Patents
Literature
128results about "Discontinuous tuning with variable tuning element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
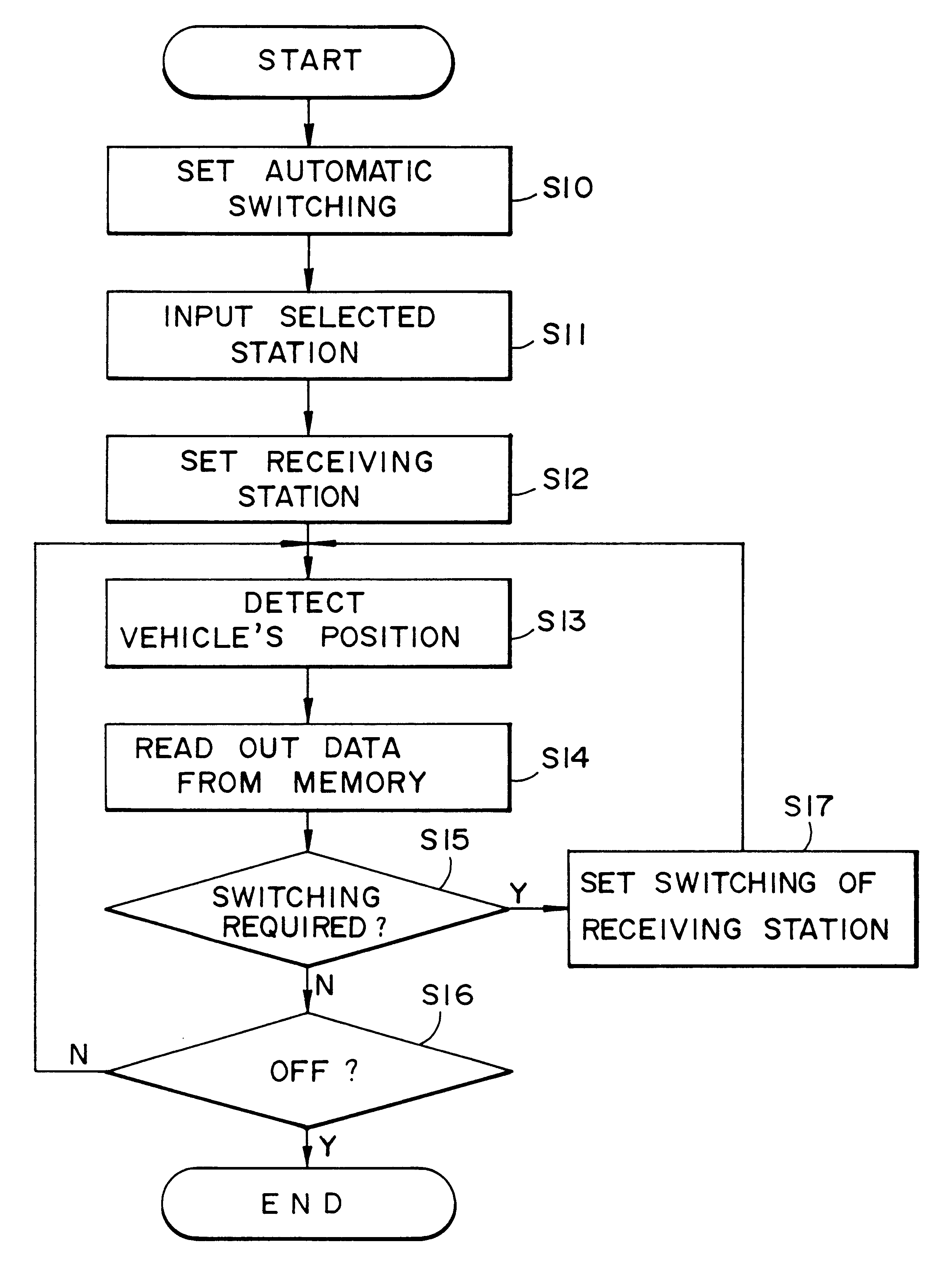
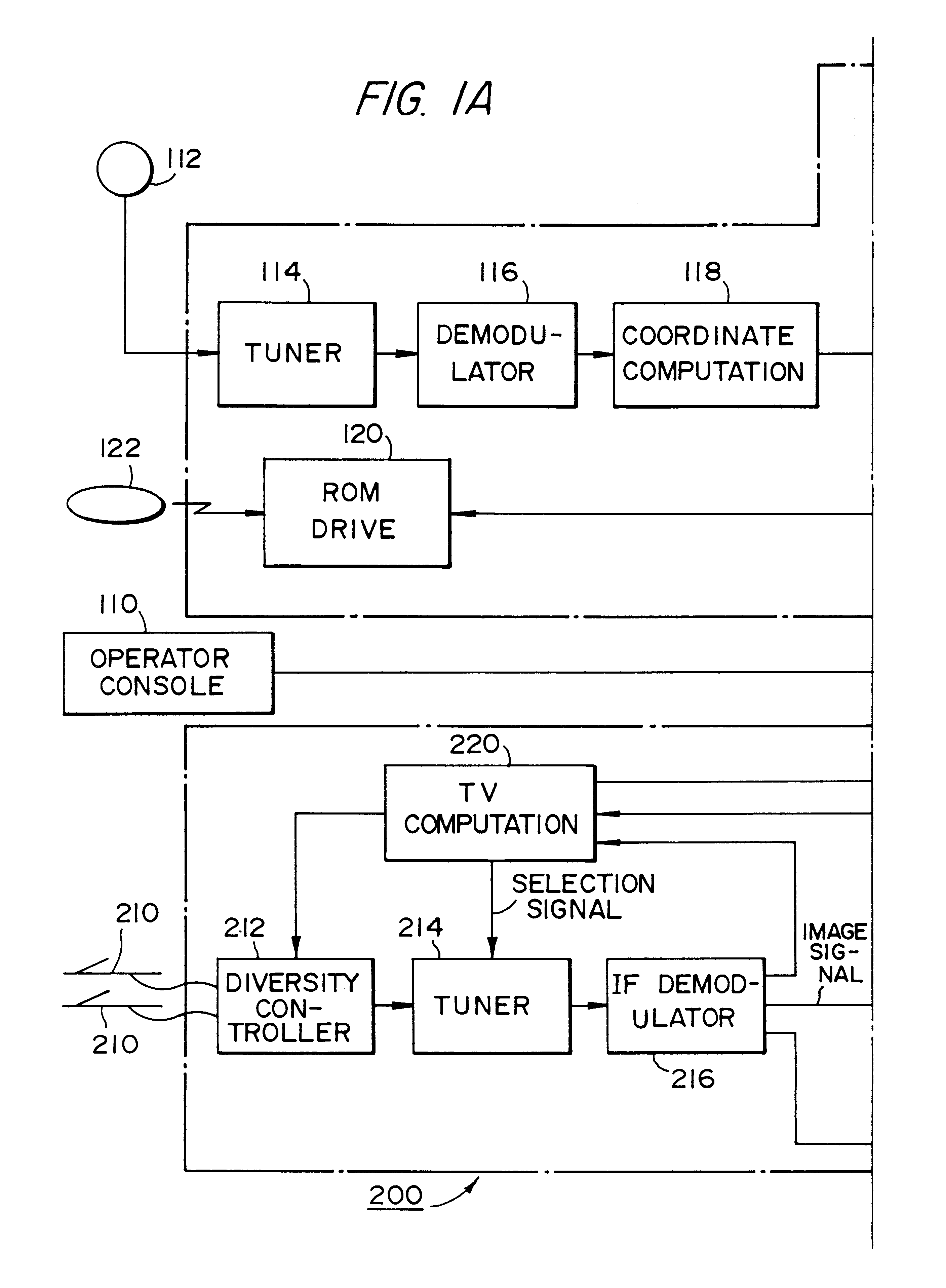
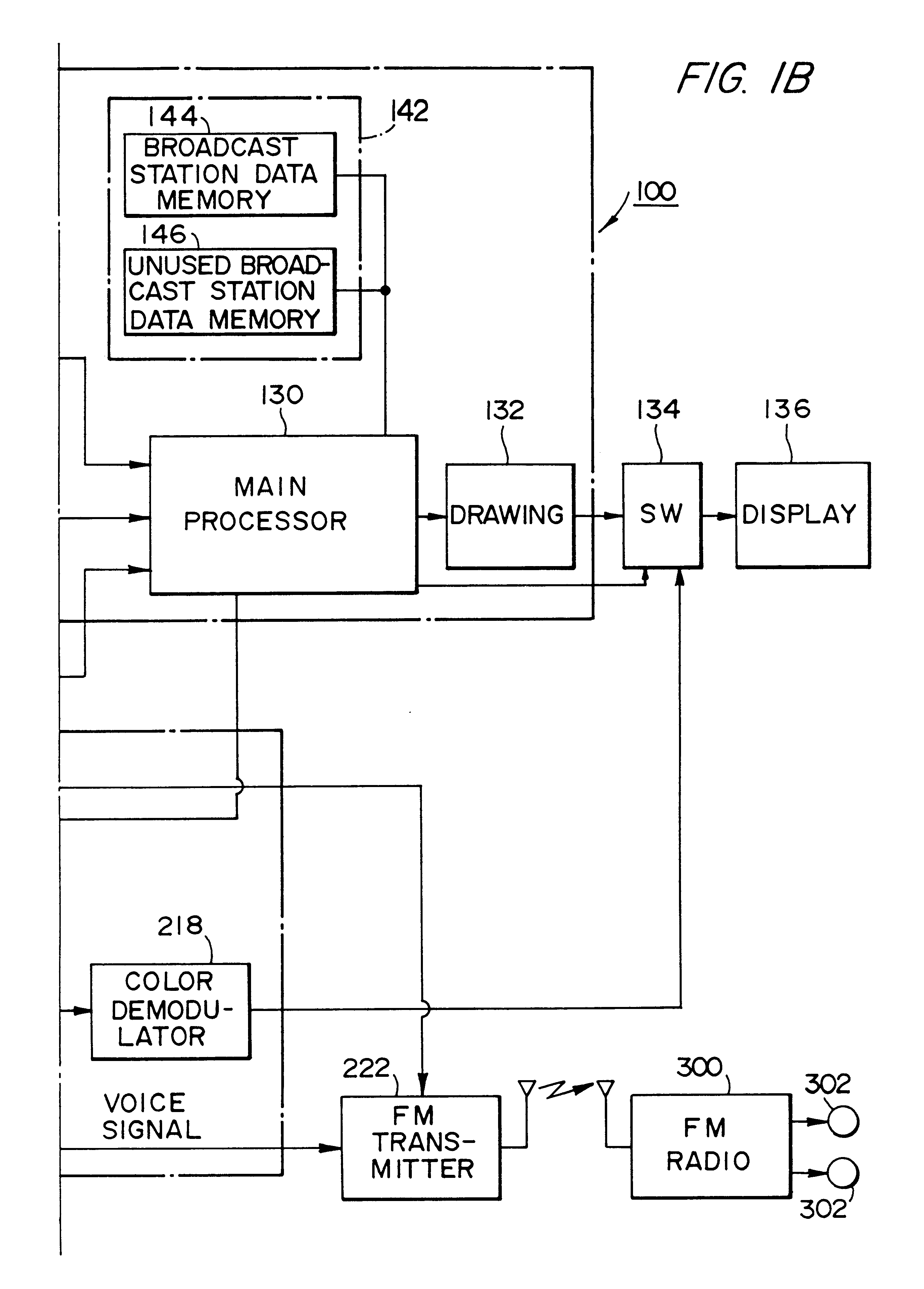
Broadcasting station data detector and broadcast receiver for moving body that search a channel map based on location
InactiveUS6181921B1Simple structureTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationChannel dataDisplay device
The present invention provides a system for a moving body which enables a user to know a receivable broadcast station at the current position in real time and to select smoothly a desired broadcast station in a receiver even in an unfamiliar area. This system includes a broadcast station data memory that stores the channel data of a receivable broadcast station for each area, and a main processing circuit which is responsive to the vehicle's current position sensed by a coordinate computing unit for referring to the channel data and for showing the channel data of a receivable broadcast station at the current position on a display.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
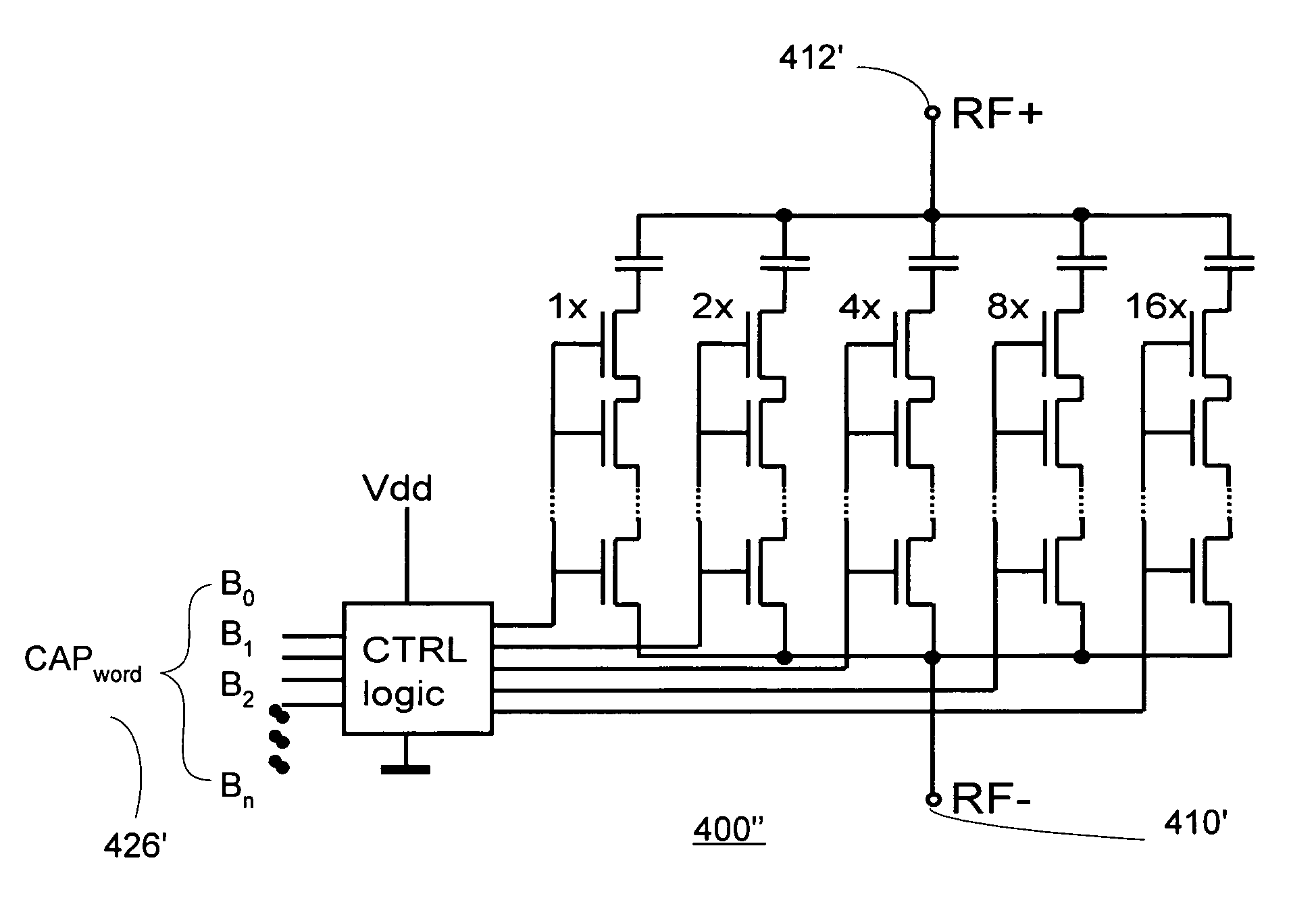
Method and apparatus for use in digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS9024700B2Easy to controlHigh Power Handling CapabilityMultiple-port networksImpedence matching networksCapacitanceLeast significant bit
Owner:PSEMI CORP
System and method for automatic tuning of a magnetic field generator
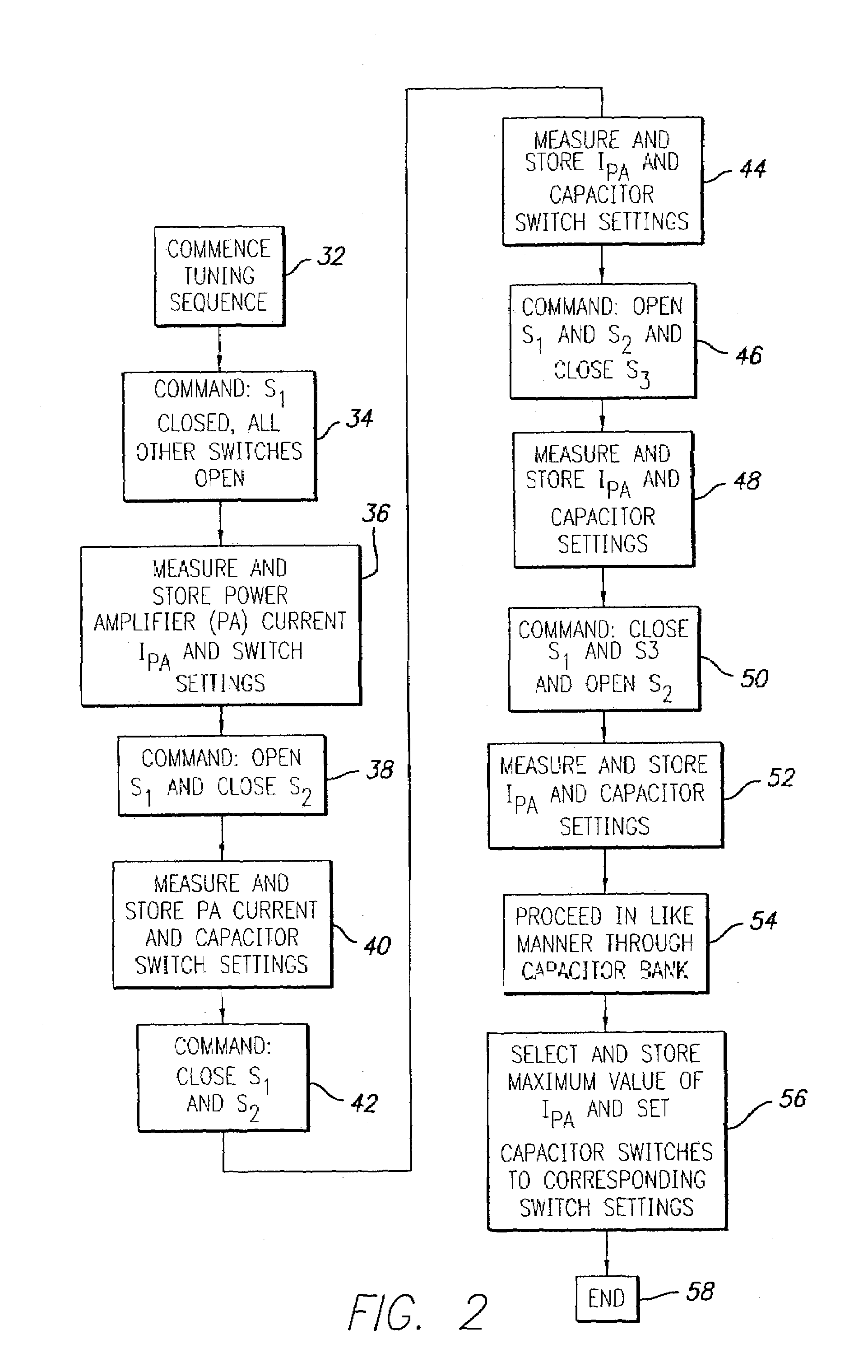
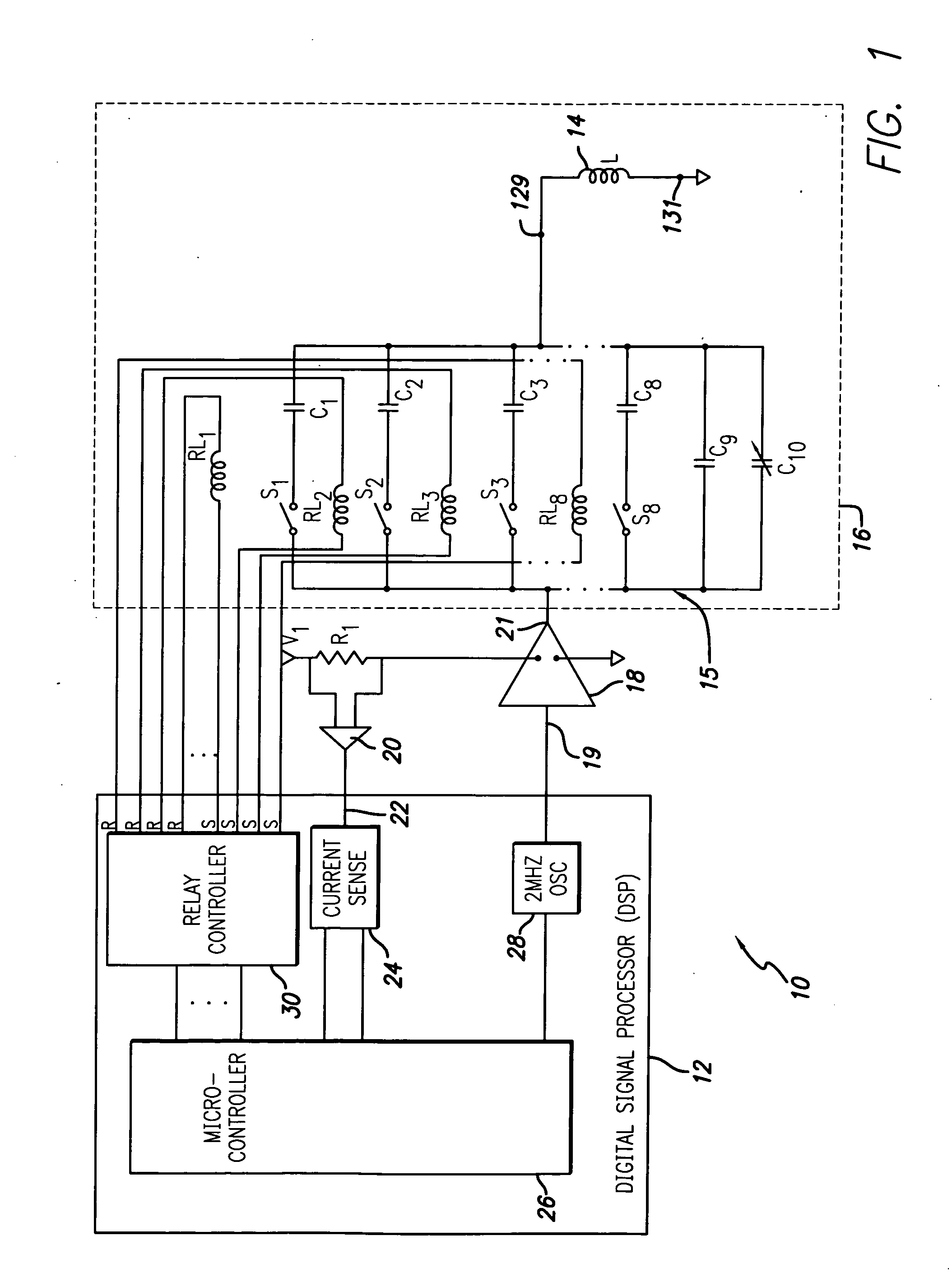
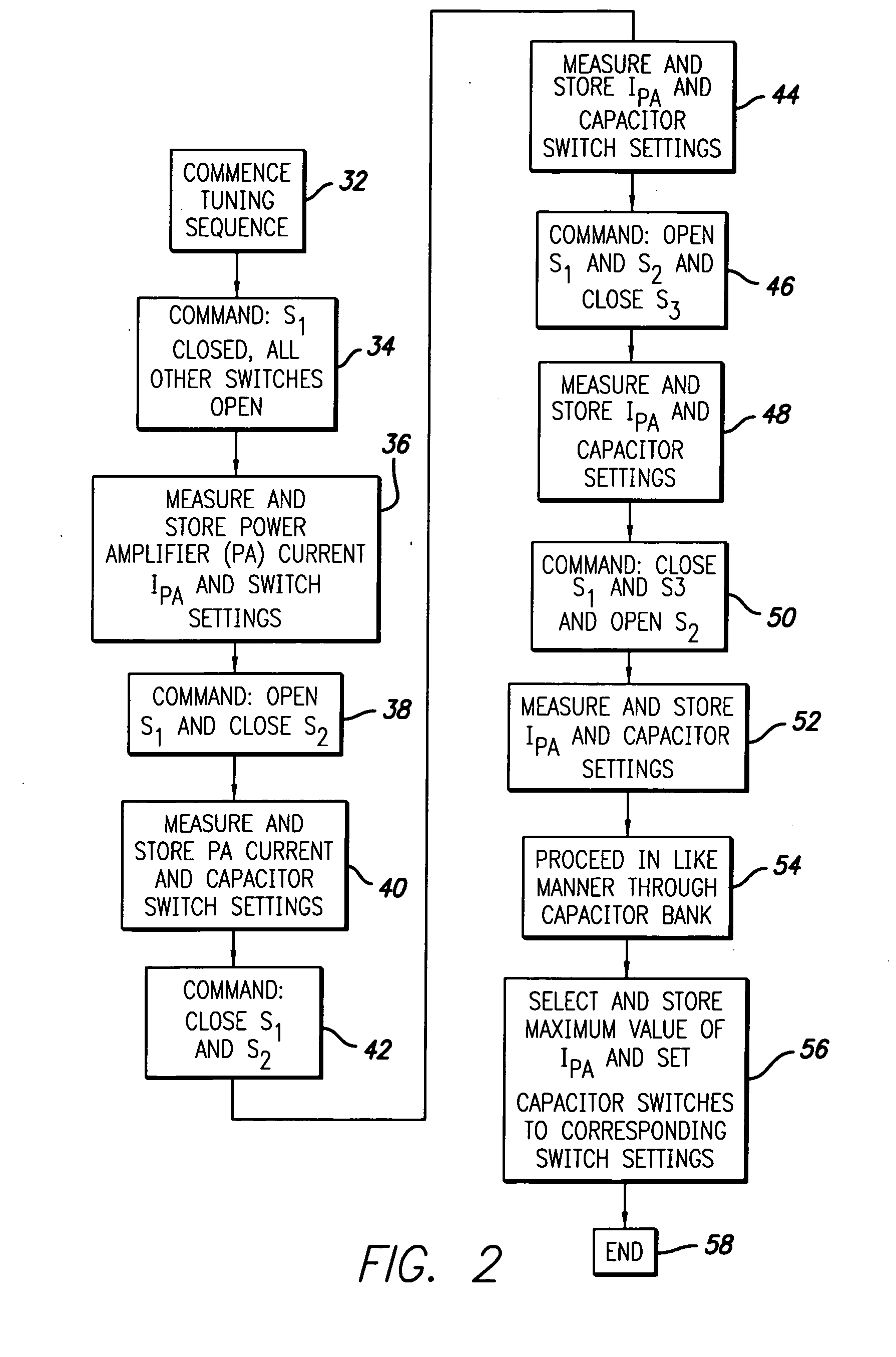
ActiveUS7015769B2Power maximizationMaximize power outputTransmission control/equlisationElectrotherapyCapacitanceControl parameters
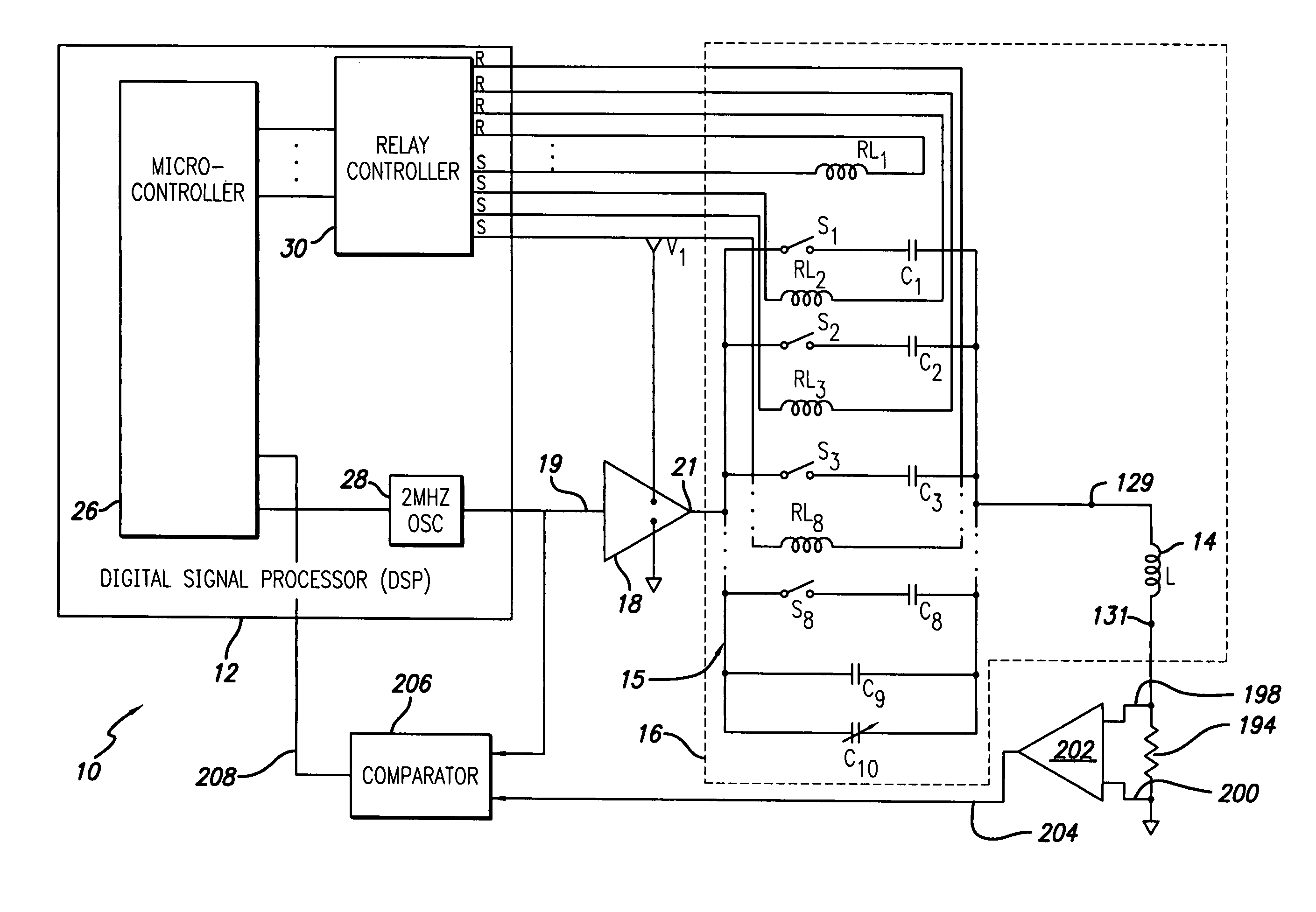
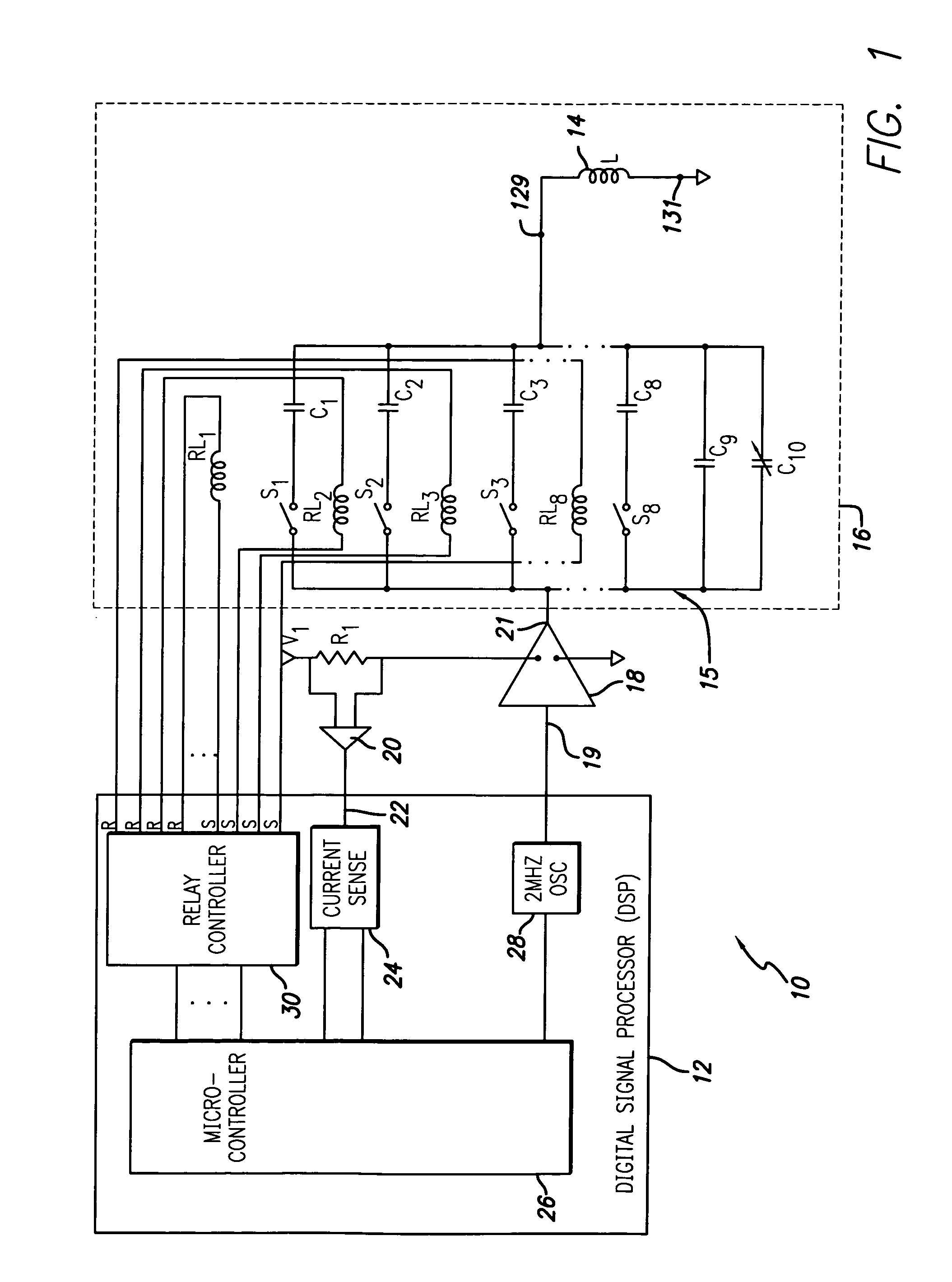
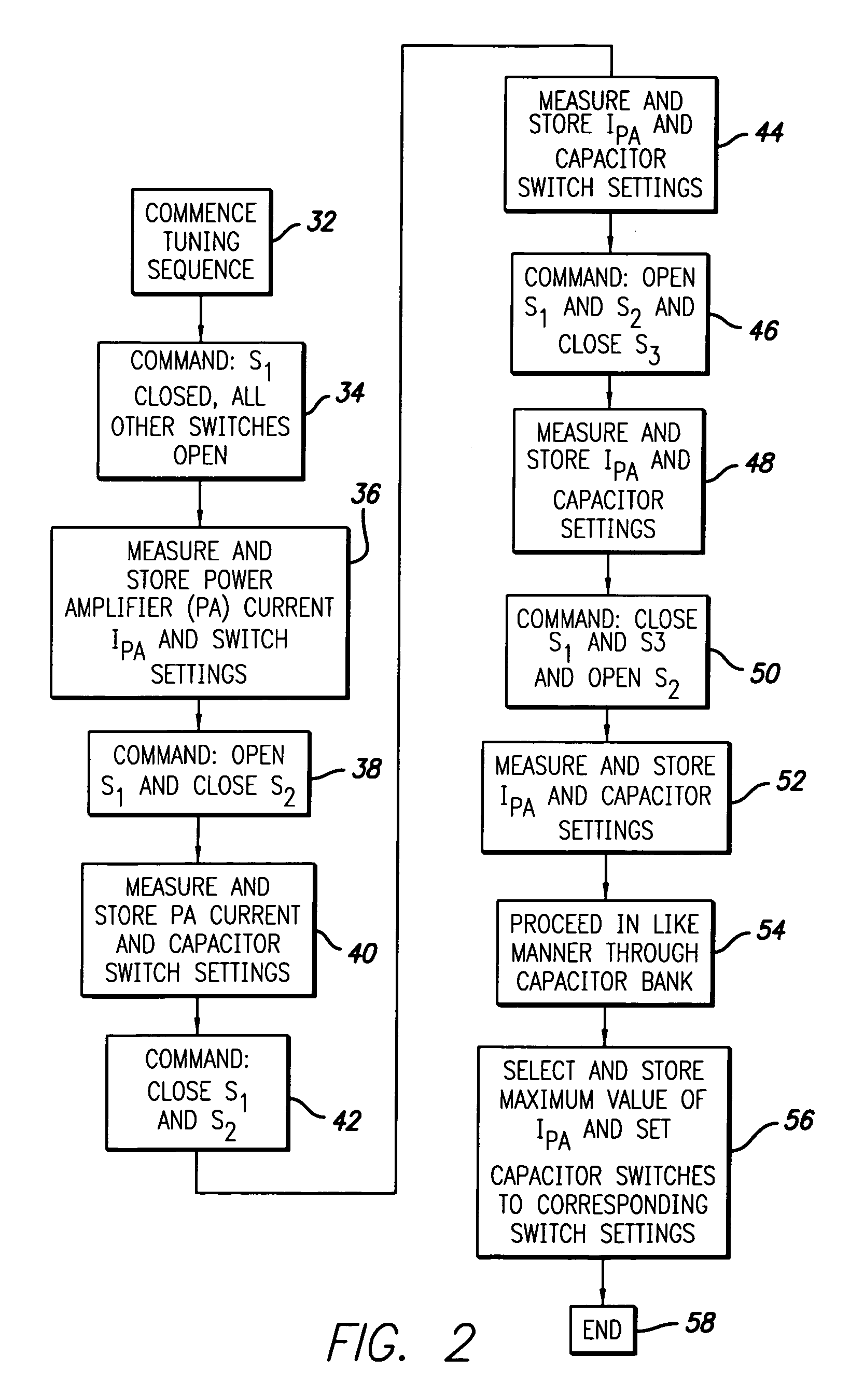
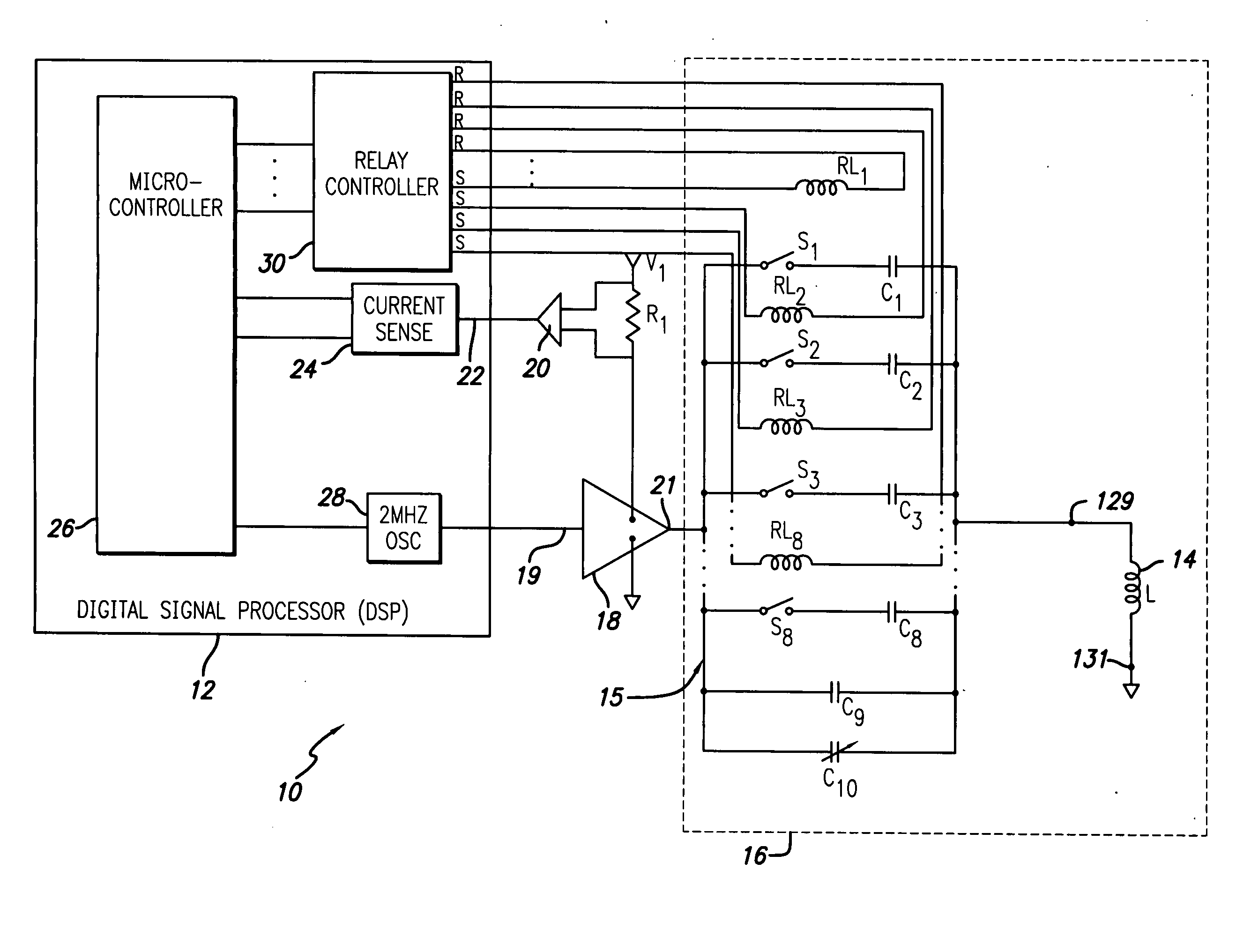
An automatic tuning system for a magnetic field generating tuned circuit includes a processor configured to maintain the resonant frequency of a tuned circuit equal to a reference frequency. The tuned circuit is driven by a power amplifier whose output provides an amplified signal at the reference frequency. The tuned circuit includes a magnetic field generating inductor and a bank of individually switchable capacitors controlled by the processor capable of adding and removing the respective capacitances to and from the tuned circuit. The inductor includes a Faraday shield to shield the tuned circuit from the influence of electric fields. A power sense circuit monitors the power delivered by the power amplifier to the tuned circuit and the processor sequentially switches the capacitors in a binary progression format to achieve maximum power delivery indicative of conforming the resonant frequency of the tuned circuit to the reference frequency. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the inductor includes a plurality of taps that provide individually selectable inductance values available for use in the process of conforming the resonant frequency of the tuned circuit to the reference frequency. In further alternate embodiments, the variable capacitor is in the form of a motor driven variable capacitor and the tuning sequence relies on a phase locked loop using the phase of a reference frequency signal and the phase of the inductor current as control parameters.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Antenna unit and communication device using the same
InactiveUS6300909B1Wide bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceCoupling
