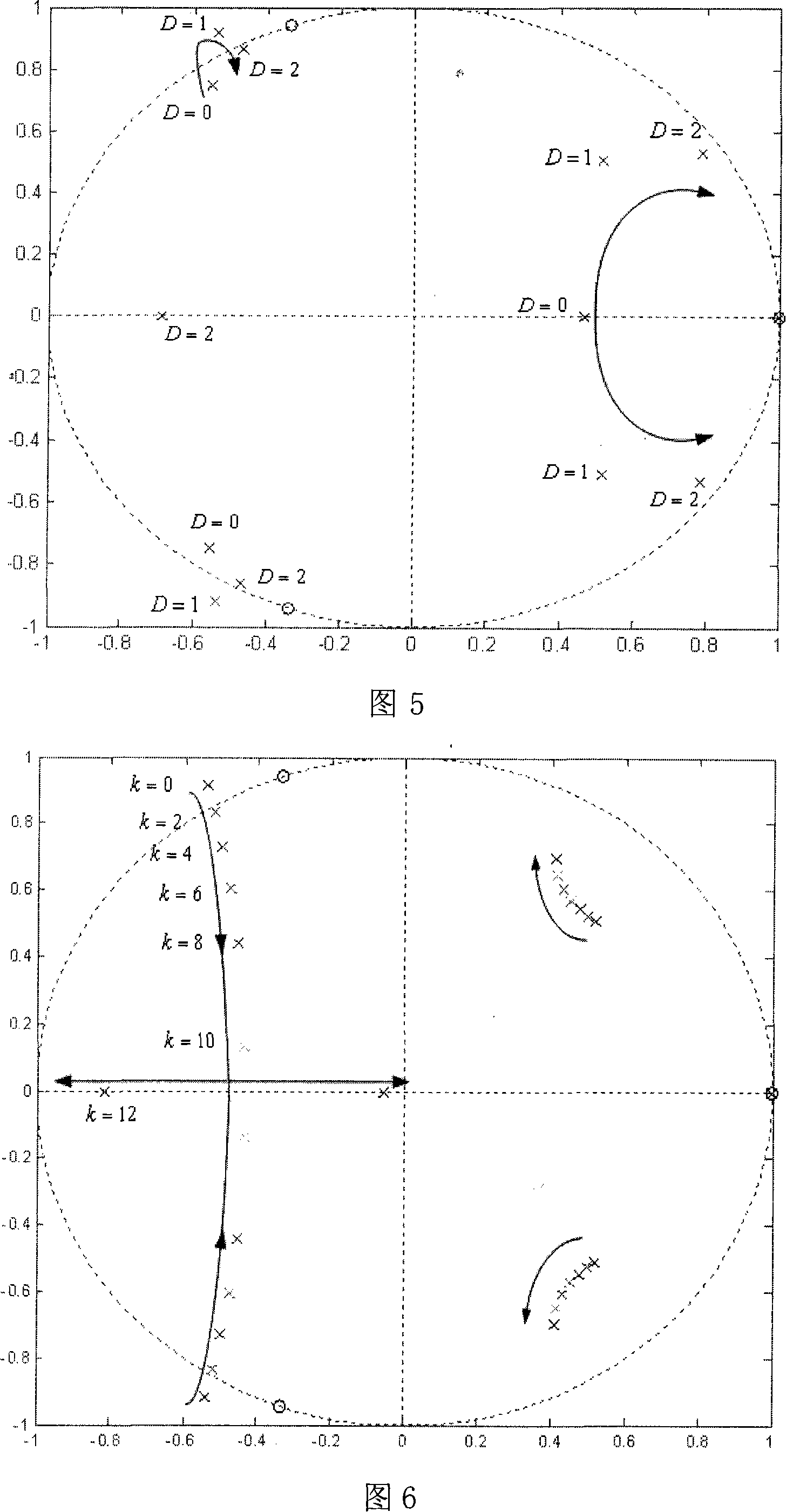Patents
Literature
188 results about "Active rectification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Active rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification by replacing diodes with actively controlled switches such as transistors, usually power MOSFETs or power BJTs. Whereas normal semiconductor diodes have a roughly fixed voltage drop of around 0.5-1 volts, active rectifiers behave as resistances, and can have arbitrarily low voltage drop.
Active rectifier and wireless power receiving apparatus using the same that can reduce reverse current leakage
ActiveUS20150263534A1Total current dropAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformersReverse currentDelayed time
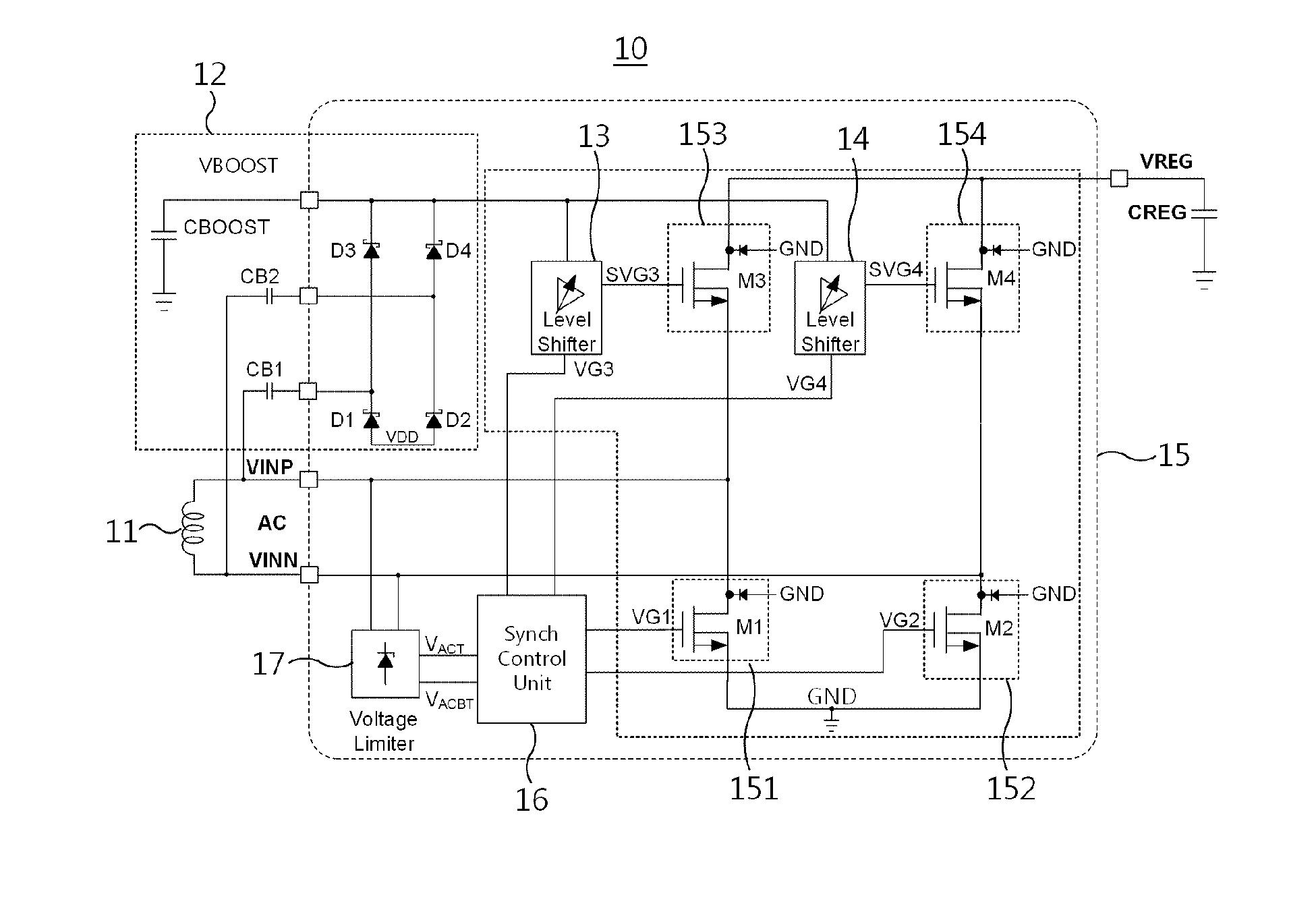
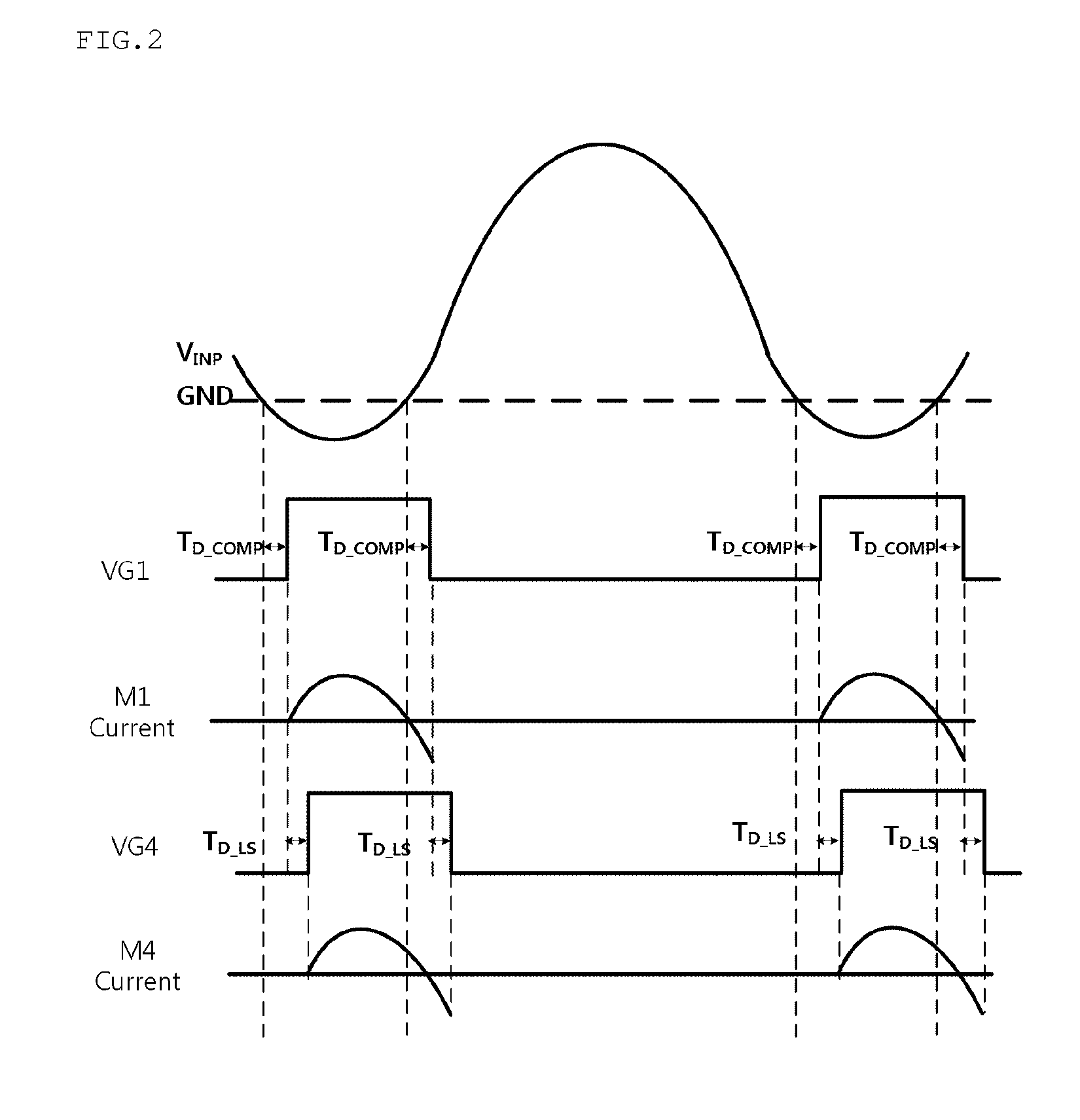
An active rectifier and a wireless power reception apparatus using the same are disclosed herein. The active rectifier includes first and fourth switches, second and third switches, and a synchronization control unit. The first and fourth switches are turned on while the voltage of an alternating current (AC) input is negative, and apply the current of the AC input to a rectifying capacitor. The second and third switches are turned on while a voltage of the AC input is positive, and apply the current of the AC input to the rectifying capacitor. The synchronization control unit compensates for the delay time of the comparator for detecting zero-crossing of the AC input so as to switch the first to fourth switches.
Owner:SKAI CHIPS
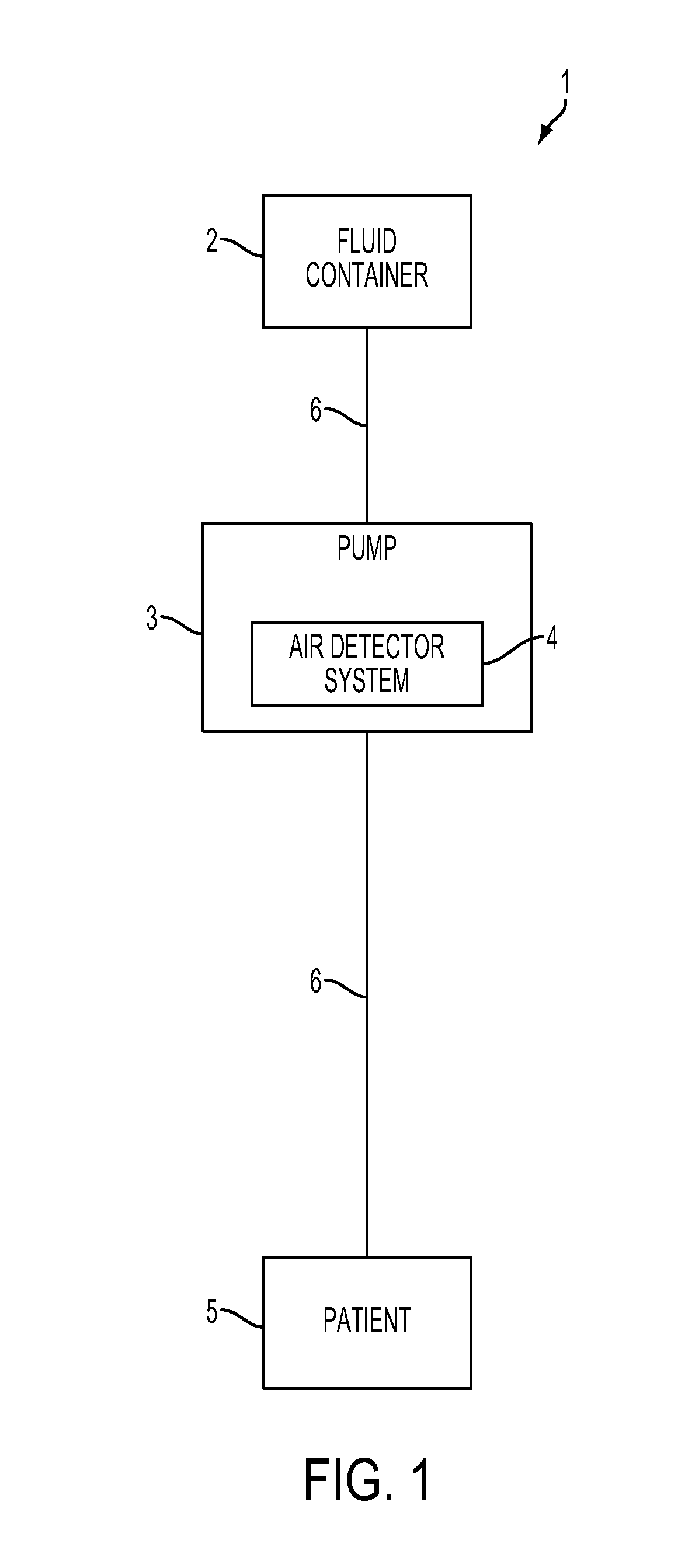
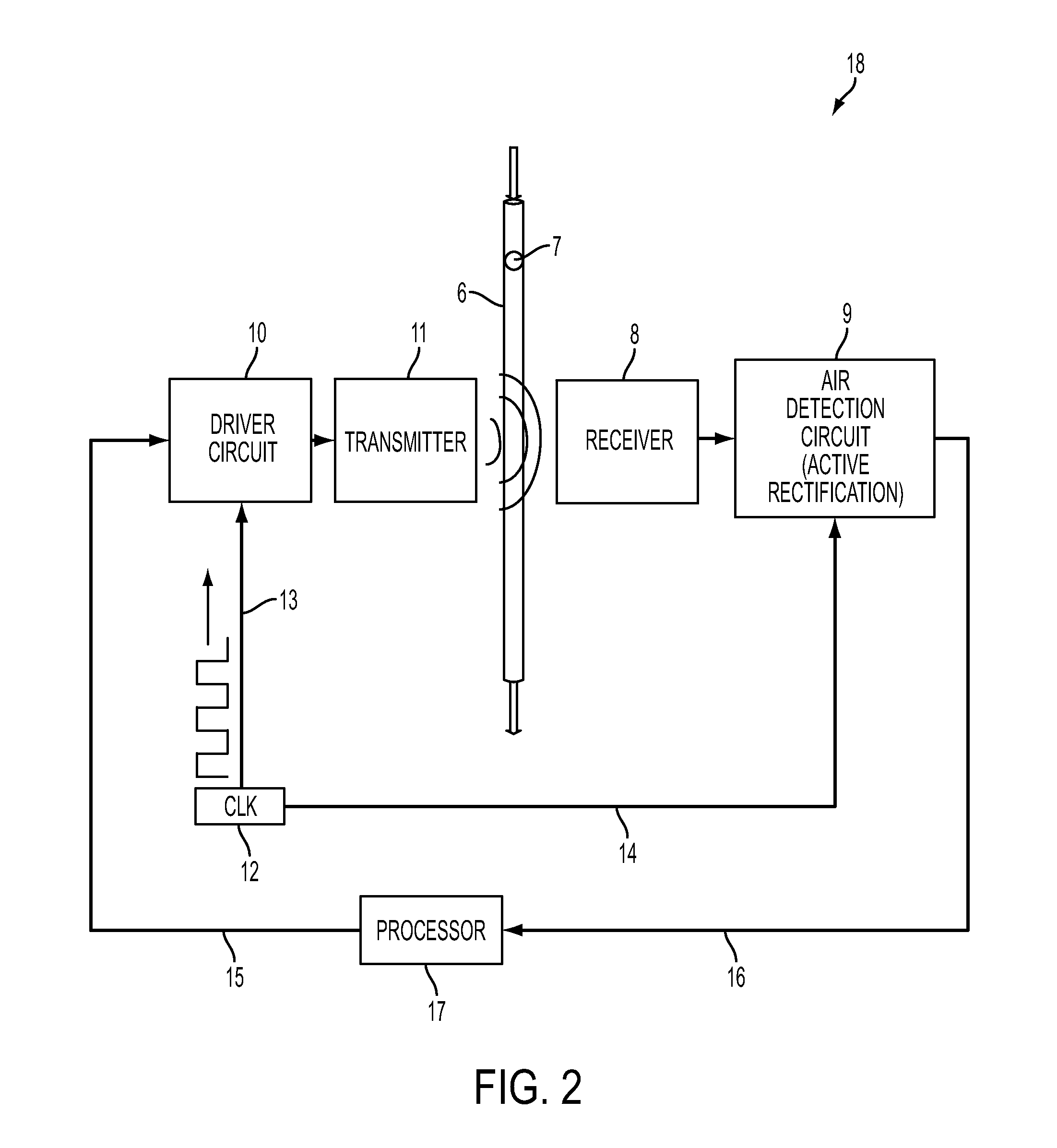
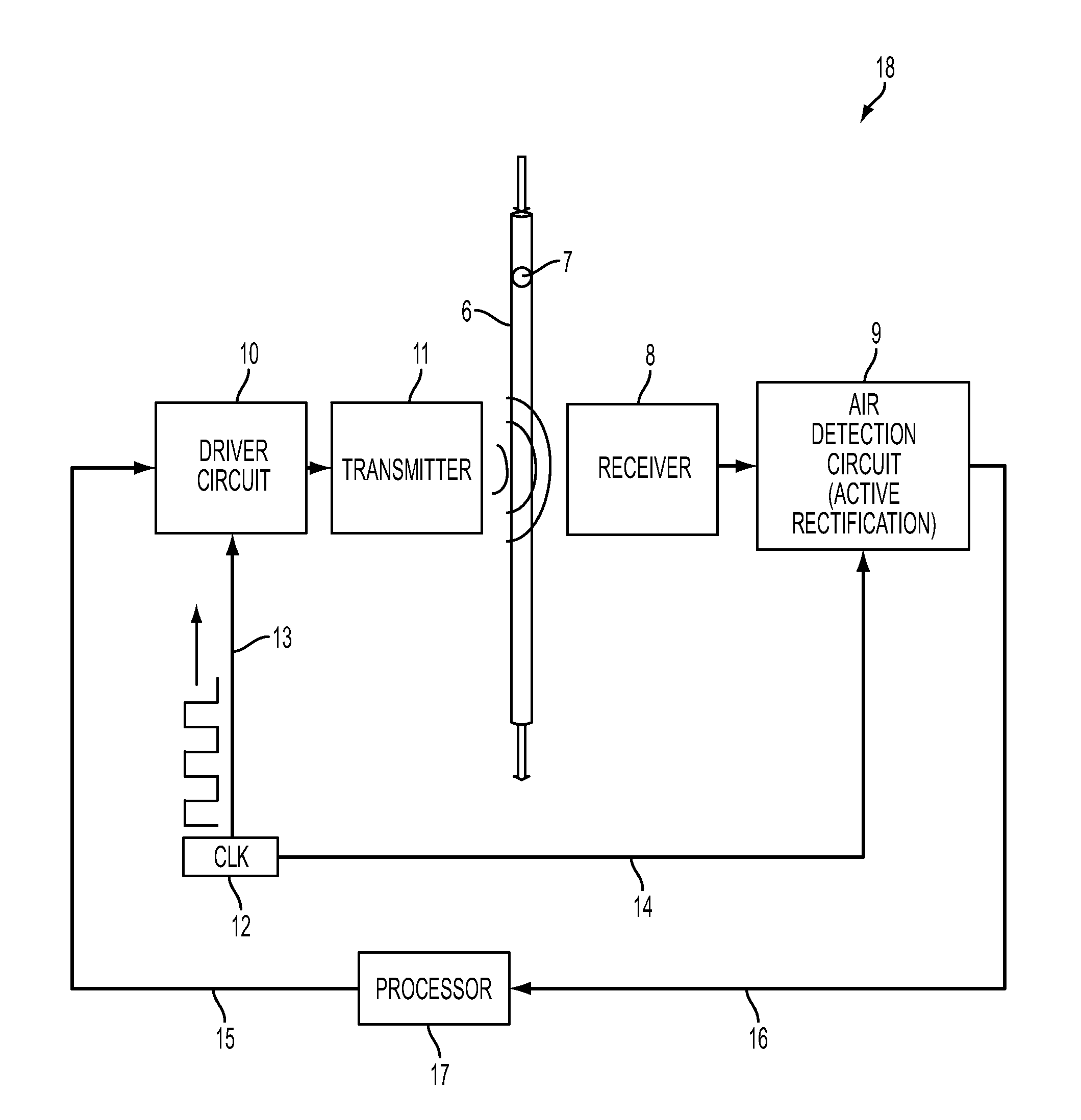
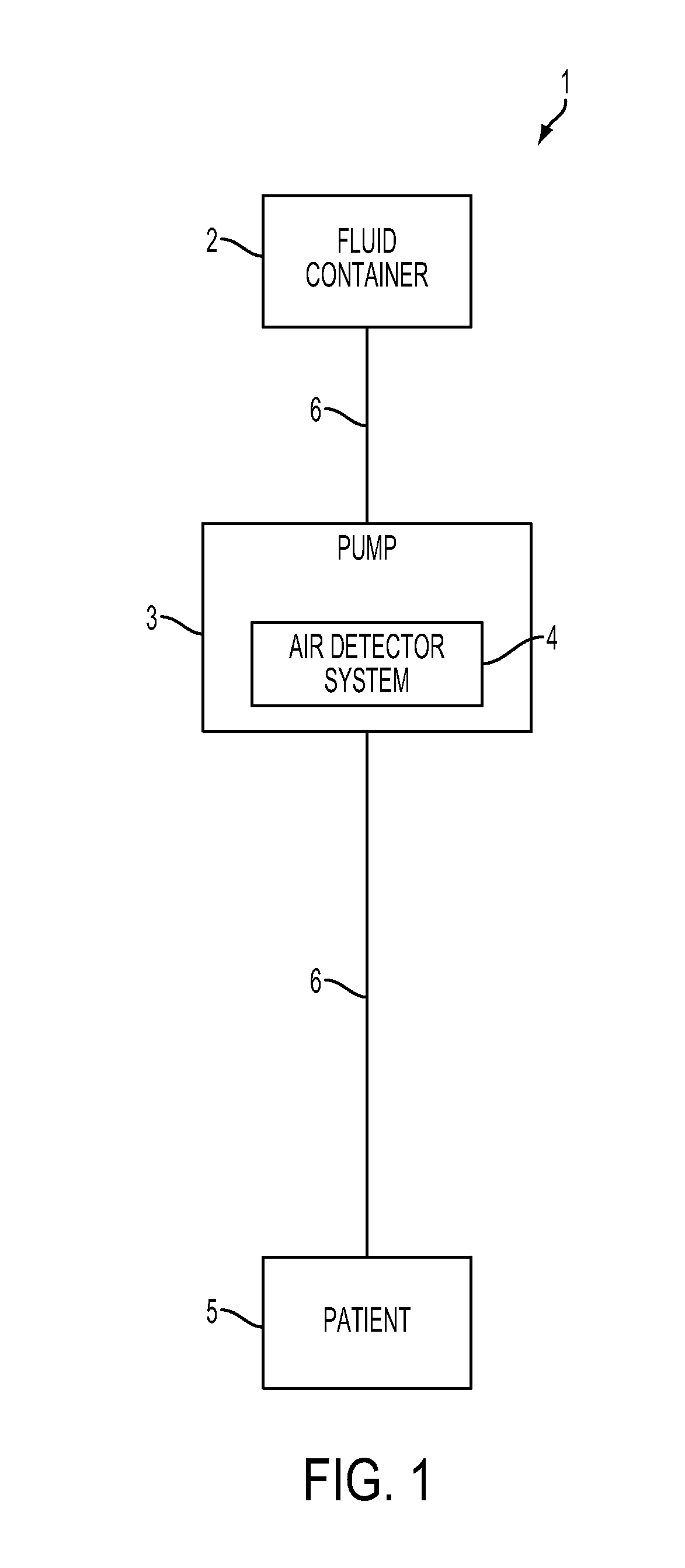
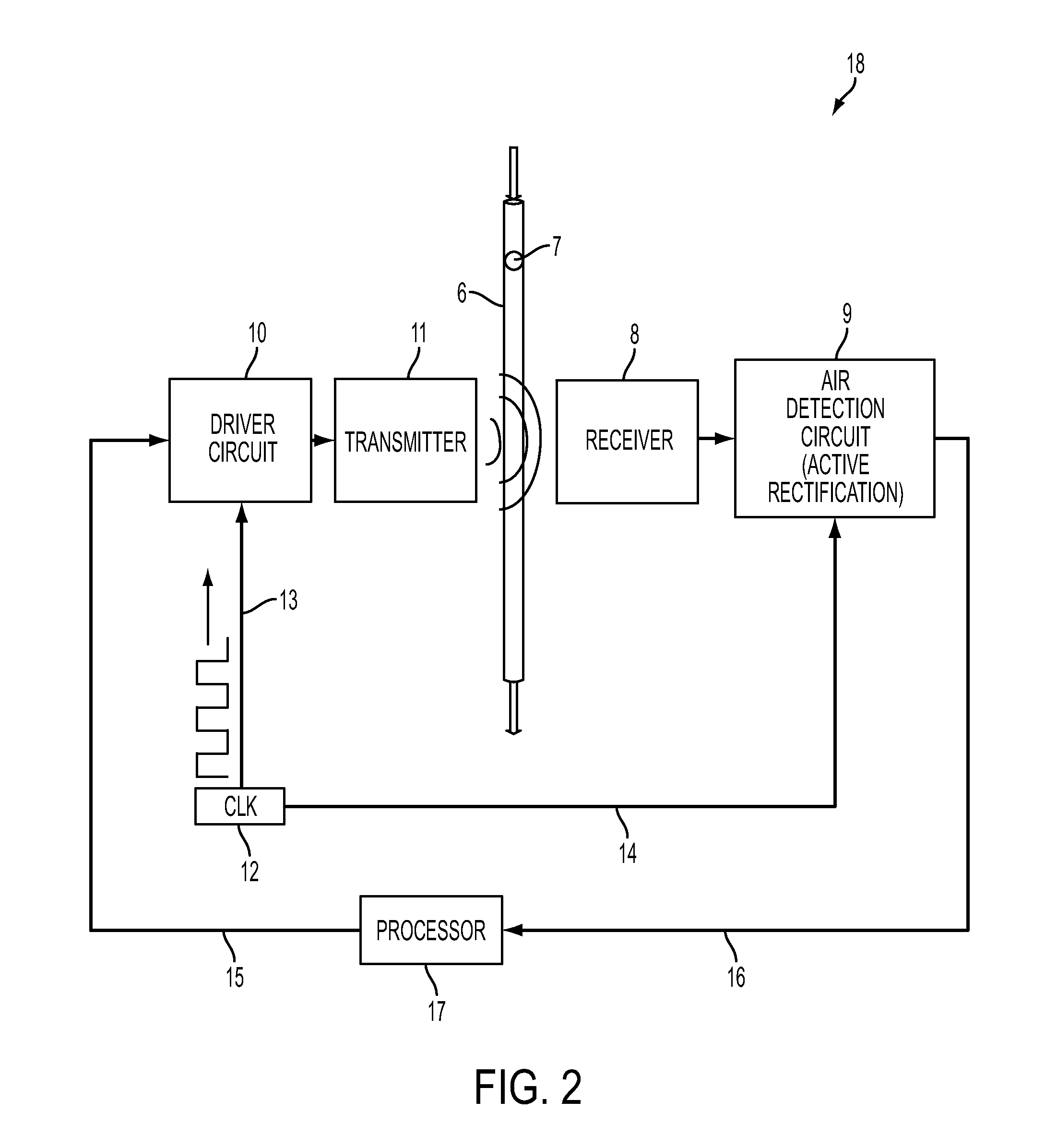
System, Method, and Apparatus for Detecting Air in a Fluid Line Using Active Rectification
ActiveUS20140165703A1Reduce errorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLine tubingElectrical and Electronics engineering
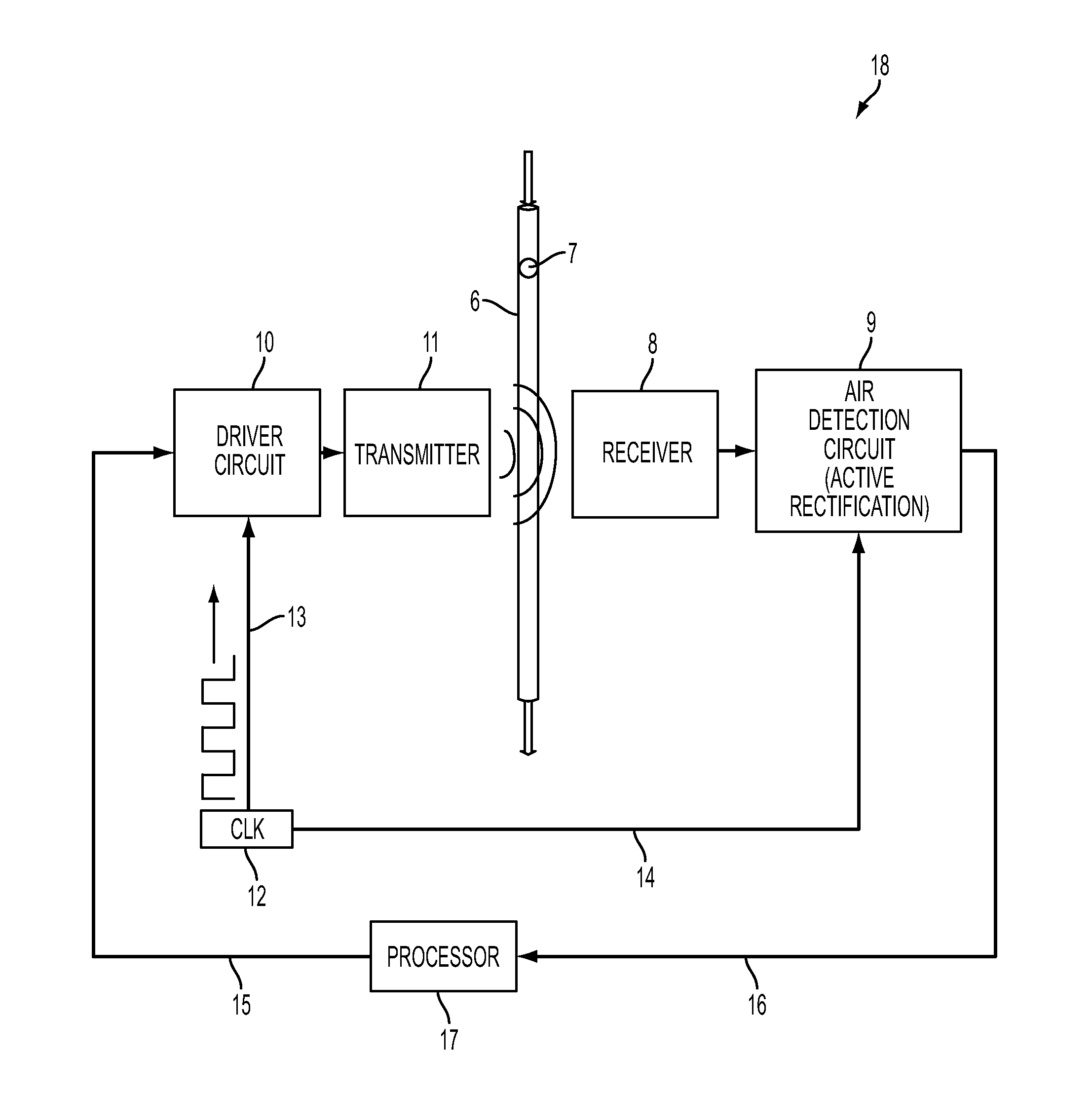
