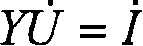Patents
Literature
57 results about "Two-level scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
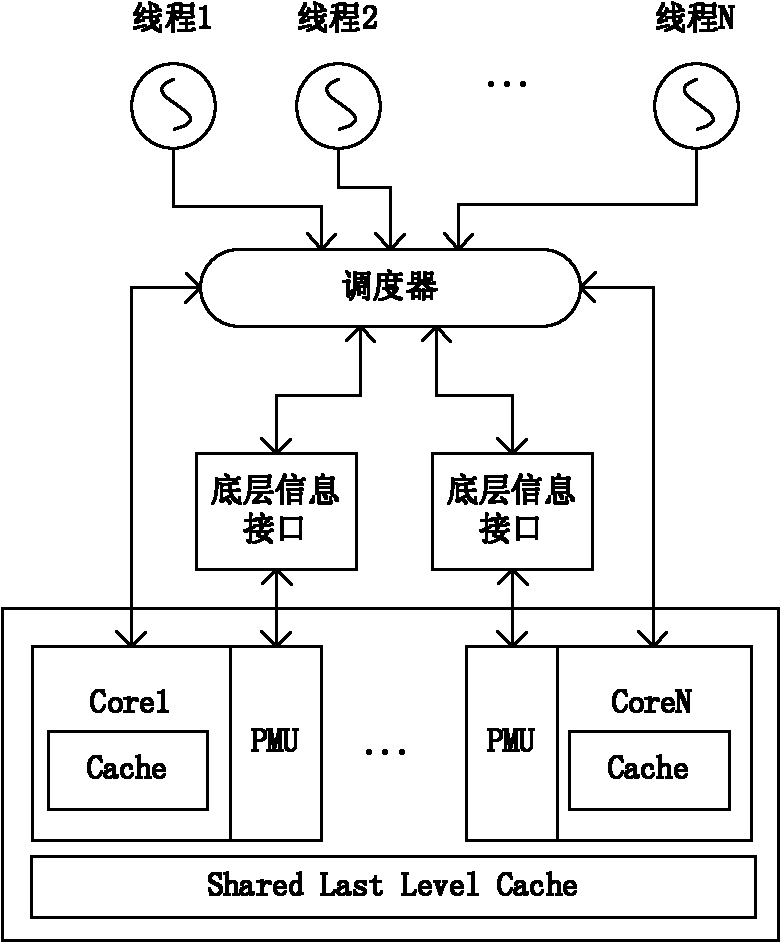
Two-level scheduling is a computer science term to describe a method to more efficiently perform process scheduling that involves swapped out processes. Consider this problem: A system contains 50 running processes all with equal priority. However, the system's memory can only hold 10 processes in memory simultaneously. Therefore, there will always be 40 processes swapped out written on virtual memory on the hard disk. The time taken to swap out and swap in a process is 50 ms respectively.
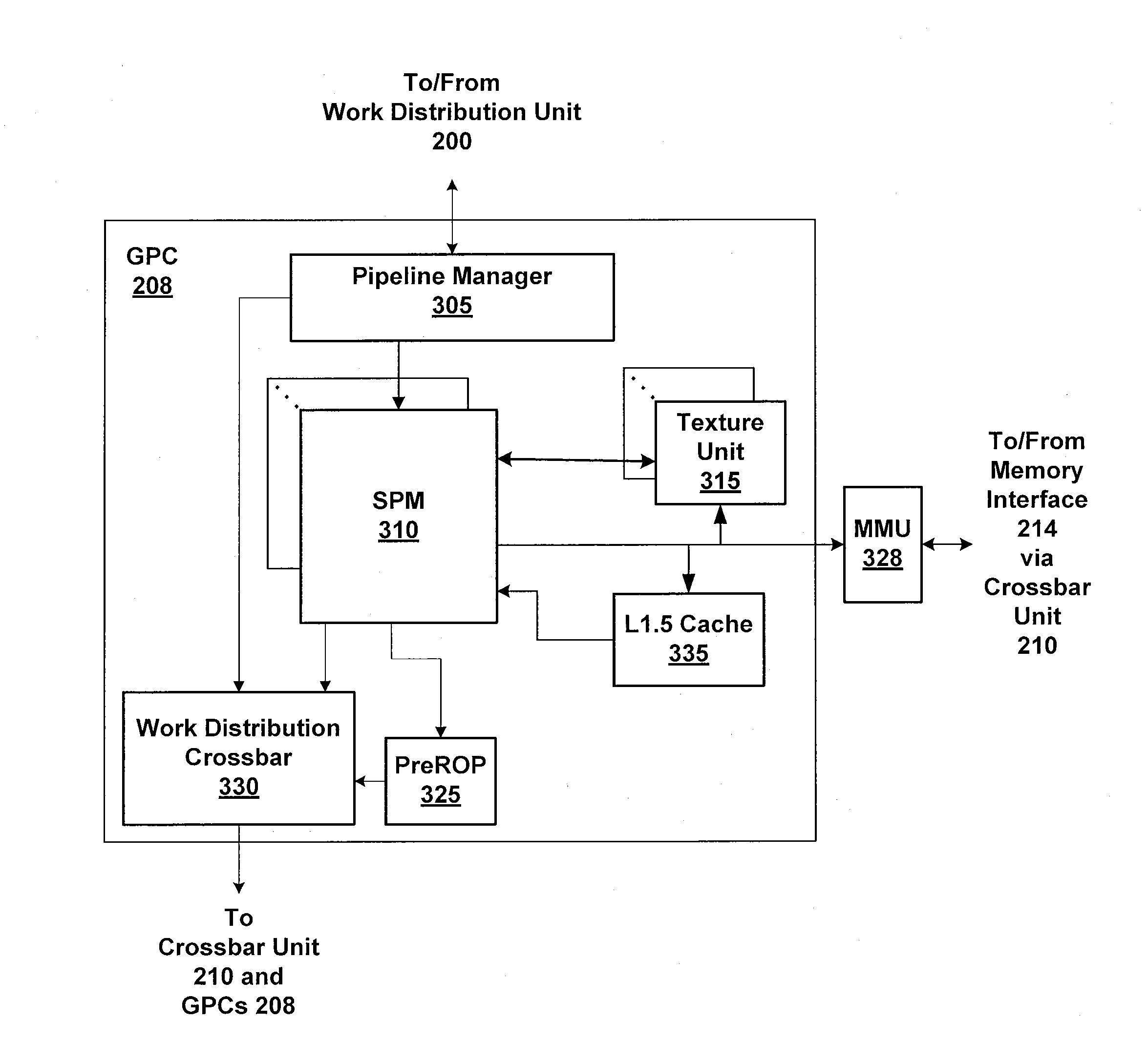
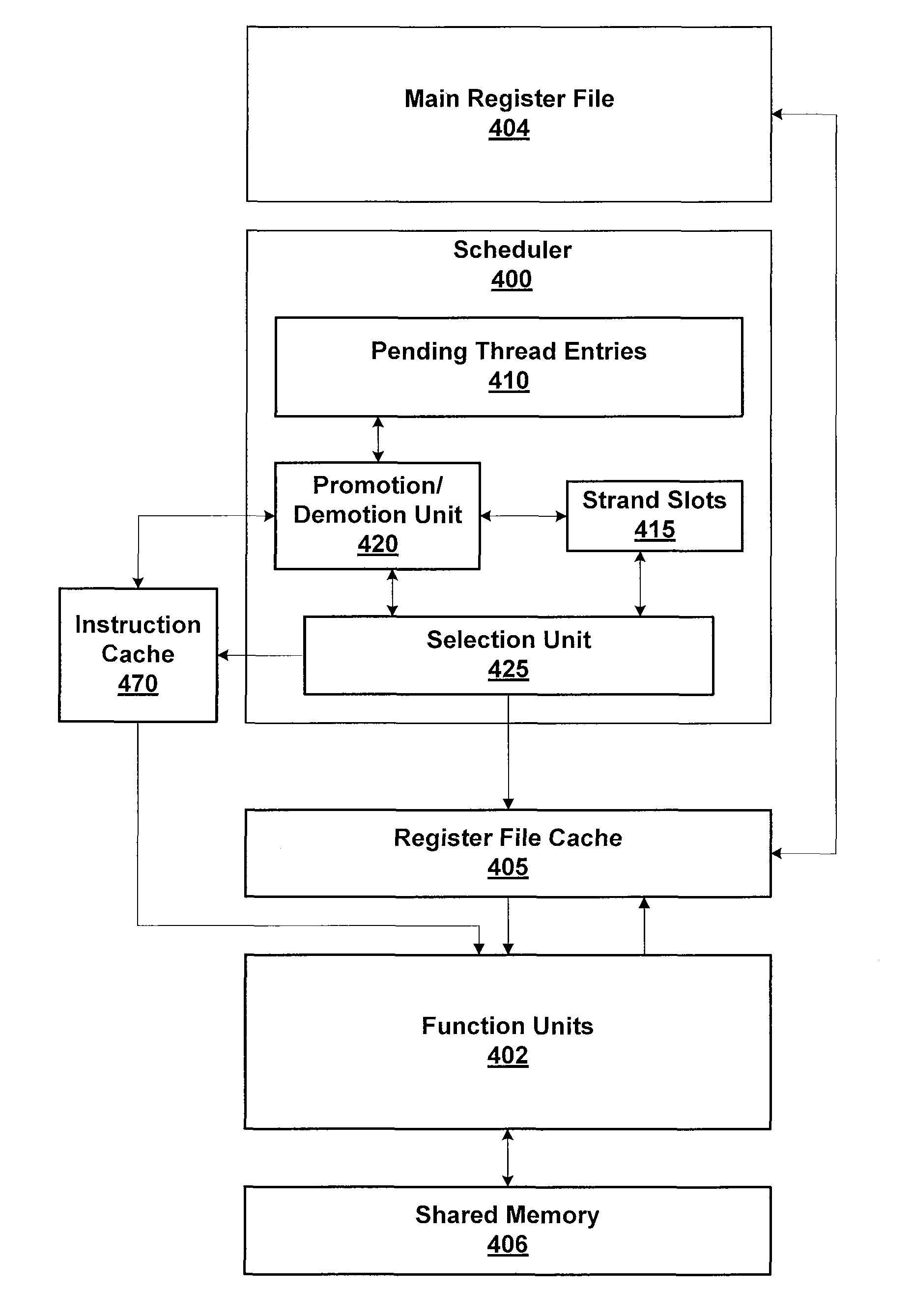
Two-Level Scheduler for Multi-Threaded Processing
ActiveUS20120079503A1Reduce power consumptionReduce areaProgram initiation/switchingMemory systemsLong latencyLocal memories
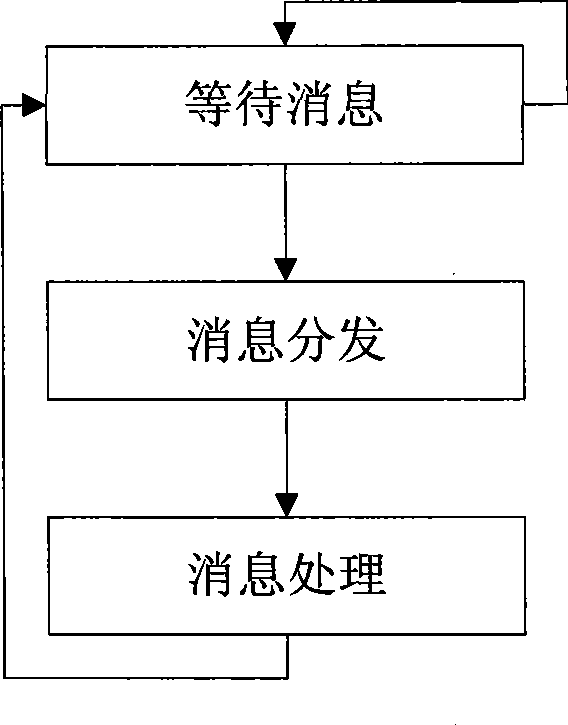
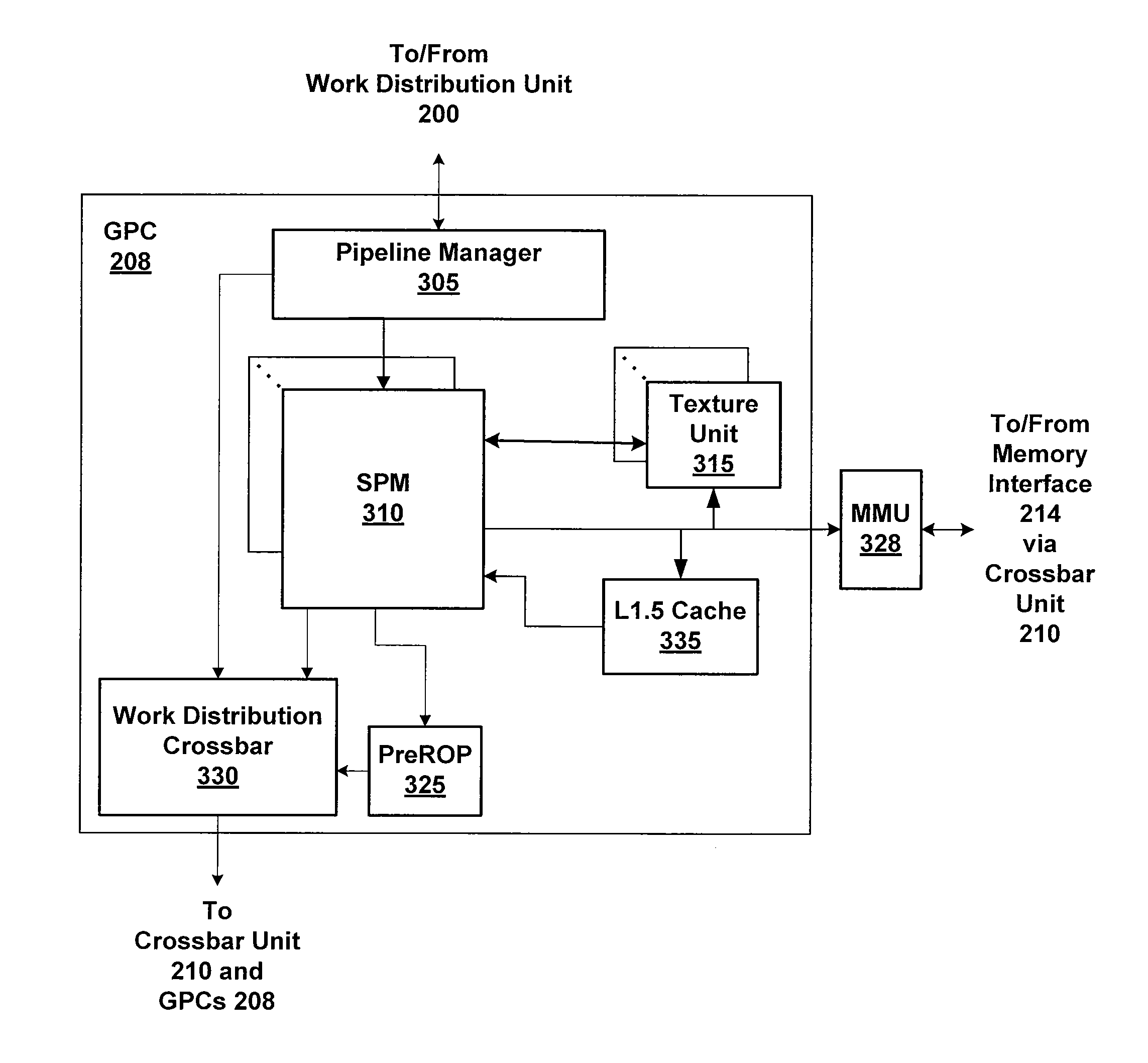
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for scheduling thread execution in a multi-threaded processing environment. A two-level scheduler maintains a small set of active threads called strands to hide function unit pipeline latency and local memory access latency. The strands are a sub-set of a larger set of pending threads that is also maintained by the two-leveler scheduler. Pending threads are promoted to strands and strands are demoted to pending threads based on latency characteristics. The two-level scheduler selects strands for execution based on strand state. The longer latency of the pending threads is hidden by selecting strands for execution. When the latency for a pending thread is expired, the pending thread may be promoted to a strand and begin (or resume) execution. When a strand encounters a latency event, the strand may be demoted to a pending thread while the latency is incurred.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
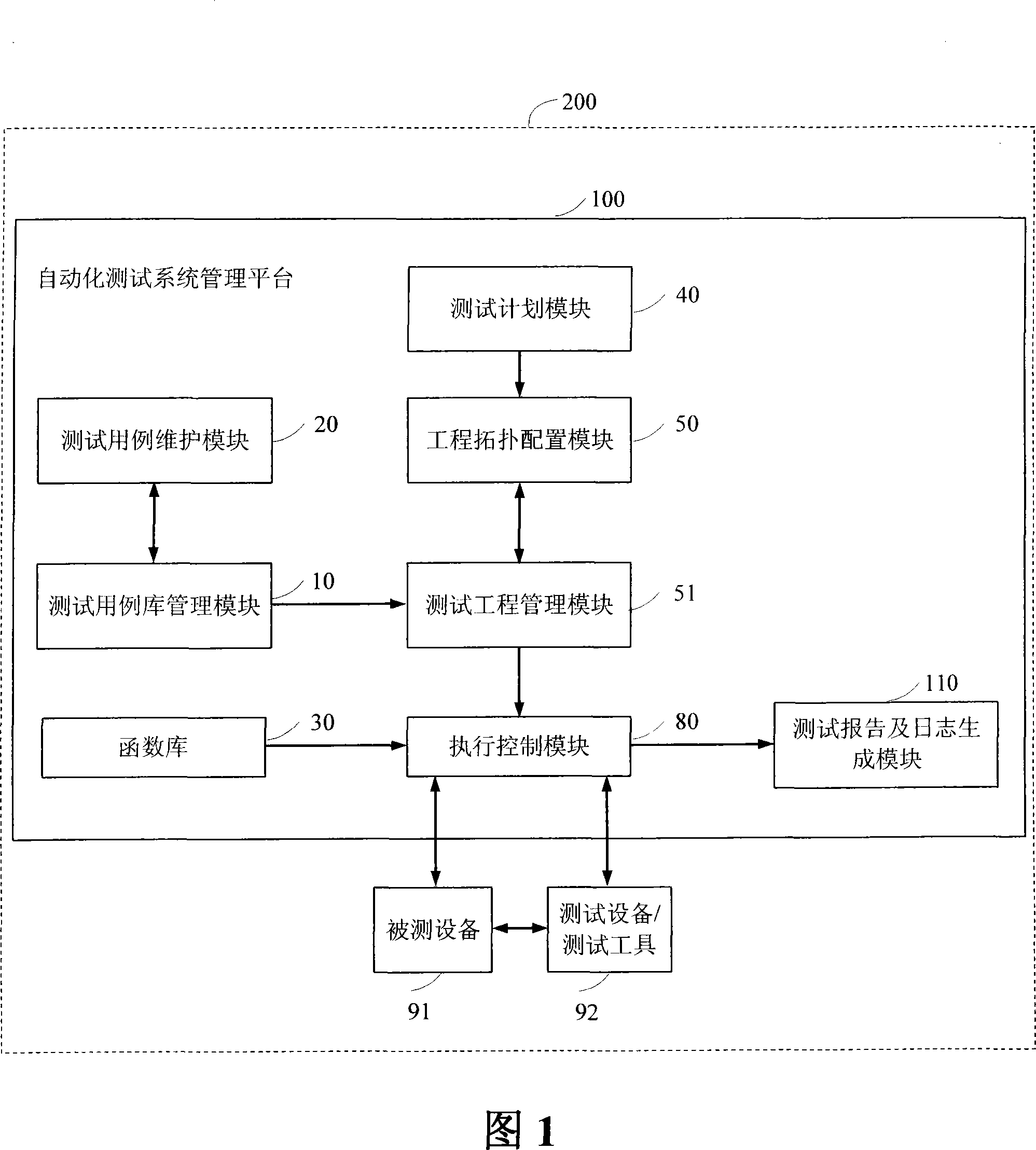
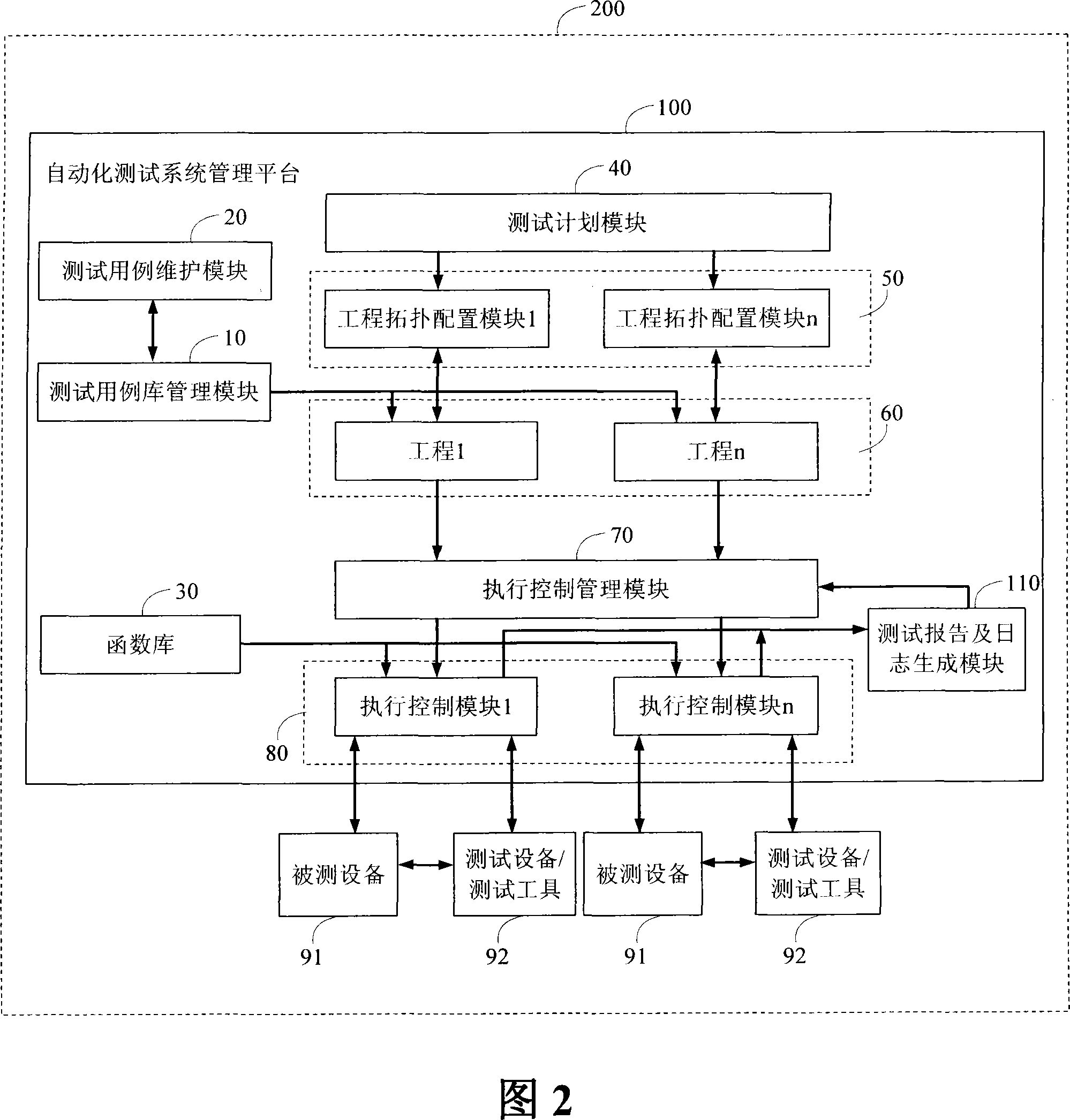
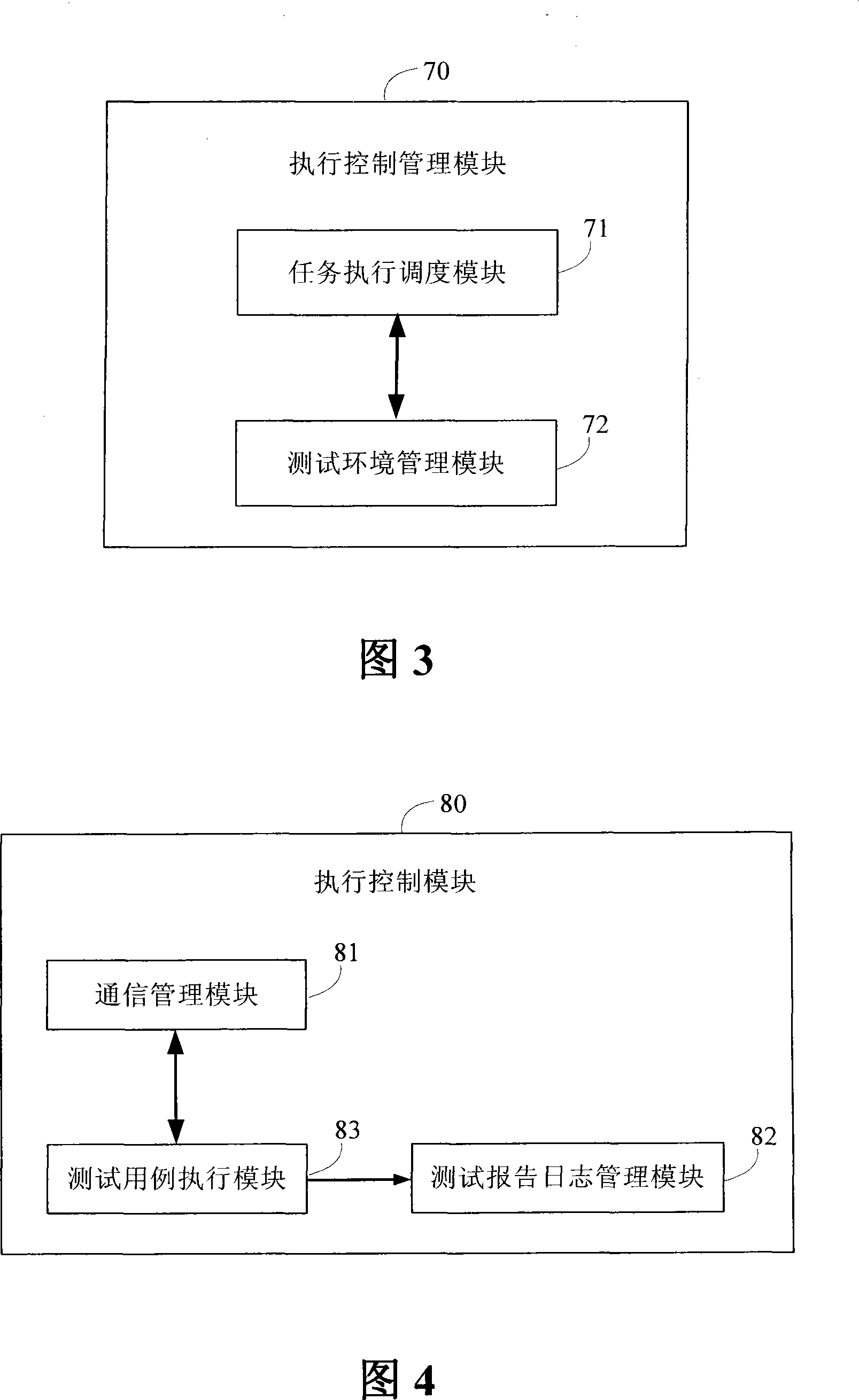
System for parallel executing automatization test based on priority level scheduling and method thereof
InactiveCN101227350ATake advantage ofImprove test efficiencyData switching networksResource utilizationExecution control
The invention discloses a parallel execution automation test system and a method which are based on priority scheduling, the system comprises a test plan module which is used to manage and draw up testing contents, an engineering topology configuring module which is used to topologically allocate test environment and manage the essential information of test environment, a test report and journal generating module for generating test journal and / or test report and a execution control module which is responsible for executing a plurality of test environment, and the invention also comprises an execution control management module, a connection execution control module, an engineering topology configuring module, a test report and journal generating module, a testing use case group with higher priority level which controls the execution control module to preferentially operate in test environment according to testing use case group, when the priority level is same, the relative testing use case group is operated in parallel. The invention greatly improves testing efficiency, which improves recourse utilization ratio, timely avoids ineffective test, and improves availability of test.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Scheduling system