In an antenna unit, the generation of capacitances between each of the open ends of first and second microstrip antennas and a control electrode is controlled by turning a switch on and off, both antenna frequencies being simultaneously changed. The antenna unit has a basic body having first and second main surfaces and at least one end surface extending between the main surfaces; a grounding electrode provided on the first main surface of the basic body; a first radiation electrode forming a first antenna, having an open end at one end thereof, and provided on the second main surface of the basic body; a second radiation electrode forming a second antenna, having an open end at one end thereof, and provided on the second main surface of the basic body; a first connecting electrode for connecting the first radiation electrode to the grounding electrode, and provided on an end surface of the basic body; a second connecting electrode for connecting the second radiation electrode to the grounding electrode, and provided on an end surface of the basic body; a feeding electrode for transmitting a signal to at least one of the first radiation electrode and the second radiation electrode, and provided on the basic body; and a control electrode on the basic body for providing coupling capacitances between the open end of the first radiation electrode and the control electrode and between the open end of the second radiation electrode and the control electrode, and provided so as to be close to each of the open ends.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
System and method for automatic tuning of a magnetic field generator
ActiveUS7515012B2Power maximizationMaximize power outputElectrotherapyTransmission control/equlisationHemt circuitsEngineering
An automatic tuning system for a magnetic field generating tuned circuit includes a processor configured to maintain the resonant frequency of a tuned circuit equal to a reference frequency. The tuned circuit is driven by a power amplifier whose output provides an amplified signal at the reference frequency. The tuned circuit includes a magnetic field generating inductor and a bank of individually switchable capacitors controlled by the processor capable of adding and removing the respective capacitances to and from the tuned circuit. The inductor includes a Faraday shield to shield the tuned circuit from the influence of electric fields. In an embodiment of the invention, the variable capacitor is in the form of a diode variable capacitor (varicap) in parallel circuit relationship with the tuned circuit capacitor and the inductor. In an alternate embodiment the inductor and a fixed capacitor are in series circuit relationship with the varicap in parallel circuit relationship with the fixed capacitor and the tuning sequence relies on a phase locked loop using the phase of a reference frequency signal and the phase of the inductor voltage as control parameters.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
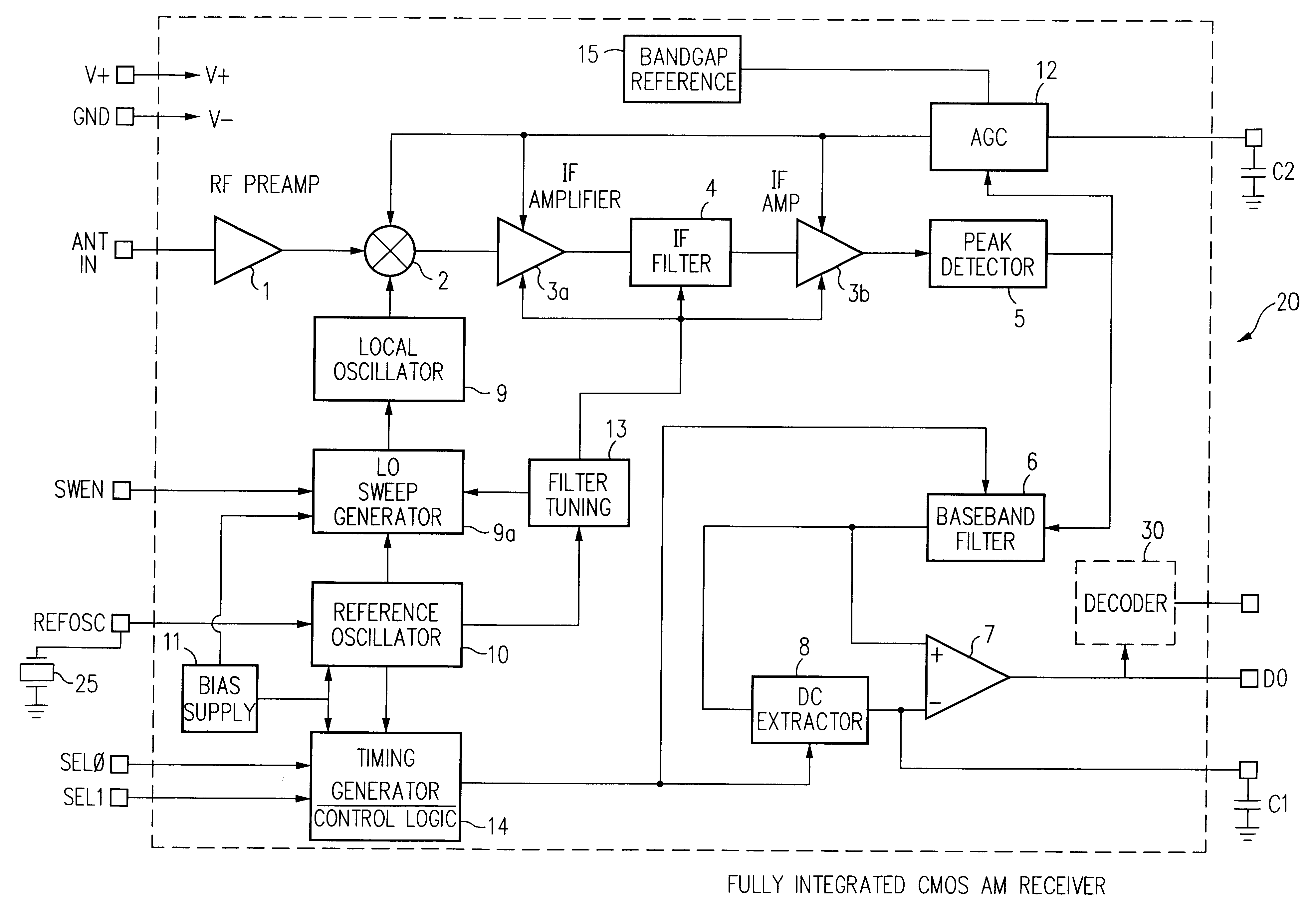
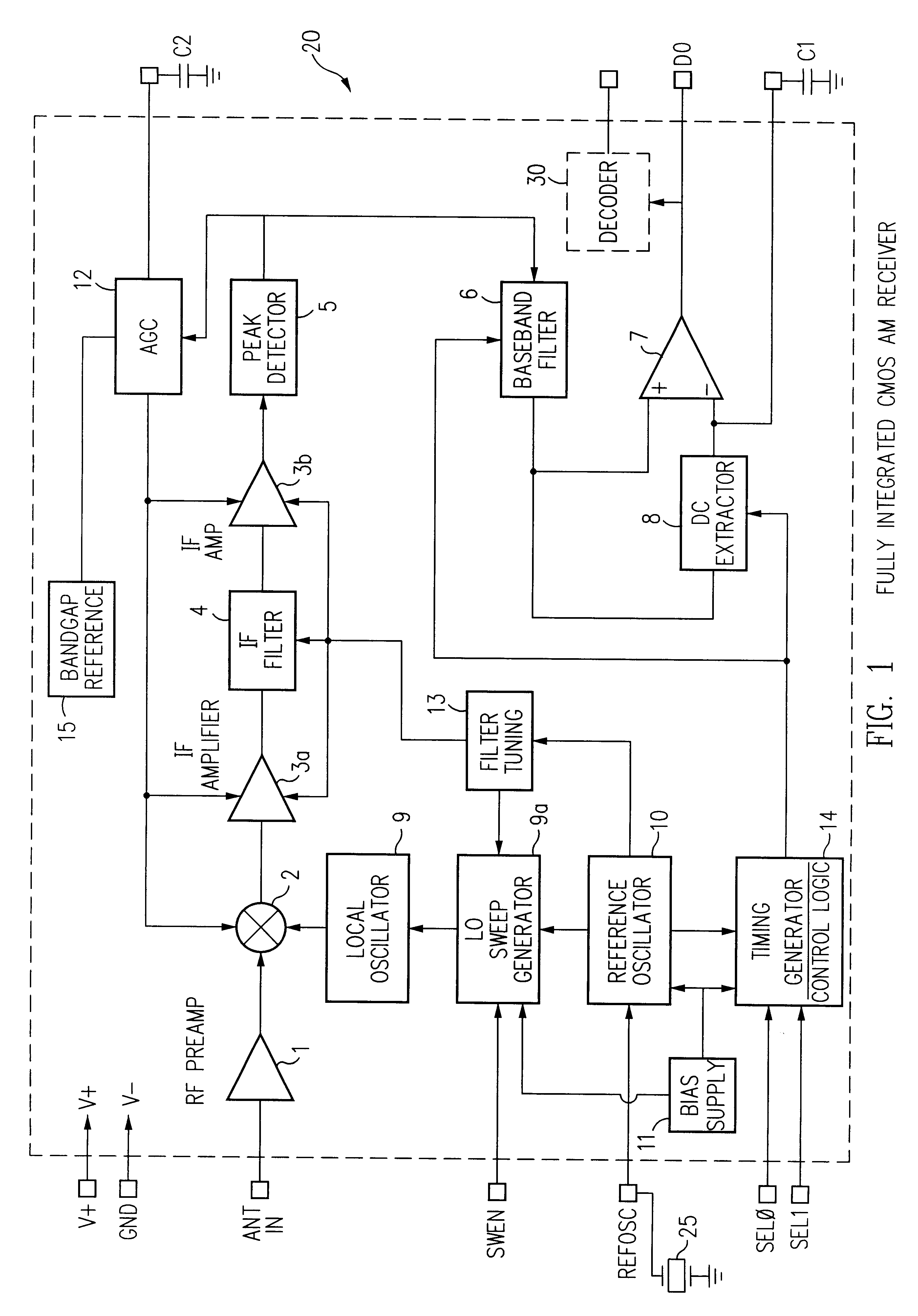
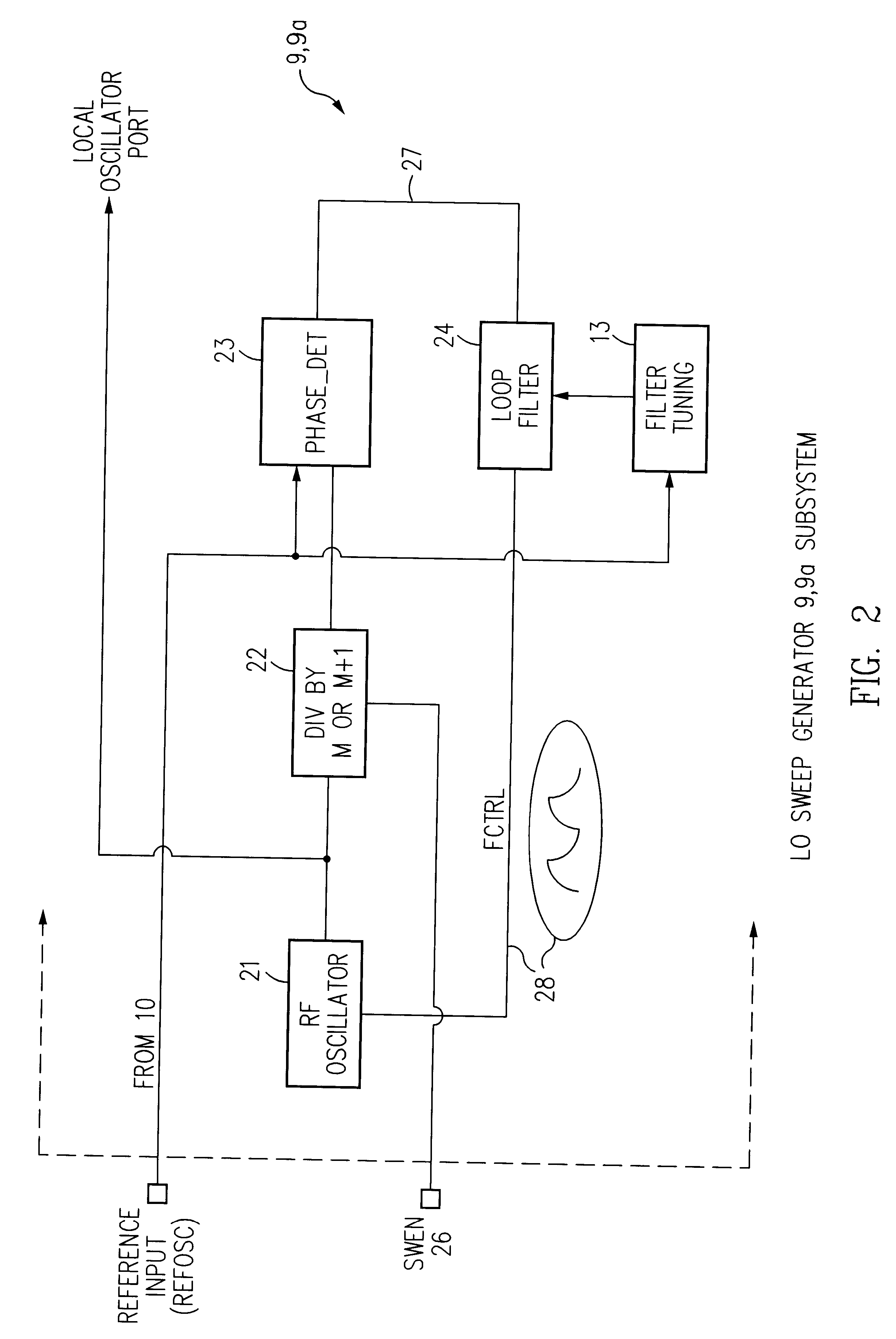
Fully integrated all-CMOS AM receiver
InactiveUS6167246AEasy to controlLower requirementPulse automatic controlTelephonic communicationCMOSSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
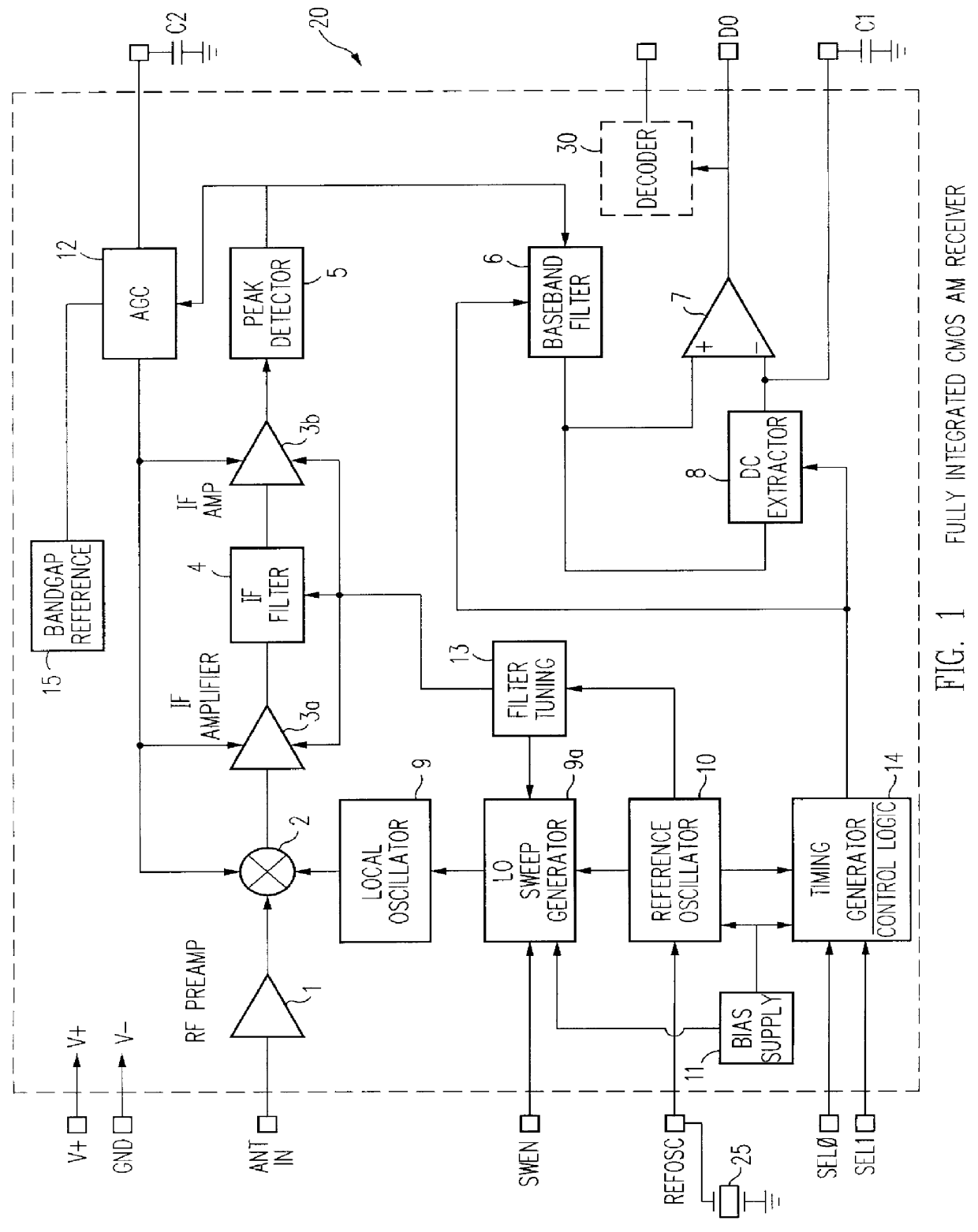
A single chip superhetrodyne AM receiver including a local oscillator which sweeps through a frequency range at a rate higher than a modulation frequency of the incoming RF signal. The local oscillator frequency is mixed with the incoming RF signal. An IF filter passes a selected frequency band from the mixer to a demodulator. The demodulator is tuned to demodulate any signal within a band of frequencies determined by the sweeping of the local oscillator. This increases the signal to noise ratio of the receiver since it allows for variations in the transmitter output frequency. The frequency responses of the various filters are tied to the reference frequency and allows the user to set the tuning and alignment of the receiver. To compensate for process variations in the implementation of the IC, bias currents setting the operating conditions for various amplifiers and other components in the system are adjusted based on frequency control signals in a PLL circuit in the local oscillator.
