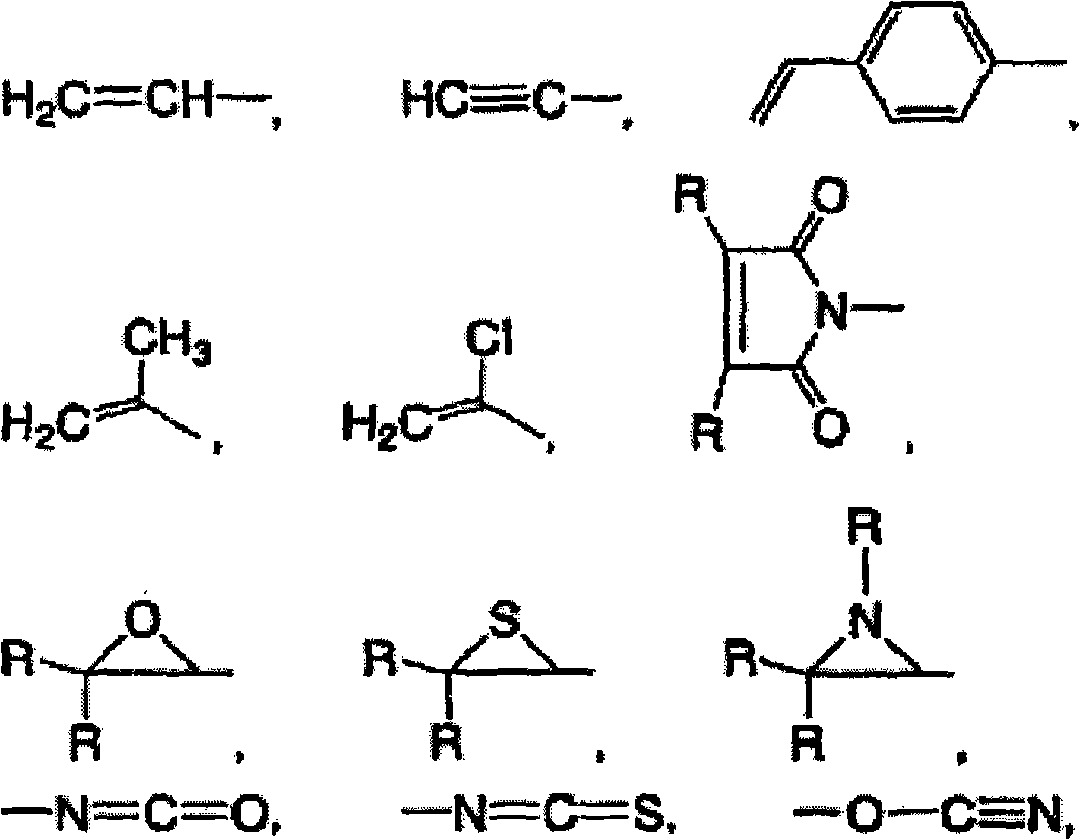
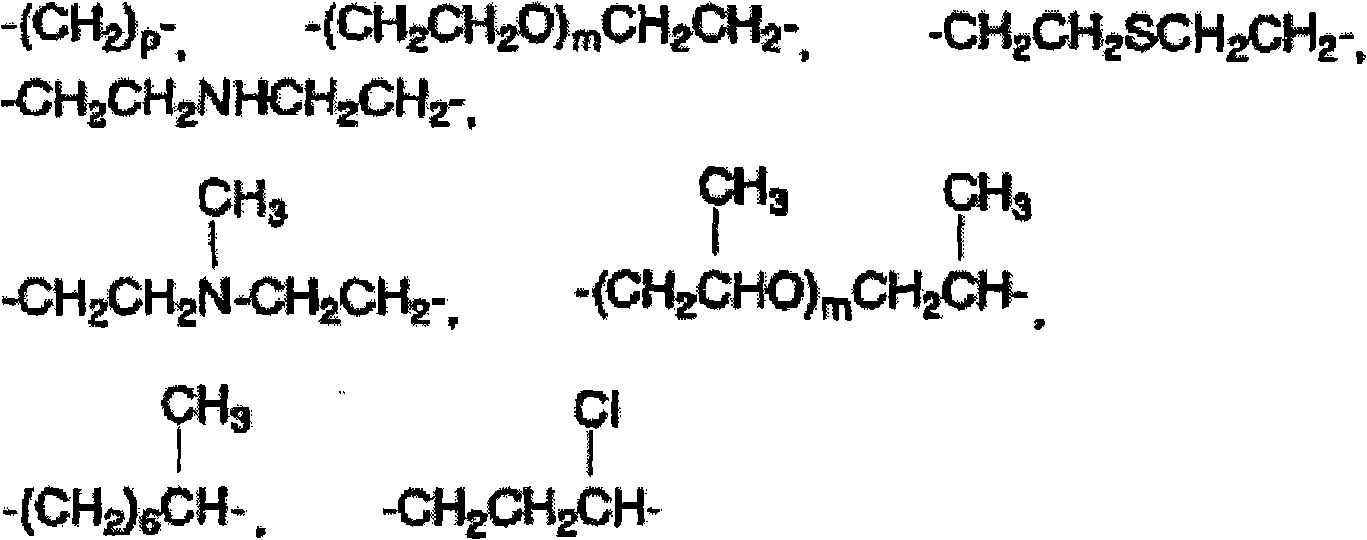
Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Suppresses color shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
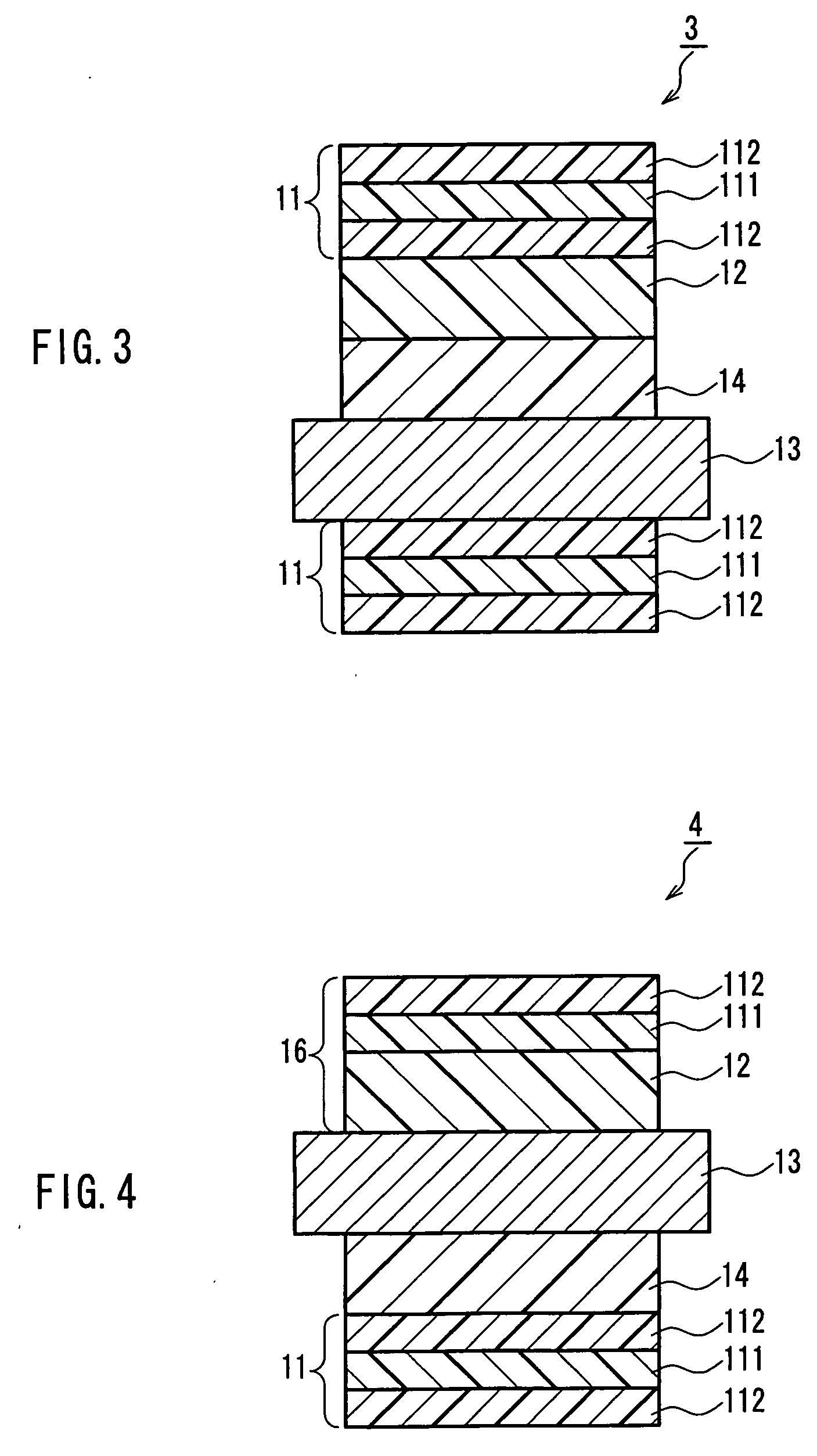
Colored composition, cured film, color filter, method for producing color filter, solid-state image sensor, and image display device
ActiveUS20160146987A1Increase resistanceImprove solubilityPhotosensitive materialsOptical filtersPolymer chemistryPhotochemistry
Provided are a colored composition which enables the formation of a pattern having excellent heat resistance and excellent solubility in solvents and has inhibited color migration; and a cured film, a color filter, a method for producing a color filter, a solid-state image sensor, and an image display device, each of which uses the colored composition.The colored composition includes a polymer anion having a repeating unit containing a weakly nucleophilic anionic structure, and a dye having a cationic structure, in which the weakly nucleophilic anionic structure represents an anionic structure produced by dissociating an organic acid having a lower pKa value than the pKa value of sulfuric acid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
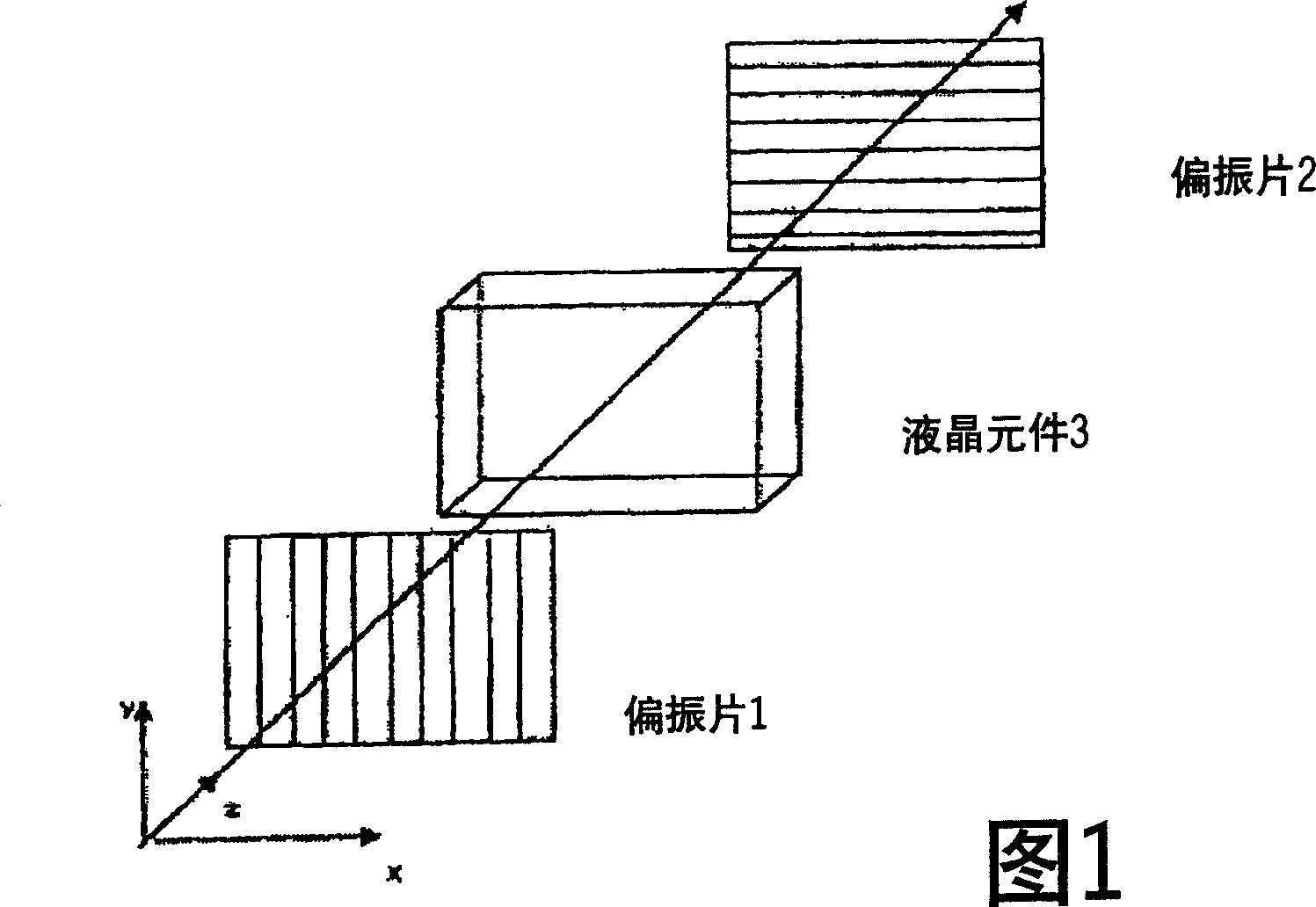
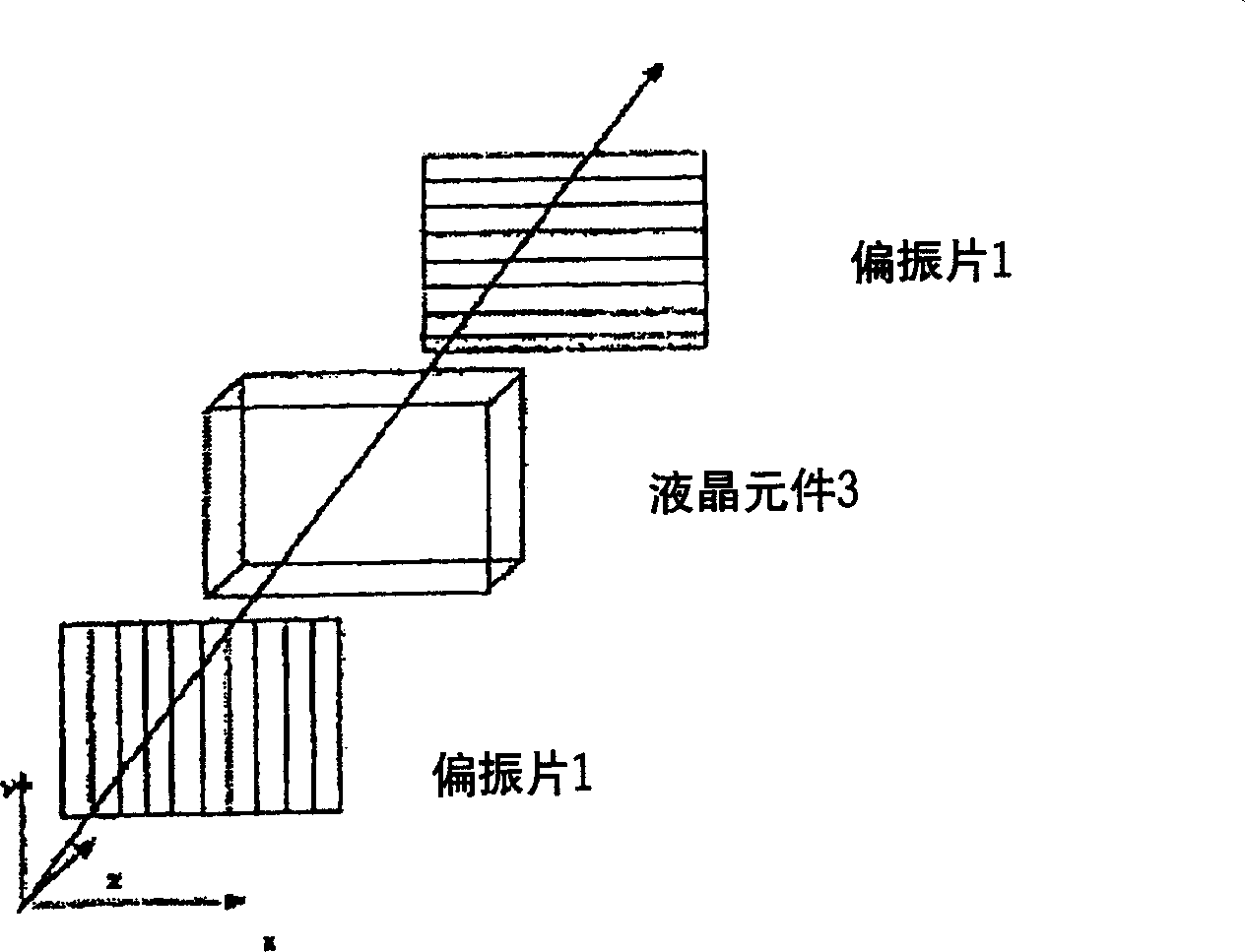
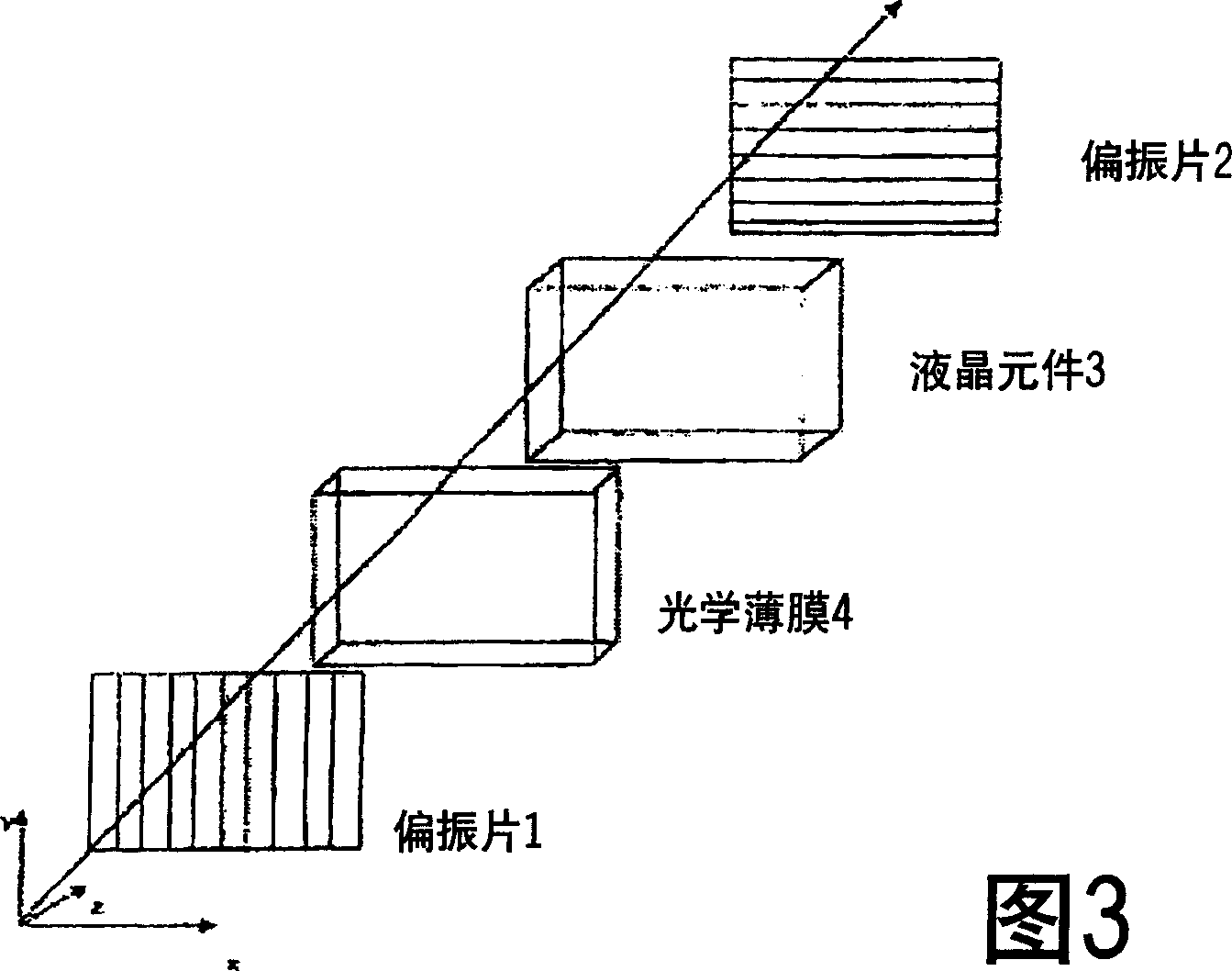
Optical member, polarizing plate set, and liquid crystal display apparatus
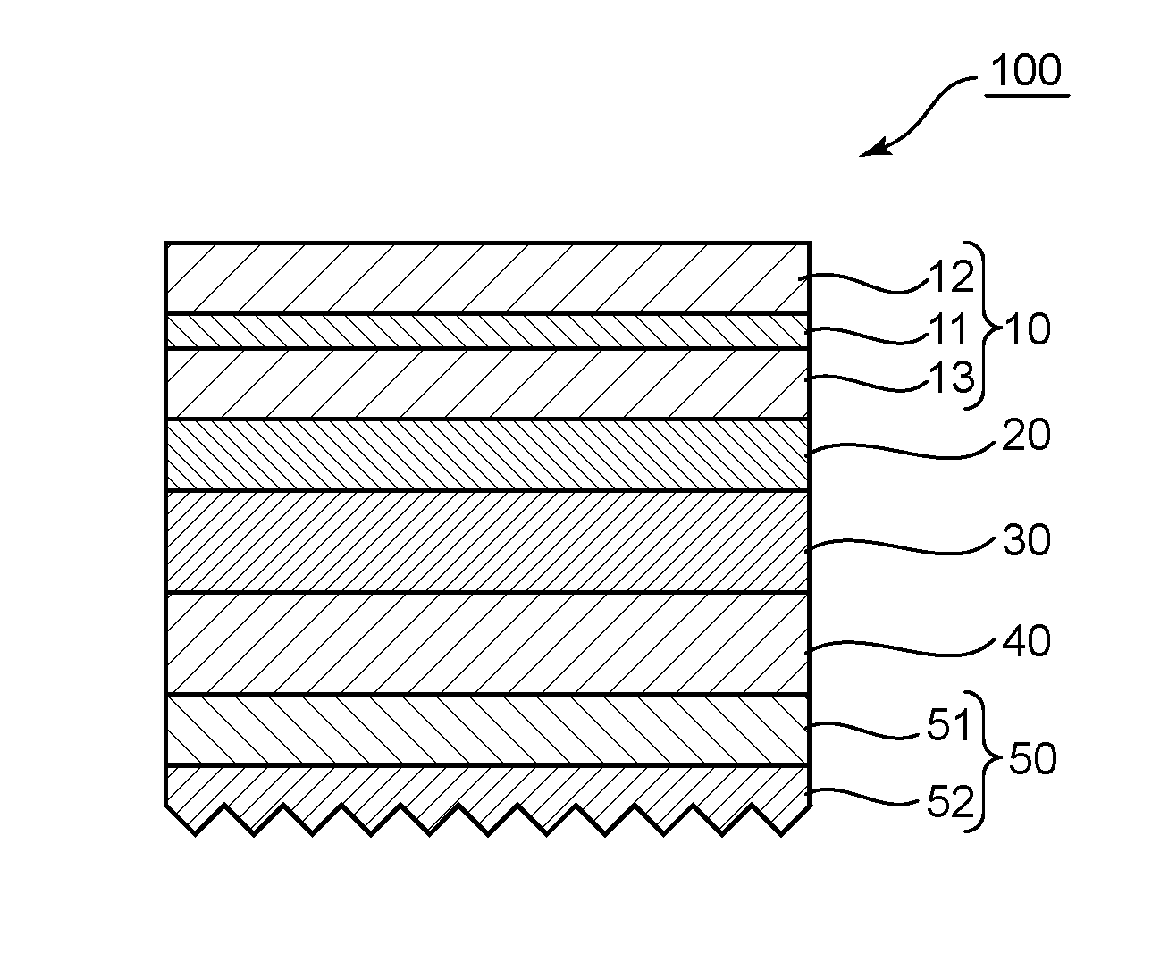
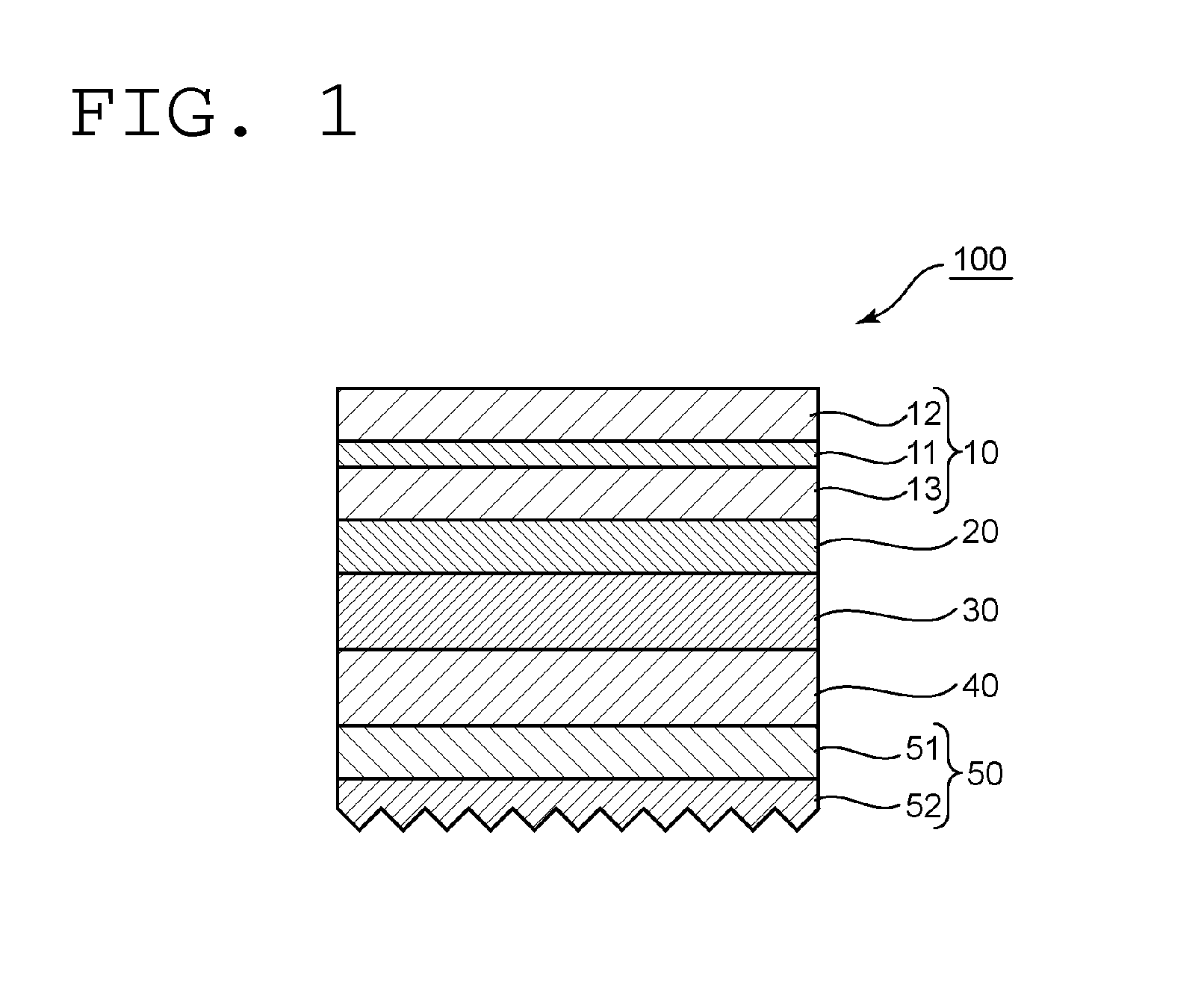
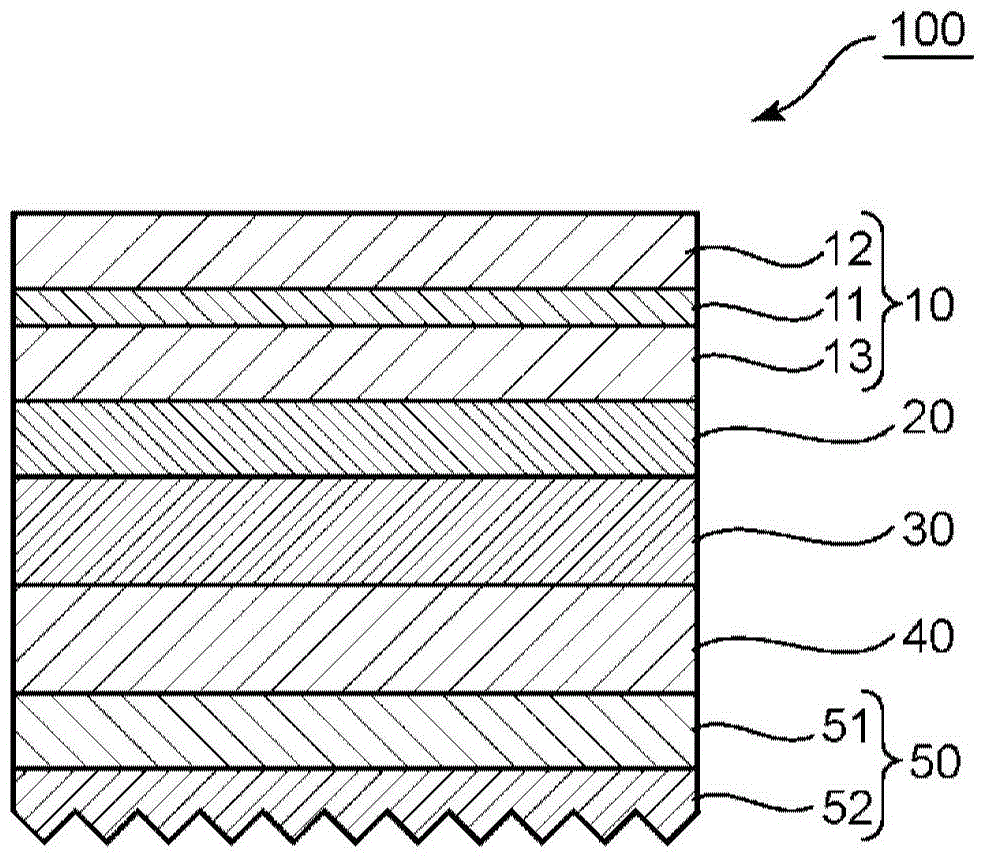
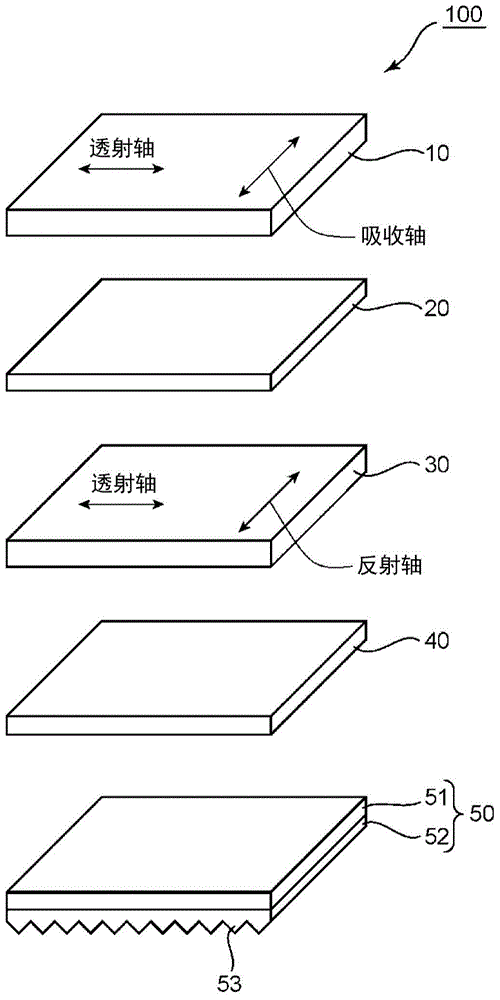
InactiveUS20150277012A1High mechanical strengthSuppresses color shiftPrismsPolarising elementsColor shiftLiquid-crystal display
Provided is an optical member that can realize a liquid crystal display apparatus that is excellent in mechanical strength and suppressed in color shift. The optical member includes: a polarizing plate; a reflective polarizer; a low refractive index layer having a selected refractive index; and a prism sheet.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Imaging device and imaging method
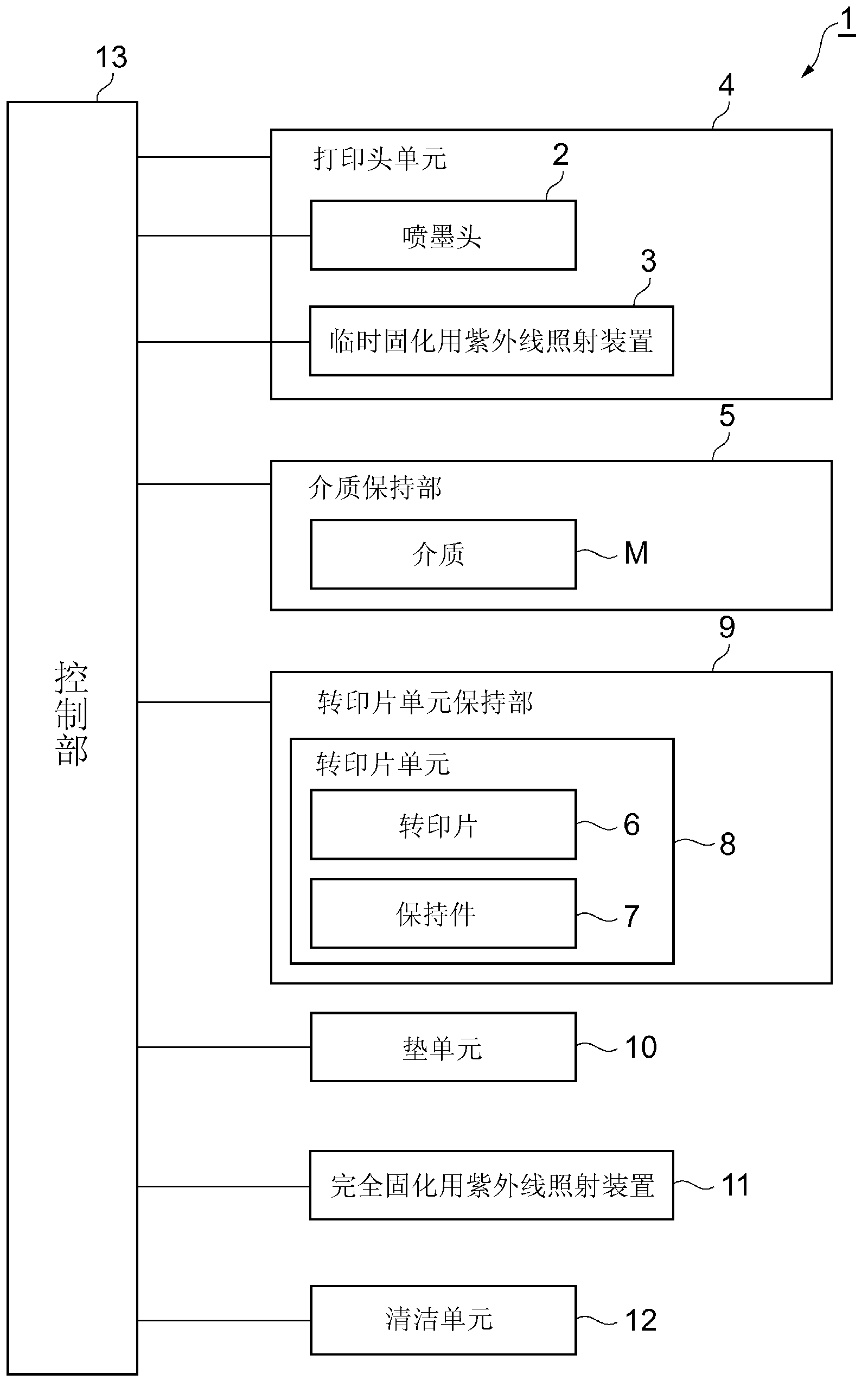
ActiveCN102883888AAvoid deformationShorten the formation timeDuplicating/marking methodsTypewritersUltravioletImage formation
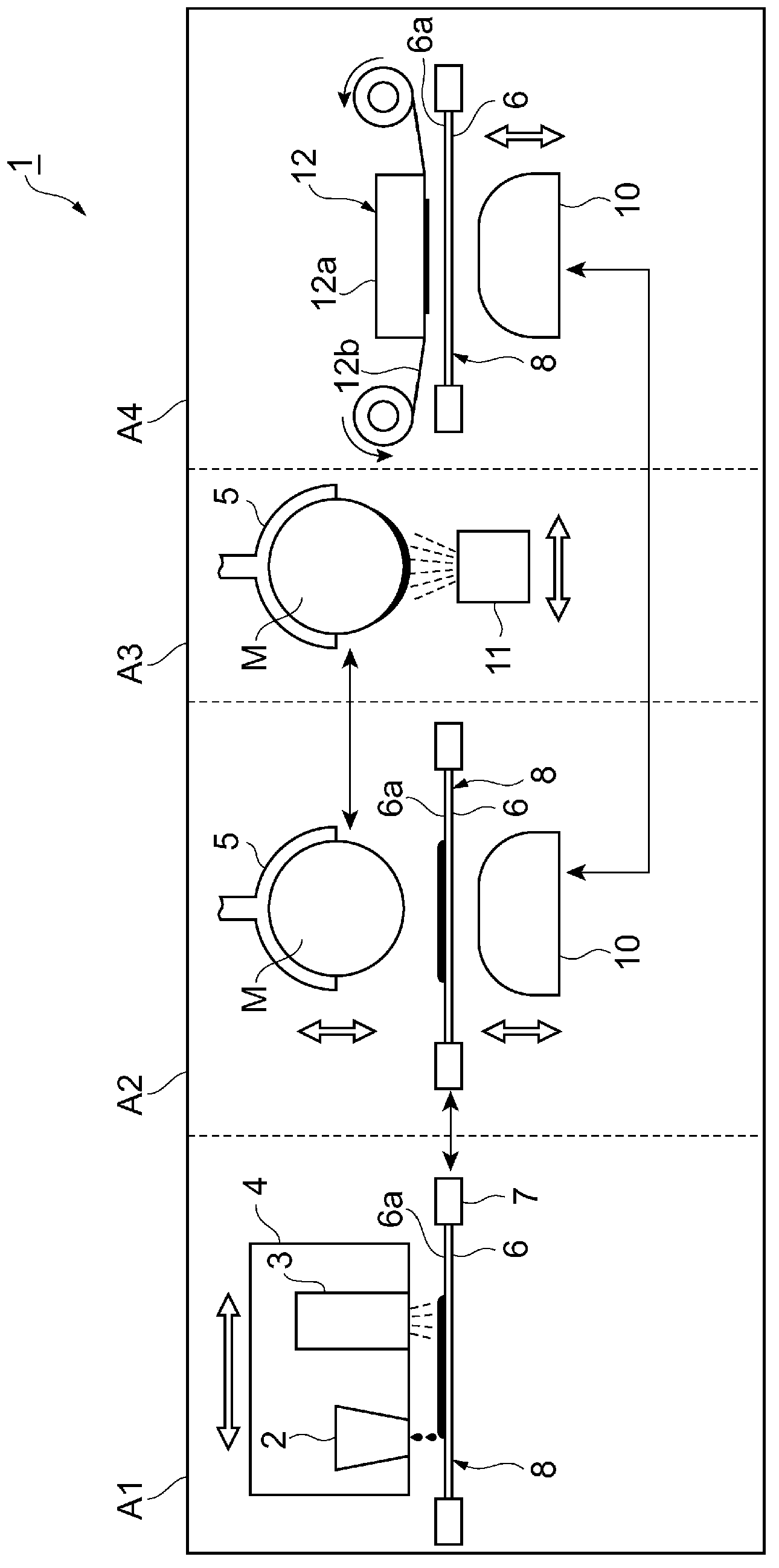
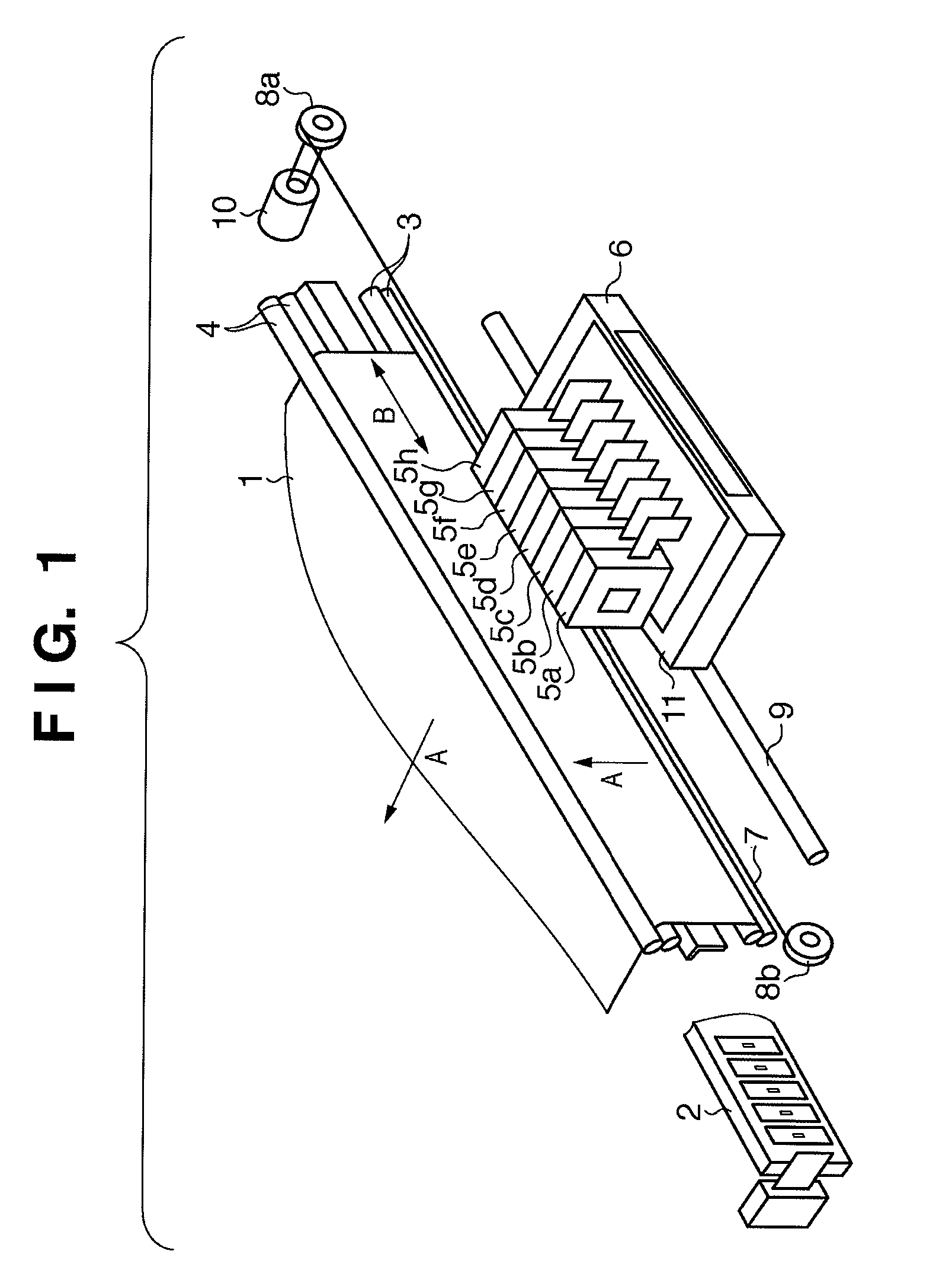
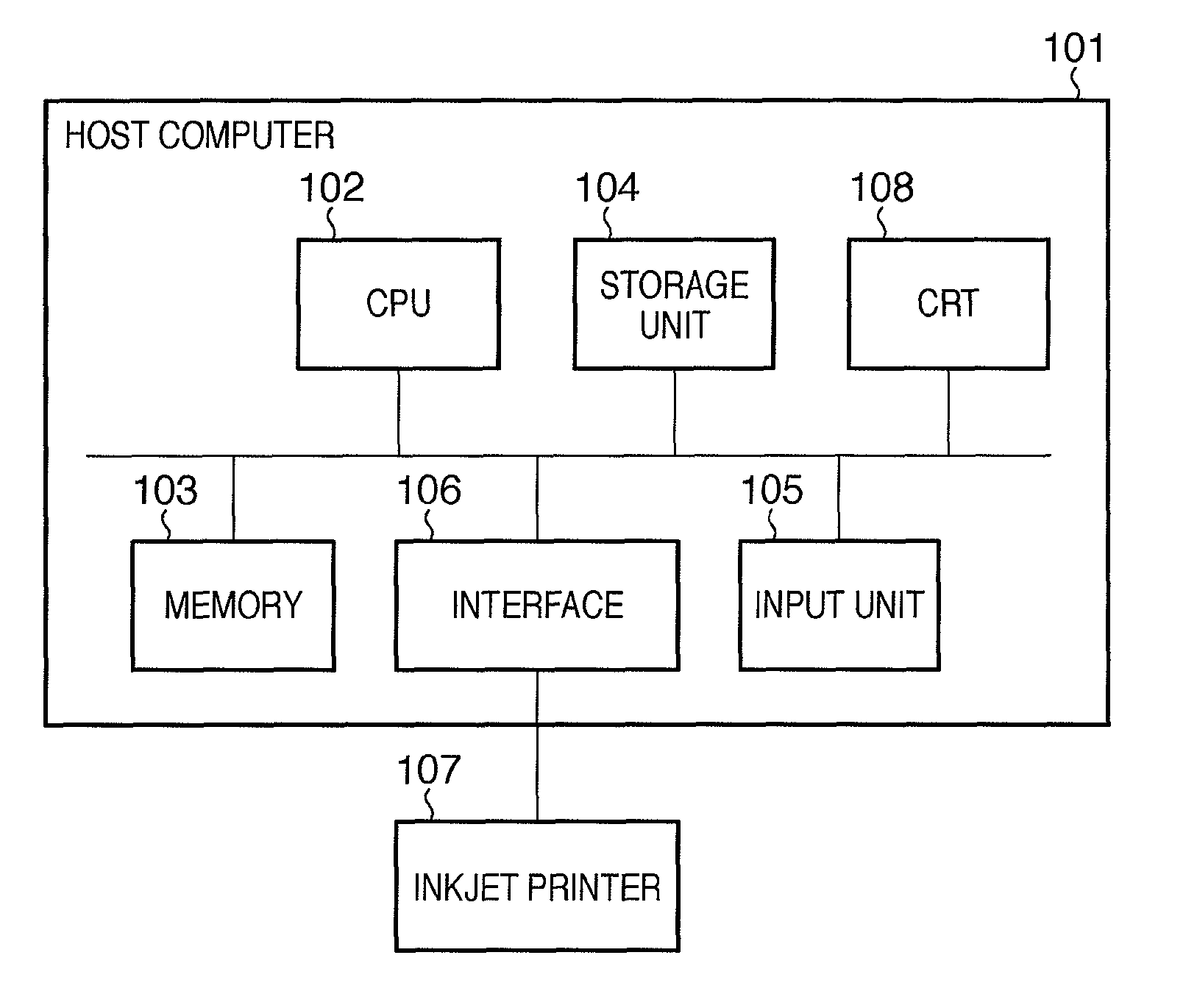
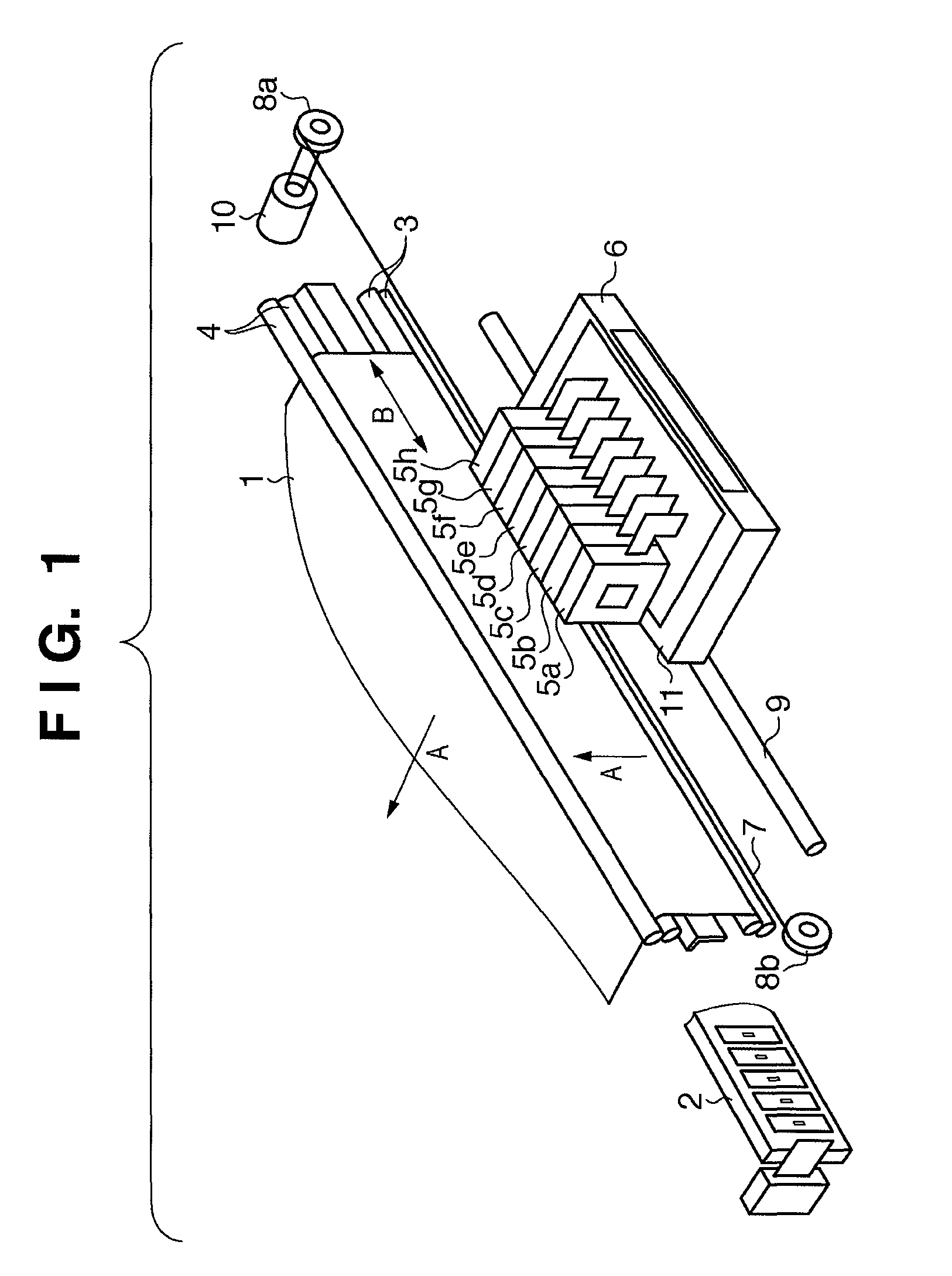
The present invention relates to an imaging device and an imaging method. The object of the present invention is to form, quickly and at low cost, a high-quality image on a medium formed with a curved surface. In order to achieve this object, the imaging device is equipped with: an ink-jet head (2); a pre-curing ultraviolet irradiation device (3); a head unit (4) in which is installed the ink-jet head (2) and the pre-curing ultraviolet irradiation device (3); a medium holding unit (5) that holds a medium (M); a transfer sheet unit holding unit (9) that holds a transfer sheet unit (8), in which a transfer sheet (6) is mounted to a transfer sheet holder (7); an elastic pad unit (10); a final curing ultraviolet irradiation device (11); a cleaning unit (12); and a control unit (13). The ink-jet head (2) applies ink to the transfer sheet (6) and the pad unit (10) pushes the transfer sheet (6) against the medium (M), thus providing a pressure transfer of the ink applied to the transfer sheet (6) to the medium (M).
Owner:MIMAKI ENG
Display apparatus
InactiveCN103219357ANo color shift at high viewing anglesSolved the problem of color shift at high viewing anglesStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesRefractive indexColor filter array
Owner:CANON KK
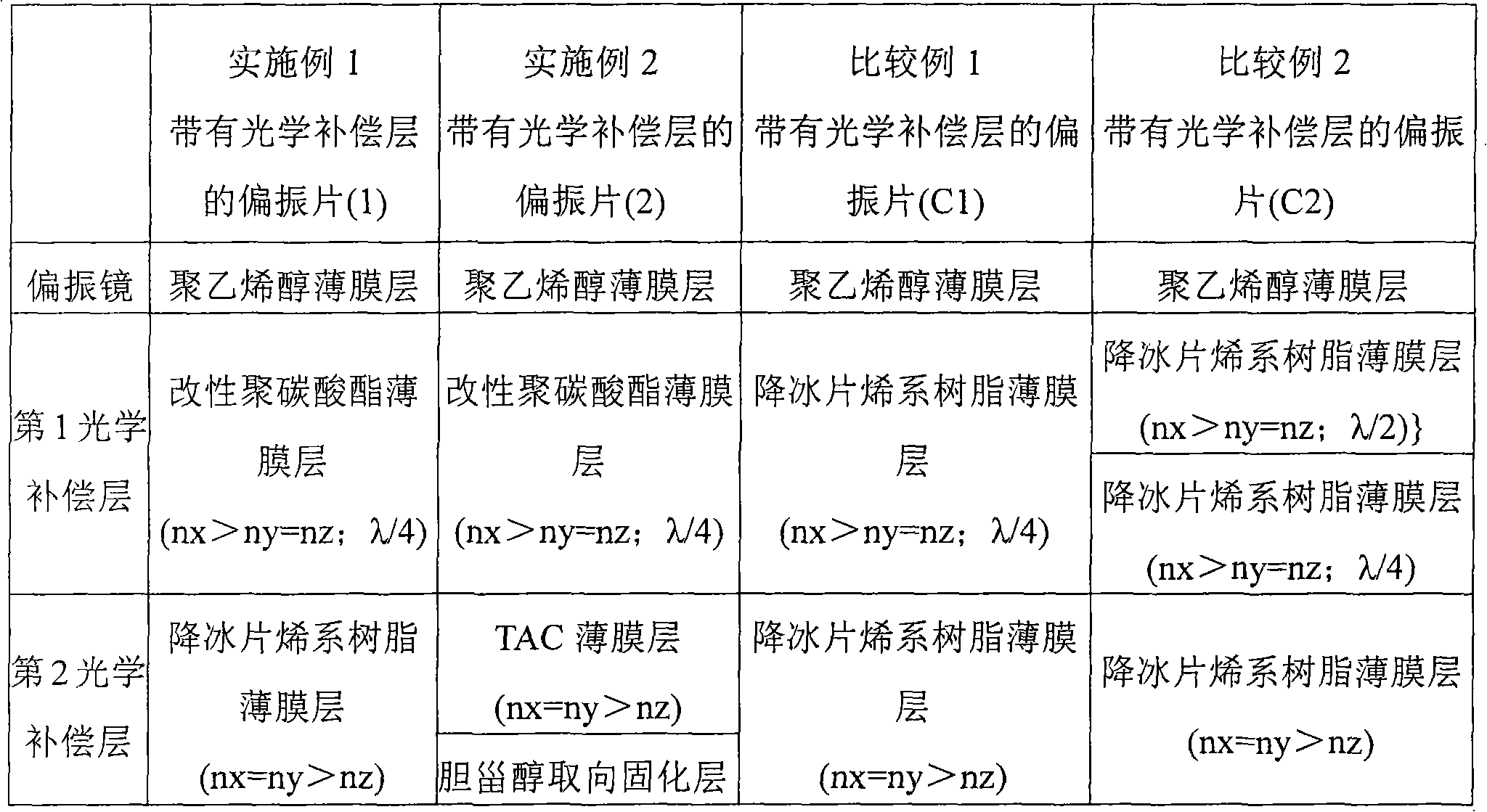
Polarizing plate having optical compensation layer, liquid crystal panel using the polarizing plate having optical compensation layer, liquid crystal display device, and image display device
