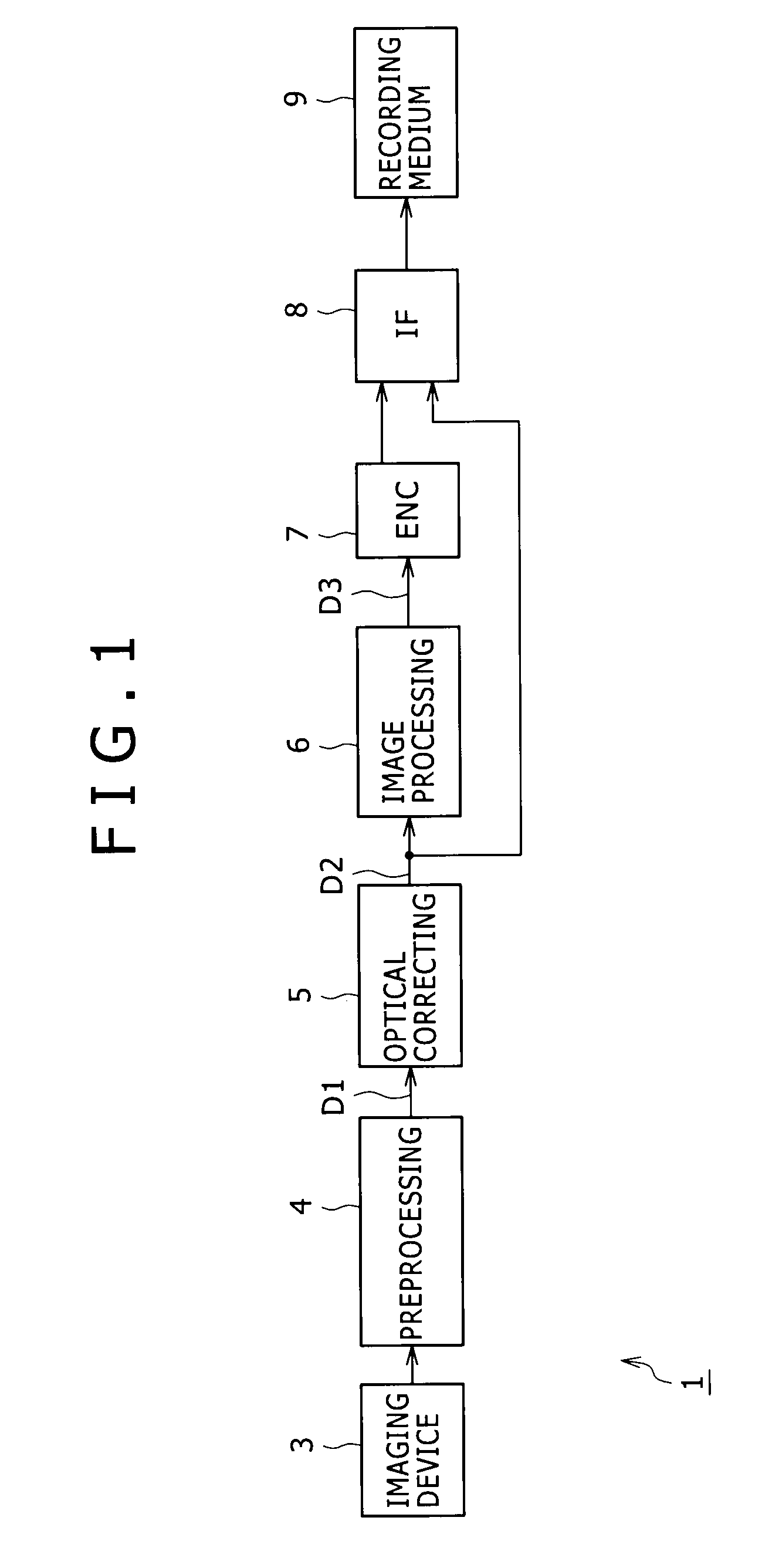
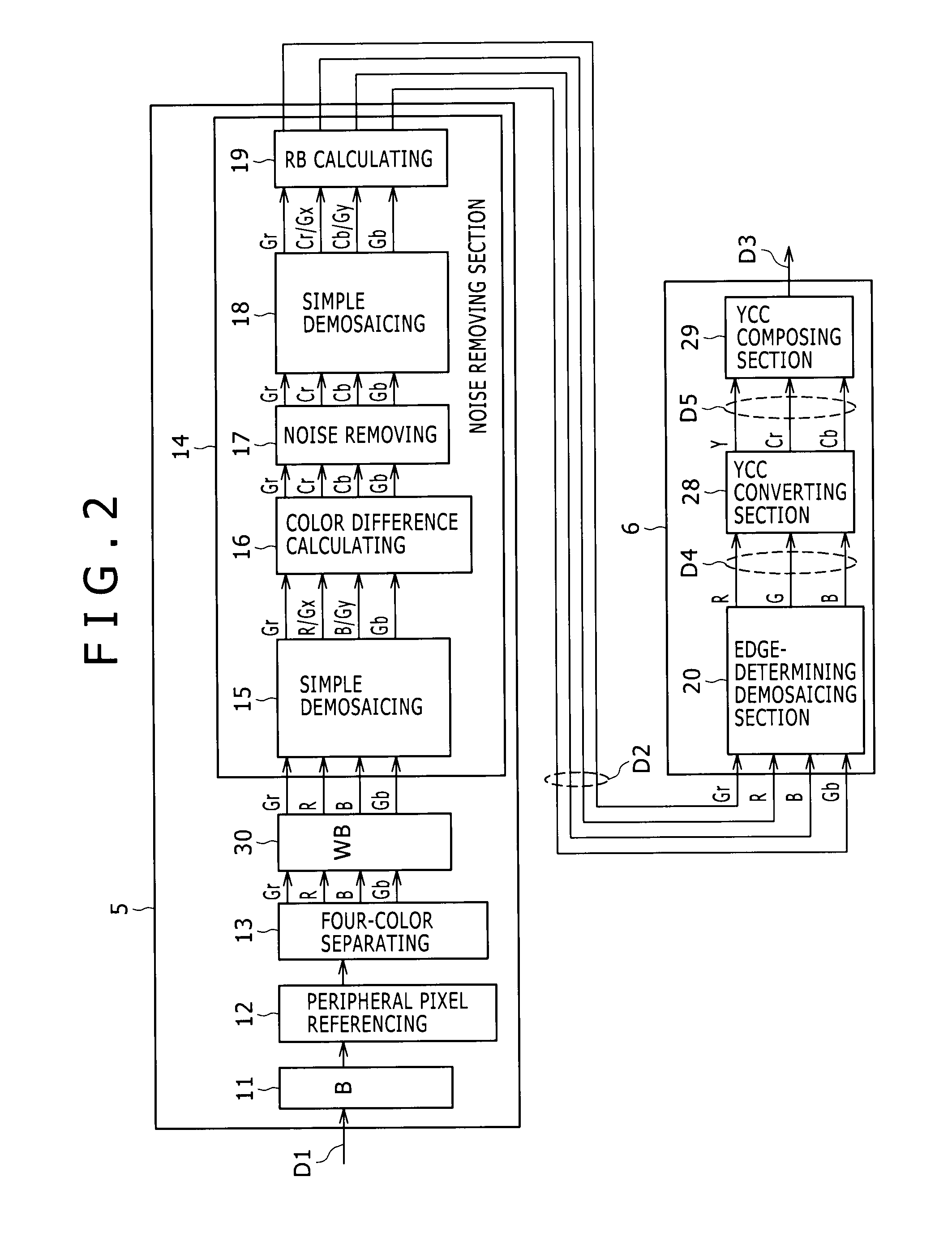
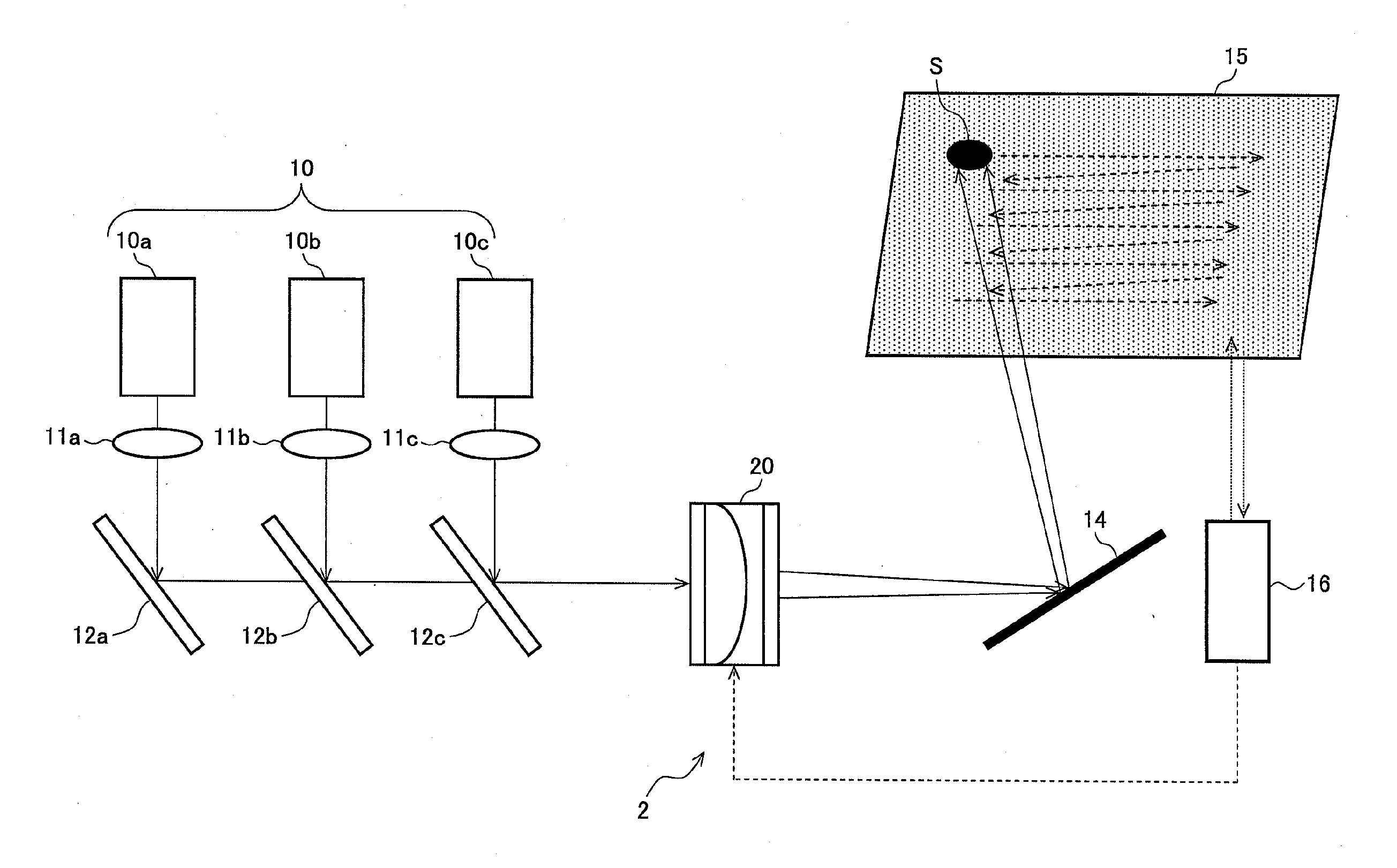
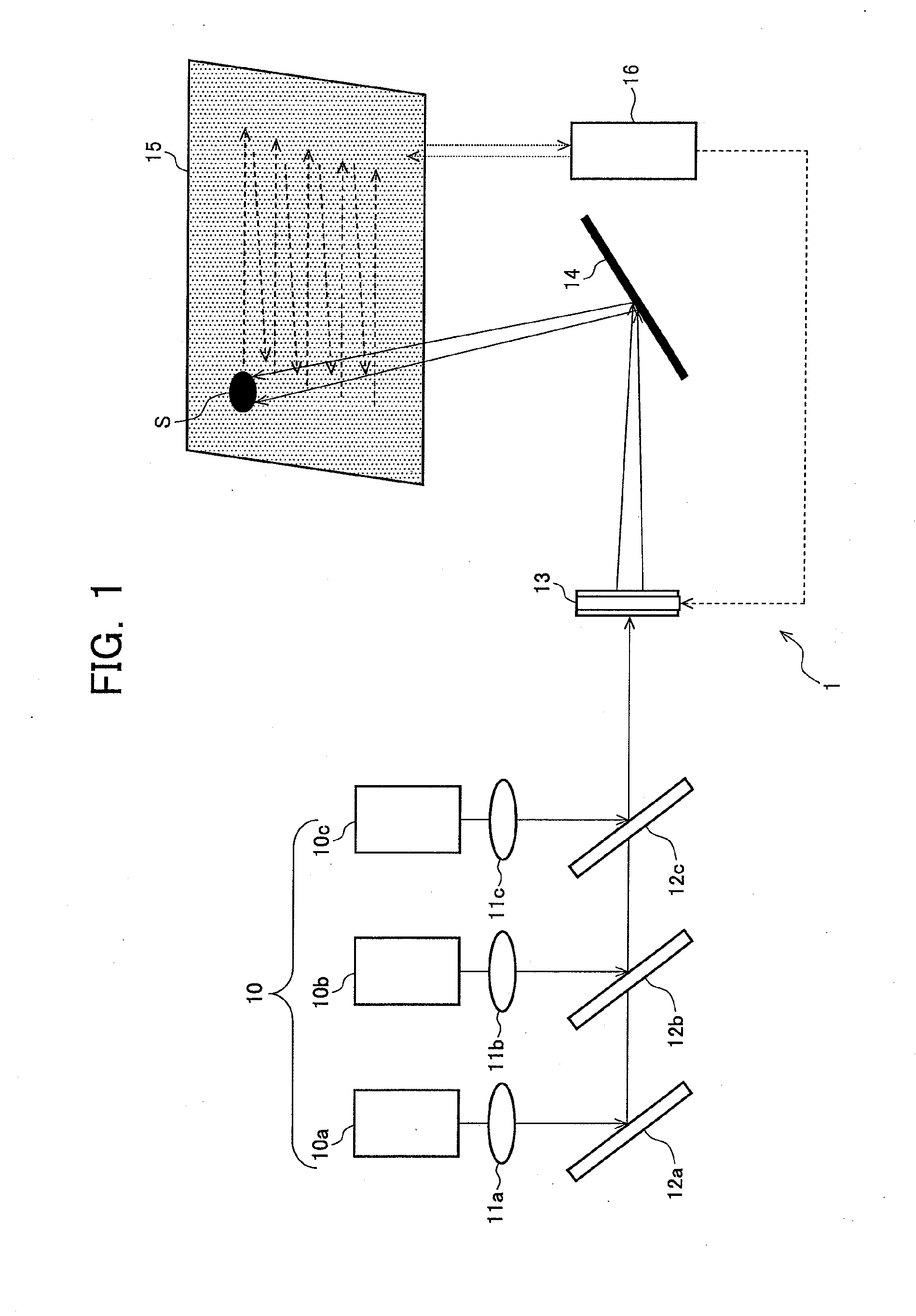
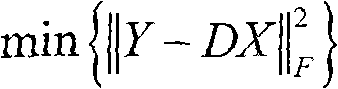Patents
Literature
412 results about "Image quality degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
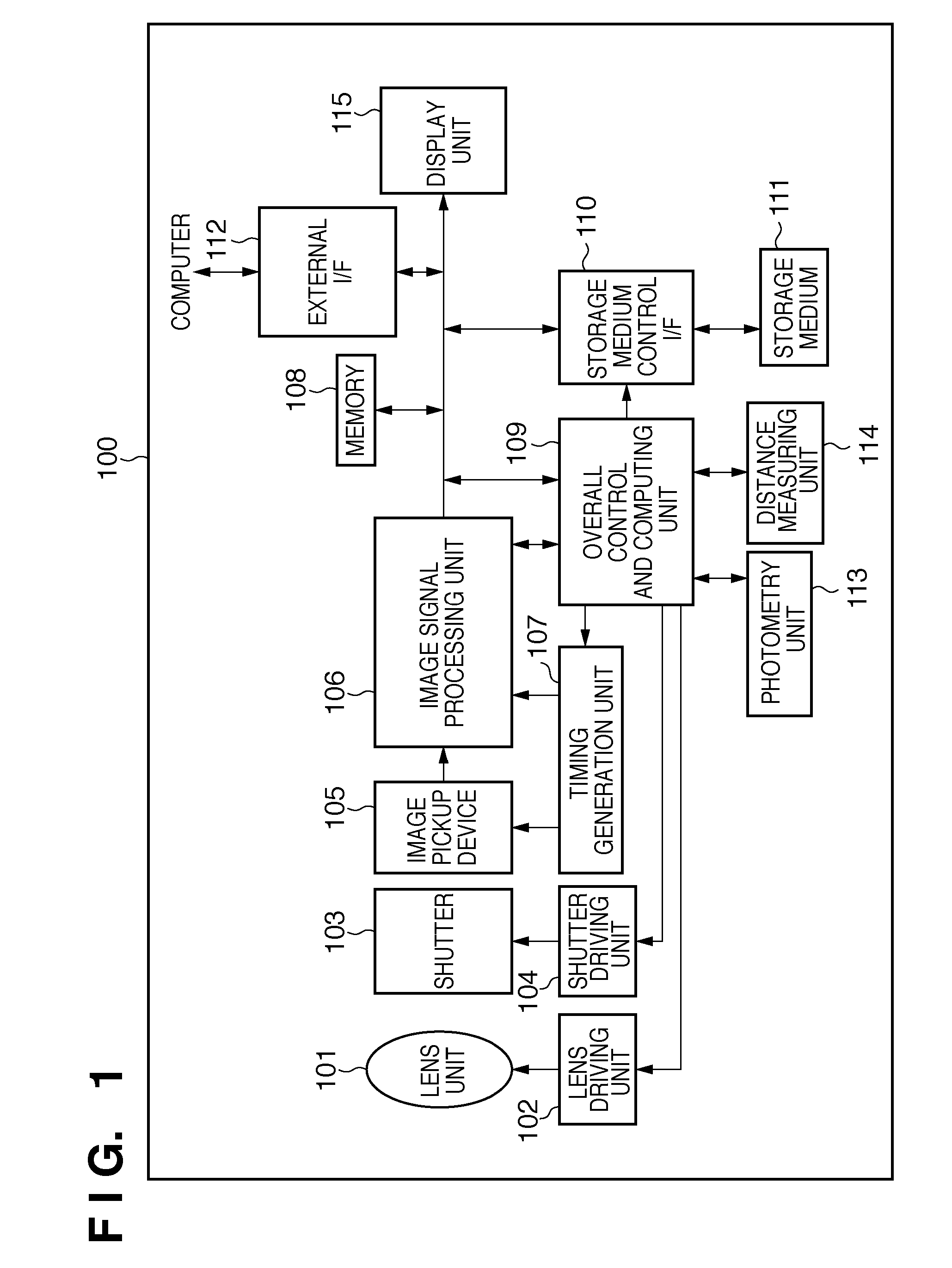
Liquid crystal display device
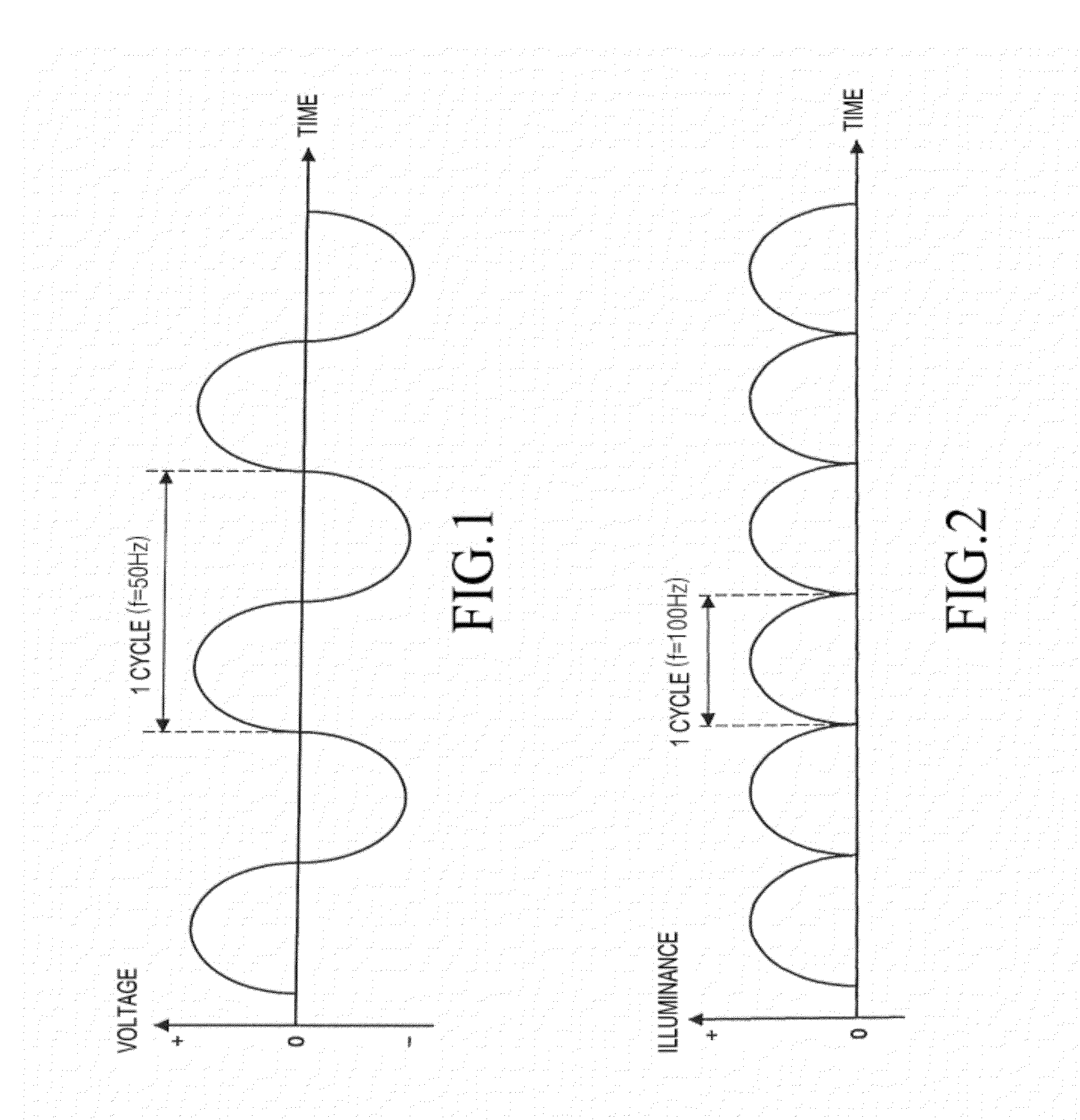
InactiveUS20050259064A1Avoid injuryImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
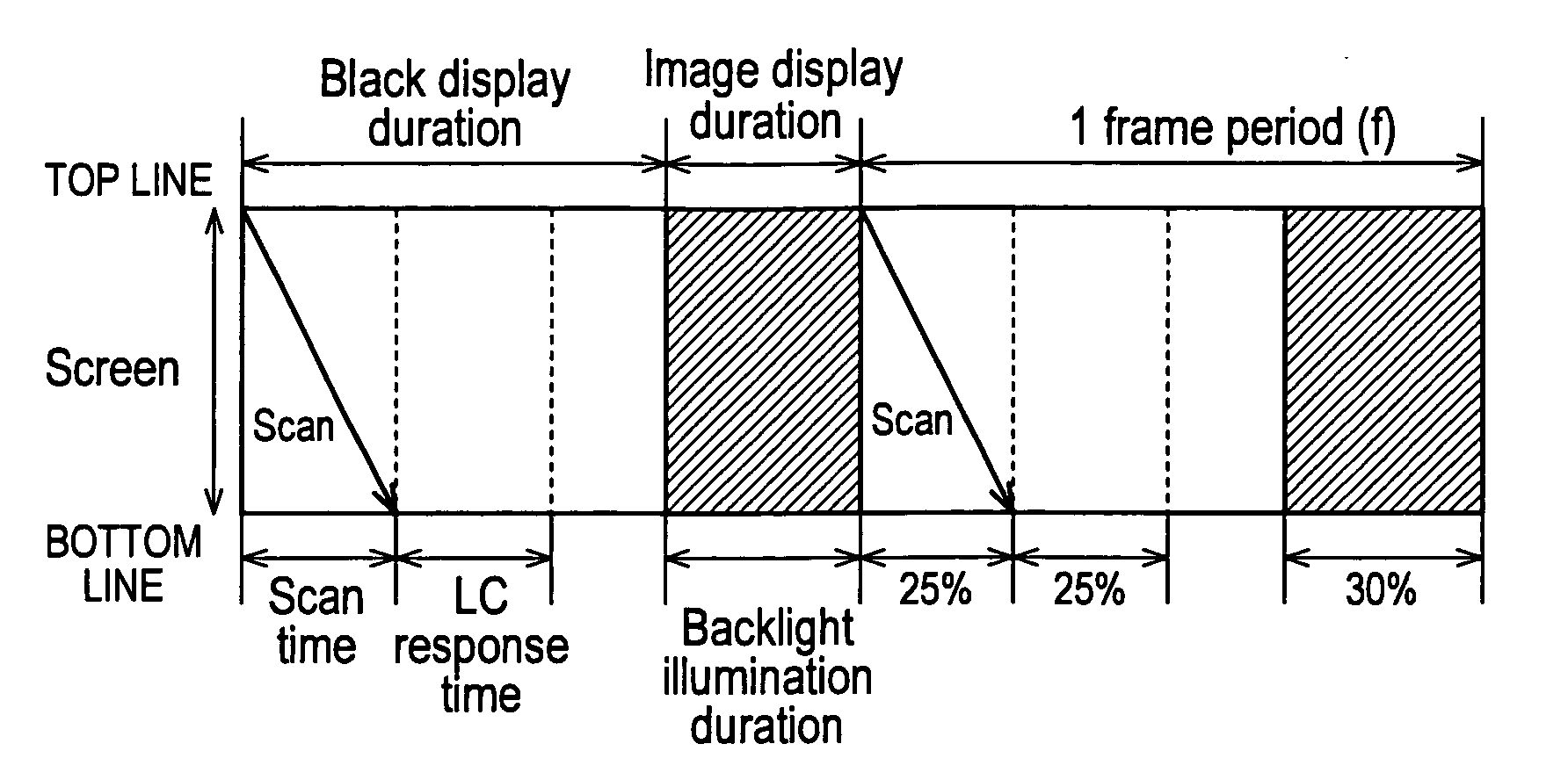
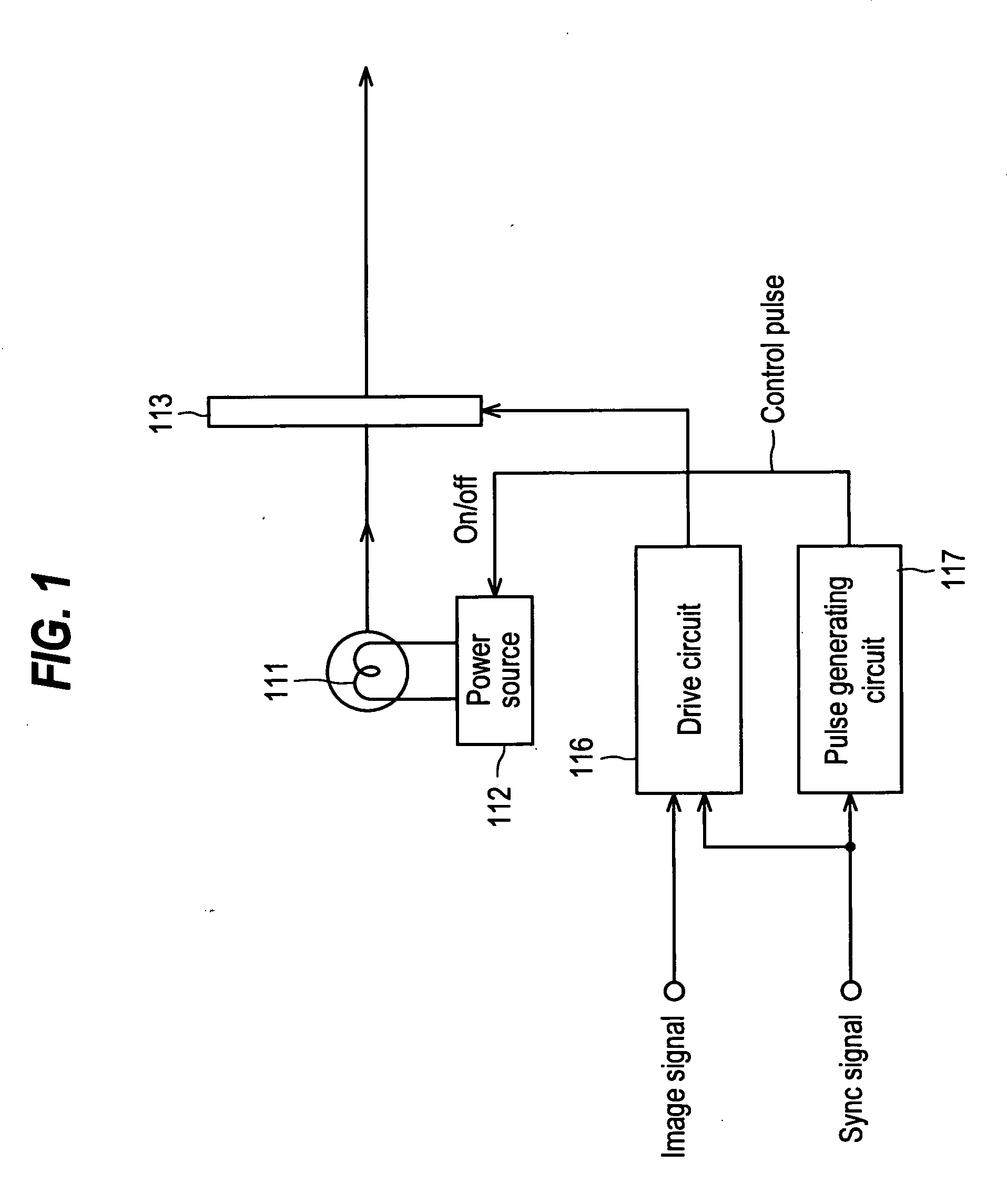
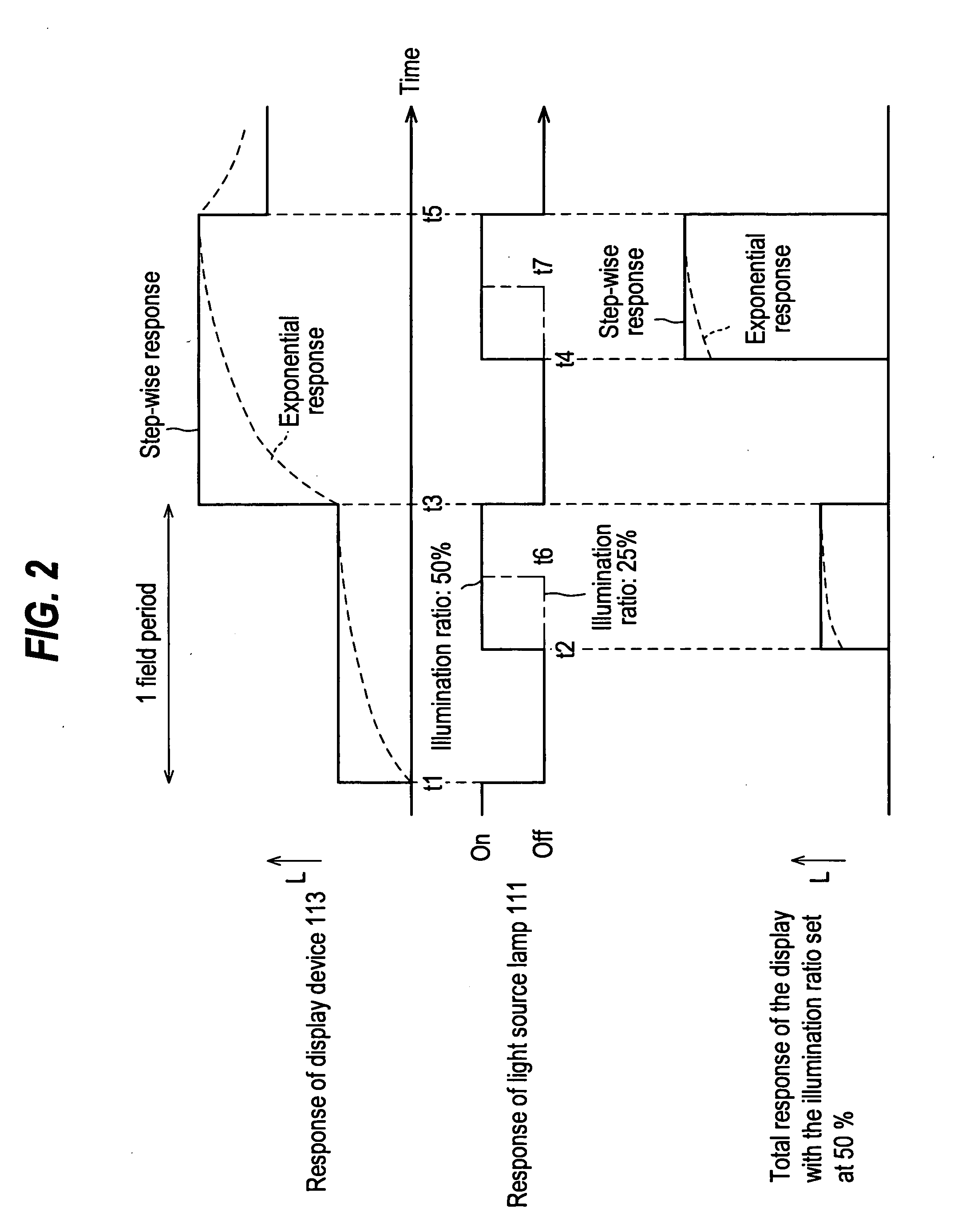
A liquid crystal display device in which a frame of the image signal to be displayed is written into a liquid crystal display panel while a backlight is activated intermittently within one frame period so as to prevent blur injury arising when displaying motion pictures includes: sections and for variably controlling the illumination duration of the backlight based on the detected type of the image content to be displayed. This configuration makes it possible to appropriately control the image quality degradation caused by blur injury, stroboscopic effect and flickering, hence realize total image quality improvement.
