Patents
Literature
57results about How to "Adequate access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
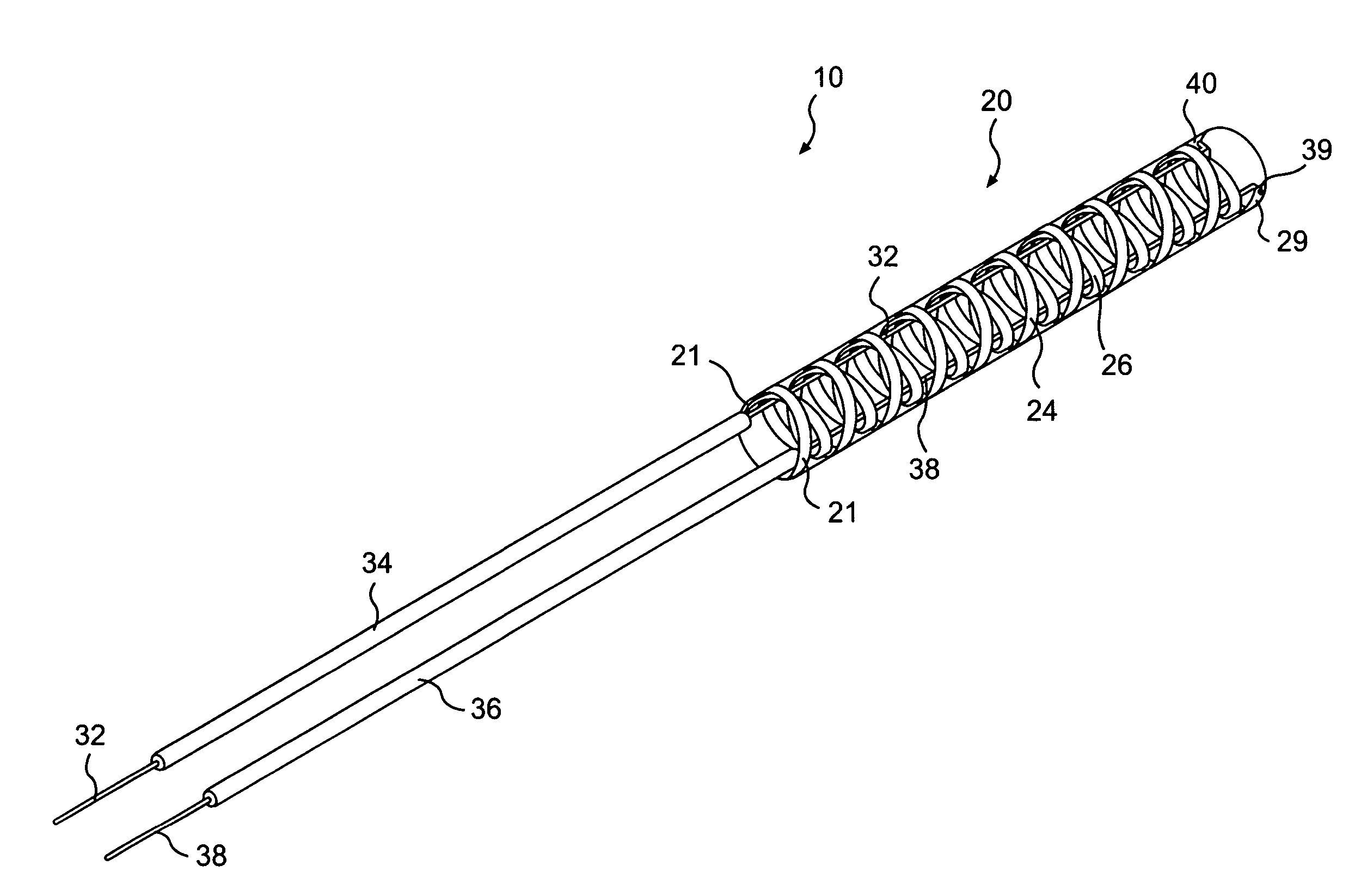
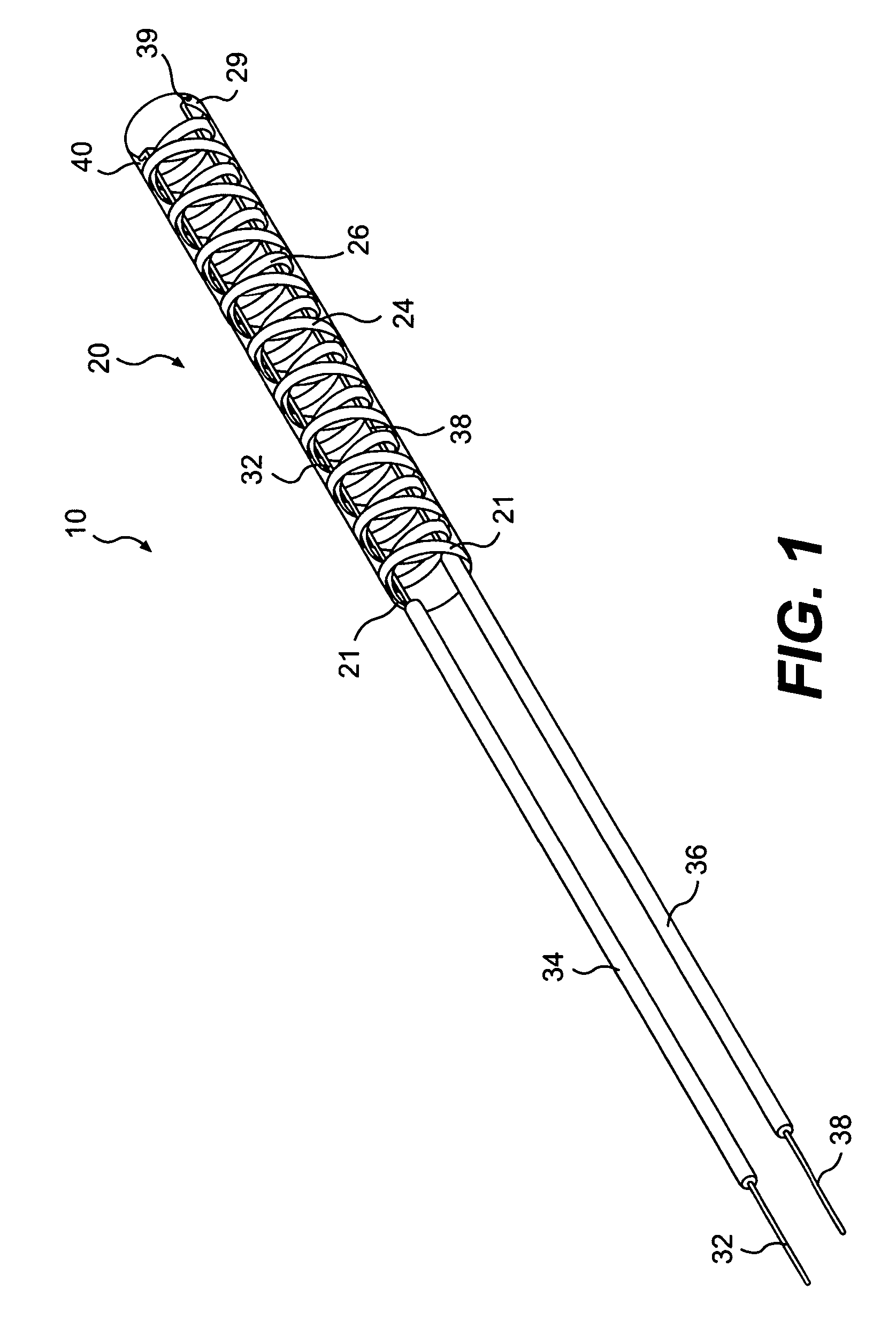
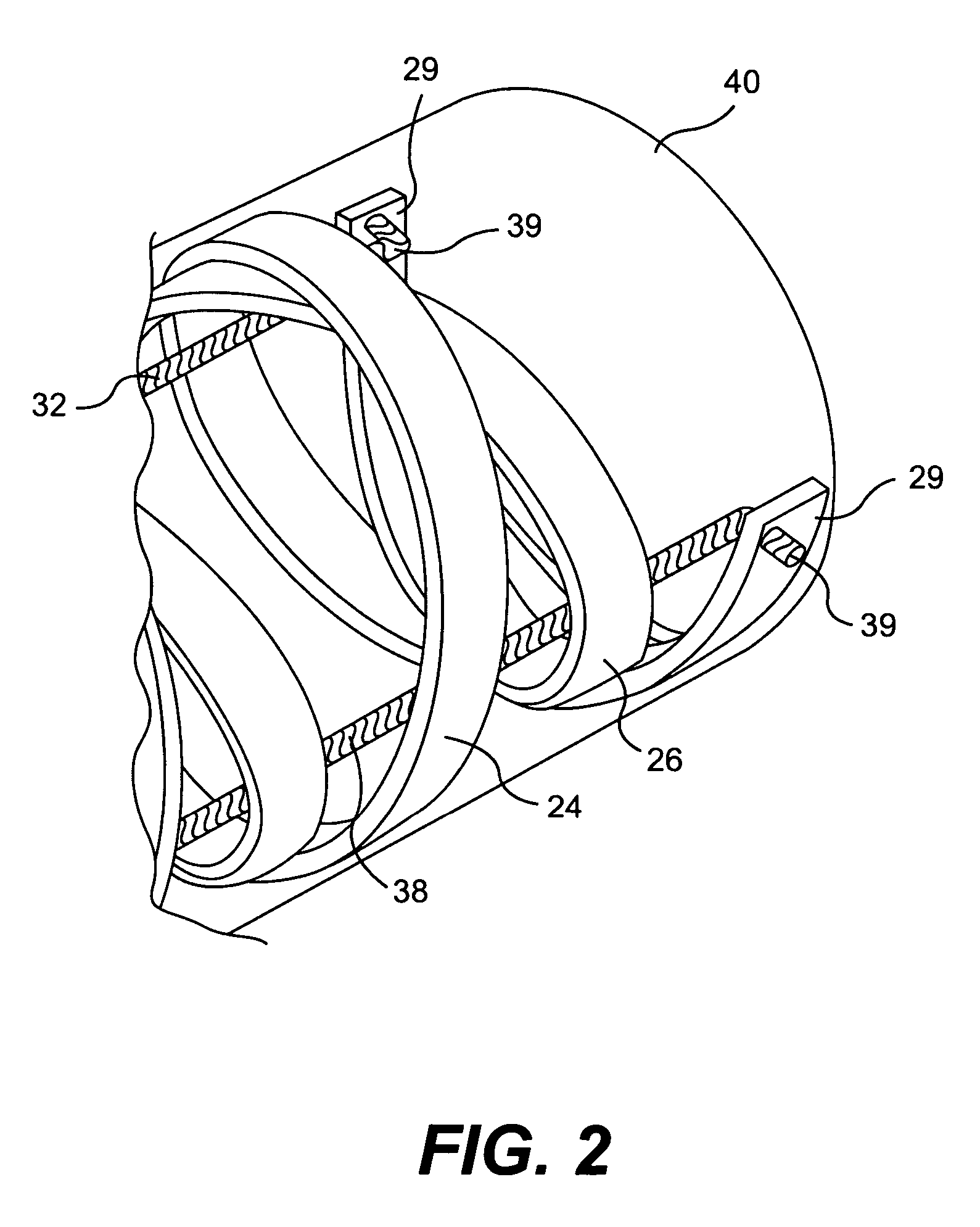
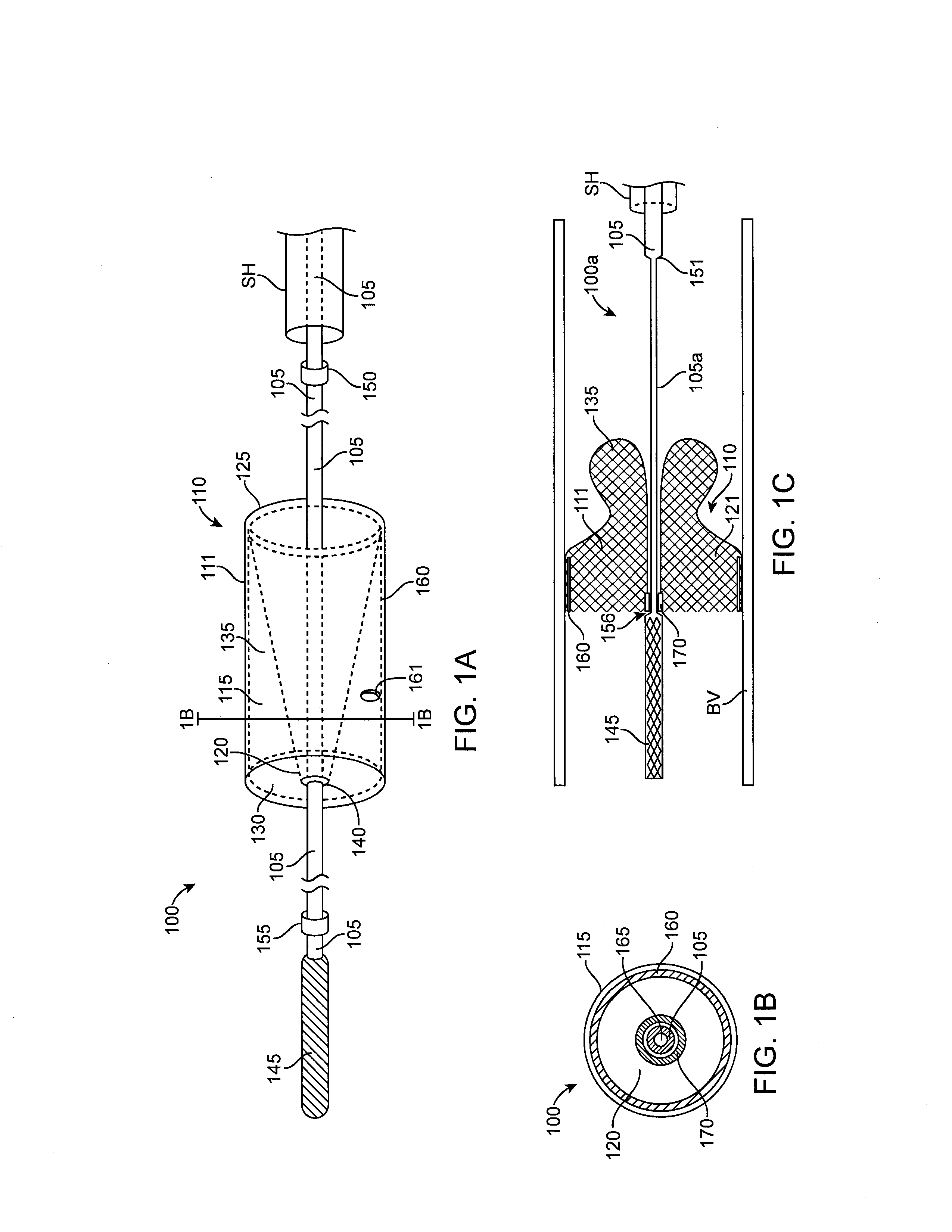
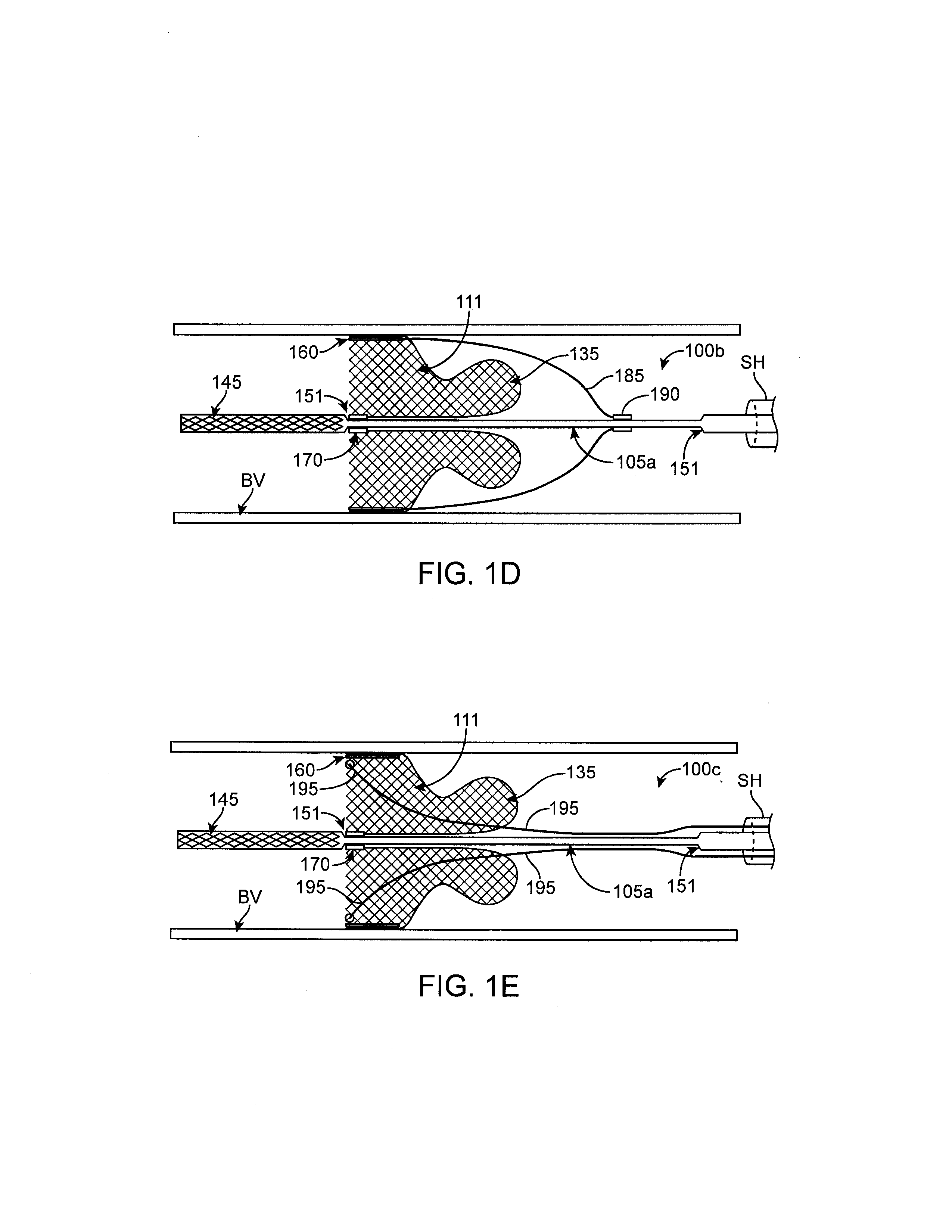
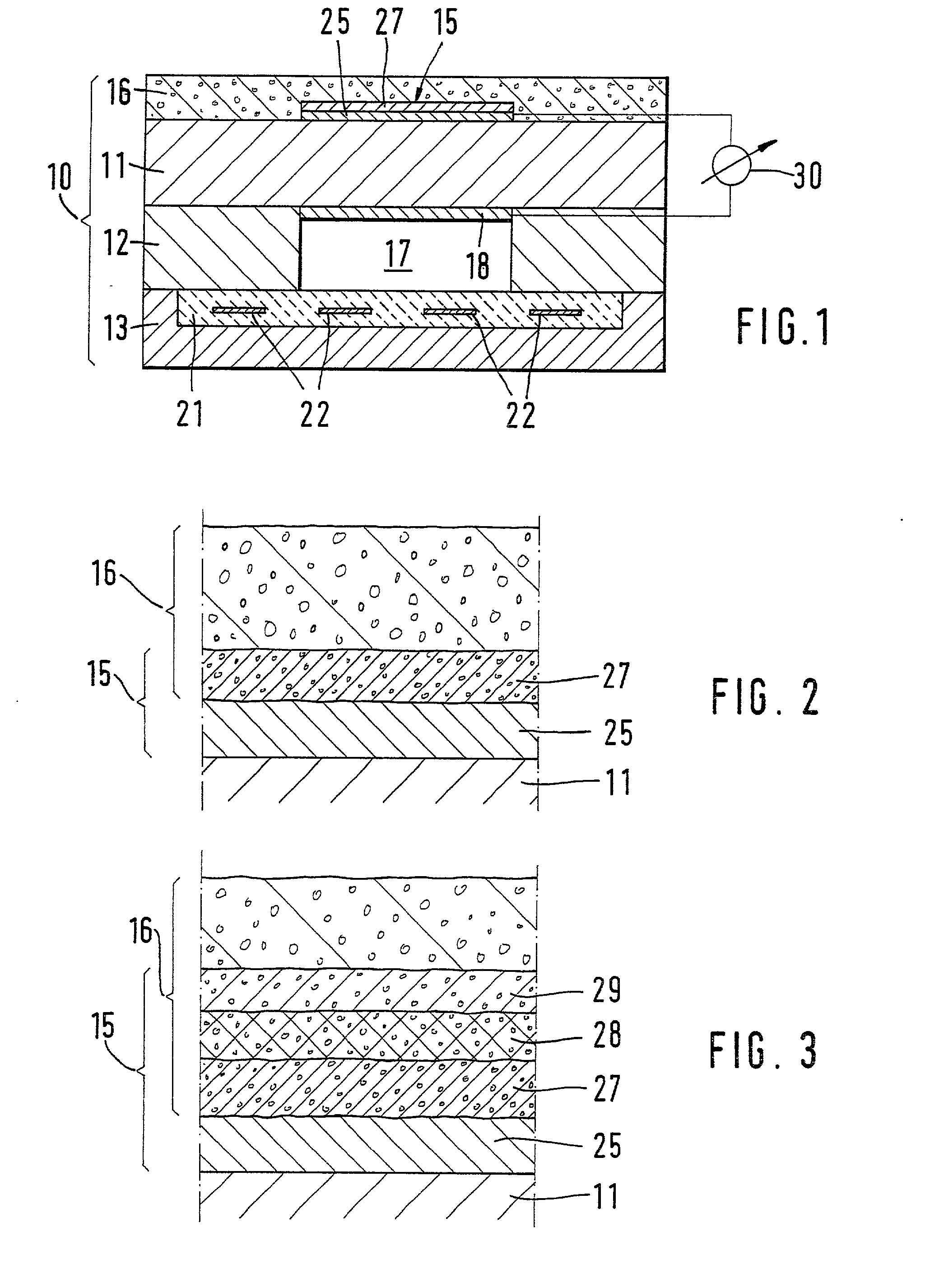
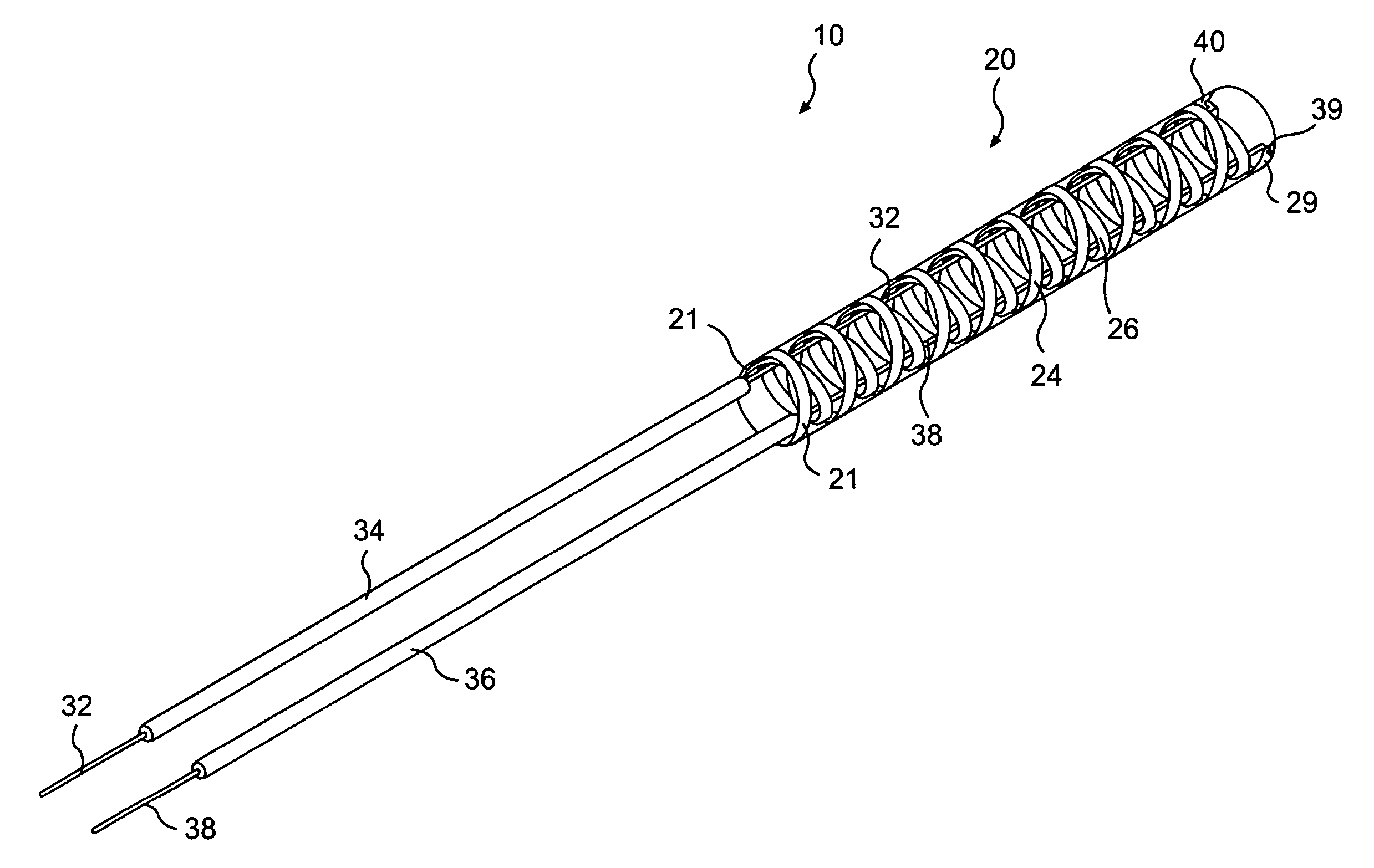
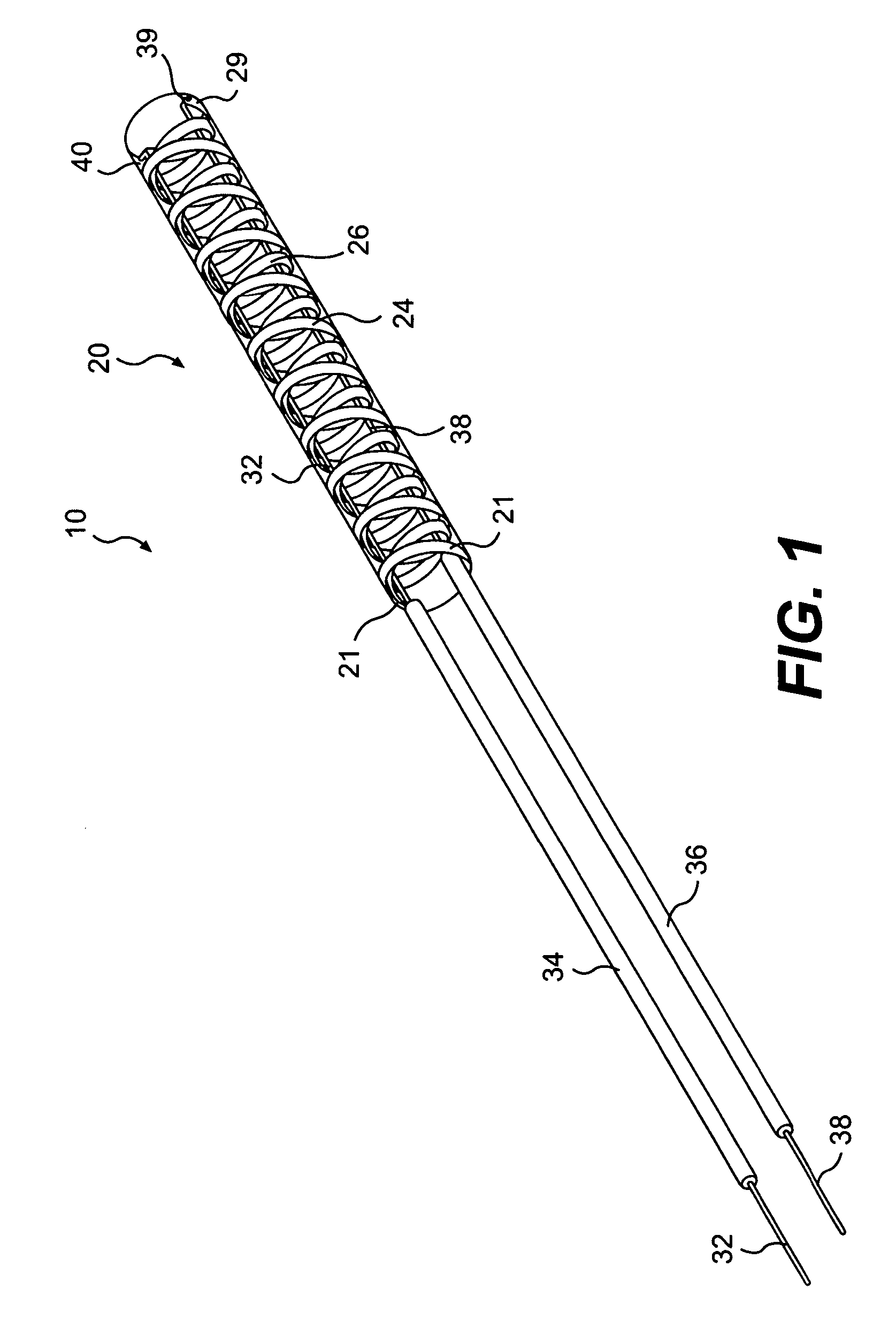
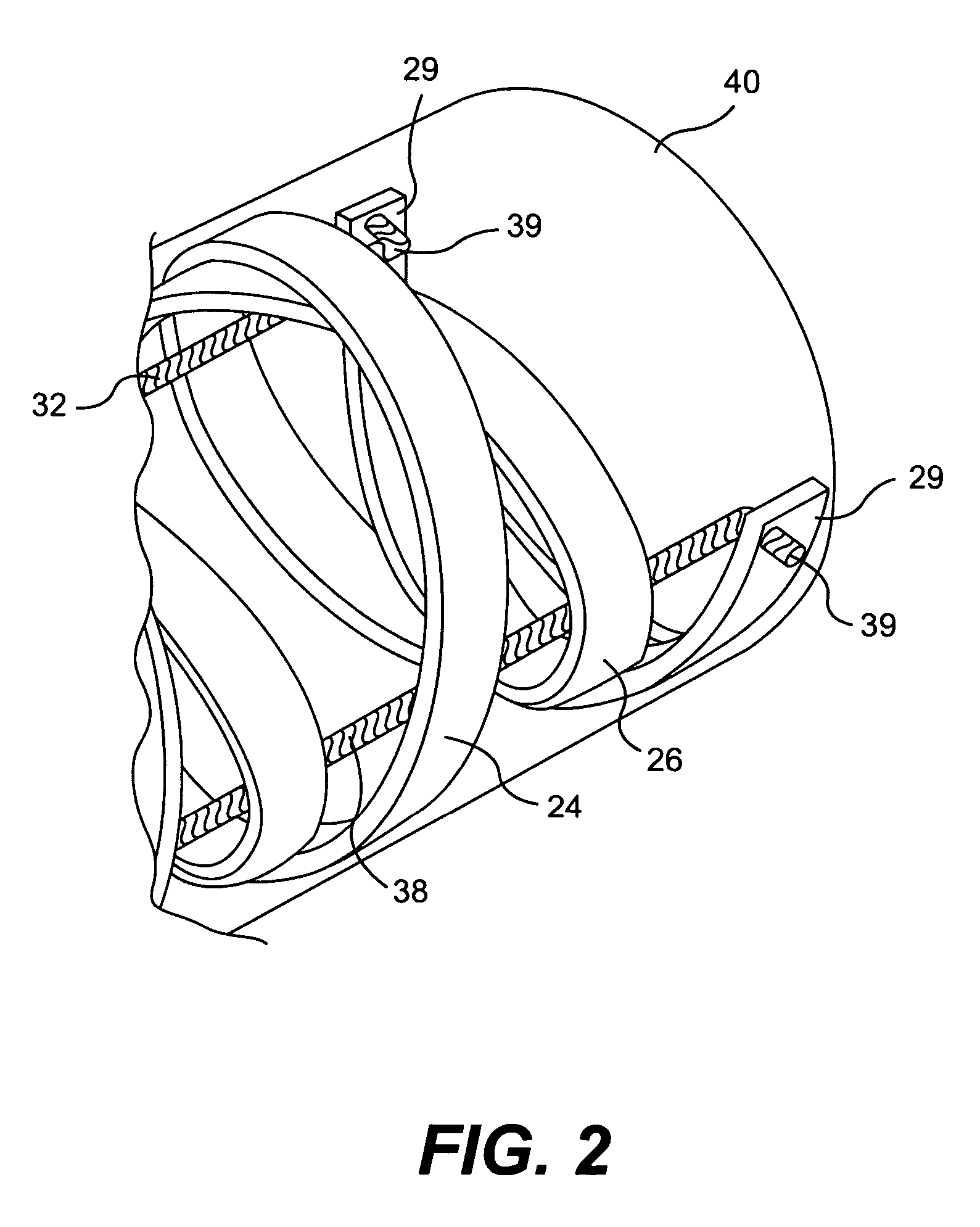
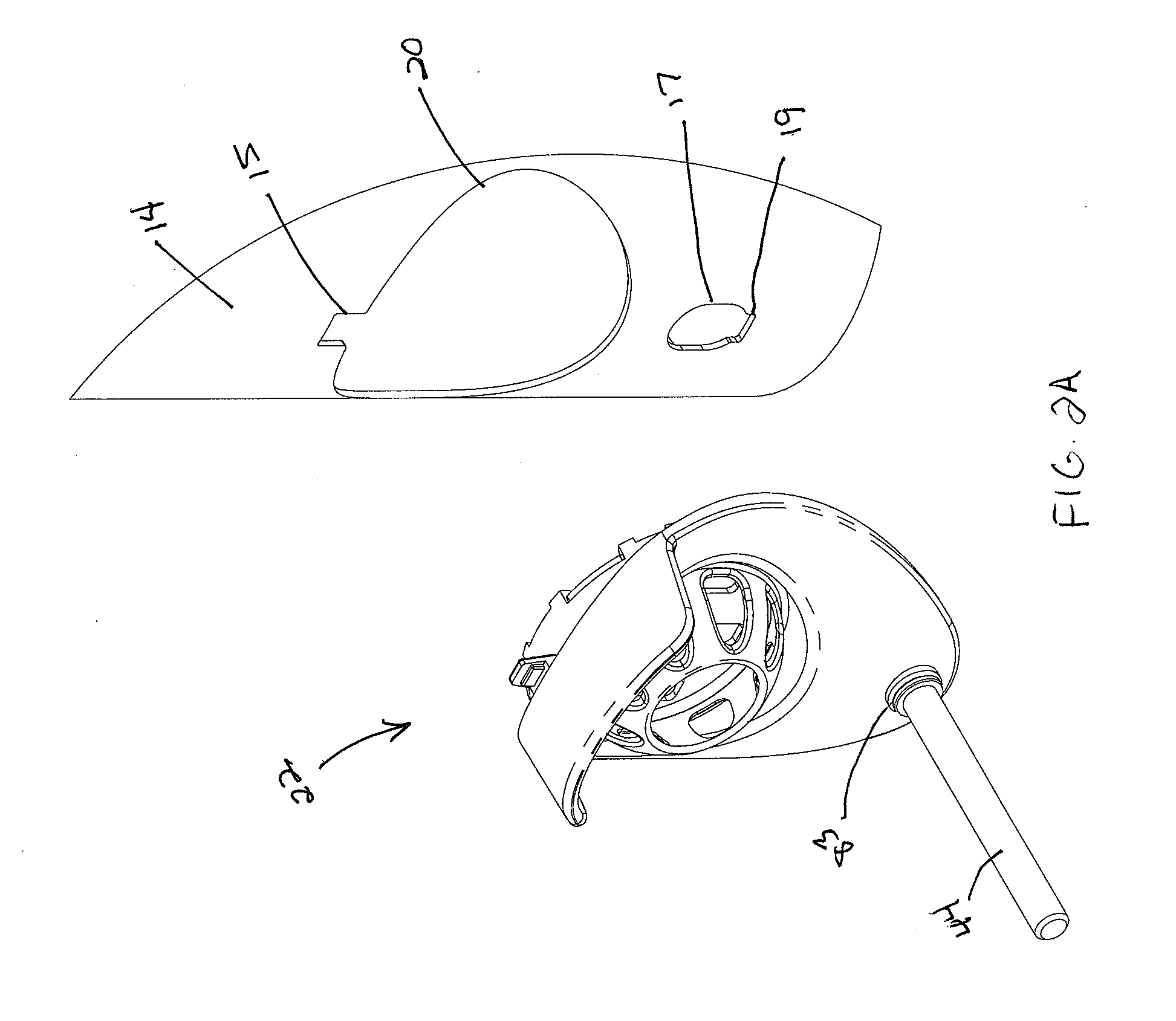
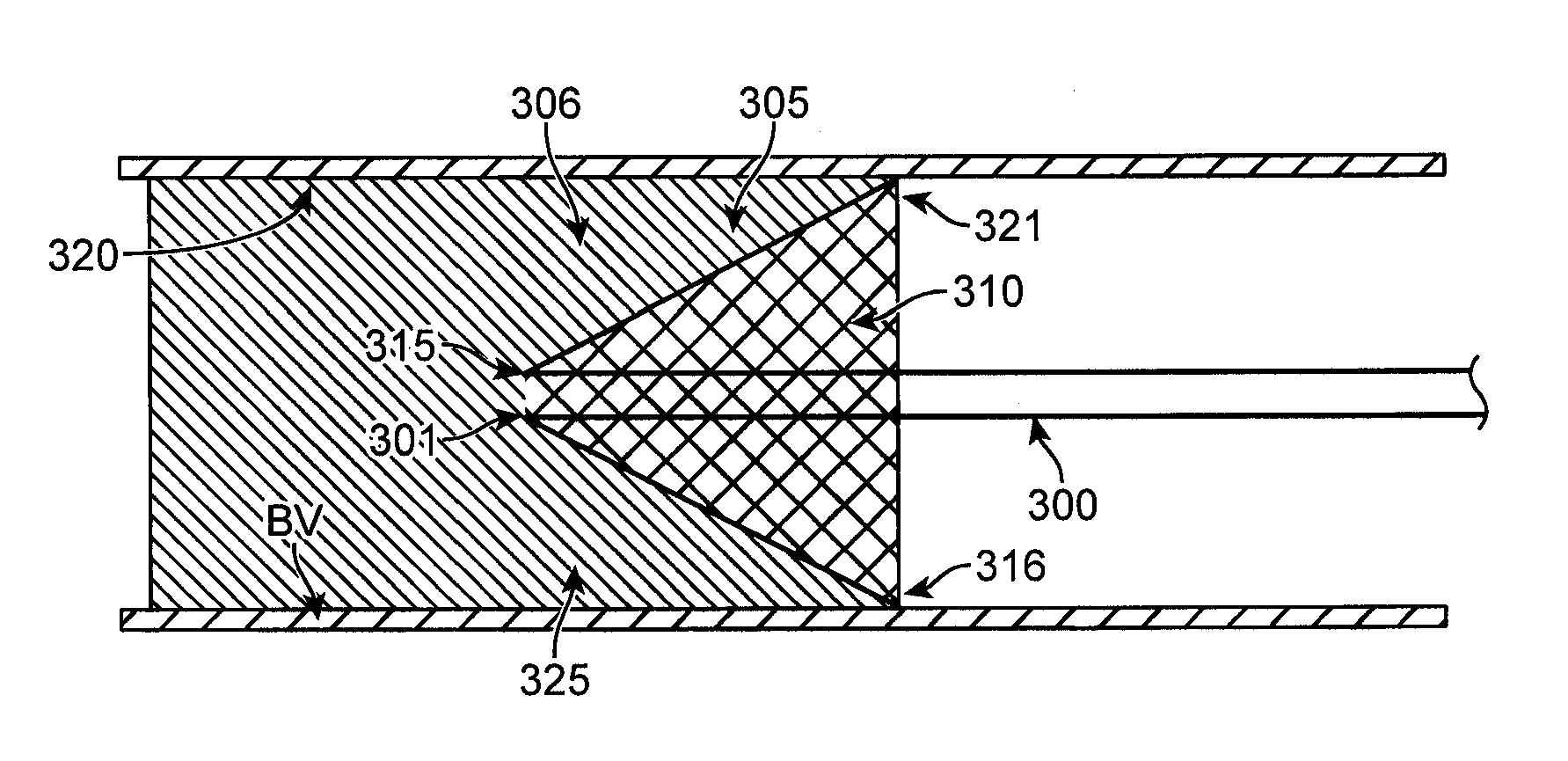
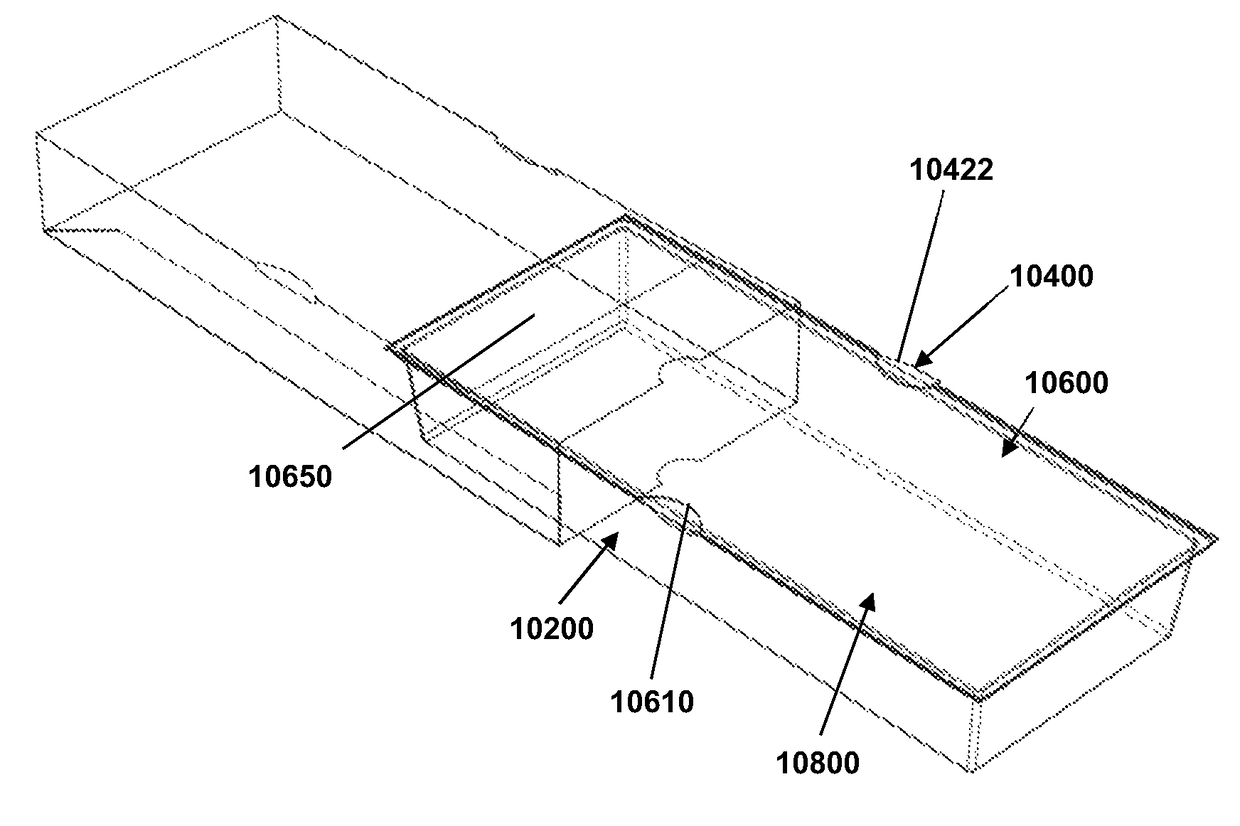
Access catheter having dilation capability and related methods
ActiveUS7476232B2Adequate accessIncrease the cross-sectional areaSurgeryDilatorsMedical deviceGuide tube
Various embodiments of a medical device having a dilation capability and related methods are disclosed. For example, the medical device may include a distal assembly having a radially expandable body defining a passageway therethrough, and a control member extending from the distal assembly to a proximal end of the device. Actuation of the control member may apply a compressive force to the body, causing the body to radially expand and a cross-sectional area of the passageway to increase.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
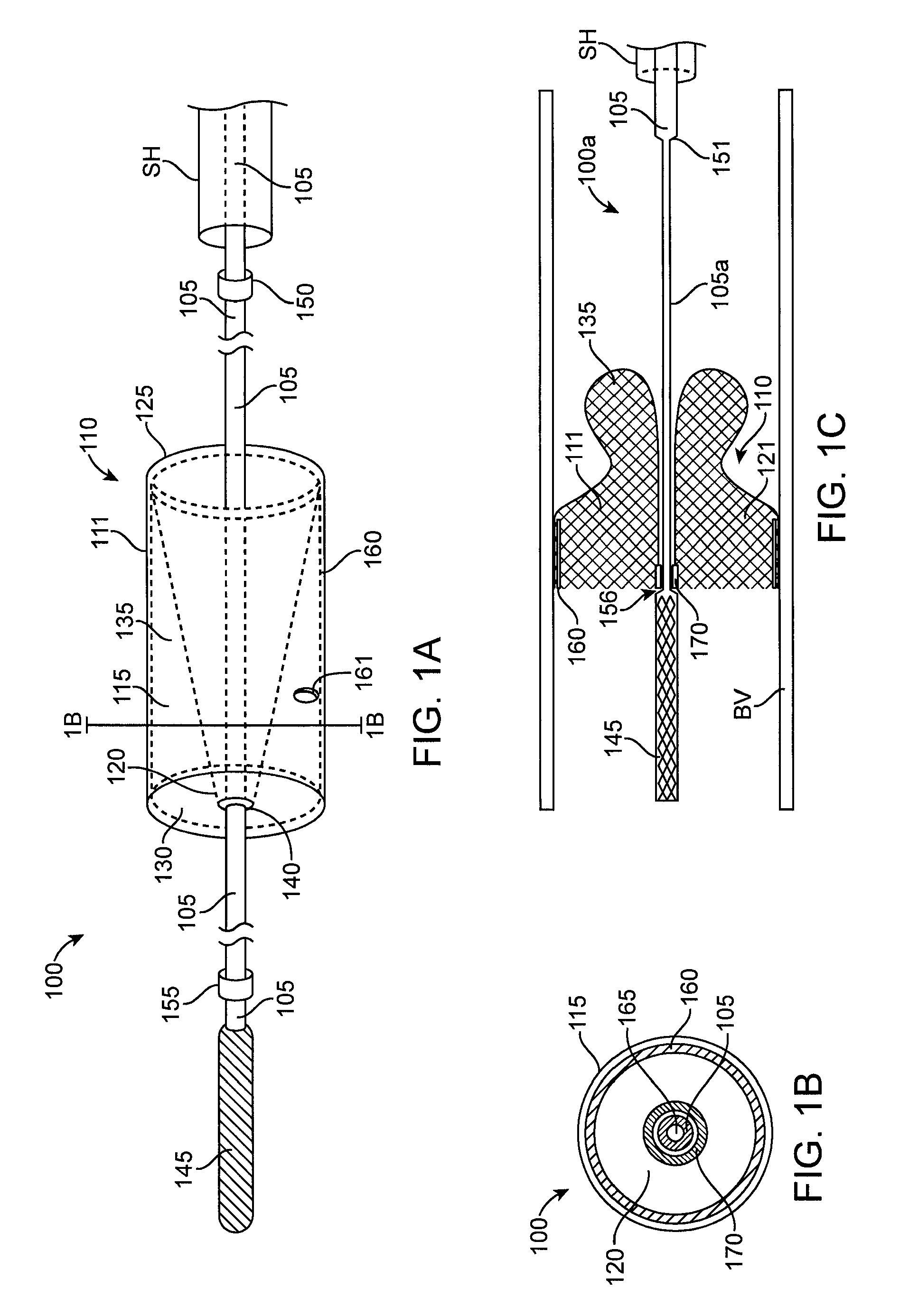
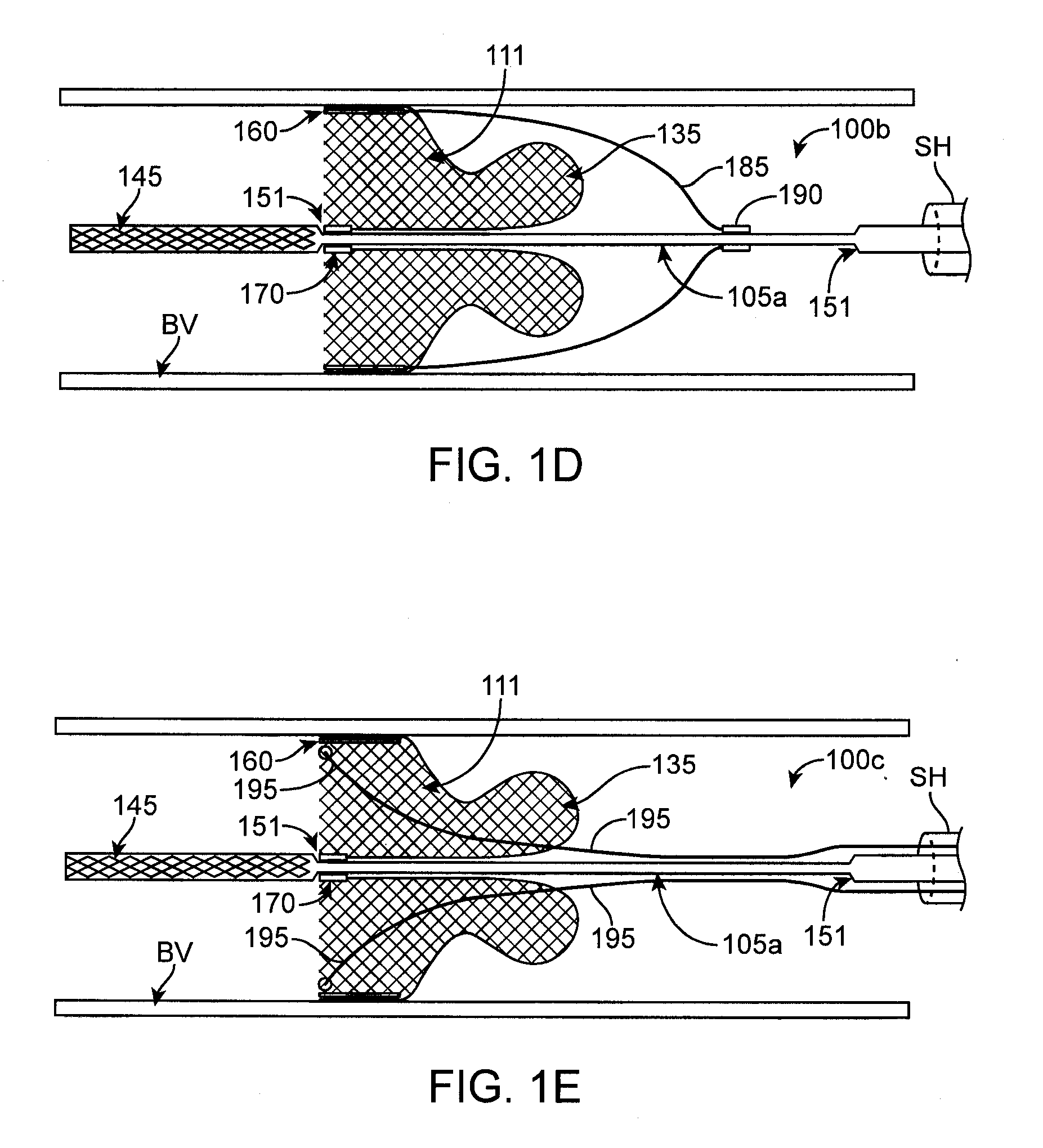
Integrated embolic protection devices
ActiveUS20130178891A1Promote resultsMinimization requirementsHeart valvesSurgeryDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
Embolic protection elements are integrated with a catheter or access sheath for any catheter. A catheter with an integrated embolic protection element comprises a catheter shaft, an embolic filter slidably mounted on a distal portion of the shaft, a proximal stop for limiting the proximal movement of the embolic filter, and a distal stop for limiting the distal movement of the embolic filter. The filter comprises a porous mesh material defining a collection chamber for captured emboli and has a collapsed and a deployed configuration. The filter may be collapsed by an access sheath used with the catheter. An access sheath may comprise a tubular main body and an embolic filter mounted on the distal portion of the tubular main body. The embolic filter may evert into the central lumen of the sheath or may be constrained on the exterior of the sheath with a larger diameter outer tube.
Owner:EMBOLINE
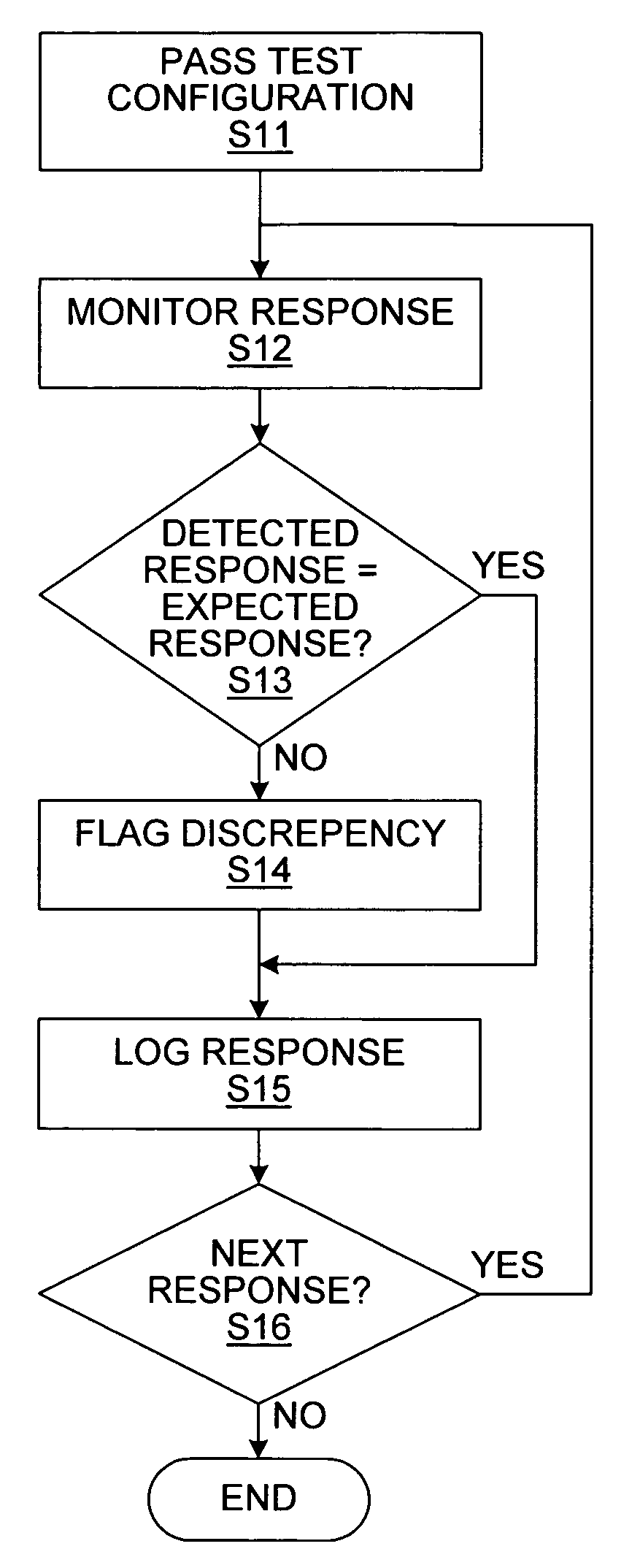
