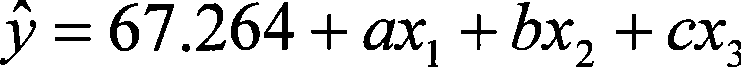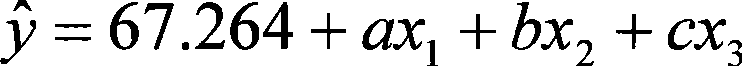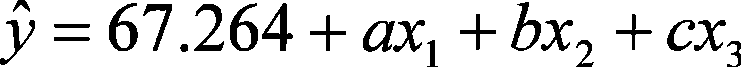Patents
Literature
155 results about "Ultrasound scanner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrasound scan. An ultrasound scan is a procedure that uses high frequency sound waves to create a picture of a part of the inside of your body. The ultrasound scanner has a microphone that gives off sound waves. The sound waves bounce off the organs inside your body, and the microphone picks them up.
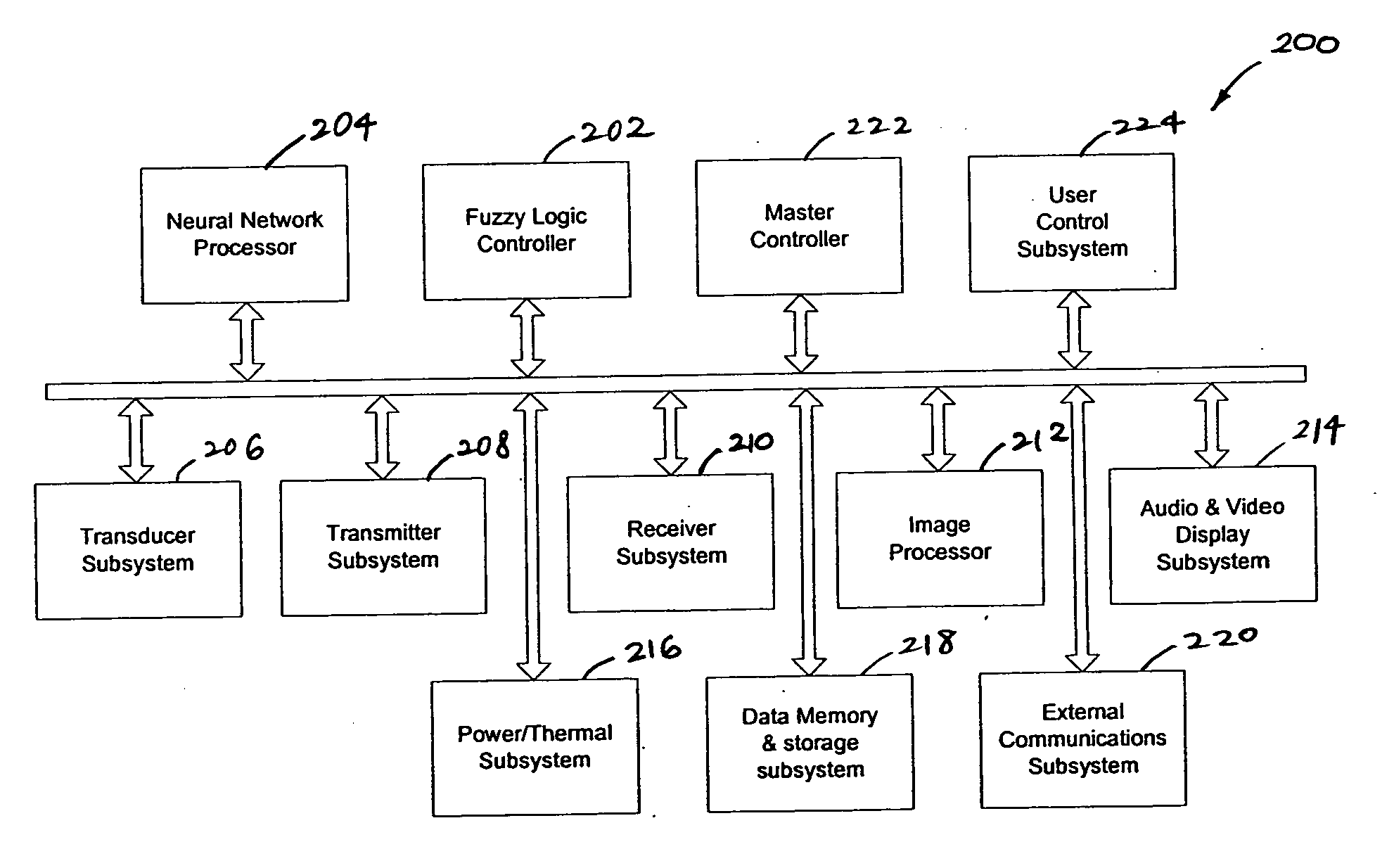
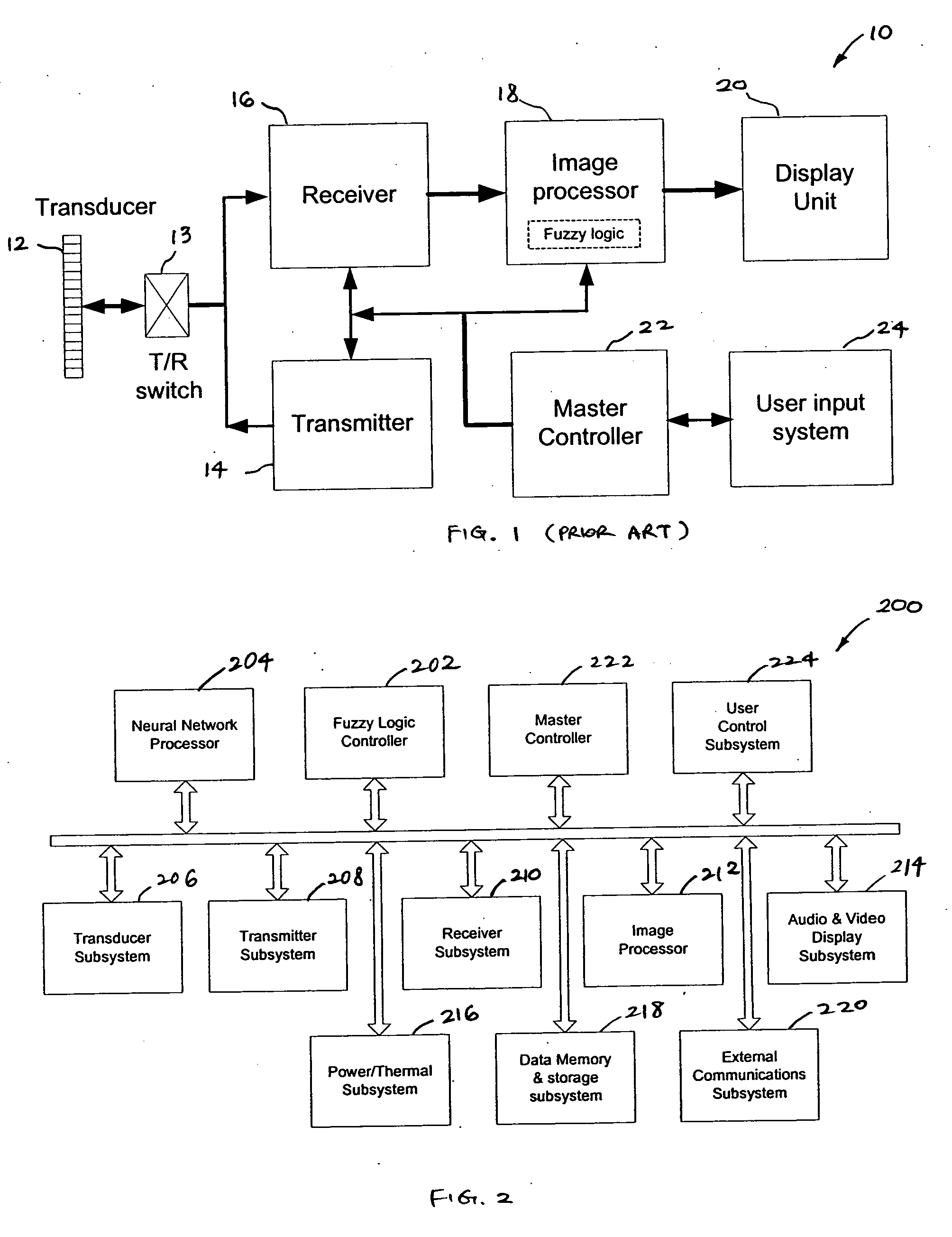
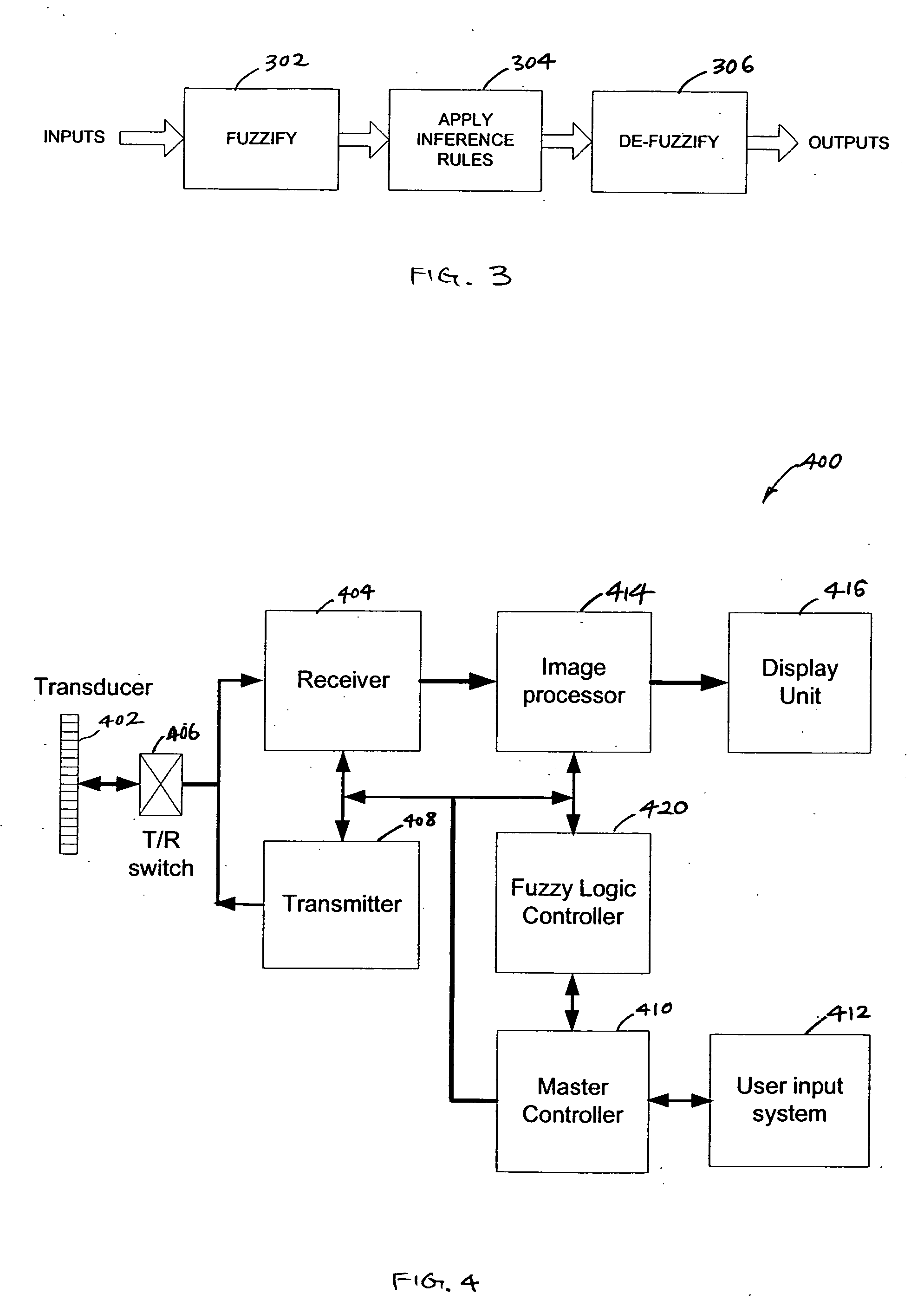
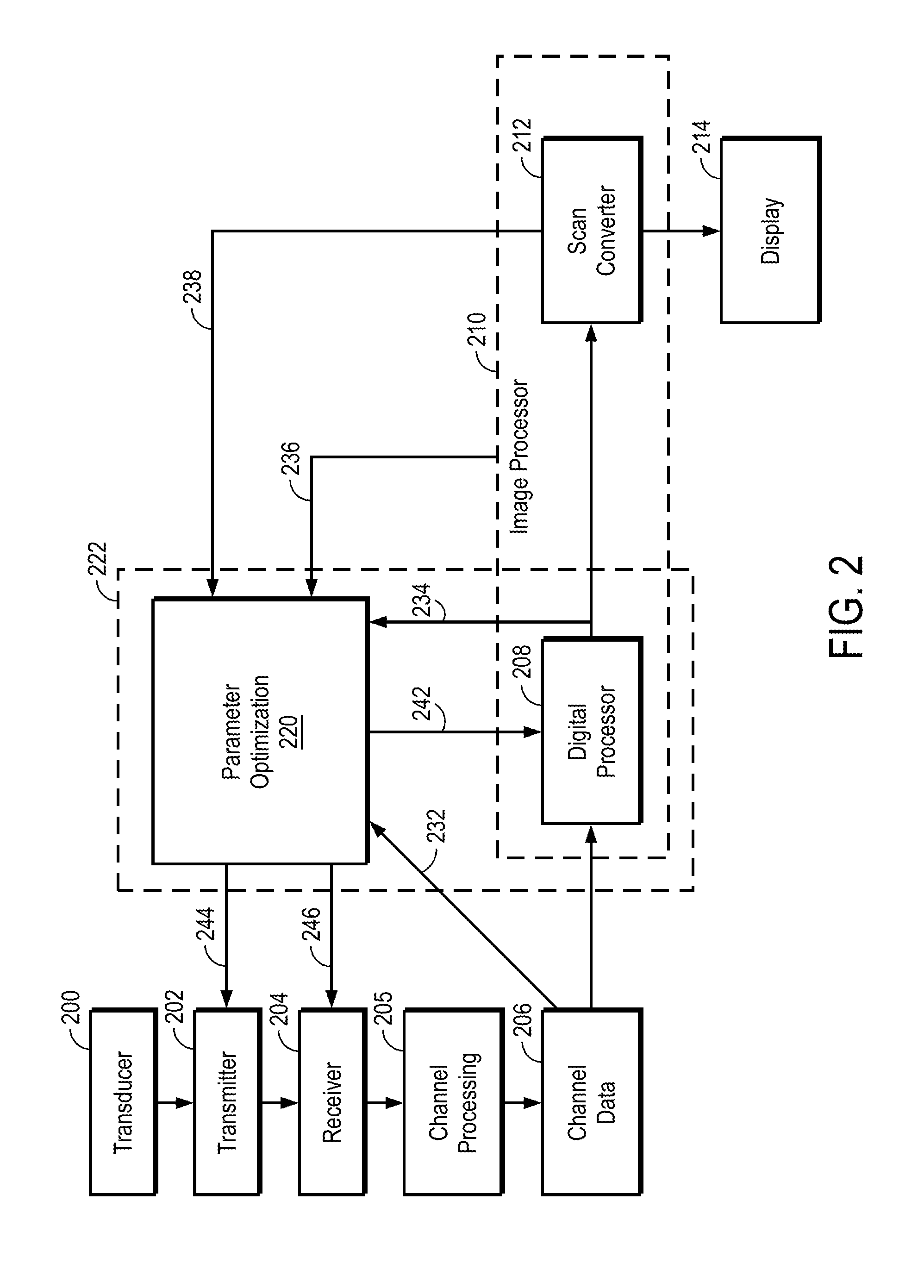
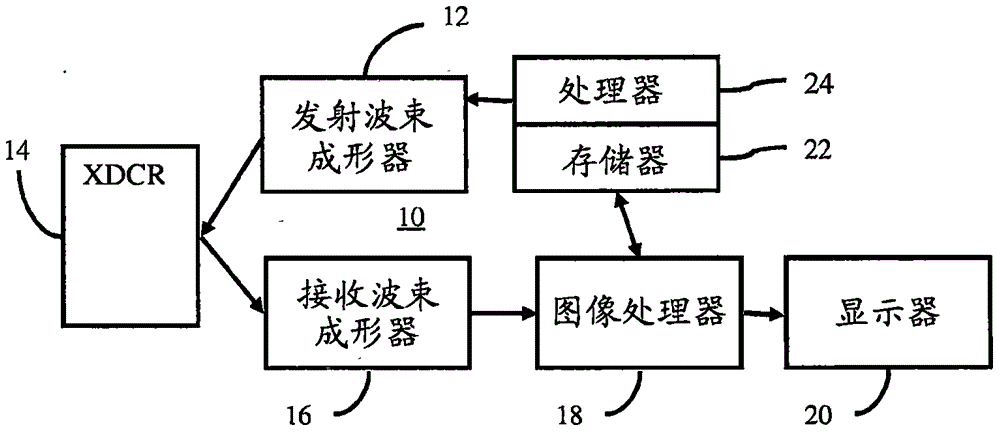
Ultrasound imaging system parameter optimization via fuzzy logic
ActiveUS20060079778A1Easy to adaptWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesImaging processingUltrasonic imaging
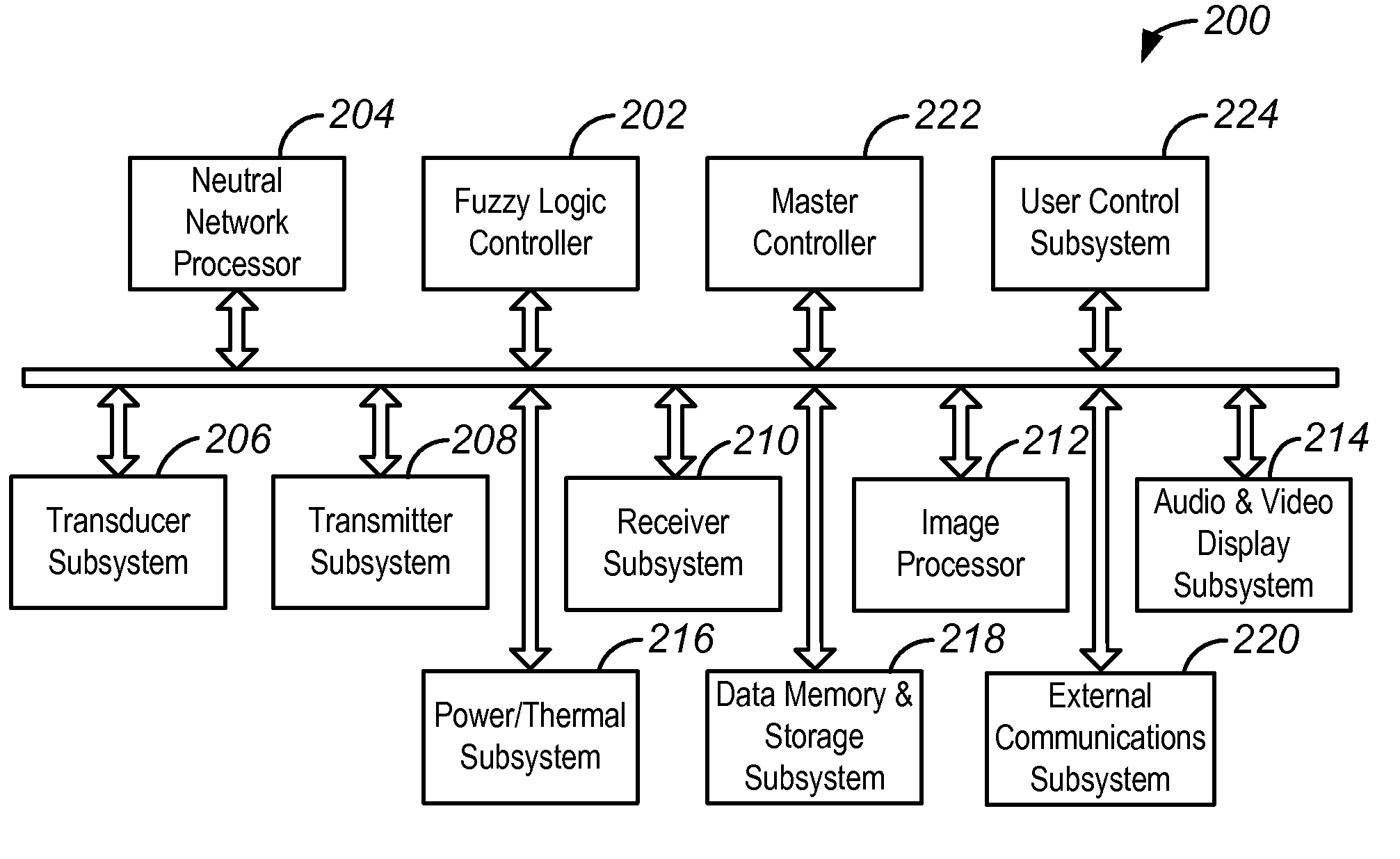
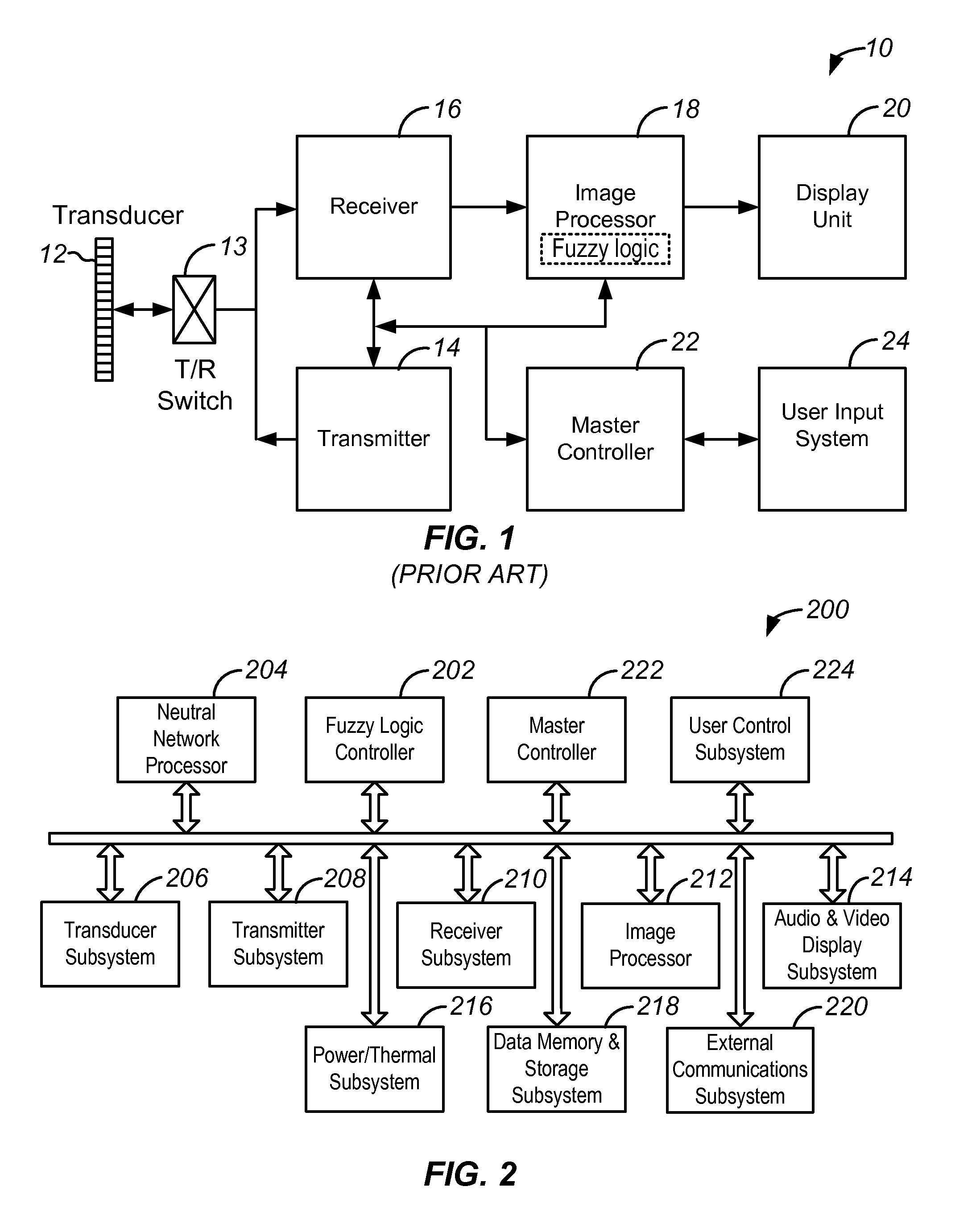
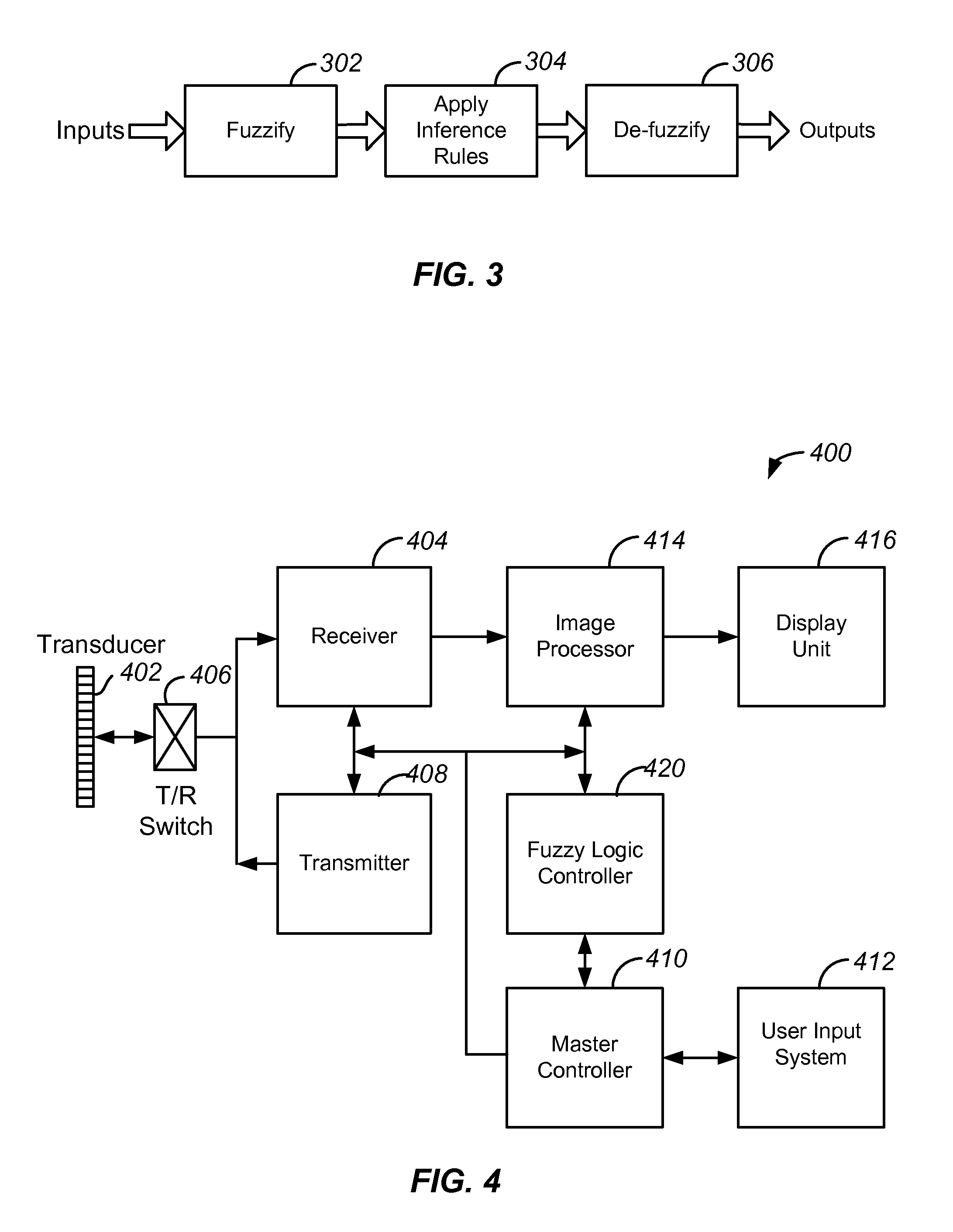
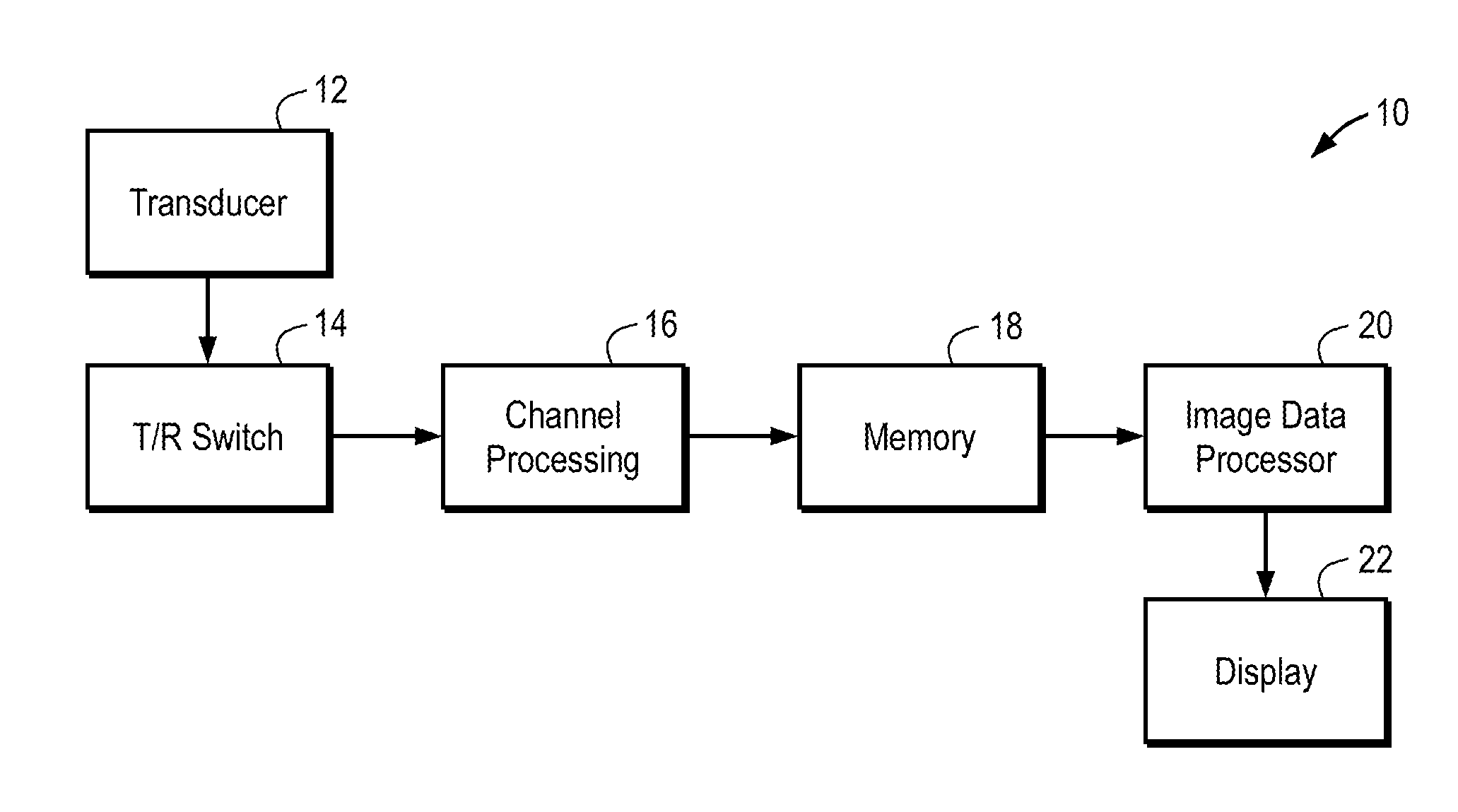
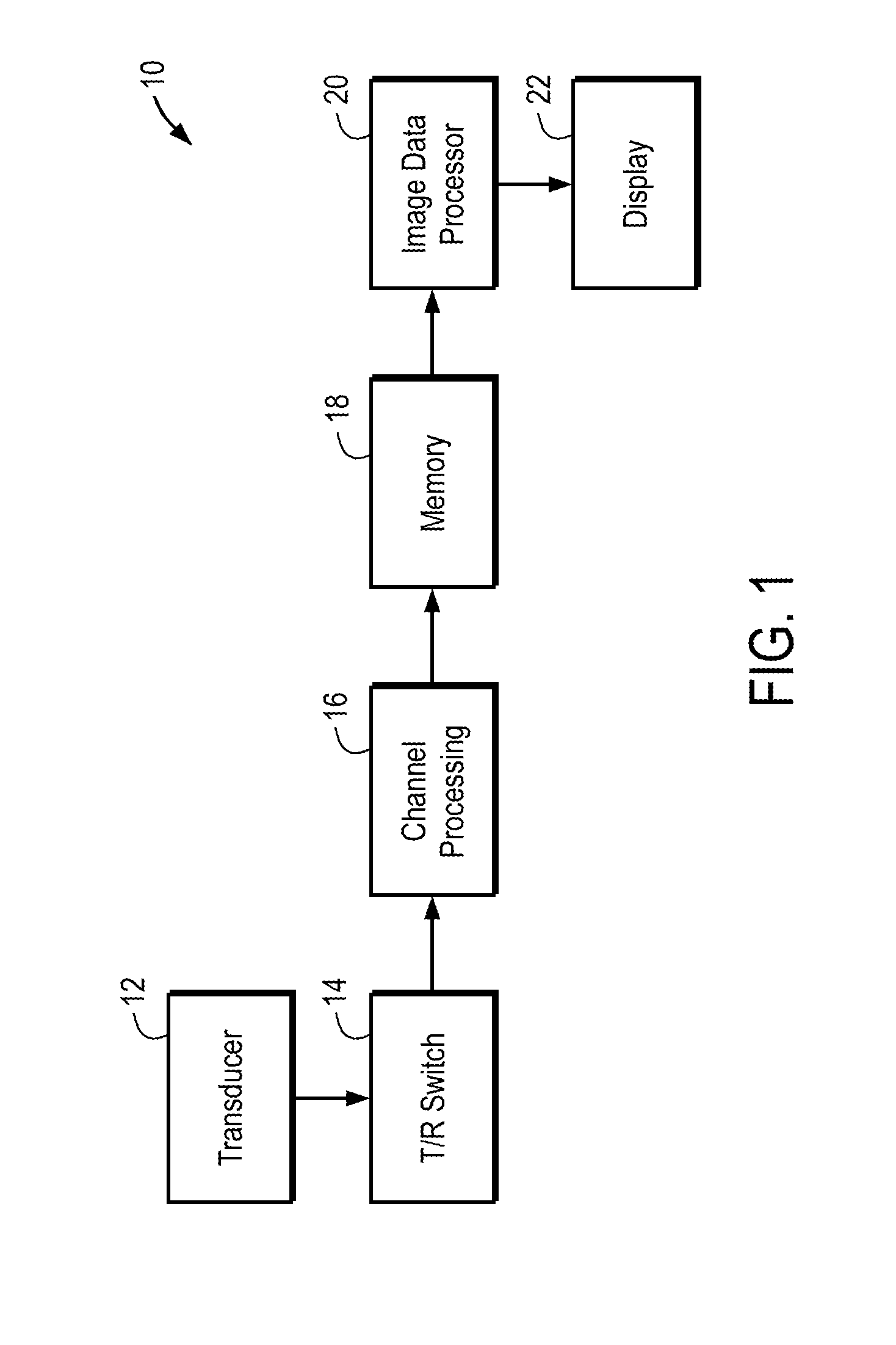
An ultrasound scanner is equipped with one or more fuzzy control units that can perform adaptive system parameter optimization anywhere in the system. In one embodiment, an ultrasound system comprises a plurality of ultrasound image generating subsystems configured to generate an ultrasound image, the plurality of ultrasound image generating subsystems including a transmitter subsystem, a receiver subsystem, and an image processing subsystem; and a fuzzy logic controller communicatively coupled with at least one of the plurality of ultrasound imaging generating subsystems. The fuzzy logic controller is configured to receive, from at least one of the plurality of ultrasound imaging generating subsystems, input data including at least one of pixel image data and data for generating pixel image data; to process the input data using a set of inference rules to produce fuzzy output; and to convert the fuzzy output into numerical values or system states for controlling at least one of the transmit subsystem and the receiver subsystem that generate the pixel image data.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
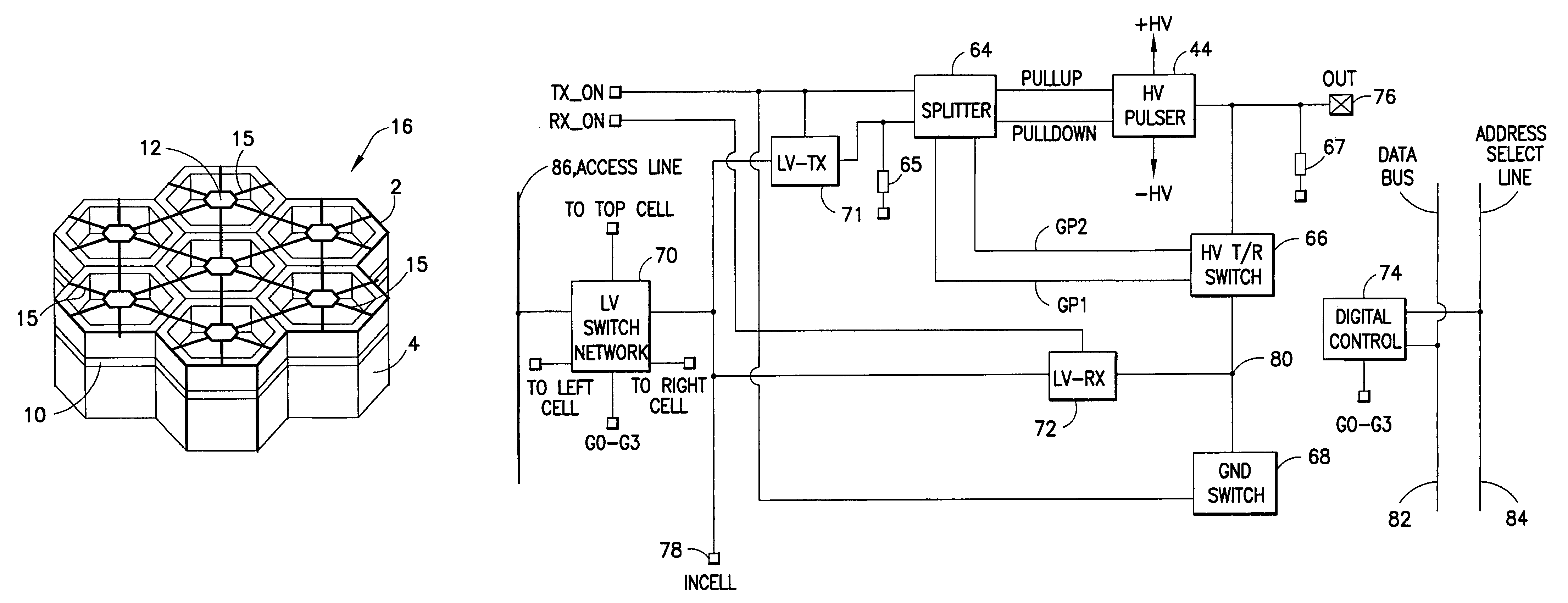
Transmit and receive interface array for highly integrated ultrasound scanner
InactiveUS20070016026A1Minimal expenditure of powerSmall footprintWave based measurement systemsInfrasonic diagnosticsLow voltageControl signal
An ultrasonic transducer probe having a highly integrated interface circuit array. Low-voltage transmit control signals from the system are transmitted on the system transmit channels via the ultrasound probe cable and into the interface circuit array. These transmit control signals are routed through the interface circuit array using a dense switching matrix. Once the low-voltage transmit control signals reach individual cells within the interface array, they are decoded and used to control local high-voltage pulser circuits to drive individual ultrasound transducer elements made up of selected subelements that are co-integrated with the interface electronics. The interface cell circuitry further comprises a high-voltage transmit / receive switch, which is closed when the high-voltage pulser is transmitting to protect the low-voltage components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus to produce ultrasonic images using multiple apertures
ActiveUS20080103393A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioNarrow thicknessDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging ProceduresIntercostal space
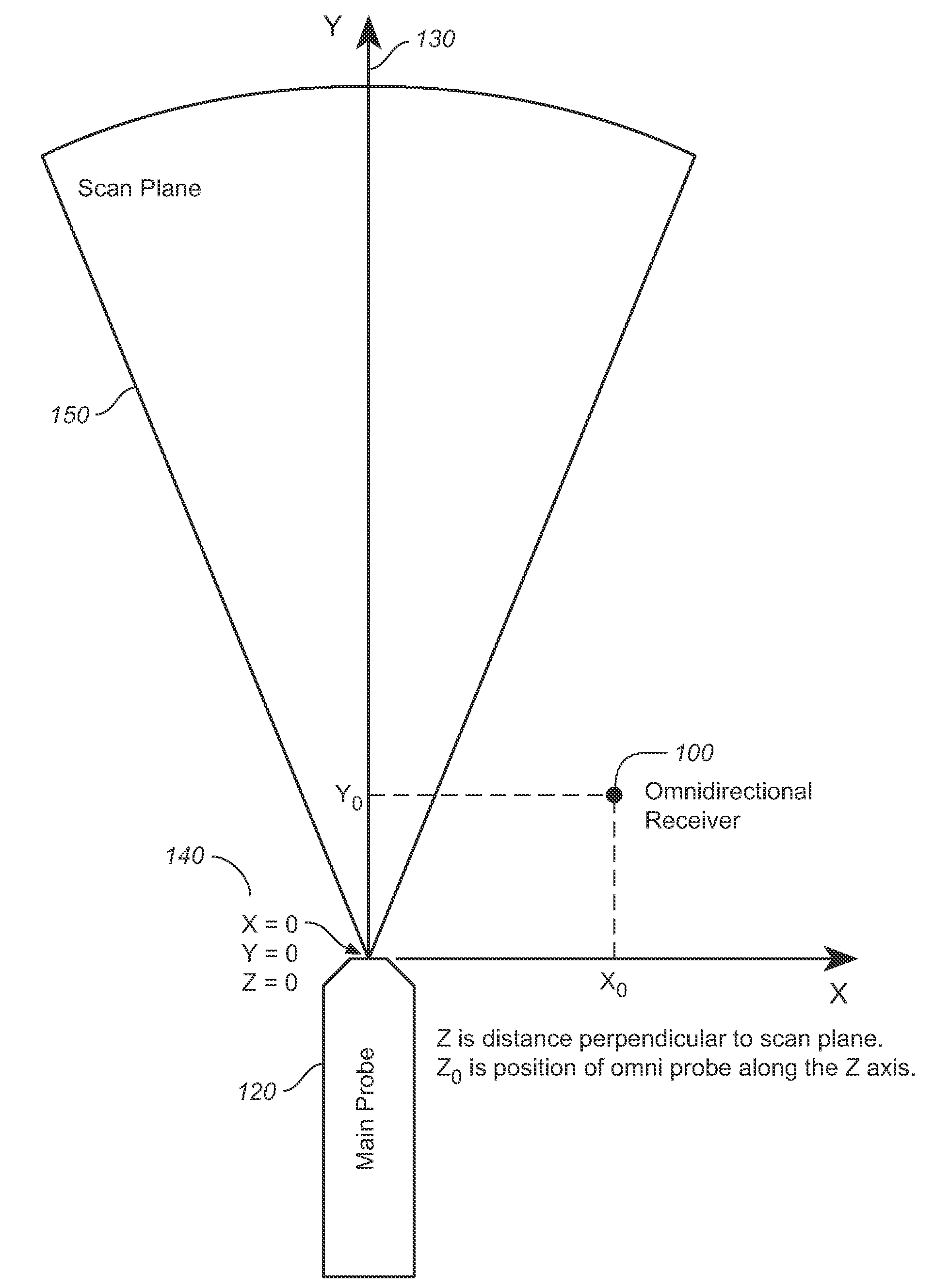