Owner:MICREL
Switch assembly with integrated tuning capability
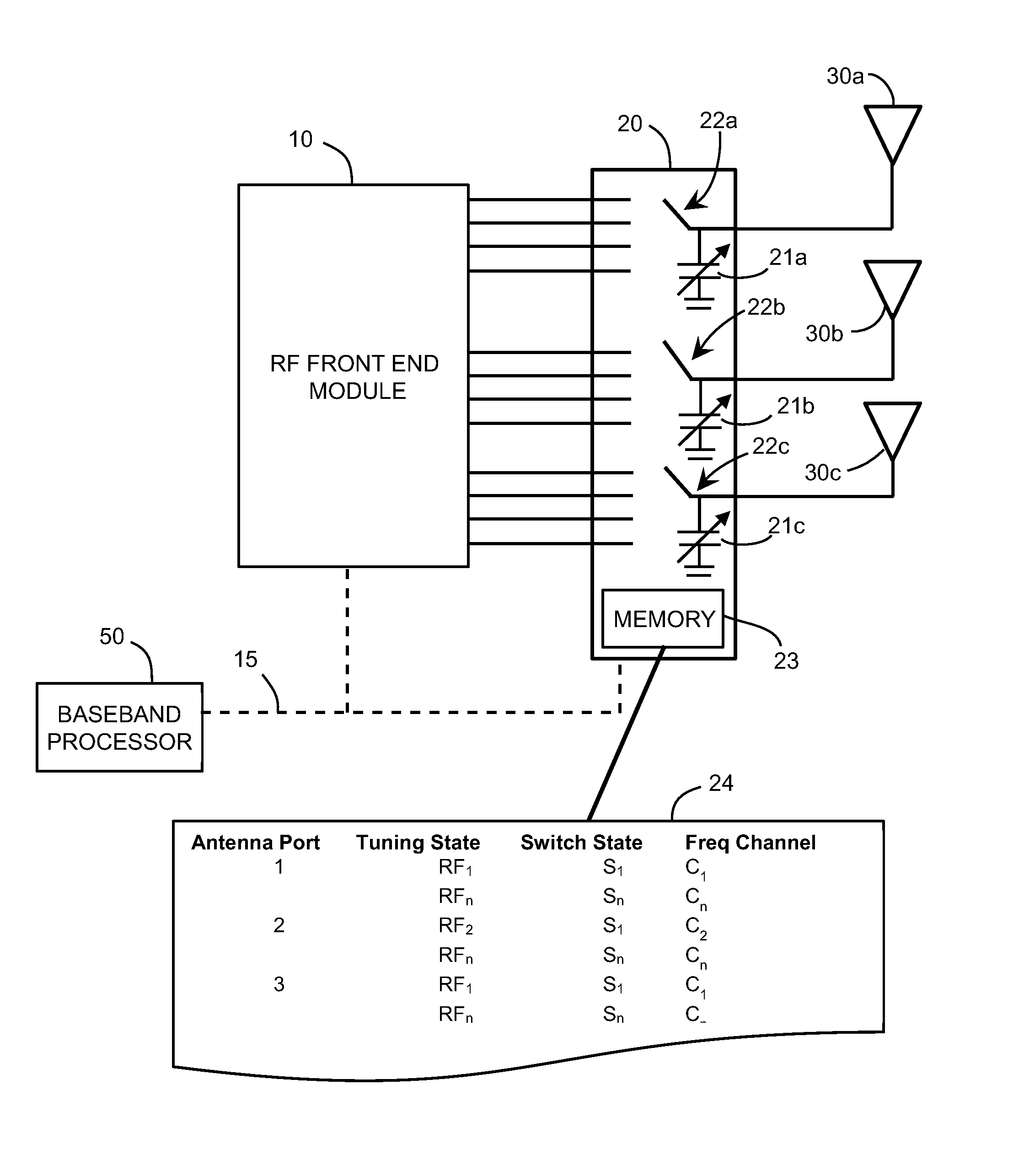
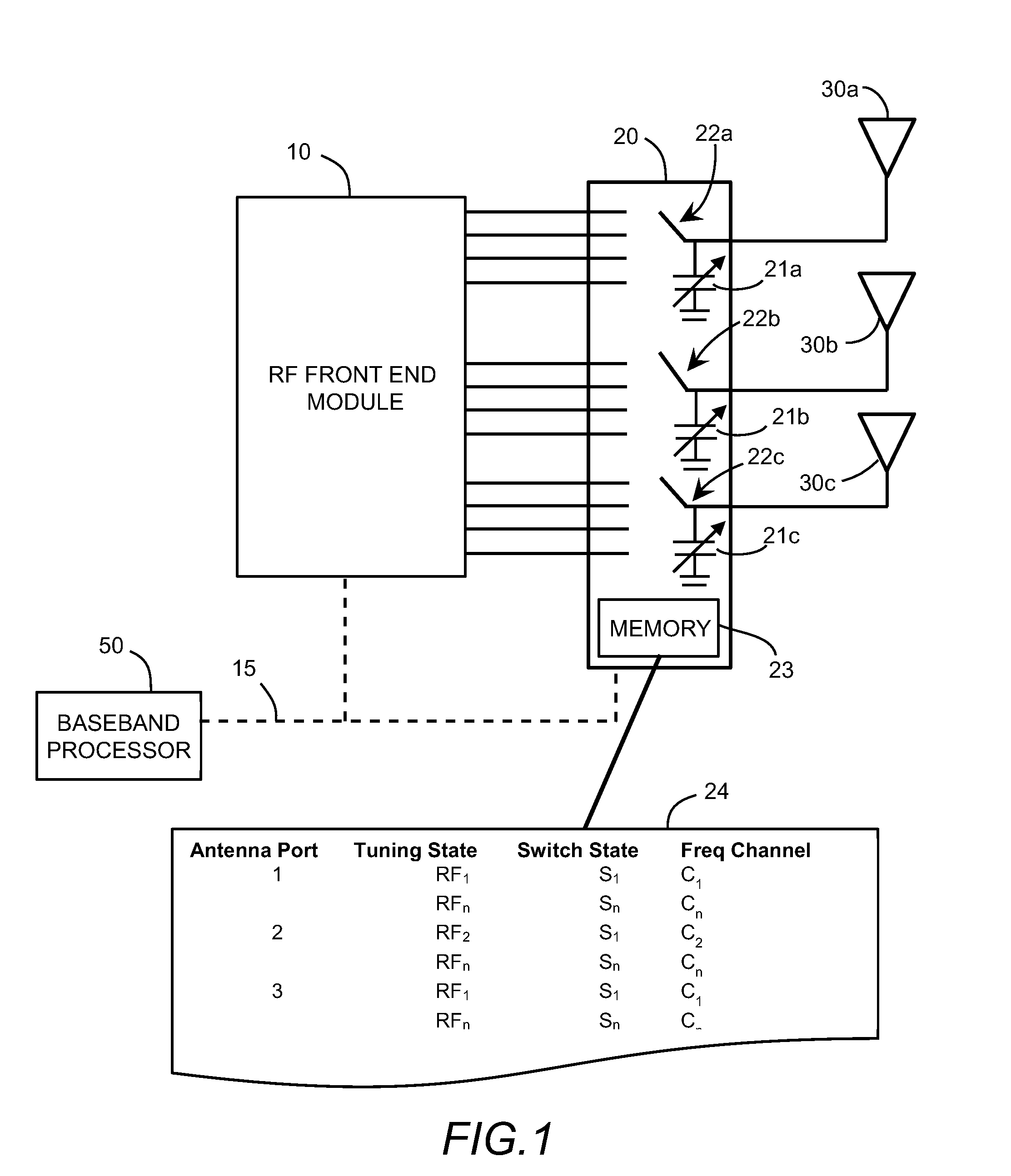
ActiveUS20150340769A1Particular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsCommunications systemRF front end
A multiport RF switch assembly with integrated impedance tuning capability is described that provides a single RFIC solution to switch between transmit and receive paths in a communication system. Dynamic tuning is integrated into each switch sub-assembly to provide the capability to impedance match antennas or other components connected to the multiport switch. The tuning function at the switch can be used to shape the antenna response to provide better filtering at the switch / RF front-end (RFFE) interface to allow for reduced filtering requirements in the RFFE. Memory is designed into the multiport switch assembly, allowing for a look-up table or other data to reside with the switch and tuning circuit. The resident memory will result in easier integration of the tunable switch assembly into communication systems.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Communication terminal device
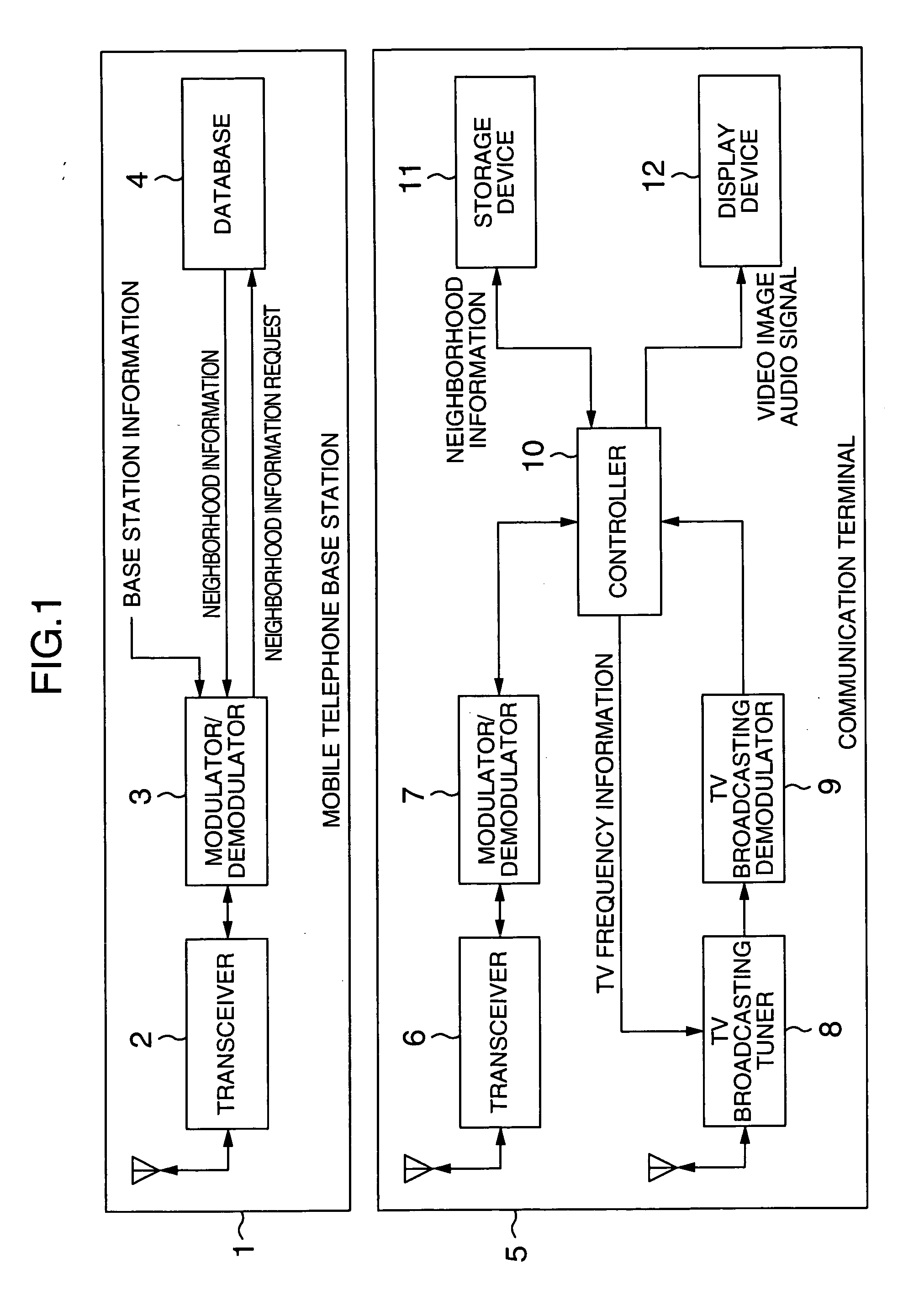
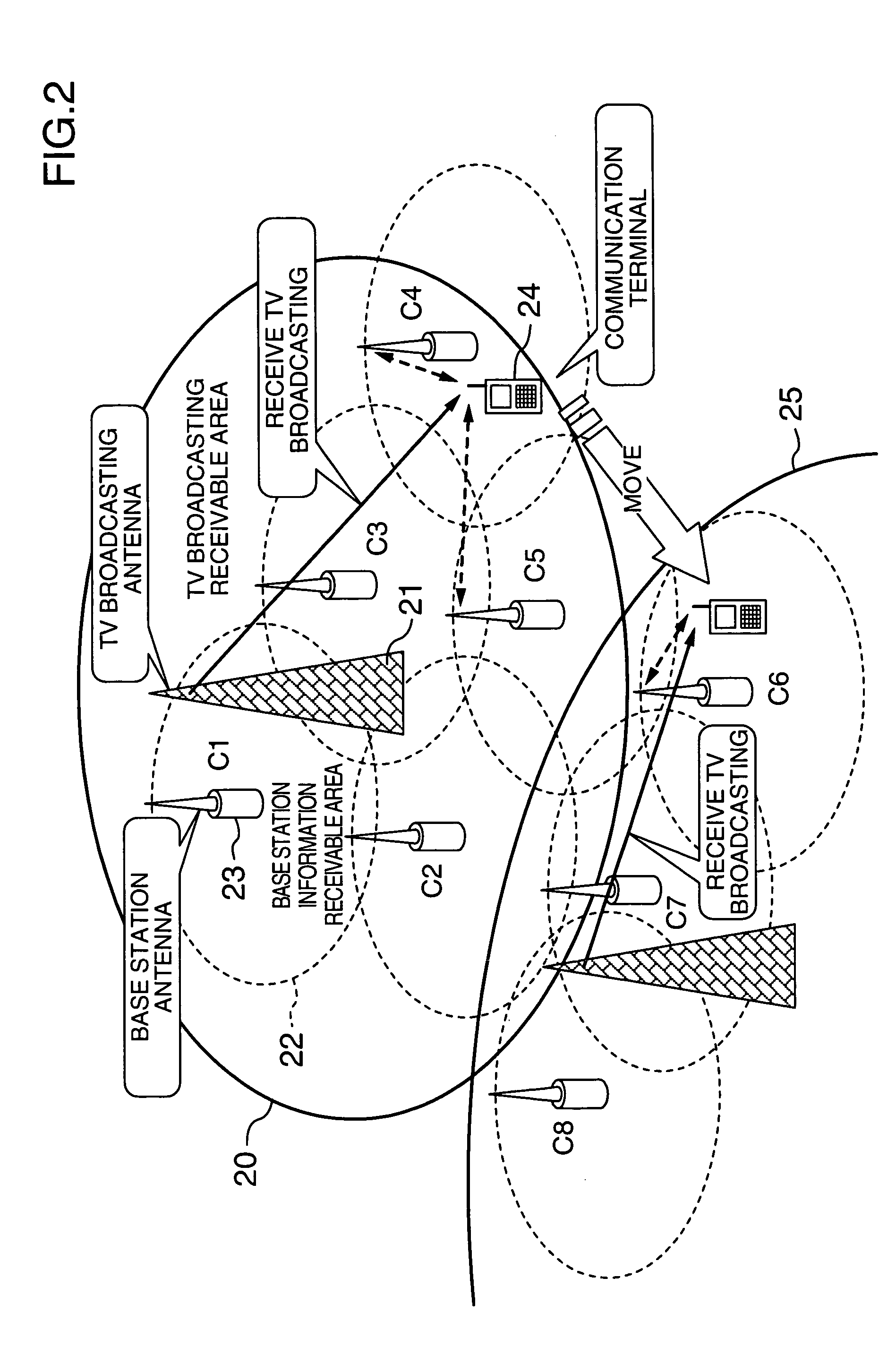
InactiveUS20050122429A1Improve usabilityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTransceiverTerminal equipment
A communication terminal device comprising a TV broadcasting tuner for receiving a TV broadcasting, a display device for displaying a video image of the received TV broadcasting, and a transceiver for communicating with a base station. The transceiver acquires base station information for an optional one of base station areas, and acquires a TV broadcasting frequency corresponding to the optional base station area. The TV broadcasting tuner receives the TV broadcasting at the acquired TV broadcasting frequency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Linear voltage controlled capacitance circuit
InactiveUS6853272B1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemContinuous tuning detailsOne-port networksCapacitanceEngineering
A linear voltage controlled capacitance circuit is provided that includes a plurality of MOS varactor pairs. Each MOS varactor pair is operable to receive a first tuning voltage, a second tuning voltage, and a bias voltage unique to the MOS varactor pair. The capacitance circuit is operable to generate a positive tank node signal and a negative tank node signal based on the first and second tuning voltages and the bias voltages. A means to control voltage-to-capacitance gain is also provided to compensate for coarse tuning capacitance change.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
System and method for automatic tuning of a magnetic field generator
ActiveUS20060192628A1Power maximizationMaximize power outputTransmission control/equlisationElectrotherapyFixed capacitorInductor
An automatic tuning system for a magnetic field generating tuned circuit includes a processor configured to maintain the resonant frequency of a tuned circuit equal to a reference frequency. The tuned circuit is driven by a power amplifier whose output provides an amplified signal at the reference frequency. The tuned circuit includes a magnetic field generating inductor and a bank of individually switchable capacitors controlled by the processor capable of adding and removing the respective capacitances to and from the tuned circuit. The inductor includes a Faraday shield to shield the tuned circuit from the influence of electric fields. In an embodiment of the invention, the variable capacitor is in the form of a diode variable capacitor (varicap) in parallel circuit relationship with the tuned circuit capacitor and the inductor. In an alternate embodiment the inductor and a fixed capacitor are in series circuit relationship with the varicap in parallel circuit relationship with the fixed capacitor and the tuning sequence relies on a phase locked loop using the phase of a reference frequency signal and the phase of the inductor voltage as control parameters.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