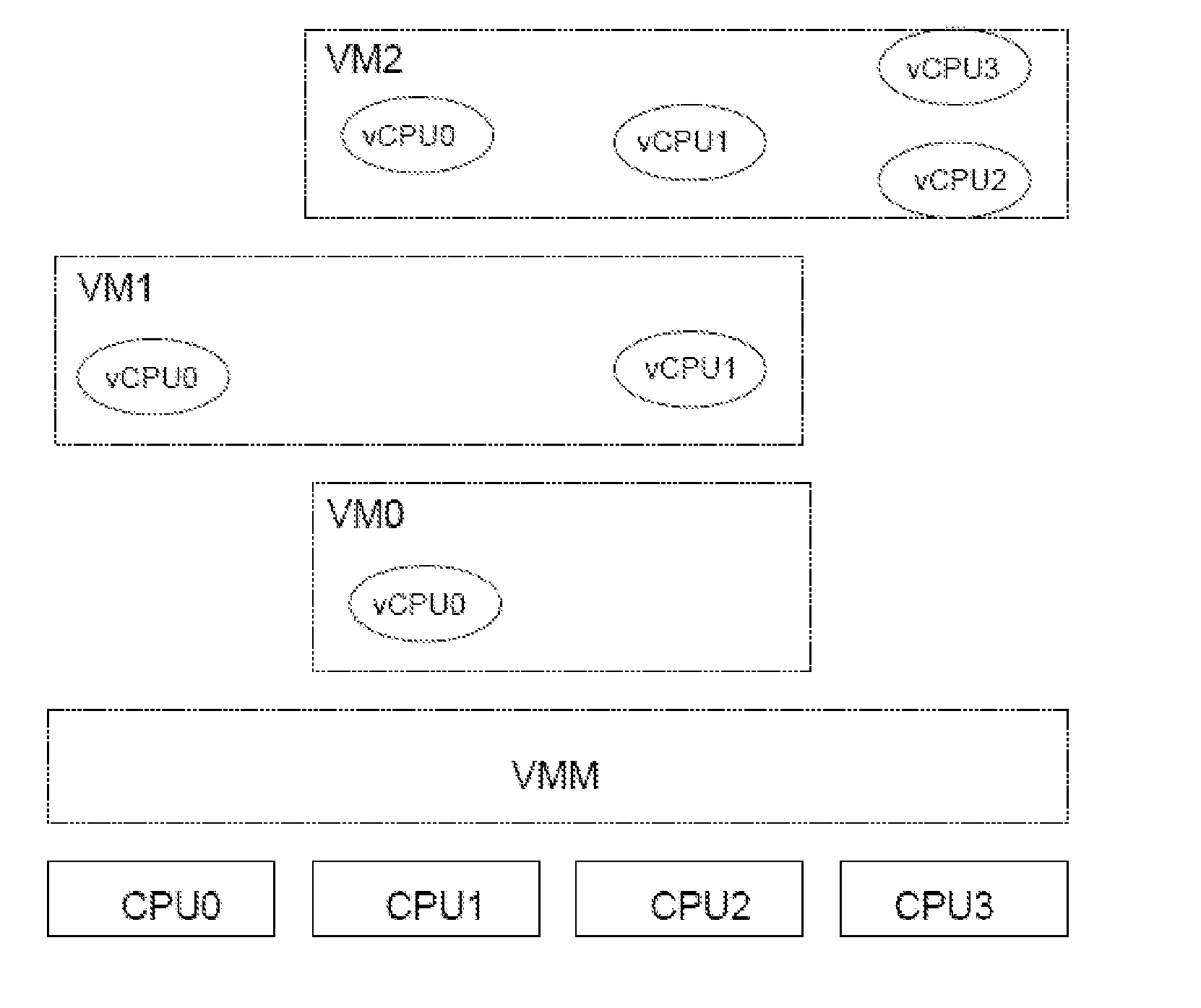
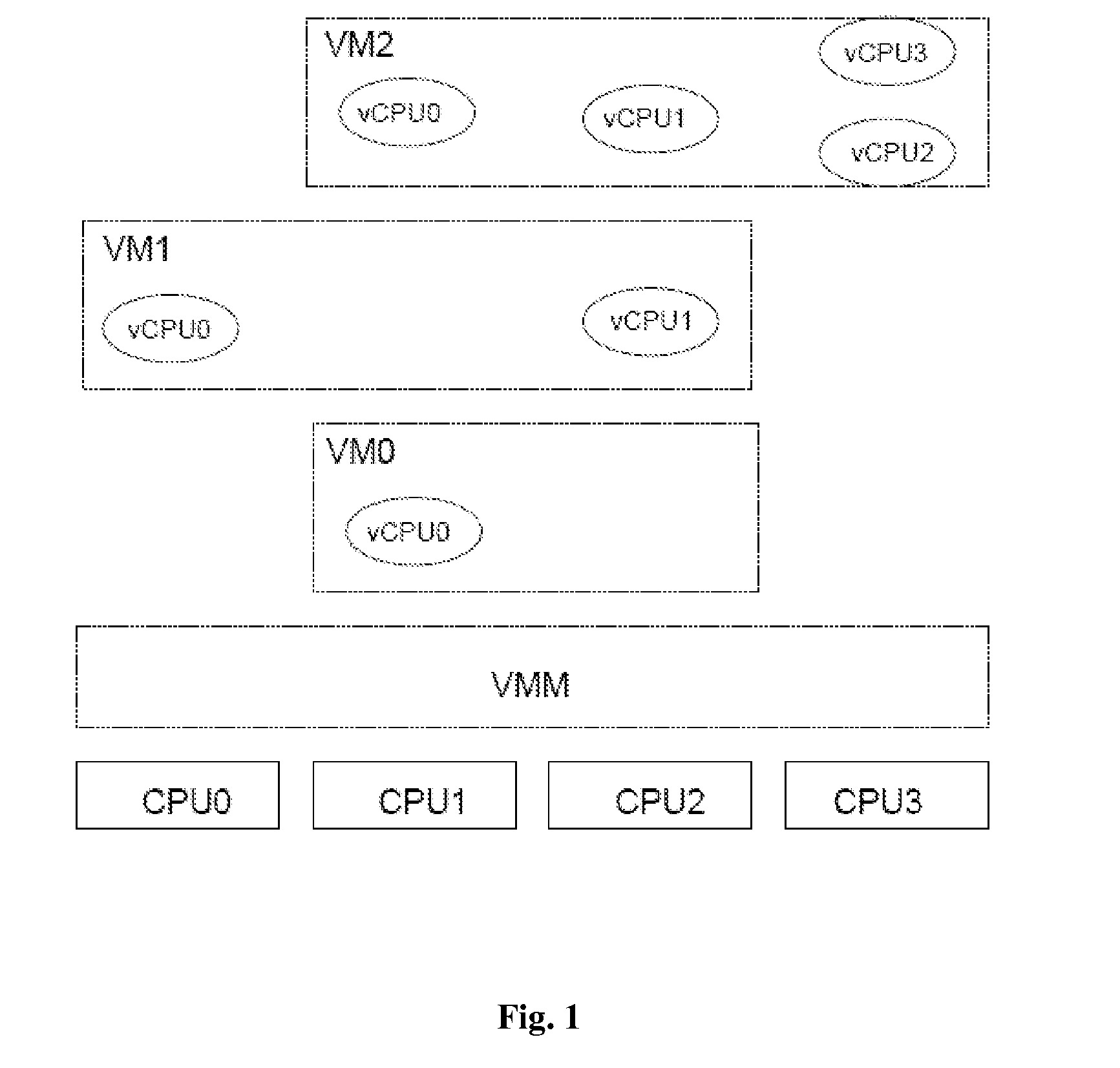
ActiveUS20110119422A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsData processing systemTwo-level scheduling
The present invention provides a scheduling method for a data processing system comprising at least one physical CPU, and one or more virtual machines each assigned to one or more virtual CPUs, the method comprising: a first scheduling step in which one of said virtual machines is elected to run on said physical CPU; and a second scheduling step in which at least one of the virtual CPUs assigned to the elected virtual machine is elected to run on said physical CPU. The second scheduling step is applied to the virtual machine only. When a virtual machine instance is elected to run on a given CPU, the second level scheduling determines the virtual CPU instance to run. The second level scheduling is global and can cause a virtual CPU migration from one physical CPU to another. In order to ensure correct task scheduling at guest level, virtually equivalent (in terms of calculation power) virtual CPUs should be provided to the scheduler. This is achieved by the second level scheduler using a virtual CPU election criteria based on time statistics.
Owner:VIRTUALLOGIX
Task processing system for distributed computation and task processing method for distributed computation
InactiveCN102763086AImprove processing efficiencyImprove scheduling flexibilityResource allocationStore-and-forward switching systemsHandling systemDistributed computing
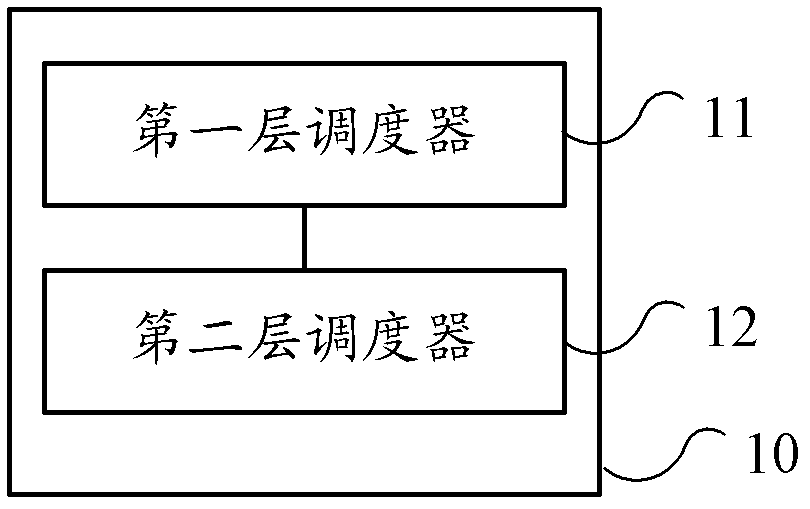
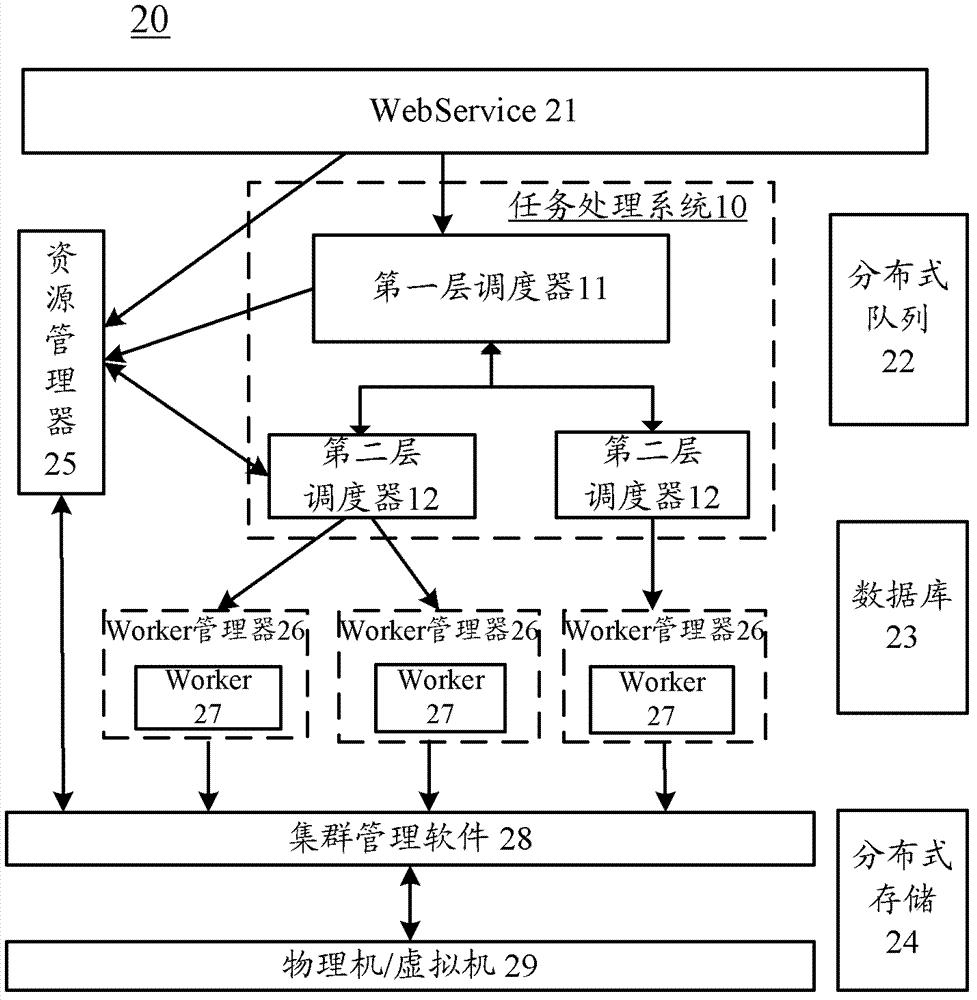
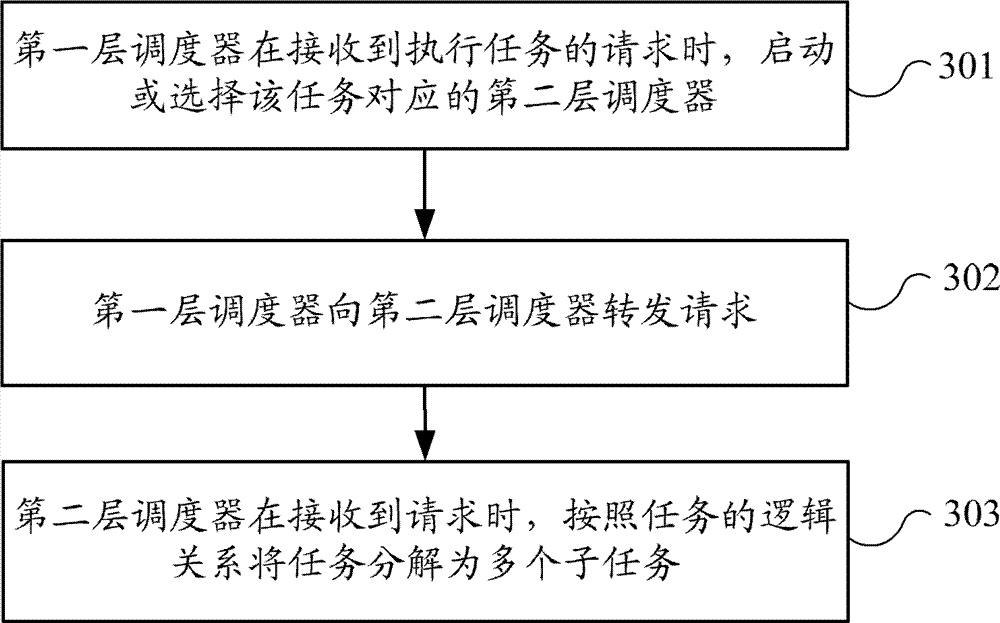
Embodiments of the invention provide a task processing system for distributed computation and a task processing method for the distributed computation. The task processing system comprises a first level scheduler which is used for receiving requests of executing a task, starting or selecting a second level scheduler according to the task, and transmitting the requests to the second level scheduler; and the second level scheduler which is used for decomposing the task into a plurality of subtasks according to a logical relationship of the task when receiving the requests are transmitted by the first level scheduler. The embodiments of the invention employ a two-level scheduling frameworks, with the second level scheduler corresponding to the task and the first level scheduler starting or selecting the second level scheduler corresponding to the task, so that the task processing system and the task processing method can be used in different tasks, and processing efficiency and scheduling flexibility are improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Micro-architecture sensitive thread scheduling (MSTS) method
InactiveCN102081551AImprove hit rateRun fastMultiprogramming arrangementsOperational systemRelevant information
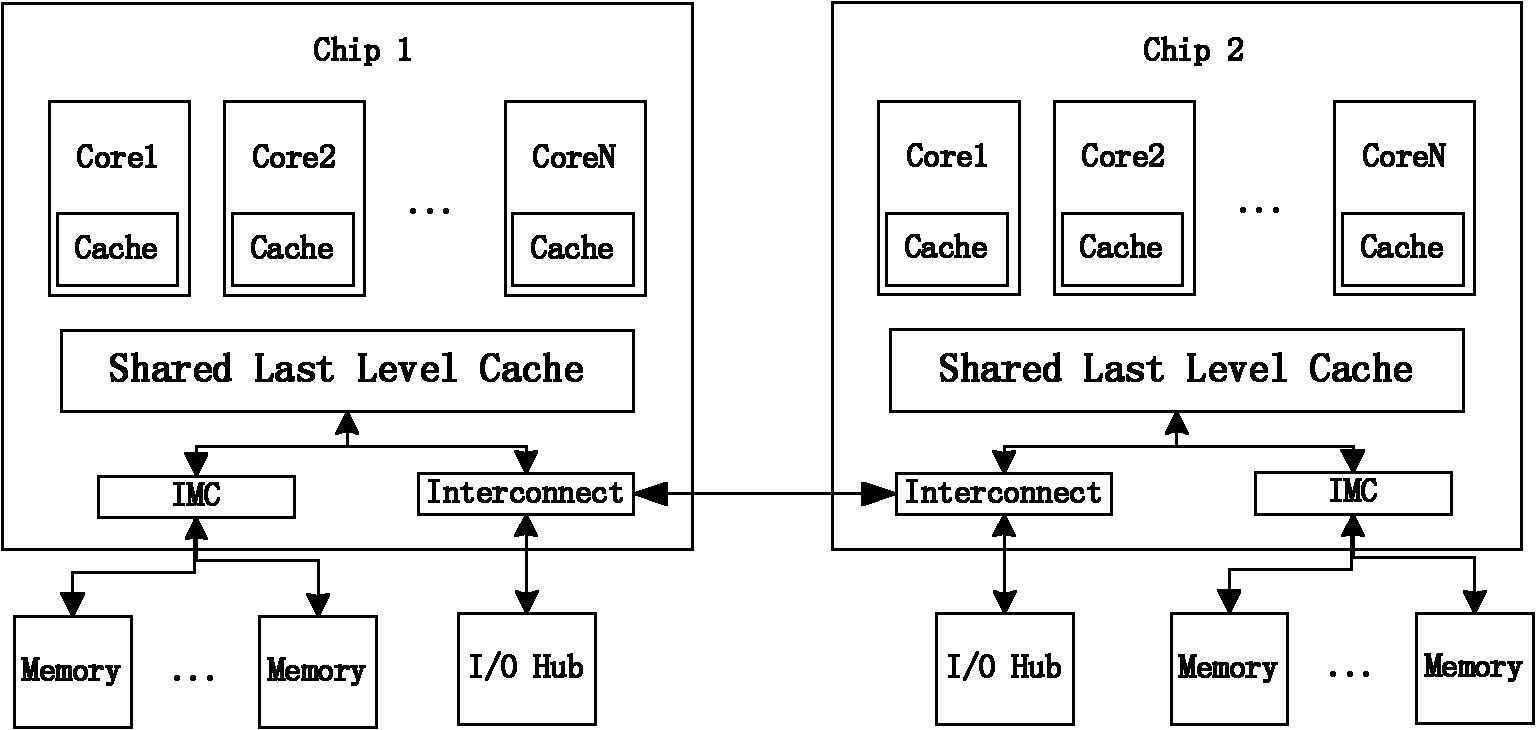
