Patents
Literature
62 results about "Cubic inch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cubic inch (symbol in³) is a unit of measurement for volume in the Imperial units and United States customary units systems. It is the volume of a cube with each of its three dimensions (length, width, and depth) being one inch long.
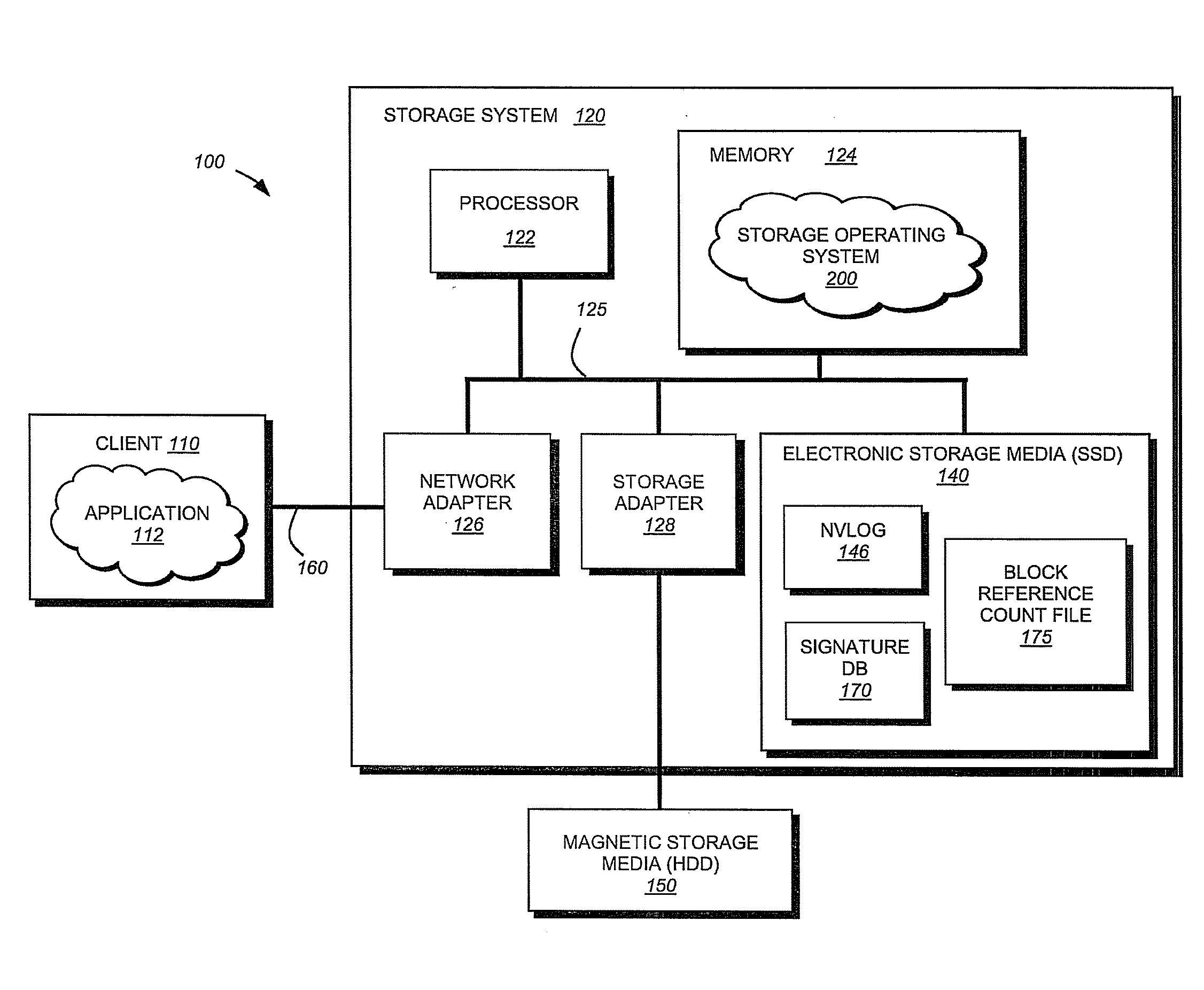
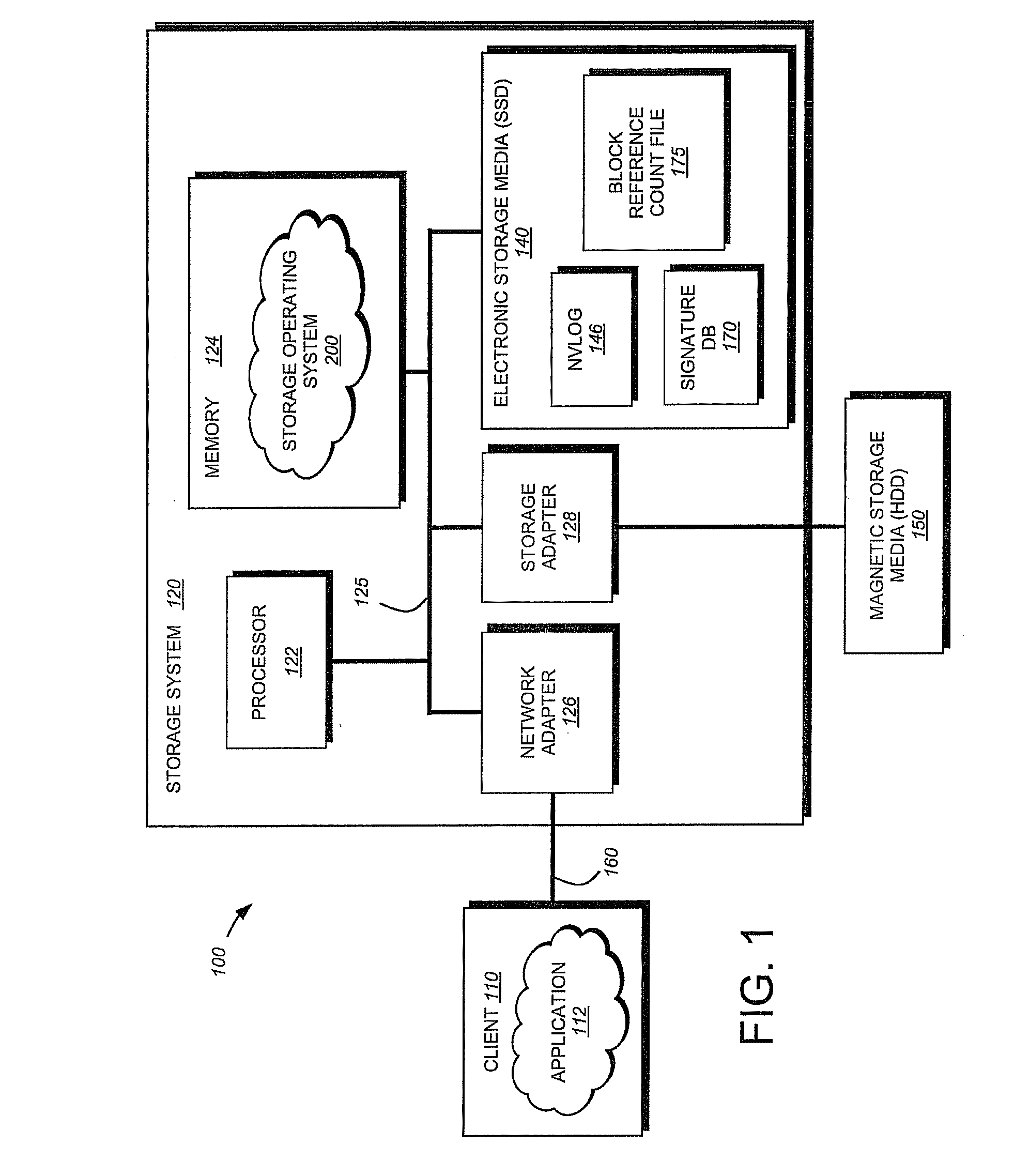
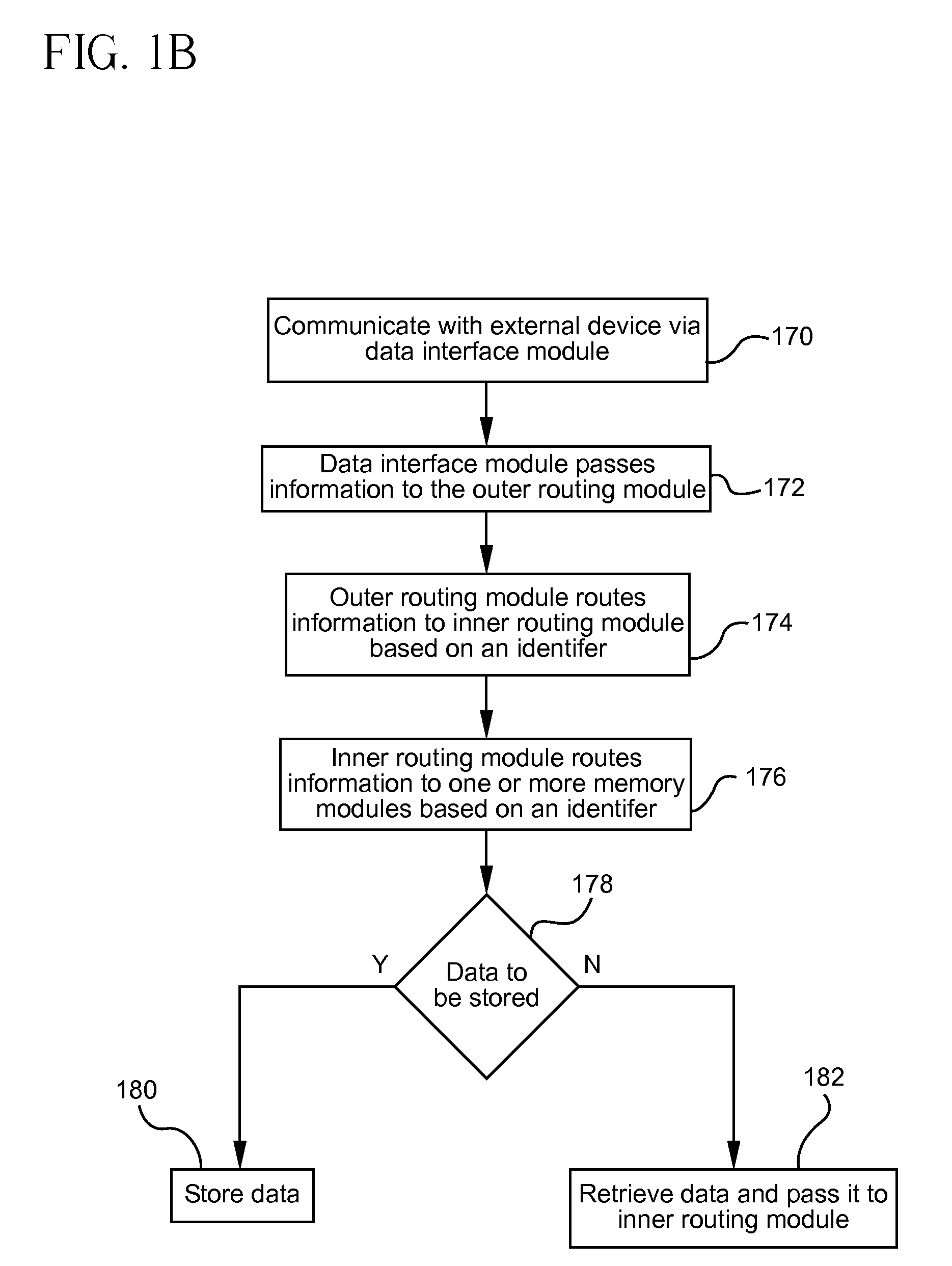
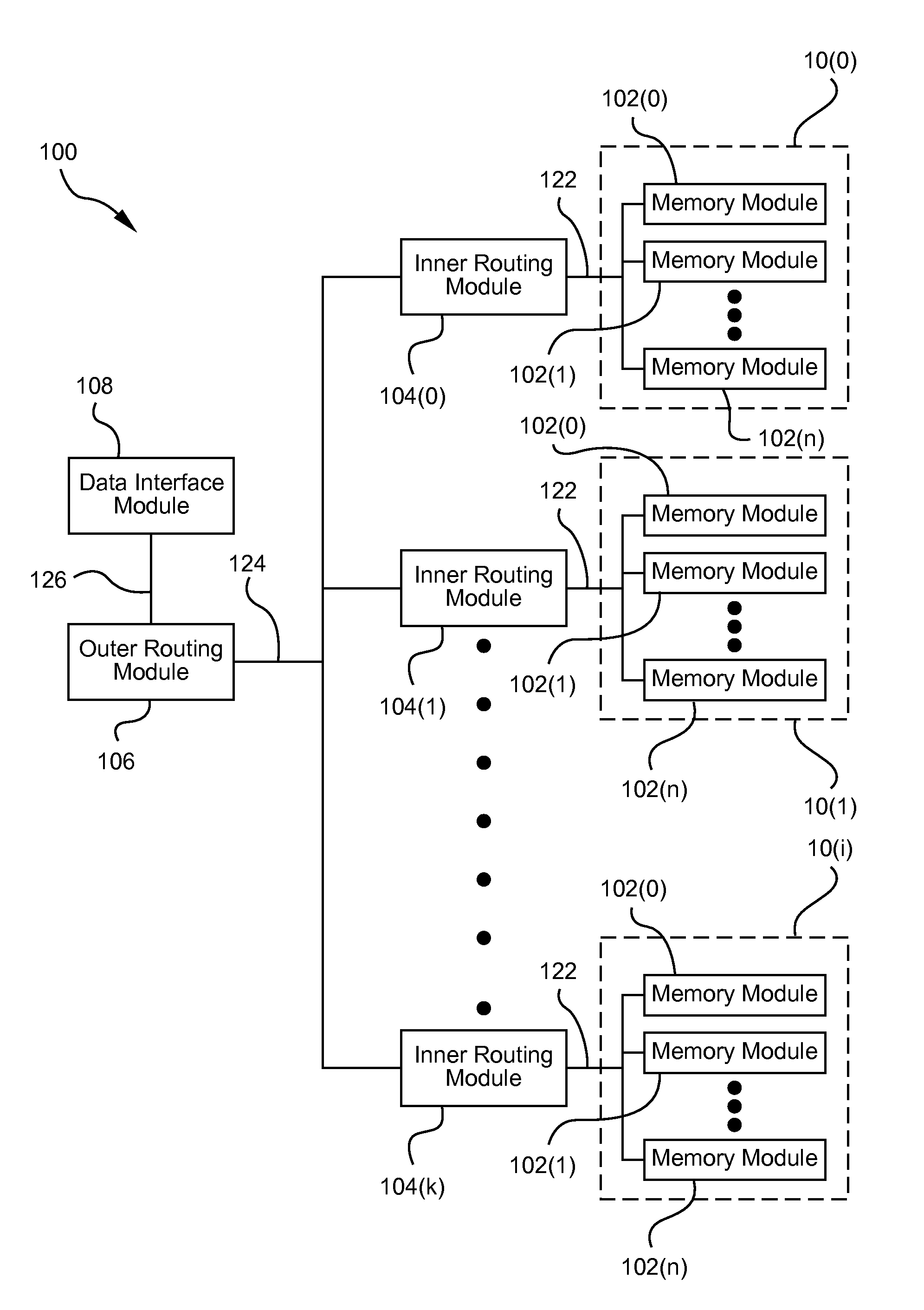
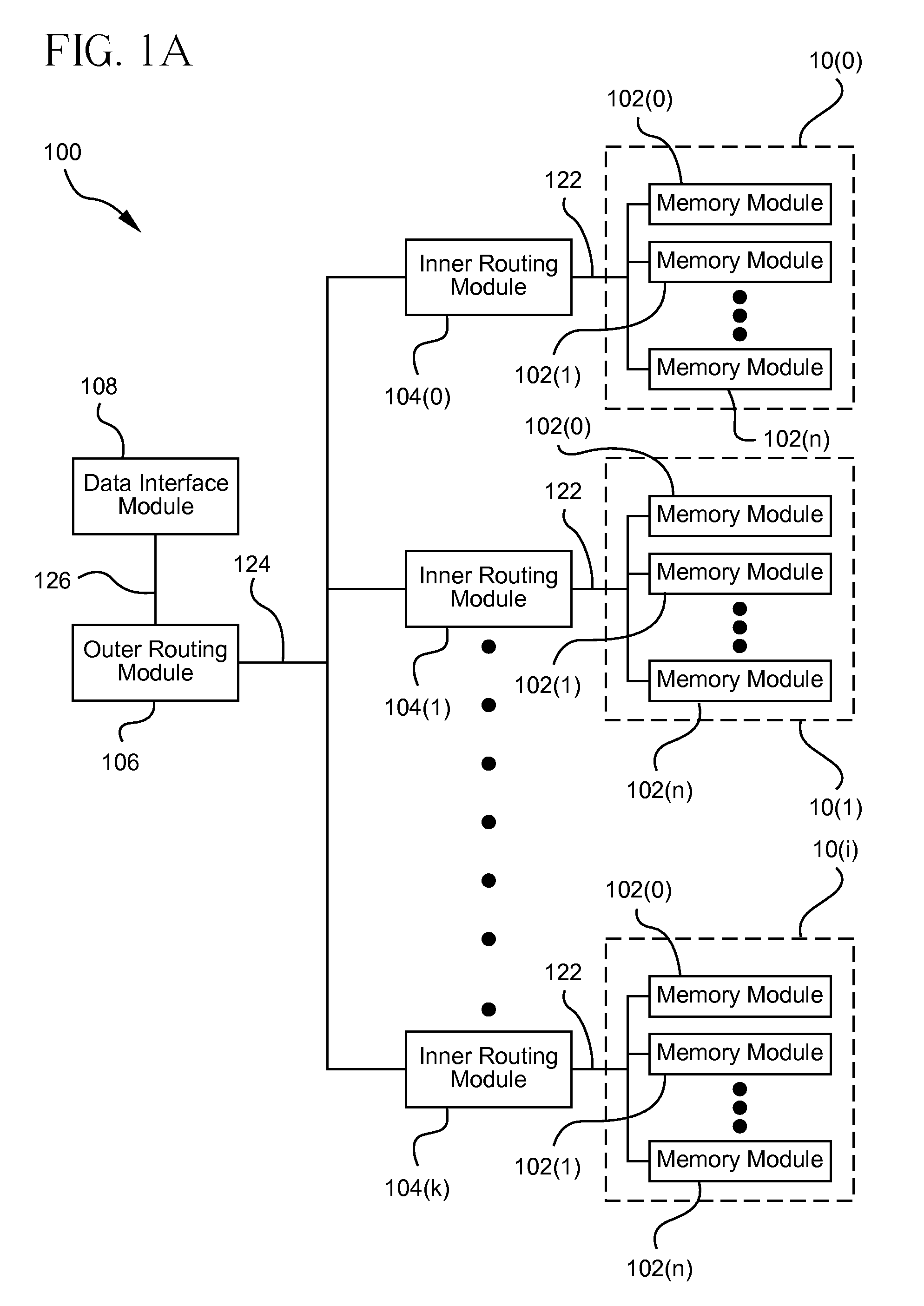
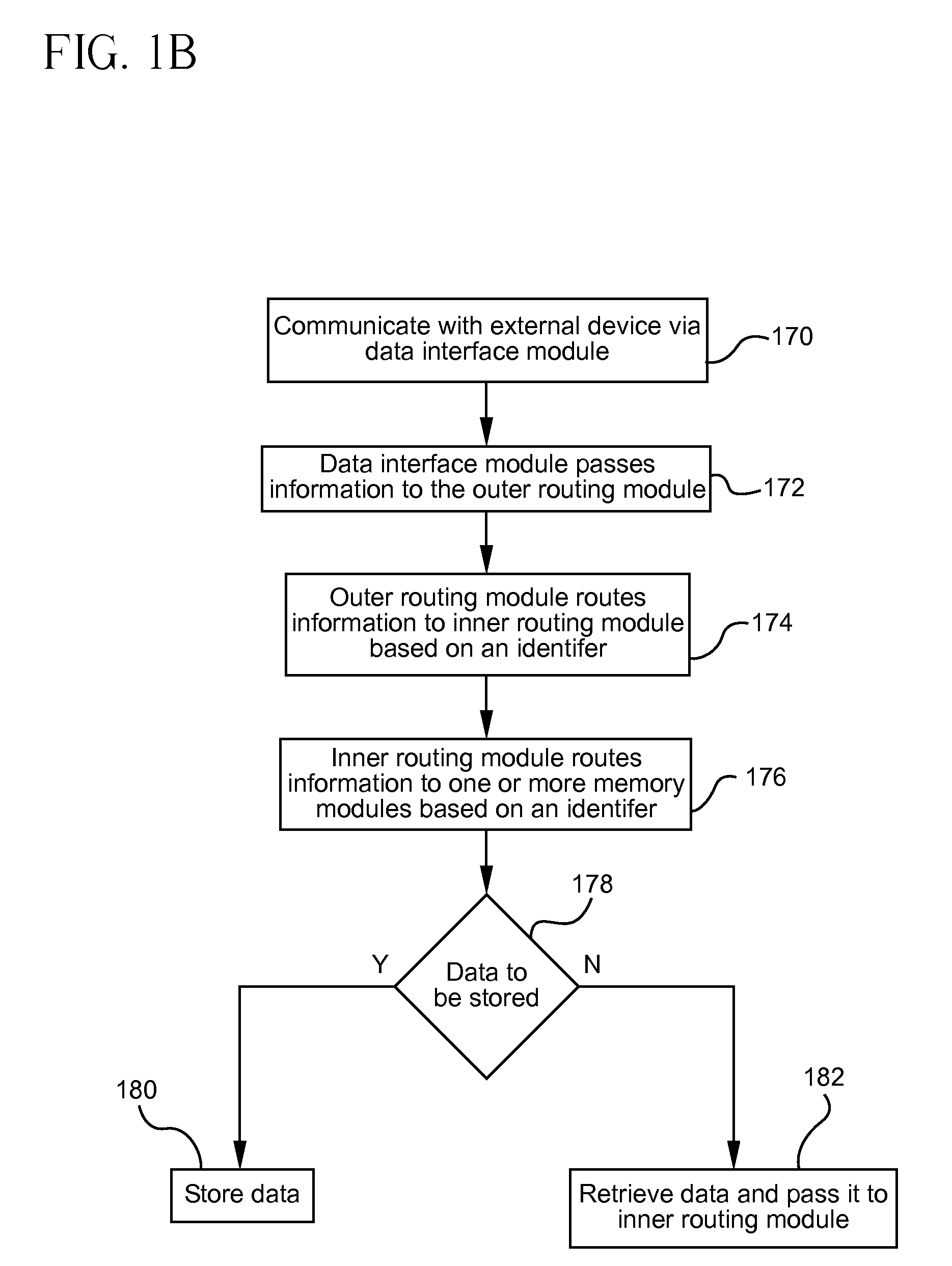
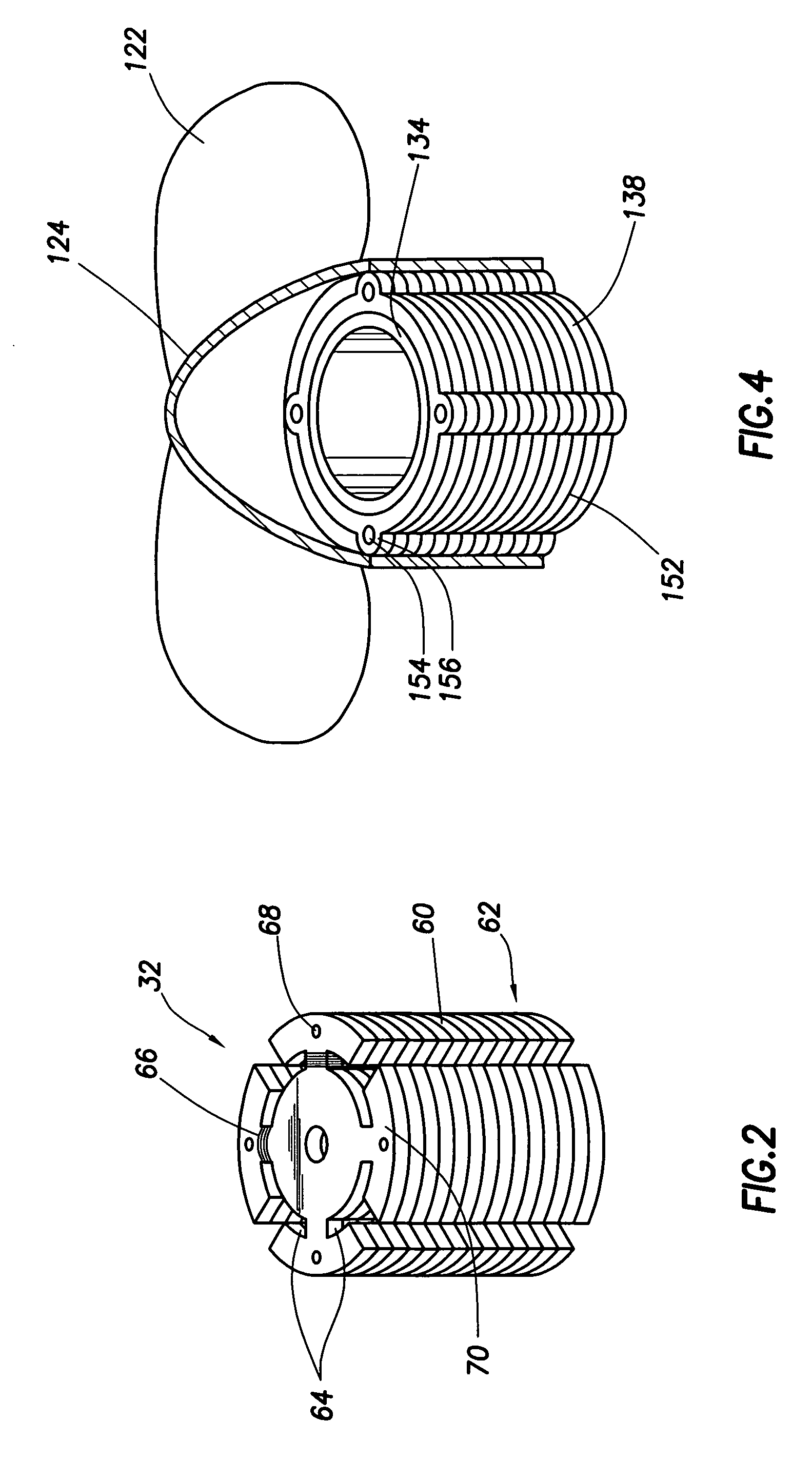
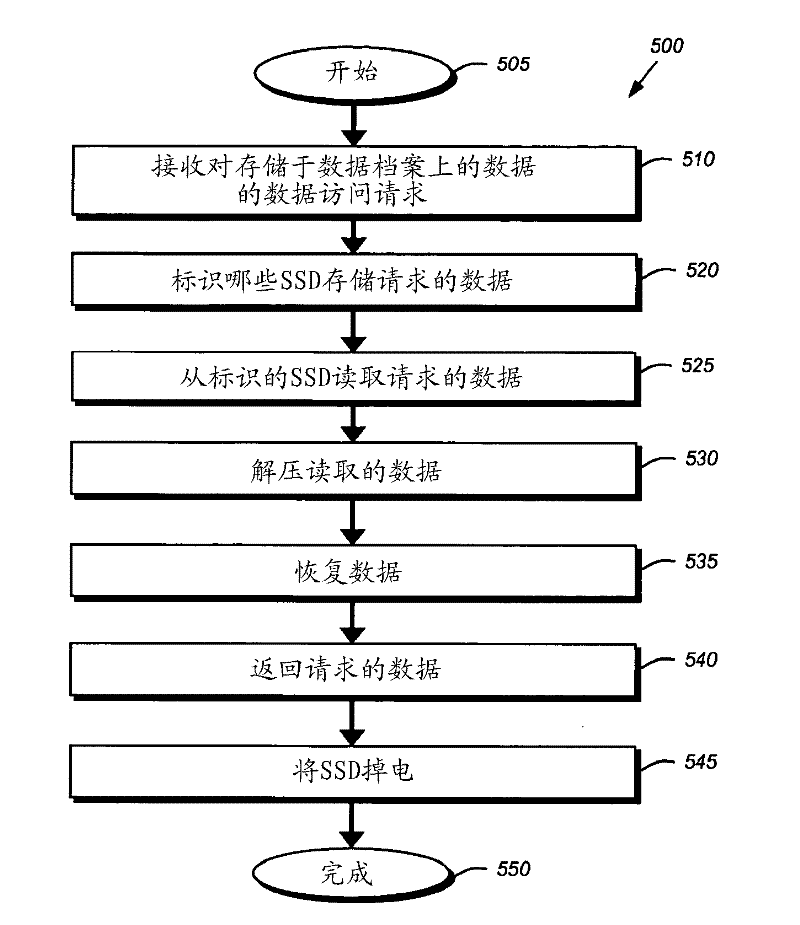
Flash-based data archive storage system
InactiveUS20100281207A1Large capacityMore capacityEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionMass storageMagnetic tape
A flash-based data archive storage system having a large capacity storage array constructed from a plurality of dense flash devices is provided. The flash devices are illustratively multi-level cell (MLC) flash devices that are tightly packaged to provide a low-power, high-performance data archive system having substantially more capacity per cubic inch than more dense tape or disk drives. The flash-based data archive system may be adapted to employ conventional data de-duplication and compression methods to compactly store data. Furthermore, the flash-based archive system has a smaller footprint and consumes less power than the tape and / or disk archive system.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Attack tool
In one aspect of the invention, an attack tool has a wear-resistant base suitable for attachment to a driving mechanism. A first end of a generally frustoconical first cemented metal carbide segment bonded to the base. A second metal carbide segment is bonded to a second end of the first carbide segment at an interface opposite the base. The first end has a cross sectional thickness of about 0.250 to 0.750 inches and the second end has a cross sectional thickness of about 1 to 1.50 inches. The first cemented metal carbide segment also has a volume of 0.250 cubic inches to 0.600 cubic inches.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Scalable mass data storage device
ActiveUS20090094406A1Improve data transfer rateHigh bulk densityEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData centerVolumetric density
