Patents
Literature
185results about How to "Big choice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
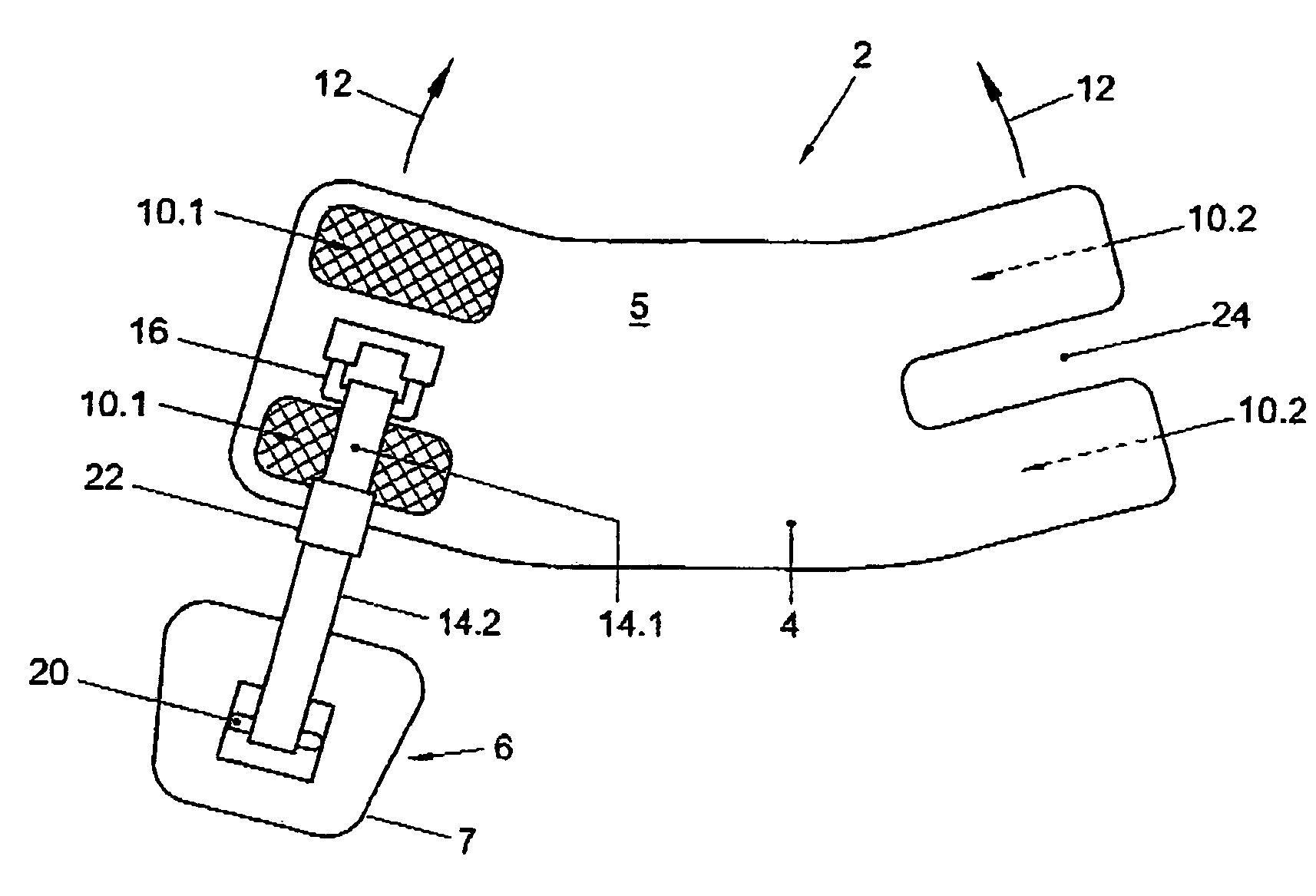
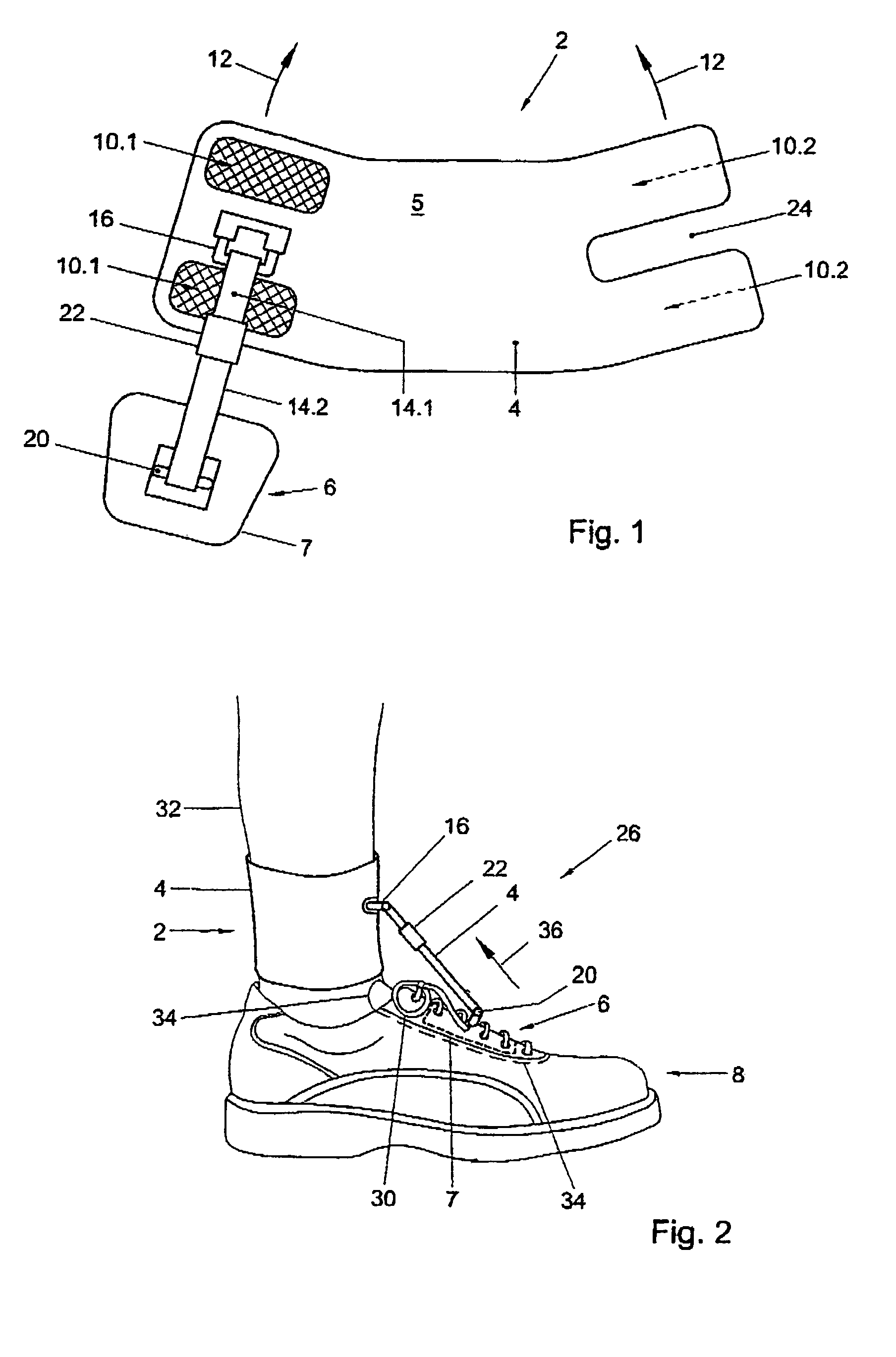
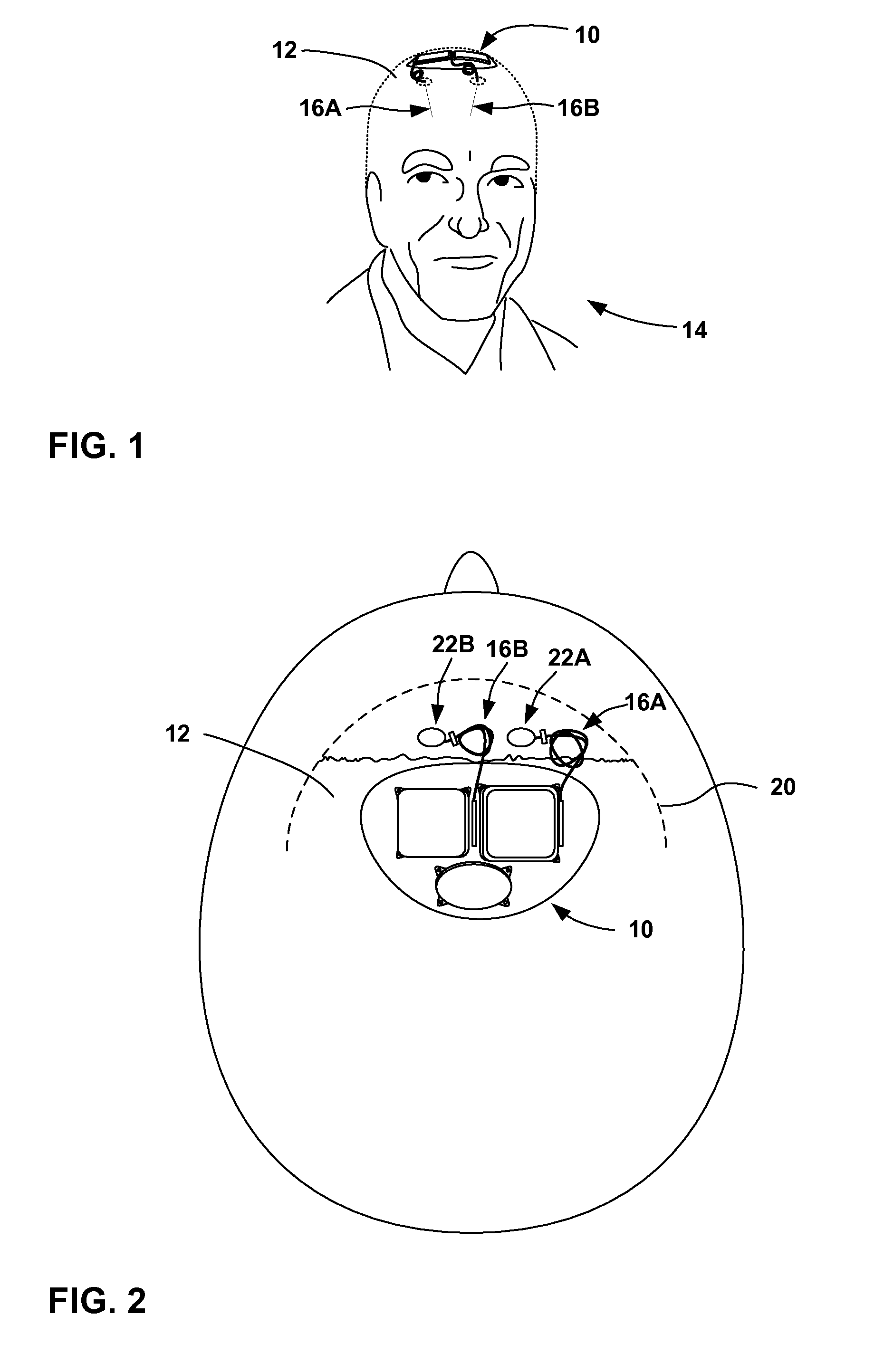
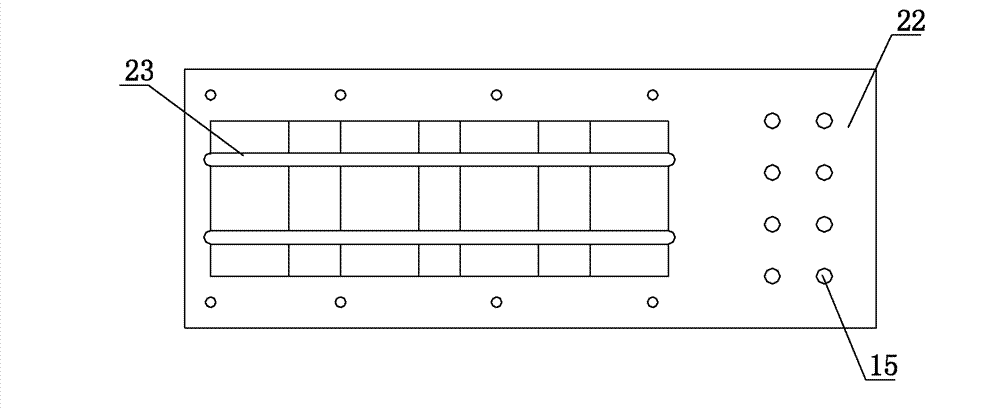
Drop foot device
ActiveUS7674212B2The degree of freedom becomes largerBig choiceClubsResilient force resistorsDropping footDropped foot
The invention relates to assembly of an accessory and a shoe for providing support to a foot-drop affected foot relative to a lower leg belonging to the foot such that the foot is prevented from dropping downwards relative to the lower leg when the foot is raised by the lower from a supporting surface, the accessory being provided with a first attachment member for attachment of the accessory to the lower leg, a second attachment member for attachment of the accessory to an upper side of the shoe and a connecting body joining together the first attachment member and the second attachment member, wherein the second attachment member is provided with an attachment plate which, in use, is positioned under an upper part of the shoe. The invention also relates to the accessory of the assembly.
Owner:OSSUR EURO
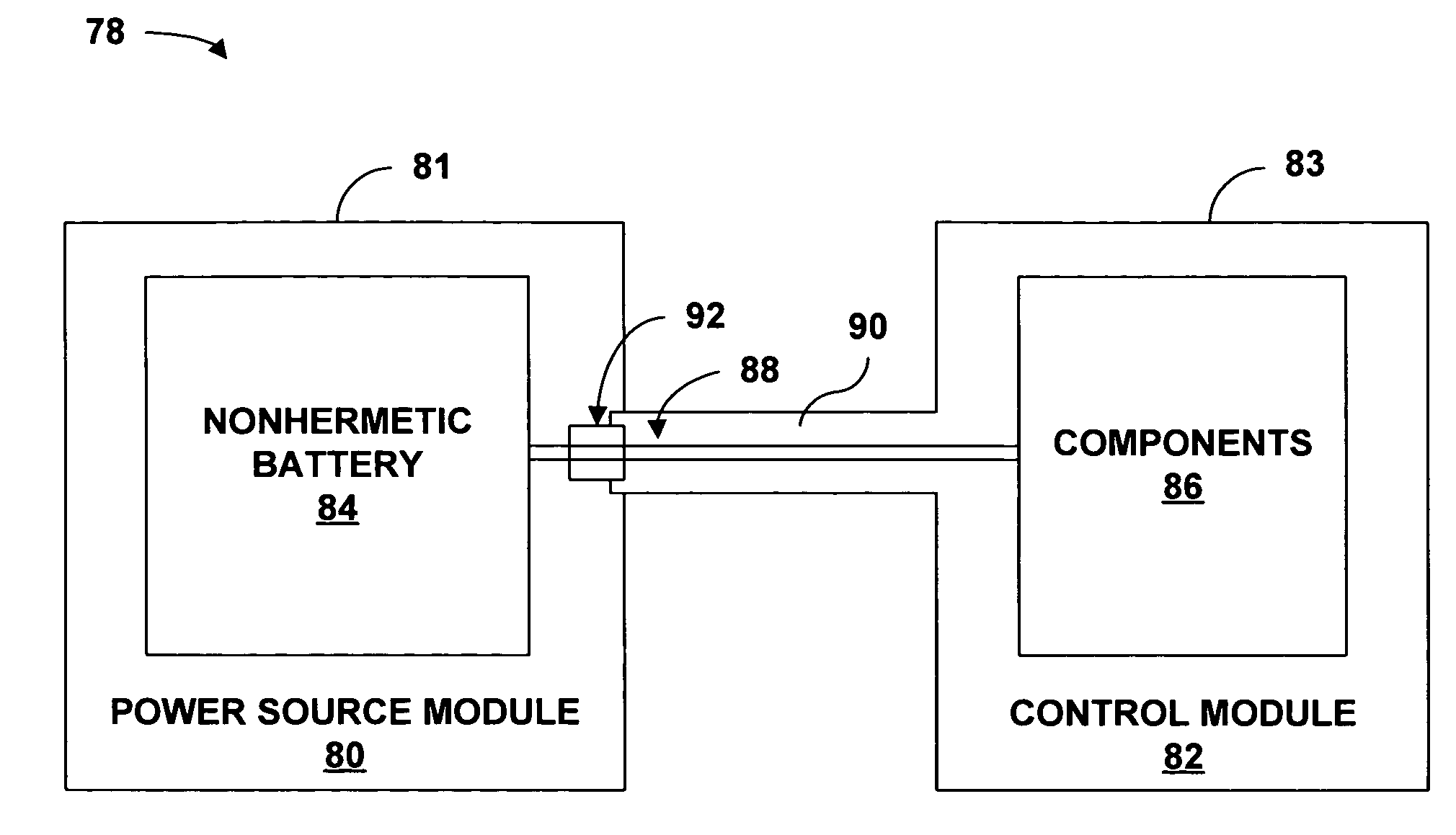
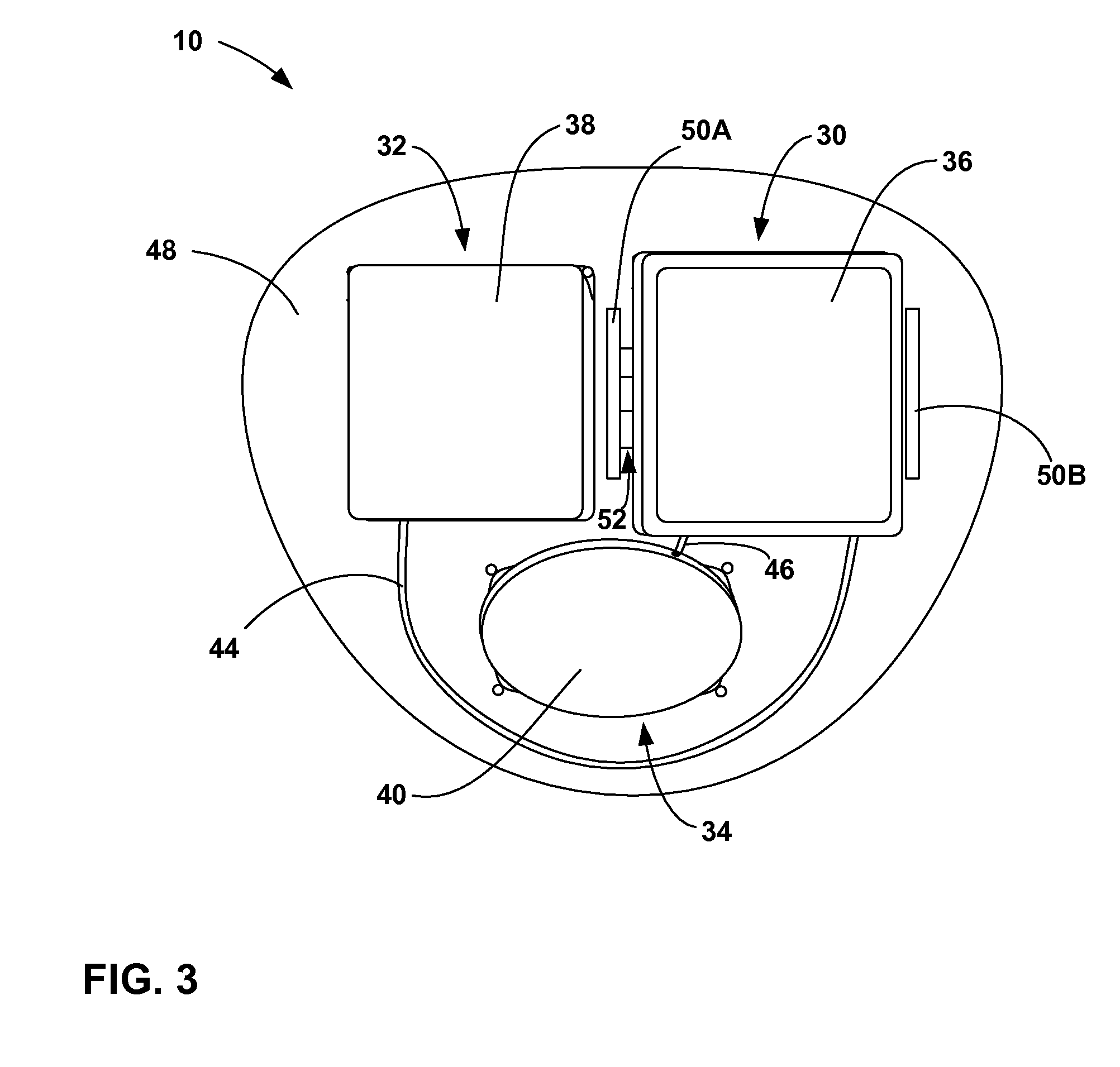
Implantable medical device with a nonhermetic battery
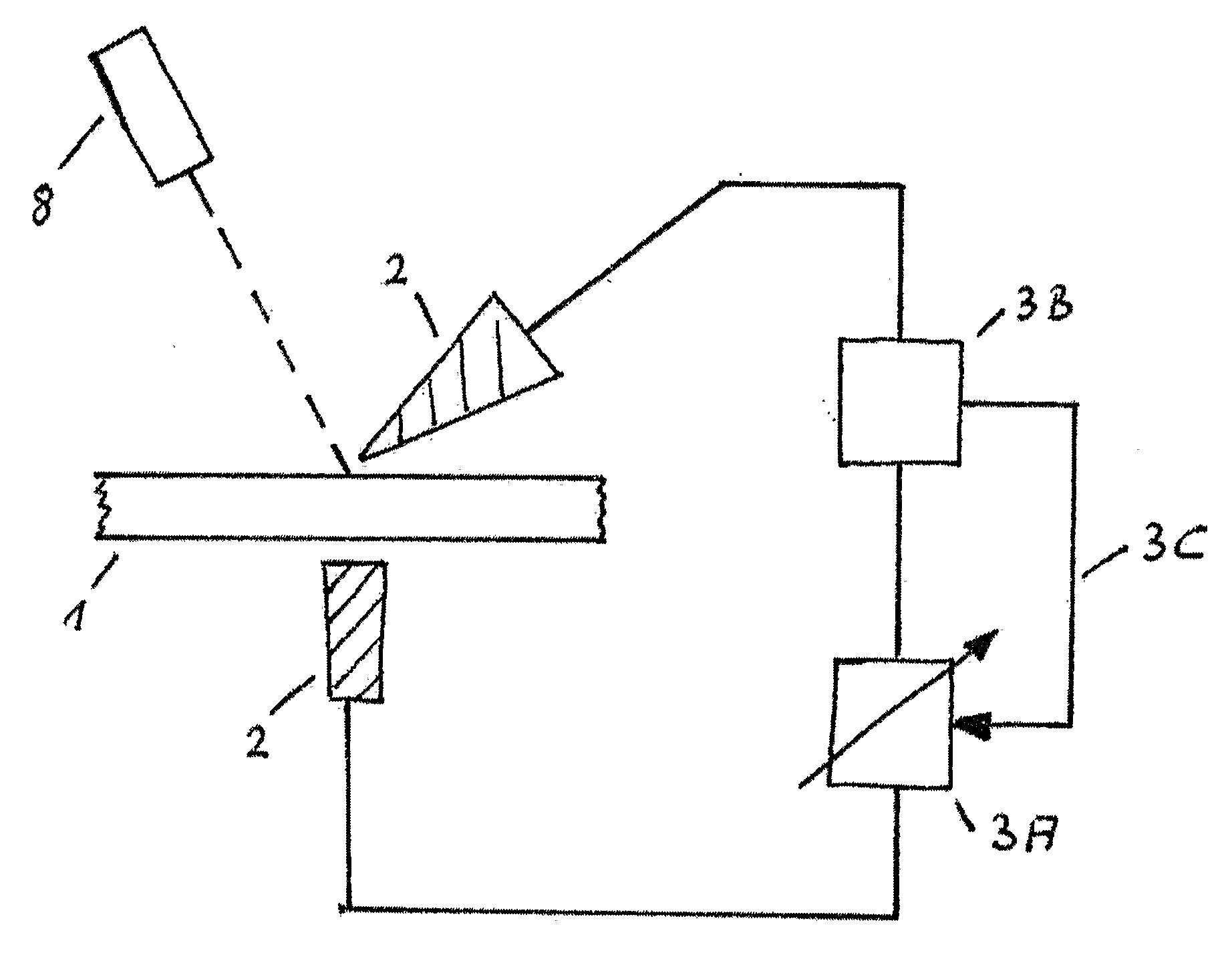
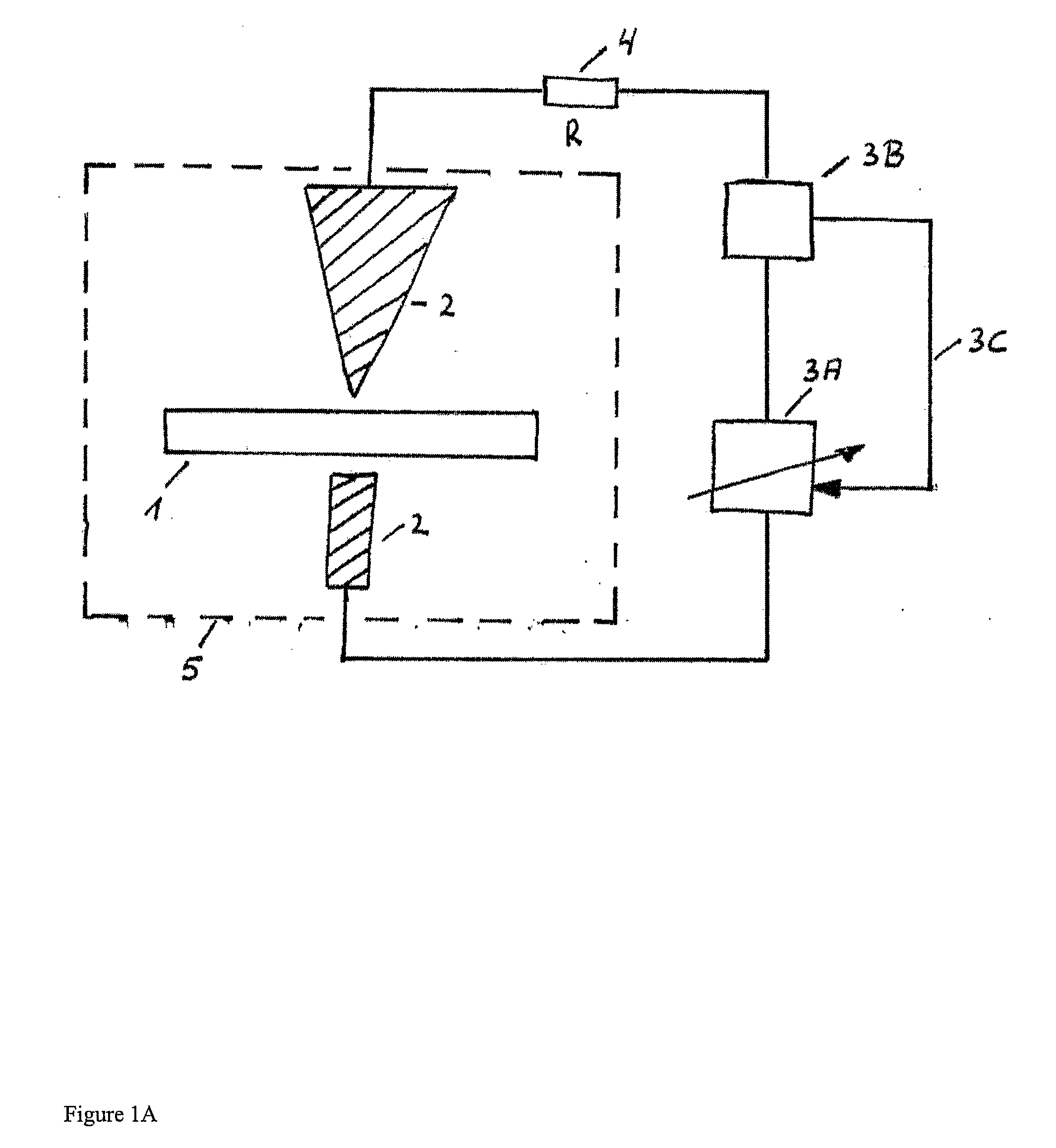
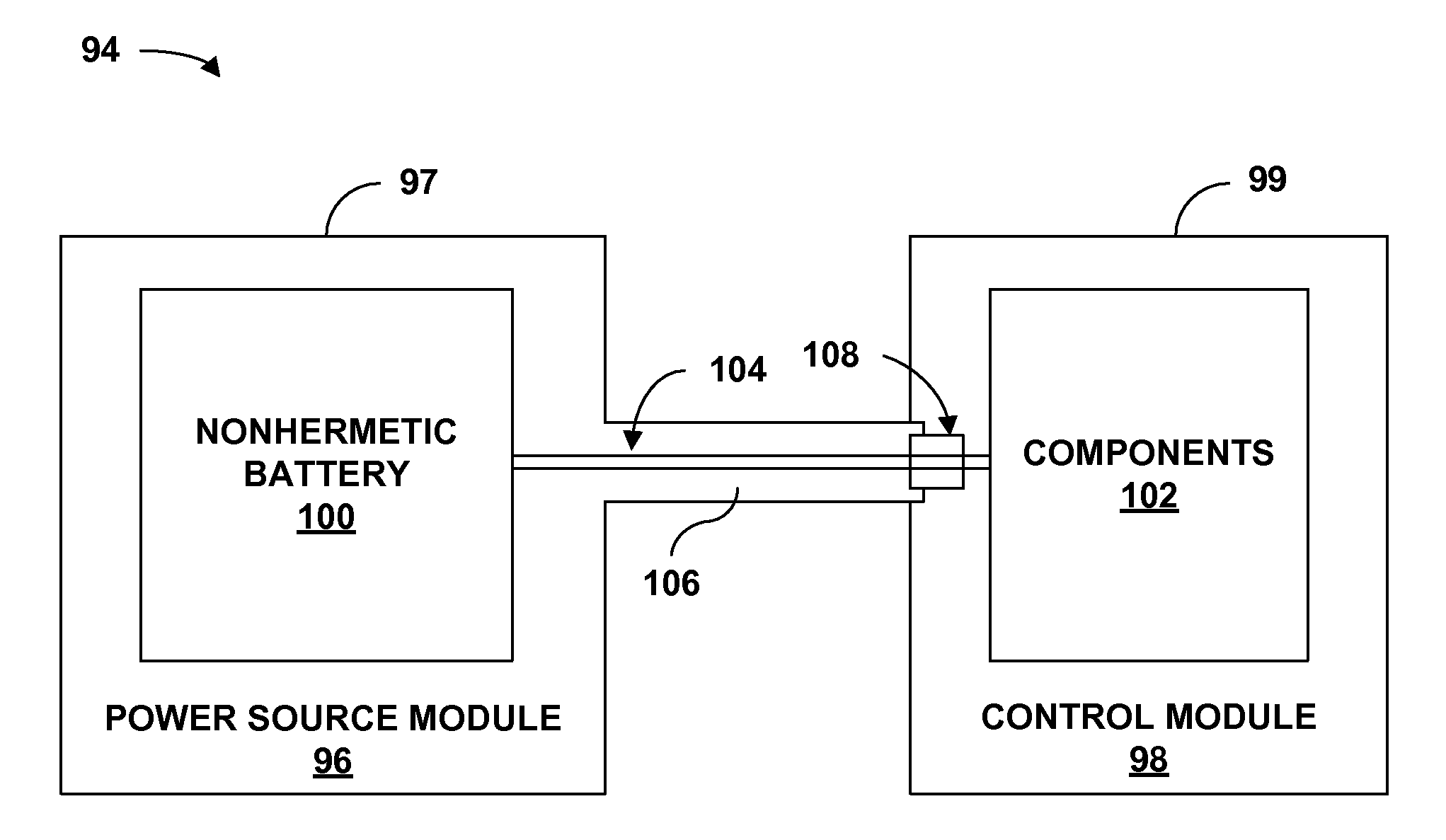
InactiveUS7263401B2Damage to componentEasy to useInternal electrodesHermetically-sealed casingsElectrical batteryEngineering
An implantable medical device (IMD) including a nonhermetic battery is described. The IMD includes components and a power source module that includes the nonhermetic battery. The IMD also includes a barrier to substantially impede movement of substances from the nonhermetic battery to the components. The barrier may include a hermetic feedthrough, a gel, a polymer, or a solid electrolyte within the nonhermetic battery, and a seal member. The barrier may also be a material that encapsulates the nonhermetic battery and a getter within the IMD. In some embodiments, the IMD comprises a modular IMD including an interconnect member. In that case, the barrier may include a material that fills at least a portion of a void defined by the interconnect member. A length and a cross-sectional area of the interconnect member may also act as a barrier.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
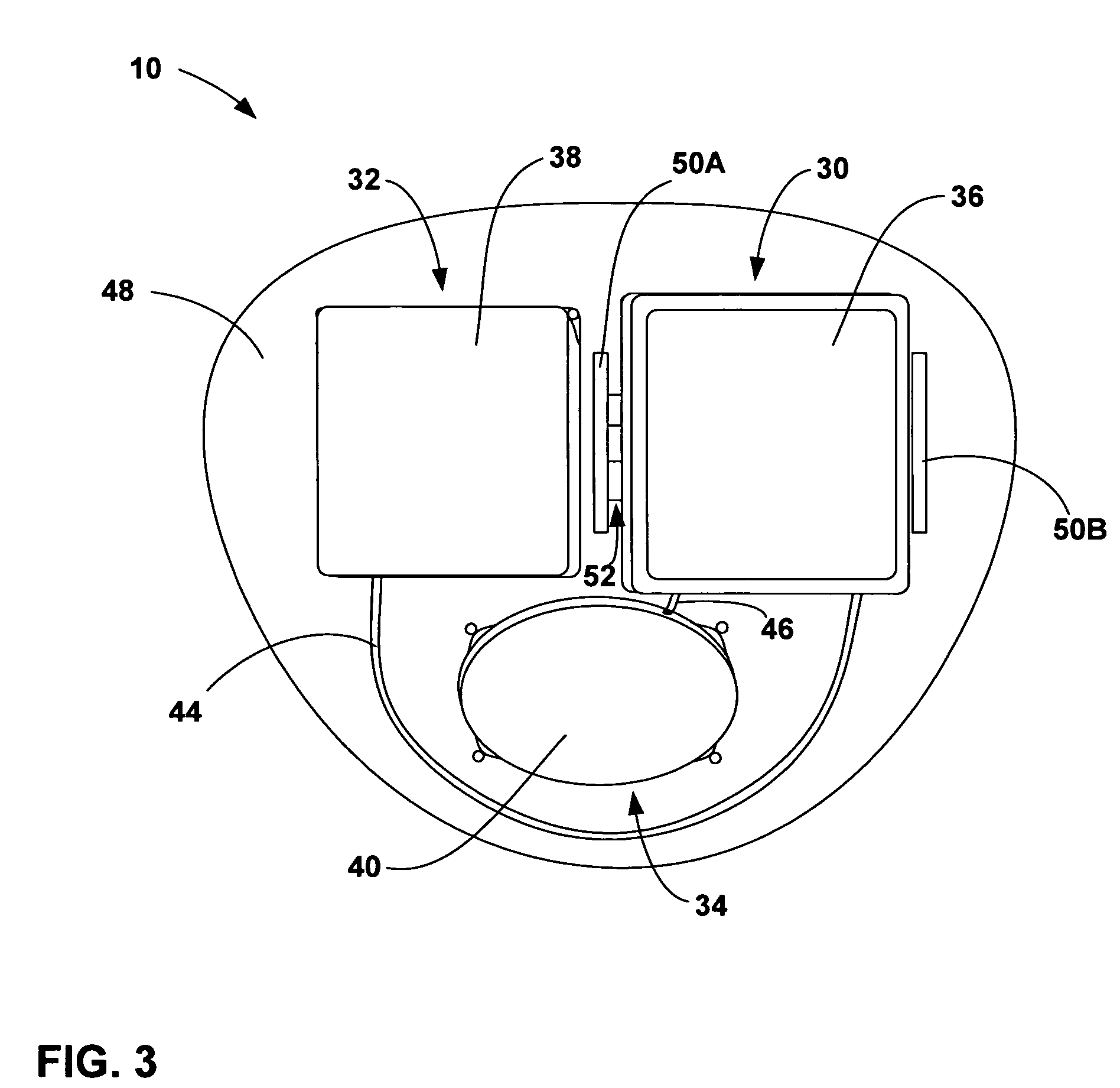
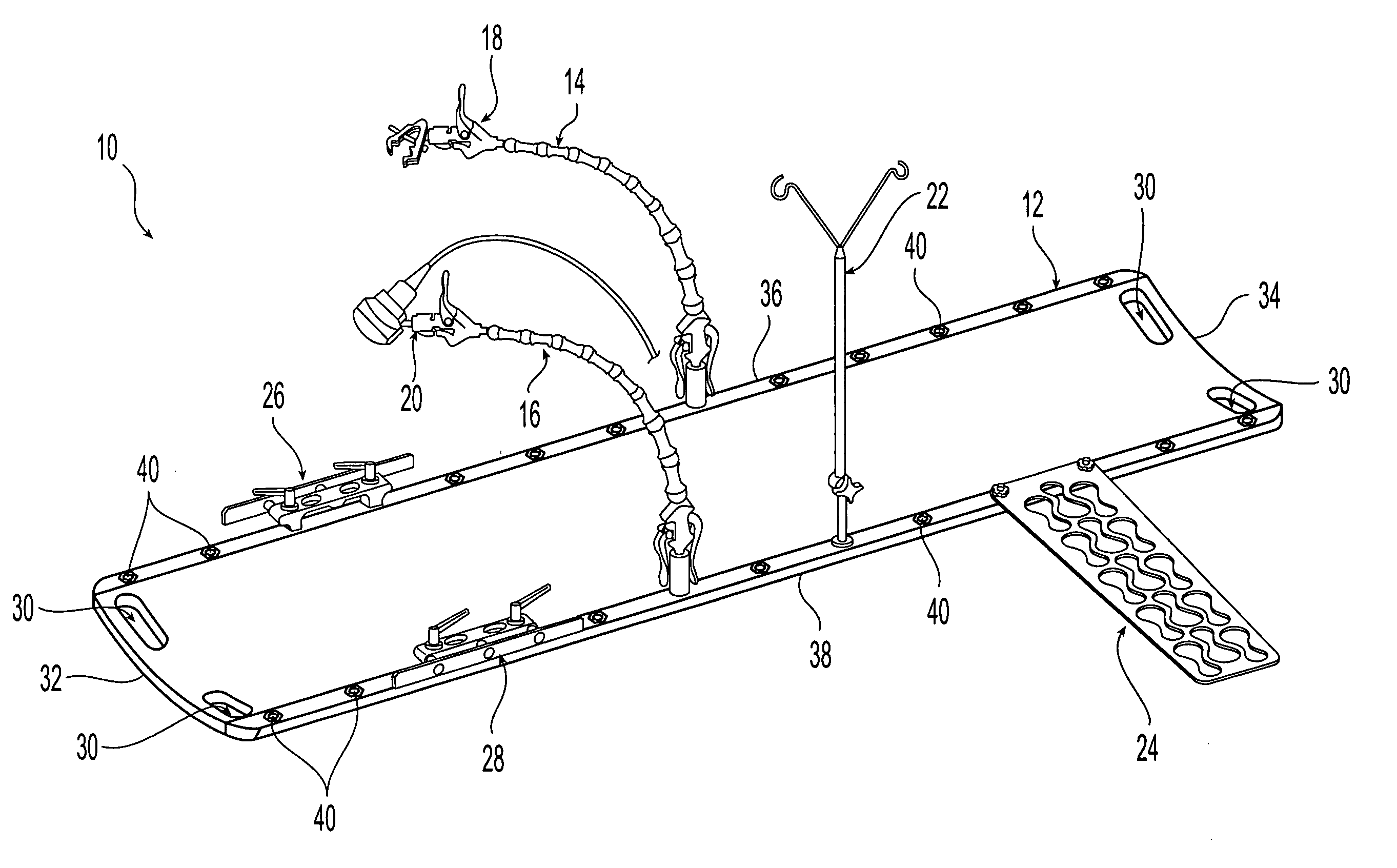
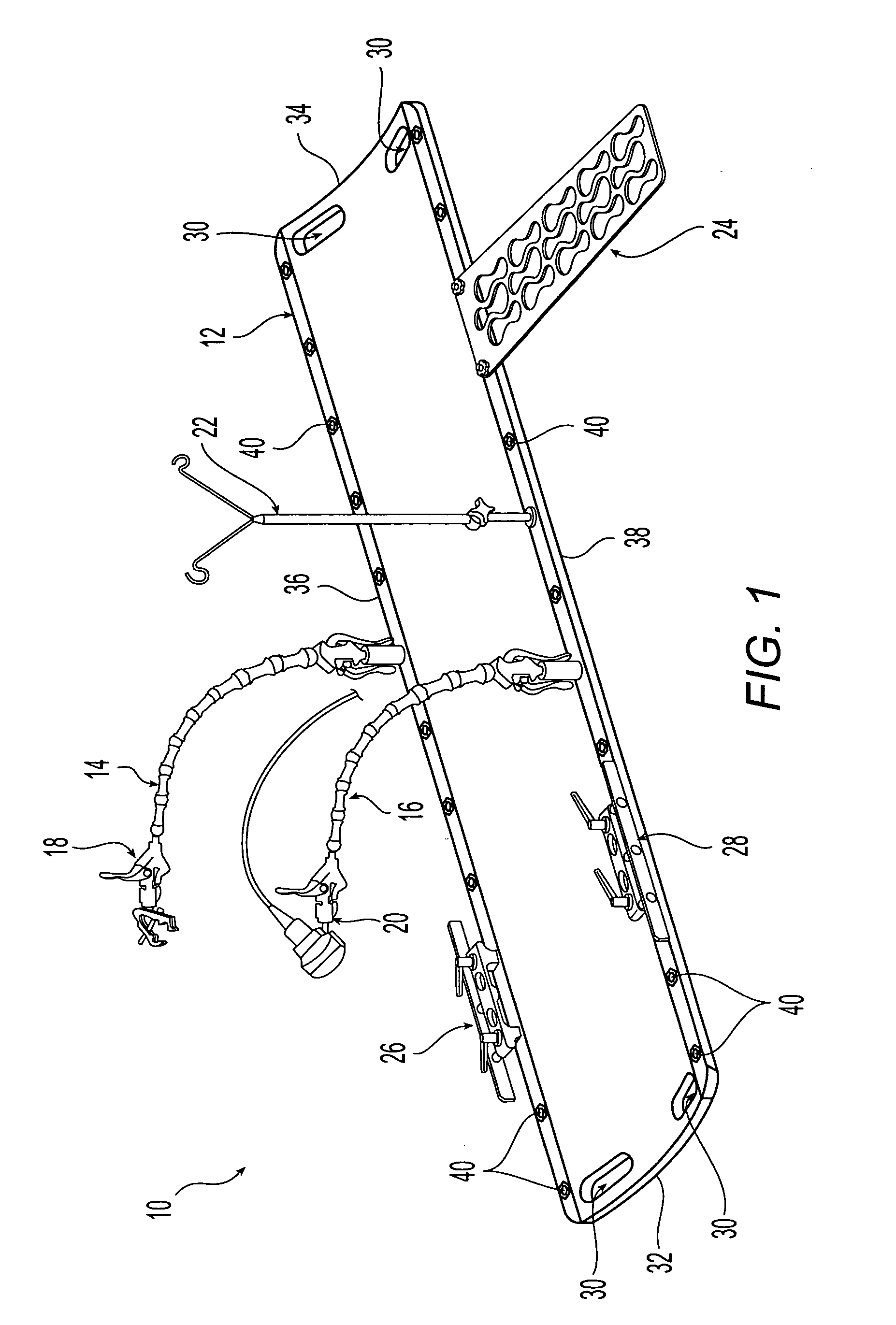
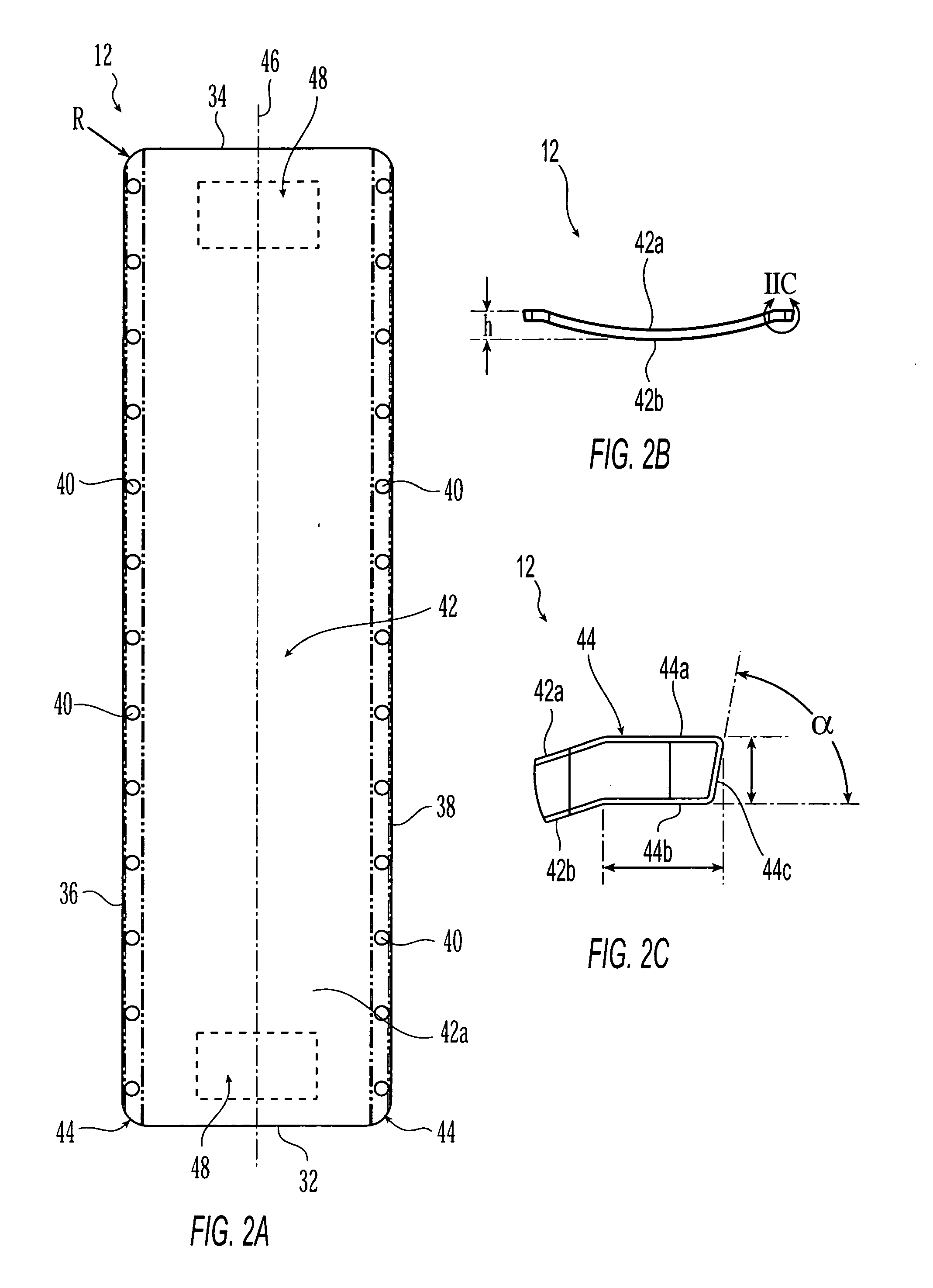
Support system for use when performing medical imaging of a patient
InactiveUS20060016006A1Solve the quick positioningQuick fixOperating tablesStretcherSupporting systemEngineering
A system is provided for supporting a patient during computed axial tomography imaging. The system includes a movable platform formed of a radiolucent material, a discrete attachment region in the platform, and a curvilinear articulating arm coupled to the platform at the discrete attachment region. A method for supporting a patient during a plurality of procedures also is provided. The method includes: disposing the patient on a movable platform formed of a radiolucent material; positioning a device with respect to the patient, the device being disposed on a curvilinear articulating arm coupled to the platform; placing the platform, positioned device, and patient in a computed axial tomography imaging system and performing an imaging procedure.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
