Patents
Literature
193 results about "Nerve fibre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
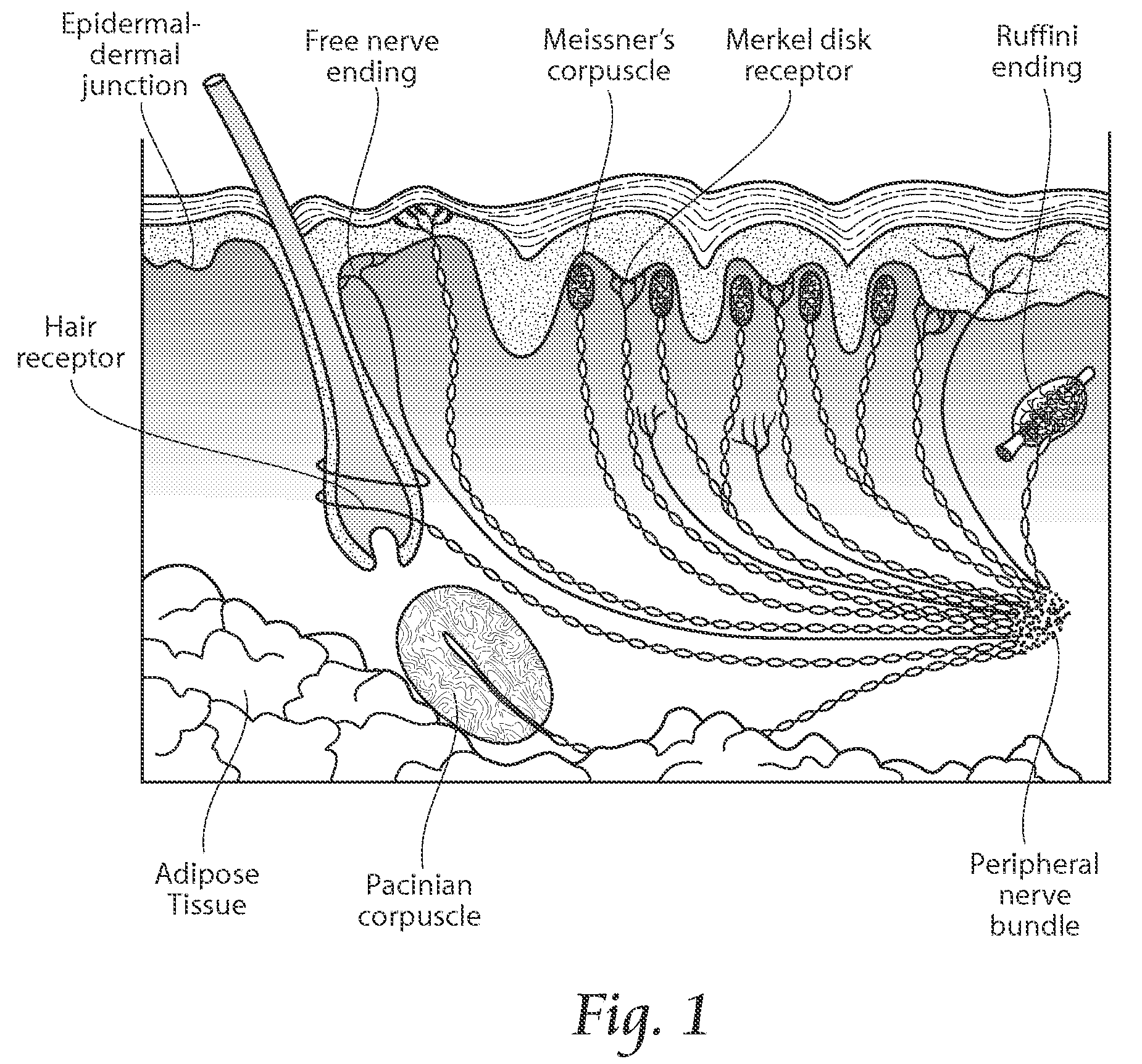
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis) or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials, away from the nerve cell body.
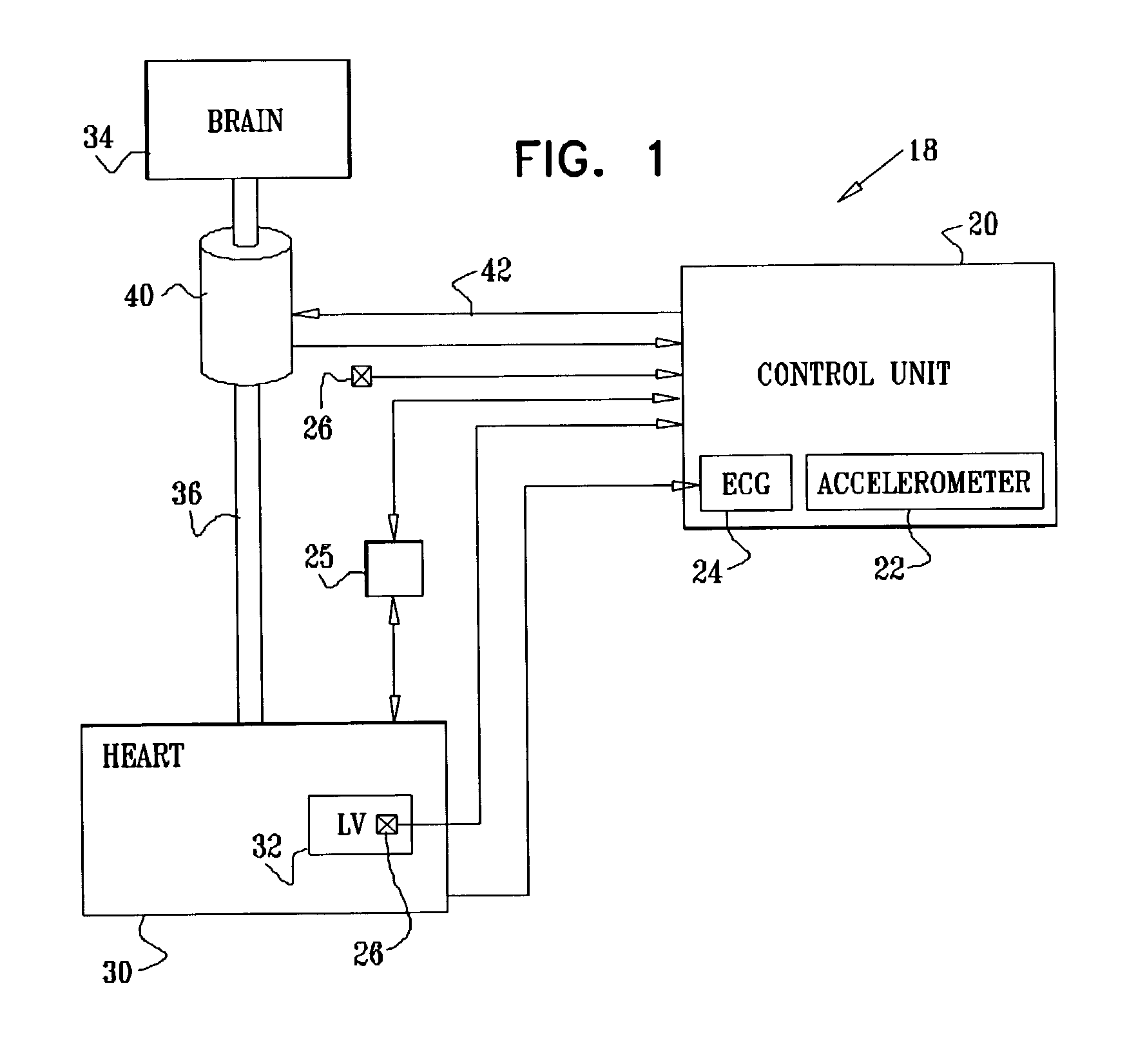
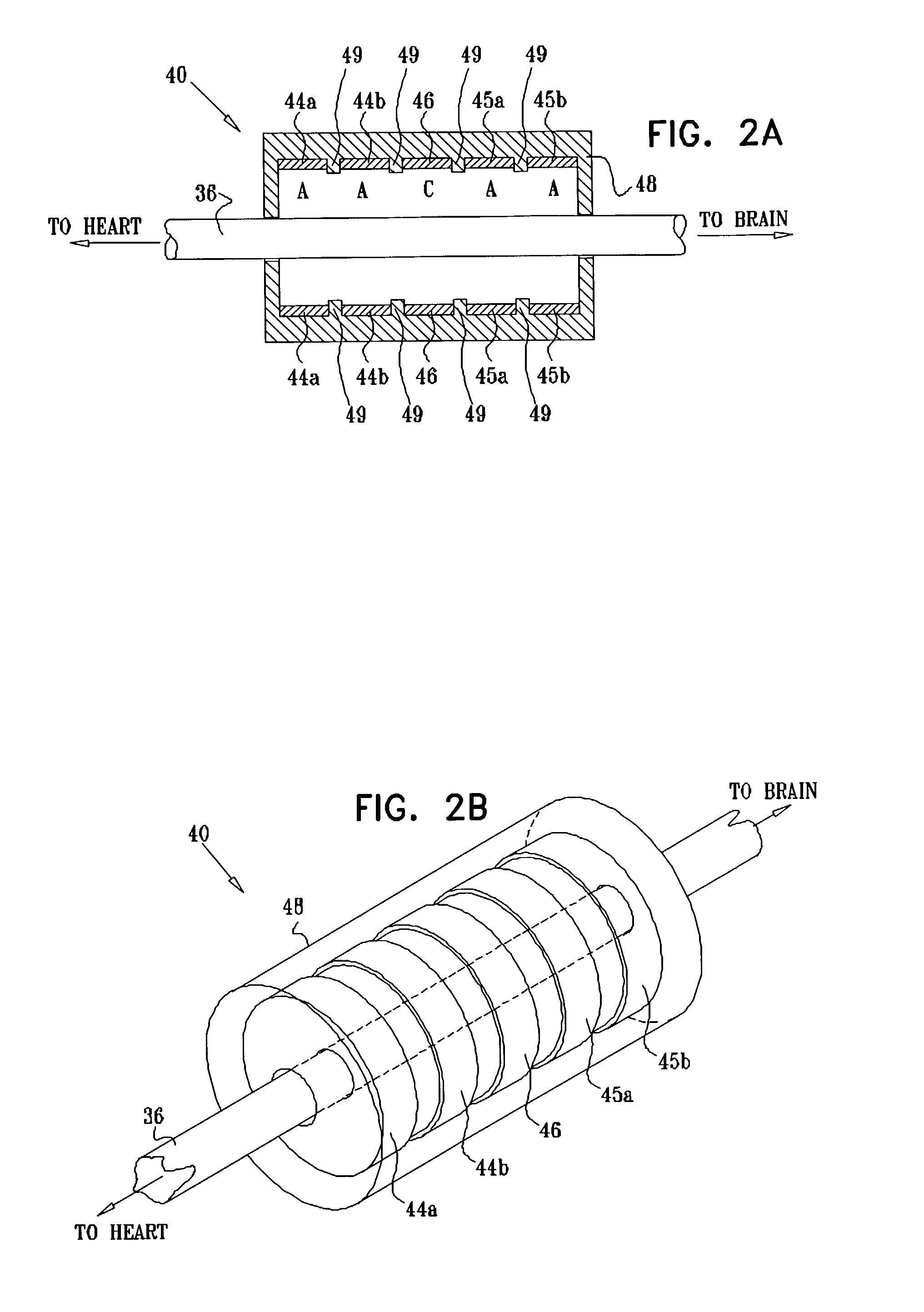
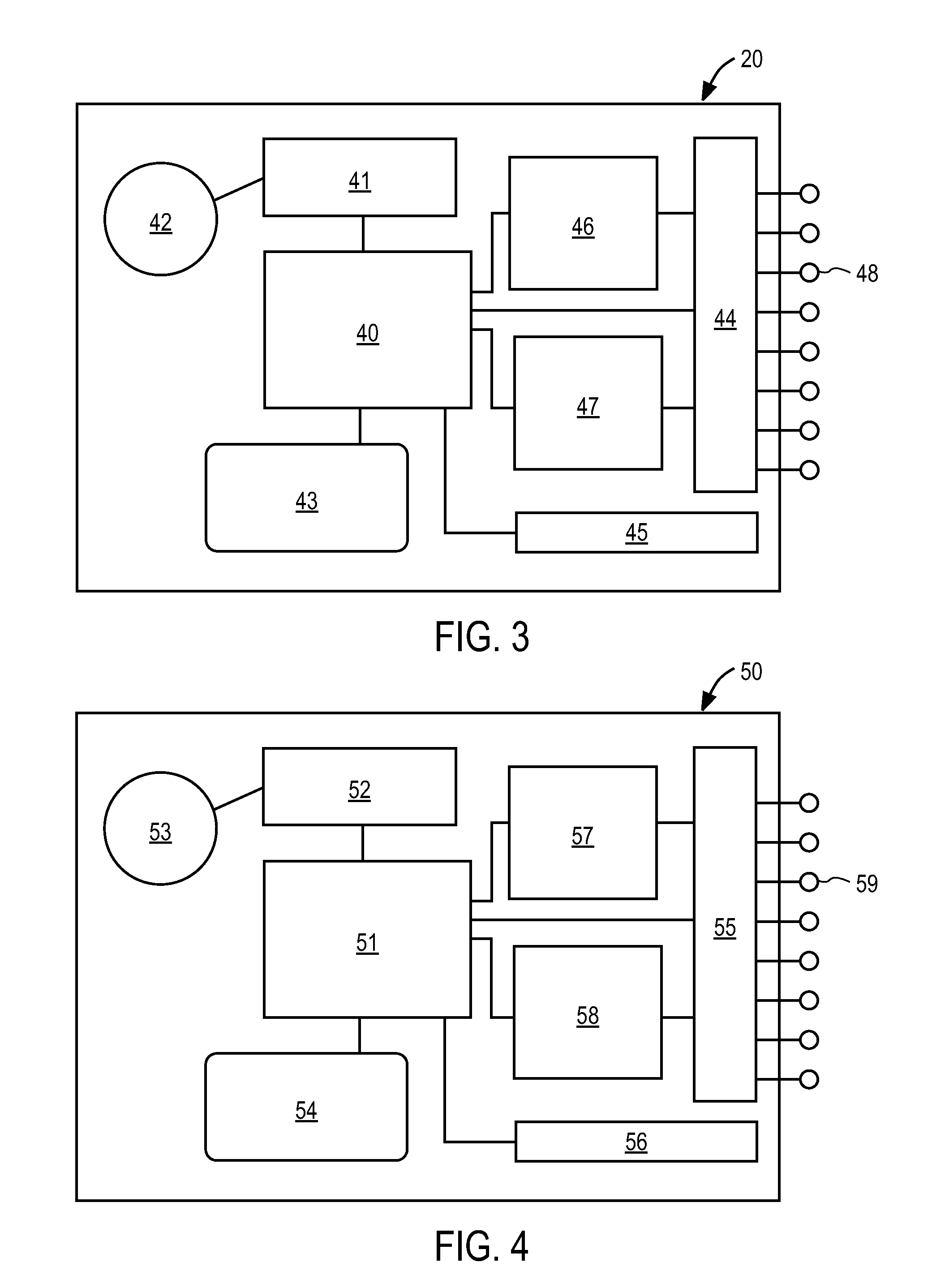
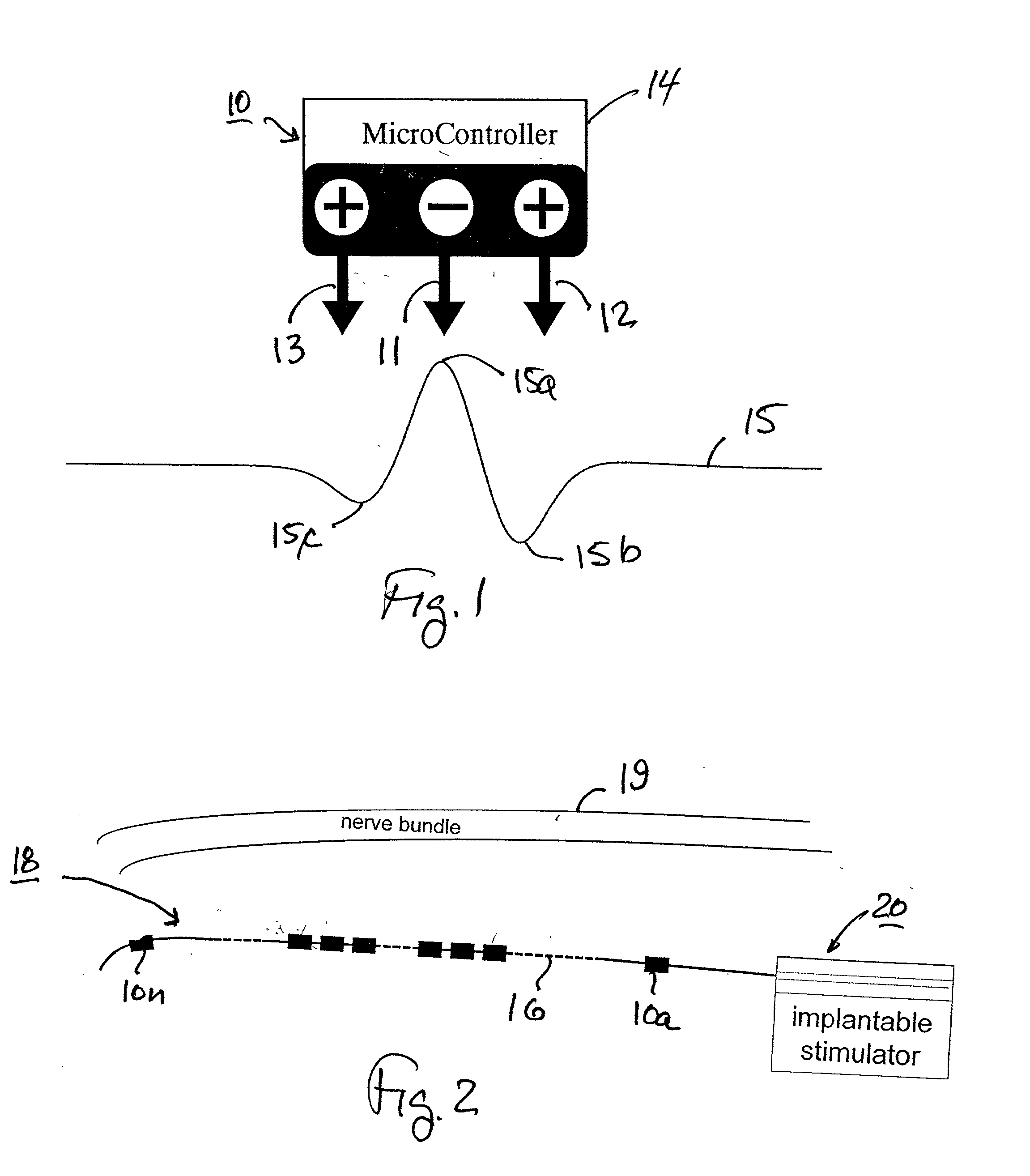
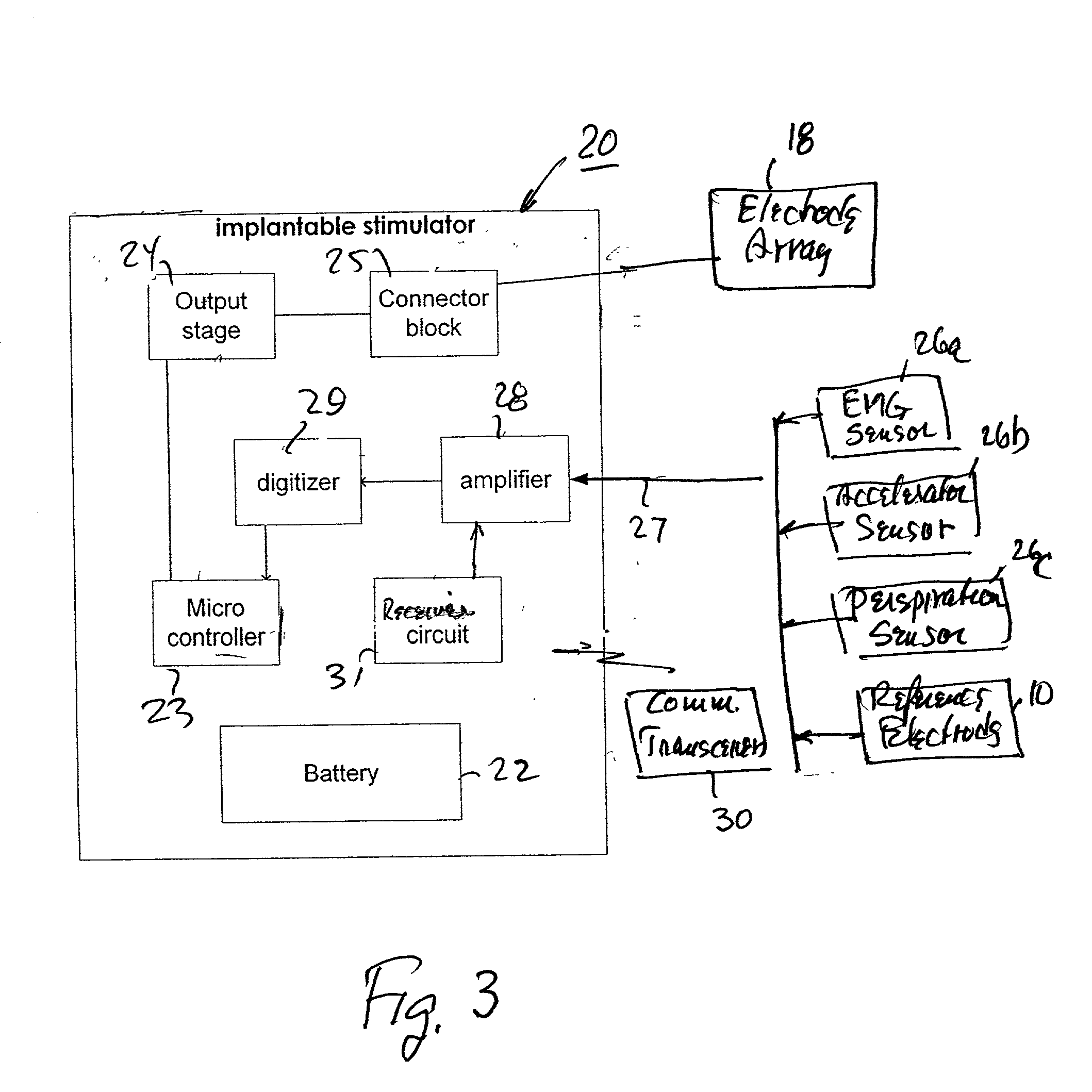
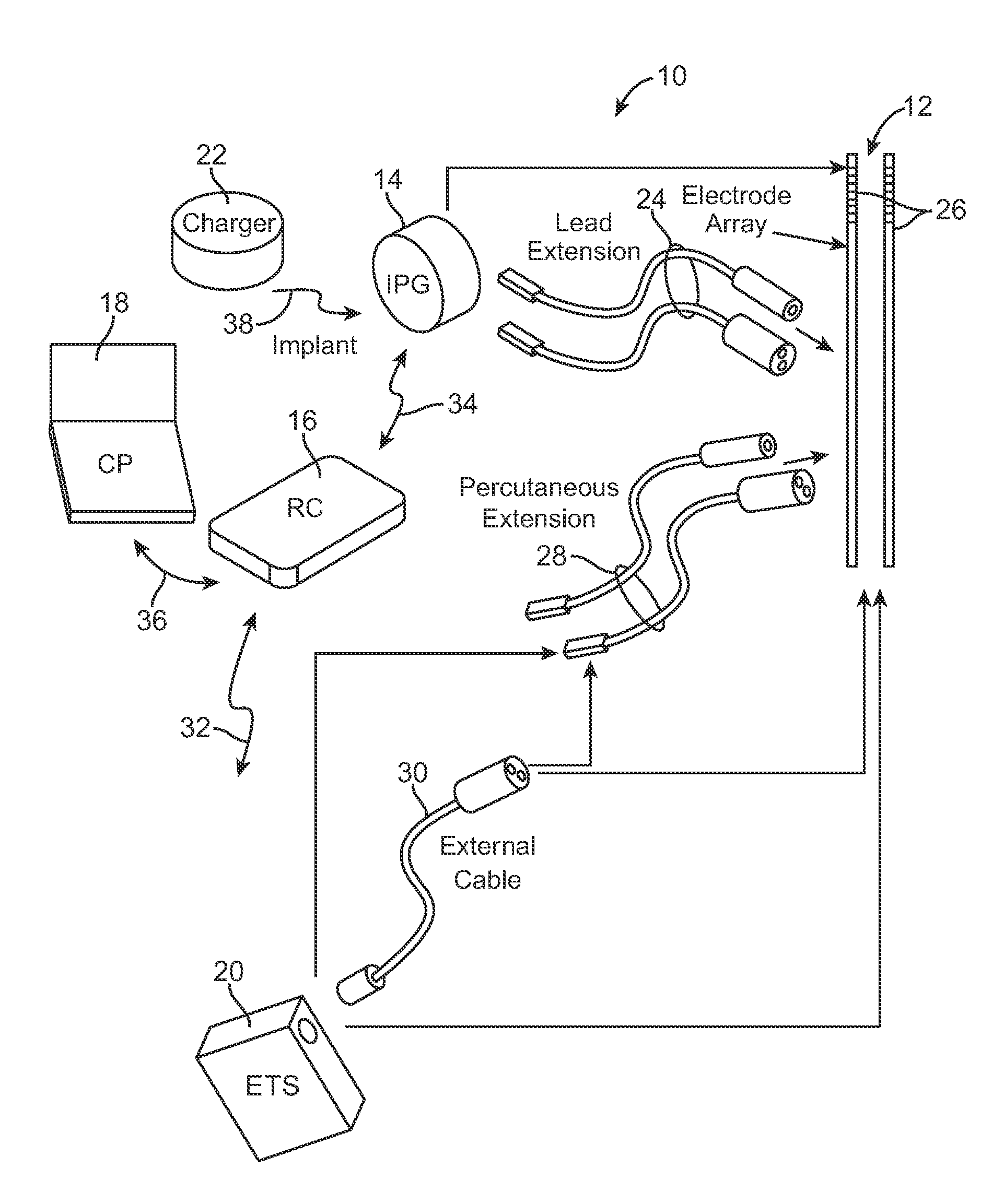
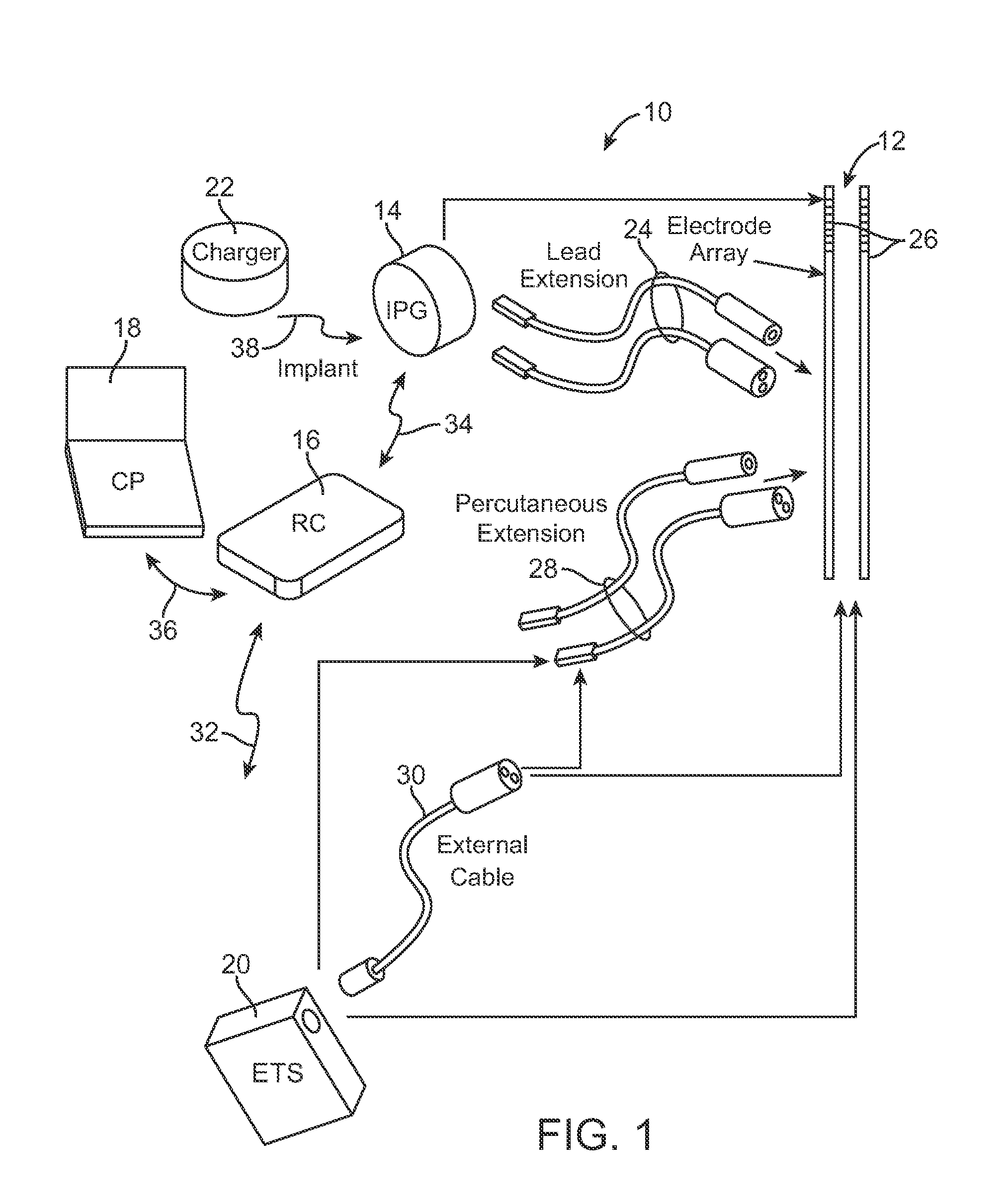
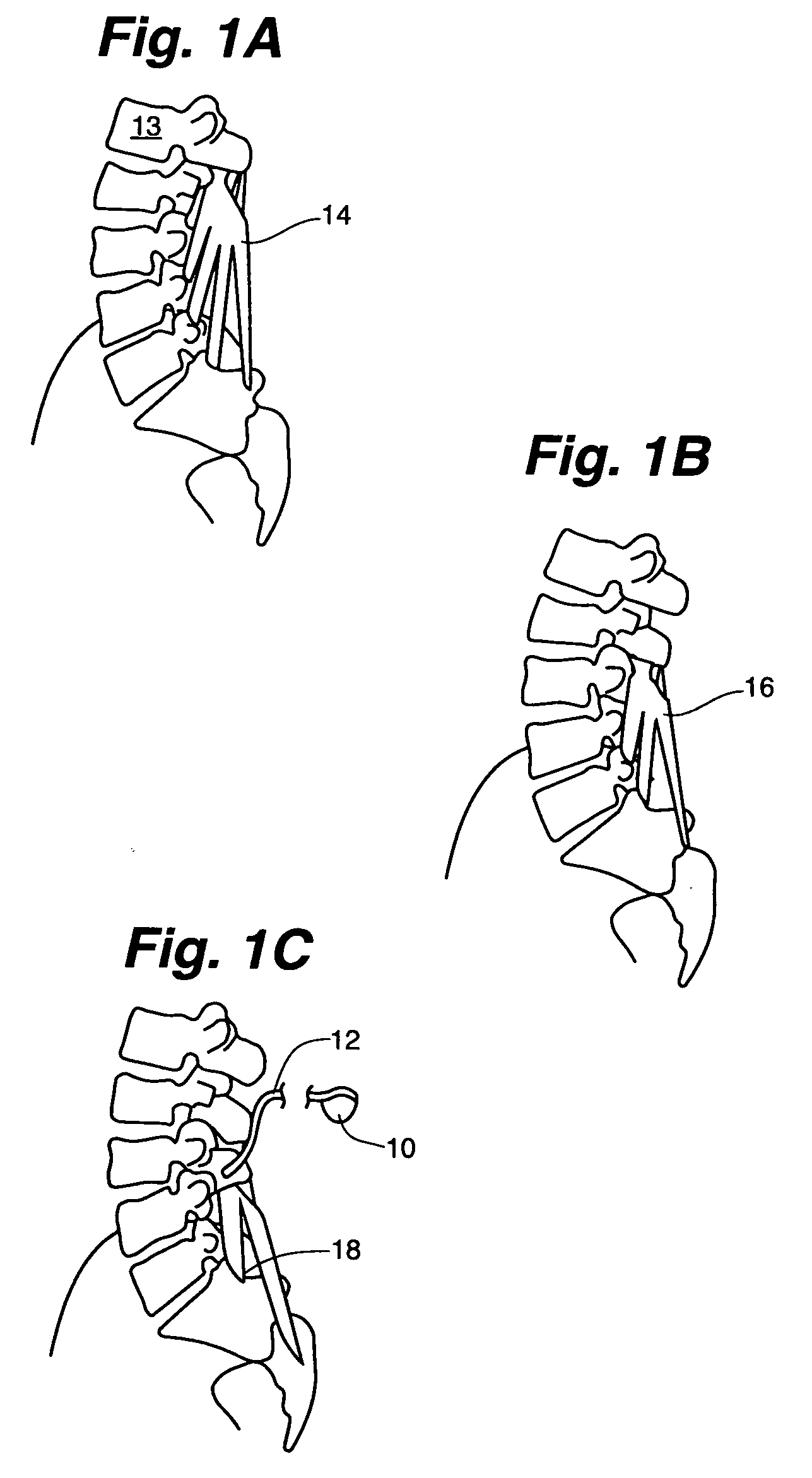
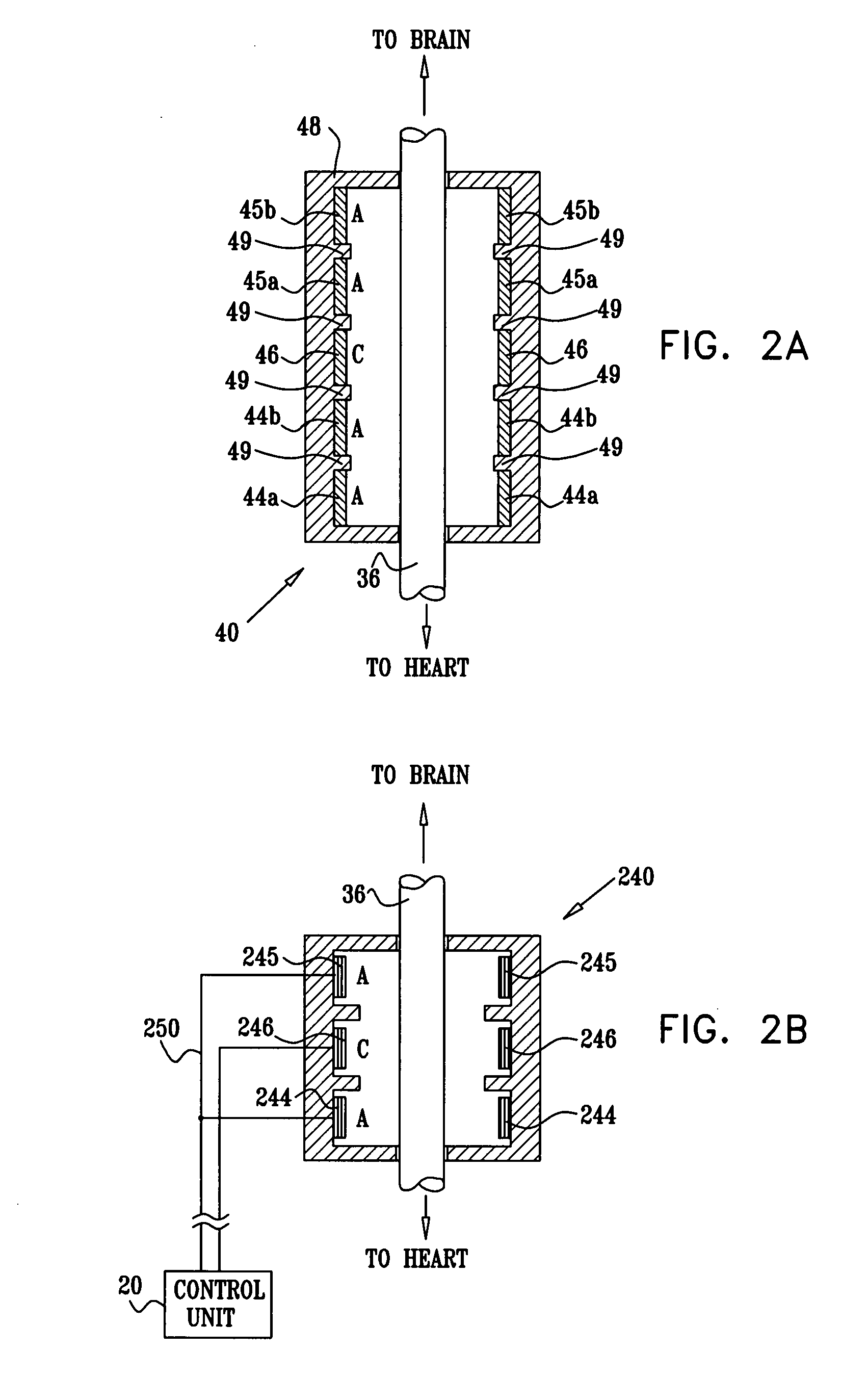
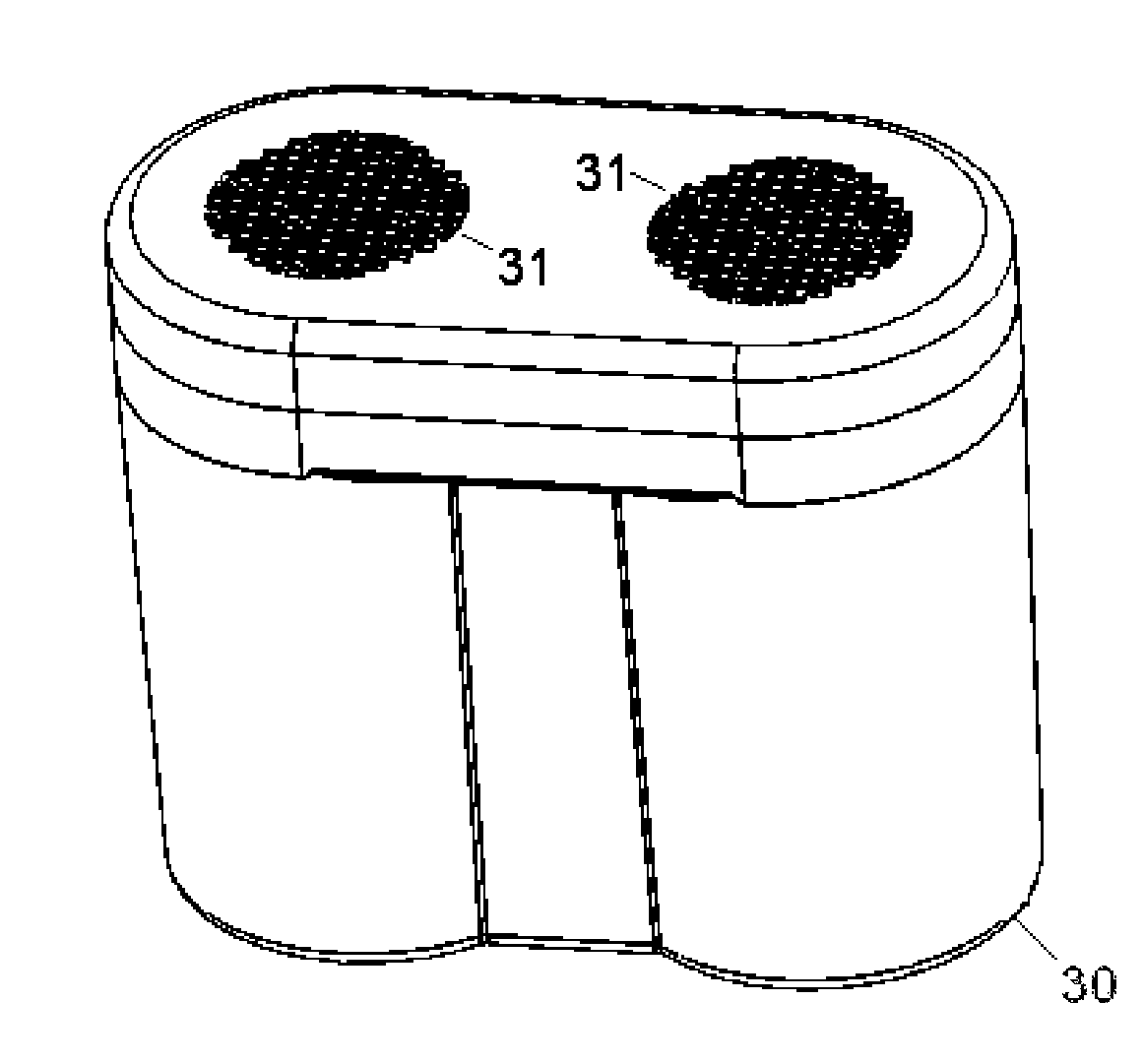
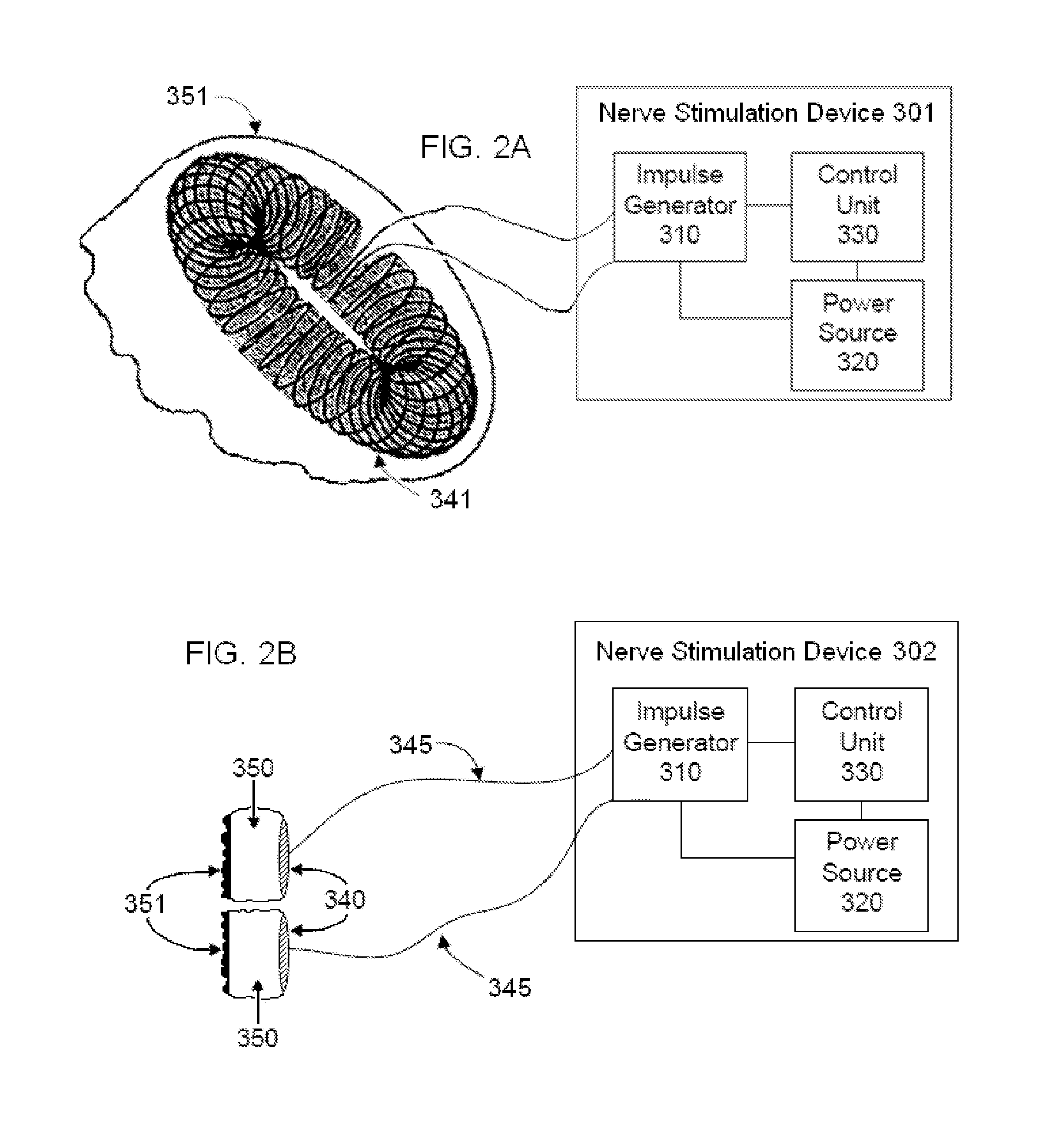
Selective nerve fiber stimulation
InactiveUS20060100668A1Modify heart rate variabilityReduce heart rate variabilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationNerve fiber bundleControl cell
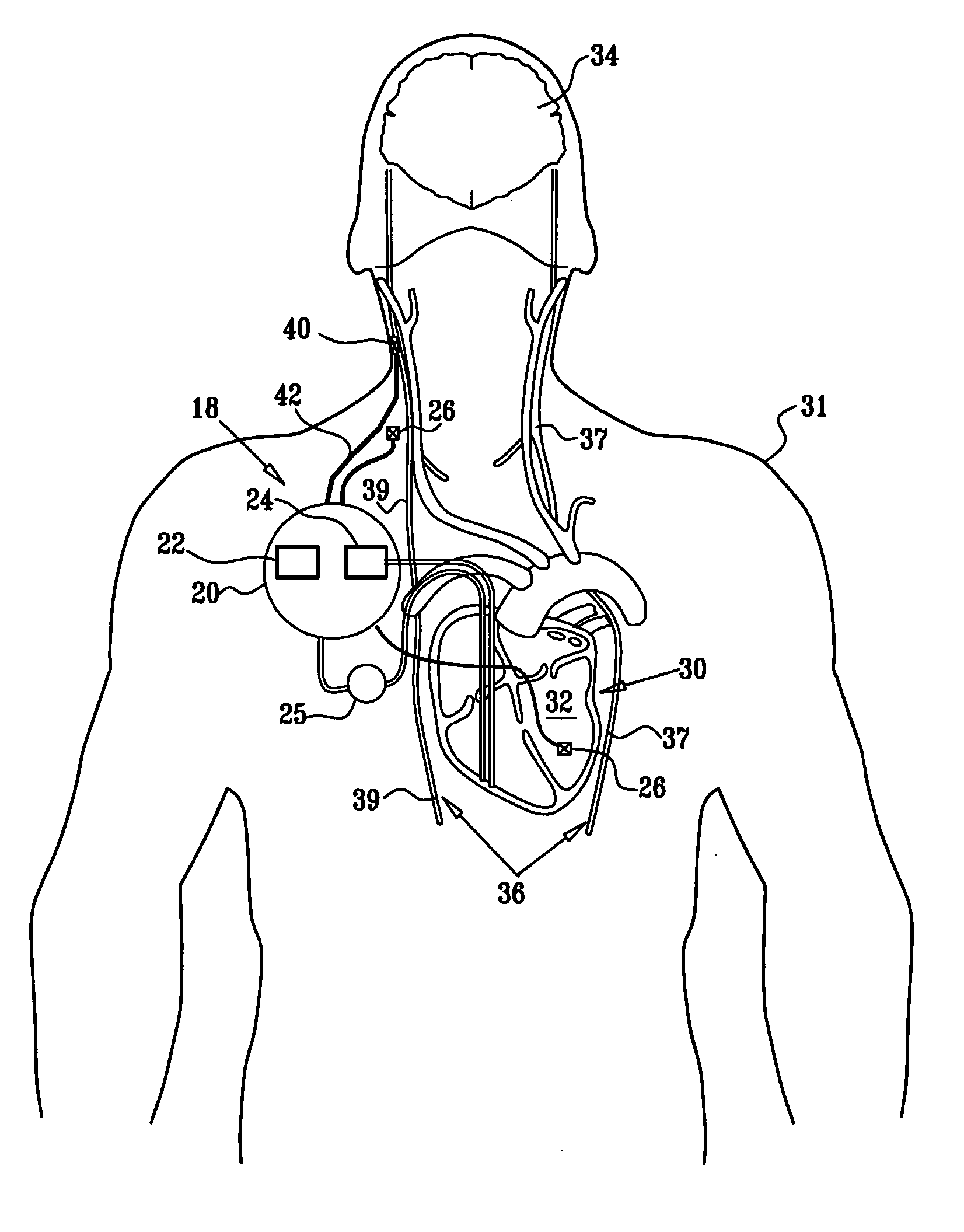
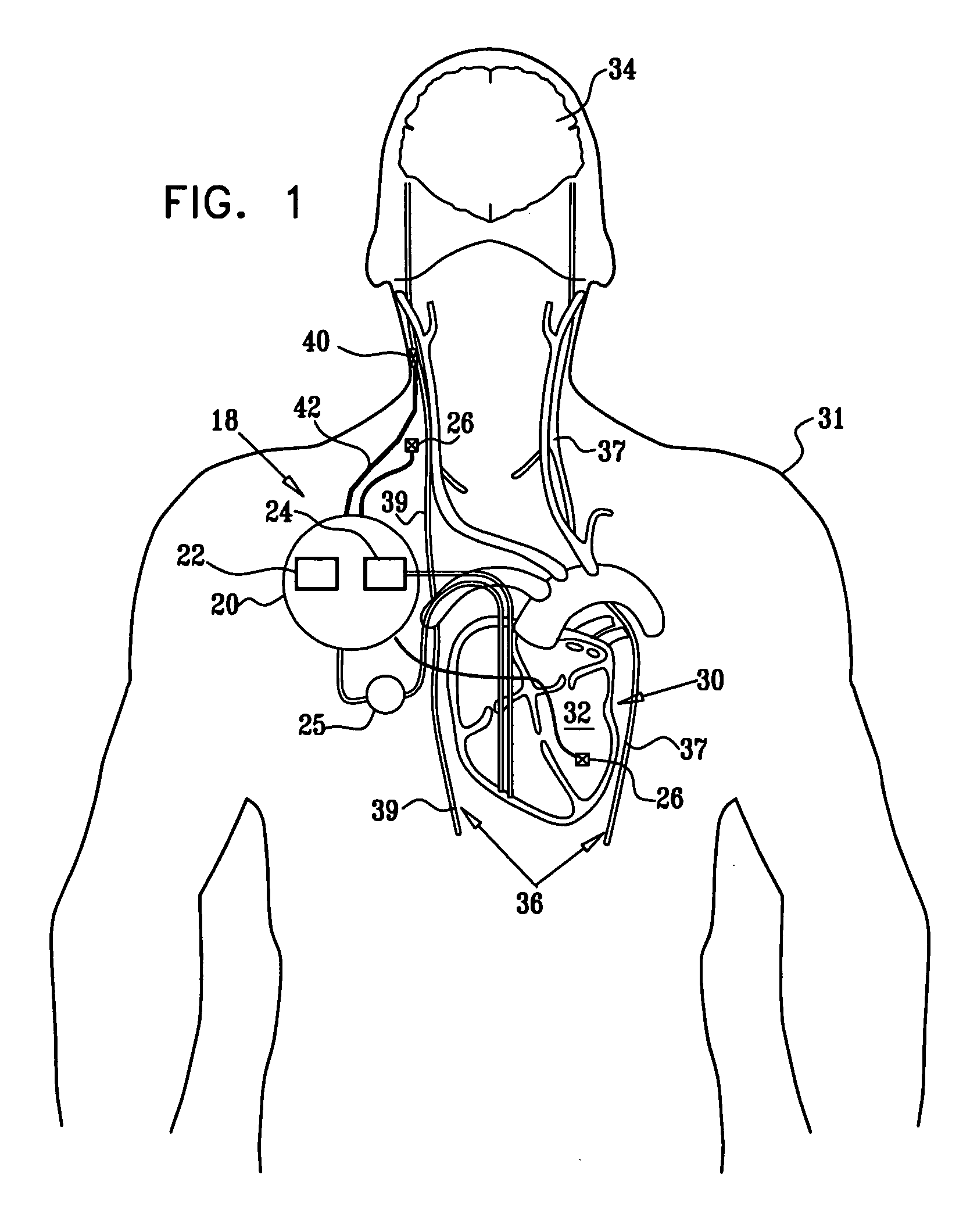
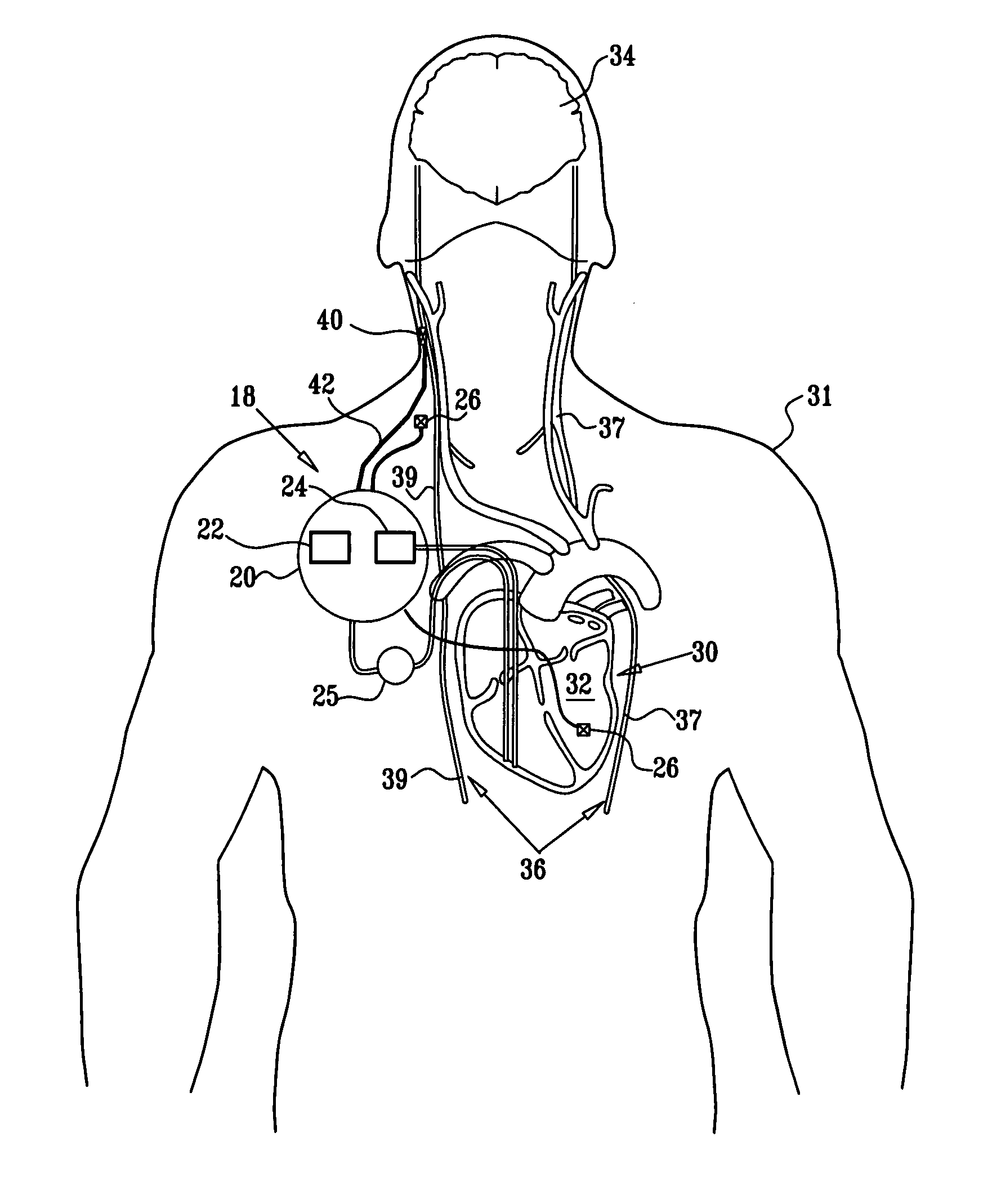
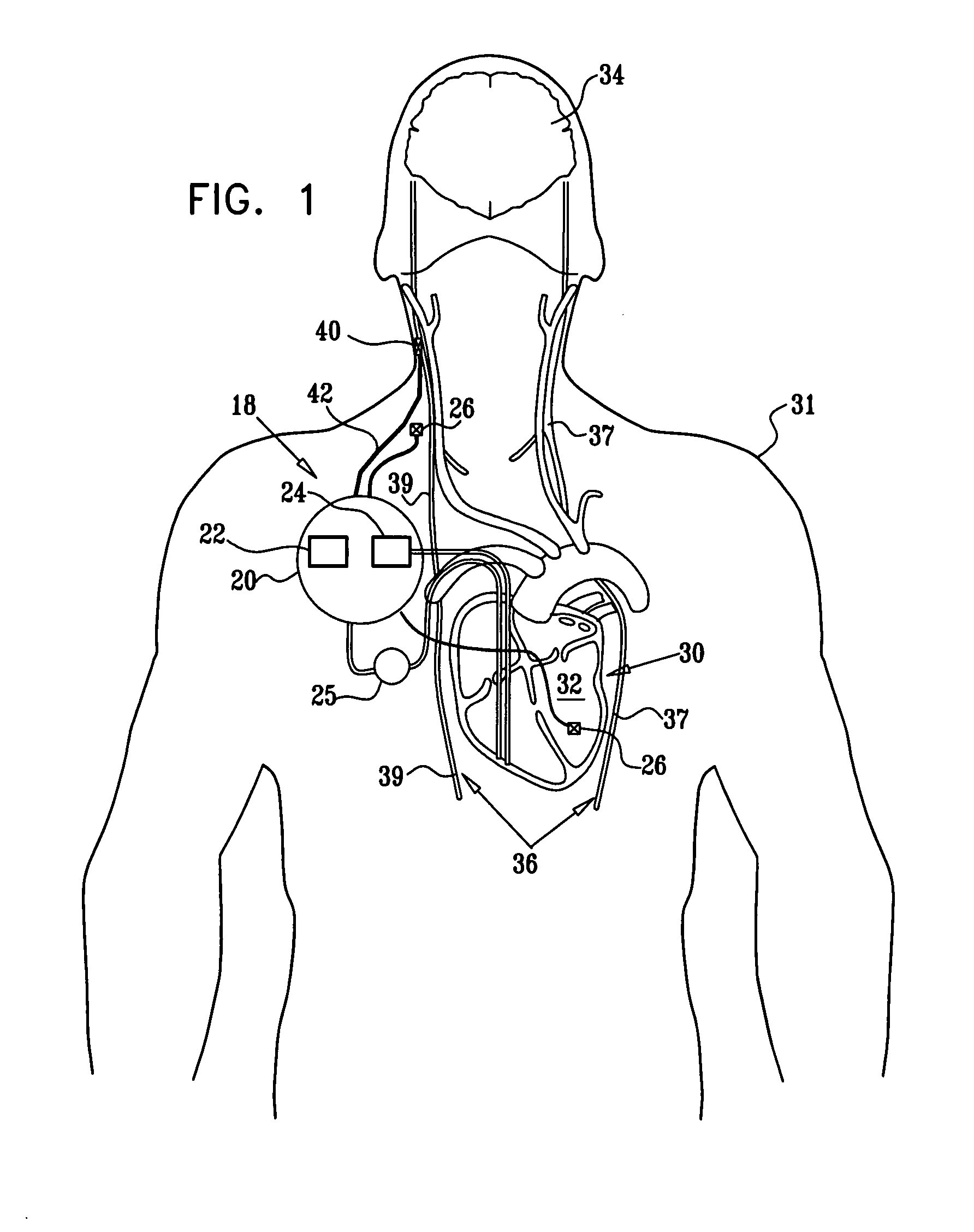
Apparatus is provided for treating a condition of a subject, including an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to an autonomic nerve of the subject, and a control unit. The control unit is adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the nerve a stimulating current, which is capable of inducing action potentials in a therapeutic direction in a first set and a second set of nerve fibers of the nerve, and to drive the electrode device to apply to the nerve an inhibiting current, which is capable of inhibiting the induced action potentials traveling in the therapeutic direction in the second set of nerve fibers, the nerve fibers in the second set having generally larger diameters than the nerve fibers in the first set. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Selective nerve fiber stimulation for treating heart conditions
InactiveUS7778703B2Minimizing adverse side effectRegulate heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleStimulus current
Apparatus for treating a heart condition of a subject is provided, including an electrode device, which is adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of the subject. A control unit is adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve a stimulating current, which is capable of inducing action potentials in a therapeutic direction in a first set and a second set of nerve fibers of the vagus nerve. The control unit is also adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve an inhibiting current, which is capable of inhibiting the induced action potentials traveling in the therapeutic direction in the second set of nerve fibers, the nerve fibers in the second set having generally larger diameters than the nerve fibers in the first set.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable microstimulators and methods for unidirectional propagation of action potentials
