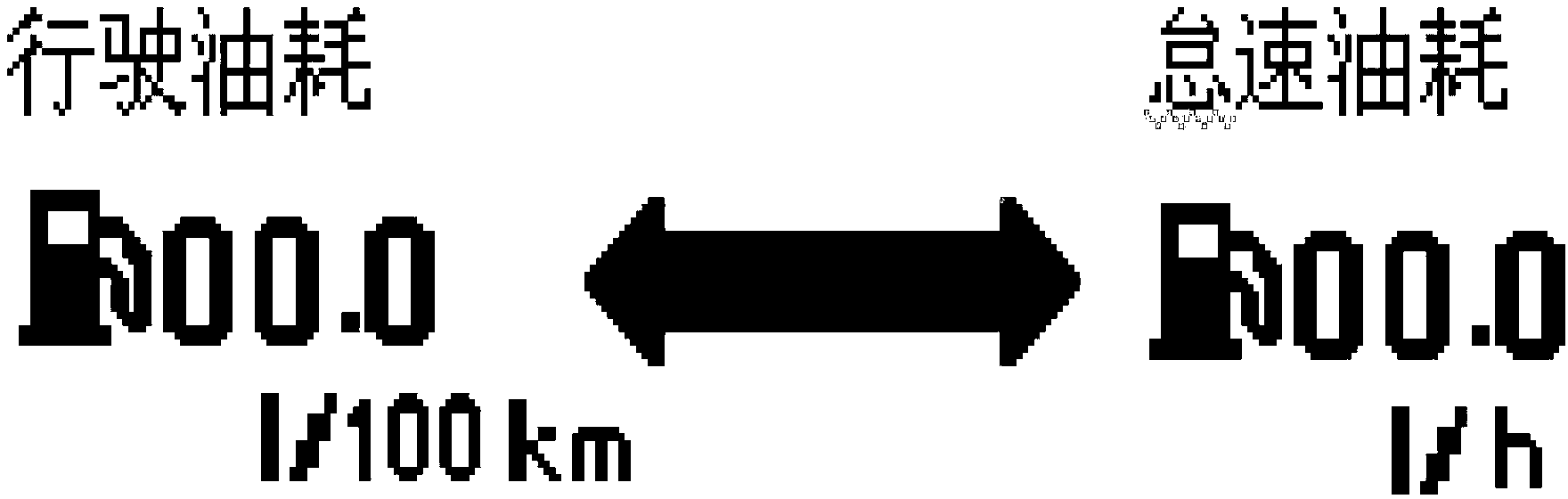Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Reasonable access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and device for selecting mobile management entity and providing load information
InactiveCN101605316AGuaranteed balanceReasonable accessNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionReal-time computingUser equipment
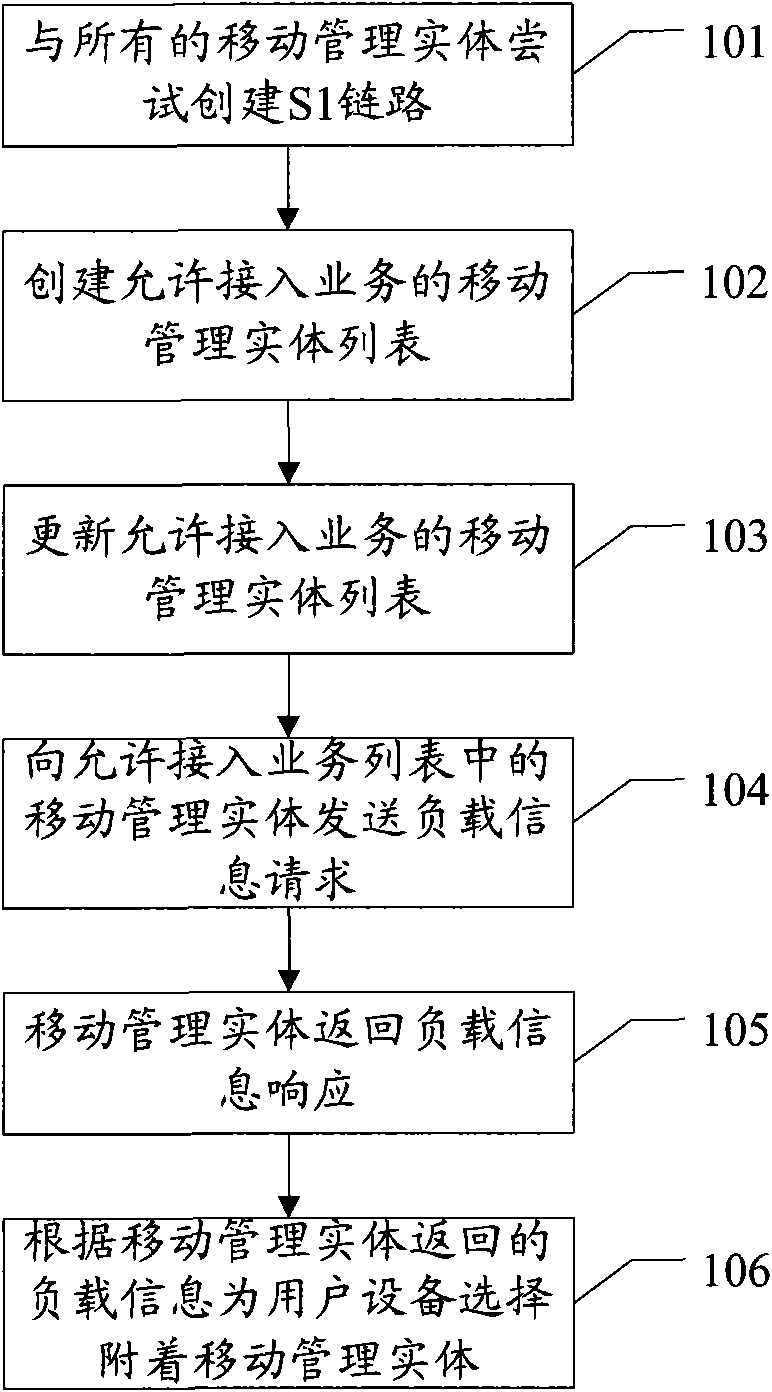
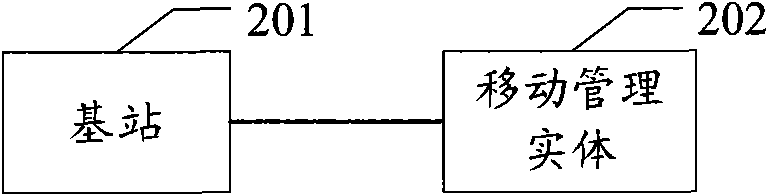
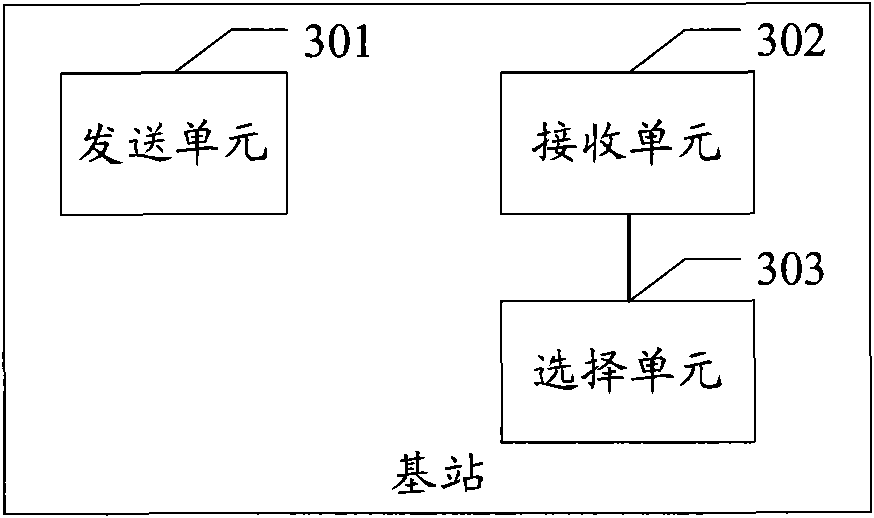
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for selecting an attached mobile management entity for user equipment, and a method and a device for providing load information, wherein one method comprises the following steps: sending a load information request to at least one mobile management entity allowing service access; receiving the load information response returned from the at least one mobile management entity, wherein the load information response carries with the load information of the mobile management entity; and selecting the attached mobile management entity for the user equipment from the at least one mobile management entity according to the load information. The other method comprises the following steps: receiving the load information request sent by a base station; acquiring the load information; and returning the load information response to the base station according to the load information request, wherein the load information response carries with the load information. The methods and the device can effectively use resources and ensure the balance of MME loads in an MME pool.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
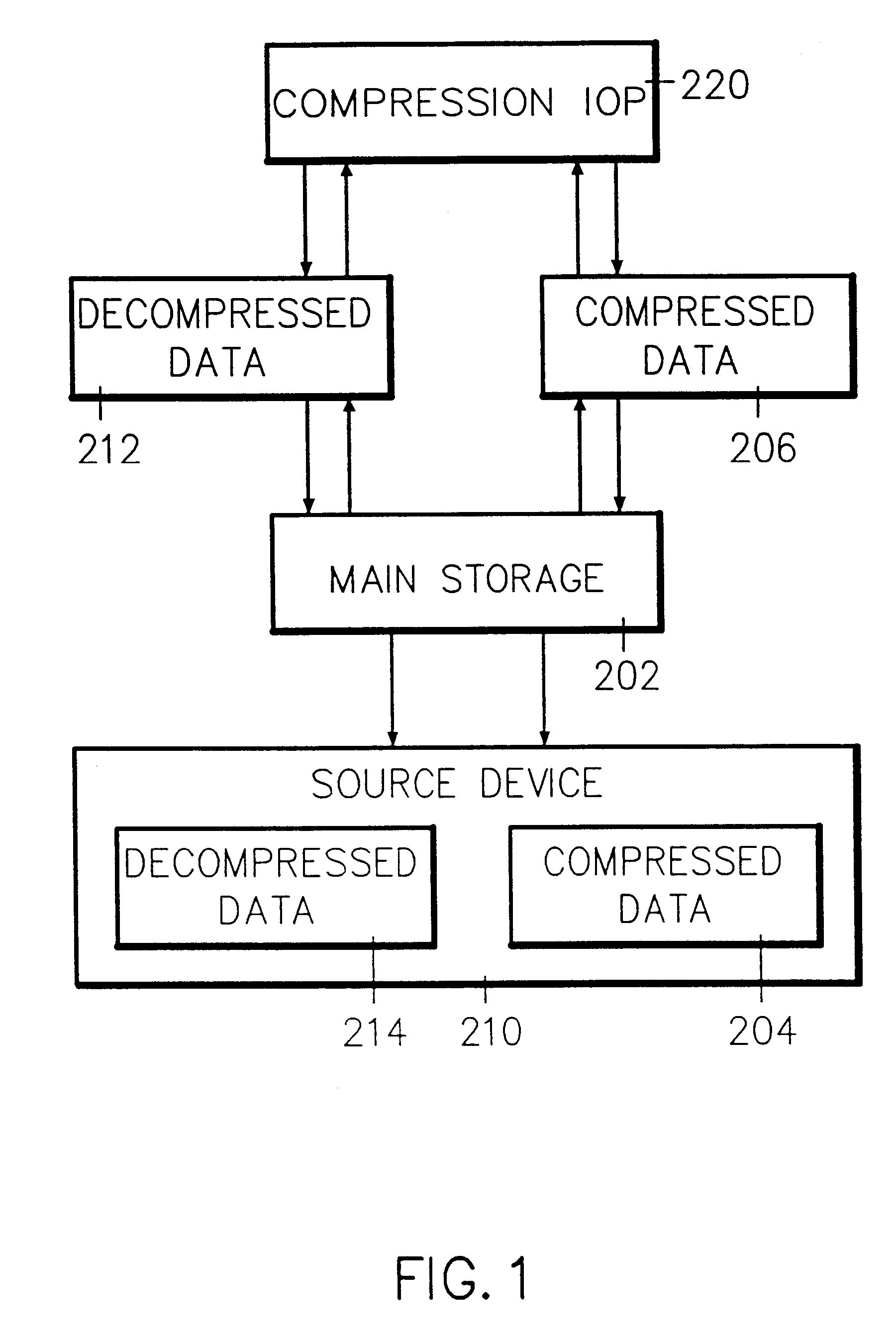
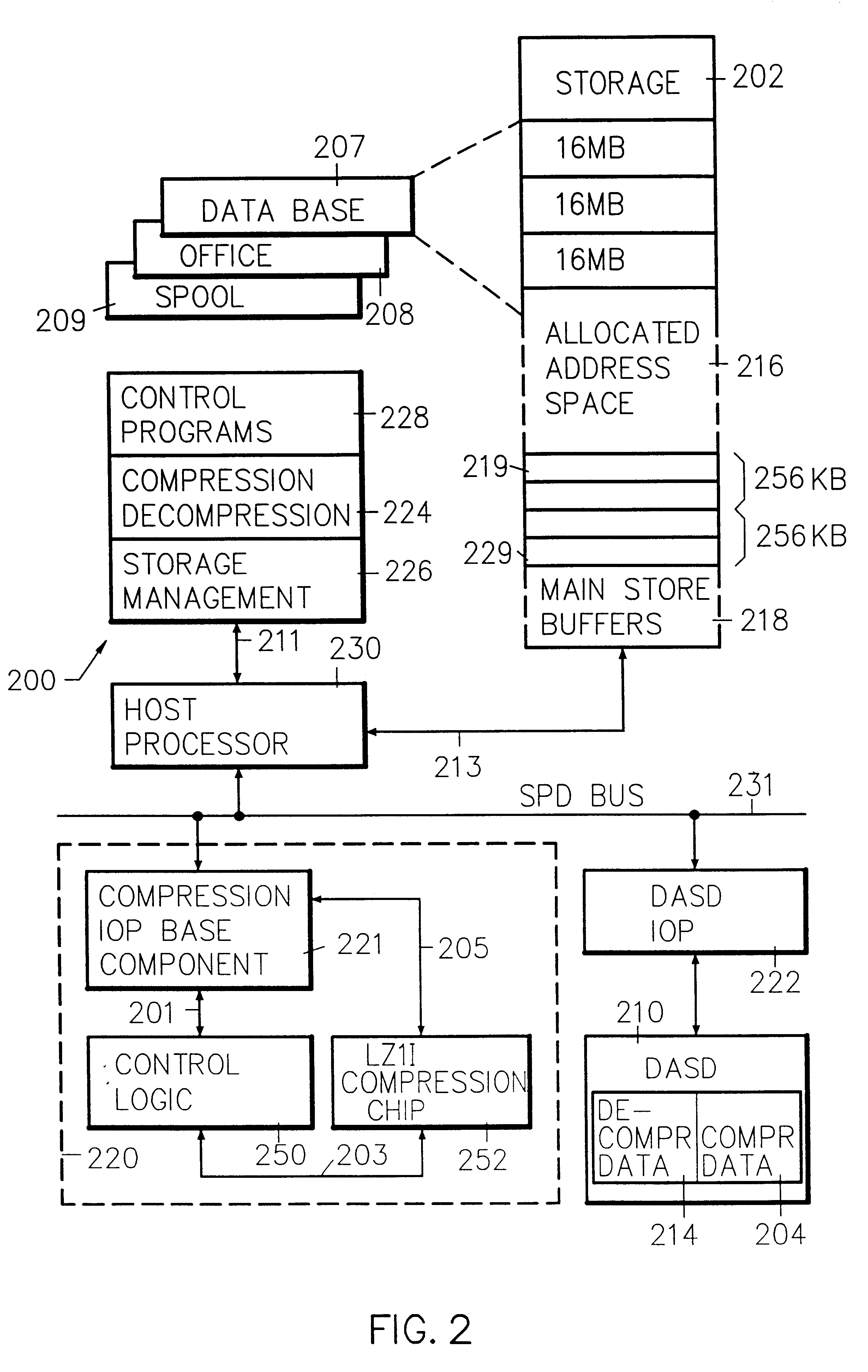
Dedicated input/output processor method and apparatus for access and storage of compressed data
InactiveUS6317747B1Minimal access penaltyEasy to useInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsData life cycleSystems management
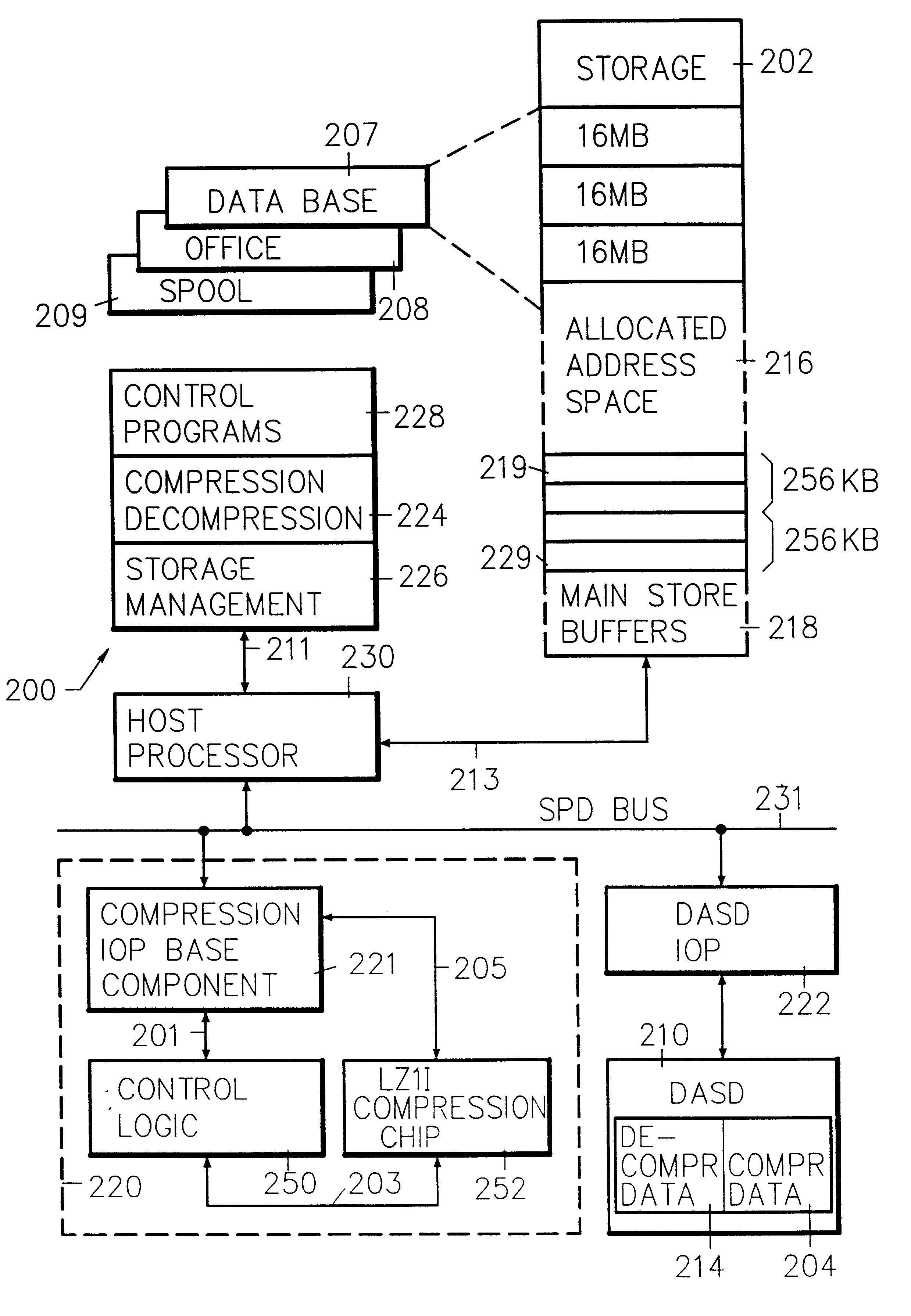
System control of compression and decompression of data based upon system aging parameters, such that compressed data becomes a system managed resource with a distinct place in the system storage hierarchy. Processor registers are backed by cache, which is backed by main storage, which is backed by decompressed disk storage, which is backed by compressed disk storage then tape, and so forth. Data is moved from decompressed to compressed form and migrated through the storage hierarchy under system control according to a data life cycle based on system aging parameters or, optionally, on demand: data is initially created and stored; the data is compressed at a later time under system control; when the data is accessed, it is decompressed on demand by segment; at some later time, the data is again compressed under system control until next reference. Large data objects are segmented and compression is applied to more infrequently used data. A dedicated compression input / output processor (IOP) is controlled by host system defined data structures which include a bus transport mechanism (BTM) which is DMA loaded to the compression IOP storage. The BTM includes a request response control block (RRCB) comprising a compress or decompress operation command, a data out descriptor (DOD) for providing the address of data in host storage that needs to be compressed or decompressed, and data in descriptor (DID) for providing the address in host storage where the resulting decompressed or compressed data is to be stored.