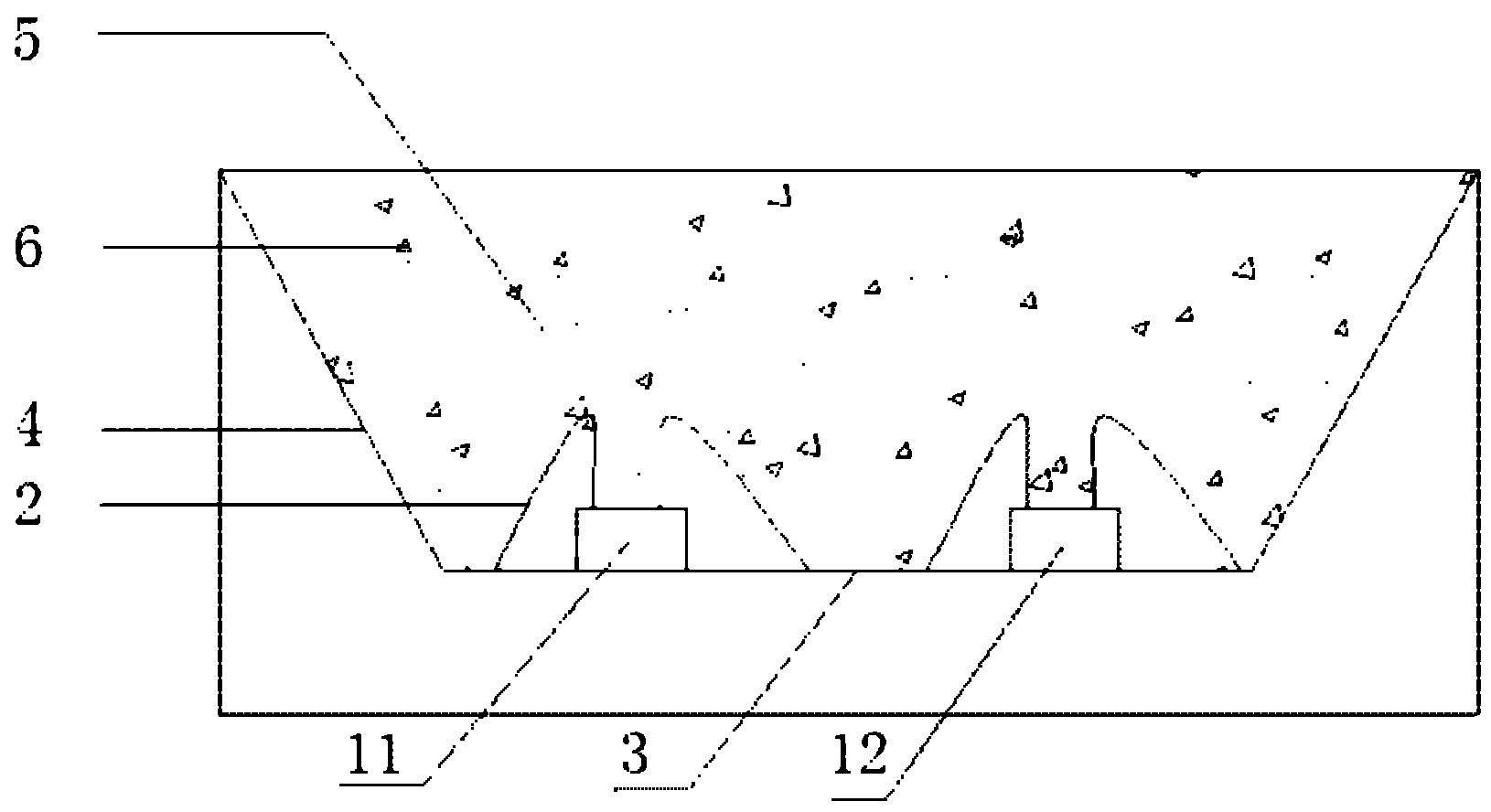
Manufacturing and Use of Microperforated Substrates
ActiveUS20080047935A1Precise definitionDrop in electrical substrate resistanceElectric discharge heatingArc welding apparatusVoltage amplitudeNatural science
This invention relates to methods and devices for the production of micro-structured substrates and their application in natural sciences and technology, in particular in analysis and detection systems based on artificial and biological lipid membranes. The structure is preferably a hole or a cavity or channel and is obtained by spark perforation. Energy, preferably heat, is applied to the region to be structured so as to reduce the amplitude of voltage required and / or soften the material. The electrical parameters of the spark perforation are feedback-controlled.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Implantable medical device with a nonhermetic battery
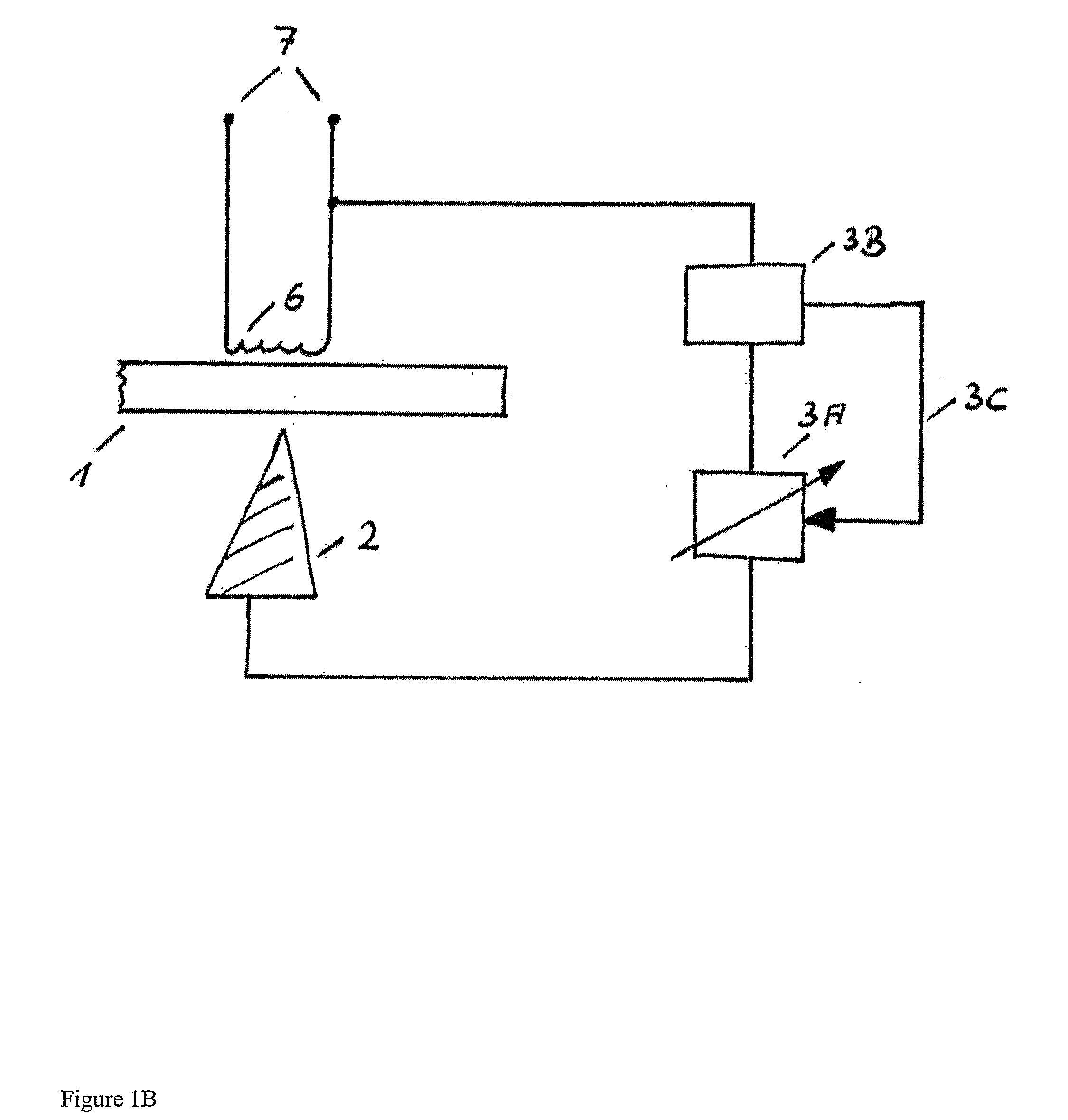
InactiveUS7881796B2Damage to componentEasy to useInternal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical batteryEngineering
An implantable medical device (IMD) including a nonhermetic battery is described. The IMD includes components and a power source module that includes the nonhermetic battery. The IMD also includes a barrier to substantially impede movement of substances from the nonhermetic battery to the components. The barrier may include a hermetic feedthrough, a gel, a polymer, or a solid electrolyte within the nonhermetic battery, and a seal member. The barrier may also be a material that encapsulates the nonhermetic battery and a getter within the IMD. In some embodiments, the IMD comprises a modular IMD including an interconnect member. In that case, the barrier may include a material that fills at least a portion of a void defined by the interconnect member. A length and a cross-sectional area of the interconnect member may also act as a barrier.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Variable-friction damper
The invention discloses a variable-friction damper which comprises a plurality of steel plates stacked or sleeved together. The middle portions of at least one pair of adjacent steel plates are in concave-convex surface contact, every two remaining adjacent steel plates are in plane contact, friction materials are adhered between other steel plates, the other surface of each steel plate with one surface being a concave surface or a convex surface is a plane, the steel plates arranged at intervals form a group of steel plate groups, a first steel plate group and the friction materials adhered to the first steel plate group are provided with at least one group of corresponding bolt holes, a second steel plate group and the friction materials adhered to the second steel plate group are provided with strip-shaped sliding grooves corresponding to the bolt holes along the steel plate length direction, and bolts enabling the steel plates and the friction materials to be connected together penetrate into each group of bolt holes respectively. Linear damping is provided in a friction mode by means of changes of positive pressure, and the variable-friction damper has good damping performance.
Owner:CABR TECH CO LTD
Light-emitting diode device
InactiveCN102543986ALarge dominant wavelength rangeBig choiceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectricityEpoxy
The invention relates to a light-emitting diode device, which comprises a substrate, a support, a light-emitting diode chip and fluorescent flue, wherein an insulating layer and a conducting layer which is arranged on the insulating layer are arranged on the substrate; the support forms an inwards concave opening and is matched with the substrate to form a reflector cup; the light-emitting diode chip is arranged on the substrate and is electrically connected with the conducting layer of the substrate; and the fluorescent glue is prepared by using hot-setting transparent sealing resin such as high-transparency silica gel or epoxy resin and fluorescent powder according to certain weight percentage. Moreover, the light-emitting diode chip consists of at least one blue light chip and at least one green light chip; and the fluorescent powder is excited to emit red light. The light-emitting diode device has the advantages that the working conditions of the chips are consistent, the support structure and the external circuit design are simple, the selection range of the fluorescent powder is wide and the production is facilitated.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
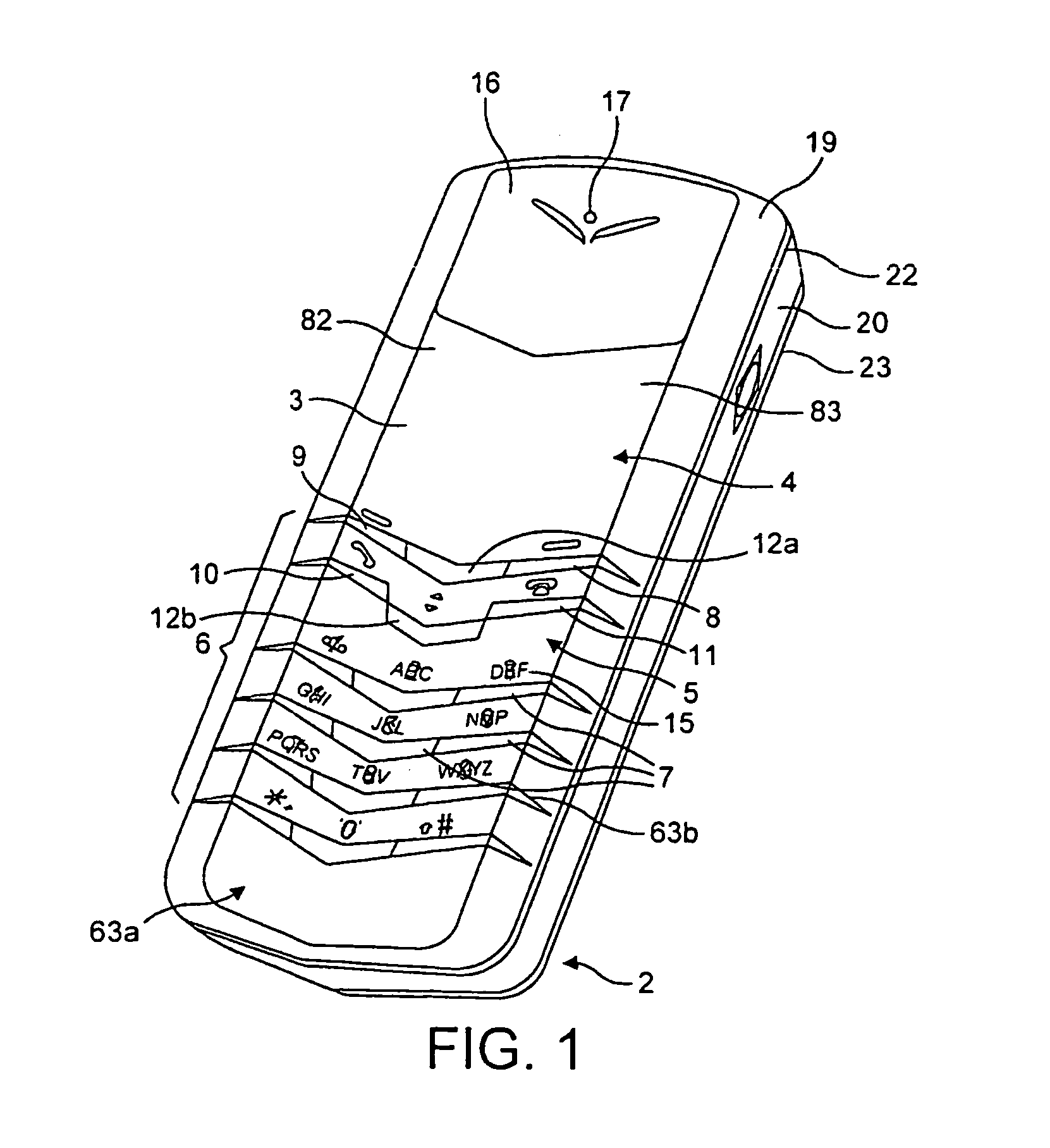
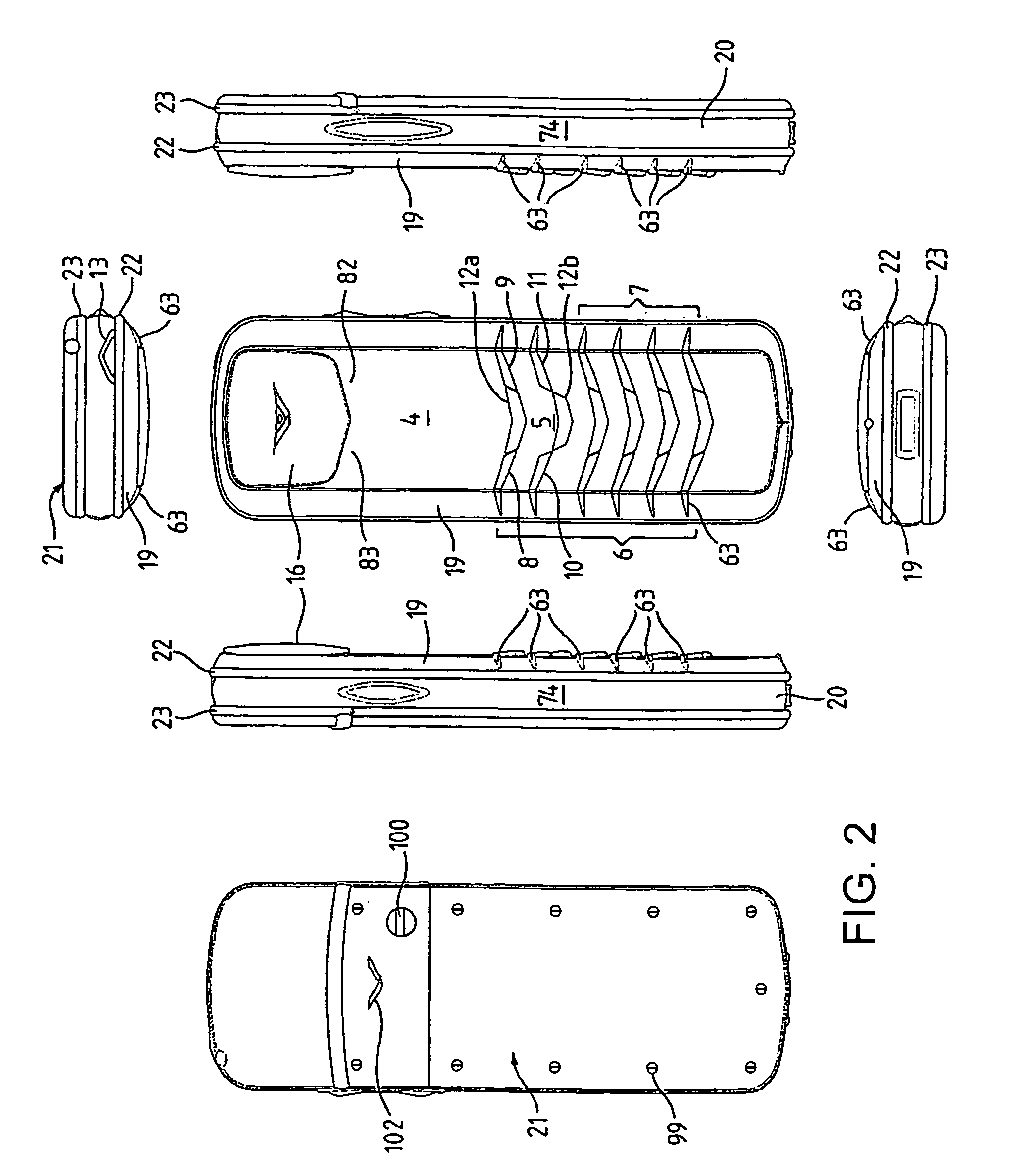
Casing for portable communication device
InactiveUS7418282B2Protection from damageGreat individualityDigital data processing detailsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsUser inputDisplay device
The invention relates to a casing for a portable communication device. The casing has an operating face carrying user input elements and a display, and rails are provided along an intersection between adjacent housing elements to obscure the edges of the housing elements, on the exterior of the assembled housing.
Owner:RITTALWERK RUDOLF LOH GMBH & CO KG
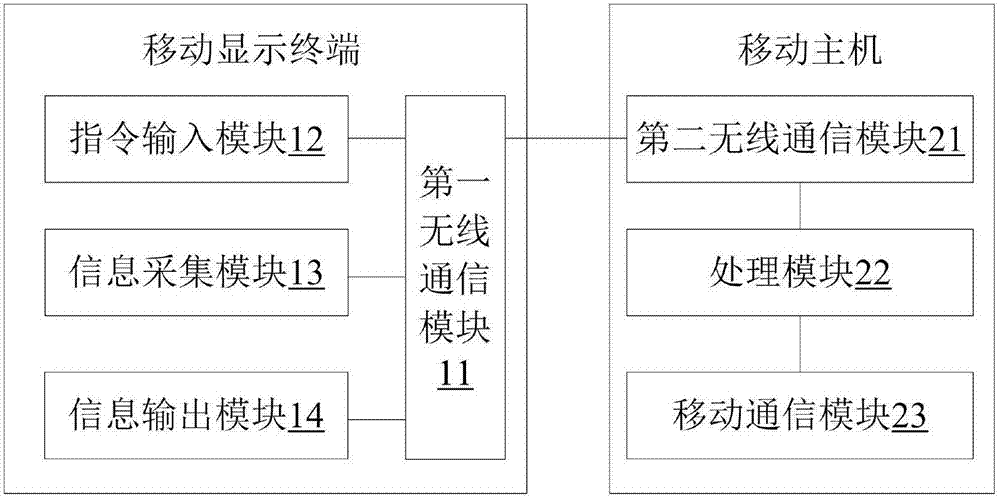
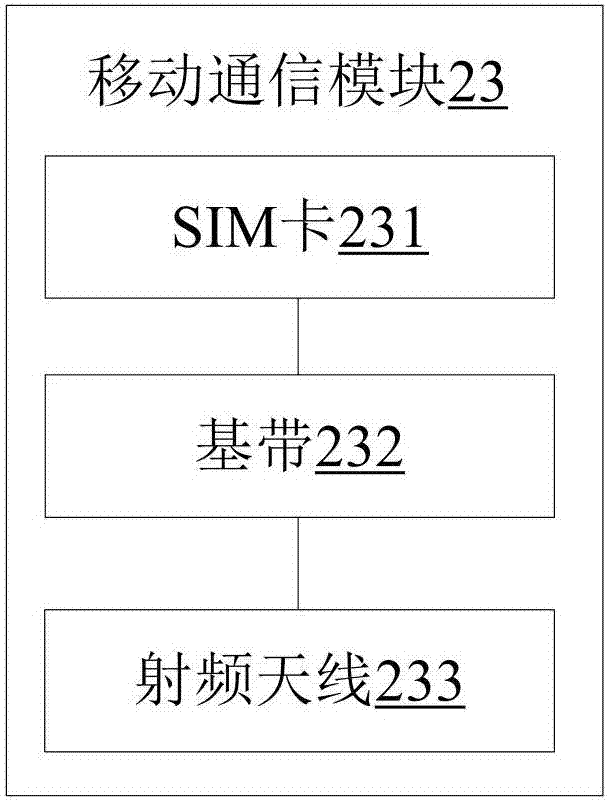
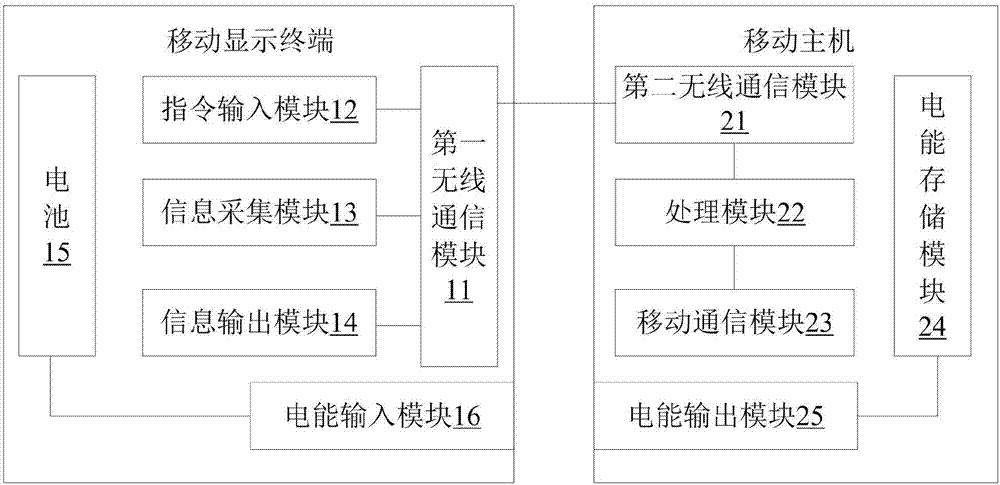
Separate communication device and mobile host
InactiveCN107070478AReduce power consumptionImprove battery lifeTransmissionTelephone set constructionsComputer moduleComputer terminal
The invention discloses a separate communication device and a mobile host. The device comprises a mobile display terminal and a mobile host, the mobile display terminal comprises a first wireless communication module, and an instruction input module, an information collection module and an information output module connected with the first wireless communication module, the mobile host comprises a second wireless communication module, a processing module and a mobile communication module, which are connected in sequence, and the first wireless communication module communicates with the second wireless communication module. The existing mobile terminal is set into the mobile display terminal and the mobile host, only necessary components of user interaction are arranged in the mobile display terminal handheld operated by a user, and an SIM card, a base band, a radio frequency antenna, a processing module, a memory and other power consumption components and parts of the mobile communication module are omitted, thereby greatly reducing the power consumption of the mobile display terminal and improving the cruising ability of the mobile display terminal and the lighting and thinning of a battery, and thus the lighting and thinning design of the mobile display terminal is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN WATER WORLD CO LTD