Owner:SHARP KK
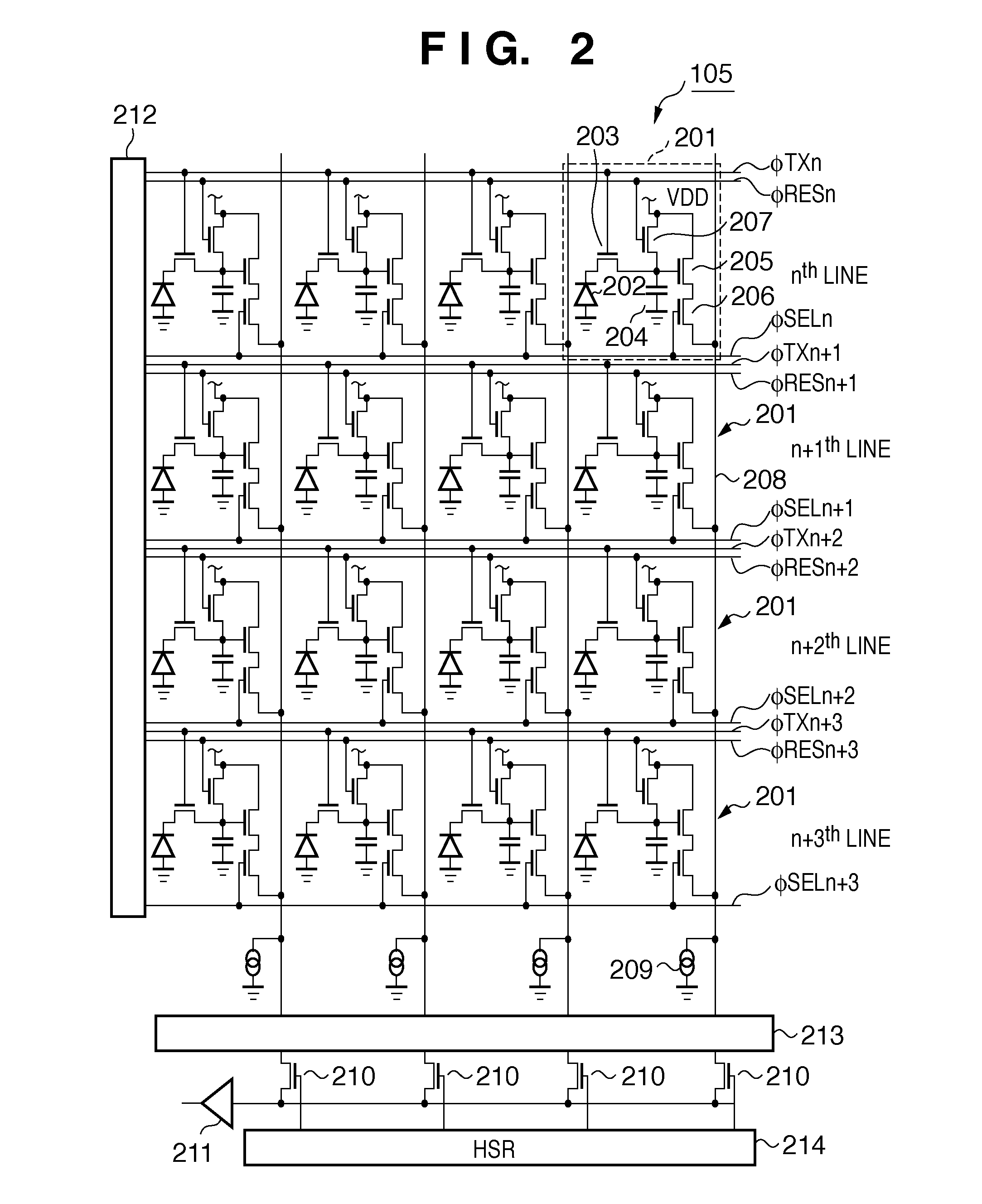
Imaging device, image processing device, image processing method, program for image processing method, and recording medium having program for image processing method recorded thereon
ActiveUS20090052797A1Color noise can be suppressedLuminescence signal can be reducedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingNoise removal
A method and apparatus to remove color noise included in raw data while effectively preventing image quality degradation. For Interest pixels serially set onto a mosaic image formed of raw data, conversion is executed into a pixel value for noise removal based on a processing reference pixel value having a unified color signal component in each interest pixel, noise is removed from the pixel value for noise removal, and the pixel value for noise removal with noise removed is converted into the source pixel value, whereby only color noise can be removed without affecting a luminance signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image display apparatus
InactiveUS20100315605A1Reduce impactProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementImage formationLight beam
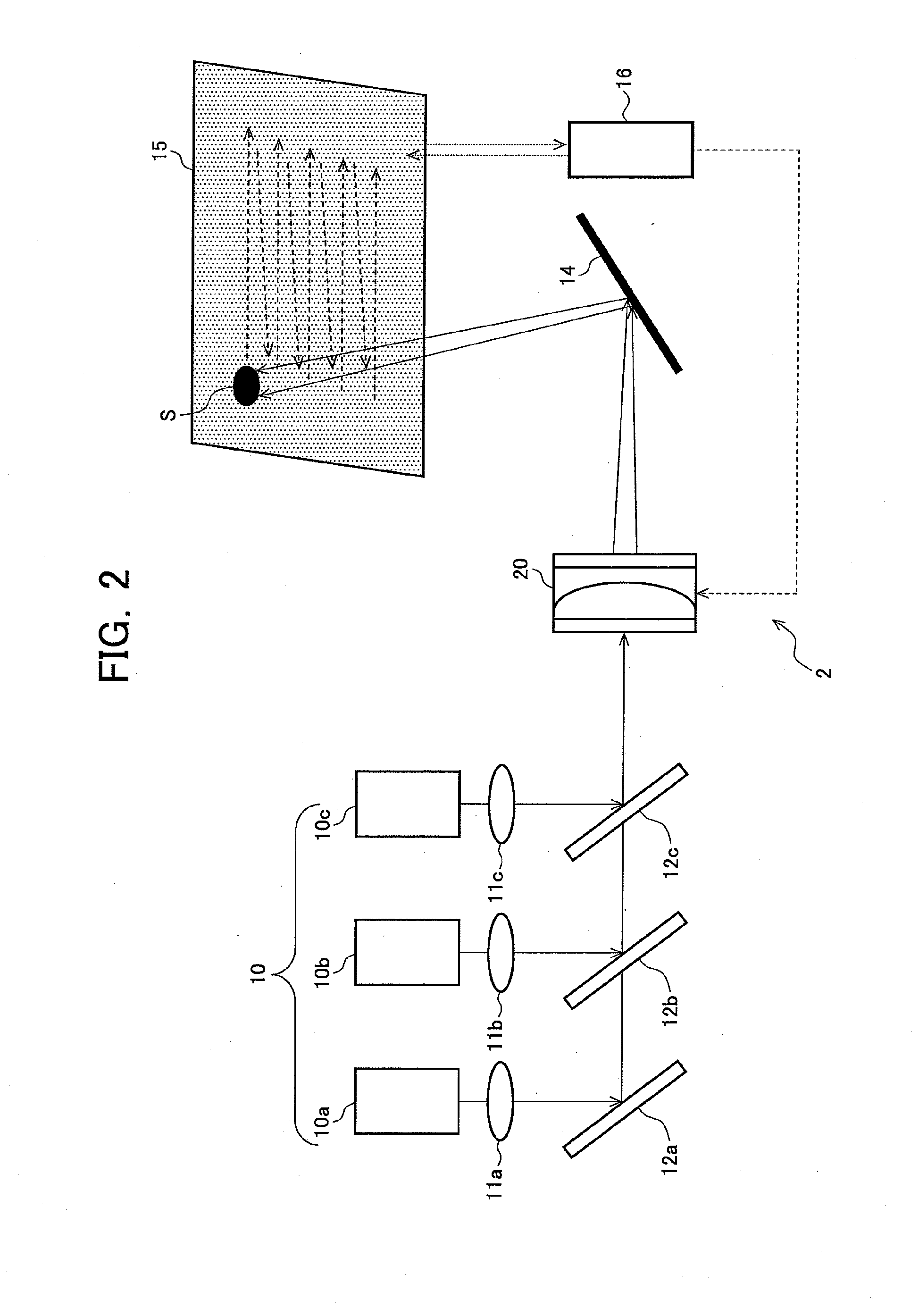
Provided is an image display apparatus which can reduce the influence of image quality degradation caused by a spot size on a screen generated when using a light source having a high directivity such as a laser beam and scan-type image formation means. The image display apparatus includes: a light source device (10) which emits light; scan-type image formation means (such as an MEMS mirror (14)) which forms an image on a screen (15); a variable focus device (13) arranged in the optical path of the light emitted from the light source device (10) to reach the image formation means; and control means which controls the variable focus device (13) so as to modify the spot size of the light beam projected onto the screen (15) in accordance with a projected image size or an user operation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Image pickup apparatus and lens barrel
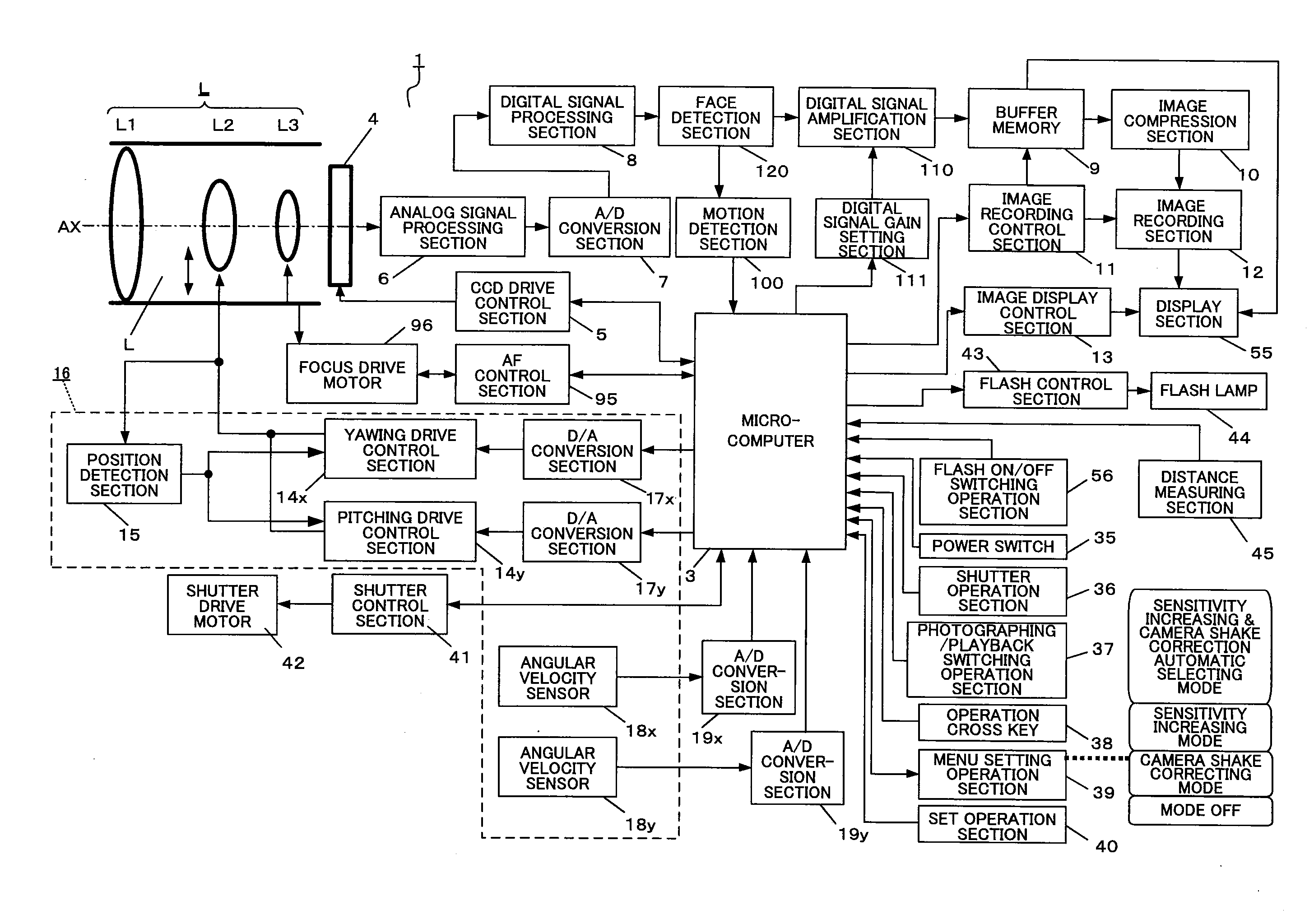
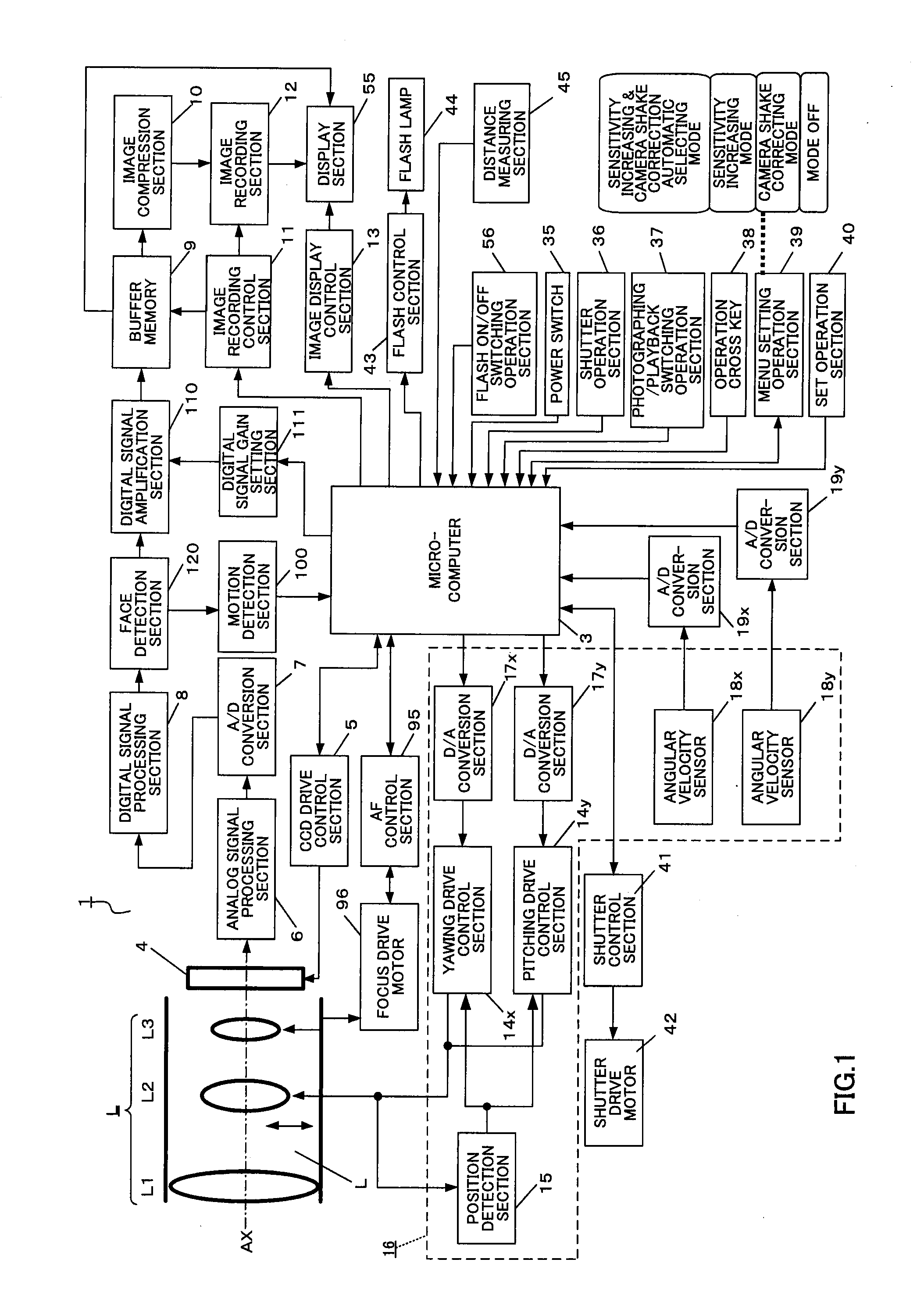
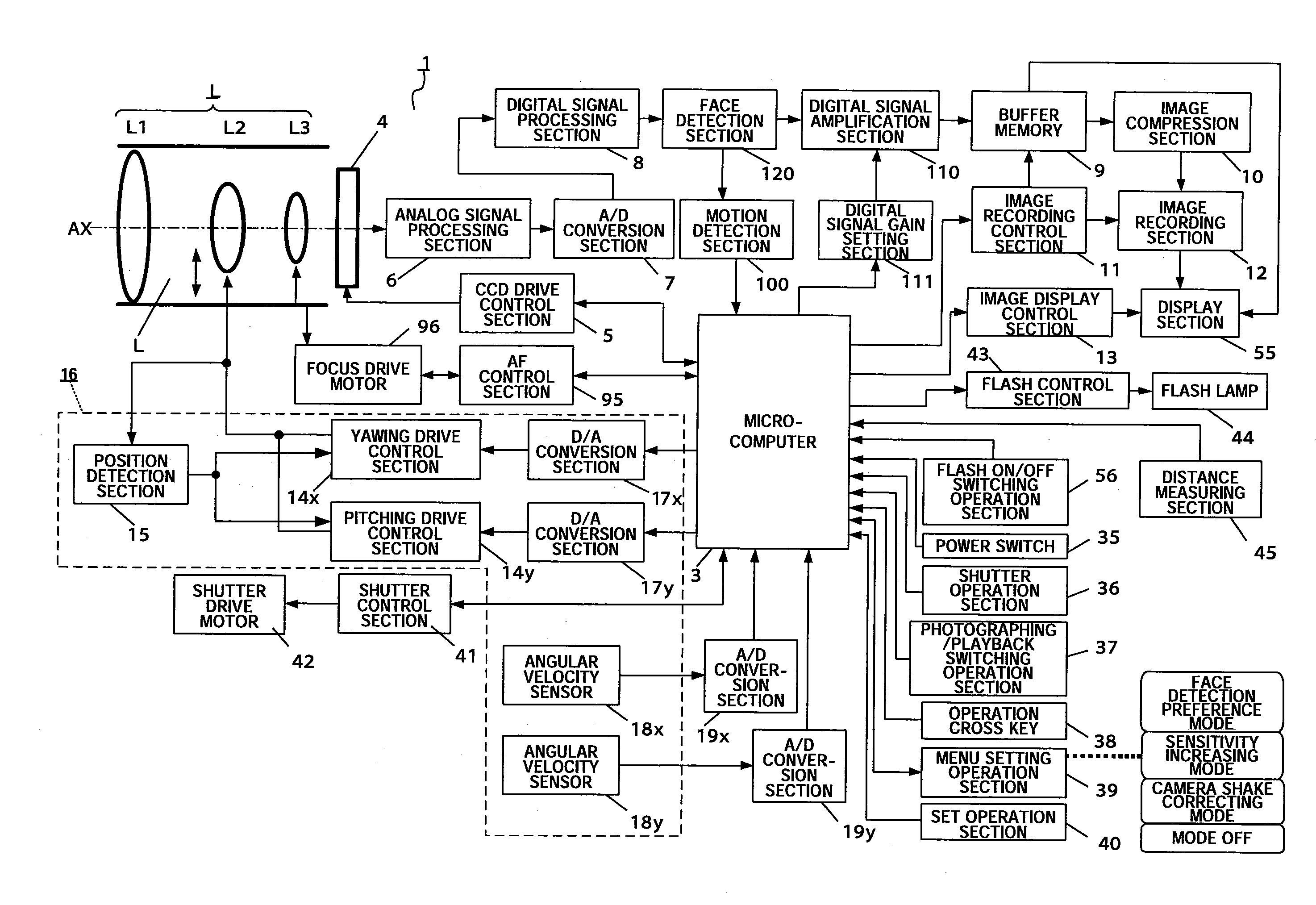
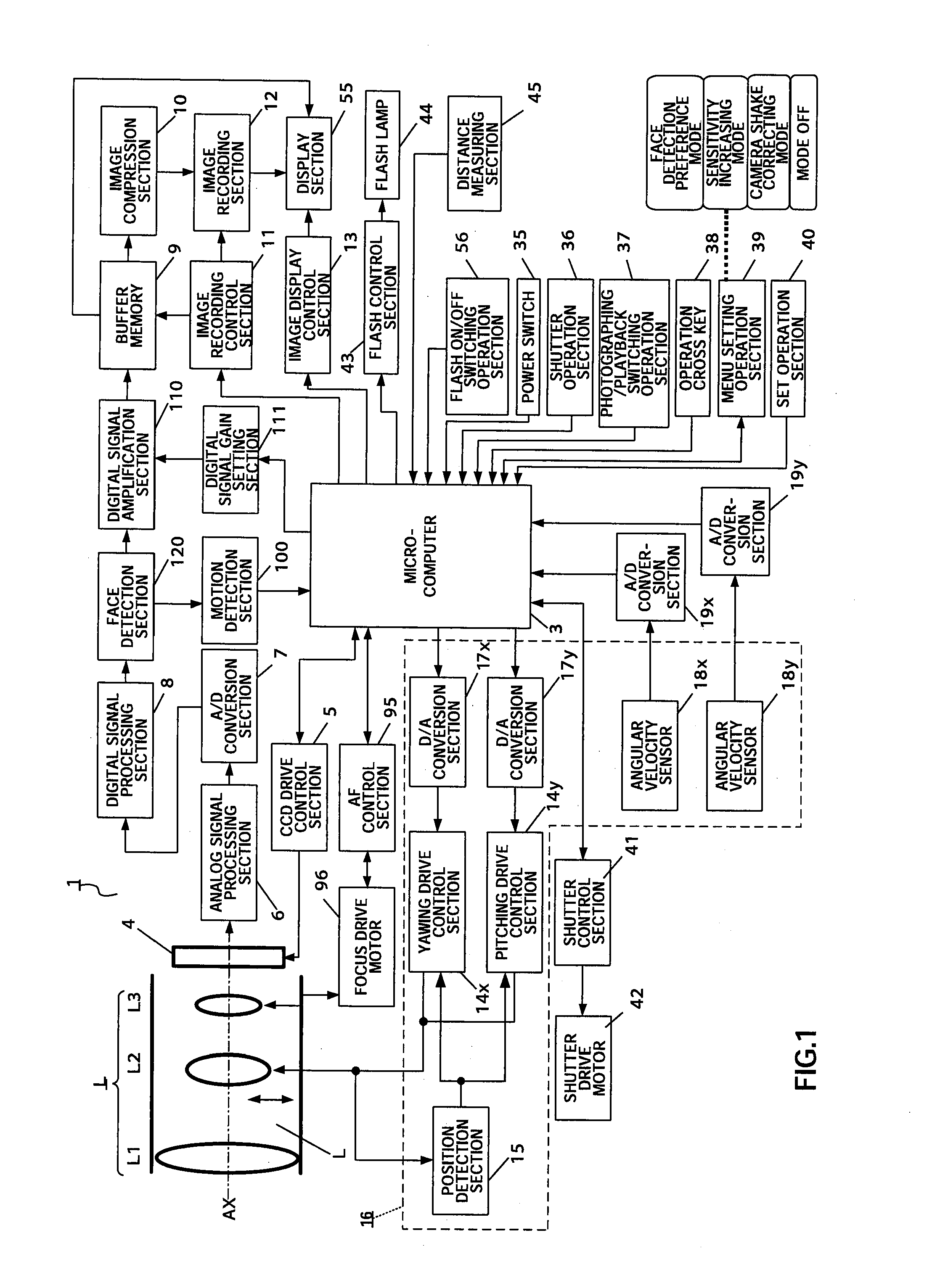
ActiveUS20080204565A1Reduce image quality degradationQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrintersFace detectionObject based
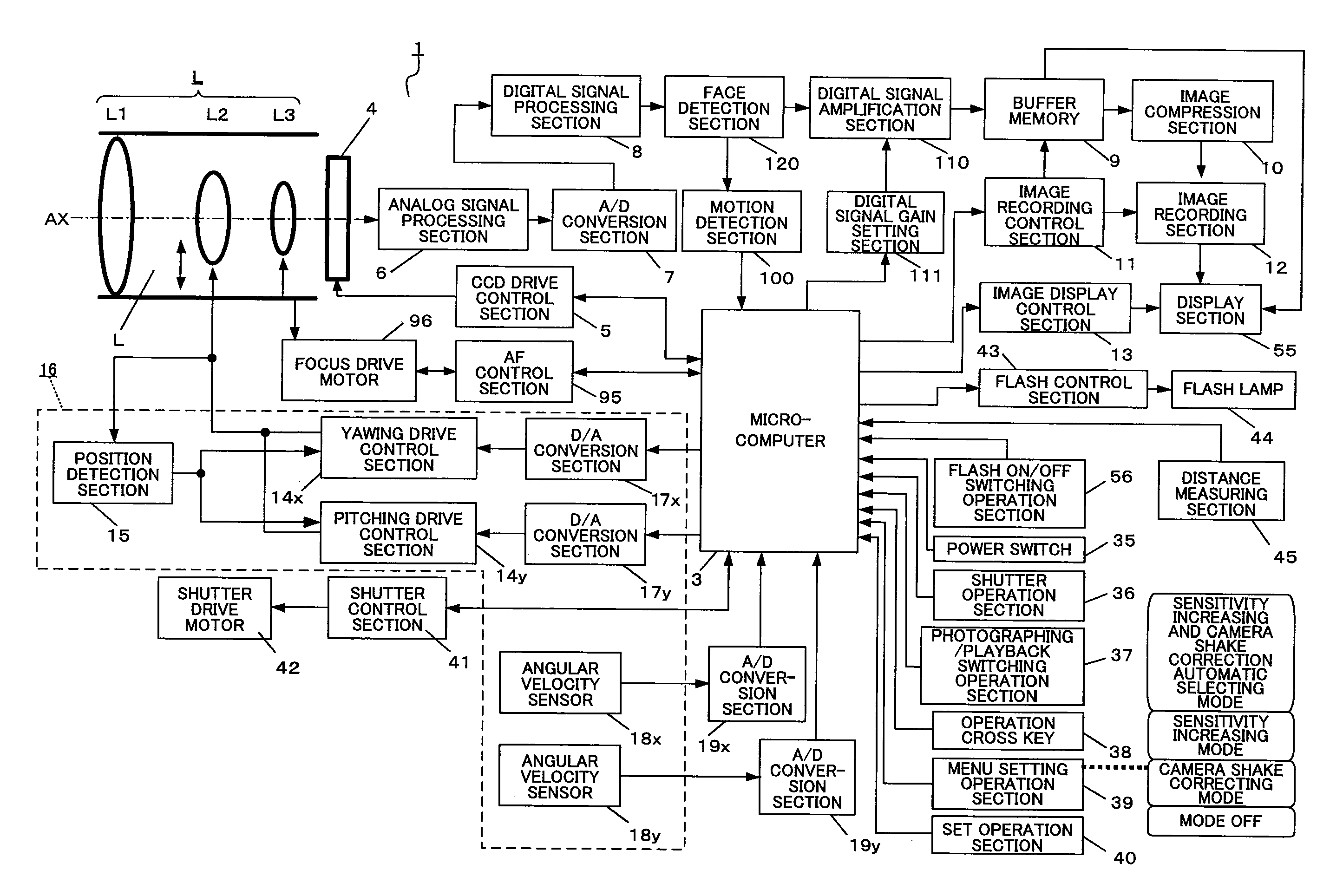
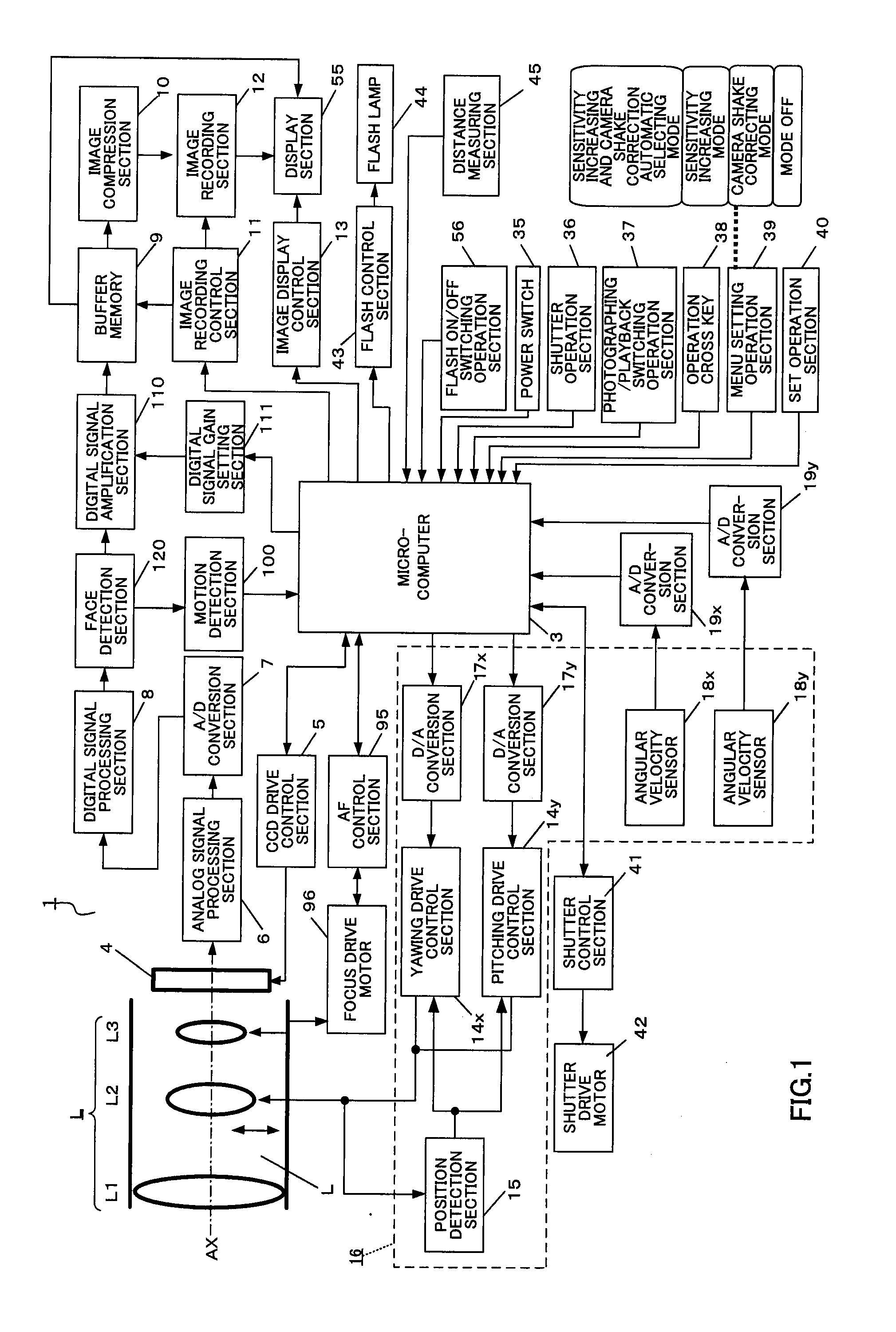
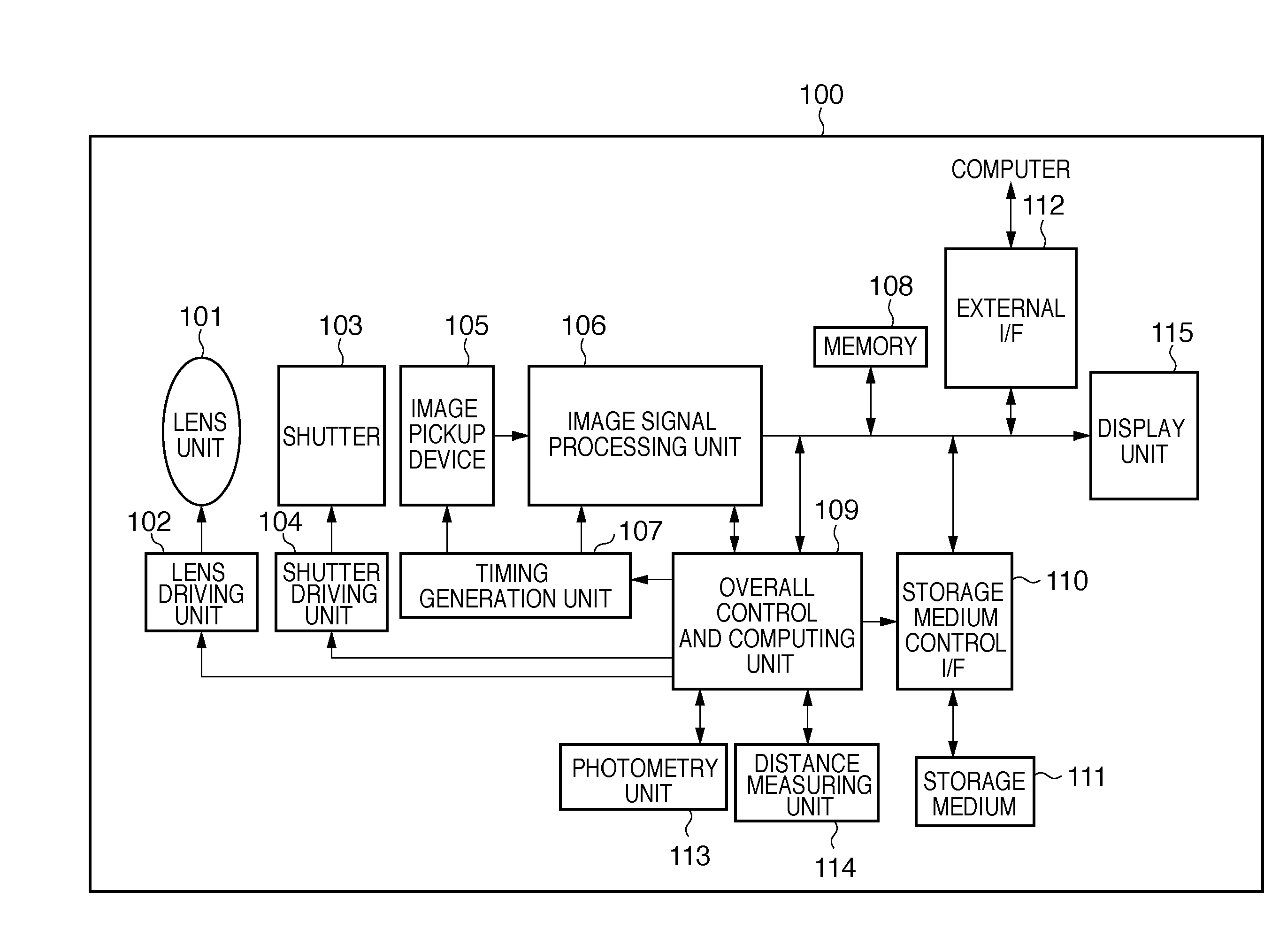
An imaging apparatus capable of preventing photographing sensitivity from being increased more than necessary, reducing image quality degradation caused by camera shake or object shake and easily photographing images in good image quality. Digital camera 1 includes image shake correcting selection 16 that corrects shake of an optical image of a photographing object formed by the imaging optical system L, digital signal amplification section 110 that amplifies an image signal with a gain set by digital signal gain setting section 111, face detection section 120 that detects a face of a fast-moving specific photographing object such as a child or pet, and motion detection section 100 that detects motion of the face of the specific photographing object based on an output of face detection section 120, wherein when a fast-moving specific photographing object such as a child or pet or the face of the specific photographing object is detected, microcomputer 3 increases the gain of a photographing sensitivity changing function compared with when no specific photographing object such as a child or pet is detected, increases ISO sensitivity, increases a shutter speed and shortens exposure time.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Intelligent face tracking system and method based on depth learning and large-scale clustering