Testing device driver hardening
InactiveUS6971048B1Easy constructionAdequate accessSoftware testing/debuggingComputer hardwareTest script
A test mechanism for testing device driver hardening includes an intercept mechanism for intercepting device driver access calls from a device driver under test and an interface for configuring the intercept mechanism to inject faults according to a determined test pattern. This mechanism enables the arbitrary introduction of typical faults. These faults may be introduced totally asynchronously and so emulate real life. A test harness module can be linked in to a test build of the driver. The test harness can intercept all of the device access calls. It mimics the normal function of these calls accessing the offset address and propagating the appropriate data. A test application is able to interpret a test script and to compare device driver responses to injected faults.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Tank top nursing bra
InactiveUS20050085160A1Easily and discretely breast feedEasy to moveBrassieresBreast feedEngineering
A tank top nursing bra for a nursing mother which provides breast support and which also allows the nursing mother to easily and discretely breast feed her baby wherein the tank top can be worn in public without the need to be covered. The tank top nursing bra includes an inner frame for securing the tank top on the nursing mother and for properly positioning the tank top relative to the breasts of the nursing mother. The inner frame includes an elastic waist or chest band which extends about the torso of the mother and below the breasts of the mother. The elastic band having a front portion and a rear portion. The inner frame further including a front sling having a pair of openings for allowing access to the woman's breasts for nursing. The sling extending from the elastic band to a set of shoulder straps which support the inner frame on the shoulders of the woman. The shoulder straps having back edges which are joined either directly or indirectly to the elastic band. The tank top nursing bra further including at least one breast supporting inner nursing flap having a bottom edge joined to the elastic waistband and a top edge which is selectively interengageable with the inner support structure. The tank top nursing bra further including an outer tank top having a front and back portion. The front portion of the tank top being attached to the at least one nursing flap and the back portion being attached to the inner frame.