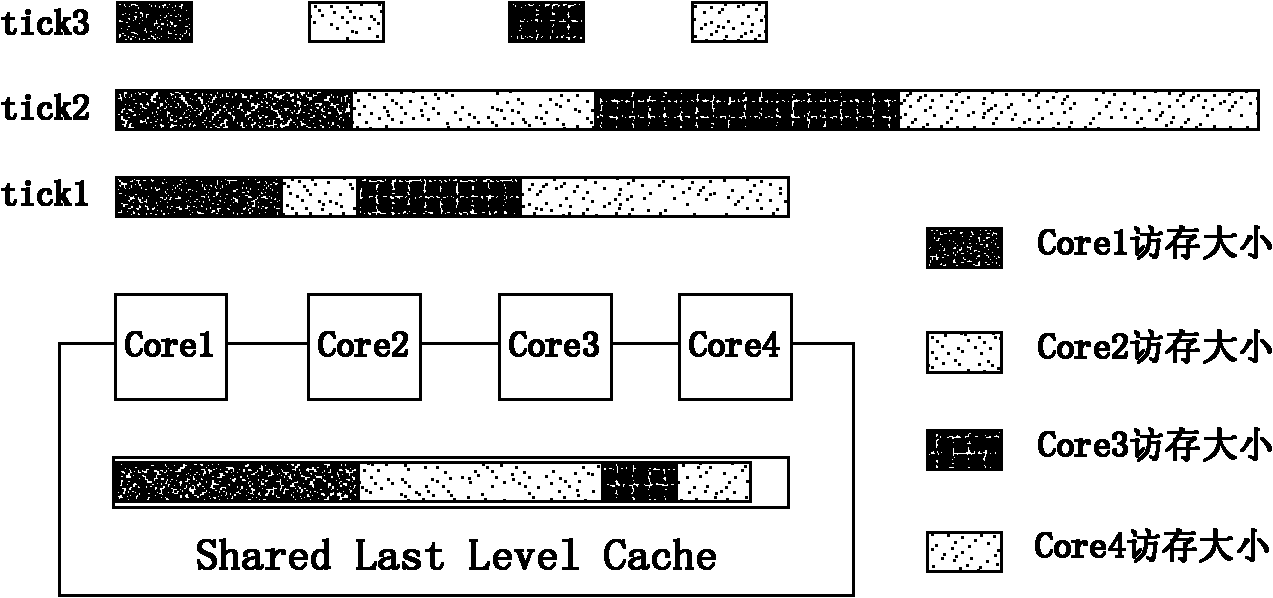
The invention relates to a micro-architecture sensitive thread scheduling (MSTS) method. The method comprises two-level scheduling strategies: in the inner portions of nodes, according to the structural characteristics of CMP, through acquiring relevant information of cache invalidation in real time, the threads which excessively compete for the shared cache resources operate in a staggered mode in time and spatial dimension, and the threads which can carry out effective mutual data sharing operate simultaneously or successively; and in a layer between nodes, through sampling memory data areas frequently accessed by the threads, the threads are bound to the nodes in which data are arranged as far as possible so as to reduce the access to a remote memory and reduce the amount of communication between chips. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of reducing the access delay caused by simultaneously operating a plurality of threads with large shared cache contention, and improving the operation speeds and system throughput rates of the threads.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
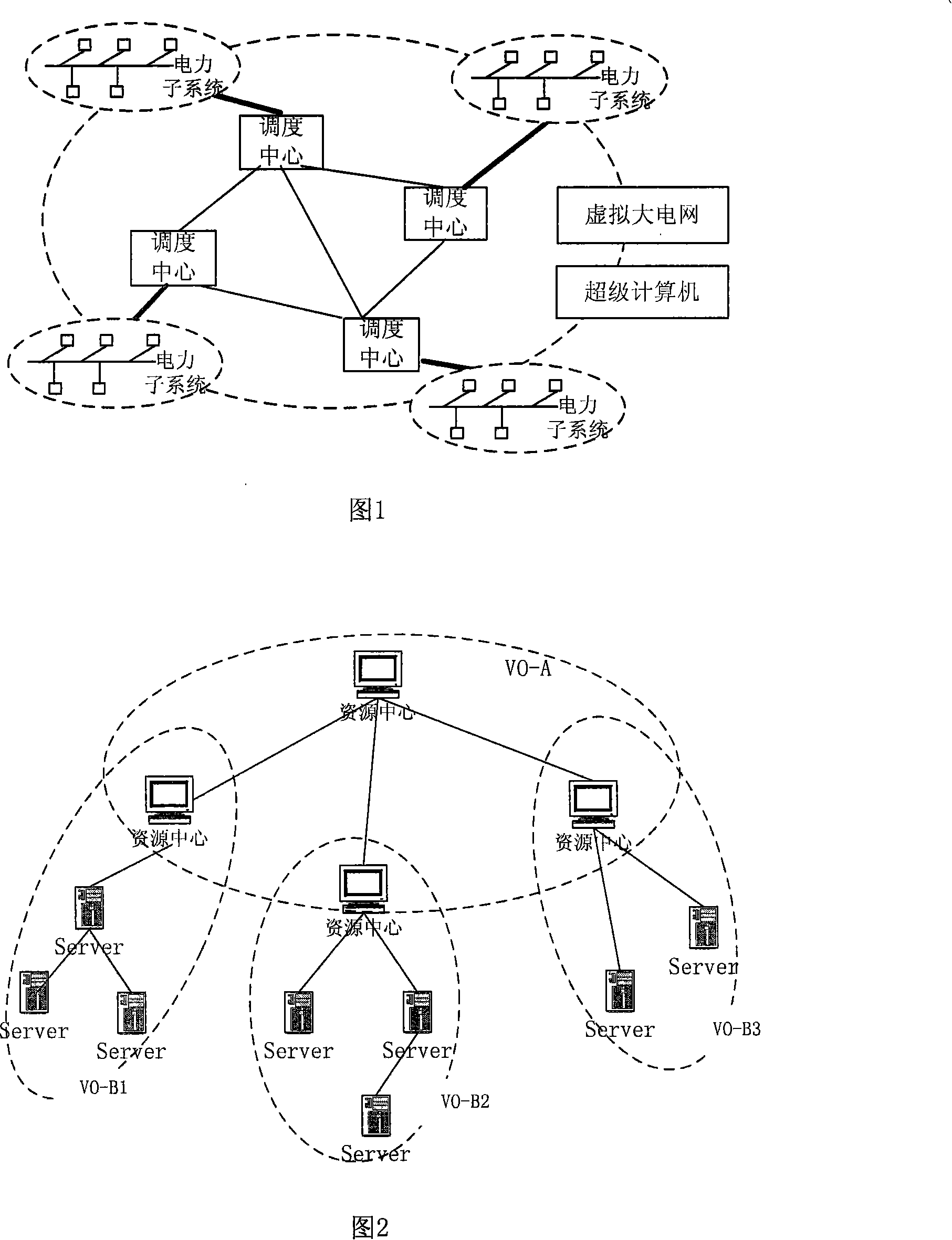
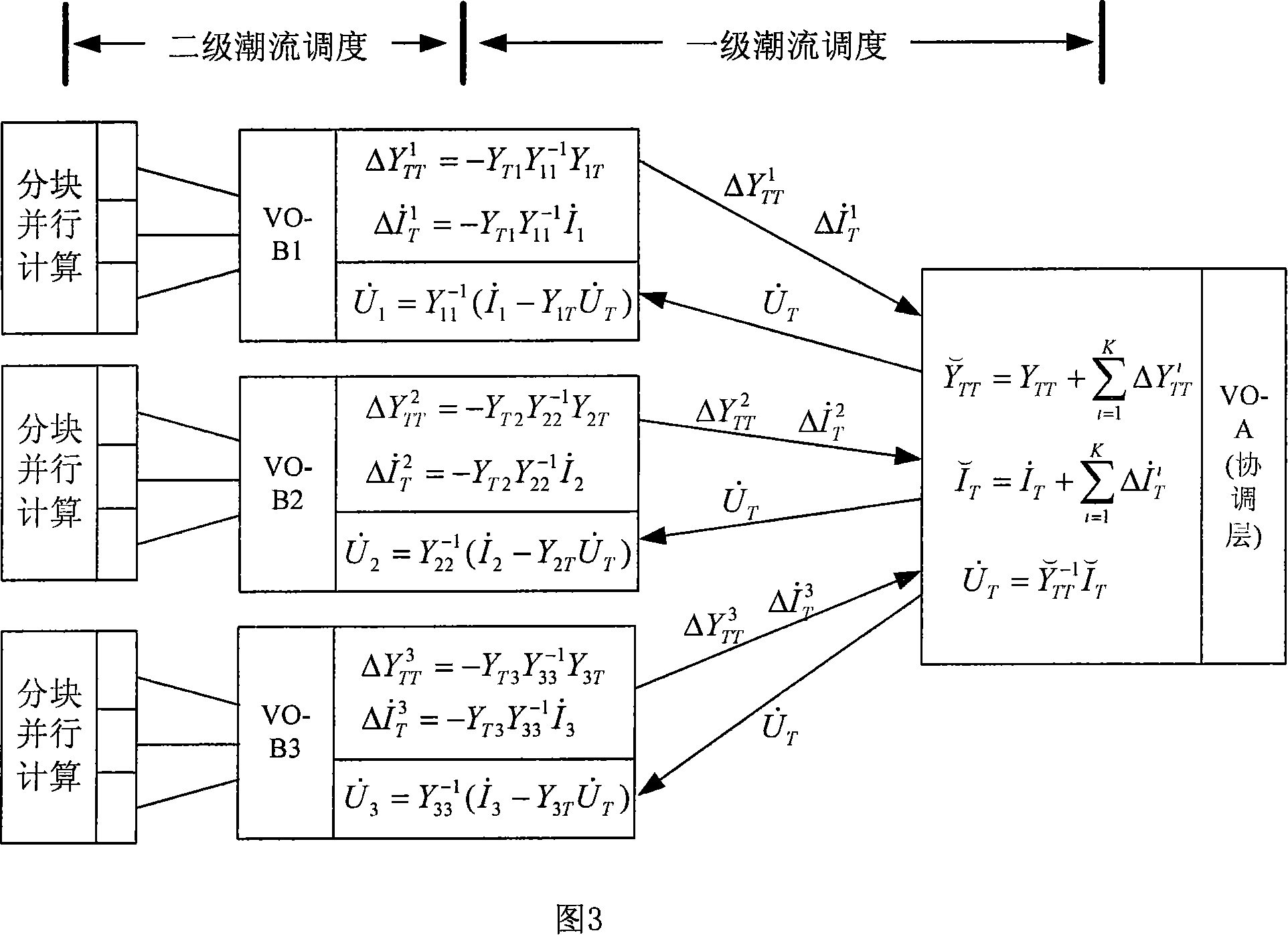
Method for implementing parallel power flow calculation based on multi-core computer in electric grid
The invention discloses a method for realizing parallel load flow computation based on a multi-core computer in power grid. The method comprises two-stage scheduling, wherein the first-stage scheduling realizes division and cooperation of load flow computation task, and the second-stage scheduling performs fine division to the computation task, in the multi-core computer, subtasks can be parallelly calculated, and after several iterative convergences, the computation results are collected and outputted by a coordination layer. The invention adopts the parallel computation and maximally utilizes the computation resource in virtual organizations, so that the computation speed is faster and the cost is lower.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
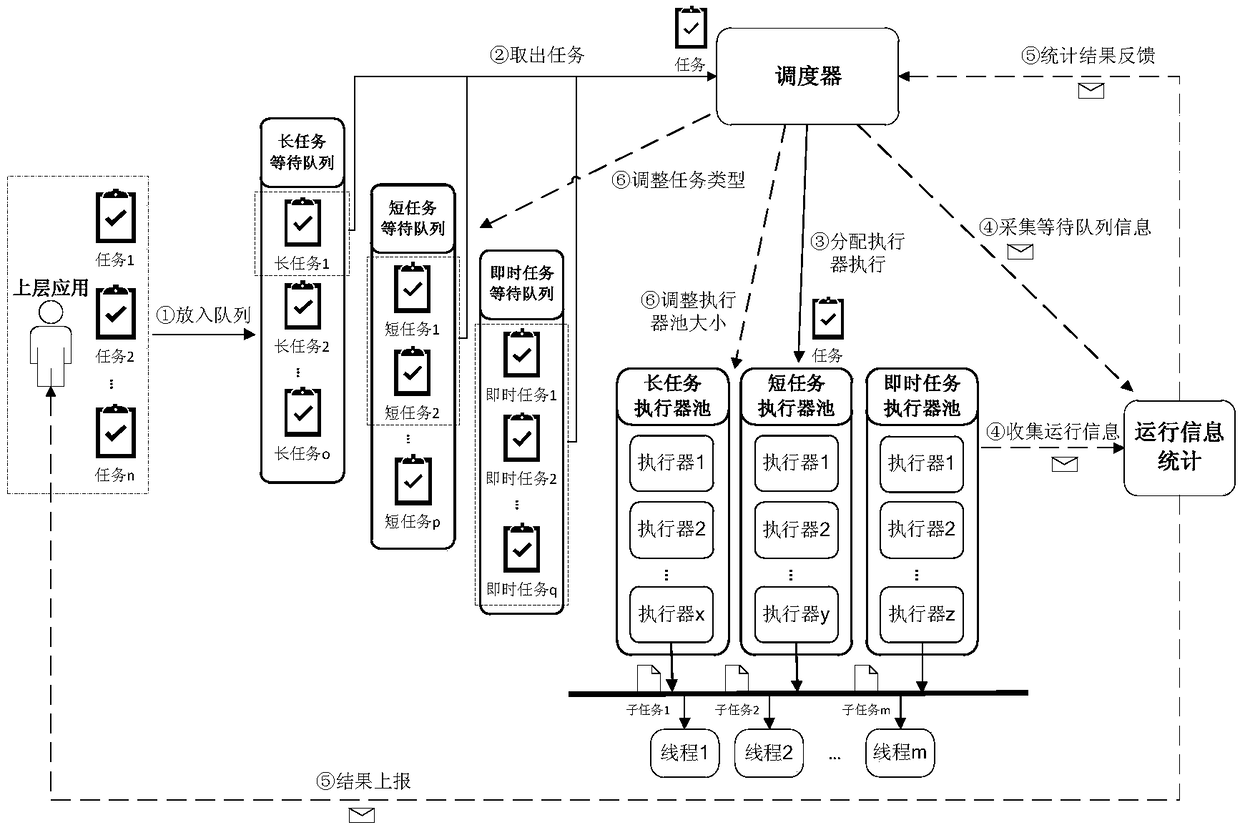
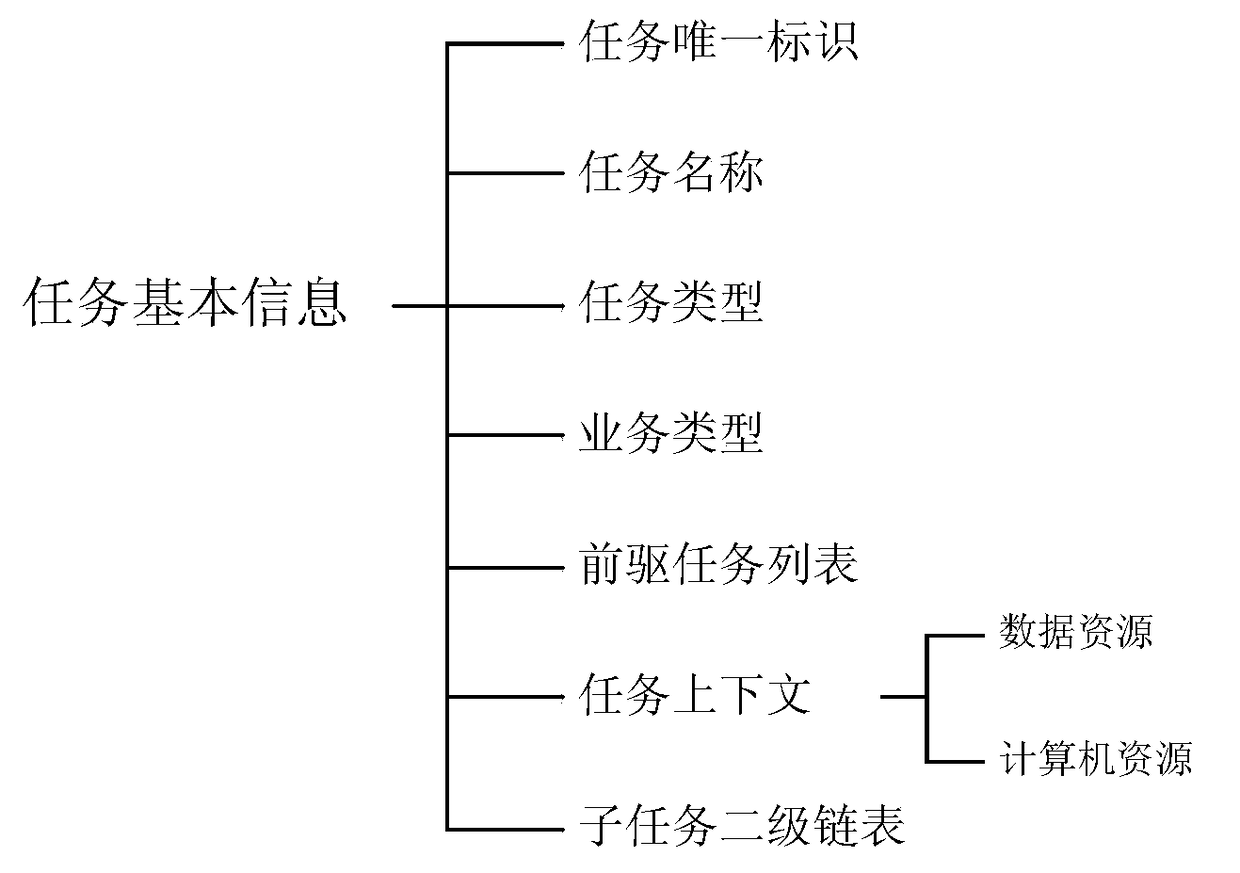
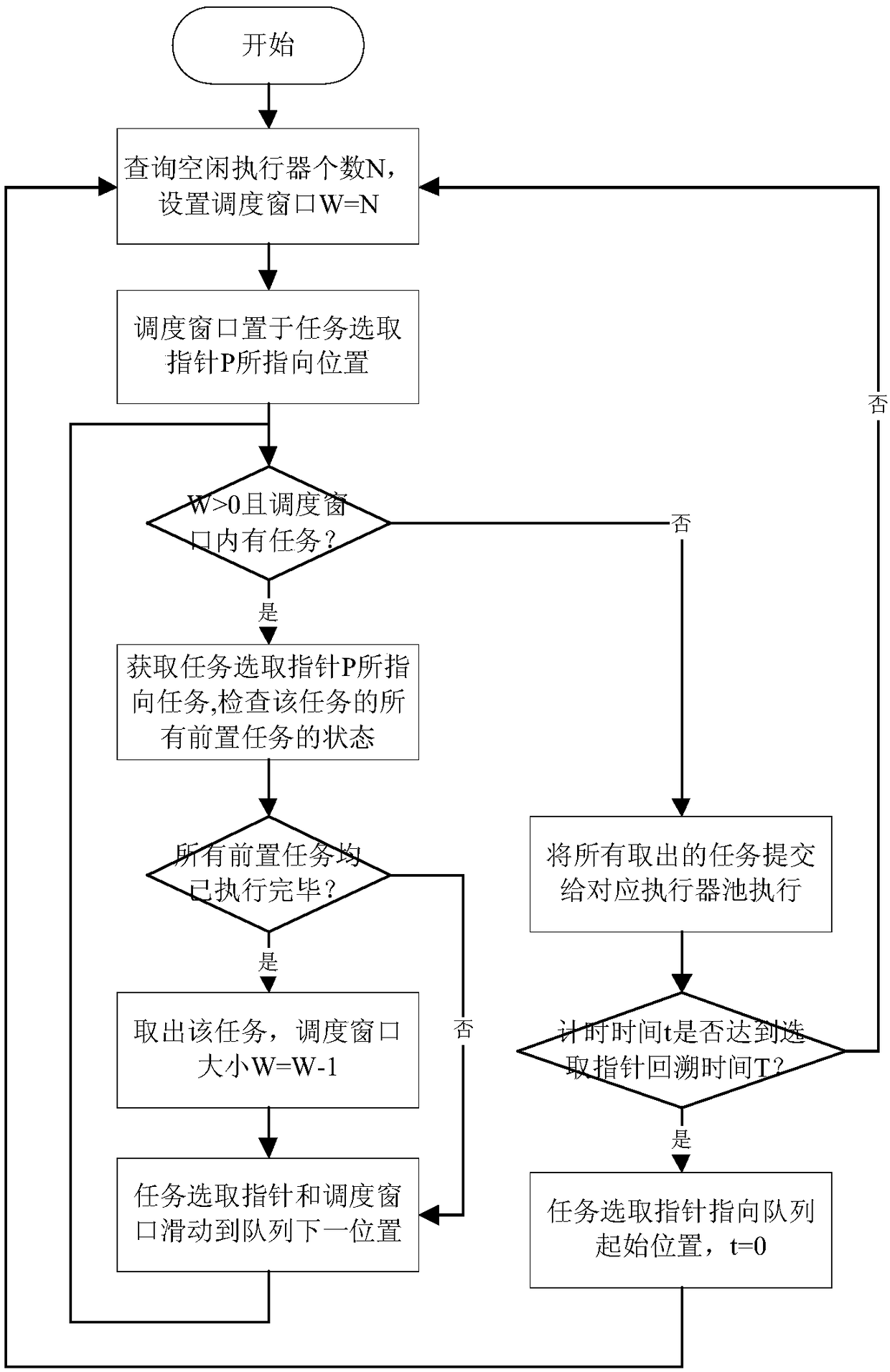
Two-stage self-adaptive scheduling method suitable for large-scale parallel data processing tasks
ActiveCN108920261ATake advantage ofSolve the difficult problem of parallel schedulingProgram initiation/switchingActuatorLarge scale data
The invention discloses a two-stage self-adaptive scheduling method suitable for a large-scale parallel data processing tasks. Two-stage scheduling is performed on tasks from a task stage and a subtask stage. By the method, the problem of parallel scheduling difficulty caused by complex dependence relationship among the tasks is solved effectively, parallelism degree is increased, orderly and efficient parallel processing of large-scale data processing tasks is realized, task waiting or executing time is reduced, and overall executing time is shortened. In addition, by the method, executor operation statistical information can be fed back to a scheduler, self-adaptive adjusting of executor pool size and task type is realized, and scheduling is constantly optimized, so that system resourceusing efficiency is improved.