A circuit for detecting air, a related system, and a related method are provided. The circuit for detecting air includes a receiver connection and an air-detection circuit. The receiver connection is configured to provide a receiver signal. The air-detection circuit is in operative communication with the receiver connection to process the receiver signal to generate a processed signal corresponding to detected air. The air-detection circuit includes one or more active-rectifying elements configured to actively rectify the receiver signal to provide the processed signal.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
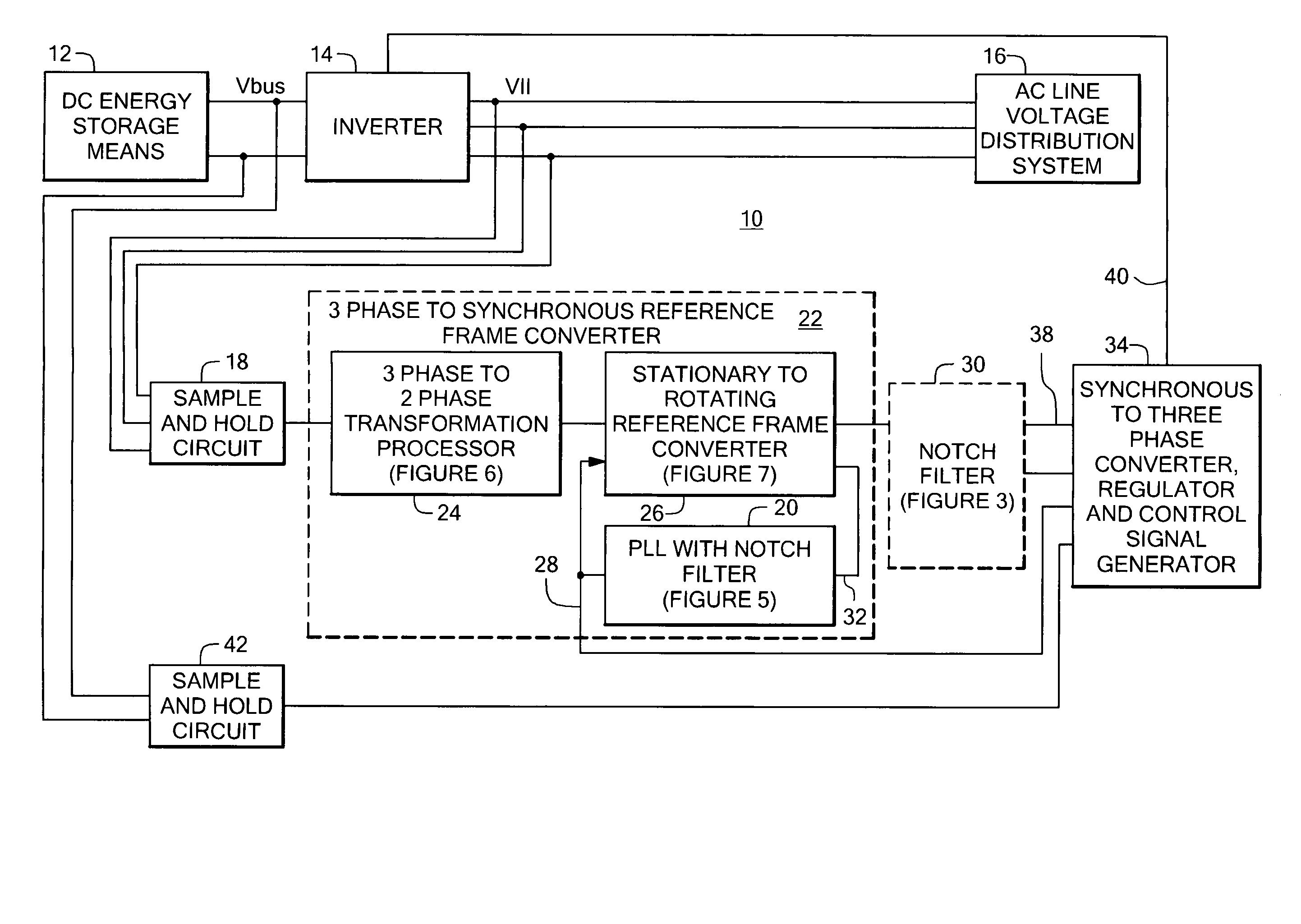
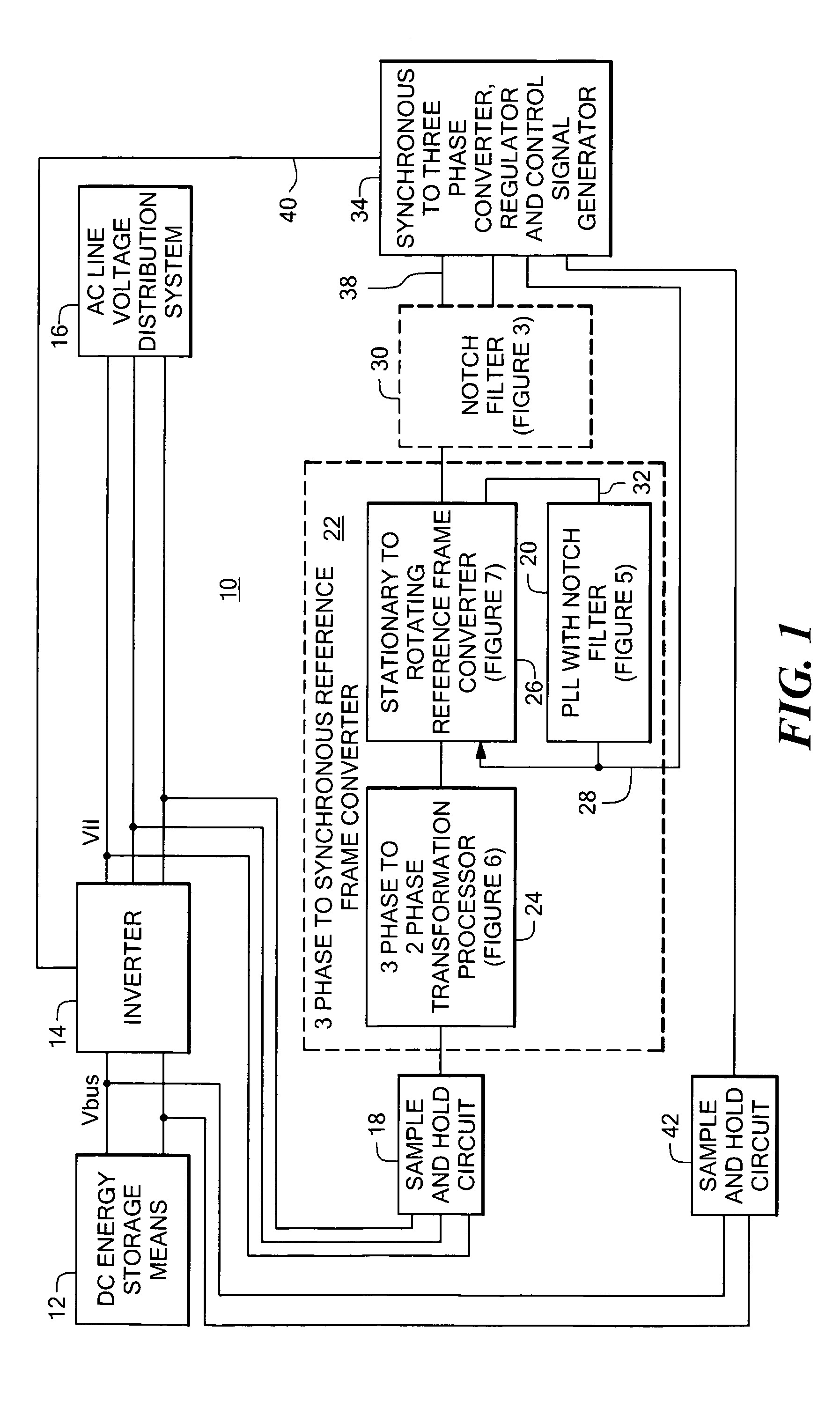
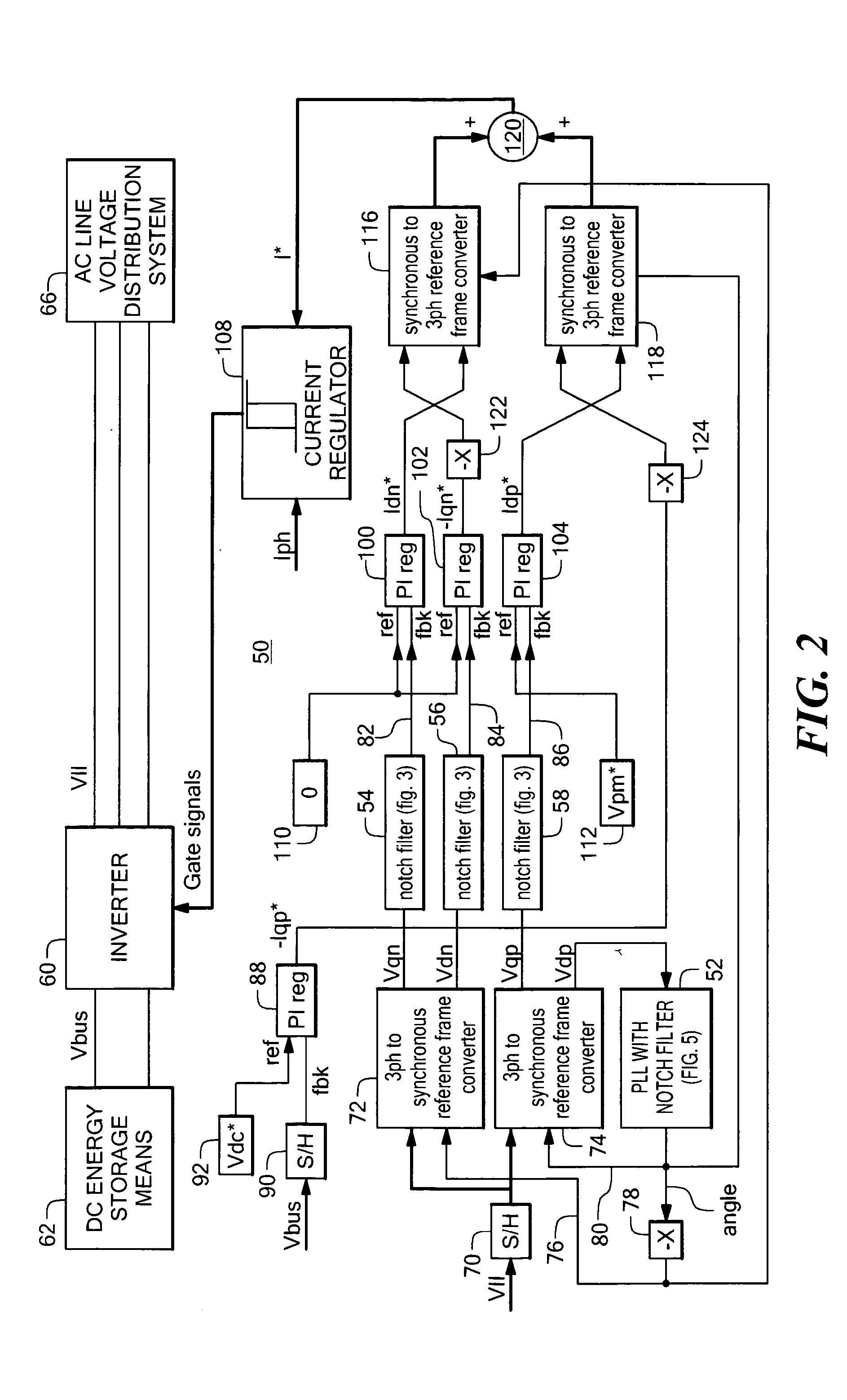
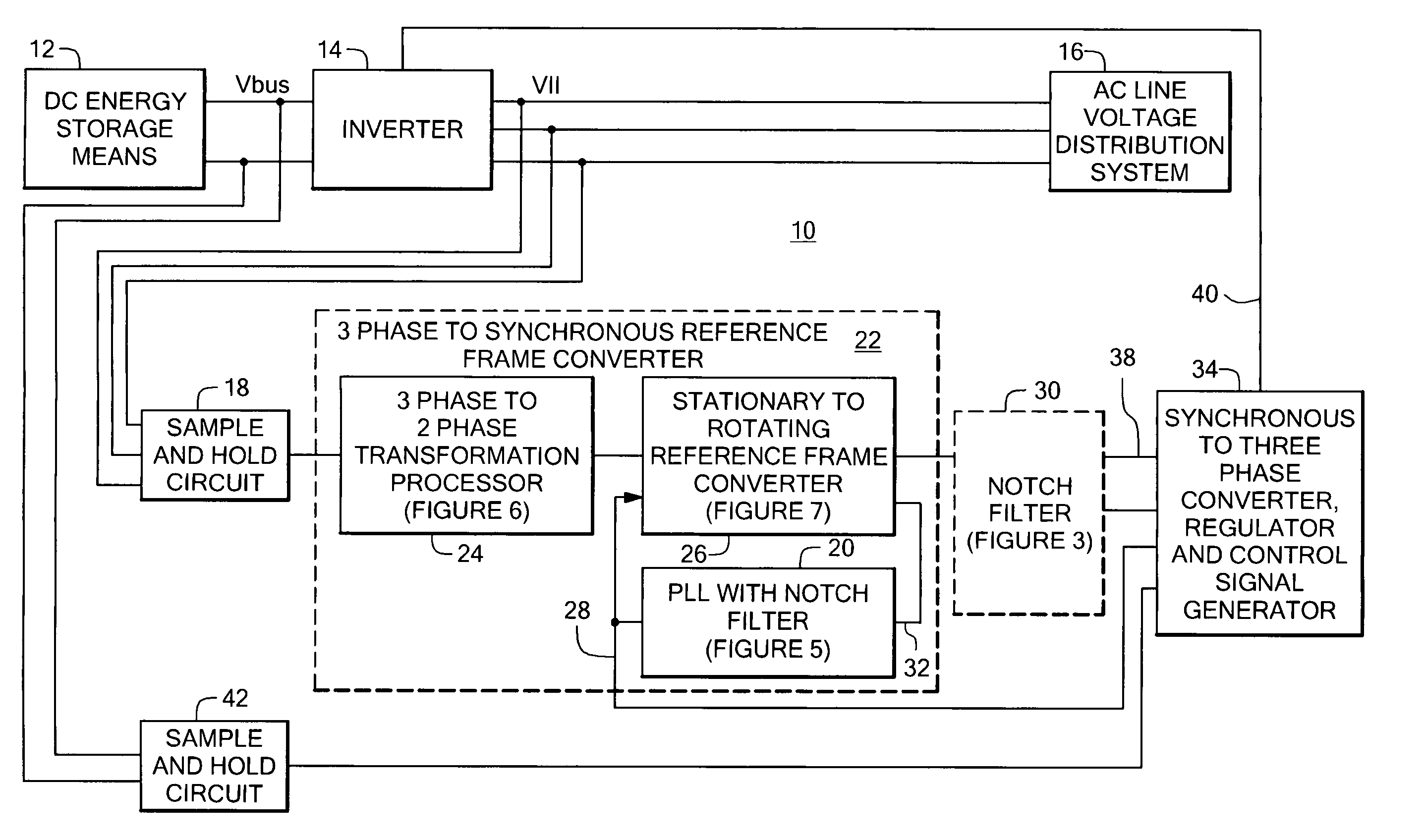
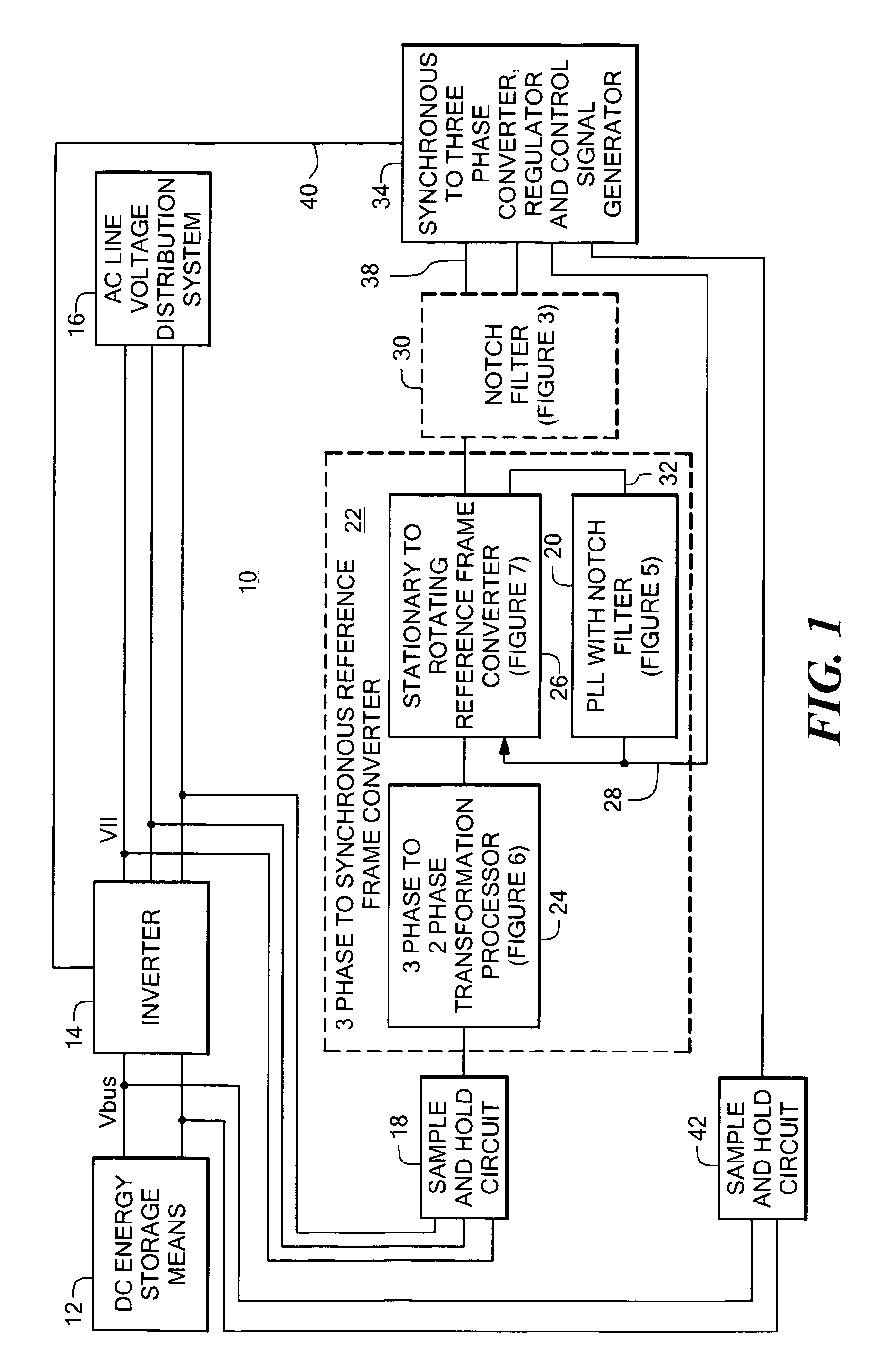
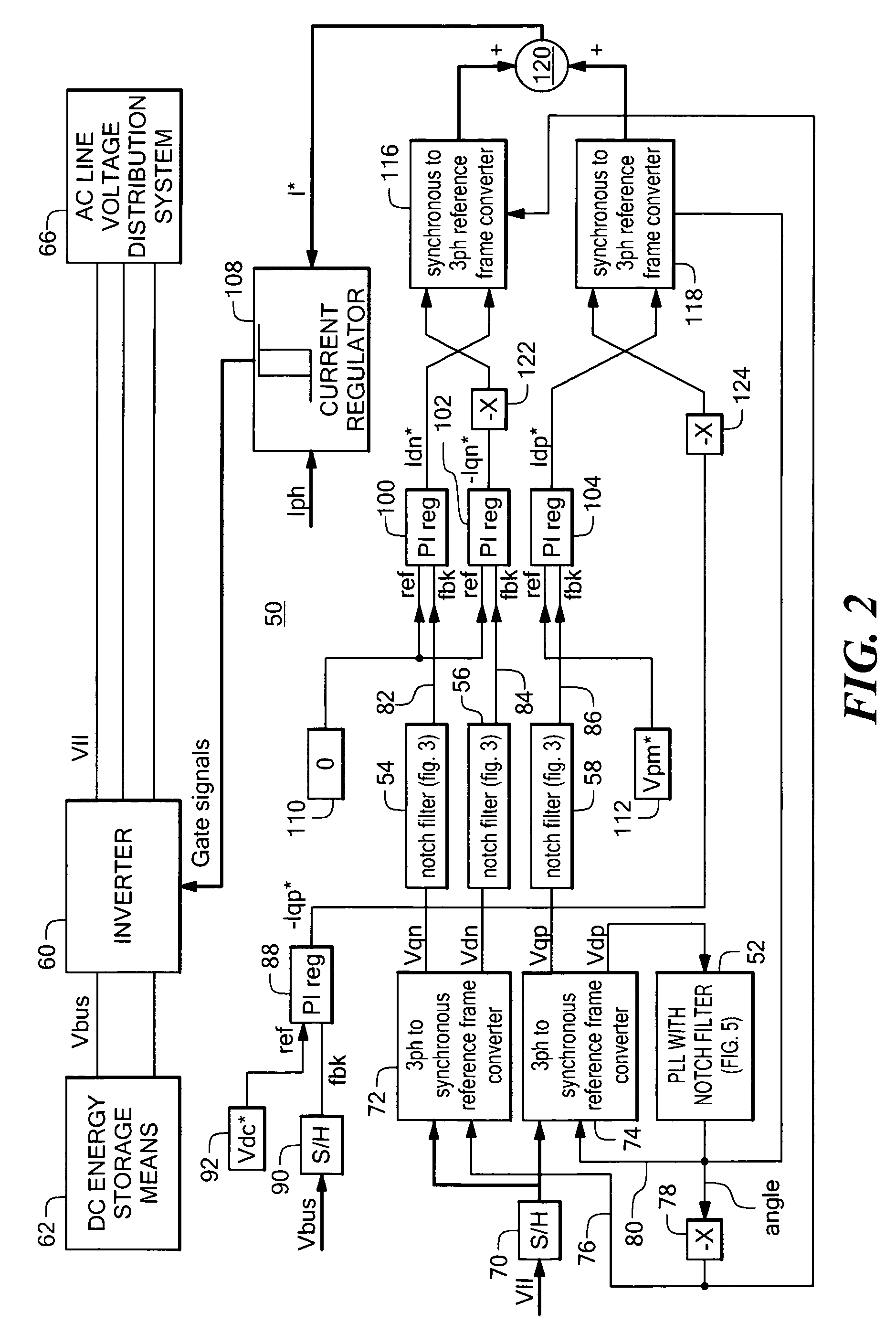
Power system having a phase locked loop with a notch filter
InactiveUS20050207190A1Highly accurate frequencyHighly accurate amplitudeAc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorHarmonic
A power system having a phase locked loop (PLL) with a notch filter for synchronous reference frame sequence separation. The notch filter includes a generalized integrator tuned to the notch frequency. The output of the generalized integrator is summed with the filter input signal and the output of the summer is fed back to the integrator input. In one embodiment, the notch filter is programmable by a control signal generated in response to the filter output signal, thereby causing the filter to self-regulate to a frequency related to the PLL input signal. Illustrative power systems include active VAR generators and active rectifiers. One or more additional notch filters may be used to remove harmonic components from derived synchronous reference frame sequence components.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
System, method, and apparatus for detecting air in a fluid line using active rectification
ActiveUS9518958B2Reduce errorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalElectrical and Electronics engineeringActive rectification
