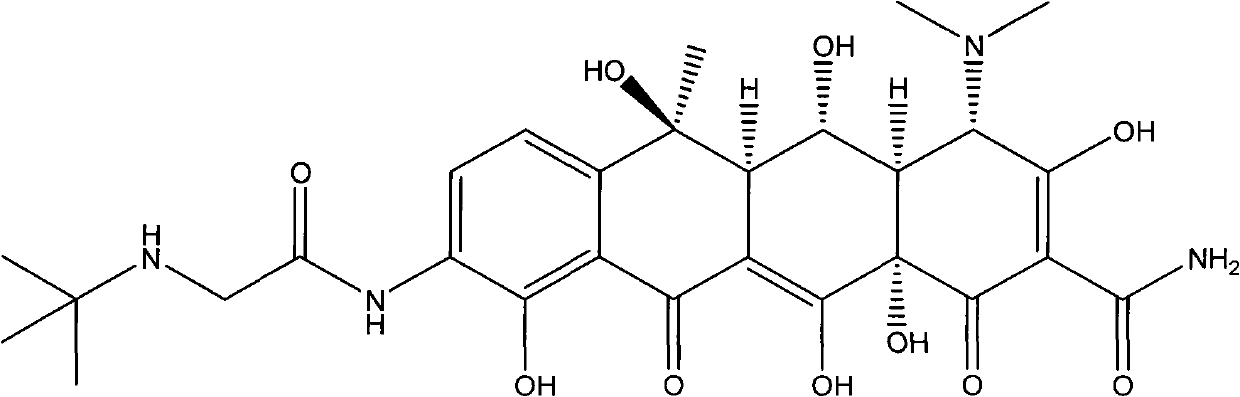
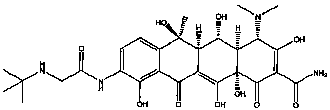
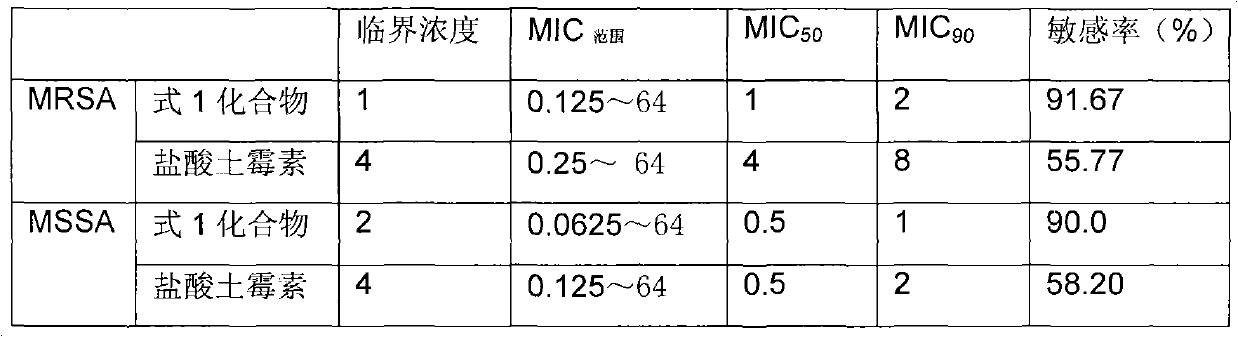
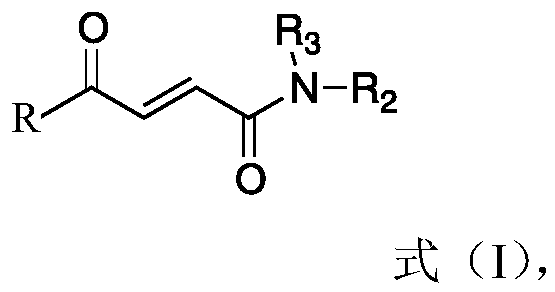
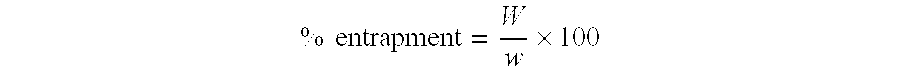Patents
Literature
30 results about "Methicillin sensitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
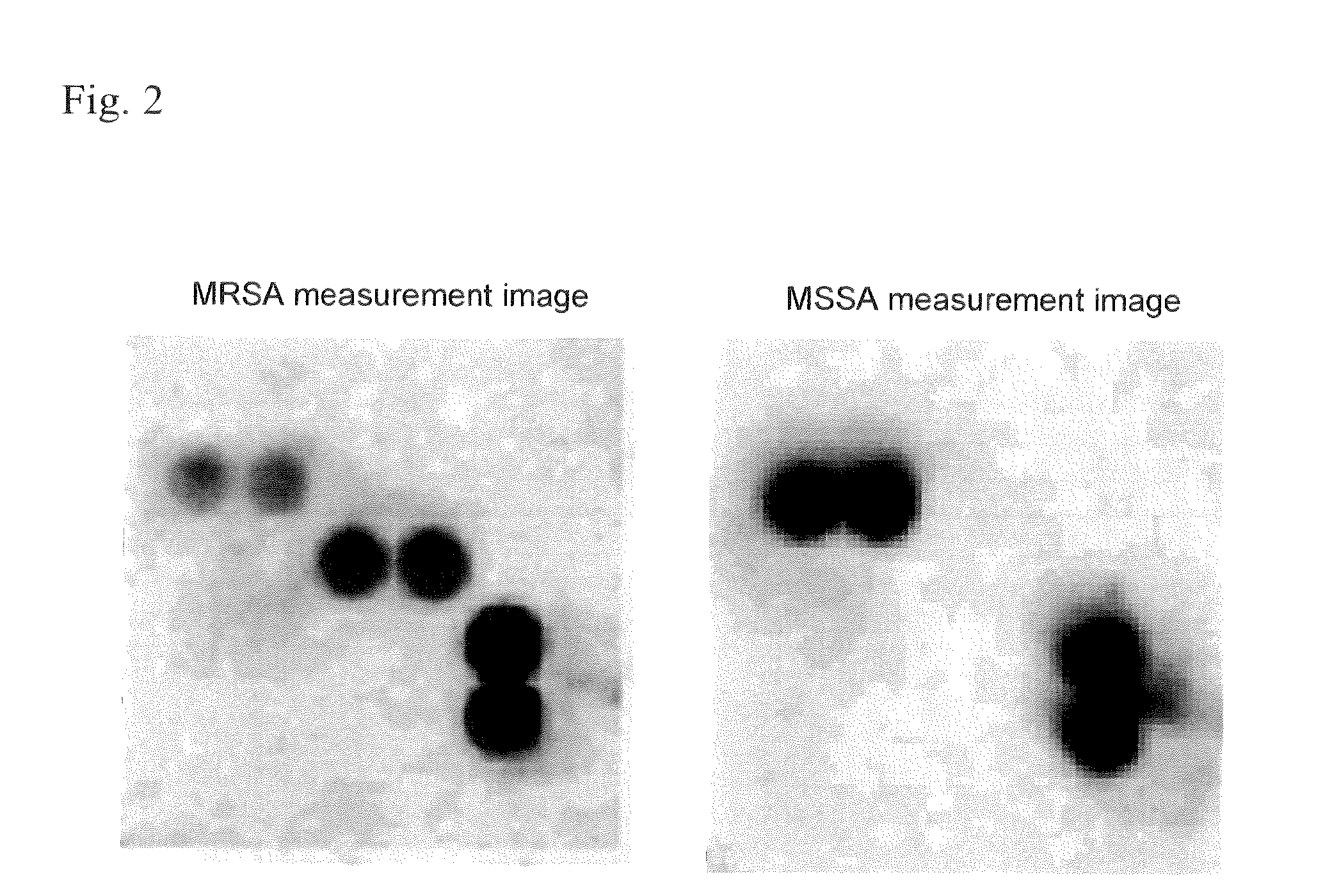
This particular bacterium is typically classified as methicillin sensitive or methicillin resistant. If the classification is MSSA, then it simply indicates that the bacterium in question is sensitive or reacts to the antibiotic drug called methicillin.
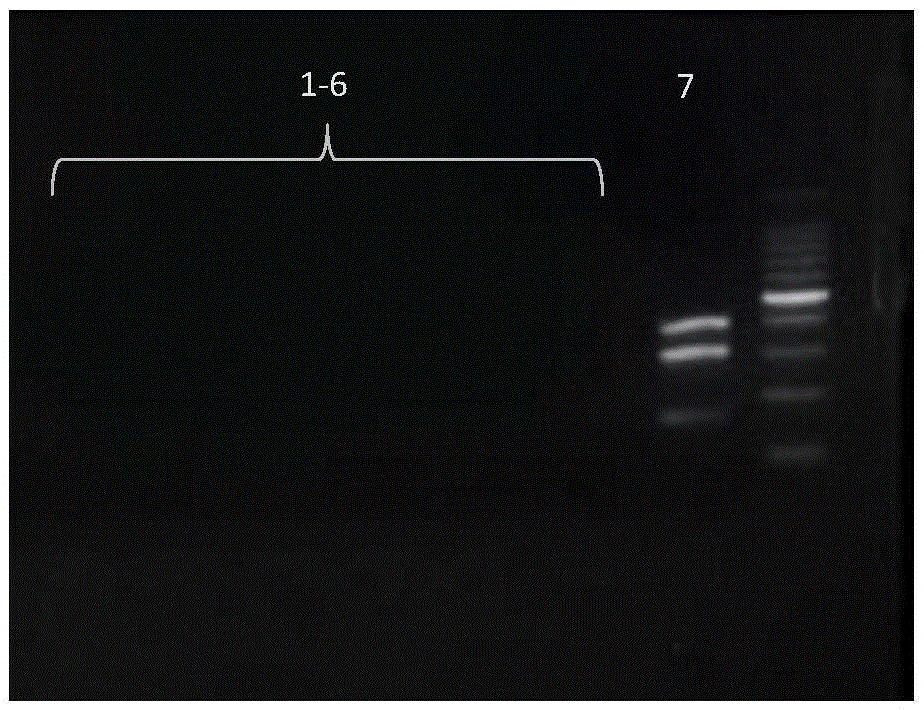
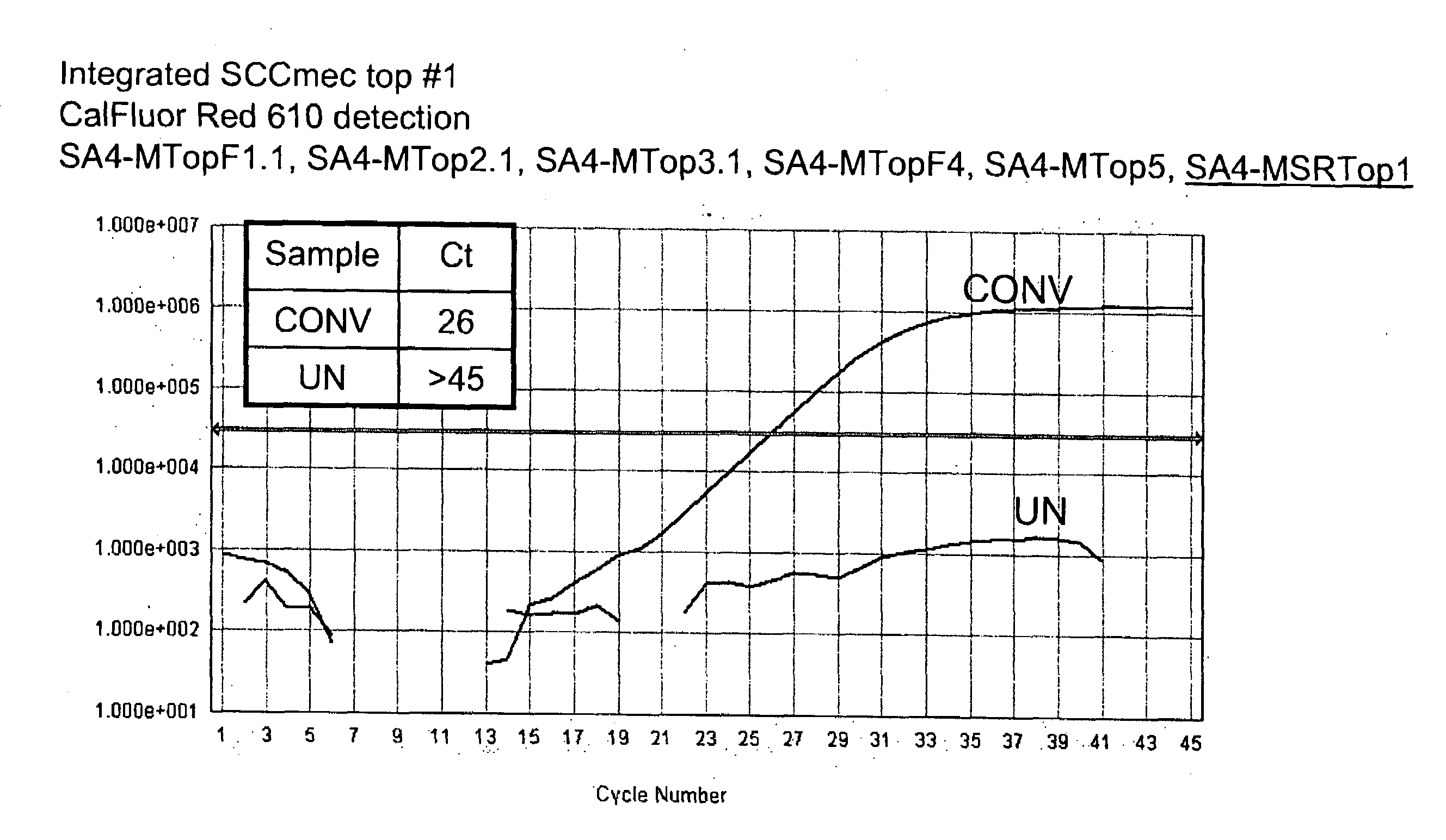
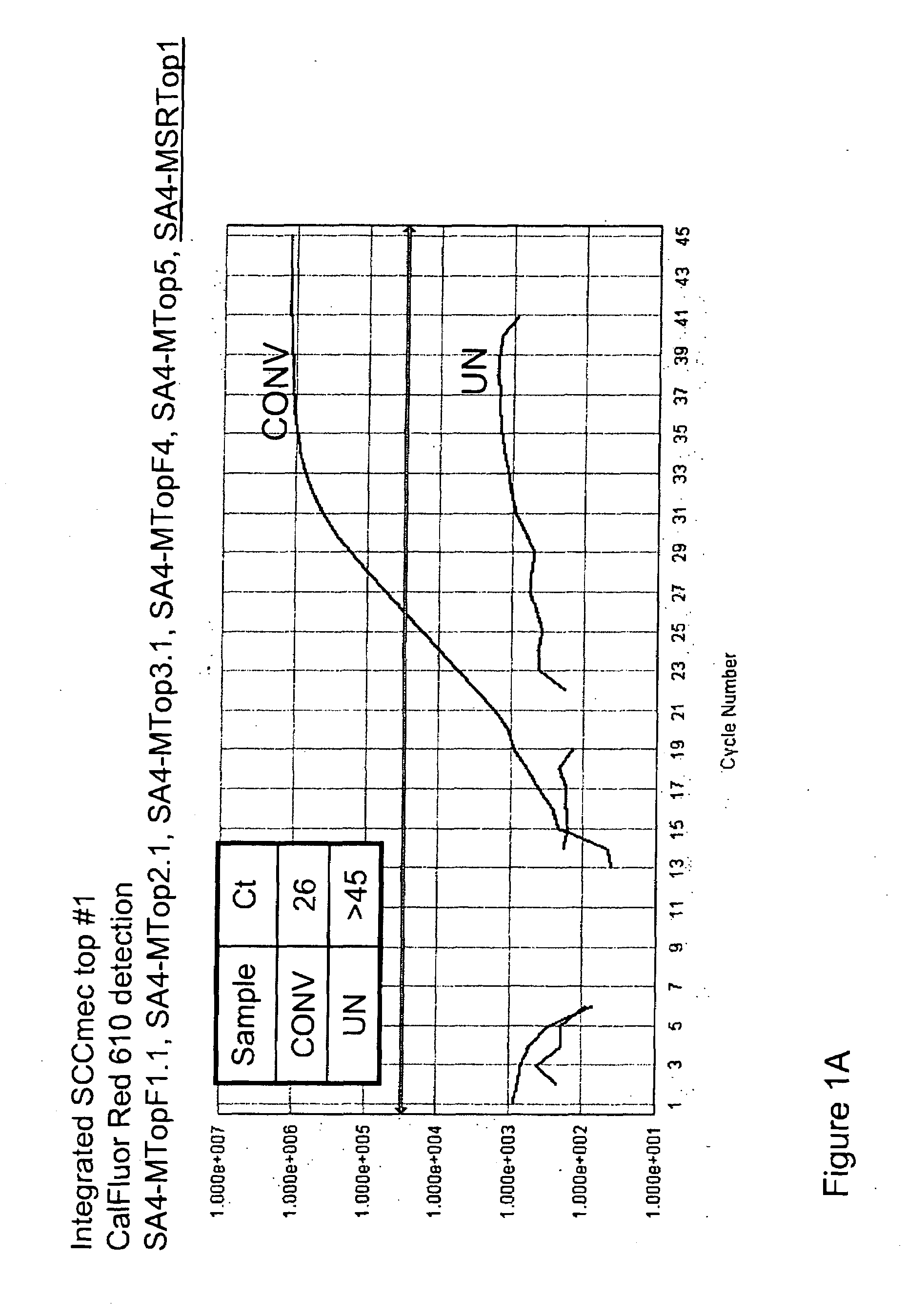
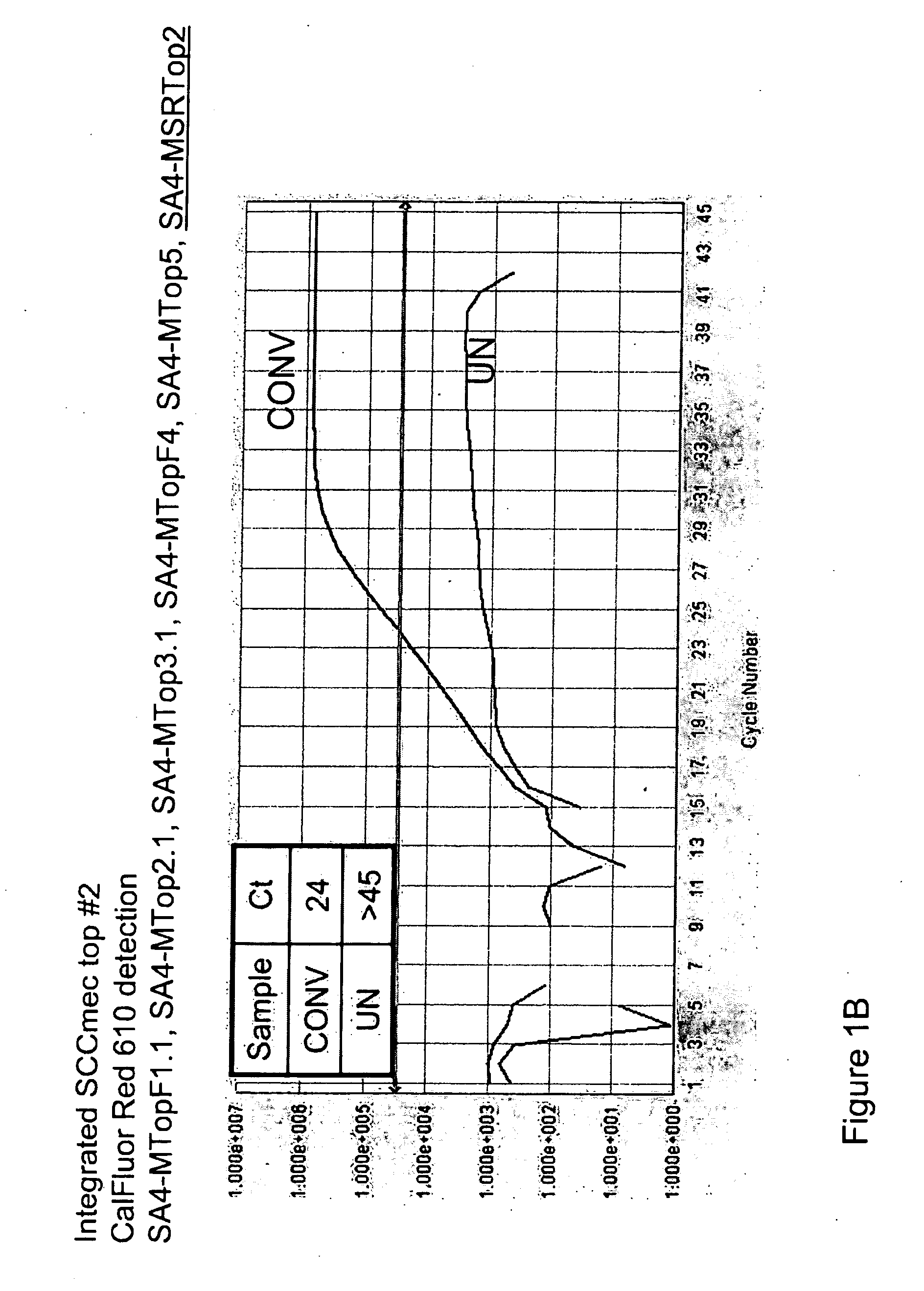
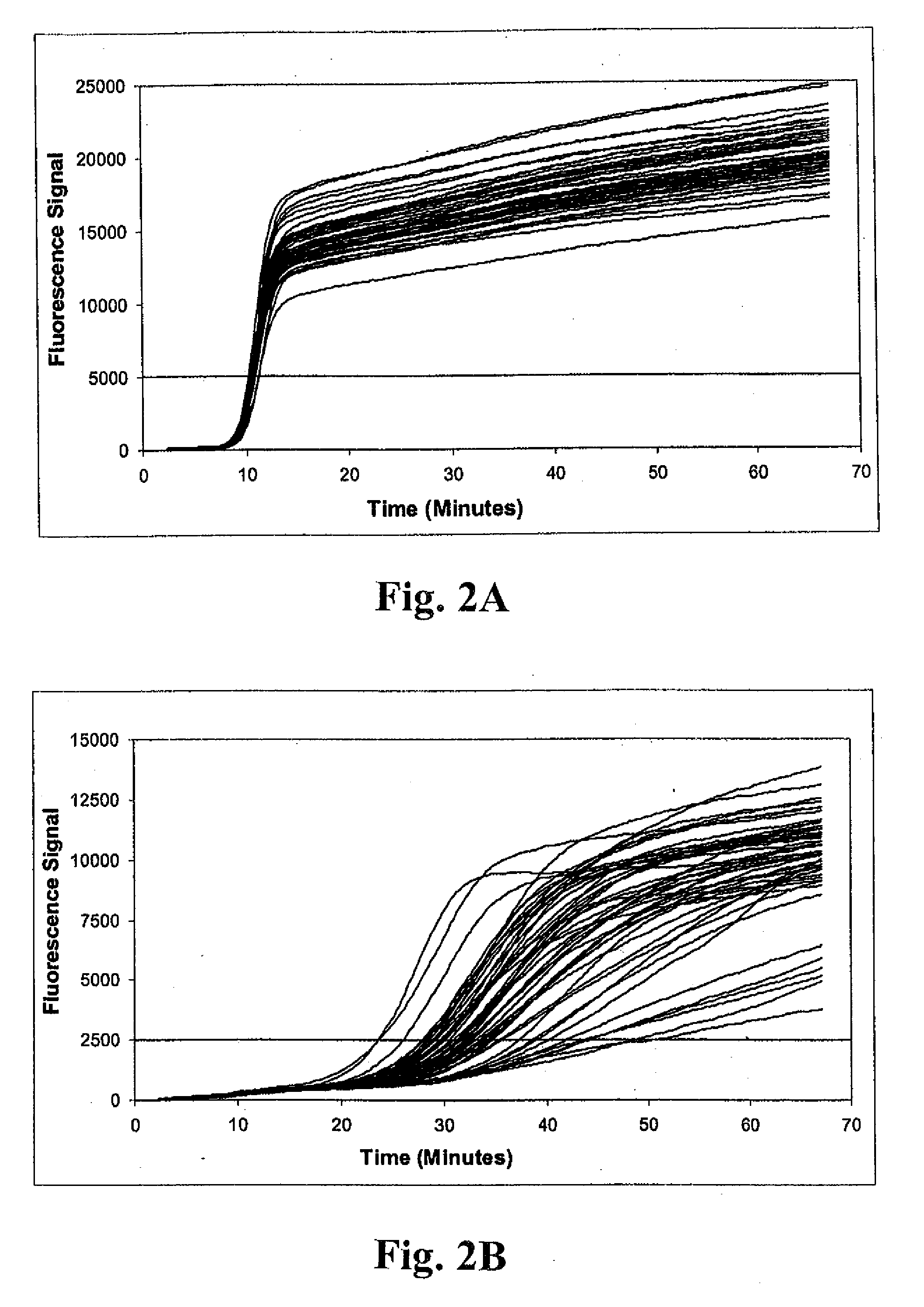
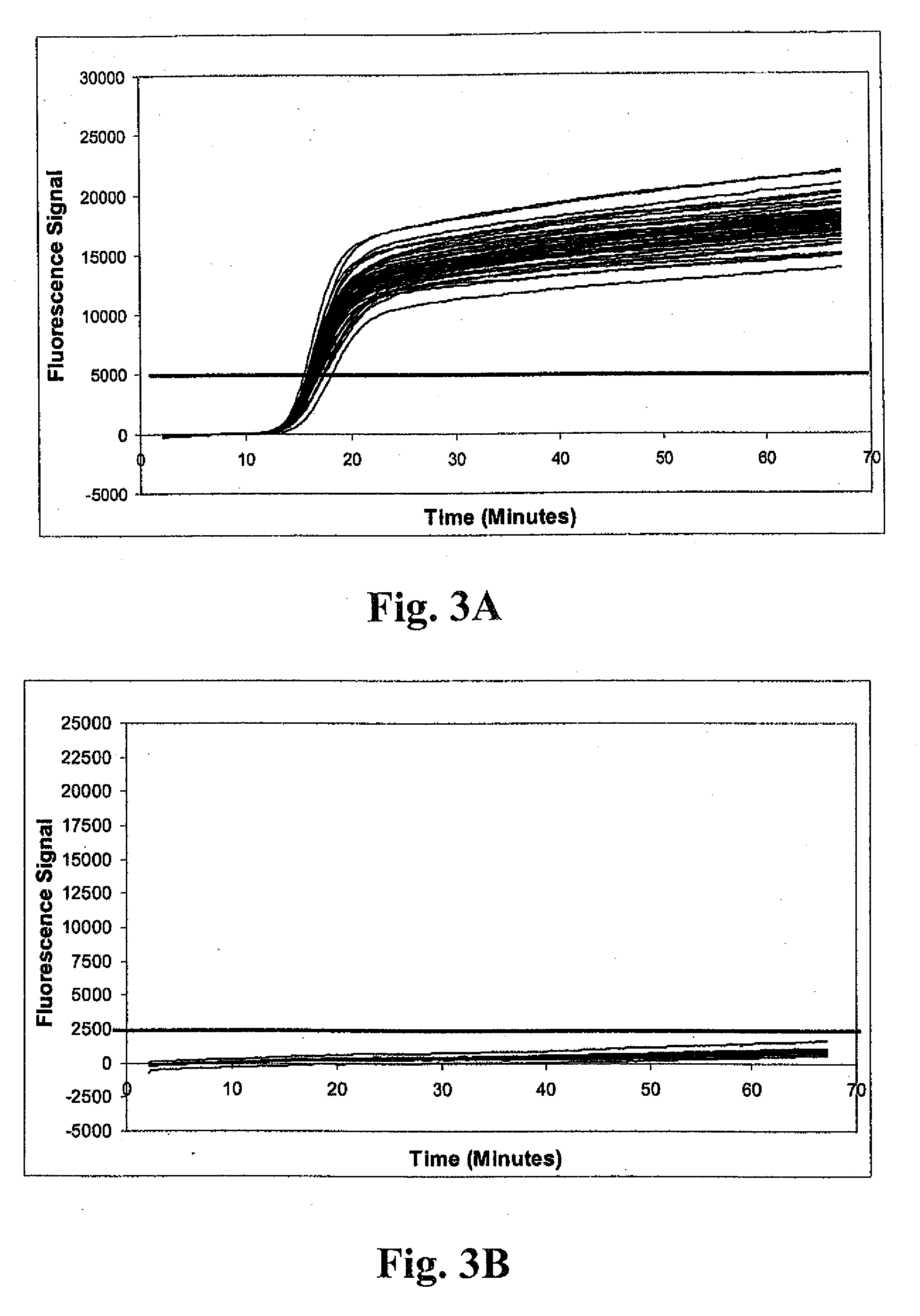
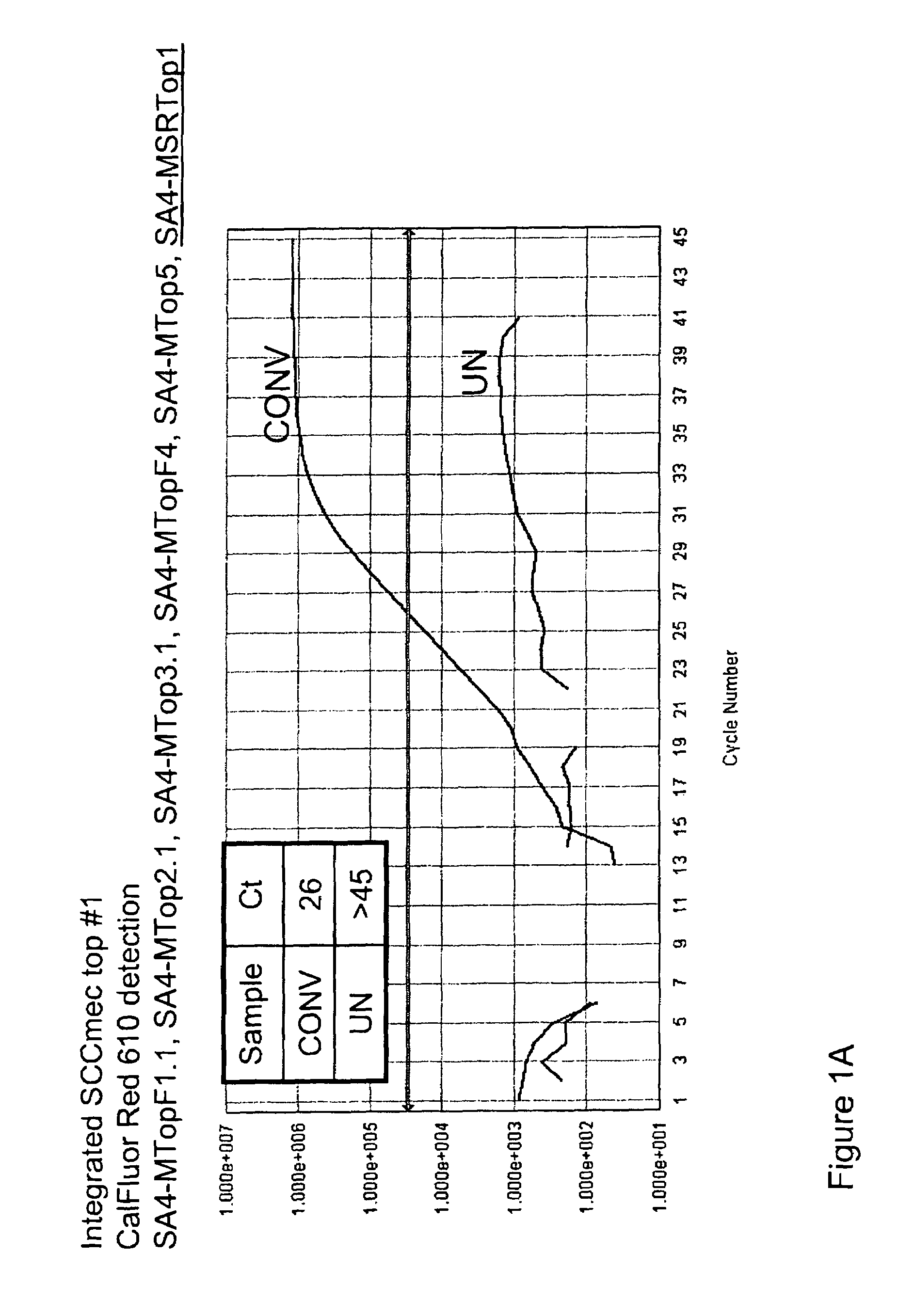
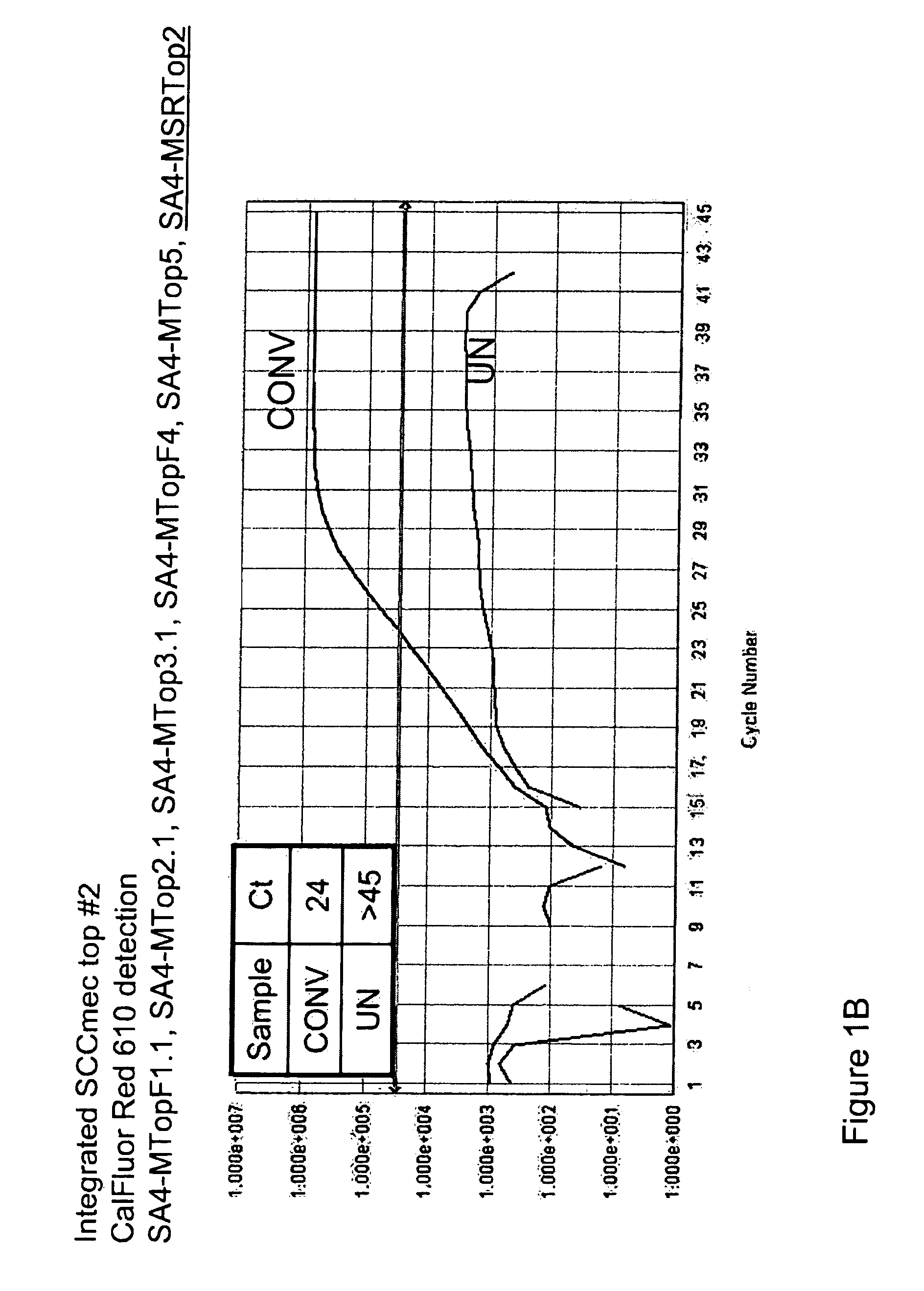
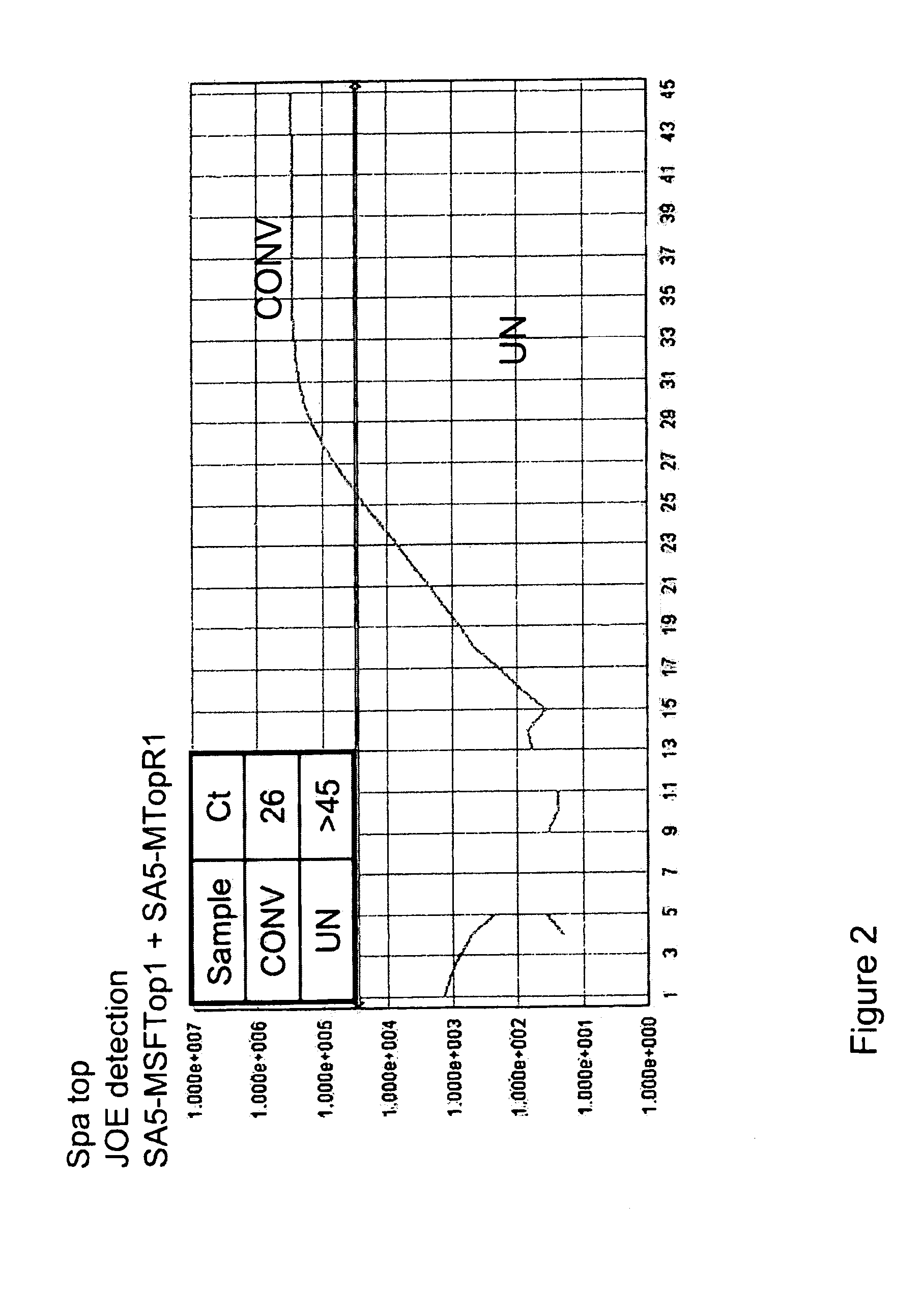
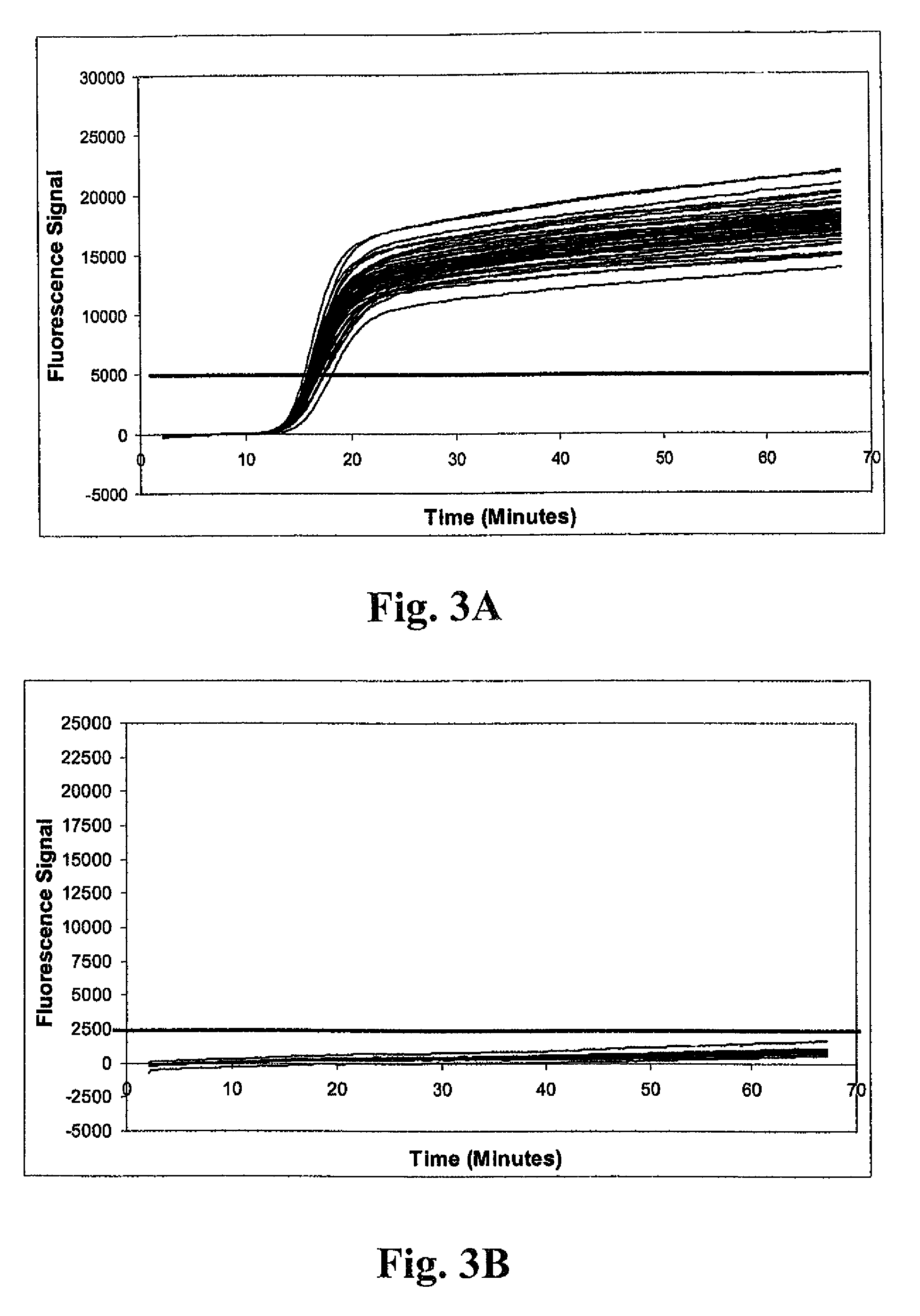
Detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus in biological samples
ActiveUS20090035780A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMethicillin resistance geneCytosine
Disclosed are methods of identifying a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) in a sample. The present invention provides a diagnostic method comprising modification of sequences of S. aureus by converting non-methylated cytosine residues ultimately into thymidine residues in the target nucleic acid. The invention further provides for the detection of modified sequences derived from the spa gene, the mecA gene, and the integrated SCCmec cassette of S. aureus.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