Owner:IBM CORP
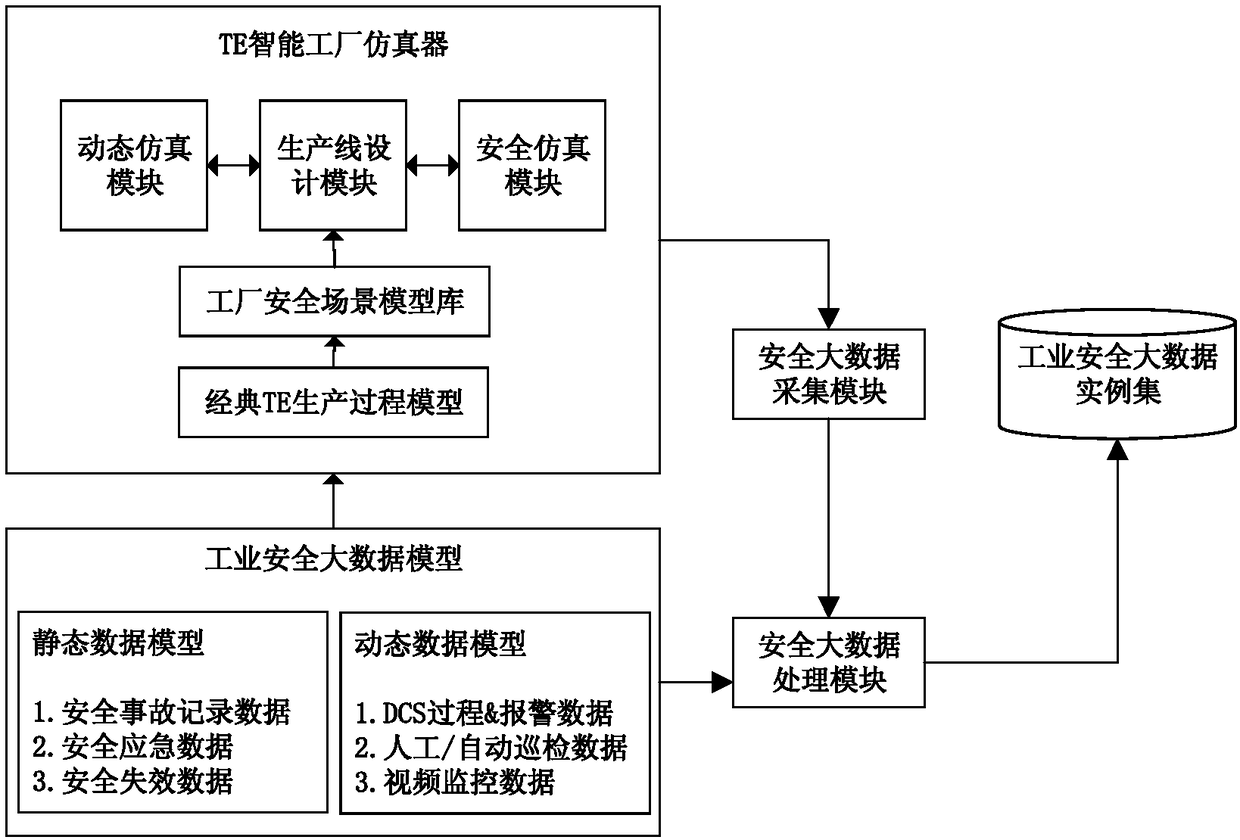
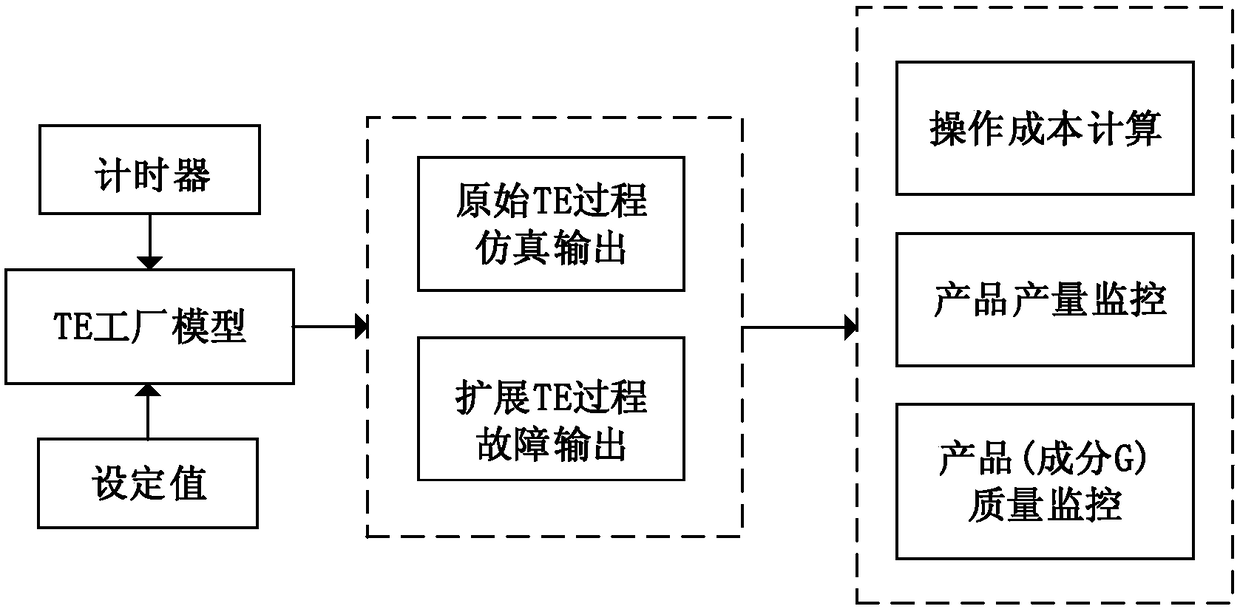
TE model based data source generation method and device of safety big data of intelligent factory
The invention discloses a TE model based data source generation method and device of safety big data of an intelligent factory. The device comprises an industrial safety big data model, a TE intelligent factor simulator, a safety data collection module, a safety data processing module and an industrial safety big data instance set; a factor safety scene model library is generated on the basis of mapping between the industrial safety big data model and a TE process model, and non-structured industrial safety big data generated by the TE intelligent factor simulator is structured; the TE intelligent factor simulator simulates an accident scene dynamically aimed at pre-embedded fault sources of a performer, a material stator, a controller and a sensor; the safety data collection module collects the industrial safety big data generated by the TE intelligent factor simulator in a classified way; the safety data processing module processes the collected industrial safety big data into instances; and the industrial safety big data processed into instances is stored in the industrial safety big data instance set. Thus, the industrial safety big data of the intelligent factor can be obtained reasonably and effectively, and targeted research and test can be carried out on the industrial safety big data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
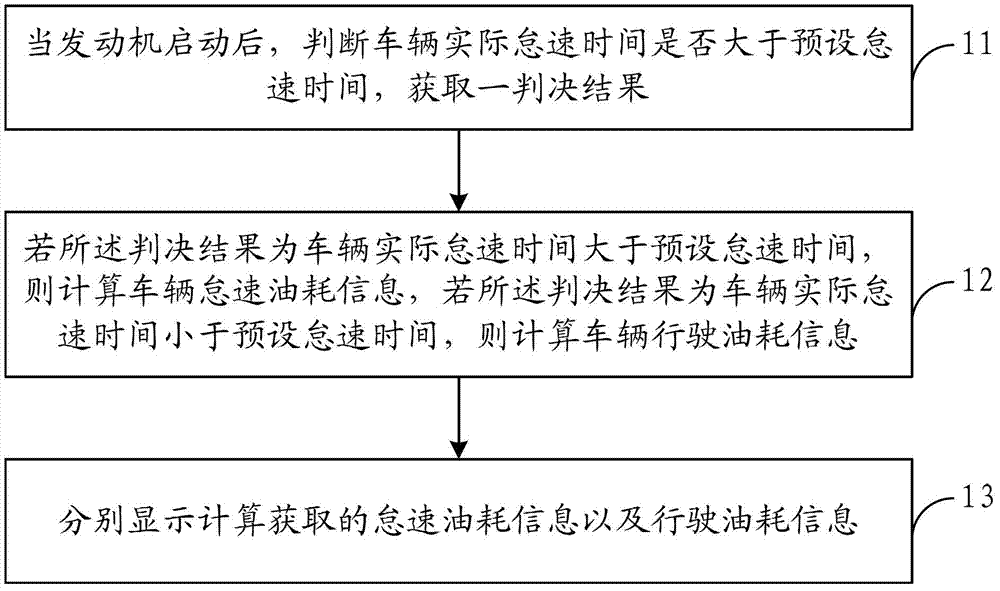
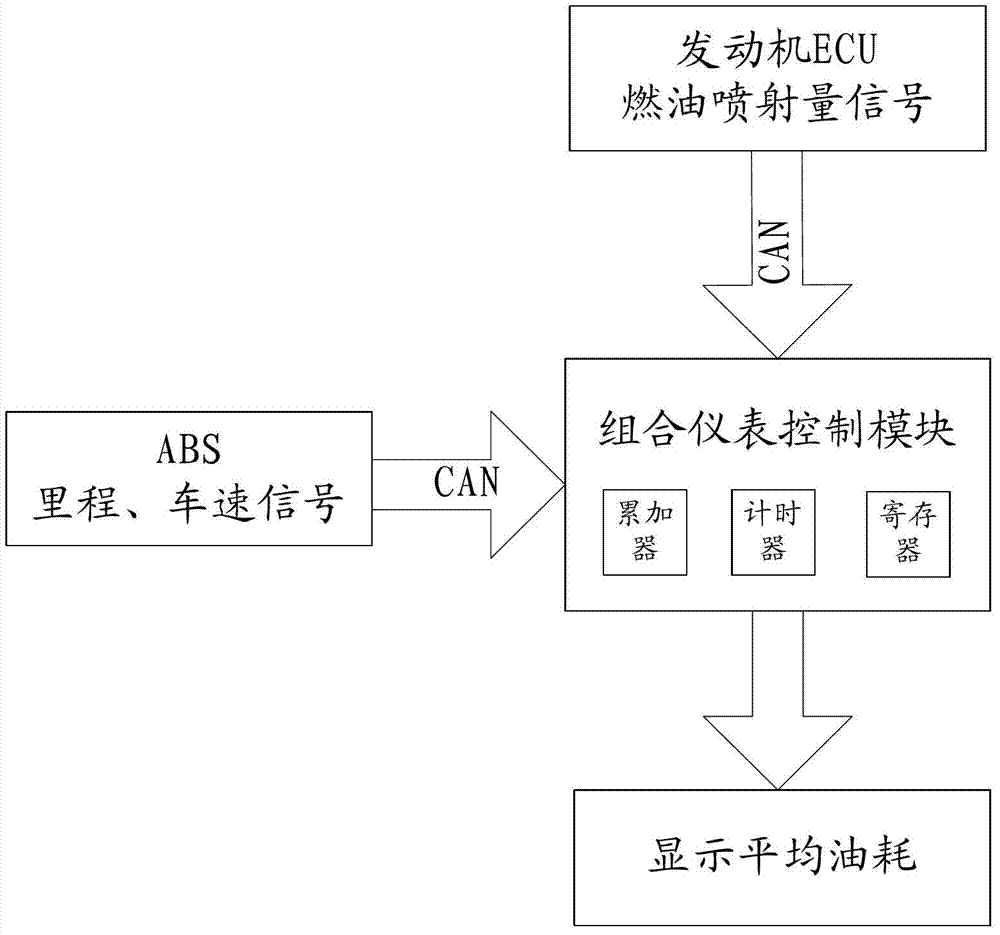
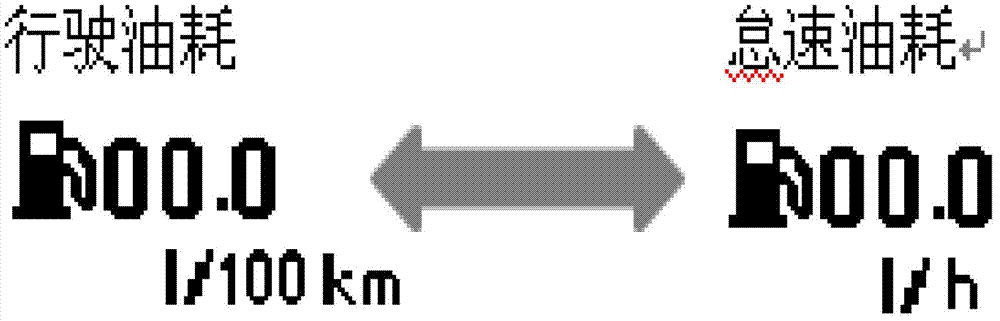
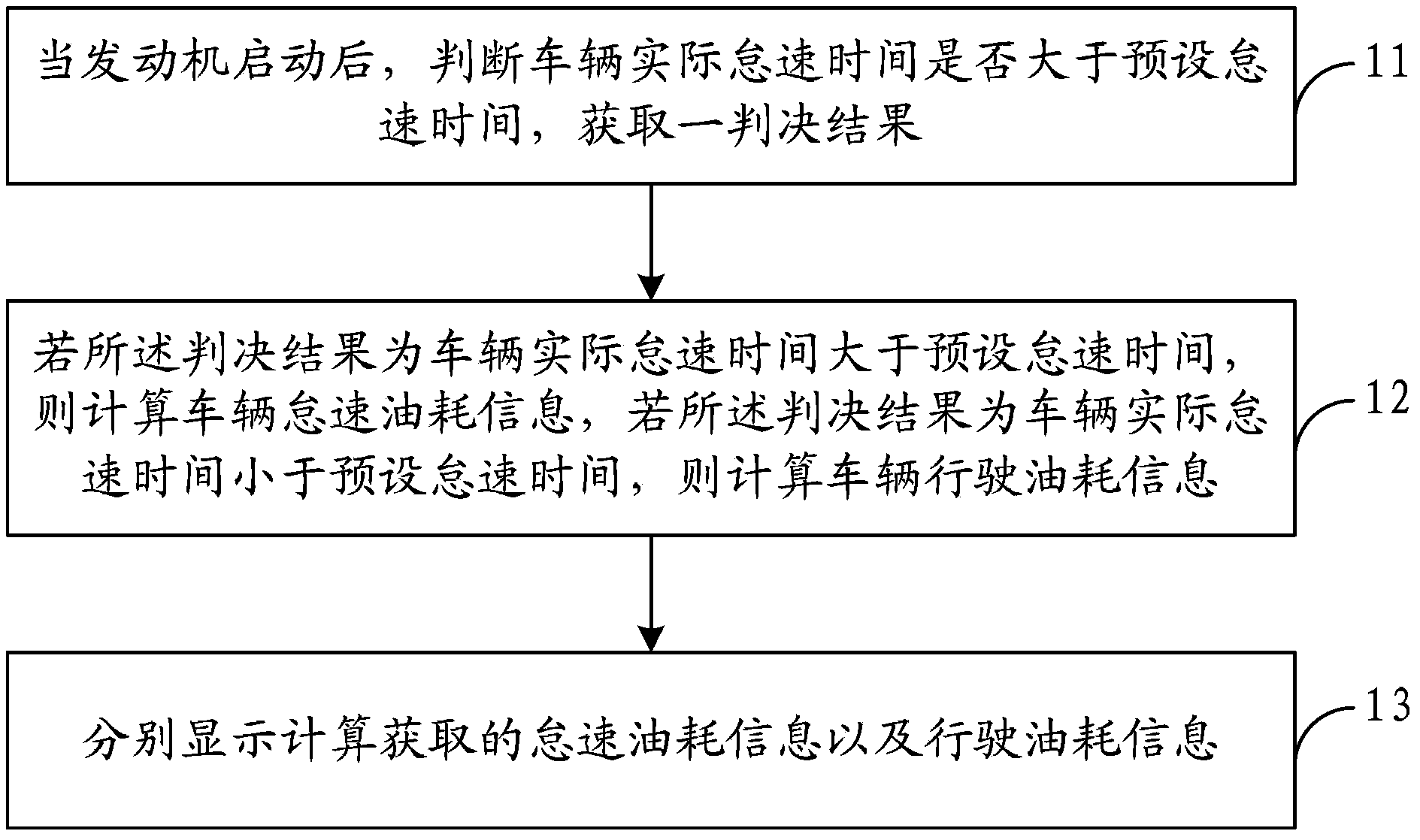
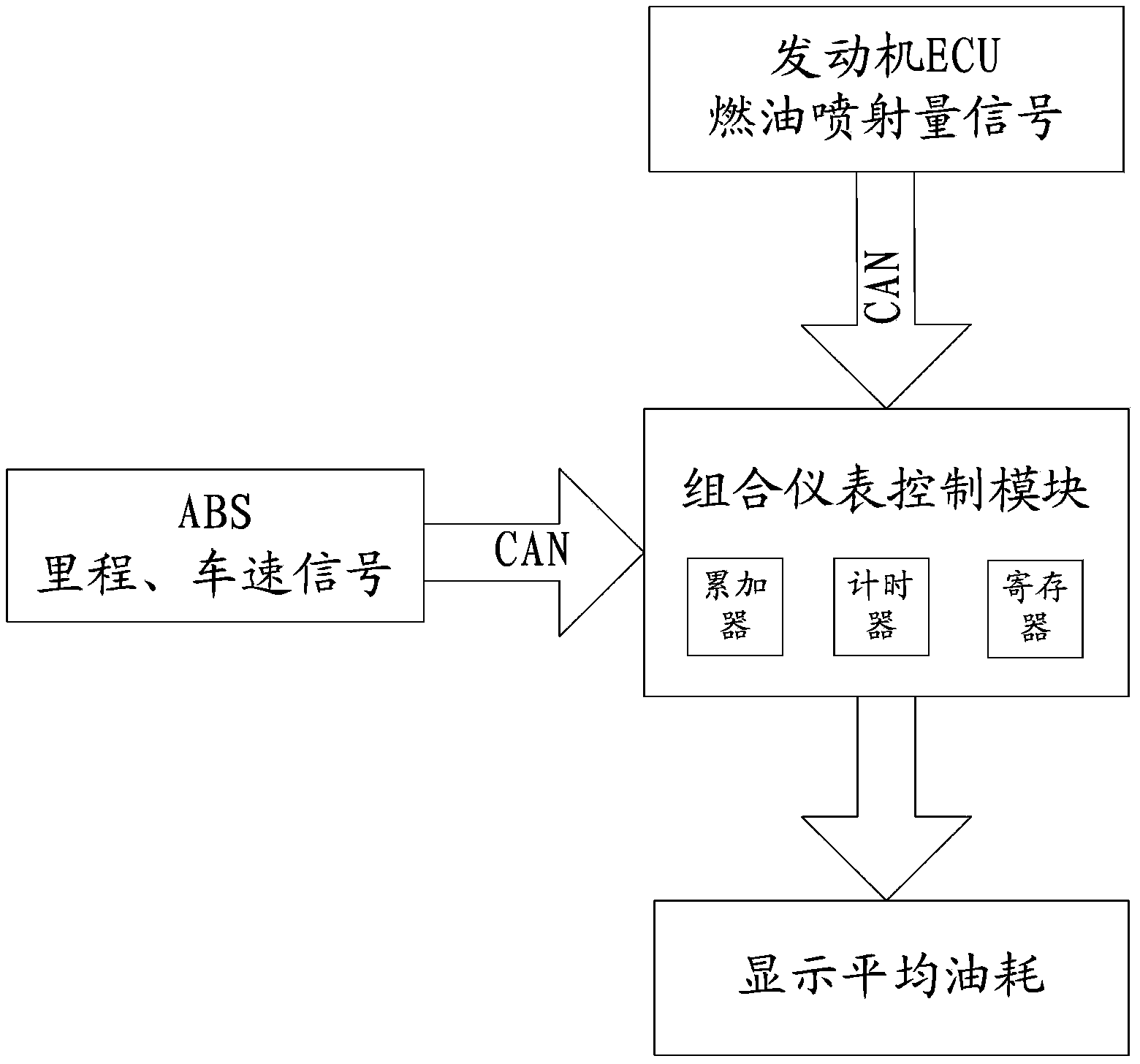
Method for calculating oil consumption of vehicle, oil consumption device and oil consumption vehicle
ActiveCN102853872AAccurate displayShow reasonableRelative volume flow measurementsIdle speedCalculation methods
The invention provides a method for calculating oil consumption of a vehicle, an oil consumption device and an oil consumption vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a determination result by judging whether actual idling speed time of the vehicle is greater than preset idling speed time or not after an engine is started; calculating idling speed oil consumption information of the vehicle if the determination result is that the actual idling speed time of the vehicle is greater than preset idling speed time; calculating driving oil consumption information of the vehicle if the determination result is that the actual idling speed time of the vehicle is smaller than the preset idling speed time; and respectively displaying the idling speed oil consumption information and the driving oil consumption information which are acquired by virtue of calculation, so that the oil consumption information of the different states of the vehicle is accurately and reasonably acquired.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
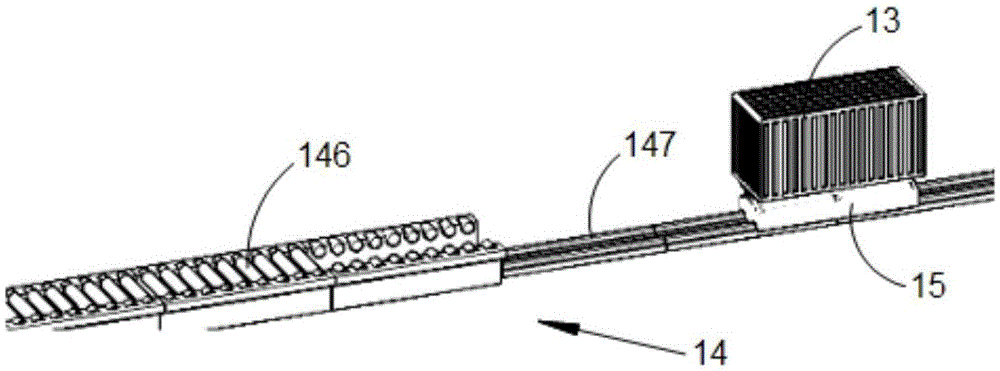
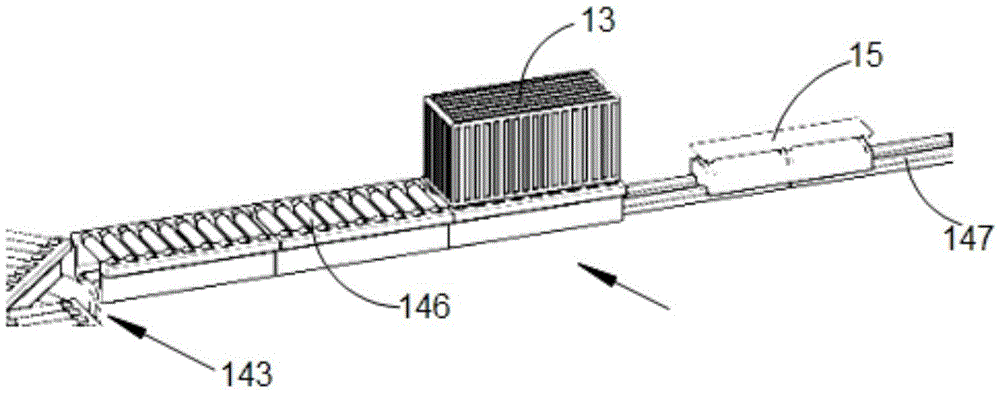
Luggage taking and placing device
The invention discloses a luggage taking and placing device, which comprises an installing plate, a folding frame, a transmission device and an extraction device, wherein lead screws with opposite screw threads are arranged at the two sides of the bottom of the installing plate, and connecting screw nuts are respectively arranged on the lead screws arranged at the two sides in a sleeving way; the lead screws are connected with a first motor; the top ends of the folding frame are respectively arranged on the connecting screw nuts arranged at the two sides, and the bottom end of the folding frame is connected with a transmission device; the transmission device comprises a bottom box and a transmission plate, a group of mutually matched gears and racks is arranged between the bottom box and the transmission plate, and the racks are connected with a second motor; the extraction device comprises a support frame, a pulley and a suction disc; the top end of support frame is arranged on the installing plate, the pulley is arranged on the support frame, a rope connected with the third motor is arranged on the pulley, the rope is connected with a screw nut lead screw, a screw nut is arranged on the screw nut lead screw in a sleeving way, and the suction disc is arranged on the screw nut. The luggage taking and placing device has the advantages that the labor work is reduced, the inconvenience in a compartment due to luggage taking and placing is reduced, the stable luggage taking and placing is realized, and the luggage can be reasonably ranged.
Owner:NANJING VOCATIONAL UNIV OF IND TECH
Robotic Arms
InactiveUS20090326714A1Minimize necessityReasonable accessProgramme controlComputer controlHand armEngineering
A robotic arm of the “top following” type, which can advance into an environment is covered is covered by a sensorised skin. The arm can thus detect a parameter of the environment, and the shape can be adjusted accordingly.