Bianisotropic Metamaterial
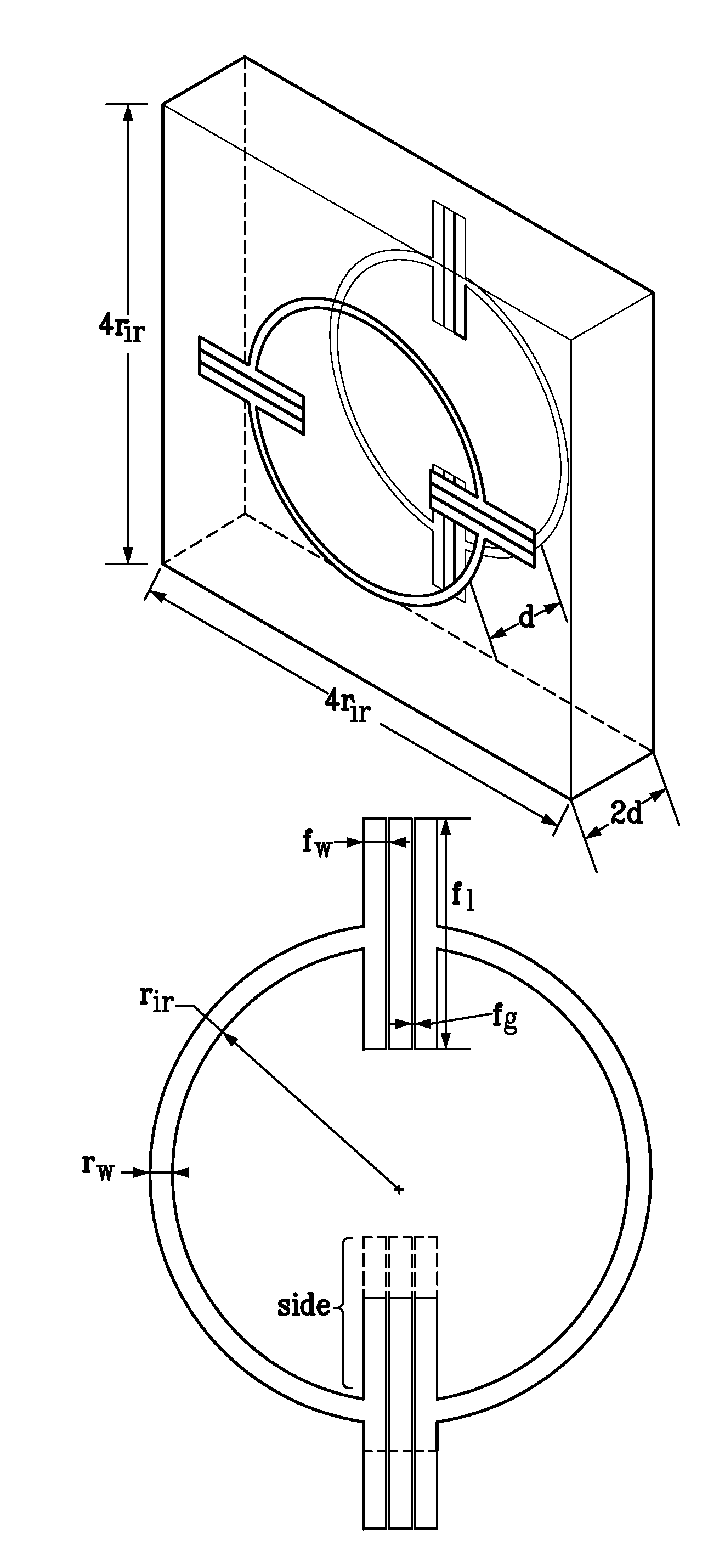
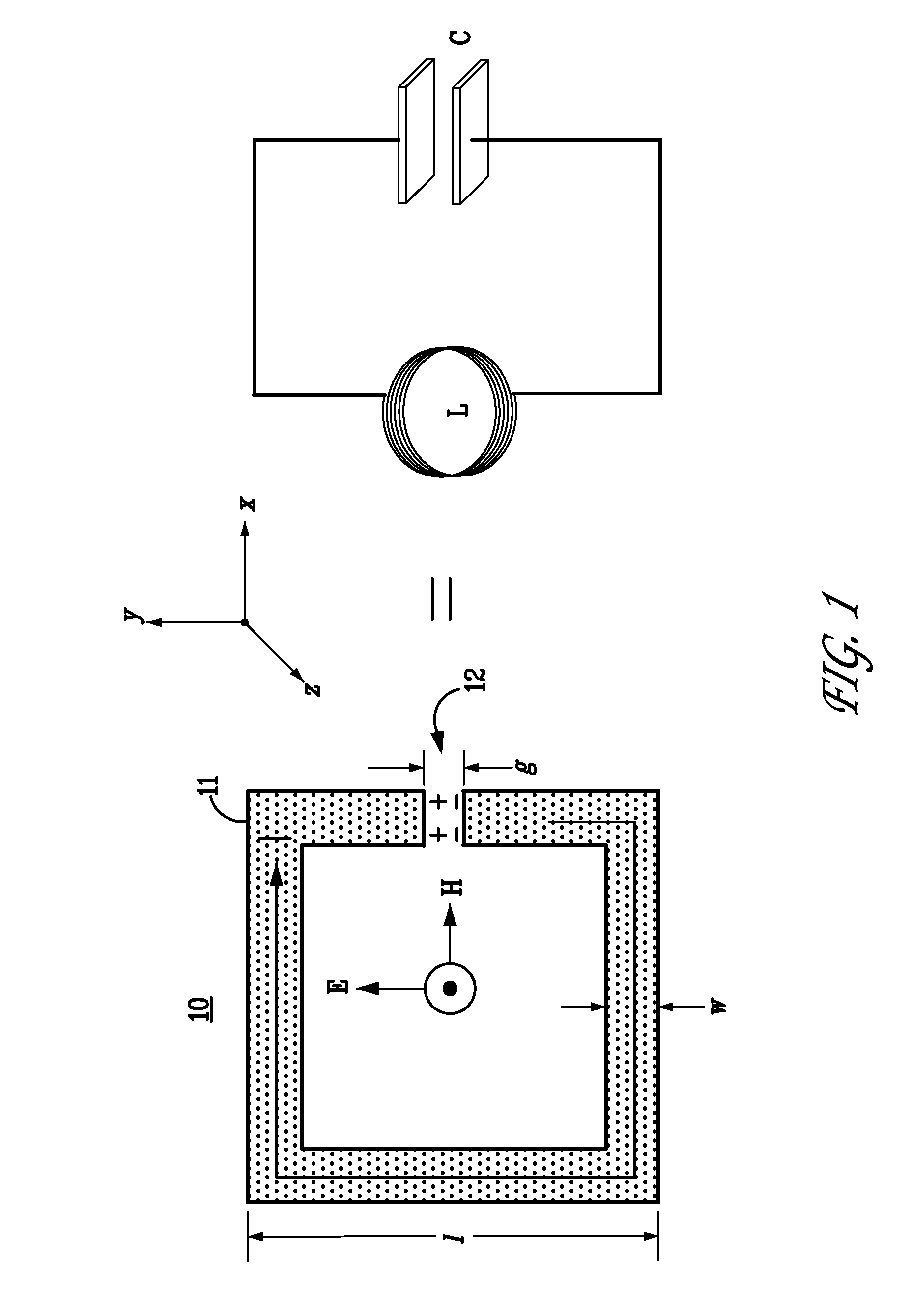
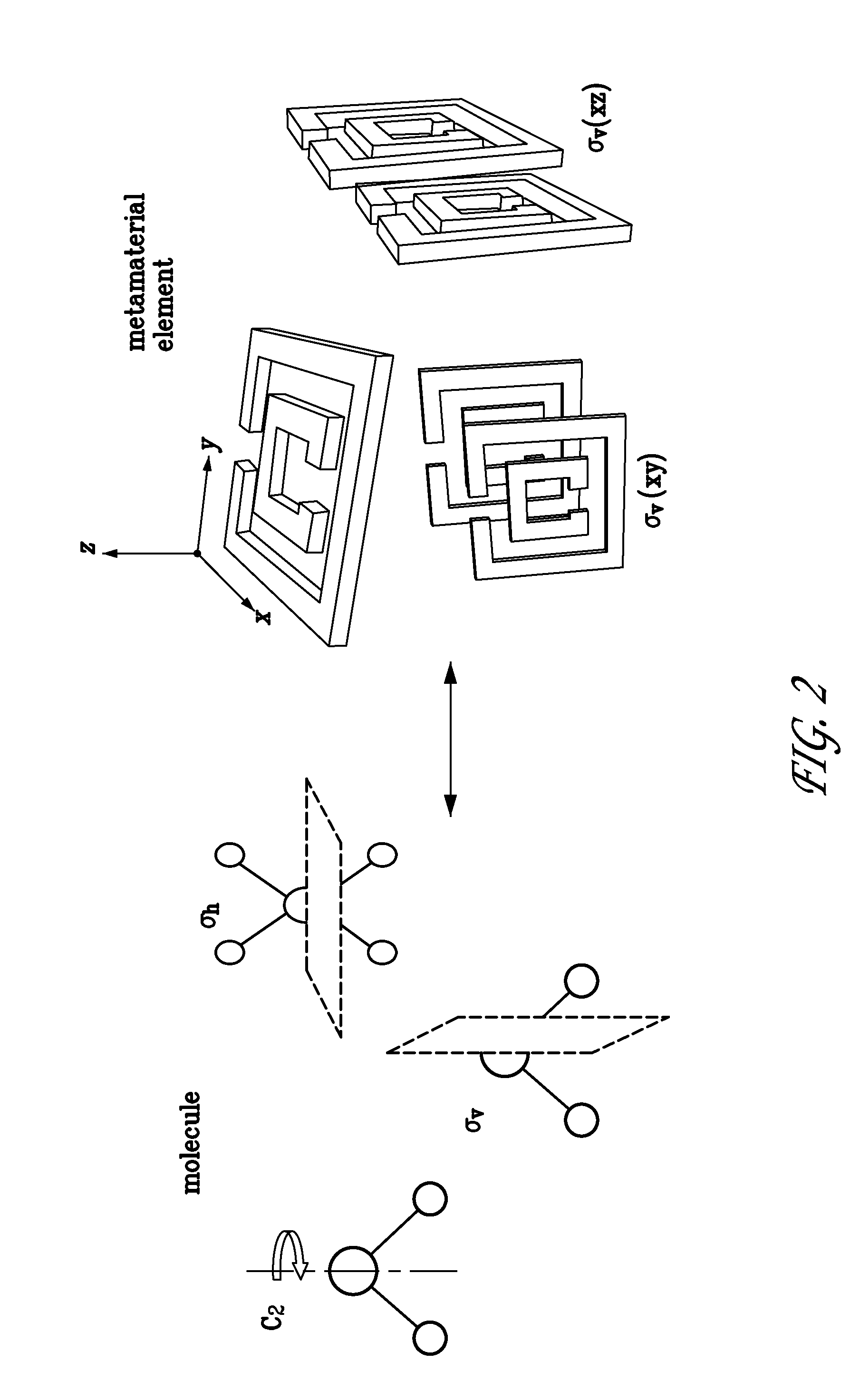
ActiveUS20150192721A1Strong couplingBig choicePolarising elementsAntennasElectromagnetic responseEngineering
The topology of the elements of a metamaterial can be engineered from its desired electromagnetic constitutive tensor using an inverse group theory method. Therefore, given a desired electromagnetic response and a generic metamaterial elemental design, group theory is applied to predict the various ways that the element can be arranged in three dimensions to produce the desired functionality. An optimizer can then be applied to an electromagnetic modeling tool to fine tune the values of the electromagnetic properties of the resulting metamaterial topology.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
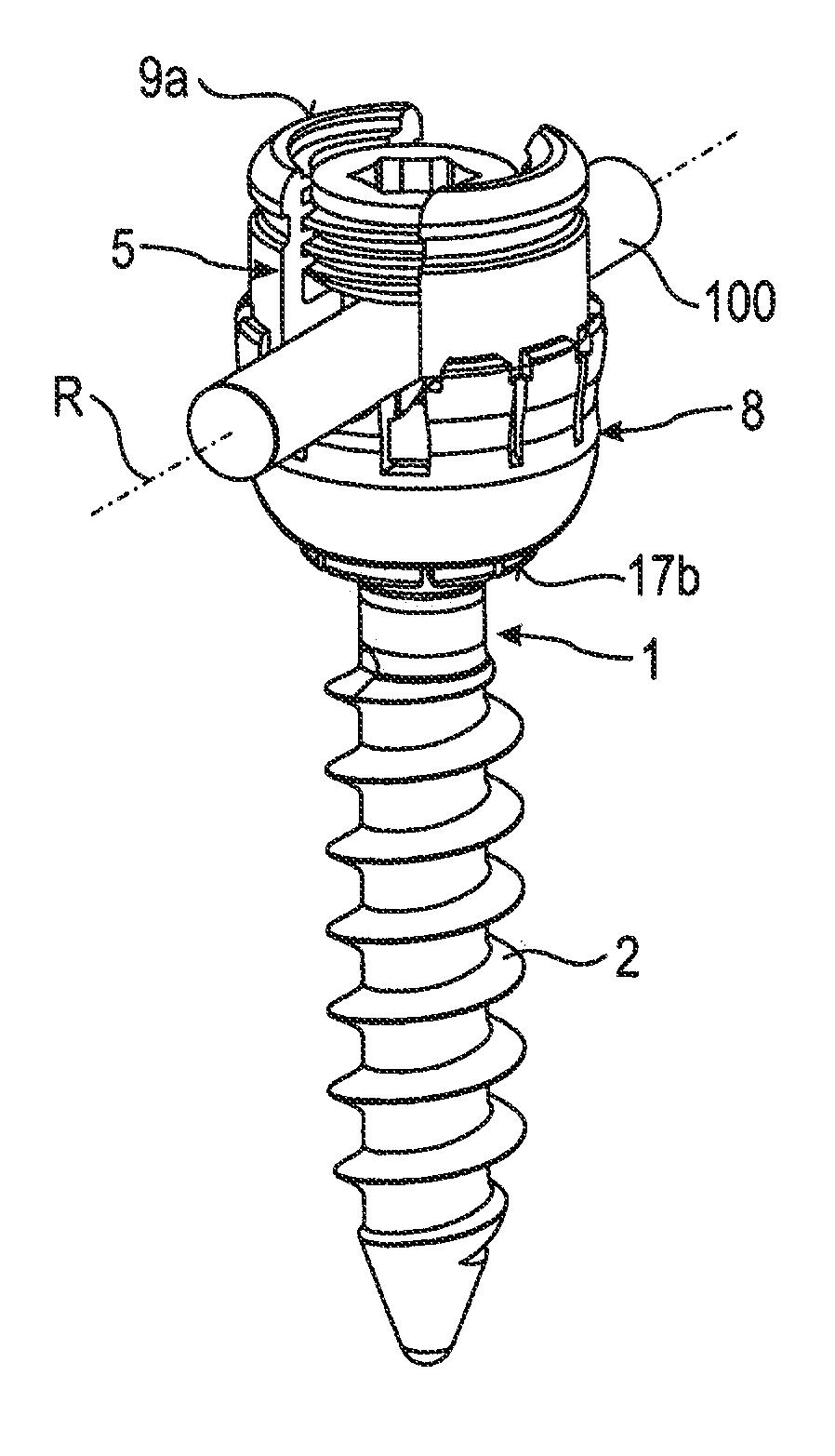
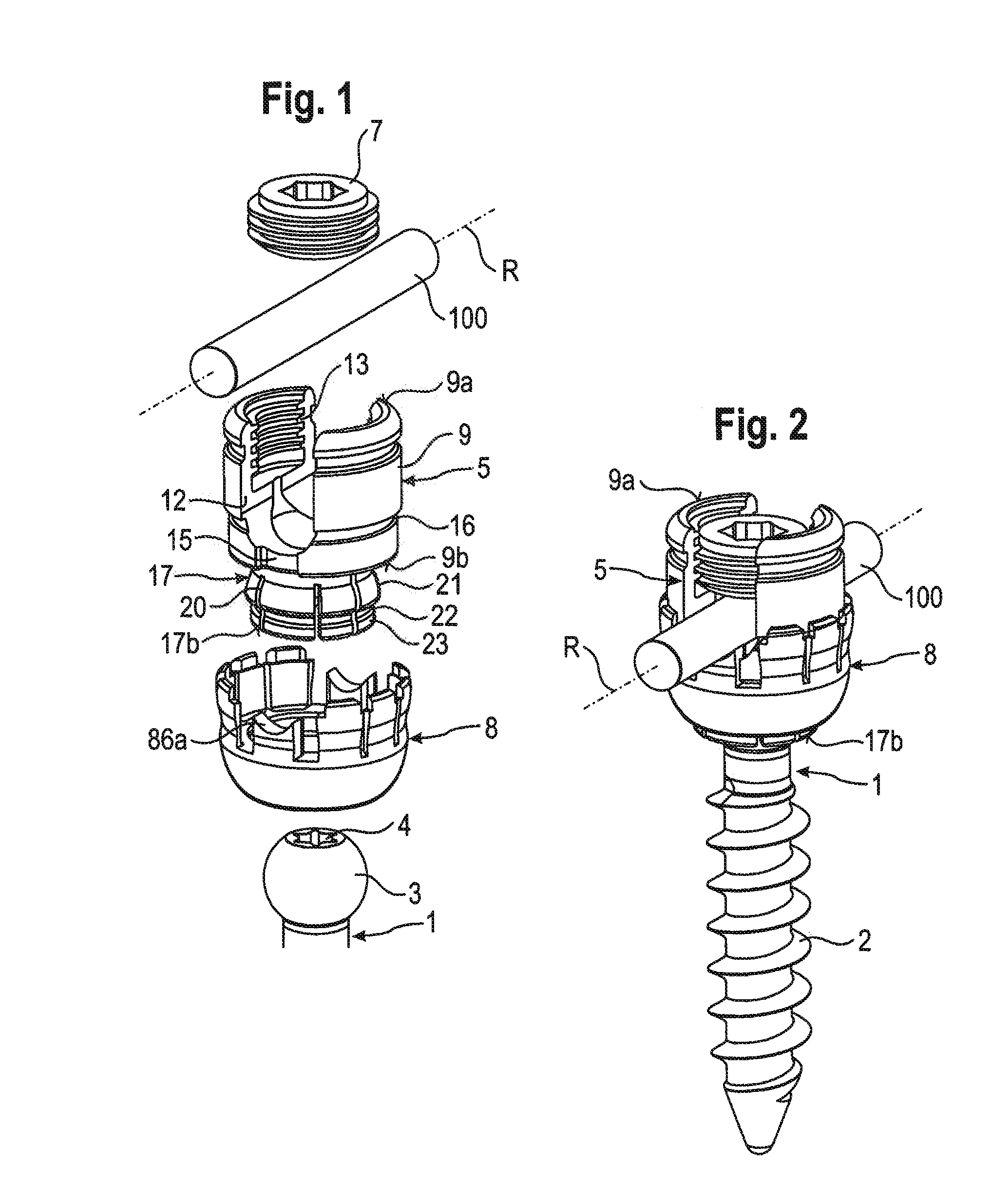
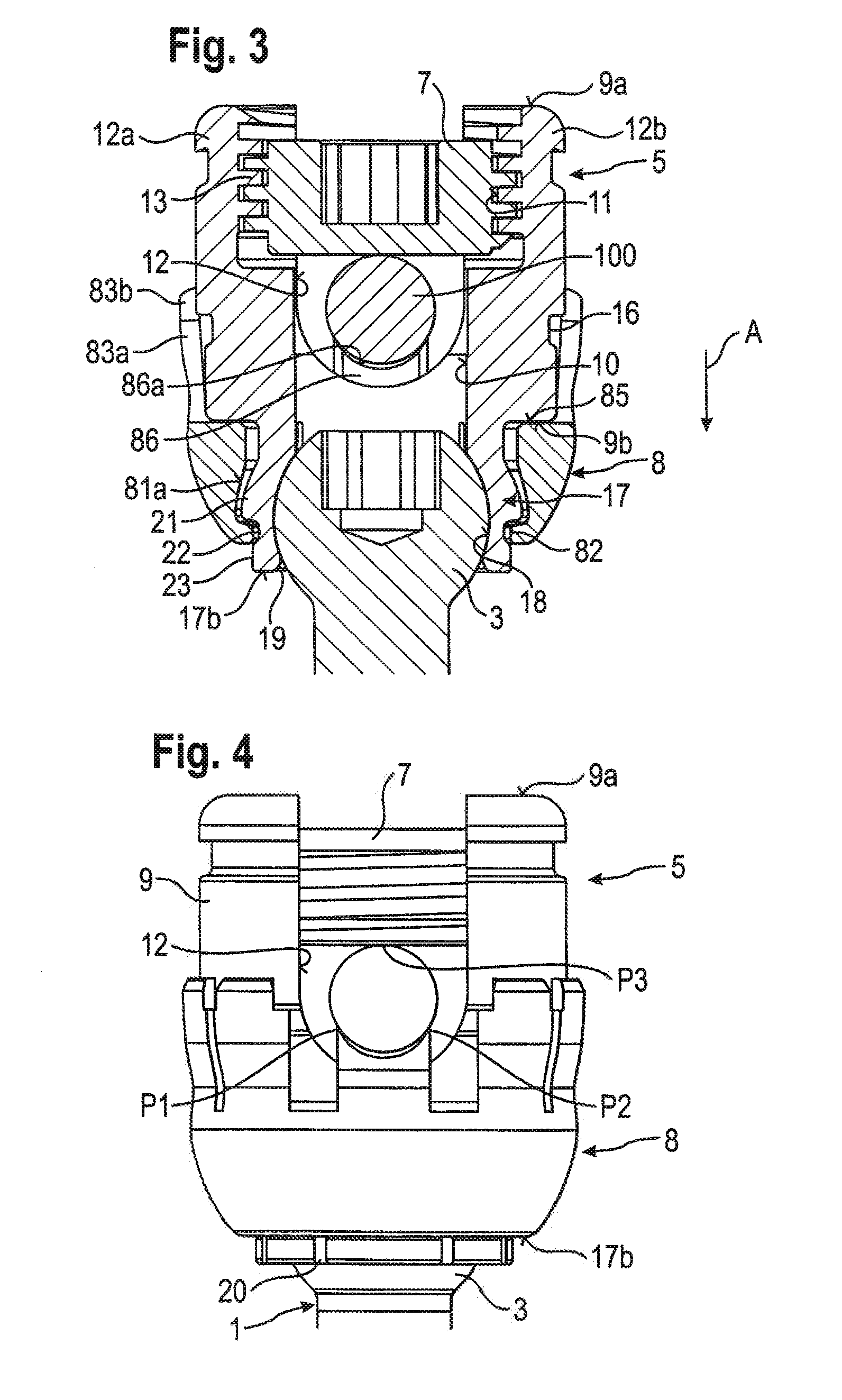
Stabilization device for stabilizing vertebrae or bone parts
ActiveUS20120165874A1Achieve modularityBig choiceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMechanical engineeringVertebra
A stabilization assembly for stabilizing a vertebra or other bone includes: at least two rods having different diameters; an anchoring element having a shaft and a head; a receiving part for interchangeably receiving any one of the rods to connect the rod to the anchoring element, the receiving part including a rod receiving portion with a channel for receiving the rod, and a head receiving portion having an open end and being flexible to allow introduction and clamping of the head; and a locking ring configured to be arranged around the head receiving portion and to clamp the head in the head receiving portion; wherein the locking ring includes a contact surface configured to contact any one of the at least two rods at at least two distinct contact areas that are spaced apart from one another in a circumferential direction of the rod.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105355818AGood effect of intercepting electrode active particlesHigh mechanical strengthCell component detailsNanofiberNanofibrous membrane
The invention discloses a compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm and a preparation method thereof. The compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm is characterized in that the compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm structurally comprises an upper layer nanofiber diaphragm layer, a middle layer nanocellulose gel layer and a lower layer nanofiber diaphragm layer, and the compound battery diaphragm containing the three-layer structure is prepared by utilizing an electrostatic spinning method and a sol-gel combination method. The preparation method of the compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm comprises the following steps: step (1), preparing nanocellulose suspension liquid; step (2), preparing a polymer electrostatic spinning solution; step (3), performing electrostatic spinning; step (4), enabling the lower layer nanofiber diaphragm layer prepared in the step (3) to be infiltrated by acid liquor of which the pH is 3 to 6; step (5), preparing the middle layer nanocellulose gel layer; step (6), preparing the upper layer nanofiber diaphragm layer. The prepared three-layer-structure compound nanofiber lithium battery diaphragm final product is the compound battery diaphragm.