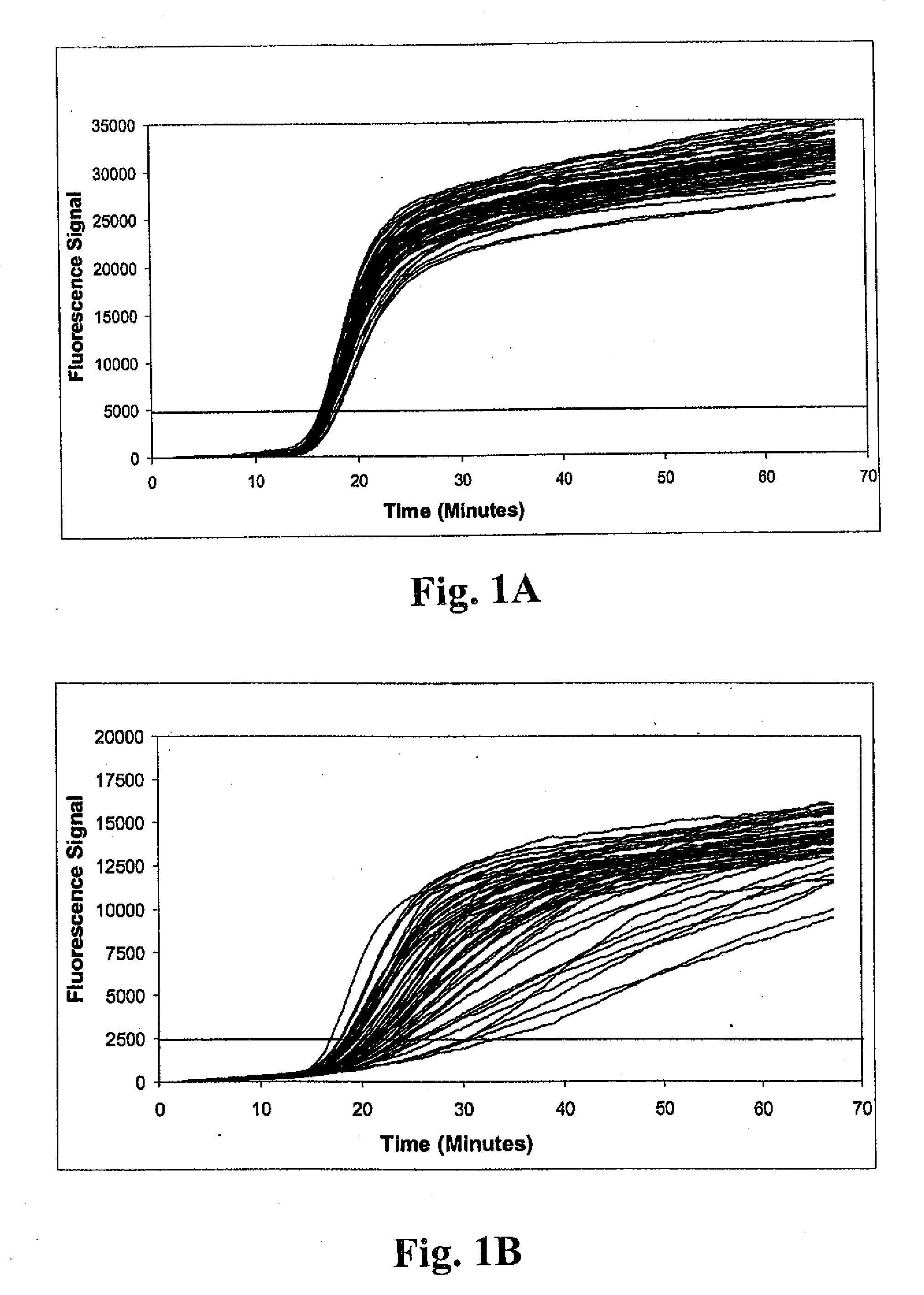
Detection of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms
ActiveUS20090181395A1Easy to separateReduce morbidityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCoagulase testMethicillin sensitive
Method of detecting methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) in a nucleic acid coamplification assay. The invention advantageously reduces the incidence of false-positive MRSA determinations in real-time assays by requiring satisfaction of a threshold criterion that excludes certain co-infections from the MRSA determination. The invention further provides for determination of MSSA, even when the MSSA is present in combination with methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative (MR-CoNS) bacteria at high or low levels.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
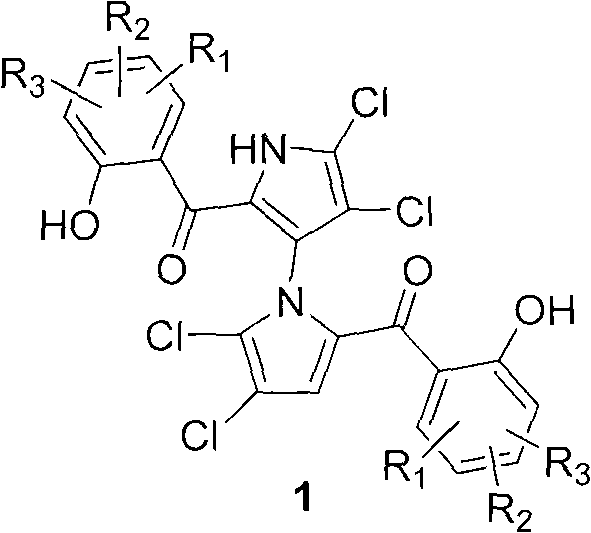
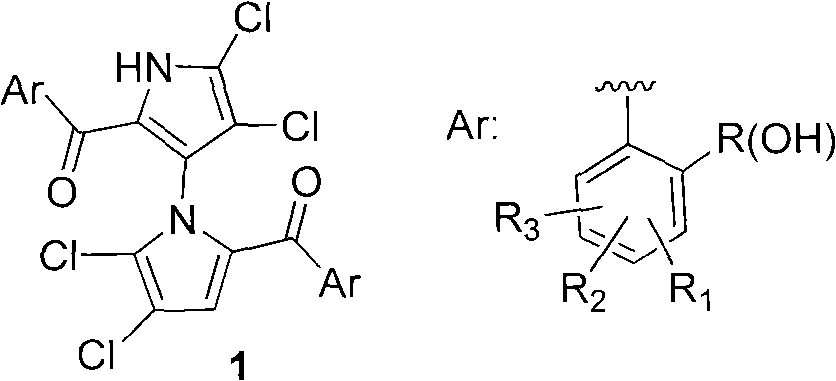
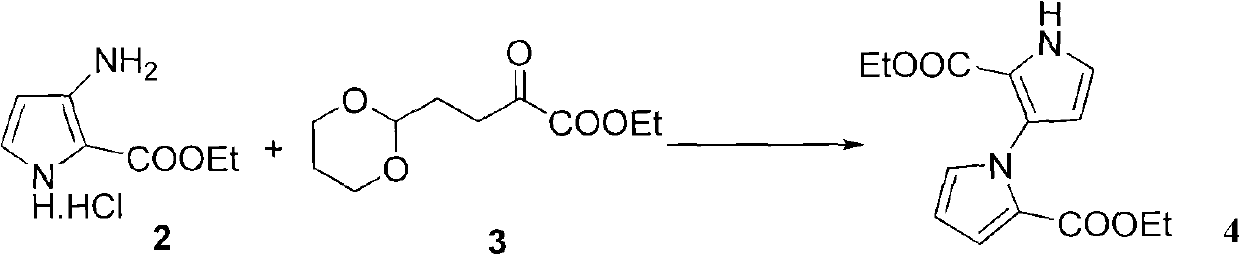
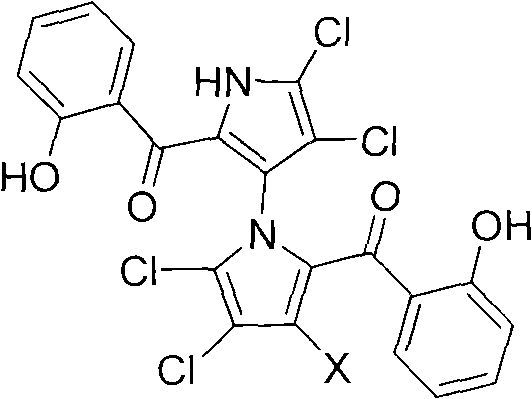
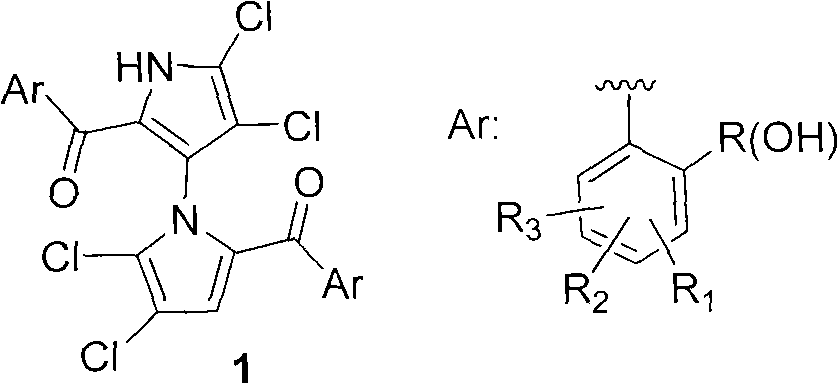
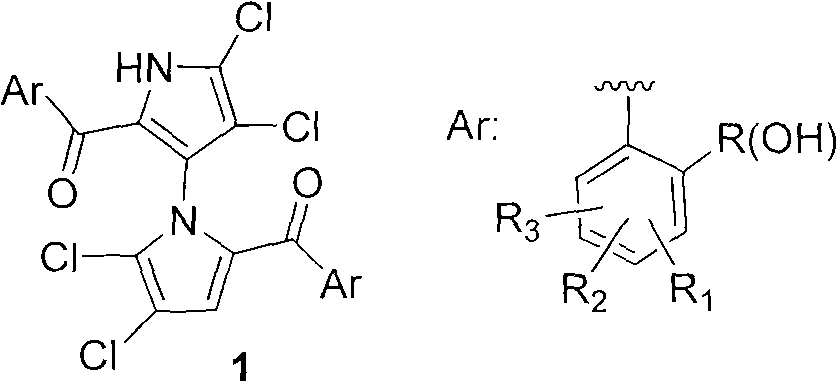
(+/-)-marinopyrrole A for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and synthesized derivative thereof
ActiveCN101786979ASmooth preparation processShort synthetic routeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention relates to an inhibition activity of a synthesized derivative of a natural product (+ / -)-marinopyrrole A, shown as the chemical structural formula 1, on gram-positive bacteria, such as methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE), oxazocilline-resistant staphylococcus aureus (ORSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and the like. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a method for preparing the (+ / -)-marinopyrrole A and the derivative thereof. The method for preparing the (+ / -)-marinopyrrole A has the advantages of short synthesis route and economy and high effectiveness. According to the study of antibacterial action in vitro, the newly synthesized derivatives of the (+ / -)-marinopyrrole A have the advantages of excellent antibiotic activity on the gram-positive bacteria, such as methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE), oxazocilline-resistant staphylococcus aureus (ORSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and the like, and potential clinical application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Enhanced microbial strains for the prevention and treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermis infection
InactiveUS20140308258A1Inhibition of colonizationIncrease heightBiocideBacteriaPathogenic microorganismMethicillin sensitive
The present invention provides enhanced microorganisms useful for inhibiting and / or preventing the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Owner:MATTHEWS CHARLES JOSEPH
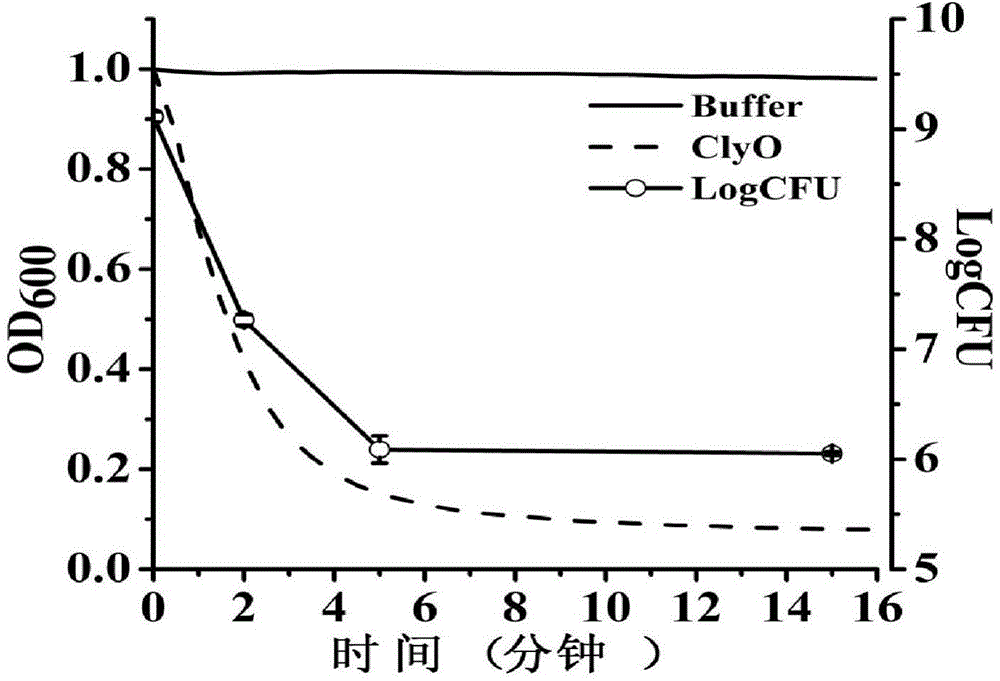
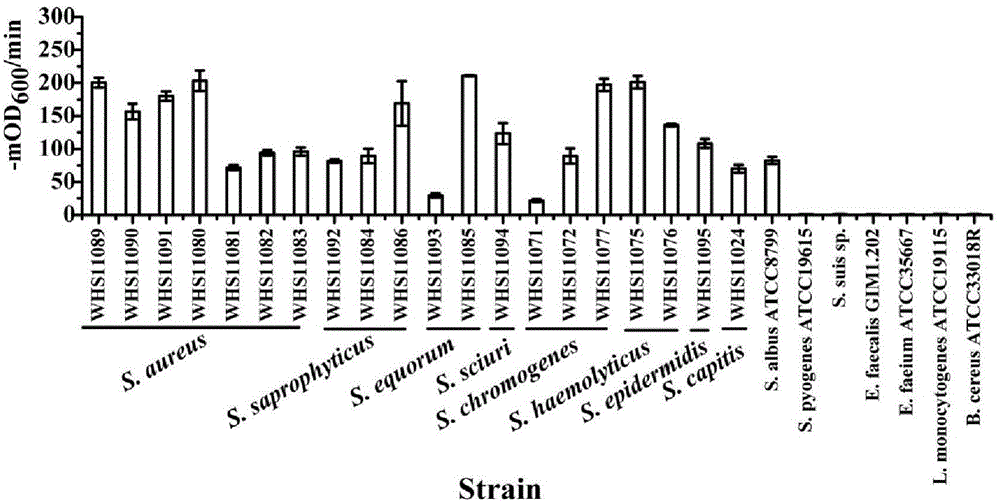
Staphylococcus lyase and application thereof
ActiveCN104805066AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin resistance
The invention discloses lyase capable of killing staphylococci and an application of the lyase, which belong to the field of biological agents. The invention discloses an amino acid sequence and a coding gene sequence of the lyase. A pH range of the lyase which plays a role is wide, the activity of cracking the