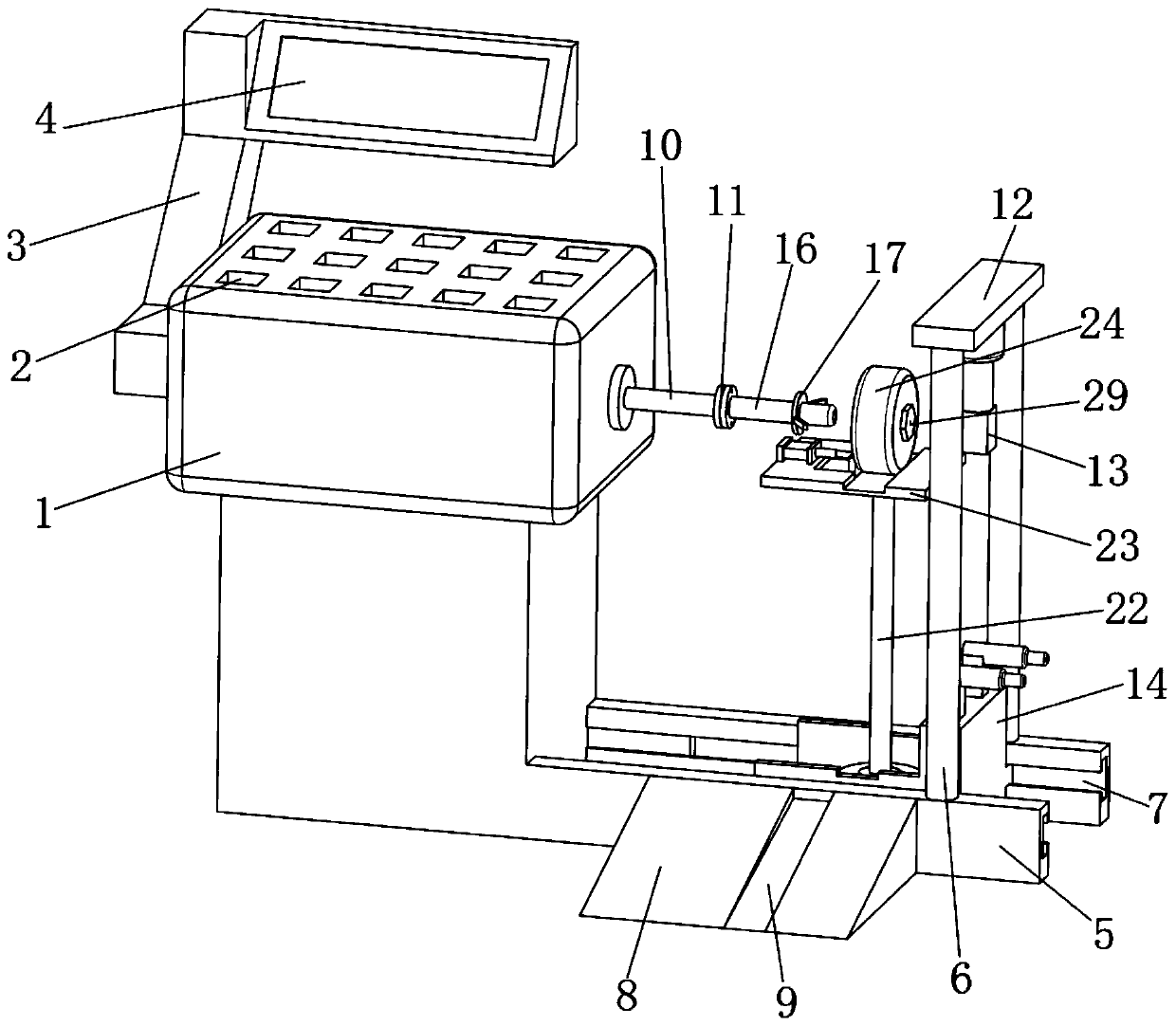
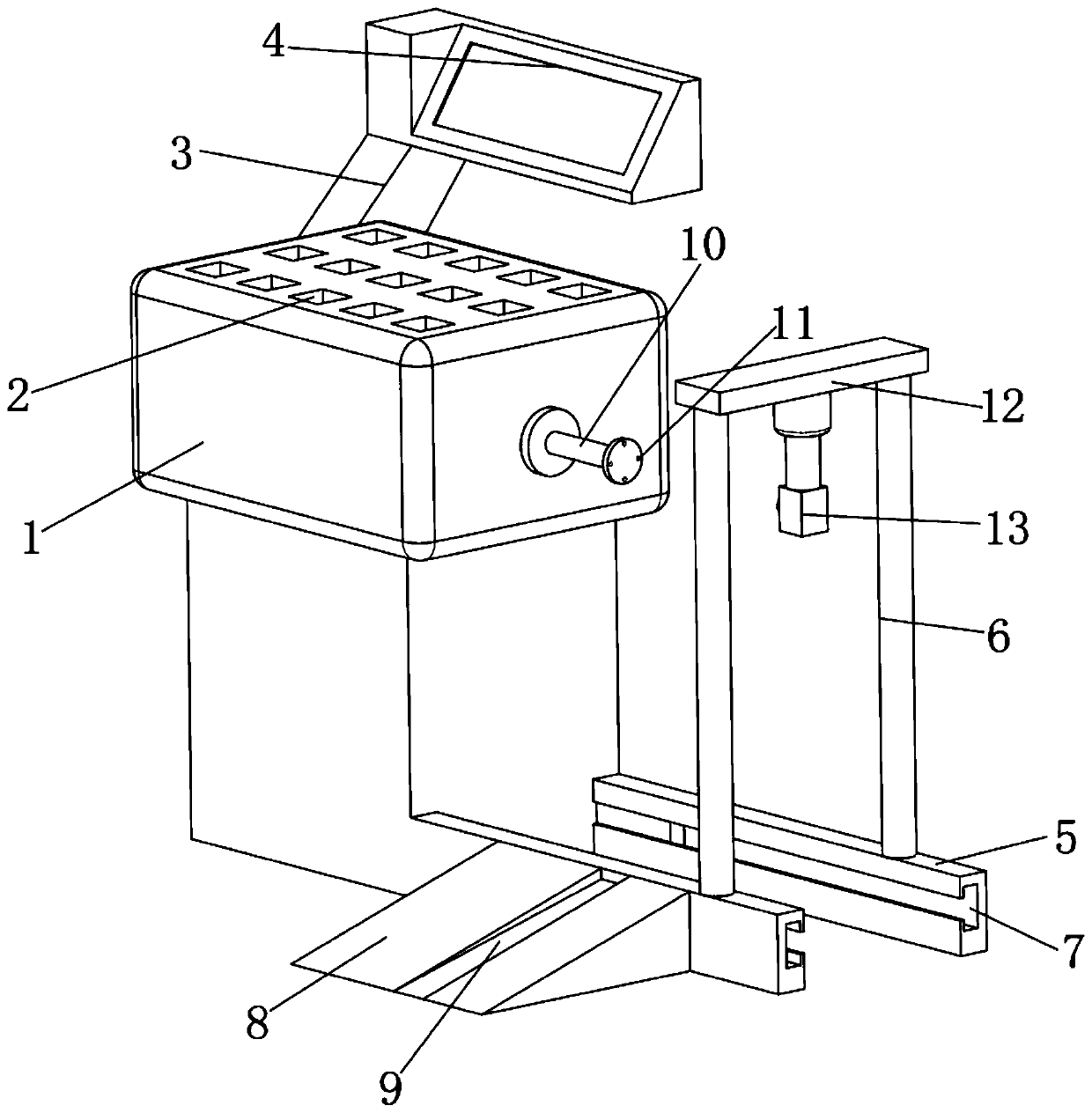
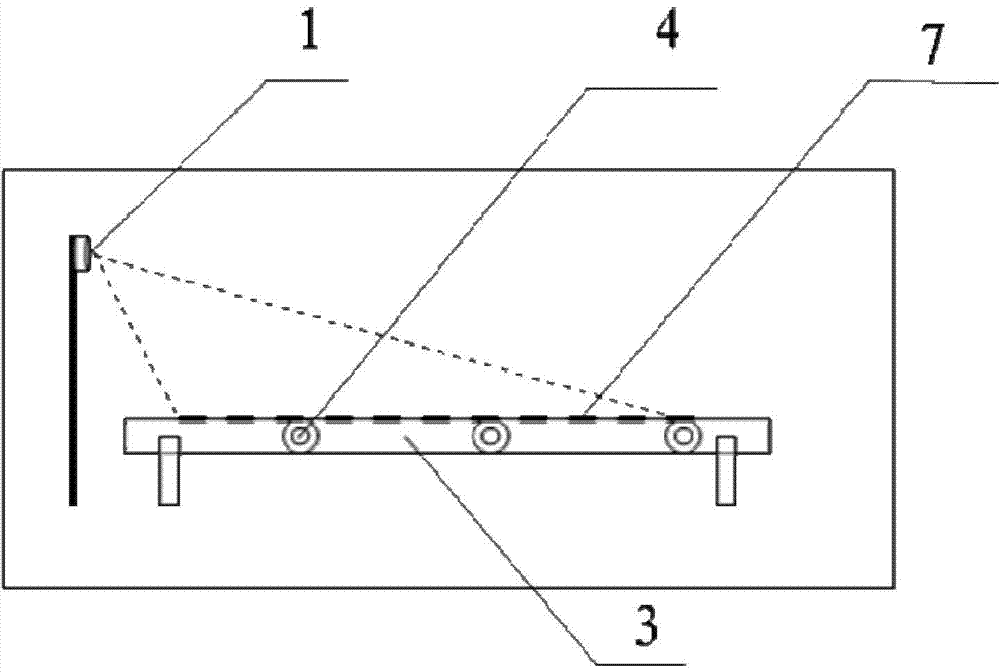
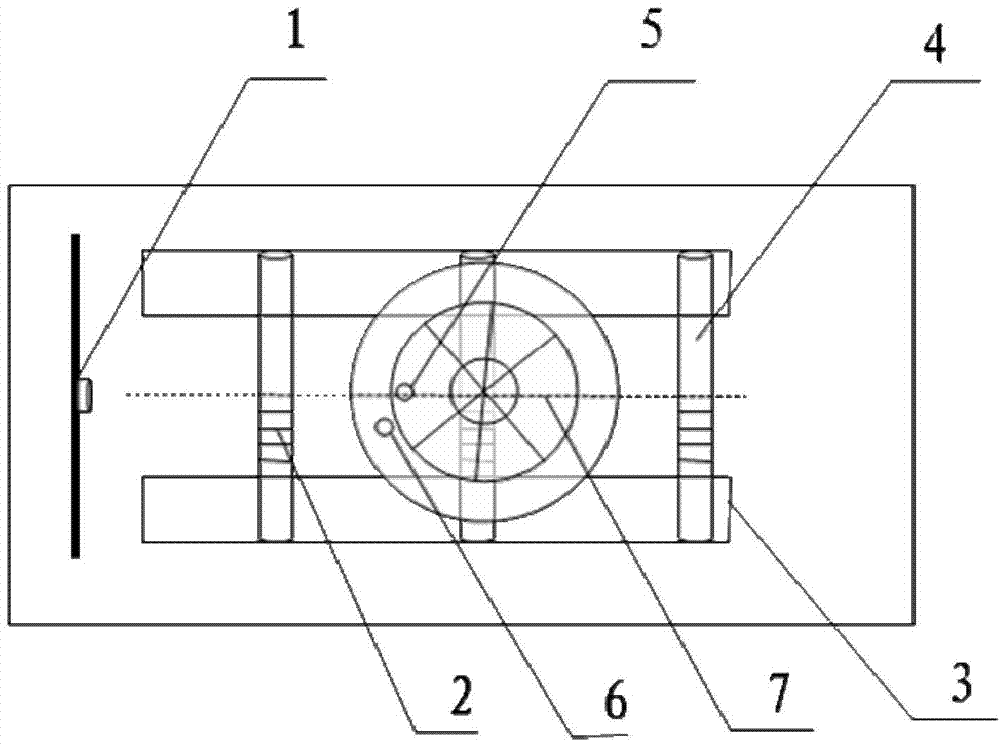
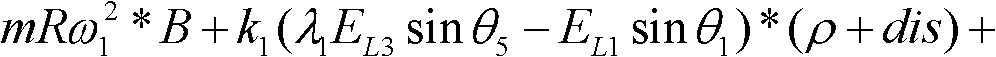Patents
Literature
83 results about "Tire balance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tire balance, also called tire unbalance or tire imbalance, describes the distribution of mass within an automobile tire or the entire wheel (including the rim) on which it is mounted. When the wheel rotates, asymmetries in its mass distribution may cause it to apply periodic forces and torques to the axle, which can cause ride disturbances, usually as vertical and lateral vibrations, and this may also cause the steering wheel to oscillate. The frequency and magnitude of this ride disturbance usually increases with speed, and vehicle suspensions may become excited when the rotating frequency of the wheel equals the resonant frequency of the suspension.
Tyre balancing compositions
InactiveUS20050159534A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove abilitiesRotating bodies balancingLaminationTire balancePolyolefin
The invention relates to tyre balancing compositions having improved balancing properties comprise a visco-plastic gel and solid bodies having an average smallest dimension in the range of 0.5-5 mm; preferably 1-4 mm, more preferably around 3 mm. When applied in a layer to the inside of a motor vehicle tyre, the compositions act by allowing the solid bodies move through the gel and to concentrate in areas to counteract imbalances. The solid bodies preferably have an average ratio α between their smallest and their largest dimension of α≦2, more preferably α≦1.5, especially around 1. The visco-plastic gel preferably has a storage modulus (G′) between 1000 Pa and 25000 Pa at 22° C., a loss modulus (G″) smaller than the storage modulus, and a critical yield stress above 3 Pa at 22° C. The bodies may be shaped as prolate or oblate ellipsoids, cylinders, rectangular paralleipipeds, or spheres, or mixtures of such bodies; they may have an apparent specific gravity in the range of 500-3000 kg / m3, preferably 600-2000 kg / m3, in particular 700-1000 kg / m3, especially 800-900 kg / m3; they may be made from polyolefins, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, polyamide, rubber or glass. The weight ratio between the solid bodies and the gel is from 10:1 to 1:10, preferably from 5:1 to 1:5, in particular from 2:1 to 3:1, such as from 1:1 to 1:2. The invention further concerns a tyre balancing kit and a method for balancing automobile wheel assemblies.
Owner:LARS BERTIL CARNEHAMMAR
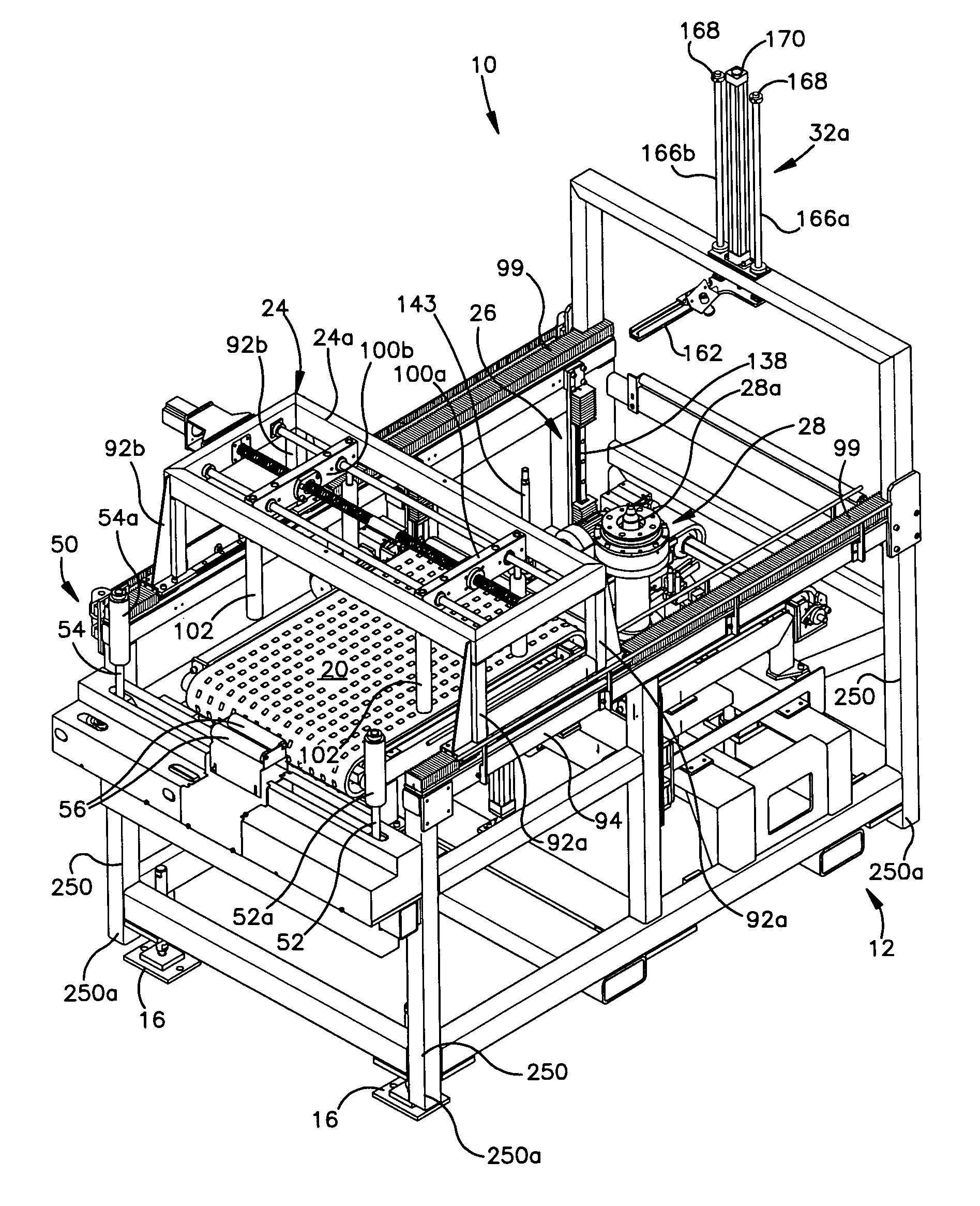
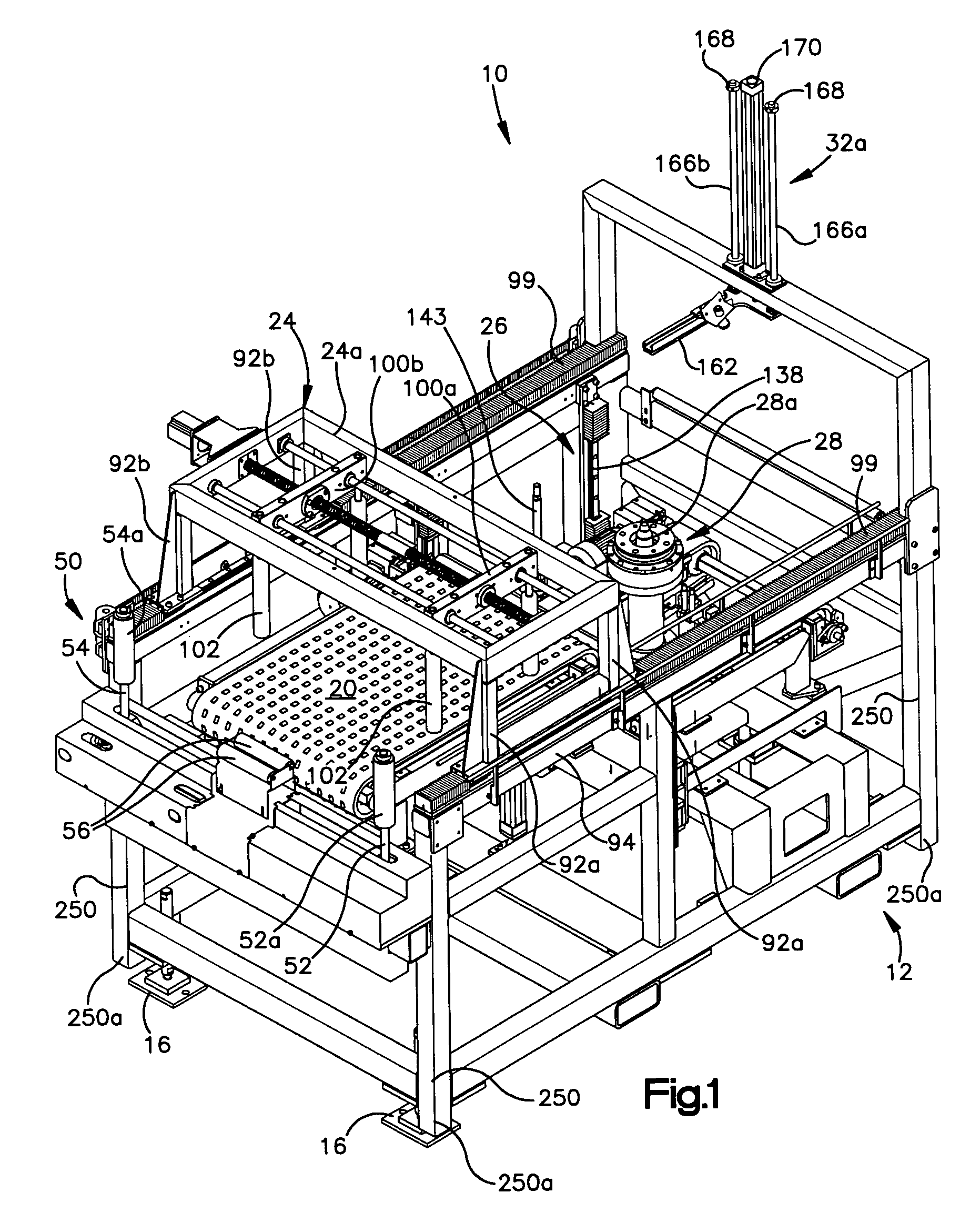
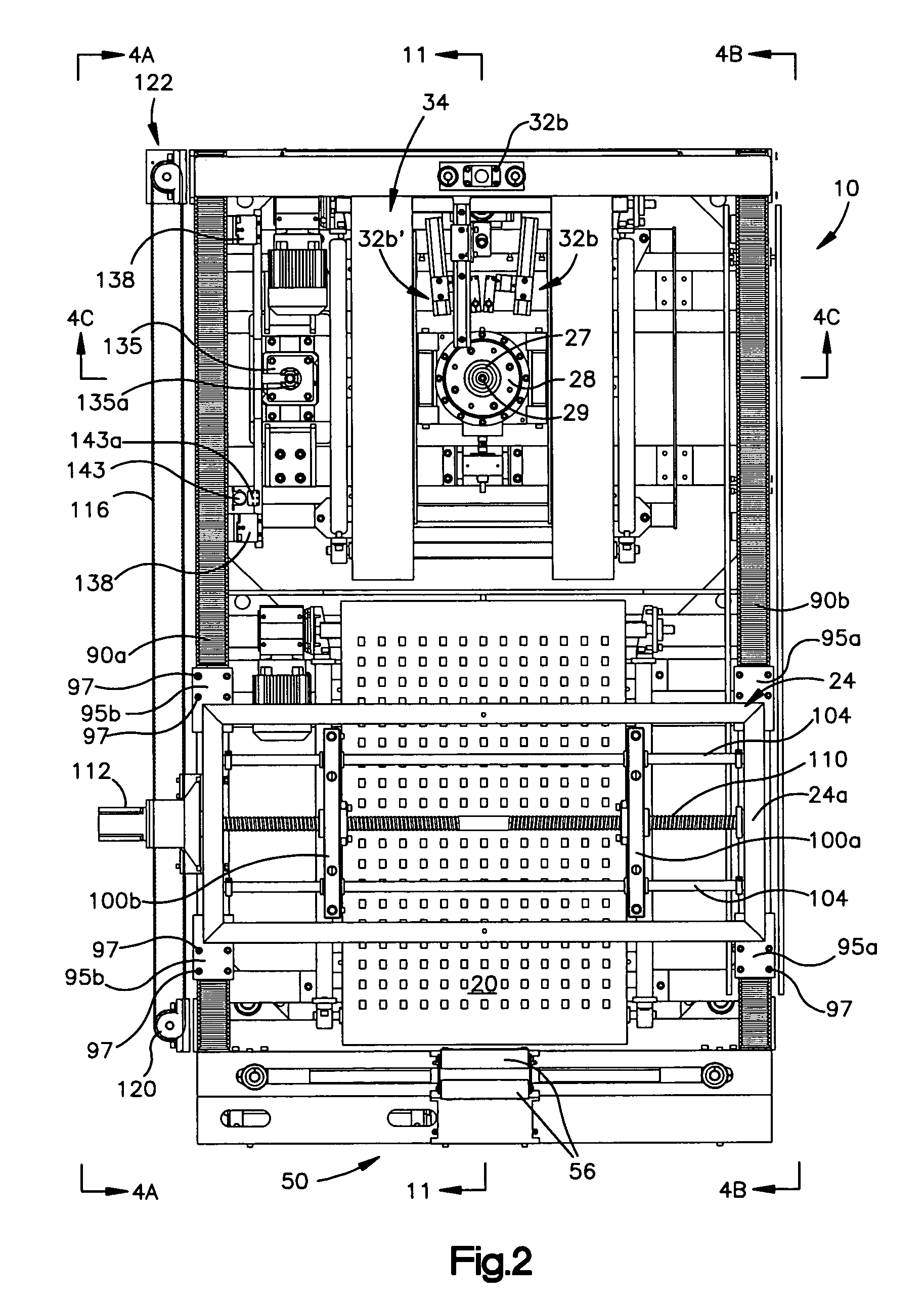
Tire balancing apparatus
InactiveUS20060016258A1Reduce maintenanceImprove reliabilityStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceEngineering
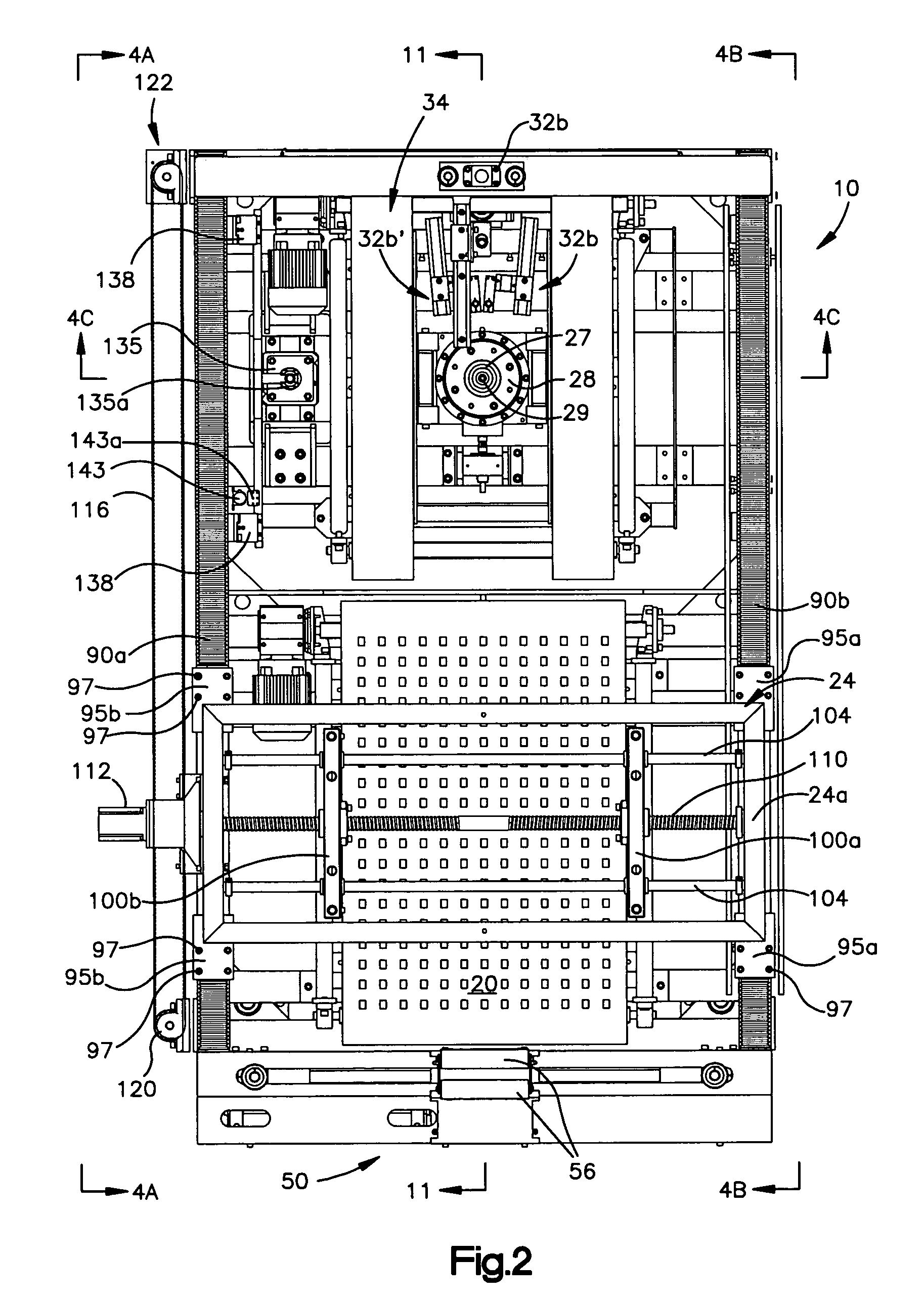
A machine and method for performing balancing measurements on a tire or tire / wheel assembly that includes a structure defining spaced apart tire centering and tire testing positions. A first conveyor moves a tire to a centering position where a shuttle assembly is operative to center the tire and, after it has been centered, engages the tire and effects the transfer of the tire from the centering station to a testing station. The shuttle assembly includes a pair of grippers that move towards and away from each other, in a lateral direction in order to engage the tire. The first conveyor permits movement of the tire in a lateral direction; whereas it substantially resists relative movement between the tire and conveyor in the longitudinal direction, i.e., the direction of movement of the conveyor. The shuttle assembly is mounted for movement in a longitudinal direction and includes a drive mechanism which allows the shuttle assembly to move relative to a tire in a longitudinal direction as the grippers engage the tire so that the shuttle assembly can align itself, in the longitudinal direction with respect to the tire. The frame structure of the machine includes three spaced apart support members providing a three point support arrangement for the machine. The machine also includes at least