode, the method can achieve the real-time accounting, improves the processing efficiency, and flexibly responds to the payment complexityand business variability.
Owner:SWIFTPLUS TECH CO LTD
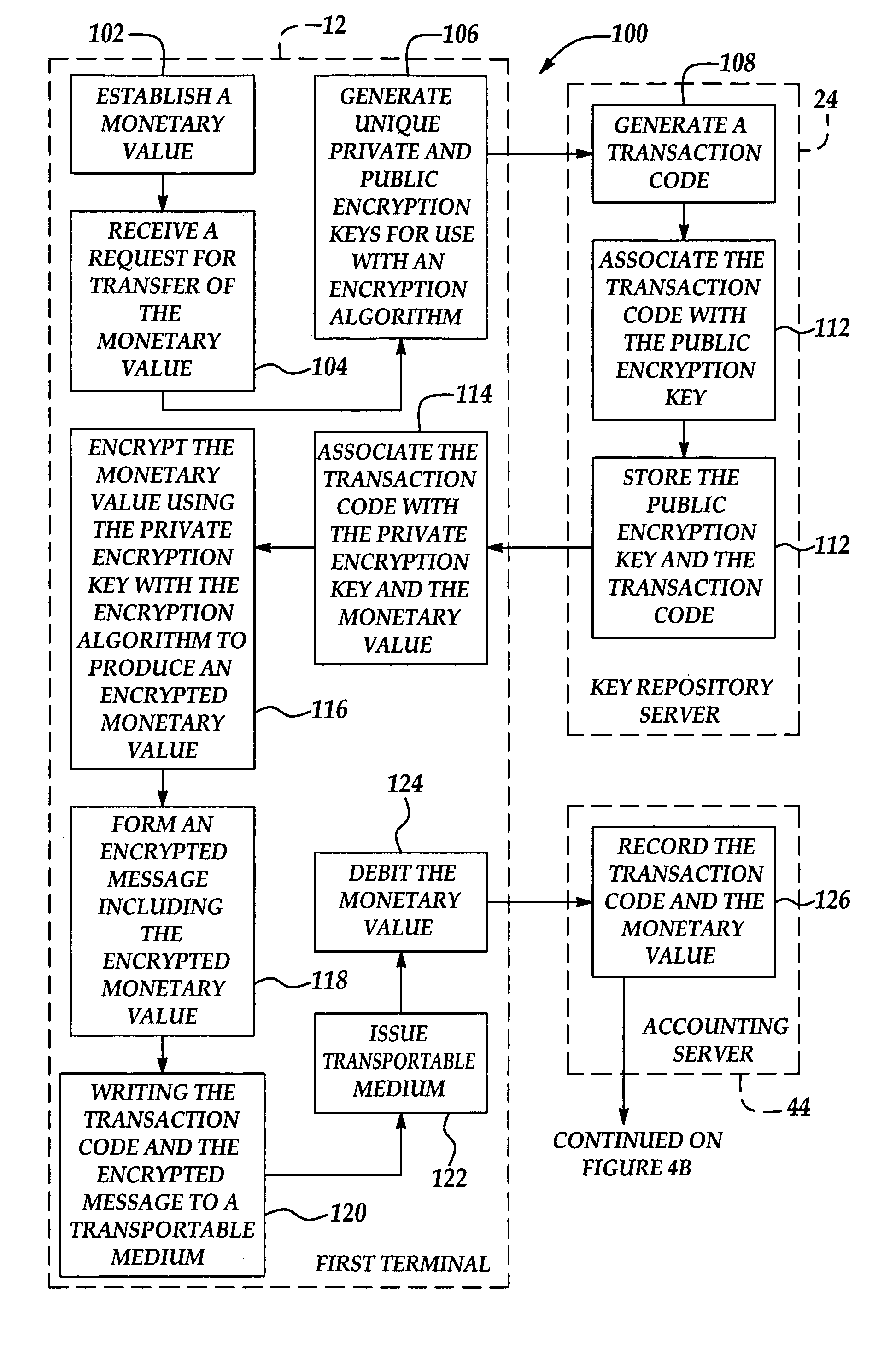
Gaming system and method of securely transferring a monetary value
ActiveUS20050234834A1Acutation objectsKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareTransport medium
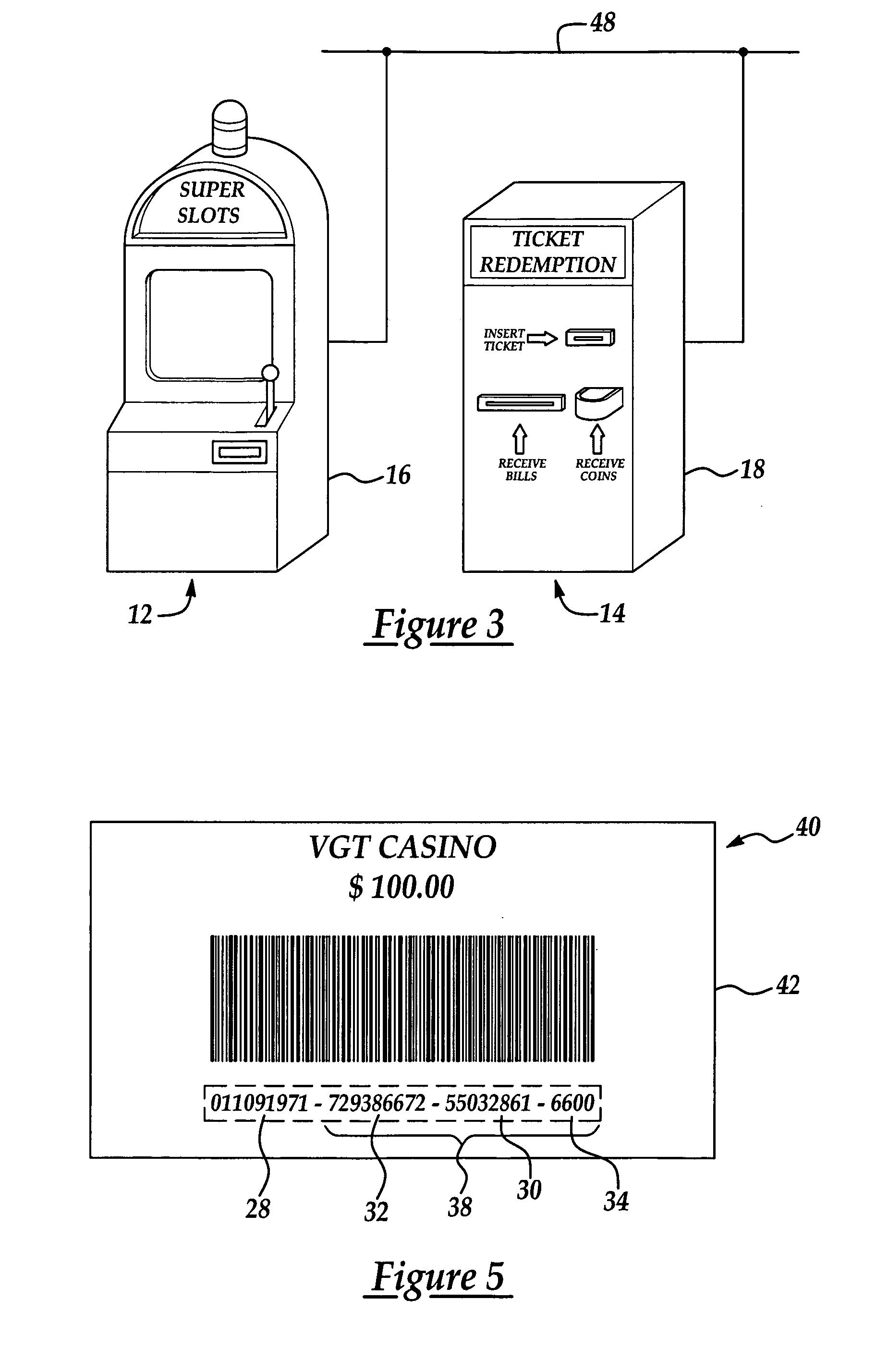
A cashless gaming system and method of securely transferring a monetary value. When “cashing-out” of a first terminal of the system, the monetary value is encrypted with an encryption key and an encryption algorithm to produce an encrypted monetary value. A transaction code is associated with encryption key and the monetary value. The transaction code and encrypted monetary value are written to a transportable medium that is issued by the first terminal. The transaction code and associated encryption key are stored in a key repository database. The transaction code and monetary value are stored in an accounting database which is securely separate from the key repository database. The transportable medium is