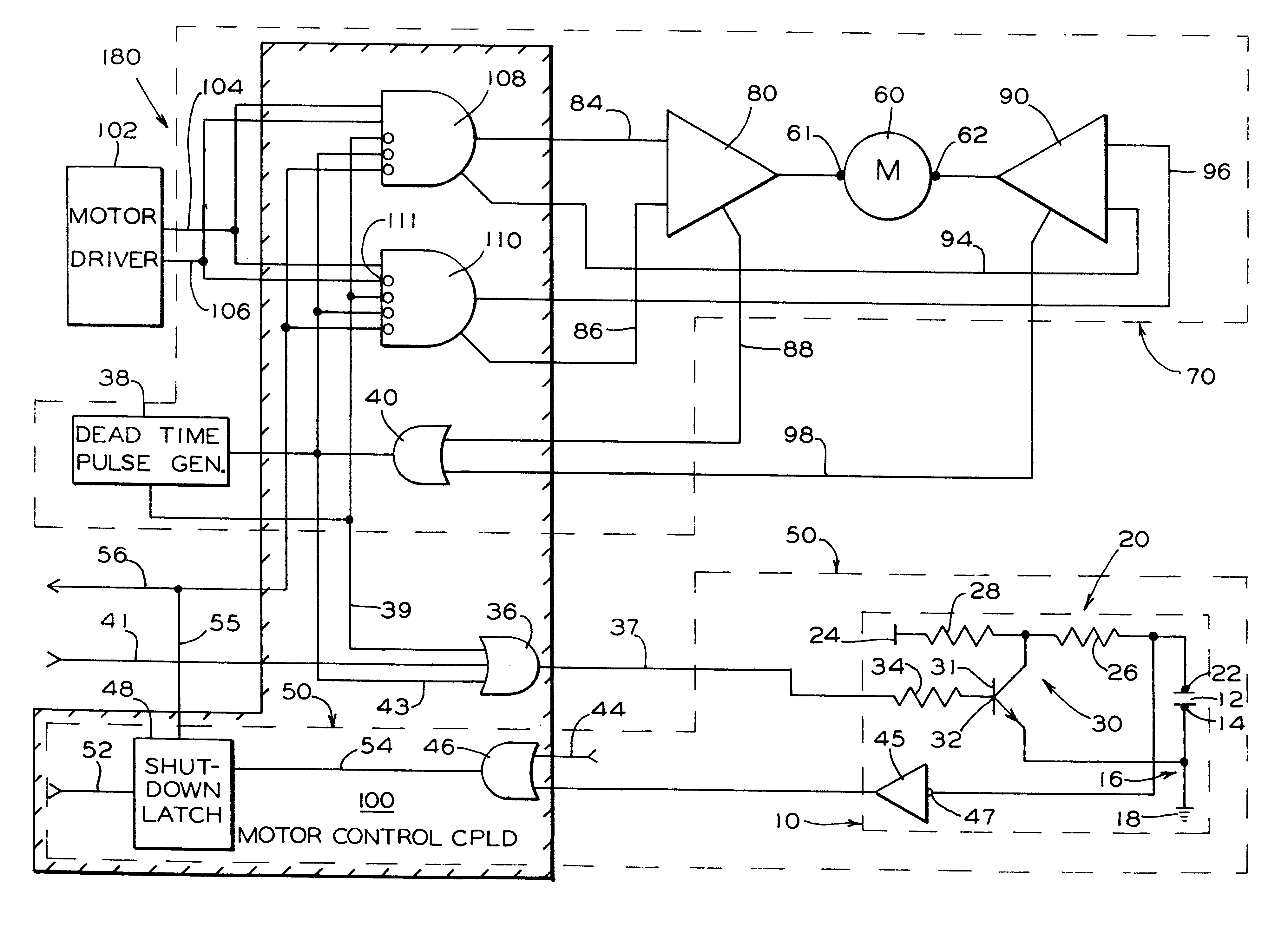
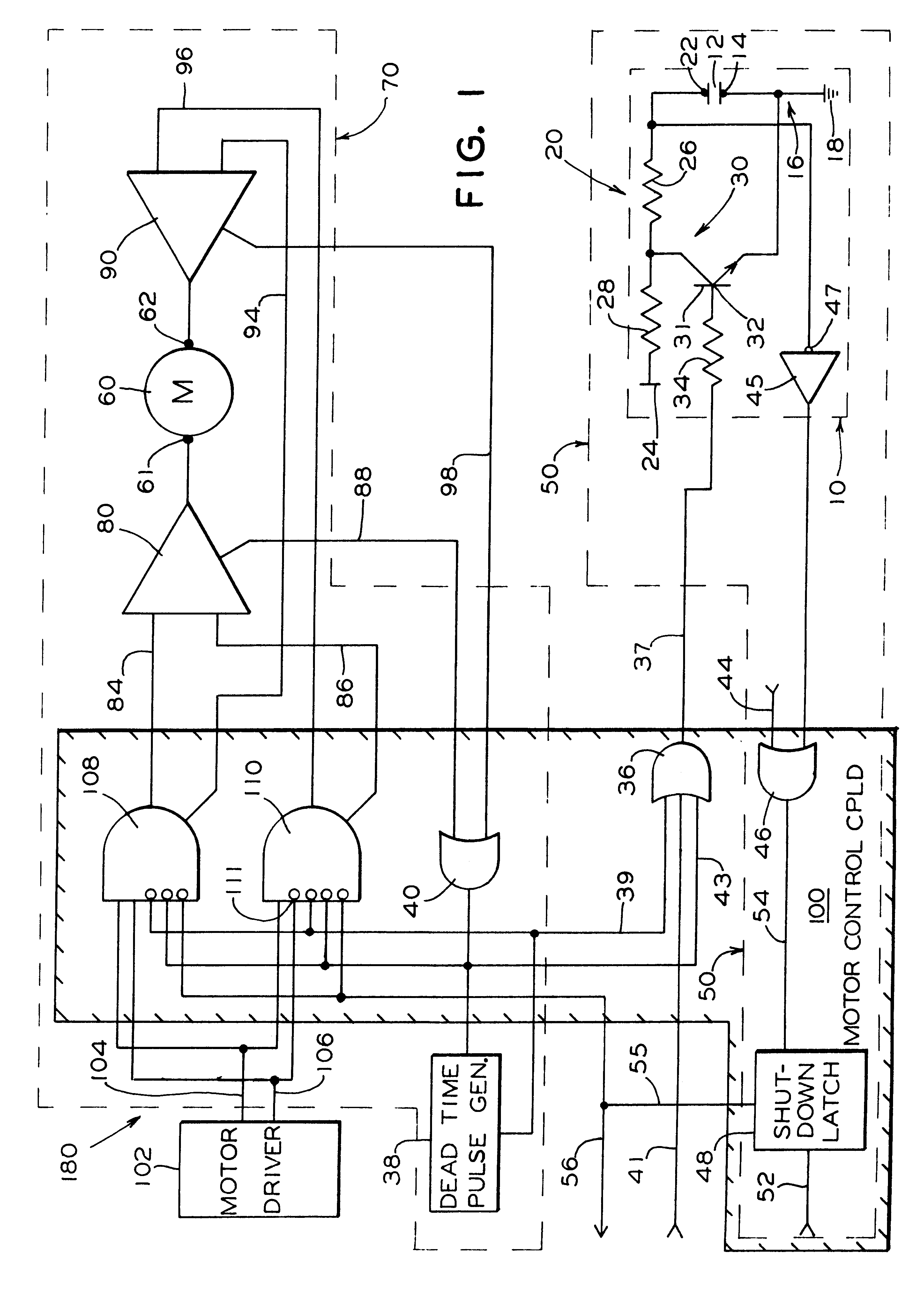
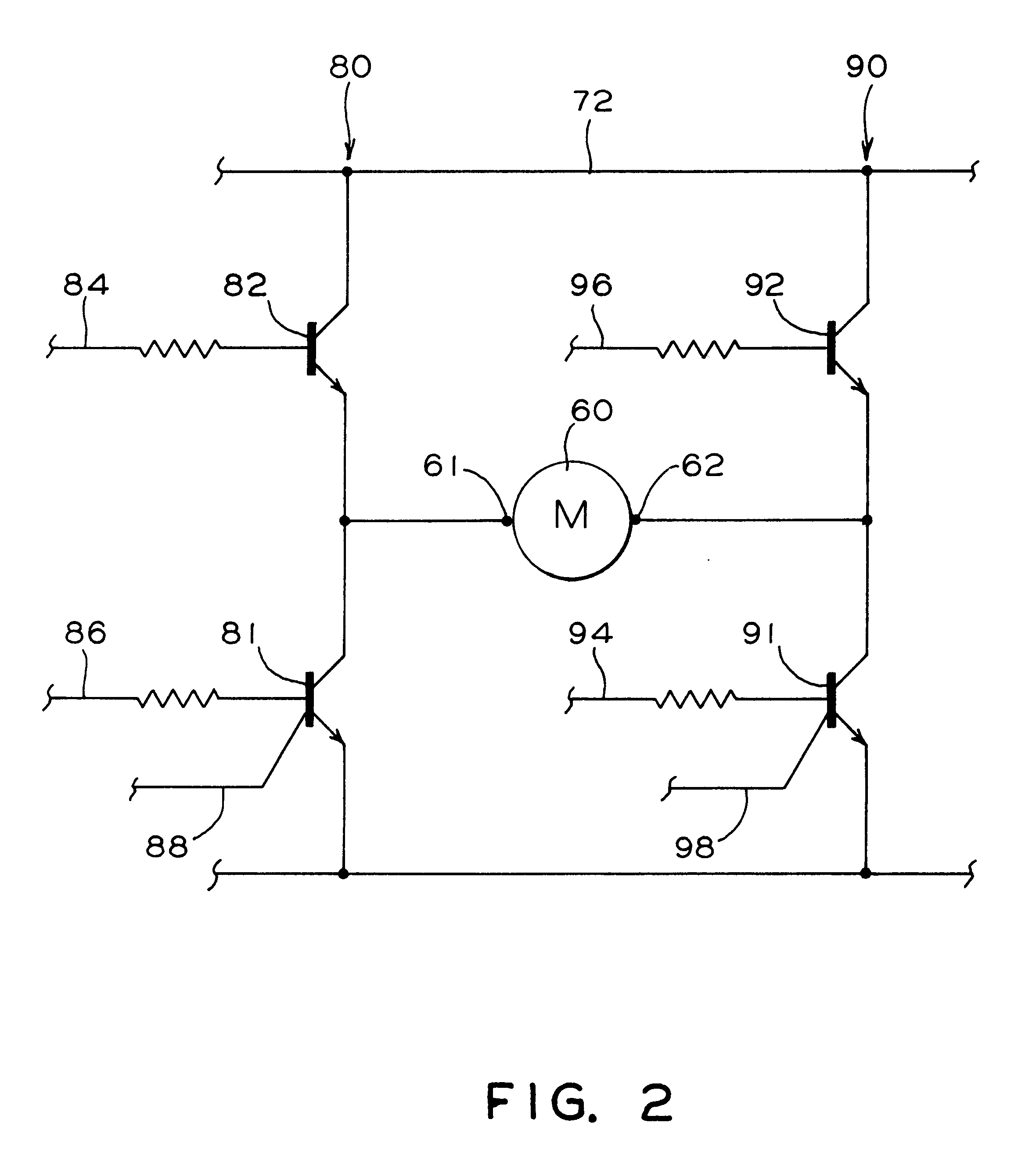
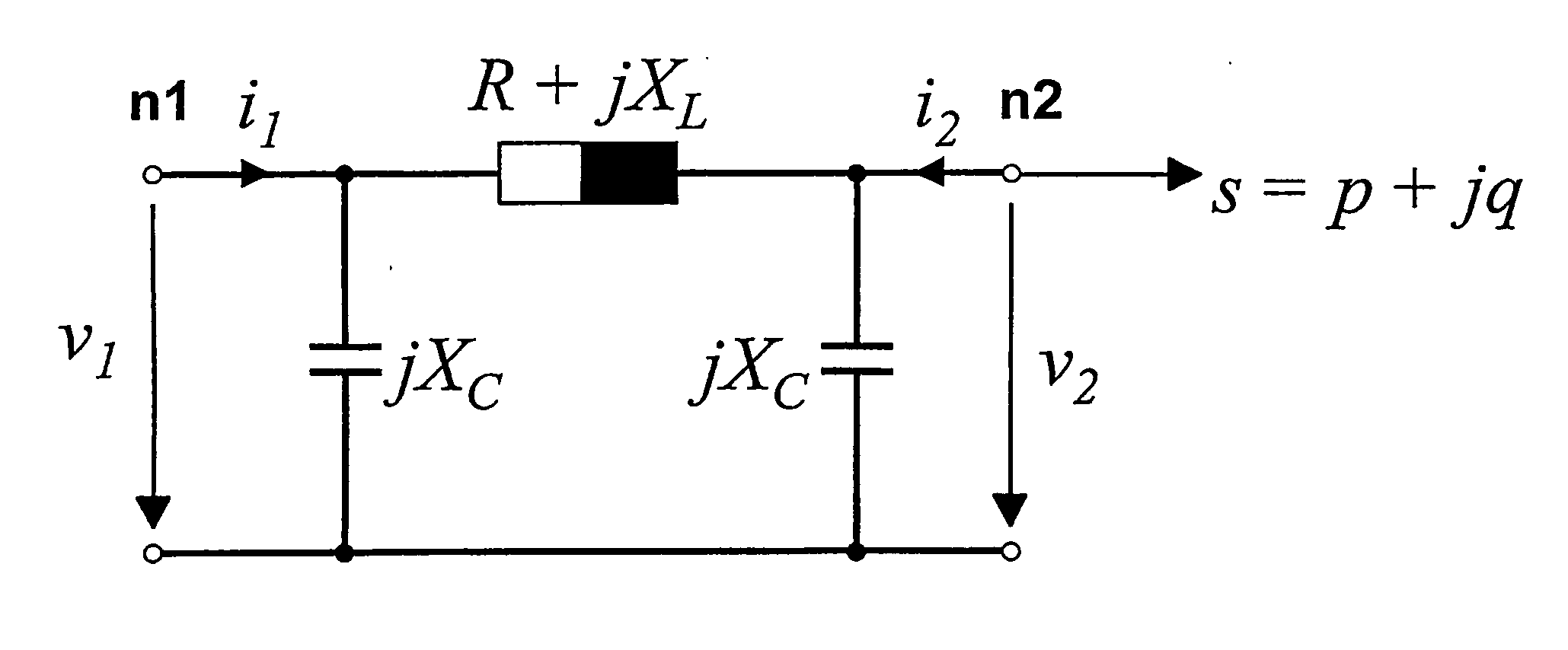
Patents
Literature
237results about "Emergency protective arrangements responsive to undesired changes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
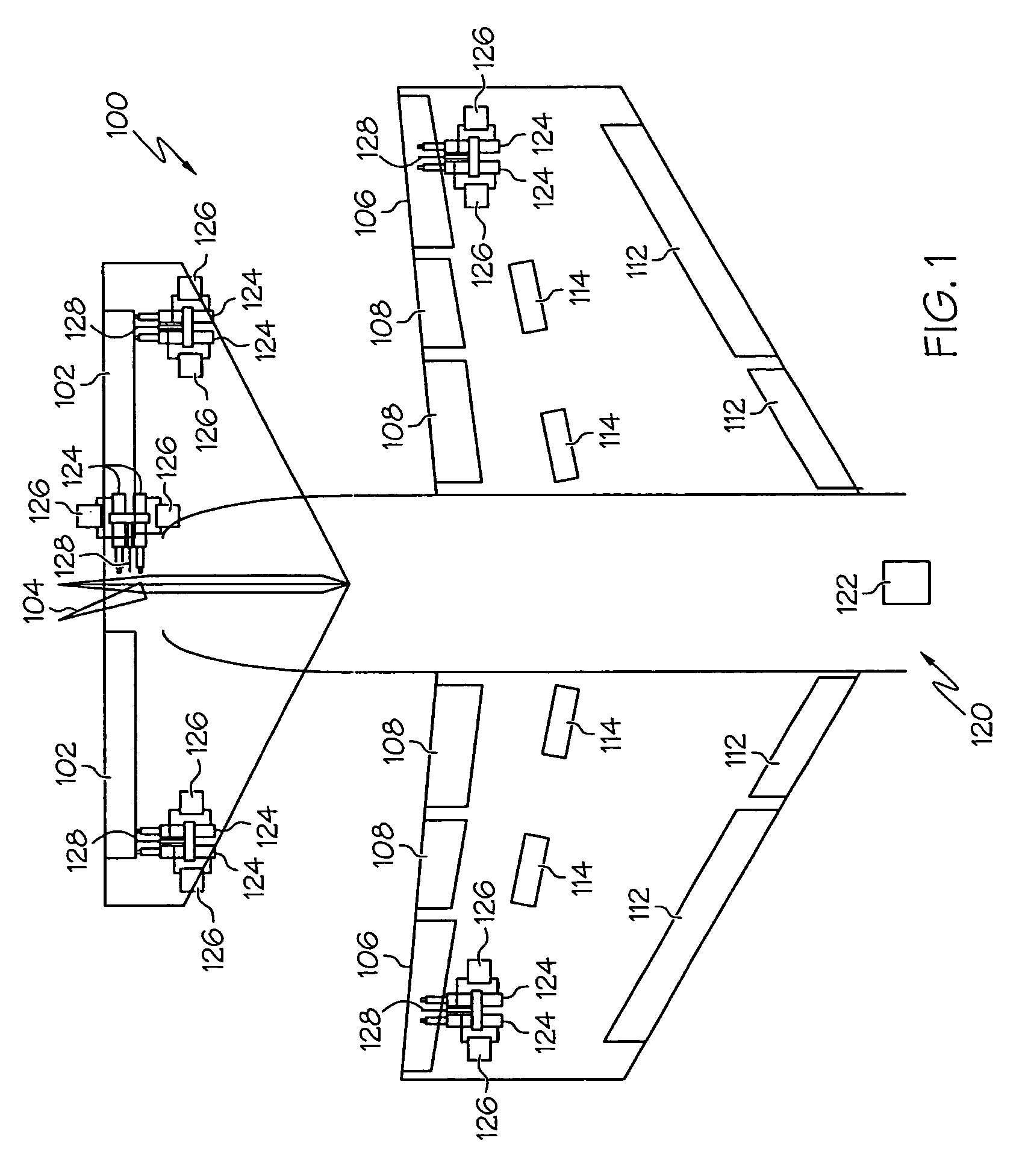
Overcurrent protection device with visual indicators for trip and programming functions
InactiveUS6055145AImprove coordinationHigh selectivityParameter calibration/settingCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsGreen ledFunctional correlation
A microprocessor based overcurrent trip unit which generates trip signals as an adjustable function of current and time, has a visual representation of the trip function on a front panel with 2-color LEDs associated with the trip function serving as indicators of trip conditions when red, and of a selected programmable parameter when green. The green LEDs flash to indicate parameter selected for modification in a program mode and illuminate steady in a view mode.
Owner:EATON CORP
Protection device for load circuits
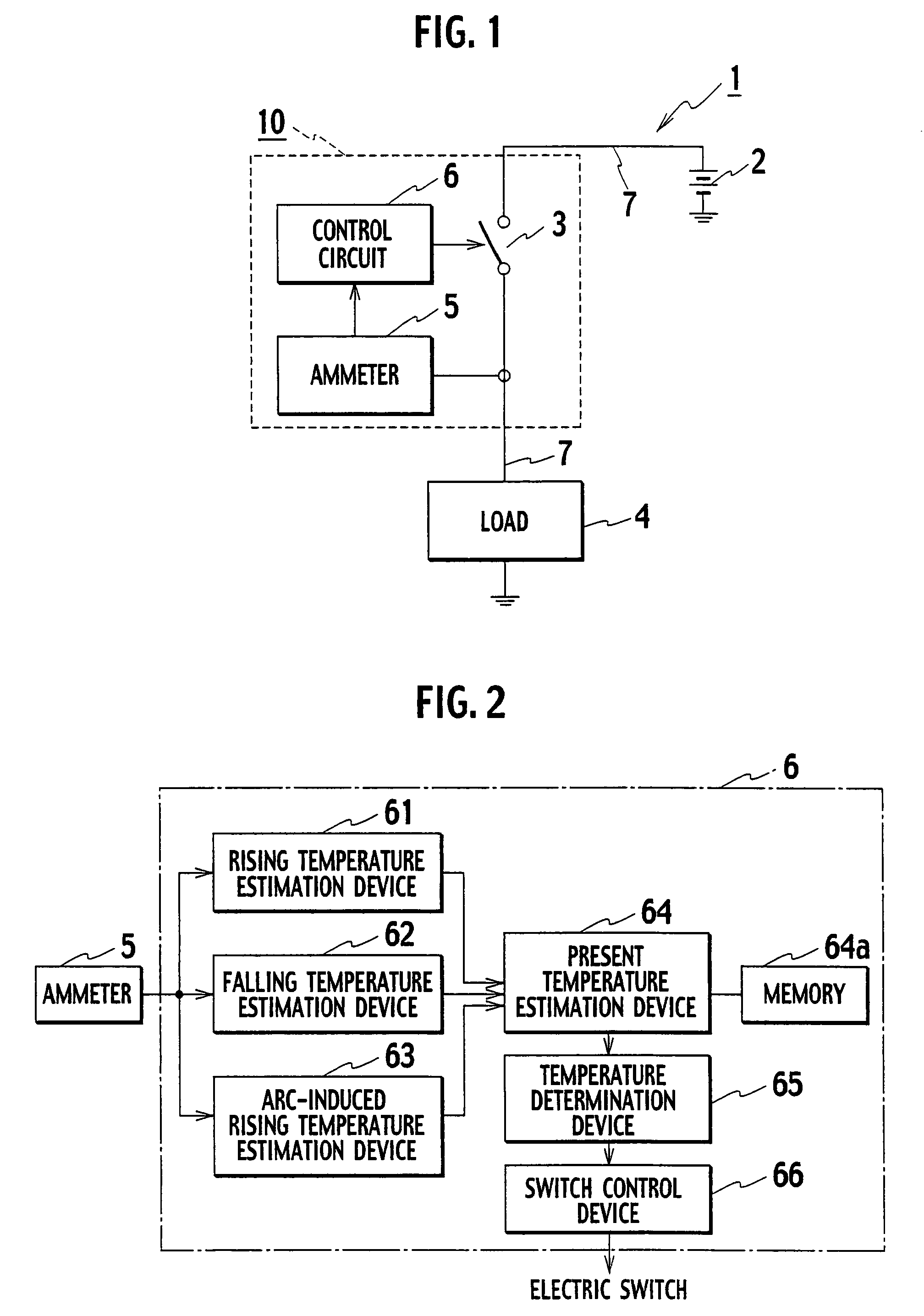
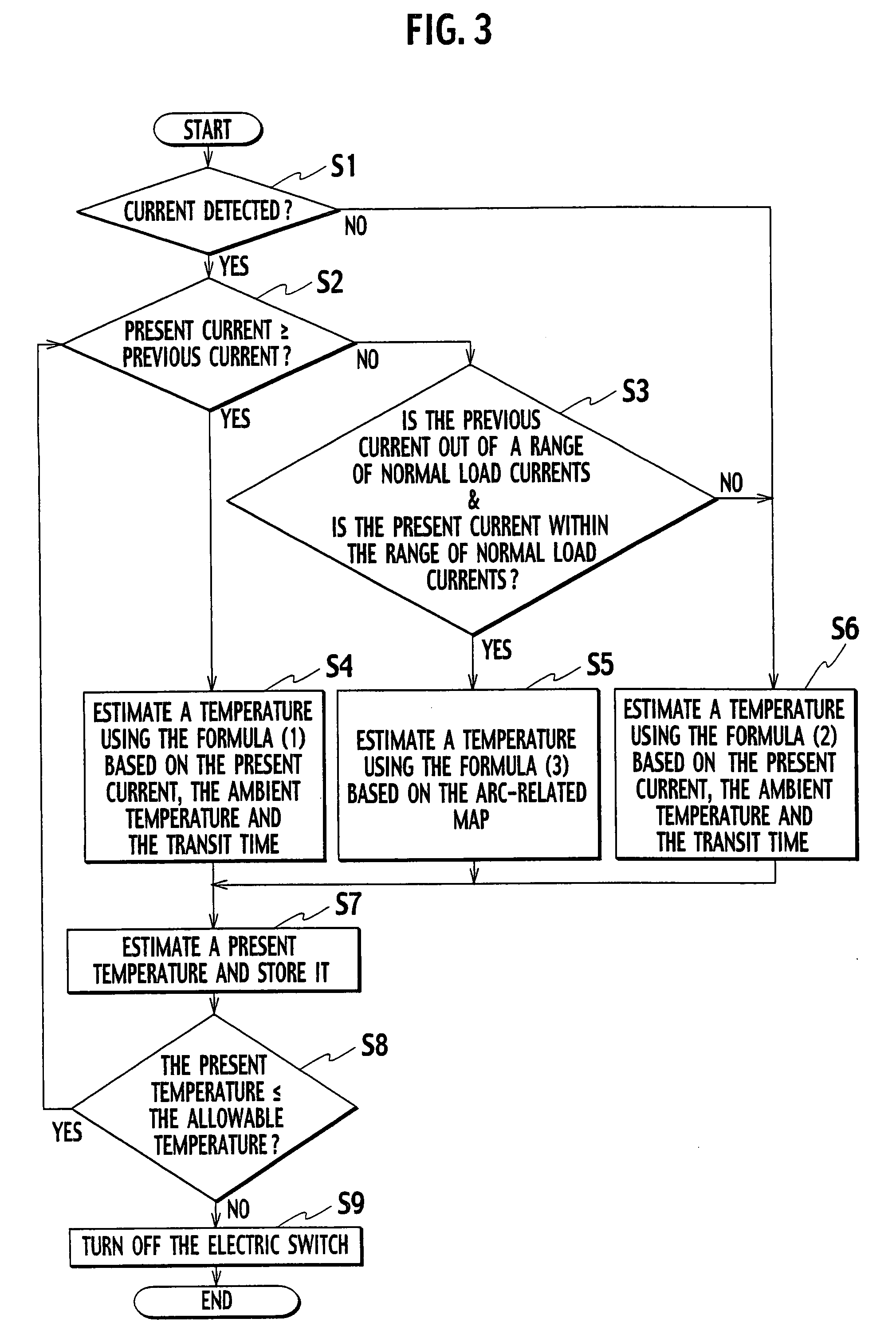
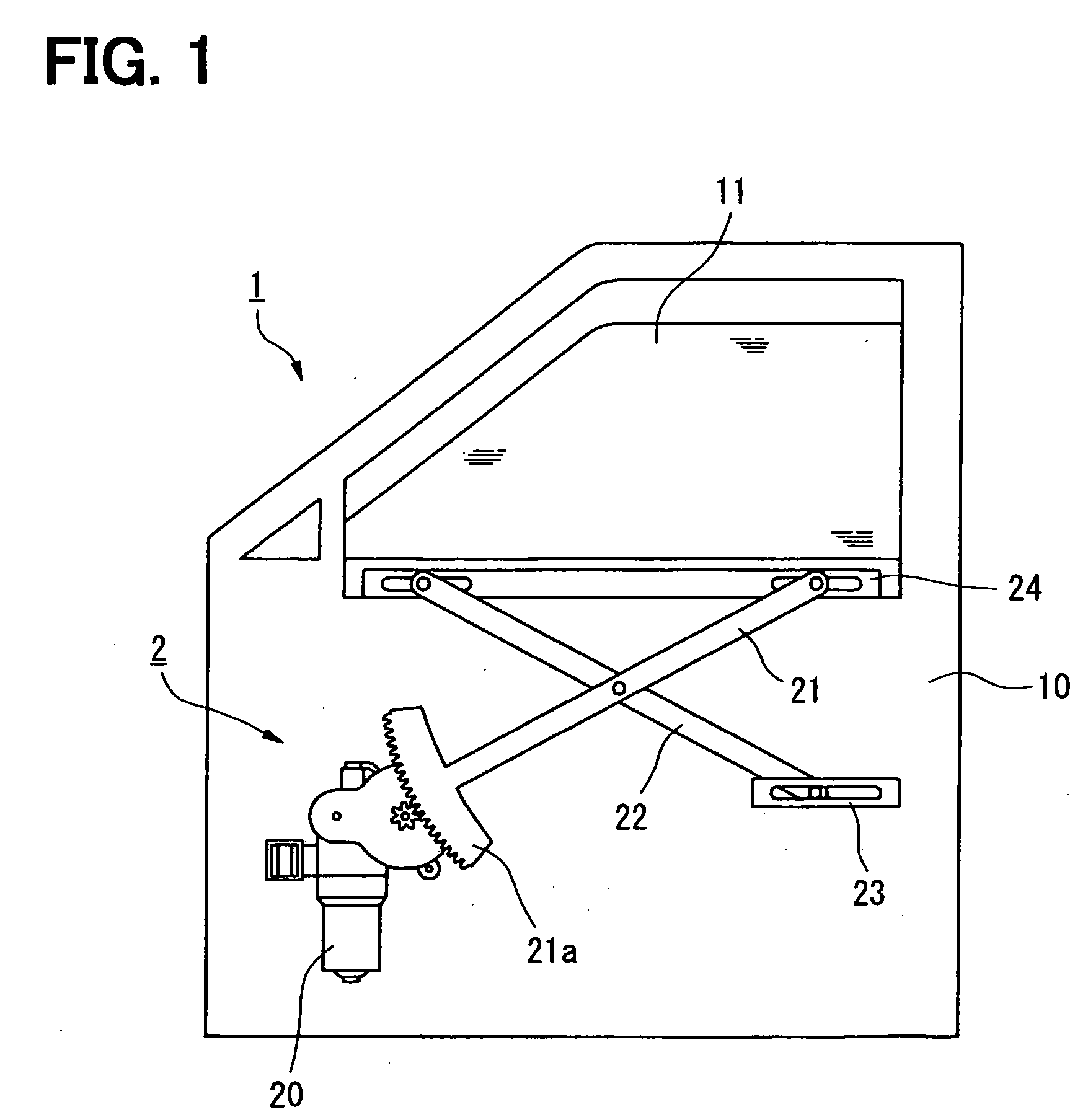
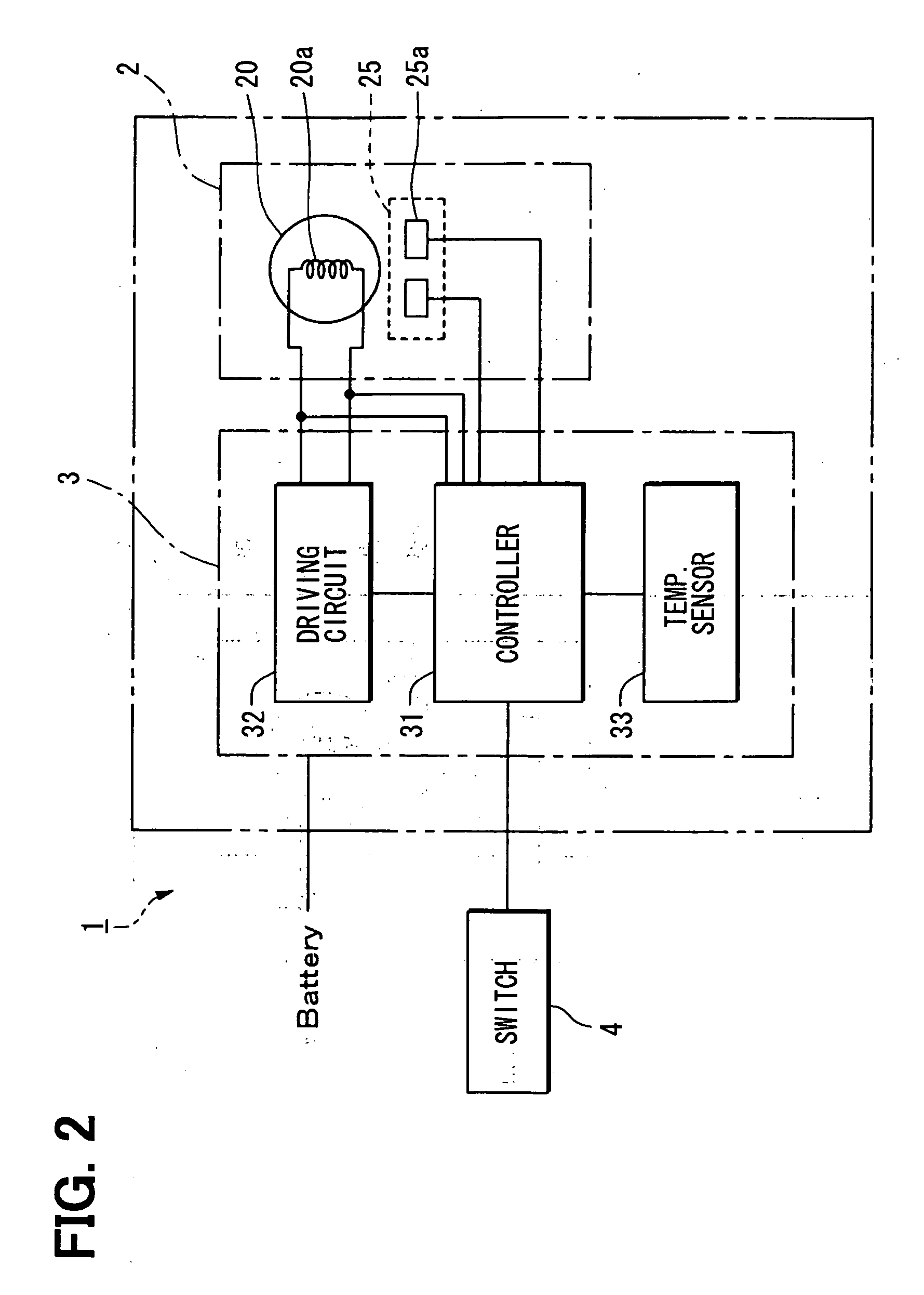
InactiveUS20070253132A1Shut down powerShutdown can be accuratelyTemperatue controlThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLoad circuitElectrical conductor
A protection device protecting a load circuit by shutting off a power thereof depending on an estimated present temperature of a wire provided in the load circuit to connect a load. The protection device has a first temperature estimation device estimating a rising temperature of a conductor including the wire based on both a current in the conductor and thermal properties of the conductor, a second temperature estimation device estimating a falling temperature of the conductor based on the thermal properties, a third temperature estimation device estimating an arc-induced rising temperature of the conductor when arcing occurs in the conductor, and a fourth temperature estimation device estimating the present temperature of the conductor deduced from the above estimated temperatures. If the estimated temperature exceeds a predetermined allowable temperature, the protection device shut off the power of the load circuit.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Control apparatus for automotive alternator having capability to accurately detect temperature of alternator
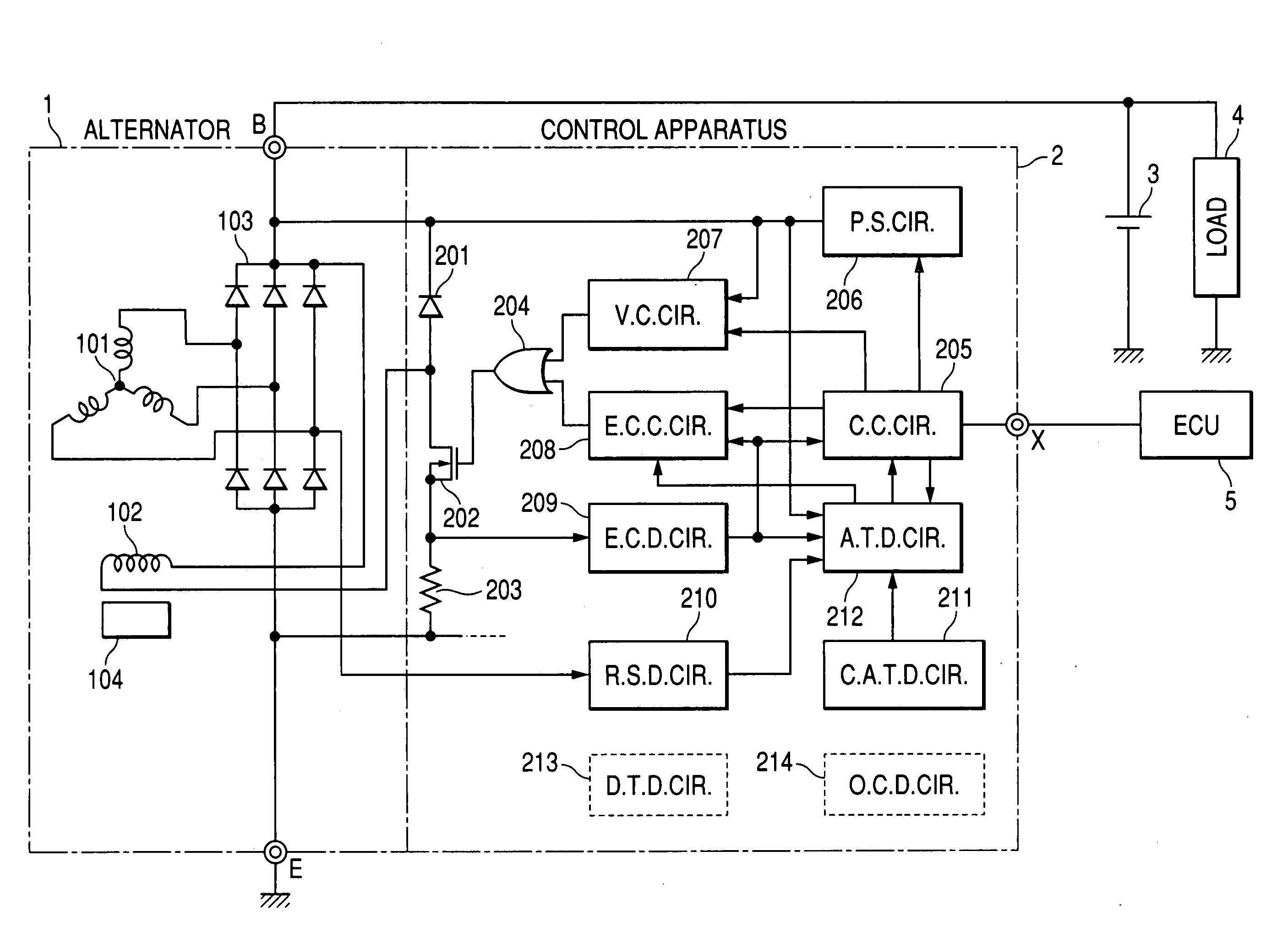
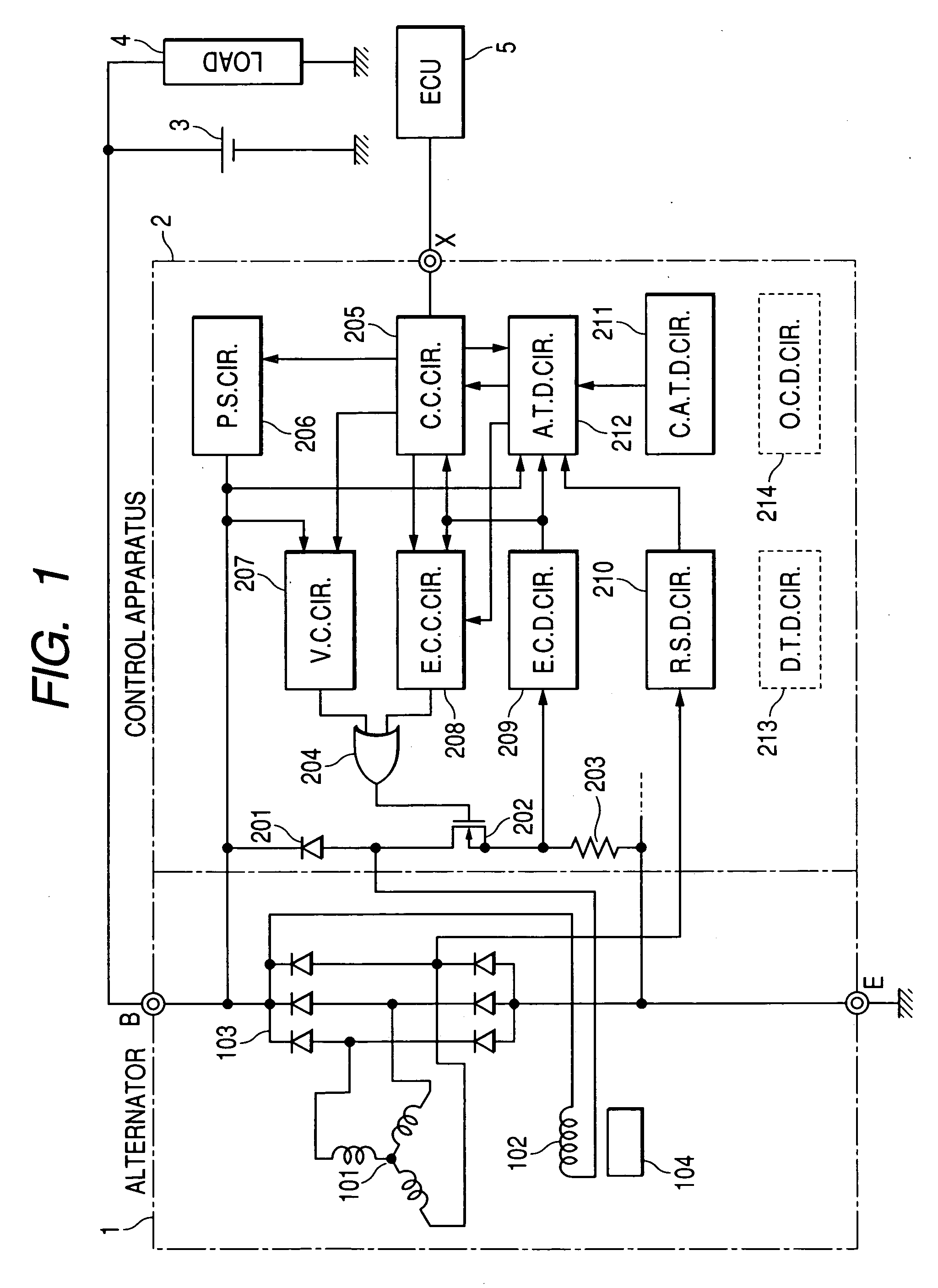
ActiveUS20060238172A1Improve accuracyControl outputMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAlternatorSignal generator
A control apparatus for a vehicle generator includes a switch, a regulator, a fault condition detector, and a PWM signal generator. The switch is selectively turned on and off so as to intermittently excite the generator. The regulator controls on / off operation of the switch so as to bring an output of the generator into agreement with a target value. The fault condition detector detects a fault condition of the generator. The PWM signal generator generates and outputs a PWM signal that has a duty determined as a function of a duty of the on / off operation of the switch and a frequency determined based on if the fault condition of the generator is detected by the fault condition detector. Consequently, the control apparatus can inform an external control apparatus of the duty of the on / off operation of the switch and the fault condition of the generator with the single PWM signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Remaining lifetime estimating method, temperature detecting structure and electronic equipment
InactiveUS6880967B2Accurate estimateAccurate conversionTesting dielectric strengthThermometers using mean/integrated valuesEngineeringElectrolytic capacitor