InactiveCN101288008AAvoid light leakageExcellent field of view characteristicsPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planePhase difference
The present invention provides a thin polarizing plate having an optical compensation layer capable of improving visual angle characteristics, realizing a high contrast, preventing interference irregularities and thermal irregularities, suppressing a color shift, exhibiting a preferable color reproducibility, and effectively preventing light leak in the black display. It is also possible to provide a liquid crystal panel and an image display device using such a polarizing plate having an optical compensation layer. The polarizing plate having the optical compensation layer includes a polarizer, a first optical compensation layer, and a second optical compensation layer in this order. The first optical compensation layer has a refractivity distribution of nx > ny = nz and exhibits wavelength distribution characteristics in which the in-plane phase difference Re1 becomes smaller as the wavelength becomes shorter and the in-plane phase difference Re1 is 90 to 160 nm. The second optical compensation layer is a film layer having a refractivity distribution of nx = ny > nz, an in-plane phase difference Re2 0 to 20 nm, and a phase difference in the thickness direction Rth2 30 to 300 nm.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical member, polarizing plate set, and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveCN104950507AHigh mechanical strengthSuppresses color shiftNon-linear opticsOptical elementsColor shiftLiquid-crystal display
Provided is an optical member that can realize a liquid crystal display apparatus that is excellent in mechanical strength and suppressed in color shift. The optical member includes: a polarizing plate; a reflective polarizer; a low refractive index layer having a selected refractive index; and a prism sheet.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Liquid crystal display devices and polarizing plate sets used therein
InactiveCN101051144ASuppress light leakageSuppresses color shiftPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsVisibilityIn plane
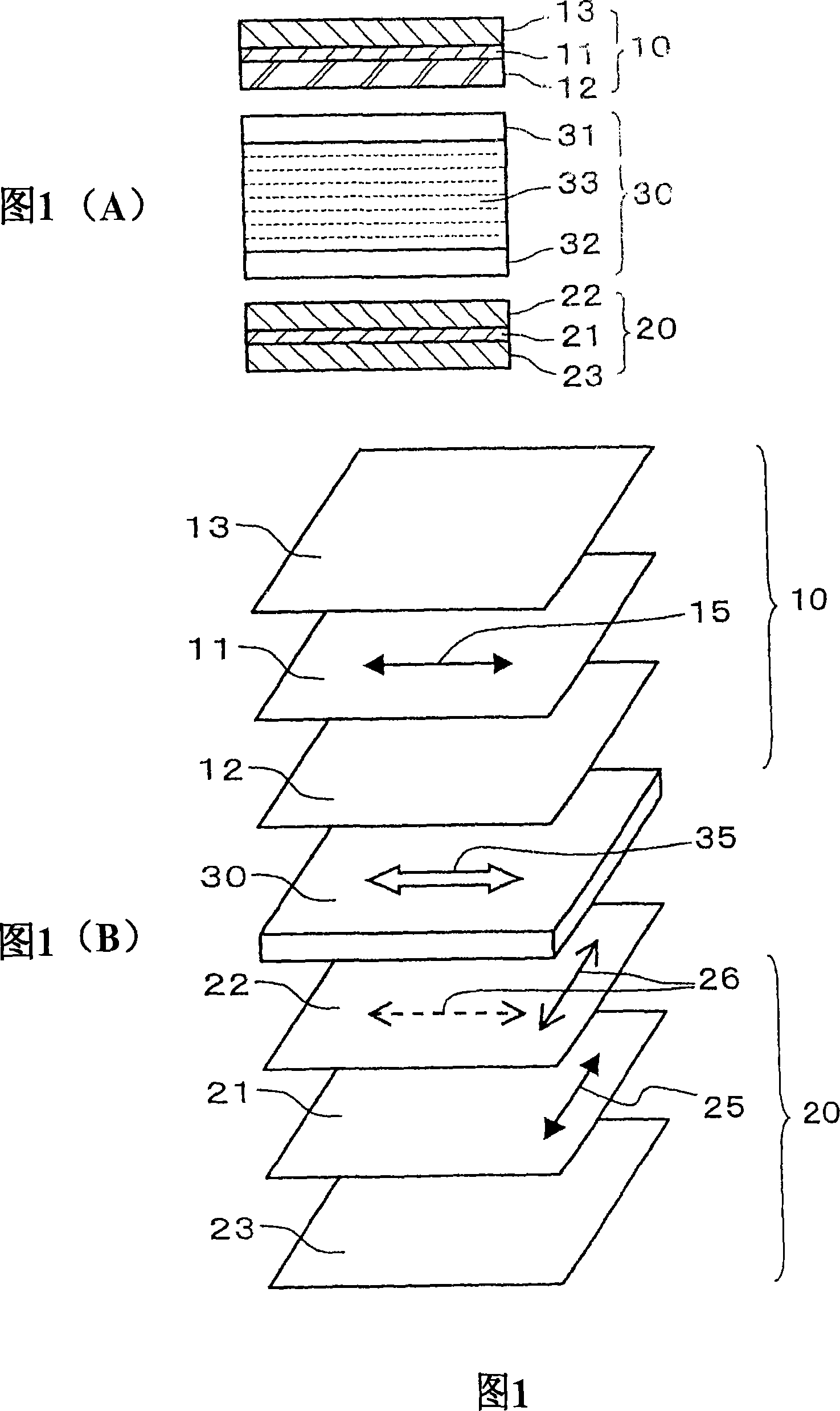
The present invention provides a IPS mode liquid crystal display device and polarizing plate set used therein, the device can improves the leakage of black brightness when side glancing, and the color migration is little caused by angle of visibility. The liquid crystal unit (30) has two pieces of base plates (31, 32) between liquid crystal layers (33) in parallel with the base plate approximately and sealed with the base plate. A pair of polarizing plates (10, 20) clamping the liquid crystal unit (30) are arranged as absorbing axles (15, 25) orthometric with the both. The base side transparent protection layer of the first polarizing plates (10) is set to be film less than 10nm in plane phase separation R<0> (1), and less than 20nm in thickness direction phase separation R<2> (2). The base side transparent protection layer of the second polarizing plates (20) is set to be film 200-300nm in plane phase separation R<0> (2), and 0.4-066 in Nz coefficient [=(n-n) / (n-n)]. In the second polarizing plates (20), the delay axle (22) of the base side transparent protection layer (20), and the absorbing axle (25) of the polarizer are in parallel or orthogonality.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Colored composition, cured film, color filter, method for producing color filter, solid-state image sensor, and image display device
ActiveUS9618665B2Increase resistanceImprove solubilityOptical filtersOrganic dyesSolubilityDisplay device
