Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Increase Computational Parallelism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
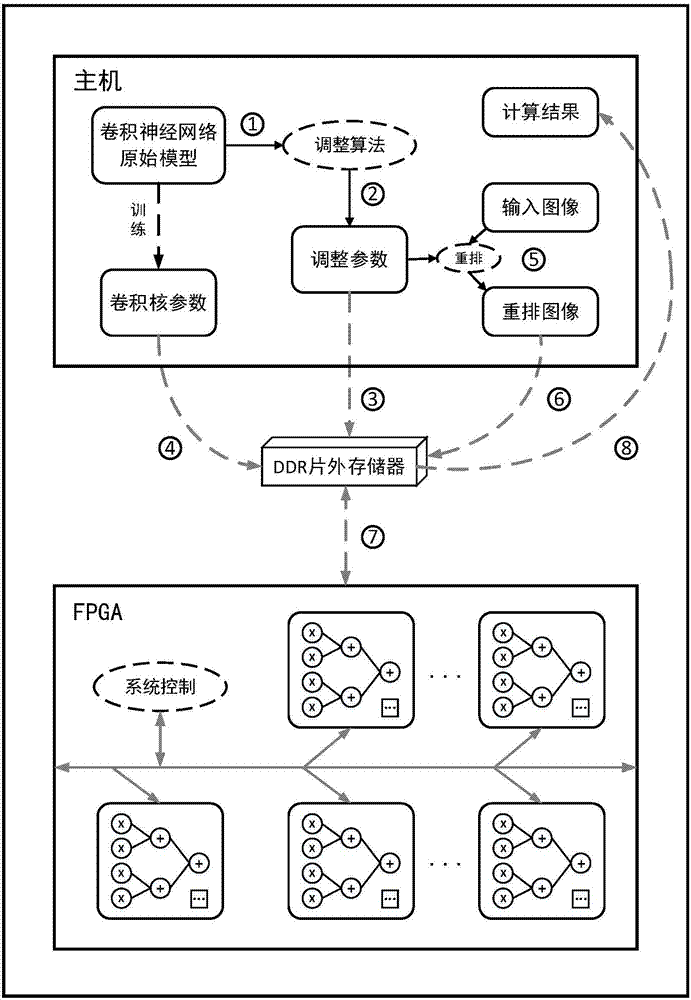
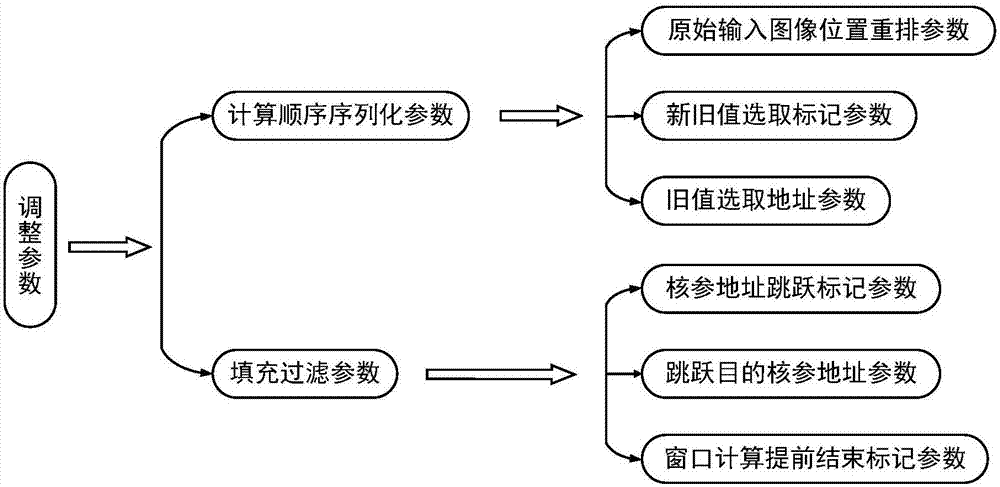
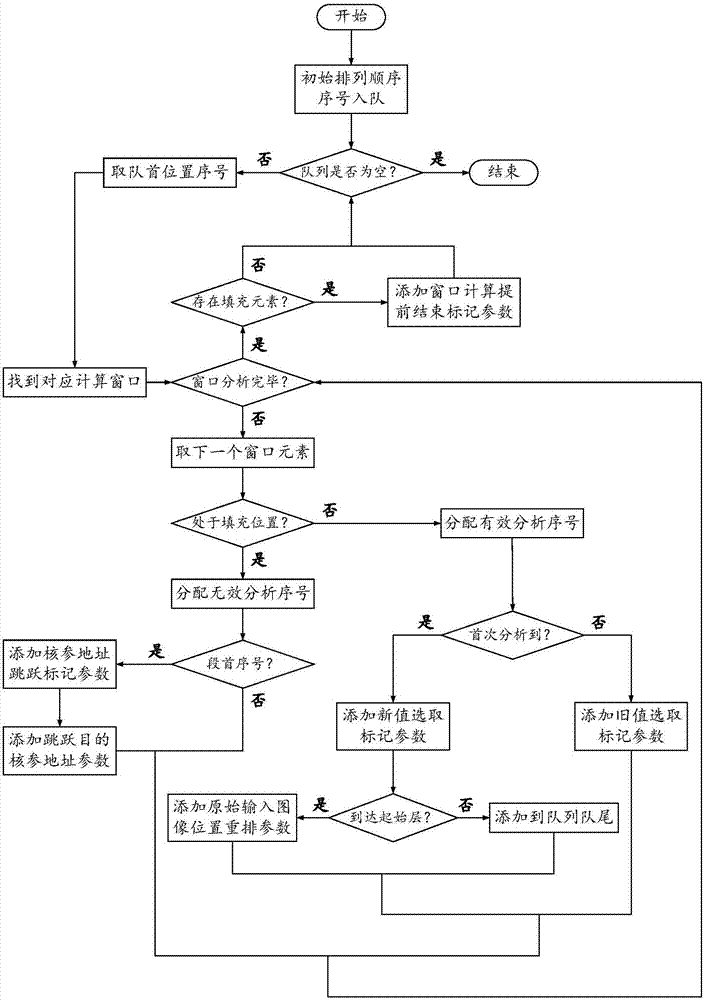
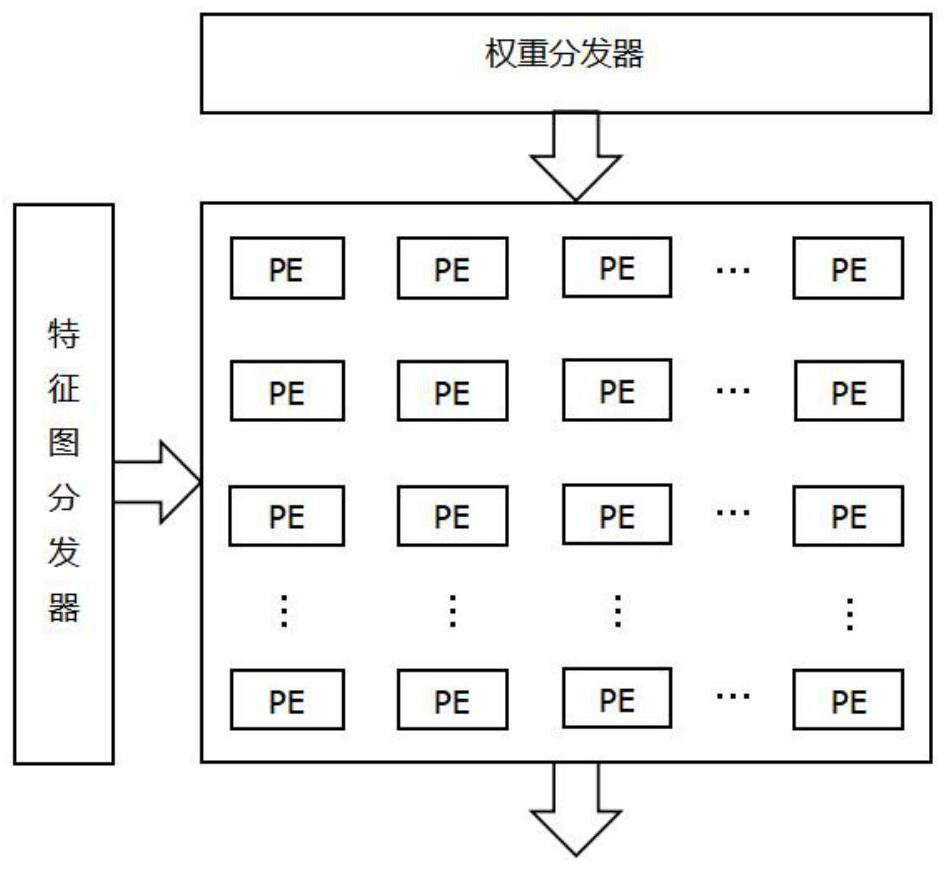
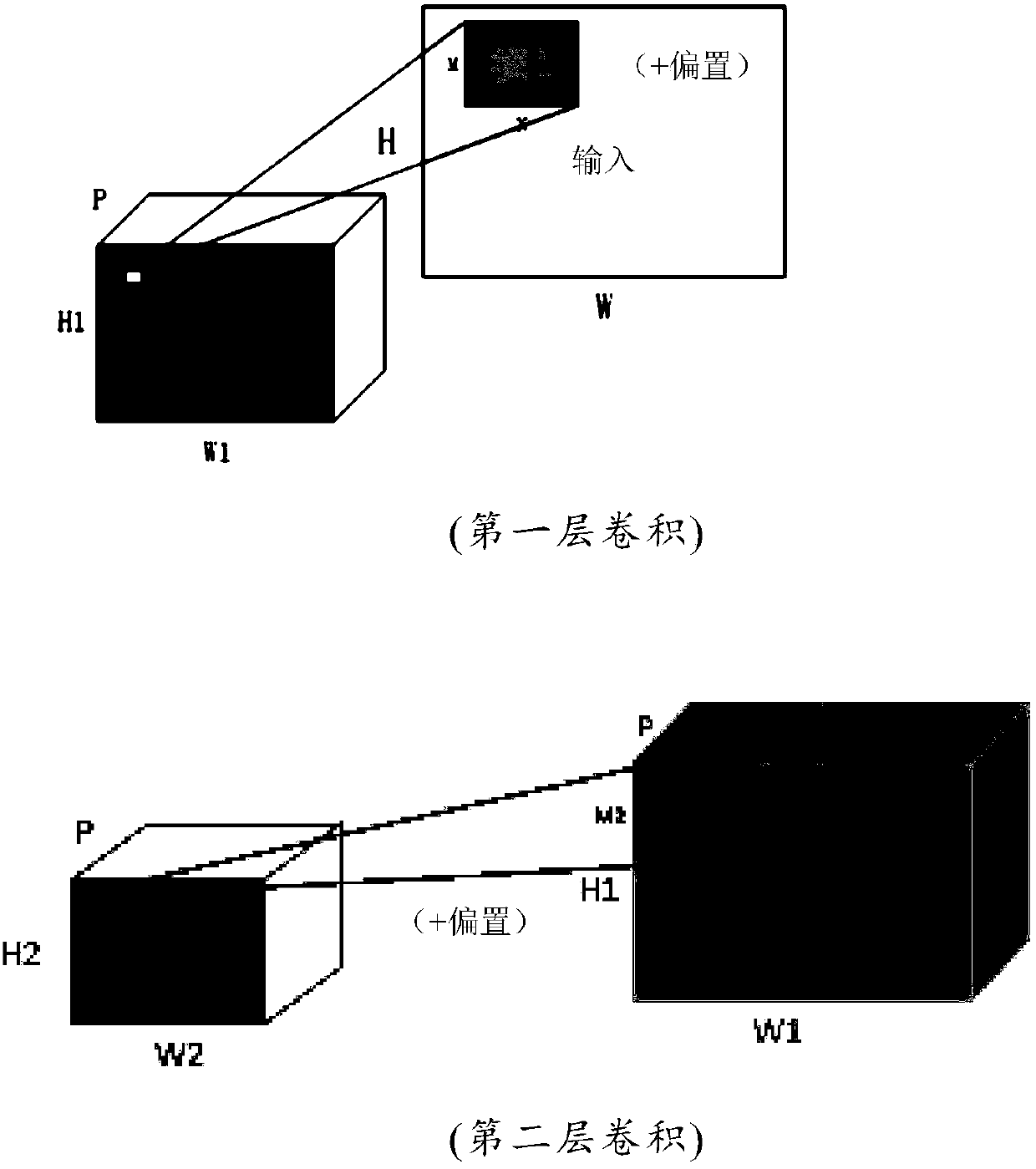
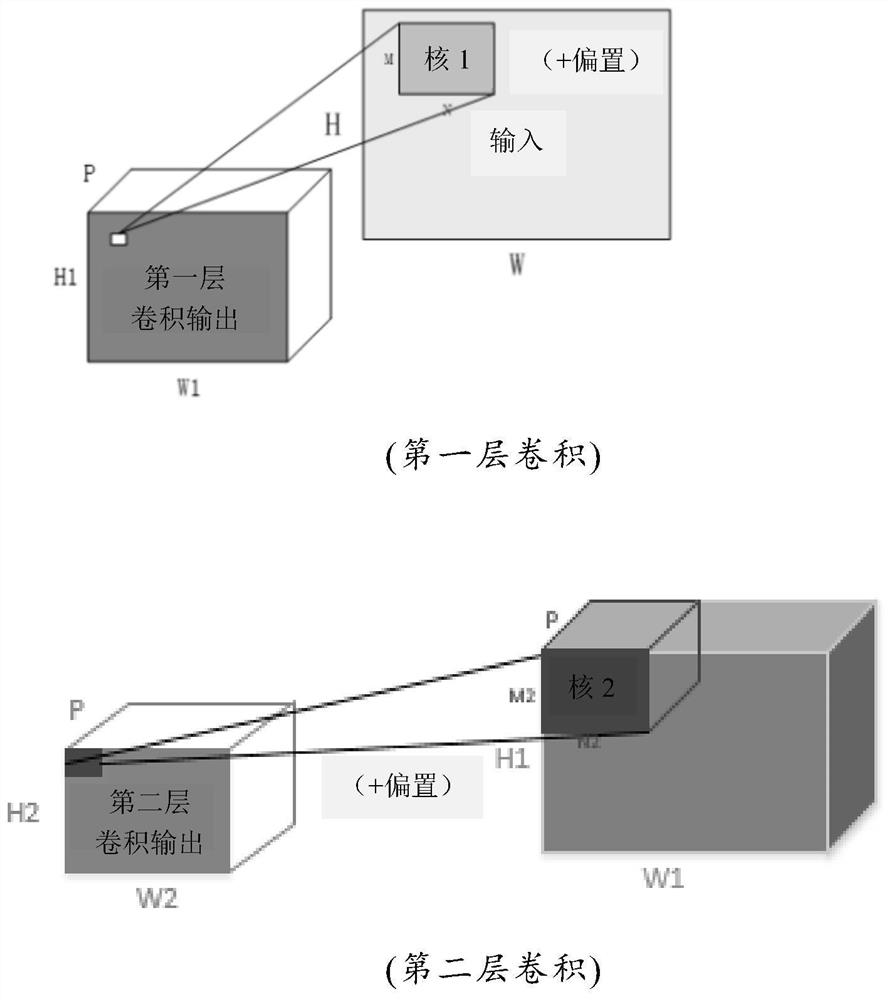
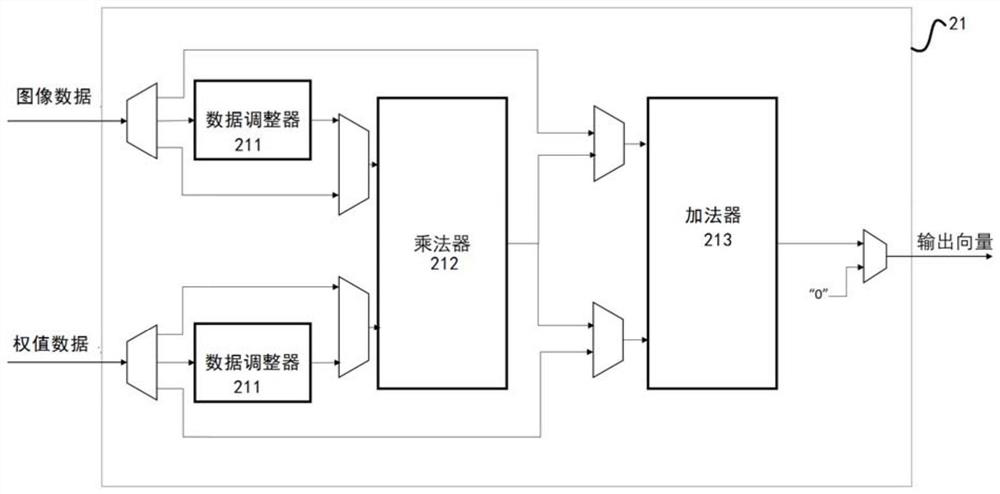
Streamlined acceleration system of FPGA-based depth convolution neural network
ActiveCN106875012AProcessing speedHighly integratedPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsComputer science
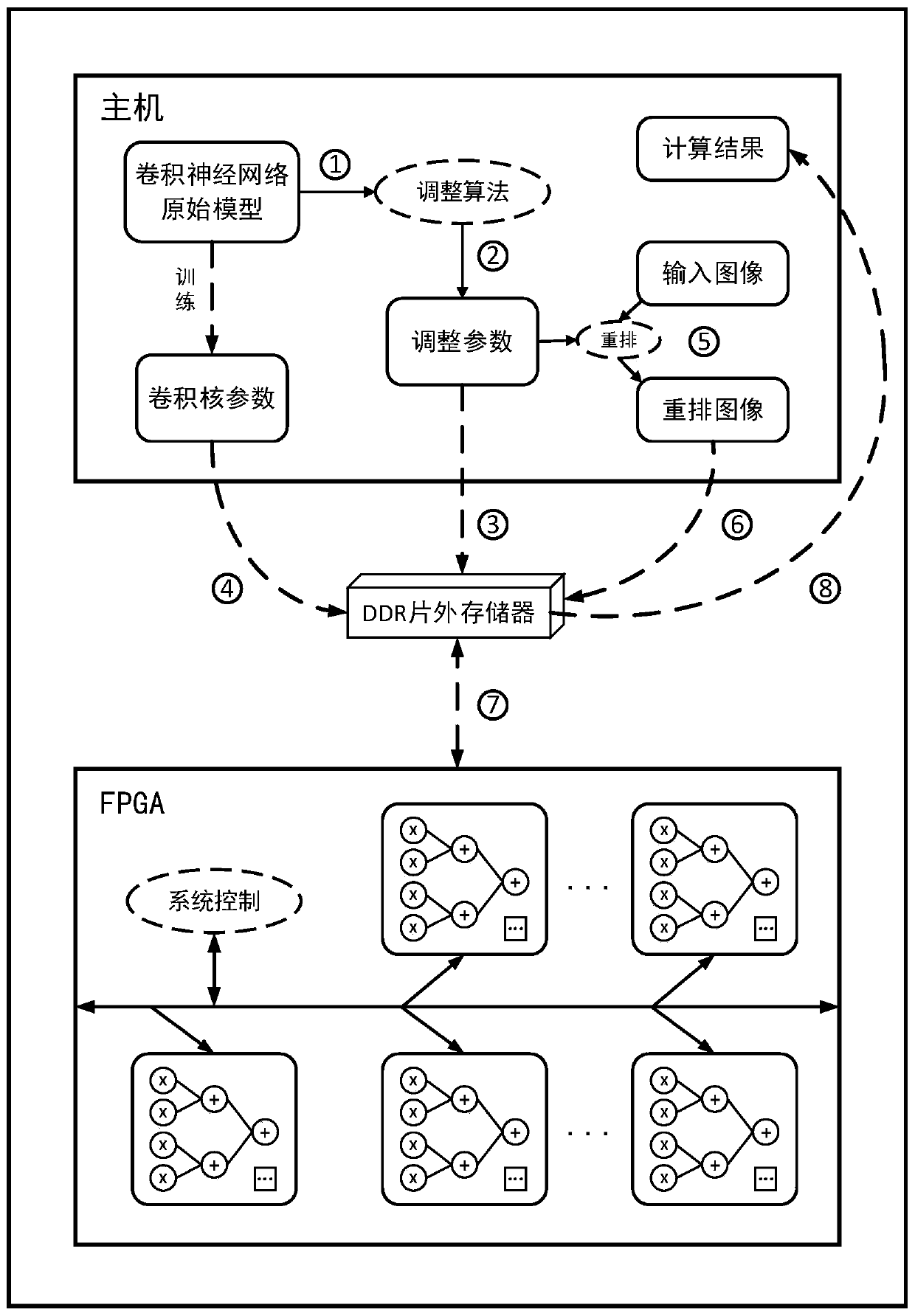
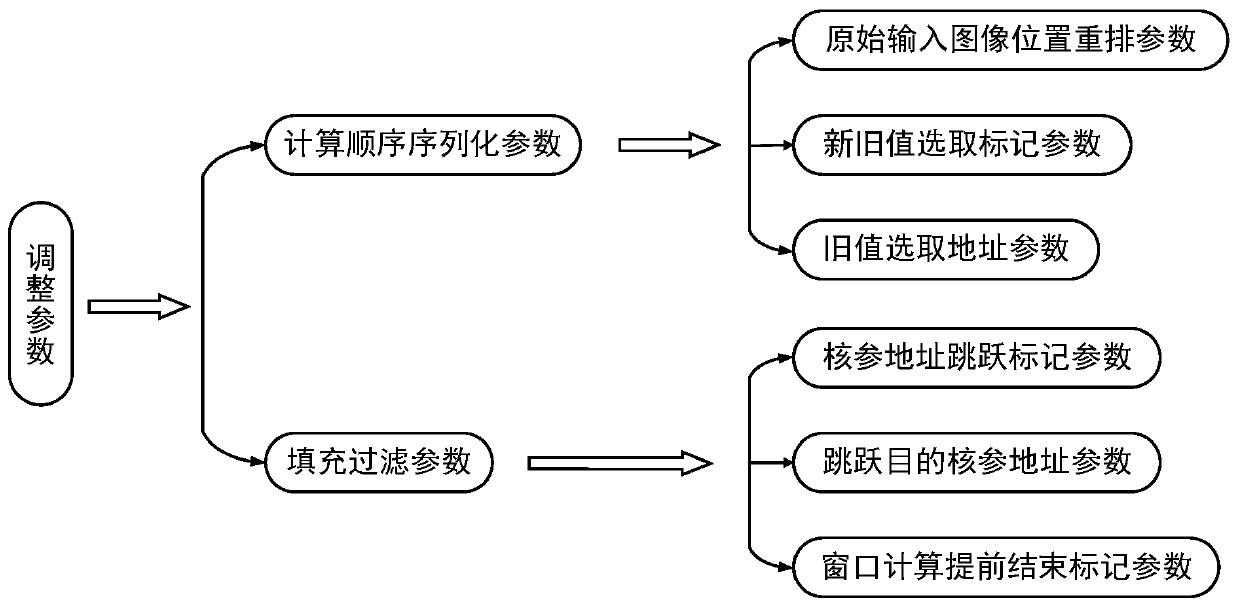
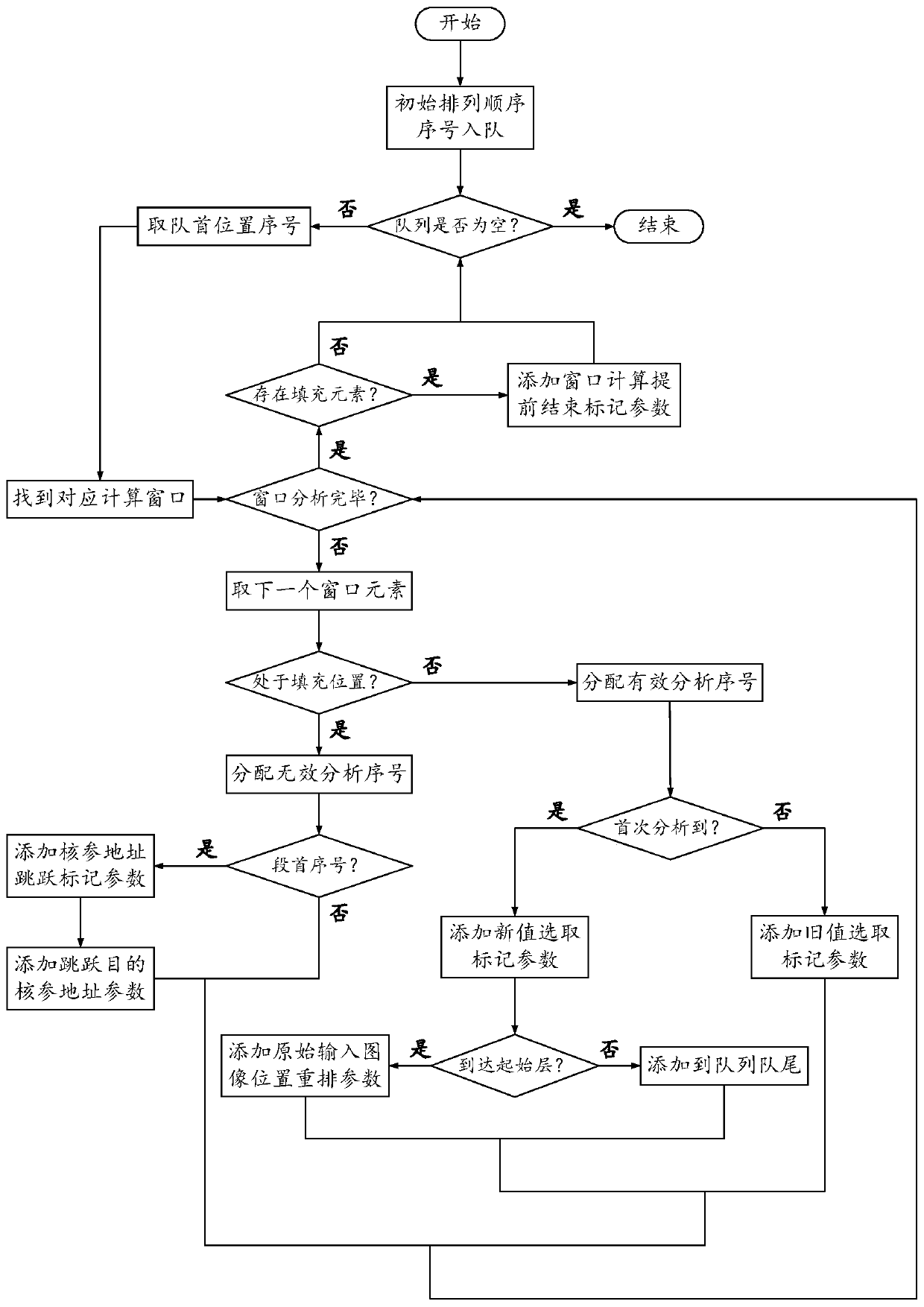
The invention brings forward a streamlined acceleration system of an FPGA-based depth convolution neural network. The streamlined acceleration system is mainly formed by an input data distribution control module, an output data distribution control module, a convolution calculating sequence serialization realizing module, a convolution calculating module, a pooling calculating sequence serialization realizing module, a pooling calculating module, and a convolution calculating result distribution control module. Moreover, the streamlined acceleration system comprises an internal system cascade interface. Through the streamlined acceleration system designed by the invention, highly efficient parallel streamlined realization can be conducted on an FPGA, problems of resource waste and effective calculation delays caused by filling operations during calculation are effectively solved, the power consumption of the system is effectively reduced, and the operation processing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:武汉魅瞳科技有限公司
Mobile ad hoc authentication method, network and system
InactiveCN101192928AImprove efficiencyMake the most of processing resourcesEnergy efficient ICTUser identity/authority verificationNetwork structureMobile ad hoc network
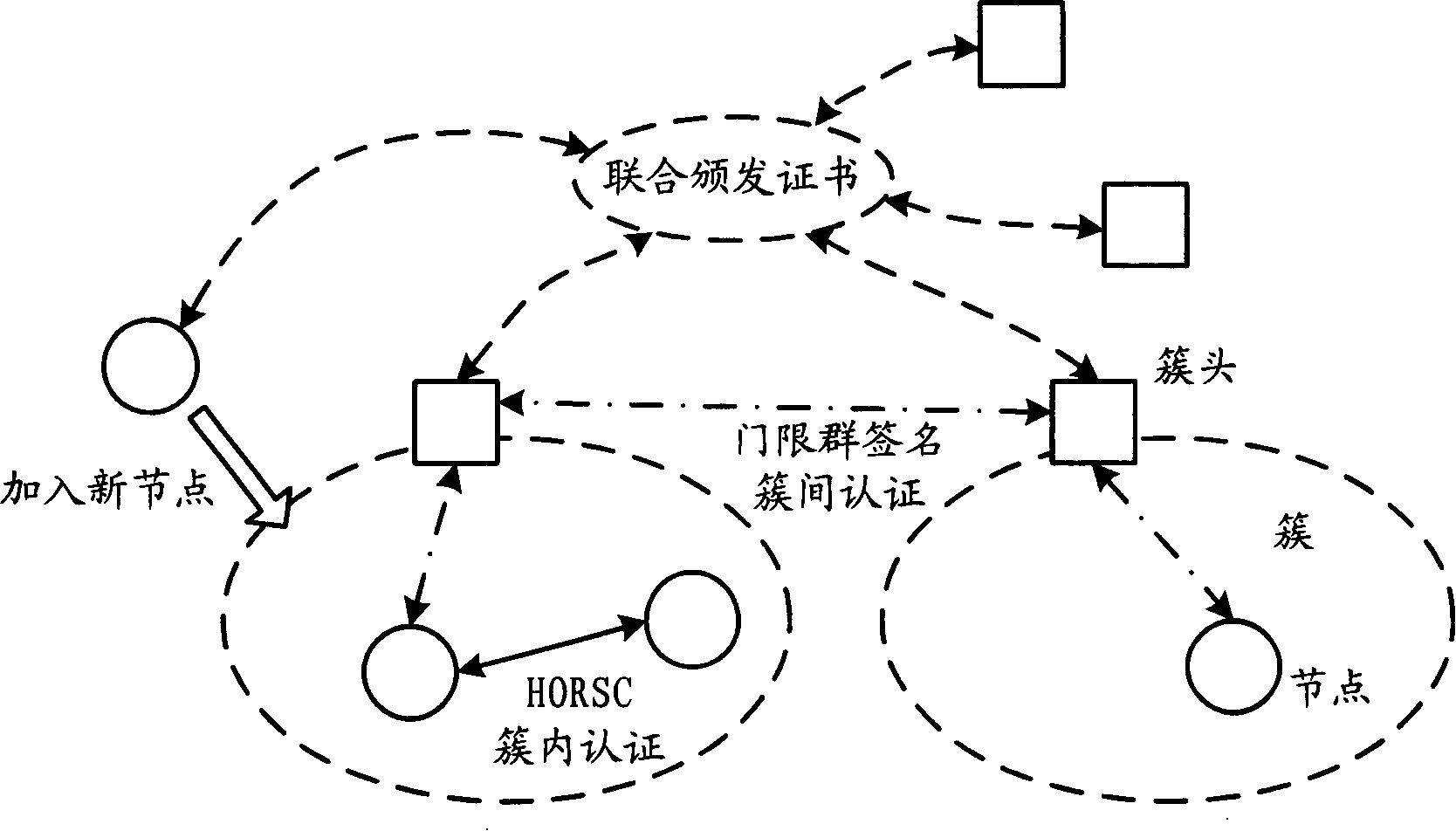
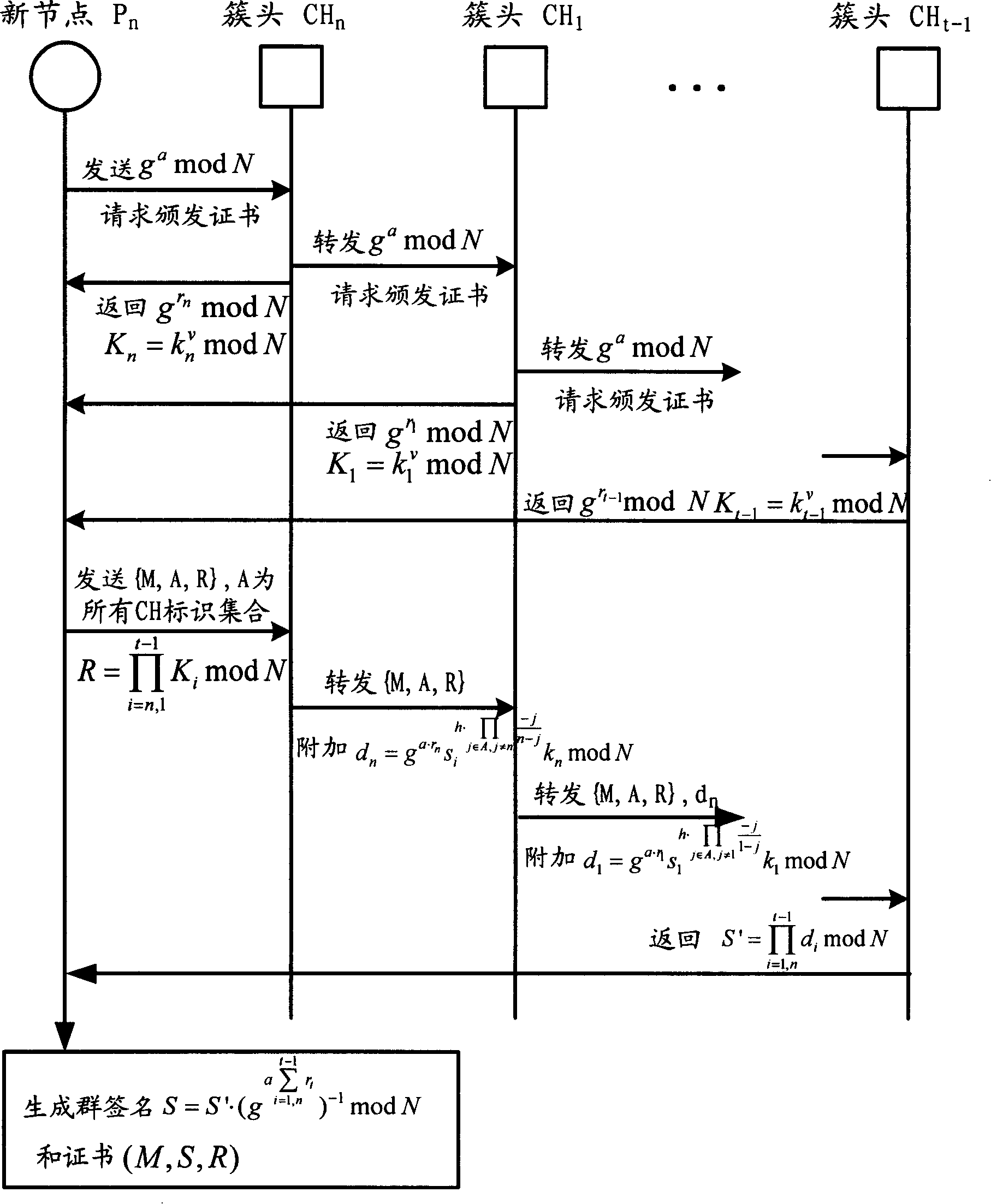
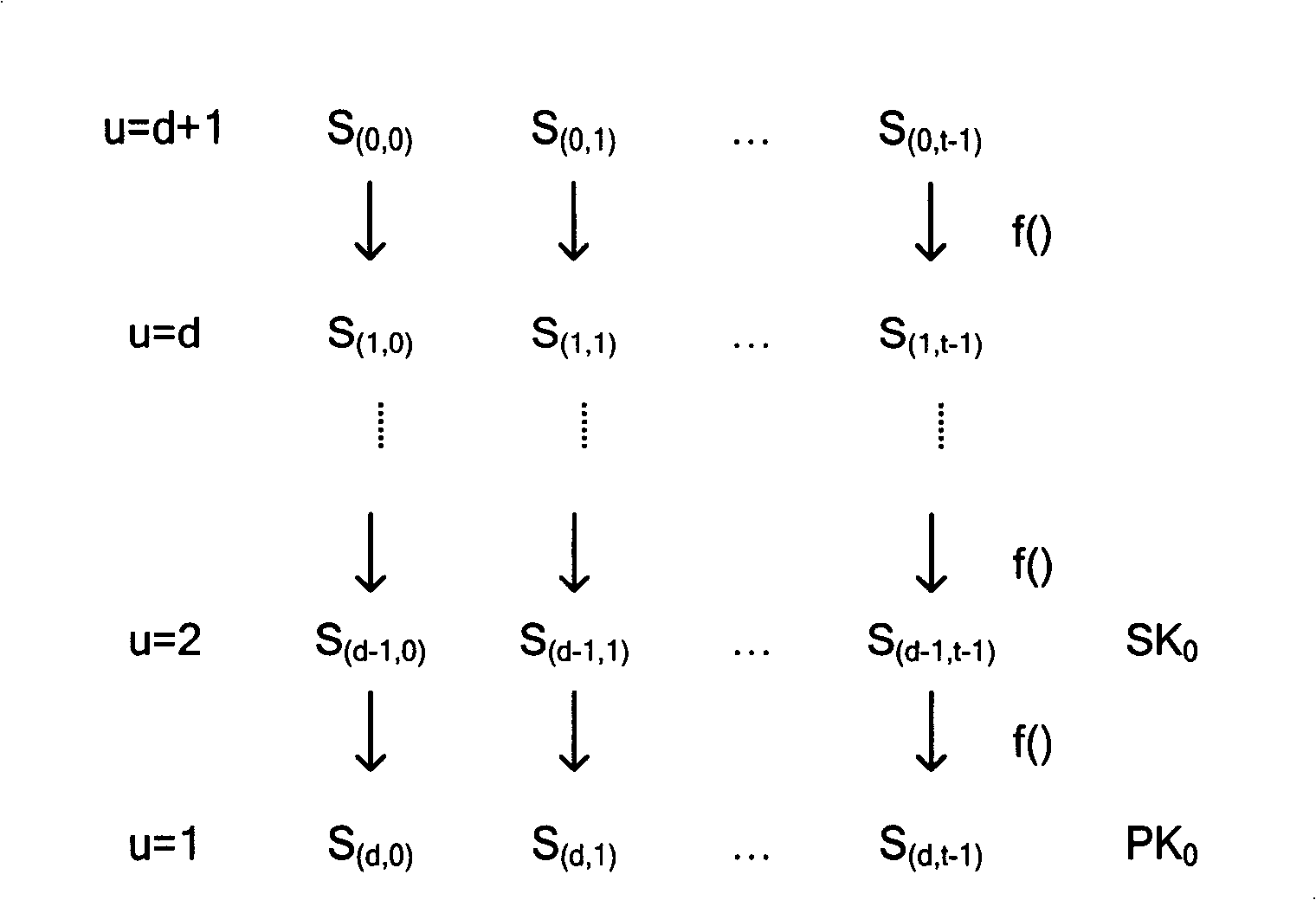
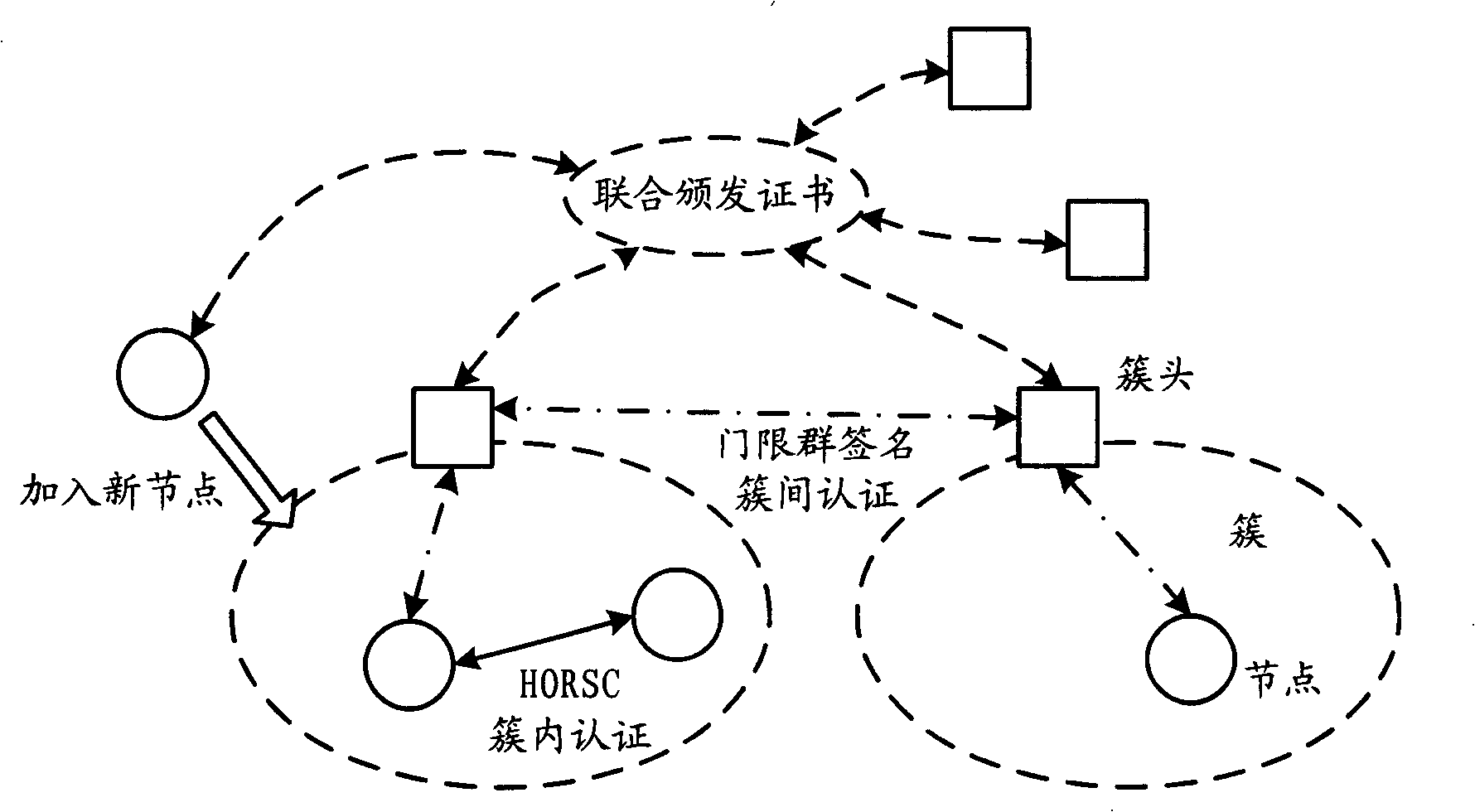
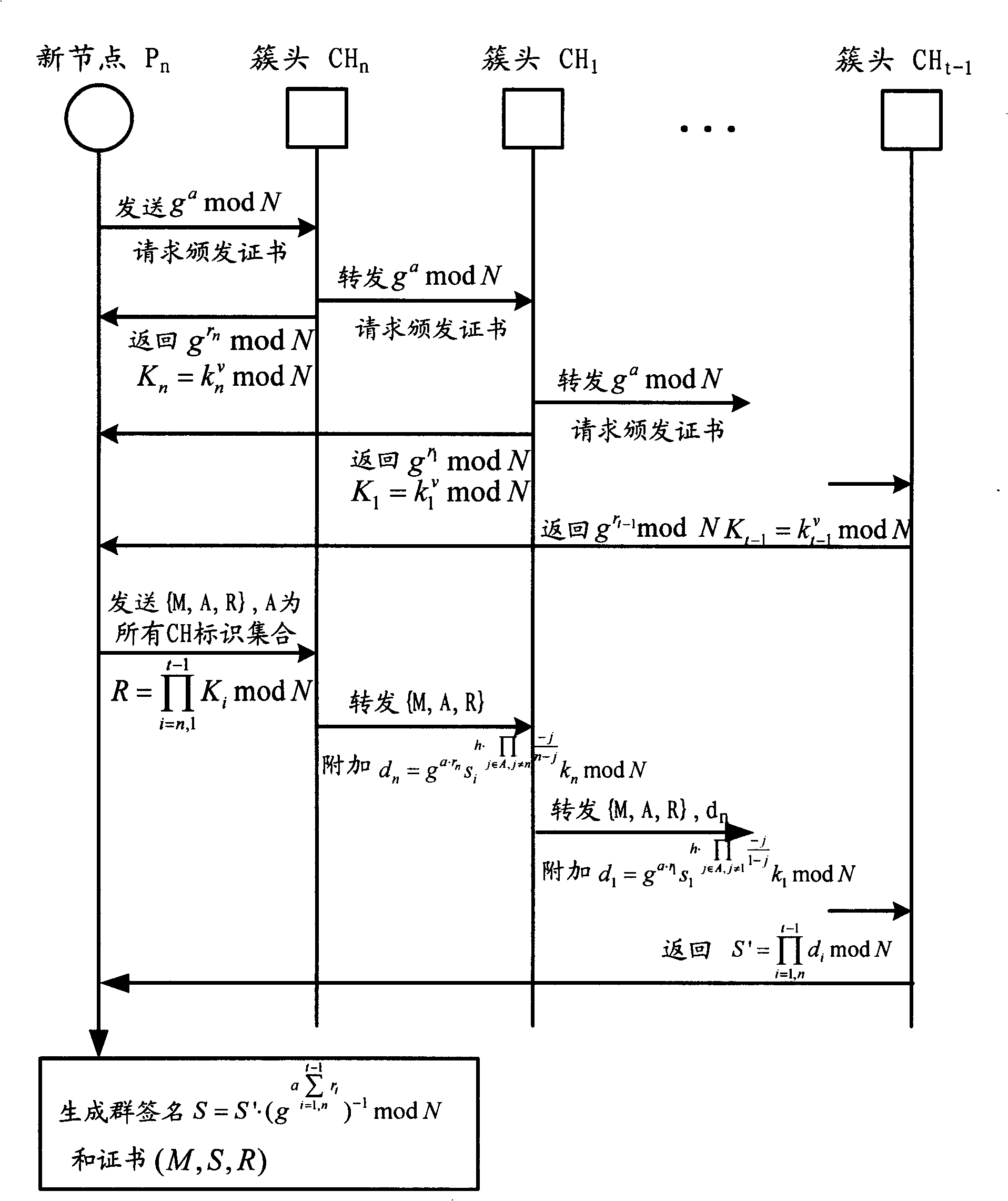