Owner:LEADING LADY
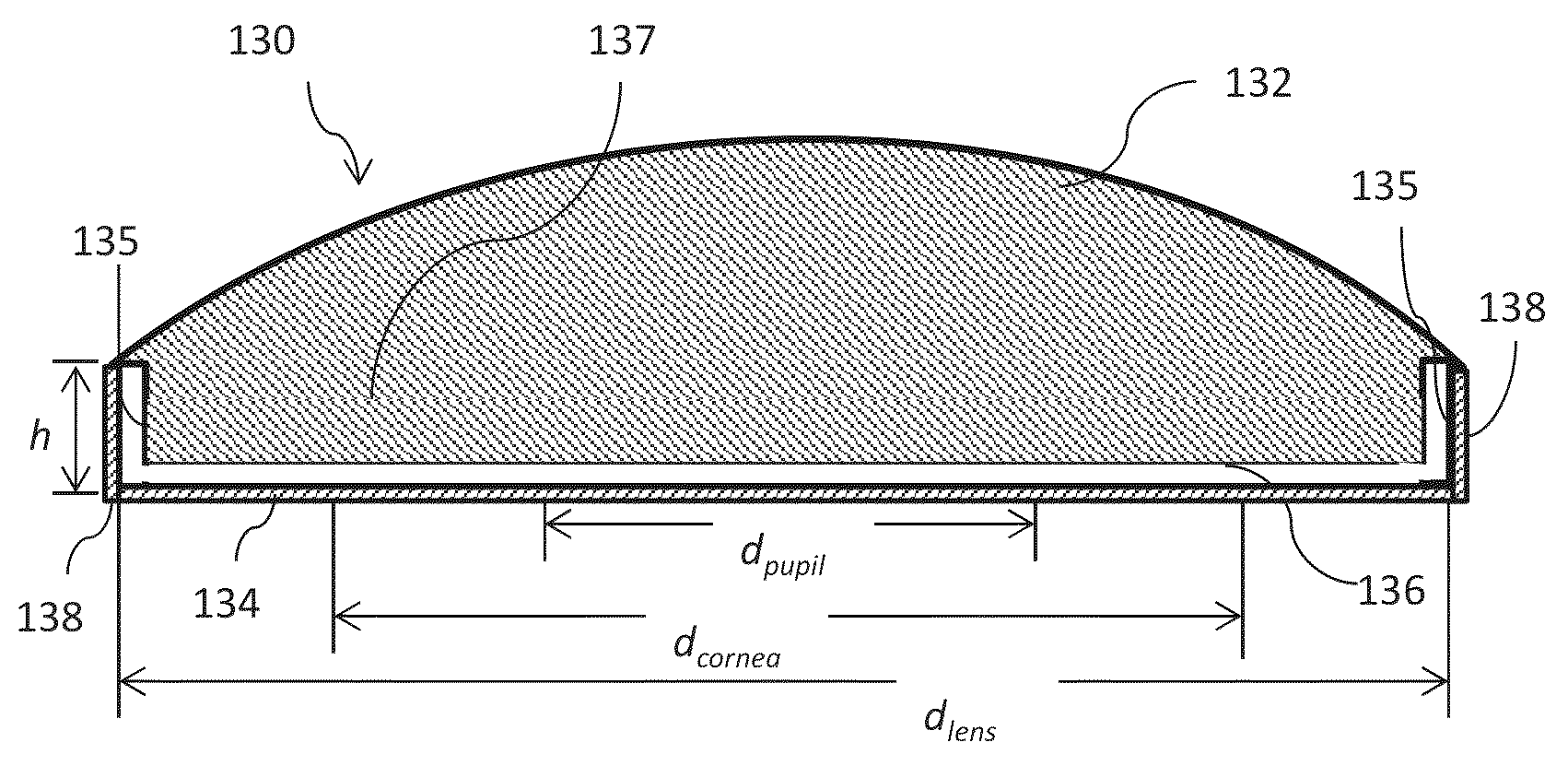
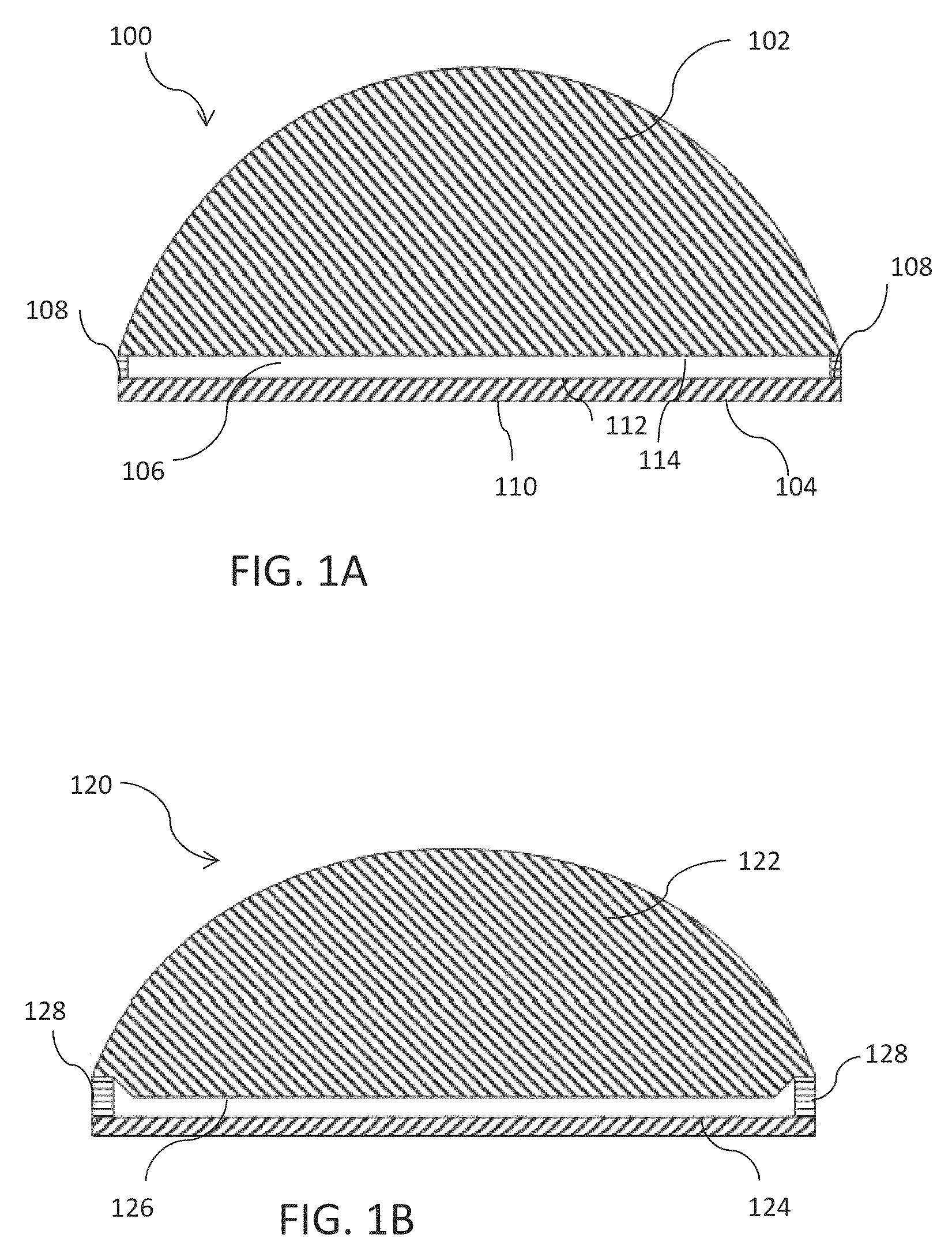
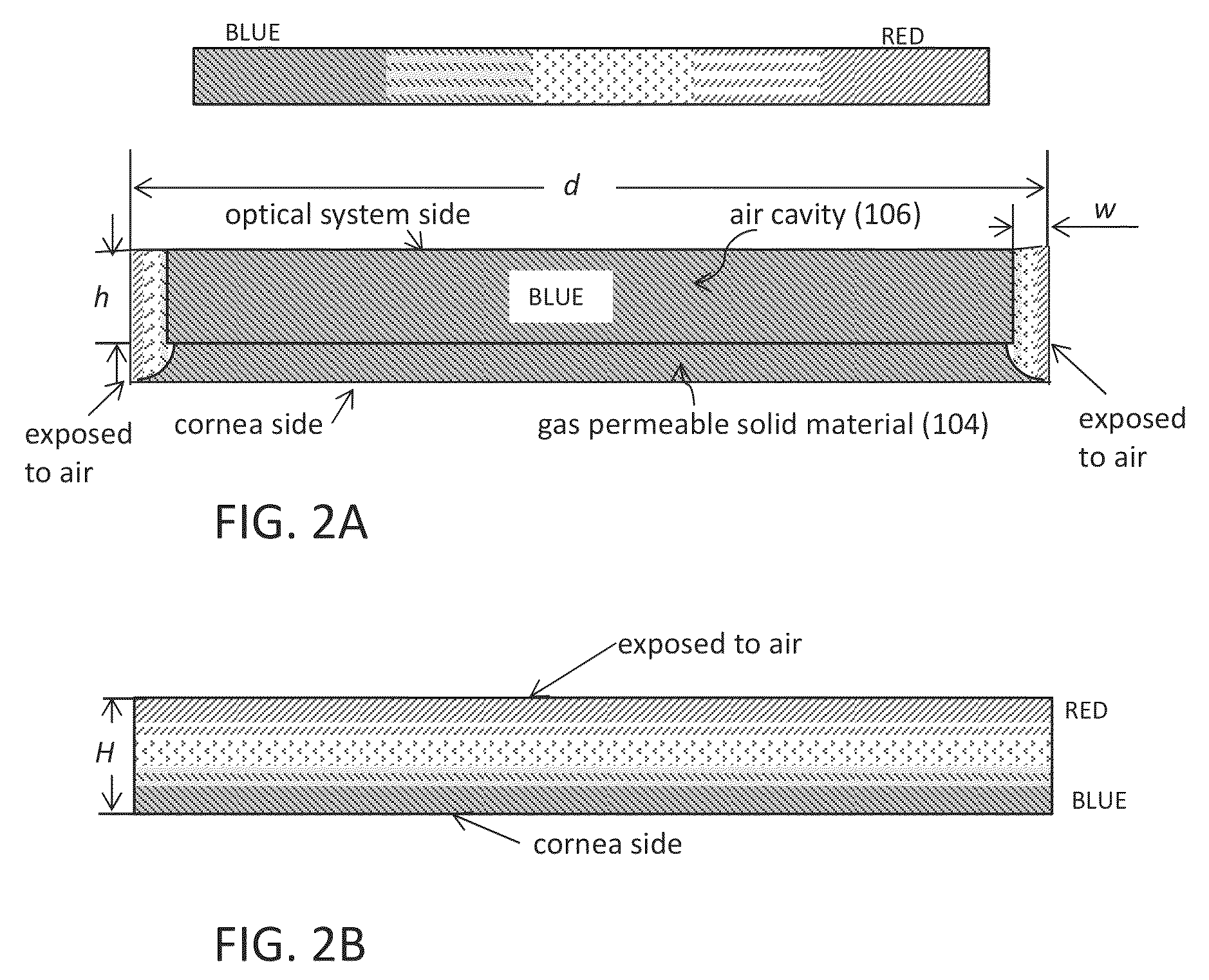
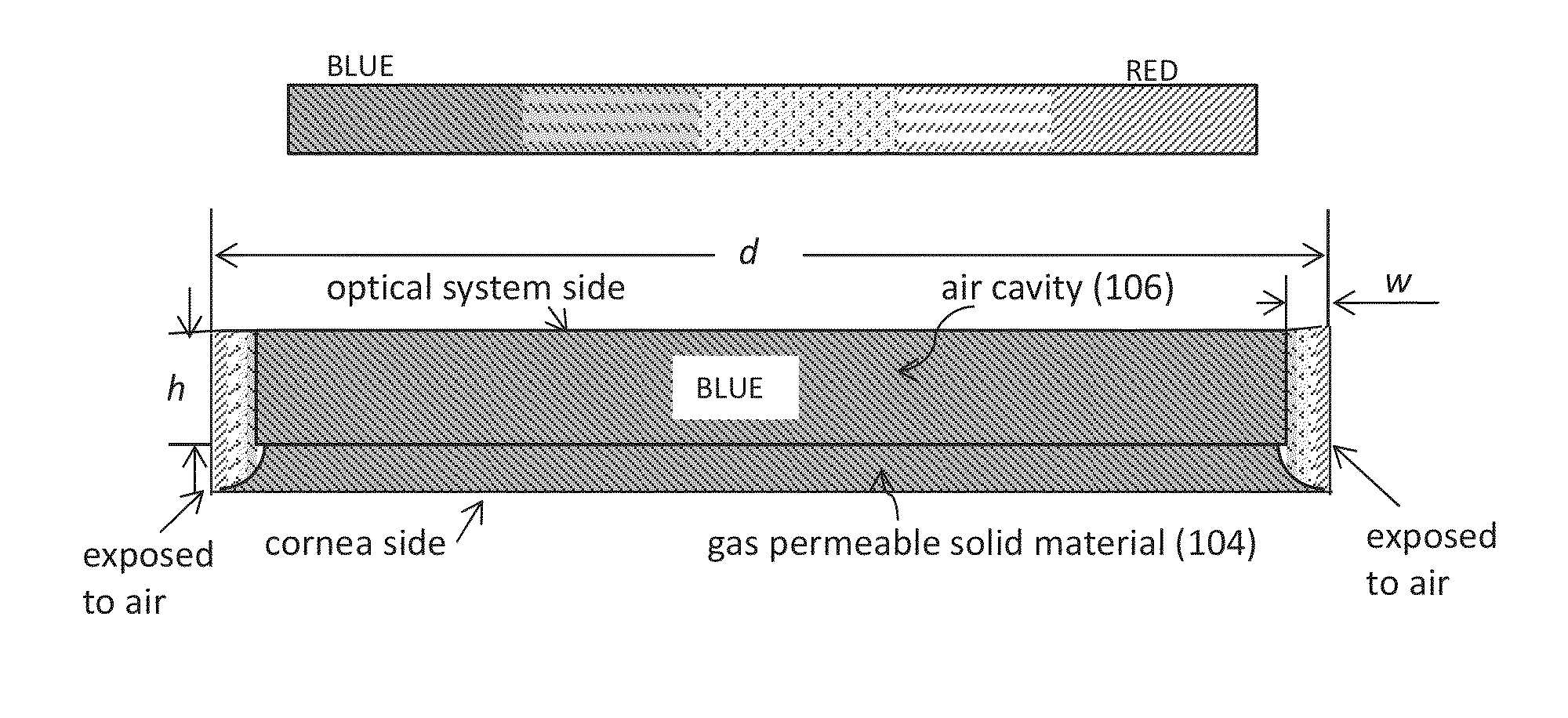
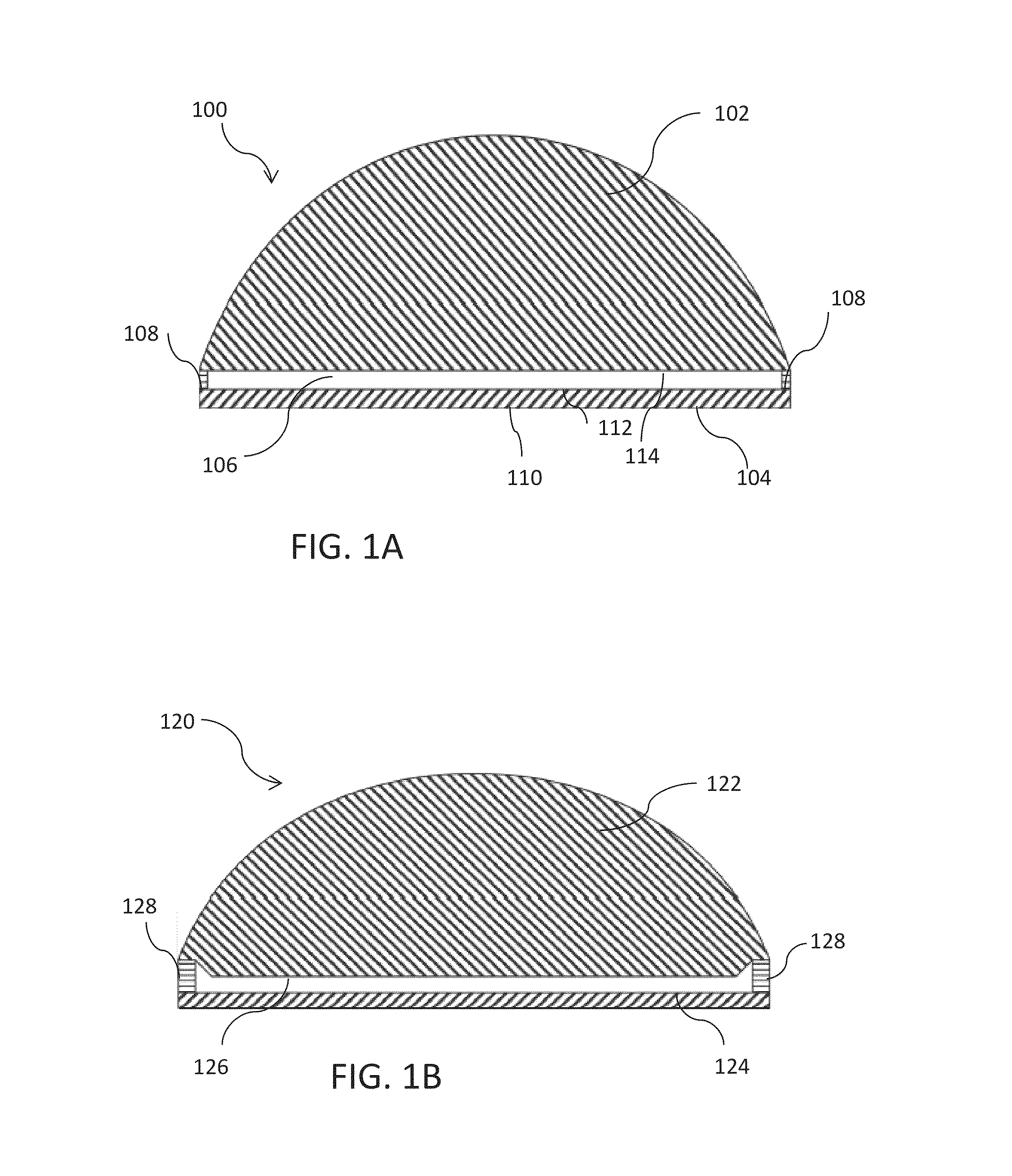
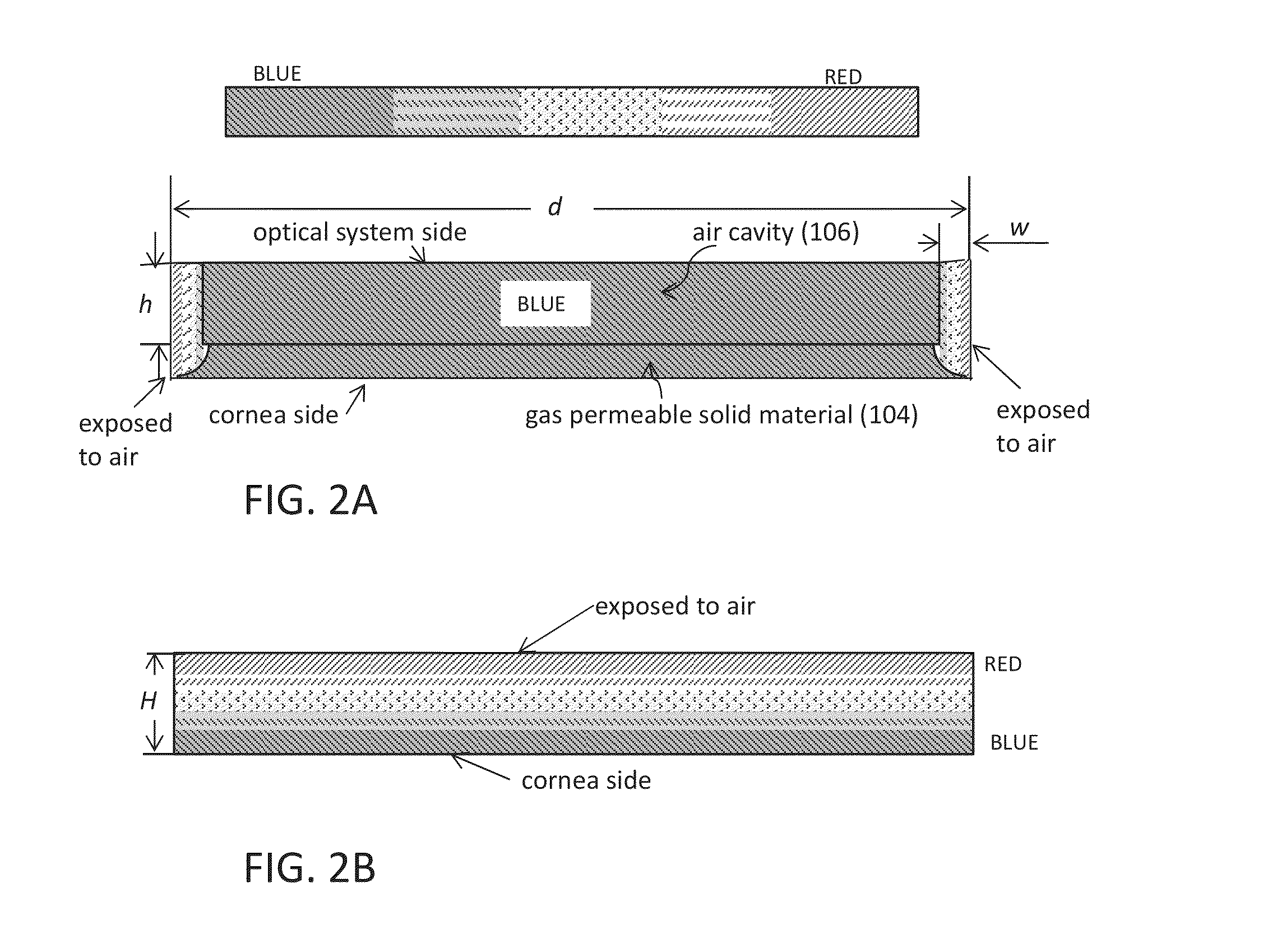
Aerated contact lens assembly
A contact lens assembly includes a proximal layer formed from a gas-permeable material, a distal layer with an optical element, an air cavity disposed between the proximal layer and the distal layer, wherein oxygen concentration across the air cavity is substantially uniform, and an gas transport region surrounding the air cavity for communicating gas between the air cavity and atmosphere. The contact lens assembly may further include a plurality of fins disposed within the air cavity where the plurality of fins has openings therethrough. One or both of the upper and lower surfaces of the air cavity may have an anti-reflection coating formed thereon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
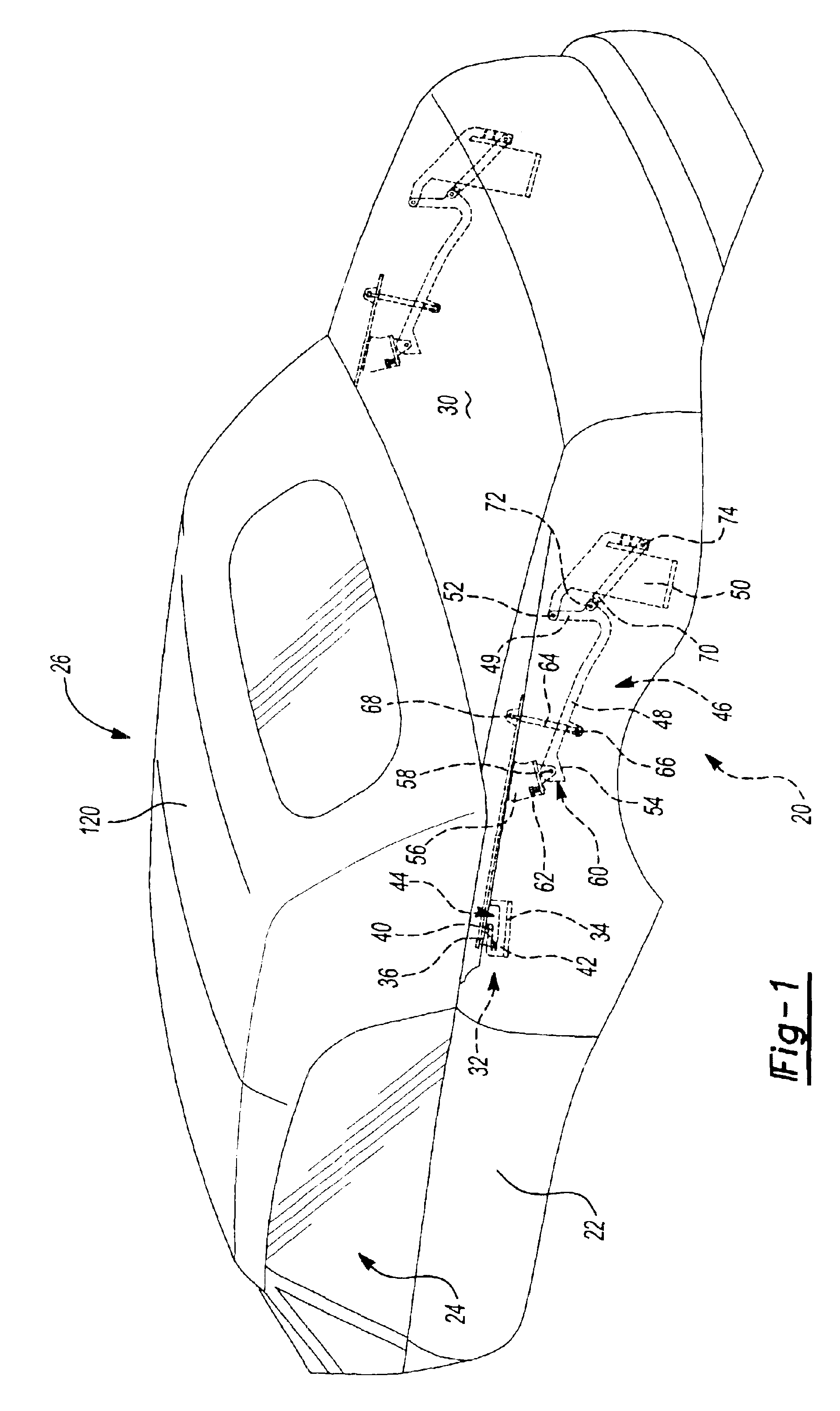
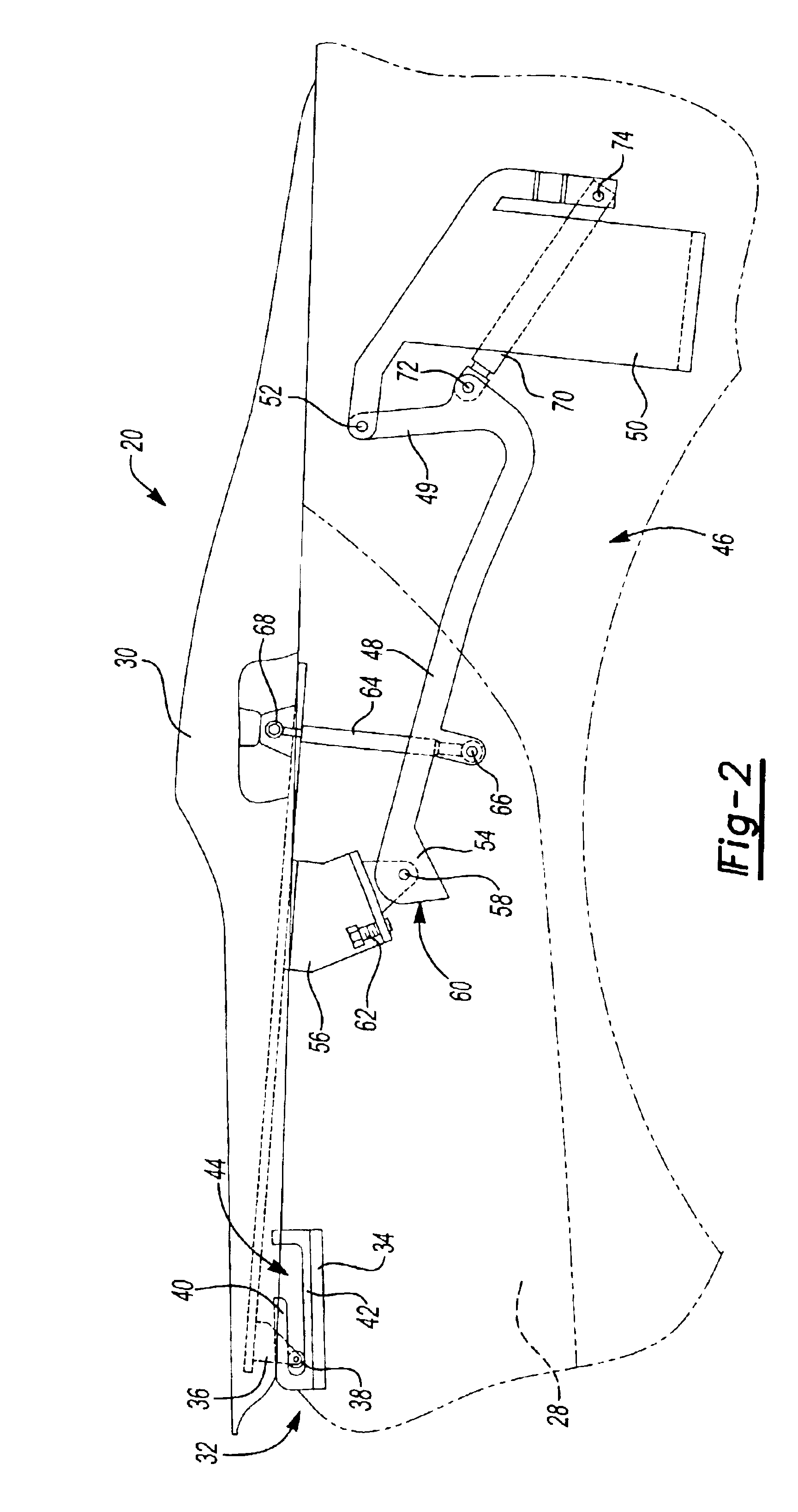
Tonneau panel mechanism
InactiveUS6866327B2Simple designLow costSuperstructure subunitsMonocoque constructionsEngineeringFace sheet
A tonneau panel mechanism engages a stationary track in a closed position and disengages from the stationary track when in the open position. The tonneau panel exhibits a first stage of motion that includes both pivotal and non-pivotal motion and a second stage of motion that consists of substantially rotational motion about a pivot. The tonneau panel mechanism can include a linkage assembly with at least one link that engages with a stop on the tonneau panel to alter the motion of the tonneau panel between the first and second stages of motion. The tonneau panel can also use an at least four-bar linkage wherein at least two of the links move relative to one another during the first stage of motion and are locked together during a second stage of motion.
Owner:SPECIALTY VEHICLE ACQUISITION
Aerated contact lens assembly
A contact lens assembly includes a proximal layer formed from a gas-permeable material, a distal layer with an optical element, an air cavity disposed between the proximal layer and the distal layer, wherein oxygen concentration across the air cavity is substantially uniform, and an gas transport region surrounding the air cavity for communicating gas between the air cavity and atmosphere. The contact lens assembly may further include a plurality of fins disposed within the air cavity where the plurality of fins has openings therethrough. One or both of the upper and lower surfaces of the air cavity may have an anti-reflection coating formed thereon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
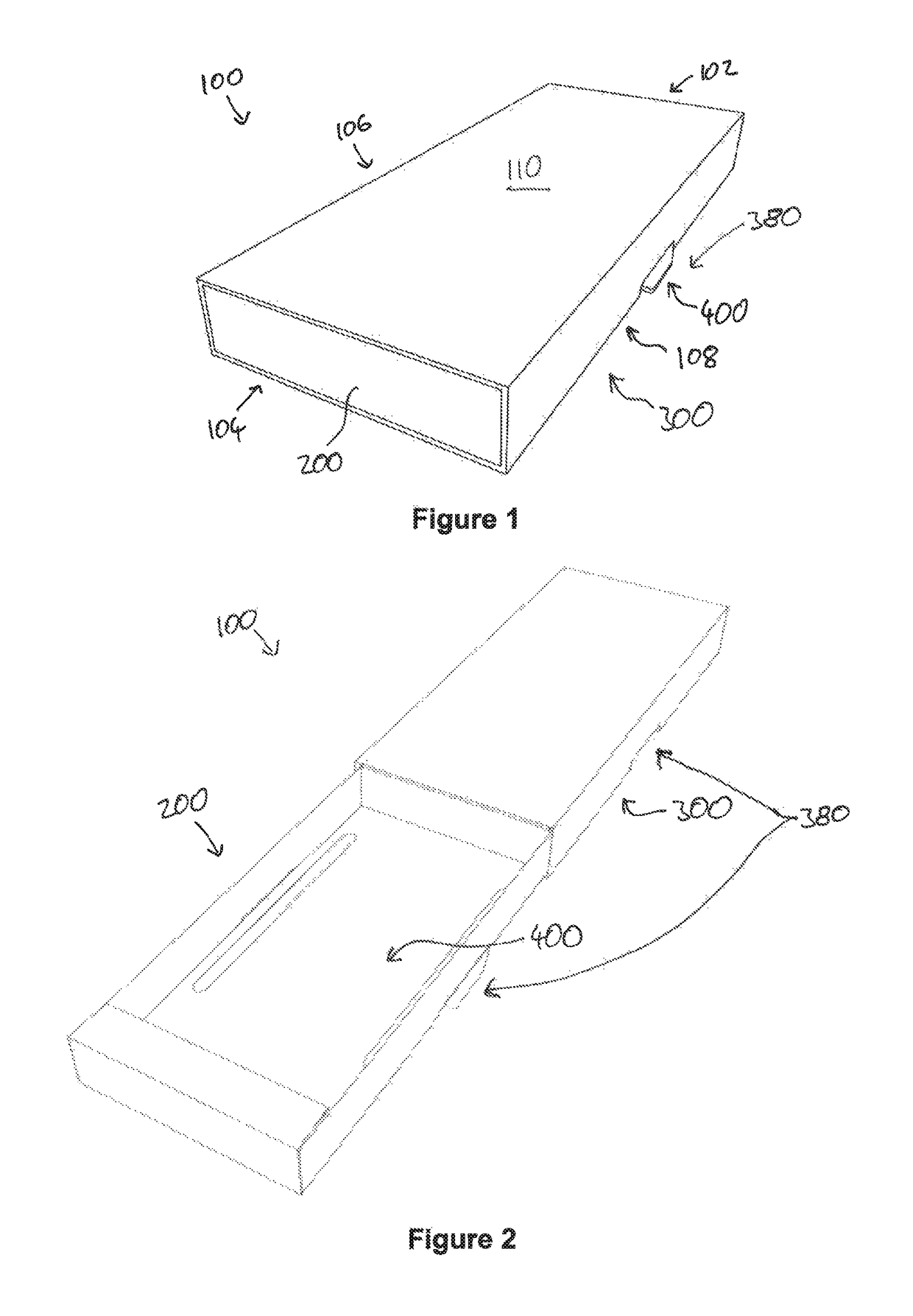
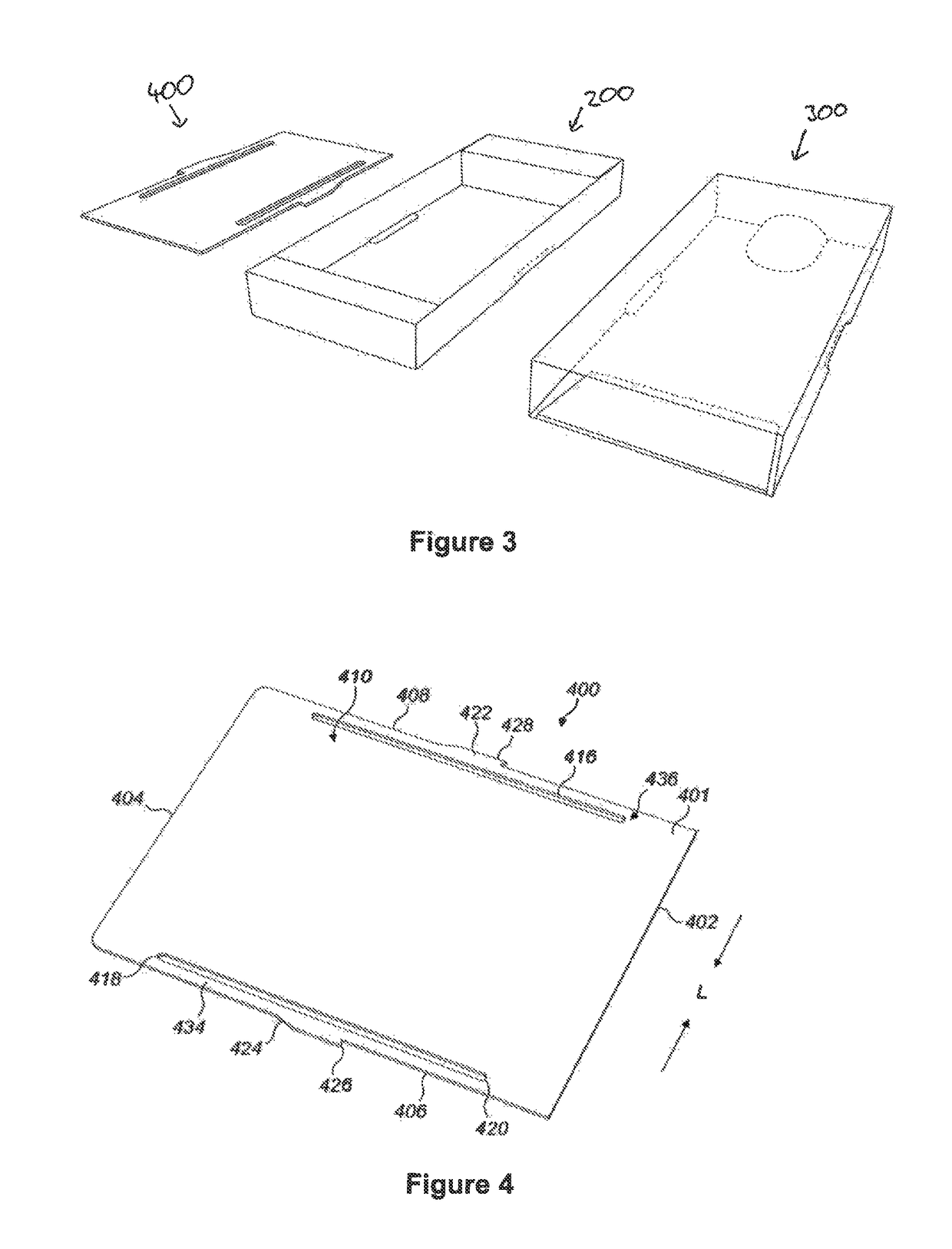
Latchable package
ActiveUS20170217658A1Enhanced couplingReduce manufacturing costSmall article dispensingClosuresEngineeringMechanical engineering
A latchable package comprises: a support for supporting one or more items; a structure for selectively blocking access to the one or more items; and a latchable insert. The latchable insert comprises a substantially planar tab member that is coupled to the support such that the insert and support are movable together in an opening direction from a first position in which the structure blocks access to the one or more items to a second position in which the one or more items are accessibly clear of the structure. The structure and the latchable insert comprise co-operating latch features configured to engage when the insert and support are arranged in the first position