A scalable data storage device which includes non-volatile memory uses a networked bus system which can be employed on a single memory storage chip level or in a multi-chip package (MCP). The scalable data storage device uses data routing modules which are adapted to store incoming data and send outgoing data thereby providing decoupling of the networked buses. This arrangement enables significantly higher data transfer rates, surpassing DRAM SSDs at a fraction of the size and cost, provides increased volumetric density (1 TB in less than 1 cubic inch), and permits concurrency of operations. The scalable data storage device can be engineered to have a rewrite capability of over 500 times that of Flash RAM and can scale down to 8 bits and up to exabytes, yottabytes and beyond. The scalable data storage device may be used in a wide range of applications from large data centers to small consumer electronic products.
Owner:STACKSPEED INC +1
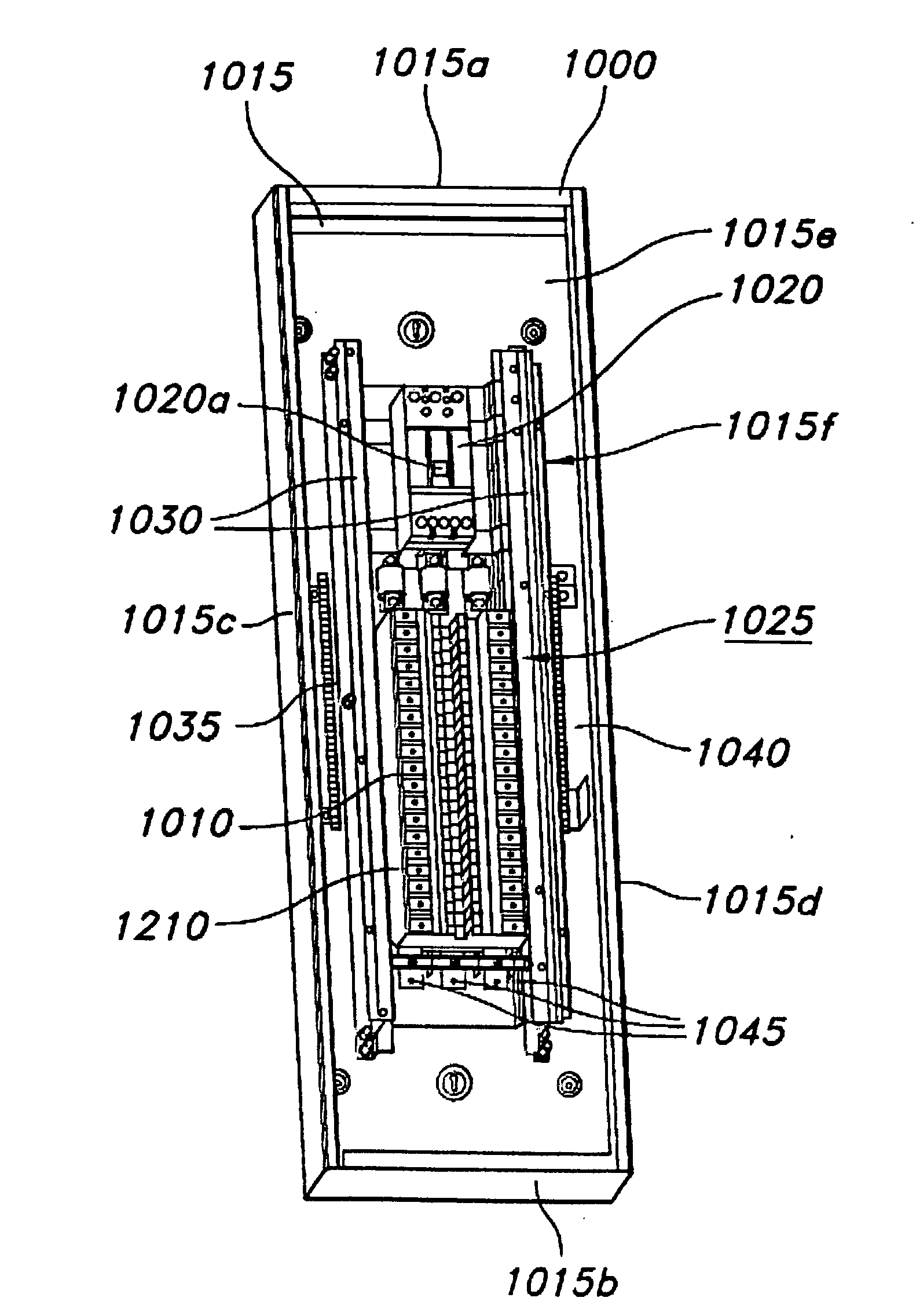
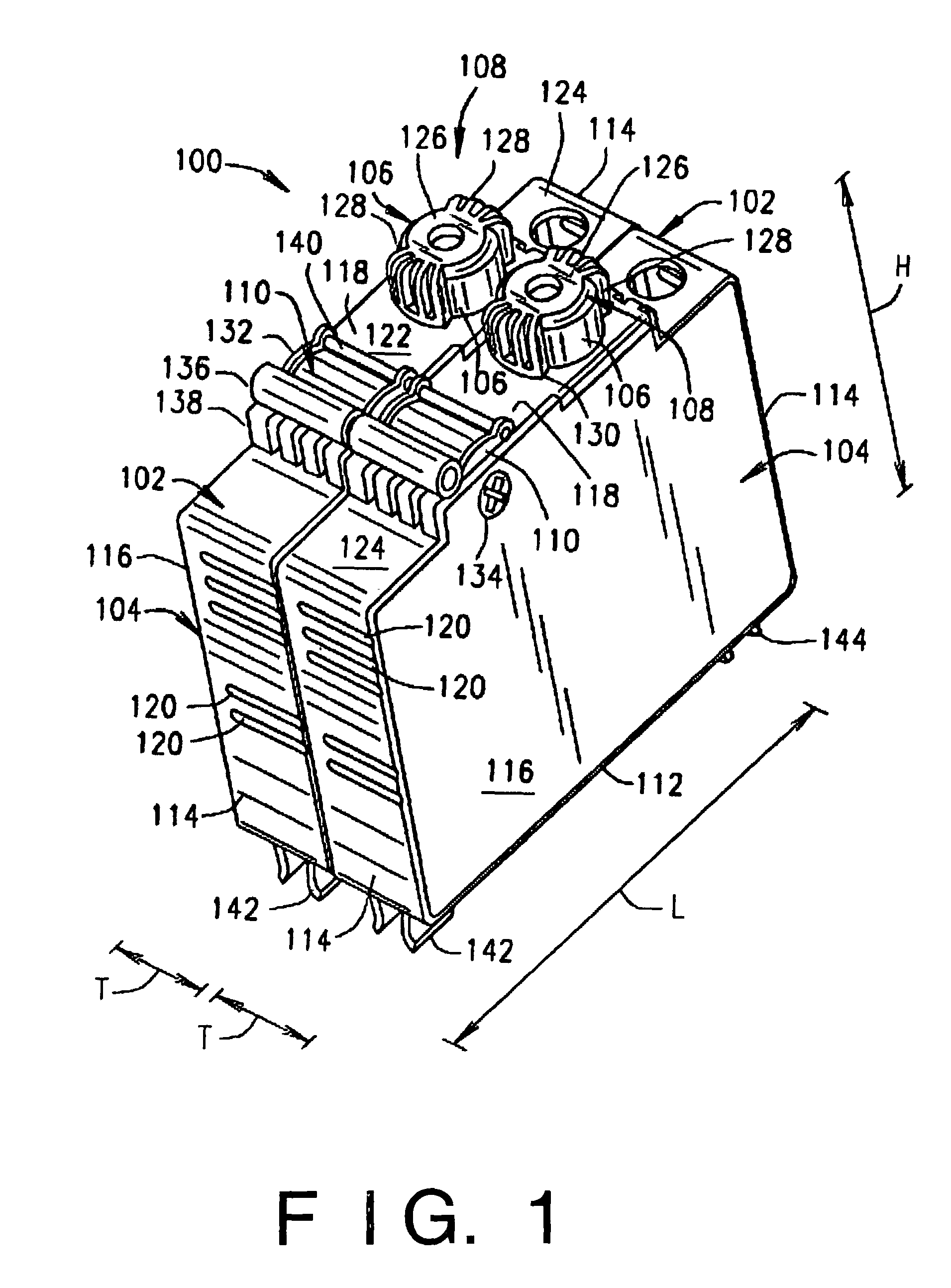
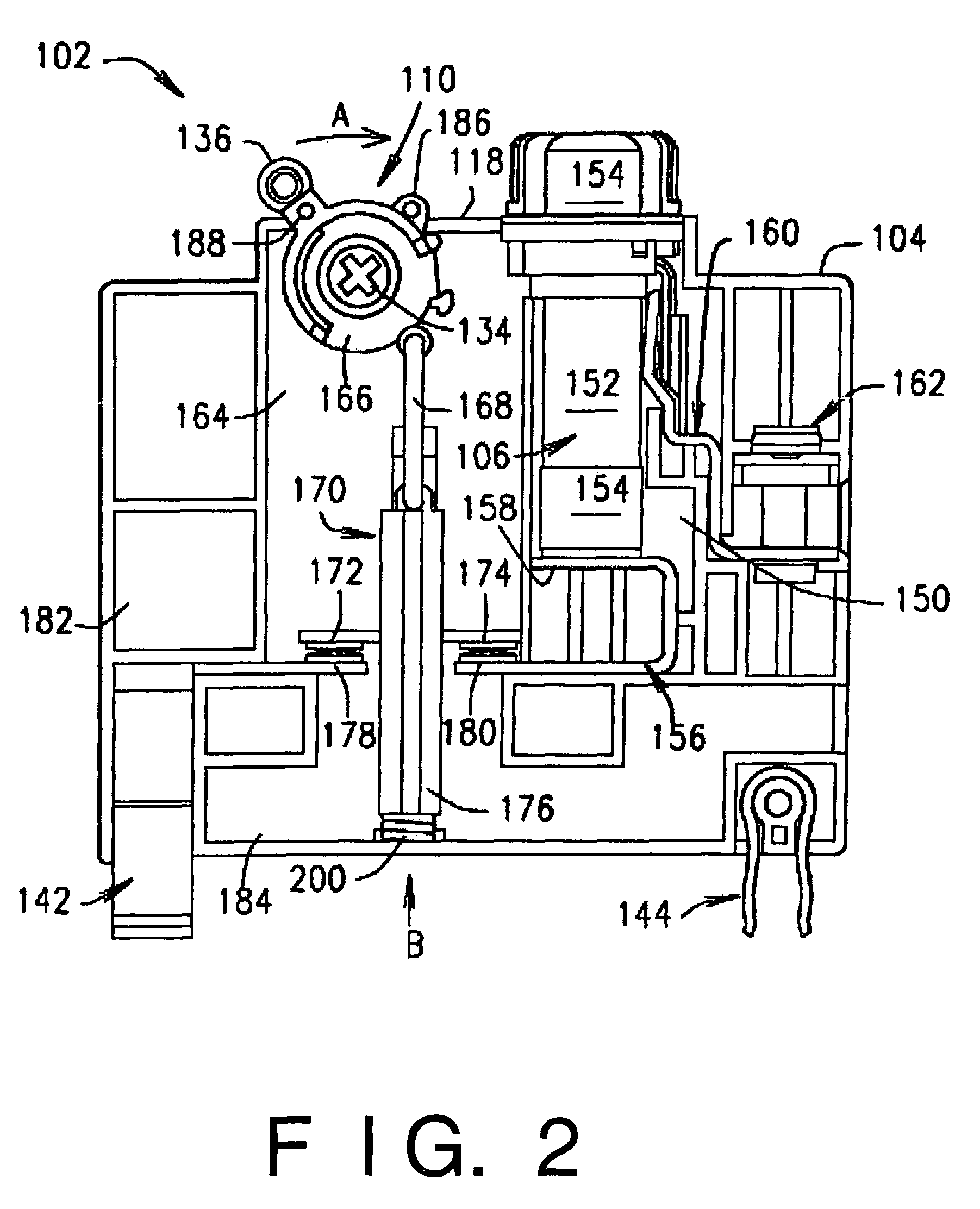
Panelboard for fusible switching disconnect devices
ActiveUS20080158788A1Switch operated by excess voltageSwitch operated by falling voltageEngineeringCircuit breaker
A panelboard for fusible switching disconnect devices. The panelboard includes a chassis coupled to a mounting enclosure. The mounting enclosure can be used indoors or outdoors. The chassis is configured to receive one or more fusible switching disconnect devices. Each of the fusible switching disconnect devices includes both a fuse and a circuit breaker-like disconnect in a single, relatively compact housing. The compactness of the housing allows the panelboard to provide a higher level of overcurrent interruption in a smaller sized mounting enclosure than conventional panelboards. For example, the panelboard can have an interruption per volume rating of at least about 33 amps per cubic inch, as compared to about 2 amps per cubic inch for most conventional panelboards.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
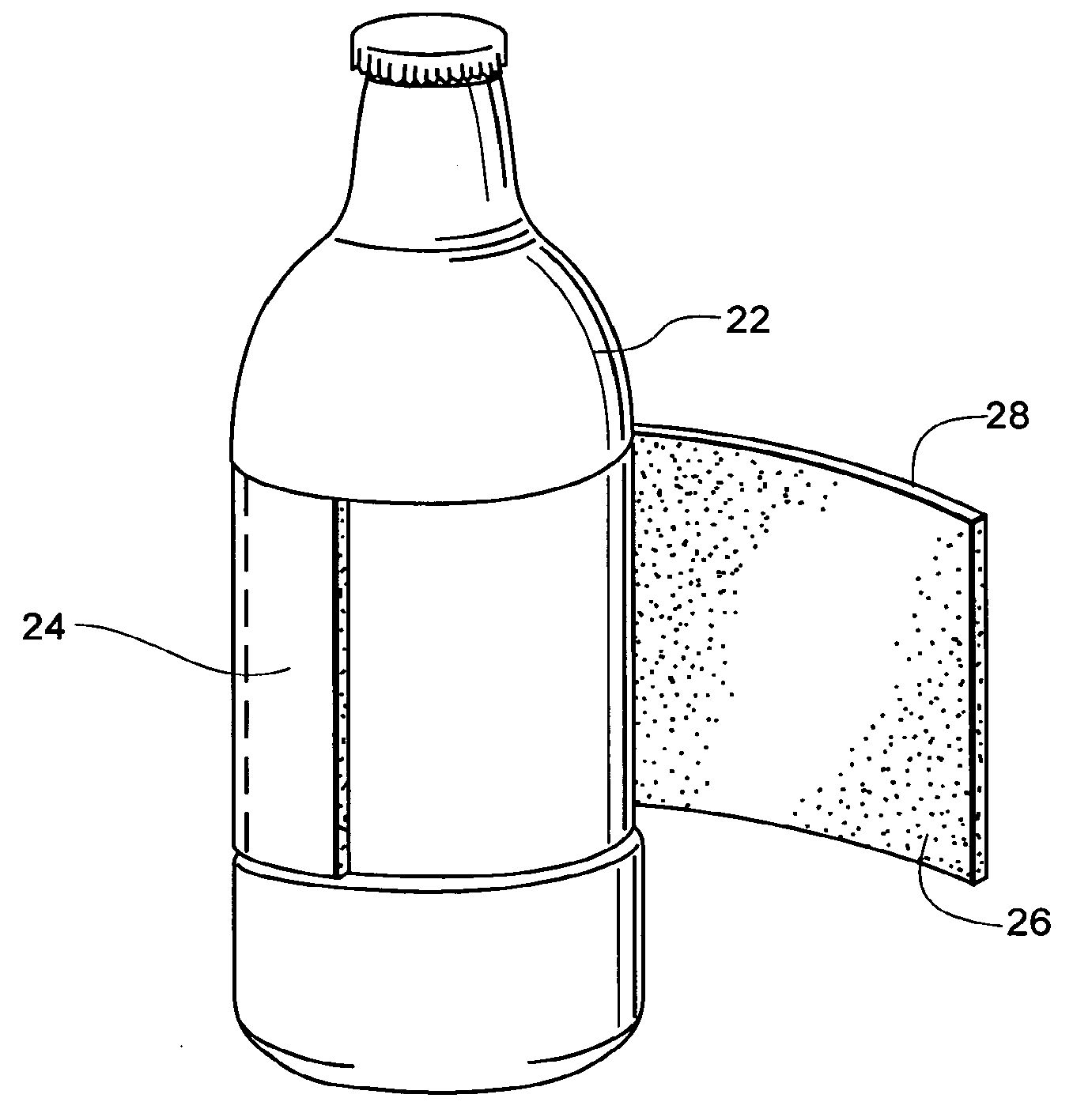
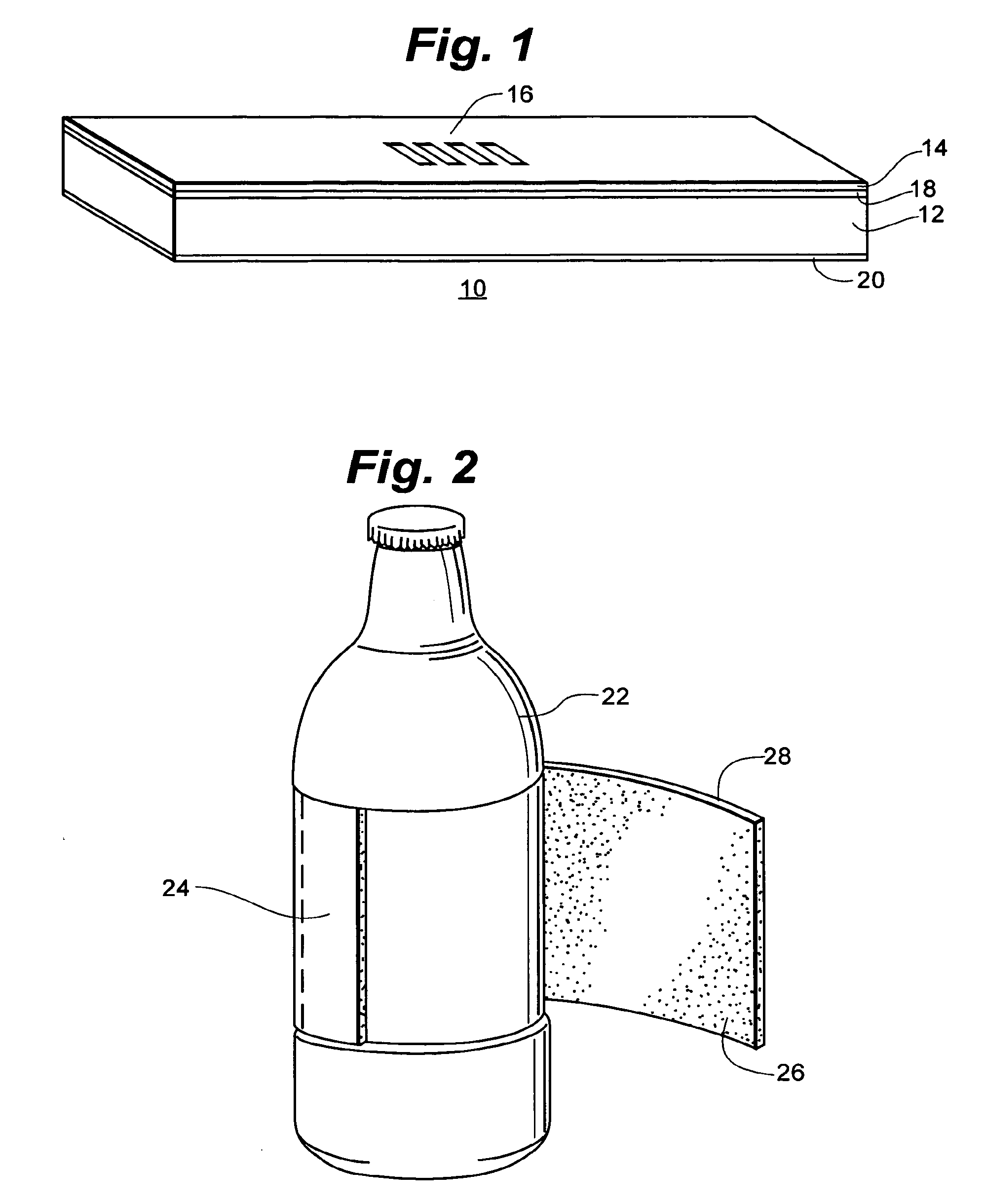
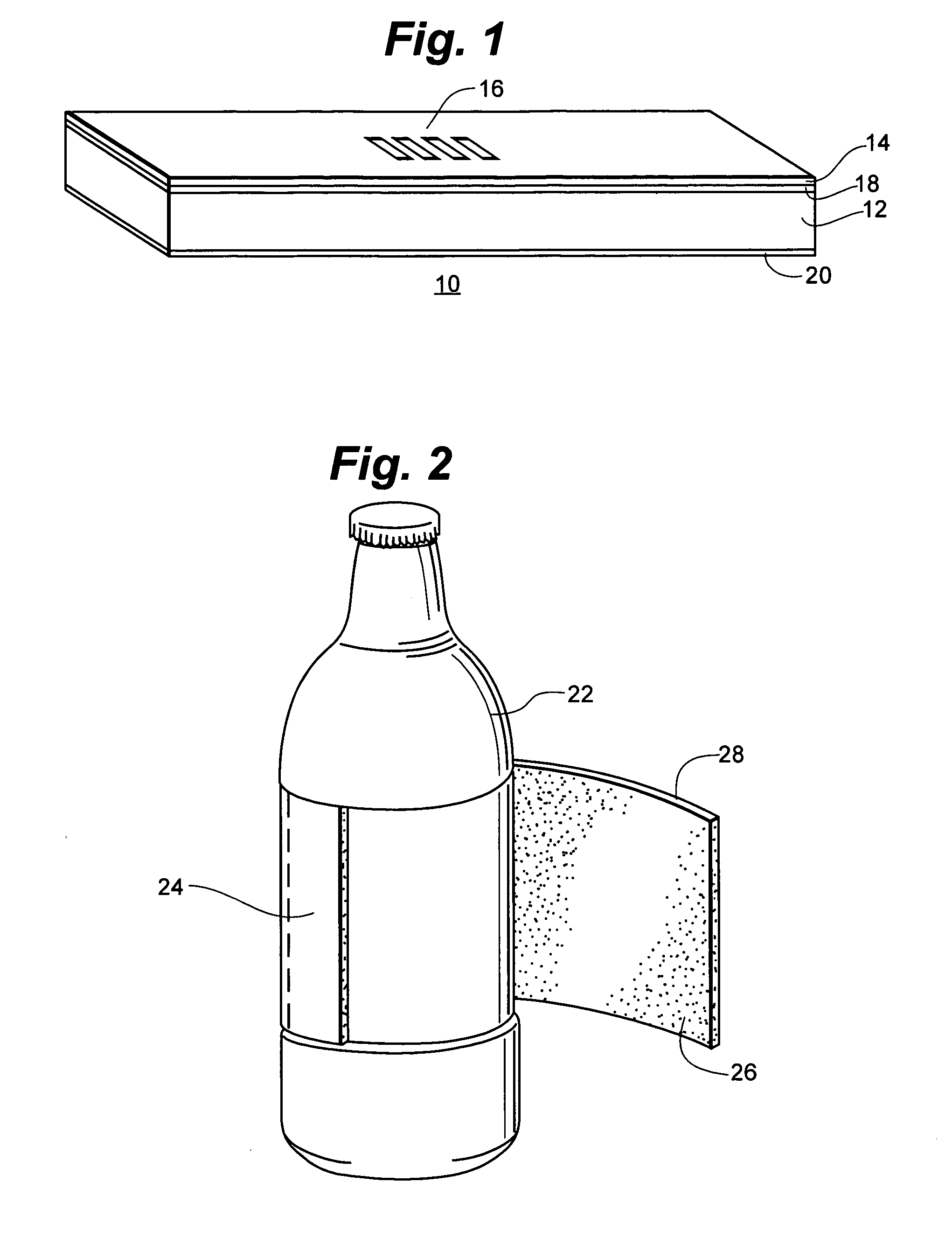
Insulating Label
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Attack Tool