A combination of an ultrasonic scanner and an omnidirectional receive transducer for producing a two-dimensional image from the echoes received by the single omnidirectional transducer is described. Two-dimensional images with different noise components can be constructed from the echoes received by additional transducers. These can be combined to produce images with better signal to noise ratios and lateral resolution. Also disclosed is a method based on information content to compensate for the different delays for different paths through intervening tissue is described. Specular reflections are attenuated by using even a single omnidirectional receiver displaced from the insonifying probe. The disclosed techniques have broad application in medical imaging but are ideally suited to multi-aperture cardiac imaging using two or more intercostal spaces. Since lateral resolution is determined primarily by the aperture defined by the end elements, it is not necessary to fill the entire aperture with equally spaced elements. In fact, gaps can be left to accommodate spanning a patient's ribs, or simply to reduce the cost of the large aperture array. Multiple slices using these methods can be combined to form three-dimensional images.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Ultrasound imaging system parameter optimization via fuzzy logic
ActiveUS7627386B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsSonificationSystem parameters
An ultrasound scanner is equipped with one or more fuzzy control units that can perform adaptive system parameter optimization anywhere in the system. In one embodiment, an ultrasound system comprises a plurality of ultrasound image generating subsystems configured to generate an ultrasound image, the plurality of ultrasound image generating subsystems including a transmitter subsystem, a receiver subsystem, and an image processing subsystem; and a fuzzy logic controller communicatively coupled with at least one of the plurality of ultrasound imaging generating subsystems. The fuzzy logic controller is configured to receive, from at least one of the plurality of ultrasound imaging generating subsystems, input data including at least one of pixel image data and data for generating pixel image data; to process the input data using a set of inference rules to produce fuzzy output; and to convert the fuzzy output into numerical values or system states for controlling at least one of the transmit subsystem and the receiver subsystem that generate the pixel image data.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
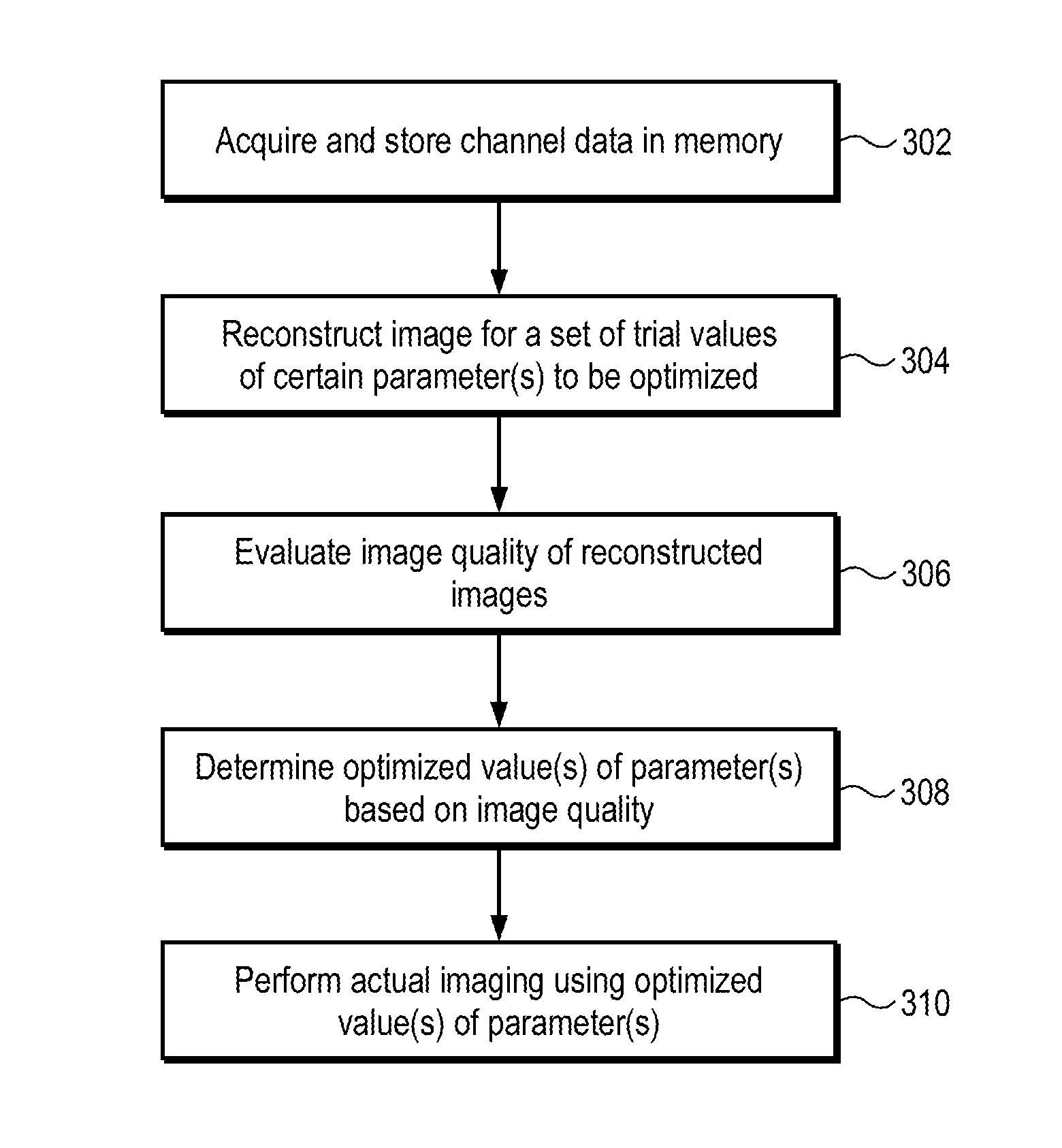
Aberration correction using channel data in ultrasound imaging system
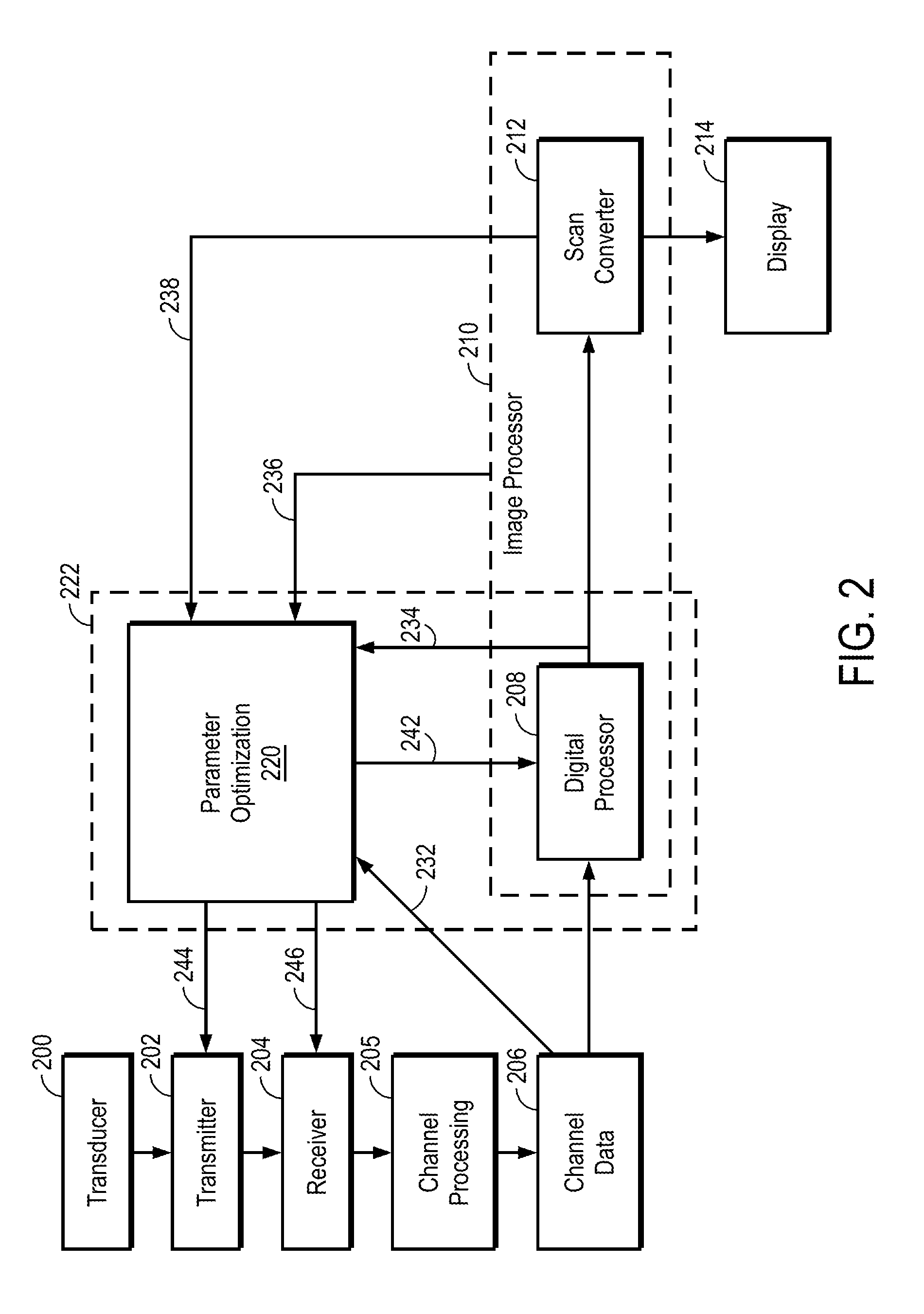
Embodiments of the present invention provide an ultrasound scanner equipped with an image data processing unit that can perform adaptive parameter optimization during image formation and processing. In one embodiment, an ultrasound system comprises a channel data memory to store channel data obtained by digitizing ultrasound image data produced by an image scan; an image data processor configured to process the stored channel data in the memory to reconstruct an ultrasound image for each of a plurality of trial values of at least one parameter to be optimized; and a parameter optimization unit configured to evaluate an image quality of the reconstructed ultrasound image for each trial value of the at least one parameter, and to determine the optimized value of the at least one parameter based on the evaluated image quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit and receive interface array for highly integrated ultrasound scanner