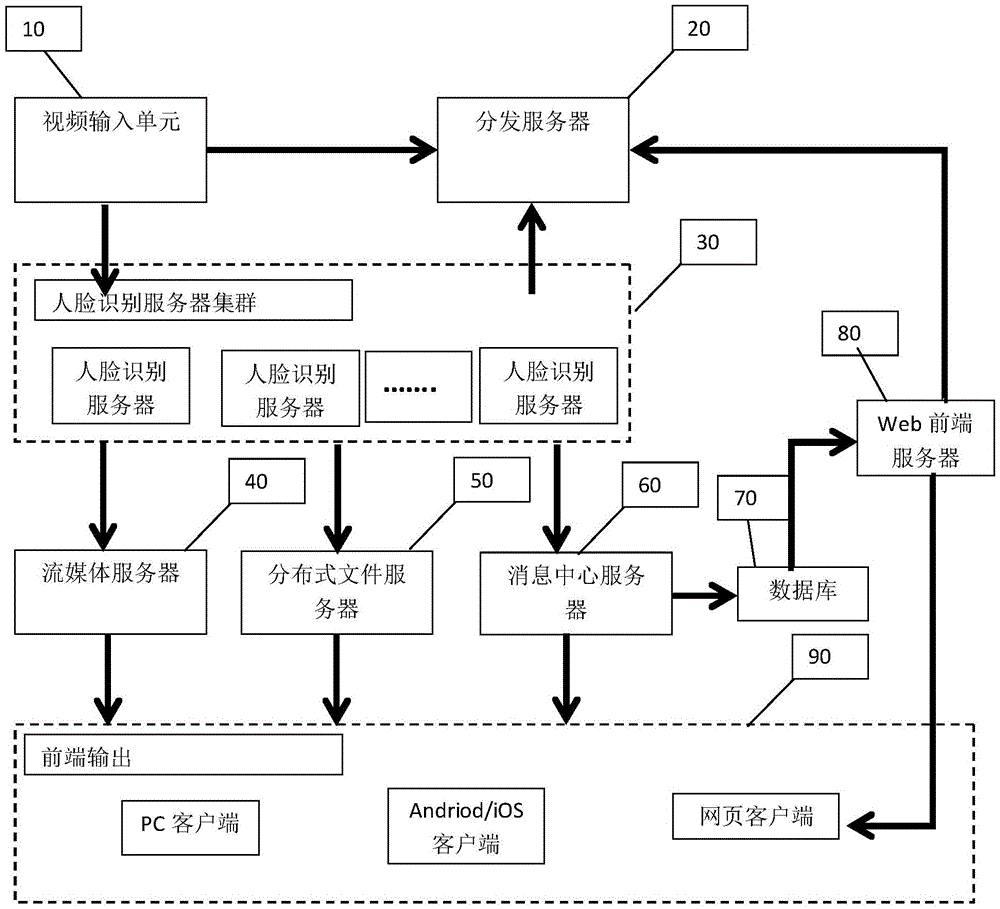
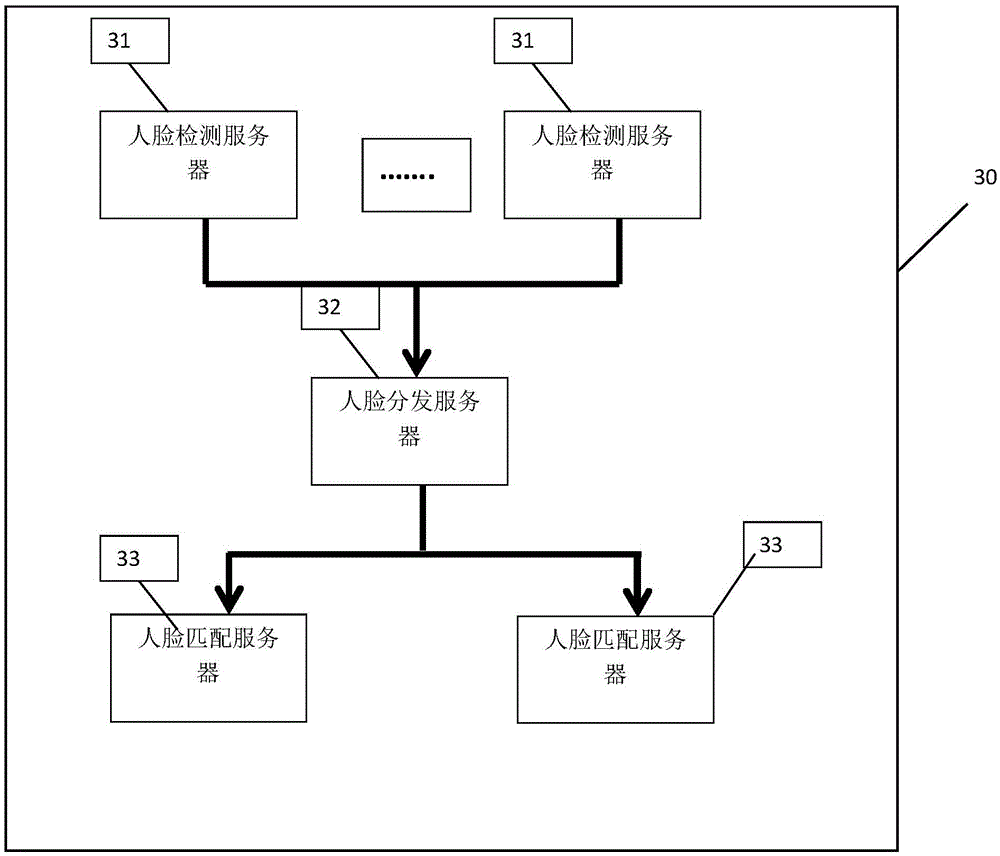
ActiveCN105574506AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionOperational systemImaging quality
The invention relates to an intelligent face tracking system and method based on depth learning and large-scale clustering. The system comprises a video input unit, a distribution server, a face identification server cluster, a streaming media server, a distributed file server, a message center server, a web front server and a client of a common operation system. According to the invention, by use of large-scale cluster servers, based on depth learning based face identification technology, a quite high identification rate can still be maintained under the condition of degraded image quality, and more important, a quite low false alarm rate and a quite low missed examination rate are maintained in a large-scale database, such that the reliability and the robustness of the intelligent tracking system can be ensured, and the intelligent tracking system based on face identification can be really applied to the field of safety protection.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENSETIME TECH CO LTD
AMOLED (active matrix/organic light emitting diode) display and driving method of AMOLED display
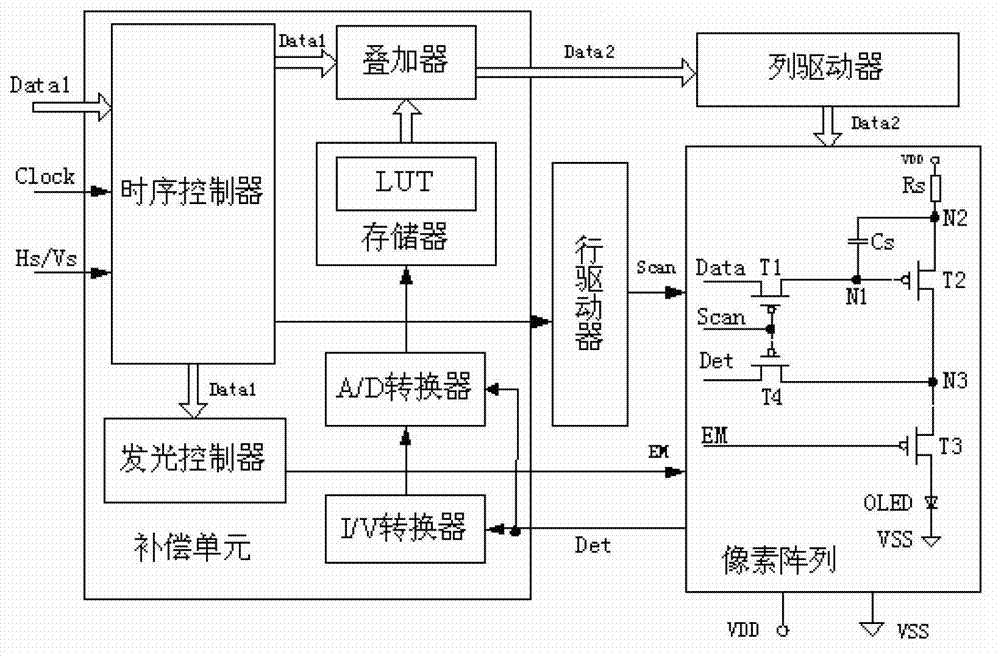
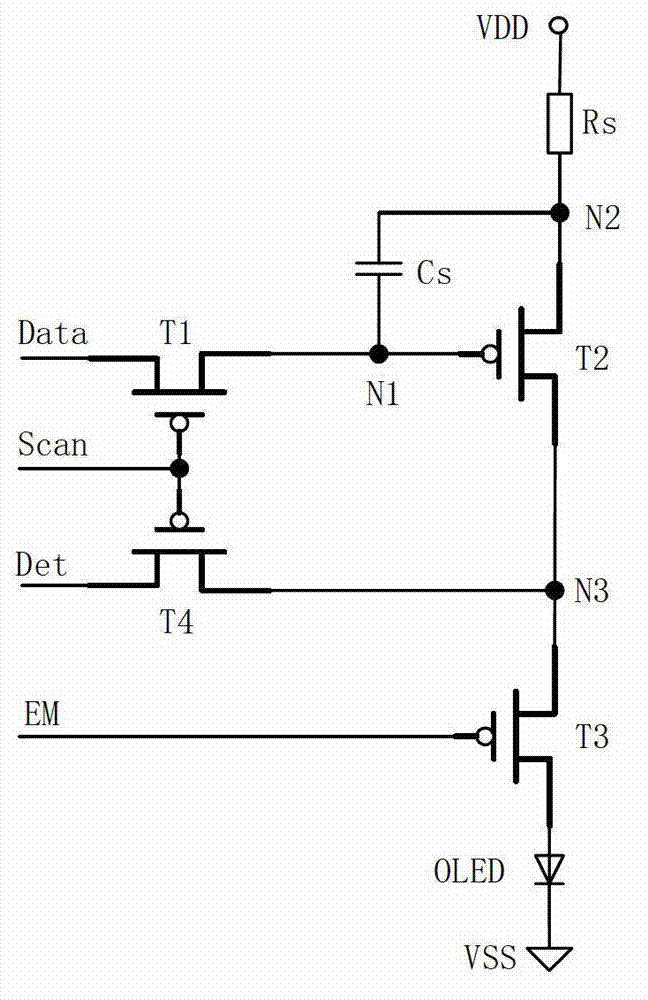
InactiveCN102768821AEliminate UniformityEliminate image retention and other phenomenaStatic indicating devicesImage quality degradationEngineering
The invention relates to an AMOLED (active matrix / organic light emitting diode) display and a driving method of the AMOLED display. The AMOLED display is provided with a compensation unit as well as a row driver and a column driver which are connected with a pixel array, wherein the compensation unit is provided with an overlaying device connected with a time sequence controller, the time sequence controller is also connected with the row driver, and the overlaying device is connected with a memory, an A / D (Analog to Digital) converter, a I / V converter and the column driver; each pixel unit of the pixel array comprises a first switch conducting element and a second switch conducting element, wherein the data conducting pins of the first switch conducting element are connected with the control pins of the column driver and a drive conducting element respectively; a capacitor is arranged between the input pin and the control pin of the drive conducting element; the input pins and the output pins of the second switch conducting element are connected with the output pins of the drive conducting element, the I / V converter and the A / D converter respectively. According to the AMOLED display and the driving method, a plurality of factors causing the image quality degradation can be compensated, the image display quality of the AMOLED display is improved, and the AMOLED display is simple in circuit structure.
