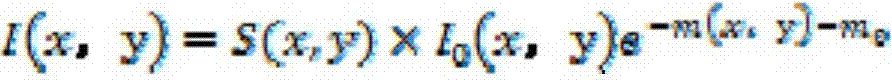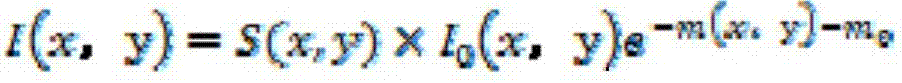Patents
Literature
161 results about "Bones parts" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
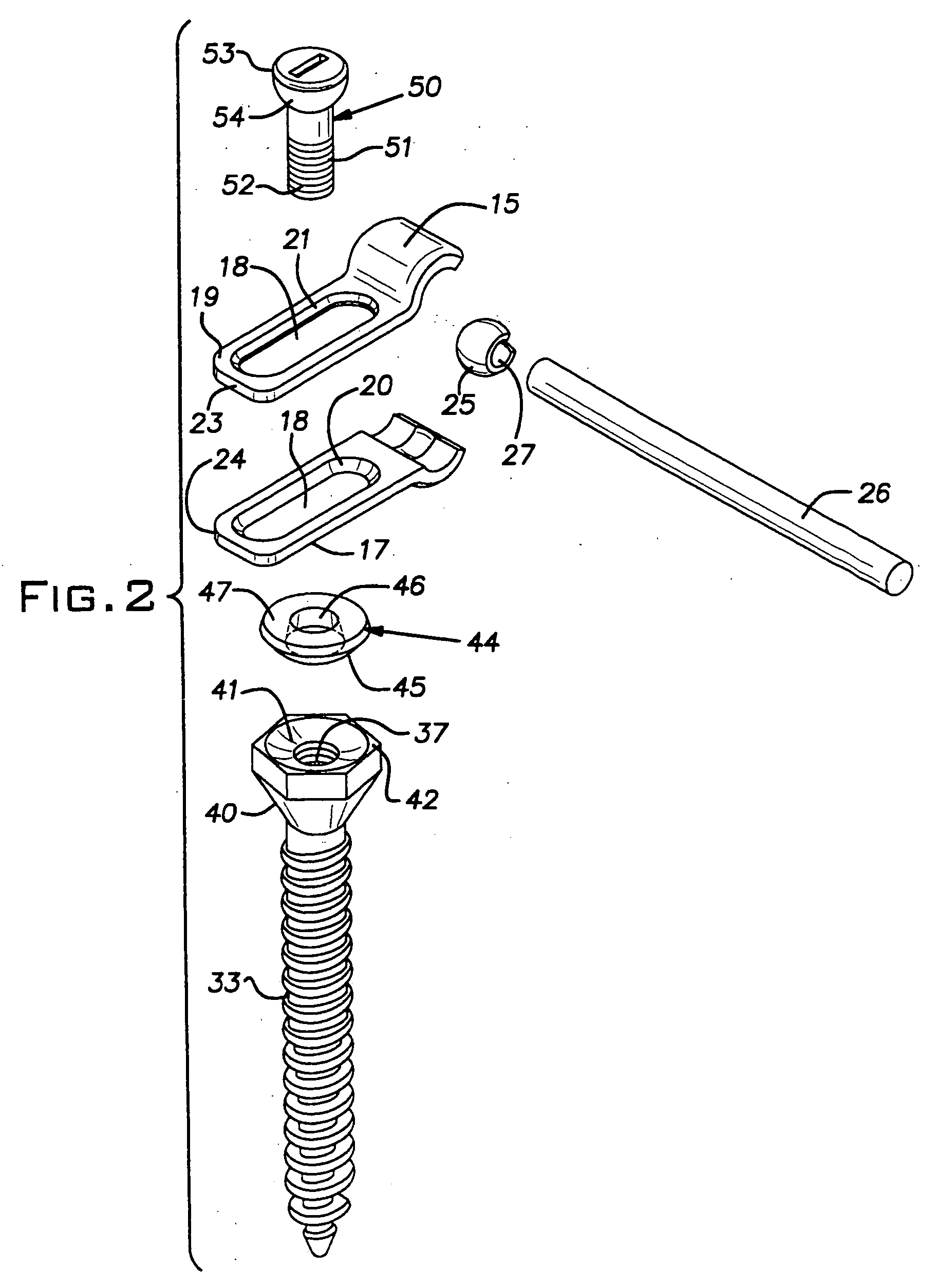
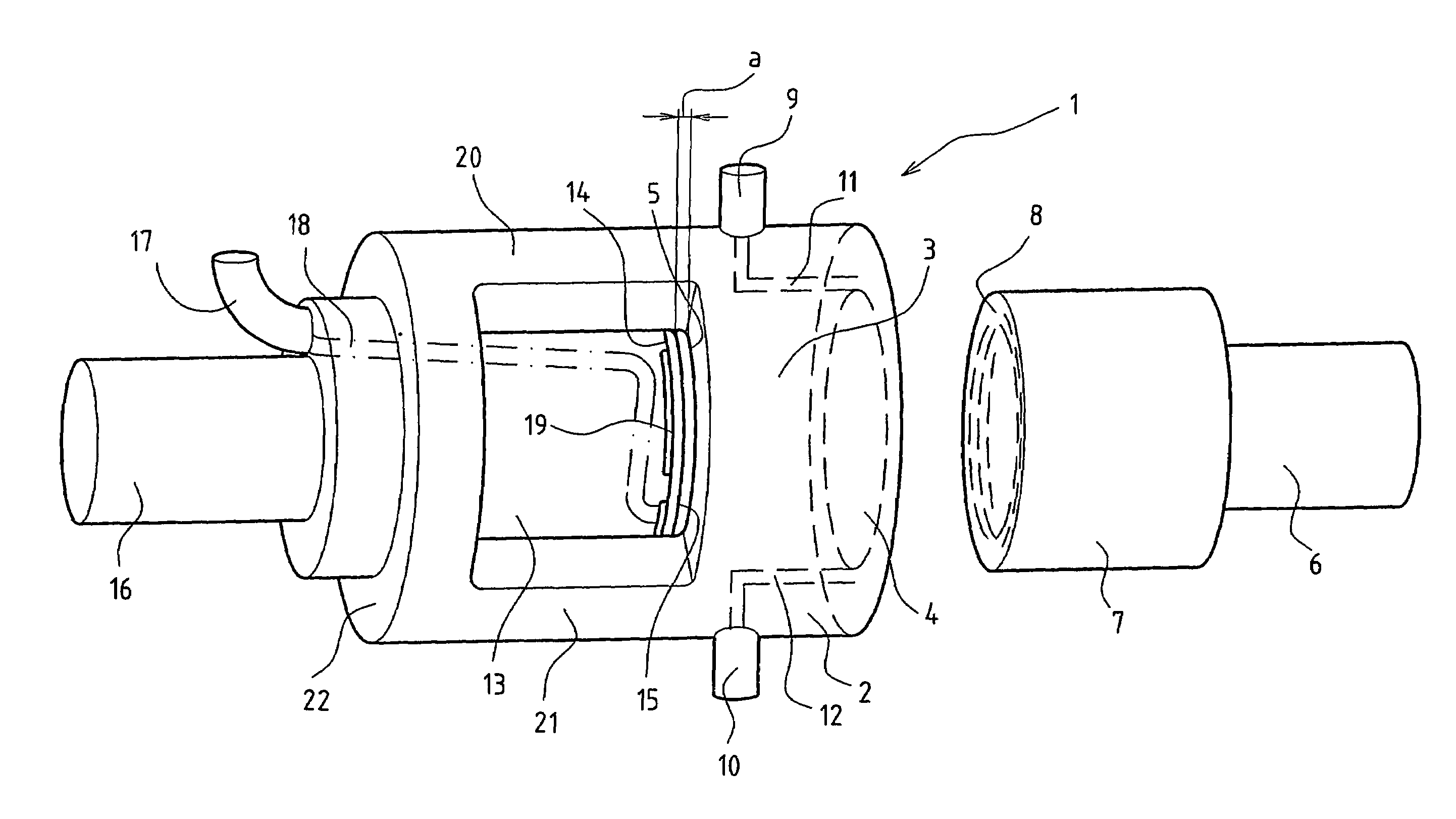
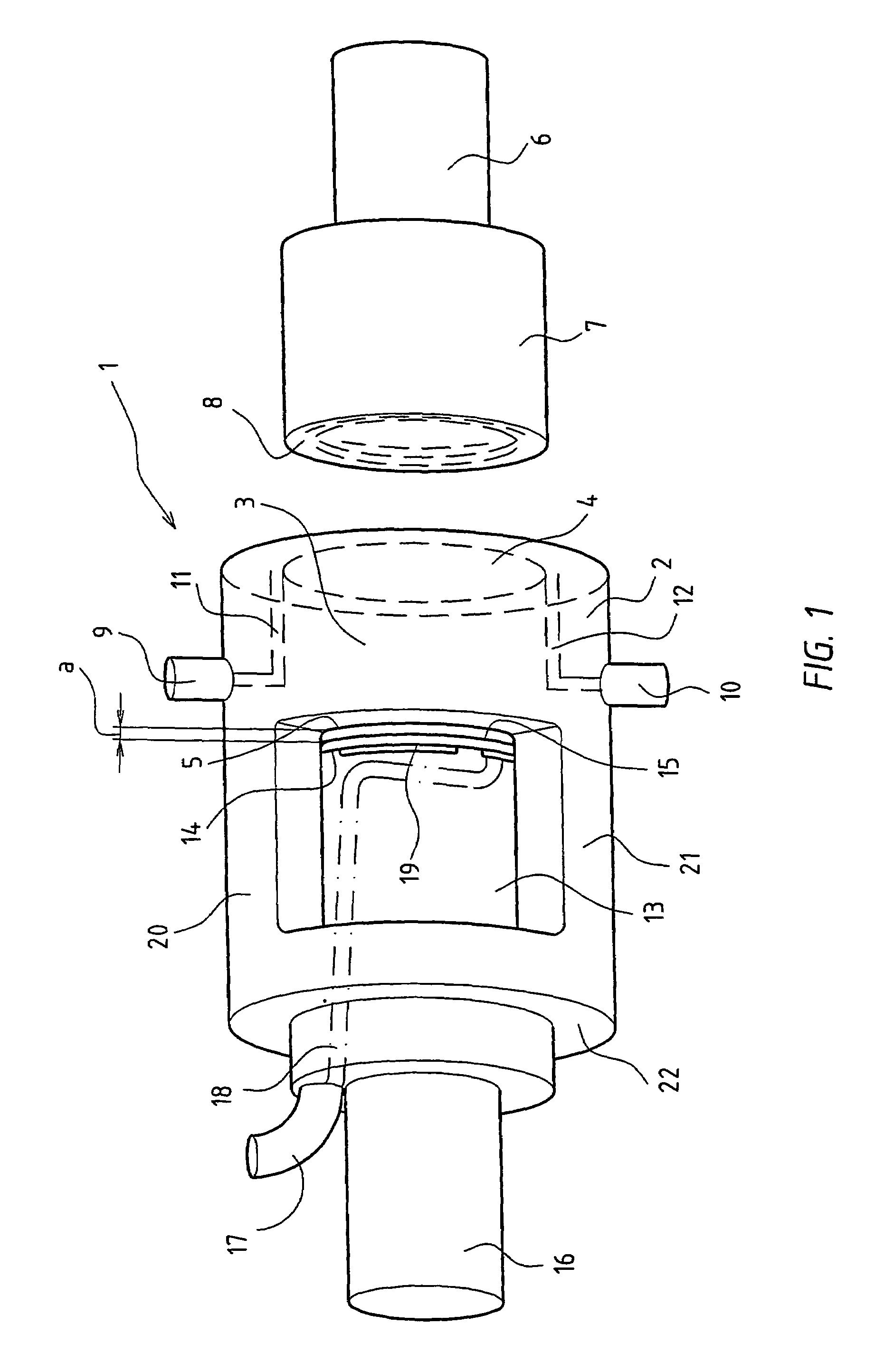
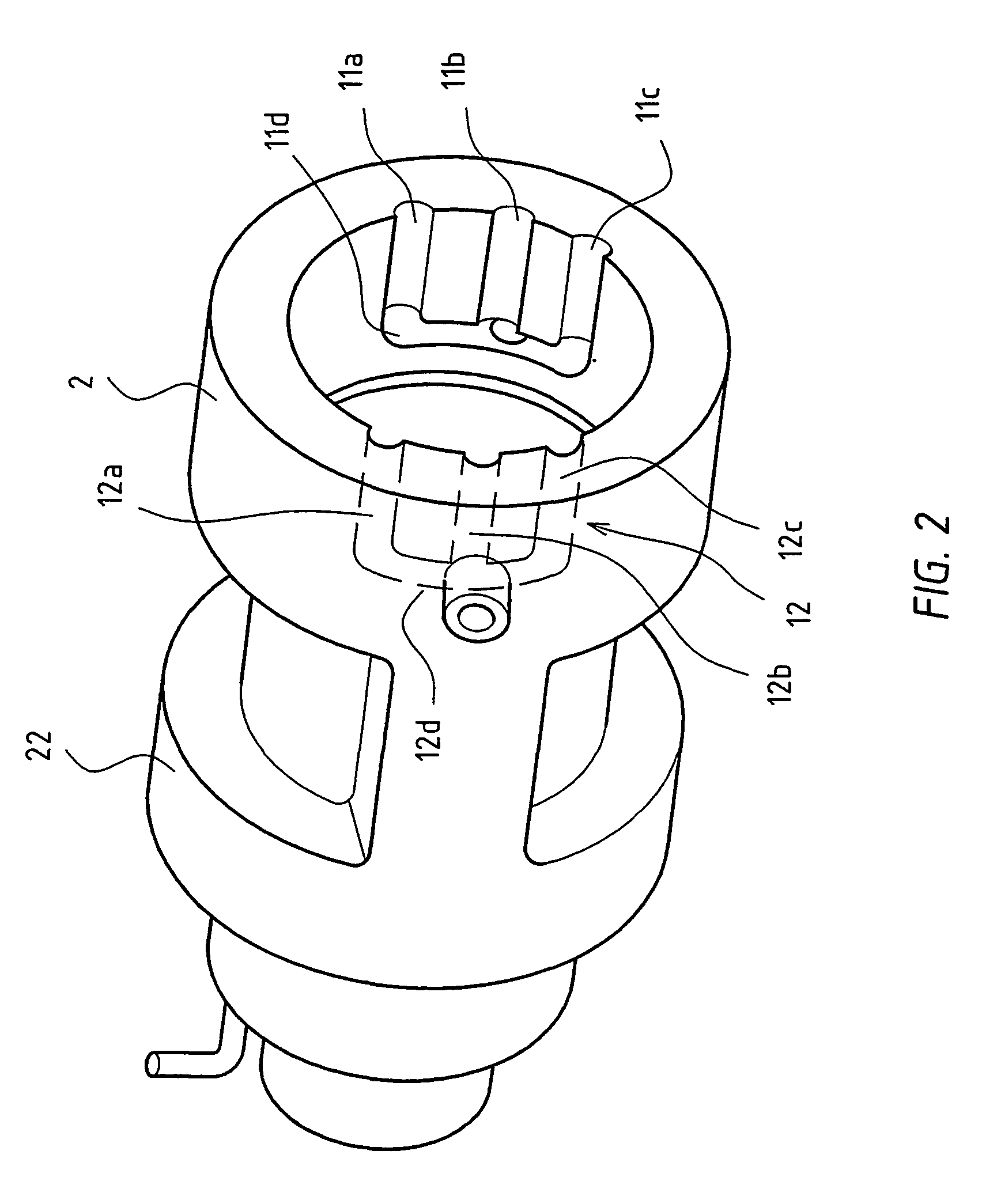
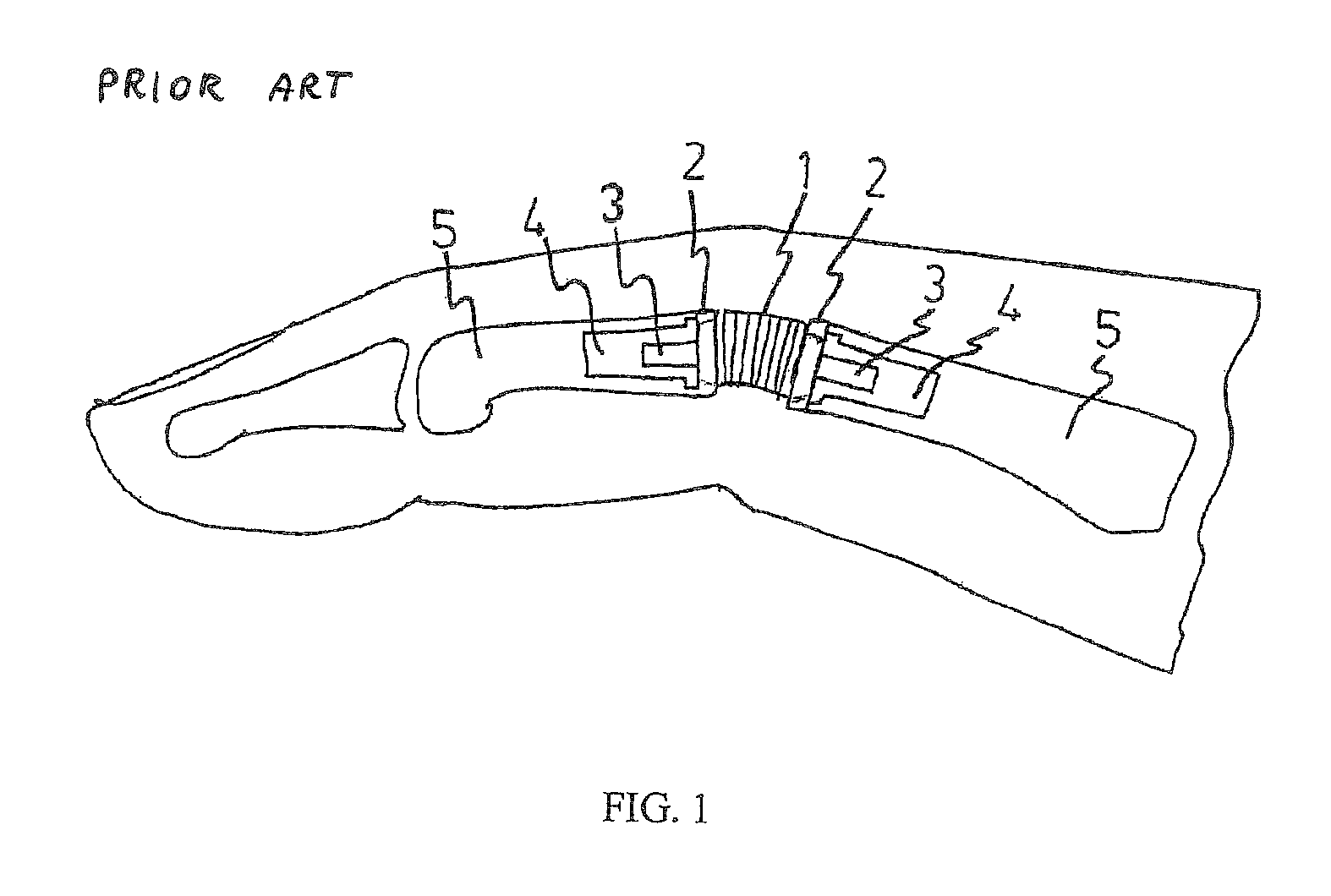
Bone plate with complex, adjacent holes joined by a bend relief zone
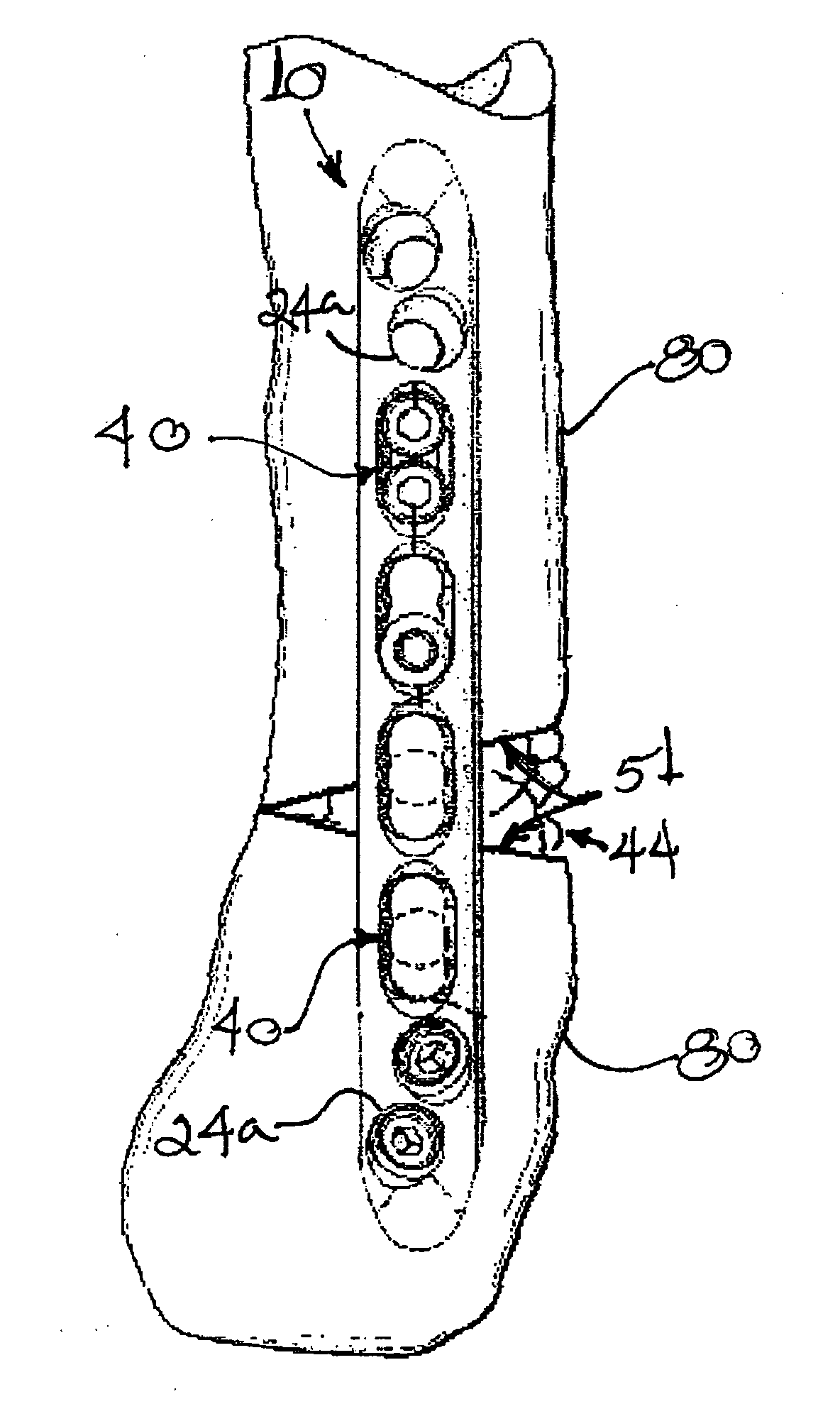
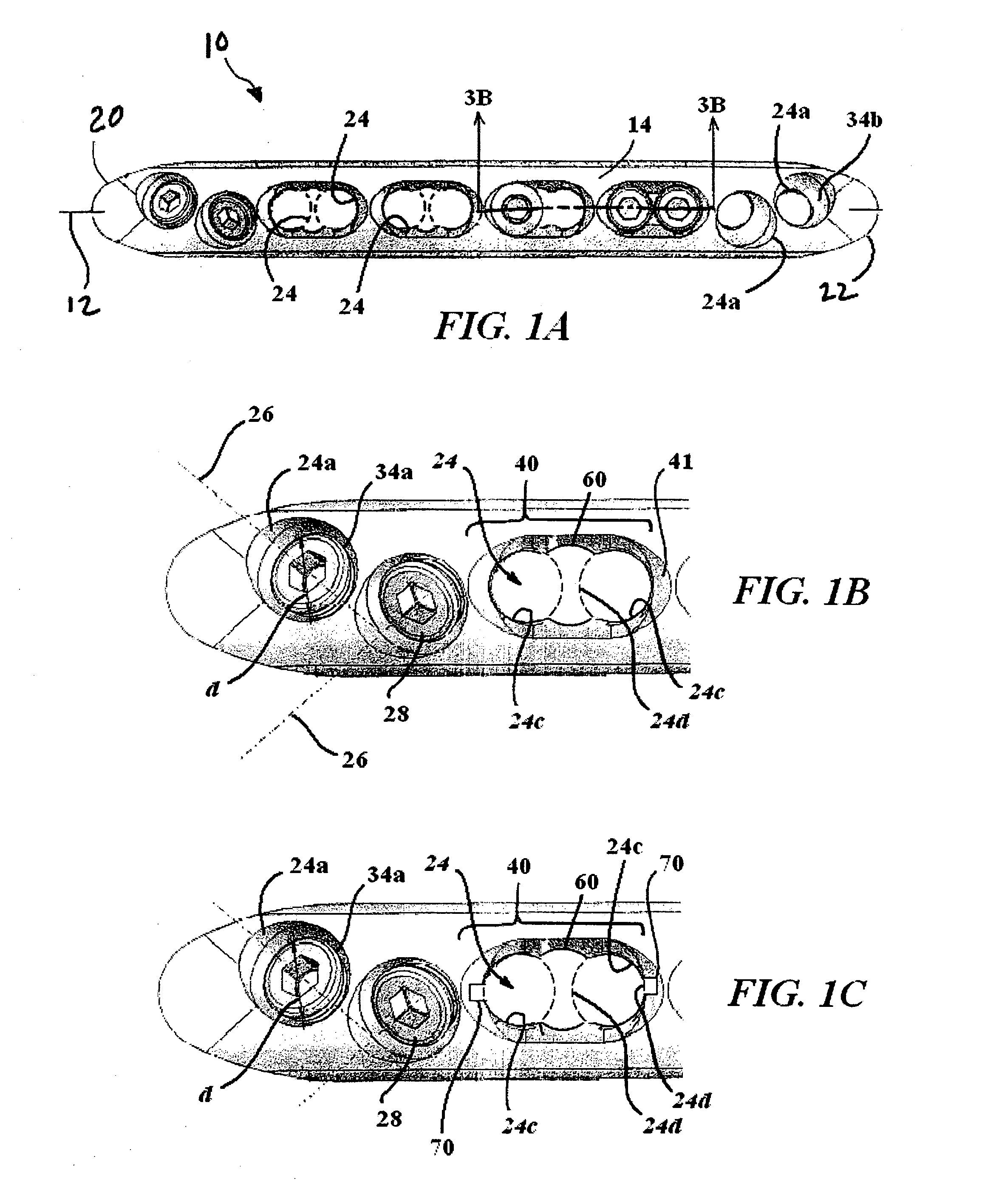
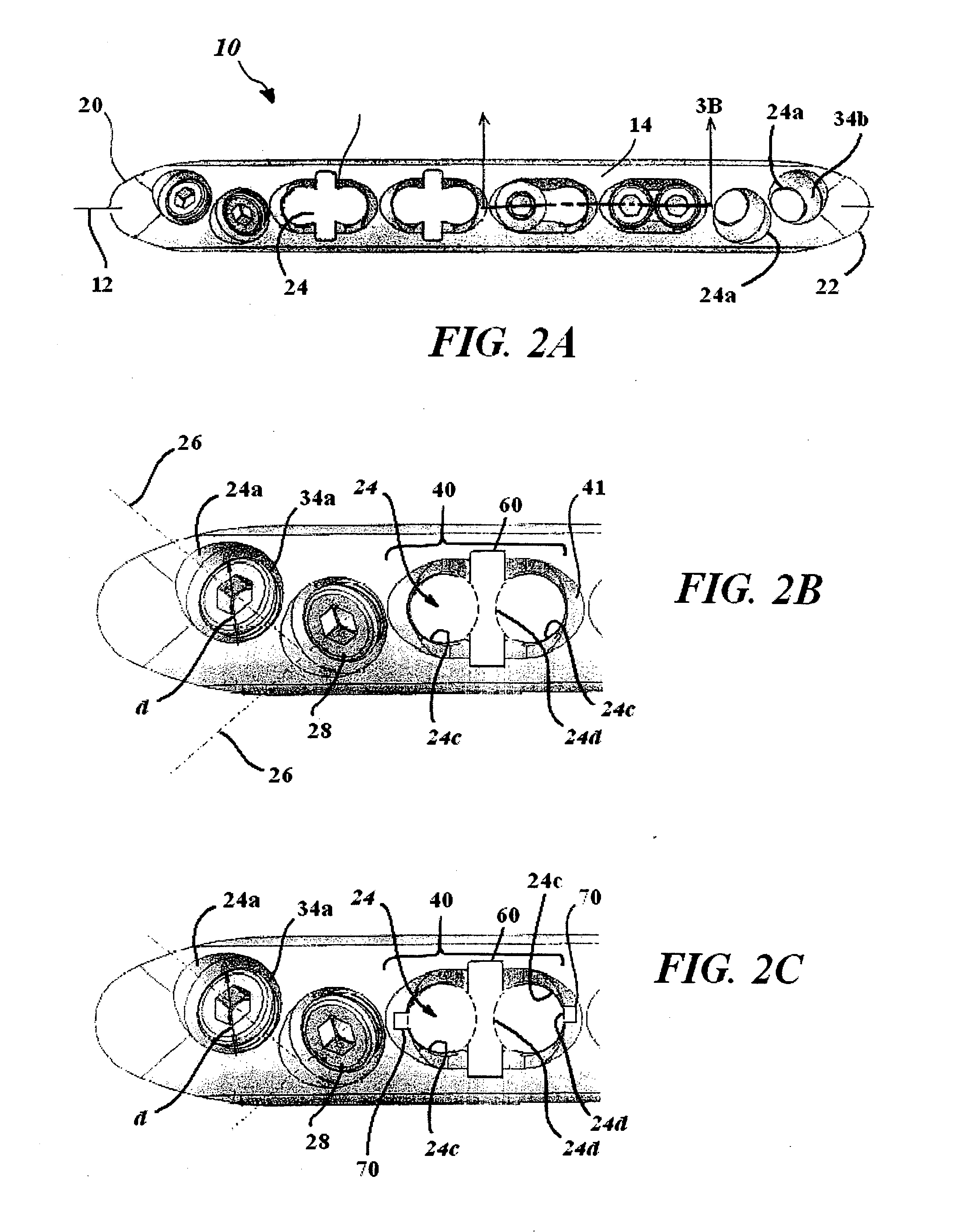
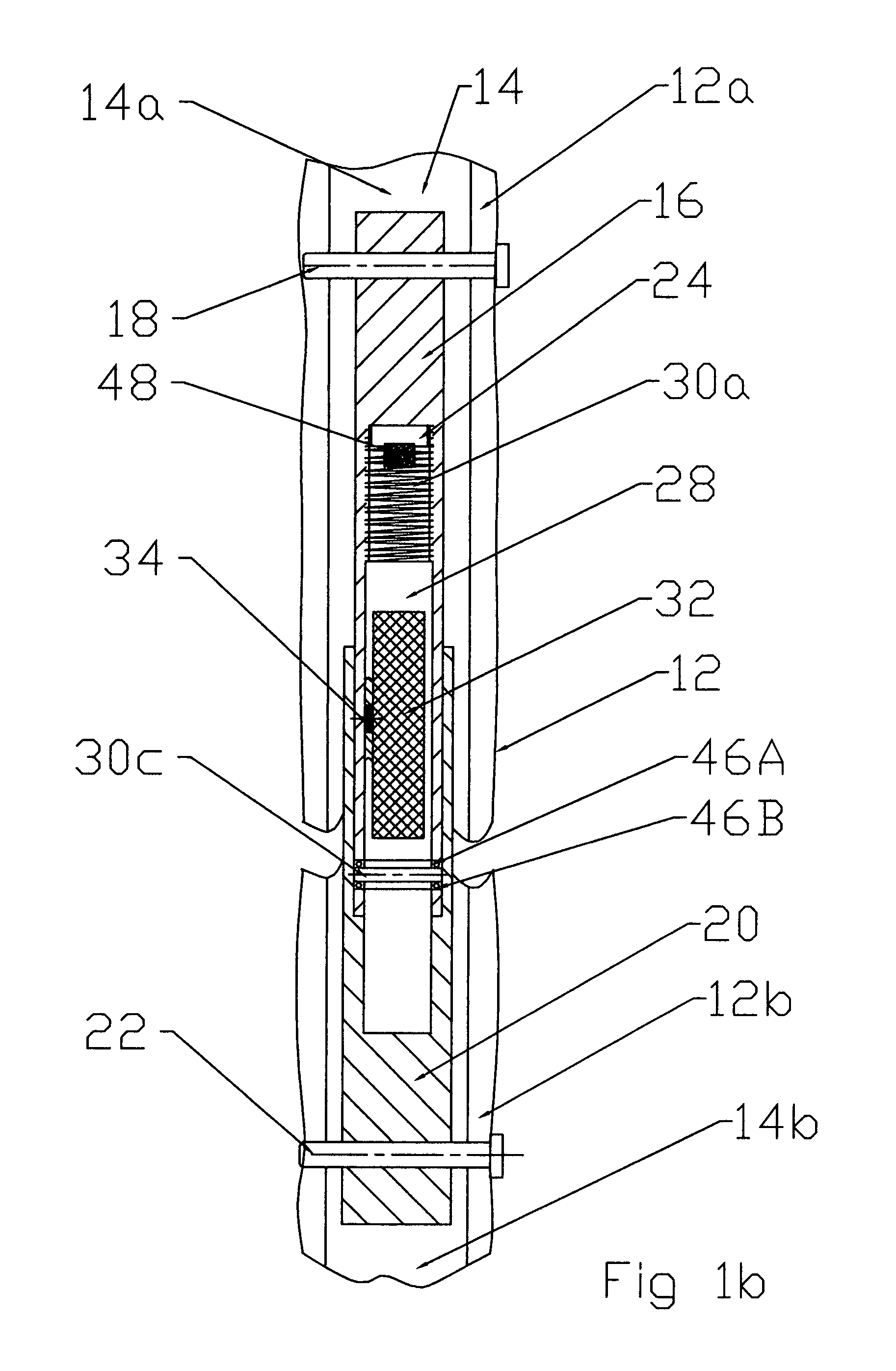
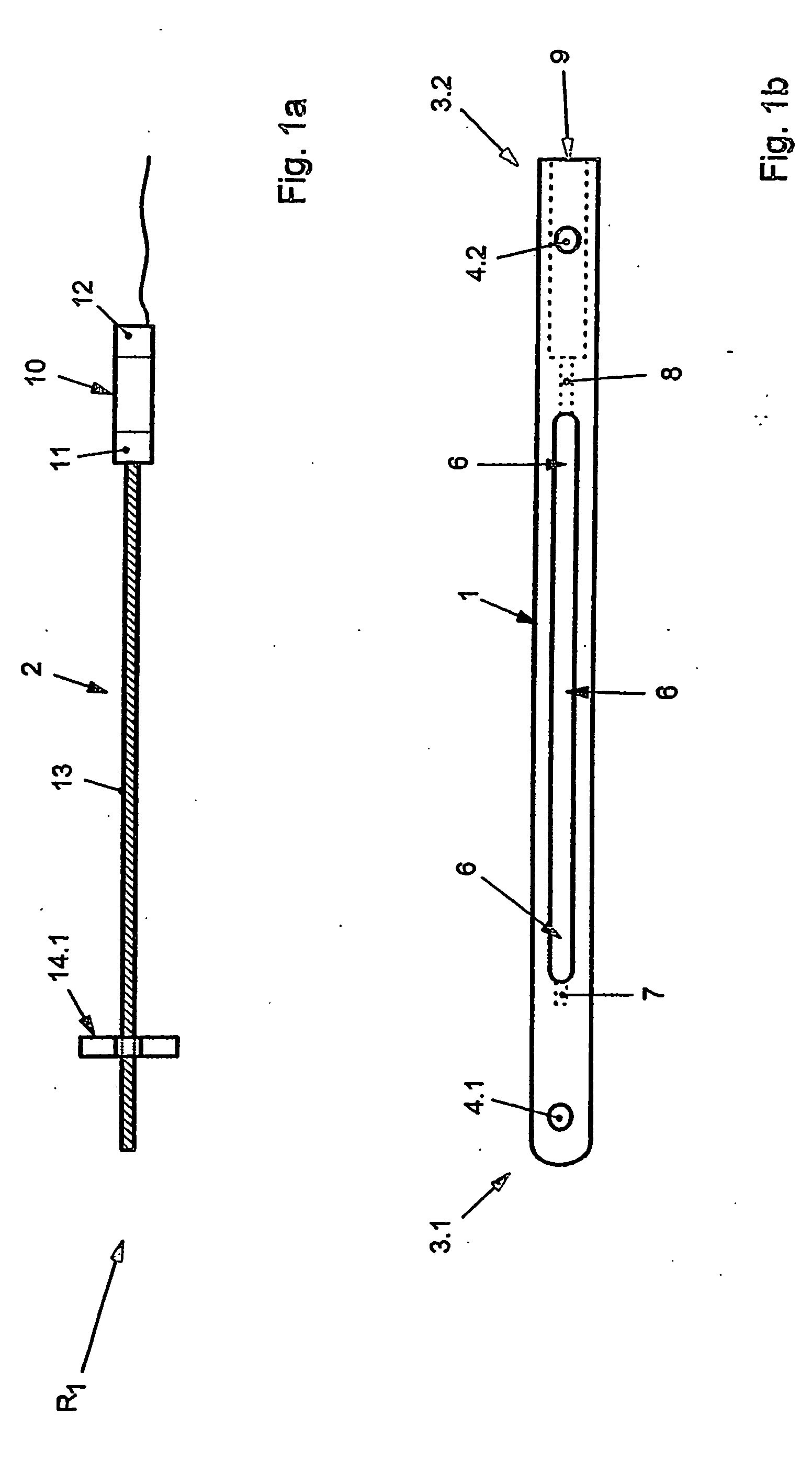
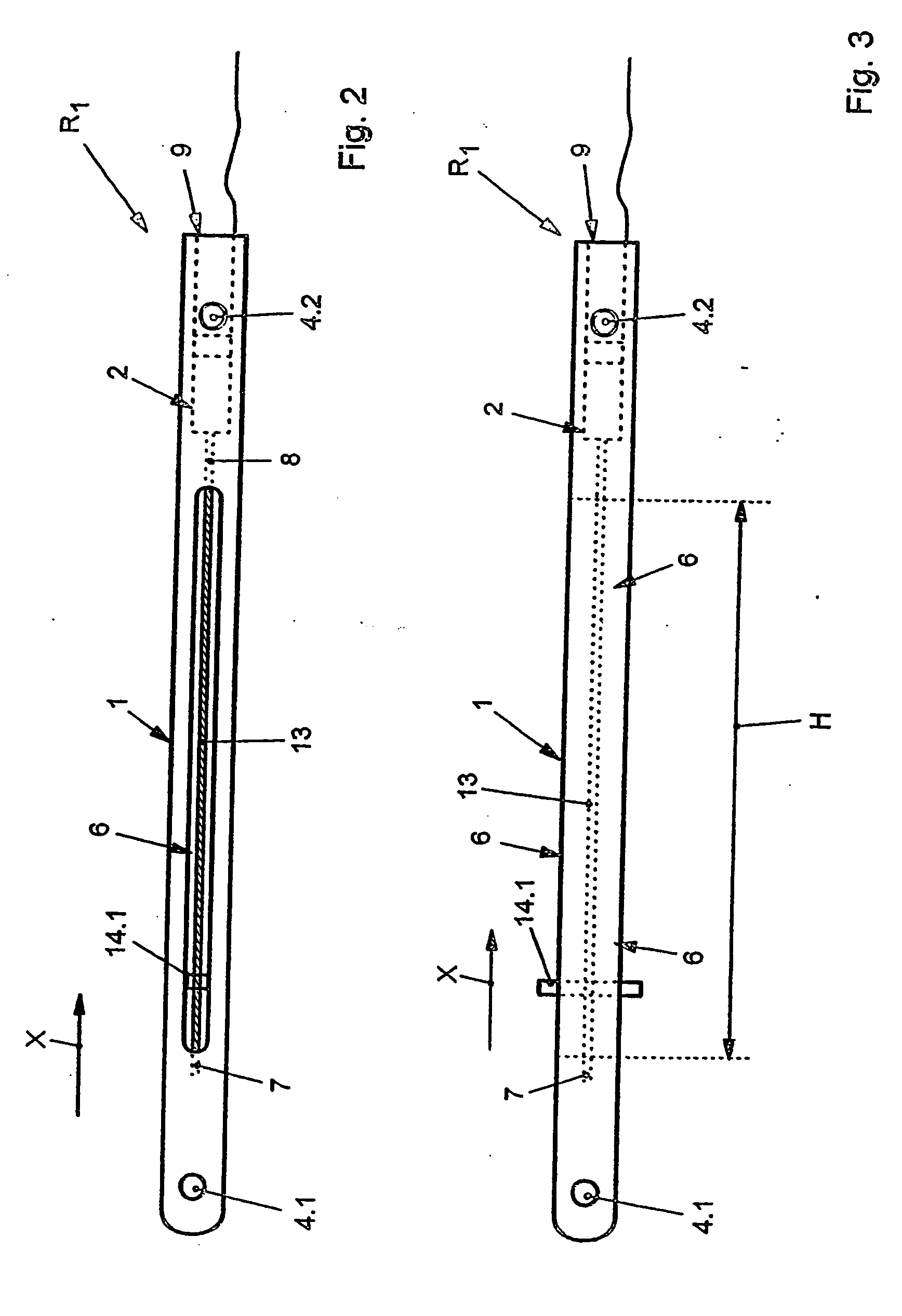
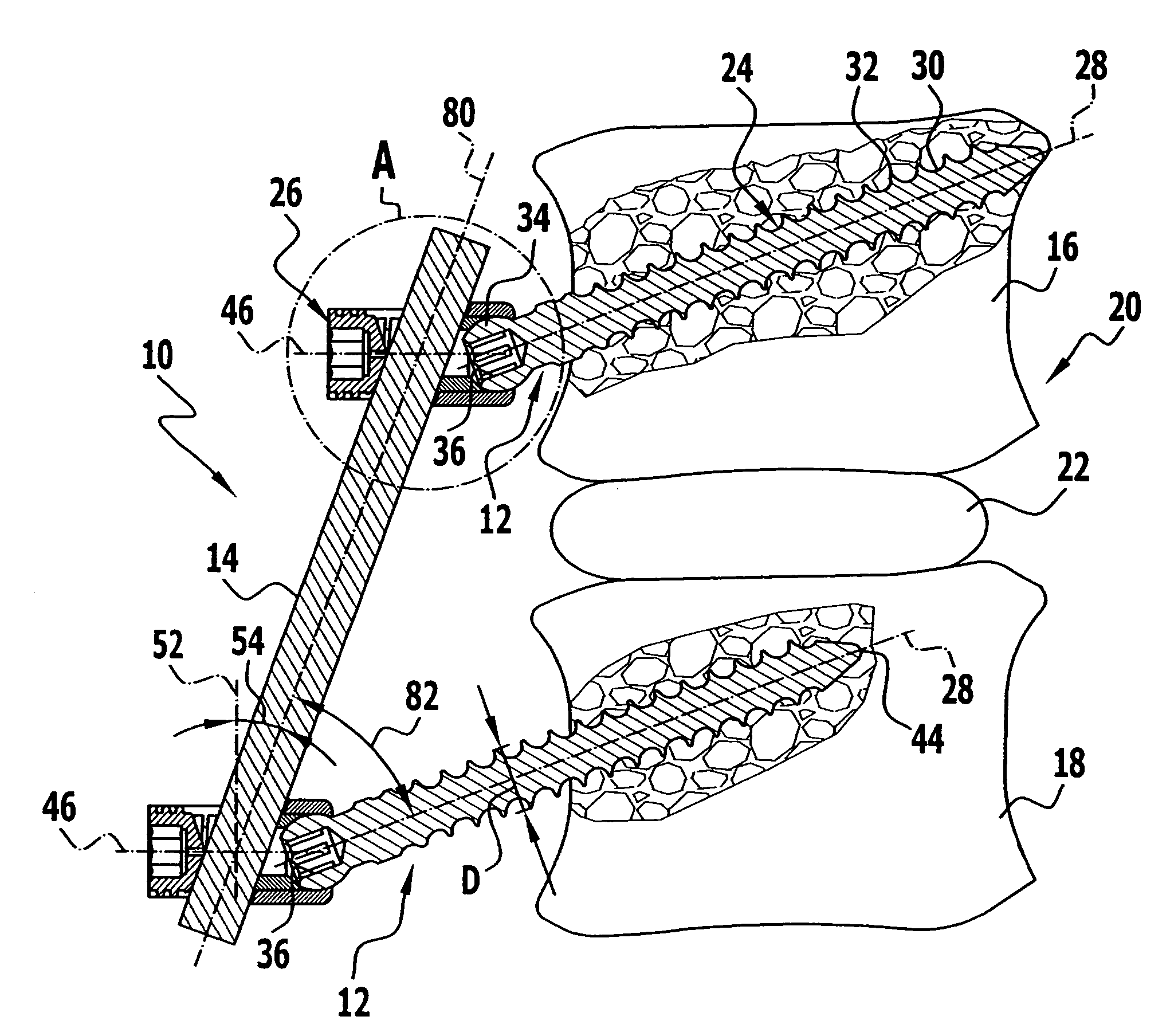
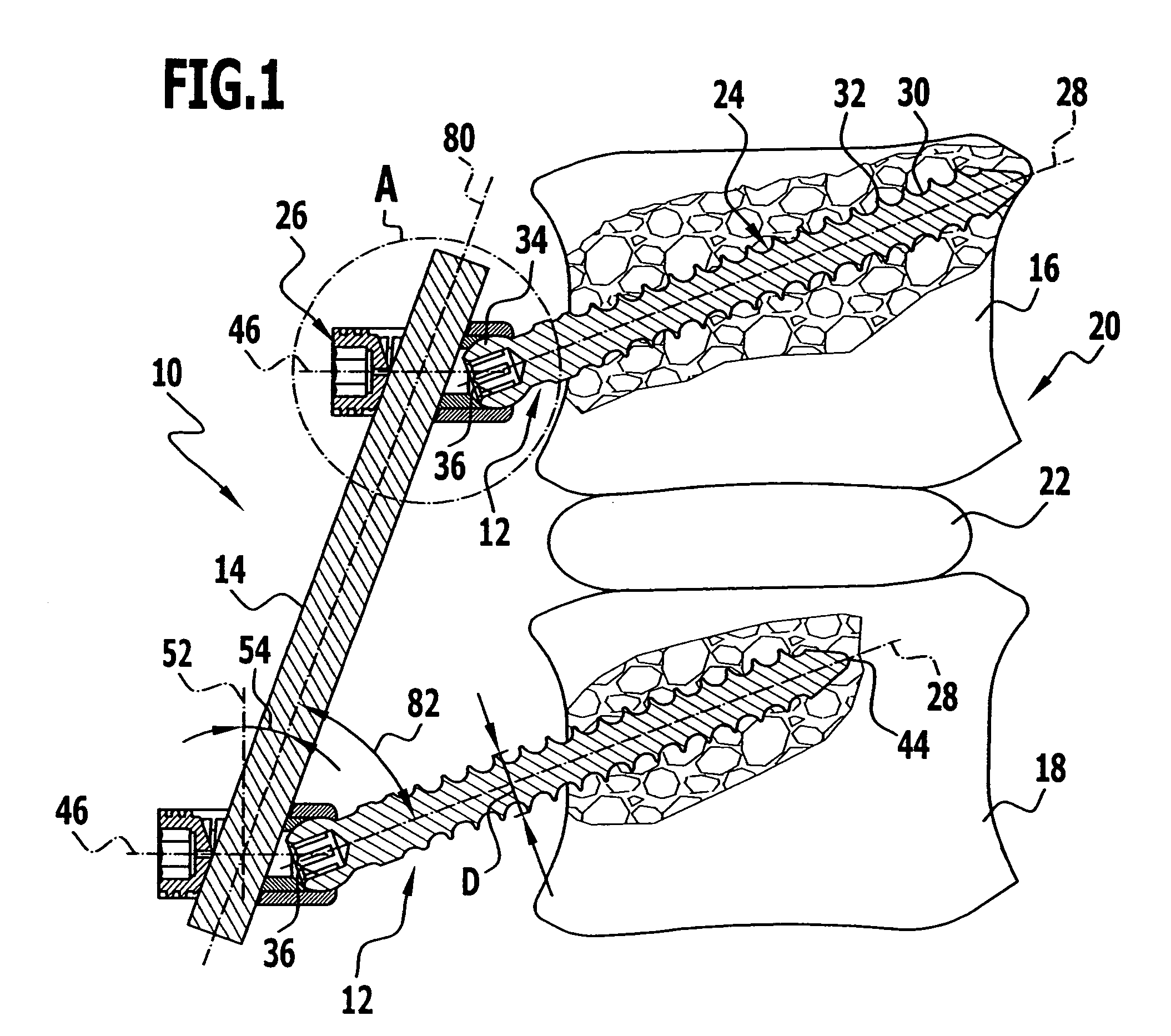
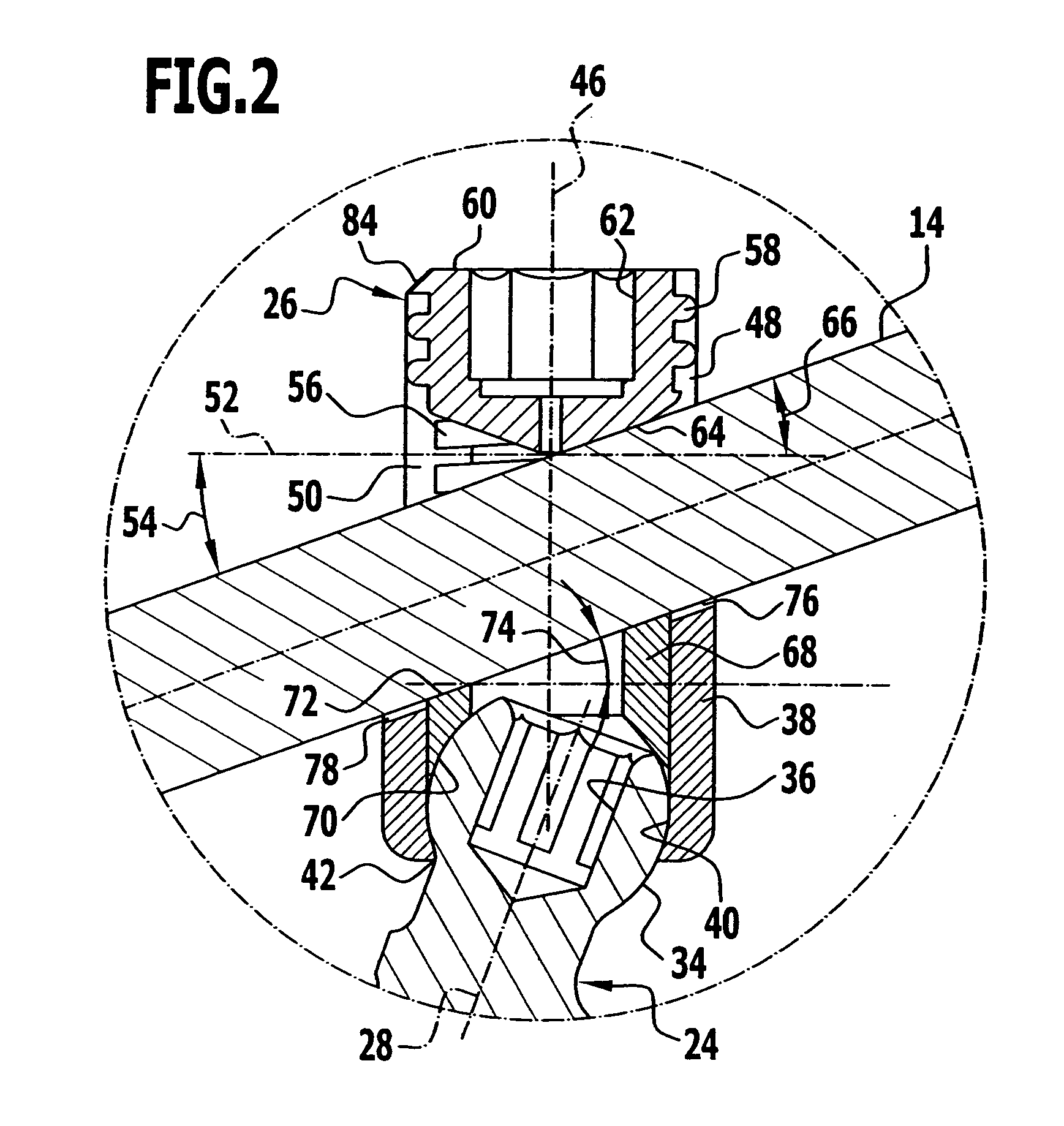
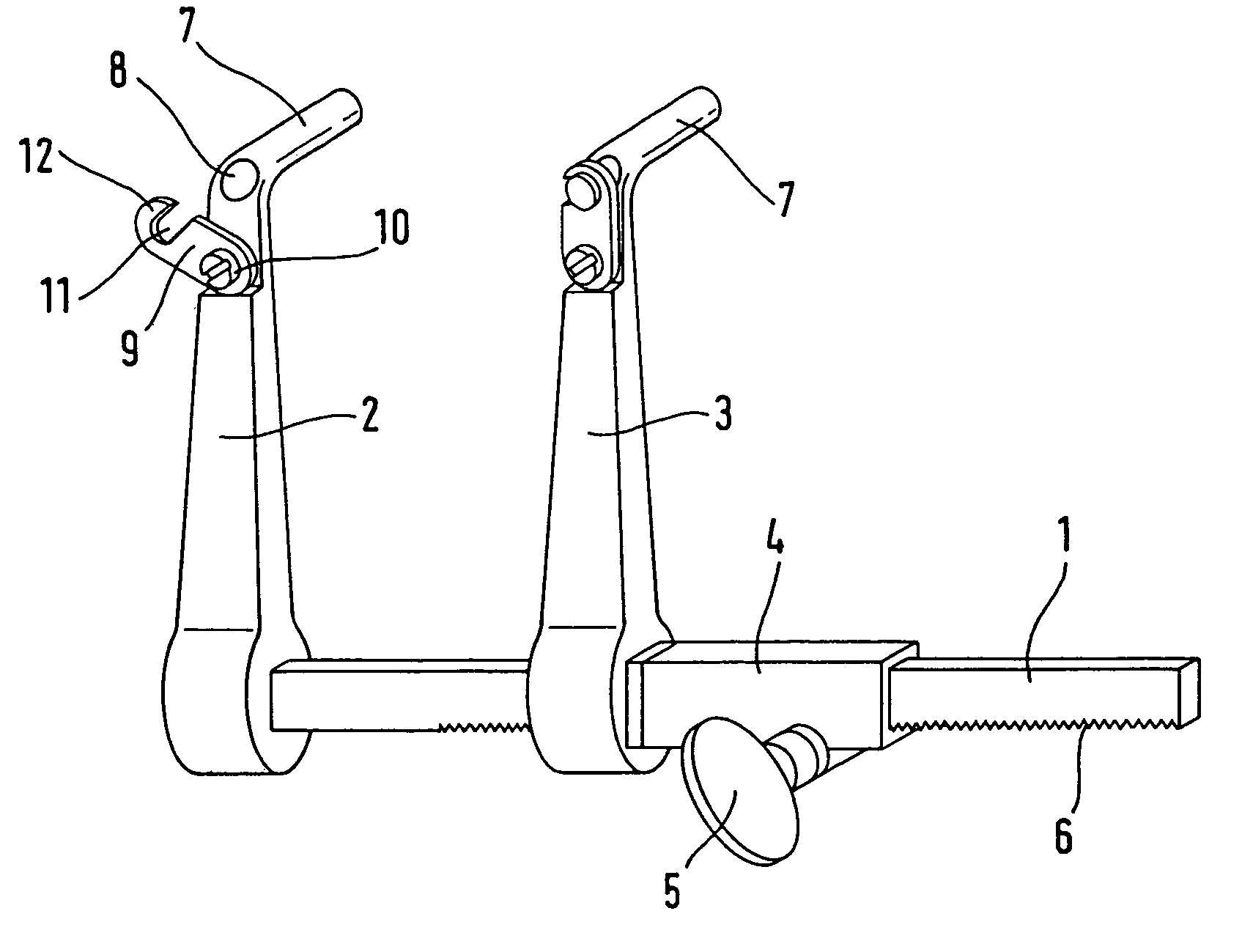
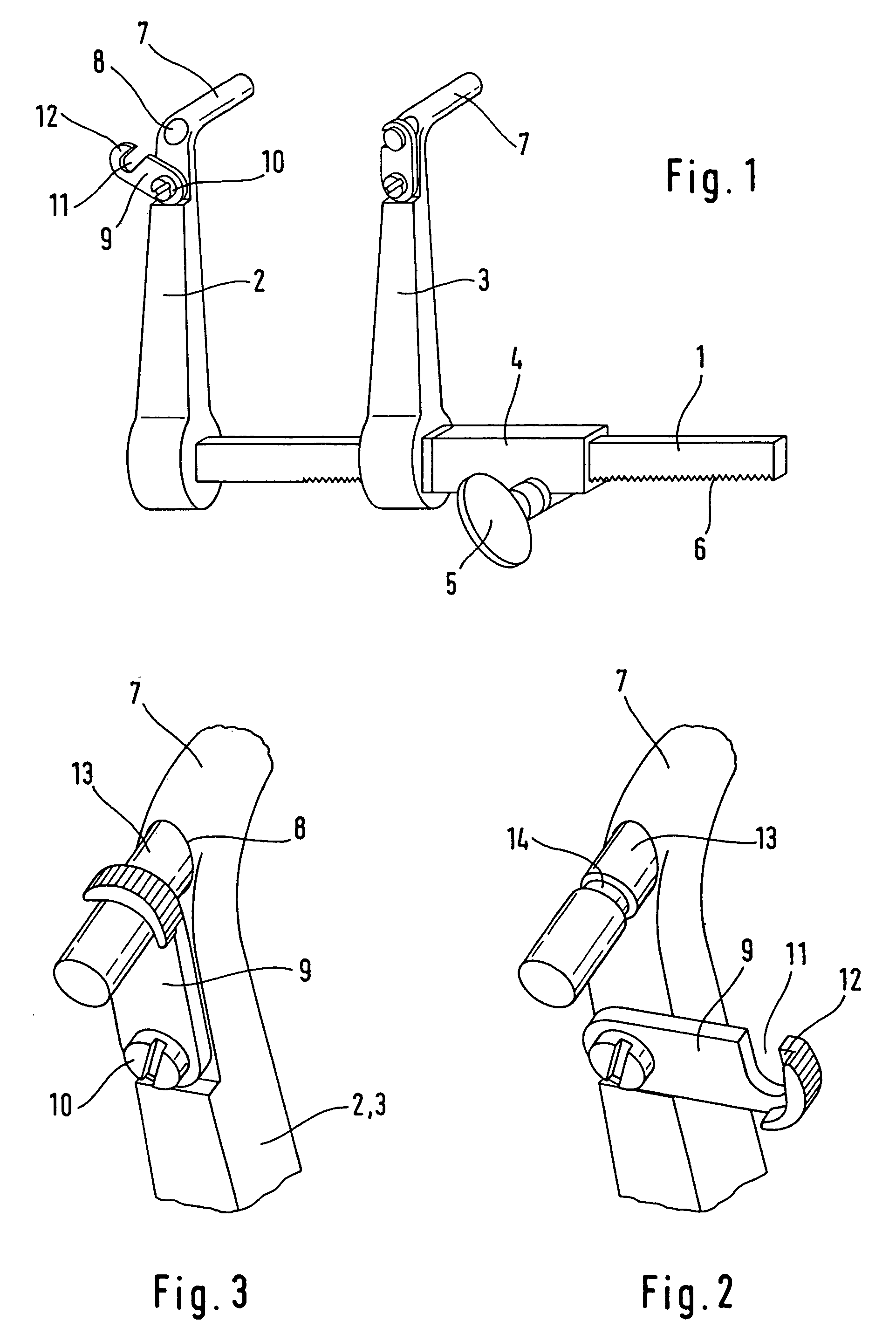
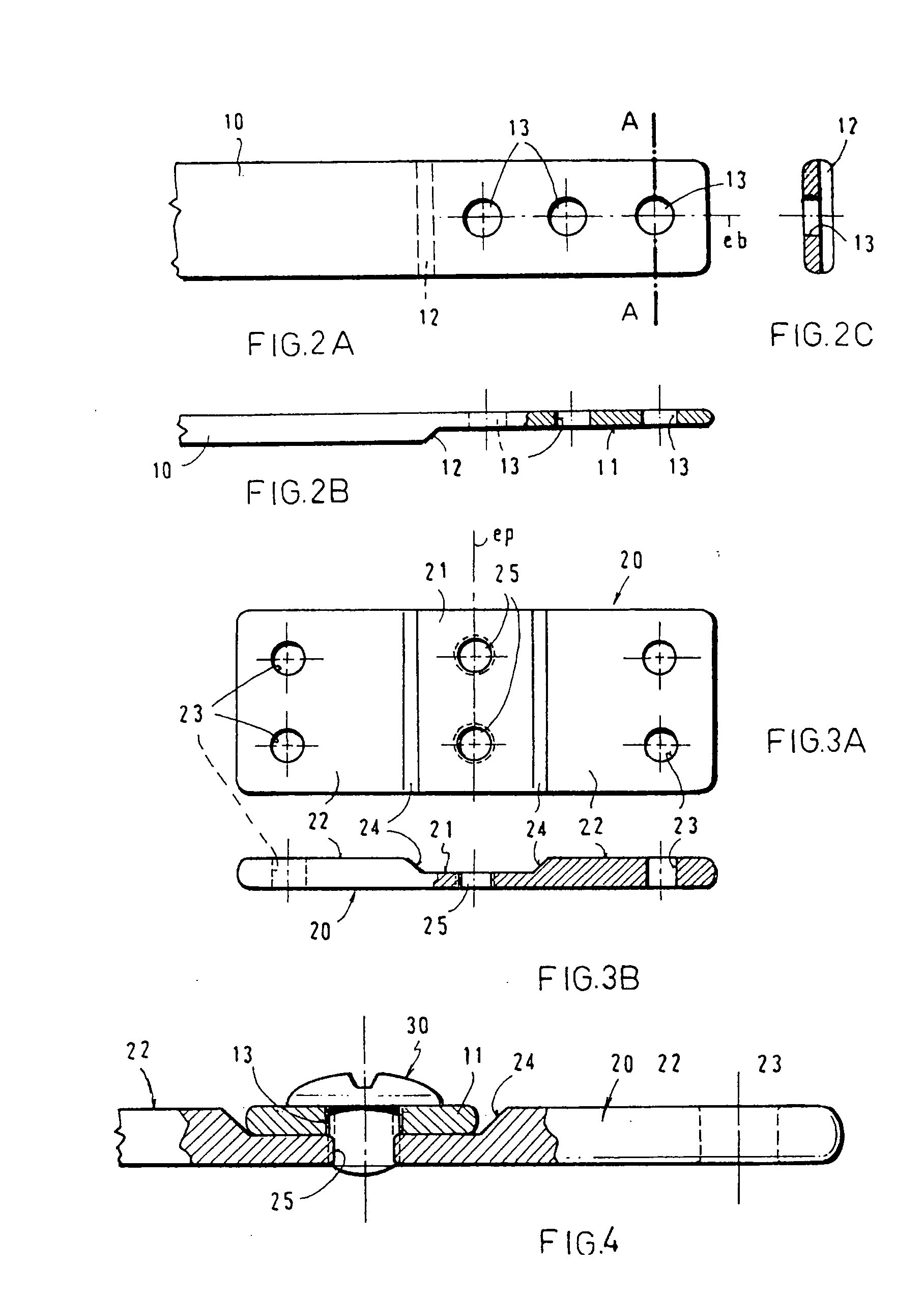
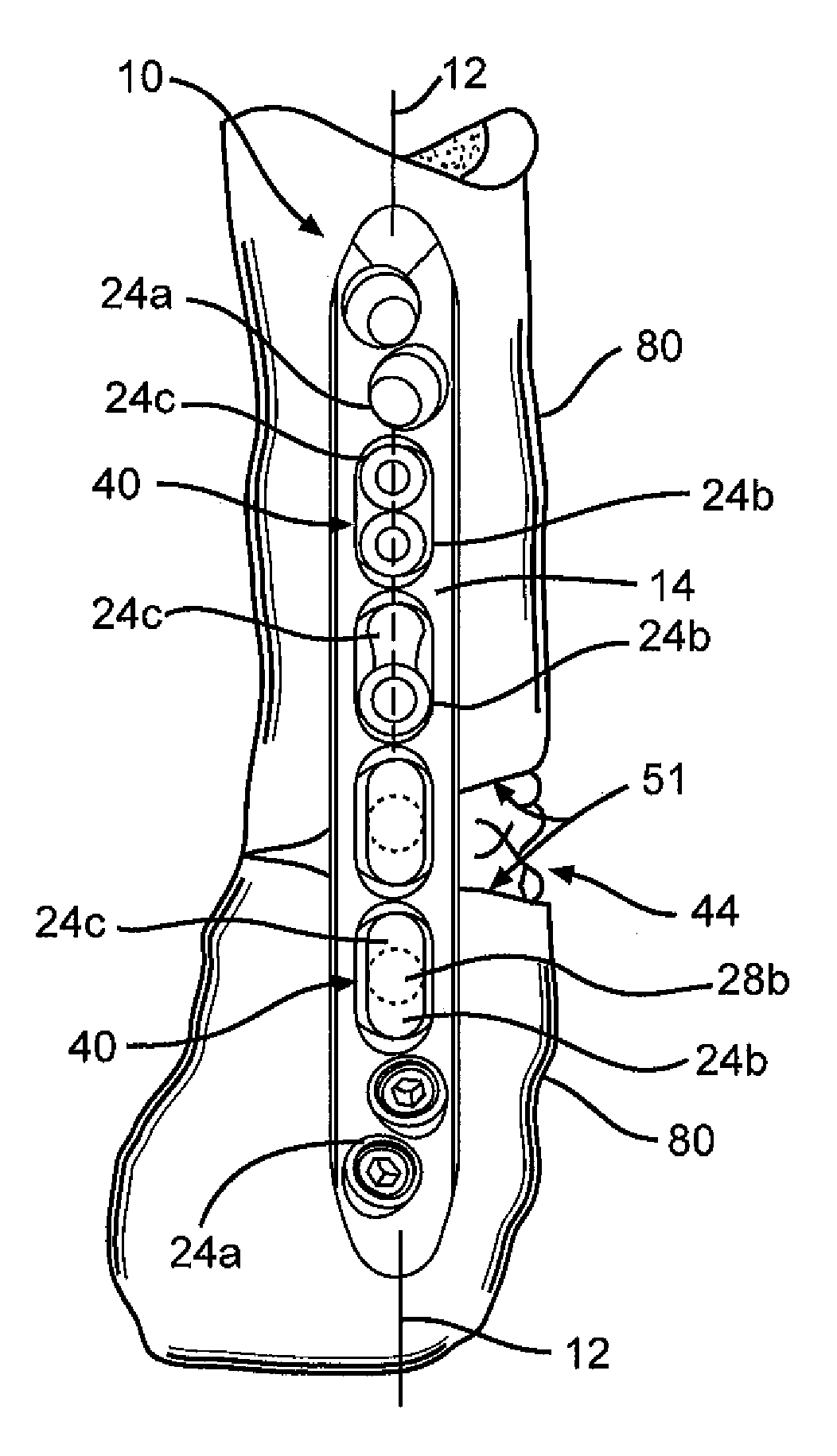
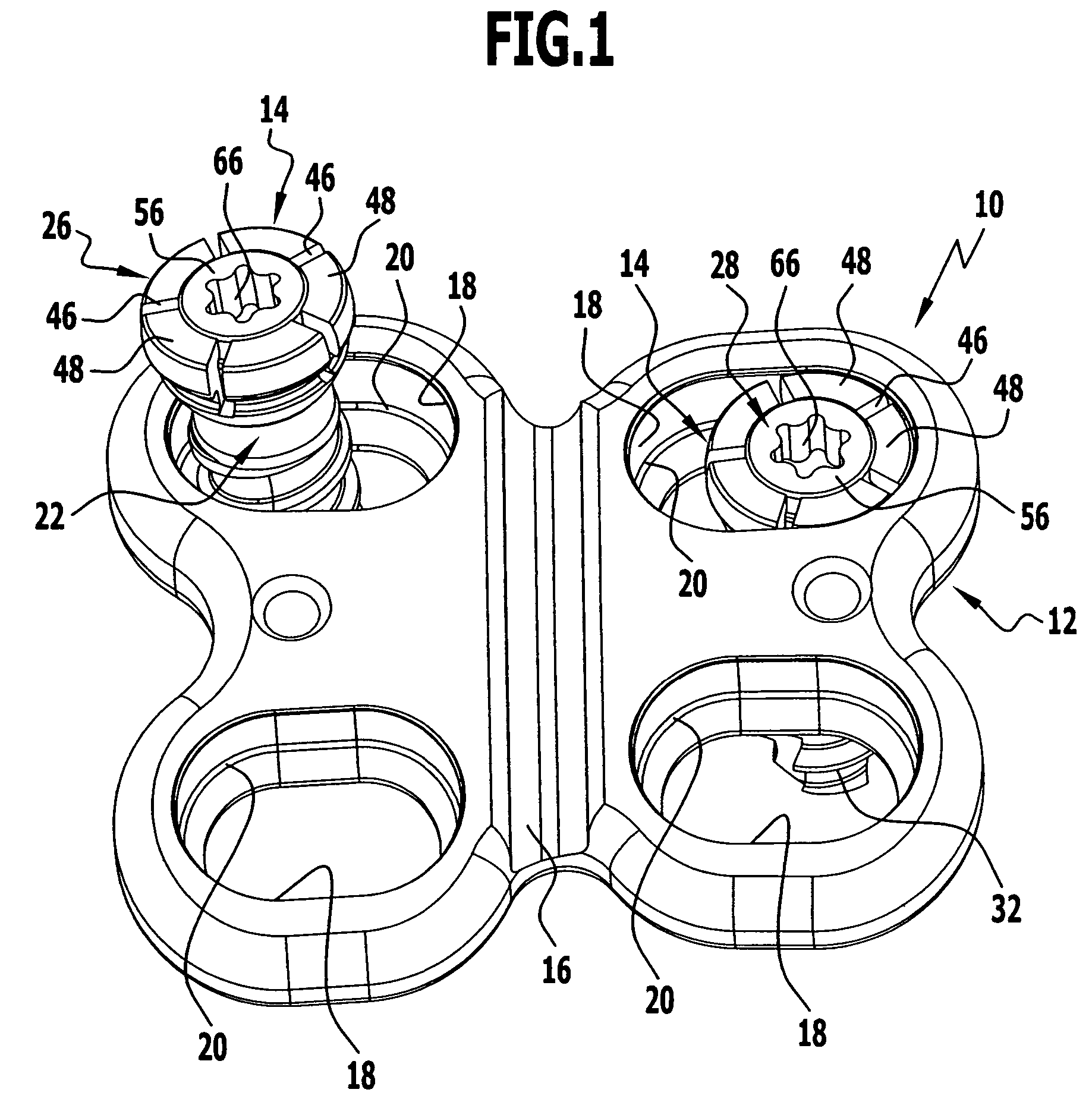
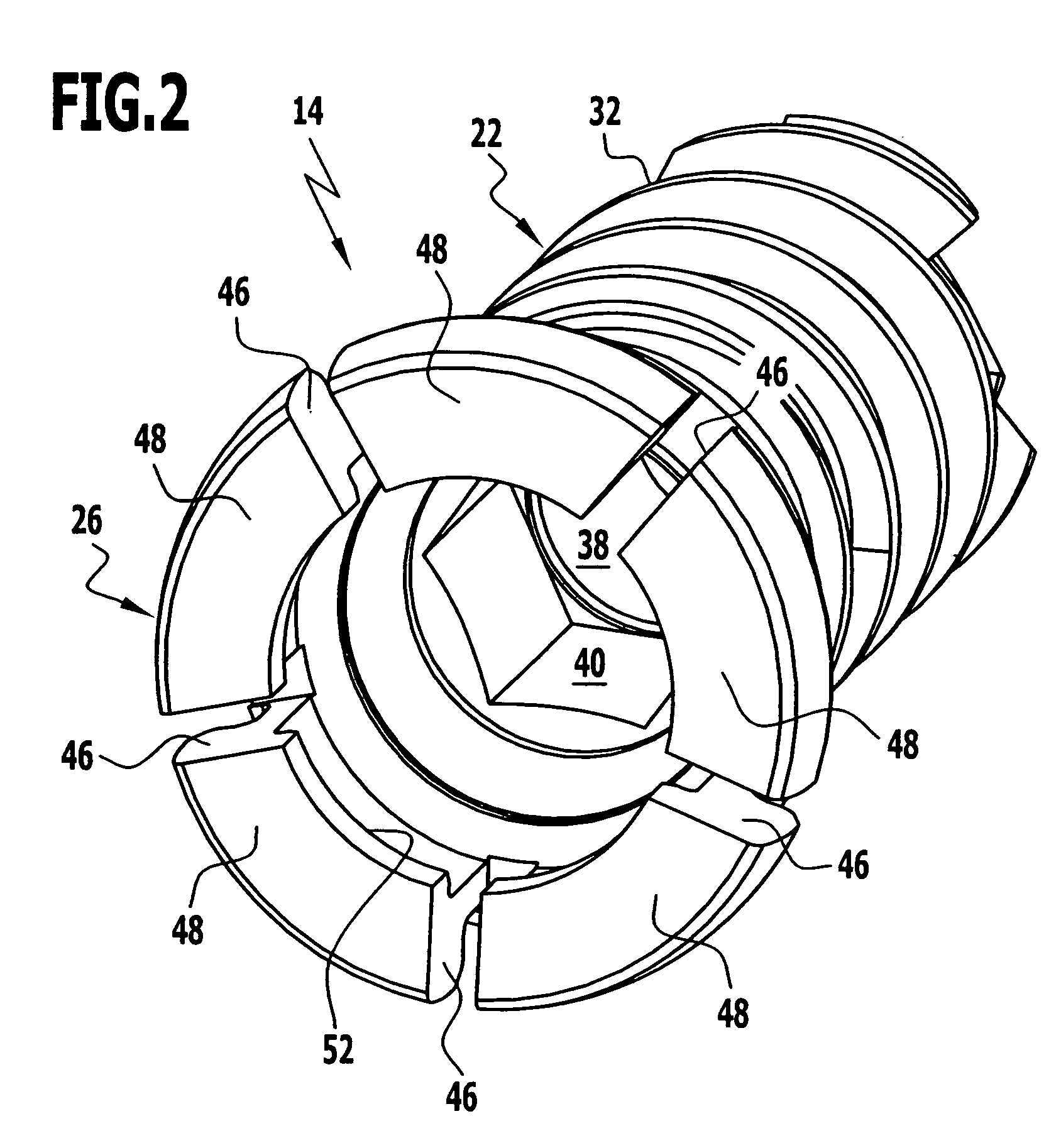
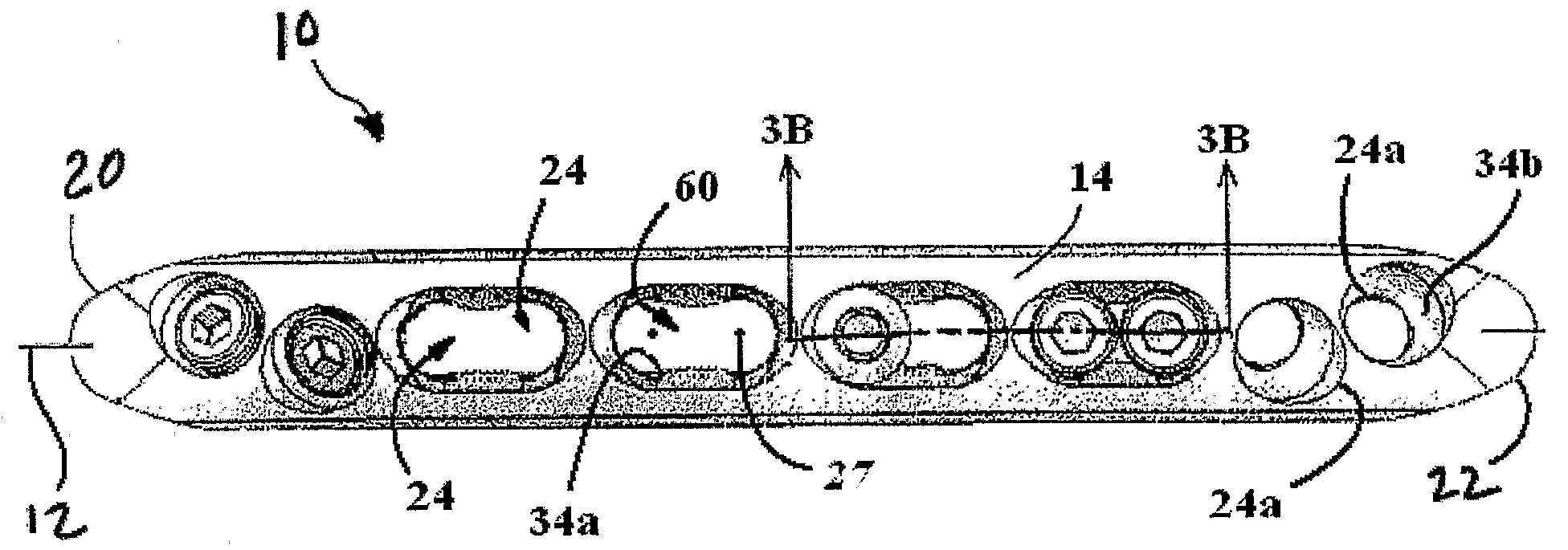
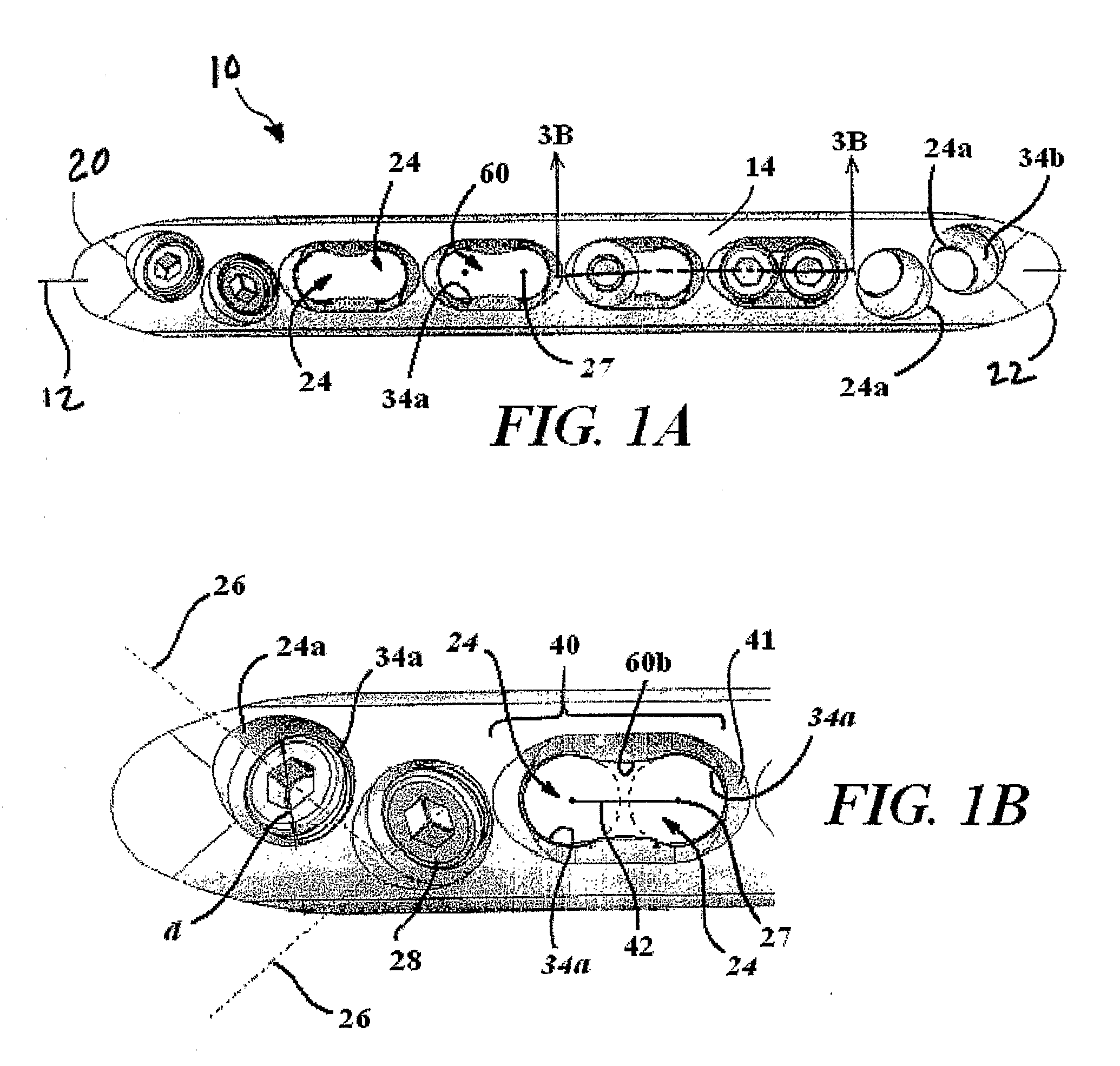
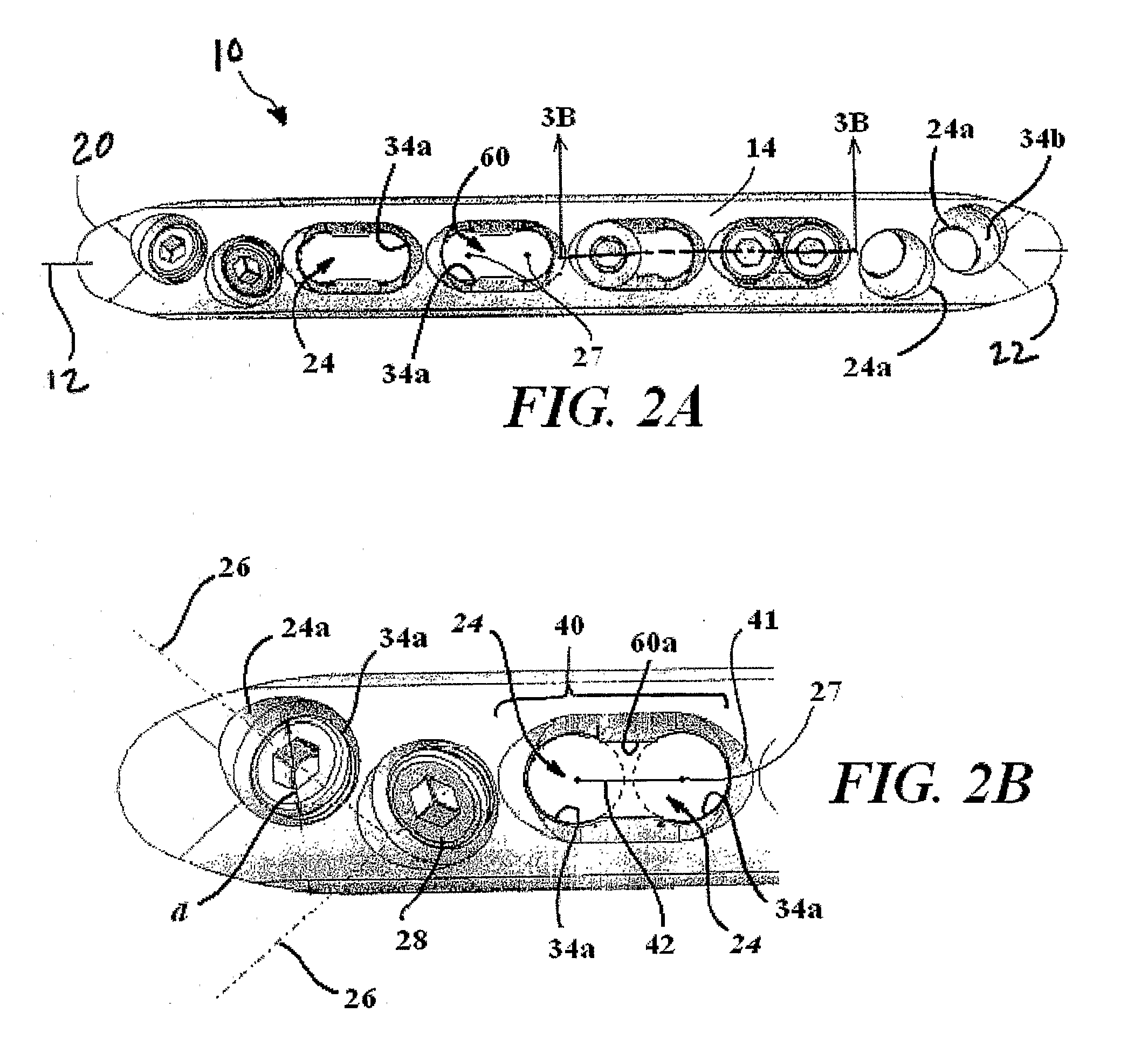
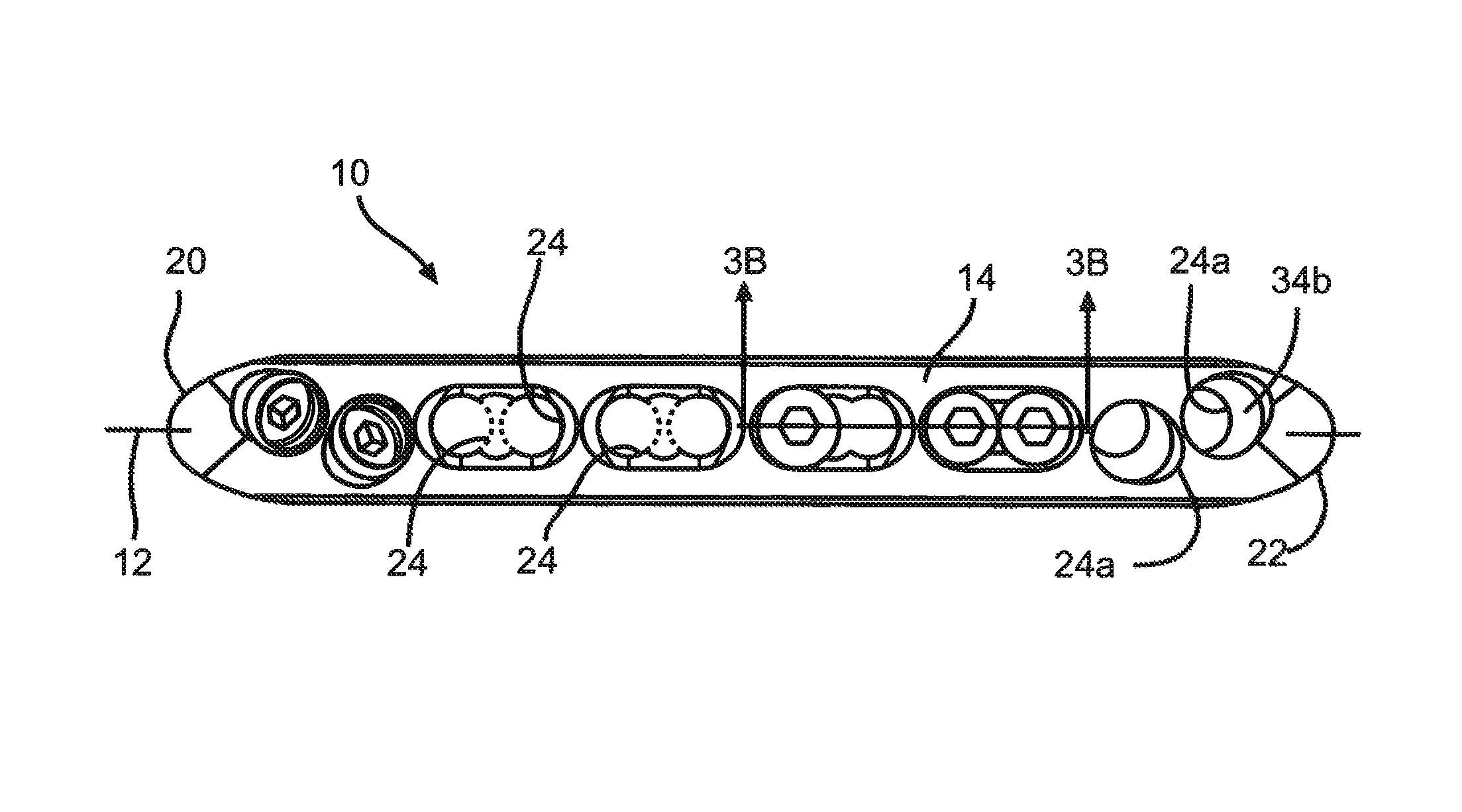
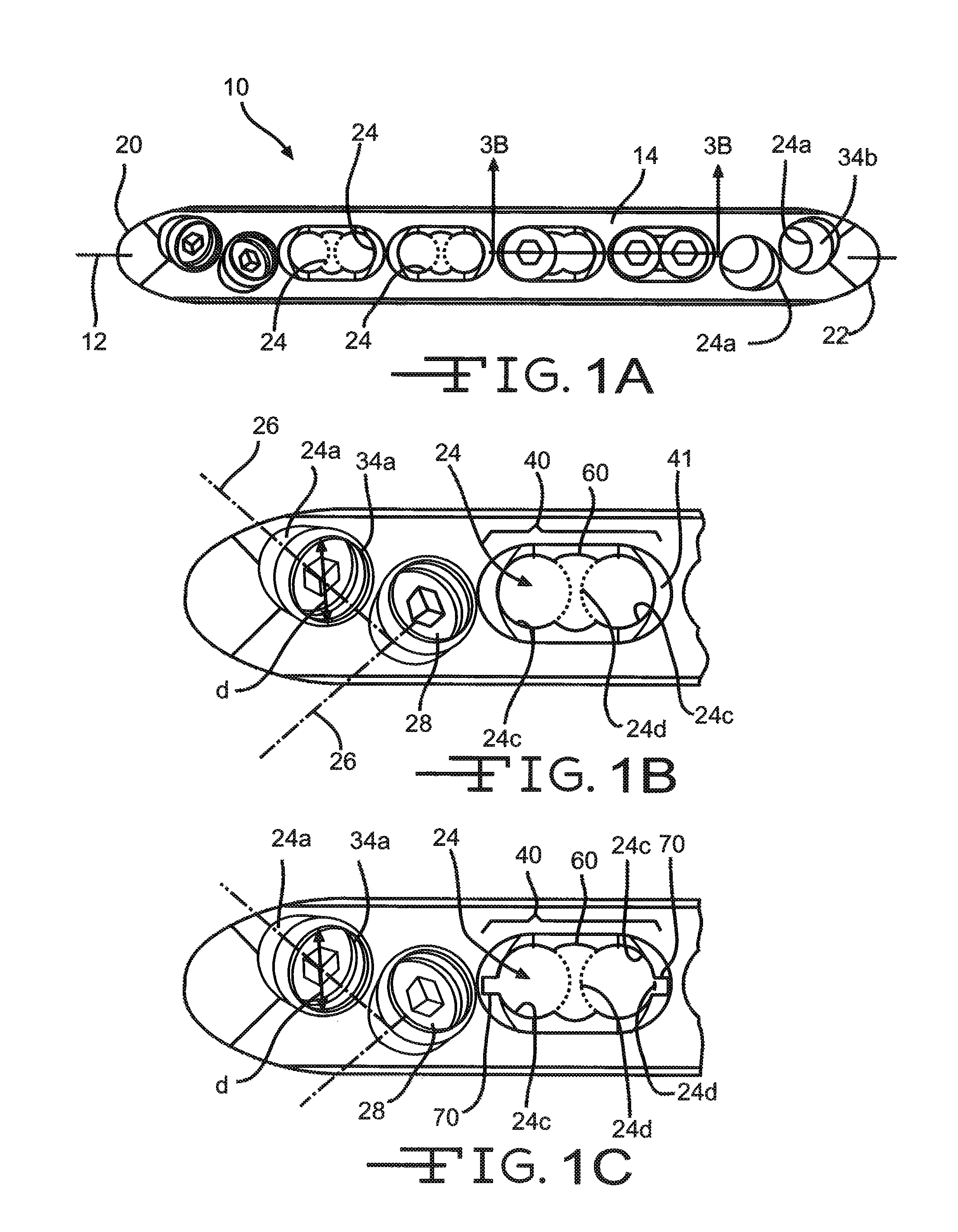
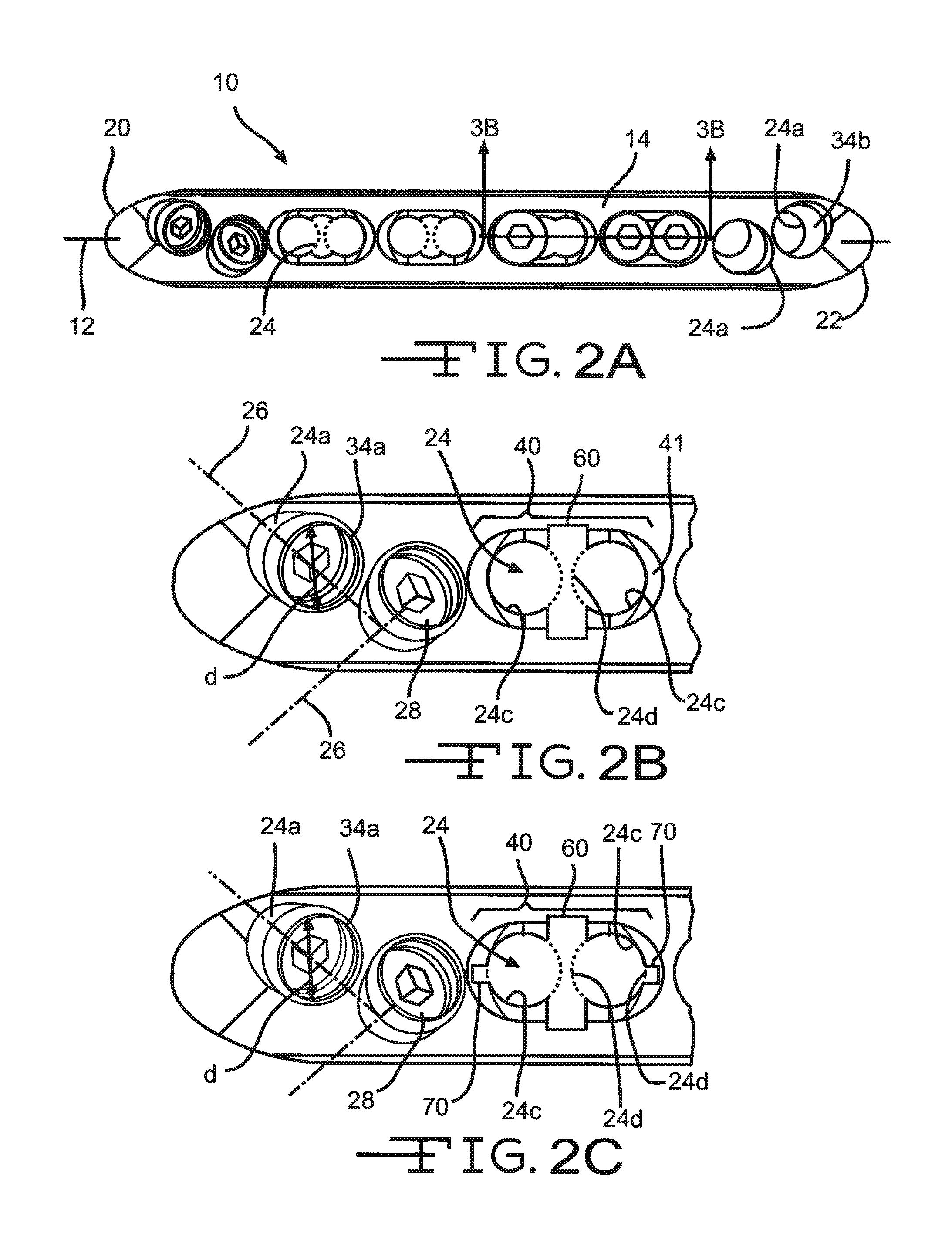
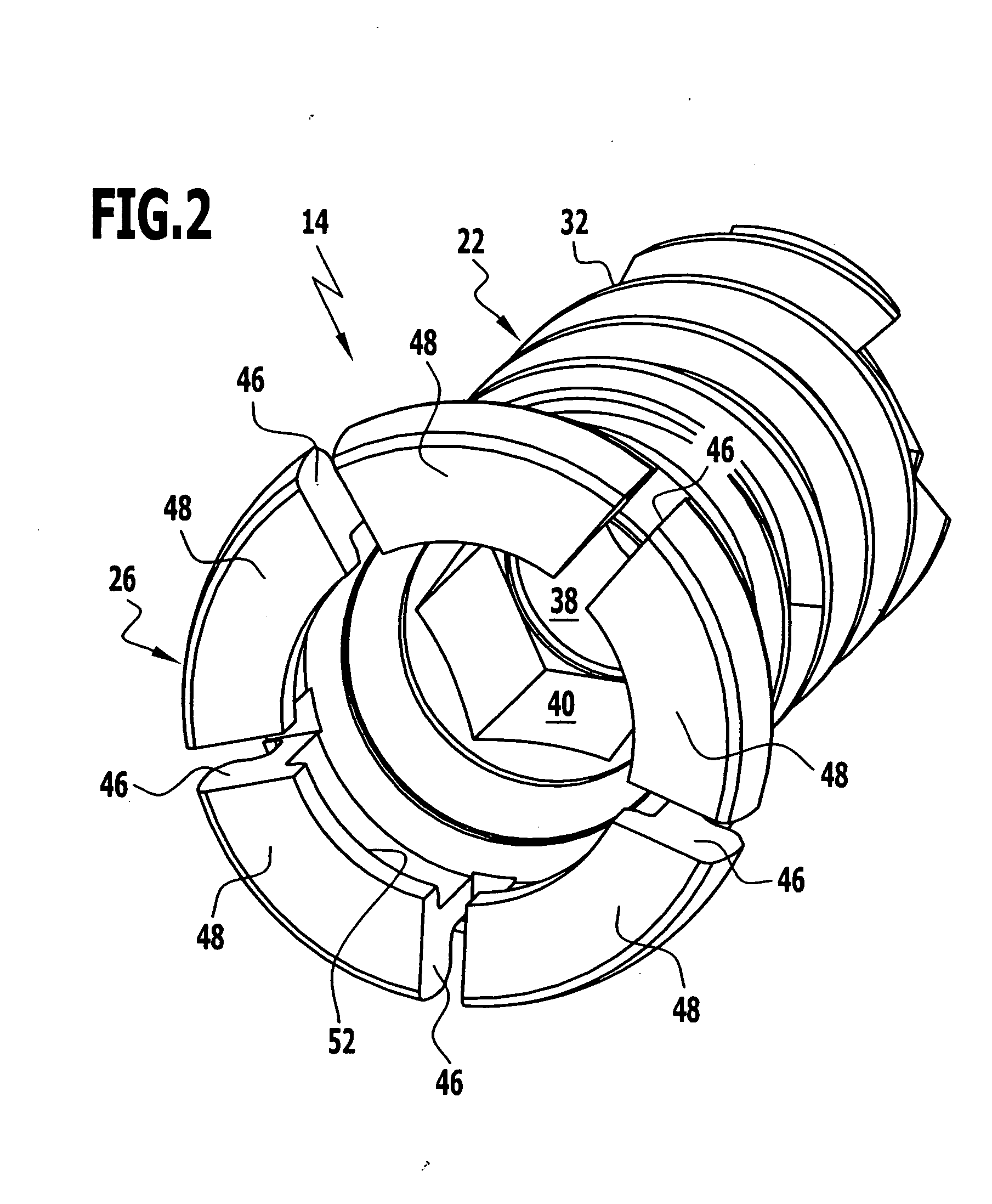
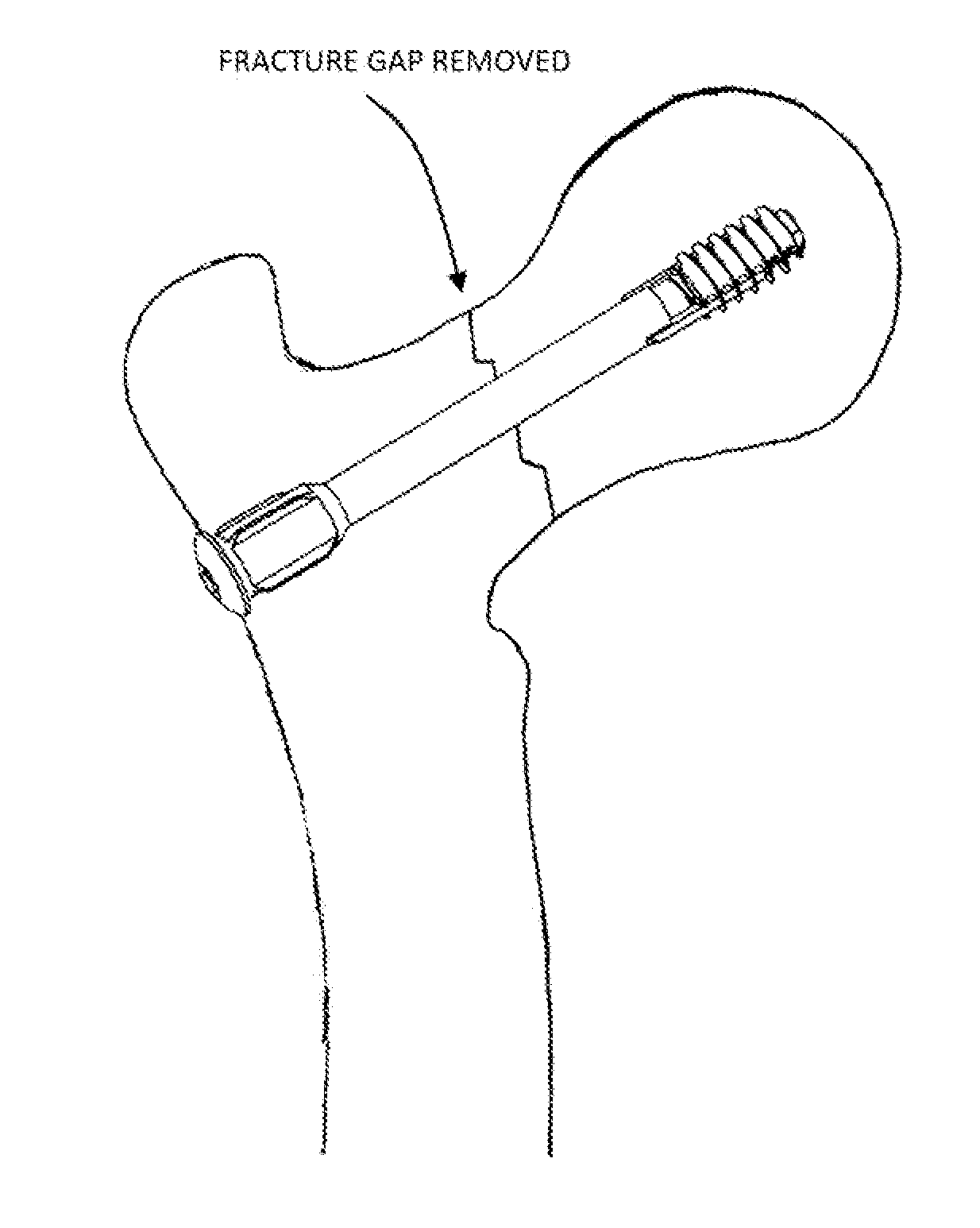