four legs which extend downwardly, but are spaced above a plane defined by the support members and inhibit tipping of the machine beyond predetermined limits. The testing station which includes a spindle assembly for rotating the tire also includes an elevator mechanism for lowering the tire on to the spindle and for raising the tire off the spindle. A lower marking mechanism forms part of the elevator and is operative to mark a predetermined location on the tire at the conclusion of a tire testing procedure. The spindle assembly includes a drive motor comprised of a drive motor housing and an armature. The armature is maintained in its operative position by a bearing arrangement associated with a shaft assembly forming part of the spindle assembly which eliminates the need for armature supporting bearings in the drive motor housing.
Owner:MICRO POISE MEASUREMENT SYST
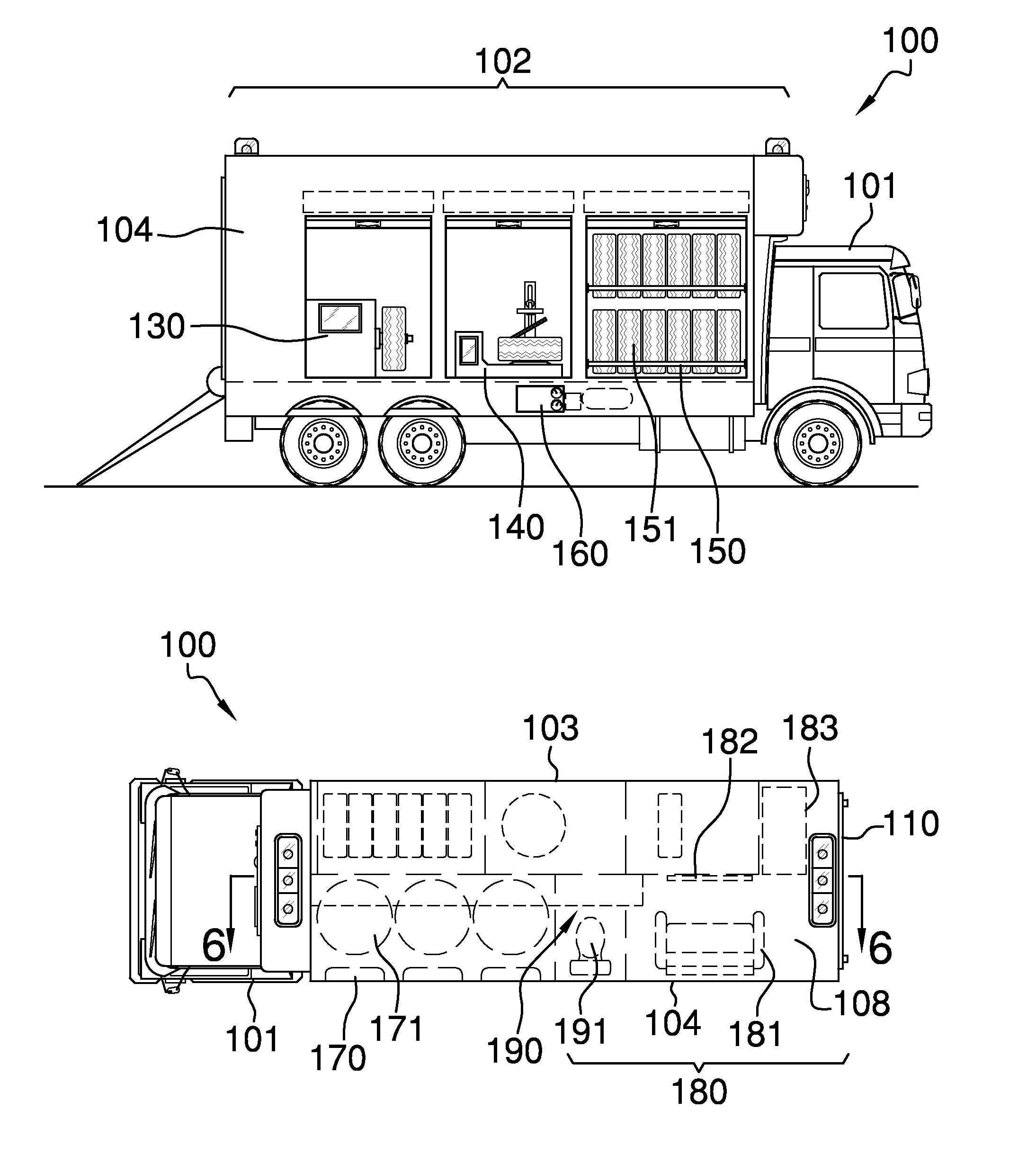
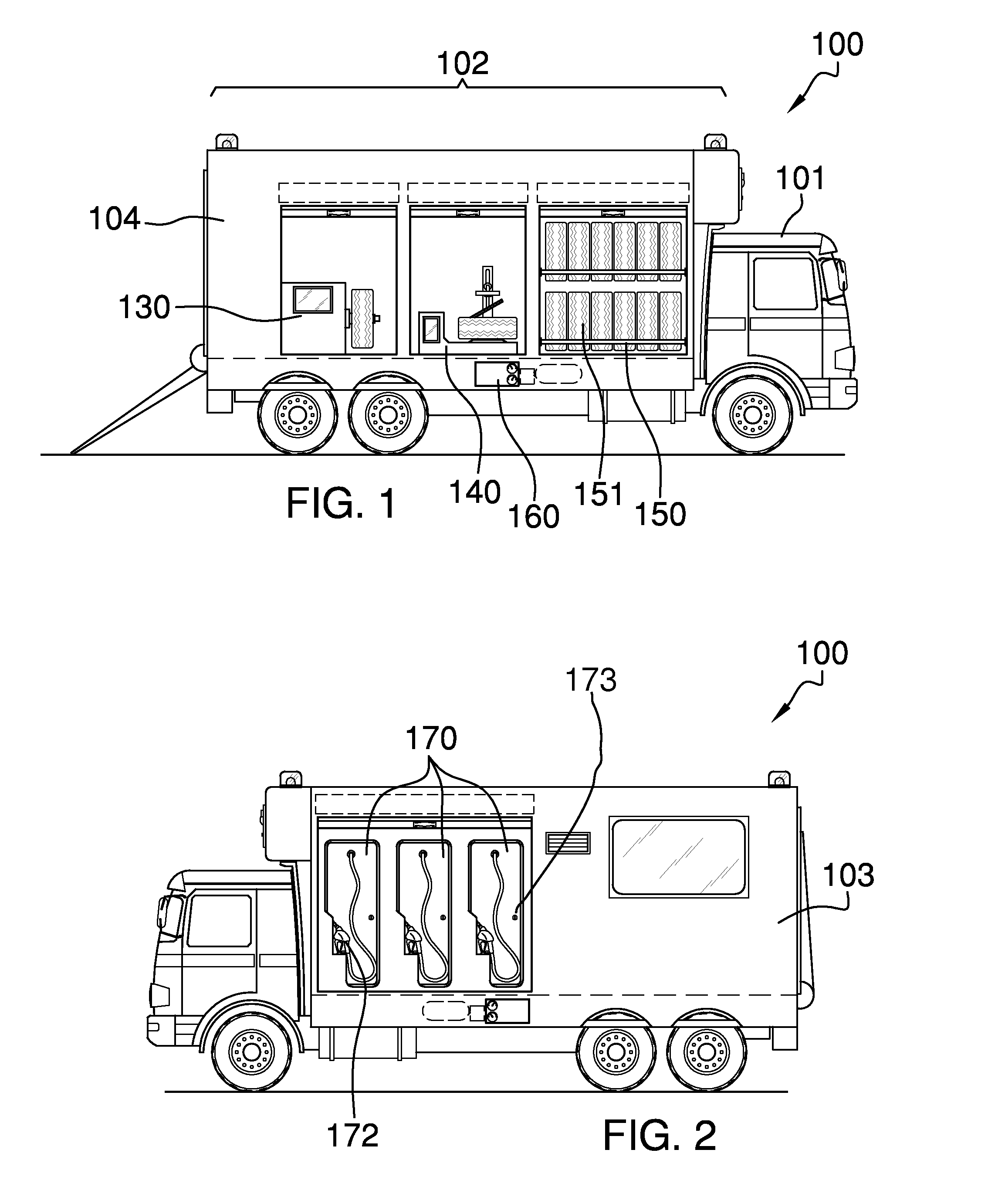
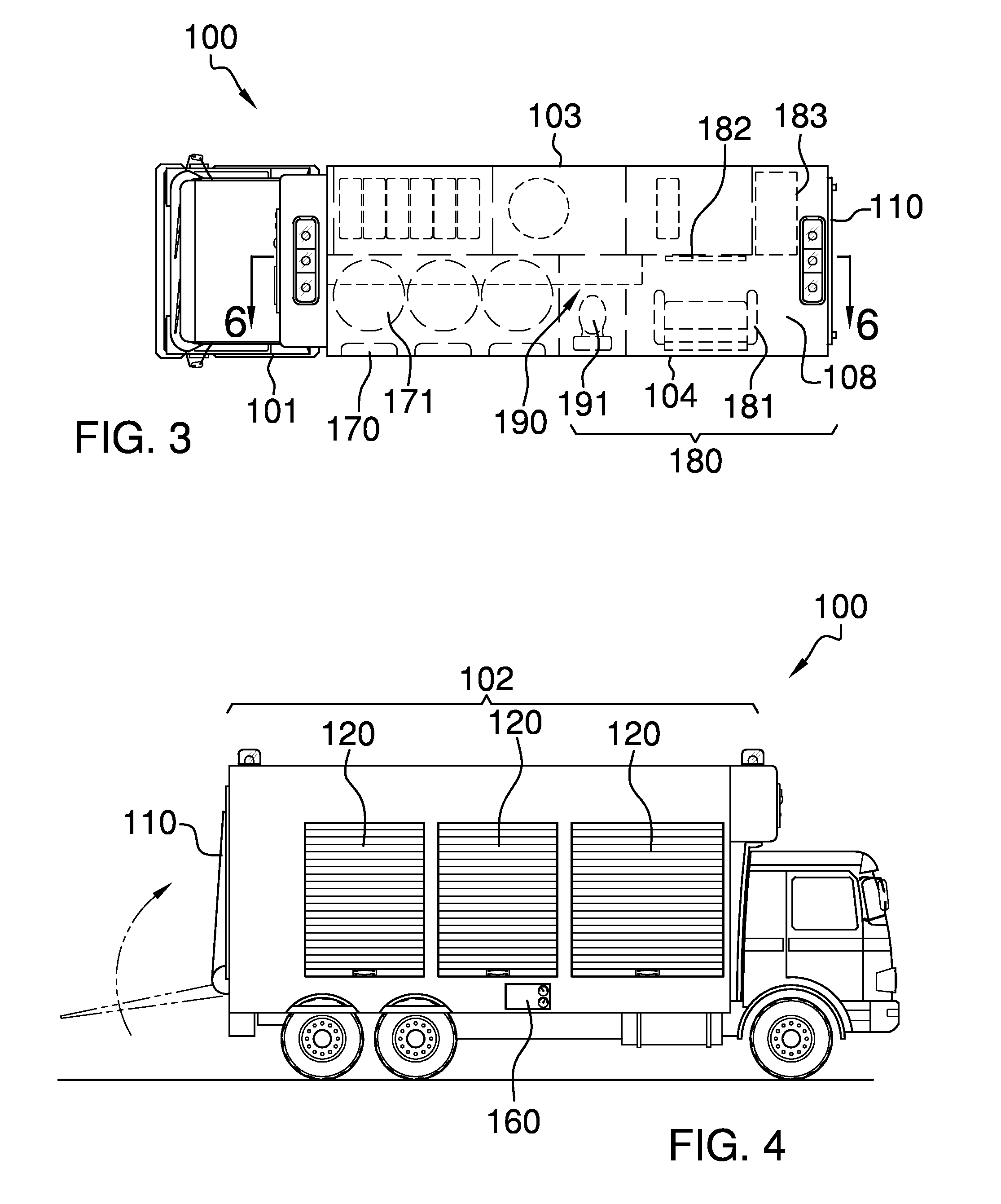
Mobile repair and response unit
The mobile repair and response unit is a truck with an attached trailer that includes a plurality of uniquely defined compartments and areas that are each provided to accomplish a particular task. The attached trailer contains a cabin within which a customer may stay while the customer's vehicle is being repaired. The attached trailer includes a tire balancing station adjacent to a tire changing station. An opposing side of the attached trailer includes a plurality of pump stations that dispense different types of fuels or lubricating oils that are customarily used to operate different types of vehicles. An air station is included on the attached trailer in order to provide pressurized air for use with pneumatically operated tools or to inflate tires of the vehicle being repaired. The rear of the attached trailer includes a ramp that folds down to enable entrance into the attached trailer.
Owner:MILLER TIMOTHY +1
Tire balancing apparatus
InactiveUS7448267B2Improve machine stabilityReduce maintenanceStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceEngineering
A machine and method for performing balancing measurements on a tire or tire / wheel assembly that includes a structure defining spaced apart tire centering and tire testing positions. A first conveyor moves a tire to a centering position where a shuttle assembly is operative to center the tire and, after it has been centered, engages the tire and effects the transfer of the tire from the centering station to a testing station. The shuttle assembly includes a pair of grippers that move towards and away from each other, in a lateral direction in order to engage the tire. The first conveyor permits movement of the tire in a lateral direction; whereas it substantially resists relative movement between the tire and conveyor in the longitudinal direction, i.e., the direction of movement of the conveyor. The shuttle assembly is mounted for movement in a longitudinal direction and includes a drive mechanism which allows the shuttle assembly to move relative to a tire in a longitudinal direction as the grippers engage the tire so that the shuttle assembly can align itself, in the longitudinal direction with respect to the tire. The frame structure of the machine includes three spaced apart support members providing a three point support arrangement for the machine. The machine also includes at least four legs which extend downwardly, but are spaced above a plane defined by the support members and inhibit tipping of the machine beyond predetermined limits. The testing station which includes a spindle assembly for rotating the tire also includes an elevator mechanism for lowering the tire on to the spindle and for raising the tire off the spindle. A lower marking mechanism forms part of the elevator and is operative to mark a predetermined location on the tire at the conclusion of a tire testing procedure. The spindle assembly includes a drive motor comprised of a drive motor housing and an armature. The armature is maintained in its operative position by a bearing arrangement associated with a shaft assembly forming part of the spindle assembly which eliminates the need for armature supporting bearings in the drive motor housing.