Owner:SICHUAN CCO DISPLAY TECH
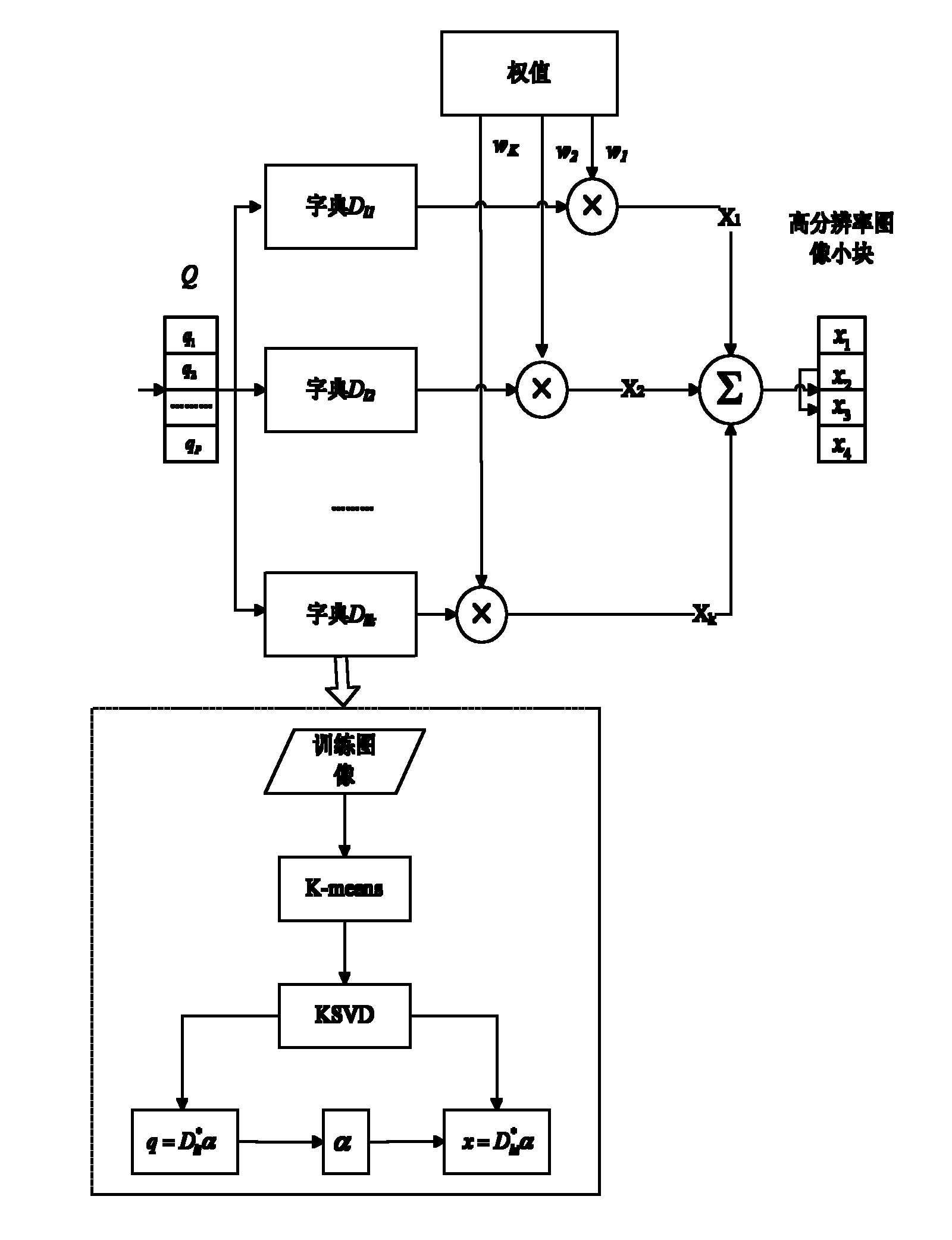
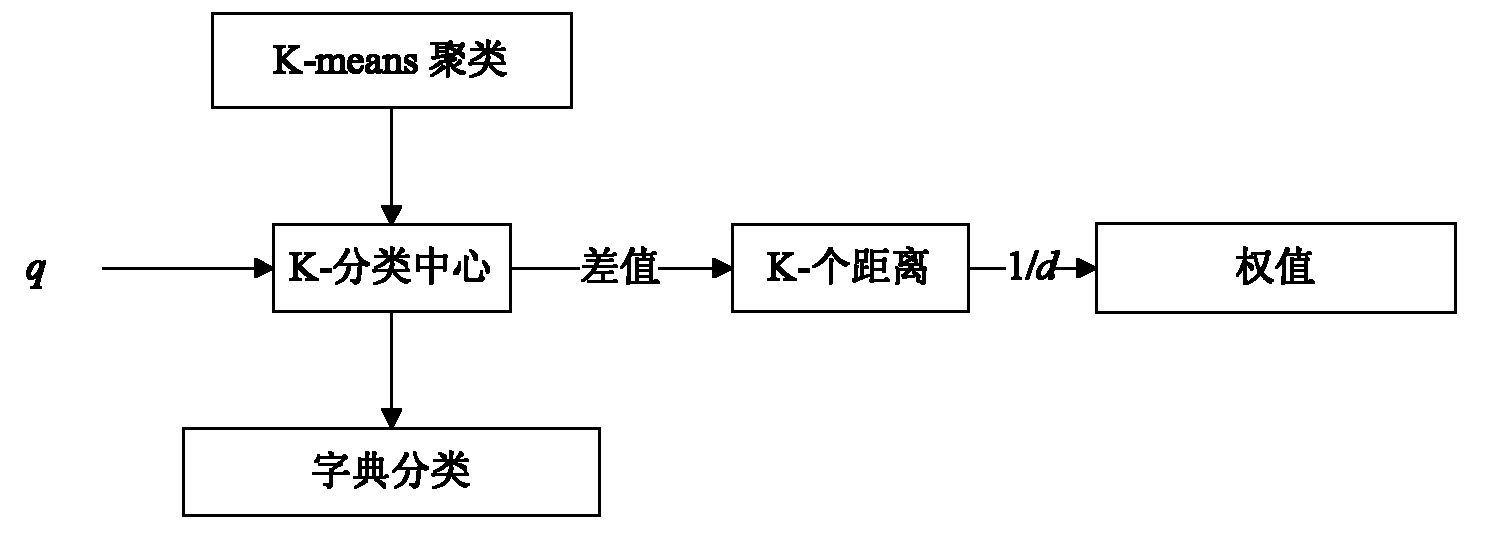
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD (K singular value decomposition) dictionary learning
ActiveCN102156875AReduce refactoring timeReduce the numberImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionFeature vector
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD (K singular value decomposition) dictionary learning, mainly aims at solving the problem that the quality of a reconstructed image of the existing method is relatively reduced seriously under a high-magnification factor. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting a training image, filteringthe image to extract characteristics; extracting tectonic characteristics vector sets of small characteristic blocks, and clustering to obtain sample pair sets {(H1, L1), (H2, L2), ..., (HK, LK)} of K to high resolution and low resolution; developing K high-resolution dictionaries Dh1, Dh2, ..., DhK and corresponding low-resolution dictionaries Dl1, Dl2, ..., DlK from the K groups of sample pair sets by means of a KSVD method; encoding low-resolution patterns input in the low-resolution dictionaries Dl1, Dl2, ..., DlK; obtaining an initial reconstruction image by encoding and high-resolution dictionaries Dh1, Dh2, ..., Dh; then implementing local constrained optimization of the initial reconstruction image; and compensating residual errors and implementing global optimization treatment toobtain a final reconstruction image. The image super-resolution reconstruction method based on multitask KSVD dictionary learning has the advantages that the various natural images can be reconstructed, the quality of the reconstructed image can be effectively improved under the condition of a high-magnification factor, and the method can be applied to the recover and identification of human, animal, plant and building and other target objects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Camera image shake correcting device
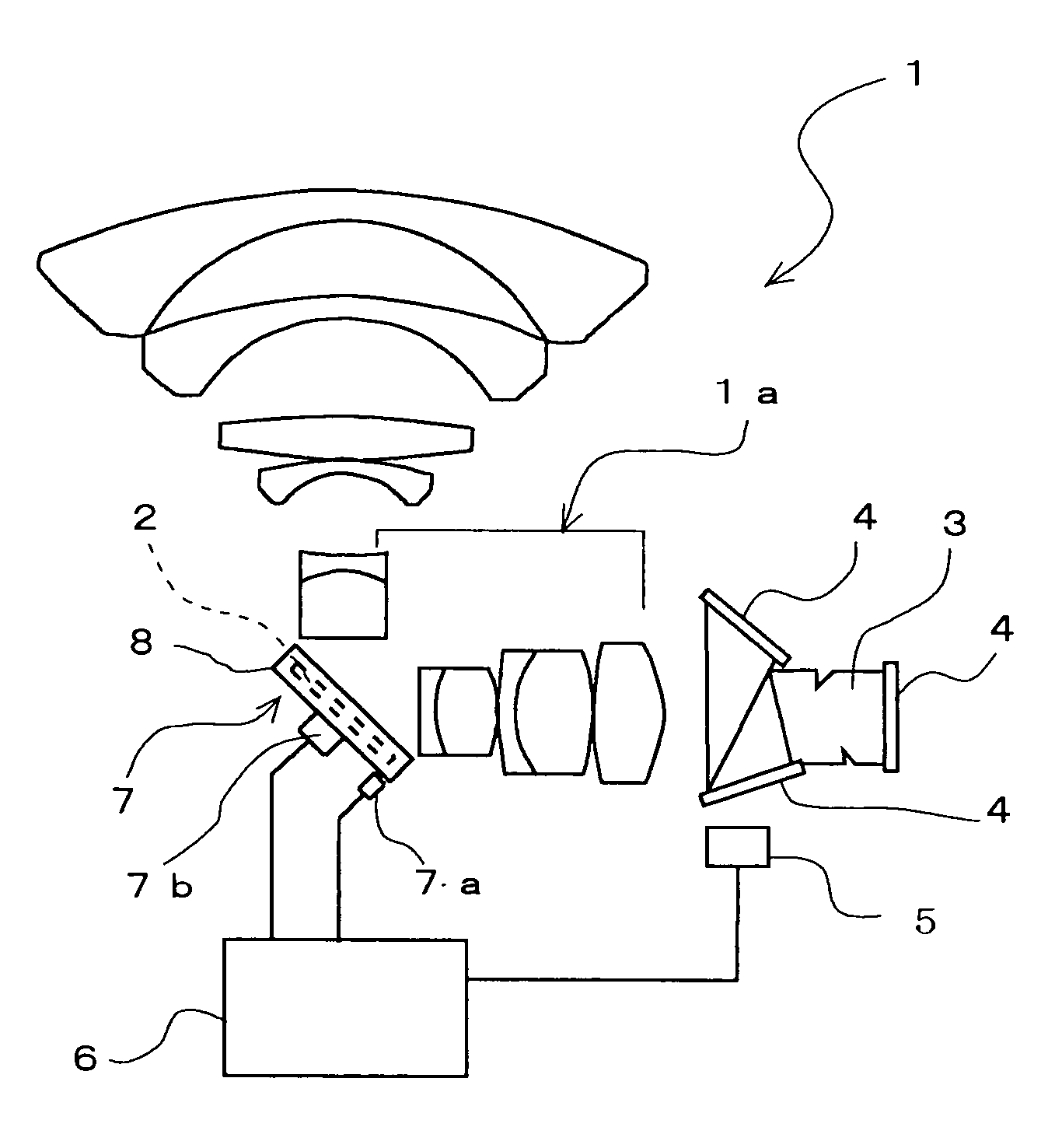
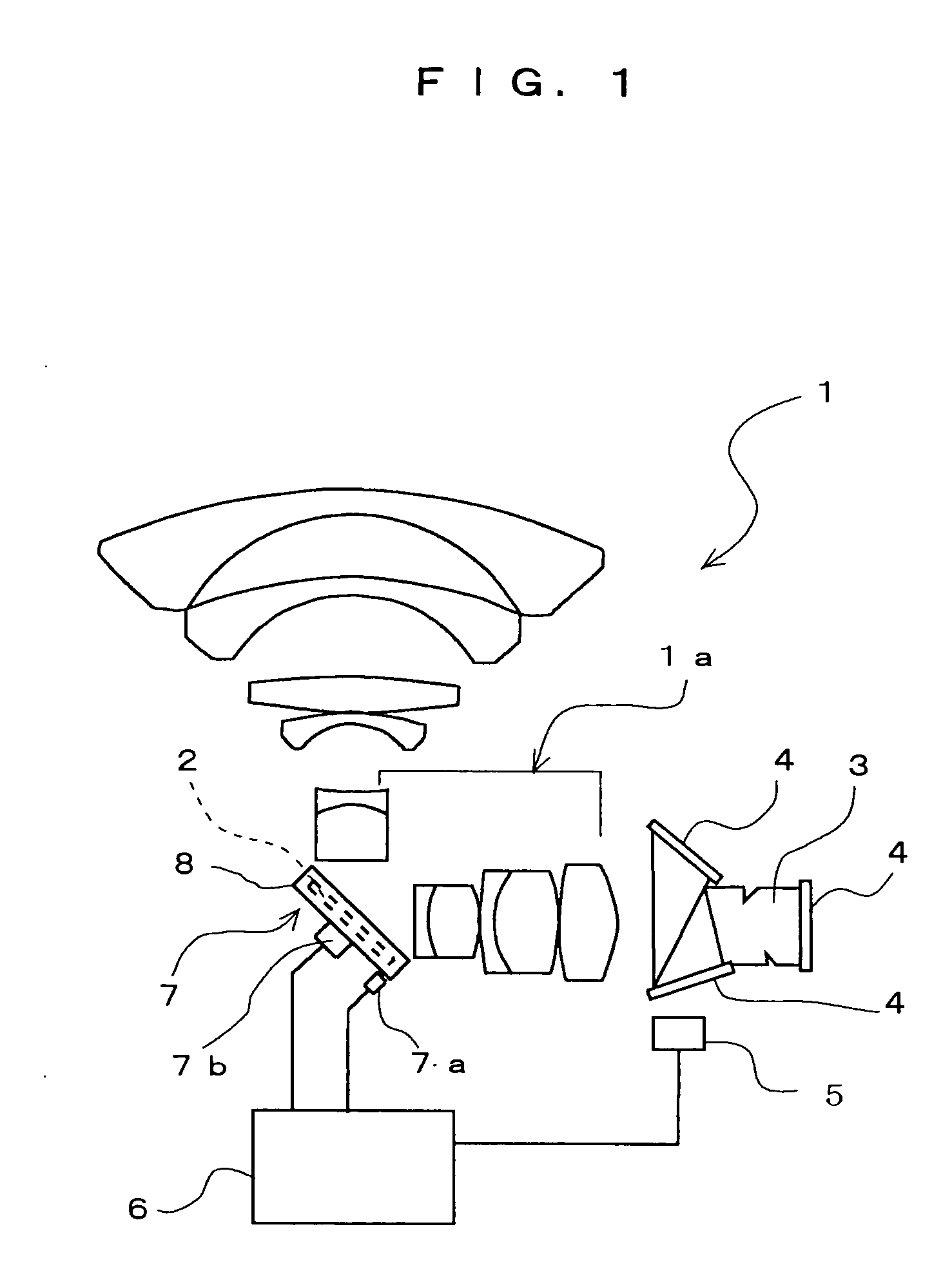
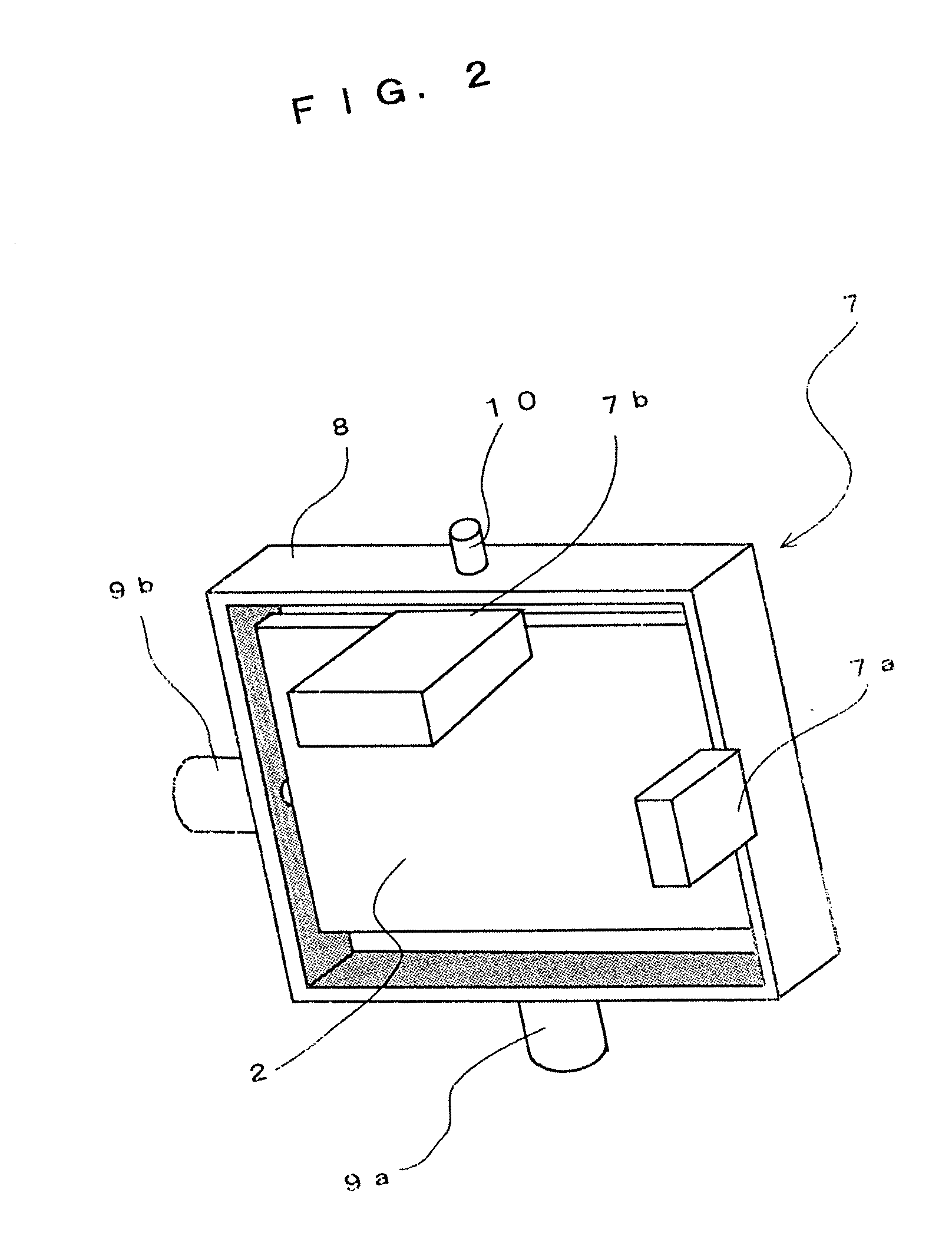
InactiveUS20050057659A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove responseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera imageImage formation
A camera image shake correcting device is provided which employs an image shake correcting system using an optical system to prevent image quality degradation and which uses a mirror (2) to allow improvement of correction response to image shake as well as miniaturization and to achieve a cost reduction. The camera image shake correcting device is characterized by having a mirror (2) disposed in an intermediate portion of an optical path connecting together an image-formation plane of an image pickup optical system of a camera and an imaging lens; mirror driving means (7) for driving the mirror (2) so that the angle of the mirror (2) is changed in correspondence to displacement of an image on the image-formation plane caused by shake of the camera to cancel the displacement of the image on the image-formation plane; and control means (6) for controlling the mirror driving means (7) by detecting the amount of shake of the camera or the amount of displacement of the image on the image-formation plane.
Owner:HASEGAWA TAKAMI
Multi-task super-resolution image reconstruction method based on KSVD dictionary learning
ActiveCN101950365AReduce refactoring timeQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDictionary learning
The invention discloses a multi-task super-resolution image reconstruction method based on KSVD dictionary learning, which mainly solves the problem of relatively serious quality reduction of the reconstructed image under high amplification factors in the existing method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting a training image, and filtering the training image to extract features; extracting image blocks to construct a matrix M, and dividing the matrix M into K classes to acquire K pairs of initial dictionaries H1, H2...Hk and L1, L2...Lk; then, training the K pairs of initial dictionaries H1, H2...Hk and L1, L2...Lk into K pairs of new dictionaries Dh1, Dh2...Dhk