In one aspect of the invention, an attack tool has a wear-resistant base suitable for attachment to a driving mechanism A first end of a generally frustoconical first cemented metal carbide segment bonded to the base. A second metal carbide segment is bonded to a second end of the first carbide segment at an interface opposite the base. The first end has a cross sectional thickness of about 0.250 to 0.750 inches and the second end has a cross sectional thickness of about 1 to 1.50 inches. The first cemented metal carbide segment also has a volume of 0.250 cubic inches to 0.600 cubic inches.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
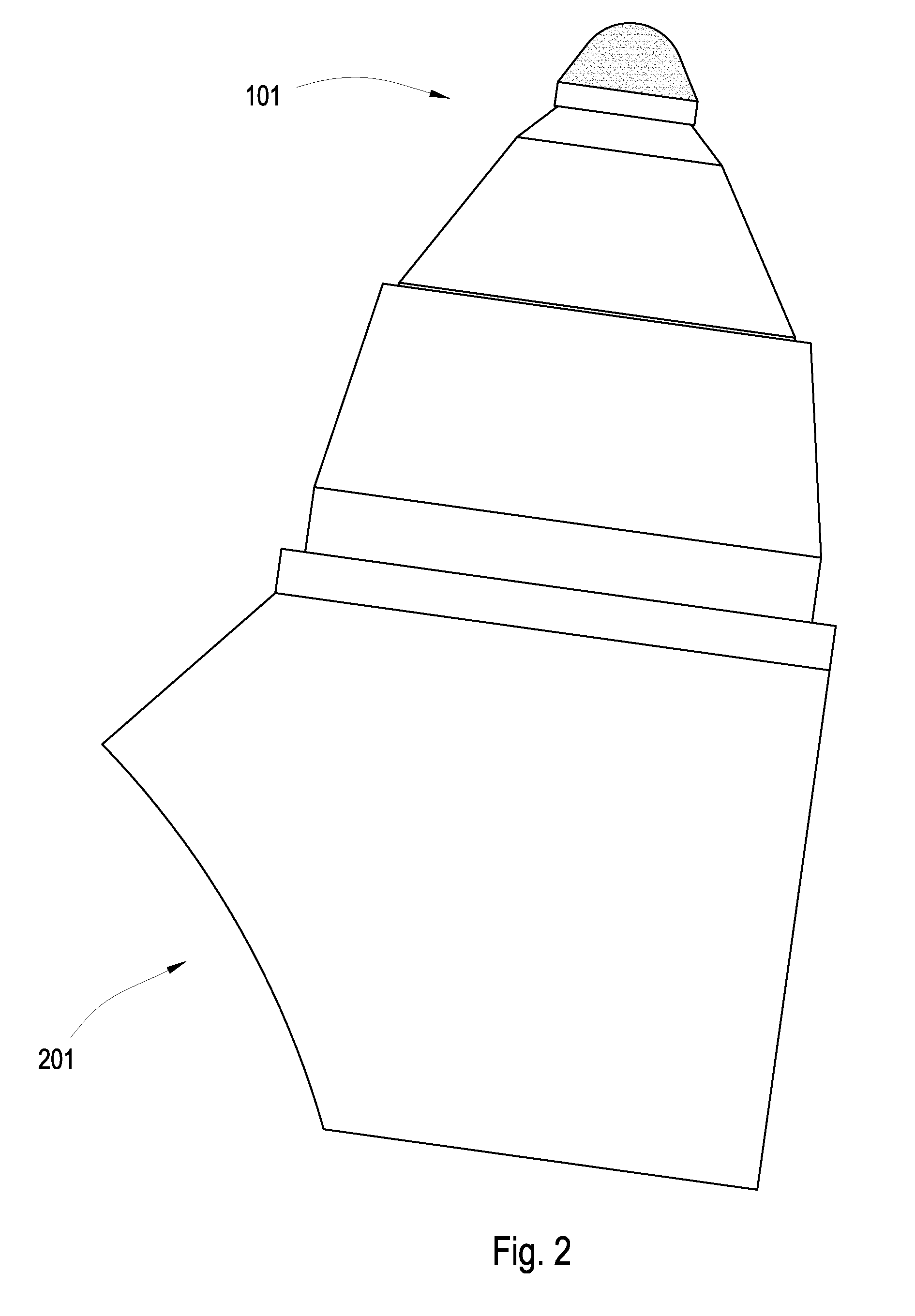
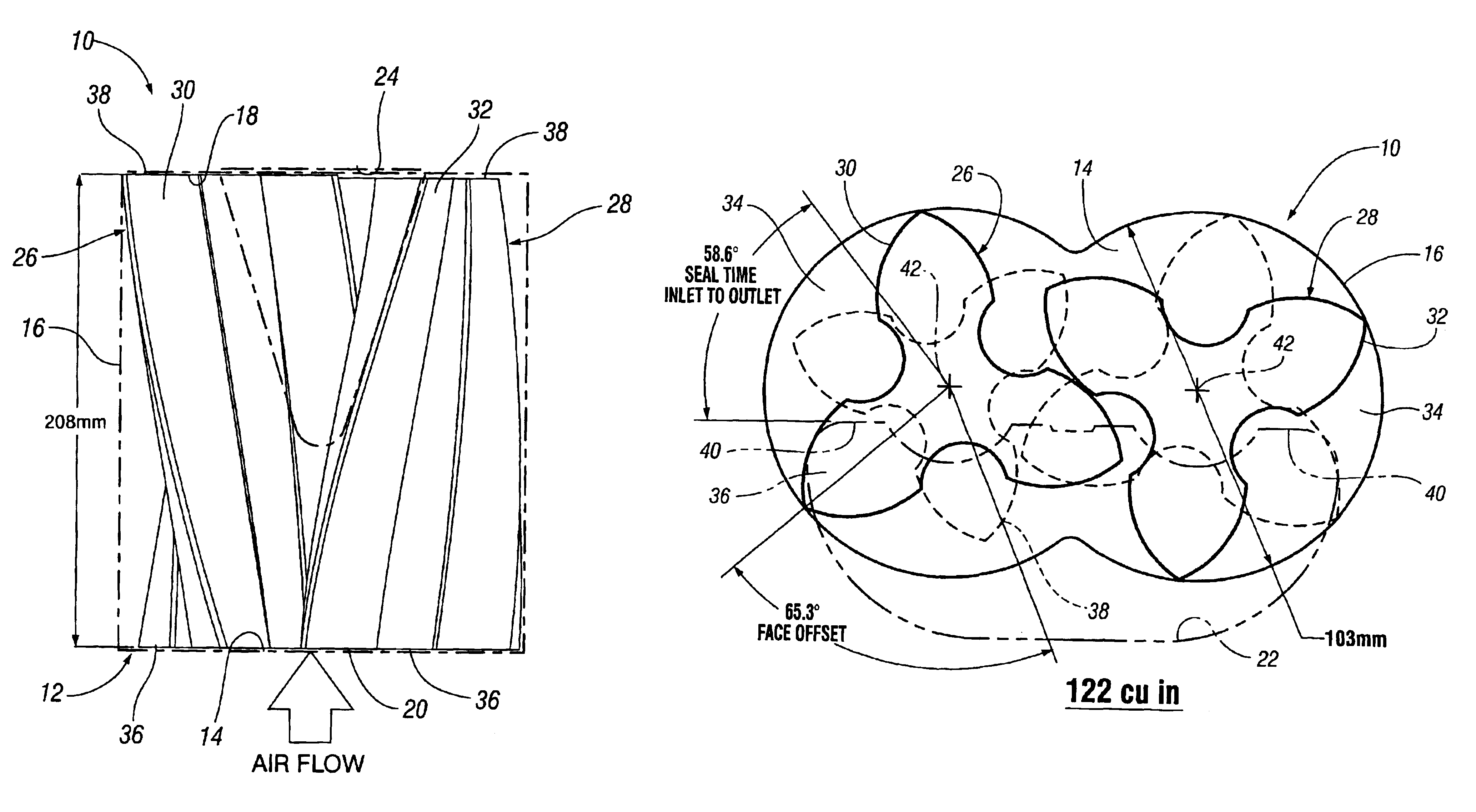
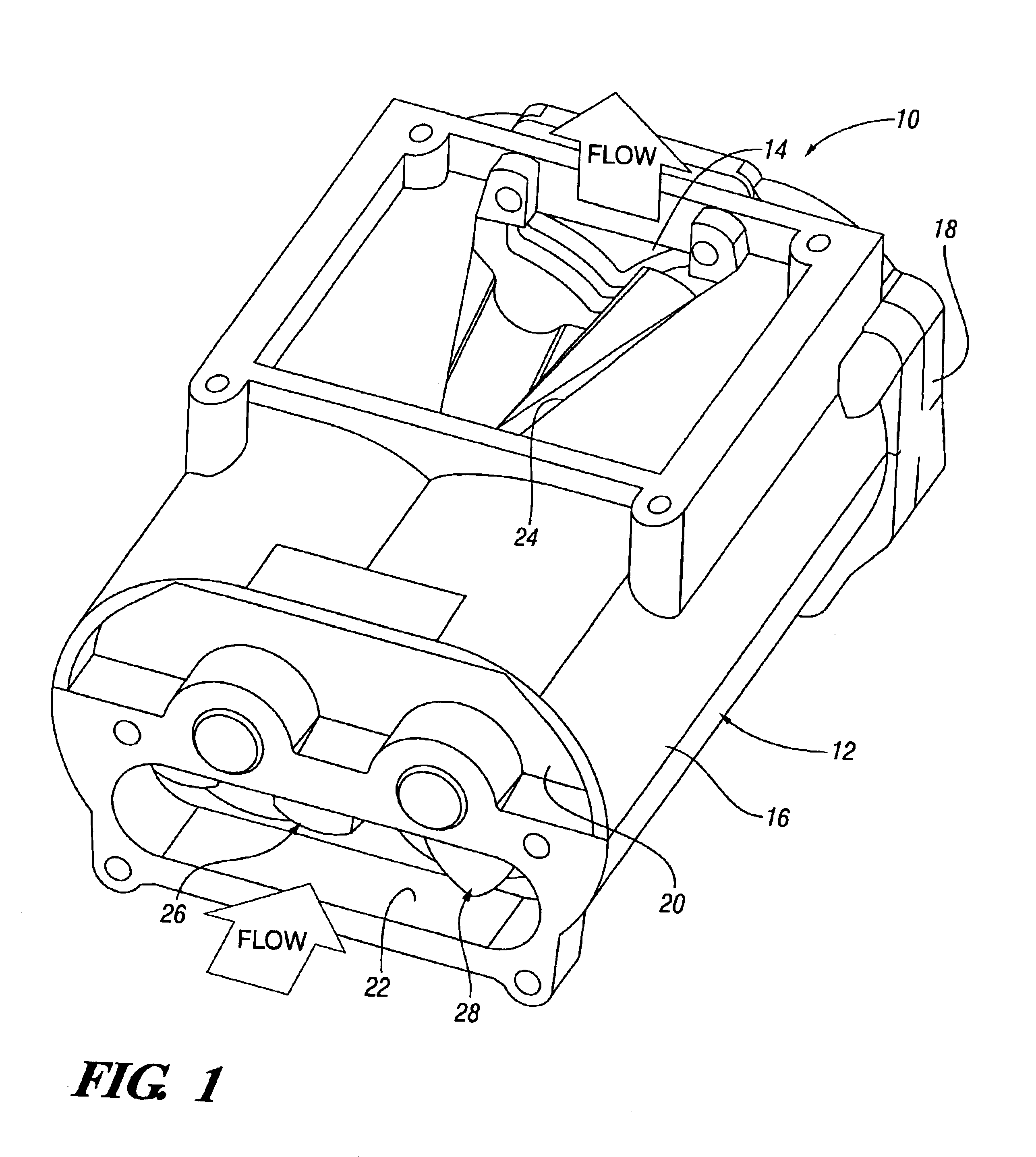
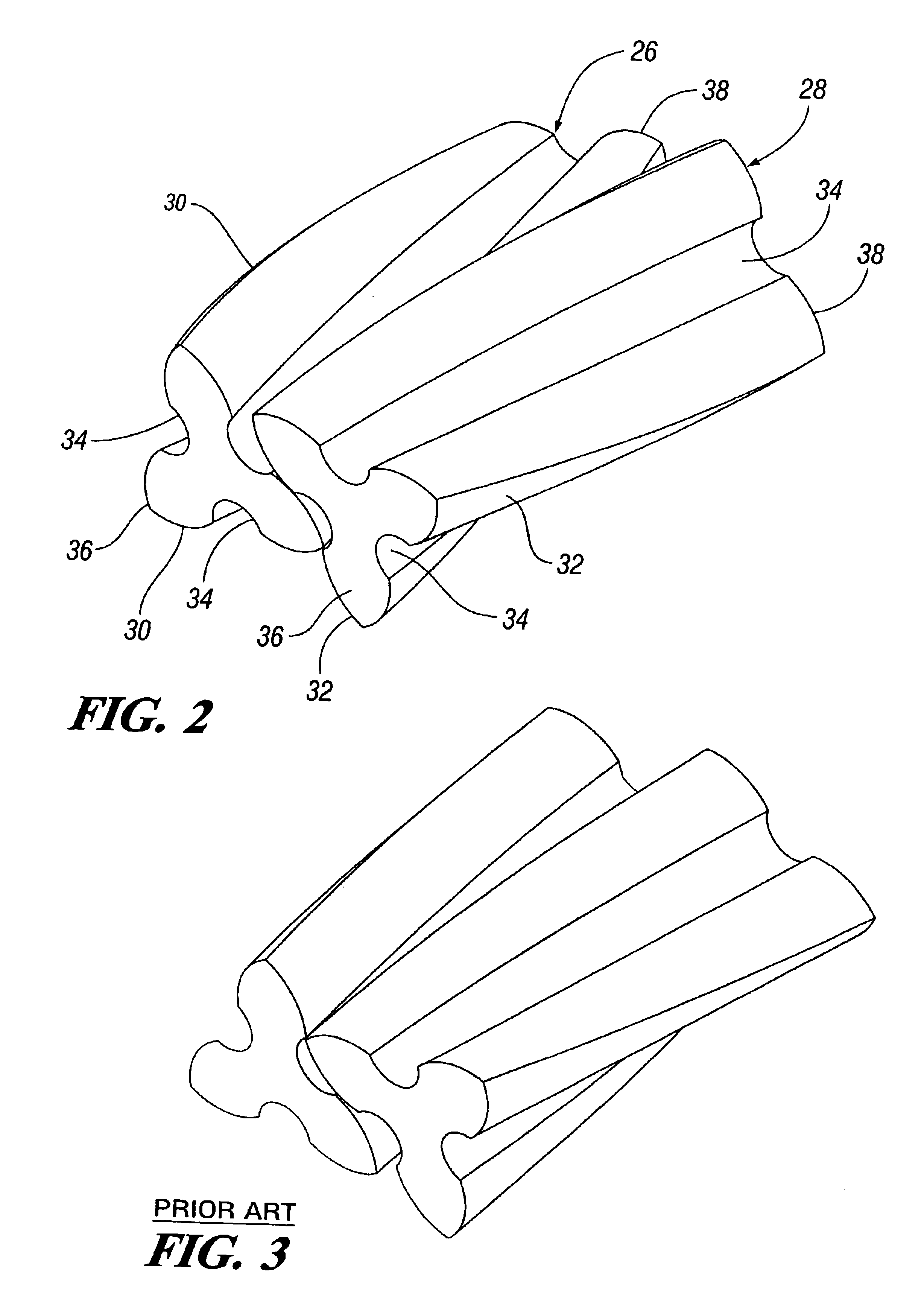
Roots supercharger with extended length helical rotors
InactiveUS6884050B2Improve efficiencyLow temperature changeOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeEngineeringHelix angle
A Roots supercharger has an extended cavity with 103 mm diameter rotors having chambers defined by interleaved helical lobes with equal angular face offsets exceeding 60 degrees from inlet to outlet end faces angled in directions opposite to directions of rotor rotation. The chambers have angular seal times of less than 67 degrees of rotation. A preferred embodiment has a displacement of 122 cu mm / revolution, rotor length of 208 mm, face offsets of 65.3 degrees and seal time of 58.6 degrees. The rotor lobe helix angle is essentially 0.314 deg / mm, equal to the helix angle of a prior art supercharger with rotors of common diameter, displacement of 112 cubic inch / revolution, rotor length of 191 mm, previously considered maximum, 60 degree face offset, previously considered optimum, and seal time of 67 degrees. Both flow volumes and efficiency of the new configuration are improved from the prior art wherein the 60 degree face offset was considered optimum.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for retarding fire
A barrier for retarding fire comprises water-permeable fabric for covering a substantial area, the fabric having at least 9 pockets per square foot, each pocket having a volumetric capacity of between about 0.03 cubic inches and about 17 cubic inches, wherein substantially all of the pockets contain between about 0.01 and about 2 grams of superabsorbent polymer per cubic inch of volumetric capacity of the pockets.