Owner:中国航天系统科学与工程研究院
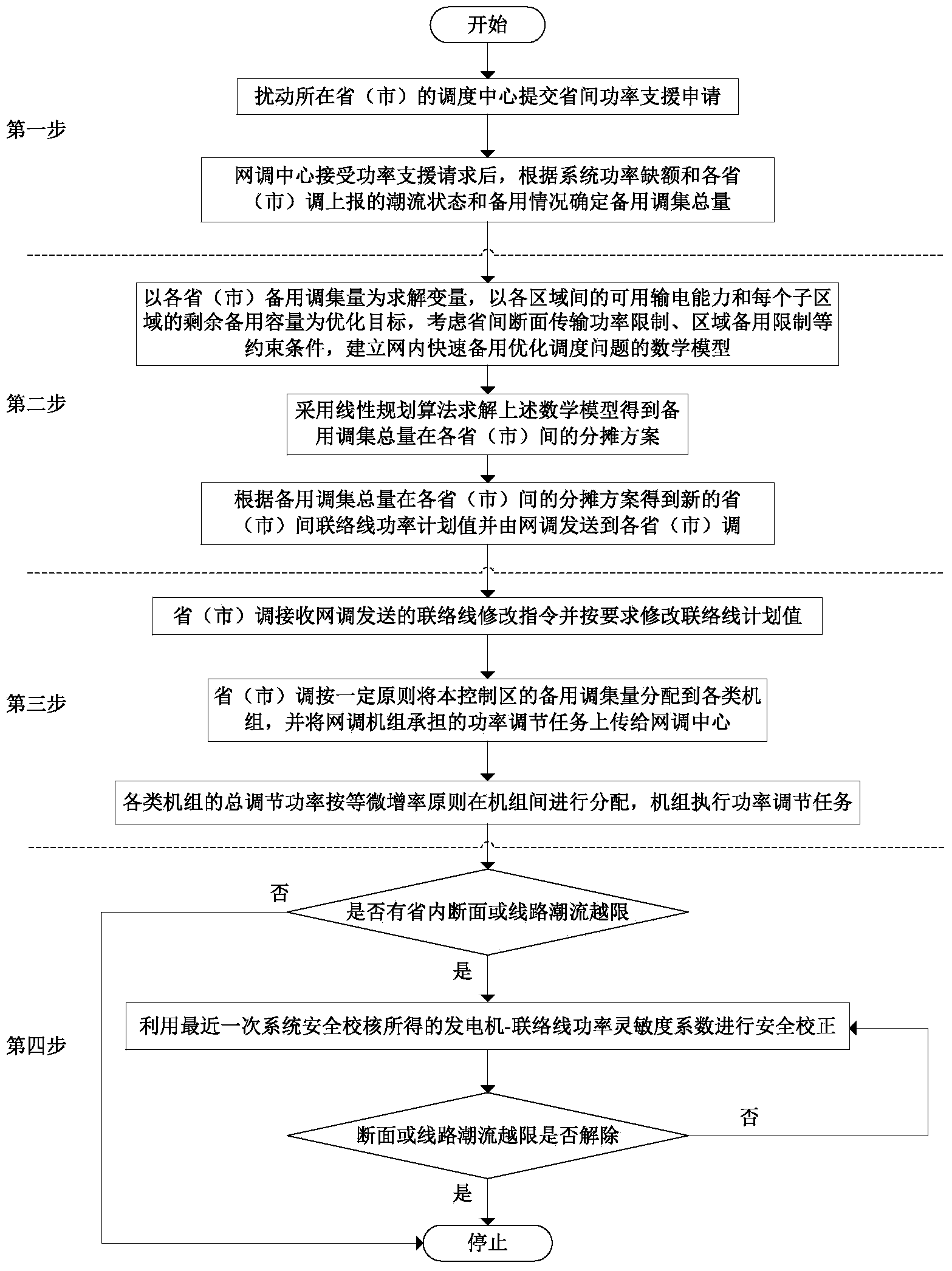
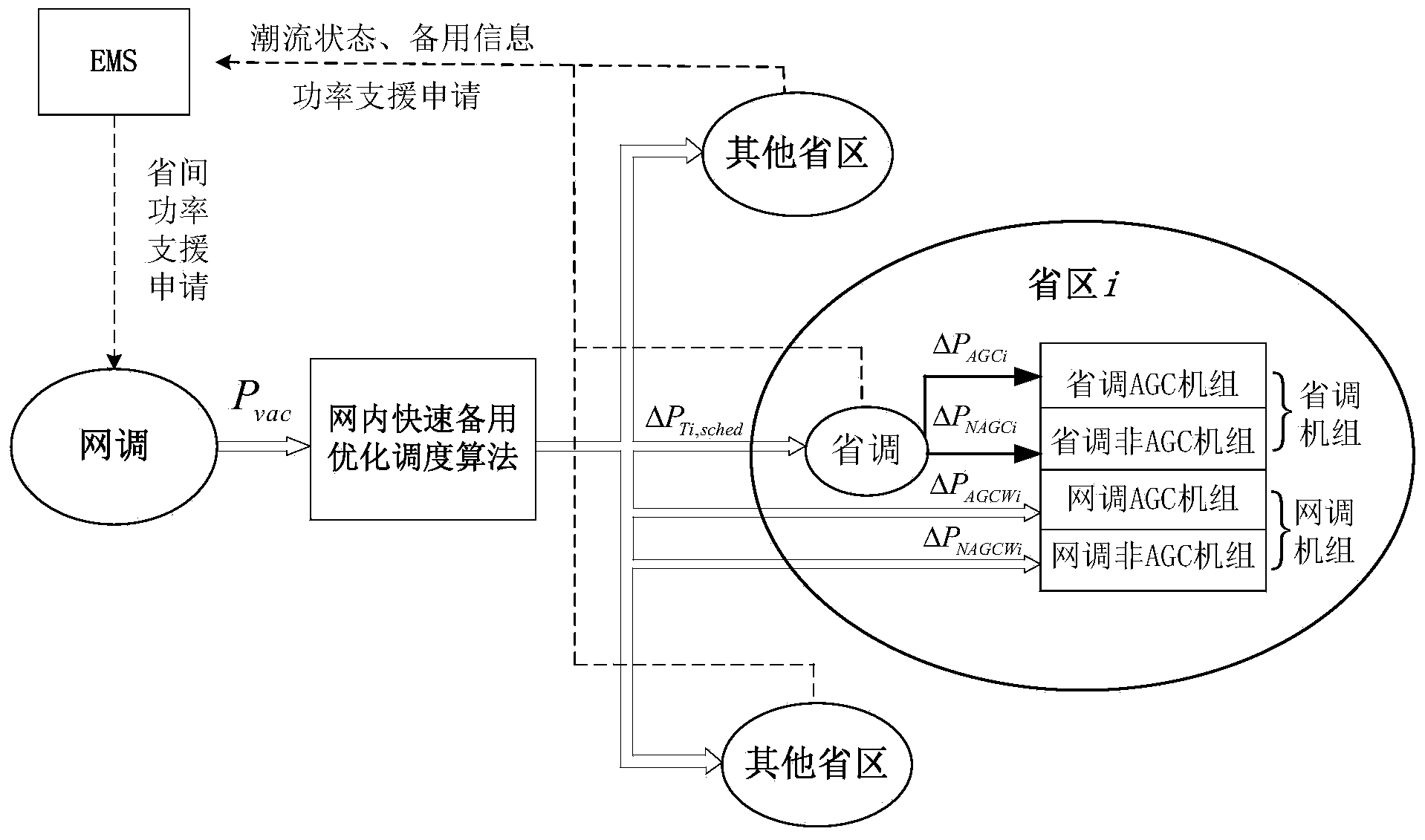
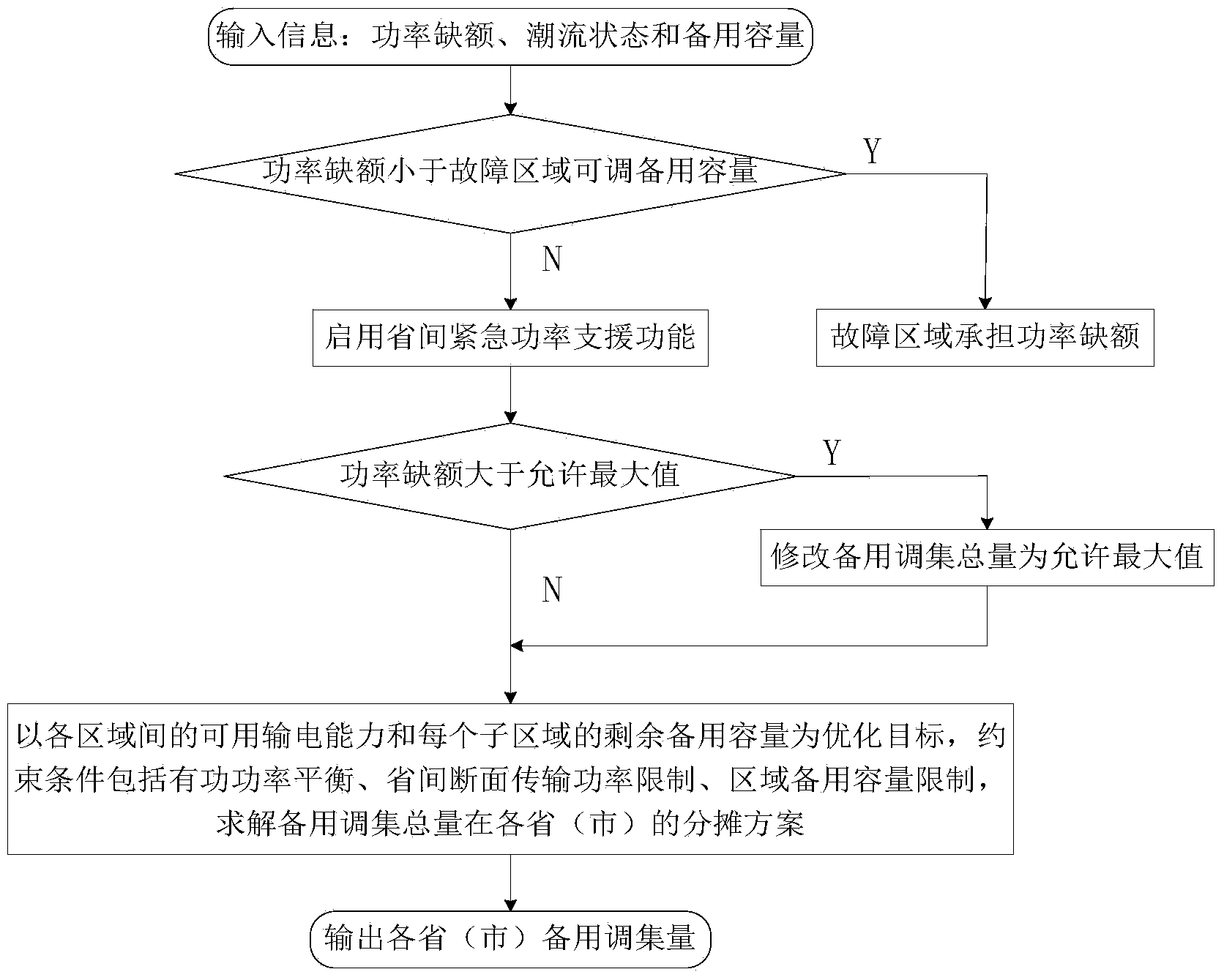
In-network quick standby coordination and optimization scheduling method used after high-power vacancy accidents
ActiveCN104300535AAccurate processingImprove the ability to control the large power gridAc network circuit arrangementsPower gridEngineering
The invention discloses an in-network quick standby coordination and optimization scheduling method used after high-power vacancy accidents. The method includes the steps that firstly, with the maximum of usable power transmitting capacity among all regions and residual standby capacity of all sub regions as the optimization target, meanwhile, the constraint conditions such as province discontinuity surface quota and region standby limit are considered, and an allocation scheme among all provinces and cities of the standby assembling amount is solved; furthermore, an allocation principle among units of the standby assembling amount of all the provinces and cities is obtained. According to the method, through network and province two-level scheduling and coordination control, the coordinated optimization scheduling of province-to-province emergency power support after the high-power vacancy accidents is achieved, and quick processing of power lack disturbance is guaranteed.
Owner:CENT CHINA GRID +1
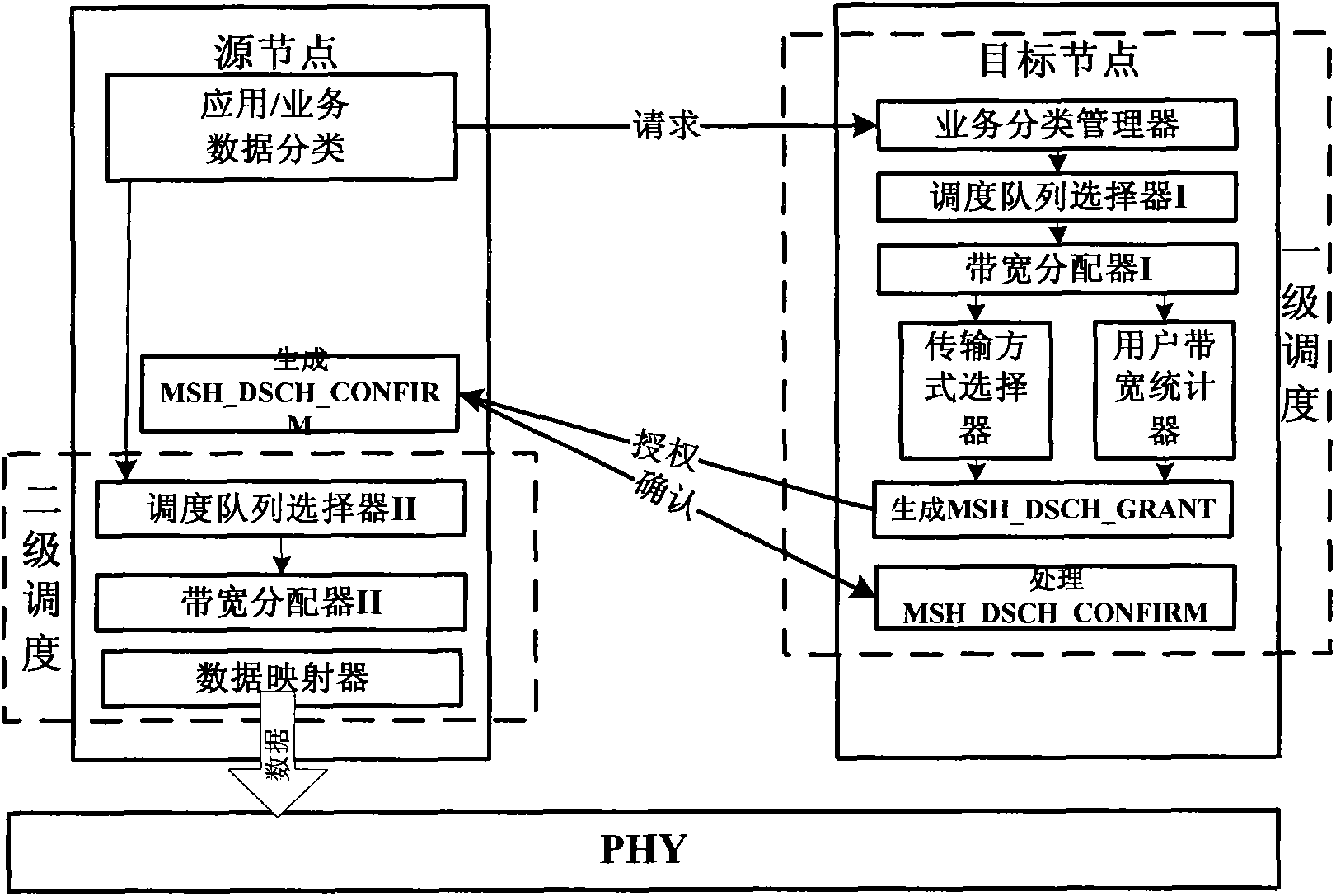
Data scheduling device and method supporting service quality in wireless MESH network
ActiveCN101820645AImprove bandwidth utilizationGuaranteed priorityNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless mesh networkPhysical layer
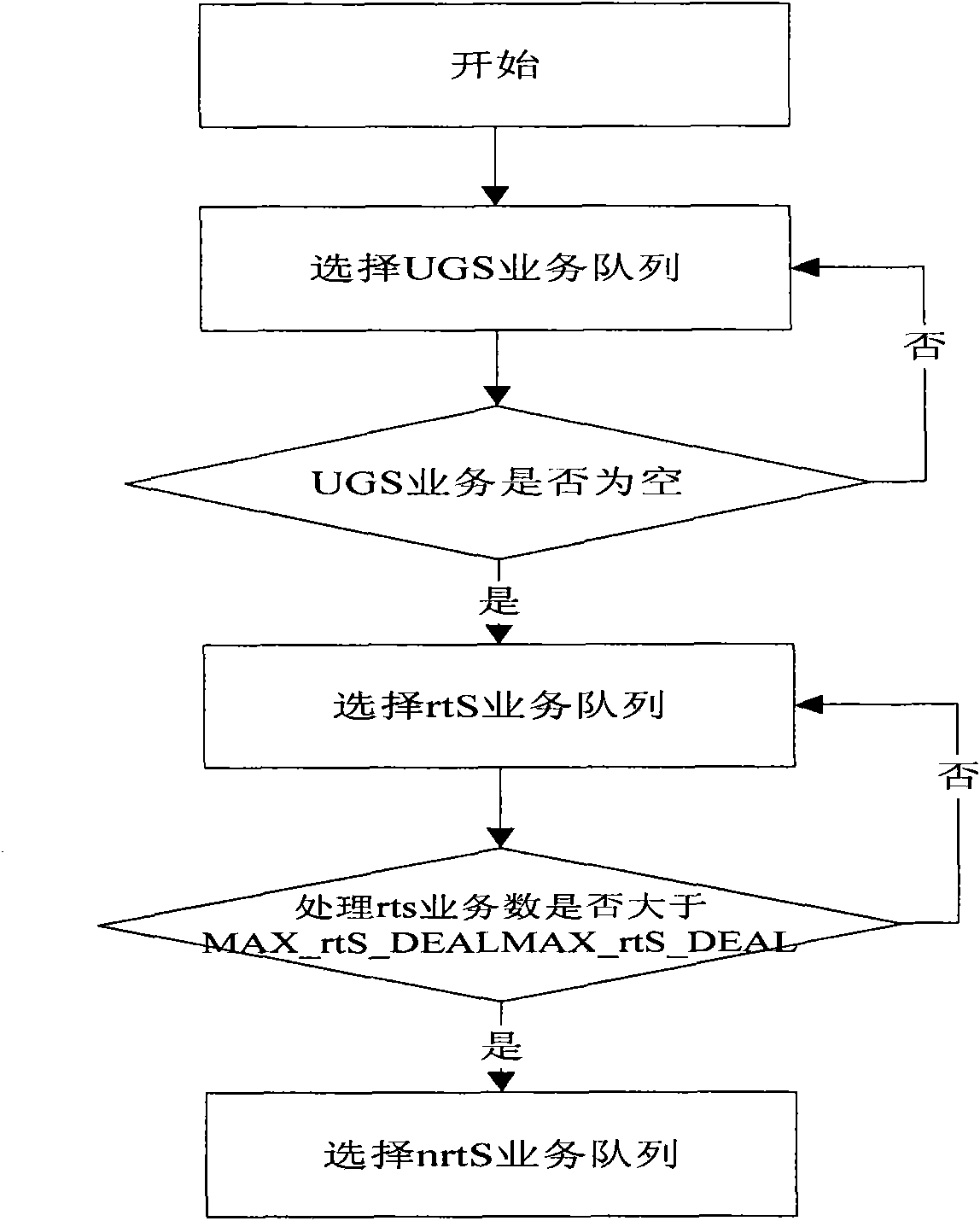
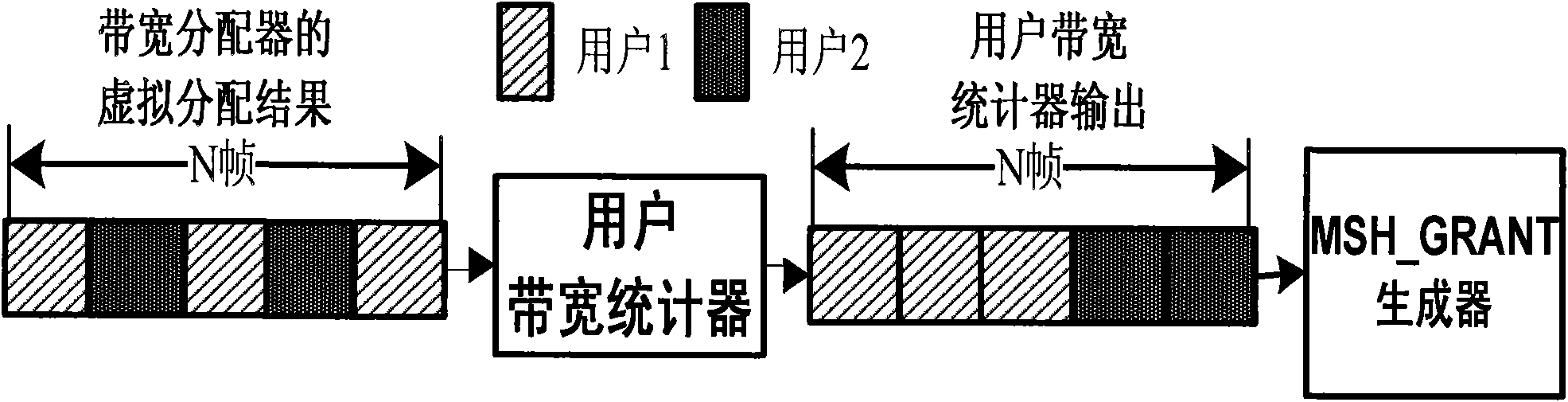
The invention provides a data scheduling device and a method supporting service quality in a wireless MESH network. The device of the invention comprises two schedulers, wherein in the primary scheduler, a service sorting manager queues requests according to service types; a scheduling queue selector I selects a request queue to be scheduled; a bandwidth allocator I virtually allocates bandwidths; a transmission mode selector provides a modulation encoding mode corresponding to connection; a user bandwidth statistic device combines discontinuous bandwidths into continuous bandwidth and sends a primary scheduling result to a source node; in the secondary scheduler, a scheduling selector II selects service of priority scheduling from the service queue; a bandwidth allocator II computes the largest / smallest sending quantity of the frame, differentiates the grades of the services and schedules the services frame by frame; and a data mapper sends the scheduled data to a physical layer and transmits to a destination node.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Task secondary scheduling module and method
ActiveCN101452399AImprove real-time performanceImprove resource utilizationMultiprogramming arrangementsOperational systemResource utilization
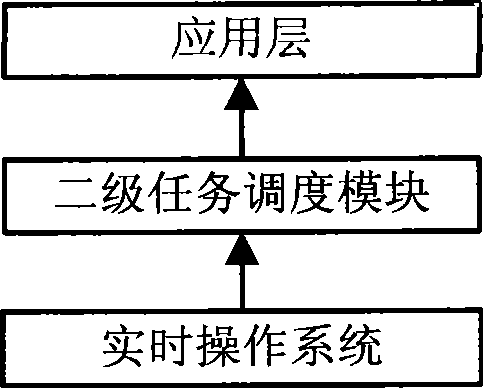
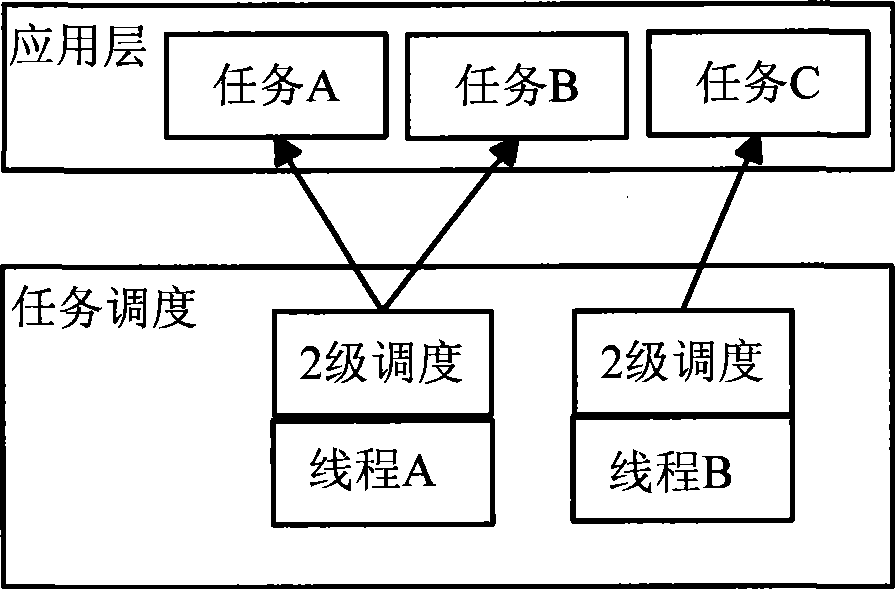
The invention provides a module and a method for task two-level scheduling. The task two-level scheduling module is applied between a real-time operating system and an application layer, and comprises an initialization submodule, a task scheduling processing submodule and a task operating submodule, wherein the initialization submodule is used for initializing the task two-level scheduling module and establishing a thread registration form to store the task information of a thread; the task scheduling processing submodule is used for receiving a thread message and directly processing inside information of the thread message, and calls an object task for processing after sending a user message to the corresponding object task; and the task operating submodule is used for completing task operation and message receiving and sending between tasks. The module and the method can realize the process of task two-level scheduling on the basis of the prior real-time operating system, thereby increasing the real-time performance and resource utilization rate of the real-time operating system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Instruction execution based on outstanding load operations
InactiveUS20120079241A1Reduce areaReduce total powerDigital computer detailsMemory systemsLong latencyLocal memories
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for scheduling thread execution in a multi-threaded processing environment. A two-level scheduler maintains a small set of active threads called strands to hide function unit pipeline latency and local memory access latency. The strands are a sub-set of a larger set of pending threads that is also maintained by the two-leveler scheduler. Pending threads are promoted to strands and strands are demoted to pending threads based on latency characteristics, such as whether outstanding load operations have been executed. The longer latency of the pending threads is hidden by selecting strands for execution. When the latency for a pending thread is expired, the pending thread may be promoted to a strand and begin (or resume) execution. When a strand encounters a latency event, the strand may be demoted to a pending thread while the latency is incurred.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