Owner:OLIVER CRISPIN ROBOTICS
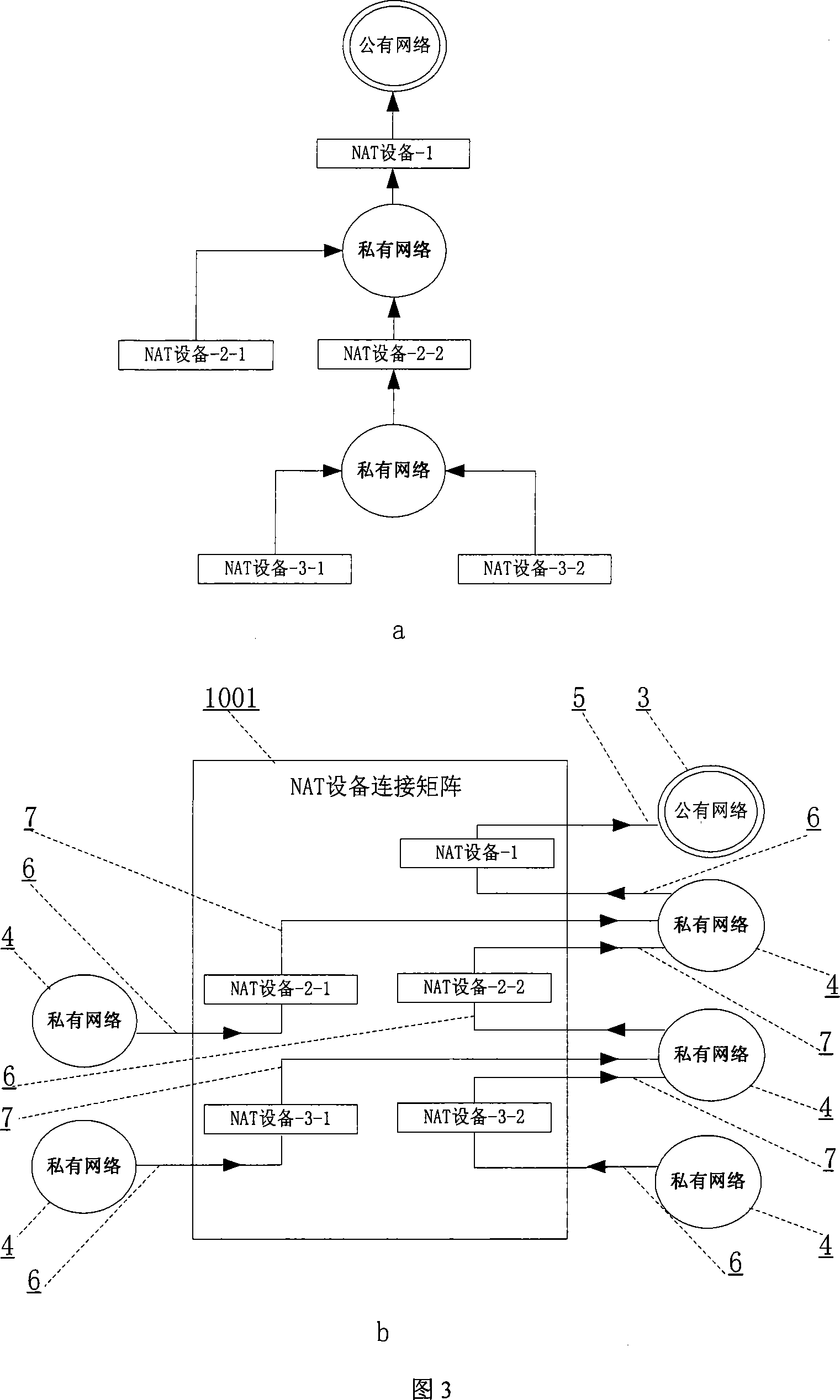
Application-oriented name registration system and its service method under multi-layer NAT environment
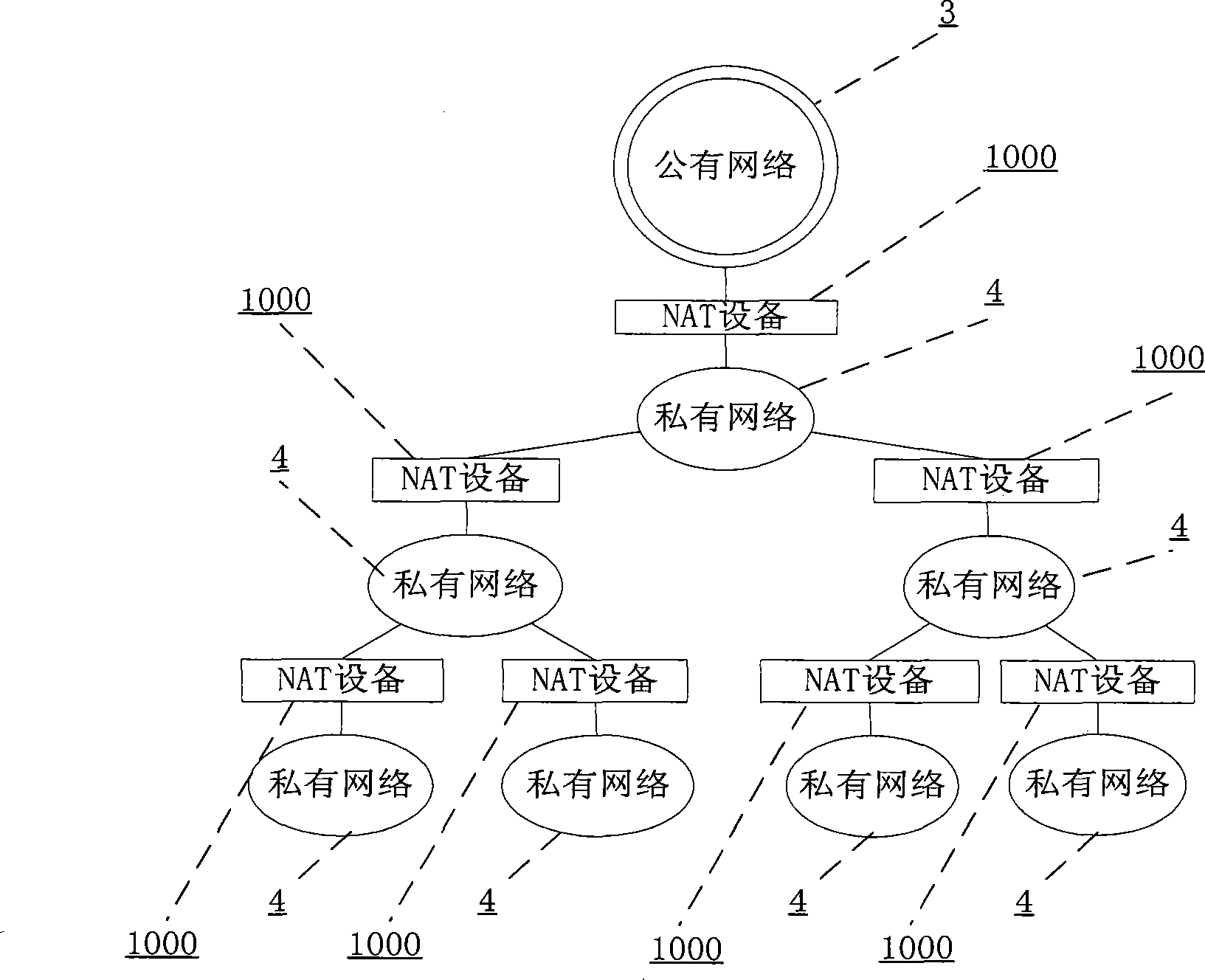
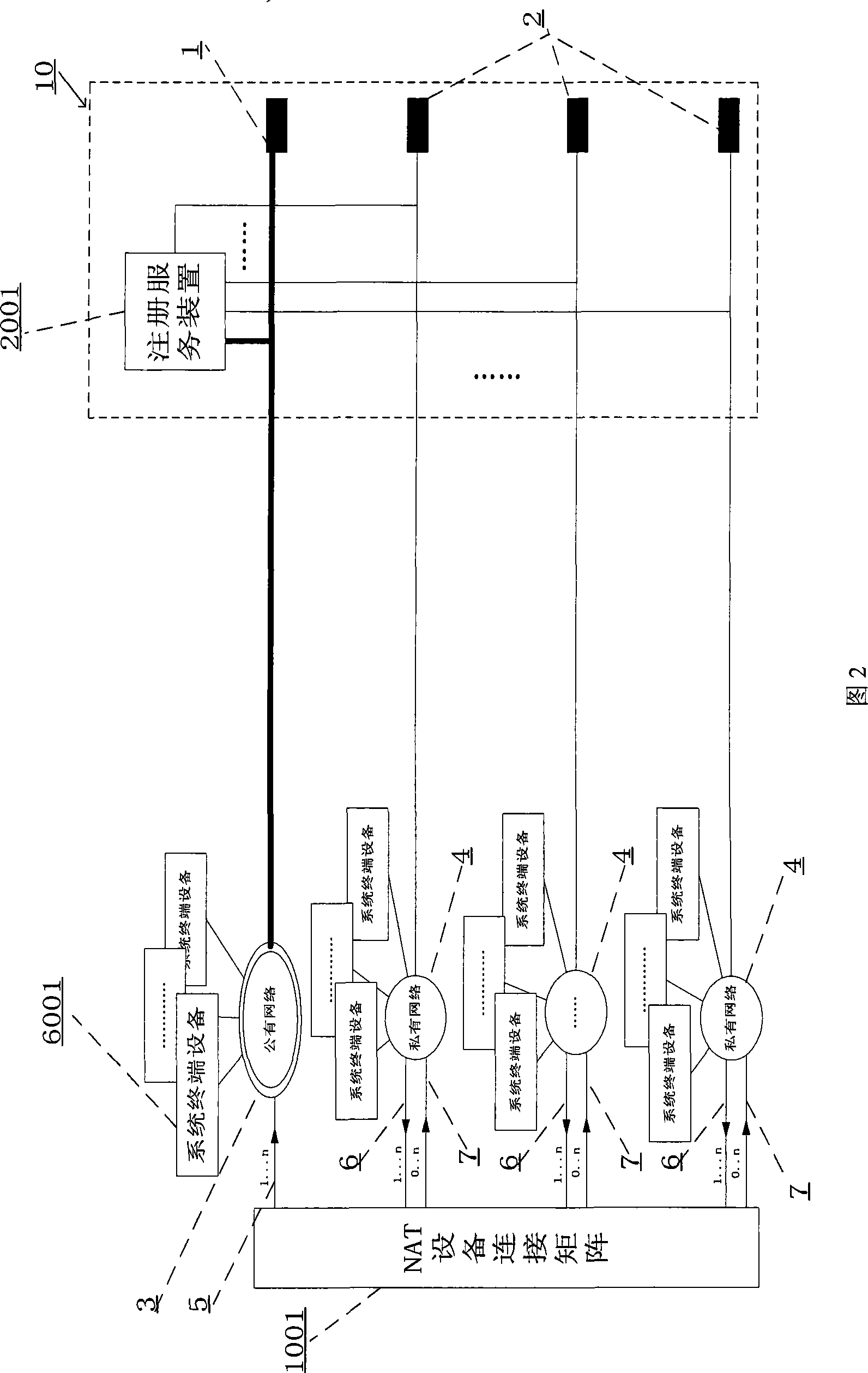
InactiveCN101242421AReasonable accessAchieve deliveryError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksEntry pointPrivate network
The invention provides an application-oriented name registration system in multi-layer NAT environment, comprising a system terminal device and a registration service unit including a top-layer registration service unit accessing public network and a basic registration service unit accessing private network; the registration service unit is used for receiving the logging request massage of the system terminal device, and recording the user logging information of the system terminal device, the user logging information at least includes a user ID, a user entry point of the user's system terminal device in the network accessed by the registration service unit, and a access point of the user's system terminal device in the network accessed by the registration service unit. The invention can locate in multi-layer NAT environment by identification, and make the service in private network visible to external network and unrelated to specific application. The invention also provides a system and a method of more reasonable access approach for external network node.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
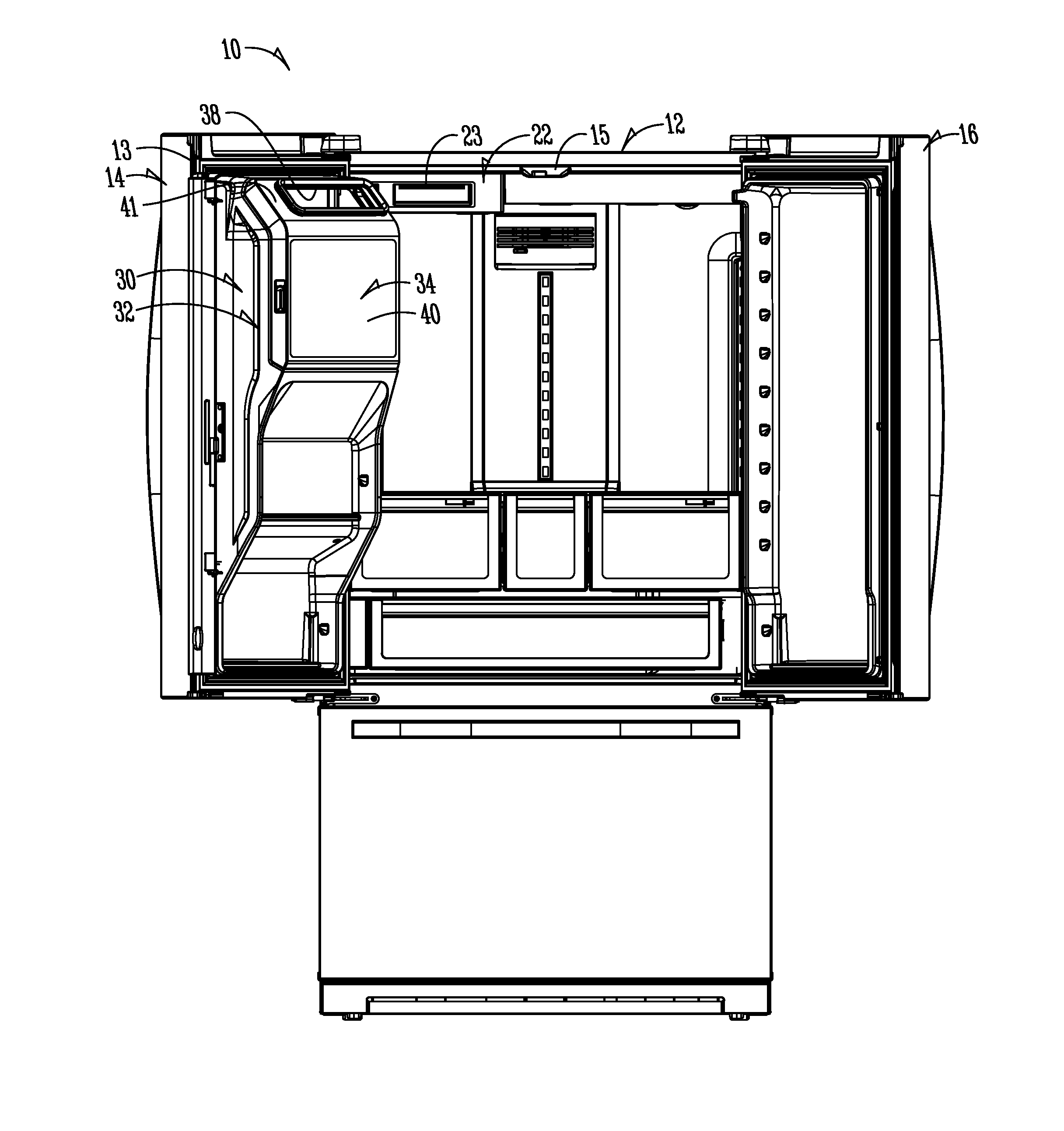
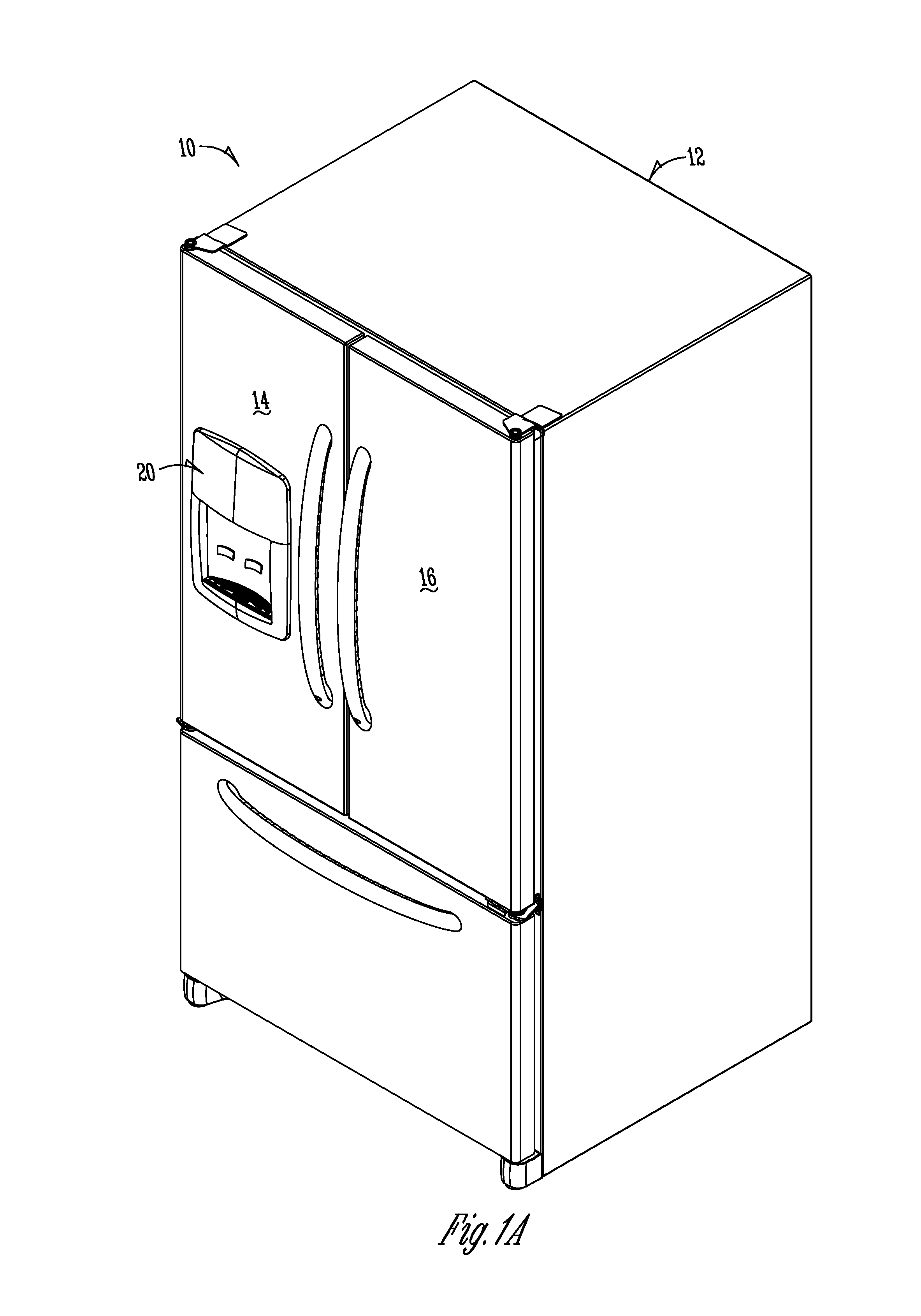
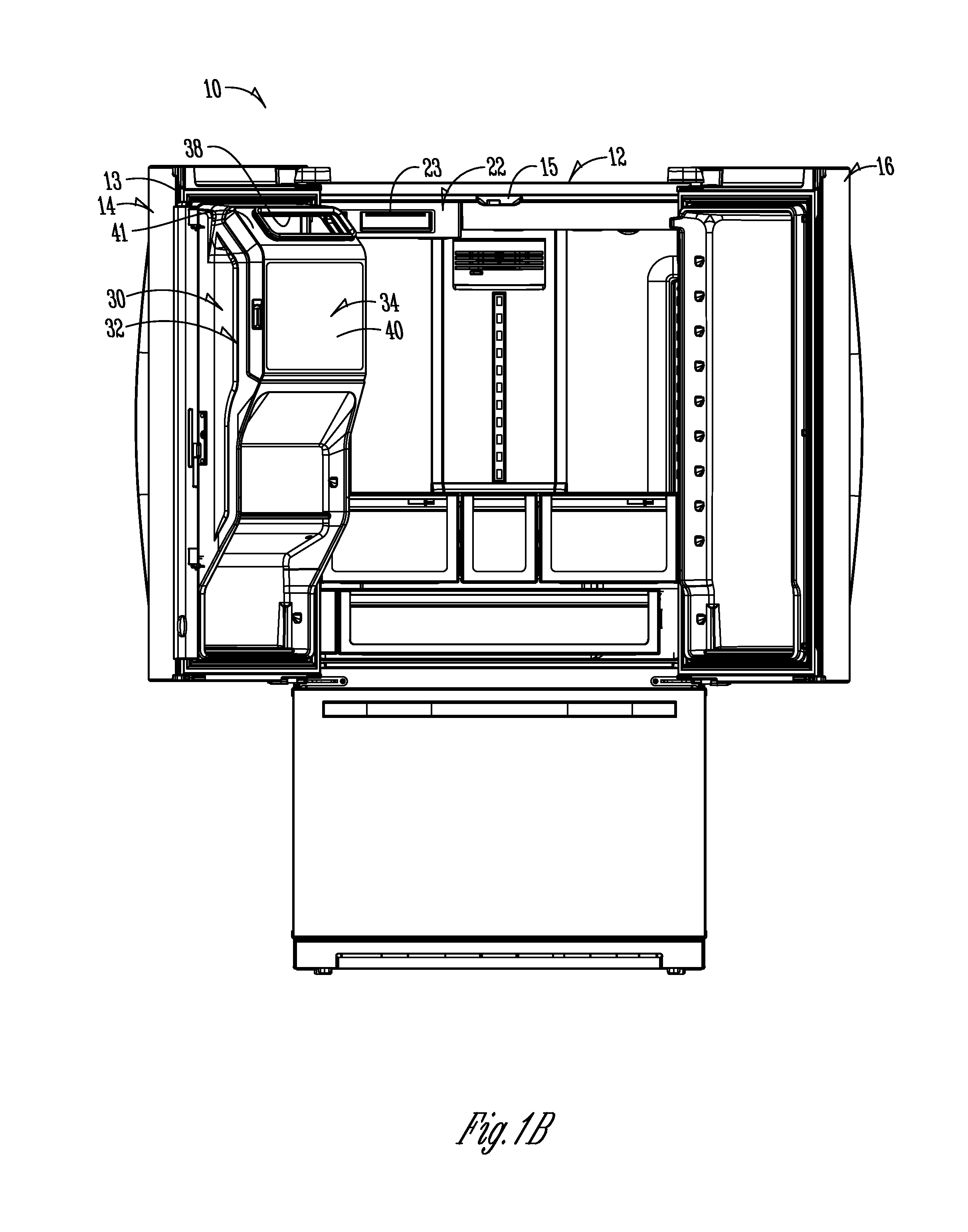
Two-plane door for refrigerator compartment
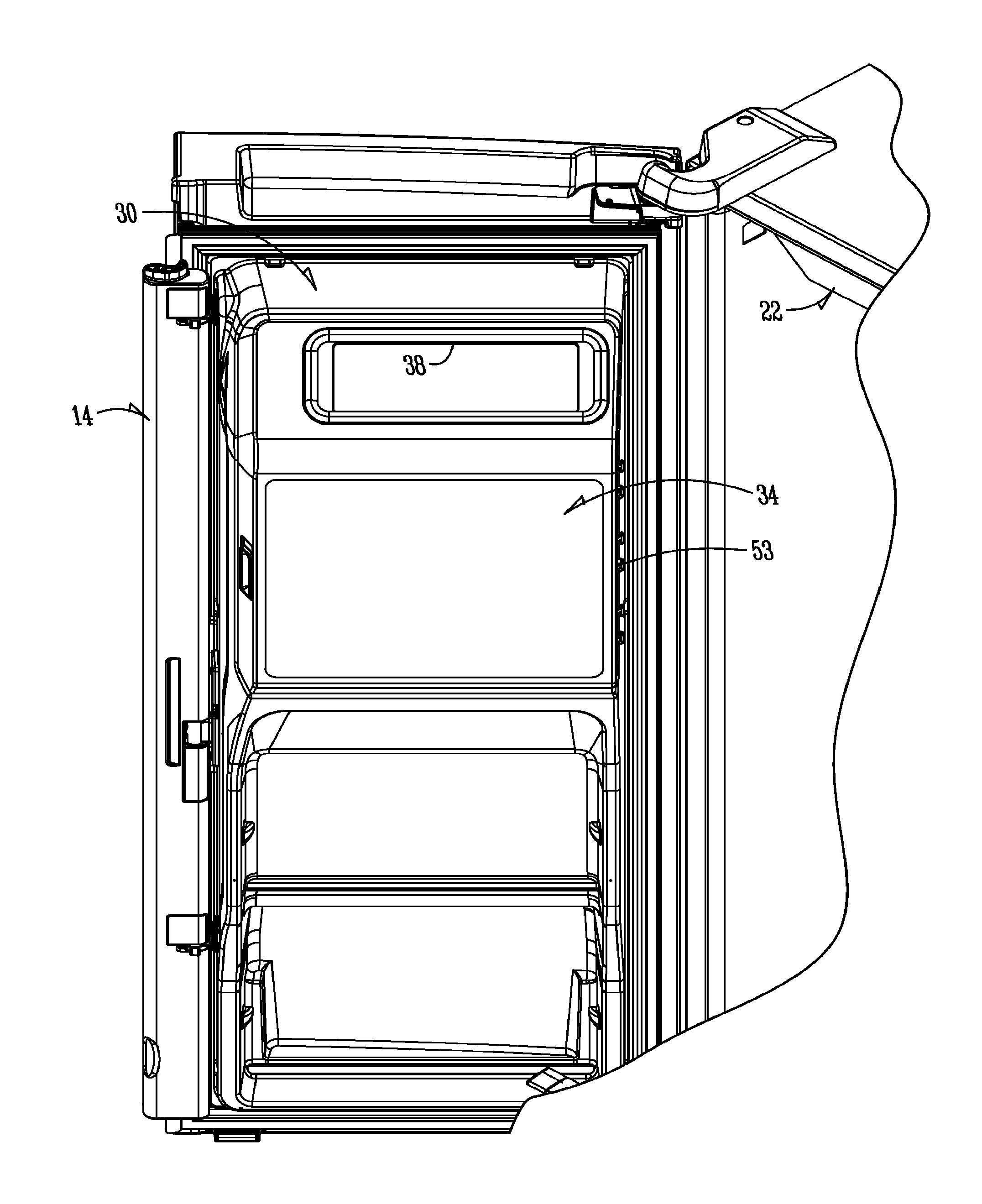
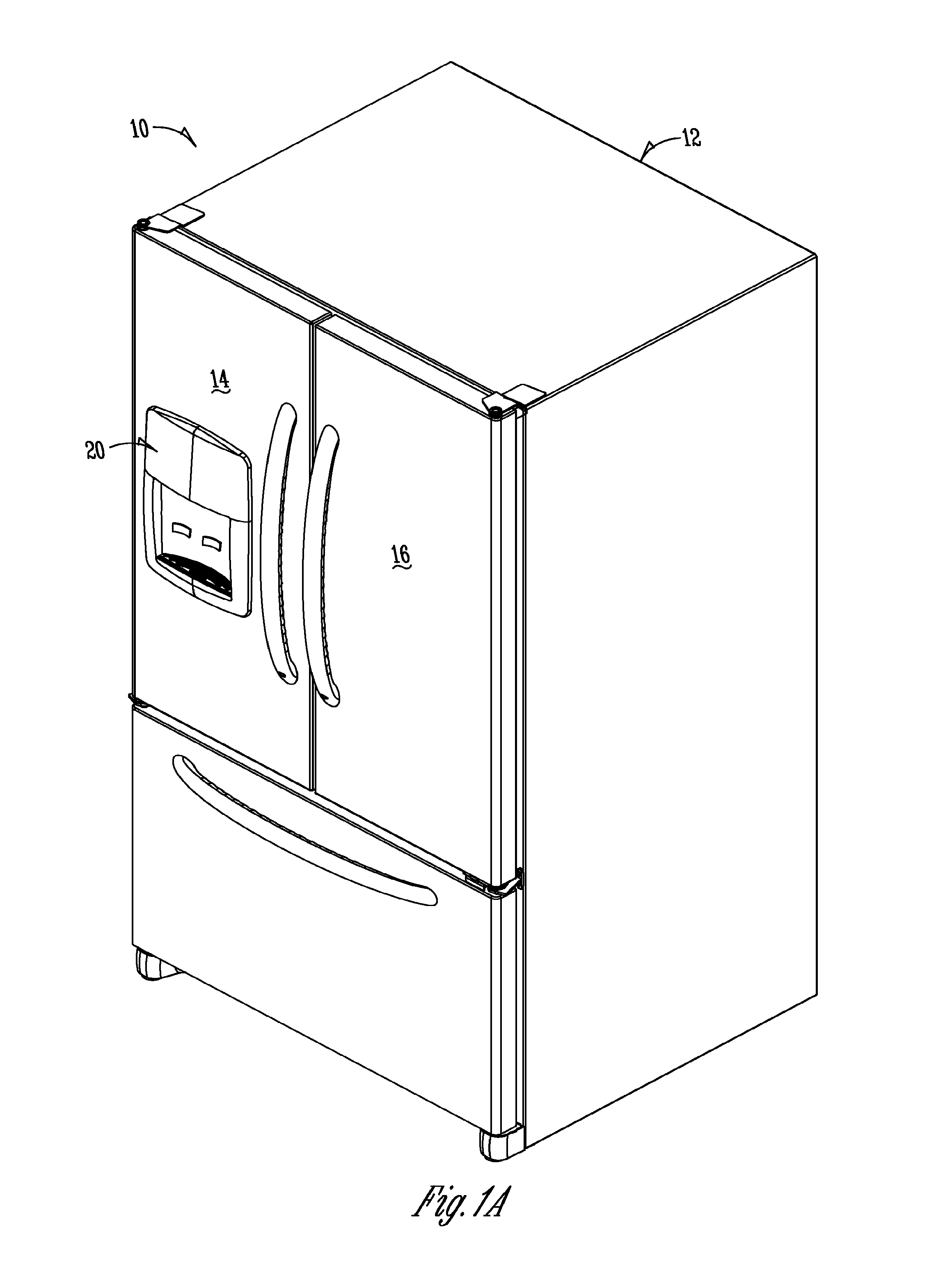
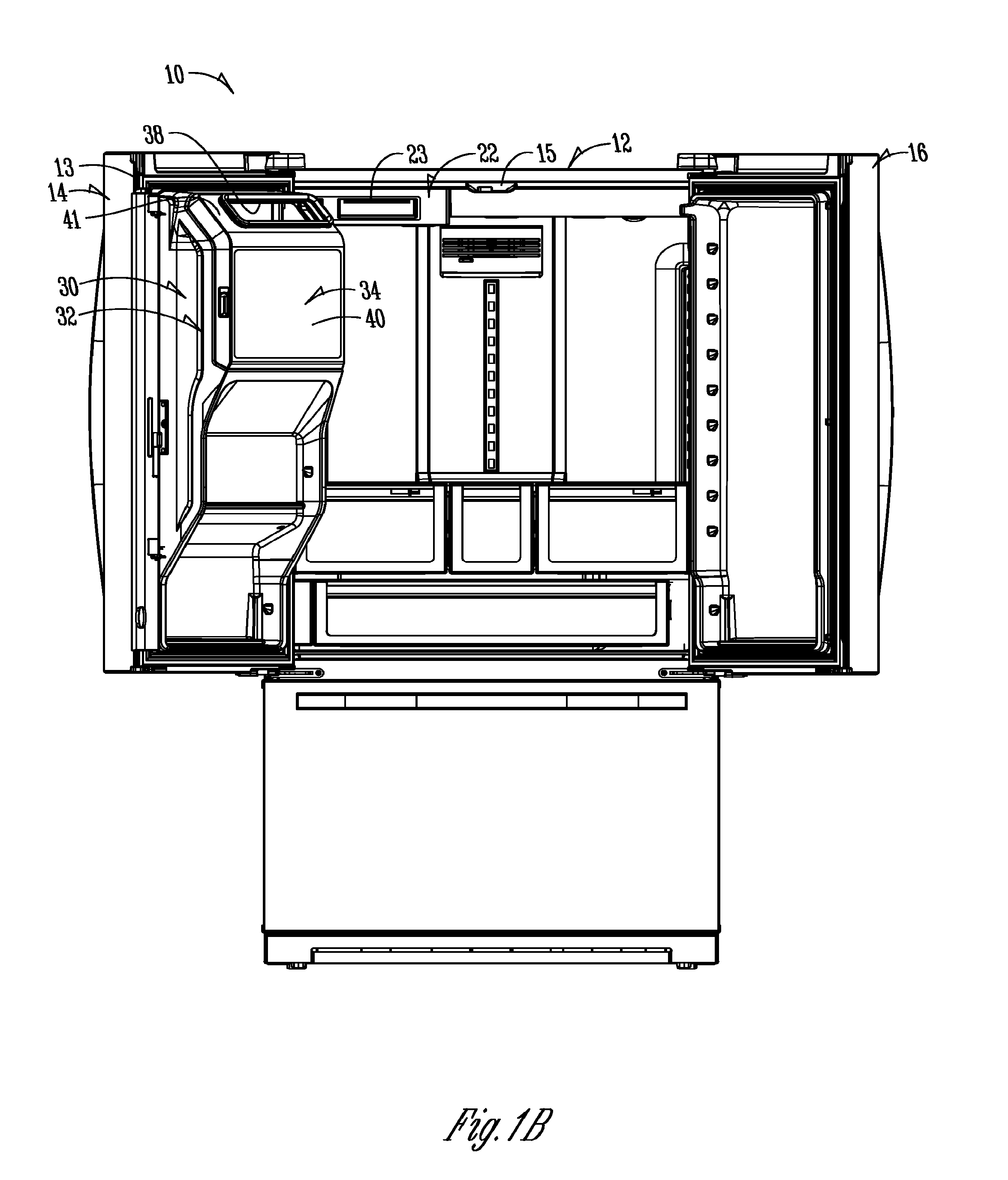
ActiveUS9441873B1Solve the real problemReasonable accessLighting and heating apparatusIce productionInterior spaceEngineering
In a refrigeration appliance, an enclosure or container defines an enclosed space. A two-plane door forms a portion of the container. The two-plane door opens along one pivot axis and allows access to the enclosed interior space. The container can be a thermally insulated in-door ice compartment of a refrigerated appliance. One example is a bottom freezer style, with the in-door ice compartment in the cold food section of the appliance.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Method and apparatus for realizing load equalizing
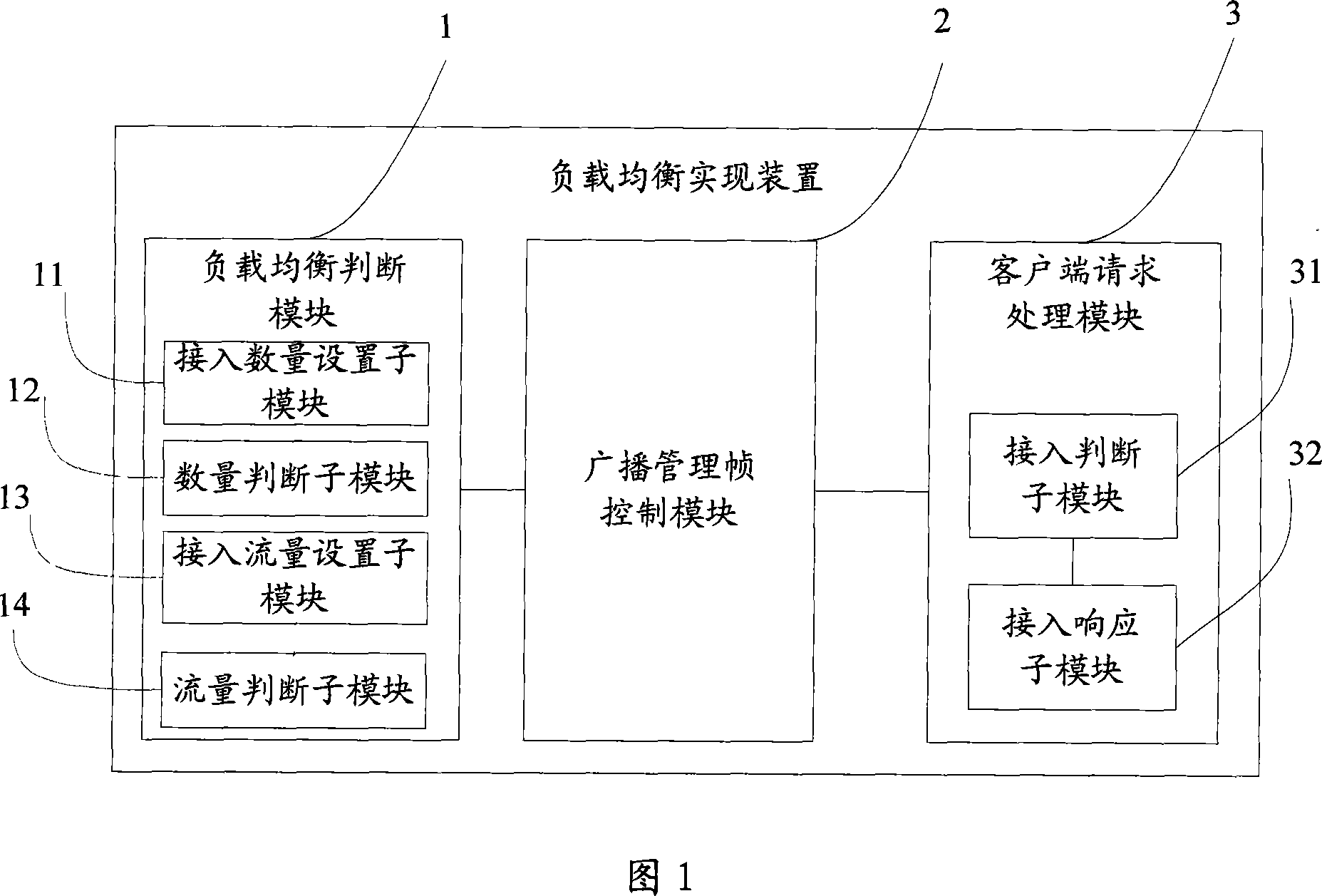
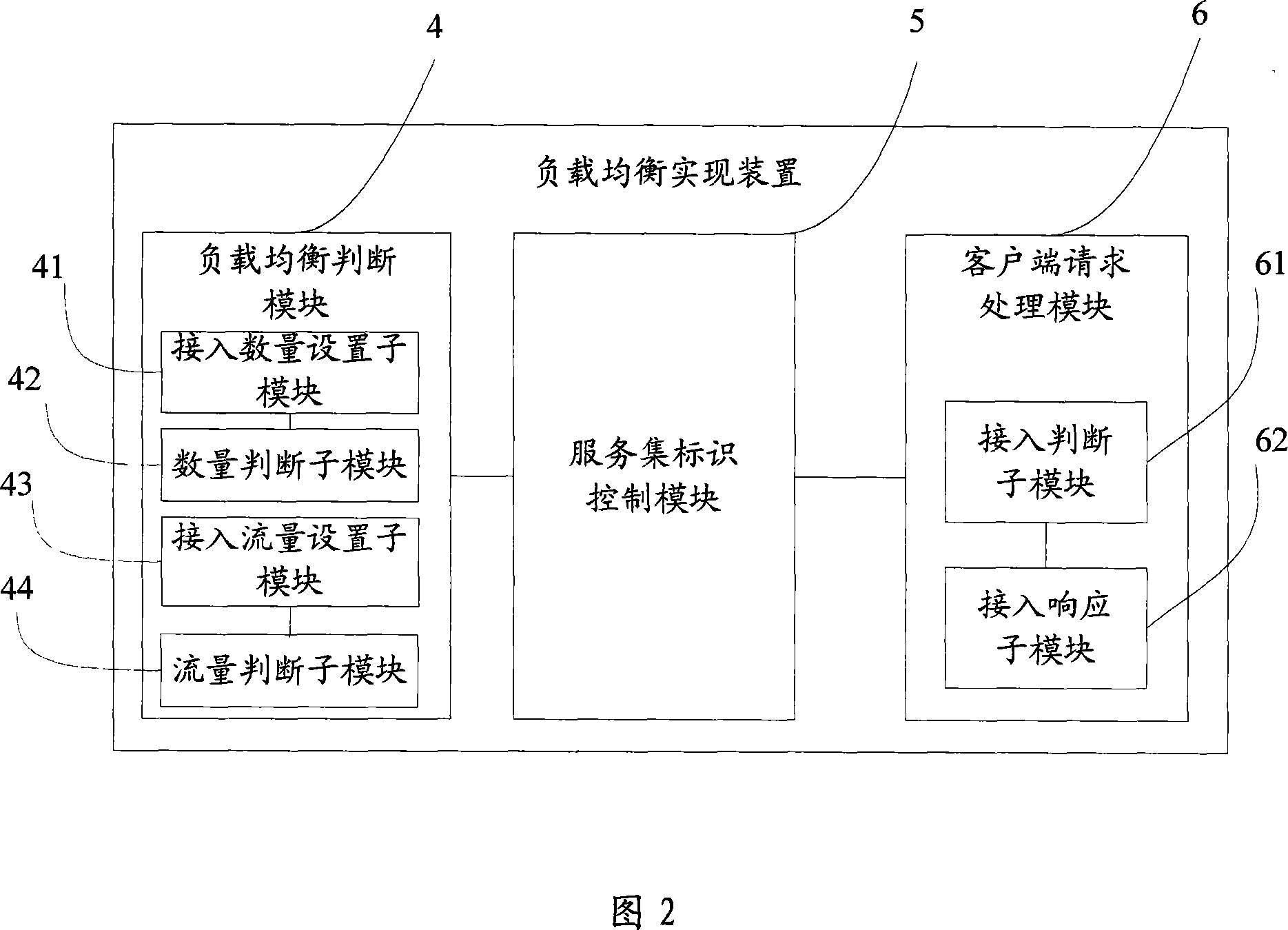
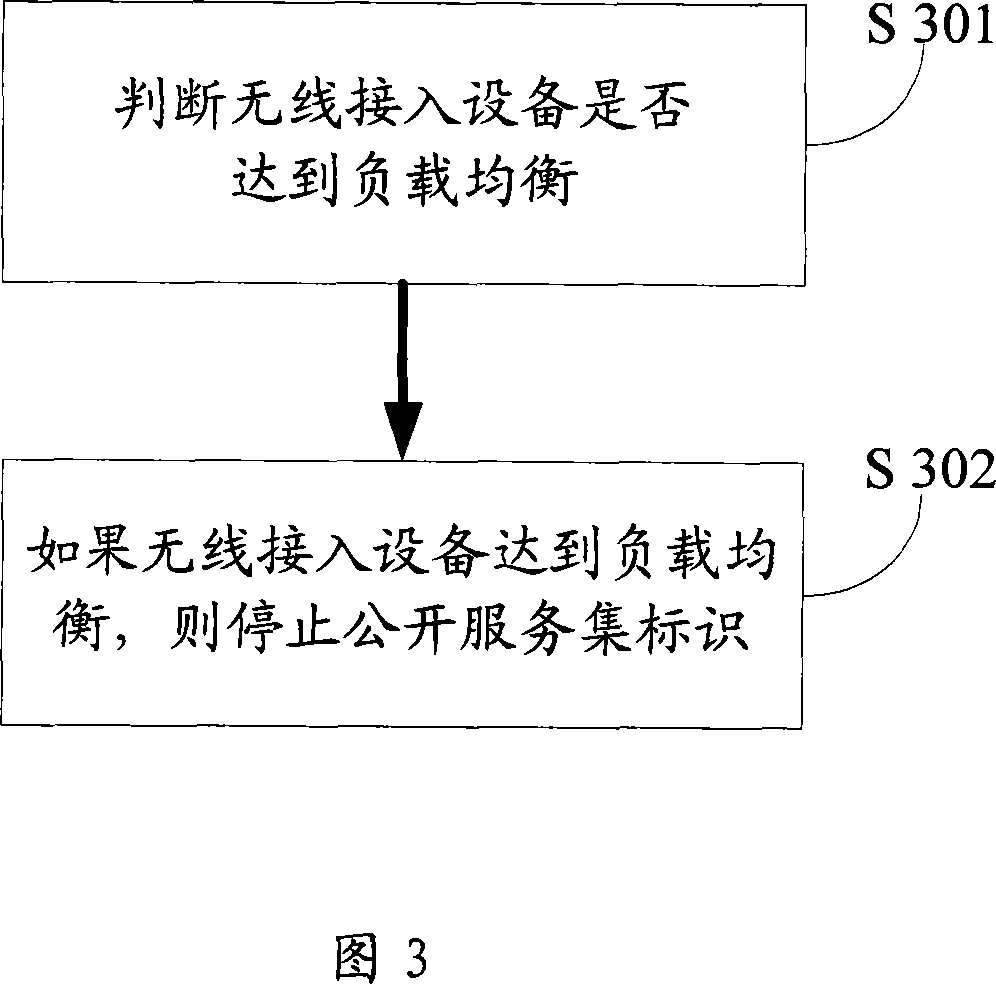
InactiveCN101043459AReasonable accessError preventionData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsClient-side
The disclosed implementation method for balance loading comprises: deciding whether the wireless access device up to balance loading; if yes, stopping the public service set mark. This invention ensures the wireless client on balance-loading environment to select effective wireless access device more properly.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Container storage device
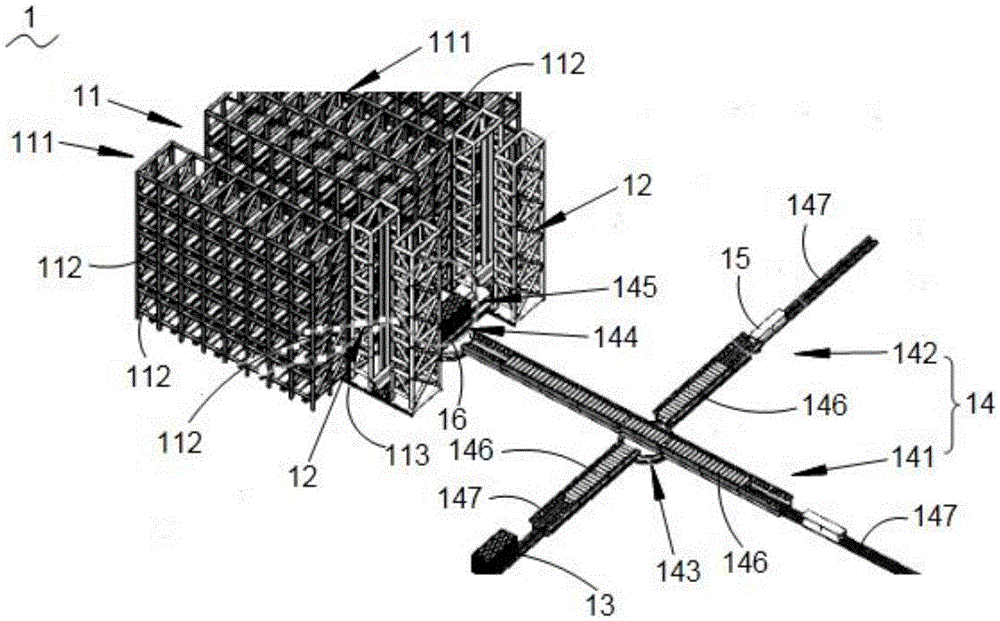
Disclosed is a container storage device. The container storage device comprises a storage chamber, roadway stackers and conveying tracks, wherein the storage chamber further comprises chamber units which are independently arranged at intervals, and chamber compartments are formed in the chamber units; the roadway stackers are disposed on the first guiding track located among the chamber units and enable containers to ascend or descend, so that the height of the containers is matched with the height of the chamber compartments of the chamber units and accordingly the containers can be stored and taken out; the conveying tracks further comprise the second guiding track and the third guiding track which are arranged in an intersecting mode, a first rotary plate is disposed at the intersection of the second guiding track and the third guiding track, a second rotary plate is disposed at the end, closely adjacent to the roadway stackers, of the conveying tracks, and the second rotary plate is in rotational butt joint with the fourth guiding track, connected with the roadway stackers, of the conveying tracks. By means of the container storage device, the space utilization rate is greatly improved; standard and reasonable storage and taking of goods is achieved; besides, the automation degree is increased, an advanced logistics system is conveniently formed, the operation efficiency is improved, and the storage cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