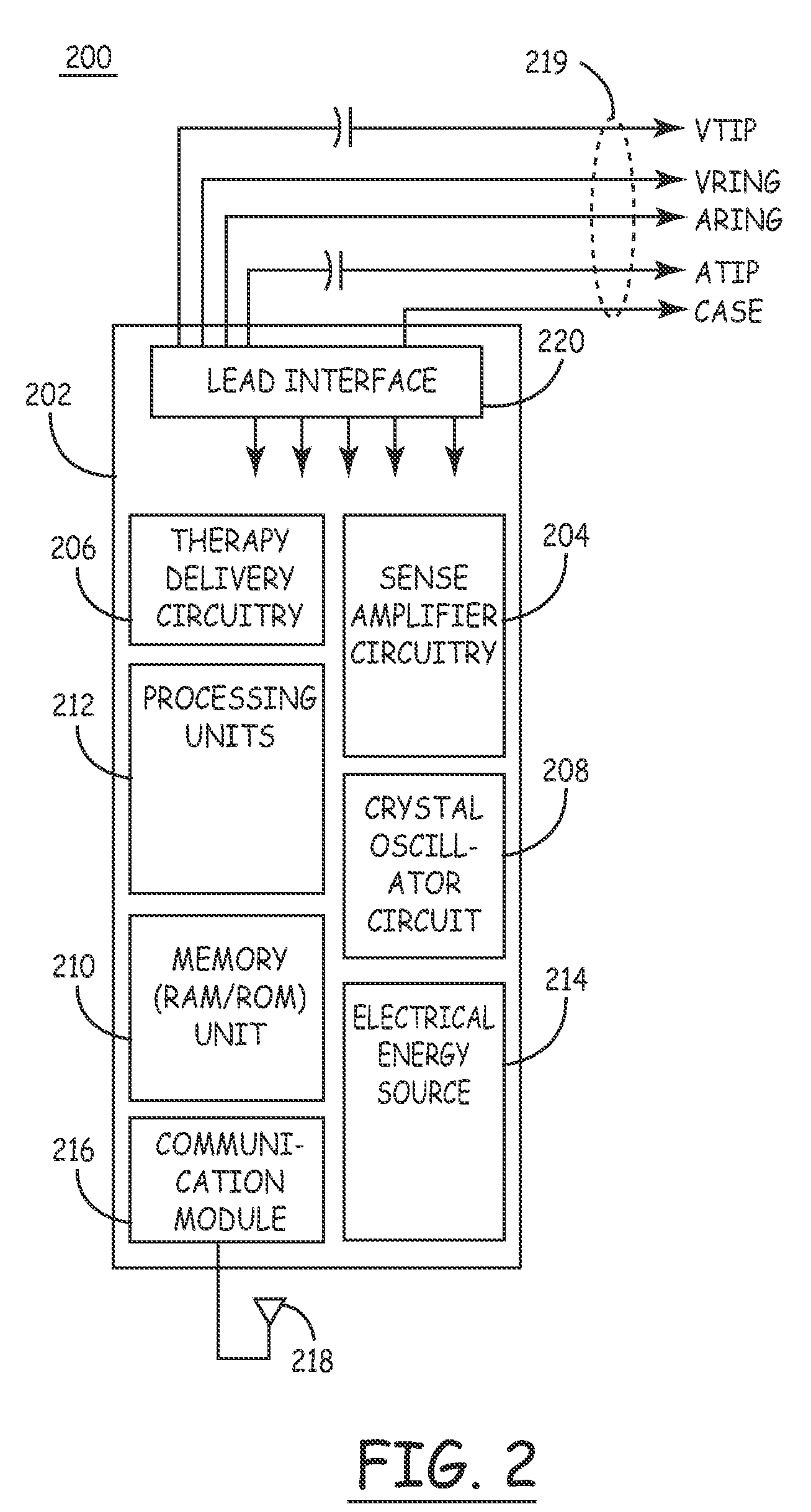
Filter circuit with variable capacitance for use with implantable medical devices
An implantable medical device (IMD) as described herein includes an input filter circuit having variable capacitor elements that can be electronically adjusted based upon current operating conditions (such as electromagnetic conditions, noise conditions, and / or environmental conditions). The variable capacitor elements can be adjusted to accommodate pre-designated operating modes of the IMD and / or dynamically in response to changing operating conditions. In one embodiment, the variable capacitor elements are realized using digitally programmable switched capacitor arrangements.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
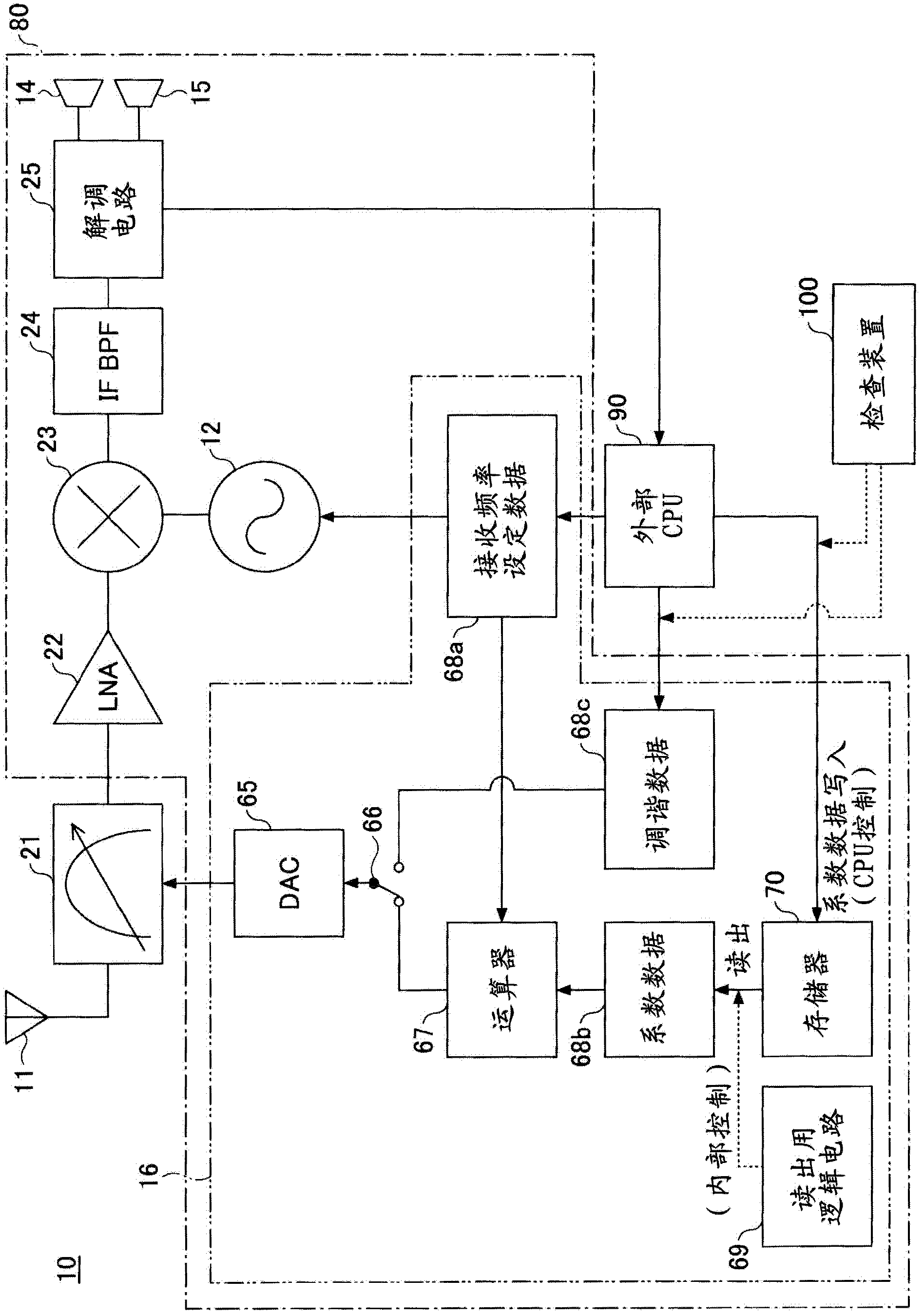
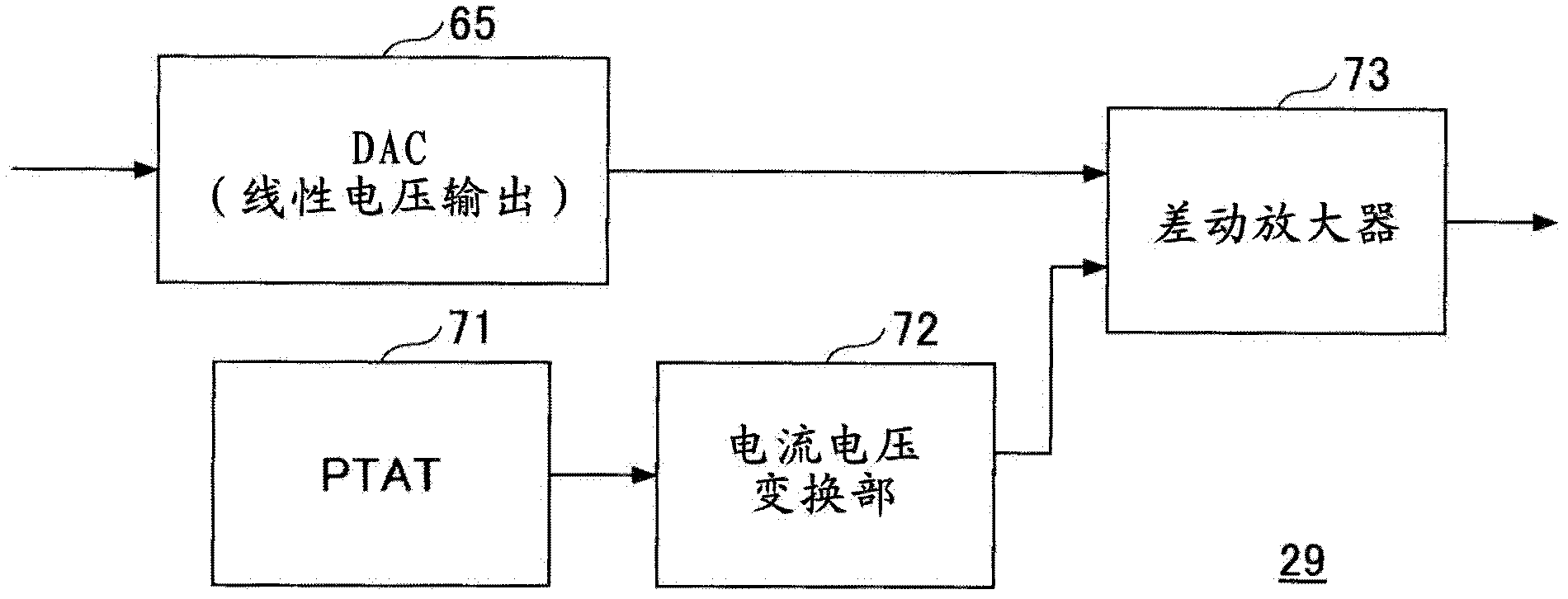
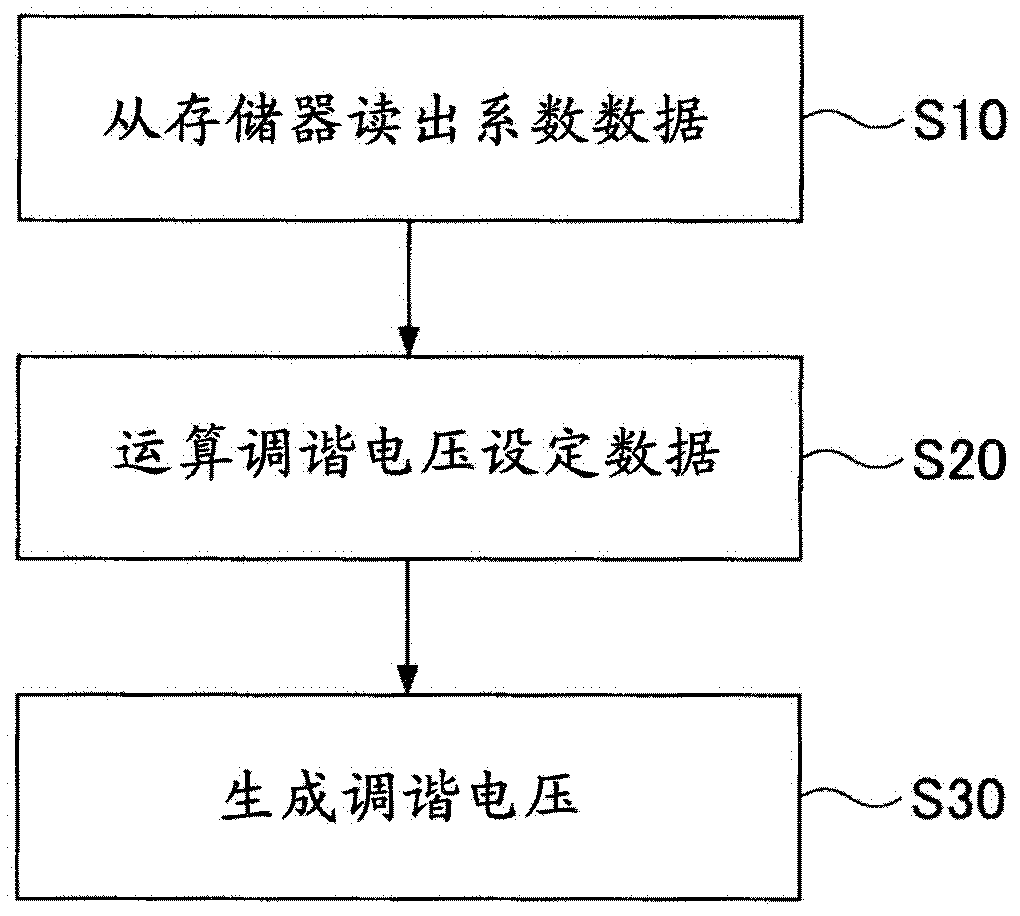
Superheterodyne receiver apparatus and reception method, and semiconductor integrated circuit for receiver apparatus
InactiveCN102484492AEasy to tuneContinuous tuning detailsResonant circuit detailsCapacitanceIntermediate frequency
A superheterodyne receiver apparatus comprises: a tuning circuit for selecting and receiving a high frequency signal, said circuit being composed of a voltage-variable capacitance element and an inductance element; and a frequency converting unit for frequency converting the high frequency signal to an intermediate frequency signal. The superheterodyne receiver apparatus further comprises: an electrically rewritable read only memory; a calculation unit for calculating tuning voltage setting data, which used to set the tuning circuit to a tuning voltage corresponding to a desired reception frequency, in accordance with a mathematical expression that uses the data stored in the memory as coefficients; and a D / A conversion unit for D / A converting the tuning voltage setting data to the tuning voltage.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
System, circuit and method for tuning a resonant circuit
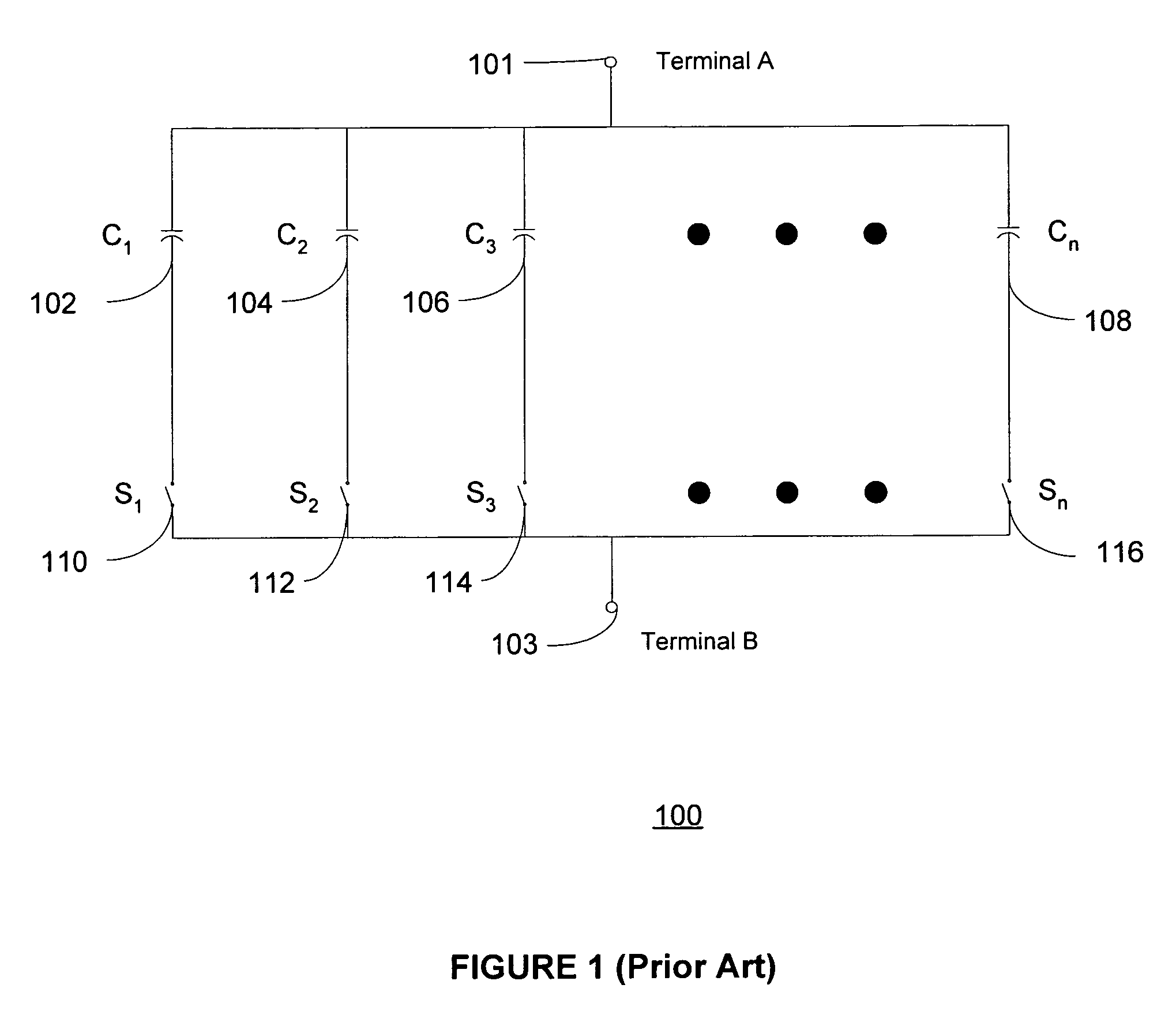
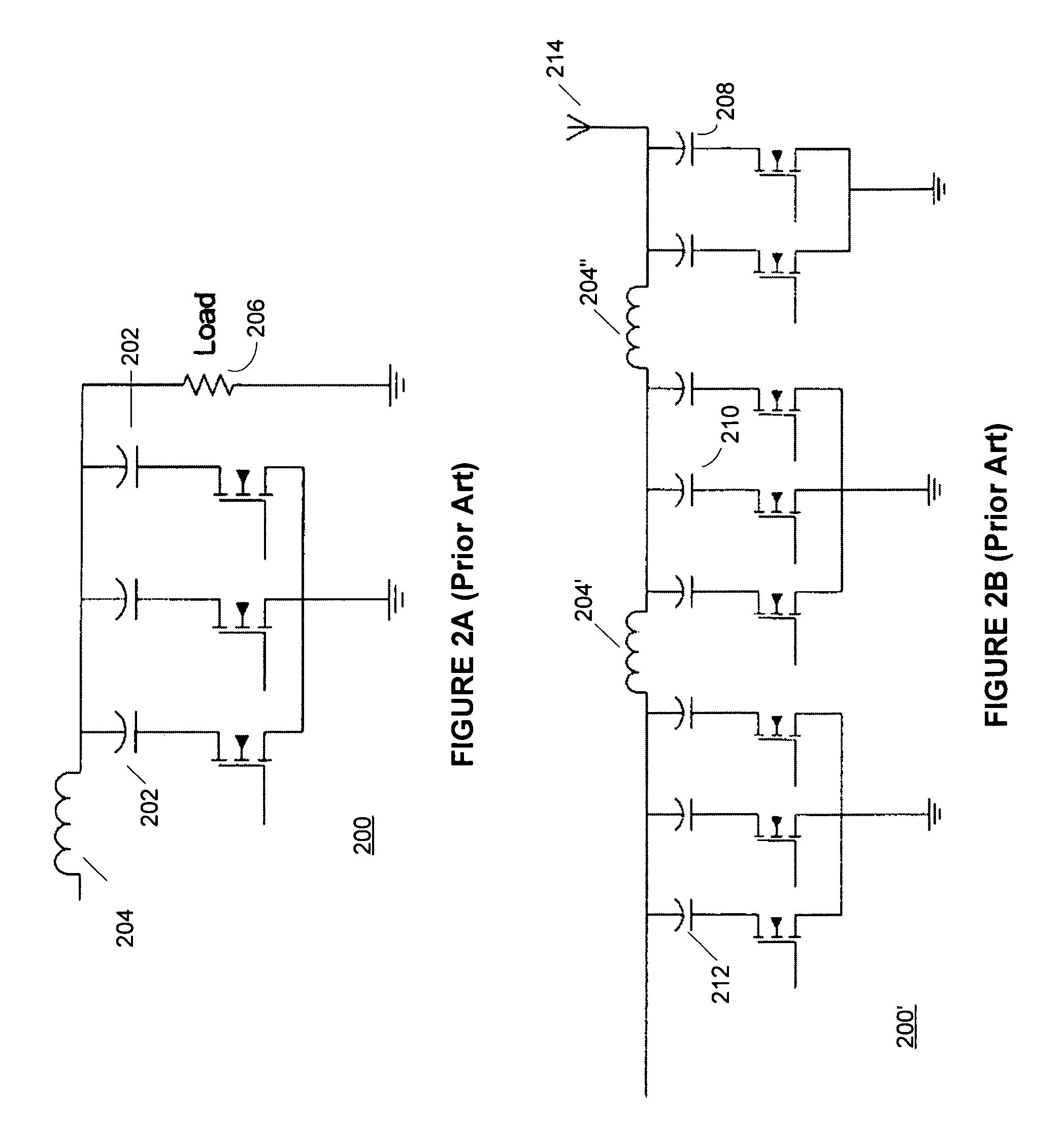
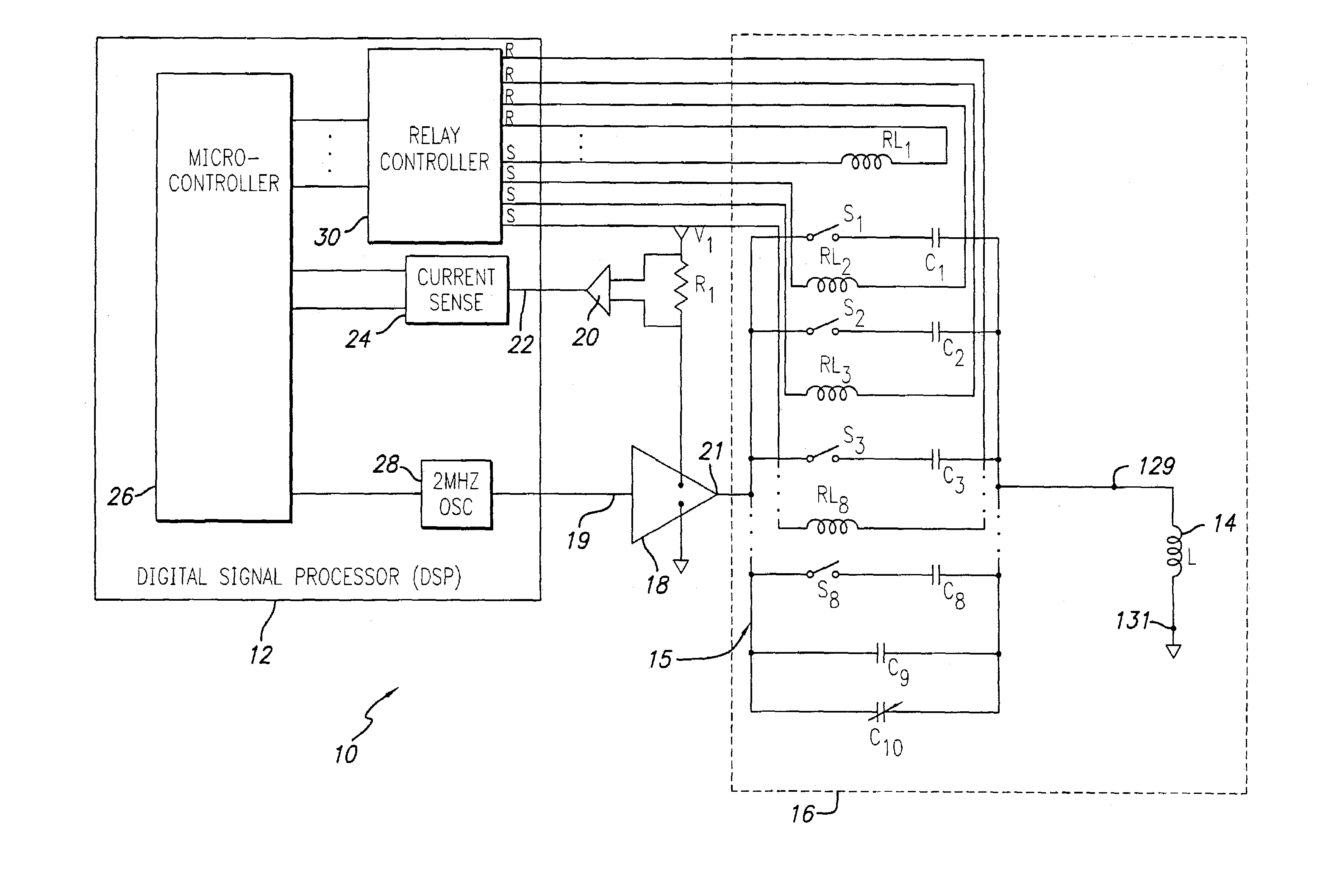
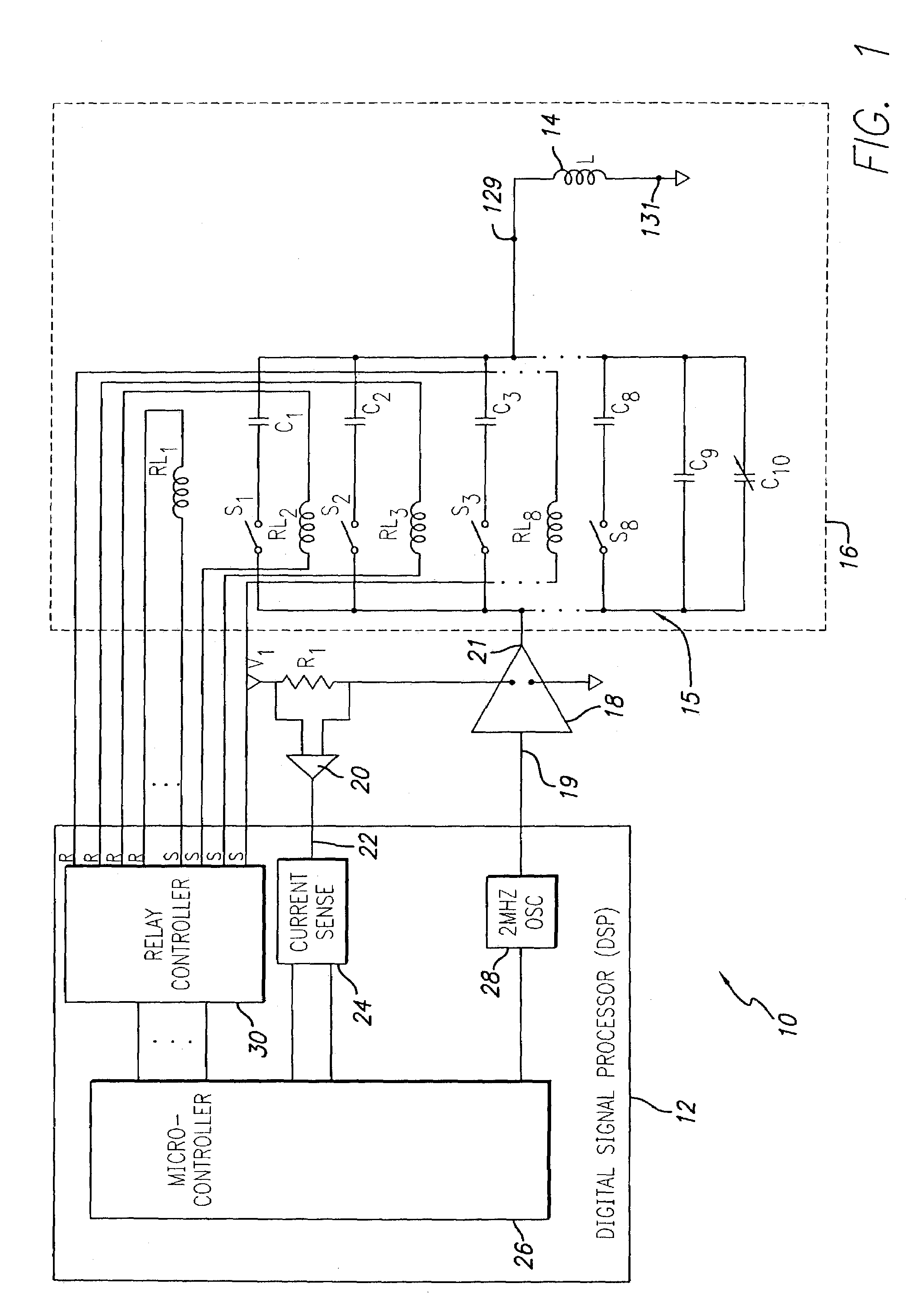
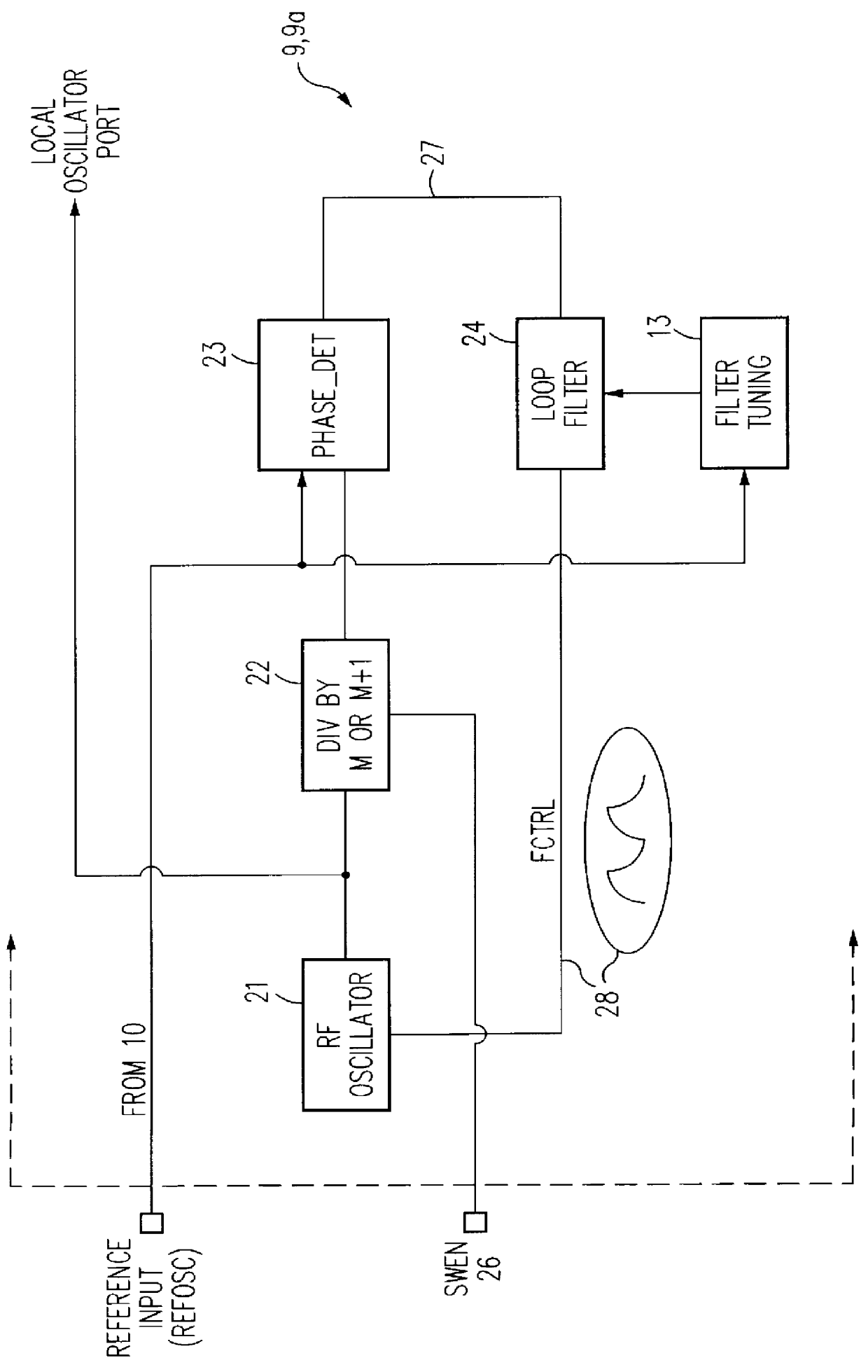
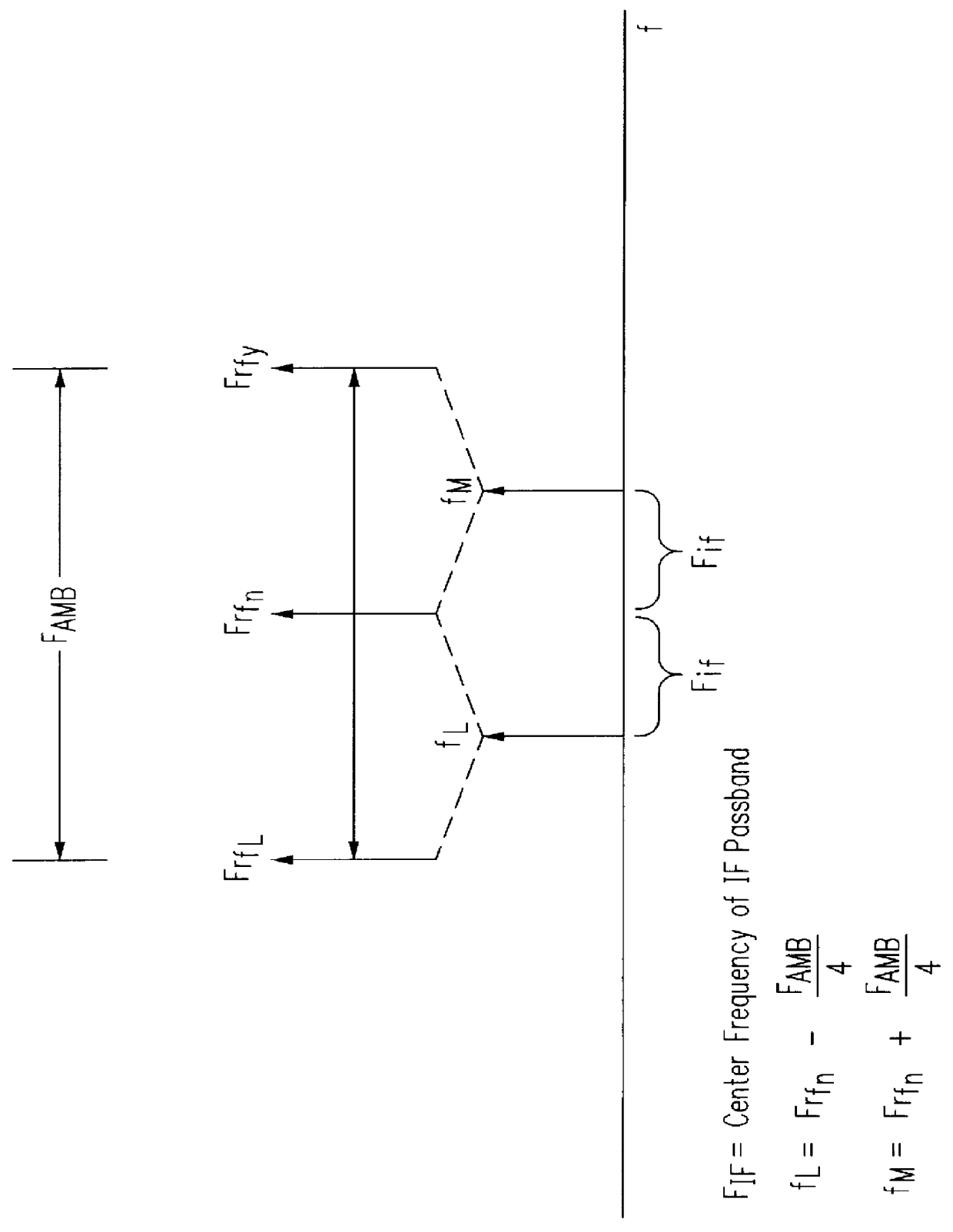
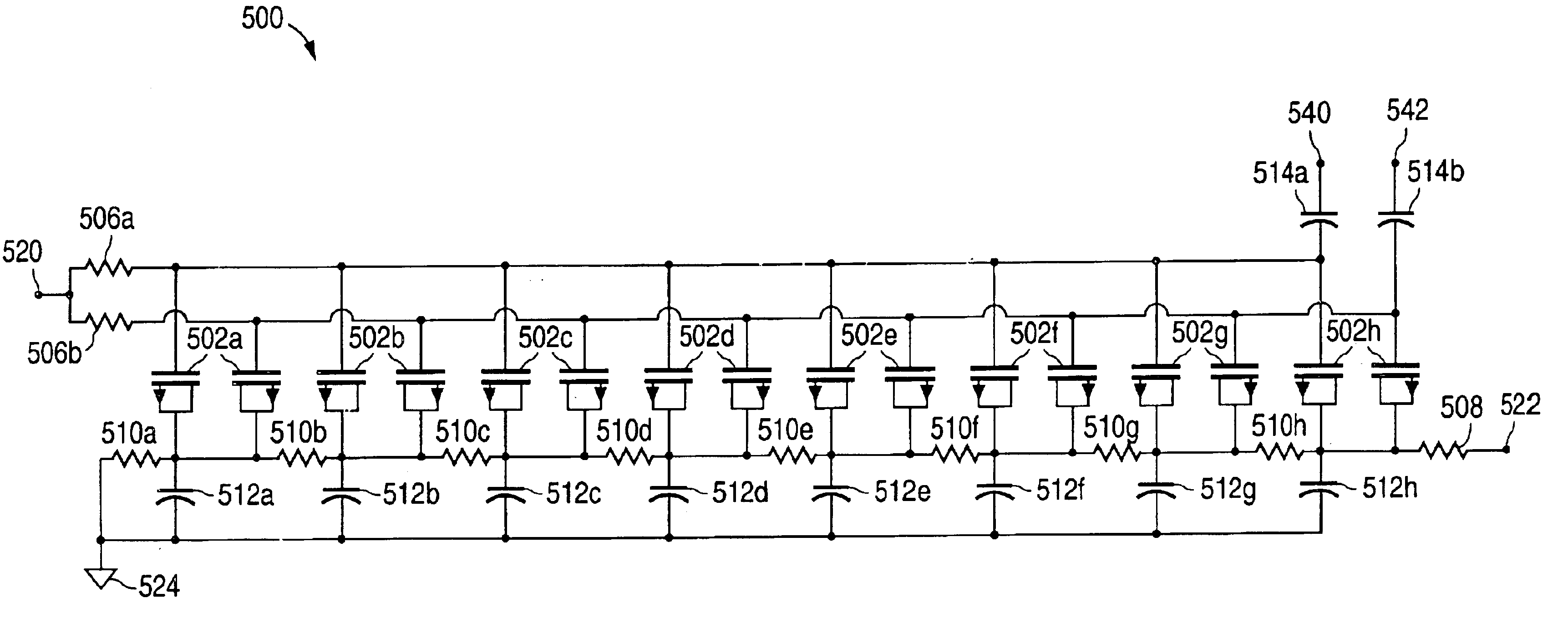
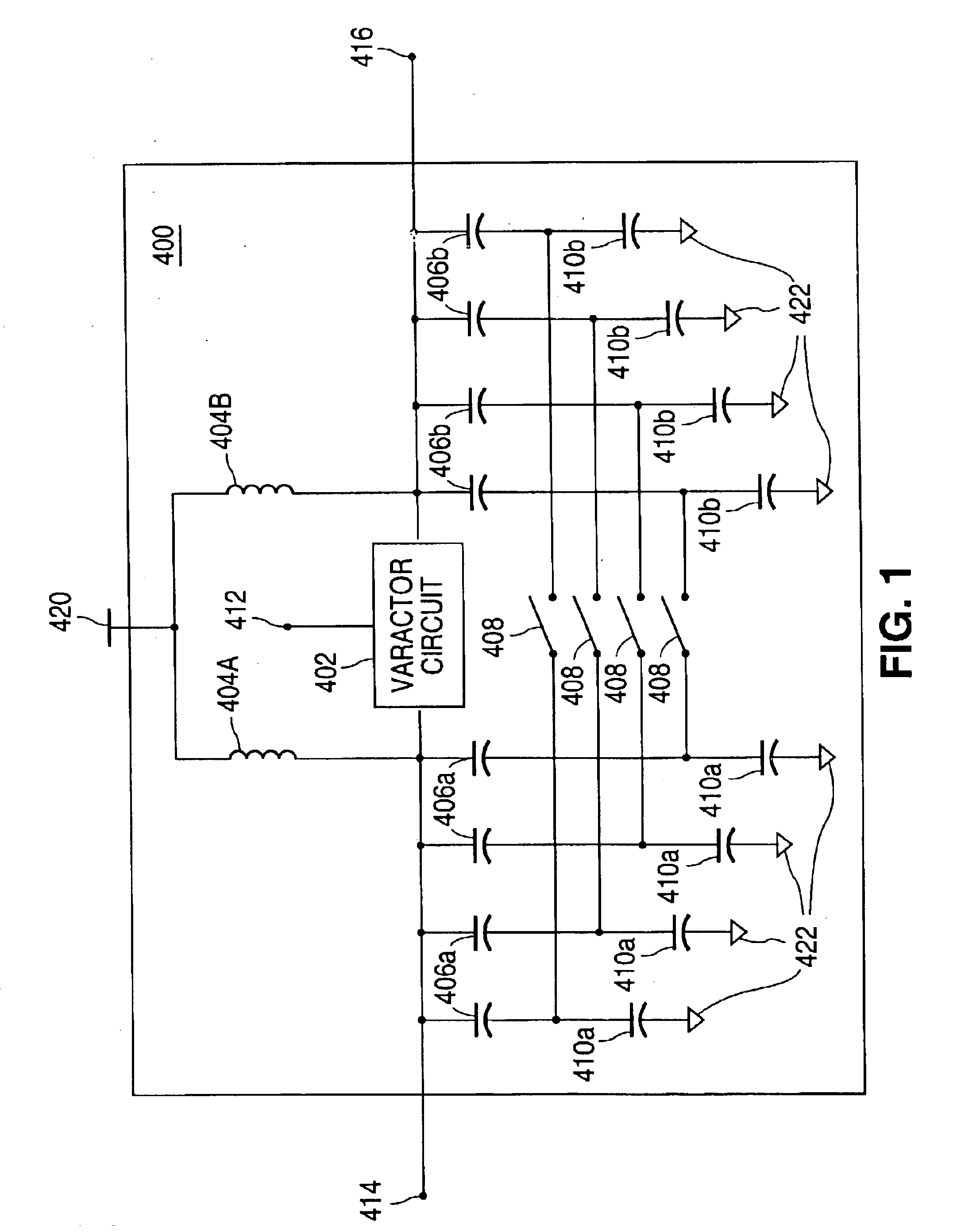
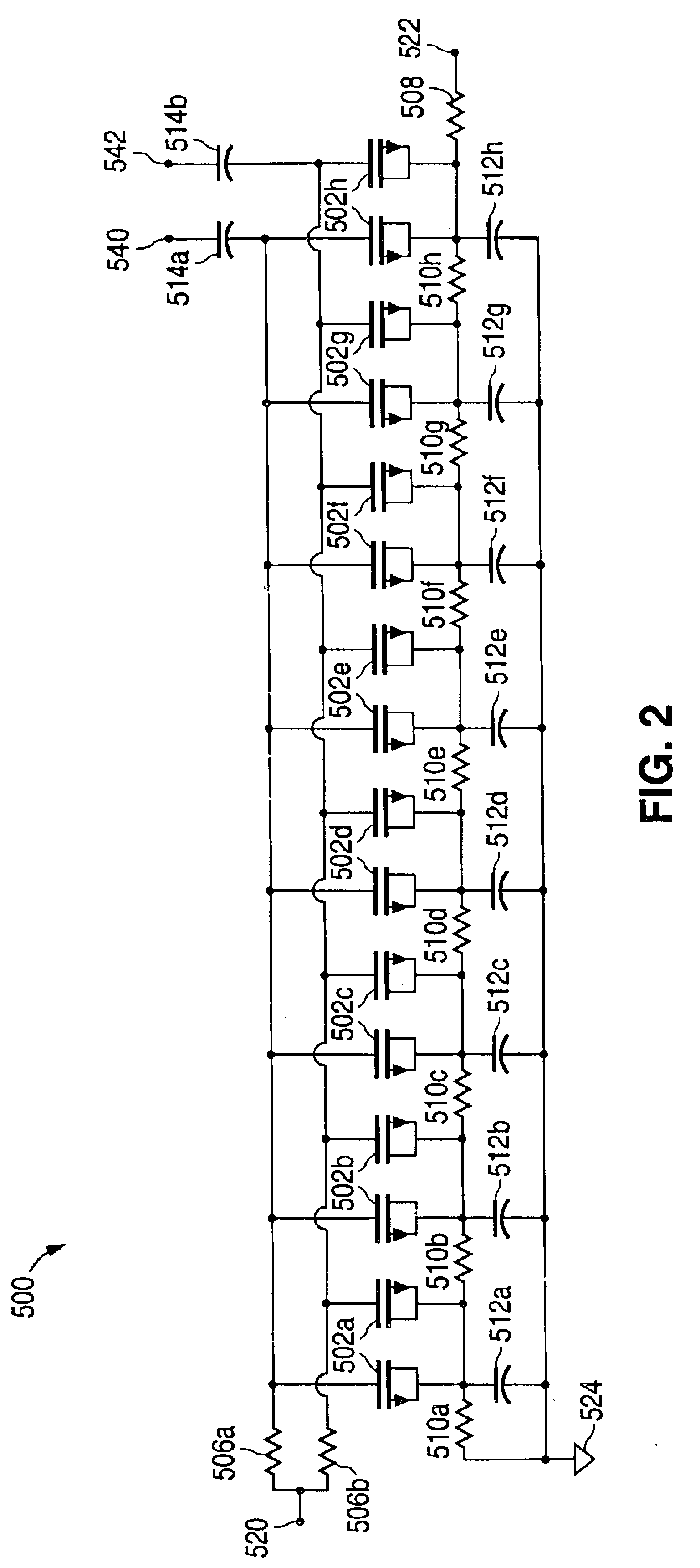
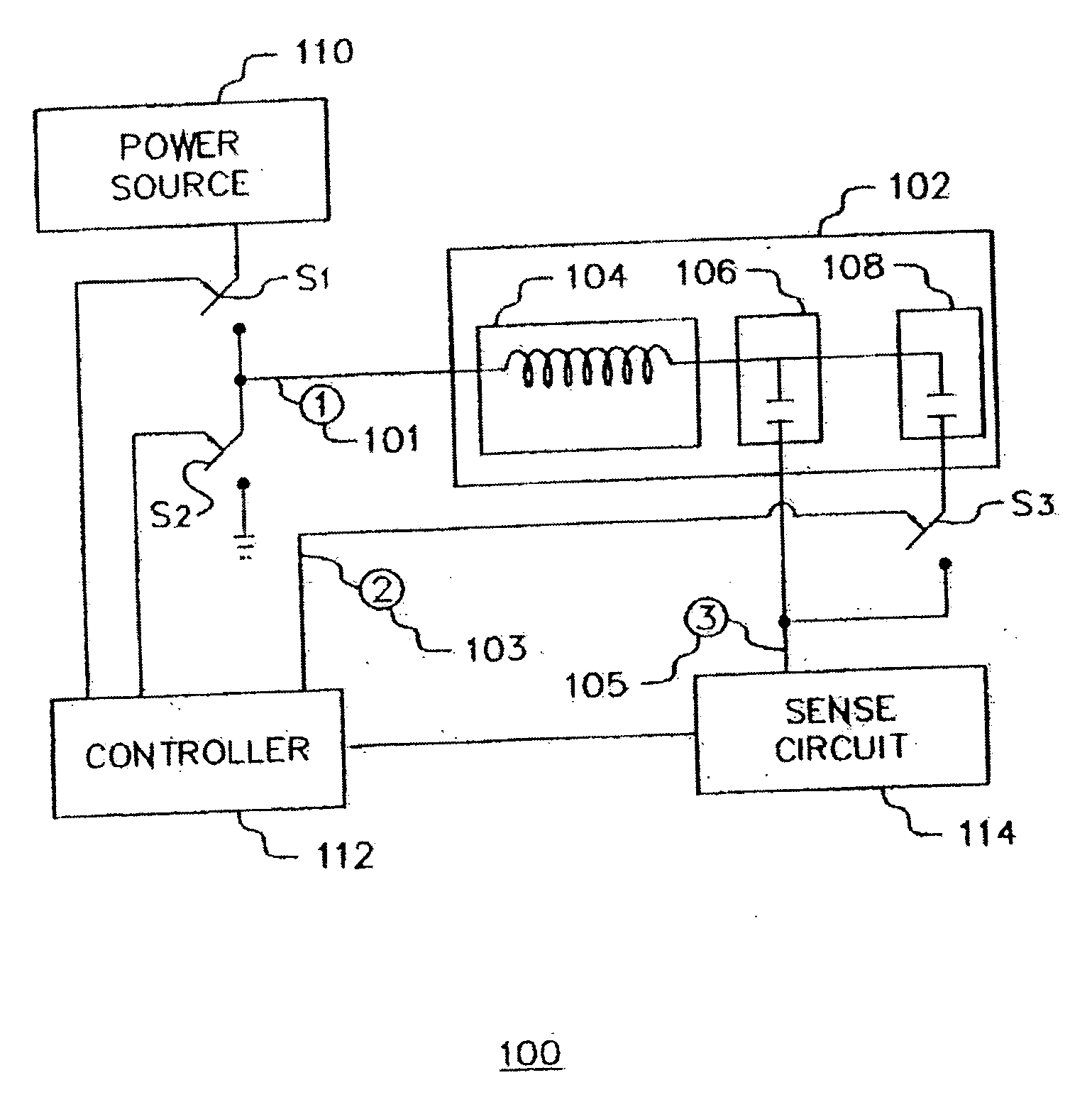
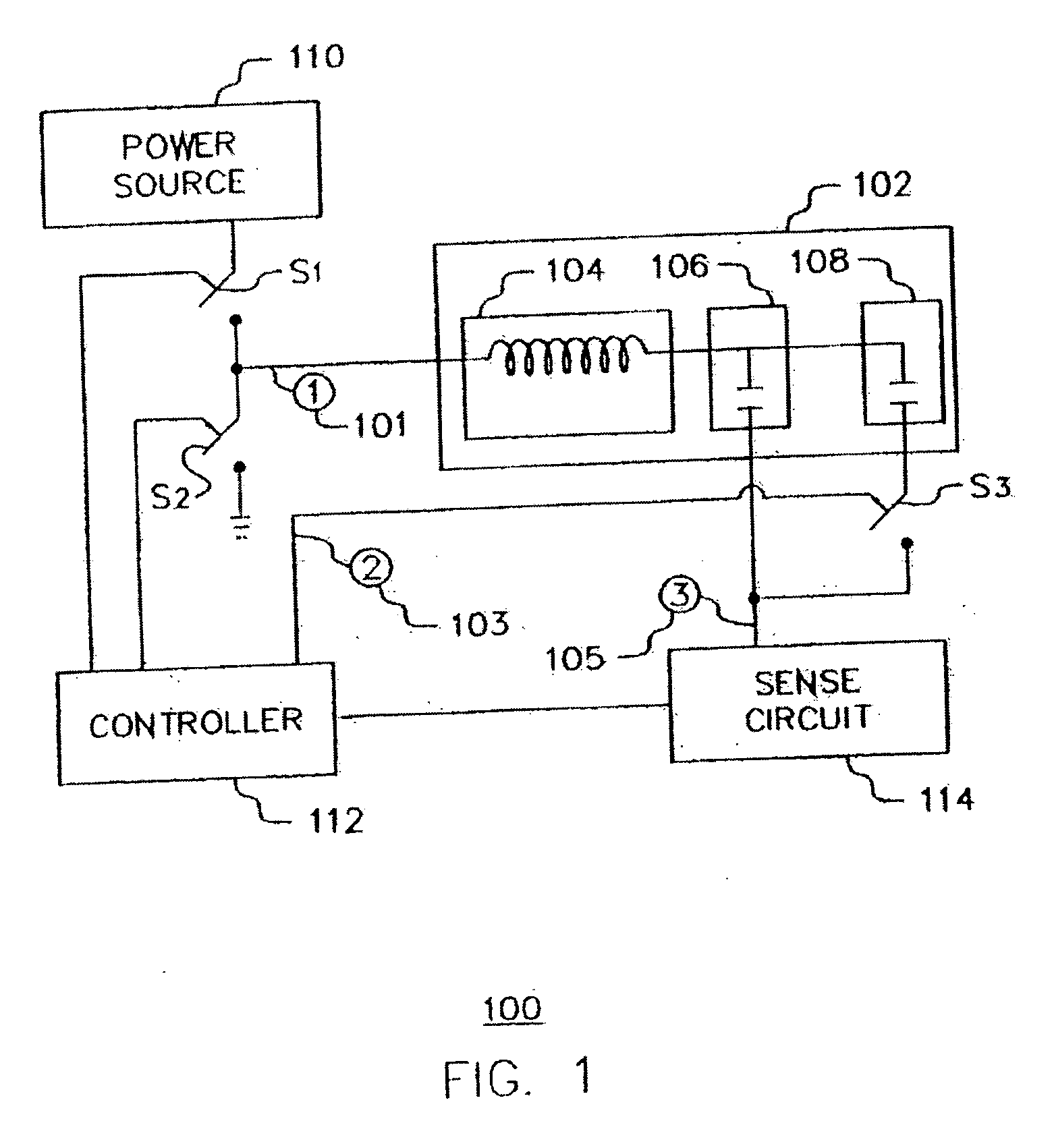
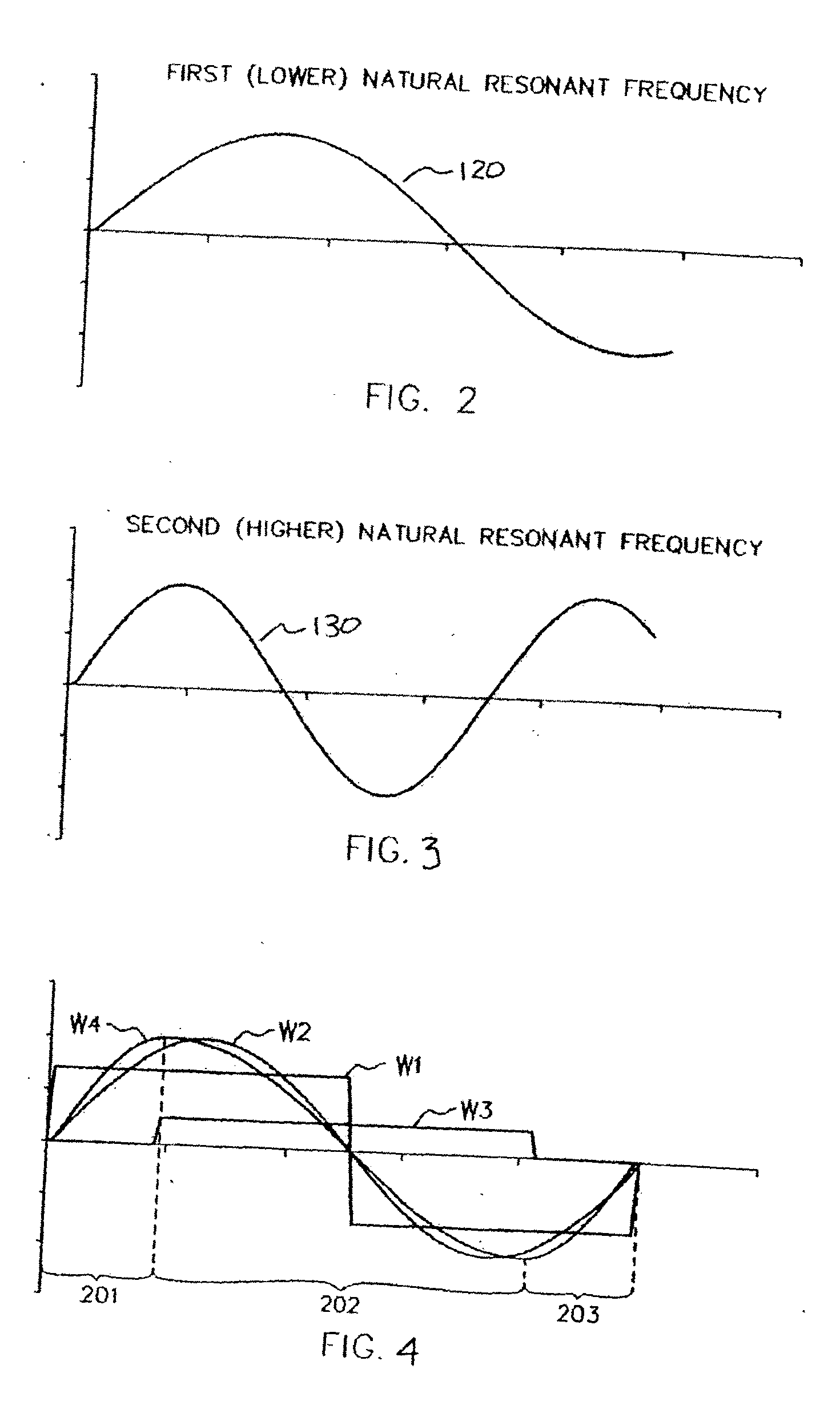
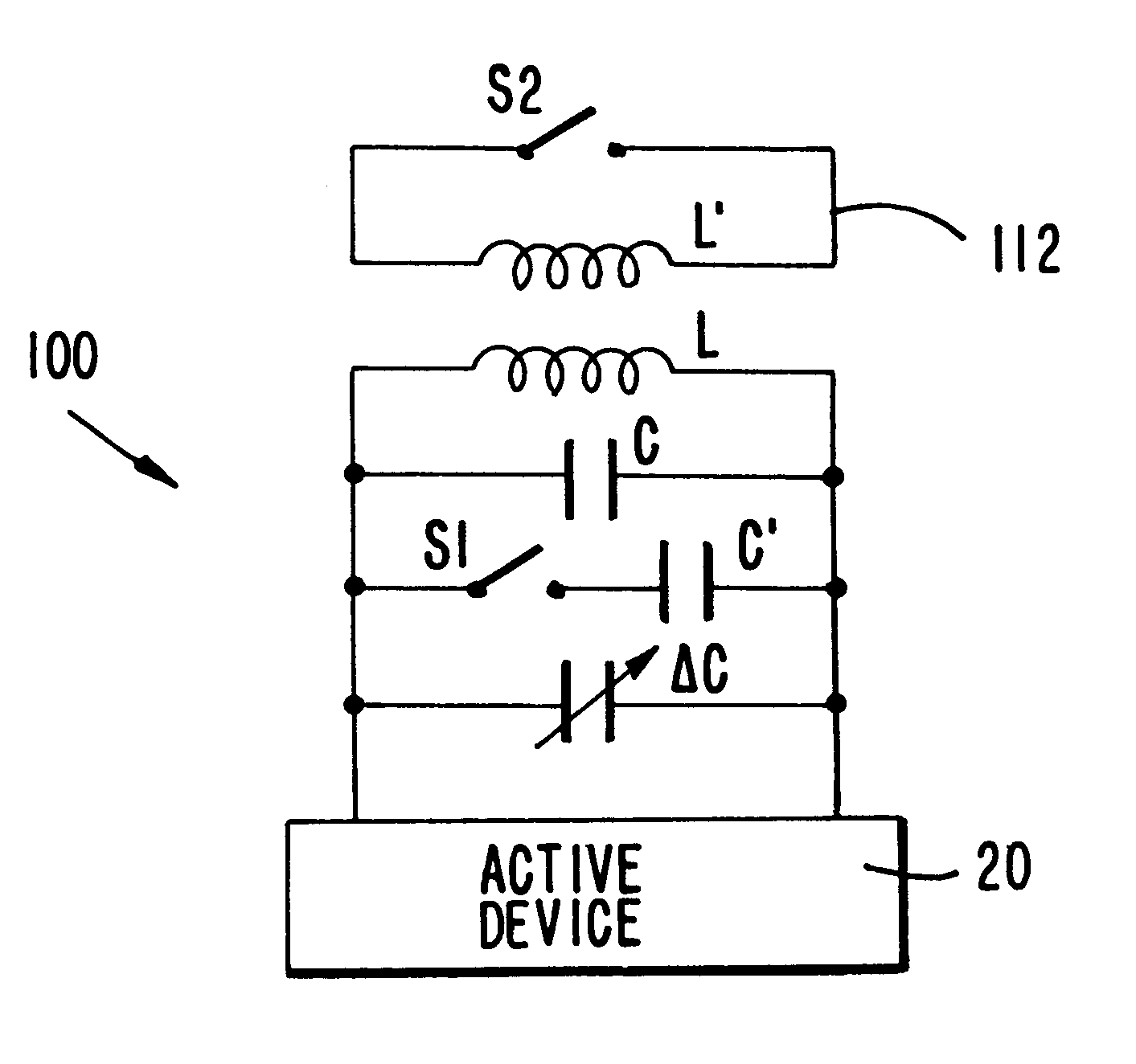
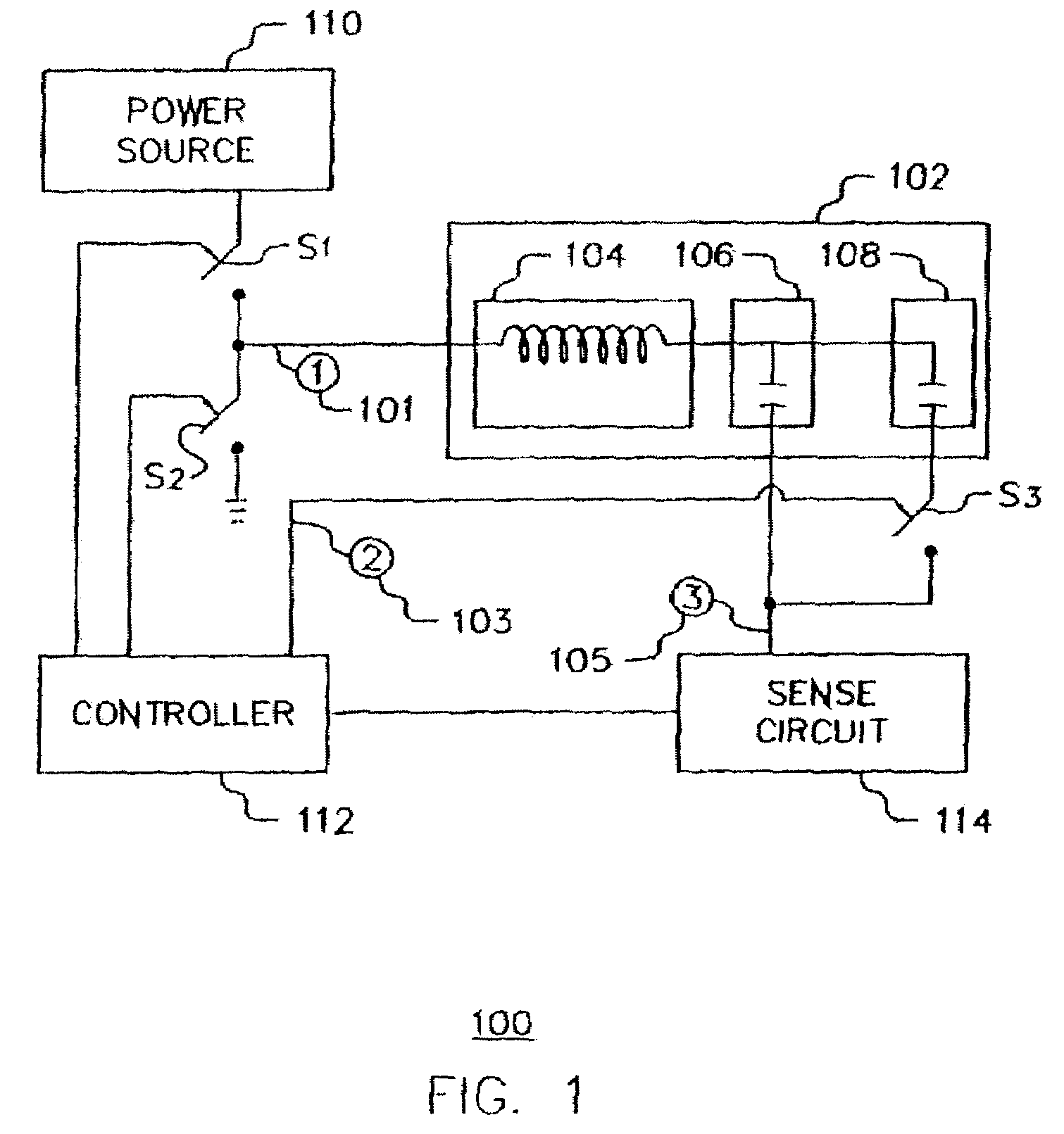
ActiveUS20060113970A1ElectrotherapyDiscontinuous tuning with variable tuning elementControl selectionElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Variable frequency oscillator circuit
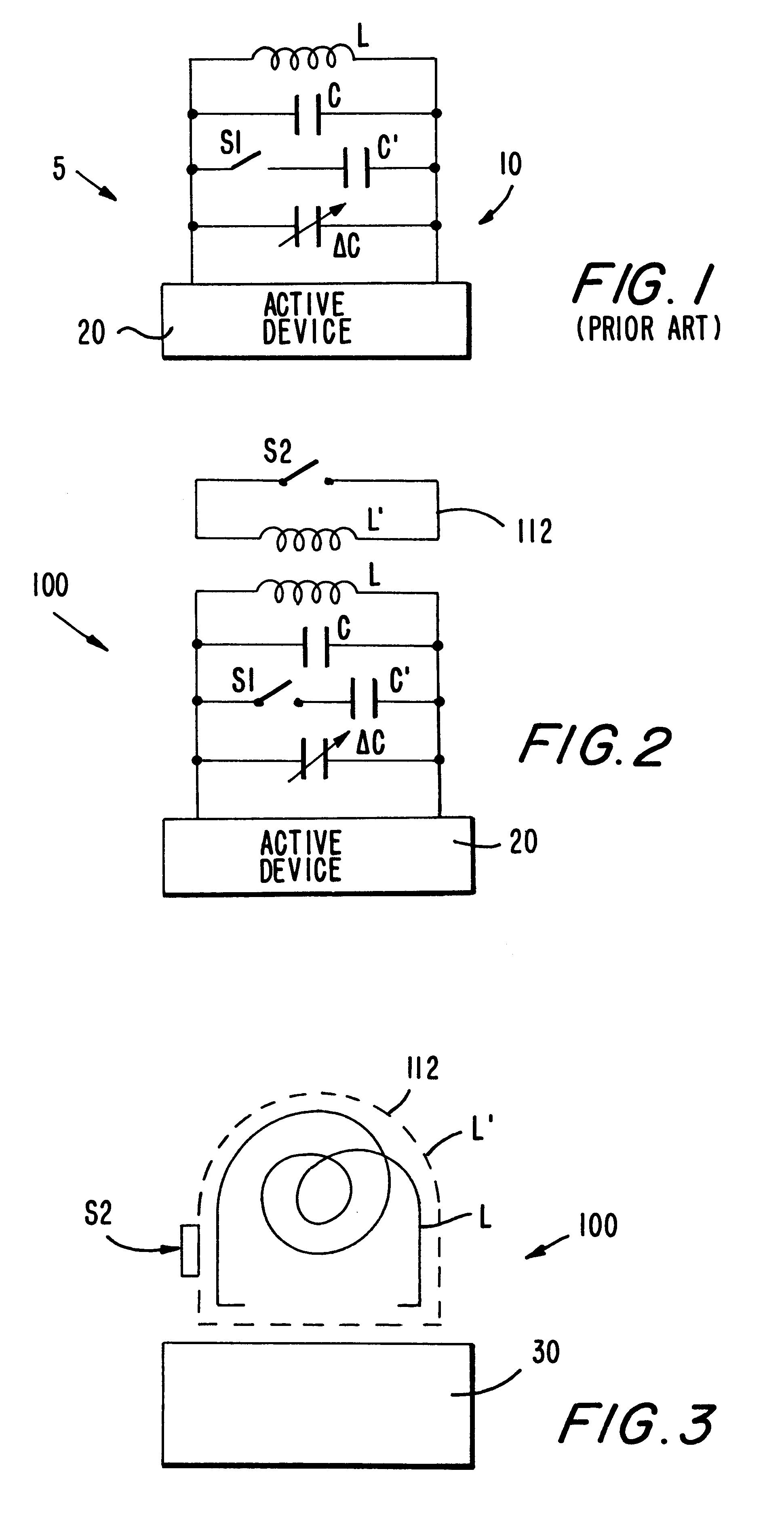
InactiveUS6255913B1Reduce inductanceIncrease working frequencyAngle modulation by variable impedenceContinuous tuning detailsInductorEngineering
A variable frequency oscillator (VFO) circuit having an increased frequency tuning range to selectively obtain operating frequencies above and below a set frequency. The circuit includes a tank inductor connected in parallel with a tank capacitor for primarily defining the set oscillating frequency of the VFO circuit. A switchable capacitor is included for selectively providing a predetermined step-wise decrease of the oscillating frequency to a frequency value below the set frequency of the circuit, and a varactor is included for accommodating selective tuning of the oscillating frequency within a range of frequency values below the set frequency. The inventive circuit selectively includes a switchable inductance element which is selectively electromagnetically coupled to the tank inductor to decrease the overall inductance value of the VFO circuit and, thereby, selectively increase the oscillating frequency above the set frequency value.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