and Dl1, Dl2...Dlk by utilizing a KSVD method; and finally, carrying out super-resolution reconstruction on the input low-resolution image by utilizing a multi-task algorithm and the dictionaries Dh1, Dh2...Dhk and Dl1, Dl2...Dlk to acquire a final reconstructed image. The invention can reconstruct various natural images containing non-texture images such as animals, plants, people and the like and images with stronger texture features such as buildings and the like, and can effectively improve the quality of the reconstructed image under high amplification factors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Resolution-converting apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060033936A1Eliminating occurrence of quality-degradingImprove clarityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionIntermediate image
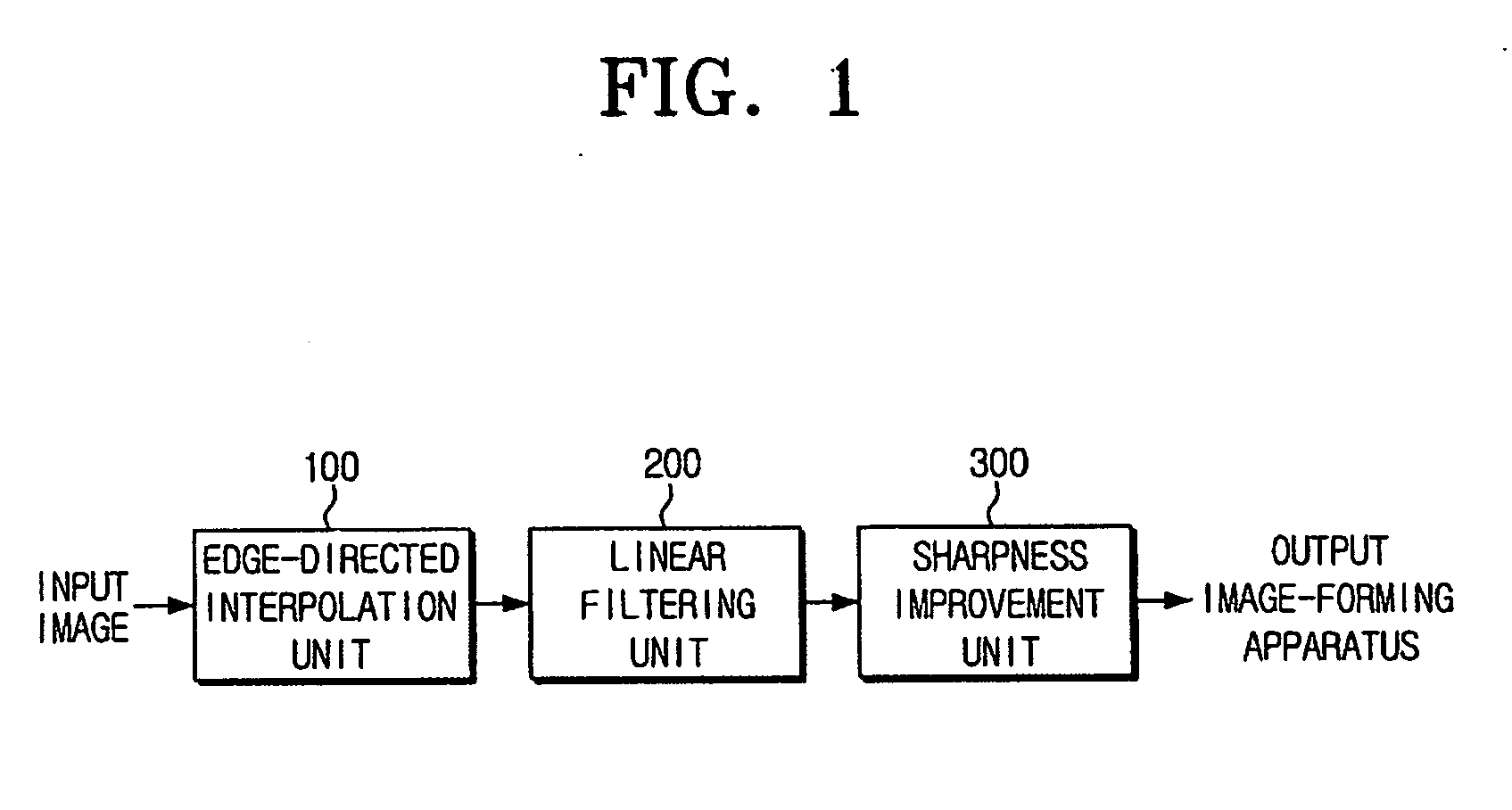
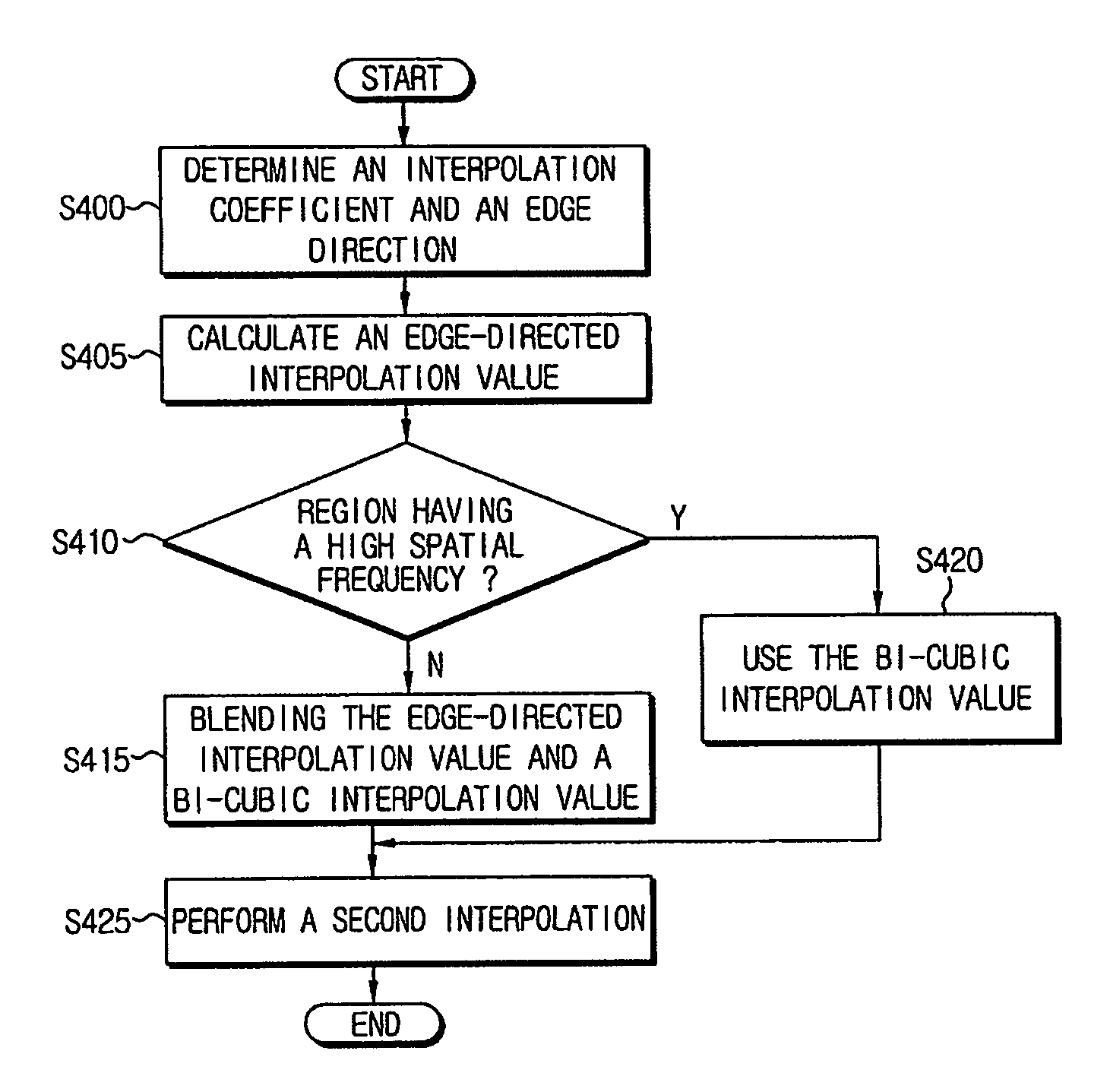
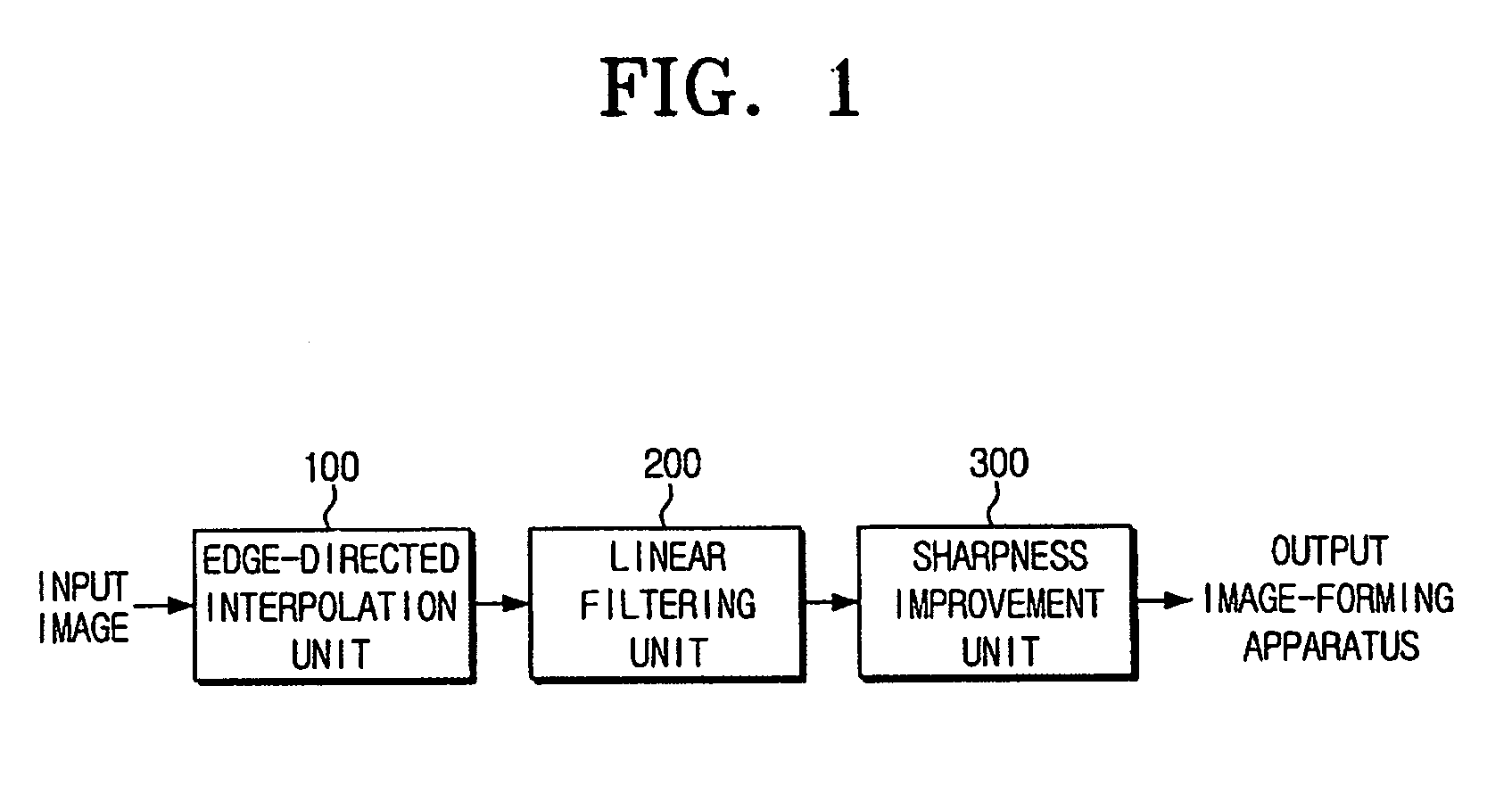
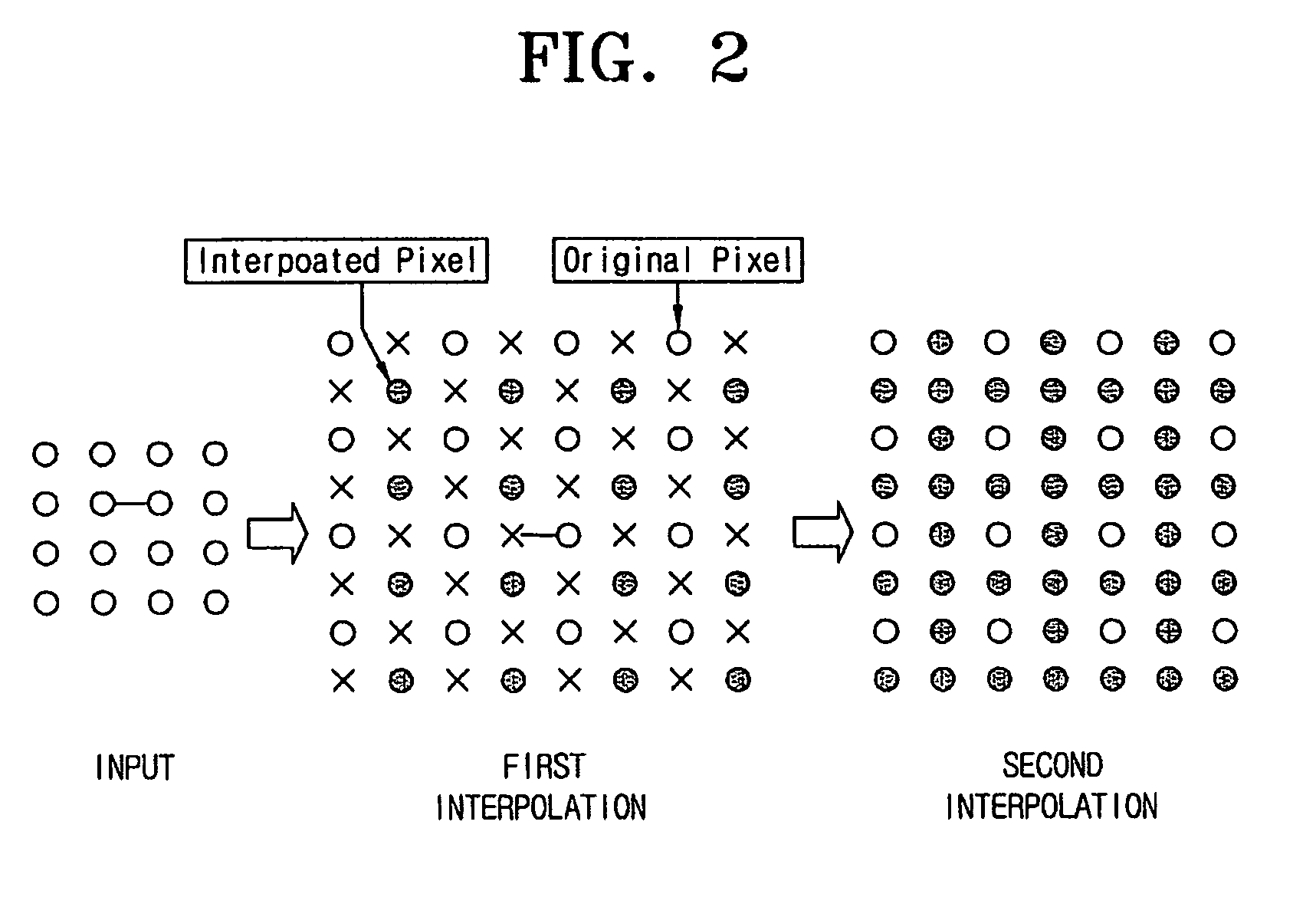
The resolution-converting method comprises steps of applying an edge-directed interpolation to an input image and producing an intermediate image; converting a sampling rate with respect to the intermediate image and producing an output image having a predetermined resolution; and improving sharpness of the produced output image. The present invention prevents image-quality degradation factors that can occur in the conventional resolution-converting method as well as obtains an output image having a resolution of a desired size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display device and electronic apparatus having a wiring connected to a counter electrode via an opening portion in an insulating layer that surrounds a pixel electrode
InactiveUS7224118B2Improve reliabilityPrevent degradationDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A display device in which variations in luminance due to variations in characteristics of transistors are reduced, and image quality degradation due to variations in resistance values is prevented. The invention comprises a transistor whose channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor, a connecting wiring connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, a light emitting element having a laminated structure which includes a pixel electrode, an electro luminescent layer, and a counter electrode, an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode, and an auxiliary wiring formed in the same layer as a gate electrode of the transistor, a connecting wiring, or the pixel electrode. Further, the connecting wiring is connected to the pixel electrode, and the auxiliary wiring is connected to the counter electrode via an opening portion provided in the insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
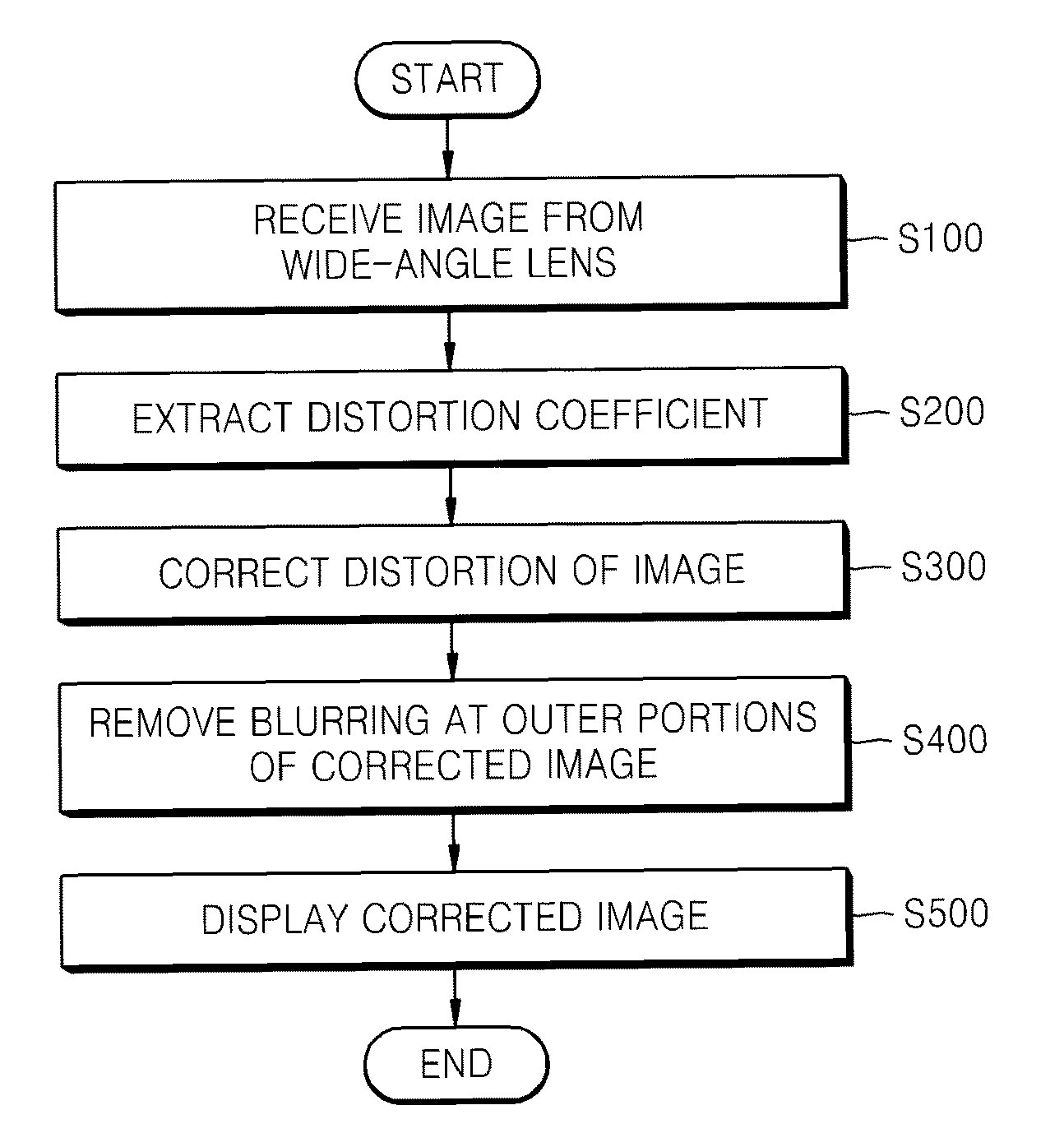
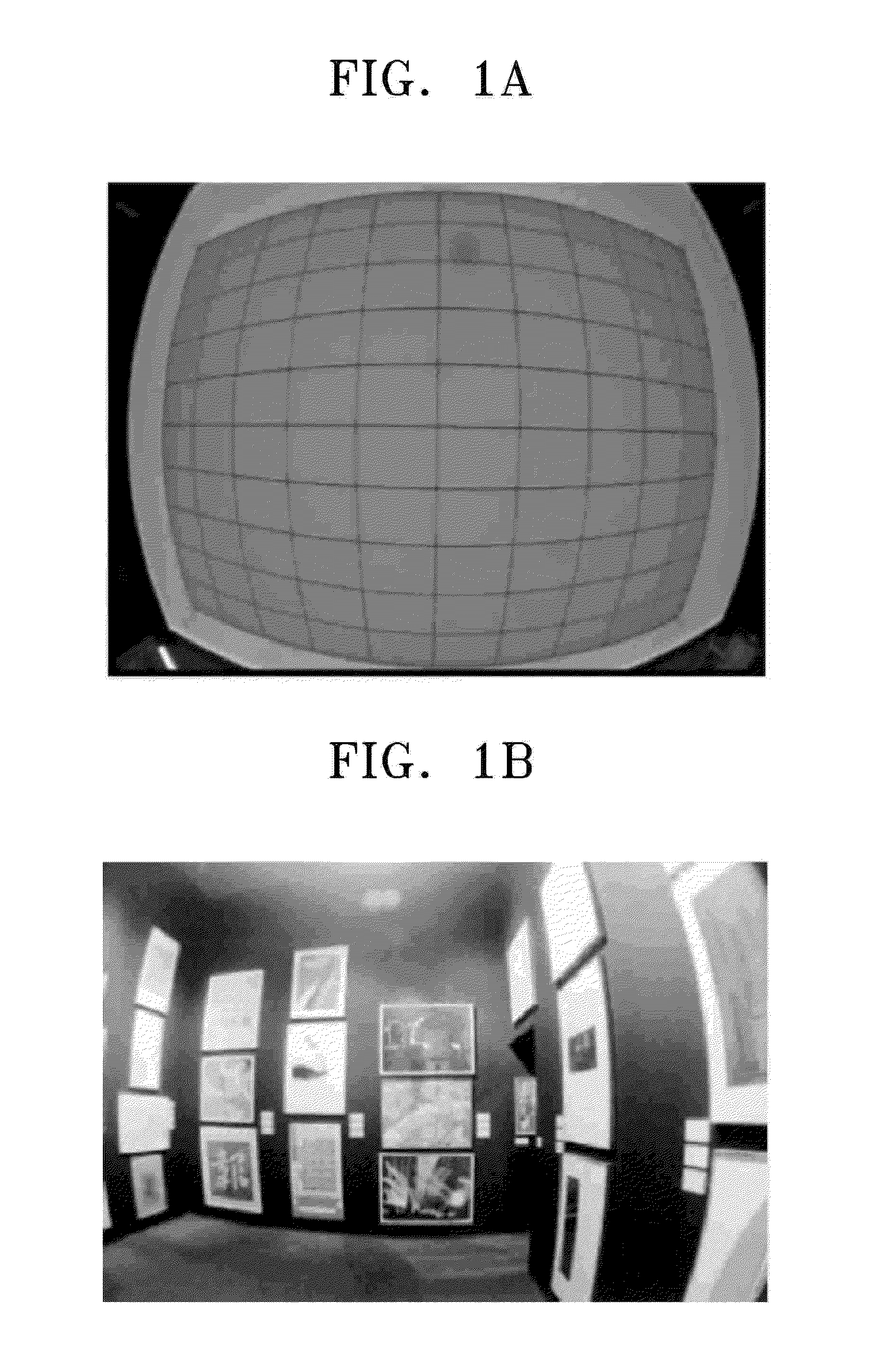
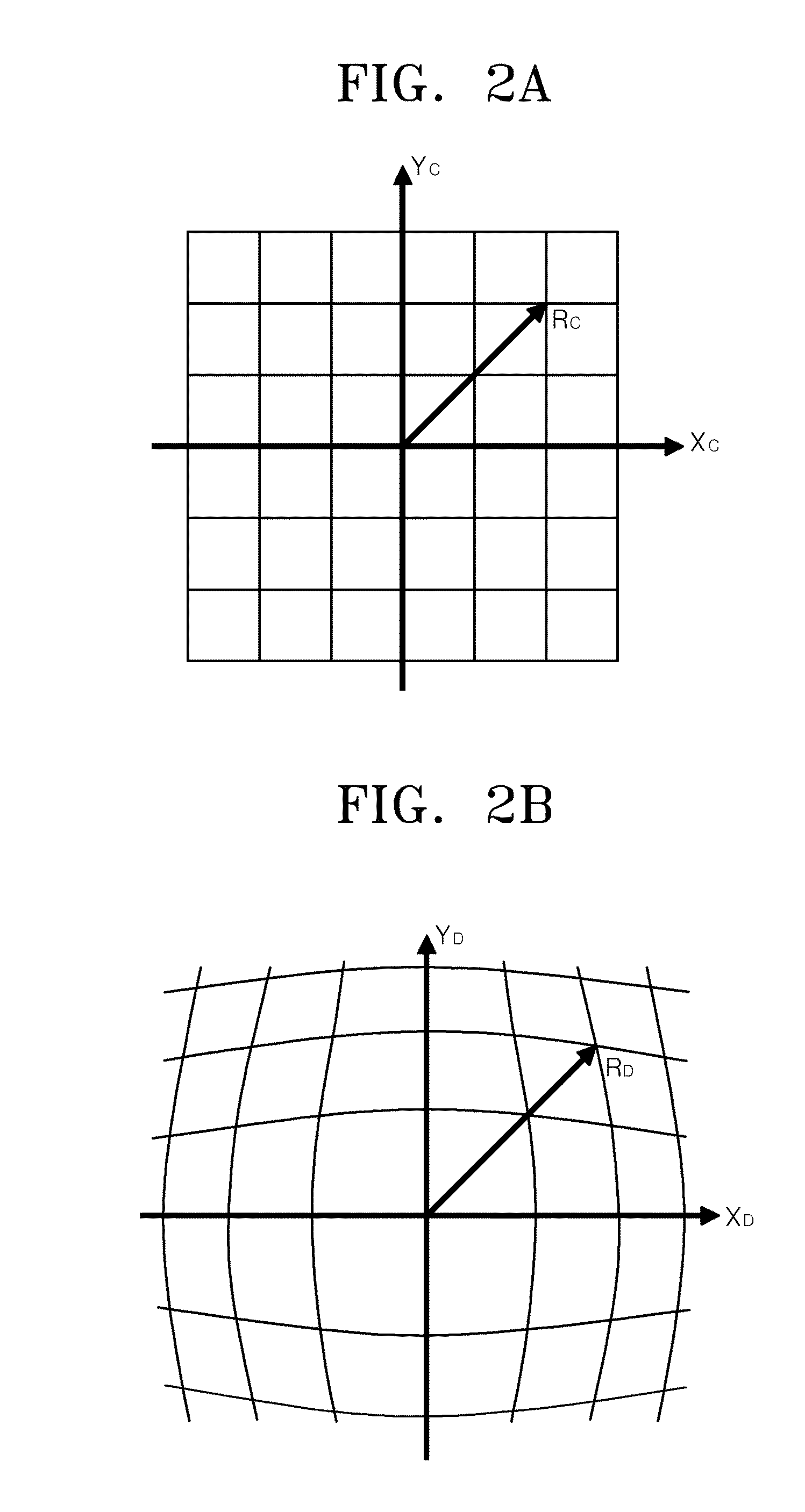
Method of correcting image distortion and apparatus for processing image using the method
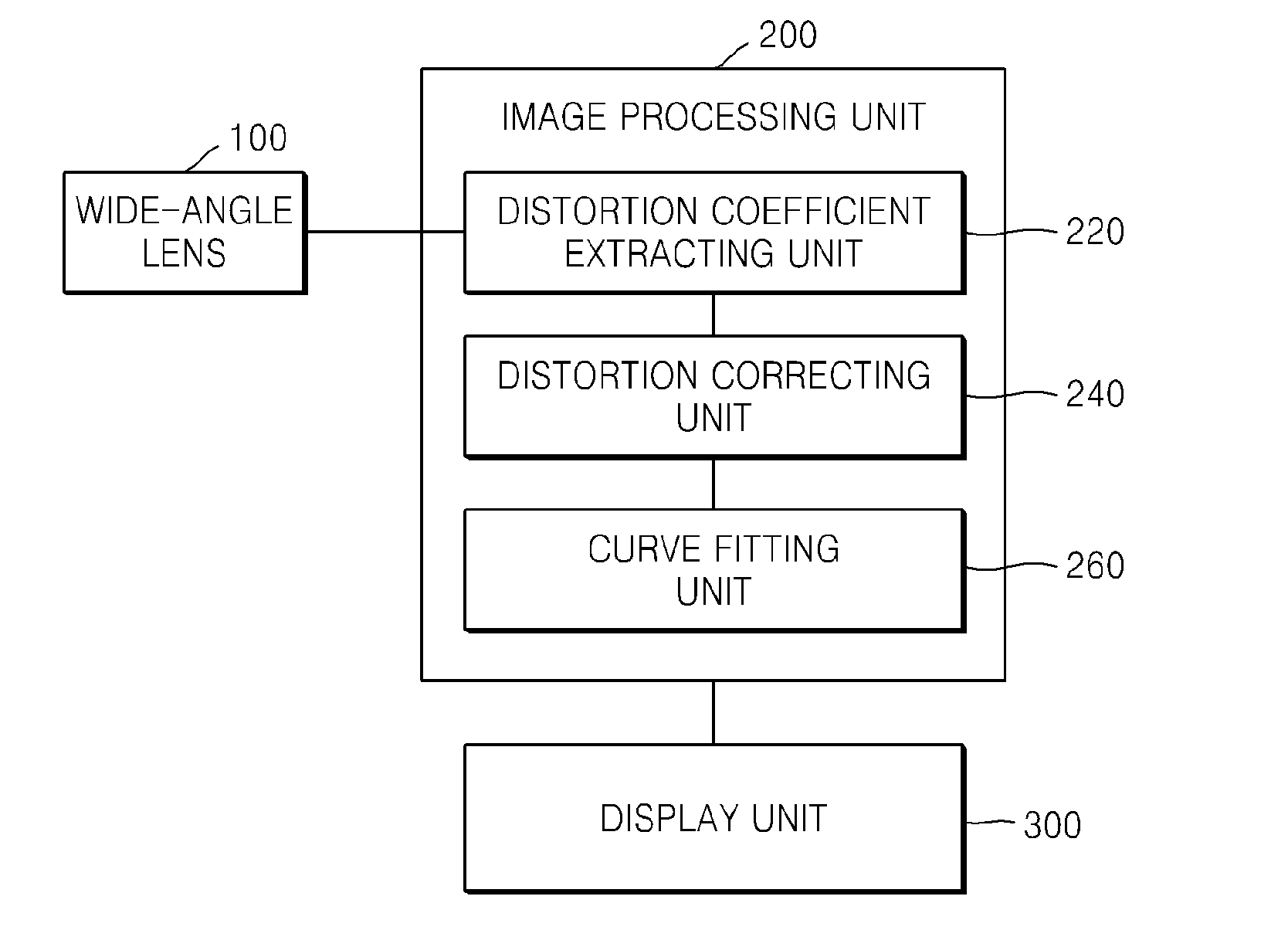
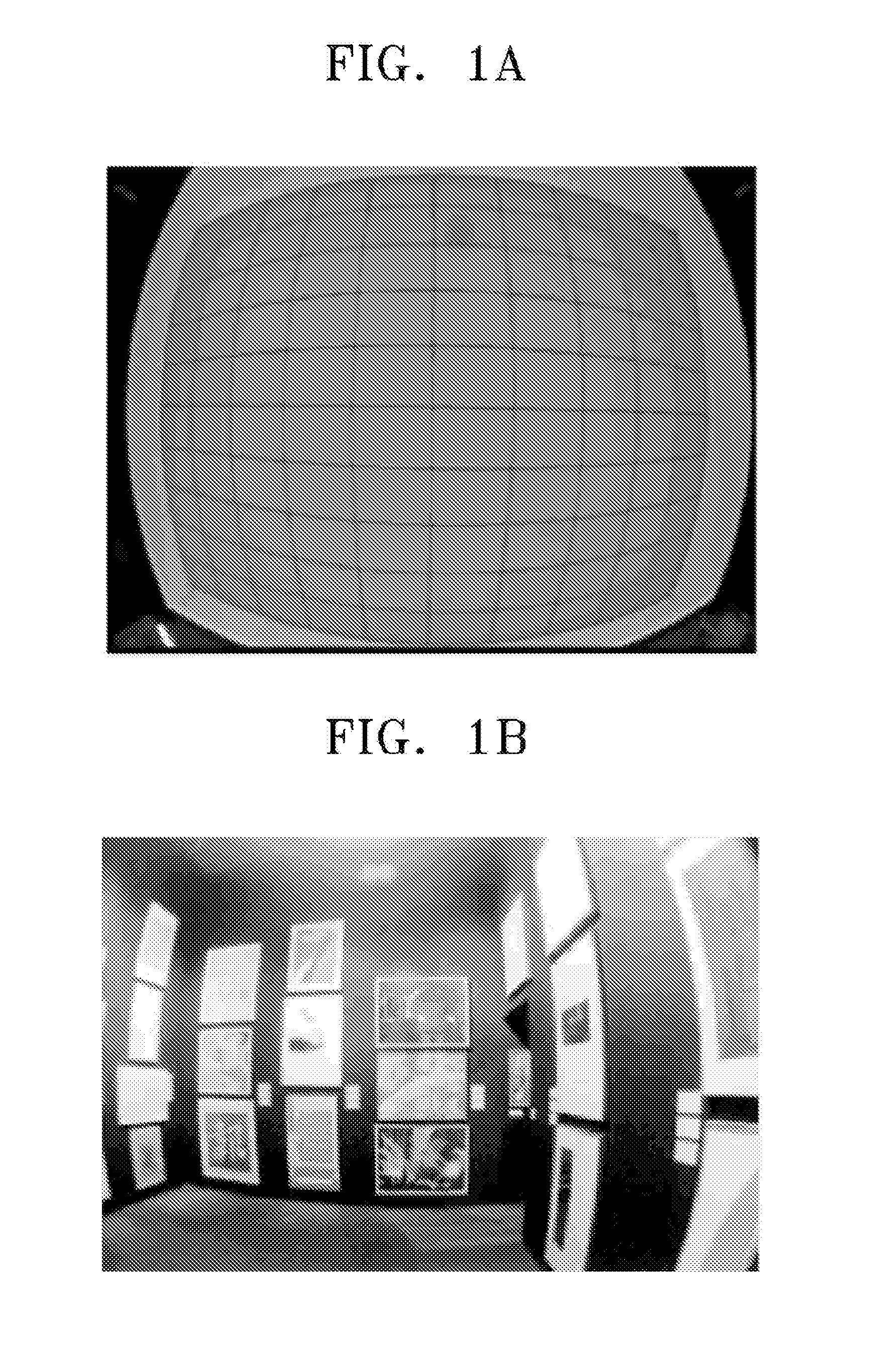
InactiveUS8000559B2Reduce image quality degradationOvercome disadvantagesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingDistortion
A method of correcting image distortion and an apparatus for processing an image using the method are provided, where the method can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional methods of correcting lens distortion and can minimize image quality degradation at outer portions,. The method includes: receiving an image from a wide-angle lens; extracting a distortion coefficient of the distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens; correcting the distortion of the image by using the extracted distortion coefficient; and displaying a corrected image. The apparatus includes: a wide-angle lens for receiving an image; an image processing unit comprising a distortion coefficient extracting unit for extracting a distortion coefficient of distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens and a distortion correcting unit for correcting the distortion of the image using the extracted distortion coefficient; and a display unit for displaying a corrected image.