A bendable bone plate (10) is disclosed which is adapted for use in situ as a conformable bone splint to fix the spatial relationship of at least two bone parts (80). The bone plate (10) has an elongated plate (11) made of a bendable material. A plurality of screw apertures (24) extending through the top (14) and bottom (16) surfaces are disposed along the length (L) of the plate. Bone screws (28) are inserted through the apertures into the underlying bone parts (80) to anchor the elongated plate (11) to the bone parts (80). At least two of the screw apertures (24) are disposed as a closely spaced pair (40) of screw apertures (24) with a “bend relief zone” (60) disposed between the closely spaced apart screw apertures (24). The bend relief zone (60) is disposed to allow the elongated plate (11) to be bent across the bend relief zone (60) up to a certain angle (A) without deforming the screw apertures (24) adjacent the bend relief zone (60)
Owner:SWISS PRO ORTHOPEDIC
Surgical fixing device for two bone parts
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Bi-directional bone length adjustment system
InactiveUS7753915B1Correction of deformationSimplified and reliable implantableInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringScrew thread
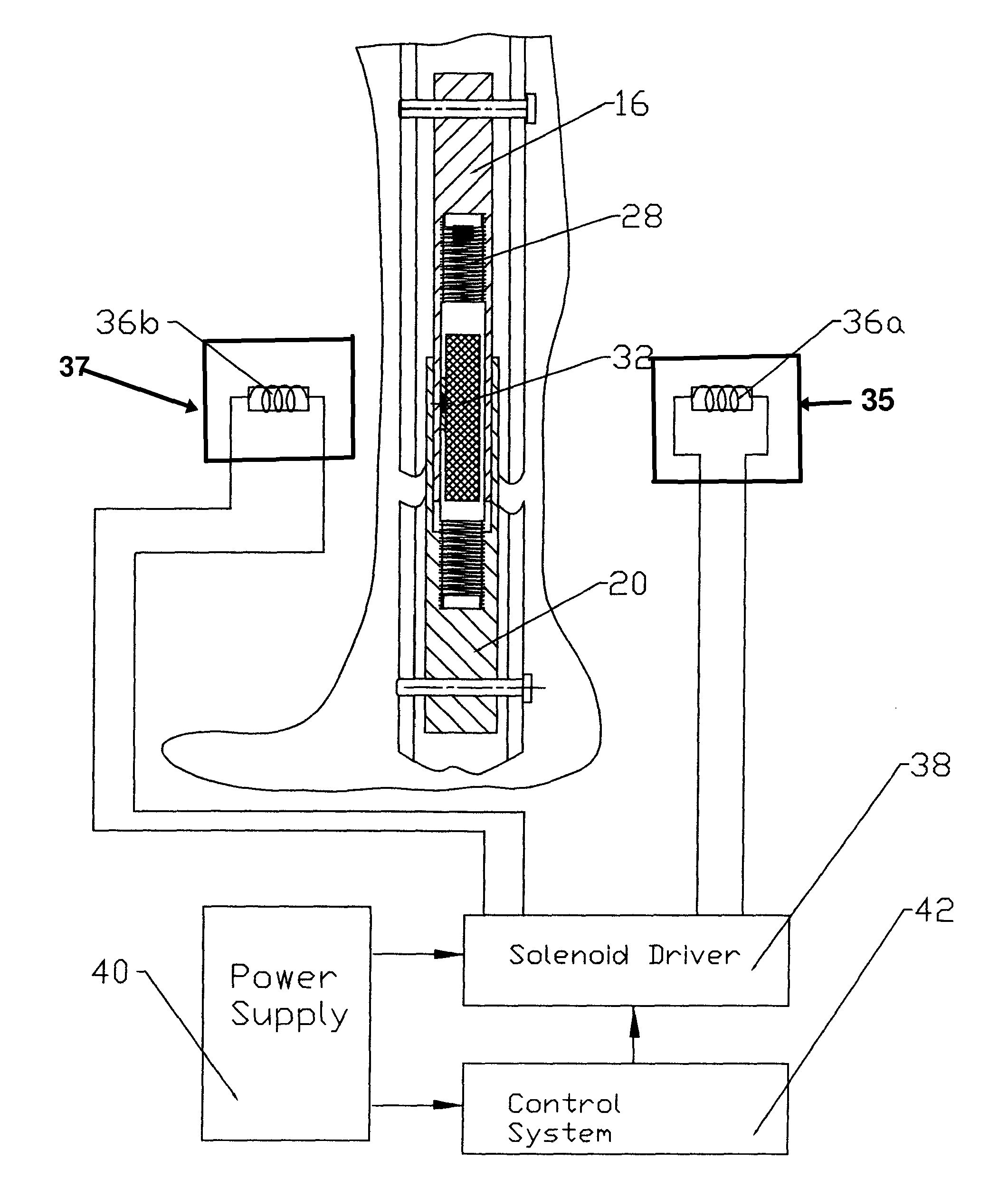
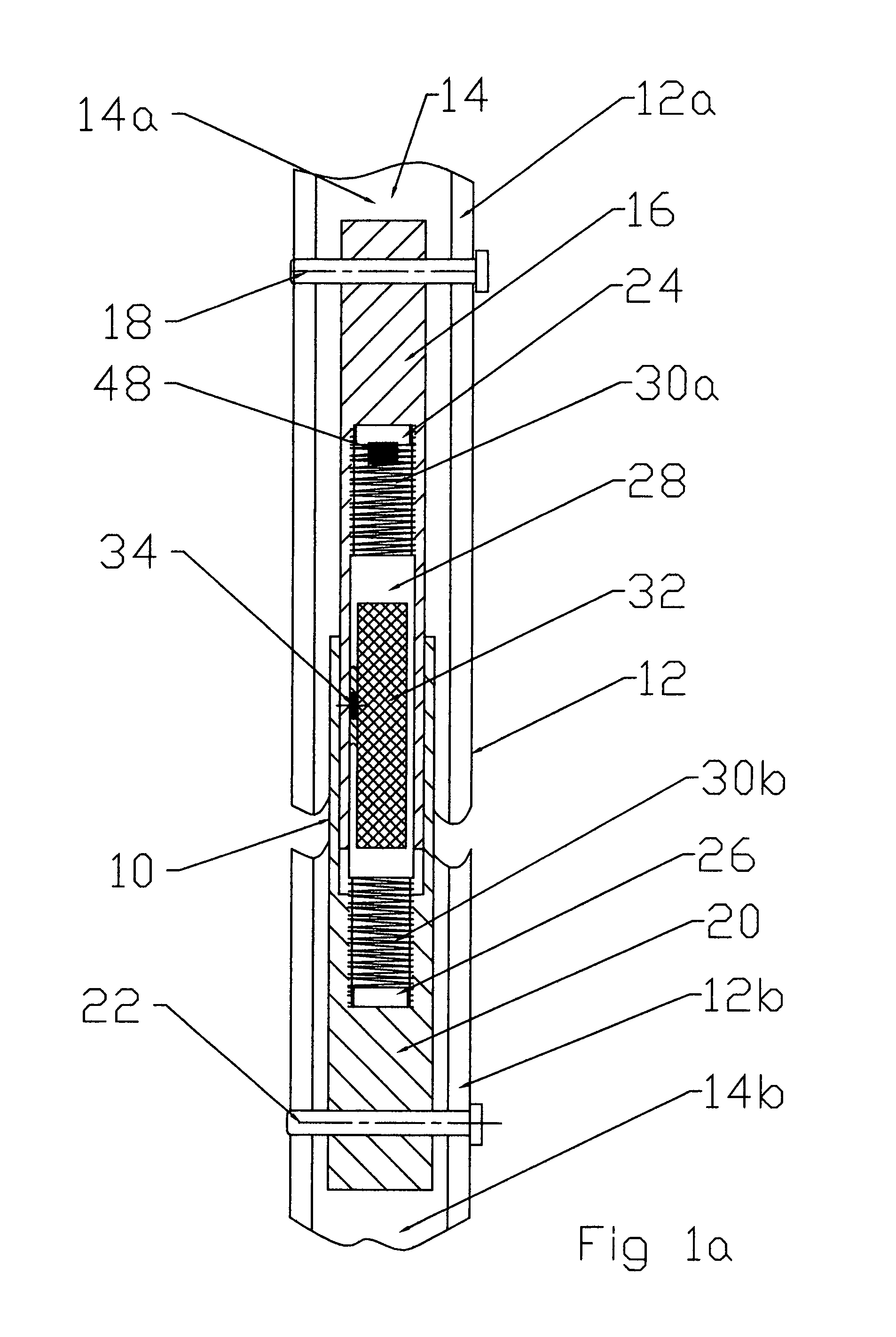
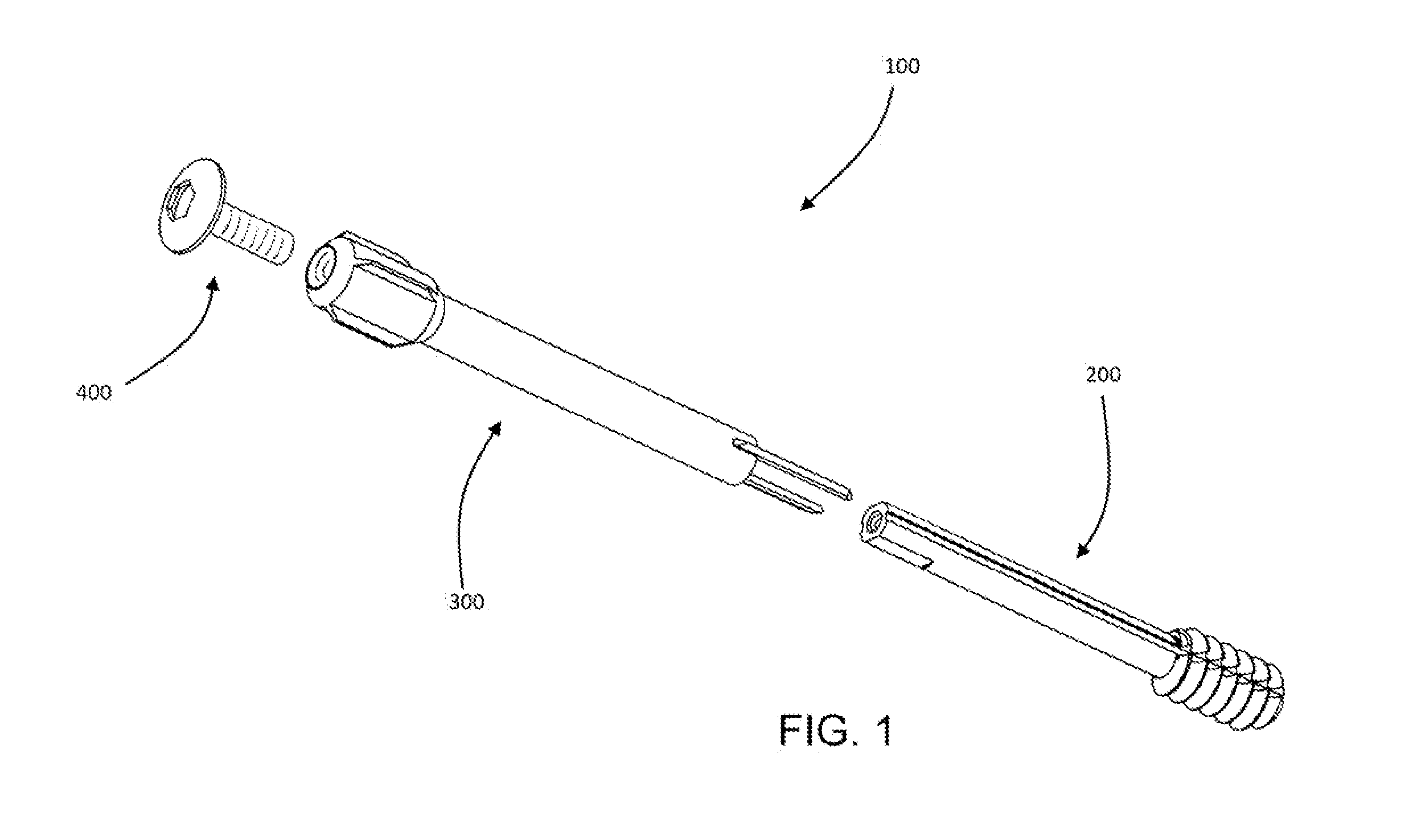
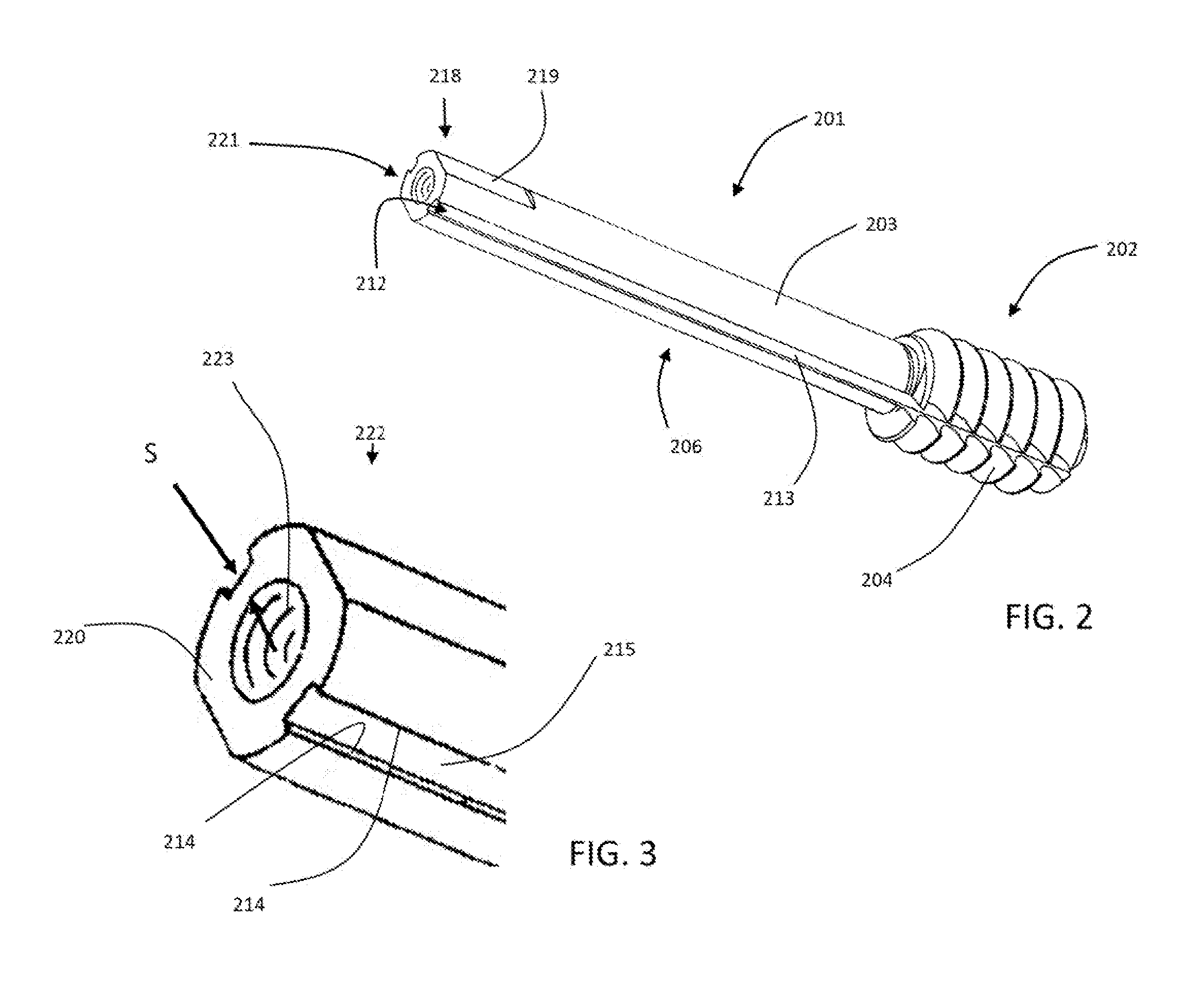
Bone length adjustment method and system includes a two-part telescopic device connected to bone parts whose length between the connection points is to be adjusted, with each part of the telescopic device being secured to the bone part, and a rod with an embedded permanent magnet which is in threaded engagement at one or both of its ends with one or both of the parts of the telescopic device. The permanent magnet in the rod