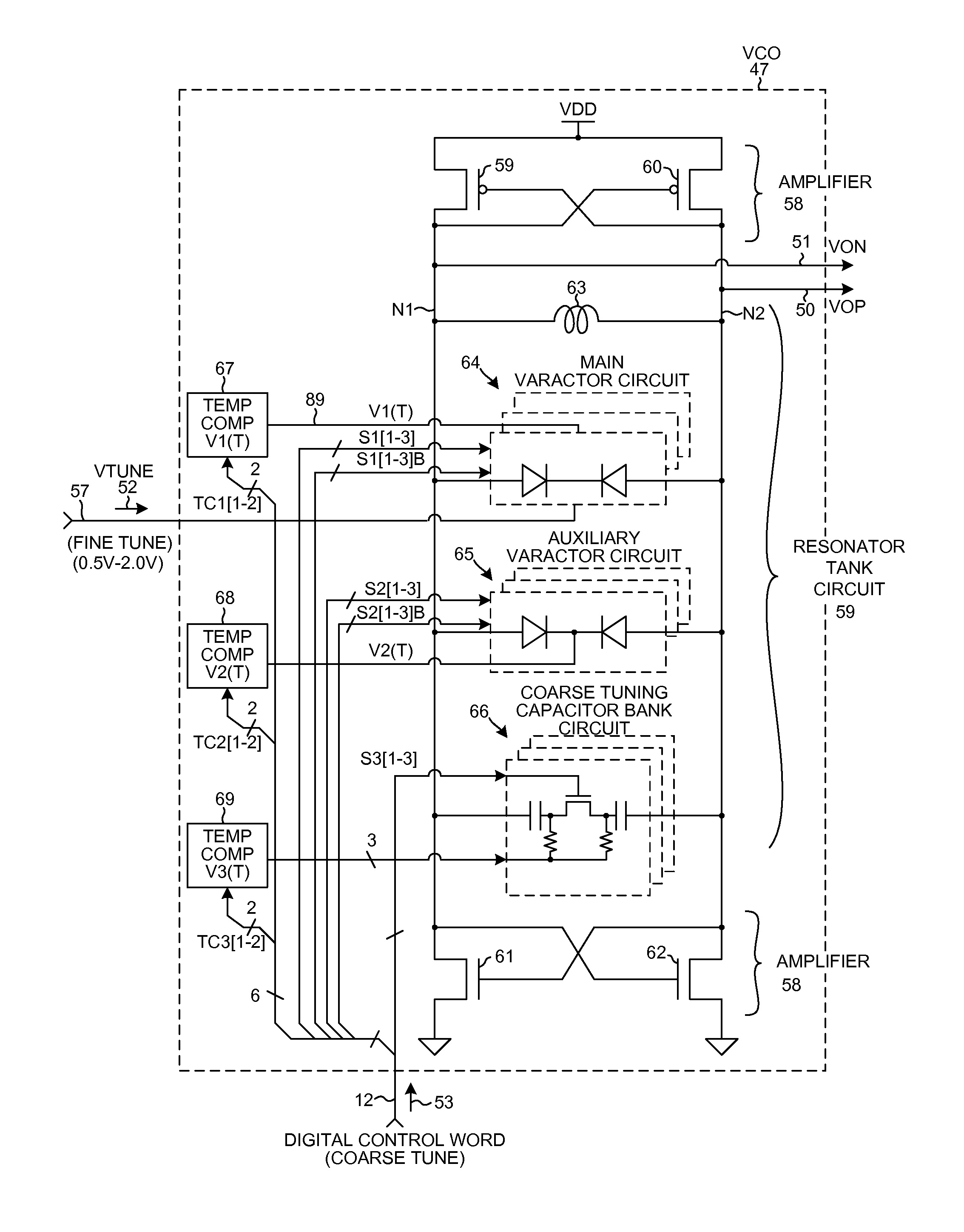
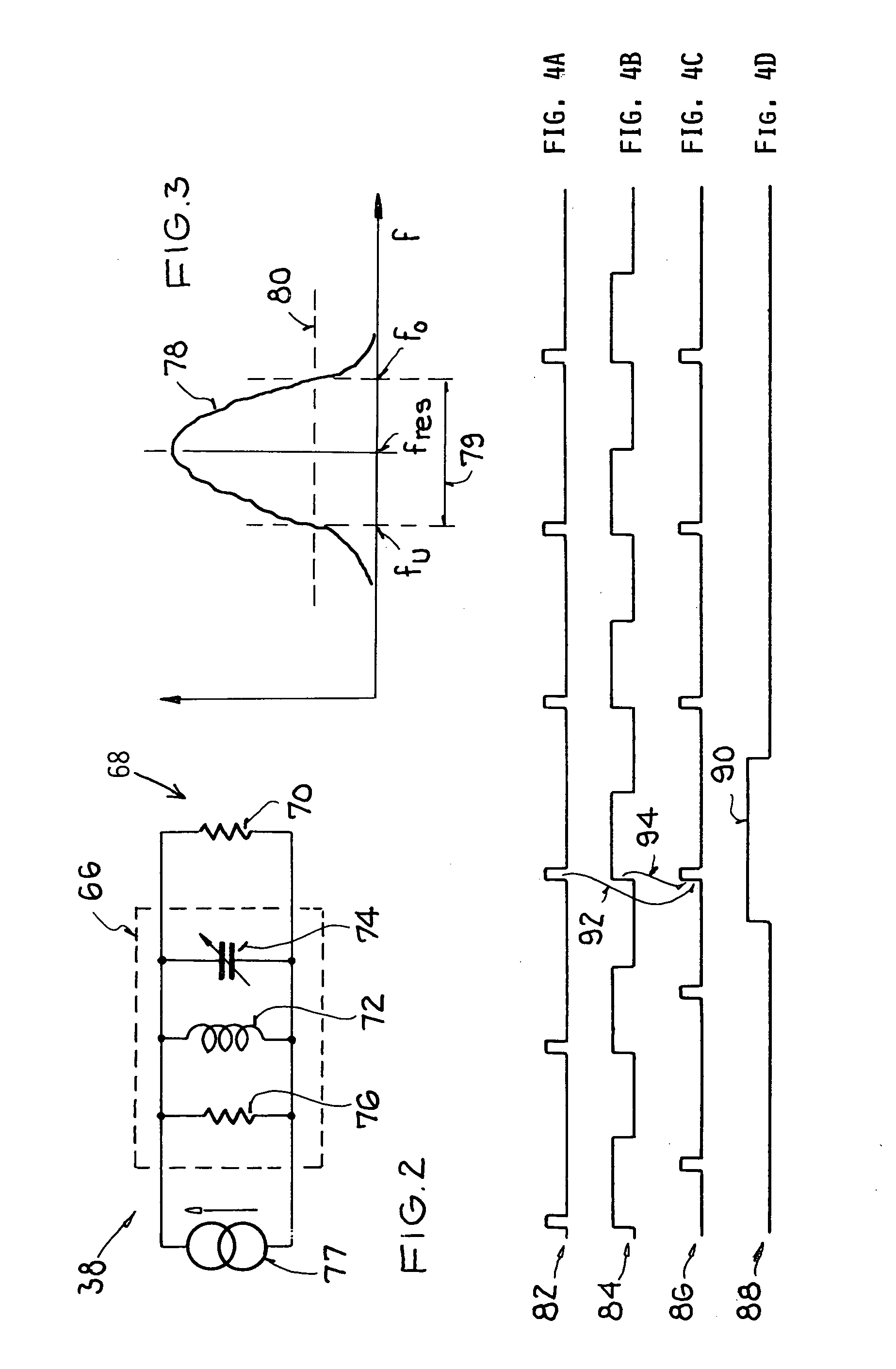
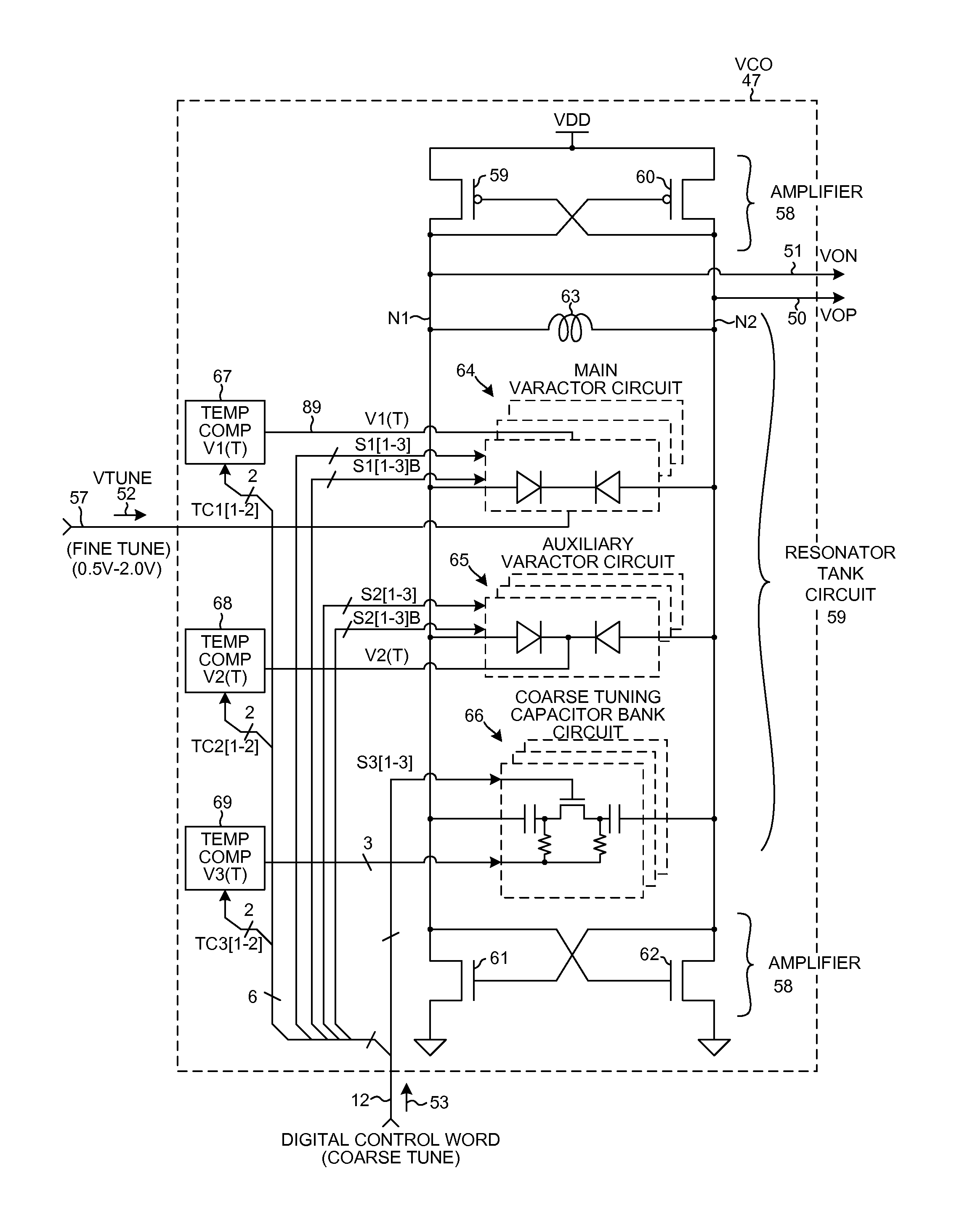
Wideband temperature compensated resonator and wideband VCO
ActiveUS8253506B2Less parasitic capacitanceReduce parasitic capacitanceAngle modulation by variable impedenceContinuous tuning detailsMultiplexingControl signal
A resonator of a VCO includes a fine tuning main varactor circuit, an auxiliary varactor circuit, and a coarse tuning capacitor bank circuit coupled in parallel with an inductance. The main varactor circuit includes a plurality of circuit portions that can be separately disabled. Within each circuit portion is a multiplexing circuit that supplies a selectable one of either a fine tuning control signal (FTAVCS) or a temperature compensation control signal (TCAVCS) onto a varactor control node within the circuit portion. If the circuit portion is enabled then the FTAVCS is supplied onto the control node so that the circuit portion is used for fine tuning. If the circuit portion is disabled then the TCAVCS is supplied onto the control node so that the circuit portion is used to combat VCO frequency drift as a function of temperature. How the voltage of the TCAVCS varies with temperature is digitally programmable.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Resonator configuration
InactiveUS7065331B2Avoid crosstalkContinuous tuning detailsPulse automatic controlSurface acoustic wave sensorControl variable
A resonator system and method are provided which includes / uses a tunable reference resonator, parts for tuning the reference resonator to a reference value via a controlled variable for the reference resonator, a tunable circuit resonator, and parts for tuning the circuit resonator which are designed such that the controlled variable for the reference resonator is used as a measure of the tuning of the circuit resonator, and wherein the reference resonator and / or the circuit resonator is / are designed as a surface acoustic wave component, a bulk acoustic wave component and / or a diaphragm oscillator.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for selection of a receiver tuning frequency
InactiveUS6957053B1Reliable and stable receptionEasy to implementResonant circuit detailsRadio data system/radio broadcast data systemQuality levelMemory bank
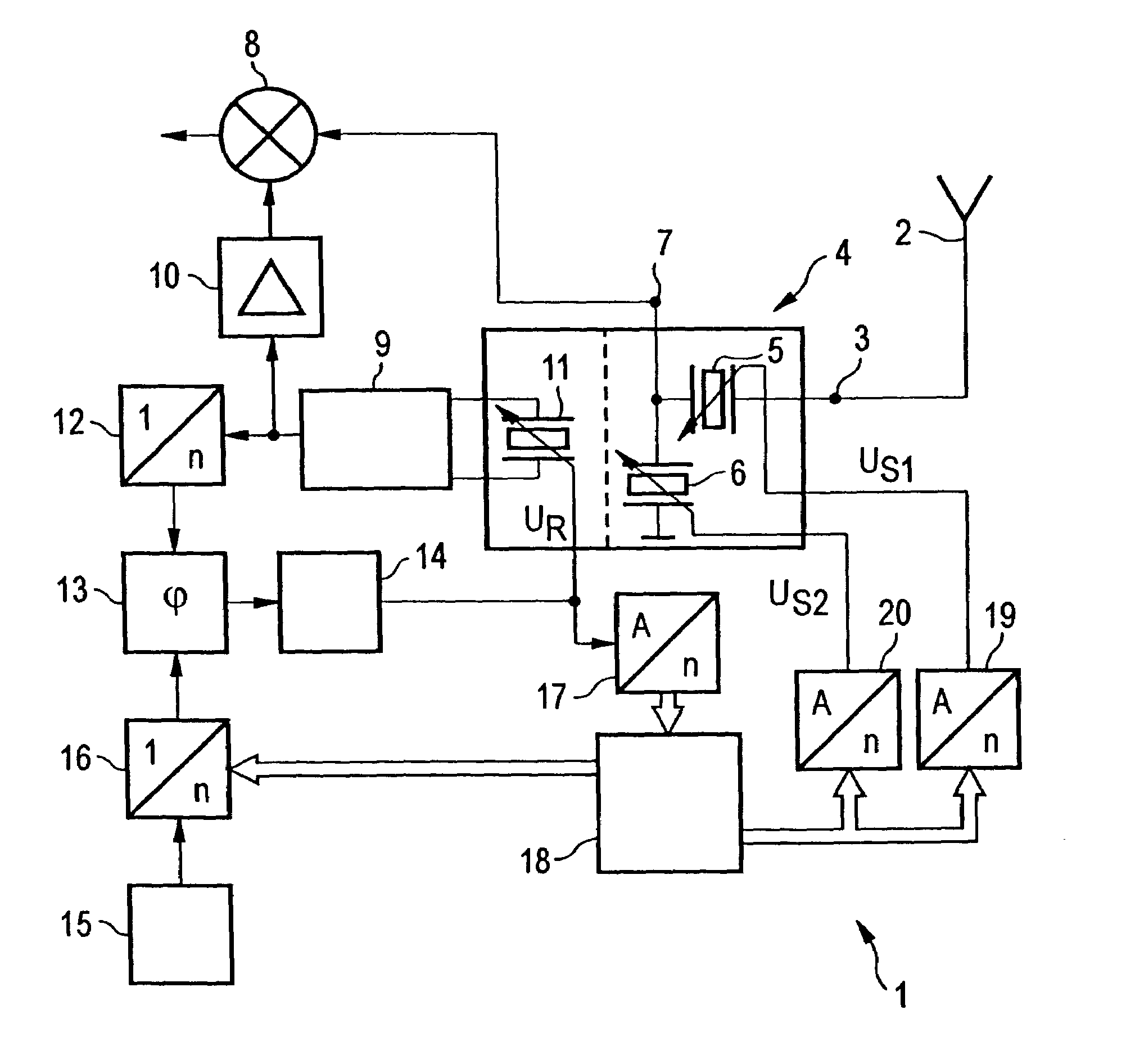
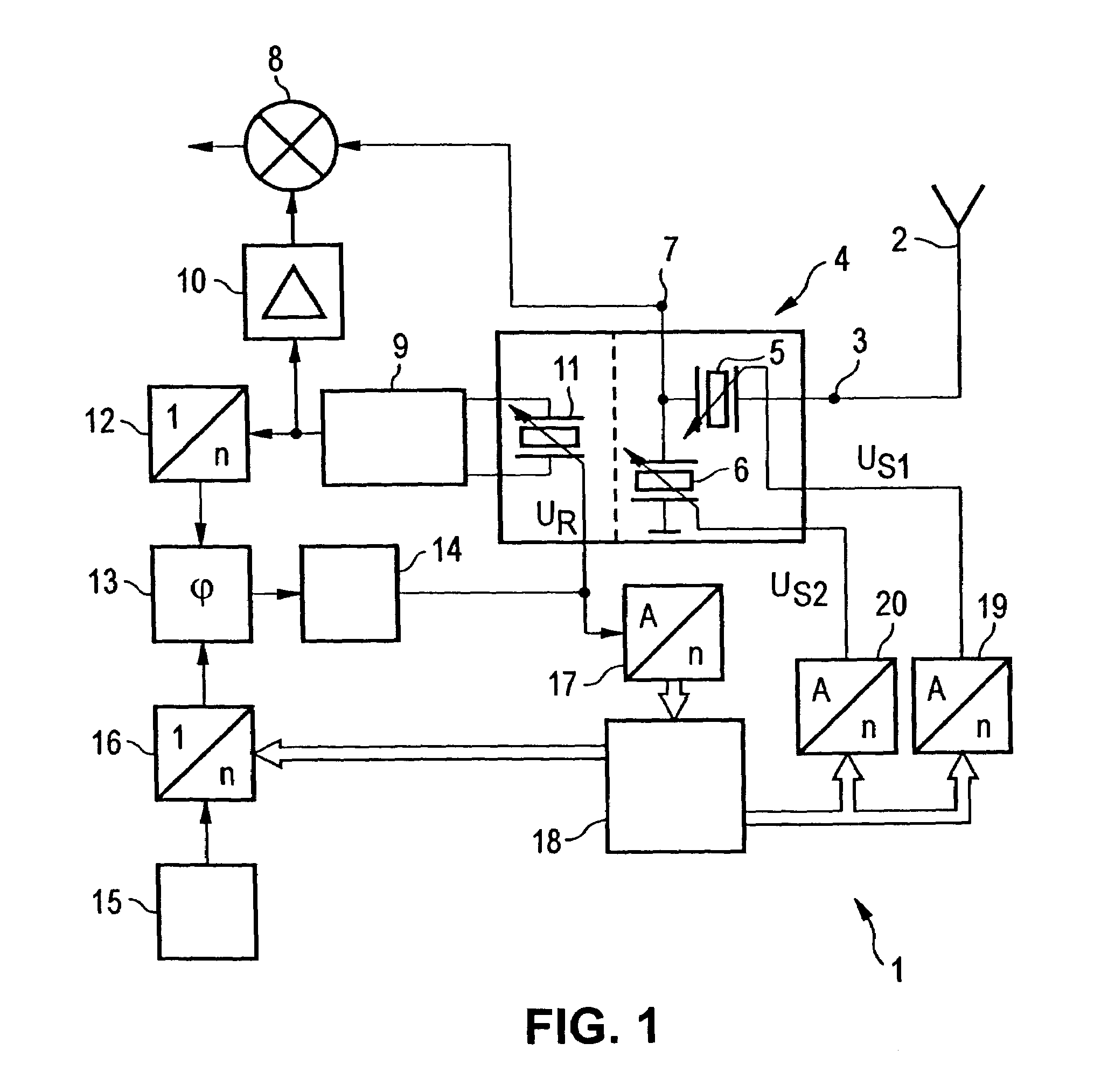
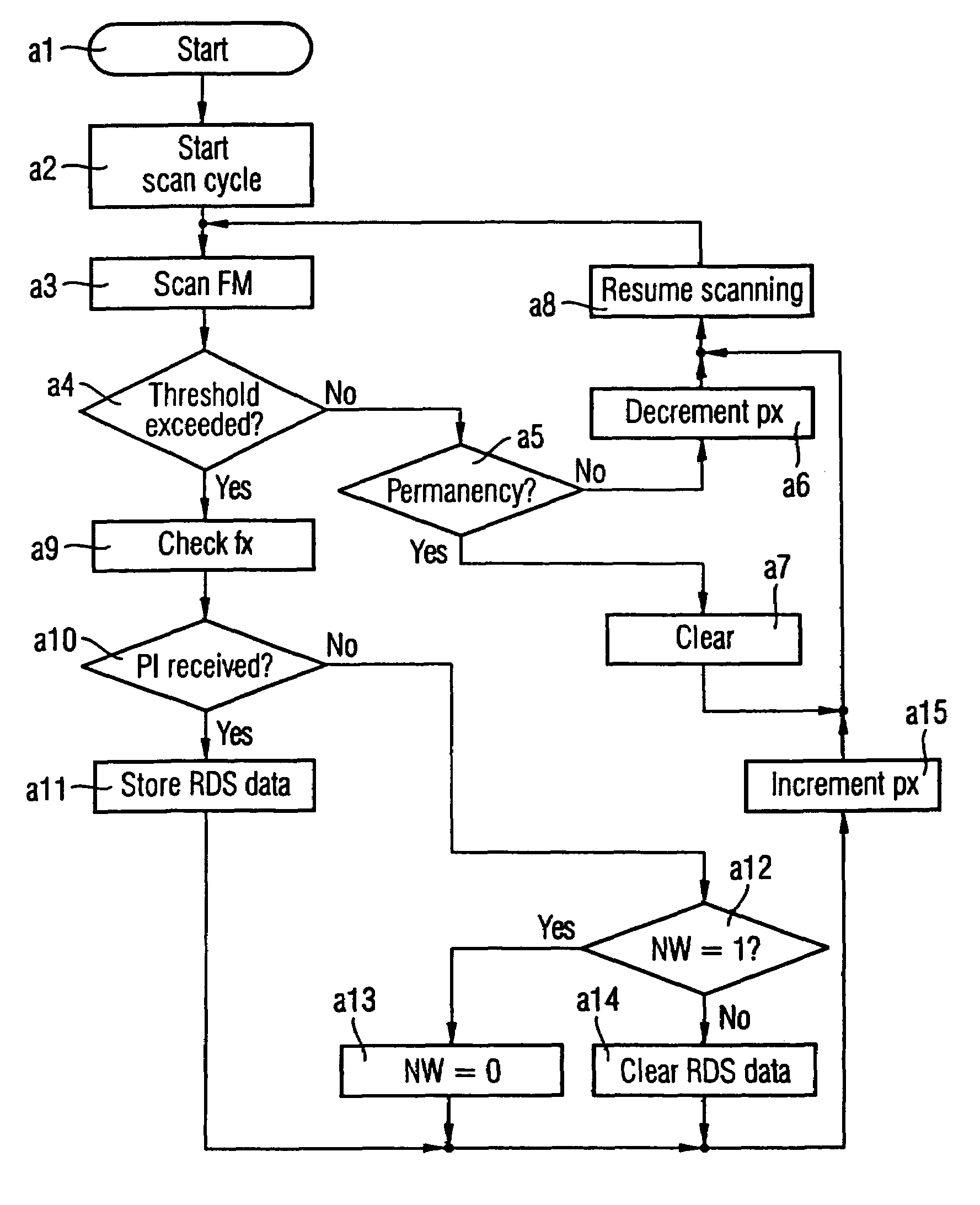
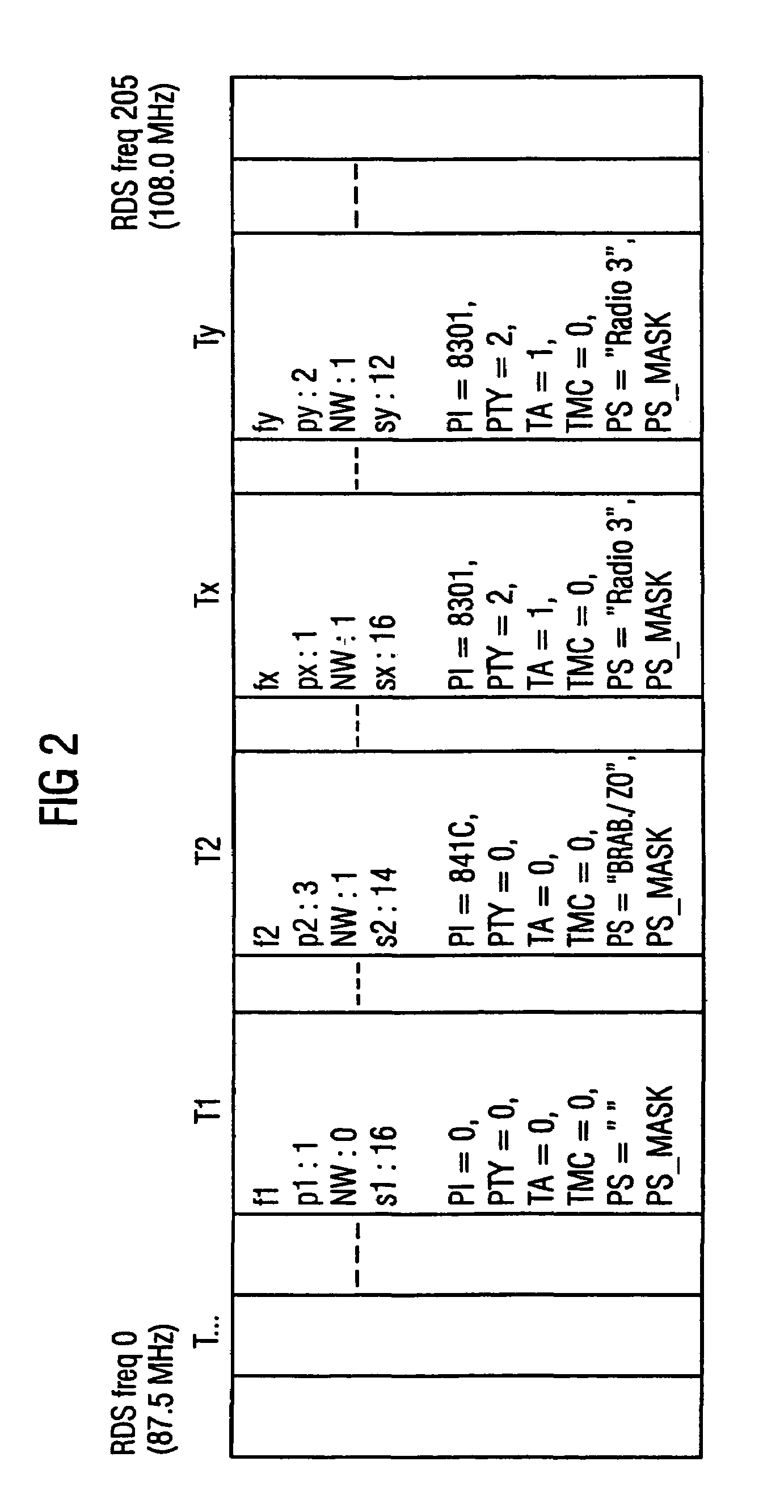
Method for tuning the reception of radio broadcast signals to an FM RDS transmitter using program related data and transmitter related data and receiver executing the method, providing a band scanning search for detecting FM RDS transmitters exceeding a predetermined reception quality level. To enhance efficiency in data processing and use of storage capacity, transmitter related data including tuning data is stored separately from program related RDS data. Per each detected transmitter a permanency factor indicating the permanency in reception quality thereof is being allocated to each detected RDS transmitter and stored in a first memory bank, along with the relevant tuning data. Per each program identification code carried in the RDS data of the so detected transmitters program related FM RDS data are being stored in a second memorybank, a linkage code defining the storage address within the second memory bank containing the program data carried by the relevant FM RDS transmitter being allocated to the transmitter data of each FM RDS transmitter and stored in the first memory bank.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Front-end integrated circuit for television receivers