staphylococci is kept within the pH range of 4 to 11, and recombinant protease constructed by adopting coding genes can be solubly expressed in colibacillus BL21(DE3). The lyase can be used for efficiently killing various staphylococci in vitro, including methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus which are clinically separated, and the lyase can be used as antibiotics for treating staphylococcal infection in vivo. The disclosed lyase can be used for quickly cracking staphylococcal cell walls and releasing substances in cells, such as triphosadenine, DNA and the like, and the staphylococci can be detected by utilizing the released substances.
Owner:TARGET ANTI-BIOPHARMACEUTICAL TECH CO LTD
Detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus in biological samples
Disclosed are methods of identifying a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) in a sample. The present invention provides a diagnostic method comprising modification of sequences of S. aureus by converting non-methylated cytosine residues ultimately into thymidine residues in the target nucleic acid. The invention further provides for the detection of modified sequences derived from the spa gene, the mecA gene, and the integrated SCCmec cassette of S. aureus.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
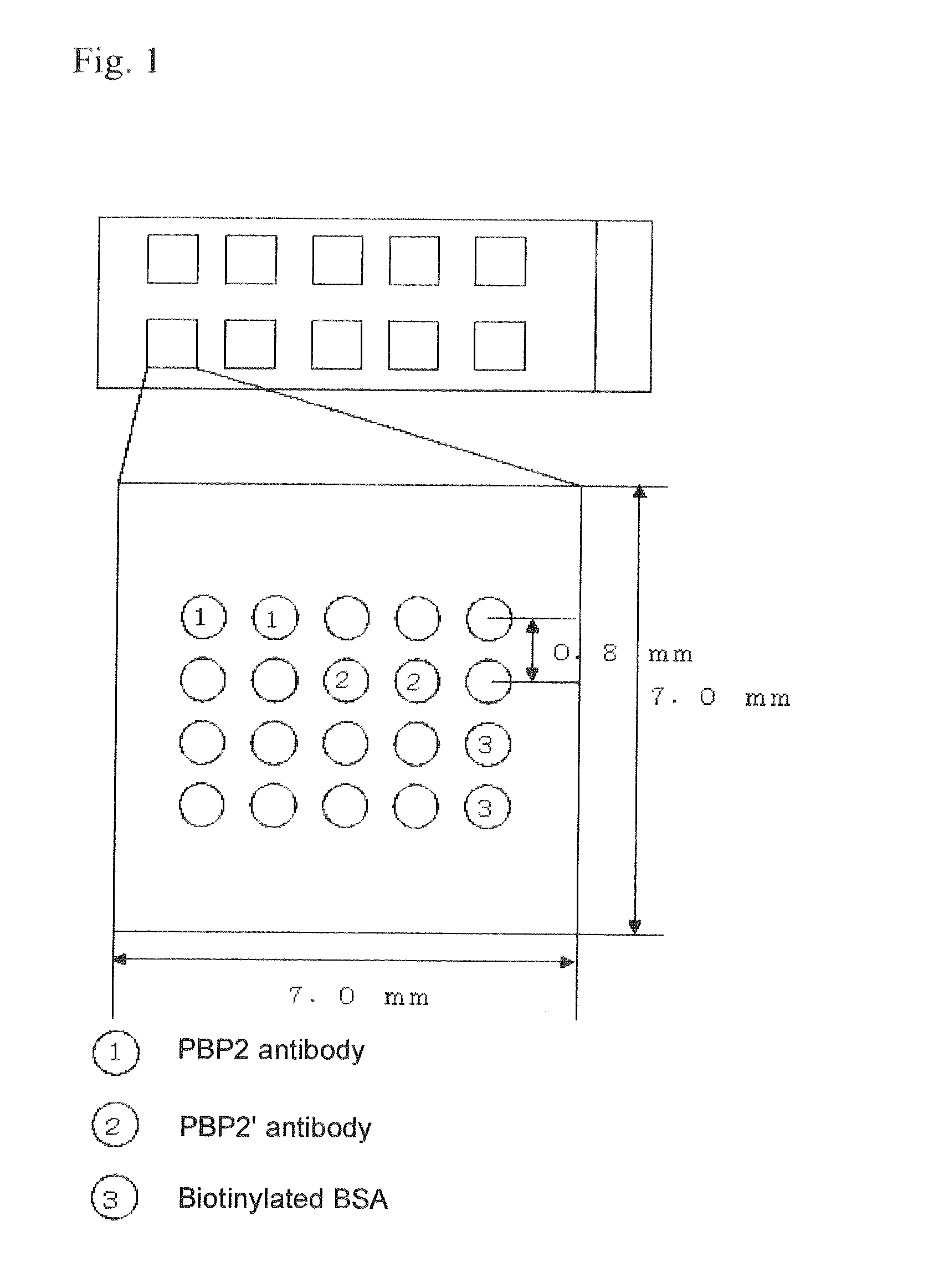
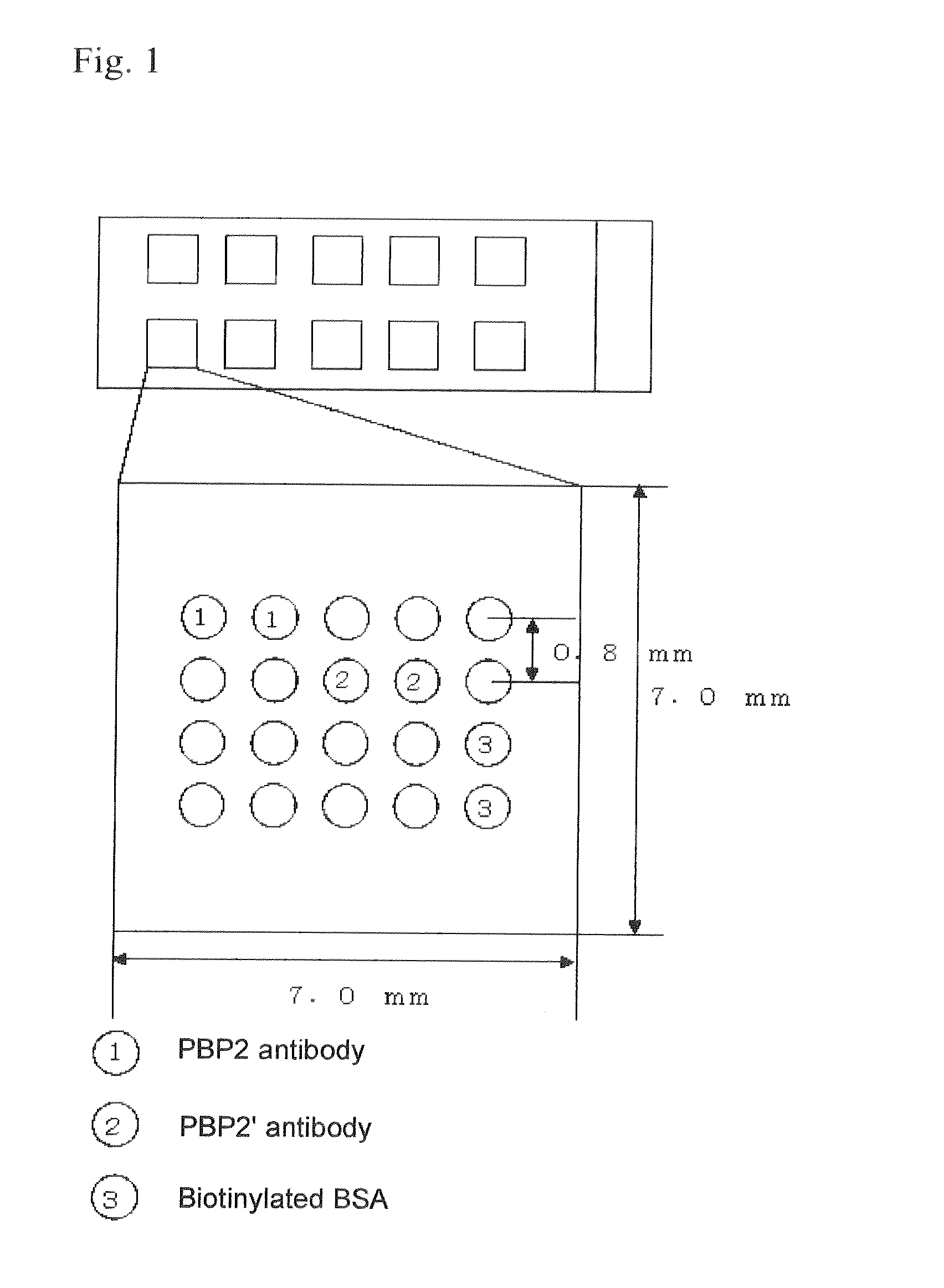
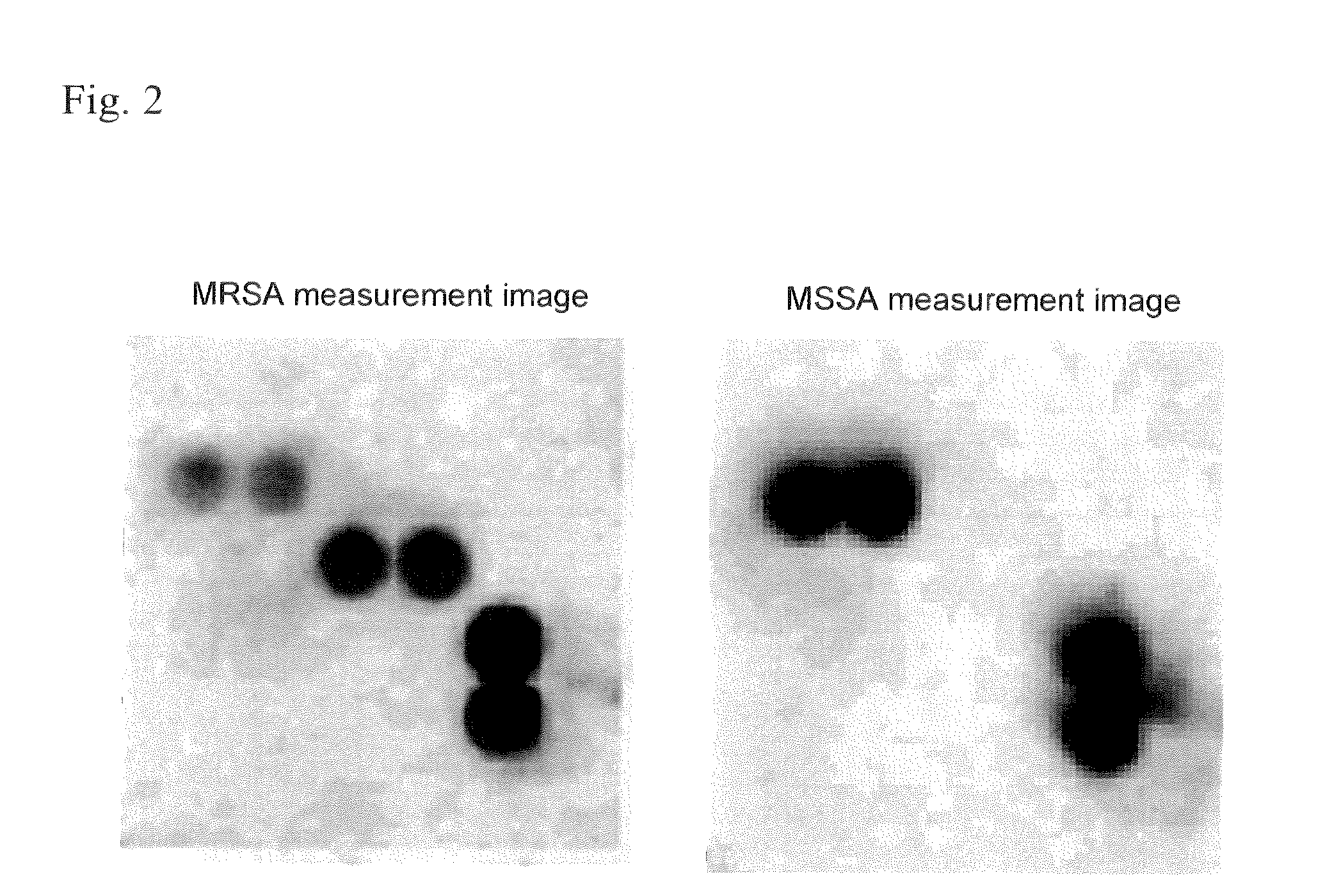
Method for extracting staphylococcus aureus antigen, reagent for extracting staphylococcus aureus antigen, and method for assessing staphyloccoccus aureus