is excited by an external solenoid arrangement to cause a radial force to develop at the rod thereby causing it to rotate. Rotation of the rod is converted via the threads at one or both of its ends to axial motion or movement of the telescopic parts relative to each other and thereby causes an increase or decrease in the bone length depending on the direction of axial movement between the telescopic parts.
Owner:EKSLER AUGUST +2
Implant for fixing two bone parts to be connected to each other
InactiveUS20070276387A1Increase distanceAvoid leaningSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringBones parts
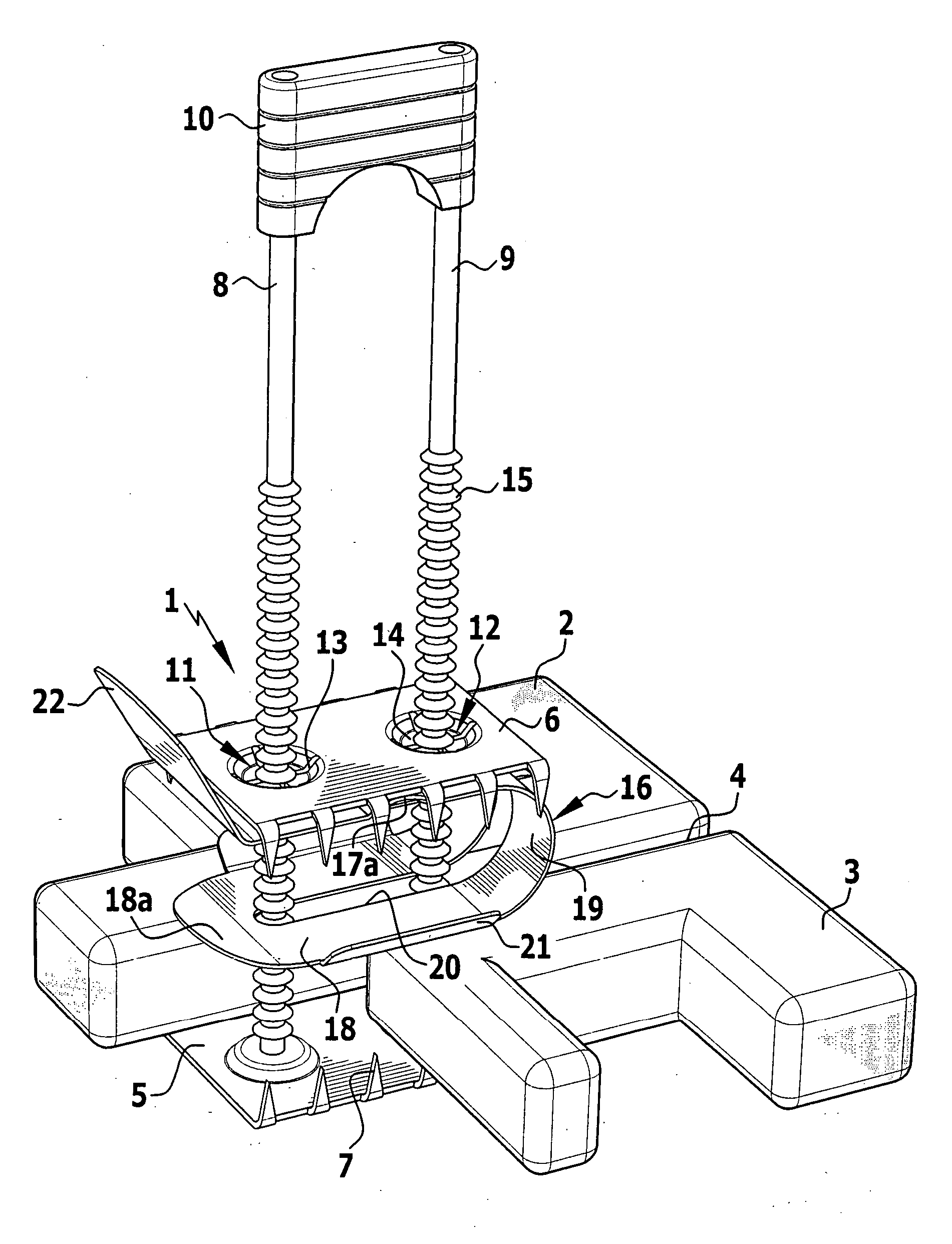
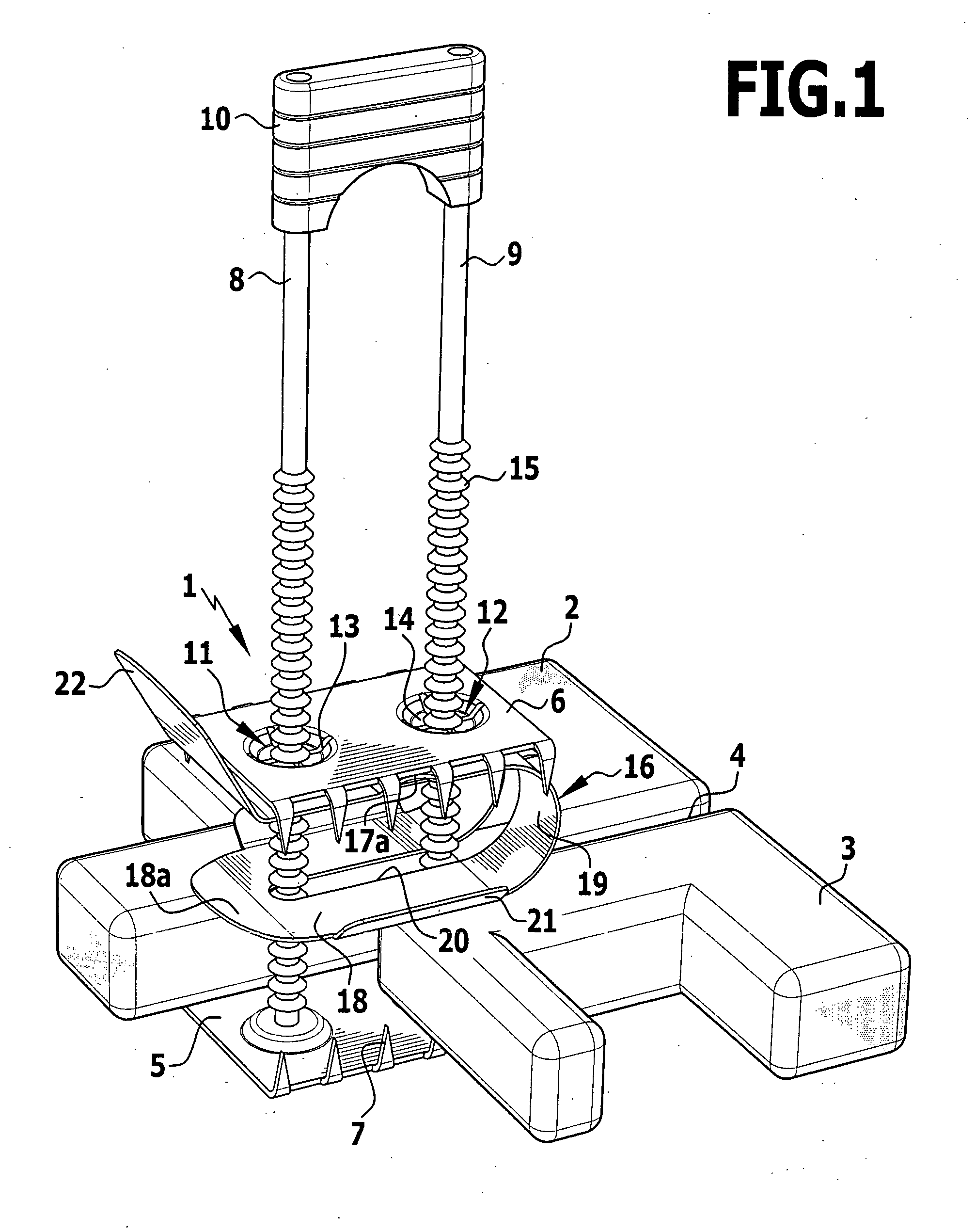
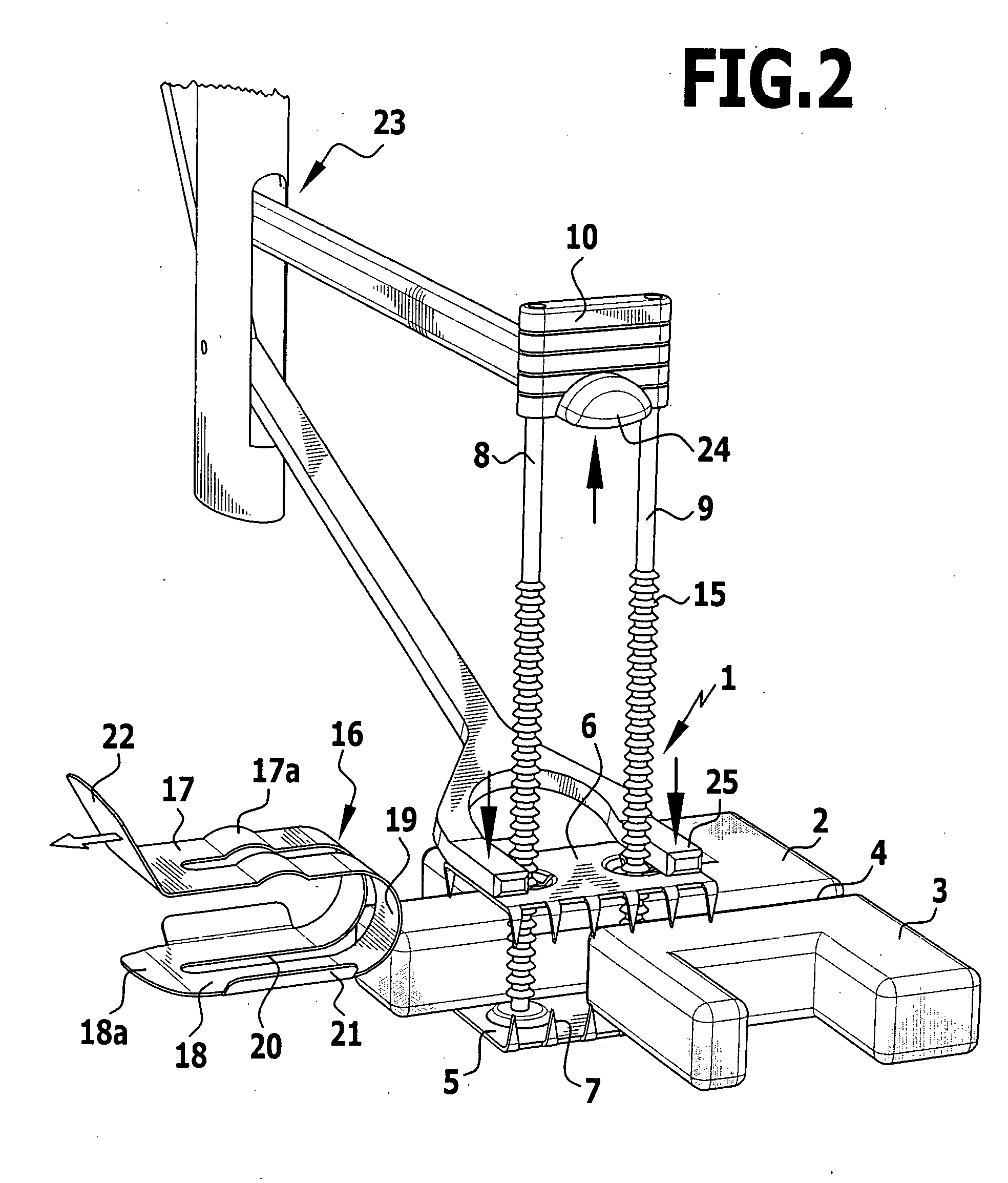
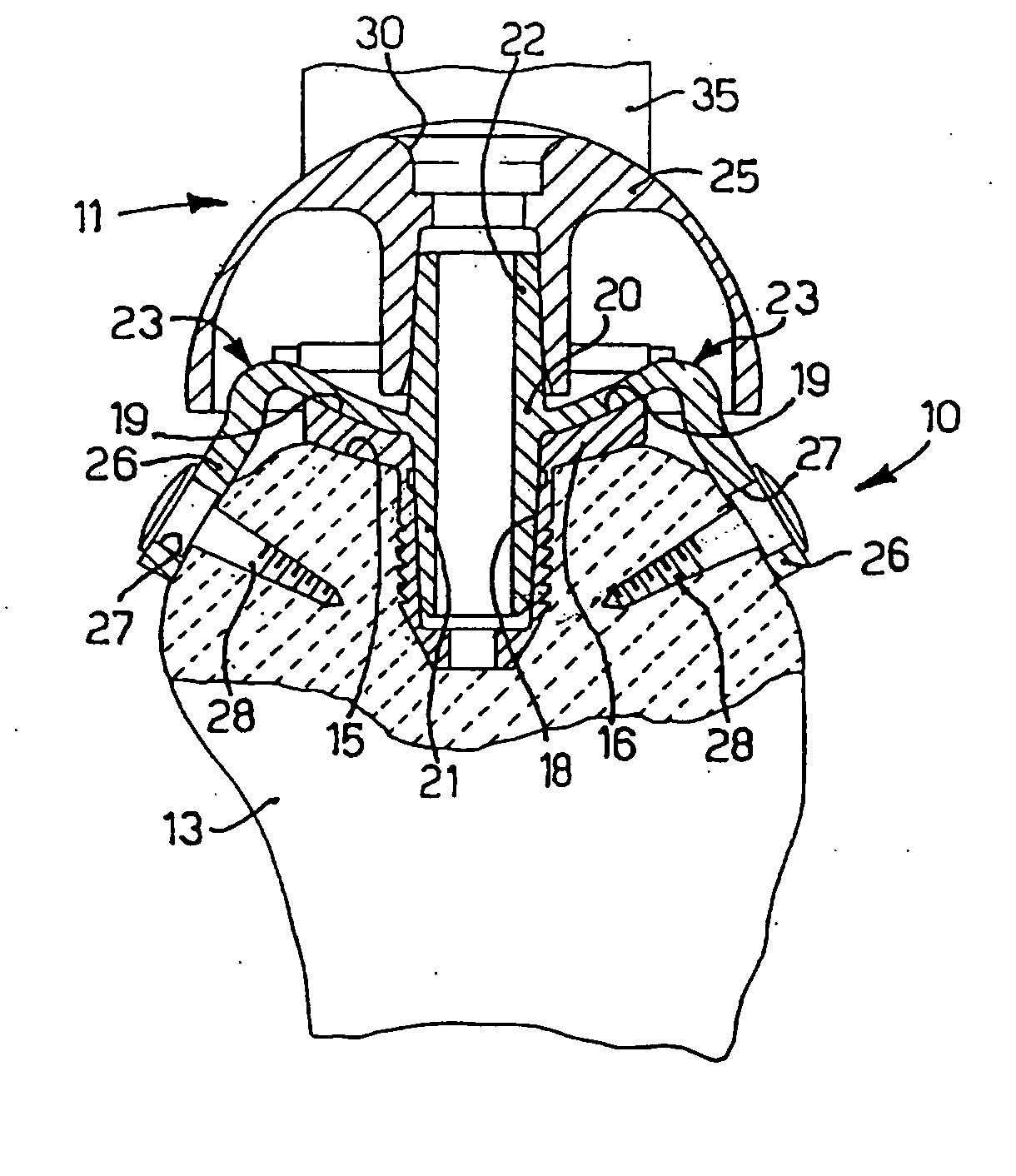
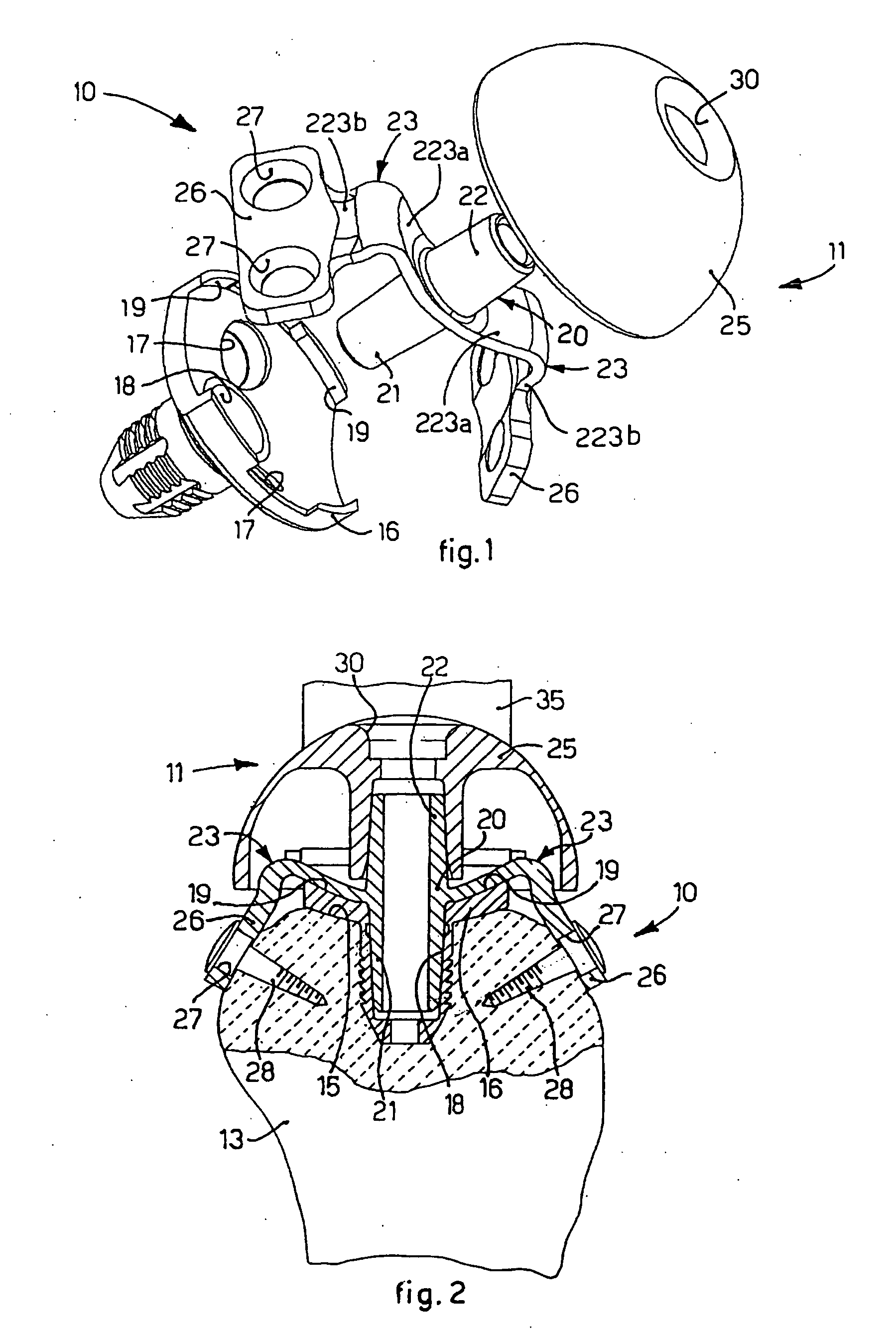
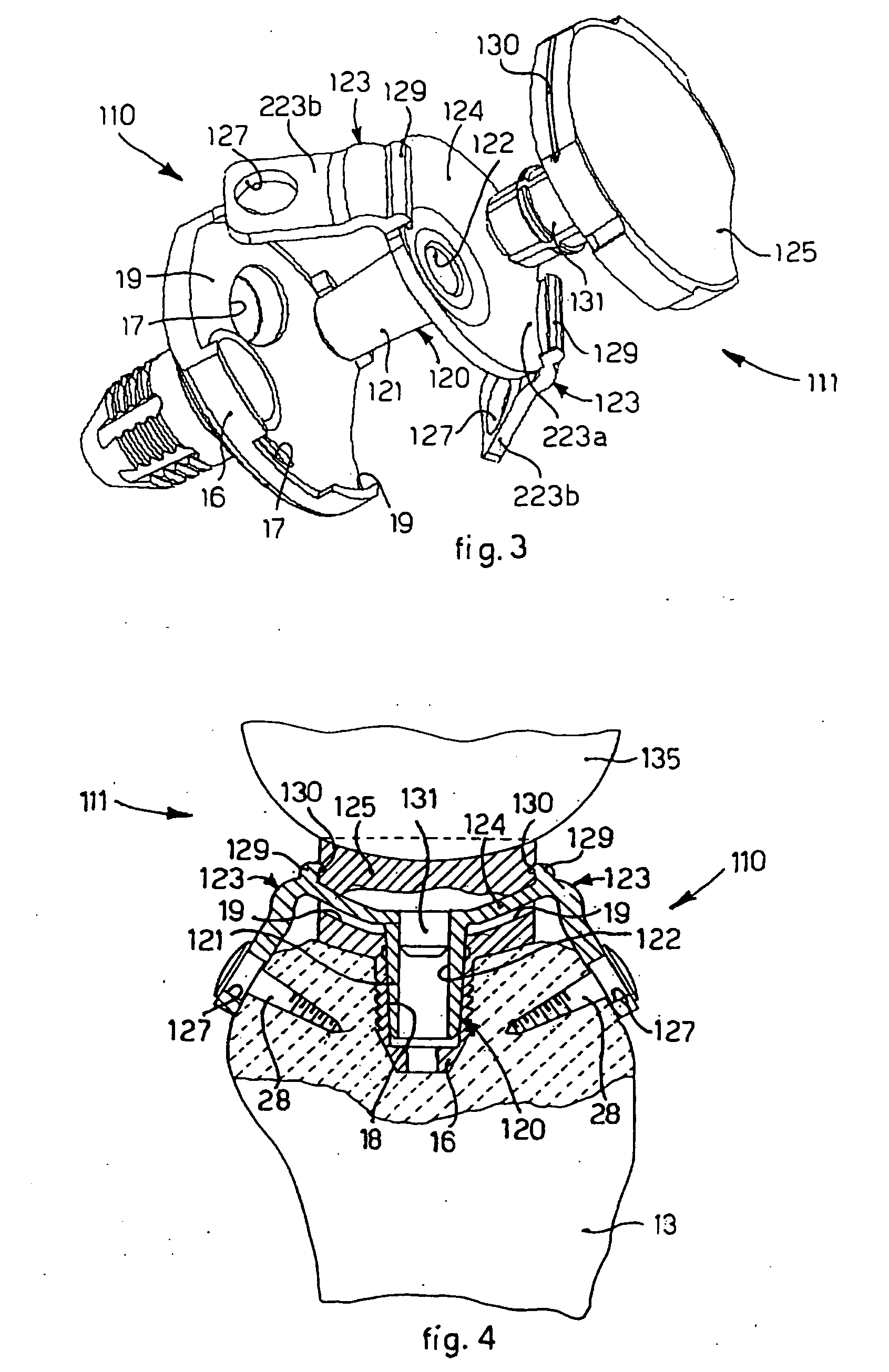
An implant for fixing two bone parts to be connected to each other is provided. The implant includes a first plate-shaped engaging element for engaging inner surfaces of the bone parts, at least two tensioning elements fixed on the engaging element and projecting transversely from it, and a second plate-shaped engaging element for engaging outer surfaces of the bone parts. The second engaging element can be tensioned with respect to the first engaging element by means of the tensioning elements brought through the interspace between the bone parts. To improve the ease of handling of the implant during tensioning, it is proposed that the tensioning elements are connected to each other at their end opposite from the first engaging element by a bridge.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Attachment element for a prosthesis for the articulation of the shoulder
ActiveUS20070100458A1Improve positional stabilityJoint implantsShoulder jointsMetatarsal bone partProsthesis
Attachment element for a prosthesis of the shoulder for the articulation of a humerus in a scapula of a shoulder having a glenoid cavity. The prosthesis comprises a first articulation element associated with the top of the humerus, and a second articulation element associated with the glenoid cavity. The attachment element comprises a first part for removable anchorage to the first or second articulation element, and a second part for attachment of the prosthesis to the bone part of the scapula in a position outside the bulk of the first and second articulation element.
Owner:LIMA CORPORATE SPA
Device for lengthening bones or bone parts
Owner:WITTENSTEIN GROUP
Bone treatment method with implants and instrumentation
A method, instrumentation and implants for a minimally invasive bone and joint treatments allow cuts in bones to be made simultaneously. This method produces a simple precise alignment of cuts on opposite sides of a joint or bone part. It eliminates many steps need to align the numerous cuts used in current joint replacement and bone treatments. In some cases only one cut will be needed. The cuts can also easily be adapted to different anatomical variation and allows implants to be implanted in a fashion where the implants oriented individually in several different planes. The method and instruments allows for other joint and bone treatments besides joint replacement.