Provided are a colored composition which enables the formation of a pattern having excellent heat resistance and excellent solubility in solvents and has inhibited color migration; and a cured film, a color filter, a method for producing a color filter, a solid-state image sensor, and an image display device, each of which uses the colored composition.The colored composition includes a polymer anion having a repeating unit containing a weakly nucleophilic anionic structure, and a dye having a cationic structure, in which the weakly nucleophilic anionic structure represents an anionic structure produced by dissociating an organic acid having a lower pKa value than the pKa value of sulfuric acid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Organic electroluminescent device, method of manufacturing organic electroluminescent device, and electronic apparatus
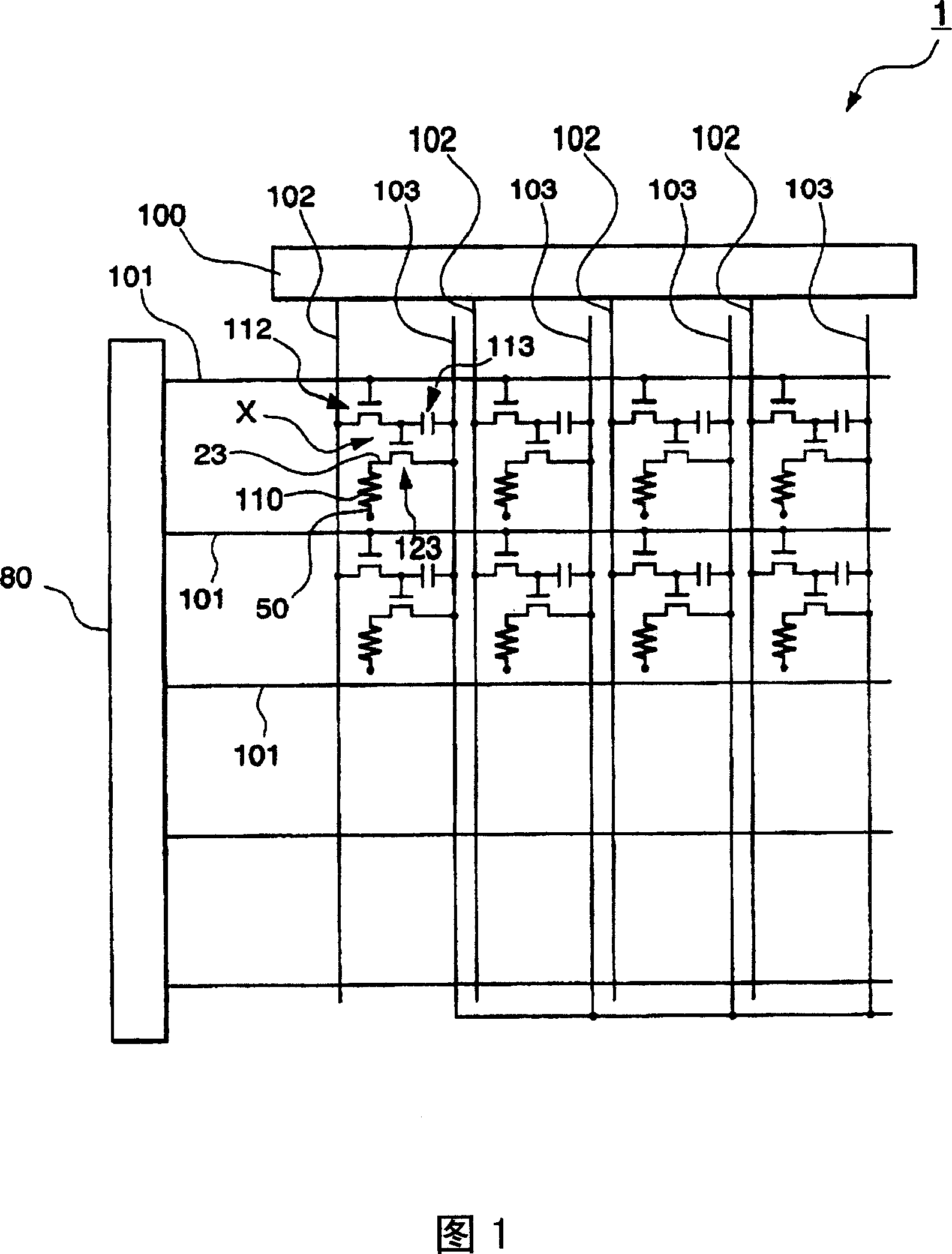
InactiveCN1929706AReduce color shiftReduce brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesColor shiftOrganic electroluminescence
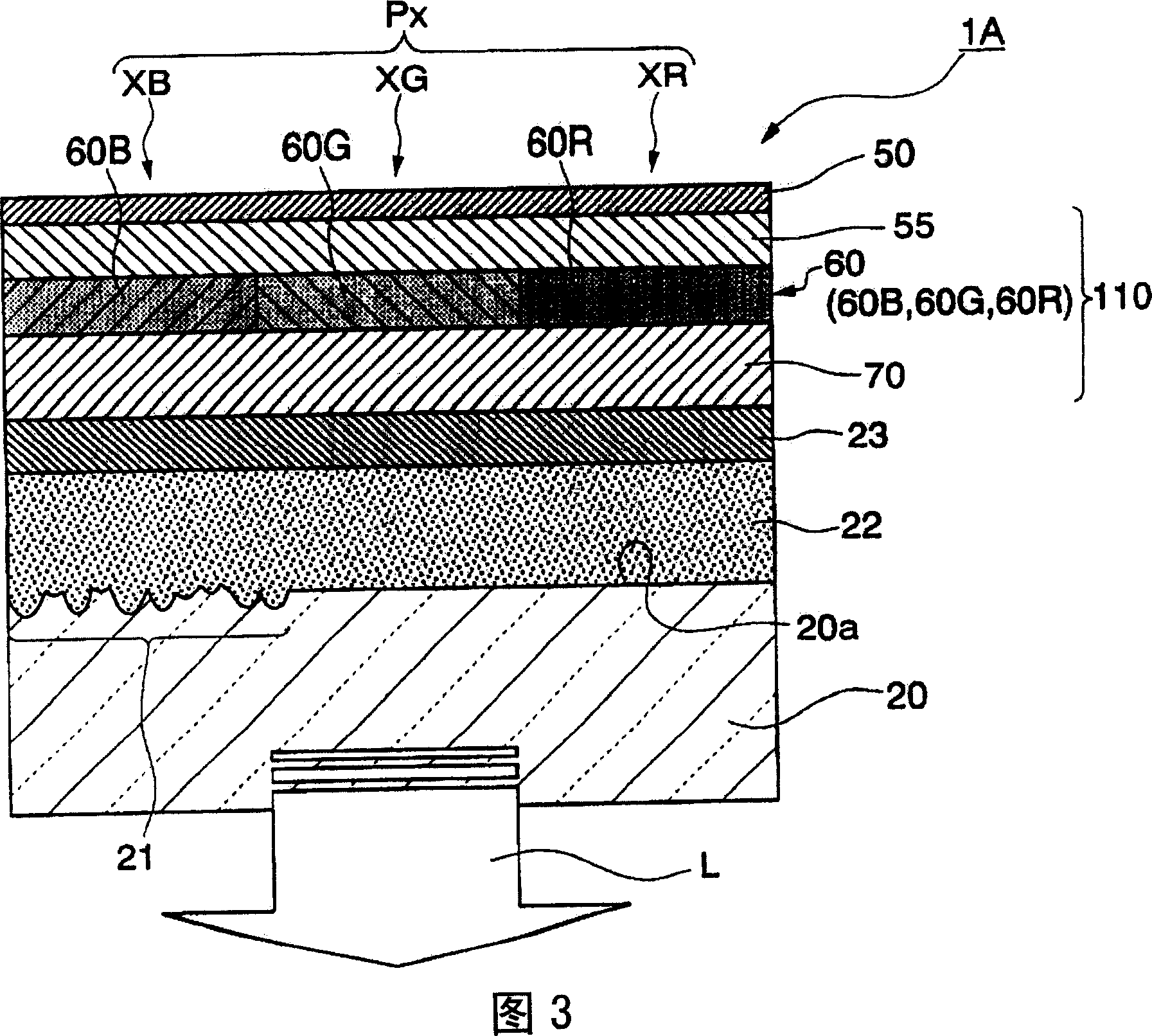
The invention provides an organic EL (ElectroLuminescent) device, a method of manufacturing an organic EL device, and an electronic apparatus free from color shift or change of brightness even when an observer sees it from front or at wide angles. Of the organic electroluminescent device 1A equipped with pixels XB, XG, XR each having a light-emitting function layer pinched by a first electrode 23 and a second electrode 50, and a unit pixel group Px consisting of a plurality of pixels XB, XG, XR, selected pixels out of the unit pixel group Px are provided with a dispersion part 21 for dispersing emission light L of the light-emitting function layer 110.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for producing light-emitting device
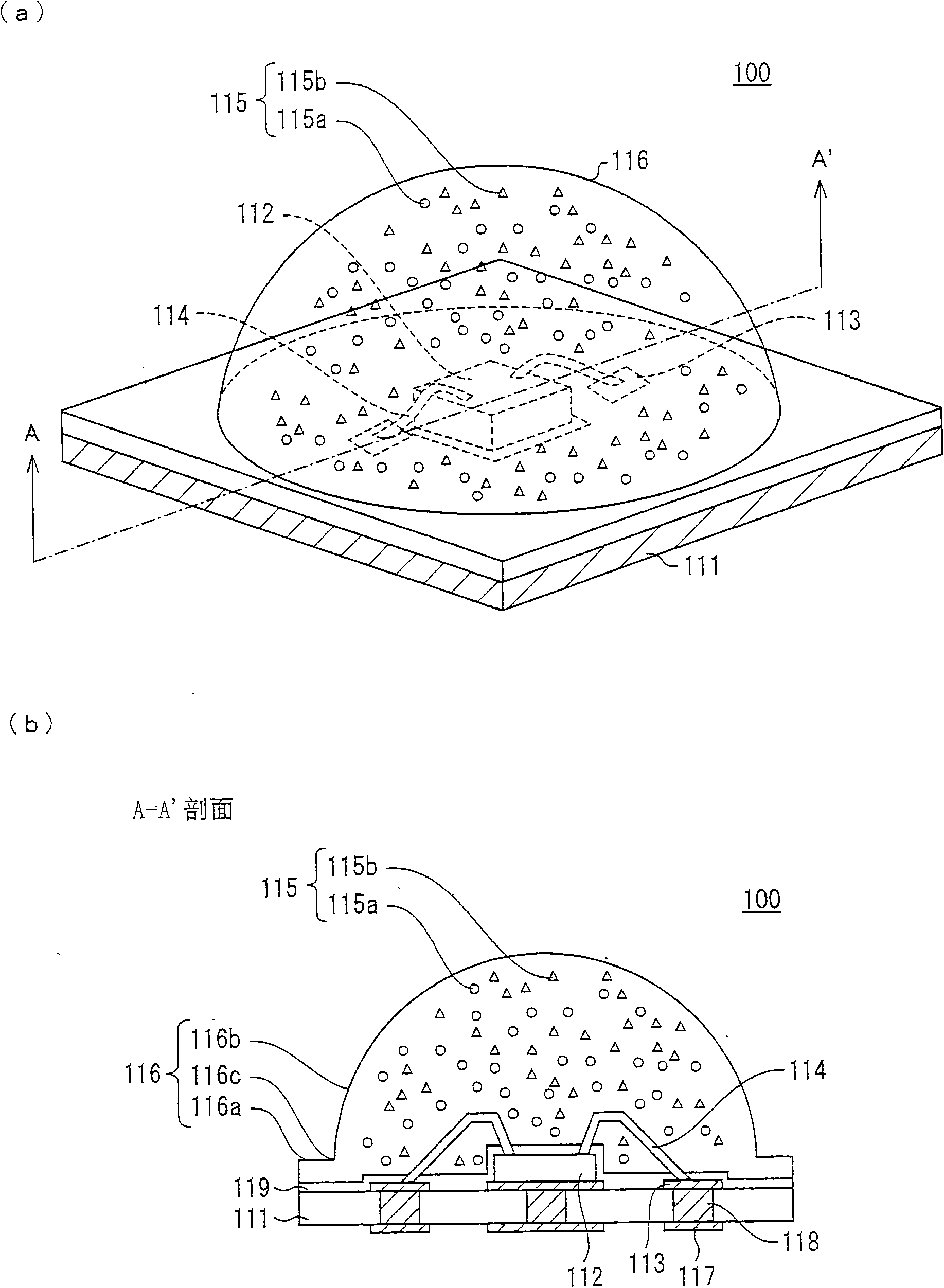
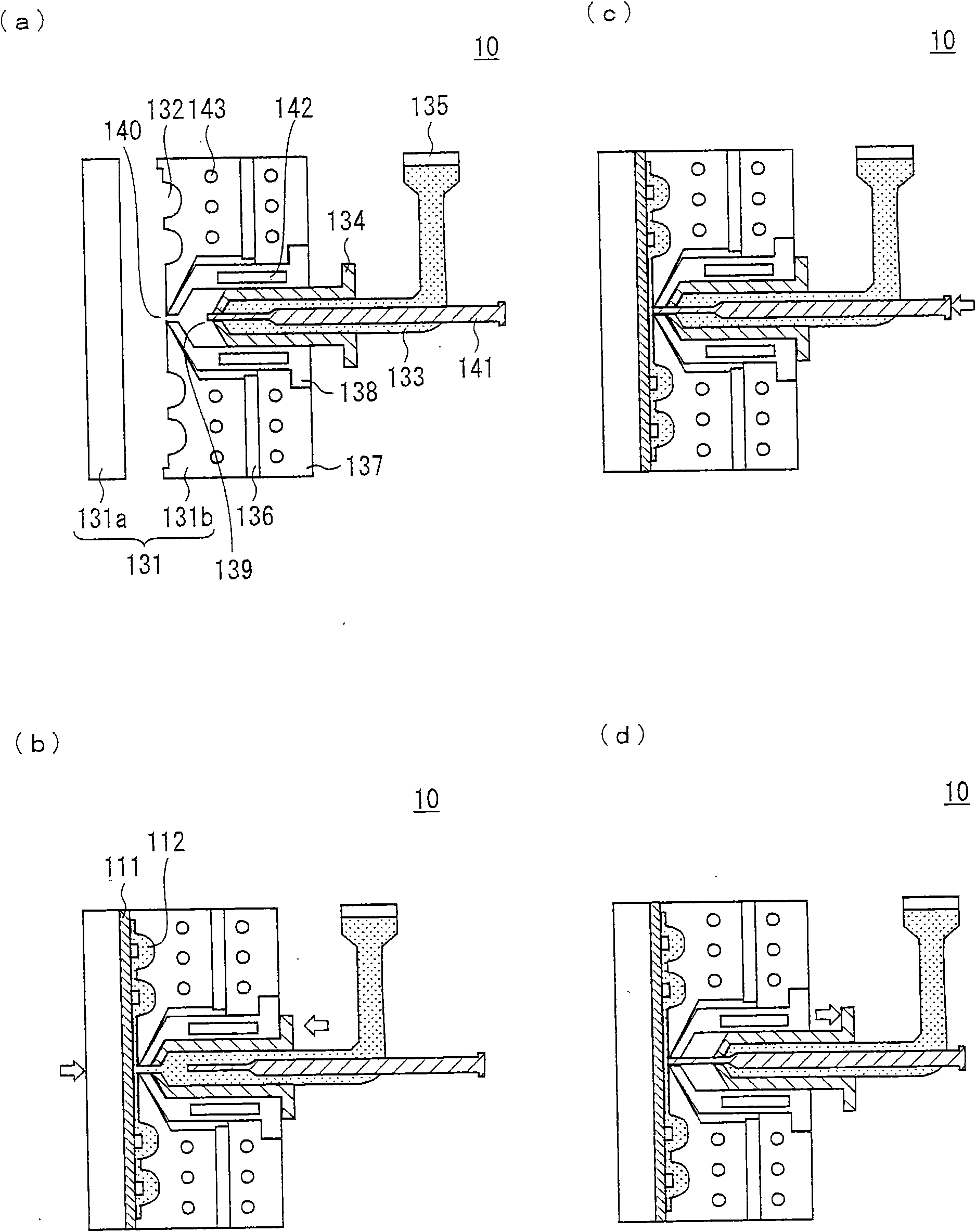
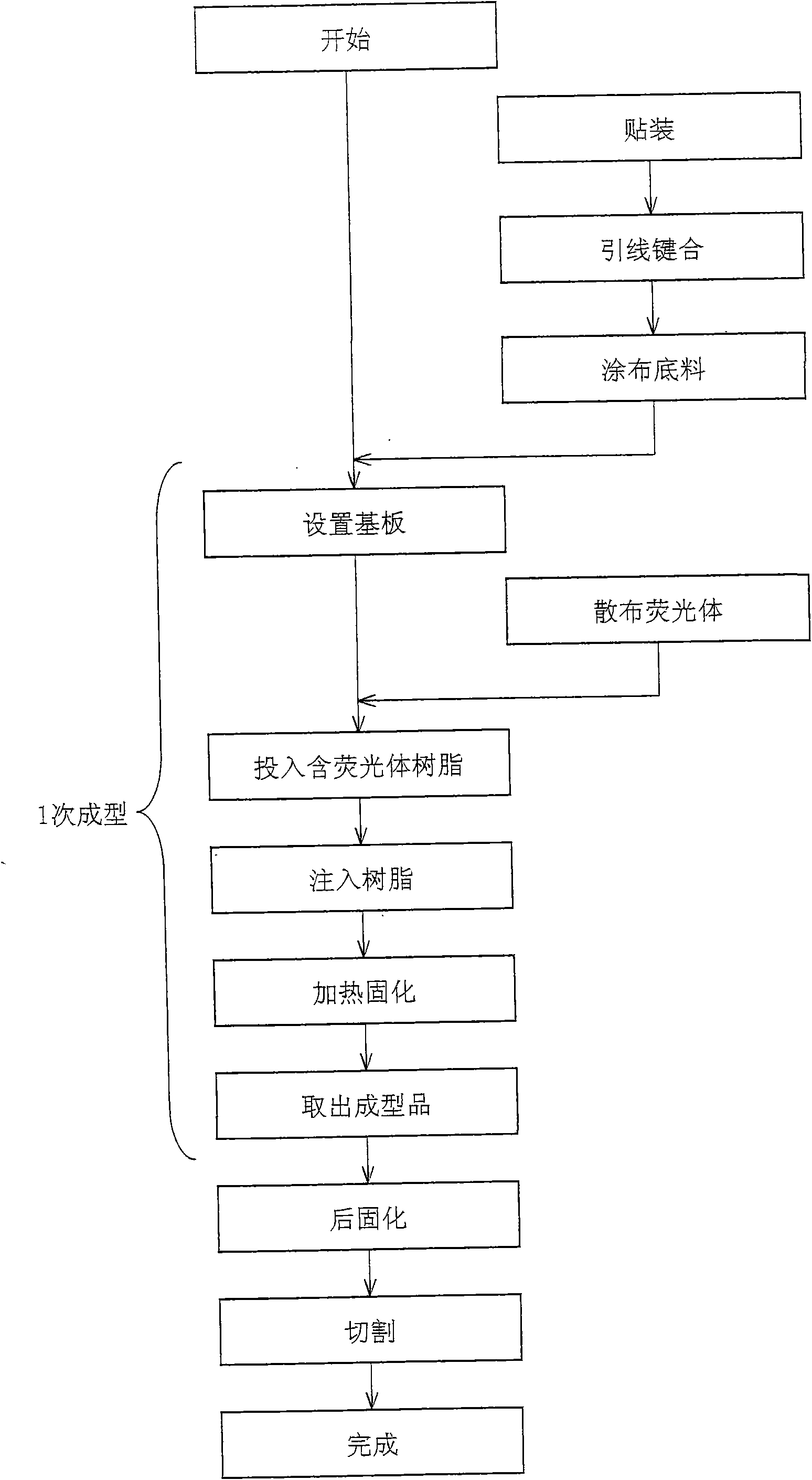
InactiveCN101635329ASuppresses color shiftSuppresses color shift of incident lightPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringDie bonding
To restrain color variation in light emitted from a light-emitting device. A method for producing a light-emitting device includes the steps of: (a) die-bonding a chip onto a substrate so as to prepare a die-bonded substrate; (b) preparing a mold having a cavity; (c) setting the die-bonded substrate such that the chip is placed in the cavity; and (d) injecting sealing resin into the cavity via a runner section. In the method, the runner section is capable of maintaining its temperature at a low temperature lower than a temperature of the mold and the step (d) injecting the sealing resin that is maintained at the low temperature in the runner section, into the cavity via the runner section.
Owner:SHARP KK
Image signal processing apparatus, image signal processing method and program
ActiveCN103533213ASuppresses color shiftImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColor signalImage signal
The invention provides an image signal processing apparatus, an image signal processing method and a program. The image signal processing apparatus includes multiple color support distortion correcting units receiving a color signal of a correction target image, performing image distortion correction of a color based on a lens distortion characteristic and generating a correction image supporting the color. Each of the multiple color support distortion correcting units performs processing of receiving a reference signal indicating a pixel position in an input image applied to calculate a pixel value of an output correction image, and setting a pixel value of the pixel position indicated by the reference signal in the input image as an output pixel value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Polarizing plate with optical compensation layer, liquid crystal panel using polarizing plate with optical compensation layer, liquid crystal display unit, and image display unit
InactiveCN101292181AAvoid light leakageContributes to thinningPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPhase differencePolarizer