A circuit for detecting air, a related system, and a related method are provided. The circuit for detecting air includes a receiver connection and an air-detection circuit. The receiver connection is configured to provide a receiver signal. The air-detection circuit is in operative communication with the receiver connection to process the receiver signal to generate a processed signal corresponding to detected air. The air-detection circuit includes one or more active-rectifying elements configured to actively rectify the receiver signal to provide the processed signal.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
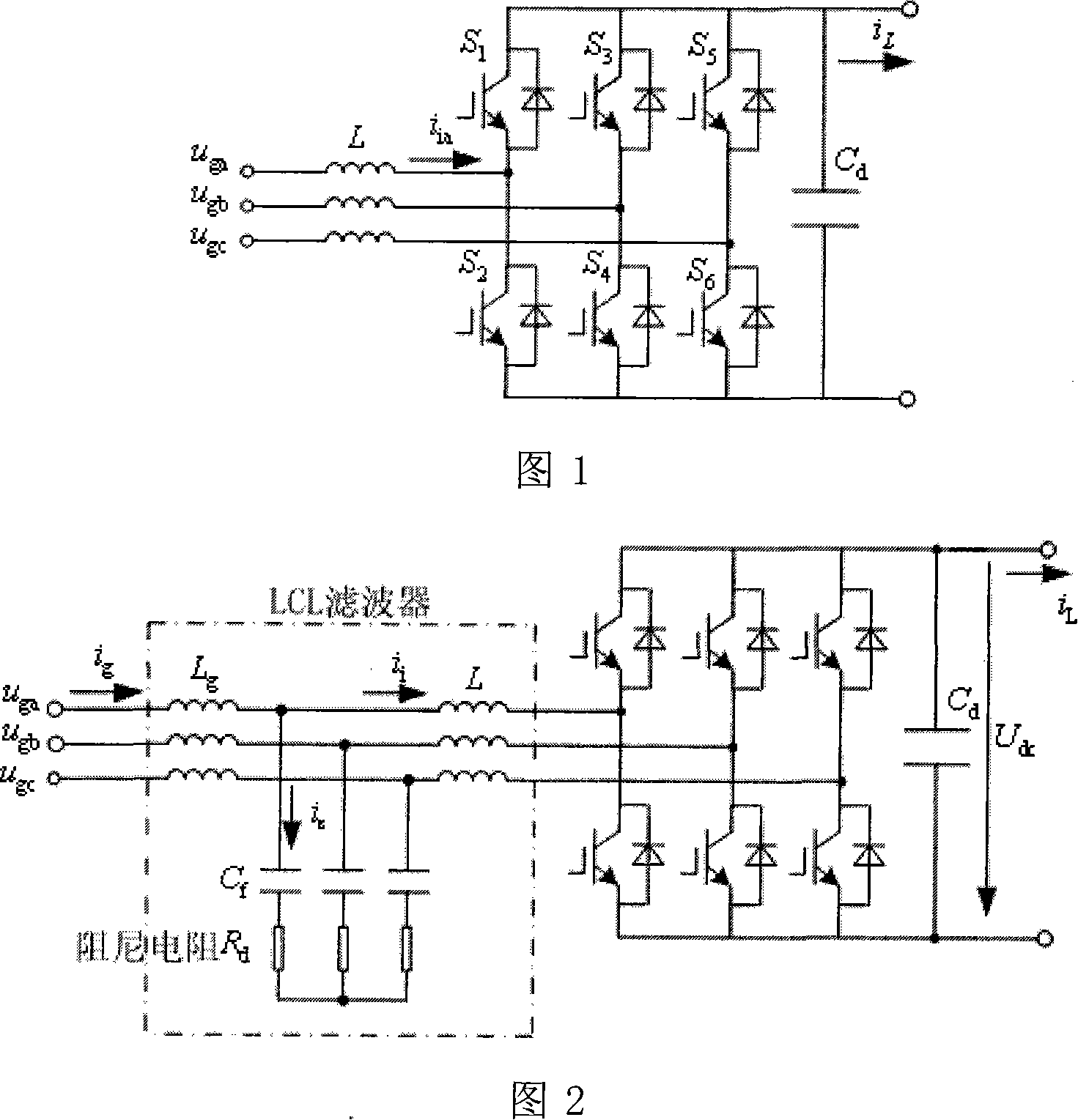
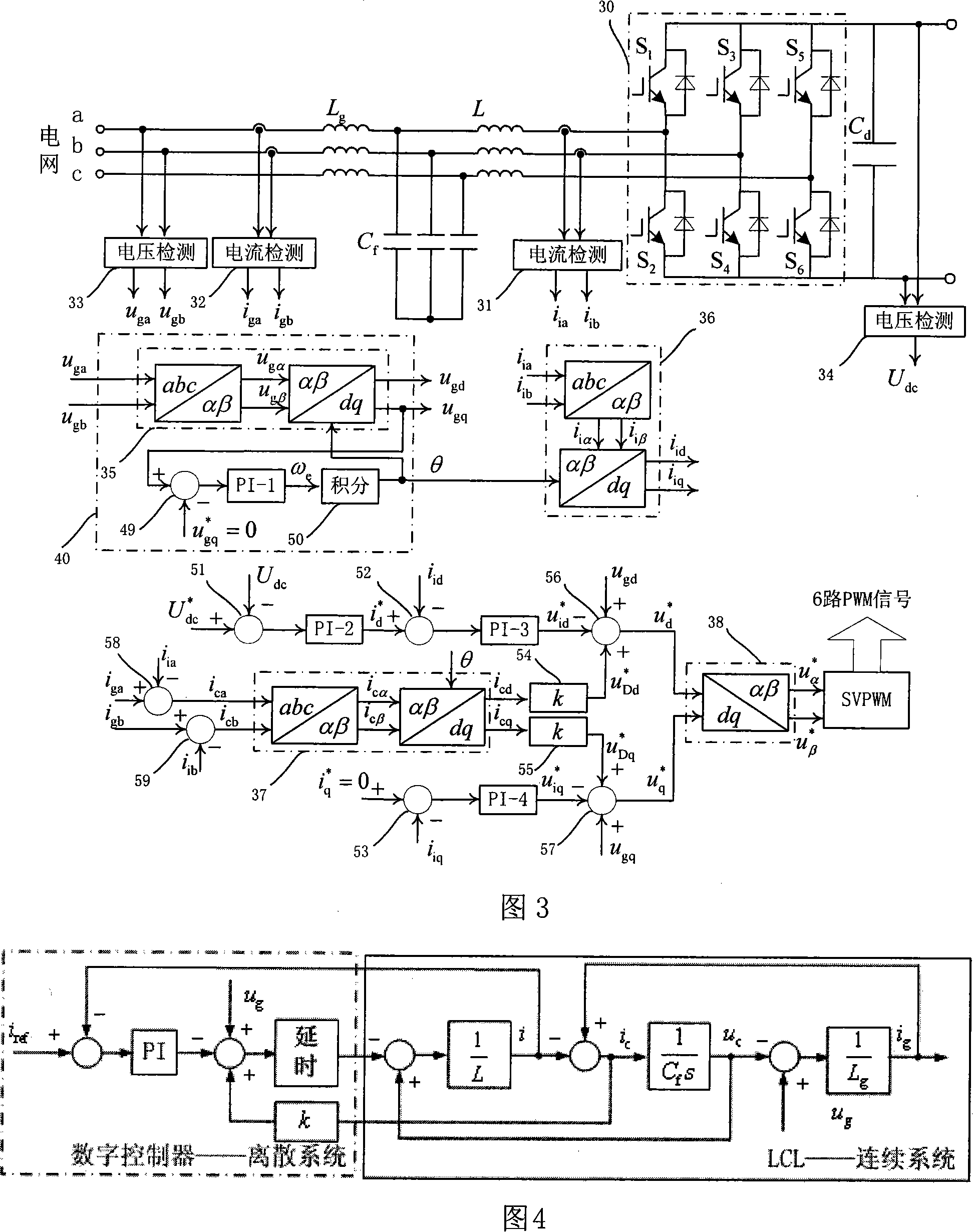
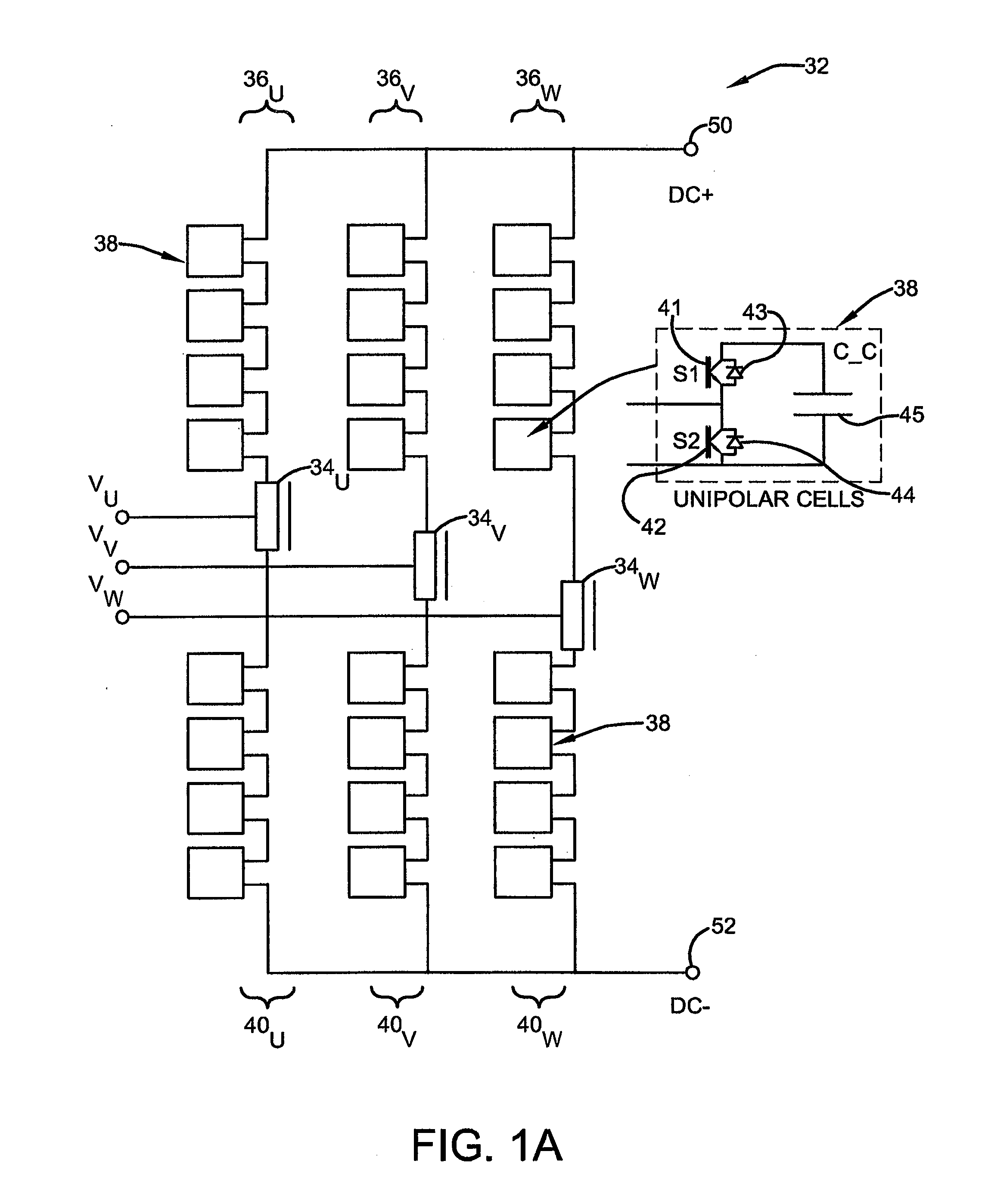
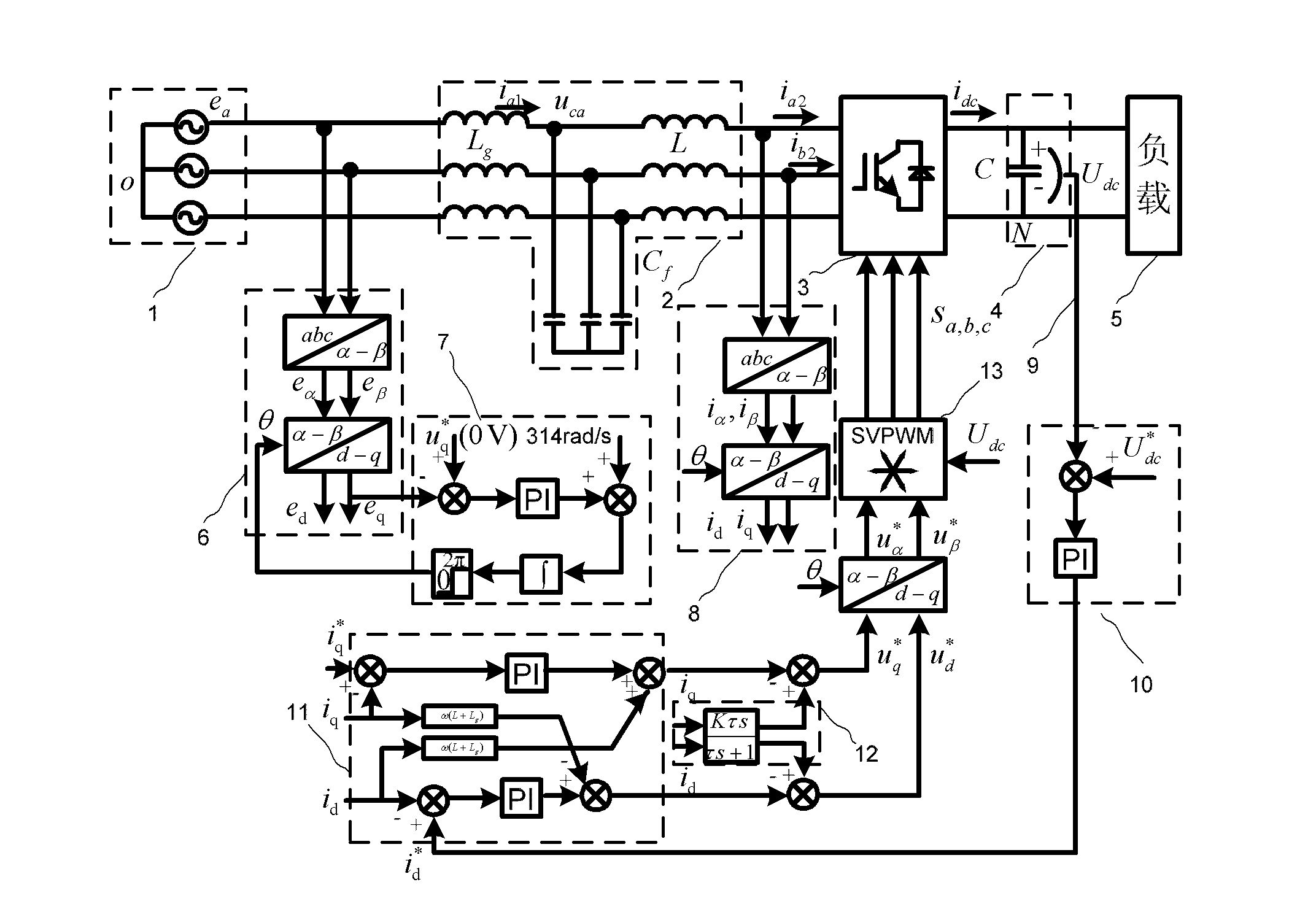
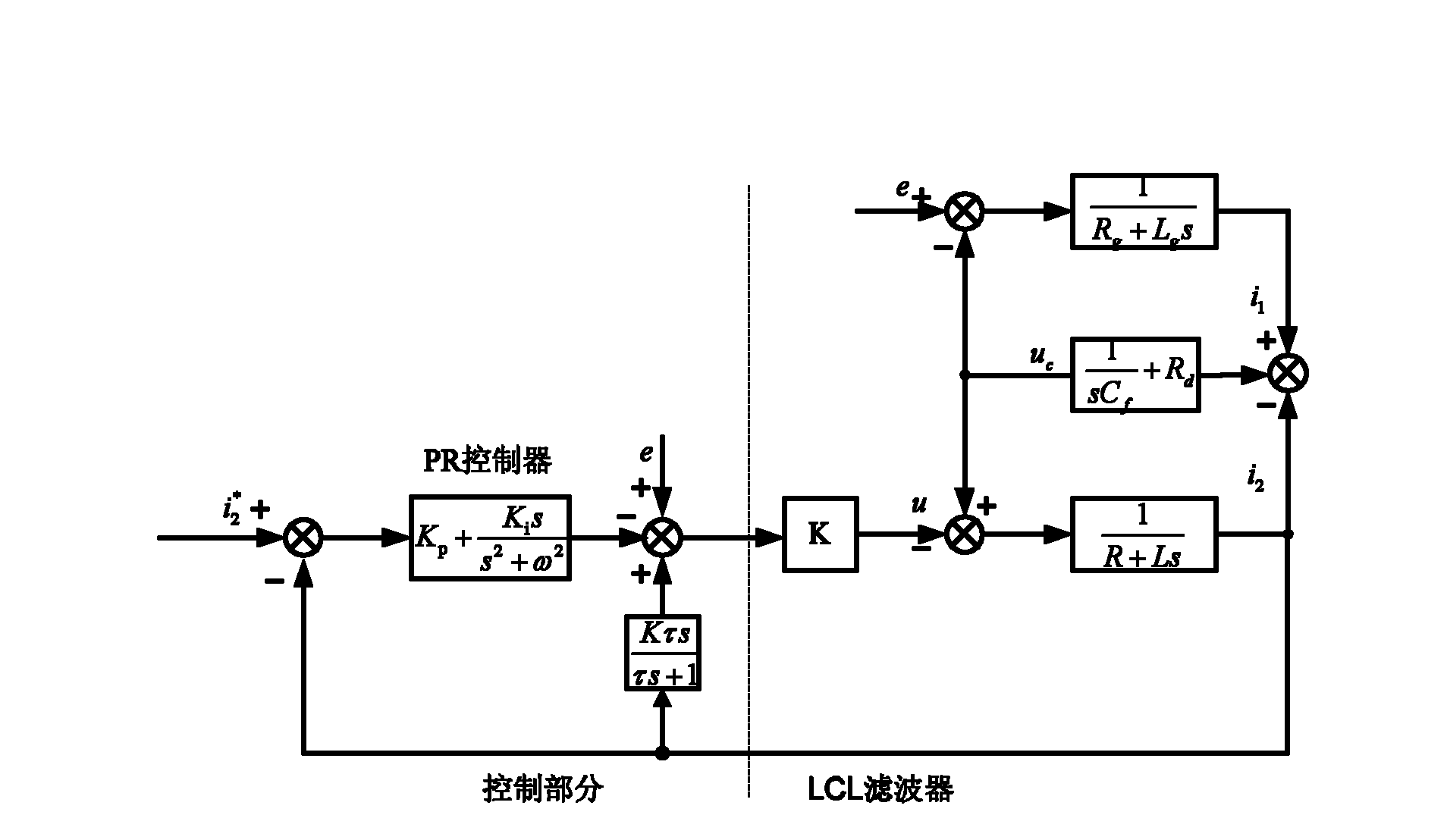
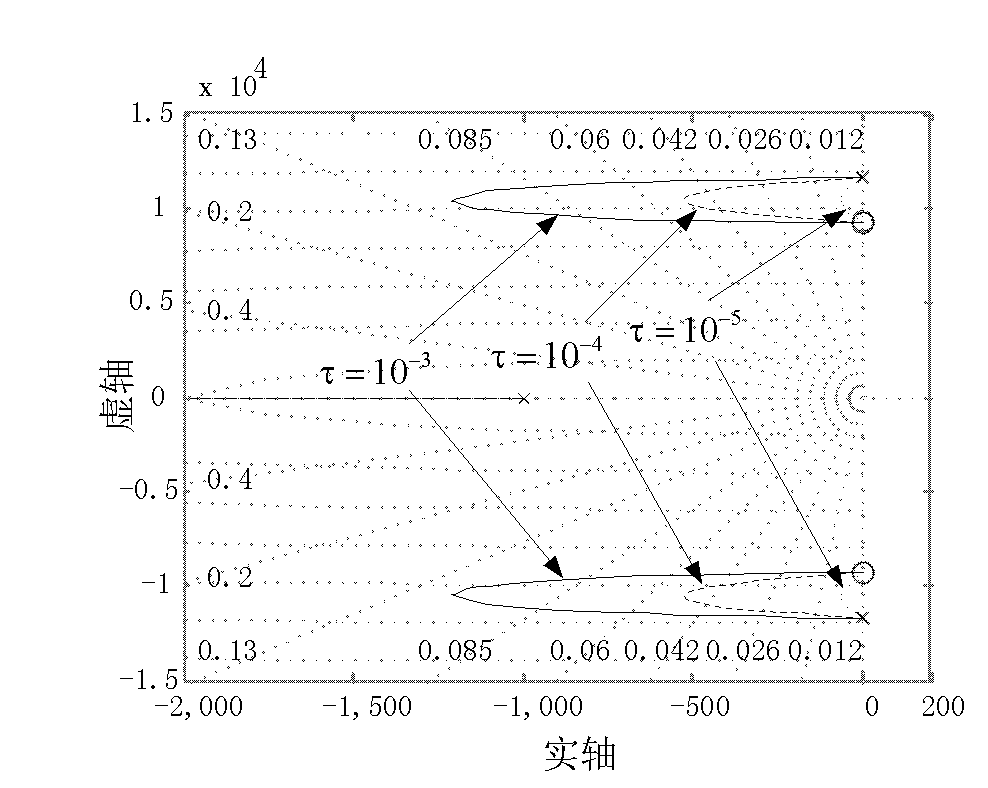
LCL filtering based voltage type active rectifier steady control system and method
InactiveCN101141100AReduce distortion rateImprove power factorEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitancePower factor
The utility model relates to a voltage type source rectifier stable control system and method based on LCL filter wave, belonging to the source rectifying technical range of electronic technology. The system comprises a DC voltage control cell, a current control cell, an active damp control cell and a voltage space vector generating cell. the utility model produces six PWM signals to gain the current signal of the filter wave capacitor branch directly or indirectly, outputs the reference value of the damp voltage and achieves the stable control on the system. The method provides an adjustable sine control on the DC voltage output and input current through the active damp vector control of the voltage type source rectifier stable control system, the damp voltage reference value outputted by the active damp vector control cell, and the network voltage to execute summation operation. The utility model has the advantages of controllable DC voltage, low aberrance rate of the network input current, high power factor, satisfying the requirement of energy double-redirection flowing, and achieving the stability of the system without increasing the quantity of hardware damp resistance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
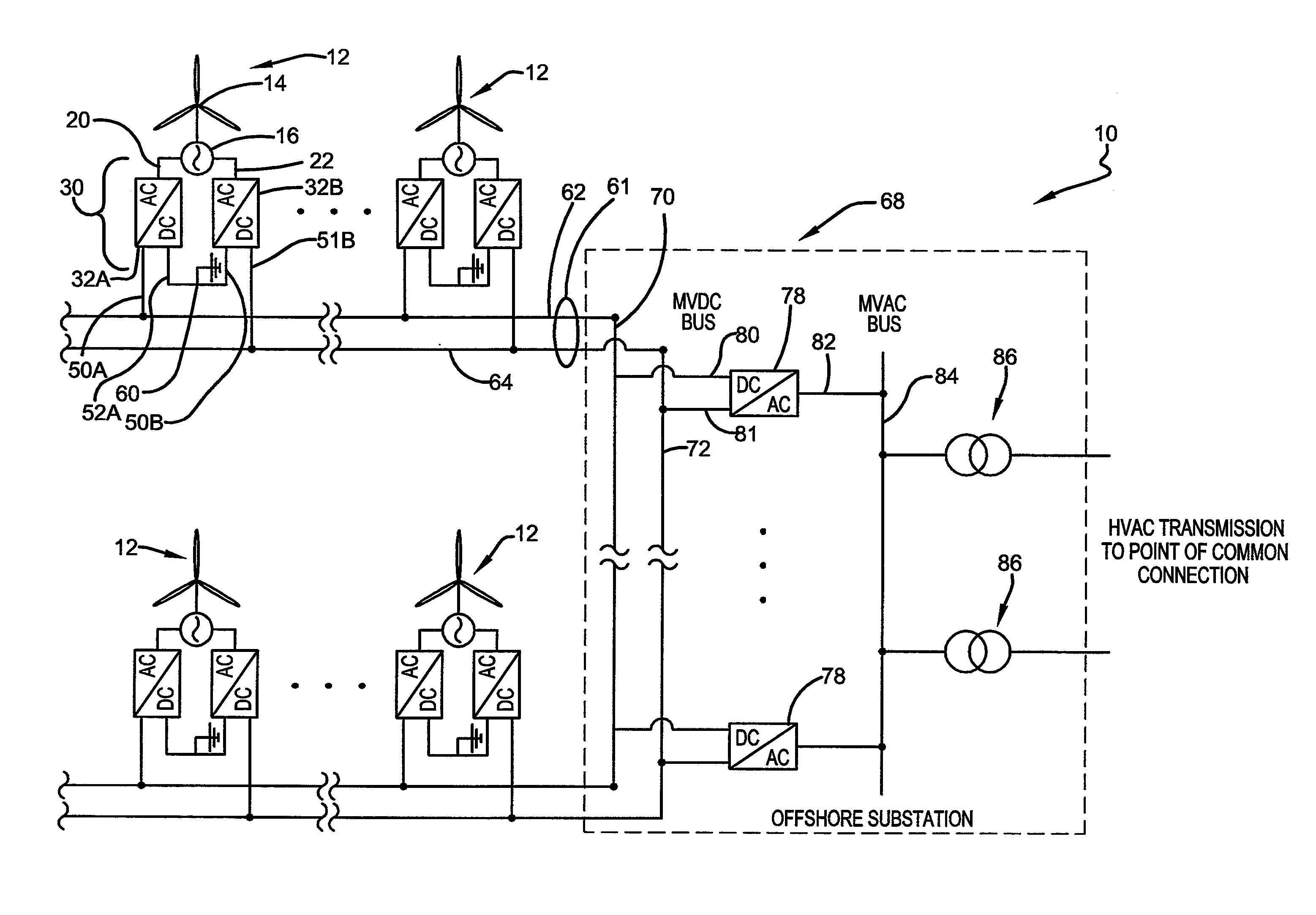
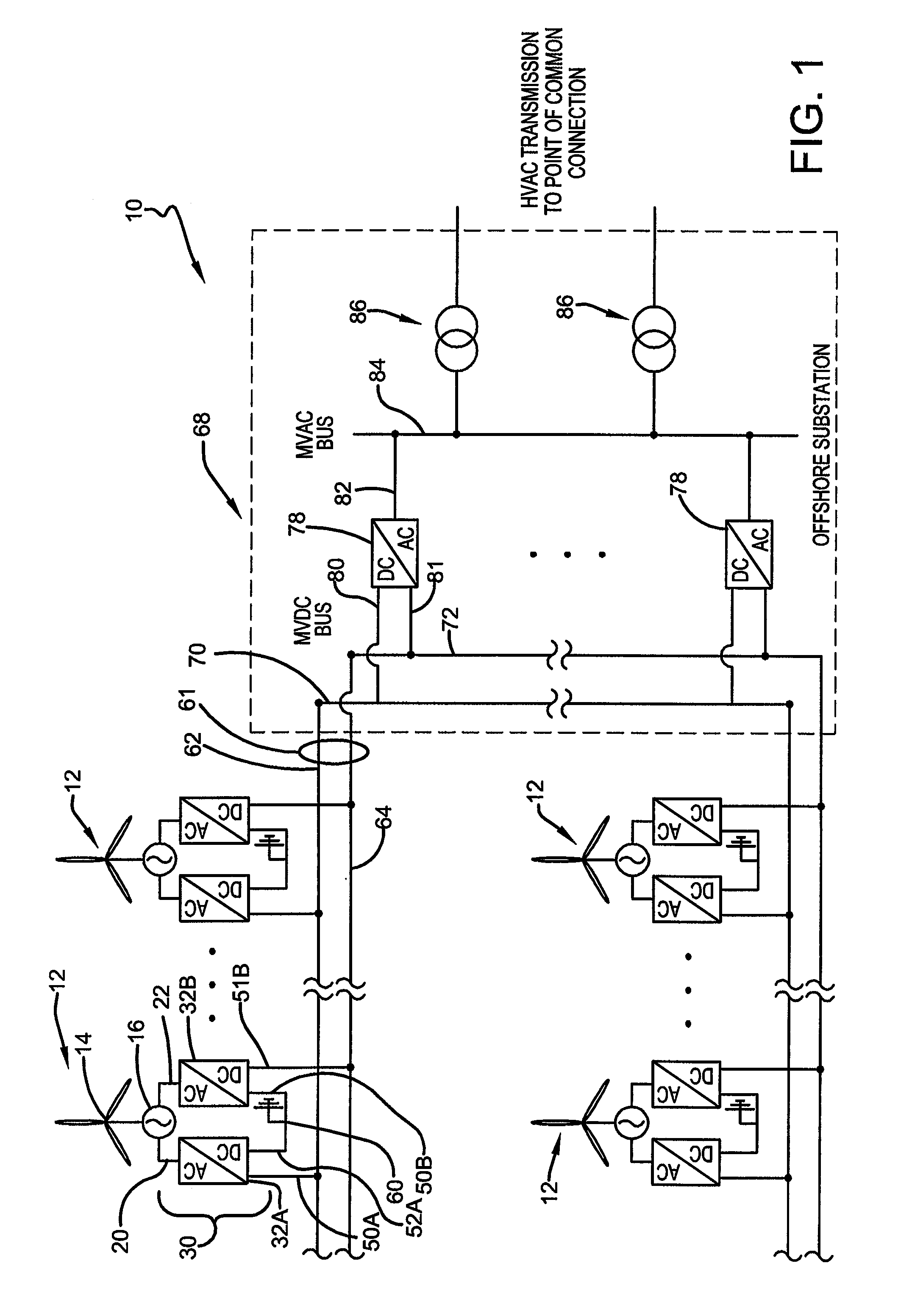
Medium voltage DC collection system
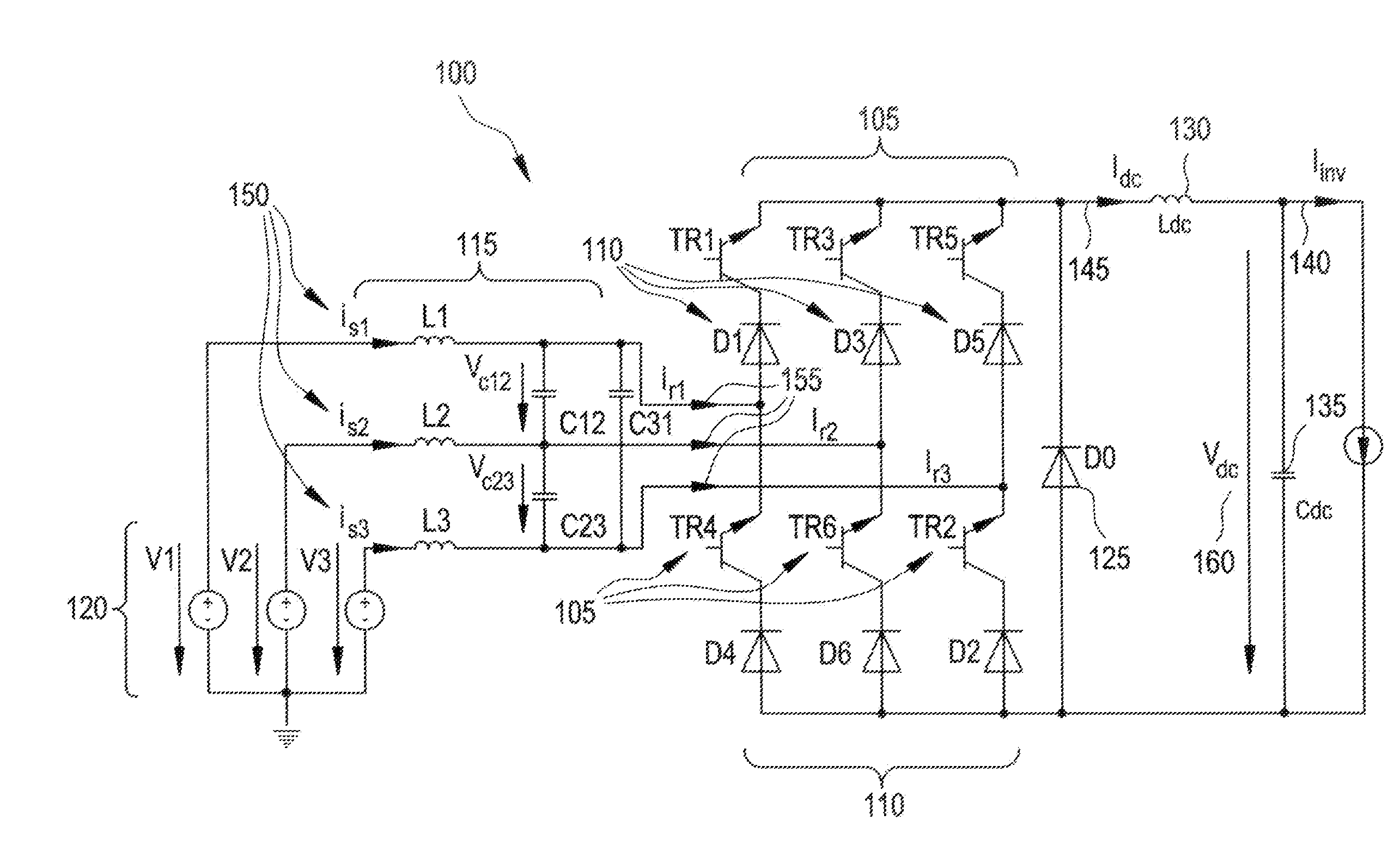
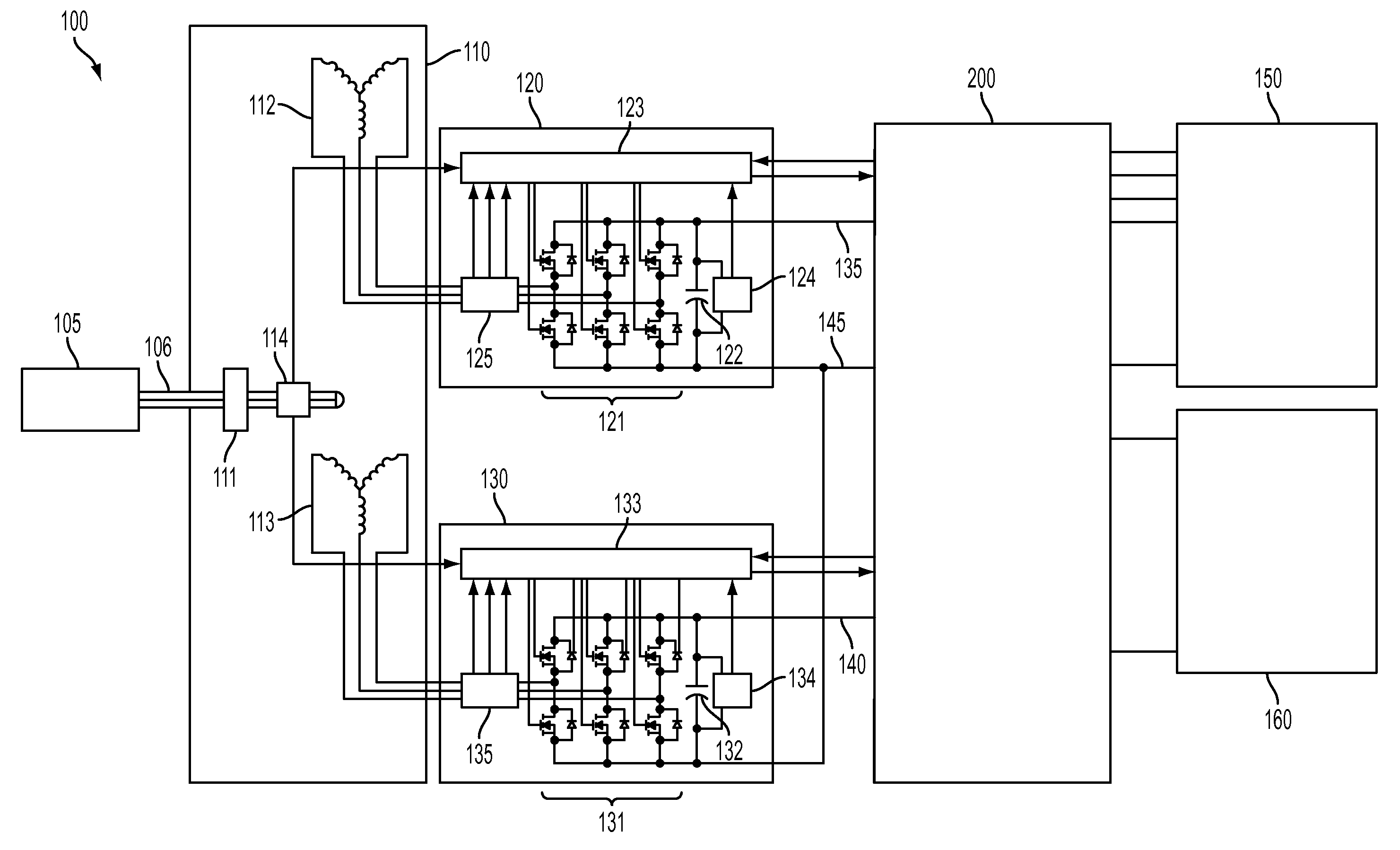
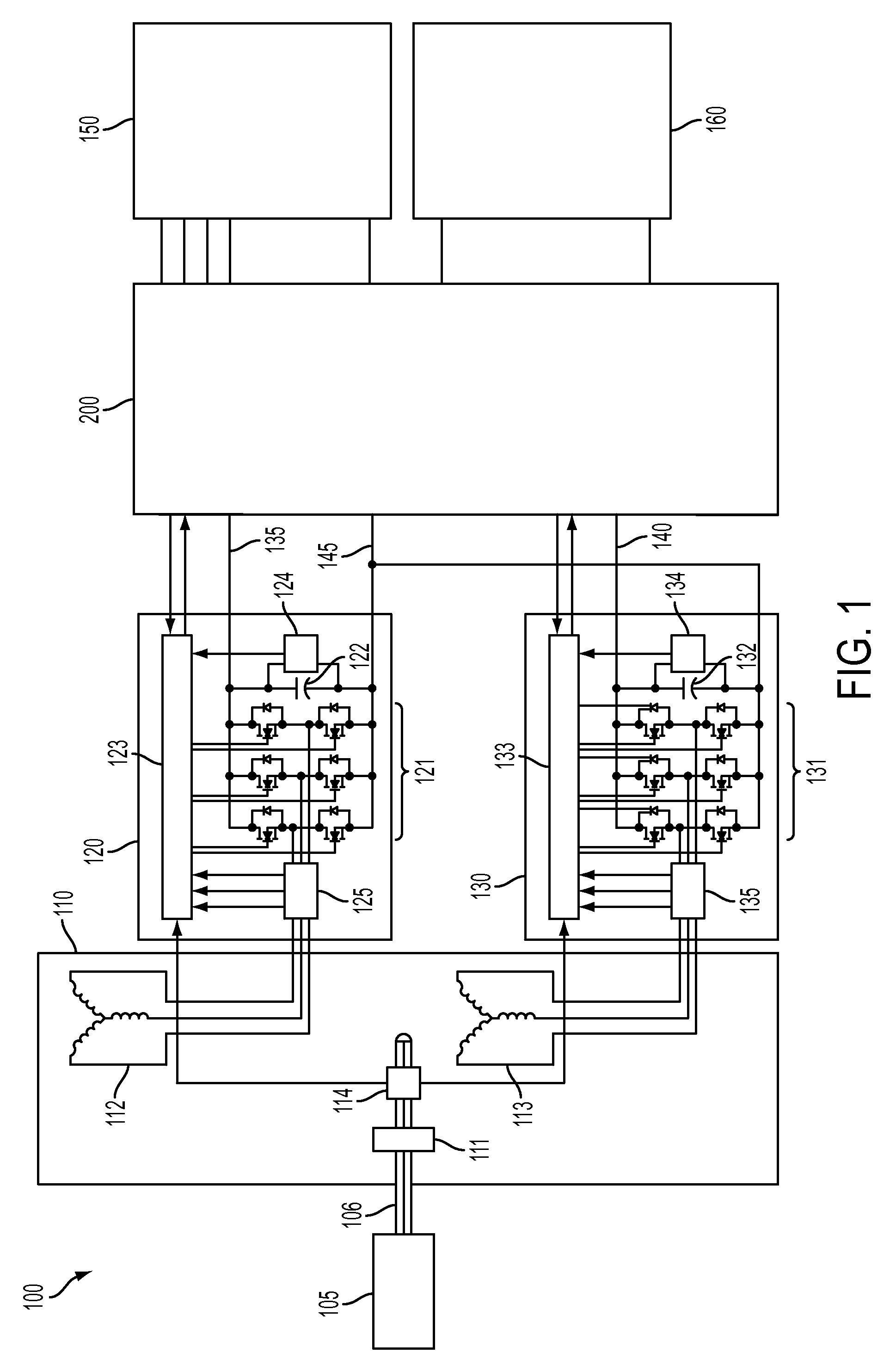