Owner:MILLER JOHN C +1
Panelboard for fusible switching disconnect devices
ActiveUS7855873B2Switch operated by excess voltageSwitch operated by falling voltageCircuit breakerCubic inch
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
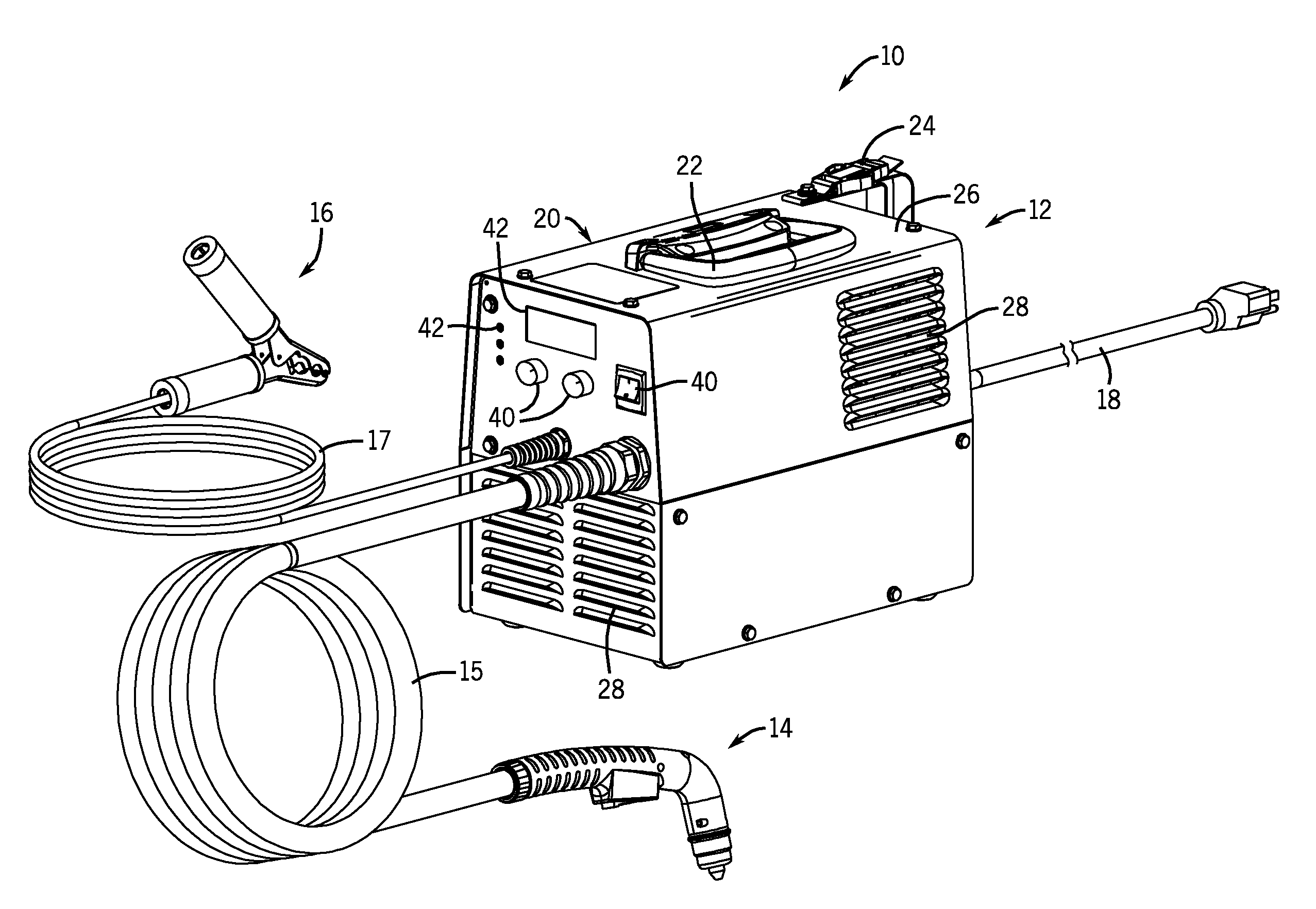
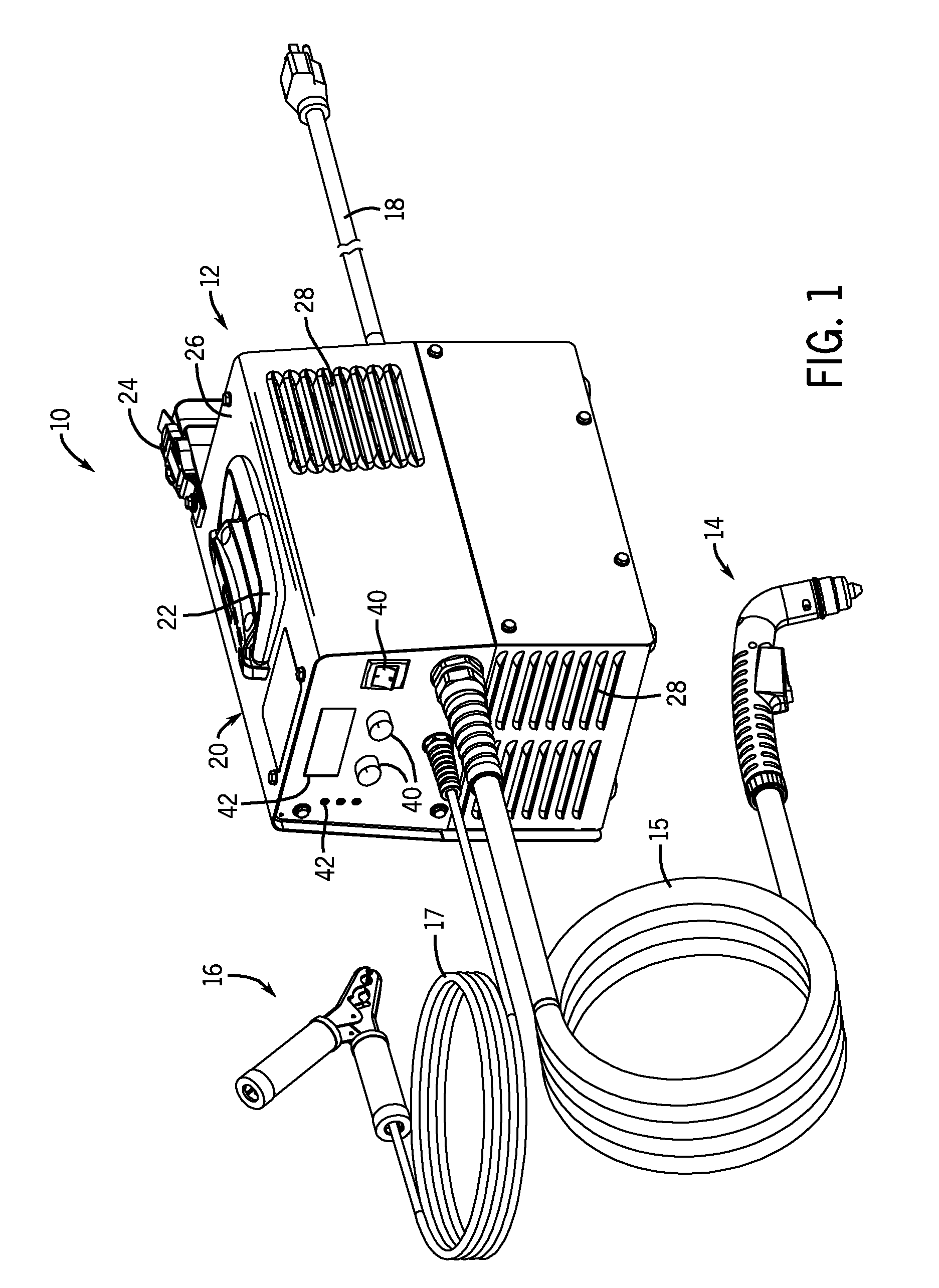
Plasma Cutter Having High Power Density
Systems and methods are provided for a torch power system having a high power density. In one embodiment, a system is provided that includes a torch power unit having a compressor and power electronics that include one or more power converters, wherein the torch power unit has a power output density of at least 2 watts per cubic inch, 80 watts per pound, or a combination thereof. A power conversion assembly for a torch power unit is provided that includes a single circuit board, a torch power converter mounted on the single circuit board, and a non-torch power converter mounted on the single circuit board. An electrical torch system is also provided that includes a circuit board and a power converter coupled to the circuit board, wherein the power converter includes a planar transformer, a foil wound transformer, or a combination thereof.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Compact infrared spectrometer, and methods and systems for manufacture and assembly of components used in same
ActiveUS7075082B2Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceMirrorsSpectrum investigationTwo dimensional detectorGrating
A compact spectrometer operable in a wavelength range of 4.5 or more microns includes an entrance slit, a collimating mirror, a grating, a focusing mirror and a first focal plane. At least some radiation passing through the slit follows an optical path in which at least some radiation passing through the slit is reflected by the collimating mirror onto the grating, which in turn reflects at least some radiation onto the focusing mirror, which in turn reflects and focuses at least some radiation at a first focal plane and onto the two-dimensional array of detectors. Each column in the two-dimensional array of detectors corresponds to a wavelength in the 4.5 or more micron range. The two-dimensional array includes a plurality of columns that collectively correspond to wavelengths spanning the 4.5 or more micron range, and each adjacent pair of columns in the two-dimensional array of detectors corresponds to two wavelengths that differ by an equal amount. The entrance slit, the collimating mirror, the grating, the focusing mirror and the first focal plane are positioned within a volume that is equal to or less than 192 cubic inches in size.
Owner:WILMINGTON INFRARED TECH
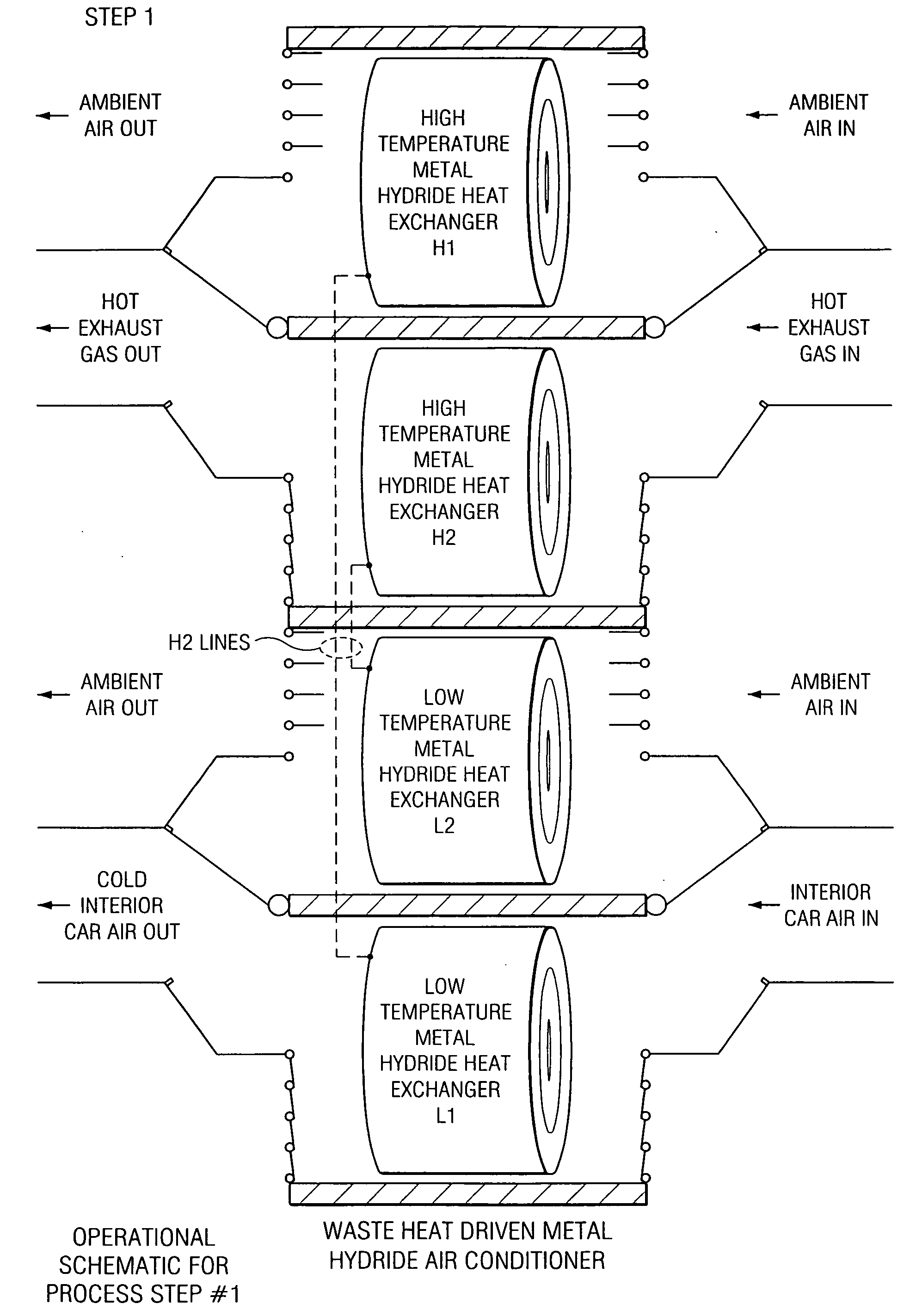
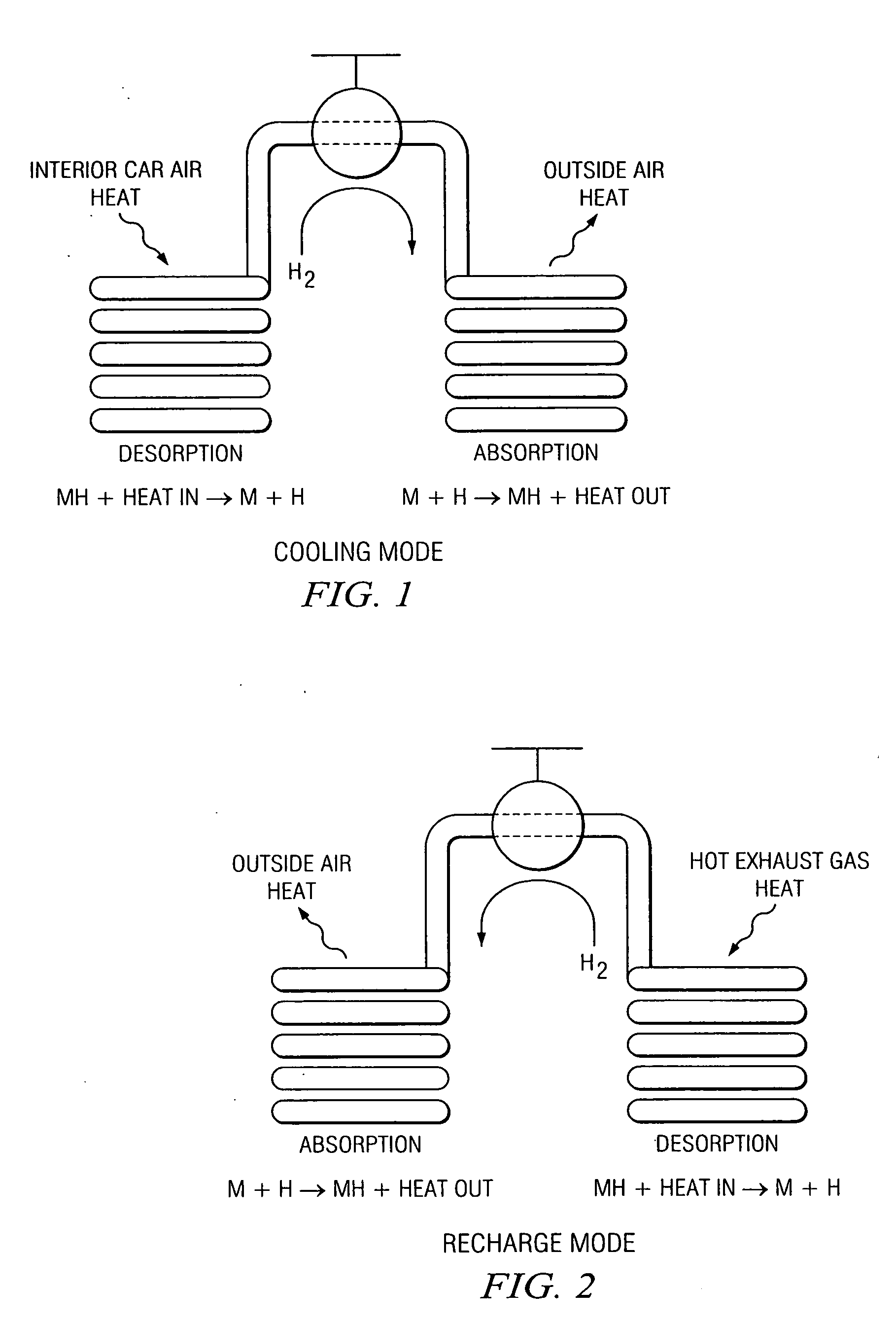
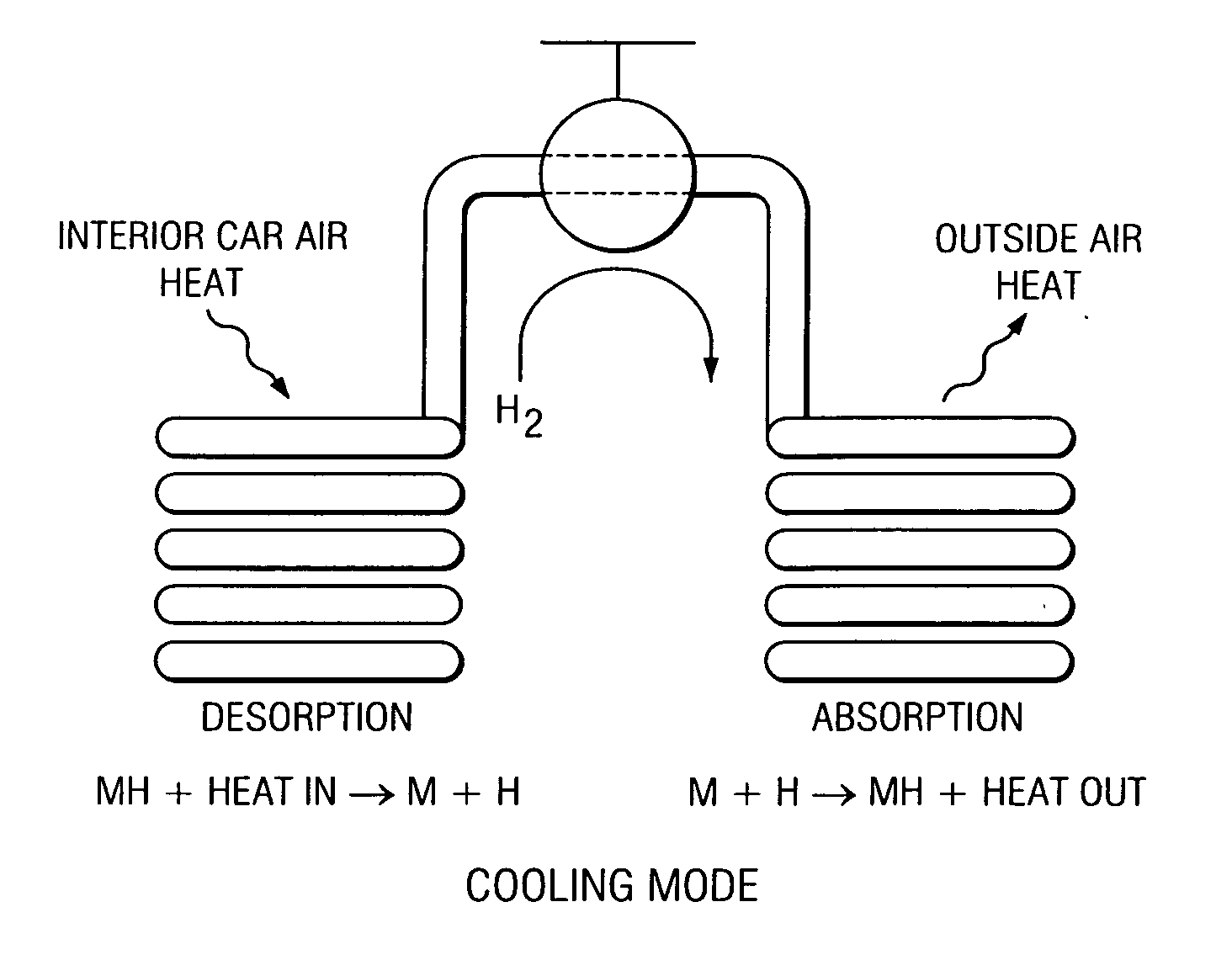
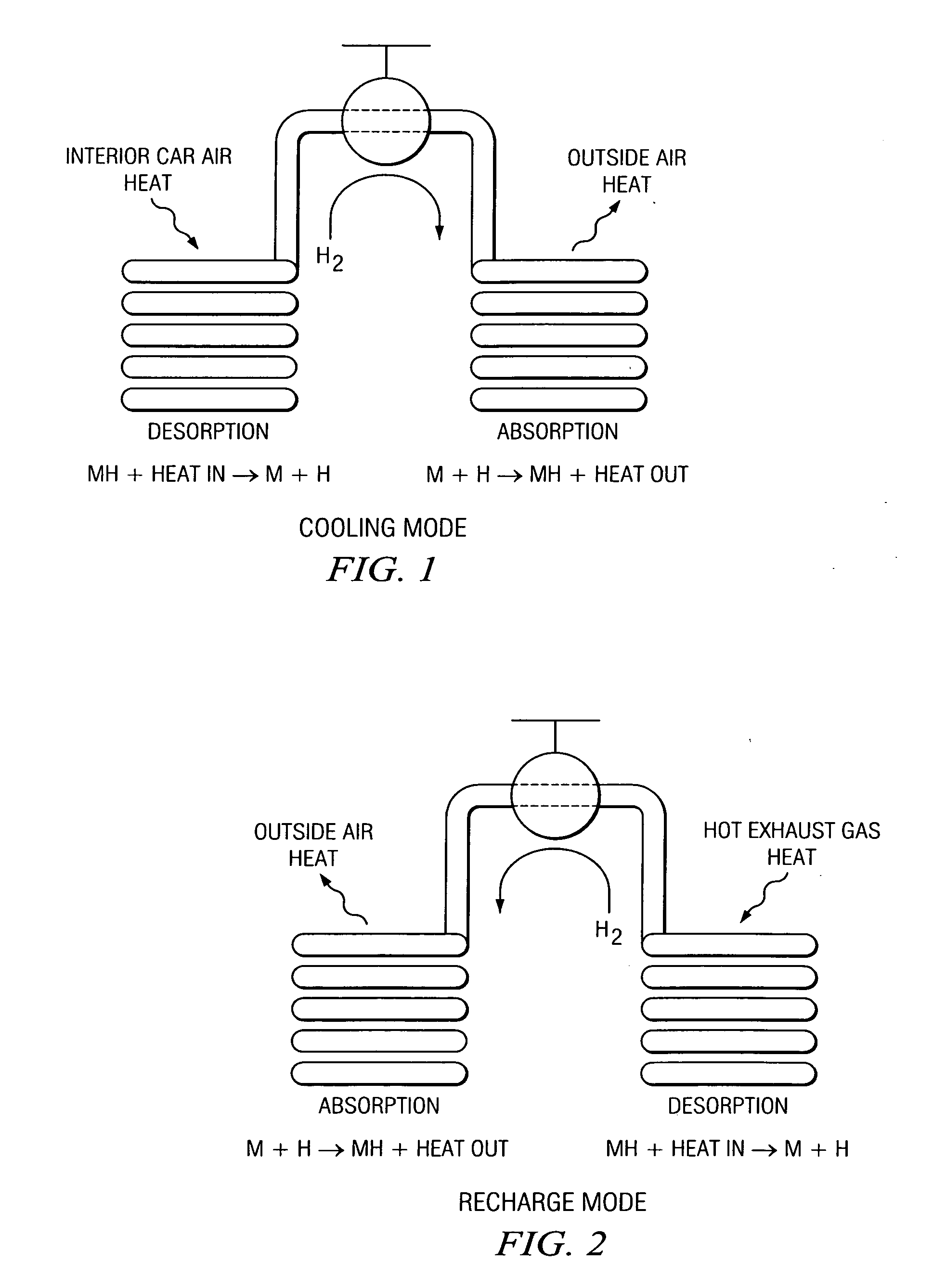
Metal hydride based vehicular exhaust cooler
InactiveUS20050274493A1Desorption can be effectedAir-treating devicesHeat storage plantsCubic inchChiller
A metal hydride heat pump comprising a first compartment, including a first fluid inlet and a first fluid outlet, wherein the first fluid inlet is configured for fluid communication with the first fluid outlet; a second compartment, including a second fluid inlet and a second fluid outlet, wherein the first fluid inlet is configured for fluid communication with the second fluid outlet; and a plurality of metal hydride vessels, each of the vessels being mounted to and disposed within each of the first and second compartments, and each of the vessels containing at least a hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, a hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material, and gaseous hydrogen, wherein the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material is in fluid communication with the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, such that heat can be transferred from (a) fluid flowing through the first compartment to (b) the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, so as to effect desorption of hydrogen from the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, and such that the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material is configured to absorb the desorbed hydrogen and generate heat upon the absorption such that the generated heat can be transferred to fluid flowing through the second compartment; wherein each of the vessels has an external surface area, and defines an internal volume for containing at least the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material, and gaseous hydrogen, wherein a ratio of the external surface area to the internal volume is greater than 45 inches2 per cubic inch.