An ultrasonic transducer probe having a highly integrated interface circuit array. Low-voltage transmit control signals from the system are transmitted on the system transmit channels via the ultrasound probe cable and into the interface circuit array. These transmit control signals are routed through the interface circuit array using a dense switching matrix. Once the low-voltage transmit control signals reach individual cells within the interface array, they are decoded and used to control local high-voltage pulser circuits to drive individual ultrasound transducer elements made up of selected subelements that are co-integrated with the interface electronics. The interface cell circuitry further comprises a high-voltage transmit / receive switch, which is closed when the high-voltage pulser is transmitting to protect the low-voltage components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
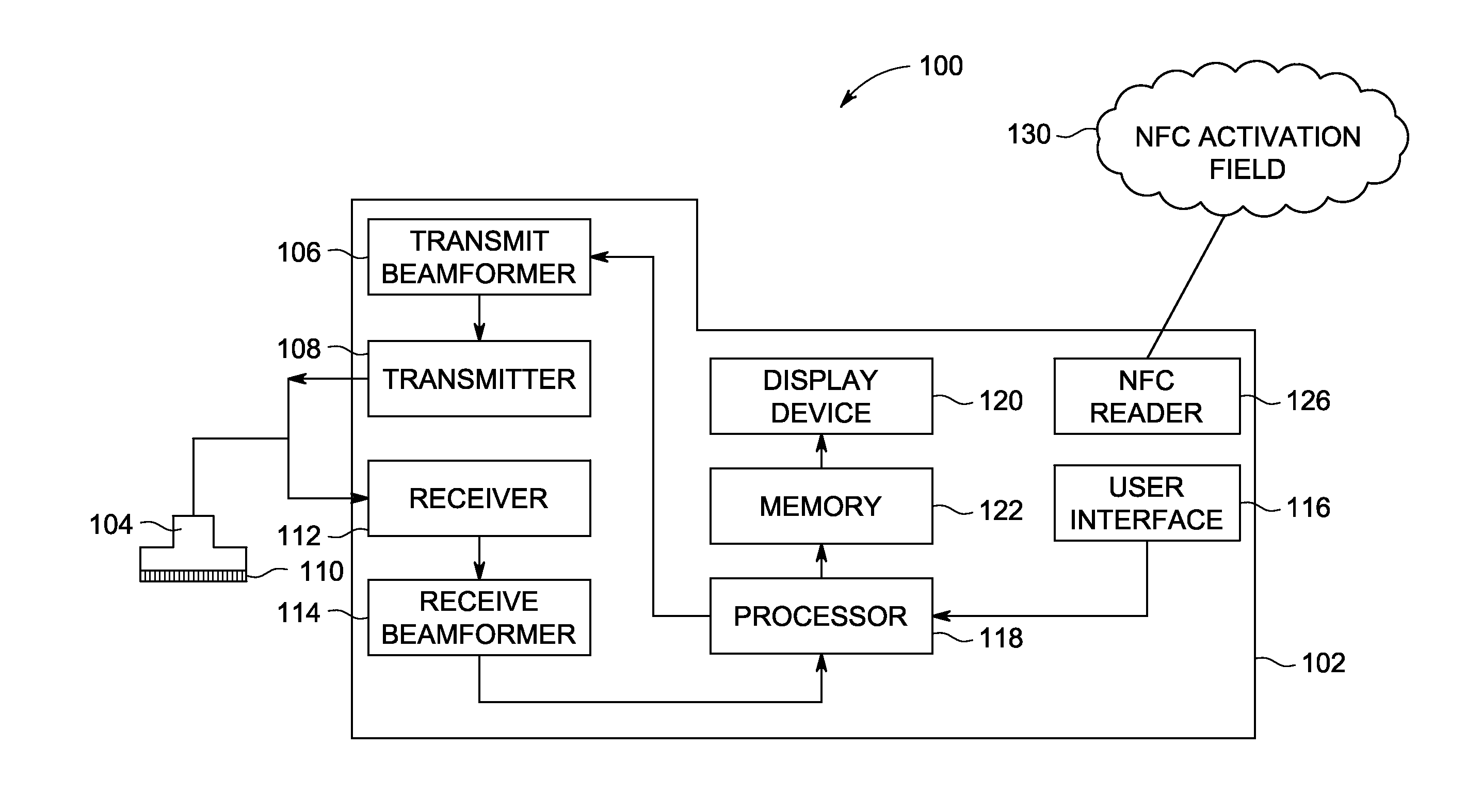
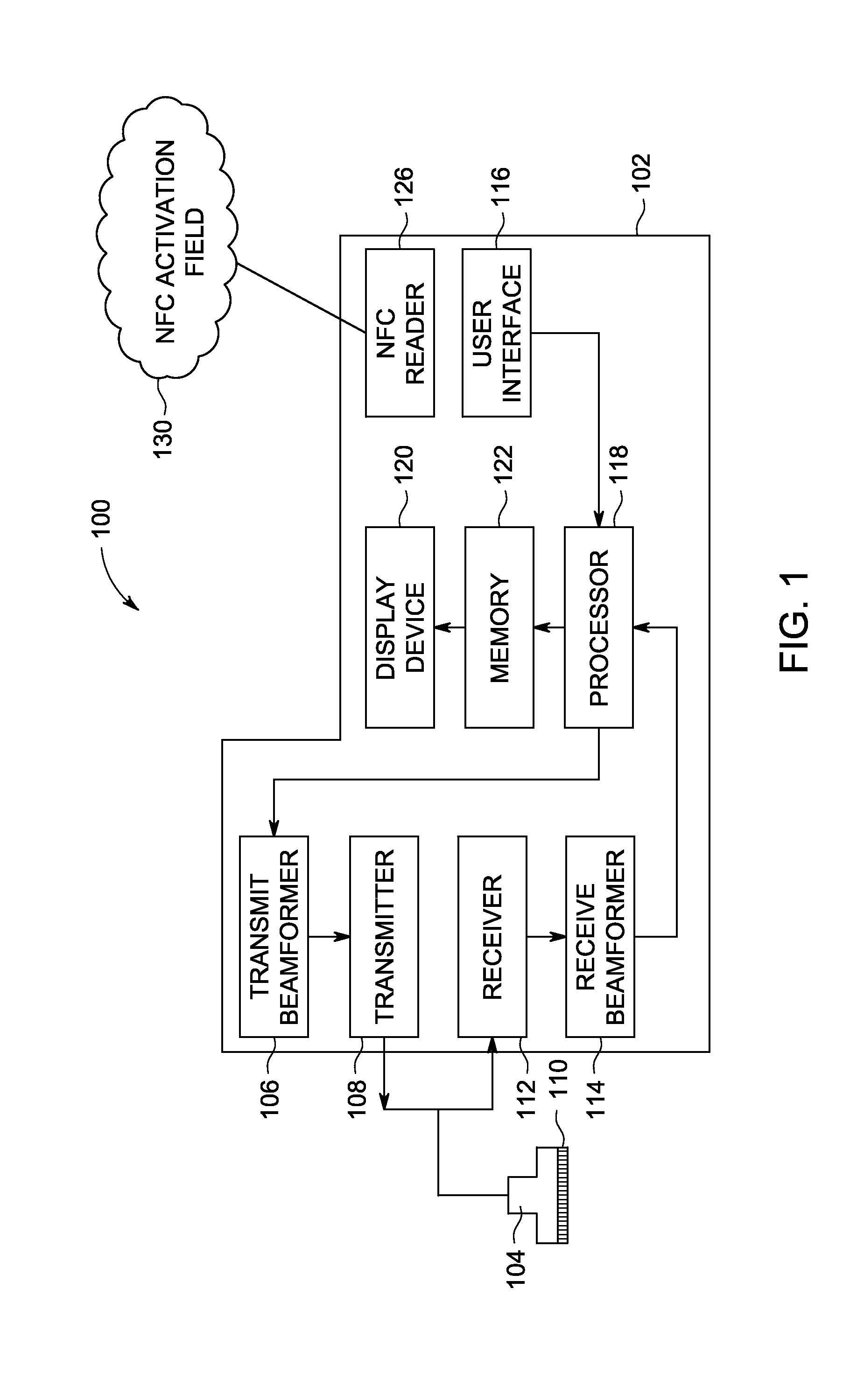
System and Method for Wireless Ultrasound Probe Pairing
InactiveUS20140180110A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBiological activationUltrasound probe
A system for pairing a wireless ultrasound probe and an ultrasound scanner is provided. The ultrasound system comprises an ultrasound scanner comprising a near field communication reader capable of generating a near field communication activation field and a wireless ultrasound probe comprising a near field communication device, wherein the probe is adapted to transmit pairing information to the scanner via a near field communication protocol.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
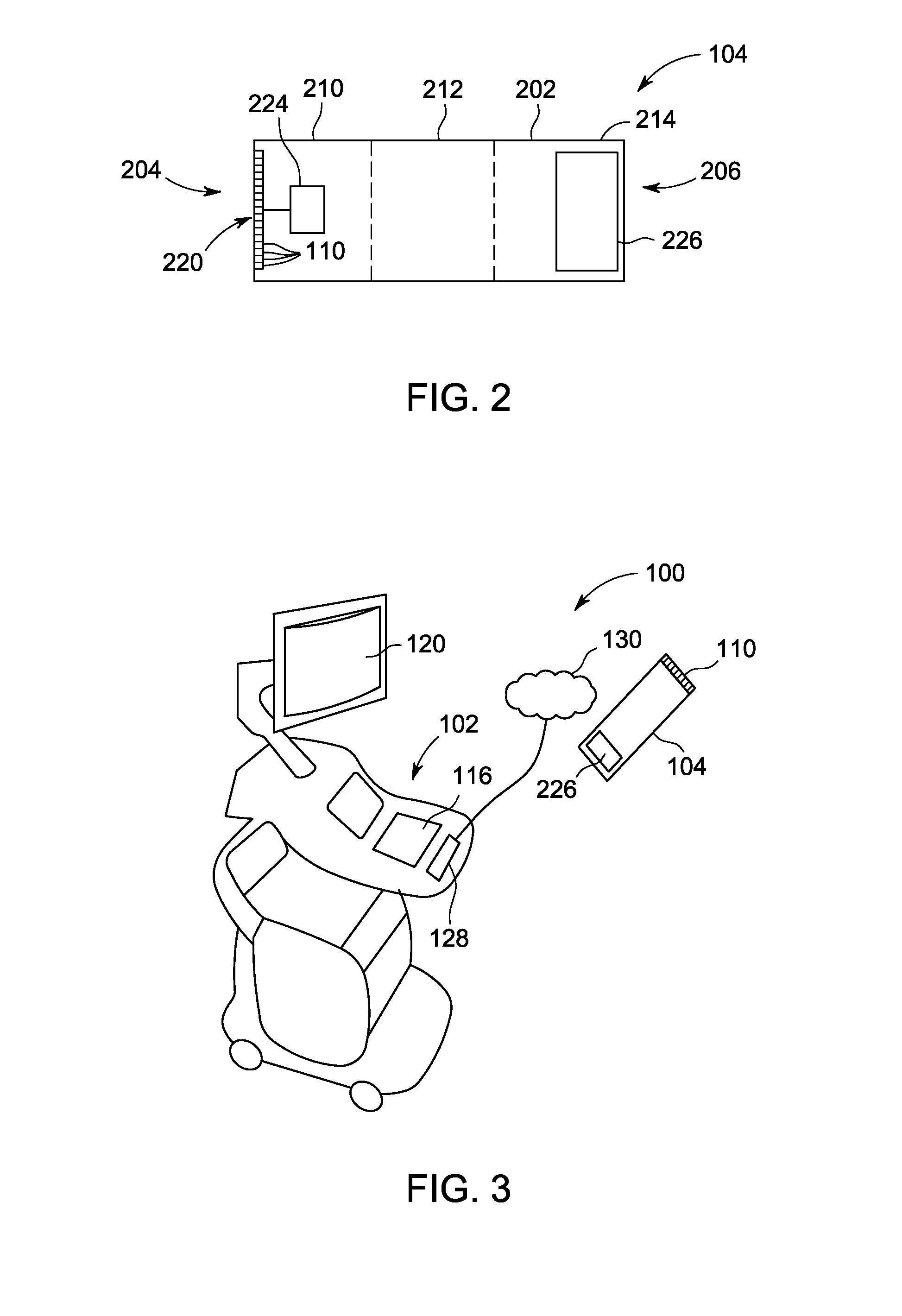
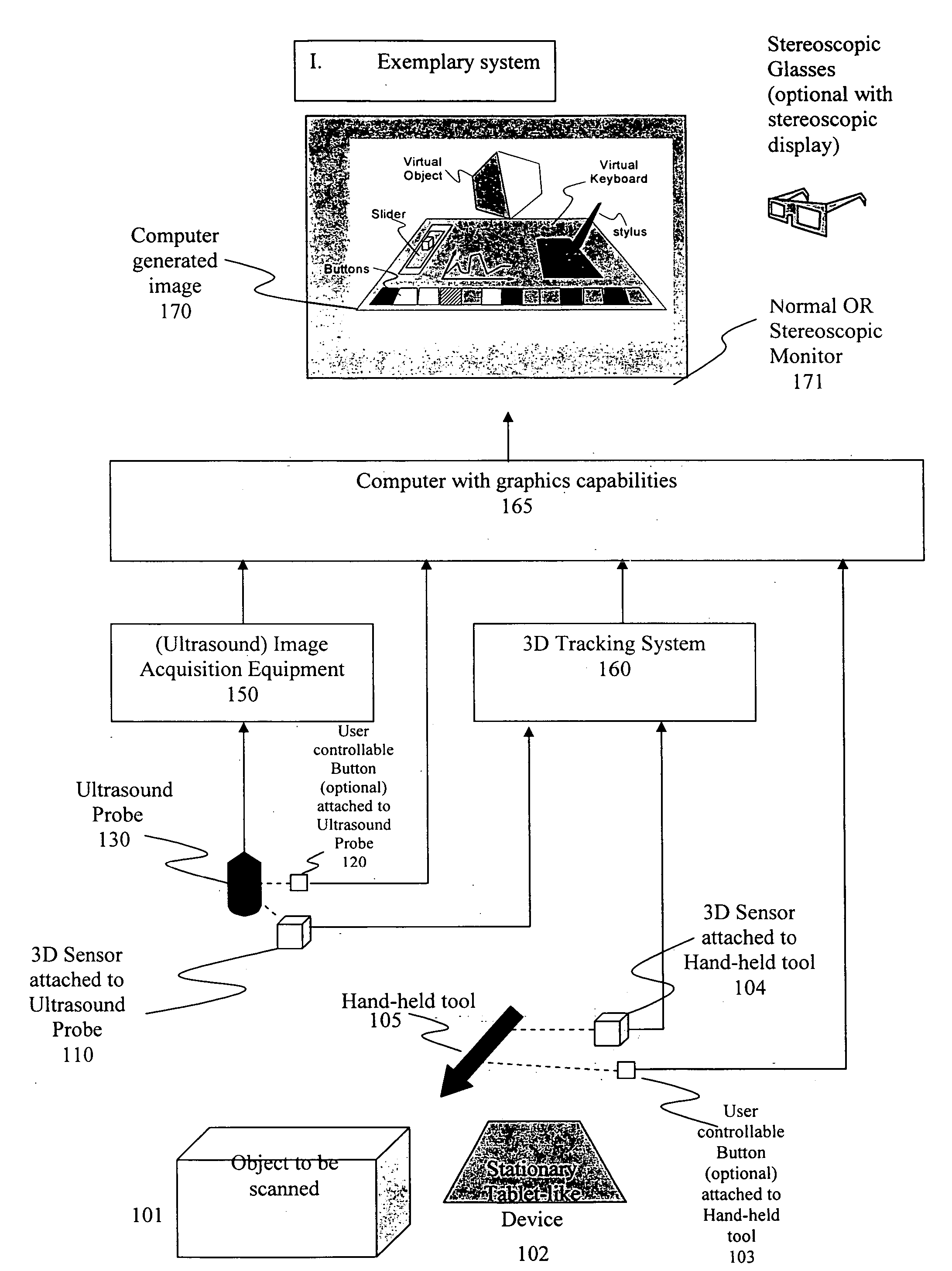
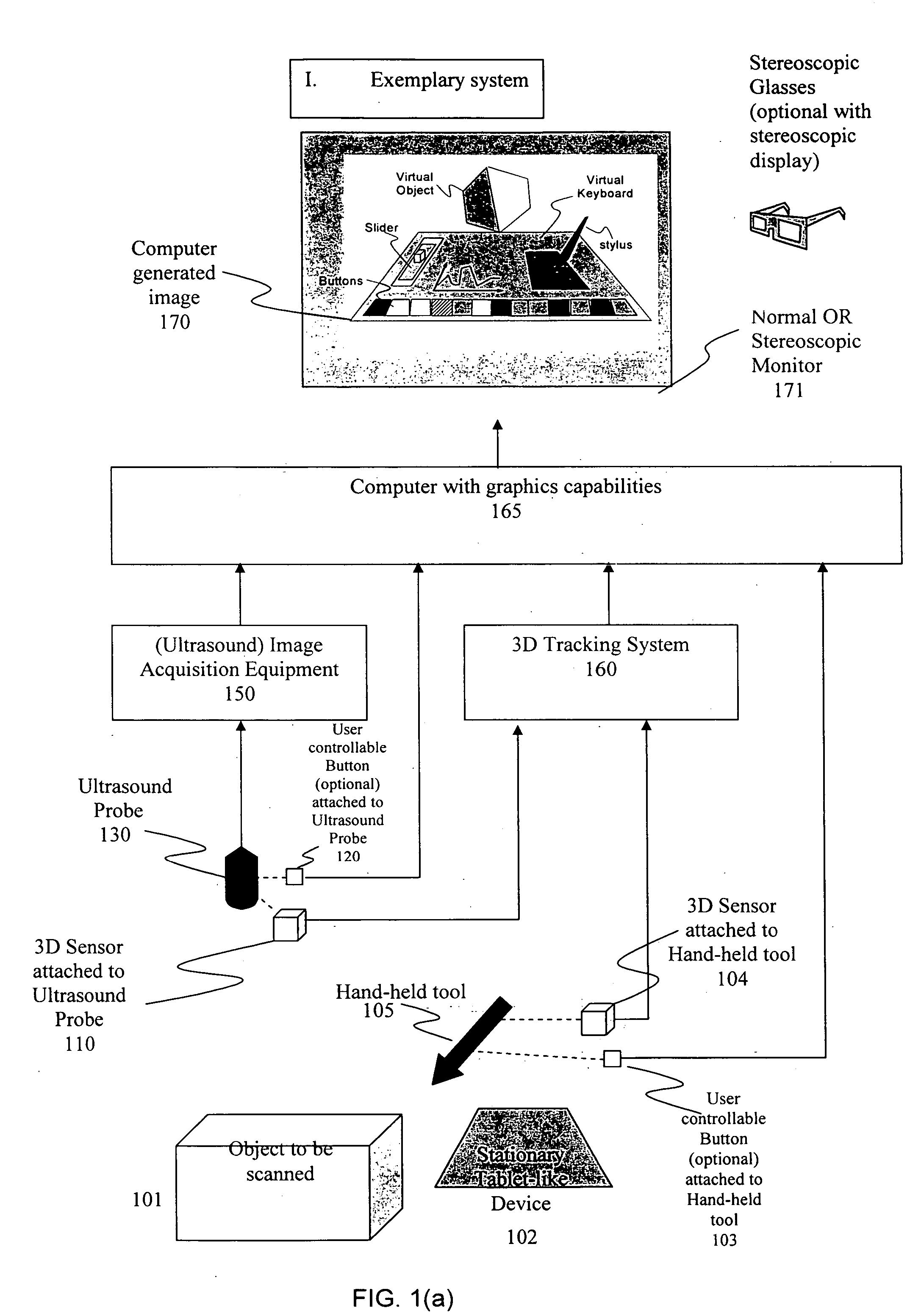
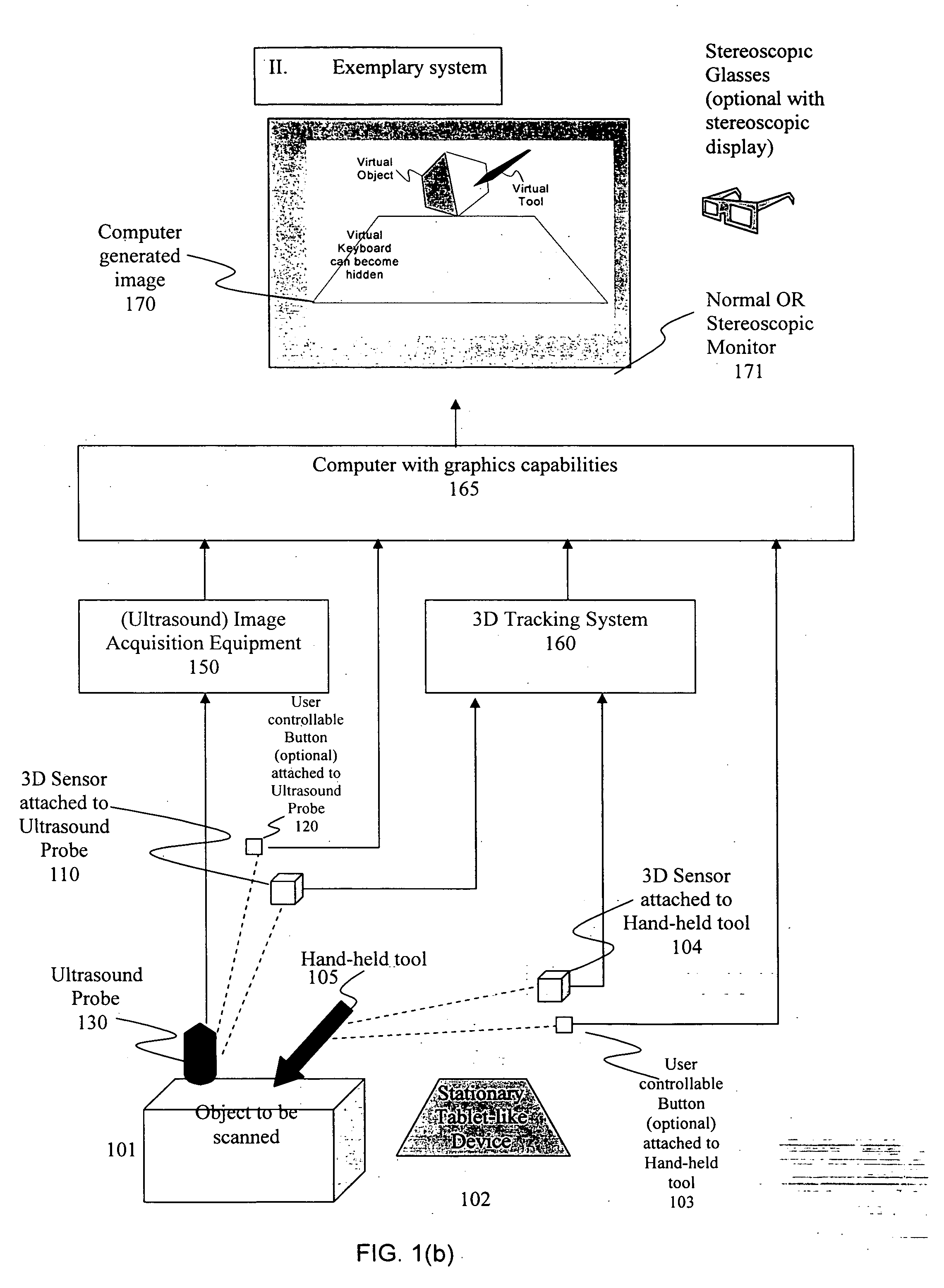
System and method for a virtual interface for ultrasound scanners
A virtual control system for substantially real-time imaging machines, such as, for example, ultrasound, is presented. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a virtual control system comprises a physical interface communicably connected to a scanner / imager, such as, for example, an ultrasound machine. The scanner / imager has, or is communicably connected to, a processor that controls the display of, and user interaction with, a virtual control interface. In operation, a user can interact with the virtual control interface by physically interacting with the physical interface. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention the physical interface can comprise a handheld tool and a stationary tablet-like device. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention the control system can further include a 3D tracking device that can track both an ultrasound probe as well as a handheld physical interface tool. In such exemplary embodiments a user can control scan and display functions of the ultrasound machine by moving a handheld tool relative to the stationary tablet, and can perform 3D interactive display and image processing operations on a displayed 3D image by manipulating the handheld tool within a defined 3D space. Alternatively, all control functions, those associated with scan and display control as well as those associated with 3D interactive display and image processing can be mapped to manipulations of the handheld tool in a defined 3D space.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Balloon anchor for endoscopically inserting ultrasound probe
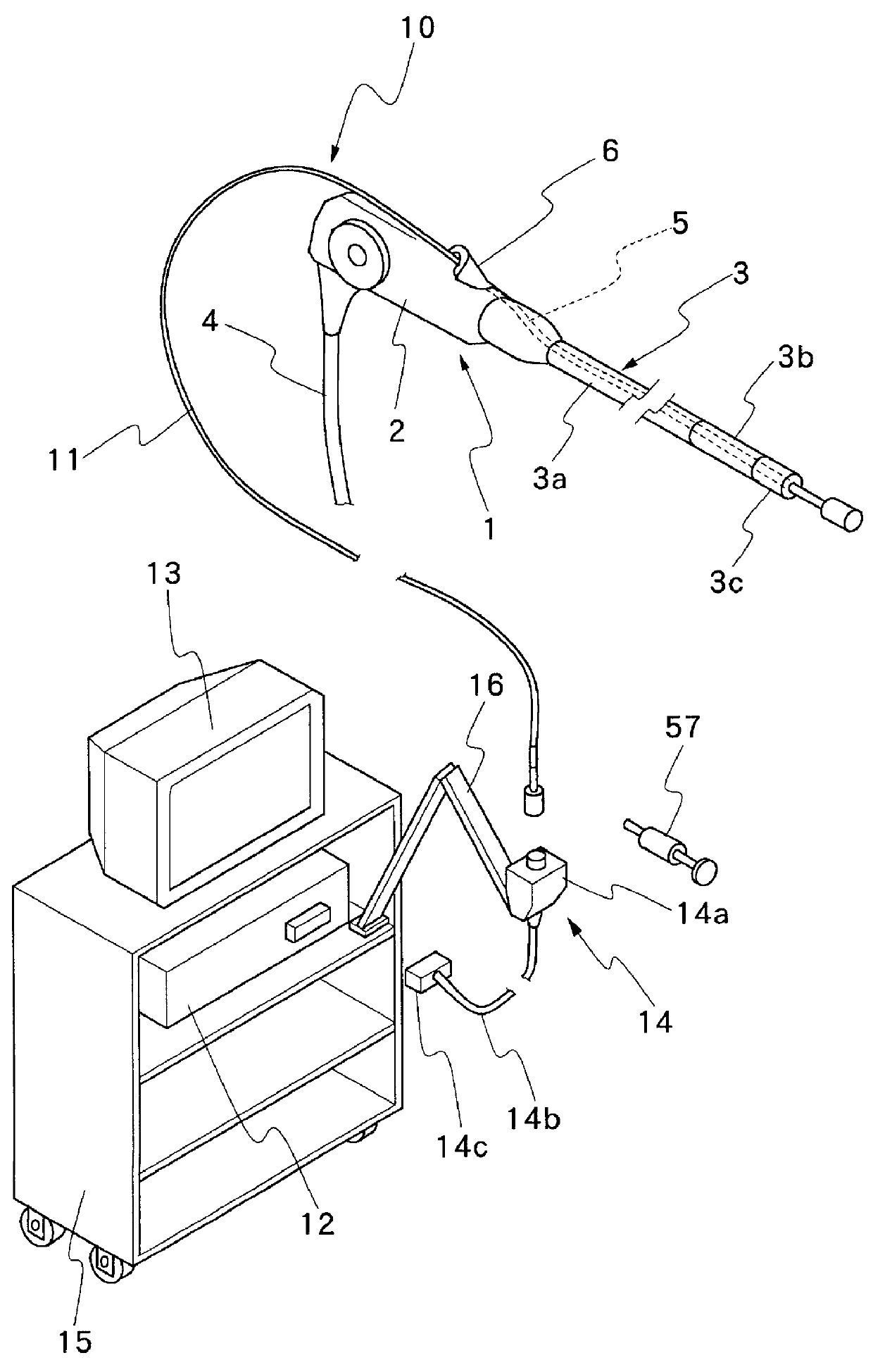