Owner:上海展恒环保科技有限公司
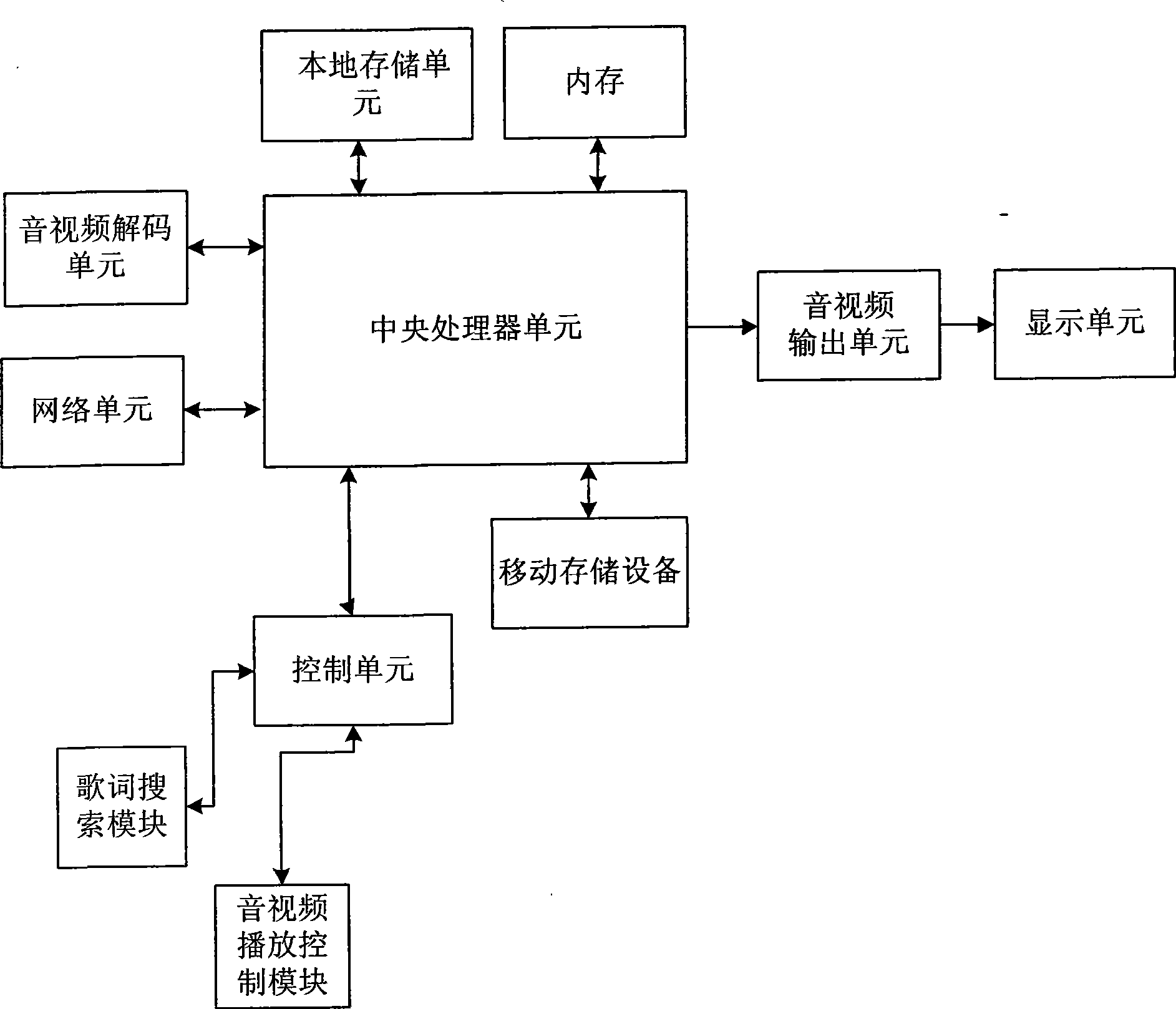
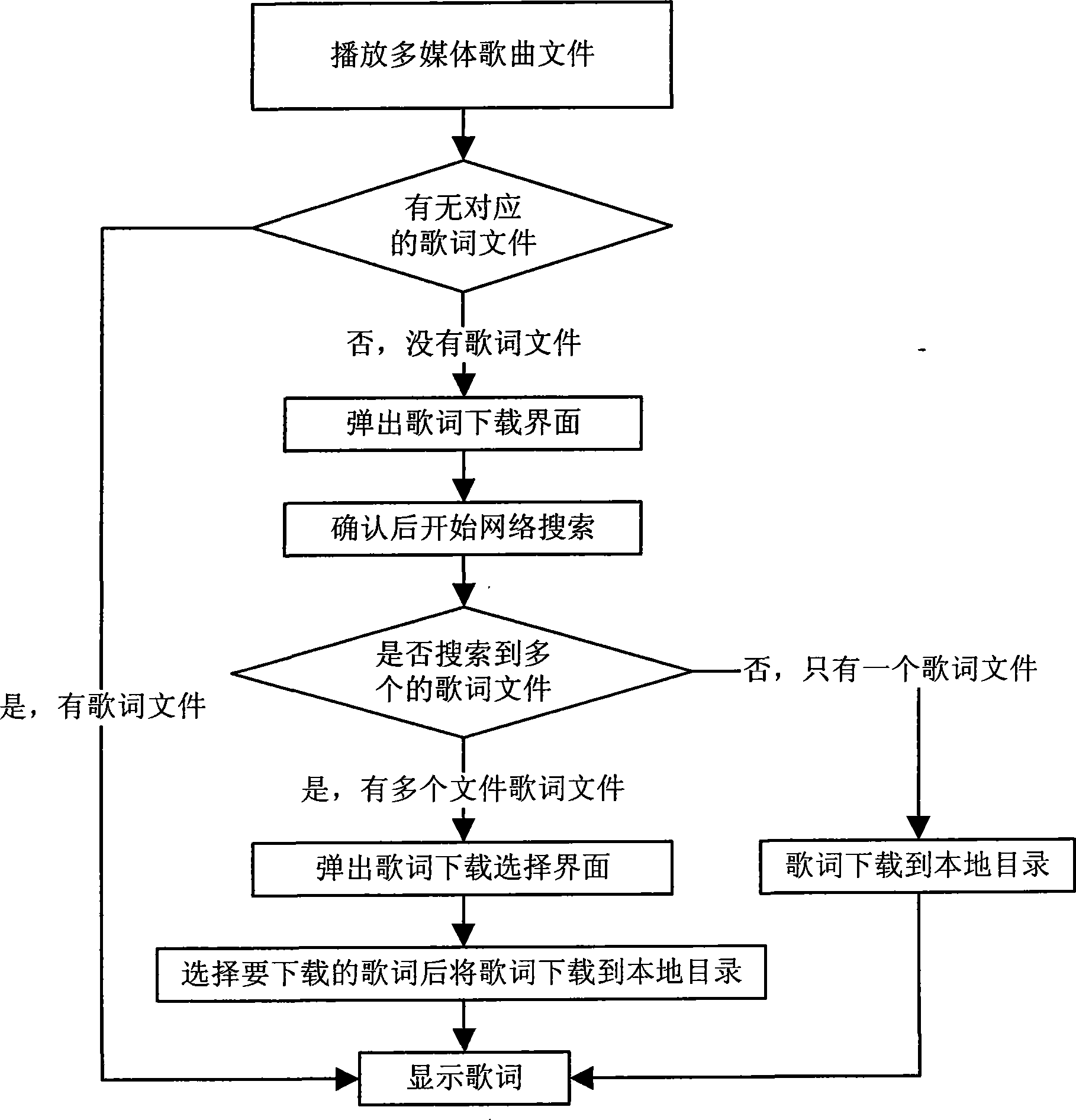
Multimedia playing system and method capable of downloading and displaying lyric
InactiveCN101452726ABig choiceRecord information storageCarrier indicating arrangementsVideo decodingMultimedia
The invention discloses a multimedia playing system and a multimedia playing method capable of downloading and displaying lyrics. The method comprises: the multimedia playing system selects a song to be played; when an audio-video playing control module inquires a storage unit of the multimedia playing system and finds no lyric file of the song to be played, the multimedia playing system is connected with a network to search the lyric file corresponding to the song and downloads the lyric file searched to the storage unit; an audio-video decoding unit plays the song; and the display unit displays the searched lyric file. The system and the method allow a user to see the lyrics when the user plays the song, thereby providing a bright point for audio playing and larger selection space for user.
Owner:KONKA GROUP
Information publishing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN110933509AOptimize the reading interaction processSave operating timeSelective content distributionTime informationProgress bar
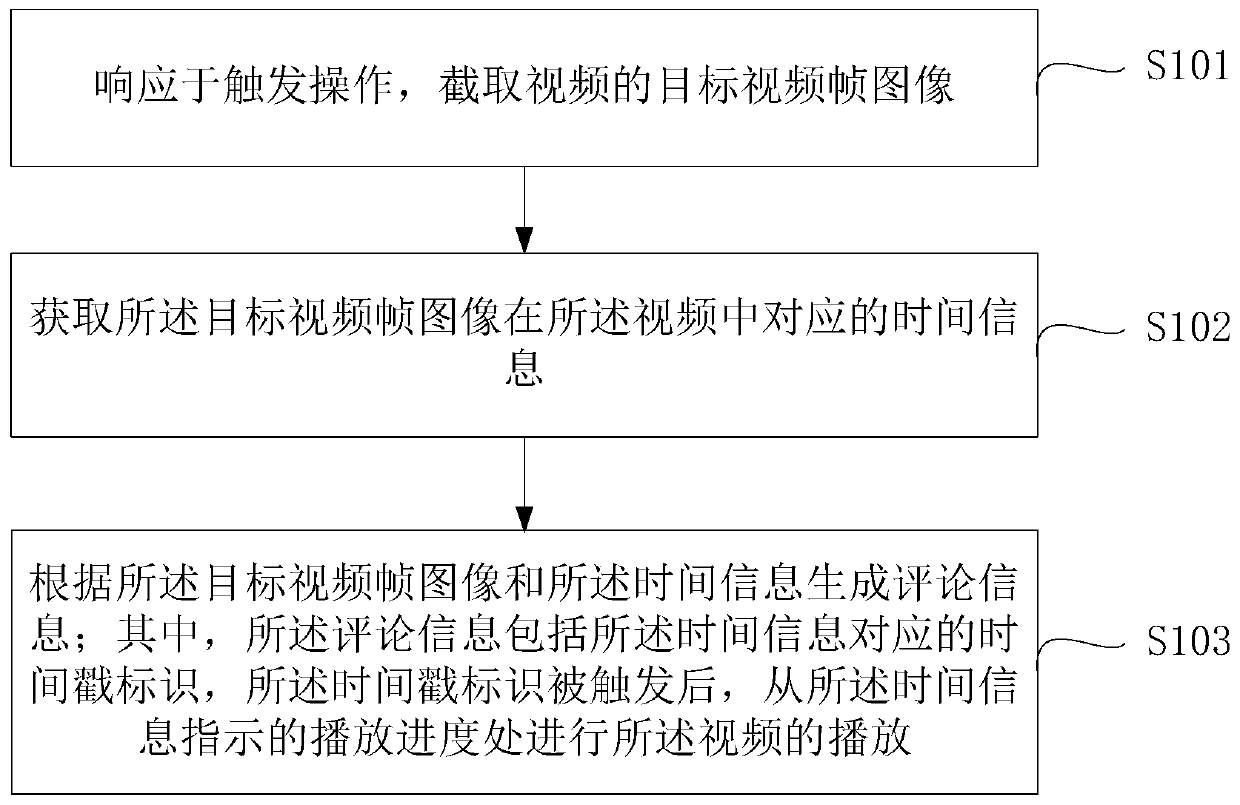
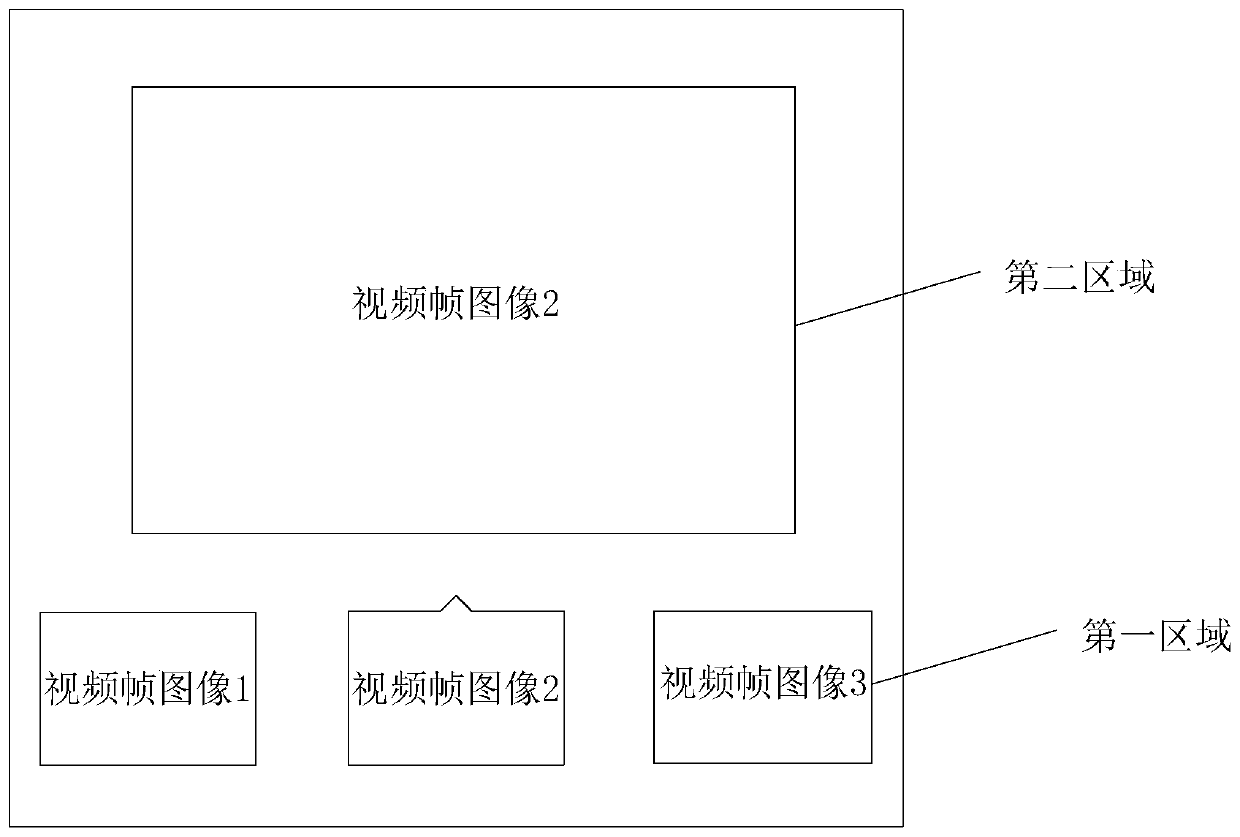
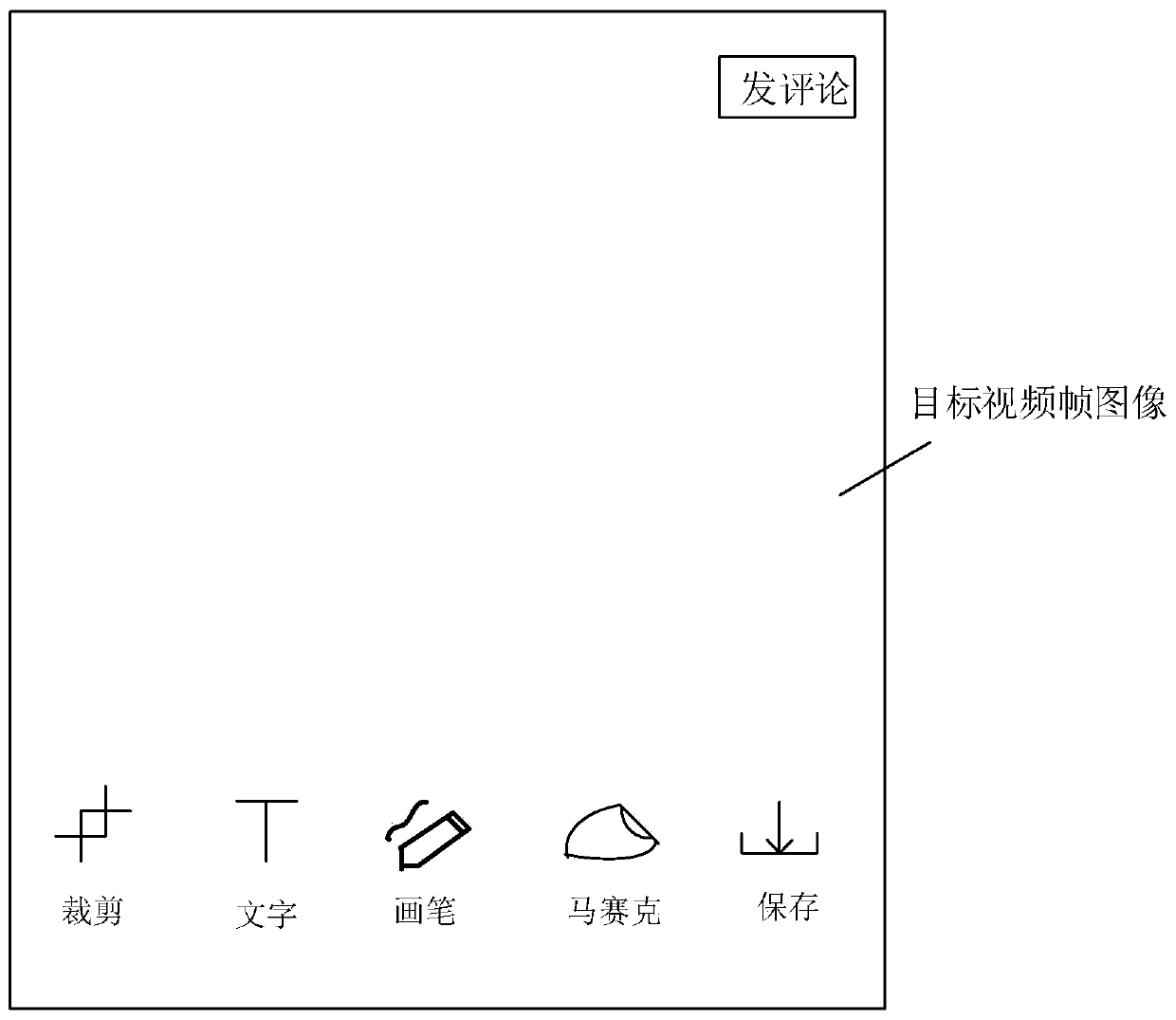
The invention provides an information publishing method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. According to the invention, the trigger operation is responded to intercept a target video frame image of the video; corresponding time information of the target video frame image in a video is acquired, then comment information is generated according to the target video frame image and the time information, the comment information comprises a timestamp identifier corresponding to the time information, and after the timestamp identifier is triggered, the video can be played from the playing progress indicated by the time information. Based on the mode, the video can be automatically skipped to the indicated playing progress to be played through the timestamp identifier without manually dragging the progress bar by a user, so that the operation time can be saved, and the reading interaction process of comment information can be optimized.
Owner:BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Display panel and OLED element thereof
ActiveCN105098094AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonant cavityEngineering
The invention provides a display panel and an OLED element of the display panel. The OLED element comprises a first electrode, an organic functional layer arranged on the first electrode, a second electrode arranged on the organic functional layer, a resonant cavity adjusting layer arranged on the second electrode, wherein the resonant cavity adjusting layer has inhomogenous thickness, and a half-transparent and half-reflecting layer arranged on the resonant cavity adjusting layer. The display panel and the OLED element of the display panel, which are provided by the invention, optimize a resonant cavity effect of the OLED element.
Owner:EVERDISPLAY OPTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
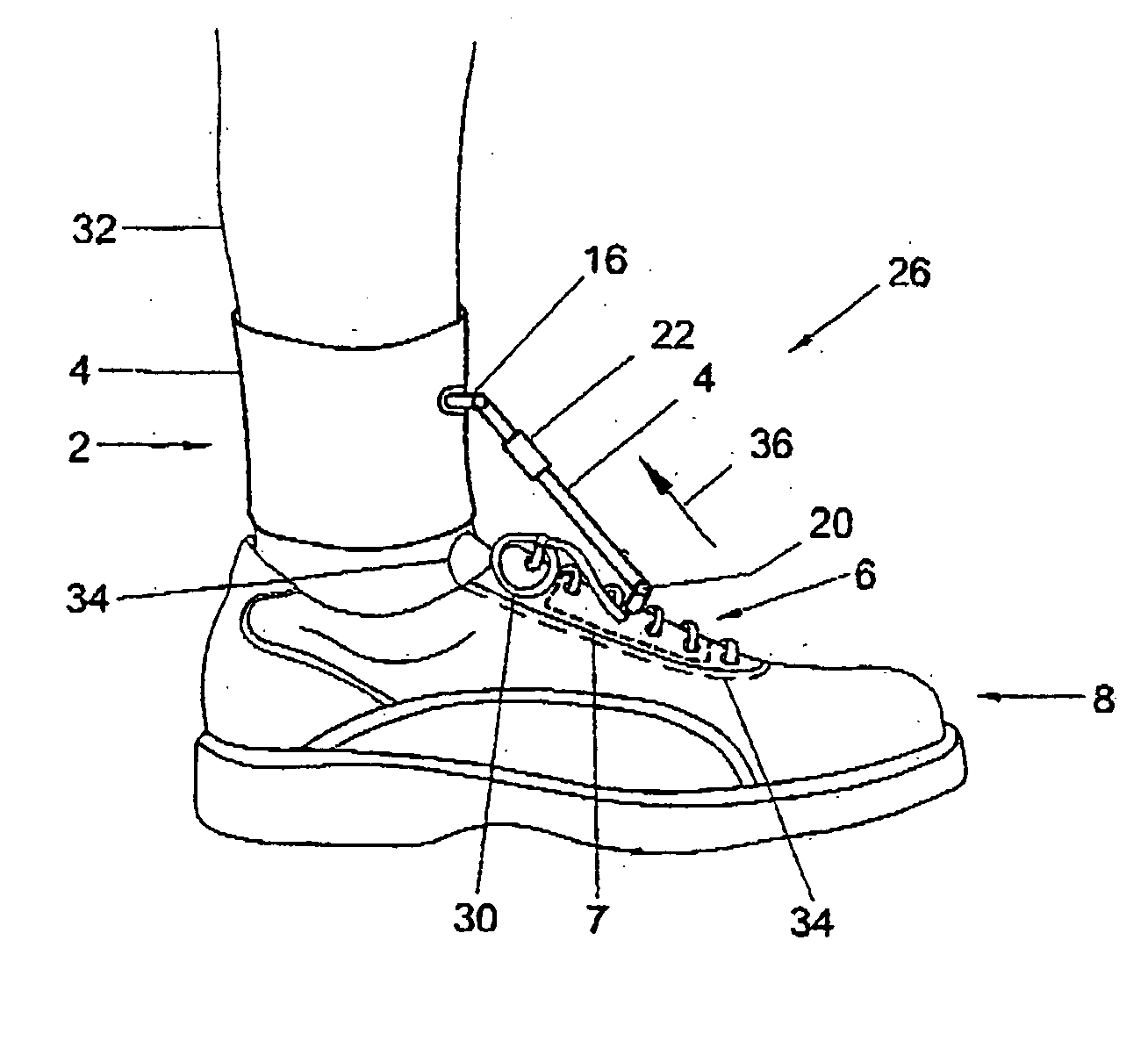
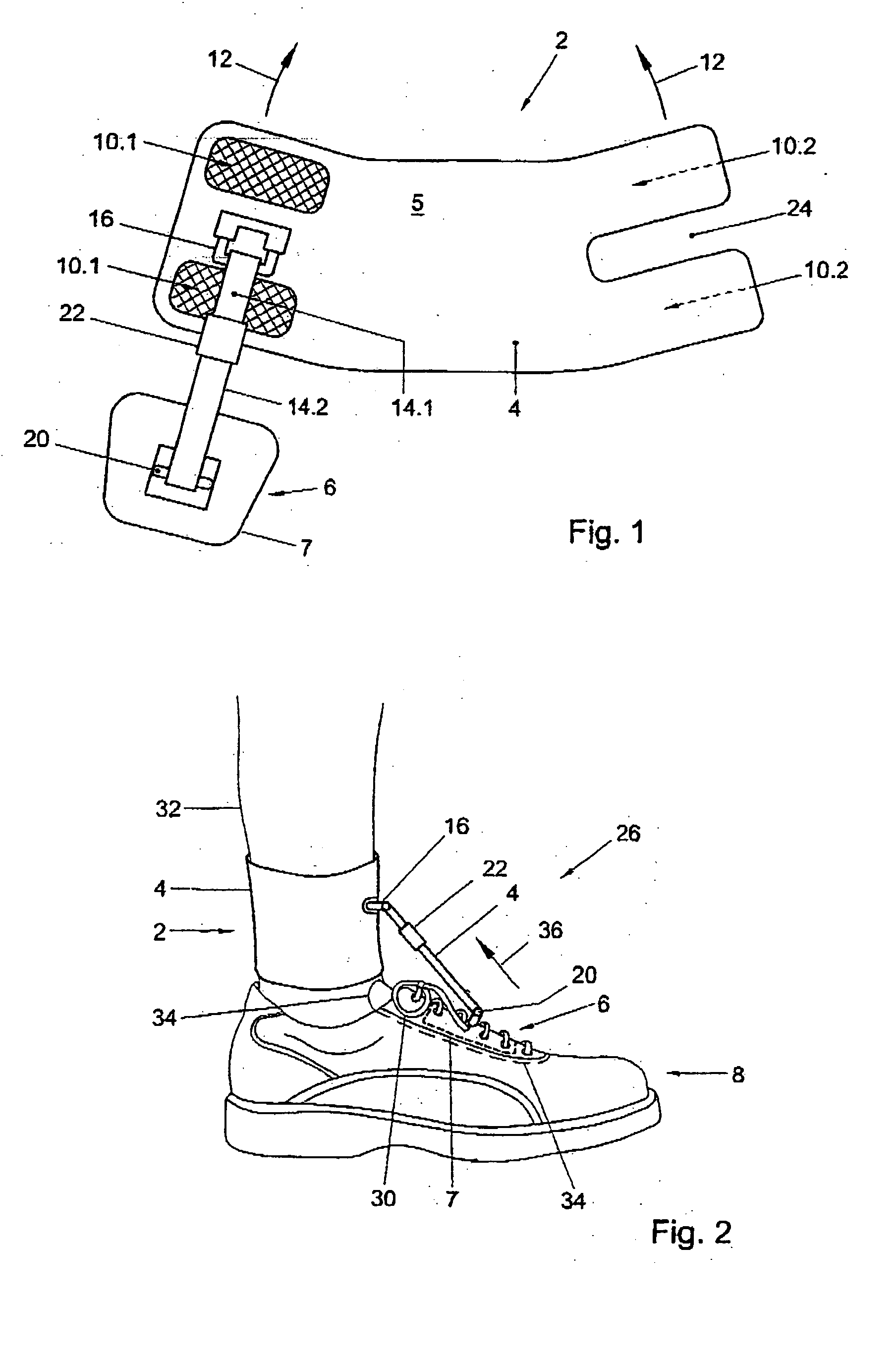
Drop foot device
ActiveUS20050126047A1The degree of freedom becomes largerBig choiceResilient force resistorsMedical scienceDropping footDropped foot
The invention relates to assembly of an accessory and a shoe for providing support to a foot-drop affected foot relative to a lower leg belonging to the foot such that the loot is prevented from dropping downwards relative to the lower leg when the foot is raised by the lower from a supporting surface, the accessory being provided with a first attachment member for attachment of the accessory to the lower leg, a second attachment member for attachment of the accessory to an upper side of the shoe and a connecting body joining together the first attachment member and the second attachment member, wherein the second attachment member is provided with an attachment plate which, in use, is positioned under an upper part of the shoe. The invention also relates to the accessory of the assembly.