Owner:HERA USA
Insulated label
The invention is an insulated label for maintaining the temperature of the contents of a package, formed from a polymeric thermoplastic closed cell foam having from about 5,000 to about 250,000 closed cells per cubic inch.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
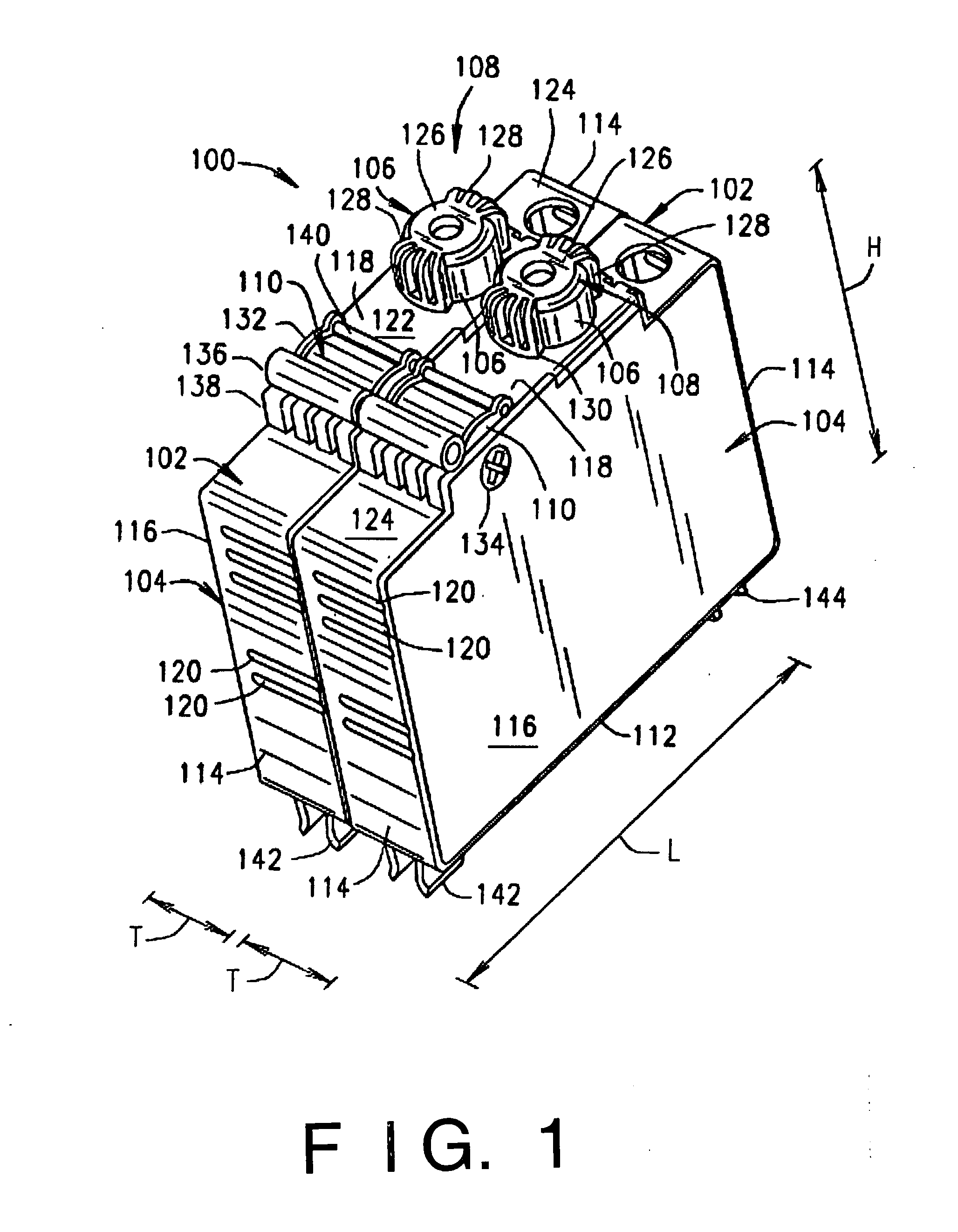
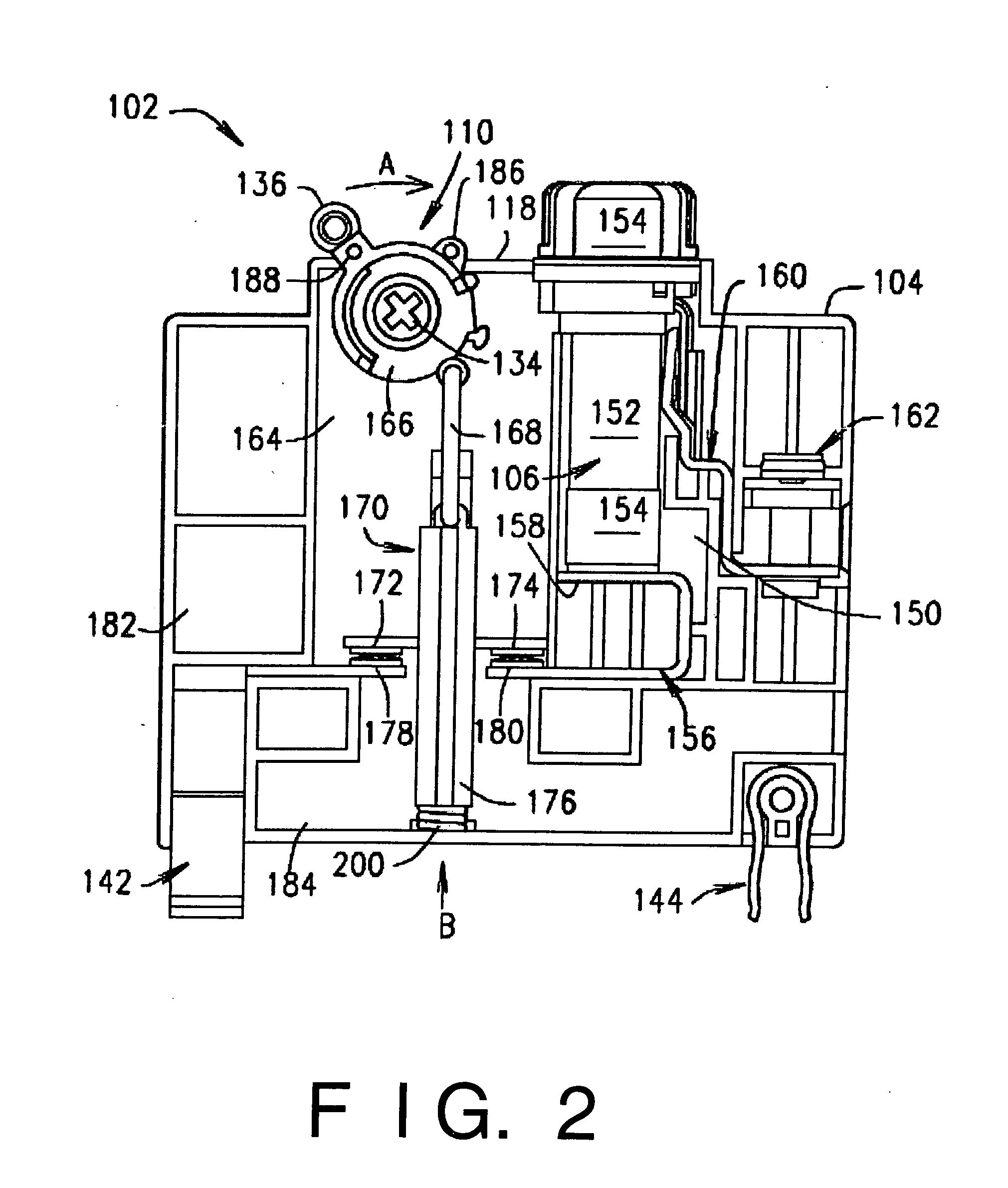
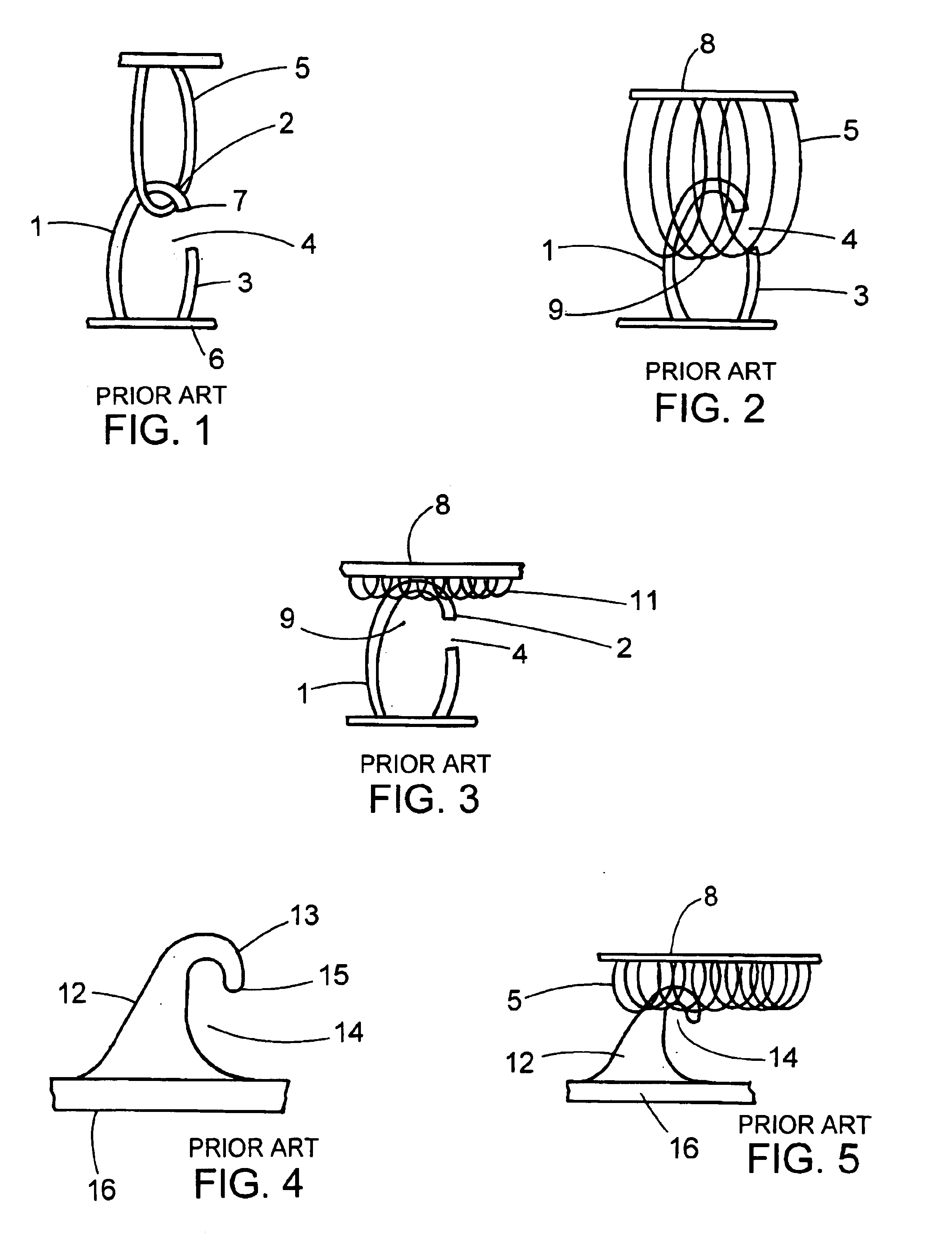
Hook for hook and loop fasteners
A plastic molded hook for use with a hook and loop fastening system especially adapted for use with low profile loops. The hook design includes a base, a stem and a crook whereby the volume of the portion of the hook penetrating into a pile of loops is defined as the displacement volume. Hooks especially adapted for use with low profile loops have a displacement volume of less than 6.times.10.sup.-6 cubic inches.
Owner:VELCRO IND BV
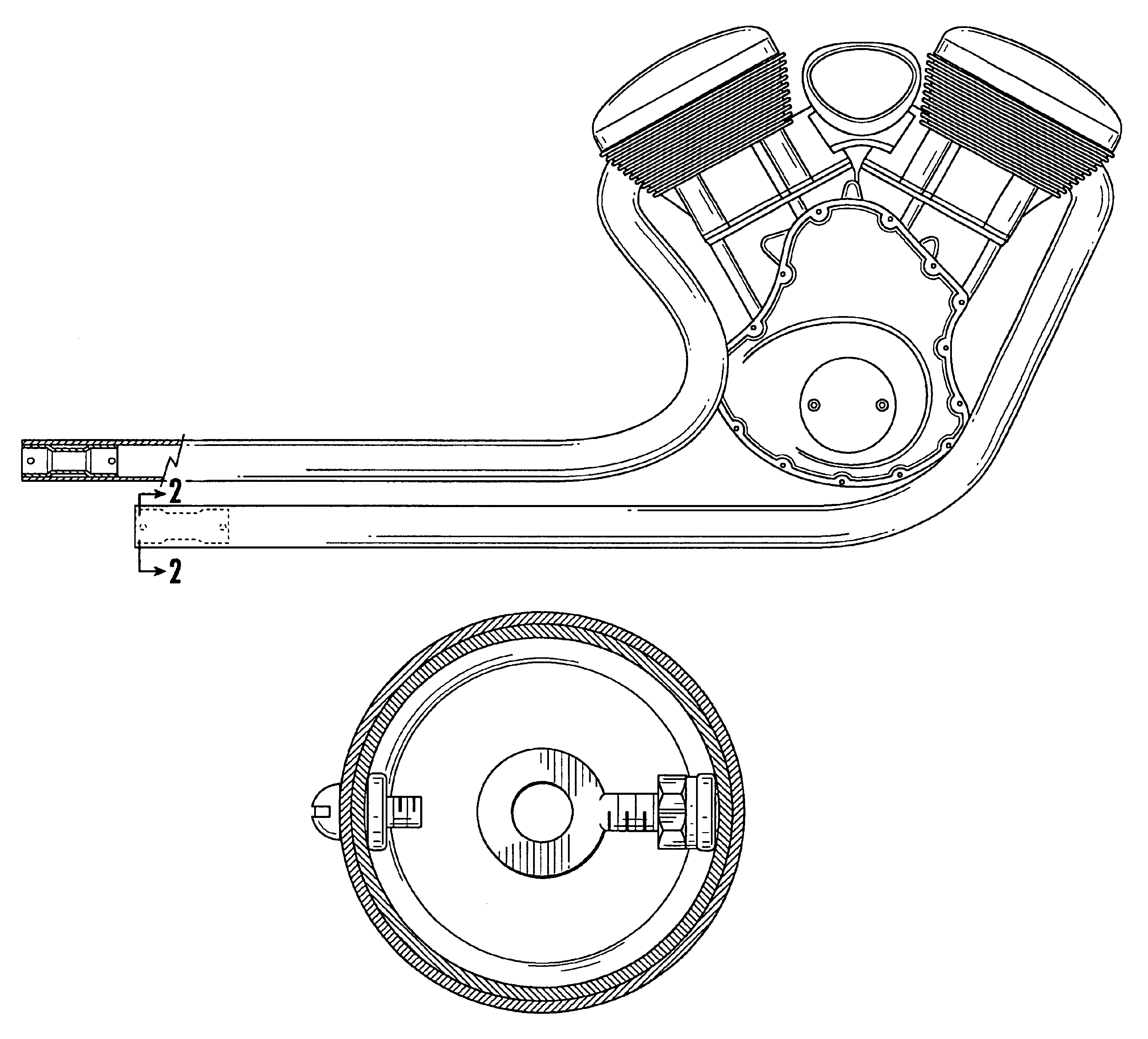
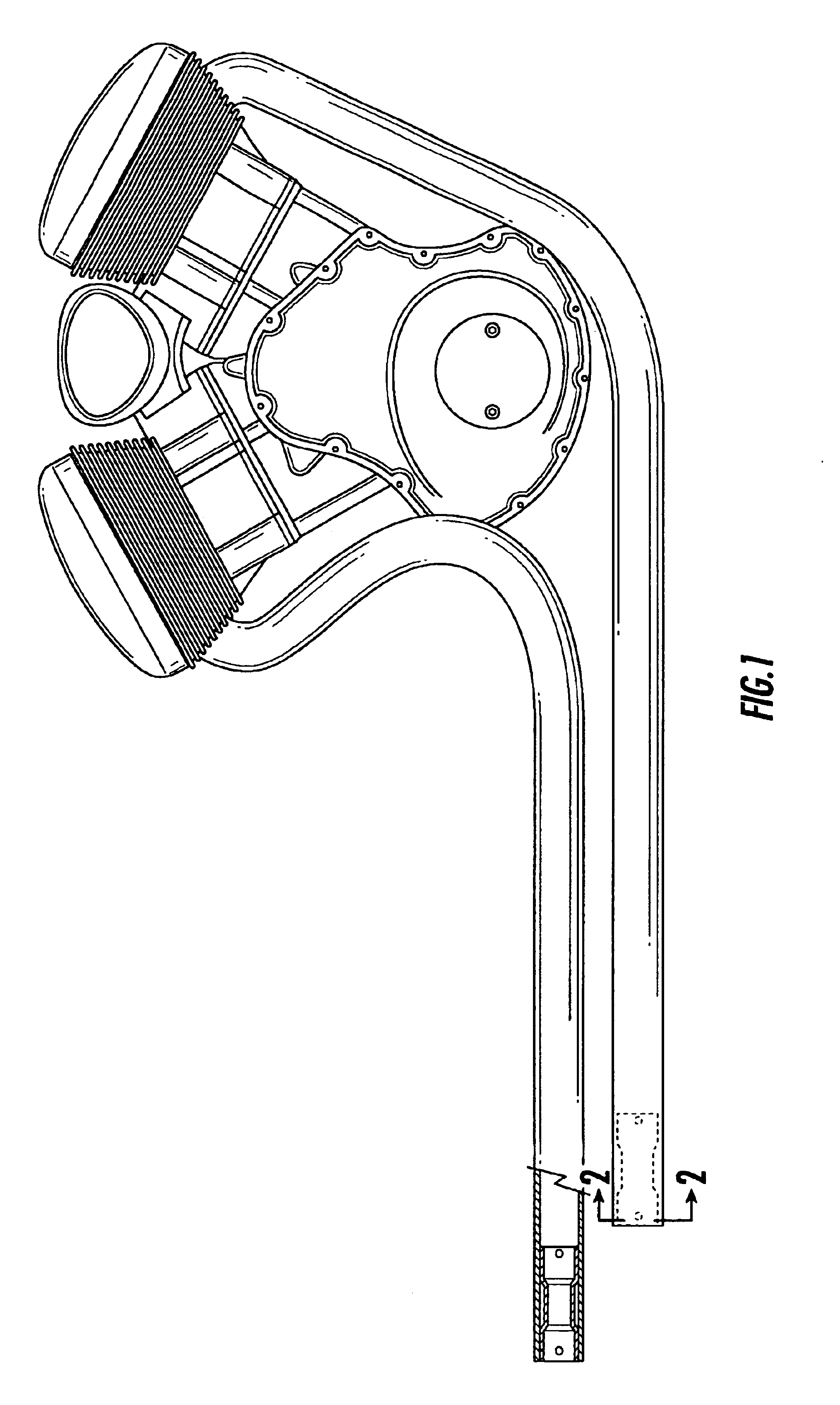
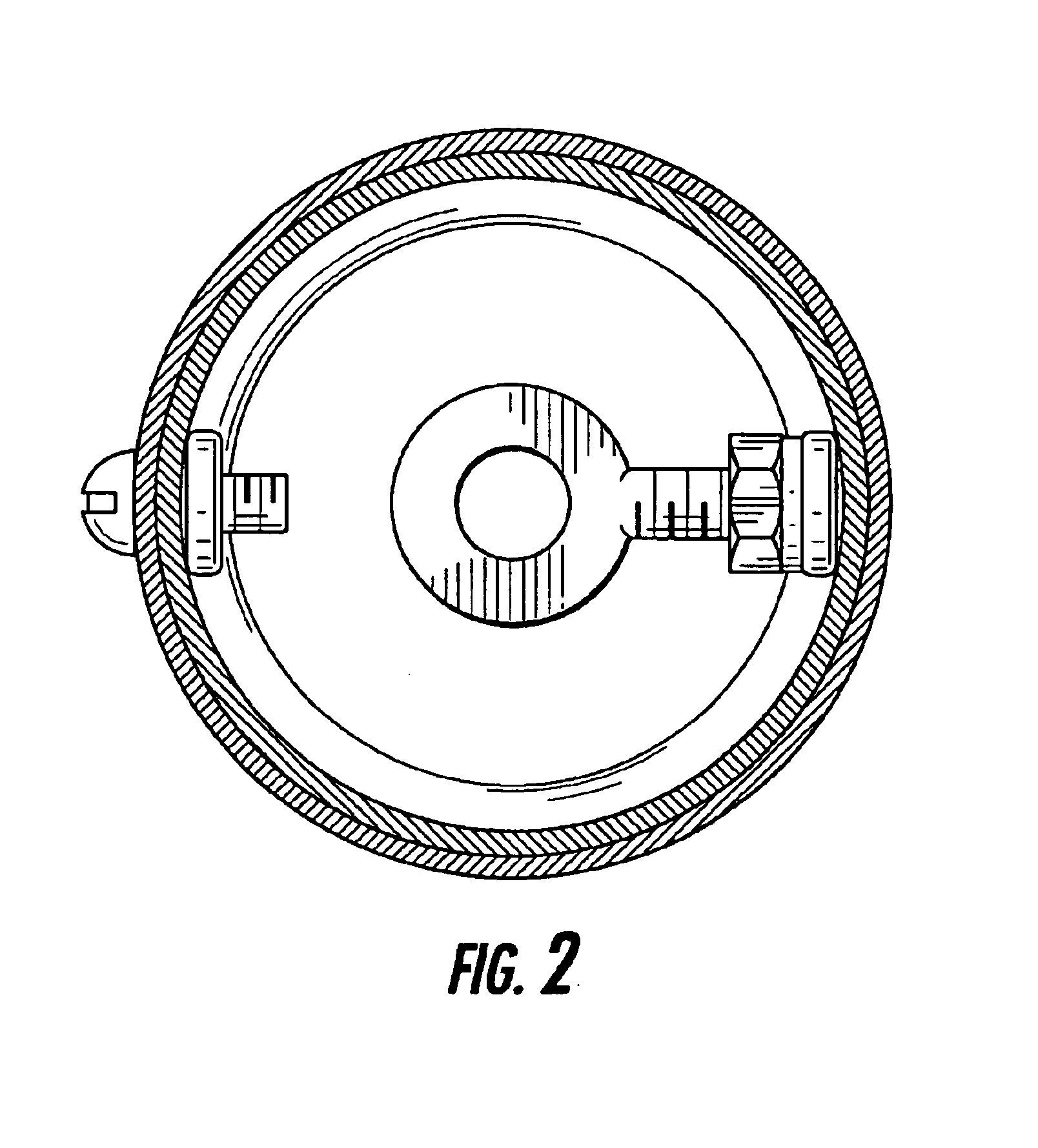
Motorcycle exhaust enhancers
InactiveUS6848252B2Increase powerImprove responseSilencing apparatusCombustion enginesIntermediate frequencyEngineering
Sound and power are an important part of the motorcycling experience. From the early days people have been attempting to get it “right” and have tried numerous ways to achieve the best of both worlds. Generally one had to be sacrificed to some degree to get the other. Tuning the exhaust rather than tuning the carburetor or increasing cubic inches is a less expensive and more efficient way to get both the sound and midrange power that motorcyclists are looking for. With the Exhaust Enhancement exhaust pipes can be tuned for sound and increased midrange power very simply and easily by installing them in the exit end of an aftermarket straight type pipe using various combinations to achieve a desired sound and not sacrifice power.