InactiveUS7860570B2Increase stimulationLess power consumptionSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationNerve fiber bundleSide effect
Miniature implantable stimulators (i.e., microstimulators) are capable of producing unidirectionally propagating action potentials (UPAPs). The methods and configurations described may, for instance, arrest action potentials traveling in one direction, arrest action potentials of small diameters nerve fibers, arrest action potentials of large diameter nerve fibers. These methods and systems may limit side effects of bidirectional and / or less targeted stimulation.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus and method for stimulation of nerves and automated control of surgical instruments
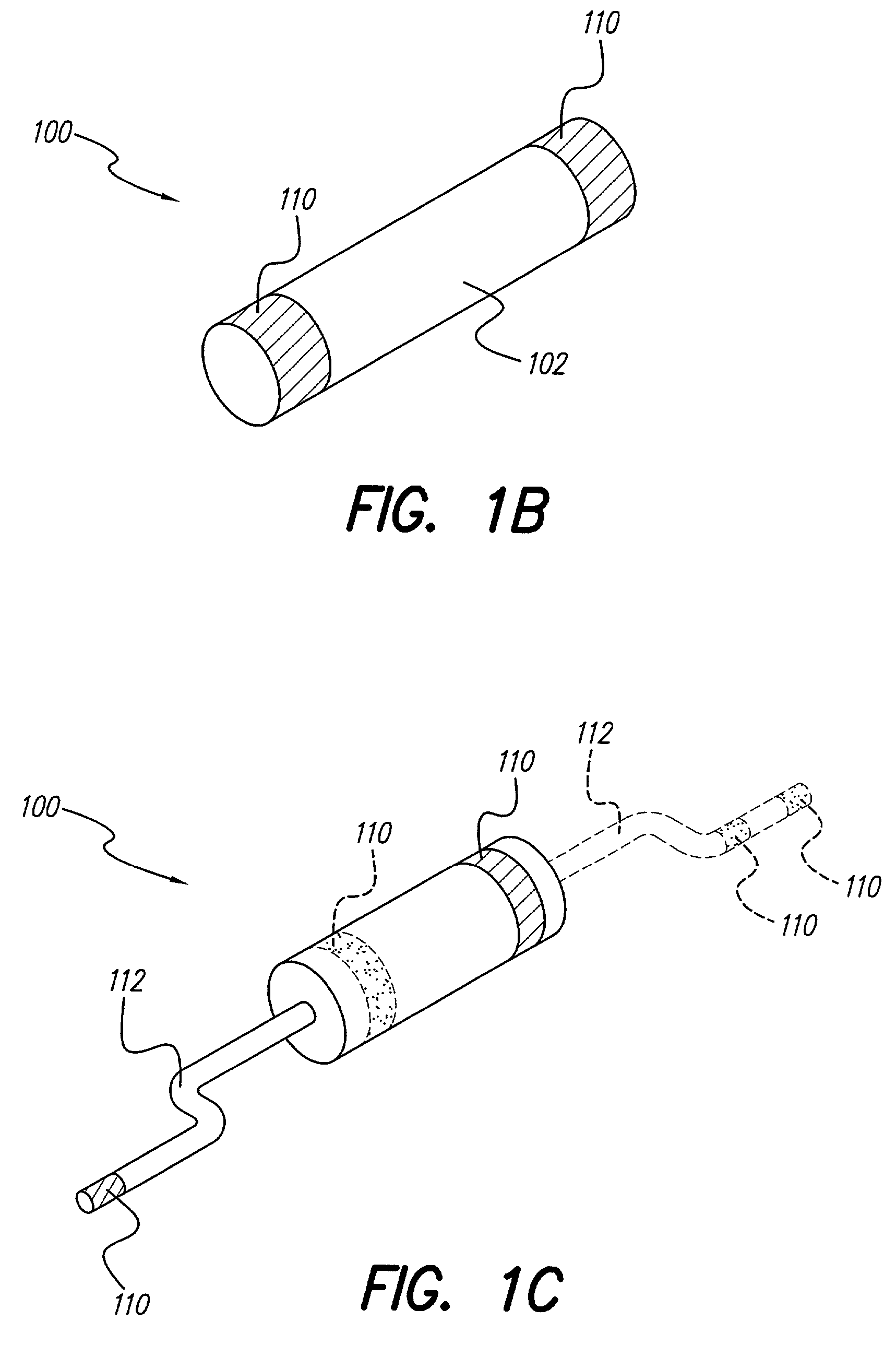
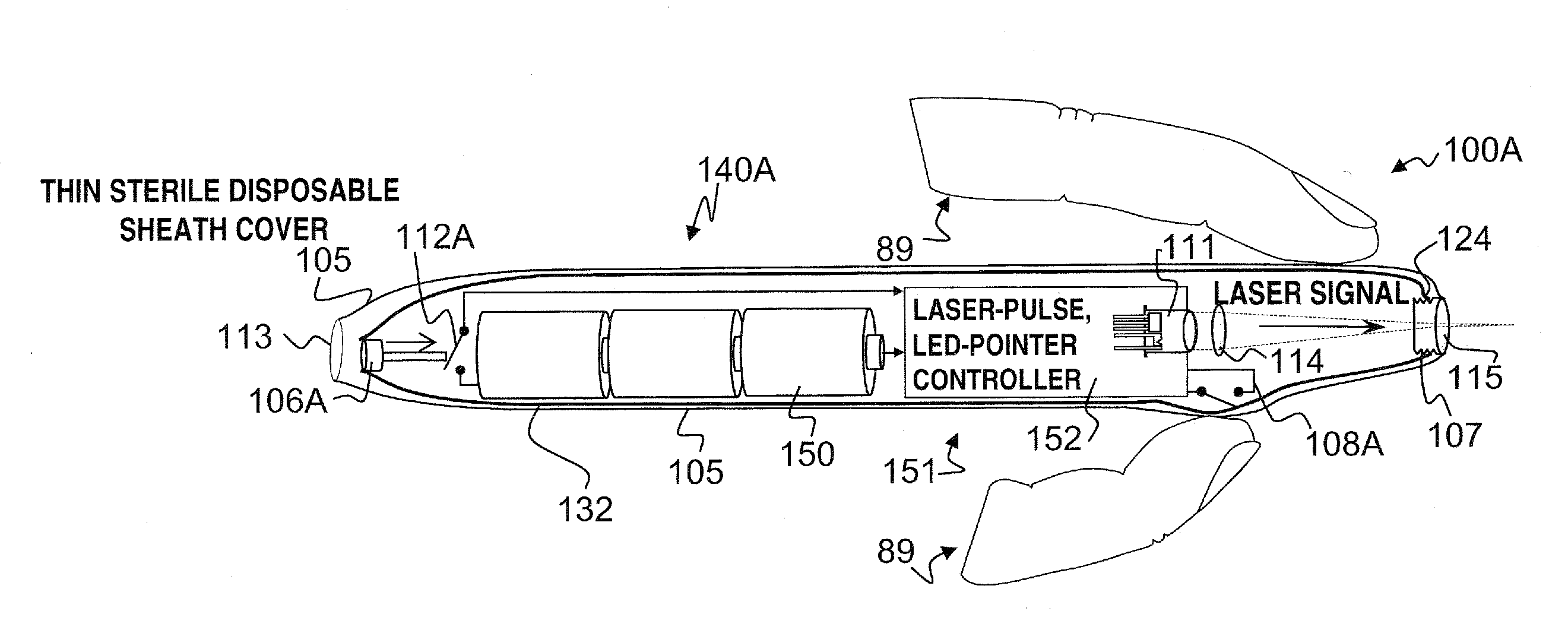
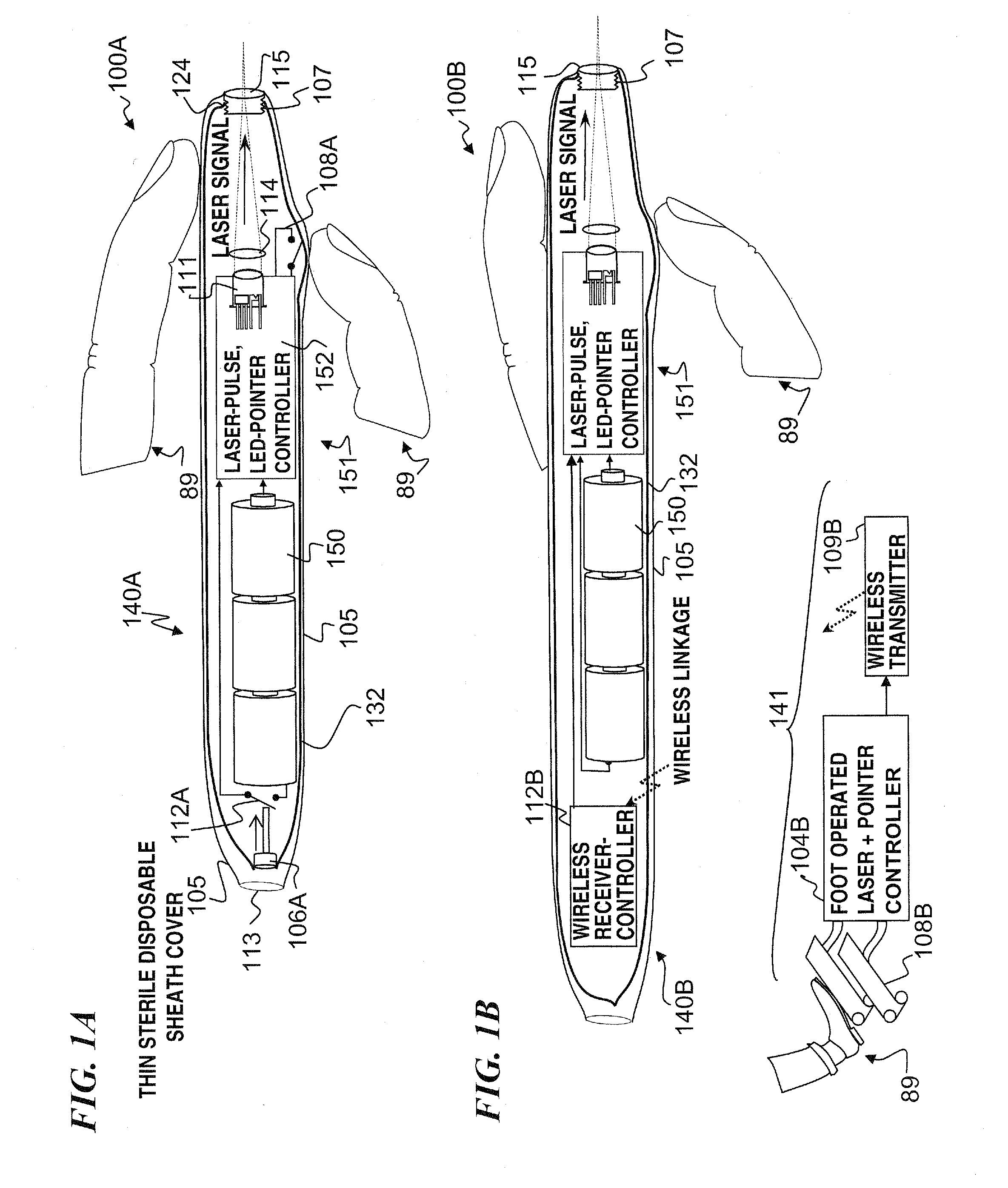
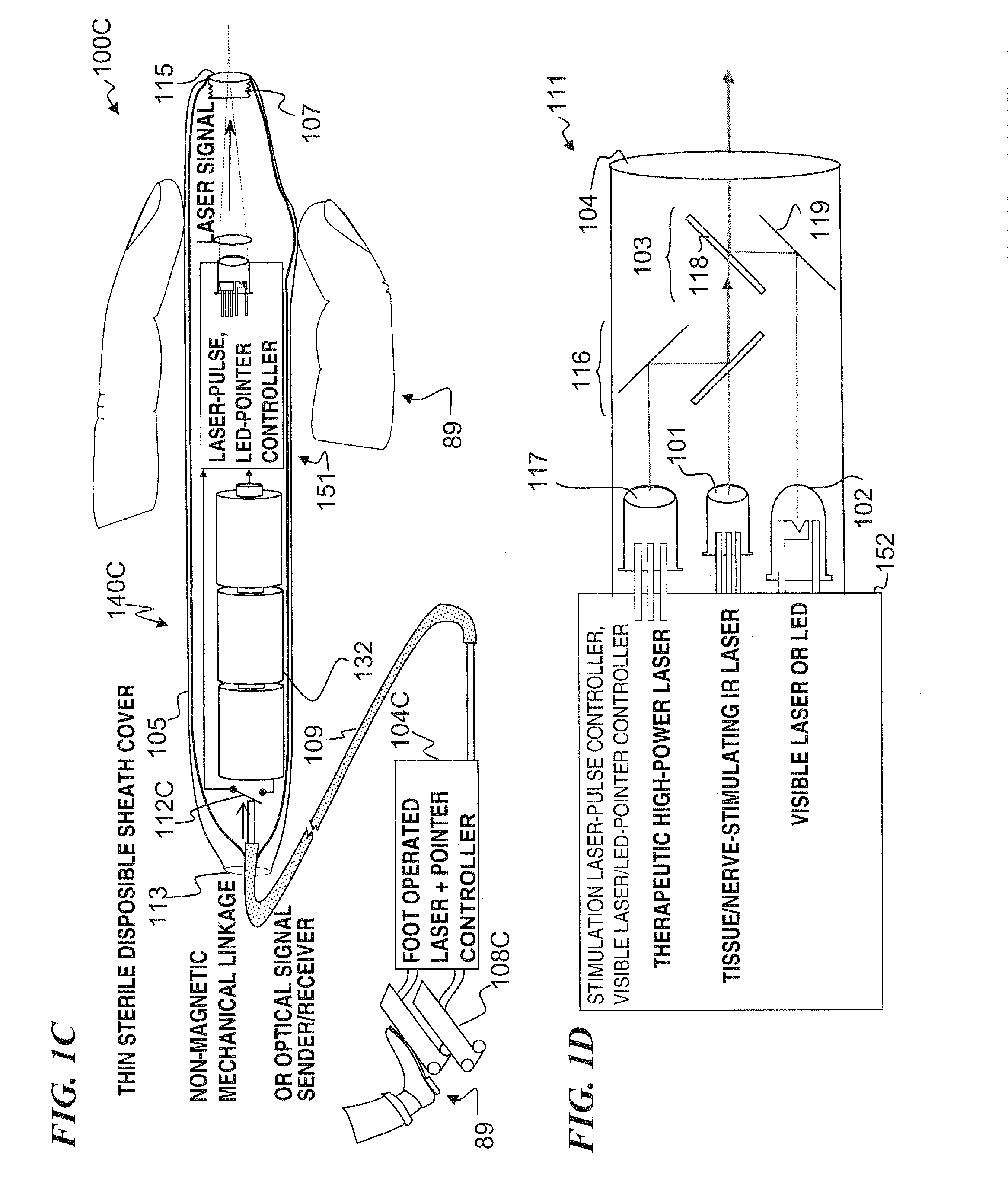
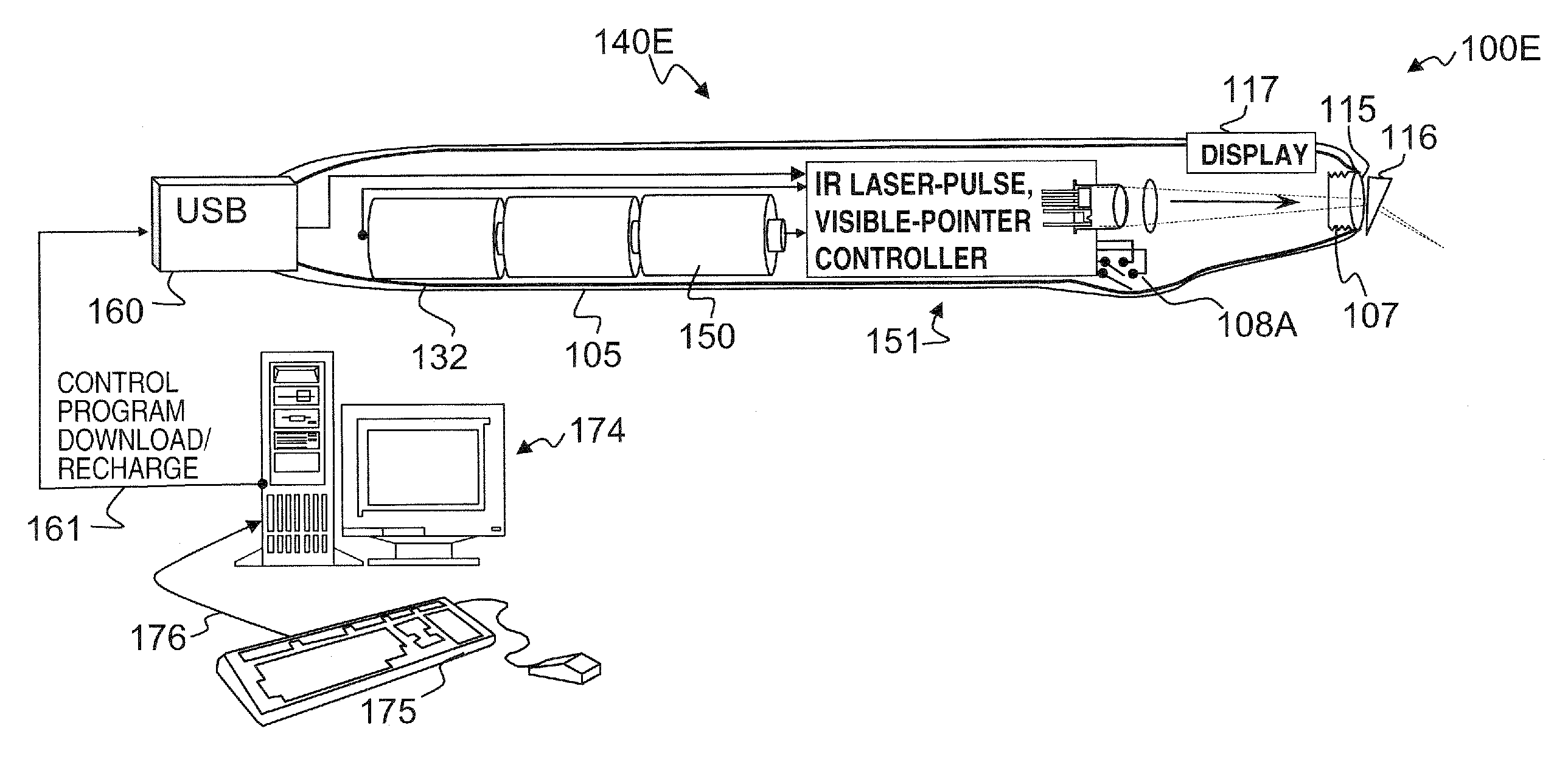
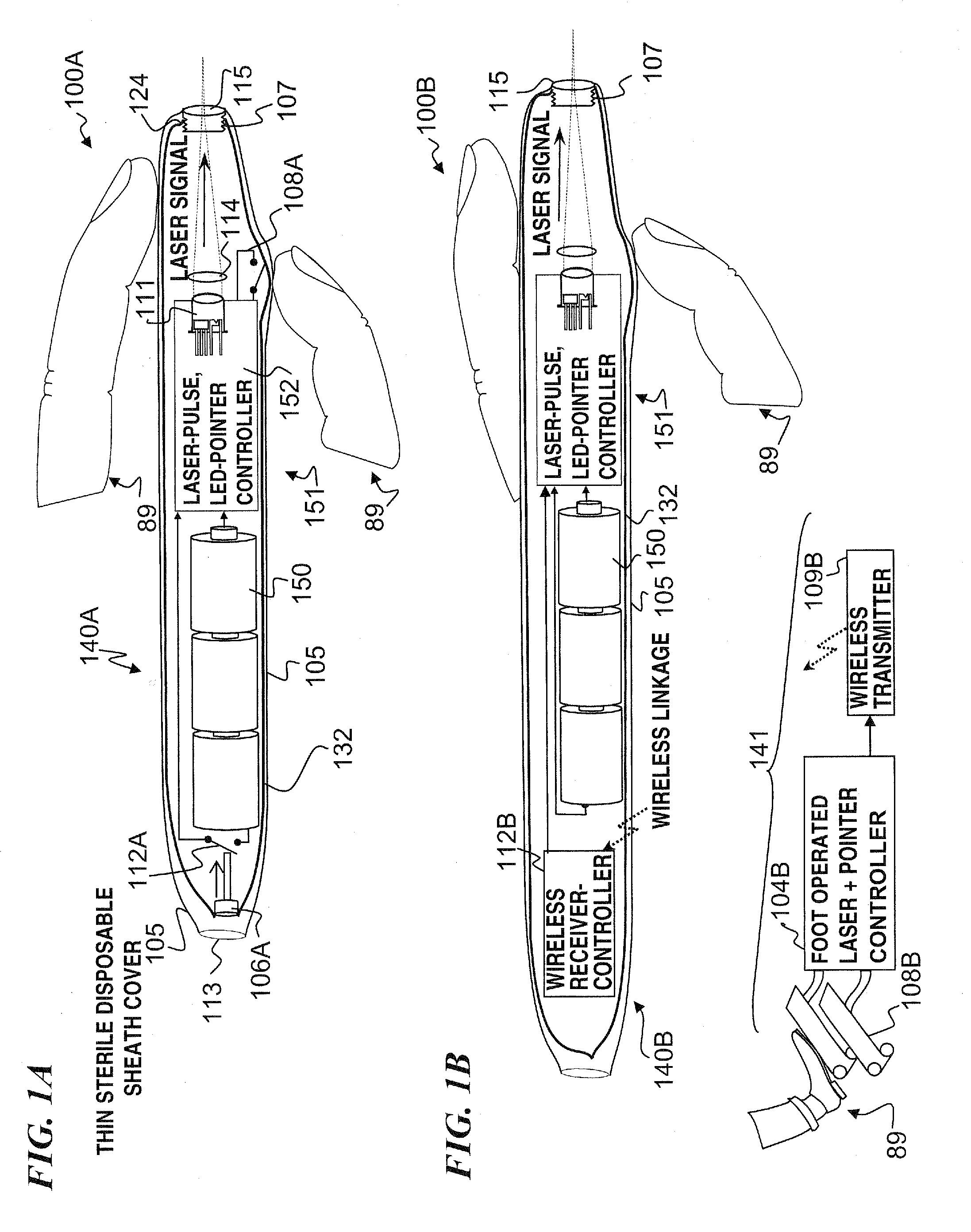
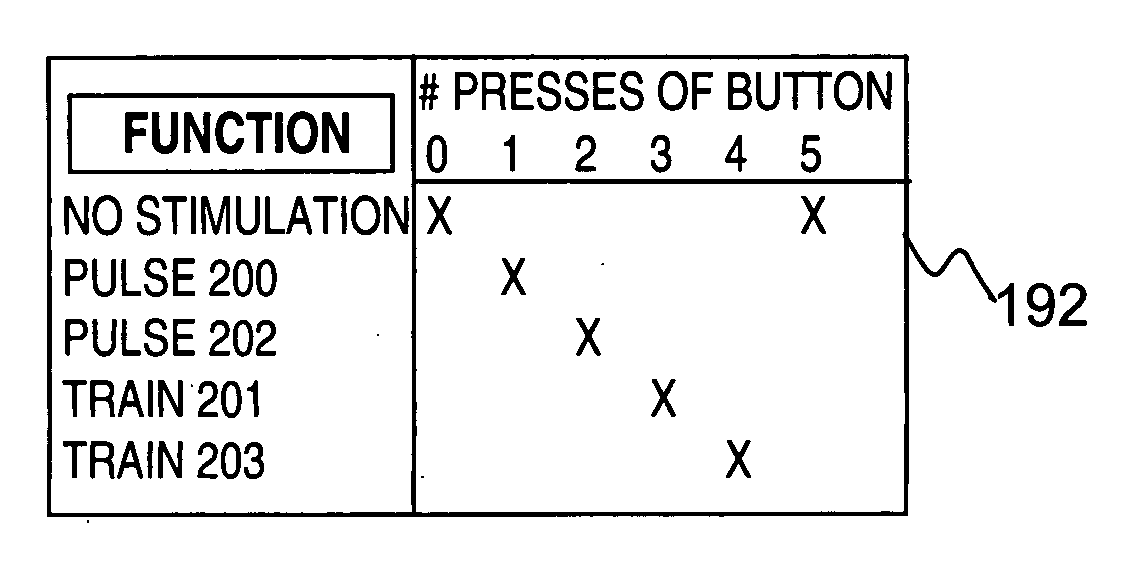
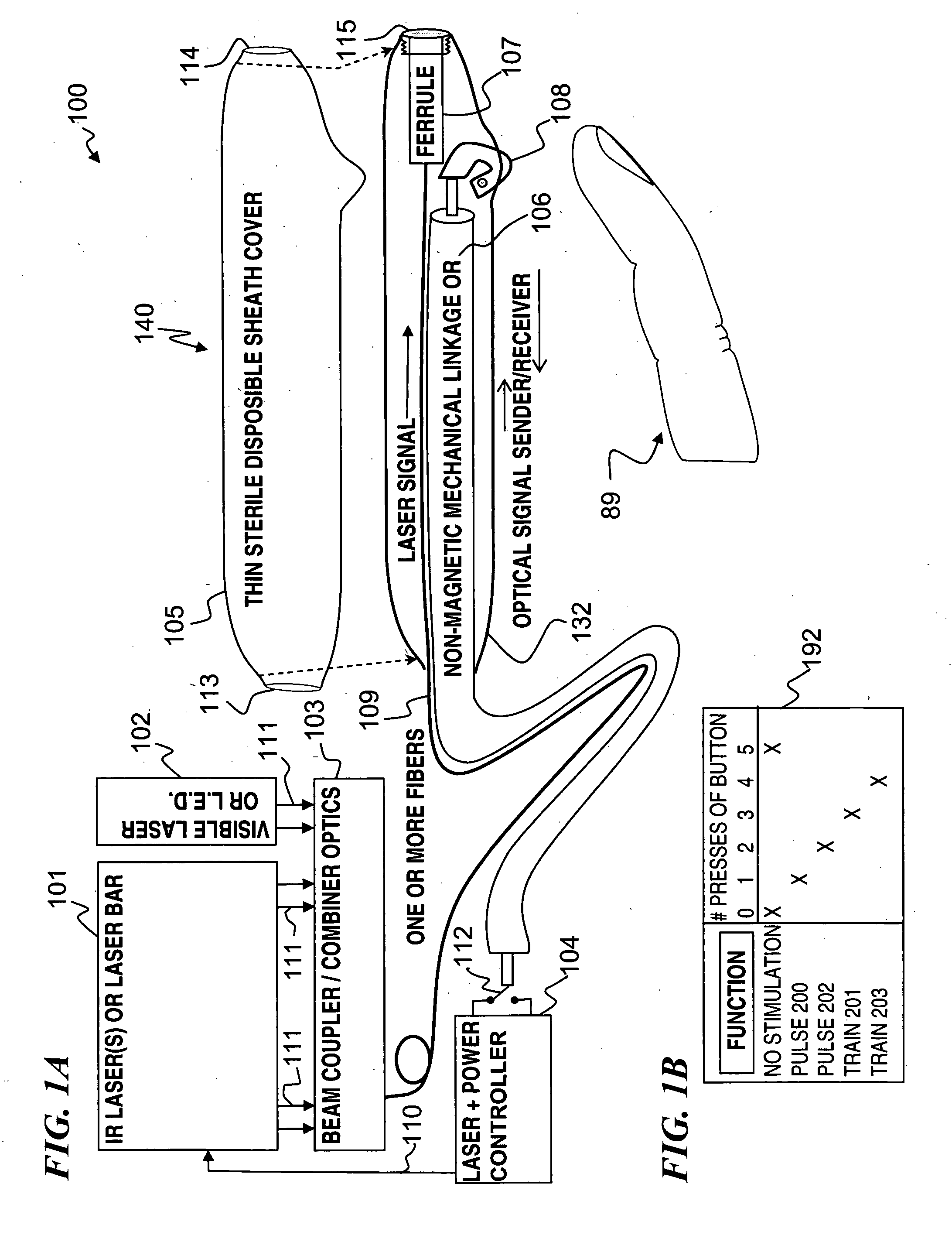
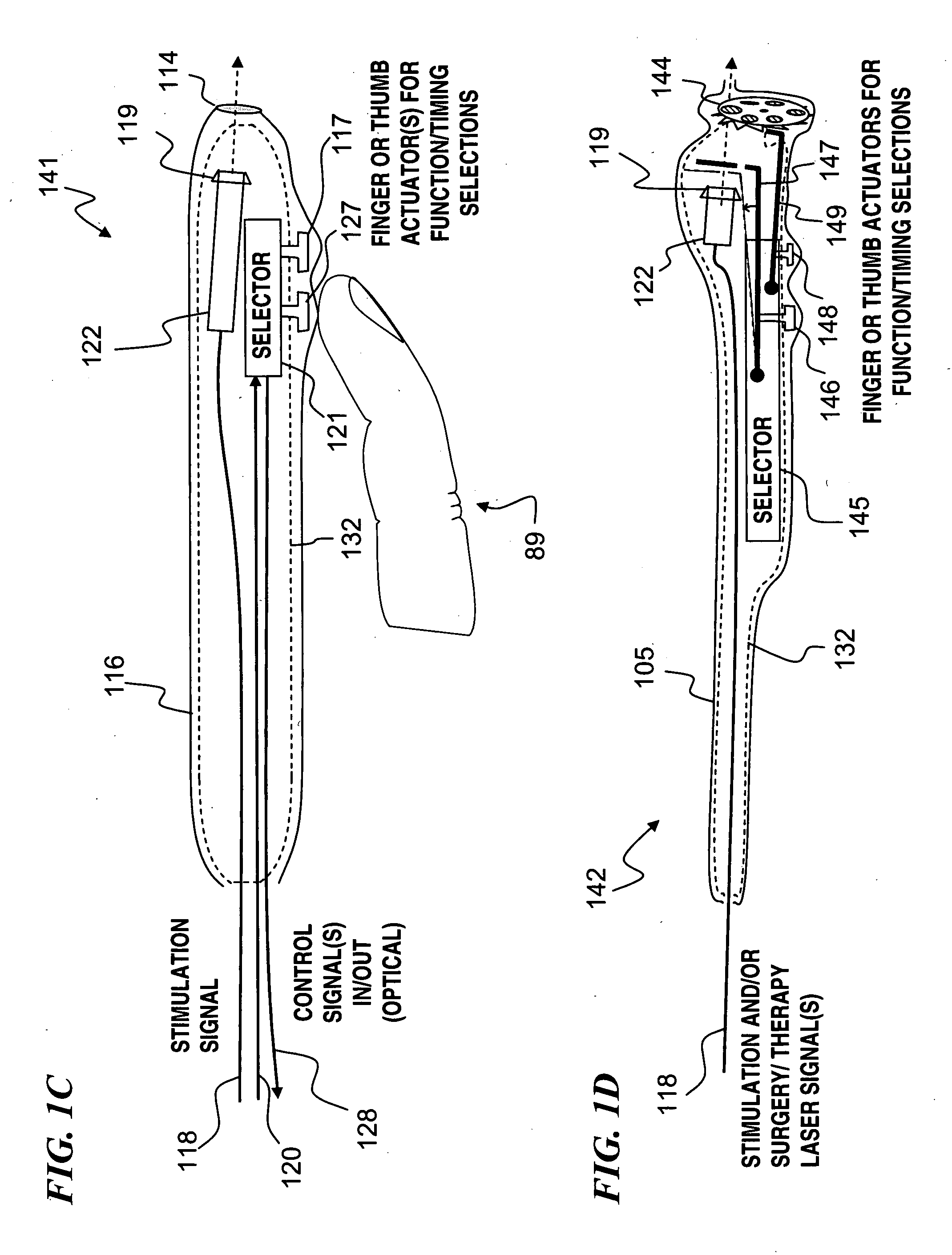
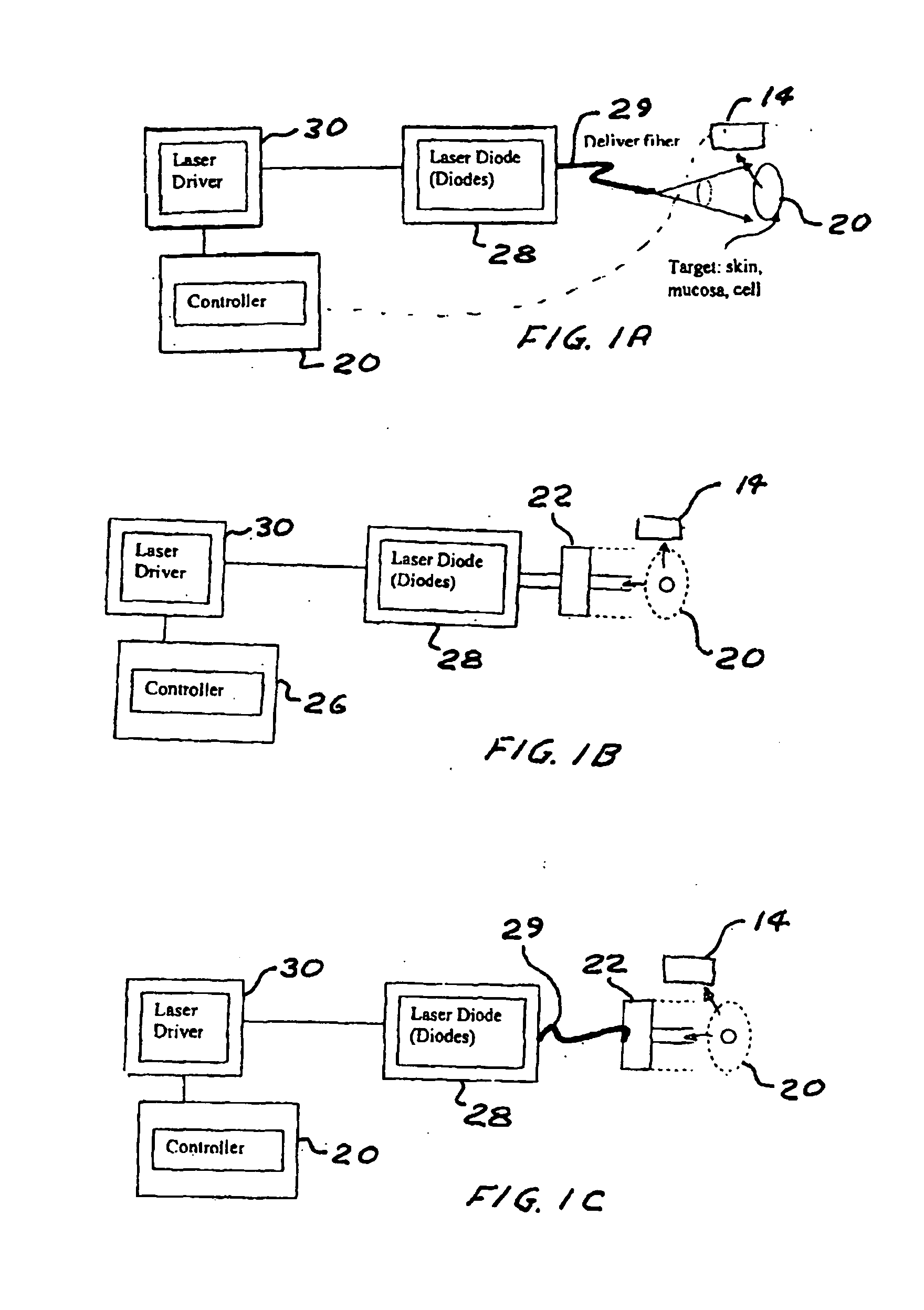
A hand-held self-contained nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light source is mounted to the handpiece. Light is passed from the light source through optical tip to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. In some embodiments, the handpiece contains a self-contained power source, such as batteries. In some embodiments, the handpiece is at least in part, activated by remote control in order to prevent moving the handpiece during activation. Some embodiments include a unit operable to sense a response of nerve stimulation and to suppress a laser-ablation surgery operation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Miniature apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A hand-held self-contained nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light source is mounted to the handpiece. Light is passed from the light source through optical tip to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. In some embodiments, the handpiece contains a self-contained power source, such as batteries. In some embodiments, the handpiece is at least in part, activated by remote control in order to prevent moving the handpiece during activation. Some embodiments include a unit operable to sense a response of nerve stimulation and to suppress a laser-ablation surgery operation.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
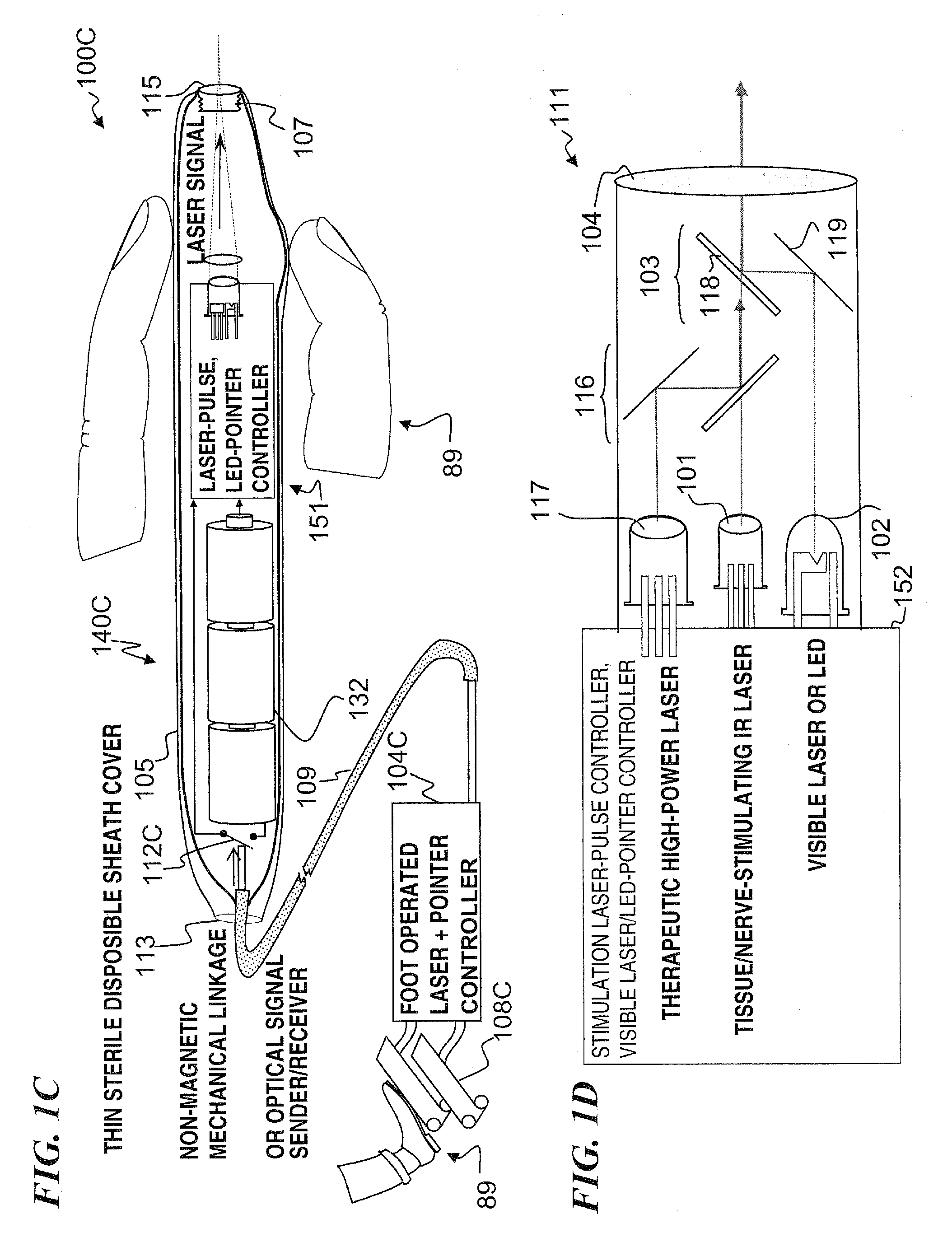
Apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light-generating source is operatively coupled to an optical fiber, which in turn is coupled to a plug in the end of a holder in a sheath. Light is then passed from the light source through the optical fiber to the holder and out a selected optical tip on the sheath to provide an efficacious amount of light to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. Some embodiments omit the fiber and use light directly from the laser diode.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