ActiveUS20120295812A1Efficiently extract PBP2′Reliably assess whether a specimenChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideOther chemical processesAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a method for extracting a Staphylococcus aureus antigen which comprises using an extraction reagent with a pH of no higher than 5.0, containing one or more acids selected from among hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid, to extract a Staphylococcus aureus antigen comprising a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus antigen and / or a methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus antigen, from Staphylococcus aureus in a specimen. The invention further provides a method for assessing Staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
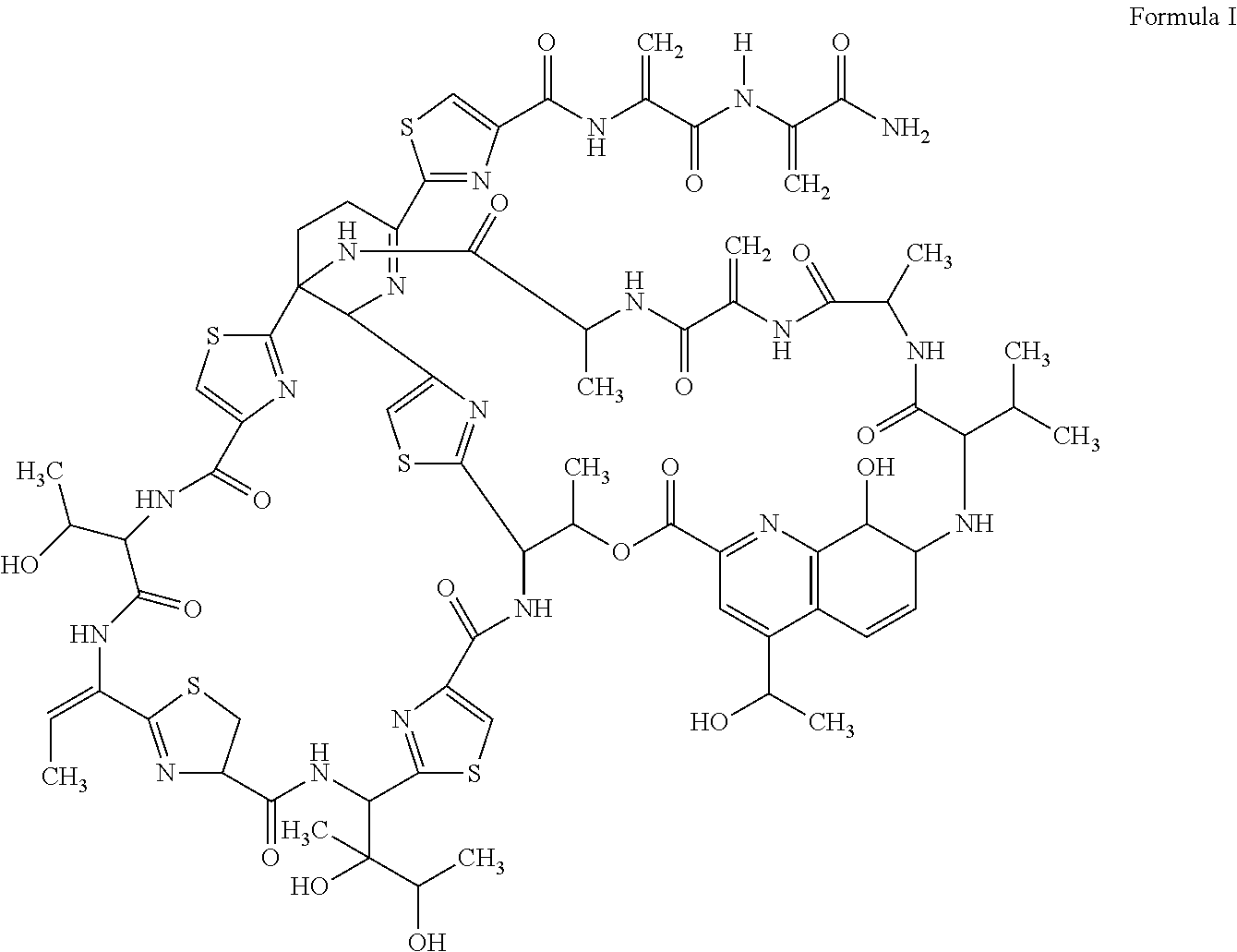
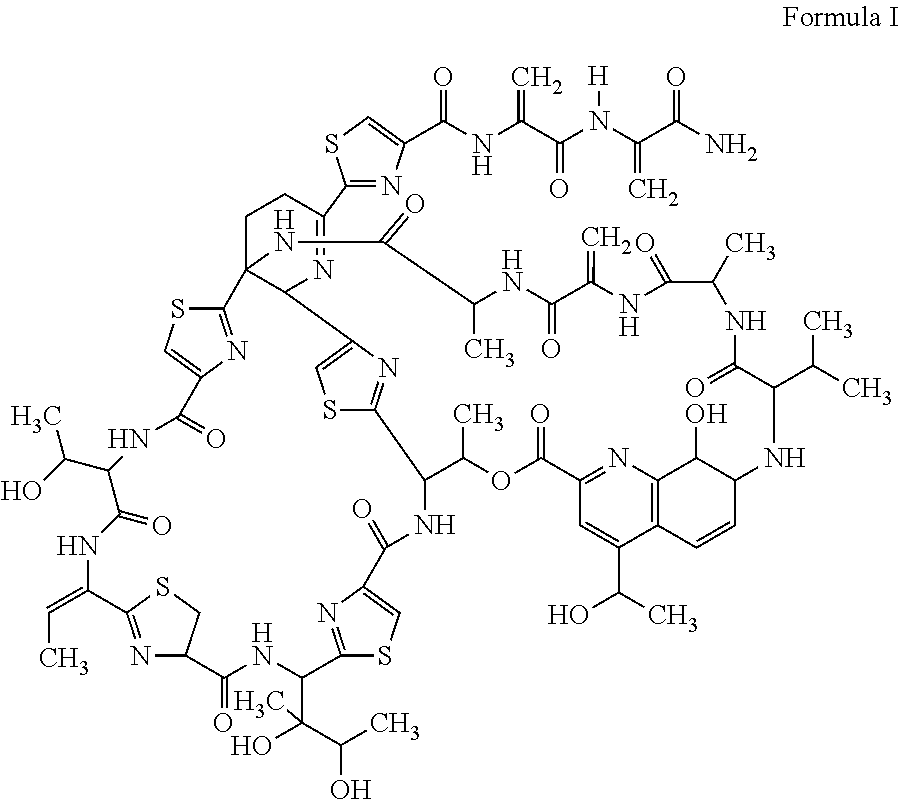
Fluoro-acrylamide derivative
InactiveCN102675311AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiMethicillin sensitive
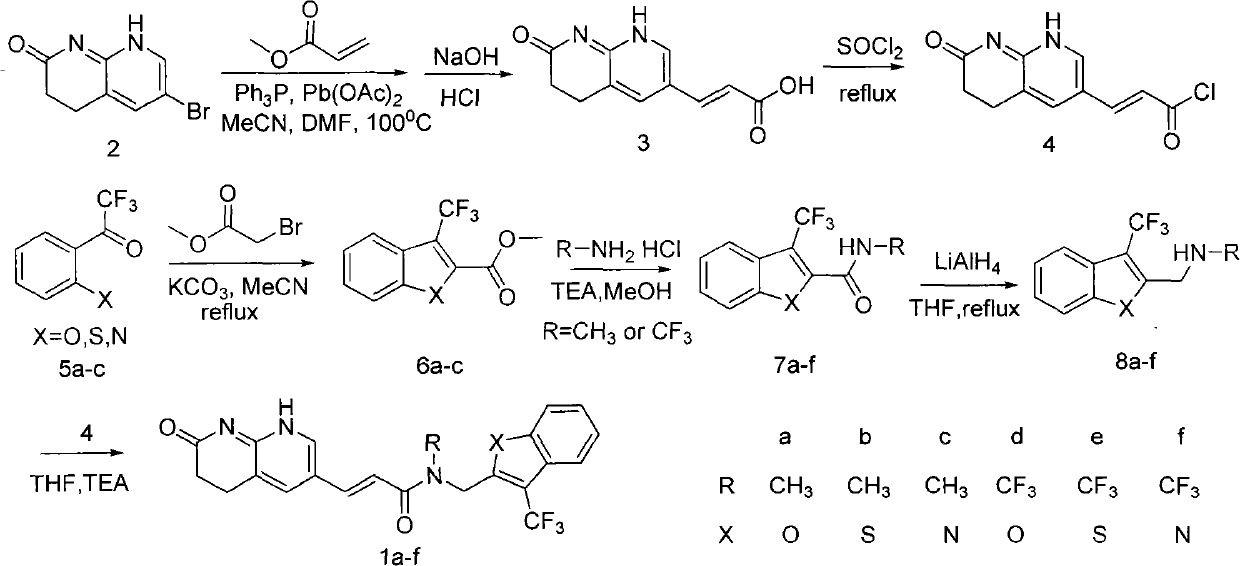
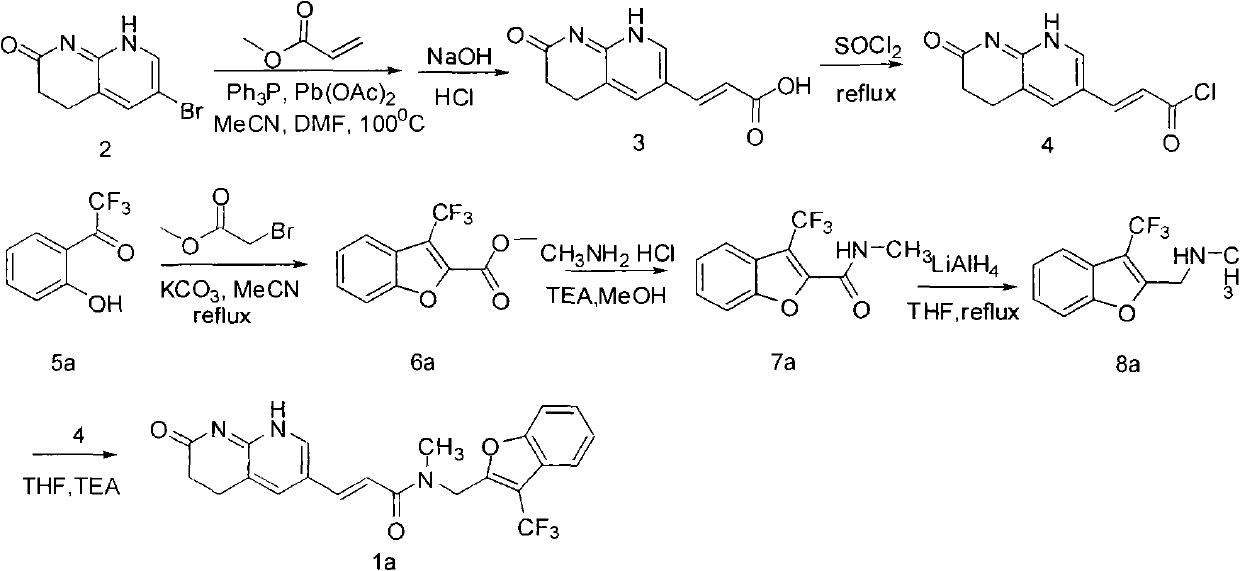
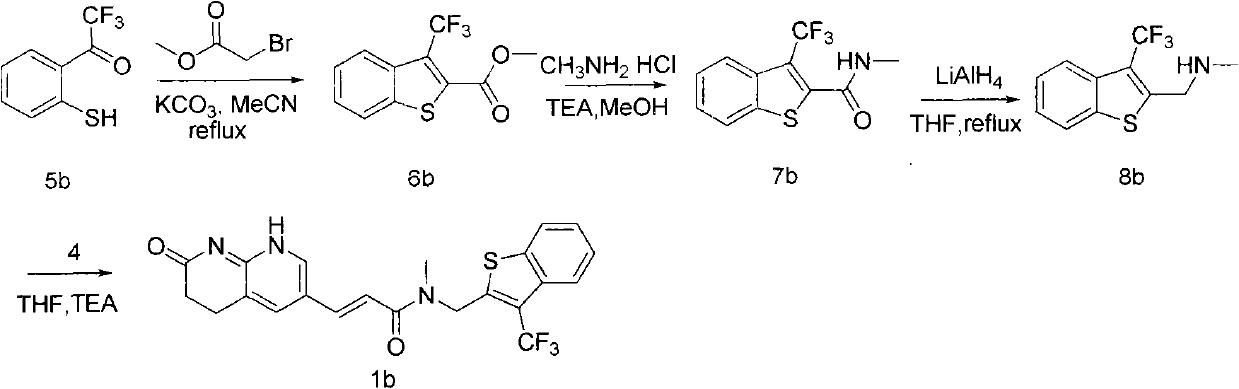
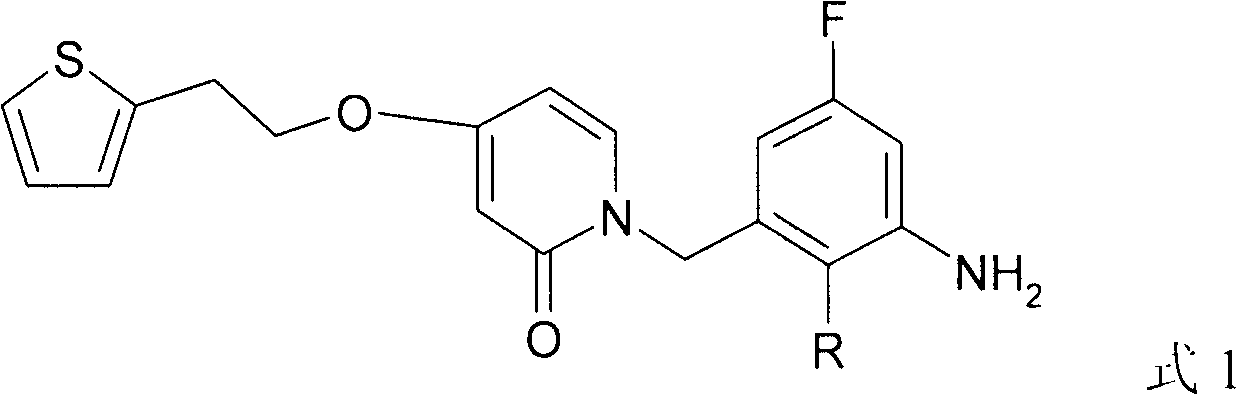
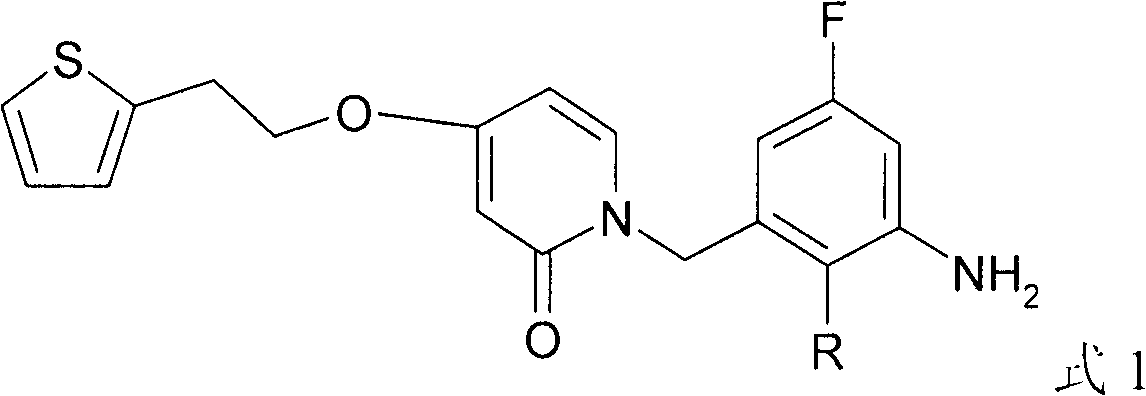
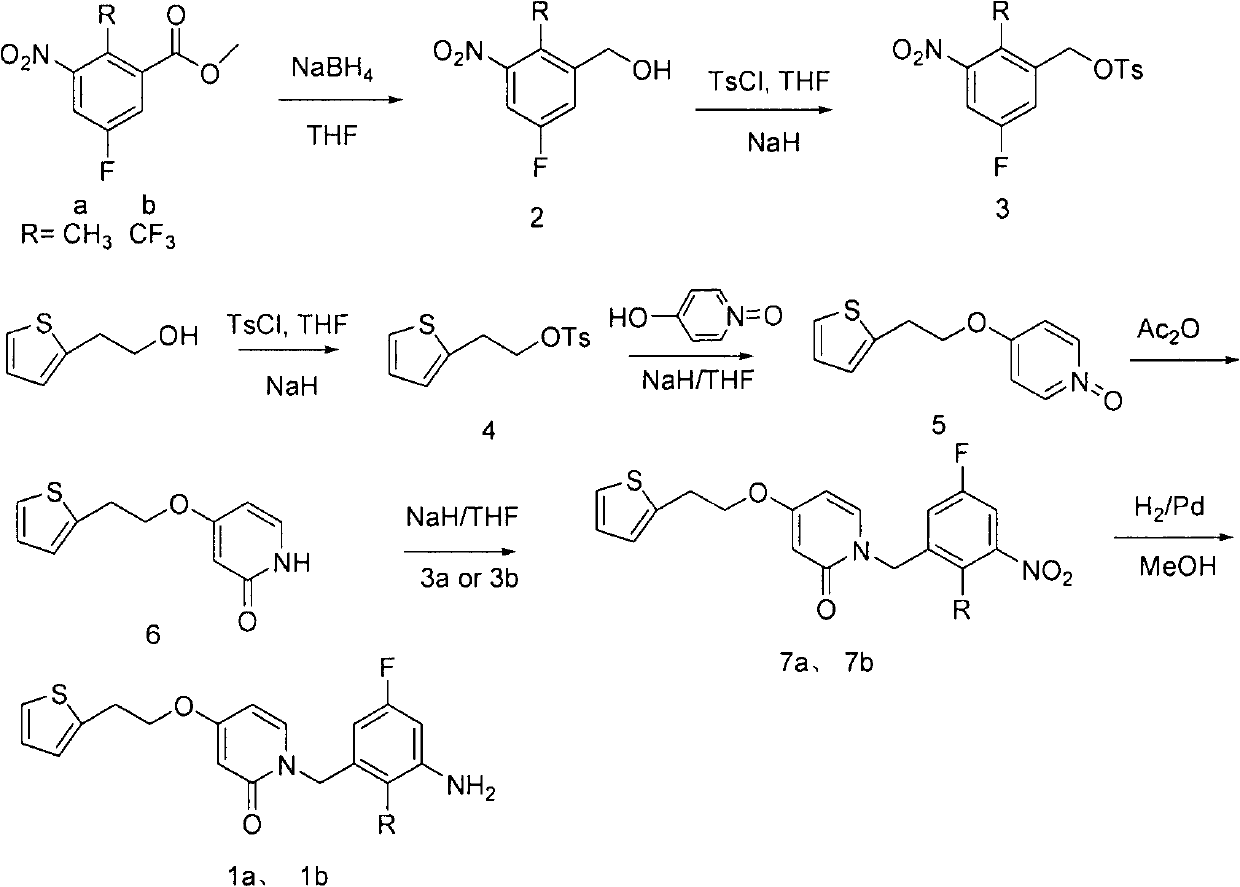
The invention relates to a new compound with remarkable antibacterial and antineoplastic activity, which has the following structure (shown in formula I), and has good antibacterial function for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) as well as good antineoplastic function for human cervical cancer Hela cells, human liver cancer BEL-7402 cells, human mucinous epidermoid lung cancer A549 cells, human breast cancer MCF-7 / s cells and human glioma U251 cells. (In the formula I,) R=-CH3 or CF3, X=O, S or N, and R1=-Cl, -F, -CH3, -CF3, -OCH3 and -OCF3.