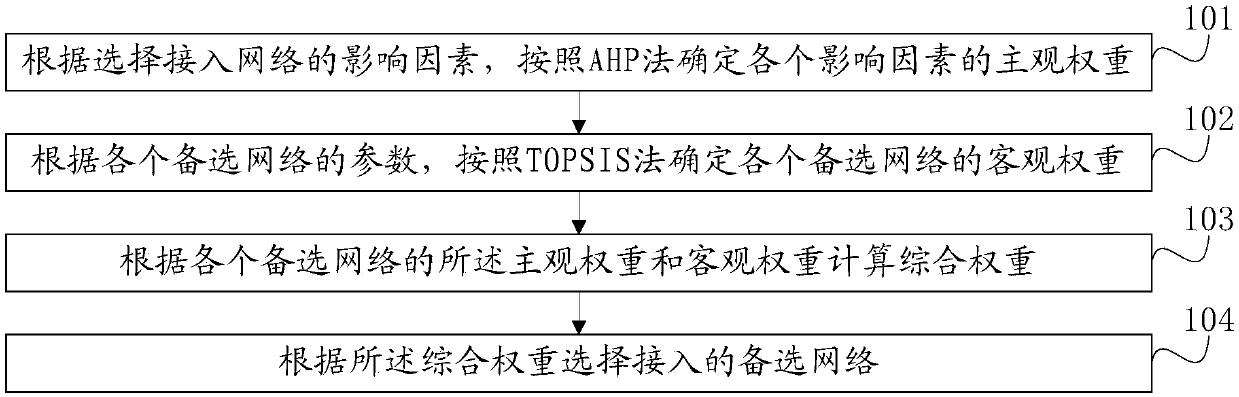
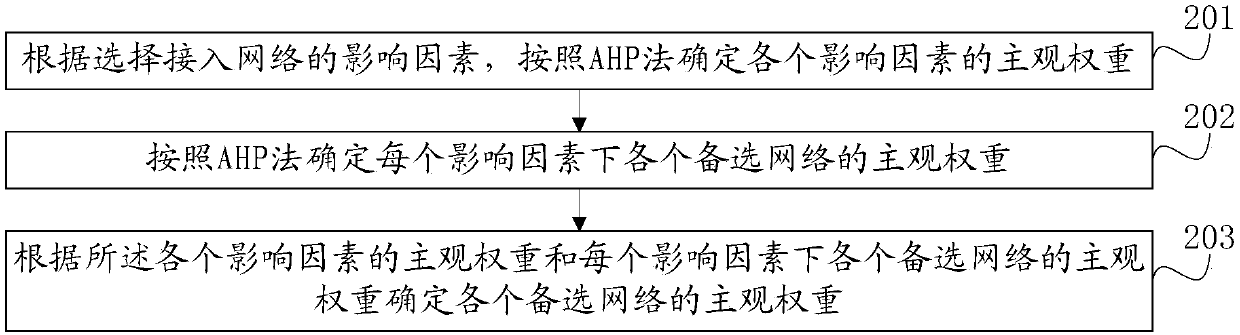
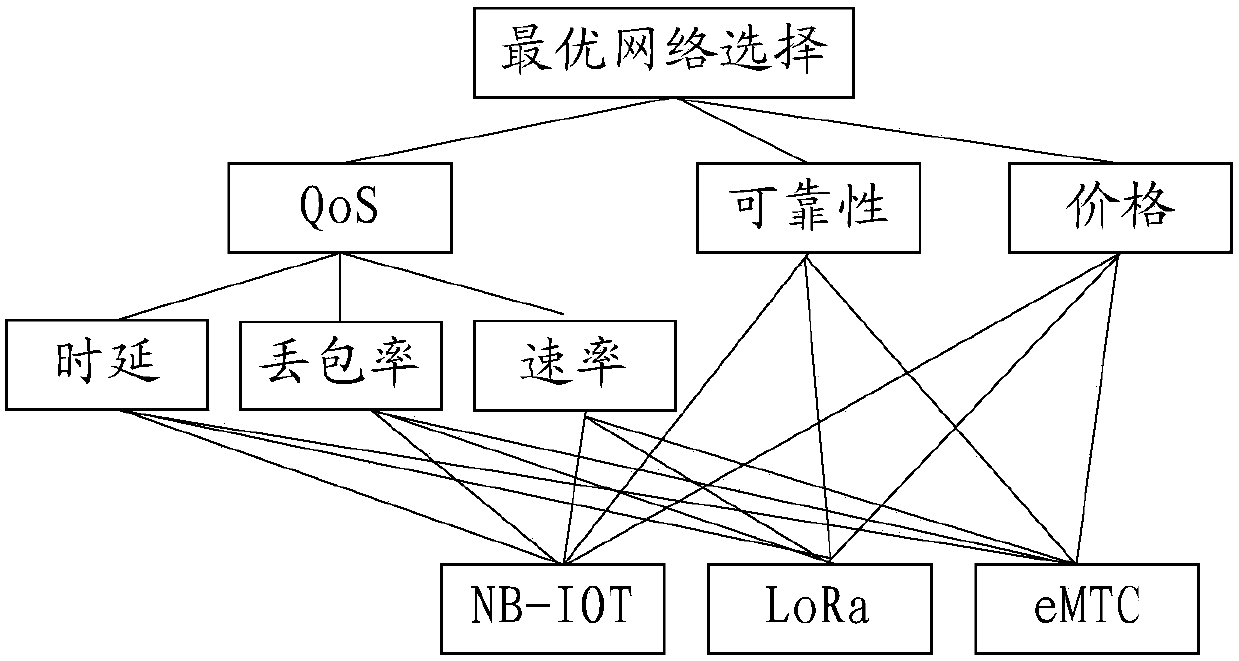
Heterogeneous network access selection method and system based on Internet of Things (IoT)
ActiveCN108024307AReasonable accessSmall amount of calculationAssess restrictionThe InternetHeterogeneous network
The invention relates to a heterogeneous network access selection method and system based on the Internet of Things (IoT). The method comprises the following steps: according to affecting factors foraccess network selection, determining subjective weights of a plurality of candidate networks through the AHP method; according to parameters of the candidate networks, determining objective weights of the candidate networks through the TOPSIS method; calculating comprehensive weights according to the subjective weights and the objective weights of the candidate networks; and selecting the candidate network to be accessed according to the comprehensive weights. The method and system provided by the invention has the following beneficial effects: 1, compared with a method and system simply adopting a subjective selection algorithm or an objective selection algorithm, the method and system achieves selection of a more reasonable network for access; 2, compared with a heterogeneous network selection algorithm combining other various algorithms, the algorithm provided by the invention achieves a smaller computation amount during a network access selection process; and 3, as the more reasonable network can be selected, the algorithm can achieve lower network expenses, a smaller network load and the like when applied in a heterogeneous network selection process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
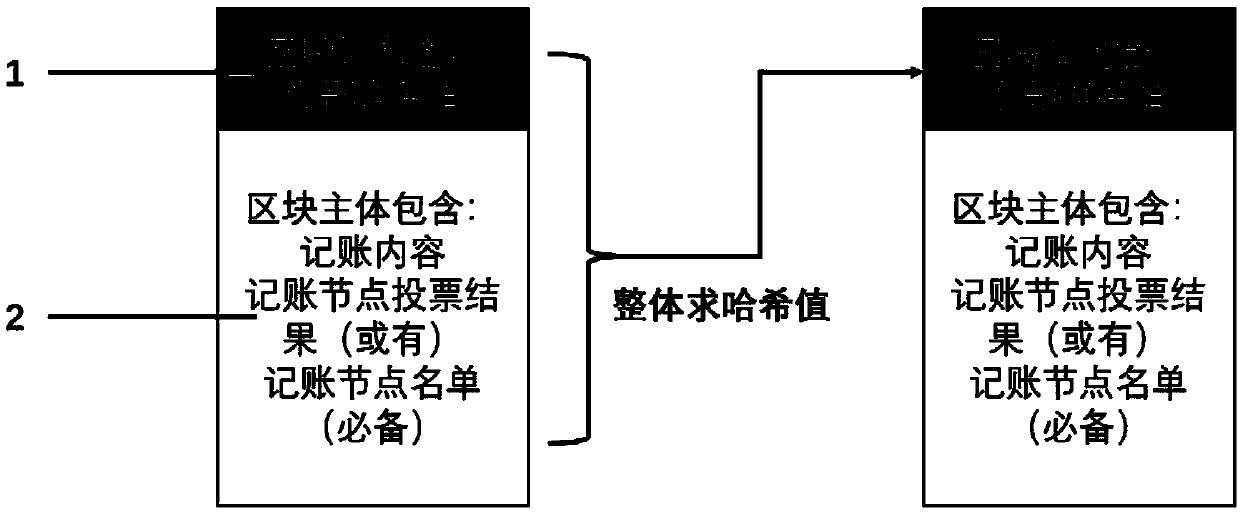
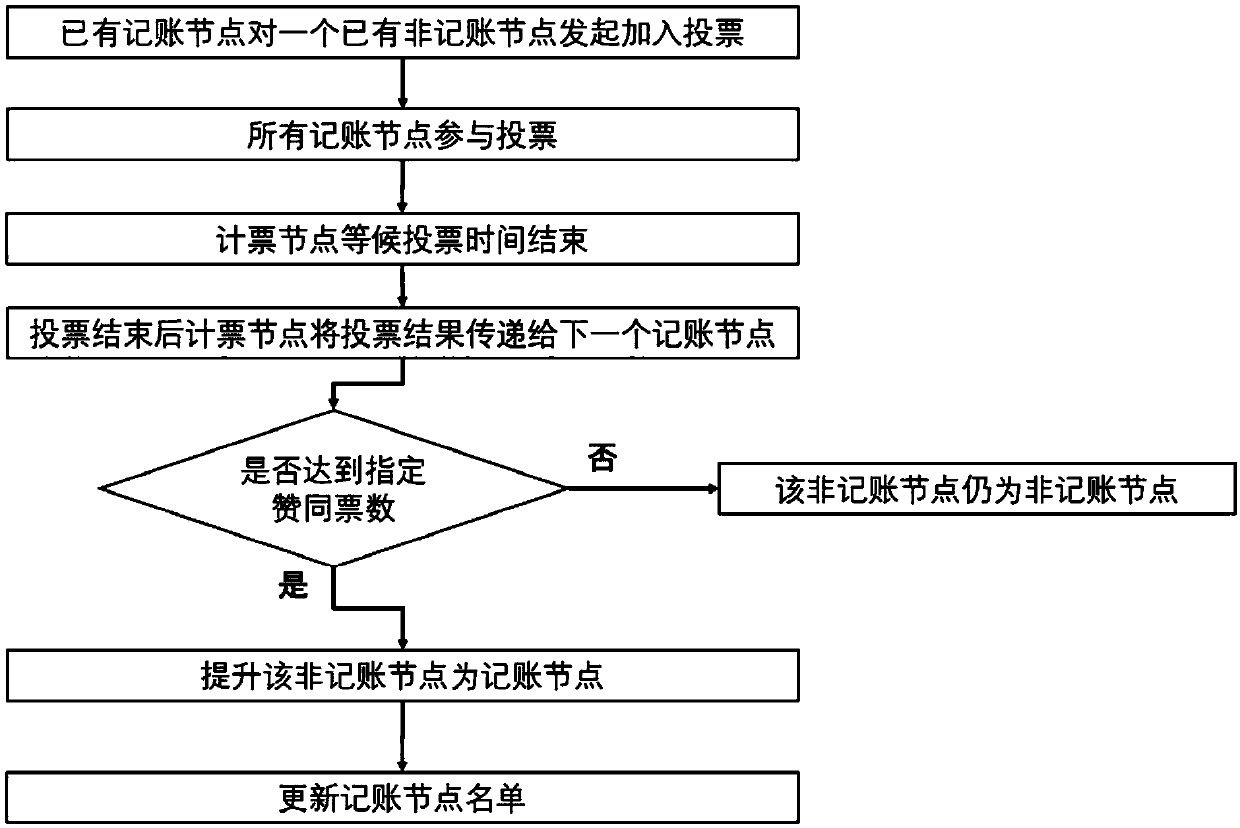
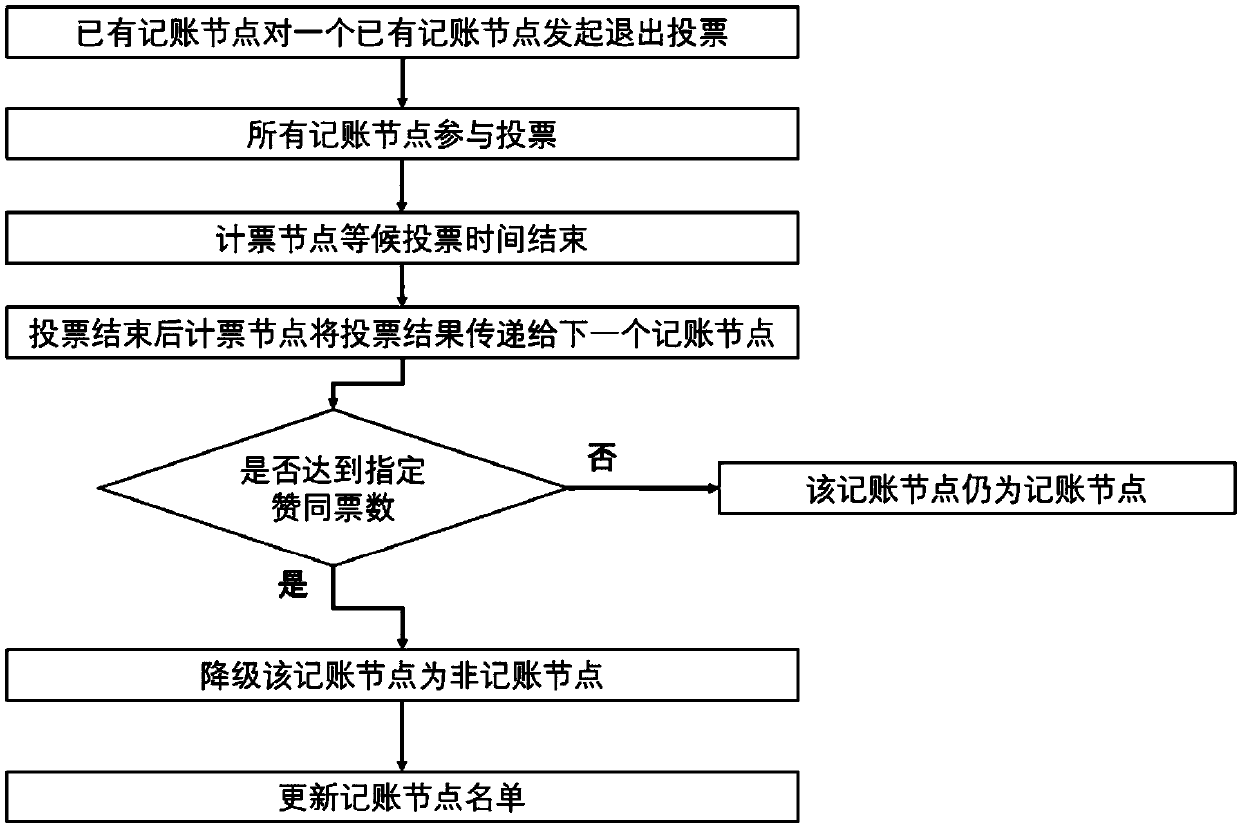
A fast consensus accounting method and a system thereof based on a block chain alliance chain
The invention relates to a fast consensus accounting method and a system thereof based on a block chain alliance chain. At least that method comprise the following step: (1) distinguishing the bookkeeping node from the non-bookkeeping node, wherein the distinguishing the bookkeeping node from the non-bookkeeping node combine the voting method, and the voting time can last for a long time; (2) allbookkeeping node reach a consensus and designate that next bookkeeping node for bookkeeping, A method for combine that next bookkeeping node with the remainder calculation method is specified in the step, and all the bookkeeping node can jointly determine the next bookkeeping node by calculation without communication, thereby reaching a common understanding, and the process of distinguishing the bookkeeping node does not affect the speed of the designated bookkeeping node. The bookkeeping method combines the voting mode to distinguish the bookkeeping nodes, the voting time can last for a longtime, and the bookkeeping nodes can be designated by combining the remainder method, and the process of distinguishing the bookkeeping nodes does not affect the speed of the designated bookkeeping nodes, so that the bookkeeping speed is fast and the efficiency is high.
Owner:孙晞瑜
Two-plane door for refrigerator compartment
ActiveUS20160298895A1Solve the real problemReasonable accessLighting and heating apparatusIce productionRefrigerator carInterior space
In a refrigeration appliance, an enclosure or container defines an enclosed space. A two-plane door forms a portion of the container. The two-plane door opens along one pivot axis and allows access to the enclosed interior space. The container can be a thermally insulated in-door ice compartment of a refrigerated appliance. One example is a bottom freezer style, with the in-door ice compartment in the cold food section of the appliance.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
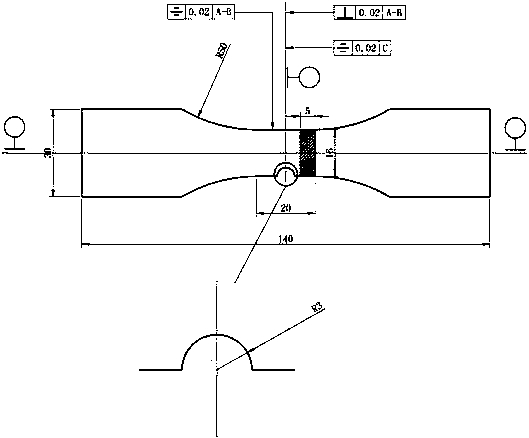