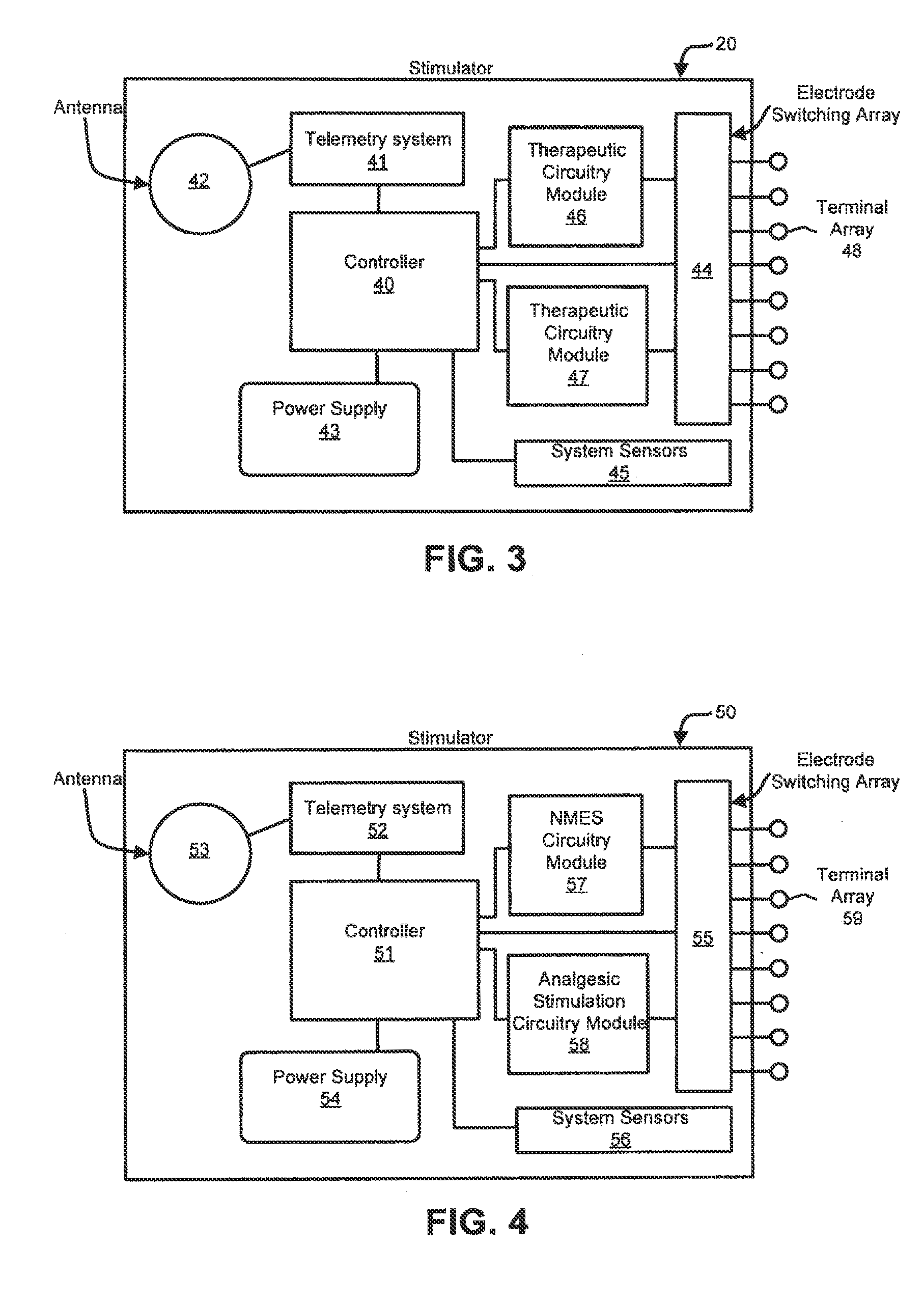
Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use
ActiveUS20110224665A1Rehabilitate spinal stabilityRestore neural driveSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsRf ablationMuscle contraction
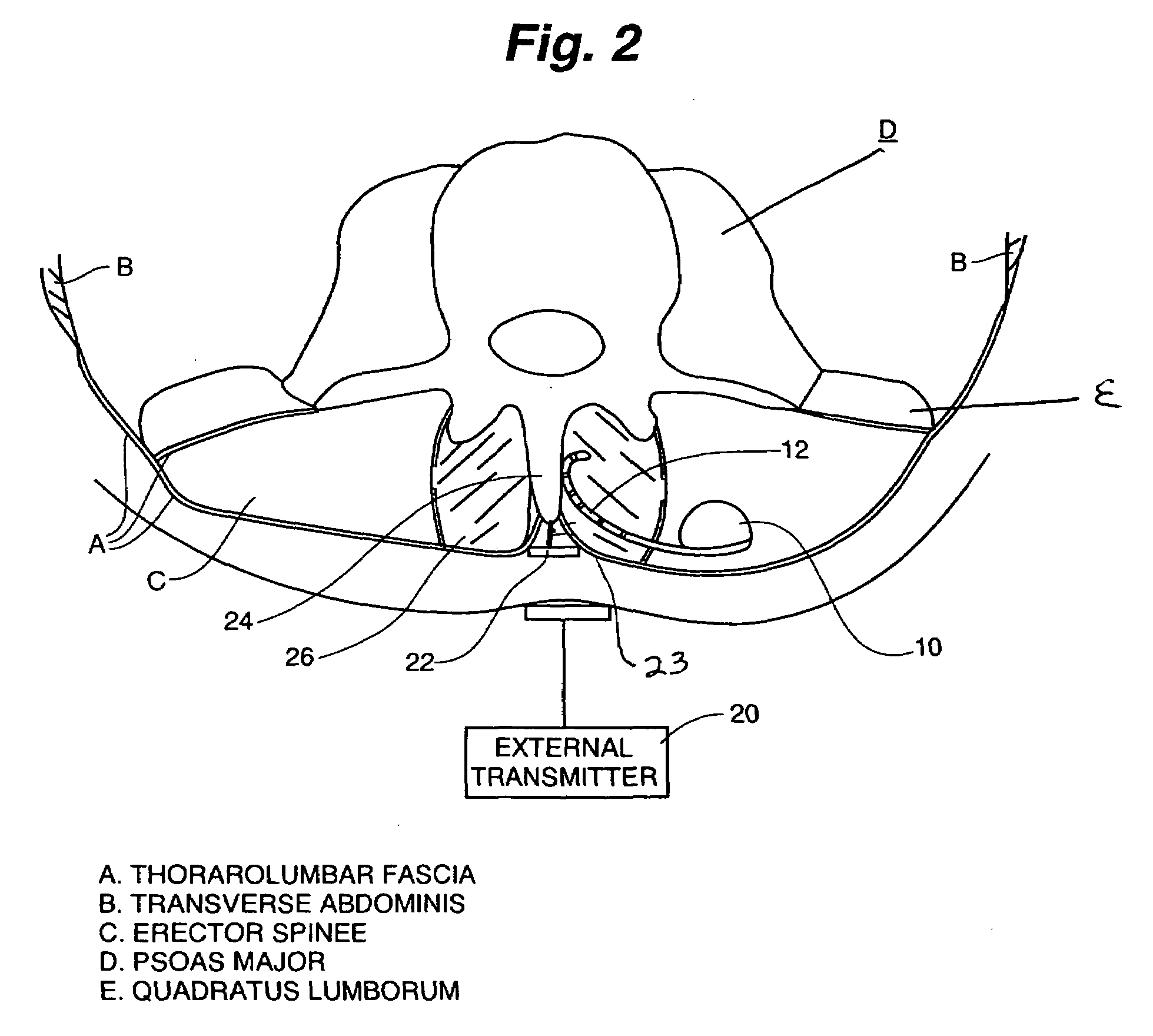
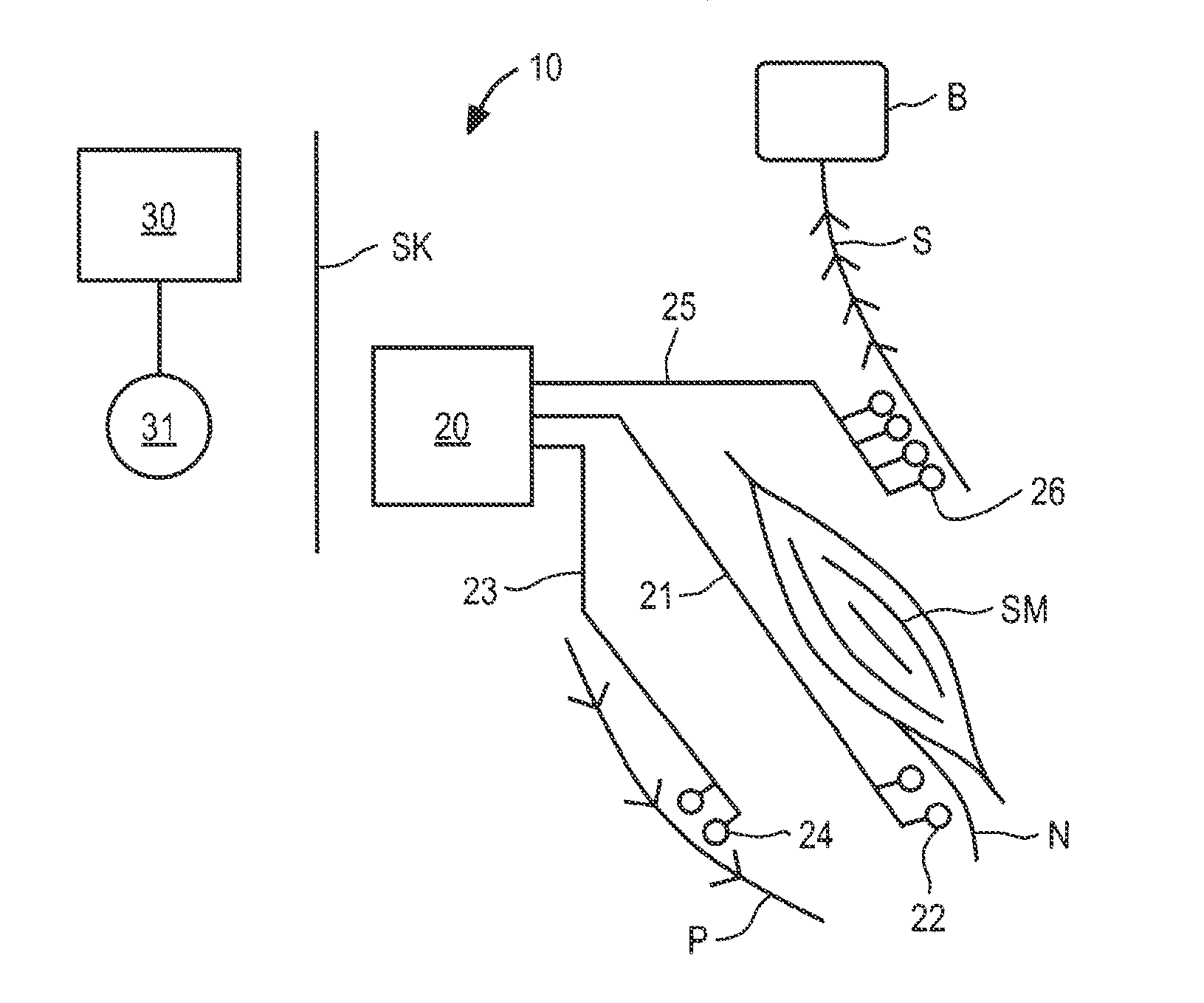
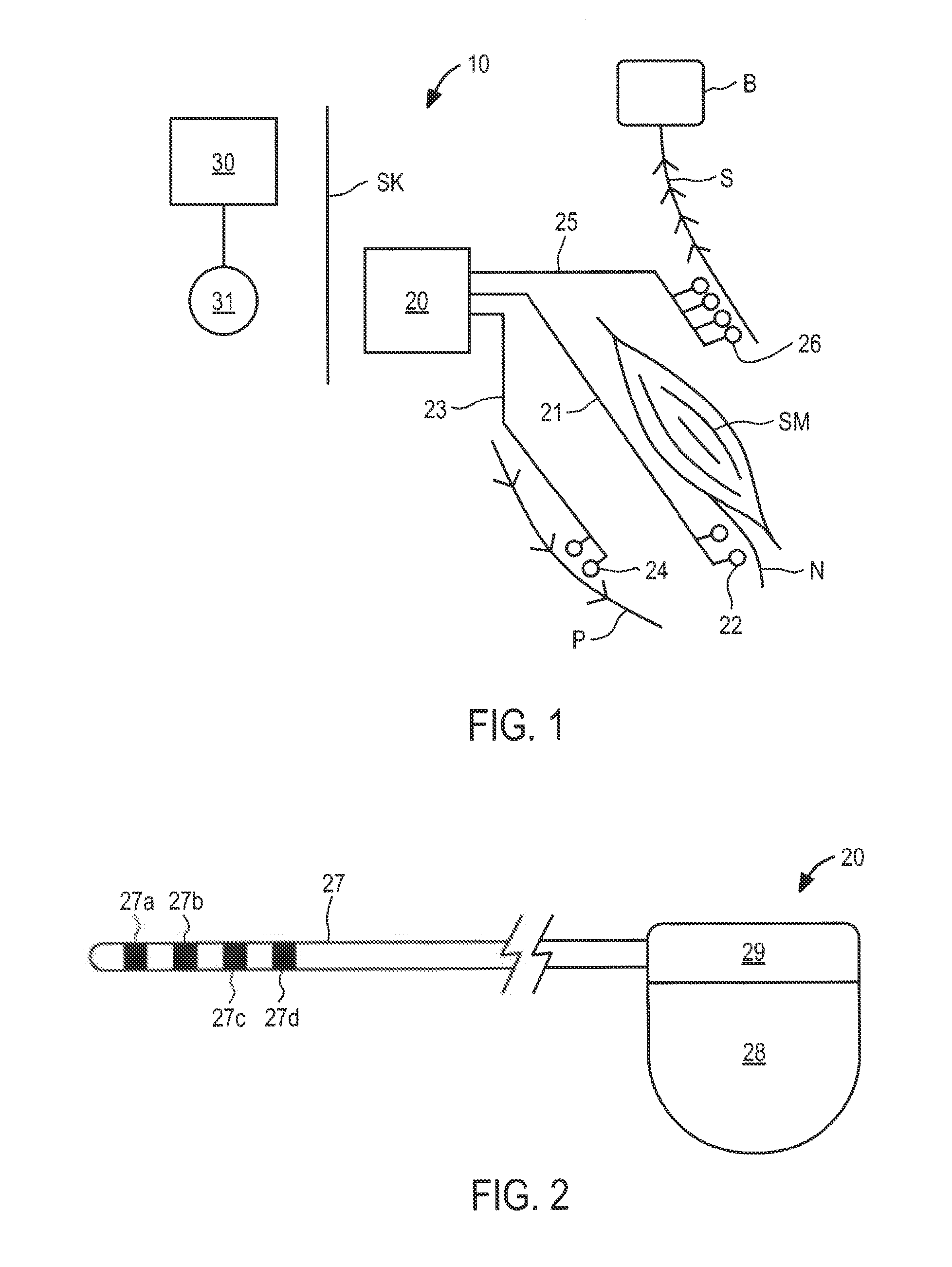
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain are provided, in which an implantable stimulator is configured to communicate with an external control system, the implantable stimulator providing a neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy designed to cause muscle contraction to rehabilitate the muscle, restore neural drive and restore spinal stability; the implantable stimulator further including one or more of a number of additional therapeutic modalities, including a module that provides analgesic stimulation; a module that monitors muscle performance and adjusts the muscle stimulation regime; and / or a module that provides longer term pain relief by selectively and repeatedly ablating nerve fibers. In an alternative embodiment, a standalone implantable RF ablation system is described.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
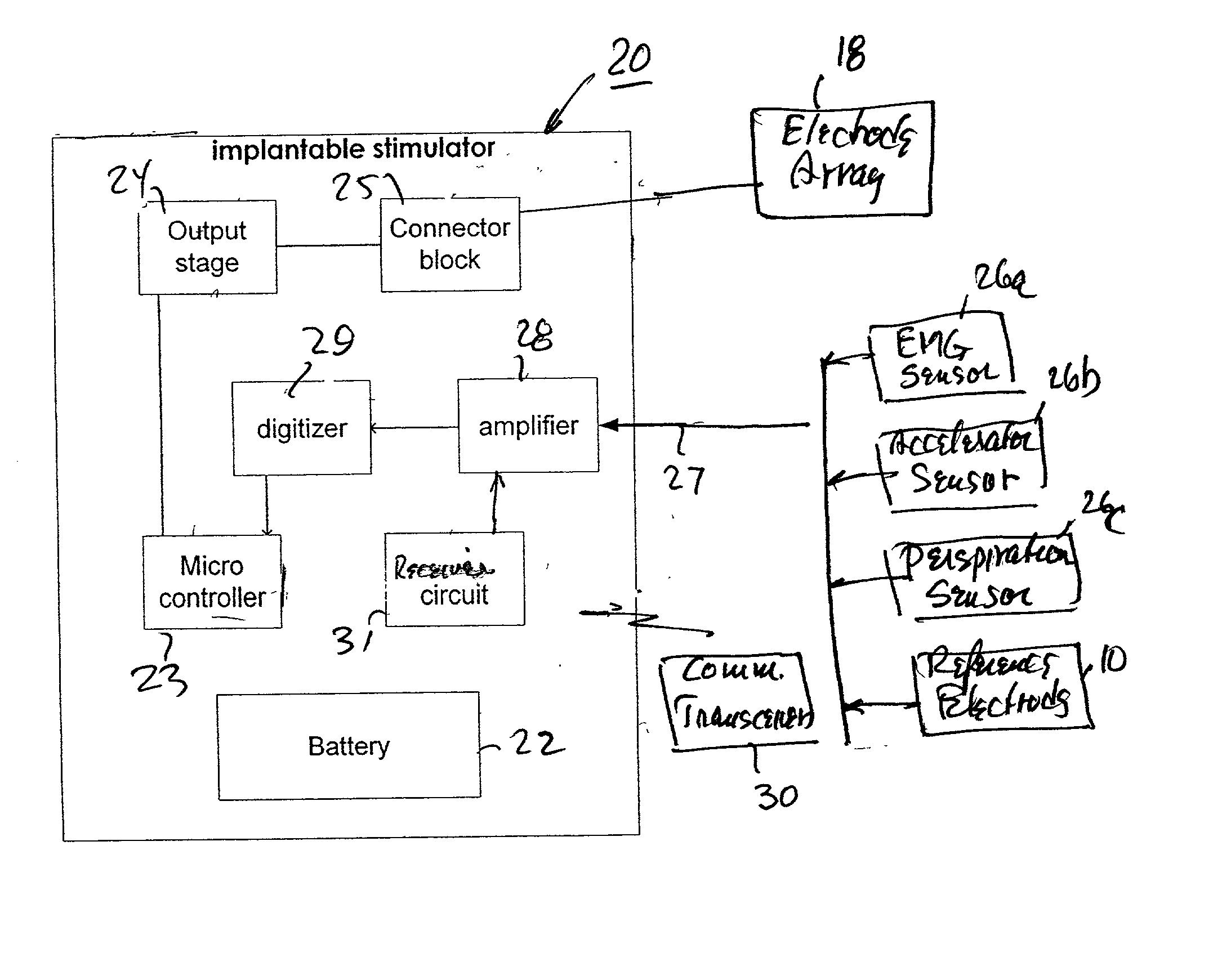
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
InactiveUS20020099419A1Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
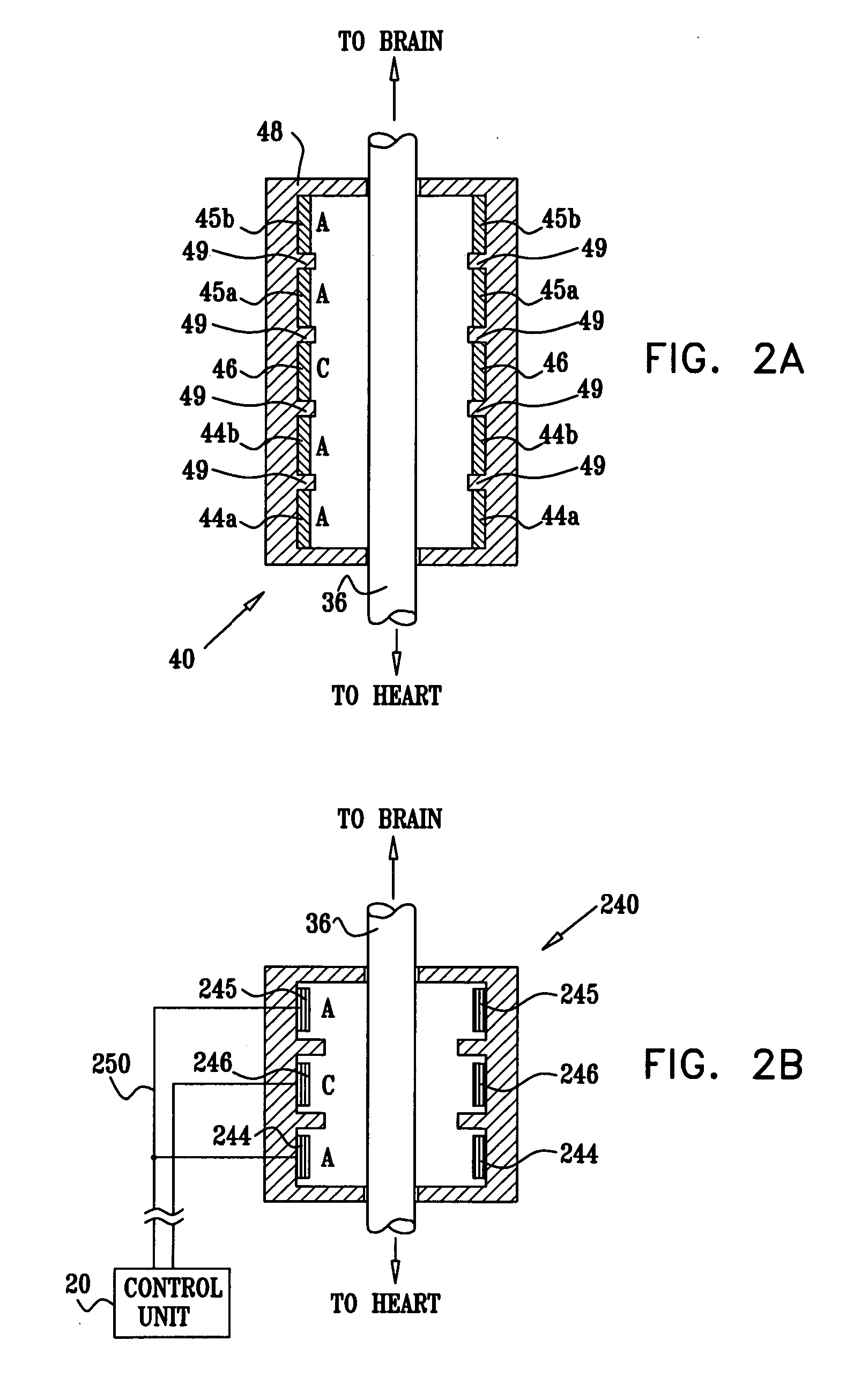
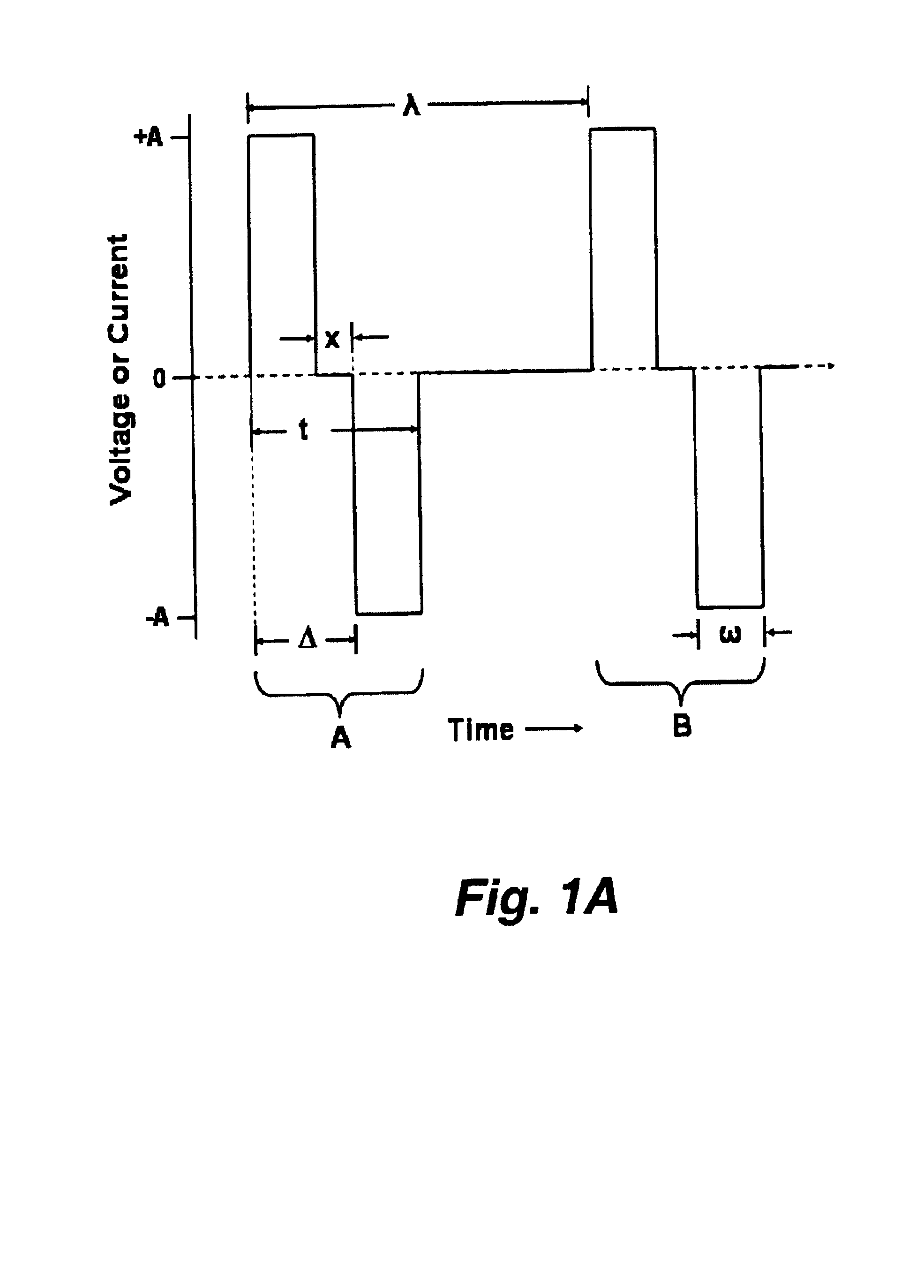
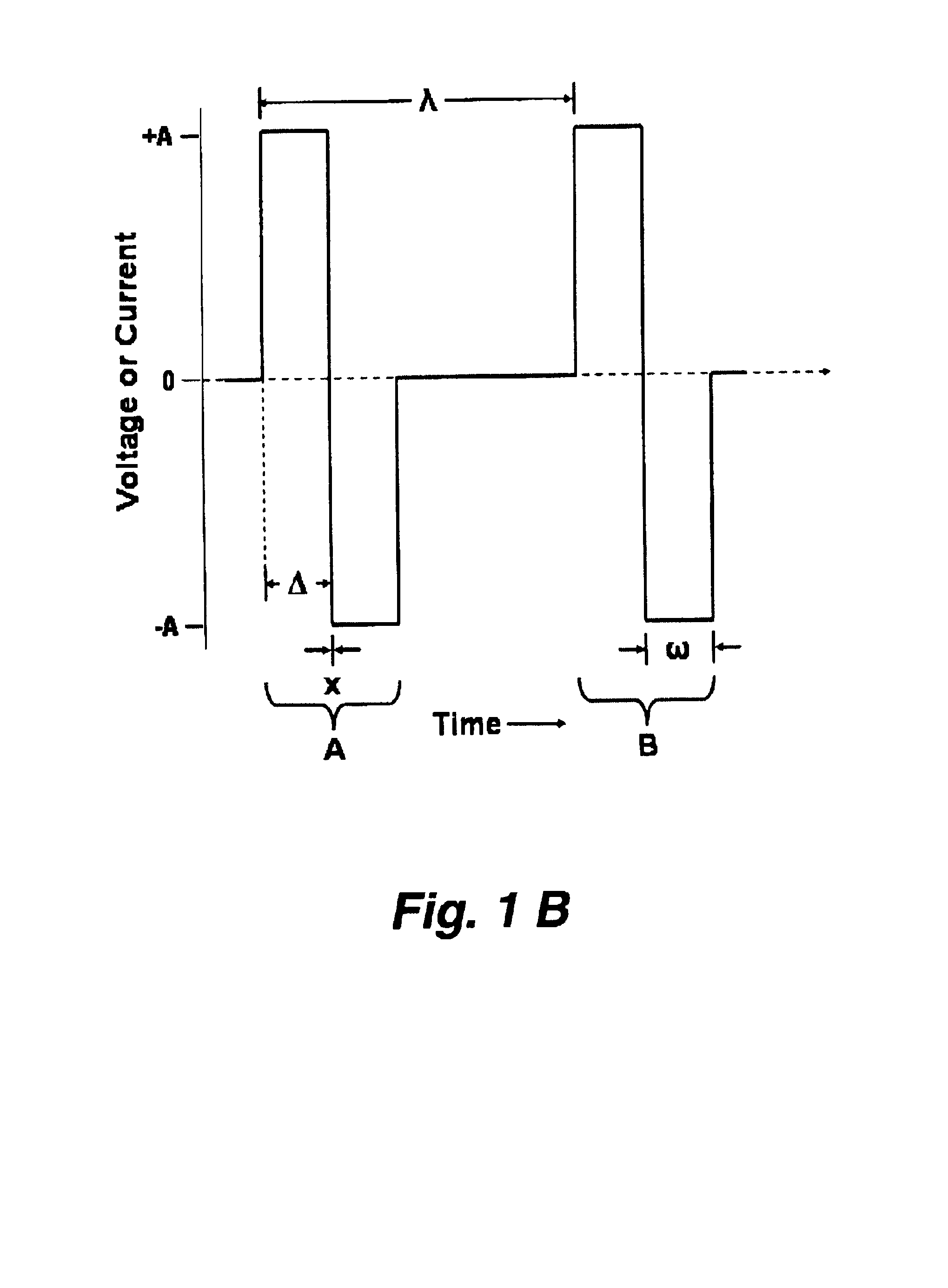
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and systems for selective control of bladder function
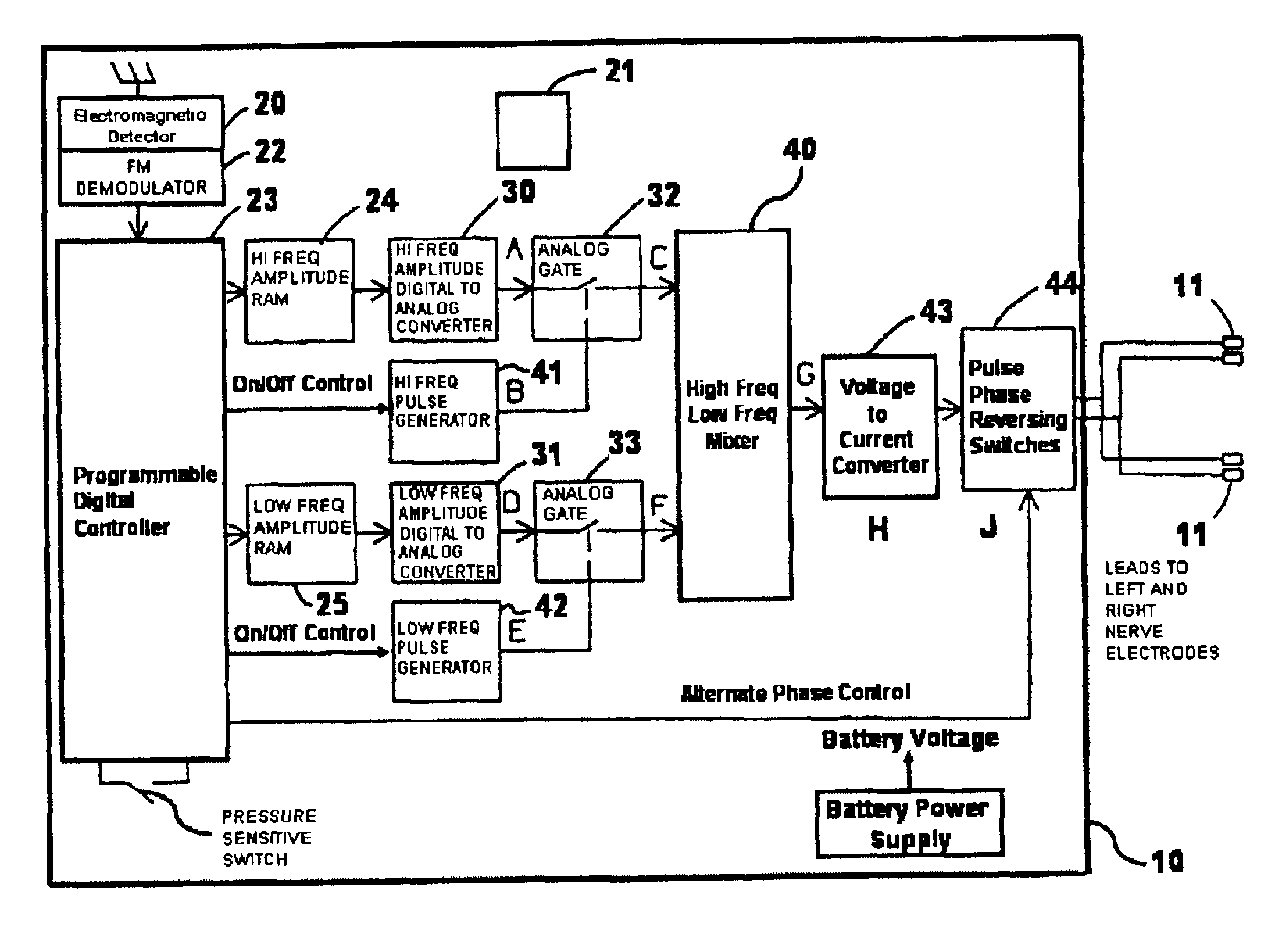
InactiveUS6990376B2Inhibiting neural transmissionStimulating neural transmissionElectrotherapyArtificial respirationNerve fibreHigh amplitude
A method and system for selective inhibition of somatic nerve fibers in a mixed nerve containing both somatic and autonomic nerve fibers where the method finds use in treatment of chronic pain, spastic muscles and for sensory and motor control of a bladder. The methods and systems utilize alternate phase rectangular electrical pulses. An electrical pulse generator is coupled to a nerve. An alternate phase high frequency, low amplitude pulse is first applied to selectively inhibit somatic nerves when present in a mixed nerve. An alternate phase low frequency, high amplitude phase pulse subsequently supplied to stimulate the autonomic nerve fibers and in the case of the sacral root will permit a controlled voiding of the bladder and bowel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Minimal Device and Method for Effecting Hyperthermia Derived Anesthesia
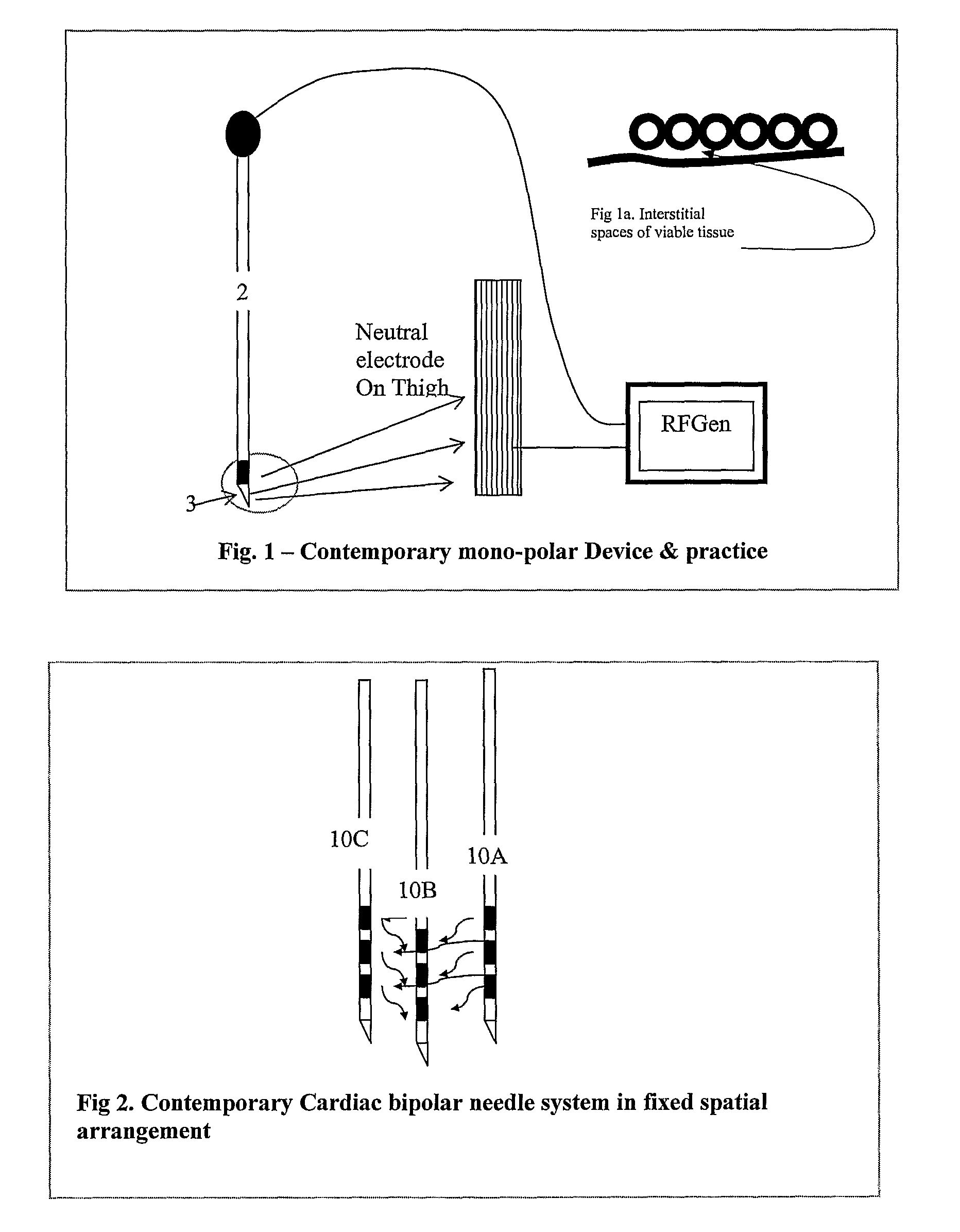
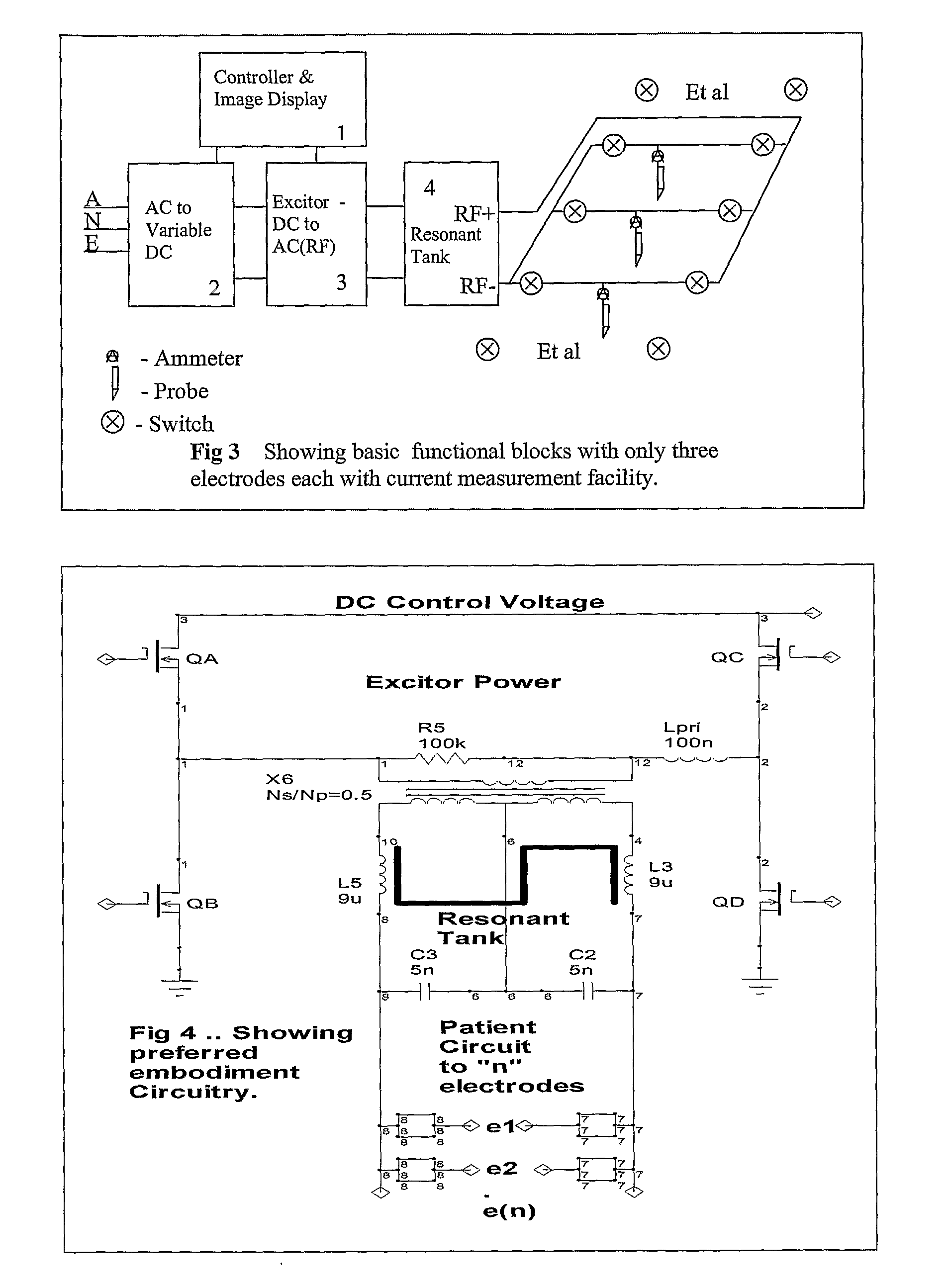
InactiveUS20080262490A1Improve comfortLess chance of physical damageElectrotherapySurgical needlesFiberMedicine