Owner:MICRO POISE MEASUREMENT SYST
Device for automatic tire inflation and tire pressure display
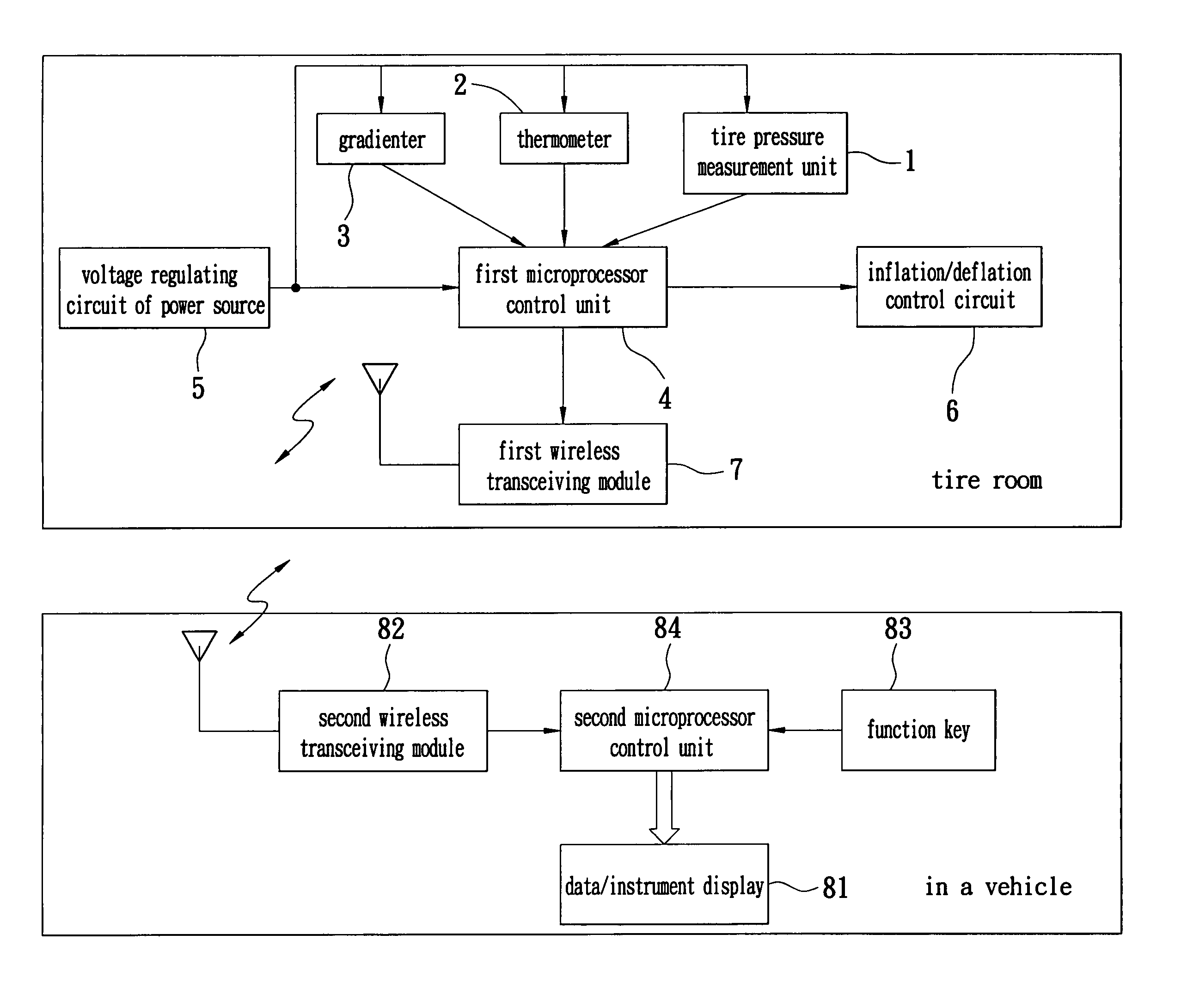
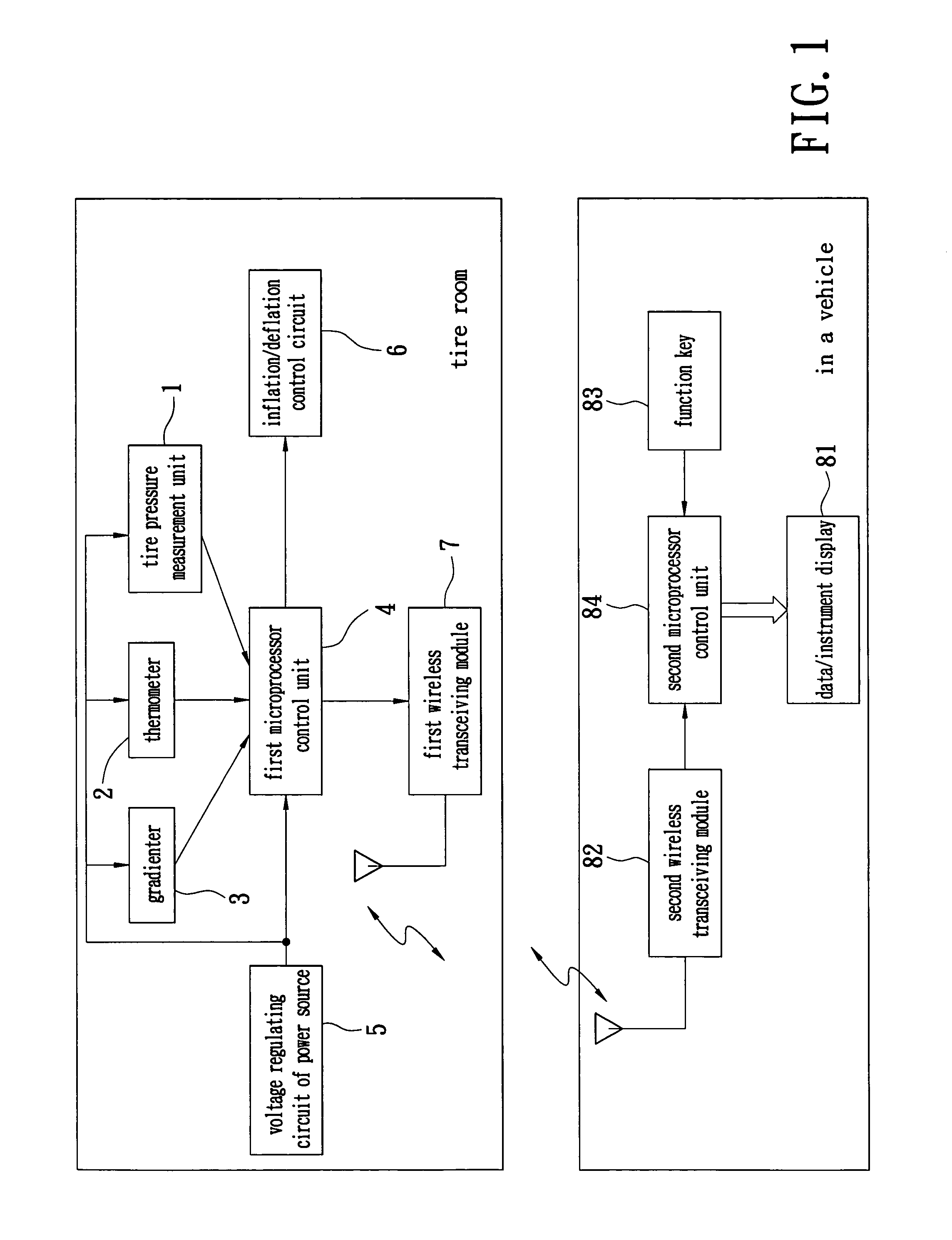
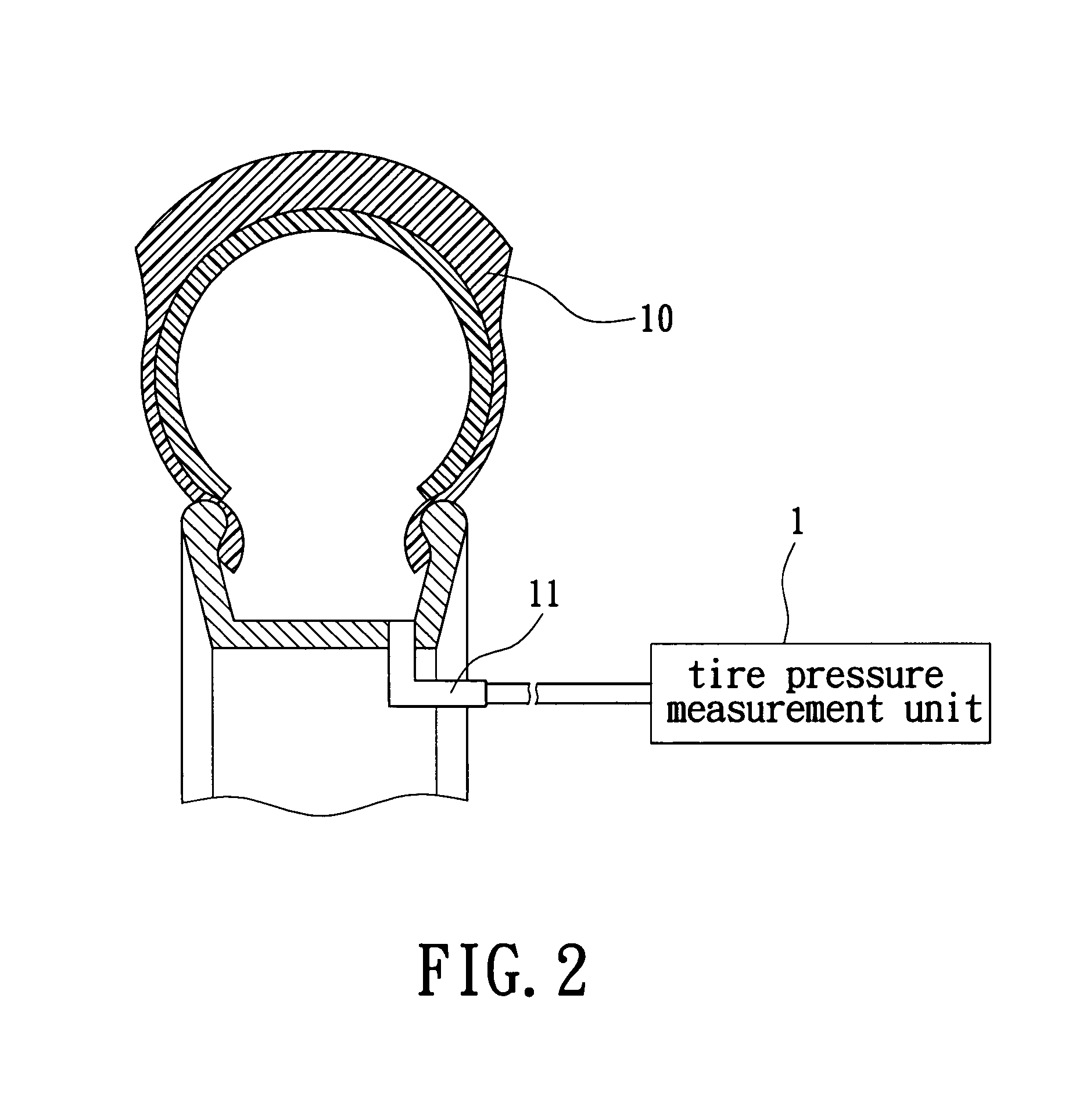
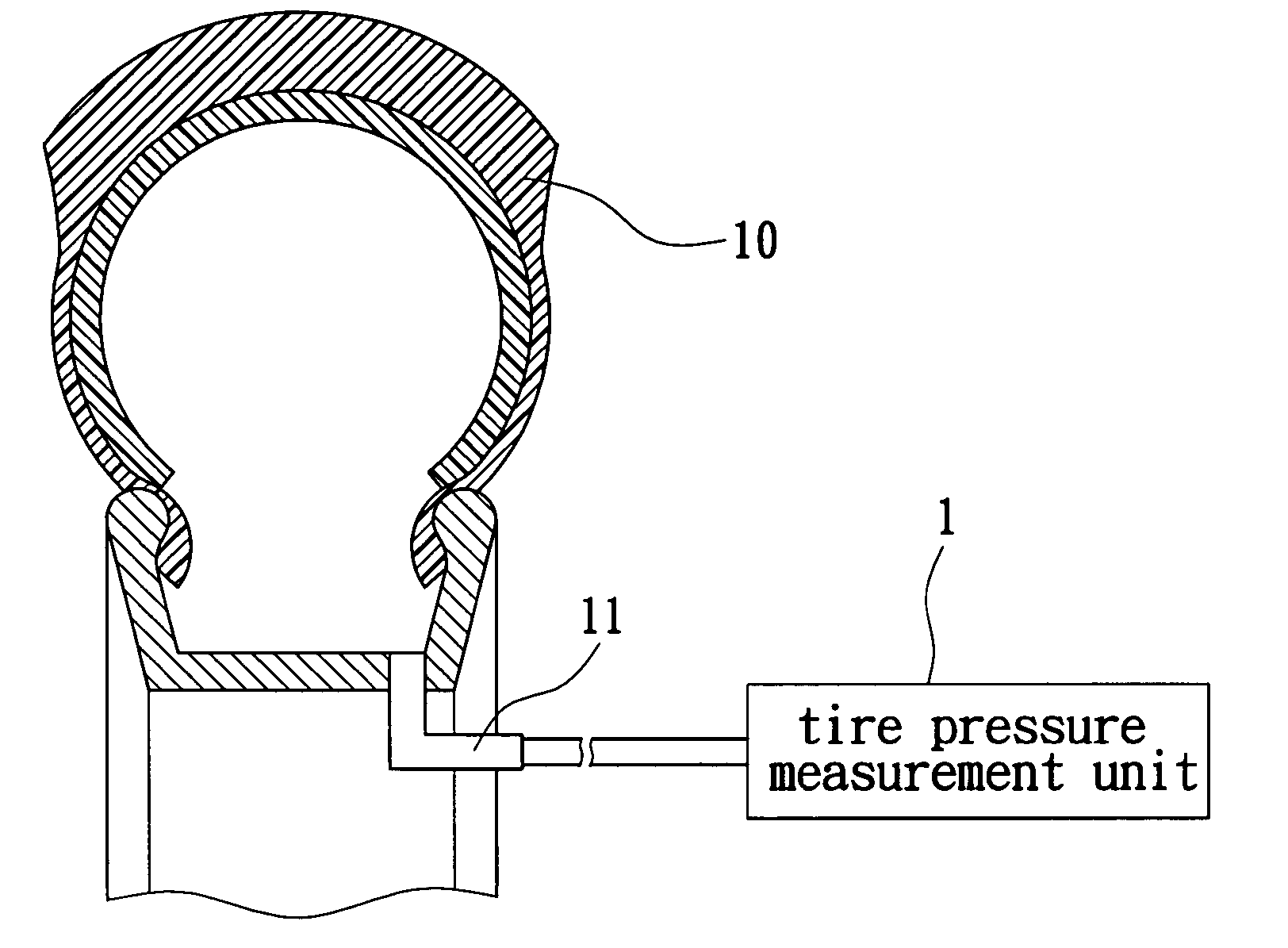
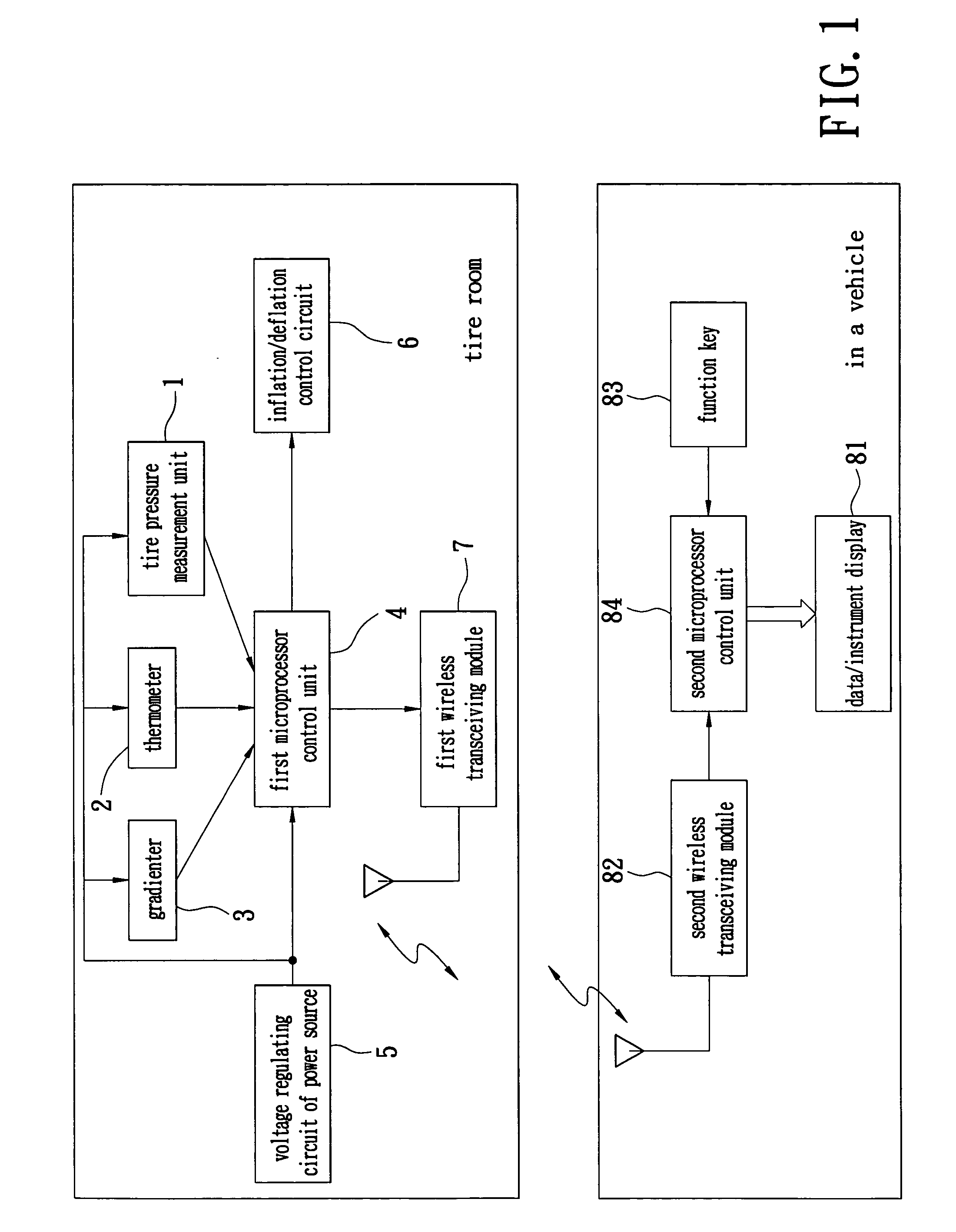
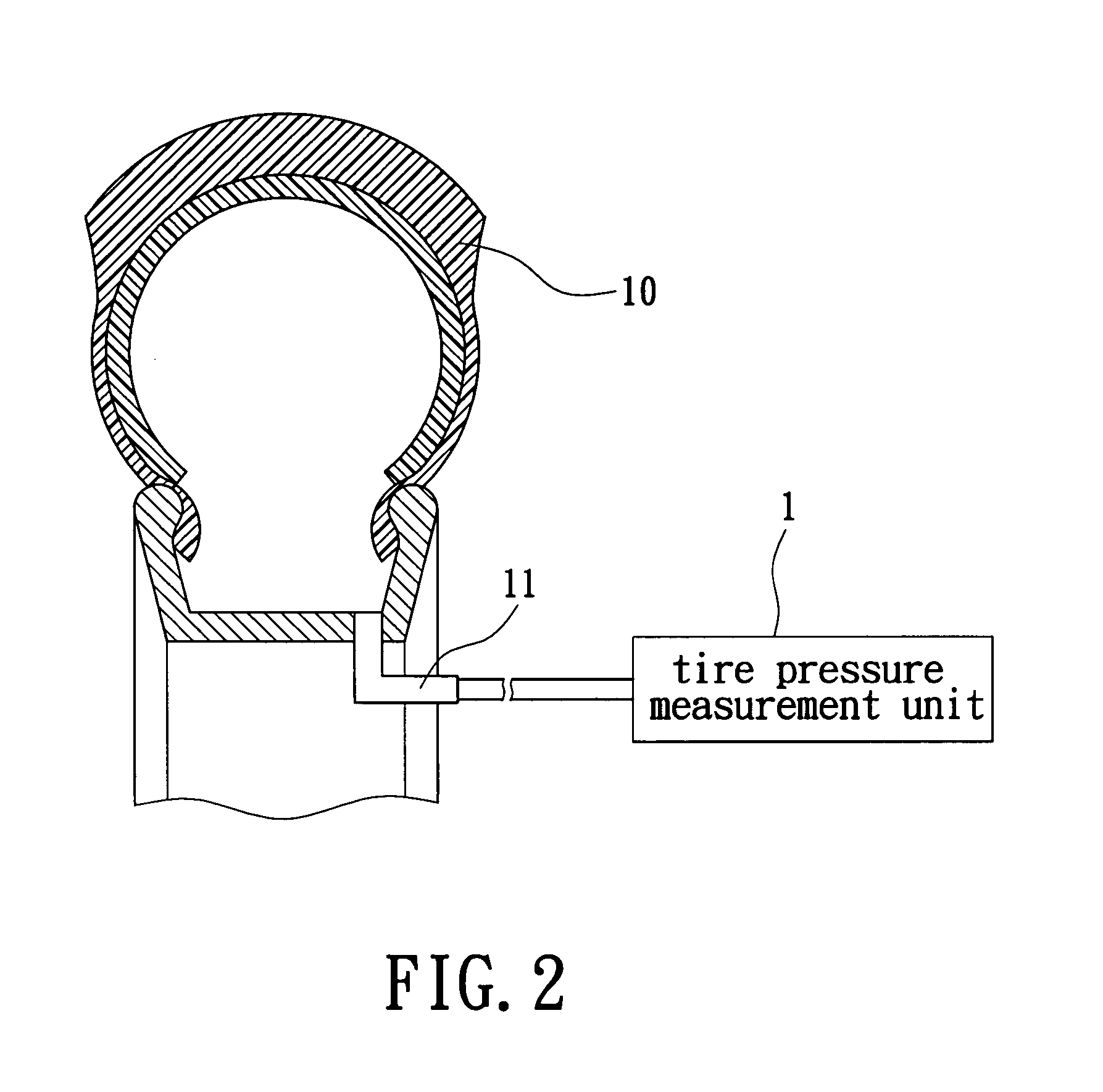
A device for automatic tire inflation and tire pressure display has a tire pressure measurement unit, a tire temperature sensor (a thermometer) and a gradienter for measuring the tire balance. The tire pressure measurement unit has a tire pressure measurement unit, a voltage regulating circuit of power source, a microprocessor control unit, a wireless transceiving module and an inflation / deflation control component. The tire pressure measurement unit measures the tire pressure value of a tested tire. The tire pressure value is then wirelessly displayed on a display unit in a vehicle so that the user can know the present status of a tire. The user can also maneuver a function key to select an operation according to the displayed data and send this message to the tire room to execute inflation or deflation of the tire.