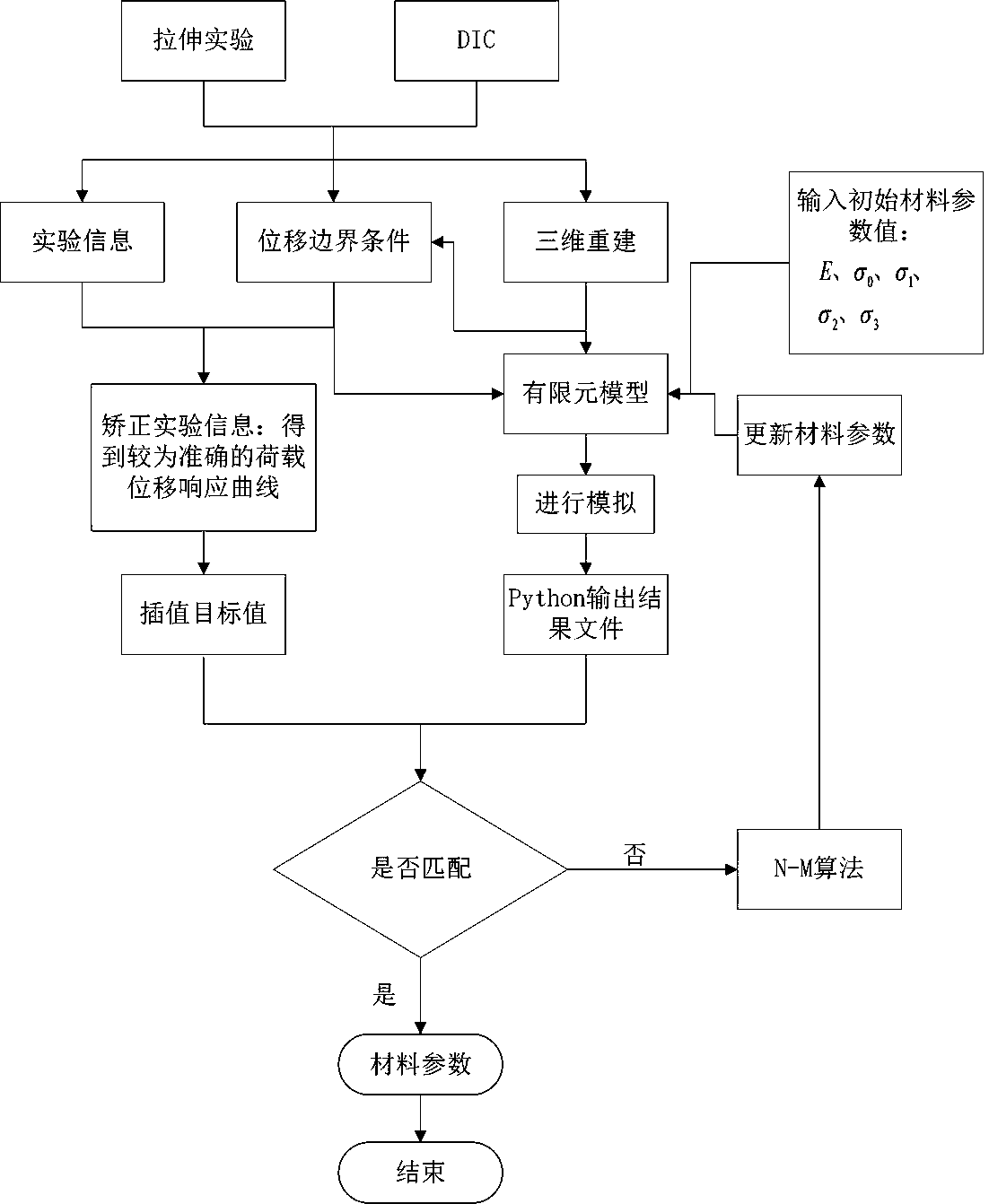
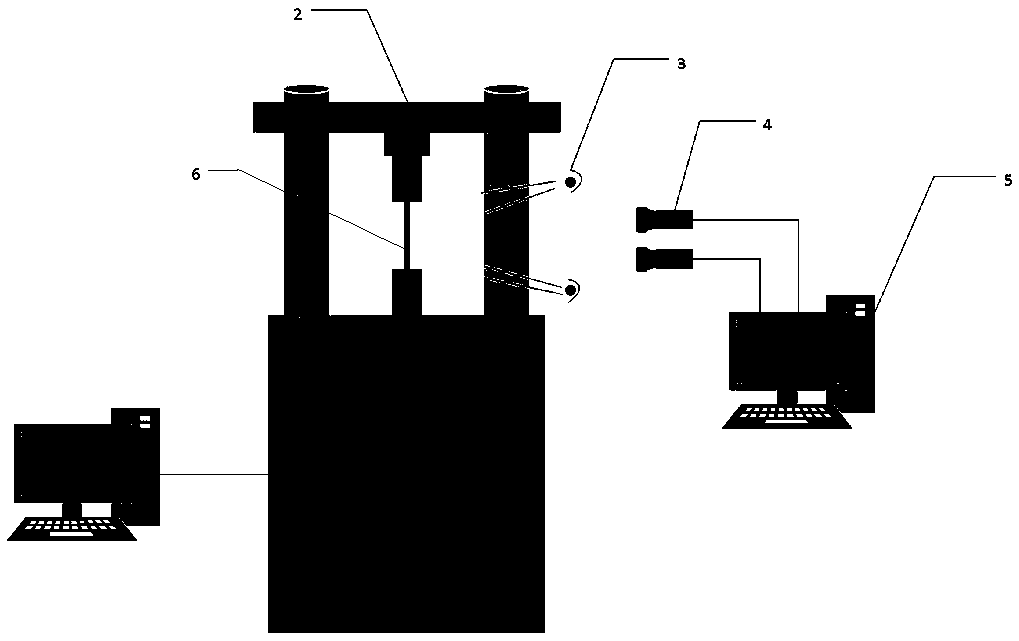
Material parameter acquisition method based on DIC technology
InactiveCN110631906ALow costReasonable accessMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelExtended finite element method
The invention discloses a material parameter acquisition method based on a DIC technology. A unilateral notch tensile experiment is carried out, speckles are sprayed on the surface of a sample, data acquisition is carried out by adopting DIC digital image measurement equipment in the experiment process, a load displacement curve of a material is obtained from a testing machine, the three-dimensional size information is obtained from the DIC, and a finite element model is established; the load displacement curve of the testing machine and a target load displacement response curve are corrected;and the load displacement information is obtained and evaluated. By combining a digital image related method and a finite element method, the material parameters of the sample can be reasonably and accurately obtained. The method is wide in applicability and can be used for metal materials and most non-metal materials. The experiment times can be greatly reduced, and the time is shortened, so that the material cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
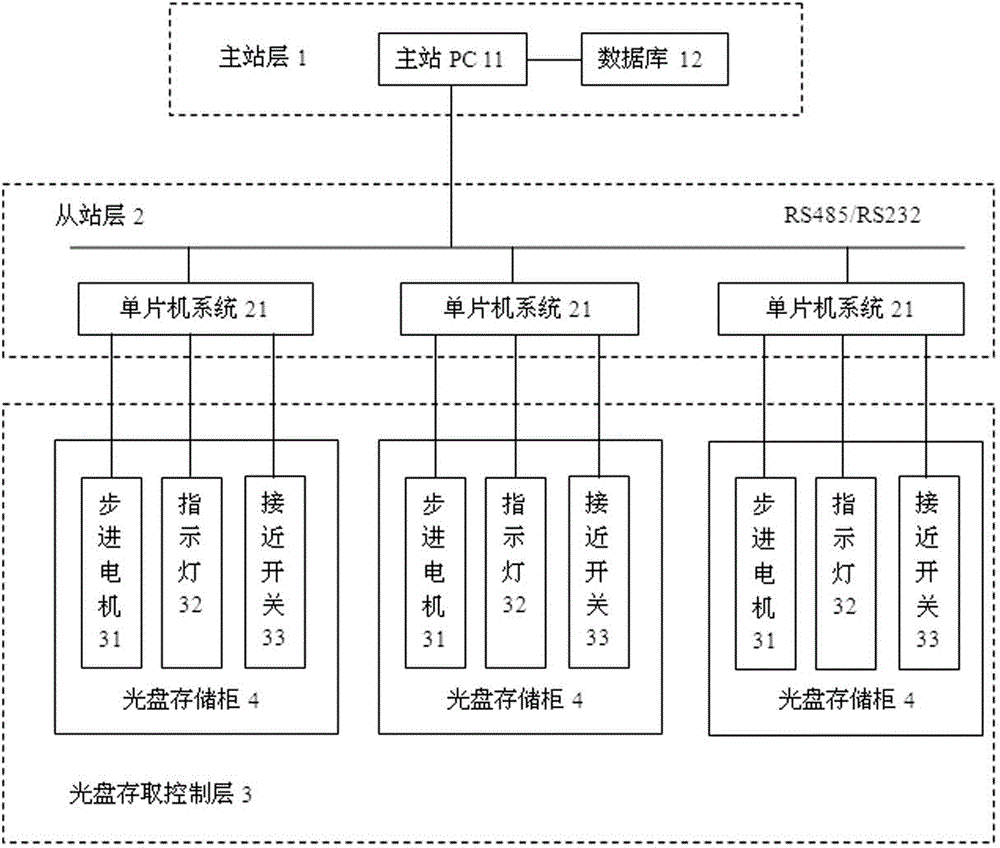
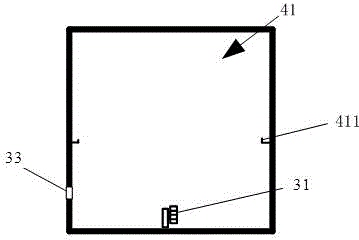
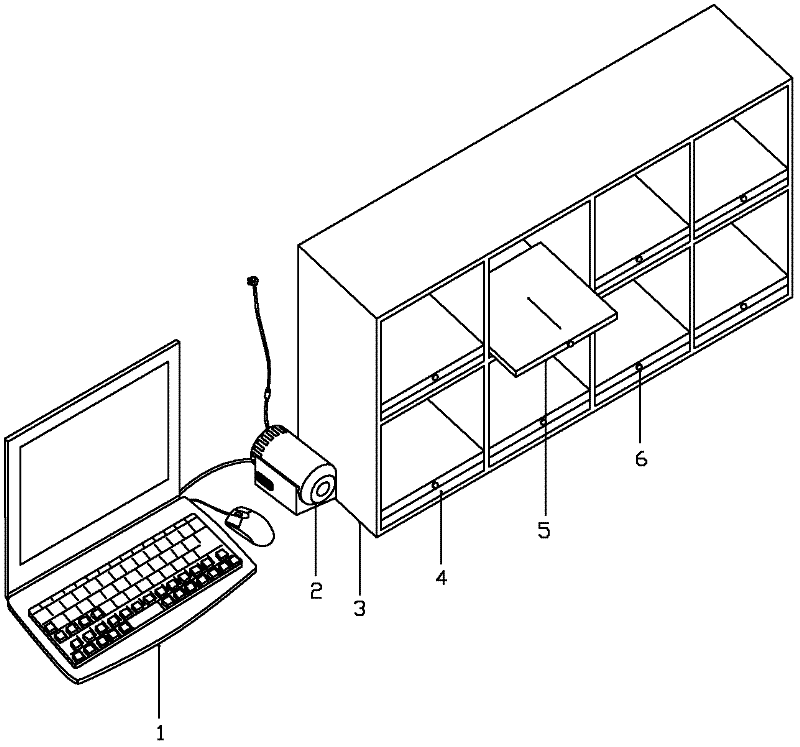
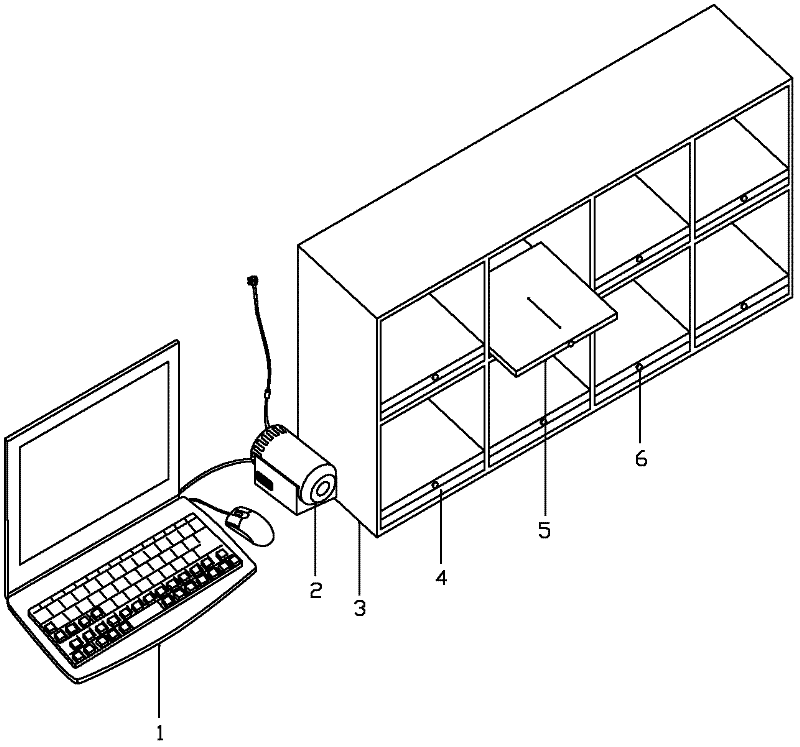
Intelligent access device for optical discs in library
The invention relates to an intelligent access device for optical discs in a library. The device comprises a main station layer, an auxiliary station layer and an optical disc access control layer, wherein the auxiliary station layer is in communication connection with the main station layer, and the optical disc access control layer is in circuit connection with the auxiliary station layer. A main station PC and a database connected with the main station PC are arranged in the main station layer. A plurality of single-chip microcomputer systems are arranged in the auxiliary station layer, and each single-chip microcomputer system is connected with the main station PC through a bus. The optical disc access control layer comprises a plurality of optical disc storage cabinets, and each optical disc storage cabinet is in circuit connection with the corresponding single-chip microcomputer system. According to the intelligent access device for the optical discs in the library, the optical discs in the library can be reasonably stored and can be managed and maintained easily, the workloads of librarians can be reduced, and the device is convenient to use, reliable and high in feasibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Intelligent book management device
The invention relates to an intelligent book management device, mainly solving the problem that books are inconvenient to look up when being stored on the traditional bookshelf. The structure of the intelligent book management device comprises a computer control device, a motor, a bookshelf, sliding rails, brackets and indicator lamps, wherein the bookshelf is of a multilayer multi-lattice frame type, the bottom of each lattice of the bookshelf is provided with the sliding rail, each sliding rail is provided with the bracket used for storing books and reference materials, the outer side of each bracket is provided with the indicator lamp, and the sliding rails, the indicator lamps and the computer control device are respectively connected with the motor. When material is required to be looked up, searching is carried out on related indexing software of a computer, location of the material required to be looked up is displayed on the computer while a taking command is input, the motor acts, the brackets on the sliding rails slide outward when being driven by the motor, and the indicator lamps on the brackets are correspondingly lightened, thus people can conveniently identify and take the material. The intelligent book management device provided by the invention has simple structure and is safe to use; files can be scientifically and reasonably stored, and the material can be conveniently and rapidly looked up.