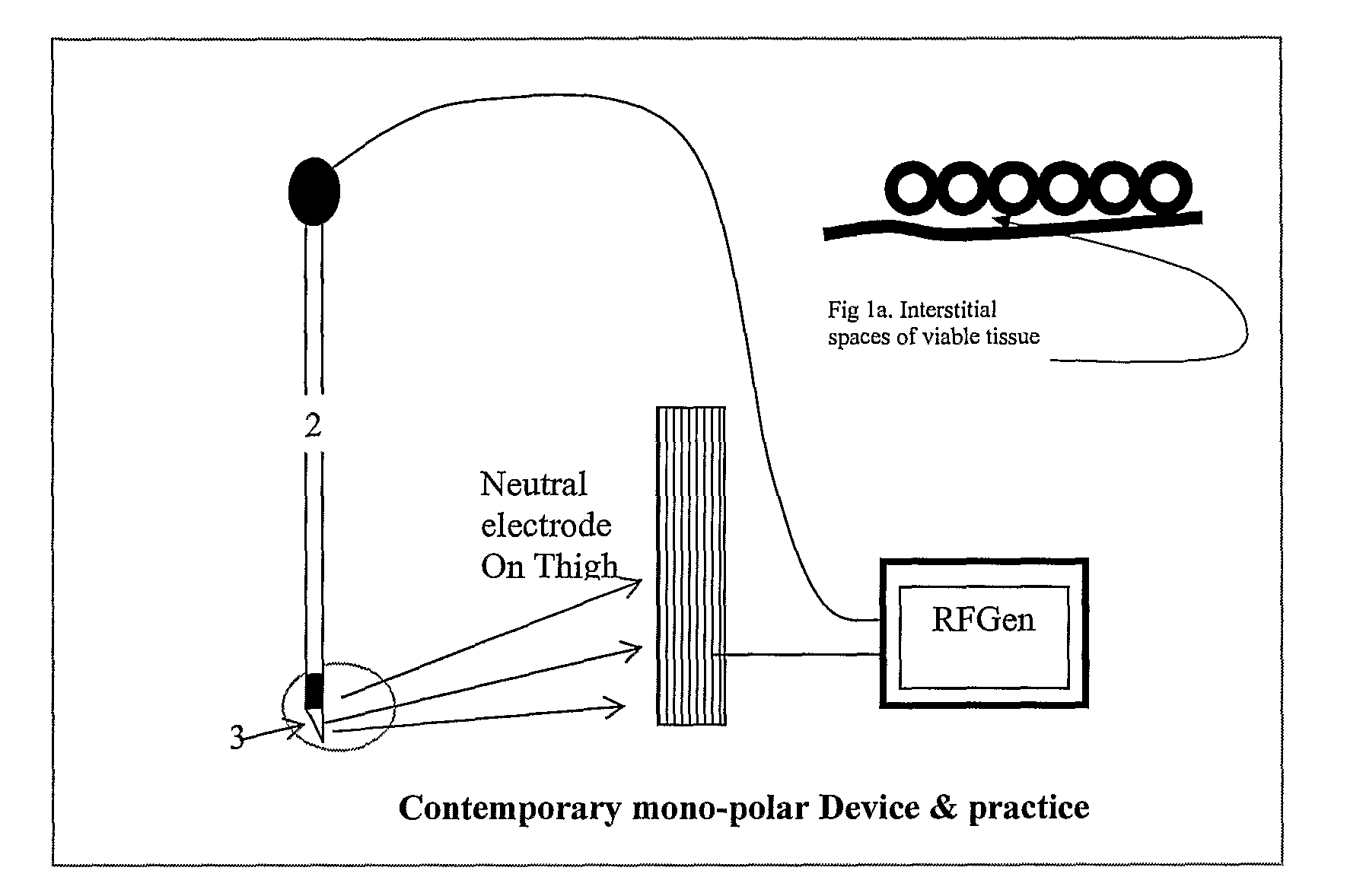
A method and device for inducing anaesthesia in mammals by the application of RF energy to create hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia. An RF generator drives a plurality of electrodes placed in tissue surrounding the target nerve fibre to desiccate the desired length of nerve fibre to be desiccated in a single deployment. The device allows high-speed selection / de-selection of bipolar electrode pairs or sets under continuous RF excitation. Activation of electrode pairs is adapted in response to sensed current density and temperature (by electrodes not in the current discharge activation phase) in order to create lesions of complex and well defined shape necessary for the production of hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia.
Owner:INTERVENTION TECH
Selective nerve fiber stimulation for treating heart conditions
ActiveUS20050187586A1Modify heart rate variabilityReduce heart rate variabilitySpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleRR interval
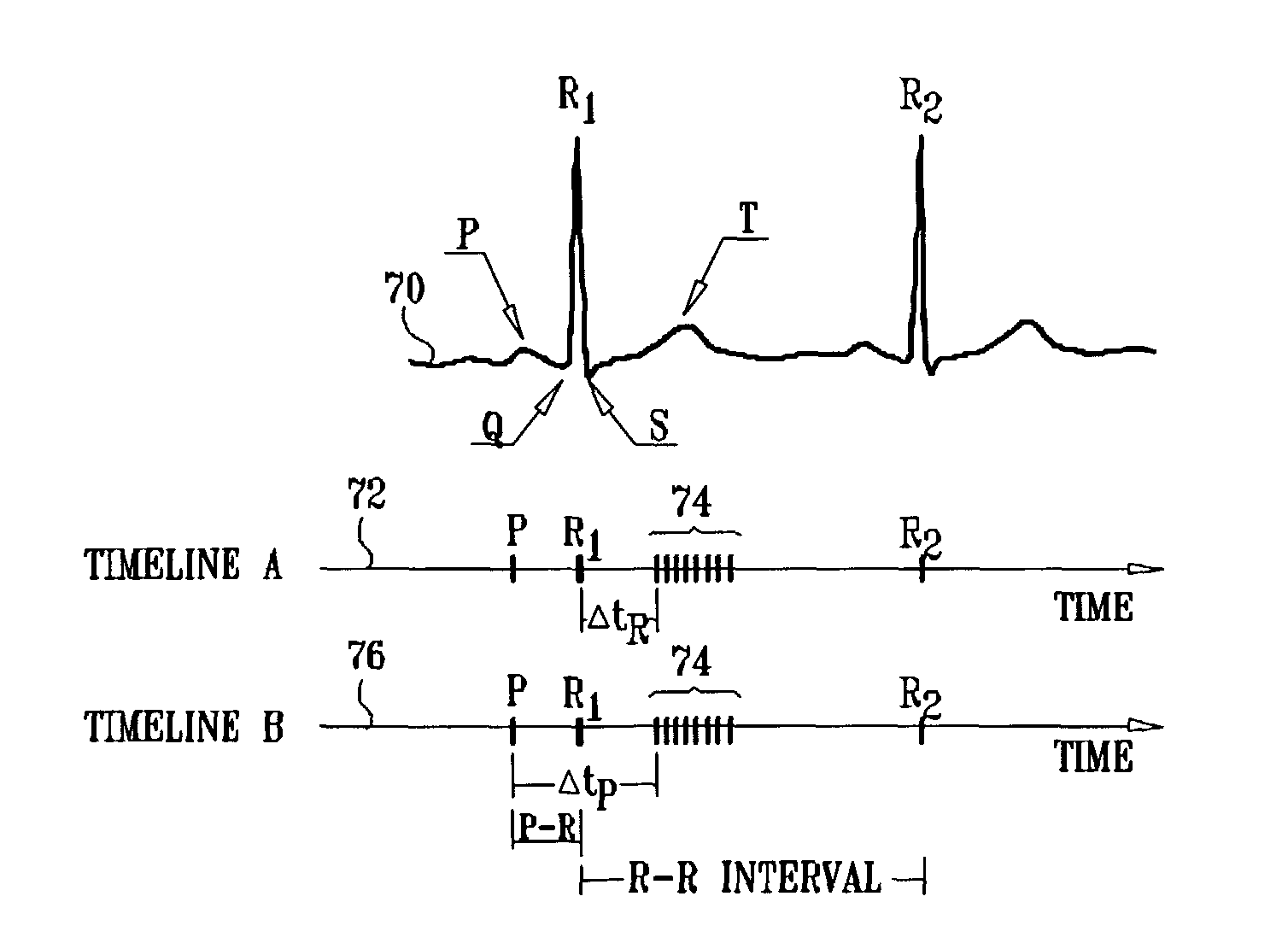
Apparatus is provided that includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of a subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject. Also provided is a method comprising applying to a vagus nerve of a subject a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
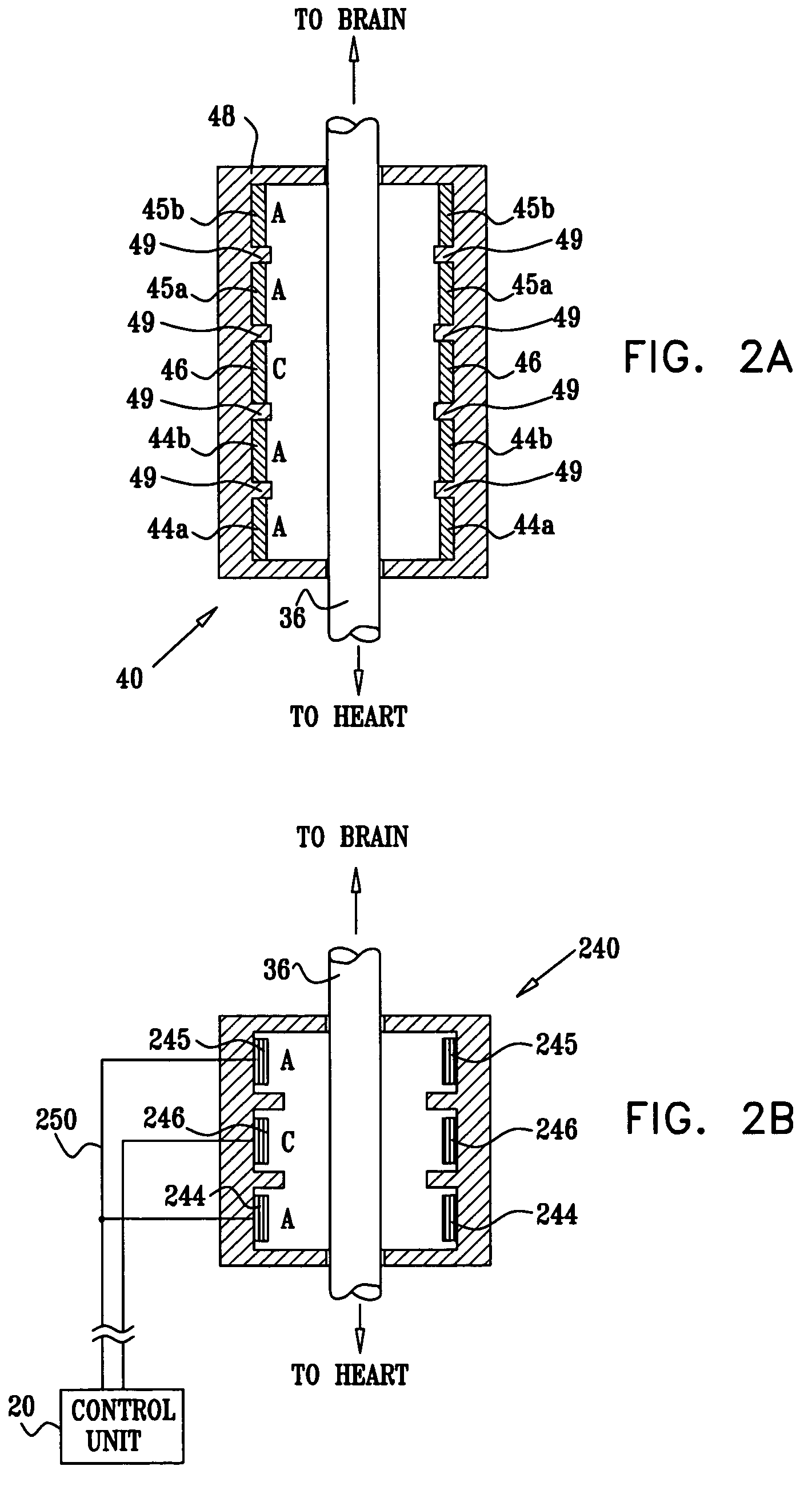
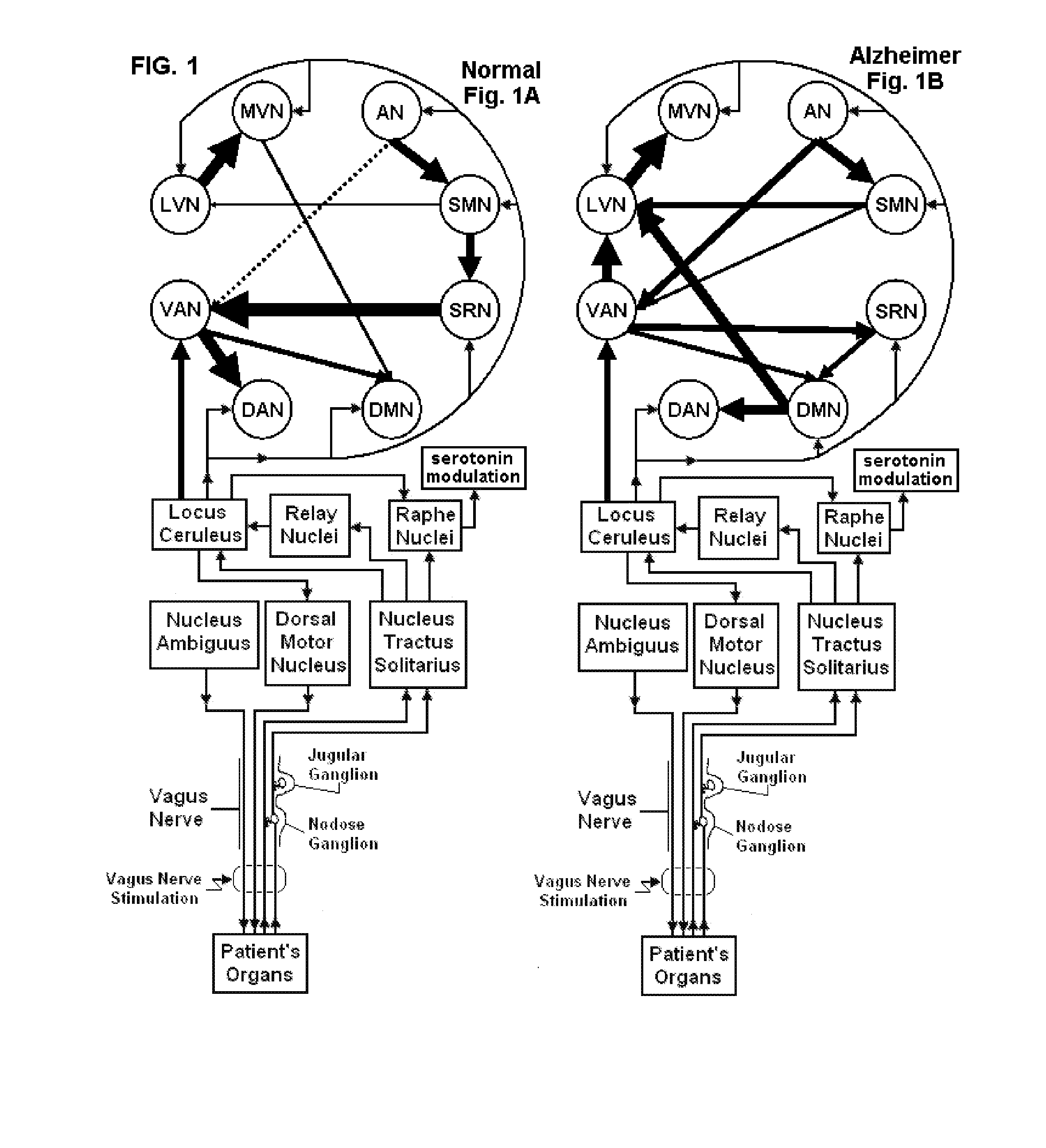
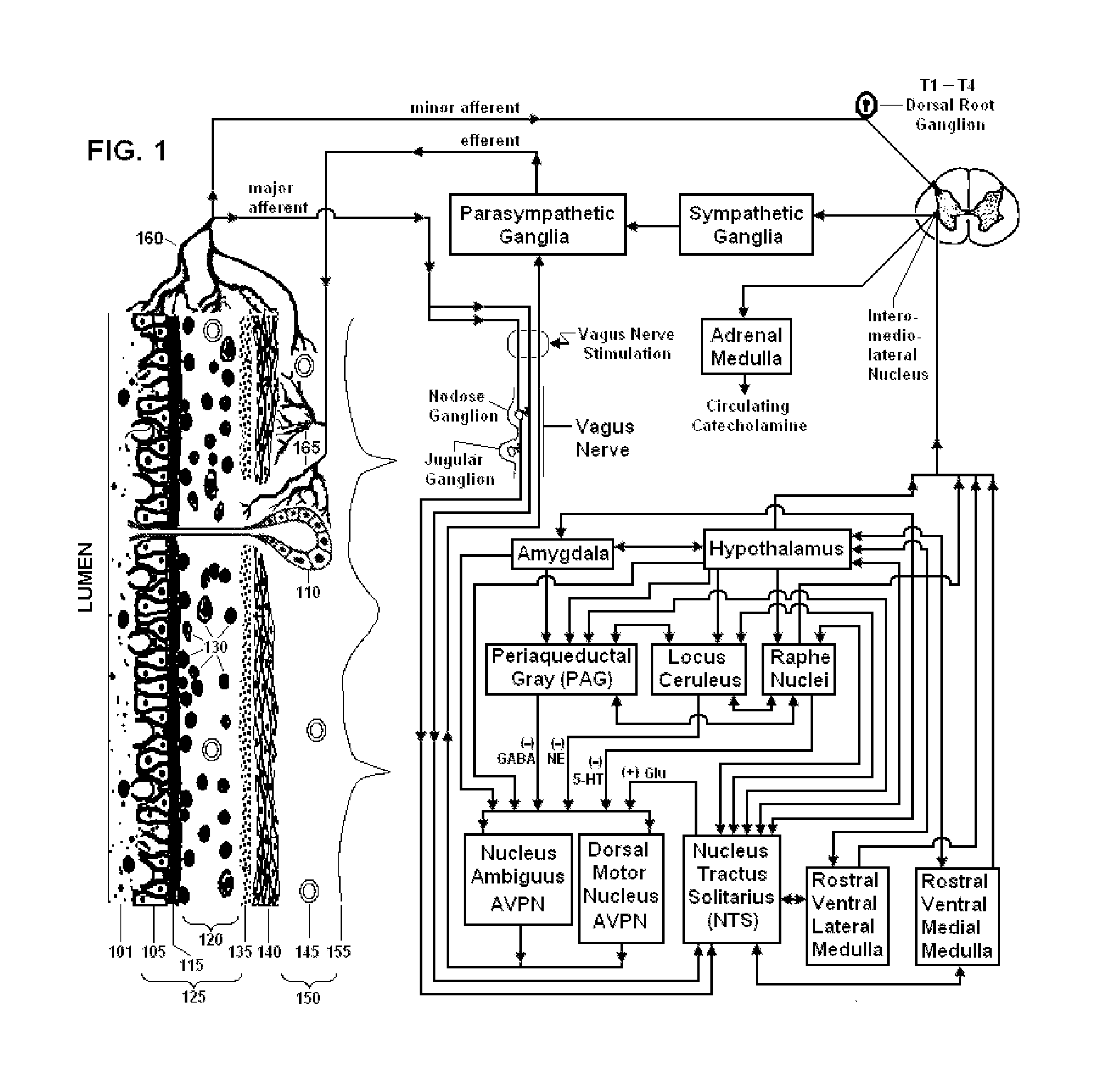
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat or prevent dementia
ActiveUS20130066392A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyAdrenergicMedicine
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve, that modulate the activity of a patient's locus ceruleus. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers to cause the locus ceruleus to release norepinephrine into regions of the brain that contain beta-amyloids. The norepinephrine counteracts neuroinflammation that would damage neurons in those regions and the locus ceruleus, thereby arresting or slowing the progression of the disease in the patient.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Neurostimulation system and method for providing therapy to patient with minimal side effects
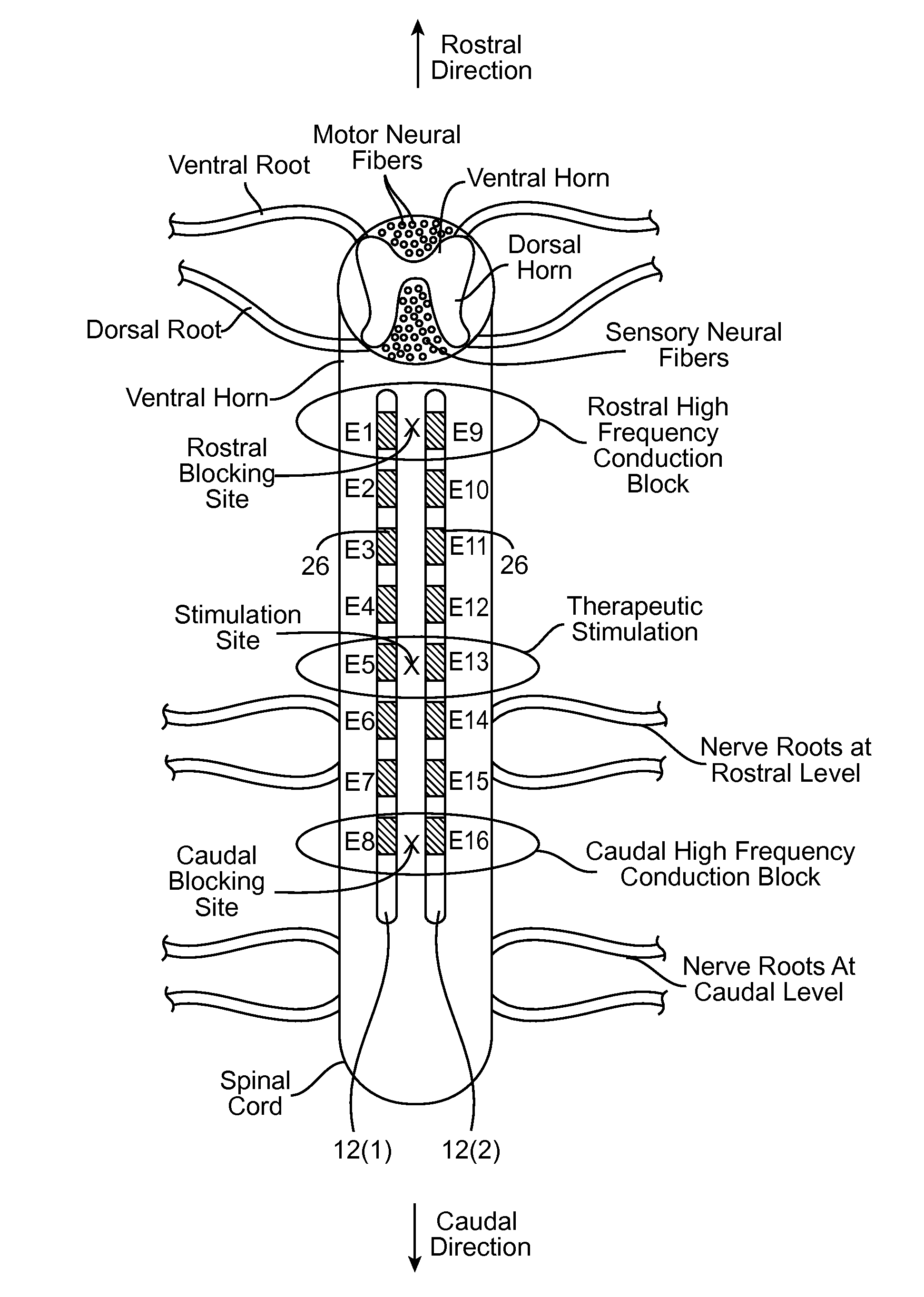
ActiveUS20120089200A1Decrease their propagationEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationSide effectMedicine
A method comprises conveying a pulsed waveform between an electrode and a stimulation site of a spinal cord, thereby evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a first sensory neural fiber creating a therapeutic effect in the tissue region, evoking the orthodromic propagation of action potentials along the first sensory neural fiber potentially creating paresthesia corresponding to the tissue region, and evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a second sensory neural fiber potentially creating a side-effect in another