Owner:DUALLOK LTD
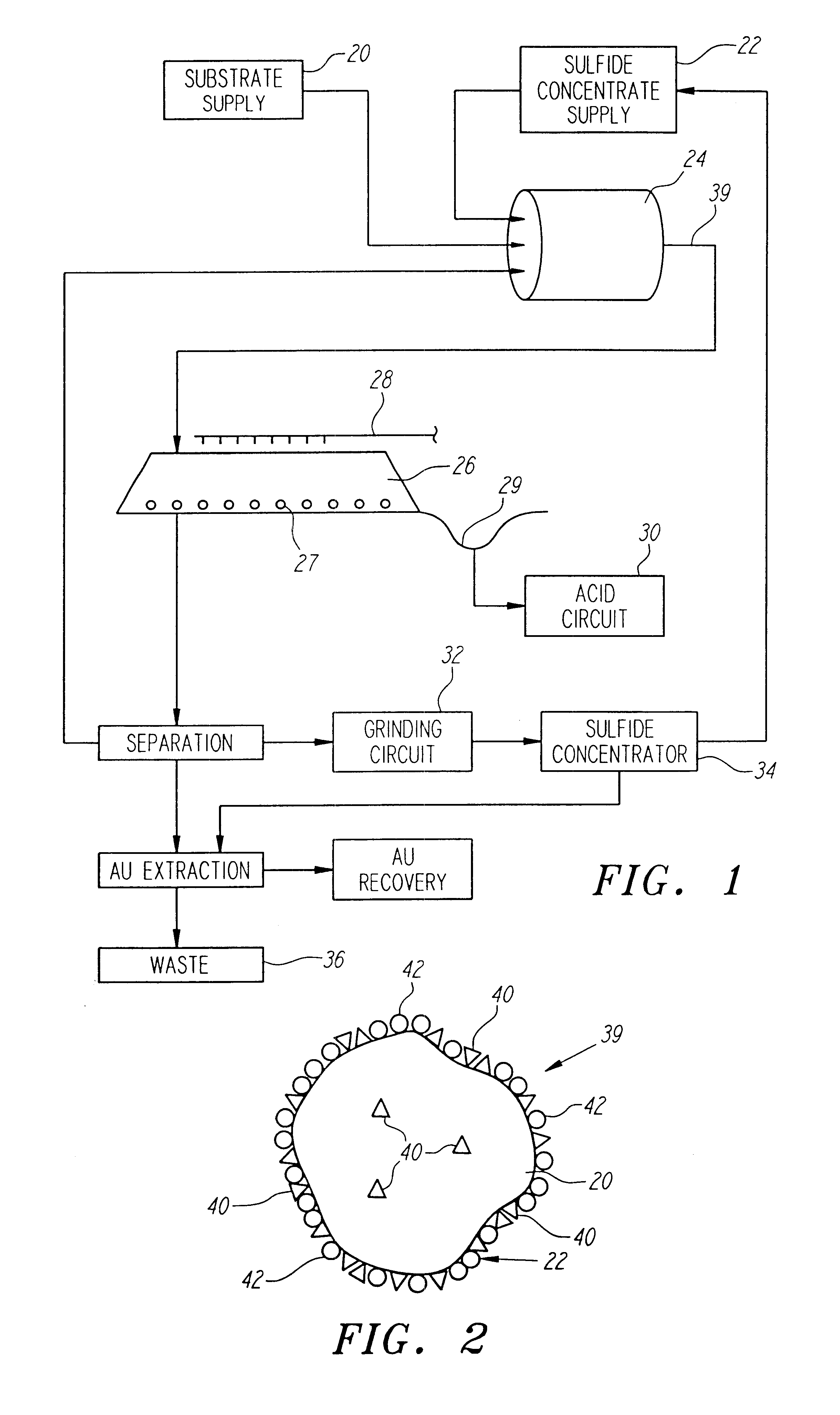
Method of biotreatment for solid materials in a nonstirred surface bioreactor
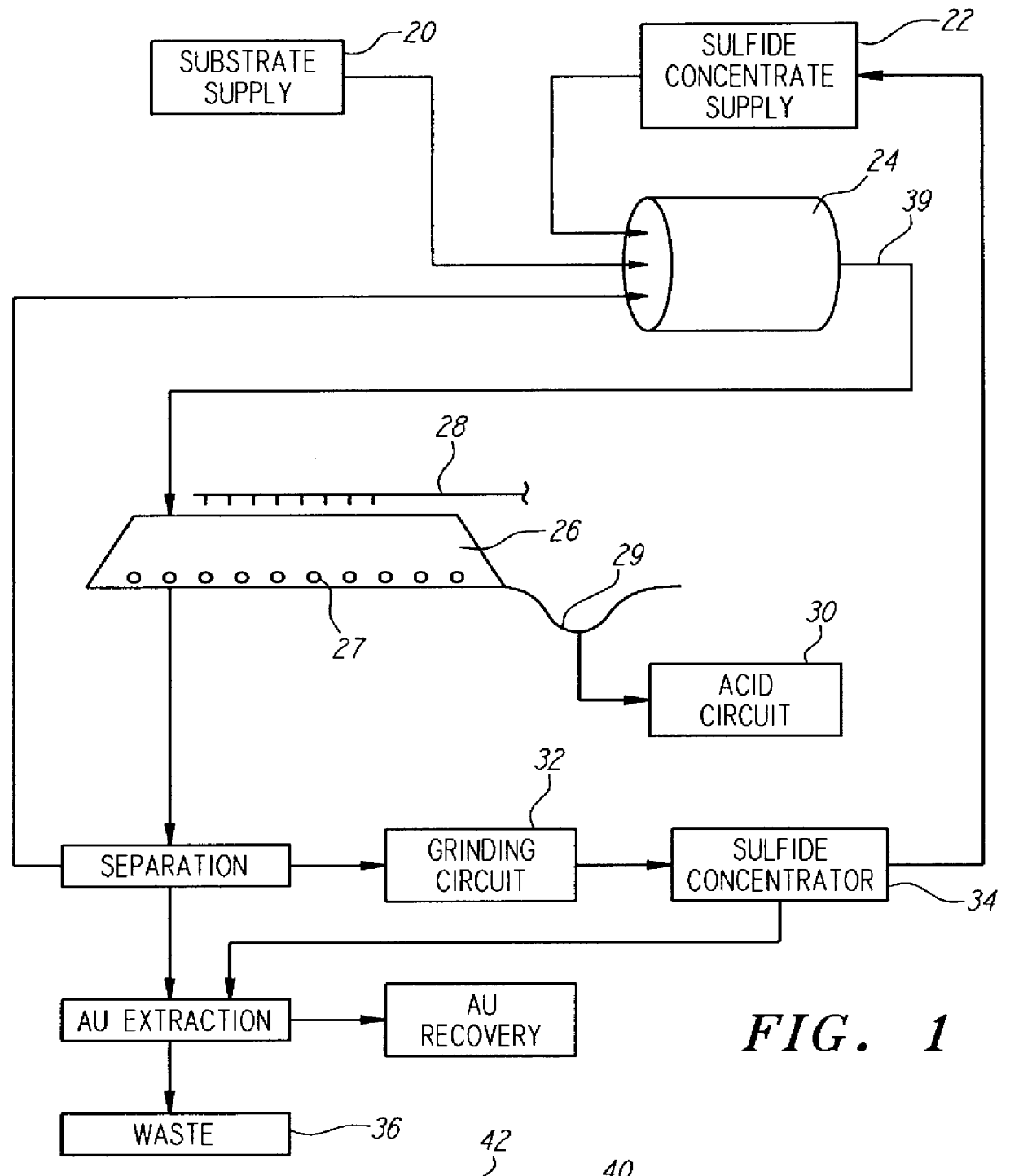
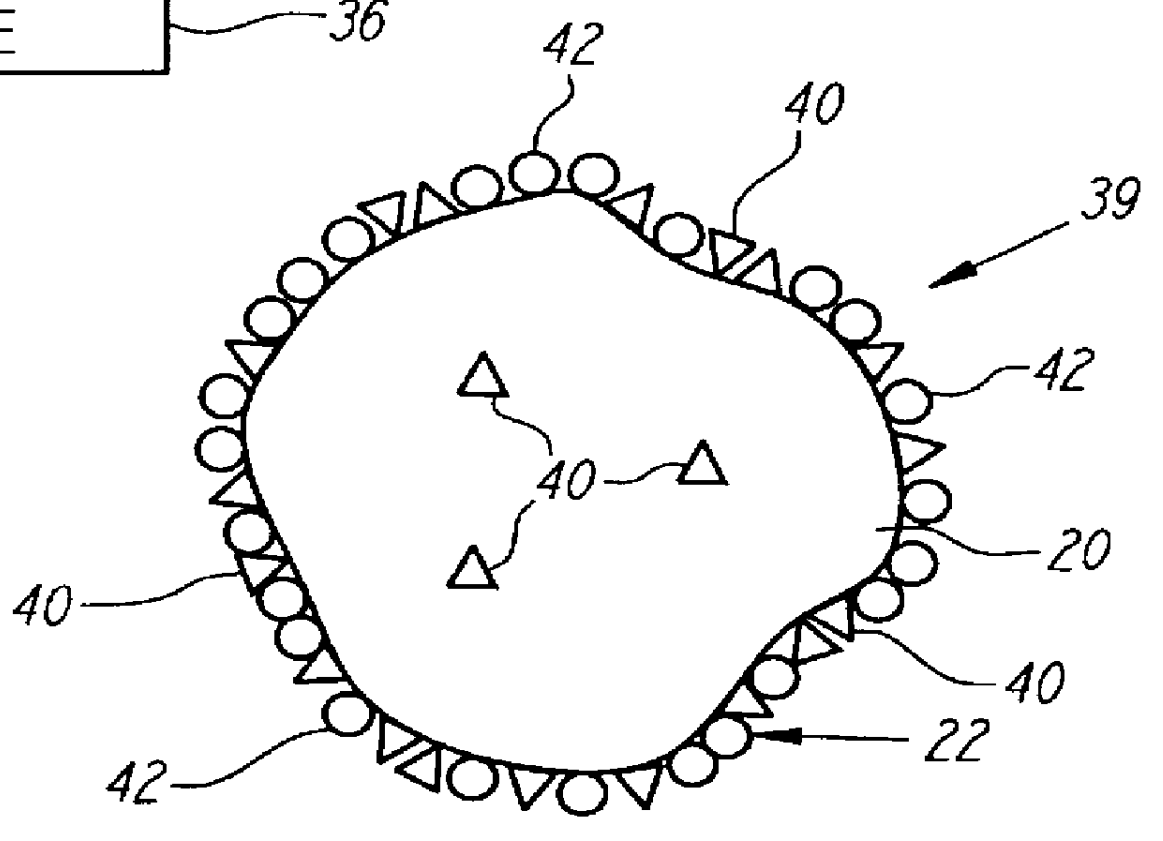
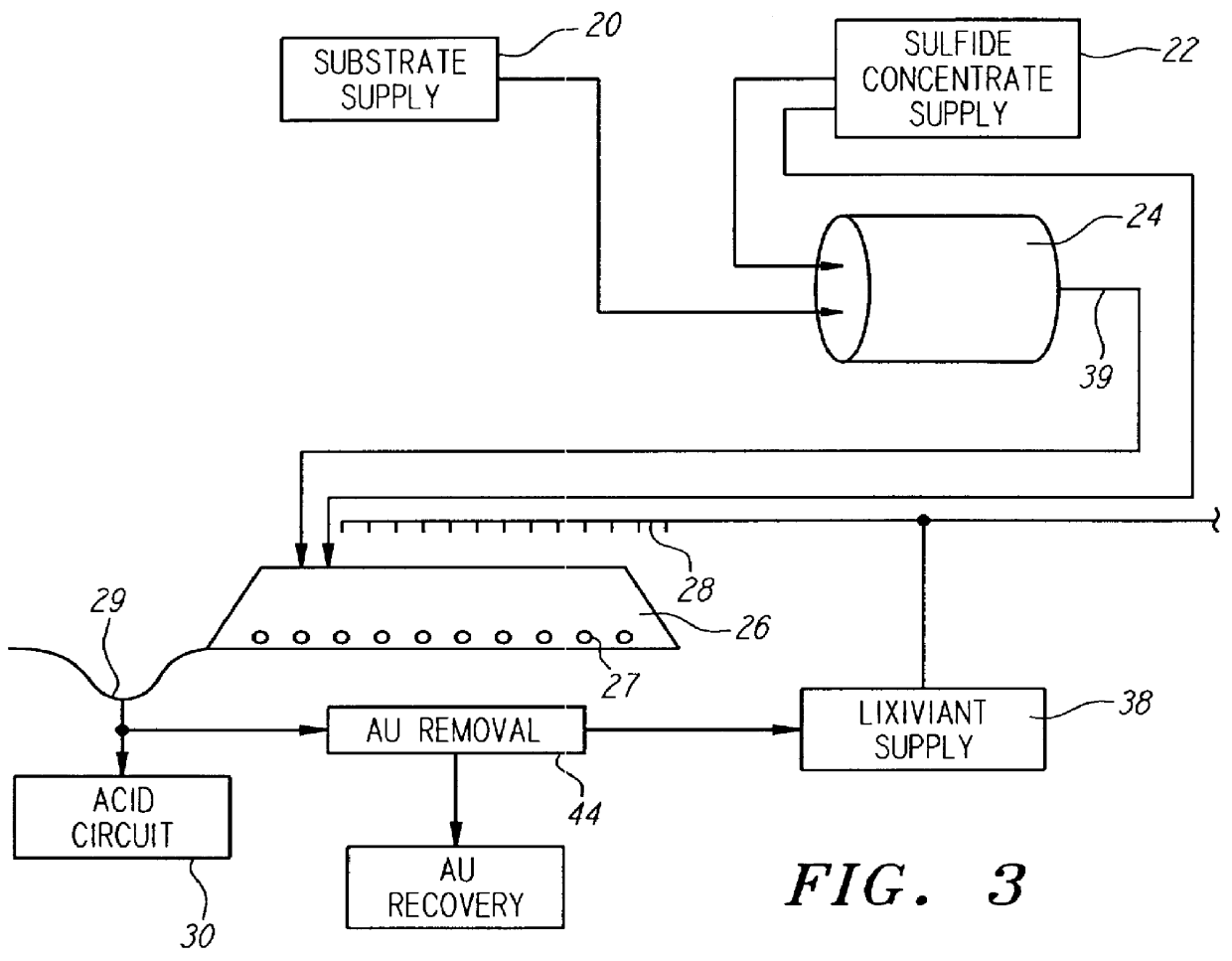
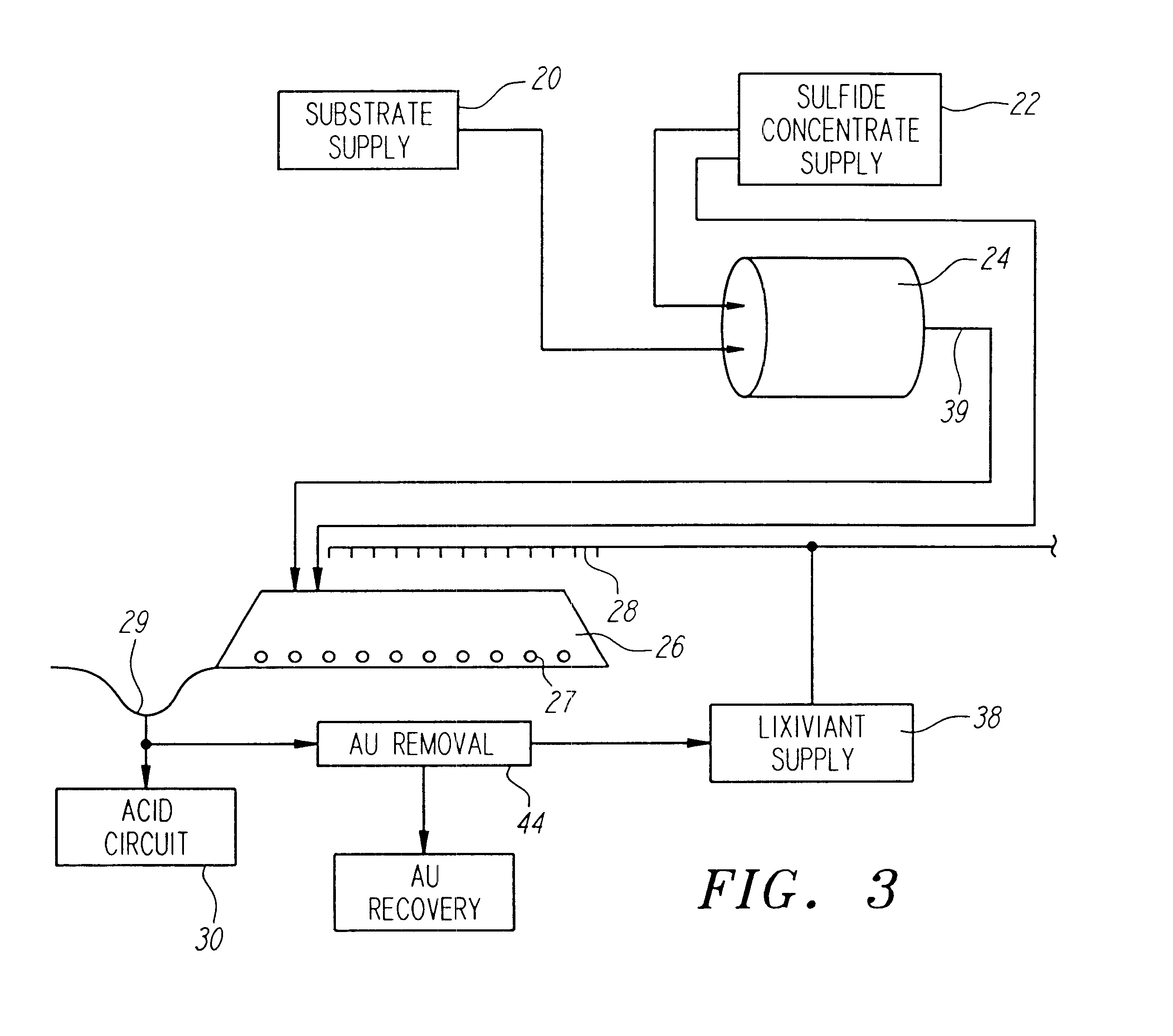
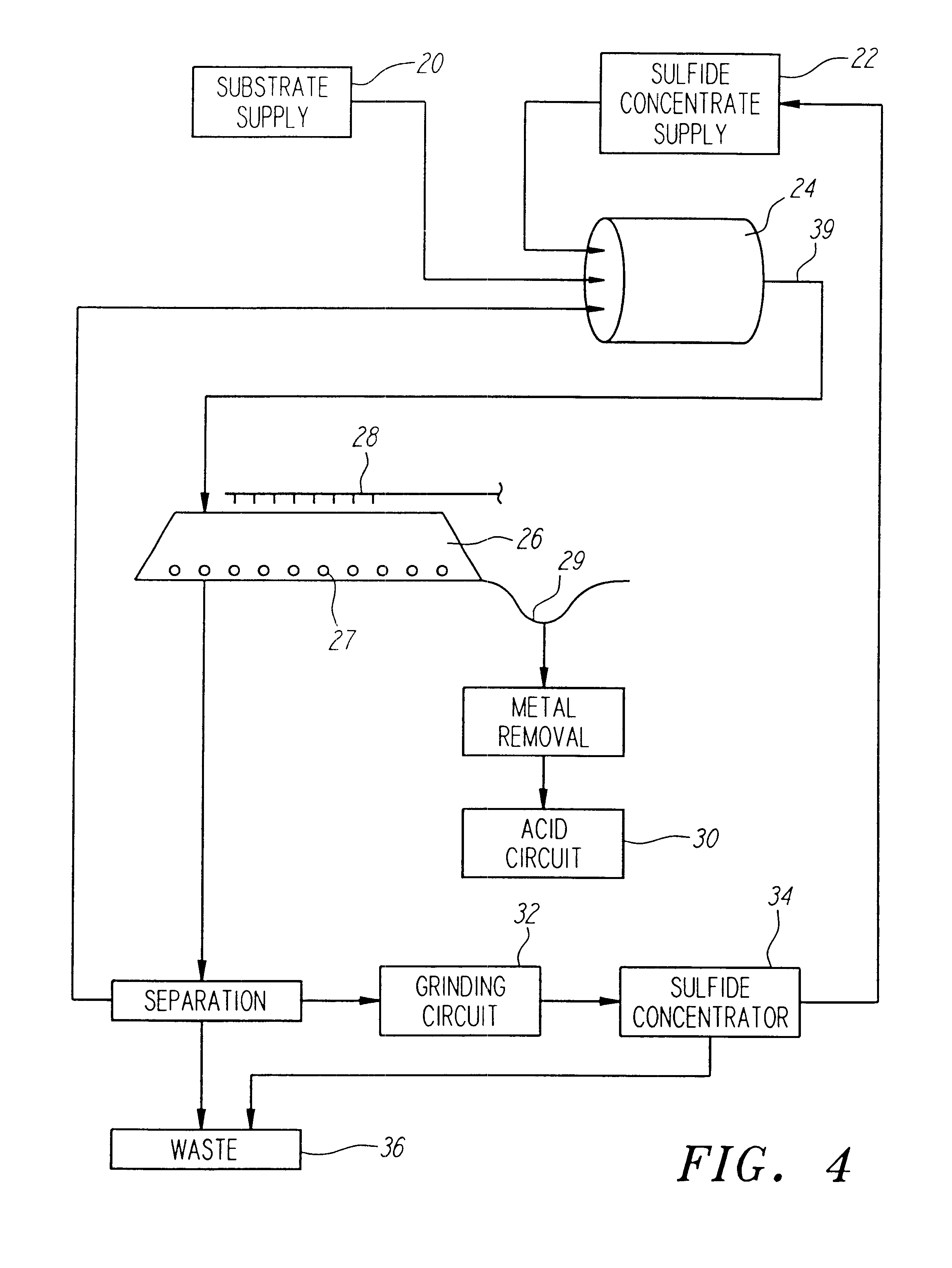
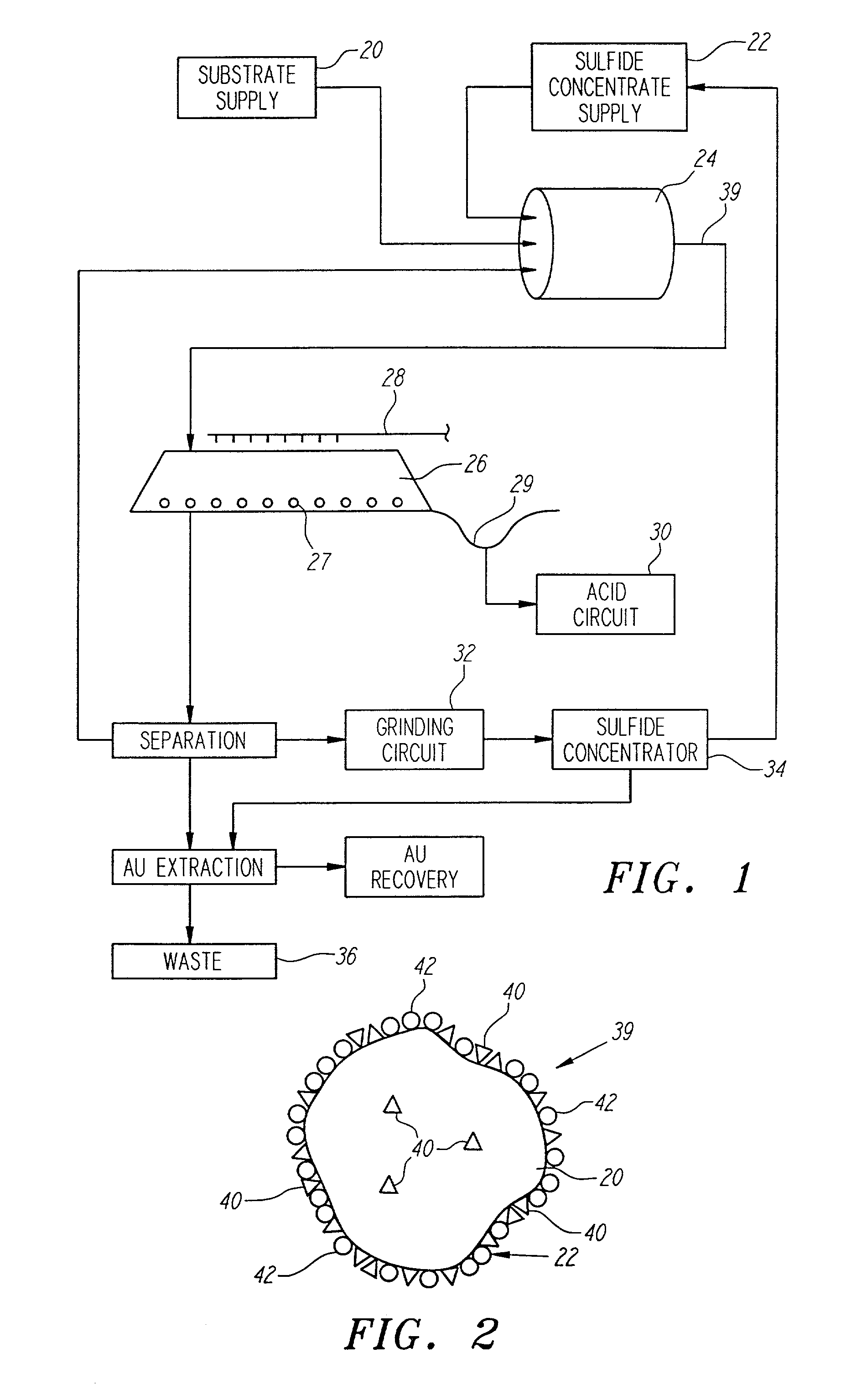
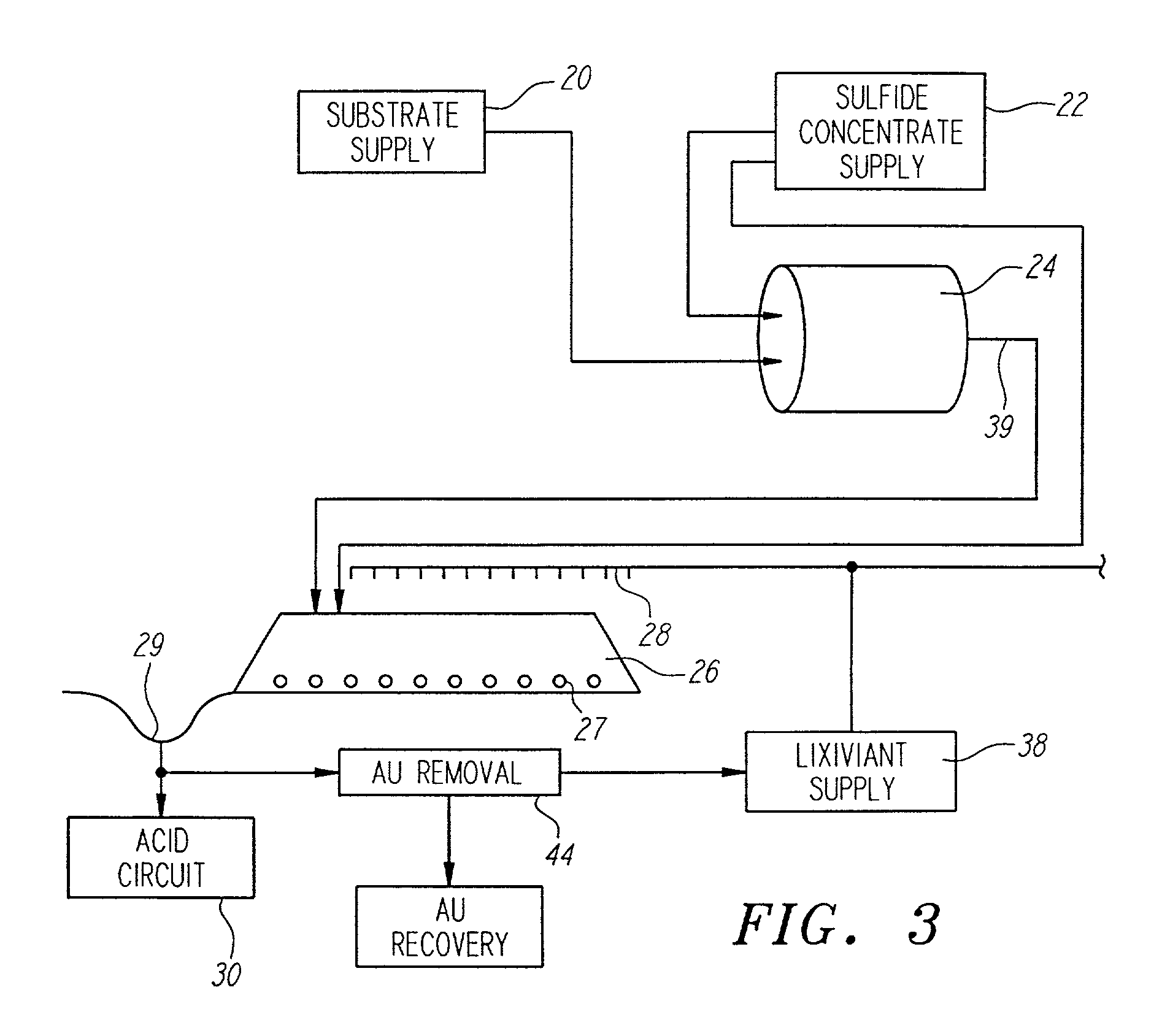
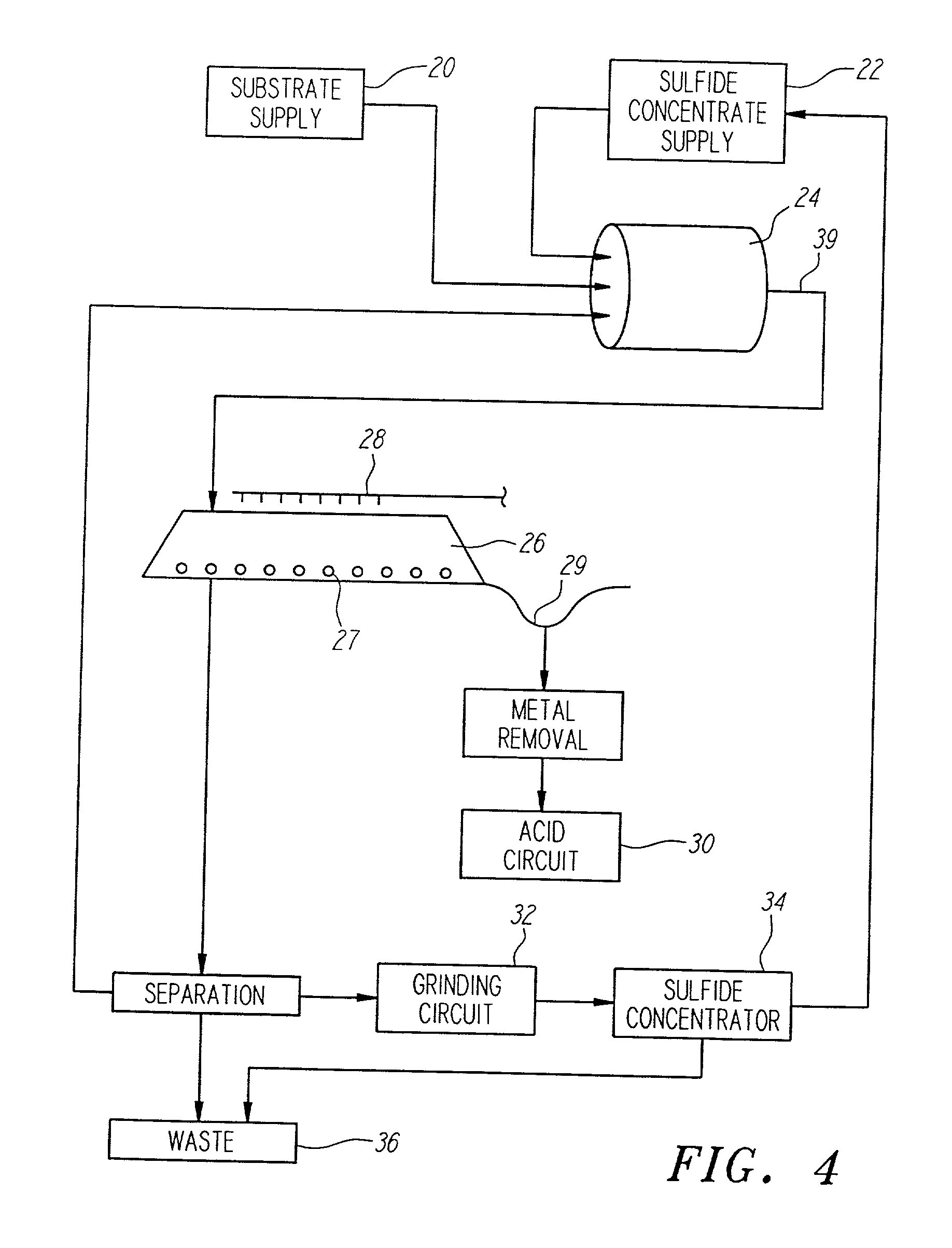
InactiveUS6159726AIncrease capacitySpeed up the processSolvent extractionSolid waste disposalMicrobial inoculationSulfide minerals
A method of biotreating a solid material to remove an undesired compound using a nonstirred surface bioreactor is provided. According to the method the surface of a plurality of coarse substrates is coated with a solid material to be biotreated to form a plurality of coated coarse substrates. The coarse substrates have a particle size greater than about 0.3 cm and the solid material to be biotreated has a particle size less than about 250 mu m. A nonstirred surface reactor is then formed by stacking the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a heap or placing the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a tank so that the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 25%. The reactor is inoculated with a microorganism capable of degrading the undesired compound in the solid material, and the solid material is then biotreated in the surface bioreactor until the undesired compound in the solid material is degraded to a desired concentration. Preferably the thickness of the solid material coating on the plurality of coarse substrates is less than about 1 mm and the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 35%. The process is useful for many different biotreatment processes, including the bioremediation of contaminated soils, the desulfurization of coal, and the biooxidation of refractory sulfide ores and concentrates. In bioremediation applications, the undesired compound is typically an organic compound. In coal desulfurization and refractory sulfide ore biooxidation applications, the undesired compound is sulfide minerals.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
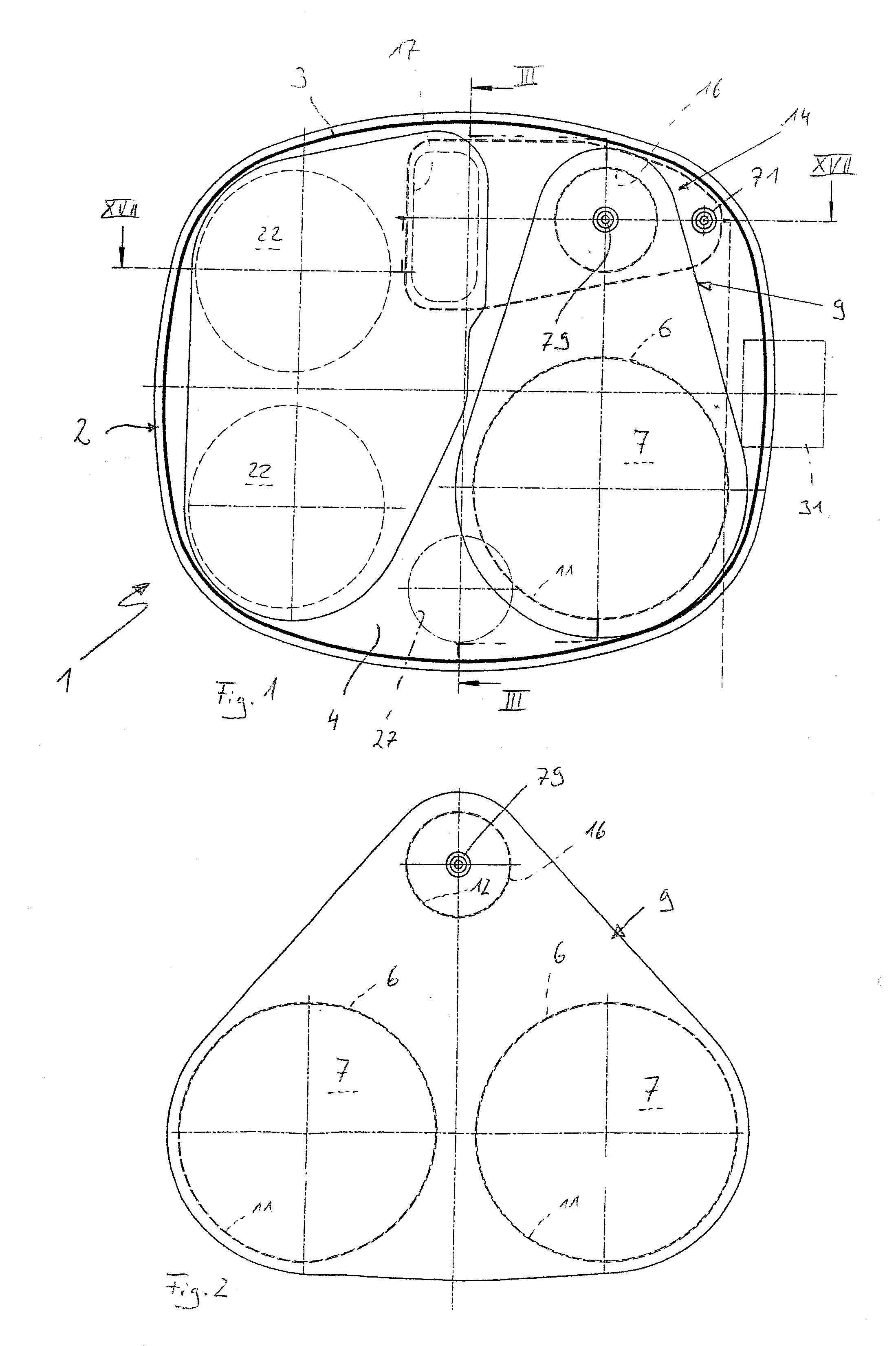
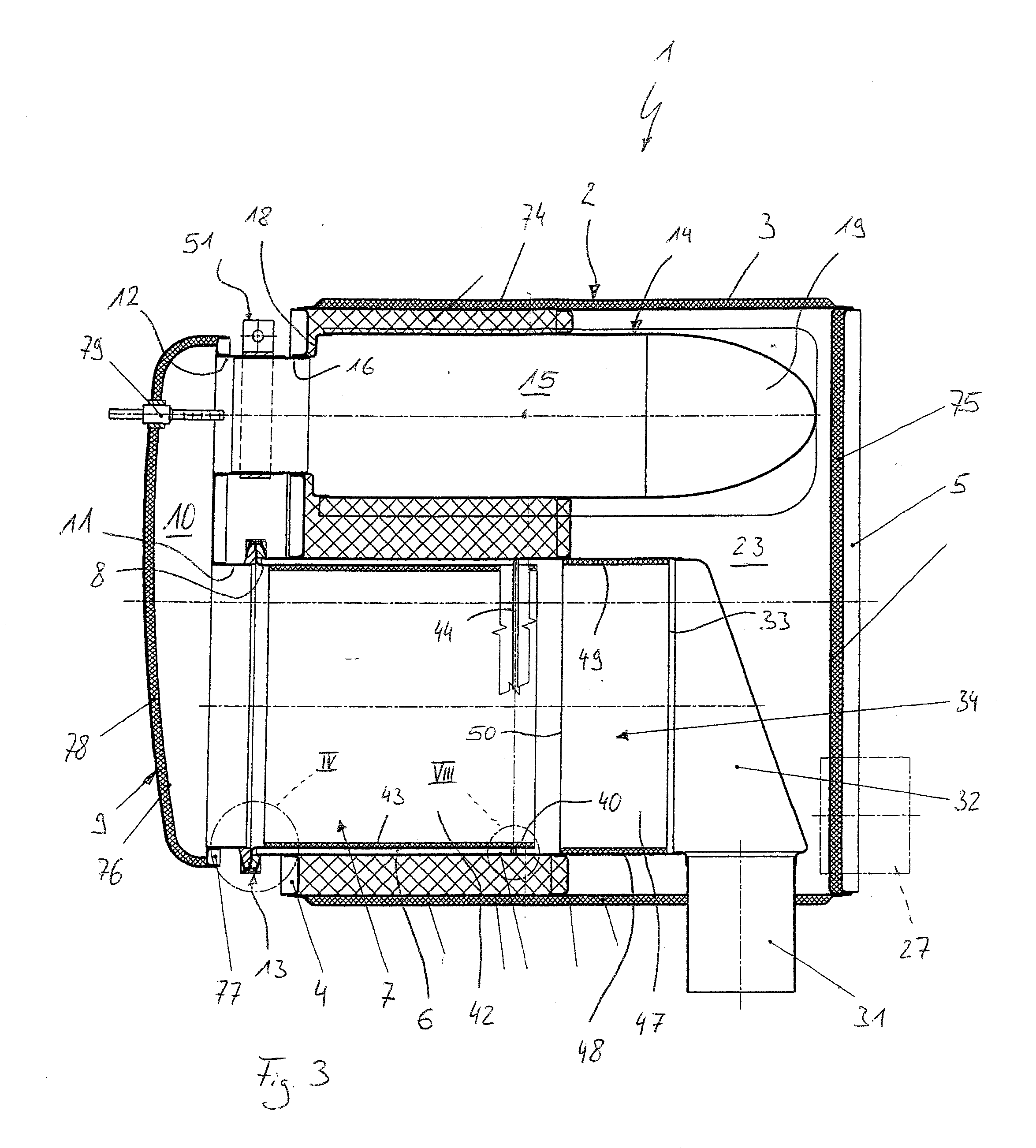
Exhaust gas-treating device
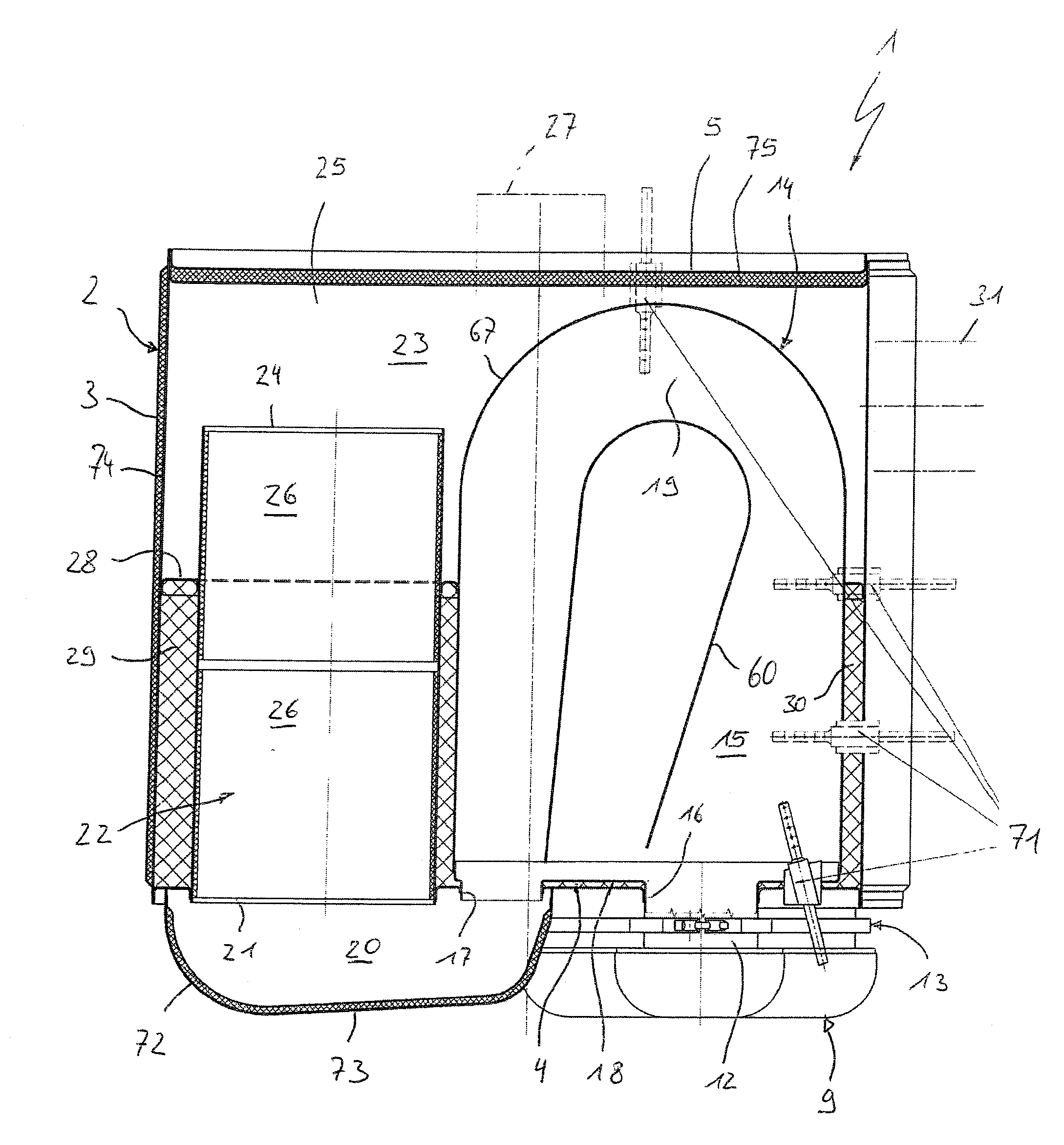
ActiveUS20100242450A1Easy to operateAdequate accessInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationExhaust fumesInternal combustion engine
An exhaust gas-treating device (1) for an exhaust system of an internal combustion engine, especially of a motor vehicle, has a housing (2), which has a jacket (3) extending circumferentially on the side and two end-side end bottoms (4, 5). Maintenance is simplified with at least one mounting tube (6), which passes through one or the first end bottom (4) and into the outlet end (8) of which a particle filter (7) is plugged axially from the outside, with a deflecting housing (9). The deflecting housing (9) contains a deflecting chamber (10), and has at least one inlet (11) communicating with the deflecting chamber (10) and at least one outlet (12) communicating with the deflecting chamber (10). A fastening device (13) is provided for detachably fastening the respective inlet (11) at the respective outlet end (8) of the mounting tube (6).