Owner:PARTNER TECH
Tire manufacturing method cover rubber stamping device used for the manufacturing method, tire rubber sheet member stamping method , and rubber sheet member stamping device
InactiveUS20060048878A1Efficient preparationHighly accurate shapeLamination ancillary operationsTyresTire balanceEngineering
A method of manufacturing a tire having first color characters or lines on at least one side wall part, includes the steps of stamping a second color side wall rubber and a first color side wall rubber on the side face of a carcass member formed in a toroidal shape by winding, a plurality of turns, a continuous second color rubber ribbon and a continuous first color rubber ribbon thereon, stamping a second color cover rubber on the outsides of the side wall rubbers by winding a rubber sheet whereon one turn in an annular shape, and molding a green tire, whereby the use of a large extrude can be eliminated, different types of tires can be efficiently manufactured since a size switching can be easily performed, the accuracies of the shape and the dimensions of the members thereof can be increased, the uniformity and the tire balance thereof can be increased, and the sharp profile of the first color characters or lines can be assumed, thus eliminating problems associated with the appearance.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
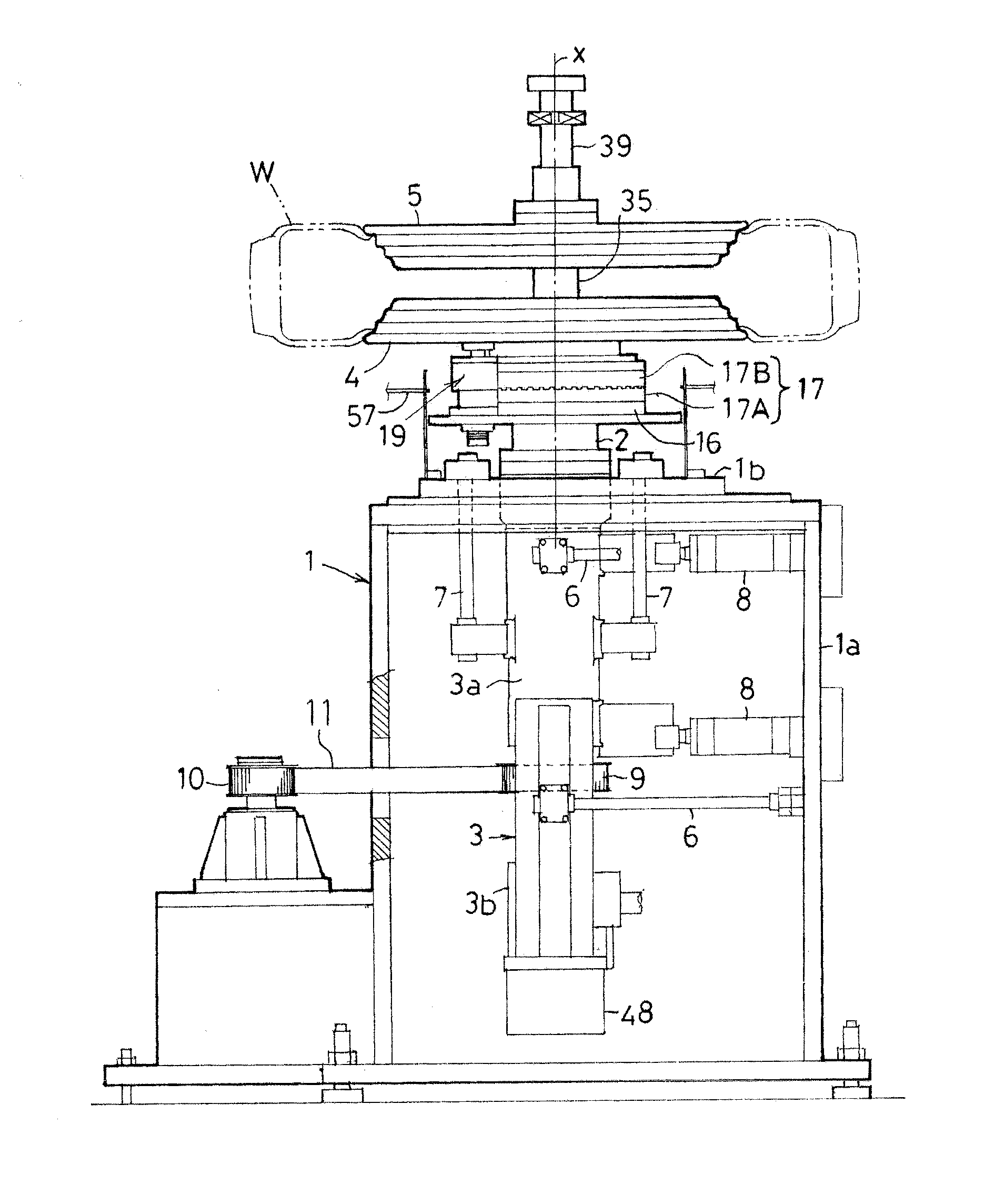
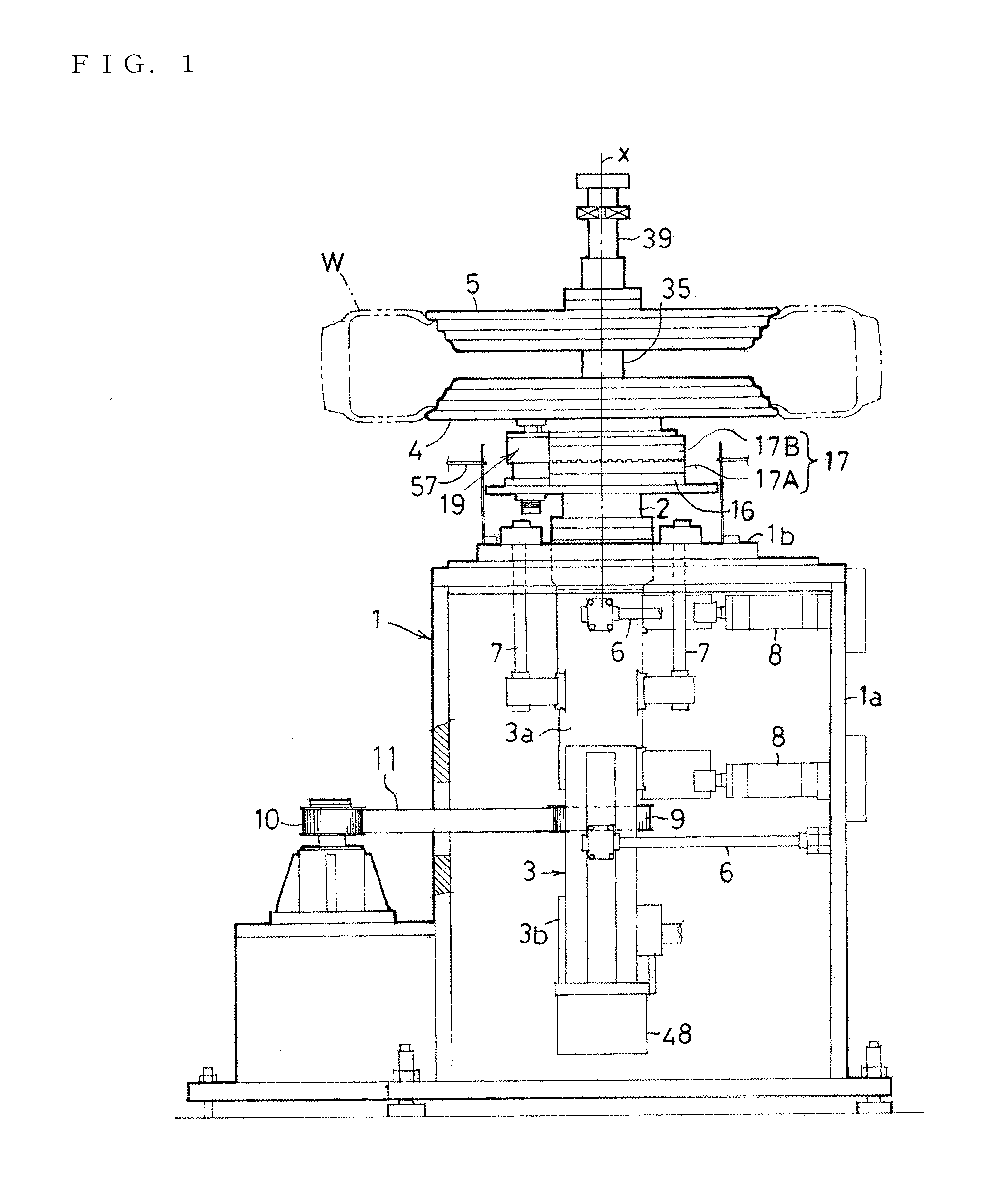
Combined machine for assembly, disassembly and balance tests of tires as well as method for manufacturing and using same
InactiveCN101612868AReduce distanceConvenient distanceStatic/dynamic balance measurementTyre repairingTire balanceBalance test
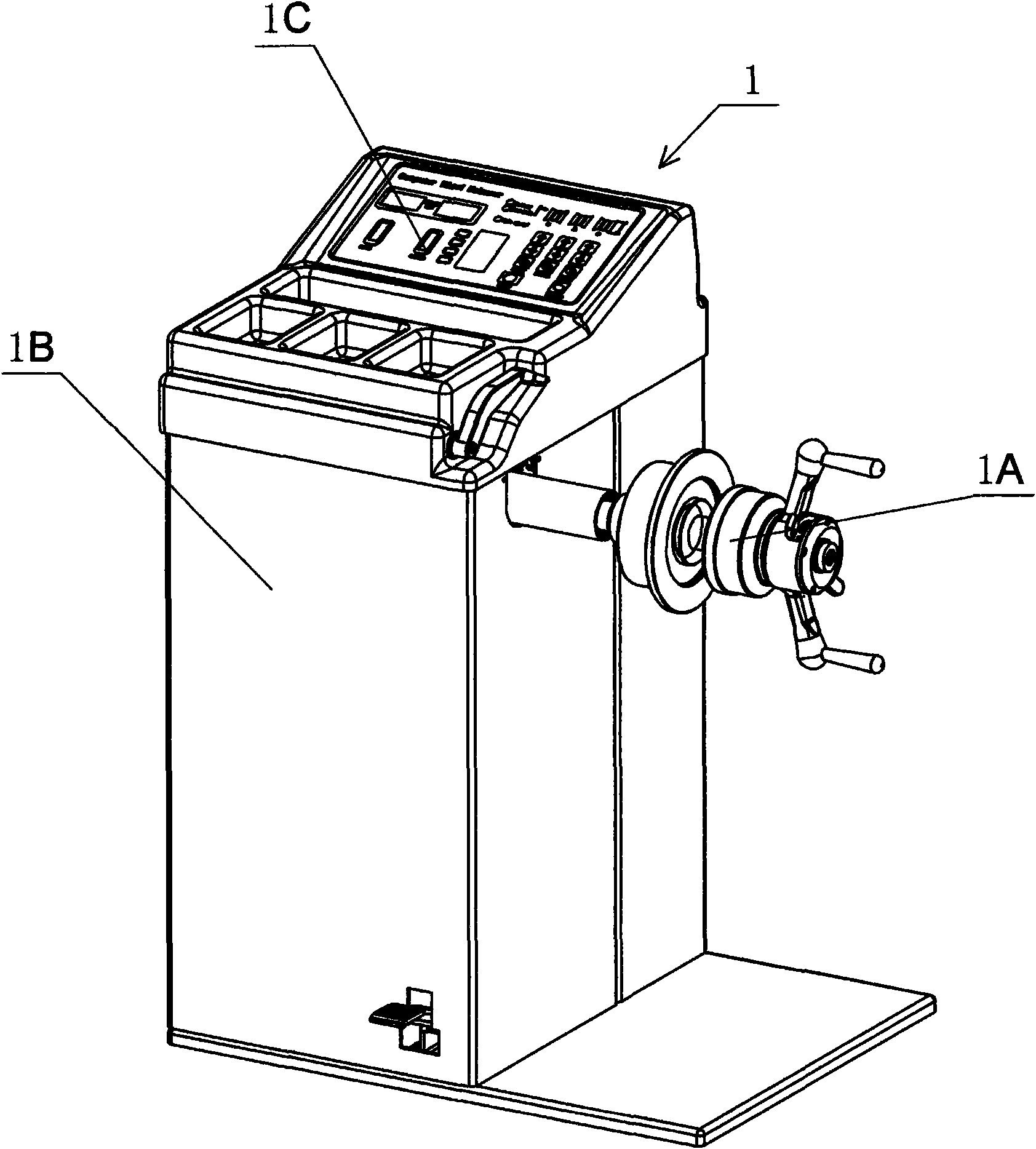
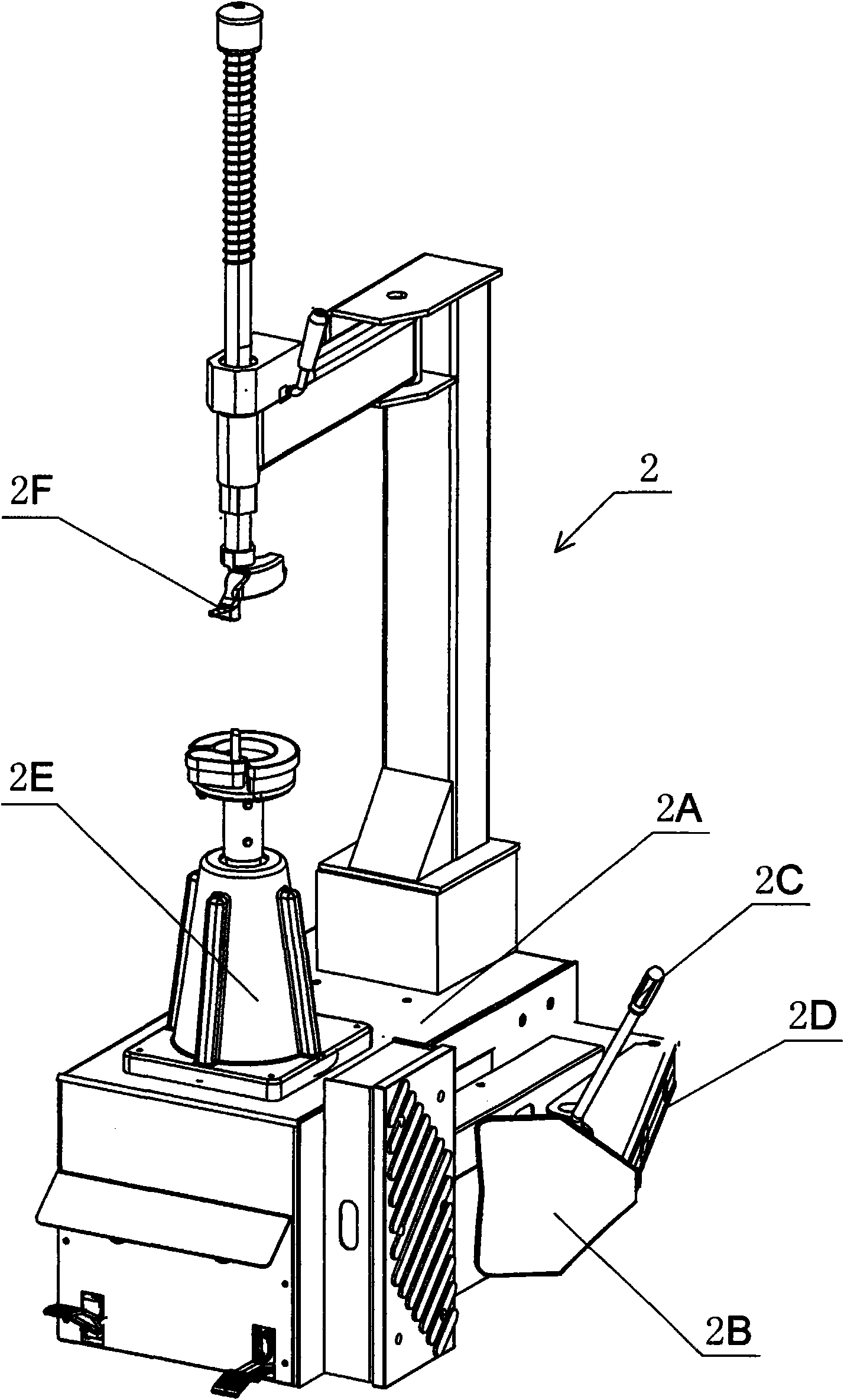
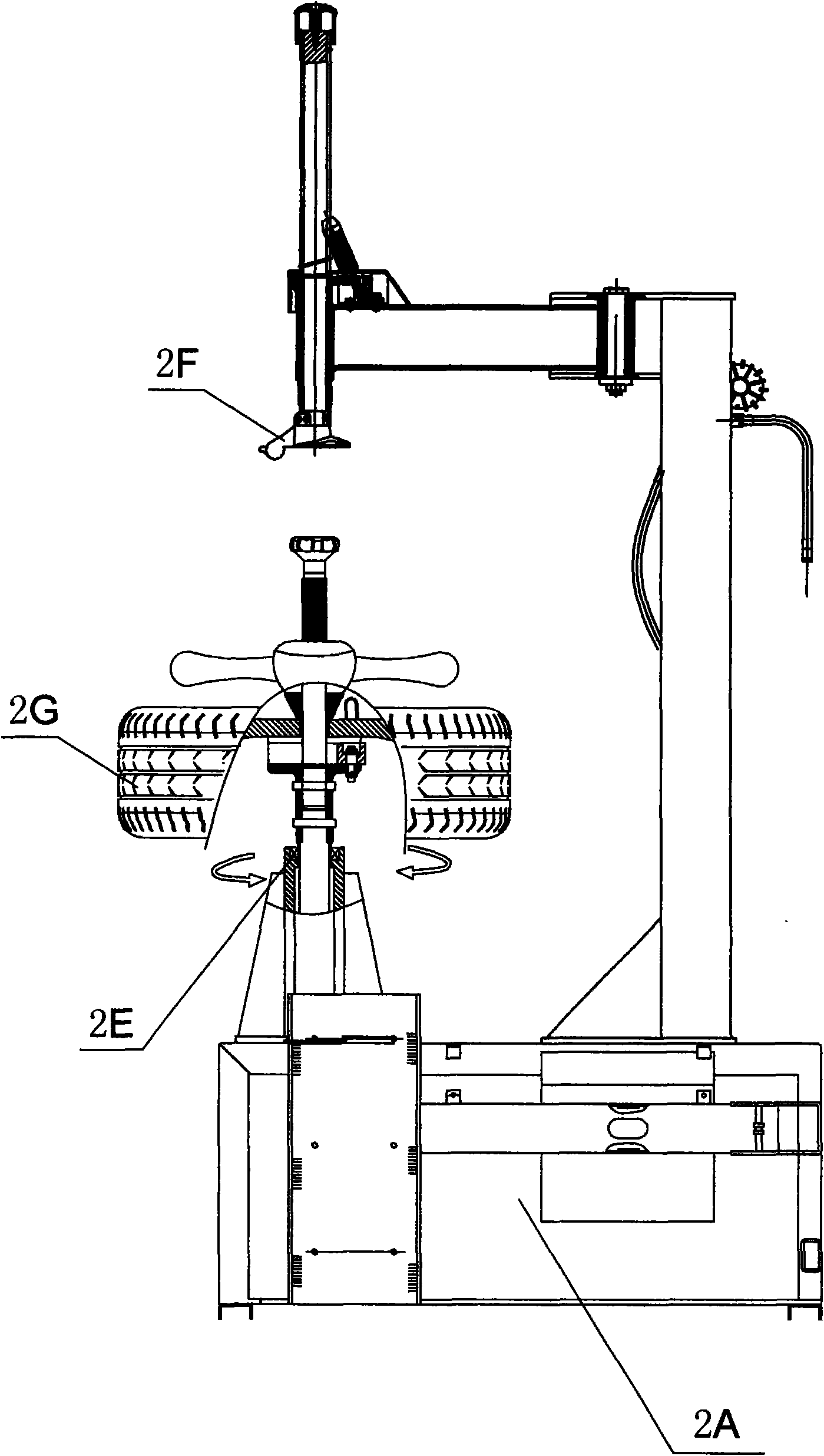
The invention provides a combined machine for the assembly, disassembly and balance test of tires as well as a method for manufacturing and using the combined machine, relating to the technical field of assembly, disassembly and test of automobile tires and applying to the assembly, disassembly and test of automobile tires. The tire balance test machine comprises a cabinet (1B), a data input device (1C) located in the upper cover of the cabinet, and a tire mounting shaft assembly (1A), and the machine is characterized in that the cabinet (1B) is provided with a gap (1D) located in a three-dimensional spatial position where the tire balance test machine is placed in adjacent three-dimensional spatial position of the tire assembly / disassembly machine, and the gap (1D) is internally provided with a shovel-arm assembly (2D) of a tire-pressing shovel (2B) at one side of the base (2A) of the tire assembly / disassembly machine. The invention has the advantages that the jointly-occupied area of the tire assembly / disassembly machine and the tire balance test machine is reduced, the distance for carrying tires is shorter, and the structure is compact and reasonable.
Owner:科星(中山)汽车设备有限公司
Tyre balancing compositions
InactiveUS20100252174A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove abilitiesStatic/dynamic balance measurementLaminationTire balancePolyolefin
Owner:CARNEHAMMAR LARS BERTIL PROF DR
Mobile tyre changing system
InactiveCN101148158ASave fuelReduce wearWheel mounting apparatusItem transportation vehiclesTire balanceBalancing machine
The movable tyre replacing system includes available truck head and chassis, one tyre changer, one air compressor, one tyre storage rack, one power supply unit, one tyre balancing machine, and one tyre nitrogen filler. The movable tyre replacing system is for out tyre change, and can facilitate tyre change and collect used tyre for concentrated treatment.