A temperature of an electrolytic capacitor 24 incorporated in equipment is detected, a remaining lifetime in actual use is calculated based on a temperature-lifetime law, and the remaining lifetime is indicated. A thin film tape 23 is wound around a temperature sensor 22 for insulation, and the electrolytic capacitor 24 and the temperature sensor 22 are accommodated in a heat-shrinkable tube 25, the secondary temperature sensor 22 is brought into tight contact with the primary electrolytic capacitor 24.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Electric motor, electric motor winding temperature detection method and device as well as electric motor winding thermal protection method and device
ActiveCN102156000ARealize real-time monitoringFully reflect the effect of temperature riseThermometer detailsTemperature measurement in motorsElectric machineEngineering
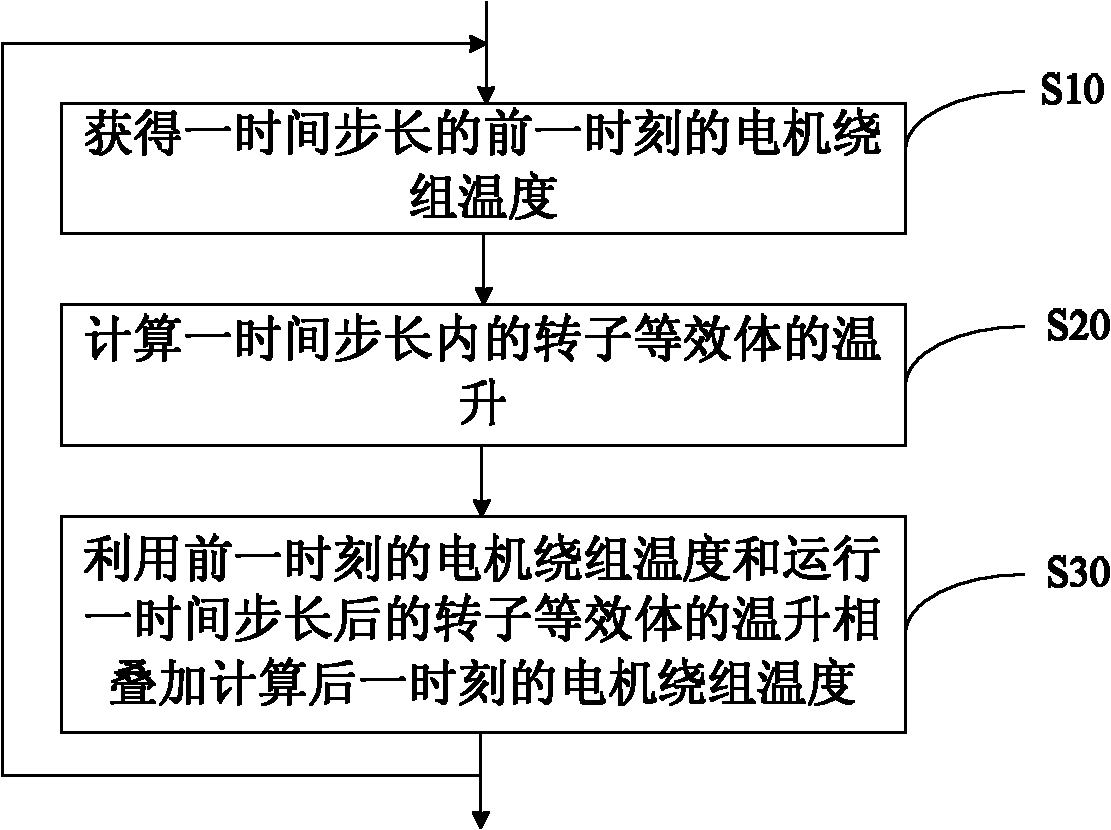
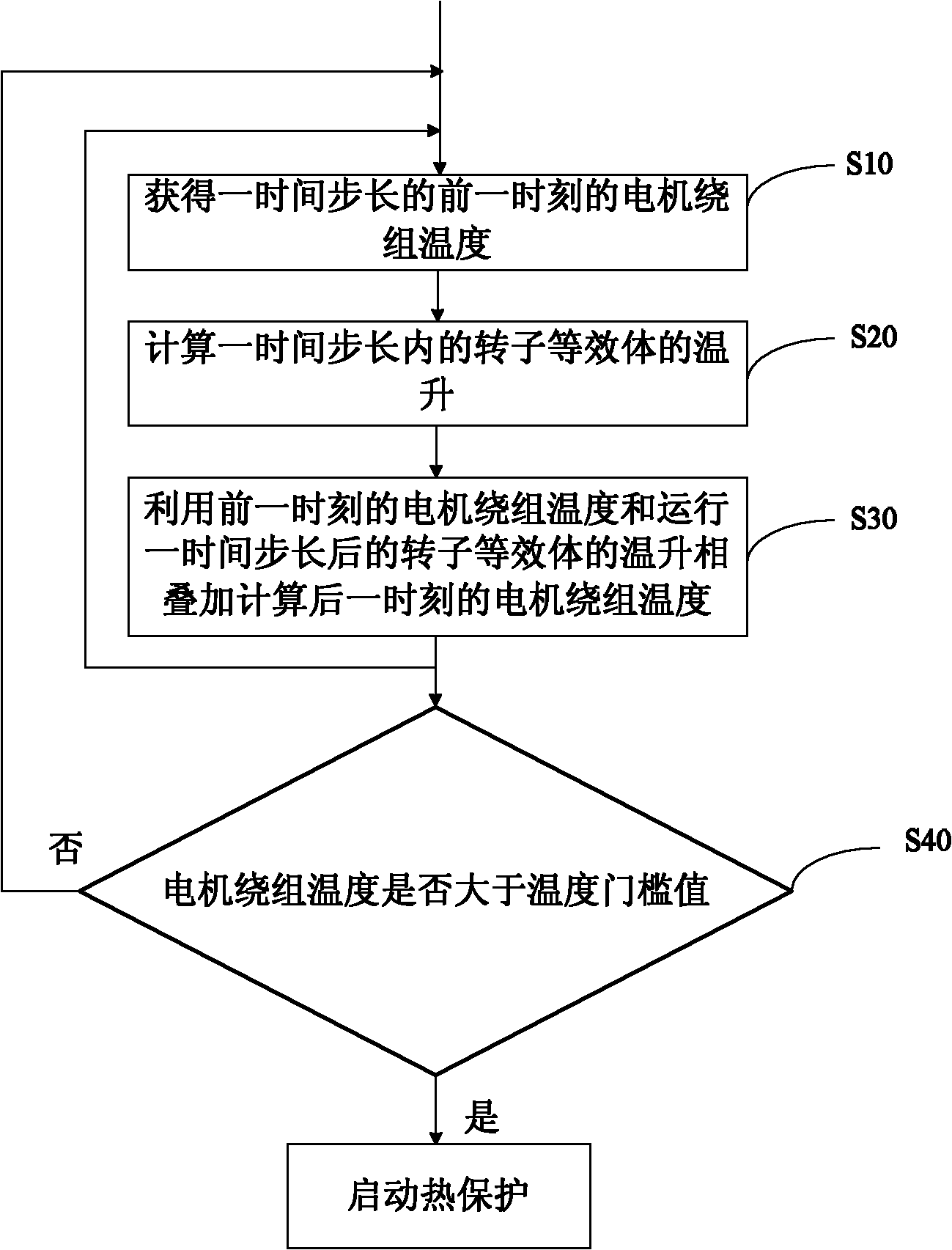
The invention discloses an electric motor, an electric motor winding temperature detection method and device as well as an electric motor winding thermal protection method and device. The electric motor winding temperature detection method comprises the following steps: acquiring the electric motor winding temperature at the previous moment; then calculating temperature rise of a rotor equivalentbody after operating for one time step; and finally calculating the electric motor winding temperature at the next moment by superimposing the electric motor winding temperature at the previous moment with the temperature rise of the rotor equivalent body after operating for one time step. According to the electric motor winding temperature detection method, the electric motor winding temperatureis monitored in real time; the performance of the electric motor is exerted; and the sensitivity of the electric motor is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JINGWEI HIRAIN TECH CO INC
Motor controller
ActiveUS20070058303A1Easy to adjustEstimated temperatureMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlMotor controllerMotor control
A motor controller includes: a motor control part for driving and controlling a motor; an estimated temperature computing part for computing an estimated temperature of a winding of the motor; and a motor protecting part for protecting the motor from being burned when the estimated temperature becomes larger than a predetermined temperature. A temperature rise value of the estimated temperature is computed according to operating conditions of the motor at the time of passing electric current through the winding. This temperature rise value is added to an estimated temperature stored in the estimated temperature storing part to update the estimate temperature. To compute the temperature rise value, an optimum temperature rise value is computed by the use of a plurality of temperature-rise value computing expressions.
Owner:DENSO CORP
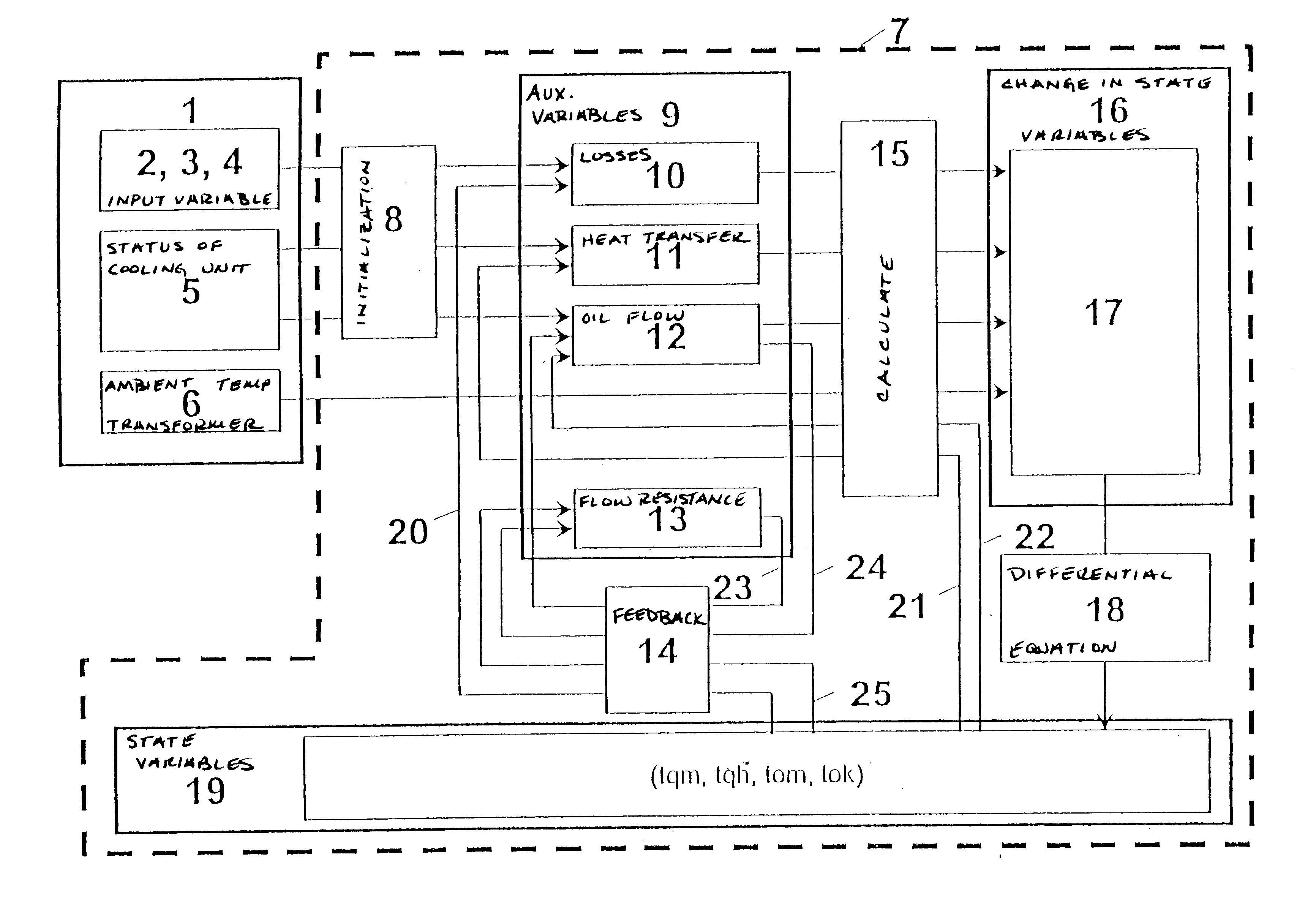
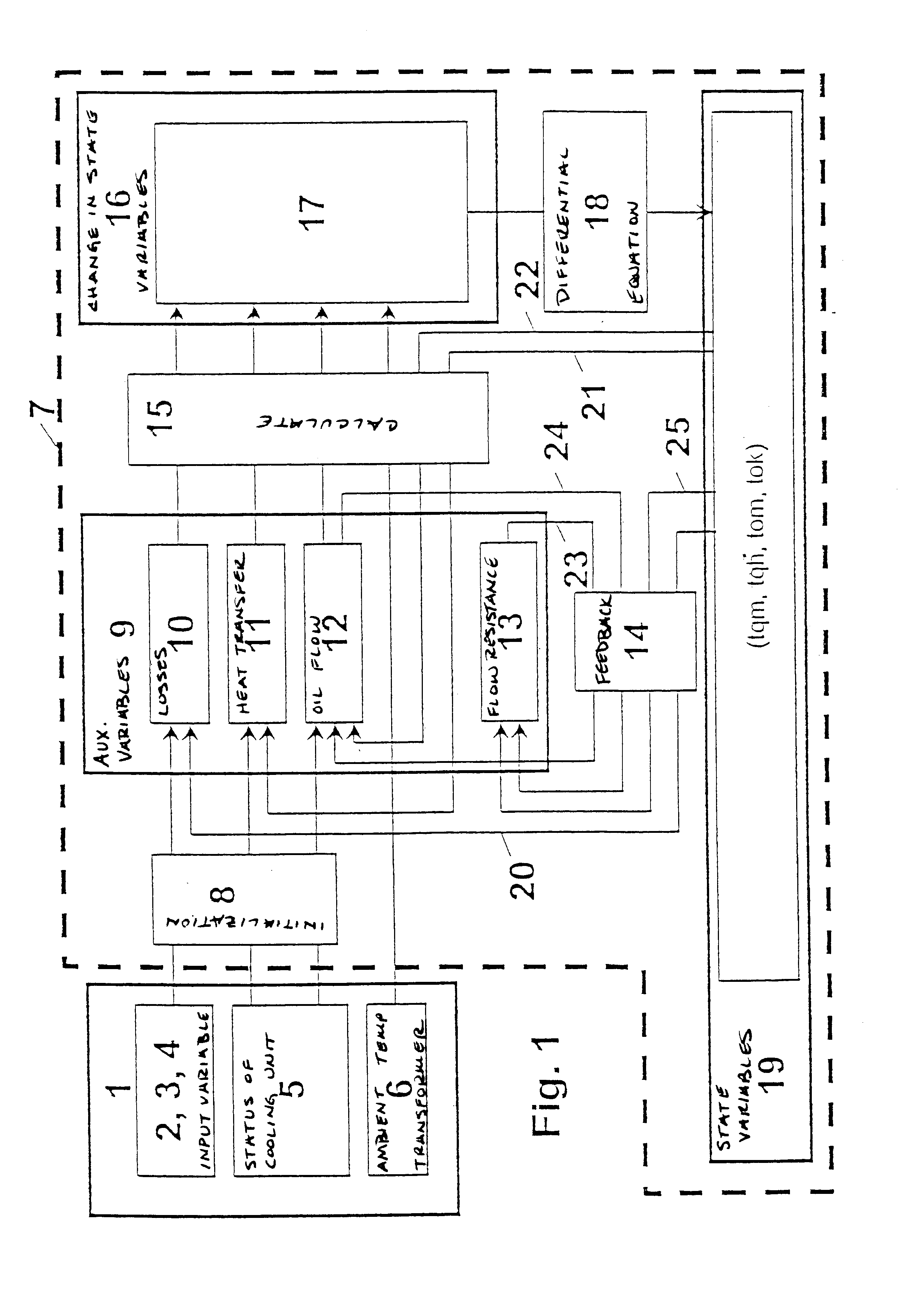
Method and arrangement for ascertaining state variables
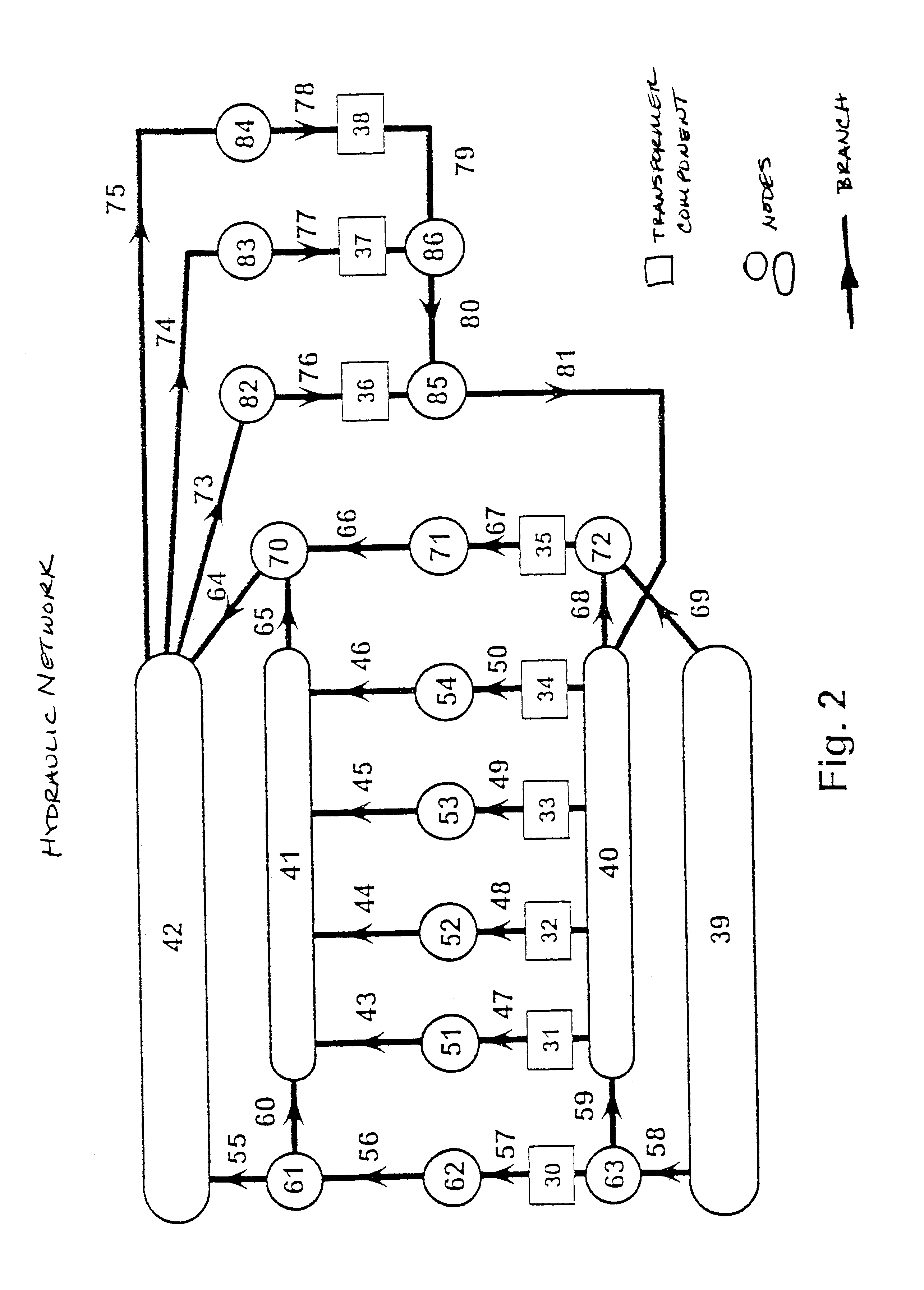
In a method for ascertaining temperatures (tqm, tqh, tom, tok) in an oil-cooled transformer, the transformer terminal voltages (2), the winding currents (3) and the ambient temperature (6) are measured. Furthermore, the status (5) of fans and pumps and the switch position (4) of a stepping switch are established. The measured and established variables (2, 3, 4, 5, 6) are fed to a thermohydraulic model (7), in which state variables (19) are calculated with auxiliary variables (9), which are losses (10) in the transformer, heat transfer parameters (11), flow resistances (13) and the oil flow (12), and a hydraulic network of the oil circuit, which has branches and nodes. The state variables (19) are the average temperatures (tqm) and the hotspot temperatures (tqh) in loss-producing parts of the transformer and the average oil temperatures in branches (tom) and in nodes (tok) of the hydraulic network of the oil circuit. When there is a change in the variables measured and established (2, 3, 4, 5, 6), the auxiliary variables (9) are adapted appropriately, and the rate of change of the state variables (19) is subsequently ascertained and new state variables (19) are consequently calculated. With this method, temperatures (tqm, tqh, tom, tok) and their changes in the transformer are ascertained without temperature sensors, whereby the optimum operation of the transformer is ensured, an early detection of errors and risks takes place and the optimum point in time for service work can be established.