Owner:徐德钦
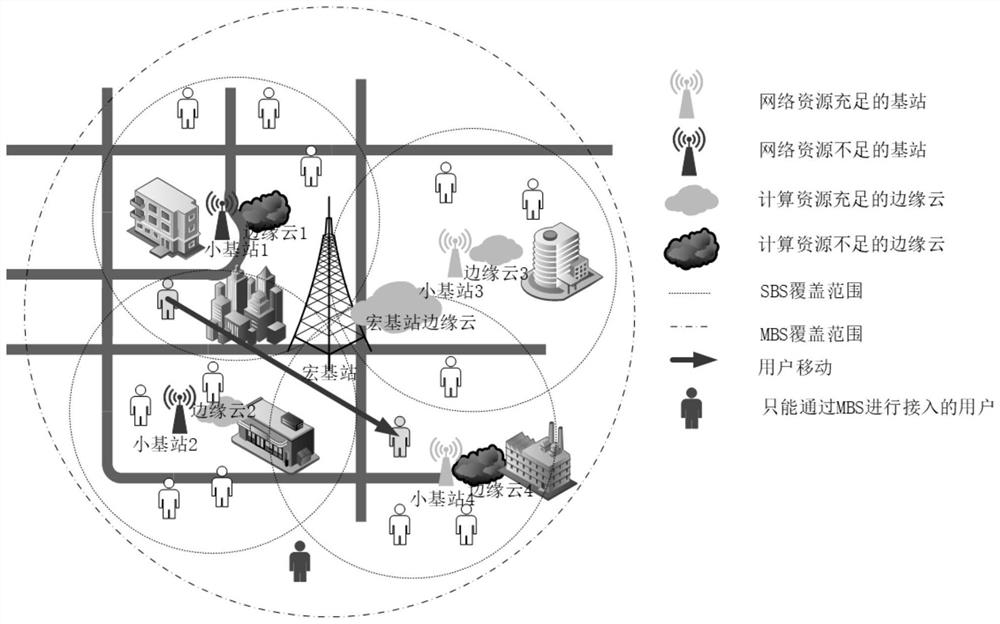
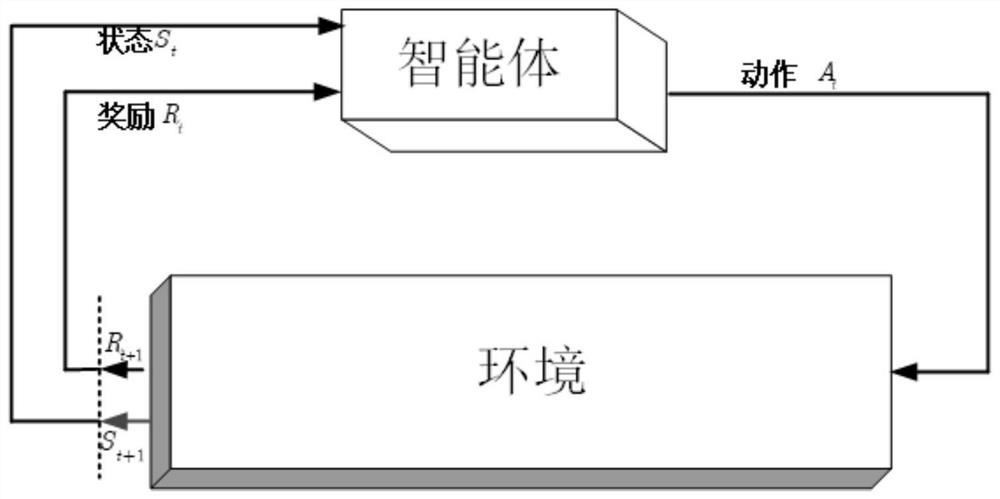
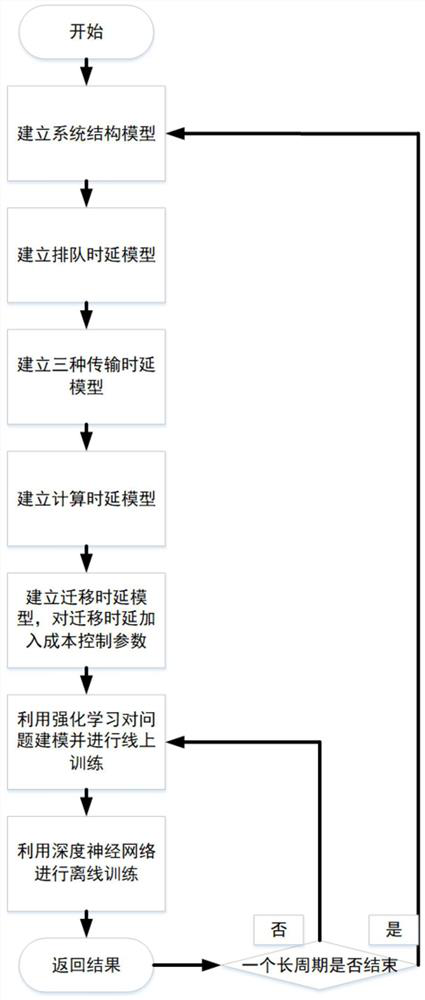
Mobile edge computing service placement strategy based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN113163409AQuality improvementReasonable accessTransmissionNetwork planningMacro base stationsService placement
The invention relates to a mobile edge computing service placement strategy based on artificial intelligence, and the strategy comprises the following steps: carrying out the modeling of a whole network system, and needing to build a macro base station model, a small base station model, and a user model; dividing the delay model of the user into a switching delay model and a non-switching delay model, wherein the non-switching delay model is divided into a queuing delay model, a transmission delay model and a calculation delay model; establishing a queuing model of the user; after the steps are completed, calculating the total delay perceived by the user; and finally, modeling the problem by using a reinforcement learning method, and establishing a state space, an action space, a revenue signal and a Bellman equation, so that the problem can be solved through an algorithm based on artificial intelligence. The mobile edge computing service placement strategy based on artificial intelligence can provide base station selection and service placement decisions, and realizes network selection and service placement decoupling on the basis of controllable cost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
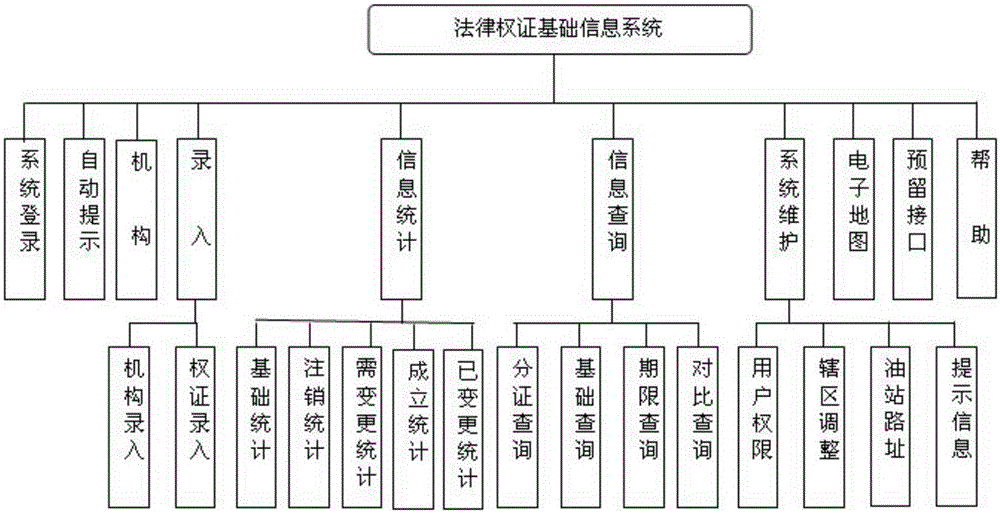
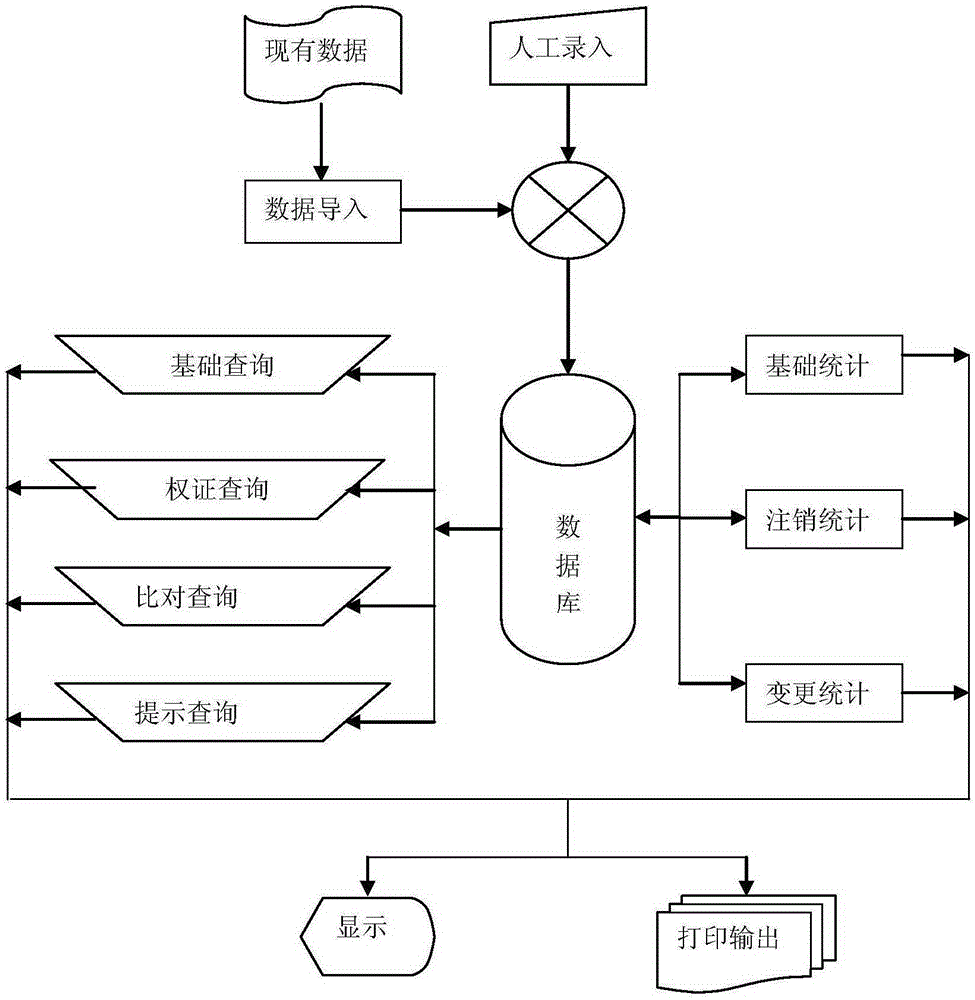
Warrant basic information system
A warrant basic information management system comprises a warrant information data recording module; a system automatic prompting module; an information query module; an information statistics module; a system maintenance module; and an electronic map module. The information data recording module, the information query module, and the information statistics module in the entire system all use a mechanism organization structure of a holding company as an overall framework, and use a mechanism attachment area, a mechanism type, a specific warrant legal document and a duration as main prompting symbols of prompting and supervision; a mechanism is an independent business unit of the holding company; all the modules share one data background to ensure data reliability and uniqueness; a function of the system automatic prompting module is to prompt an expired warrant automatically, and prompting states are divided into three states of red, orange and blue according to an expired time limit; and for all warrants with valid duration, the warrants with valid duration are compared with search dates and should be subjected to list query according to "an expiration in less than one month" and "expired", and a form should contain an item of "expiry date".