Owner:OSSUR EURO
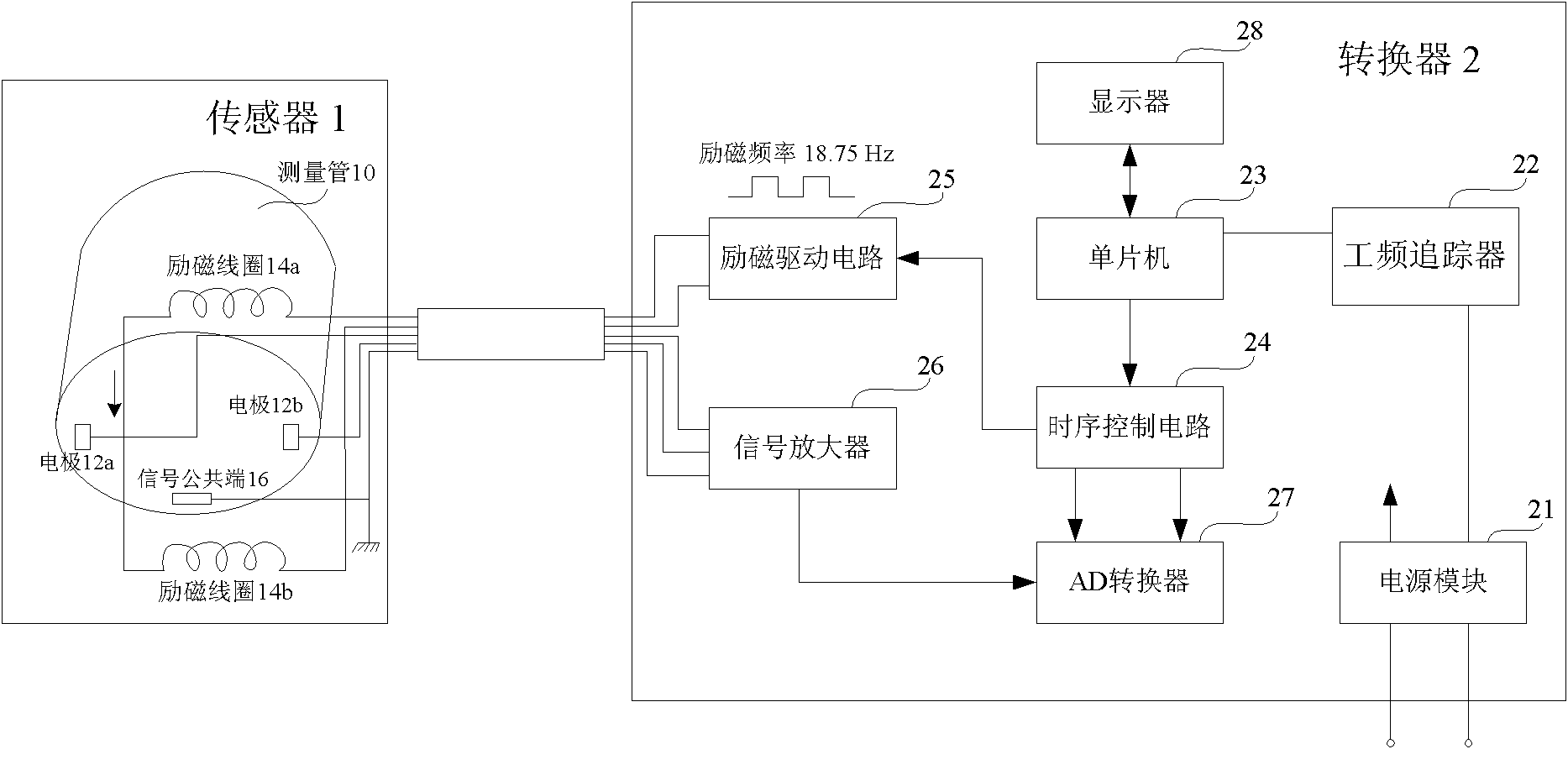
Electromagnetic flowmeter
ActiveCN102654411AImprove dynamic response performanceBig choiceVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersExcitation currentTransverter
The invention provides an electromagnetic flowmeter comprising a sensor and a converter, wherein the sensor comprises an exciting coil, an electrode and a conduit; the converter comprises an exciting drive circuit, a central processing unit and an electrode signal measurement unit; the exciting drive circuit produces an exciting current; and particularly, the exciting current has an exciting frequency of a fractional frequency which is an uneven number multiple of the power frequency. Compared with the prior art, the gap between two adjacent stages of exciting frequencies is small and the option is wide; and therefore, the minimization of low-frequency noise interference and the stable output both are taken into account.
Owner:SHANGHAI WELLTECH AUTOMATION CO LTD +1
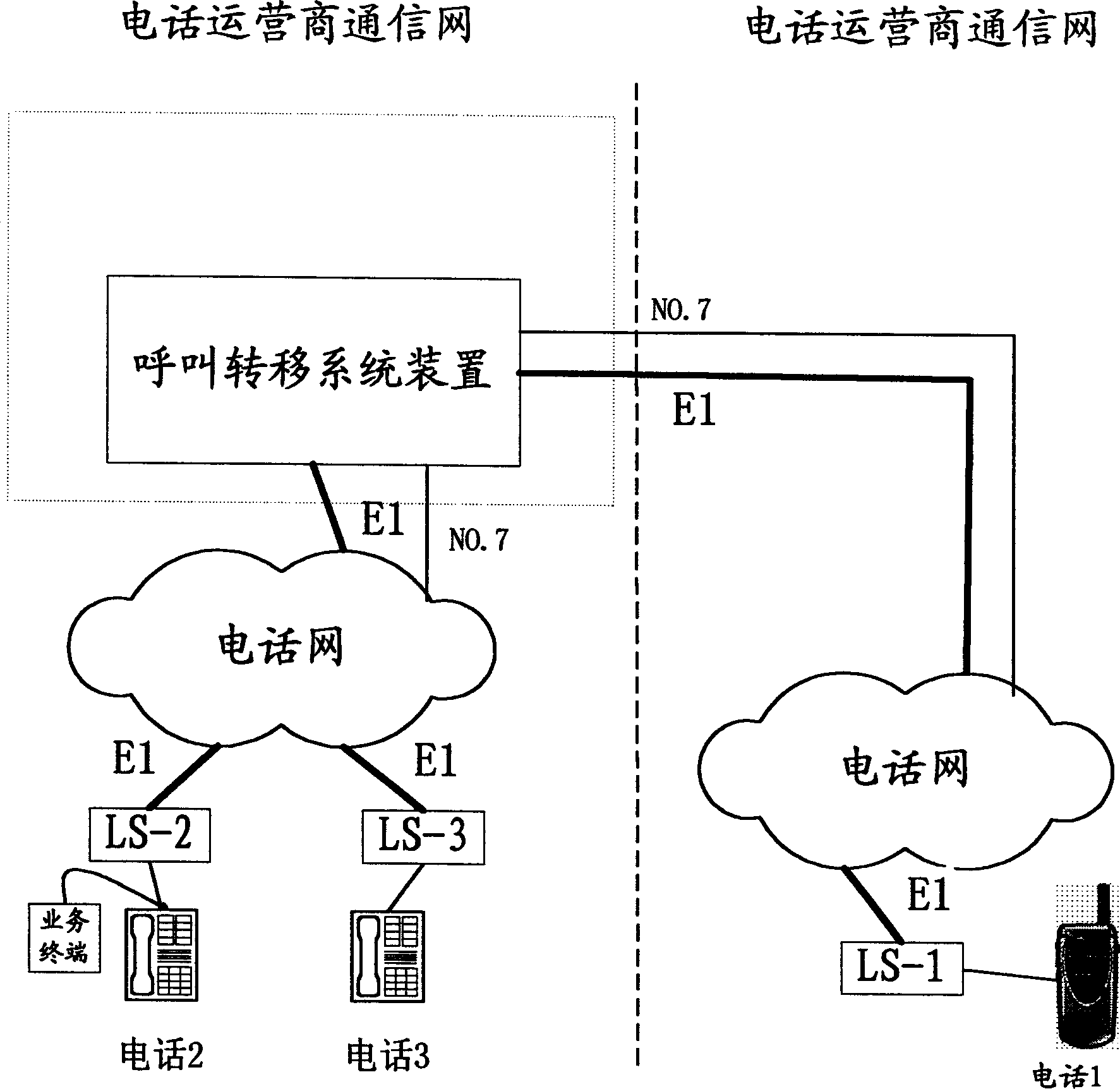
Method for network system of telecommunication operation trader to provide calling transfer for users of other telecommunication network
InactiveCN1406043ASave communication feeEasy to operateSpecial service for subscribersMobile telephonyControl function
The method is to construct the devices of the call back transferring system. The said devices can be the computer communication system platform, the intelligent network, the next generator network system, IP communication system. The one end of these devices is linked to one network system of the operation dealer through the repeat circuit. The other end of these devices is linked to one network system of the telephone operation dealer the user of the call back transferring telephone belongs to. The said devices provide the functions of the service control, the service data and service exchange. The invention separates apart the call back transferring function of mobile phones and phones of the other telecom from the exchanger in end offices of communication network.
Owner:中国电信集团广东省电信公司
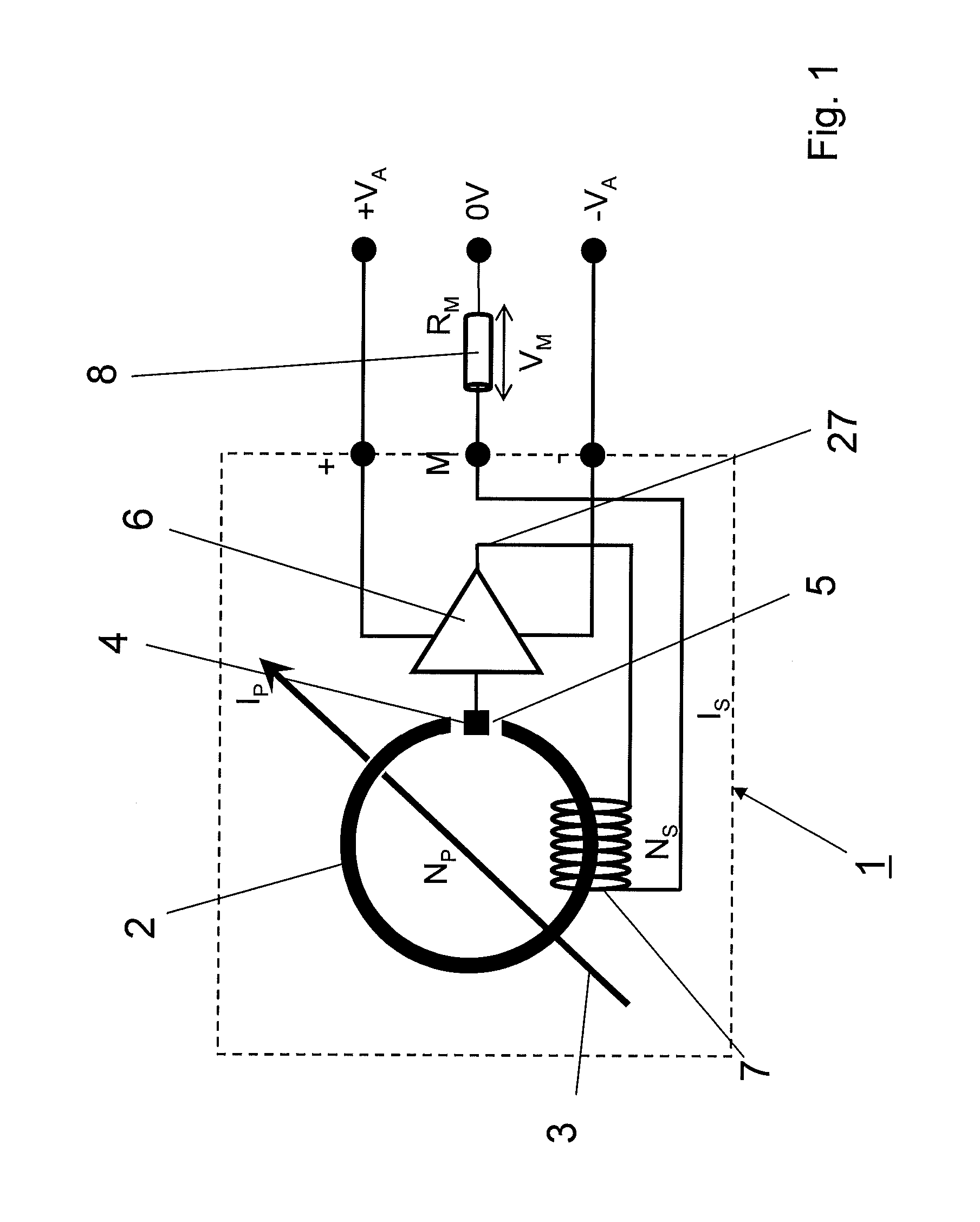
Current sensor operating in accordance with the principle of compensation
ActiveUS20120268108A1Low maximum lossesLow costMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsElectrical measurementsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An exemplary current sensor operating in accordance with the principle of compensation includes a primary winding creating a magnetic field based on a current to be measured, a secondary winding generating a magnetic field compensating the primary winding based on a compensation current. The current sensor also includes a magnetic core, a terminating resistor connected in series to the secondary winding, and sensor means. A booster circuit is connected downstream of the sensor means and feeds the compensation current to the secondary winding via the terminating resistor. The booster circuit includes a switched mode amplifier with a pulse width and density modulator that operates based on pulse width and density modulation, turning the compensation current into a pulse width and density modulated current. The switched mode amplifier having a switching frequency that is high at when the compensation current is small and low when the compensation current is high.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
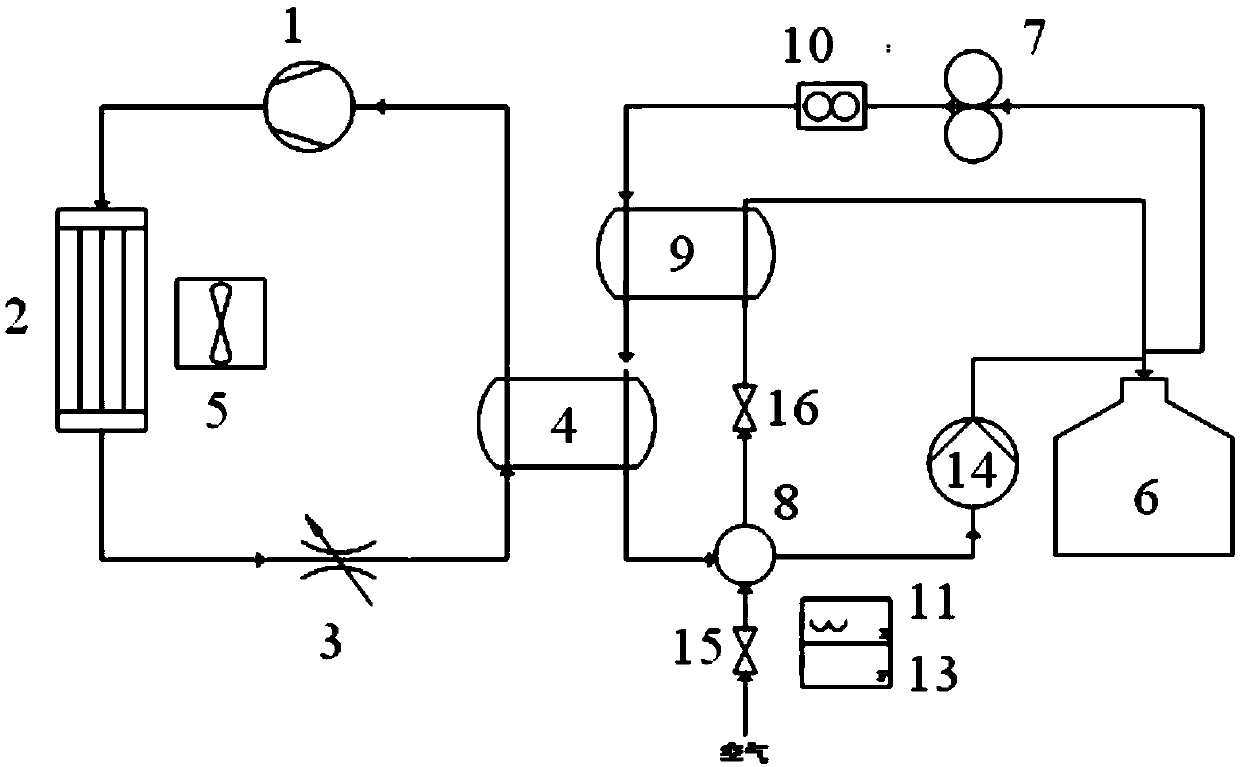
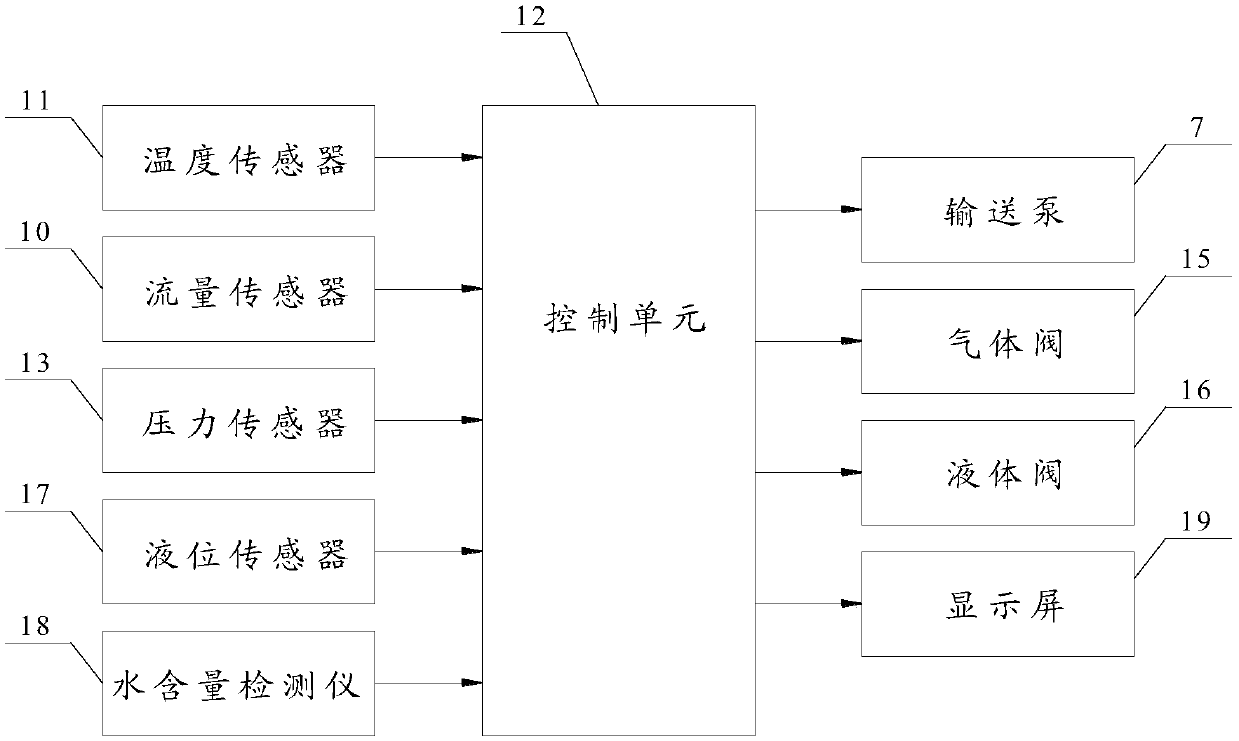
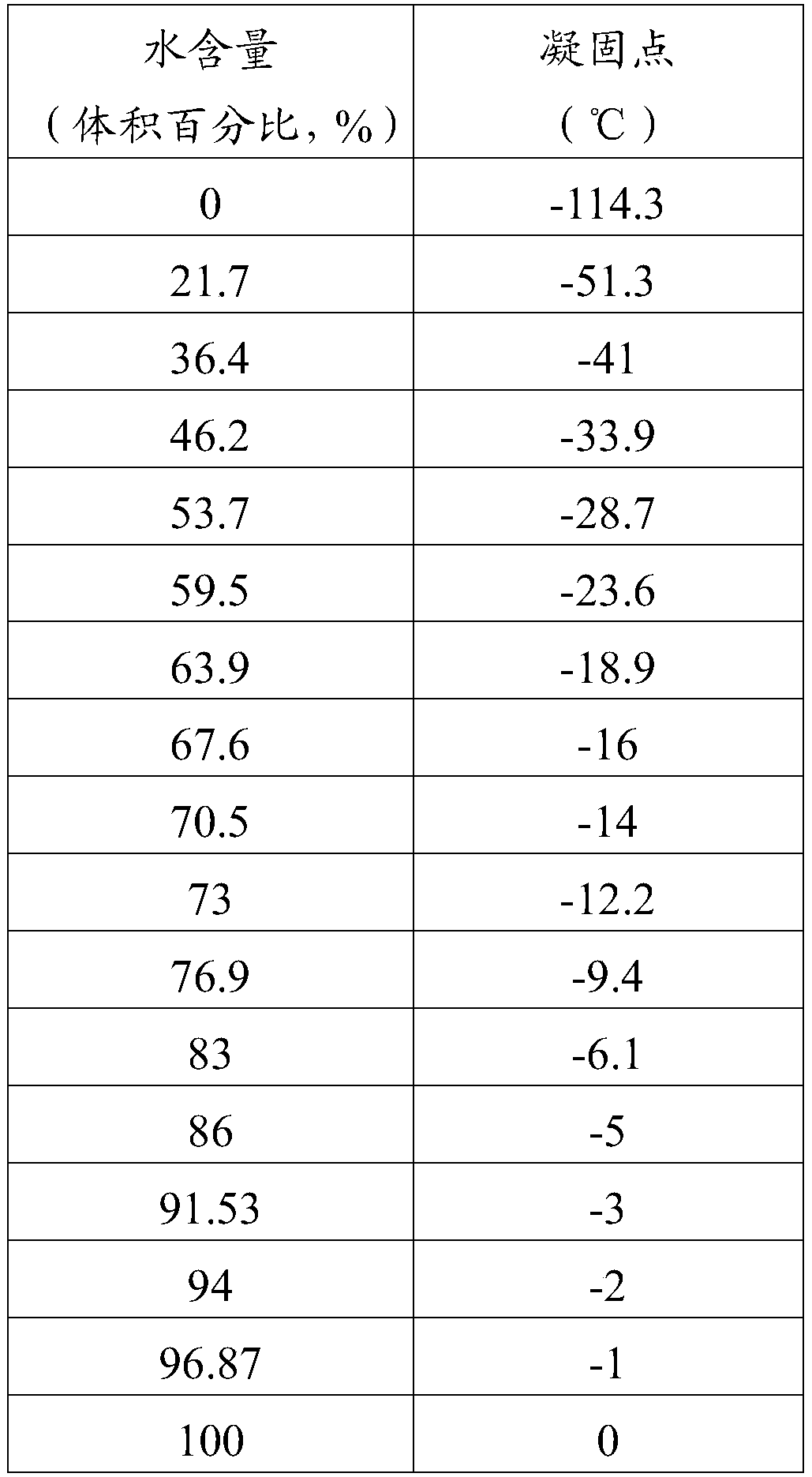
Treatment equipment for medical cryoplasty
ActiveCN109674525AReduce trafficReliable supplyCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingTherapeutic DevicesLiquid storage tank
The invention discloses treatment equipment for medical cryoplasty. The treatment equipment comprises a refrigeration device for providing a cold source, a liquid storage tank, a conveying pump and aheat exchanger, wherein the liquid storage tank is used for storing a liquid treatment working medium with a freezing point lower than a threshold value; the conveying pump is used for pumping the working medium in the liquid storage tank to a treatment working medium cycle; the heat exchanger is used for carrying out heat exchange to replace the cooling capacity of a cold source to the treatmentworking medium, so as to provide the treatment working medium cooled to treatment temprature to the cryoplasty, wherein the treatment working medium flowing out from the cryoplasty in the treatment working medium cycle can reflow back to the liquid storage tank. Compared with the prior art, the treatment equipment provided by the scheme provides the heat exchange cooling capacity to the liquid treatment working medium through a refrigeration cold source and a formation mechanism of the treatment cooling capacity is changed, so that the surgical safety and economical performance can be comprehensively improved.