Owner:朱戈宇
Vehicle service system with variable-lens imaging sensors
A optical imaging sensor assembly for a machine-vision vehicle service system comprising a variable lens optical assembly. The variable lens optical assembly is controlled in response to direction from a vehicle service software application to alter an optical characteristic such as a field of view, a lens focal length, or an optical axis alignment to acquire images for use in a vehicle service procedure such as a vehicle wheel alignment procedure, vehicle tire balancing procedure, or tire changing procedure.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
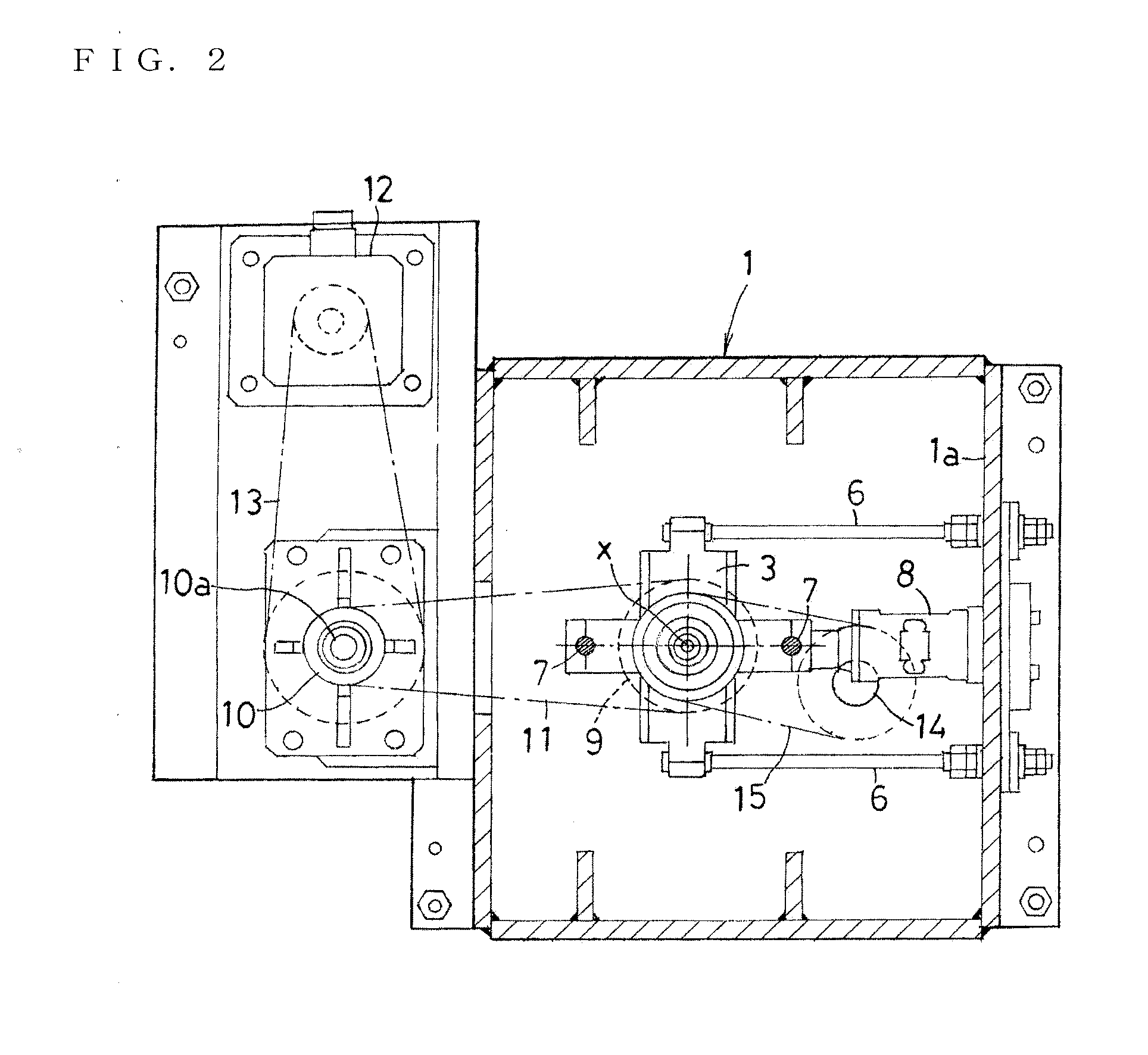
Rim replacing device in tire balance measuring device
ActiveUS20140191480A1Easily and promptly performInconvenience being requiredSleeve/socket jointsStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceCoupling
A lower side coupling of a Hirth coupling is coaxially coupled and fixed to a spindle, an upper side coupling of the Hirth coupling is coaxially coupled and fixed to a lower rim, the upper side coupling of the lower rim is meshed with the lower side coupling of the spindle, and upward separation of the lower rim from the spindle is prevented by chuck mechanisms.
Owner:YAMATO SCALE CO LTD
Production technique of run-flat tire resistant to deflation caused by puncturing
InactiveCN103386863AStrong initial adhesionIncrease stickinessMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesLiquid surface applicatorsTire balanceAdhesive
The invention relates to a production technique of a run-flat tire resistant to deflation caused by puncturing. The run-flat tire comprises a tire body. The production technique comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a liquid adhesive; (2) carrying out atomized spraying by spraying the adhesive on the cleaned inner surface of the tire body uniformly with a sprayer; (3) heating the coating to dryness for shape-fixing; and (4) repeating step (2) and step (3) for a plurality of times until a tire inner coating with a thickness between 0.2 and 10 mm is formed. The technique employs liquid raw material, atomized technology, spray flow control, and drying for shape-fixing. The technique is suitable for producing different models of run-flat tires, which are resistant to deflation caused by puncturing, to satisfy the needs of different users. The technique is characterized by high driving efficiency and safety performance, small tire balancing bias, and a uniform, thin, light inner coating with good heat sink performance and thermal stability, etc.
Owner:杭州绿奇科技有限公司
Detector for detecting degree of balance of automobile tires
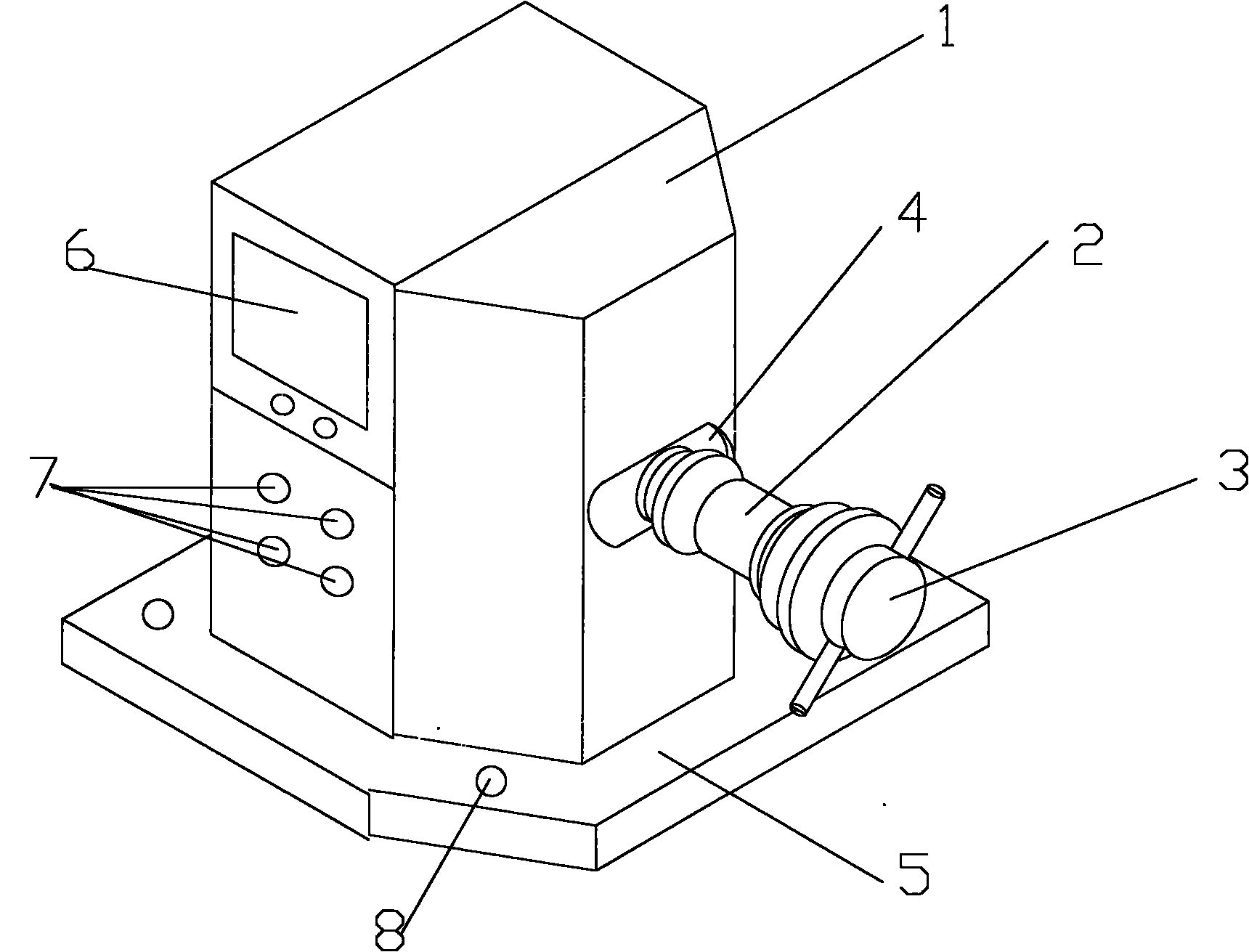
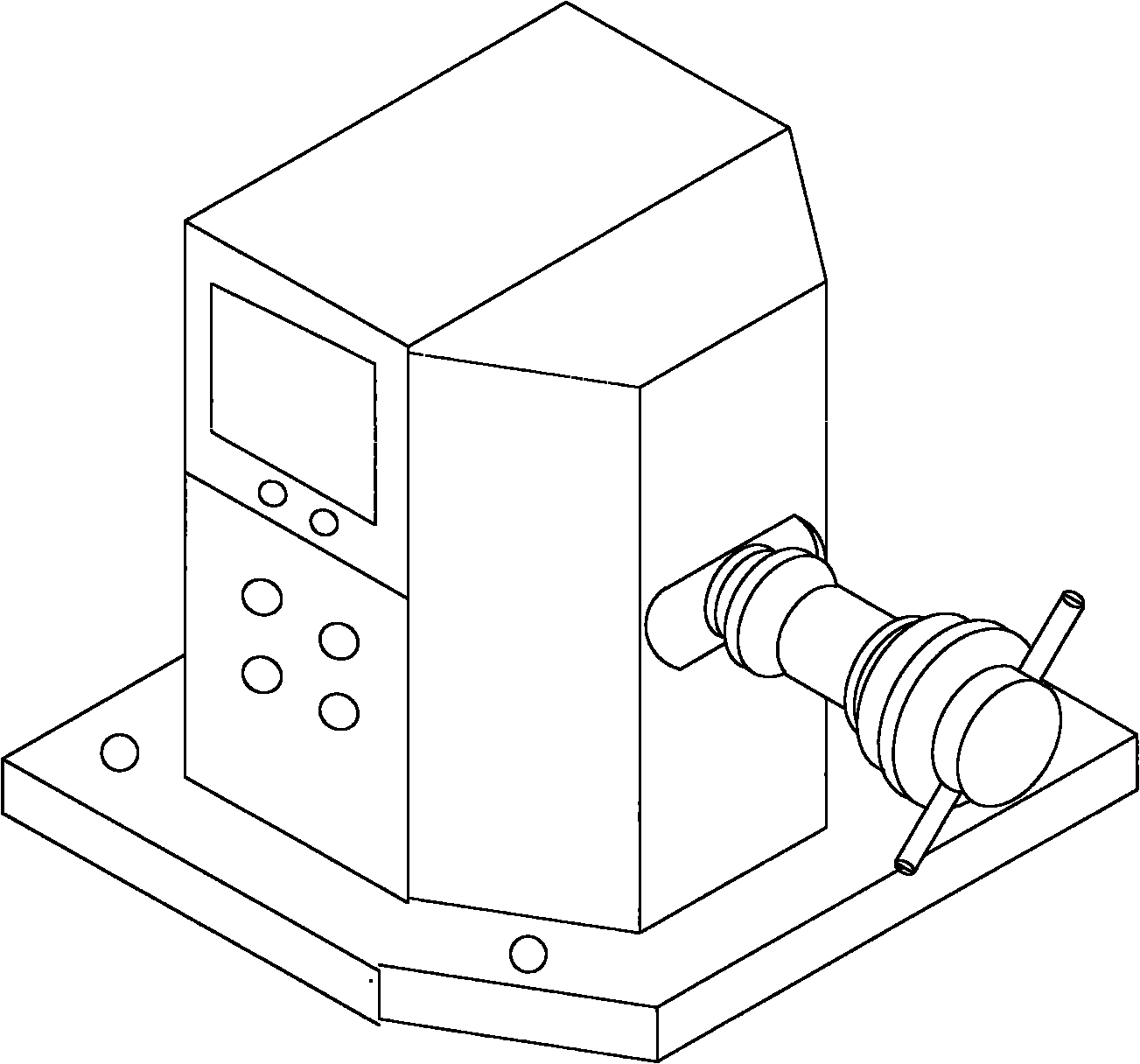
InactiveCN102095553AReasonable designSimple structureStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceLiquid-crystal display
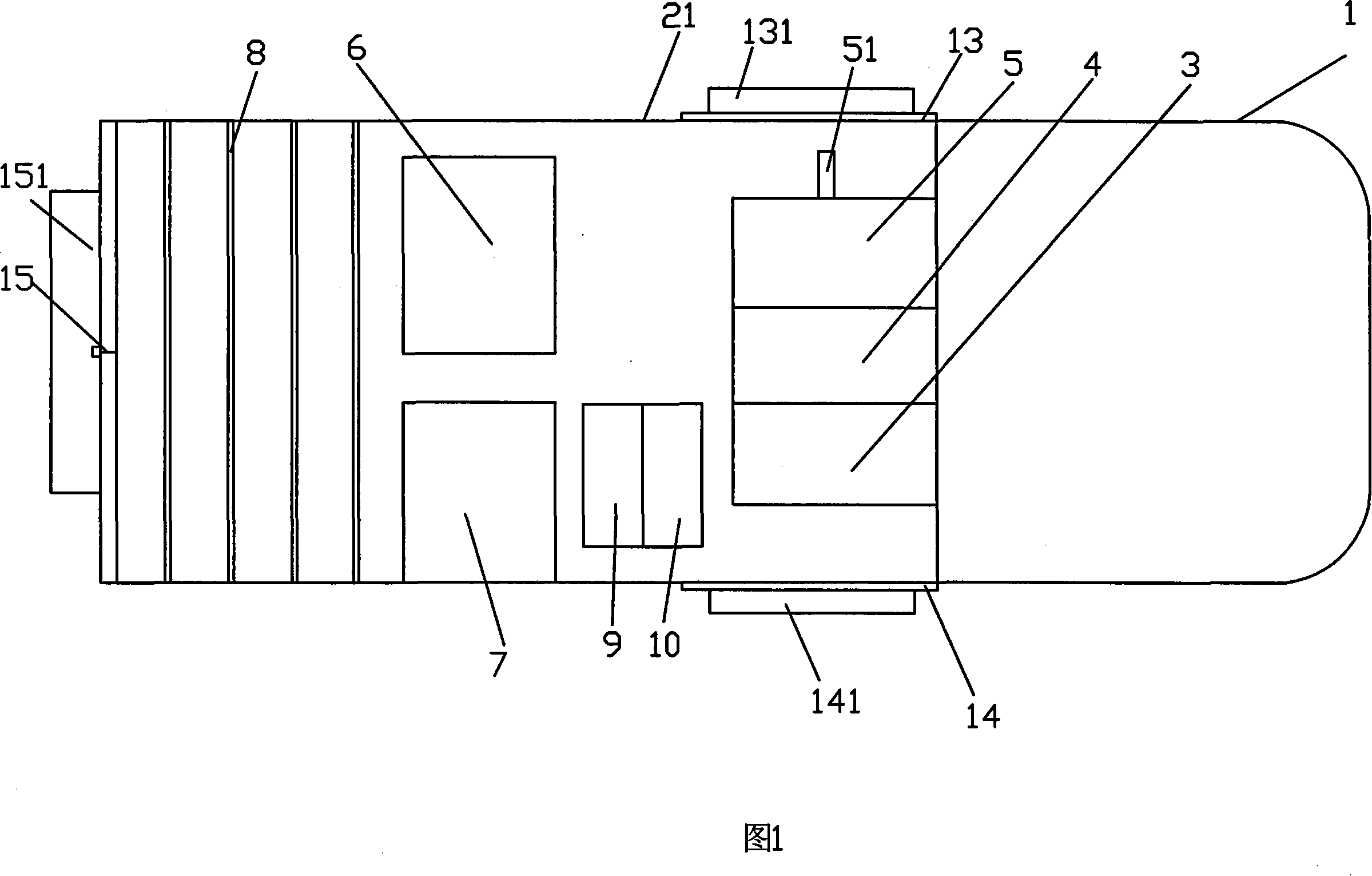
The invention provides a detector for detecting the degree of balance of automobile tires, which comprises a box body 1, a main shaft 2, a shaft end locking device 3 and a pedestal 5, wherein a pressure sensor inside the box body 1 receives, via the main shaft 2, axial and radial pressure changes fed back when the automobile tires rotate, a liquid crystal display screen 6 and a control button 7 are arranged on the side face of the box body, the main shaft 2 stretches out of an annular notch 4, the end part of the main shaft 2 is tightly fixed by the shaft end locking device 3, and the pedestal 5, which is integrally designed with the box body 1, is tightly fixed on the ground by screws. The invention discloses the detector for detecting the degree of balance of the automobile tires, which is reasonable in design, simple in structure, convenient in installation and convenient and fast in usage, can accurately measure the degree of balance of the automobile tires when the automobile advances and turns, and prevent elements and devices of the automobile from being damaged due to too much vibration in order to avoid unnecessary loss.