Owner:CORELOGIC
Imaging apparatus and imaging method
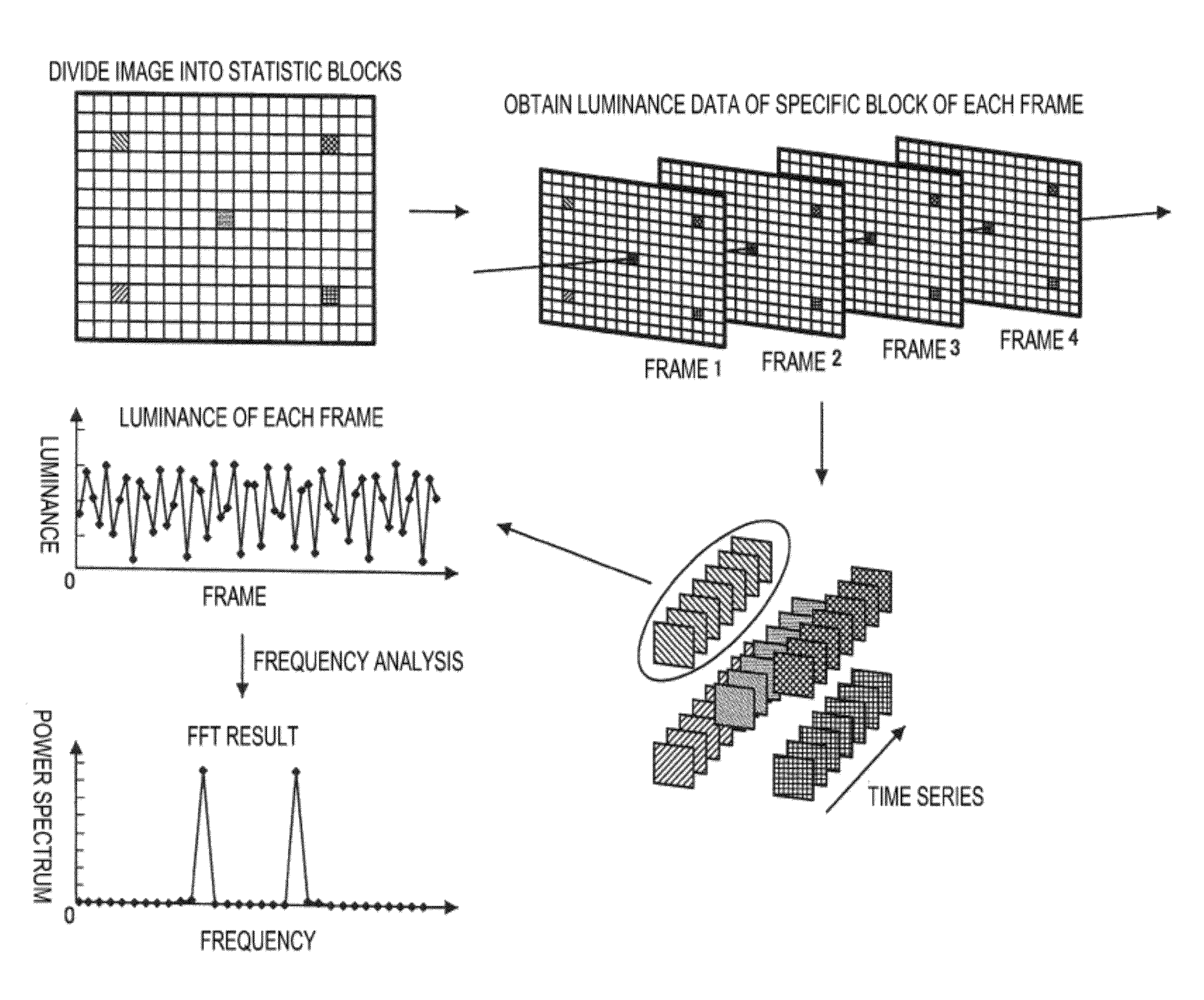
InactiveUS20120154629A1Increase in amount of calculationDegradation of image qualityColor signal processing circuitsConversion by changing video signal frequencyImaging equipmentCalculator
Disclosed is an imaging apparatus with a flicker detector that restrains an increased calculation amount and image quality degradation. The apparatus includes a frame rate controller for setting a frame rate of an acquired image to a first frame rate or different second frame rate, a luminance calculator for calculating a first luminance difference between two images of a first group continuously acquired at the first frame rate and a second luminance difference between two images of a second group continuously acquired at the second frame rate, and a flicker detector for comparing the first and second luminance differences with first and second threshold, respectively, and determining whether flickers of a first frequency and a different second frequency are generated or not.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image pickup apparatus and lens barrel
InactiveUS20080204564A1Quality improvementReduce image quality degradationTelevision system detailsPrintersFace detectionImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus capable of preventing photographing sensitivity from being increased more than necessary, reducing image quality degradation caused by camera shake or object shake and easily photographing images in good image quality. Digital camera 1 includes image shake correcting selection 16 that corrects shake of an optical image of a photographing object formed by an imaging optical system L, digital signal amplification section 110 that amplifies an image signal with a gain set by digital signal gain setting section 111, and face detection section 120 that detects a face of a photographing object, and microcomputer 3 calculates an object speed based on the detected motion of the face of the photographing object, decides whether or not the object speed is equal to or higher than a threshold A, and operates, when the object speed is lower than the threshold A, image shake correction by controlling image shake correcting section 16 or increases, when the object speed is equal to or higher than the threshold A, the gain of digital signal gain setting section 111, increases ISO sensitivity to increase the shutter speed and shorten the exposure time.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20070222380A1Lower on-resistanceImage quality can be hinderedDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A display device in which variations in luminance due to variations in characteristics of transistors are reduced, and image quality degradation due to variations in resistance values is prevented. The invention comprises a transistor whose channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor, a connecting wiring connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, a light emitting element having a laminated structure which includes a pixel electrode, an electro luminescent layer, and a counter electrode, an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode, and an auxiliary wiring formed in the same layer as a gate electrode of the transistor, a connecting wiring, or the pixel electrode. Further, the connecting wiring is connected to the pixel electrode, and the auxiliary wiring is connected to the counter electrode via an opening portion provided in the insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Driver device for liquid crystal display, computer program and storage medium, and liquid crystal display
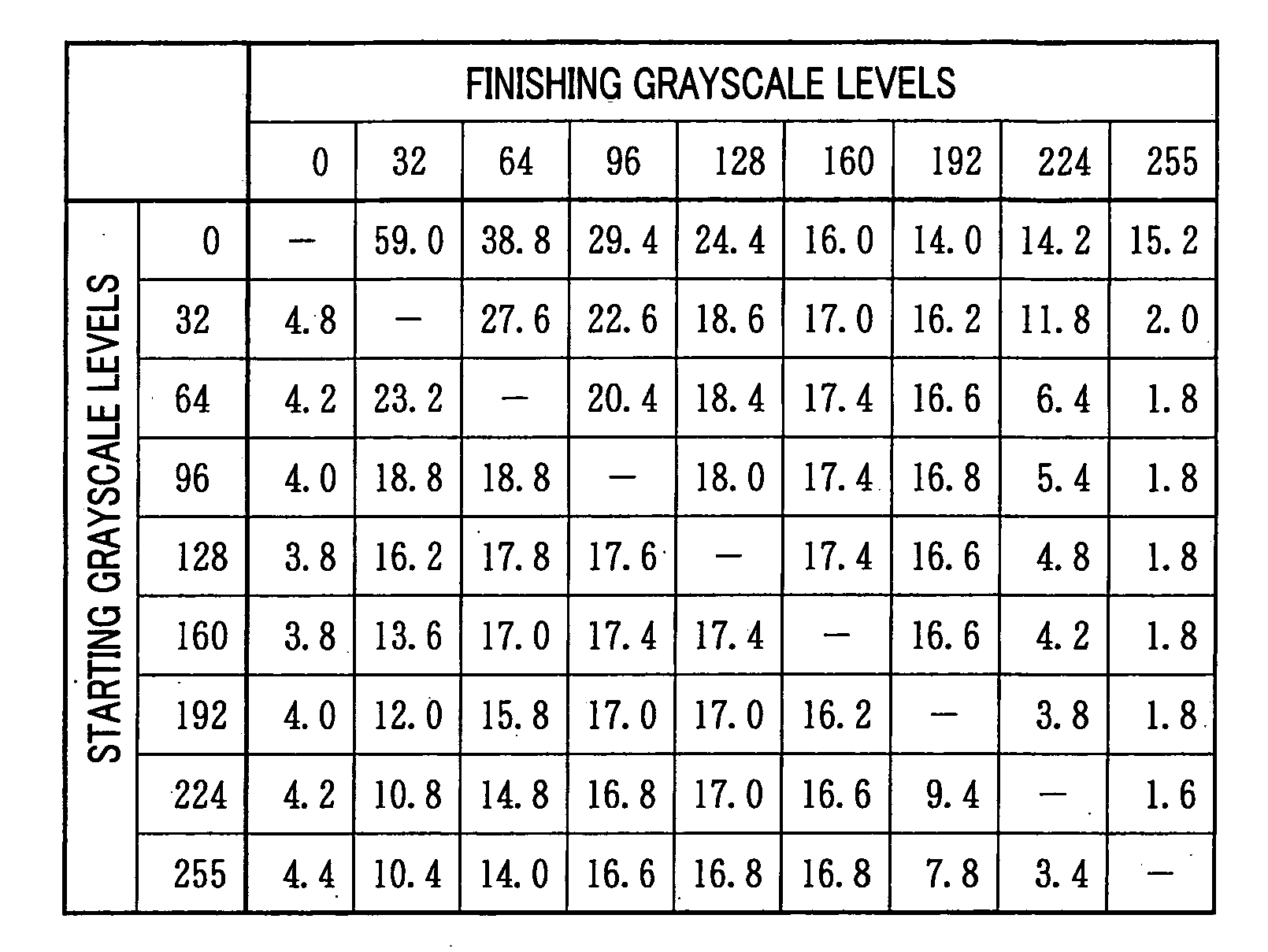
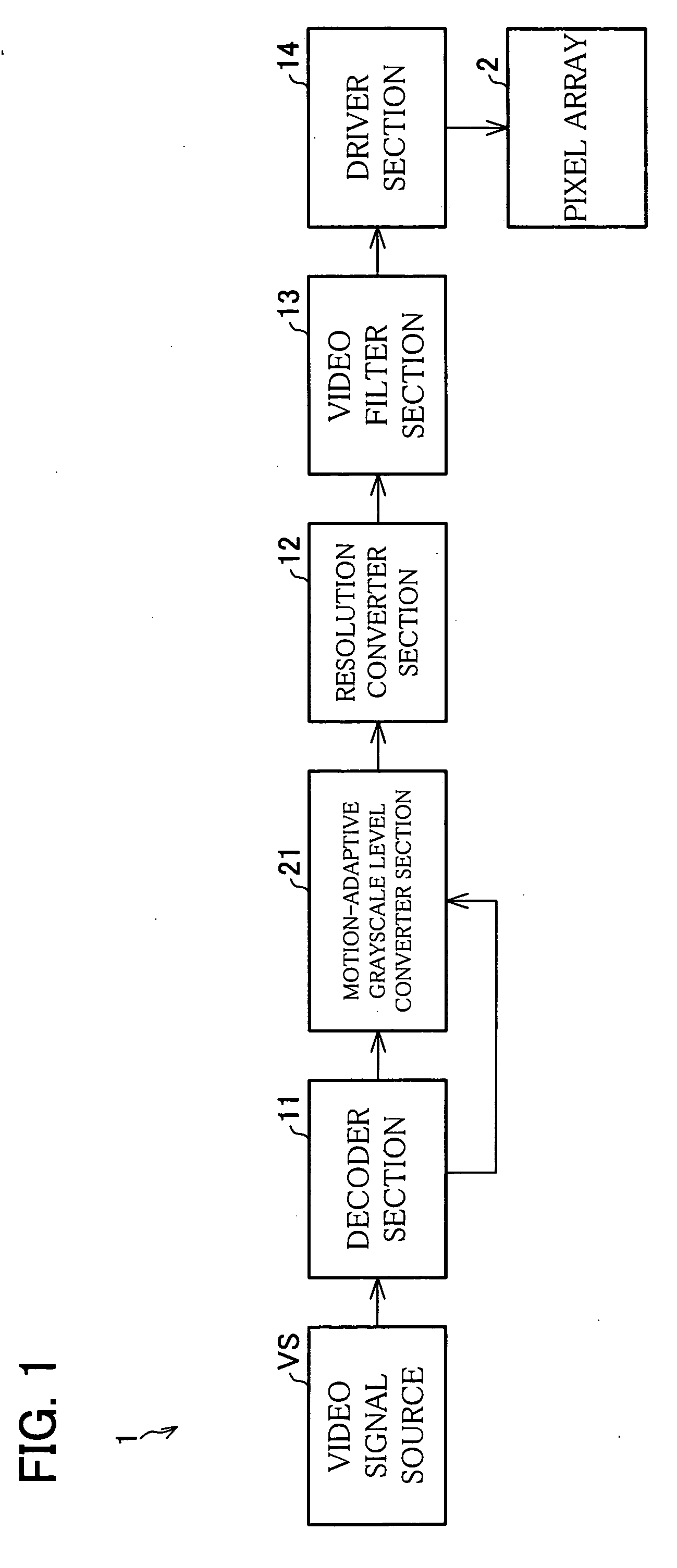
ActiveUS20060017678A1Lack of image qualityMaintain contrastStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLevel dataLevel converter
There is provided a motion-adaptive grayscale level converter section between a video signal source and a pixel array. The pixel array includes a liquid crystal cell of normally black and vertically aligned mode. The motion-adaptive grayscale level converter section determines based on information from a decoder section whether the pixels of an image represented by a video signal is in a moving image area. If a pixel is in a moving image area, the motion-adaptive grayscale level converter section changes the grayscale level data representing the grayscale level of the pixel so that there is no darker grayscale level than a predetermined first grayscale level. The resultant data is output as a video signal. Accordingly, we can provide a liquid crystal display capable of easing image quality degradation due to insufficient response when displaying a moving image while maintaining the contrast ratio achieved for a still image display.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device and projection type display apparatus
InactiveUS20050248556A1Improve picture qualityCapacitance can be smallProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
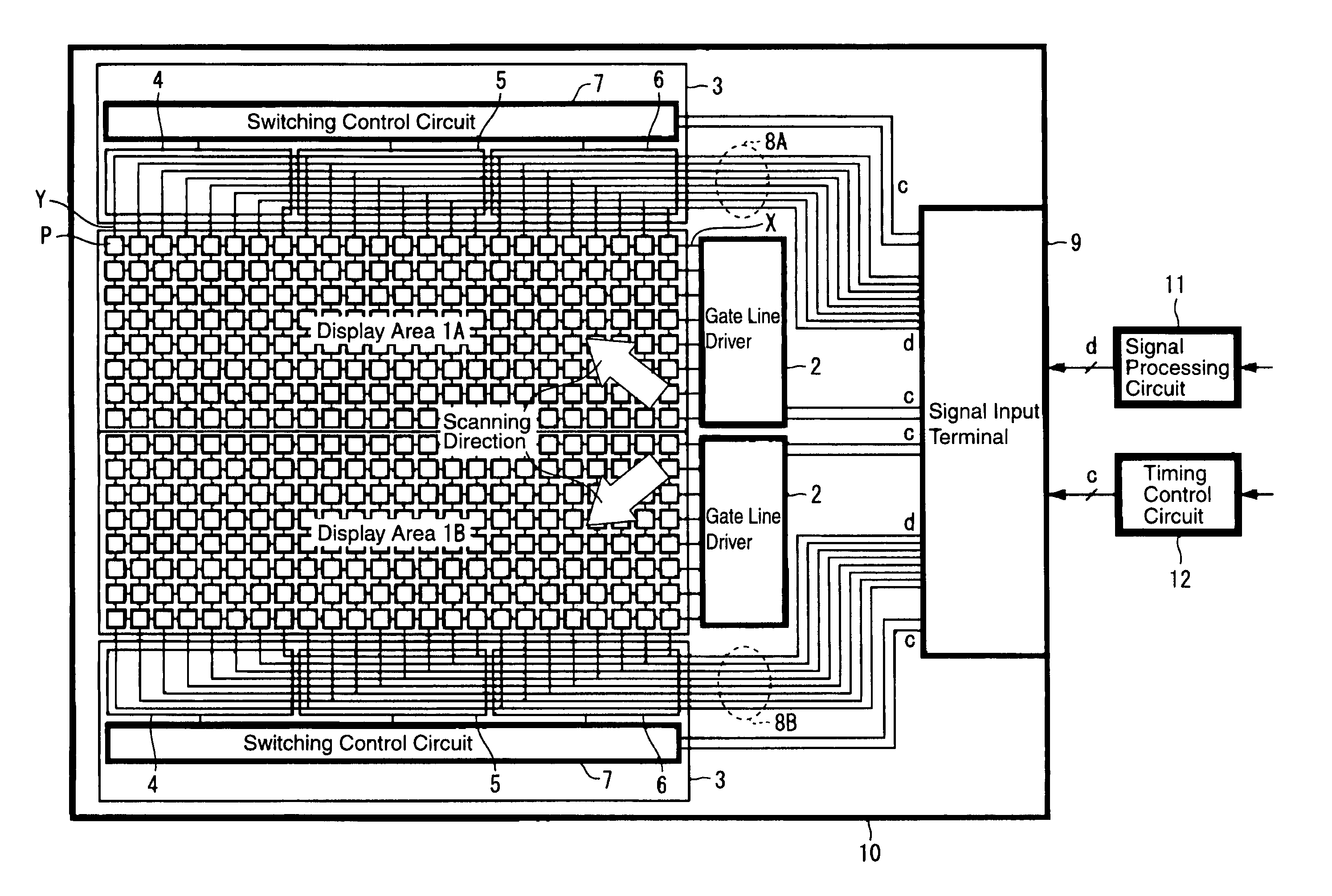
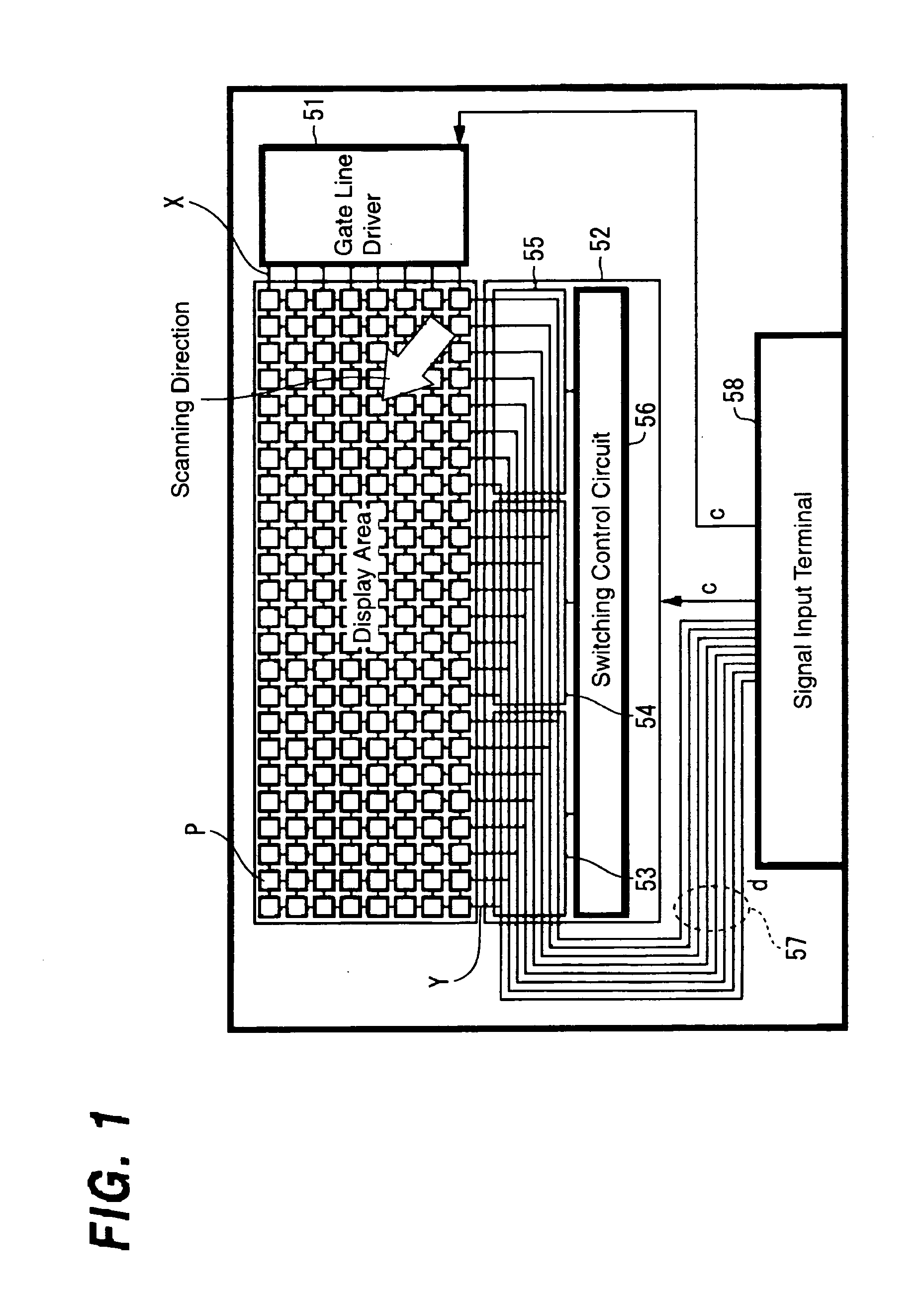
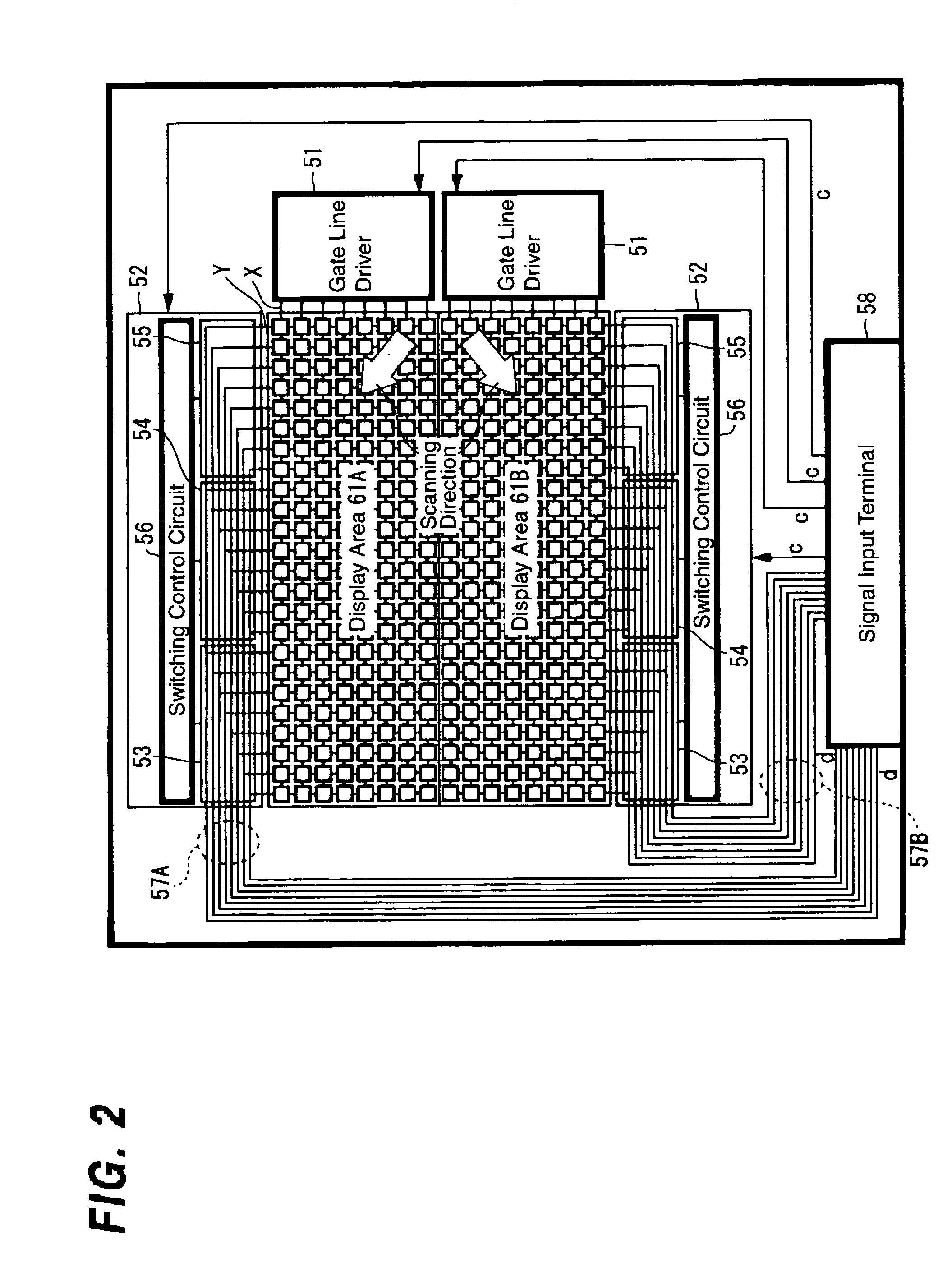
A display device having extremely short writing time to a pixel such as the liquid crystal display device of a dot sequential drive method using a single-crystal silicon transistor as a switching element is provided in which in the case where a display area is divided into two or more areas, the degradation of picture quality is prevented to perform a high definition display. In a display device of a matrix drive method in which gate lines X in the row direction and data lines Y in the column direction are arranged in matrix shape and a pixel P is arranged at the intersection of the gate line and the data line, a display area is divided into two or more areas 1A and 1B which are driven independently from each other; wiring layout of signal lines 8A and 8B which transfer display data d to each of the areas 1A and 1B is approximately symmetrical with a division boundary line of those areas positioned in between; and control unit 12 which makes a control to perform writing of the display data at least to the pixels P next to each other with the division boundary line positioned in between at approximately the same timing.
Owner:SONY CORP
Structure of Stereoscopic Image Data, Stereoscopic Image Data Recording Method, Reproducing Method, Recording Program, and Reproducing Program
InactiveUS20090102916A1Little image quality degradationIncrease the compression ratioColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsParallaxData recording
It is made possible to record stereoscopic image data of parallel-ray one-dimensional IP type in a format at a high compression rate with little image quality degradation. This stereoscopic image data can be efficiently decompressed and reproduced. A stereoscopic image data structure includes: a parallax component image data representing n or more parallax component images, each having accumulated pixels that cause the pixels to generate the parallel light rays in the same parallax direction in the viewing zone, and having different numbers of horizontal pixels. N combined images with the same numbers of vertical and horizontal pixels are a unit to be converted into a parallax interleaved image, the n combined images being formed by combining two or more parallax component images with parallax directions different from each other by n.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
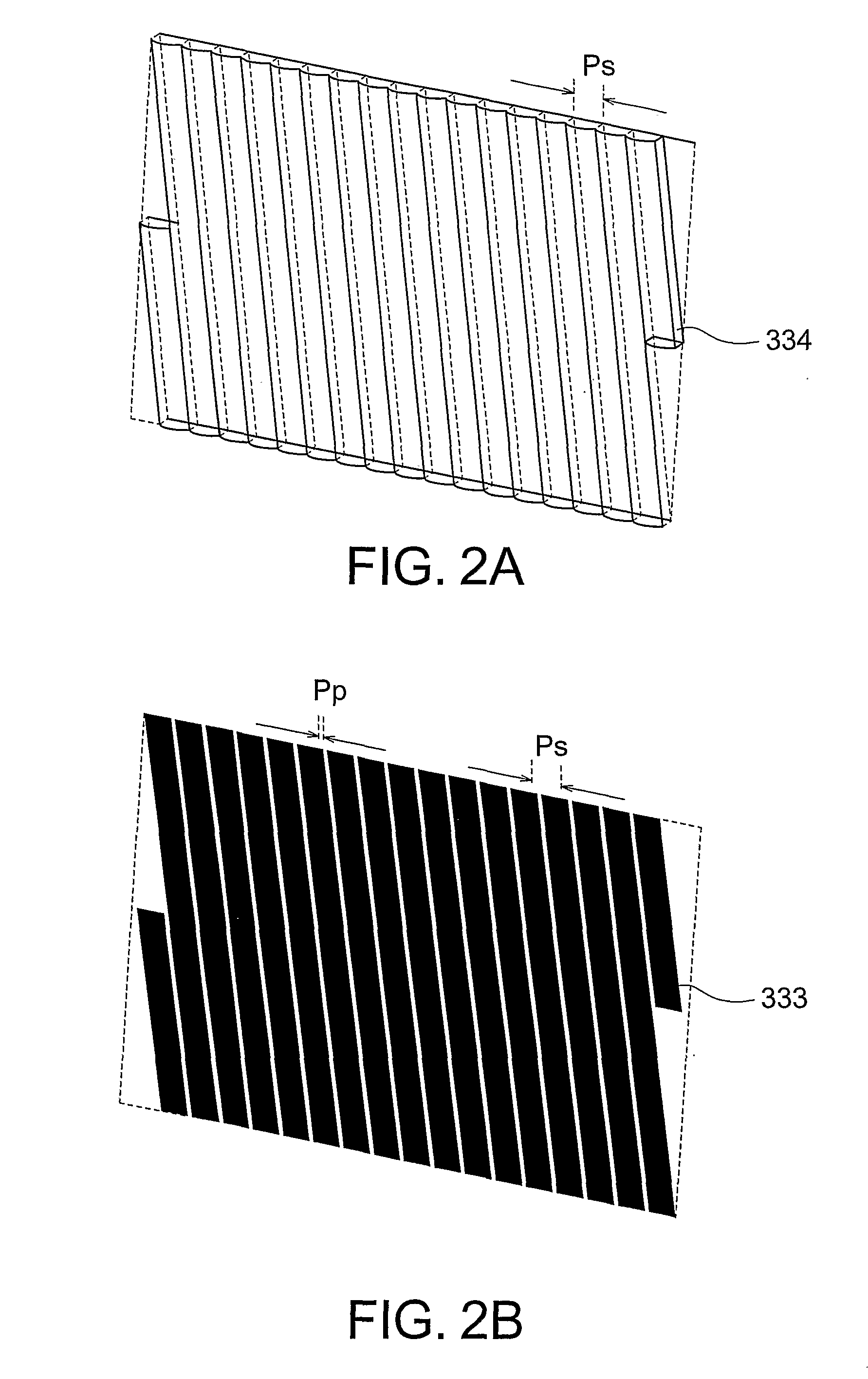
Image correcting apparatus and method, program, storage medium, image reading apparatus, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7477426B2Quality improvementImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImaging qualityImage correction
An image correcting apparatus is provided for preventing a degraded image quality which can be caused by a three-dimensional distortion correction made to a scanned image distorted in a trapezoidal shape. Divergent distortion angles α, β of a scanned image are detected using a page contour of a book document which can be found near the upper or lower edge of the scanned image in a main scanning direction. The scanned image is corrected for a divergent distortion based on the divergent distortion angles α, β, followed by a correction of the scanned image for a shape distortion in a sub-scanning direction. In this way, the image quality can be prevented from degradation possibly caused by the three-dimensional distortion correction, if made to such a scanned image distorted in a trapezoidal shape.