ActiveUS20080198269A1Television system detailsElectronic switchingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Television receivers
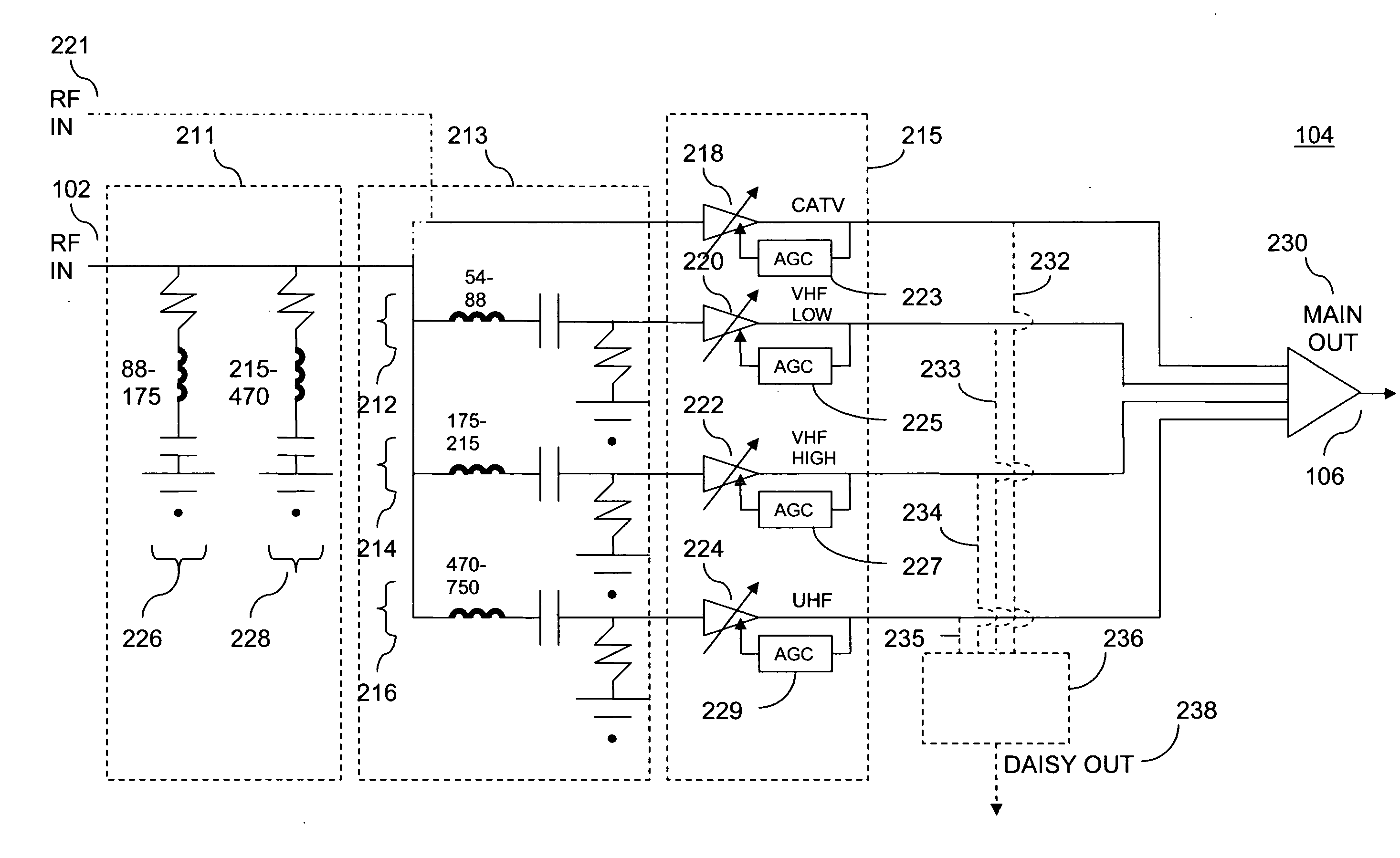
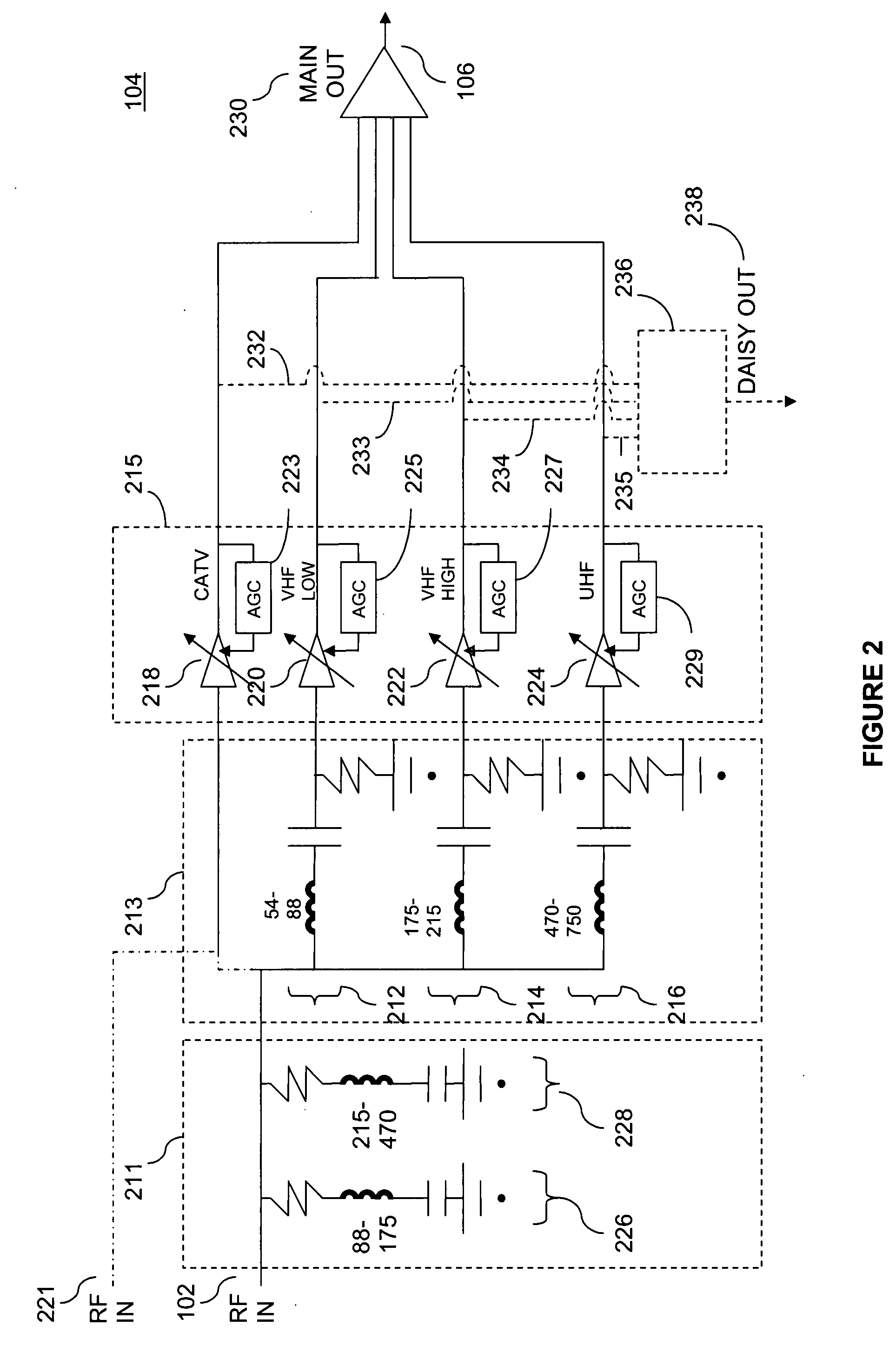
A tuner front-end circuit for processing a radio frequency (RF) signal includes a first filter block that terminates the RF signal for unwanted frequency bands; a second filter block that provides selectivity within the unterminated signal by separating the unterminated signal into a plurality of separate signals, each of a different desired frequency band; and an amplifier block that amplifies each of the separate signals. One or more of the amplified separate signals can be provided to a tuner. The circuit can also include a daisy chain output block that provides the amplified separate signals to one or more additional tuners. One or more tracking filter blocks can also be included to provide further selectivity to the amplified separate signals and to reject signals at specific harmonics to prevent degradation of a signal-to-noise ratio. A method of processing an RF signal is also presented.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Location specific in-vehicle frequency tuning data
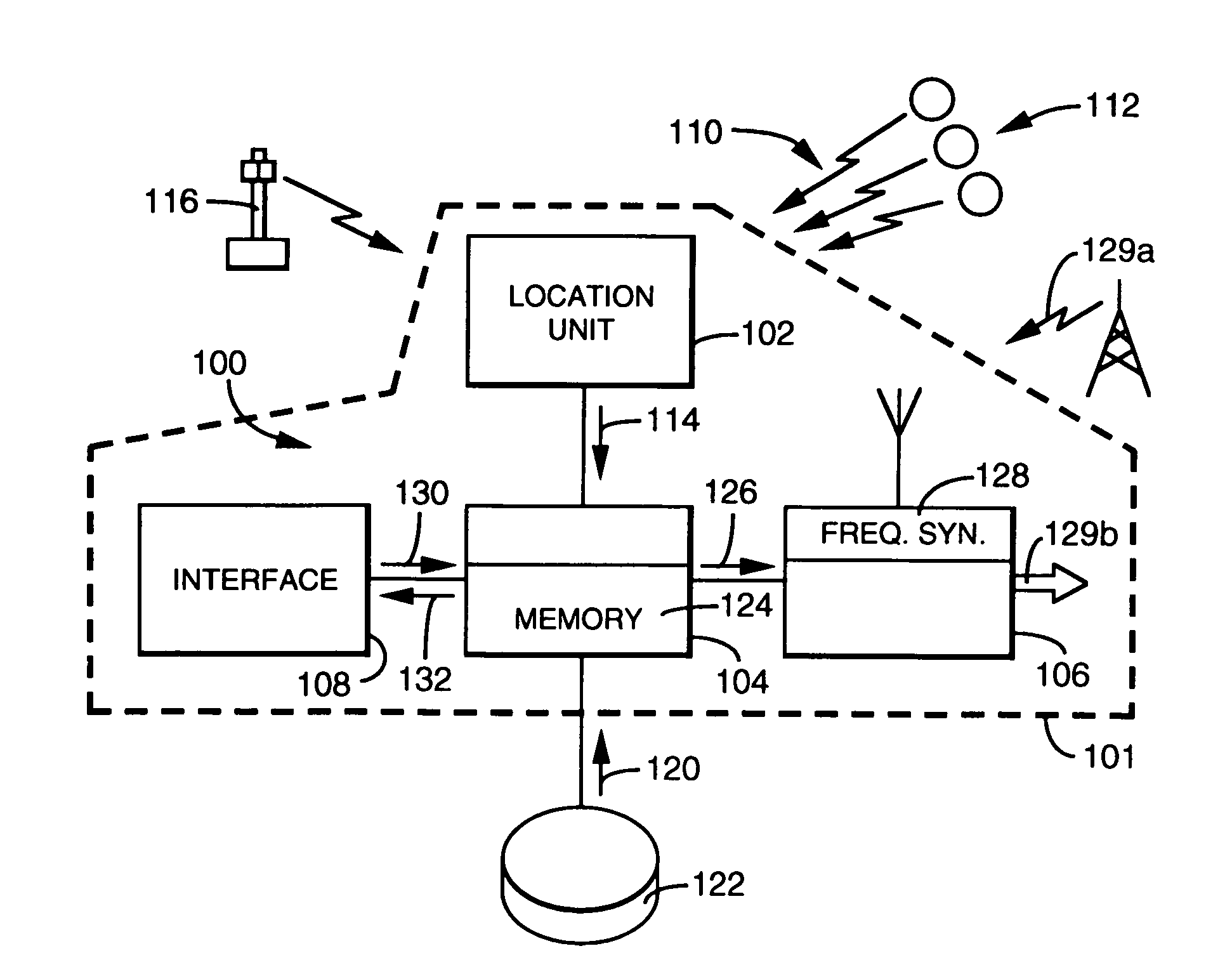
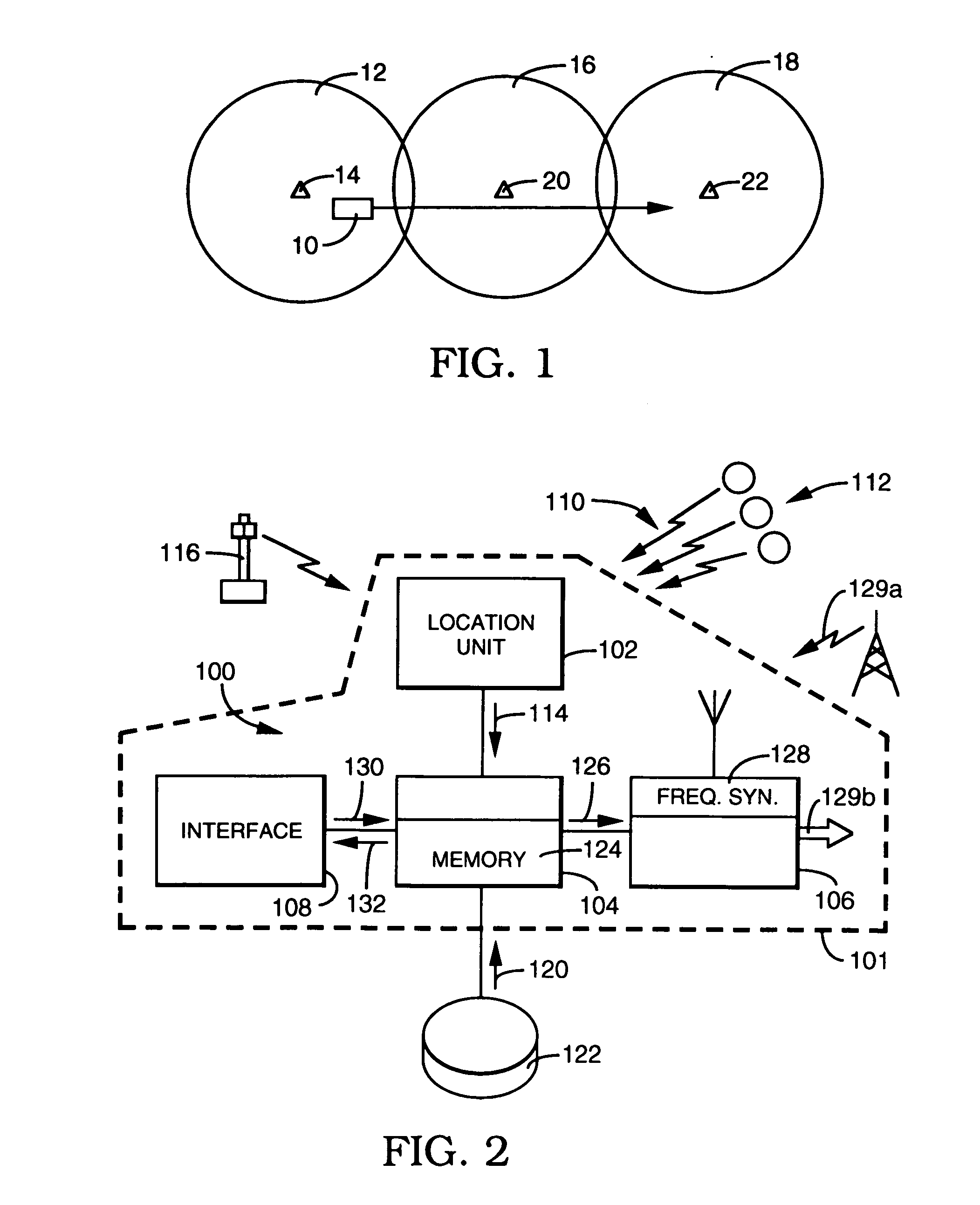
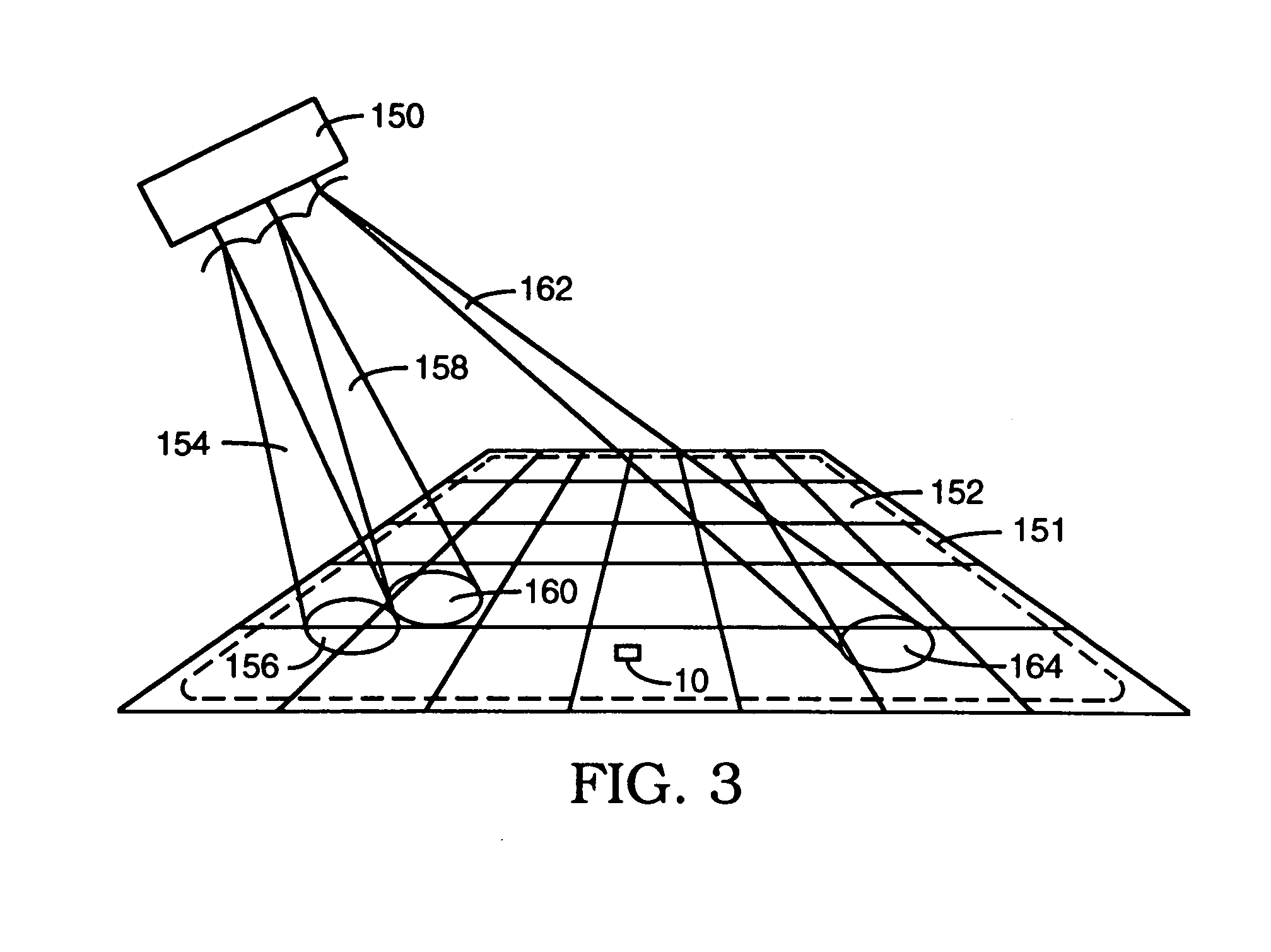
An in-vehicle system comprises a location unit, a frequency selection unit, and a receiving unit. Frequency tuning data is loaded into the selection unit. The frequency tuning data includes a radio signal reception area for each unique frequency in the tuning data. The location unit determines the system location and passes the location information to the frequency selection unit. The selection unit selects tuning data for a particular frequency having a signal reception area that encompasses the present vehicle location, and passes the selected data to the receiving unit. The receiving unit uses the selected tuning data to tune the radio signal.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Method and circuit arrangement for synchronizing plural oscillators
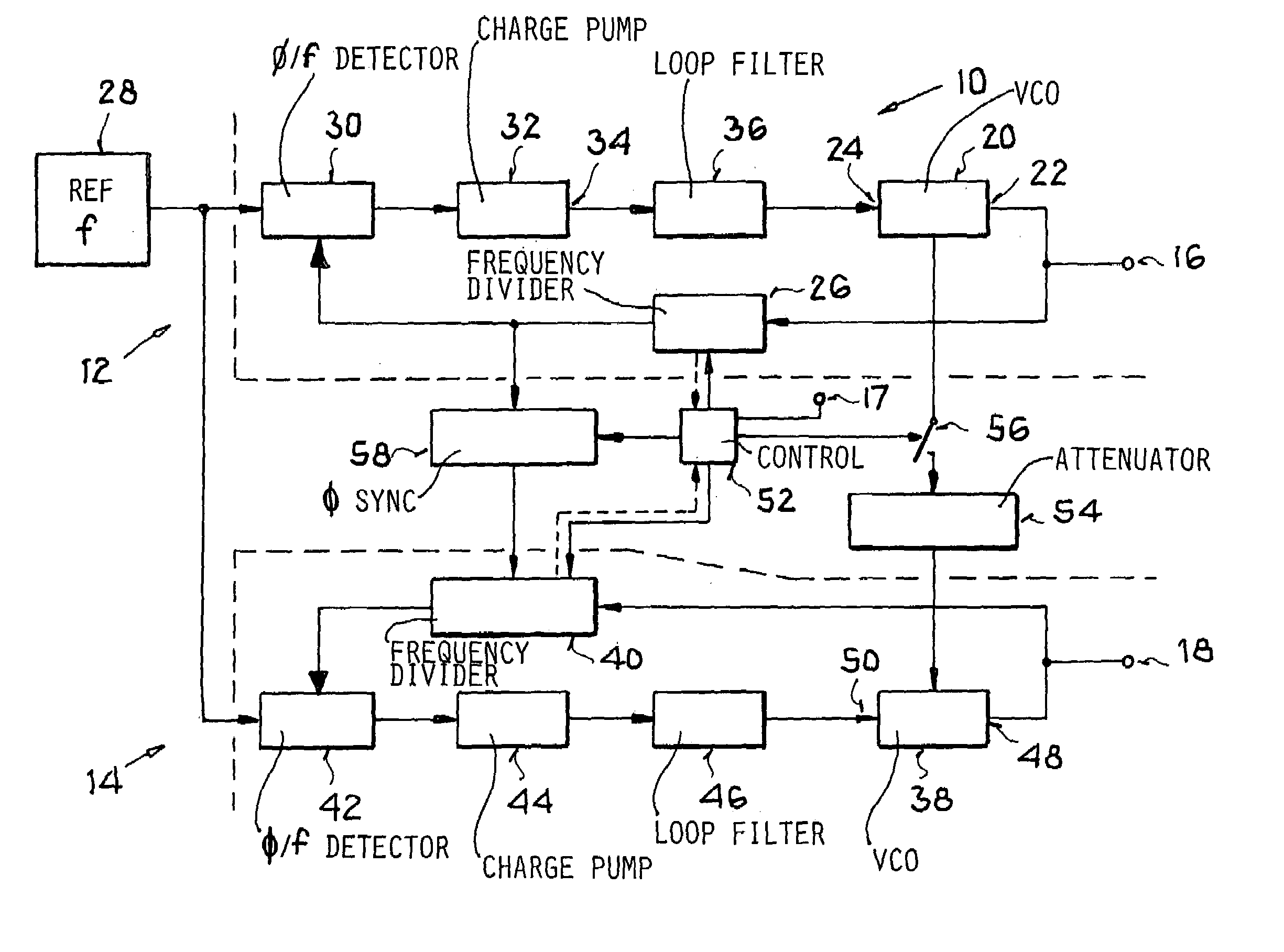
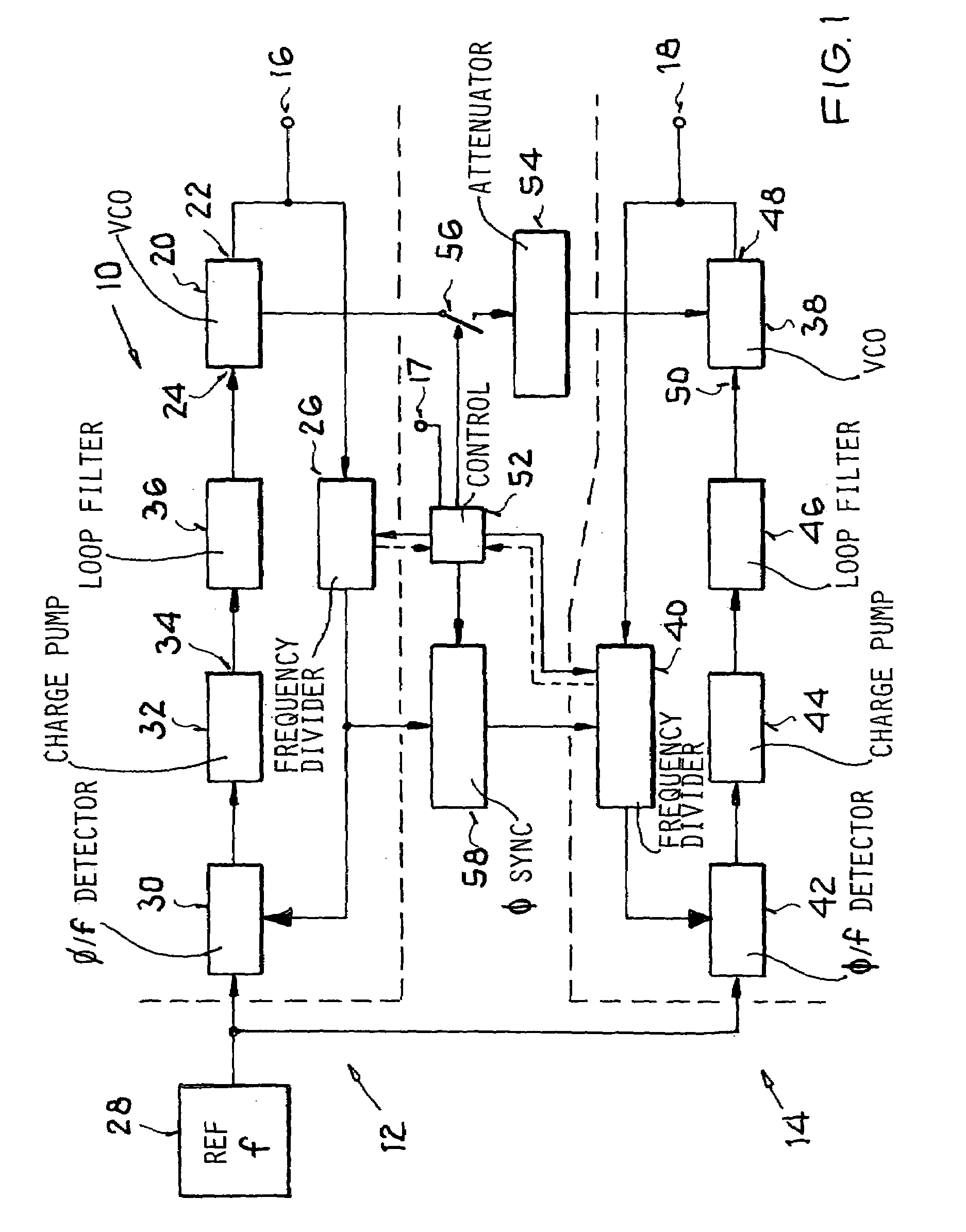
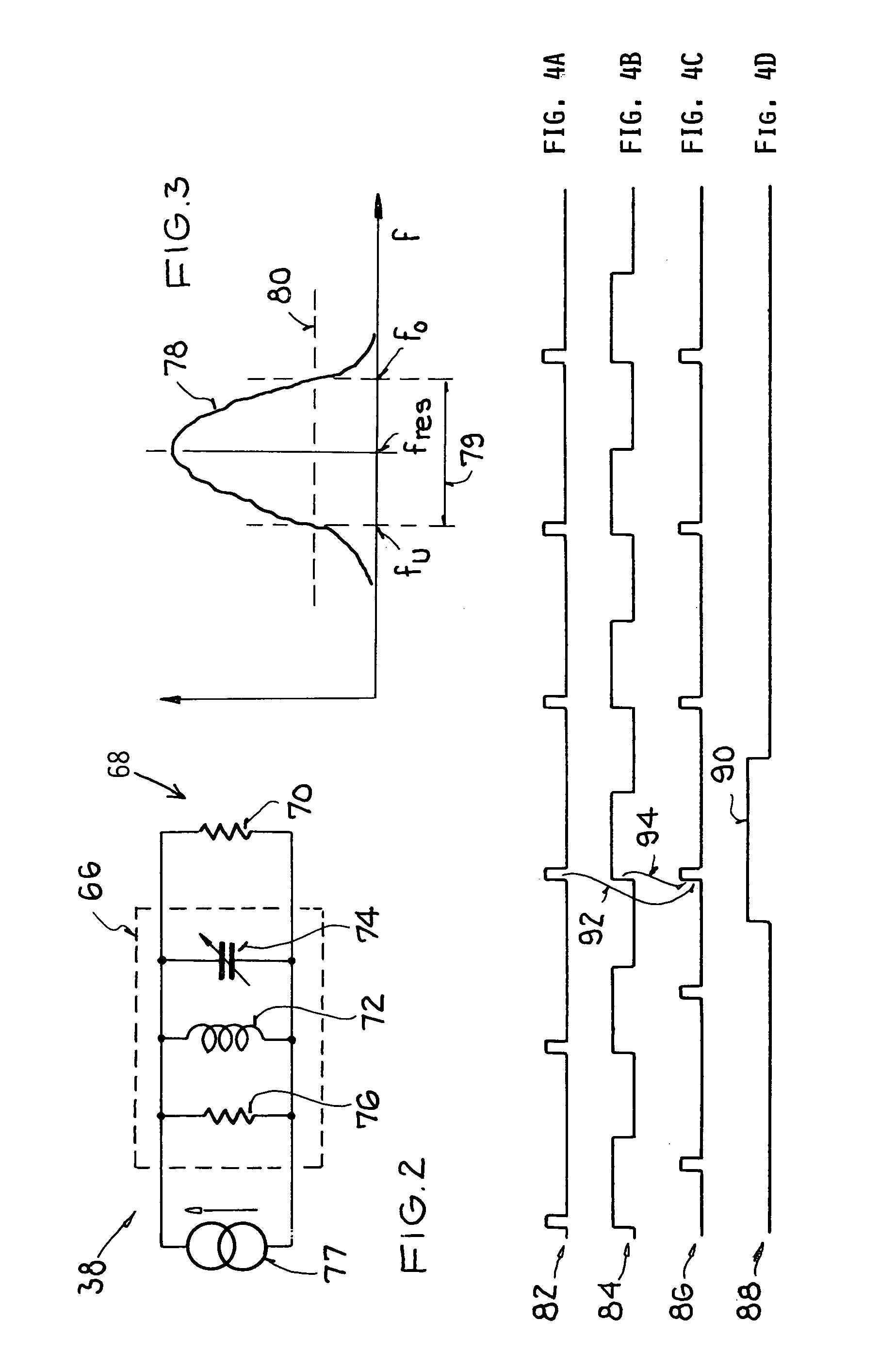
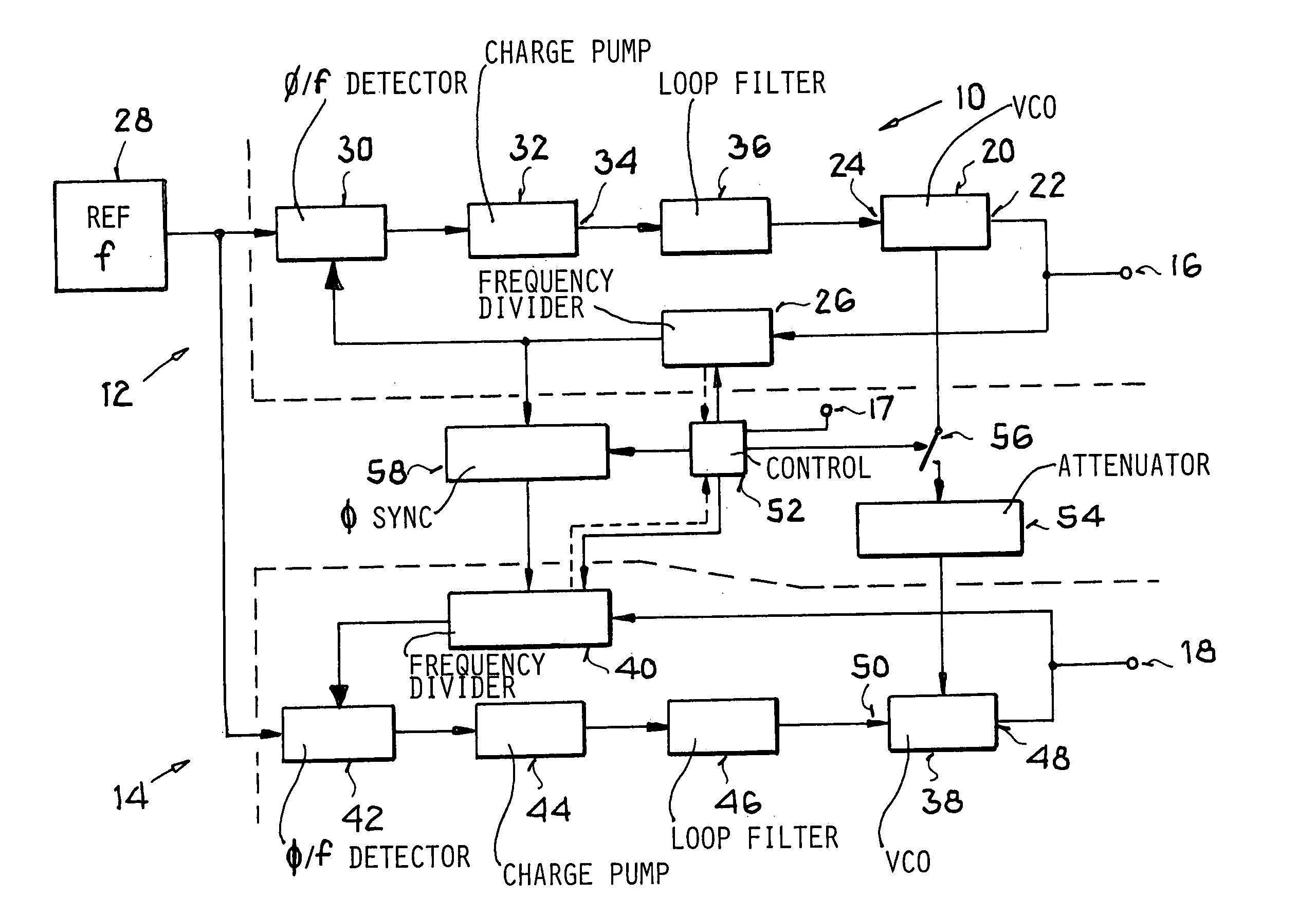
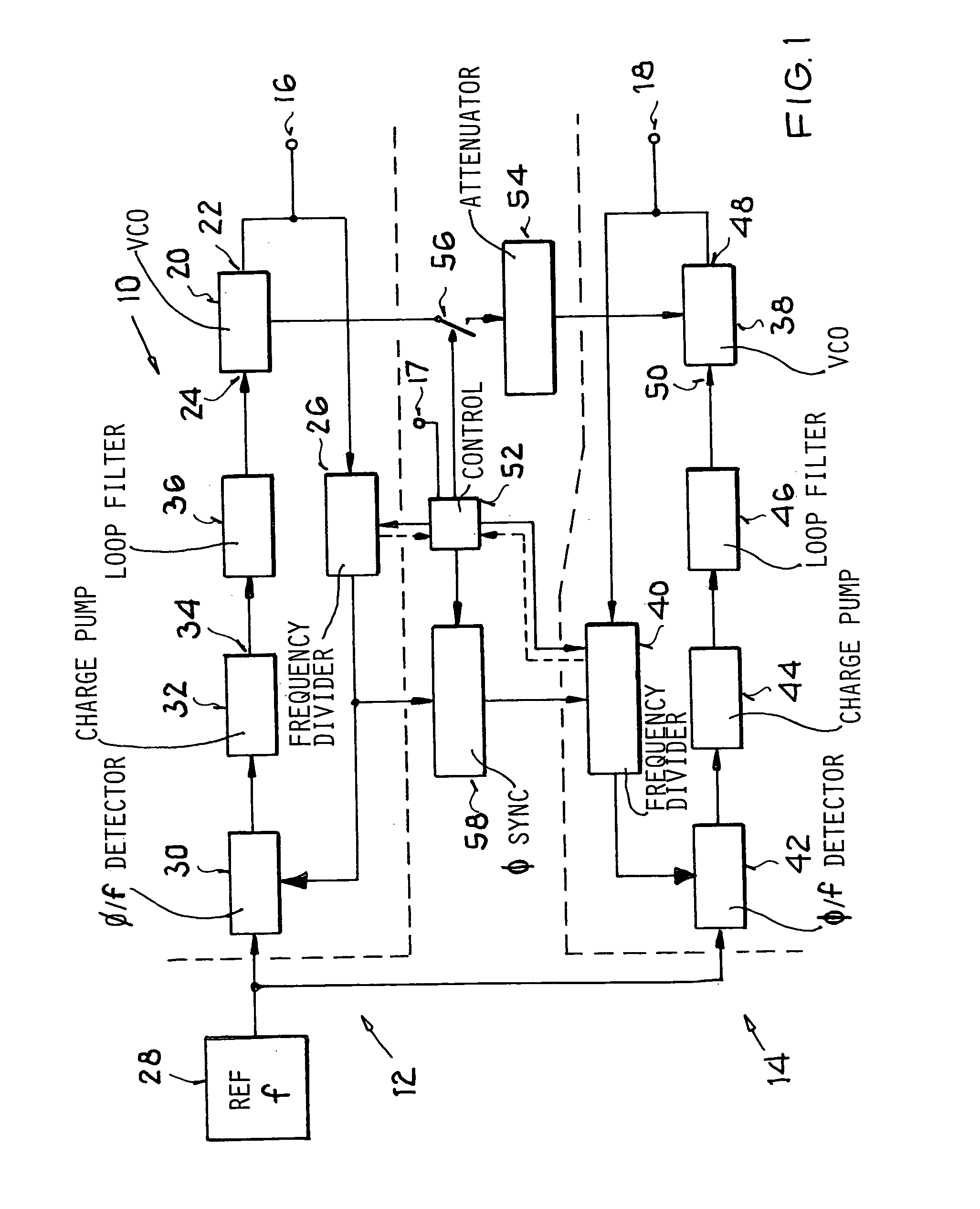
InactiveUS7109803B2Simple and economical technologySimple or uncomplicated filter tuning or balancingPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionOperation modeFrequency matching
A circuit arrangement includes a first phase locked loop to generate a first oscillator frequency, a second phase locked loop to generate a second oscillator frequency, a reference frequency emitter connected to a reference frequency input of both phase locked loops, and a signal attenuator and optionally a switch connected between a master signal output of the first (master) loop and an input of the second (slave) loop. In a method, a common reference frequency is provided to both loops, the first loop generates a first oscillator frequency, and the second loop generates a second oscillator frequency that matches the first oscillator frequency in at least one operating mode and optionally differs from the first oscillator frequency in another operating mode. The frequency matching in one of the modes involves feeding an attenuated signal from the first loop operating as a master into the second loop operating as a slave.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY
Method and circuit arrangement for synchronizing plural oscillators
InactiveUS20050104666A1Economical and simpleSimple and uncomplicated filter tuningPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionEngineeringFrequency matching