taken to a second terminal where the encrypted monetary value and transaction code are read. The encryption key associated with the transaction code is retrieved and used to decrypt the encrypted monetary value. The monetary value is then credited to the second terminal.
Owner:VIDEO GAMING TECH
Near-field magnetic communication and proximity relation detection based mobile phone payment system and method
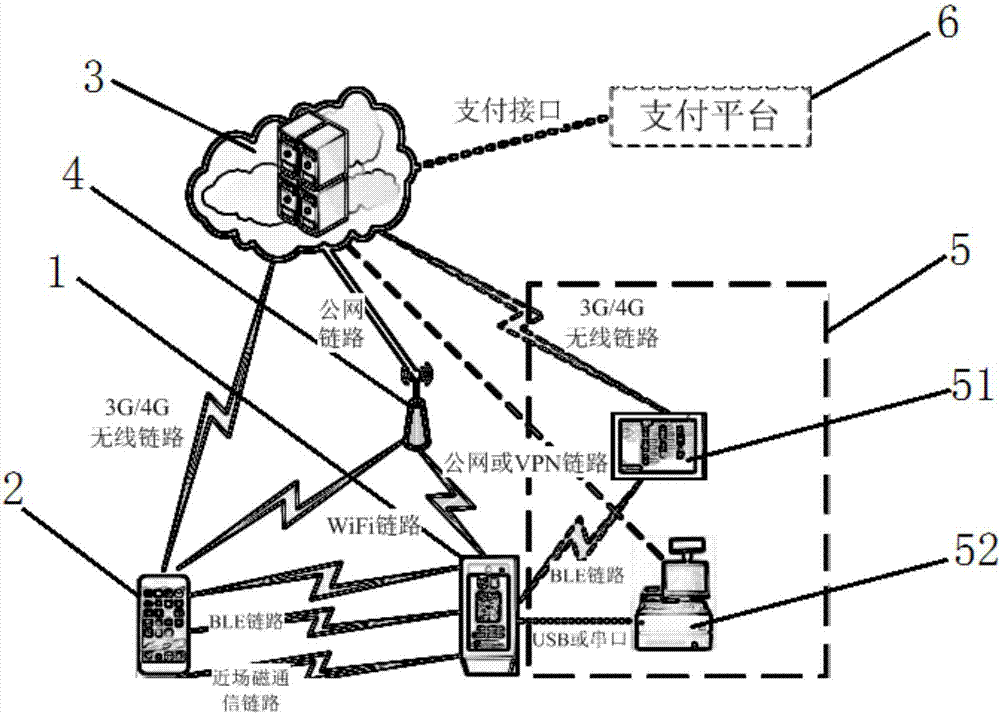
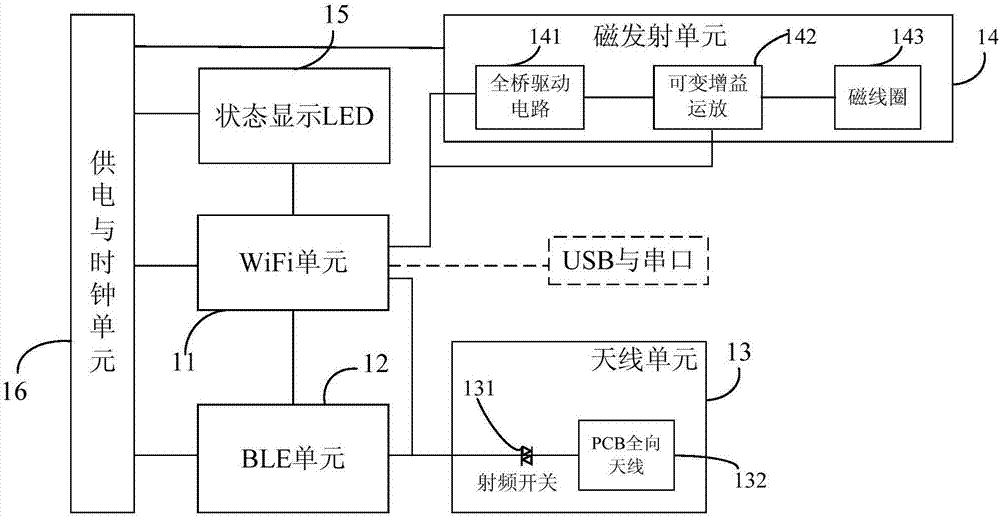
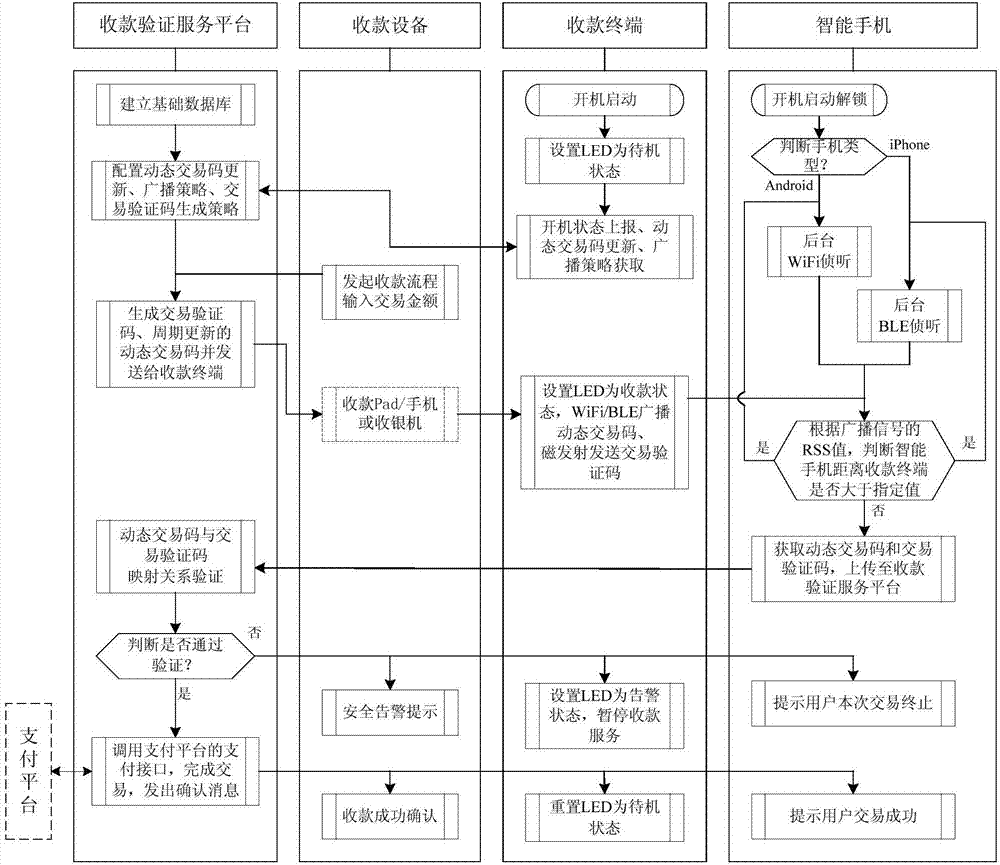
PendingCN107194689AImprove securityImprove payment experienceNear-field transmissionProtocol authorisationTelecommunications linkPayment transaction
The invention provides a near-field magnetic communication and proximity relation detection based mobile phone payment system and method. The near-field magnetic communication and proximity relation detection based mobile phone payment method comprises the steps of initiating a money collection process through a money collection device by a payee; enabling a money collection verification service platform to be connected with a money collection terminal; sending a transaction verification code and a dynamic transaction code generated by the transaction to a money collection terminal; broadcasting the dynamic transaction code through WiFi or a BLE link by the money collection terminal; sending the transaction verification code through the near-field magnetic communication link; after a smart phone obtains the dynamic transaction code and the transaction verification code, packaging the codes into a verification request message and sending the message to the money collection verification service platform for safety verification; verifying the uploaded transaction verification code and dynamic transaction code by the money collection verification service platform; and after the verification passes, finishing the payment transaction through a payment interface provided by the payment platform. The payment in the system approaches the immediate payment; the payment movement can be reduced, the payment time can be shortened, and the payment experience can be improved; and the unique transaction verification code generated in the transaction and the dynamically and periodically updated dynamic transaction code guarantee the payment safety.