Owner:MAYBECK JAMES CHARLES
Wearable Implantable Medical Device Controller
A miniaturized controller includes communication and control circuitry for monitoring and controlling an implantable medical device (IMD). The miniaturized controller includes a display that allows it to essentially mimic the IMD control functionality of a traditional IMD controller. The size of the miniaturized controller, which may be approximately 1.1 cubic inches, enables it to be carried discreetly by a patient during the patient's daily activities. While the miniaturized controller functions as a standalone IMD controller in a first mode of operation, it is also wearable by the patient to function as a smartwatch, for example, in a second mode of operation. In the second mode of operation, the miniaturized controller, which may include sensors for measuring physiological parameters of the patient as well as patient motion when worn by the patient, is capable of providing closed-loop control of the IMD.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method and apparatus for retarding fire
A barrier for retarding fire comprises water-permeable fabric for covering a substantial area, the fabric being porous, hydrophilic and flammable, and having at least 9 pockets per square foot, each pocket having a volumetric capacity of between about 0.03 cubic inches and about 17 cubic inches, wherein substantially all of the pockets contain between about 0.01 and about 2 grams of superabsorbent polymer per cubic inch of volumetric capacity of the pockets.
Owner:MILLER JOHN C +1
Comb-shaped power bus bar assembly structure having integrated capacitors
ActiveUS20090080158A1So as not to breakElectrically conductive connectionsDigital data processing detailsSurface mountingEngineering
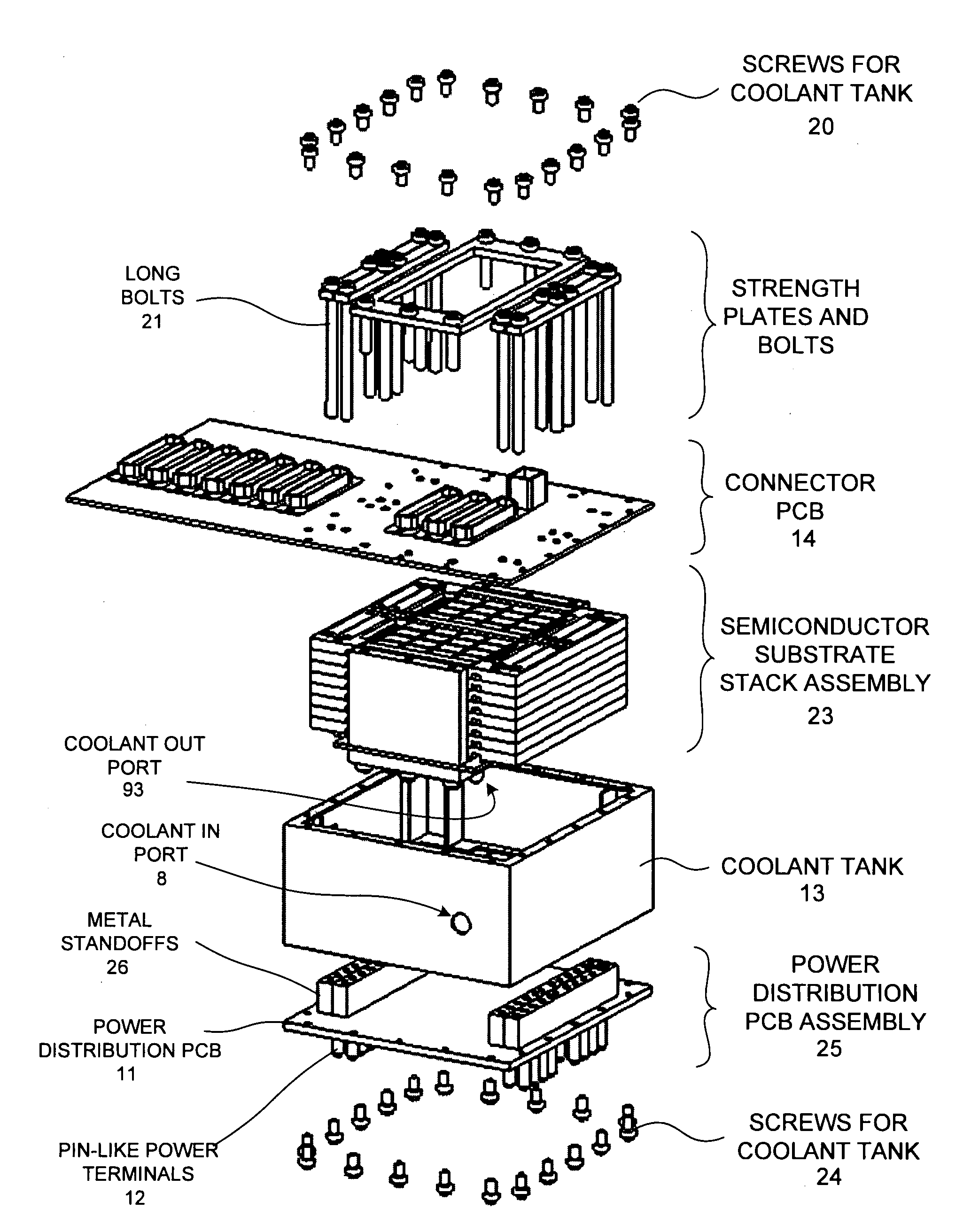
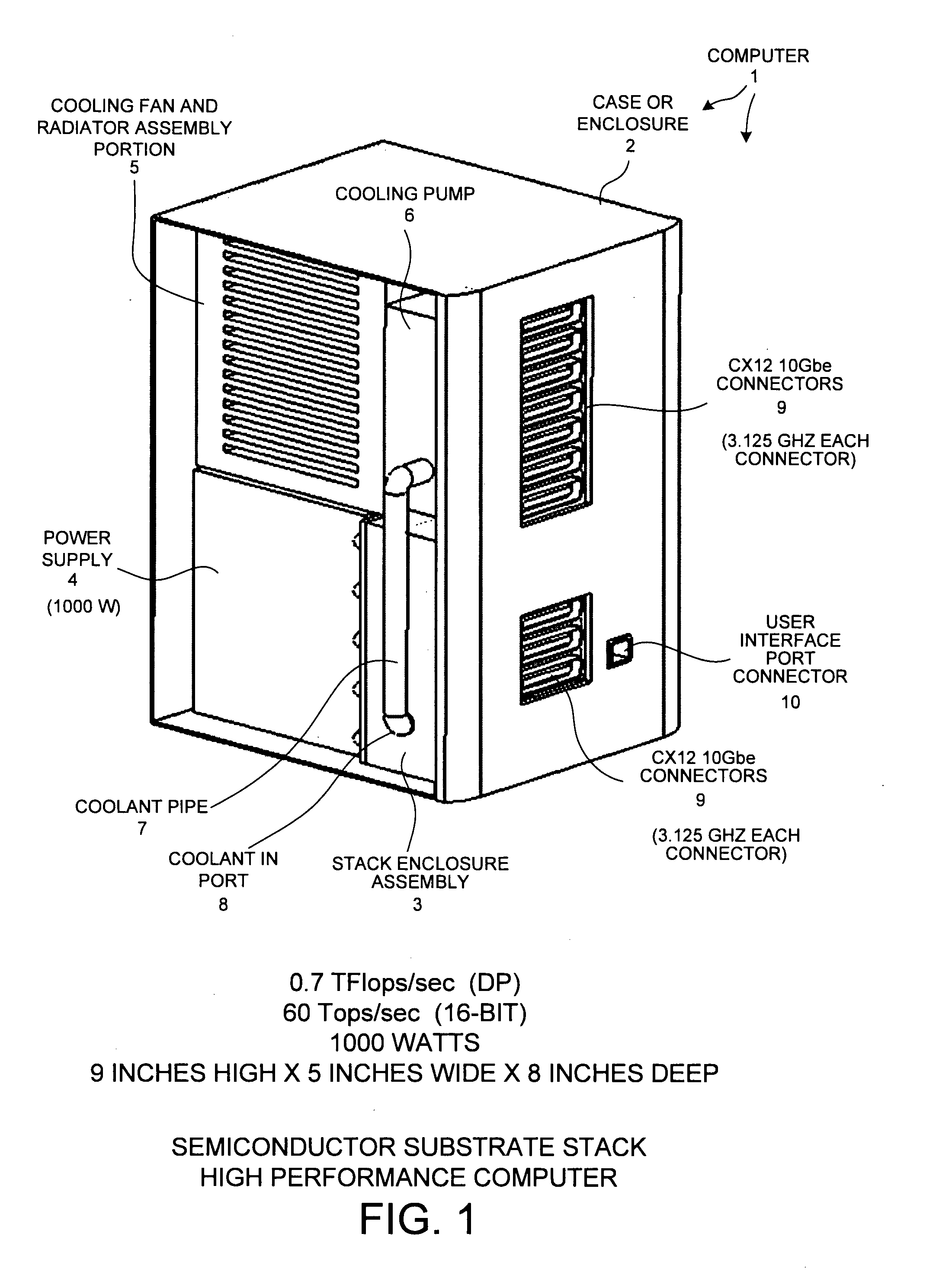
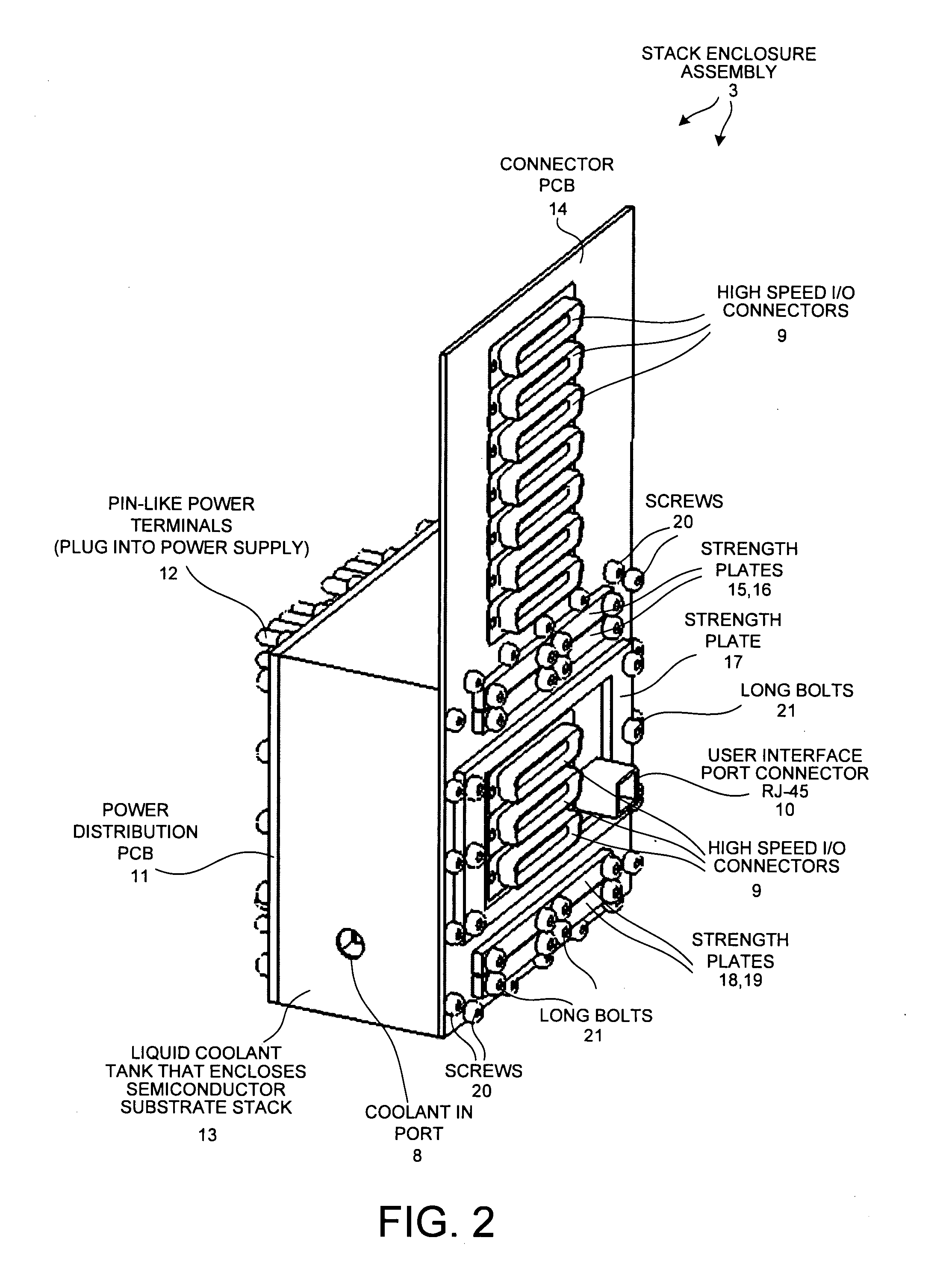
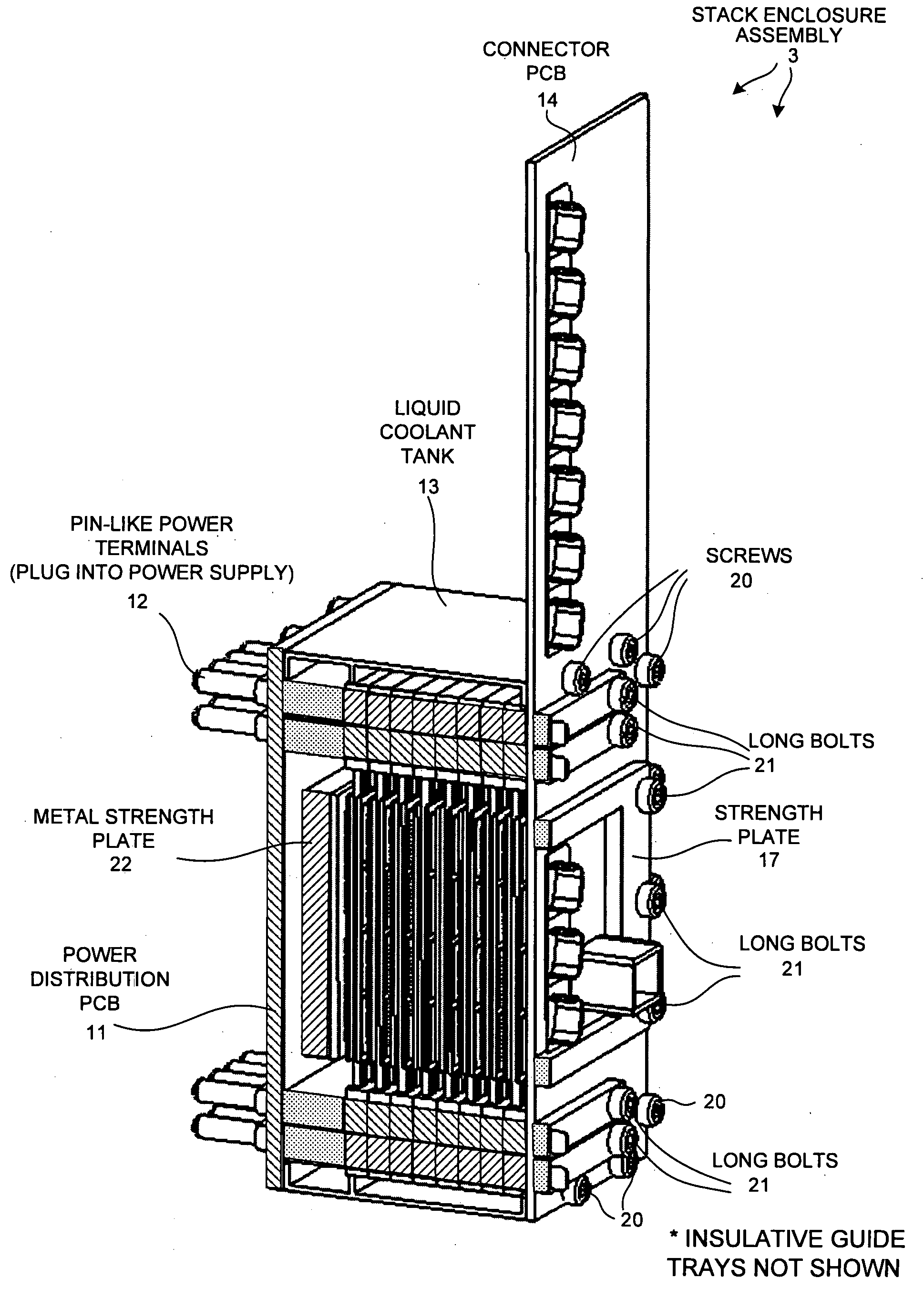
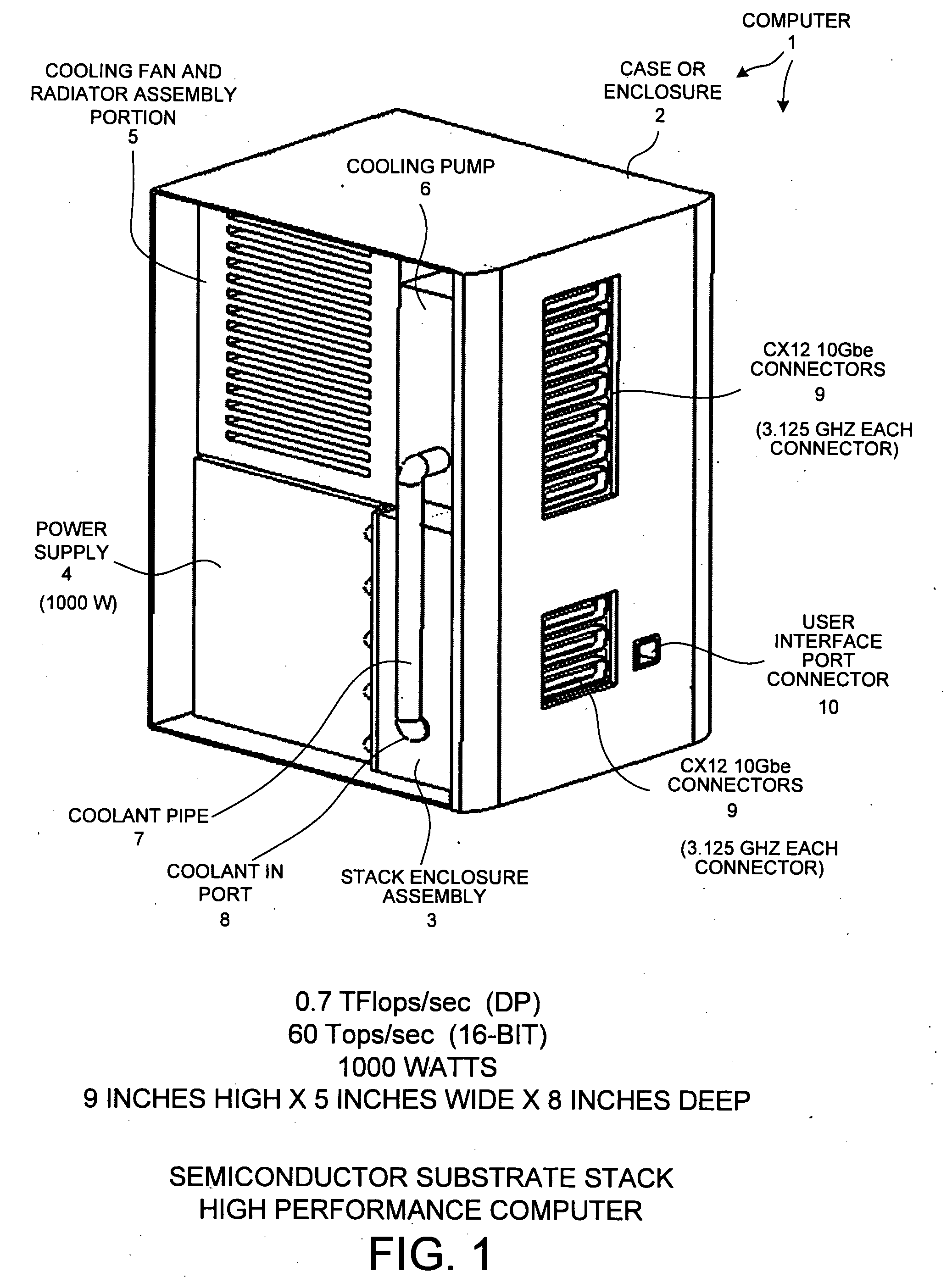
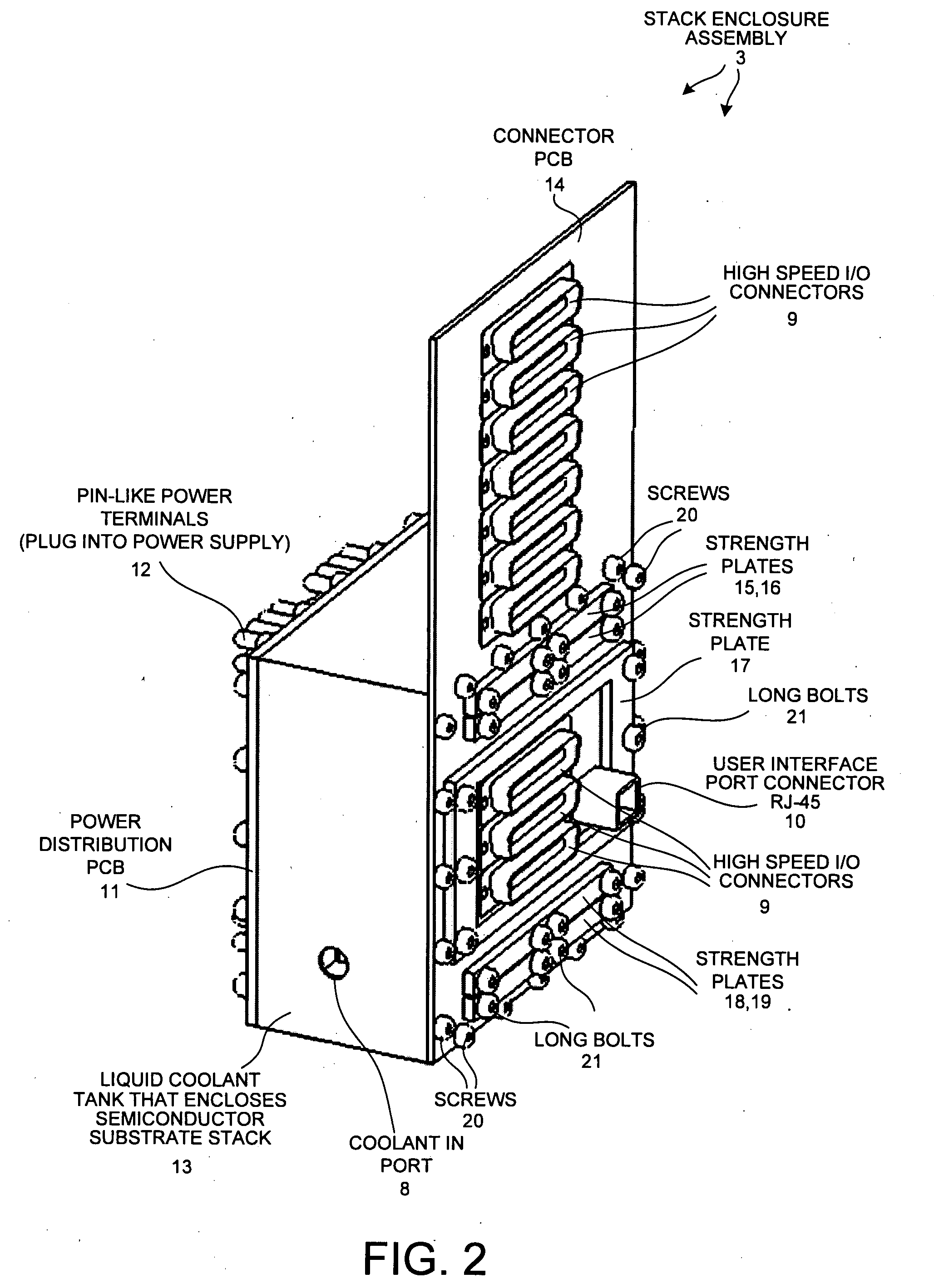
A reconfigurable high performance computer occupies less than 360 cubic inches and has an approximate compute power of 0.7 teraflops per second while consuming less than 1000 watts. The computer includes a novel stack of semiconductor substrate assemblies. Some semiconductor substrate assemblies involve field programmable gate array (FPGA) dice that are directly surface mounted, as bare die, to a semiconductor substrate. Other semiconductor substrate assemblies of the stack involve bare memory integrated circuit dice that are directly surface mounted to a semiconductor substrate. Elastomeric connectors interconnect adjacent semiconductor substrates proceeding down the stack. Tines of novel comb-shaped power bus bar assembly structures extend into the stack to supply DC supply voltages. The supply voltages are supplied from bus bars, through vias in the semiconductor substrates, and to the integrated circuits on the other side of the substrates. The power bus bars also serve as capacitors and guides for liquid coolant.