A balloon anchor for use with an endoscopically inserting ultrasound probe having an ultrasound transducer element accommodated in an ultrasound scanner head at the fore distal end of a flexible cord to be placed in an endoscopic biopsy channel. The balloon anchor includes an anchor tube which is adapted to be fitted in the endoscopic biopsy channel in such a way that it is partly projected from fore distal end of the endoscopic biopsy channel. Connected to the projected fore end of the anchor tube is a balloon support member of a larger diameter as compared with the endoscopic biopsy channel. A passage of a large diameter is formed axially through the anchor tube and through the balloon support member. A balloon stopper portion is provided on the outer periphery of the balloon support member to anchor a resilient ring of a balloon therein.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
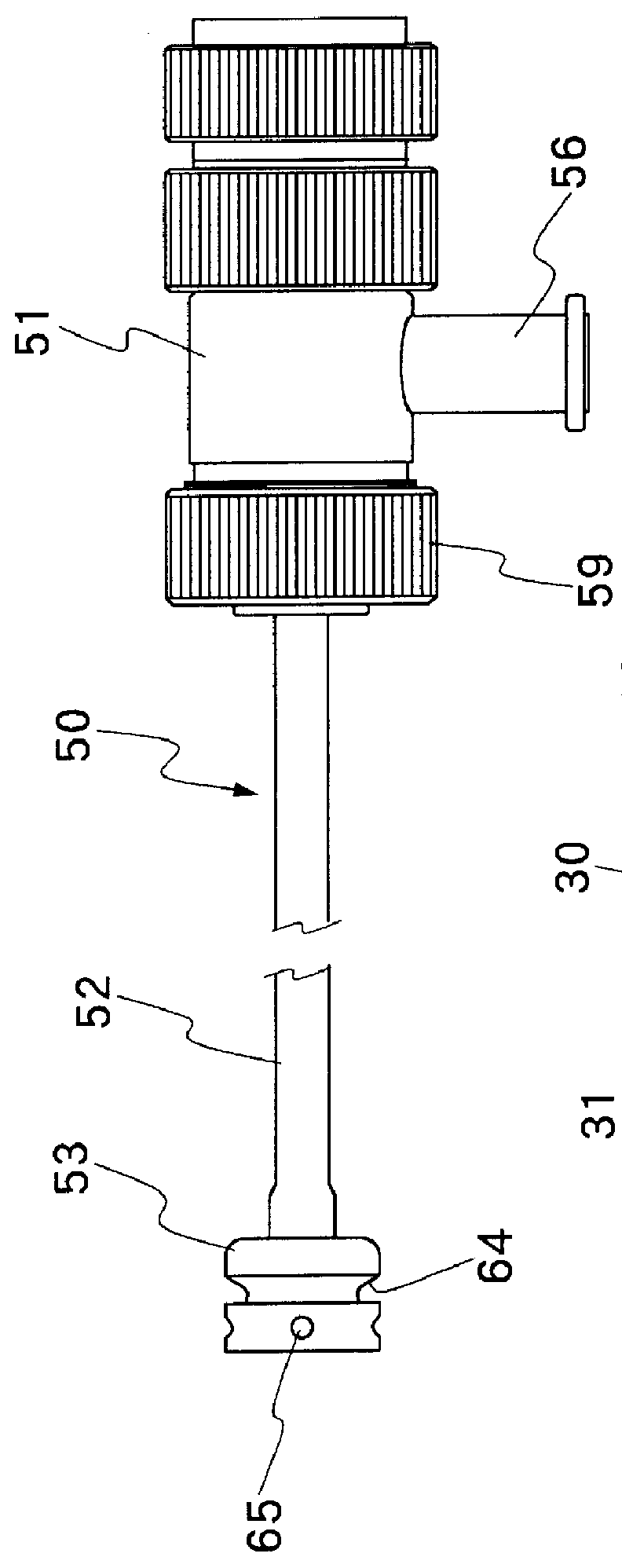
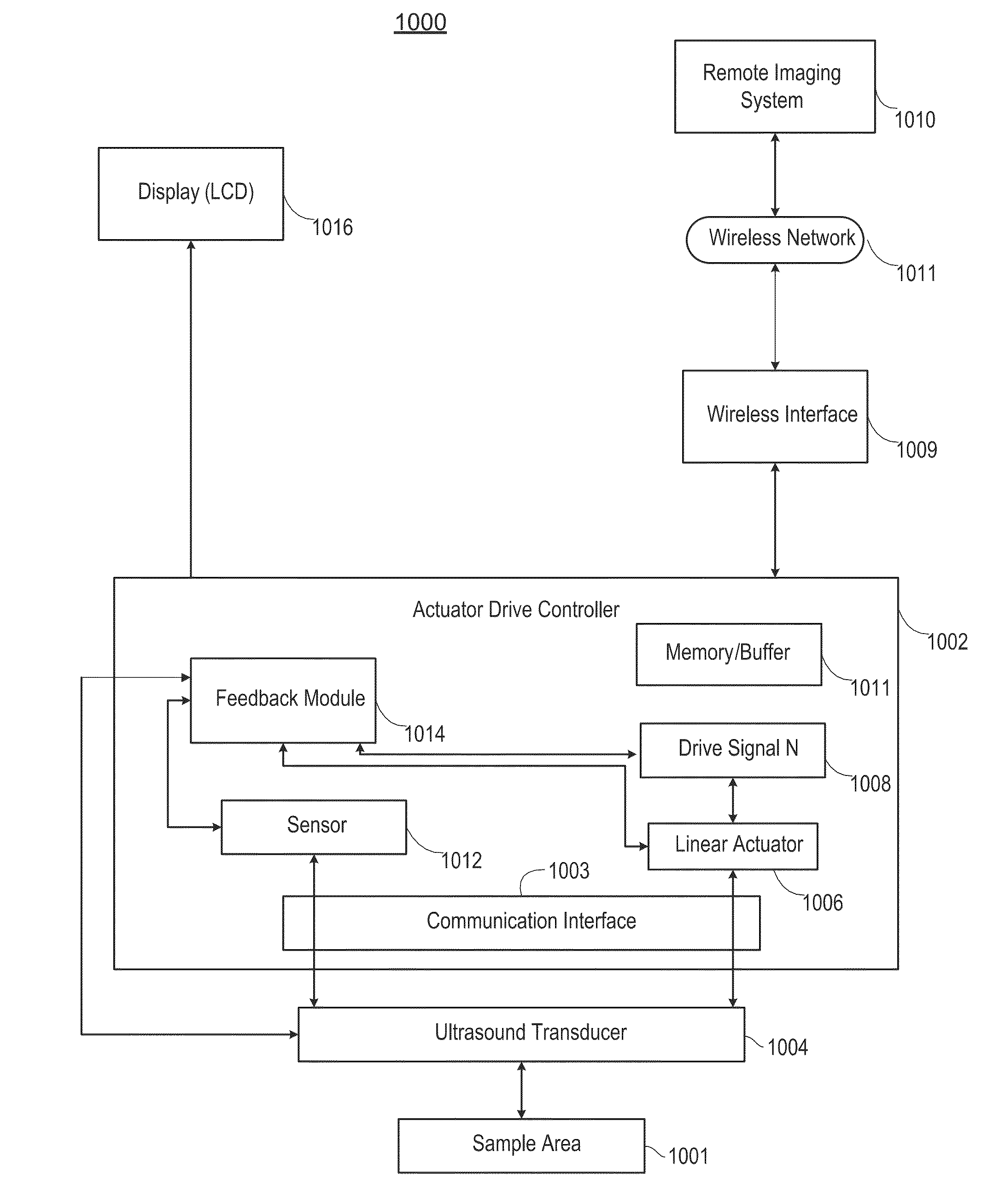
Linear magnetic drive transducer for ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20130345566A1Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
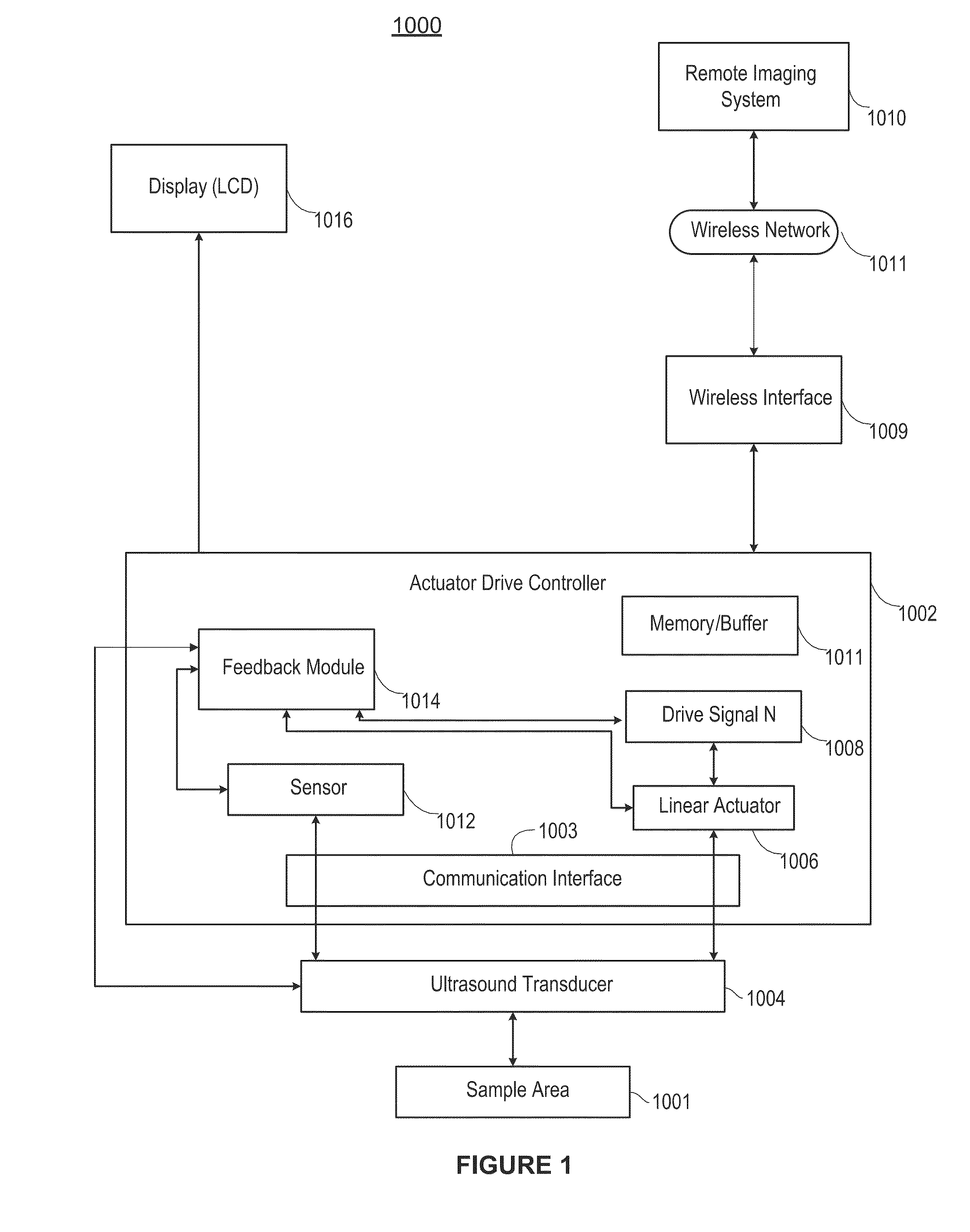
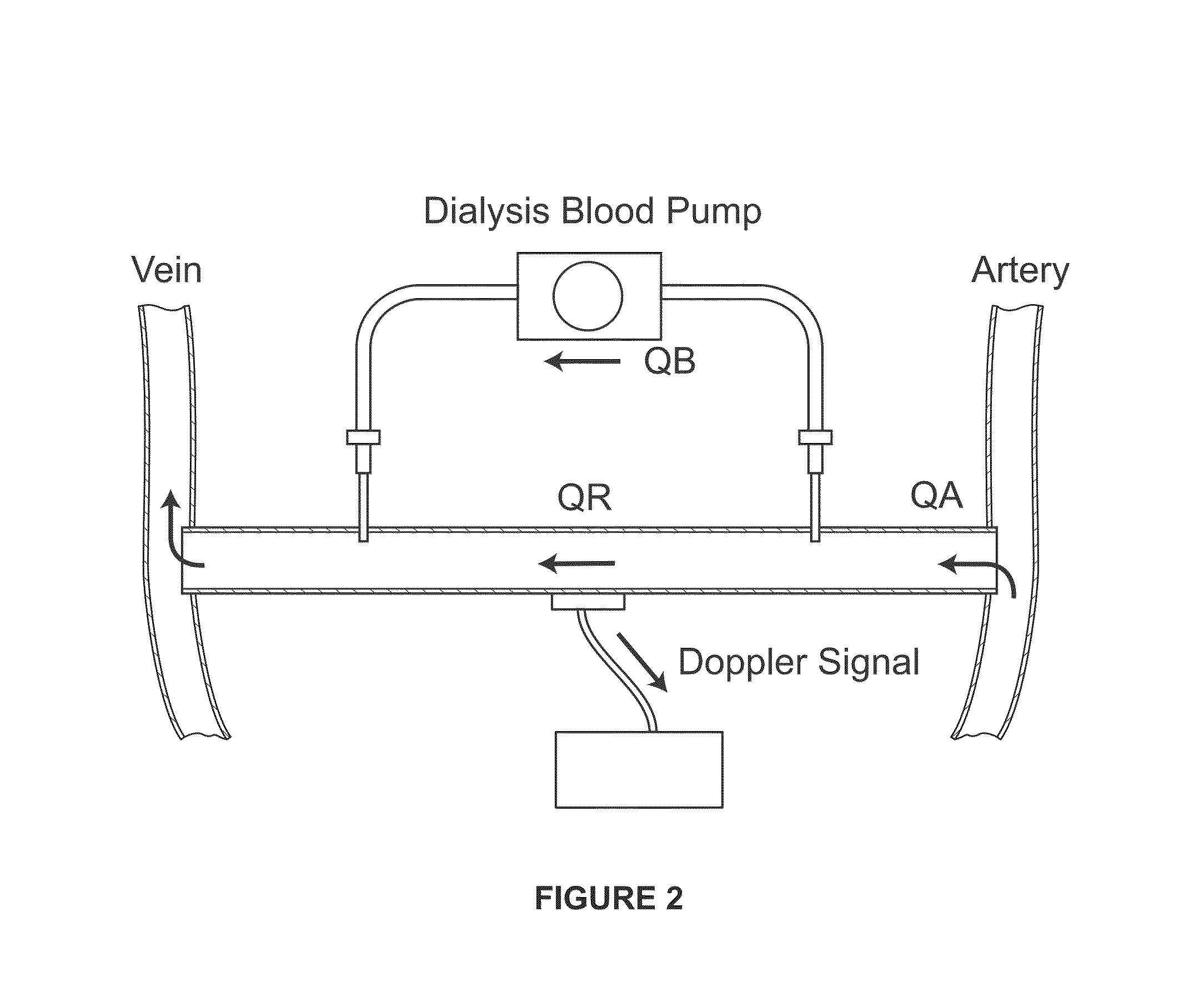
An ultrasound imaging system uses a magnetic linear motor driven ultrasound scanner, with accurate track and hold operation and / or other motion feedback, to scan a two dimensional or three dimensional area of a sample. The scanner is implemented in a low-power and low-bandwidth handheld device and is connected with a remote image processing system that receives raw data and performs full ultrasound image analysis and creation, allowing the handheld to be used for scanning, pre-processing, and display.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
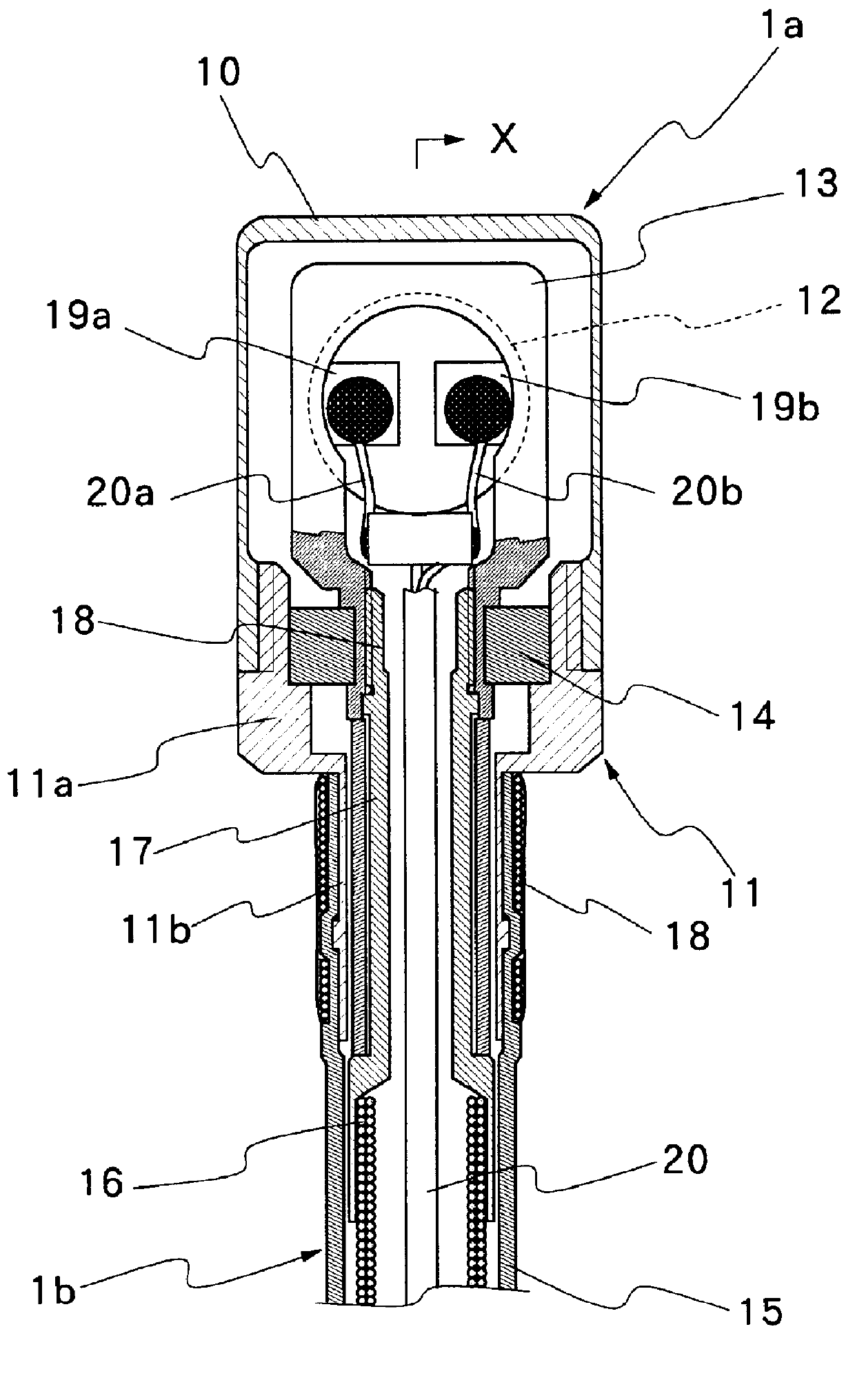
Ultrasound probe having an insulating sleeve member
InactiveUS6017311AHigh strengthPrevent leakageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsDrive shaftTransducer
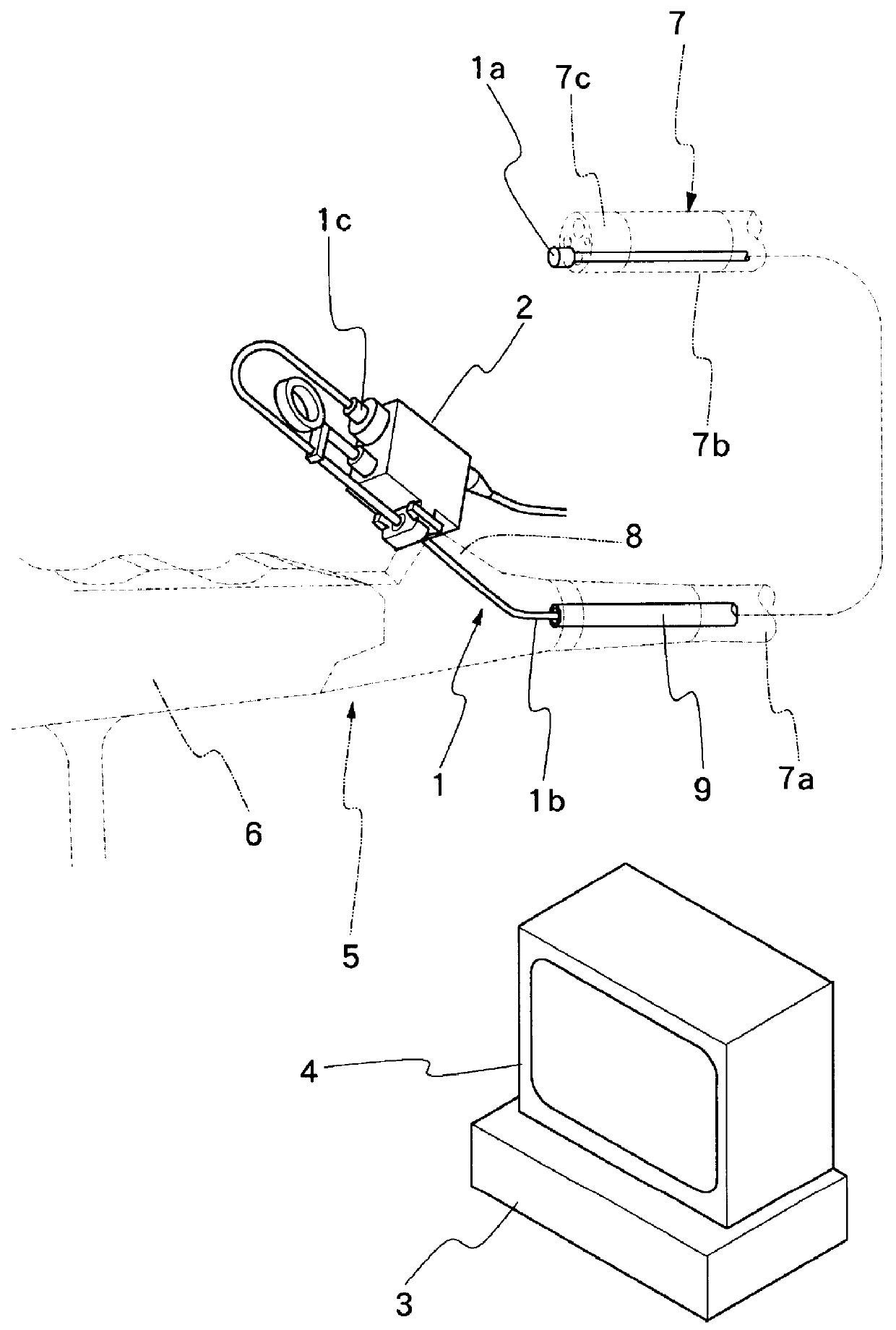
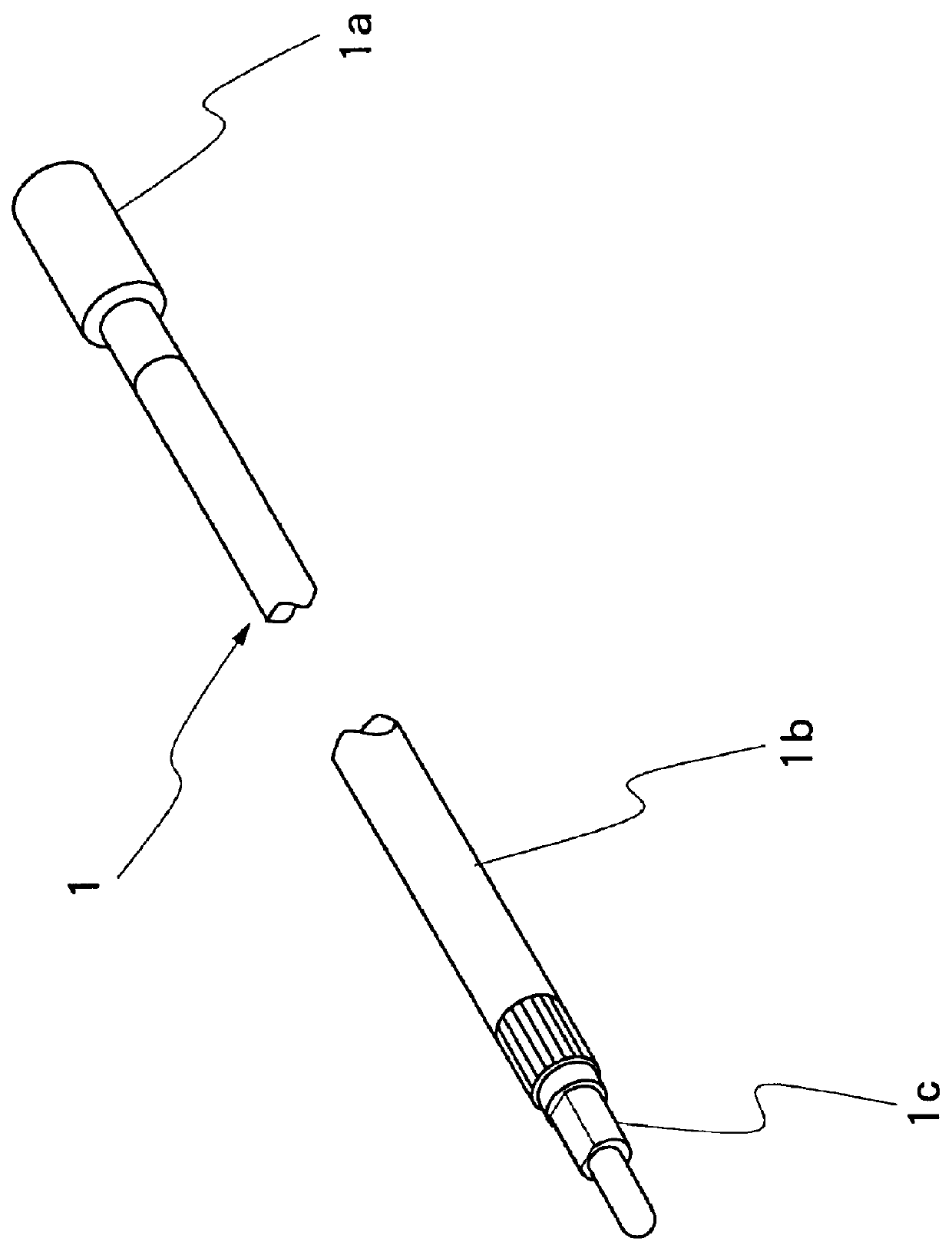
An ultrasound probe of the type having, successively from its head to tail end, an ultrasound scanner head assembly accommodating an ultrasound transducer element rotatably within an end cap, an elongated flexible cord having a flexible transmission shaft of tightly wound metal wire coils within an outer sheathing tube, and a tail end connector. The ultrasound probe is characterized by a joint construction for the ultrasound scanner head, including: a metallic joint member axially extended from the end cap of the ultrasound scanner head assembly on the proximal side thereof and joining the ultrasound scanner head with an outer sheathing tube of the flexible cord by fitting engagement therewith; a cylindrical rotating member located internally of the joint member and the outer sheathing tube, and connecting a fore end portion of the flexible transmission shaft with a rotary support member of the ultrasound transducer element at a position axially on the proximal side of a rear end of the joint member; and an insulating sleeve member fitted on the cylindrical rotating member and keeping the cylindrical rotating member out of contact with the metallic joint member for electrical insulation purposes.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
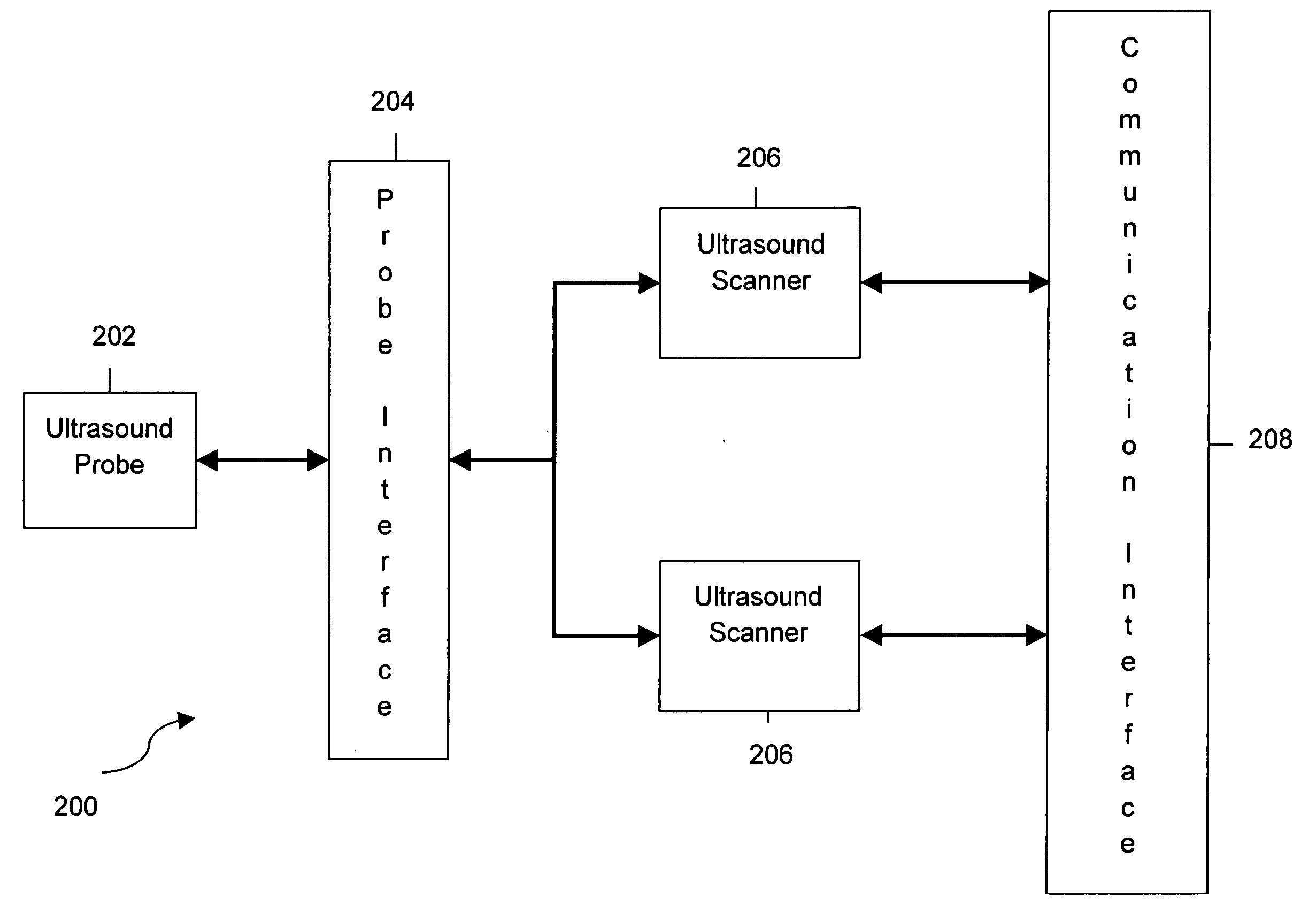
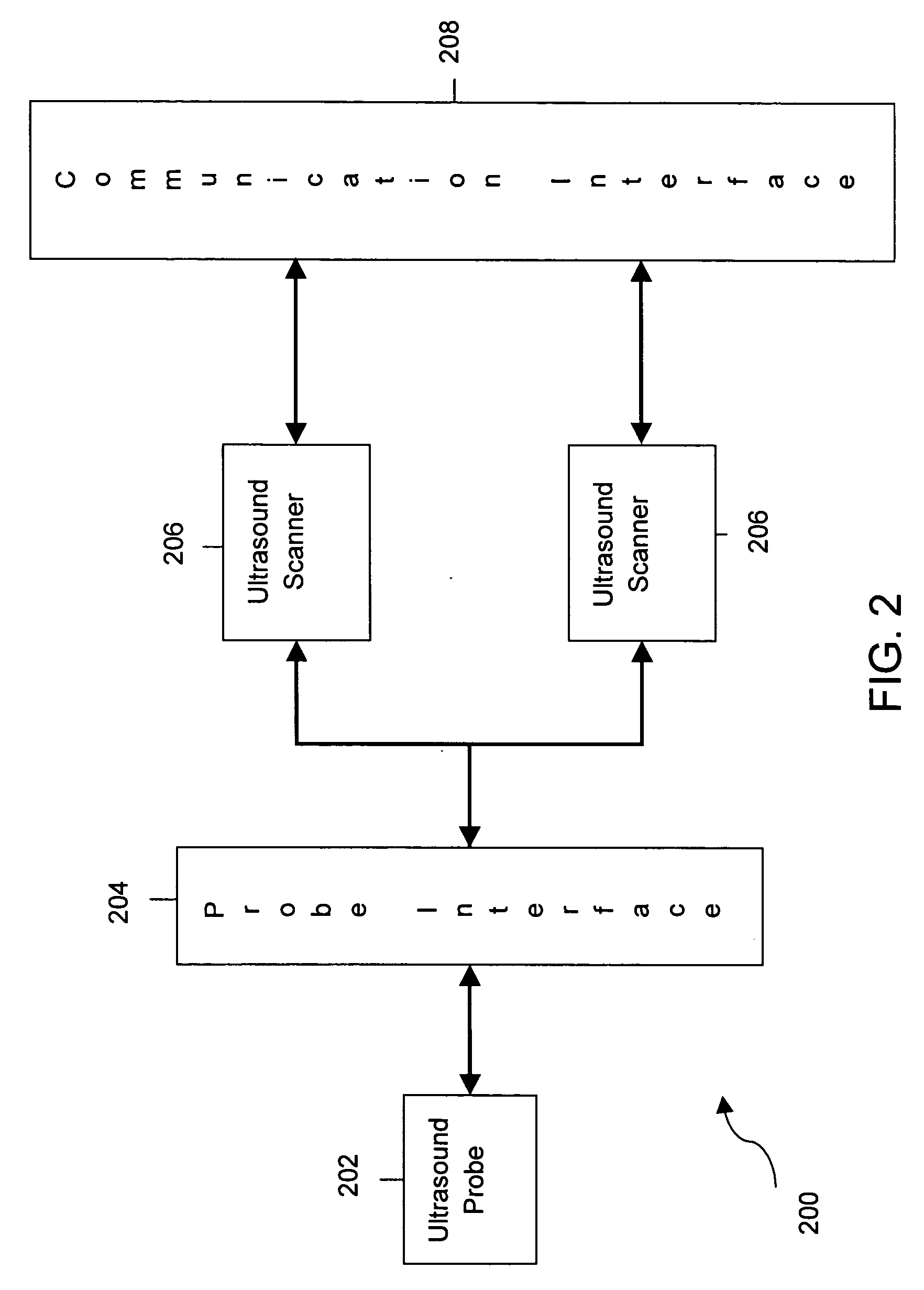
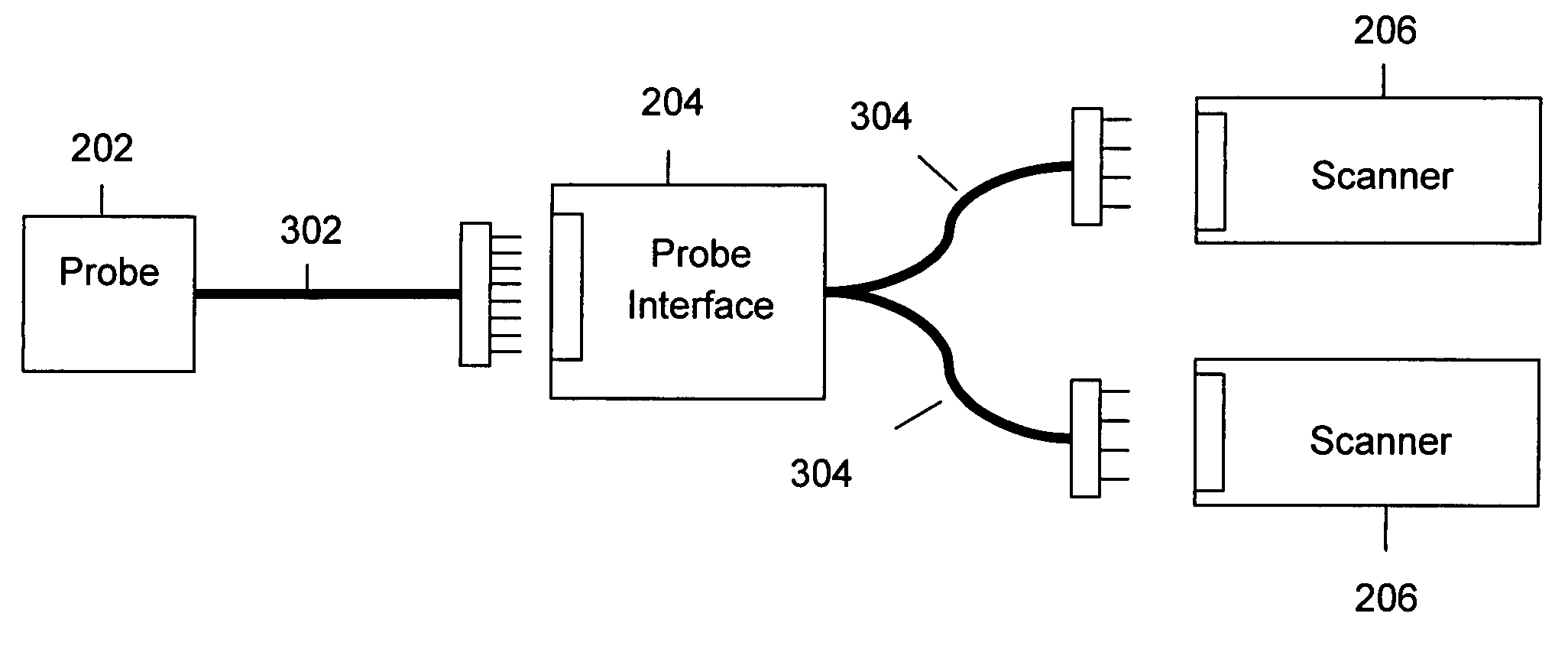
System and method for providing communication between ultrasound scanners
System and method for ganged ultrasound scanners is described. The described system includes a plurality of ultrasound scanners configured as a network and at least one connector for connecting a single ultrasound probe to the plurality of ultrasound scanners. The connector is configured to provide communication between the plurality of ultrasound scanners and the ultrasound probe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Three-dimensional ultrasonic imaging system
ActiveCN101569541AImprove accuracyLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingComputer science