Owner:VA TECH ELIN TRANSFORMATOREN
Protection apparatus of load circuit
ActiveUS20110043958A1Reduce switchingIncrease fuel consumptionArrangements responsive to excess currentEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLoad circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
A protection apparatus of a load circuit, comprises: a temperature estimation unit configured to estimate a temperature of an electric wire based on a pseudo-temperature arithmetic expression; and a breaking control unit configured to break a switch portion when the temperature estimated by the temperature estimation unit has reached an allowed temperature of the electric wire. The pseudo-temperature arithmetic expression is set in such a manner that, in a temperature arithmetic expression of the electric wire, the temperature arithmetic expression using the elapsed time counted by the timer, the current detected by the current detection unit, and a heat capacity and conductor resistance of the electric wire, a pseudo-heat capacity smaller than the heat capacity of the electric wire is assigned to the heat capacity, and a pseudo-conductor resistance larger than the conductor resistance of the electric wire is assigned to the conductor resistance.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Motor protection for a powered door system
InactiveUS6198241B1Quick responseDC motor speed/torque controlAsynchronous induction motorsElectrical conductorCapacitor voltage
A motor protection circuit for an electric motor driven by a pulse width modulated amplifier. It has a capacitor and a first conduction path connected to a first terminal of the capacitor and connectable to a first conductor. It also has a second conduction path connected to the second capacitor terminal and connectable to a second conductor. There is a DC voltage difference between the first conductor and the second conductor. There is a third conduction path between the first terminal and the second terminal. The third conduction path having a resistance which is lower than the resistance of the first conduction path plus the resistance of the second conduction path. The third conduction path passes through a switch which has an input connection to be opened and closed thereby. The input connection is for receiving a signal indicating a motor overload condition, whereby the capacitor discharge switch is closed when the signal indicates the motor overload condition and the capacitor discharge switch is opened when the signal does not indicate the motor overload condition. A charge on the capacitor increases when the signal does not indicate the motor overload condition and the charge on the capacitor decreases when the signal indicates the motor overload condition. The circuit also has a voltage comparator receiving the voltage of the capacitor. The voltage comparator produces a signal for shutting down the motor.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE CO
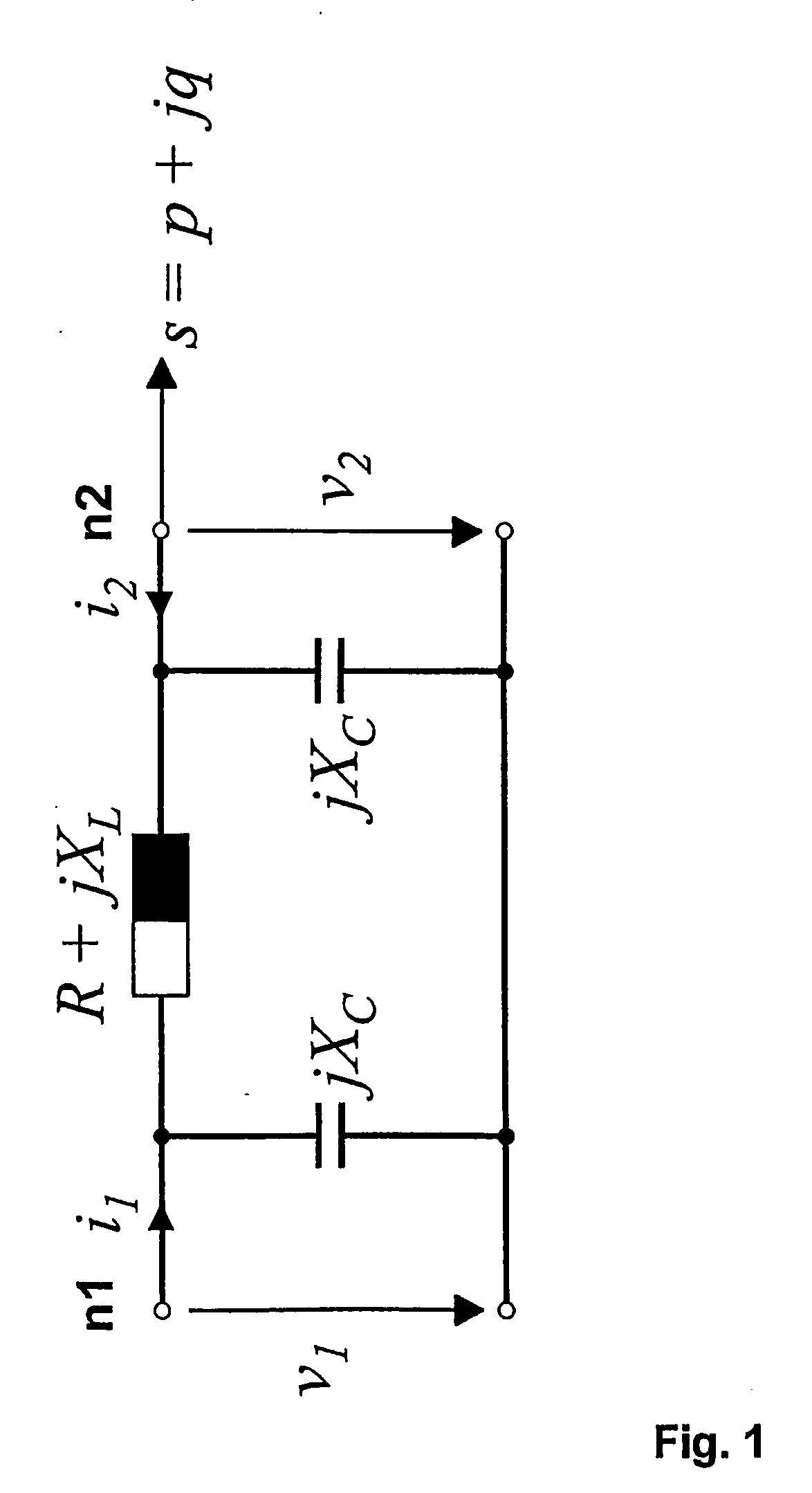
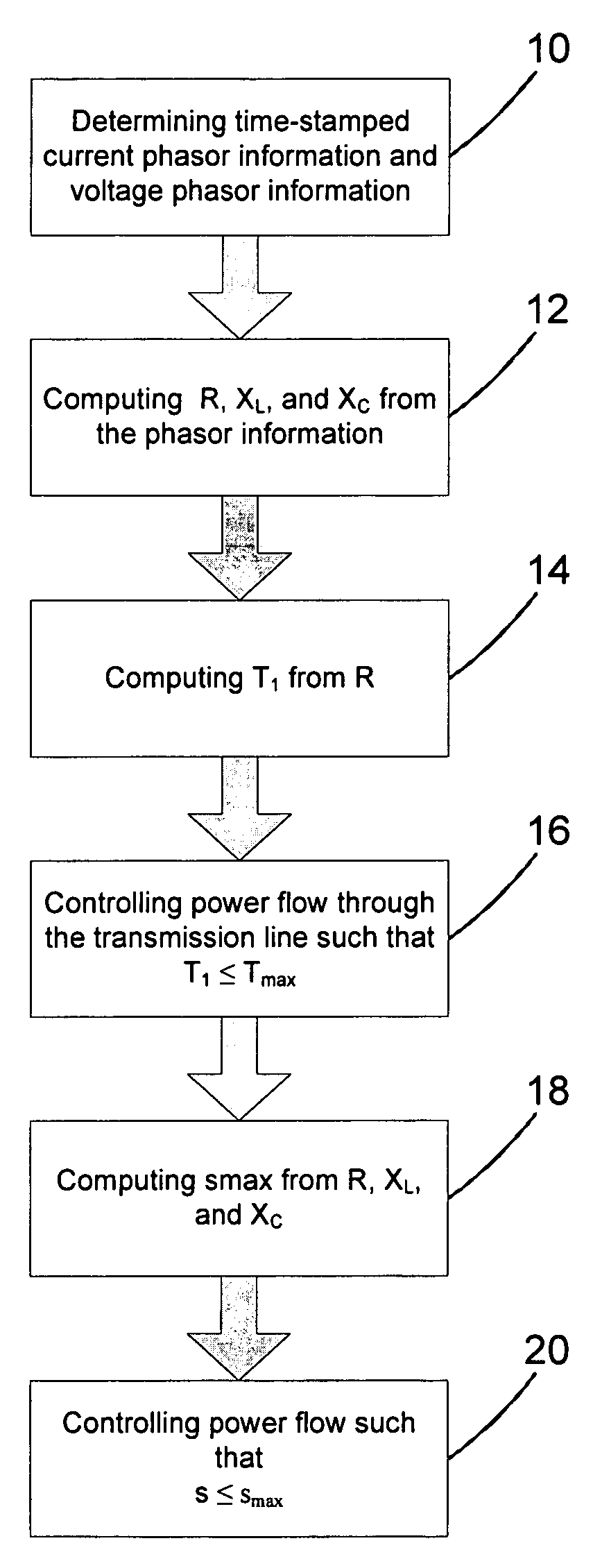
Determining an operational limit of a power transmision line
InactiveUS20050222808A1High resolutionTemporal resolutionSpectral/fourier analysisElectric signal transmission systemsElectric power transmissionElectrical resistance and conductance
In a method, computer program and system for determining an operational limit of a power transmission line, time-stamped current phasor information and voltage phasor information for a first end and a second end of the line are determined, an ohmic resistance of the line is computed from the phasor information, and an average line temperature is computed from the ohmic resistance. This allows to determine the average line temperature without dedicated temperature sensors. The average line temperature represents the actual average temperature and is largely independent of assumptions regarding line parameters.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
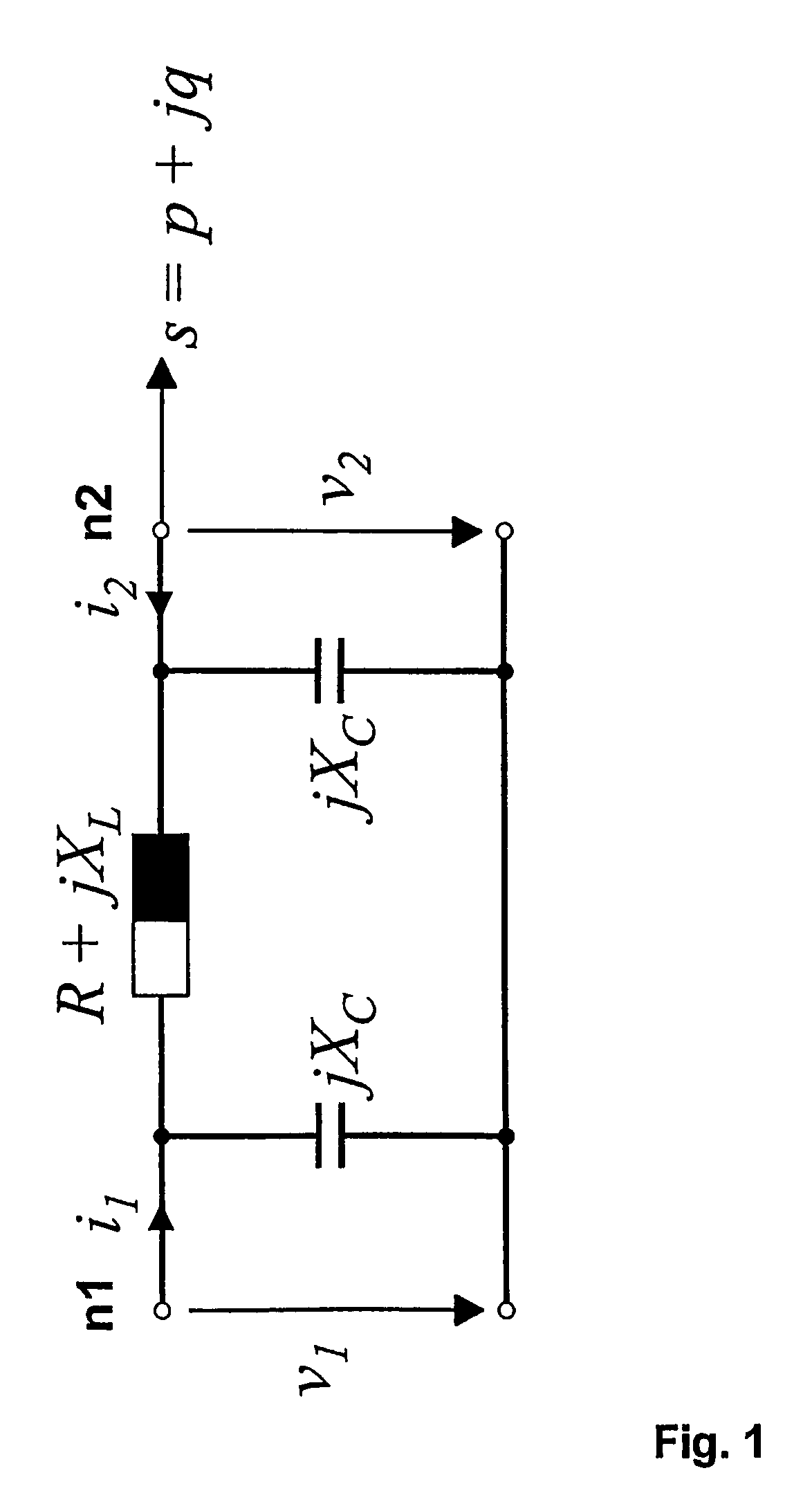
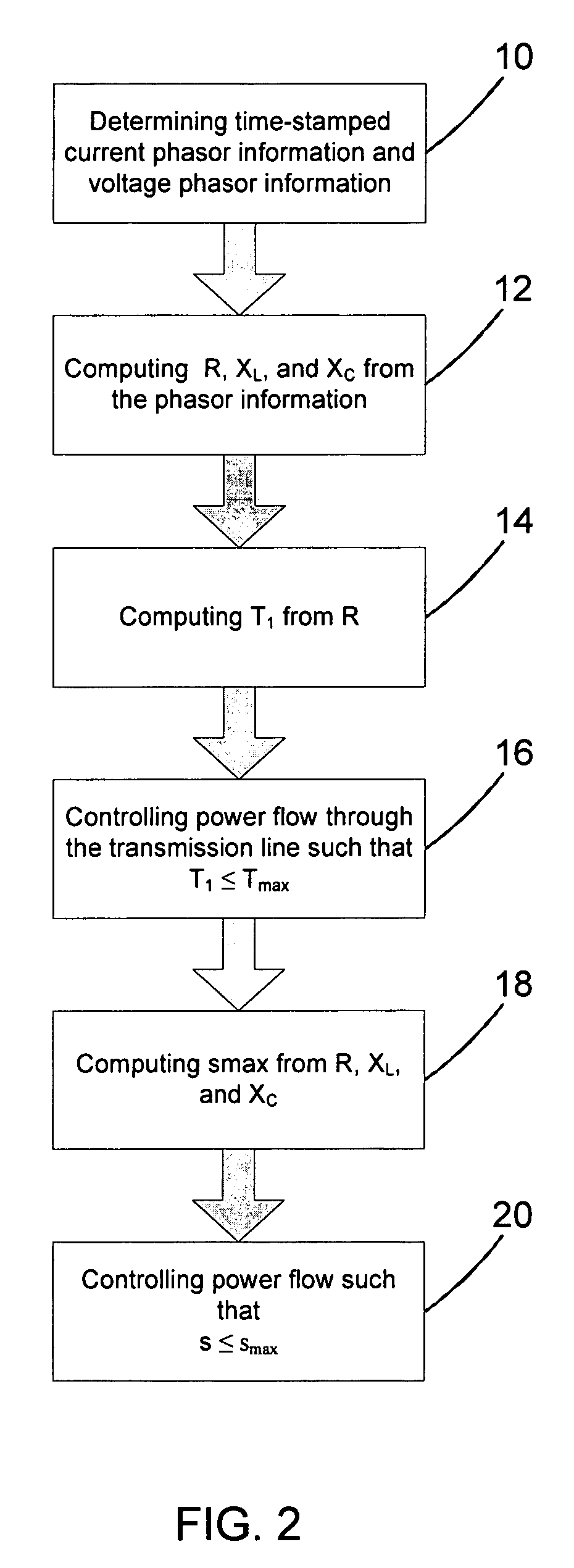
Determining an operational limit of a power transmission line
InactiveUS7107162B2Good precisionClosing operationSpectral/fourier analysisDc network circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectrical resistance and conductance
In a method, computer program and system for determining an operational limit of a power transmission line, time-stamped current phasor information and voltage phasor information for a first end and a second end of the line are determined, an ohmic resistance of the line is computed from the phasor information, and an average line temperature is computed from the ohmic resistance. This allows to determine the average line temperature without dedicated temperature sensors. The average line temperature represents the actual average temperature and is largely independent of assumptions regarding line parameters.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
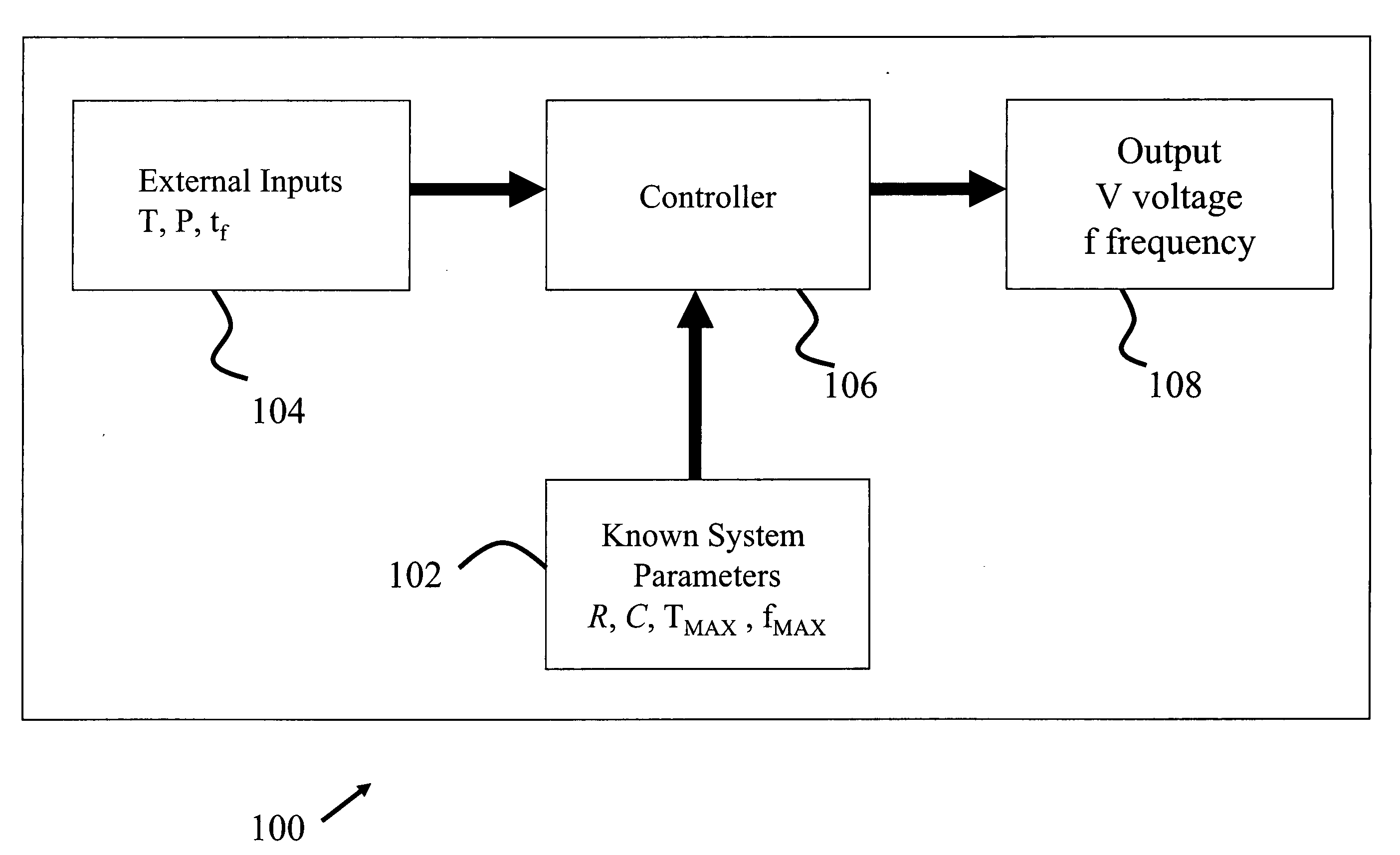
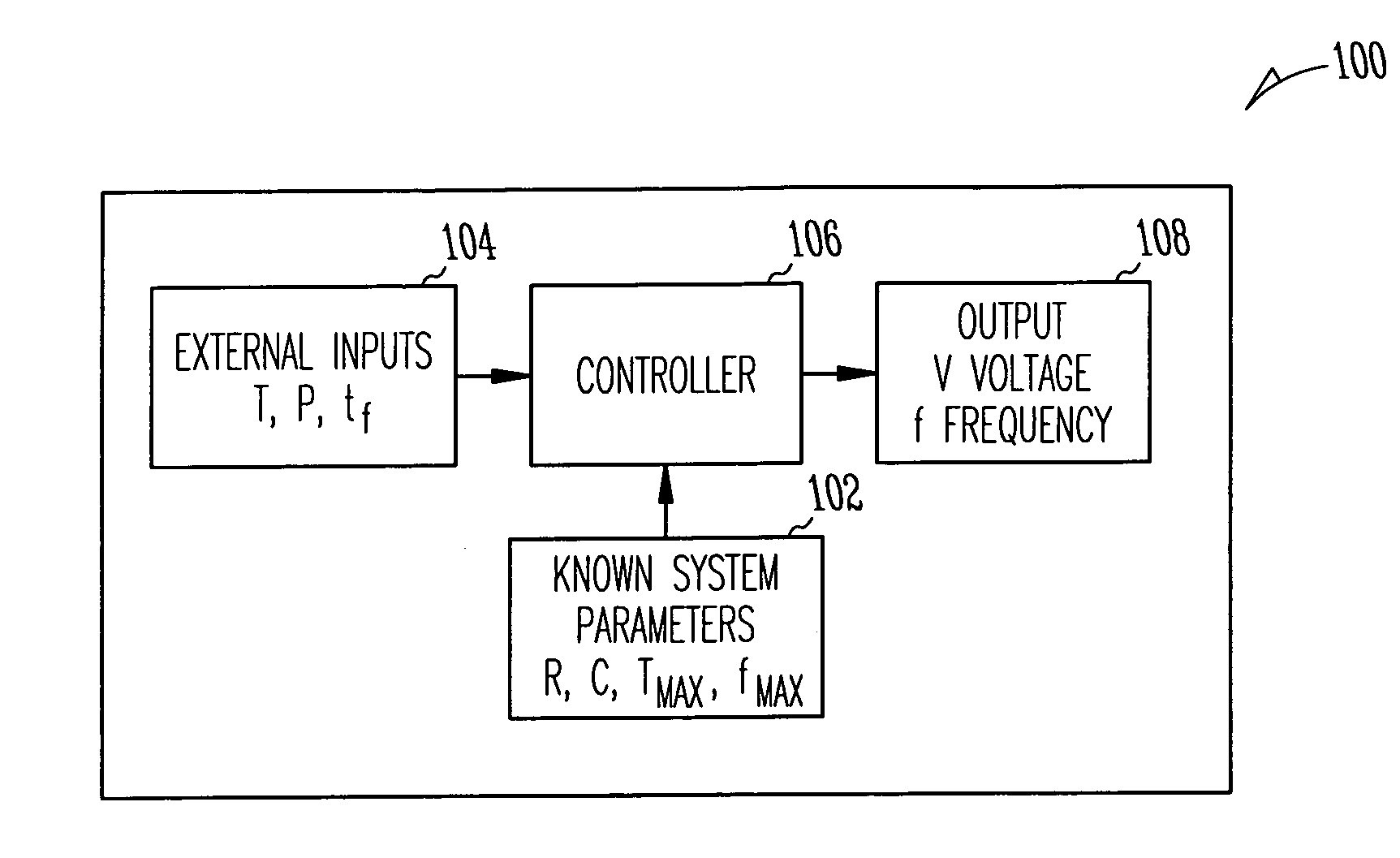
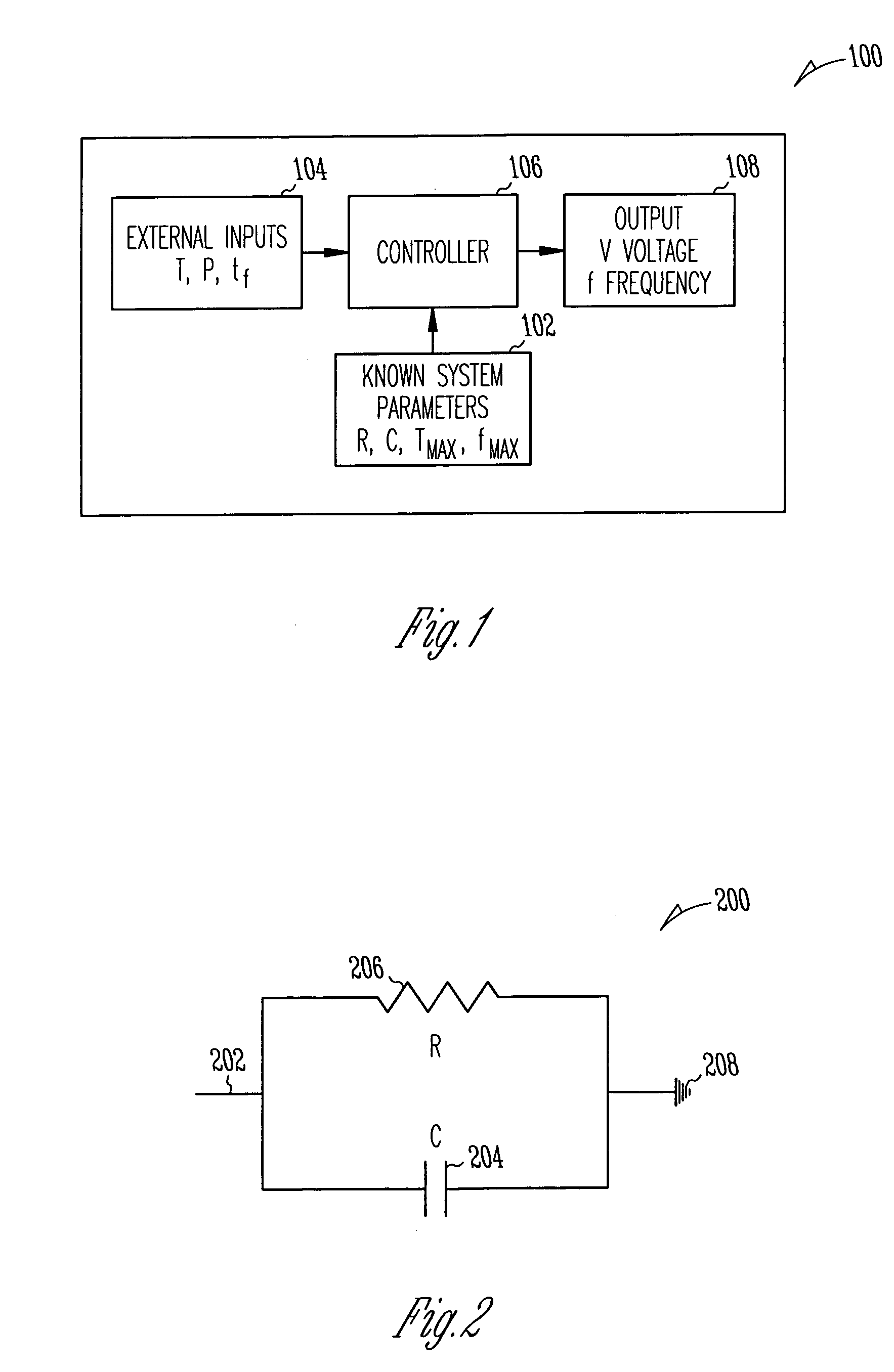
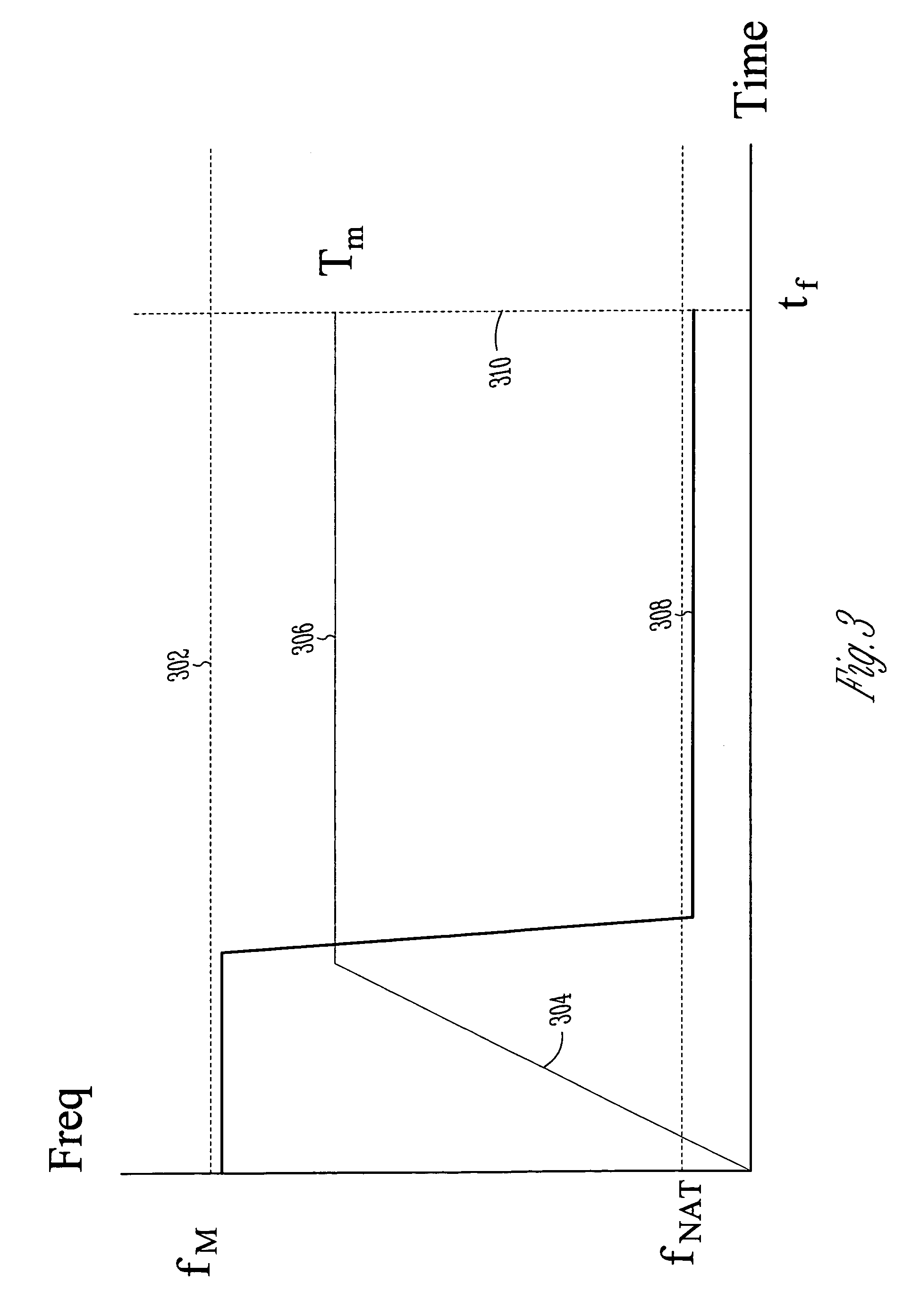
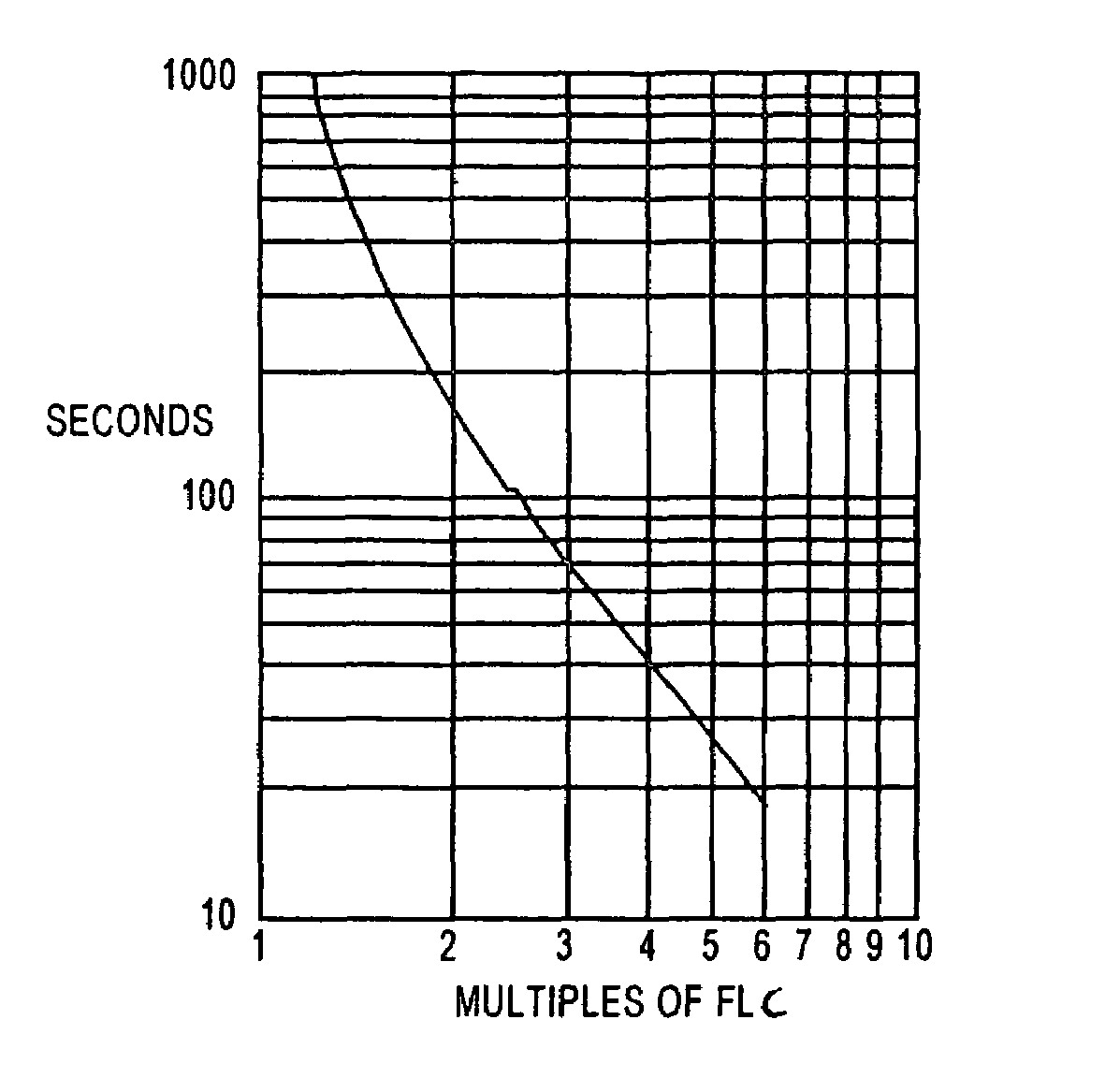
Methods and apparatus for optimal voltage and frequency control of thermally limited systems
Methods, apparatus, and articles of manufacture control a device or system that has an operational limit related to the rate or frequency of operation. The frequency of operation is controlled at a variable rate calculated to maximize the system or apparatus performance over a calculated period of time short enough that a controlling factor, such as power consumption, does not vary significantly during the period. Known system parameters, such as thermal resistance and capacitance of an integrated circuit (IC) and its package, and measured values, such as current junction temperature in an IC, are used to calculate a time-dependent frequency of operation for the upcoming time period that results in the best overall performance without exceeding the operational limit, such as the junction temperature.