tissue region. The method further comprises conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site rostral to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the first sensory neural fiber and reducing the paresthesia, and conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site caudal to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the second sensory neural fiber and reducing the side-effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
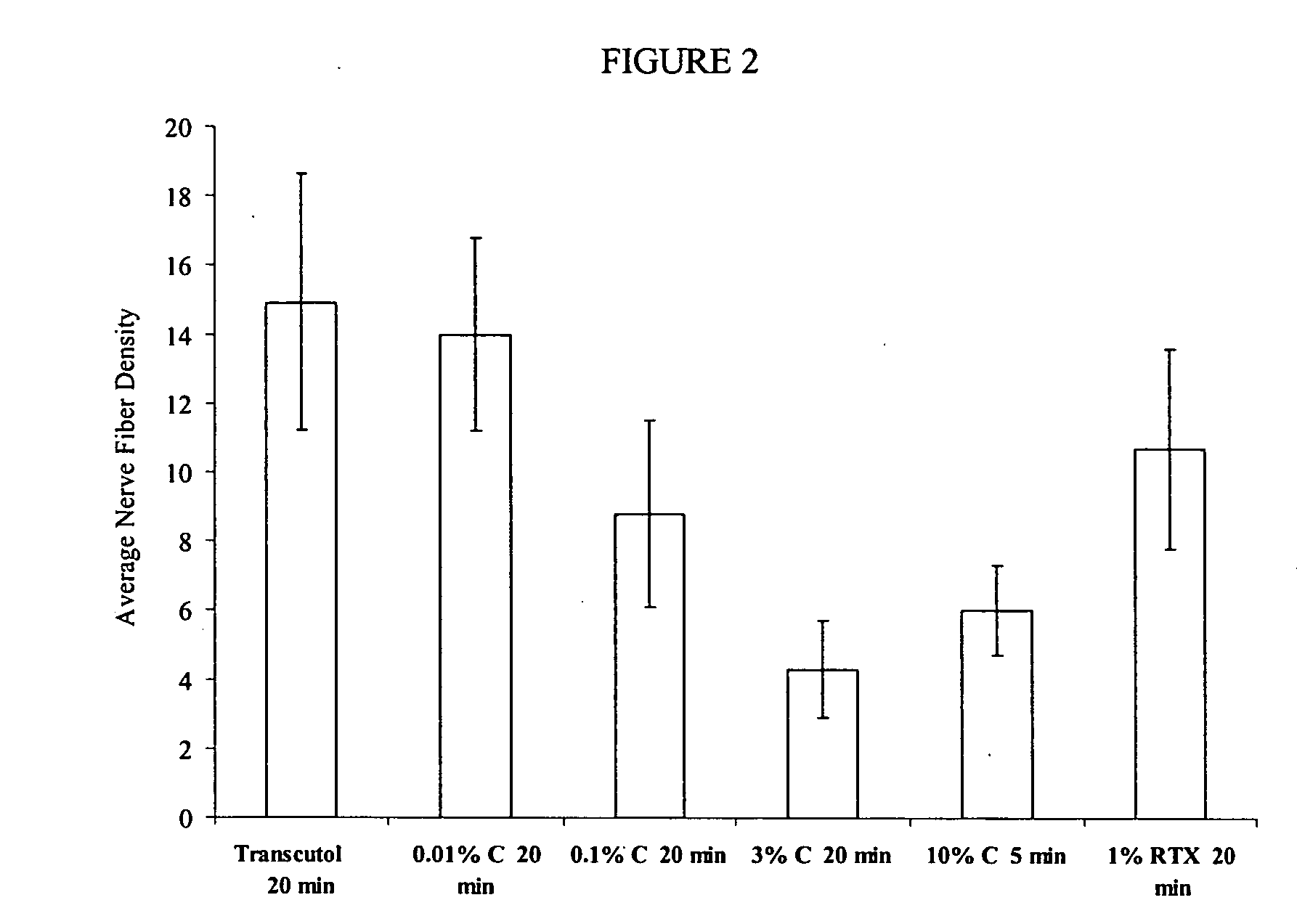
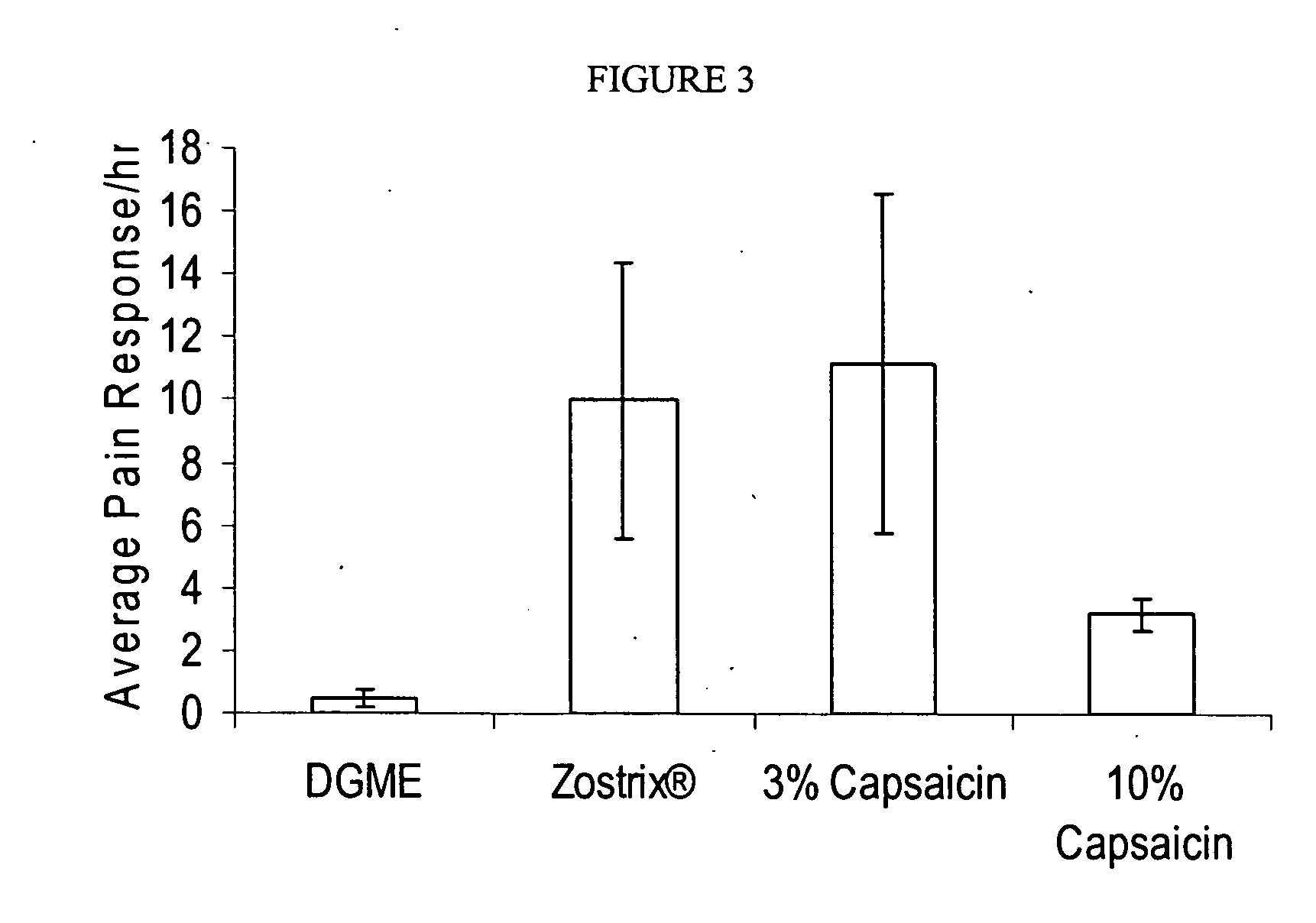
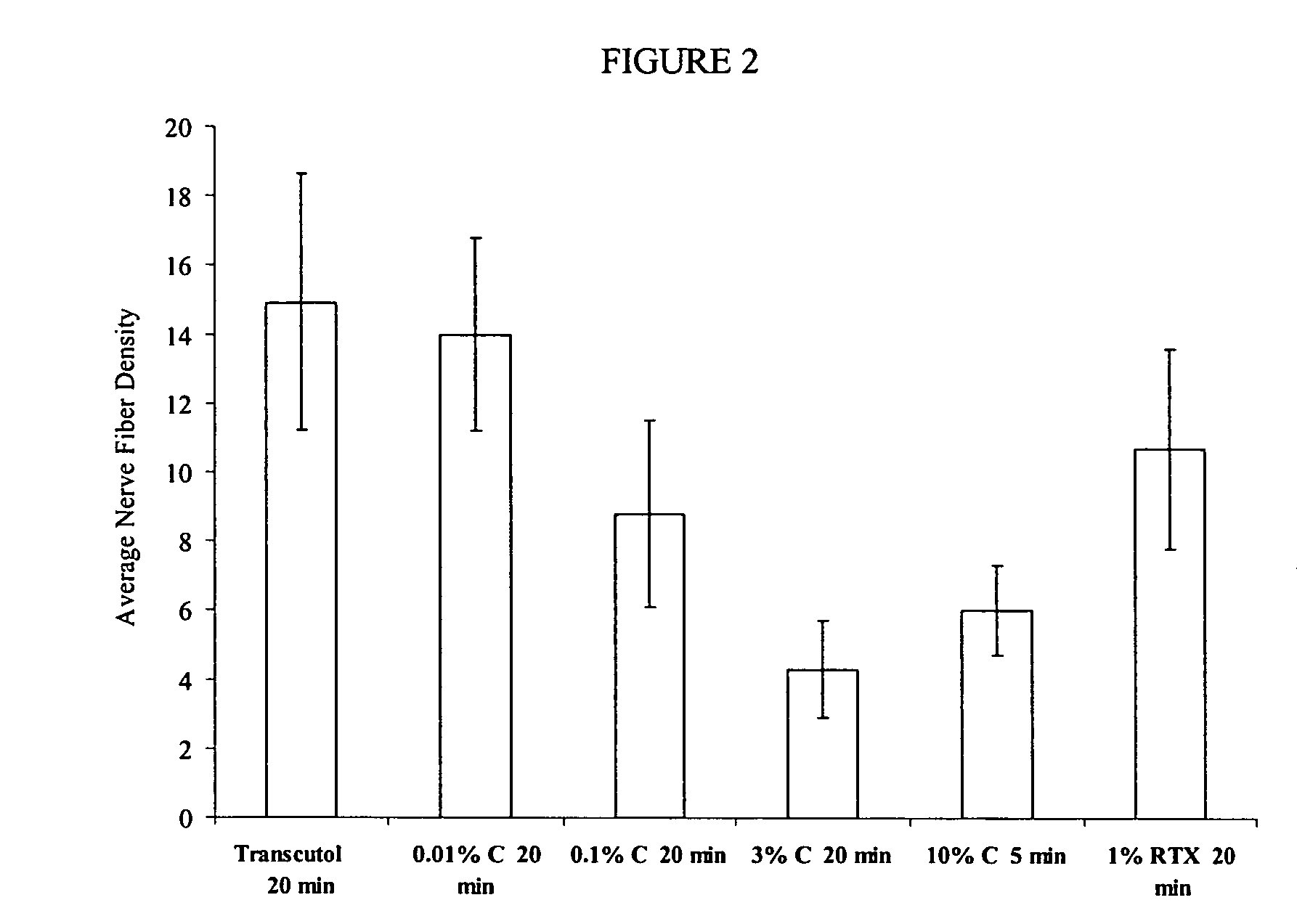
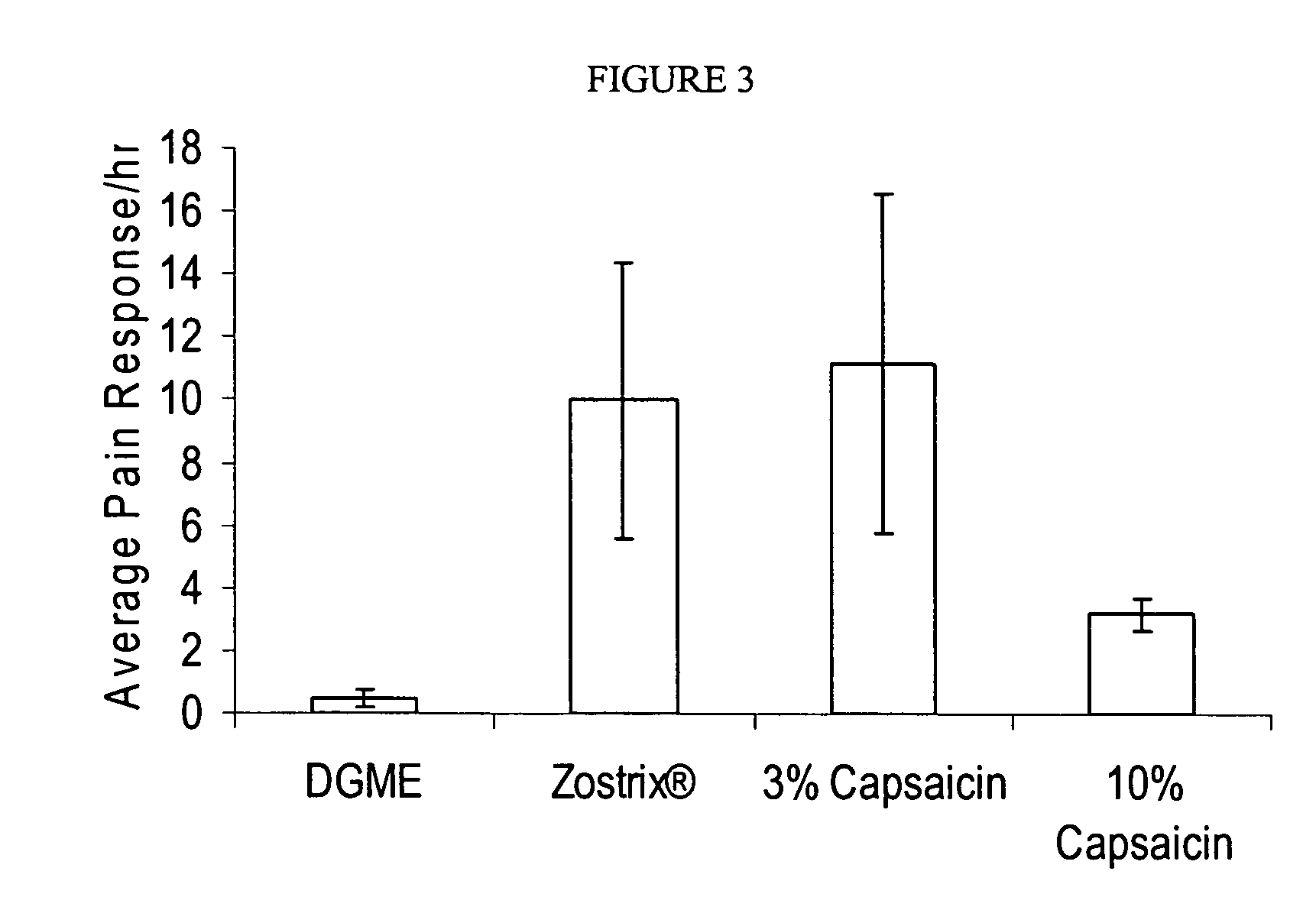
Methods and compositions for administration of TRPV1 agonists
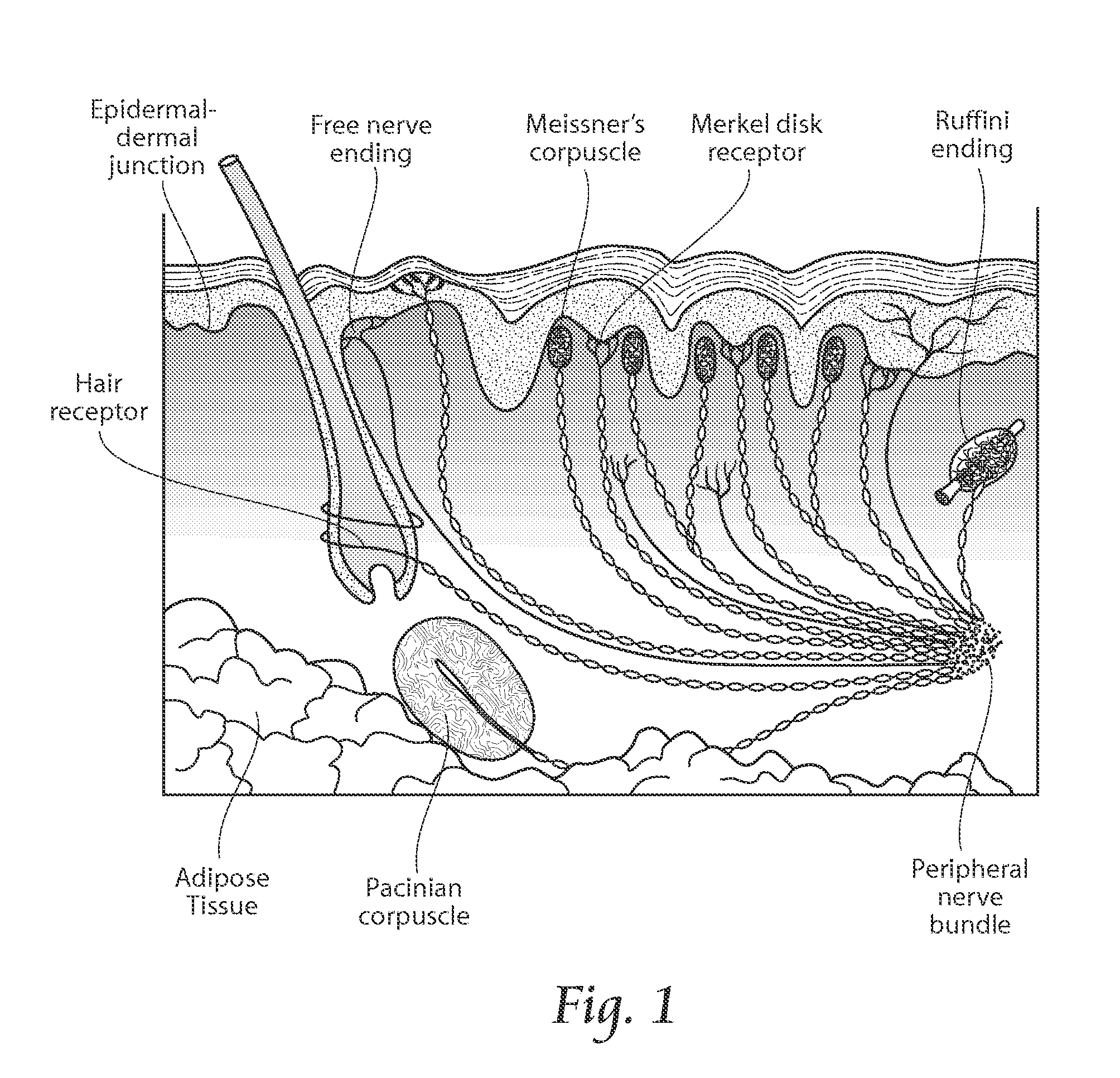
Compositions are provided that contain a TRPV1 agonist, such as capsaicin, and a solvent system. Topical application of the composition results in rapid delivery of agonist to the dermis and epidermis. Method of using the compositions for reducing nociceptive nerve fiber function in subjects, and for treatment of capsaicin-responsive conditions are also provided.
Owner:GRT US HLDG INC
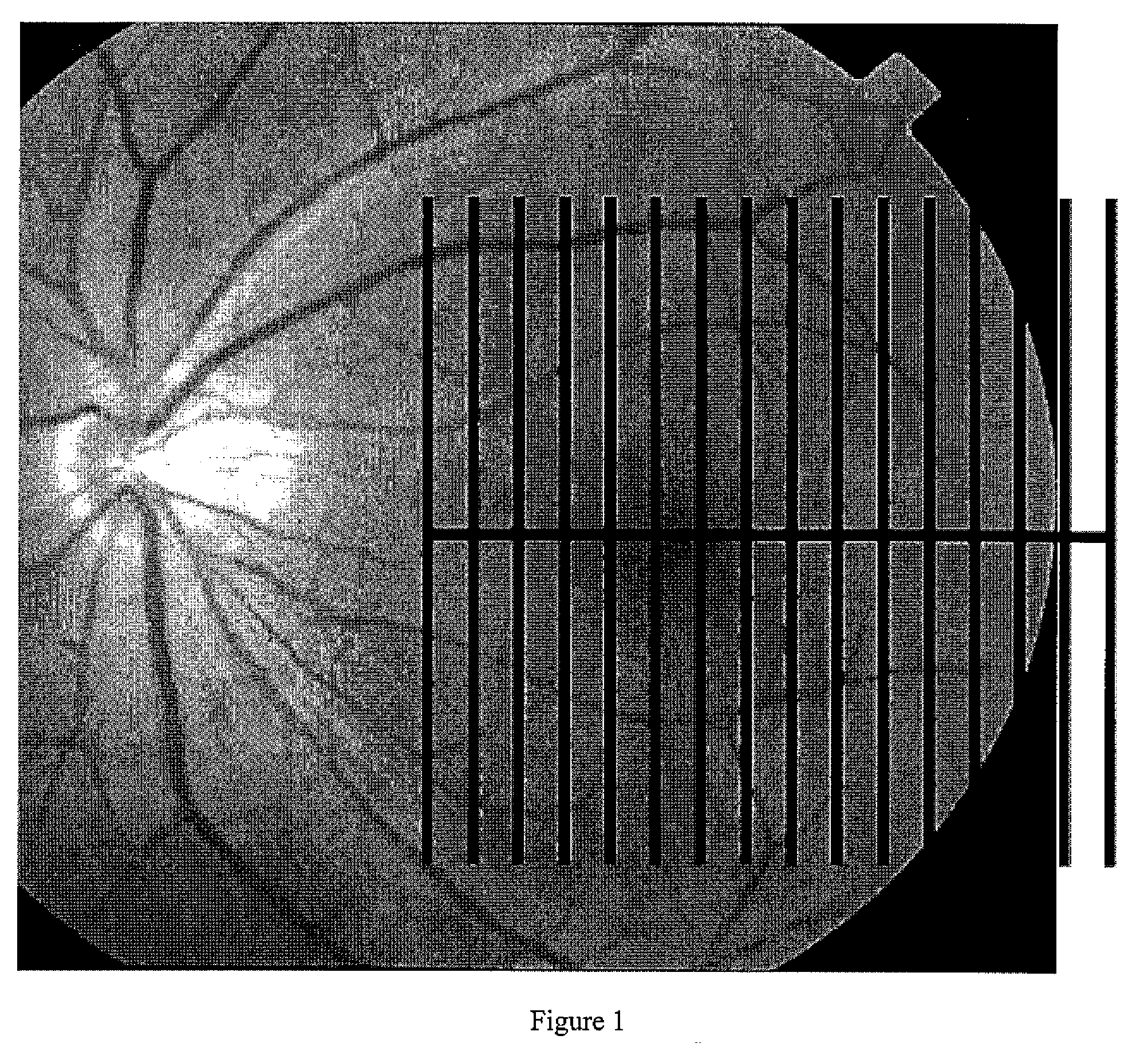
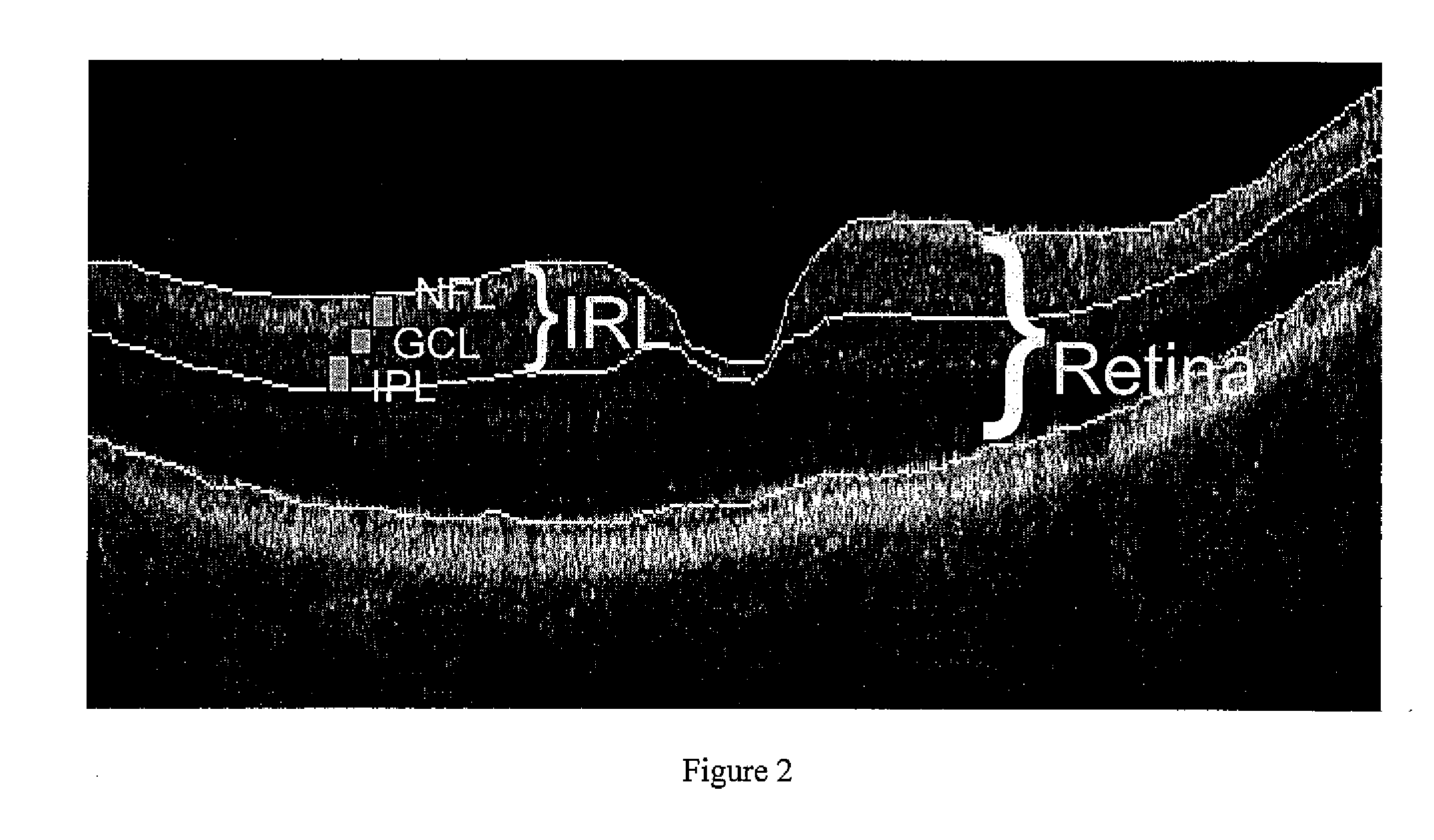
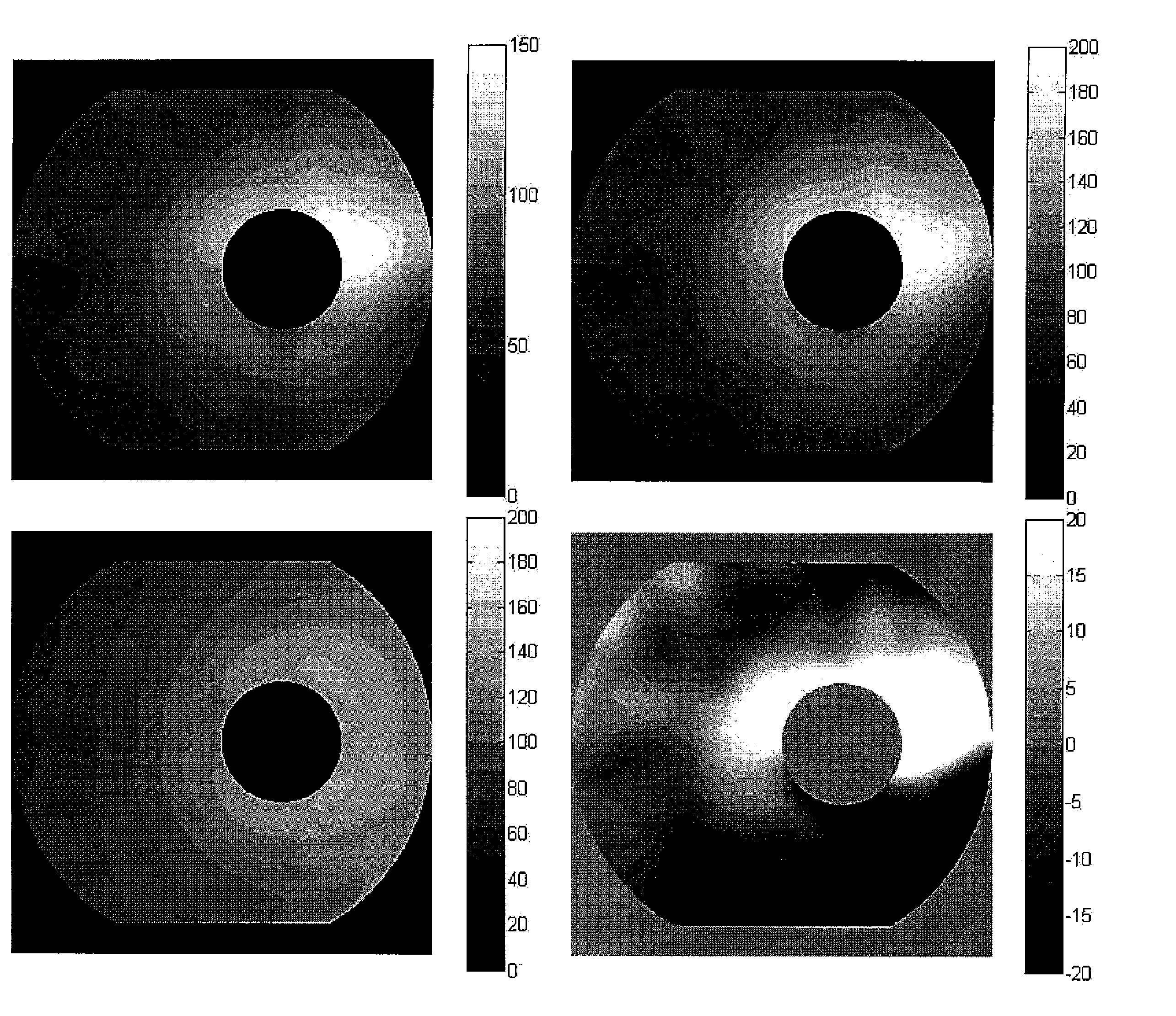
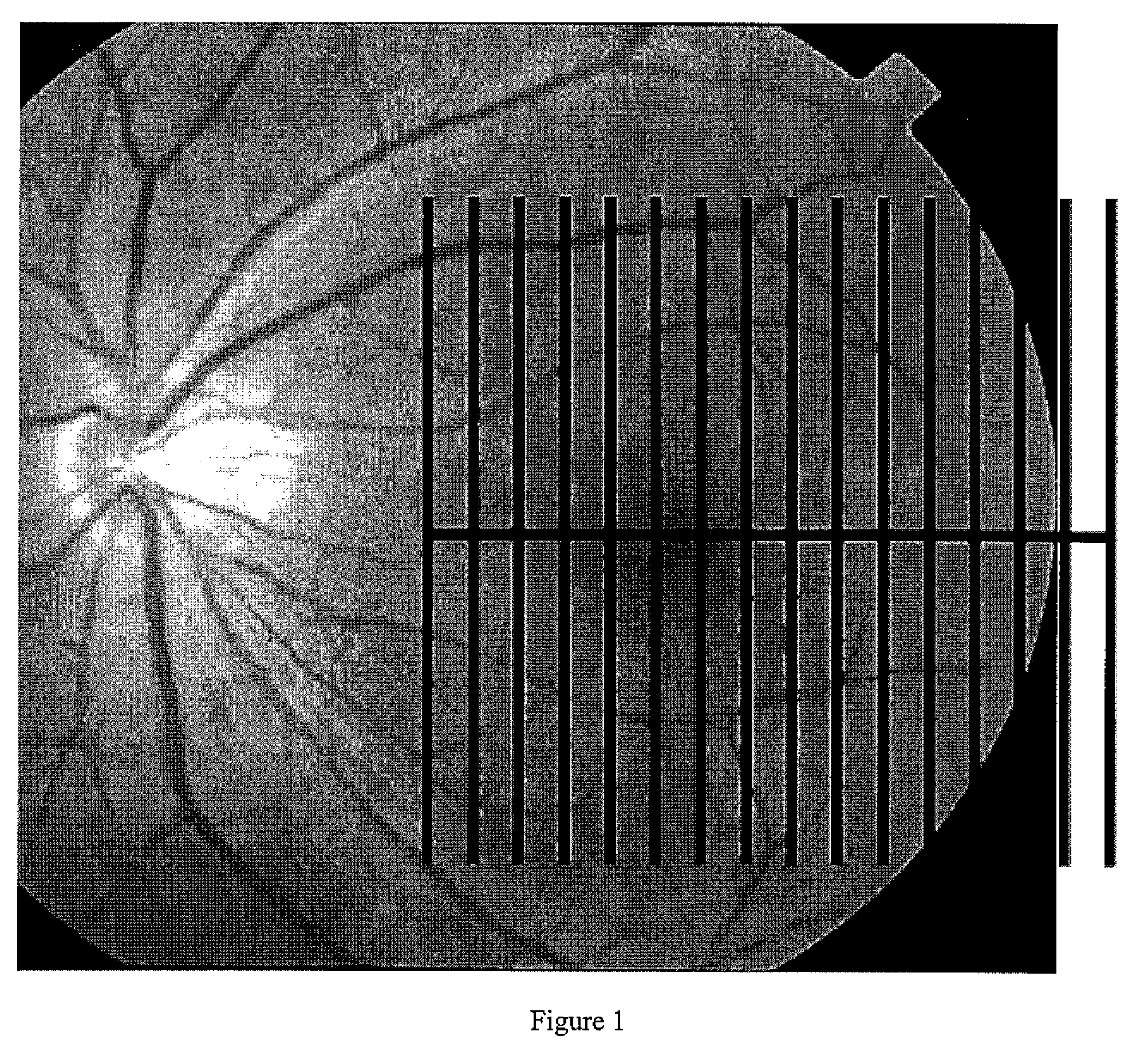
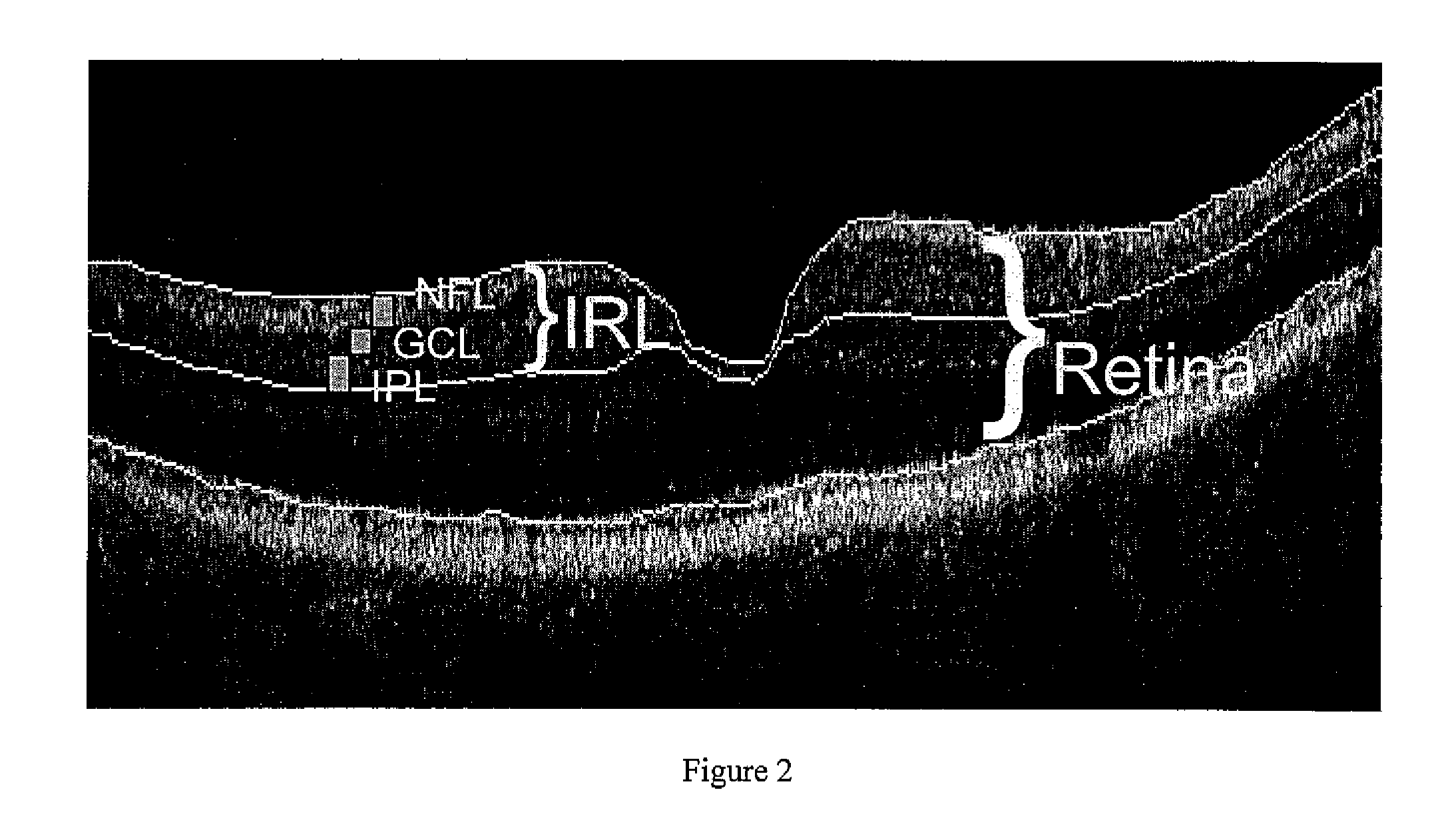
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
System and method for adjusting automatic pulse parameters to selectively activate nerve fibers
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Muscle stimulator
ActiveUS20080228241A1Reduce severityExcellent toneSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNerve fiber bundleLigament structure
An implantable medical device for treating the back of a patient. Stimulation energy is delivered to muscles or joint capsules or ligaments or nerve fibers to improve the heath of the back.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use
ActiveUS20150374992A1Rehabilitate spinal stabilityRestore neural driveSpinal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsSpinal columnMuscle contraction
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain are provided, in which an implantable stimulator is configured to communicate with an external control system, the implantable stimulator providing a neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy designed to cause muscle contraction to rehabilitate the muscle, restore neural drive and restore spinal stability; the implantable stimulator further including one or more of a number of additional therapeutic modalities, including a module that provides analgesic stimulation; a module that monitors muscle performance and adjusts the muscle stimulation regime; and / or a module that provides longer term pain relief by selectively and repeatedly ablating nerve fibers. In an alternative embodiment, a standalone implantable RF ablation system is described.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
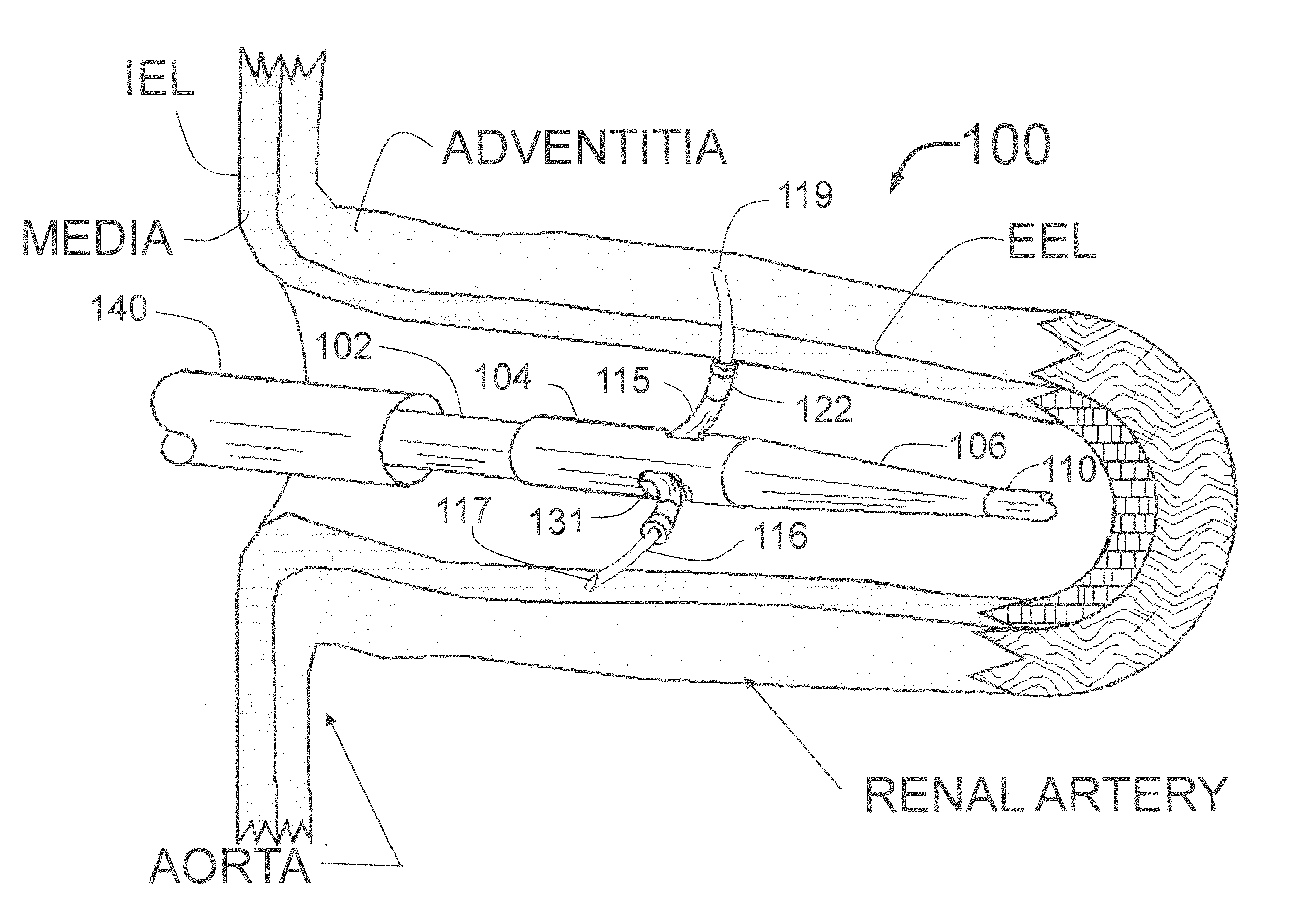