Owner:南京维智感网络科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for verifying a person's identity or entitlement using one-time transaction codes
ActiveUS8947197B2Improve securityReduce riskElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
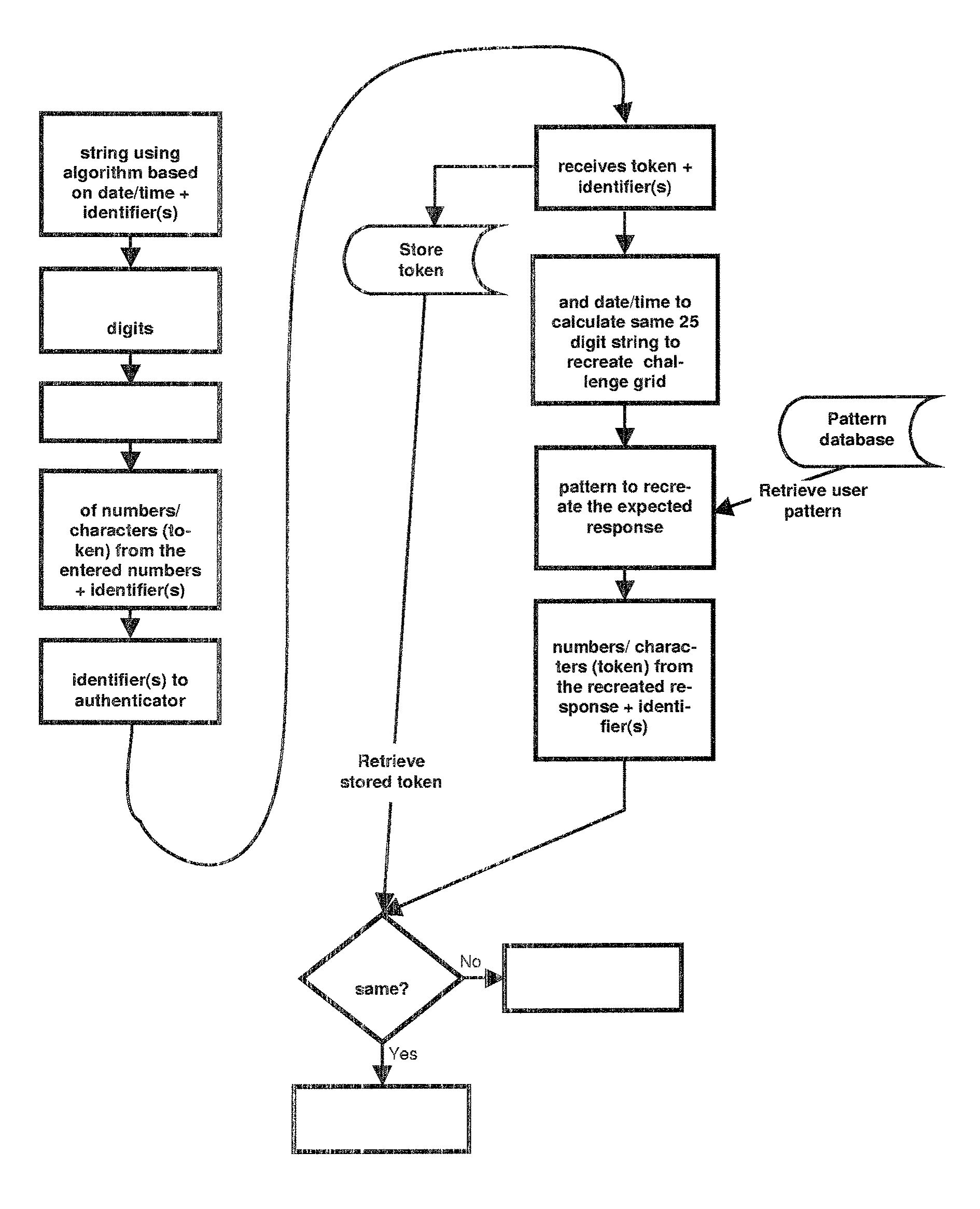
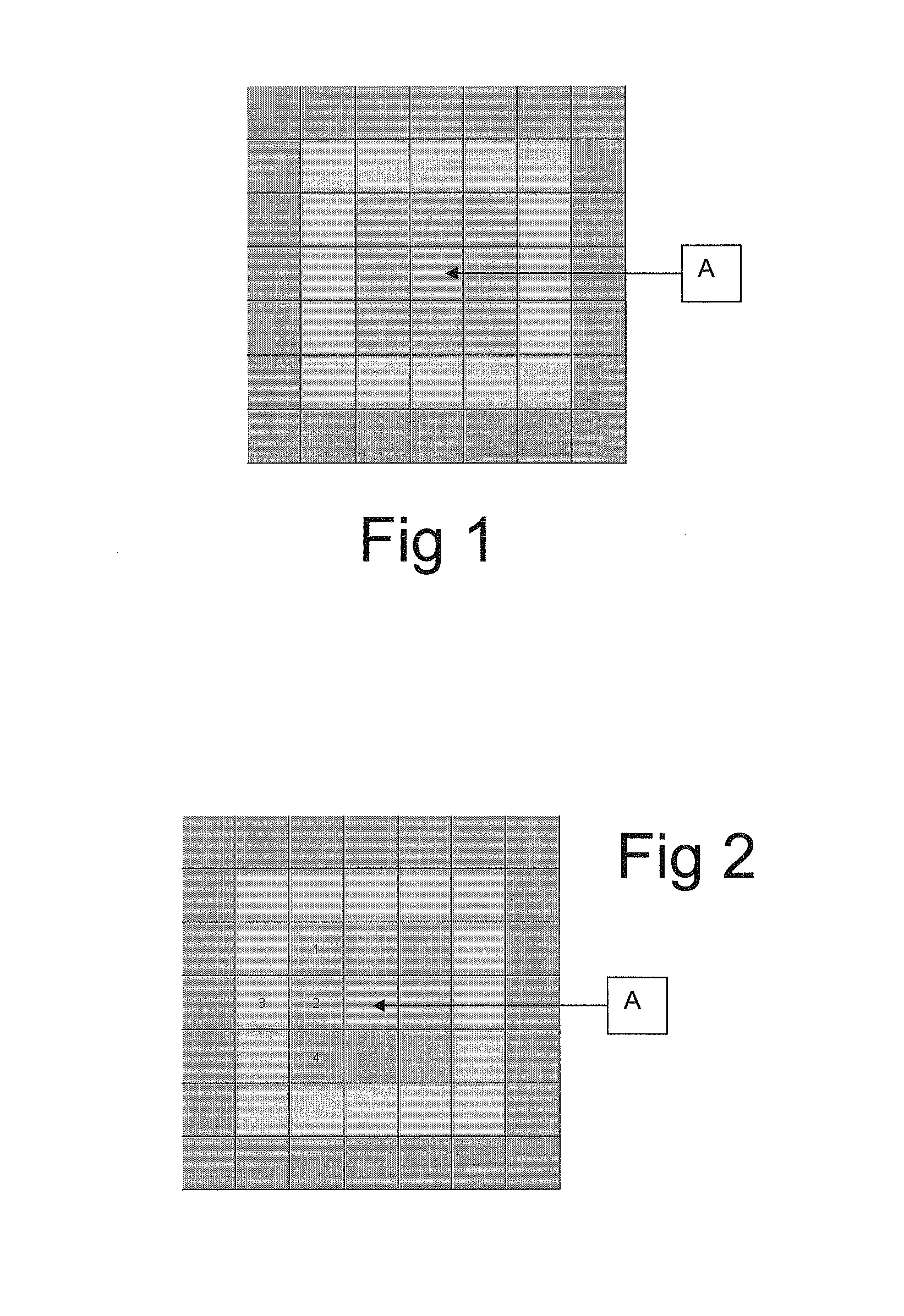
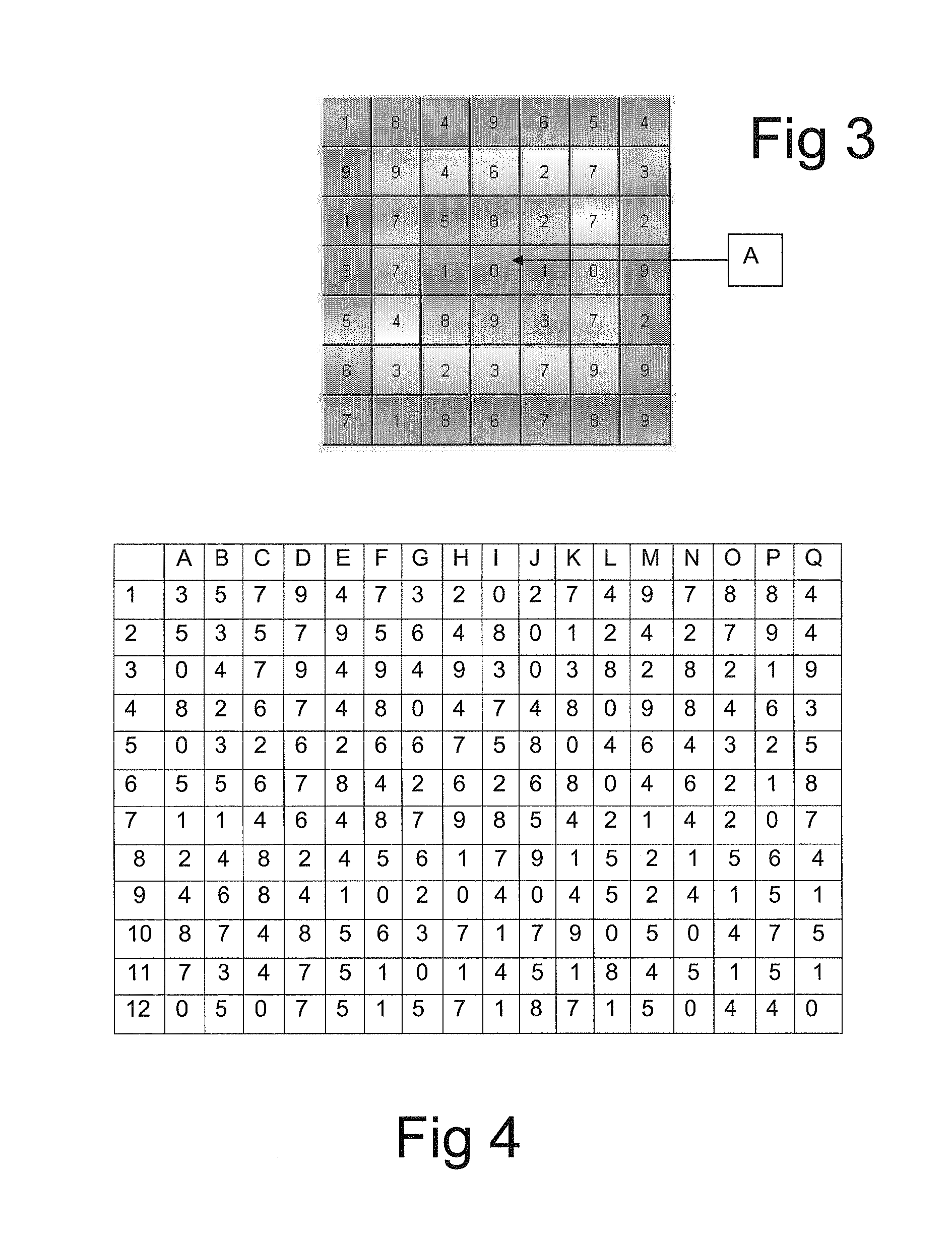
A method for verifying a person's identity is of the general type which comprises storing a personal pattern of a pre-determined number of locations on a grid in association with personal identification data, and subsequently using the pattern in a verification process. According to the invention, the subsequent verification process comprises the steps of: (a) presenting to the person a challenge grid of locations occupied by a pseudo-random set of symbols, and challenging the person to identify a response set of symbols occupying locations in the challenge grid corresponding to the stored personal pattern; (b) receiving from the person the response set; (c) generating from the challenge grid and the stored pattern a verification set of symbols occupying locations in the challenge grid corresponding to the stored personal pattern; (d) comparing the response set of symbols with the verification set of symbols; and (e) verifying the identity of the person if the response set is the same as the verification set.