Owner:INTEL CORP
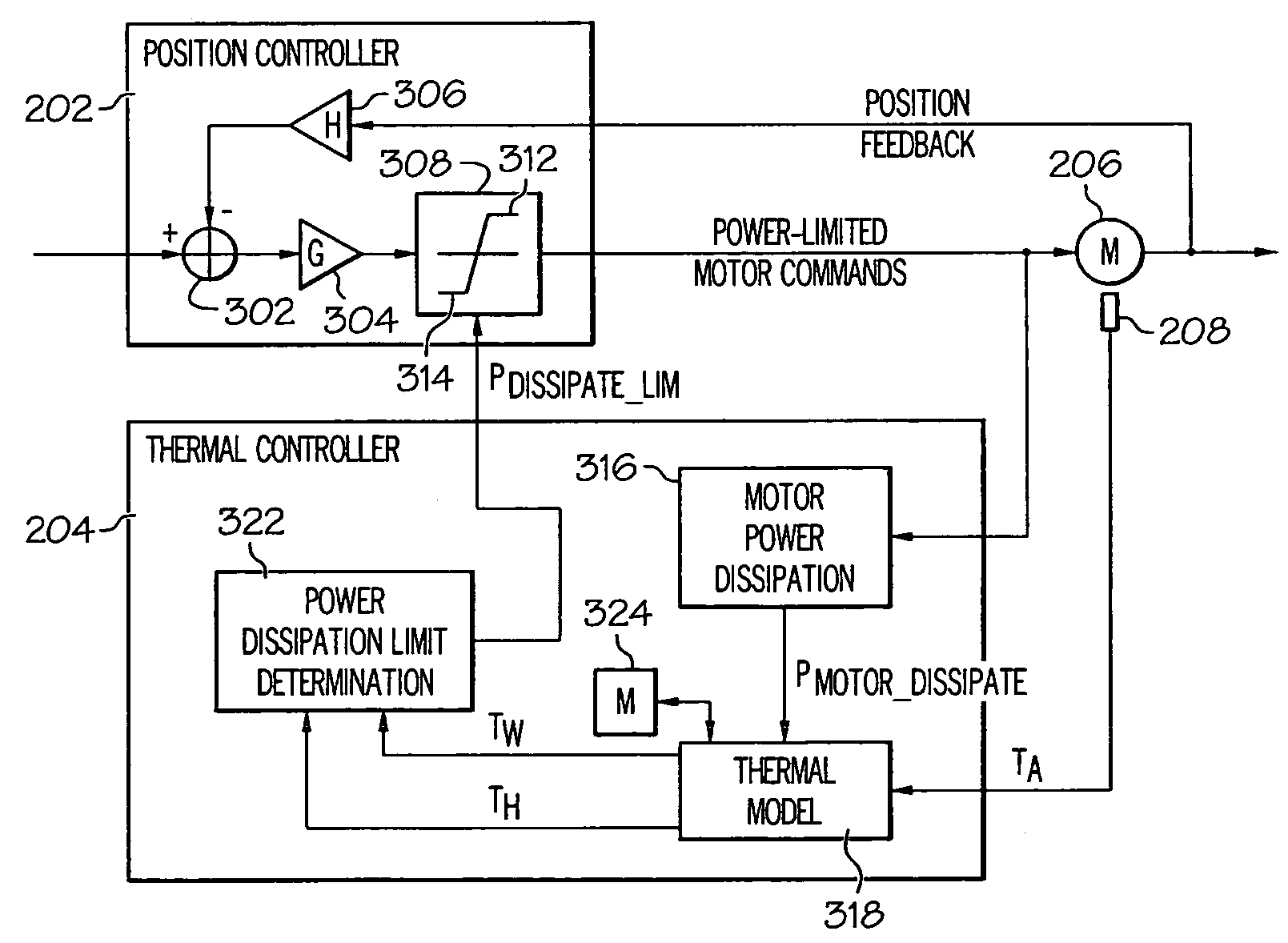
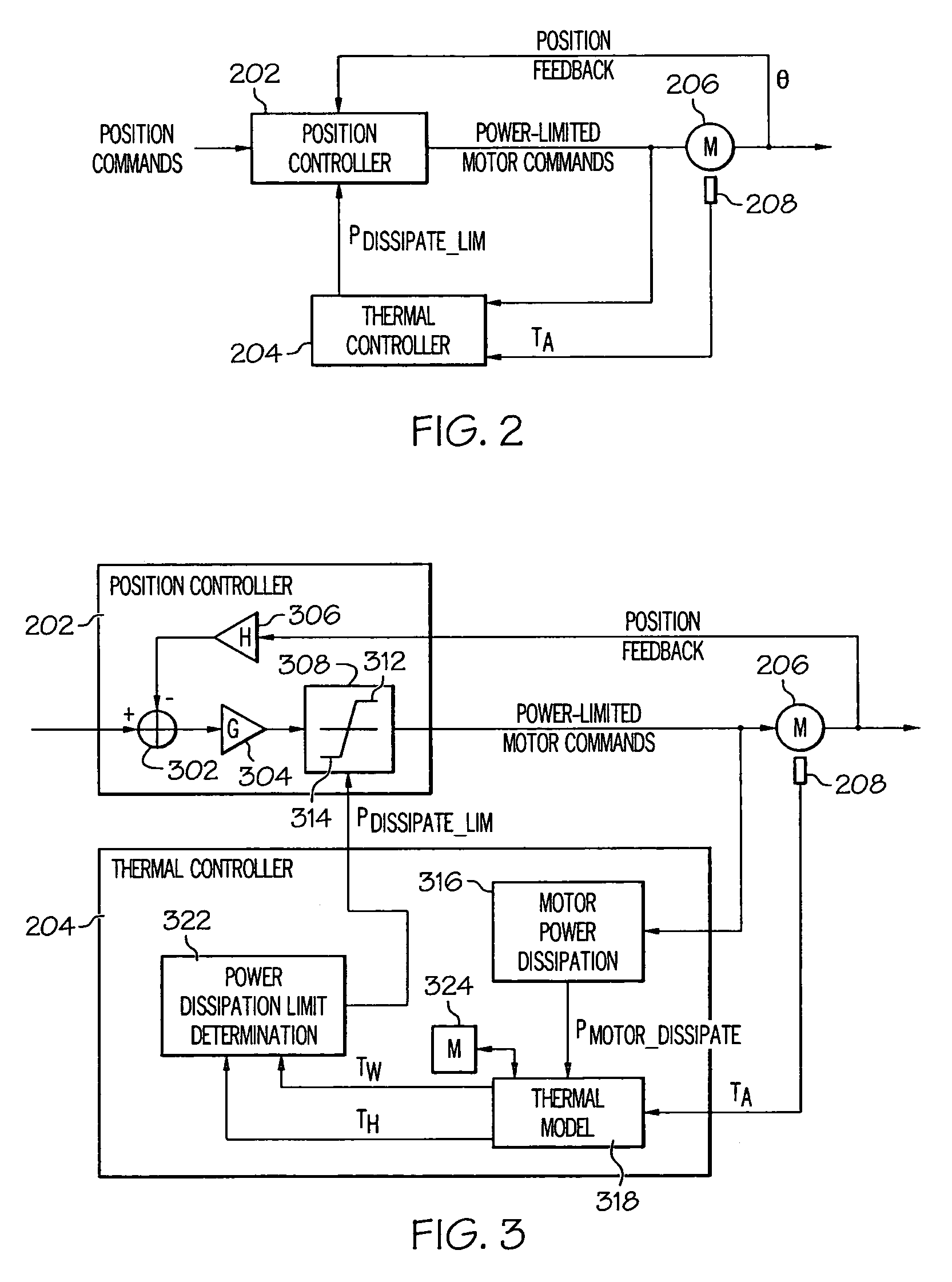
Motor temperature control using estimated motor temperature based on motor power dissipation
InactiveUS7248009B1Avoid overall overheatingSingle-phase induction motor startersProgramme controlTemperature controlMotor drive
A system and method of controlling motor temperature is based on computed motor power dissipation and a thermal model of the motor, rather than a measured motor temperature, in a control loop that limits the motor drive to prevent overheating. An ambient temperature sensor senses the ambient temperature near the motor, and a determination is made of the motor power dissipation. The motor winding temperature is estimated based on the sensed ambient temperature and the determined motor power dissipation. A maximum motor power dissipation that would raise the motor temperature to a predetermined maximum temperature value is determined based on the estimated temperature. The motor power dissipation is limited to a value that is below the determined maximum power dissipation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
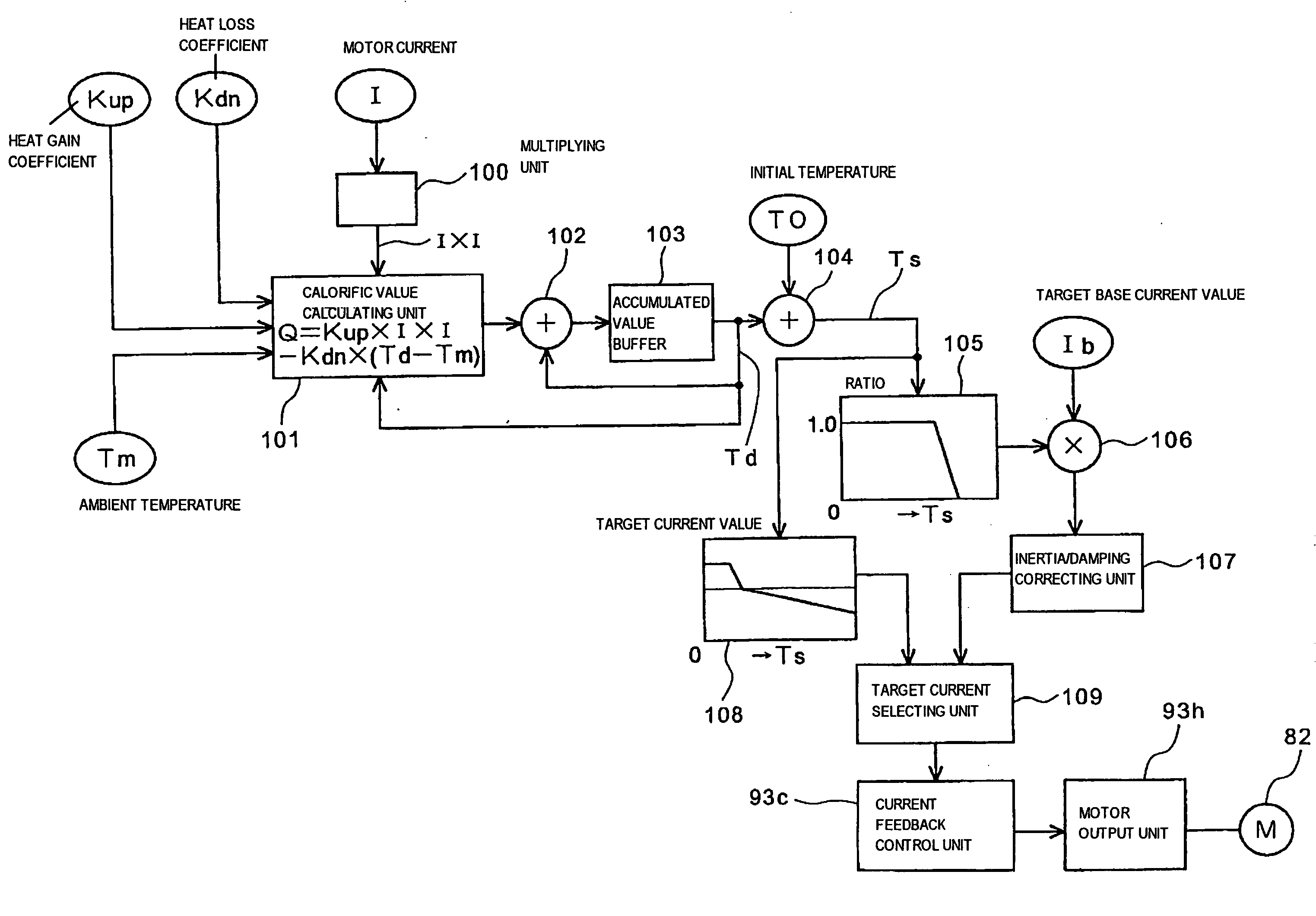
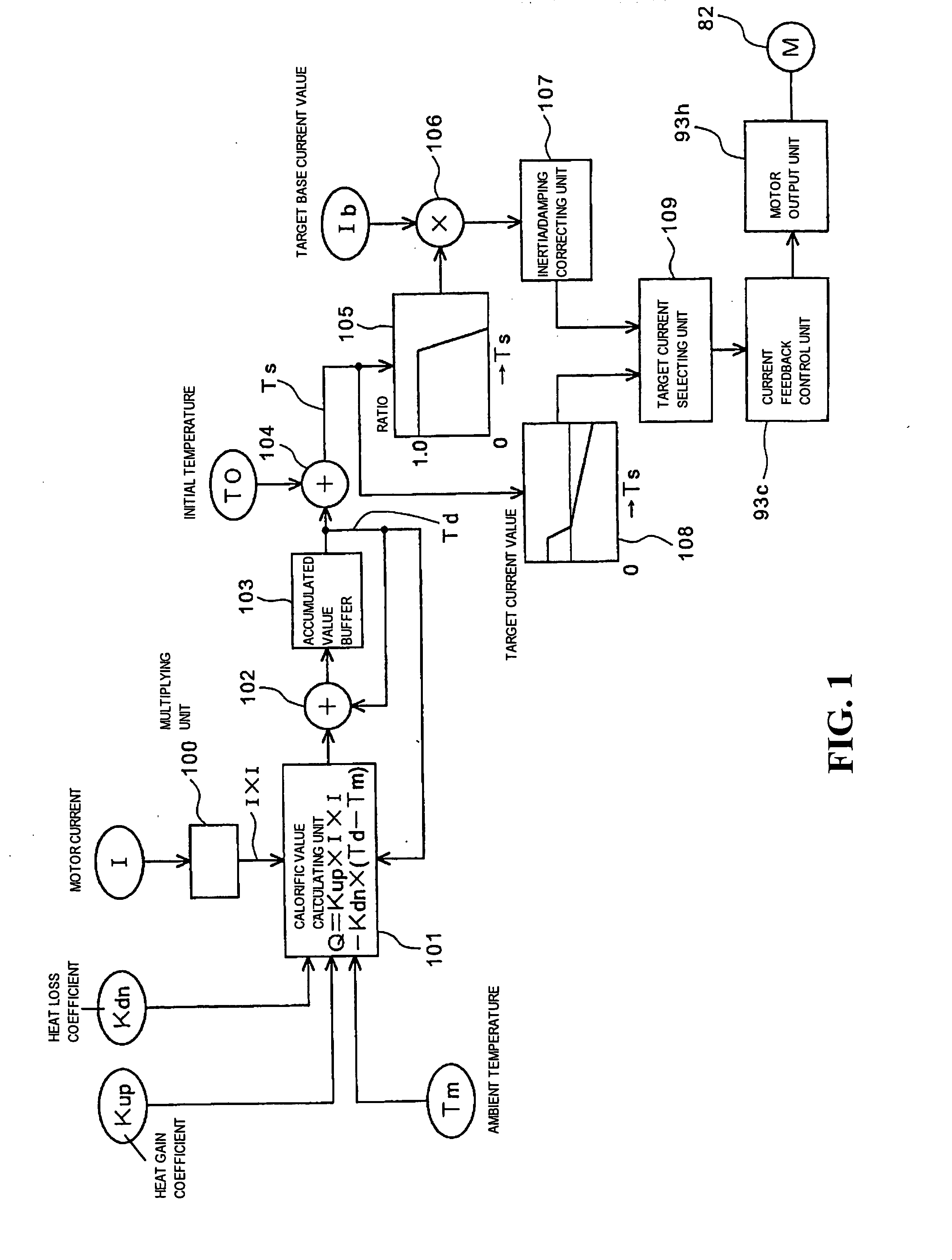
Motor protection system
InactiveUS20080024080A1Accurate temperatureAvoid overall overheatingDC motor speed/torque controlTemperatue controlEngineeringControl theory
To precisely detect the temperature of a power assist motor without using a temperature sensor and enhance an overheating protection function. A calorific value calculating unit calculates a calorific value based upon the difference between a calorific value by current supplied to a motor and the quantity of heat radiation. The output of the calorific value calculating unit is accumulated and an accumulated value is input to an accumulated value buffer. A cumulative value TS acquired by adding initial temperature T0 to a cumulative value Td is input to a ratio map of a target current value, ratio is read, and a target base current value is limited according to the ratio. The cumulative value TS used in the map is not an actual motor current value and is calculated based upon unlimited current acquired in an unlimited current calculating unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
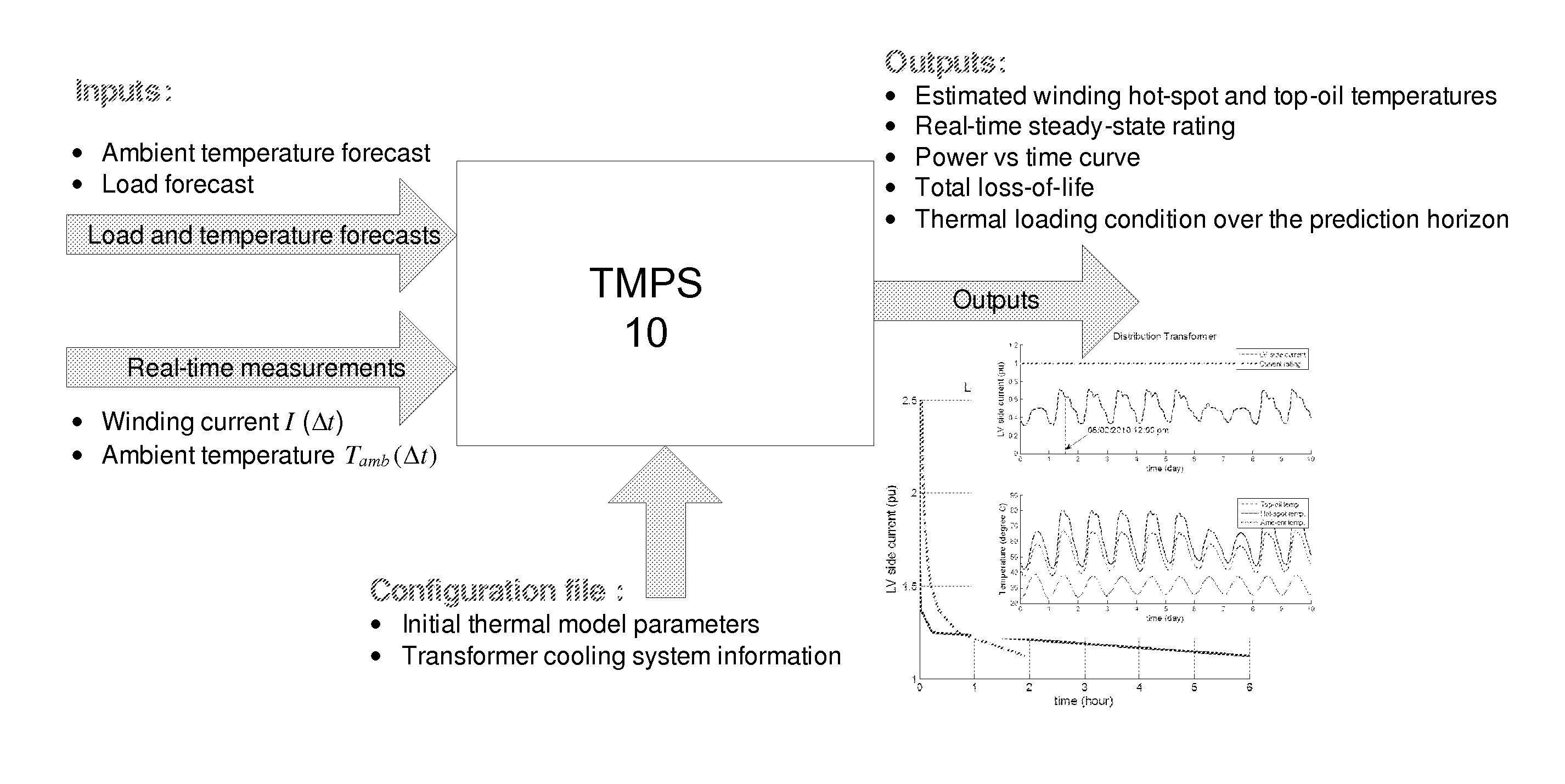
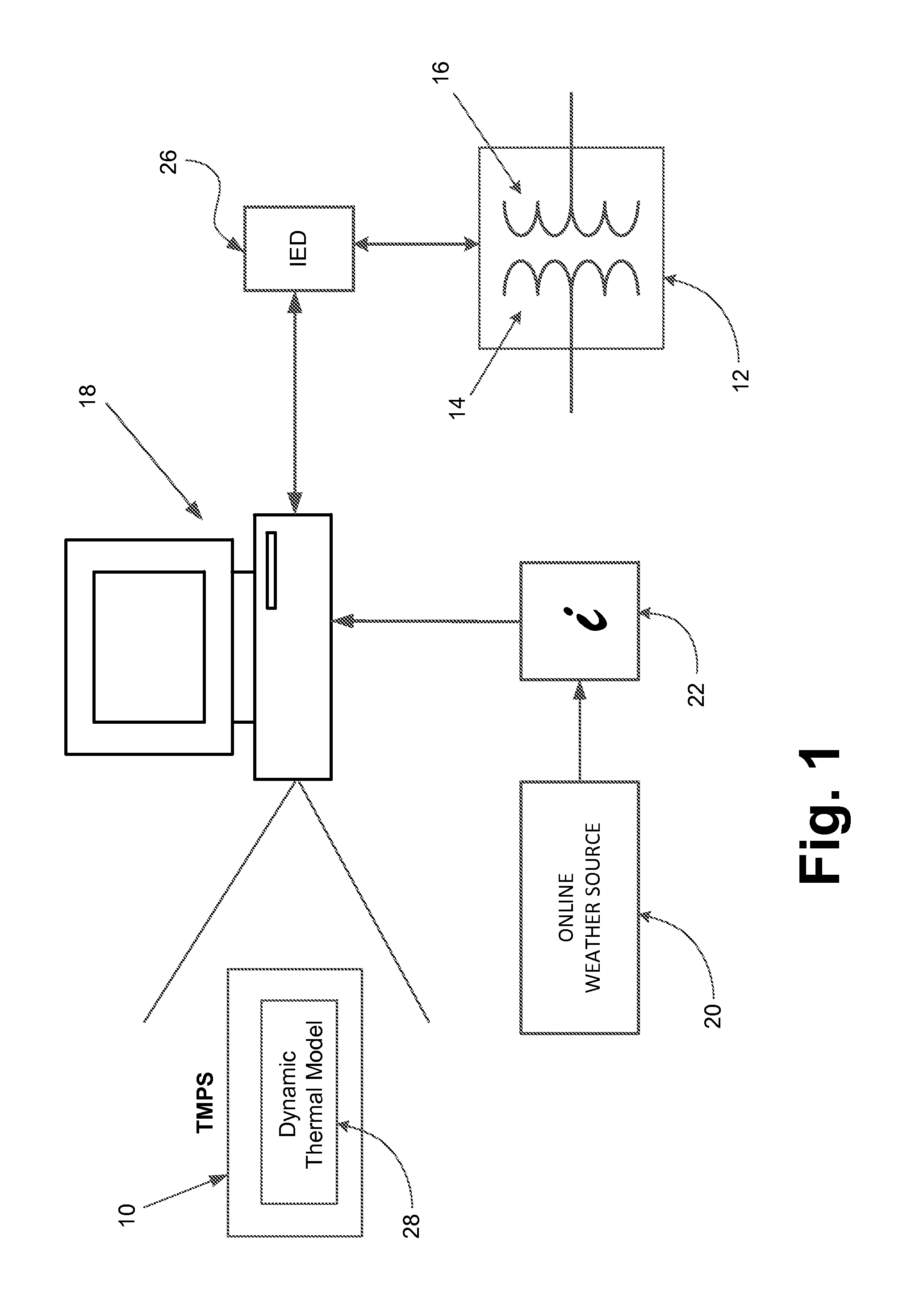
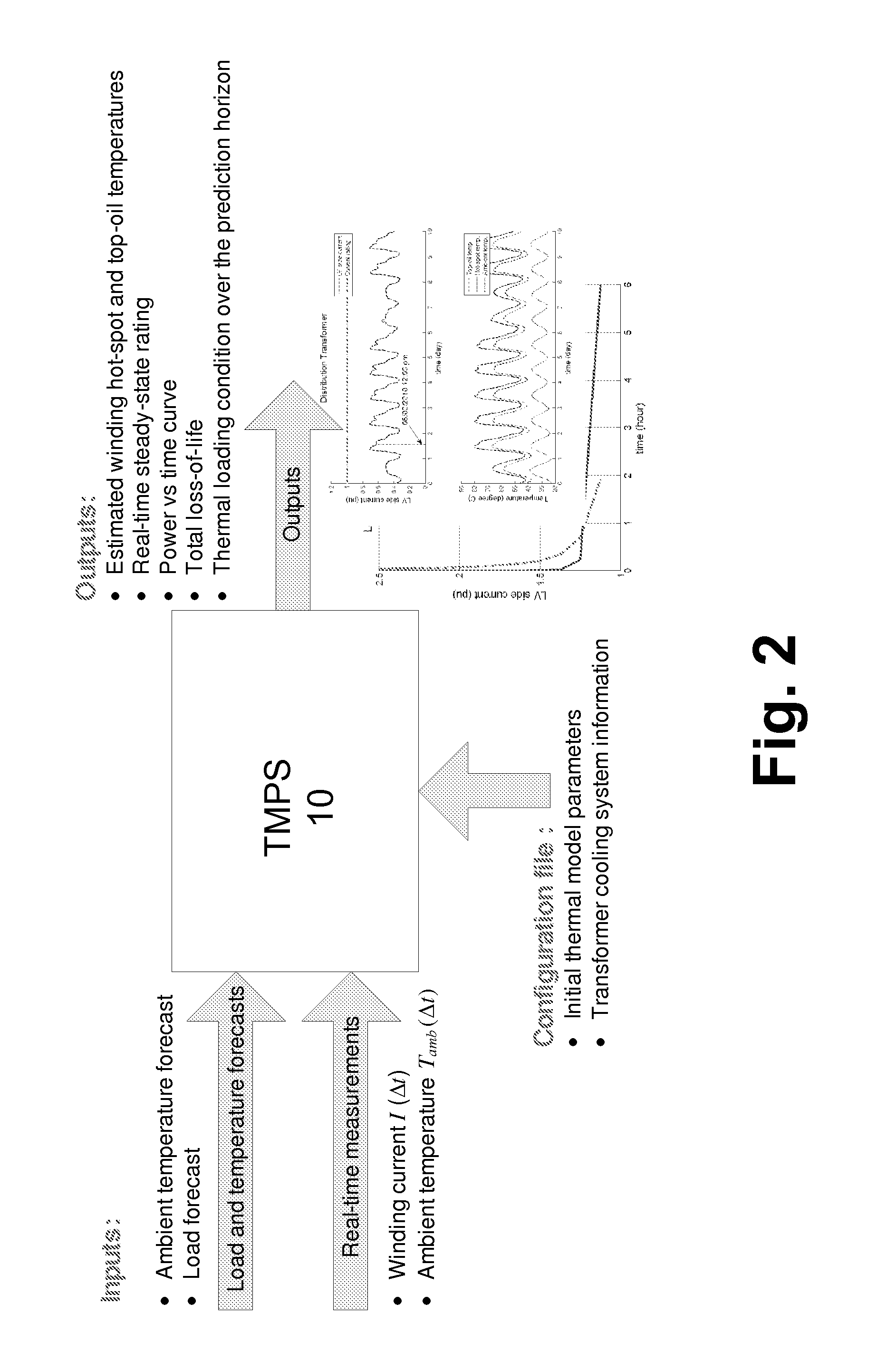
Oil-immersed transformer thermal monitoring and prediction system
InactiveUS20160252401A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermal monitoringTransformer
A real time thermal monitoring and prediction system (TMPS) is provided for use in monitoring and operating a transformer. The TMPS may be used to estimate a maximum loading level for the transformer over a future time period using a dynamic thermal model for the transformer and ambient temperature forecasts. The transformer may be loaded to its maximum loading level during power congestion or a service restoration process.