The invention relates to the communication field and discloses an authentication method, a network and a system of mobile ad hoc network, which ensures the realization of layer distribution type authentication scheme of cluster mobile ad hoc network; and the requirement on computer processed resources is rational, which can be realized in practical application environment. The invention adopts a group network structure of cluster mobile ad hoc network and advocates layer distribution identity authentication scheme; and the inter-cluster communication used an improved new threshold group signature protocol which improves the original threshold group signature method based on GQ and decreases power index calculation times, improves calculation parallelism and reduces the requirement on processed resources; at the time of initialization, a certificate and a sub key are issued by the system uniformly; cluster heads which have enough numbers of sub keys can jointly recover system keys, thereby carrying out the group signature to issue certificates to new added nodes and using multi-leap serial communication for realizing united group signature.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
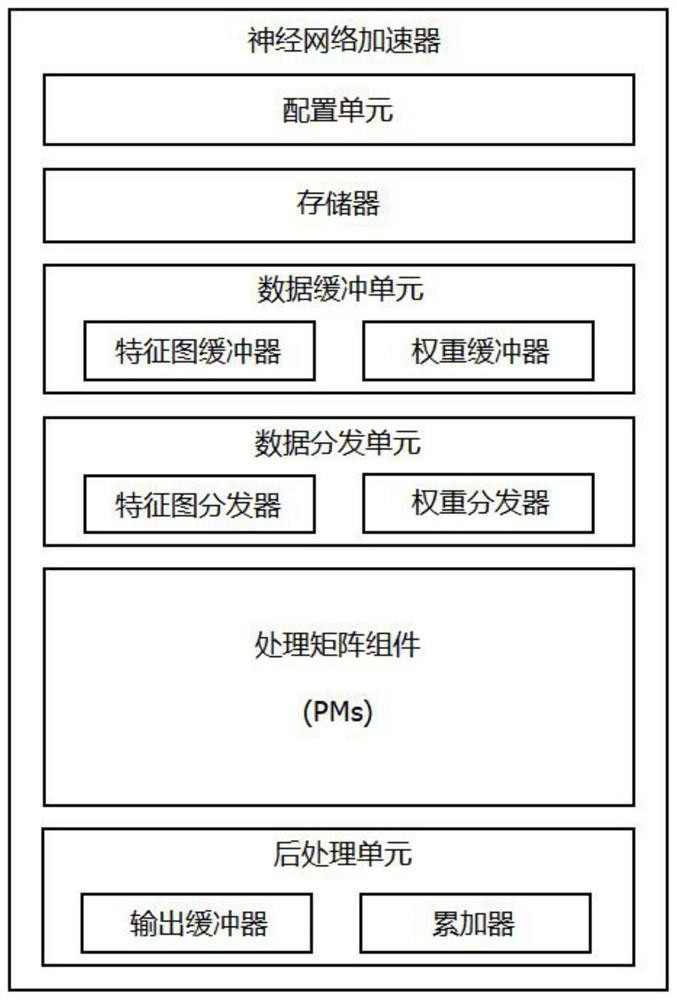
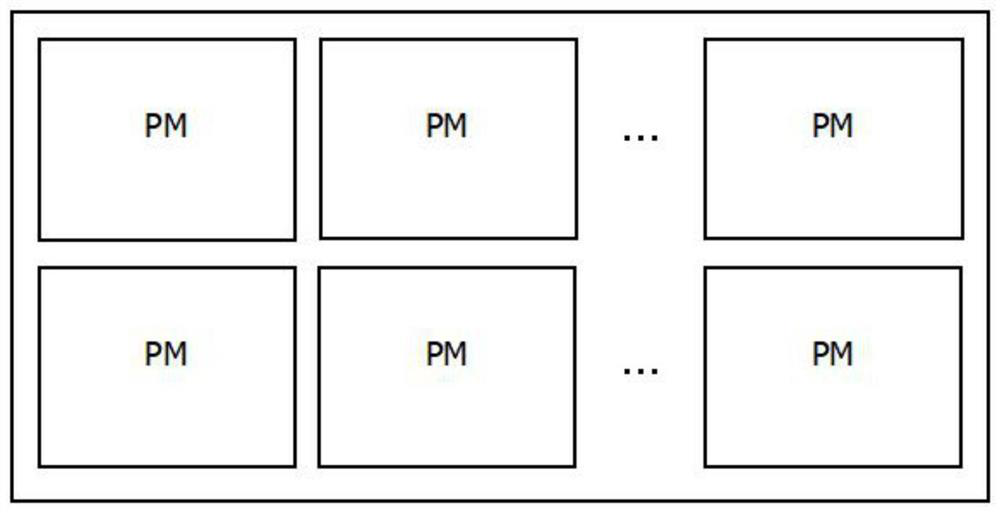
Neural network accelerator suitable for edge equipment and neural network acceleration calculation method
ActiveCN111667051ARealize multiplexingImprove reuse rateDigital data processing detailsNeural architecturesMultiplexingProcessing element
The invention discloses a neural network accelerator suitable for edge equipment and a neural network acceleration calculation method, and relates to the technical field of neural networks. The network accelerator comprises a configuration unit, a data buffer unit, a processing matrix component (PMs) and a post-processing unit, and a main controller writes feature parameters of different types ofnetwork layers into a register of the configuration unit to control the mapping of different network layer operation logics to the processing matrix hardware, so as to realize the multiplexing of theprocessing matrix component, i.e., the operation acceleration of different types of network layers in the neural network is realized by using one hardware circuit without additional hardware resources; and the different types of network layers comprise a standard convolution layer and a pooling network layer. The multiplexing accelerator provided by the invention not only ensures the realization of the same function, but also has the advantages of less hardware resource consumption, higher hardware multiplexing rate, lower power consumption, high concurrency, high multiplexing characteristic and strong structural expansibility.