A polarizing plate with an optical compensation layer capable of contributing to its thinning, realizing high contrast with viewing angle characteristics improved, preventing interference non-uniformity and thermal non-uniformity, being limited in color shift, delivering a good color reproducing feature, and favorably preventing light leakage at black displaying; and a liquid crystal panel, a liquid crystal display unit and an image display unit using such a polarizing plate with an optical compensation layer. The polarizing plate with an optical compensation layer comprises a polarizer, a first optical compensation layer, an adhesive layer, and a second optical compensation layer sequentially in the order mentioned, wherein the first optical compensation layer has a refractive index distribution, nx>ny=nz, with its in-plane phase difference Re1 exhibiting wavelength dispersion characteristics that gradually decrease toward a short-wavelength side and with its in-plane phase difference Re1 being 90-160 nm, and the second optical compensation layer is a coating layer, has a refractive index distribution, nx=ny>nz, with its in-phase difference Re2 being 0-20 nm, its phase difference Rth2 in thickness direction being 30-300 nm and its thickness being 0.5-10 [mu]m.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display using the same
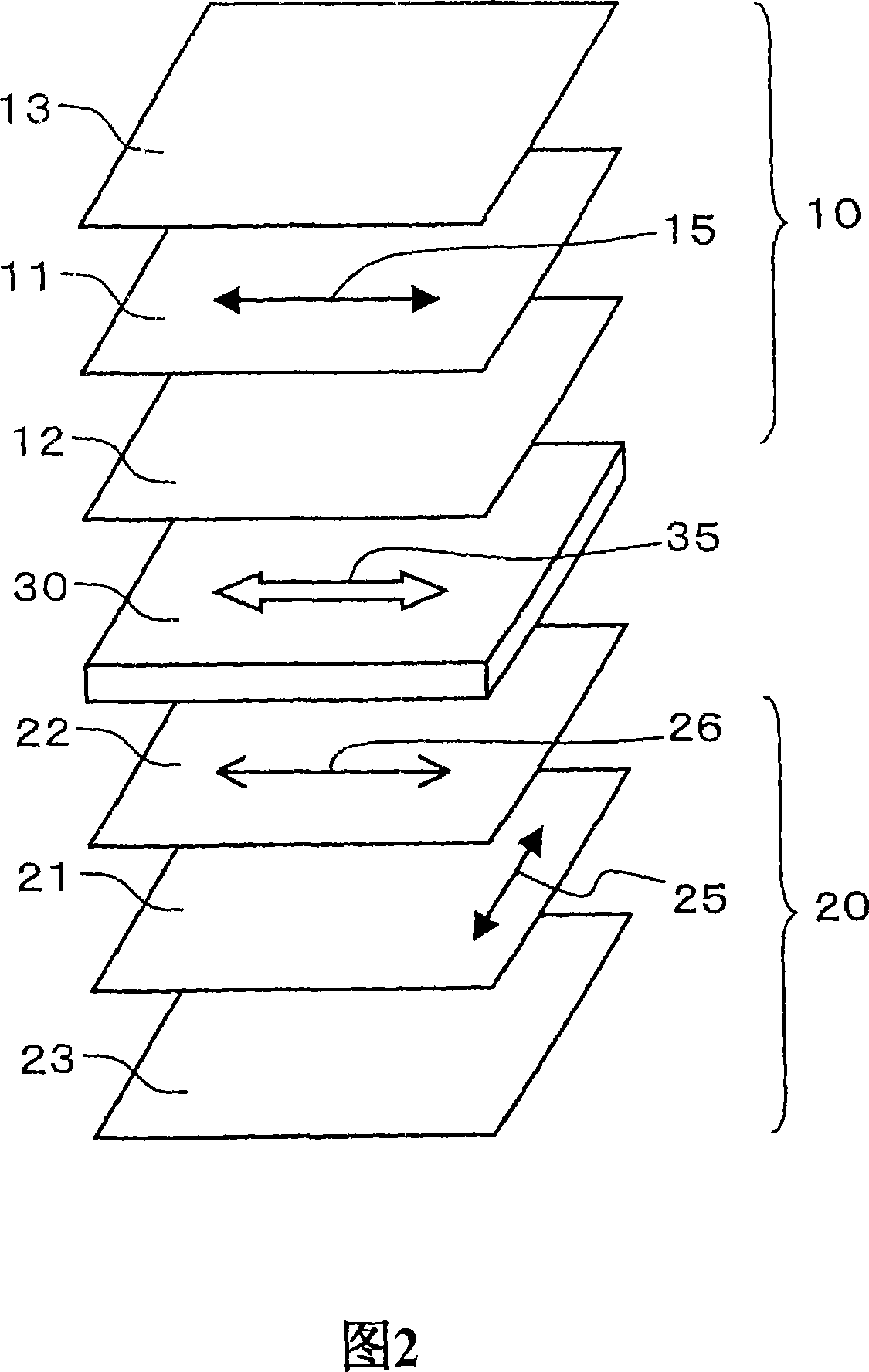
InactiveUS20070013844A1Suppresses color shiftIncrease contrastNon-linear opticsLength waveContrast ratio
A liquid crystal panel that has a high contrast ratio over a wide range and can suppress color shifting effectively is provided. In a liquid crystal panel including between two polarizing plates arranged in a crossed Nicols state a birefringent layer A with nx>ny≧nz, a birefringent layer B with nx≧ny>nz and a VA-mode liquid crystal cell C, it is set that a wavelength dispersion characteristic (α40(A)) of the birefringent layer A, a wavelength dispersion characteristic (α40(B)) of the birefringent layer B and a wavelength dispersion characteristic (α40(C)) of the liquid crystal cell C satisfy conditions α40(B)>α40(C)>α40(A) and 1>α40(A). The wavelength dispersion characteristic α40 represents a ratio of a retardation Re measured with incident light at 430 nm to that measured with incident light at 550 nm, the incident light being inclined by 40° with respect to a normal direction (0°) of a surface of the birefringent layer or a surface of the liquid crystal cell.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical film, optical compensation film, polarization sheet and liquid crystal device using same
InactiveCN1916666AReduce light leakageImprove viewing angle contrastPolarising elementsThin material handlingCopolymerChemistry
Disclosed are the optical film represented by inequalities (1) to (4) and contains a specified kind of polycarbonate copolymer with a specified copolymerization ratio and / or a blend body containing the polycarbonate copolymer, the optical compensating film using the same, wherein (1) 0.1 G02B 1 / 00 G02F 1 / 13363 G02B 5 / 30 9 79 6 2006 / 8 / 17 1916666 2007 / 2 / 21 000000000 Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. Japan Nakayama Moto Ohashi Yusuke yu hui 72002 NTD Patent & Trademark Agency Ltd. Units 1805-6, 18th Floor, Greenfield Tower, Concordia Plaza, No.1 Science Museum Road, Tsimshatsui, east, Kowloon, Hong Kong 100045 Japan 2005 / 8 / 17 236856 / 2005
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image forming method and image forming system
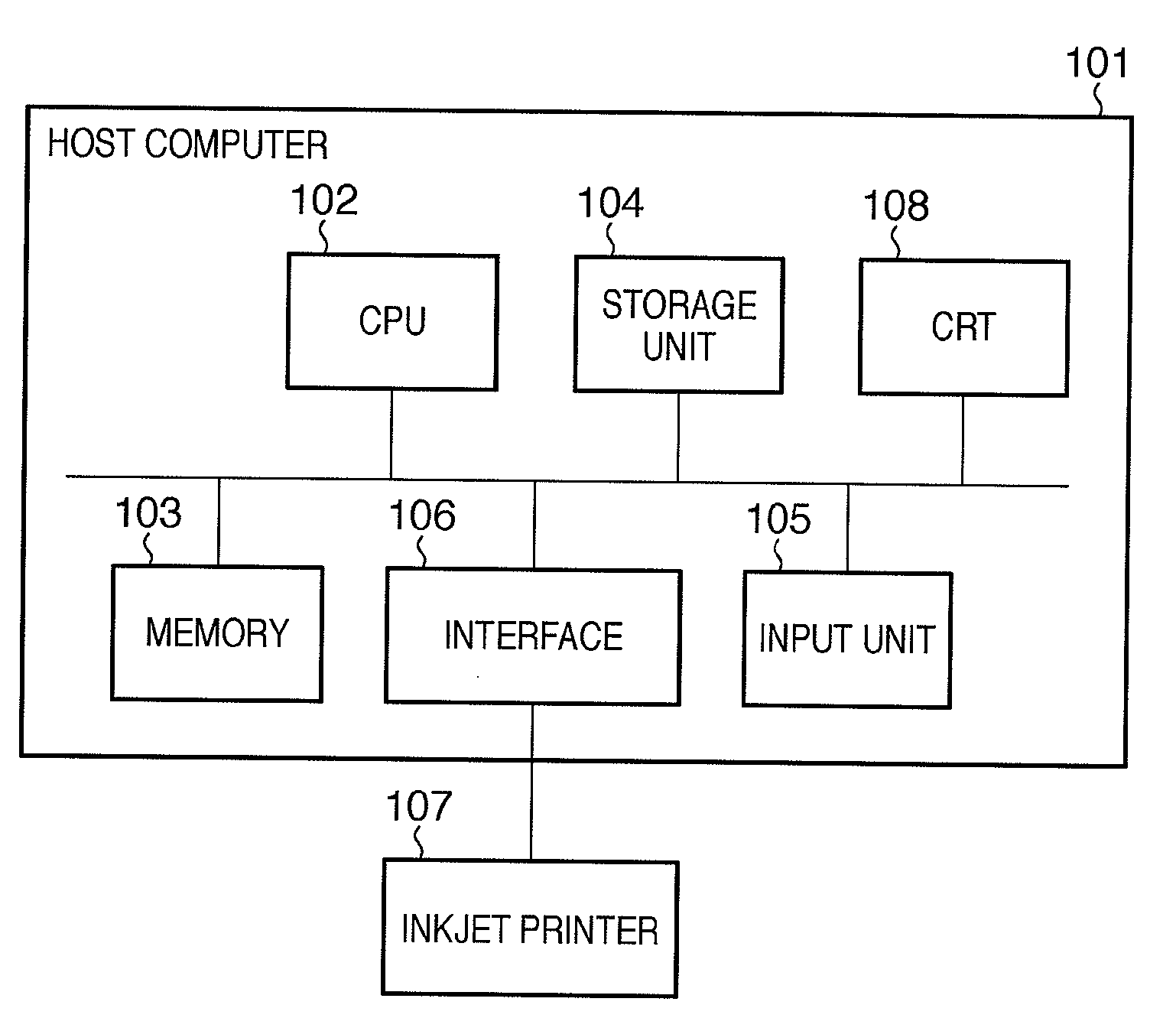
InactiveUS20100157336A1Eliminate the problemSuppressing color shifts in correspondenceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsHueSignal transition
An image forming apparatus sets one of a plurality of modes including a monochrome mode of forming a monochrome image, converts a multivalued luminance signal into signal values of color material amounts to be used to form the image and forms the image using color materials based on the signal values. The color materials used in the forming when the monochrome mode is set include an achromatic color material and at least two auxiliary color materials which have hues opposite to each other and a chroma larger than that of the achromatic color material.