Owner:常熟市普利擎汽车维修保养有限公司
Tire balancing devices and methods
InactiveUS20070000322A1Facilitate concentric engagementEasy to useStatic/dynamic balance measurementVehicle tyre testingTire balanceHand held
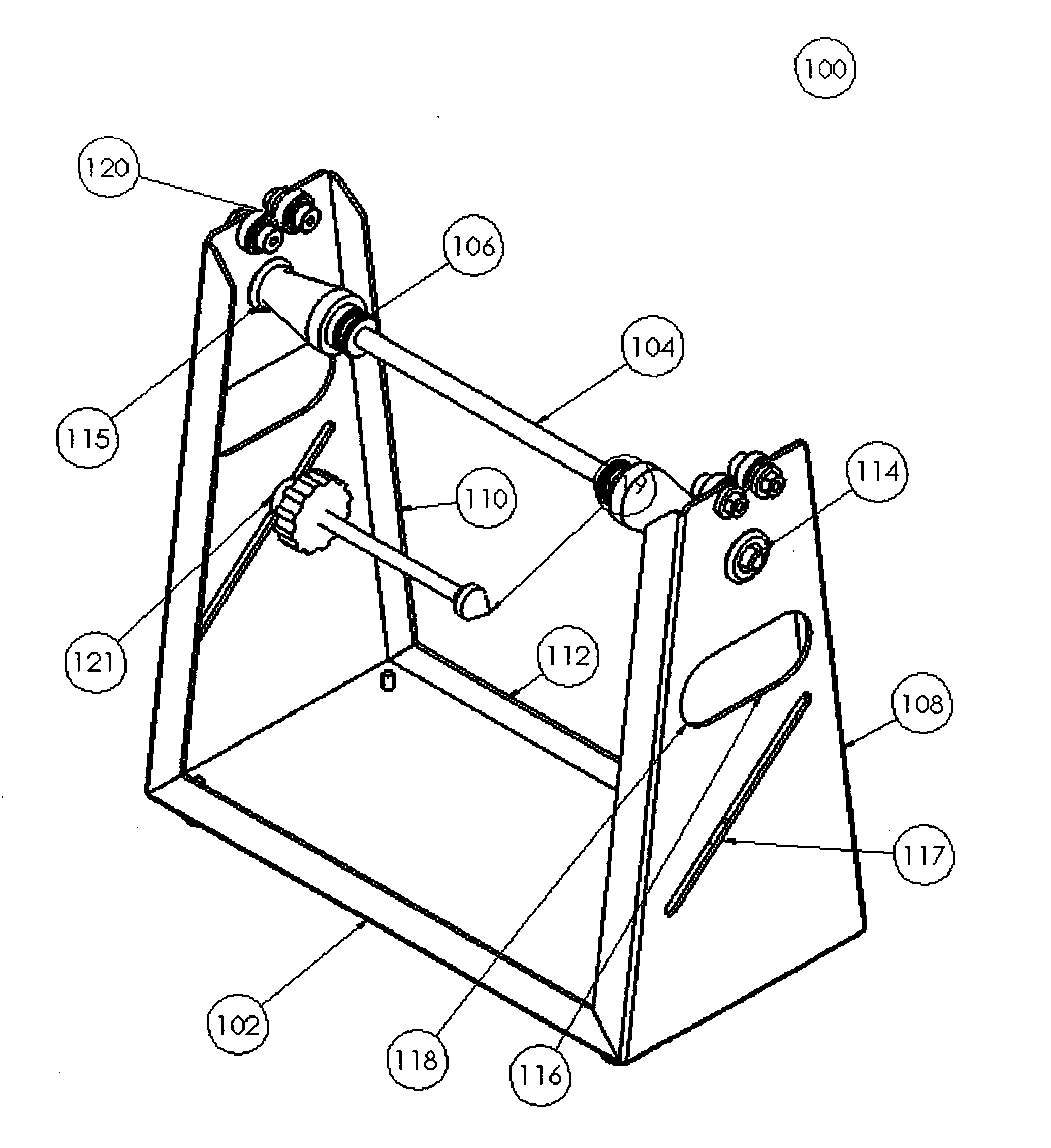
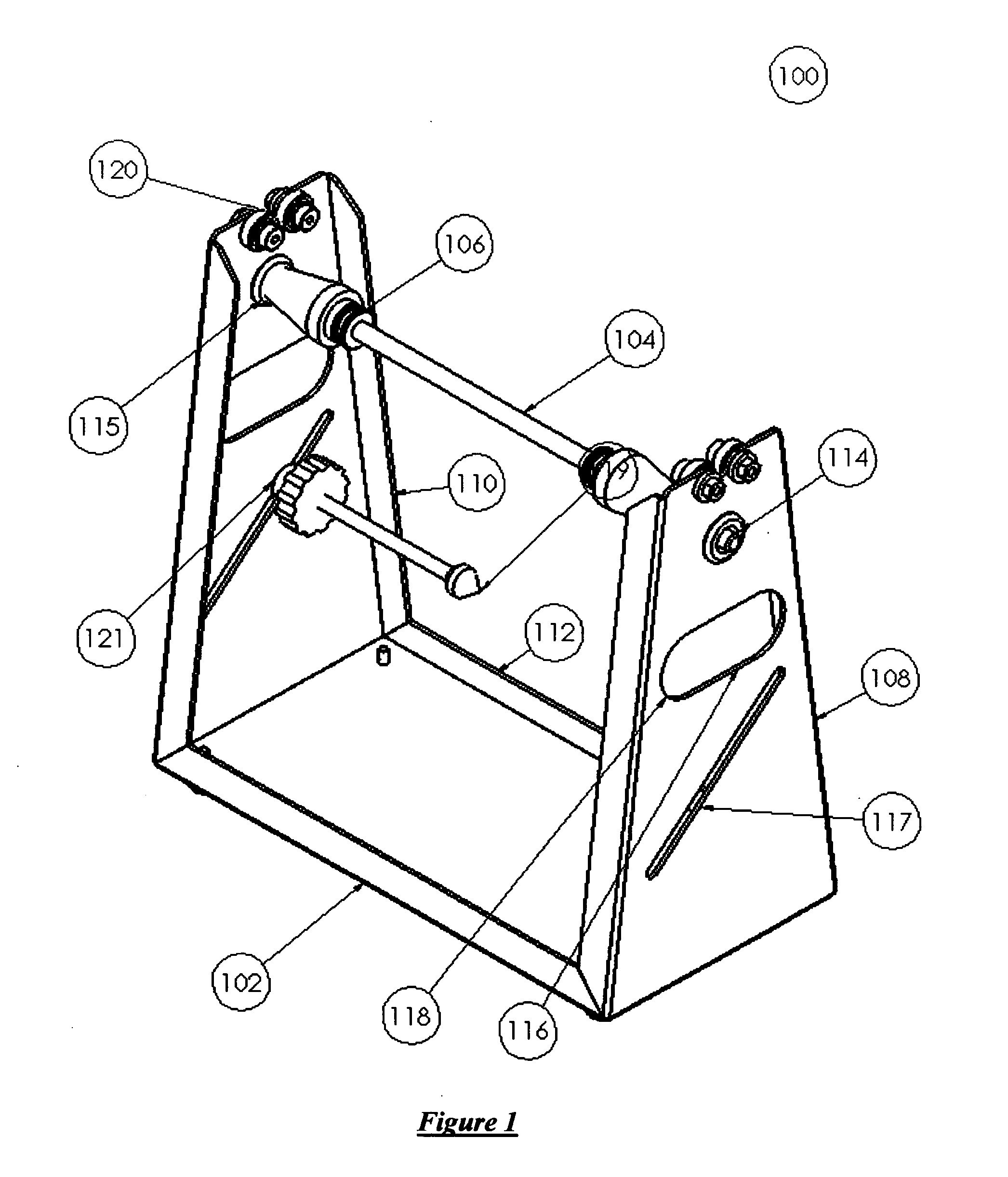
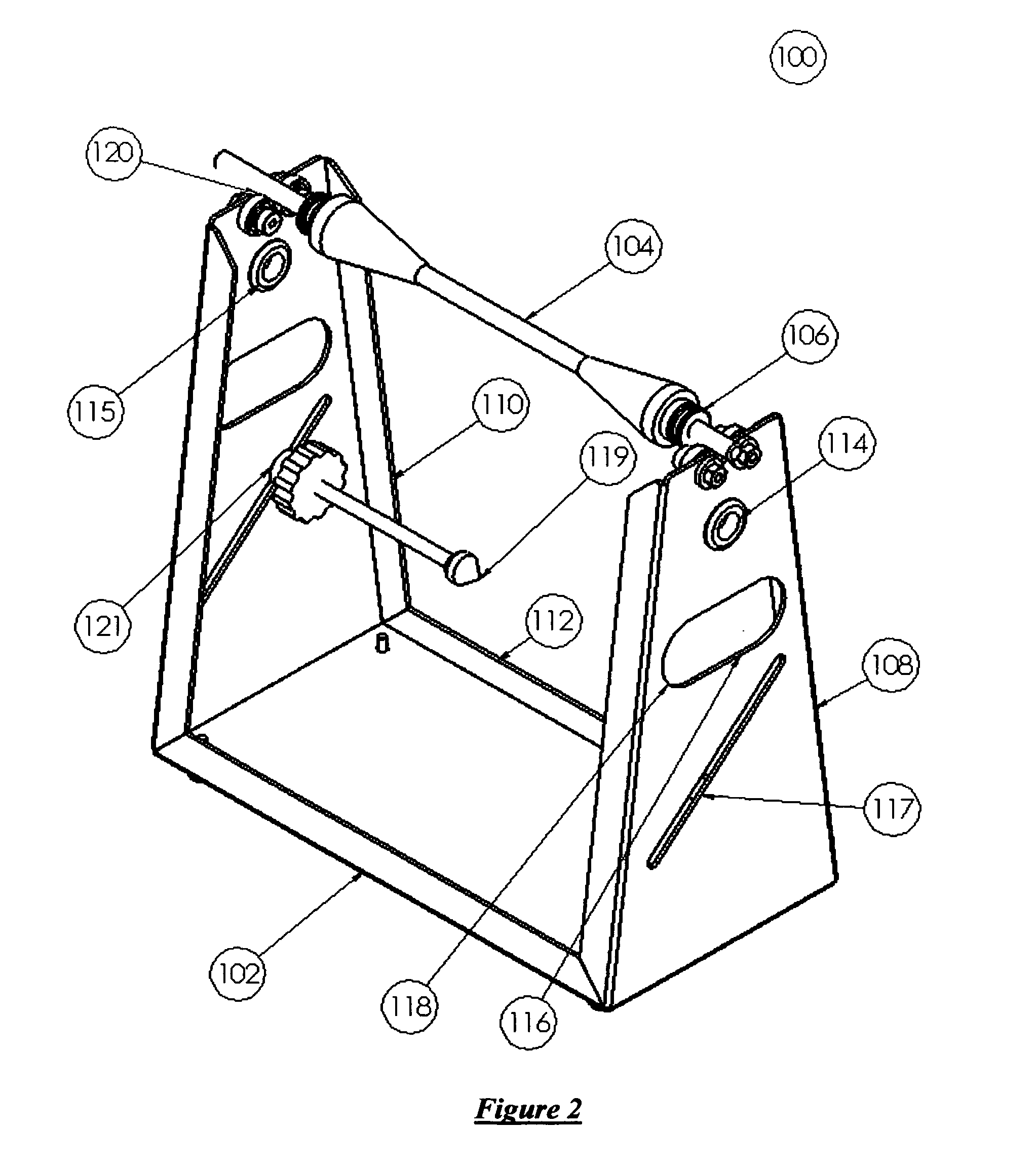
Apparatus for performing static balancing or axial or radial run-out inspection on an axially symmetrical disc or wheel assembly. The apparatus consists of a contemplated design of a rigid frame portion with features for easy transport, wheel run-out inspection attachments with high-resolution adjustment, anti-vibration and anti-marring non-skid isomeric feet, integrated frame hand-holds, integrated arbor storage that utilizes the primary locking function of the tool-less arbor tooling itself as a means to engage the arbor shaft into the frame, tool-less quick-changeover arbors of a locking ball and ramp design, arbors that act as a means of a hand-hold for transport, and arbors for non-traditional rotating member mounting to address the issue of thin cross-sectional wheel assemblies.
Owner:SLER RICHARD J JR
Laser measurement and positioning device and using method of wheel balancer
ActiveCN103728100ARealize automatic measurementSolve collection problemsStatic/dynamic balance measurementLaser transmitterTire balance
The invention discloses a laser measurement and positioning device and a using method of a wheel balancer. The laser measurement and positioning device adopts a stepping motor to drive a laser transmitter to rotate till laser is pointed to the inner side edge of a measured tire, calculates an optical distance by utilizing the time from laser transmitting and laser receiving according to an optical principle so as to obtain a straight line distance from a laser head to a laser indication point, utilizes a geometrical mathematic model to calculate tire parameters according to an installing position constant of the laser measurement and positioning device, achieves automatic measurement of various tire parameters and is accurate in measurement and simple in operation. After tire balance calculation is finished, a microprocessor is adopted to convert a triangular side function formed by the detected unbalance position and an original point of the laser transmitter into an angle differential parameter and then sends an instruction to the stepping motor, the stepping motor drives the laser transmitter to rotate to a converted angle, and the laser transmitter enables the laser to be transmitted onto the unbalance position so as to achieve laser positioning of the unbalance position of the measured tire.
Owner:科星汽车设备(珠海)有限公司
Automobile body system with chassis having stress sensor
The invention relates to an automobile body system with a chassis having a stress sensor and belongs to the technical field of automobiles. The automobile body system comprises a controller, a wiring harness, pressure sensors, deflating valves, a front-end stress sensor, a rear-end stress sensor, an automobile roof stress sensor and a chassis stress sensor, wherein the front-end stress sensor and the controller are arranged at the front part of an automobile body, the rear-end stress sensor is arranged at the rear end of the automobile body, the chassis stress sensor is mounted on the chassis, the pressure sensors and the deflating valves are arranged on tires, the deflating valves are all electromagnetic valves, and the controller is respectively connected with the pressure sensors and the deflating valves through the wiring harness. According to the automobile body system, when the controller monitors that the front or rear end of an automobile is subjected to collision or the roof or chassis of the automobile is bumped, the deflating valves of four tires can be opened, so that the pressure of the four tires can be equal. The automobile body system is reasonable in structure and simple in design and is applicable to the design of automobile tire balancing systems.
Owner:董超
System calibration method of tire balancing machine
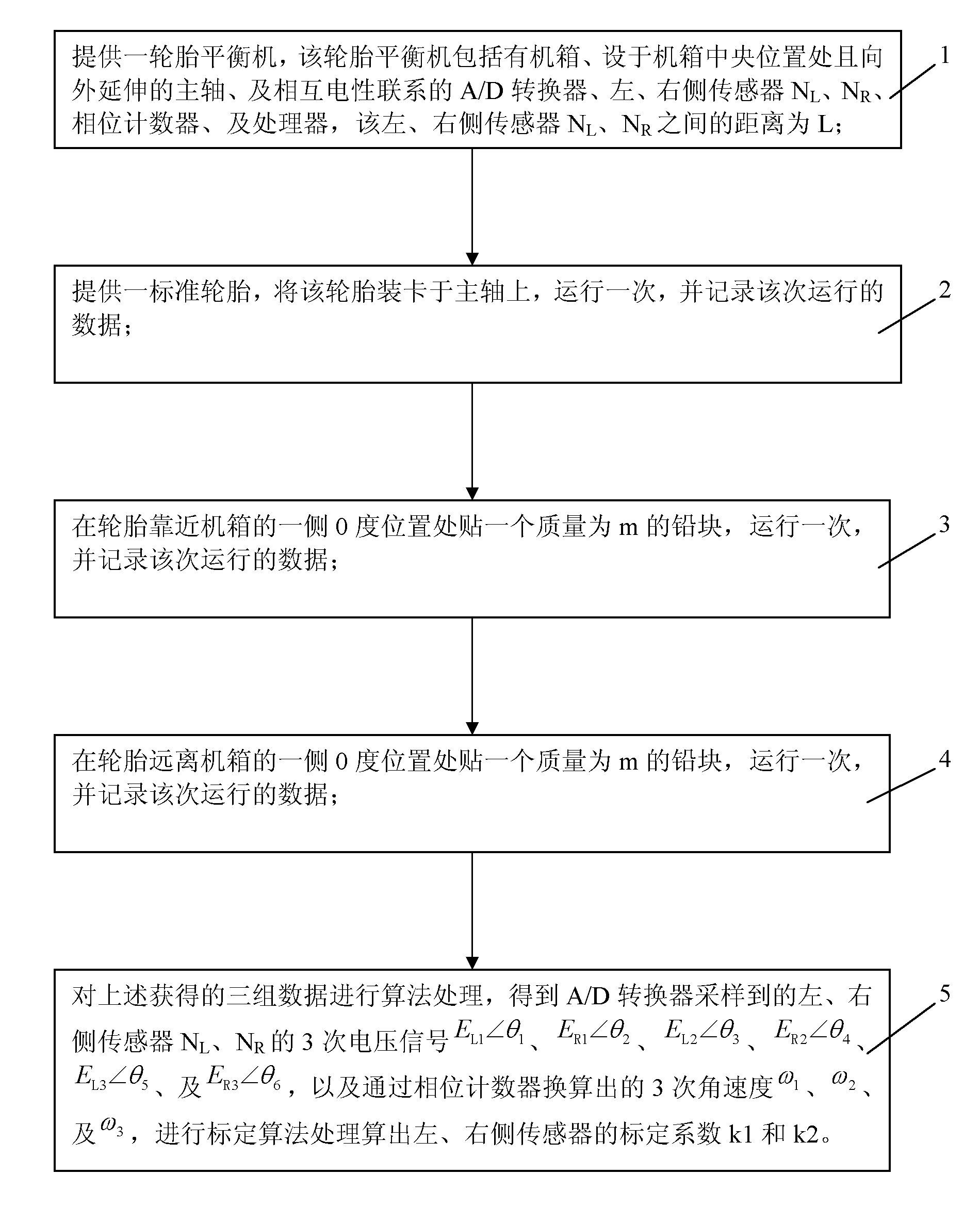
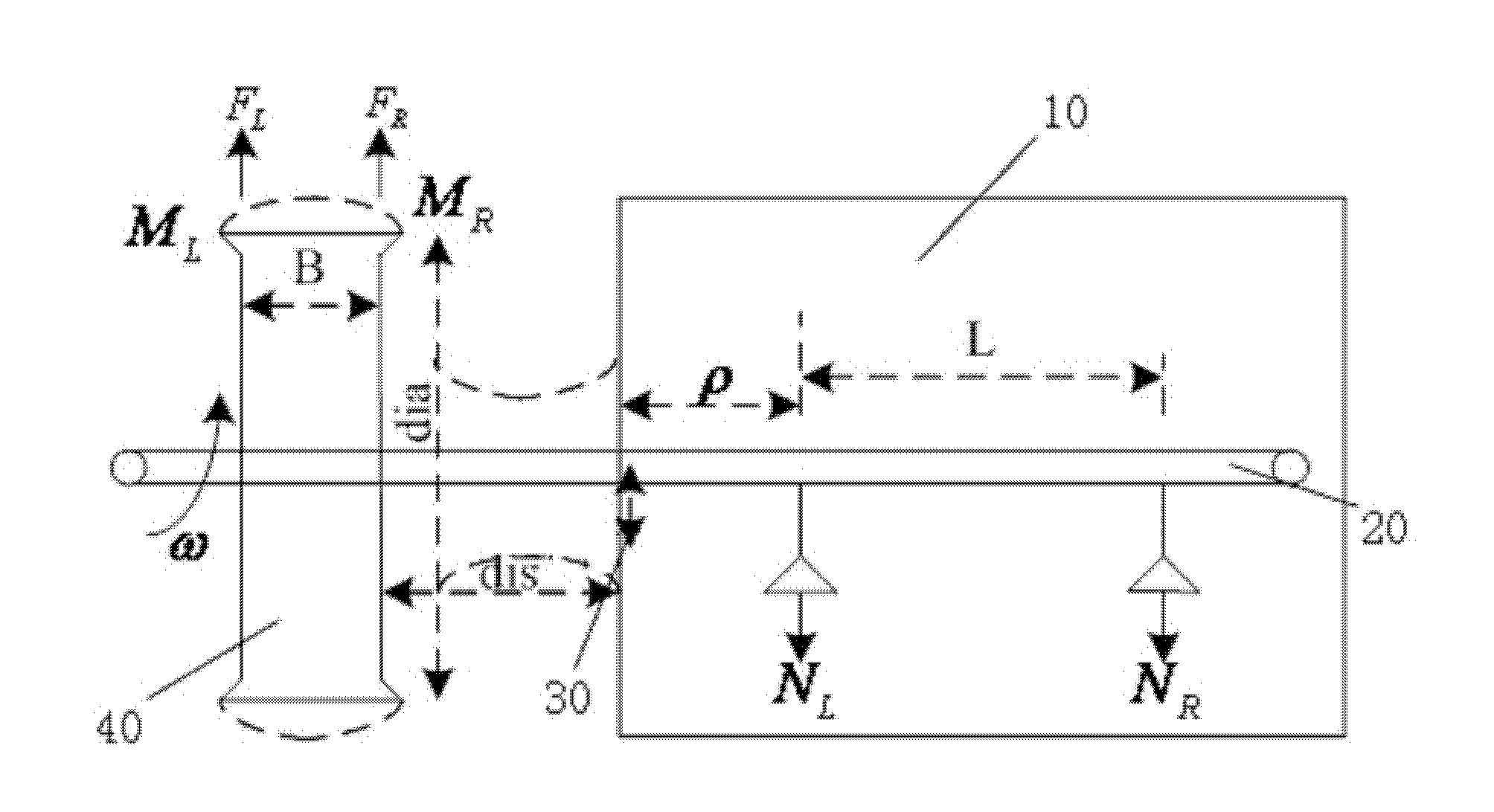
ActiveCN102156025AAccurate measurementOvercome the influence of factors affecting measurement resultsStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceBalancing machine
The invention provides a system calibration method of a tire balancing machine, comprising: step I, supplying a tire balancing machine; step II, supplying a standard tire, clamping the tire on a main shaft, running the tire once, and recording the running data; step III, pasting a lead m in weight at a 0-degree position at one side of the tire close to a case, running the lead once and recording the running data; step IV, pasting a lead m in weight at a 0-degree position at one side of the tire far away the case, running the lead once and recording the running data; step V, performing algorithm processes for the obtained three datum, and performing a calibration algorithm process to calculate the calibration coefficients k1 and k2 of left and right sensors. In the invention, before the tire balancing machine is used for measuring, the linear relation between an inductor force and an induction voltage signal of the sensor is calibrated, the calibration coefficients k1 and k2 of left and right sensors are determined, and the size and position of dynamic and static unbalance amount of the tire can be measured accurately, so that the error of the system calibration is reduced to the minimum value.
Owner:LAUNCH SOFTWARE DEV
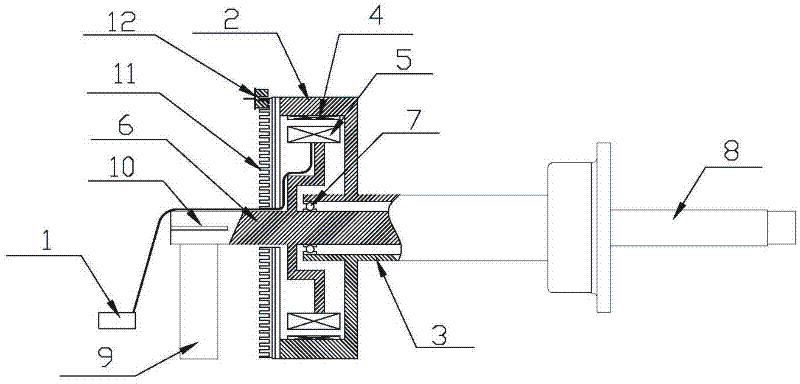
Tire shaft dynamic balance detection and correction device
InactiveCN110749395AQuick installationImprove detection efficiencyStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceLaser transmitter
The invention relates to the technical field of tire balancing machines, in particular to a tire shaft dynamic balance detection and correction device. The tire shaft dynamic balance detection and correction device comprises a balancing main machine, a material frame is arranged on the upper end face of the balancing main machine, a rocker arm is rotatably mounted on the left end face of the balancing main machine, a main rotating shaft is arranged on the upper side of the right end face of the balancing main machine, and a pair of guiding rails which are symmetrically in the front-rear direction and extend rightwards are vertically arranged at the lower end of the right side of the balancing main machine. The tire shaft dynamic balance detection and correction device has the beneficial effects that by arranging an auxiliary shaft adopting a connecting flange for connecting, quick mounting between the auxiliary shaft and the main rotating shaft is achieved, the detecting efficiency isfurther improved, and the mounting and demount processes are simplified; by arranging a sliding trolley with the lifting effect, meanwhile, a hydraulic cylinder is utilized to realize lifting of tires, and the purposes of labor saving and convenient and quick mounting are achieved; and by arranging cooperation of a module and a laser emitter, the tires, the auxiliary shaft and the laser source arelocated on the same axis, thus the tires are accurately mounted, the abrasion to the outer wall of the rotating shaft by the tires is avoided, and the detection precision is improved.