Owner:上海赛昉科技有限公司
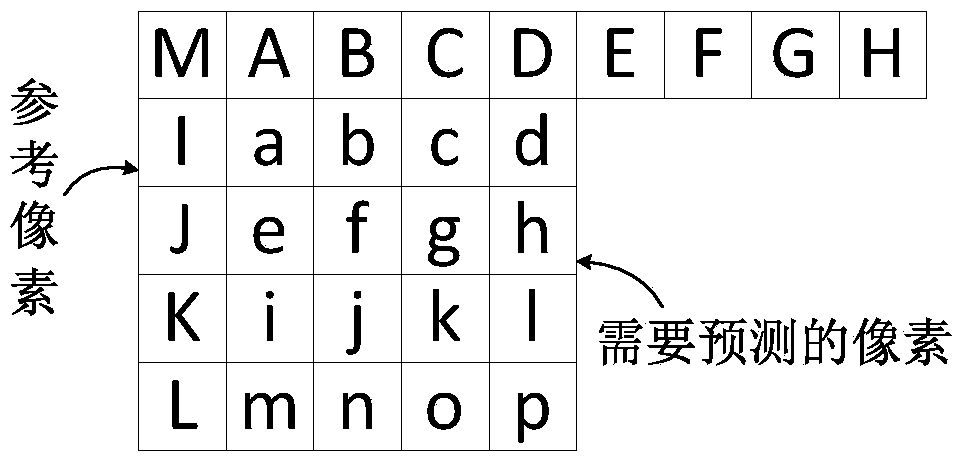
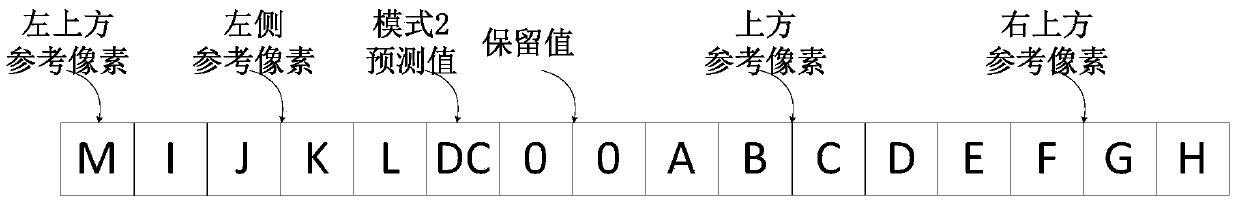
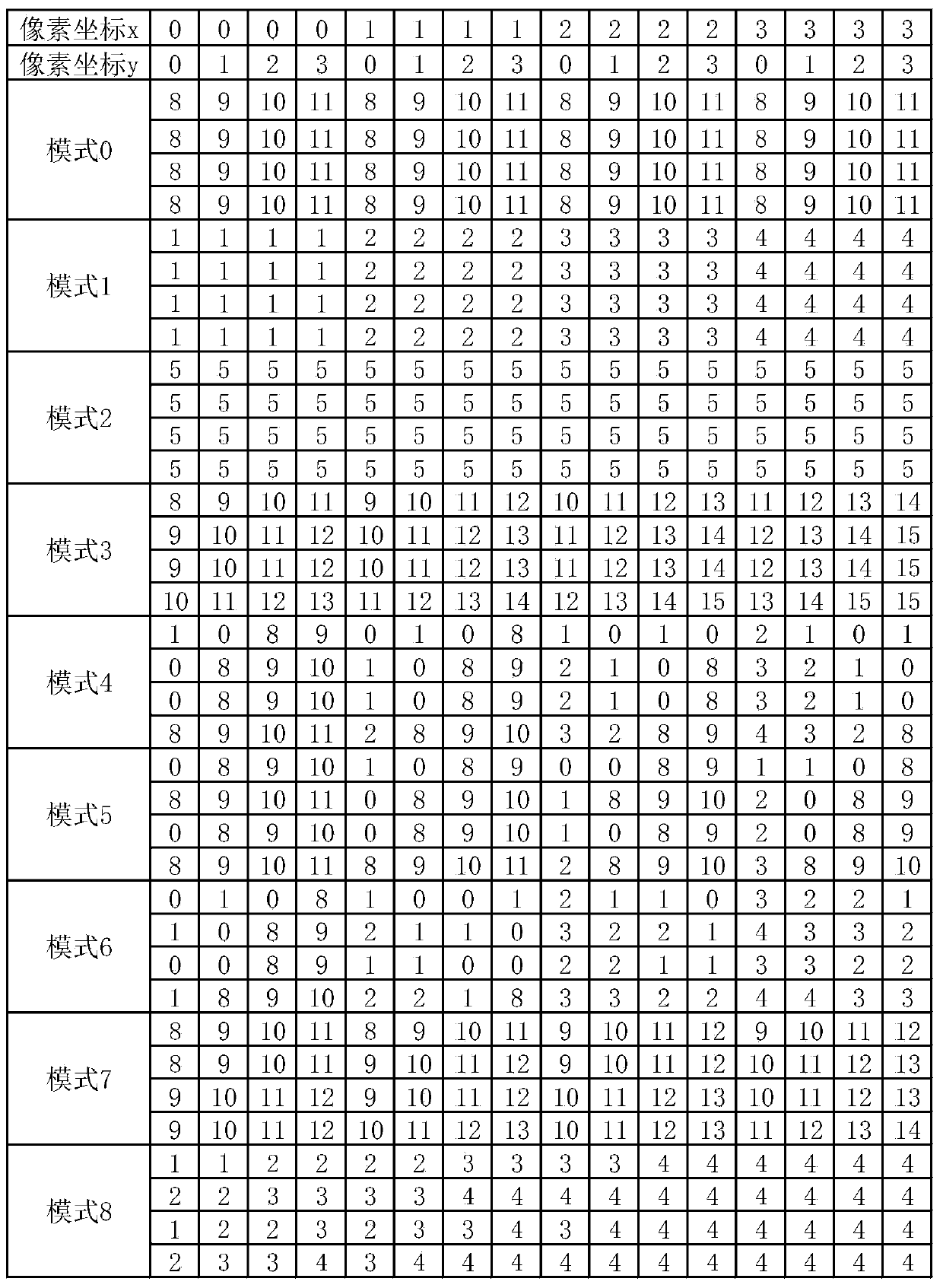
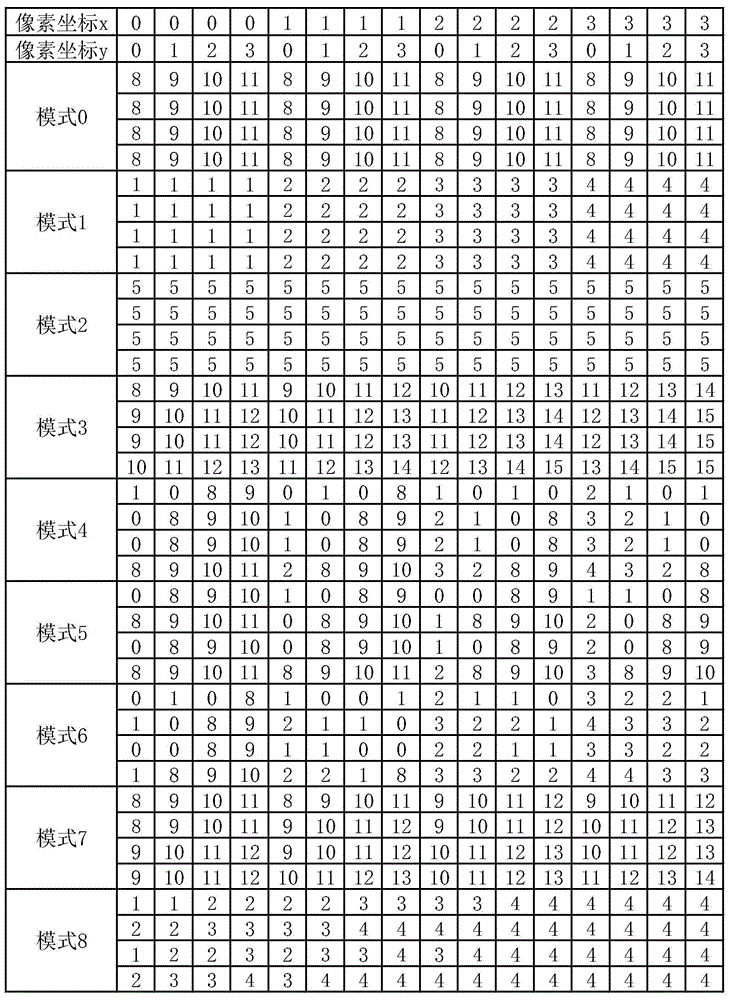
Method for 4*4 sub-macroblock parallel intraframe prediction in H.264/AVC
ActiveCN103747250AIncrease Computational ParallelismEliminate branch statementsDigital video signal modificationArray data structureParallel algorithm
The present invention discloses a method for 4*4 sub-macroblock parallel intraframe prediction in H.264 / AVC, comprising the steps of: a unified intraframe prediction formula, a reference value array, a reference position table and a concrete implementation step of parallel intraframe prediction. The unified intraframe prediction formula is improved based on the feature of a CUDA and an intraframe prediction formula, by the corresponding prediction formulas of 9 prediction modes to be transformed into one formula to meet the requirements of the CUDA multi-thread single instruction multiple data stream, to achieve the fine-grained parallel in the intraframe prediction sub-macroblock. The reference value array and the reference position table are designed to cooperate with the unified intraframe prediction formula and to completely eliminate a large number of branch statements that affects the parallel algorithm performance. The present invention in the process of the intraframe prediction achieves the pixel level parallel, can effectively use multi-core resources in a GPU to accelerate the process of intraframe prediction, and shorts a coding time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
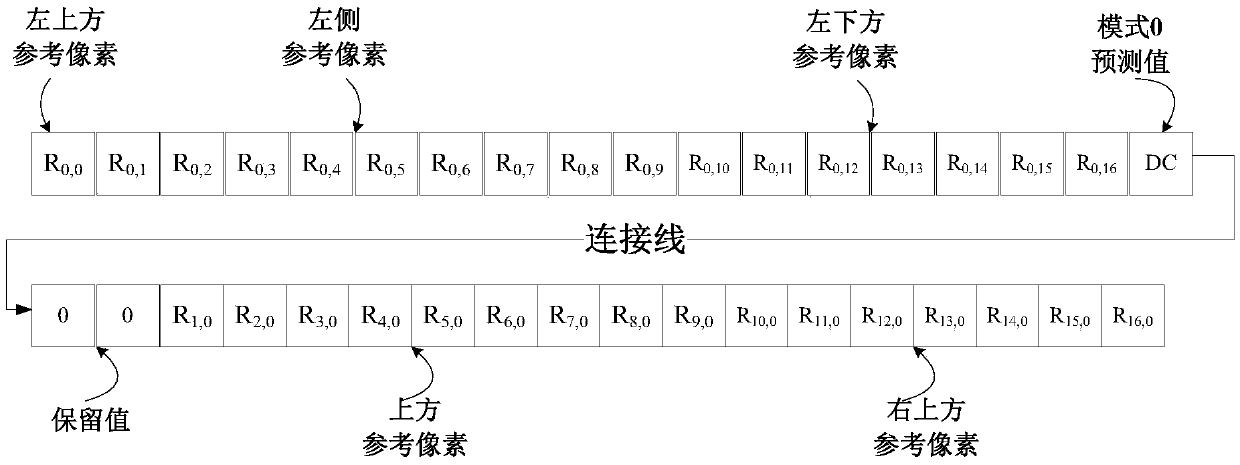
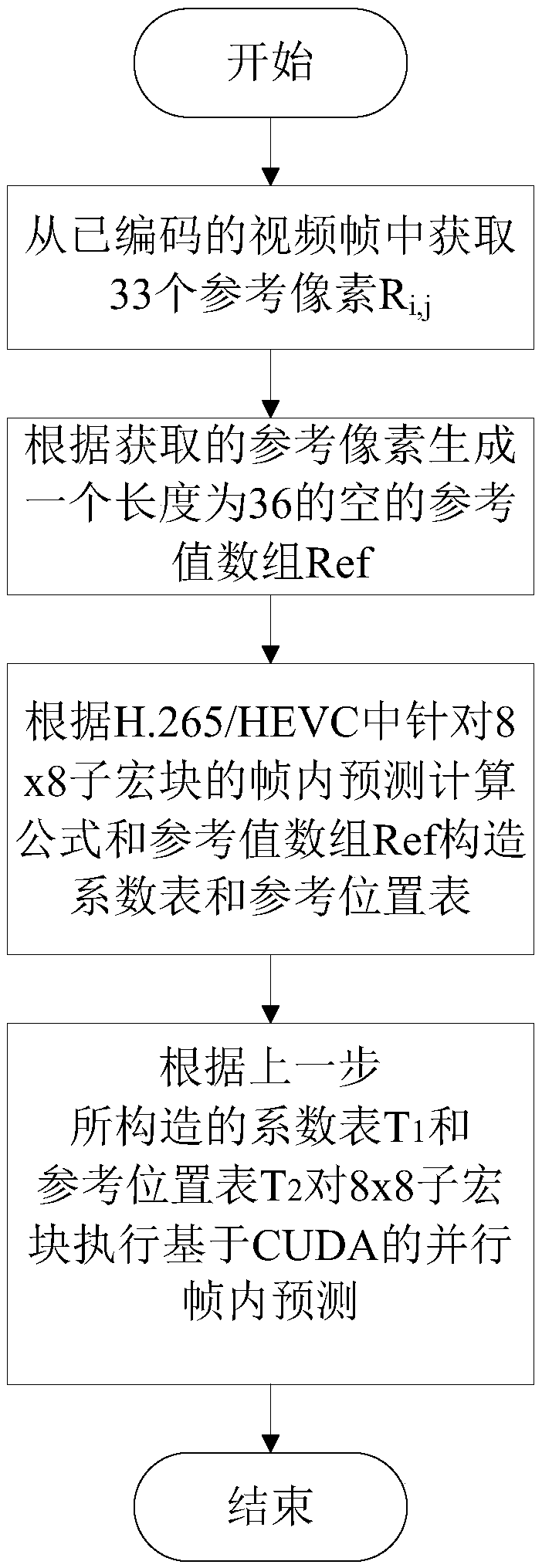
Parallel intra-frame prediction method of 8*8 sub-macroblocks in H.265/HEVC
ActiveCN105516728AIncrease Computational ParallelismEliminate branch statementsDigital video signal modificationData streamGranularity
The invention discloses a parallel intra-frame prediction method of 8*8 sub-macroblocks in H.265 / HEVC. The method comprises the following steps: unifying an intra-frame prediction formula form, establishing a coefficient table and a reference position table and a specific execution step of parallel intra-frame prediction, wherein the unification of the intra-frame prediction formula form and the establishment of the coefficient tale and the reference position are formulated according to the characteristics of the CUDA and an intra-frame prediction computational formula, so that the prediction of 64 to-be-predicted pixels and the corresponding 35 prediction modes in the 8*8 sub-macroblocks through a unified prediction formula is more benefited, the requirement of single-instruction multi-data stream of CUDA multi-thread is satisfied, the intra-frame prediction of the fine granularity parallel in the sub-macroblocks is realized, and a large number of branch statements influencing the parallel algorithm performance are eliminated. The pixel level parallel is realized in the intra-frame prediction process, the many-core resource in the GPU can be effectively used for accelerating the intra-frame prediction process, and the encoding time is shortened.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
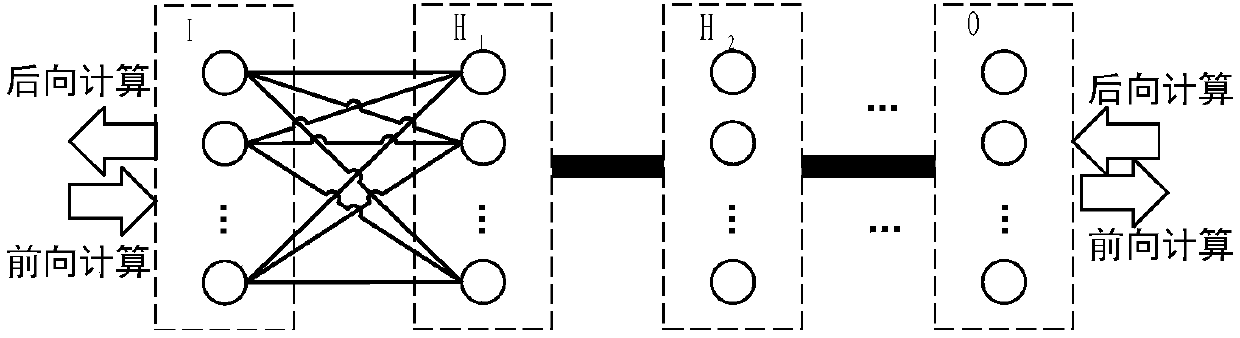
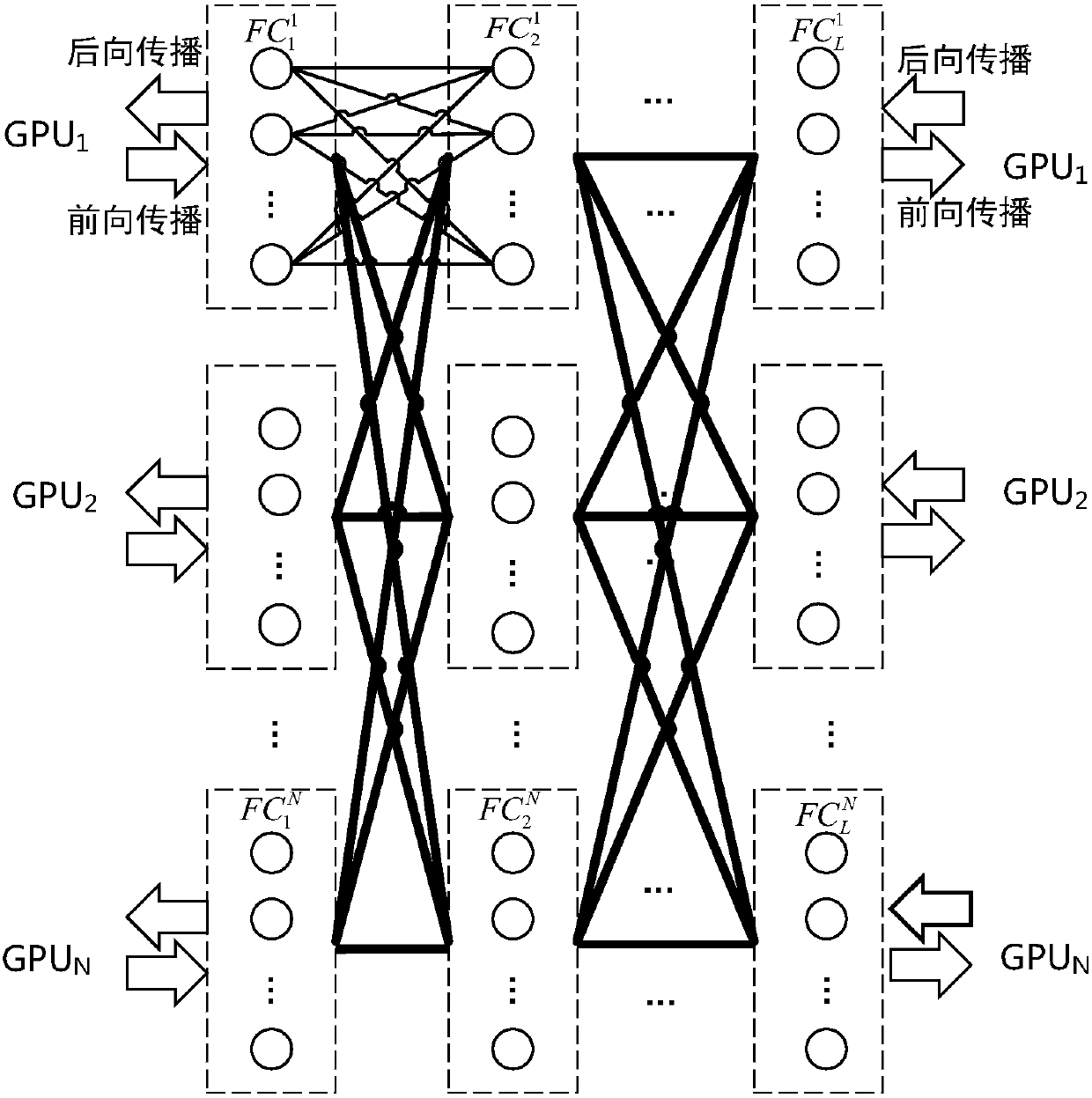
Model-parallel full-connected layer data exchange method and system for deep neural network
ActiveCN106991474AIncrease Computational ParallelismReduce overheadNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsMachine learningNetwork model
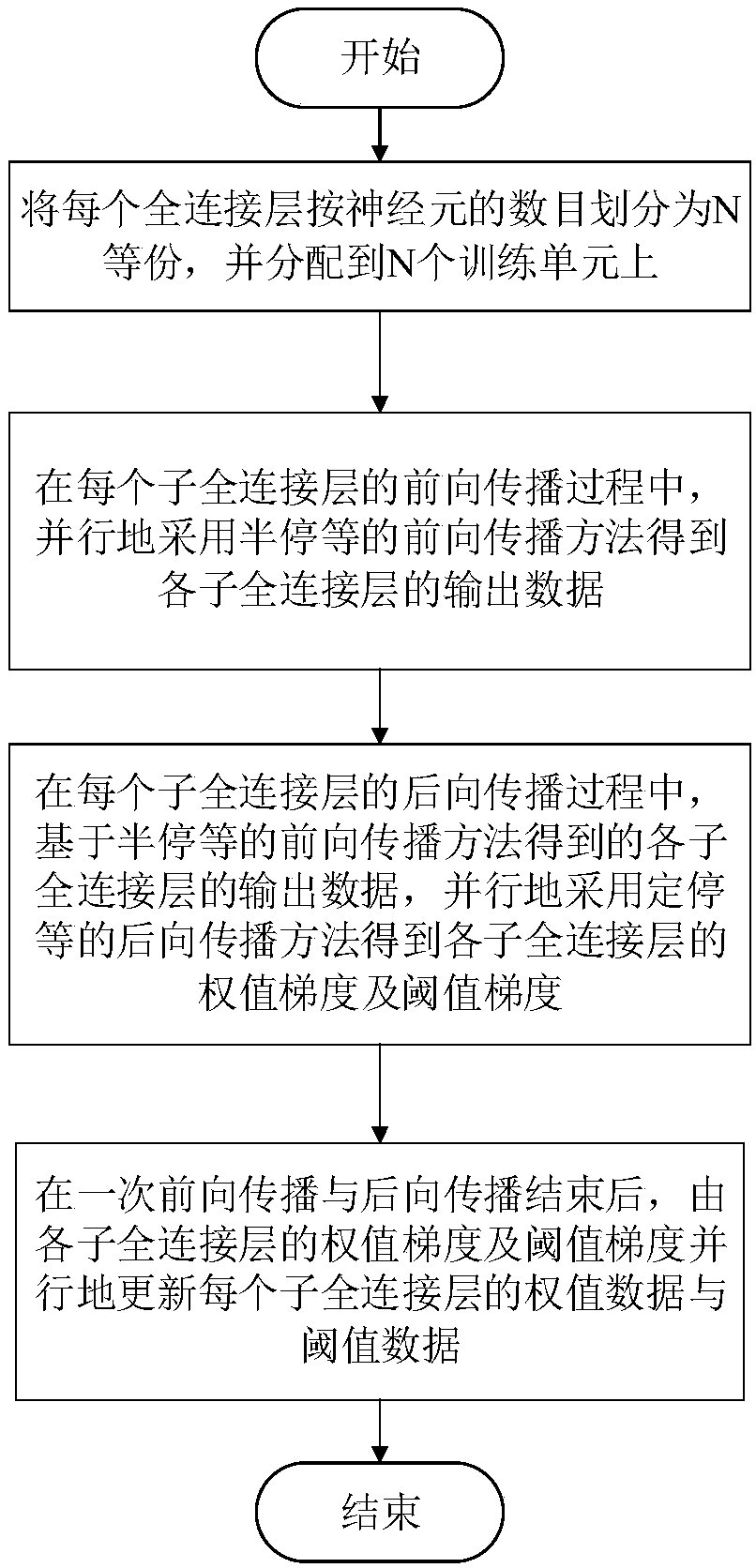
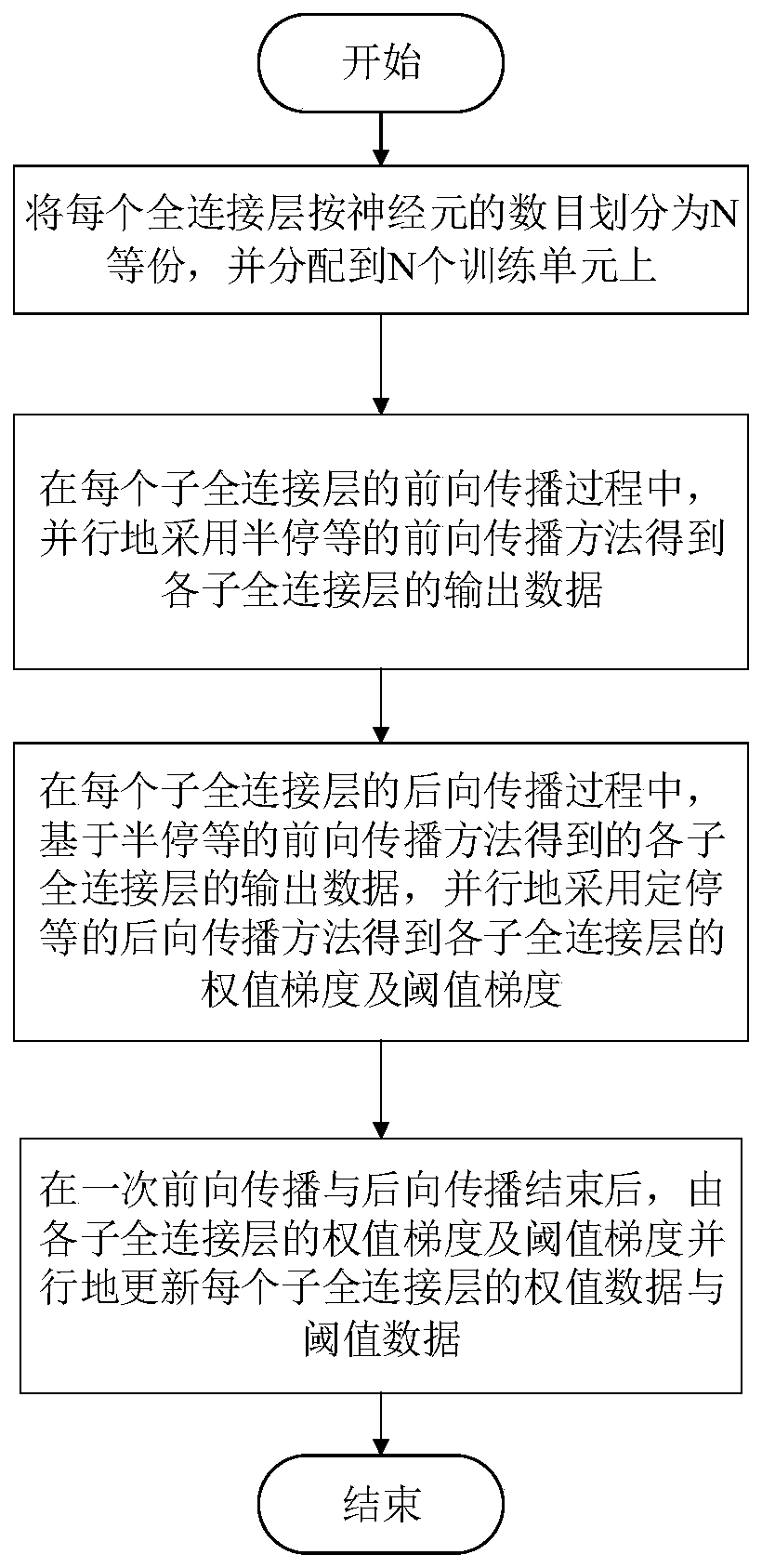