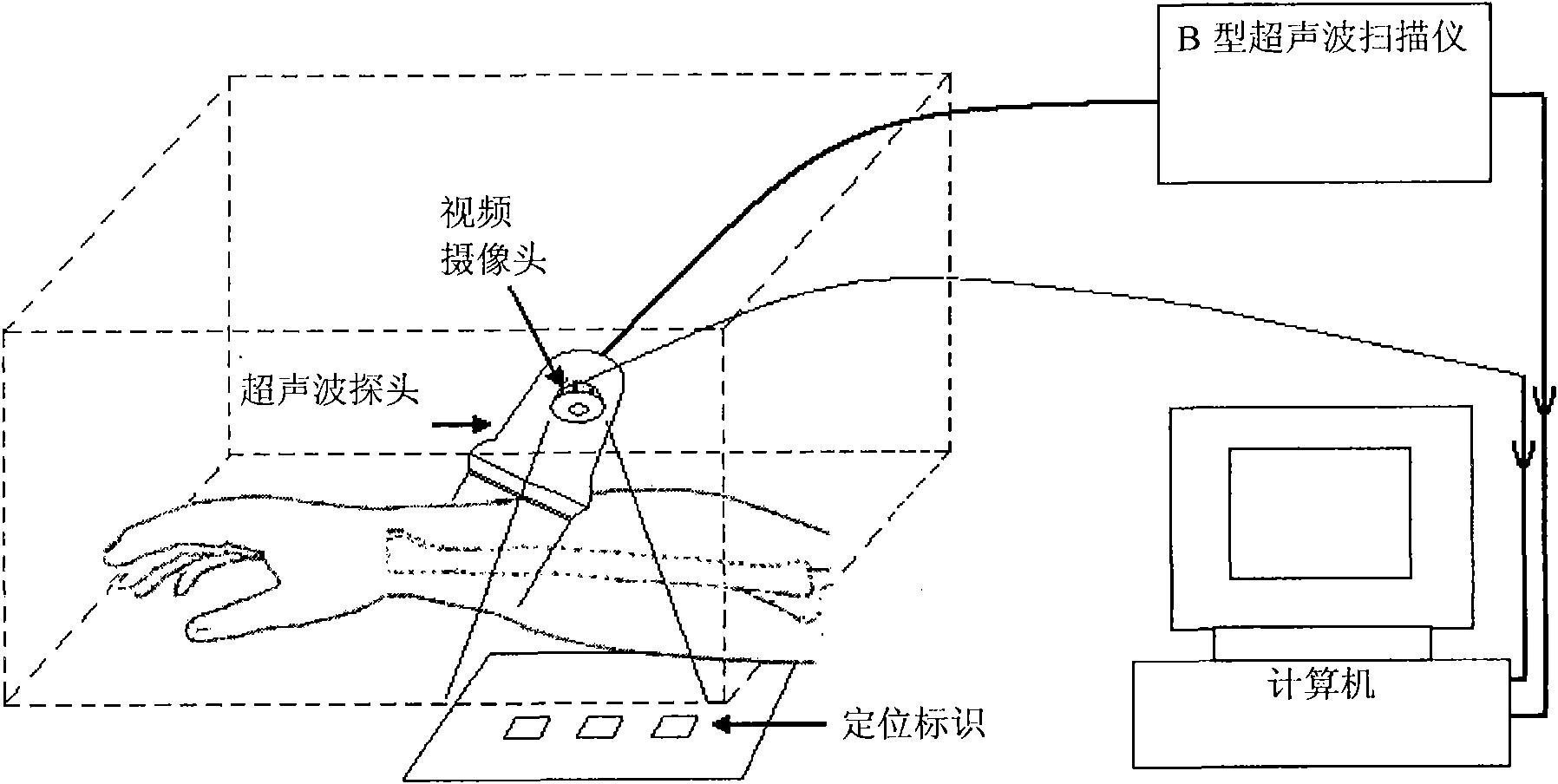
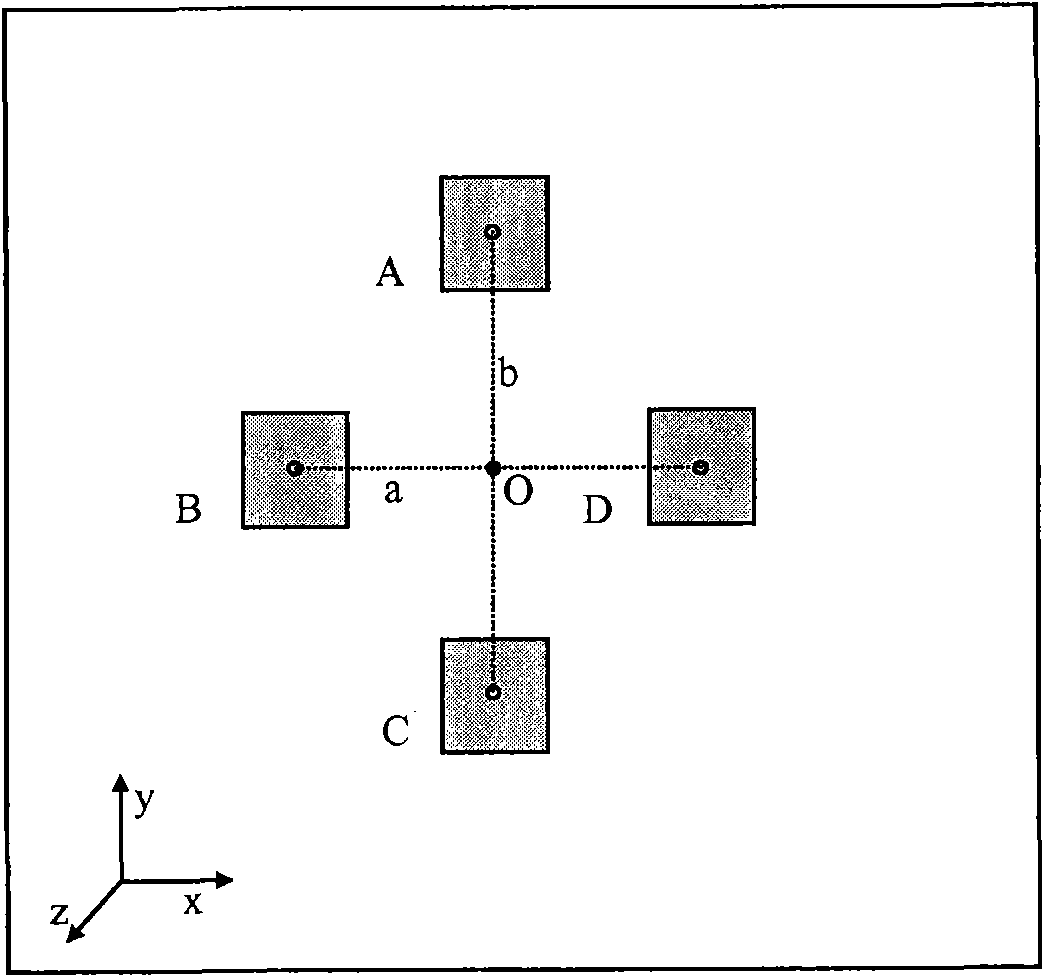
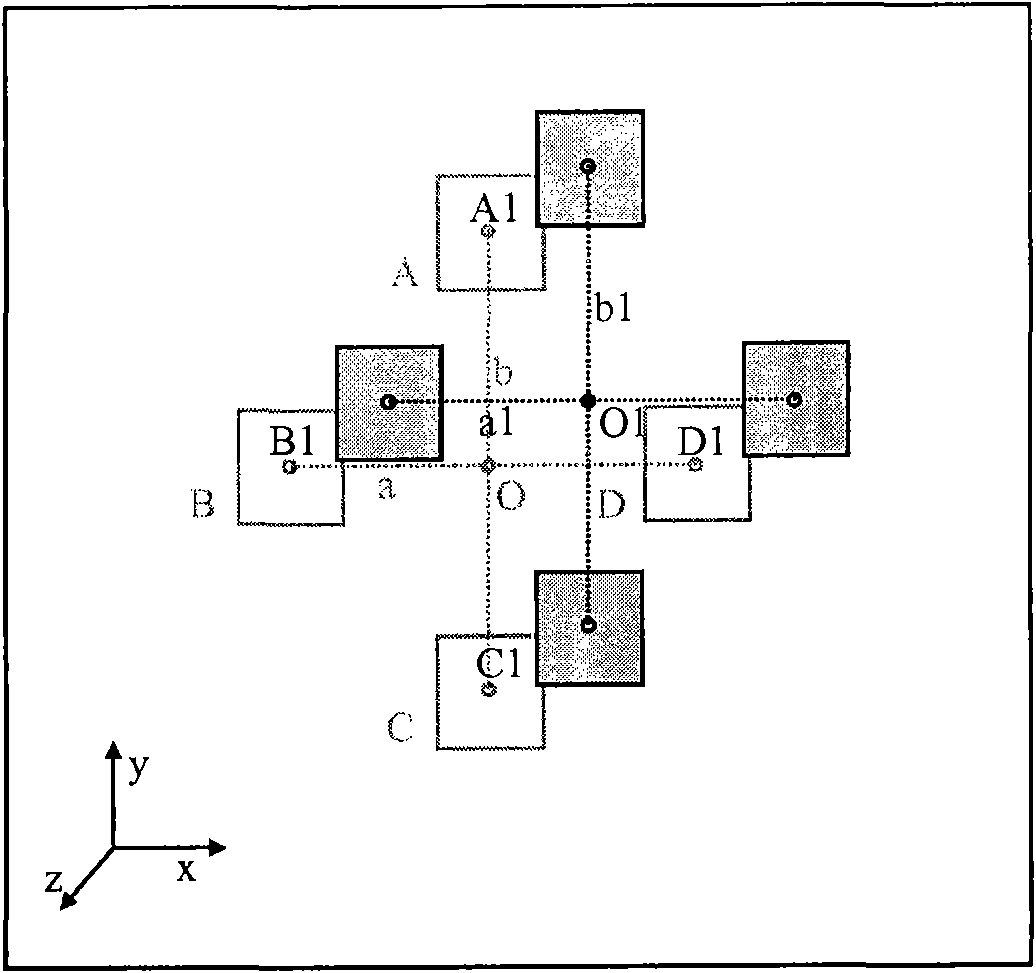
The invention provides a three-dimensional ultrasonic imaging system which comprises an ultrasonic probe, a camera, a positioning module, an ultrasonic scanner and a computing module; wherein the camera is attached to the ultrasonic probe; the positioning module is placed within the viewfinder range of the camera; the ultrasonic scanner provides ultrasonic images corresponding to each part of a body, and meanwhile, the camera provides real time video; and the computing module simultaneously collects scanned pictures and videos and conducts corresponding three-dimensional pictures generated by computing. The invention has the advantages of low cost and is capable of increasing the accuracy of three-dimensional ultrasonic imaging space tracking.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
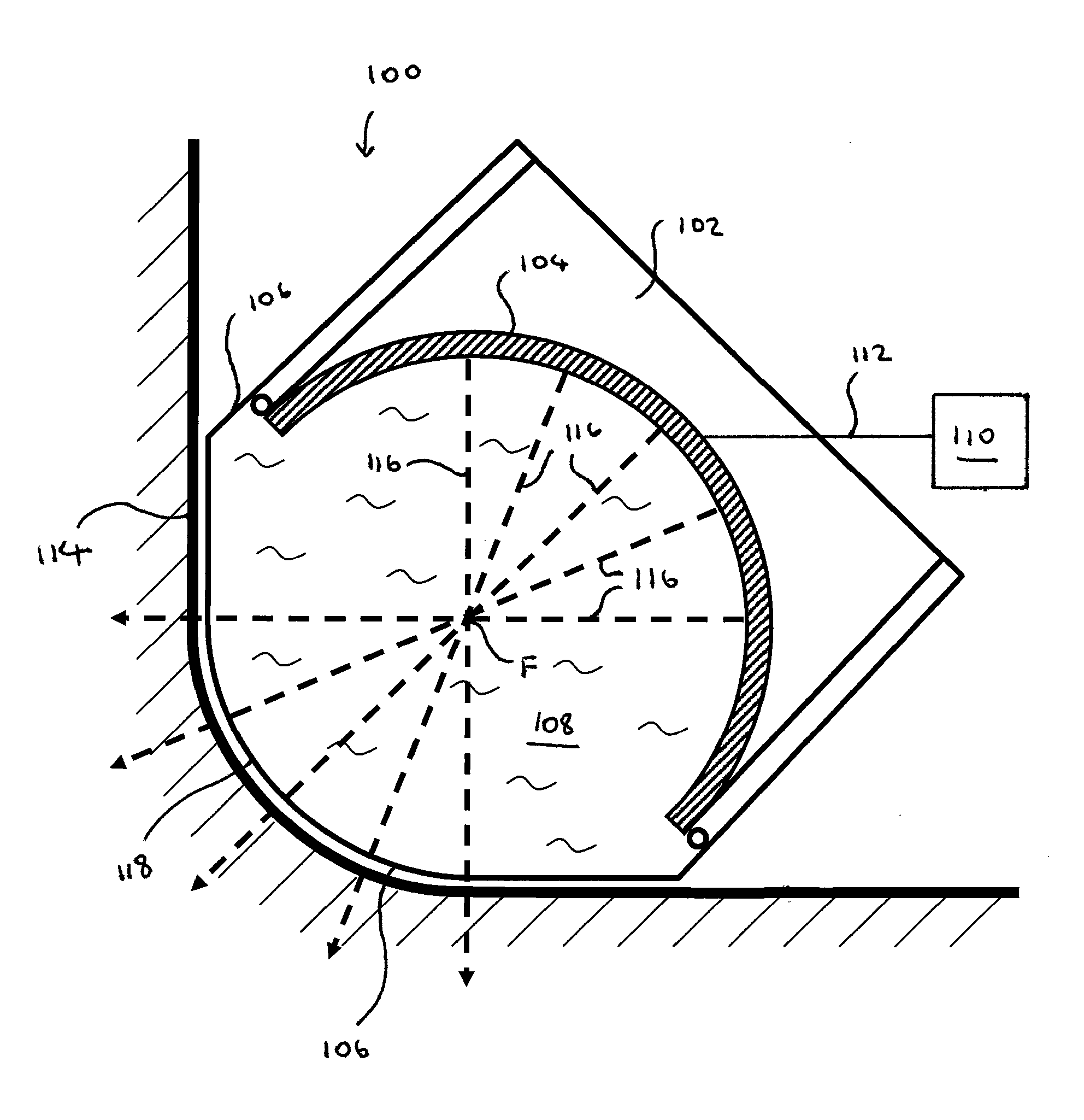
Lithotripter with stone tracking and locking localization system
InactiveUS20080146908A1Precise positioningHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryShock waveLocalization system
A lithotripter with stone tracking and locking localization system comprises an X-ray machine, an ultrasound scanner, an ultrasound probe, a movable platform, a monitor, a system controller and a stone tracking and locking localization system. The X-ray generator is mounted on the end of rotational arm, capable of illuminating across a range from 0 to 30 degrees, especially at 0 and 30 degrees, whereby the position of stones embedded in a patient's body can be located in a three-dimensional way. The ultrasound probe is located under the movable platform and shock-cup, whereby the image of a stone embedded in the patient can be displayed on the monitor after the ultrasound probe moves and contacts the surface of body. The stone tracking and locking localization system then lock on the position of the stone. And starts the tracking process by driving the movable platform to always keep the stone in the focal point F2 or using the locking process to pulverize the stone which is on the focal point F2 (if the stone moves out of the focal point F2, the shock waves will not be triggered until the stone moves into the F2 again).
Owner:LITE MED
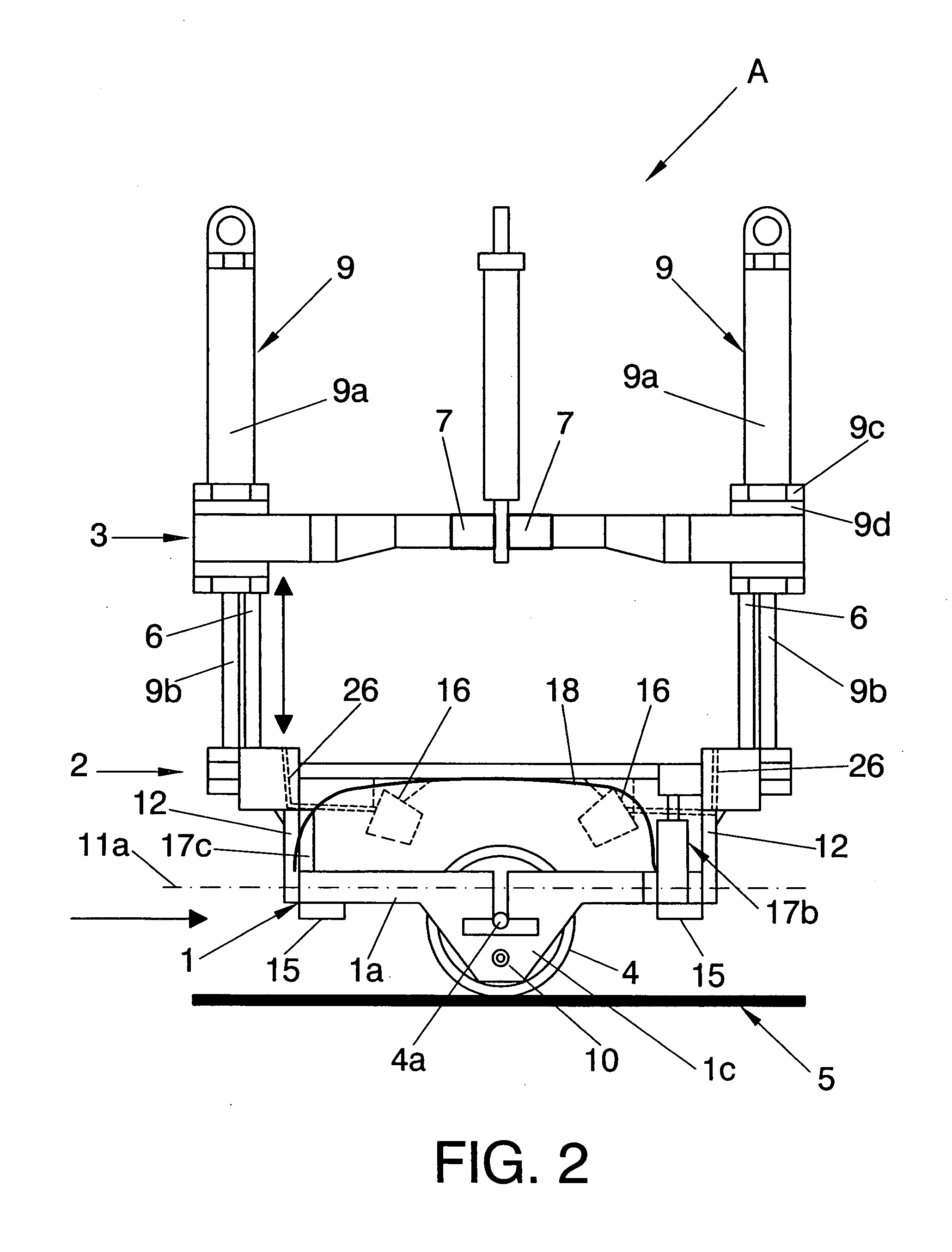
Head with roller for pulse-echo ultrasonic inspection of parts in an automatic parts inspection facility
InactiveUS20080066553A1Minimize impactLarge deformationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansEngineeringCoupling system
Head for ultrasonic inspection with a semidry coupling system involving a roller (4) and an ultrasound scanner that rolls on the surface (5) of the part to be inspected and that includes a first frame (1) to which the roller (4) is connected and pivots around an stationary axis (4a) in direction that is perpendicular to the probe's movement; a second frame (2) from which linear vertical guides (6) emerge and is connected in an oscillatory manner to the first frame (1) through an oscillating axis (11a) that is perpendicular to the stationary axis (4a): a third frame (3) that slides vertically through the linear guides (6); at least two actuators of the vertical adjustment (9) anchored to the third frame (3) and to the second frame (2); their corresponding laterally aligned pivotal axis (10), connected to the first frame (1) in a rotating manner and parallel to and lower from the plane of the stationary axis (4a) and the respective ends of the stationary axis (4a).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
Blind guide robot, blind guide system and blind guide method
InactiveCN110368275ASimple mechanical structureImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationControl theoryBlind persons