Owner:HYGEA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Virtual human movement simulation frame
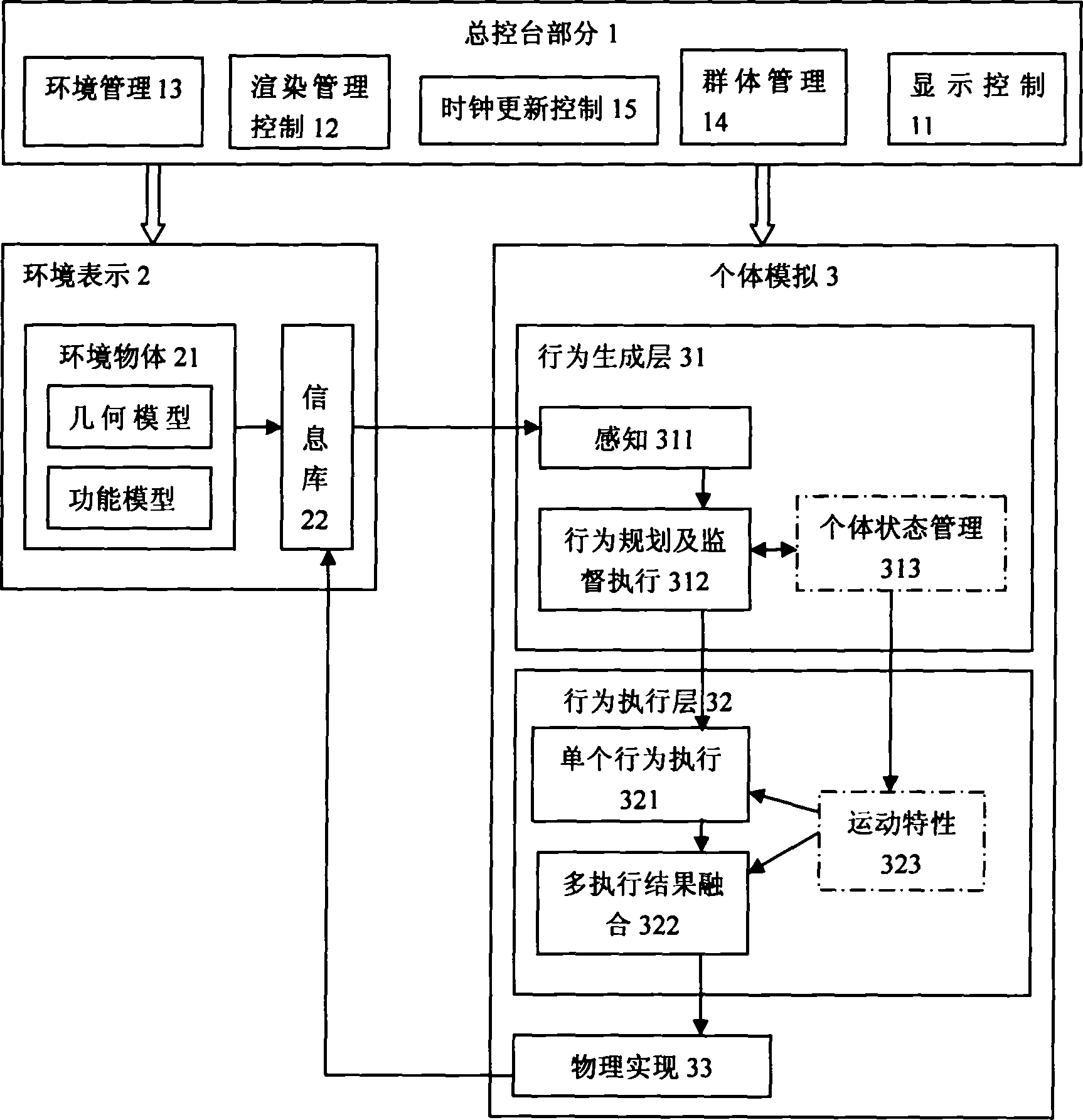
InactiveCN1889044APromote sportsImprove general performanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSimulationCrowds
The invention discloses an emulate frame of the dummy human movement, which includes: 1) the general controller is made up of the vision control, the romance management, the environment management, the colony management and the clock renovating control, they provide the all distributions and the scheduling management; 2) the environment expressing part which manages the environment information and supports the query and the renovation of the information; 3) the individual analogue part is made up of the motion formation layer, the motion performing layer and the physical realization layer, it provides the simulation of the individual movement to reach the movement emulation of the colony. The emulate frame has the good versatility, the reality and the adaptability, so it can emulate the dummy human movement in all kinds of the environment and the scenes.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bi-telecentric camera lens based on machine vision
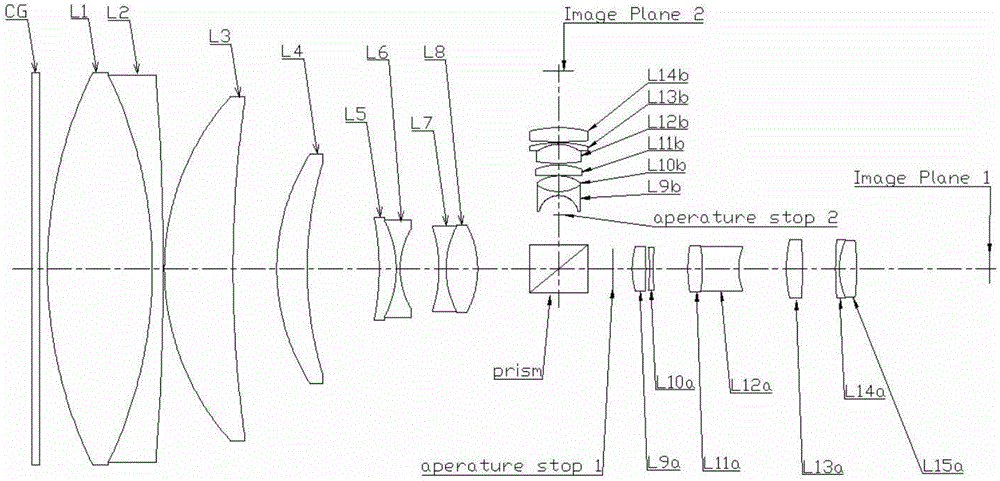
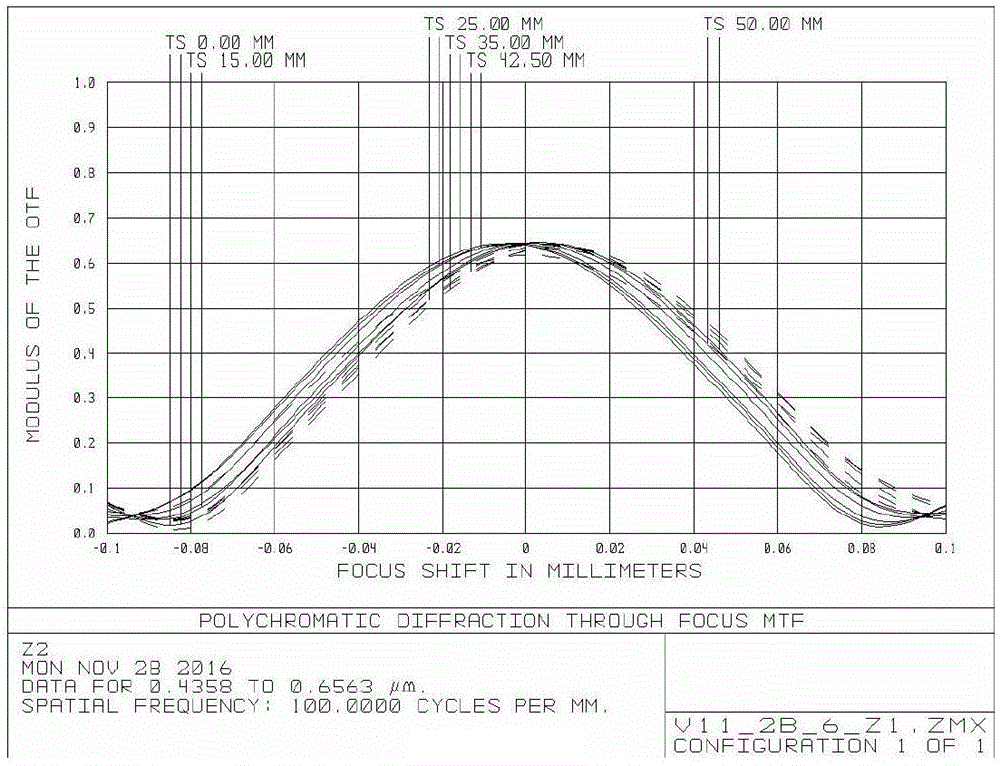
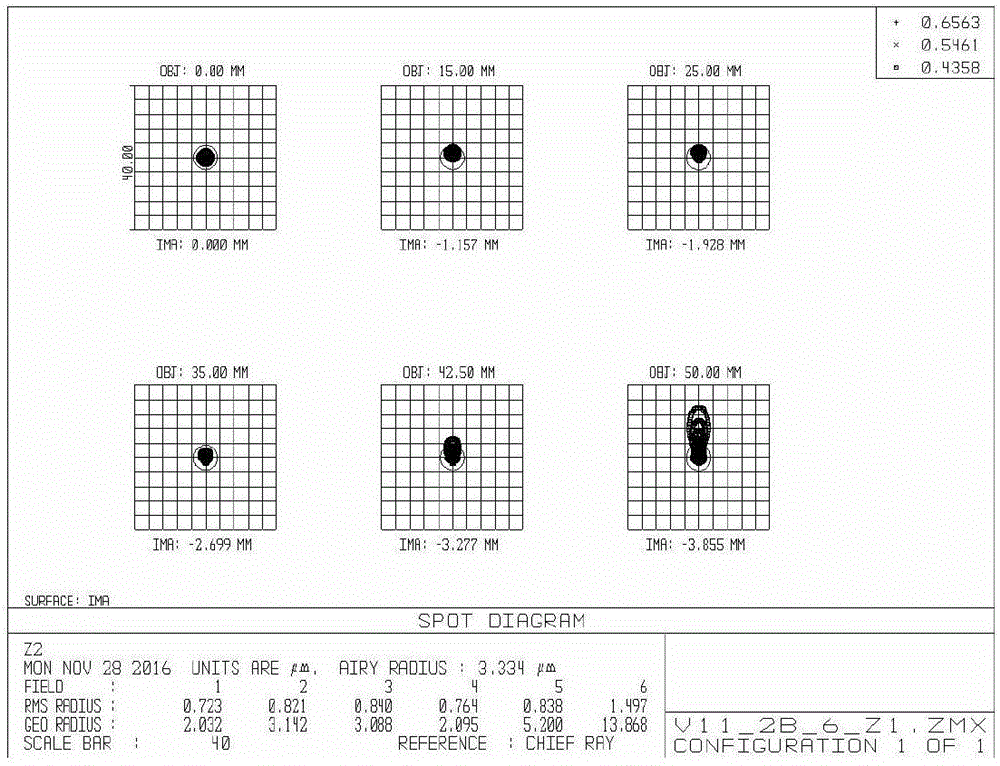
ActiveCN106483642AEnsure consistencyGood for correcting distortionOptical elementsCamera lensMachine vision
A bi-telecentric camera lens based on machine vision comprises, in sequence from left to right, protective glass, a front lens group, a half-transmitting and half-reflecting device, a diaphragm, a first rear lens group for low-magnification measurement, and a second rear lens group for high-magnification measurement. The front lens group includes eight lenses, which are a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens, a seventh lens and an eighth lens in sequence from left to right. The front lens group forms a bi-telecentric light path together with the first rear lens group and the second rear lens group. The first lens and the second lens constitute a doublet, and the agglutination surface is bent towards the object plane. The third lens and the fourth lens are crescent-shaped and bent towards the diaphragm. The fifth lens and the sixth lens constitute a doublet which has negative focal power. The seventh lens and the eighth lens constitute a doublet, and the agglutination surface is bent towards the diaphragm. The bi-telecentric camera lens can be connected with two CCDs or CMOSs at the same time to measure an object at different magnifications.
Owner:舜宇光学(中山)有限公司
System for making a cosmetic product by mixing components from several single-use packaging units
ActiveUS20170304789A1Promote perfectionBig choiceShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersMixer accessoriesEngineeringSingle use
Disclosed is a system for production of a cosmetic product including: at least one first single-use packaging unit including a preset quantity of a first phase of a cosmetic product, at least one second single-use packaging unit including a preset quantity of a second phase of a cosmetic product, a machine including a mixer inside of which the mixture of the preset quantity of the first phase and the preset quantity of the second phase is done automatically in order to end up with a cosmetic product directly consumable by the end consumer. The mixing is done in a manner such that neither the first phase nor the second phase are in direct contact with any part of the mixer which is not single use, thus avoiding dirtying the mixer.
Owner:SEB SA +1
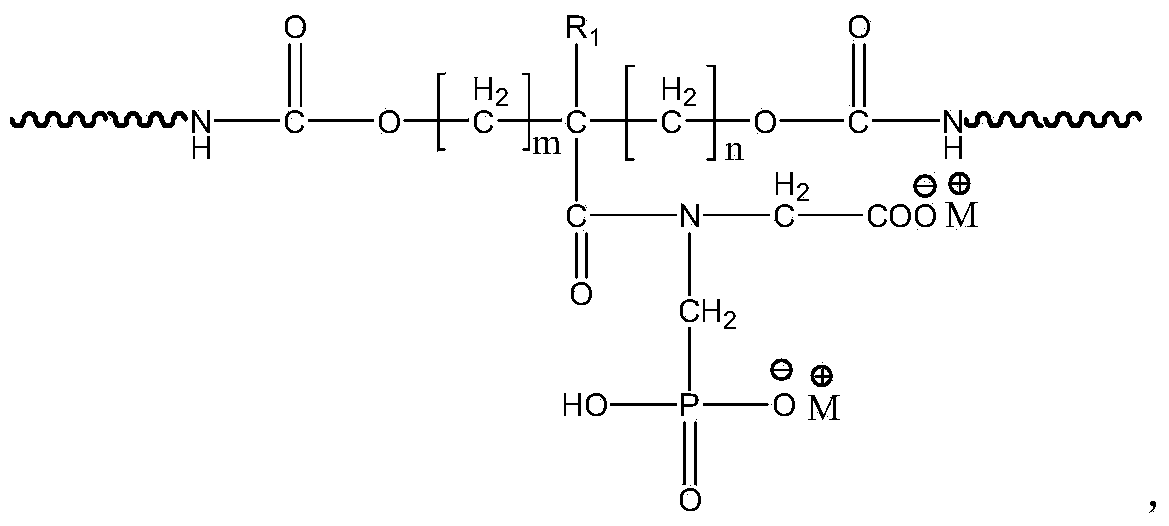
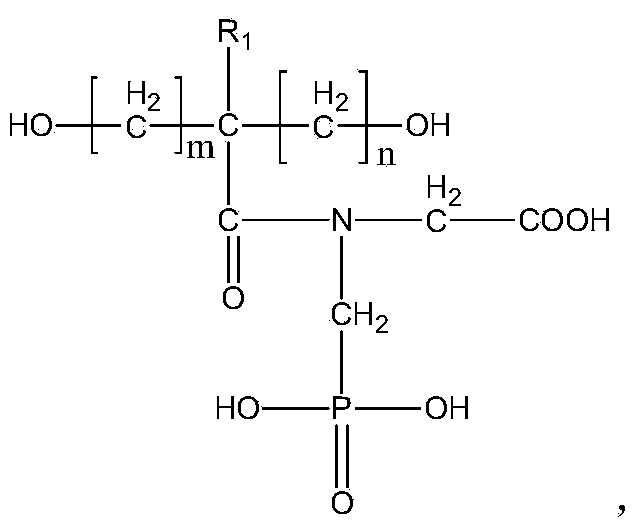
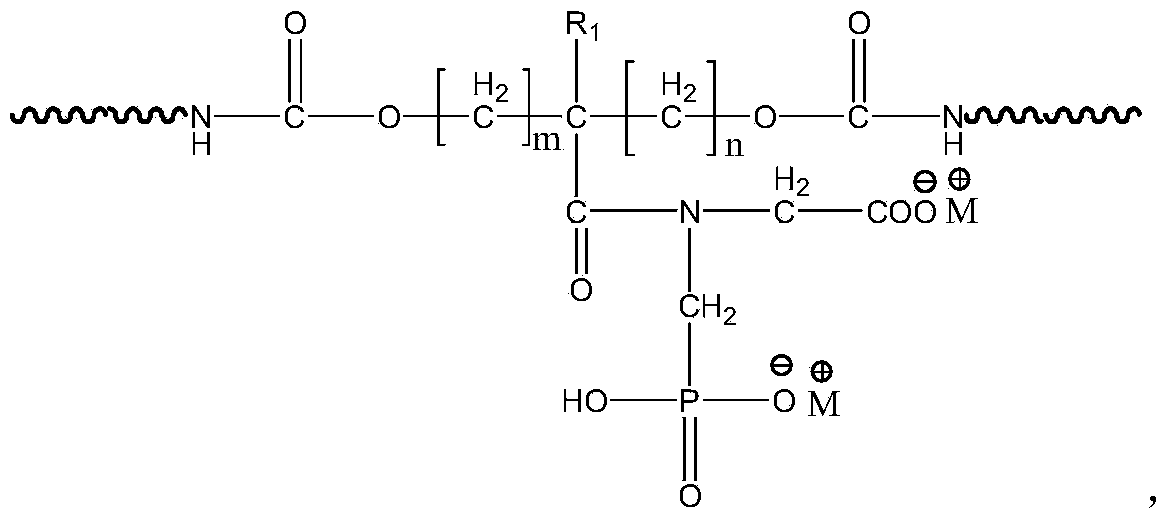
Waterborne polyurethane emulsion and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a waterborne polyurethane polymerization monomer, and relates to a waterborne polyurethane emulsion which is obtained by polymerizing the waterborne polyurethane polymerization monomer. The waterborne polyurethane emulsion is prepared by the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 5-20% of oligomer polyols, 0-5% of micromolecule chain extender, 5-14% of diisocyanate, 1-5% of hydrophilic chain extender, 1-5% of saltifying reagent, 0.1-0.5% of catalyst and 50-70% of deionized water. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the waterborne polyurethane emulsion. The waterborne polyurethane emulsion provided by the invention has strong chemical stability, good water tolerance and solvent resistance, excellent adhesive force and favorable flame retardance, so that the research gap of waterborne polyurethane products simultaneously containing phosphoric acid hydrophilic group and carboxylic acid hydrophilic group in the prior art is filled.
Owner:FUJIAN POLYTECH TECH CO LTD
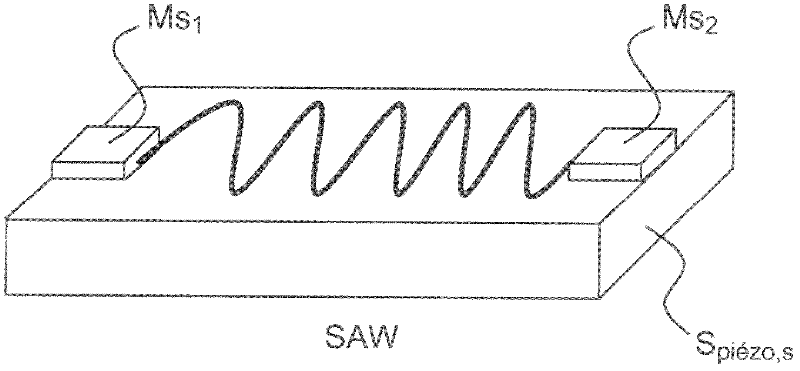
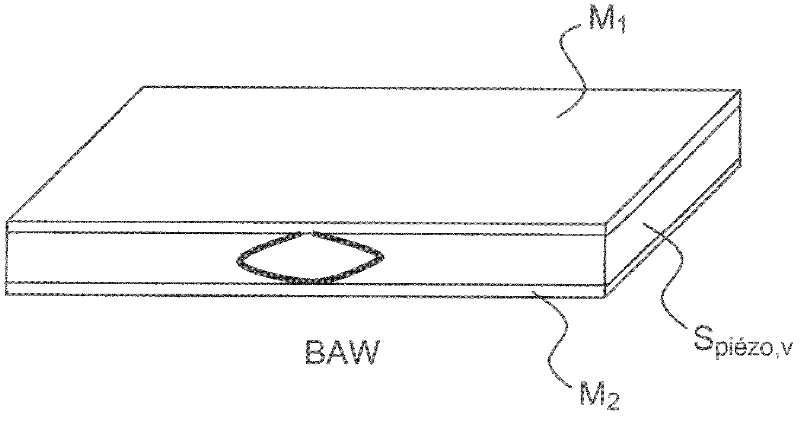
Acoustic wave device including a surface wave filter and a bulk wave filter, and method for making same
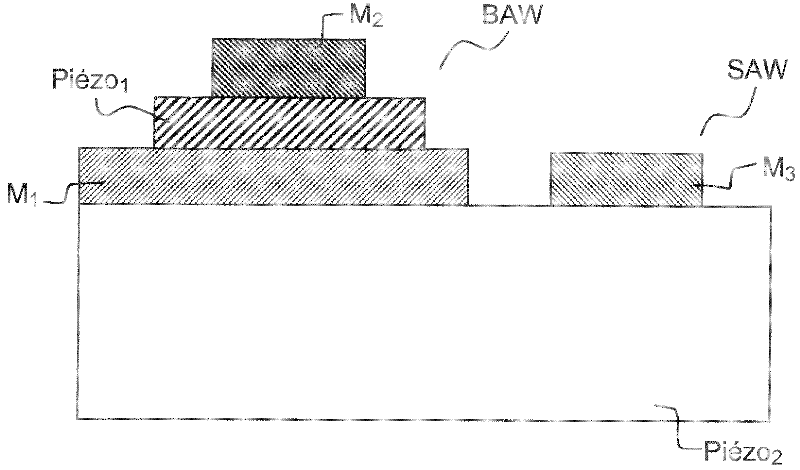
The invention relates to an acoustic wave device comprising at least one surface acoustic wave (SAW) filter and one bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filter, characterized in that it includes, on a substrate comprising a second piezoelectric material (Piezo2): a stack of layers comprising at least a first metal layer (M1) and a layer of a first monocrystalline piezoelectric material (Piezo1), wherein the stack of layers is partially etched so as to define a first area in which the first and second piezoelectric materials are present and a second area in which the first piezoelectric material is absent; a second metallization (M2) at the first area for defining the bulk acoustic wave filter integrating the first piezoelectric material, and a third metallization (M3) at the second area for defining the surface acoustic wave filter integrating the second piezoelectric material. The invention also relates to a method for making the device of the invention, advantageously using application steps similar to those used is the Smart Cut TM method or mechanical bonding / thinning steps.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Ultrasonic controlled release medicine elution balloon catheter and preparation method
ActiveCN104841060AHigh drug loadingHigh drug loading efficiencyBalloon catheterMedical devicesLipophilicityLesion site
The invention discloses an ultrasonic controlled release medicine elution balloon catheter and a preparation method. The surface of the medicine elution balloon catheter is coated with a medicine coating, the medicine coating is composed of a fat-soluble medicine carrying microcapsule having a ultrasonic response characteristic and an adhesive having a water-soluble characteristic. Medicine of the medicine elution balloon catheter is wrapped in a lipophilic medicine carrying microcapsule which is hard to dissolve in the blood, so medicine loss caused by blood washing can be reduced. When the ultrasonic controlled release medicine elution balloon catheter is used, the medicine elution balloon catheter is sent to a lesion portion and unfolds, a balloon contacts with the lesion tissues, ultrasound inducts the lesion portion at the external, the medicine carrying microcapsule can be speeded up to be separated from the hydrophilic adhesive, medicine can diffuse in the fat-soluble lesion tissues, at the same time, the medicine carrying microcapsule having the ultrasonic response characteristic breaks under the function of the ultrasound and discharges the medicine, the efficiency of medicine absorption and utilization by the target lesion tissues can be greatly raised. The amount and time of medicine discharge can be controlled through adjusting the characteristic and the ultrasonic characteristic of the medicine carrying microcapsule, the validity and safety of the medicine elution balloon catheter can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG RIENTECH MEDICAL TECH