The invention discloses a model-parallel full-connected layer data exchange method and system for a deep neural network. The model-parallel full-connected layer data exchange method for a deep neural network includes the steps: uniformly dividing the full-connected layer of the deep neural network to N training units according to the number of nerve cells, and forming a network model being parallel with the full-connected layer model in the deep neural network; during the forward propagation process of the full-connected layer, utilizing a half-stop waiting forward propagation method to employ the processing modes of partial arrival, partial calculation, overall output and overall propagation on the input data of the front layer; during the backward propagation process of the full-connected layer, utilizing a quantified half-stop waiting backward propagation method to employing the processing modes of quantified arrival, quantified calculation and quantified propagation on the residual error data of the back layer; and after completing the primary forward and backward propagation, according to the solved weight gradient and threshold gradient, parallelly updating the weight data and threshold data of each layer. The model-parallel full-connected layer data exchange method for a deep neural network can overlap data communication and data calculation of the full-connected layer, and can accelerate convergence of the acceleration model on the premise of guaranteeing the correct rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Neural network acceleration circuit and method
ActiveCN110956258AIncrease Computational ParallelismImprove computing powerPhysical realisationEnergy efficient computingClock rateEngineering
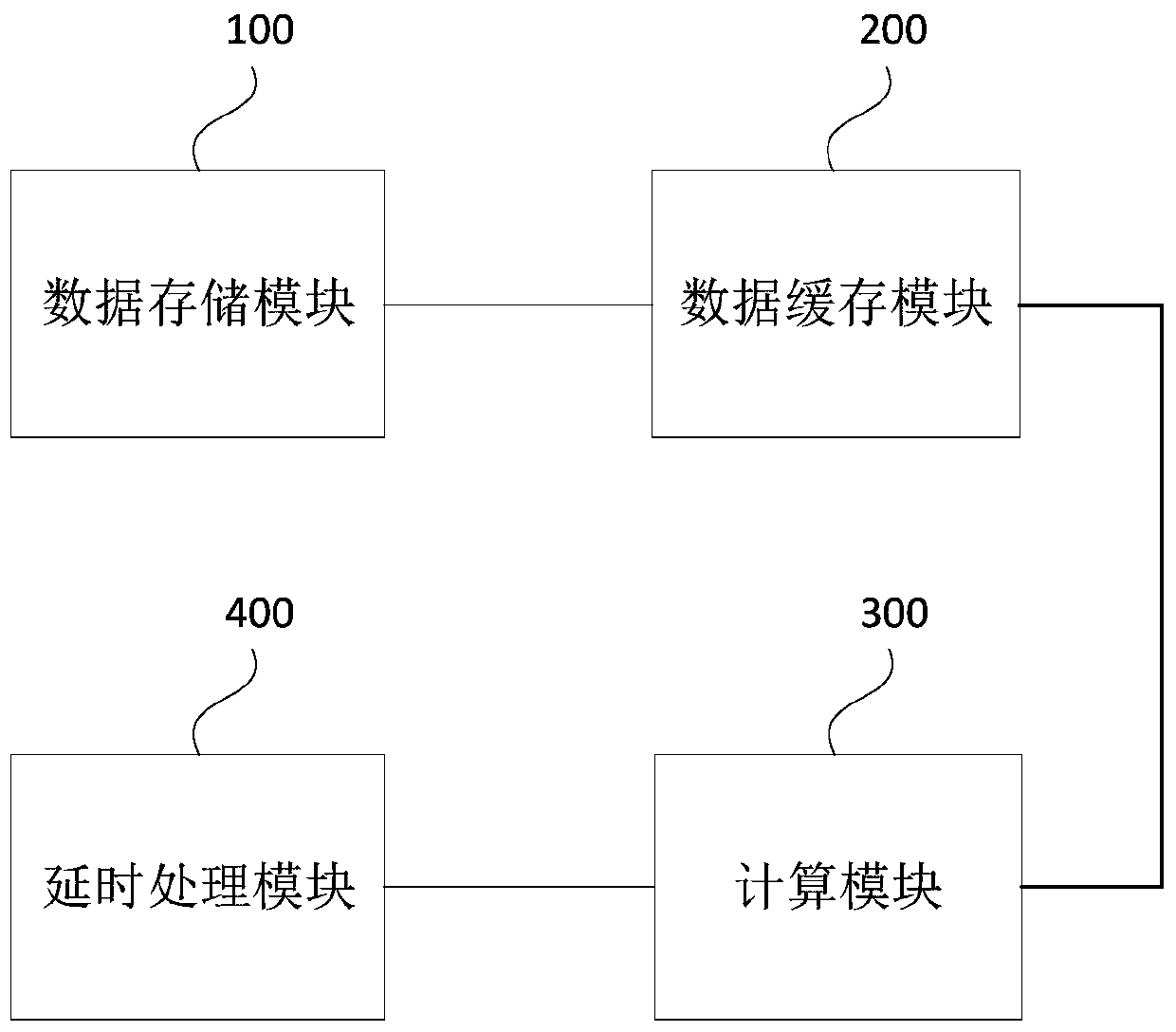
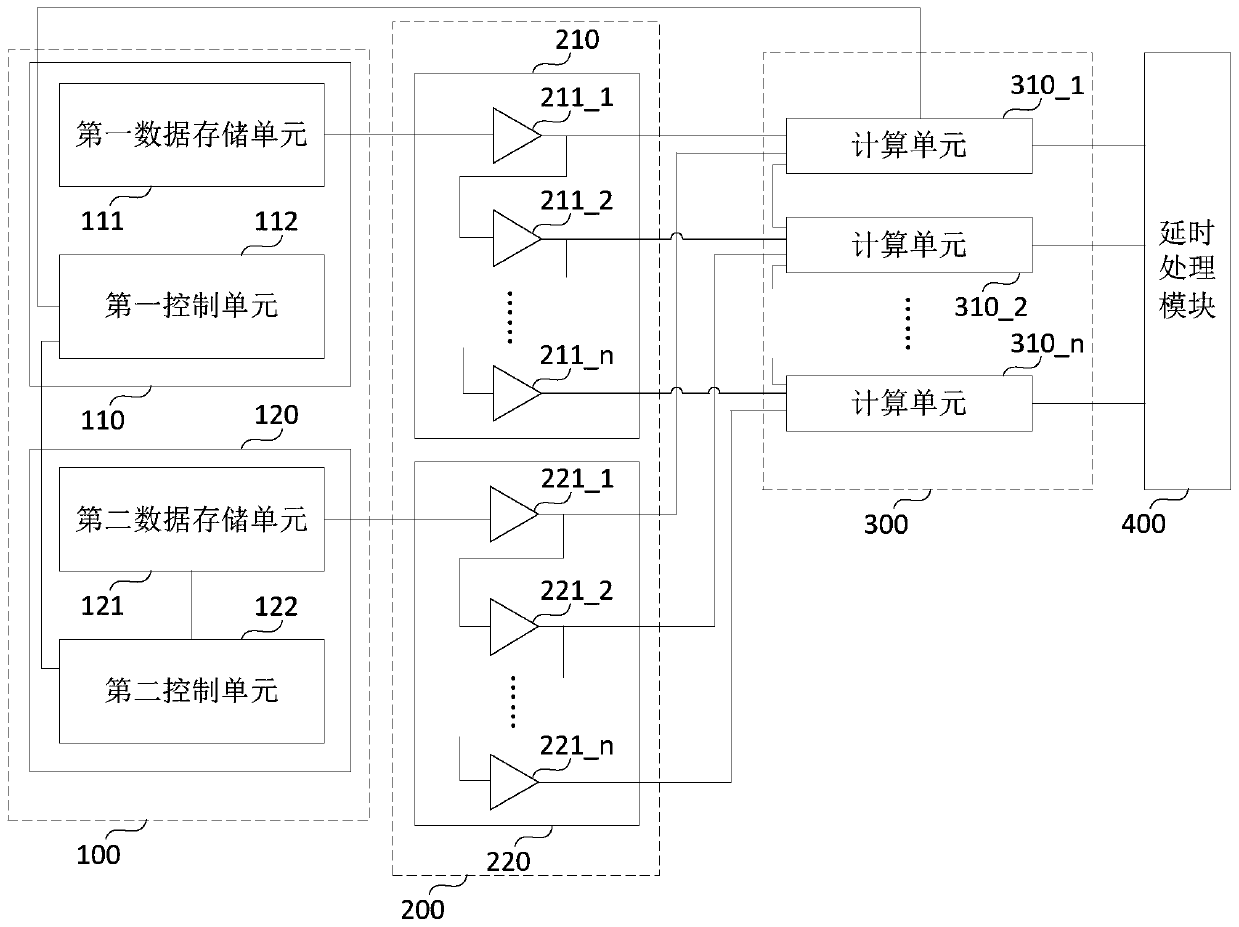
The embodiment of the invention discloses a neural network acceleration circuit and method. The neural network acceleration circuit comprises a data storage module which is used for storing the inputdata needed by the calculation of a neural network, a data caching module which is used for caching the input data output by the data storage module, a calculation module which comprises a plurality of calculation units which are used for calculating the input data output by the data caching module to obtain output data, and a delay processing module which is used for carrying out delay processingon the output data and simultaneously outputting the output data after delay processing. According to the neural network acceleration circuit provided by the embodiment of the invention, the contradiction between the time sequence and the calculation parallelism degree in the neural network acceleration circuit is solved, so that the neural network acceleration circuit can have high calculation parallelism degree when working at a high clock frequency, and the calculation capability of the neural network acceleration circuit is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CORERAIN TECH CO LTD
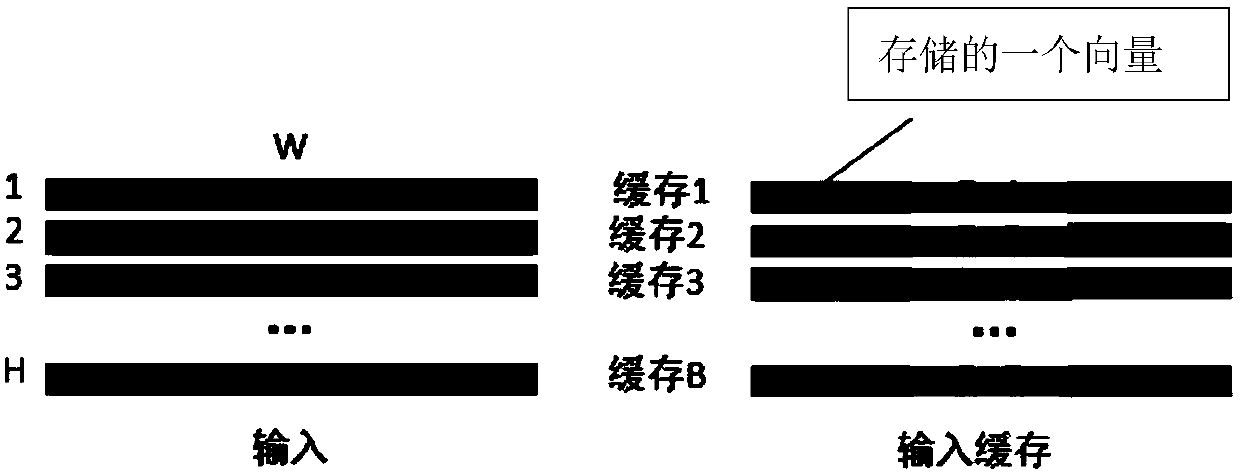
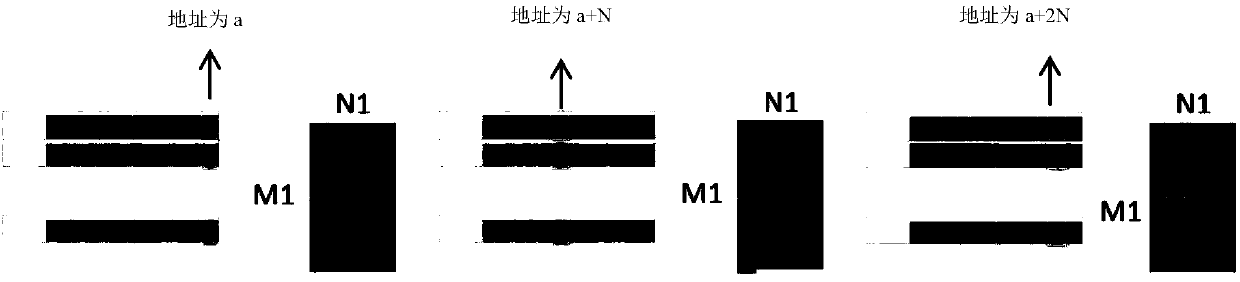
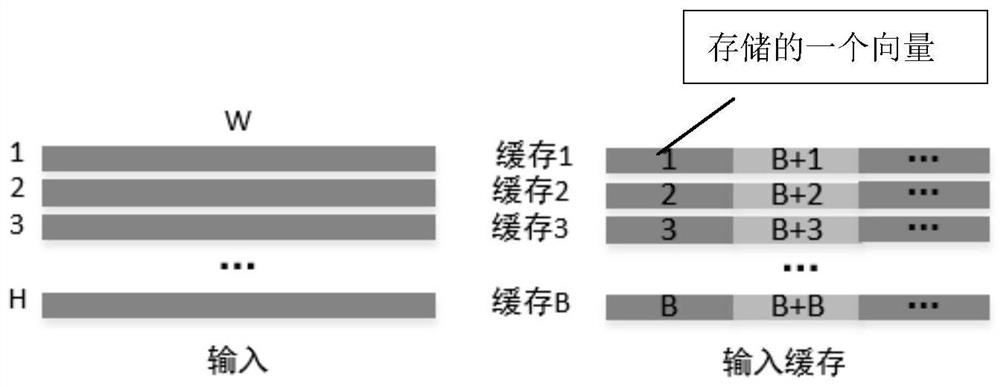
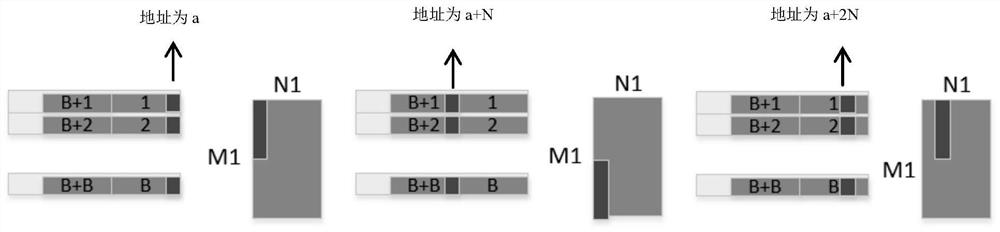
Data access method and device, hardware accelerator, computing equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110309912ASave resourcesLow costNeural architecturesPhysical realisationFeature vectorAccess method
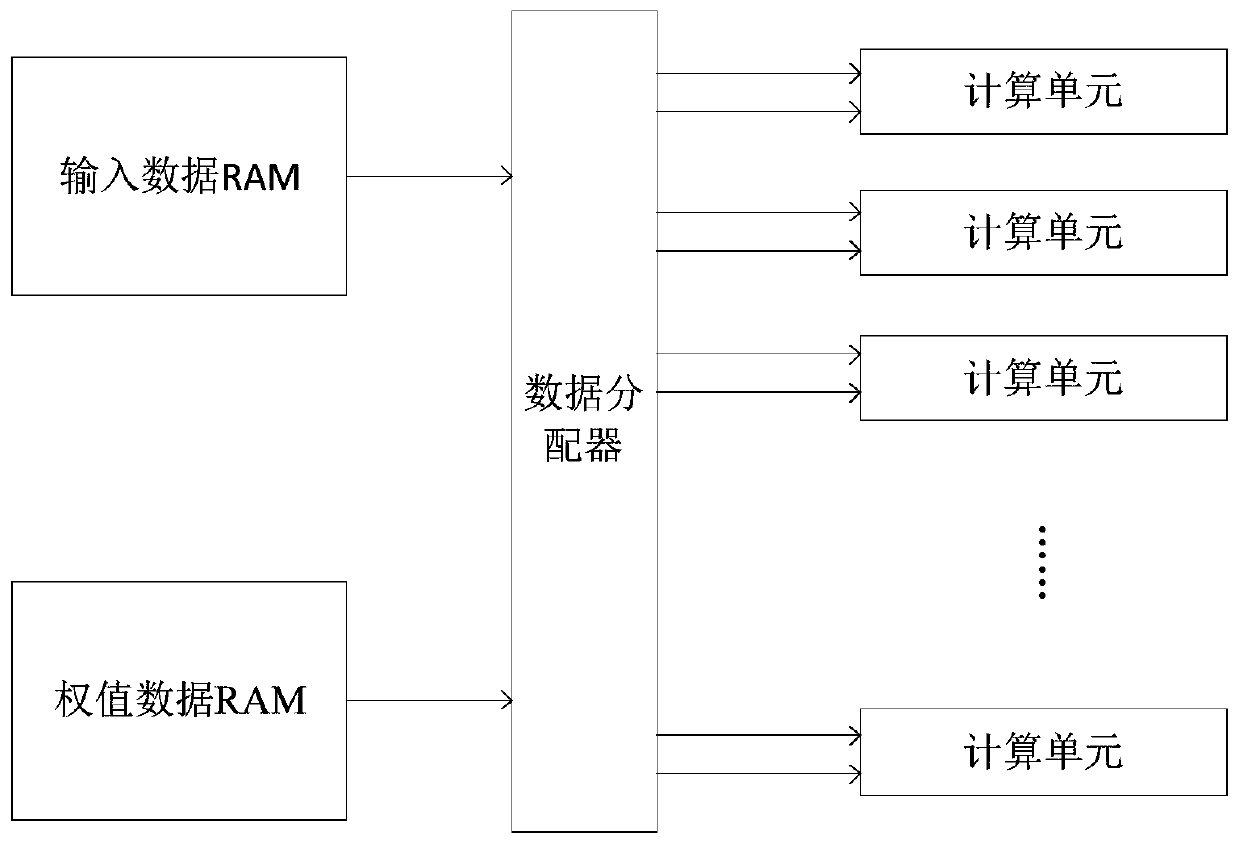
The invention discloses a data access method and device, a hardware accelerator, computing equipment and a storage medium. The data access method comprises the following steps of: storing the ith input feature vector in the i%Bth cache block in the B cache blocks under the condition that input data is received and stored by taking a feature vector as a unit, at the moment, the storage address of the ith input feature vector being the next of the last storage address in the i%Bth cache block, wherein B and i are both natural numbers. Efficient data access in a convolutional neural network witha large convolution kernel size is realized. Therefore, hardware resources are saved, cost and power consumption are reduced, high calculation parallelism is supported, and system performance is improved.
Owner:XILINX INC
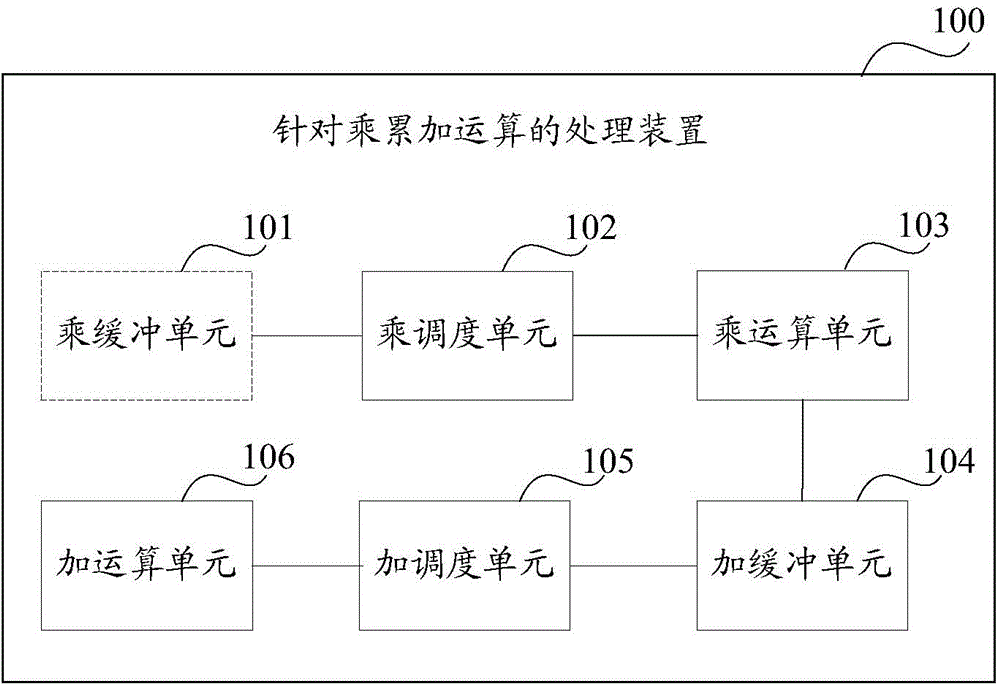
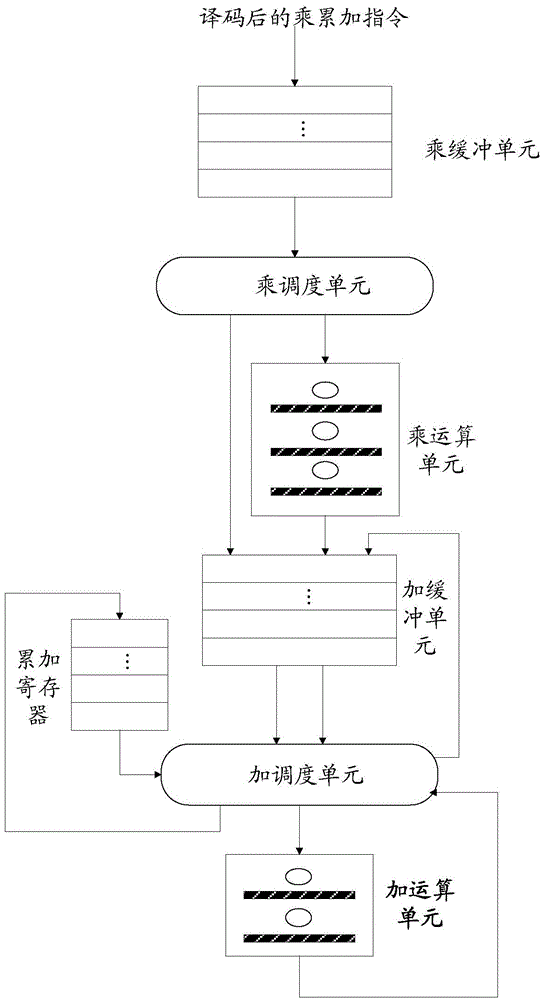
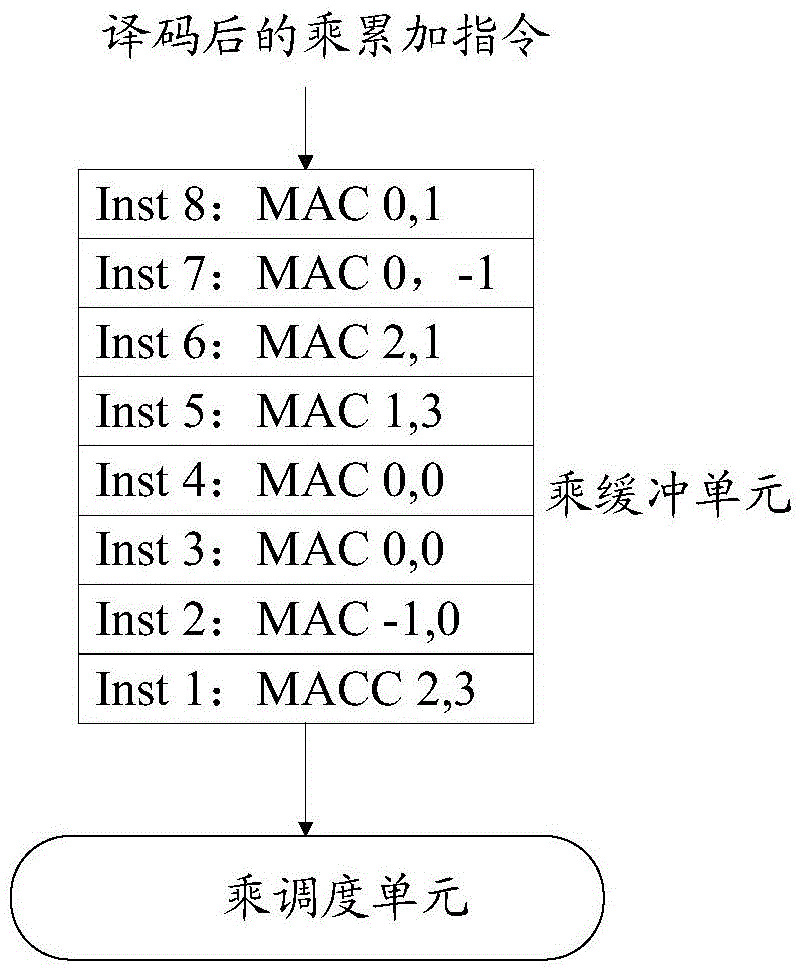
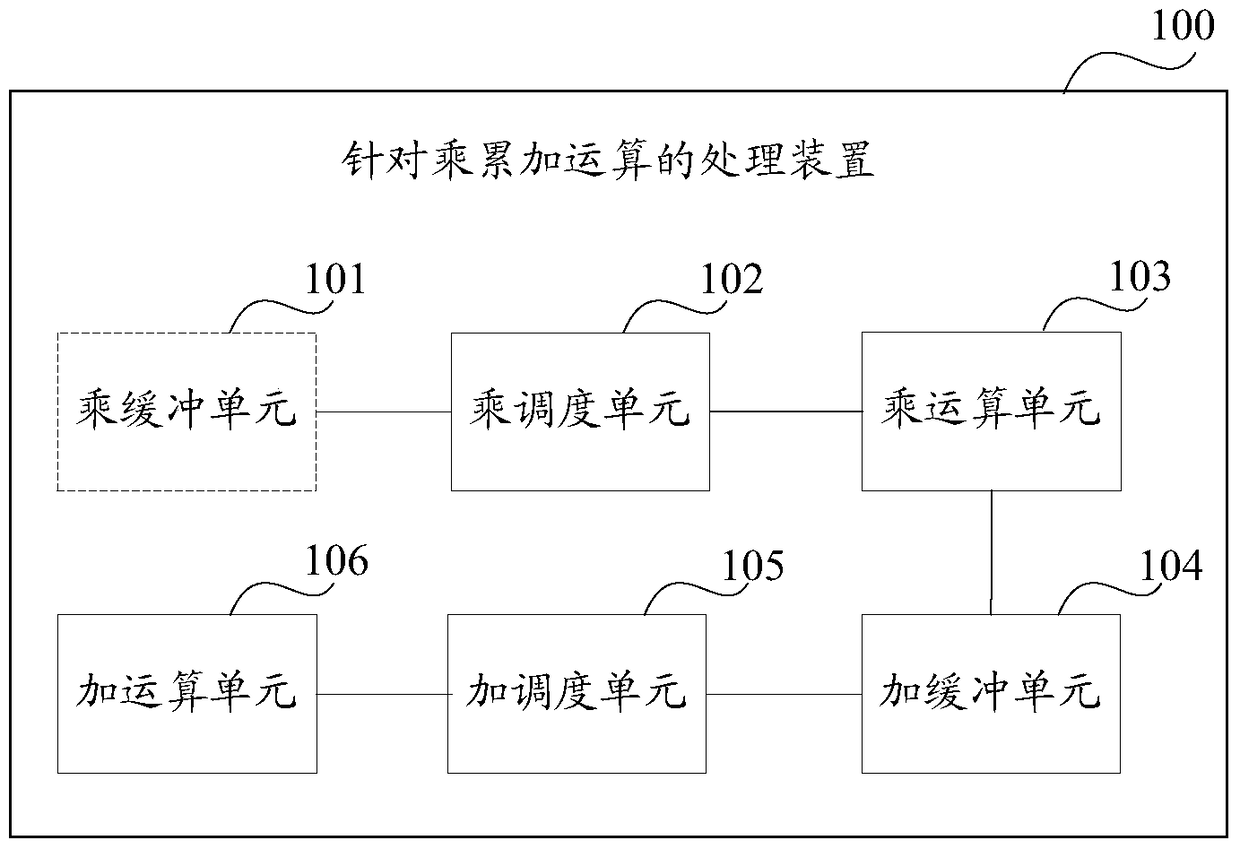
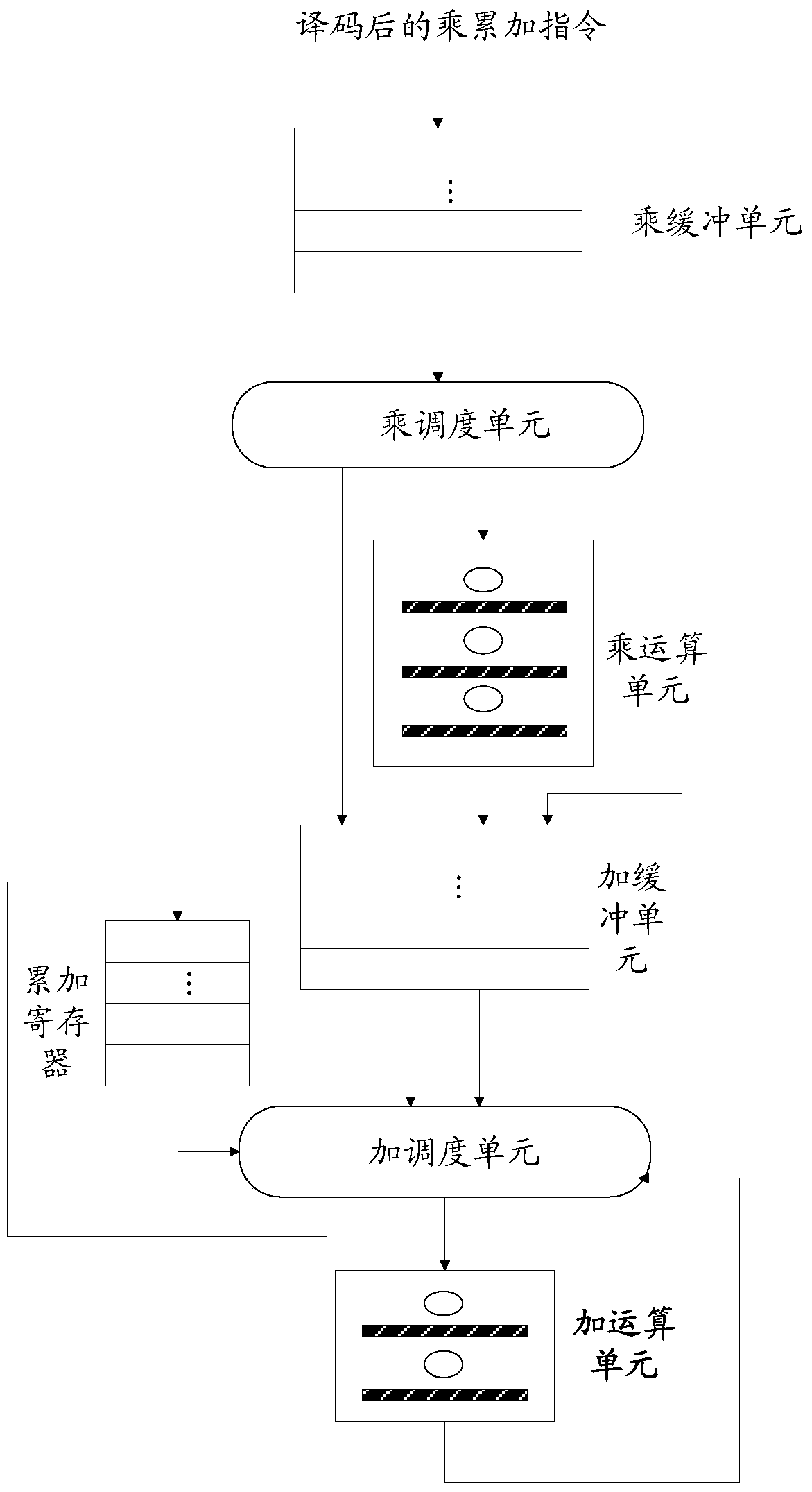
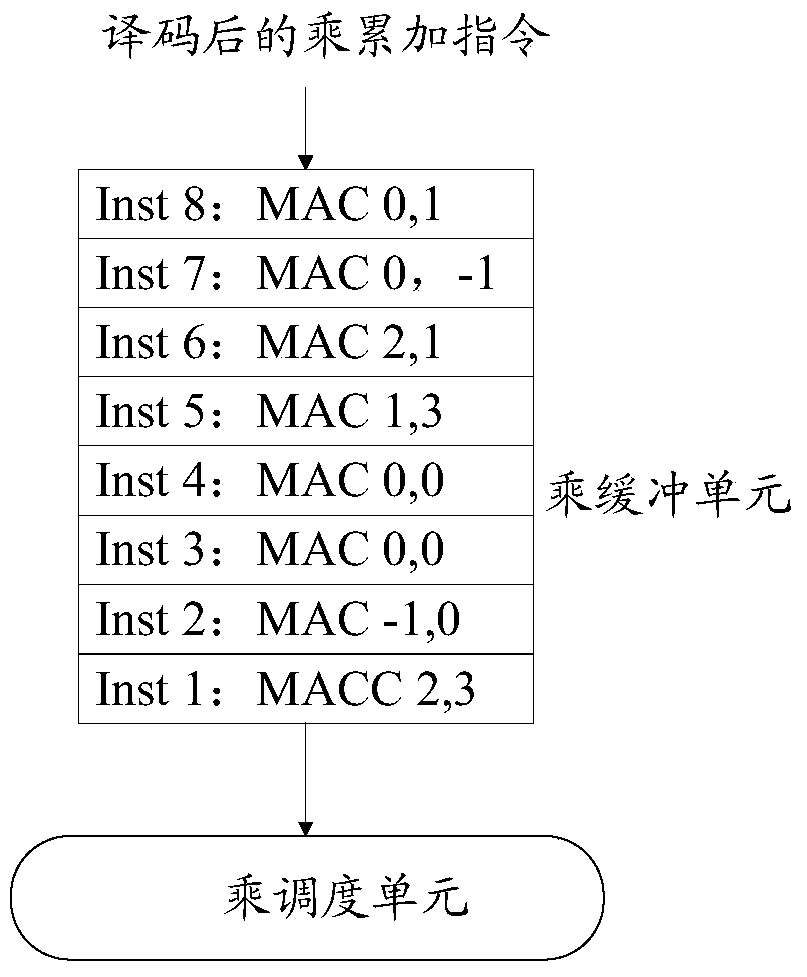
Processing method and device for multiplication and accumulation operation