Owner:HYDE EDWARD ROBERT JR
Implant system and fastening element for an implant system
InactiveUS20060195098A1Easy to optimizeStable supportSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAxis of symmetryEngineering
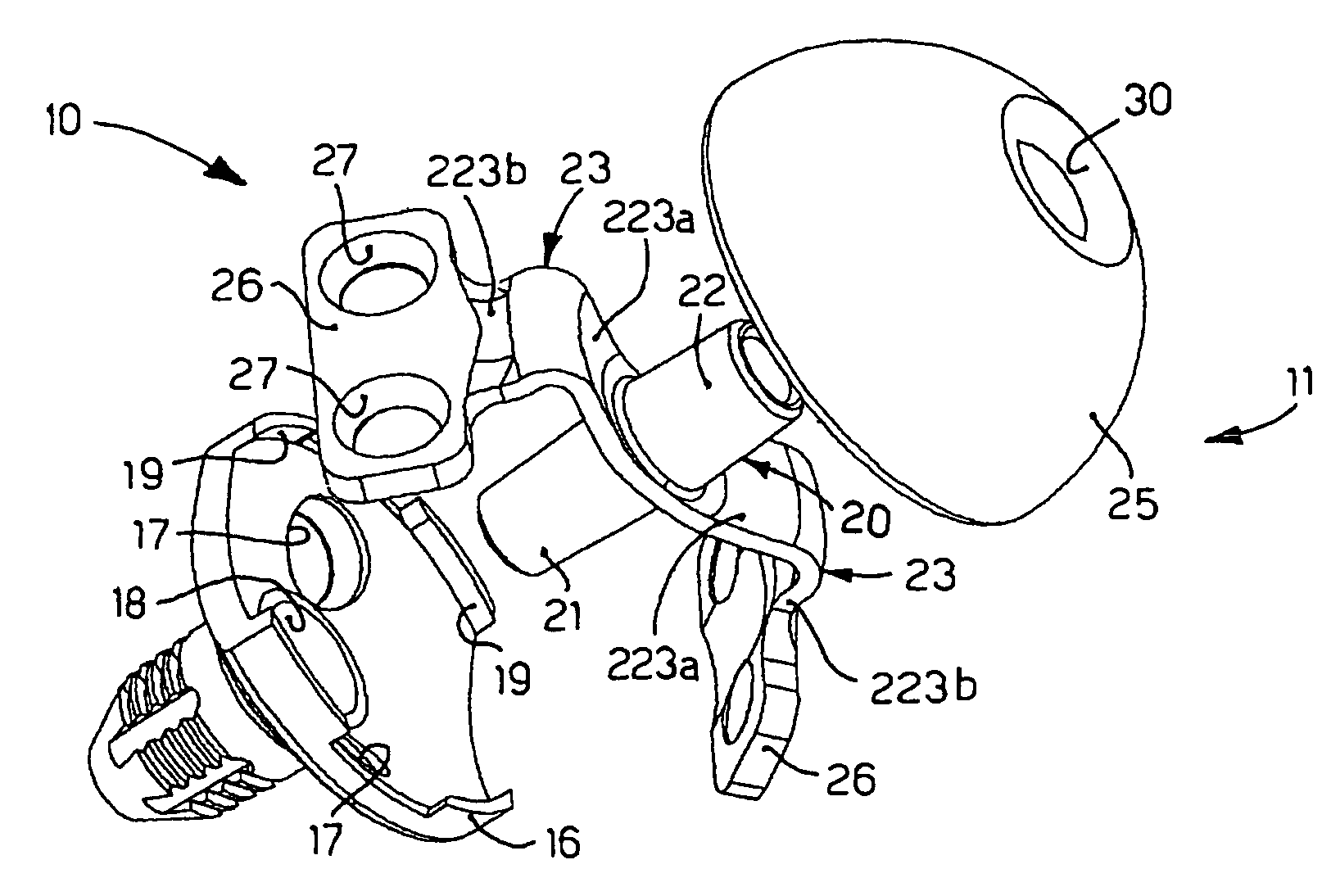
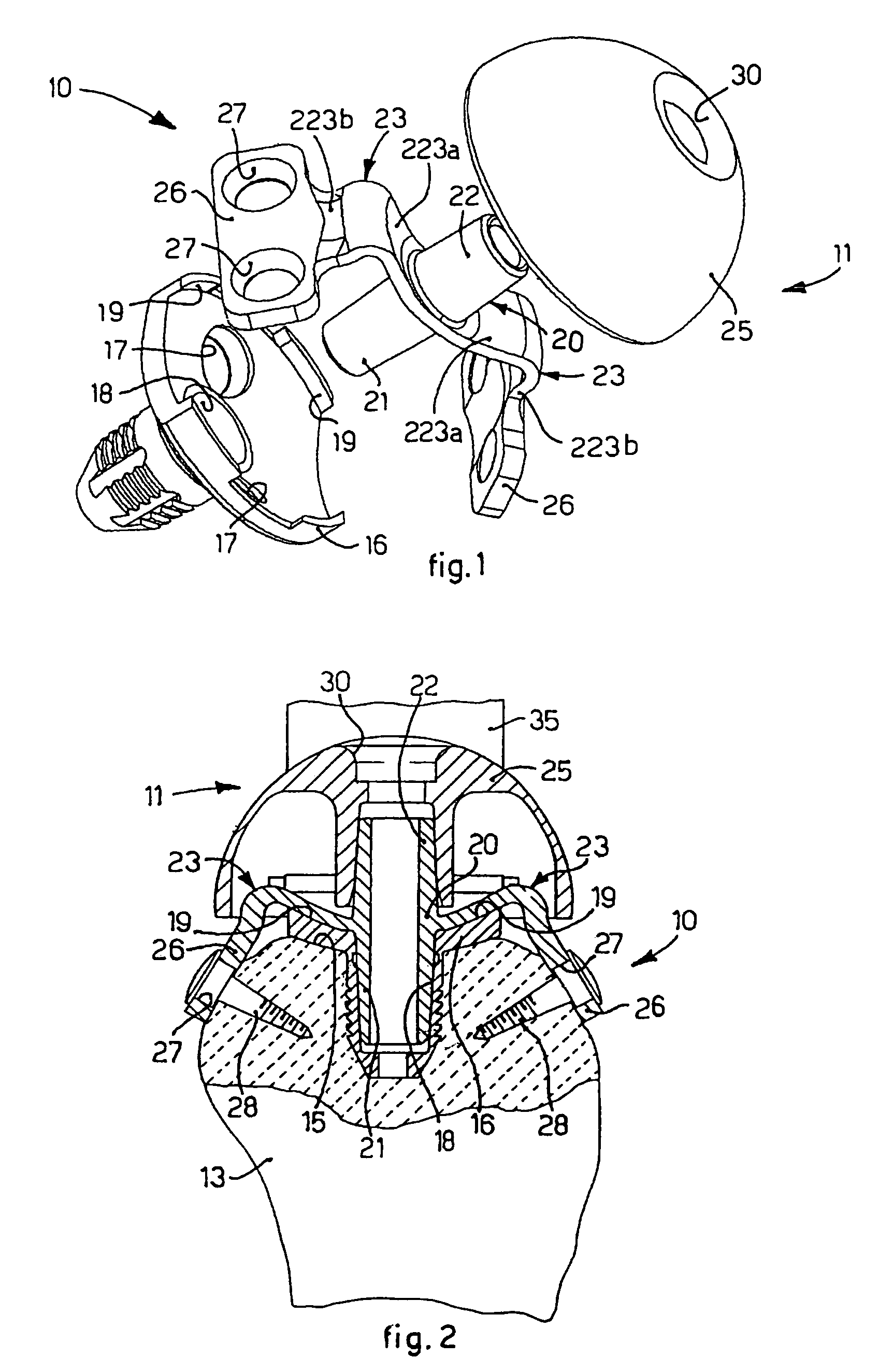
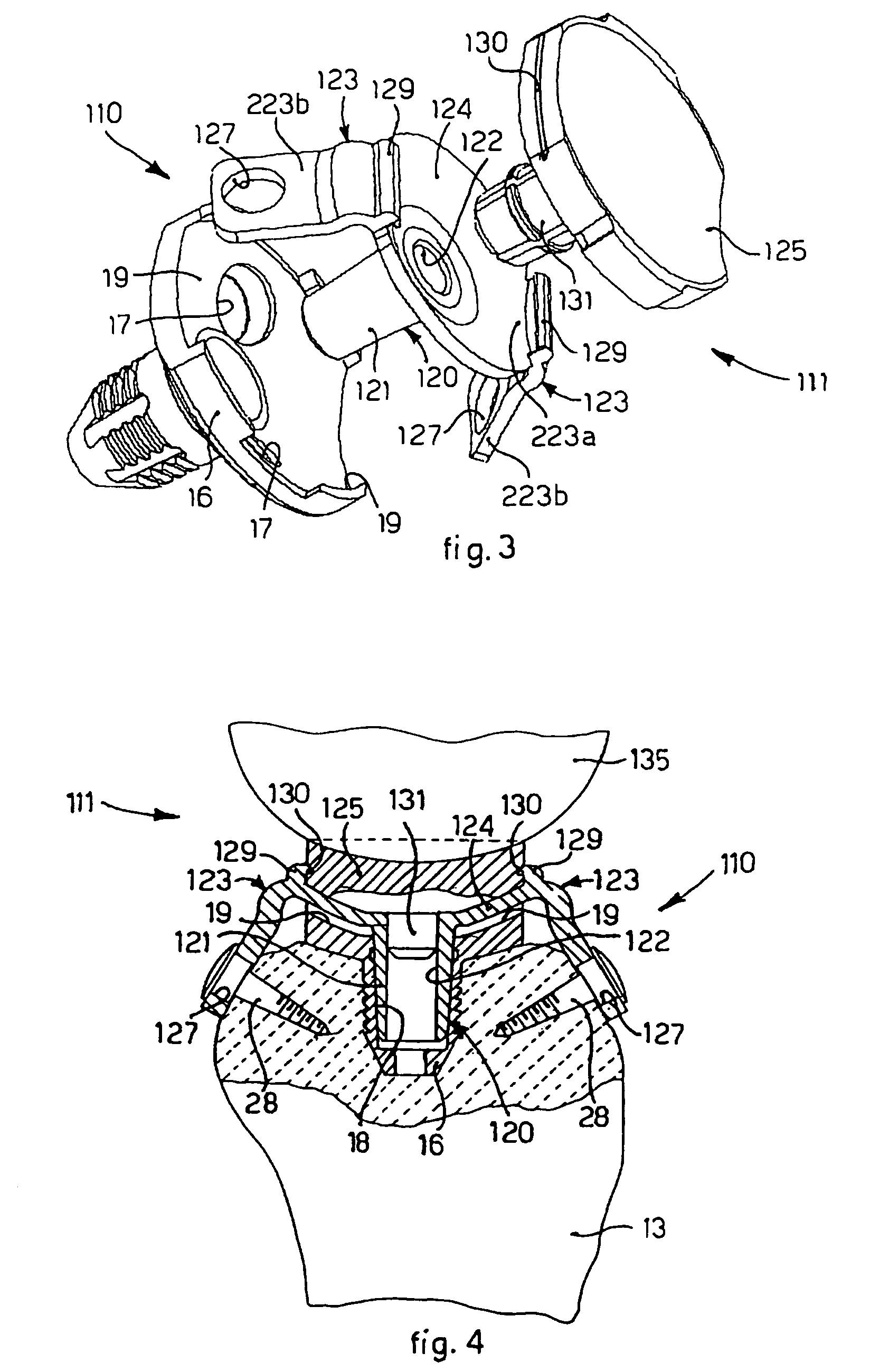
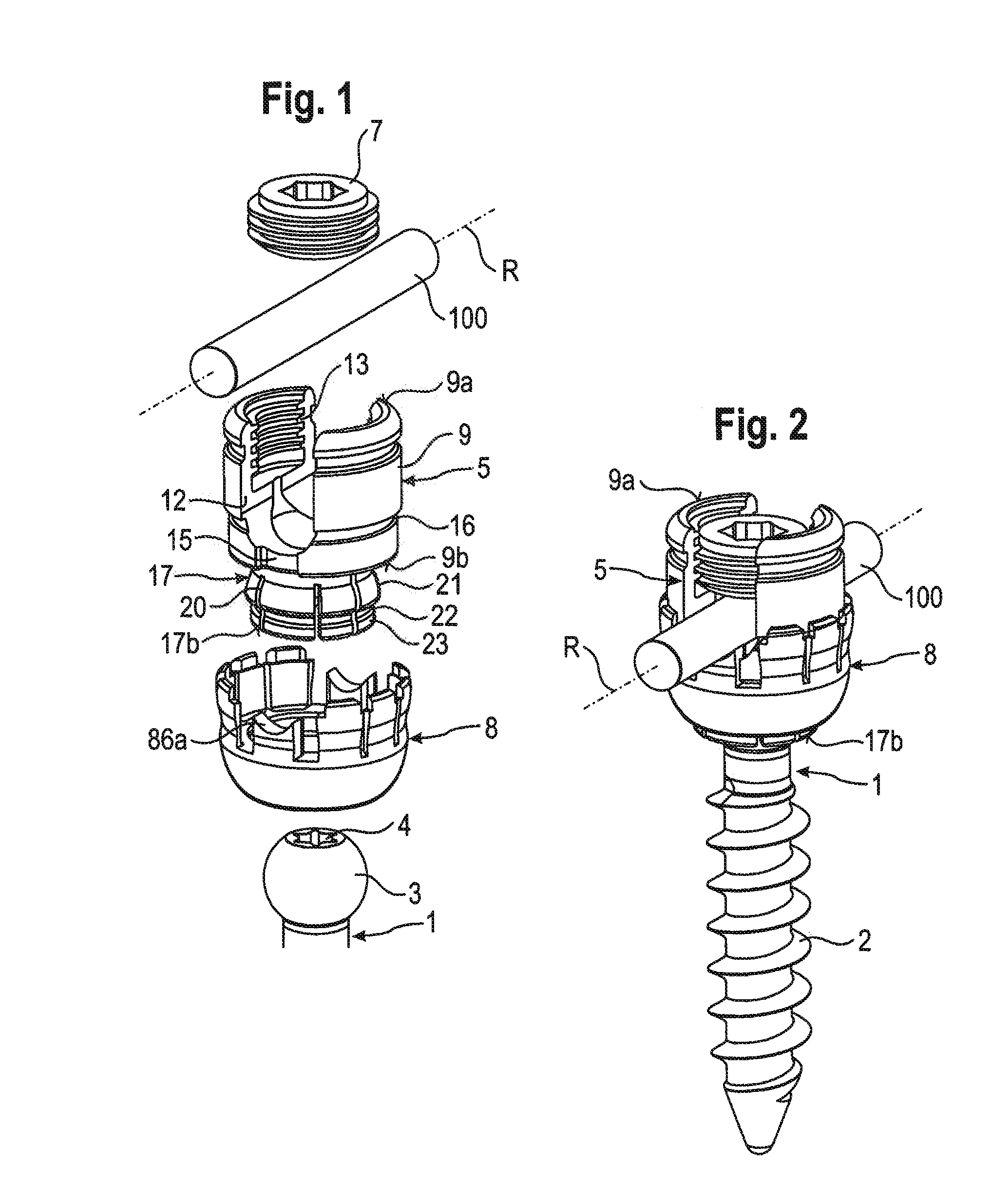
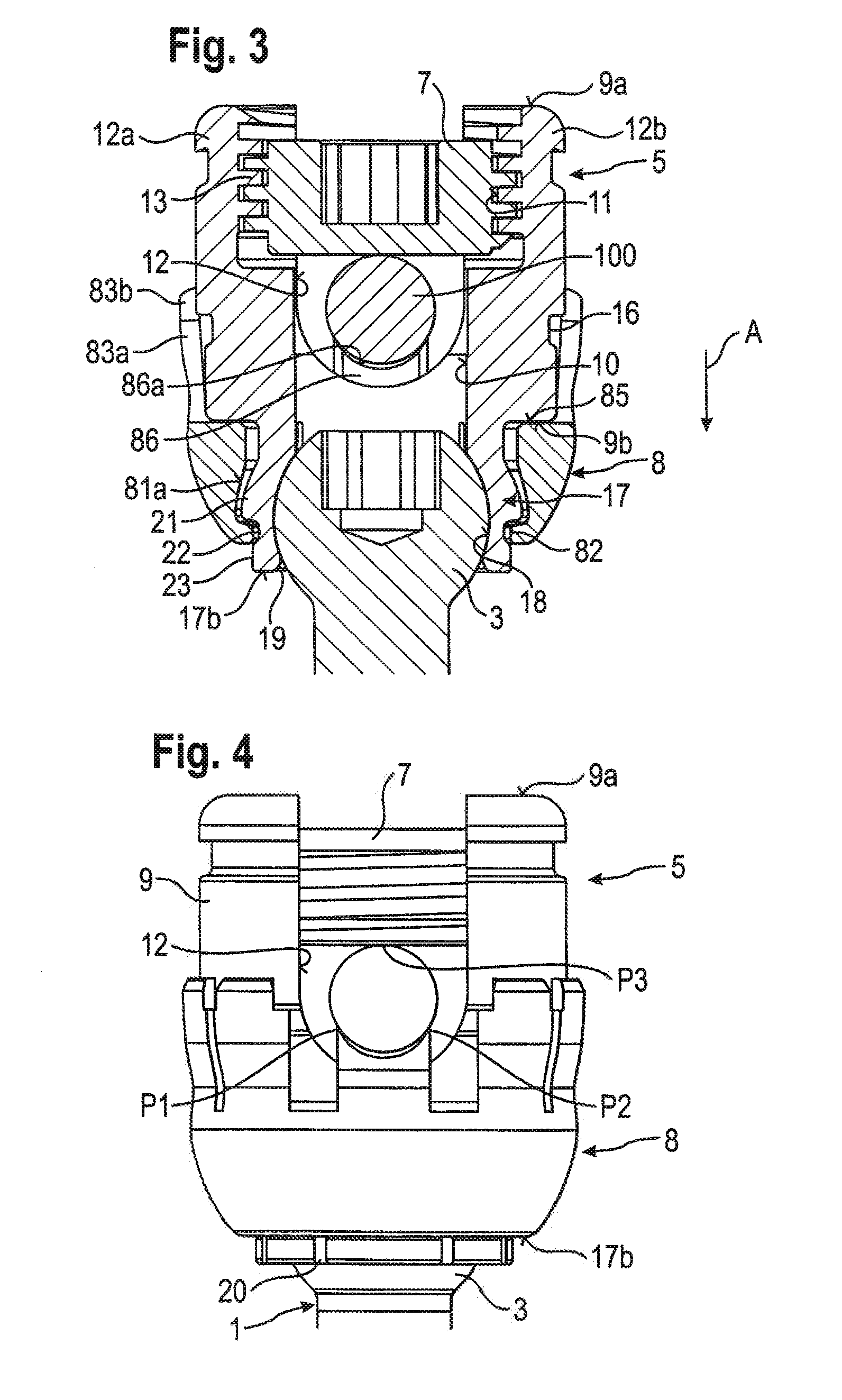
The present invention relates to a fastening element for an implant system, which comprises at least two fastening elements fixable to bone parts or the like and at least one connecting element fixable to the at least two fastening elements, wherein the fastening element comprises a fastening part with a fastening portion at the distal end as well as a receiving part connected to the fastening part, wherein the receiving part comprises a connecting-element receiver for receiving the connecting element as well as a fixing element for fixing the fastening element in the connecting-element receiver, wherein the connecting-element receiver is designed asymmetrically in relation to an axis of symmetry or longitudinal axis of the fixing element.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Preparation for repairing cartilage defects or cartilage/bone defects in human or animal joints
InactiveUS6858042B2Reduce absorptionResistant to resorptionBone implantJoint implantsRepair tissueCyst
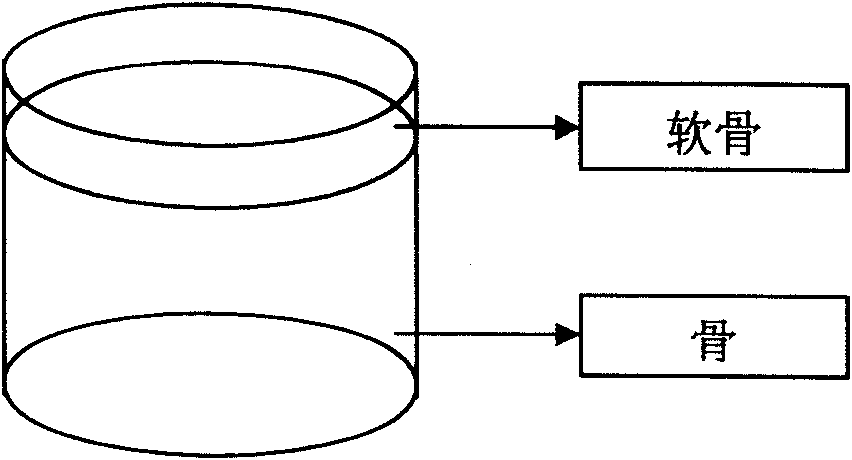
Repairs of cartilage defects or of cartilage / bone defects in human or animal joints with the help of devices including a bone part (1), a cartilage layer (2) and a subchondral bone plate (4) or an imitation of such a plate in the transition region between the cartilage layer (2) and the bone part (1). After implantation, the bone part (4) is resorbed and is replaced by reparative tissue only after being essentially totally resorbed. In a critical phase of the healing process, a mechanically inferior cyst is located in the place of the implanted bone part (1). In order to prevent the cartilage layer (2) from sinking into the cyst space during this critical phase of the healing process the device has a top part (11) and a bottom part (12), wherein the top part (11) consists essentially of the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) and the bottom part (12) corresponds essentially to the bone part (1) and wherein the top part (11) parallel to the subchondral bone plate (4) has a larger diameter than the bottom part (12). After implantation in a suitable opening or bore (20), the cartilage layer (2) and the subchondral bone plate (4) are supported not only on the bone part (1) but also on native bone tissue having a loading capacity not changing during the healing process. Therefore, the implanted cartilage layer cannot sink during the healing process.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
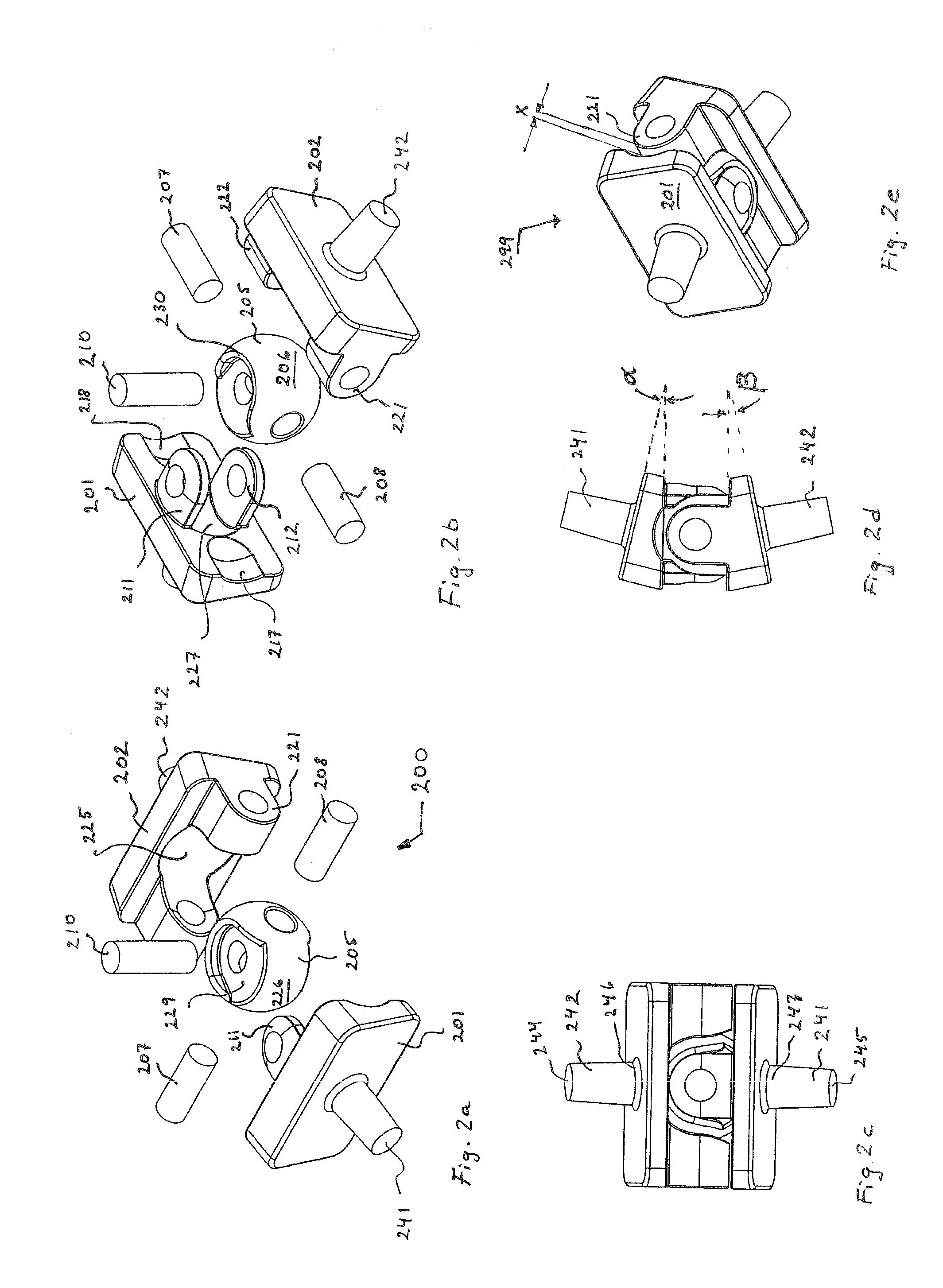
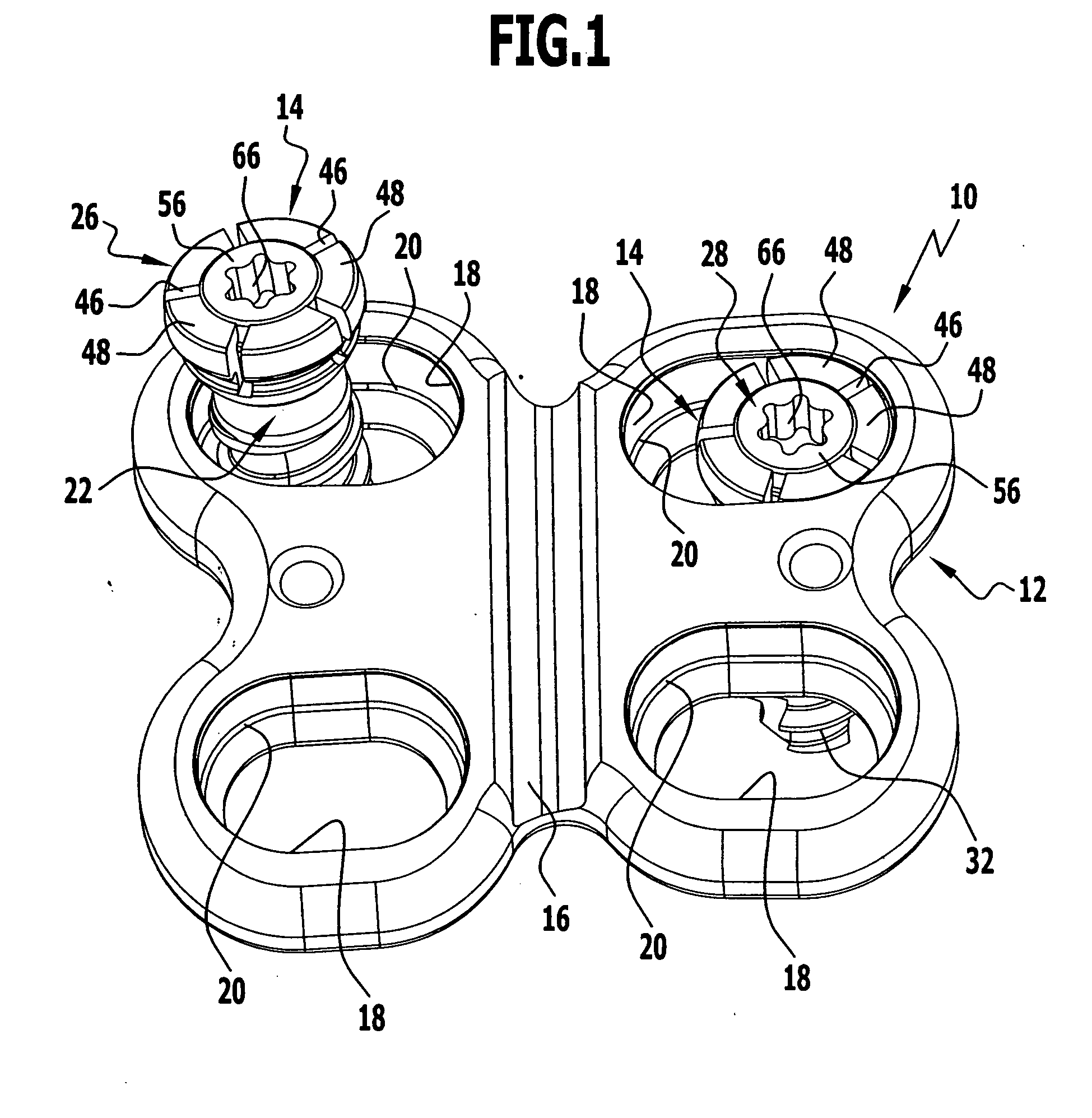
Bone fastener assembly for bone retention apparatus
ActiveUS20060149231A1Good adhesionEasily attached to applianceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisThumb oppositionBearing surface
A bone fastener assembly, comprising a bone fastener, an adjusting member and a securing fastener is provided for fastening an appliance to a bone body so that a plurality of the bone fastener assemblies and the appliance constitute an apparatus that acts to retain a plurality of bone bodies in a desired spatial relationship. Each bone fastener has an attaching portion for attaching the bone fastener to a bone or bone part, a supporting portion for supporting the adjusting member for universal movement relative to the supporting portion, and a securing portion for securing the bone fastener to the securing fastener. The securing fastener has a first end that passes through an aperture in the appliance and an opening in the adjusting member and is secured to the securing portion of the bone fastener. A second end of the securing fastener has a bearing surface that adjustably bears against the appliance in opposition to an engaging surface of the adjusting member that engages the appliance.
Owner:BRAY ROBERT S JR DR
Attachment element for a prosthesis for the articulation of the shoulder
ActiveUS7608109B2Improve positional stabilityJoint implantsShoulder jointsMetatarsal bone partArticular cavity
Attachment element for a prosthesis of the shoulder for the articulation of a humerus in a scapula of a shoulder having a glenoid cavity. The prosthesis comprises a first articulation element associated with the top of the humerus, and a second articulation element associated with the glenoid cavity. The attachment element comprises a first part for removable anchorage to the first or second articulation element, and a second part for attachment of the prosthesis to the bone part of the scapula in a position outside the bulk of the first and second articulation element.
Owner:LIMA CORPORATE SPA
Bone separator
ActiveUS7927337B2Arrangement is especially simple and clearInternal osteosythesisProsthesisTransverse grooveEngineering
A bone spreader includes two tubular pin holders which are connected to one another by a parallel guide system, and two pins that are configured to be connected to the bone parts that are to be spread apart. In order to give the bone parts that are to be spread apart a more secure position in relation to one another, at least one of the pin holders is provided with a locking device for a pin located in the pin holder. This locking device includes a locking finger which is movable tangentially with respect to the pin holder and which, in the locking position, engages in a transverse groove of the associated pin and can be formed by a pivotably mounted hook.