A power generation system includes at least one generator having at least two sets of stator windings, an active rectifier comprising power cell based modular converters associated with each set of generator windings. Each set of windings is connected to an AC voltage side of the associated active rectifier, with each active rectifier having a positive DC voltage output and a negative DC voltage output. The DC voltage outputs of active rectifiers are connected to each other in series. A medium voltage DC (MVDC) collection network comprises positive pole cables and negative pole cables, wherein each positive pole cable is connected to the positive DC voltage output of a first active rectifier and each negative pole cable is connected to the negative DC voltage output of a last active rectifier. A substation receives the negative and positive pole cables of the MVDC collection network for further transformation and transmission.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
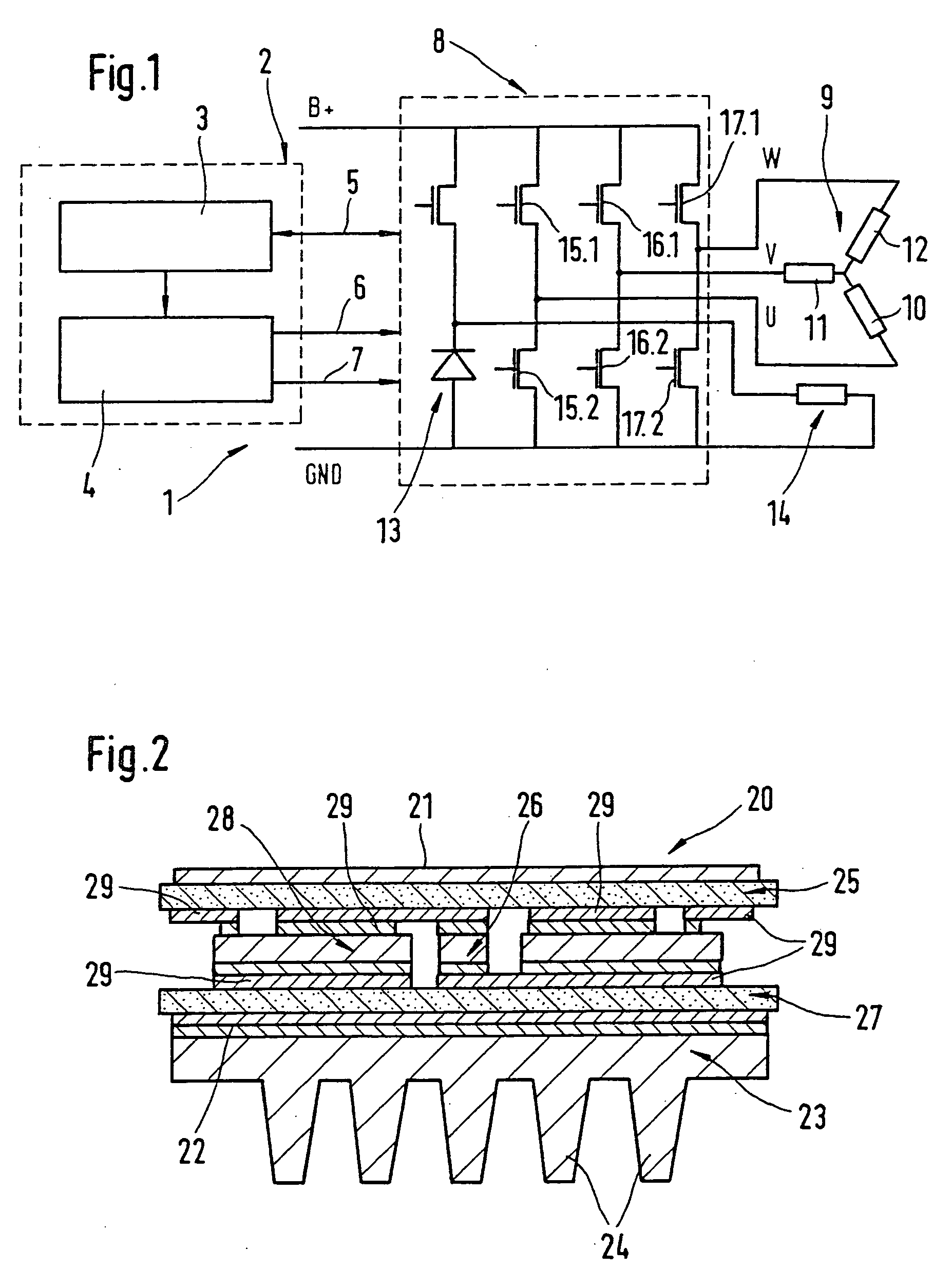
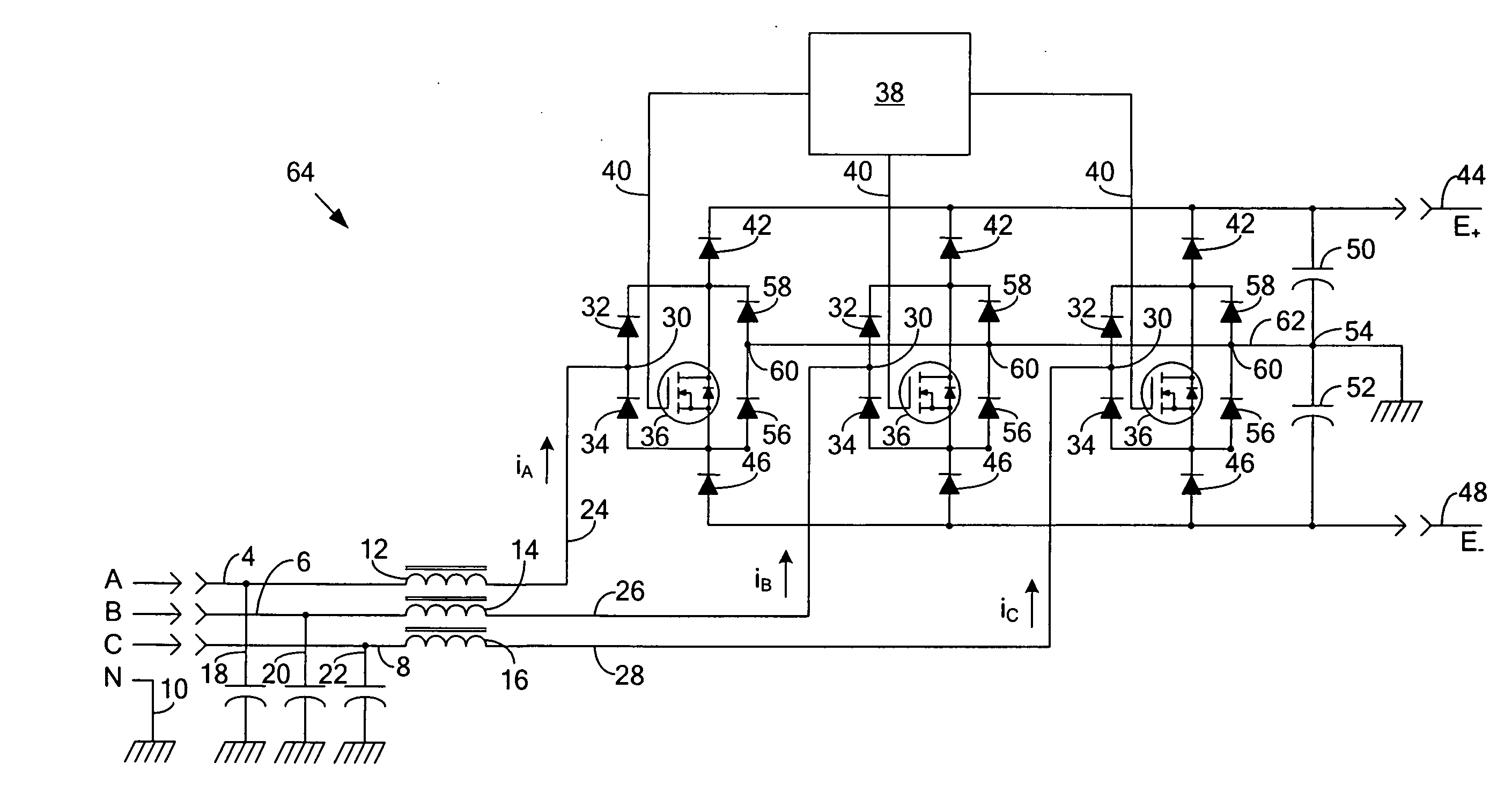
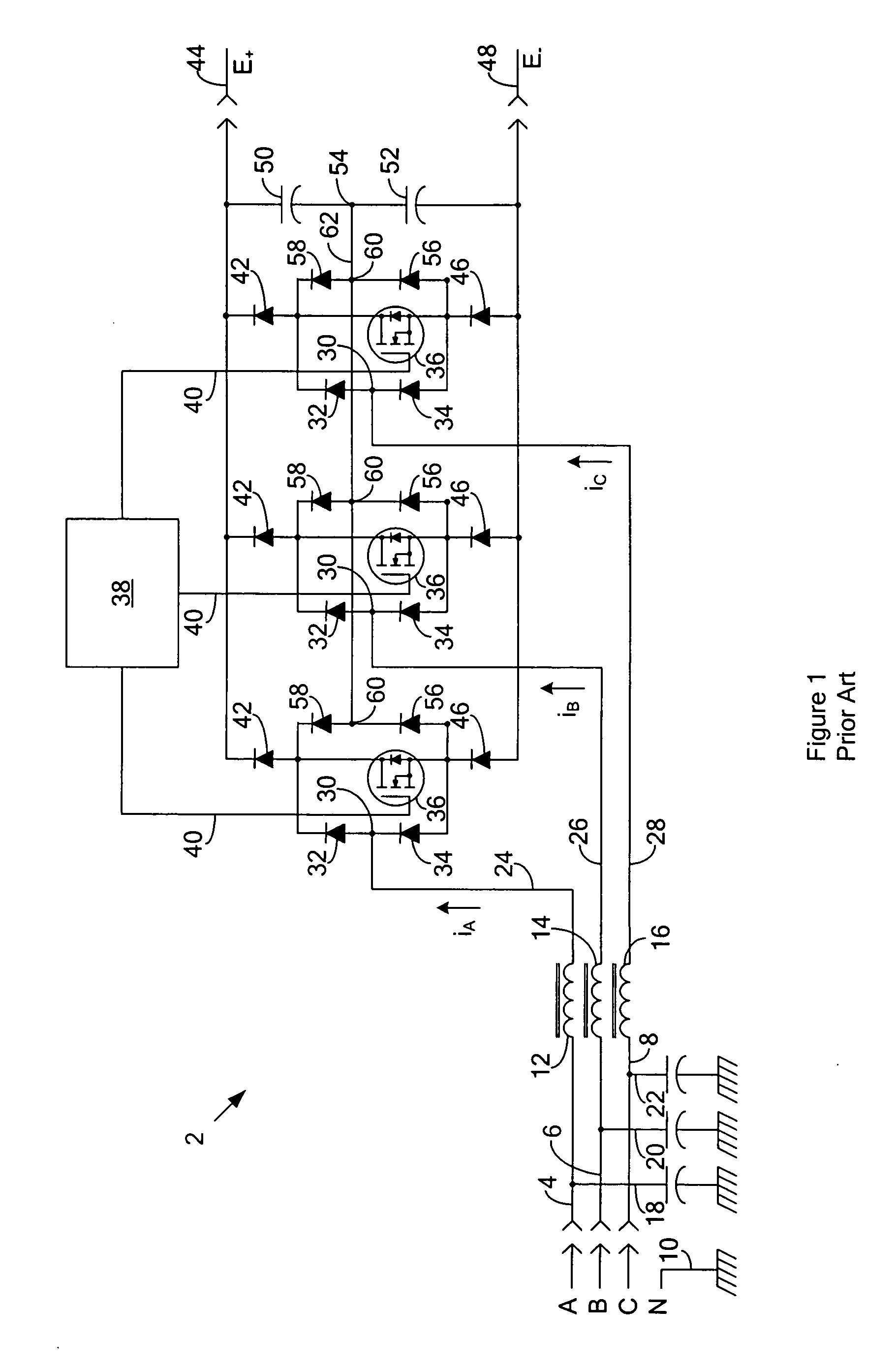
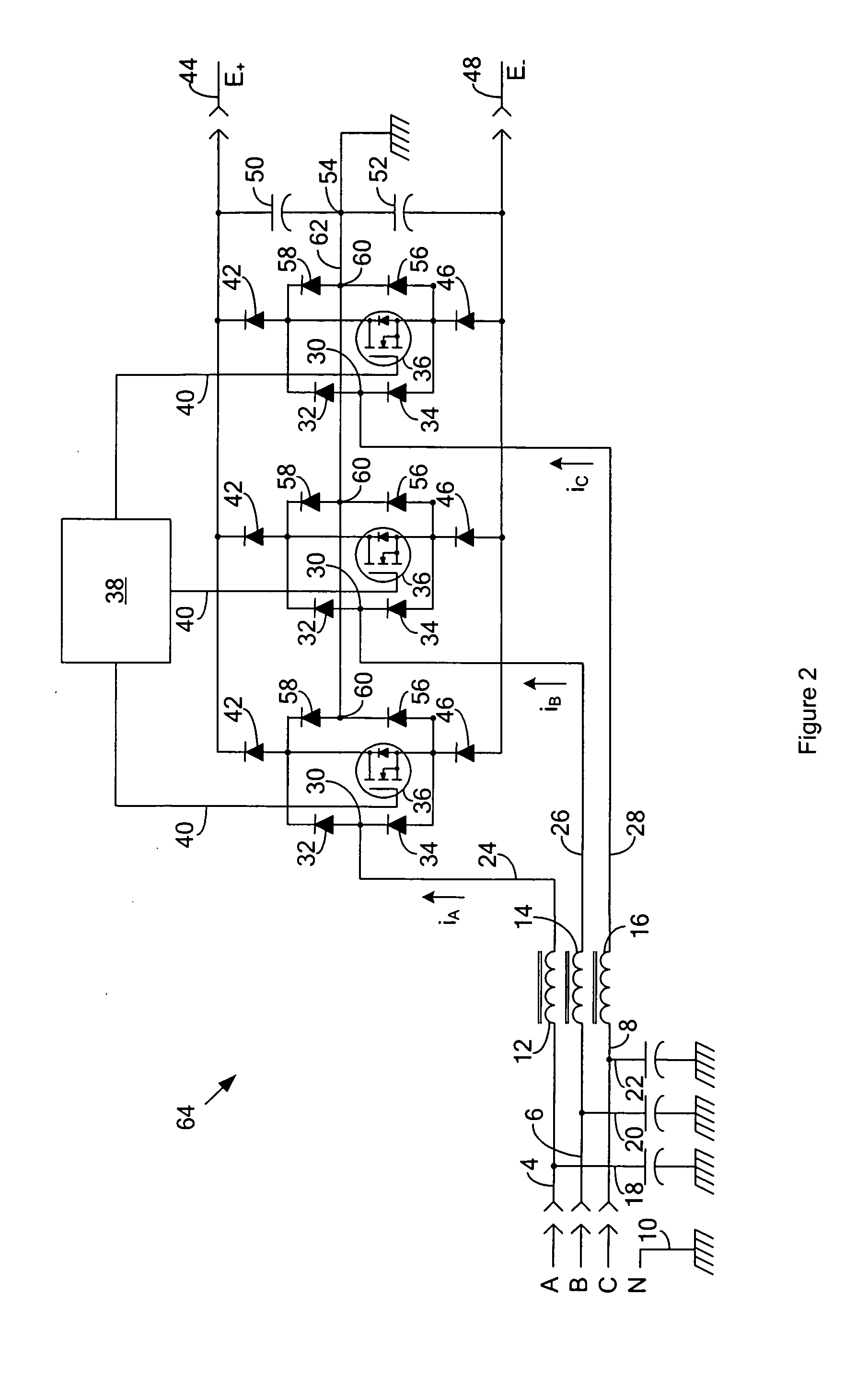
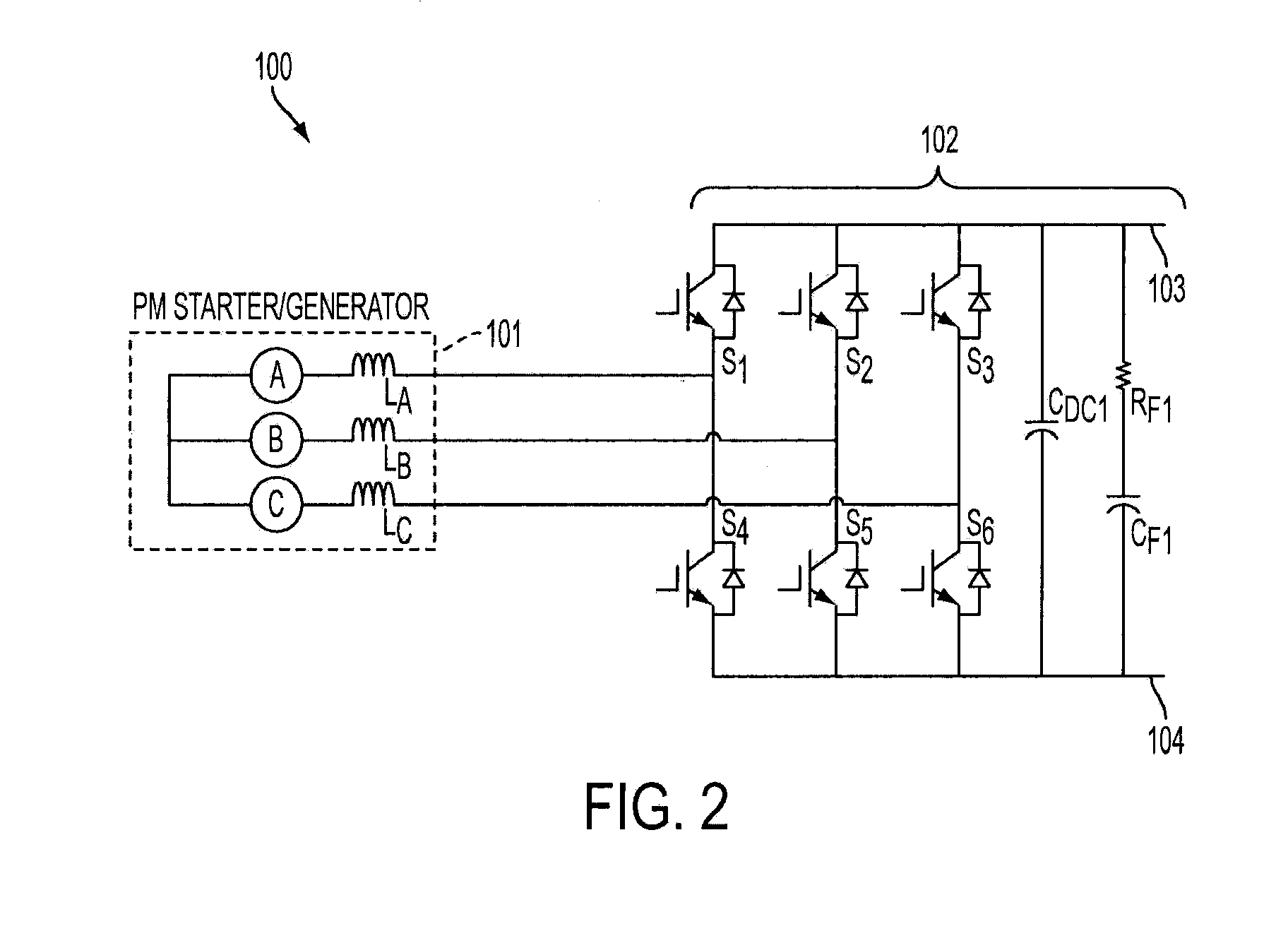
Active rectifier module for three-phase generators of vehicles
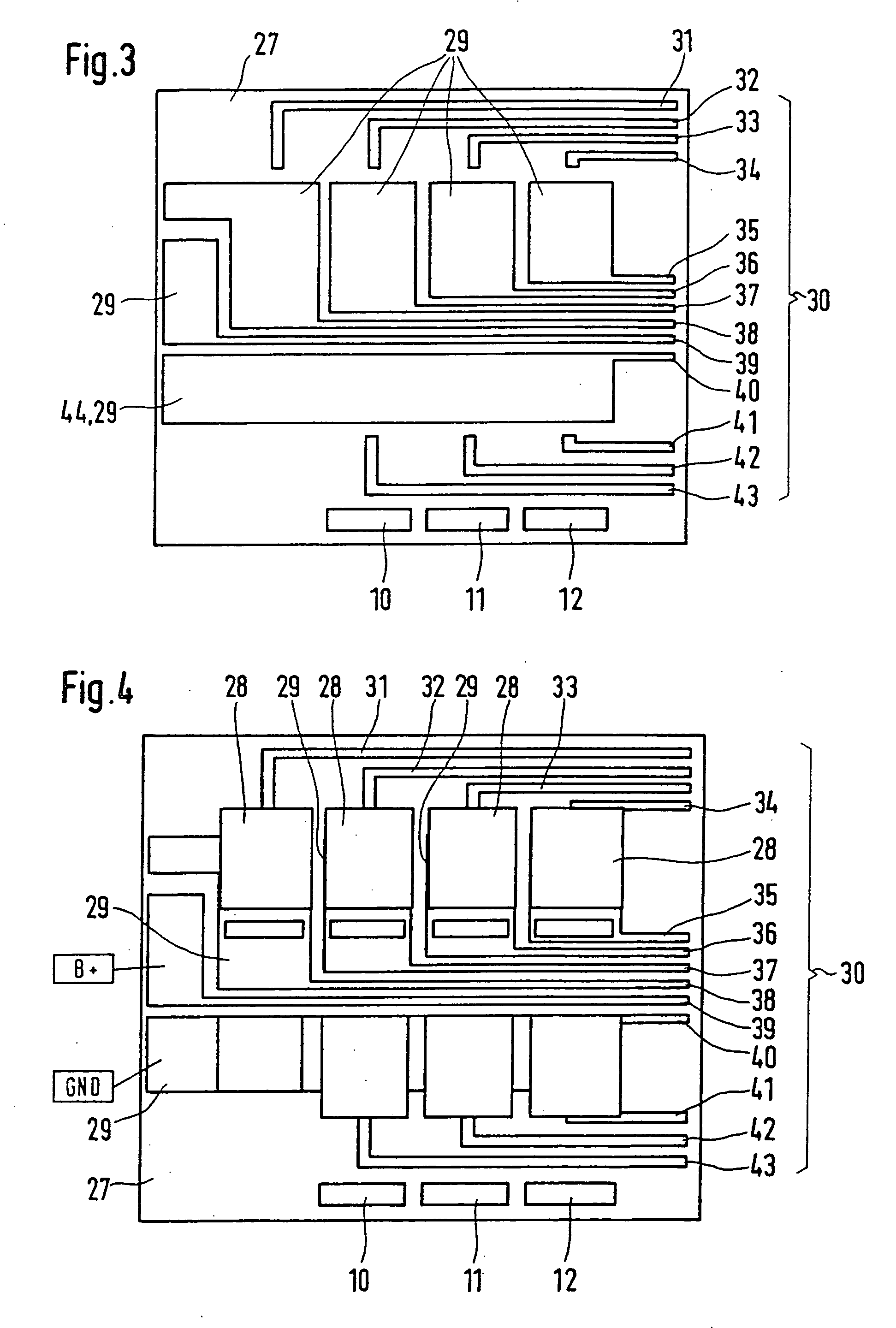
InactiveUS20060151874A1Improve efficiencyGuaranteed usageBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalThree-phaseAlternating current
A rectifier for rectifying alternating current into direct current is described, in which a three-phase generator includes a three-phase stator winding. The phases of the stator winding are triggered via switching elements of a power circuit. The power circuit is controlled via a control part, which includes a controller component. The rectifier includes a control part (control module) having control terminals and a power circuit (power module) controlled by the control module and optionally provided with a cooling device, in which all the power-conducting components are designed as power MOS components and integrated in a stacked construction.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rectifier circuit
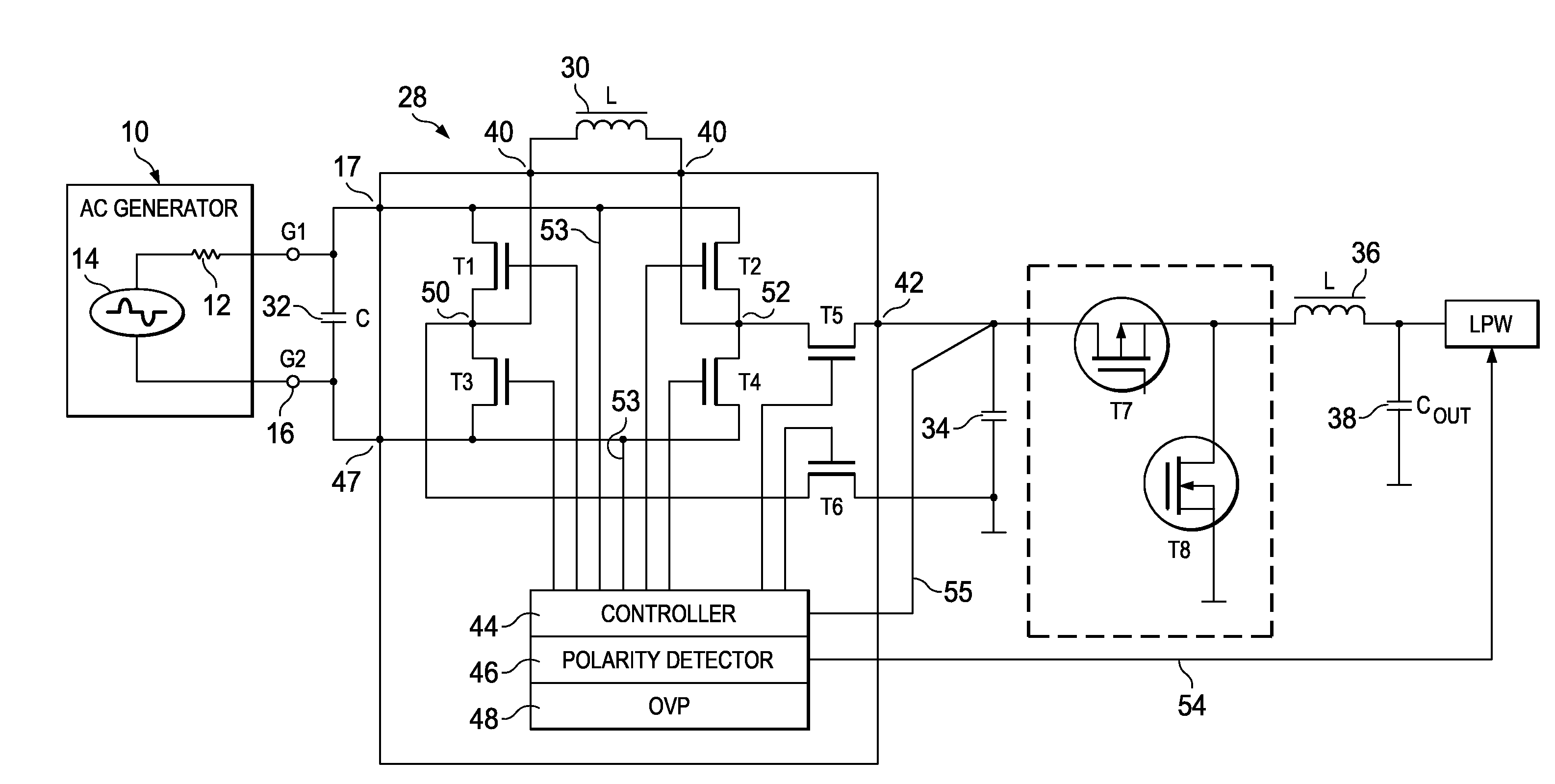
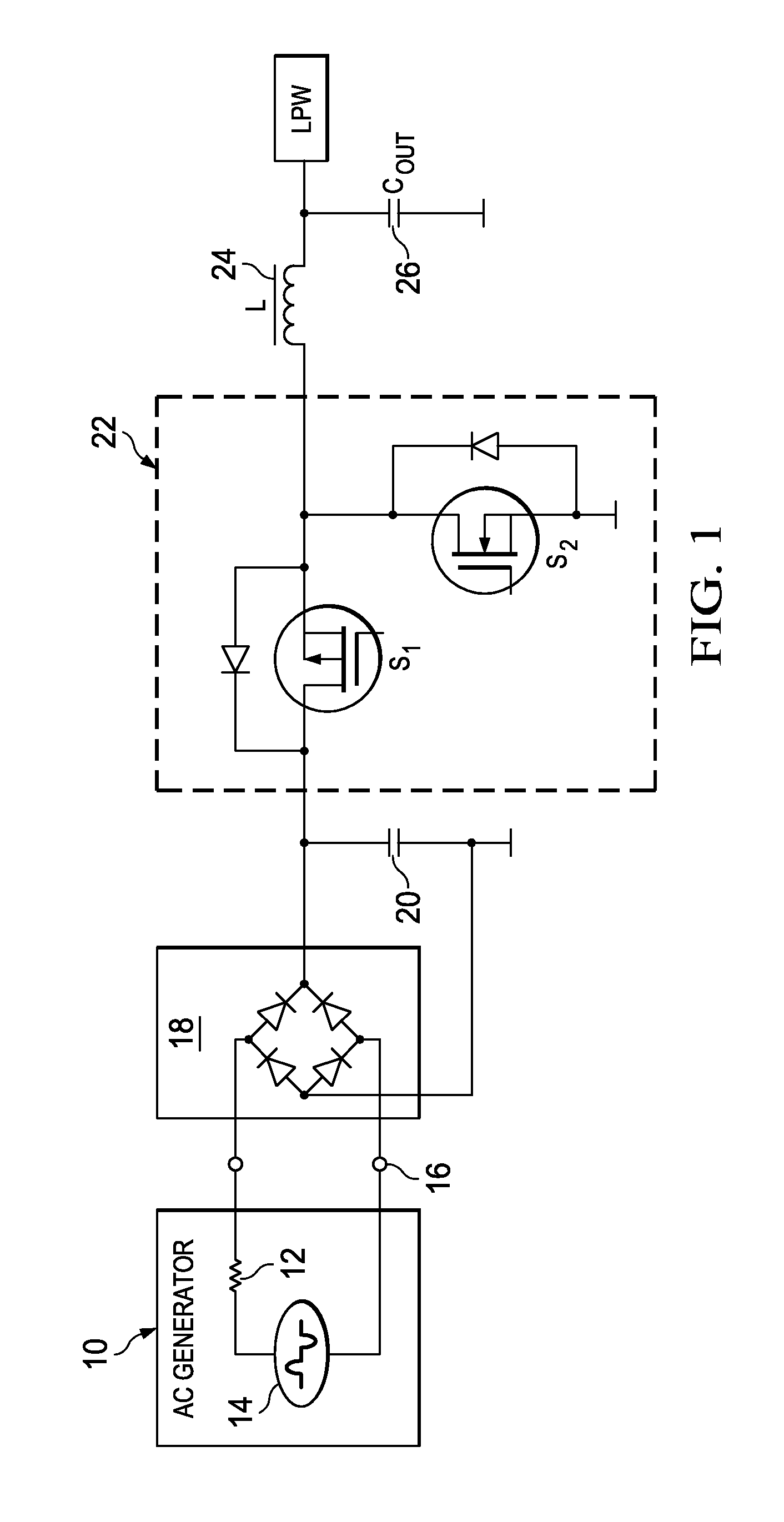