Owner:苏春华 +1
Method for extracting Staphylococcus aureus antigen, reagent for extracting Staphylococcus aureus antigen, and method for assessing Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS8679812B2Efficiently extract PBP2′Reliably assess whether a specimenChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideNitrogen compoundsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a method for extracting a Staphylococcus aureus antigen which comprises using an extraction reagent with a pH of no higher than 5.0, containing one or more acids selected from among hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid, to extract a Staphylococcus aureus antigen comprising a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus antigen and / or a methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus antigen, from Staphylococcus aureus in a specimen. The invention further provides a method for assessing Staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
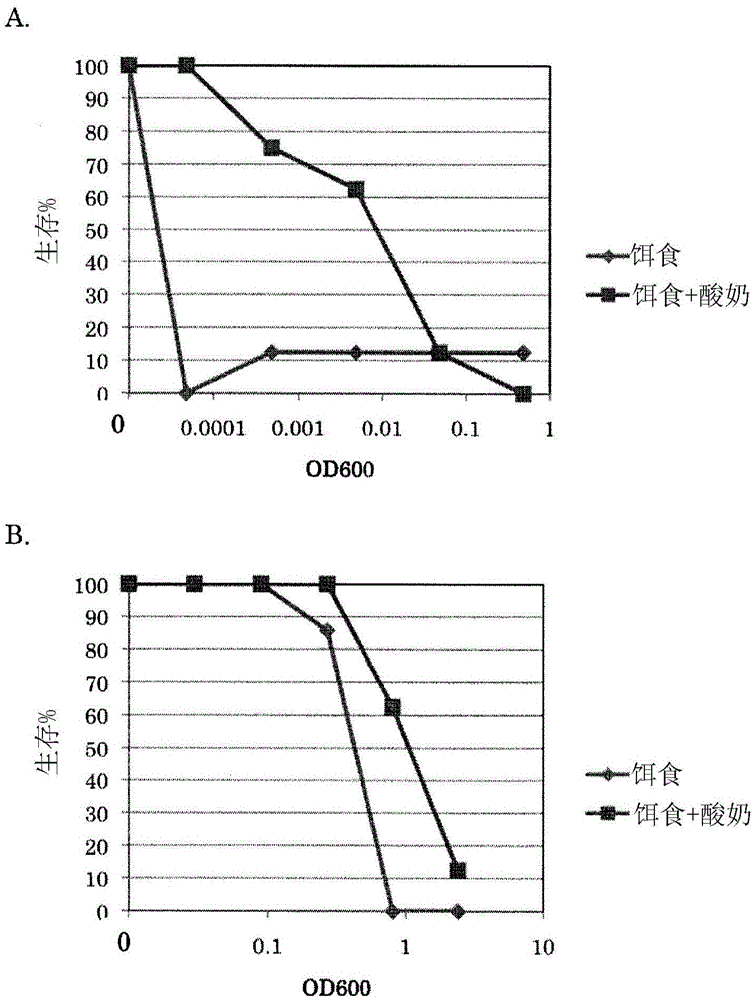
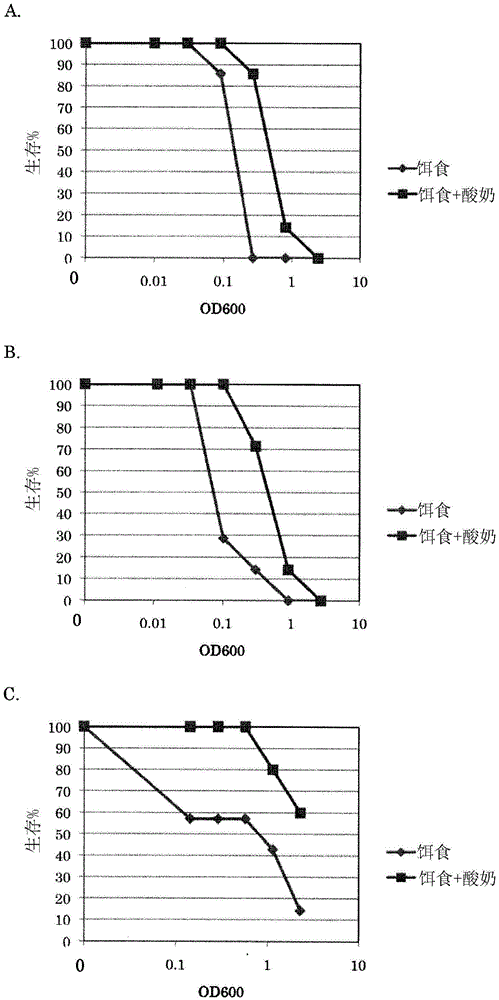
New lactic acid bacterium, natural immunostimulant having new lactic acid bacterium as active ingredient, and food or drink containing new lactic acid bacterium
ActiveCN105637084AHigh innate immune activation capacityImprove the immunityMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesGenus Lactococcus
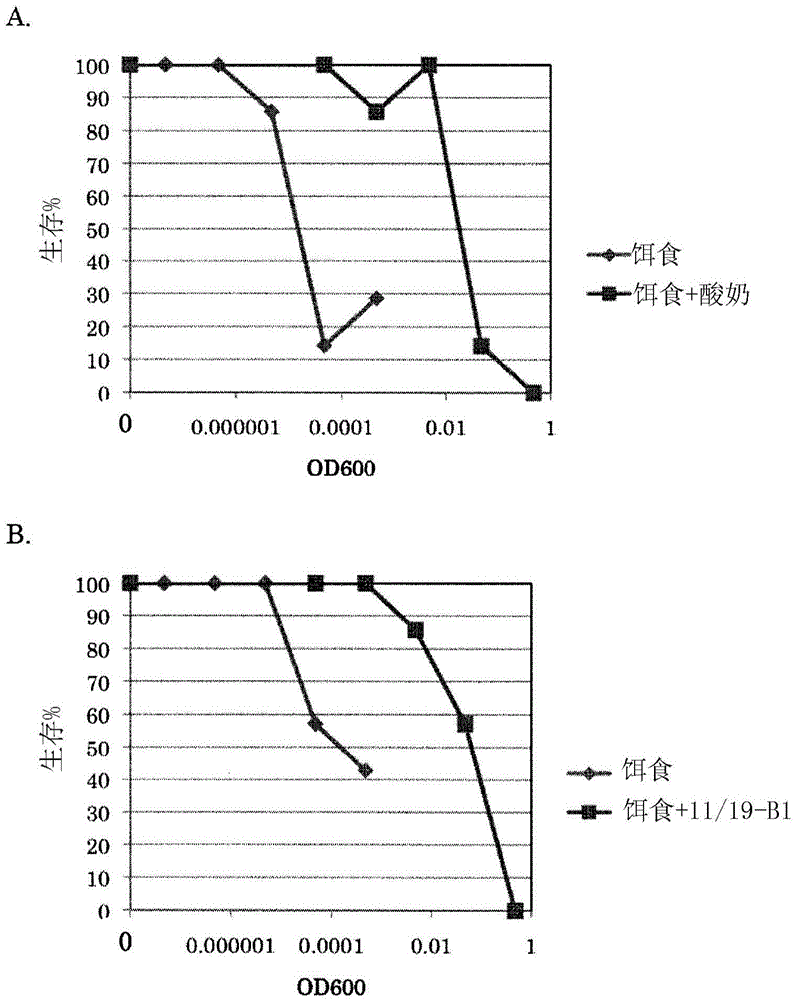
The present invention pertains to a lactic acid bacterium belonging to the genus Lactococcus and having a receipt number NITE ABP-01694 with the Patent Microorganisms Depositary (NPMD) of the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE), a natural immunostimulant having this lactic acid bacterium as an active ingredient, a food or drink containing this lactic acid bacterium or this natural immunostimulant, and yogurt containing lactic acid bacteria, wherein the yogurt has resistance to at least one bacterium selected from the group comprising methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococcus mundtii.
Owner:GENOME PHARMA INST +2
Genetically Modified Bacteriophage (Bio-Phage)
InactiveUS20170333500A1Improve abilitiesViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsBacteriophagesBacteroidesMethicillin sensitive
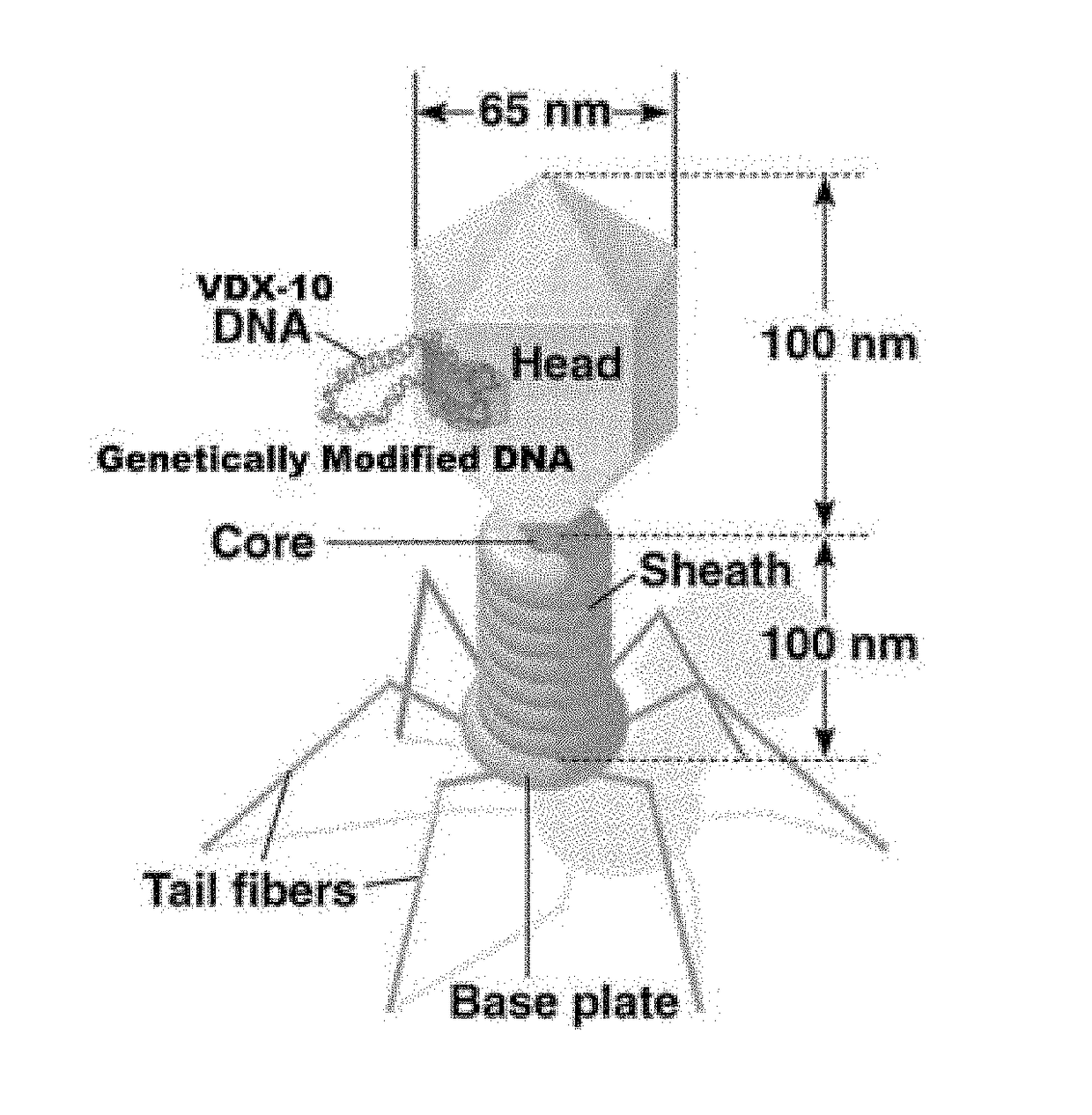
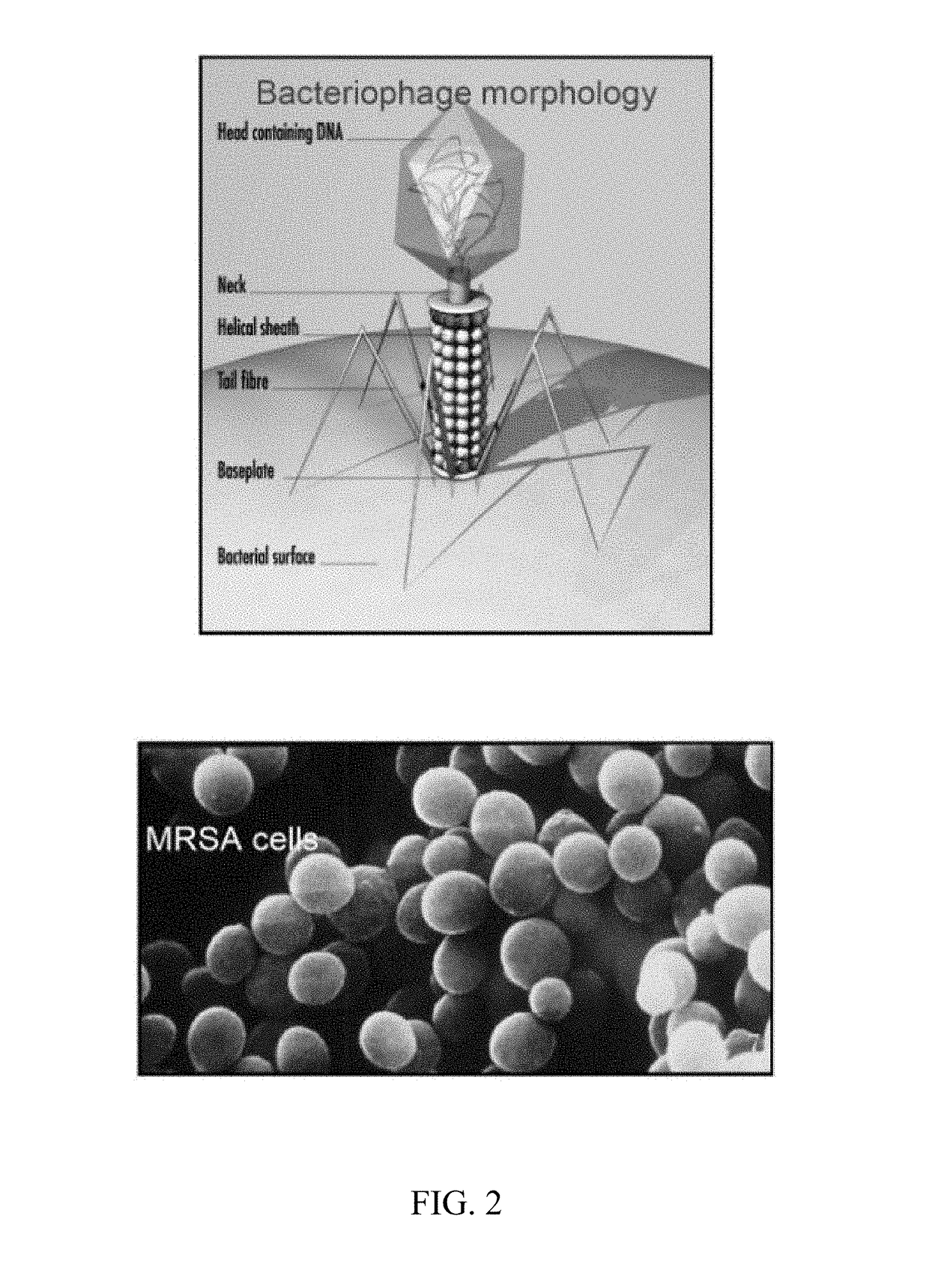
The present invention describes a genetically modified Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage VDX-10 comprising the DNA of the bacteriophage VDX-10 being altered by inserting a gene sequence that increases the ability of the bacteriophage to replicate faster as compared to unmodified VDX-10 bacteriophage; a method of producing the genetically modified Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage VDX-10; and a method of treating infection in a patient by administering an amount of the genetically modified Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage effective to eliminating the Staphylococcus bacteria cells, where the infection can be Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) or bacteremia as incited by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcal aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcal aureus (MSSA).