Owner:EBERSPACHER EXHAUST TECH GMBH & CO +1
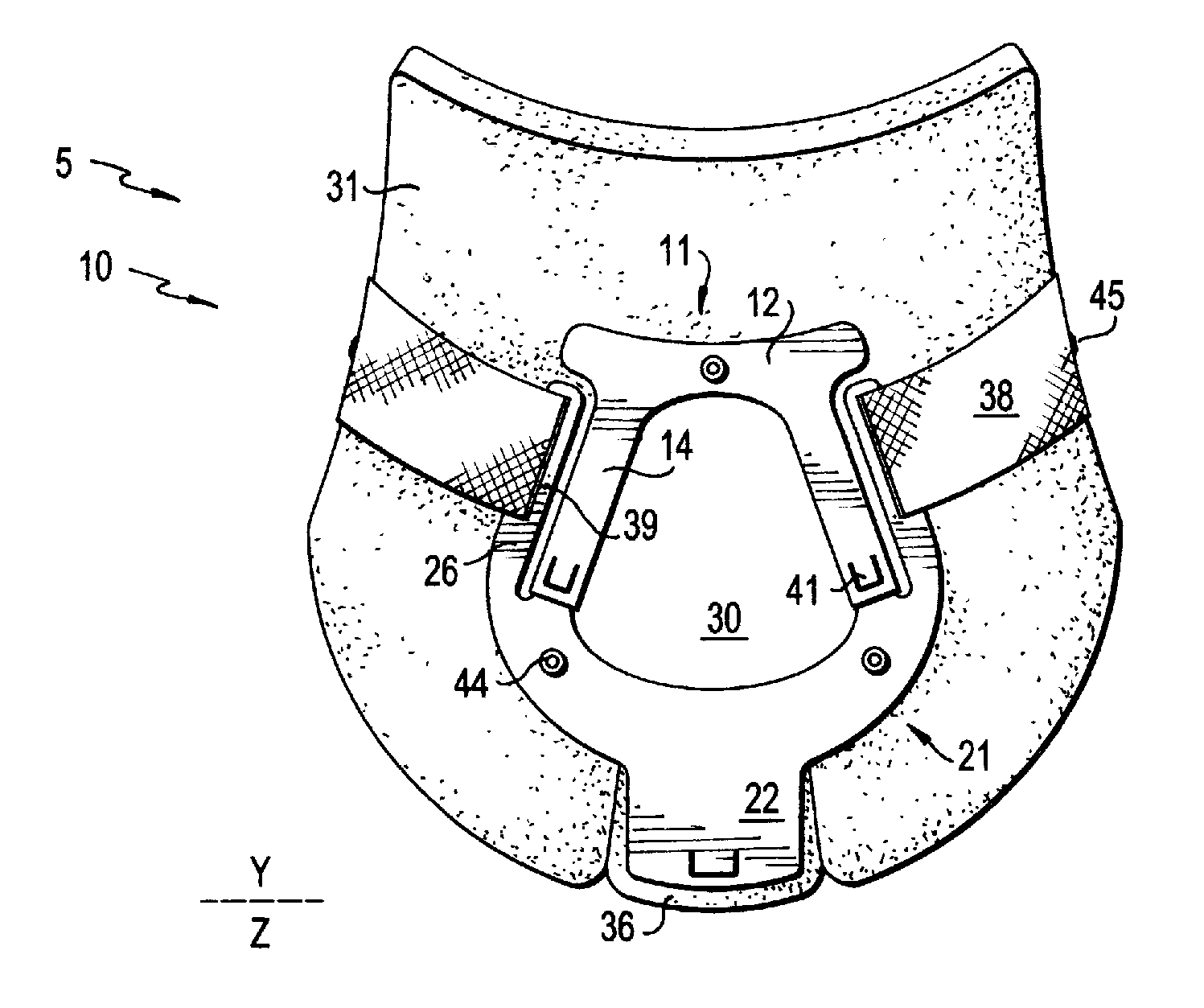
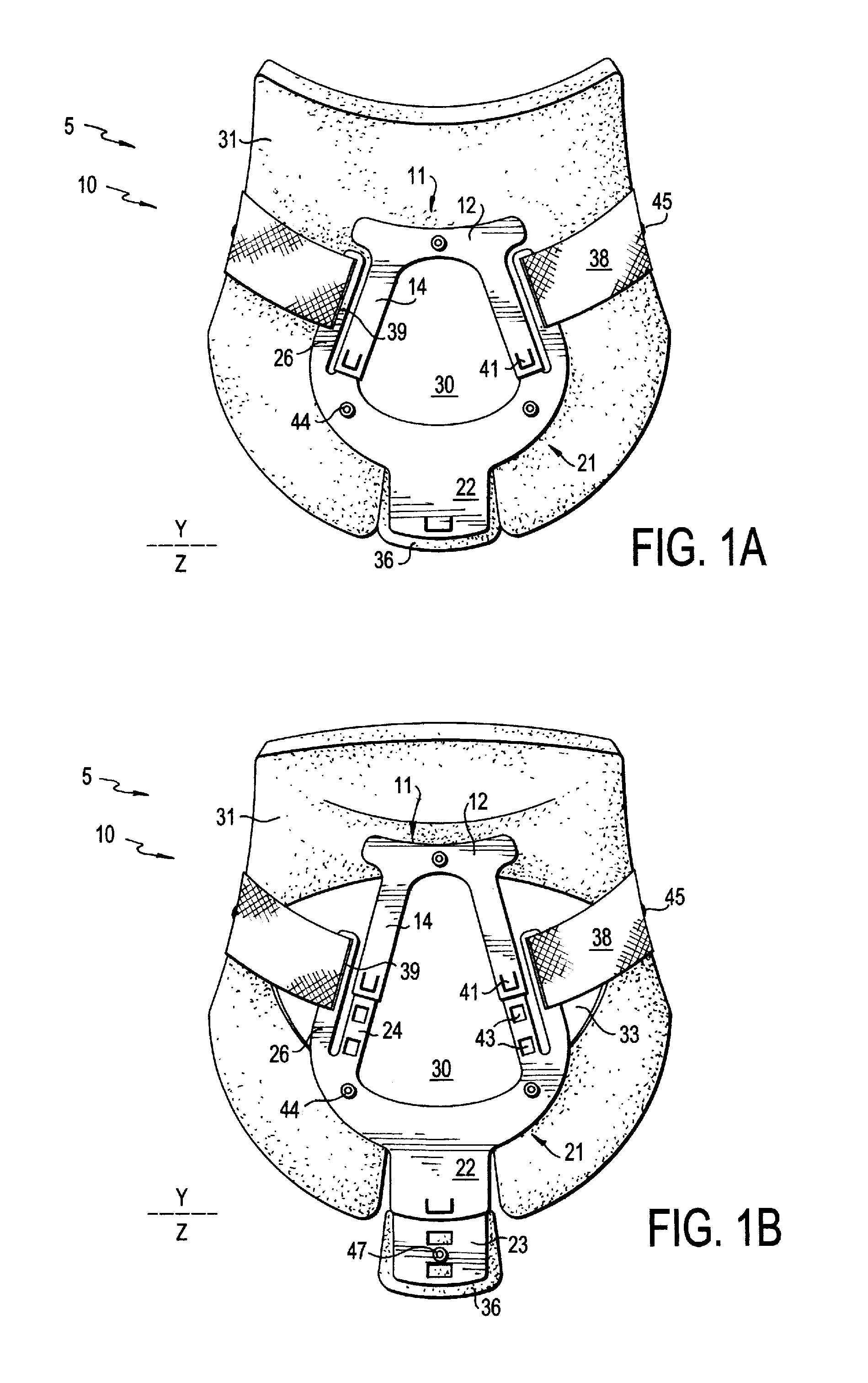
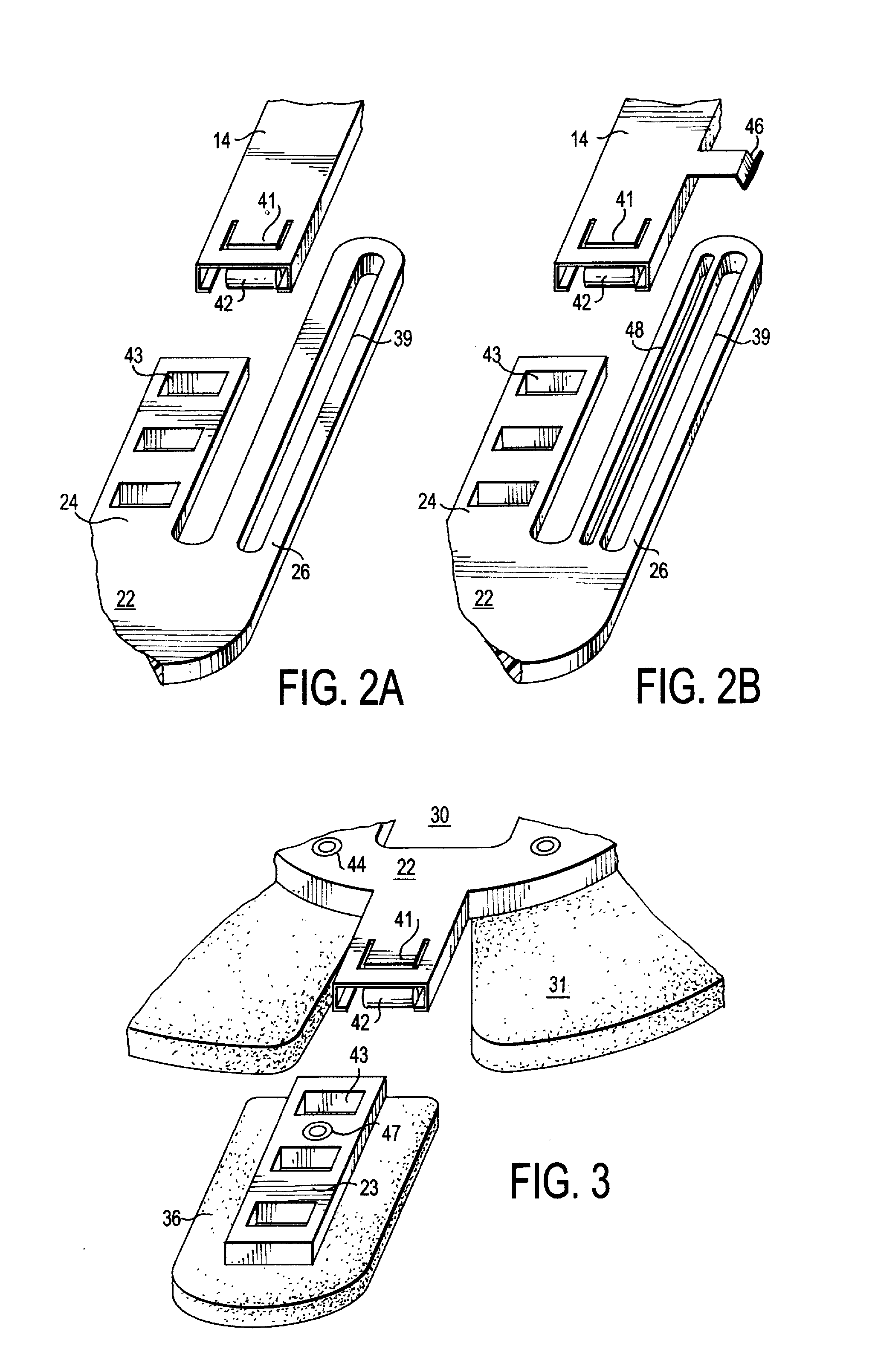
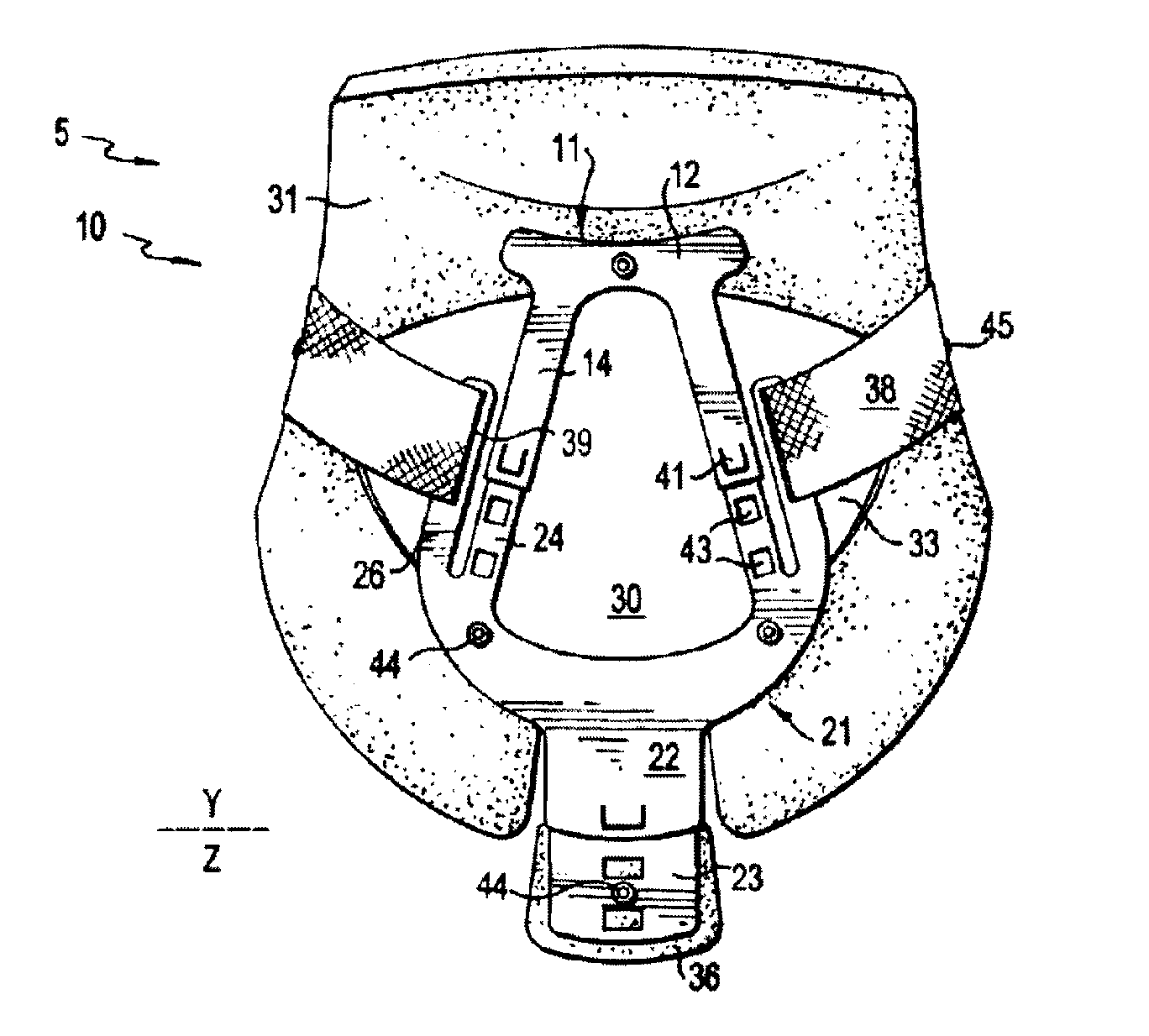
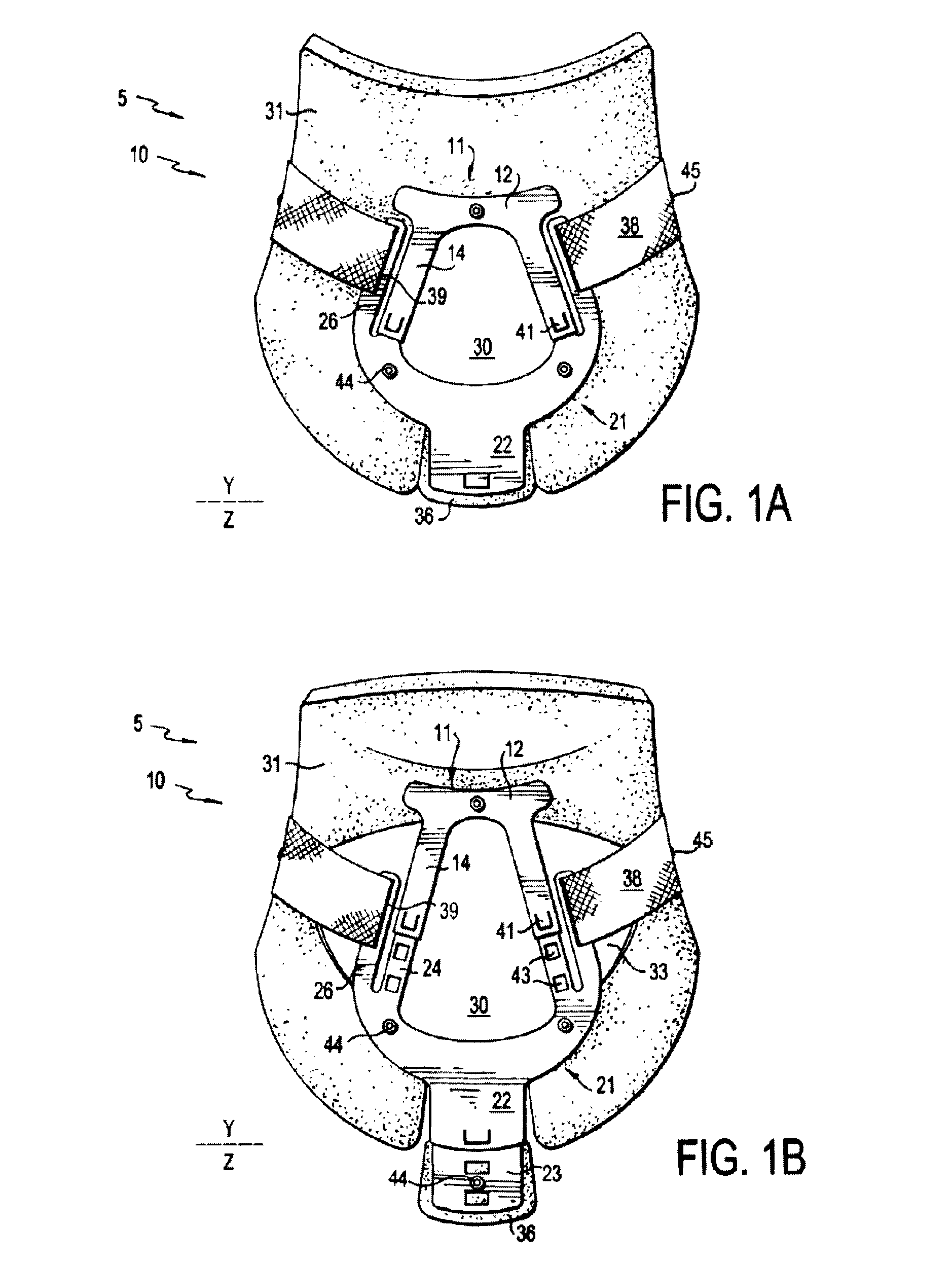
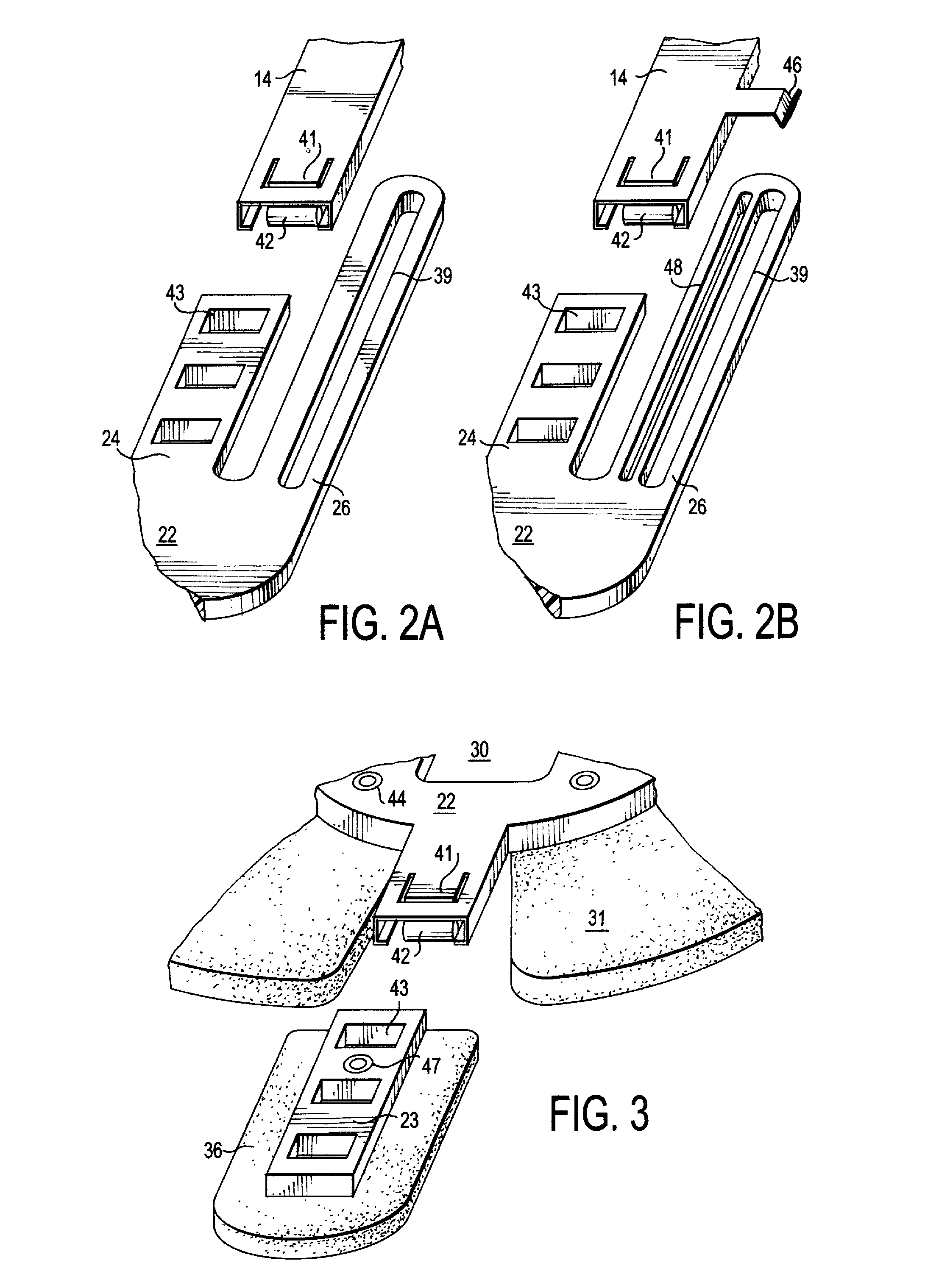
Cervical collar with independent height and circumference adjustability
ActiveUS20120165712A1Limit range of motionLimited rangeFractureProsthesisPhysical medicine and rehabilitationOccipital bone
An adjustable cervical collar designed to accommodate a broad range of prospective wearers with unique physical attributes, and to restrict the movements of the wearer's cervical spine, including rotation, flexion, extension, and lateral bending. The cervical collar includes a front portion and back portion, which may be adjusted in relation to one other to vary the circumference of the cervical collar. The front portion includes upper and lower plastic portions which may be adjusted to vary the height of the cervical collar, and a front thoracic extender which may be adjusted to achieve a desired restrictiveness of flexion movement. The back portion includes occipital and back thoracic extenders which may be adjusted to achieve a desired restrictiveness of extension movement. The adjustable features may be operated independently of one another. The adjustable features include locking means to ensure that the cervical collar is securely applied to the wearer.