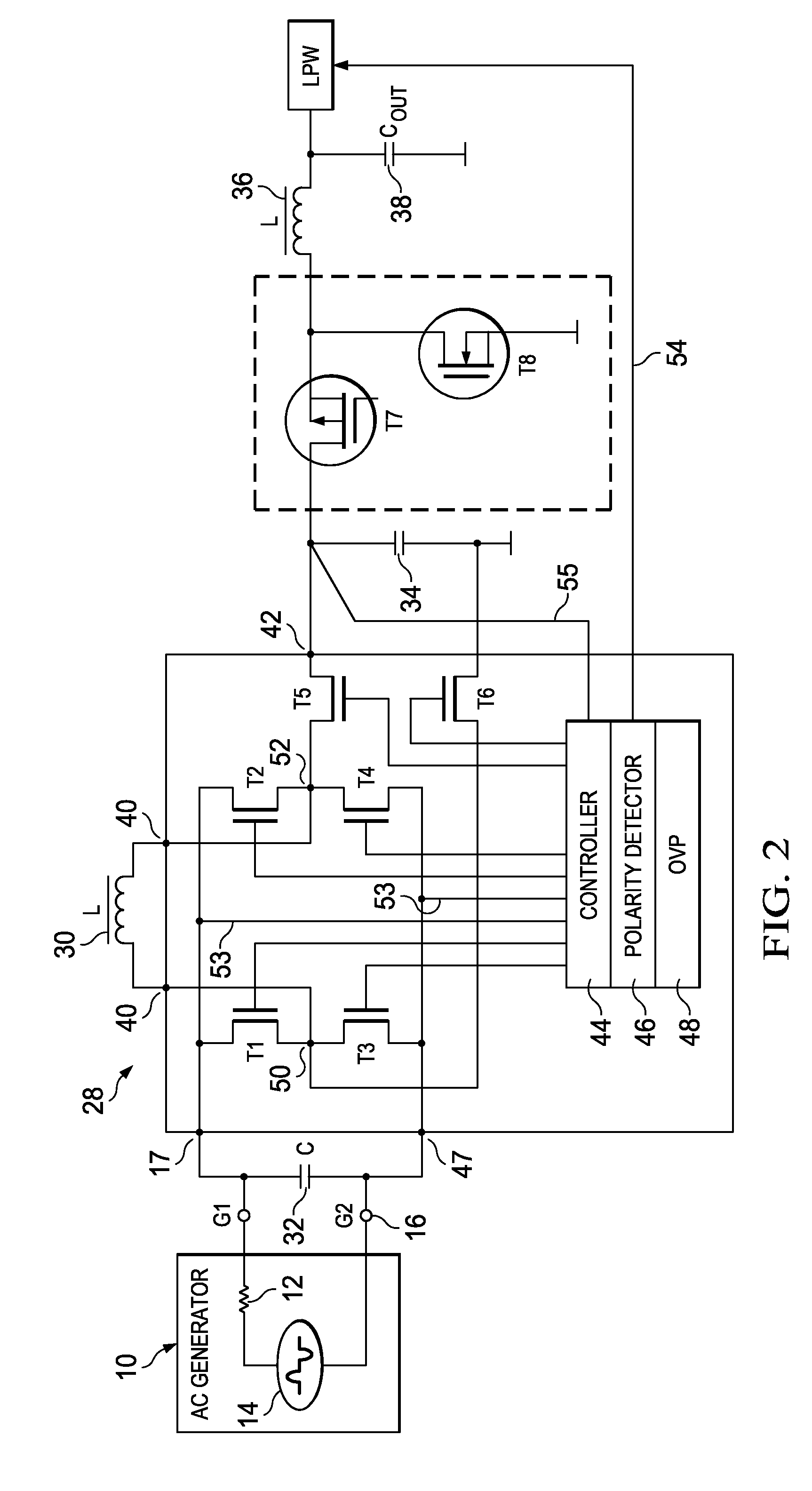
InactiveUS20100165686A1Lower average energyLow energy conversionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSwitching cycleMechanical energy
A rectifier circuit for use in an energy harvesting application in which mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by using an AC generator using an active rectifier bridge with a pair of input terminals adapted to be connected to an output of the AC generator and a pair of output terminals, an inductor connected across the output terminals of the active rectifier bridge and a storage capacitor. A pair of output switches selectively connects the storage capacitor across the inductor. A controller controls the active rectifier bridge and the pair of output switches such that in successive switching cycles within any half wave of AC input voltage from the output of the AC generator the inductor is first loaded by current from the output of the AC generator and then discharged into the storage capacitor. An energy harvesting system which uses an AC generator for generating electrical energy out of mechanical energy, a rectifier circuit which is connected with the input to the output of the AC generator and a low power wireless system as application unit. A method of rectifying an AC output voltage of an AC generator for use in an energy harvesting application.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Converter and method for extracting maximum power from piezo vibration harvester
ActiveUS20110227543A1Avoids large amount of powerA large amountBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalCapacitanceDc dc converter
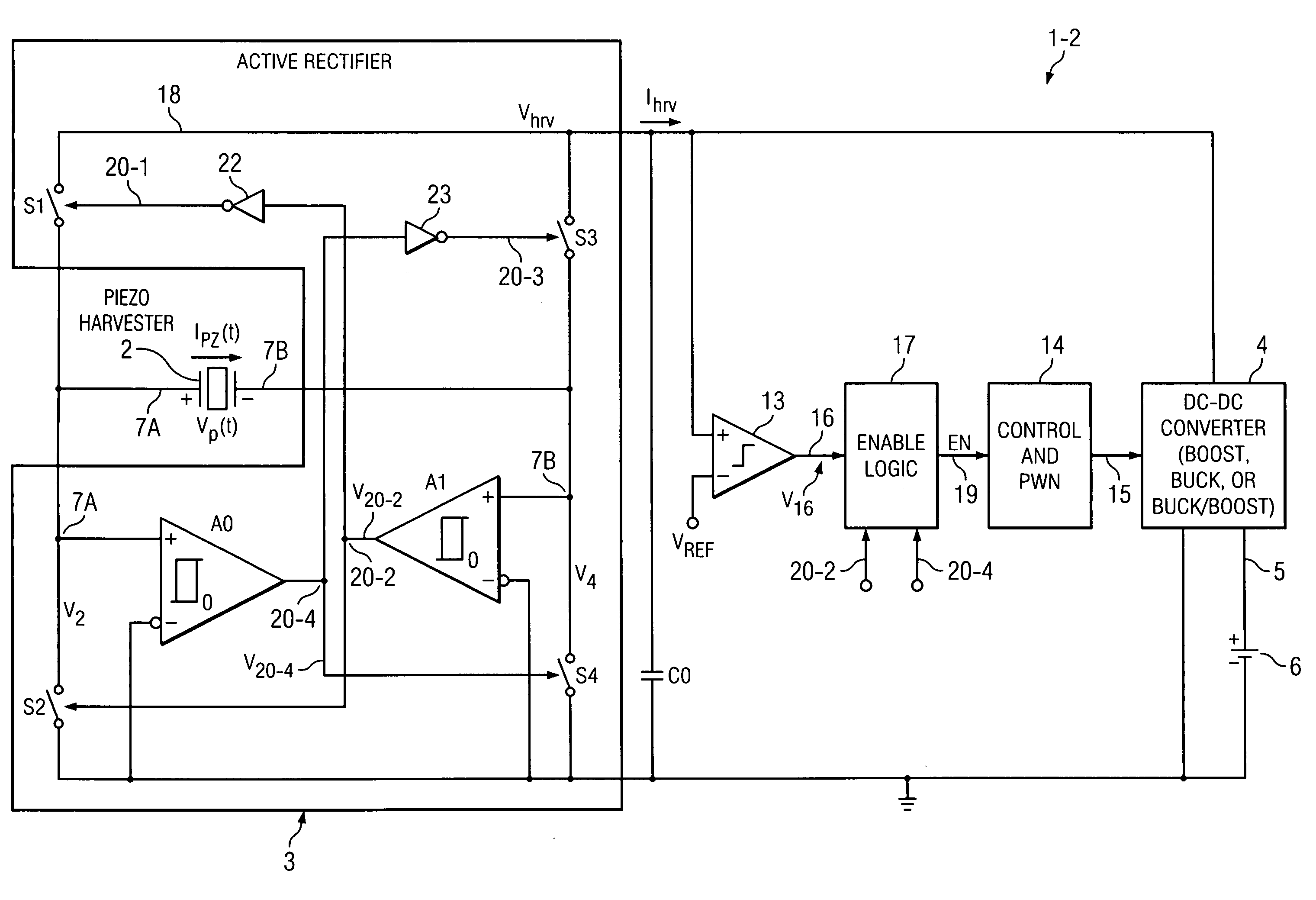
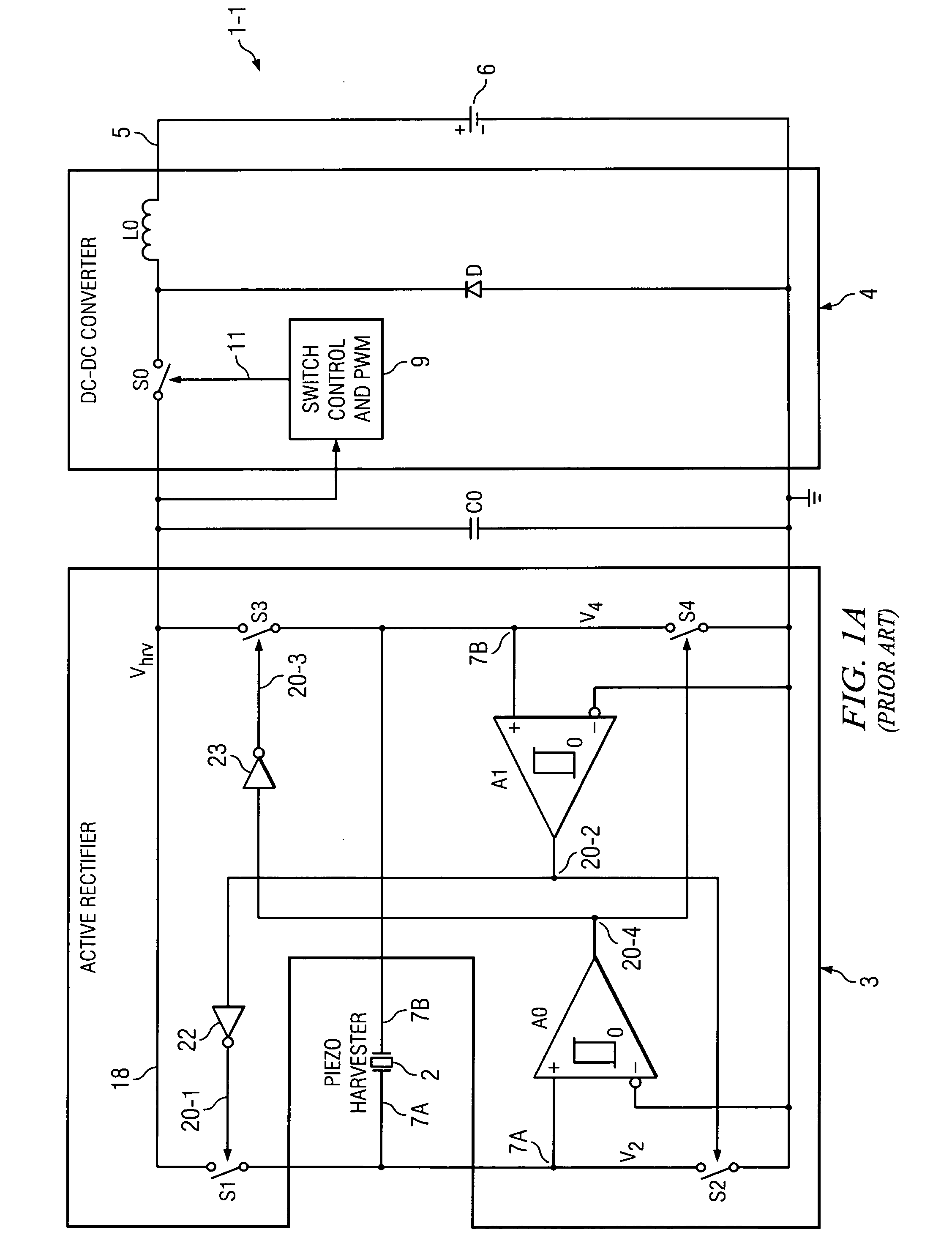
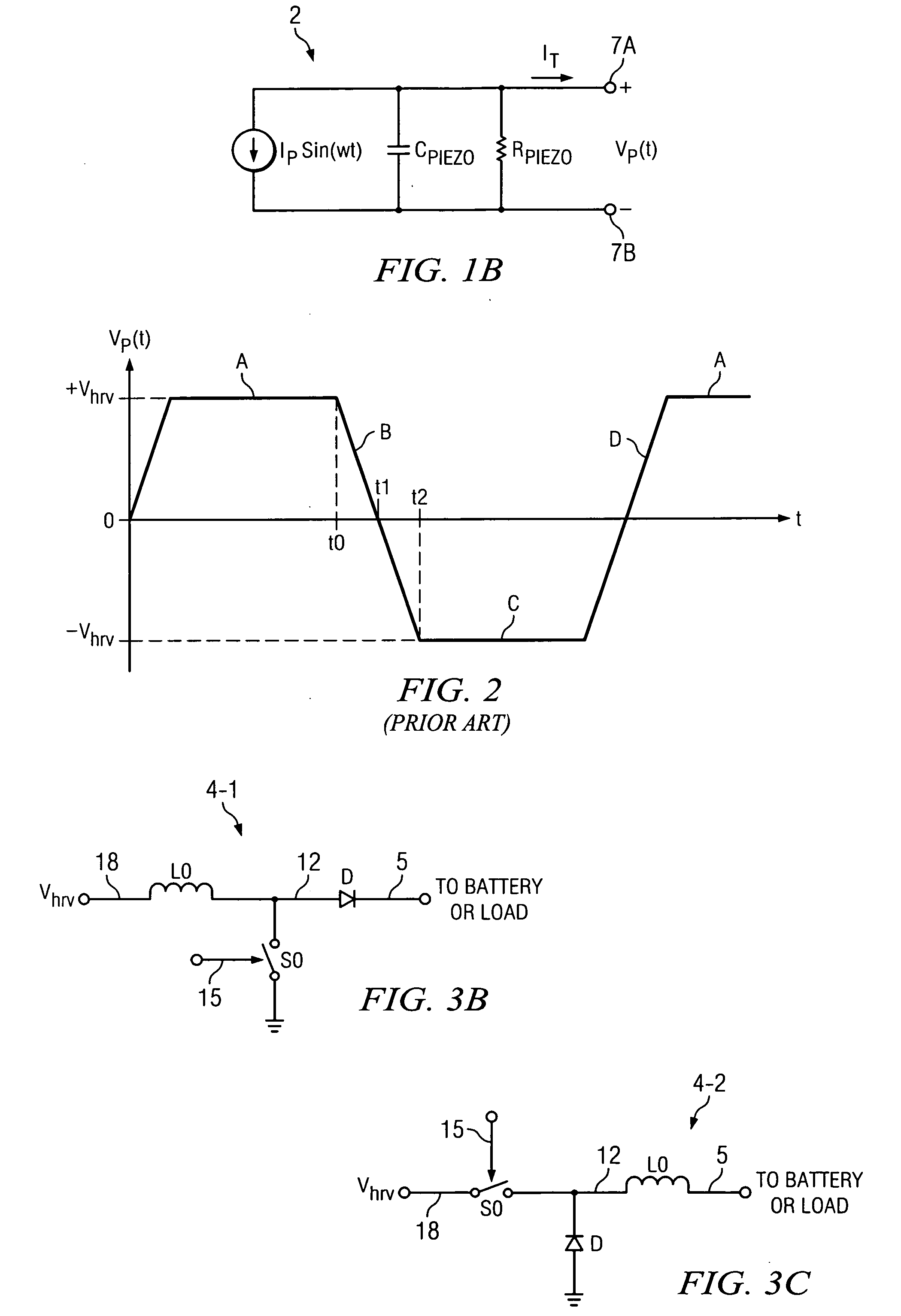
A system (1-2) for efficiently transferring harvested vibration energy to a battery (6) includes a piezo harvester (2) generating an AC output voltage (VP(t)) and current (IPZ(t)) and an active rectifier (3) to produce a harvested DC voltage (Vhrv) and current (Ihrv) which charge a capacitance (C0). An enable circuit (17) causes a DC-DC converter (4) to be enabled, thereby discharging the capacitance into the converter, when a comparator (A0,A1) of the rectifier which controls switches (S1-S4) thereof detects a direction reversal of the AC output current (IPZ(t)). Another comparator (13) causes the enable circuit (17) to disable the converter (4) when the DC voltage exceeds a threshold (VREF), thereby causing the capacitance be recharged.