Owner:CERVITECH INC
Apparatus for the correction of chest wall deformities such as pectus carinatum and method of using the same
InactiveUS20040117016A1Easy to compressEasy to insertBone implantJoint implantsChest wall deformityEngineering
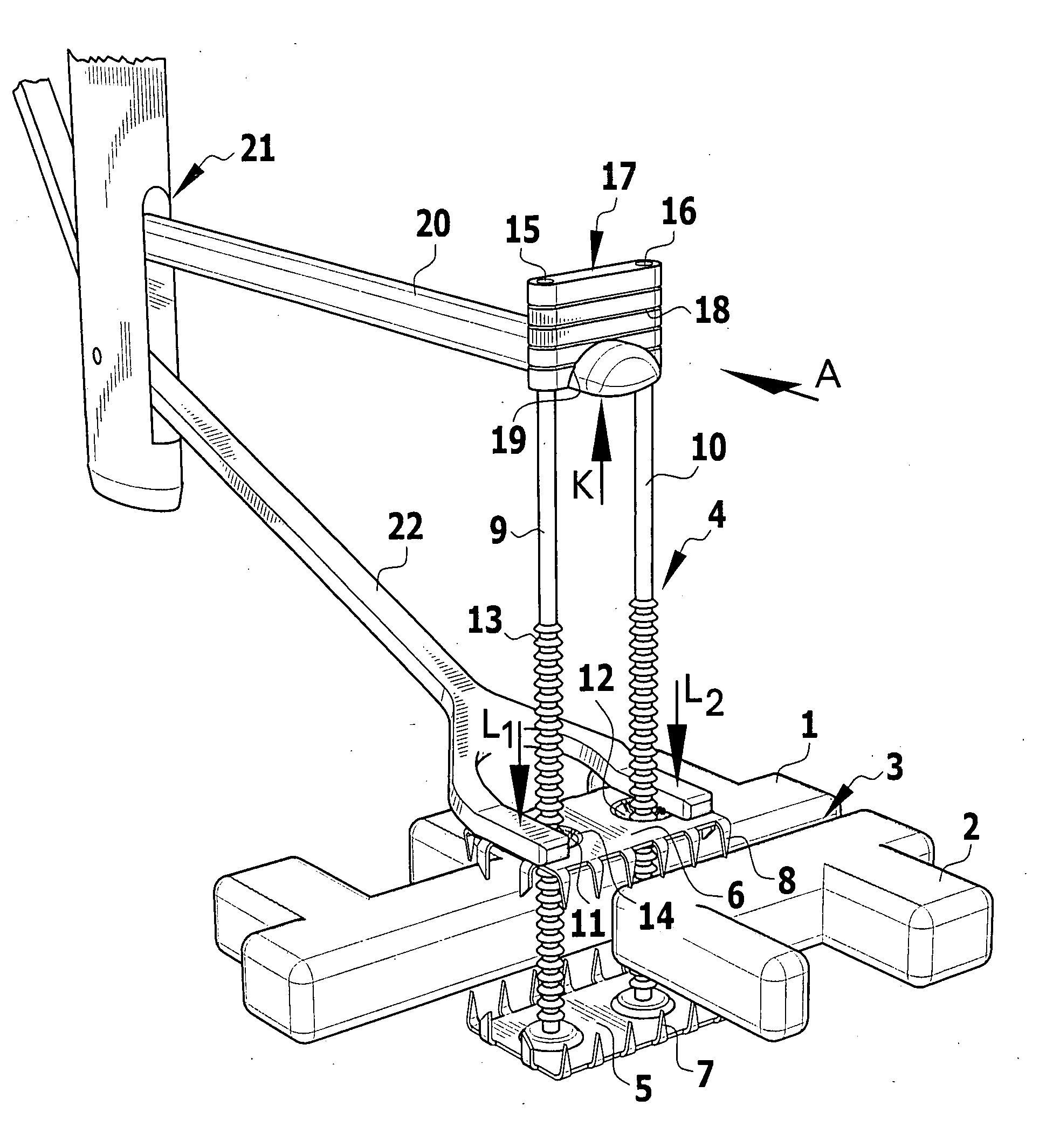
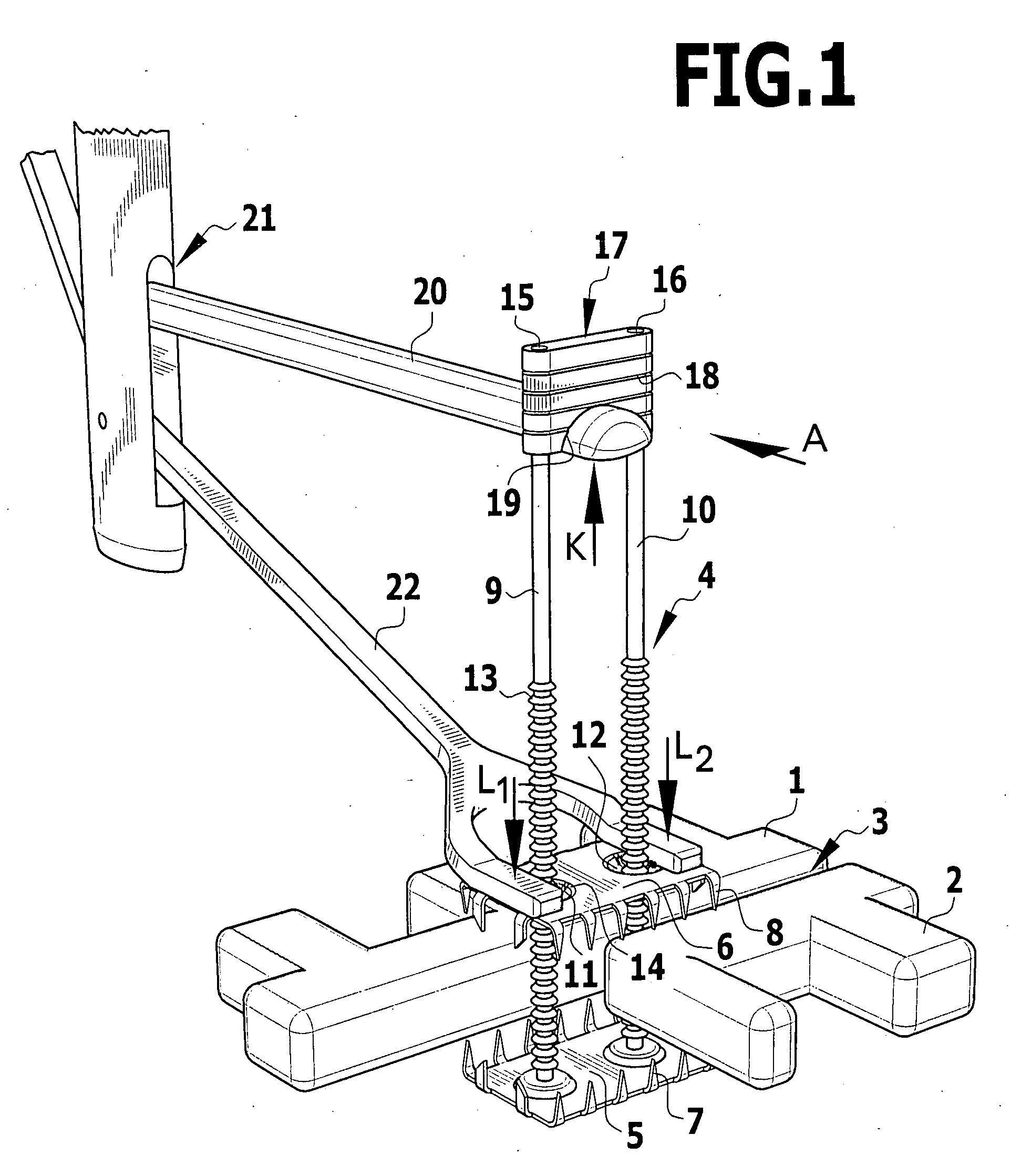
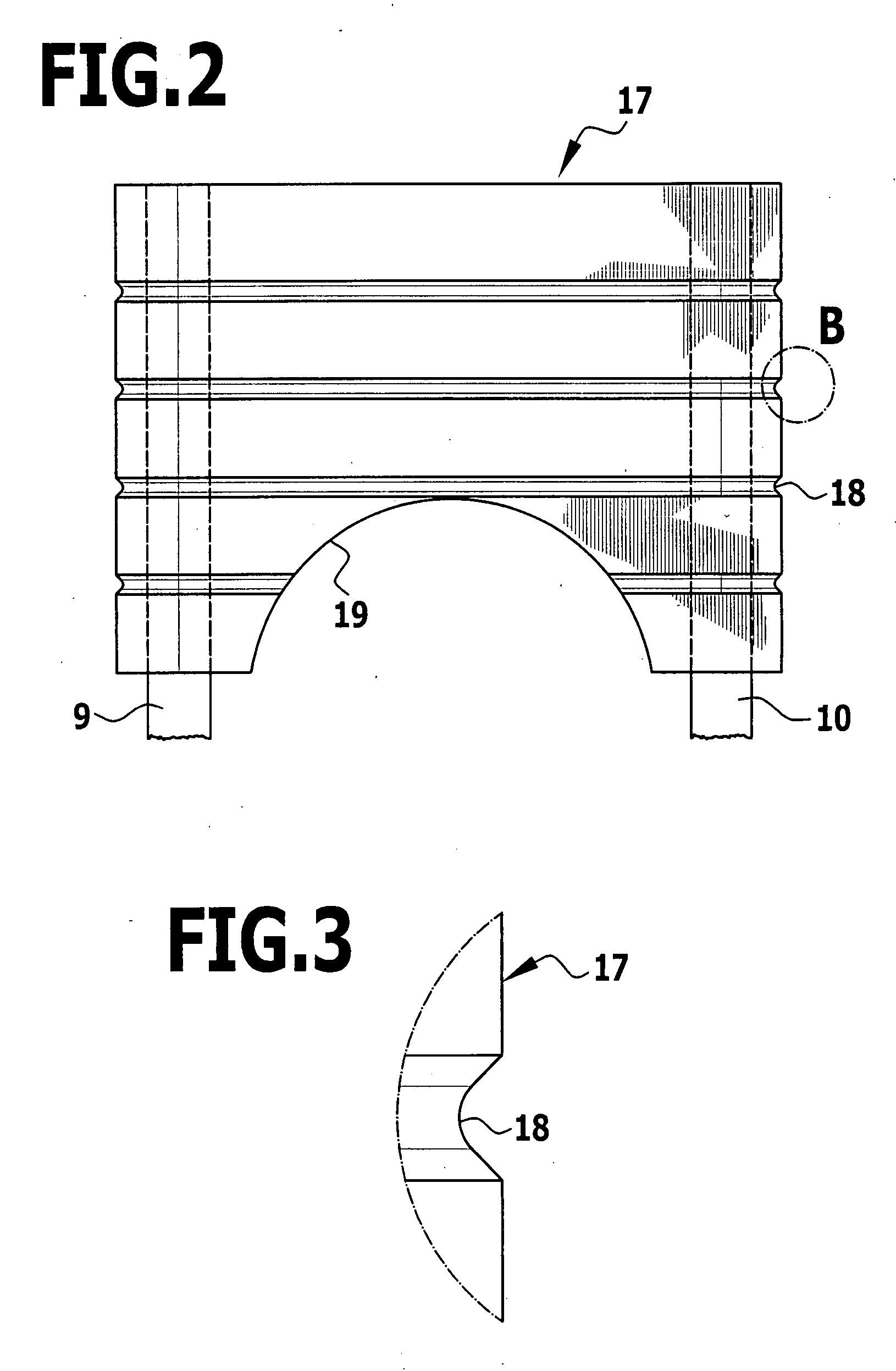
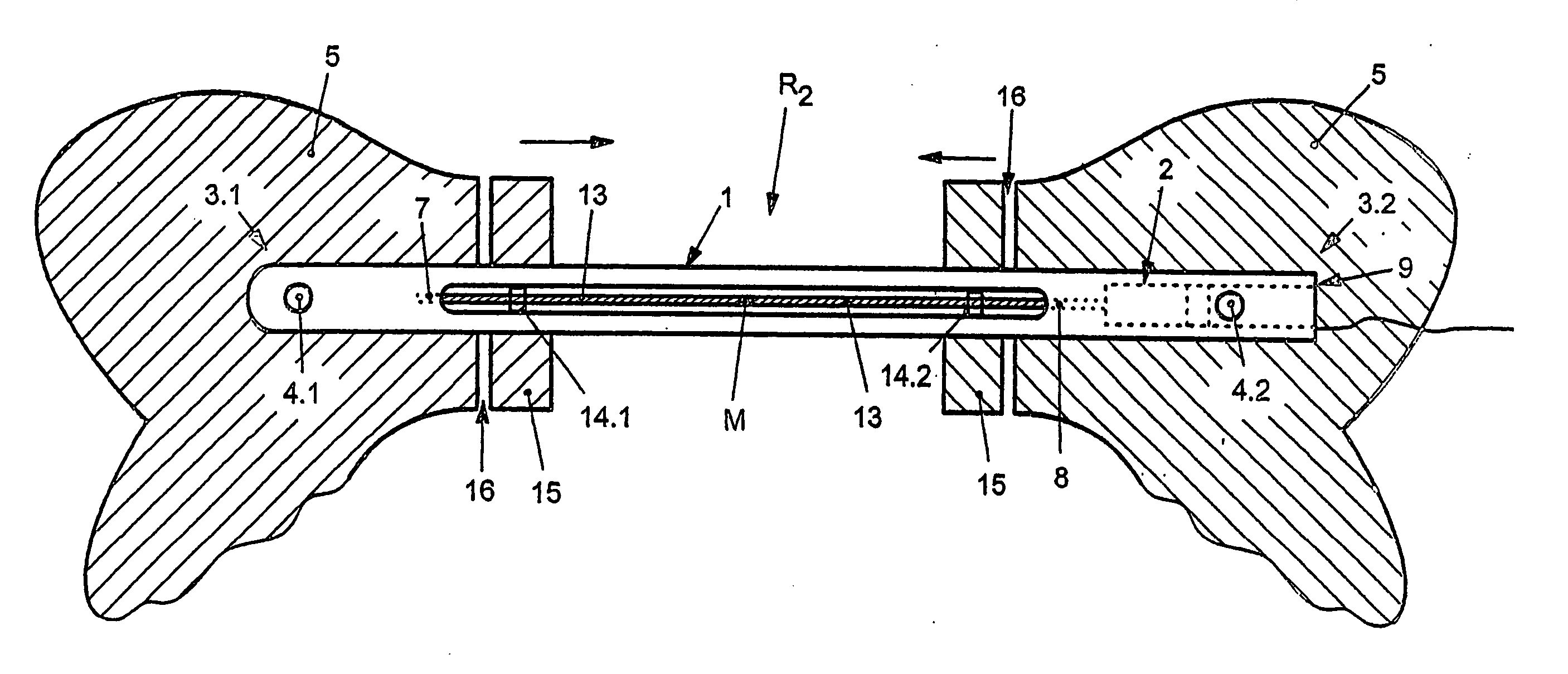
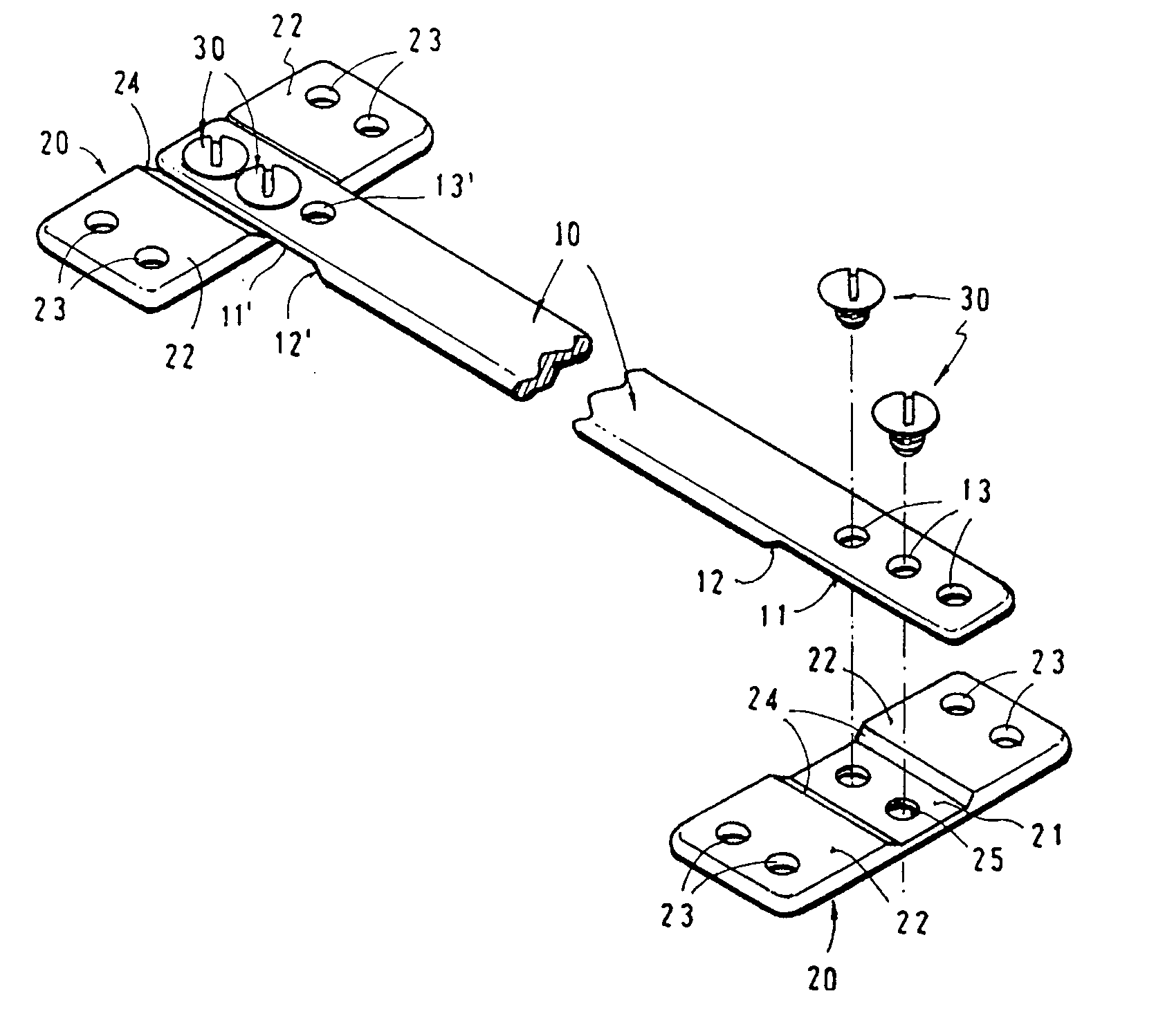
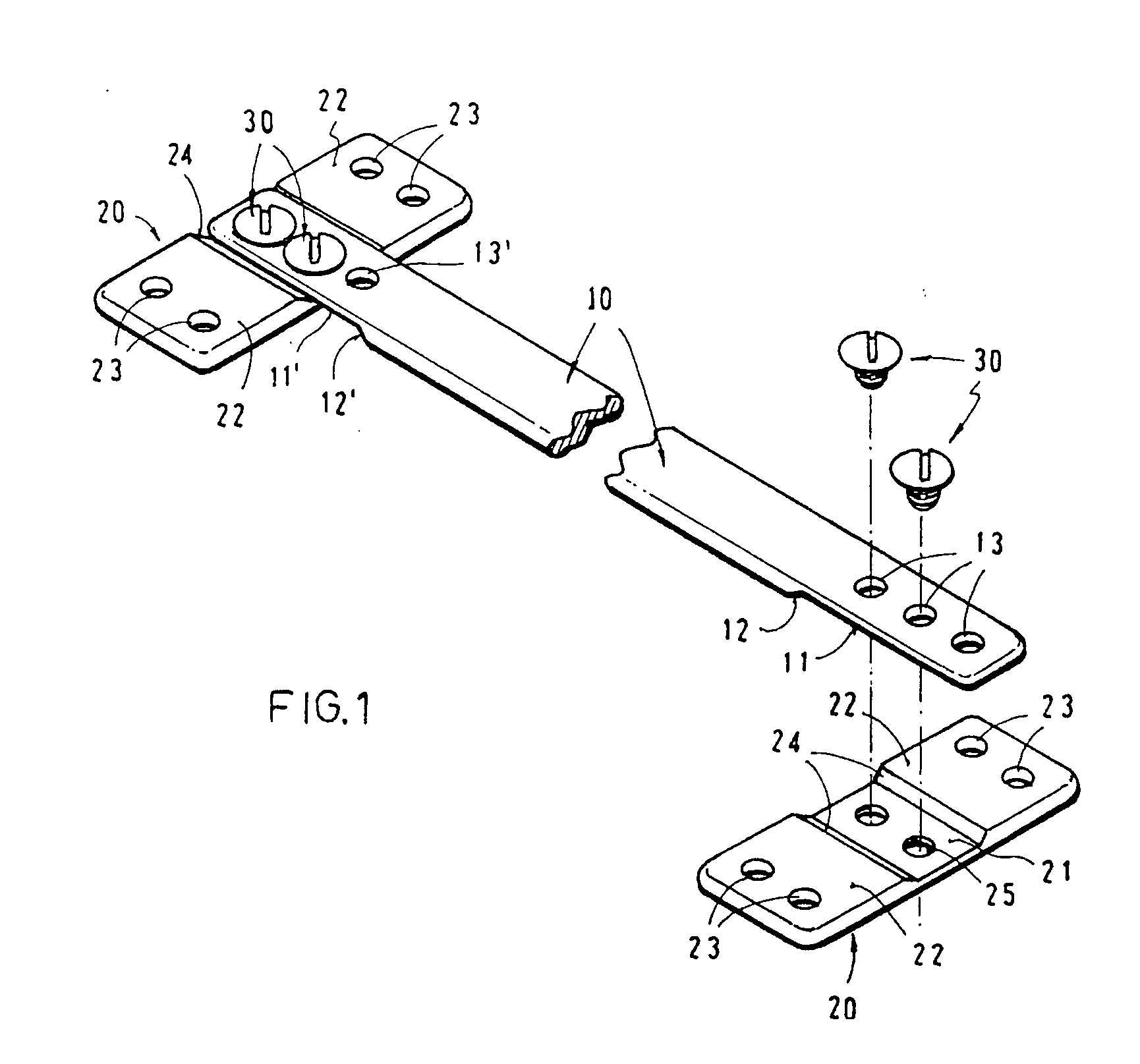
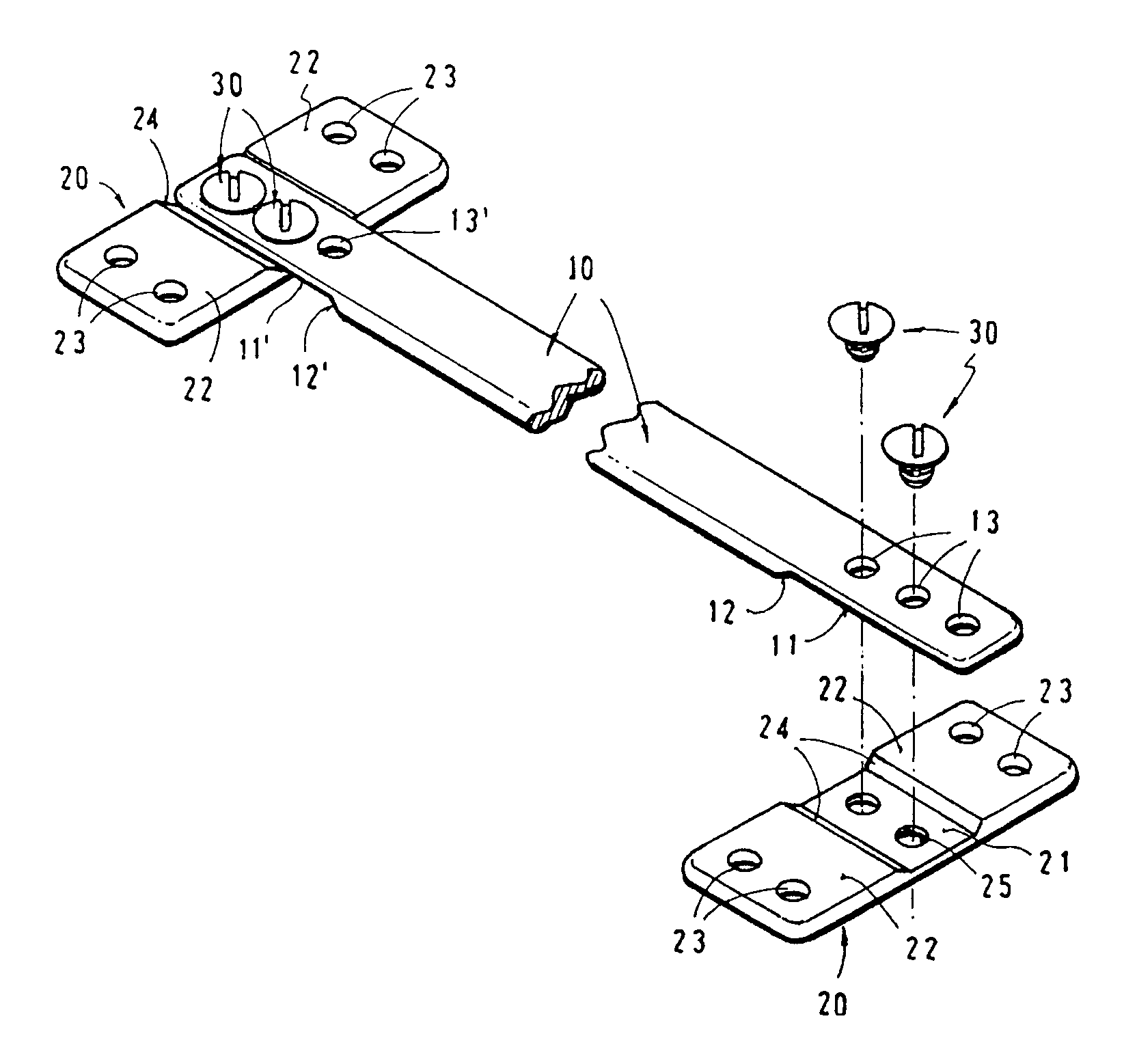
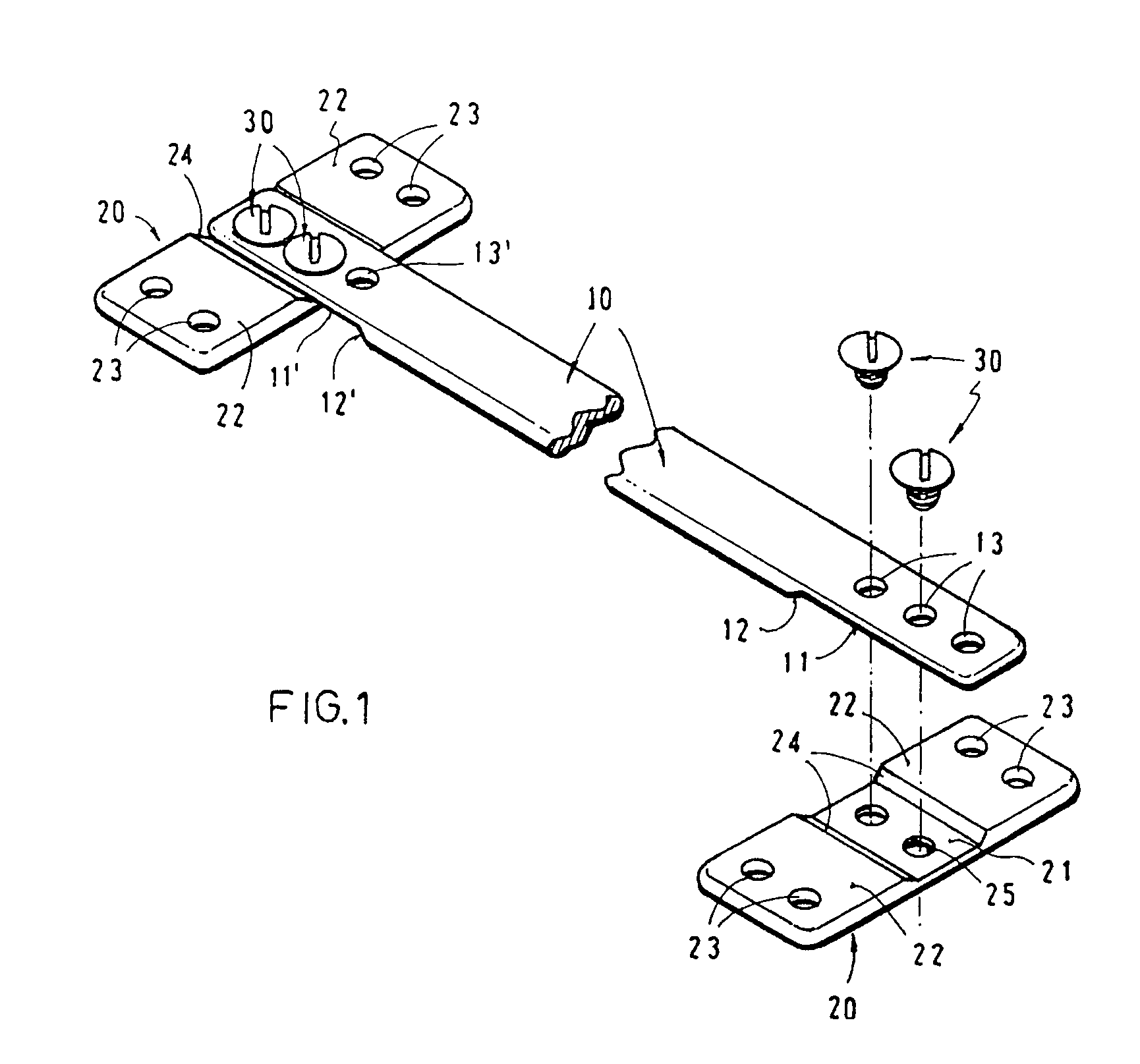
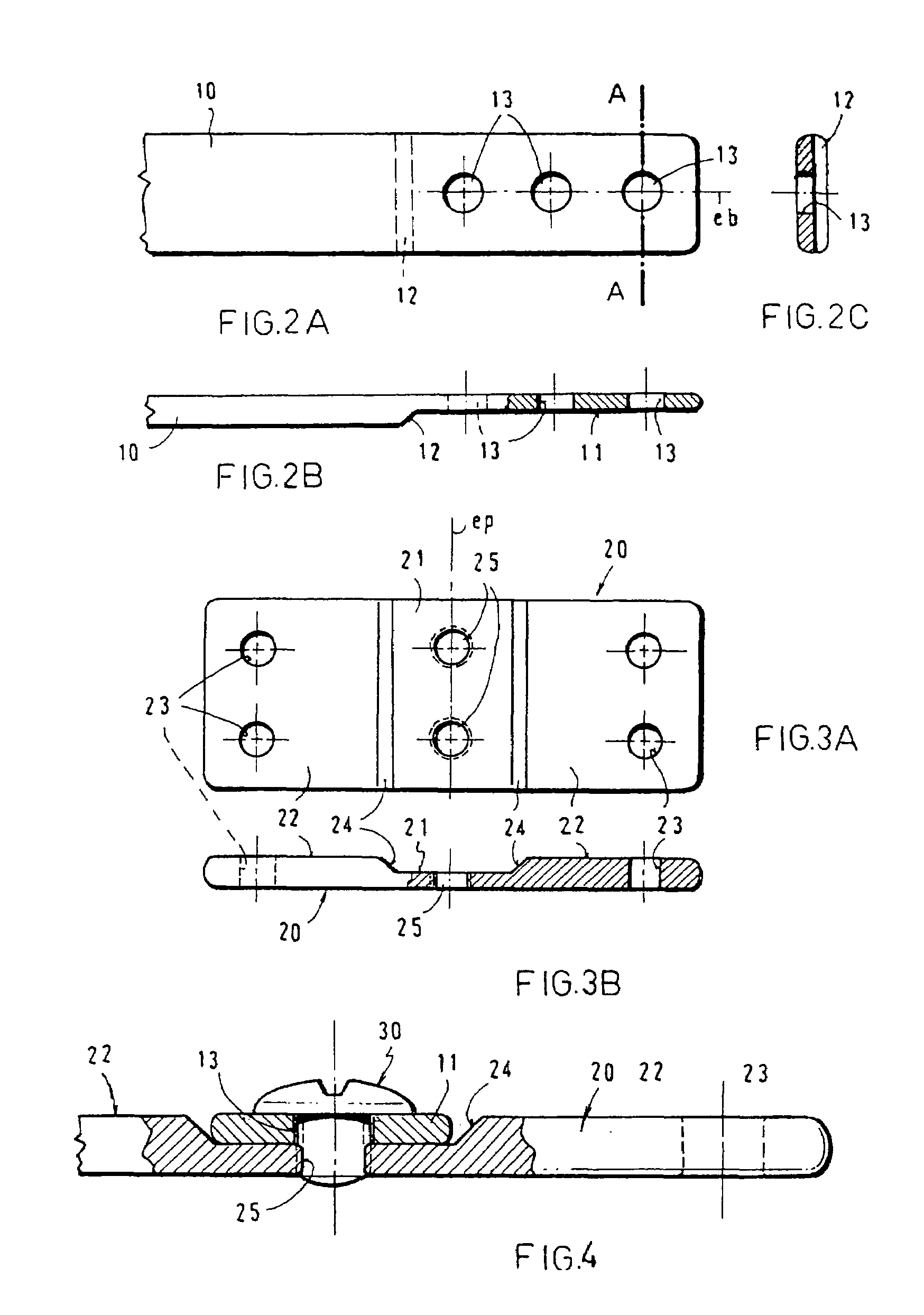
An apparatus for the correction of wall chest deformities, such as "Pectus Carinatum", comprising: a bar (10) having a flattened cross-section, having a minimum bending strength according to the values defined by ASTM F382-95, plates (20) having a slot (21) in the medium portion so as to fit the corresponding end of the bar (10) and peripheral holes (23) for securing the bone parts. The bar ends comprise planar grooves (11-11') determining the wall thickness substantially similar to the height of the slot (21) of the plate (20). The wall of the grooves (11-11') has aligned holes (13) in order to form with the respective plate (20) and by using screws (30), a fixed removable attachment that allows the axial registration of the bar (10). Method for the correction of Pectus Carinatum using said apparatus in order to achieve a normal anatomic shape of the chest wall.