Owner:无锡创悟信息科技有限公司
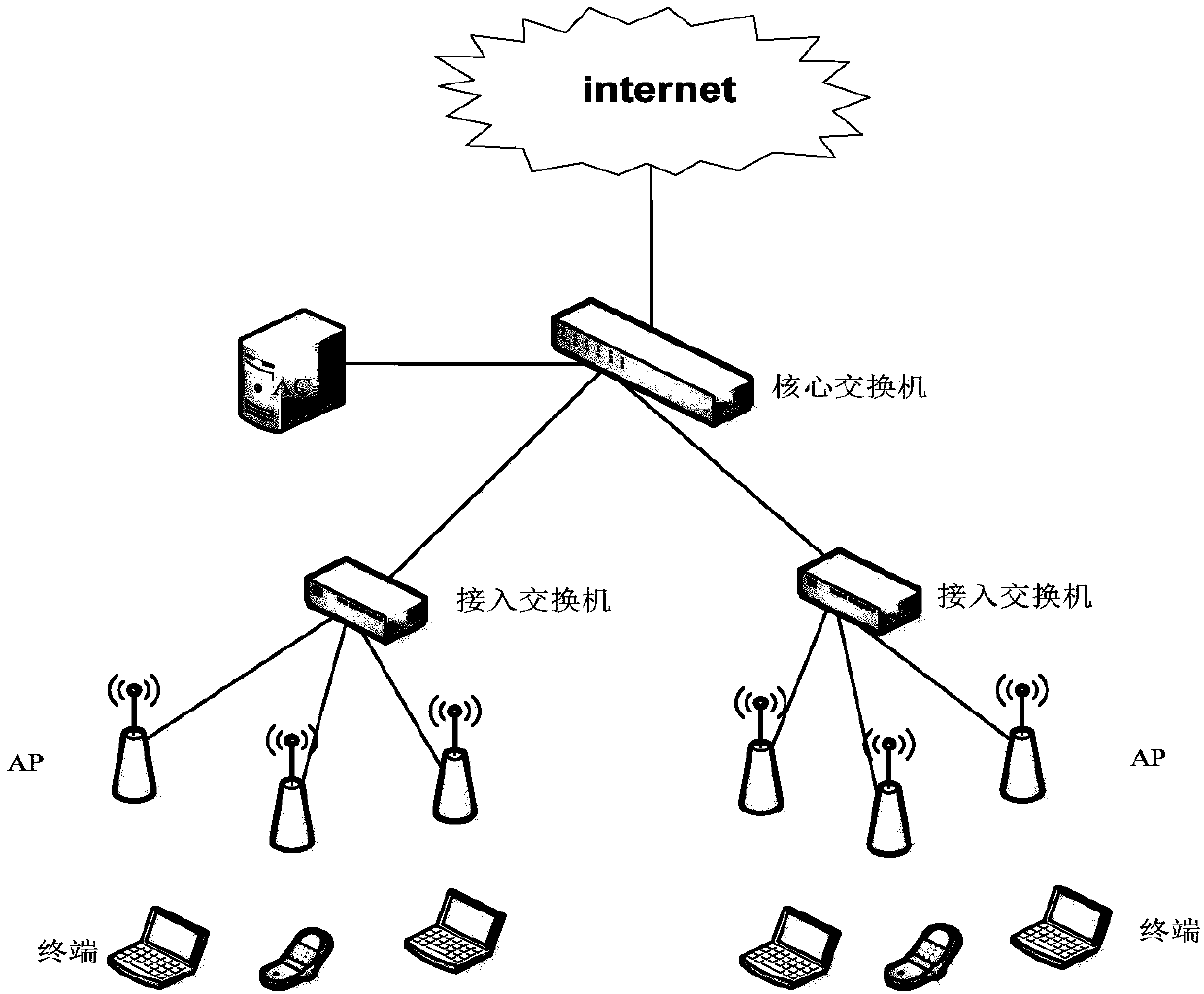
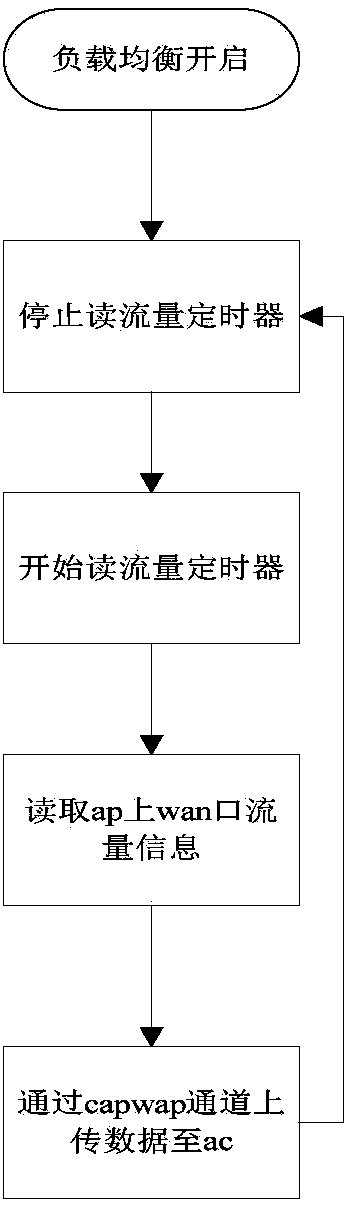
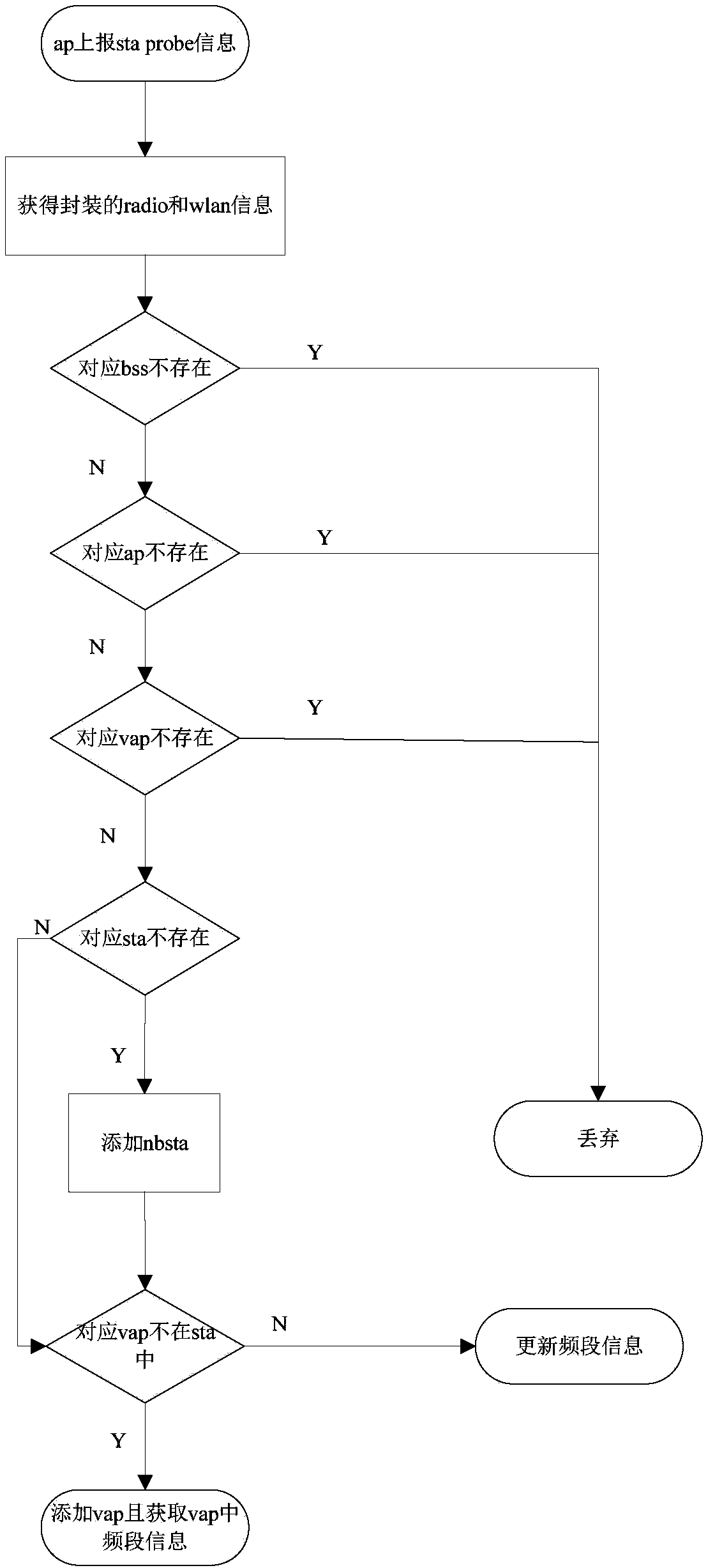
Wireless controller and wireless load balancing method
InactiveCN107567058AFlexible Mode SelectionLoad balancingNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityWireless
The invention discloses a wireless controller and a wireless load balancing method. According to the invention, a wireless controller is configured with relevant load balancing parameters and an AP needing load balancing is bound to a load balancing group configured in an AC; the AC collects a flow, reported by the AP regularly, of a WAN port and a received probe frame; and then the AC searches for an AP with the optimal load based on a configured threshold rule during terminal association. According to the wireless controller and the wireless load balancing method, a load mode is selected flexibly, the optimal-load AP is selected in a visible range of the terminal, and priority access of the 5-G frequency band is taken into consideration during the load balancing process, so that a properAP access is selected for the terminal effectively and a load balancing effect is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAUD DATA COMM
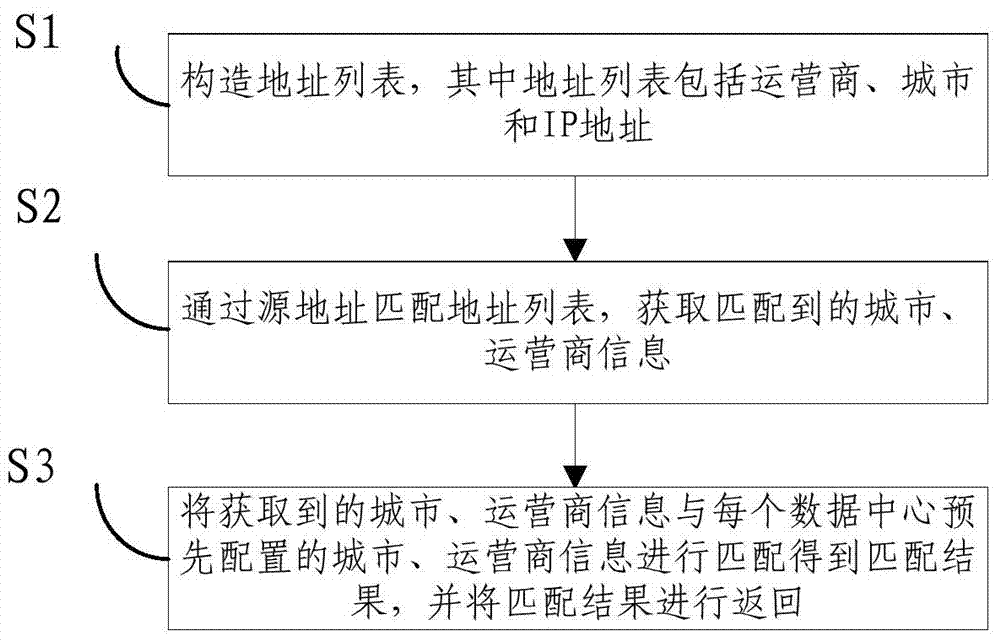
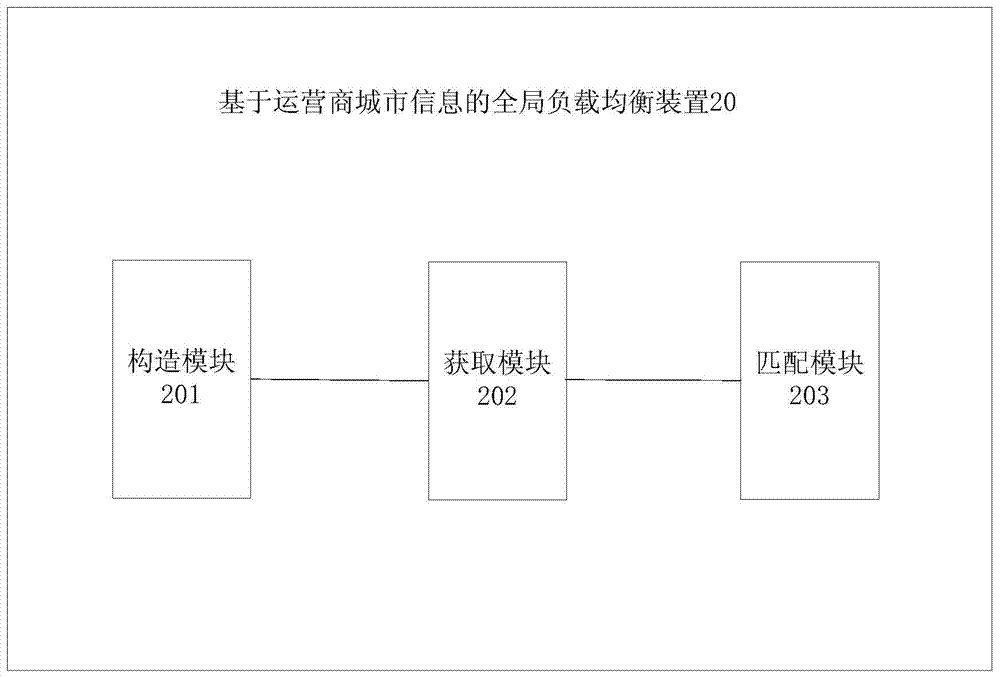
Global load balancing method and device based on operator city information
The invention relates to a global load balancing method based on operator city information. The method particularly comprises the steps of S1, constructing an address list, S2, obtaining matched city and operator information by matching of a source address and the address list, and S3, conducting matching on the obtained city and operator information and city and operator information preset by each data center to obtain a matching result, and returning the matching result. According to the global load balancing method and device based on the operator city information, the corresponding address list among an operator, the city and an IP address section can be constructed, global load balancing equipment conducts scheduling according to the comparison between local configuration information and list layering, and a user have the access to the global resources more rapidly and reasonably. The invention further discloses a global load balancing device based on the operator city information.
Owner:OPZOON TECH
PON system and state updating method thereof
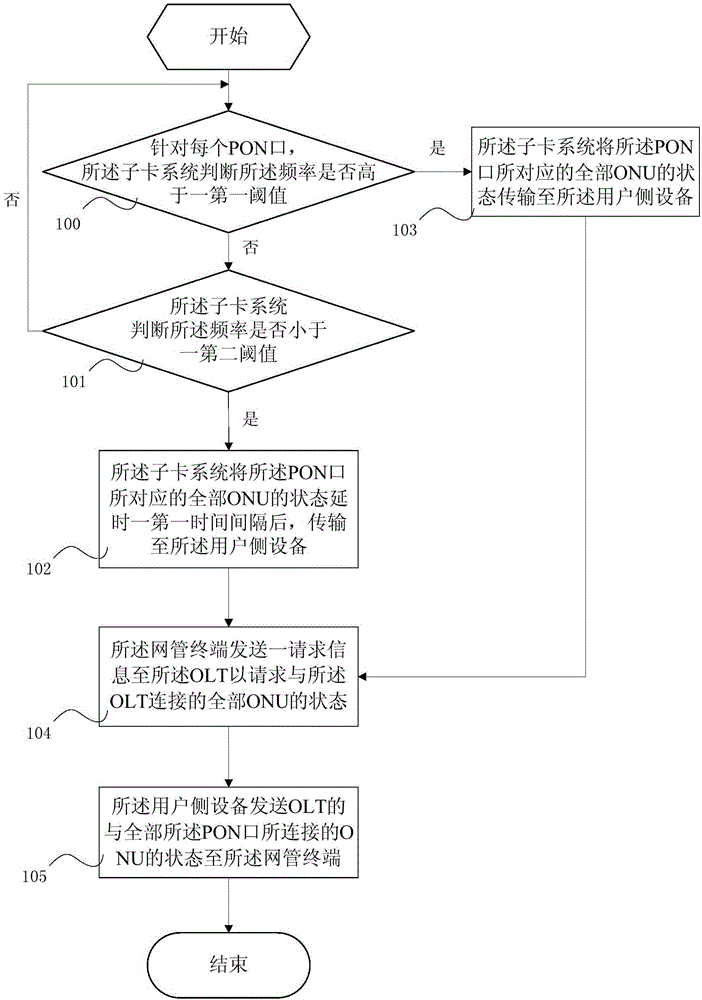
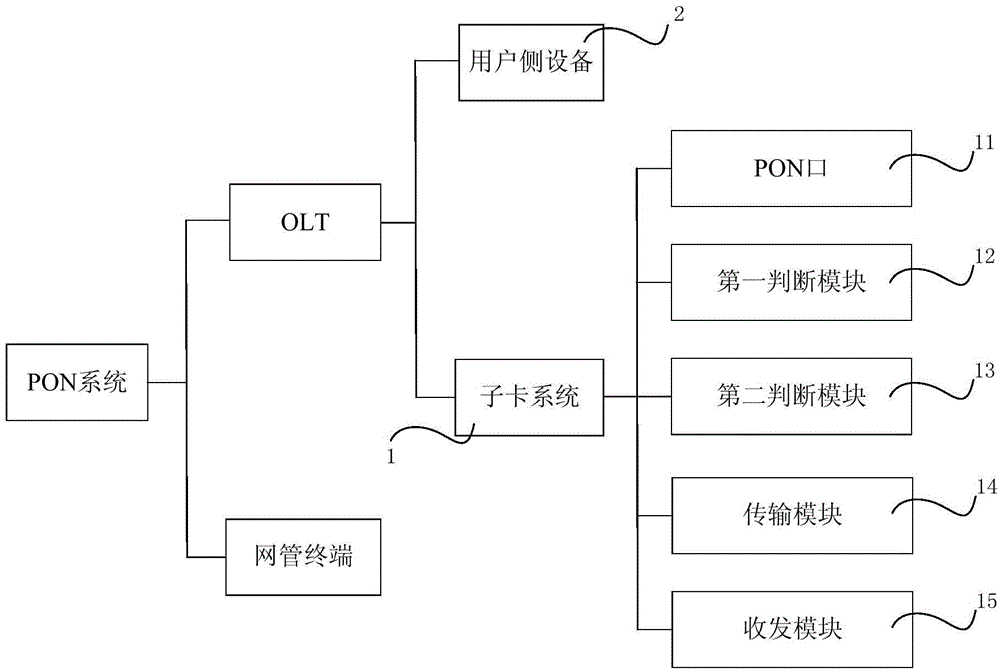
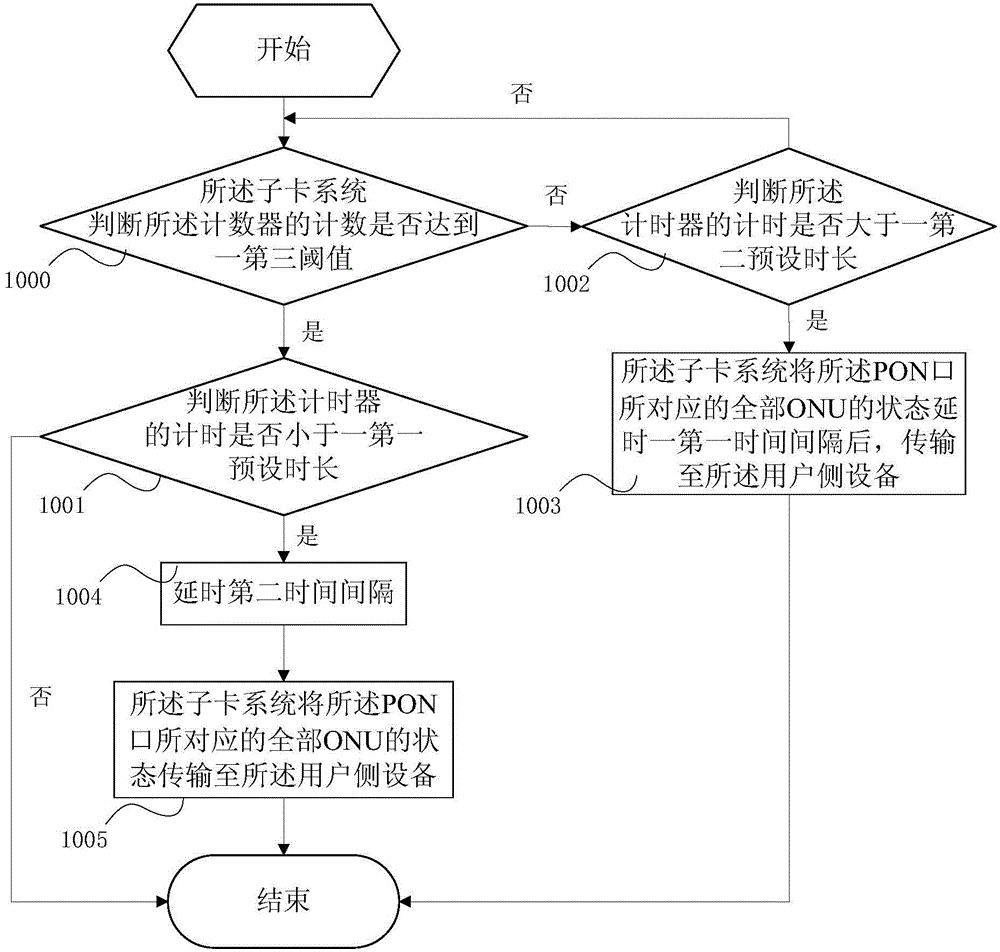
ActiveCN104426684AEasy maintenanceReasonable accessMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksState variationEmbedded system
The invention discloses a PON system and a state updating method thereof. The PON system comprises an OLT. The OLT comprises a piece of user-side equipment and a sub card system. The sub card system comprises a plurality of PON ports of which each is correspondingly connected with a plurality of ONUs. The state updating method comprises the following steps: S1, for each PON port, the sub card system judges whether a frequency is higher than a first threshold, executes the step S2 if the frequency is higher than the first threshold, and executes the step S1 again if the frequency is not higher than the first threshold, wherein the frequency is the frequency of state change of all the ONUs corresponding to the PON port acquired by the sub card system; and S2, the sub card system transmits the states of all the ONUs corresponding to the PON port to the user-side equipment. The internal communication pressure of the OLT of the PON system is small, the performance of the PON system is more stable and reliable, and the user-side equipment can acquire the states of the ONUs more reasonably and accurately.
Owner:宋易霄
Method for calculating oil consumption of vehicle, oil consumption device and oil consumption vehicle
ActiveCN102853872BAccurate displayShow reasonableRelative volume flow measurementsEngineeringIdle speed
The invention provides a method for calculating oil consumption of a vehicle, an oil consumption device and an oil consumption vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a determination result by judging whether actual idling speed time of the vehicle is greater than preset idling speed time or not after an engine is started; calculating idling speed oil consumption information of the vehicle if the determination result is that the actual idling speed time of the vehicle is greater than preset idling speed time; calculating driving oil consumption information of the vehicle if the determination result is that the actual idling speed time of the vehicle is smaller than the preset idling speed time; and respectively displaying the idling speed oil consumption information and the driving oil consumption information which are acquired by virtue of calculation, so that the oil consumption information of the different states of the vehicle is accurately and reasonably acquired.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
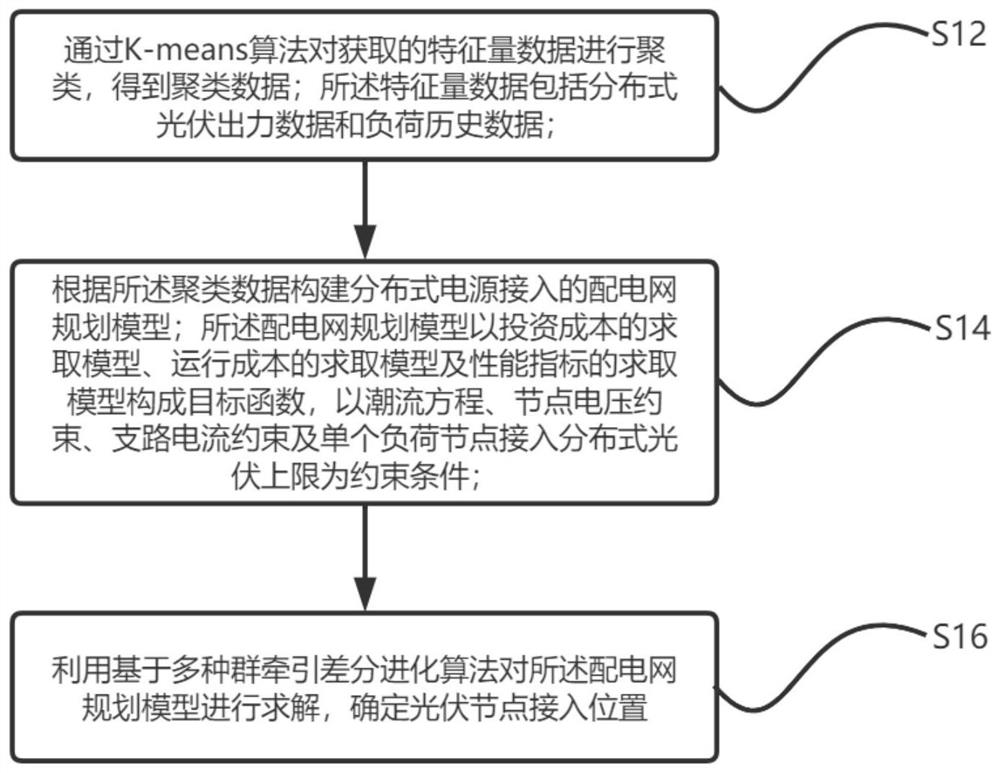
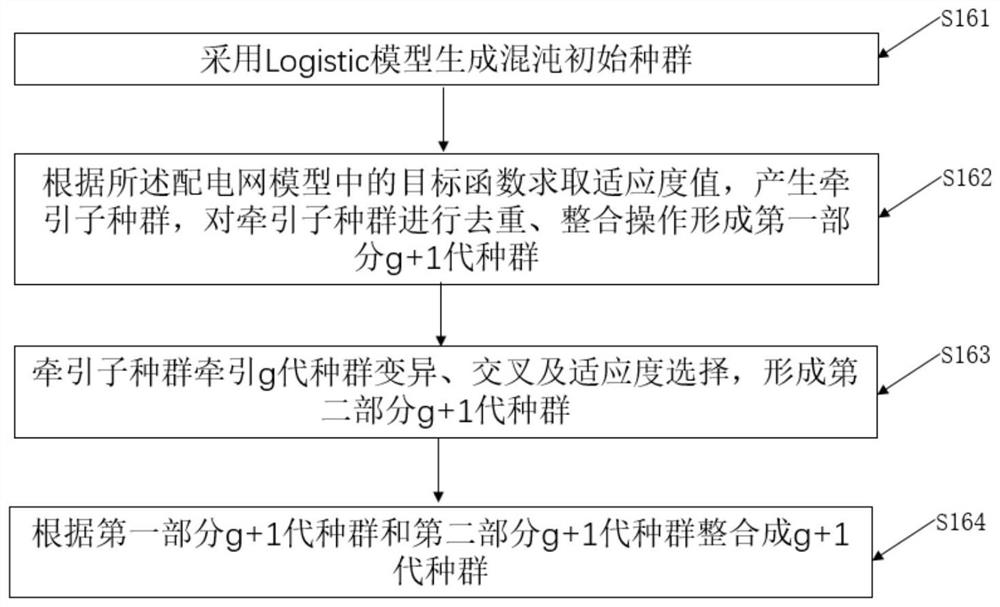
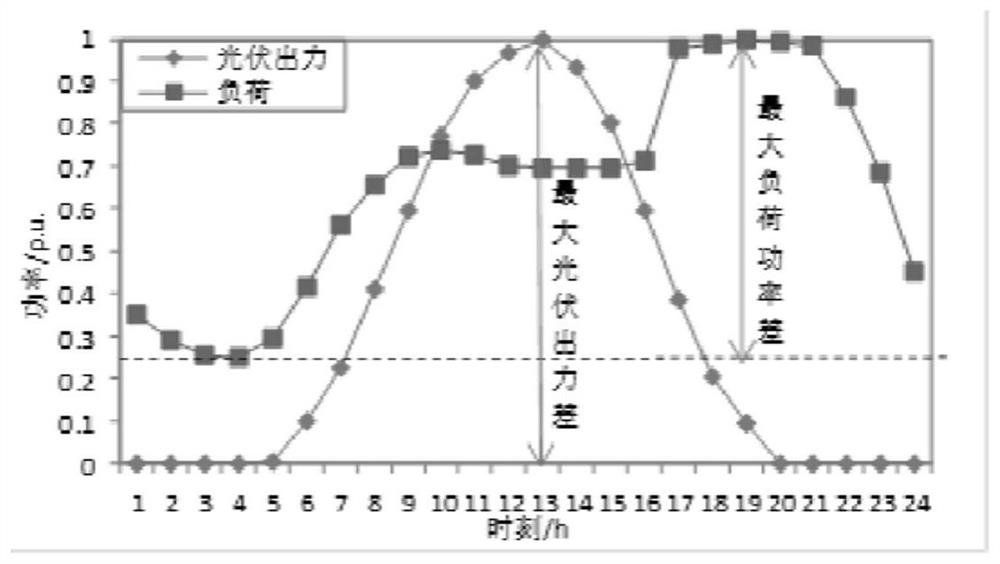
Multi-population traction differential evolution power distribution network planning method and device and storage medium
ActiveCN113222383AIncrease diversityReasonable accessMarket predictionsCharacter and pattern recognitionClustered dataPower flow
The invention discloses a multi-population traction evolution method power distribution network planning method, equipment and a storage medium. Based on a multi-population traction differential evolution algorithm, the method is used for determining access positions of distributed photovoltaic distribution points, and comprises the following steps: clustering acquired characteristic quantity data through a K-means algorithm to obtain clustering data; constructing a power distribution network planning model connected with the distributed power supply according to the clustering data; enabling a calculation model of the investment cost, a calculation model of the operation cost and a calculation model of the performance index of the power distribution network planning model to form a target function, and taking a power flow equation, node voltage constraint, branch current constraint and a single load node access distributed photovoltaic upper limit as constraint conditions; solving the power distribution network planning model based on a multi-population traction differential evolution algorithm, and determining a photovoltaic node access position. By implementing the method, the iteration speed and quality are improved, the diversity of populations adopted in the iteration process is ensured, and more reasonable access of distributed photovoltaic distribution points is ensured.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
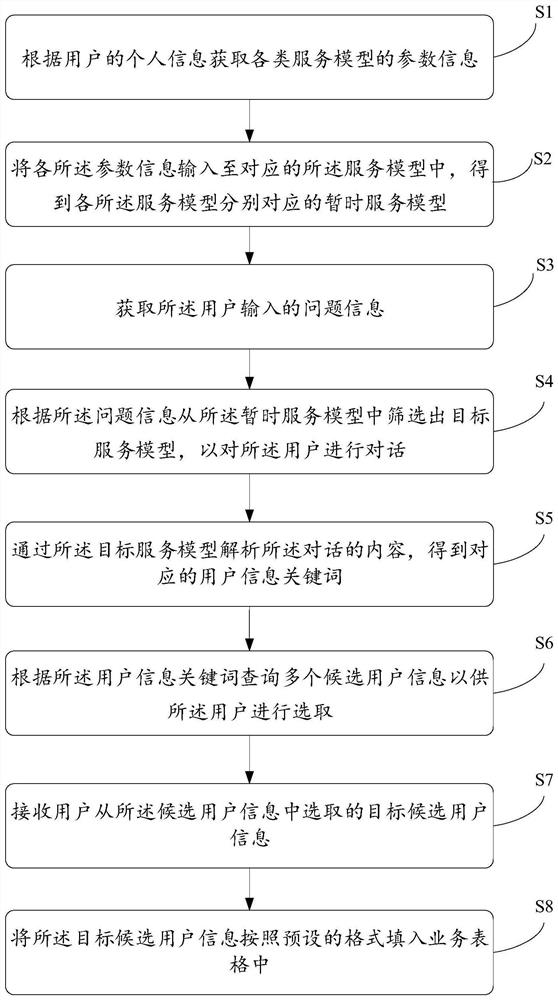
User information filling method and device and computer equipment
PendingCN112579751AReasonable accessFill in correctlySemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionService modelEngineering
The invention provides a user information filling method and device and computer equipment, and the method comprises the steps: screening a target service model according to the personal information of a user, so as to carry out the conversation of the user; and analyzing the content of the dialogue through the target service model, and filling the user information into a service table according to a preset format. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the method selects the proper service model for the dialogue of the user according to the personal information of the user, obtainsthe user information keywords from the dialogue according to the corresponding service model, enables the obtaining of the user information keywords to be more reasonable, obtains the corresponding target candidate user information according to the user information keywords, and converts the user information into a preset format and filling the service table with the user information, thereby correctly and quickly filling the service table with the user information.