Owner:SAFENET UK
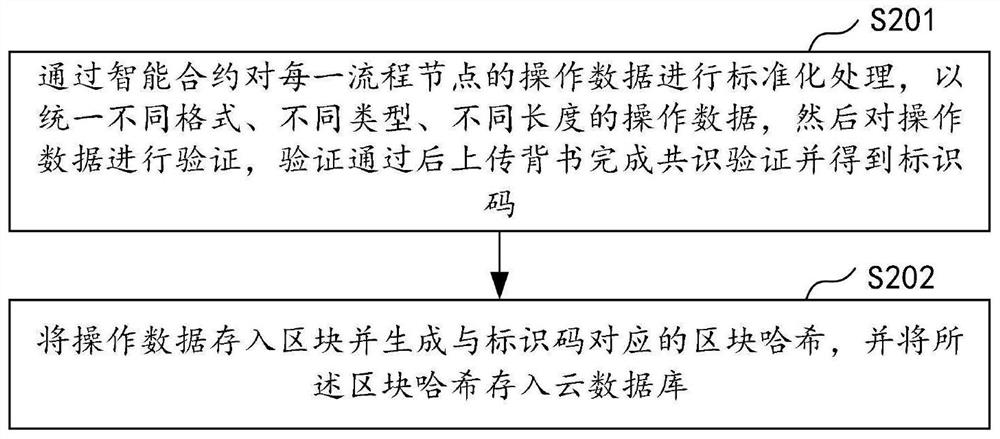
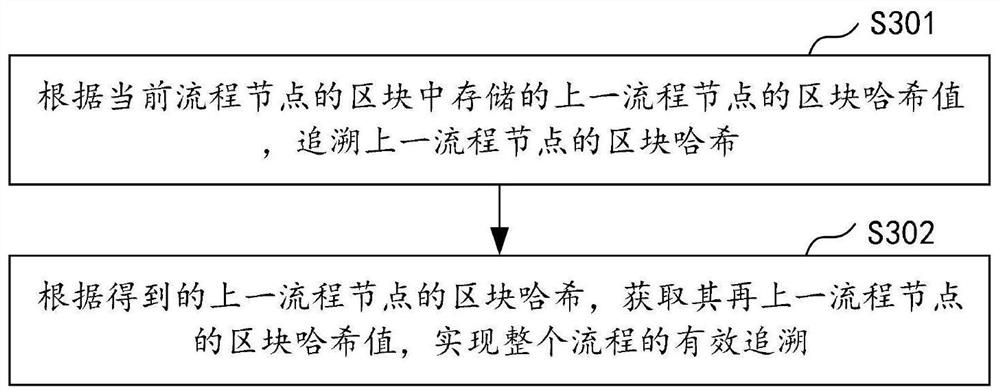
Data tracing method and device based on block chain, computer equipment and storage medium
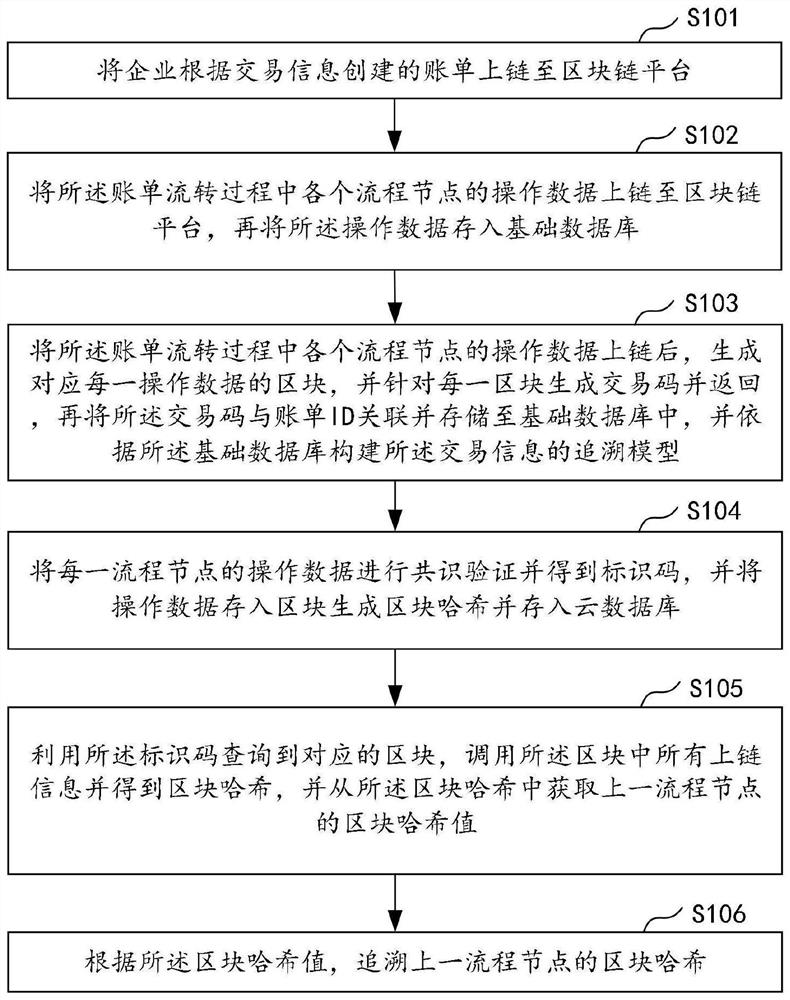
PendingCN112150149ARealize full process traceabilityImprove securityProtocol authorisationParallel computingEngineering
The invention discloses a data tracing method and device based on a block chain, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of uploading operation data of each process node in a bill circulation process and storing the operation data into a basic database; and performing consensus verification on the operation data of each process node to obtain an identification code,storing the operation data into a block generation block hash, and storing the operation data into a cloud database. According to the invention, the block corresponding to the transaction code duringuplink can be inquired through the transaction code, and the corresponding data is acquired from the block; the corresponding block hash can be traced and acquired through the identification code, the block hash value of the previous process node is acquired from the block hash of the current process node, the block hash of the previous process node is acquired according to the block hash value,and the whole process tracing of the bill is realized through repeated tracing, so that the step-by-step tracing from the bottom layer data is realized, and the tracing efficiency is improved. And thesecurity and authenticity of the data are improved.