Owner:ABRAMSON HORACIO
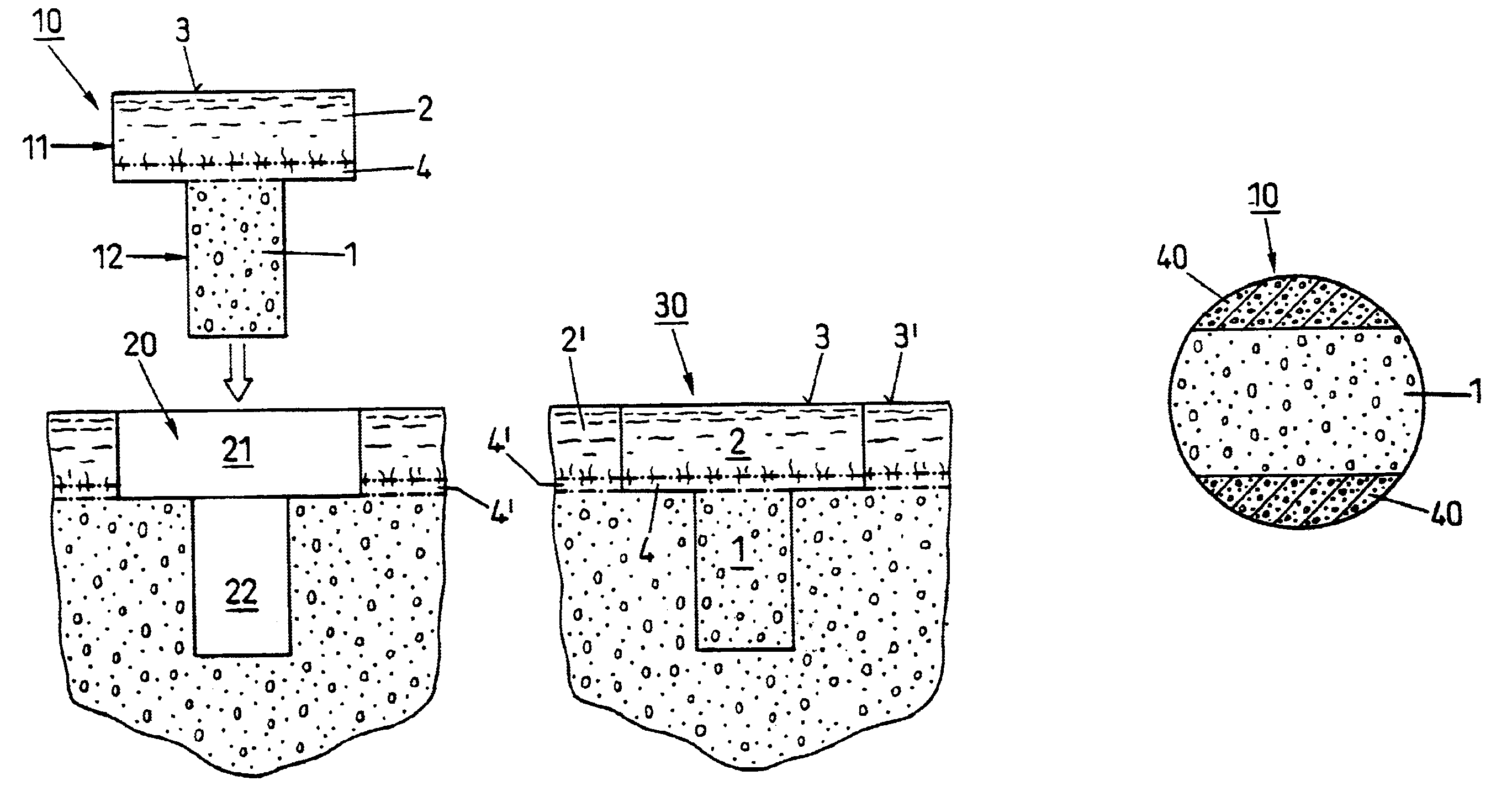
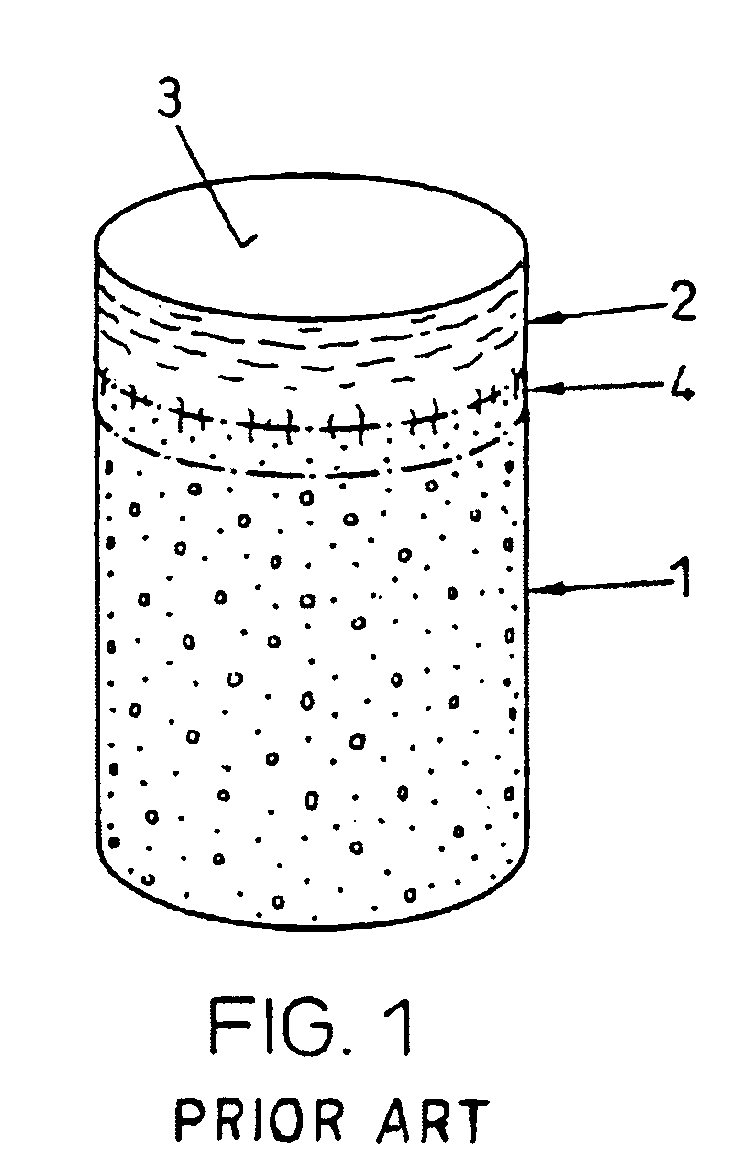
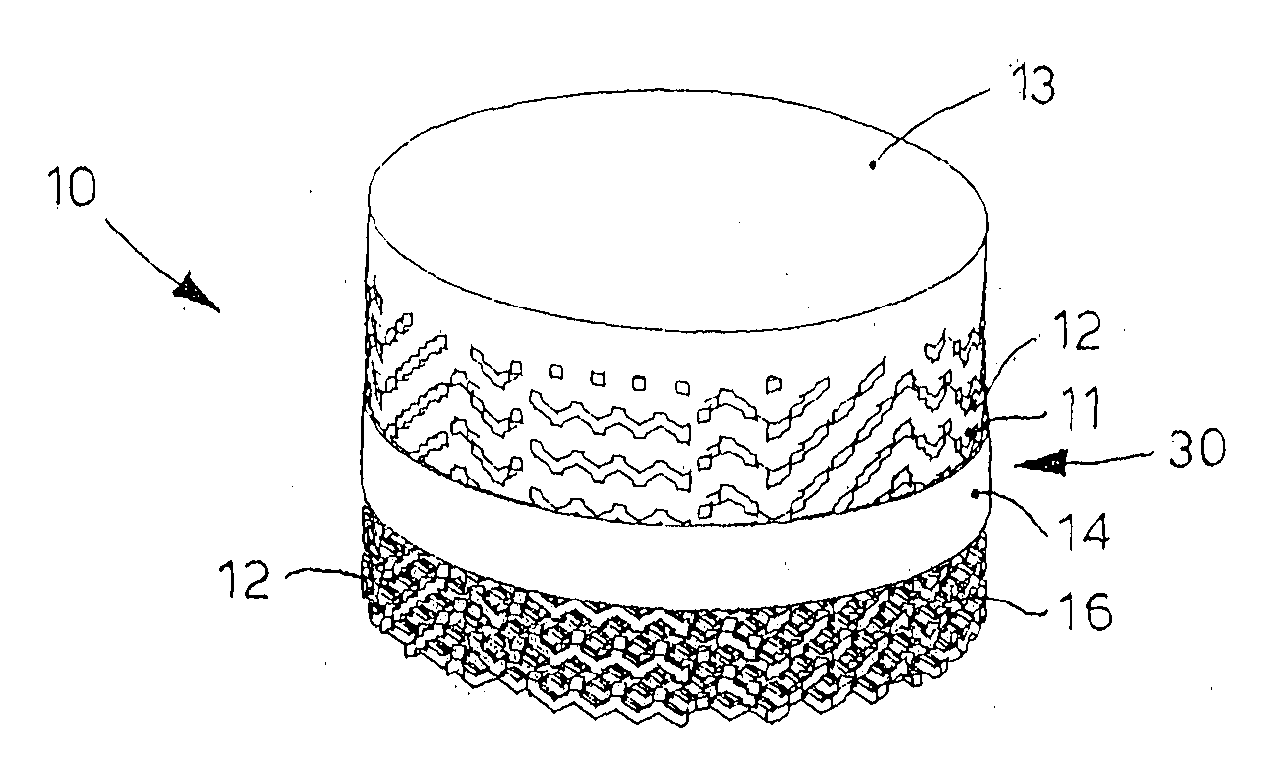
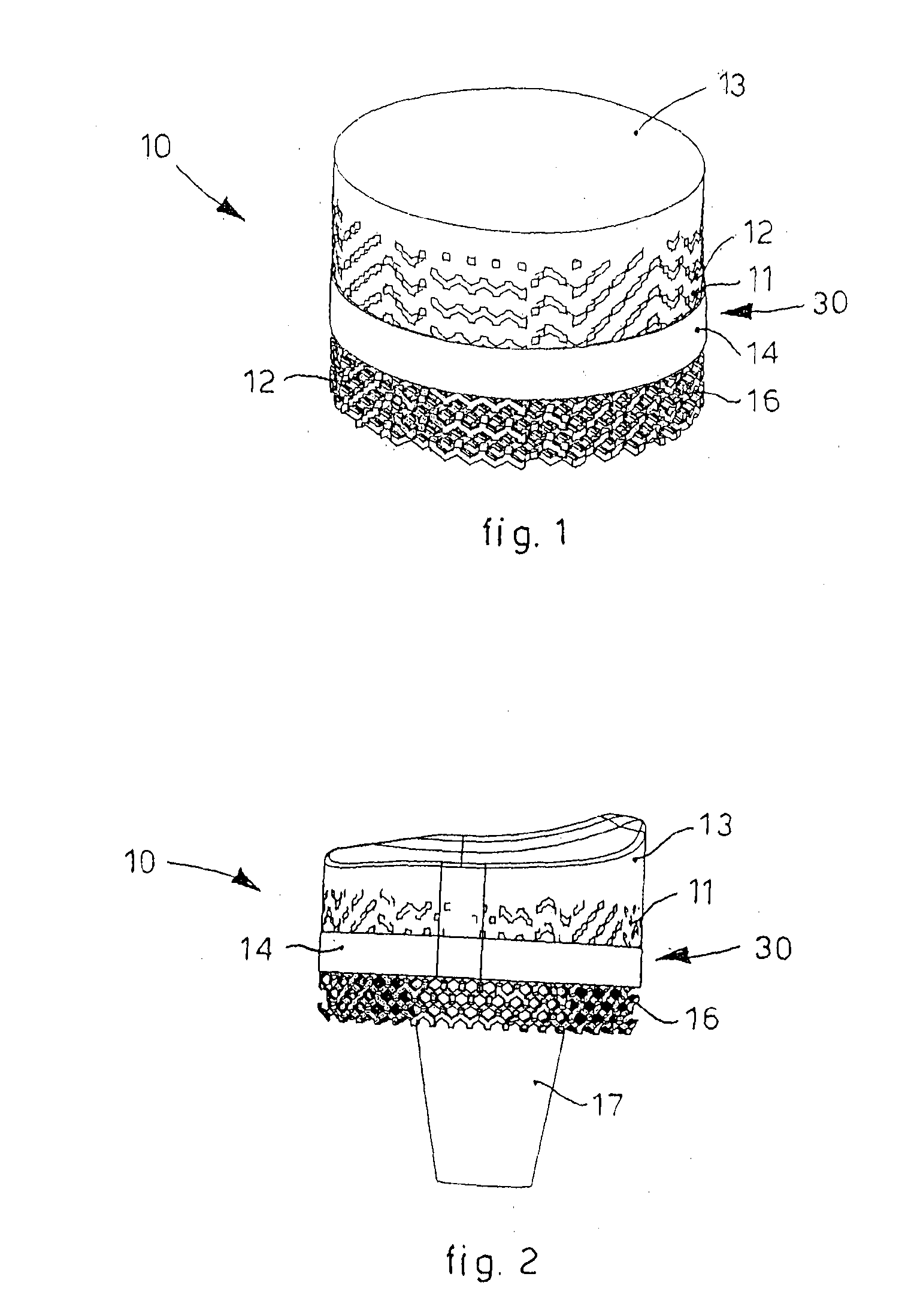
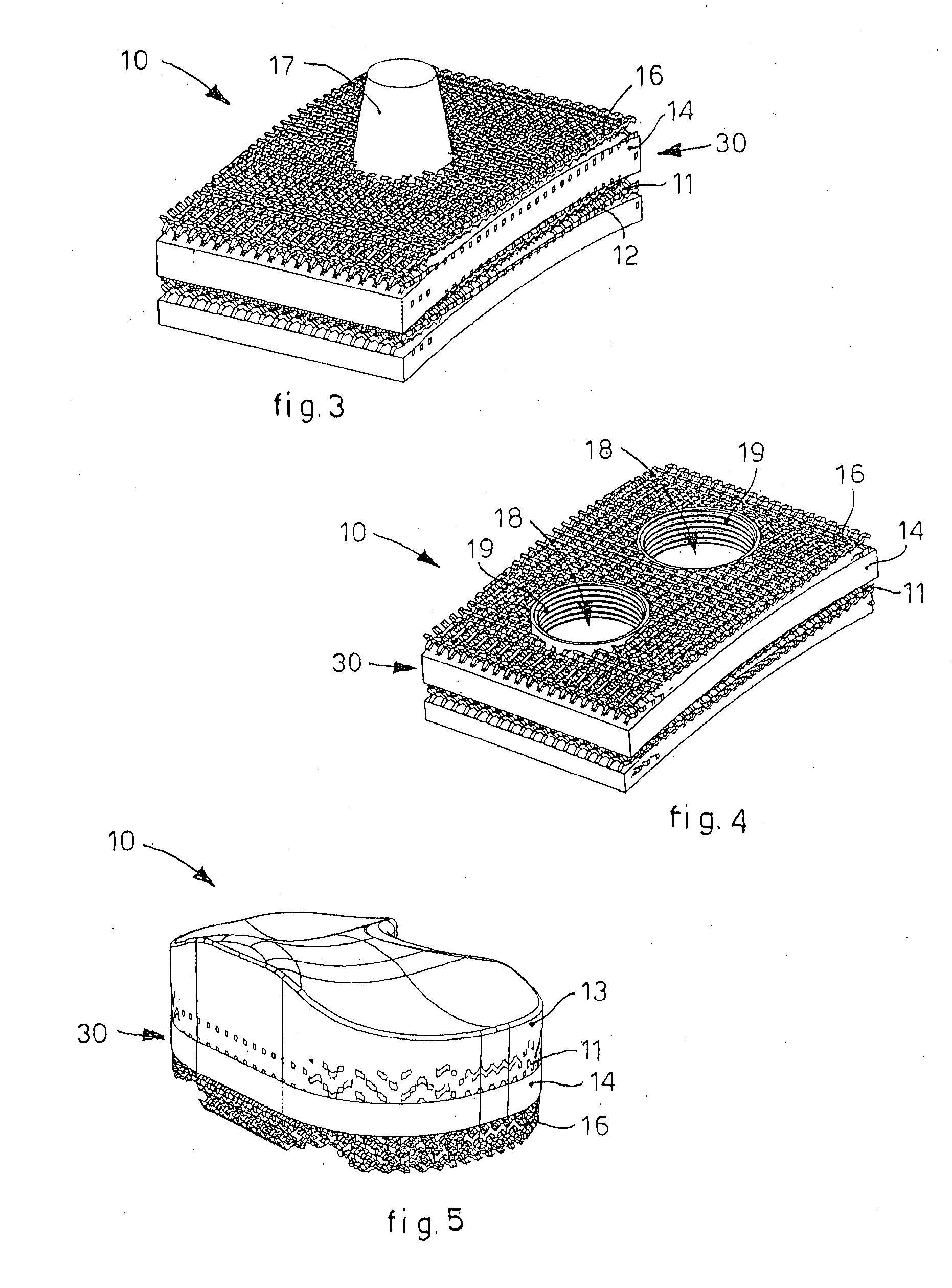
Bone Plate with Complex, Adjacent Holes Joined by a Relief-Space
InactiveUS20090171399A1Great flexibility of choiceSuture equipmentsSurgical furnitureBiomedical engineeringIncenter
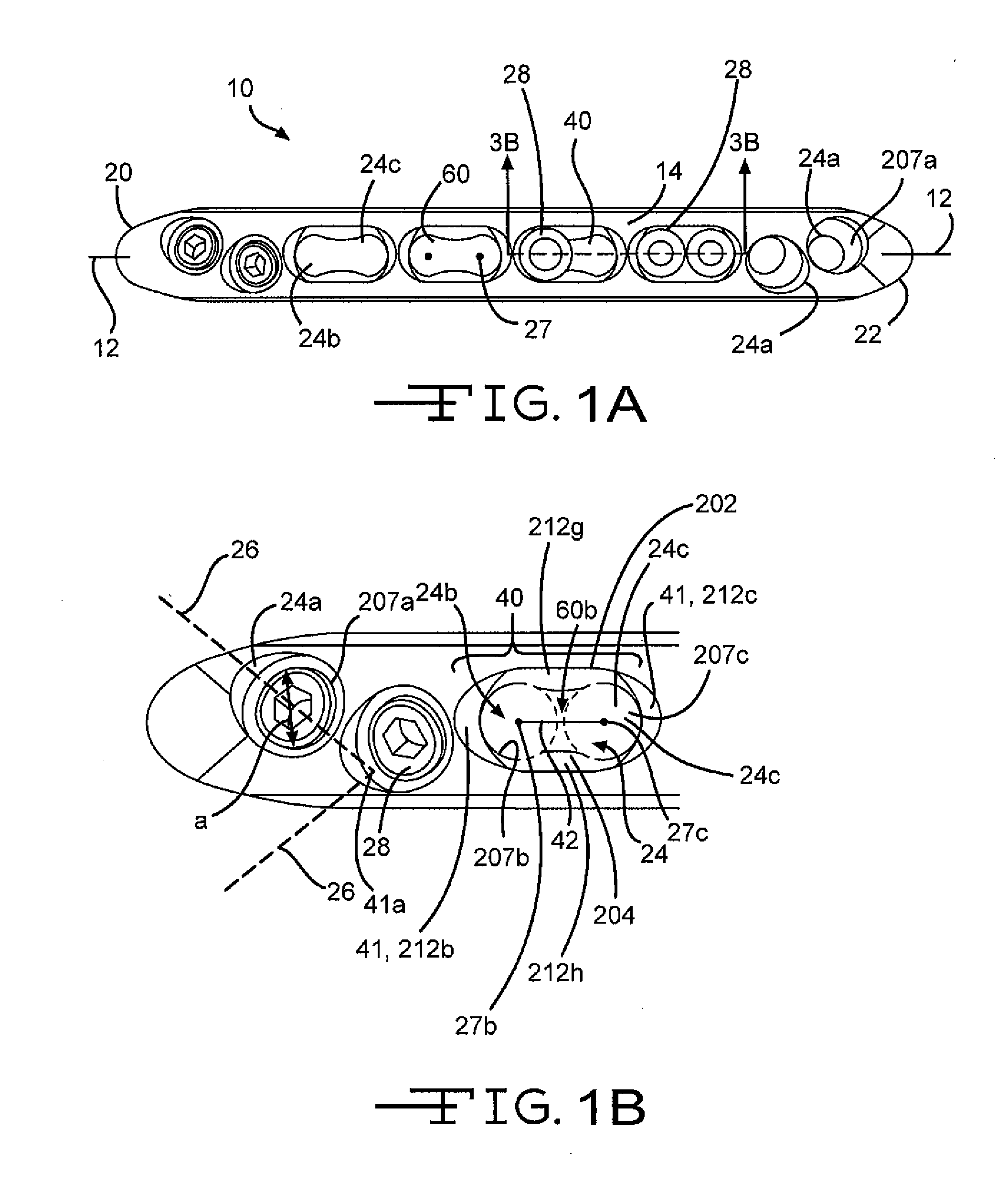
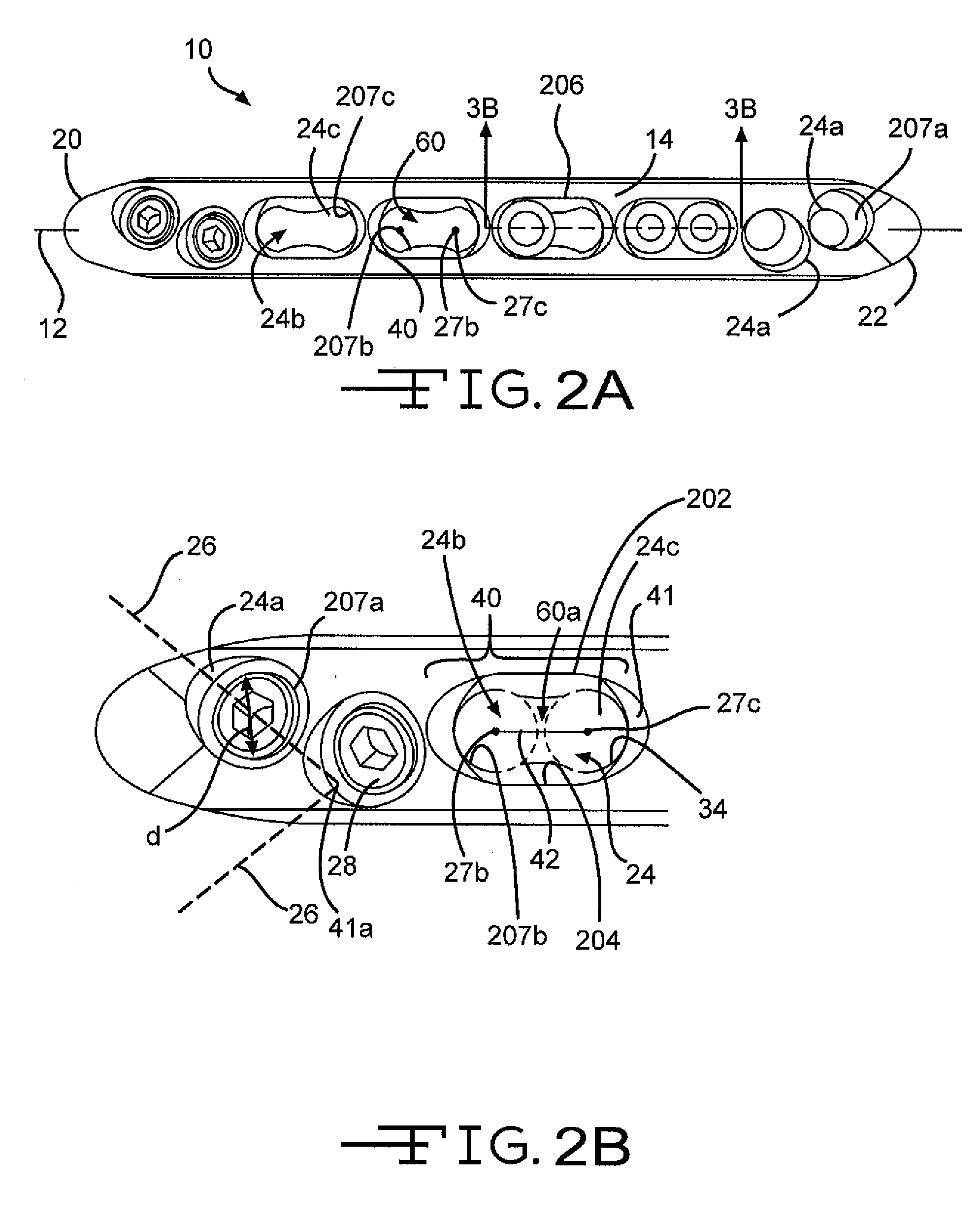
A bone plate is described which is adapted for use in situ to fix a spatial relationship of at least two bone parts. The bone plate has at least one pair of the bone screw apertures that are adjoined by a relief-space contiguous with the open space of the screw apertures themselves. An adjoined aperture pair forms a complex aperture and has a center-to-center distance d of the apertures along an axis running through the centers of the apertures. The center-to-center distance d is equal to or greater than the sum of the radii (r1+r2) of the heads of the individual bone screw used with the aperture pair.
Owner:SWISS PRO ORTHOPEDIC
Apparatus for the correction of chest wall deformities such as Pectus Carinatum and method of using the same
InactiveUS7156847B2Enlarge regionEasy to compressBone implantJoint implantsEngineeringChest wall deformity
An apparatus for the correction of wall chest deformities, such as “Pectus Carinatum”, comprising: a bar (10) having a flattened cross-section, having a minimum bending strength according to the values defined by ASTM F382-95, plates (20) having a slot (21) in the medium portion so as to fit the corresponding end of the bar (10) and peripheral holes (23) for securing the bone parts. The bar ends comprise planar grooves (11–11′) determining the wall thickness substantially similar to the height of the slot (21) of the plate (20). The wall of the grooves (11–11′) has aligned holes (13) in order to form with the respective plate (20) and by using screws (30), a fixed removable attachment that allows the axial registration of the bar (10). Method for the correction of Pectus Carinatum using said apparatus in order to achieve a normal anatomic shape of the chest wall.
Owner:ABRAMSON HORACIO
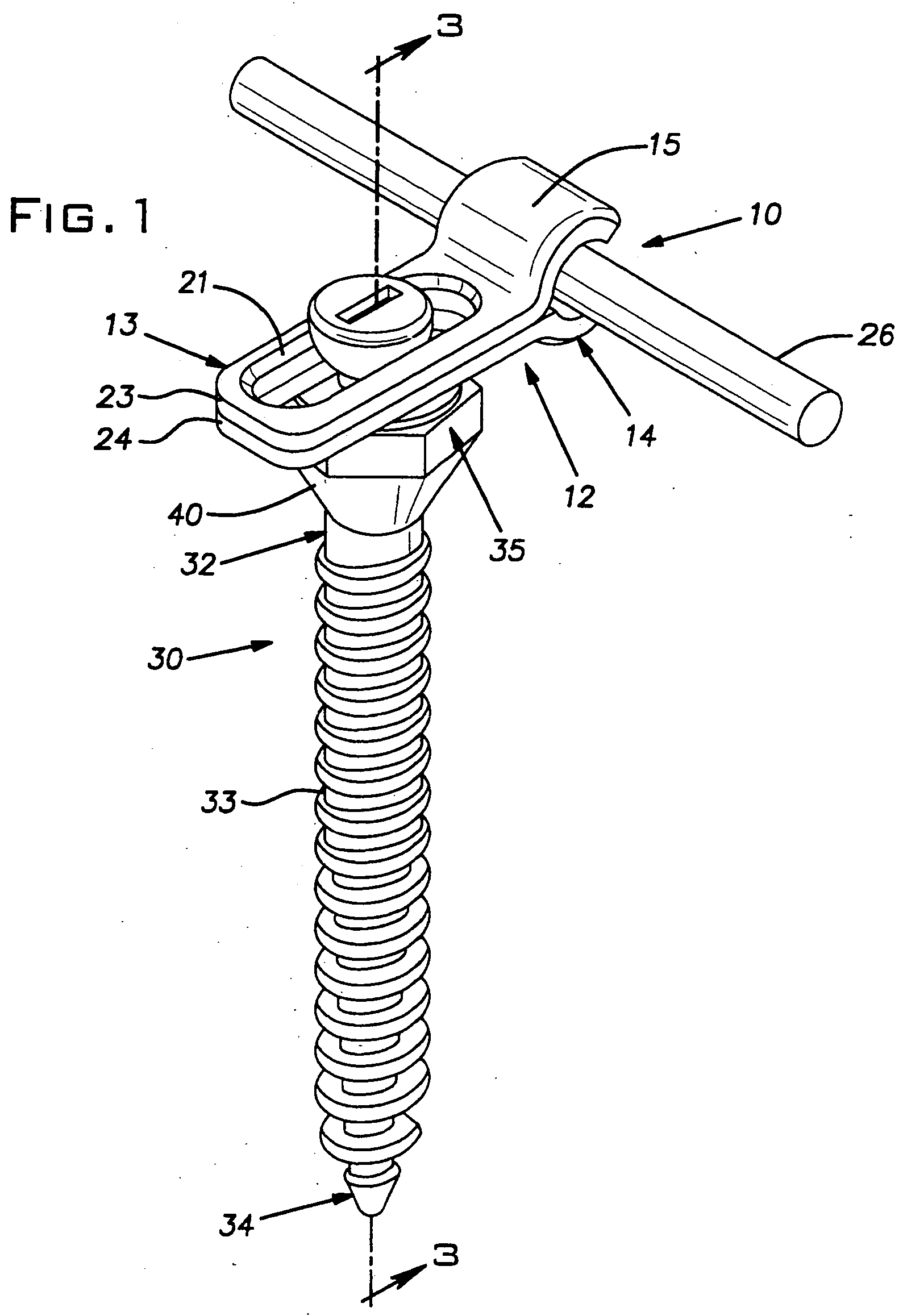
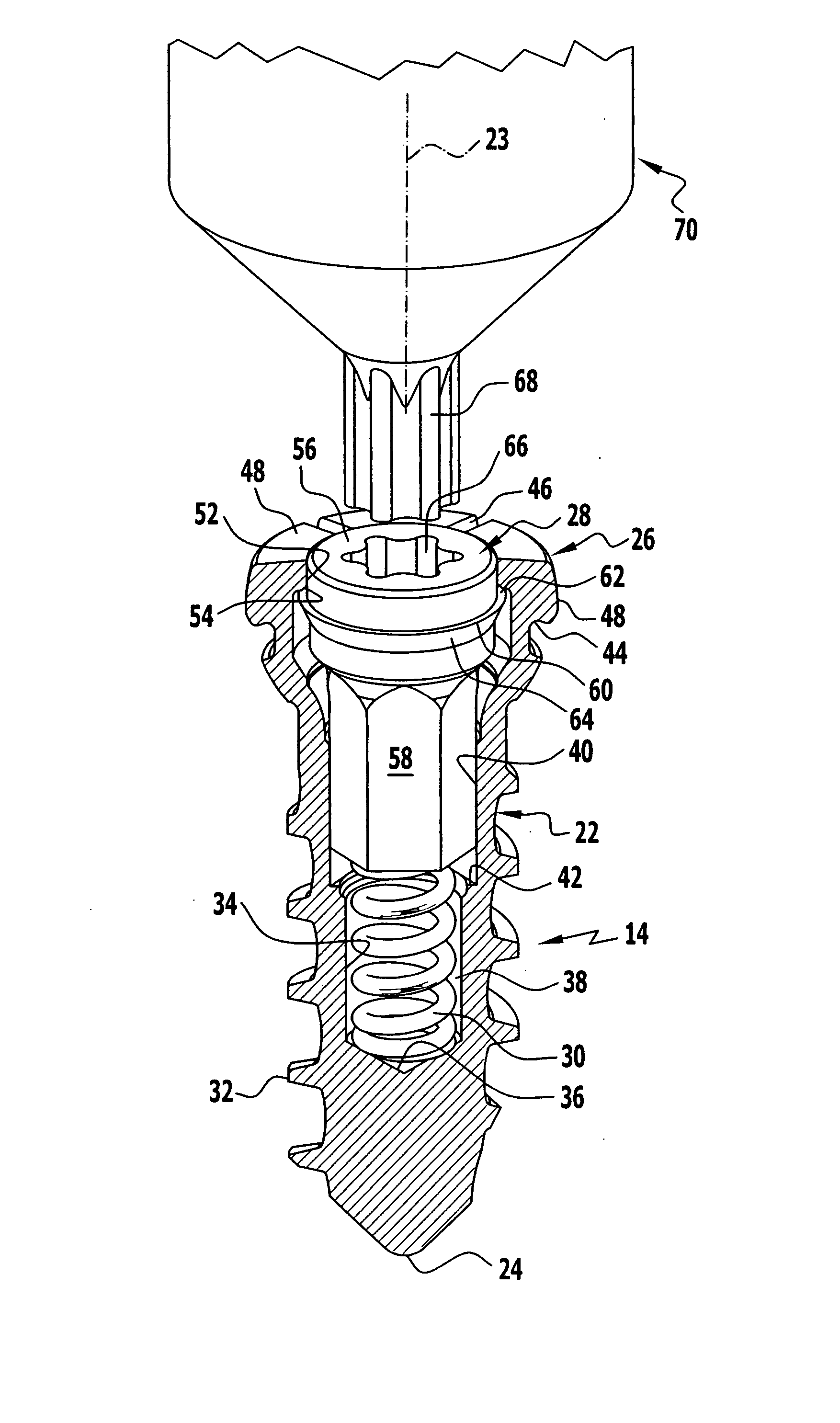
Bone screw
ActiveUS7988714B2Avoid the securing elementImprove stabilitySuture equipmentsLigamentsBiomedical engineeringBone screws
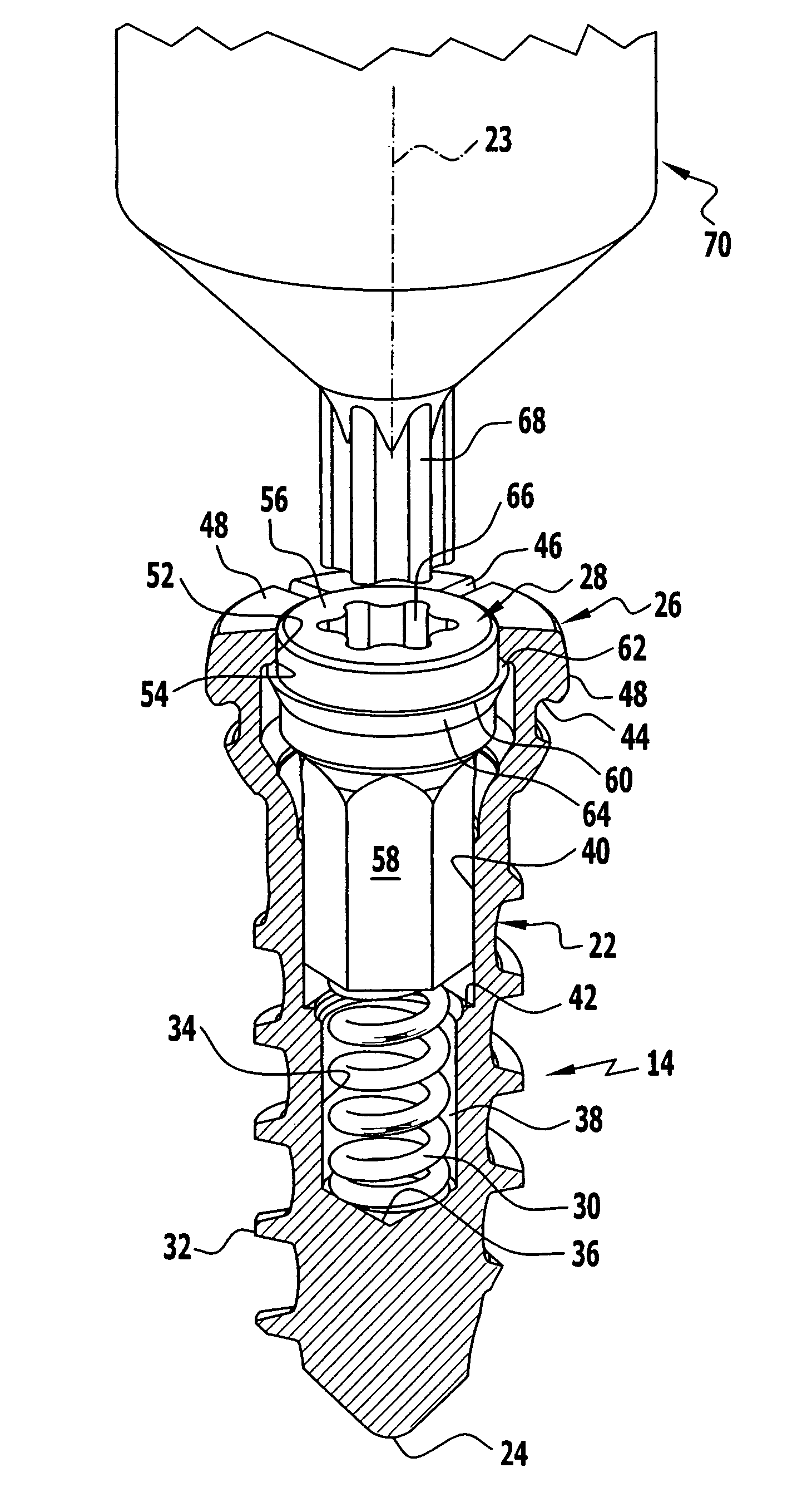
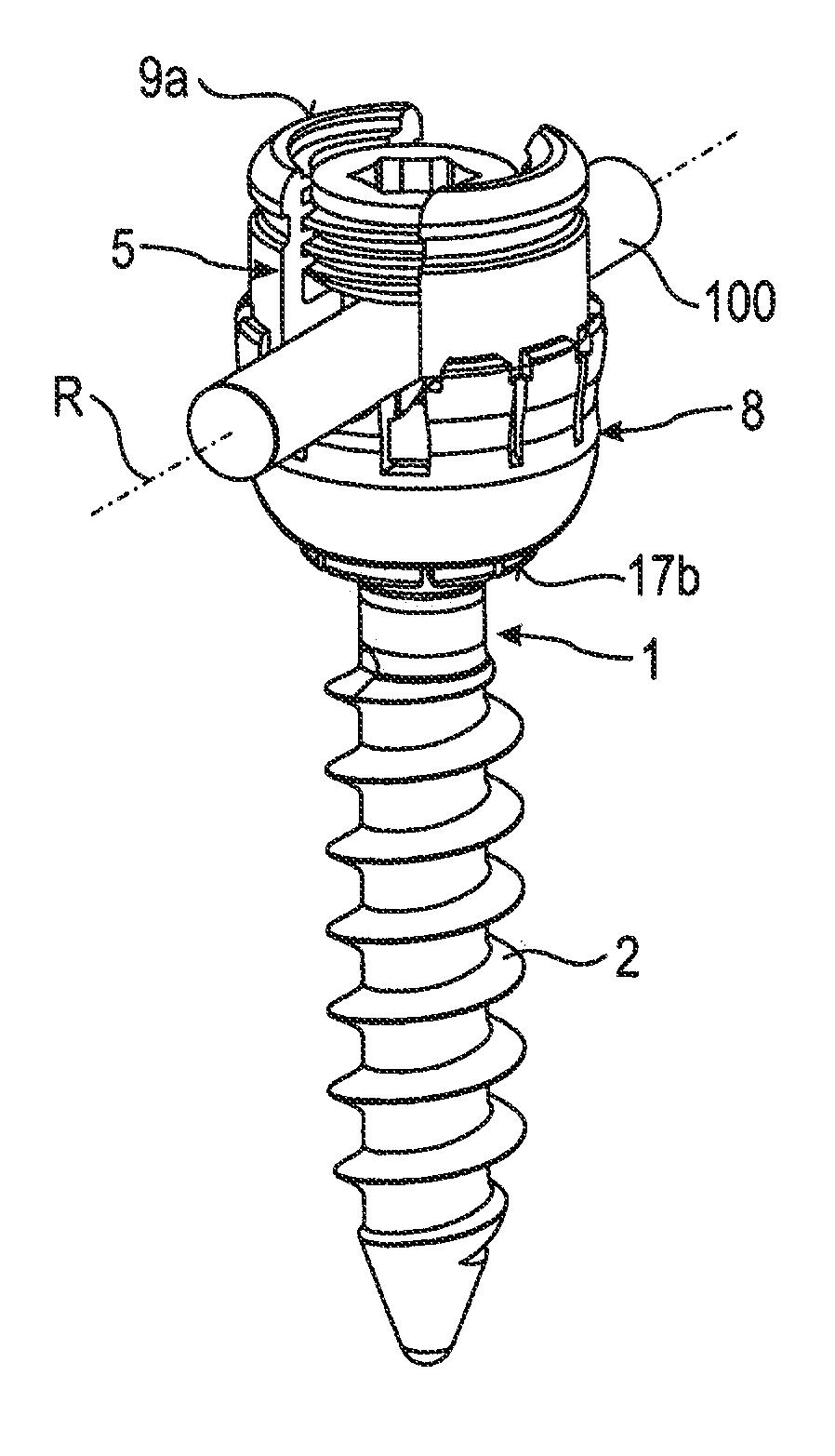
In order to improve a bone screw with a shaft defining a longitudinal axis and with a head which can be brought into engagement with a bone screw receiving means of a bone plate for the releasable connection of the bone screw to the bone plate, wherein a securing element for securing a connection between the bone screw and the bone plate is provided, wherein the bone screw can be brought from a position of engagement, in which the bone screw is held on the bone plate, into a release position, in which the bone screw can be released from the bone plate, wherein the securing element can be brought from a non-securing position, in which the bone screw can be brought into the release position, into a securing position for securing the connection between the bone screw and the bone plate, in which the bone screw takes up the position of engagement, such that a bone plate can be fixed to bone parts more easily and more securely it is suggested that the securing element be supported on the bone screw so as to be movable.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Bone Plate with Complex, Adjacent Holes Joined by a Relief-Space
InactiveUS20090292318A1Great flexibility of choiceSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringSelf locking
Owner:SWISS PRO ORTHOPEDIC
Bone plate with complex, adjacent holes joined by a bend relief zone
A bendable bone plate (10) is disclosed which is adapted for use in situ as a conformable bone splint to fix the spatial relationship of at least two bone parts (80). The bone plate (10) has an elongated plate (11) made of a bendable material. A plurality of screw apertures (24) extending through the top (14) and bottom (16) surfaces are disposed along the length (L) of the plate. Bone screws (28) are inserted through the apertures into the underlying bone parts (80) to anchor the elongated plate (11) to the bone parts (80). At least two of the screw apertures (24) are disposed as a closely spaced pair (40) of screw apertures (24) with a “bend relief zone” (60) disposed between the closely spaced apart screw apertures (24). The bend relief zone (60) is disposed to allow the elongated plate (11) to be bent across the bend relief zone (60) up to a certain angle (A) without deforming the screw apertures (24) adjacent the bend relief zone (60).