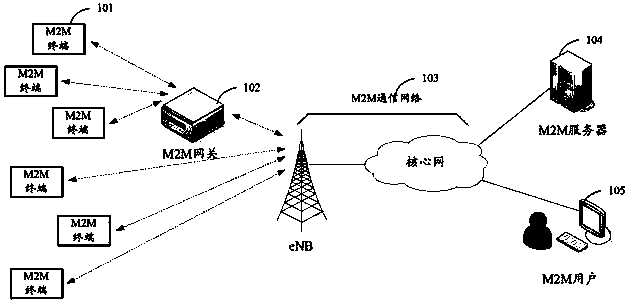
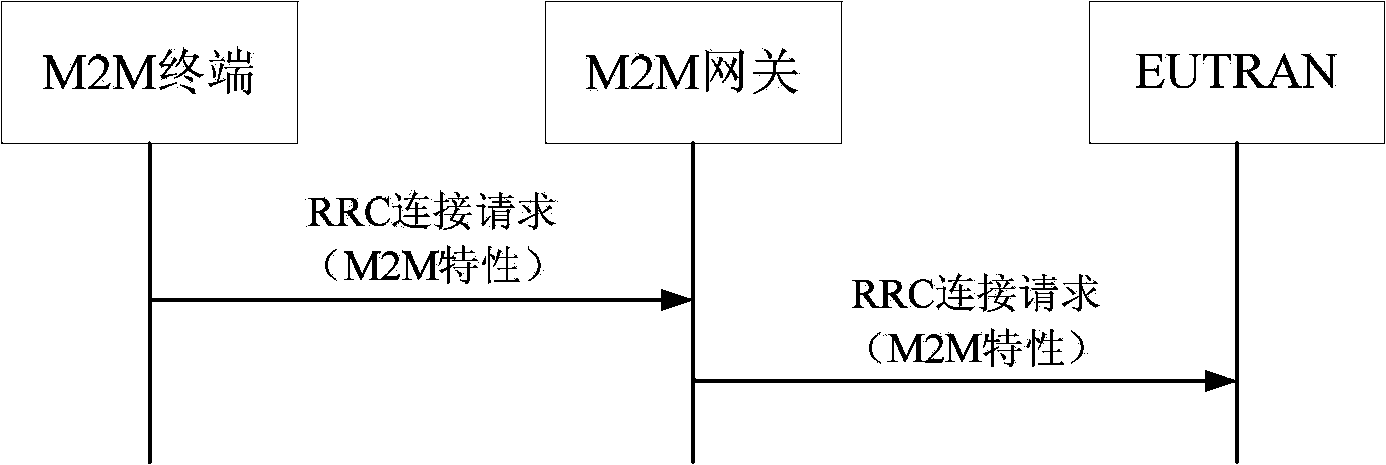
M2M (machine to machine) terminal group management method
The invention discloses an M2M (machine to machine) communication terminal group management method. The method includes: A, M2M terminals report their supported features or device types to a base station, and the base station distributes the supported common features or the M2M terminals to a same M2M group; B, the base station informs an M2M group identifier and a device identifier of each M2M terminal through RRC (radio resource control) signaling; C, with the M2M group as a unit, the base station dispatches the M2M terminals by means of two-level dispatching; in the first-level dispatching which is physical layer dispatching, wireless resources that carry M2M group dispatching information usage are indicated by a PDCCH (physical downlink control channel); in the second-level dispatching which is MAC (media access control) dispatching, wireless sources that each M2M terminal uses are indicated. The method has the advantages that system PDCCH resources can be saved effectively and the system can contain mass M2M terminals.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
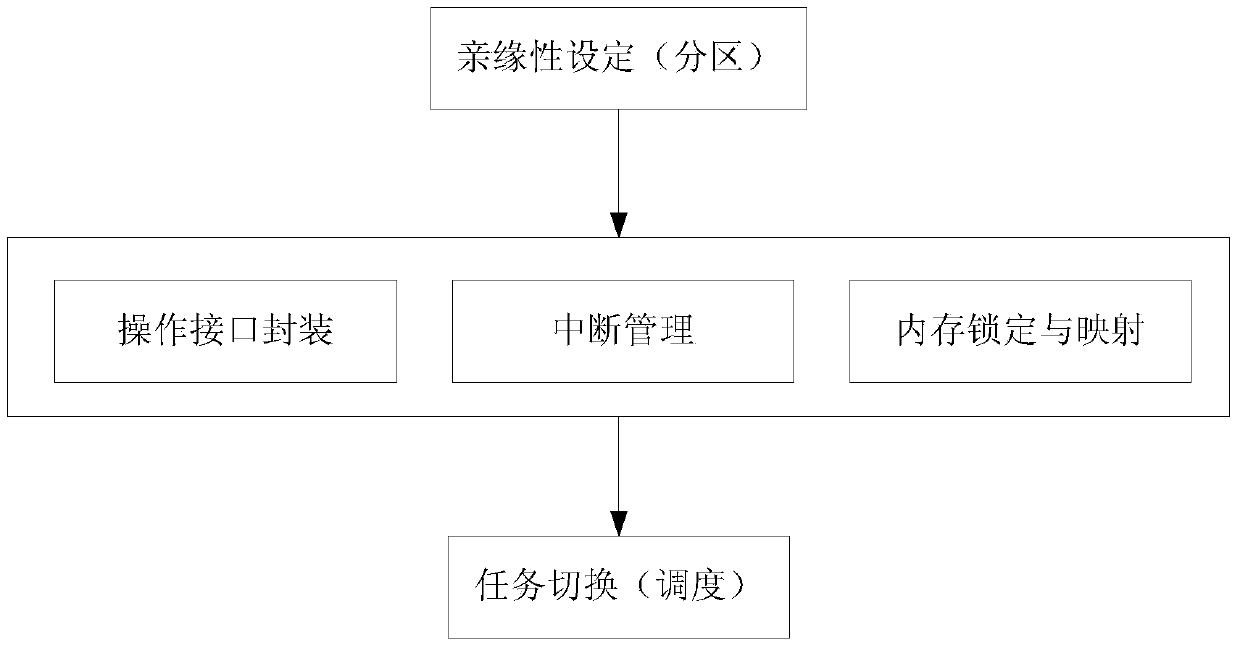
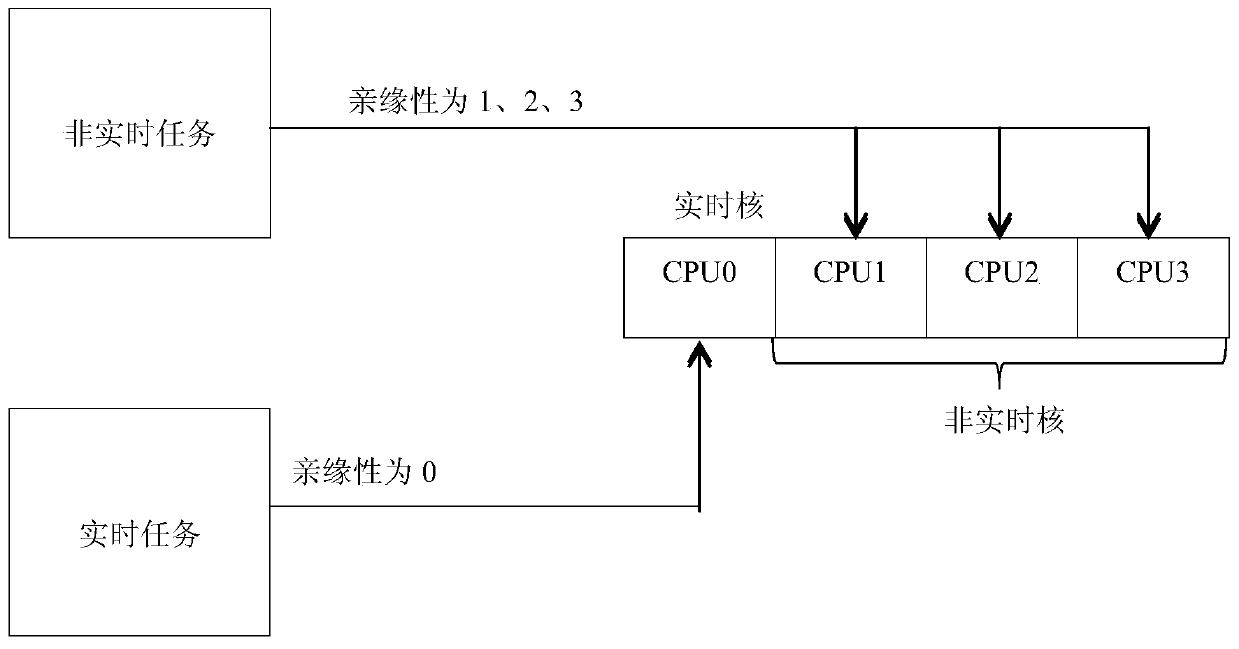
Two-stage scheduling method of real-time extension of Windows system
ActiveCN103744726AResolve task switchingSolve real-timeProgram initiation/switchingTime extensionAdvanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
The invention relates to a two-stage scheduling method of real-time extension of the Windows system. According to the method, by means of affinity settings of the Windows system, reallocating the CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources of the system, and specifying a running core of real-time tasks in order to ensure resources needed by the real-time tasks; setting an IOAPIC(I / O Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) redirection table to enable external interrupt to point to specific core processing and to not affect the operation of real-time kernel; meanwhile, using a clock interrupt counter of Local APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) to provide task scheduling with high-precision clock signals; using WinDbg to obtain operation function entry addresses of the process and the thread of Windows from NTDLL to be packaged as DLL, and forming a basic interface of task control; locking and mapping kernel task control blocks and task queues to enable the writing and debugging of a scheduling algorithm can be performed in a user mode, and finally linking into the interrupt handling routine of the high-precision clock of the Local APIC so as to complete the real-time kernel scheduling algorithm.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Implementation method for integrating provincial dispatch organization PAS system and local-level dispatch organization PAS systems in electric power system
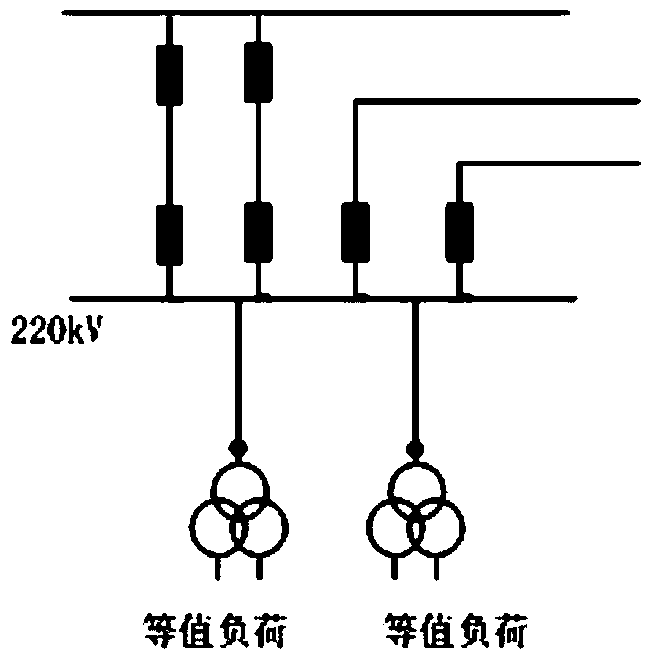
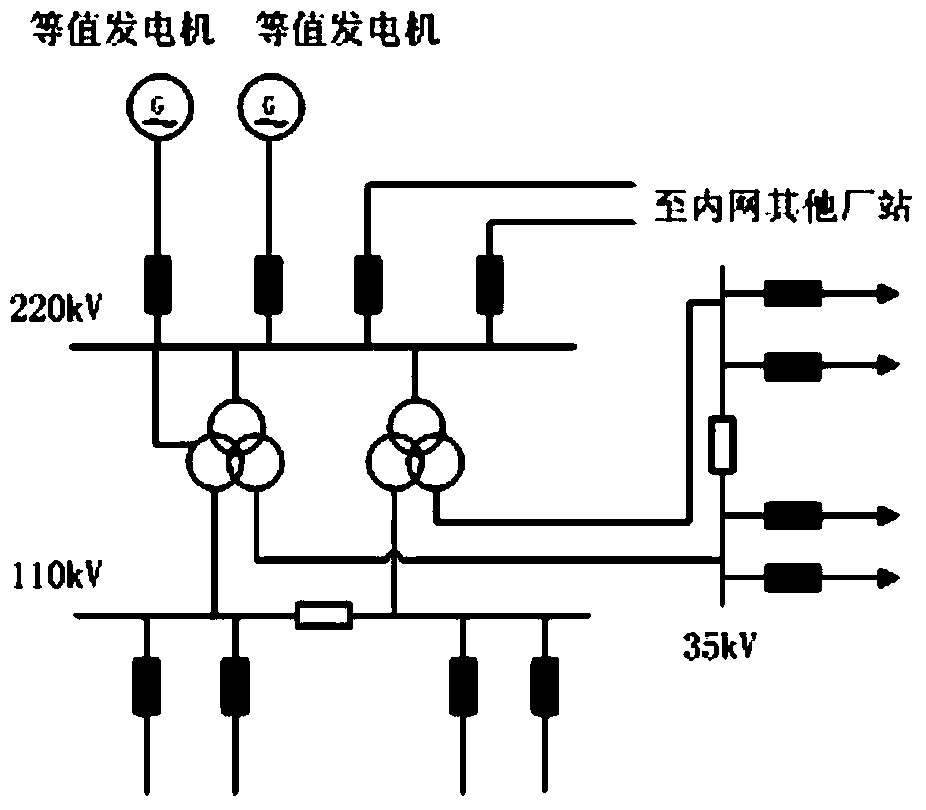
ActiveCN101860024ARealize integrationGood effectTransmissionAc network circuit arrangementsElectric power systemPower grid
The invention discloses an implementation method for integrating provincial dispatch organization PAS system and local-level dispatch organization PAS systems in an electric power system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) splicing a provincial dispatch organization power grid model with local-level dispatch organization power grid models; (2) and arranging an integrated PAS system by using a centralized analytical calculation service mode, wherein the local-level dispatch organization PAS systems do not carry out construction or deployment any longer, and the integrated PAS system simultaneously has all the functions of the provincial dispatch organization PAS system and the local-level dispatch organization PAS systems and is arranged at a provincial dispatch organization server. The integrated PAS system comprises a front-end application layer, an application service layer and a model service layer, wherein the clients of the provincial dispatch organization and local-level dispatch organization are connected to a provincial dispatch organization PAS application service layer. The invention can enhance the accuracy and the practicality of network analysis calculation of provincial and local-level dispatch centers and realize the integration of the provincial dispatch organization PAS system and the local-level dispatch organization PAS systems.
Owner:云南电力调度中心 +1
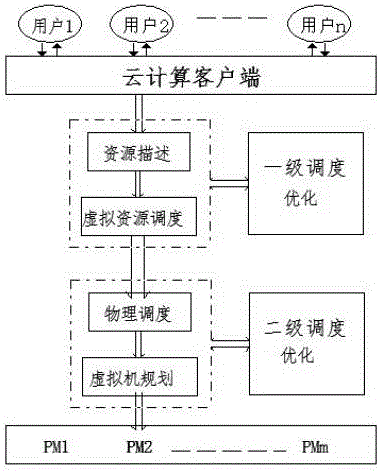
An energy consumption optimization management method for cloud platform based on fusion genetic algorithm and ant colony algorithm
InactiveCN109213585AImprove performanceReduce energy consumptionProgram initiation/switchingArtificial lifeGenetic algorithmCloud resources