Owner:PINGAN PUHUI ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT CO LTD
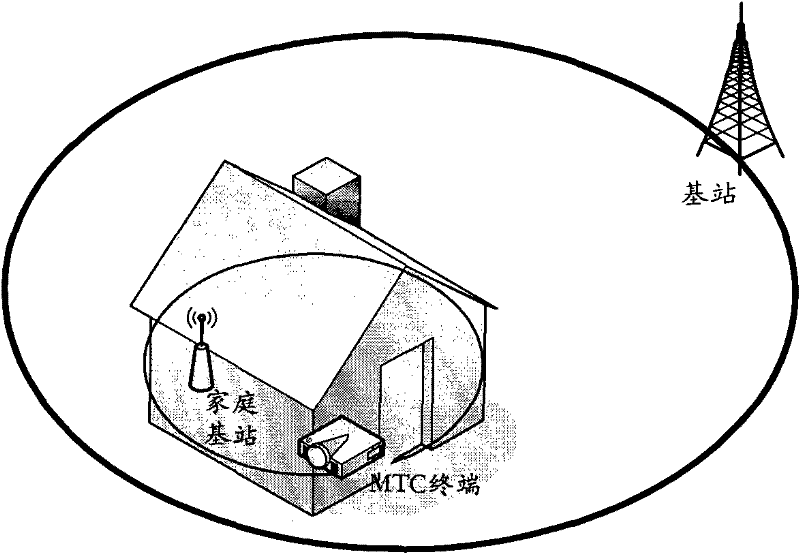
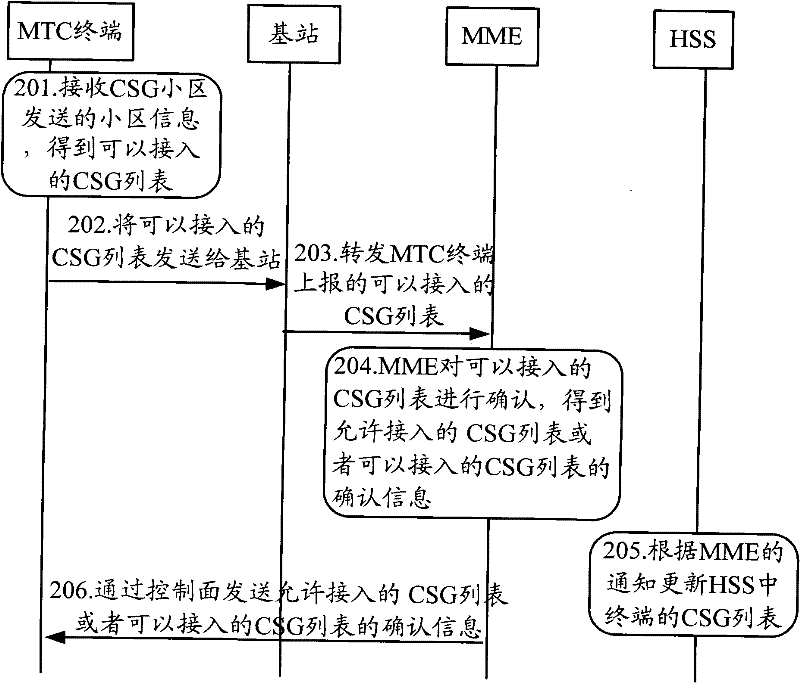
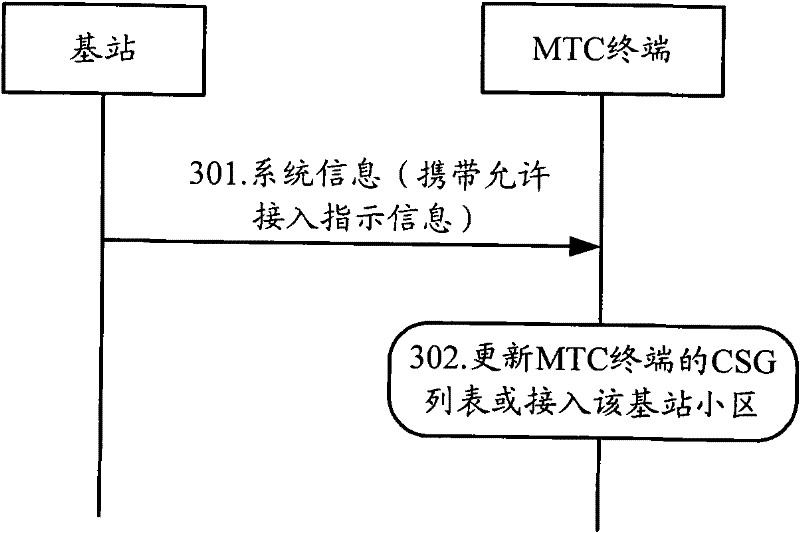
Method and equipment for controlling updating and access of closed subscriber group (CSG) cell information
InactiveCN102685711AReasonable accessImprove utilization efficiencyAssess restrictionConnection managementAccess networkClosed subscriber groups
The invention discloses a method and equipment for controlling updating and access of closed subscriber group (CSG) cell information. The method comprises the following steps that: a terminal receives cell information transmitted by a CSG cell, acquires accessible CSG cell information according to the received cell information, and transmits the accessible CSG cell information to a network side; and the terminal receives CSG cell information which is returned by the network side and allowed to access or confirmation information of the accessible CSG cell information, and the CSG cell information of the terminal is updated according to the CSG cell information which is allowed to access or the confirmation information. The terminal receives the cell information transmitted by the CSG cell, acquires the CSG cell information and transmits the CSG cell information to the network side, and the CSG cell information transmitted by the terminal is determined and informed to the terminal for updating through equipment on the network side, so that the terminal can be ensured to access network resources reasonably, and the utilization efficiency of the network resources is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
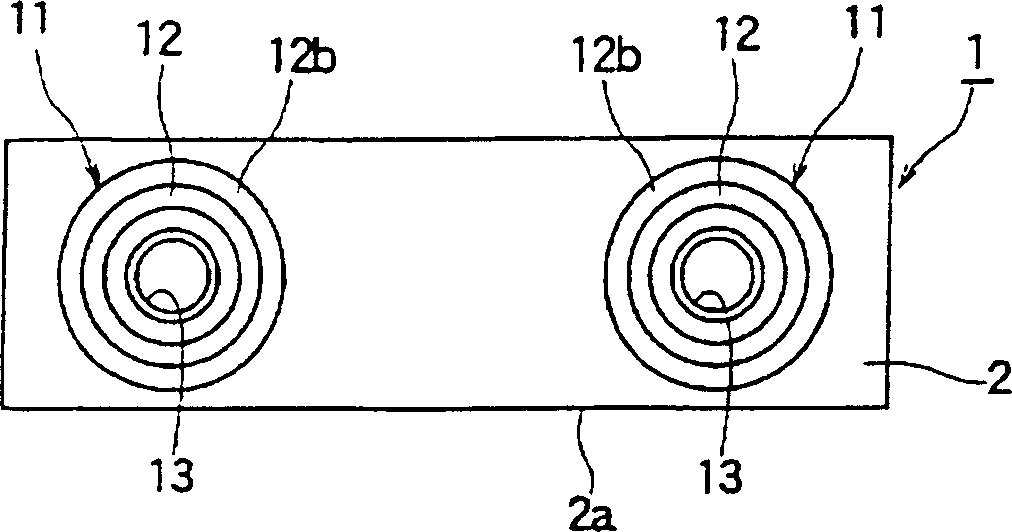
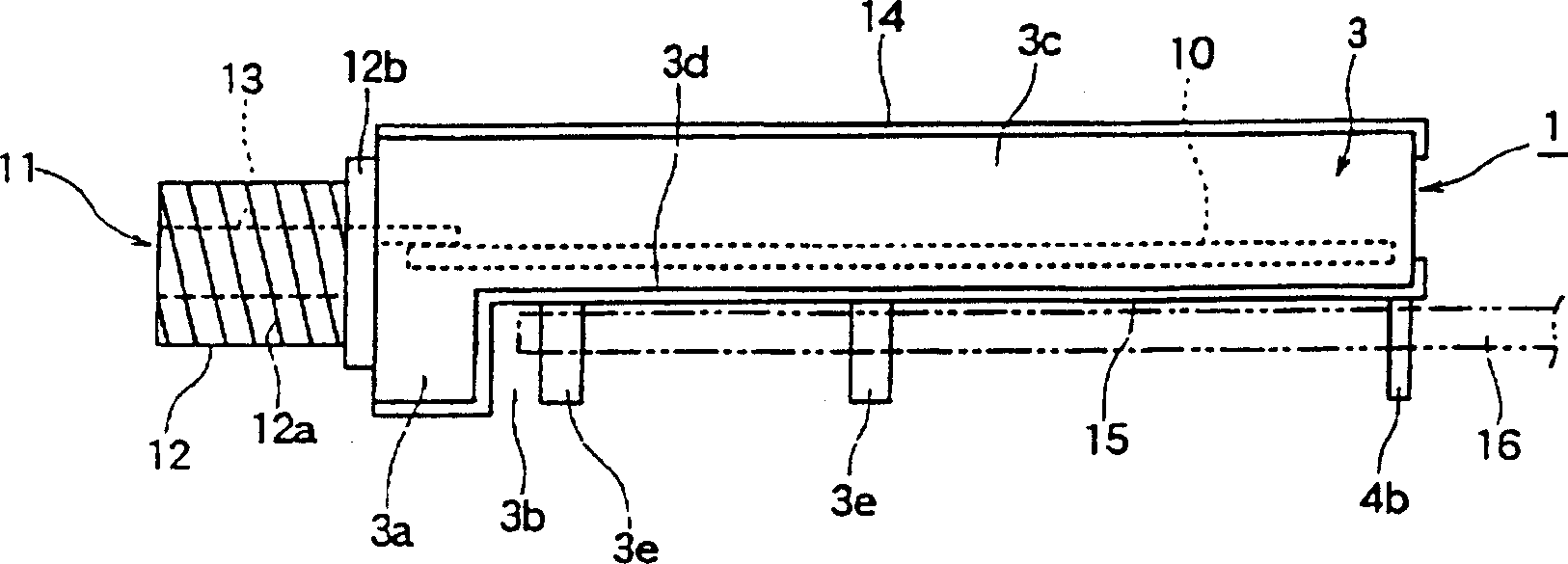
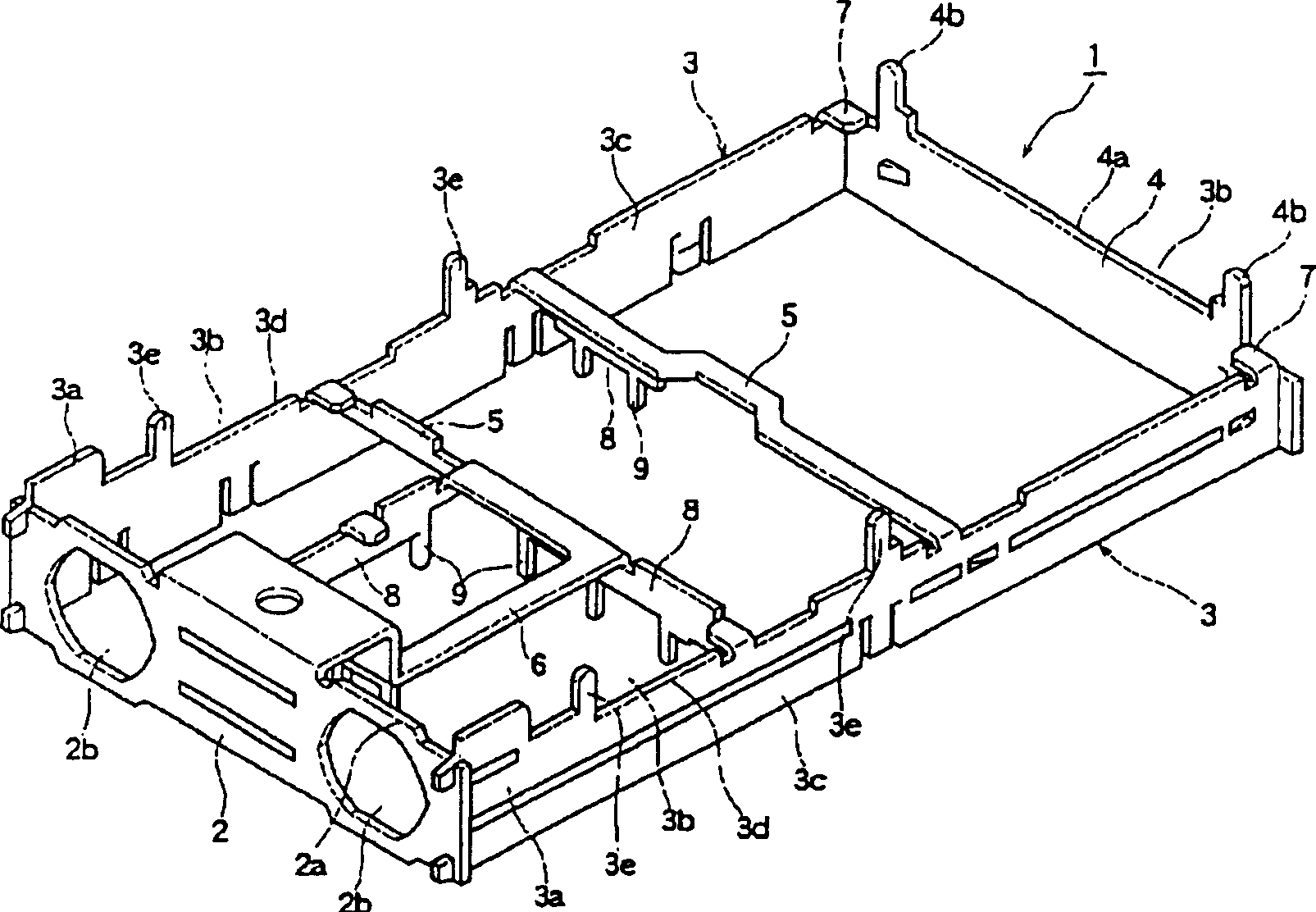
High frequency component and installation structure thereof
InactiveCN1525807AReasonable accessLow priceTelevision system detailsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsEngineeringHigh frequency
Provided is an inexpensive high-frequency unit which can be made small-sized, thin, and lightweight and is efectively using the material and its fitting structure. A frame body 1 has a rectangular front plate 2, a couple of side plates 3 which extend backward from the short side of the front plate 2, and a rear plate 4 which closes the rear side of the couple of side plates 3. The couple of side plates 3 each have a thin-width part 3c which is narrower than the width of the front plate 2 in the height direction and formed over the rear end while having a step 3b with the upper edge or lower edge of the front plate 2 and a fitting leg 3e which extends from one edge 3d of the thin width part 3c toward the step 3b, so the frame body 1 is a rectangular parallelepiped shape formed between a couple of thin parts 3c which are smaller than the front plate 2, and the frame body is made smaller than before and requires less materials to make it lightweight.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
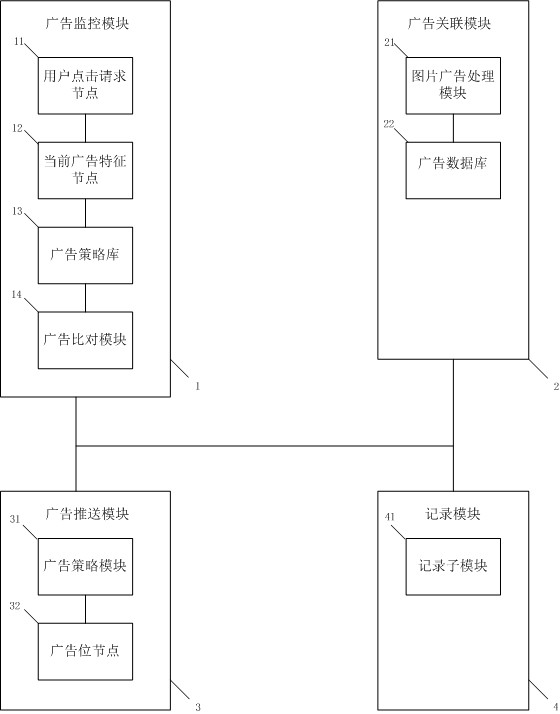
Commercial advertisement redirection system and method
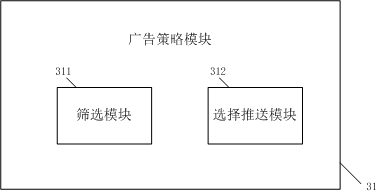
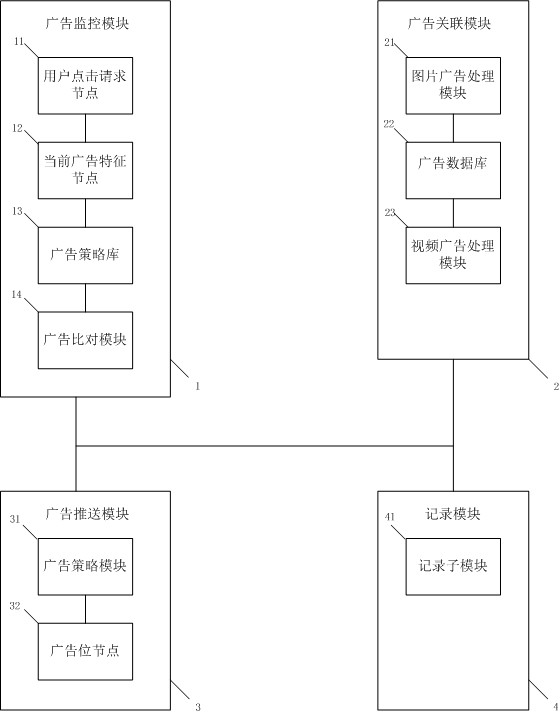
PendingCN111861584AReasonable accessImprove experienceAdvertisementsTransmissionEngineeringData bank
When an advertiser modifies an advertisement delivery strategy, a delivered advertisement needs to be redirected. A commercial advertisement redirection system comprises an advertisement monitoring module, an advertisement association module, an advertisement pushing module and a recording module. The advertisement monitoring module comprises a user click request node, a current advertisement feature node, an advertisement strategy library and an advertisement comparison module. The advertisement association module comprises a picture advertisement processing module and an advertisement database. The advertisement pushing module comprises an advertisement strategy module and an advertisement position node. The recording module comprises a recording sub-module. The system not only reduces the amount of transmitted information and the load of the server, but also ensures the timeliness of advertisement putting.
Owner:上海酷量科技有限公司
Auxiliary archives management device and archives management system with same
PendingCN110179261AEasy to managePrevent theftBook cabinetsPower-operated mechanismEmbedded systemElectricity
The invention provides an auxiliary file management device. The auxiliary file management device comprises a box body, and an emergency driving mechanism containing unit, an inquiry terminal and a power supply body which are arranged in the box body, wherein the emergency driving mechanism containing unit contains an emergency driving mechanism for providing input power for an file cabinet when power failure occurs; the emergency driving mechanism comprises a driving part and a transmission part connected with the driving part; the transmission part is movably connected with a plurality of transmission units of the file cabinet to select files in the file cabinet; the inquiry terminal is in wired or wireless network connection with a file information database of the file cabinet to realizedata transmission and sharing; and the power supply body is electrically connected with the inquiry terminal and the emergency driving mechanism. The design of the whole device is reasonable and theauxiliary file management device is easy to operate; and when the power failure occurs, the emergency driving mechanism is used for lifting and lowering of a cabinet door and selection and preservation of files, so that the problems of file theft caused by the failure to take out the files or the failure to close the file cabinet door during the power failure are solved, and the management of files is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU XUNJIE HARNESS TECH
Networking reminding method, device, terminal and readable medium for smart socket
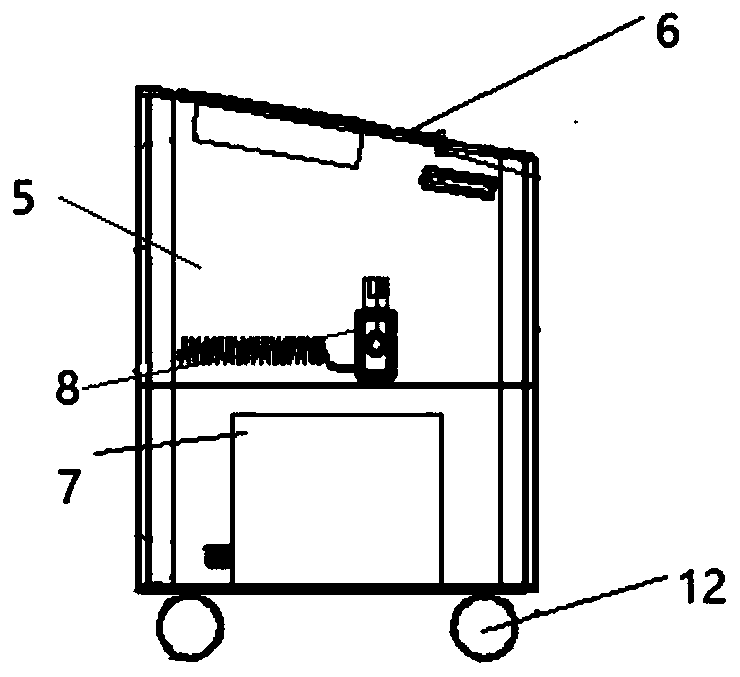
ActiveCN109061287ARealization of network reminderImprove securityElectrical measurementsHome automation networksComputer terminalElectrical equipment
Owner:昆山品源知识产权运营科技有限公司
Prompt method and device for smart socket and smart socket
InactiveCN108919635ARealize smart reminderImprove securityCoupling device detailsElement comparisonEmbedded systemElectrical equipment
Owner:昆山品源知识产权运营科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com