Owner:RICOH KK
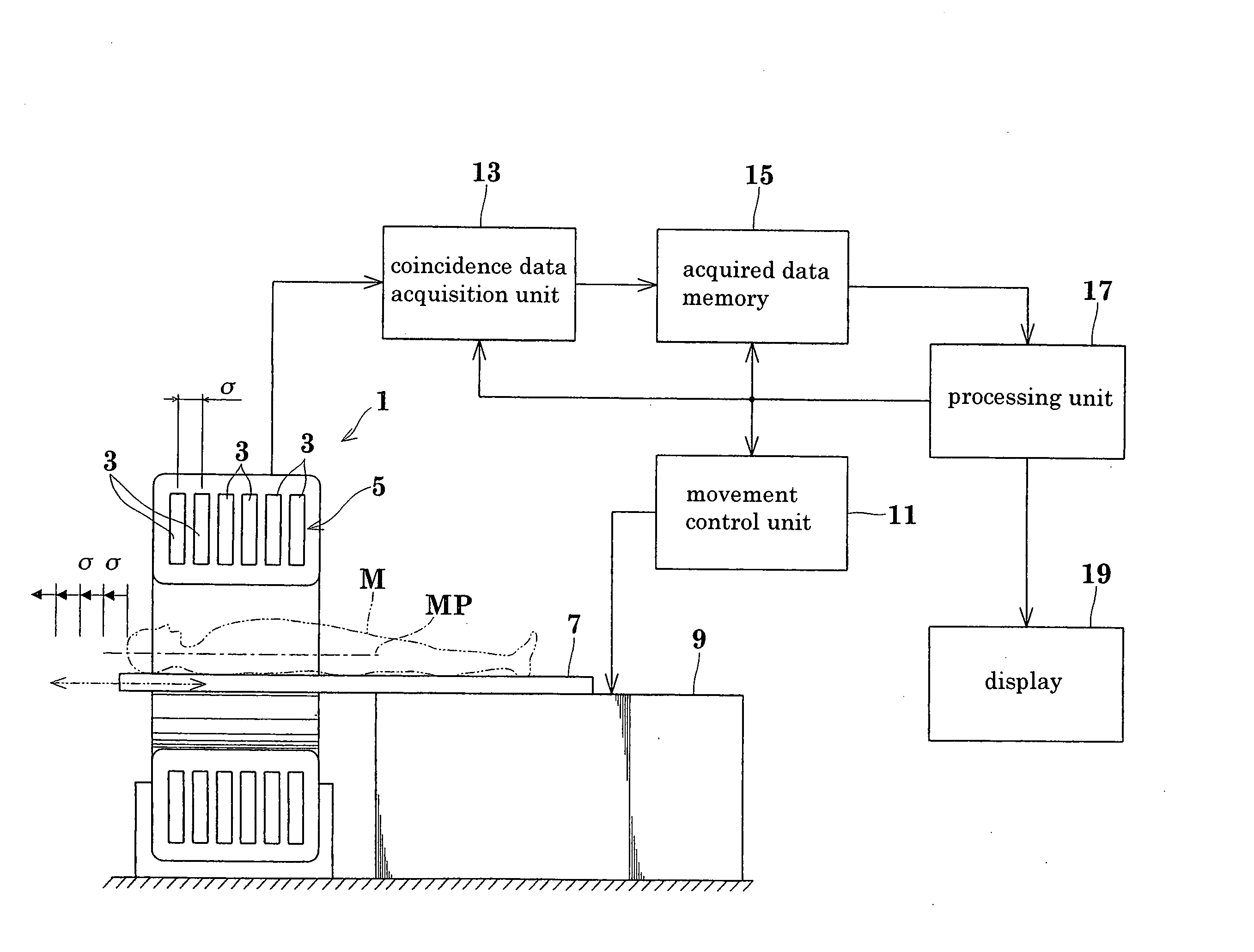
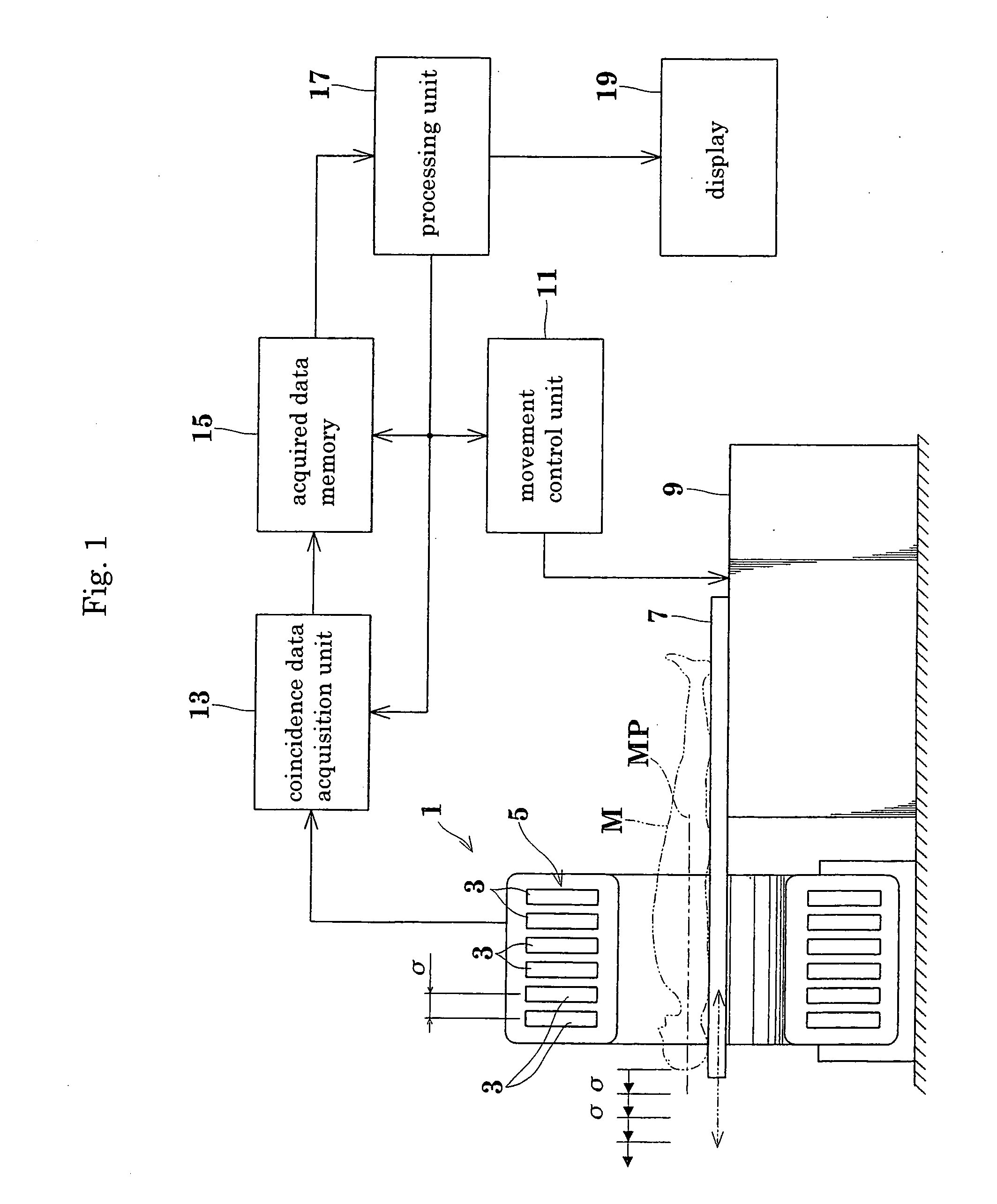
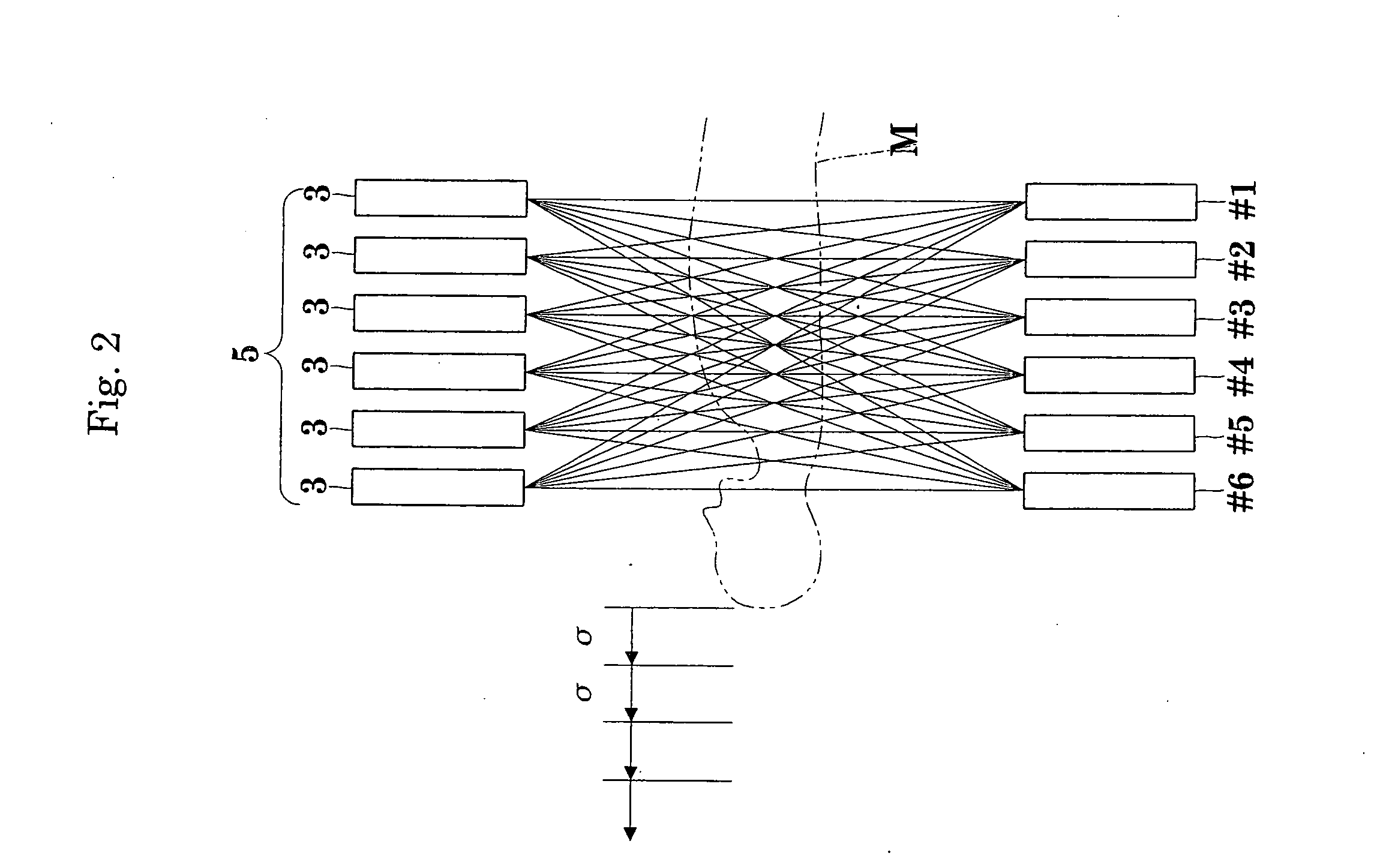
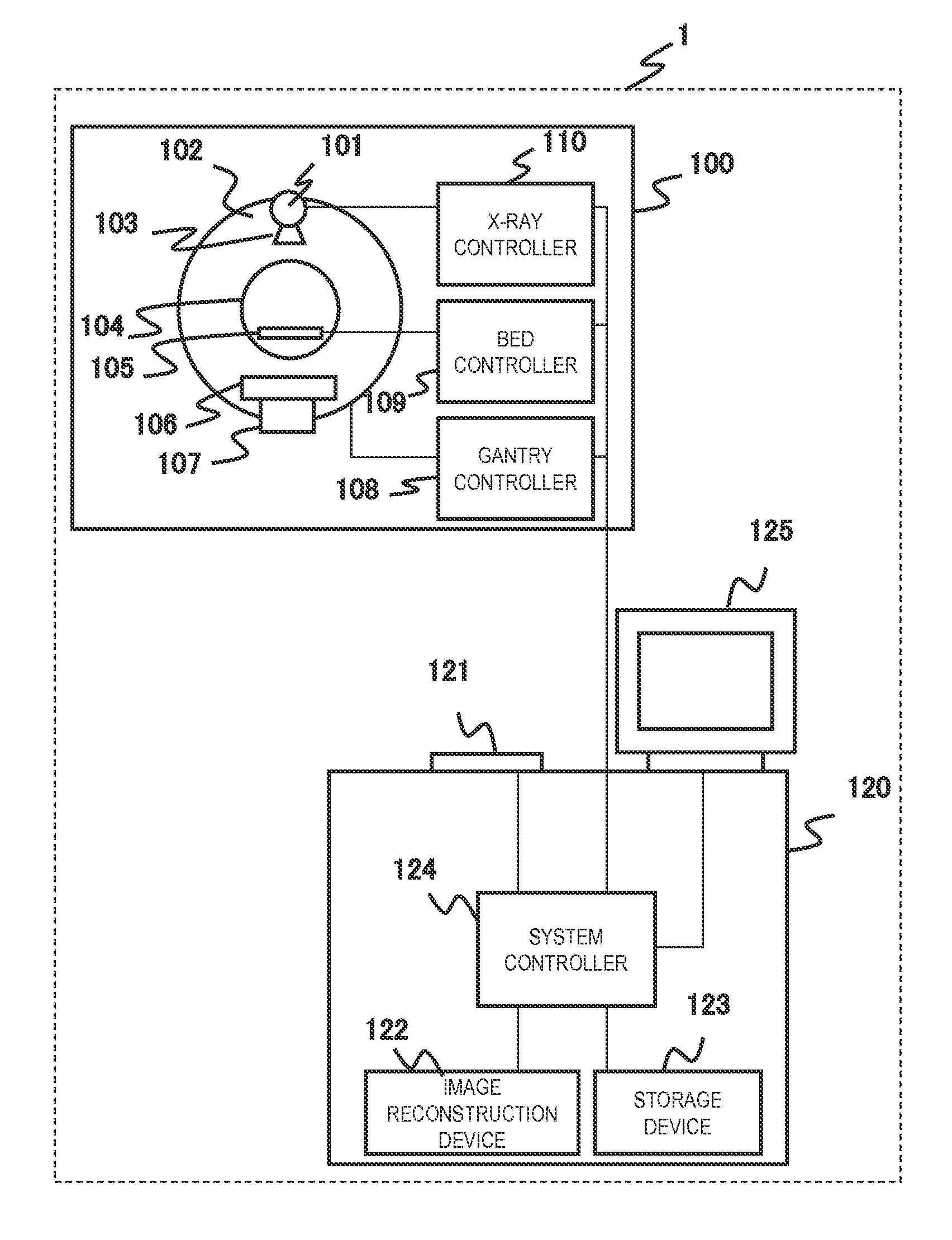
3D image reconstructing method for a positron CT apparatus, and positron CT apparatus
InactiveUS20070018108A1Eliminate unevennessReduce image qualityMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentUltrasound attenuation3d image
Image quality deterioration due to a drop in resolution or lowering of S / N ratio while reducing the amount of data stored during a 3D data acquisition process, and shortening the time from the start of an examination to the end of imaging. The method and apparatus of this invention perform, in parallel with the 3D data acquisition process, addition of sinograms, reading of subsets of the sinograms having been added, and image reconstruction. Consequently, the amount of data stored is reduced, and the time from the start of an examination to the end of imaging is shortened. At the same time, since 3D iterative reconstruction is not accompanied by conversion from 3D data to 2D data, a drop in resolution due to errors occurring with the conversion from 3D data to 2D data is avoided. The 3D iterative reconstruction can directly incorporate processes such as an attenuation correction process. It is thus possible to avoid also a lowering of S / N ratio resulting from an indirect incorporation of such processes.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Imaging apparatus and imaging method
ActiveUS20080260375A1Reduce image quality degradationImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementMicrocomputerFace detection
An imaging apparatus and an imaging method capable of reducing image quality degradation due to camera shake or object shake and photographing images in good image quality in a simple manner. Digital camera 1 is provided with face detection section 120 that detects faces of a plurality of photographing objects, microcomputer 3 performs continuous shooting in optimum photographing conditions in accordance with the number of faces of the photographing objects for each face of the plurality of photographing objects by a single shutter operation and performs control by assigning serial photographing object numbers to the images of the plurality of photographing objects taken by continuous shooting and recording the images in a single continuous-shooting image folder. Furthermore, microcomputer 3 performs continuous shooting in predetermined order in accordance with the number of faces of the photographing objects and detects, when the photographing object speed is equal to or higher than a predetermined value, the photographing object speed again after photographing other photographing objects.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method of correcting image distortion and apparatus for processing image using the method
InactiveUS20090059041A1Remove jagged-edge artifactMinimize blurringTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingComputer science
A method of correcting image distortion and an apparatus for processing an image using the method are provided, where the method can overcome the disadvantages of the conventional methods of correcting lens distortion and can minimize image quality degradation at outer portions,. The method includes: receiving an image from a wide-angle lens; extracting a distortion coefficient of the distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens; correcting the distortion of the image by using the extracted distortion coefficient; and displaying a corrected image. The apparatus includes: a wide-angle lens for receiving an image; an image processing unit comprising a distortion coefficient extracting unit for extracting a distortion coefficient of distortion in the image caused by the wide-angle lens and a distortion correcting unit for correcting the distortion of the image using the extracted distortion coefficient; and a display unit for displaying a corrected image.
Owner:CORELOGIC
Display device and terminal unit using the same
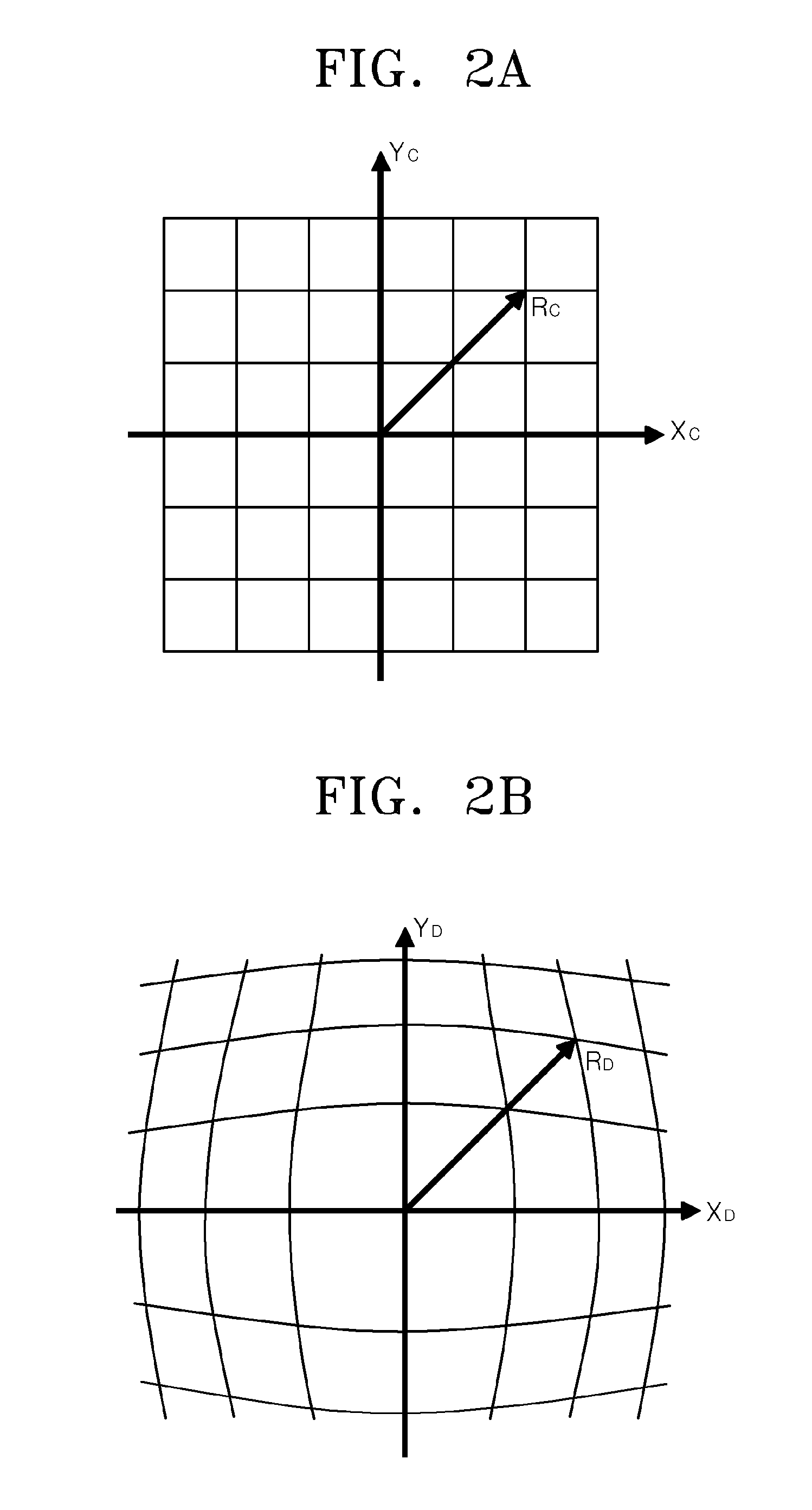
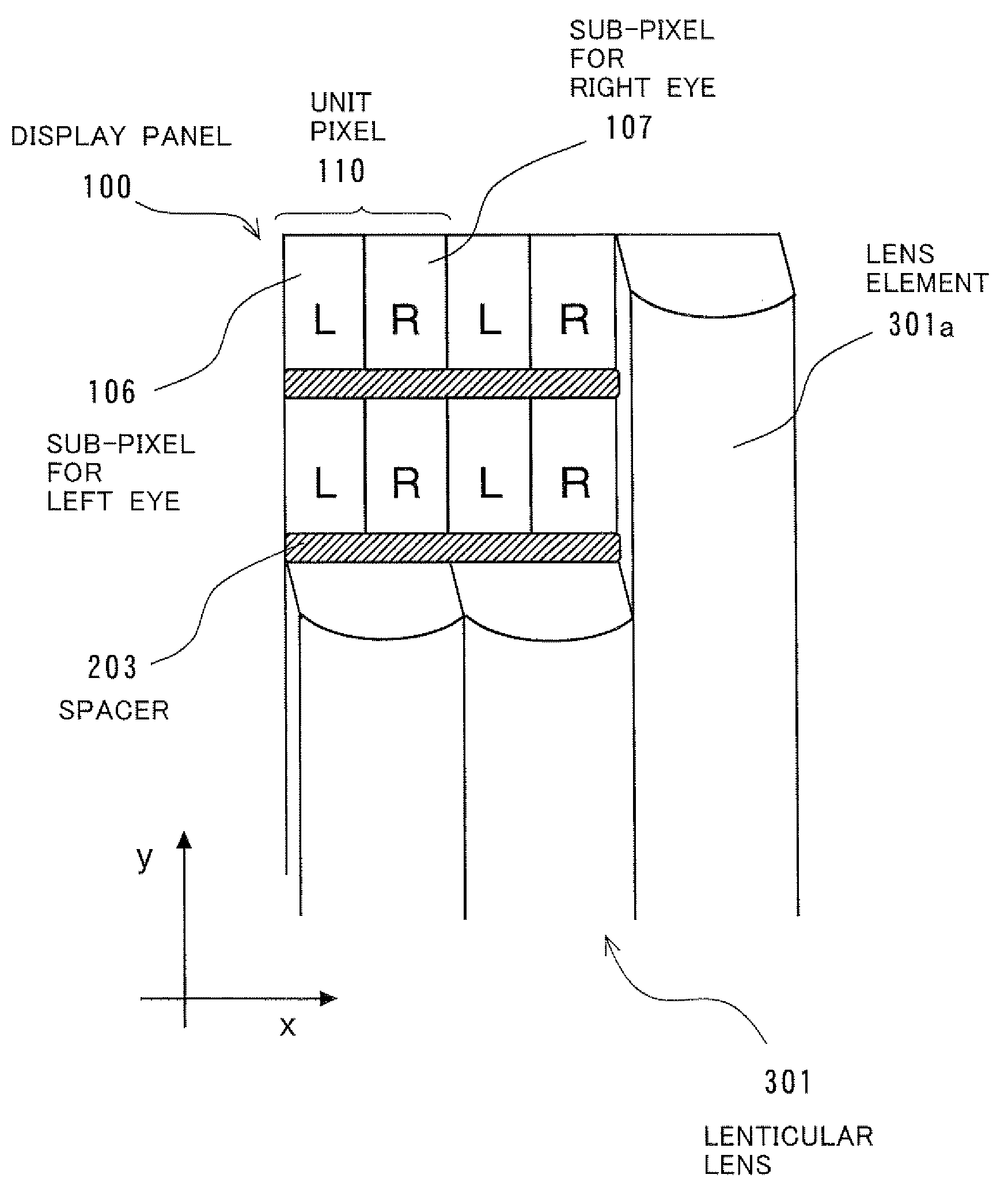
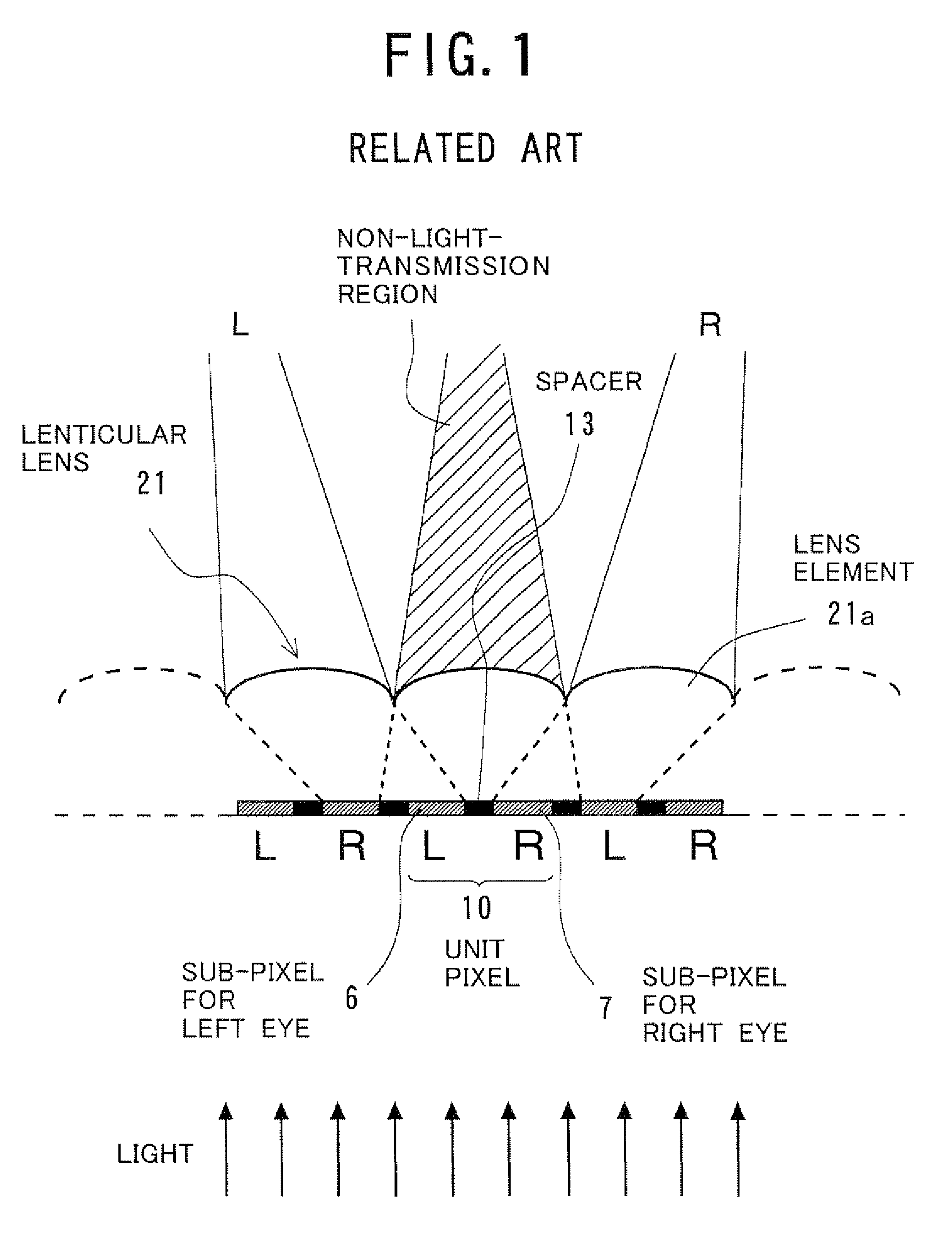
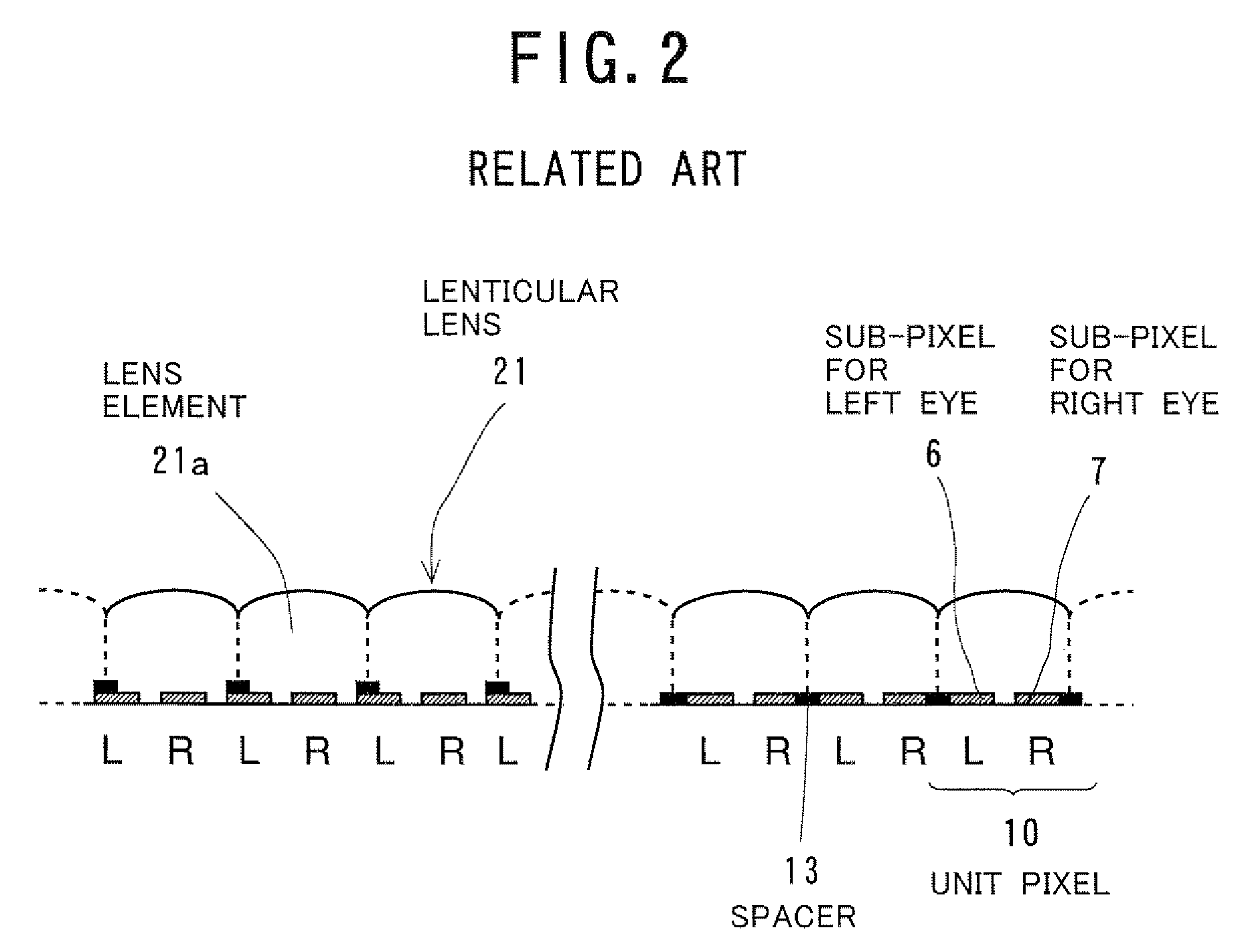
ActiveUS20090168167A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce image quality degradationSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsImaging qualityDisplay device
A display device reduces the image quality degradations by suppressing the effect of the defective alignment regions caused by the spacers while minimizing the aperture ratio lowering, and prevents the image quality change dependent on the observation positions. The display device has a display panel and a lenticular lens. Each unit pixel of the display panel includes the sub-pixel for the left eye and the sub-pixel for the right eye. To keep the pair of substrates at a predetermined gap, spacers are arranged at predetermined positions in the gap. The spacers are stripe-shaped and extended along a direction perpendicular to the image separation axis of the lenticular lens. The spacers are equally overlapped with the sub-pixels for the left eye and those for the right eye. The spacers may be isolated for the respective unit pixels, or the first or second sub-pixels.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
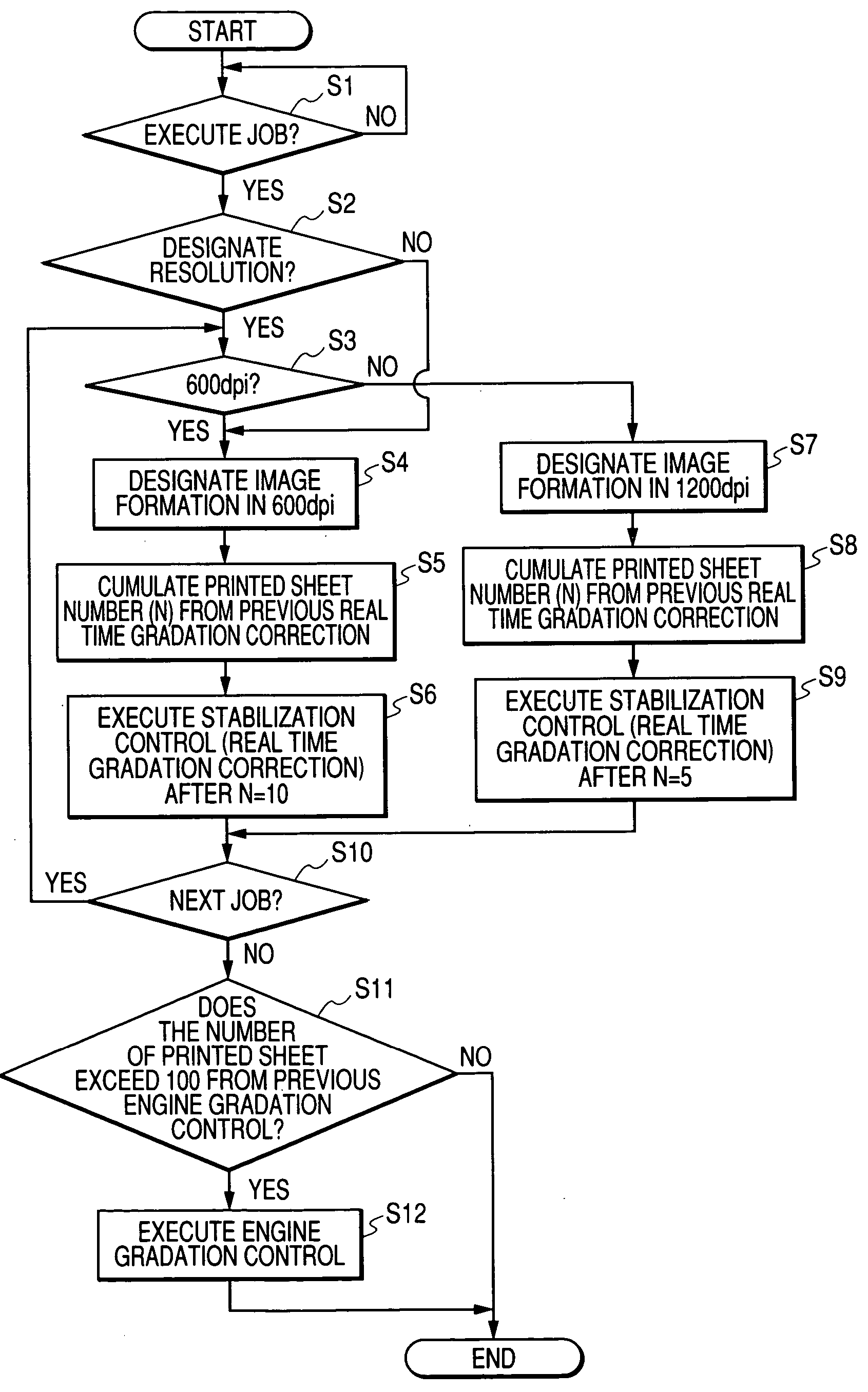
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20050007609A1Inhibit deteriorationShorten the timeDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage resolutionImaging quality
The image forming apparatus includes image forming device for forming an image, switching device for switching resolution of an image formed by the image forming device, processing device for performing stabilization processing for stabilizing quality of the image formed by the image forming device and changing device for changing a processing procedure of the stabilization processing in accordance with the resolution switched by the switching device. With these features, it is possible to avoid deterioration of image quality even if the resolution is switched.