ActiveCN106325812AImprove throughputImprove processing efficiencyComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerOperand
The invention discloses a processing method and device for multiplication and accumulation operation, used for solving the problems of low data processing efficiency and high power consumption of a computer in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of distributing a register identifier to each read multiplication and accumulation instruction, after processing each multiplication and accumulation instruction to obtain an add operand, taking the add operand and the register identifier distributed to the multiplication and accumulation instruction as binary groups to cache, reading one binary group as a reference binary group, taking the add operand included in the reference binary group as the first add operand, reading an associated binary group, taking the add operand included in the associated binary group as the second add operand, or, reading data in a register corresponding to the register identifier included in the reference binary group as the second add operand, generating an add calculation result based on the first add operand and the second add operand, and storing the add calculation result in the source of the second add operand. Thereby, the calculation parallelism, the data throughout and the data processing efficiency are increased; and the power consumption of the computer is reduced.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Deep learning accelerator suitable for stacked hourglass network
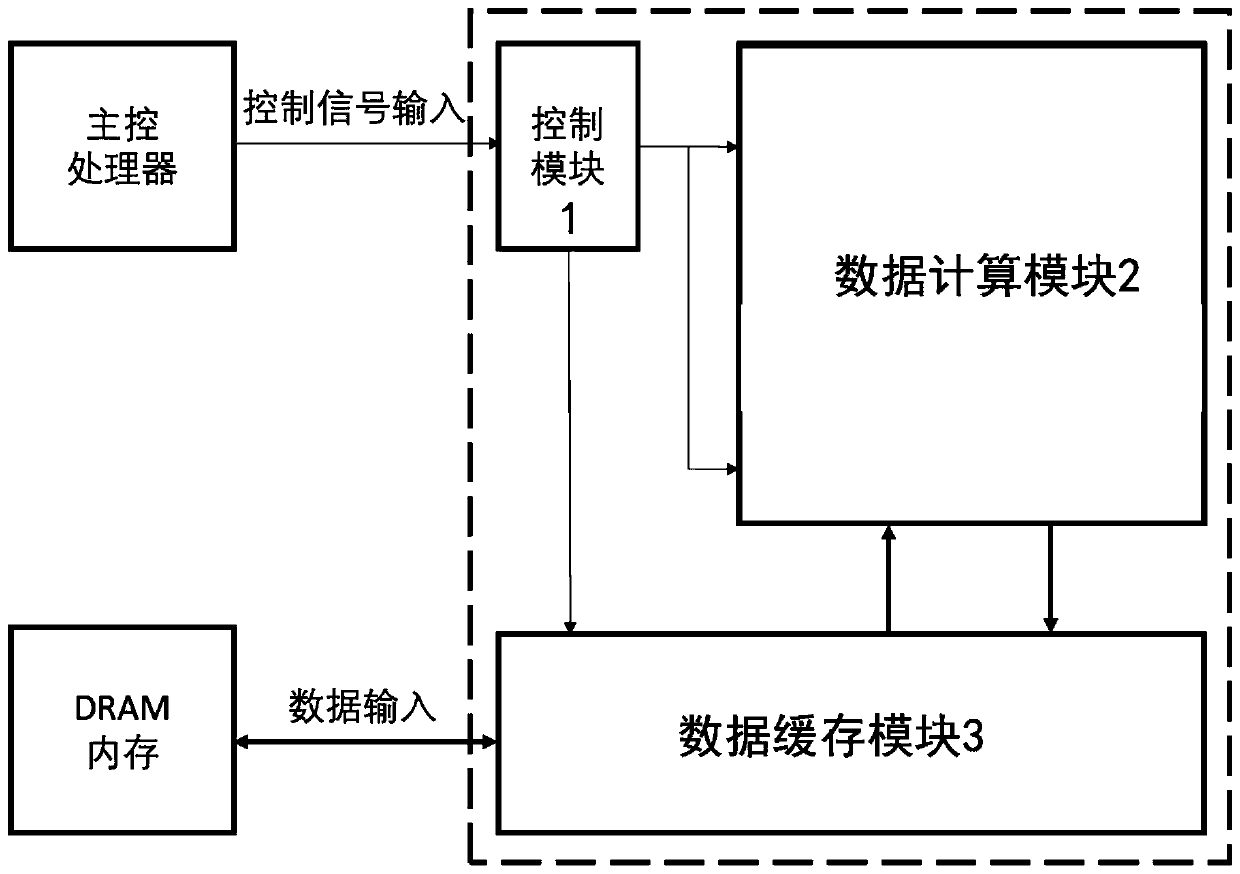
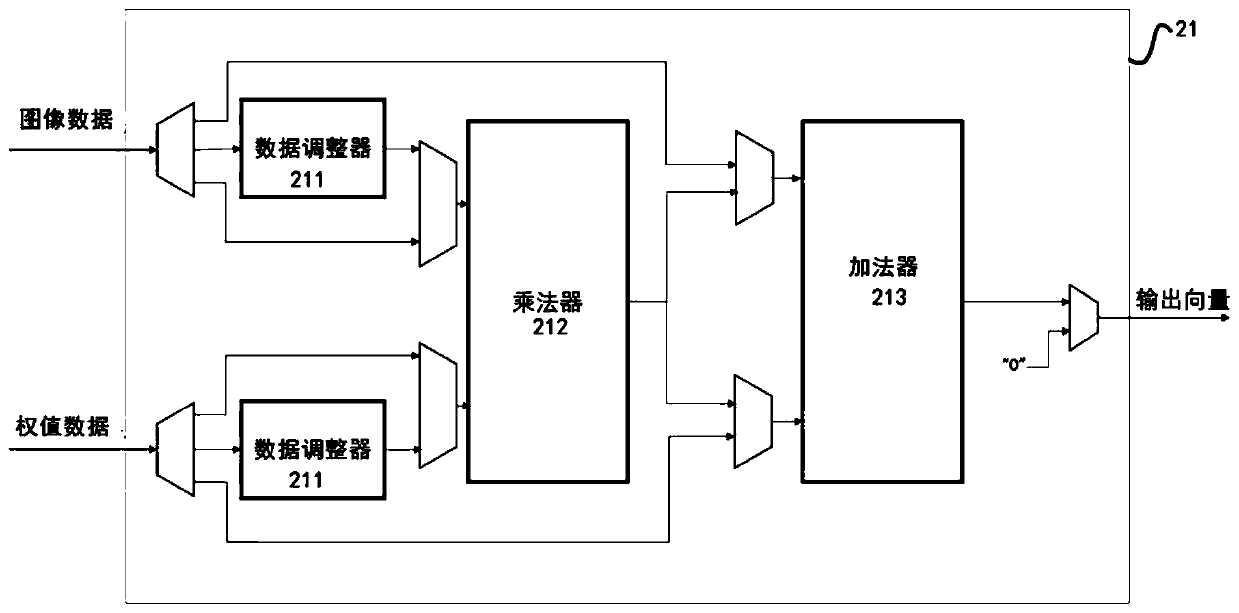
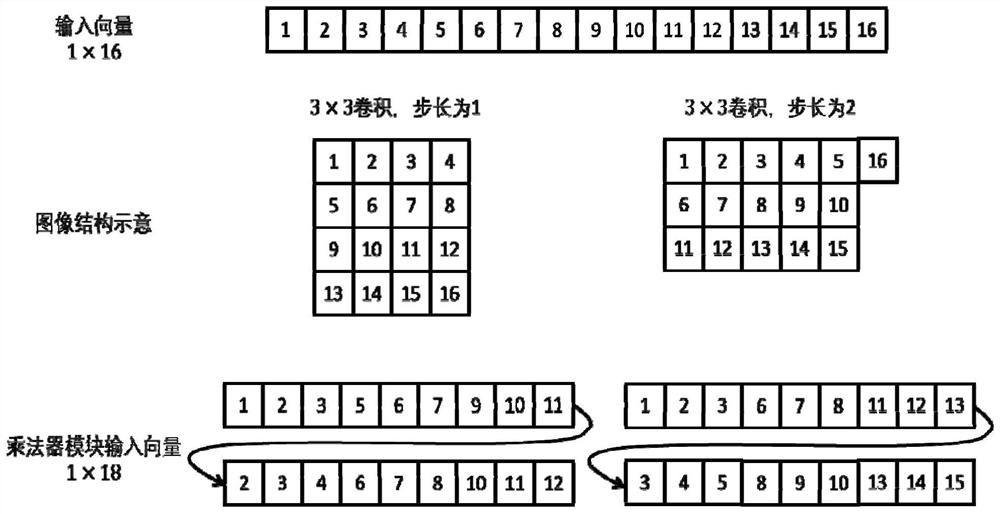
ActiveCN109993293AAchieve Computational Acceleration PerformanceCalculation speedNeural architecturesPhysical realisationTime delaysData acquisition
The invention discloses a deep learning accelerator suitable for a stacked hourglass network. A parallel computing layer computing unit improves the computing parallelism, and a data caching module improves the utilization rate of data loaded into the accelerator while accelerating the computing speed; and meanwhile, a data adjuster in the accelerator can carry out self-adaptive data arrangement sequence change according to different calculation layer operations, so that the integrity of acquired data can be improved, the data acquisition efficiency is improved, and the time delay of a memoryaccess process is reduced. Therefore, according to the accelerator, the memory bandwidth is effectively reduced by reducing the number of memory accesses and improving the memory access efficiency while the algorithm calculation speed is increased, so that the overall calculation acceleration performance of the accelerator is realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Deep convolutional neural network acceleration method and system suitable for NPU
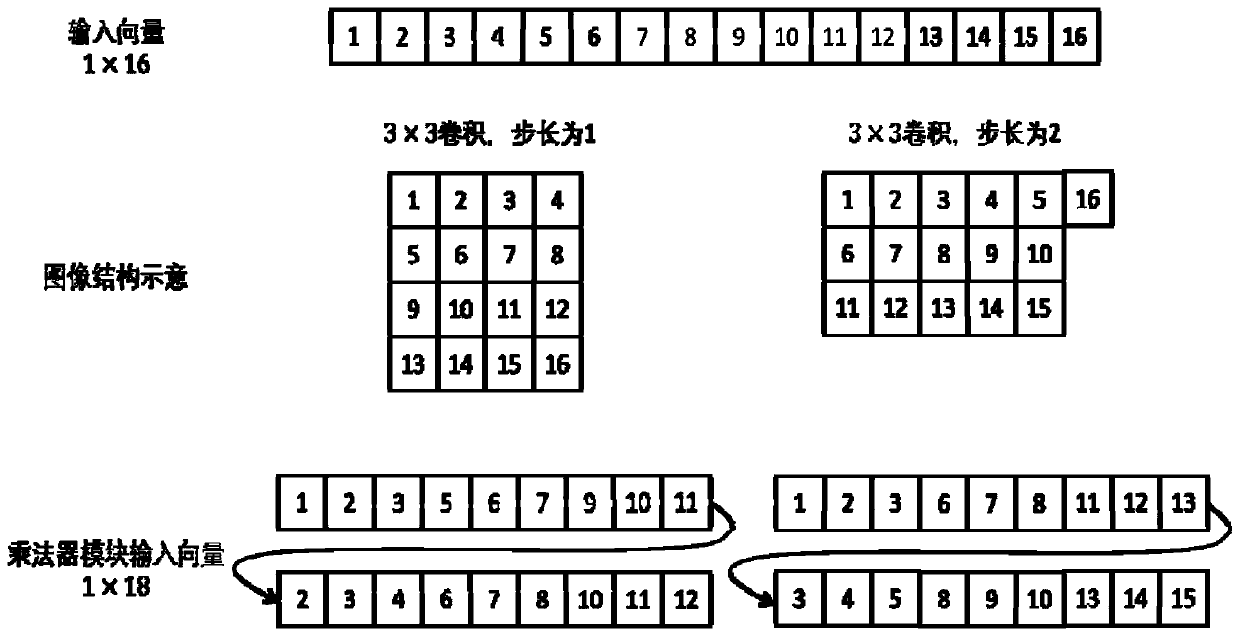
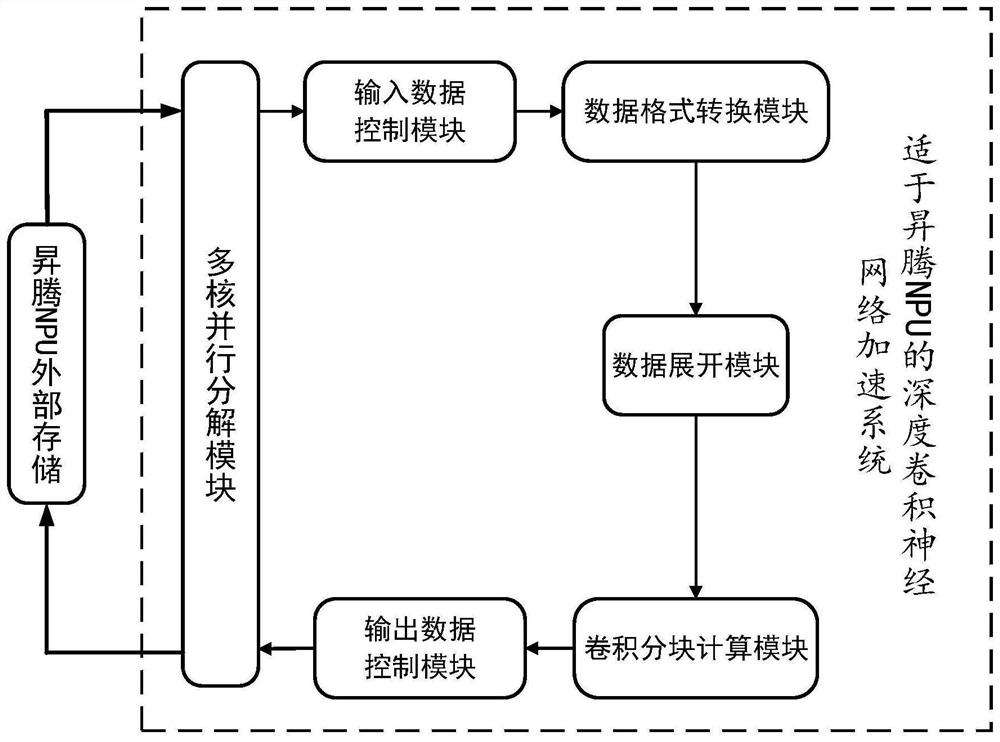
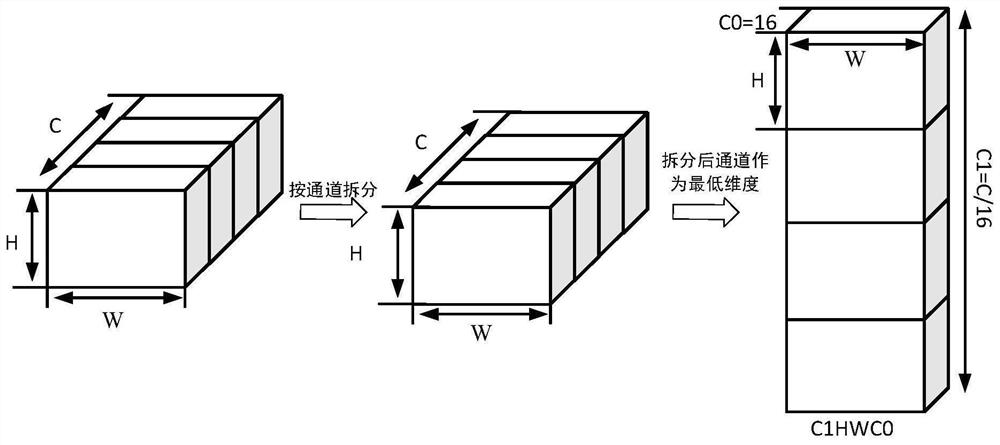
ActiveCN113469350AIncrease Computational ParallelismAddress underutilizationNeural architecturesPhysical realisationData streamAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a deep convolutional neural network acceleration method and system suitable for NPU. According to the NPU calculation unit structure, the data arrangement format of the input parameters of the convolutional layer is adjusted in advance; therefore, the problem that the calculation units are not fully utilized in the convolution calculation process is solved, and the throughput of the matrix calculation units is fully utilized. and execution assembly line of the calculation instruction in the NPU is rearranged, the convolution calculation capability of the NPU is mined, and the calculation parallelism in the deep convolutional neural network is enhanced. According to the acceleration method provided by the invention, the arrangement mode of the data streams and the instructions in the deep convolutional neural network is modified, so that the efficient and rapid convolutional neural network can be realized on the NPU.