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
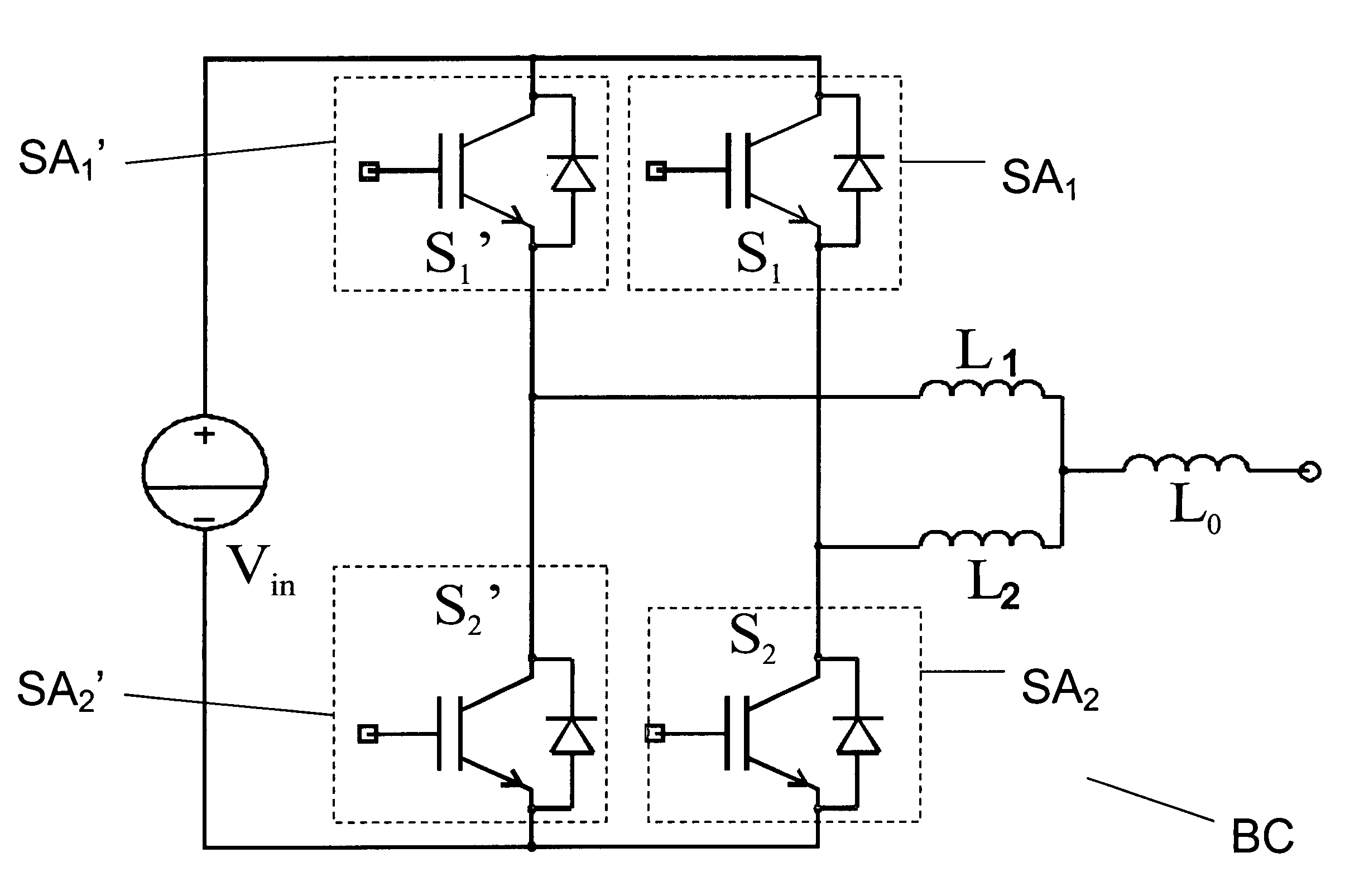
Interleaved soft switching bridge power converter
InactiveUS7423894B2Reduce switching lossesReduce recoveryConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionMotor driveReverse recovery
An interleaved soft switching bridge power converter comprises switching poles operated in an interleaved manner so as to substantially reduce turn-on switching losses and diode reverse-recovery losses in the switching pole elements. Switching poles are arranged into bridge circuits that are operated so as to provide a desired voltage, current and / or power waveform to a load. By reducing switching turn on and diode reverse recovery losses, soft switching power converters of the invention may operate efficiently at higher switching frequencies. Soft switching power converters of the invention are well suited to high power and high voltage applications such as plasma processing, active rectifiers, distributed generation, motor drive inverters and class D power amplifiers.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
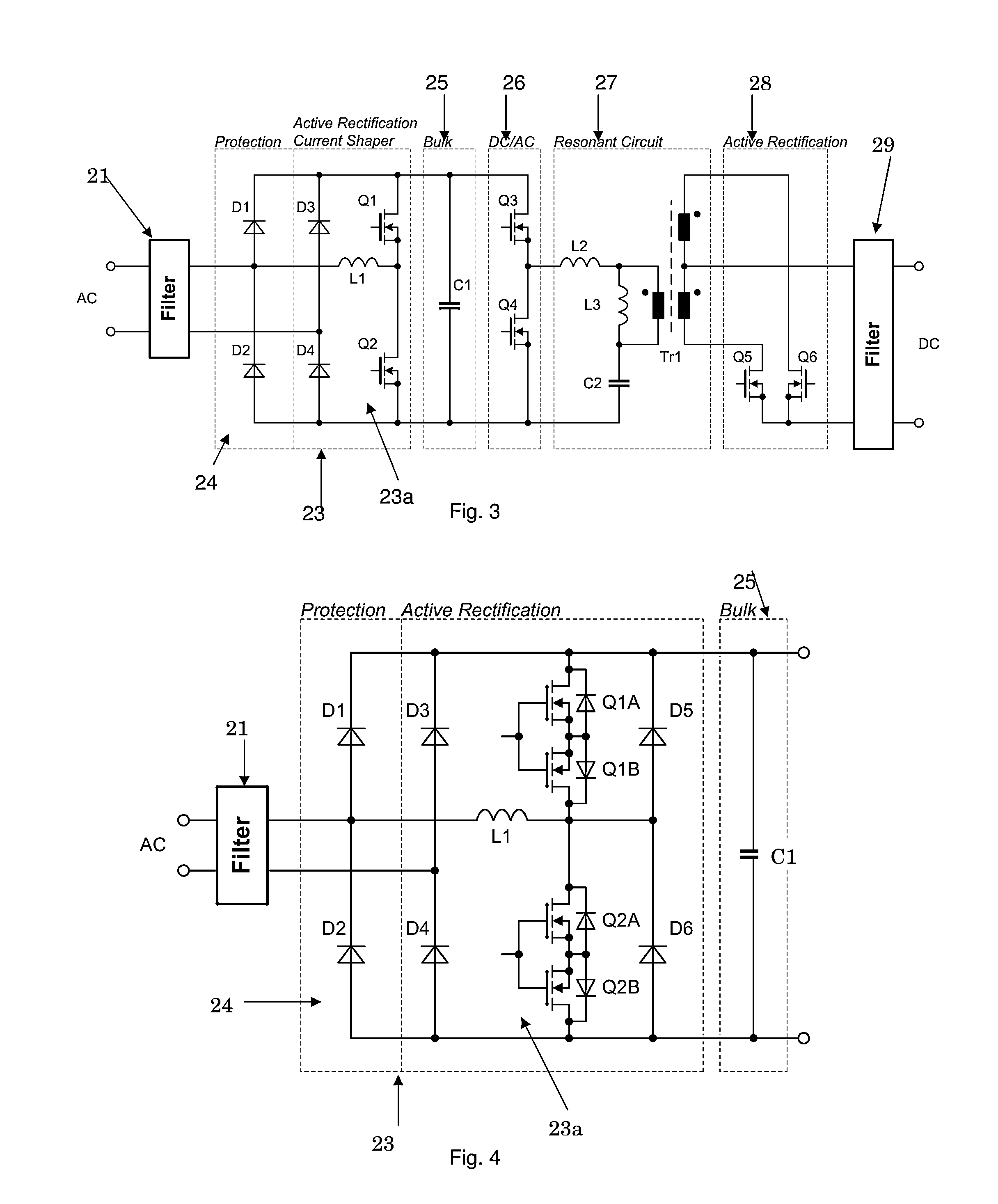
AC/DC power converter with active rectification and input current shaping
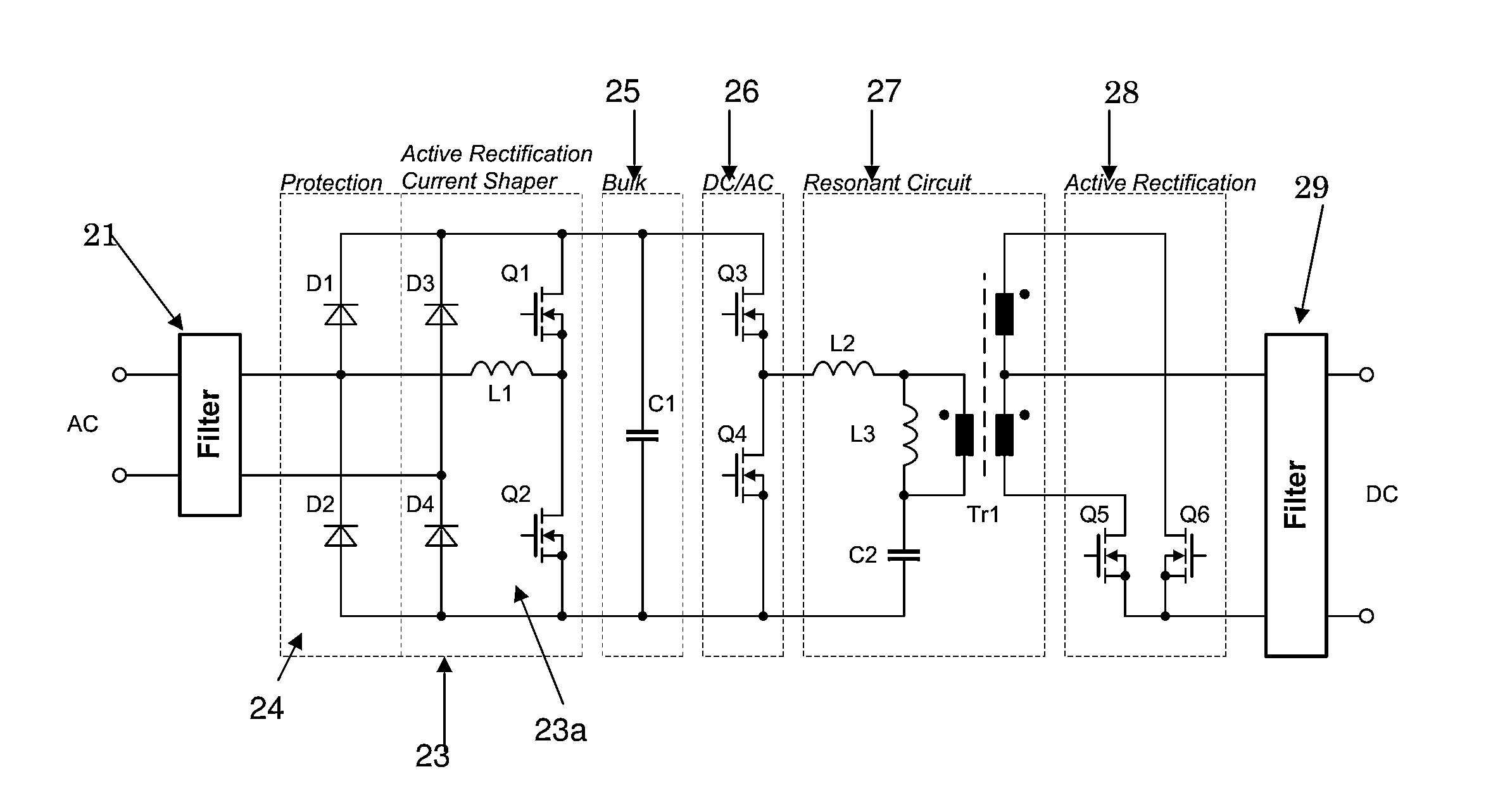
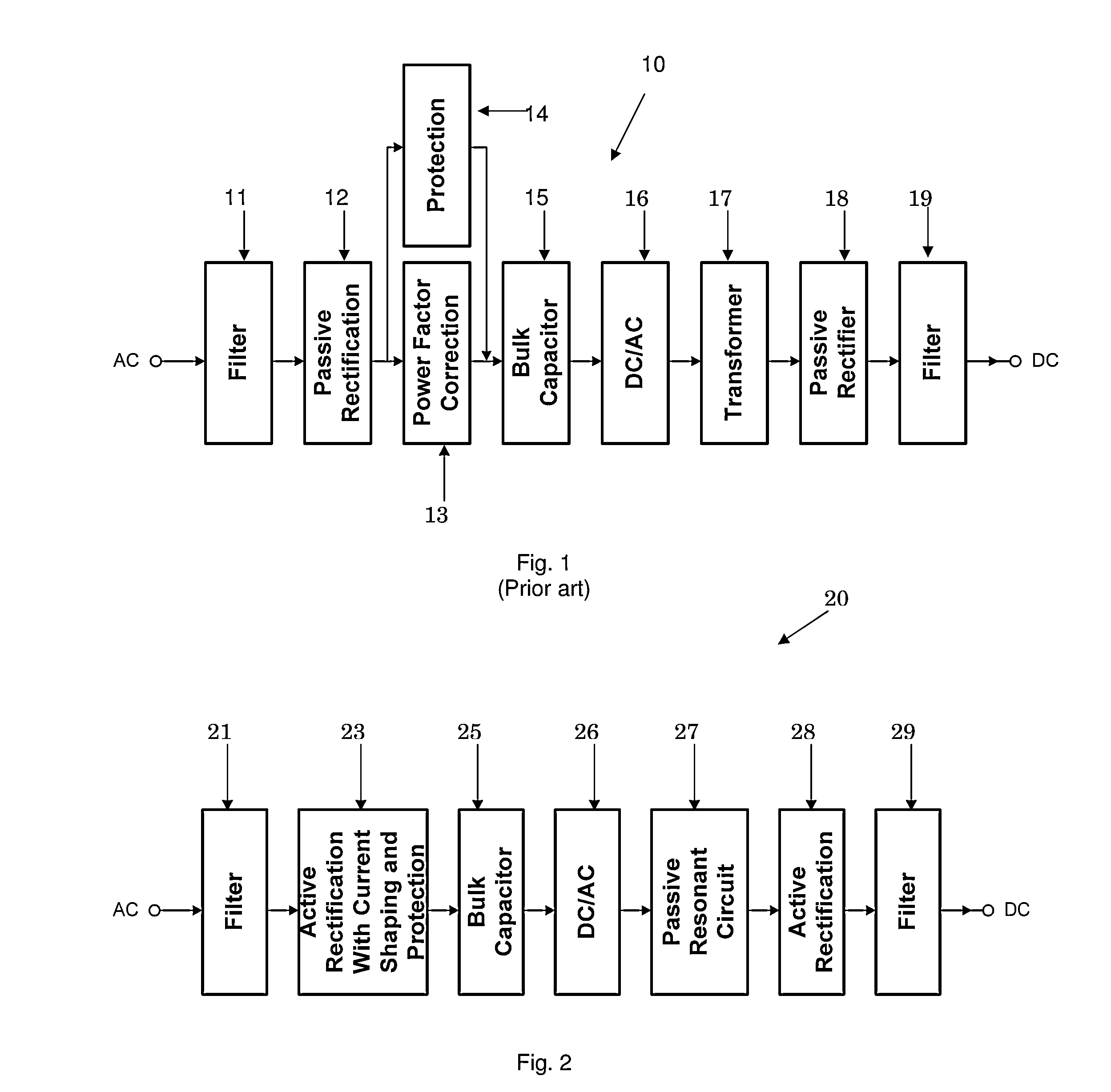
ActiveUS8503199B1Improve efficiencyReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringCapacitor
An AC / DC power converter has an AC input and a DC output, with an input rectifier circuit coupled to the AC input. The input rectifier circuit includes a passive half-bridge rectifier circuit functional to provide passive rectification of an AC input power sign and at least one current shaper circuit. The current shaper circuit includes an input inductor coupled between the AC input and a switch node in the input active rectifier circuit. The input current shaper circuit is functional to shape an AC input current signal