Owner:CANON KK
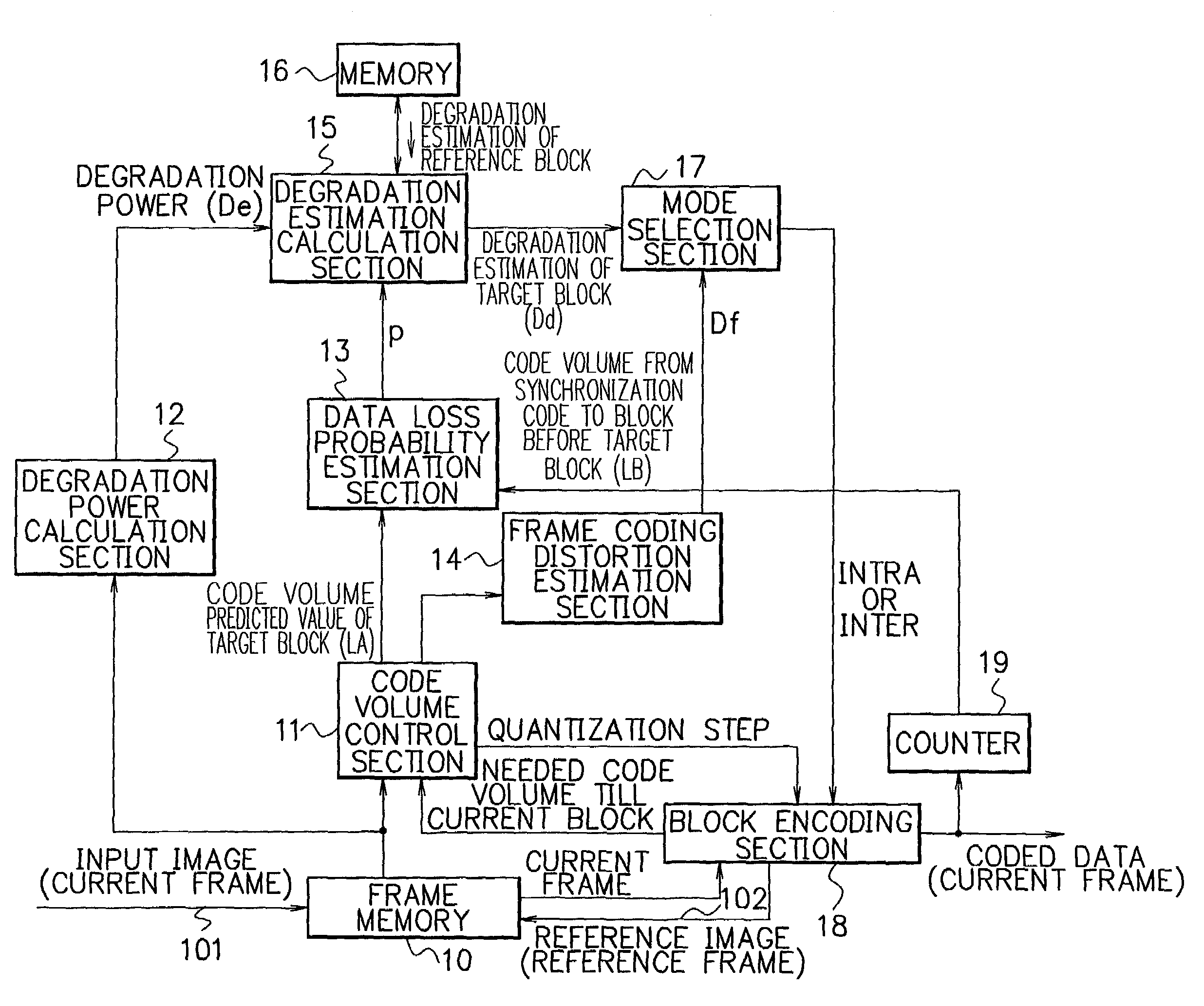
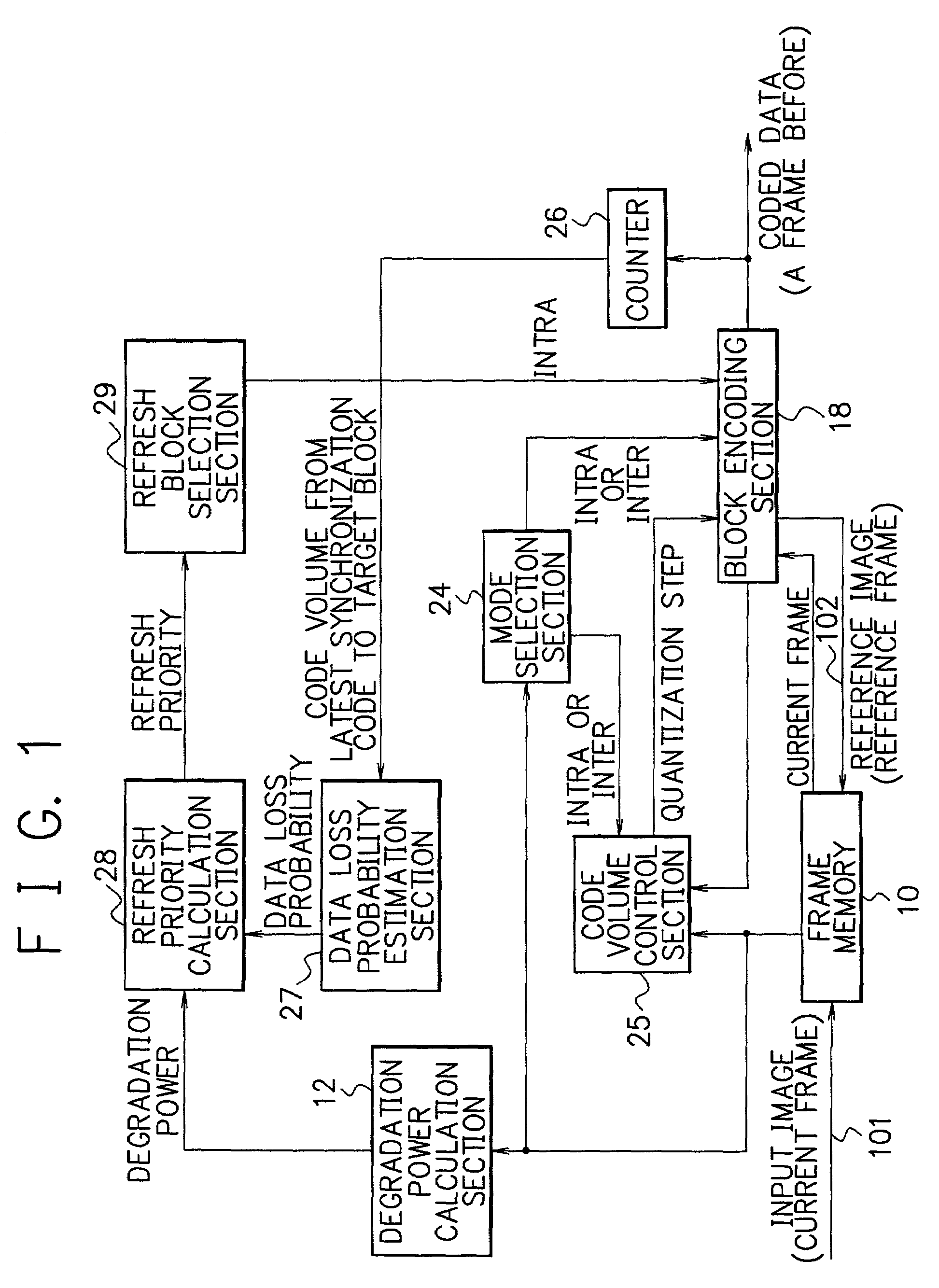
Device and method for motion video encoding reducing image degradation in data transmission without deteriorating coding efficiency
InactiveUS7161982B2Image degradation can be reduced without deteriorating the coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareProbability estimation
A code volume control section refers to an input image and a reference image stored in a frame memory and thereby sets a quantization step for each block so that the volume of coded data generated for a frame will be a preset volume. A data loss probability estimation section estimates a data loss probability (the probability that data loss will occur to a target block due to transmission error) based on a code volume predicted value of the target block obtained by the code volume control section and the code volume from the latest synchronization code pattern to a block just before the target block. A degradation estimation calculation section calculates an estimate of degradation of the target block caused by errors based on image degradation power and the data loss probability. A mode selection section selects an optimum encoding mode for the target block based on the degradation estimate of the target block and an estimate of frame coding distortion. Forced refresh (intra-frame encoding of a block) is carried out properly and effectively, thereby image degradation is reduced without deteriorating coding efficiency.
Owner:NEC CORP
Image processing device and method, program recording medium
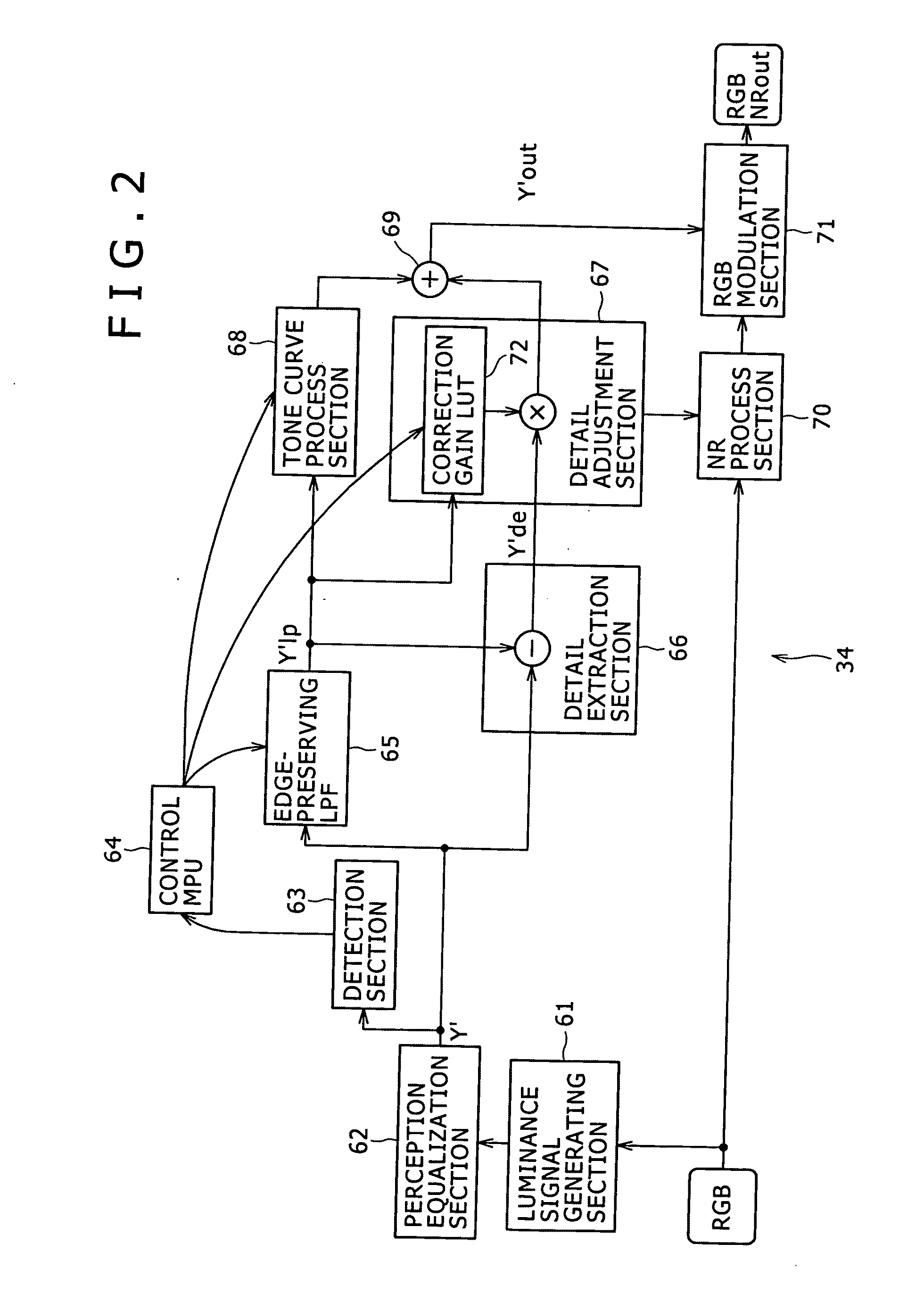
InactiveUS20100310189A1Suppresses image quality degradationSimple configurationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingEqualization
The present invention relates to an image processing device and method, program and recording medium for achieving grayscale compression capable of suppressing image quality degradation using a simple configuration. A detection section 63 performs a detection process of a signal Y′ that has been subjected to the processes of a luminance signal generating section 61 and perception equalization section 62, thus finding average intensities of lighting in bright and dark areas of an input image. A control MPU 64 finds adaptation gains kAr and kBr based on the average intensities. Processing the signal Y′ with an edge-preserving LPF 65 provides a lighting component signal Y′lp. A detail extraction section 66 computes the difference between the signal Y′ and lighting component signal Y′lp, thus extracting a detail component signal Y′de of the image of the signal Y′. Thereafter, the lighting component of the signal Y′ is subjected to grayscale compression by a tone curve process section 68, while the detail component of the image of the signal Y′ is subjected to grayscale compression by a detail adjustment section 67.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image restoration method
InactiveCN101635050AEffective recoveryImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityImage restoration
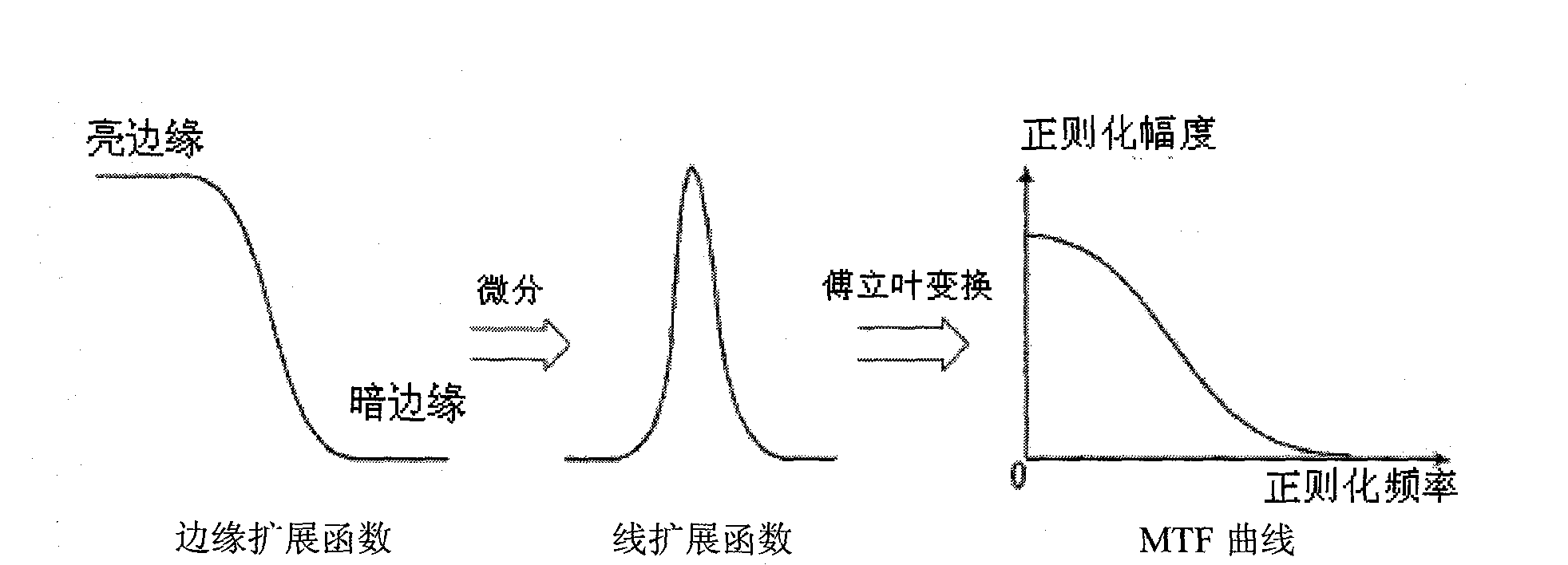
An image restoration method based on MTF includes the following steps: firstly, calculating MTF curve of an image; secondly, constructing dimensional MTF matrix; thirdly, carrying out image restoration in frequency domain by utilizing the MTF matrix. The method aims at remote sensing image with large data volume and is based on MTF theory and image quality degradation theory; and the method provided by the invention is effective for image restoration. Practice shows that the method can effectively restore image and improve image quality and has high algorithm efficiency. Currently, the method is successfully applied in domestic ground satellite pre-treatment system, and practice shows that the method is correct, feasible and universal.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Resolution-converting apparatus and method
ActiveUS7876979B2Eliminating occurrence of quality-degradingImprove clarityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersIntermediate imageImage resolution
The resolution-converting method comprises steps of applying an edge-directed interpolation to an input image and producing an intermediate image; converting a sampling rate with respect to the intermediate image and producing an output image having a predetermined resolution; and improving sharpness of the produced output image. The present invention prevents image-quality degradation factors that can occur in the conventional resolution-converting method as well as obtains an output image having a resolution of a desired size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image pickup apparatus and control method thereof
InactiveUS20100066897A1Avoid changeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityComputer science
When luminance of an object changes, aperture value and shutter speed are changed. Shutter speed, in case of an electric shutter, is changed immediately. On the other hand, aperture value is driven over the span of several frames, due to delays in communication between the lens and the camera body or mechanical delays. During aperture driving duration, the aperture value deviates from the program diagram, leading to inappropriate exposure and drop in image quality. Correction coefficient B is calculated from ratio of luminance values of certain regions of a frame that are appropriately exposed according to the program diagram and a frame that are inappropriately exposed and deviates from the program diagram. Then, correction of gain is performed on the frames that are inappropriately exposed using the correction coefficient B, obtaining output image signals for which deterioration in image quality due to inappropriate exposure is suppressed.
Owner:CANON KK
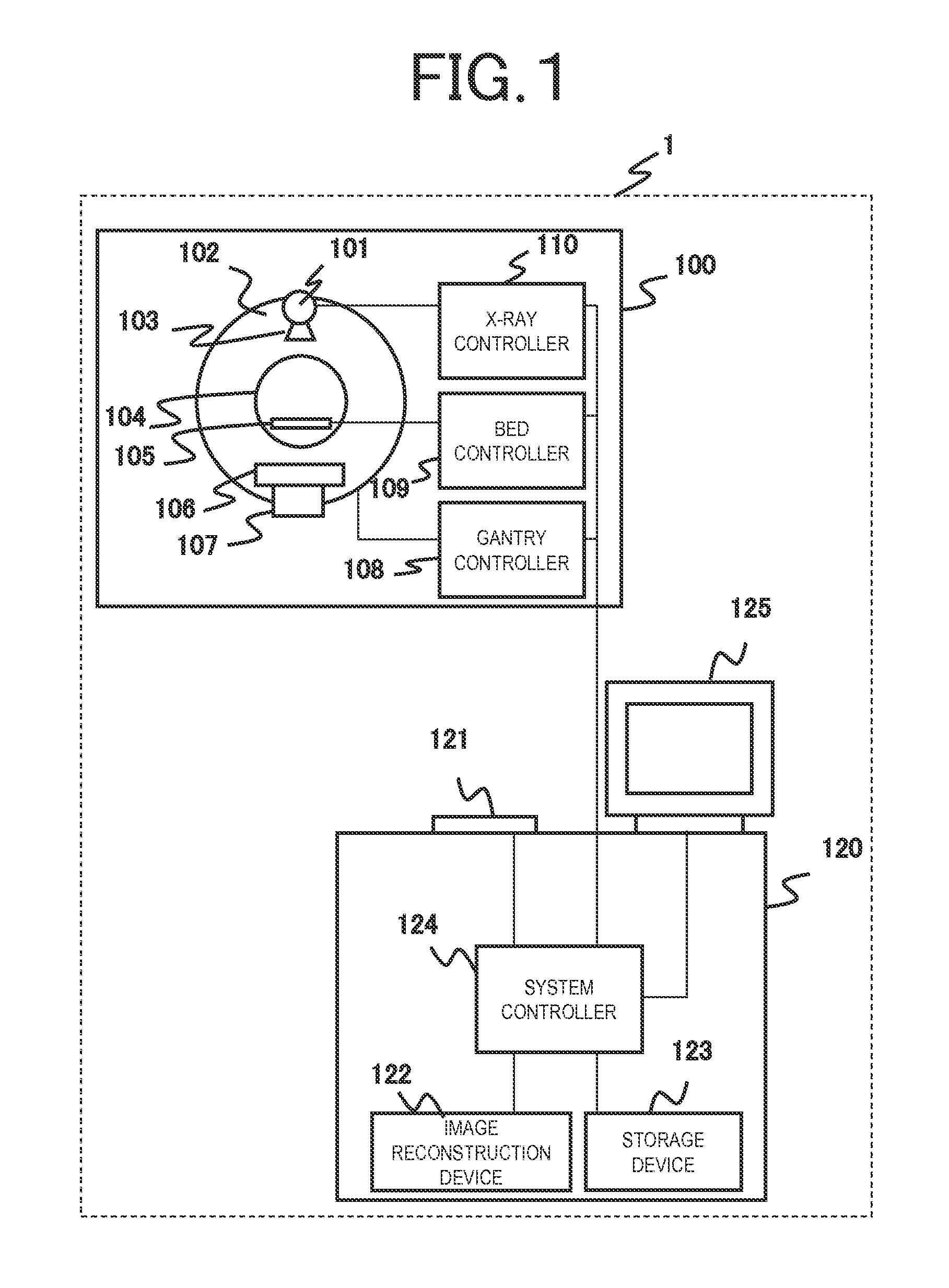
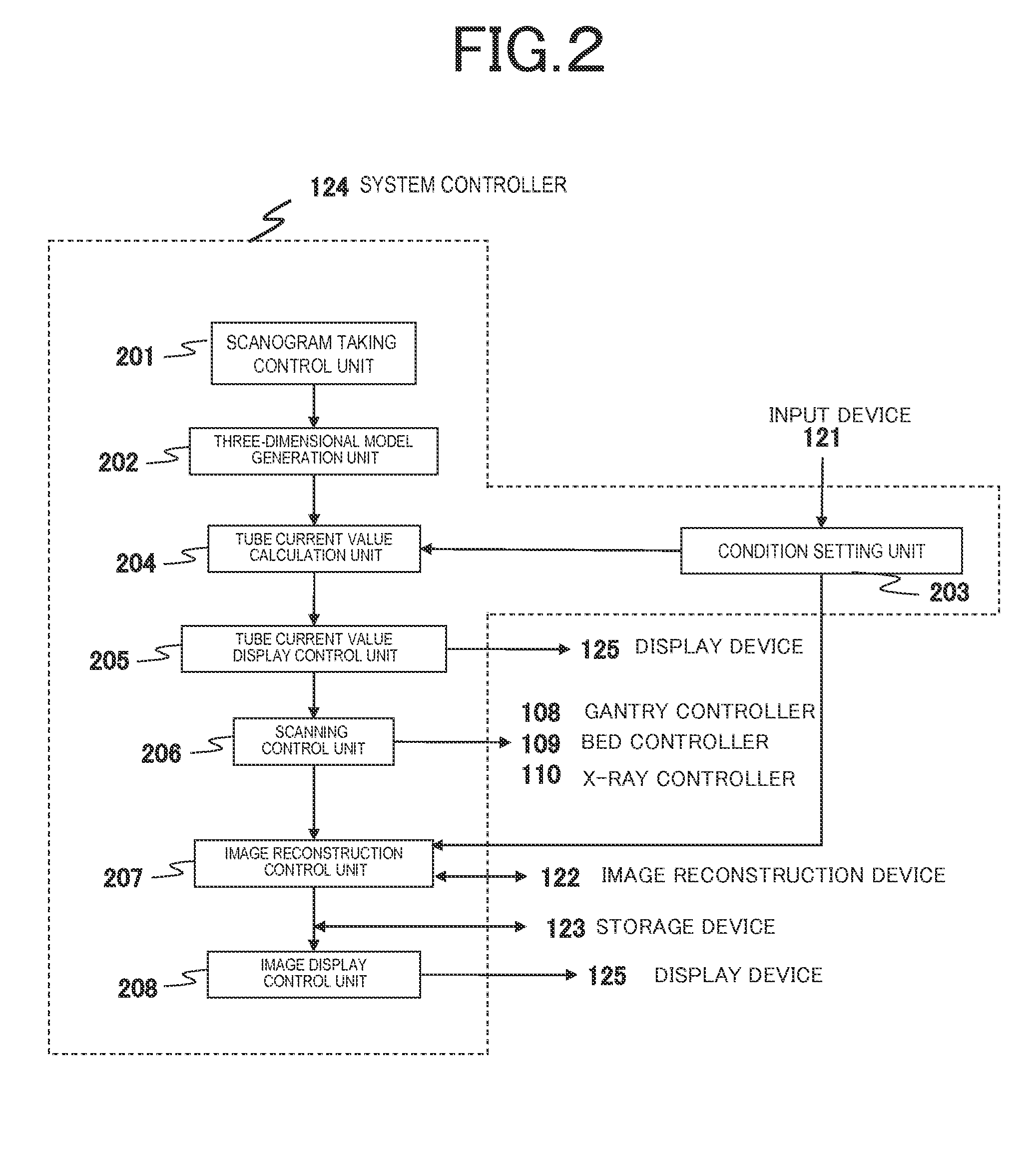
X-ray ct apparatus and tomography method
ActiveUS20150297165A1Little image quality degradationImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPower flowObject based
In order to provide an X-ray CT apparatus with little image quality degradation even though a tube current value of the X-ray tube is suppressed, an X-ray CT apparatus of the present invention includes: a system controller that calculates a tube current value of an X-ray tube based on a successive approximation process condition selected from a plurality of successive approximation process conditions and input a scanning condition and / or a reconstruction condition and that performs scanning based on the calculated tube current value of the X-ray tube; and an image reconstruction device that reconstructs a tomographic image of an object, based on the selected successive approximation process condition and the reconstruction condition, from an amount of transmitted X-rays detected by an X-ray detector after being emitted from an X-ray source to the object based on the calculated tube current value of the X-ray tube and being transmitted through the object.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com