Owner:武汉魅瞳科技有限公司
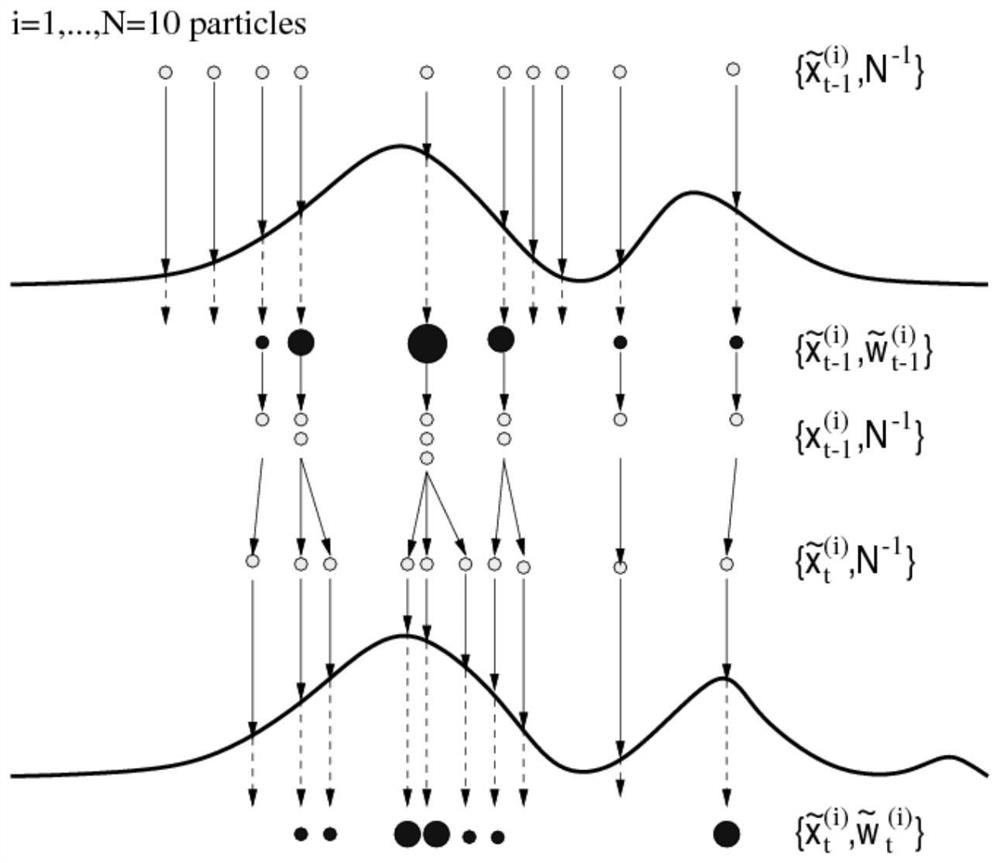
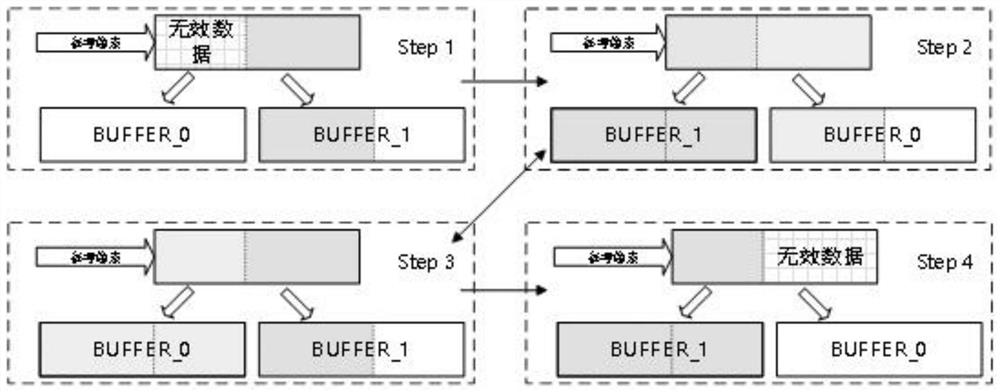
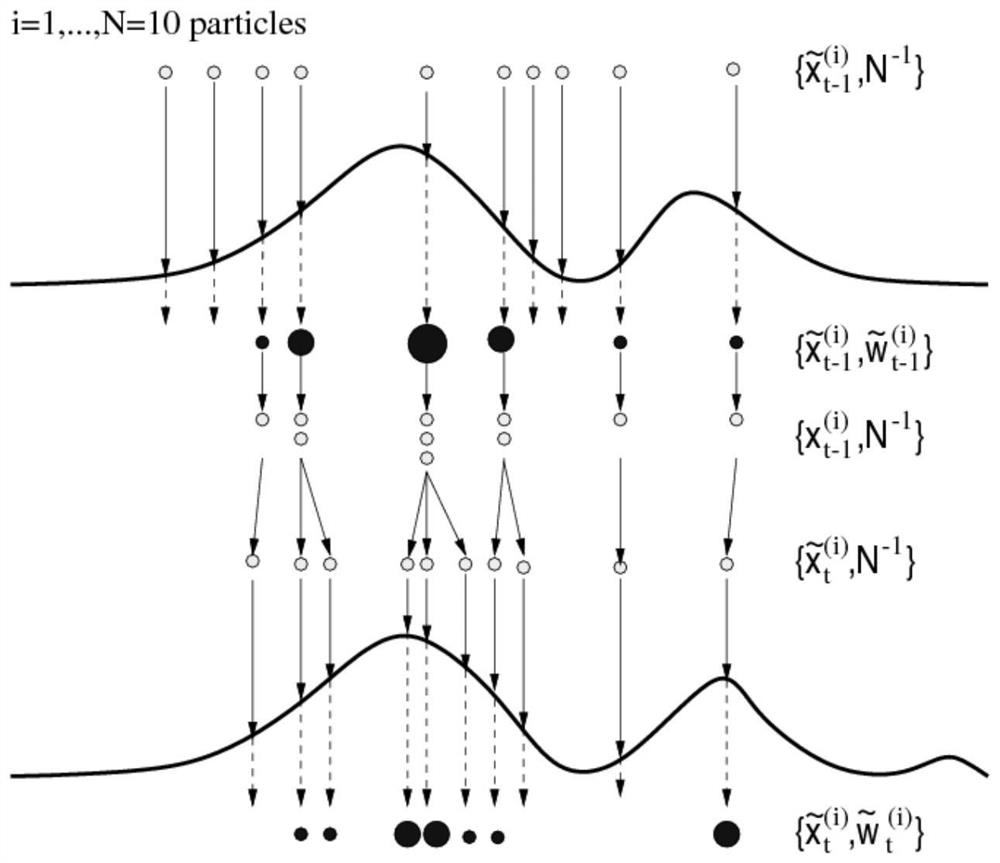
FPGA hardware implementation method and device based on Bayesian resampling particle filtering and a target tracking method
ActiveCN112732637AGuarantee sufficiencyDiversity guaranteedArchitecture with single central processing unitElectric digital data processingEngineeringComputational science
The invention discloses an FPGA hardware implementation method and device based on Bayesian resampling particle filtering and a target tracking method. The FPGA hardware implementation method comprises the steps that a particle sampling unit reads old particles from a particle cache block, receives random numbers from a random number generator, and samples and updates the read old particles in parallel; a weight updating unit reads the observed value, performs weight calculation on the updated particles in parallel, and stores the generated weight into a weight cache block; the Bayesian resampling unit adopts a Bayesian resampling method, performs resampling in parallel according to all weight values in the weight cache blocks, and stores index output values back to the corresponding index cache blocks; the pseudo-random arrangement generator reads the address of a new particle from the index cache block and randomly allocates the new particle to each particle cache block to achieve exchange in particle parallel computing; and the steps are circularly executed until iteration of all the time steps is completed, and state estimation of the system is completed. According to the invention, the calculation speed of the particle filtering system can be improved.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
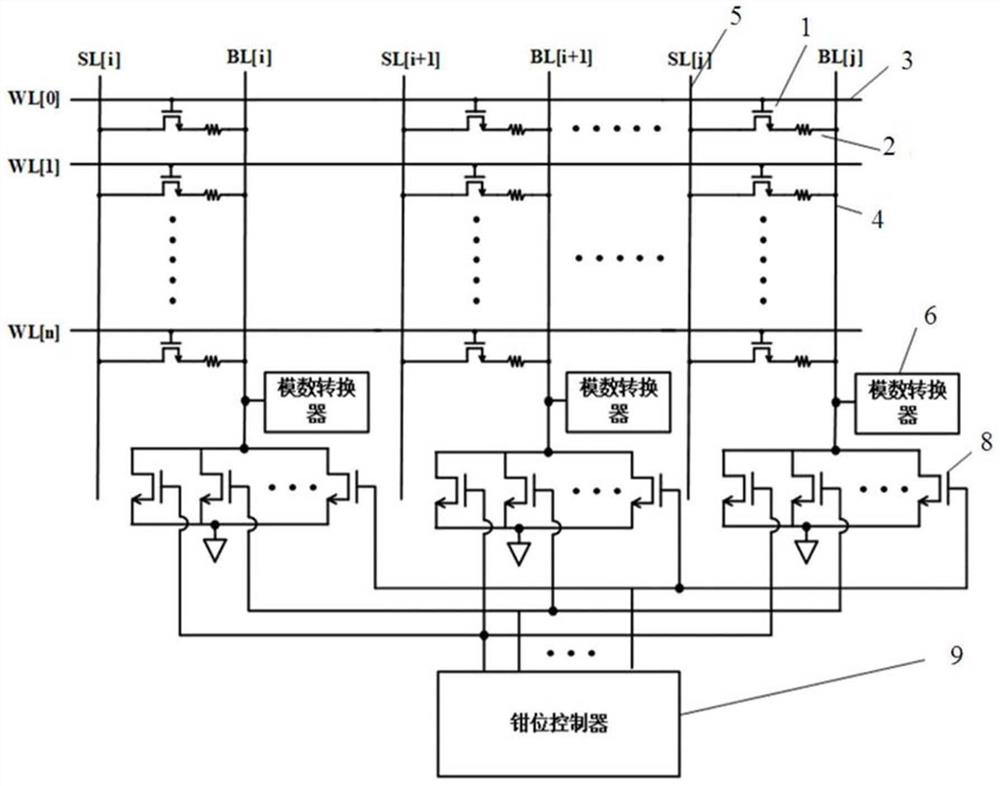
In-memory computing circuit based on local multiplication-global addition structure, memory and equipment
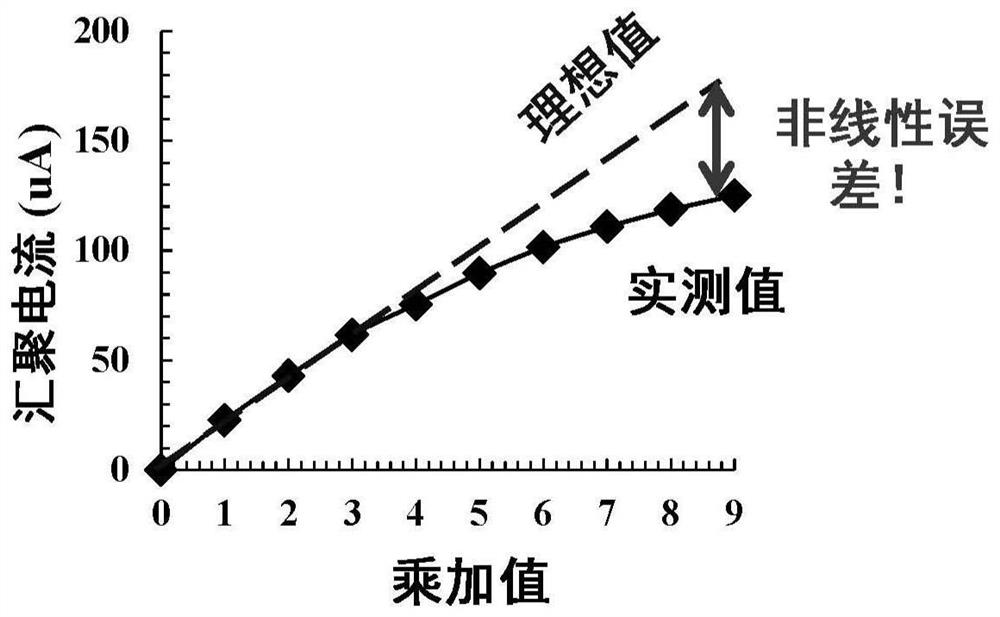
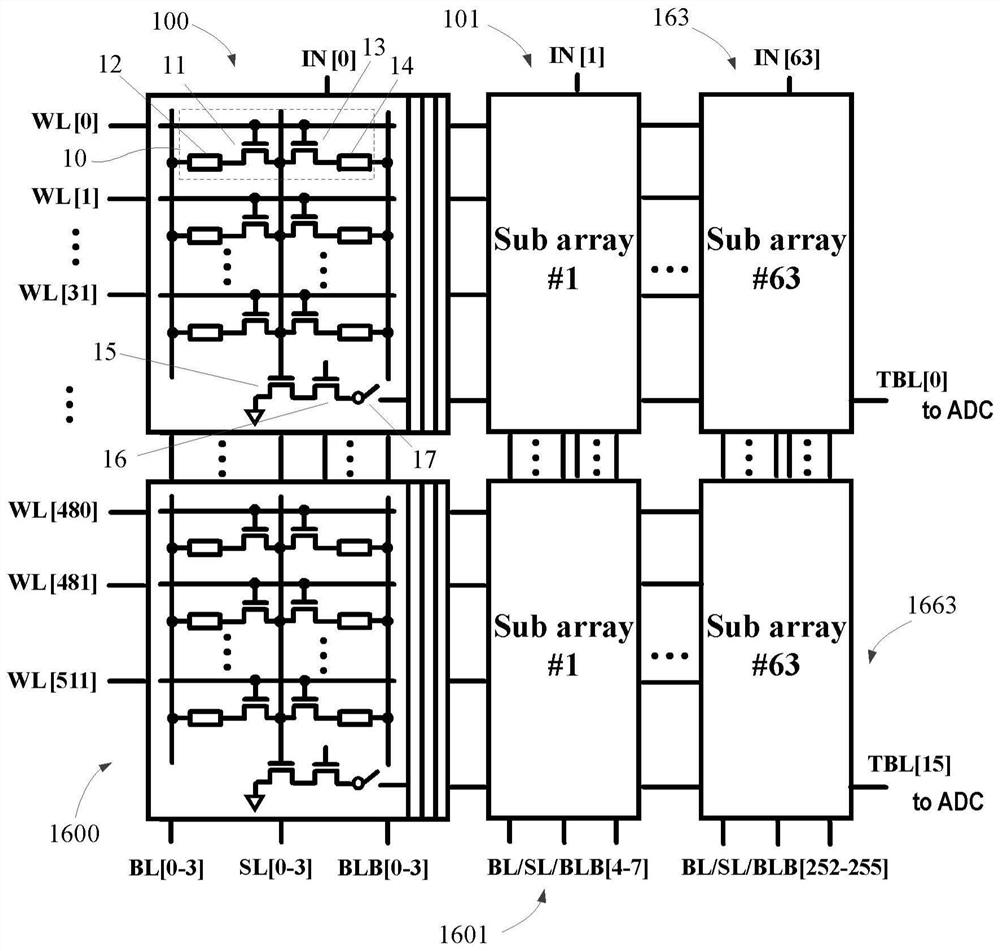
PendingCN114863964AReduce power consumptionSolve the problem of excessive convergence currentDigital storageEnergy efficient computingComputer architectureParallel computing
The invention provides an in-memory computing circuit based on a local multiplication-global addition structure. The in-memory computing circuit comprises a plurality of sub-computing arrays, a plurality of word lines, a plurality of bit lines, a plurality of complementary bit lines and a plurality of source lines, the sub-calculation arrays in each row are connected with a common word line, and the sub-calculation arrays in each column are connected with a common bit line, a common complementary bit line and a common source line; the calculation unit in each sub calculation array comprises a first transistor, a first memory, a second transistor and a second memory; the grid of the transistor is connected with the word line, and the source is connected with the source line; the drain of the first transistor is connected with a first memory, and the other end of the first memory is connected with a bit line; the drain of the second transistor is connected with the second memory, and the other end of the second memory is connected with the complementary bit line; the grid electrode of the third transistor is connected with the source line, the source electrode is grounded, and the drain electrode is connected with the source electrode of the fourth transistor; the grid of the fourth transistor is connected with the input line, and the drain is connected with the calculation line through the switch. The invention also provides a memory and electronic equipment.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