Owner:ABB INC
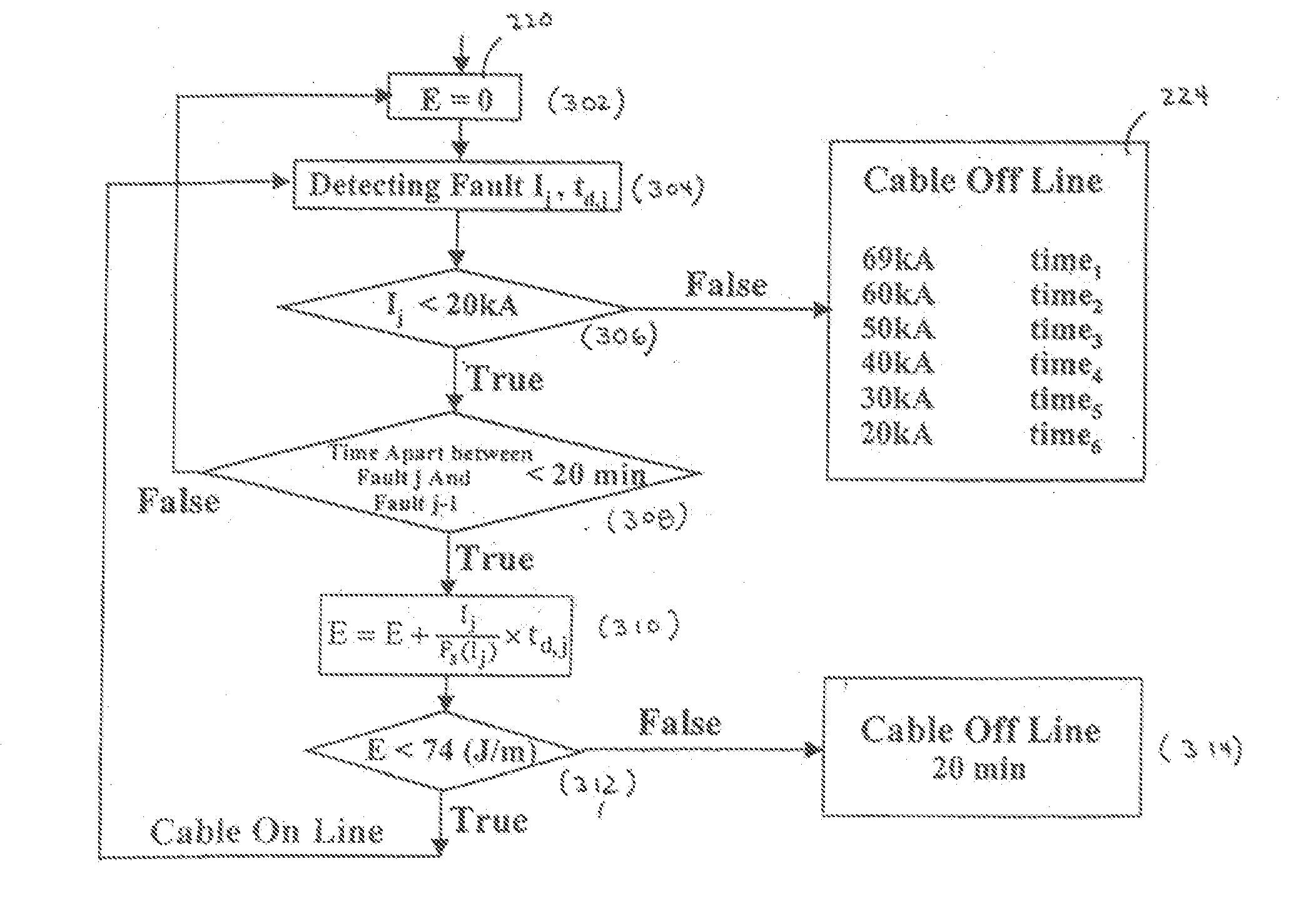
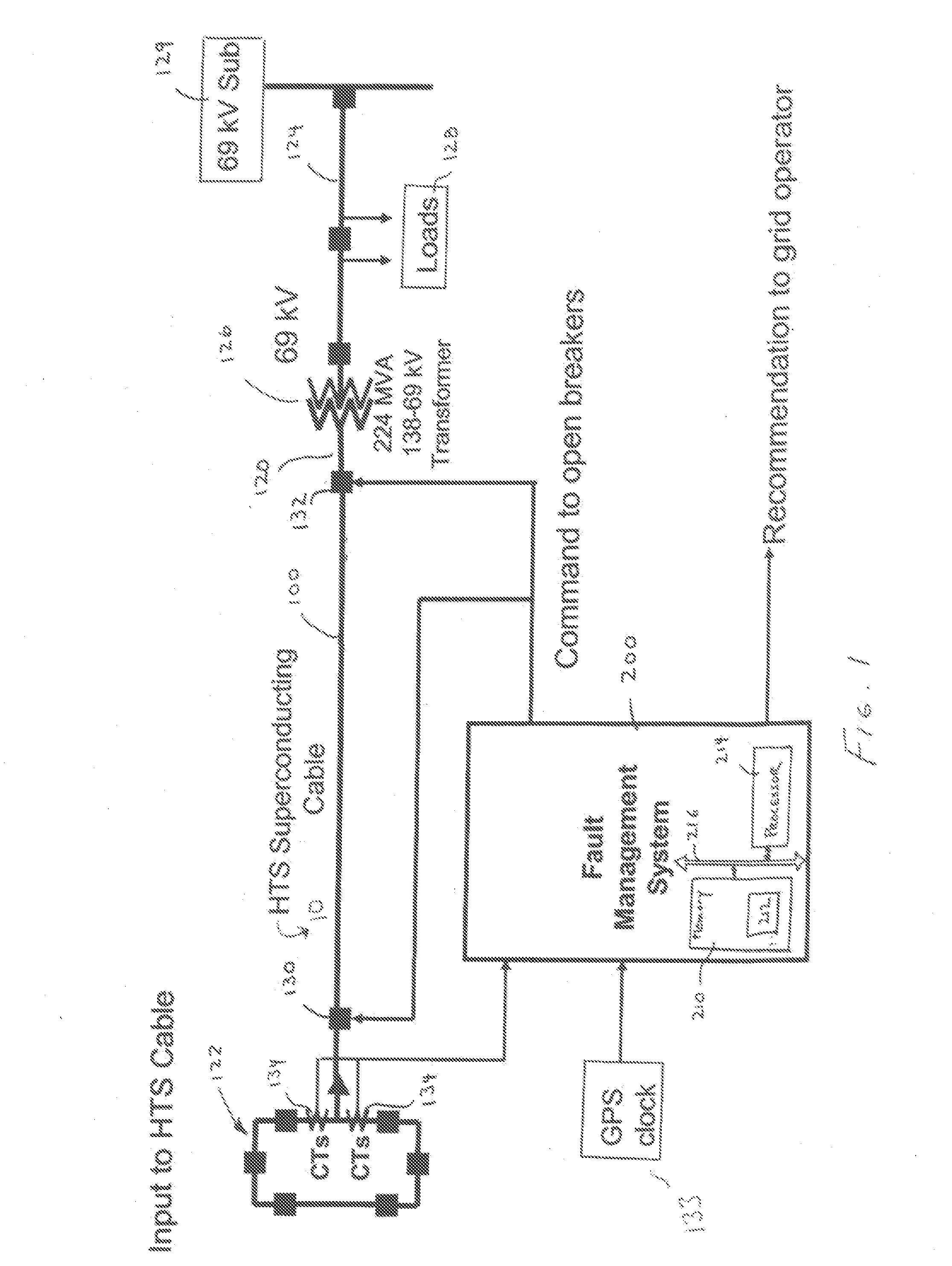
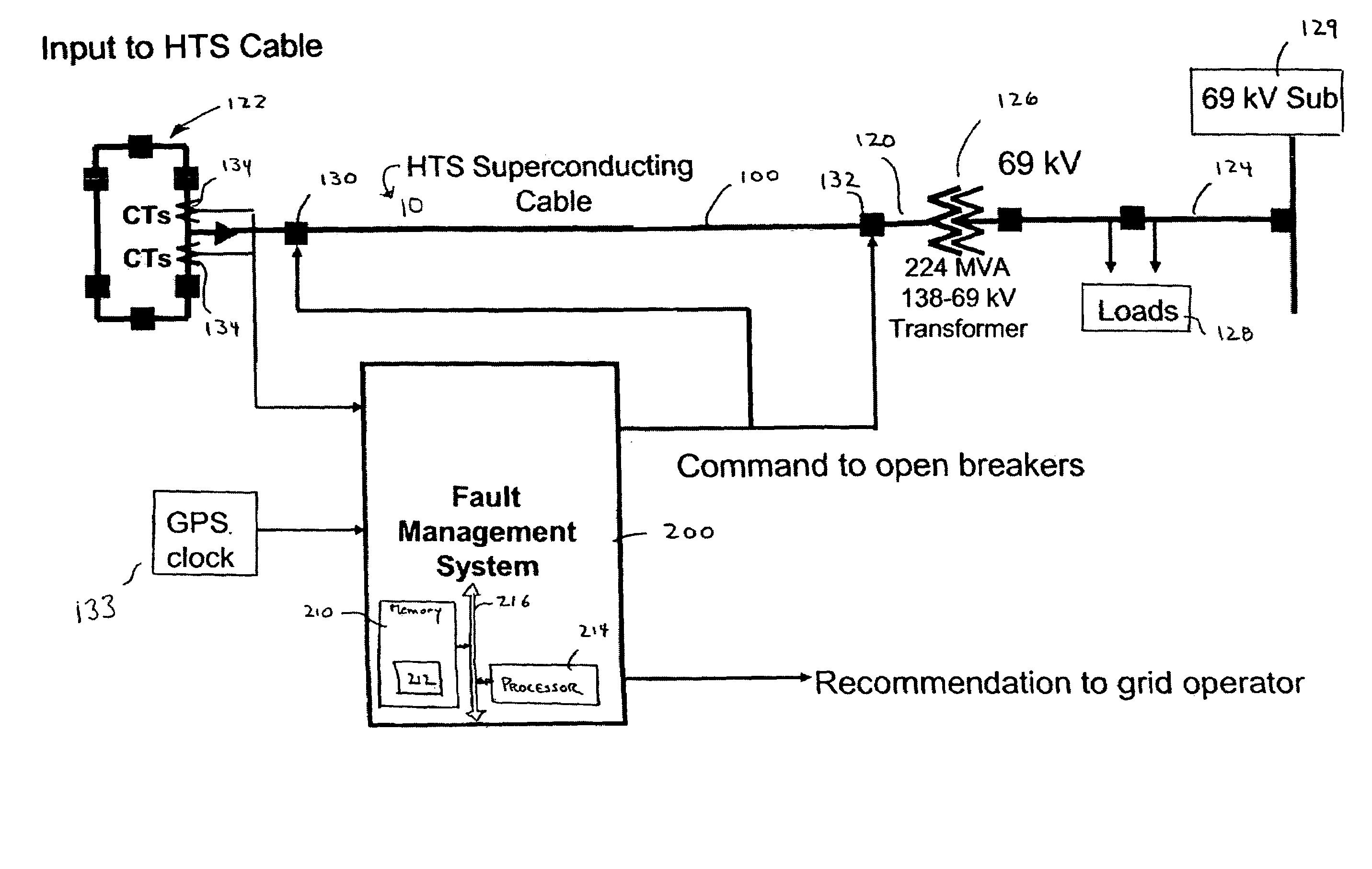
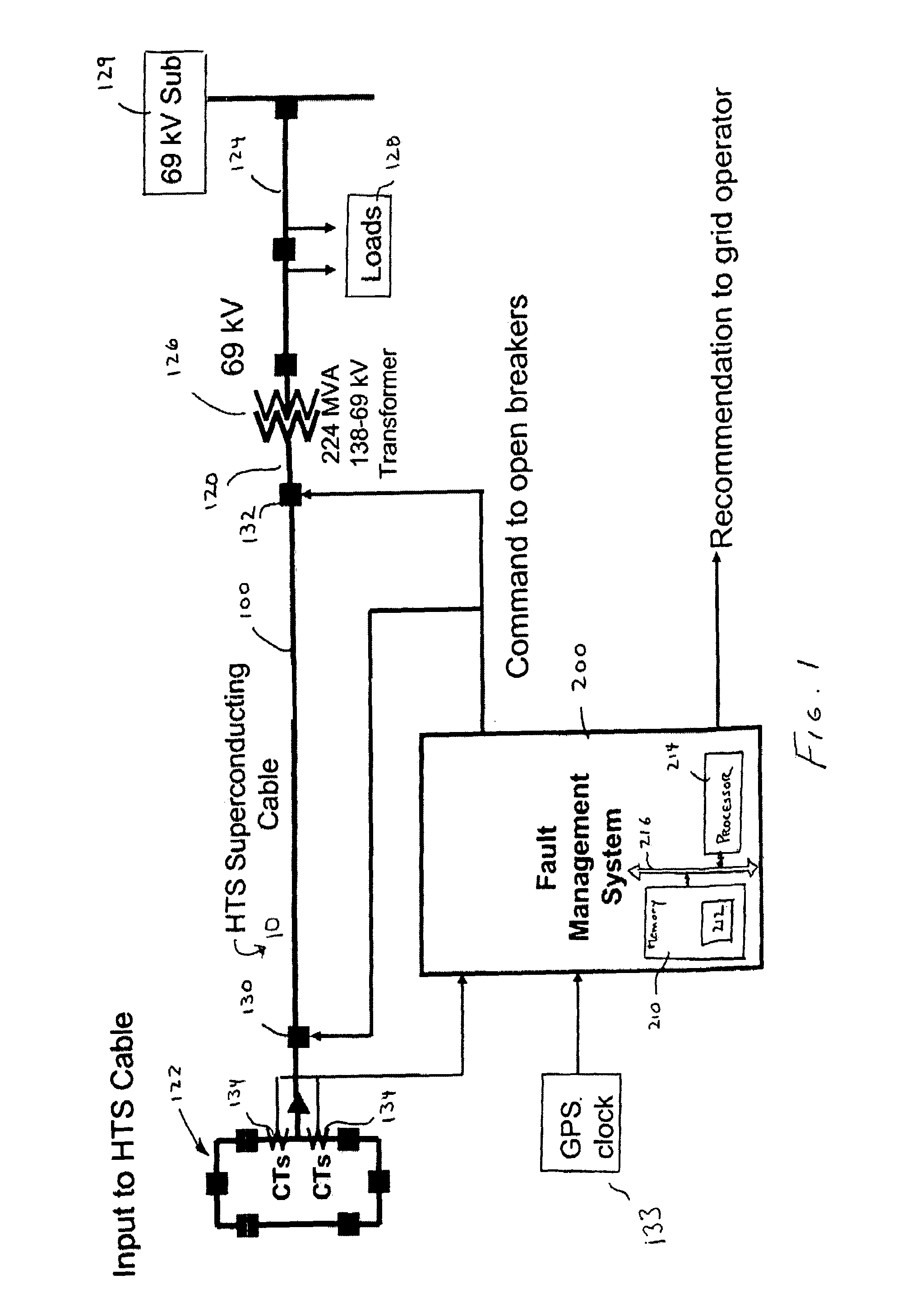
Fault Management of HTS Power Cable
A method and system for providing protection for a superconducting electrical cable located in a utility power network includes detecting a fault current on the superconducting electric cable, determining the cumulative total energy dissipated in the superconducting electrical cable from the fault current and at least one prior fault current over a predetermined time period, and determining whether to disconnect the superconducting electrical cable from the utility power network on the basis of the cumulative total energy dissipated.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR +1
Electrical Power Grid Monitoring Apparatus, Articles of Manufacture, and Methods of Monitoring Equipment of an Electrical Power Grid
InactiveUS20150094965A1Testing/monitoring control systemsElectrical testingCommunication interfaceElectricity
Electrical power grid monitoring apparatus, articles of manufacture, and methods of monitoring equipment of an electrical power grid are described. According to one aspect, an electrical power grid monitoring apparatus includes a communications interface configured to access electrical data indicative of electrical energy received at a plurality of consumer locations from an electrical power grid at a plurality of moments in time, the consumer locations being coupled with one or more unbalanced single phase feeders of a distribution system of an electrical power grid and which individually comprise a plurality of components configured to conduct the electrical energy from at least one electrical energy source to the consumer locations, and processing circuitry coupled with the communications interface and configured to use the electrical data to estimate a state of the electrical power grid and to identify one of the components as being in a potentially degraded state using the estimation of the state of the electrical power grid.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
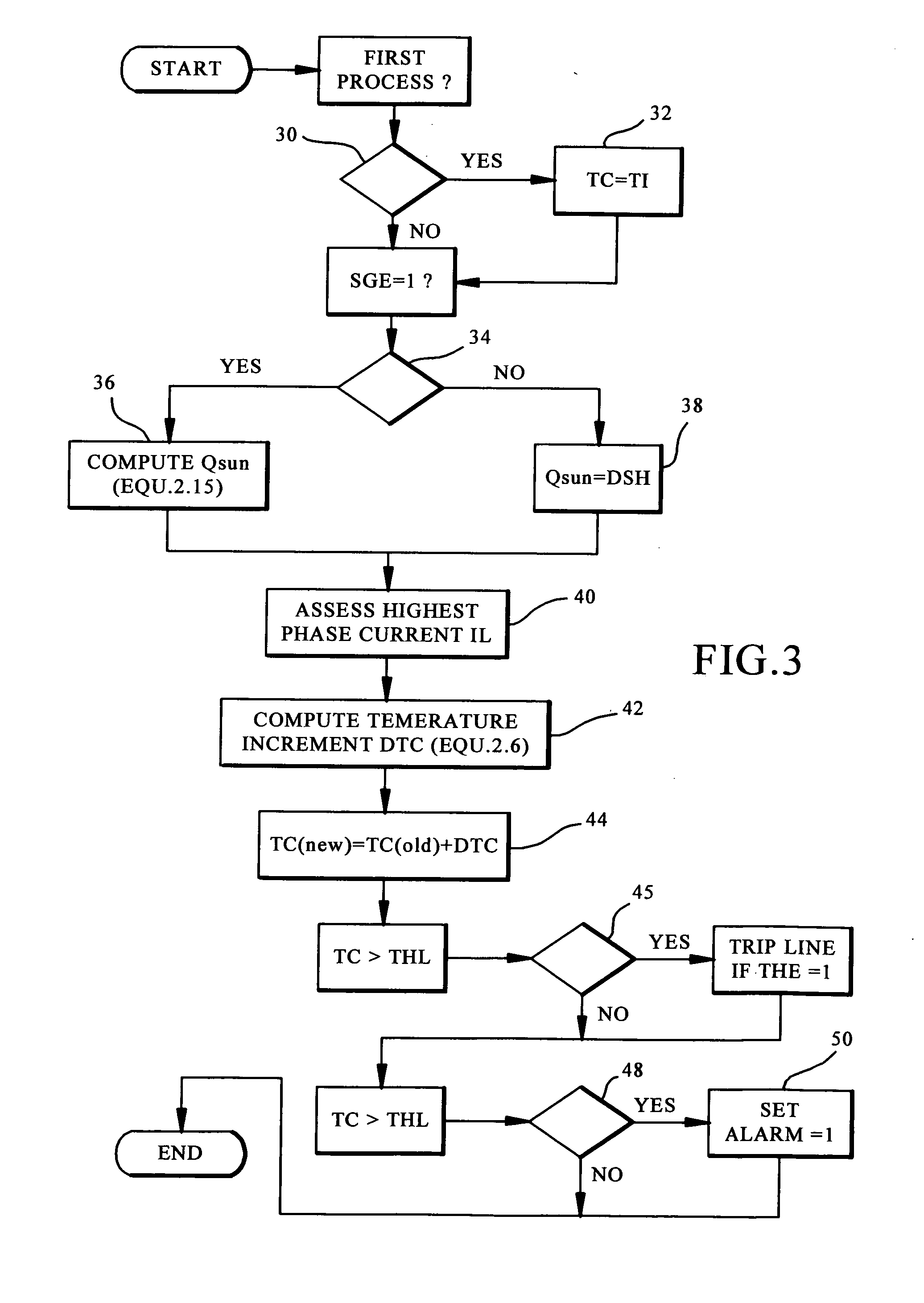
Distance protective relay using a programmable thermal model for thermal protection
ActiveUS20050047043A1Parameter calibration/settingEmergency protective arrangements responsive to undesired changesElectrical conductorUser input
The system includes a distance protective relay for power lines which includes a logic capability which is responsive to settings entered into the relay by an end user to implement the value of those settings into stored thermal model equations which emulate the temperature of the power line conductor. The logic within the relay is organized and has the capability of receiving the setting values entered by the user and to use those in the logic equations to determine the temperature of the conductor.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Method and device for an overload detection in hand-guided power tools
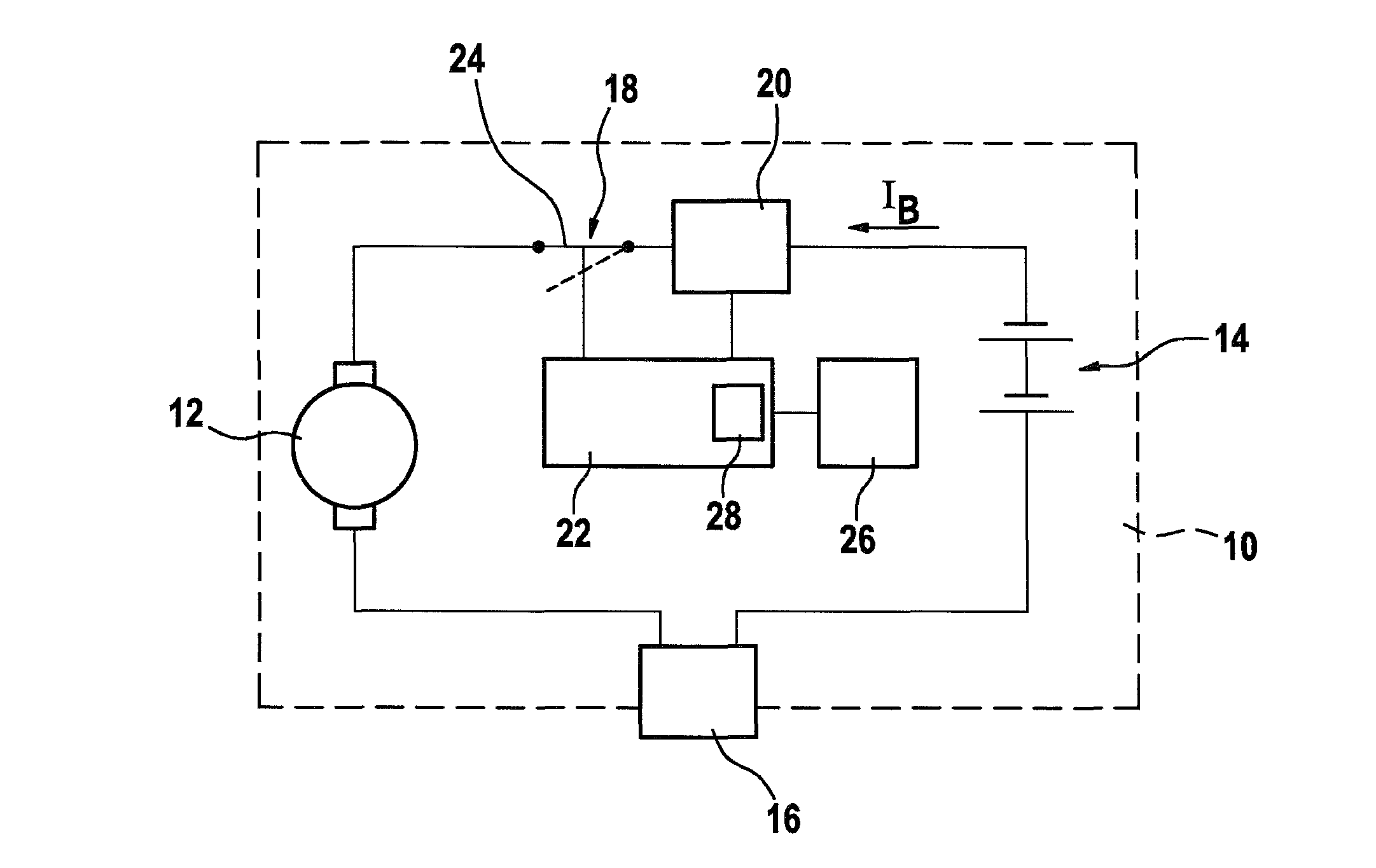
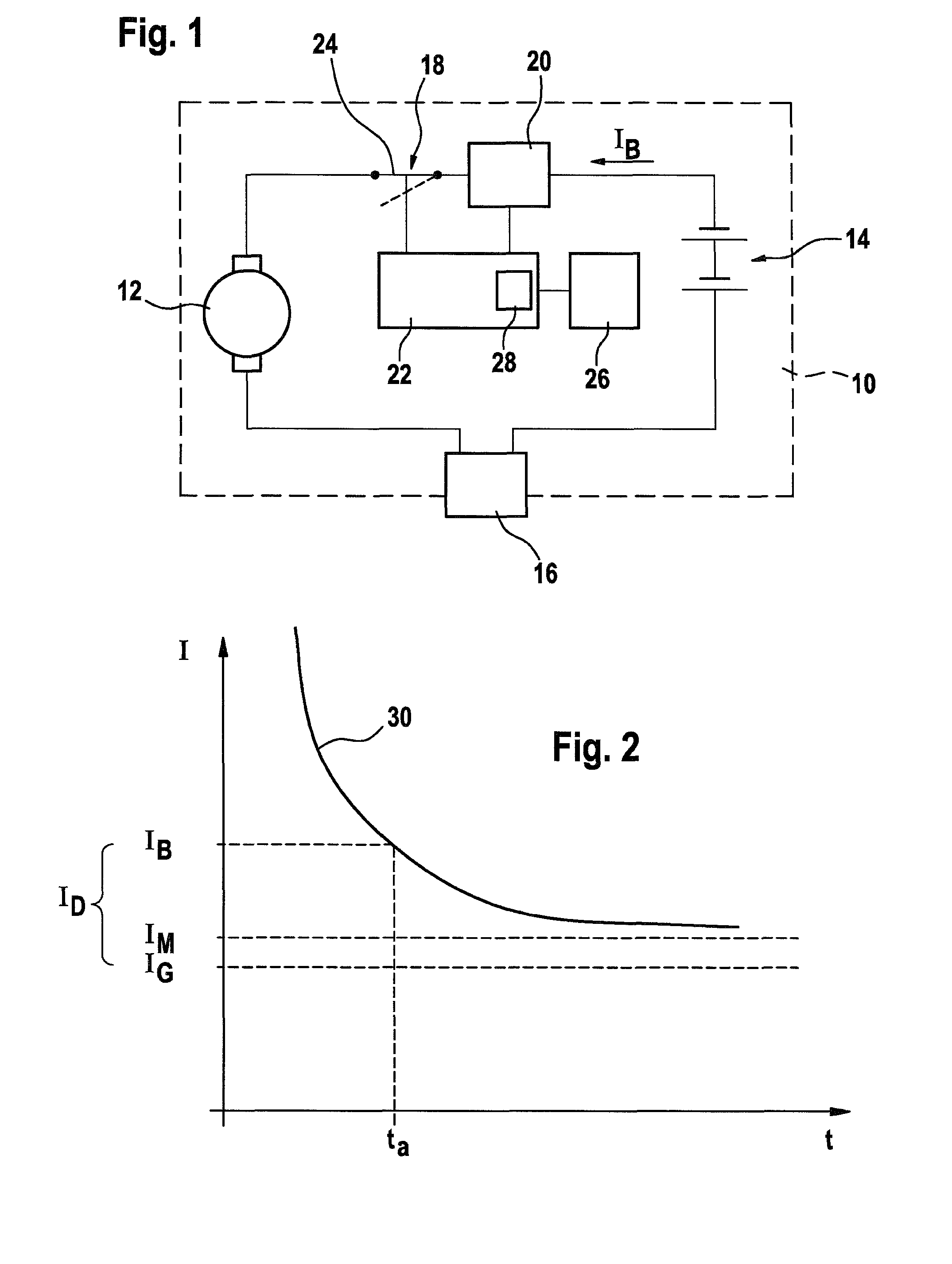
InactiveUS8018182B2Minimizes calculation amount of calculationGood depictionAC motor controlVector control systemsHand heldEngineering
The invention relates to a method for detecting an overload in an electric hand tool (10) comprising an electric motor (12), in particular a battery-driven electric hand tool (10). According to the invention, an operating current (iB) of the electric motor (12) is determined, the difference (ID) between the value of the operating current (IB) and at least one stored current value (IG) is determined and a thermal overload of the electric hand tool (10) is deduced from said difference (ID). The invention also relates to a corresponding monitoring device (22).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fault management of high temperture superconductor cable