Owner:CANON KK
Color image formation apparatus
InactiveUS20050001897A1Precise positioningSuppresses color shiftInking apparatusElectrographic process apparatusColor imageElectrical conductor
In an image formation apparatus having a photoconductor unit including a photoconductor and a developing unit for storing toner supplied to the photoconductor, the developing unit is displaceably placed in an apparatus main unit, and then, the photoconductor unit is detachably placed in the apparatus main unit and is positioned at a predetermined position, thereby the displaceable developing unit previously placed is positioned relative to the photoconductor unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Color image formation apparatus
InactiveUS6943817B2Precise positioningSuppresses color shiftInking apparatusElectrographic process apparatusColor imageImage formation
An optical unit includes an incidence optical member for giving a different angle to each of a plurality of laser beams to form a color image and making the laser beam incident on a single polygon mirror rotation body; a single first reflecting mirror for reflecting the laser beam for each color reflected on the polygon mirror in the opposite direction to the incidence direction; and a single or plurality of second reflecting mirrors having Fθ characteristics for forming an image of each reflected laser beam reflected on the first reflecting mirror on the image formation position for each color.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light emitting device, light source for illumination, and illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20150194412A1Good colorSuppresses color shiftSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
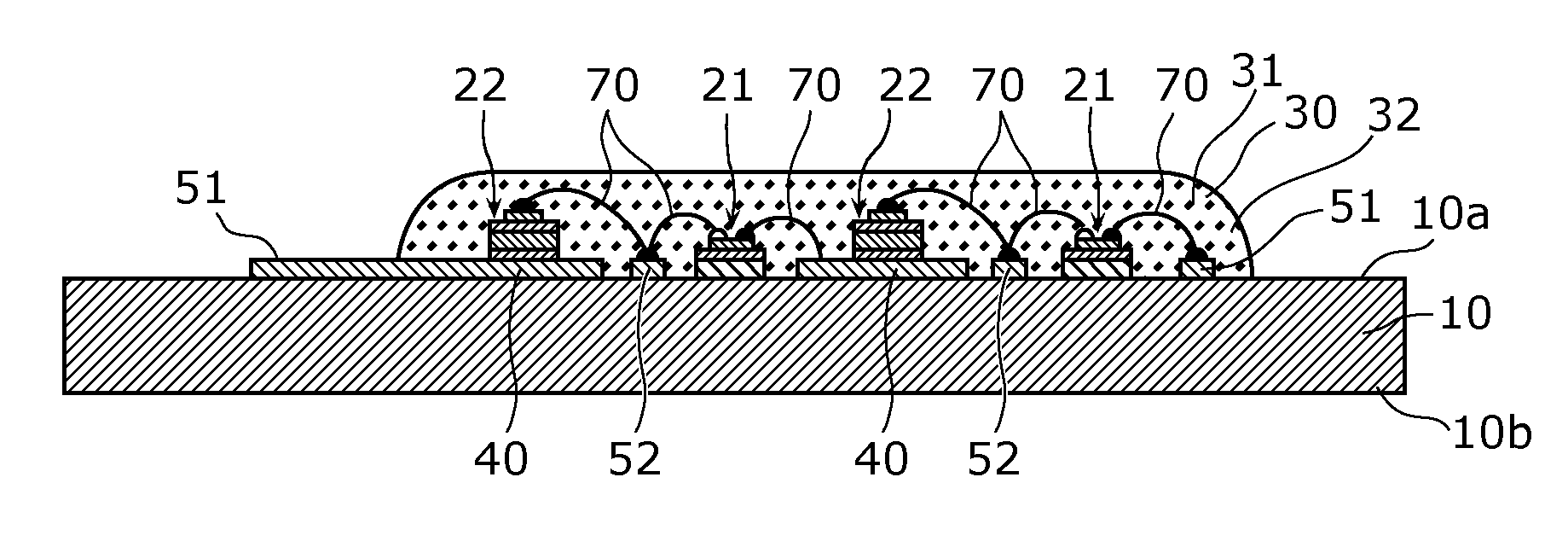
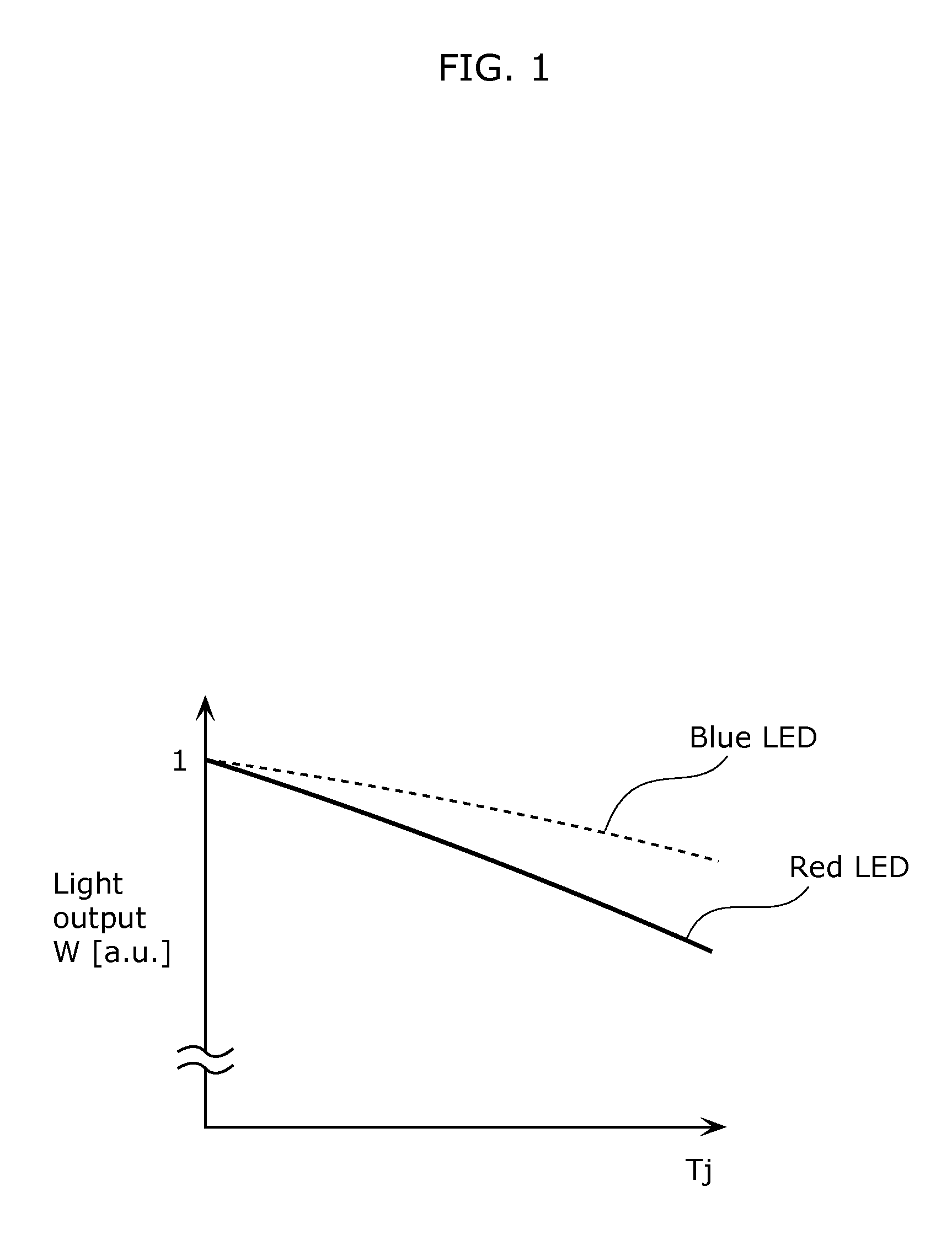
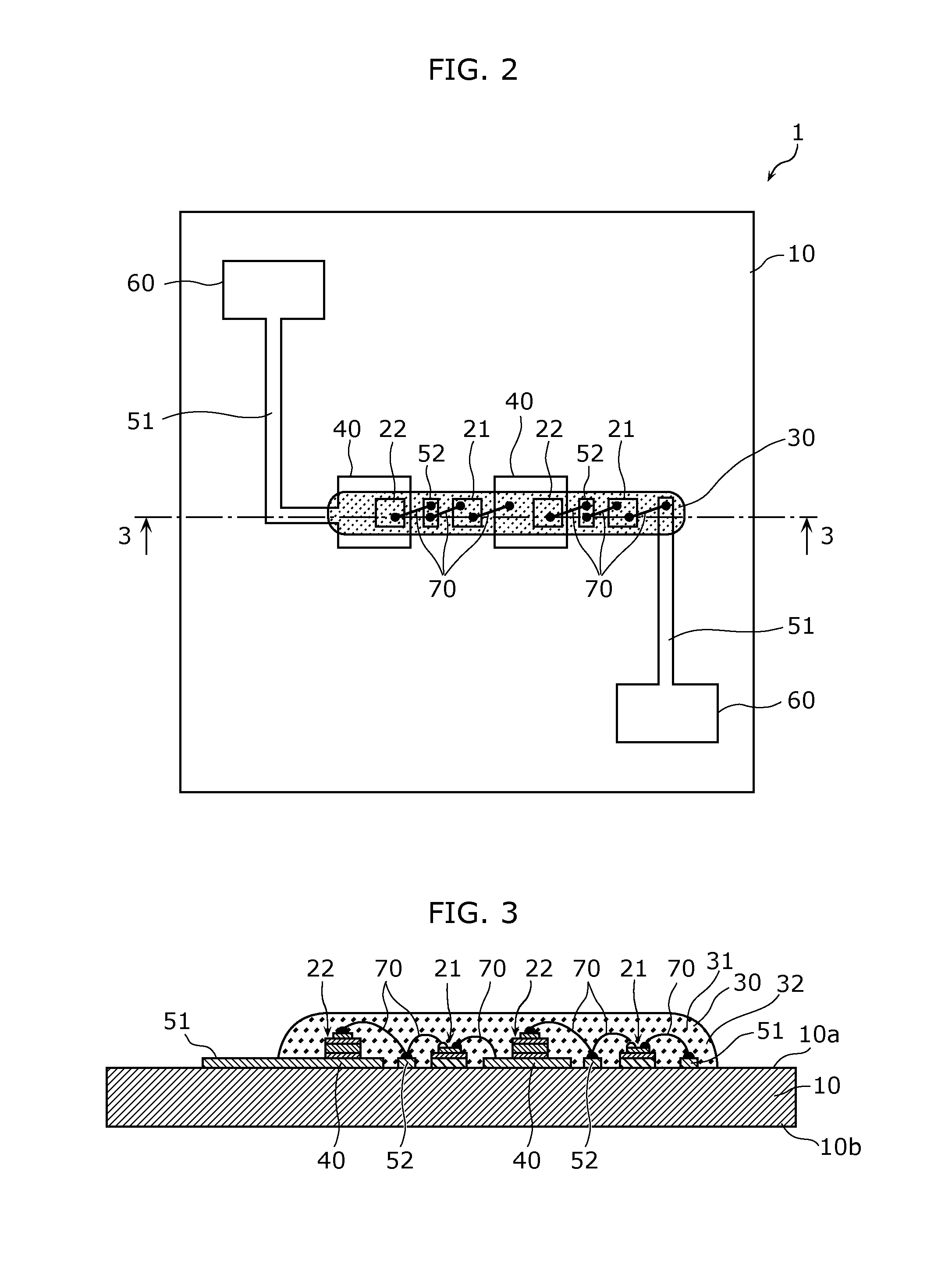
A light emitting device includes: a substrate; a first light emitting element and a second light emitting element that are mounted above the substrate; and a heat transfer pattern that is formed on the substrate. A rate of decrease in light output with respect to a temperature increase is greater for the second light emitting element than for the first light emitting element. The second light emitting element is mounted above the substrate via the heat transfer pattern, and the first light emitting element is mounted above the substrate without the heat transfer pattern
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
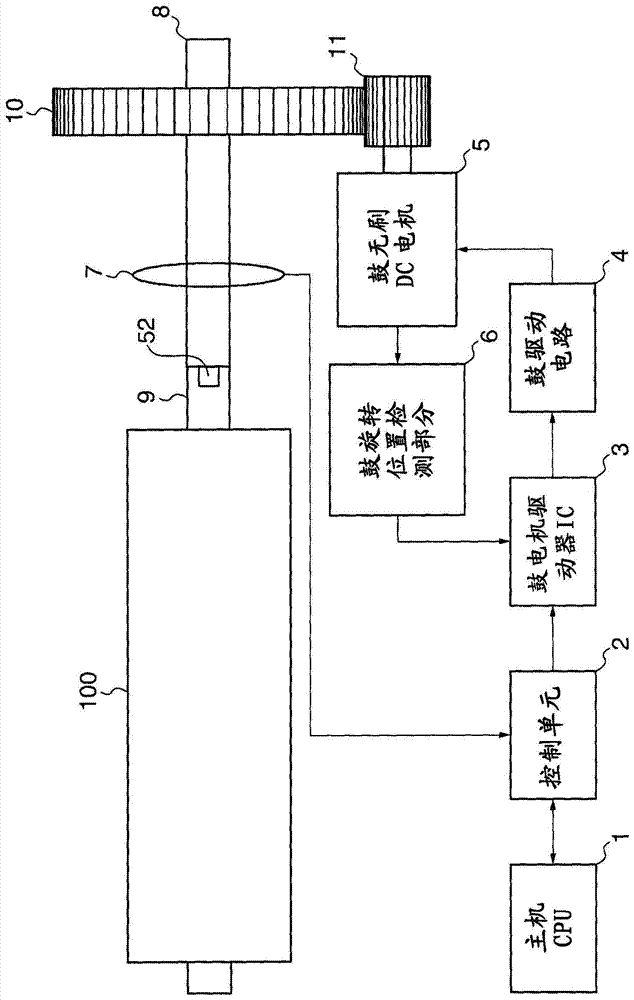
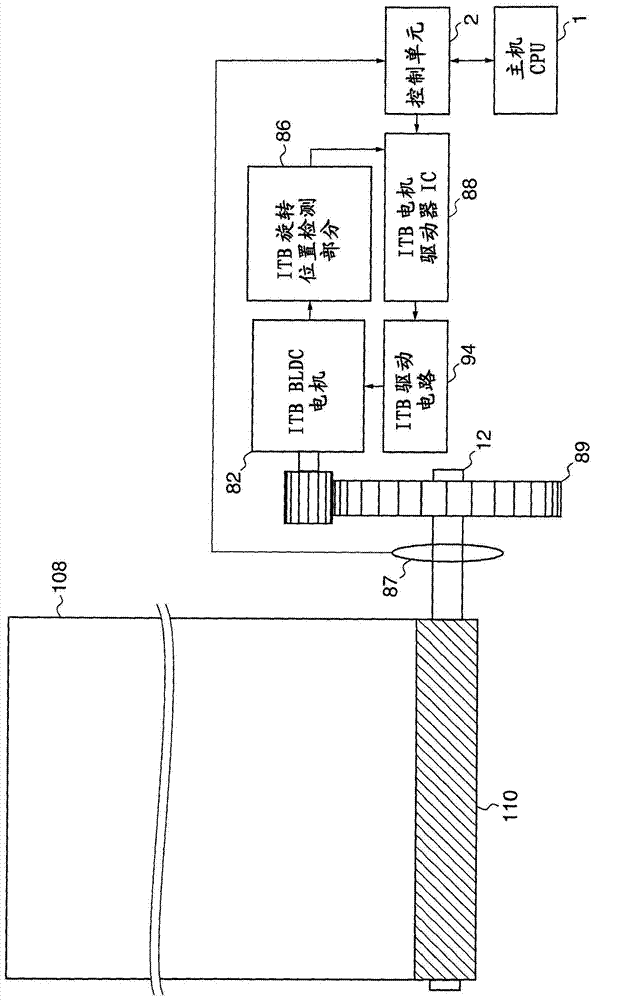
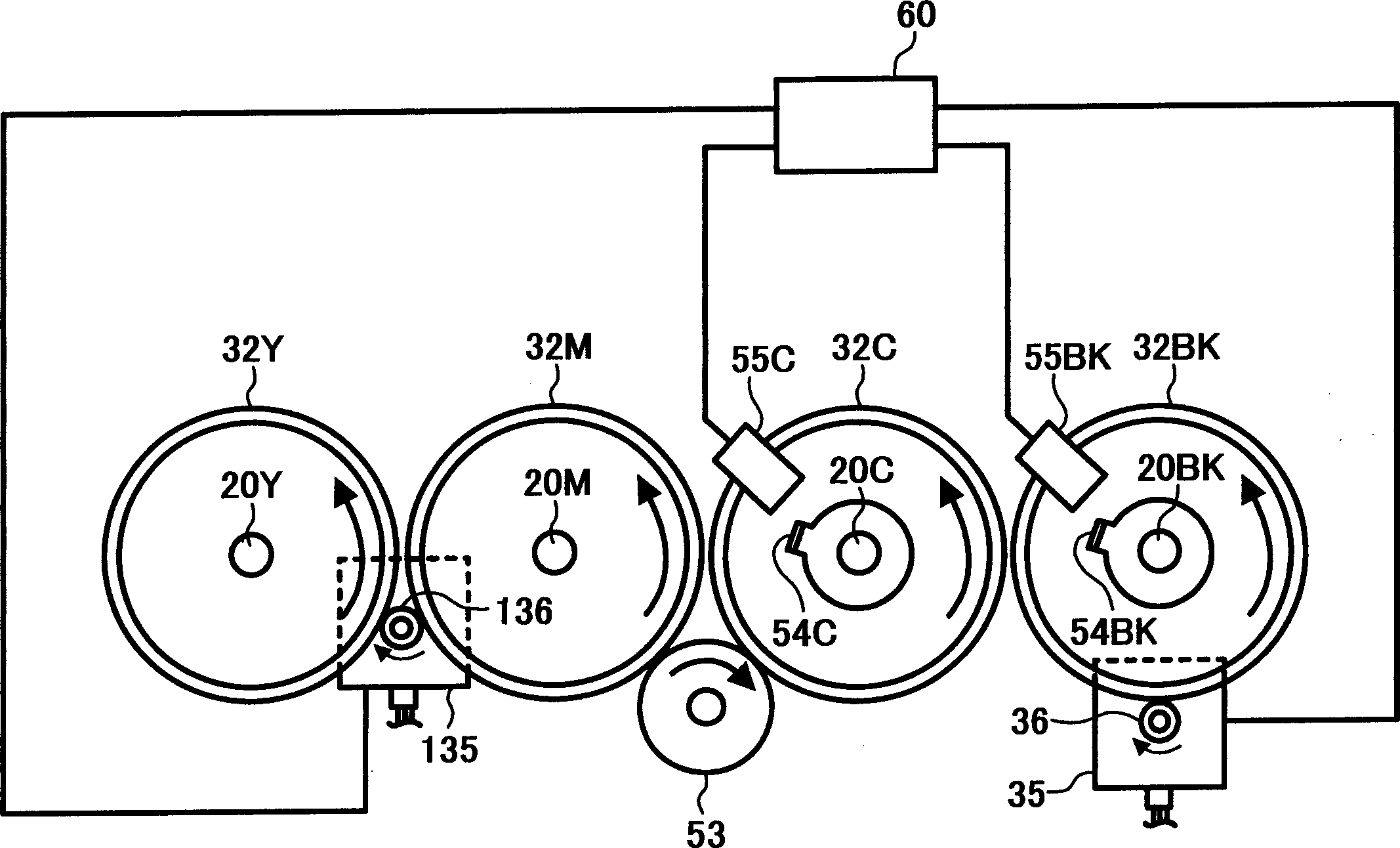
ActiveCN107009756ASuppresses color shiftTransfer printingPrinting mechanismsImage formationThermal Head
In order to provide an image forming apparatus which can reduce color deviation at the time of forming an image on a medium, the present printing apparatus comprises an image forming unit which forms an image by superimposing images, each formed with corresponding color of ink, on a transfer film (46) while heating a thermal head (40), a film conveying device which conveys a transfer film (46), a sensor (Se1) which detects a stretch of the transfer film (46) occurring due to heating with the thermal head (40), a controller which controls the image forming unit to change a line cycle of the thermal head (40) in accordance with a stretch of the transfer film (46) detected by the sensor (Se1).