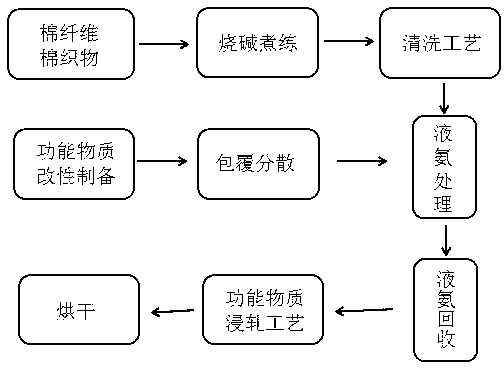
Filled type cotton fiber and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of the filled type cotton fiber. The preparation method of the filled type cotton fiber comprises the following steps: conducting a caustic scouring process on the cotton fiber or cotton fabrics; conducting a cleaning process; conducting modified preparation of functional substances; dispersing the functional substances in liquid ammonia; conducting a liquid ammonia treatment process; recycling the liquid ammonia; and dehydrating and stoving; The caustic scouring process is used for eliminating impurities in a center chamber of the cotton fiber and enabling most of the end ports of the center chamber of the cotton fiber to be opened, the modified preparation of the functional substances refers to put the cotton fiber into the liquid ammonia which is provided with functional particles in a diffusion mode to be treated, and the functional particles are enabled to be permeated into the center chamber and holes of the cotton fiber by means of a permeation function of the center chamber of the cotton fiber and the function which detaches hydrogen bonds of cellulose molecules. The invention further discloses a filled type cotton fiber. The cotton fiber prepared by the method has the advantages of being anti-bacterial, health-care, capable of releasing negative ions, ultraviolet-resistant and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU YDTEX GRP LTD
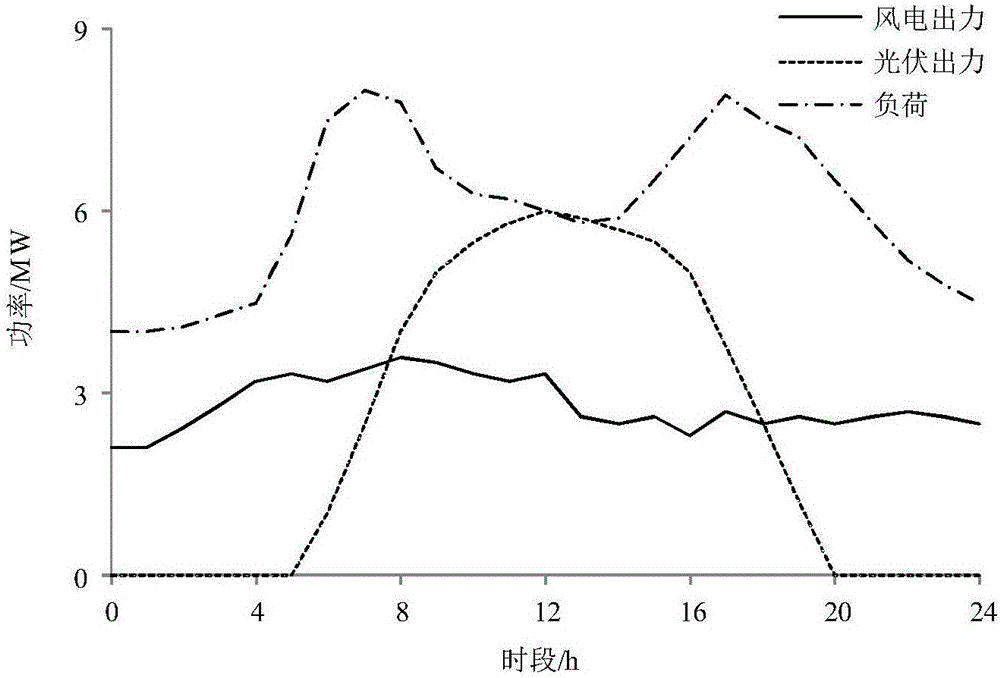
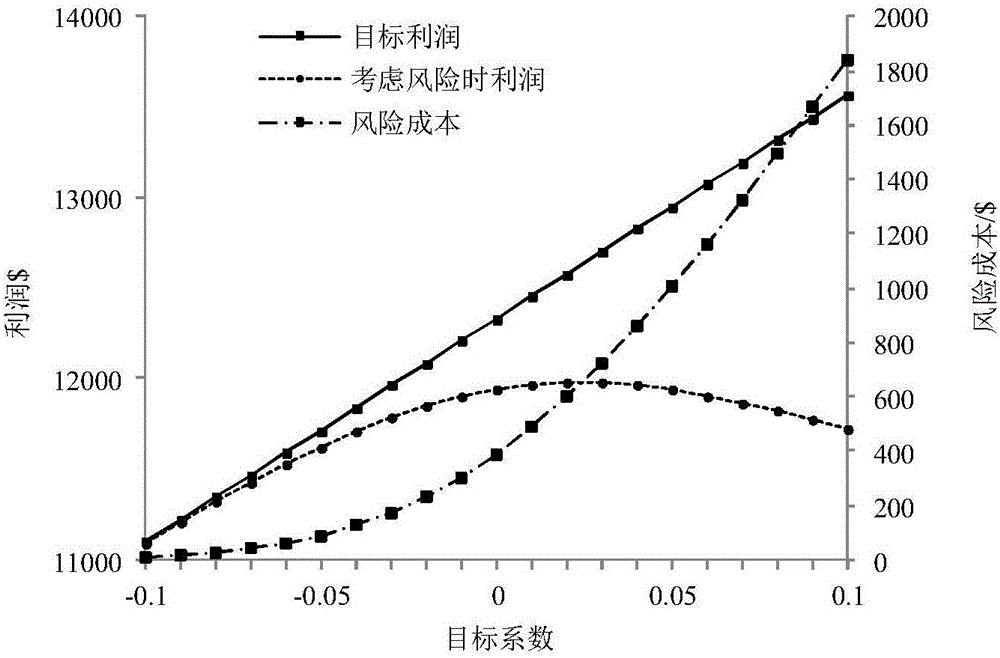
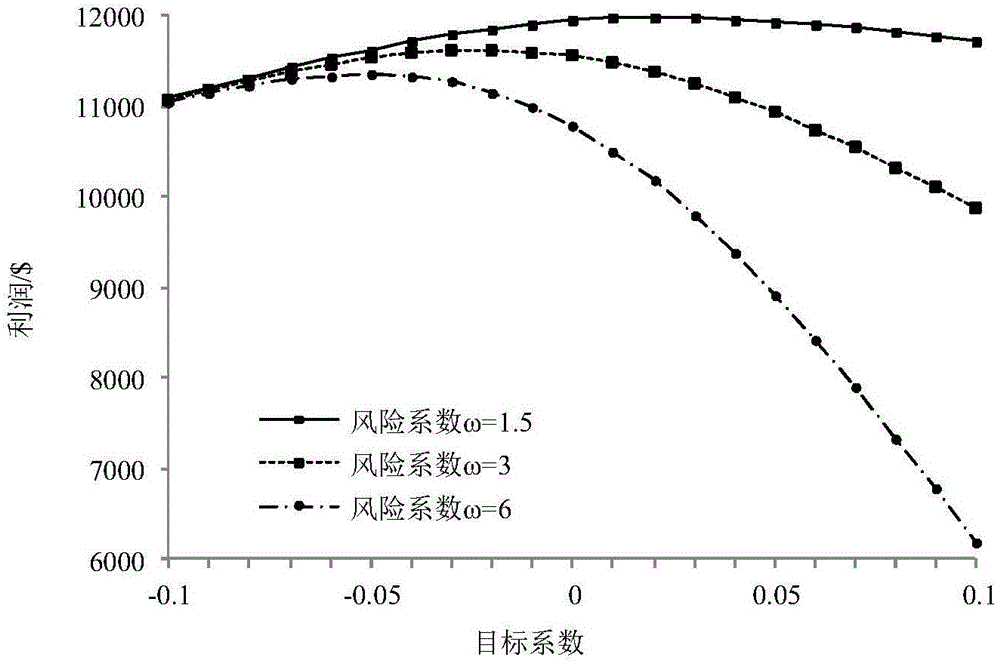
Virtual power plant day-ahead scheduling optimization model
InactiveCN106169102ASolve the problem of dealing with the uncertainty of wind power output at the same timeIncrease profitForecastingSystems intergating technologiesDecision schemeOptimal decision
The invention provides a virtual power plant day-ahead scheduling optimization model. A model aggregation unit comprises a gas turbine, a wind turbine generator set, a photovoltaic set, a water drawing energy storage power station and loads. For the characteristics that the electricity price probability distribution description is relatively accurate and the prediction is relatively high, random programming is adopted to process the uncertainty of the electricity price; and for the characteristics that the wind power and photovoltaic output probability distribution is difficult to precise describe and the prediction precision is relative low, an information gap decision theory (IGDT) is adopted to process the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic output, different weights are provided to wind power and photovoltaic output deviation coefficients, and the IGDT is enabled to simultaneously process the uncertainty of wind power and photovoltaic output. In addition, for the blindness of uncertainty decisions and the different risk degrees of different strategies, the risk cost is introduced, and the risks corresponding to different decision schemes are quantified. According to the invention, a larger decision making space is provided for a decision maker, and the VPP is enabled to make the optimal decision under more conditions, so that the benefit of the virtual power plant (VPP) is increased.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
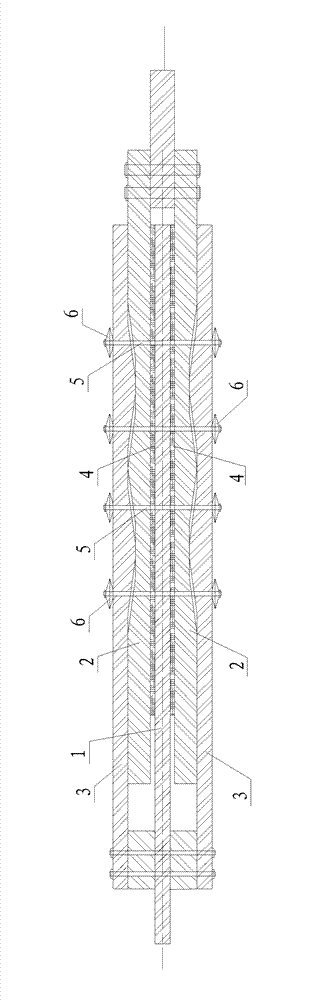
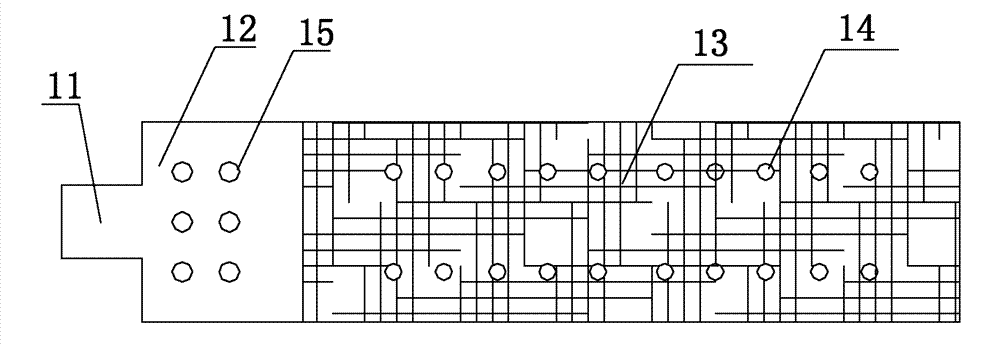
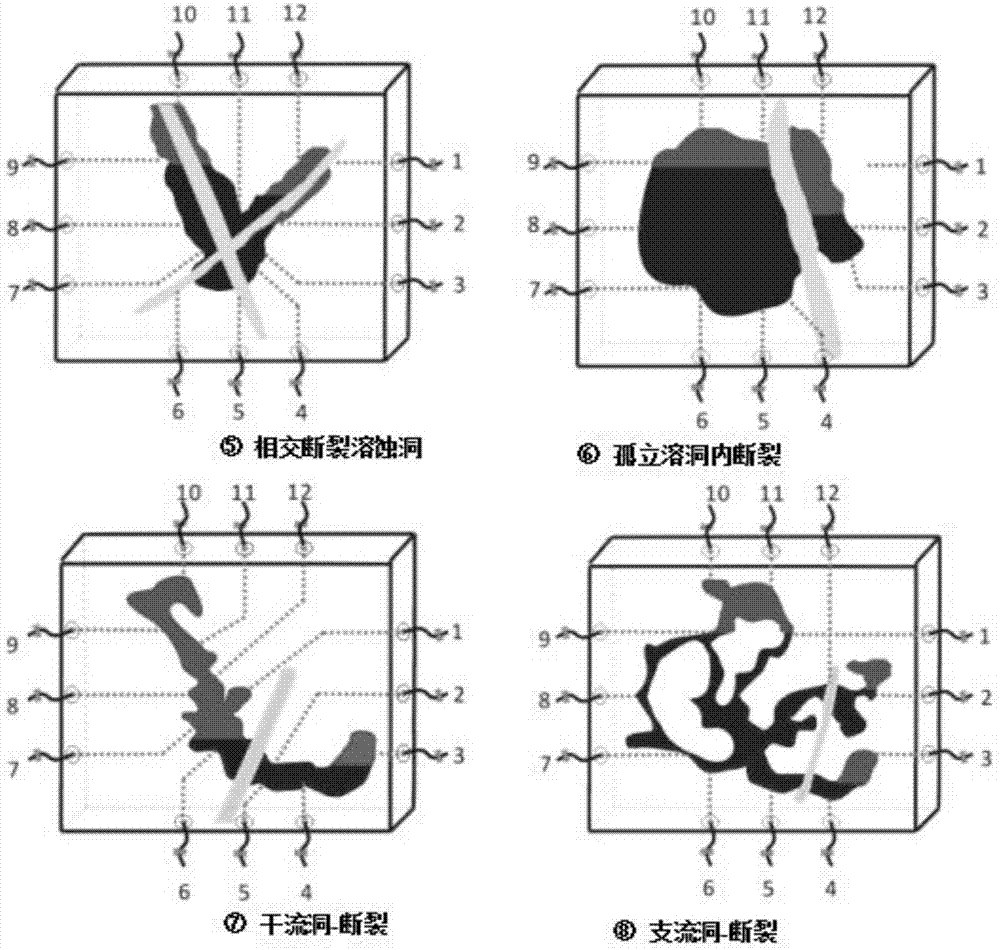
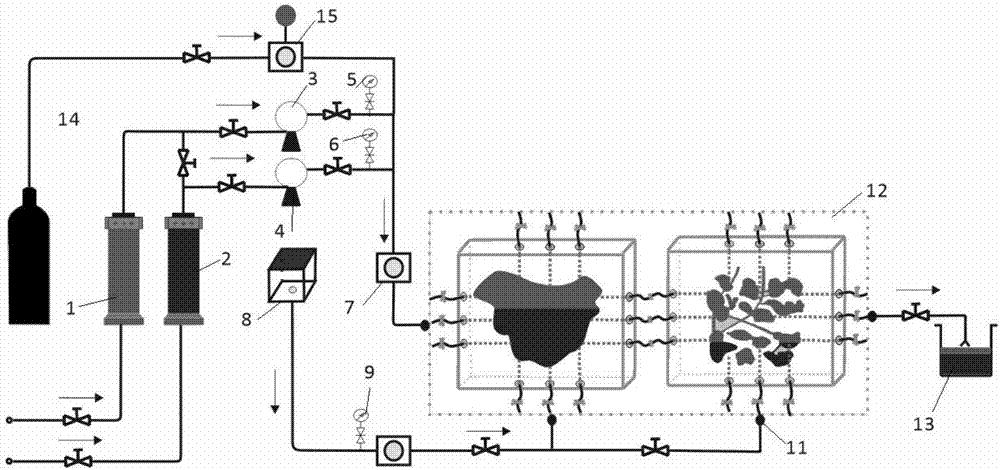
Carbonatite fracture-cave type reservoir displacement physical model combination method and experiment device
InactiveCN107461193AVerify rationalityGood for combination experimentsBorehole/well accessoriesData processing systemPhysical model
The invention discloses a carbonatite fracture-cave type reservoir displacement physical model combination method and an experiment device. 15 kinds of typical fracture-cave structures are extracted; 14 fracture-cave combination modularized units are finally obtained; and 25 kinds of fracture-cave combination modes are summarized by analyzing different main control factors and combining the practical fracture-cave units. A fracture-cave type reservoir displacement experiment physical model system combination module experiment device for performing the experiment on the carbonatite fracture-cave type reservoir displacement physical model combination method comprises a raw material storage system, a fracture-cave combination device, a pressure supply device, a power supply, a metering system, a data processing system and relevant accessories such as a pipeline and a valve. A serious of novel fracture-cave combination modes for the experiment are provided; devices required by the experiment method are subjected to integral experiment device and technical flow process design; and a whole set of fracture-cave type reservoir displacement experiment physical model system combination module experiment device is finally formed.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
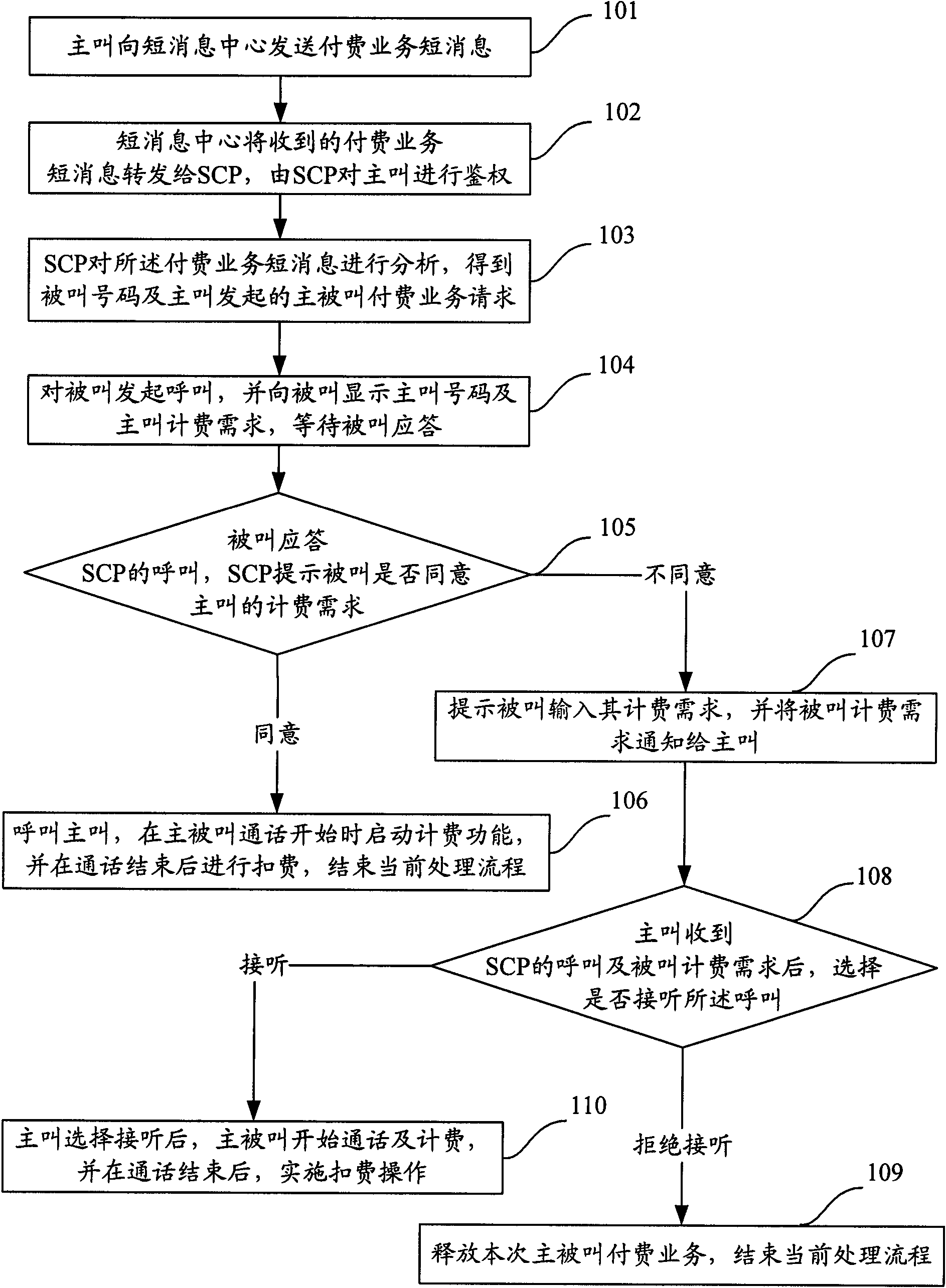
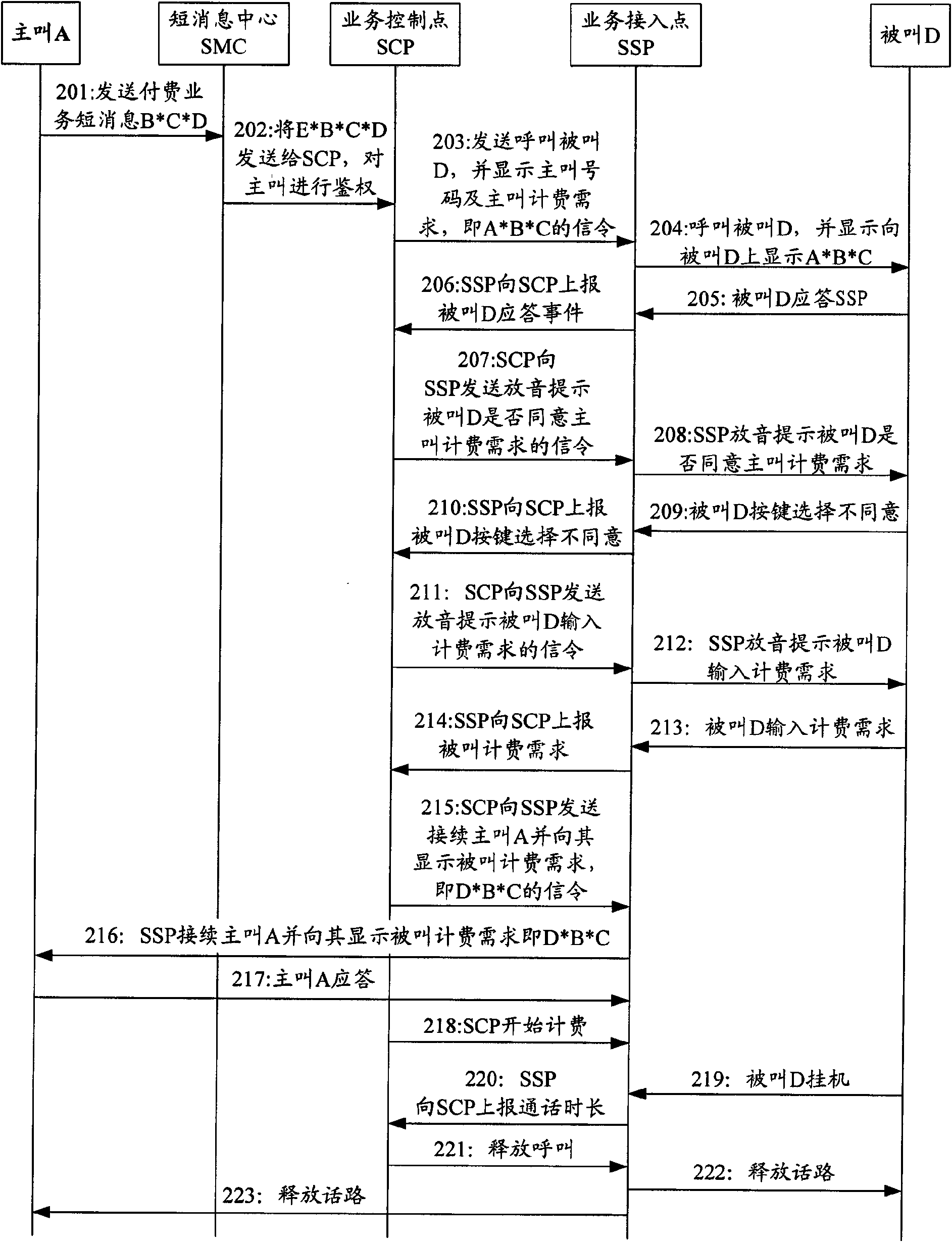
Implementing method of paying service of calling party and called party and system
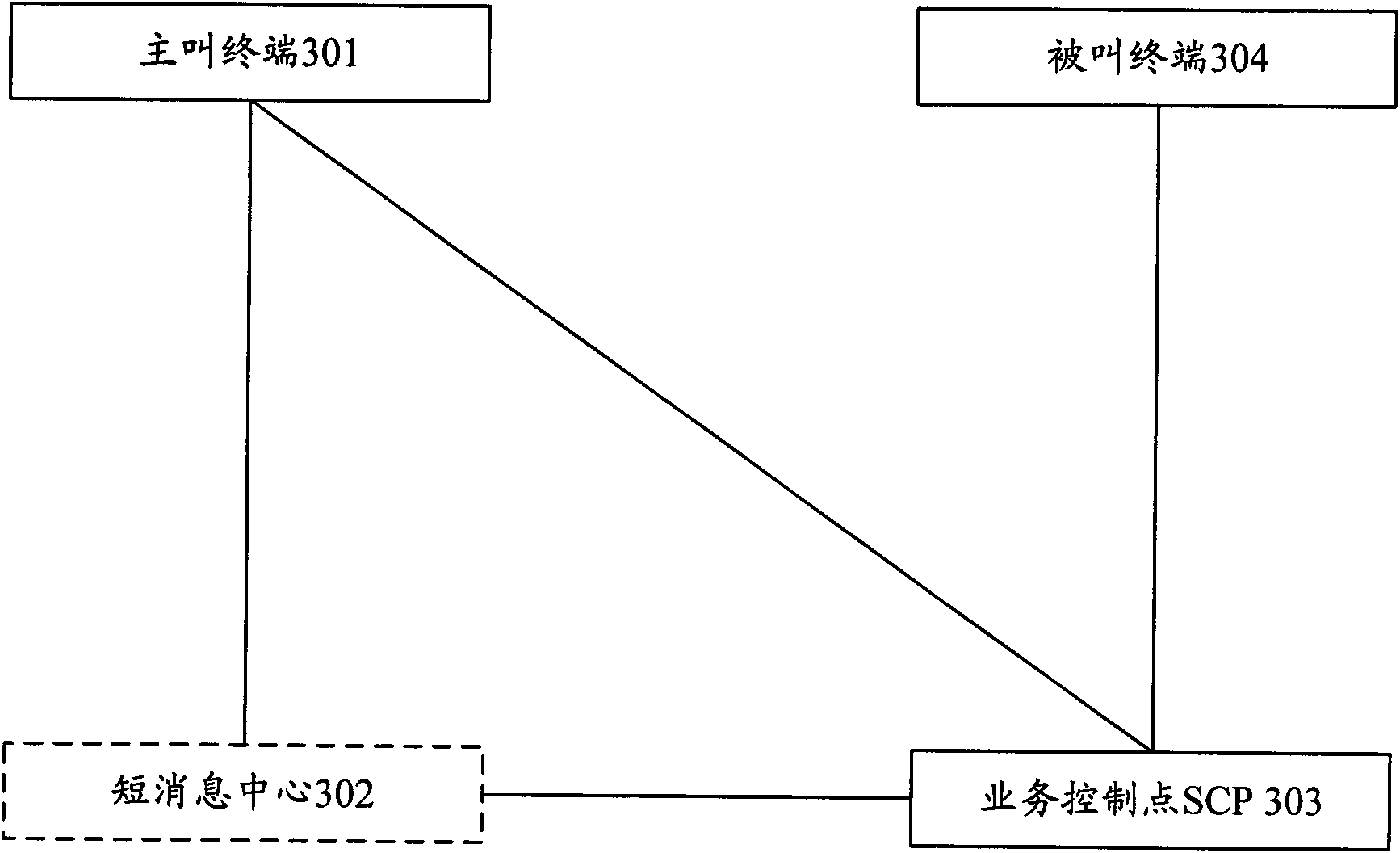
ActiveCN101616391AFlexible serviceComprehensive serviceAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationTelecommunicationsService control point
The invention discloses an implementing method of a paying service of a calling party and a called party. The method comprises the following steps: the calling party sends a short message of the paying service and triggers the paying service of the calling party and the called party; a service control point (SCP) informs the number of the calling party requiring the paying service of the calling party and the called party and the charging needs calling party to the called party, and waits for the answer of the called party; after the called party answers, that whether the called party agrees the charging needs of the calling party is determined, if the called agrees, the calling party is called; if the called party does not agree, the self charging need thereof is expressed. Correspondingly, the invention also discloses a system of the paying service of the calling party and the called party, comprising a calling terminal, a short message center, an SCP and a called terminal. Therefore, the invention can realize the paying function of negotiation charging of the calling party and the called party.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com