A method and system for providing protection for a superconducting electrical cable located in a utility power network includes detecting a fault current on the superconducting electric cable, determining the cumulative total energy dissipated in the superconducting electrical cable from the fault current and at least one prior fault current over a predetermined time period, and determining whether to disconnect the superconducting electrical cable from the utility power network on the basis of the cumulative total energy dissipated.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR +1
Overload protection system for an electrical device
ActiveUS20060126250A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical devicesEngineering
A protection system for an electrical device may include at least one temperature sensitive element located in a region adjacent to a component of the electrical device and configured to provide an output related to an actual temperature in the region. The system may also include a controller configured to determine the actual temperature in the region based on the output of the at least one temperature sensitive element and to determine a predicted temperature of the component based on the actual temperature in the region and on a predetermined heat dissipation characteristic of the electrical device.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Predictive method for surplus life, temperature testing structure and electronic device
InactiveCN1439867AThermometers using mean/integrated valuesElectrolytic capacitorsElectrolysisPredictive methods
Owner:ORMON CORP
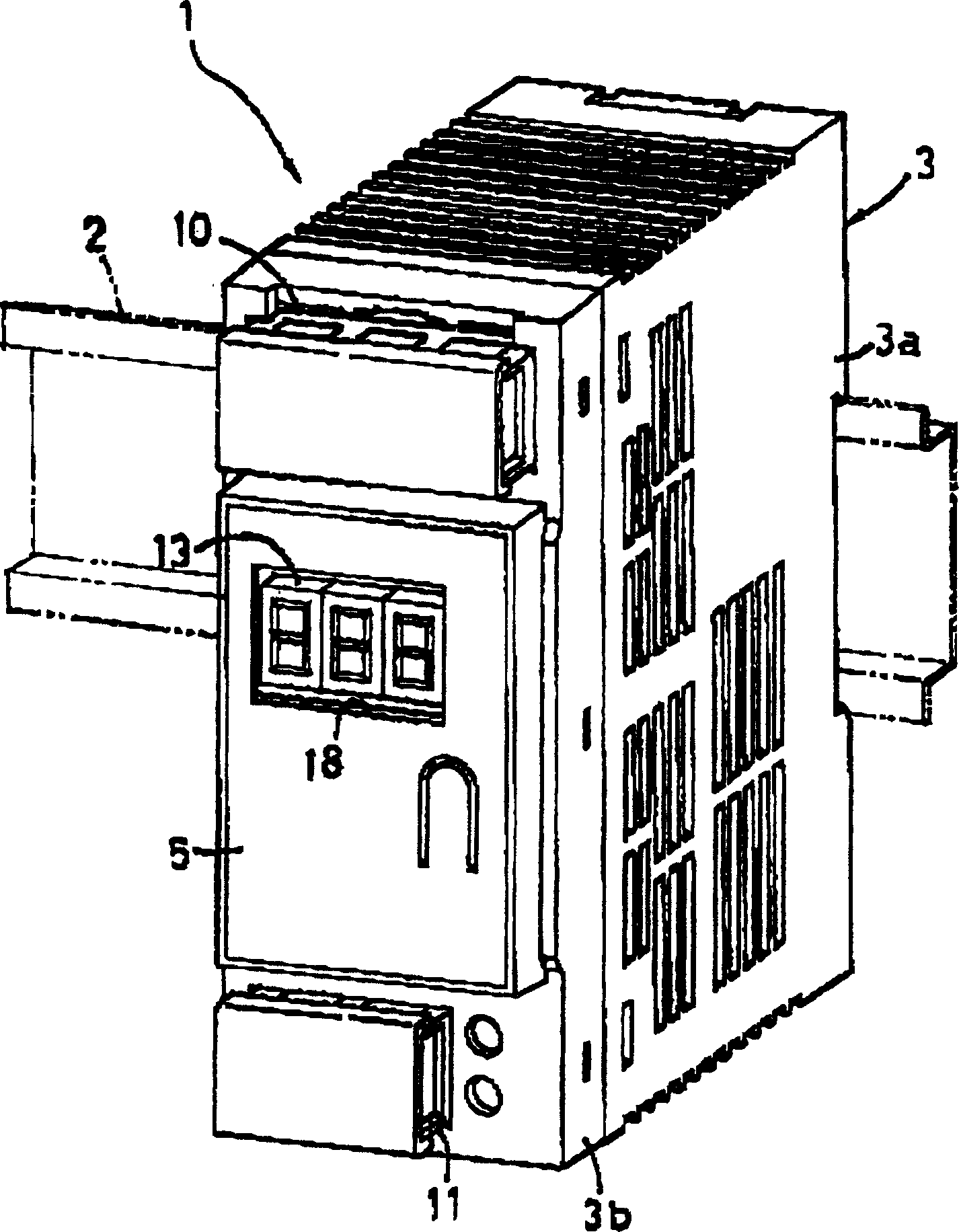
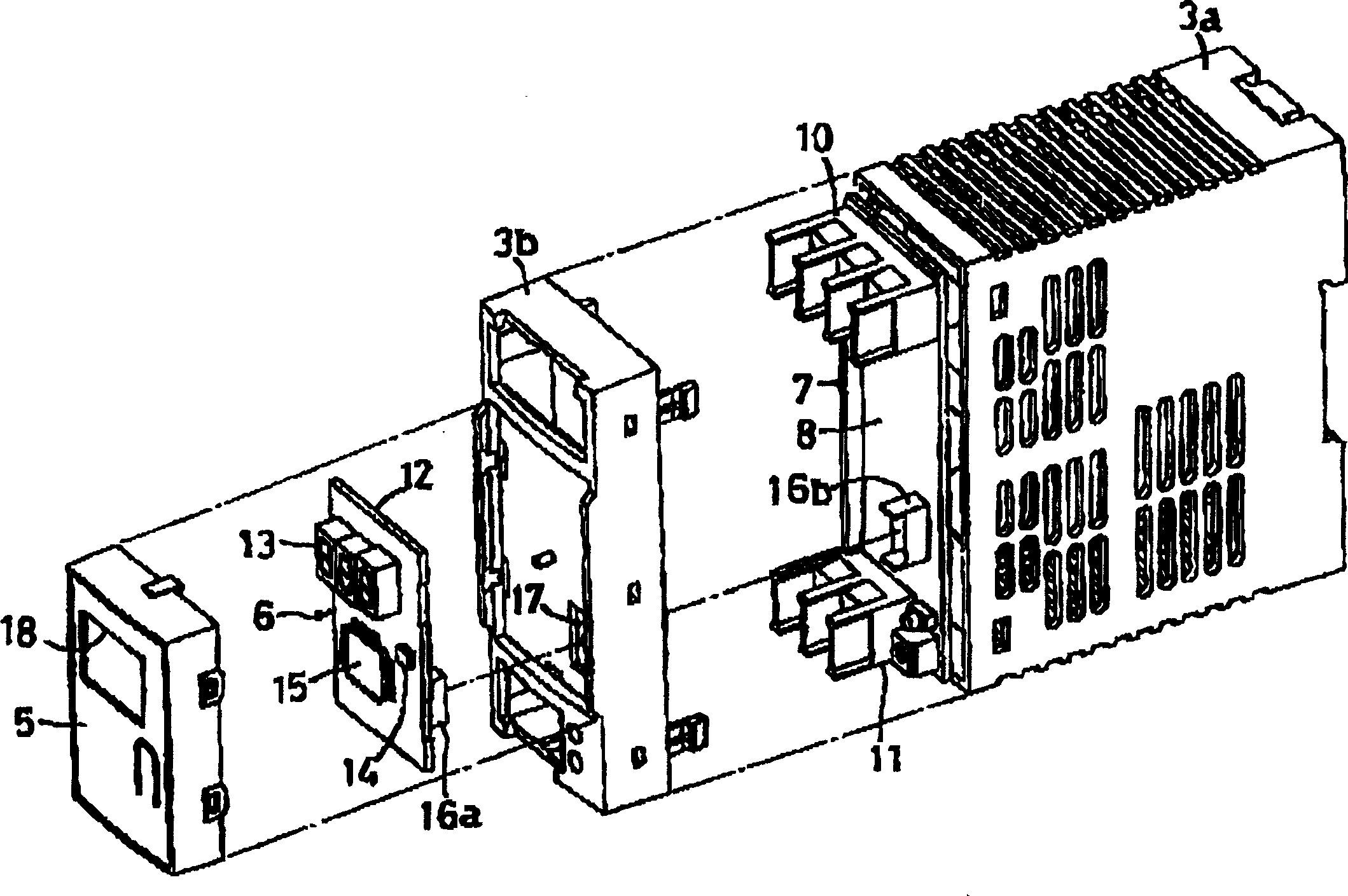
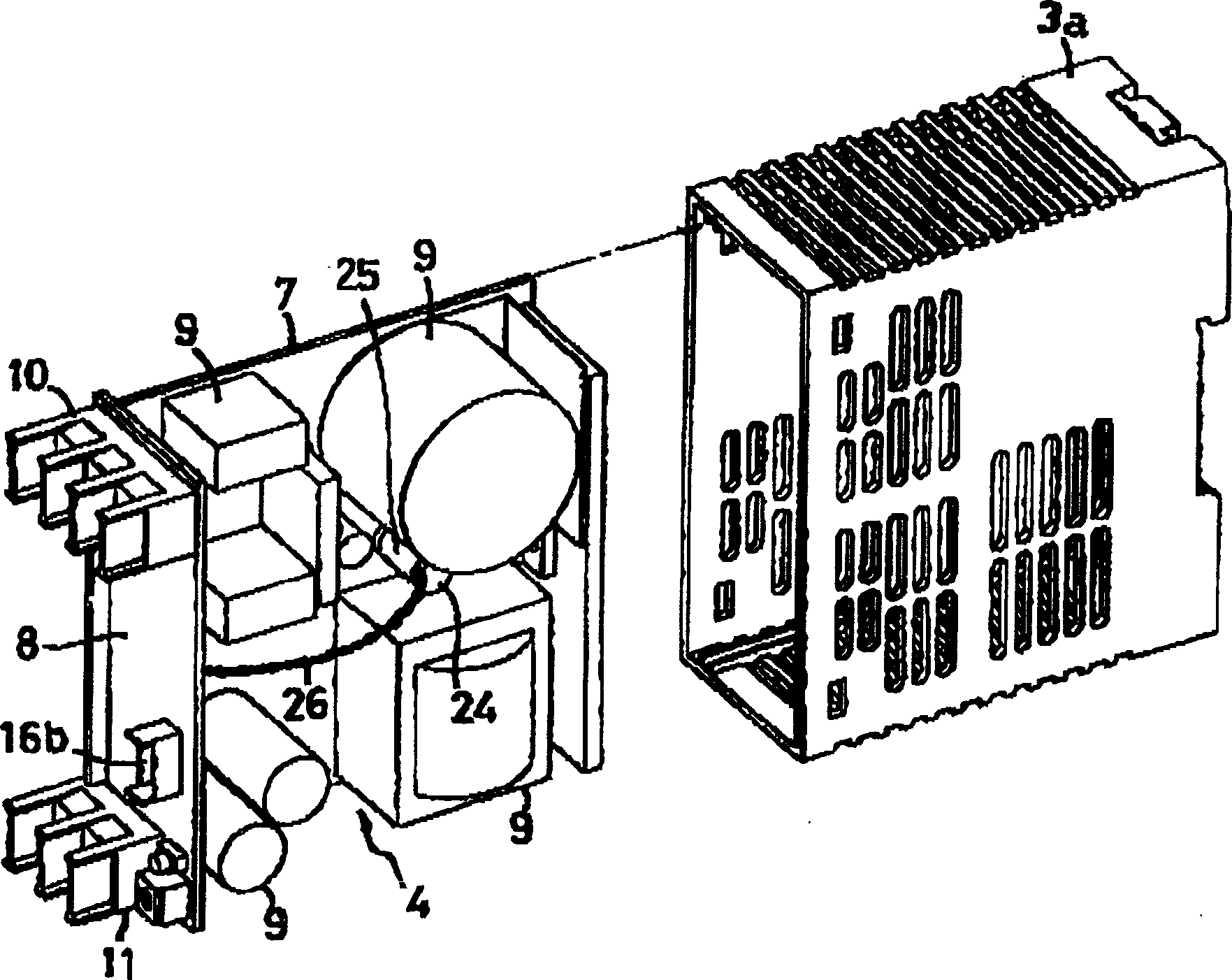
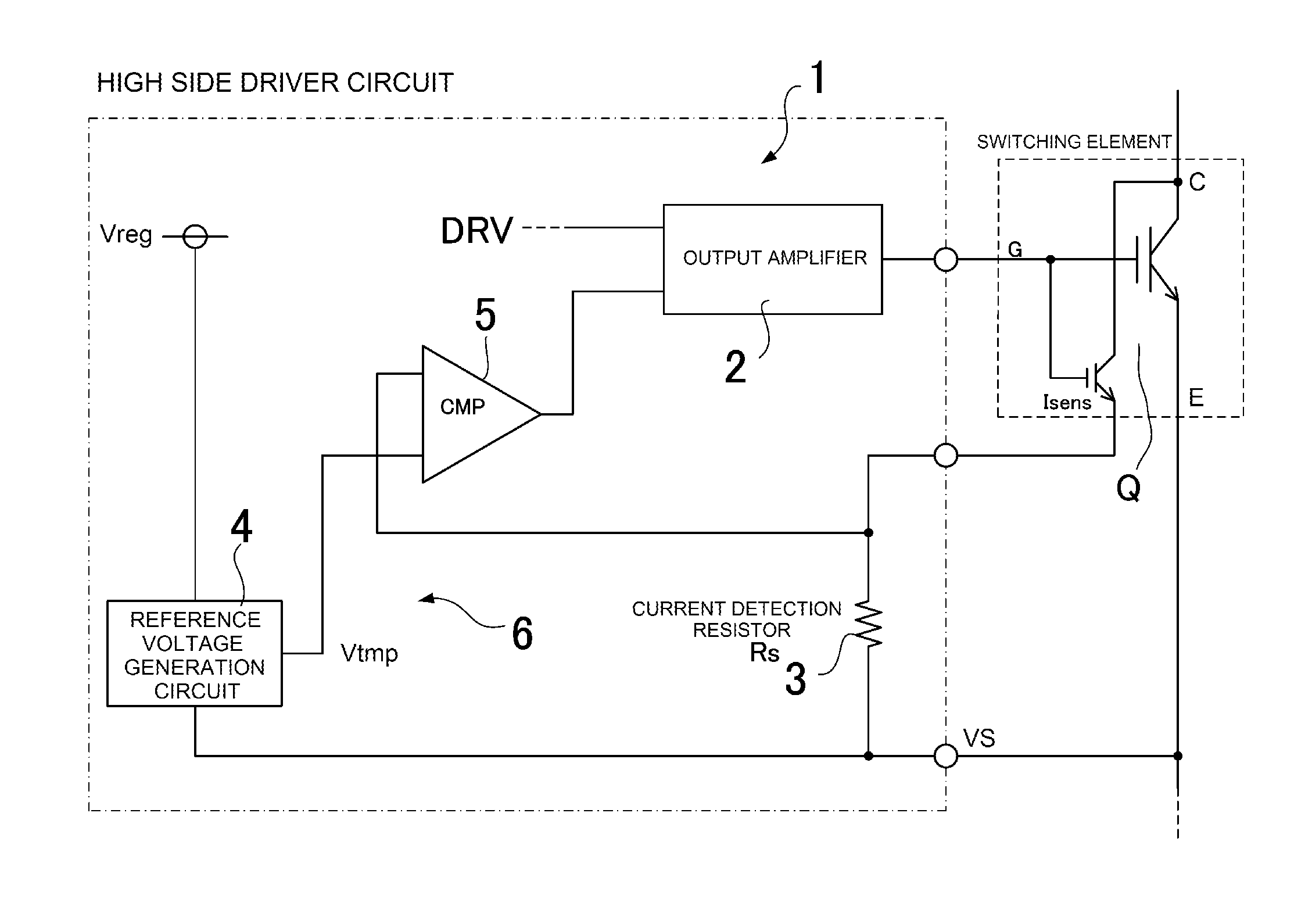
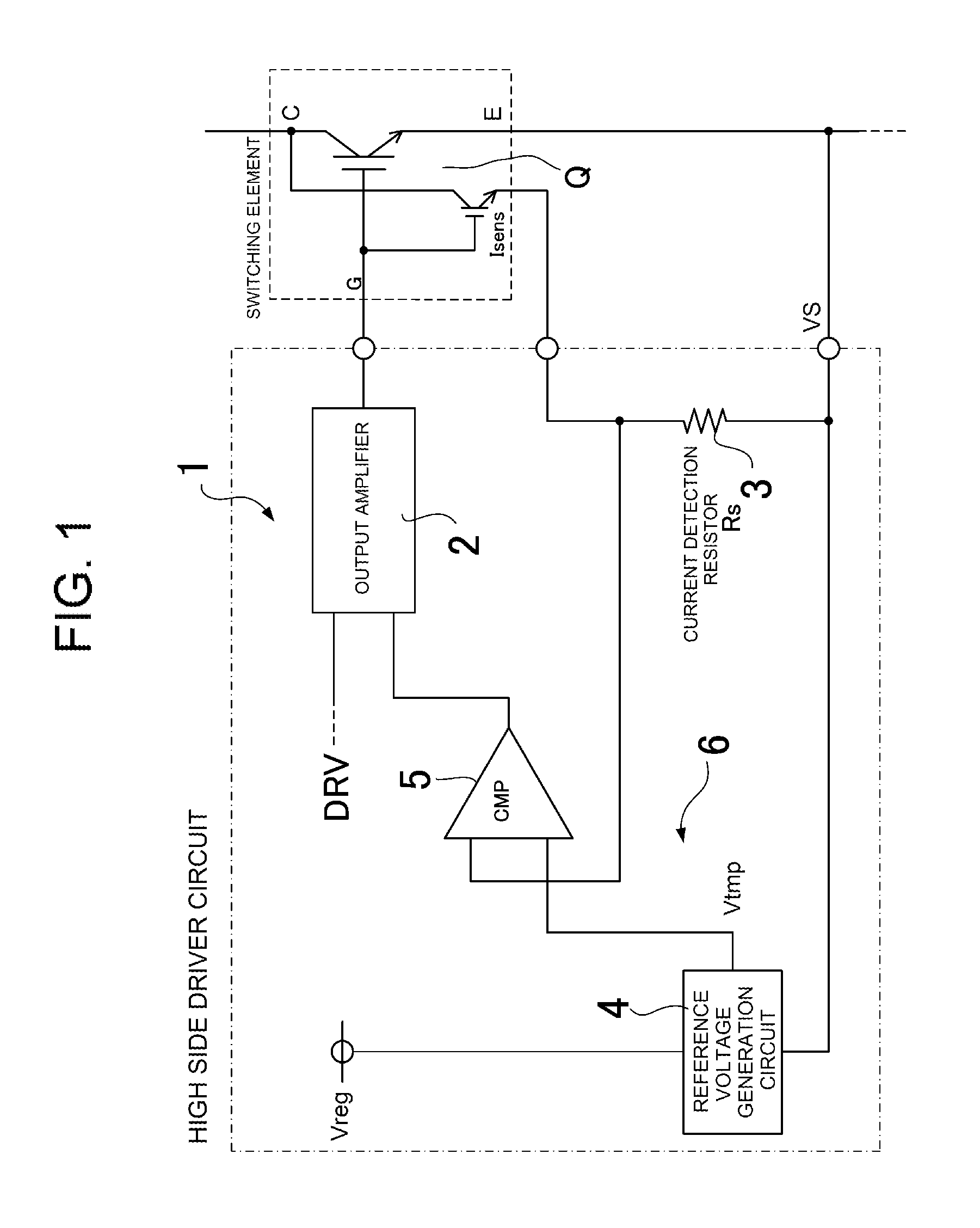
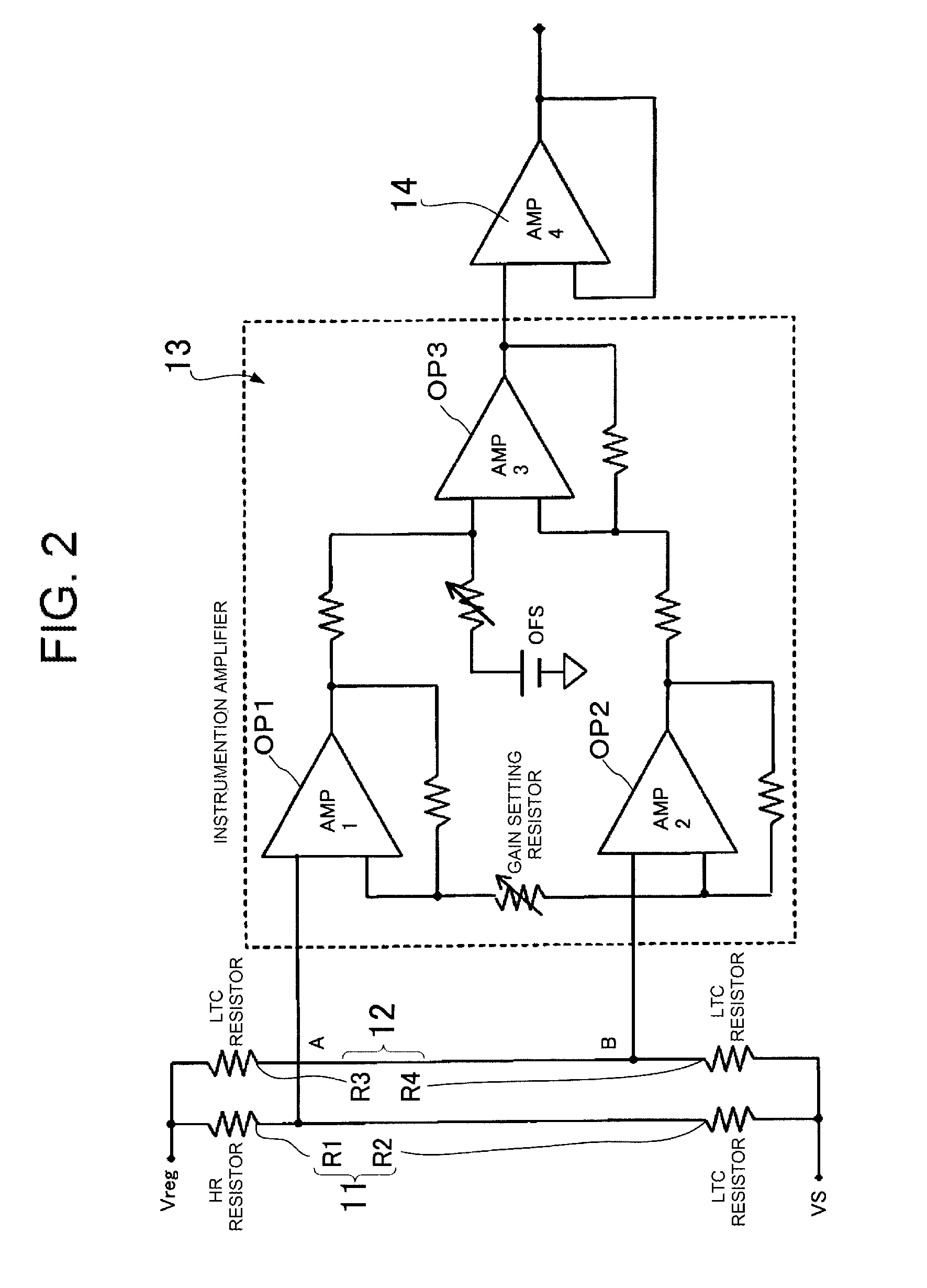
Overcurrent detection circuit
ActiveUS20150309090A1Accurate and stable detectionStable generationCurrent/voltage measurementDc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
An overcurrent detection circuit includes a current detection resistor that generates a voltage in proportion to current flowing through a switching element and a comparator that compares the voltage detected via the current detection resistor and a reference voltage generated by a reference voltage generation circuit to thereby detect overcurrent flowing through the switching element. In particular, the reference voltage generation circuit includes: a first resistance voltage dividing circuit that resistance-divides a standard voltage by connecting, in series, two types of resistors having different temperature characteristics; a second resistance voltage dividing circuit that resistance-divides the standard voltage by connecting, in series, resistors having the same temperature characteristics; and an instrumentation amplifier that generates the reference voltage according to the difference between the divided output voltages of the first and second resistance voltage dividing circuits.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Power supply controller
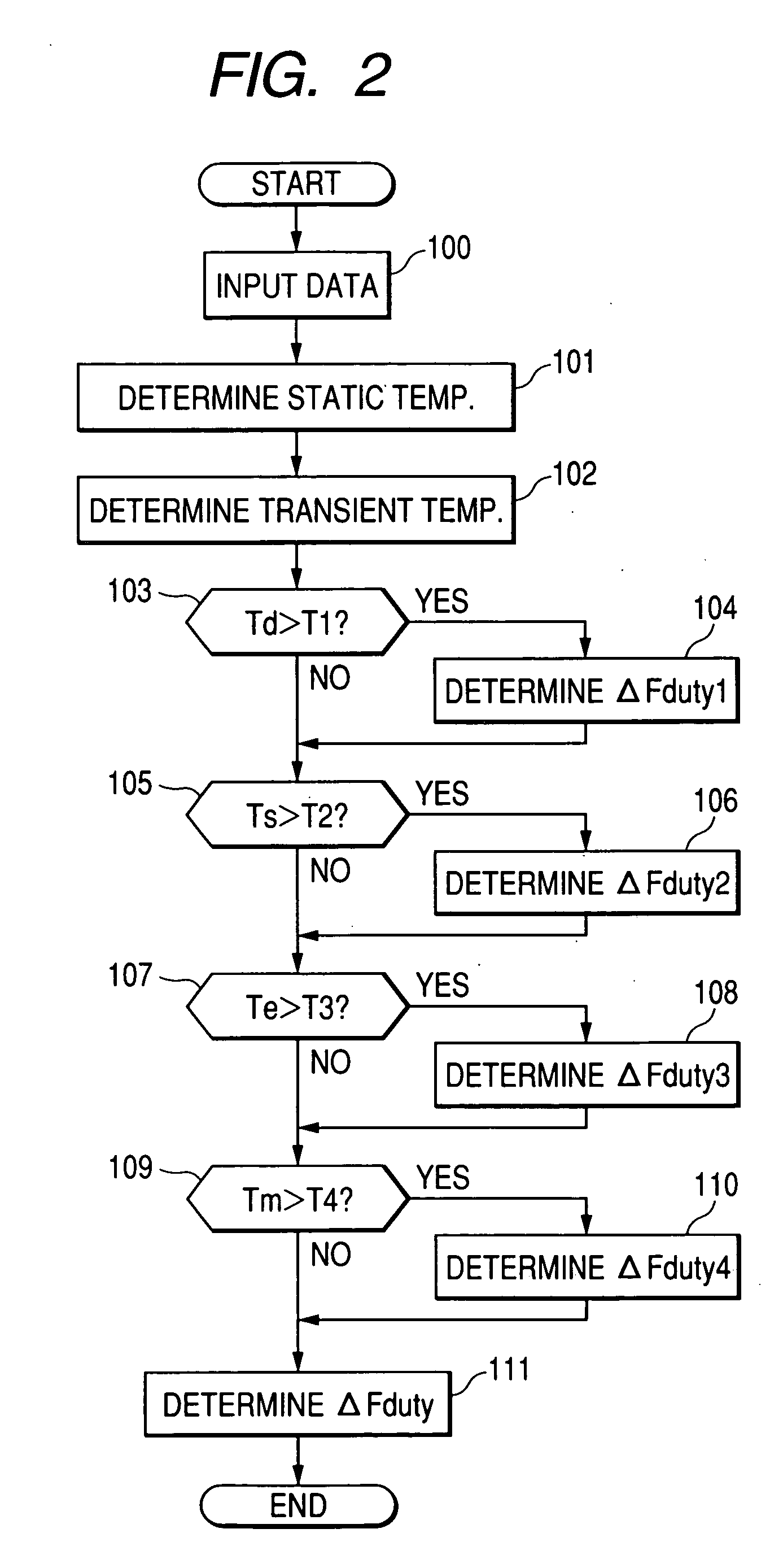
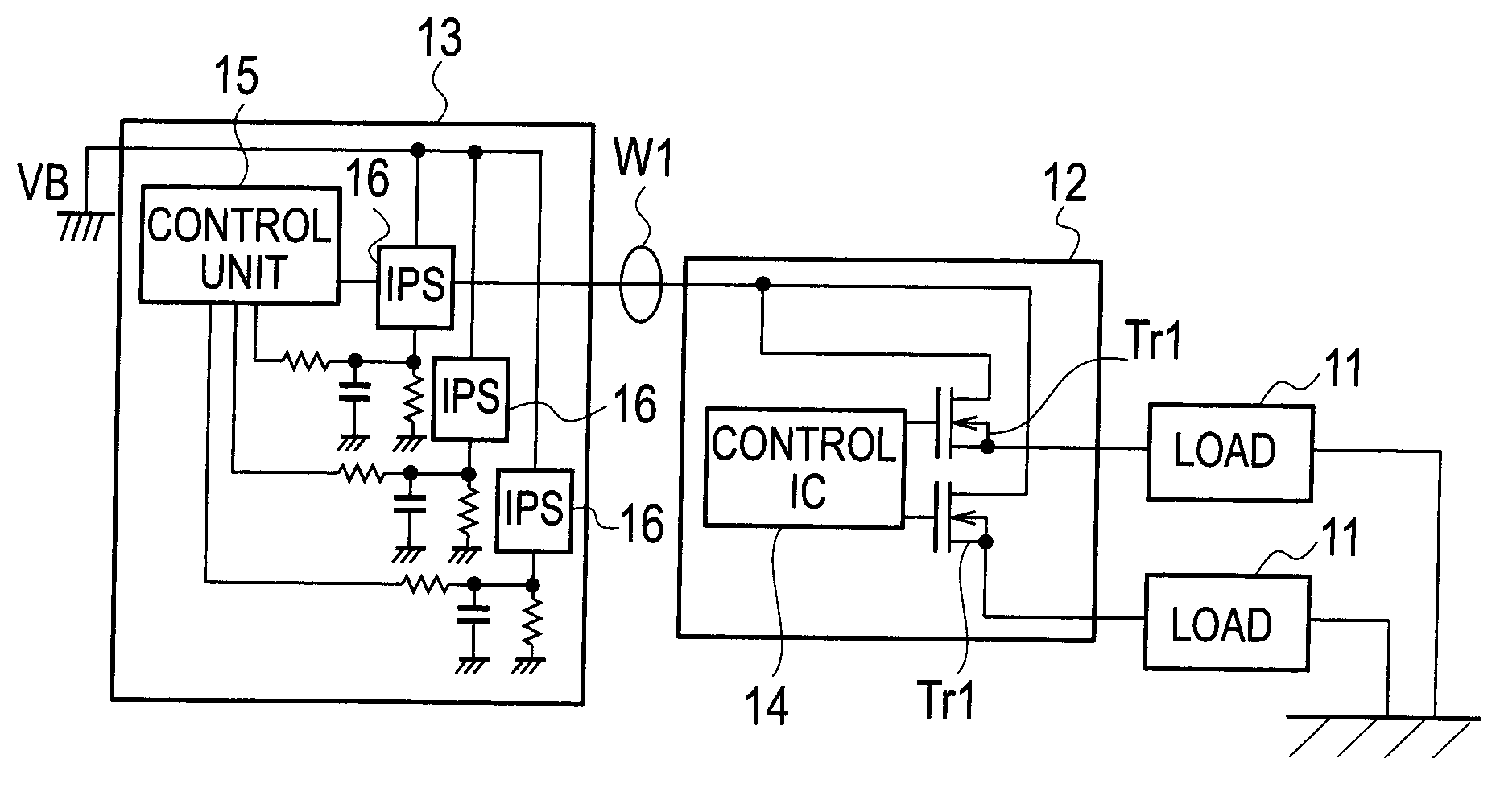
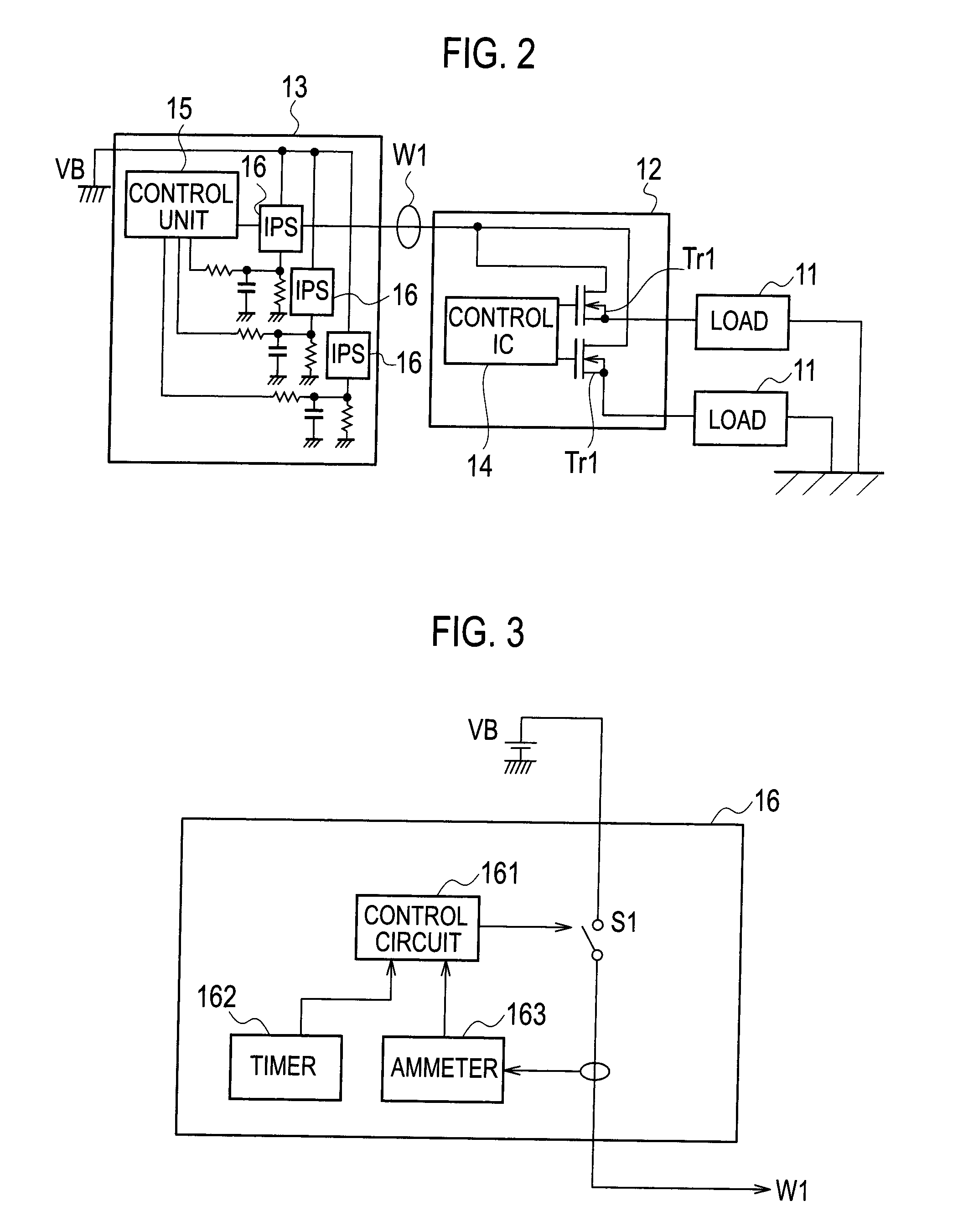
ActiveUS20120176115A1Reduce in quantityElectronic switchingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPower controllerCurrent threshold