The invention discloses a cloud platform energy consumption optimization management method based on a fusion genetic algorithm and an ant colony algorithm. The invention adopts a two-level dispatchingmode. The first-level dispatching dispatches a task to a virtual machine for execution according to the preference selection of a user on performance and cost. According to the task attributes and resource load, the second-level scheduling searches for the appropriate cloud resources to allocate to the virtual machine. The invention divides the demand of the user for the service quality into an energy consumption demand and a cost demand. The energy consumption demand reduces the energy consumption by reducing the calculation energy consumption, transmission energy consumption and storage energy consumption of the physical resources, and the cost demand reduces the calculation cost through the comprehensive energy consumption demand and the scheduling cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
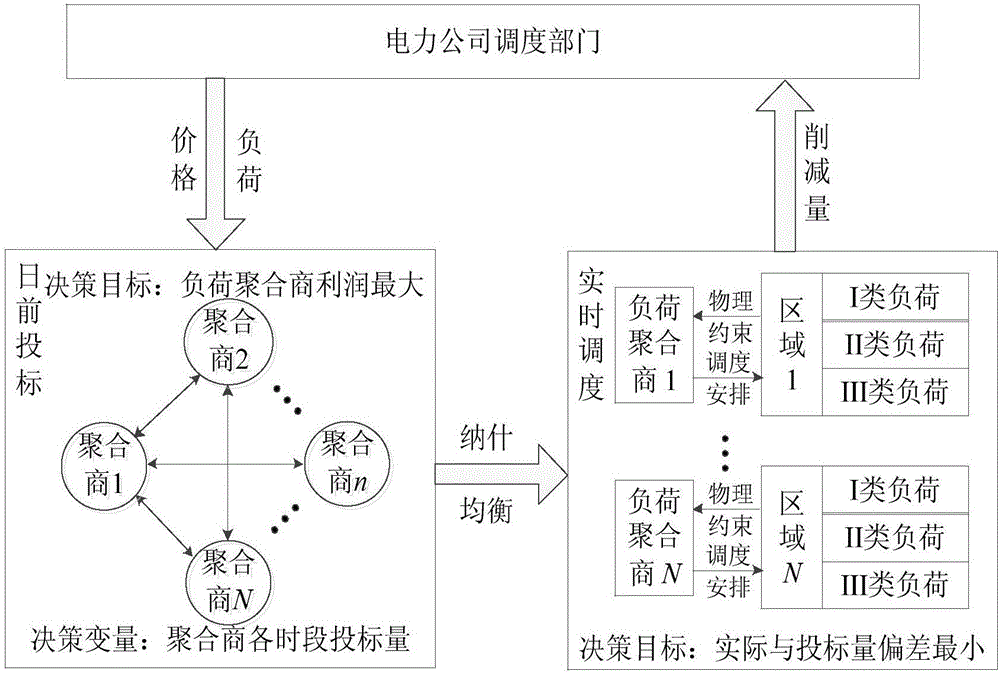
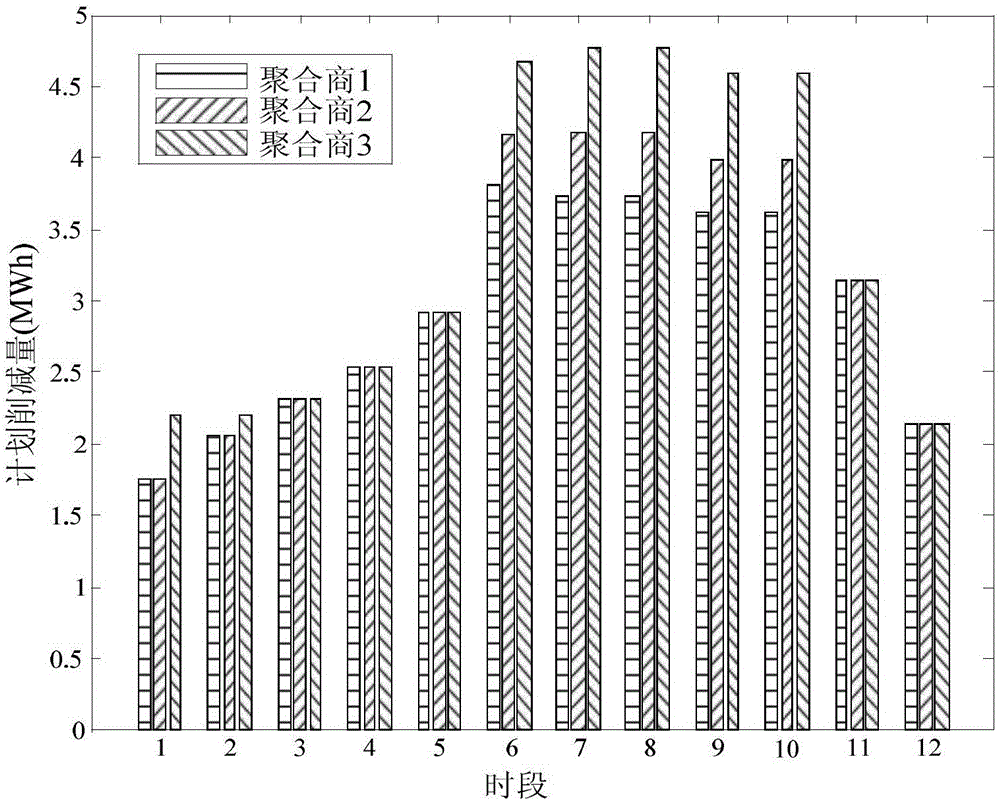
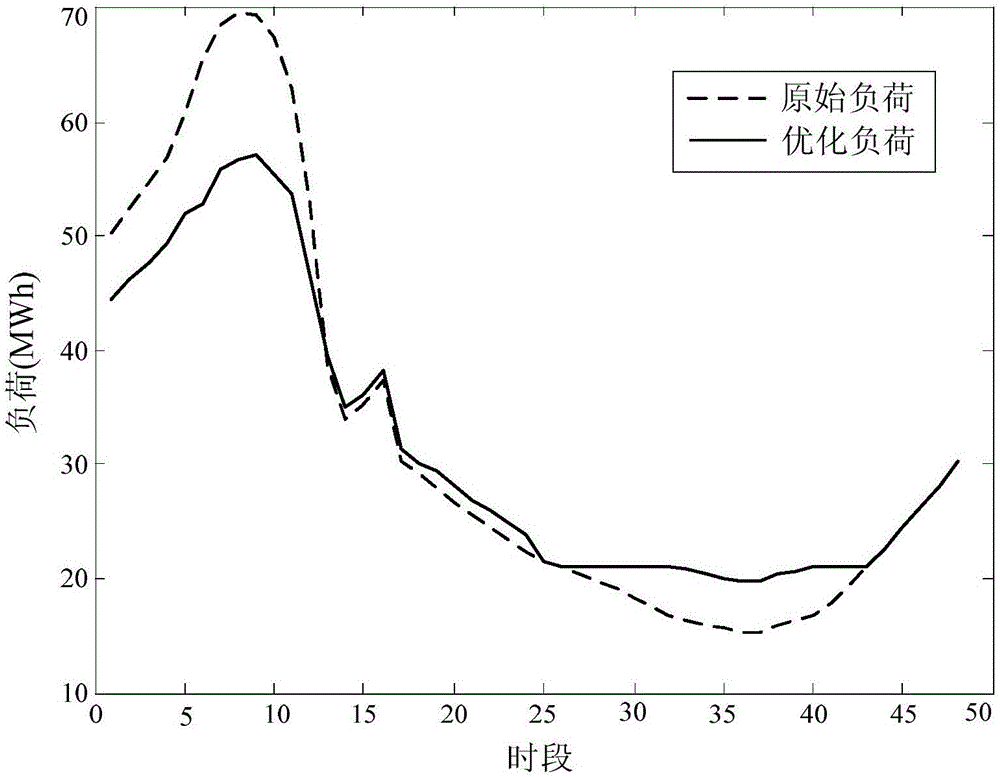
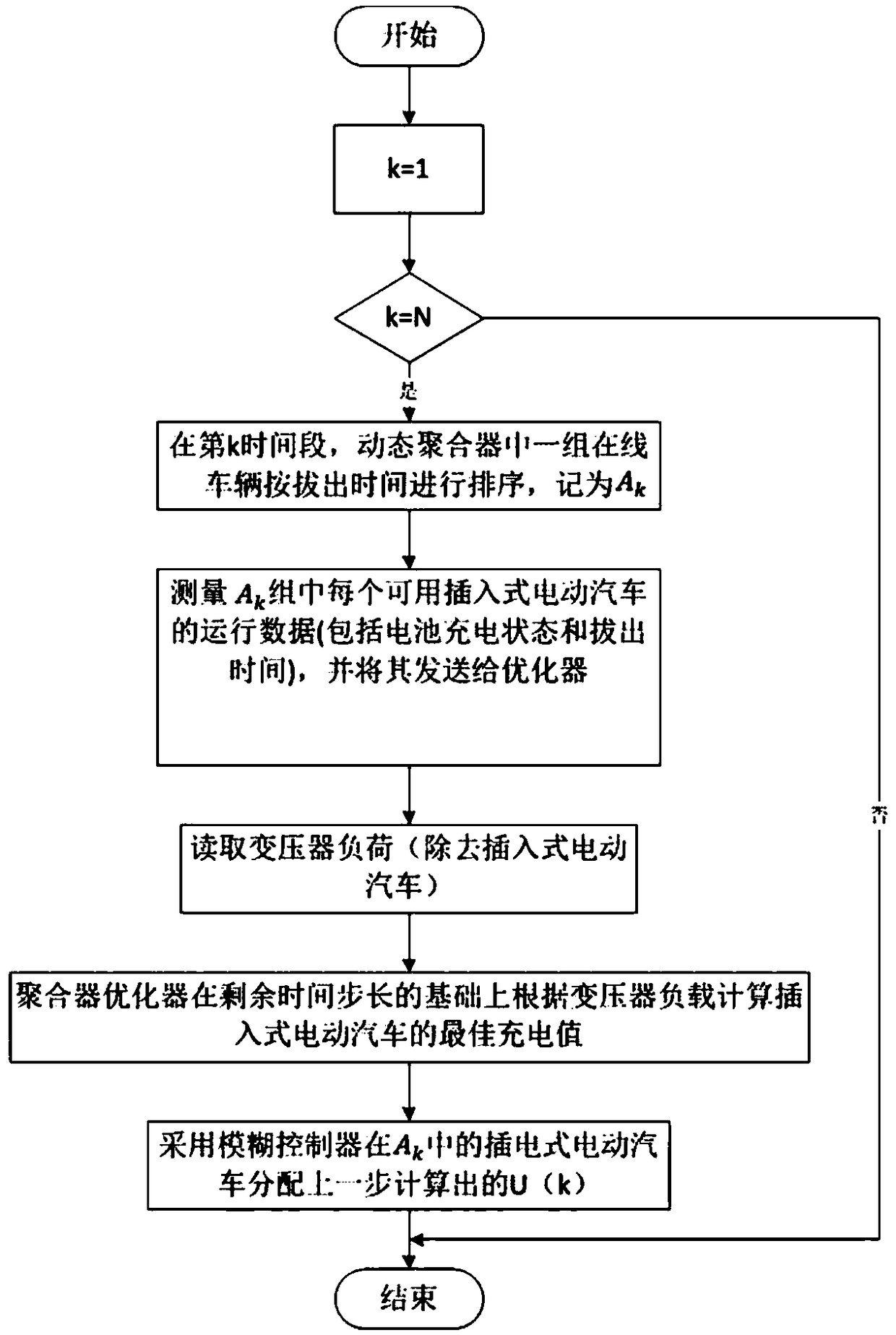
Non-cooperative game-based residential load two-level scheduling optimization method
ActiveCN106846179AIncrease profitGuaranteed comfortData processing applicationsPeak loadDistributed computing
The invention discloses a non-cooperative game-based residential load two-level scheduling optimization method, which comprises the following steps: S1: constructing a load aggregator non-cooperative game model for an upper market side; S2: constructing a resident load real-time scheduling model for a lower user side; S3: by solving the non-cooperative game model and the real-time scheduling model, allowing the load aggregator to obtain the optimal load reduction bid amount and the most reasonable load scheduling strategy. The non-cooperative game idea is introduced into the demand response, and a load aggregator profit function is converted into the non-cooperative game model according to the non-cooperative game idea; the aggregator obtains the optimal load reduction bid amount at the peak load period by solving the non-cooperative game module, i.e., finding a Nash equilibrium solution; the optimal real-time scheduling of user load is carried out based on the bid amount according to three types of load electricity physical characteristics of users, so that the profit of the aggregator is maximized under the condition of ensuring the comfort degree of the users.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
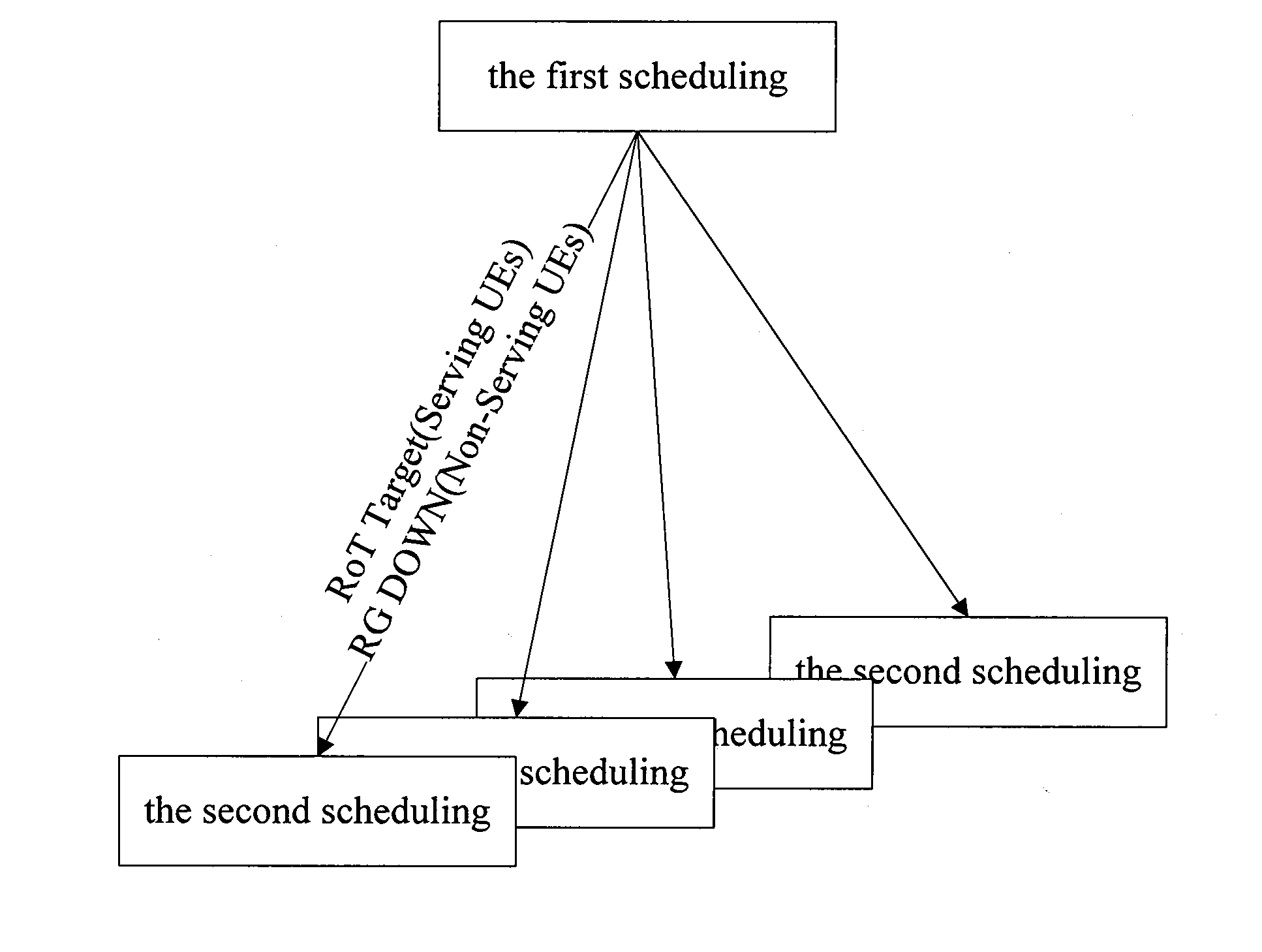
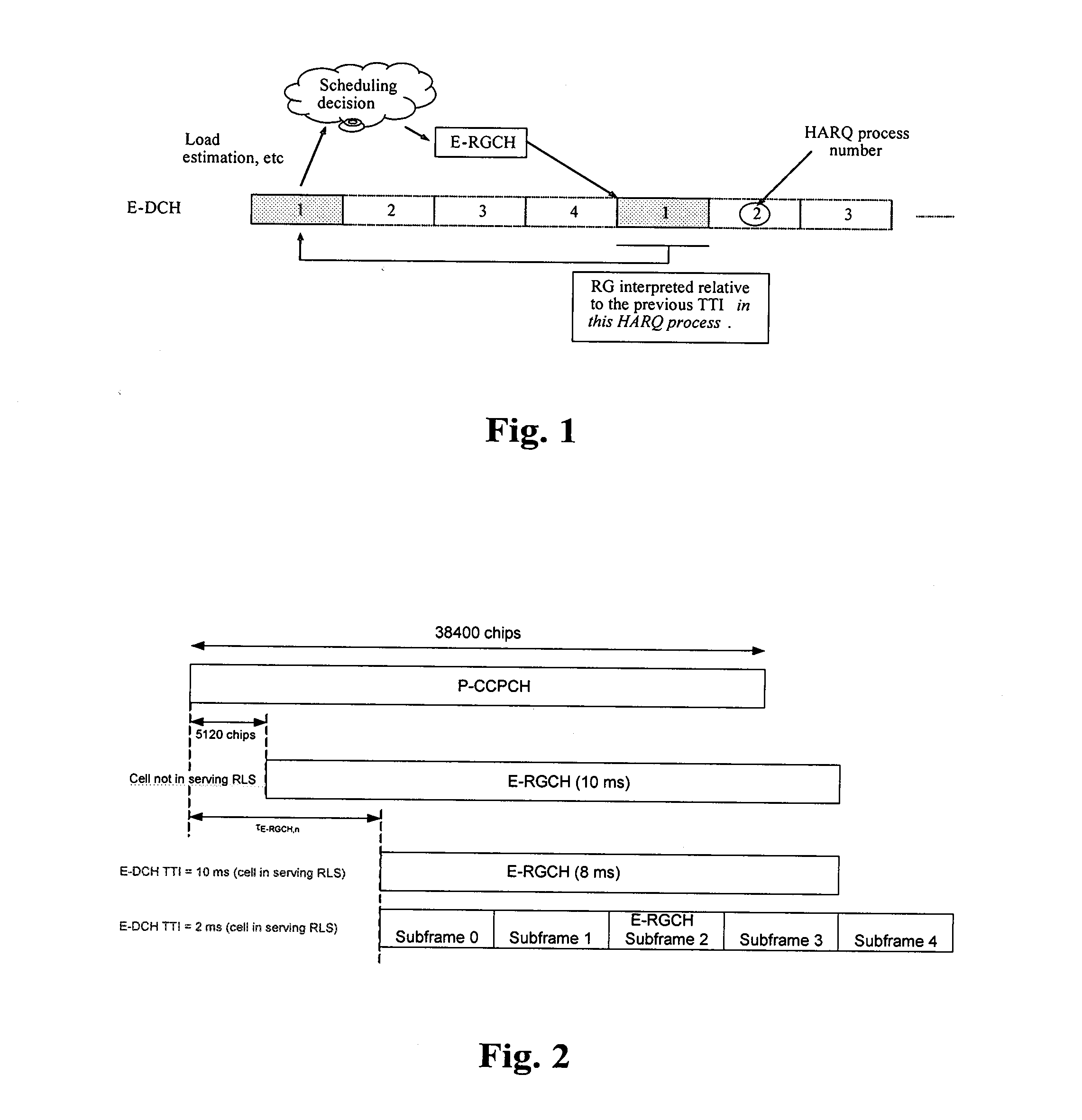
Scheduling method and system for high speed uplink packet access
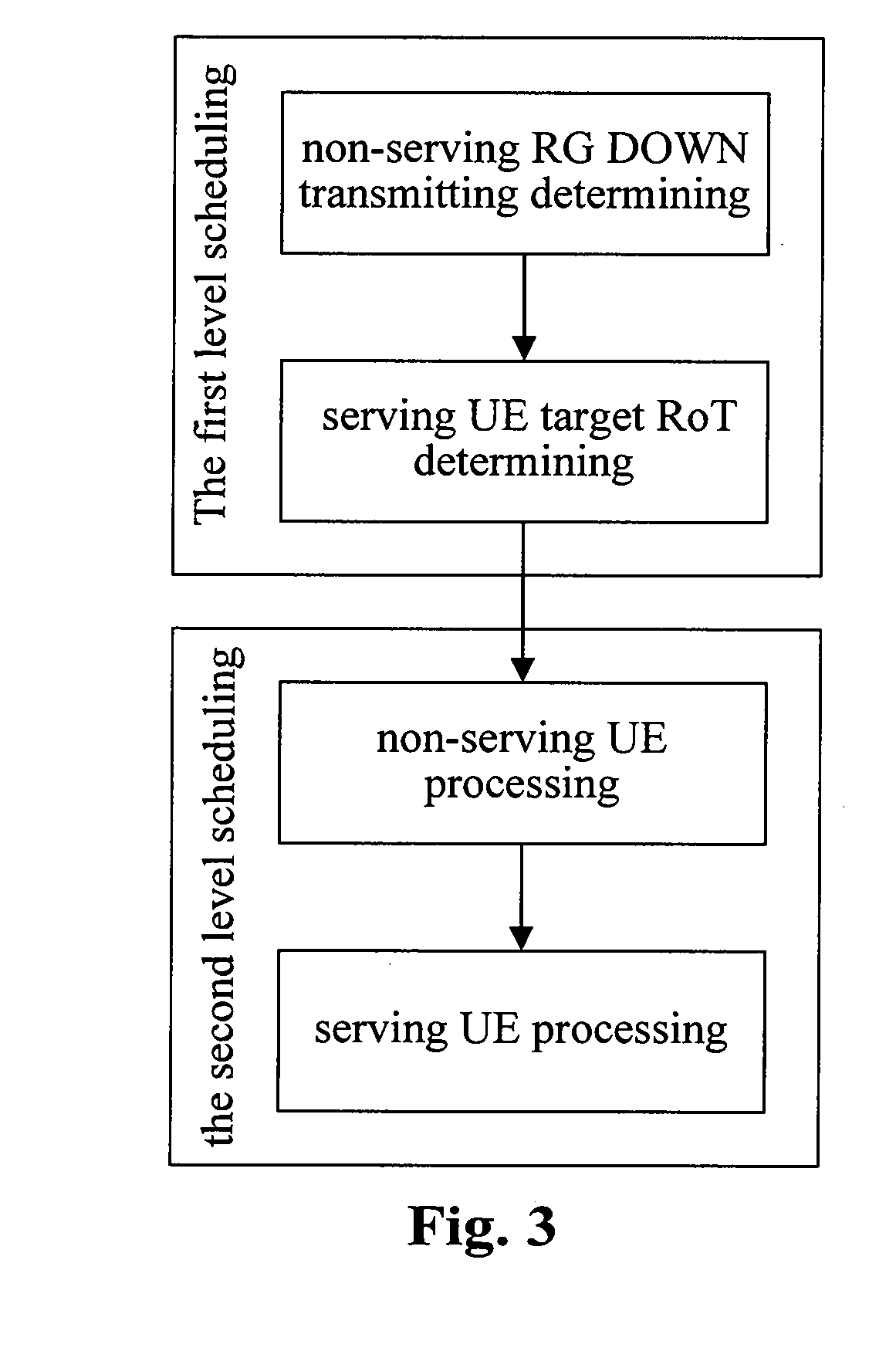
ActiveUS20110038323A1Simplify the scheduling processLower performance requirementsStore-and-forward switching systemsWireless commuication servicesDistributed computingRise over thermal
A scheduling method and system for high speed uplink packet access which comprises the following two-level scheduling: a first level scheduling for distributing the target rise over thermal (RoT) of each user equipment (UE); and a second level scheduling for tracking the assigned to target RoT via transmitting a relative authority instruction, according to the current authority and channel quality of the UE.
Owner:ZTE CORP
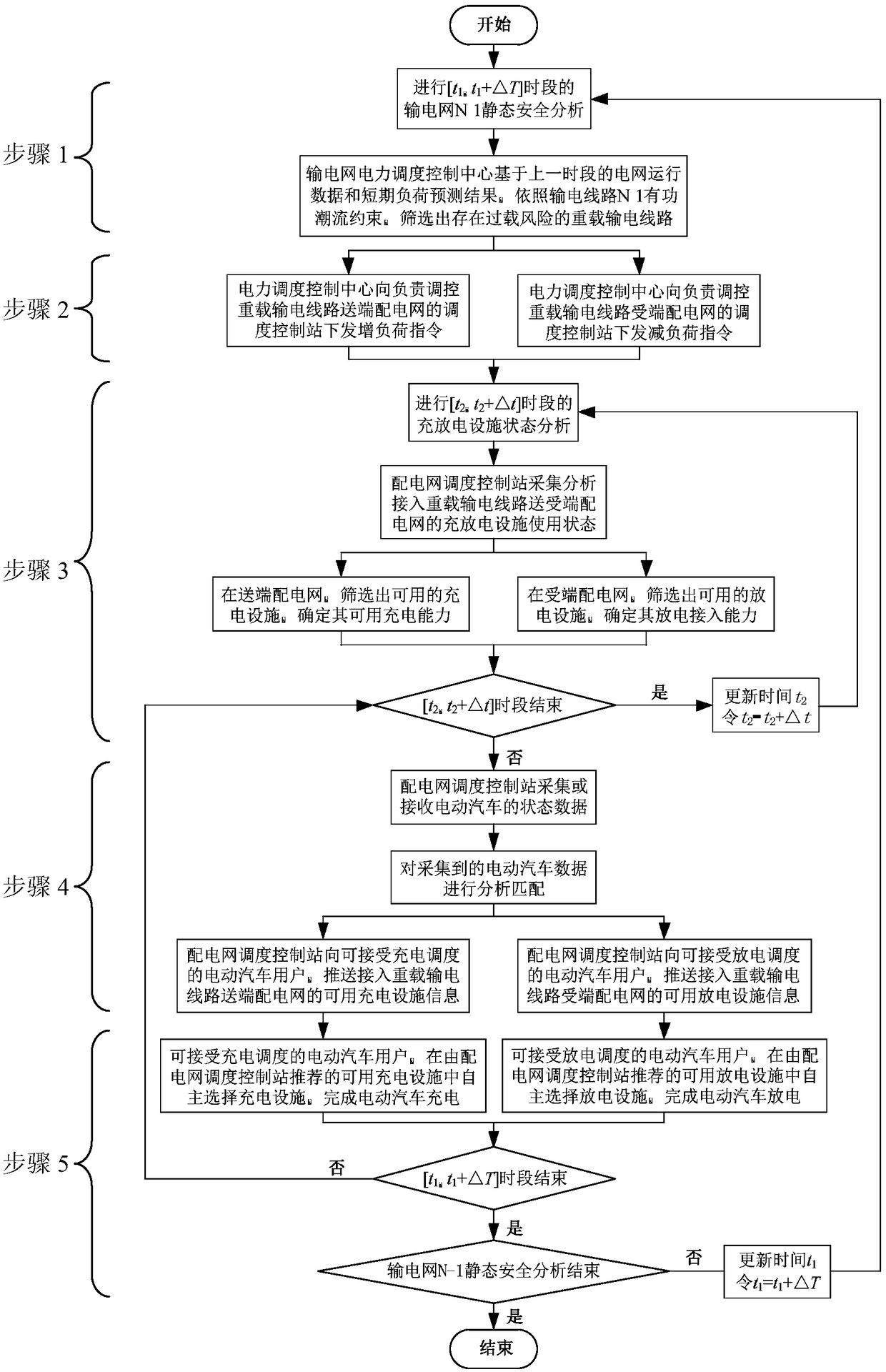
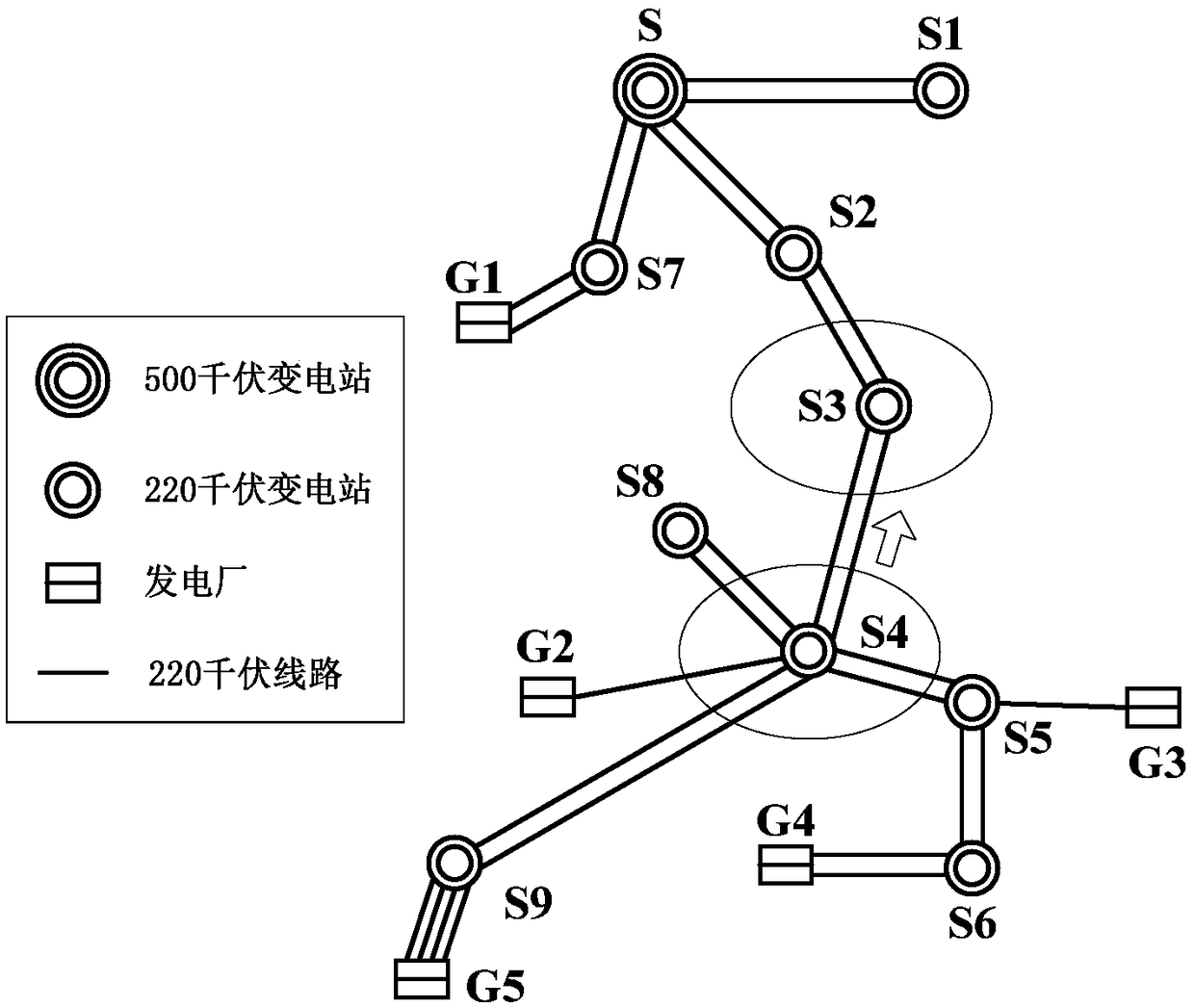
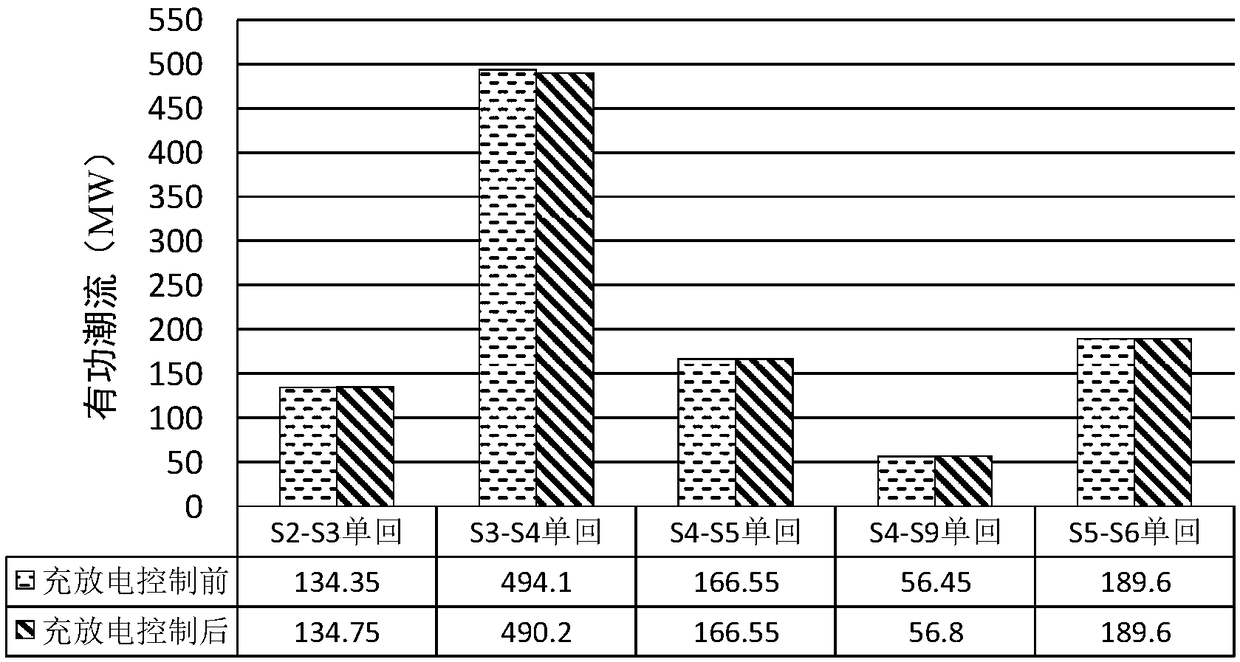
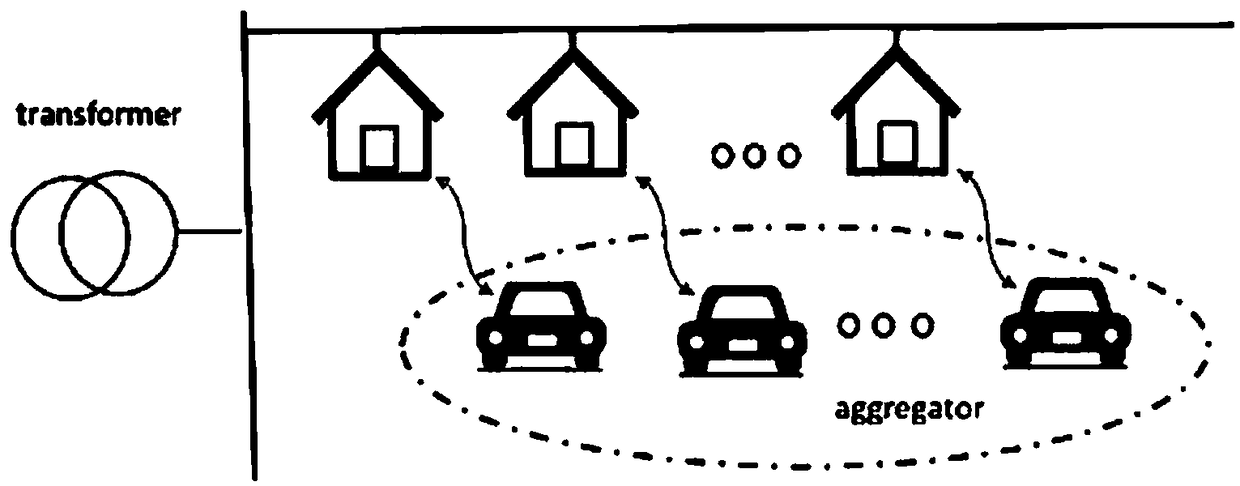
Orderly charging and discharging control method for electric automobile considering operation constraints of transmission network
ActiveCN108631344AImprove static securityRealize coordinated controlAc network load balancingEngineeringGlobal Positioning System
The invention discloses an orderly charging and discharging control method for an electric automobile considering the operation constraints of a transmission network. Coordinated control of a power grid and the electric automobile is realized through the two-level scheduling mechanism of a transmission network power scheduling control center and a distribution network scheduling control station under the consideration of N-1 power flow constraint of a transmission network, the power constraint of a charging and discharging facility, the charge state constraint of the electric automobile, the user charging and discharging demand and the scheduling willingness based on wireless communication, a GPS (Global Positioning System), a GIS (Geographic Information System) and electric automobile V2G. Compared with an existing orderly charging and discharging control method for the electric automobile, the method has the advantages that the peak-shaving effect and scheduling flexibility of charging and discharging for large-scale electric automobiles can be brought into better play; the interaction between the electric automobile and the power grid is expanded to the level of the transmissionnetwork; the charging and discharging behaviors of the electric automobile respond to the operation state of transmission network; and the N-1 static security of the power grid can be further enhanced.