Owner:HATFIELD ROC
METHOD AND DEVICE FOR ANNIHILATION OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS20190126063A1Cyclic peptide ingredientsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentImaging studyMethicillin sensitive
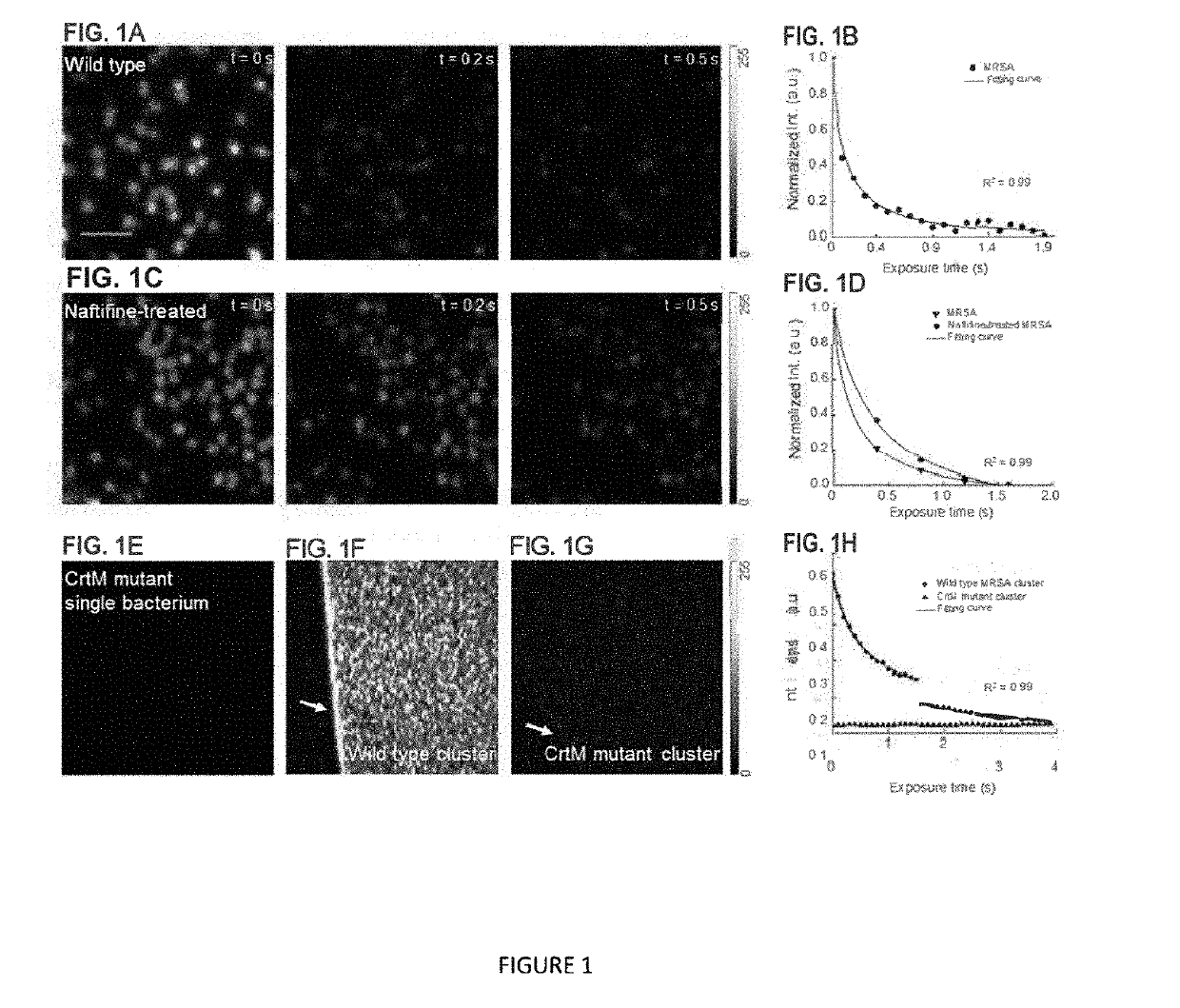
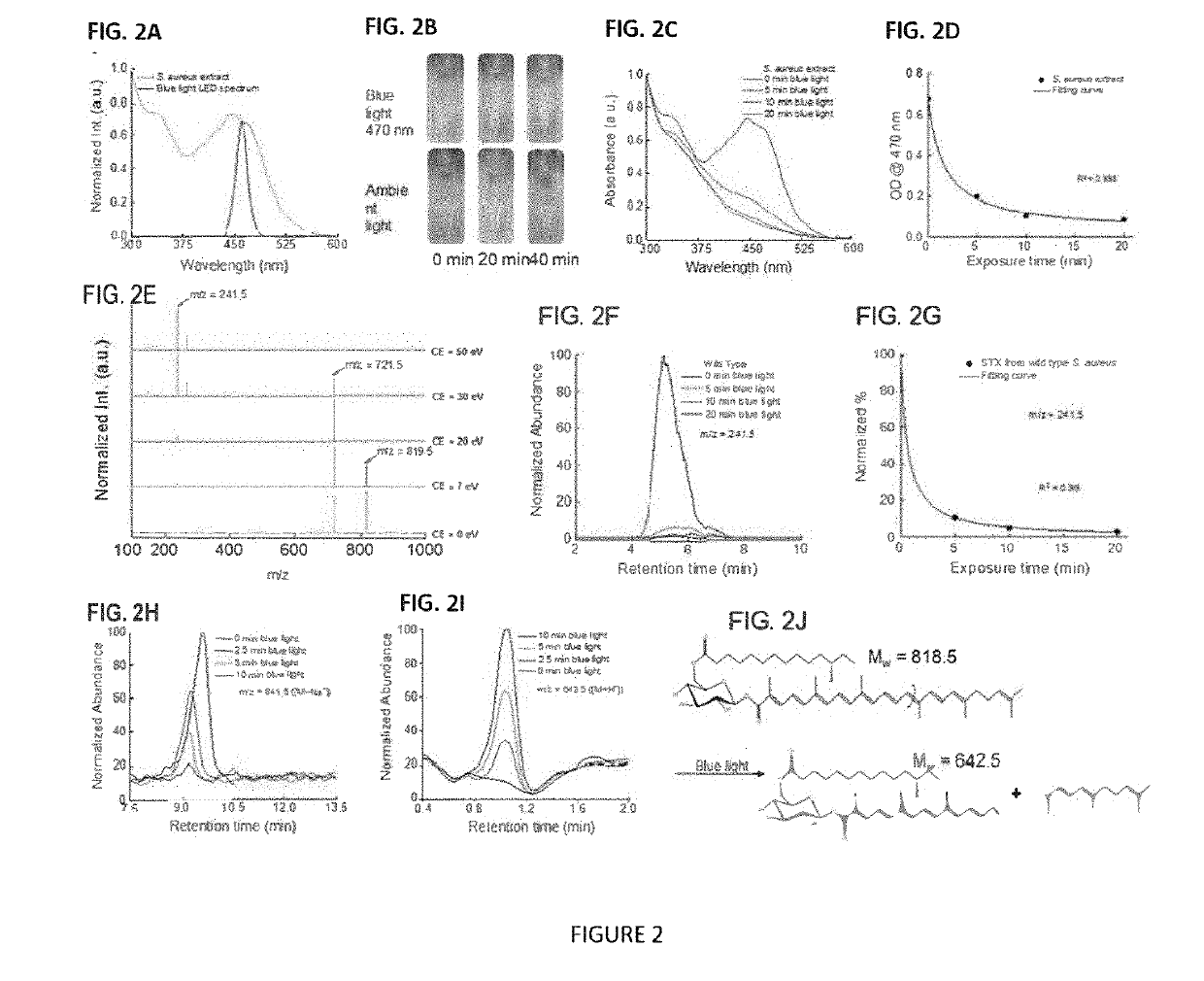
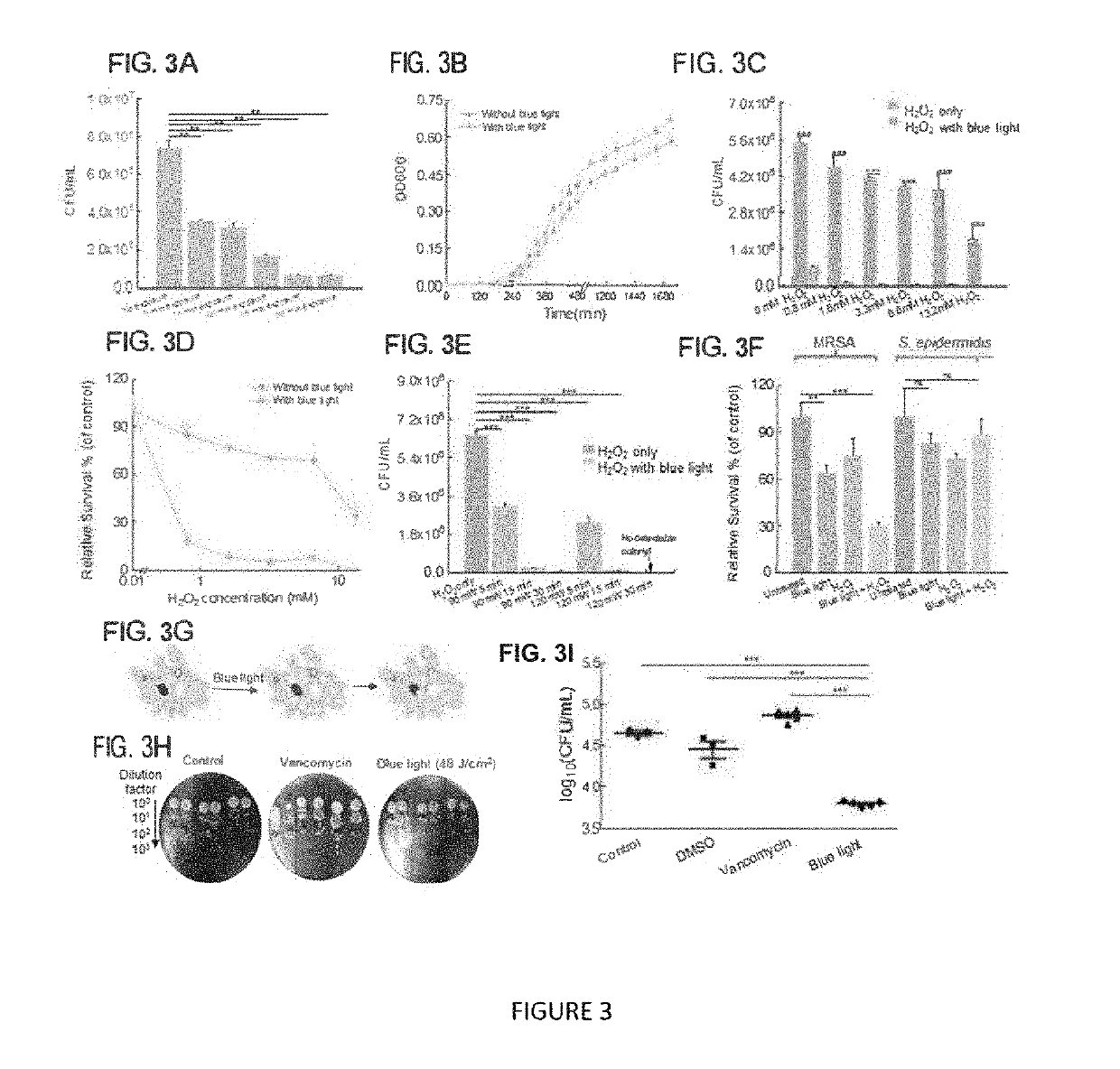
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) possesses array of strategies to evade antibiotics through mutational inactivation, hiding inside host immune cells or concealing inside the biofilm in a sessile form. We report a drug-free approach to eradicate MRSA through blue-light bleaching of staphyloxanthin (STX), an anti-oxidative carotenoid residing inside the cell membrane of S. aureus. The photobleaching process, uncovered through a transient absorption imaging study and quantitated by mass spectrometry, decomposes STX and sensitizes MRSA to reactive oxygen species attack. Consequently, photobleaching using low-level blue light exhibits high-level synergy when combined with low-concentration of hydrogen peroxide. Antimicrobial effectiveness of this synergistic therapy is validated in MRSA culture, MRSA-infected macrophage cells, biofilm, and a mouse wound infection model. Collectively, these findings highlight broad applications of STX photobleaching for MRSA-infected diseases.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
(+/-)-marinopyrrole A for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and synthesized derivative thereof
ActiveCN101786979BSmooth preparation processShort synthetic routeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
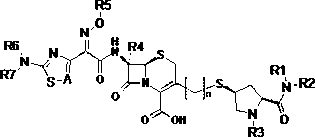
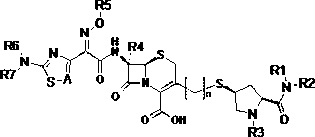
Cephalosporins compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
InactiveCN102977123AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
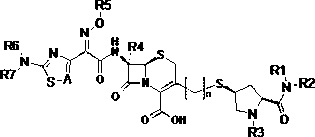
The invention discloses a cephalosporins compound and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, preparation methods of the compounds, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compounds or the salt thereof, and applications in preparing the pharmaceutics for treating and / or preventing infectious diseases. The cephalosporins compound has a good bacteriostatic activity to gram-positive bacteria such as MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), MSSA (Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus Aureus) and MRSE (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis), and gram-negative bacteria such as drug-resistant bacteria producing ESBLs (Extended Spectyum beta Lactamase), is wide in antibacterial spectrum, strong in antibacterial activity, low-toxicity, and anti-drug resistance, thereby having extremely high research and development values.
Owner:广州烜华生物科技有限公司
Fasamycins compounds, preparation method thereof and application thereof to preparation of antibacterial medicines
InactiveCN108503522ANovel structureStrong antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryResistant bacteriaStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses Fasamycins compounds, a preparation method thereof and the application thereof to preparation of antibacterial medicines. Eight novel Fasamycins compounds are separated and purified from a fermented product of Streptoverticillium morookaense SC1169. In-vitro antibacterial activity testing results show that the Fasamycins compounds have a very strong effect of inhibiting methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-sensitive enterococcus faecium (VSE) and vancomycin-resistant enterococcus faecium (VRE). The Fasamycins compounds are novel in structure, especially have significant antibacterial activity for drug-resistant bacteria and have a very high research and development potential. The Fasamycins compounds can be applied as novel antibiotics to the control of the drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A New Antibacterial Compound Containing Fluorine
InactiveCN102267987AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveStructural formula
A compound with remarkable antibacterial activity has the following structure: (Formula I), which has good antibacterial effect on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA).
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGKE DRUG R&D
Staphylococcus Lysin and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20180291357A1Improve survival rateStrong cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliMethicillin sensitive
The present invention discloses a lysin that is capable of killing Staphylococcus and the use thereof, belonging to the field of biological agents. The present invention discloses the amino acid sequence and the encoding gene sequence of the lysin. This lysin keeps active in a wide range of pH. It has lytic activity against Staphylococcus in pH 4-11. The recombinant protease constructed by the encoding gene can be solubly expressed in E. coli strain BL21 (DE3). The lysin can be used to effectively kill multiple species Staphylococcus in vitro, including methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated in clinics. This lysin can be used as an antibiotic for the treatment of staphylococcal infections in vivo. This lysin is also able to rapidly lyse staphylococcal cell wall; as a result, intracellular substances such as ATP and DNA are released. Those released substances can be used to detect the type of Staphylococcus.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
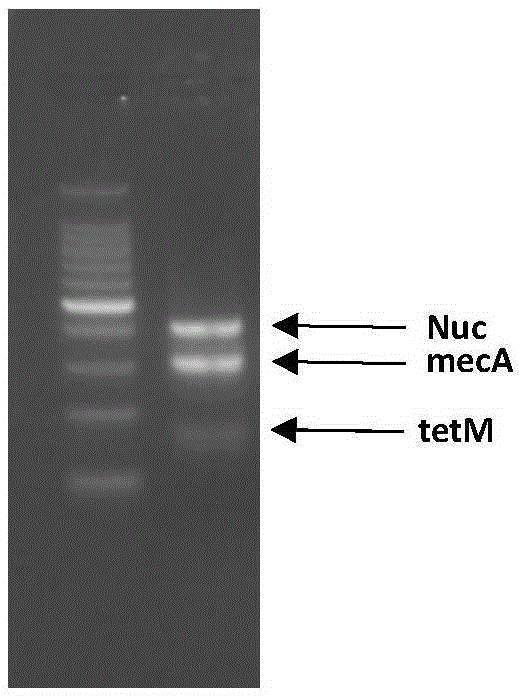
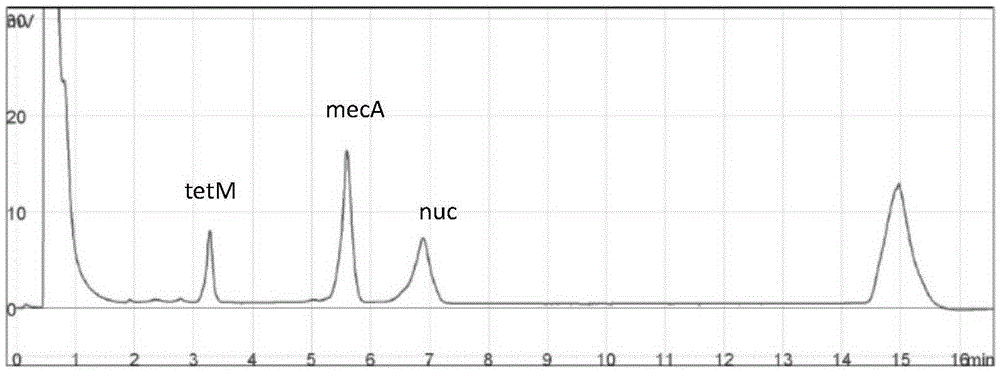
Composition used for detection of methicillin-resistant and/or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN104212900AMeet the needs of rapid and accurate detectionShort inspection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStaphylococcus cohniiMethicillin sensitive
The invention provides a composition used for detection of methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus. The composition used for detection of the methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus comprises a primer pair shown in SEQ ID No.1 / 2 and at least one of primer pairs shown in SEQ ID NO.3 / 4 and SEQ ID NO.5 / 6; meanwhile, an mPCR-DHPLC / electrophoresis detection kit and method are further constructed on the basis, and pathogenic staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus drug resistant strains in food are detected; and bacterial strain identification is carried out on staphylococcus aureus by utilizing the composition and the method which are disclosed by the invention, and MRSA and a tetracycline-resistant gene can be detected at the same time, so that staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and erythromycin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in a sample can be identified at the same time during one-step detection. The composition used for detection of methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus has the advantages of high speed and high throughput; and meanwhile, detection time is short, operation is simple, labour and cost can be greatly saved, and the rapid detection requirement can be met.