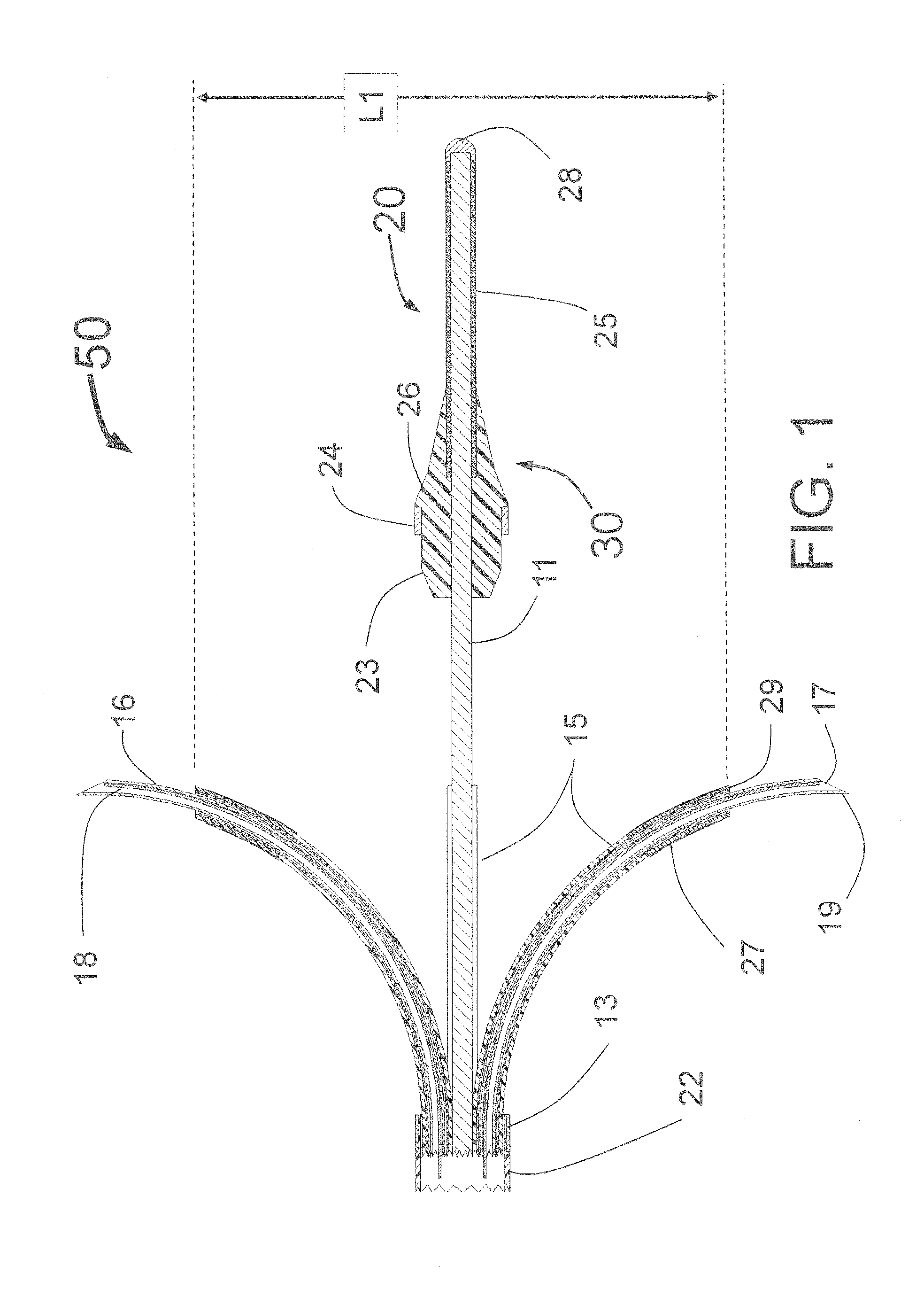
Peri-vascular tissue ablation catheter with unique injection fitting
ActiveUS20140316351A1Reduce or eliminate patient discomfort and painAvoiding needlestick injuriesBalloon catheterDiagnosticsVascular tissueGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through supported guide tubes which expand around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The system may also include a means to limit and / or adjust the depth of penetration of the ablative fluid into and beyond the tissue of the vessel wall. The catheter may also include structures which provide radial and / or lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes expand uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened injection needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
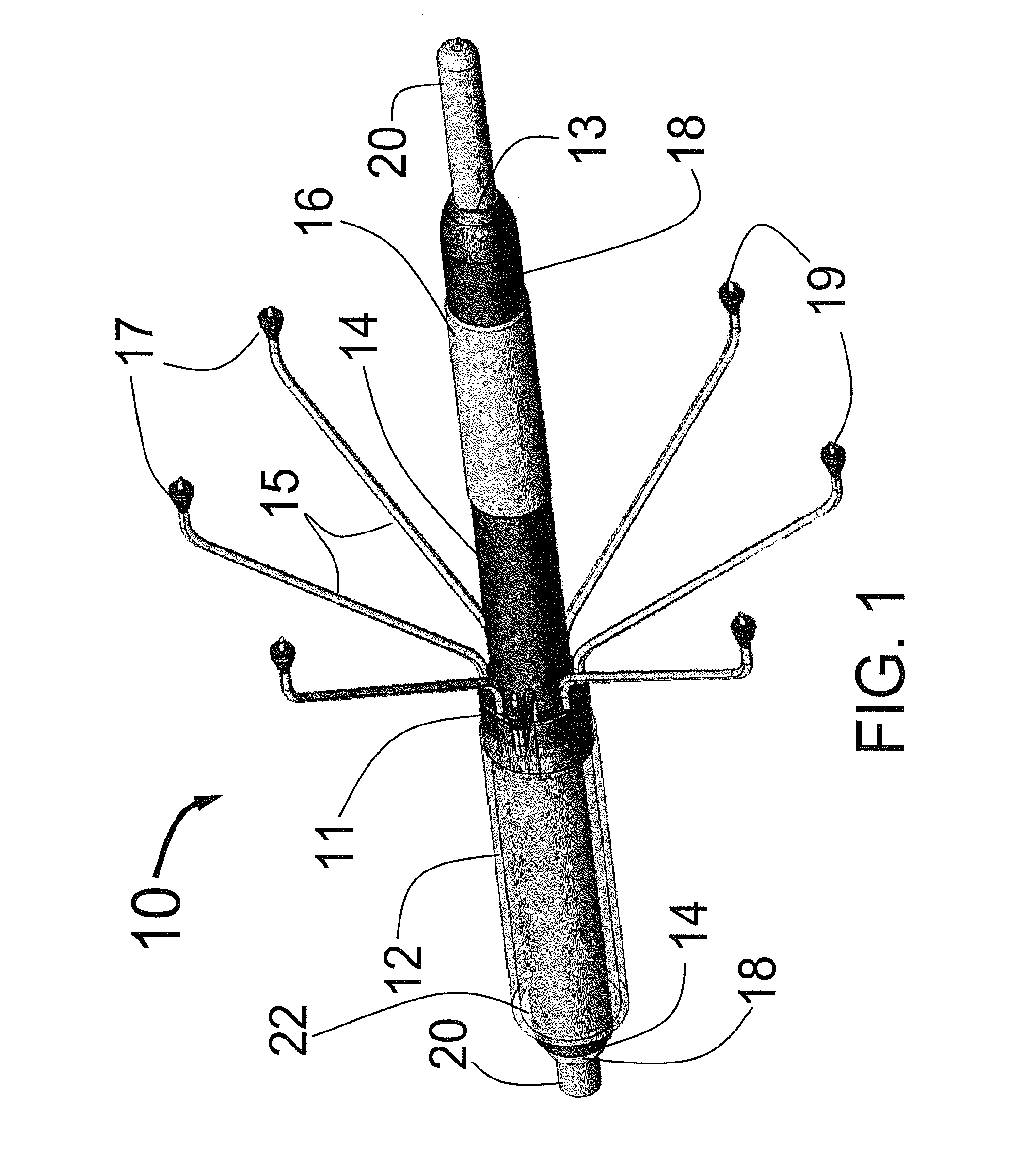
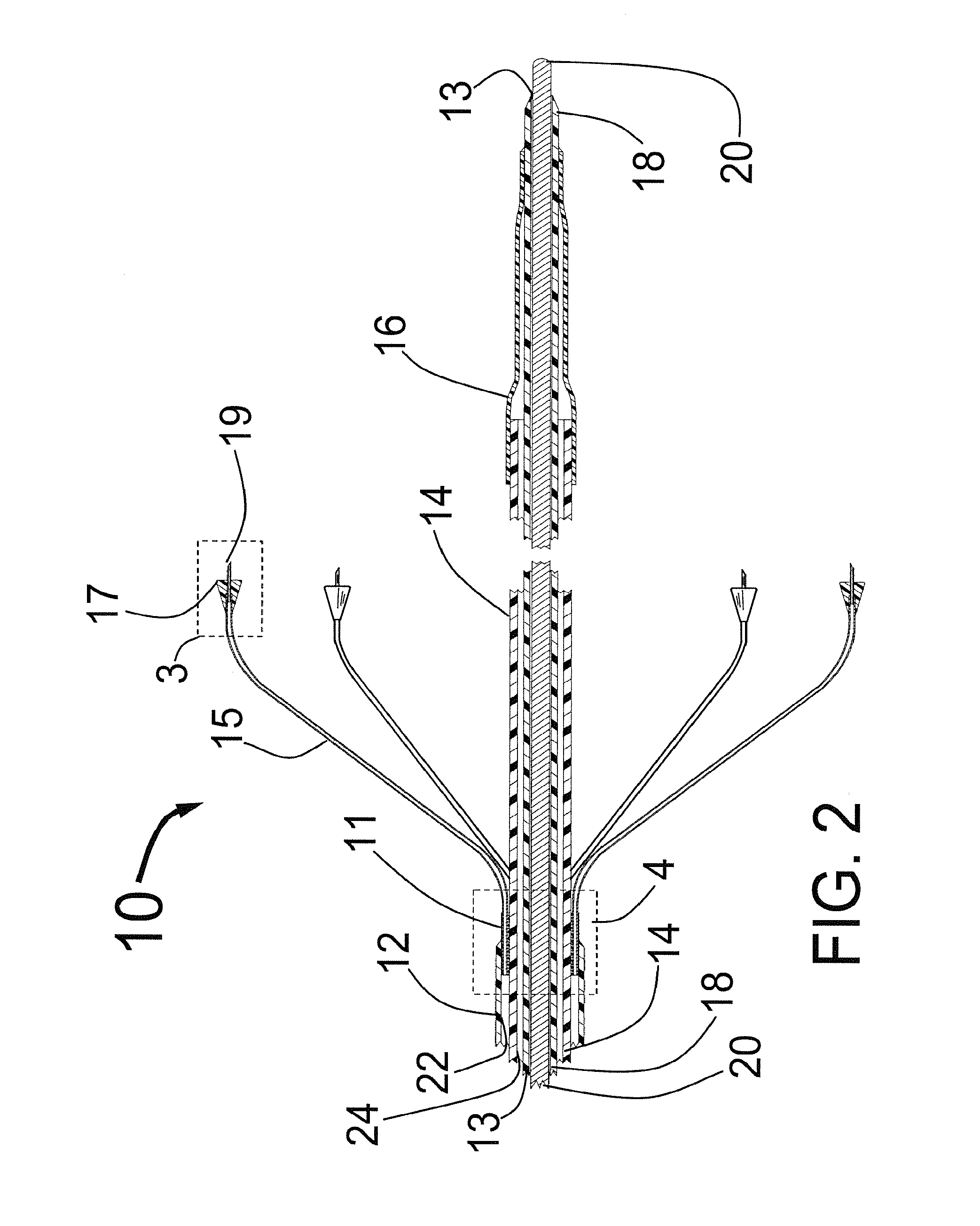
Systems and methods for the treatment of pain through neural fiber stimulation
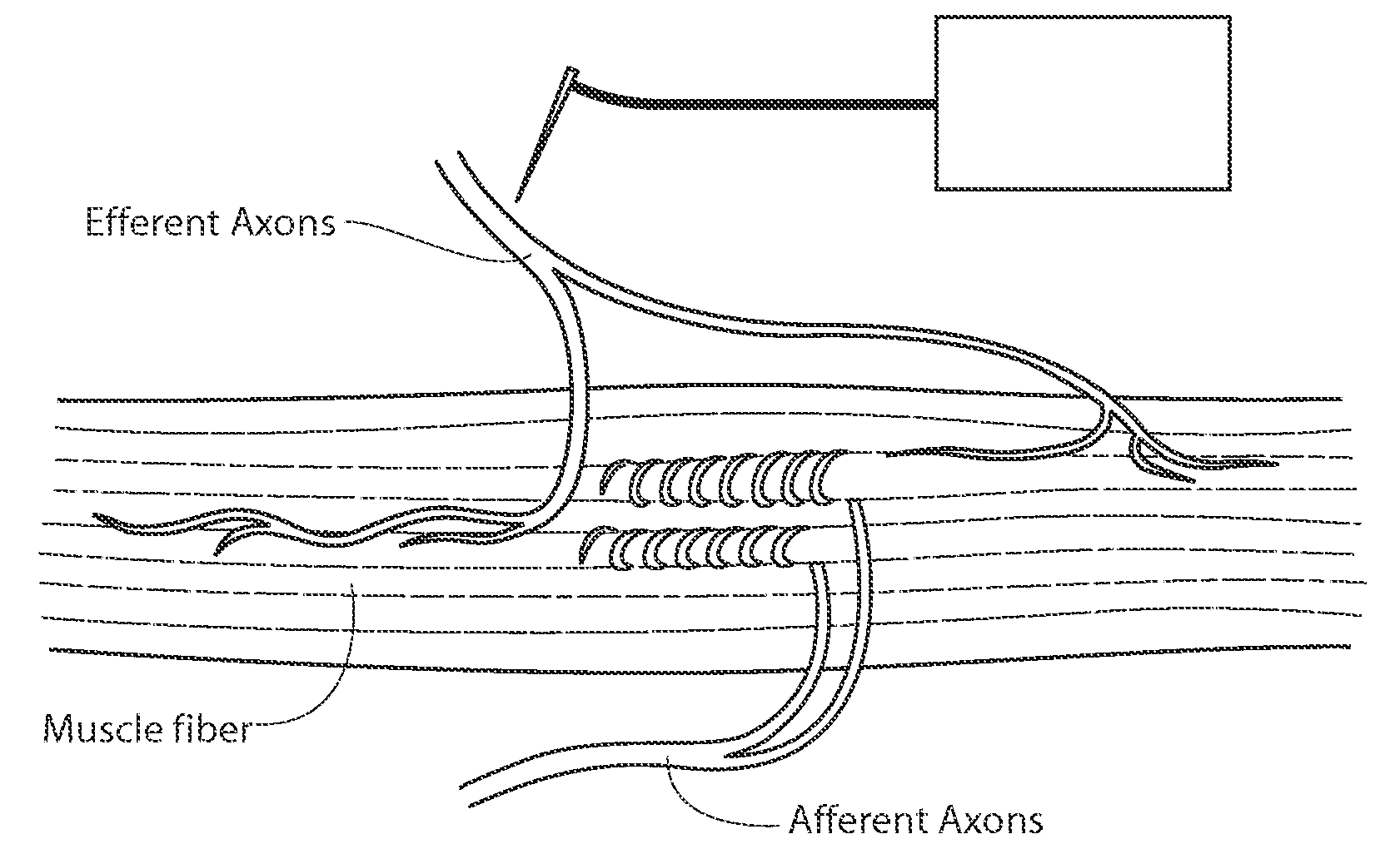
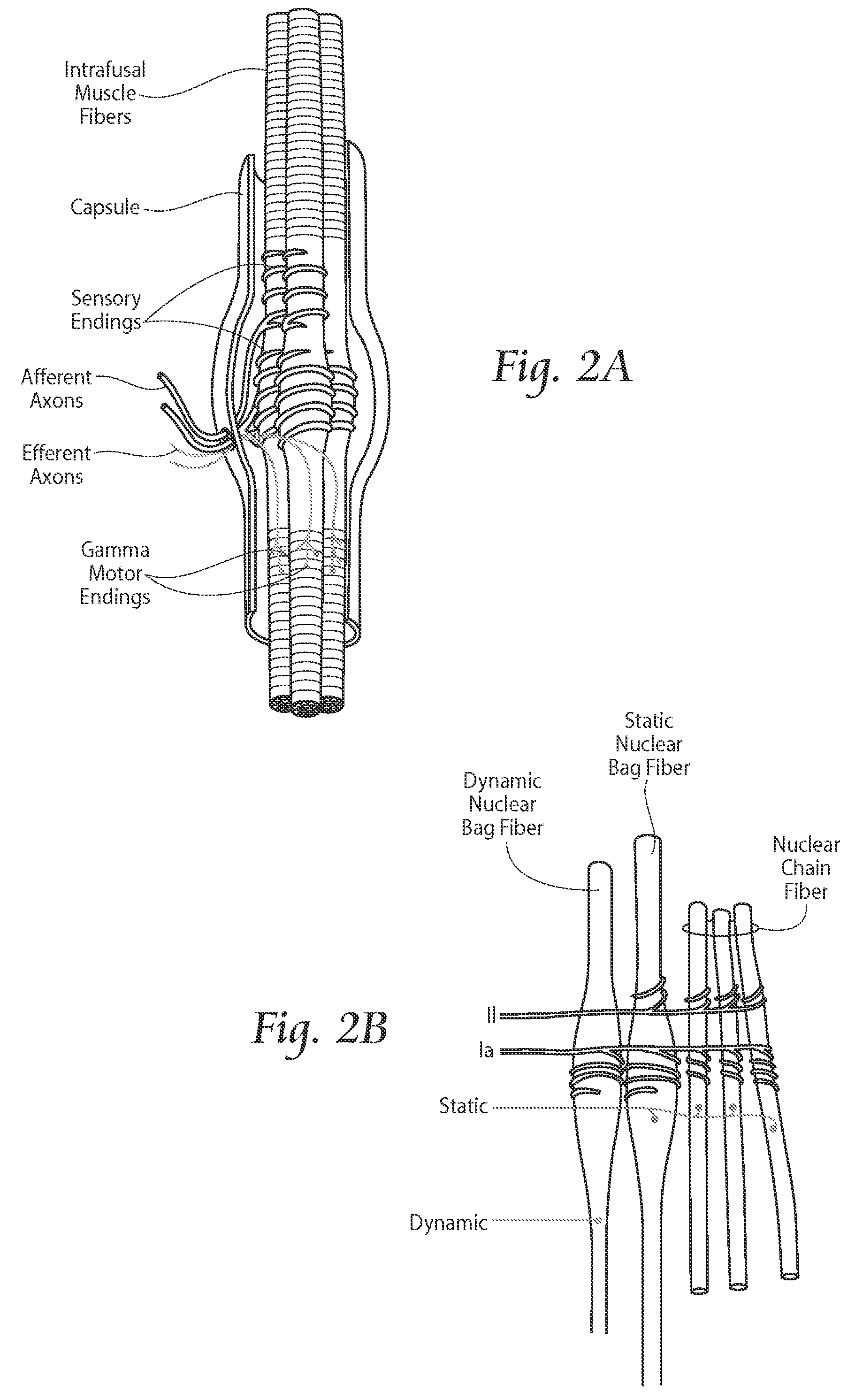
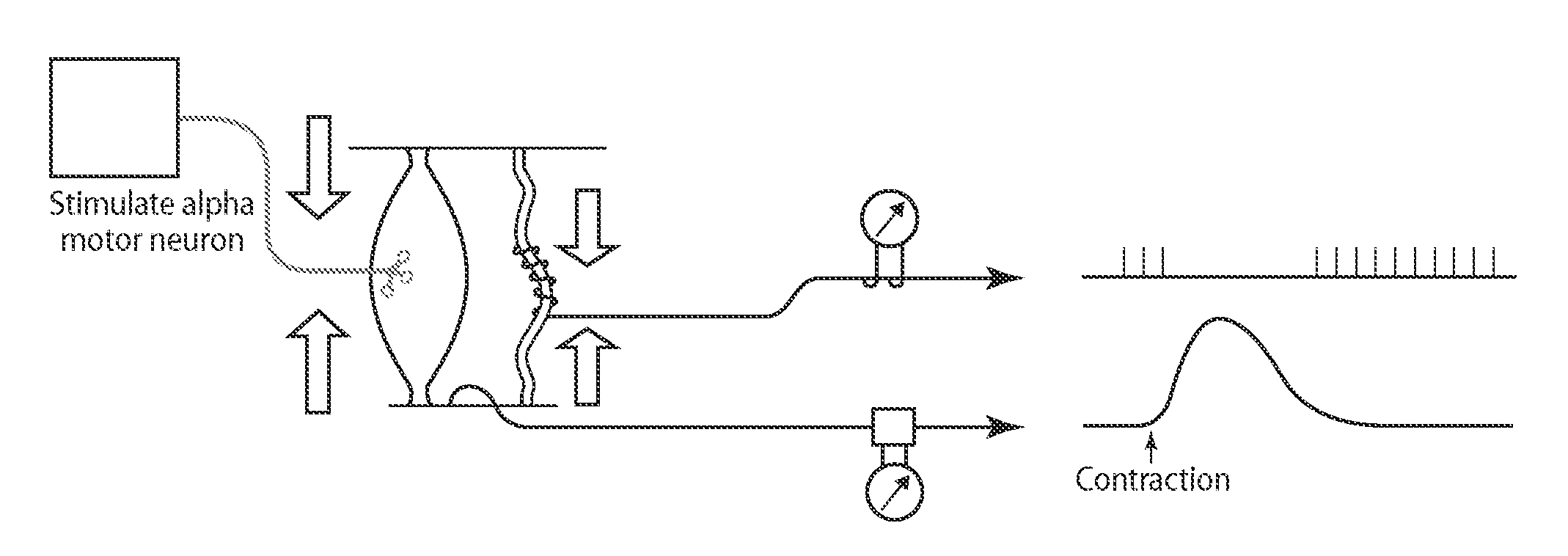
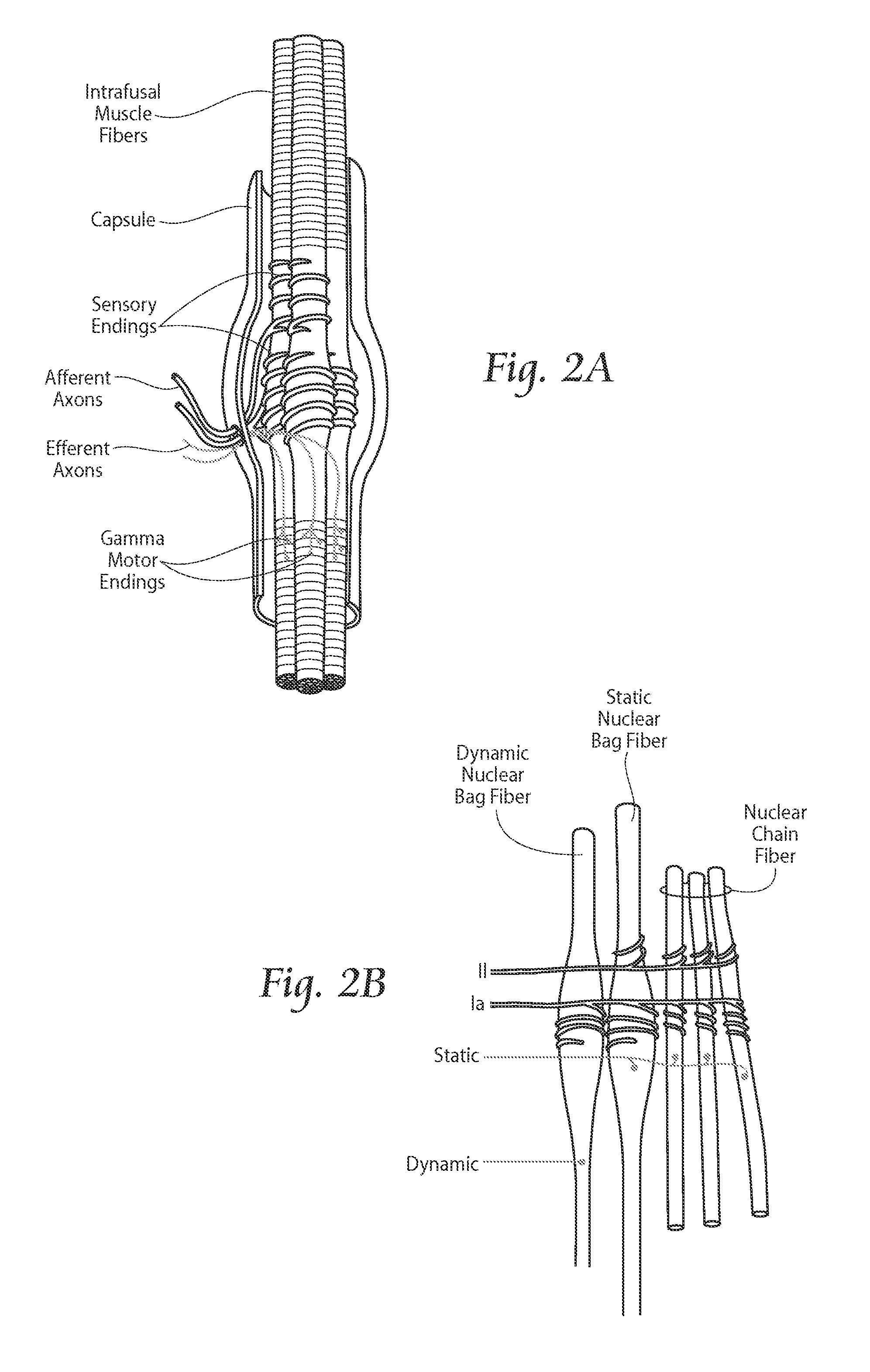
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for the treatment of pain through activation of select neural fibers. The neural fibers may comprise one or more afferent neural fibers and / or one or more efferent neural fibers. If afferent fibers are stimulated, alone or in combination with efferent fibers, a therapeutically effective amount of electrical stimulation is applied to activate afferent pathways in a manner approximating natural afferent activity. The afferent fibers may be associated with primary receptors of muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, secondary receptors of muscle spindles, joint receptors, touch receptors, and other types of mechanoreceptors and / or proprioceptors. If efferent fibers are stimulated, alone or in combination with afferent fibers, a therapeutically effective amount of electrical stimulation is applied to activate intrafusal and / or extrafusal muscle fibers, which results in an indirect activation of afferent fibers associated therewith.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
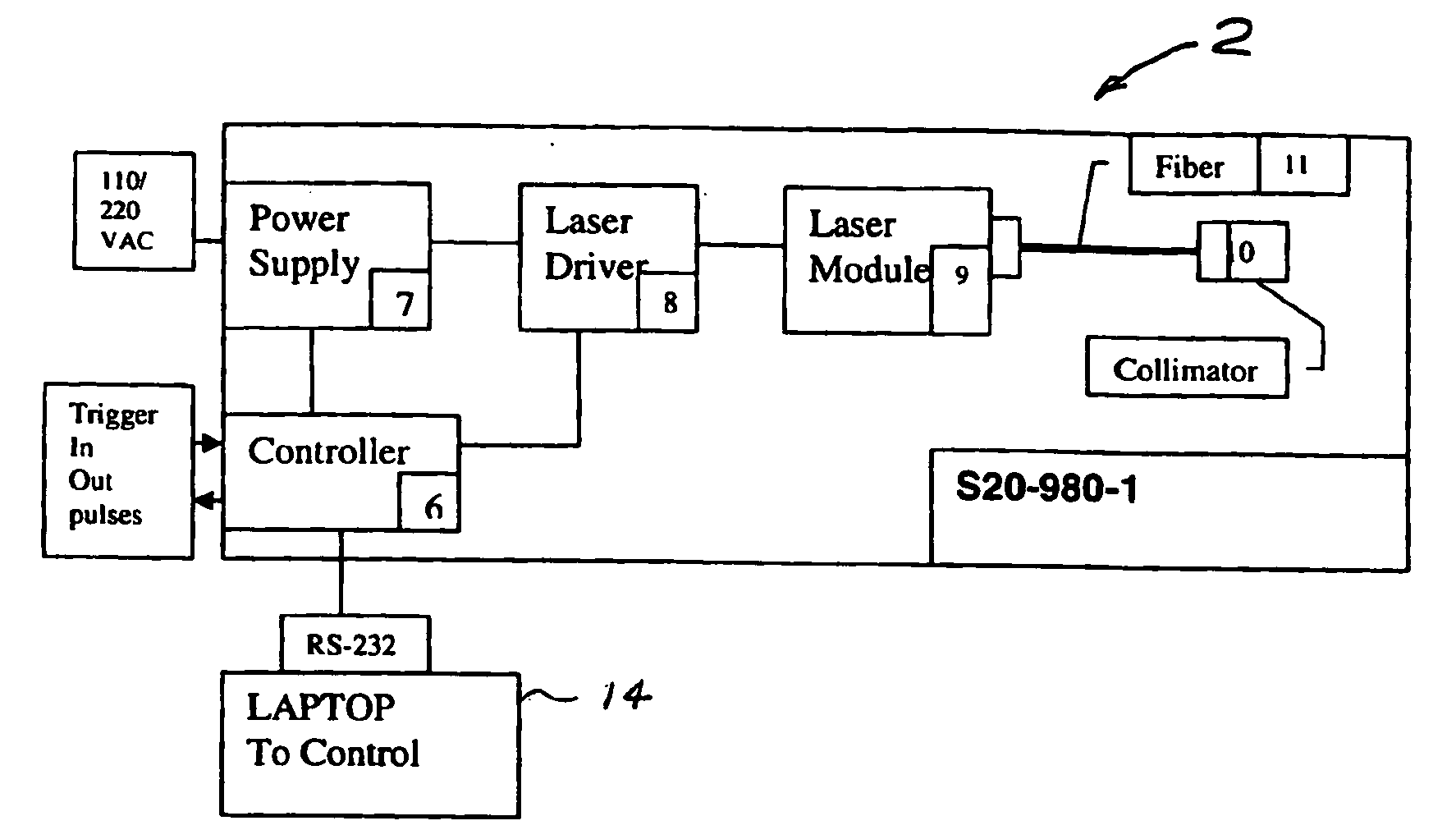
Portable laser and process for pain research
ActiveUS20080269847A1Accurately determineDiagnostics using lightSurgical instrument detailsElectrophysiology studyFiber
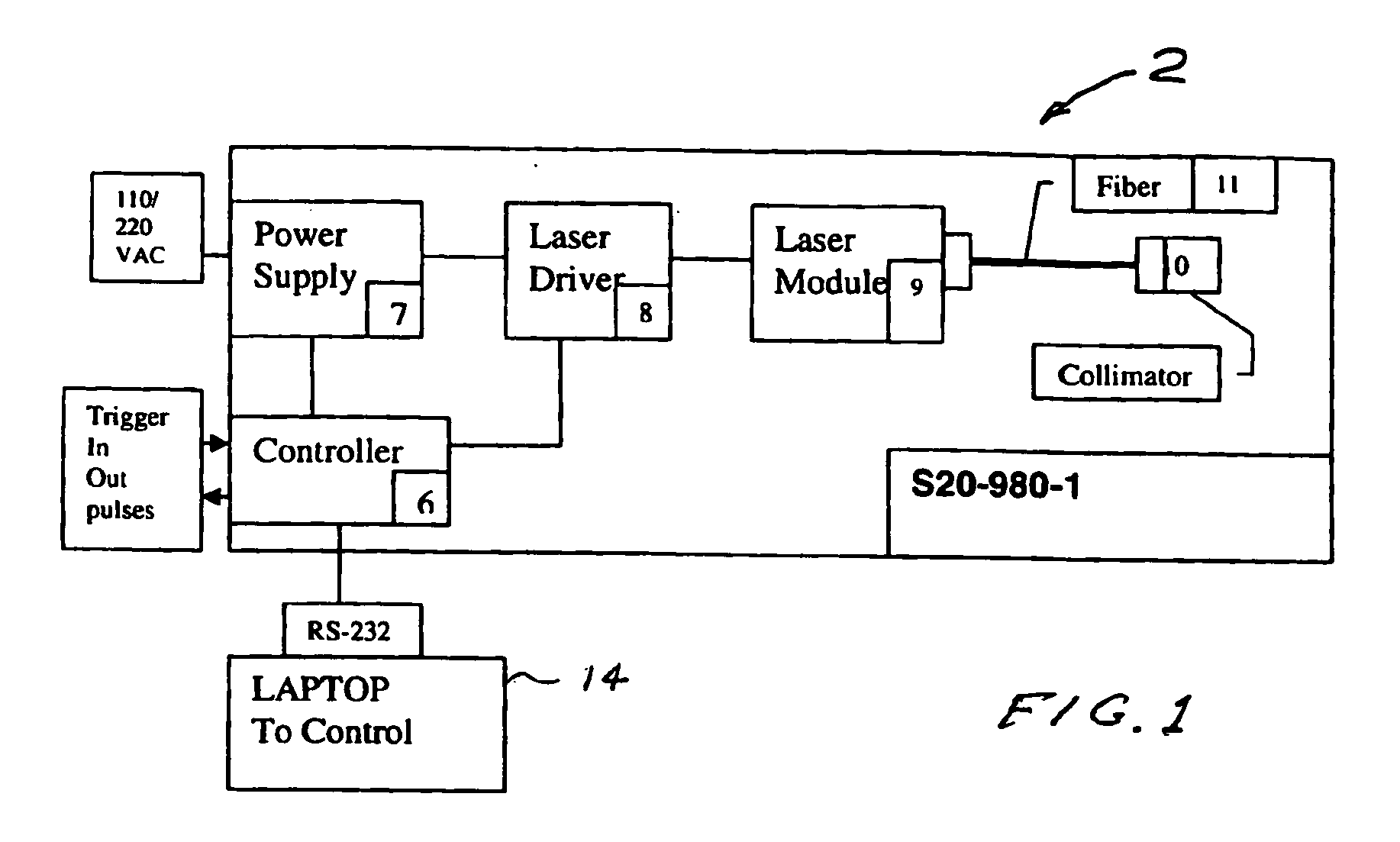
A process and laser system for in vitro and in vivo pain research, pain clinical testing and pain management. In preferred embodiments of the present invention a diode laser operating at a 980 nm wavelength is used to produce warmth, tickling, itching, touch, burning, hot pain or pin-prick pain. The device and methods can be used for stimulation of a single nerve fiber, groups of nerve fibers, nerve fibers of single type only as well as more the one type of nerve fibers simultaneously. The present invention is especially useful for research of