The power supply controller performs the power-supply-path protection operation to restrict power supply through the switch element if a value of temperature increase of the power supply path W with respect to the reference temperature To exceeds the temperature threshold value and remove the restriction if the temperature decreases to the temperature threshold value or lower. And the controller performs the switch protection operation to restrict the power supply through the switch element if the value of the flowing current exceeds the current threshold value and remove the restriction after the reference time H elapses. And also the controller adds the additional value F to the value of temperature increase on condition that the value of the flowing current exceeds the current threshold value in the power supply protection operation and compares a post-addition temperature to the temperature threshold value.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
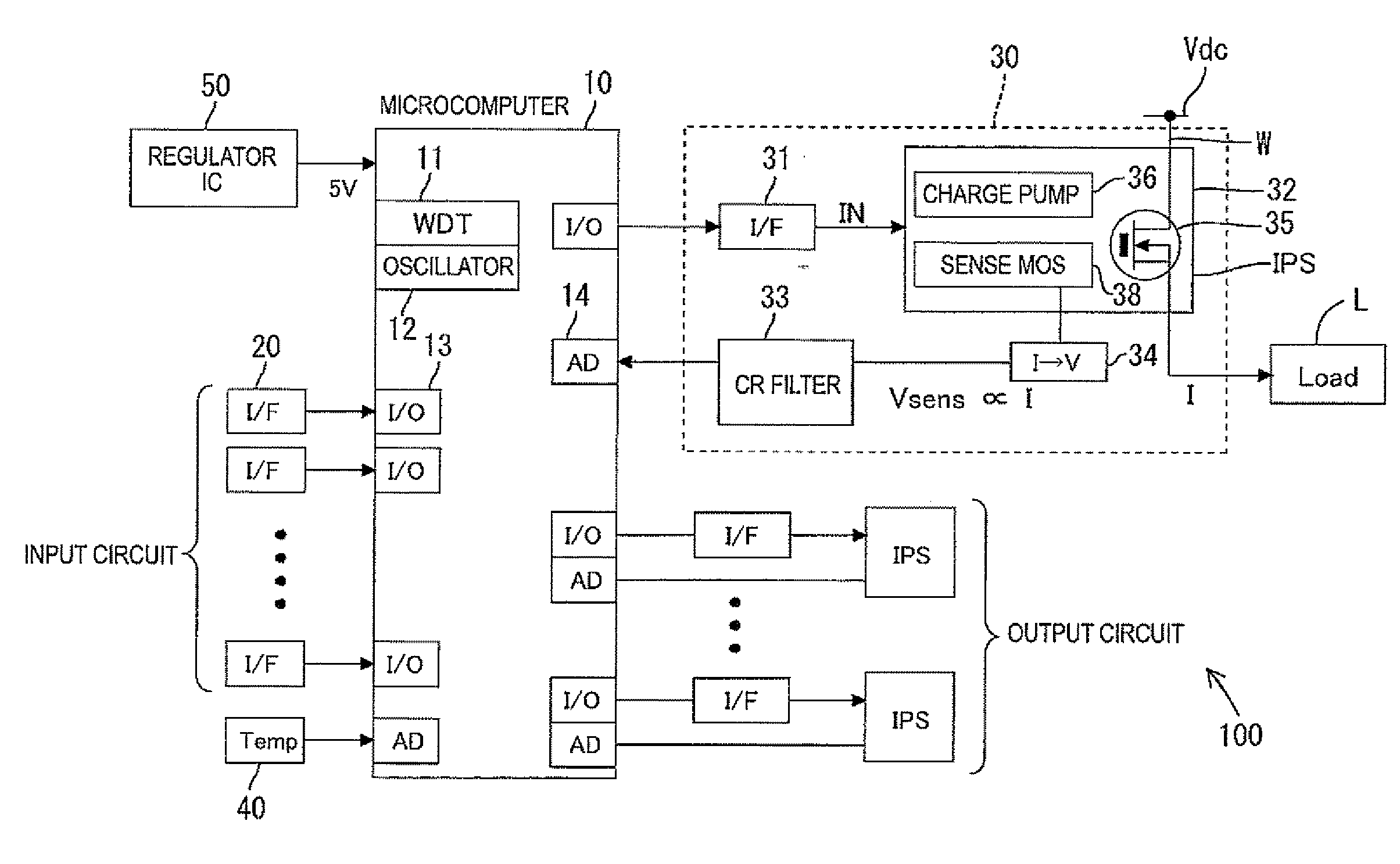
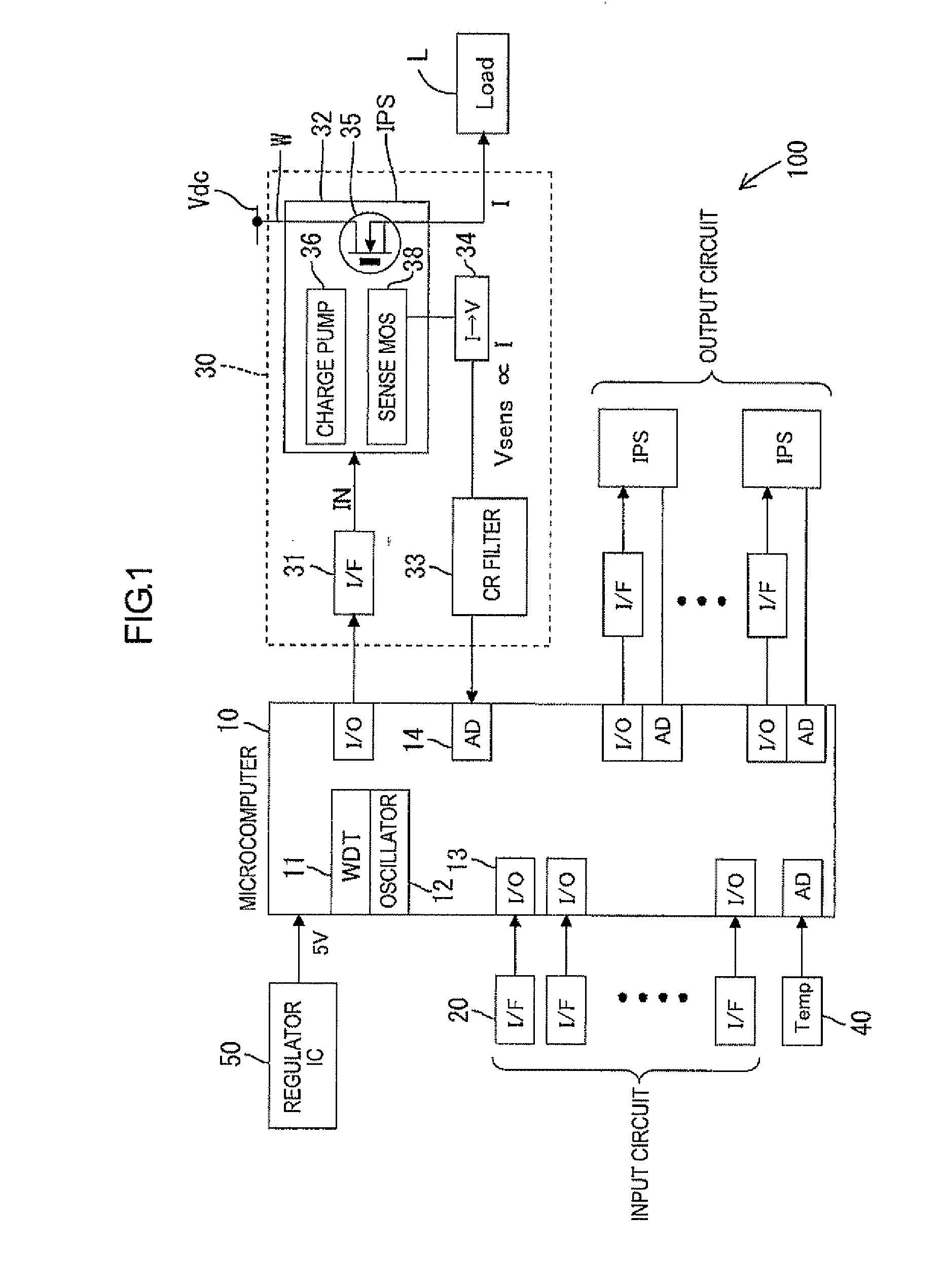
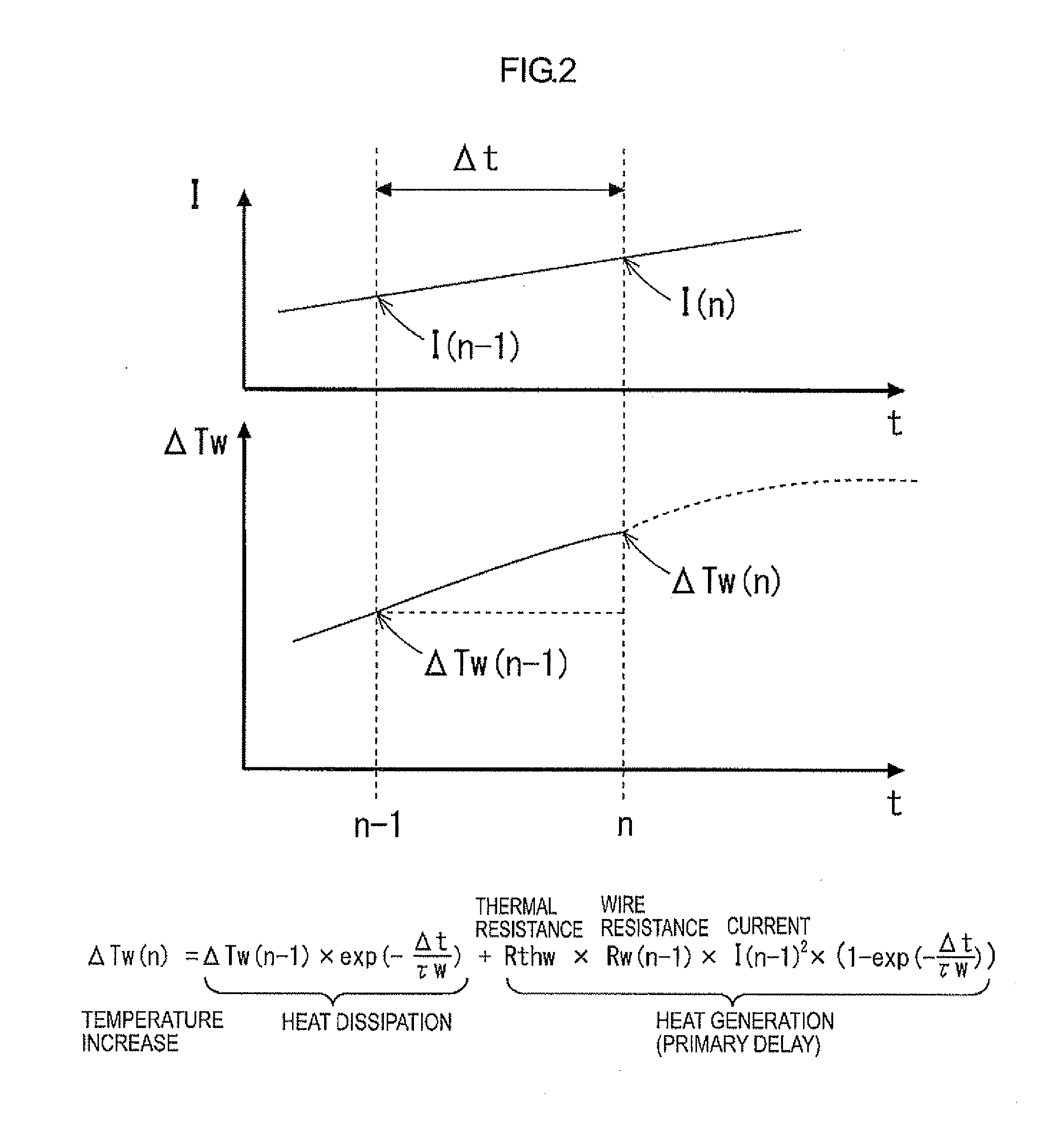
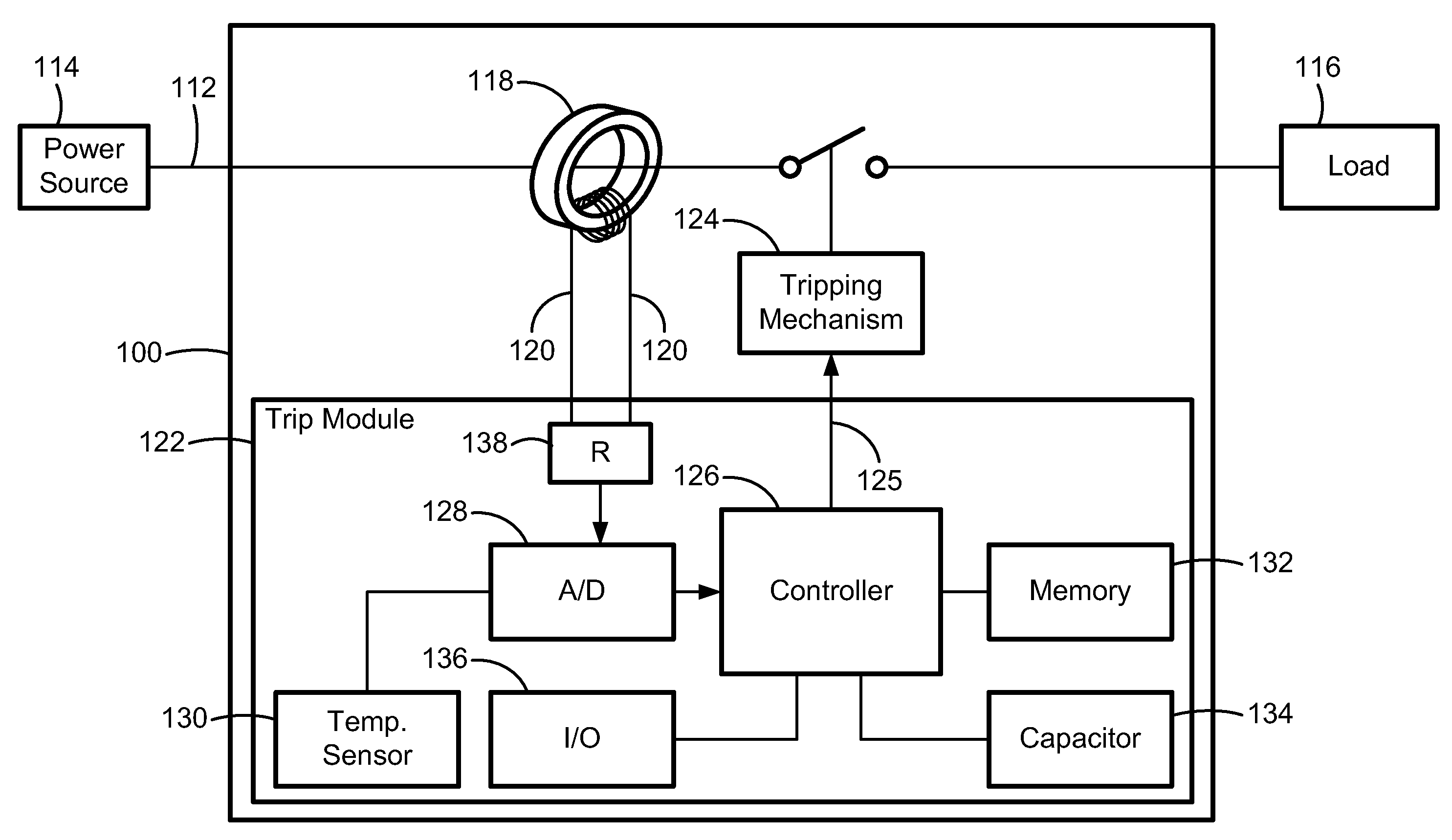
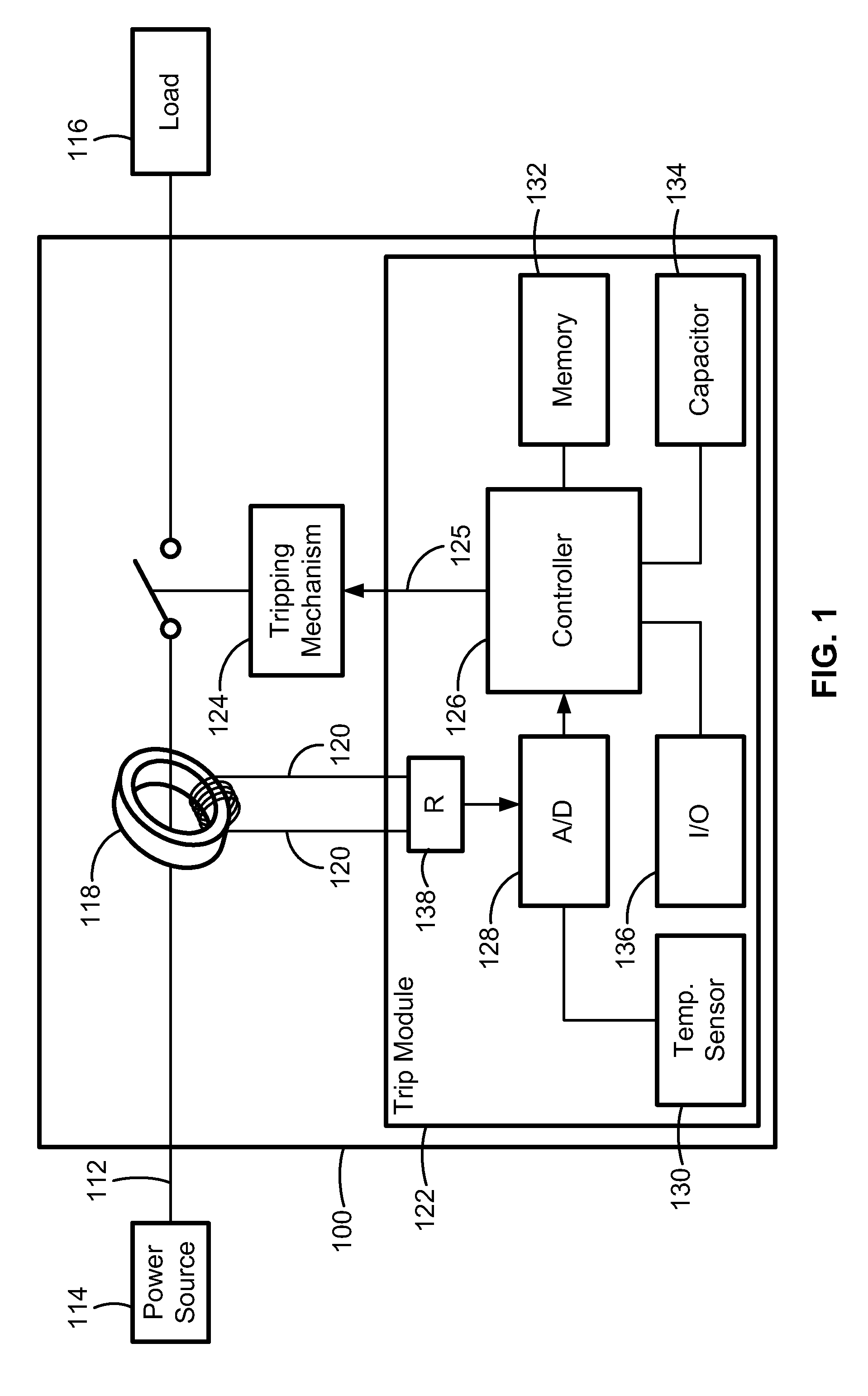
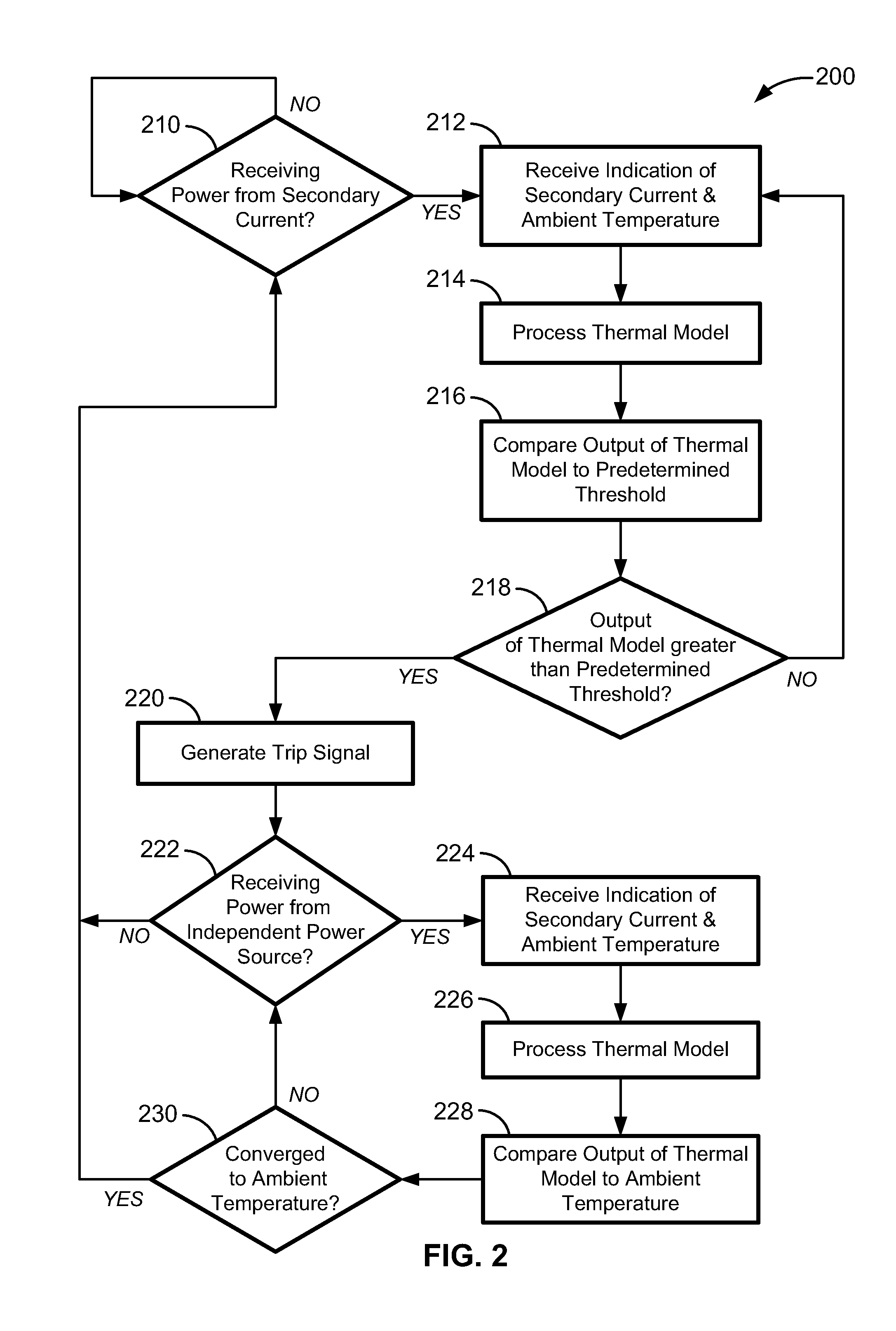
Thermal Memory In A Fault Powered System
ActiveUS20120123762A1Precise, flexible, and easy-to-implementMaximum flexibilityEmergency protection for supplying operative powerAerodynamics improvementMicrocontrollerElectrical conductor
A circuit breaker system for providing thermal protection to a conductor conducting current from a power source to a load. While the power source is connected to the load, a microcontroller is powered by the current passing through the conductor to thermally model the temperature of the conductor. If the microcontroller determines that the temperature of the conductor has risen to an undesirable or unsafe level, the circuit breaker disconnects the power source from the load and the current no longer passes through the conductor. With no current passing through the conductor, the microcontroller no longer receives power from the conductor. Instead, the microcontroller continues to model the temperature of the conductor as the conductor cools to an ambient temperature by receiving power from an energy storage device. Accordingly, the microcontroller continuously models the temperature of the conductor until the temperature of the conductor cools to the ambient temperature.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Methods and apparatus for optimal voltage and frequency control of thermally limited systems
Methods, apparatus, and articles of manufacture control a device or system that has an operational limit related to the rate or frequency of operation. The frequency of operation is controlled at a variable rate calculated to maximize the system or apparatus performance over a calculated period of time short enough that a controlling factor, such as power consumption, does not vary significantly during the period. Known system parameters, such as thermal resistance and capacitance of an integrated circuit (IC) and its package, and measured values, such as current junction temperature in an IC, are used to calculate a time-dependent frequency of operation for the upcoming time period that results in the best overall performance without exceeding the operational limit, such as the junction temperature.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Rotor thermal model for use in motor protection
ActiveUS7161778B2Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements responsive to undesired changesElectric machineInduction motor