Owner:郑秋月 +4
New antibacterial compound
InactiveCN101948403AAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationMethicillin sensitiveStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
The invention relates to a new compound with significant antibacterial activity, the structure is as follows: (formula I), and the new compound has great antibacterial effect for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). (Formula I).
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGKE DRUG R&D
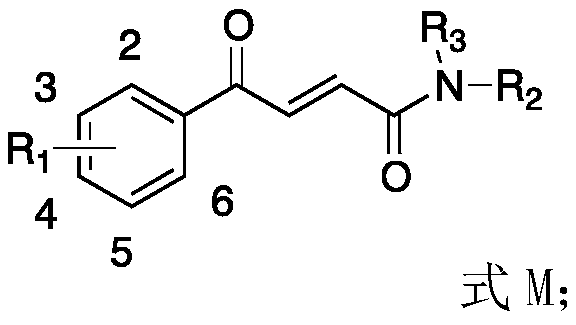
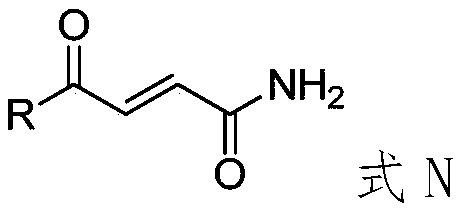
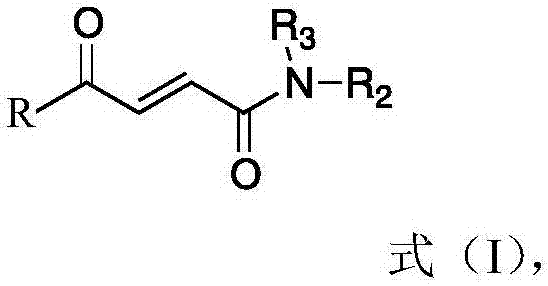
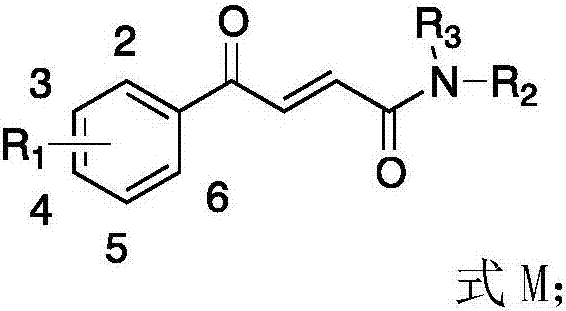
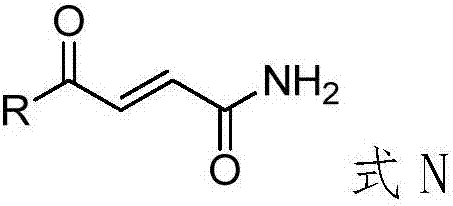
Application of 4-oxo-2-butenamide derivatives in the preparation of antibacterial agents
ActiveCN106860441BAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention discloses application of a 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative to preparation of bacteriostatic agents. The structure of the 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative is shown as a formula (I). The 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative has a bacteriostatic effect; good antibacterial activity can be realized on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, vancomycin drug-resistant enterococcus faecalis, vancomycin drug-resistant enterococcus faecium, methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus epidermidis, vancomycin-sensitive enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-sensitive enterococcus faecium. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Microparticle formulation for pulmonary drug delivery of anti infective molecule for treatment of infectious diseases
ActiveUS20130125879A1Reduce drug associated systemic toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisMethicillin sensitive
The present invention relates to a biodegradable, inhalable microparticle formulation comprising a compound of formula I obtained by fermentation of a microorganism of the Streptomyces species (PM0626271 / MTCC5447), as described in PCT application publication WO2011027290, and a biodegradable lipid for drug delivery wherein the ratio of drug (compound of formula I) to lipid is 1:15 to 1:25. The present invention also relates to the process for preparation of the formulation and to the method of treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis, multi drug resistant tuberculosis (MDRTB), methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonias and methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) pneumonias by administering therapeutically effective amount of the formulation to a mammal in need thereof. The present invention further relates to a method of delivering the microparticle formulation to a mammal in need thereof, wherein the formulation is administered by inhalation or intratracheal instillation for pulmonary delivery.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ANTARCTIC & OCEAN RES NCAOR +1
Staphylococcus lysin and use thereof
ActiveUS10626387B2Low cytotoxicityIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveStaphyloccocus aureus
The present invention discloses a lysin that is capable of killing Staphylococcus and the use thereof, belonging to the field of biological agents. The present invention discloses the amino acid sequence and the encoding gene sequence of the lysin. This lysin keeps active in a wide range of pH. It has lytic activity against Staphylococcus in pH 4-11. The recombinant protease constructed by the encoding gene can be solubly expressed in E. coli strain BL21 (DE3). The lysin can be used to effectively kill multiple species Staphylococcus in vitro, including methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated in clinics. This lysin can be used as an antibiotic for the treatment of staphylococcal infections in vivo. This lysin is also able to rapidly lyse staphylococcal cell wall; as a result, intracellular substances such as ATP and DNA are released. Those released substances can be used to detect the type of Staphylococcus.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
Methacycline derivative
InactiveCN101967108BAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationStaphylococcus cohniiMethicillin sensitive
The invention discloses a methacycline derivative with remarkable antimicrobial activity. The methacycline derivative has the following structure: FORMULA (I), which has good very good antibacterial action on meticillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA).
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGKE DRUG R&D
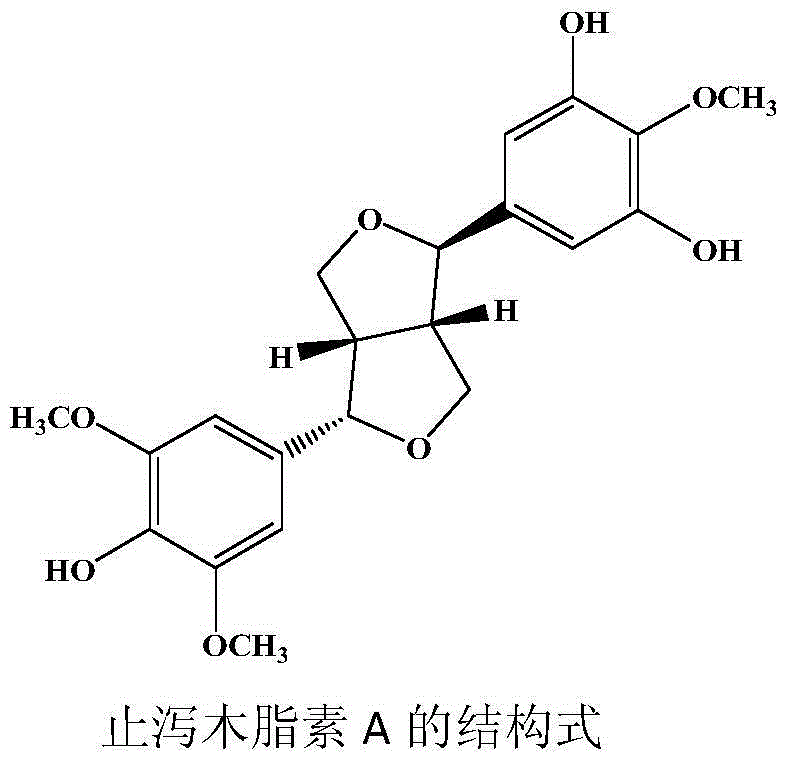
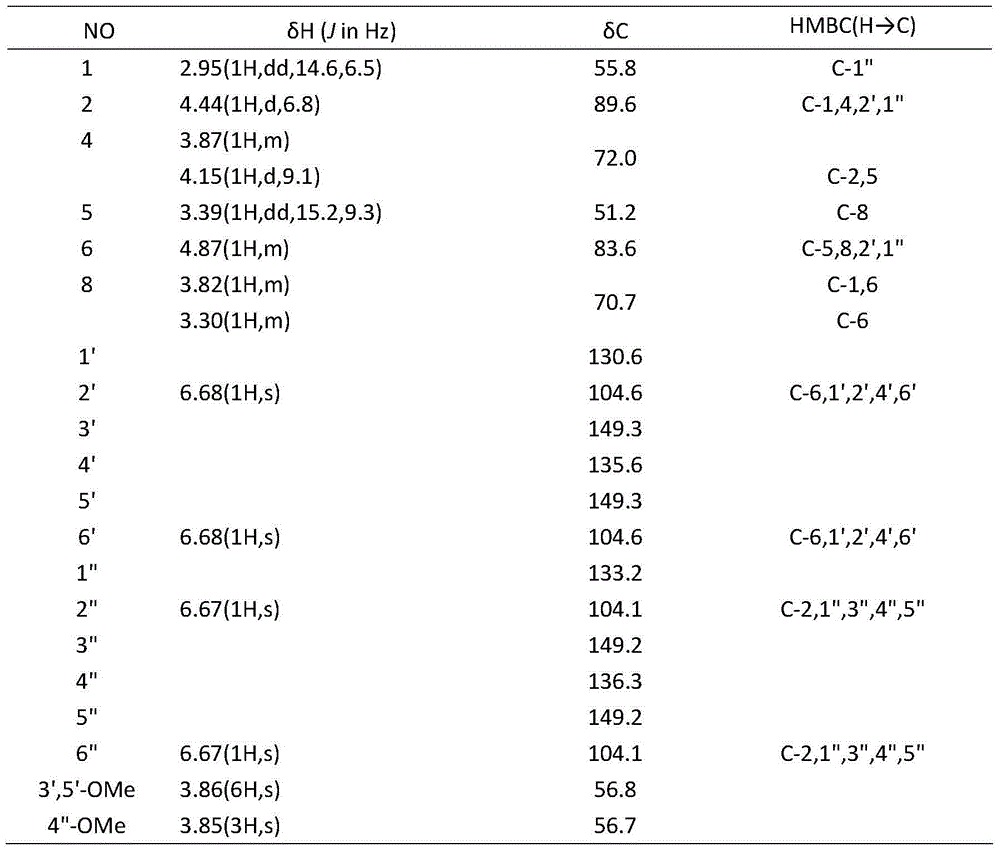
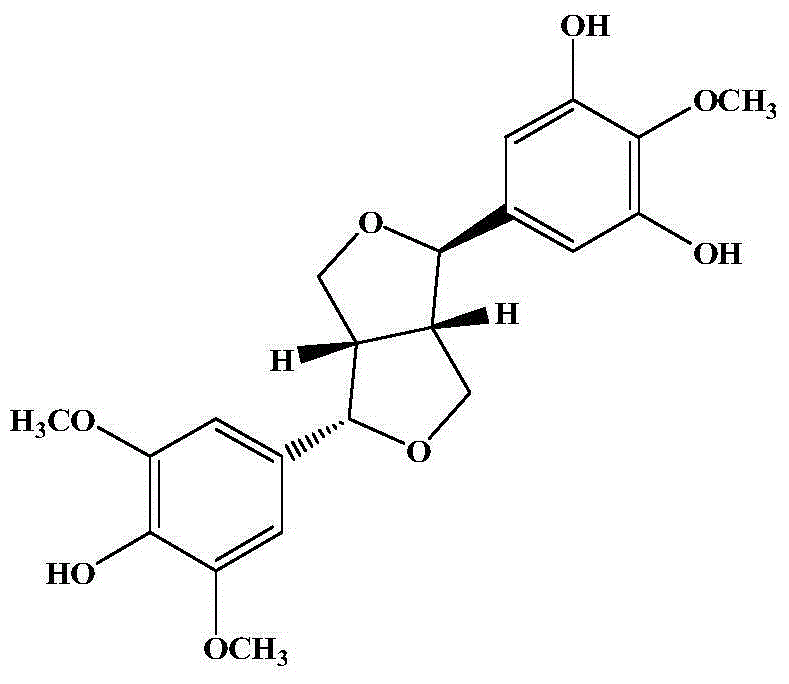
Antidiarrheal ligan compound A with antibacterial activity and application thereof
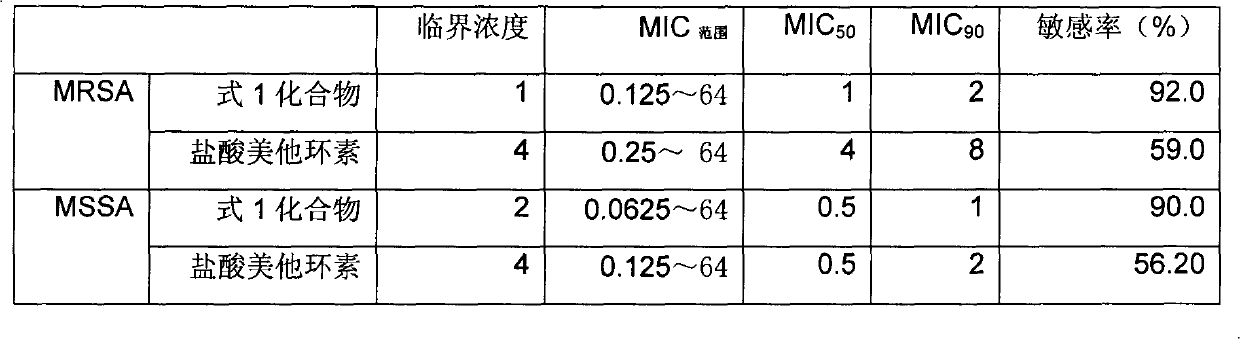
InactiveCN104804012AHas antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCompound aMethicillin sensitive
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and discloses a structure of an antidiarrheal ligan compound A with natural bacteriostatic activity and application of the antidiarrheal ligan compound A to bacteriostasis. In-vitro culture screening experiments and in-vitro bacteriostatic activity tests show that the antidiarrheal ligan compound A has a relatively obvious inhibitory activity on two selected bacteriostatic strains. The specific data is that the antidiarrheal ligan compound A has an extremely strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus, and the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) is 128 [mu]g / mL; the antidiarrheal ligan compound A also has an extremely strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant staphylocccus aureus, and the MIC value is 128 [mu]g / mL.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Compositions for the detection of methicillin-resistant and/or tetracycline-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN104212900BMeet the needs of rapid and accurate detectionShort inspection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMethicillin sensitiveStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a composition used for detection of methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus. The composition used for detection of the methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus comprises a primer pair shown in SEQ ID No.1 / 2 and at least one of primer pairs shown in SEQ ID NO.3 / 4 and SEQ ID NO.5 / 6; meanwhile, an mPCR-DHPLC / electrophoresis detection kit and method are further constructed on the basis, and pathogenic staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus drug resistant strains in food are detected; and bacterial strain identification is carried out on staphylococcus aureus by utilizing the composition and the method which are disclosed by the invention, and MRSA and a tetracycline-resistant gene can be detected at the same time, so that staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and erythromycin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in a sample can be identified at the same time during one-step detection. The composition used for detection of methicillin-resistant and / or tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus aureus has the advantages of high speed and high throughput; and meanwhile, detection time is short, operation is simple, labour and cost can be greatly saved, and the rapid detection requirement can be met.
Owner:郑秋月 +4
Microparticle formulation for pulmonary drug delivery of anti infective molecule for treatment of infectious diseases
ActiveUS8697653B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisMethicillin sensitive
The present invention relates to a biodegradable, inhalable microparticle formulation comprising a compound of formula I obtained by fermentation of a microorganism of the Streptomyces species (PM0626271 / MTCC5447), as described in PCT application publication WO2011027290, and a biodegradable lipid for drug delivery wherein the ratio of drug (compound of formula I) to lipid is 1:15 to 1:25. The present invention also relates to the process for preparation of the formulation and to the method of treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis, multi drug resistant tuberculosis (MDRTB), methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonias and methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) pneumonias by administering therapeutically effective amount of the formulation to a mammal in need thereof. The present invention further relates to a method of delivering the microparticle formulation to a mammal in need thereof, wherein the formulation is administered by inhalation or intratracheal instillation for pulmonary delivery.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ANTARCTIC & OCEAN RES NCAOR +1
New antibacterial compound
InactiveCN101948403BAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationStaphylococcus cohniiMethicillin sensitive
The invention relates to a new compound with significant antibacterial activity, the structure is as follows: (formula I), and the new compound has great antibacterial effect for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). (Formula I).
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGKE DRUG R&D
A kind of compound antidiarrheal lignan a with anti-drug resistance activity and use thereof
InactiveCN104804012BHas antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryMethicillin sensitiveStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and discloses a structure of an antidiarrheal ligan compound A with natural bacteriostatic activity and application of the antidiarrheal ligan compound A to bacteriostasis. In-vitro culture screening experiments and in-vitro bacteriostatic activity tests show that the antidiarrheal ligan compound A has a relatively obvious inhibitory activity on two selected bacteriostatic strains. The specific data is that the antidiarrheal ligan compound A has an extremely strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus, and the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) is 128 [mu]g / mL; the antidiarrheal ligan compound A also has an extremely strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant staphylocccus aureus, and the MIC value is 128 [mu]g / mL.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Detection of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms
ActiveUS8911946B2Reduce morbidityEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMicroorganismCo infection
Method of detecting methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) in a nucleic acid coamplification assay. The invention advantageously reduces the incidence of false-positive MRSA determinations in real-time assays by requiring satisfaction of a threshold criterion that excludes certain co-infections from the MRSA determination. The invention further provides for determination of MSSA, even when the MSSA is present in combination with methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative (MR-CoNS) bacteria at high or low levels.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Application of 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative to preparation of bacteriostatic agents
ActiveCN106860441AAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention discloses application of a 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative to preparation of bacteriostatic agents. The structure of the 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative is shown as a formula (I). The 4-oxo-2-crotonamide derivative has a bacteriostatic effect; good antibacterial activity can be realized on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, vancomycin drug-resistant enterococcus faecalis, vancomycin drug-resistant enterococcus faecium, methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus epidermidis, vancomycin-sensitive enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-sensitive enterococcus faecium. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com