Owner:刘咏
Tire balance point aligning method and device
ActiveCN103754062AGuaranteed pass rateReduce rework rateStatic/dynamic balance measurementTyresTire balanceEngineering
The invention discloses a tire balance point aligning method and a tire balance point aligning device, and belongs to the field of assembly and production of automobile tires. The method is performed according to the following steps: step 1, determining an onsite reference, fixing the placing position of a hub by the reference, and enabling the heavy point of the hub to place at the center of a roller bed to serve as the reference line for aligning to the light point of the tire; step 2, making reference dimension scales to ensure the control of staffs on the offset dimension of the tire; step 3, adjusting the position of the light point of the tire placed on the hub and aligning the point to the point, according to the reference dimension scales and a tire offset dimension statistical table. According to the method provided by the invention, the problem that the tire is poor in alignment offset is solved, the percent of pass of the produced tires is ensured, the remade rate of the staffs is reduced, the alignment operation is simple, convenient and rapid, and the cost is effectively reduced.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
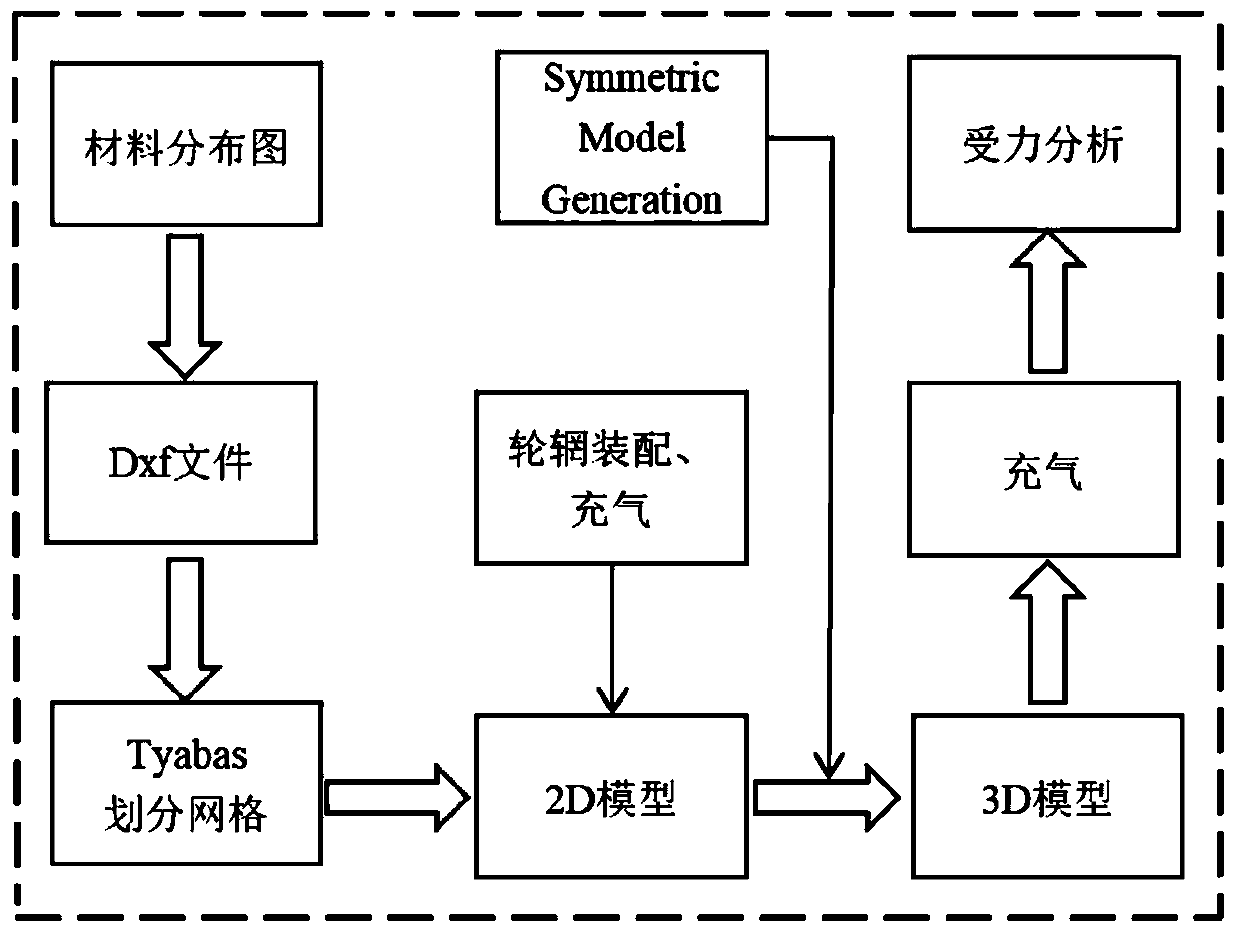
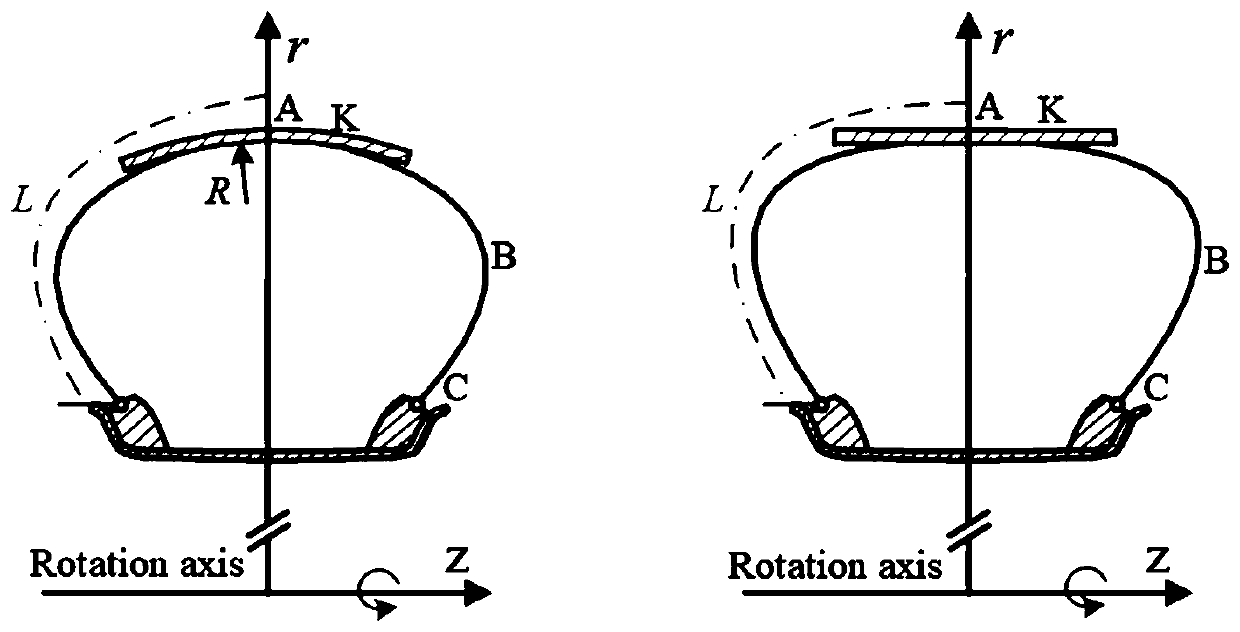
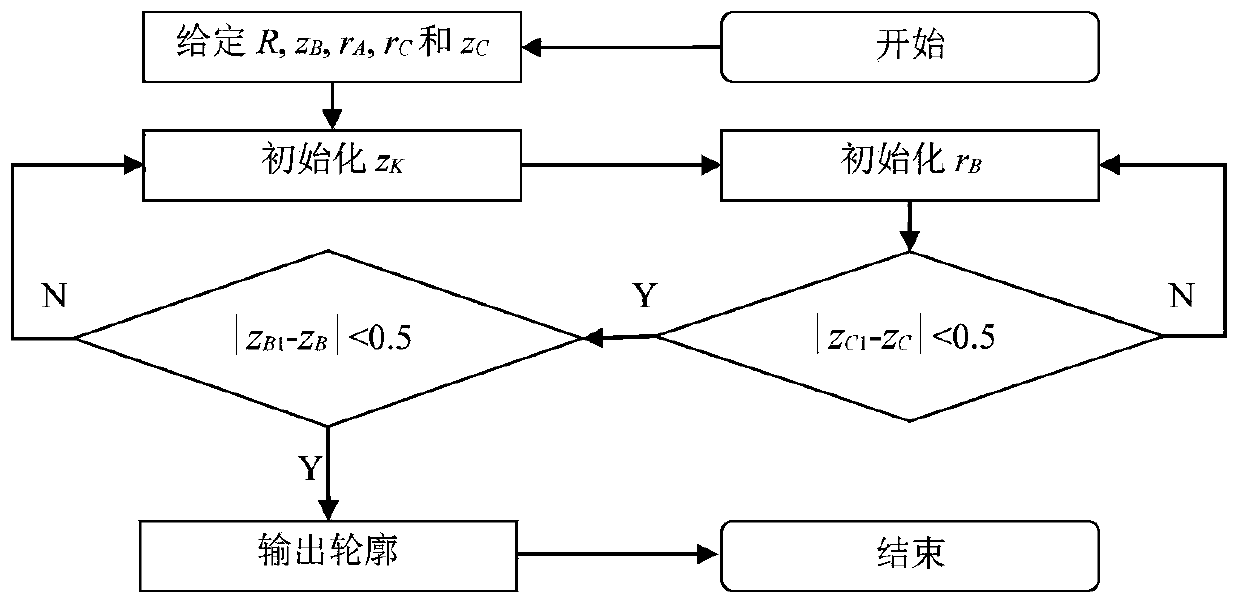
Tire structure design method and application thereof
The invention discloses a tire outline and carcass simulation design method, and particularly relates to an all-steel meridian (TBR) tire. The tire stress and deformation capacity, the tire body contour, the tire tread contour and the tire balance contour are considered, and the purpose of improving the durability of the tire is achieved.
Owner:ZHONGCE RUBBER GRP CO LTD
Self-driven balancing machine rotating component and corresponding tire balancing machine
ActiveCN102183337AImprove coaxialityAccurate balance detectionStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceBalancing machine
The invention relates to a tire balancing device, in particular to a self-driven balancing machine rotating component and a corresponding tire balancing machine. The existing tire balancing machine has a complicated structure and low efficiency, is inconvenient to manufacture, and has transmission error. The self-driven balancing machine rotating component comprises an outer rotor and an inner stator, which are both fixed on the same axis. The self-driven balancing machine rotating component has large torque, high efficiency and convenient control, and is suitable for various balancing machines; and the tire balancing machine assembled with the rotating component has accurate detection, and is suitable for being used for balancing various tires.
Owner:杨爱国 +1
Method for measuring amount of unbalance of tire dynamic balance and tire balancer
ActiveCN102121862AAccurate amplitudePhase accurateStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceBalancing machine
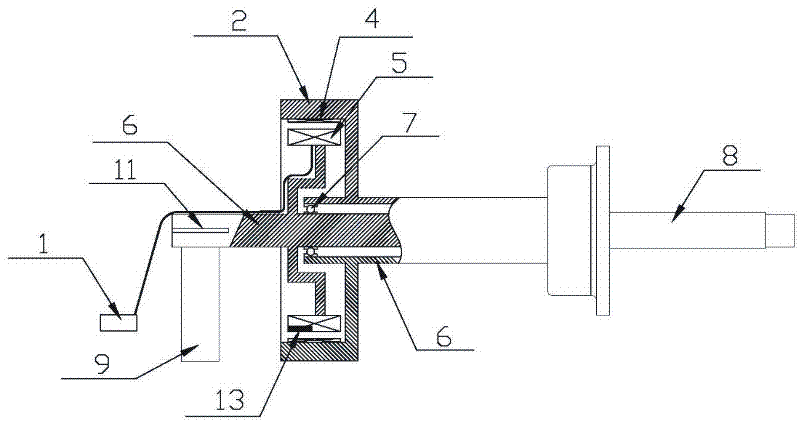
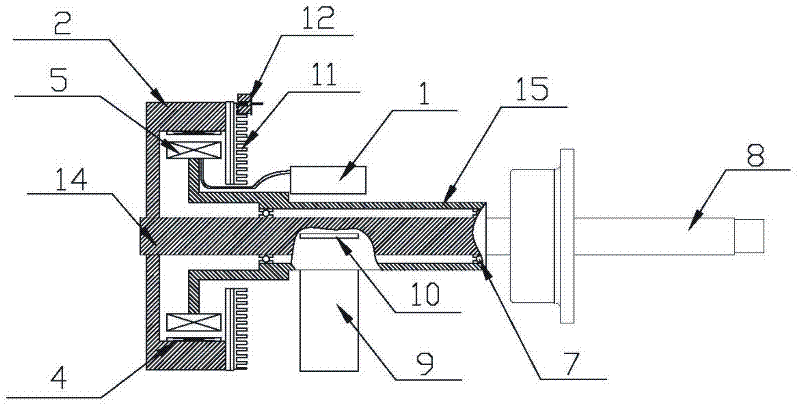
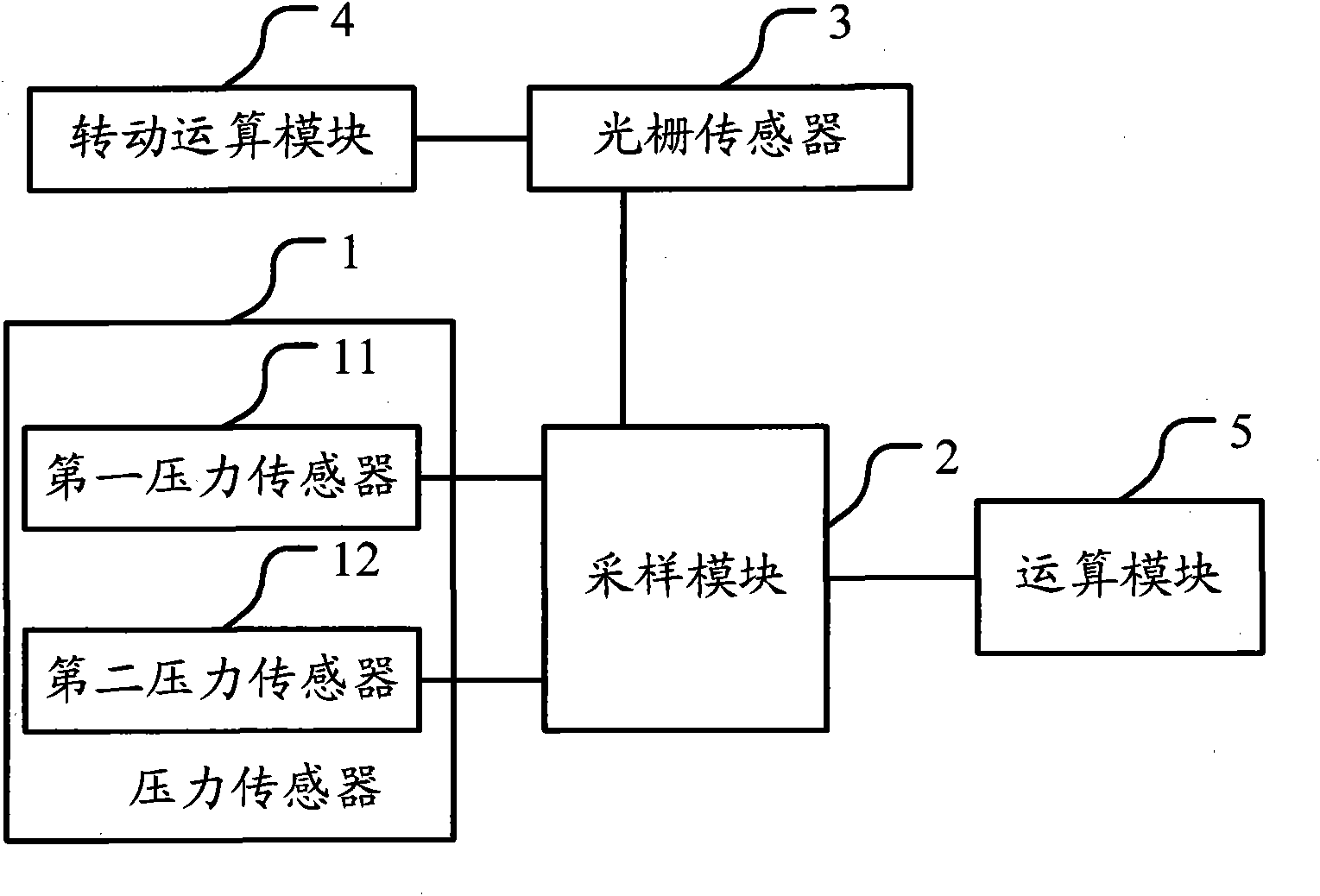
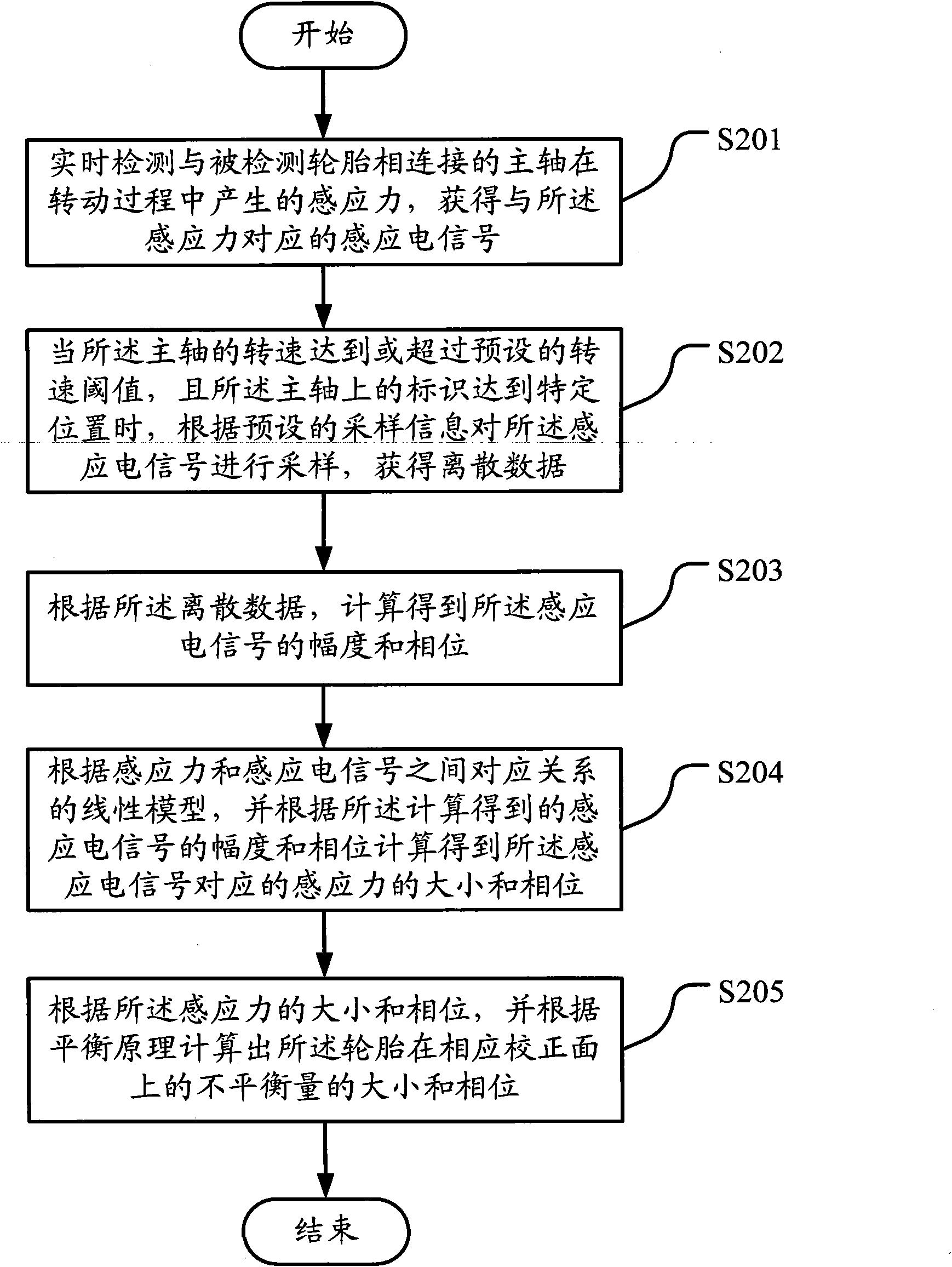
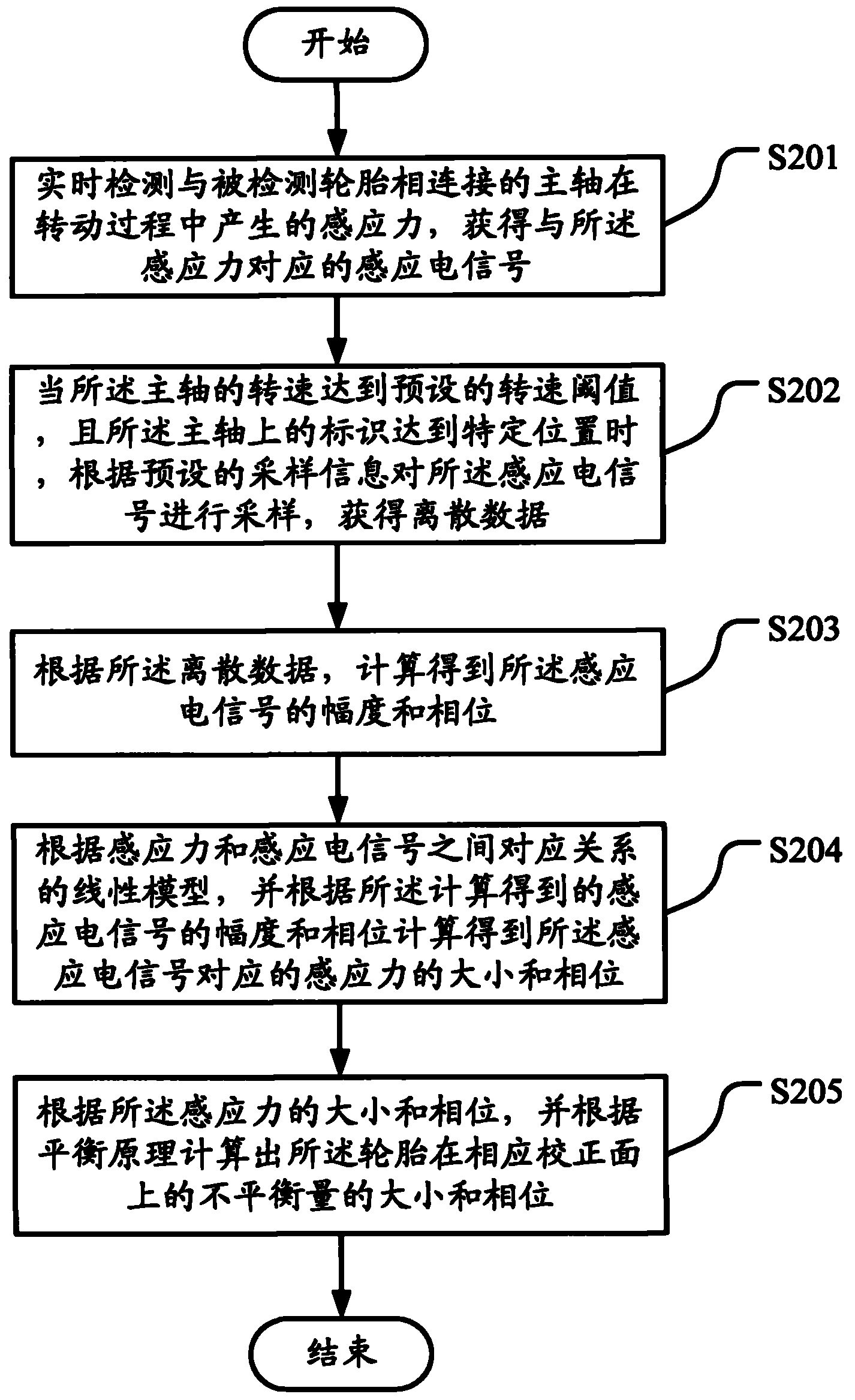
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for measuring the amount of unbalance of tire dynamic balance, which comprises the following steps of: detecting an induction electrical signal of a main shaft connected with a tire in real time in a rotating process; if the rotating speed of the main shaft reaches a preset rotating speed threshold value and an identifier on the main shaft reaches a given position, sampling the induction electrical signal according to preset sampling information to obtain discrete data; calculating the amplitude and phase of the induction electrical signal according to the discrete data; calculating the magnitude and phase of an induced force corresponding to the induction electrical signal according to a linear model of corresponding relationships between the induced forces and the induction electrical signals; and calculating the magnitude and phase of the amount of unbalance of the tire on a corresponding corrected surface according to the magnitude and phase of the induced force and a balance principle. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a tire balancer. By the method of the tire balancer, the high-accuracy magnitude and phase of the amount of unbalance of the dynamic balance can be simply and conveniently measured and calculated.
Owner:LAUNCH SOFTWARE DEV
Device for automatic tire inflation and tire pressure display
A device for automatic tire inflation and tire pressure display has a tire pressure measurement unit, a tire temperature sensor (a thermometer) and a gradienter for measuring the tire balance. The tire pressure measurement unit has a tire pressure measurement unit, a voltage regulating circuit of power source, a microprocessor control unit, a wireless transceiving module and an inflation / deflation control component. The tire pressure measurement unit measures the tire pressure value of a tested tire. The tire pressure value is then wirelessly displayed on a display unit in a vehicle so that the user can know the present status of a tire. The user can also maneuver a function key to select an operation according to the displayed data and send this message to the tire room to execute inflation or deflation of the tire.