Owner:MICROSS ADVANCED INTERCONNECT TECH LLC
Pre-packaged, flexible container of ice and air
InactiveUS7900471B2Facilitate easy openingImprove distributionDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusMechanical engineeringCubic inch
Owner:S I INC DBA SERV ICE
Sterilizing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20180221803A1Dispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingCubic inchInstrument tray
A sterilization container for retaining surgical instruments in a sterilizer comprising a plurality of walls defining an interior volume sized to receive at least one instrument tray, least one of the walls defining a venting pass through area, and a filter occluding the venting passage area, wherein a ratio of the venting pass through area to the interior volume is at least 1 square inch:125 cubic inches.
Owner:TURBETT SURGICAL
Automatic transfer switch for power busways
ActiveCN106662904ACompact switchIncrease flexibilityVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingTransfer switchComputer module
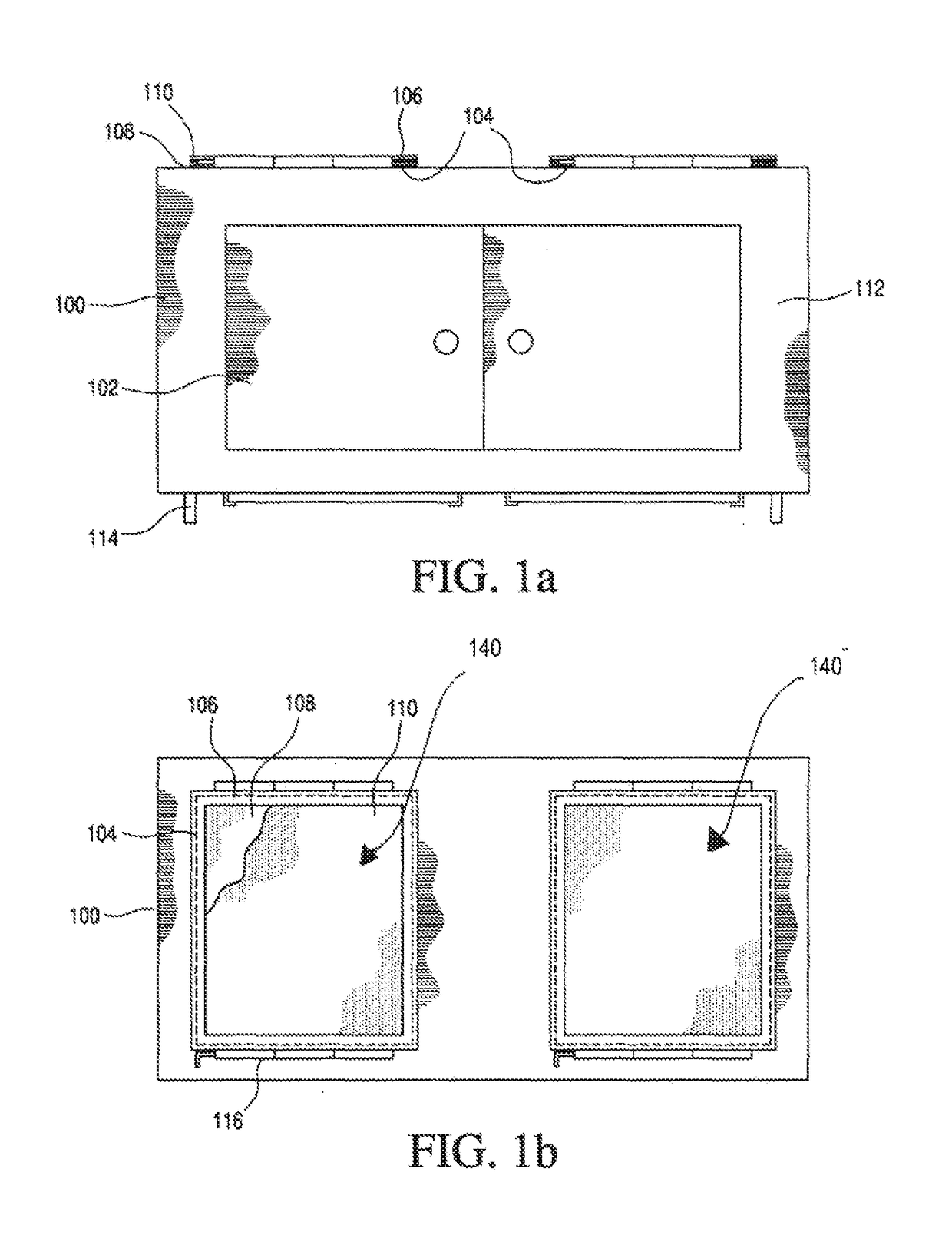
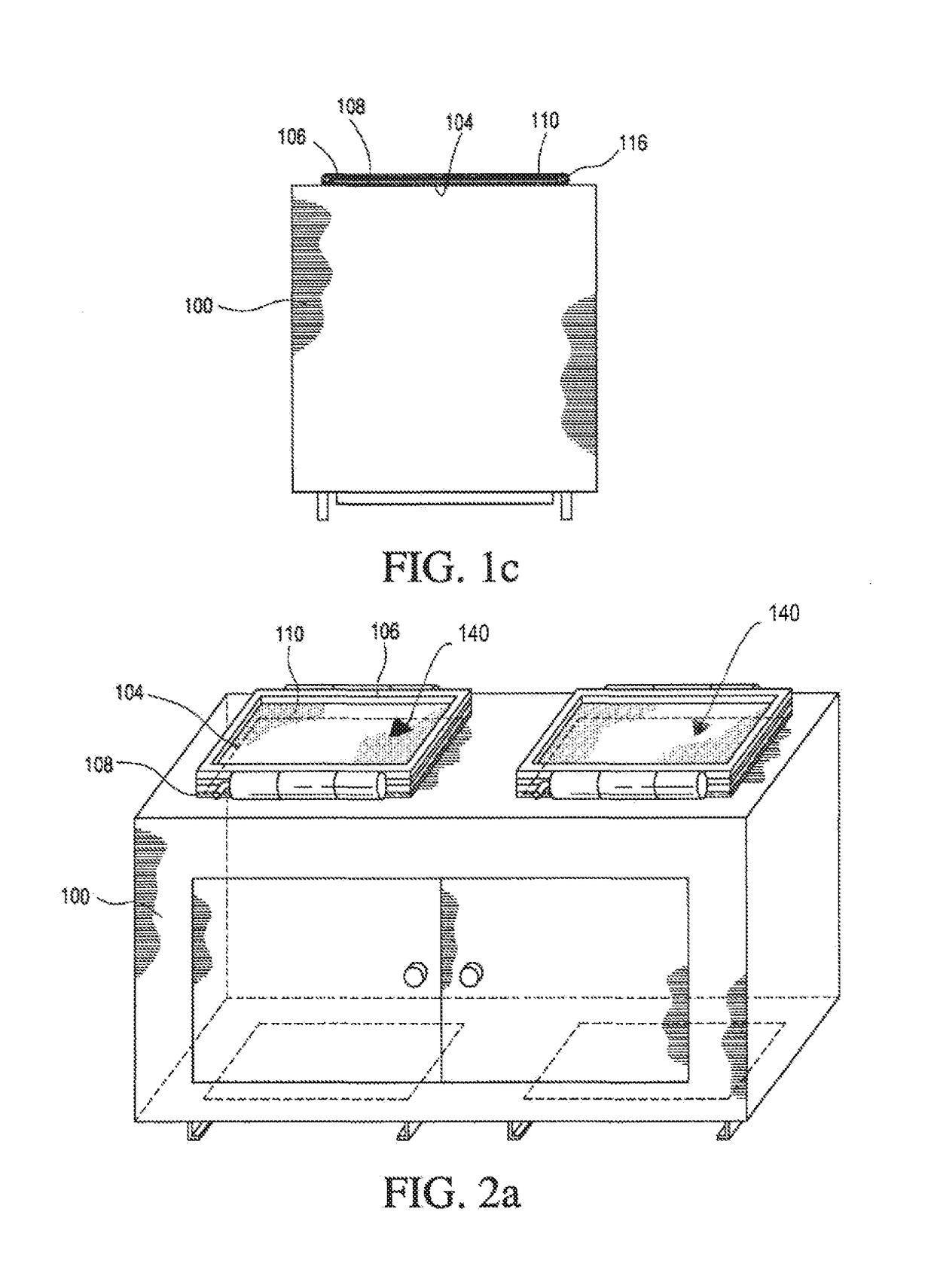
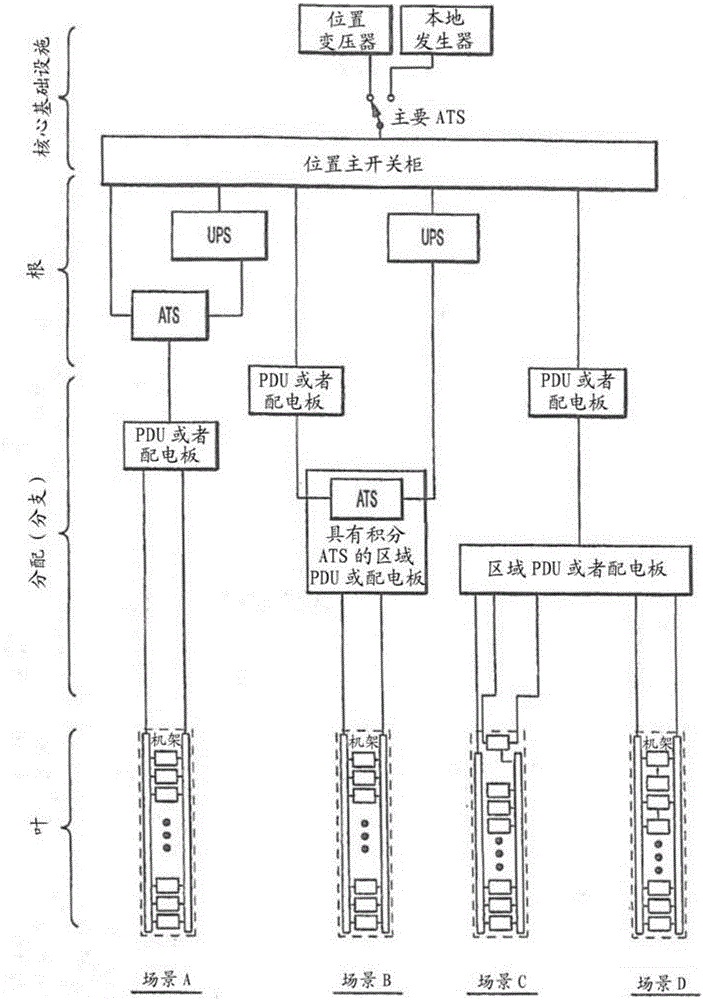
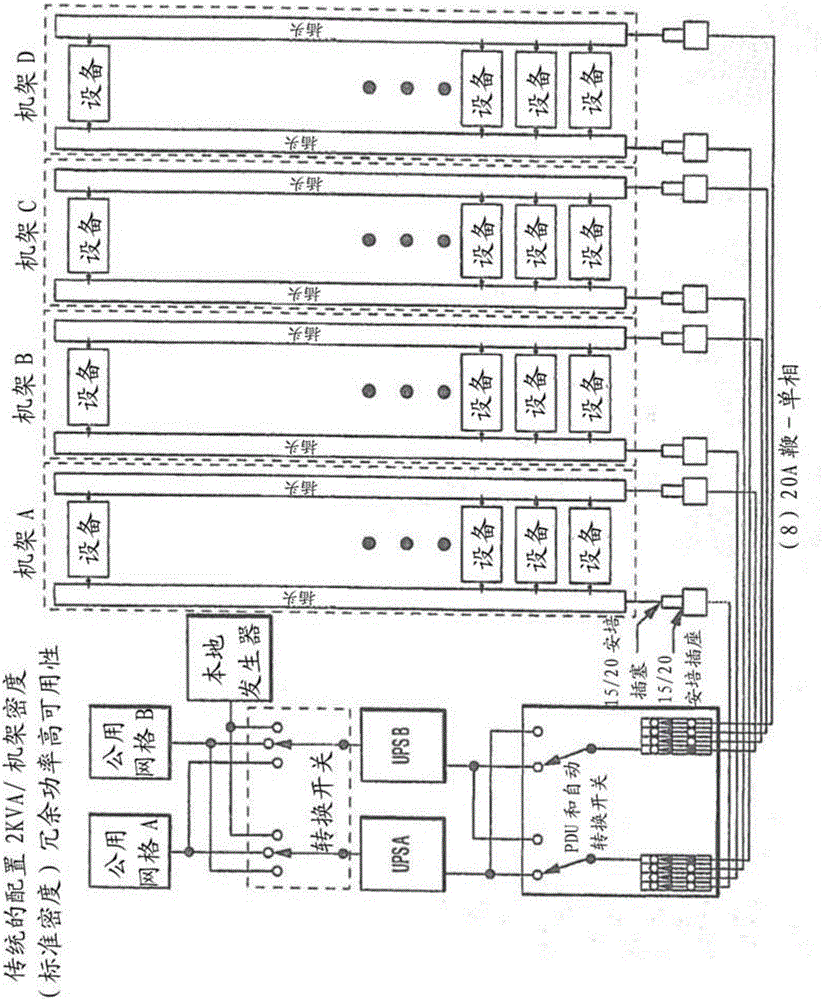
Systems and methods are provided for reliable redundant power distribution. Some embodiments include micro automatic transfer switches (micro-ATSs), including various components and techniques for facilitating reliable auto-switching functionality in a small footprint (e.g., less than ten cubic inches, with at least one dimension being less than a standard NEMA rack height). Other embodiments include systems and techniques for integrating a number of micro-ATSs into a parallel auto-switching module for redundant power delivery to a number of devices. Implementations of the parallel auto-switching module are configured to be mounted in, on top of, or on the side of standard equipment racks. Still other embodiments provide power distribution topologies that exploit functionality of the micro-ATSs and / or the parallel micro-ATS modules.
Owner:ZONIT STRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
Semiconductor substrate elastomeric stack
ActiveUS20090079058A1So as not to breakAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElastomerSurface mounting
A reconfigurable high performance computer occupies less than 360 cubic inches and has an approximate compute power of 0.7 teraflops per second while consuming less than 1000 watts. The computer includes a novel stack of semiconductor substrate assemblies. Some semiconductor substrate assemblies involve field programmable gate array (FPGA) dice that are directly surface mounted, as bare die, to a semiconductor substrate. Other semiconductor substrate assemblies of the stack involve bare memory integrated circuit dice that are directly surface mounted to a semiconductor substrate. Elastomeric connectors interconnect adjacent semiconductor substrates proceeding down the stack. Tines of novel comb-shaped power bus bar assembly structures extend into the stack to supply DC supply voltages. The supply voltages are supplied from bus bars, through vias in the semiconductor substrates, and to the integrated circuits on the other side of the substrates. The power bus bars also serve as capacitors and guides for liquid coolant.
Owner:MICROSS ADVANCED INTERCONNECT TECH LLC
Metal hydride based vehicular exhaust cooler
InactiveUS20050274492A1Desorption can be effectedAir-treating devicesHeat storage plantsDesorptionEngineering
A metal hydride heat pump comprising a first compartment, including a first fluid inlet and a first fluid outlet, wherein the first fluid inlet is configured for fluid communication with the first fluid outlet; a second compartment, including a second fluid inlet and a second fluid outlet, wherein the first fluid inlet is configured for fluid communication with the second fluid outlet; and a plurality of metal hydride vessels, each of the vessels being mounted to and disposed within each of the first and second compartments, and each of the vessels containing at least a hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, a hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material, and gaseous hydrogen, wherein the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material is in fluid communication with the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, such that heat can be transferred from (a) fluid flowing through the first compartment to (b) the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, so as to effect desorption of hydrogen from the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, and such that the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material is configured to absorb the desorbed hydrogen and generate heat upon the absorption such that the generated heat can be transferred to fluid flowing through the second compartment; wherein each of the vessels has an external surface area, and defines an internal volume for containing at least the hydrided form of a low temperature metal hydride material, the hydridable form of a high temperature metal hydride material, and gaseous hydrogen, wherein a ratio of the external surface area to the internal volume is greater than 45 in2 per cubic inch.
Owner:HERA USA
Hybrid all-terrain, four-wheel drive vehicle with two cylinder engine
ActiveUS9545838B1Large loading capacityIncrease powerBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesTerrainTransfer case
A v-twin motorcycle engine, 100 to 140 cubic inches (1600 cc to 2300 cc) is mounted longitudinally in a tubular chassis behind dual seats. A chain drive is mounted to the crankshaft that further drives a clutch device. A transmission / transfer unit is mounted in front of and below the engine and receives a clutch output shaft. The transfer case has two output drive shafts, one to a front differential and the other to a rear differential located under the engine. The differentials each have two shafts that drive the four wheels. The wheels have disk brakes and typical independent suspension for driven wheels of such types of vehicles. The present invention provides an off road, sports utility vehicle having the power between an ATV and a 4 cylinder (VW) engine. Further an adjustable engine mount allows for the selection of different engines.