N level sub-pixel search method based on whole pixel searching result
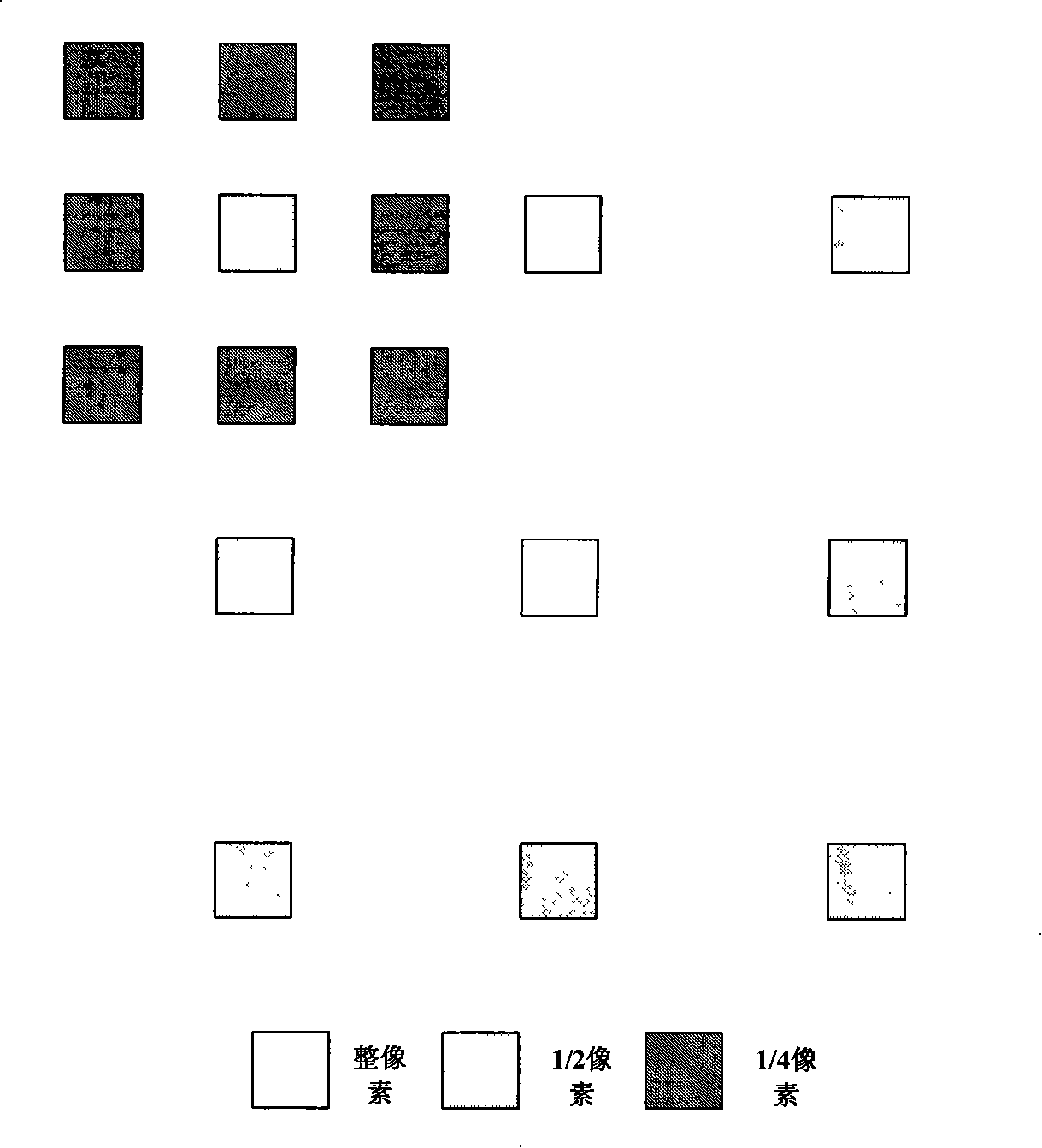
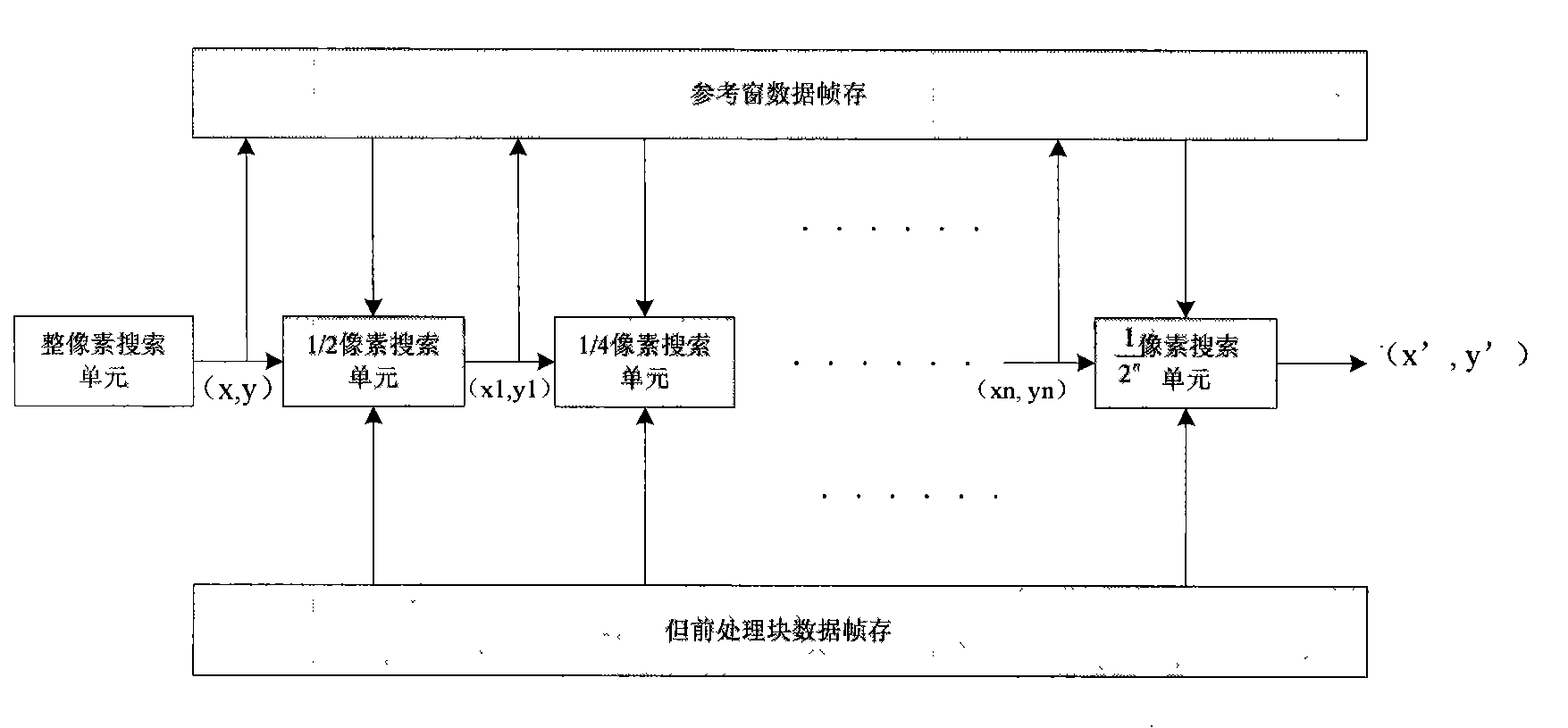
InactiveCN101299818BProcessing speedIncrease Computational ParallelismTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoError function
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
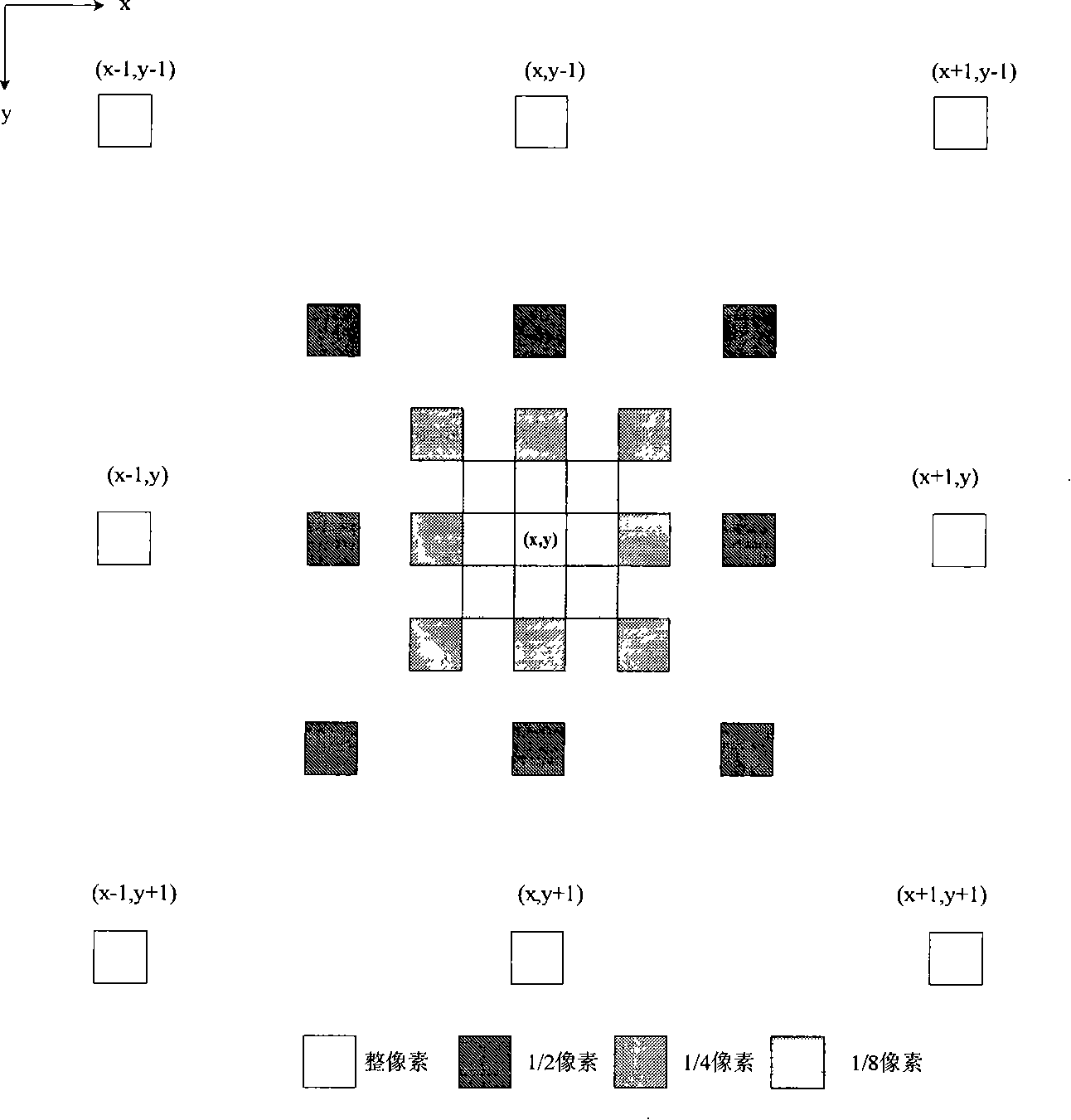
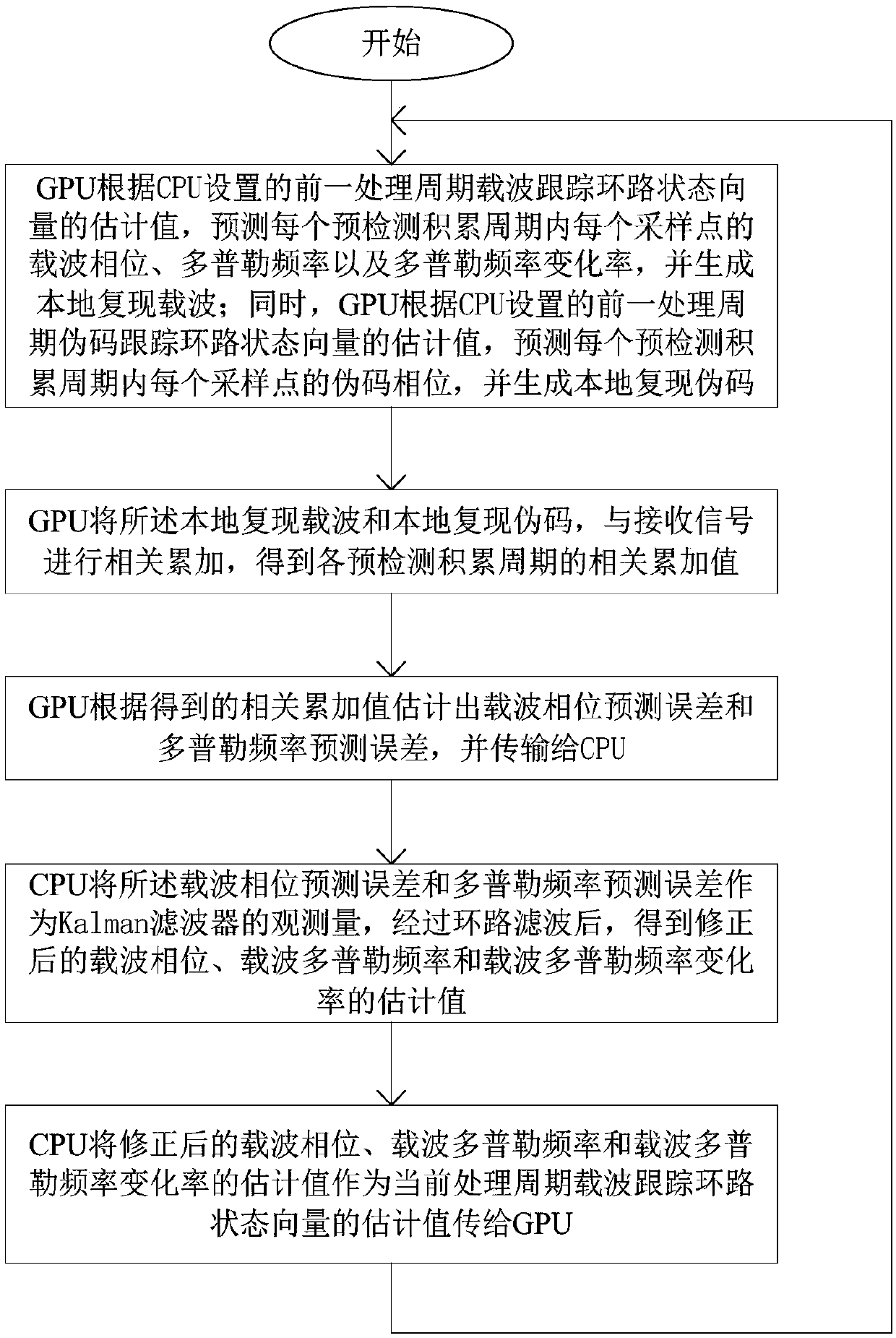
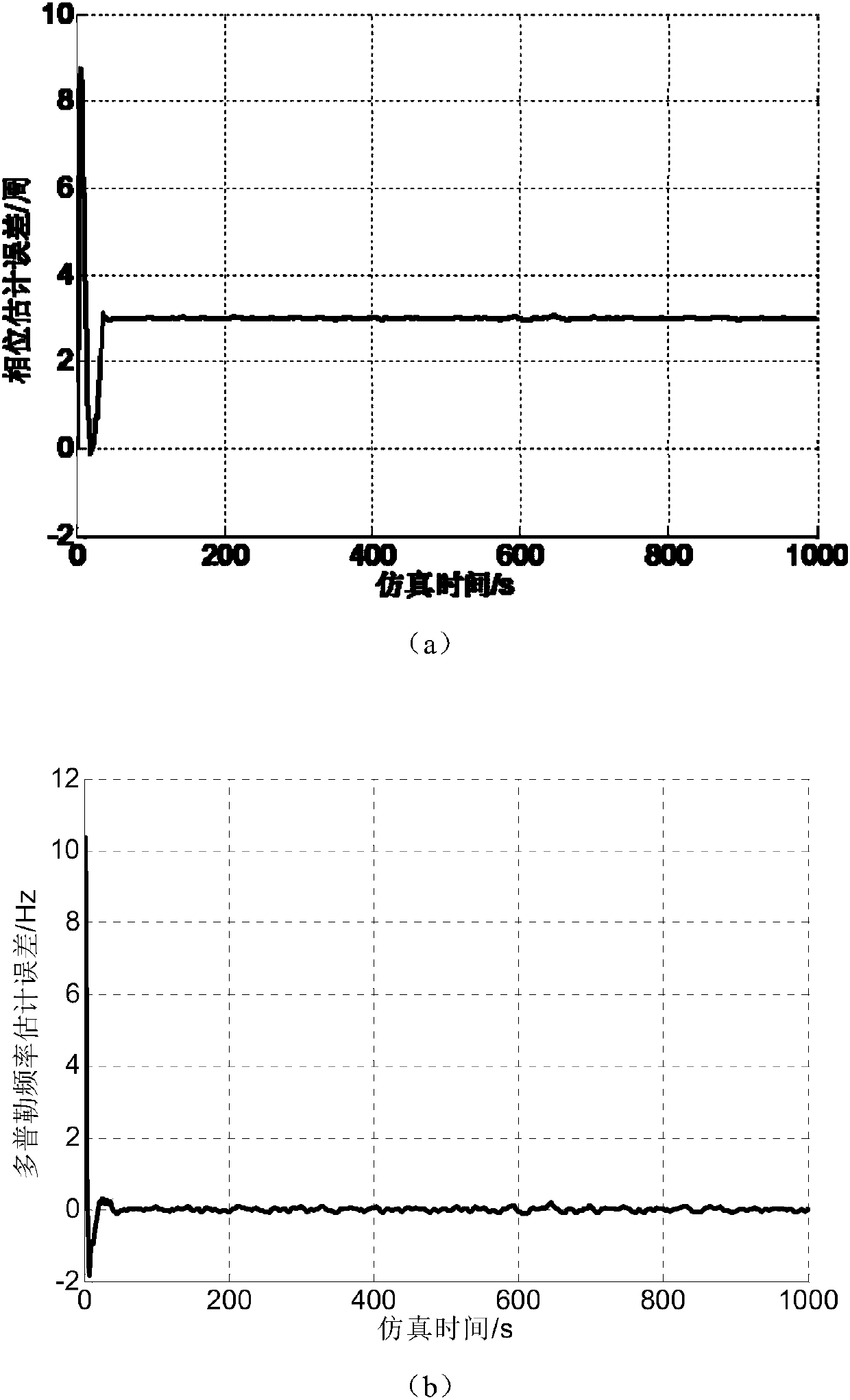
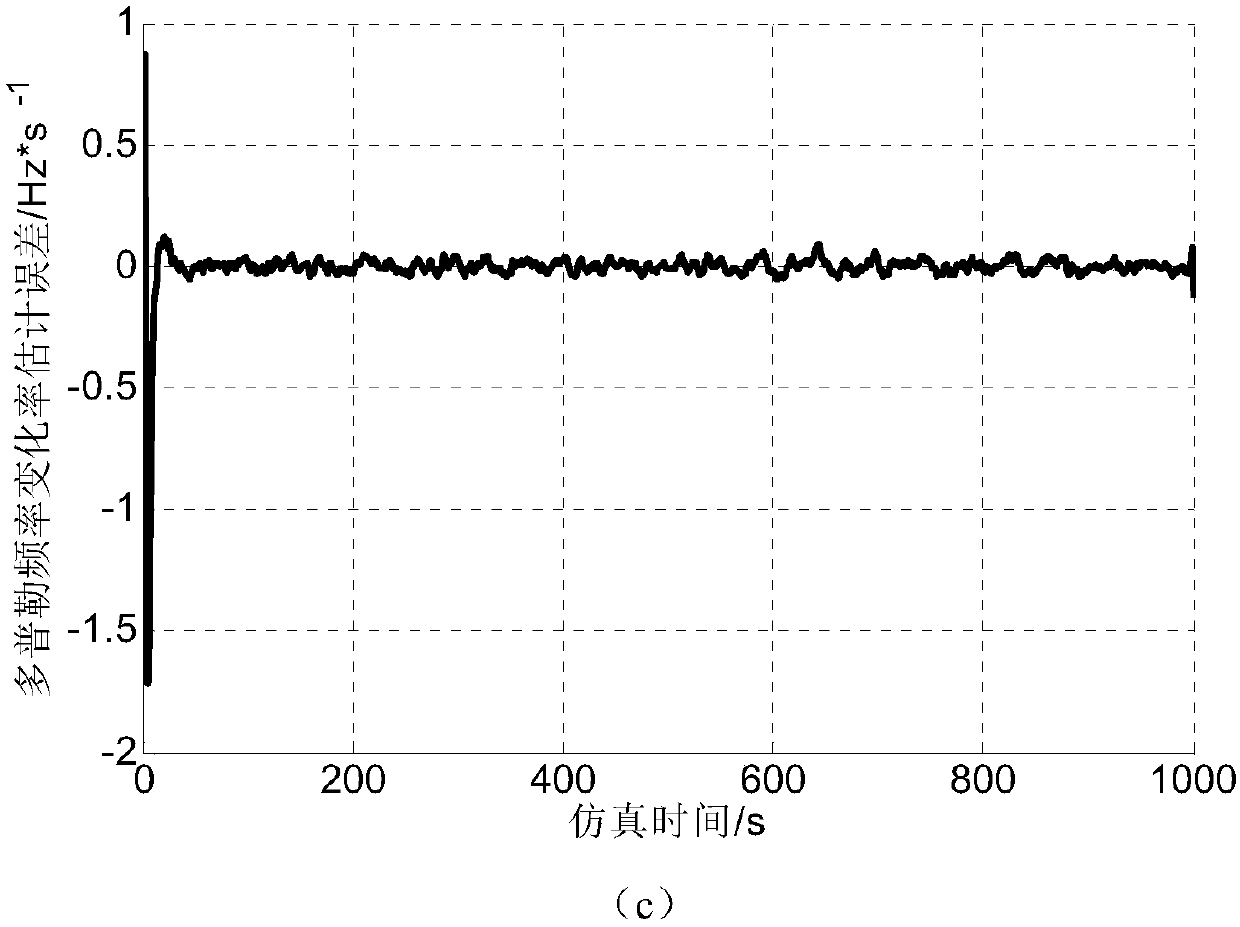
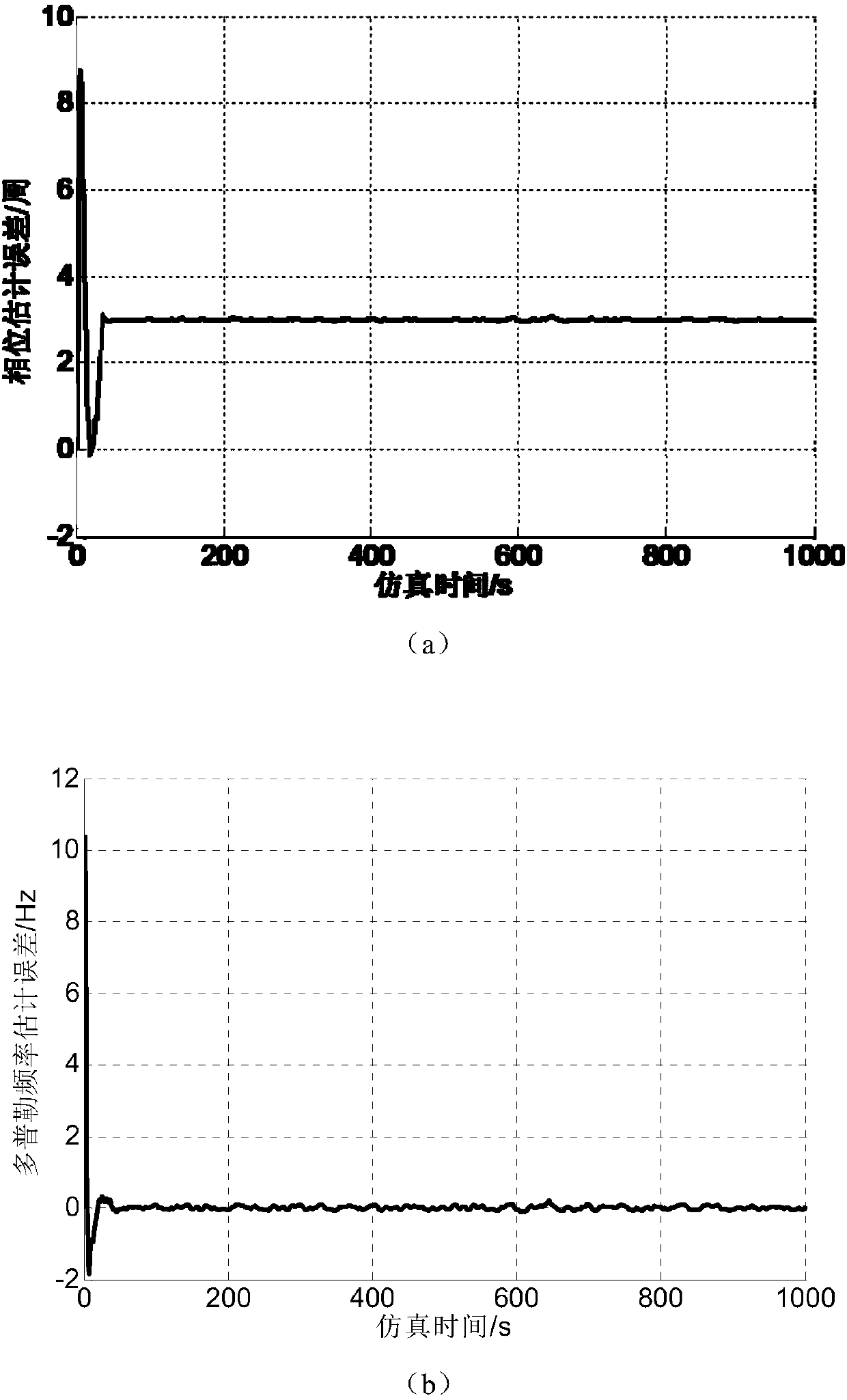
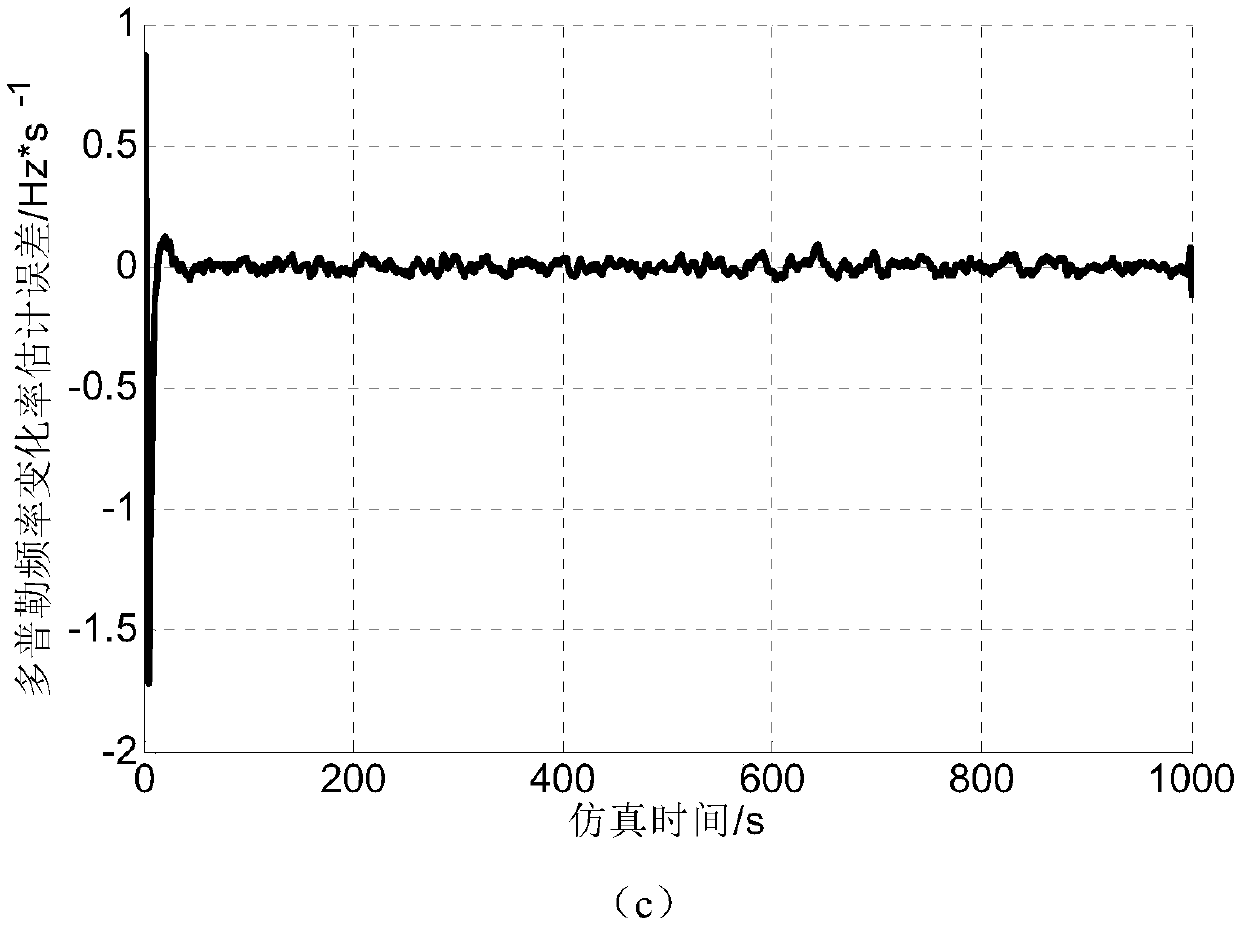
Low-updating-frequency satellite navigation carrier wave tracing method
ActiveCN107870338AShorten the update cycleGuaranteed stabilitySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalSatellite navigation
The invention discloses a low-updating-frequency satellite navigation software receiver carrier wave tracing method. The method includes that in a single processing period of a carrier wave tracing loop, a GPU completes multiple times of pre-detection accumulation at the same time and estimates carrier wave phase prediction and Doppler frequency error according to multiple related accumulated values; the CPU takes the error as observation quantity of a Kalman filter, corrects a prediction value, configures related accumulation parameters of the GPU of the next period after loop filtering and finally completes carrier wave loop tracing. Compared with conventional carrier wave tracing algorithms, the method has the advantage that stability and accuracy of carrier wave loop tracing can be ensured at low processing frequency.
Owner:湖南跨线桥航天科技有限公司
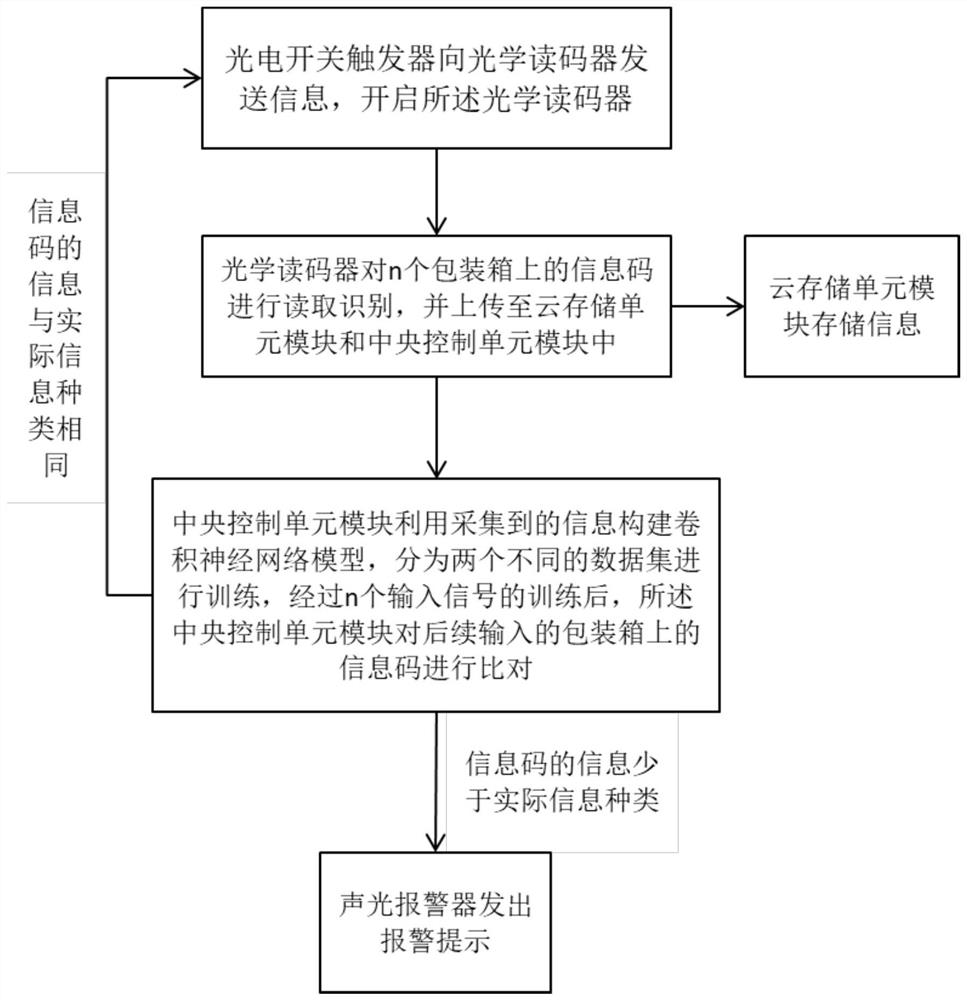
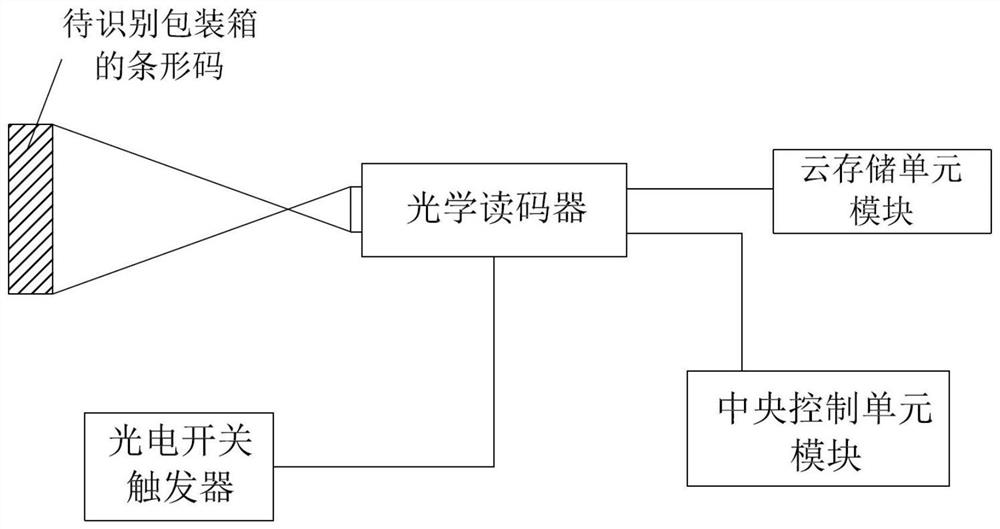
Packaging box information code optical identification and comparison method and system
PendingCN113962231AImprove recognition accuracyIncrease Computational ParallelismCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric transmission signalling systemsData setPhotoswitch
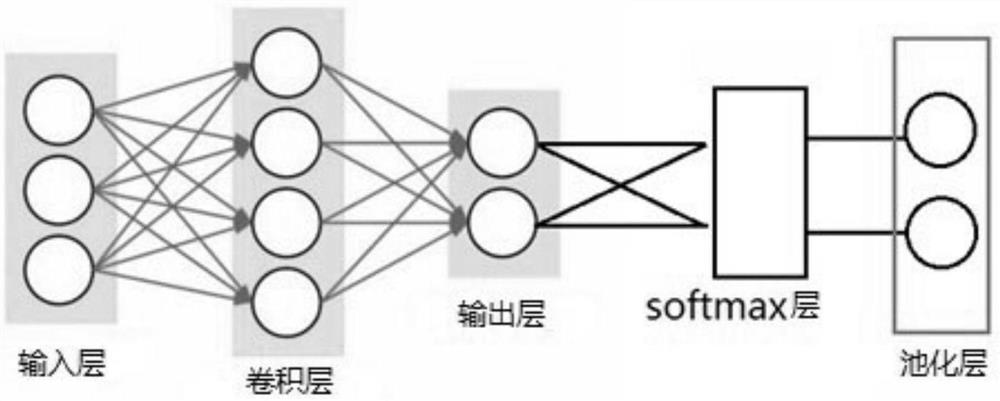
The invention provides a packaging box information code optical identification and comparison method and system. A photoelectric switch trigger starts an optical code reader; the optical code reader reads and identifies an information code; a cloud storage unit module performs cloud storage; a central control unit module decodes and compares the information, constructs a convolutional neural network model, divides the convolutional neural network model into two different data sets for training and self-adaption, and compares subsequently input information codes on a packaging box after training; if the information of the compared information code is less than the actual information type, a signal is sent to an audible and visual alarm; and the audible and visual alarm gives an alarm prompt. After the convolutional neural network model with the Softmax layer is constructed, data self-adaption and separation of the two training sets are performed, so that the calculation parallelism is improved, and the recognition precision is improved on the premise of fewer parameters and lower calculation amount; and a mode of post-processing the classification probability of the convolutional neural network is adopted, so that the recognition precision of the model is effectively improved.