A circuit arrangement includes a first phase locked loop to generate a first oscillator frequency, a second phase locked loop to generate a second oscillator frequency, a reference frequency emitter connected to a reference frequency input of both phase locked loops, and a signal attenuator and optionally a switch connected between a master signal output of the first (master) loop and an input of the second (slave) loop. In a method, a common reference frequency is provided to both loops, the first loop generates a first oscillator frequency, and the second loop generates a second oscillator frequency that matches the first oscillator frequency in at least one operating mode and optionally differs from the first oscillator frequency in another operating mode. The frequency matching in one of the modes involves feeding an attenuated signal from the first loop operating as a master into the second loop operating as a slave.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY
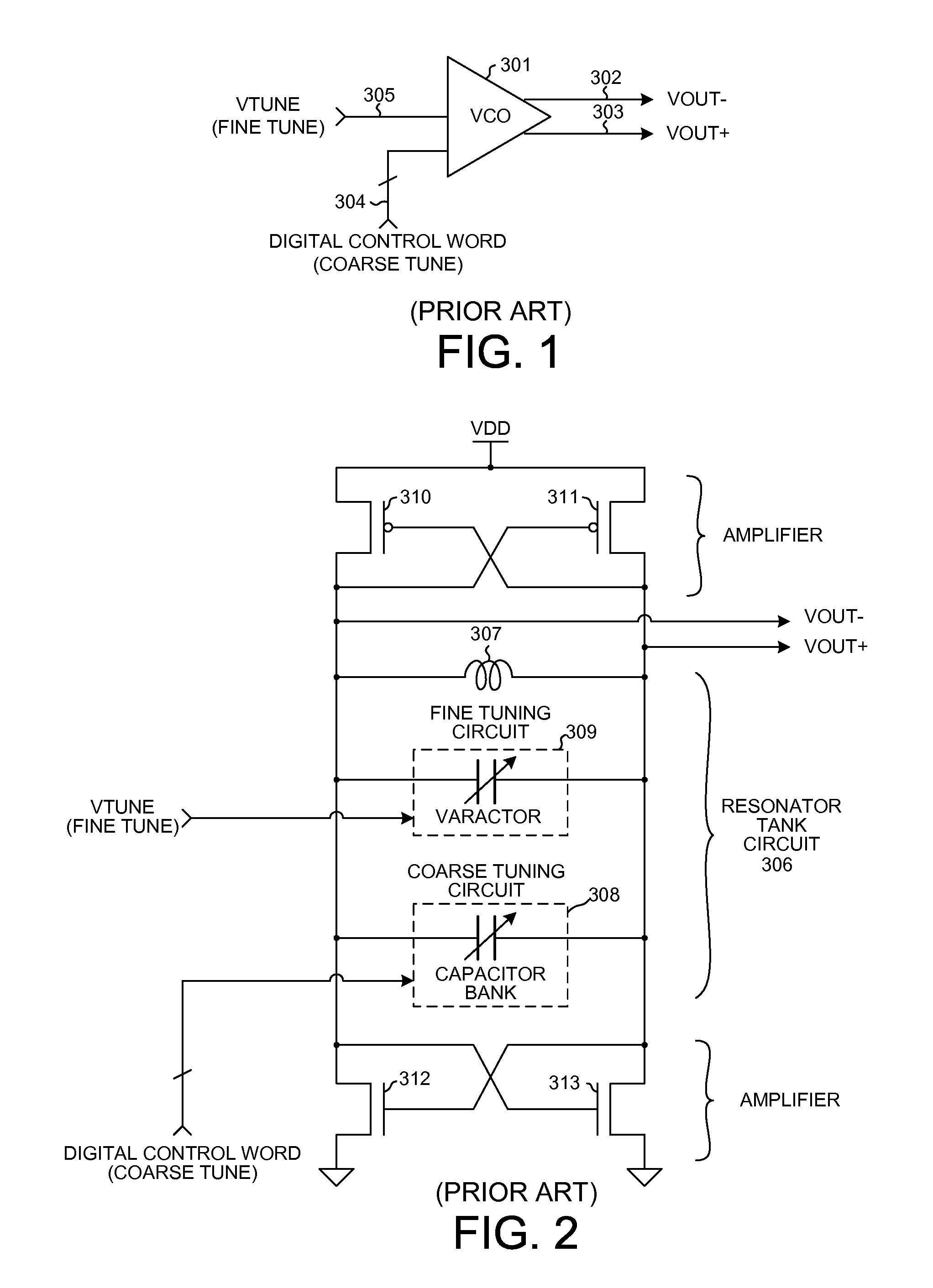
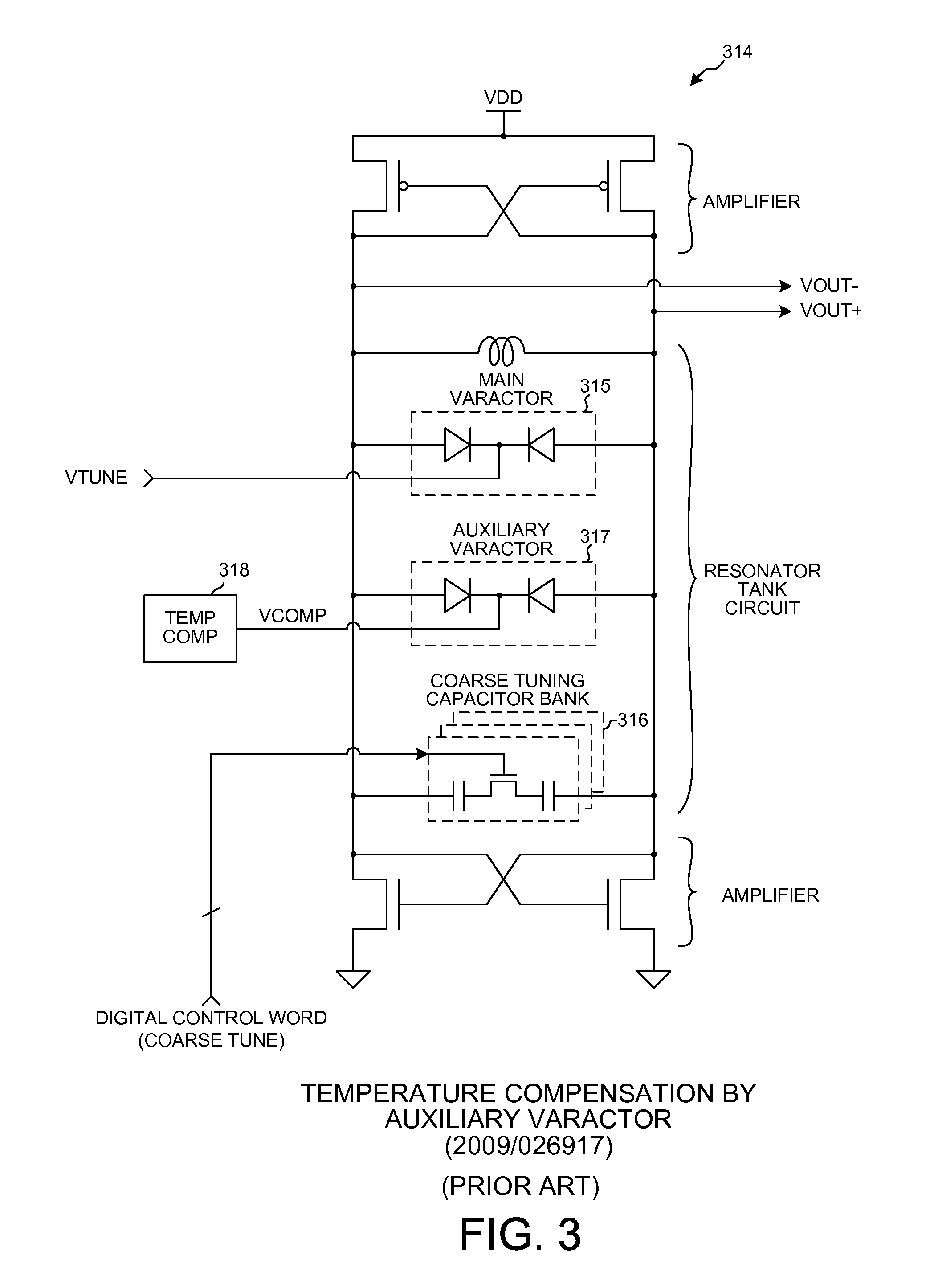
Wideband temperature compensated resonator and wideband vco
ActiveUS20120081188A1Facilitates increased tuning rangeLess parasitic capacitanceContinuous tuning detailsPulse automatic controlMultiplexingControl signal
A resonator of a VCO includes a fine tuning main varactor circuit, an auxiliary varactor circuit, and a coarse tuning capacitor bank circuit coupled in parallel with an inductance. The main varactor circuit includes a plurality of circuit portions that can be separately disabled. Within each circuit portion is a multiplexing circuit that supplies a selectable one of either a fine tuning control signal (FTAVCS) or a temperature compensation control signal (TCAVCS) onto a varactor control node within the circuit portion. If the circuit portion is enabled then the FTAVCS is supplied onto the control node so that the circuit portion is used for fine tuning. If the circuit portion is disabled then the TCAVCS is supplied onto the control node so that the circuit portion is used to combat VCO frequency drift as a function of temperature. How the voltage of the TCAVCS varies with temperature is digitally programmable.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
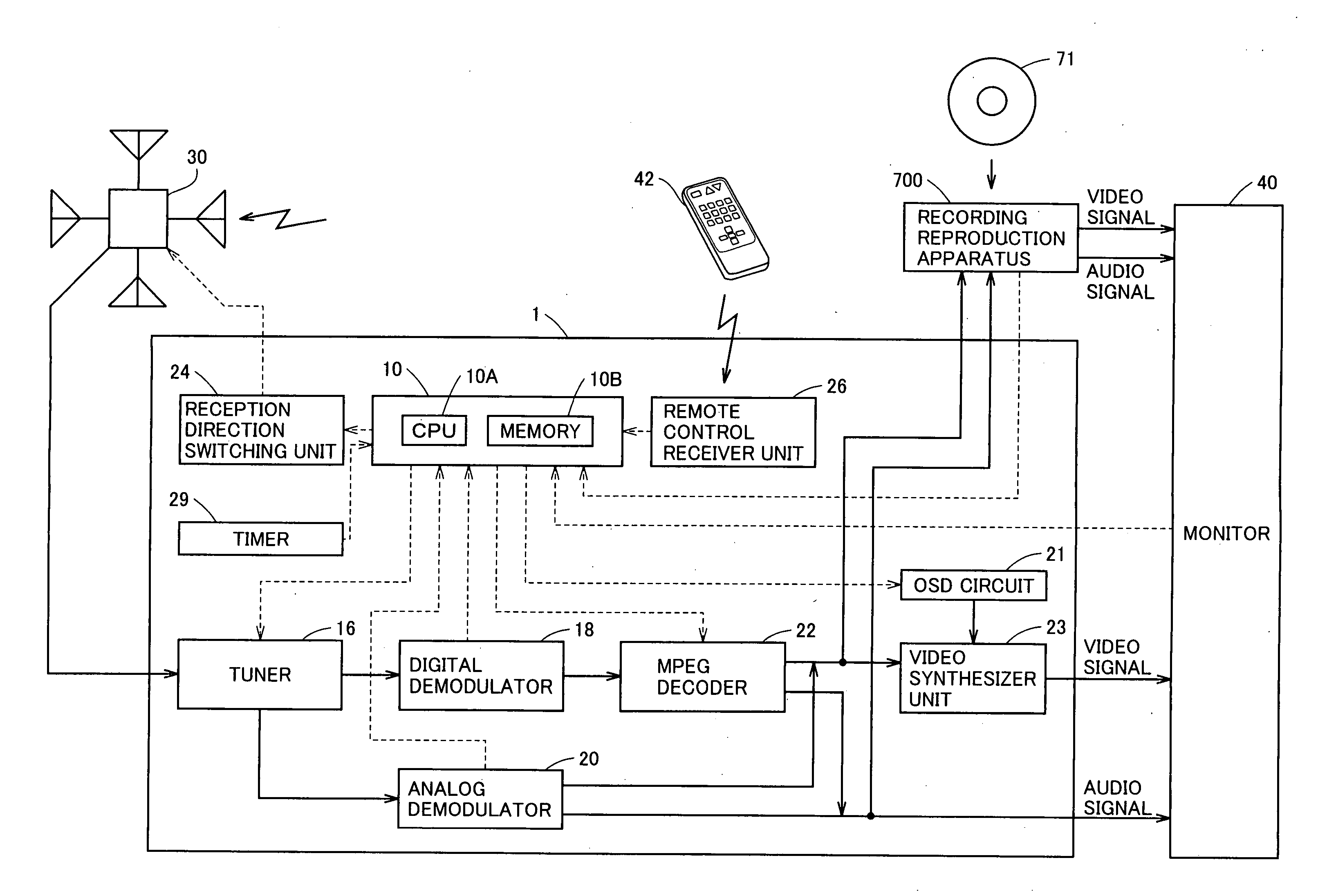
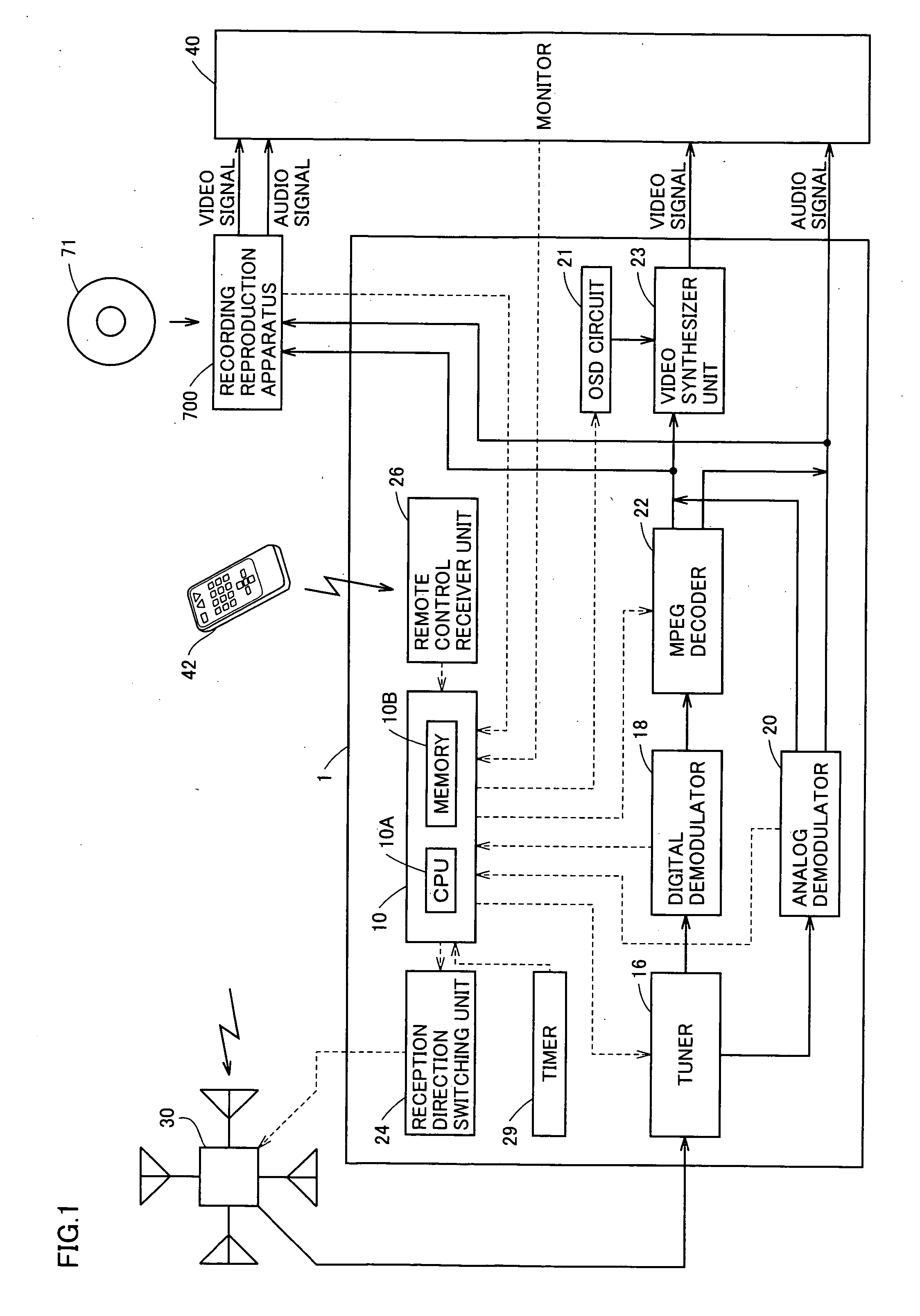
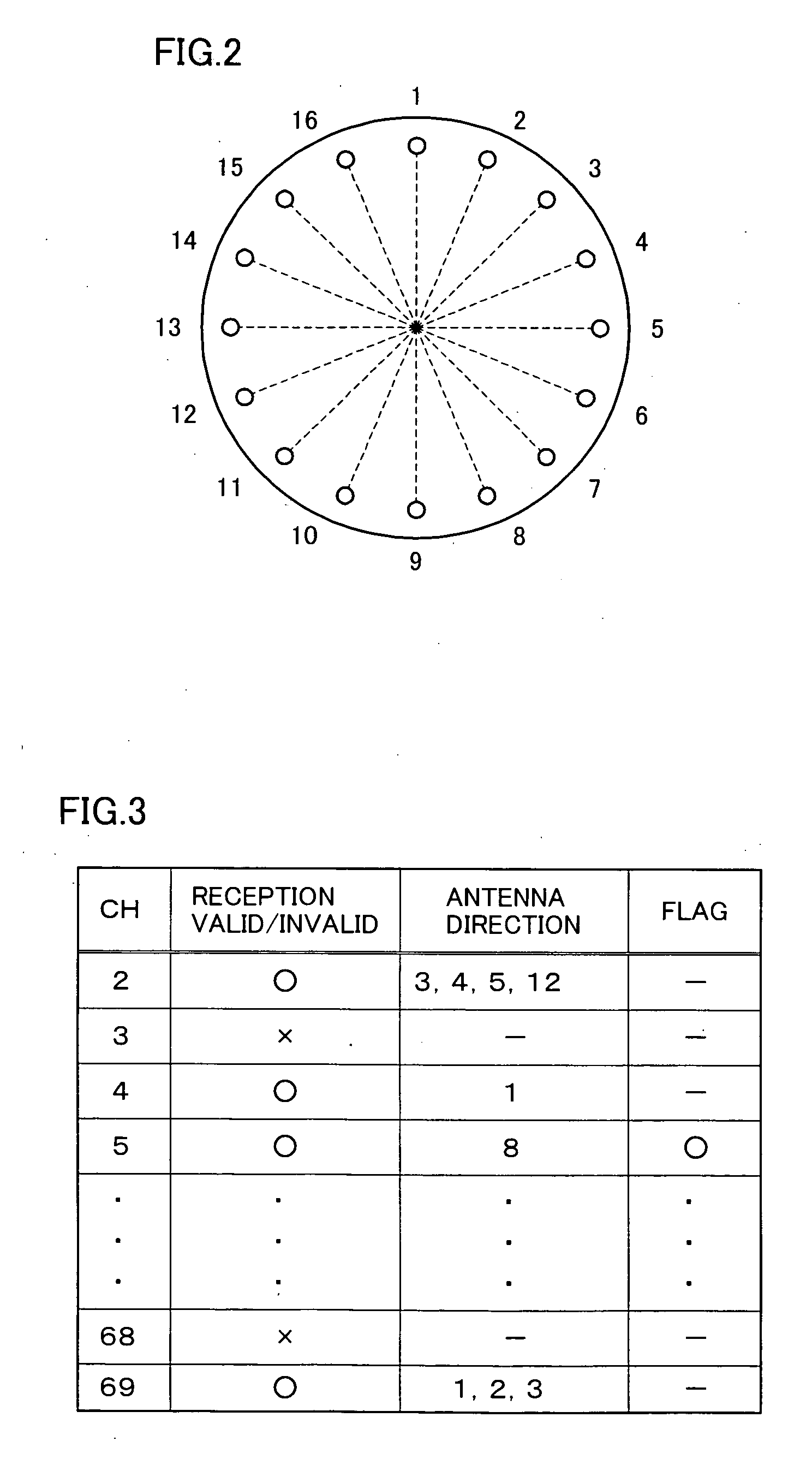
Broadcast receiver receiving broadcasts utilizing variable directional antenna
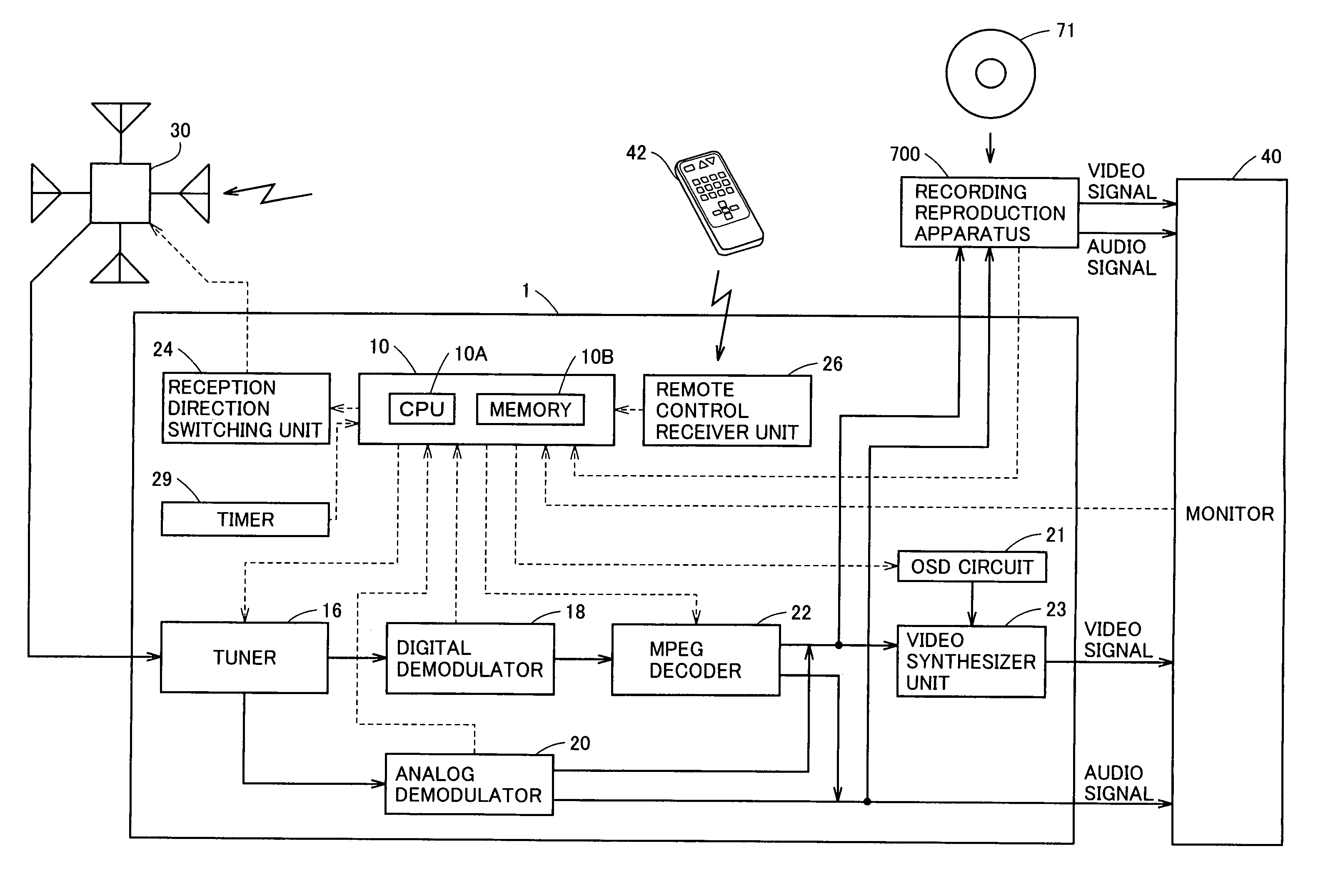
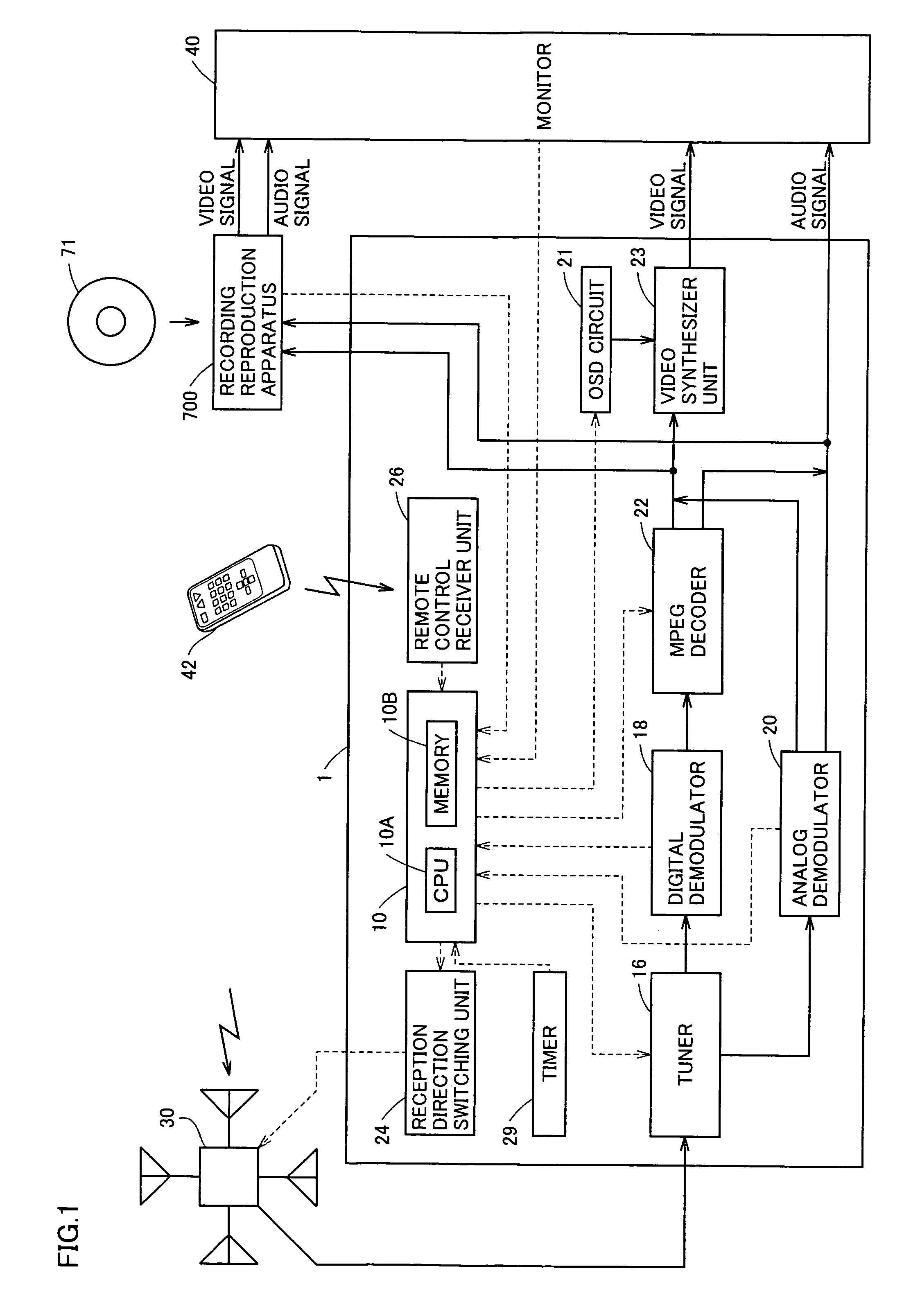
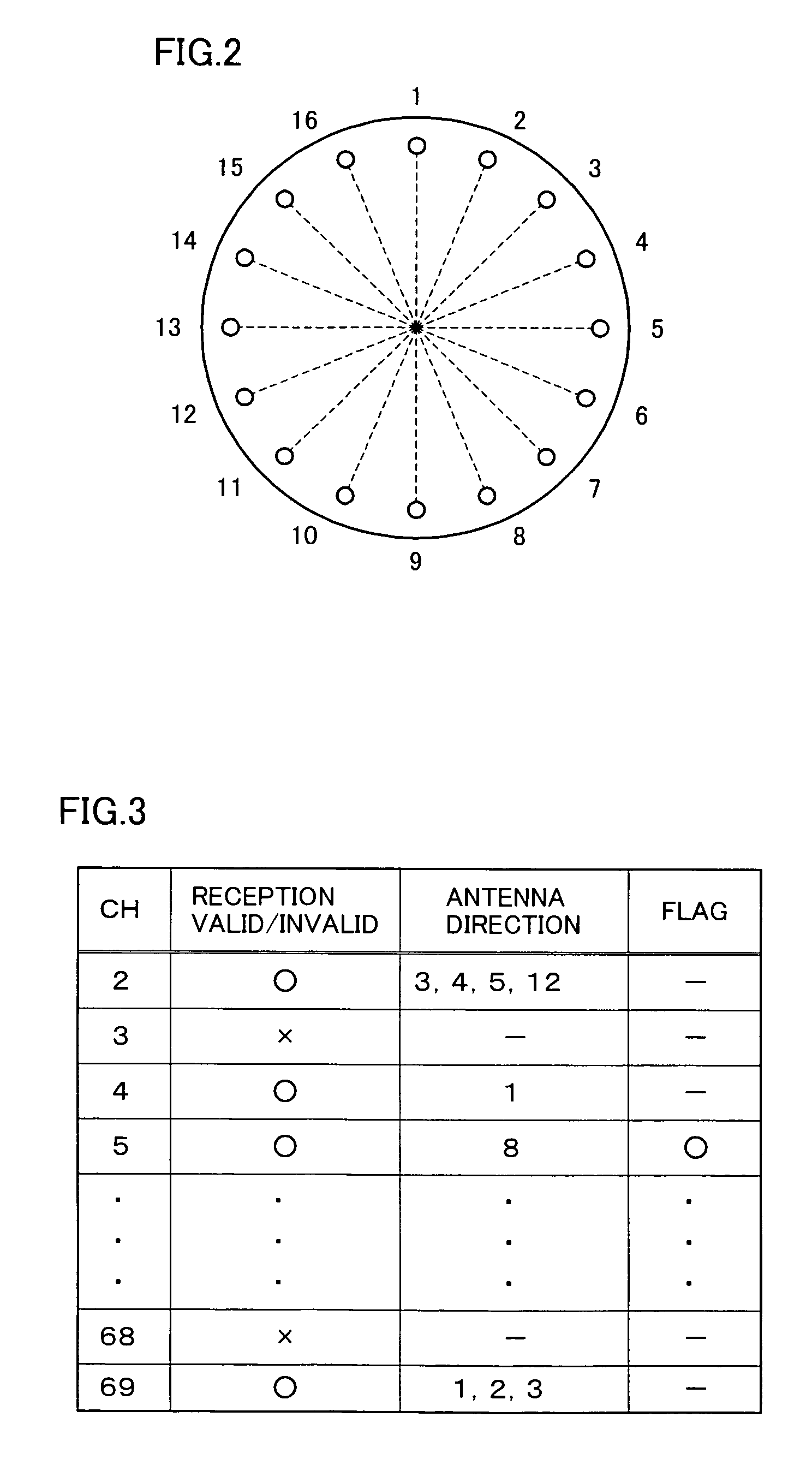
InactiveUS7502590B2Efficient conductionShort timeTelevision system detailsReceiver side switchingDirectional antennaBroadcasting
In a broadcast receiver, determination is made, as channel search, whether a broadcast wave is valid for reception for all reception directions by a variable directional antenna with respect to only the frequency having the information stored as being invalid for reception in a storage unit.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Bias signal generator in radio receiver
InactiveUS6278866B1Easy to controlLower requirementPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionDigital dataRadio receiver
A single chip superhetrodyne AM receiver is disclosed herein. To compensate for process variations in the implementation of the IC, bias currents setting the operating conditions for various amplifiers and other components in the system are adjusted based on frequency control signals in a PLL circuit in the local oscillator. Since the magnitude of the control signal reflects the process variations, the bias currents are adjusted based on the control signal to offset these variations in other portions of the receiver. To further improve the signal to noise ratio of the receiver, the IF filter is tuned within a range so as not to include any integer multiple or integer divisor of the timing reference frequency. Various techniques are described for enabling a complete superhetrodyne AM receiver to be implemented on a single chip which receives an antenna input signal and outputs a digital data signal.