human / animal sensitivity, pain management, drug investigation and testing, and psychophysiology / electrophysiology studies. The device and methods permit non-contact, reproducible and controlled tests that avoid risk of skin damage. Applicant an his fellow workers have shown that tests with human subjects with the process and laser of the present invention correlate perfectly with laboratory tests with nerve fibers of rats. The device and the methods can be applied in a wide variety of situations involving the study and treatment of pain. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide laser systems and techniques that permit mapping and single mode activation of C fibers and A-delta fibers.
Owner:NEMENOV MIKHALL
Selective nerve fiber stimulation for treating heart conditions
InactiveUS20080125827A1Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleRR interval
Apparatus is provided that includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of a subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject. Also provided is a method comprising applying to a vagus nerve of a subject a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
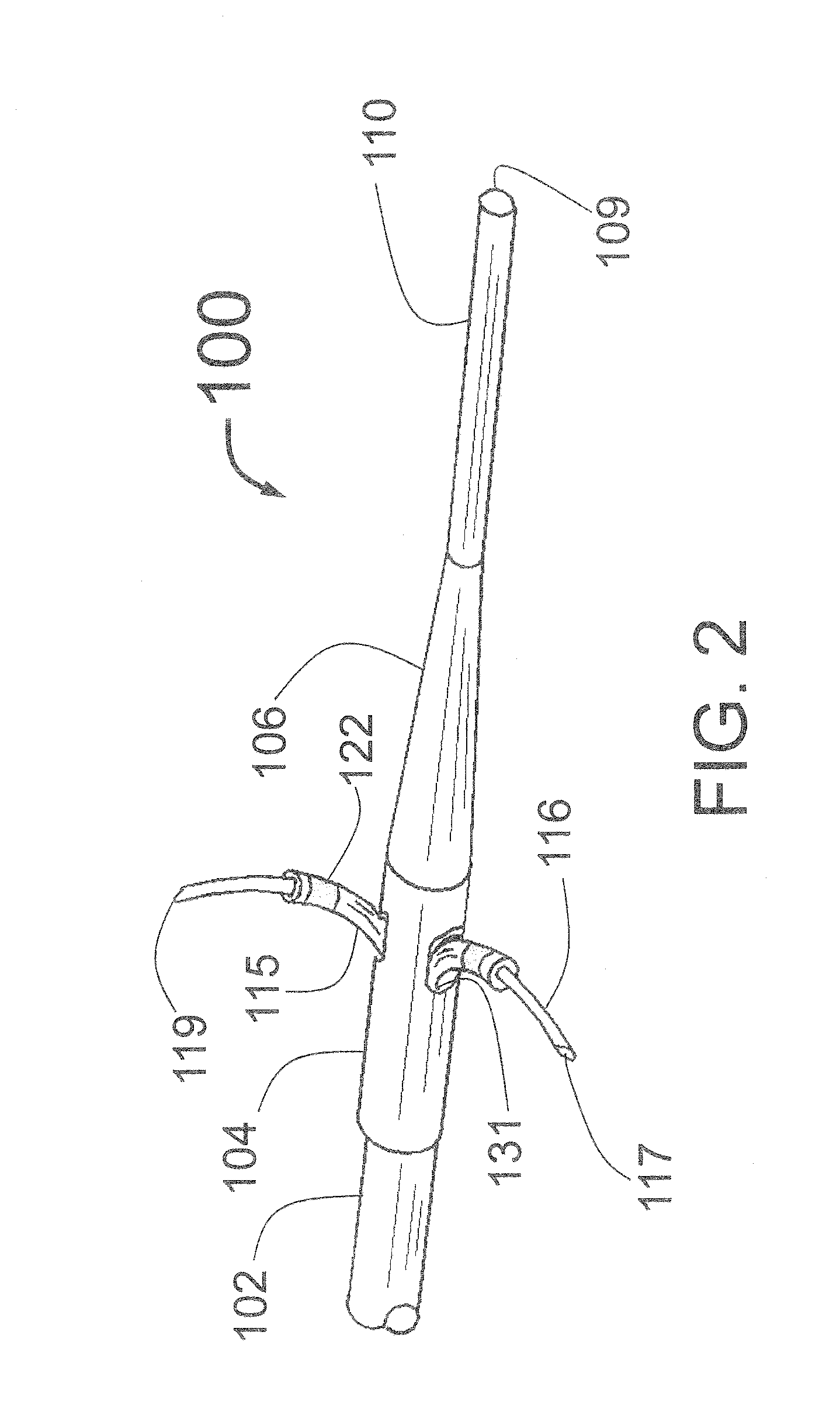
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20160235464A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS8983629B2Inhibition releaseInhibits mucous productionElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma, anaphylaxis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), exercise-induced bronchospasm and post-operative bronchospasm. The treatment comprises transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers that activate neural pathways to reduce the release of acetycholine from airway-related vagal preganglionic neurons within the brain of the patient. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers to produce the bronchodilation.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Double-layer artificial nerve catheter and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an artificial nerve conduit of double layer and the method for preparing same. The said nerve conduit comprises an inner conduit and an outer layer, which are made from degradable and adsorptive material in living body. The slit between said inner conduit and outer conduit is filled with fiber albumen glue (used for regeneration of nervous tissue and blood vessel). The artificial nerve conduit of double layer can be used for bypass surgery for damaged round nerve and spinal marrow, and it will be degraded and adsorbed in living body after nerve regeneration. The said artificial nerve conduit possesses good elasticity and strength, and the degradation time is adaptive to growing speed of nervous fiber (about 1-6 months).
Owner:首都医科大学北京神经科学研究所
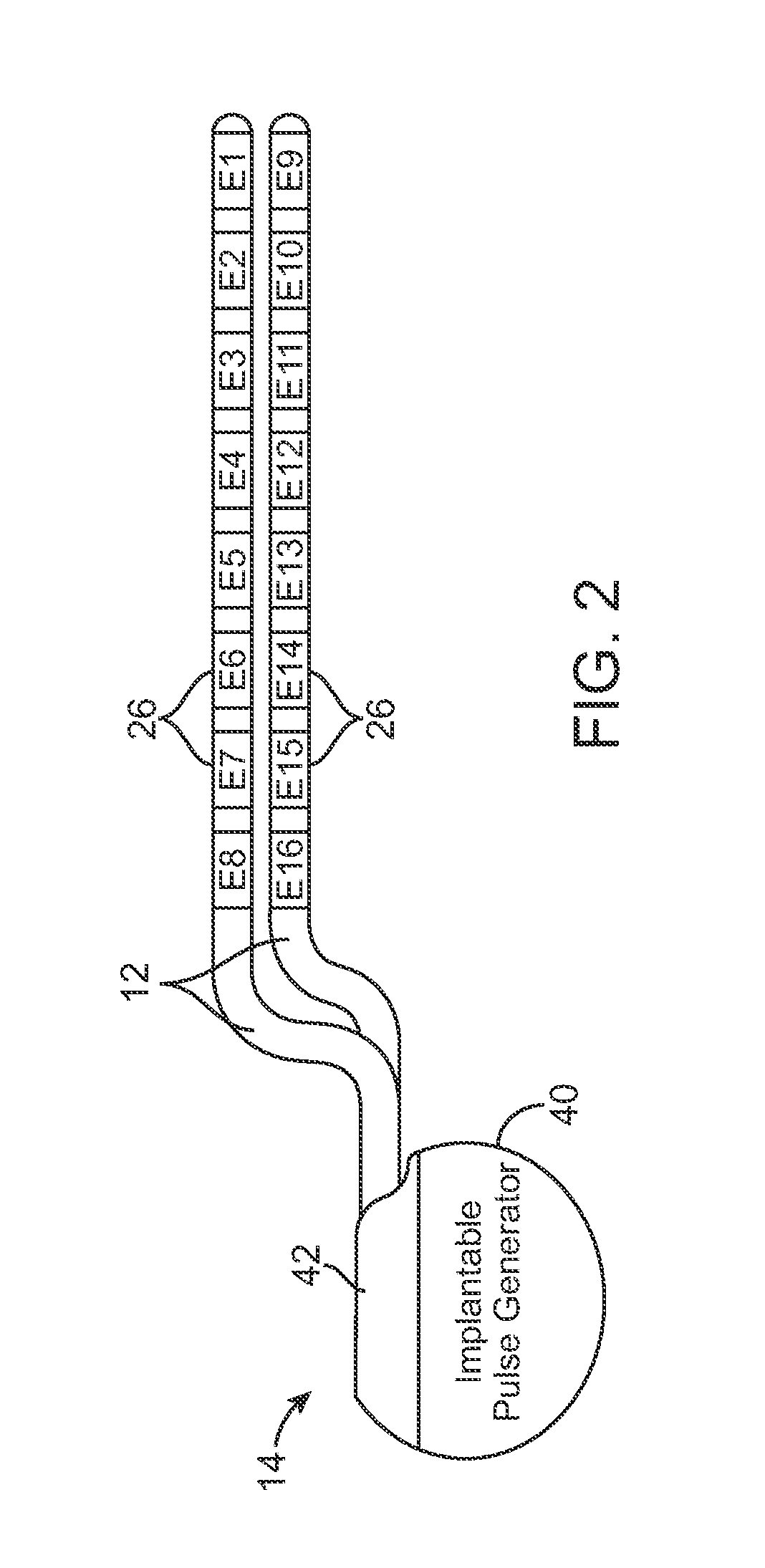
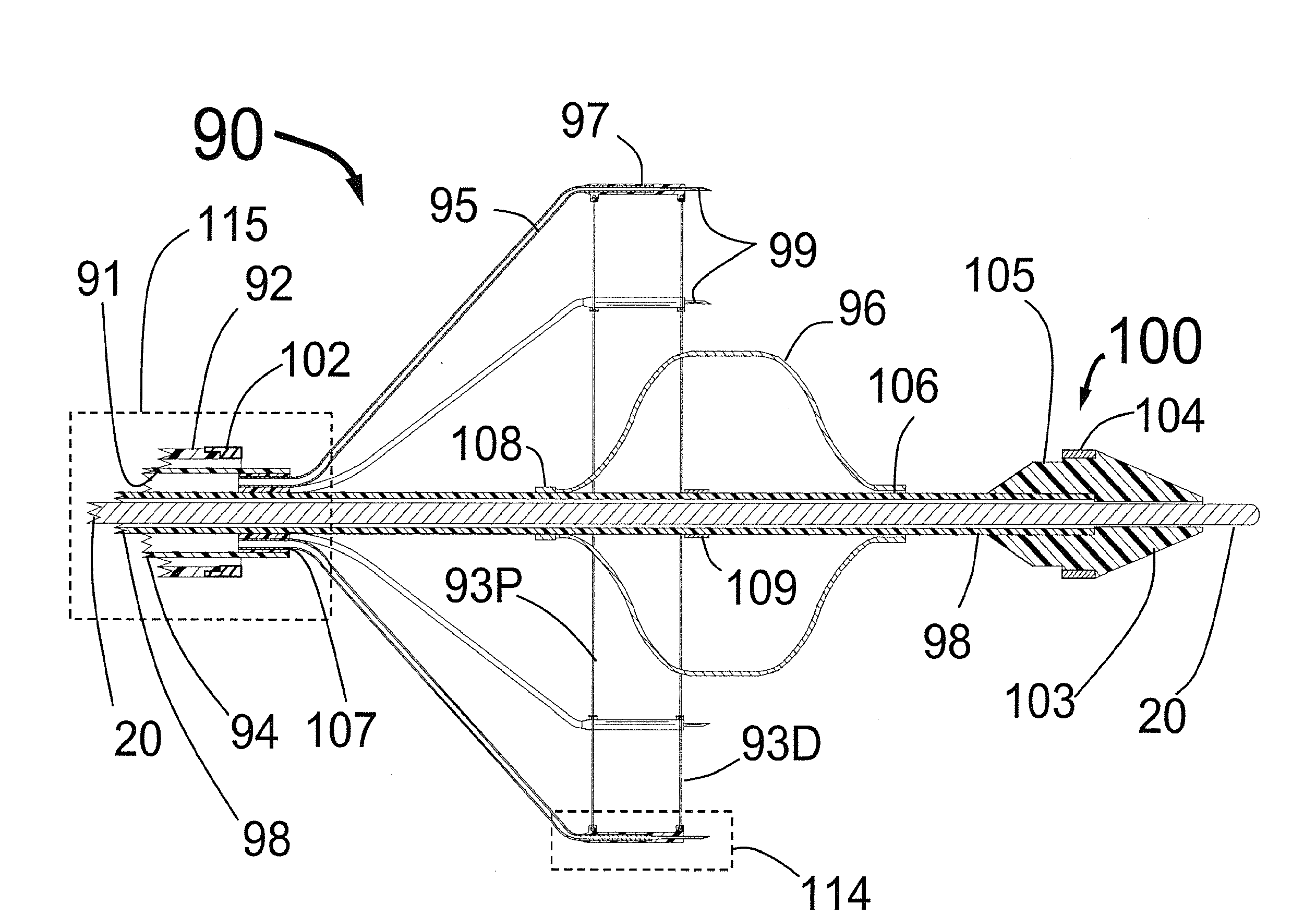
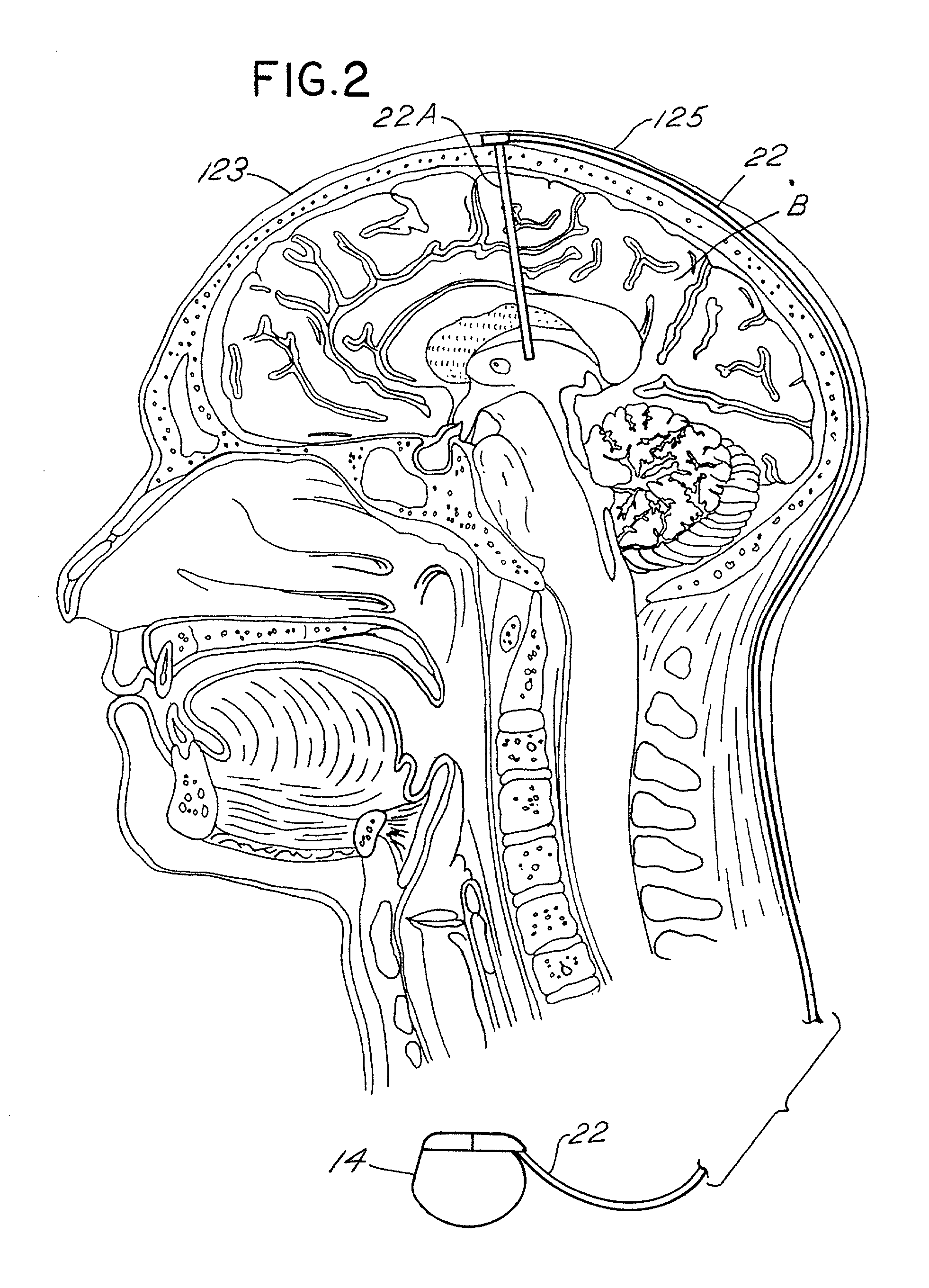
Techniques for selective activation of neurons in the brain, spinal cord parenchyma or peripheral nerve