Owner:SC IP
Cervical collar with independent height and circumference adjustability
An adjustable cervical collar designed to accommodate a broad range of prospective wearers with unique physical attributes, and to restrict the movements of the wearer's cervical spine, including rotation, flexion, extension, and lateral bending. The cervical collar includes a front portion and back portion, which may be adjusted in relation to one other to vary the circumference of the cervical collar. The front portion includes upper and lower plastic portions which may be adjusted to vary the height of the cervical collar, and a front thoracic extender which may be adjusted to achieve a desired restrictiveness of flexion movement. The back portion includes occipital and back thoracic extenders which may be adjusted to achieve a desired restrictiveness of extension movement. The adjustable features may be operated independently of one another. The adjustable features include locking means to ensure that the cervical collar is securely applied to the wearer.
Owner:SC IP
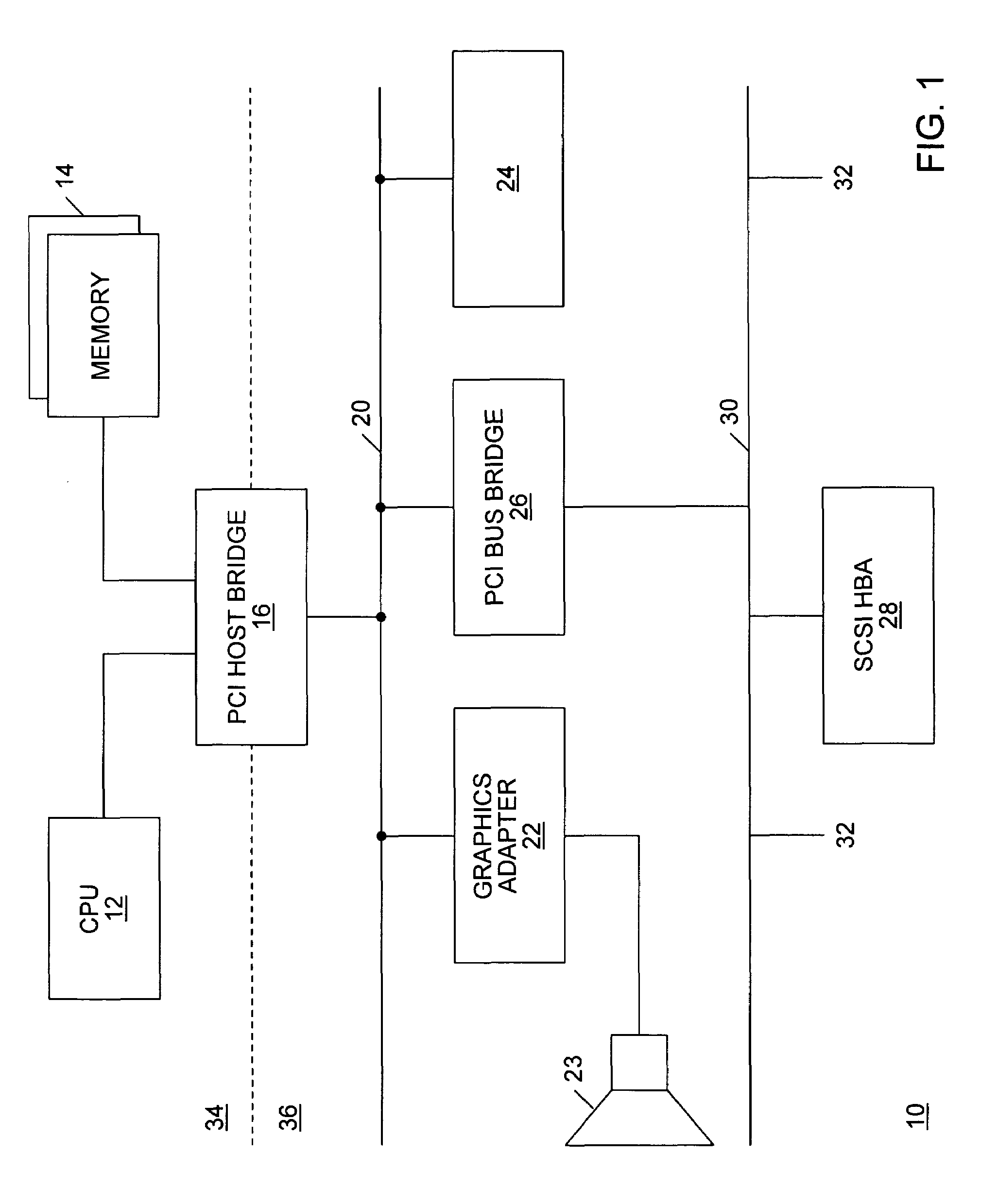
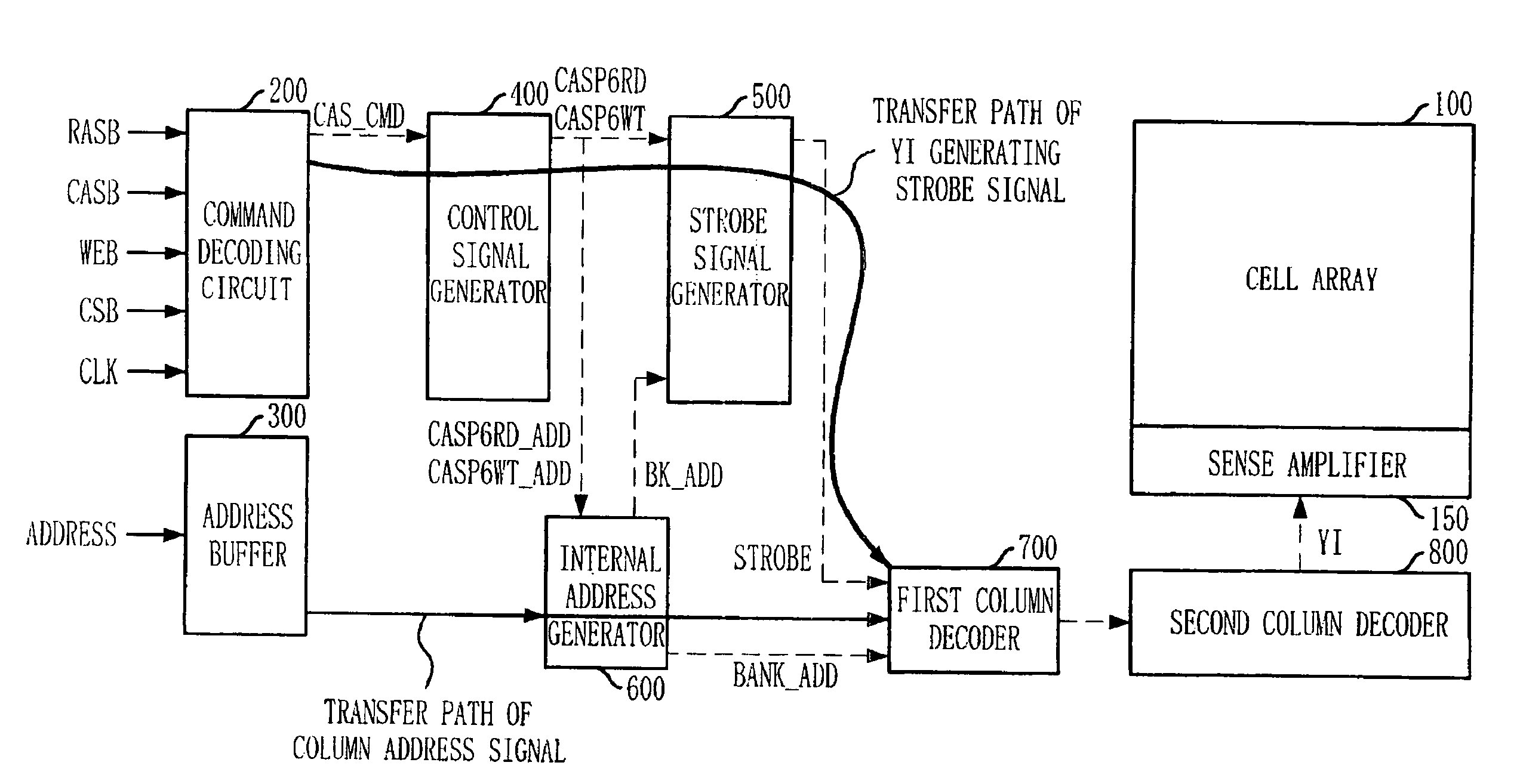
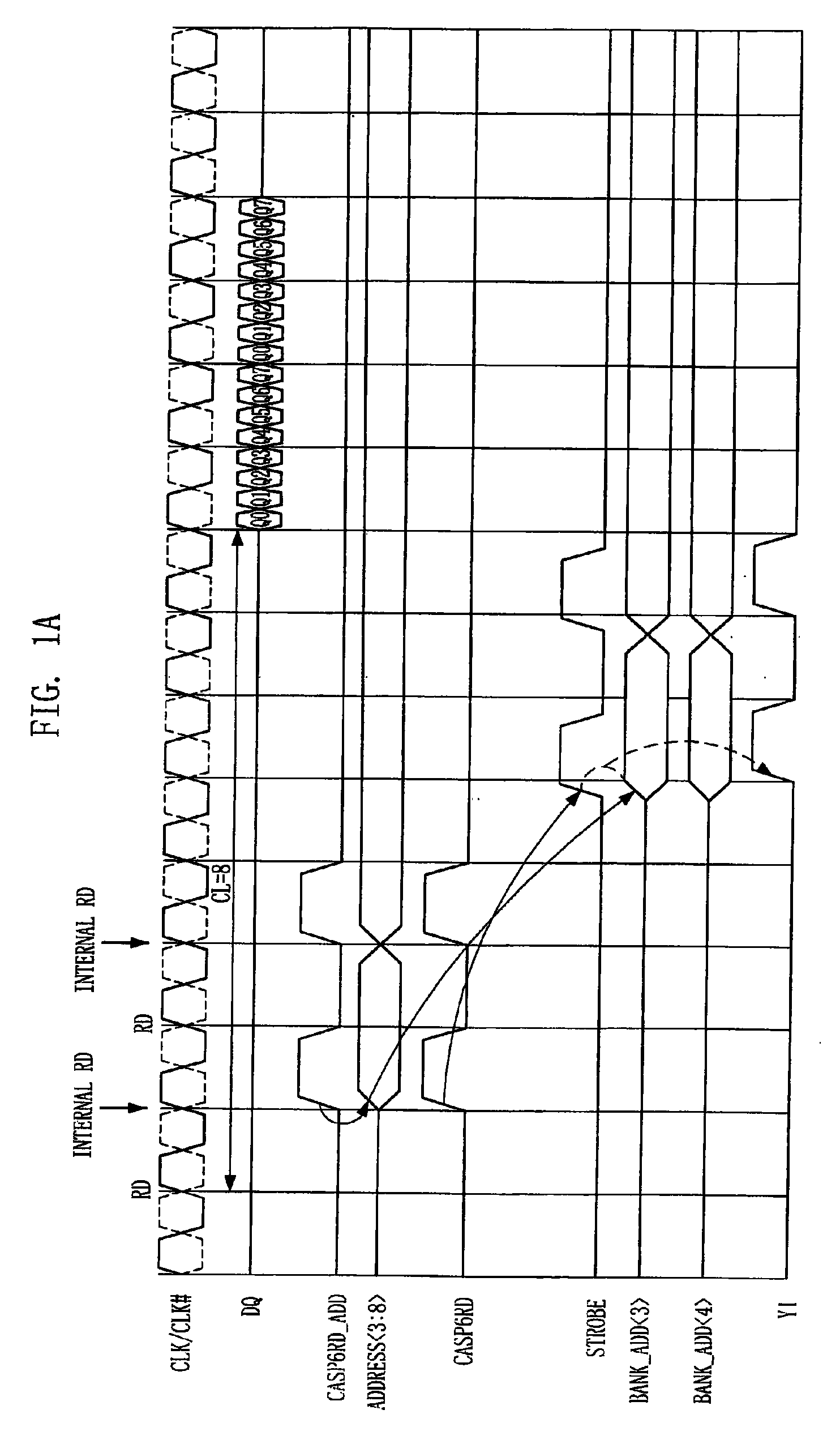
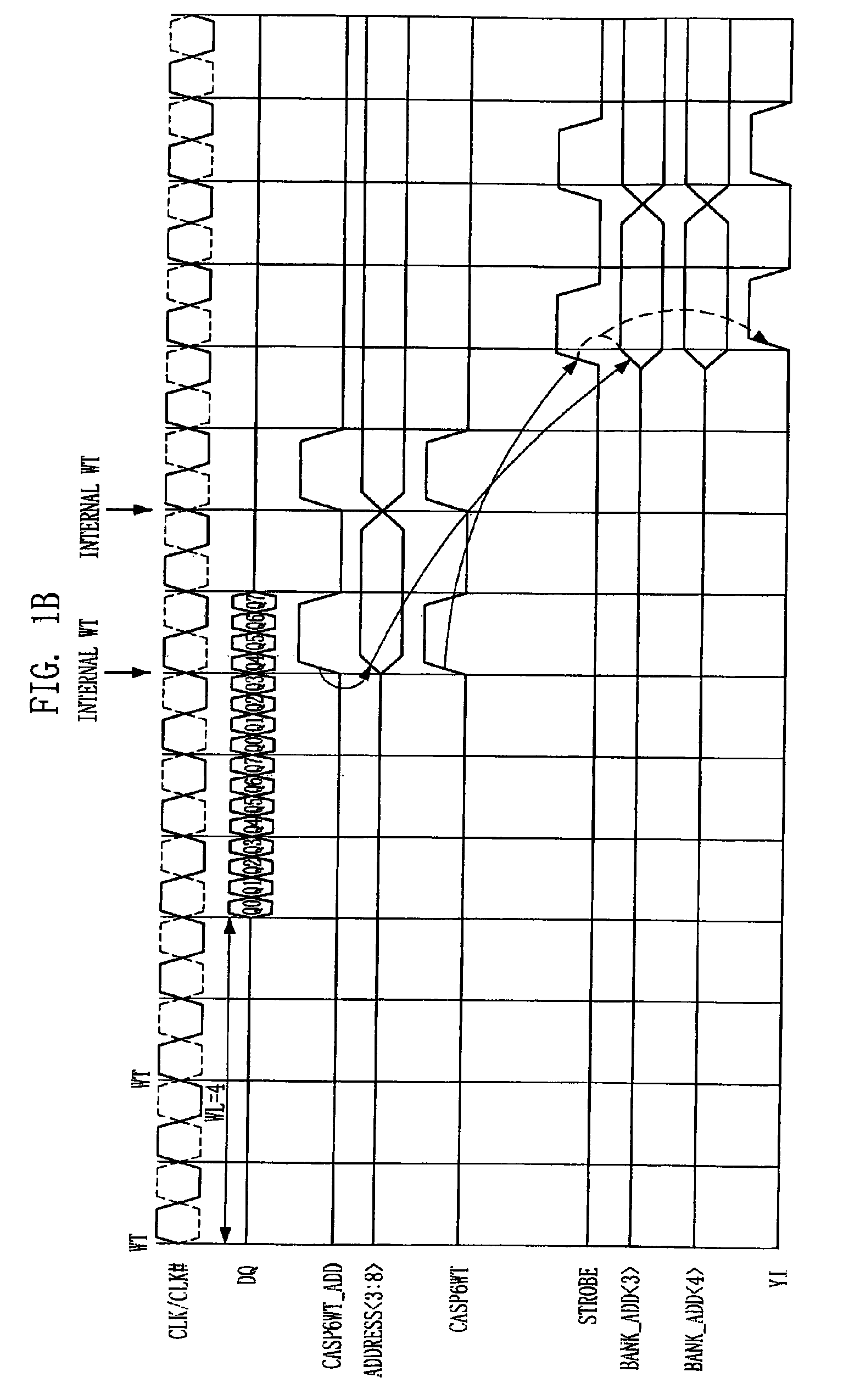
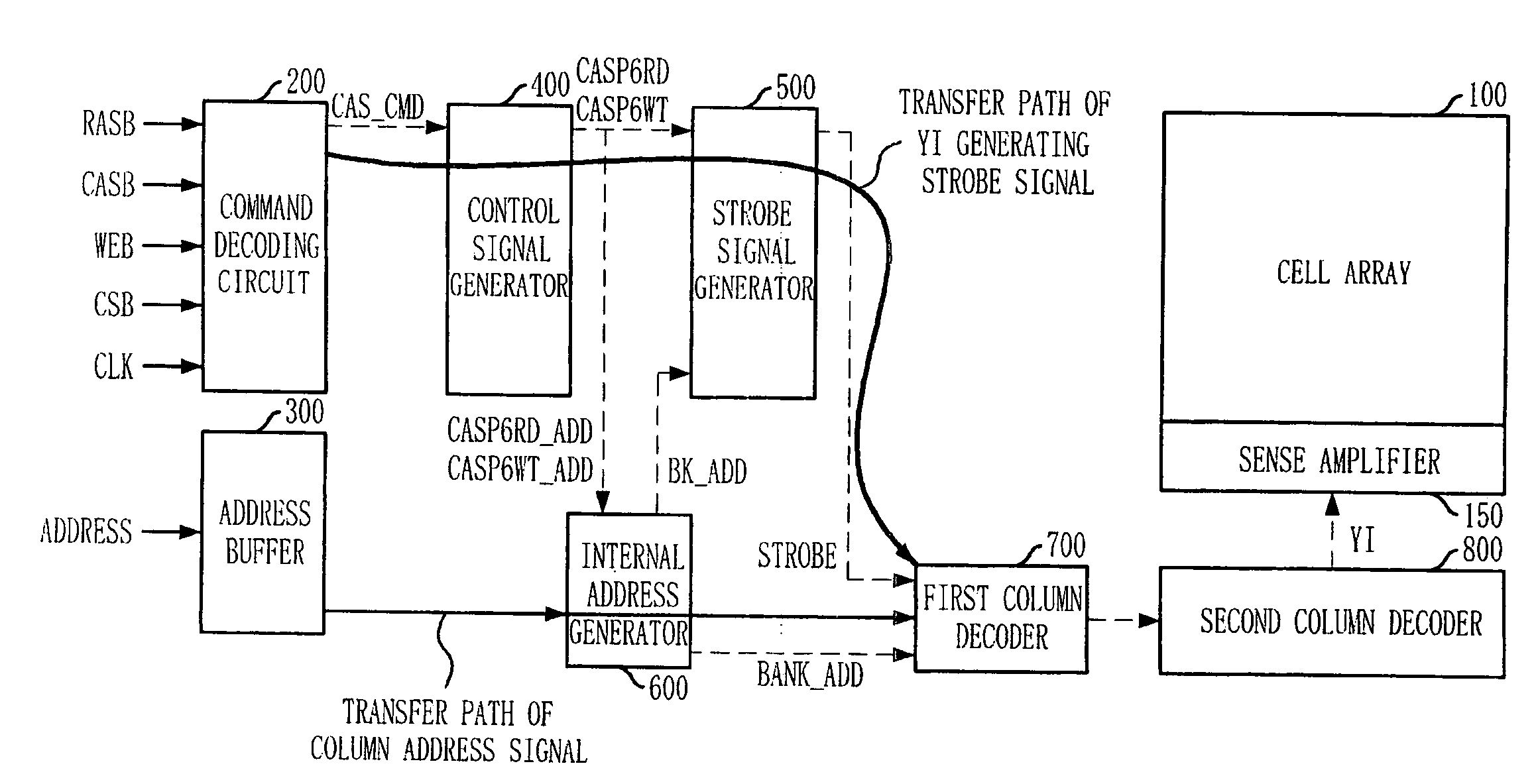
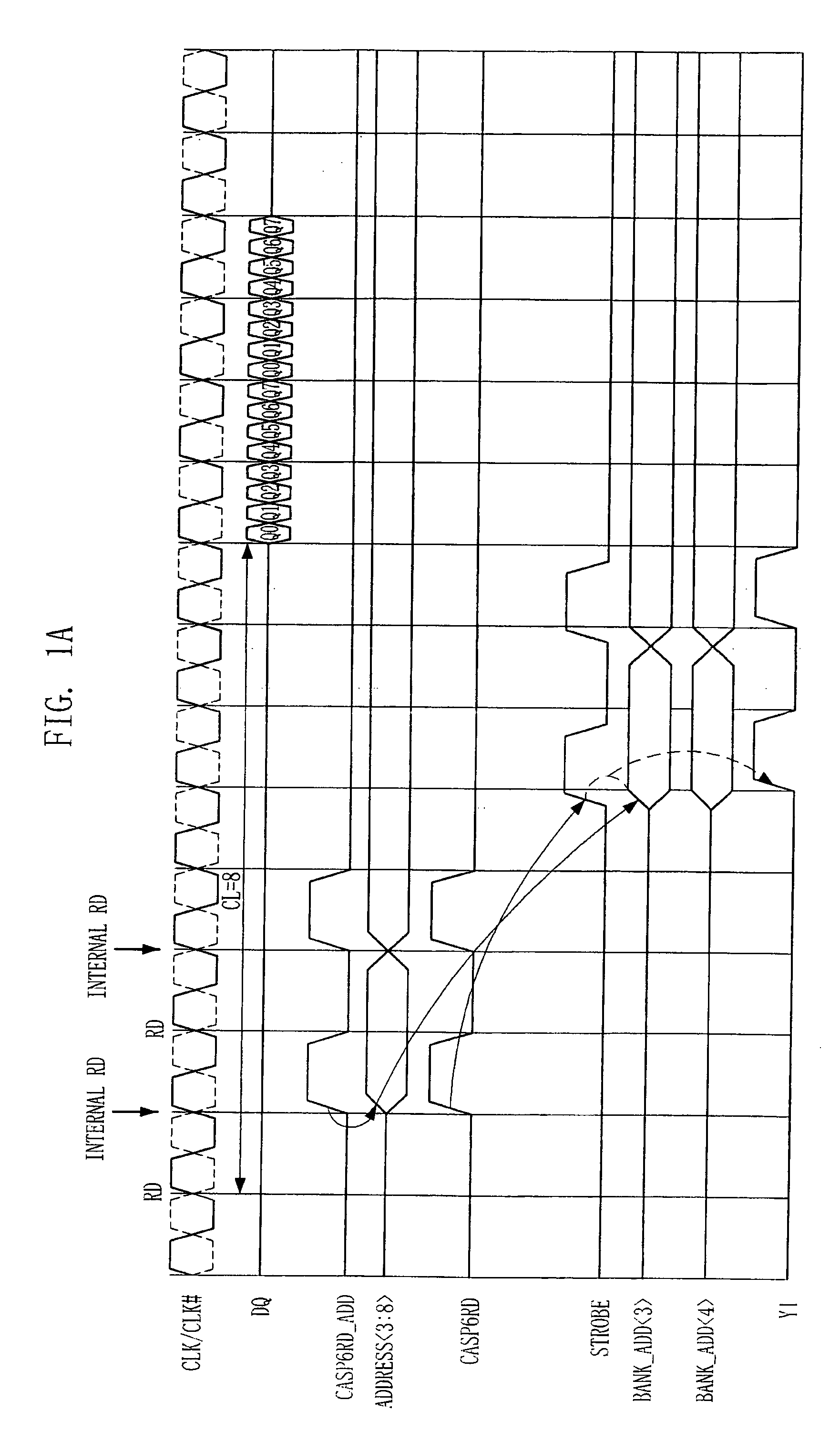
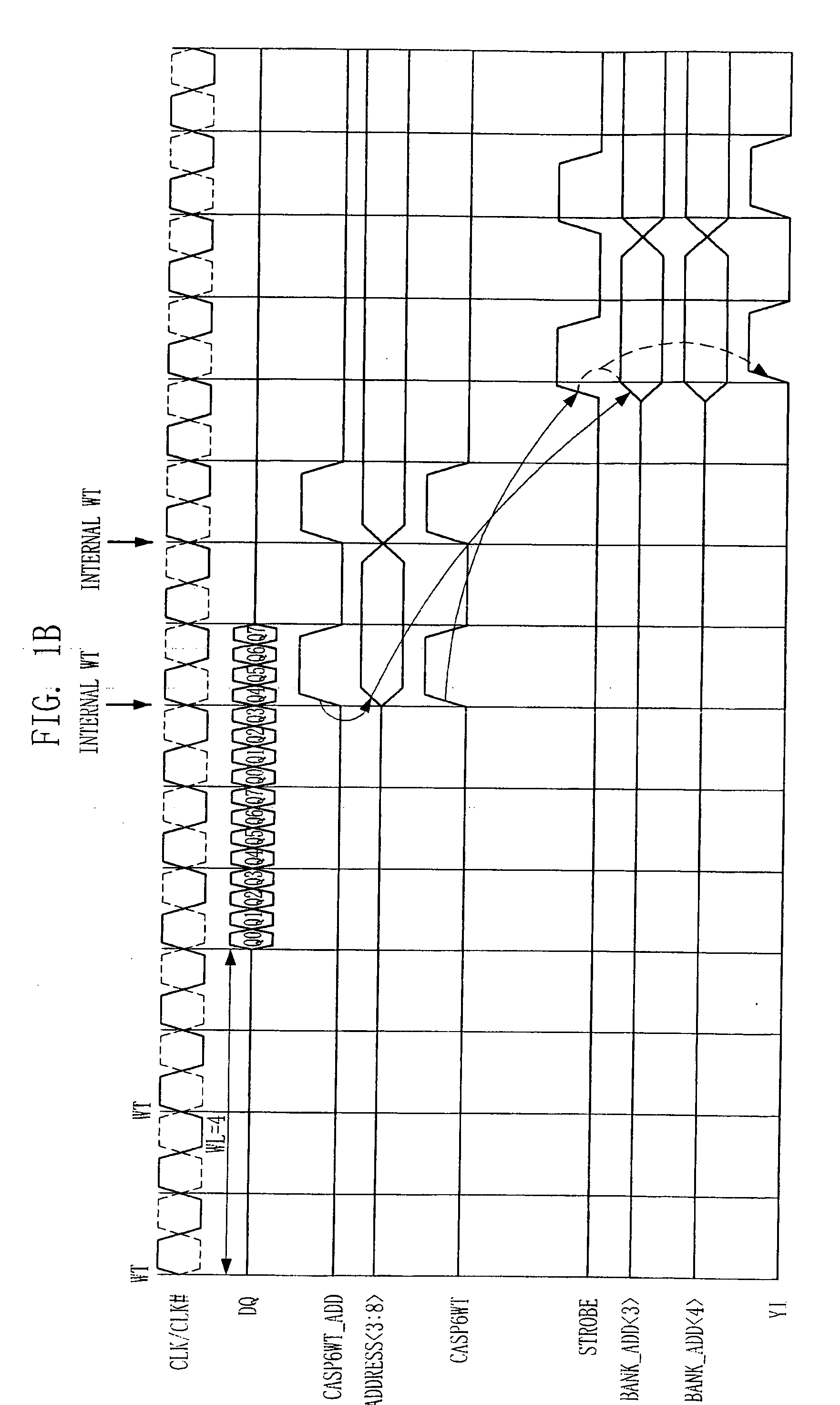
Semiconductor memory device and operation method of the same
A semiconductor memory device has a timing margin for internal operations. The semiconductor memory device can activate an internal control signal for controlling an external address sooner than an internal control signal for controlling an external command to secure a sufficient time for data access. The semiconductor memory device includes a command decoding circuit configured to decode an external command to output an internal command signal for an internal operation corresponding to the external command, a control circuit configured to generate a strobe signal for controlling the internal operation in response to the internal command signal and an internal address signal by decoding an address signal received from outside such that the internal address signal activates sooner than the strobe signal, and a column decoding circuit configured to generate a data access signal when both the internal address signal and the strobe signal are activated.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
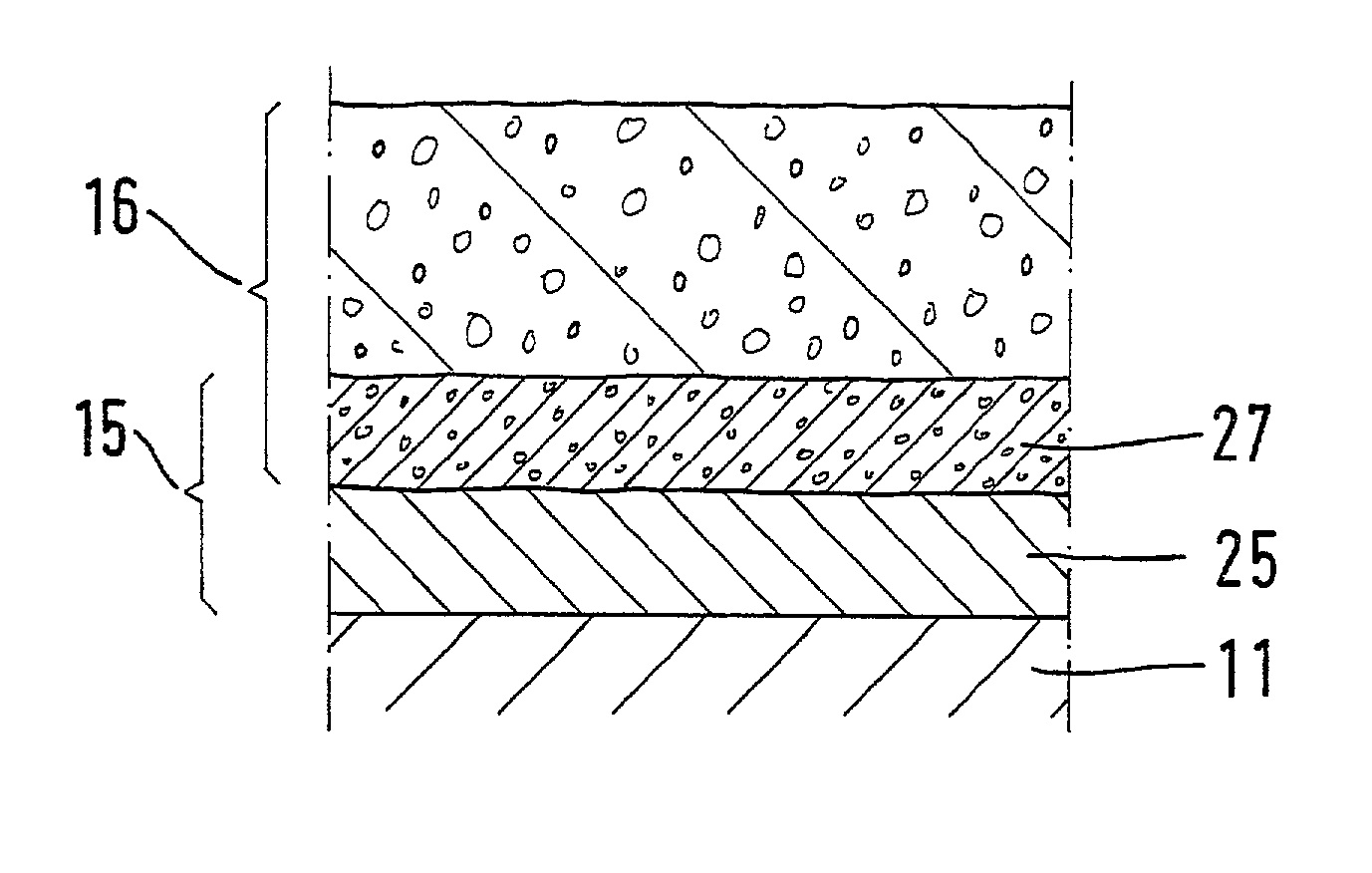
Gas sensor and corresponding production method
InactiveUS20020023838A1Modify the catalytic activity of the electrodeGood precisionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPretreated surfacesVitrificationElectricity
A gas sensor and a method for its manufacture are described. The gas sensor has a solid electrolyte (11) having at least one measuring electrode (15) and one porous protective coating (16). The measuring electrode (15) has an electrically conductive base layer (25) and a further layer (27), the further layer (27) being deposited in the pores of the porous protective coating (16) adjacent to the base layer (25) via galvanic deposition. In order to deposit the further layer (27) via galvanic deposition, the basic body (10), which has been fused with the base layer (25) and the protective coating (16) via vitrification, is immersed in a galvanizing bath, the base layer (25) being connected as the cathode.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
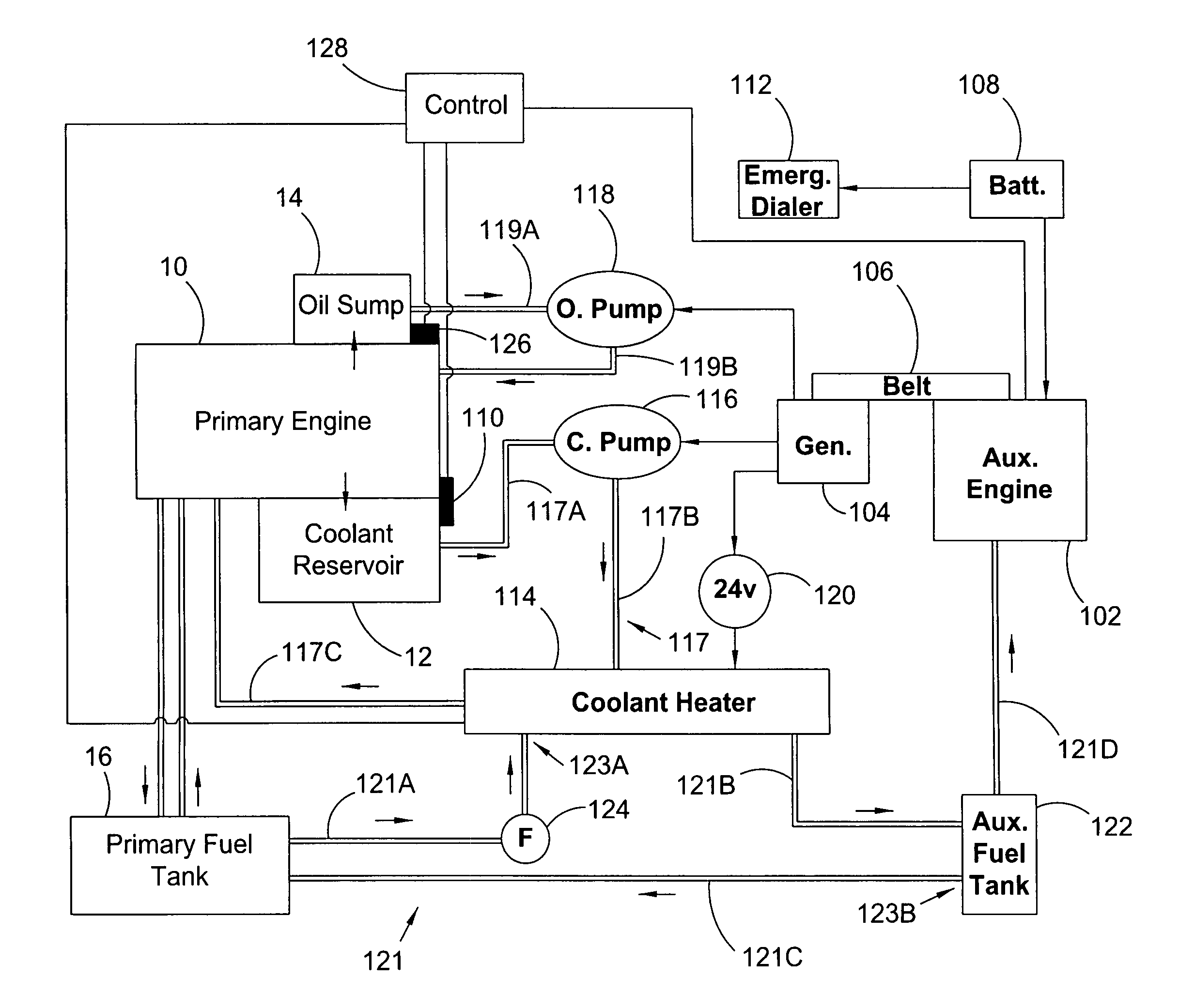
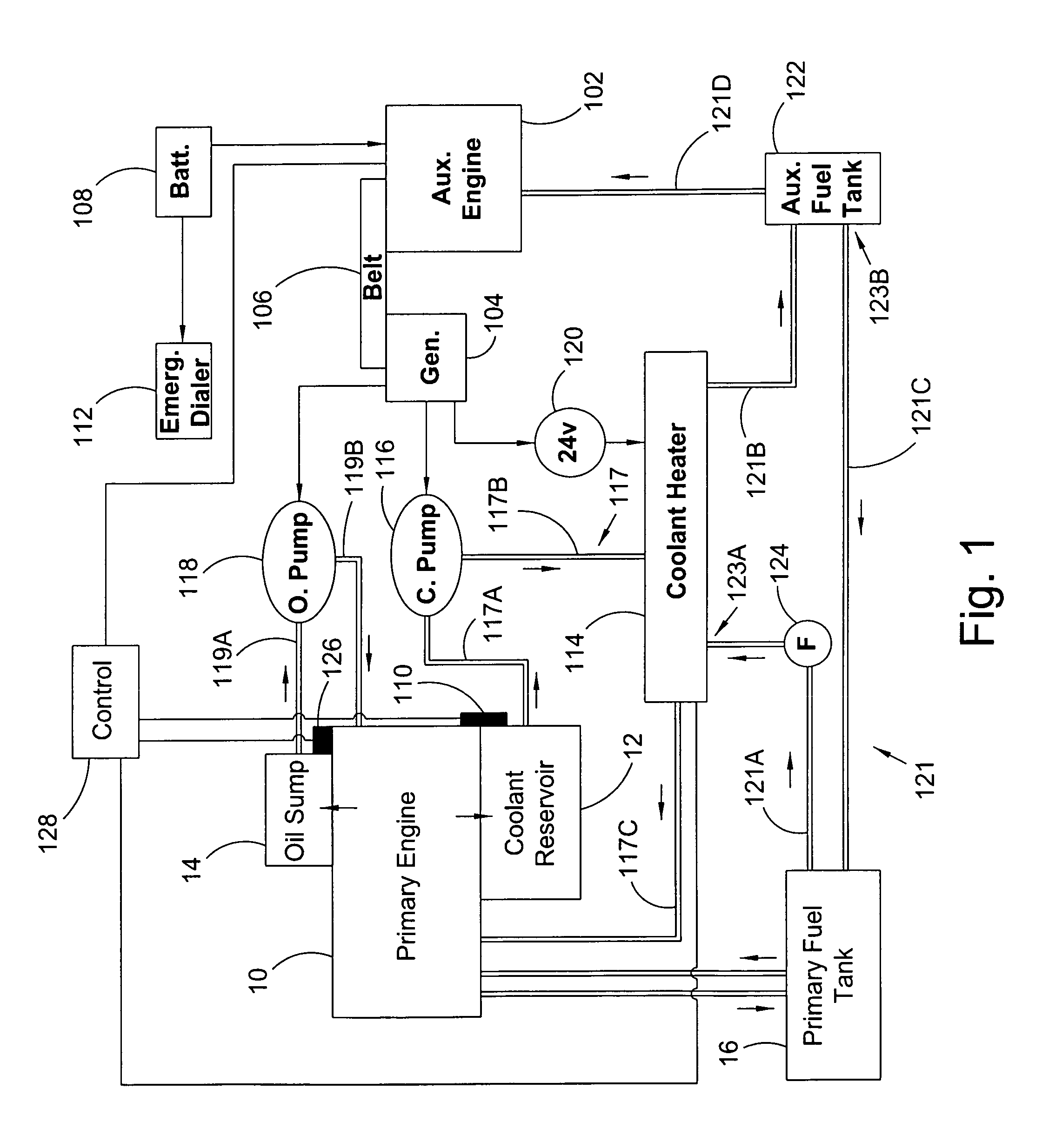
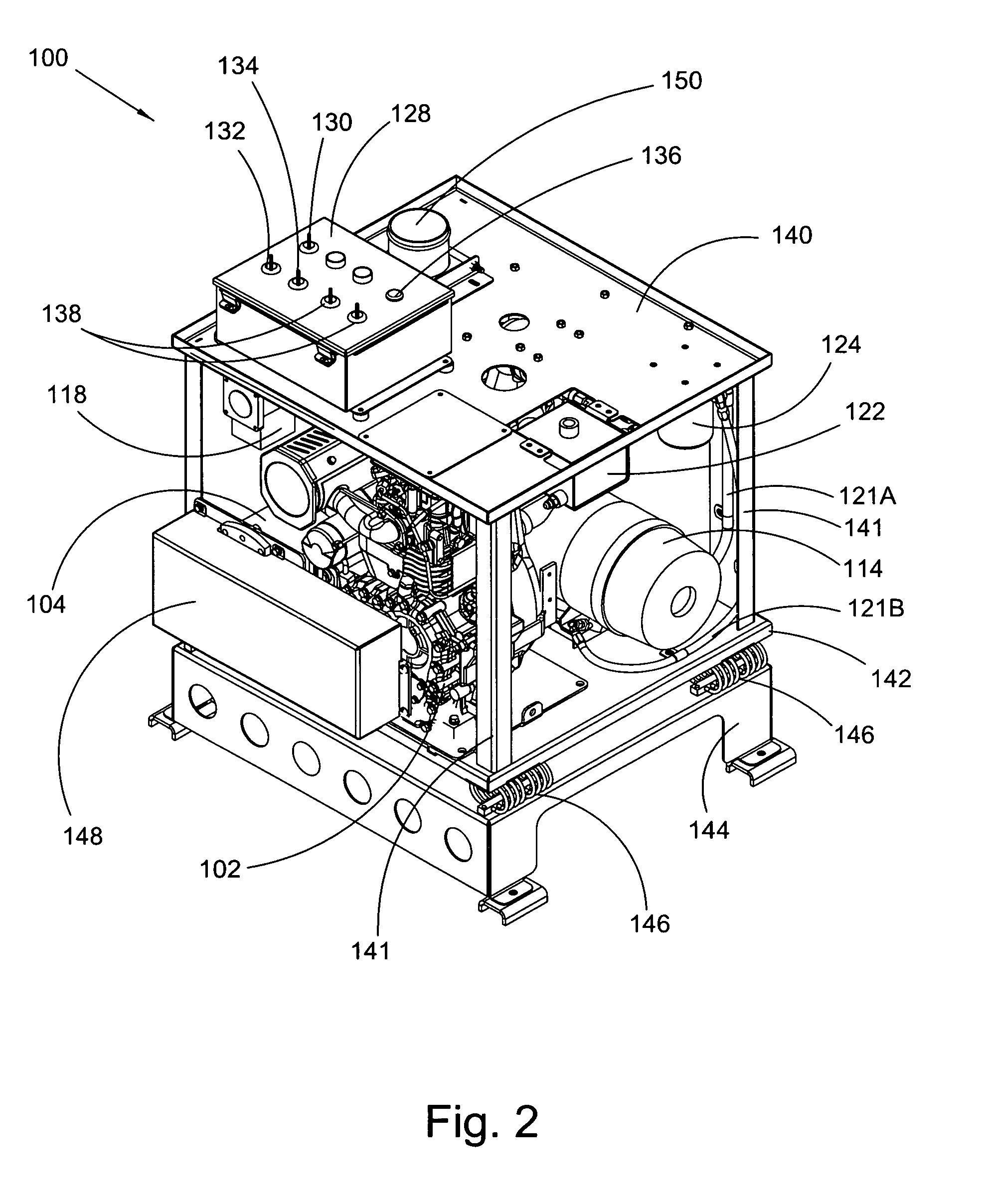
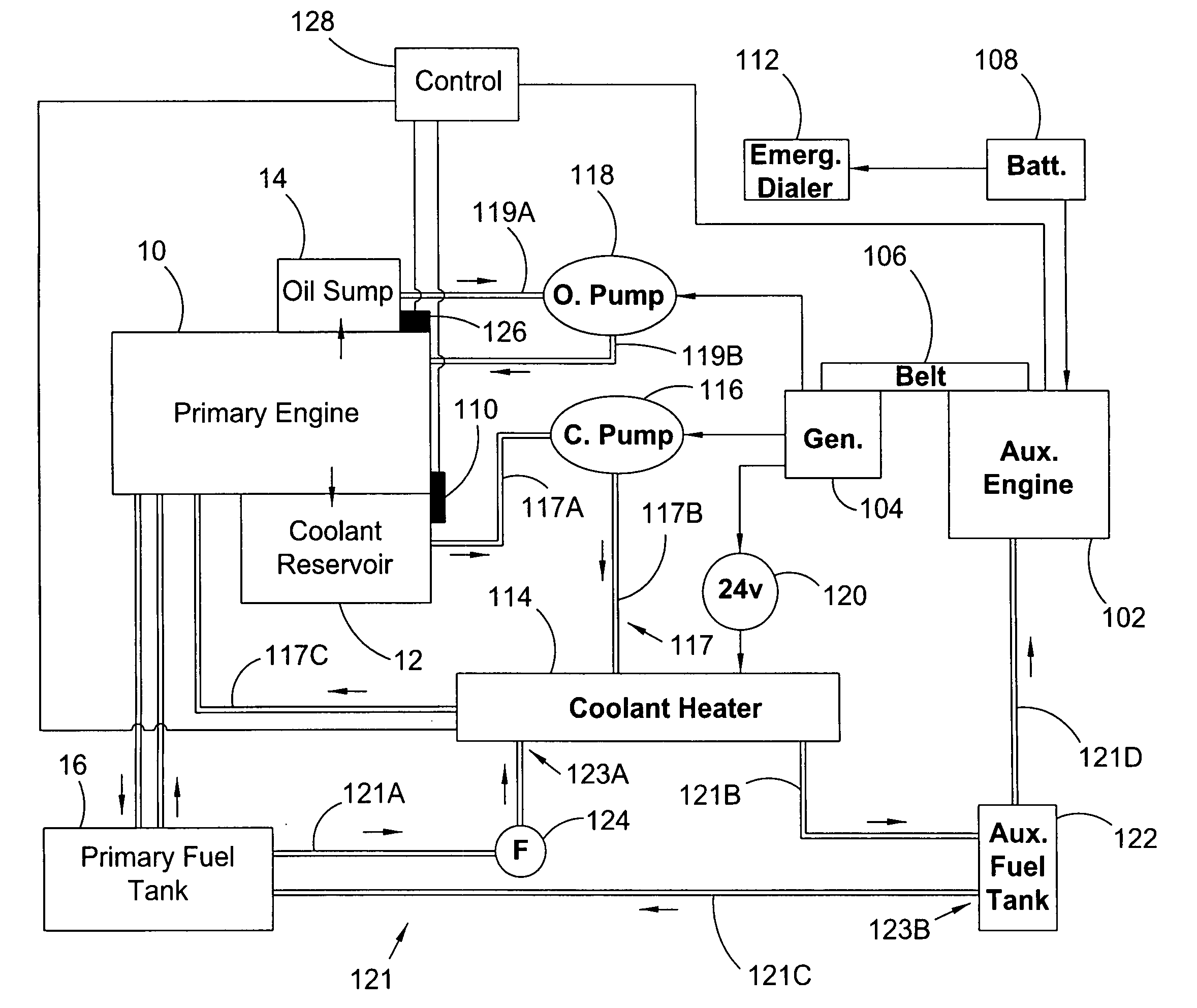
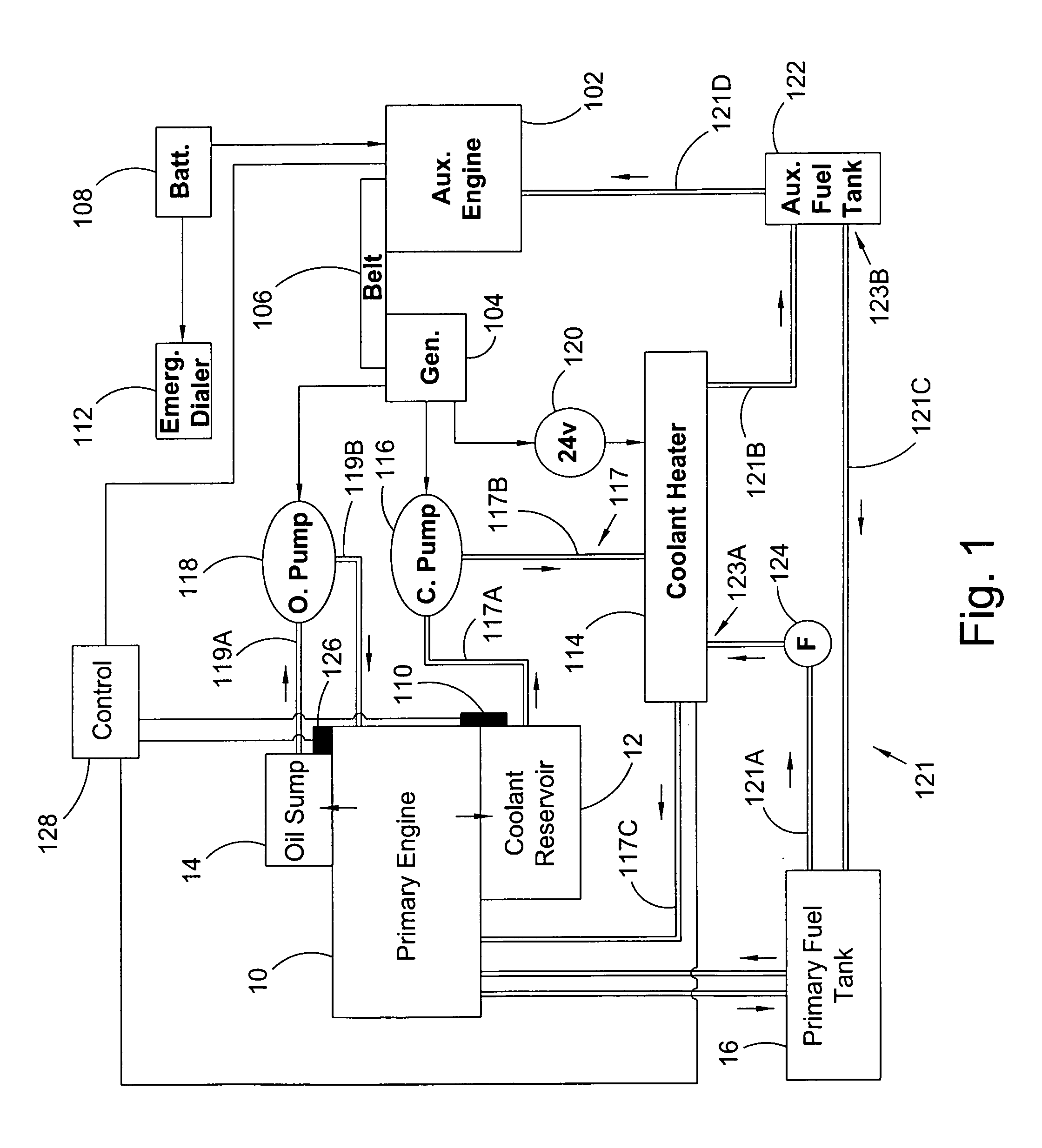
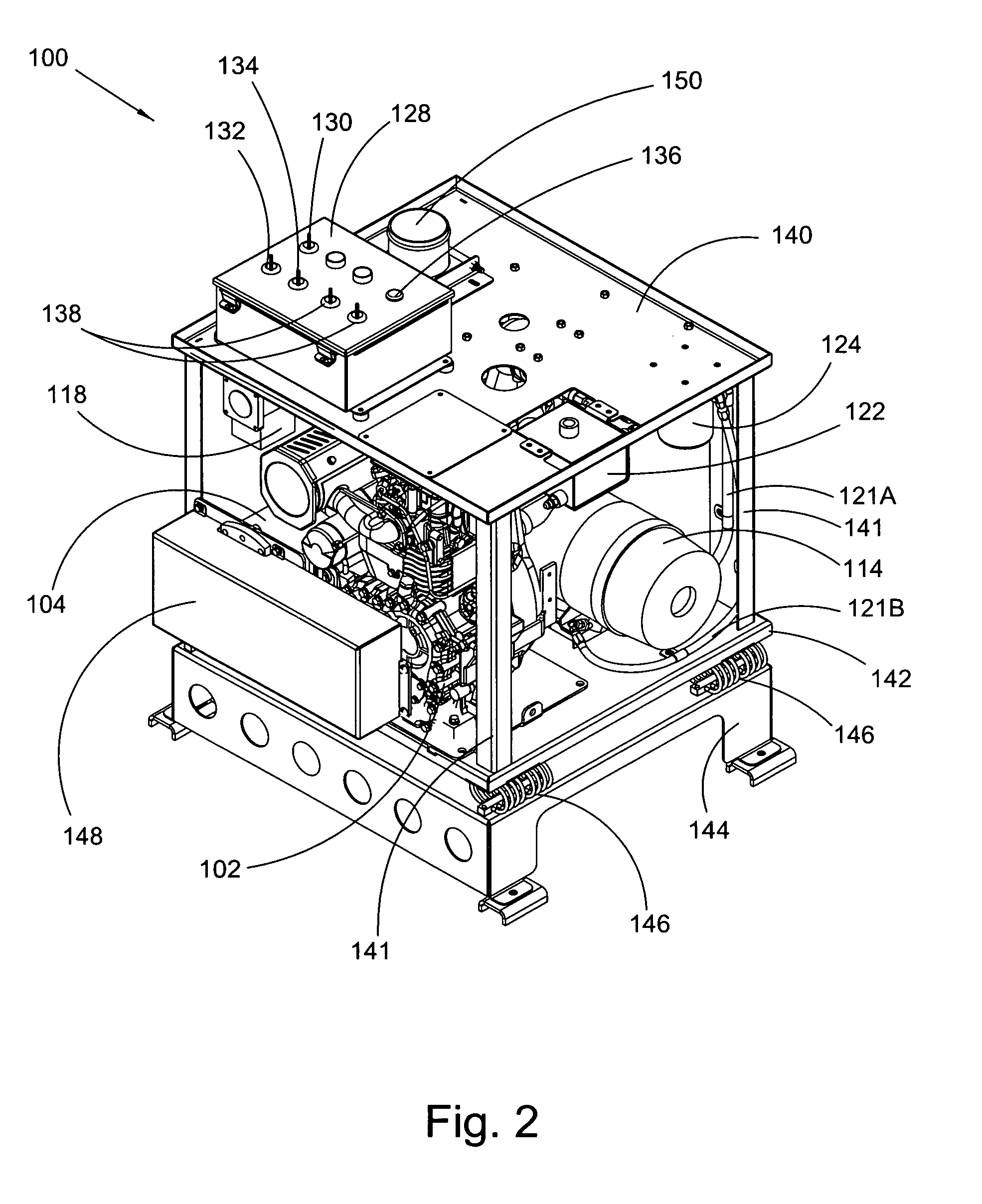
Auxiliary locomotive engine warming system
InactiveUS7769537B2Reduce transmissionAvoid damageAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersDiesel locomotiveFuel tank
An auxiliary engine warming system for a primary engine in a diesel locomotive including: a modular engine assembly including an auxiliary diesel engine, the assembly displaceable as a unit from and to a frame for the engine warming system; an auxiliary fuel tank including a fuel line detachably connected to the auxiliary engine and including a first fitting detachably connectable to a first fuel line for a fuel tank for the diesel; at least one temperature sensor interfacable with the diesel locomotive and arranged to monitor at least one temperature condition for the diesel locomotive; and an emergency dialer for automatically dialing a preprogrammed number and transmitting an alert message in response to an alarm signal from the at least one temperature sensor.
Owner:POWER DRIVES
Access catheter having dilation capability and related methods
ActiveUS20060200184A1Adequate accessIncrease the cross-sectional areaSurgeryDilatorsMedical treatmentCatheter