Owner:MICREL
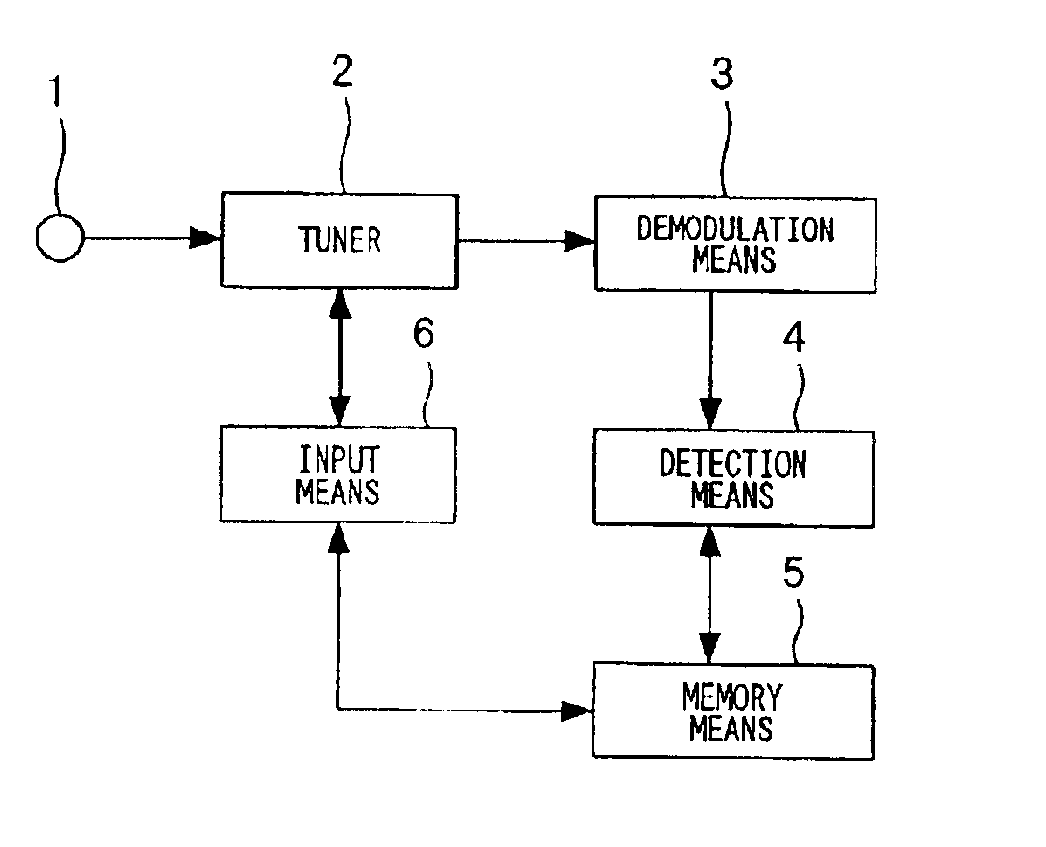
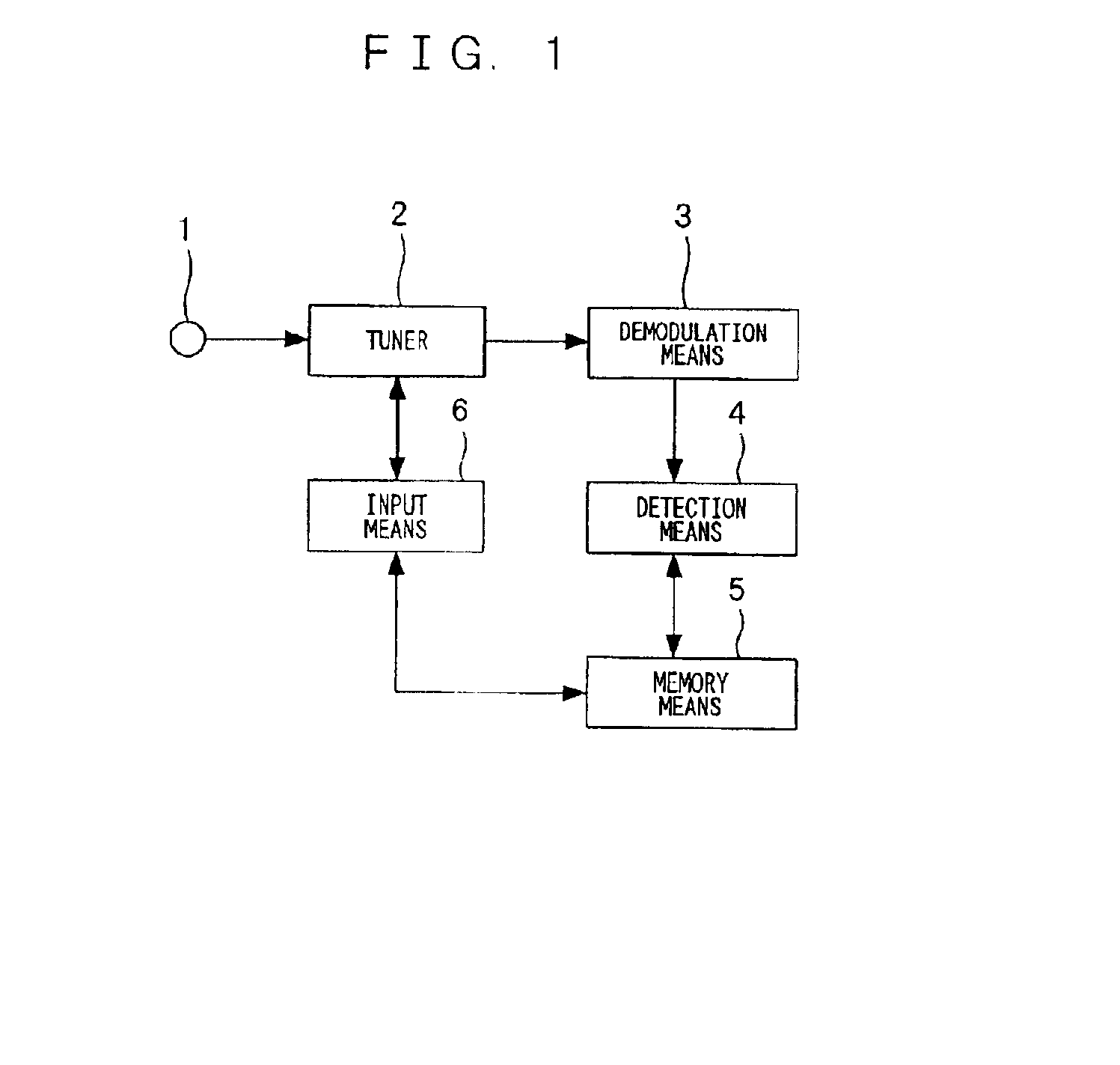
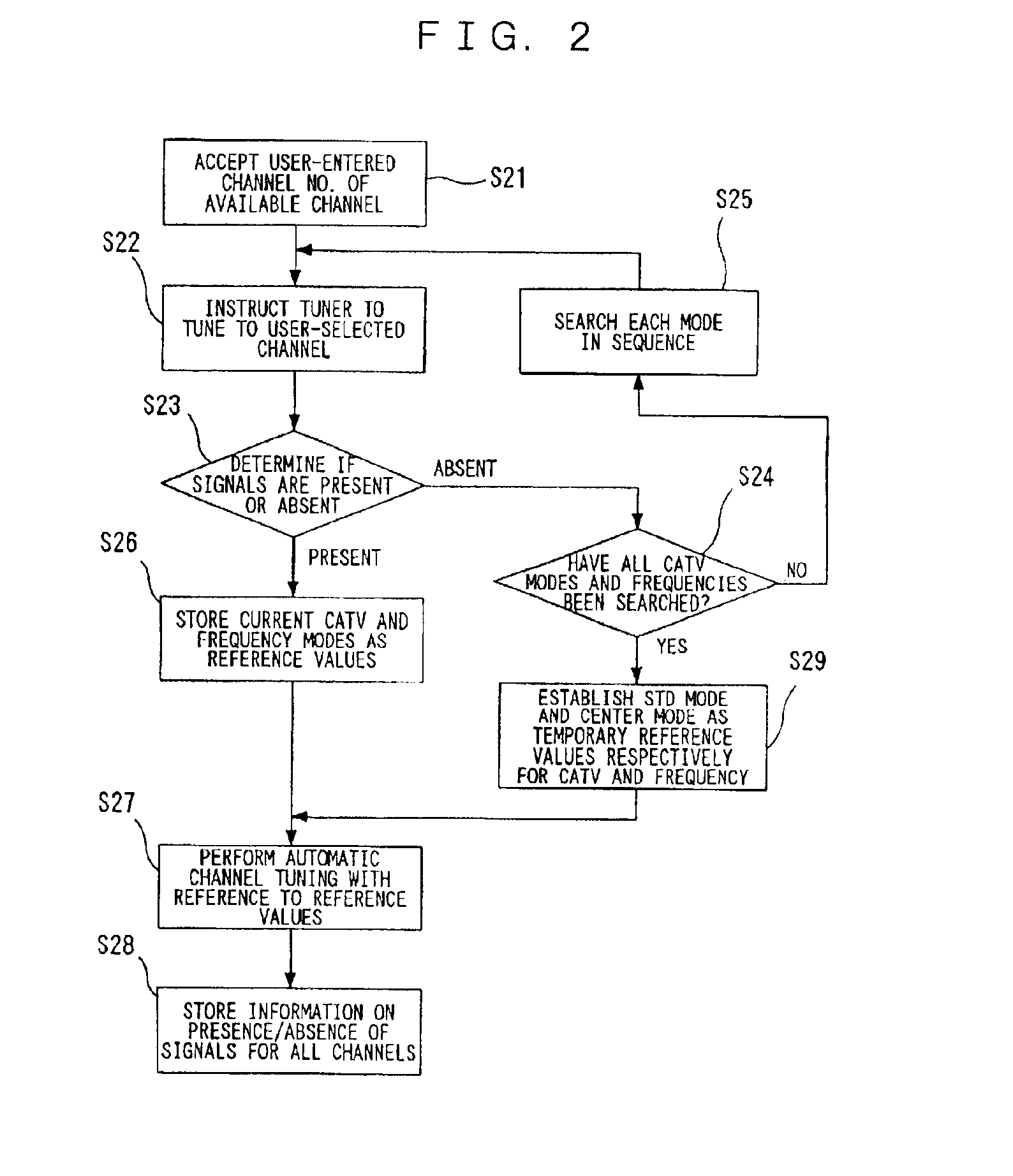
Channel tuning apparatus
InactiveUS6864926B2Easy to operateReliable channel tuningTelevision system detailsModulated-carrier systemsOperabilityDemodulation
A channel tuning apparatus which improves operability by eliminating a need for a user to select a CATV mode and allows reliable channel tuning without misjudging the presence or absence of signals even if a frequency of a CATV broadcast is shifted. The channel tuning apparatus includes a tuner (2) for receiving signals from an antenna (1), a demodulation unit (3) for demodulating the received signals coming from the tuner (2), an input unit (6) for selecting a specific channel for the tuner (2), a detection unit (4) for determining receive mode, and a memory unit (5) for storing the detected data by the detection unit (4), in which the channel tuning apparatus is configured to, before performing automatic channel tuning, tune to a specific channel determined by the input unit (6), detect the receive mode and shift in the received frequency, and store them for use as initial data for automatic channel tuning.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Broadcast receiver receiving broadcasts utilizing variable directional antenna
InactiveUS20060116094A1Efficient conductionShort timeTelevision system detailsReceiver side switchingDirectional antennaBroadcasting
In a broadcast receiver, determination is made, as channel search, whether a broadcast wave is valid for reception for all reception directions by a variable directional antenna with respect to only the frequency having the information stored as being invalid for reception in a storage unit.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus and method for tuning a broadcast channel
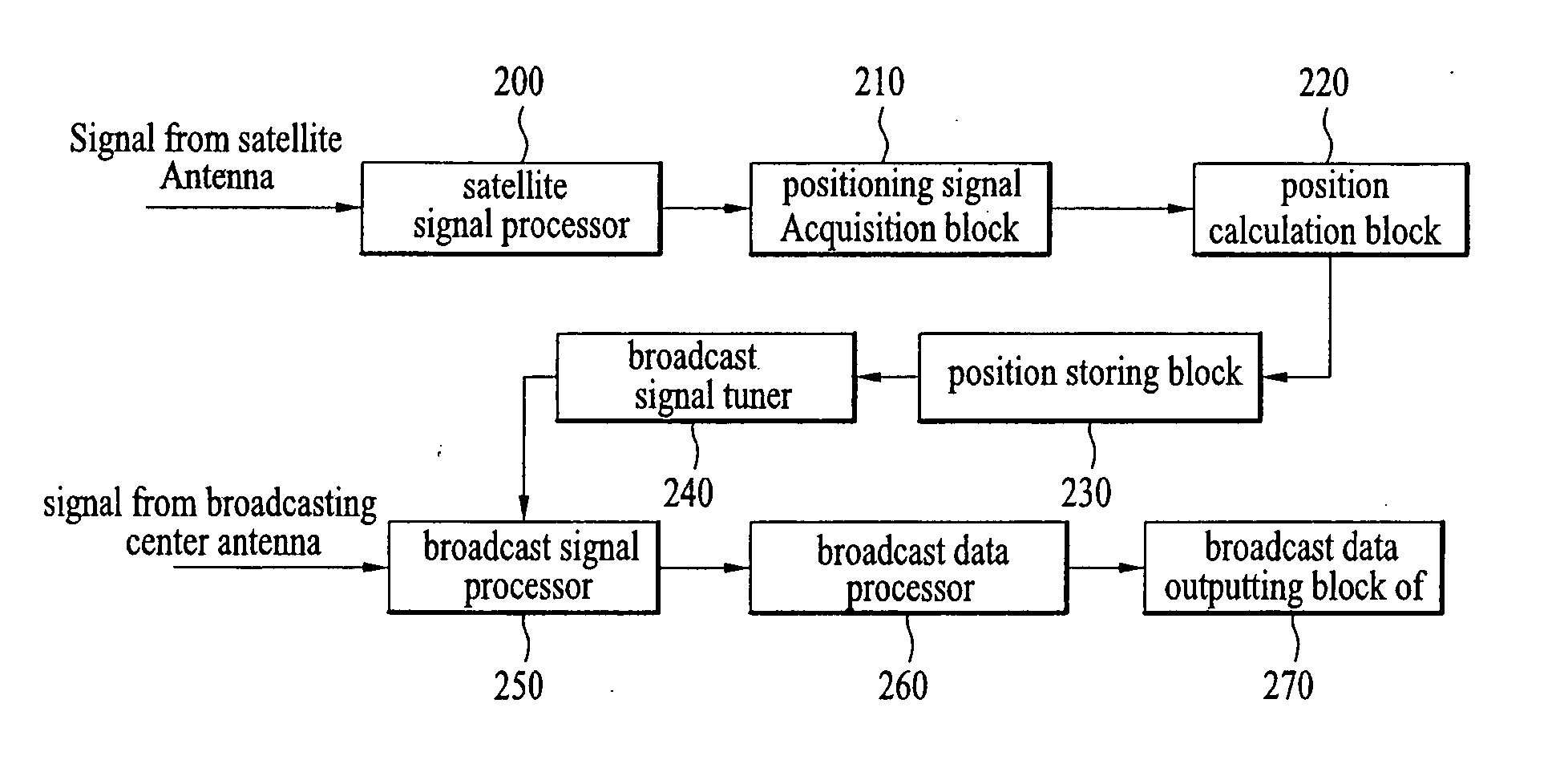
InactiveUS20060099962A1Television system detailsAssess restrictionBroadcast channelsGlobal Positioning System
An apparatus for tuning a broadcast channel and method thereof are disclosed, by which a broadcast channel is tuned using a global positioning system (GPS) in a mobile multimedia broadcast receiving terminal, and by which a first broadcast channel is changed to a second broadcast channel responsive to the terminal position. In tuning one of a plurality of broadcast channels belonging to a broadcasting station, the present invention includes an acquisition block acquiring position information, a calculation block calculating a position of a terminal using the position information, and a tuner for changing the broadcast channel responsive terminal position.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System, circuit and method for tuning a resonant circuit
ActiveUS7190153B2ElectrotherapyDiscontinuous tuning with variable tuning elementControl selectionEngineering
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Digital broadcasting receiver and channel information registration processing method in digital broadcasting receiver
InactiveUS7221412B2Shorten the time periodTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsTelecommunicationsSignal on
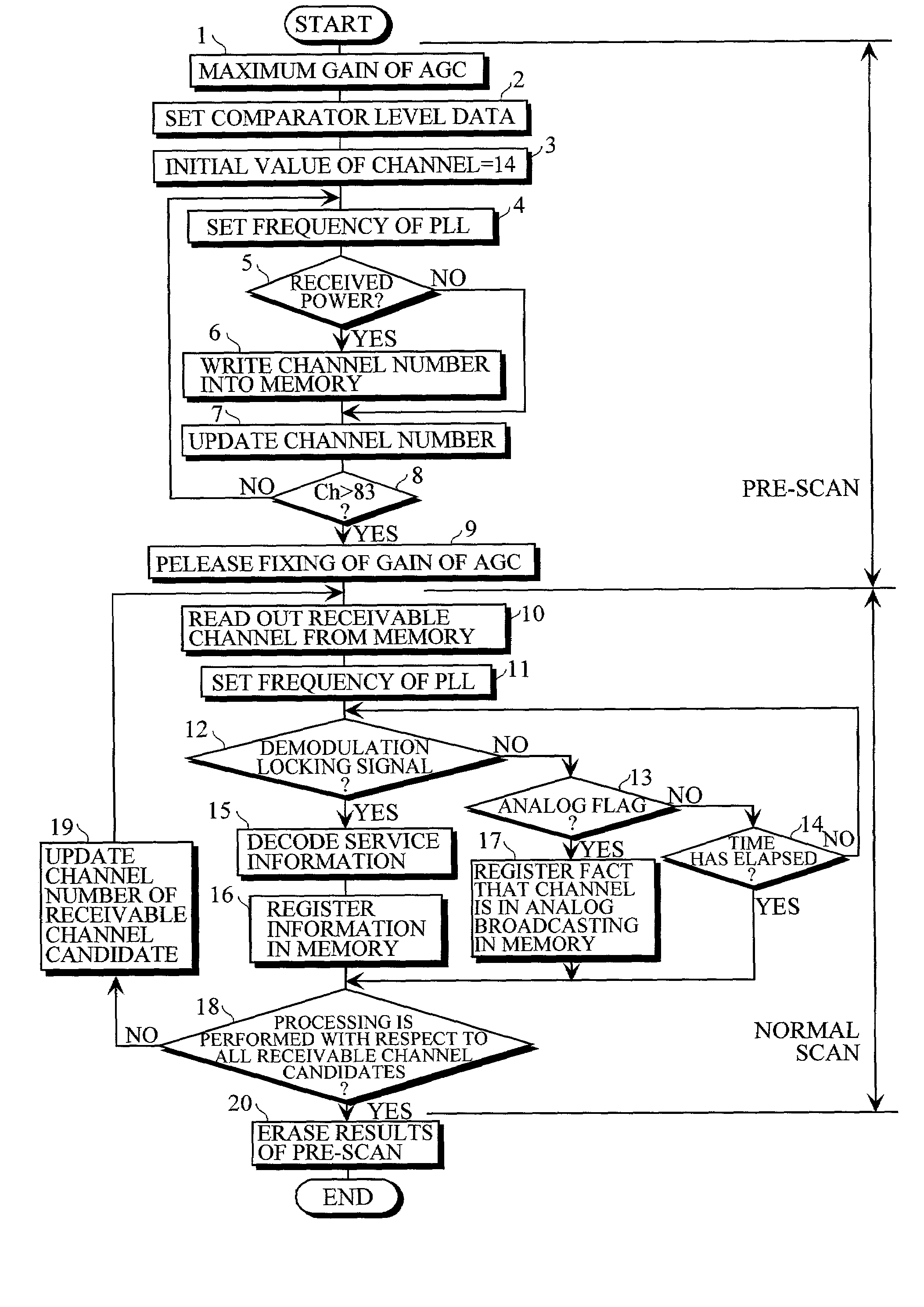
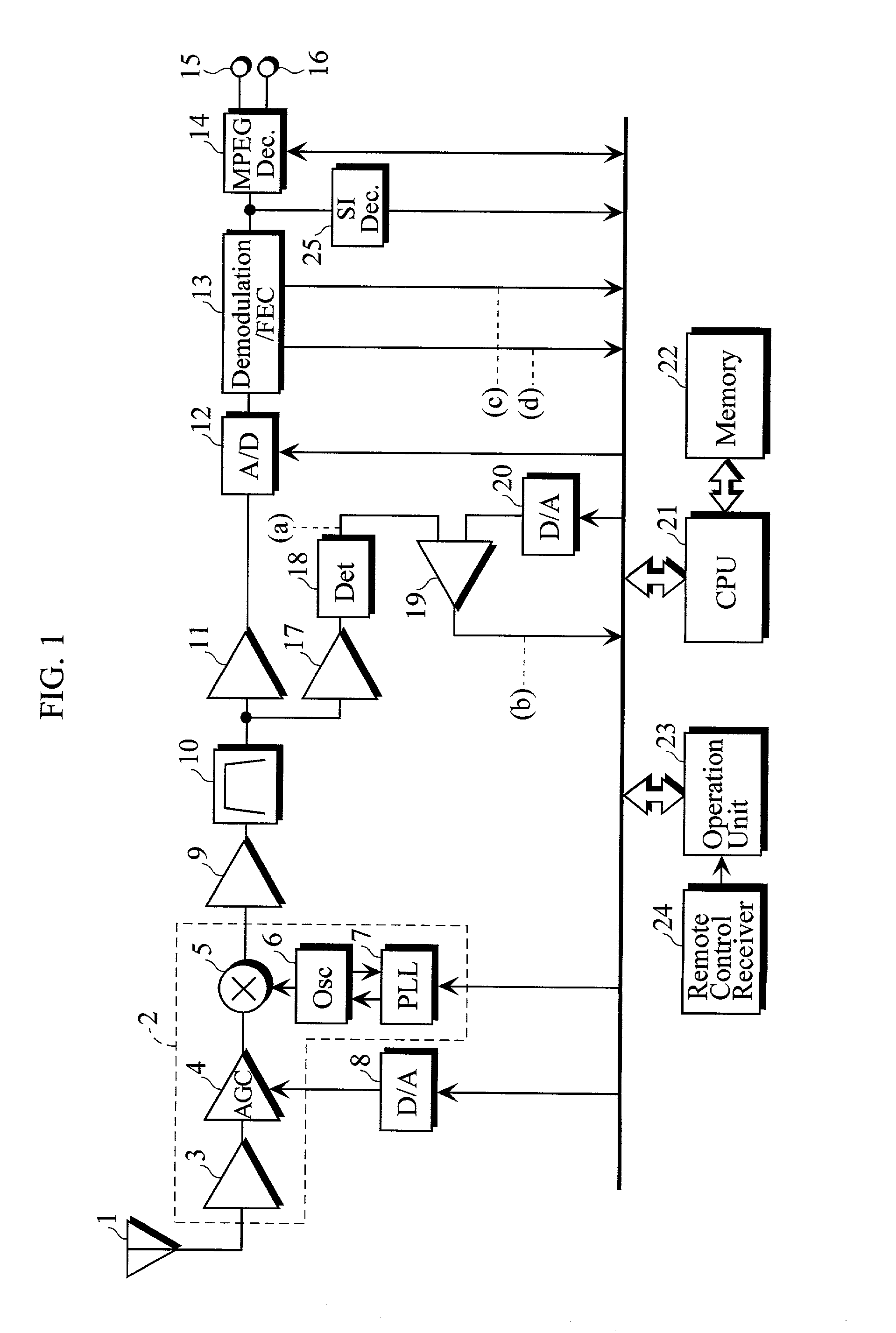
Disclosed in a digital broadcasting receiver comprising first means for performing pre-scan processing for successively tuning in on channels previously set, to examine whether or not a received signal on each of the channels is of a predetermined quality or more, and temporarily registering the channel numbers of the channels on which the received signals are of the predetermined quality or more in a storage device as receivable channel candidates, and second means for performing normal scan processing for successively tuning in on the receivable channel candidates temporarily registered in the storage device by the first means, to acquire and register necessary channel information.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
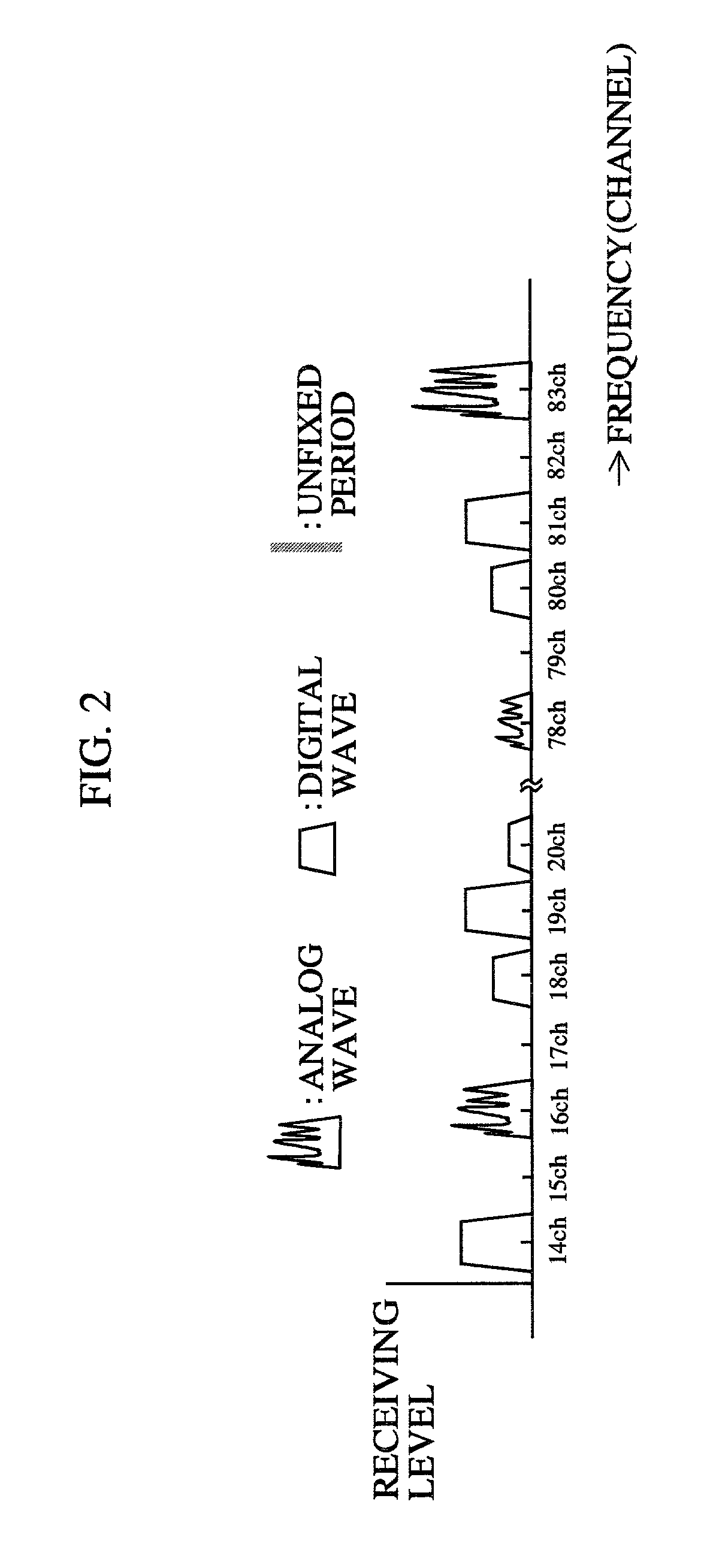
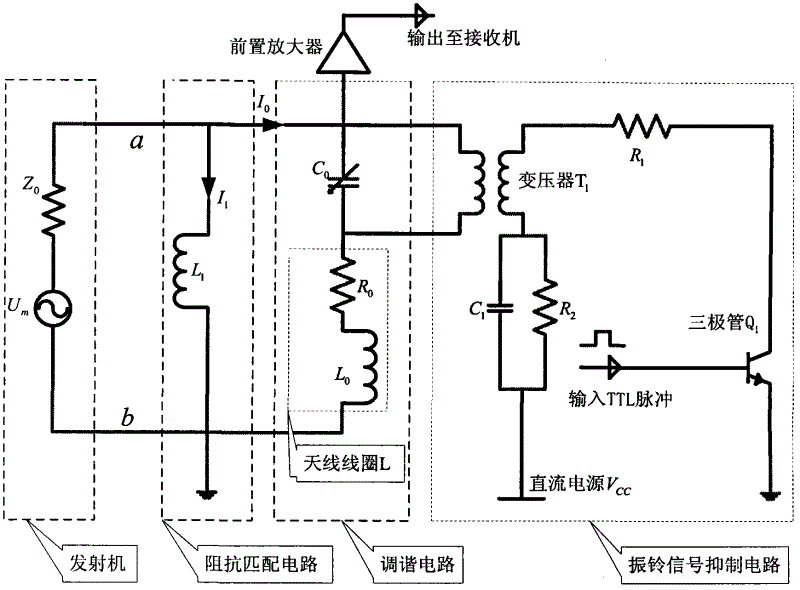
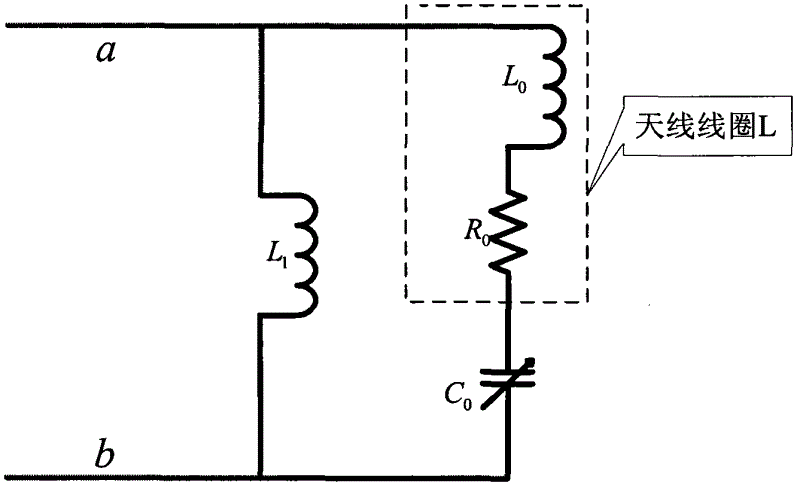
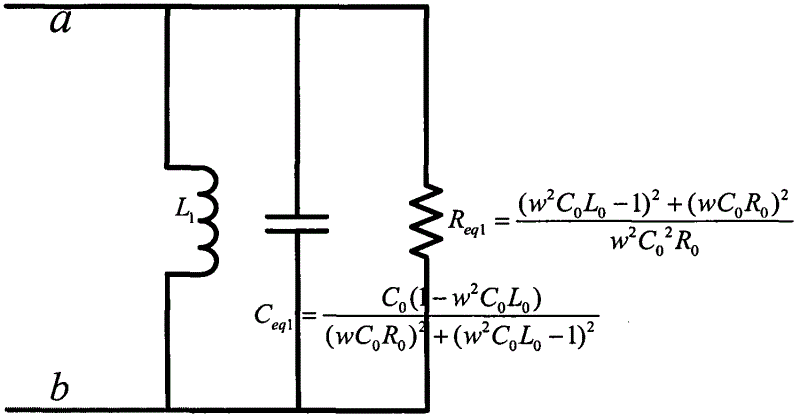
Low frequency tuning antenna applicable to explosive detection
InactiveCN102624411AMultiple-port networksAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceStopped workResonance
The invention discloses a low frequency tuning antenna applicable to explosive detection, which comprises a high Q-value tuning circuit, an impedance matching circuit and a ringing signal suppression circuit. The high Q-value tuning circuit receives radio frequency pulse containing characteristic frequency of a sample to be tested and output from a high-power transmitter. The impedance matching circuit is used for turning complex impedance of the high Q-value tuning circuit into 50 ohm, and a phase is 0. The ringing signal suppression circuit has effects that when the transmitter works, Q value of the circuit is high, and the antenna ringing signal suppression circuit does not work; and when the transmitter stops working, the Q value of the circuit is low, and residual energy stored in an antenna coil is consumed as soon as possible through the antenna ringing signal suppression circuit. Therefore, time from closing the transmitter to opening a receiver is shortened, the Q value of the circuit is high during a nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) signal receiving period, and detecting sensitivity on weak NQR signals is improved, namely a process that the Q value of a resonance circuit becomes smaller then bigger in a detection process is required.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Popular searches
Navigational calculation instruments Position fixation Color television details Broadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognition Broadcast characteristics identification/recognition Broadcast receiving circuits Selective content distribution Transmission Electric signal transmission systems Semiconductor/solid-state device details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com