Owner:HILL DAVID
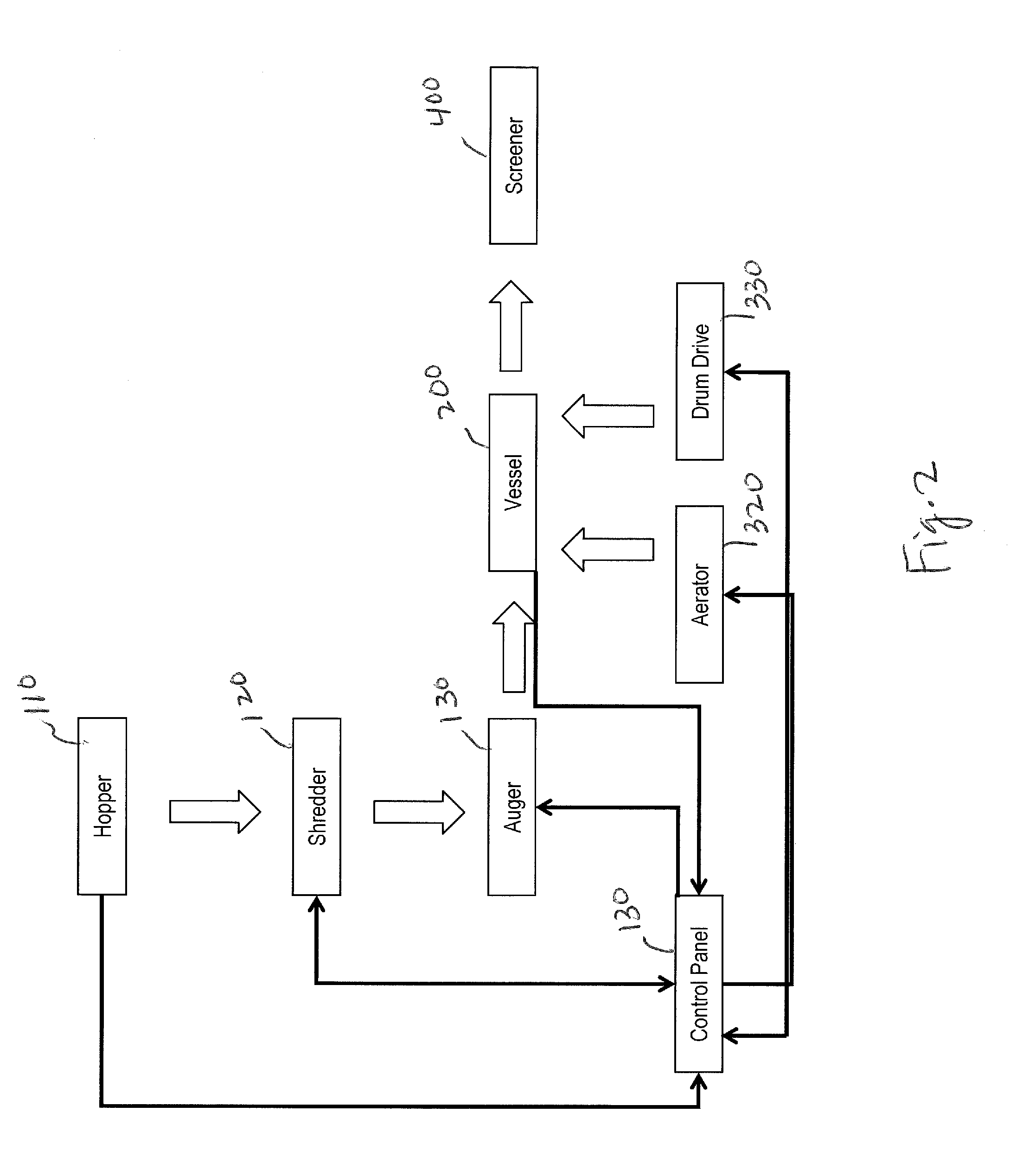
Composting machine
ActiveUS20120196357A1Reduce in quantityPromote digestionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingNutrientProcess control
An apparatus for the in-vessel composting of feedstock into nutrient-rich compost comprising means for shredding said input material, said means configured and powered for shredding said feedstock into a particle size no larger than one cubic inch, a vessel having an input port on top of such vessel and a discharge port, said vessel comprising one chamber, said vessel configured and powered composting said shredded feedstock, and said vessel tilted from the input port to the discharge port, means for passing said feedstock from said means for shredding into said vessel, means for rotating said vessel, means for introducing air into said vessel and a process controller, said process controller communicating with said means for shredding, said vessel, said means for rotating said vessel and said means for introducing air into said vessel.
Owner:FOR SOLUTIONS IP
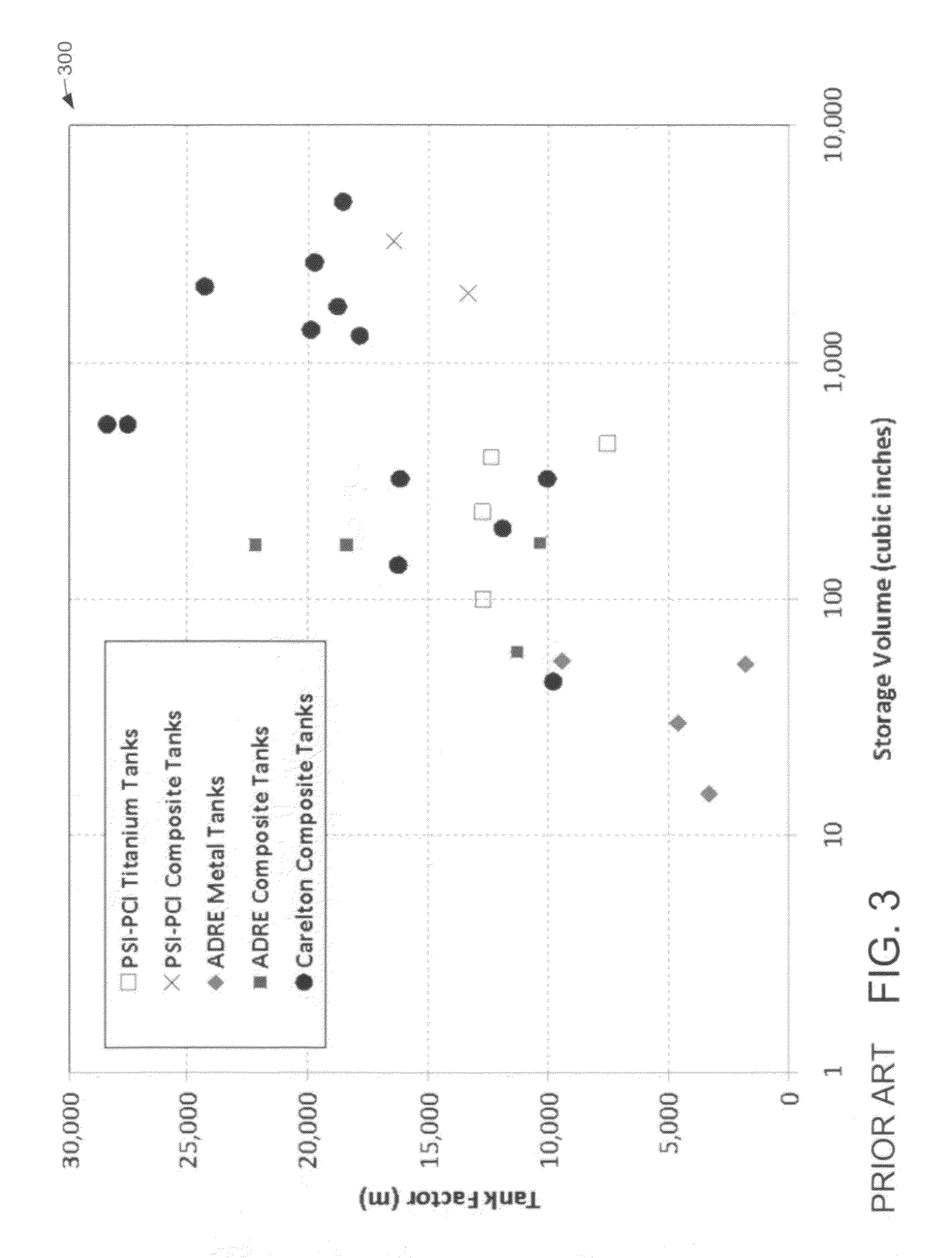
Small-scale metal tanks for high pressure storage of fluids
ActiveUS20130098918A1Simple structureThe overall structure is light in weightLarge containersPressure vesselsMetal foilEngineering
Small scale metal tanks for high-pressure storage of fluids having tank factors of more than 5000 meters and volumes of ten cubic inches or less featuring arrays of interconnected internal chambers having at least inner walls thinner than gage limitations allow. The chambers may be arranged as multiple internal independent vessels. Walls of chambers that are also portions of external tank walls may be arcuate on the internal and / or external surfaces, including domed. The tanks may be shaped adaptively and / or conformally to an application, including, for example, having one or more flat outer walls and / or having an annular shape. The tanks may have dual-purpose inlet / outlet conduits of may have separate inlet and outlet conduits. The tanks are made by fusion bonding etched metal foil layers patterned from slices of a CAD model of the tank. The fusion bonded foil stack may be further machined.
Owner:VENTIONS LLC
Scalable mass data storage device
ActiveUS8397011B2Improve data transfer rateHigh bulk densityEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData centerVolumetric density
A scalable data storage device which includes non-volatile memory uses a networked bus system which can be employed on a single memory storage chip level or in a multi-chip package (MCP). The scalable data storage device uses data routing modules which are adapted to store incoming data and send outgoing data thereby providing decoupling of the networked buses. This arrangement enables significantly higher data transfer rates, surpassing DRAM SSDs at a fraction of the size and cost, provides increased volumetric density (1 TB in less than 1 cubic inch), and permits concurrency of operations. The scalable data storage device can be engineered to have a rewrite capability of over 500 times that of Flash RAM and can scale down to 8 bits and up to exabytes, yottabytes and beyond. The scalable data storage device may be used in a wide range of applications from large data centers to small consumer electronic products.
Owner:STACKSPEED INC +1
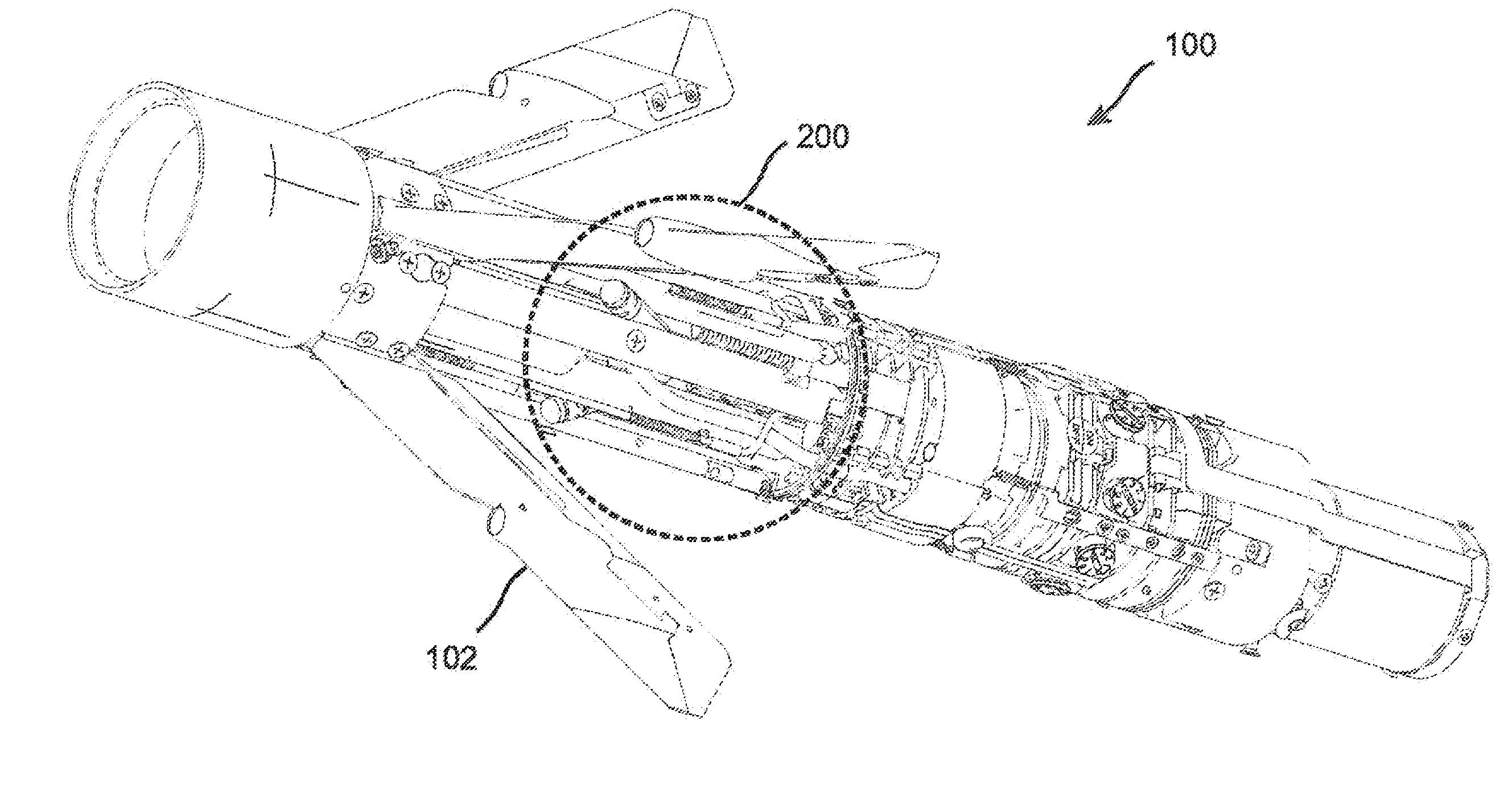
Torsion spring wing deployment initiator
ActiveUS20120119014A1Light weightLimited spaceDirection controllersSelf-propelled projectilesCentrifugal forceRocket
A compact, purely mechanical wing deployment assisting mechanism uses torsion springs and lever arms to apply a deploying force to a guidance wing during its initial deployment through a wing slot in a rocket or missile, thereby assisting the wing to burst through a cover seal protecting the wing slot. The wings are then fully deployed by centrifugal force. Various embodiments include two “extreme duty” springs and two lever arms per wing, working in parallel. Embodiments provide a total of at least 24 pounds of force per wing at the end of a spring travel of 0.30 inches. In some embodiments, the entire mechanism weighs less than 0.5 pounds and / or occupies less than 2.5 cubic inches per wing. In embodiments, an assembled group, including two springs and two lever arms, is located between each pair of wings, whereby each assembled group applies one lever arm to each adjoining wing.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
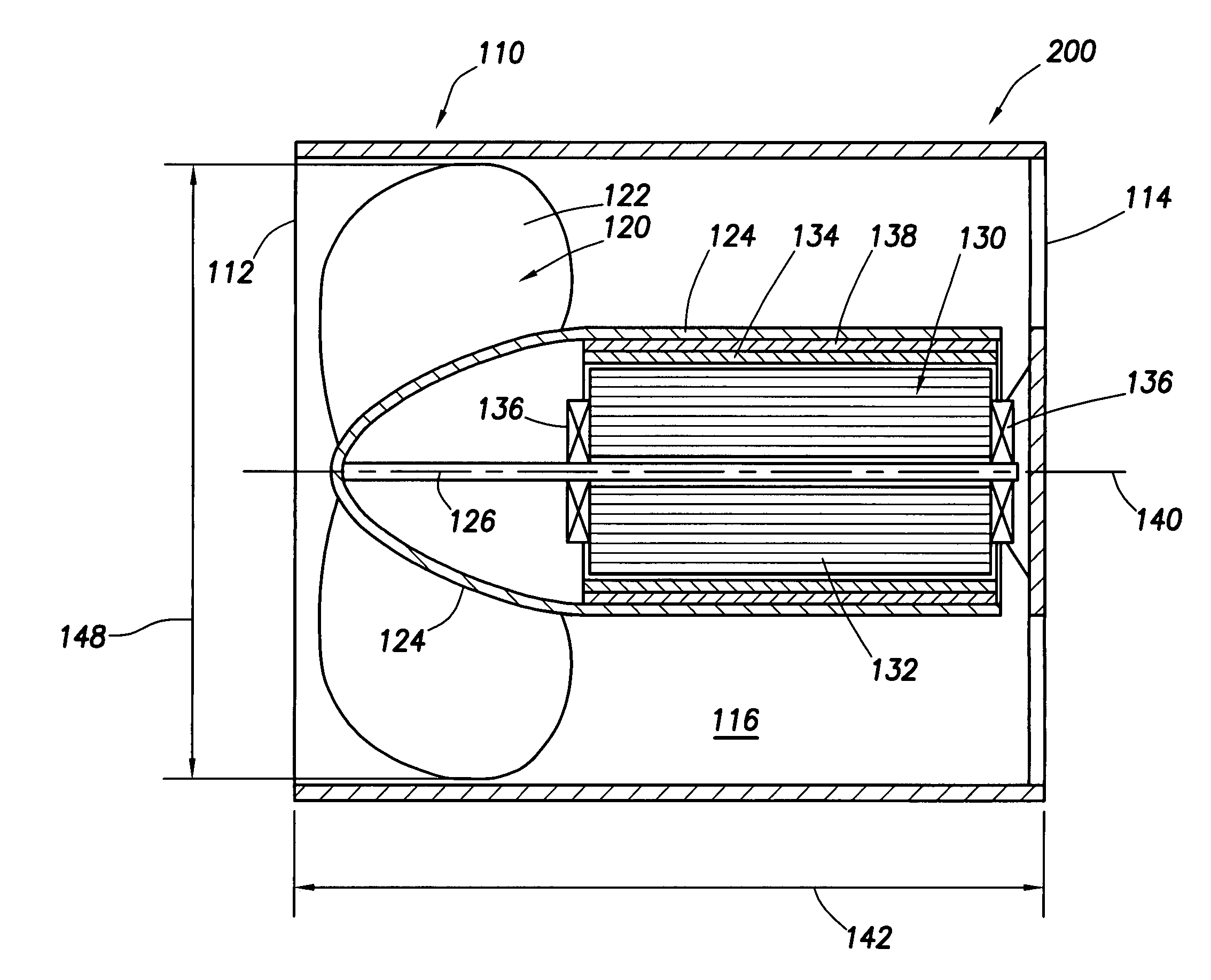
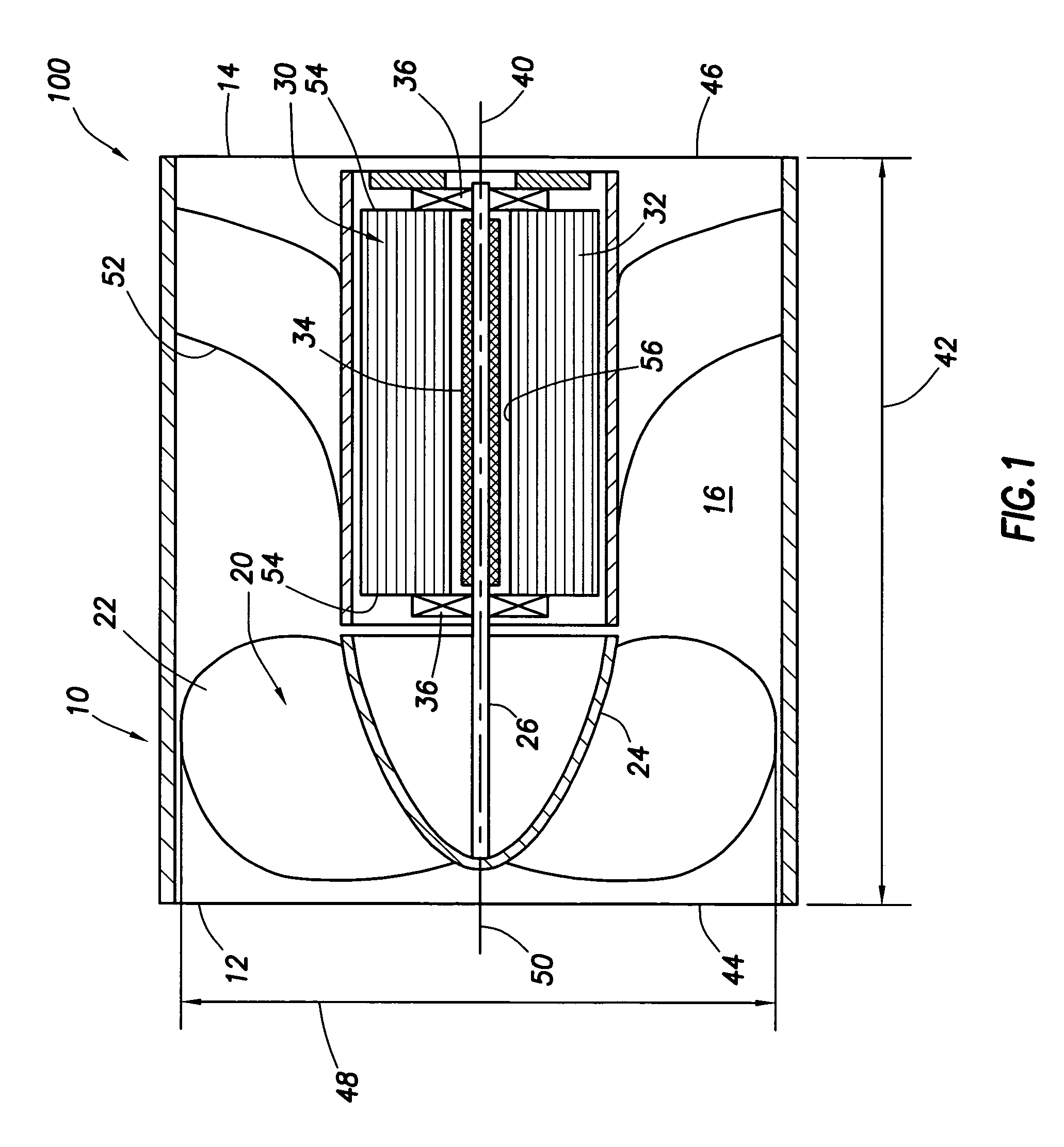
Axial duct cooling fan
A cooling fan comprising a housing that connects to a chassis that is operable to support an electronic component. An axial duct runs through the housing. A blade assembly is rotatably disposed within the duct and comprises a plurality of fan blades that extend radially from a hub to a fan diameter. The axial duct has a chord length at least equal to the fan diameter. A motor assembly is disposed within the axial duct and coupled to said blade assembly. The cooling fan provides a cooling capacity of at least 1.5 air horsepower per cubic inch volume of the cooling fan.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Flash-based data archive storage system
InactiveCN102460371ARandom access is fast and efficientEnergy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersMass storageSmall footprint
A flash-based data archive storage system having a large capacity storage array constructed from a plurality of dense flash devices is provided. The flash devices are illustratively multi-level cell (MLC) flash devices that are tightly packaged to provide a low-power, high-performance data archive system having substantially more capacity per cubic inch than more dense tape or disk drives. The flash-based data archive system may be adapted to employ conventional data de-duplication and compression methods to compactly store data. Furthermore, the flash-based archive system has a smaller footprint and consumes less power than the tape and / or disk archive system.
Owner:网络存储技术公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com