associated with an AC input power signal to a substantially sinusoidal current signal. A bulk capacitor circuit is coupled to the input active rectifier circuit. A DC / AC converter circuit is coupled to the bulk capacitor circuit. A resonant circuit is coupled to the DC / AC converter circuit and an output rectifier circuit may be coupled between the resonant circuit and the DC output.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
Active damping control method of lcl filter controllable rectification with current feedback on converter side
InactiveCN102290820AEasy to controlFix stability issuesAc-dc conversionPower oscillations reduction/preventionCapacitanceControl cell
The invention relates to a LCL (Lower Control Unit) filtering controlled rectifying active damping control method of electric currents on a feedback variable current side, belonging to an active rectifying method of power electronics. The method comprises the following steps: a direct current voltage control unit is used for finishing the control on a direct current voltage and producing d-shaft active currents of an electric current control unit; a q-shaft current given is used for controlling reactive components of a rectifier; a soft phase locking unit is used for locking a power grid voltage phase position and realizing the synchronous rotational transformation of the power-grid voltage and sampling currents on the variable current side; the current given and a sampling actual value are fed into the electric current control unit; the output quantity of the electric current control unit is accumulated with the electric current on the variable current side which is fed back by usinga first-order high-pass filter to generate the given quantity of a voltage space vector unit; and finally, the voltage space vector unit generates six PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) signals to finish the control on the rectifier. The method solves the stability problem of a LCL (Low Control Unit) filtering voltage type controlled rectifier and realizes the control of the rectifier on direct-currentvoltages and currents on line side under the condition that the electric current or voltage detection of a capacitor branch is not needed.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Power system having a phase locked loop with a notch filter