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
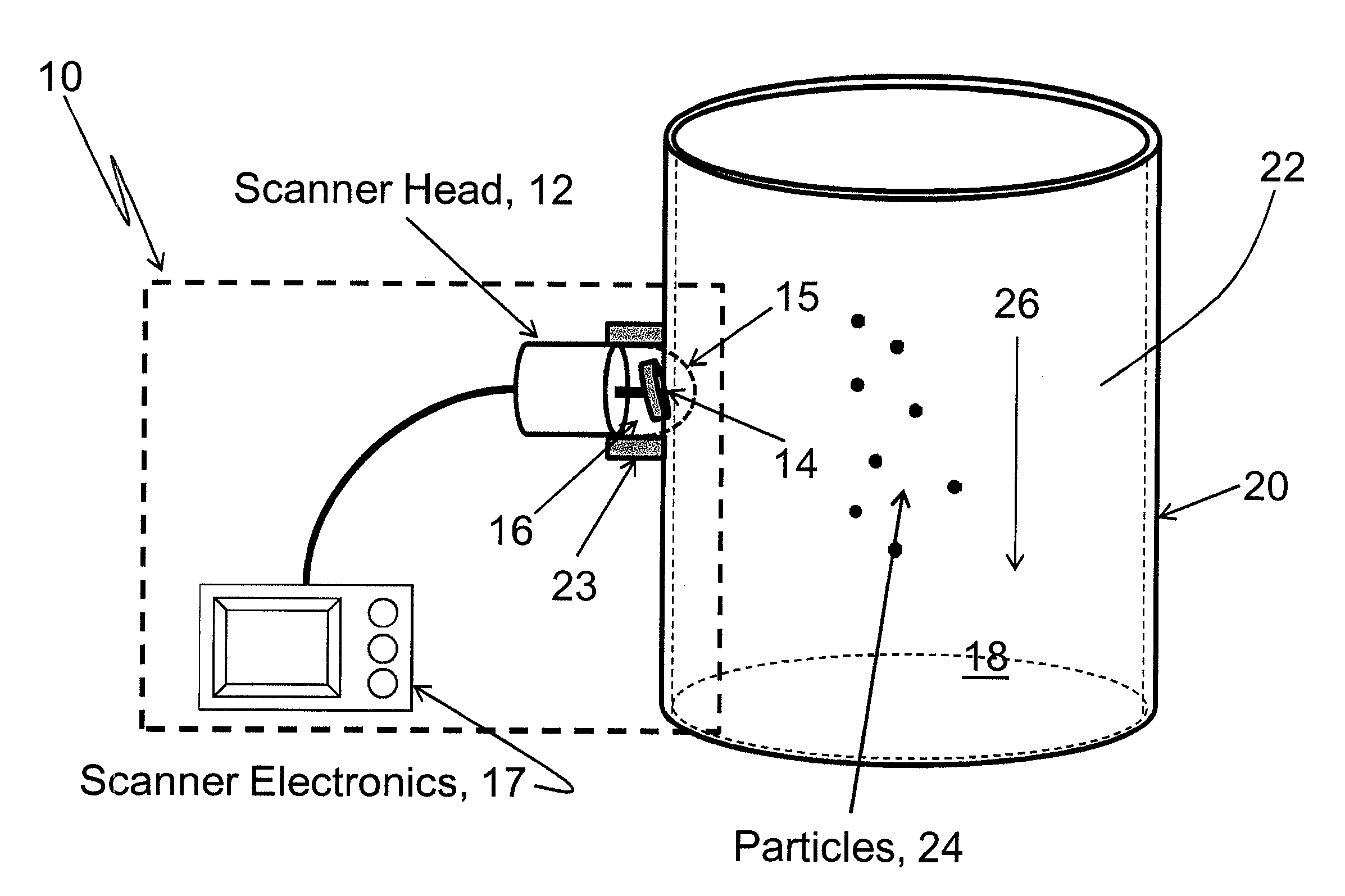
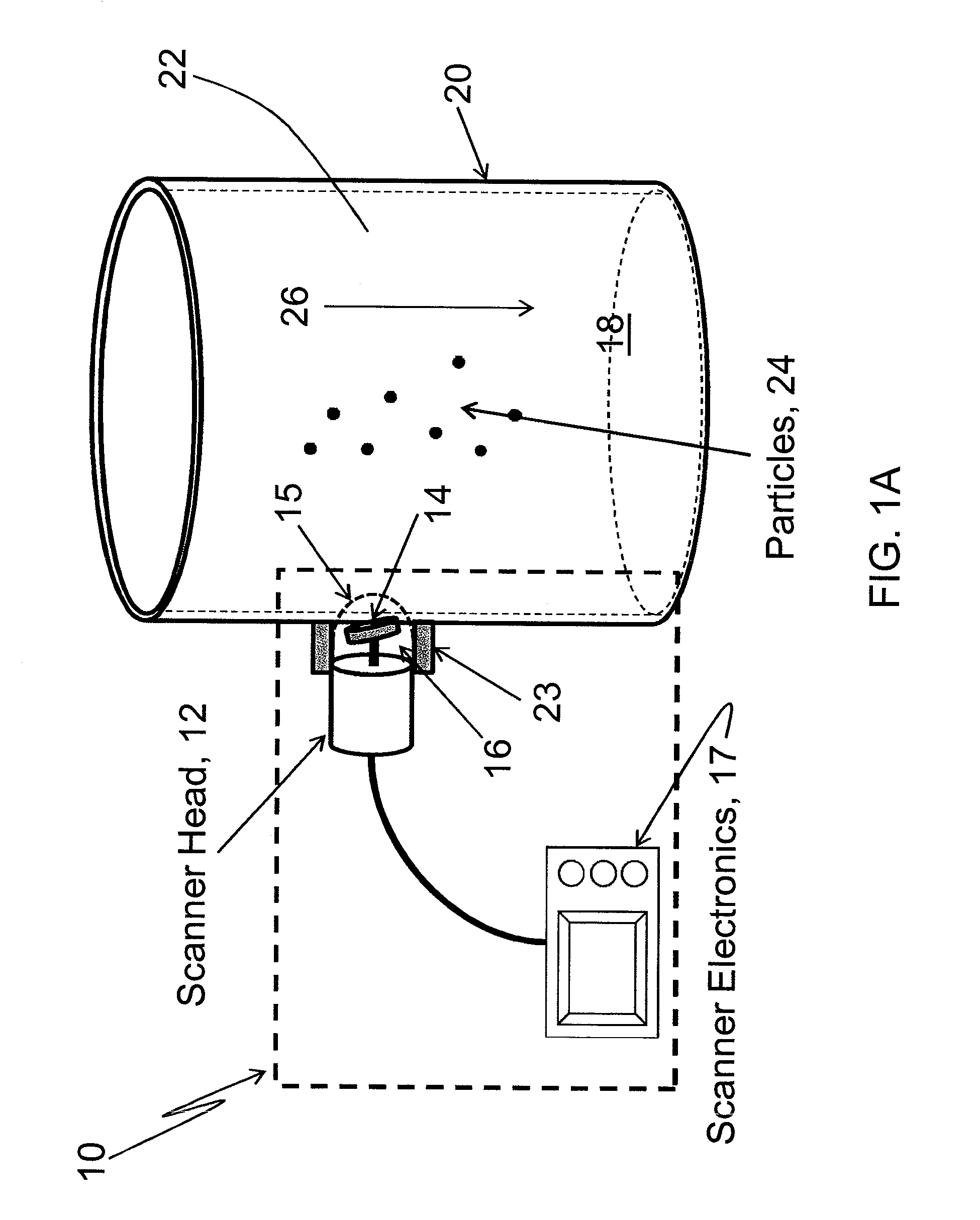
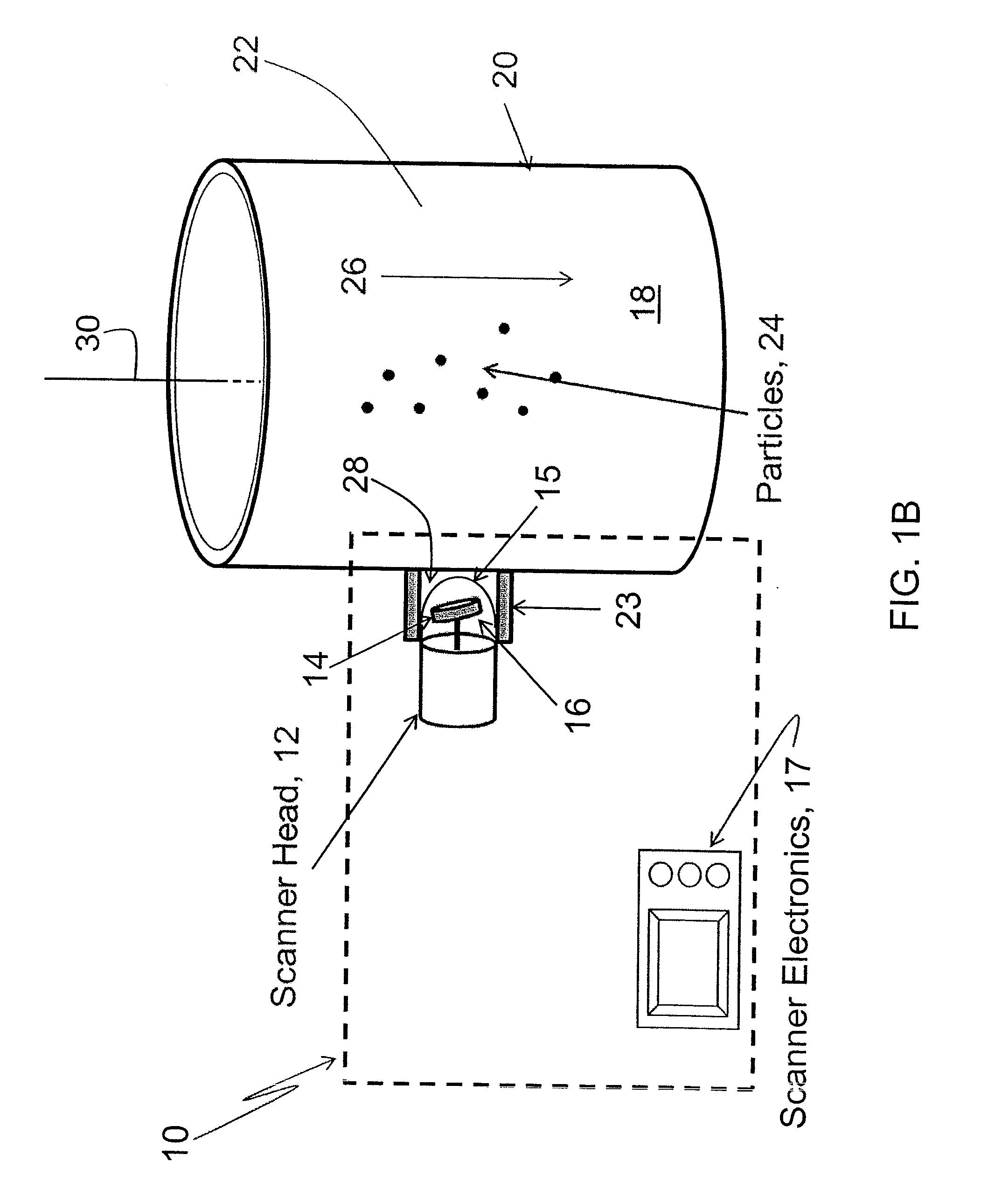
Apparatus and method for visualization of particles suspended in a fluid and fluid flow patterns using ultrasound
ActiveUS20120227473A1Easy to moveMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementParticulatesSonification
An apparatus and method for real-time visualization of particulate matter suspended in a static or flowing fluid and fluid flow patterns in a pipe, tube, conduit, or other container, are described. Ultrasonic scanning and detection of scattered sound from the particles in the fluid create a real-time image of the particles, or of flow patterns in the liquid. A mechanical wobbler directs a piezoelectric transducer over a chosen angle in an oscillatory manner. The transducer is operated in a pulse-echo mode wherein the same transducer detects the return signal from the target region through which particles are passing and / or a flow is present. The pulse-echo measurements are made rapidly and continuously during a single sweep of the transducer over the chosen angle. Received signals are processed in the ultrasound scanner electronics module and displayed as an image in real-time.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
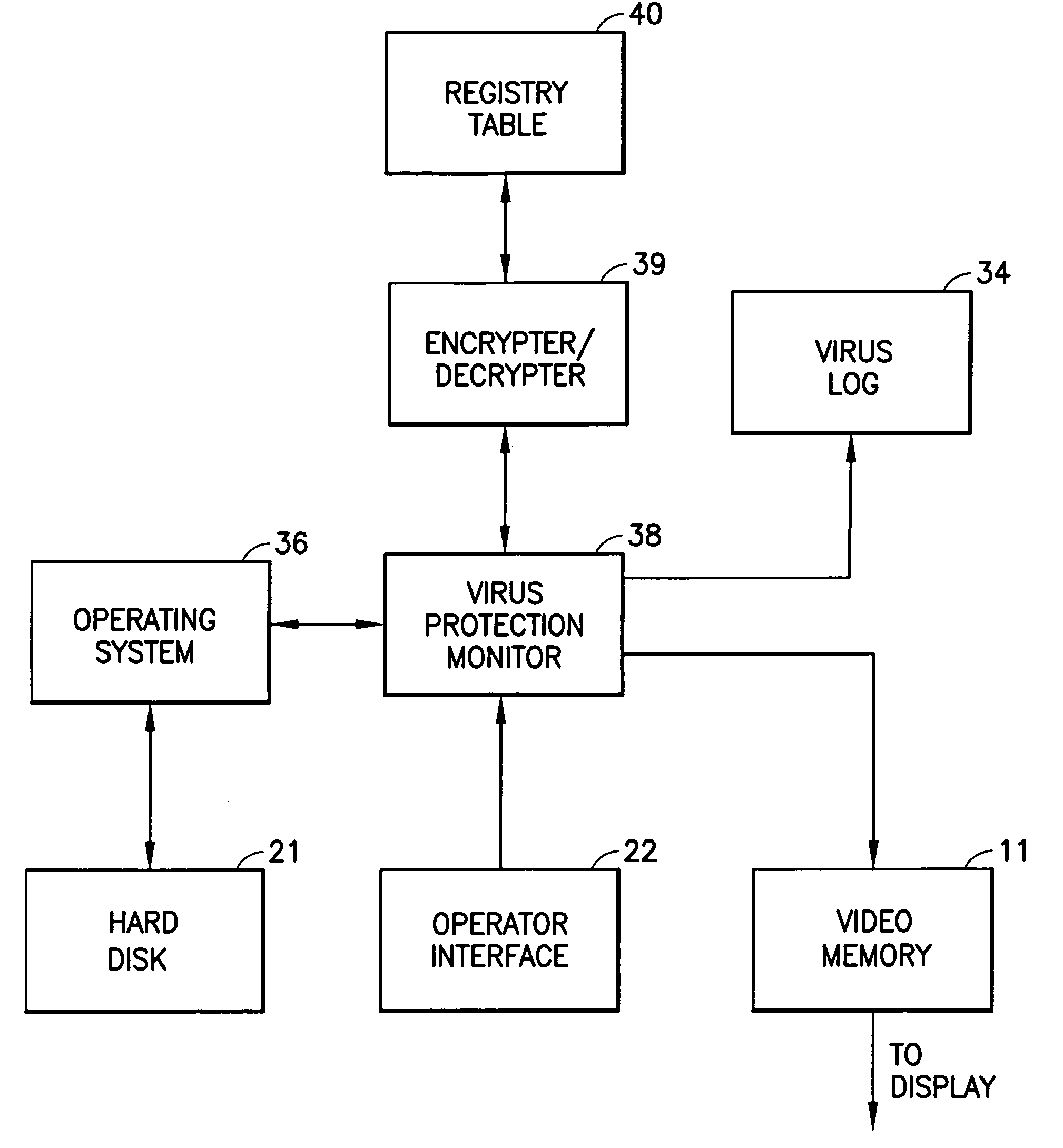
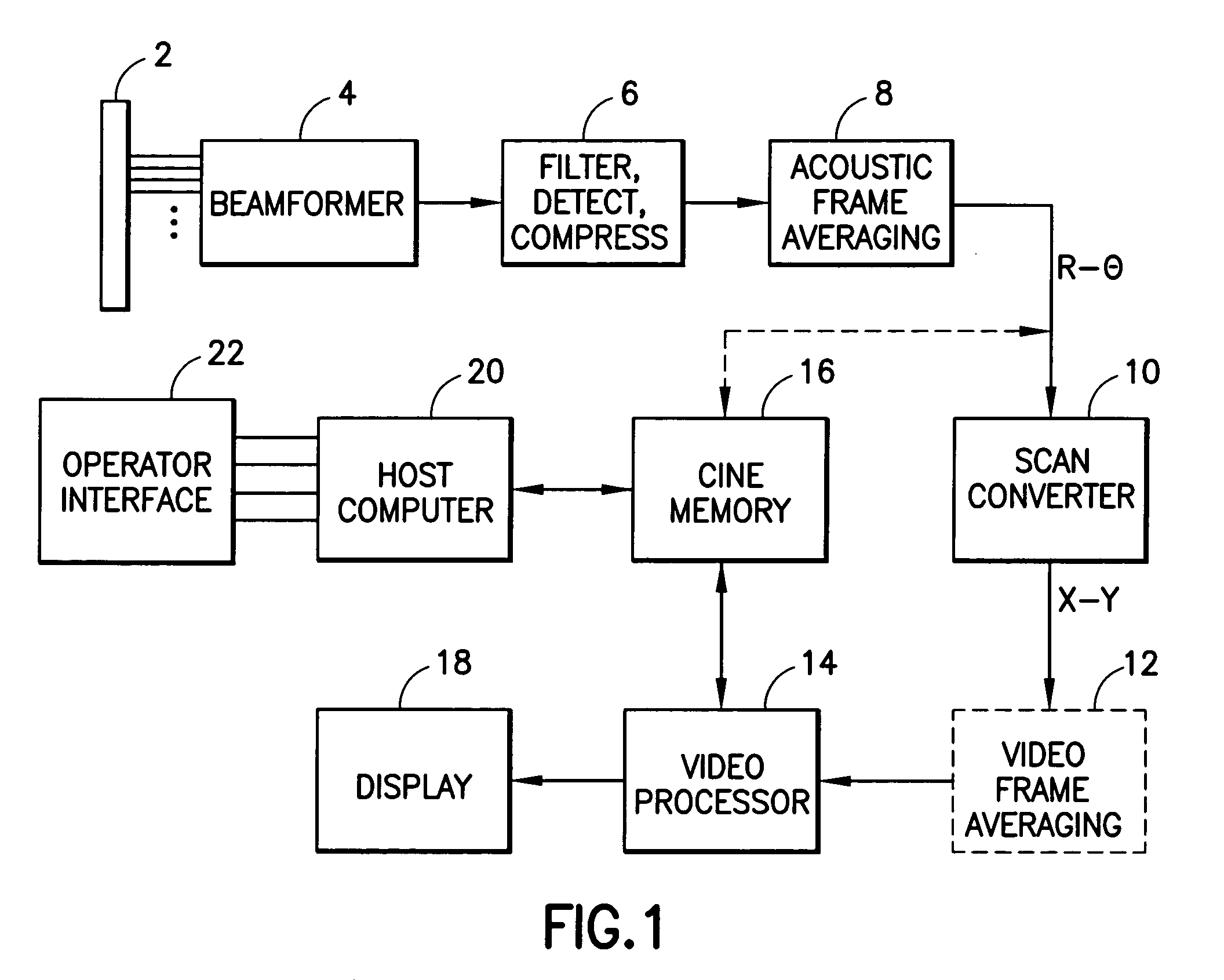
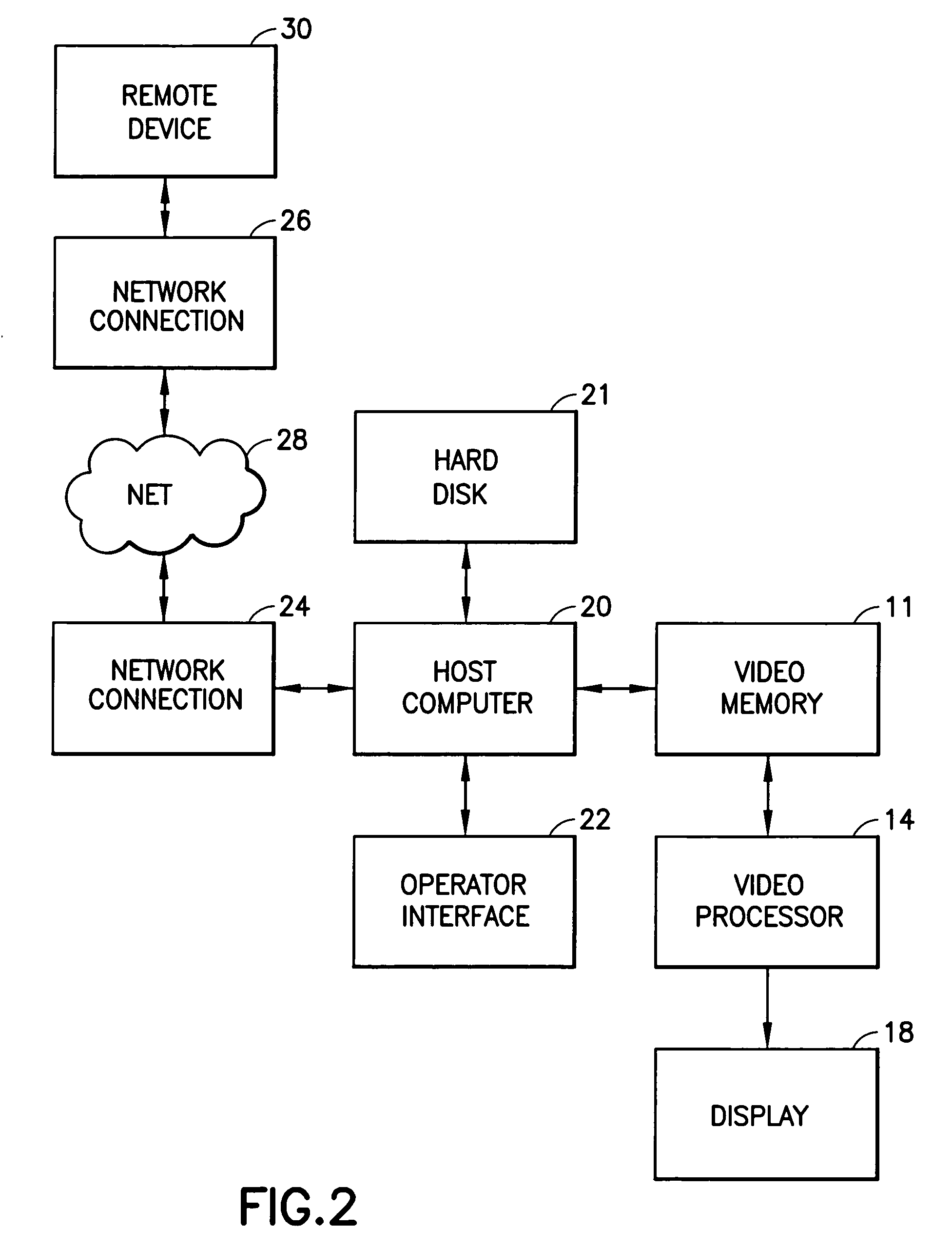
Ultrasound imaging system having computer virus protection
InactiveUS7263616B1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound imaging system is provided with virus protection. Each file that enters the system (via the hard disk or the networking port) is scanned to detect the presence of any virus in the file. Before each file is written to the hard disk of the scanner, the Checksum and Size of the file are verified, along with other virus-identifying attributes, to determine if the file is infected with a virus or if the file itself is a virus. If there is a discrepancy in either the Checksum or Size, then a dialogue box appears, warning the system operator that the file being installed may contain a virus. In order to provide additional protection for the ultrasound scanner, all processes starting to run on the scanner are monitored. Each time a new process is started on the scanner, virus protection monitoring software will suspend the process and search for encrypted data identifying the starting process in a Registry table. If the starting process is listed in the table, then the starting process is un-suspended without the user ever knowing what happened. If the virus protection monitor does not find a match in the table, then a dialogue box appears on the screen, warning the system operator that the application may be a virus.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System and method for providing communication between ultrasound scanners
System and method for ganged ultrasound scanners is described. The described system includes a plurality of ultrasound scanners configured as a network and at least one connector for connecting a single ultrasound probe to the plurality of ultrasound scanners. The connector is configured to provide communication between the plurality of ultrasound scanners and the ultrasound probe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
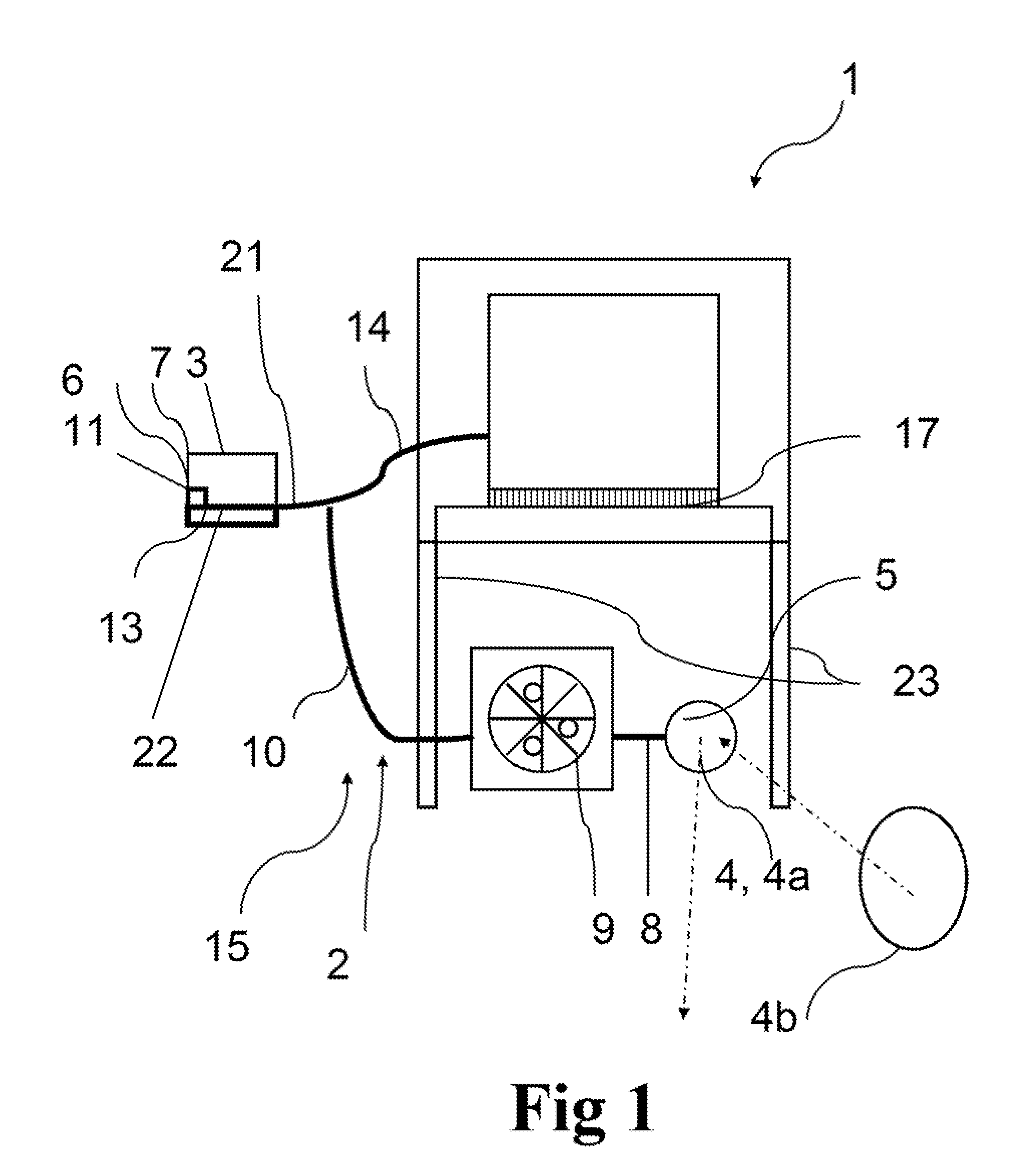
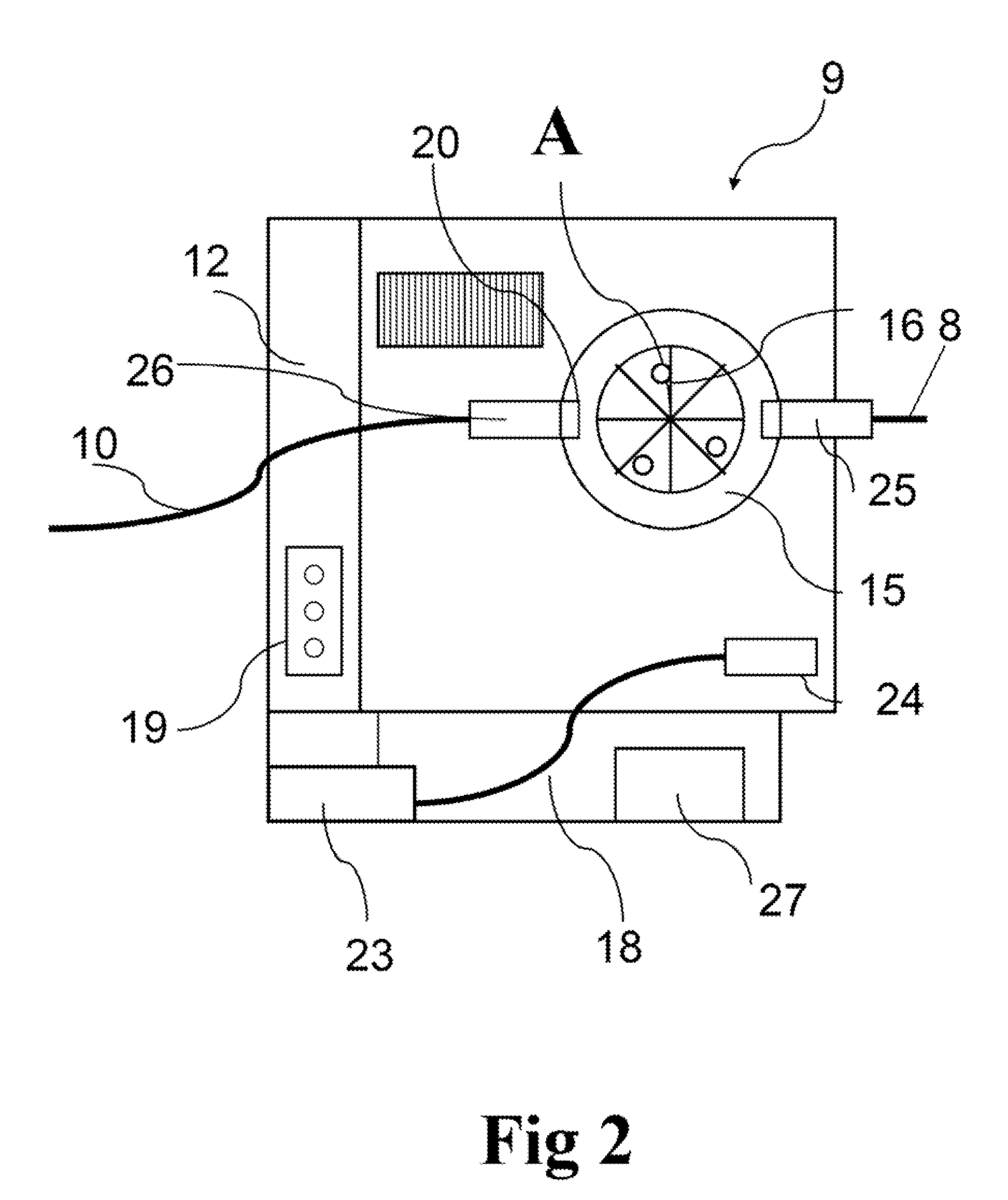
Fully automatic ultrasonic scanner and scan detection method
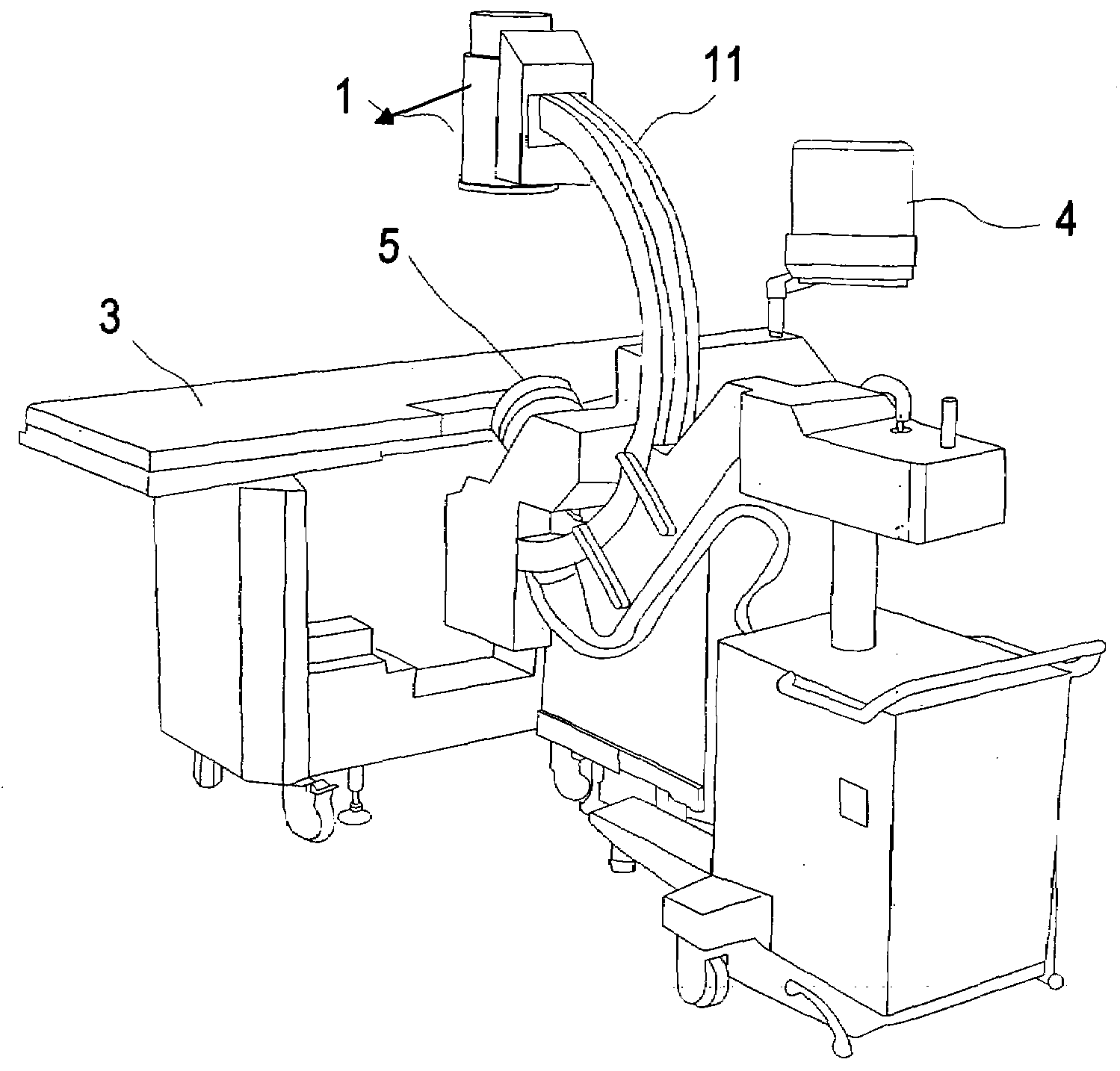
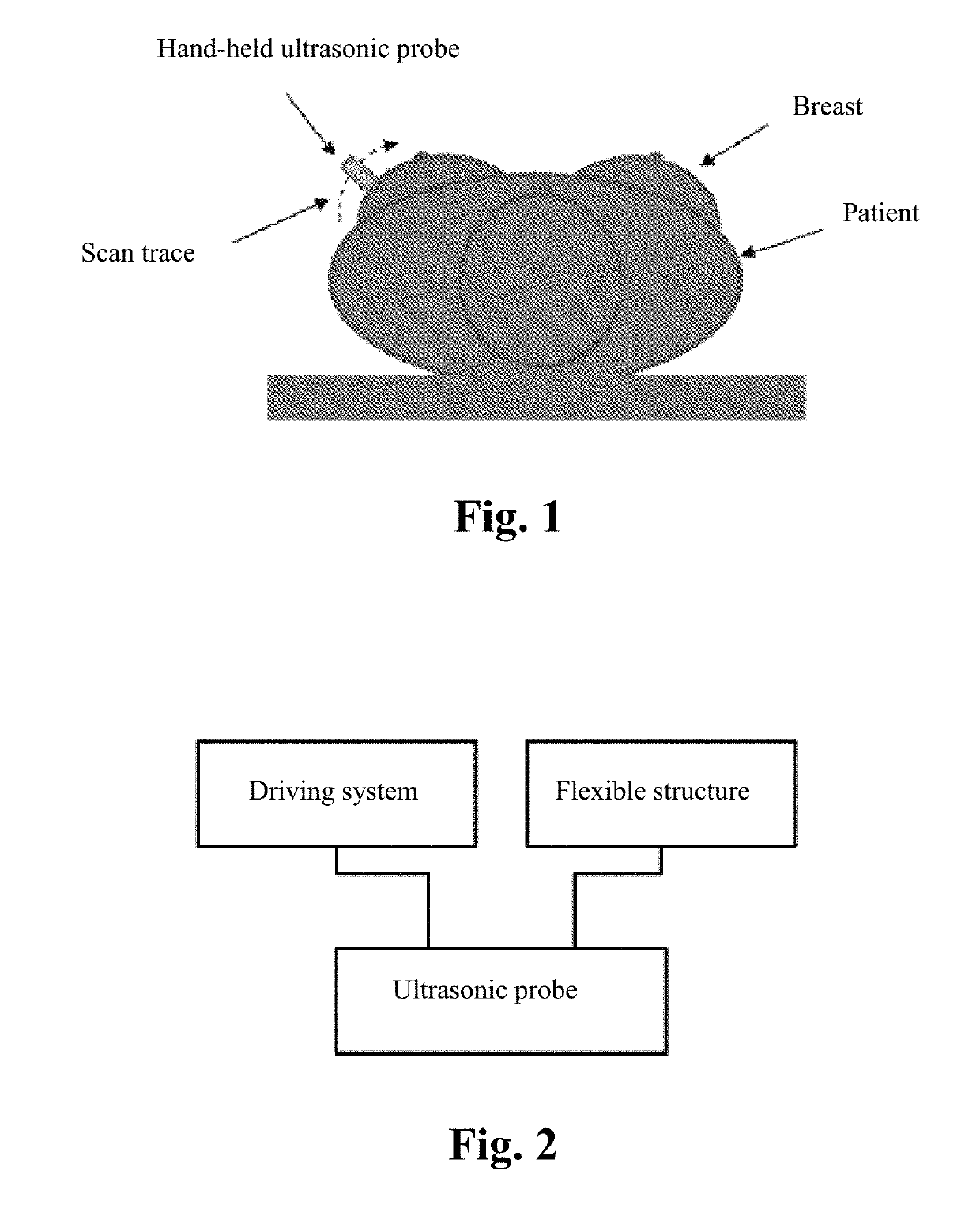
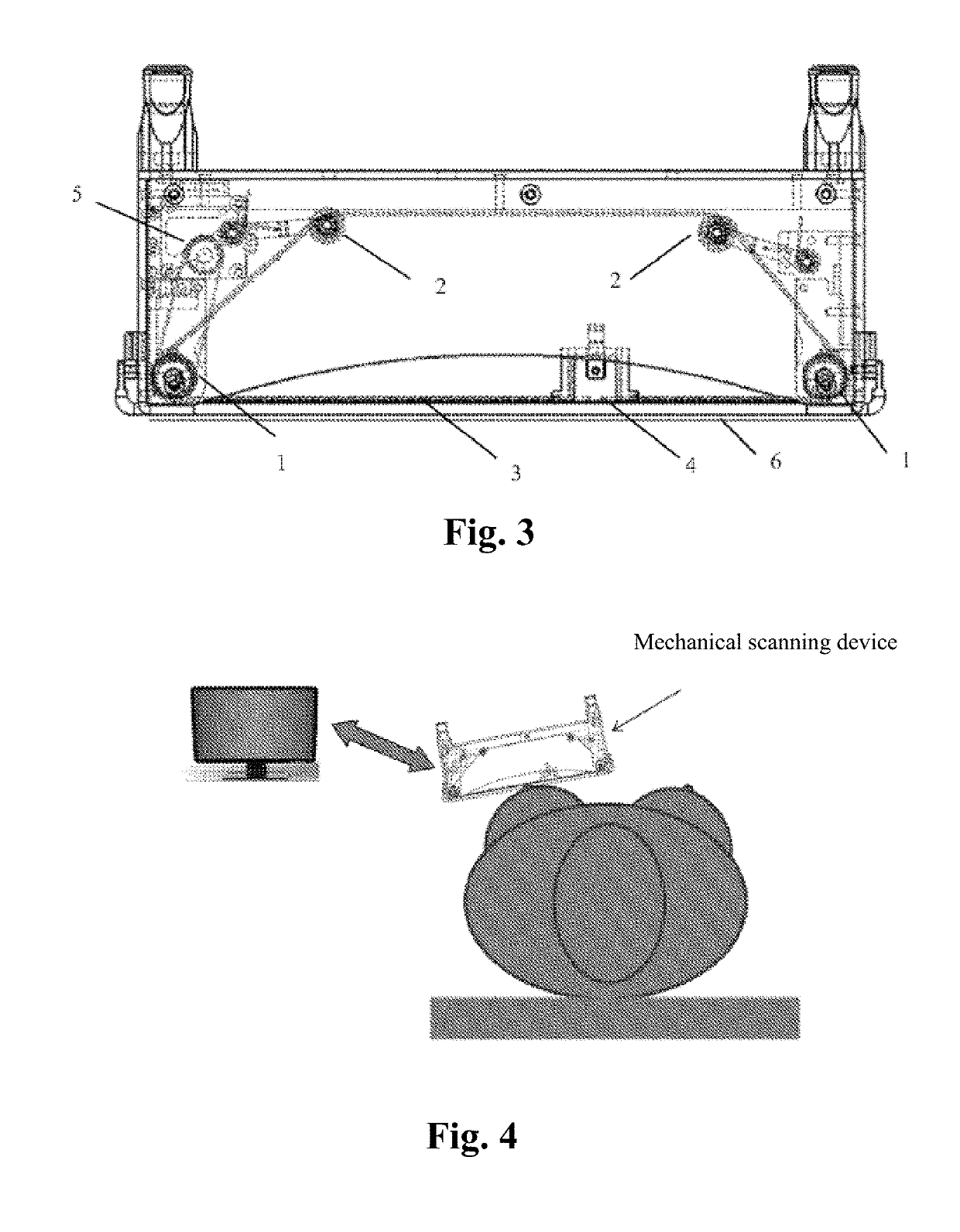
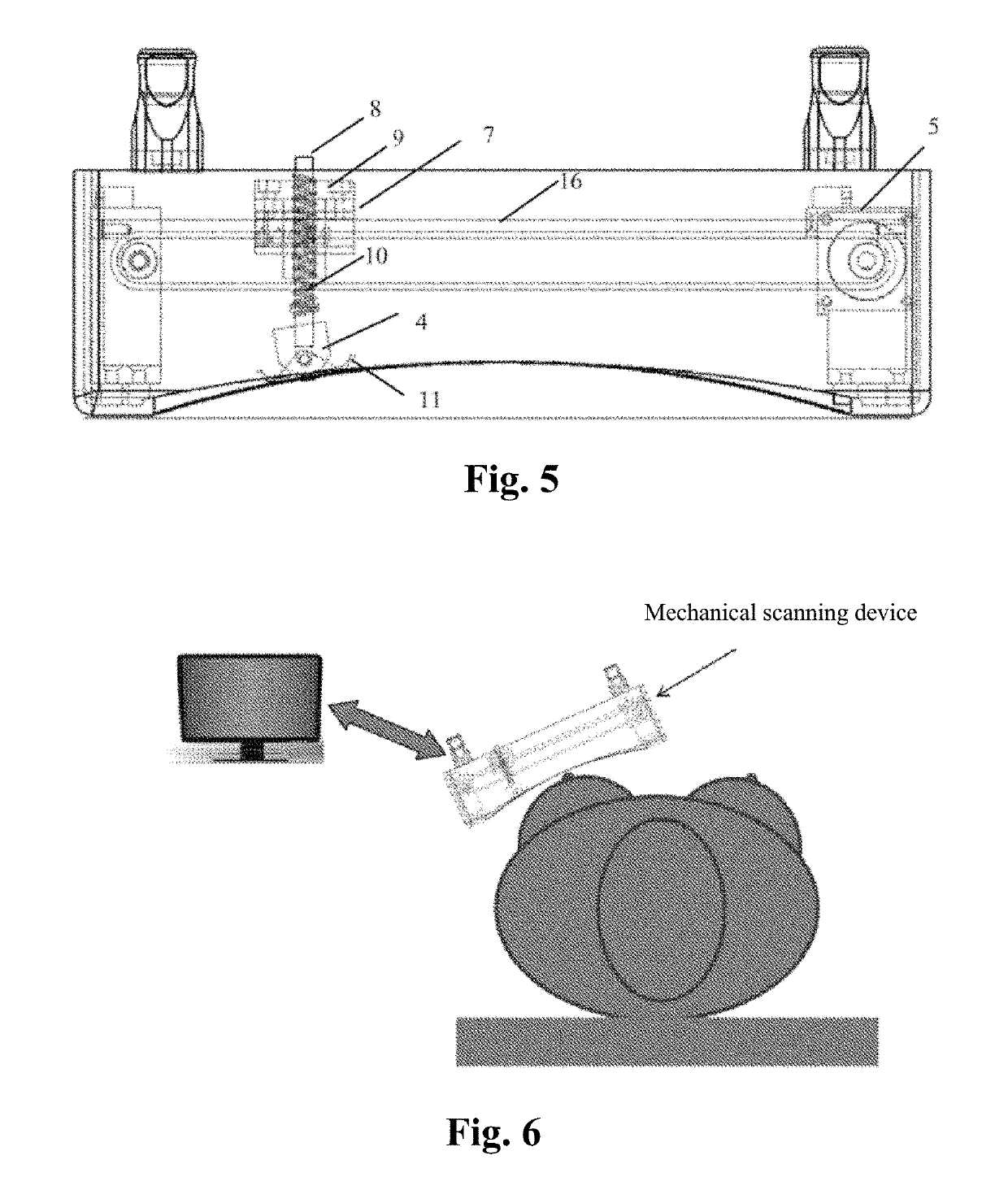