Owner:STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER +1
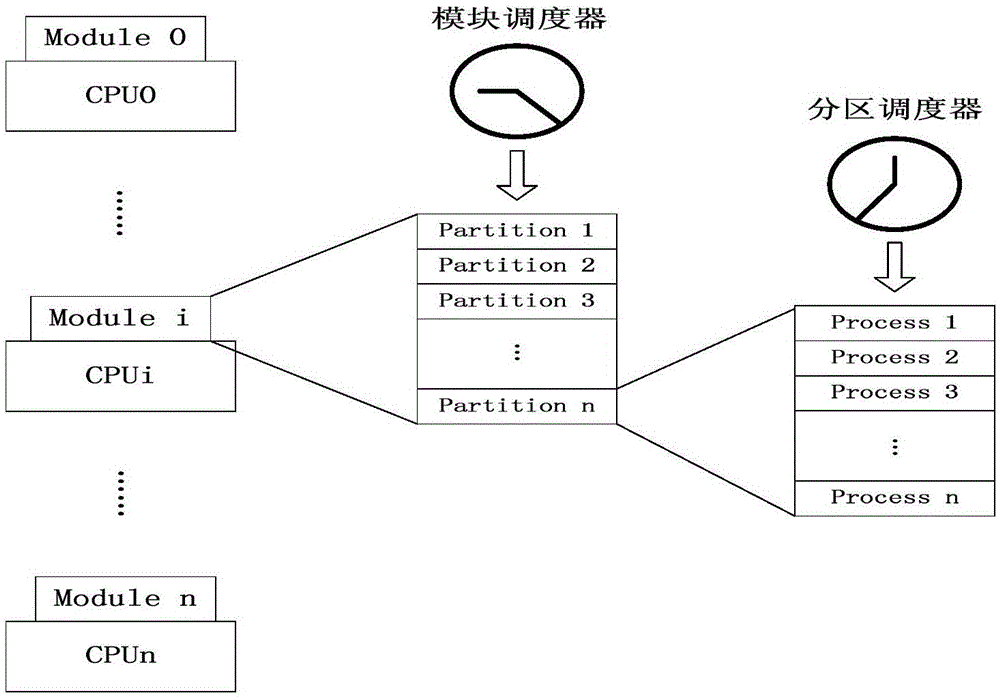
Method for partition scheduling in Windows operating system environment
ActiveCN105045666AImprove practicalityGuaranteed resourcesProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationARINC 653Operational system
The invention discloses a method for partition scheduling in a Windows operating system environment, and the method is used to solve the technical problem that an existing partition scheduling method is low in practicality. The technical scheme is that by using affinity setting of the Windows system, CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources of the system are reallocated, and a running core of a real-time task is appointed, so that resources needed by the real-time task can be ensured; a two-level scheduling model is adopted, wherein the model comprises two levels of schedulers: a module scheduler of a scheduling partition, and a partition scheduler of a process in the scheduling partition; and a secondary scheduling model is inclined to a cycle round-robin scheduling partition of the module scheduler, and the partition scheduler preempts a scheduling process based on a fixed priority. According to the scheduling method, in the Windows environment, a virtual two-level scheduling policy of ARINC 653 is created, thereby providing a good development and debugging environment for embedded software; and the method is high in practicality and reduces development cost.
Owner:智盈未来(西安)信息技术有限公司
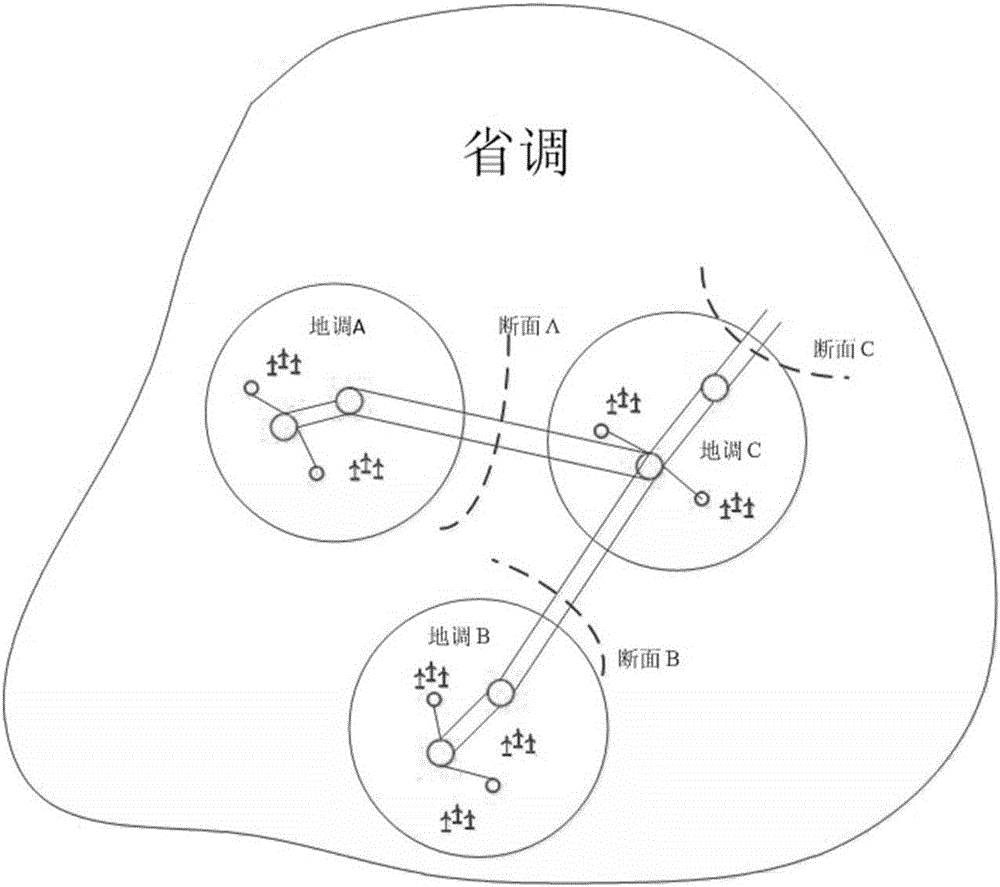
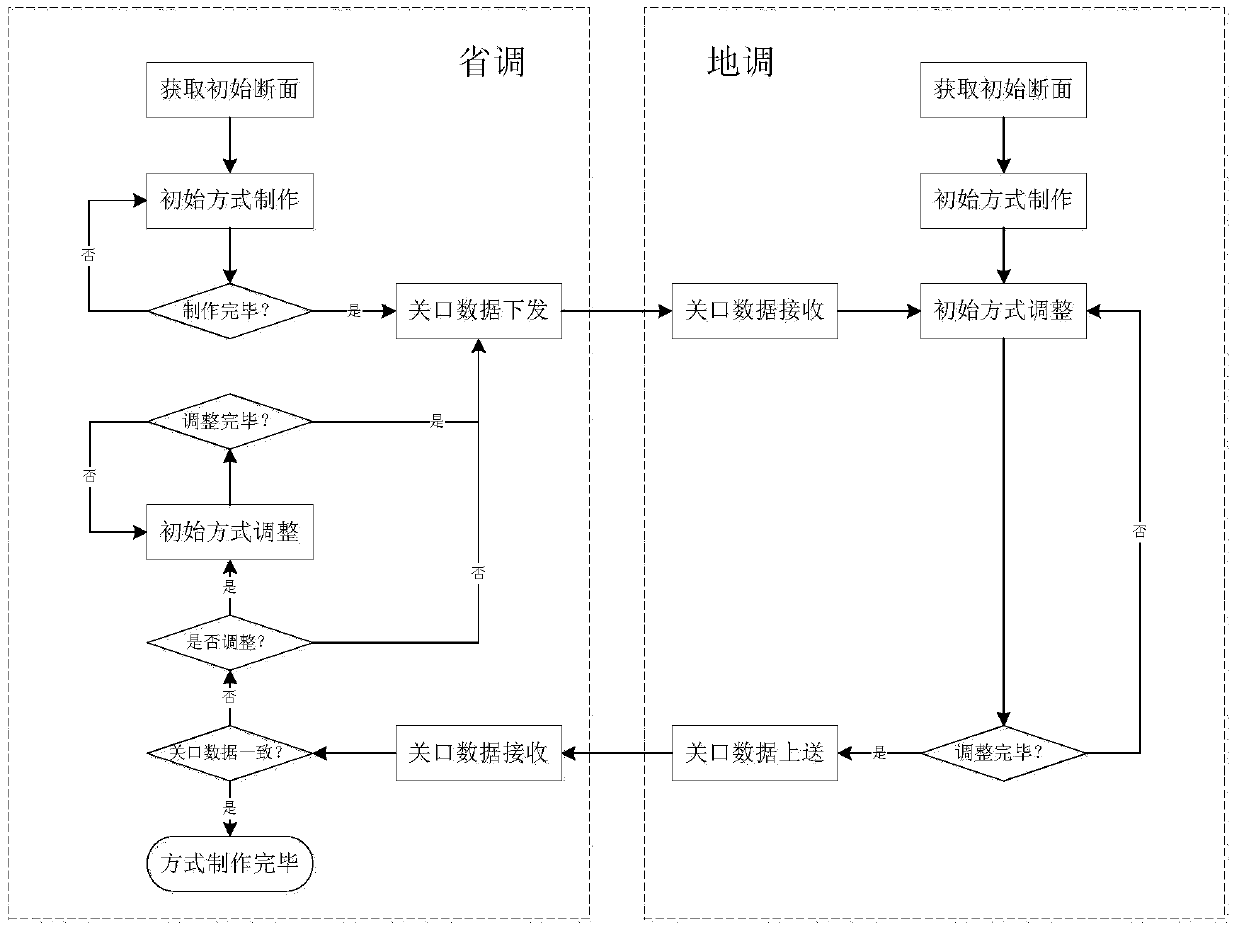
Provincial and local two-level dispatching section coordination and control method
ActiveCN106602613AMaximize consumptionGuarantee the safety of power transmission sectionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationTransmitted powerNew energy
The invention discloses a provincial and local two-level scheduling section coordination and control method which is characterized in that maximum electricity generation power new energy of a local dispatching center is calculated via the local dispatching center based on section limit value issued by a provincial dispatching center and limit value of transmitting power of neighboring local dispatching centers; utilization conditions of limit value of transmitting power of neighboring zones are monitored in real time; if the limit value is not fully used, underused conveying capacity of the neighboring zones is additionally issued and used via control over a new energy filed station; if the conveying capacity of the neighboring zones surpasses the limit value of transmission, control operation is performed based on original section limit value, statistics are run on over-issued limit value, and provincial dispatching centers are assisted in relevant performance examination indicator calculation. The beneficial effects of the method are that new energy electricity generation space of each local dispatching center is calculated at a provincial dispatching side in a unified manner, the electricity generation space is corrected after a section operation state is monitored in real time at a local dispatching side, power transmission capacity of the power transmission section can be fully used while safety of a power transmission section of a power grid is ensured, and maximum new energy can be absorbed.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
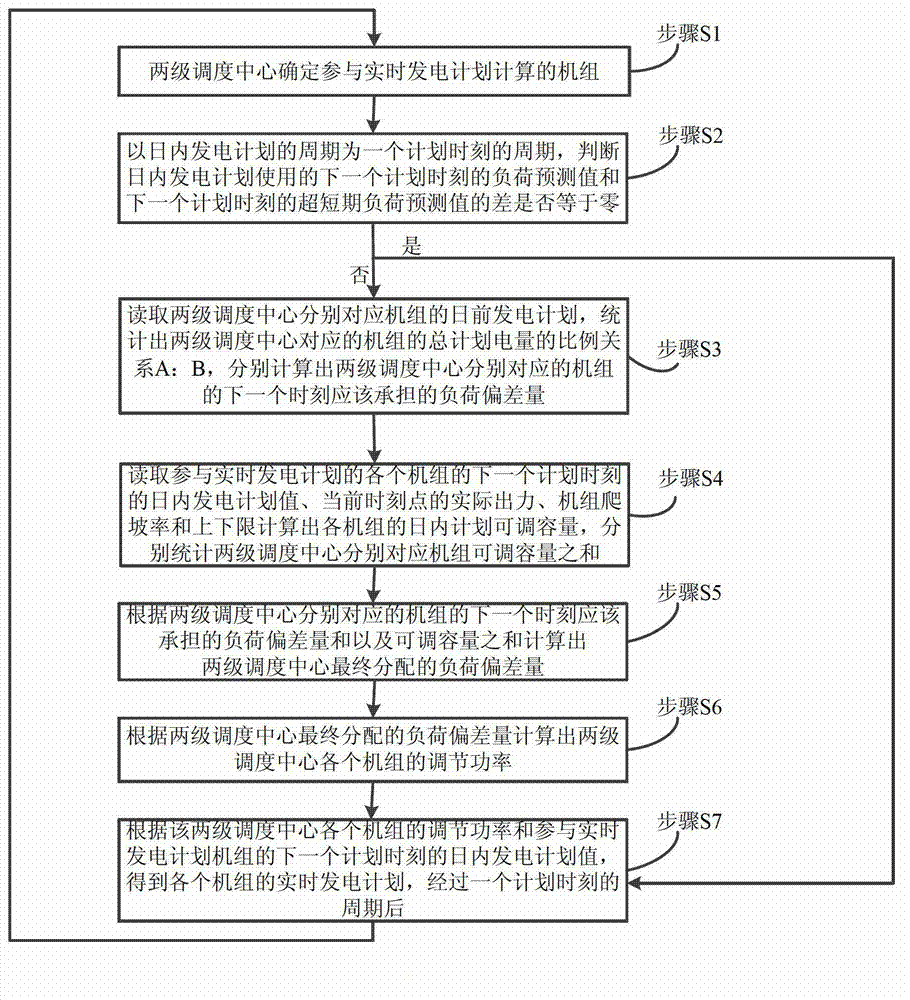
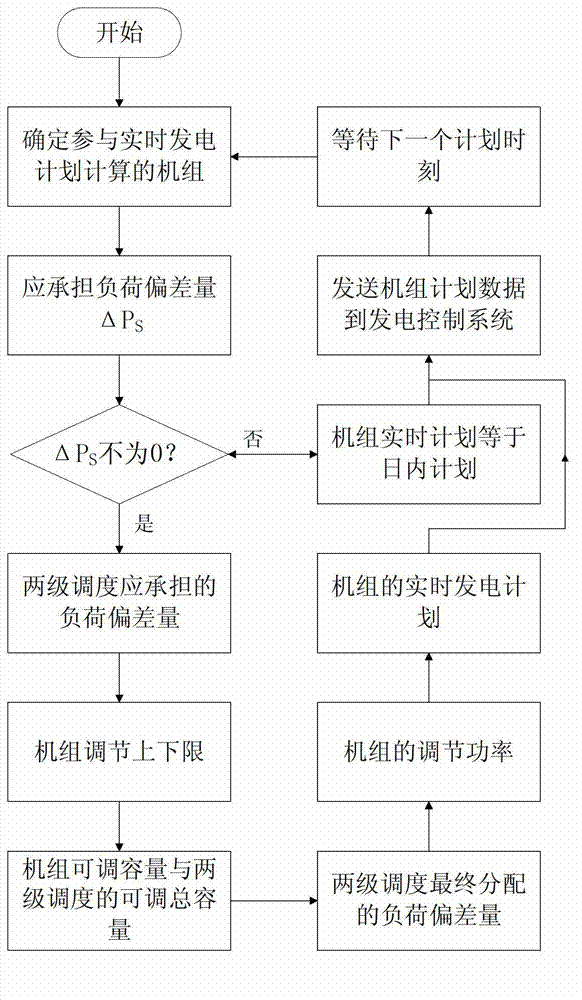
Minor-cycle real-time generation schedule
ActiveCN103051001AEfforts closeHandle balanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsShort termsTwo-level scheduling
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
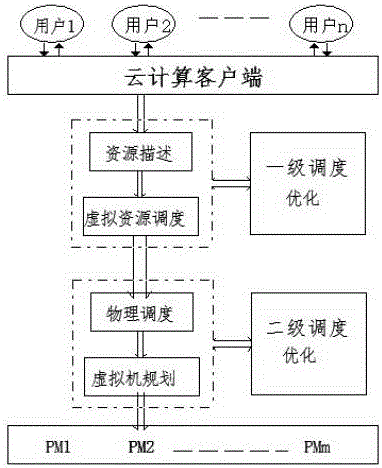
Virtual machine two-level optimization scheduling management platform based on cloud computing
InactiveCN106095591AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove service qualityResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOptimal schedulingResource consumption
The invention provides a virtual machine two-level optimization scheduling management platform based on cloud computing. The platform comprises a cloud computing platform portal, a first-level scheduling module, a second-level scheduling module, a first-level scheduling optimization module, a second-level scheduling optimization module and a physical resource distribution module. In the invention, the first-level scheduling optimization module and the second-level scheduling optimization module are introduced to the two-level scheduling model of traditional cloud computing; and the two-level scheduling optimization module optimizes the resource scheduling distribution of the first-level scheduling module and the second-level scheduling module by adopting different bionic intelligent algorithms, static and dynamic globally optimal solutions are provided for the load balancing of the cloud virtual machine, an optimal scheduling scheme is obtained, the resource consumption for the virtual machine migration is effectively reduced, the utilization efficiency of the cloud computing resources is increased, and the service quality of users is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU YUYA TECH
Two-level scheduler for multi-threaded processing
ActiveUS8732711B2Reduce areaReduce total powerMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsLong latencyLocal memories
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for scheduling thread execution in a multi-threaded processing environment. A two-level scheduler maintains a small set of active threads called strands to hide function unit pipeline latency and local memory access latency. The strands are a sub-set of a larger set of pending threads that is also maintained by the two-leveler scheduler. Pending threads are promoted to strands and strands are demoted to pending threads based on latency characteristics. The two-level scheduler selects strands for execution based on strand state. The longer latency of the pending threads is hidden by selecting strands for execution. When the latency for a pending thread is expired, the pending thread may be promoted to a strand and begin (or resume) execution. When a strand encounters a latency event, the strand may be demoted to a pending thread while the latency is incurred.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Queue-based multi-target scheduling strategy for heterogeneous resources
InactiveCN104852860ALoad balancingImprove resource utilizationData switching networksQuality of serviceResource utilization
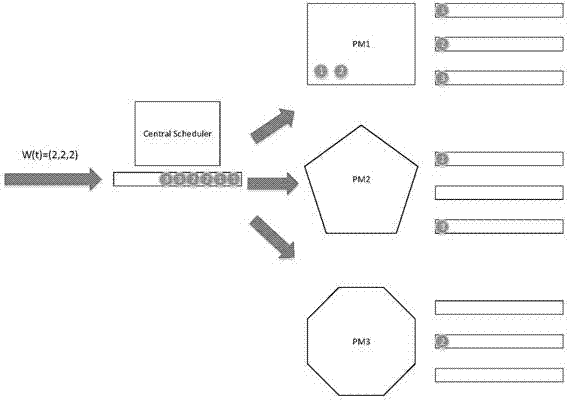
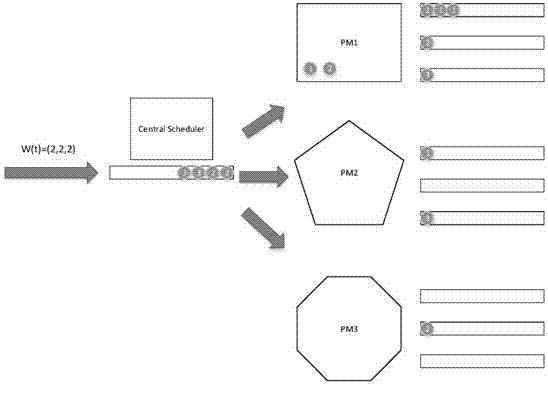
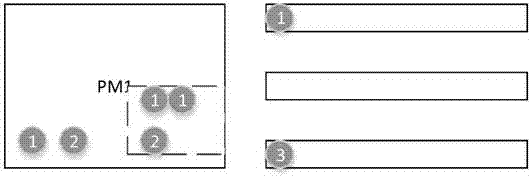
The present invention relates to a strategy for scheduling resources at a heterogeneous cloud data center, wherein the strategy is provided based on the queuing theory to fully consider the heterogeneity of resources and improve the utilization rate of resources. In this way, the service quality (QoS) of tasks and the load balancing of the cloud data center are ensured. Meanwhile, the energy consumption of the cloud data center is greatly reduced. The strategy comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a two-stage scheduling framework for the data center by means of a queuing model, and dividing the execution of all tasks into two stages, namely task allocating and task scheduling; 2, during the task allocating period, considering the heterogeneity of resources, and evenly allocating an acquired classification task set W(t) to all servers (PW) by means of the HPAC algorithm; 3, during the task scheduling period, considering the resource utilization rate and the service quality (QoS), establishing a virtual machine based on tasks queued in all the PMs by means of the MIUS algorithm, and executing the tasks.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Teaching plan manufacturing method in multi-level scheduling integrated mode in training system