Owner:深圳市中装智链科技有限公司
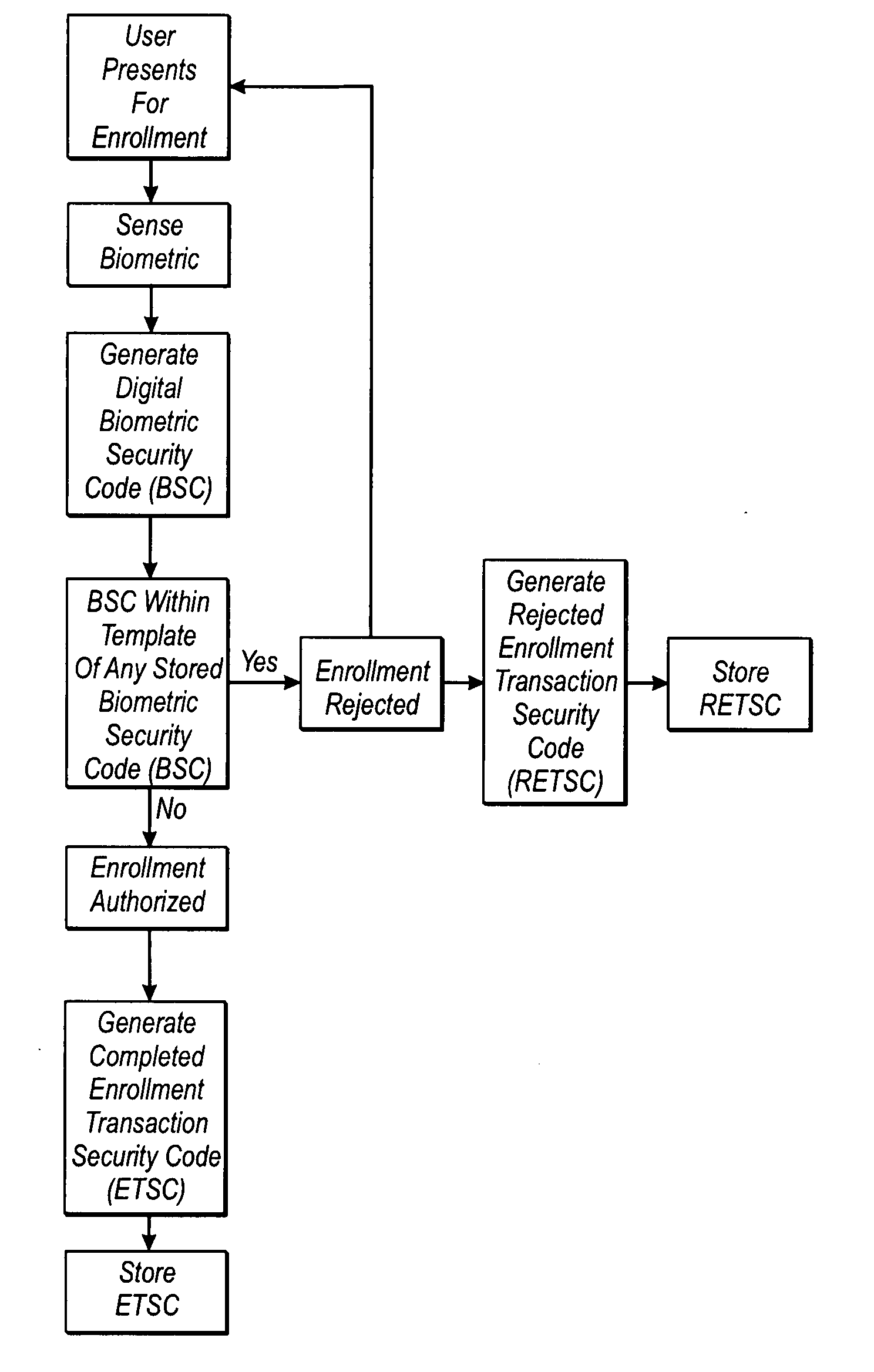
Apparatus and method for secured commercial transactions
InactiveUS20080262973A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsTransaction securityData library
A transaction security code database and a method and apparatus for generating the transaction security code database. The transaction security code database is comprised of multiple transaction security codes, each transaction security code constituting a transaction code generated based upon a transaction initiated by a user, which is appended to or linked to a security code which is based upon a biometric sensor code generated by a biometric sensor from a biometric presentation of a biometric feature of the user.