Owner:COPYER
Back reflector and back projecting picture displaying appts. using same
InactiveCN1540368ASuppresses color shiftSuppress brightnessMirrorsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsBack reflectorColor shift
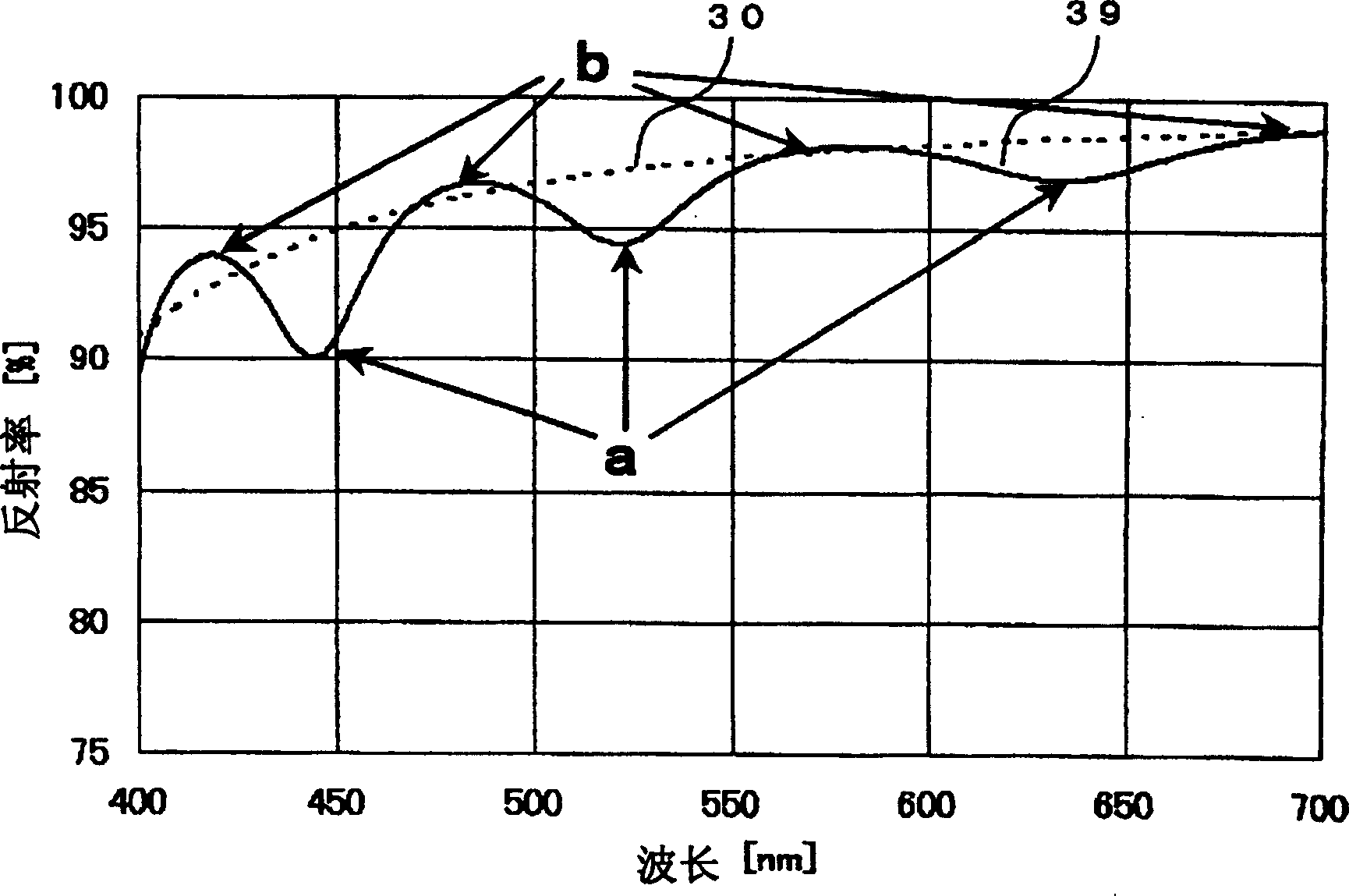
In the present invention, there is disclosed a reflective mirror whose contrast or resolution performance is equal to that of a surface mirror of a glass mirror for general use and which does not have any problem in reliability of resistance to environment and whose color shift or brightness performance is inhibited from being degraded. For this, in the present invention, a reflective film is formed on a glass substrate by use of silver mirror reaction, and a topcoat is formed of a colorless / transparent resin. At this time, a wavelength of a crest of a ripple indicated by a reflectance characteristic is constituted to substantially agree with that of a green luminescent line. Accordingly, a back projection type video display device which is satisfactory in the contrast or resolution performance can be prepared.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
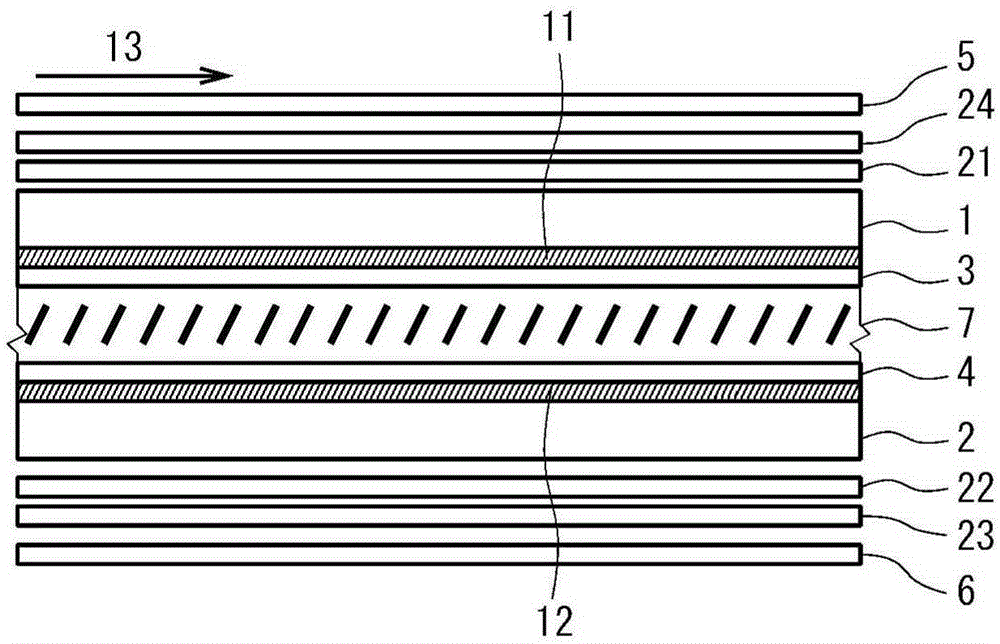
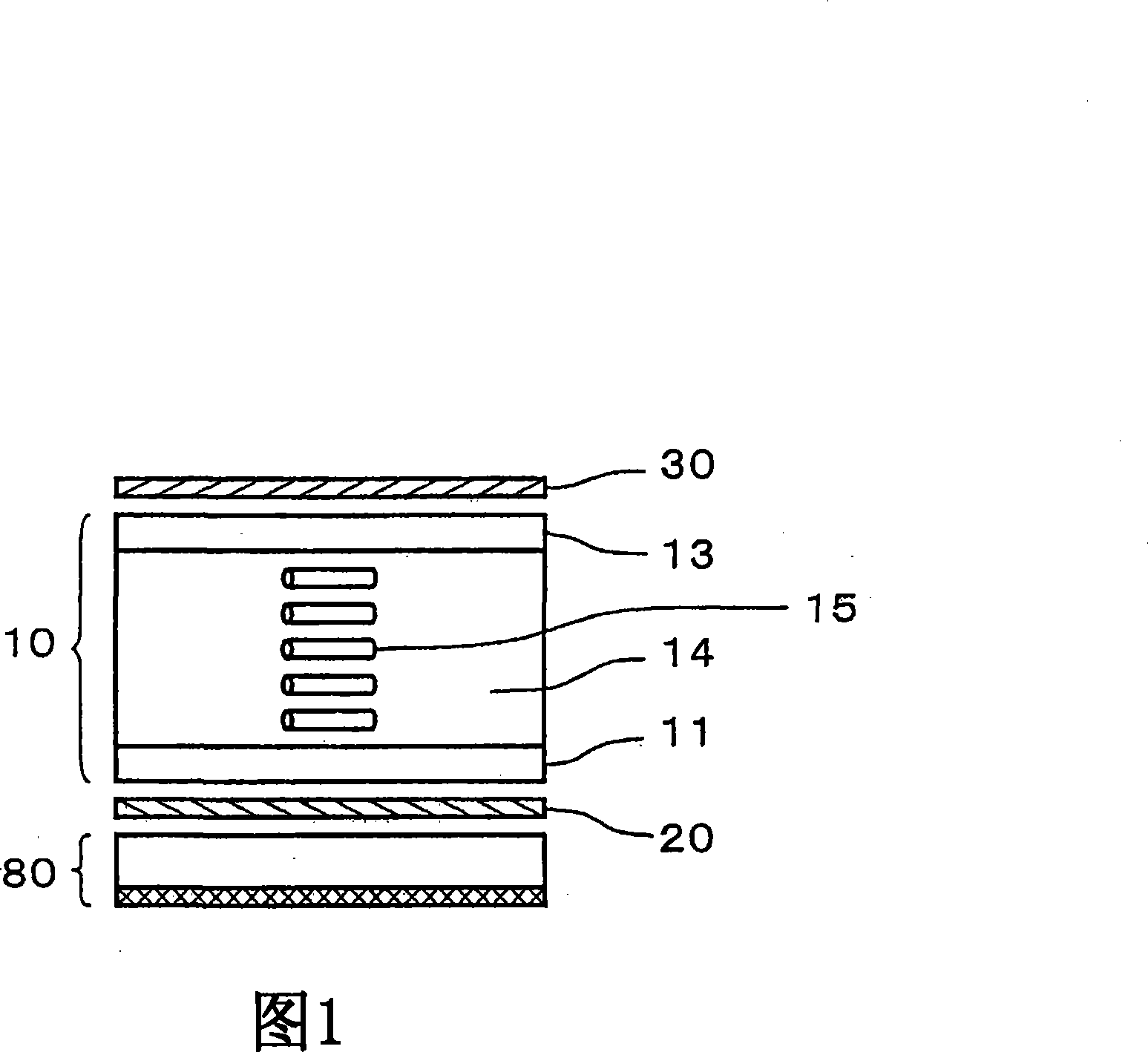
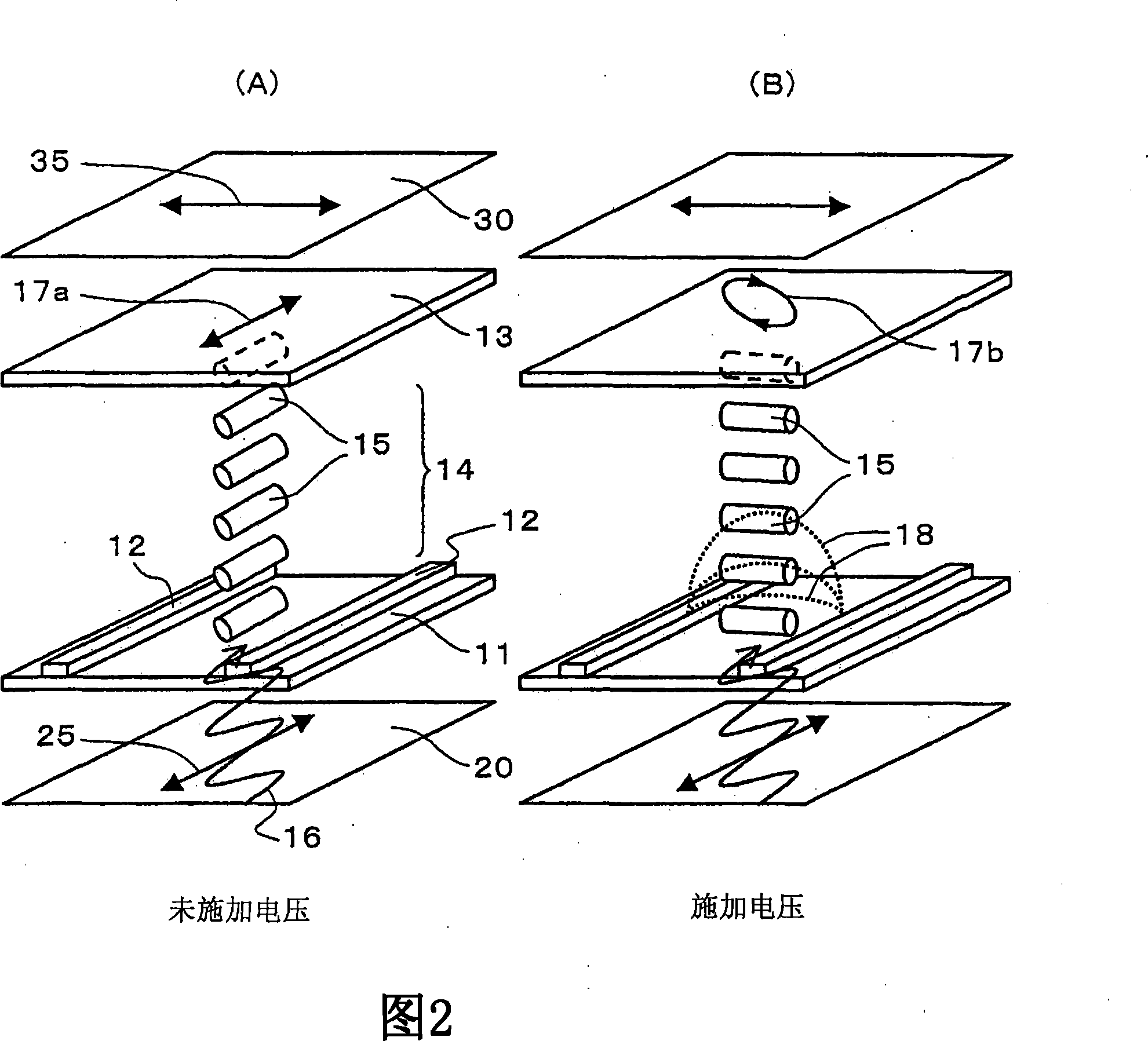
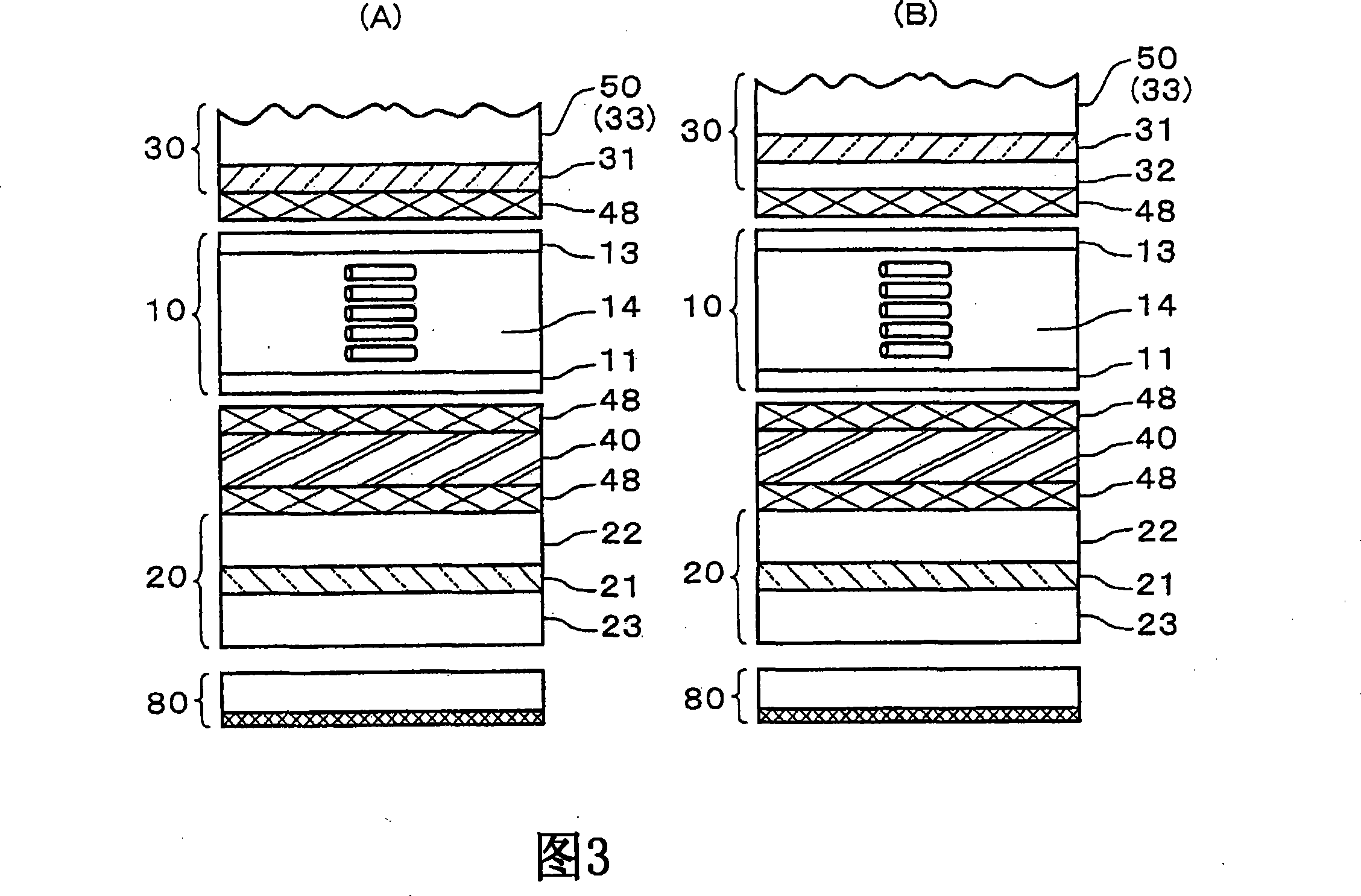
Liquid crystal display device
The invention provides a liquid crystal display device which can restrain color offset of a normally white displayed vertical oriented liquid crystal display device in observation in a left-and-right direction. The liquid crystal display device is provided with a first substrate, a second substrate, a liquid crystal layer, a first polarizing plate, a second polarizing plate, a first optical board, a second optical board and a third optical board. The absorption axes of the polarizing plates are configured approximately perpendicular with one another. Furthermore each polarizing plate is configured at an angle of approximate 45 DEG relative to the orienting direction of an approximately central part in the layer thickness direction of the liquid crystal layer when an electric field is applied. The first optical board is a 1 / 4 wavelength board, and the in-surface slow axis is configured at an angle of approximate 45 DEG relative to the absorption axis of the first polarizing plate. The second optical board is a 1 / 4 wavelength board, and the in-surface slow axis is configured at an angle of approximate 45 DEG relative to the absorption axis of the second polarizing plate. The third optical board has negative biaxial optical anisotropy, and the in-surface slow axis is configured to be approximately perpendicular with the absorption axis of the first polarizing plate.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Liquid crystal display apparatus and polarizing panel group
ActiveCN101271217BGood anti-glare effectSuppress light leakageStatic indicating devicesPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayPhase difference
Polarization plates (20, 30) are configured at two sides of a liquid plasma panel (10) of IPS mode. A phase separation plate (40) is configured between a polarization plate (20) at back side and the liquid plasma panel (10); the sum of phase difference Rth at the thickness direction of a double refraction layer existed between one side of the liquid plasma surface a polarizer (21) at back side and a base plate (11) surface at back side of the liquid plasma panel (10) is in the range of -40 nm to +40 nm as well as the sum R0 of the plane phase difference is in the range of 100 nm to 300 nm. A polarization plate (31) at the front side includes a polarizer (31) and a transparent protective layer (33) at visual side; the phase difference Rth at the thickness direction between the side plane of the liquid plasma panel of the polarizer (31) and the surface of a base plate (13) at the front side of the liquid plasma panel (10) is in the range of -10 nm to +40 nm; the transparent protective layer (33) at visual side includes a glare-proof layer (50) whose surface is provided with a fine concavo convex satisfied with the ruled optical feature.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveCN104280949ASuppresses color shiftSuppress flickerStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPhysics
The present invention includes first pixels formed to have a first slit having an inclination angle with respect to a rubbing direction and second pixels formed to have a second slit having an inclination angle opposite to the first slit, and at least one of the first pixels having a positive polarity allocated thereto and at least one of the first pixels having a negative polarity allocated thereto exist in the same frame, and at least one of the second pixels having the positive polarity allocated thereto and at least one of the second pixels having the negative polarity allocated thereto exist in the same frame.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
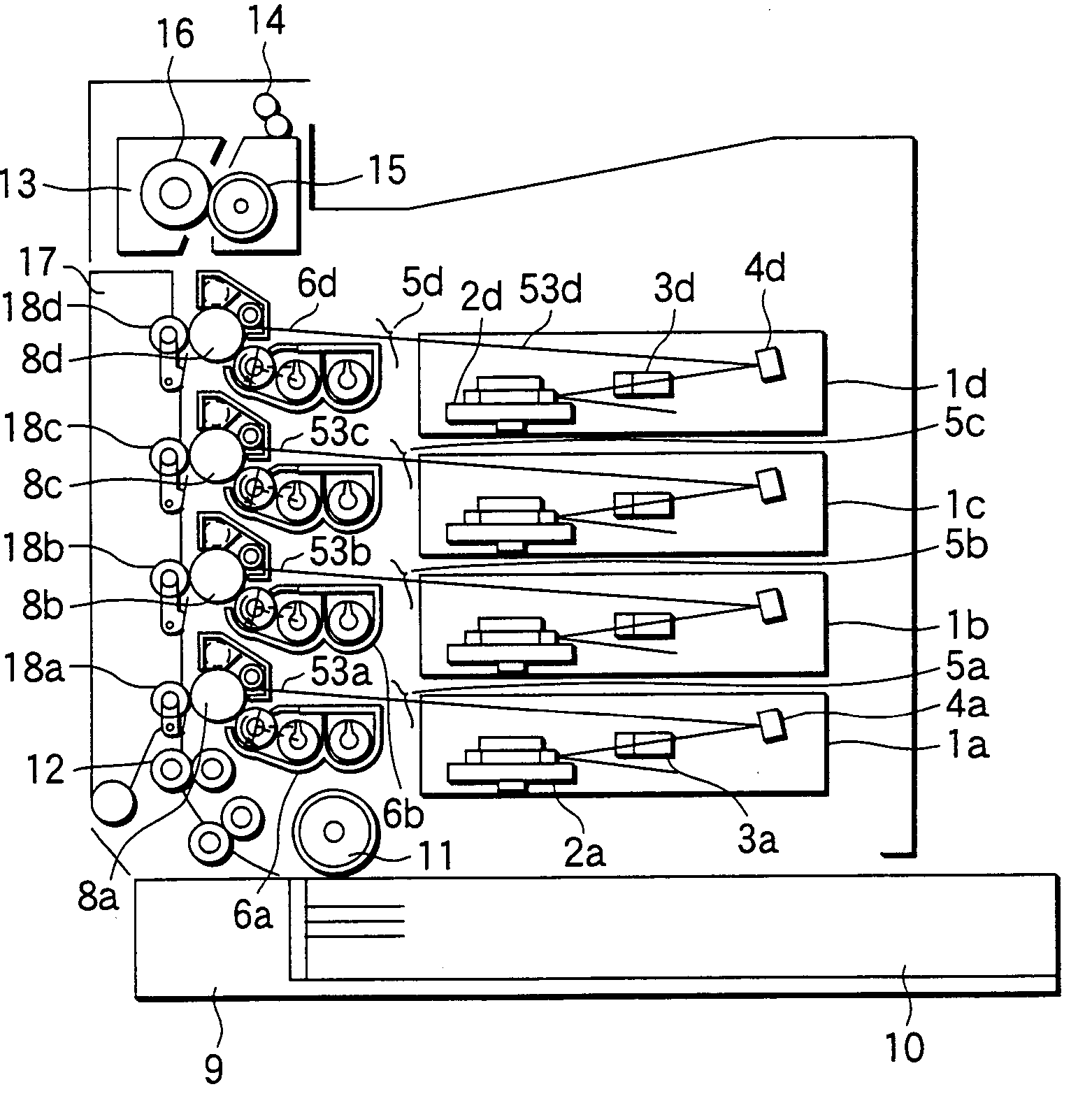
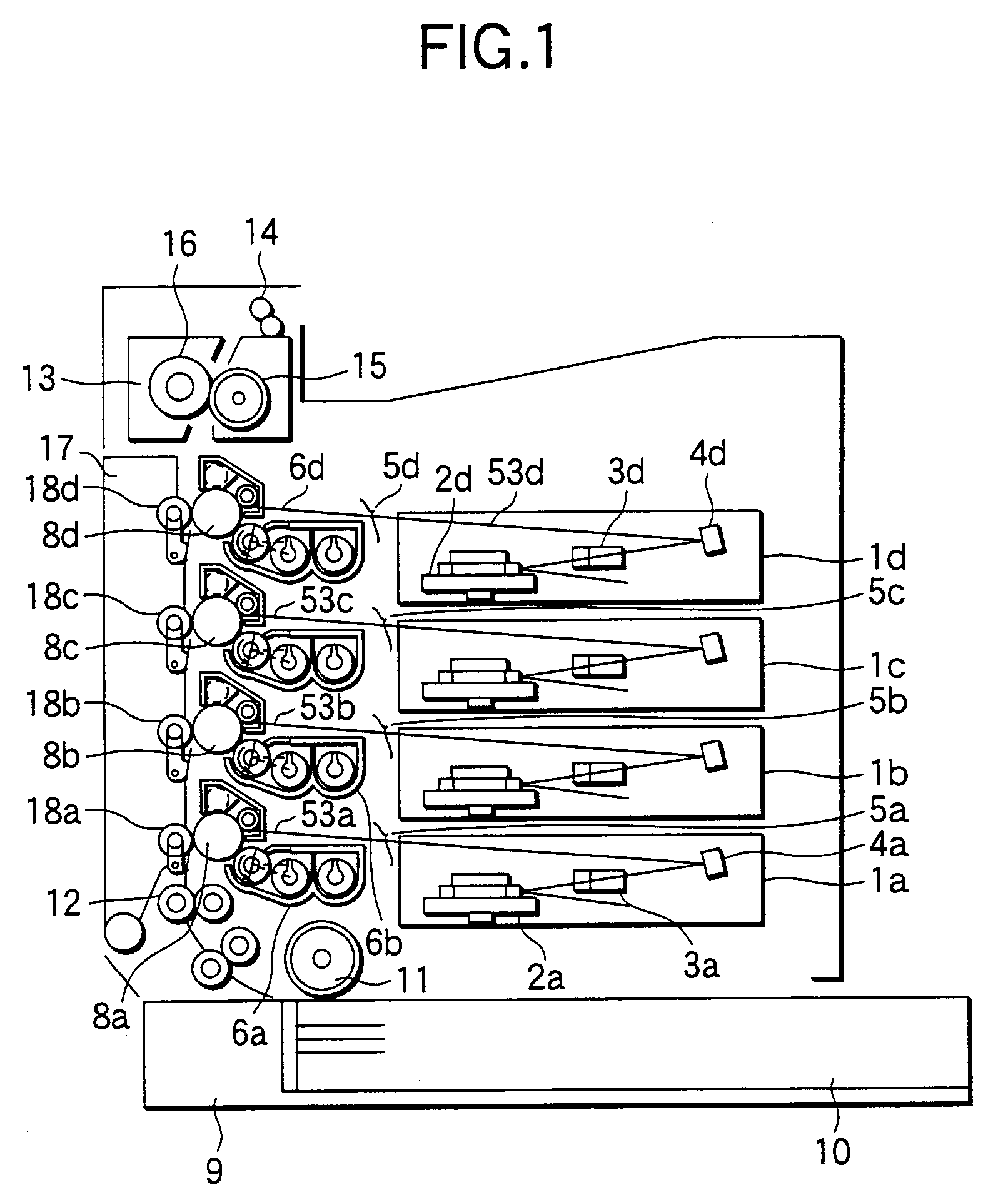
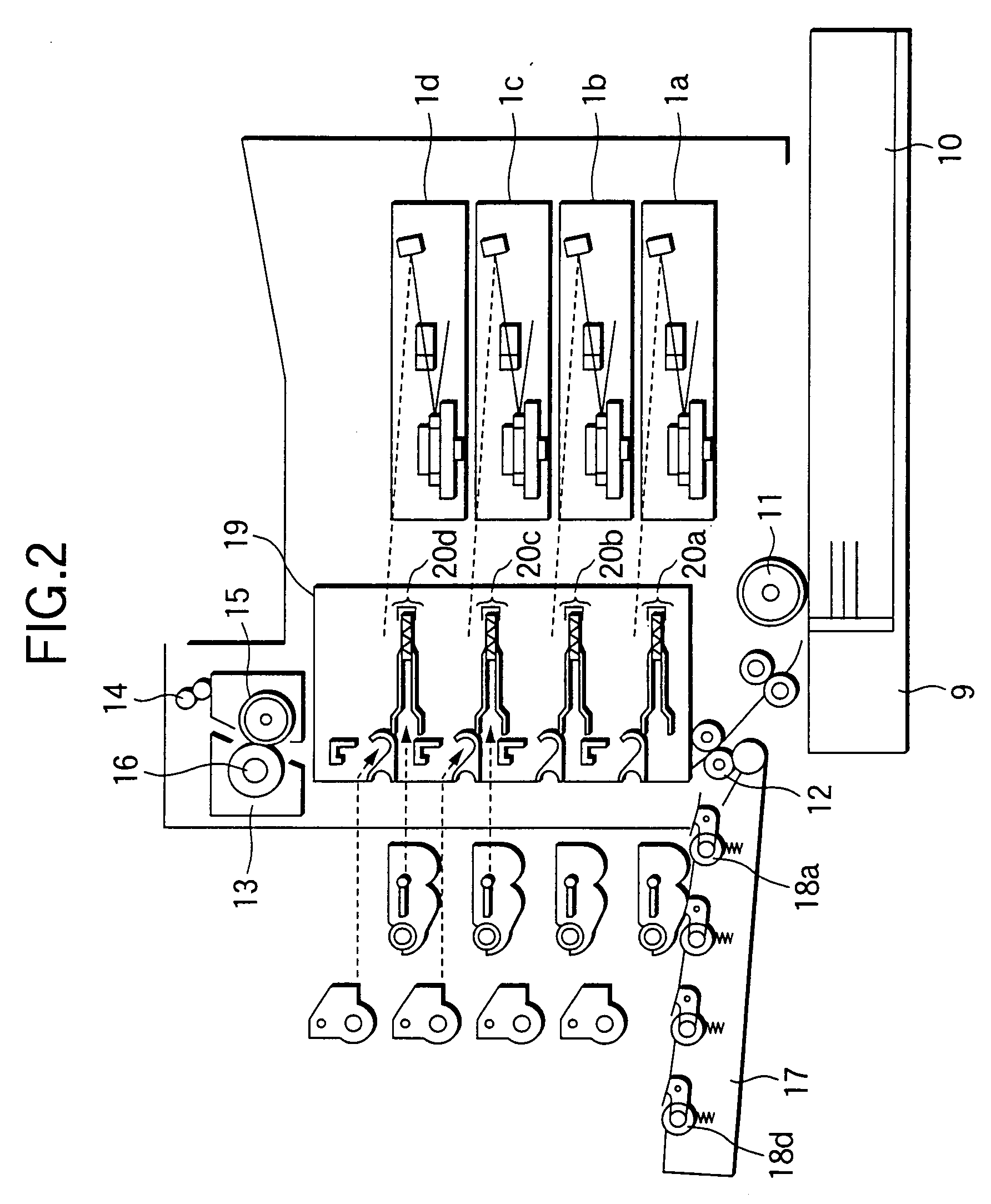
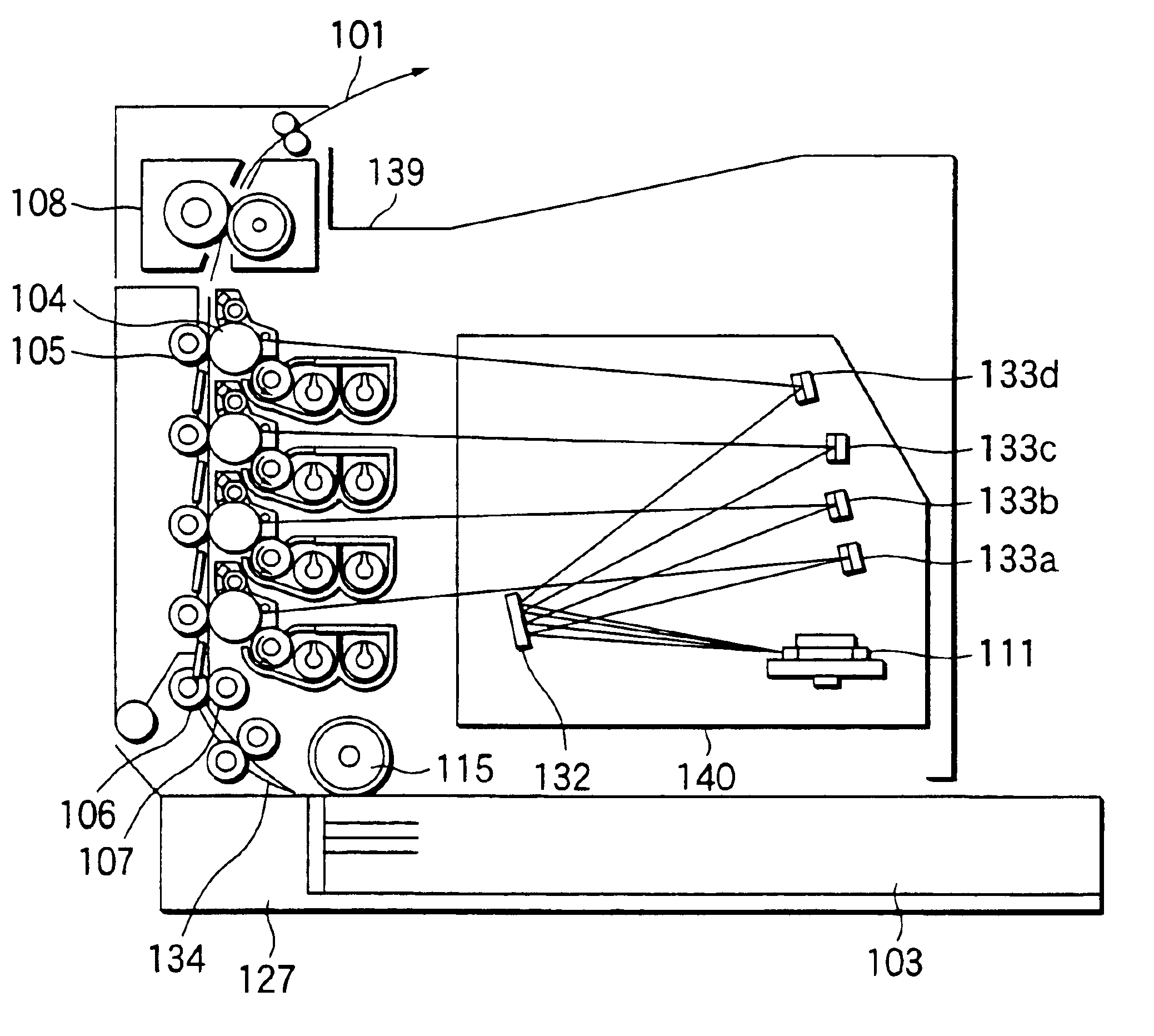
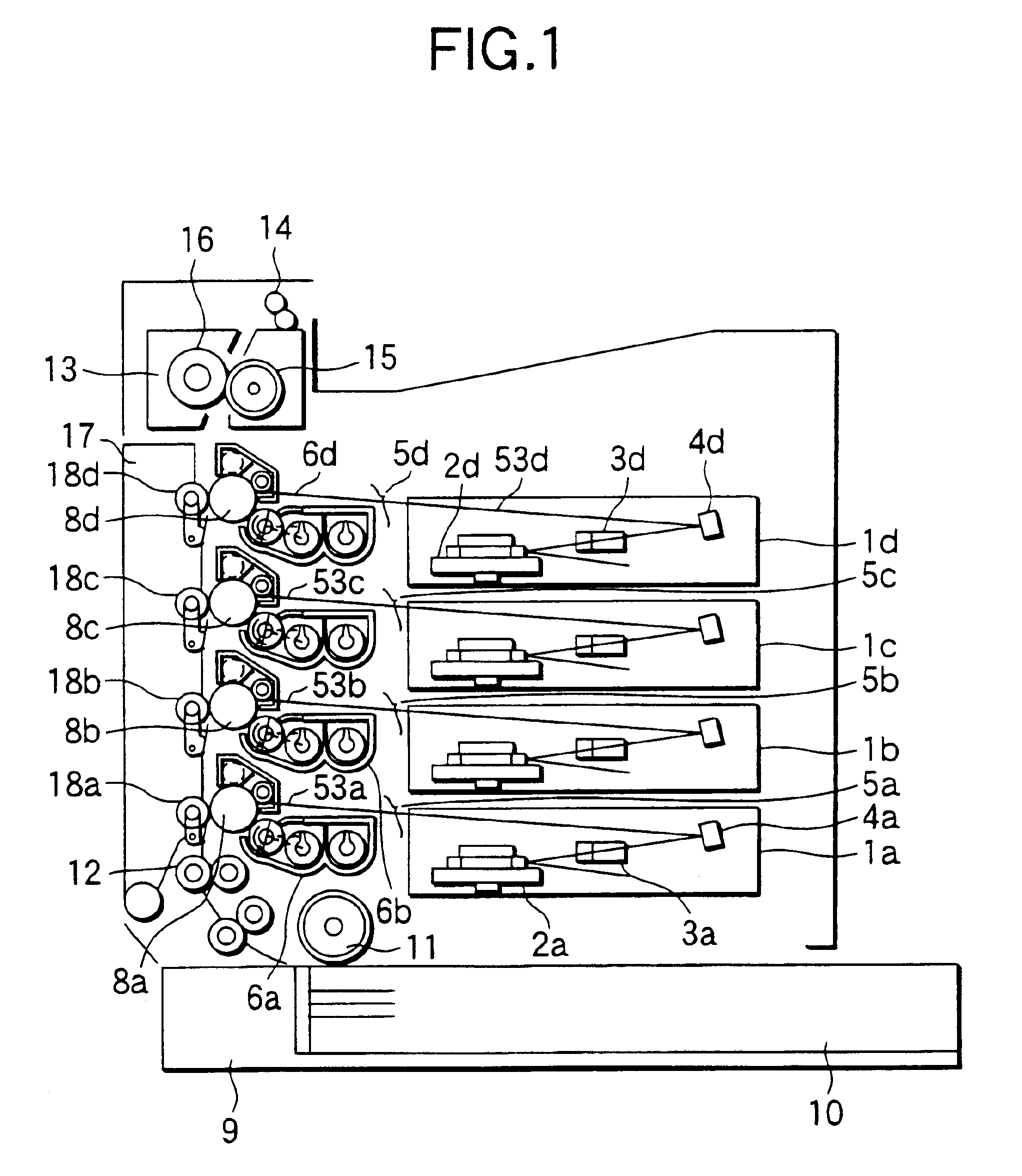
Image forming apparatus suppressing occurrence of color shift in images and method of controlling same
InactiveCN103869650ASuppresses color shiftElectrographic process apparatusPictoral communicationColor shiftImage transfer
An image forming apparatus that suppresses occurrence of color shift in images transferred from image bearing members onto an intermediate transfer member. A surface of each of a first photosensitive drum and second photosensitive drums is charged. An exposure device, provided for each photosensitive drum, forms an electrostatic latent image by exposing an associated one of the charged photosensitive drums. A developing device, provided for each photosensitive drum, develops the electrostatic latent image with toner. An intermediate transfer belt friction-drives the photosensitive drums for rotation and has the developed images transferred thereon. Timing for exposing the second photosensitive drums is controlled based on a first surface distance from an exposure light irradiated position to a primary transfer position of the first photosensitive drum, and a second surface distance from an exposure light irradiated position of each second photosensitive drum to a primary transfer position thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Led Illumination Device And Led Light-emission Module
InactiveCN103883900AReduce absorptionSuppresses color shiftPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsEffect lightDaylight
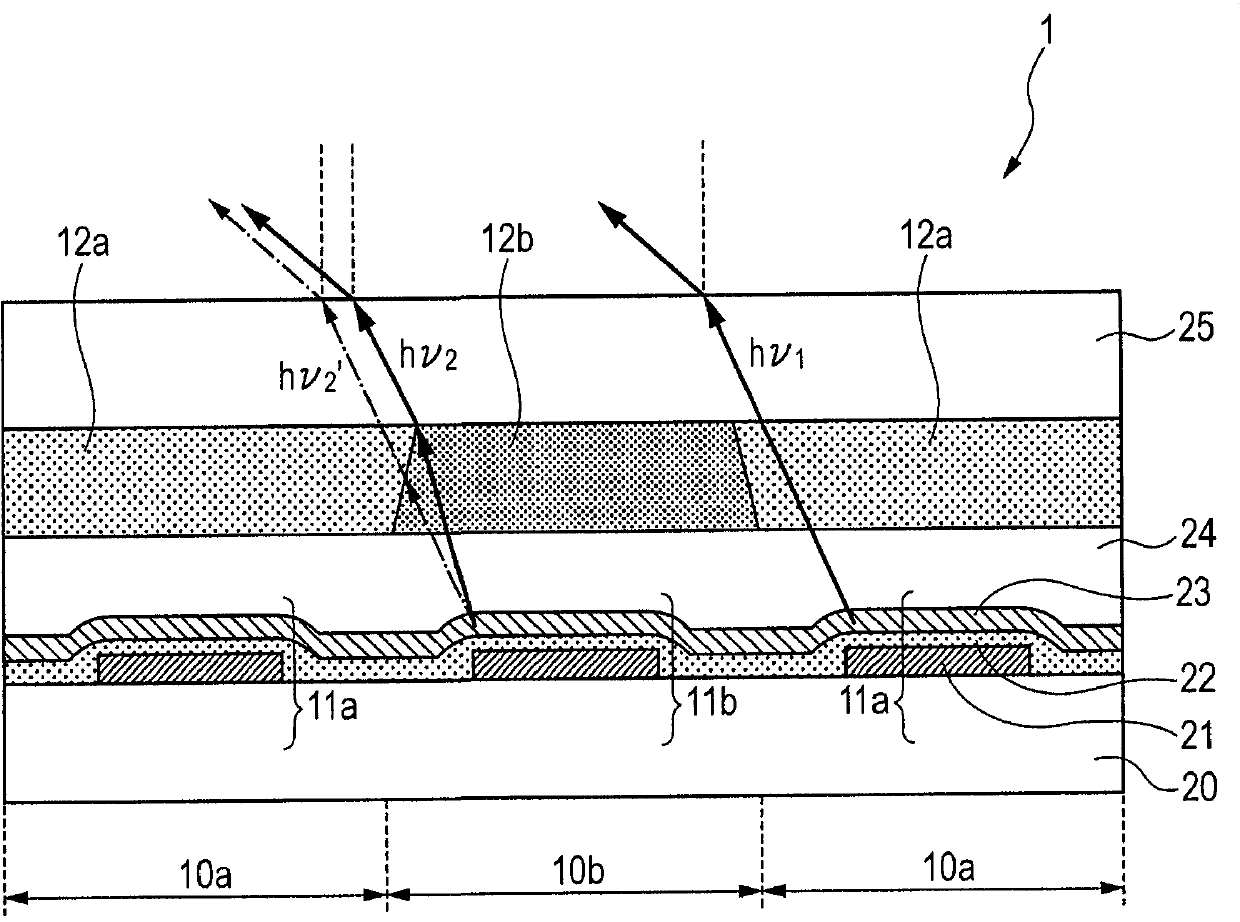
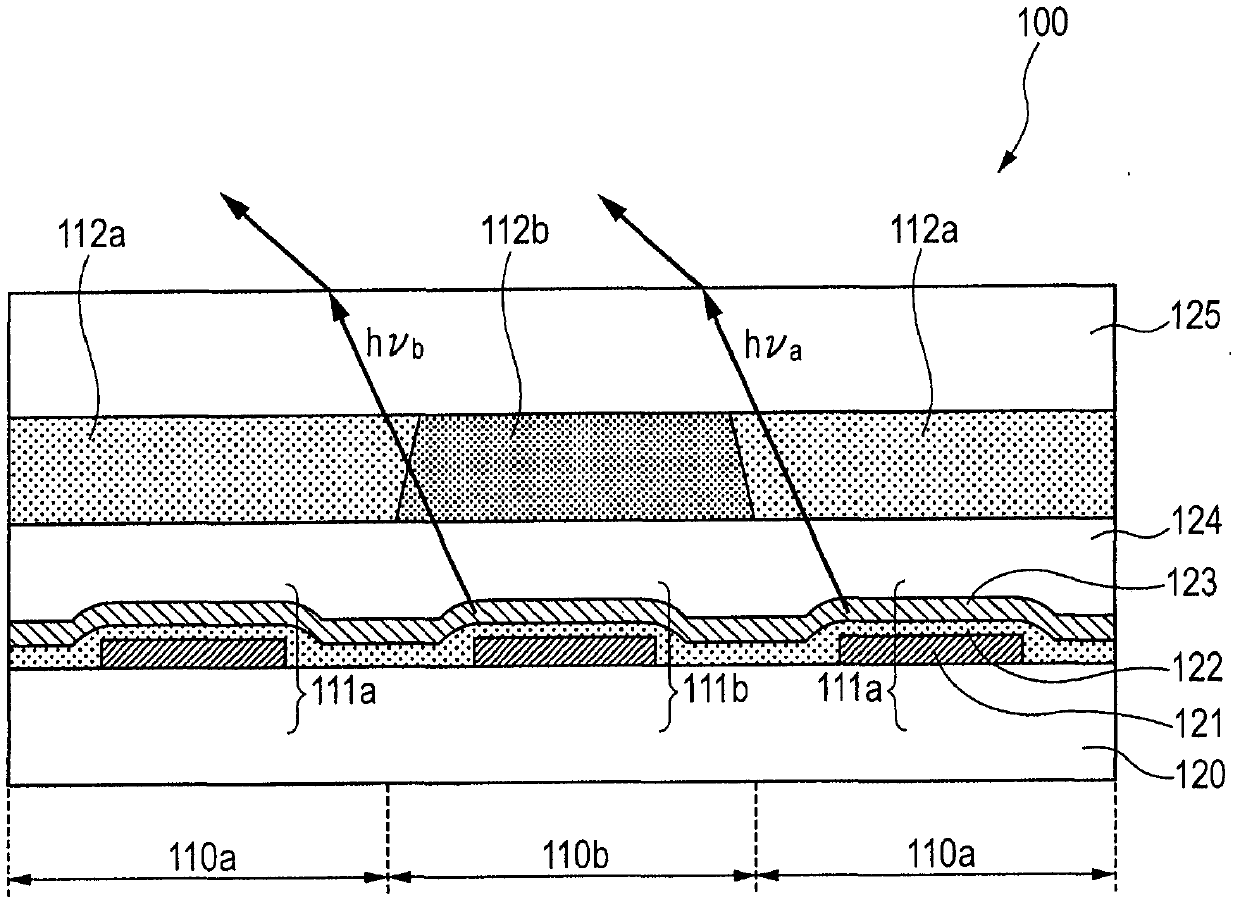
An illumination device and a light-emission module suppressing a change in color temperature when light emitted from a light-emission unit passes through an optical member. The illumination device (3) has a lighting apparatus that includes: a first light-emission part (12a) emitting light of a daylight color temperature; a second light-emission part (12b) emitting light of an incandescent lamp color temperature; and the optical member (50), which is disposed on an optical path of the light emitted from the light-emission parts (12a, 12b). A correlated color temperature of the light emitted from the second light-emission part (12b) is set to 2238 K. Due to this, in a spectrum of the light emitted from the second light-emission part (12b), a maximum intensity within a wavelength range from 400 nm to 500 nm is no greater than one-tenth of a maximum intensity within a wavelength range from 300 nm to 800 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Phase Difference Film, Polarizing Plate And Liquid Crystal Display Device
InactiveCN107272101ASuppression of haze riseSuppresses color shiftPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsDichloromethaneSolubility
The present invention relates to a phase difference film, a polarizing plate and a liquid crystal display device. The phase difference film 13 is the phase difference film of a cellulose ester system of which the delay Ro in an in-plane direction is more than 20 nm, is used as an additive, and contains a first nitrogenous heterocyclic compound having the solubility less than 2% relative to the dichloromethane and a second nitrogenous heterocyclic compound having the solubility more than 15% relative to the dichloromethane.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