Owner:PARTNER TECH
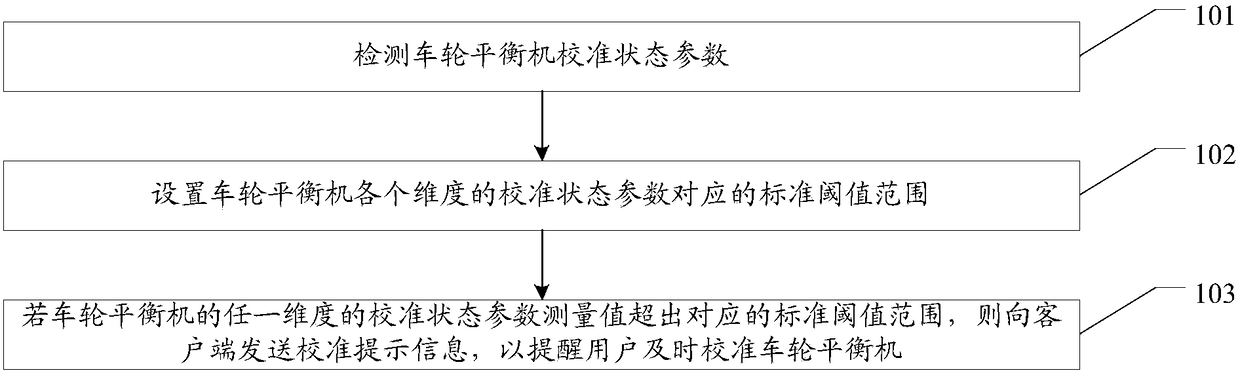
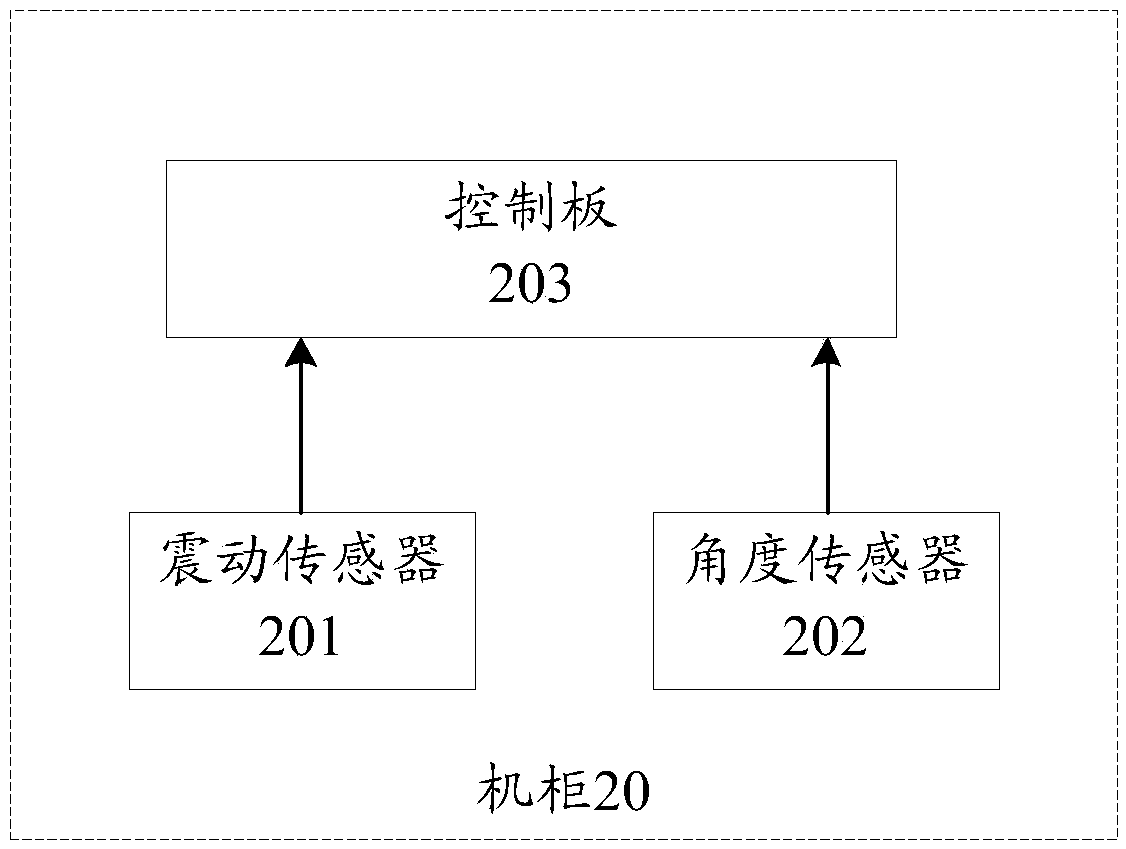
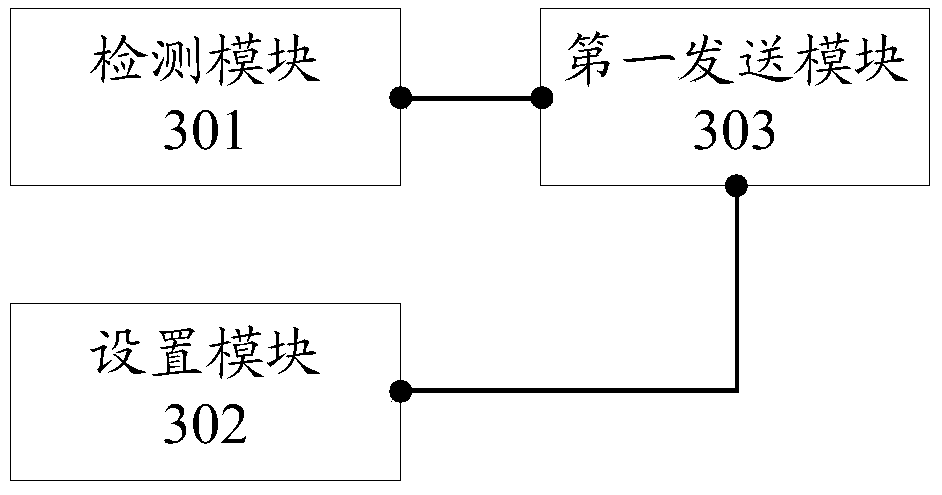
Tire balance machine calibration prompt method and system and related equipment
Embodiments of the invention provide a tire balance machine calibration prompt method and system and related equipment, and are used for reminding a user to carry out equipment calibration in time according to the change of calibration state parameters of a tire balance machine. The method of the embodiments of the invention comprises the following steps of detecting the calibration state parameters of the tire balance machine; setting standard threshold ranges corresponding to the calibration state parameters of each dimension of the tire balancing machine; and if the measurement value of thecalibration state parameter of any dimension of the tire balance machine exceeds the corresponding standard threshold value range, sending the calibration prompt information to a client so as to remind the user to timely calibrate the tire balance machine.
Owner:LAUNCH TECH CO LTD
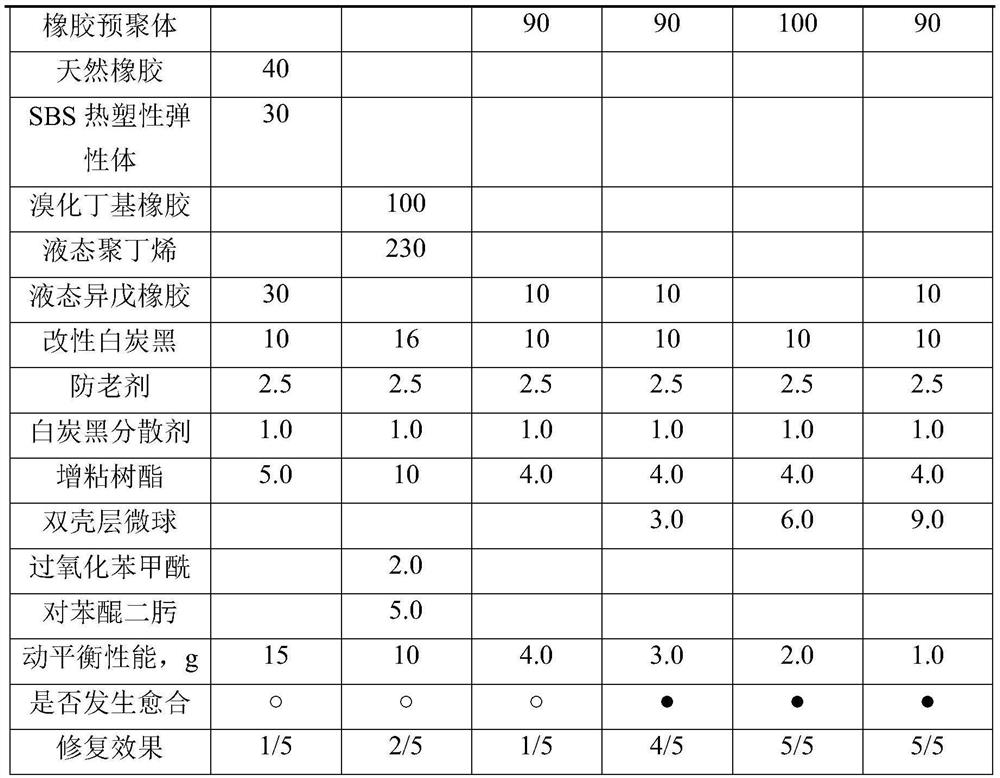
Self-repairing rubber composition for tires and preparation method of self-repairing rubber composition
ActiveCN113502135AExtended service lifeSelf-sealingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesTyresRubber materialTire balance
The invention belongs to the technical field of self-repairing tires, provides a self-repairing rubber composition for tired and a preparation method of the self-repairing rubber composition, and aims at solving the problems that an existing tire self-sealing repairing material is unrecyclable, poor in flow sealing effect and may influence the balance performance of the tire. Various materials such as reverse vulcanized rubber prepolymer, liquid isoprene, triglyceride, silicon dioxide-gel-catalytic repair polymerizing agent double-shell microspheres, modified white carbon black and tackifying resin are matched for use. The prepared self-repairing rubber material has high repairing rate and good repairing effect, has recoverability, can be applied to the inner wall of a tire to play a self-sealing role, and can remarkably improve the life safety of a driver and passengers in the running process of the tire and effectively prolong the service life of the tire.
Owner:EVE RUBBER RES INST
Tire manufacturing method, cover rubber stamping device used therefore, tire, as well as rubber sheet member stamping method, and device
InactiveUS7622013B2Efficient preparationHighly accurate shapeLamination ancillary operationsLaminationTire balanceEngineering
A method of manufacturing a tire having first color characters or lines on at least one side wall part, includes the steps of stamping a second color side wall rubber and a first color side wall rubber on the side face of a carcass member formed in a toroidal shape by winding, a plurality of turns, a continuous second color rubber ribbon and a continuous first color rubber ribbon thereon, stamping a second color cover rubber on the outsides of the side wall rubbers by winding a rubber sheet whereon one turn in an annular shape, and molding a green tire, whereby the use of a large extrude can be eliminated, different types of tires can be efficiently manufactured since a size switching can be easily performed, the accuracies of the shape and the dimensions of the members thereof can be increased, the uniformity and the tire balance thereof can be increased, and the sharp profile of the first color characters or lines can be assumed, thus eliminating problems associated with the appearance.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Tire balancer control method and system and related device
InactiveCN109115406AEasy to operateFriendly operation interfaceProgramme controlComputer controlTire balanceBalancing machine
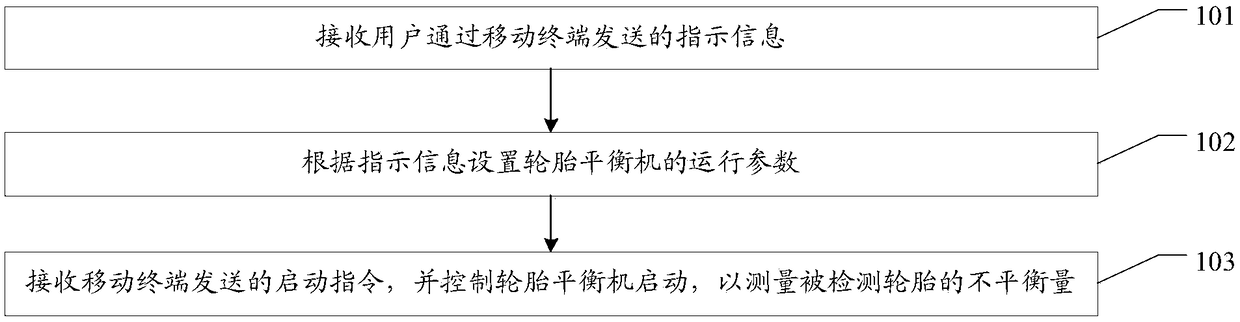
The embodiments of the application provide a tire balancer control method and system and a related device. The control operation of a tire balancer is simplified based on the tire balancer control system and a mobile terminal. The method provided by one embodiment of the invention includes the following steps: receiving indication information sent by a user through a mobile terminal; setting the operation parameters of a tire balancer according to the indication information; and receiving a starting instruction sent by the mobile terminal, and making the tire balancer started to measure the unbalance quantity of a detected tire.
Owner:LAUNCH TECH CO LTD
Dam bursting re-blockage construction method based on waste and old tires
The invention discloses a construction method for dam breakage and blockage restoration based on waste tires. Heavy blocks; drive positioning piles, so that the positioning piles are inserted into the soil layer with high strength; lap the containment wall, and evenly insert the waste tire counterweights and connecting plates, and finally form the waste tire counterweights and connecting plates alternately distributed 1. Two parallel containment wall structures connected by connecting plates between each row of positioning piles 8; fill in the cut-off material, fill in the cut-off material within the length of a construction unit and compact it; repeat the above process until the dragon mouth closes. The waste tire counterweight in the present invention is simple to manufacture, low in overall price, simple and convenient in construction, fast in construction speed, and meets the urgent needs of flood fighting and emergency rescue. Multiple rows of positioning piles and waste tire counterweights overlap each other to form a containment wall. The overall rigidity is large and the stability is high.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Self-driven balancing machine rotating component and corresponding tire balancing machine
ActiveCN102183337BImprove coaxialityAccurate balance detectionStatic/dynamic balance measurementTire balanceBalancing machine
The invention relates to a tire balancing device, in particular to a self-driven balancing machine rotating component and a corresponding tire balancing machine. The existing tire balancing machine has a complicated structure and low efficiency, is inconvenient to manufacture, and has transmission error. The self-driven balancing machine rotating component comprises an outer rotor and an inner stator, which are both fixed on the same axis. The self-driven balancing machine rotating component has large torque, high efficiency and convenient control, and is suitable for various balancing machines; and the tire balancing machine assembled with the rotating component has accurate detection, and is suitable for being used for balancing various tires.
Owner:杨爱国 +1
Passenger car tire balance point identification system
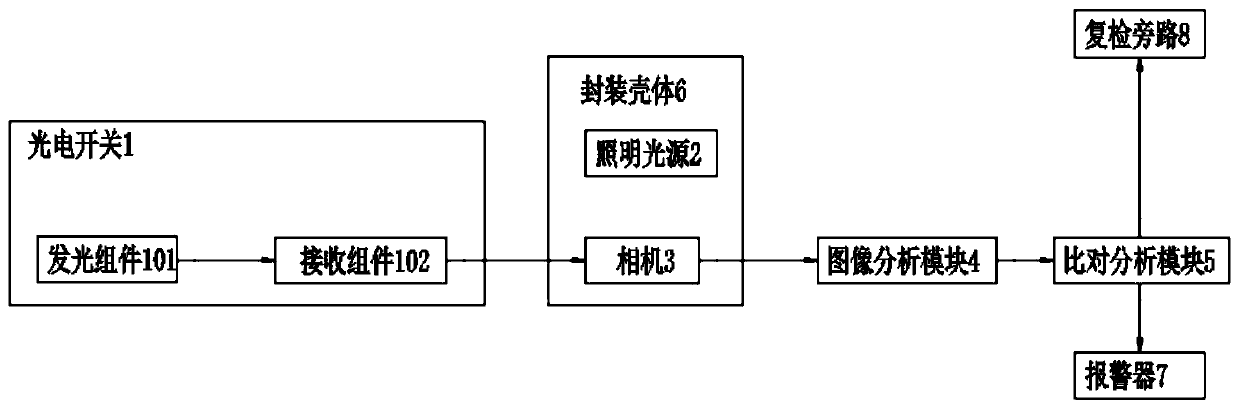
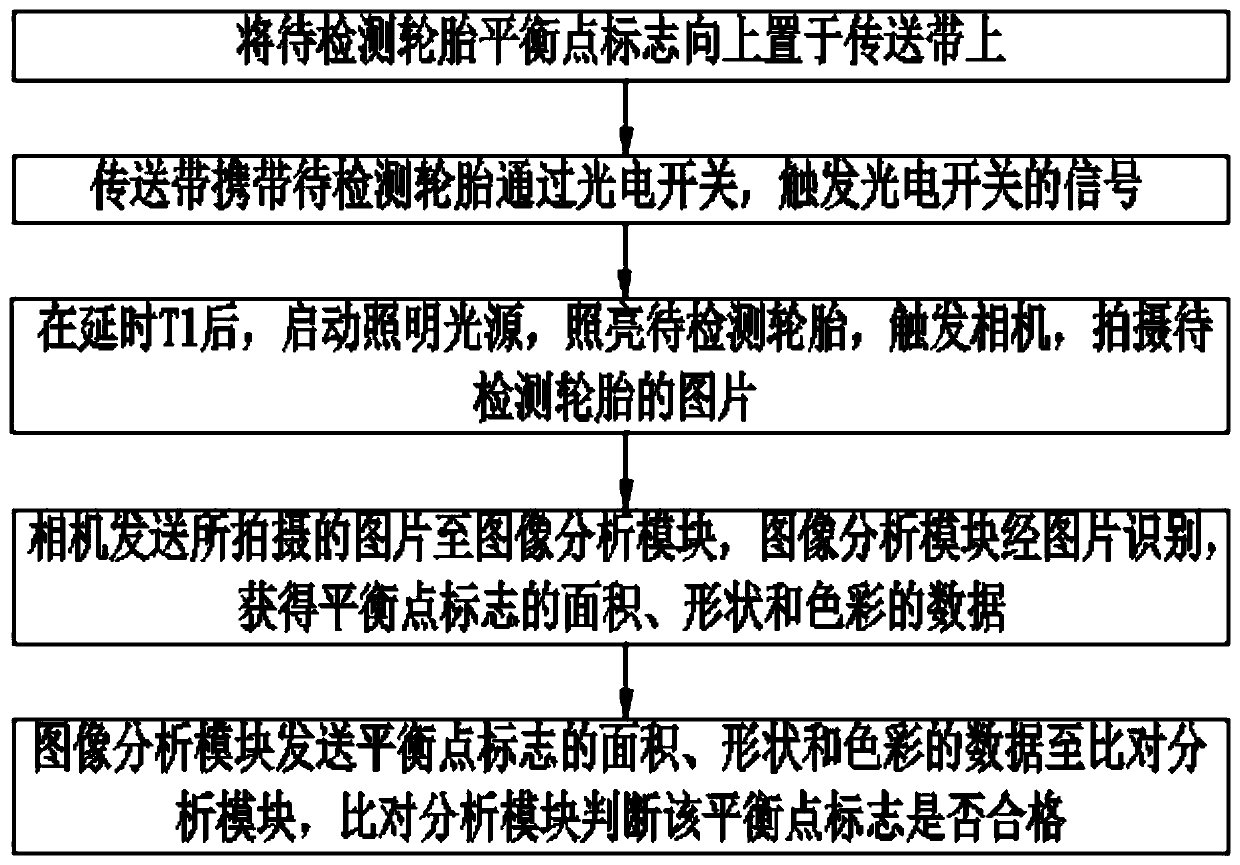
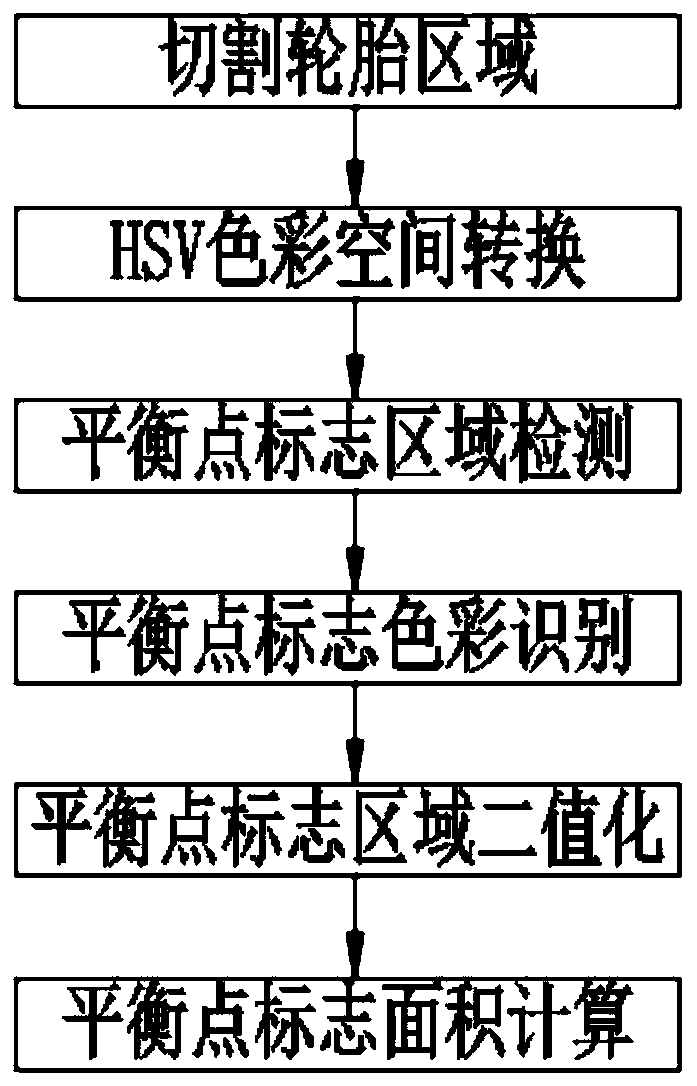
InactiveCN109709107AShort exposure timeImprove clarityMaterial analysis by optical meansTire balancePhotoswitch
The invention provides a passenger car tire balance point identification system, thereby solving a technical problem that the existing equipment can not be upgraded and modified by the existing spot mark detection scheme in the prior art. The system comprises a conveyor belt, a photoelectric switch, an illumination source, a camera, an image analysis module and a comparison analysis module. The photoelectric switch includes a light-emitting assembly and a receiving assembly that are arranged at the two sides of the conveyor belt; the photoelectric switch is connected to the camera and triggersthe camera to work; the illumination source and the camera are arranged above the conveyor belt; and the illumination source and the camera work cooperatively. According to the system provided by theinvention, the camera is controlled by the photogate to work; and the structure is simple and the cost is low. A few of devices are installed for the conveyor belt and modification of most of existing spot mark devices can be realized. The camera exposure time is short and the picture definition is improved; with an HSV color model, the work difficulty of the image analysis module is reduced andthe working efficiency of the image analysis module is improved; and because of an externally arranged processing module, remote control of the identification system is realized.
Owner:上海深视信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com