ActiveUS20190150895A1Easy to operateAccurate pressurePatient positioningOrgan movement/changes detectionSkin surfaceMissed diagnosis
A fully automatic ultrasonic scanner and a scan detection method is provided. The fully automatic ultrasonic scanner comprises: an ultrasonic probe (4); a driving system (5) for driving the ultrasonic probe (4) to move; and a flexible structure on which the ultrasonic probe (4) is mounted, wherein the flexible structure enables the ultrasonic probe (4) to be always along a curve of a skin surface and keep perpendicular to the skin surface during scanning. The flexible structure of the fully automatic ultrasonic scanner has self-adaptive effect, can adjust the scan trace and the probe angle in real time according to different curves of the human body, and ensure that the ultrasonic probe (4) scans against the skin surface and keeps perpendicular to the skin surface, which improves the quality of the scanned images, so as to enhance the detection rate and accuracy rate of early screening, and reduces the probability of missed diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENBO MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
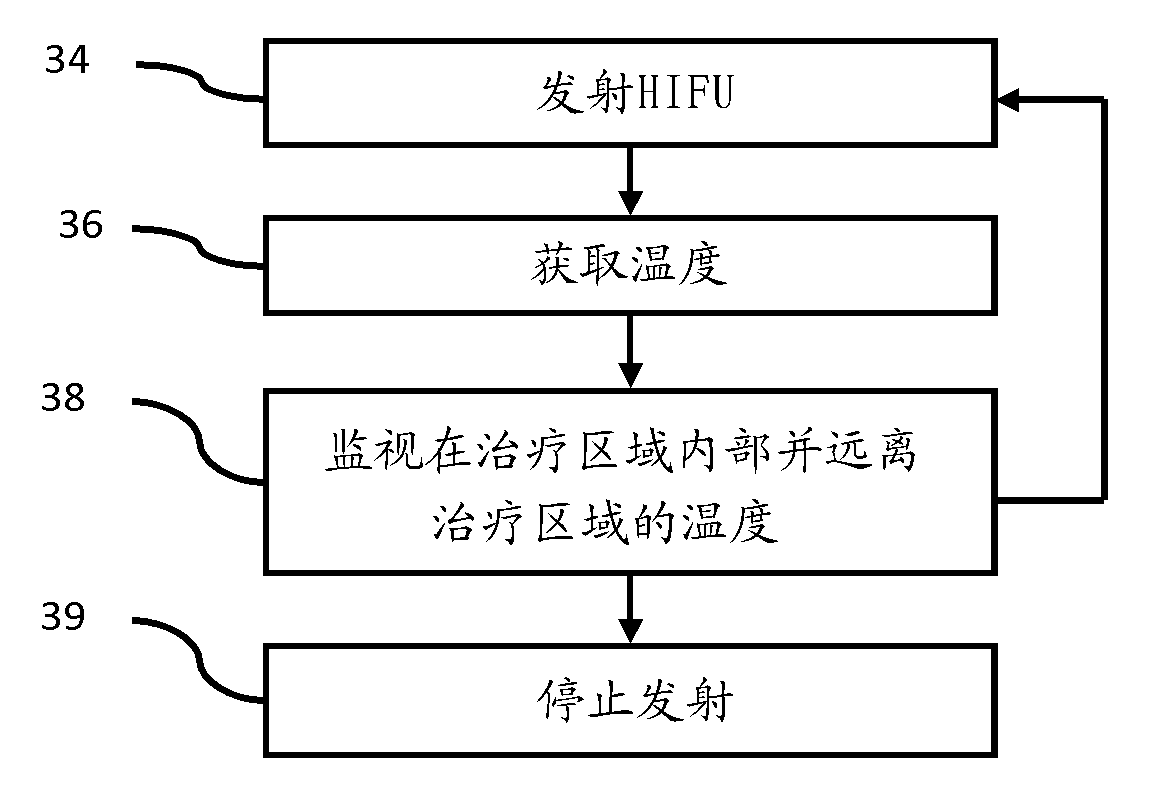
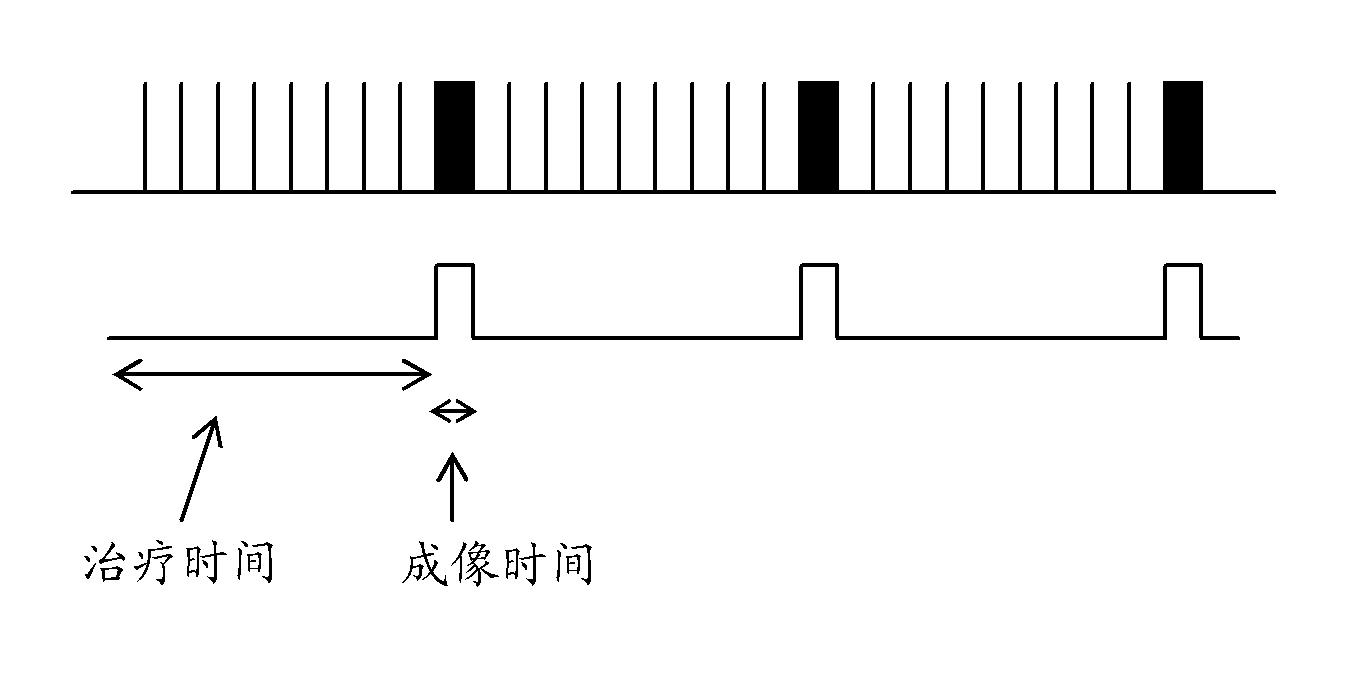
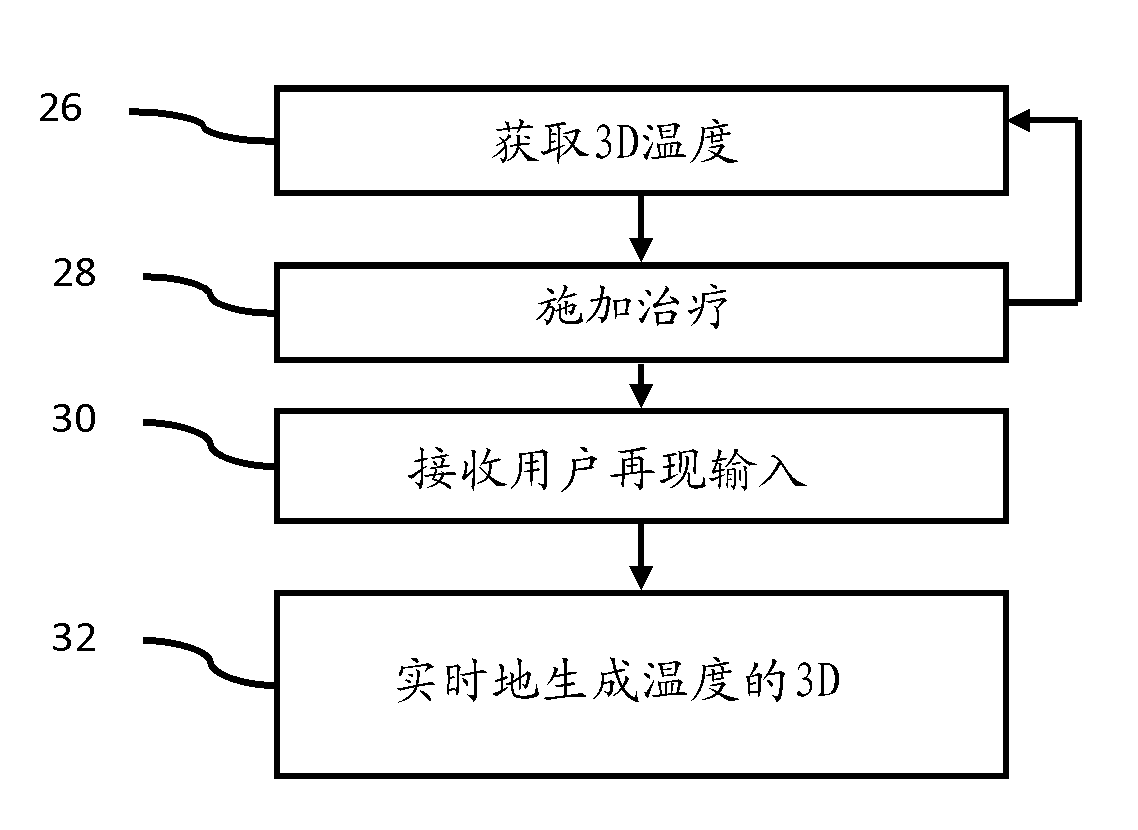
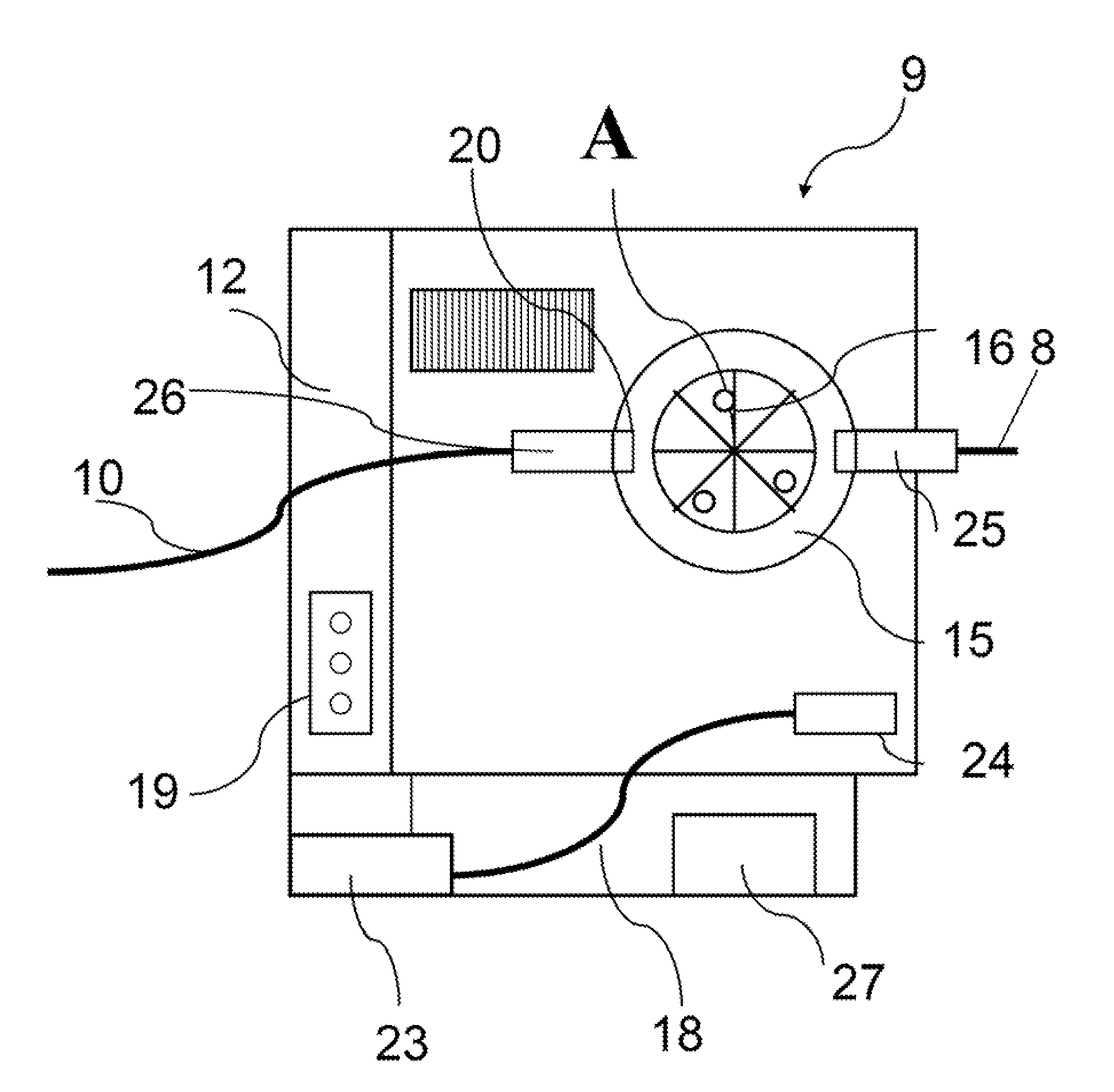
Ultrasound for therapy control or monitoring
InactiveCN103381097AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTherapy controlUltrasound scanner
Therapy control and / or monitoring is performed with an ultrasound scanner. The ultrasound scanner detects temperature to monitor therapy, and perform HIFU beam location refocusing of the therapy system based on the temperature. The monitoring is synchronized with the therapy using a trigger output of the ultrasound scanner. The trigger output responds to a scan sequence of the ultrasound scanner. To meet a given therapy plan, the scan sequence is customized, resulting in the customized trigger sequence. Three dimensional or multi-planar reconstruction rendering is used to represent temperature for monitoring feedback. The temperature at locations not being treated may be monitored. If the temperature has an undesired characteristic (e.g., too high), then the therapy is controlled by ceasing, at least temporarily.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Ultrasound scanner with gel dispenser device attached to or integrated with at least one probe and use
InactiveUS20110190635A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryInsertion stentBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to an ultrasound scanner comprising a gel distributing device which is attached, or built into, at least one signal emitting probe. The ultrasound scanner is provided with a gel holder for gel used to transmit ultrasound waves for medical, paramedical and / or veterinary procedure purposes. The holder is fixed to the probe and has an opening in the vicinity of the signal emitting or receiving window of the probe. The holder is a tight, sterile, supple pouch, which is tightly connected by tubes or the equivalent to a pump which, in turn, is tightly connected to at least one probe. The invention also relates to the use of the fluid circuit of the ultrasound scanner, comprising at least the tight, sterile, supple pouch that is tightly connected via the tube to the pump set which, in turn, is tightly connected via the tube for supplying the signal emitting and / or receiving window of the probe with gel, in order to automatically prevent the operator from having to manually supply the gel and to stop the gel remaining for subsequent procedures from coming into contact with the air, the patient, or any other sources of contamination.