The protective relay for an induction motor includes a first program function which establishes a first thermal threshold value for a start condition of the motor, using a start condition thermal model. The thermal condition of the motor is determined by measuring the motor's thermal response to stimulus. A comparator compares the start condition thermal representation with the first thermal threshold value and monitors whether the first thermal threshold value is exceeded by the start condition thermal representation. A second thermal threshold value is established for a run condition of the motor, including a selected time constant which results in the time-current curves of the start and run conditions being substantially continuous. A representation of the thermal condition of the motor is then developed in response to stimulus current. A comparator then compares the run condition thermal representation with the second thermal threshold value.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Detection of loss of cooling air to traction motors
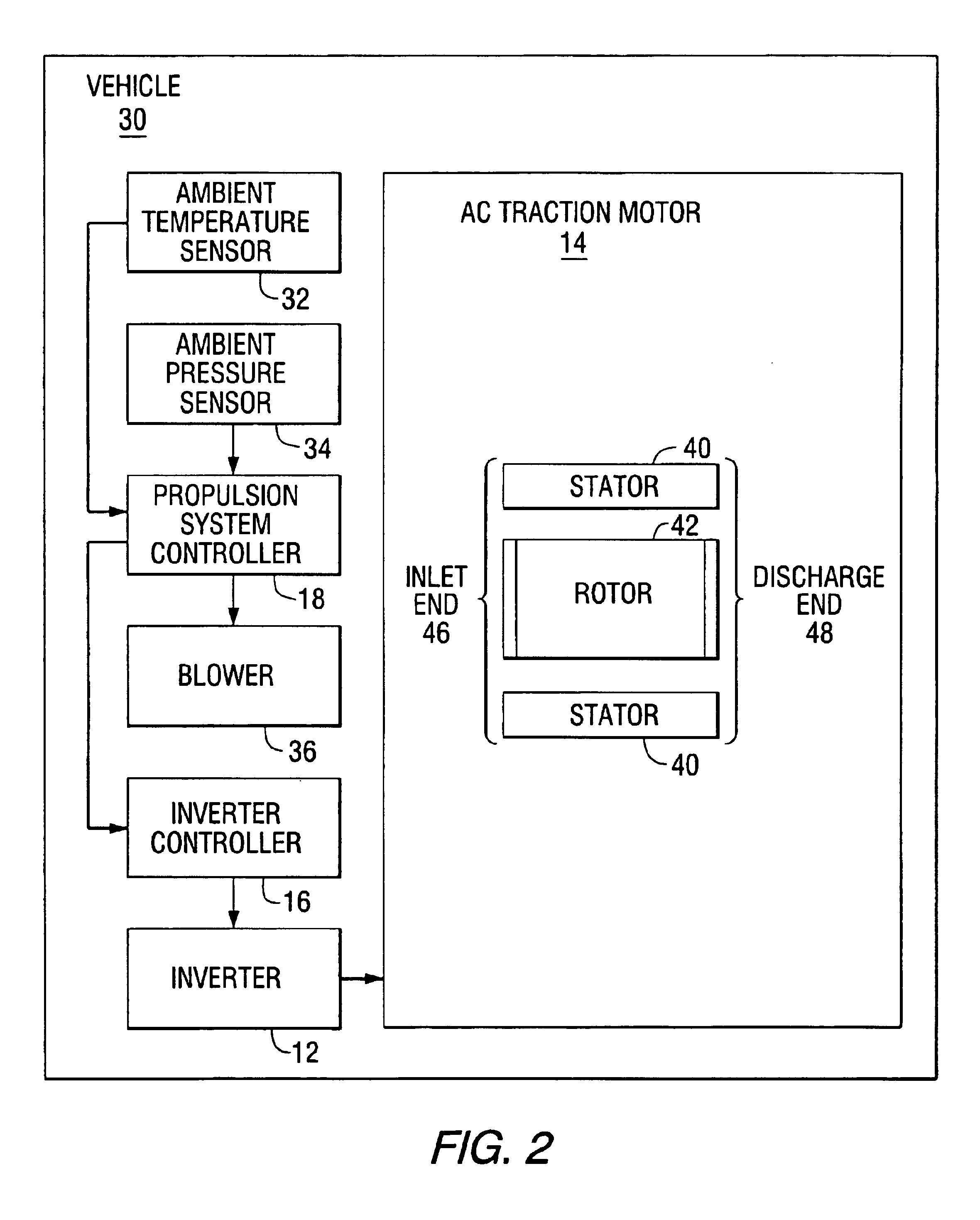
InactiveUS6847187B2Increase speedReduce motor speedThermometer detailsSingle-phase induction motor startersControl theoryThermal protection
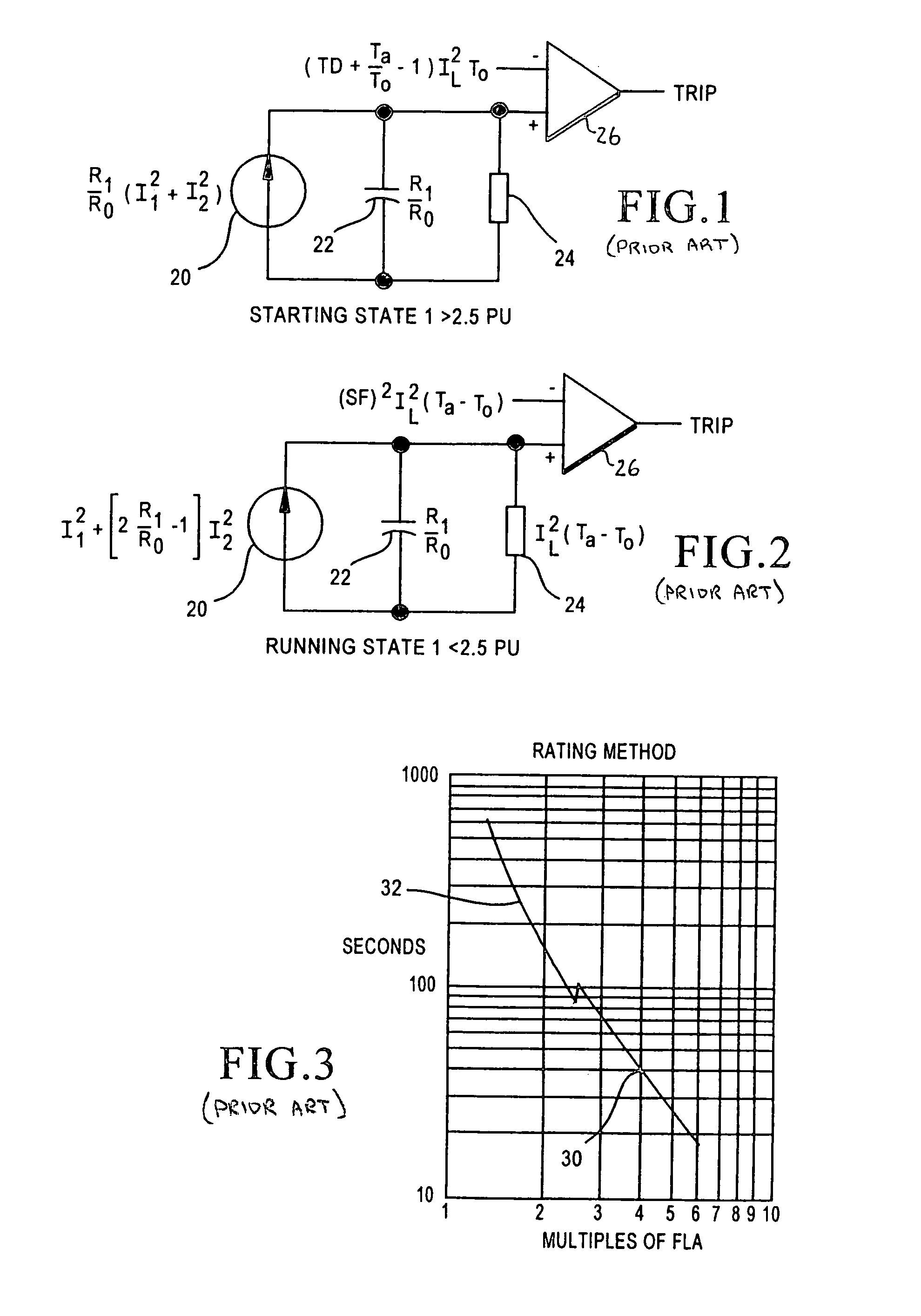
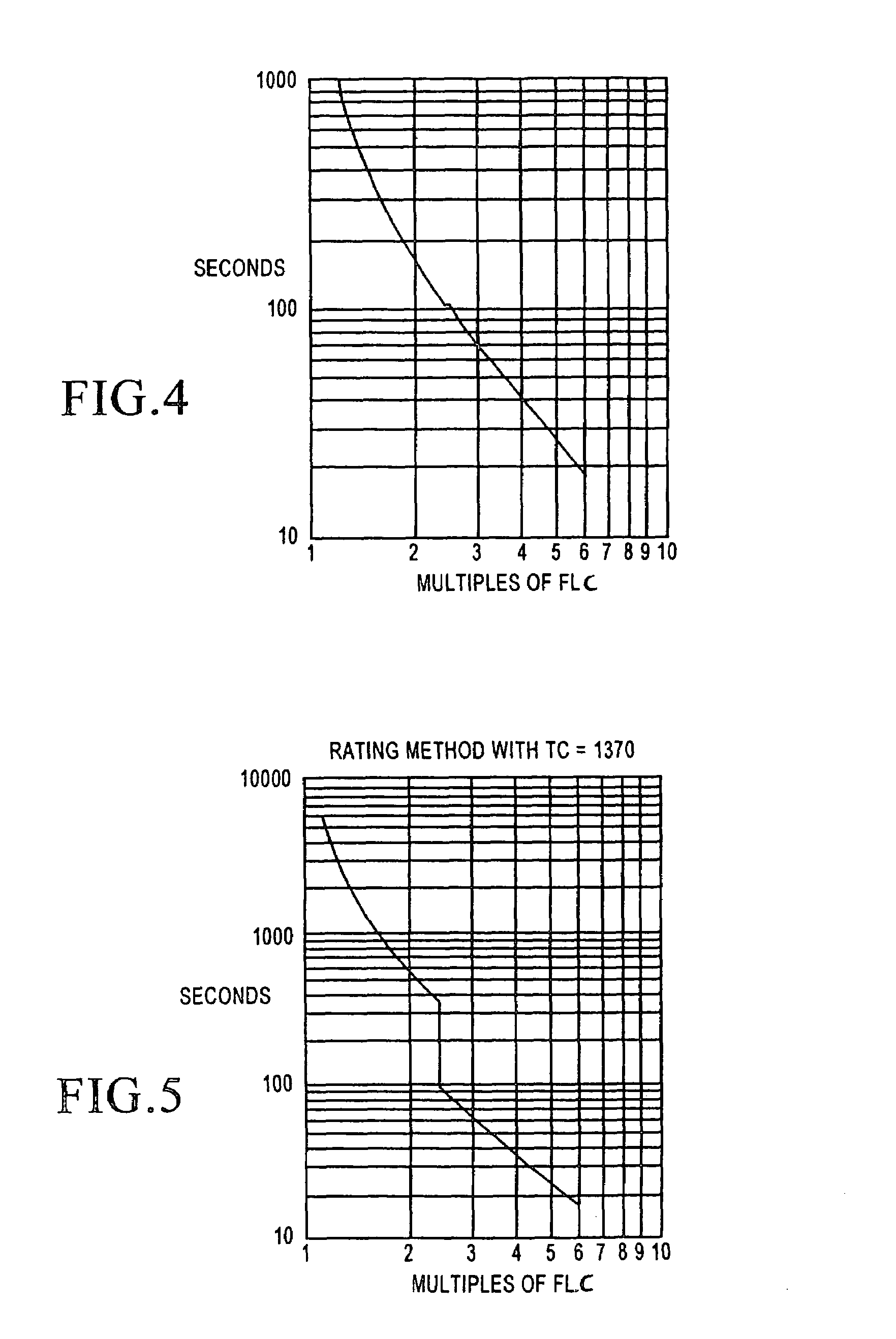
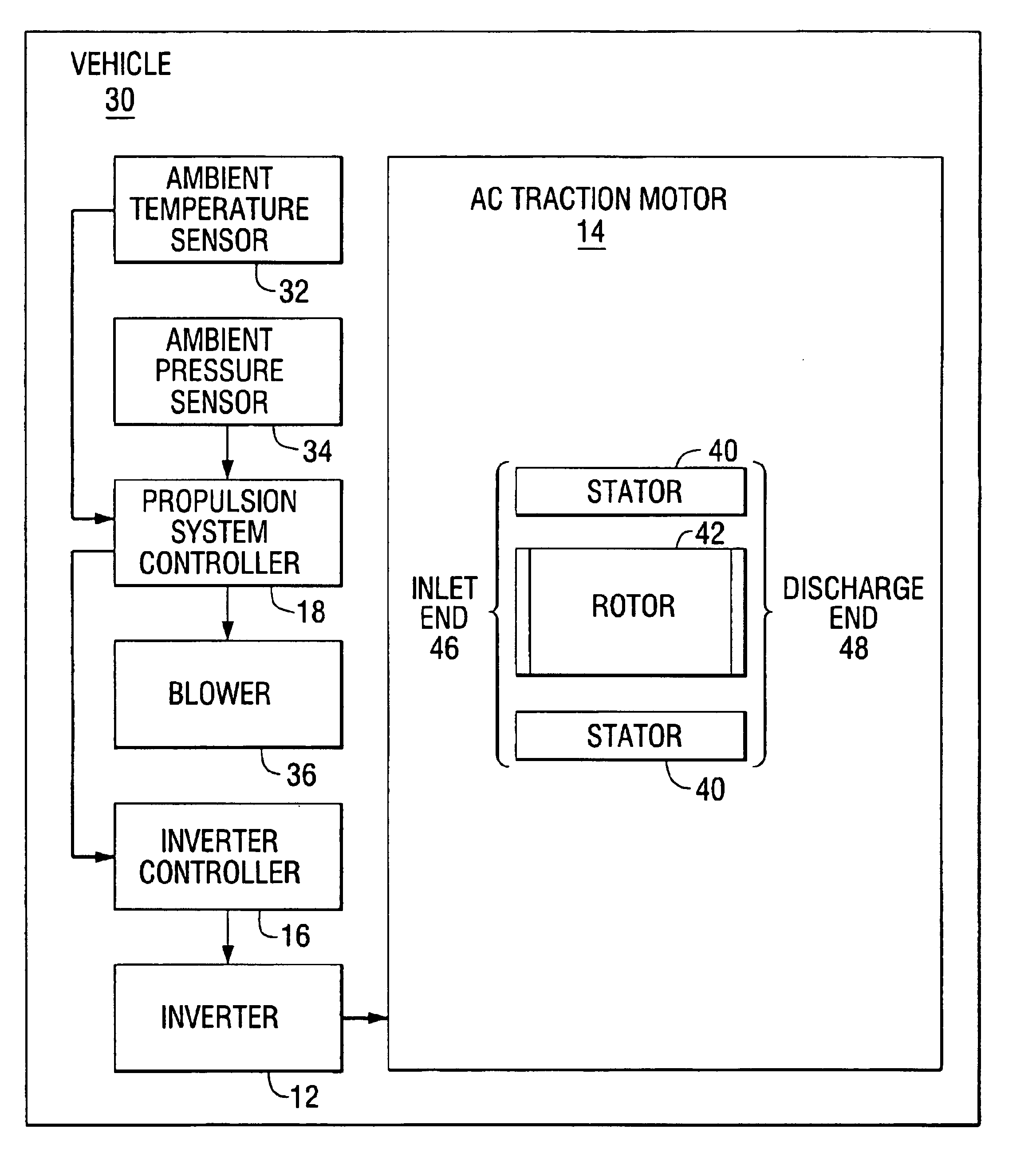
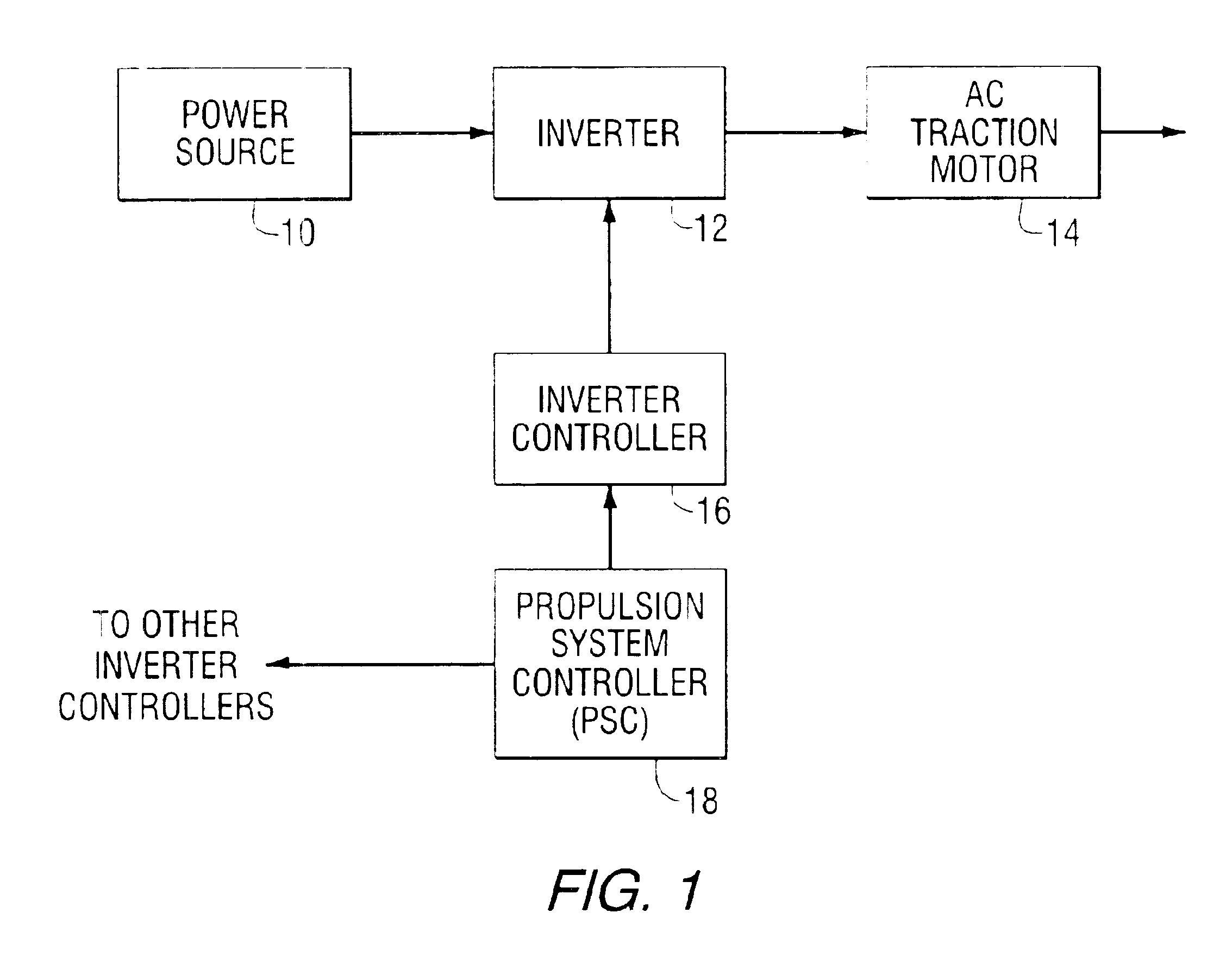
A thermal protection apparatus for an AC traction motor including a stator, a rotor, a blower fan and an inverter includes a method and apparatus for predicting the motor temperature assuming that the blower is operational. The method and apparatus also determines an estimated motor temperature by measuring the motor resistance or the rotor slip. The estimated motor temperatures compared to the predicted motor temperature to determine the condition of the motor cooling system.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Motor control system
ActiveUS20070103820A1Reduce power consumptionTemperatue controlVolume/mass flow measurementControl systemMotor control
A controller is operable in one of a plurality of operational modes, which include an estimated temperature computation performing mode for performing computing of an estimated temperature of the motor and an estimated temperature computation non-performing mode for stopping the computing of the estimated temperature of the motor. An operational mode of the controller is changed from the estimated temperature computation performing mode to the estimated temperature computation non-performing mode according to a predetermined condition in a stopped state of the motor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
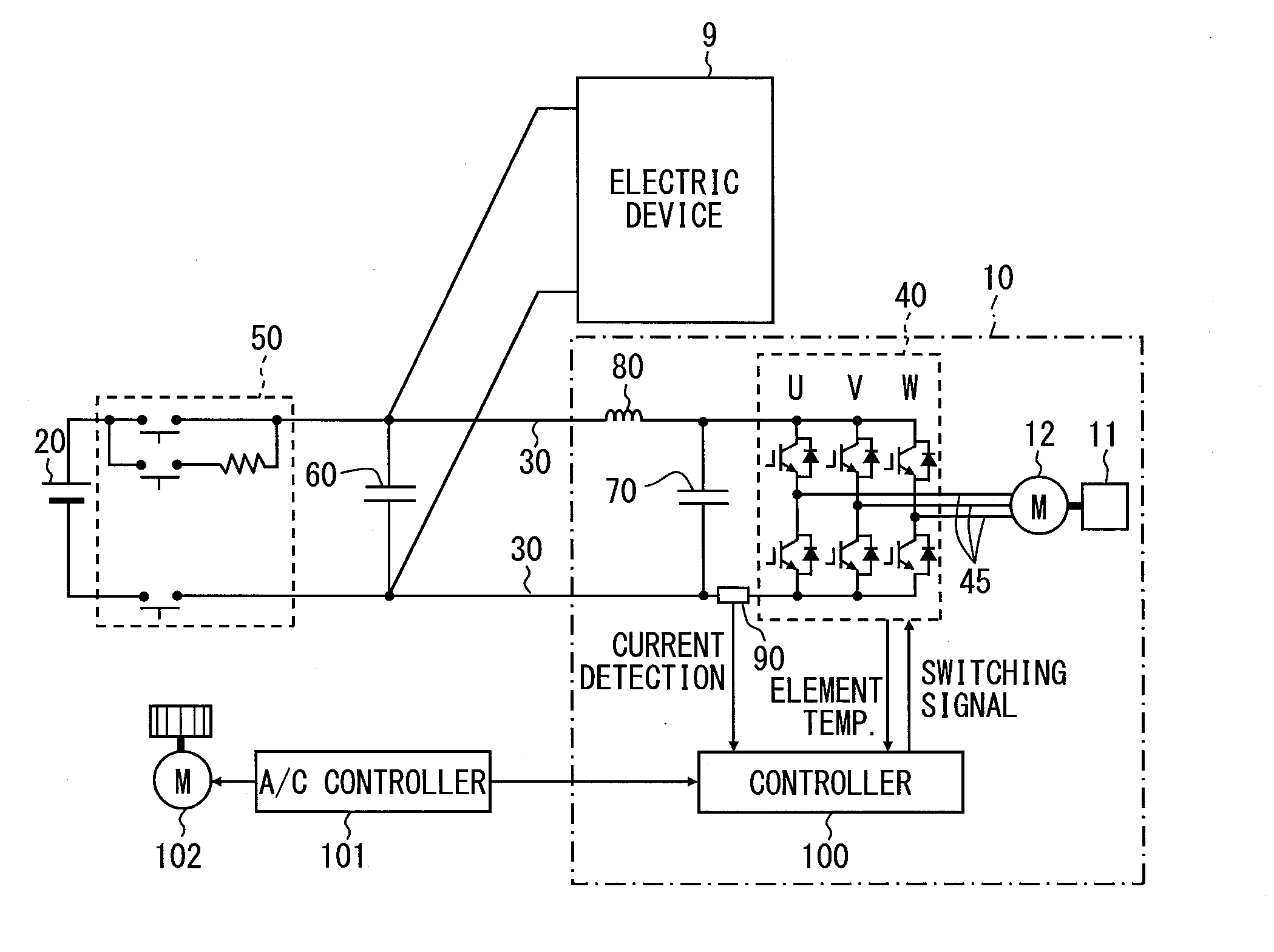
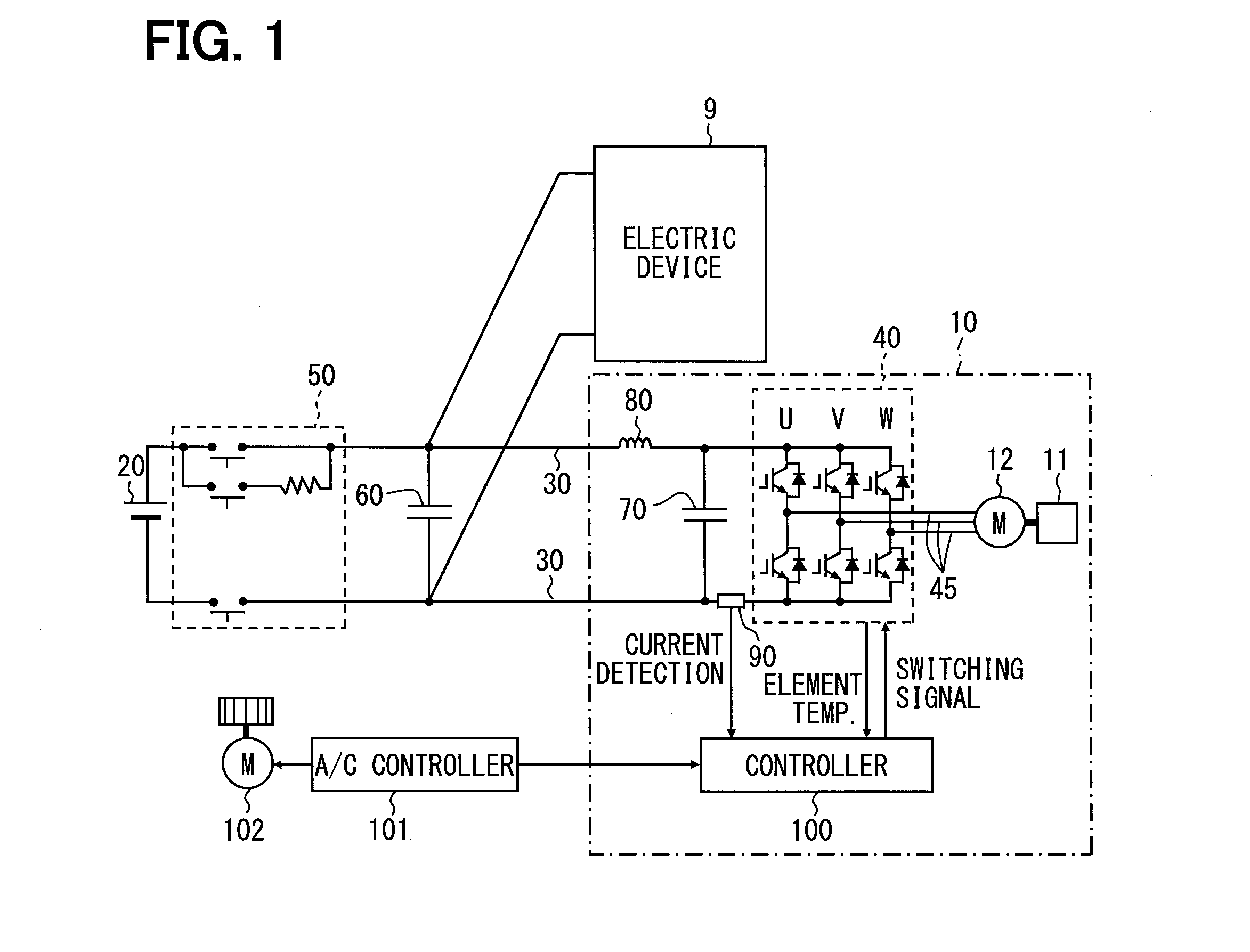
Electric compressor
ActiveUS20150295532A1Reduce in quantityReduce the temperatureDC motor speed/torque controlTemperatue controlEngineeringTemperature drop
A controller for an electric compressor sets a temperature rise region A, a temperature drop region B, and a steady region C from change in temperature of switching elements, and sets a carrier frequency for each of the set regions. In the region A, the carrier frequency is changed according to the element temperature so that the carrier frequency decreases with increase of the element temperature at startup of a motor. In the region B and the region C, the carrier frequency is changed according to the number of revolutions of a compression mechanism, so that the carrier frequency decreases with increase of the number of revolutions of the compression mechanism, regardless of the element temperature.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Popular searches
Emergency protective arrangement details Instruments Using electrical means Electric switches Switch operated by excess current and arc fault Multiple motor speed/torque control Generation protection through control Dynamo-electric converter control Generator control by field variation Apparatus with intermediate ac conversion
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com