The invention discloses a teaching plan manufacturing method in a multi-level scheduling integrated mode in a training system. The method comprises the steps of determining all levels of scheduling model boundary gates when united training simulation is performed on multi-level scheduling (network scheduling and province scheduling as well as province scheduling and local scheduling); coordinating a power grid initial mode manufacturing process; coordinating a load curve teaching plan manufacturing process; coordinating an event teaching plan manufacturing process. The load teaching plan manufacturing method in the multi-level scheduling integrated environment is wide in applicable range, has extremely high flexibility and operability, can effectively improve the teaching manufacturing efficiency of united training simulation, and improves reliability of united training simulation.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Cloud computing based virtual machine two-level optimization scheduling management platform
InactiveCN106161640AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove service qualityTransmissionQuality of serviceOptimal scheduling
The invention provides a cloud computing based virtual machine two-level optimization scheduling management platform which comprises a cloud computing platform portal, a first-level scheduling module, a second-level scheduling module, a first-level scheduling optimization module, a second-level scheduling optimization module and a physical resource allocation module. The first-level scheduling module and the second-level scheduling module are introduced on the basis of a traditional cloud computing based two-level scheduling model, resource scheduling distribution of the first-level scheduling module and the second-level scheduling module is optimized by the adoption of the two-level scheduling optimization modules, a static and dynamic global optimal solution is provided for load leveling of a cloud virtual machine, the optimal scheduling scheme is acquired, resource cost in migration of the virtual machine is effectively reduced, utilization rate of cloud computing resources is increased, and meanwhile, service quality of users is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU YUYA TECH
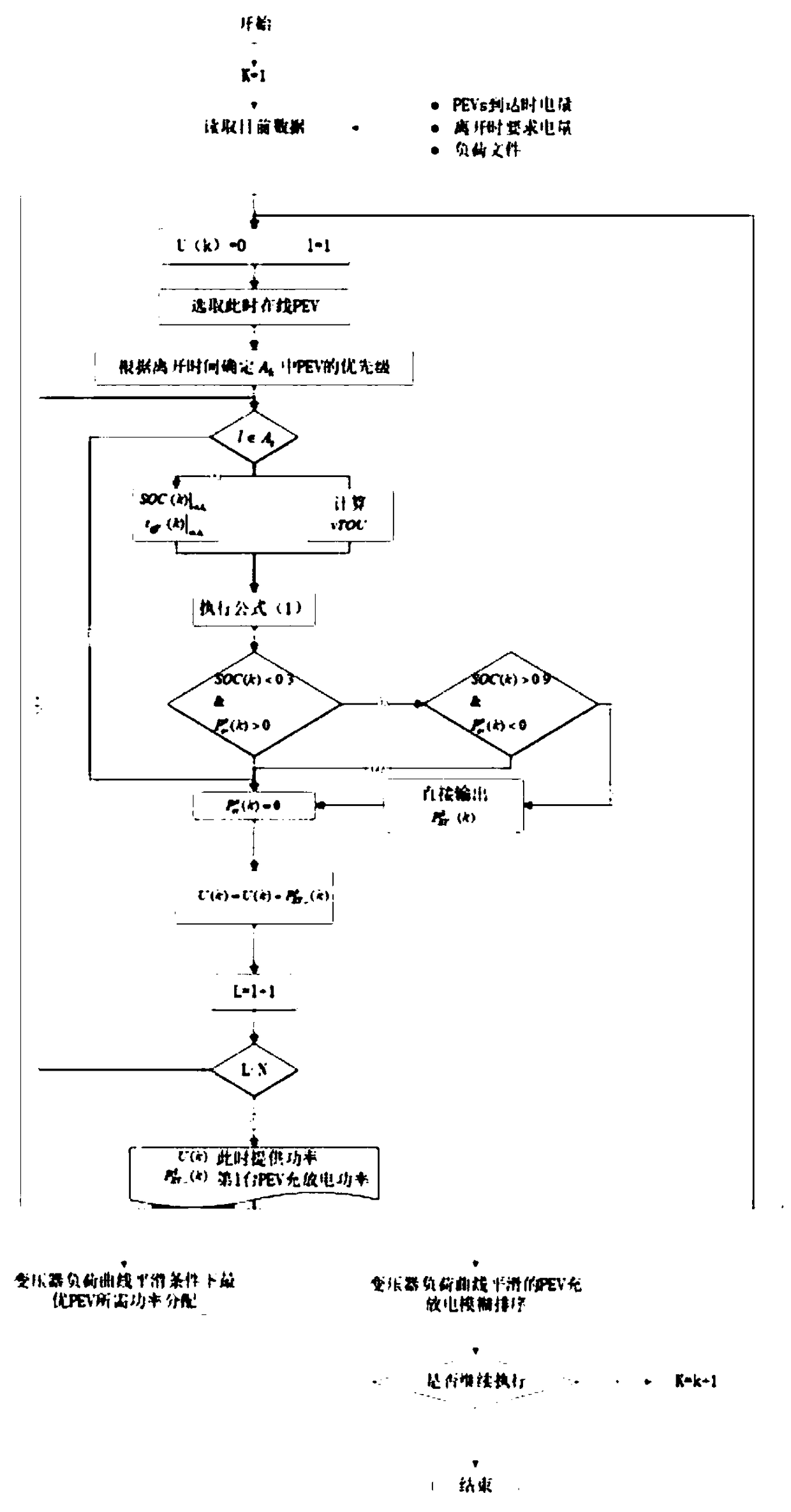
Intelligent V2G charging method with two-stage scheduling structure based on dynamic integrator
InactiveCN109378845ASmooth load distributionRational energy managementAc network load balancingIntegratorElectrical battery
The invention relates to an intelligent V2G charging method with a two-stage scheduling structure based on a dynamic integrator. The method takes the influence of charging and discharging of a plug-inelectric vehicle (PEV) on the power grid into account, and considers its influence on the performance of a distribution transformer. In the first stage, the BEE algorithm (BA) is used as an aggregator to optimize and calculate the optimal charging of each plug-in electric vehicle; and in the second stage, the fuzzy logic controller (FLC) is used to distribute power between electric vehicles (EVS). The framework considers nonlinear dynamic characteristics of the plug-in electric vehicle battery in various practical conditions. The main advantages of this method are that the method reduces theload peak, smoothes the load distribution of a transformer, considers the nonlinear dynamic characteristics of the plug-in electric vehicle battery, and performs reasonable energy management of the battery when a charging station disconnects a power supply from time to time.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI & RES INST OF STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER CO +3
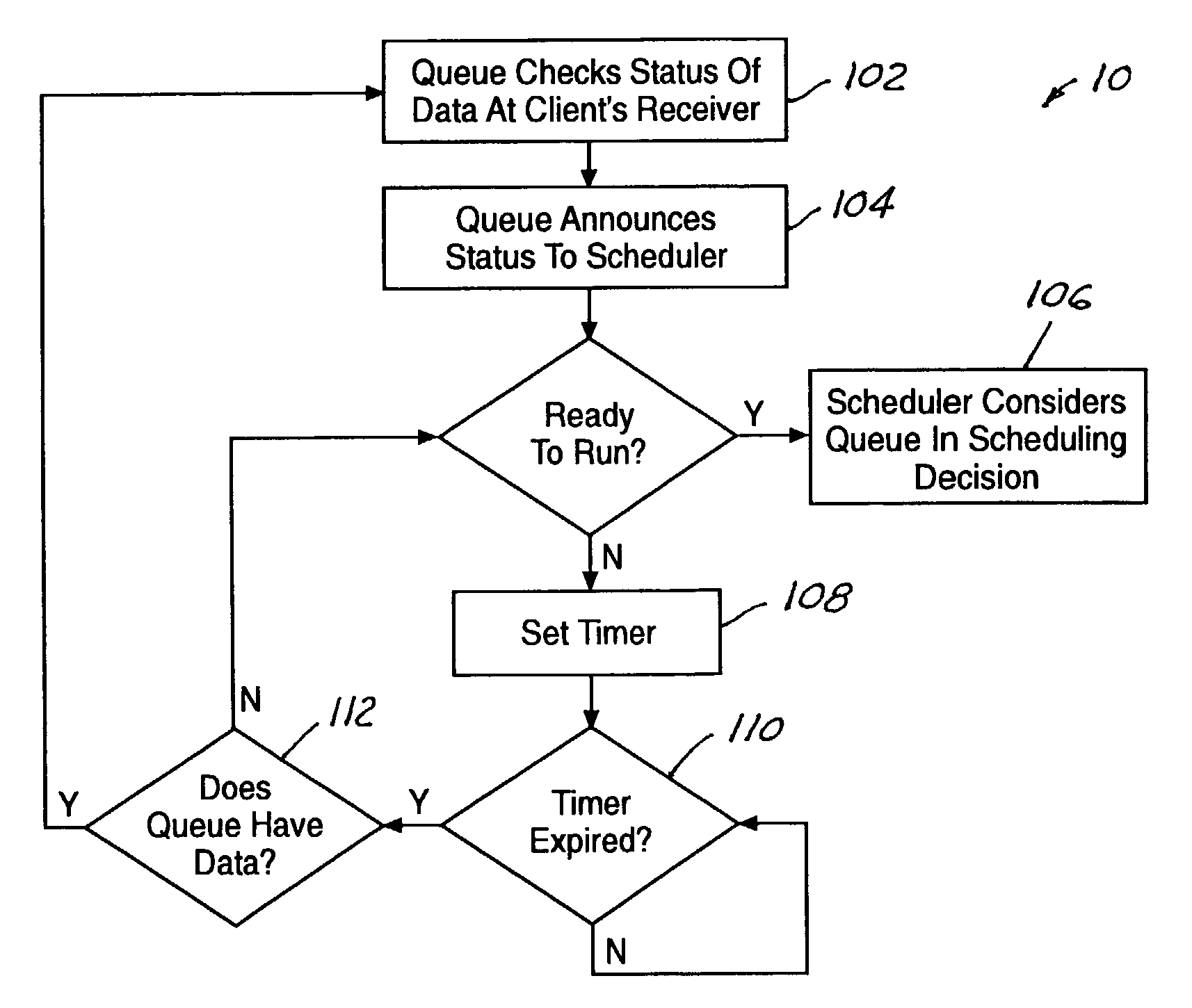
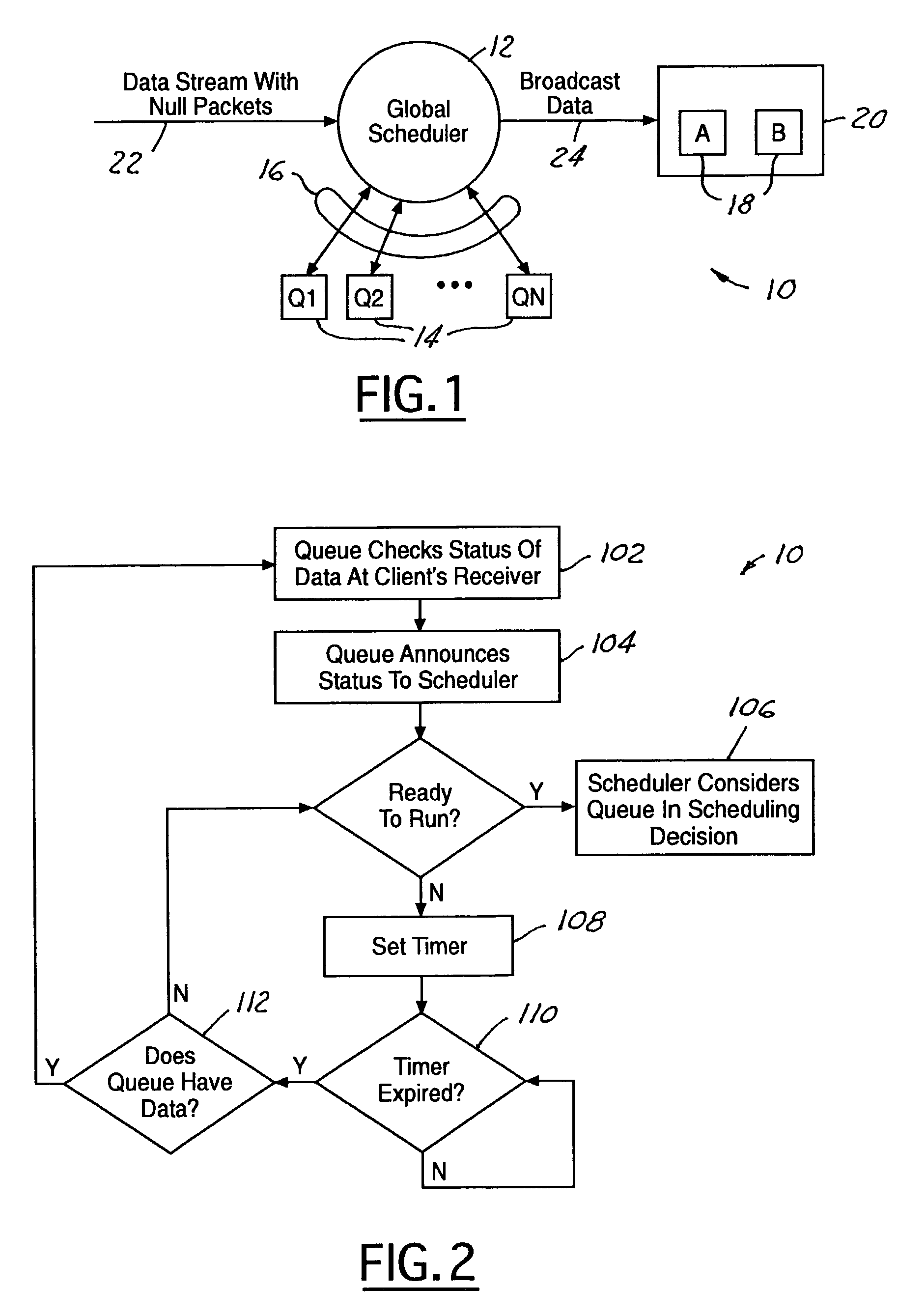
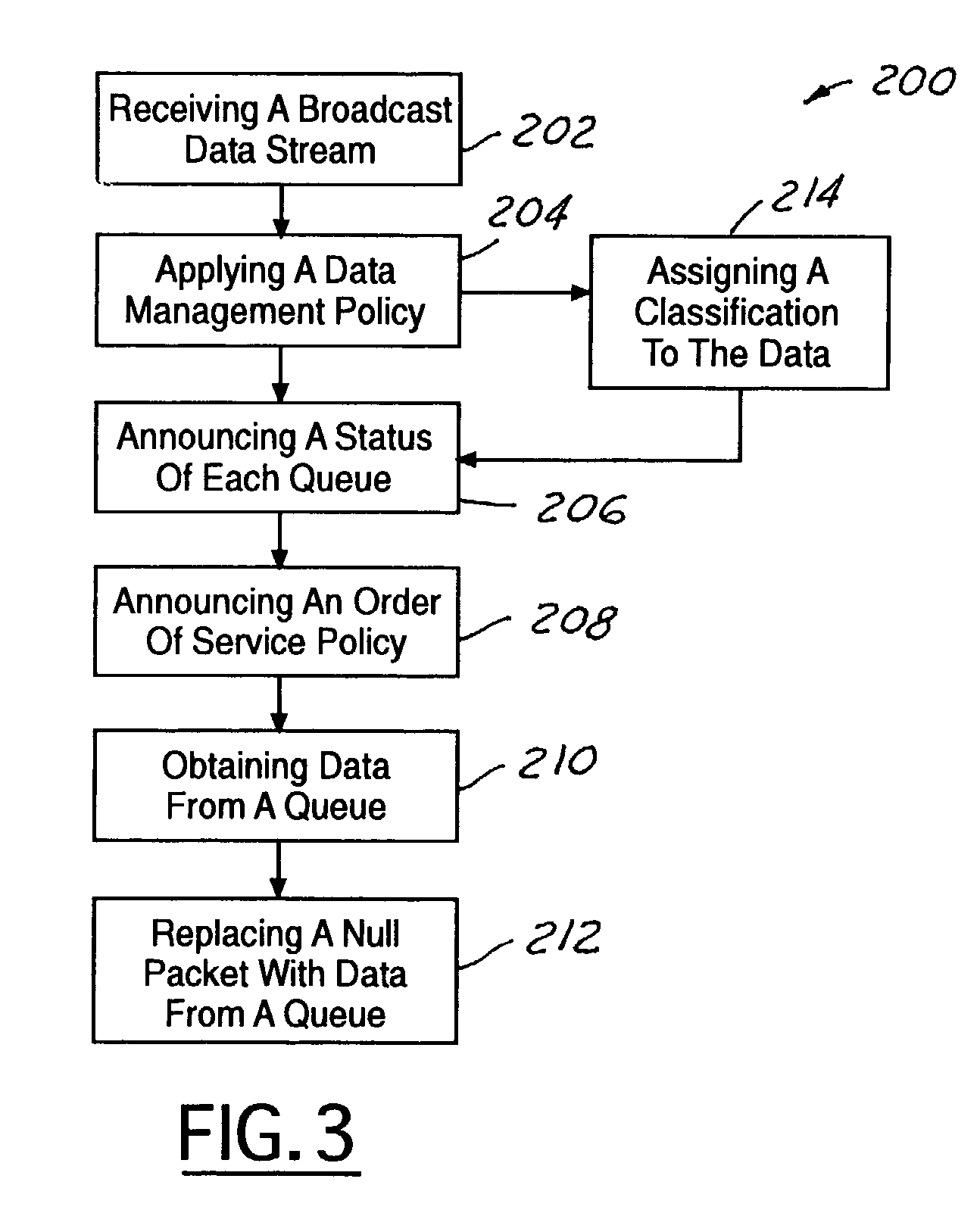
Null packet replacement with bi-level scheduling
InactiveUS7286473B1Maximize bandwidthEasy to useError preventionTransmission systemsData streamData rate
A system and method for null packet replacement having a global scheduler (12) select data from a plurality of self-managed queues (14) to insert in to the data stream in place of null packets. The queues (14) managed by the global scheduler have rules that are private to each queue Q1, Q2, . . . QN. The global scheduler (12) has a set of rules (16) for prioritizing the queues (14). The global scheduler (12) knows the average data rate for each queue (14) and has a priority assigned to each queue (14). Rules for the global scheduler policy (16) are limited to the order of service for the queues. The present invention is advantageous in that the order of service may be changed at the global scheduler (12) without affecting the independent queues (14).
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
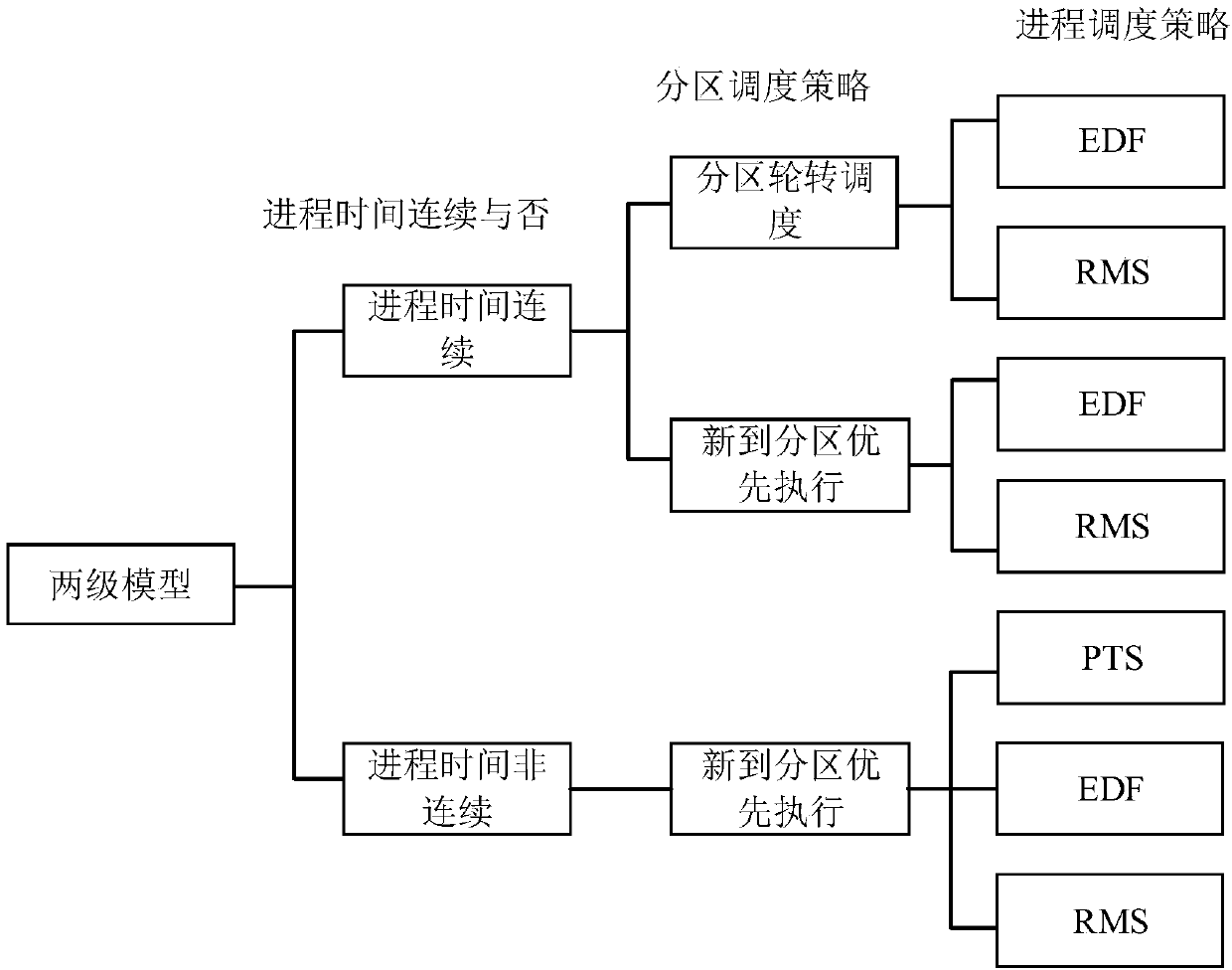
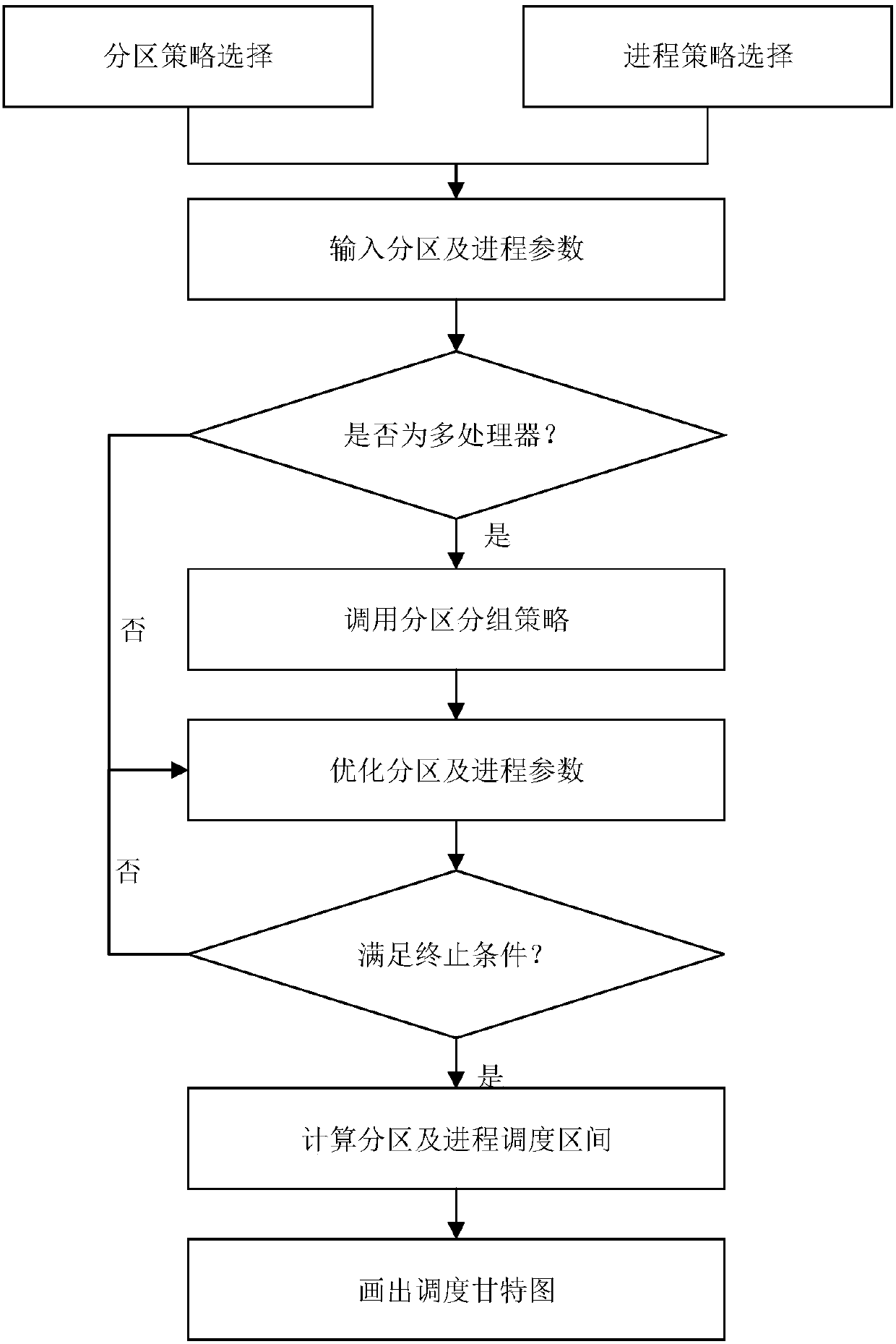
Integrated modular avionics system two-stage scheduling model and prototype platform
The invention discloses an integrated modular avionics system two-stage scheduling model and a prototype platform, and belongs to the technical field of avionics. The two-stage scheduling model is divided into three categories of combination ways according to whether process time is continuous and according to a partition scheduling strategy and a process scheduling strategy, the optimization of unknown parameters is independently finished by aiming at each category of combination ways, and finally, a reasonable scheduling scheme and a reasonable scheduling Gantt chart are generated. On the basis of a classical partition and process scheduling model, an IMA (Integrated Modular Avionics) system two-stage scheduling model is expanded, the prototype platform has the advantages of complete structure and function, various two-stage scheduling models and any partitioning and process parameter can be conveniently verified, and a platform is provided for researching an efficient IMA two-stagescheduling strategy; and the prototype platform adopts a modular structure to support to add a new scheduling strategy and a new scheduling algorithm, each module can be conveniently replaced, and themodel exhibits good expandability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Quick clustering preprocessing method for massive image eigenvectors
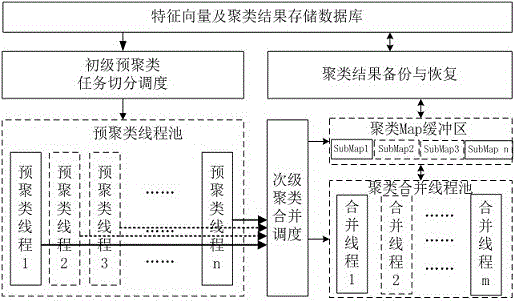
ActiveCN106547890AReduce memory requirementsReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data indexingFeature vectorPretreatment method
The invention relates to the field of image processing and discloses a quick clustering preprocessing method for massive image eigenvectors. The method comprises the following steps of (A) two-stage thread pool processing; and (B) two-stage Map storage structure processing. A two-stage thread pool comprises a primary preprocessing thread pool which performs simple pre-clustering, and a secondary combination thread pool which performs secondary clustering combination; and in a two-stage Map storage structure, a large clustering result Map is divided into sub-Maps, and combination and comparison operations of the sub-Maps are carried out in parallel. The method has the beneficial effects that a clustering operation process is suitable for running in a multi-core server through the two-stage scheduling design; and through the two-stage Map storage structure, the influence of blockage between clustering comparison and clustering update tends to 0.
Owner:SHENZHEN INTELLIFUSION TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com