Techniques capable of selectively affecting and adjusting a volume of neural tissue in the brain, parenchyma of the spinal cord, or a peripheral nerve are disclosed. A lumen having at least one opening at its distal end that is capable of directing a lead outwardly along a predetermined trajectory is preferred. The lumen is capable of accepting a plurality of leads that can project outward in different directions from the distal end of the lumen. The leads have one or more electrodes at its ends and are thereby configured by the lumen in accordance with a predetermined two- or three-dimensional geometry. Anode / cathode relationships may be established between the electrodes by the operator to stimulate the neural tissue surrounding these electrodes. The operator may also adjust the stimulation to selectively stimulate the desired portion of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve. Sensor feedback may be implemented to adjust the treatment therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for stimulating intraosseous nerve fibers
A method for treating a patient having pain comprises applying electrical modulation energy to a target site adjacent an intraosseous nerve fiber of the patient to modulate pain traffic within the intraosseous nerve fiber, thereby treating the pain.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems and methods for the treatment of pain through neural fiber stimulation
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for the treatment of pain through activation of select neural fibers. The neural fibers may comprise one or more afferent neural fibers and / or one or more efferent neural fibers. If afferent fibers are stimulated, alone or in combination with efferent fibers, a therapeutically effective amount of electrical stimulation is applied to activate afferent pathways in a manner approximating natural afferent activity. The afferent fibers may be associated with primary receptors of muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, secondary receptors of muscle spindles, joint receptors, touch receptors, and other types of mechanoreceptors and / or proprioceptors. If efferent fibers are stimulated, alone or in combination with afferent fibers, a therapeutically effective amount of electrical stimulation is applied to activate intrafusal and / or extrafusal muscle fibers, which results in an indirect activation of afferent fibers associated therewith.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
Methods and compositions for administration of TRPV1 agonists
Compositions are provided that contain a TRPV1 agonist, such as capsaicin, and a solvent system. Topical application of the composition results in rapid delivery of agonist to the dermis and epidermis. Method of using the compositions for reducing nociceptive nerve fiber function in subjects, and for treatment of capsaicin-responsive conditions are also provided.
Owner:GRT US HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com