Various embodiments of a medical device having a dilation capability and related methods are disclosed. For example, the medical device may include a distal assembly having a radially expandable body defining a passageway therethrough, and a control member extending from the distal assembly to a proximal end of the device. Actuation of the control member may apply a compressive force to the body, causing the body to radially expand and a cross-sectional area of the passageway to increase.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of biotreatment for solid materials in a nonstirred surface bioreactor
InactiveUS6410304B2Increase capacitySpeed up the processSolvent extractionSolid waste disposalMicrobial inoculationSulfide minerals
A method of biotreating a solid material to remove an undesired compound using a nonstirred surface bioreactor is provided. According to the method the surface of a plurality of coarse substrates is coated with a solid material to be biotreated to form a plurality of coated coarse substrates. The coarse substrates have a particle size greater than about 0.3 cm and the solid material to be biotreated has a particle size less than about 250 mum. A nonstirred surface reactor is then formed by stacking the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a heap or placing the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a tank so that the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 25%. The reactor is inoculated with a microorganism capable of degrading the undesired compound in the solid material, and the solid material is then biotreated in the surface bioreactor until the undesired compound in the solid material is degraded to a desired concentration. Preferably the thickness of the solid material coating on the plurality of coarse substrates is less than about 1 mm and the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 35%. The process is useful for many different biotreatment processes, including the bioremediation of contaminated soils, the desulfurization of coal, and the biooxidation of refractory sulfide ores and concentrates. In bioremediation applications, the undesired compound is typically an organic compound. In coal desulfurization and refractory sulfide ore biooxidation applications, the undesired compound is sulfide minerals.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
Squirrel resistant dome-shaped bird feeder port
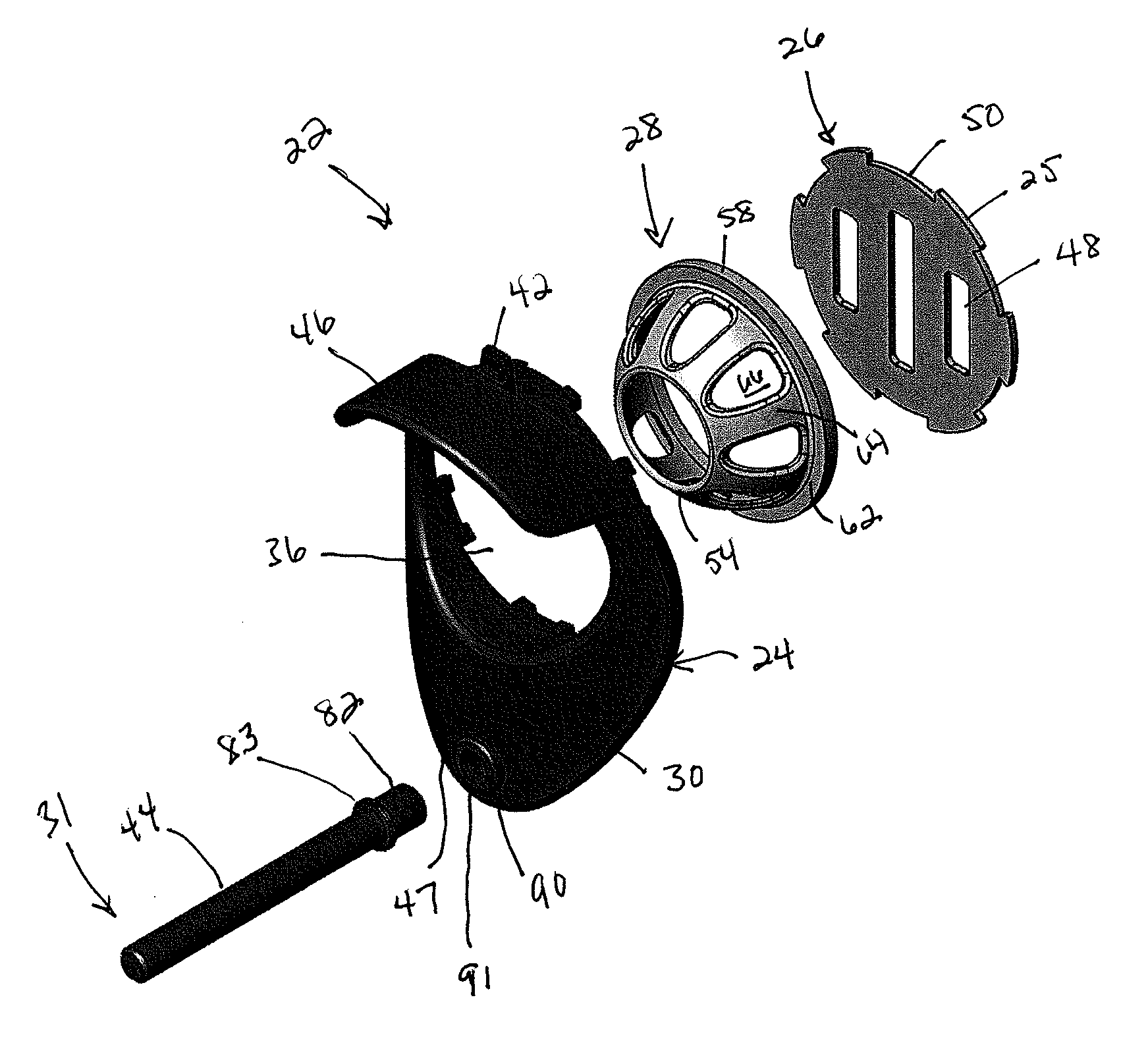
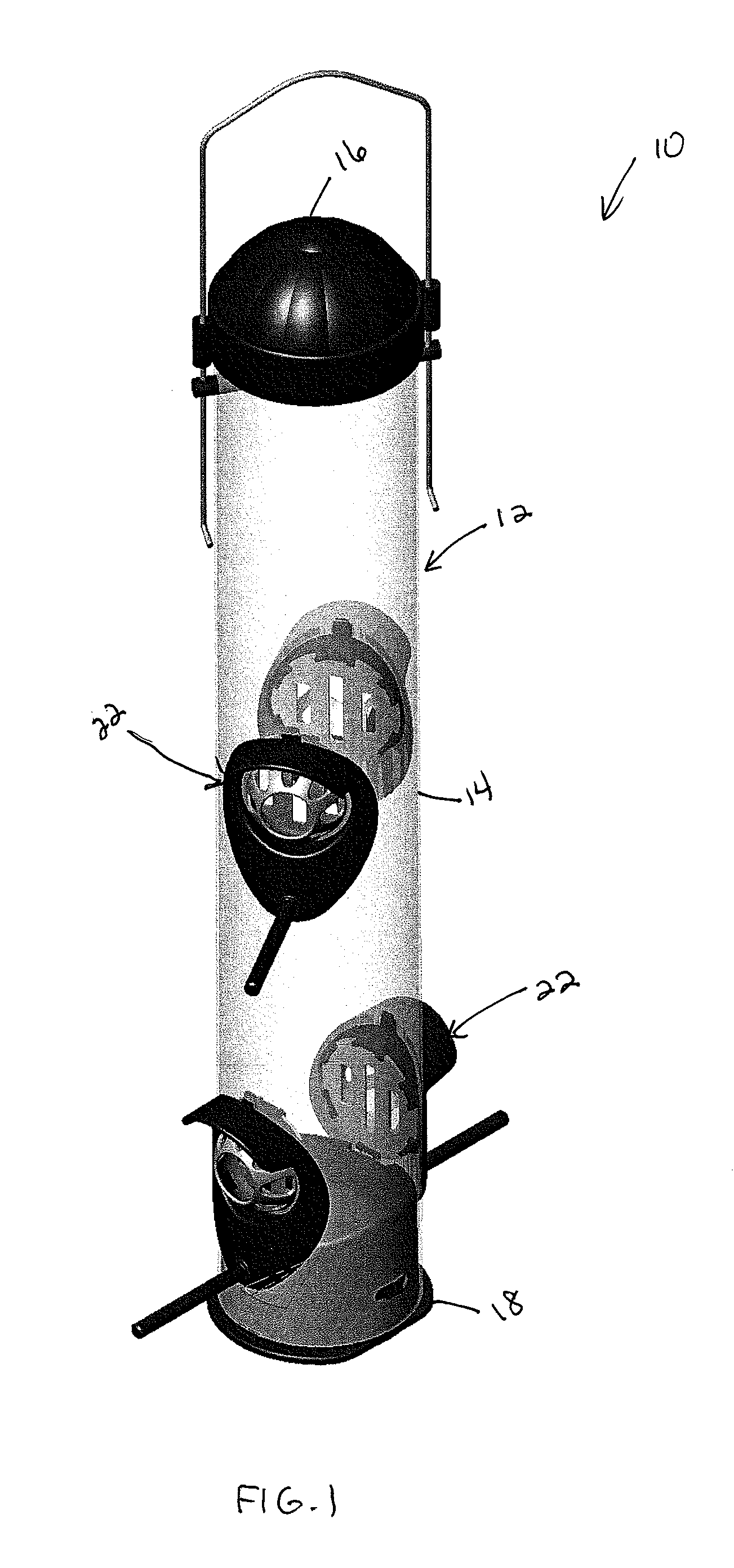
ActiveUS20140090600A1Low costEasy to installAnimal feeding devicesAnimal housingBird feederEngineering
A bird feeder is provided having a seed reservoir with a side wall that has at least one seed access opening and a squirrel resistant feed port assembly having a seed access restricter. The seed access restricter has a body with an inner opening in communication with the reservoir side wall opening and an outer seed access opening that is spaced away from the inner opening and the reservoir side wall opening while being in communication therewith. The outer seed access opening of the restricter is small enough and the length of the body is long enough that the squirrel resistant feed port assembly allows birds to access seed in the reservoir while blocking entry of the larger facial and head structure of a squirrel, thus preventing squirrels from gaining seed access.
Owner:WOODSTREAM CORP
Auxiliary locomotive engine warming system
InactiveUS20090272353A1Avoid damageQuick installationAnalogue computers for vehiclesPower operated startersDiesel locomotiveDialer
An auxiliary engine warming system for a primary engine in a diesel locomotive including: a modular engine assembly including an auxiliary diesel engine, the assembly displaceable as a unit from and to a frame for the engine warming system; an auxiliary fuel tank including a fuel line detachably connected to the auxiliary engine and including a first fitting detachably connectable to a first fuel line for a fuel tank for the diesel; at least one temperature sensor interfacable with the diesel locomotive and arranged to monitor at least one temperature condition for the diesel locomotive; and an emergency dialer for automatically dialing a preprogrammed number and transmitting an alert message in response to an alarm signal from the at least one temperature sensor.
Owner:POWER DRIVES
Integrated embolic protection devices
ActiveUS9492265B2Promote resultsMinimization requirementsHeart valvesSurgeryDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
Embolic protection elements are integrated with a catheter or access sheath for any catheter. A catheter with an integrated embolic protection element comprises a catheter shaft, an embolic filter slidably mounted on a distal portion of the shaft, a proximal stop for limiting the proximal movement of the embolic filter, and a distal stop for limiting the distal movement of the embolic filter. The filter comprises a porous mesh material defining a collection chamber for captured emboli and has a collapsed and a deployed configuration. The filter may be collapsed by an access sheath used with the catheter. An access sheath may comprise a tubular main body and an embolic filter mounted on the distal portion of the tubular main body. The embolic filter may evert into the central lumen of the sheath or may be constrained on the exterior of the sheath with a larger diameter outer tube.