Owner:N P JOHNSON FAMILY PARTNERSHIP
ETC-based gas station non-inductive payment method and system, electronic equipment and storage medium
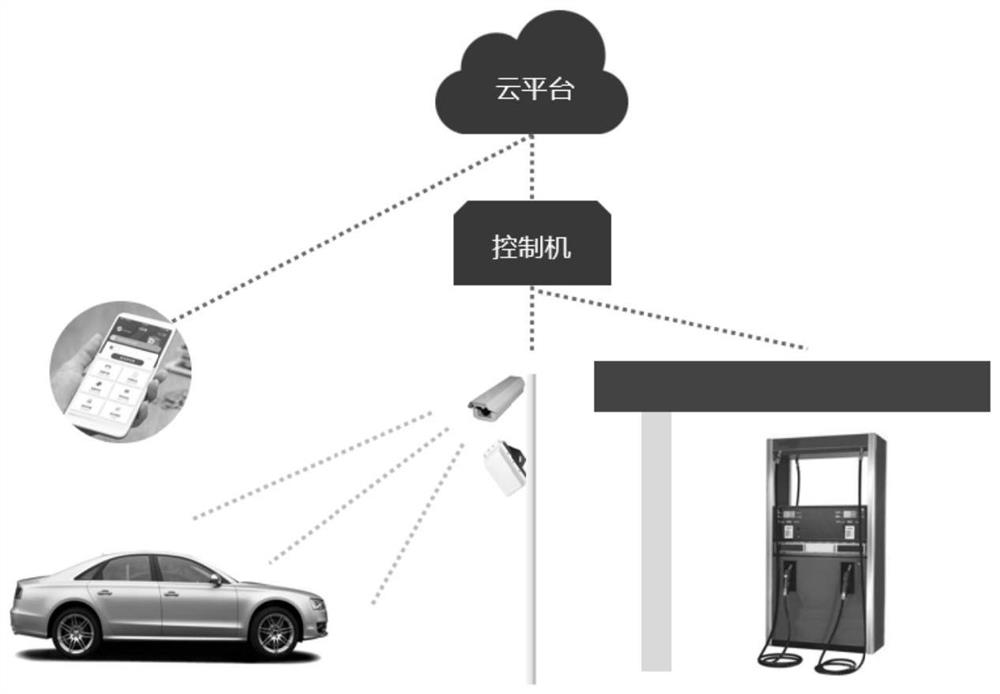
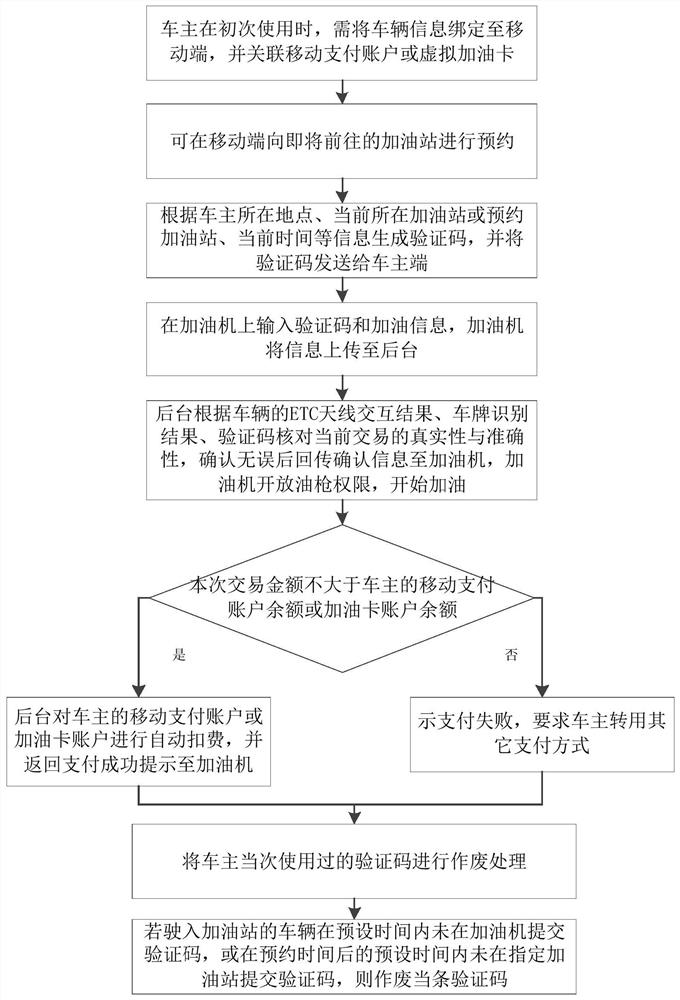
PendingCN112489303AShorten the timeEnsure safetyTicket-issuing apparatusApparatus for dispensing fluids/granular materialsFinancial transactionPetrol station
The invention provides an ETC-based gas station non-inductive payment method, which comprises the steps of: generating a verification code according to the location of a vehicle owner, a gas station and the current time, and transmitting the verification code to a vehicle owner terminal; receiving a transaction code and refueling information uploaded by a refueling machine; checking the authenticity and accuracy of the current transaction according to an ETC antenna interaction result, a license plate recognition result and the verification code of the vehicle, and returning confirmation information to the refuelling machine after confirmation; and performing fee deduction on the payment account of the vehicle owner. The invention relates to electronic equipment, a storage medium and a system. Before the vehicle owner refuels, the verification code is sent to the vehicle owner, the vehicle owner informs a worker of the verification code or inputs the verification code in the refuelingmachine in a self-service mode after the refueling machine completes refueling, refueling money is automatically deducted from a refueling card account or a mobile payment account associated with thevehicle owner after the system completes verification, the safety of the vehicle owner and a refueling station is guaranteed, the time spent by the vehicle owner in the payment process after refuelingis greatly shortened, and the field management pressure caused by queuing is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAGONG INFORMATION SOFTWARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com