Owner:SWISS PRO ORTHOPEDIC
Tissue engineering bone/cartilage double-layer scaffold and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101574540AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationBone implantCartilage collagenCells bone
The invention discloses a tissue engineering bone / cartilage double-layer scaffold and a construction method and application in medical science. The method adopts natural cartilage and bone as materials, respectively removes the antigenicity of the cartilage and the bone through de-cell, and adopts a freezing and drying method to prepare the double-layer scaffold simultaneously suitable for growthof the two issues of the bone and the cartilage. A preparation method comprises that: acellular bone is soaked in suspension of cartilage acellular matrix microfilaments, and the double-layer scaffoldof which the upper layer is a cartilage acellular matrix three-dimensional porous spongy scaffold and the lower layer is an acellular bone scaffold is prepared by the freezing and drying method and acrosslinking method. The cartilage acellular matrix spongy scaffold part of the double-layer scaffold can be introduced with factors promoting the formation of the cartilage, and the acellular bone part can be introduced with factors promoting the formation of the bone, and the factors can be respectively inoculated with cells for forming the cartilage or the bone to construct a living tissue engineering bone / cartilage complex, which is used for repairing bone and cartilage complex defect or total joint defect clinically.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Ultrasonic transmission/reception apparatus
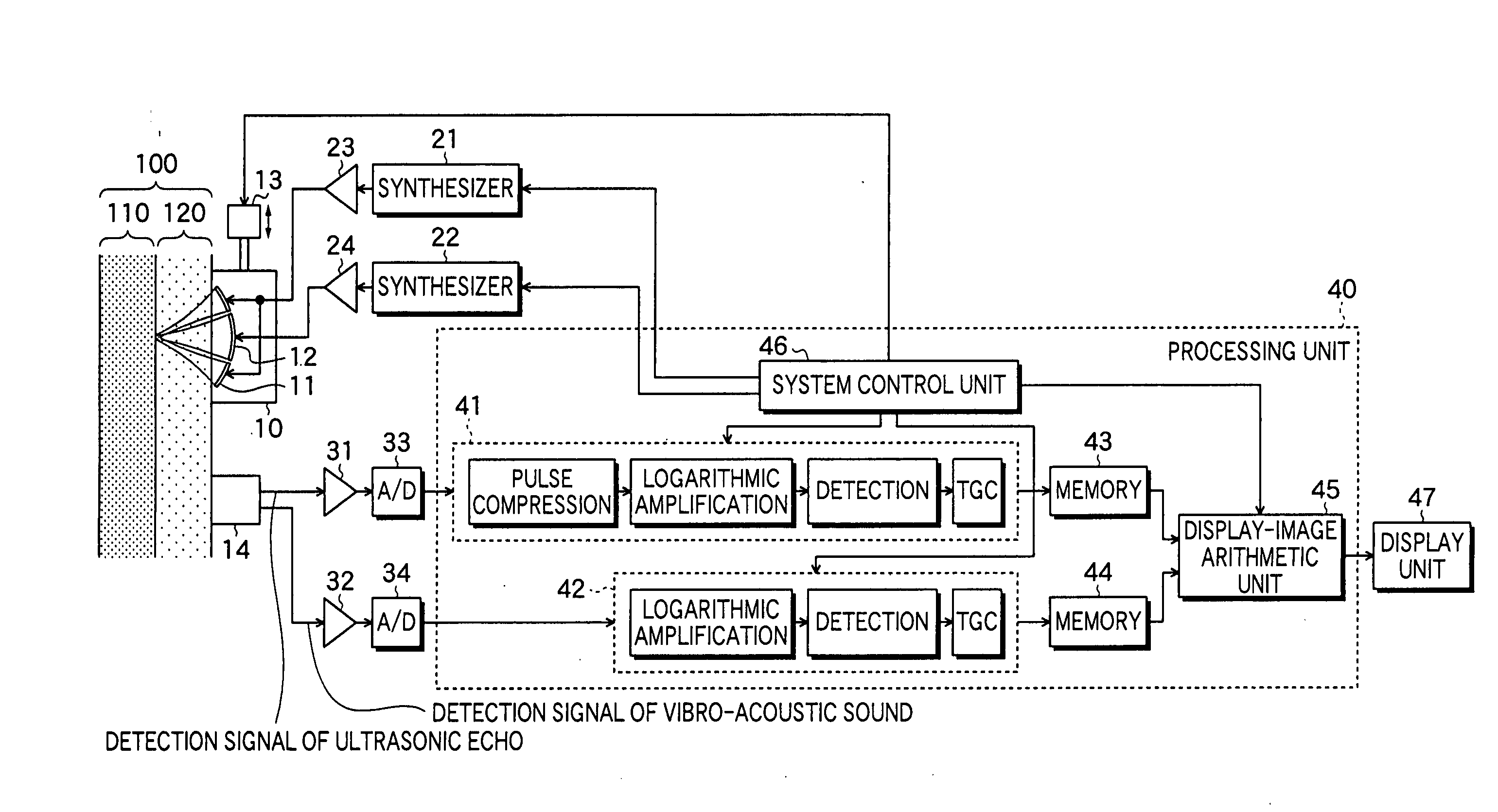
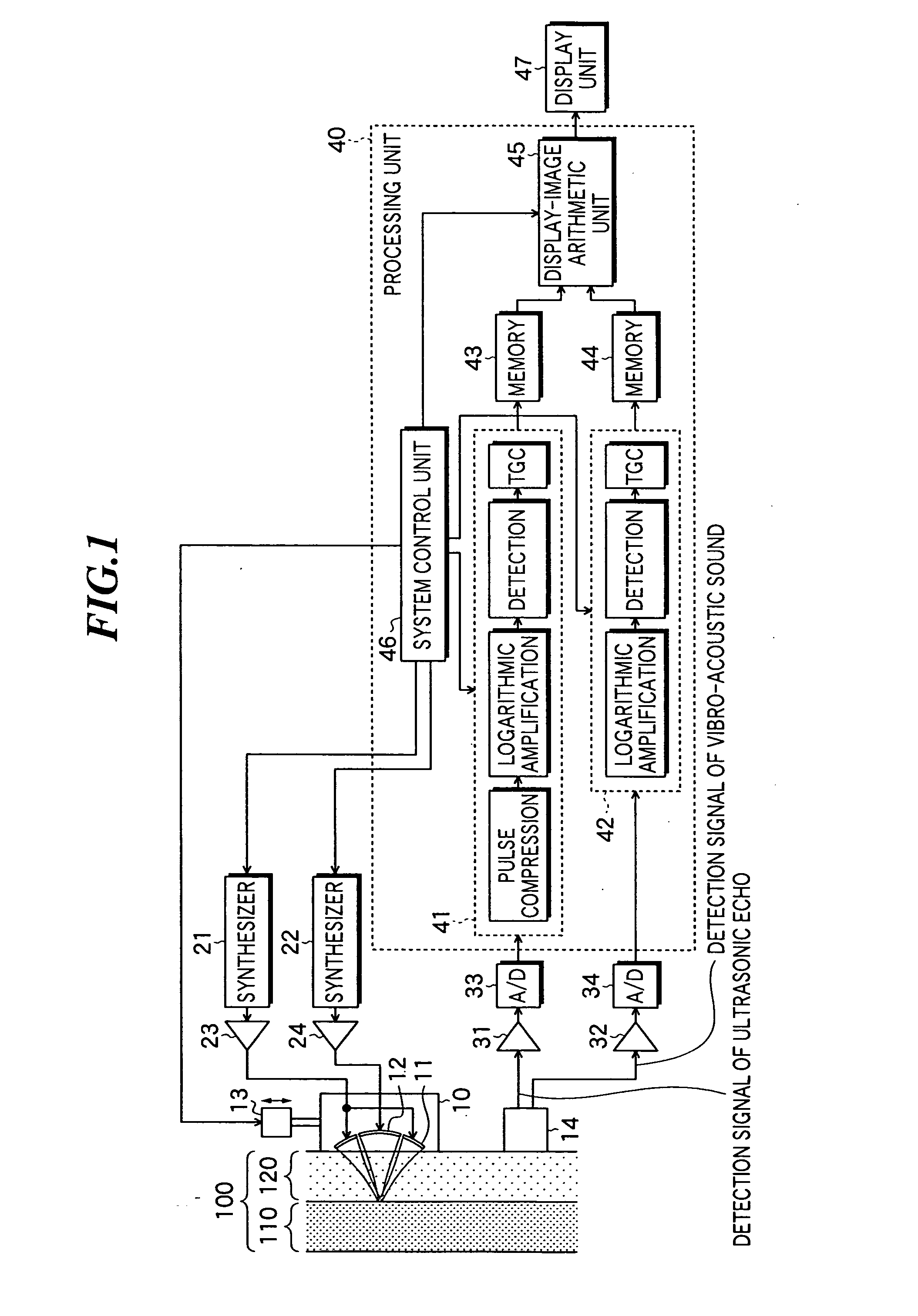
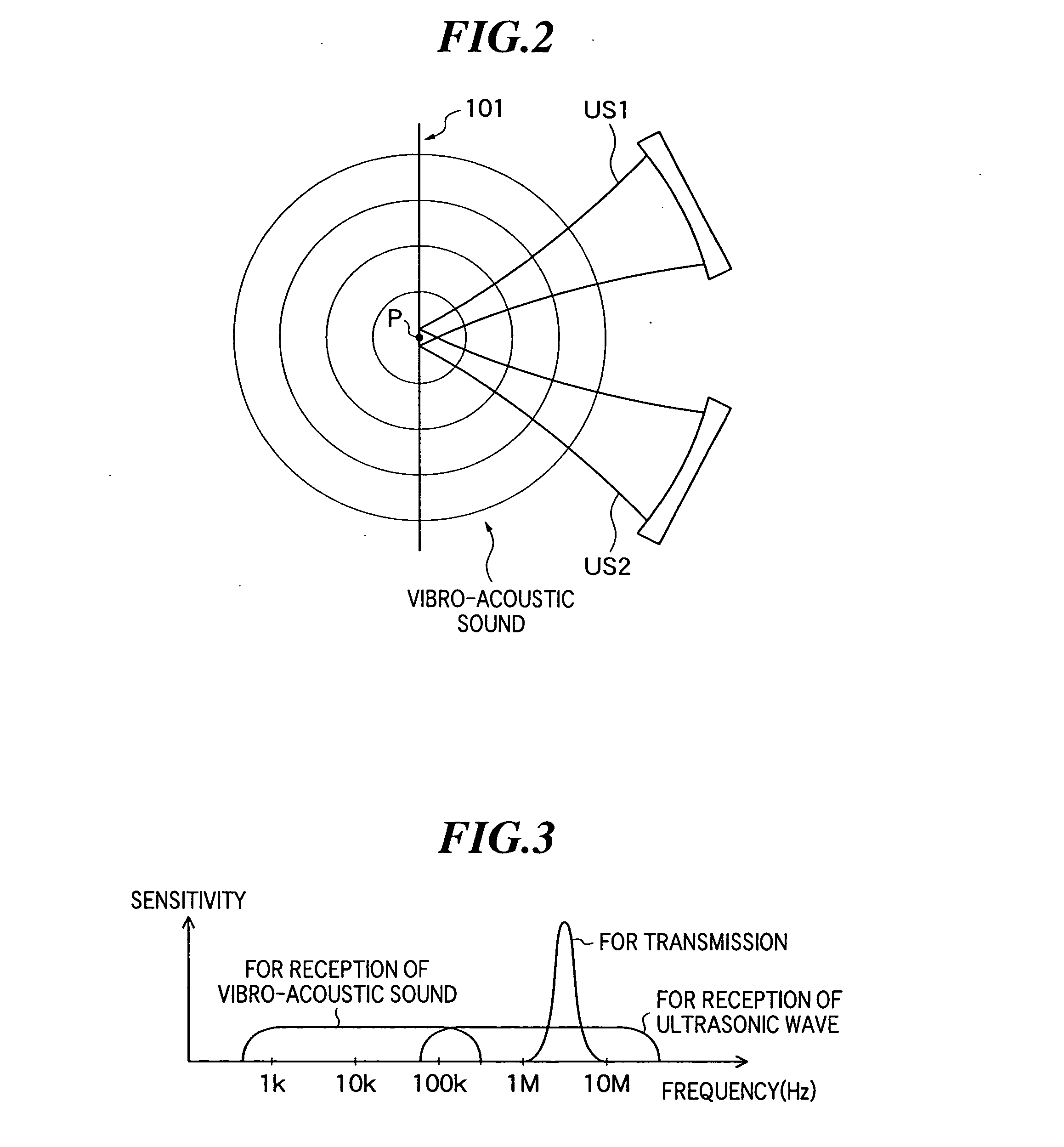
InactiveUS20050075565A1High resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationProcessing element
An ultrasonic transmission / reception apparatus which can image both a minute tissue around a bone part in an object and a minute tissue inside the bone, at a high resolution. The apparatus includes a system control unit which controls the synthesizers so that a first ultrasonic wave may be transmitted from one of the transmission elements while its frequency is being swept, and that a second ultrasonic wave may be transmitted from the other transmission element while its frequency is being swept with a predetermined difference frequency held relative to the frequency of the first ultrasonic wave, a signal processing unit which subjects the detection signal of the ultrasonic echo to predetermined signal processing, a signal processing unit which subjects the detection signal of the vibro-acoustic sound to predetermined signal processing, and a display-image arithmetic unit which generates B-mode image data based on the detection signals subjected to the signal processing.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Device and method for separating meat from bone parts
InactiveUS7029387B2Reduce stressLarge openingBone cleaning devicesPoultry processingBiomedical engineeringPlunger
In a device, assembly and method for separating meat from bone parts, at least a chamber (2) is provided for receiving bone parts which are connected to meat, having a first open end (4) and a second open end (5) which is located opposite the first open end (4), a plunger (7), first displacement means for displacing the plunger (7) inside the chamber (2) from the first open end (4) thereof, and a stop element (13) at the second open end (5) for creating a closed space (3) together with the chamber (2) and the plunger (7). A pressure is applied to the bone parts by displacing the plunger (7) in the chamber (2). The stop element (13) is arranged at a distance from the chamber (2), so that at least one gap (15) is formed between the chamber (2) and the stop element (13), for the passage of meat which has been separated from the bone parts under the influence of pressure.
Owner:STORK PMT
Artificial joint
InactiveUS8449620B2Good flexibilityImprove stress resistanceFinger jointsAnkle jointsArtificial jointsEngineering
An artificial joint for implantation in humans and animals, the joint comprising a joint body arranged between two base elements which are adapted to be connected to adjoining bone parts. The two base elements comprise horizontal and vertical retaining members respectively, that hold the joint body between them. The joint body comprises curved surfaces arranged to make sliding contact to corresponding curved surfaces of at least one base element. The joint body this way distributes the applied forces over a large surface to withstand the load initiated by the patient. The joint body is kept in position using pins held by retaining members at the base elements. The angle of motion can be predetermined by the design of the implant body to mimic the movement of a normal finger.
Owner:GS DEVMENT
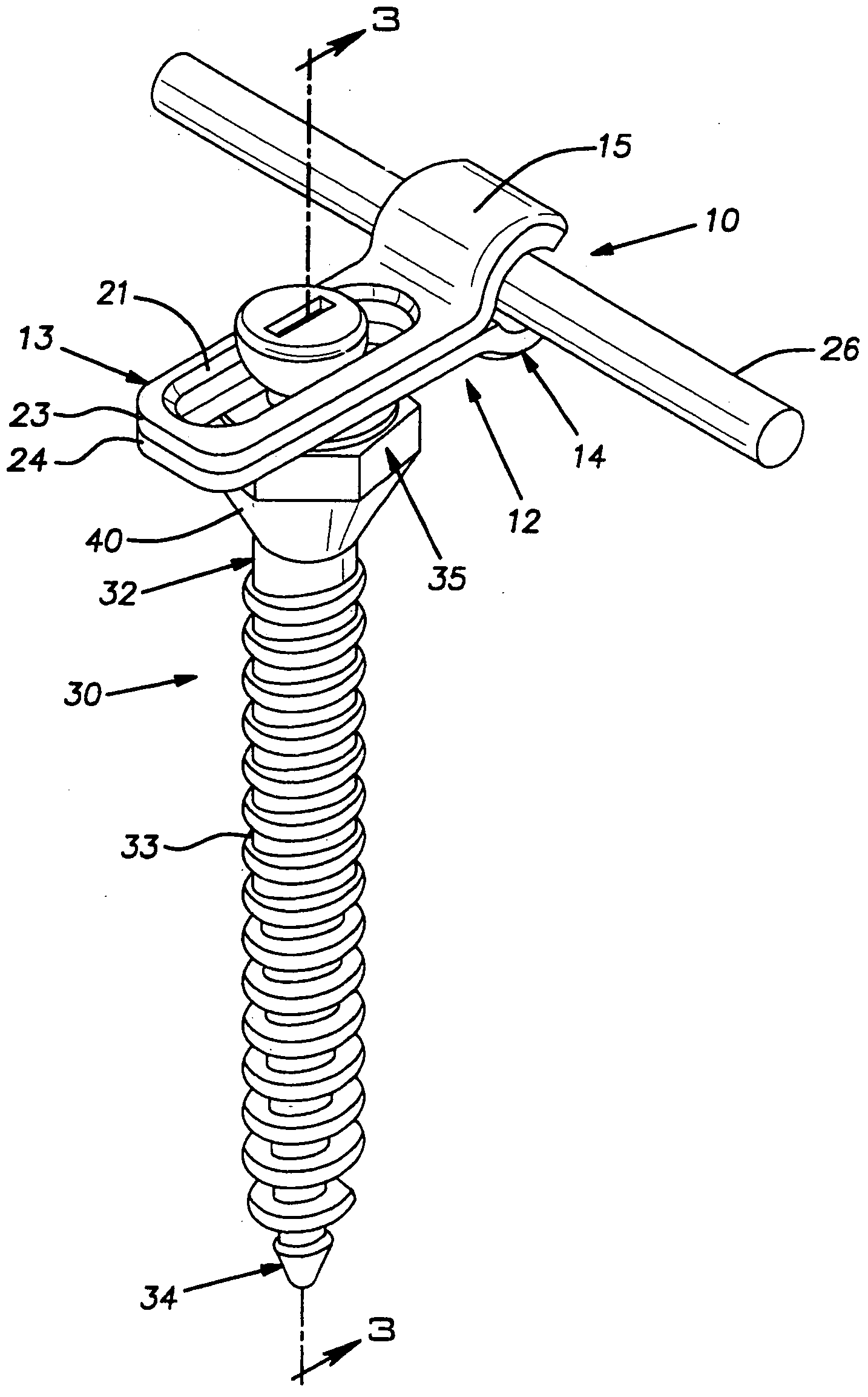
Bone Screw
ActiveUS20070288025A1Easy to assembleImprove stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMetatarsal bone partIliac screw
In order to improve a bone screw with a shaft defining a longitudinal axis and with a head which can be brought into engagement with a bone screw receiving means of a bone plate for the releasable connection of the bone screw to the bone plate, wherein a securing element for securing a connection between the bone screw and the bone plate is provided, wherein the bone screw can be brought from a position of engagement, in which the bone screw is held on the bone plate, into a release position, in which the bone screw can be released from the bone plate, wherein the securing element can be brought from a non-securing position, in which the bone screw can be brought into the release position, into a securing position for securing the connection between the bone screw and the bone plate, in which the bone screw takes up the position of engagement, such that a bone plate can be fixed to bone parts more easily and more securely it is suggested that the securing element be supported on the bone screw so as to be movable.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Joint type internal skeleton pneumatic soft hand claw
The invention discloses a joint type internal skeleton pneumatic soft hand claw. The joint type internal skeleton pneumatic soft hand claw comprises a central palm part, a plurality of soft-body tentacles fixed to the periphery of the central palm part; each soft-body tentacle part comprises a plurality of joint parts which are connected in sequence; each joint part comprises an elastic telescopiclayer and a plurality of supporting bone parts which are uniformly distributed in the elastic telescopic layer; an inner cavity of the elastic telescopic layer is supported by the supporting bone parts, the inner cavity is connected with the elastic telescopic layer, the supporting skeleton parts are hinged; an air hole is formed in the middle of the supporting skeleton part; the front end of thejoint part is provided with a fingertip bone part which is hinged to the support bone part; a finger bone part is arranged at the rear end of the joint part and is hinged to the supporting bone part;a connecting bone part is arranged between every two adjacent joint parts and is hinged to the supporting bone part; the air holes are formed in the connecting bone part and the finger bone part; andthe connecting bone part and the finger bone part are independently connected with an air pipe; the inner part of the elastic telescopic layer is filled with a plurality of circles of fiber restraintlayers, and the constraint layers correspond to the outside of the gas chamber. According to the joint type internal skeleton pneumatic soft hand claw, the rigidity and the grasping capacity of the tong are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bone fixation screw and method
ActiveUS20130317503A1Eliminates rotational motionPreventing torsional motionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsScrew threadIliac screw
Owner:J M LONGYEAR MFG LLC
Stabilization device for stabilizing vertebrae or bone parts
ActiveUS20120165874A1Achieve modularityBig choiceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMechanical engineeringVertebra
A stabilization assembly for stabilizing a vertebra or other bone includes: at least two rods having different diameters; an anchoring element having a shaft and a head; a receiving part for interchangeably receiving any one of the rods to connect the rod to the anchoring element, the receiving part including a rod receiving portion with a channel for receiving the rod, and a head receiving portion having an open end and being flexible to allow introduction and clamping of the head; and a locking ring configured to be arranged around the head receiving portion and to clamp the head in the head receiving portion; wherein the locking ring includes a contact surface configured to contact any one of the at least two rods at at least two distinct contact areas that are spaced apart from one another in a circumferential direction of the rod.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
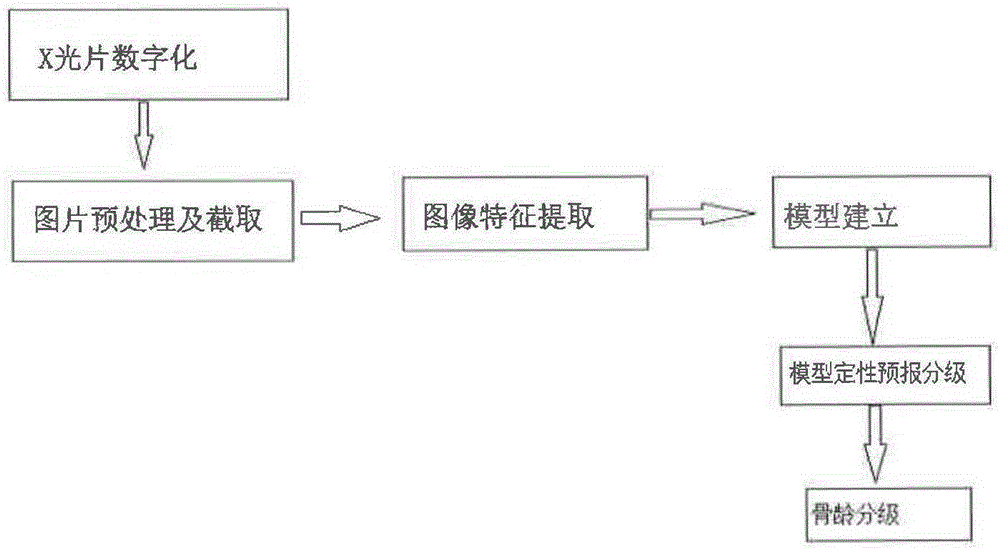
Bone age assessment method
PendingCN106340000AEase of evaluationRapid assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMathematical model
The invention discloses a bone age assessment method, which is characterized by comprising the steps of A, acquiring X-ray images of a plurality of target bone parts, and grading the acquired X-ray images according to the age group; B, performing feature extraction on a plurality of X-ray images in each grade, converting each grade of X-ray images into data by using a directional gradient histogram feature method, and building a mathematical model; and C, classifying the X-ray images in which the bone age is required to be assessed into the above grades by using a support vector machine classification algorithm. According to the bone age assessment method disclosed by the invention, an image processing technology and a computer vision technology are combined, and judgment for the bone maturity is realized through an interactive or automatic method.
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
Integrated prosthetic element
Integrated prosthetic element usable for bone implant operations or as a bone filler or replacement, comprising at least a metal support and an insert made of plastic material coupled with at least a first surface of said metal support so as to define a wear surface, or insert, of adjustable thickness. The metal support comprises, on the side opposite said first surface, a second surface intended to be coupled with the bone part on which the prosthesis or bone replacement is installed. The first surface comprises a layer having cavities or holes distributed in a substantially uniform manner and suitable for anchorage and solidarization of the plastic material that makes up the insert, while said second surface comprises a porous layer suitable to optimize the bone anchorage. The first surface and the second surface are separated by a compact layer that stops the plastic material in the step of forming the plastic insert. The cavities or holes of the first surface have bigger shapes and sizes than, and in any case different from, the pores of the second surface.
Owner:LIMA CORPORATE SPA
Bioactive graded zirconia-based structures
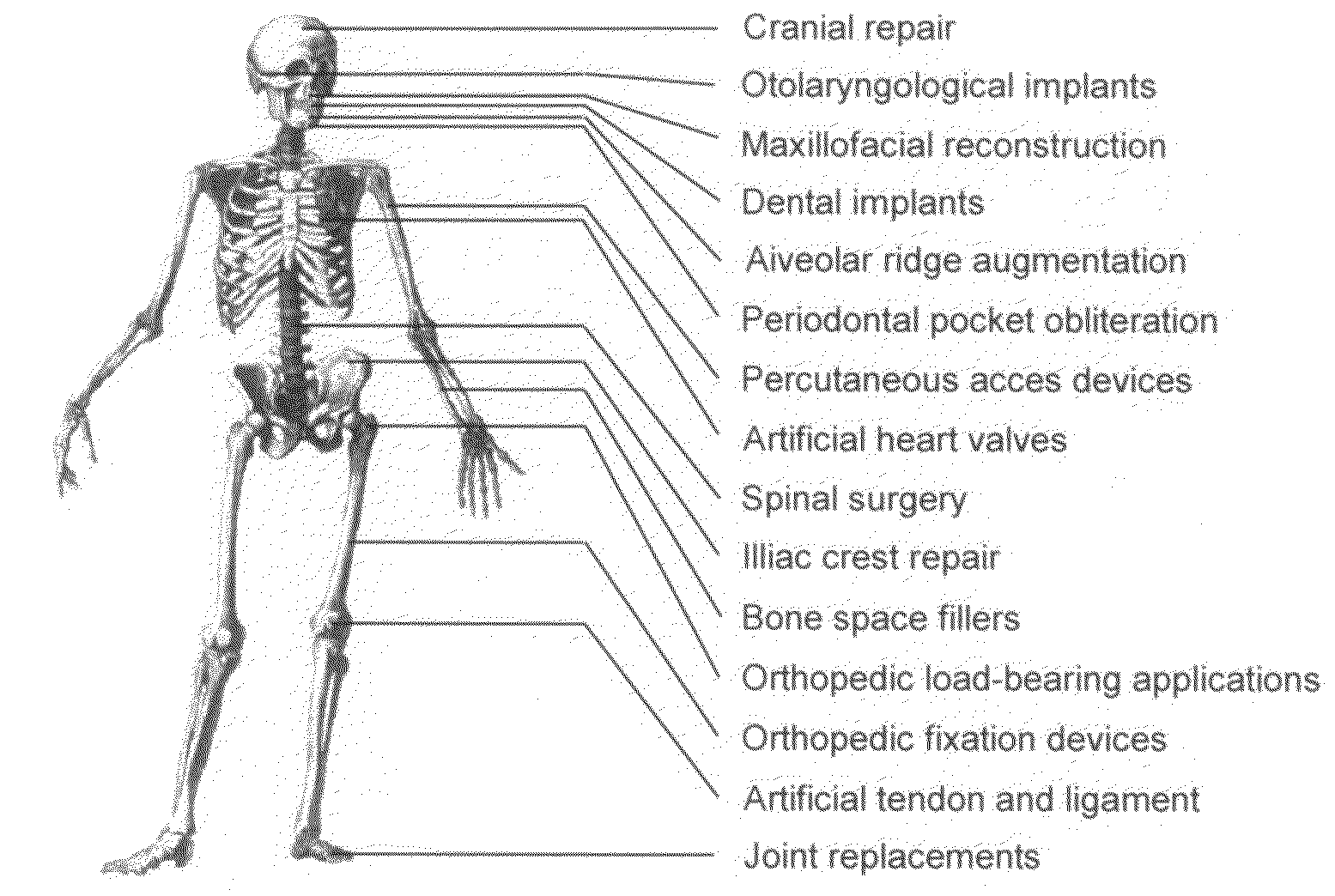
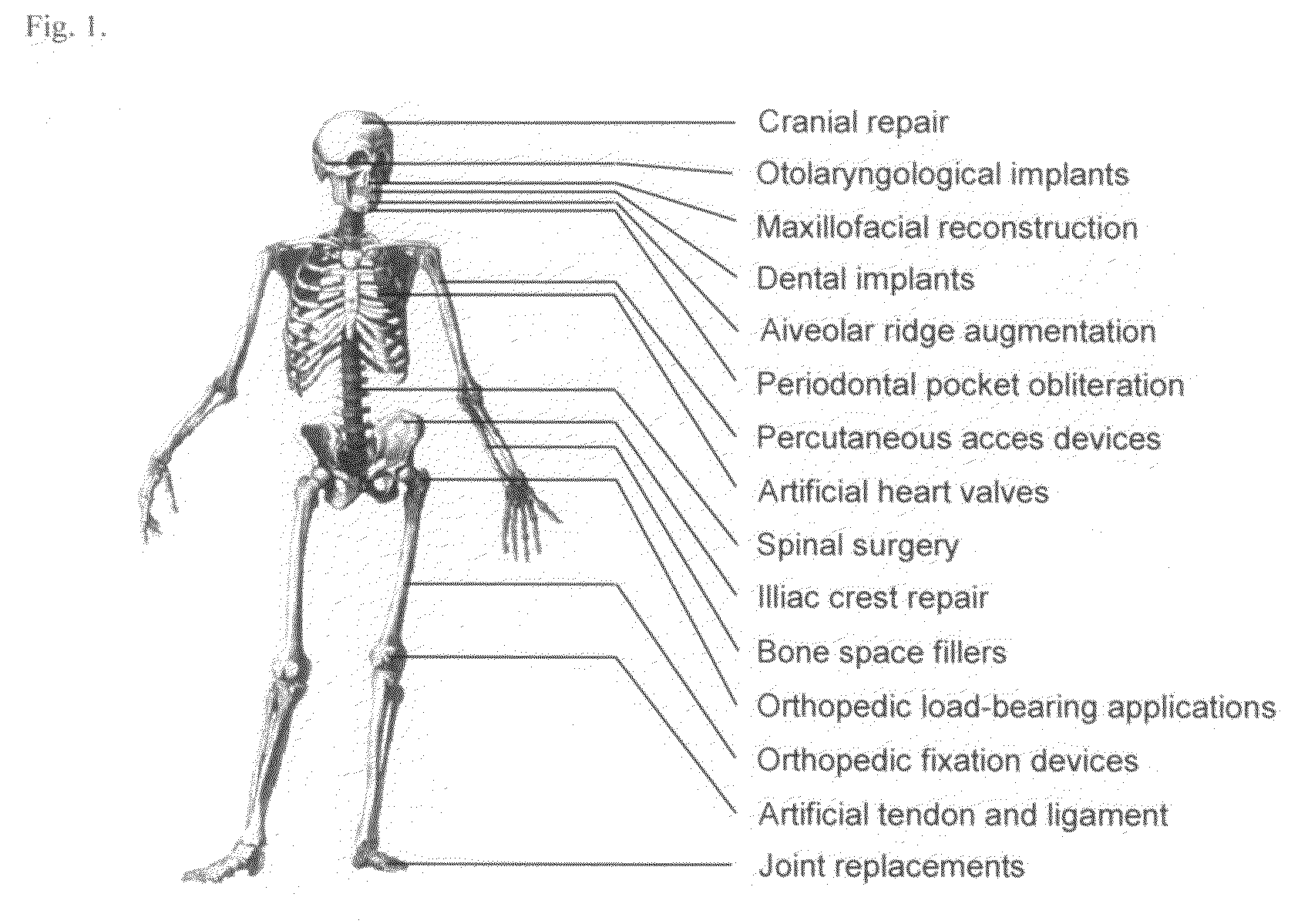
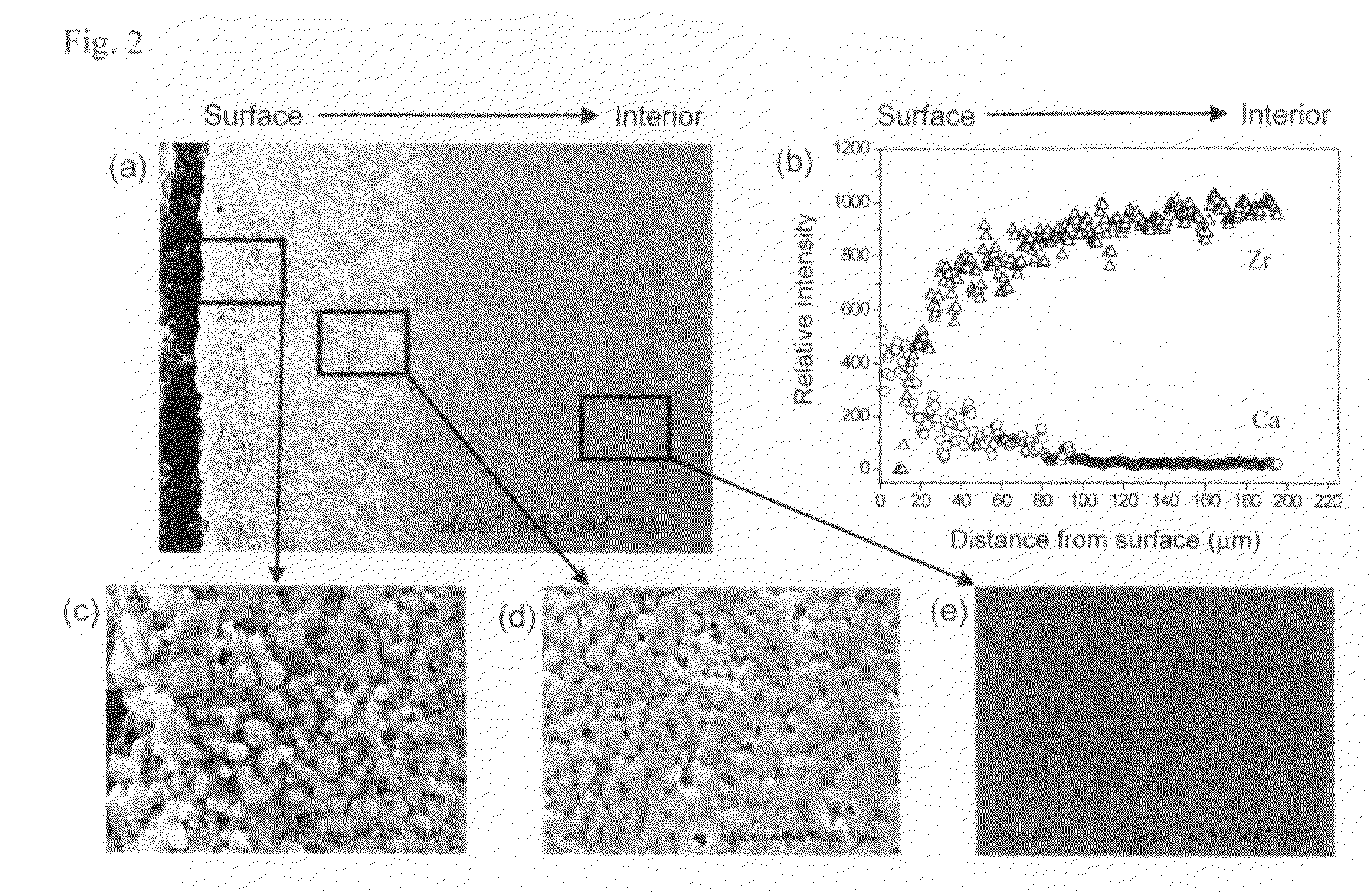
The present invention provides a functionally graded bioactive glass / ceramic composite structure or bioactive glass / ceramic / bioactive glass sandwich structure for use in such applications as damage resistant, ceramic dental implants, immediate tooth replacement, endodontic posts, orthopedic prostheses, orthopedic stems, bone substitutes, bone screws, plates, and anchors, nonunion fractures repair, alveolar ridge augmentation, missing small bone parts (e.g. fingers, toes, etc), maxilla facial reconstruction, spinal fusion, and scaffolds for bone regeneration, comprising a residual bioactive glass or glass-ceramic layer at all accessible surfaces, followed by an underlying graded glass-ceramic layer, and then an dense interior ceramic. The residual bioactive glass or glass-ceramic layer can be further transformed to a carbonate apatite (CHA) layer by immersing in calcifying solution or simulated body fluid (SBF) with electrolyte composition similar to that of serum. The interior ceramic preferably contains yttria-tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) or ceria stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Ce-TZP) or magnesia stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ) or calcia stabilized zirconia (Ca-PSZ) or alumina or zirconia-alumina composites. Further, the invention provides methods for making the same functionally graded bioactive glass / ceramic composite structure or graded bioactive glass / ceramic / bioactive glass sandwich structure.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Device for measuring bone density through reference module
ActiveCN107485405AHigh measurement accuracyEasy to operateRadiation diagnosticsBone densityDecay factor
The invention discloses a device for measuring the bone density through a reference module. The device comprises a digital X-ray imaging device used for collecting a projected image of a measured bone, an image preprocessing device used for preprocessing the image containing the measured bone, an image segmenting processing device used for segmenting the preprocessed image of the measured bone, a bone decay factor calculating device used for calculating bone decay factors of an irradiated part according to the decay characteristic of an X-ray and a bone density equivalent analysis device, wherein the bone density equivalent analysis device enables a m (x,y) value to correspond to an area with the same m (x,y) value in the image formed by a reference module with a known equivalent bone density value, and the equivalent bone density value of the corresponding reference module area is a bone density value of the measured bone part. Compared with a traditional DXA method, the device has the advantages of being high in measurement accuracy, convenient to operate and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG KANGYUAN MEDICAL DEVICE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com