Owner:EMBOLINE
Hydride-based fuel cell designed for the elimination of hydrogen formed therein
InactiveUS20050158609A1Improve stabilityAdequate accessCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsEngineering
A fuel cell for use with a hydride-based fuel, which fuel cell is designed for being sealed in a liquid-tight manner when in operation. The fuel cell comprises means for eliminating hydrogen formed inside the fuel cell. This abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:MORE ENERGY
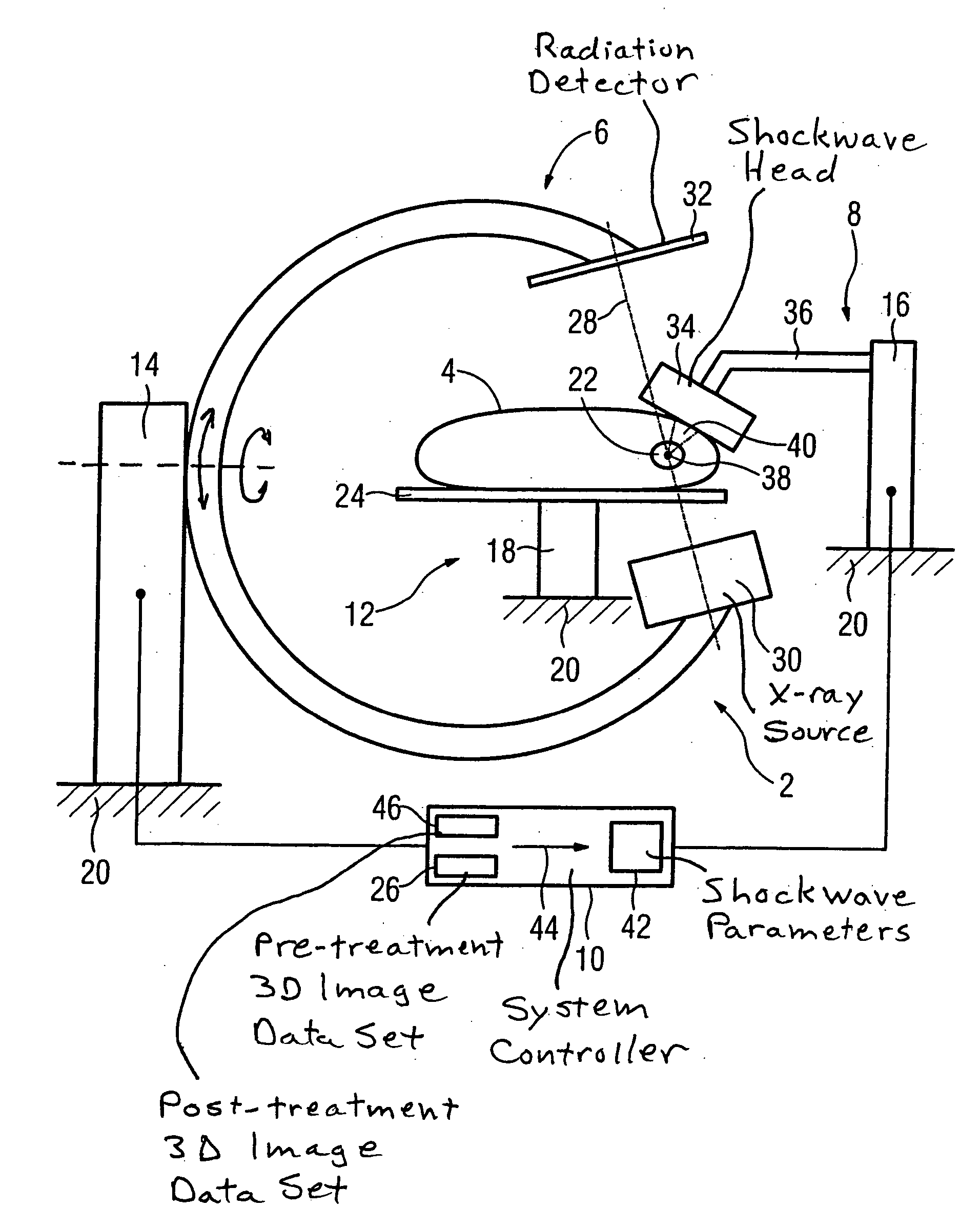
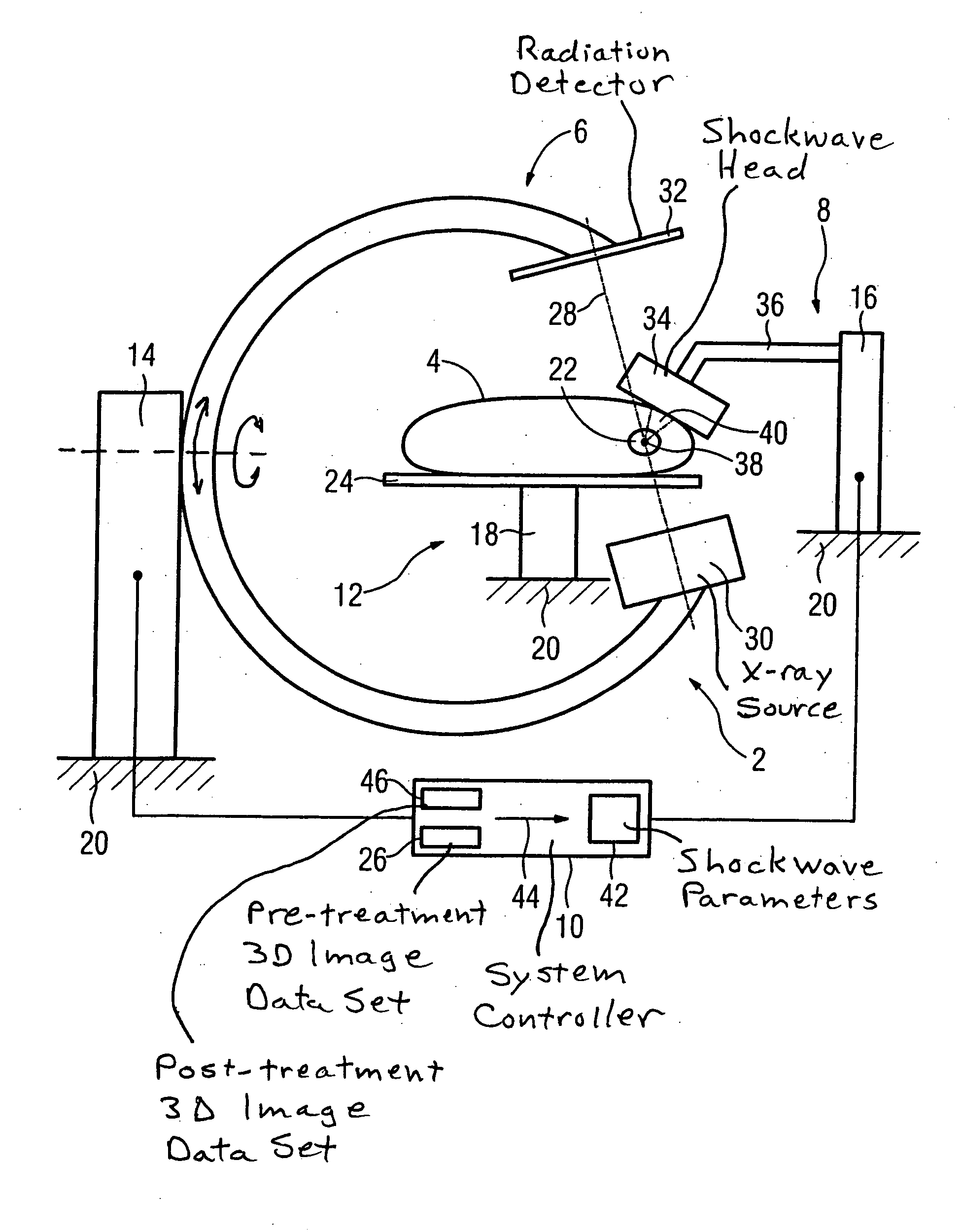
Lithotripsy method and system without patient relocation between diagnostic imaging and treatment
InactiveUS20070016114A1Adequate accessImprove matchSurgeryChiropractic devicesData setMathematical Calculus
In a method to disintegrate a calculus in a patient by shockwave lithotripsy, a 3D image data set of the patient is generated in a first step; the shockwave lithotripsy is conducted in a second step; and first step and second step are conducted with an unchanged position of the patient. A lithotripsy system to disintegrate a calculus in a patient has a shockwave system to disintegrate the calculus and a 3D imaging system to generate a 3D image data set of the patient without movement of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS AKTIENGENELLSCHAFT
Latchable package
ActiveUS9926125B2Enhanced couplingReduce manufacturing costSmall article dispensingClosuresMechanical engineeringEngineering
A latchable package comprises: a support for supporting one or more items; a structure for selectively blocking access to the one or more items; and a latchable insert. The latchable insert comprises a substantially planar tab member that is coupled to the support such that the insert and support are movable together in an opening direction from a first position in which the structure blocks access to the one or more items to a second position in which the one or more items are accessibly clear of the structure. The structure and the latchable insert comprise co-operating latch features configured to engage when the insert and support are arranged in the first position.
Owner:DUALLOK LTD
Semiconductor memory device and operation method of the same
ActiveUS20090059692A1Enough timeSufficient operation marginDigital storageTiming marginSufficient time
A semiconductor memory device has a timing margin for internal operations. The semiconductor memory device can activate an internal control signal for controlling an external address sooner than an internal control signal for controlling an external command to secure a sufficient time for data access. The semiconductor memory device includes a command decoding circuit configured to decode an external command to output an internal command signal for an internal operation corresponding to the external command, a control circuit configured to generate a strobe signal for controlling the internal operation in response to the internal command signal and an internal address signal by decoding an address signal received from outside such that the internal address signal activates sooner than the strobe signal, and a column decoding circuit configured to generate a data access signal when both the internal address signal and the strobe signal are activated.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
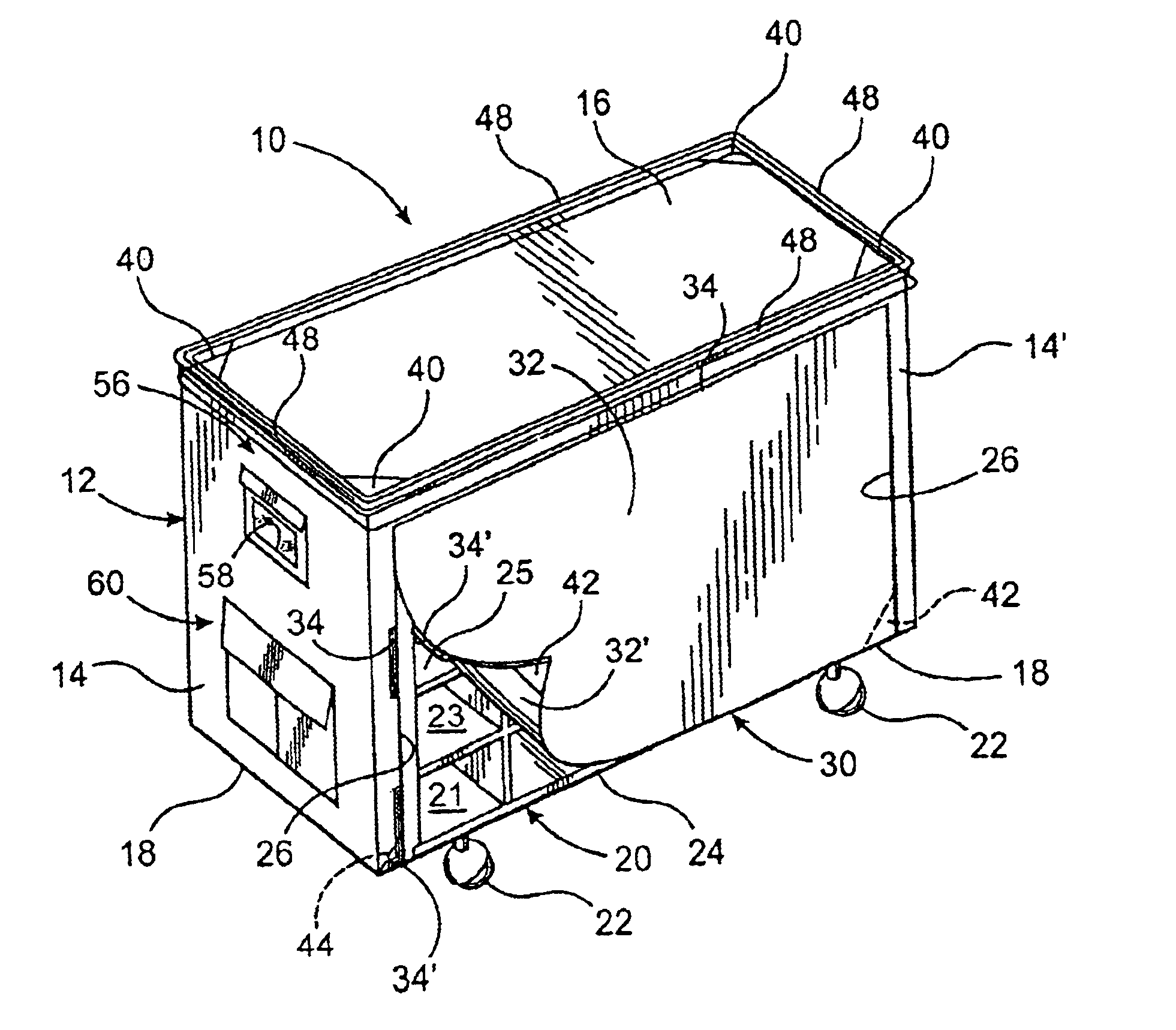
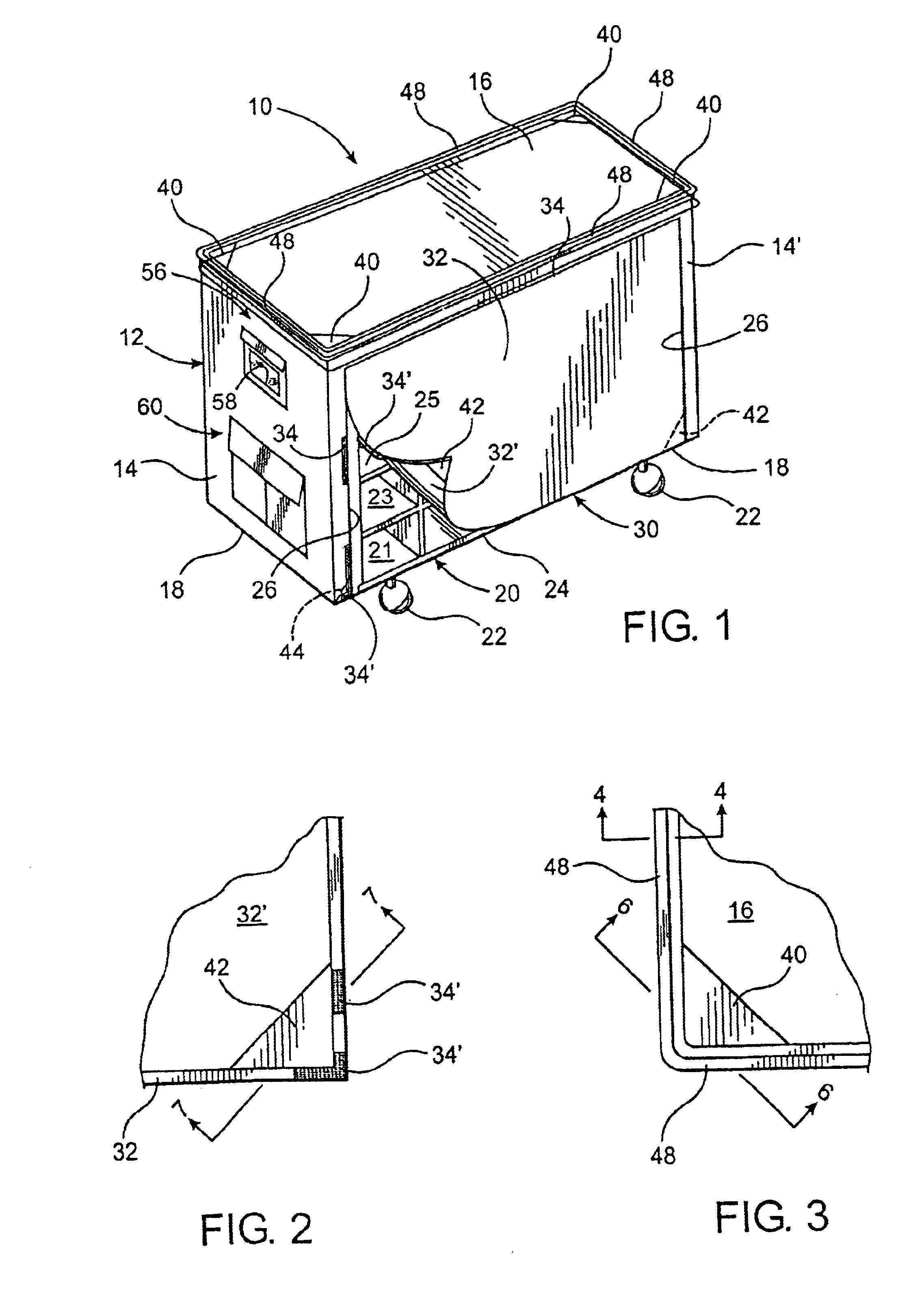
Cover assembly for hospital carts
InactiveUS6854747B2Easy maintenanceAdequate accessCarriage/perambulator accessoriesFlexible coversSterile environmentEngineering
A protective cover assembly for a cart and it's contents of the type used in hospitals and like medical facilities for the temporary storage and delivery of a plurality of items which should be maintained in a substantially sterile environment. The cover assembly comprises an enclosure formed from a flexible, preferably hypo-allergenic material dimensioned to receive substantially the entire cart therein. A plurality of reinforced portions are secured to the enclosure and are structured to prevent rupture or other physical damage thereto. A storage assembly comprises one or more compartments including at least one interior pocket disposed and structured to isolate the contents thereof.
Owner:ERICKSON TOMIKO
Cooling of power electronics circuits
ActiveUS10980103B2High resolutionPrevent high current densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorEngineering
A method for cooling power electronics circuits, in which a printed circuit board is produced according to a prescribed circuit board process and is populated with at least one power electronics components. Contact connecting at least one location on at least one metallic conductor track running on a surface of the printed circuit board that includes at least one metal element, which is both electrically conductive and heat-conductive and the physical height of which is designed to be at least as large as that of the at least one power electronics component. A cooling plate is placed in a planar manner onto the at least one power electronics component and / or the at least one metal element.
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Coil With Adjustable Opening
ActiveUS20170248666A1Improve image qualityAdequate accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMri guidedImaging quality
A configurable coil arrangement for use with MRI-guided procedures is provided that facilitates optimal imaging for both pre-procedure planning and imaging of the target sites during the procedure. The coil arrangement includes a plurality of connected coil elements. Spacers connecting the coil elements can be adjustable and / or deformable to provide one or more openings in the coil arrangement of optimal size for accessing the subject within the imaged region. Individual coil elements can also be removed to provide access openings during such procedures, or left in the array for improved pre- and post-procedure image quality. The MRI system can be configured to detect configurations of the coil arrangement and modify imaging parameters to optimize image quality.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Boiler wall tube welding tool
InactiveUS20060196043A1Easy for visual observationLimited spaceWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringScrew thread
A boiler wall tube tool for clamping together for welding adjacent ends of boiler wall tube segments in a boiler wall having narrowly spaced apart tubes. The tool includes a base with a tube engaging recess, and a pair of clamp members that attach to the base. The base has cutouts and notches to facilitate a welder's observation of the welding process. Each of the pipe clamp members includes a parallel pair of guides that are insertable between adjacent tubes of a boiler wall and are attachable by nuts and bolts to opposite sides of the base. A header that joins the guides has a threaded bore. A saddle block mounted for sliding movement between the guides is attached by a swivel nut to a clamp screw that is mounted within the threaded bore. Each saddle block is recessed for engaging an exterior surface of one of two aligned tube segments. The tool clamps aligned segments together by rotation of the clamp screws in a first direction; rotation of the screws in an opposite direction permits detaching the tool from the pipe segments. A lateral adjustment screw is provided for adjusting the tool for snug fit to adjacent, aligned tube segments.
Owner:HOLLOWAY SCOTT
Method of biotreatment for solid materials in a nonstirred surface bioreactor
InactiveUS20010001065A1Increase capacitySpeed up the processSolvent extractionSolid waste disposalMicrobial inoculationSulfide minerals
A method of biotreating a solid material to remove an undesired compound using a nonstirred surface bioreactor is provided. According to the method the surface of a plurality of coarse substrates is coated with a solid material to be biotreated to form a plurality of coated coarse substrates. The coarse substrates have a particle size greater than about 0.3 cm and the solid material to be biotreated has a particle size less than about 250 mum. A nonstirred surface reactor is then formed by stacking the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a heap or placing the plurality of coated coarse substrates into a tank so that the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 25%. The reactor is inoculated with a microorganism capable of degrading the undesired compound in the solid material, and the solid material is then biotreated in the surface bioreactor until the undesired compound in the solid material is degraded to a desired concentration. Preferably the thickness of the solid material coating on the plurality of coarse substrates is less than about 1 mm and the void volume of the reactor is greater than or equal to about 35%. The process is useful for many different biotreatment processes, including the bioremediation of contaminated soils, the desulfurization of coal, and the biooxidation of refractory sulfide ores and concentrates. In bioremediation applications, the undesired compound is typically an organic compound. In coal desulfurization and refractory sulfide ore biooxidation applications, the undesired compound is sulfide minerals.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS LLC (US)
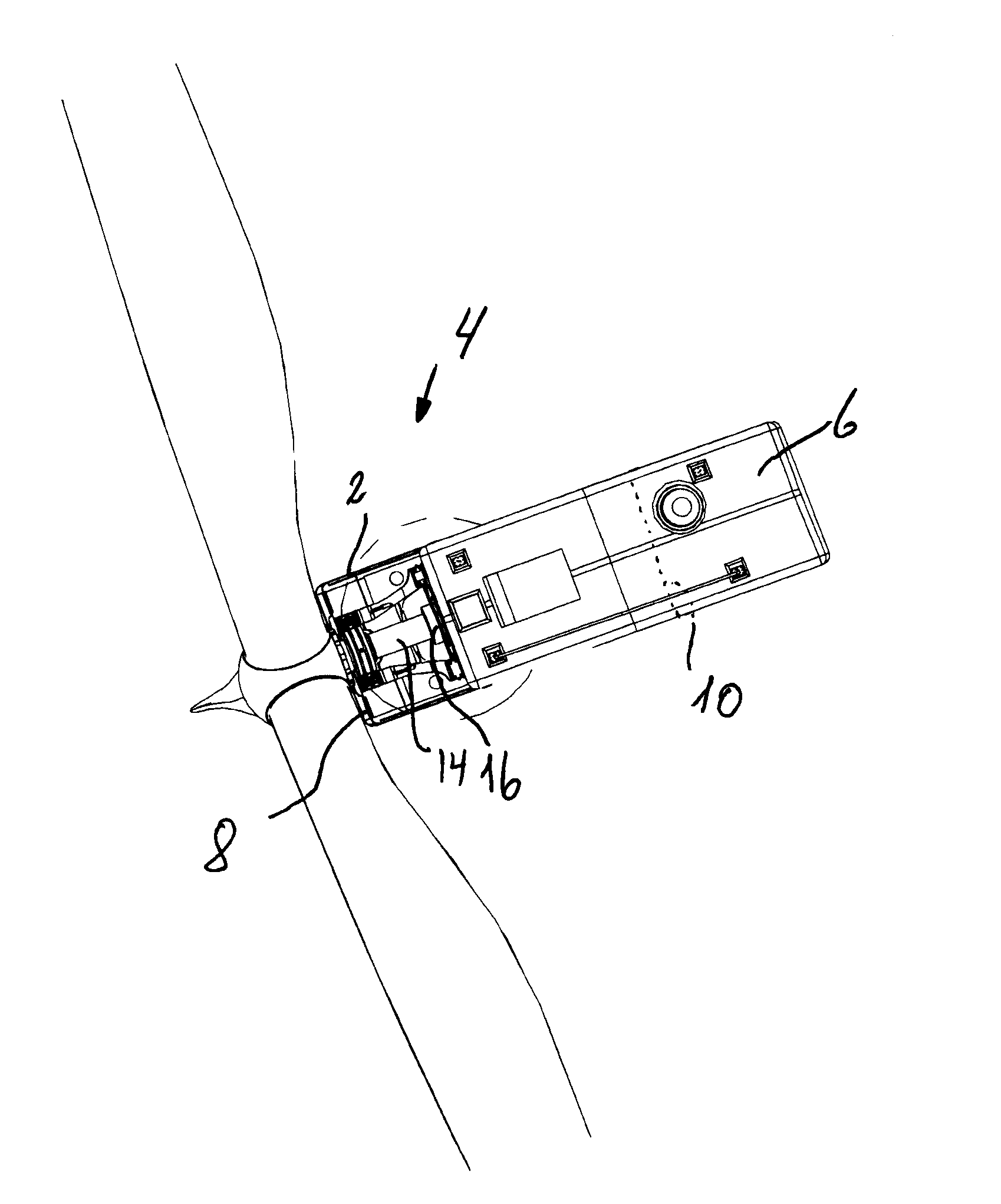
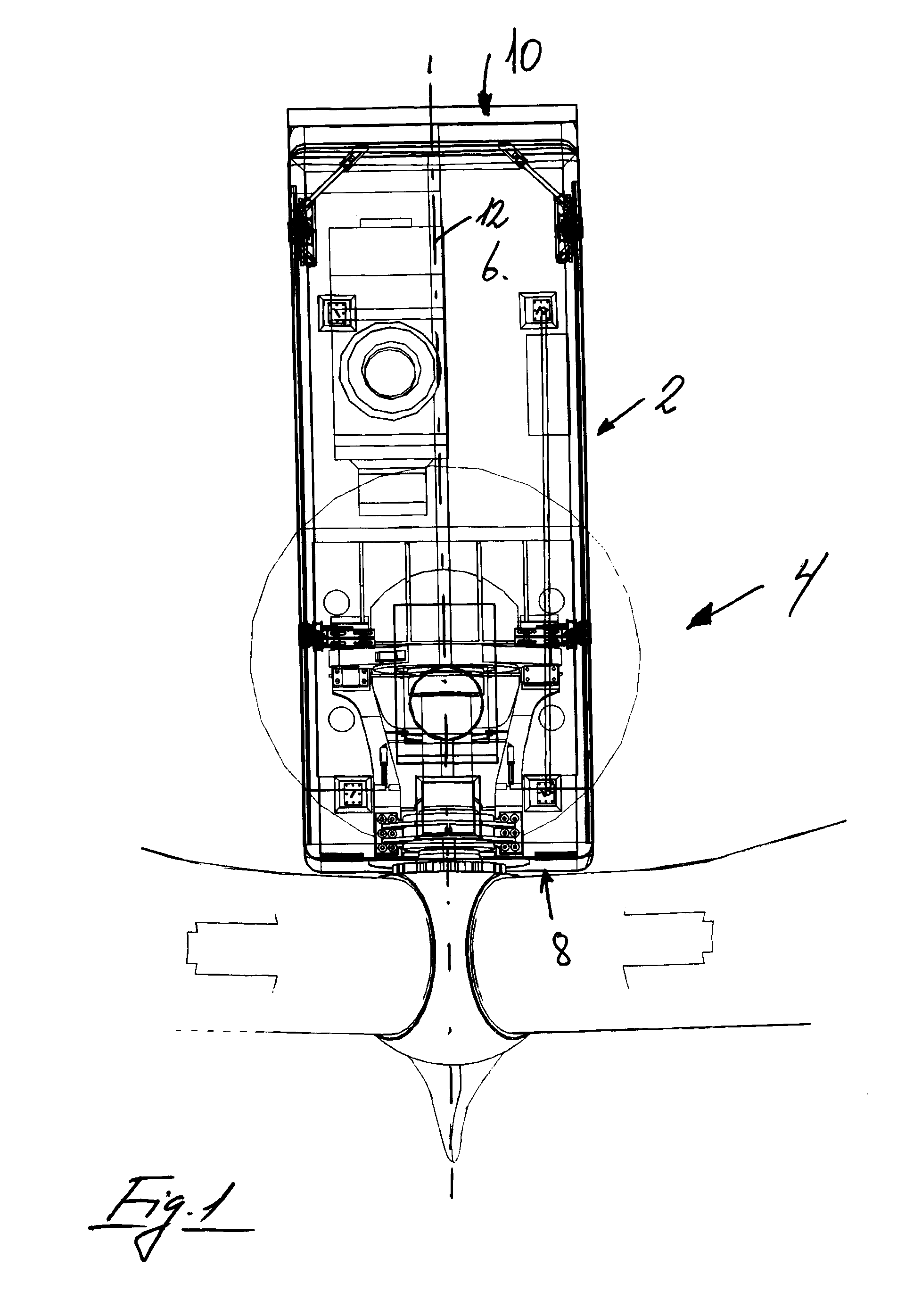
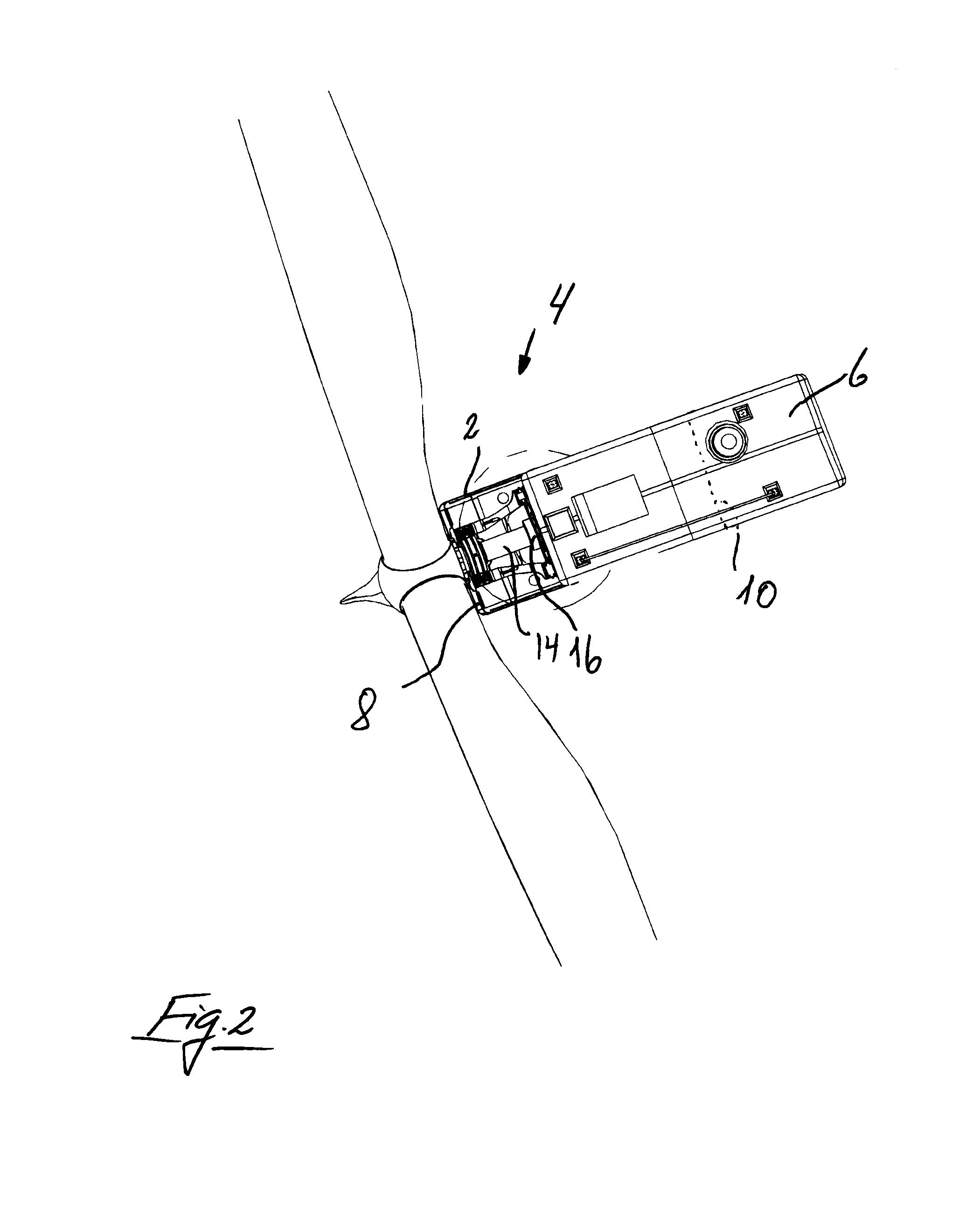
Method and means for establishing access to the main parts in the nacelle on a wind turbine
ActiveUS20150132119A1Reduce weightEasy to carryPump componentsWind motor assemblyNacelleMarine engineering
A method for establishing access for mounting and dismounting of main shafts, gearbox, generator and other main parts located in the nacelle of a wind turbine, where the cabriolet remains localized on the nacelle, and guide transfer mechanisms are provided for mounting inside the nacelle. The basic idea is that the cabriolet is lifted upon rolls or roll sets which form the guide transfer mechanisms upward facing support surfaces, and that the cabriolet is stabilized by displaceable counter holds which are displaced and locked in position above the downwards positioned mounting flange, upon which the cabriolet can be displaced on the rollers or roll sets to a partly cantilevered position over the rear end of the nacelle. By the method, service on larger wind turbines can be performed without using mobile cranes, which saves resources.
Owner:ELEVATORRA IP APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com