Owner:BOSLER FREDERIC
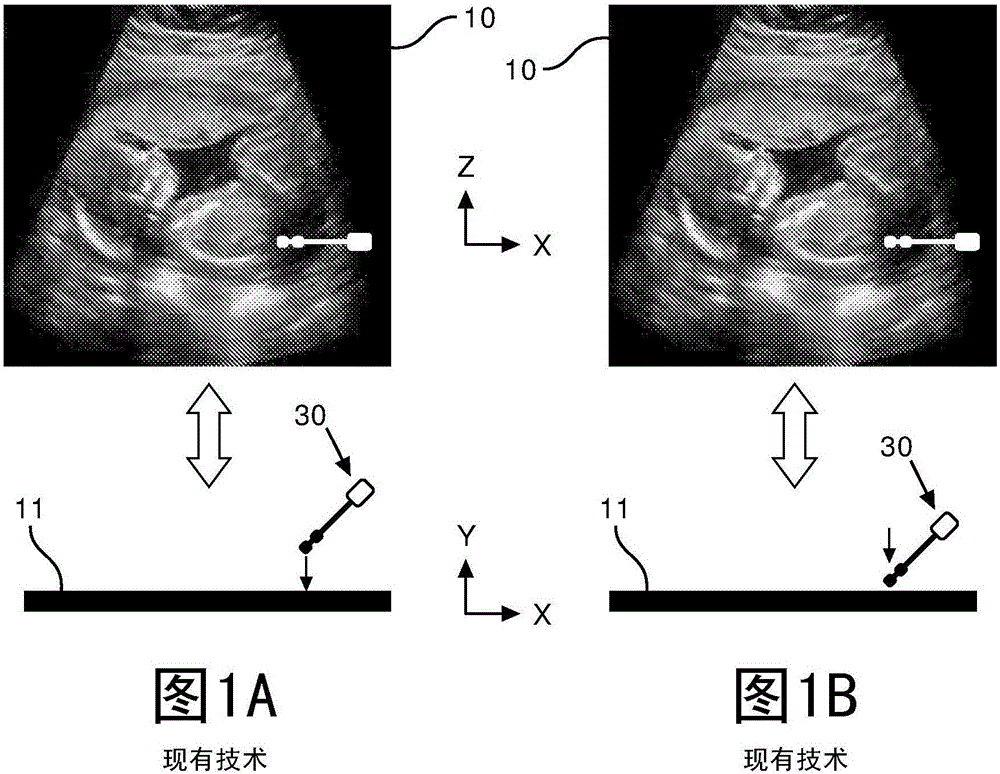
Instrument alignment and tracking with ultrasound imaging plane
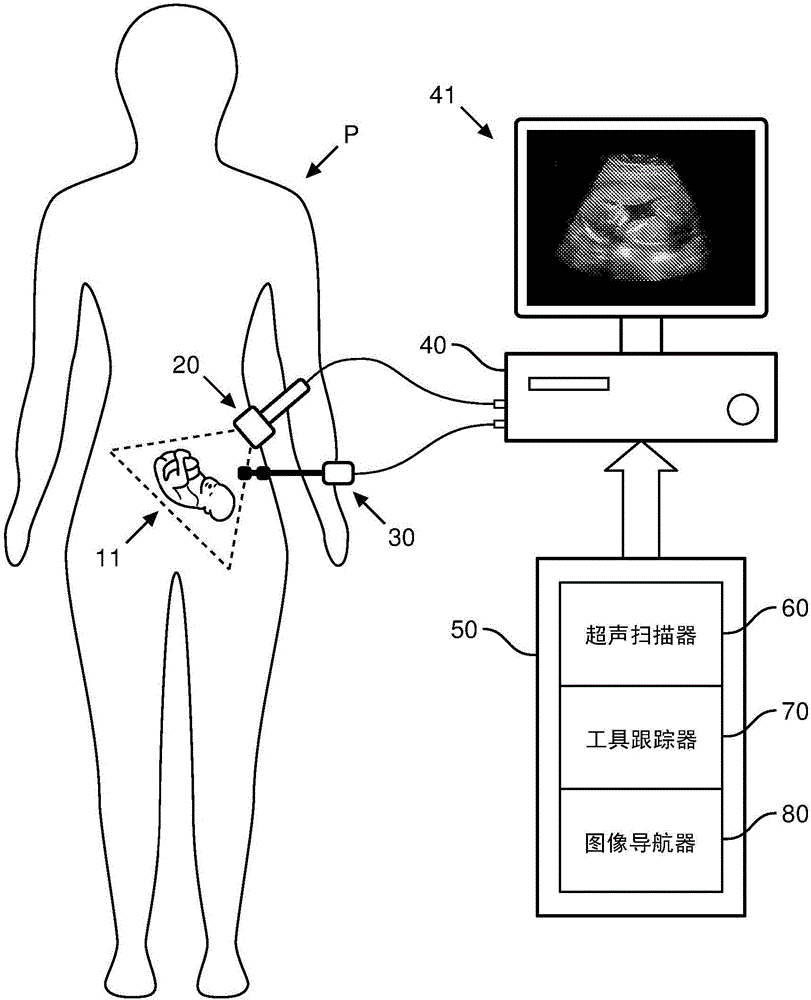
A tool navigation system employing an ultrasound probe (20), an ultrasound scanner (60), an interventional tool (30) (e.g., a needle or a catheter), a plurality of ultrasound transducers (21, 31), a tool tracker (70) and an image navigator. In operation, the ultrasound probe (20) generates an acoustic image plane for scanning an anatomical region, and the ultrasound scanner (60) generates an ultrasound image of the anatomical region from a scan of the anatomical region. During the scan, the interventional tool (30) is navigated within the anatomical region relative to the acoustic image plane, and the ultrasound transducers (21, 31) facilitate a tracks by the tool tracker (70) of a position of the interventional tool (30) relative to the acoustic image plane. The image navigator displays a graphical icon within the ultrasound image of the anatomical region as generated by the ultrasound scanner (60) for illustrating a tracking by the tool tracker (70) of a distance of the interventional tool (30) relative to the acoustic image plane. One or more aspects of the graphical icon are modulated by the image navigator responsive to the tracked distance of the interventional tool (30) relative to the acoustic image plane as the interventional tool (30) is navigated within the anatomical region.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Aberration correction using channel data in ultrasound imaging system
Embodiments of the present invention provide an ultrasound scanner equipped with an image data processing unit that can perform adaptive parameter optimization during image formation and processing. In one embodiment, an ultrasound system comprises a channel data memory to store channel data obtained by digitizing ultrasound image data produced by an image scan; an image data processor configured to process the stored channel data in the memory to reconstruct an ultrasound image for each of a plurality of trial values of at least one parameter to be optimized; and a parameter optimization unit configured to evaluate an image quality of the reconstructed ultrasound image for each trial value of the at least one parameter, and to determine the optimized value of the at least one parameter based on the evaluated image quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Detecting method and detecting system for detecting rectangular metal bars
InactiveCN102507740AGuaranteed detection accuracyImprove detection efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPersonal computerLarge distance
Owner:SHANTOU HUAXING METALLURGICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Image generation based on limited data set
InactiveUS20100054559A1Increase patient comfortReliable estimateImage enhancementImage analysisData setSonification
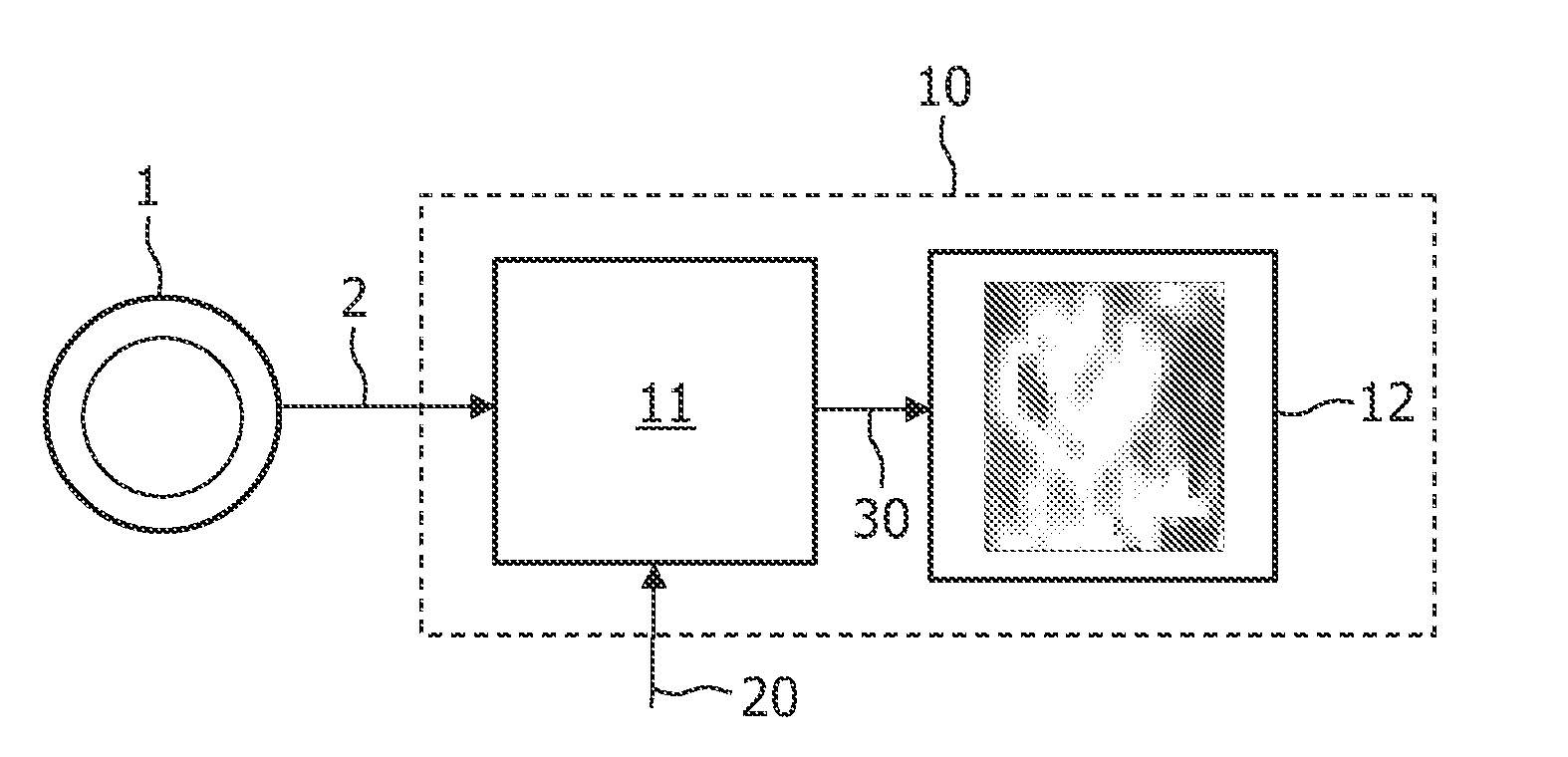
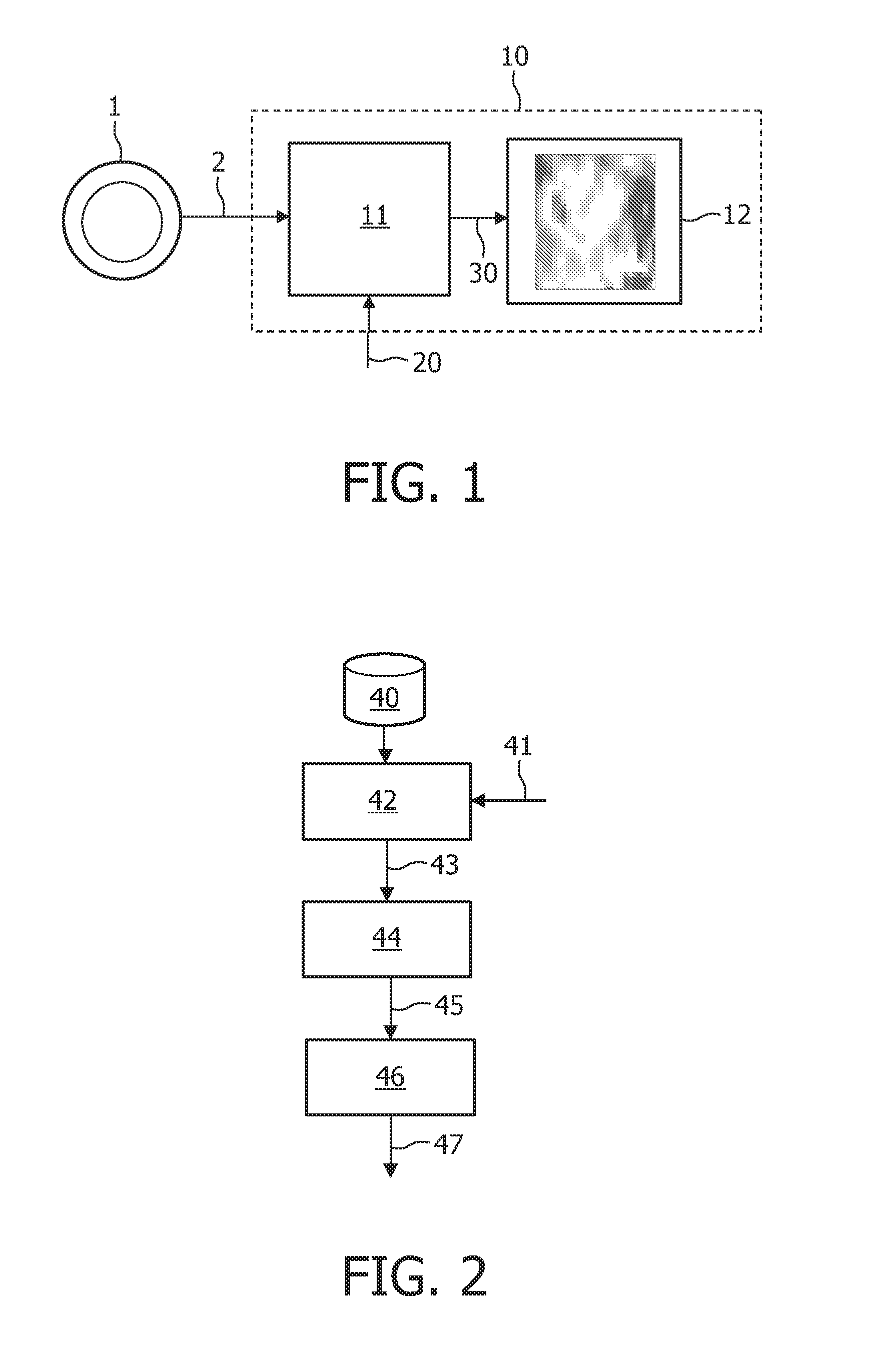
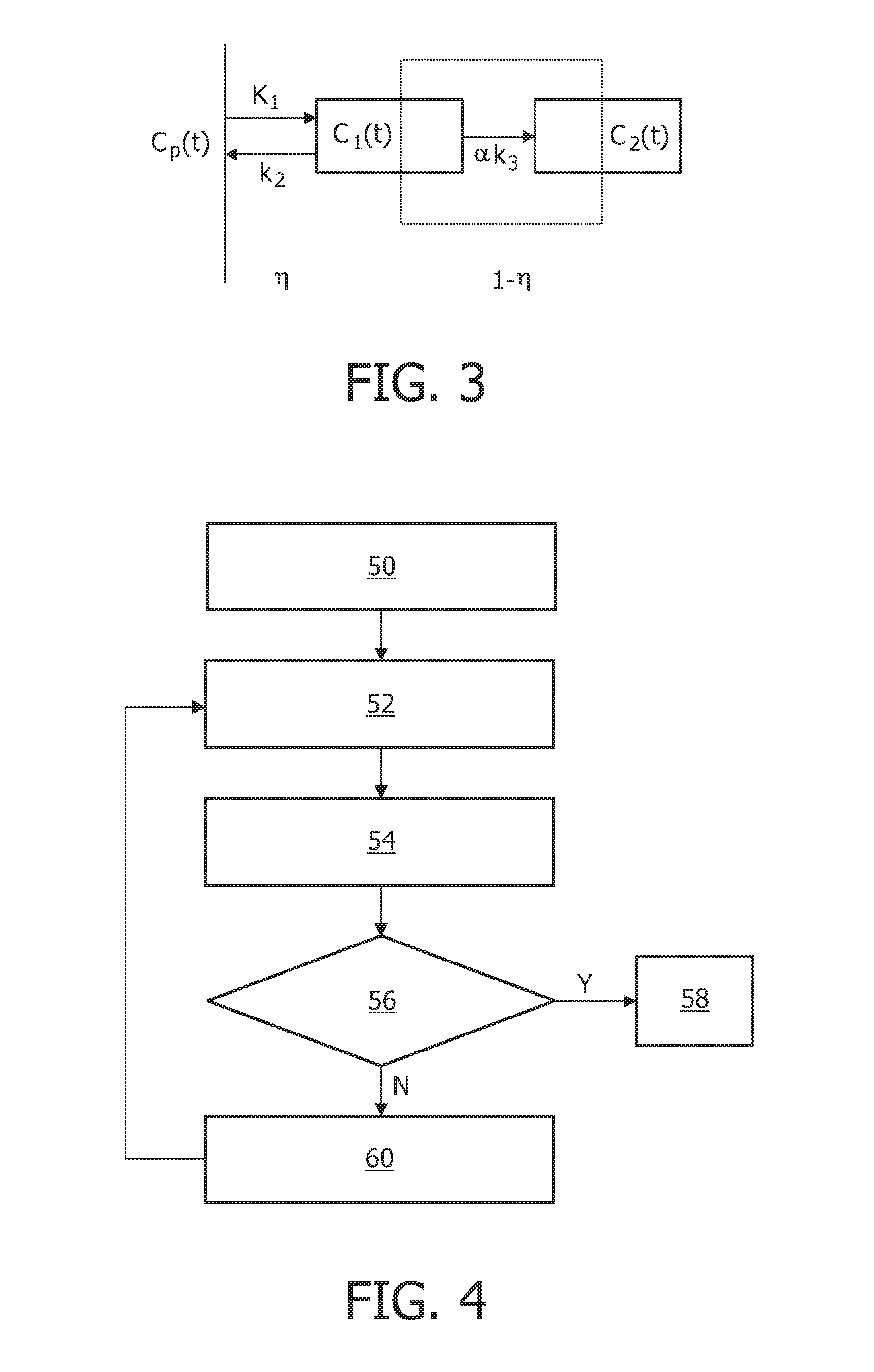
A method, signal processor, device, and system for estimating a parametric or functional image 47 mapping a biological process on the basis of a limited or incomplete sequence of biological process images 40 recorded as a function of time, e.g. by a PET or SPECT scanner after injection of a radio tracer. One or more kinetic parameters 43 are first extracted by applying a pharmacokinetic model 42 (compartmental model of the underlying tracer kinetics) to the sequence of biological process images 40. Additional data 41 are used in the model, comprising at least a predetermined kinetic parameter range (e.g. from the literature), and optionally an input function or a blood clearance function. Next, an iterative algorithm 44 is applied to arrive at a modified sequence of images 45, e.g. by inserting an estimated image into the incomplete sequence of images, utilizing the one or more kinetic parameters 43. After a stop criterion has been fulfilled, the resulting image 47 is finally estimated 46 from the modified sequence of images 45. The method can be used e.g. to estimate a hypoxia parameter k3 image in the case of a FMISO data set where only late-time images are available. The method may be implemented as part of existing PET, SPECT, CT, MR or Ultrasound scanner software, and since only a limited amount of late time post injection images are necessary to provide a reliable result, the method helps to increase patient comfort and clinical throughput.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
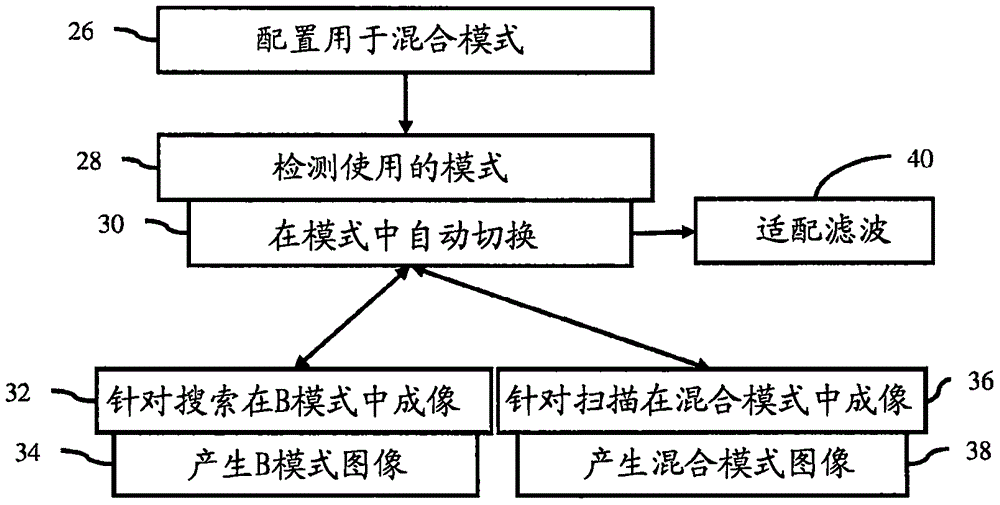
Acquisition control for mixed mode ultrasound imaging
The invention relates to acquisition control for m mixed mode ultrasound imaging. For mixed mode imaging (36), an ultrasound scanner distinguishes (28) between times when different modes of imaging (32, 36) are appropriate based on motion or transducer usage. Any switching (30) between modes, such as between B-mode and mixed mode imaging (32, 36), occurs automatically based on the detection by the ultrasound scanner of motion, alleviating the need for sonographer manual selection.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Estimation method of lean meat percentage of live pig
InactiveCN101361677AVerify accuracyVerification accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryLean meatZoology
The invention discloses a method of estimating the lean meat percentage of a live pig and relates to the field of detection technique, which aims at solving the problems of detection technique for lean meat percentage of the live pig. The method of estimating the lean meat percentage of the live pig comprises steps as follows: 1) measuring the weight of the pig with empty stomach, and determining the sizes of back fat and eye muscles of the live pig by a B-typed ultrasound scanner; 2) substituting the weight, thickness of the back fat and size of the eye muscles into a regression equation of estimating the lean meat percentage of the live pig as follows: y is equal to 67.264 plus ax1 plus bx2 plus cx3; wherein, y refers to the estimated lean meat percentage, x1 the weight, x2 the thickness of the back fat and x3 the size of eye muscles; a represents a number between -0.067 and -0.059, b represents a number between -2.206 and -2.038, and c represents a number between 0.195 and 0.215; then finally gaining an estimated lean meat percentage of the detected pig. The method of estimating the lean meat percentage of the live pig has the advantages of high accuracy and measuring speed, and can determine the lean meat percentage of live pigs, without bringing any loss caused by the slaughtering.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANIMAL EPIDEMIC PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Inspection device
InactiveUS20110100128A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsUltrasonic sensorLatex rubber
An ultrasound scanner (100) which has a pluralityofultrasound transducers (104) directed normal to a scanning surface (106) to scan a workpiece (114), the scanner (100) comprising a couplant filled latex rubber sheath (106) shaped to the surface of a workpiece (114).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Radio-frequency electrical membrane breakdown for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
InactiveUS20180028267A1Safely and effectively deployedSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnatomical structuresAnesthesia needle
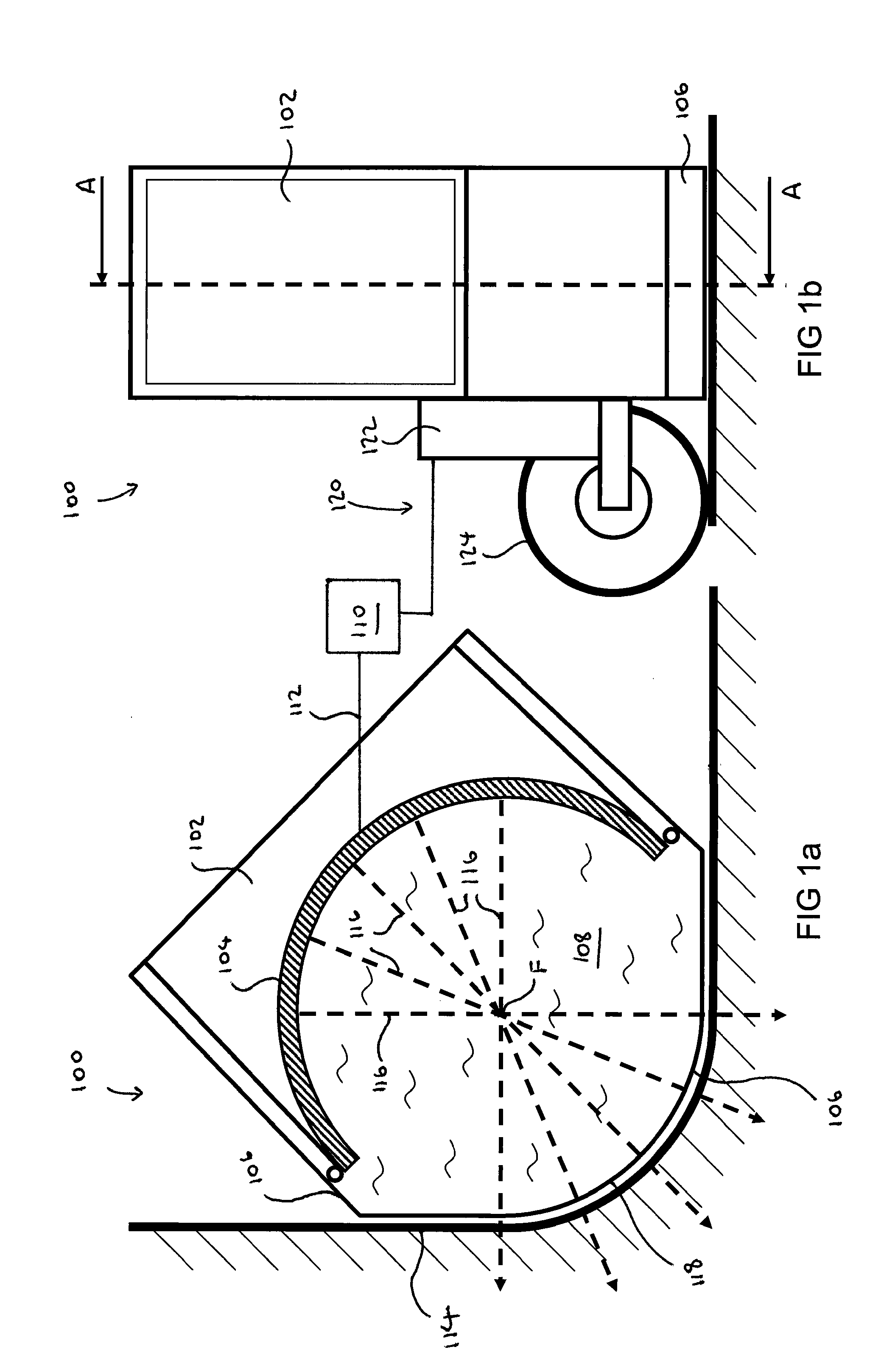
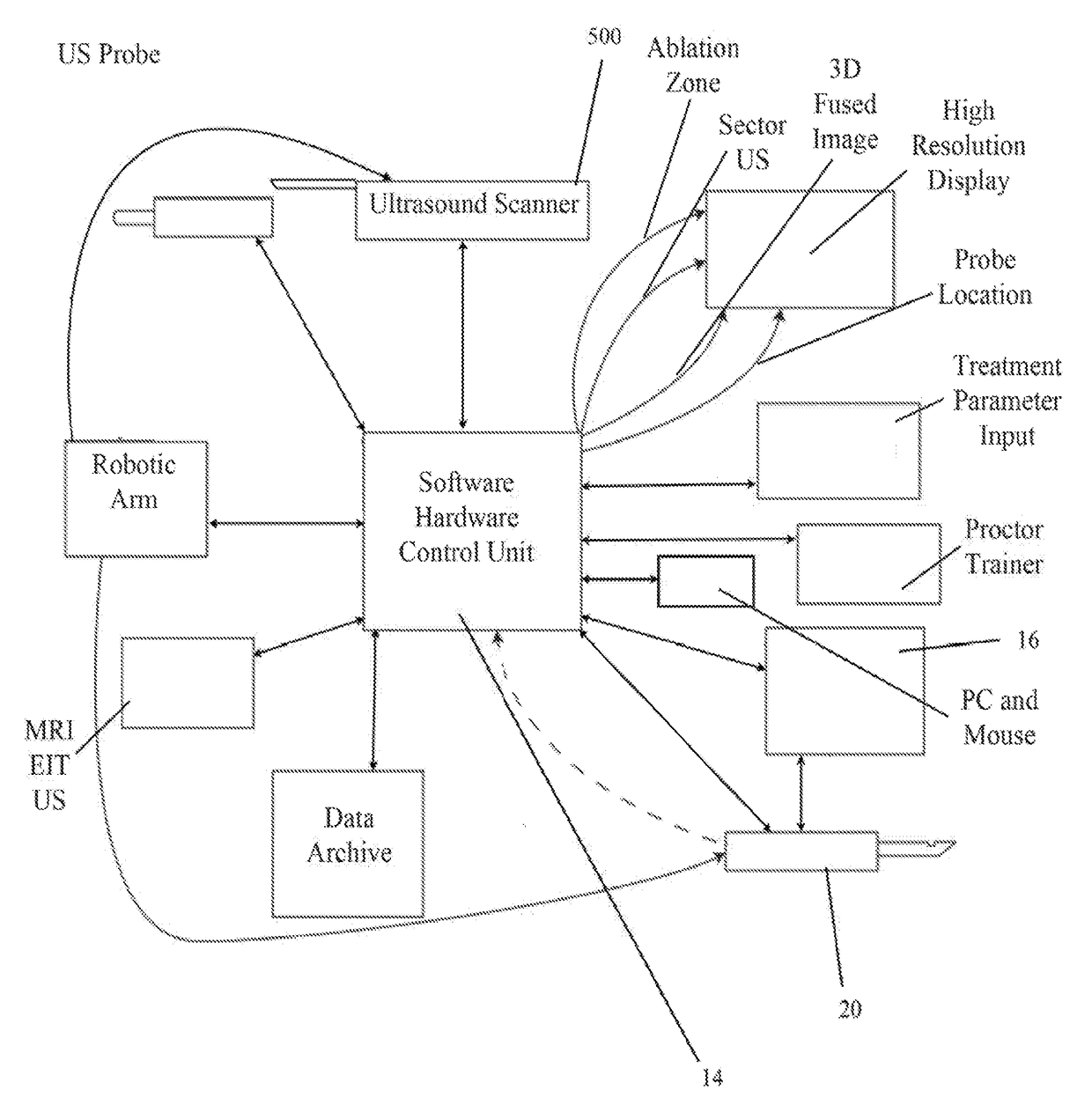
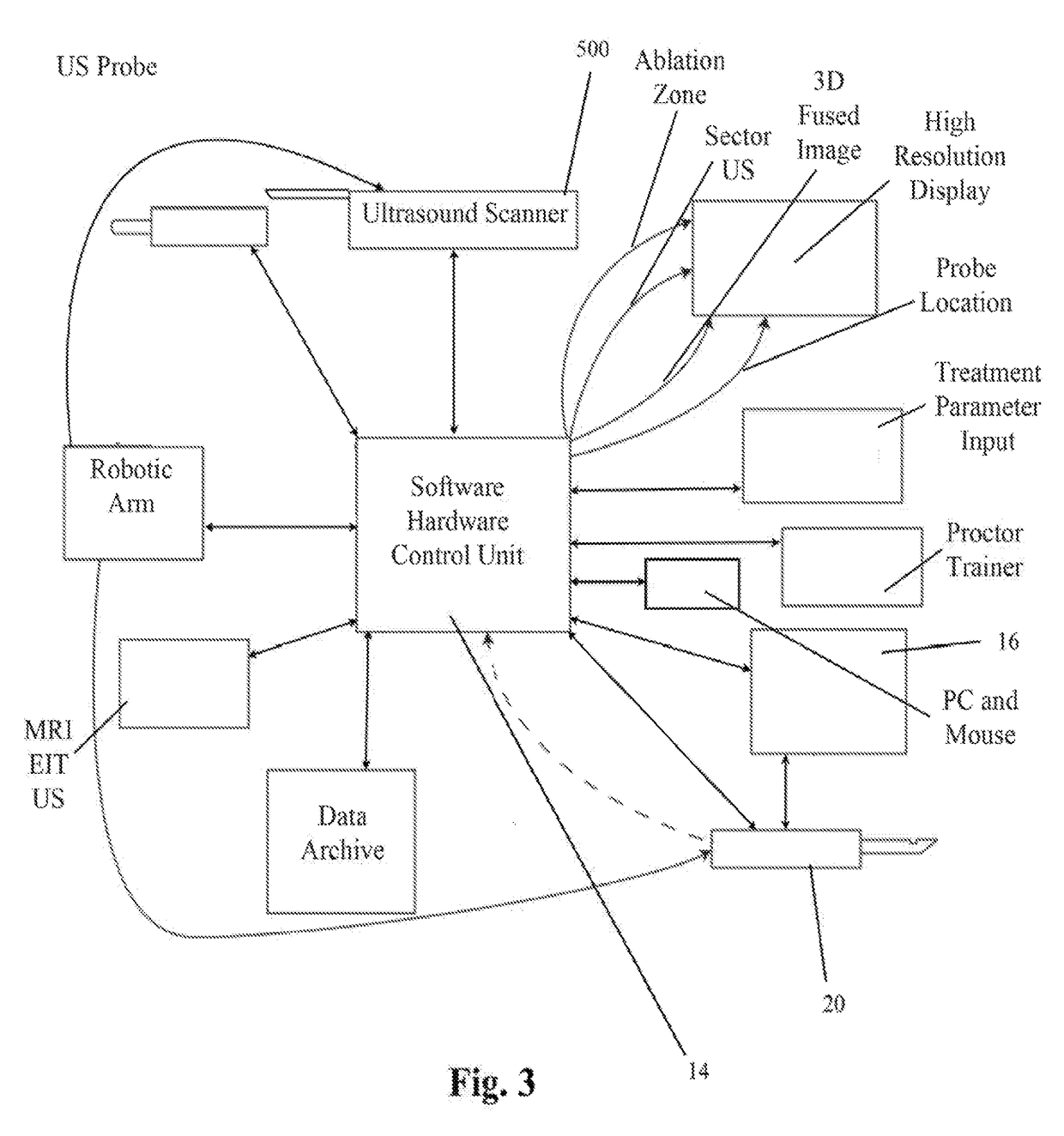
An imaging, guidance, planning and treatment system integrated into a single unit or assembly of components, and a method for using same, that can be safely and effectively deployed to treat Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in ail medical settings, including in a physician's office or in an outpatient setting. The system utilizes the novel process of Radio-Frequency Electrical Membrane Breakdown (“EMB” or “RFEMB”) to destroy the cellular membranes of unwanted BPH tissue without damaging sensitive anatomical structures in the prostate. The system preferably comprises at least one EMB treatment probe 20, at least one ultrasound scanner, at least one trackable anesthesia needle 300, and at least one controller unit for at least partially automating the treatment process.
Owner:IMMUNSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com