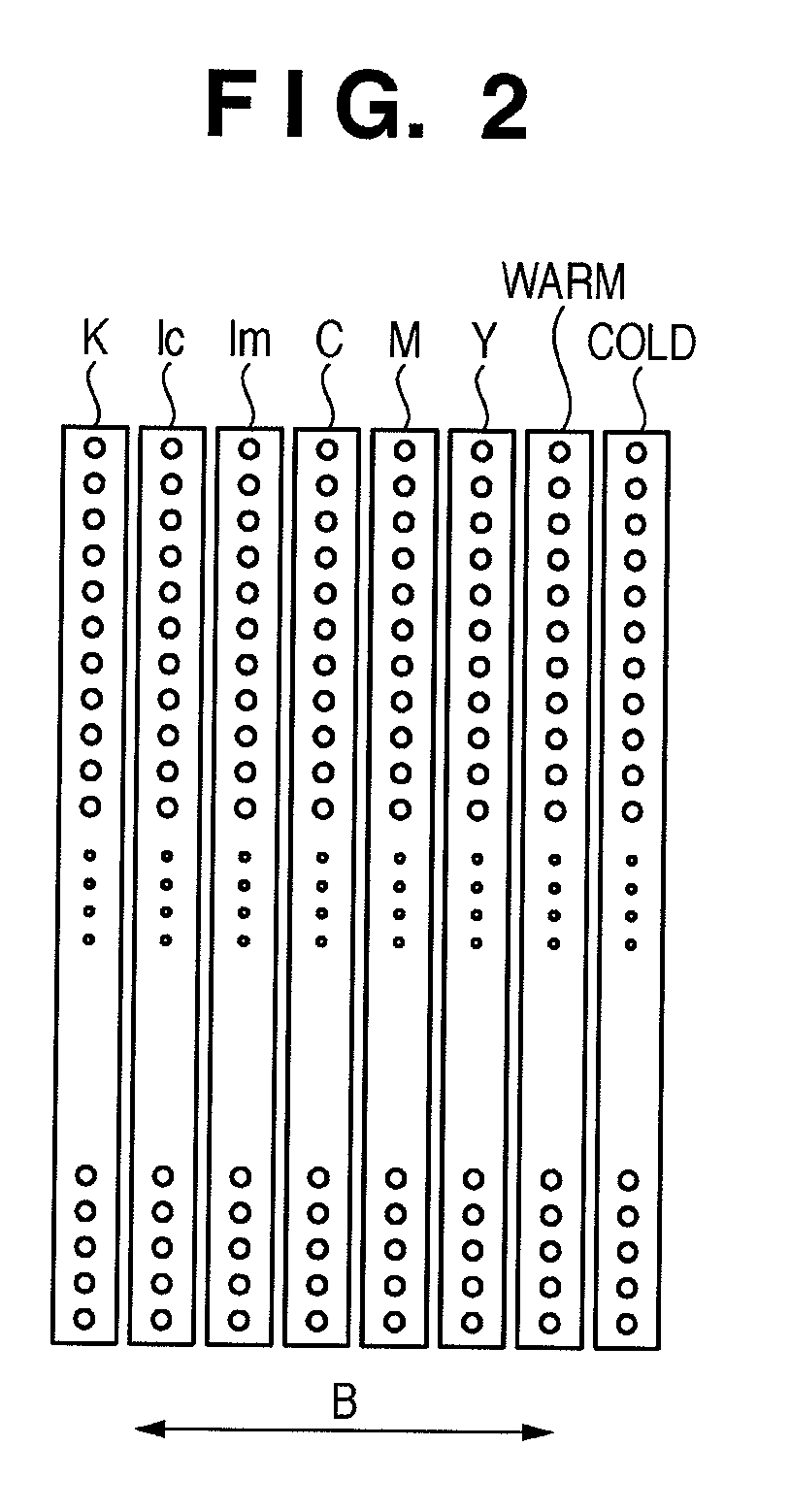
Image forming using warm and cold black tone inks
InactiveUS8508794B2Suppressing color shifts in correspondenceSuppresses color shiftDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage formationHue
An image forming apparatus sets one of a plurality of modes including a monochrome mode of forming a monochrome image, converts a multivalued luminance signal into signal values of color material amounts to be used to form the image and forms the image using color materials based on the signal values. The color materials used in the forming when the monochrome mode is set include an achromatic color material and at least two auxiliary color materials which have hues opposite to each other and a chroma larger than that of the achromatic color material.
Owner:CANON KK
Liquid crystal display device
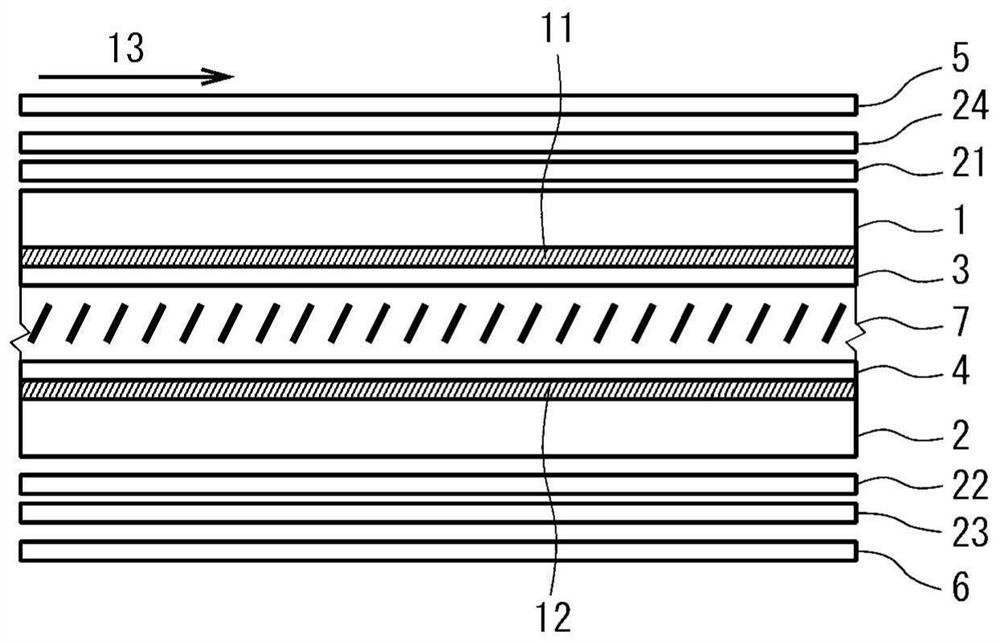
ActiveCN105629555BSuppresses color shiftLow costNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
The invention provides a liquid display device capable of suppressing color offset of a normally-white display vertical orientation liquid display device with a low cost when being viewed from the left and right direction. The liquid display device is provided with a first substrate, a second substrate, a liquid layer, a first polarization plate, a second polarization plate, a first to a third optical boards. The absorption axes of the polarization plates are substantially orthogonal, and are in 45 degrees to the orientation direction of the substantial center of the thickness direction of the liquid layer to which an electric field is applied. The first optical board is provided with negative biax optical aeolotropism and has an in-plane phase difference Re1 from 40 to 70nm. The in-plane slow axis of the first optical board is 45 degrees relative to the absorption axis of the first optical board. The second polarization plate is provided with positive single-axis optical aeolotropism. The in-plane slow axis of the second optical board is 45 degrees relative to the absorption axis of the first optical board. The in-plane phase difference Re2 of the second optical board has a relation that Re2-Re1 is greater than or equal to 200nm but less than or equal to 320nm.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Image forming apparatus and method
InactiveCN1504835APrevent local deteriorationPrevent or effectively suppress color shiftToothed gearingsDynamo-electric converter controlColor imageImage formation
Owner:RICOH KK
Liquid crystal display device
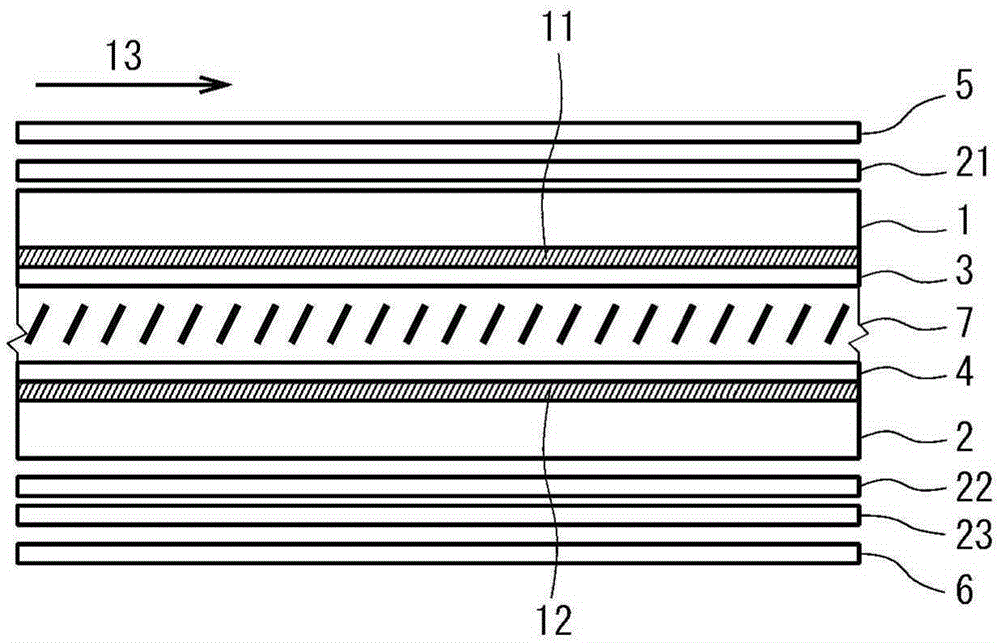
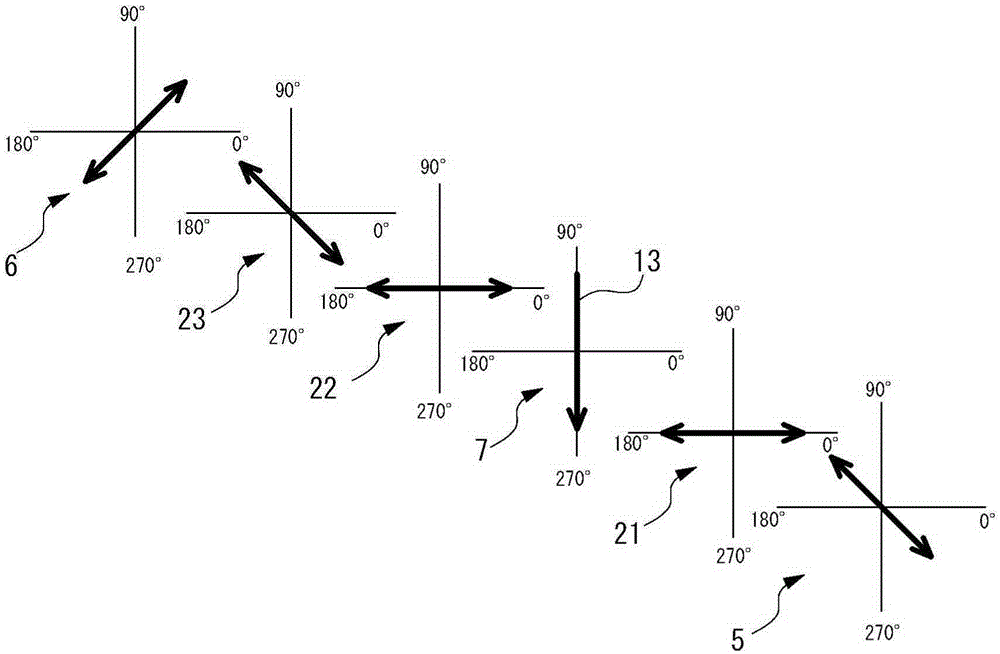
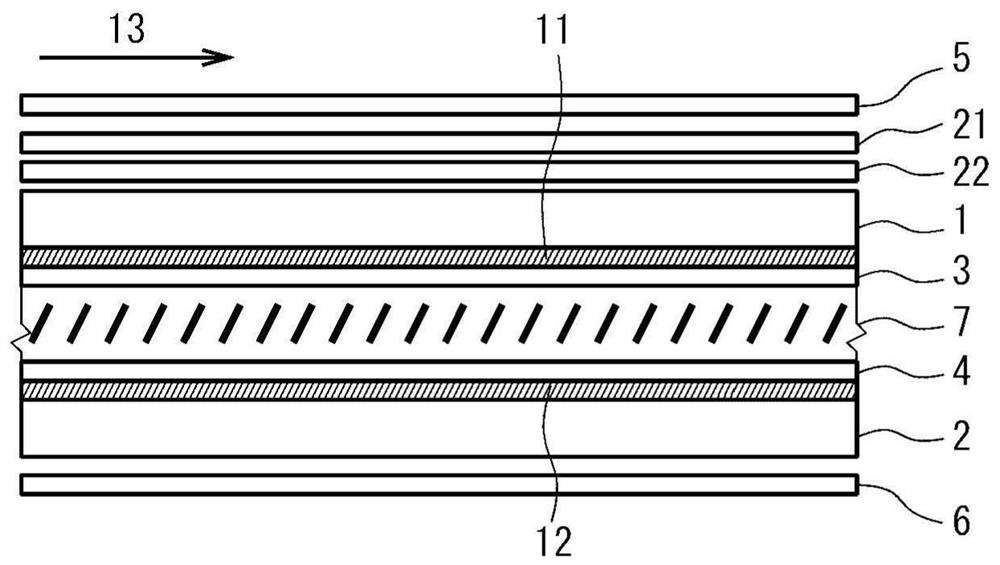
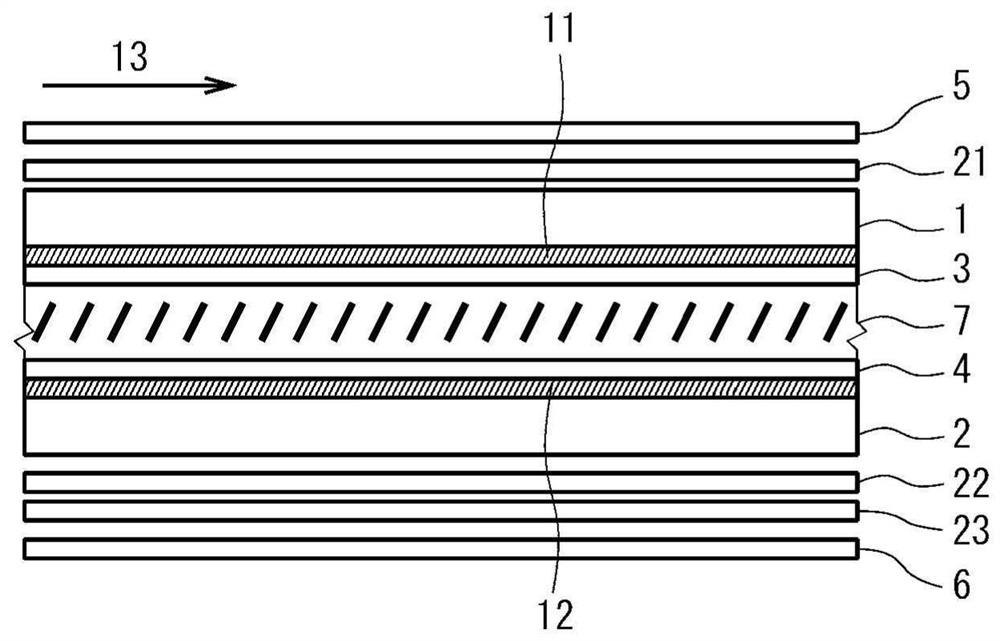
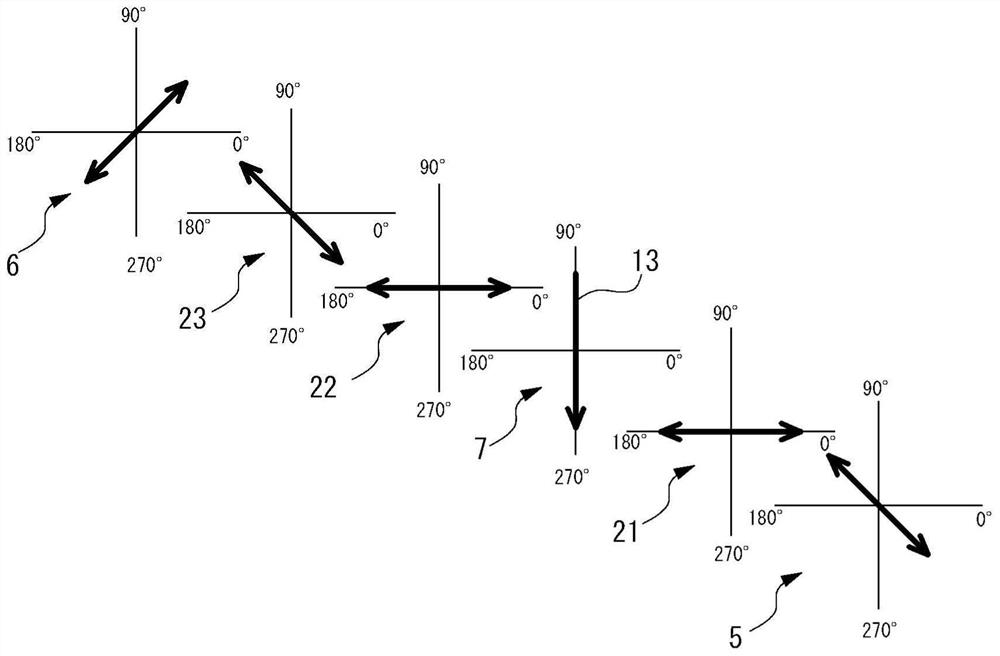
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a vertical alignment type liquid crystal display device with a normally white mode, which inexpensively suppresses a color shift occurring when the device is observed in lateral directions.SOLUTION: The liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate 1, a second substrate 2, a liquid crystal layer 7, a first polarizing plate 5, a second polarizing plate 6, and first to third optical plates 21, 22, 23. Absorption axes of the polarizing plates are disposed substantially orthogonal to each other and at an angle of about 45 with respect to an alignment direction of the liquid crystal layer at substantially the center in a layer thickness direction when an electric field is applied. The first optical plate 21 is a quarter-wave plate having an in-plane slow axis disposed at an angle of about 45° with respect to the absorption axis of the first polarizing plate 5. The second optical plate 22 is a quarter wave plate having an in-plane slow axis disposed at an angle of about 45° with respect to the absorption axis of the second polarizing plate 6. The third optical plate 23 has negative biaxial optical anisotropy and has an in-plane slow axis disposed substantially orthogonal to the absorption axis of the first polarizing plate 5.SELECTED DRAWING: Figure 1
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com