Owner:杭州胜铭纸业有限公司
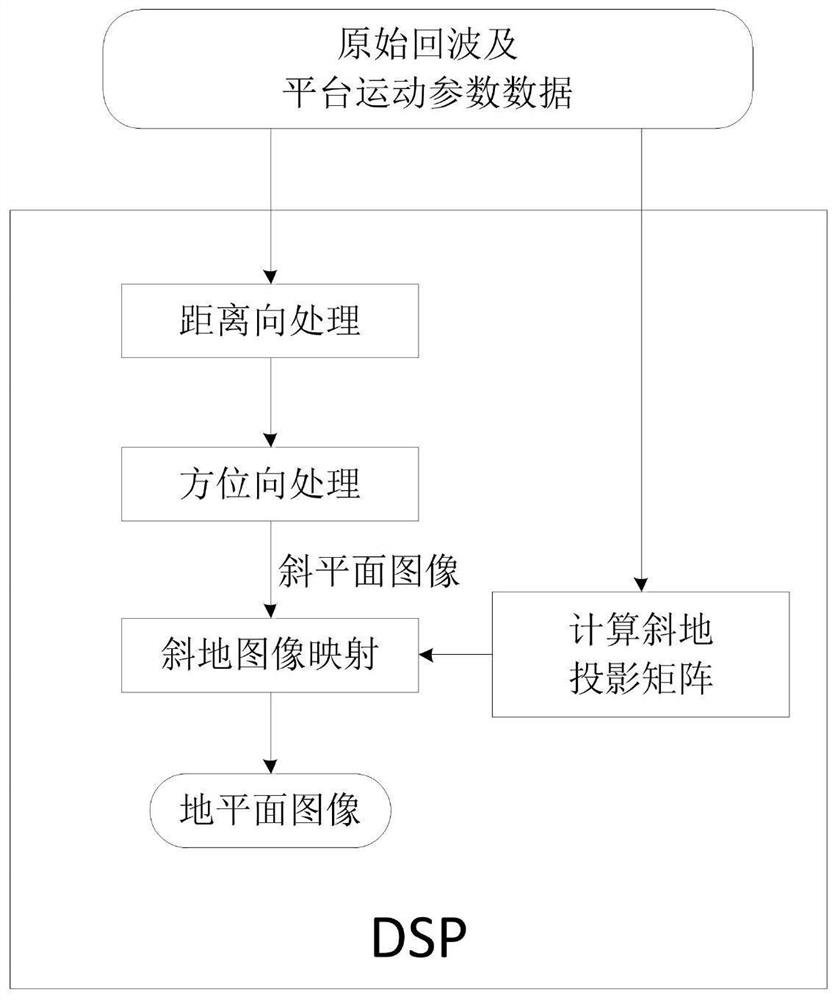
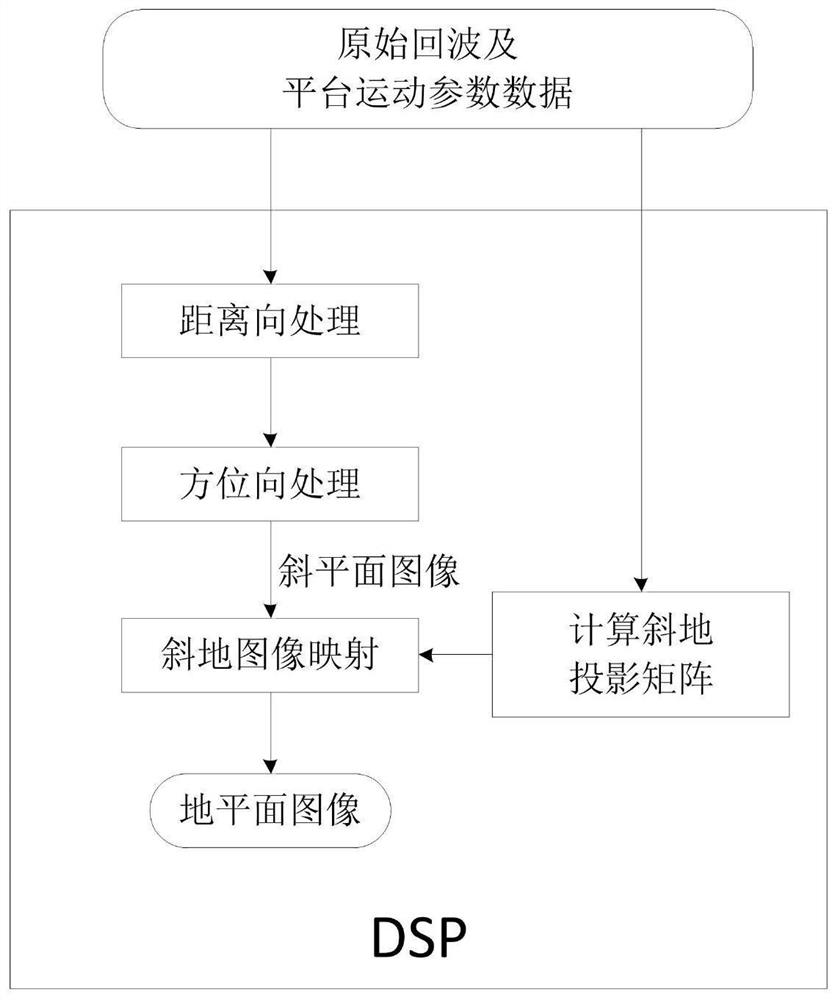
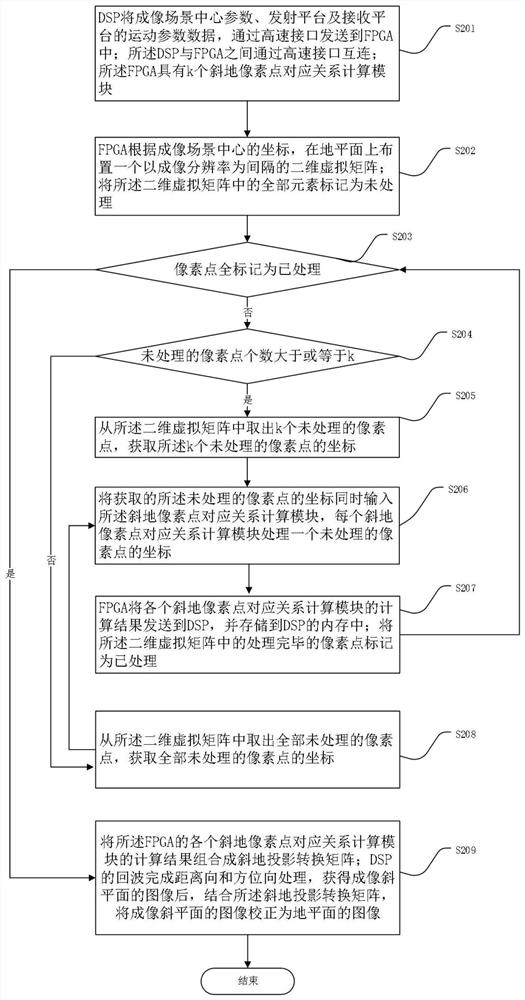
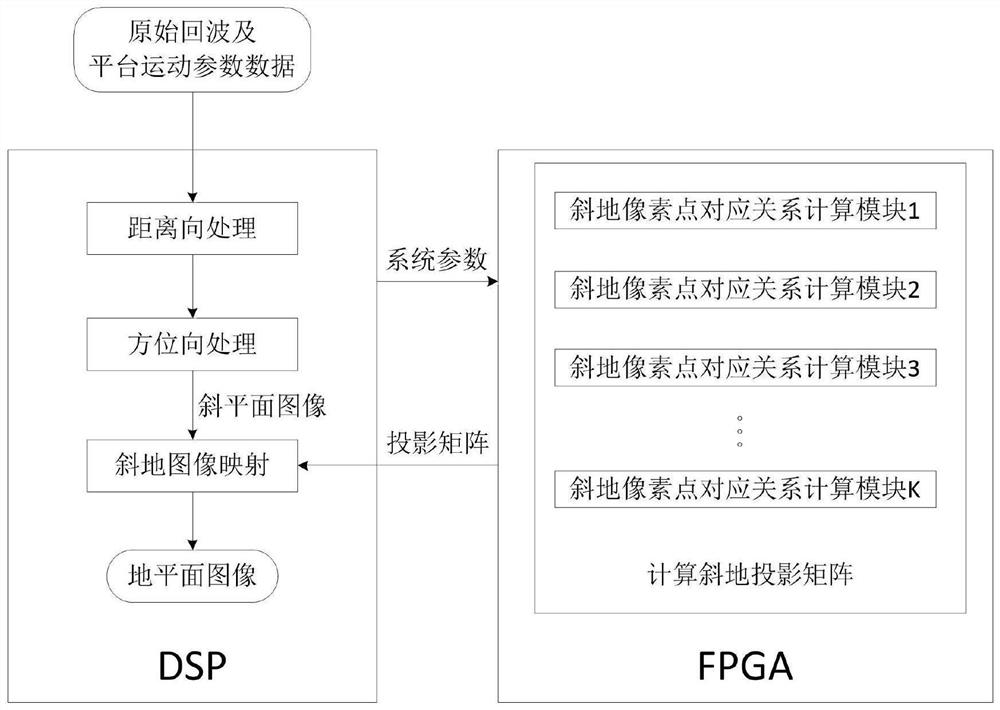
Bistatic forward-looking SAR image geometric correction method and device
ActiveCN111766582AIncrease Computational ParallelismCalculation speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer graphics (images)Radiology
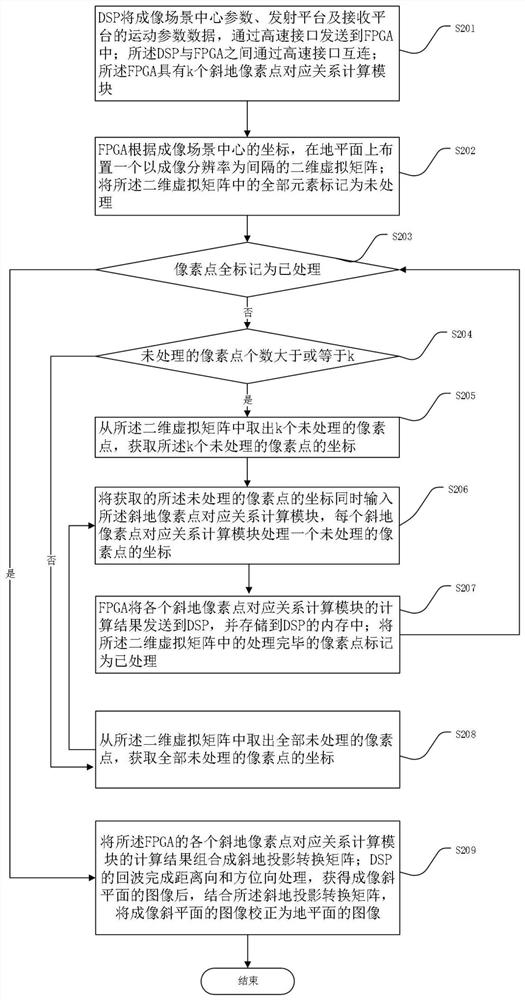
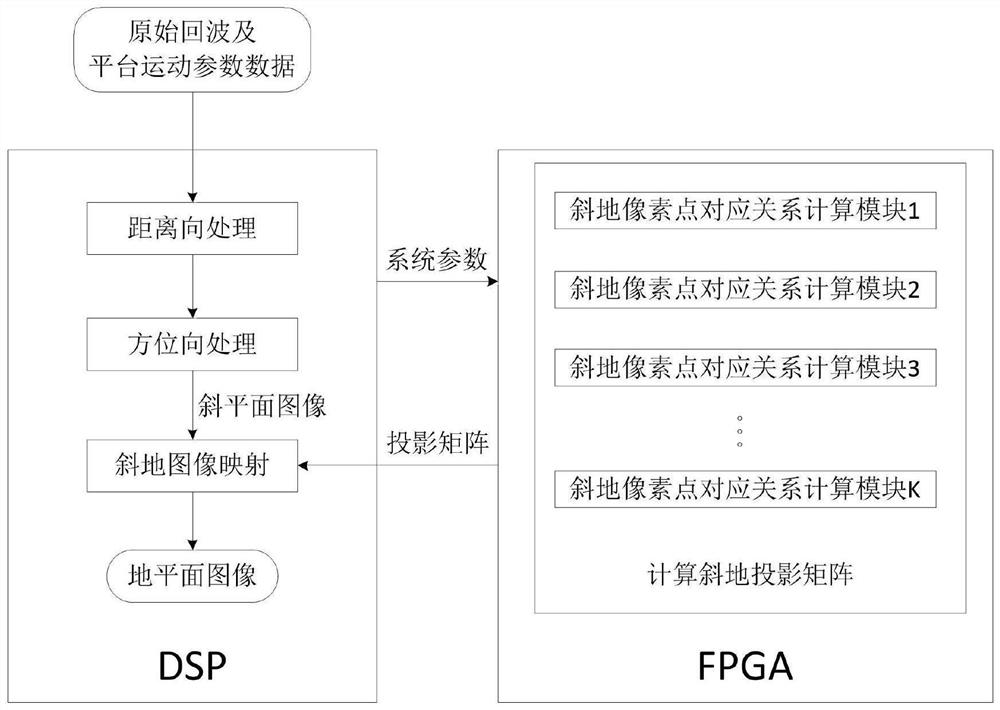
The invention provides a bistatic forward-looking SAR image geometric correction method and device based on a DSP and an FPGA. The method comprises the following steps: the DSP sends parameter data tothe FPGA; the FPGA is provided with a two-dimensional virtual matrix on the ground plane, and the FPGA is provided with k oblique ground pixel point corresponding relation calculation modules; k unprocessed pixel points and coordinates are extracted from the two-dimensional virtual matrix; the acquired coordinates of the unprocessed pixel points are simultaneously input into the oblique ground pixel point corresponding relation calculation modules, wherein each oblique ground pixel point corresponding relation calculation module processes the coordinate of one unprocessed pixel point; the calculation results of the oblique ground pixel point corresponding relation calculation modules of the FPGA are combined into an oblique ground projection conversion matrix; and the echo of the DSP completes range direction and azimuth direction processing, and after the image of the imaging oblique plane is obtained, the image of the imaging oblique plane is corrected into the image of the ground plane in combination with the oblique projection conversion matrix.
Owner:成都汇蓉国科微系统技术有限公司
Deep neural network model parallel fully connected layer data exchange method and system
ActiveCN106991474BIncrease Computational ParallelismReduce overheadNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsForward propagationNetwork model
The invention discloses a deep neural network model parallel fully connected layer data exchange method and system. The fully connected layer of the deep neural network is evenly divided into N training units according to the number of neurons to form a deep neural network. A network model in which the fully connected layer model is parallel; in the forward propagation process of the fully connected layer, the forward propagation method such as half-stop is used to process the input data of the front layer by partial arrival, partial calculation, overall output and overall propagation method; in the backward propagation process of the fully connected layer, the residual data of the rear layer is processed by using the backward propagation method such as stop and stop, and the processing methods of quantitative achievement, quantitative calculation and quantitative propagation are adopted; in a forward and backward propagation After completion, the weight data and threshold data of each layer are updated in parallel according to the obtained weight gradient and threshold gradient. It can overlap the data communication and data calculation of the fully connected layer, and accelerate the convergence of the model under the premise of ensuring the correct rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Pipelined Acceleration System of FPGA-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network
ActiveCN106875012BProcessing speedHighly integratedPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsSystems designDistribution control
The invention brings forward a streamlined acceleration system of an FPGA-based depth convolution neural network. The streamlined acceleration system is mainly formed by an input data distribution control module, an output data distribution control module, a convolution calculating sequence serialization realizing module, a convolution calculating module, a pooling calculating sequence serialization realizing module, a pooling calculating module, and a convolution calculating result distribution control module. Moreover, the streamlined acceleration system comprises an internal system cascade interface. Through the streamlined acceleration system designed by the invention, highly efficient parallel streamlined realization can be conducted on an FPGA, problems of resource waste and effective calculation delays caused by filling operations during calculation are effectively solved, the power consumption of the system is effectively reduced, and the operation processing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:武汉魅瞳科技有限公司
A Carrier Tracking Method for Satellite Navigation with Low Update Frequency
ActiveCN107870338BShorten the update cycleGuaranteed stabilitySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalSatellite navigation
Owner:湖南跨线桥航天科技有限公司
A processing method and device for multiplication and accumulation operations
ActiveCN106325812BImprove throughputImprove processing efficiencyComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerOperand
The invention discloses a processing method and device for multiplication and accumulation operation, used for solving the problems of low data processing efficiency and high power consumption of a computer in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of distributing a register identifier to each read multiplication and accumulation instruction, after processing each multiplication and accumulation instruction to obtain an add operand, taking the add operand and the register identifier distributed to the multiplication and accumulation instruction as binary groups to cache, reading one binary group as a reference binary group, taking the add operand included in the reference binary group as the first add operand, reading an associated binary group, taking the add operand included in the associated binary group as the second add operand, or, reading data in a register corresponding to the register identifier included in the reference binary group as the second add operand, generating an add calculation result based on the first add operand and the second add operand, and storing the add calculation result in the source of the second add operand. Thereby, the calculation parallelism, the data throughout and the data processing efficiency are increased; and the power consumption of the computer is reduced.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Method and device for geometric correction of double-base forward-looking SAR images
ActiveCN111766582BIncrease Computational ParallelismCalculation speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
The present invention provides a dual-base forward-looking SAR image geometric correction method and device based on DSP and FPGA. The method includes: DSP sends parameter data to FPGA; FPGA arranges a two-dimensional virtual matrix on the ground plane, and FPGA has Calculation module for k oblique pixel point correspondences; take k unprocessed pixel points and coordinates from the two-dimensional virtual matrix; simultaneously input the acquired coordinates of the unprocessed pixel points into the oblique ground pixel point correspondence relationship Calculation module, each oblique pixel point correspondence calculation module processes the coordinates of an unprocessed pixel point; the calculation results of each oblique pixel point correspondence calculation module of the FPGA are combined into an oblique projection conversion matrix; DSP After the echo is processed in the range direction and the azimuth direction, and the image of the imaging oblique plane is obtained, the image of the imaging oblique plane is corrected into an image of the ground plane in combination with the oblique projection transformation matrix.
Owner:成都汇蓉国科微系统技术有限公司
Mobile ad hoc authentication method and system
InactiveCN101192928BReduce the number of calculationsReduce processing resource requirementsEnergy efficient ICTUser identity/authority verificationNetwork structureEngineering
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
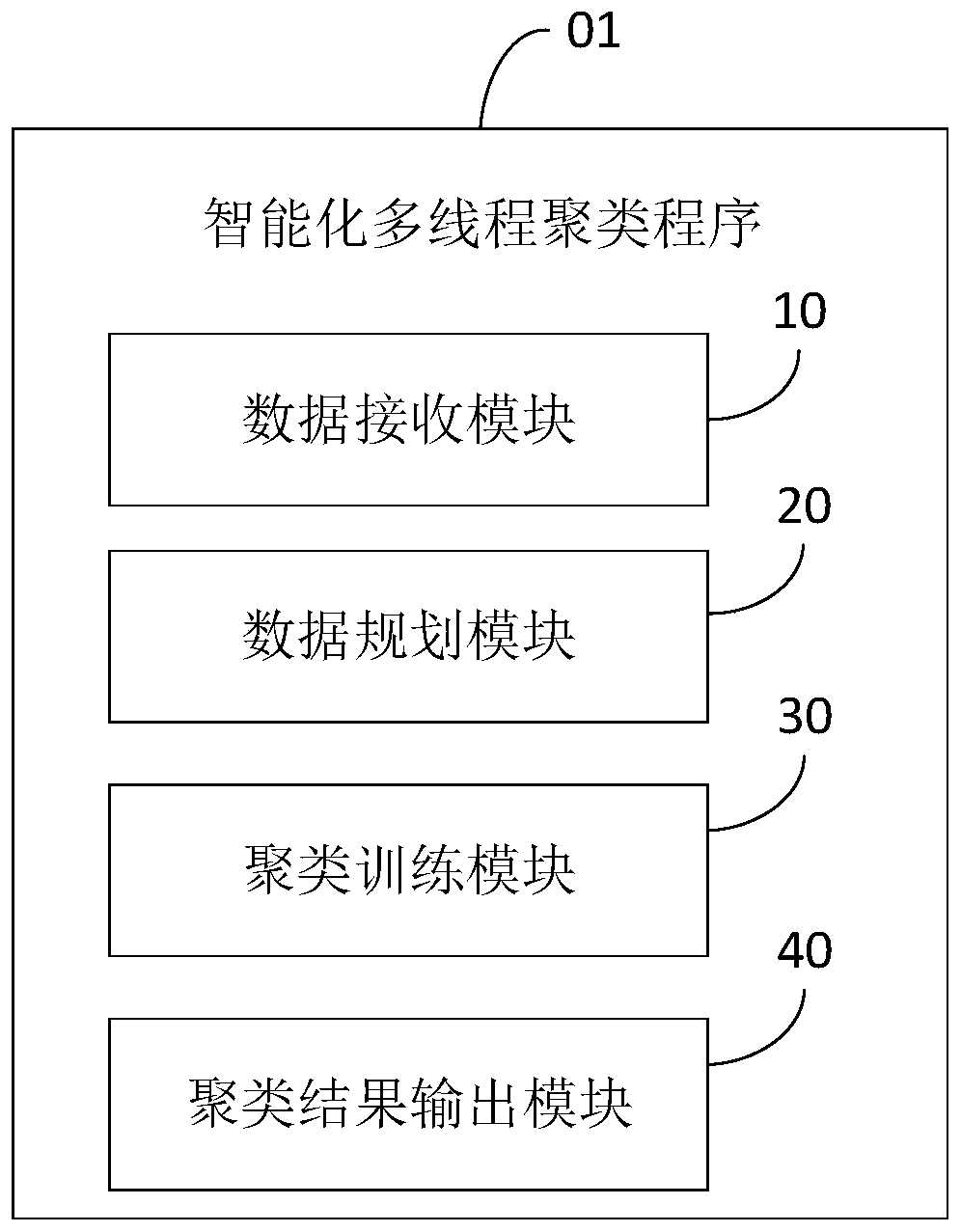
Intelligent multi-thread clustering method and device and computer readable storage medium
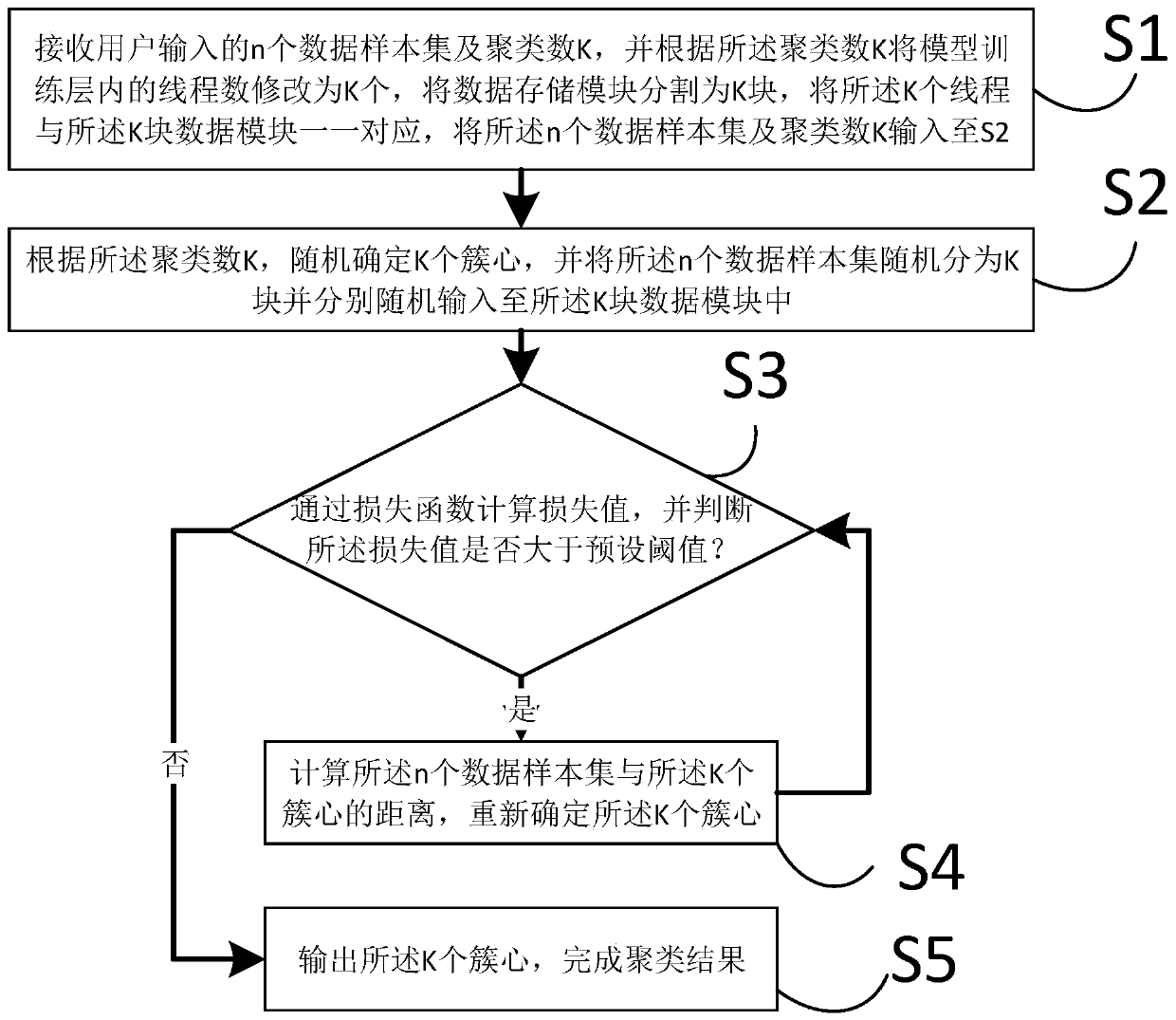
PendingCN110717517AImprove operational efficiencyIncrease Computational ParallelismDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to an artificial intelligence technology, and discloses an intelligent multi-thread clustering method, which comprises the following steps of: receiving n data sample sets and aclustering number K input by a user, randomly determining K cluster centers according to the clustering number K, randomly dividing the n data sample sets into K blocks, and inputting the K blocks into K data modules; reading the sample sets in the K data modules by K threads, calculating the loss values of the K cluster centers and the n data sample sets, and judging the size relationship betweenthe loss values and a preset threshold value; and when the loss value is greater than the preset threshold value, re-determining the K cluster centers, re-calculating the loss value and judging the size relationship with the preset threshold value, and when the loss value is less than the preset threshold value, outputting the K cluster centers to complete a clustering result. The invention further provides an intelligent multi-thread clustering device and a computer readable storage medium. According to the invention, an accurate intelligent multi-thread clustering function can be realized.
Owner:CHINA PING AN PROPERTY INSURANCE CO LTD
A Parallel Intra-frame Prediction Method for 4x4 Sub-Macroblocks in H.264/AVC
ActiveCN103747250BIncrease Computational ParallelismEliminate branch statementsDigital video signal modificationData streamParallel algorithm
The present invention discloses a method for 4*4 sub-macroblock parallel intraframe prediction in H.264 / AVC, comprising the steps of: a unified intraframe prediction formula, a reference value array, a reference position table and a concrete implementation step of parallel intraframe prediction. The unified intraframe prediction formula is improved based on the feature of a CUDA and an intraframe prediction formula, by the corresponding prediction formulas of 9 prediction modes to be transformed into one formula to meet the requirements of the CUDA multi-thread single instruction multiple data stream, to achieve the fine-grained parallel in the intraframe prediction sub-macroblock. The reference value array and the reference position table are designed to cooperate with the unified intraframe prediction formula and to completely eliminate a large number of branch statements that affects the parallel algorithm performance. The present invention in the process of the intraframe prediction achieves the pixel level parallel, can effectively use multi-core resources in a GPU to accelerate the process of intraframe prediction, and shorts a coding time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Data access method, device, hardware accelerator, computing device, storage medium
ActiveCN110309912BSave resourcesLow costNeural architecturesPhysical realisationMemory addressAccess method
Owner:XILINX INC
High-speed split multiply accumulator MAC apparatus
InactiveCN100465877CFast working frequencyNot much depthDigital data processing detailsData selectionOperating frequency
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Deep Learning Accelerator for Stacked Hourglass Networks
ActiveCN109993293BAchieve Computational Acceleration PerformanceCalculation speedNeural architecturesPhysical realisationComputational scienceConcurrent computation
The invention discloses a deep learning accelerator suitable for a stacked hourglass network. The parallel calculation layer calculation unit improves the calculation parallelism, and the data cache module improves the utilization of data loaded into the accelerator internal cache while accelerating the calculation speed. At the same time, the data adjuster inside the accelerator can make adaptive changes in the order of data arrangement according to the operation of the computing layer, which can increase the integrity of the acquired data, improve the efficiency of data acquisition, and reduce the delay of the memory access process. Therefore, while improving the computing speed of the algorithm, the accelerator effectively reduces the memory bandwidth by reducing the number of memory accesses and improving memory access efficiency, thereby realizing the overall computing acceleration performance of the accelerator.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Integer motion estimation method and system for video coding and storage medium
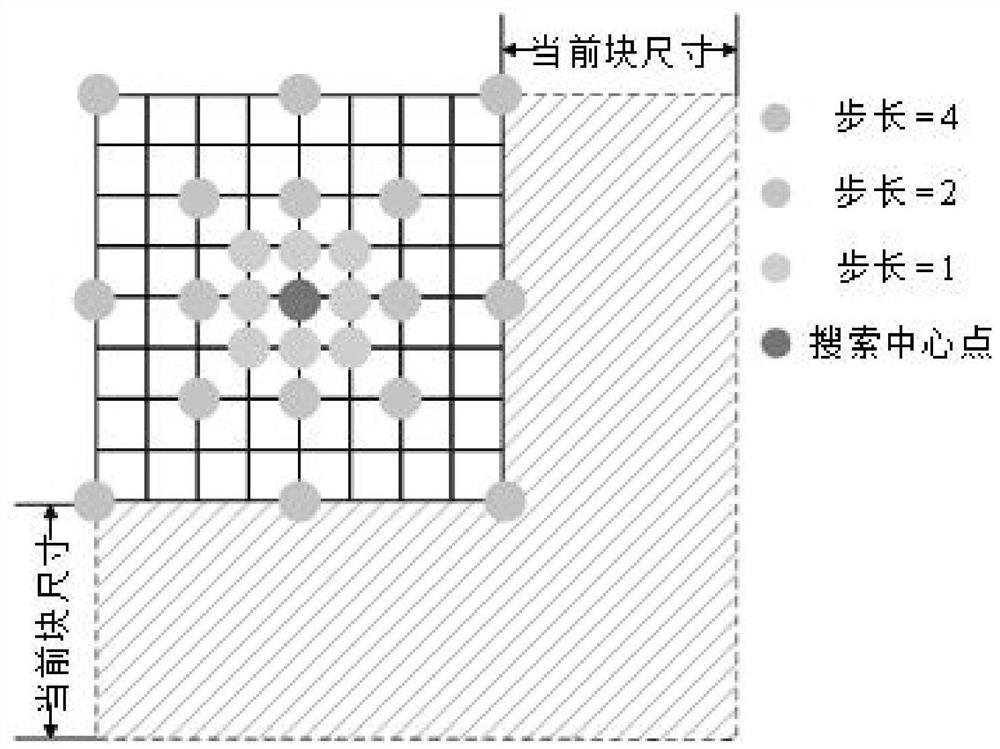
PendingCN114727115AFew stepsReduce operation stepsDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingMotion vector
The invention relates to the technical field of video coding, and discloses an integer motion estimation method for video coding, which comprises the following steps of: calculating a first SAD value of a current block of a zero point according to a central point, and outputting a relative coordinate of the central point as an optimal motion vector under the condition that the first SAD value is smaller than a threshold value; calculating a second SAD value of the current block of the dense area according to the first search point, and outputting the relative coordinate of the first search point as an optimal motion vector under the condition that the second SAD value is smaller than a threshold value; and under the condition that the optimal motion vector is not determined in the current block of the dense region, calculating a third SAD value of the current block of the sparse region according to the second search point, and under the condition that the third SAD value is smaller than a threshold value, outputting the relative coordinates of the second search point as the optimal motion vector. The problems that existing integer motion estimation correlation calculation is long in consumed time and large in consumed storage space are solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of fpga hardware implementation method, device and target tracking method of particle filter based on Bayesian resampling
ActiveCN112732637BGuarantee sufficiencyDiversity guaranteedArchitecture with single central processing unitElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareComputational science
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com