InactiveUS6977827B2Highly accurate frequency and amplitude and phase estimateAc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorHarmonic
A power system having a phase locked loop (PLL) with a notch filter for synchronous reference frame sequence separation. The notch filter includes a generalized integrator tuned to the notch frequency. The output of the generalized integrator is summed with the filter input signal and the output of the summer is fed back to the integrator input. In one embodiment, the notch filter is programmable by a control signal generated in response to the filter output signal, thereby causing the filter to self-regulate to a frequency related to the PLL input signal. Illustrative power systems include active VAR generators and active rectifiers. One or more additional notch filters may be used to remove harmonic components from derived synchronous reference frame sequence components.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Active rectifier system with power factor correction
InactiveUS20080013352A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringAlternating current
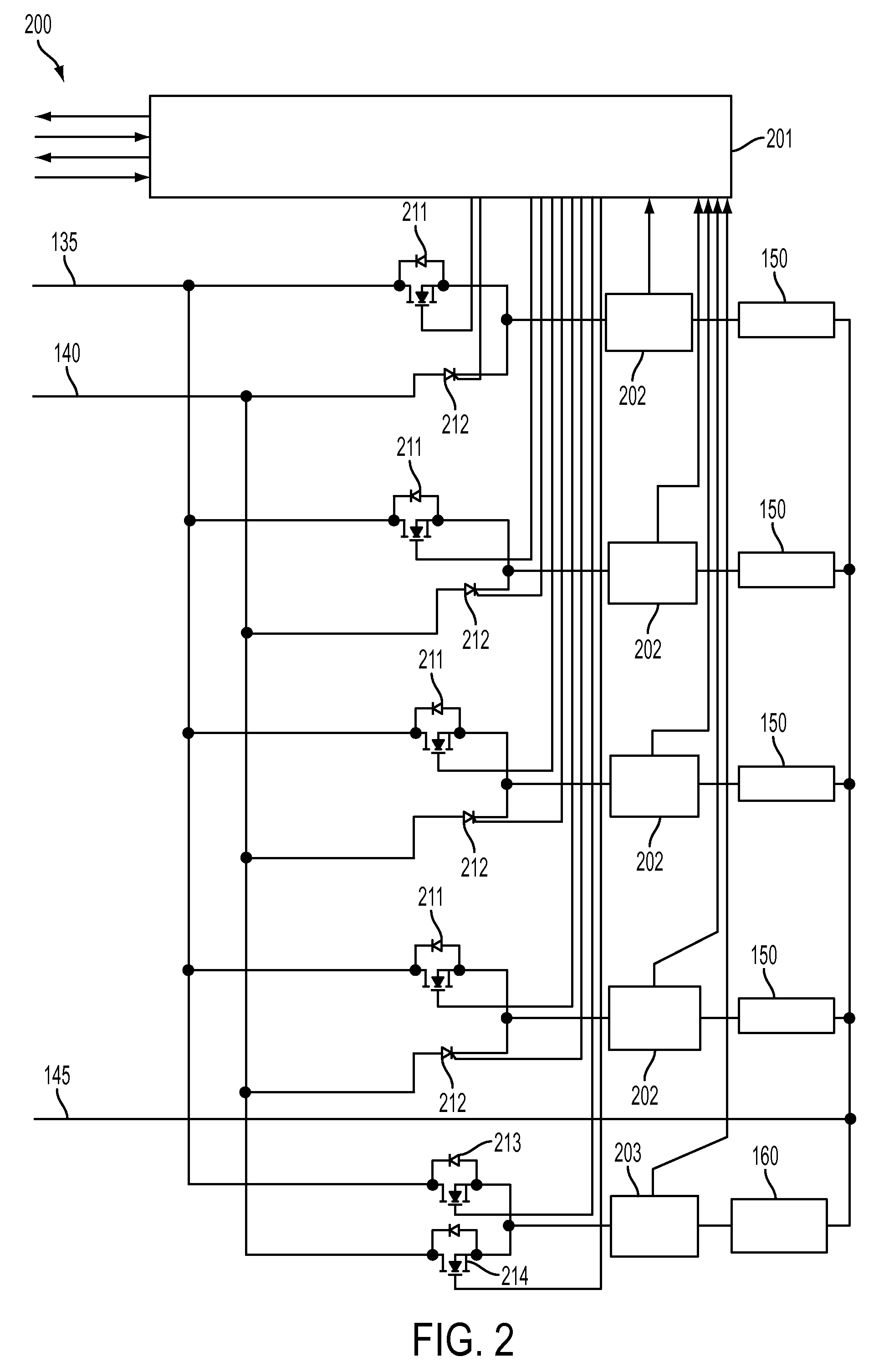
A polyphase alternating current (AC) active rectifier system converts polyphase AC from an AC source to direct current (DC) on a DC bus comprising a positive DC bus line and a negative DC bus line with a switching element for each phase configured to direct current from the AC source to the DC bus through four different conducting paths with three electrical potential levels, including a positive DC level on the positive DC bus line, a negative DC level on the negative DC bus line and a neutral DC level between the positive and negative DC level on a neutral DC bus line and suppresses AC common mode electrical potential from the DC bus, comprising: a ground path between the neutral DC bus line and a system ground coupled to a neutral point for the AC source that clamps the level of the neutral DC level to the AC source neutral.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
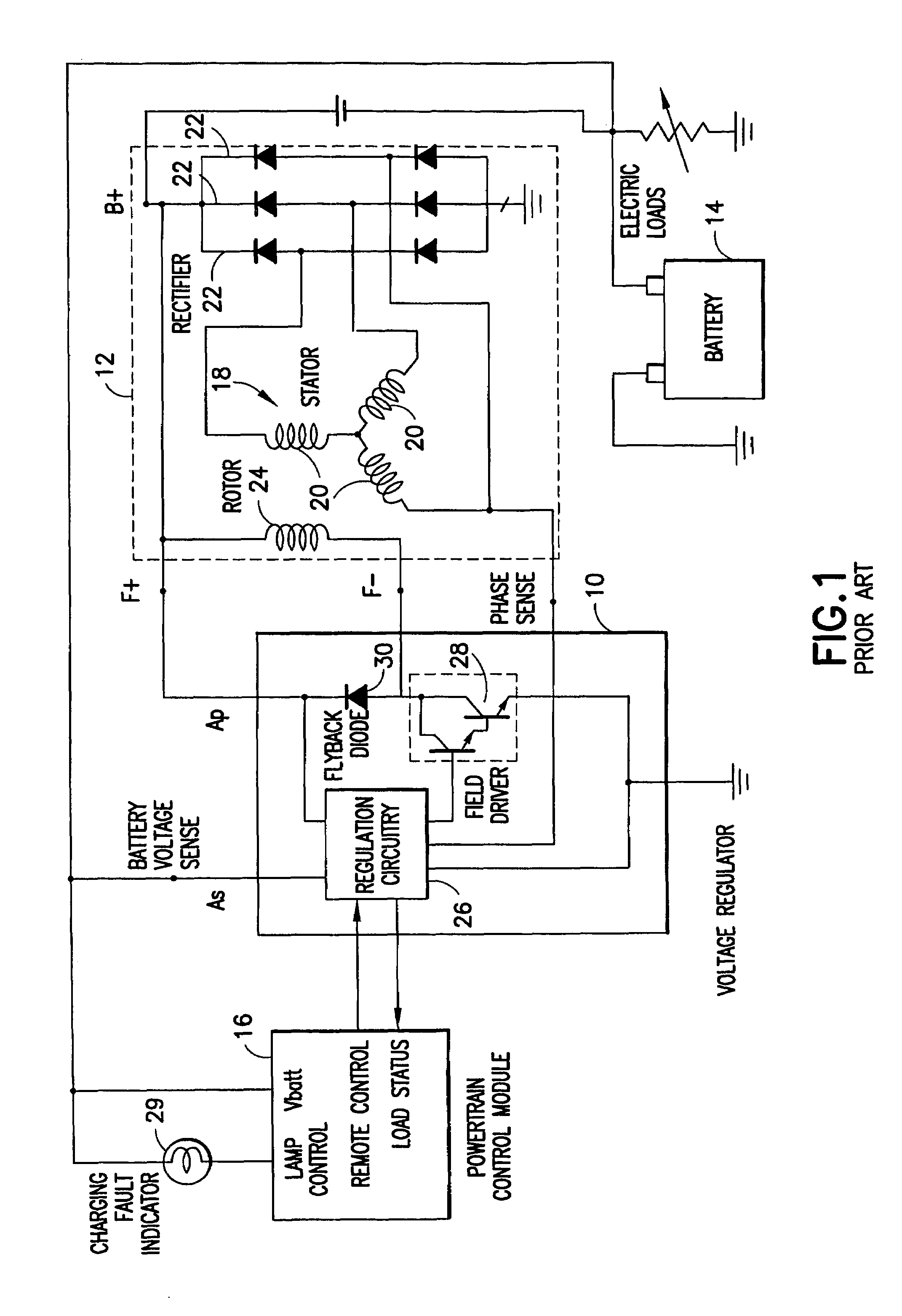
Active integrated rectifier regulator
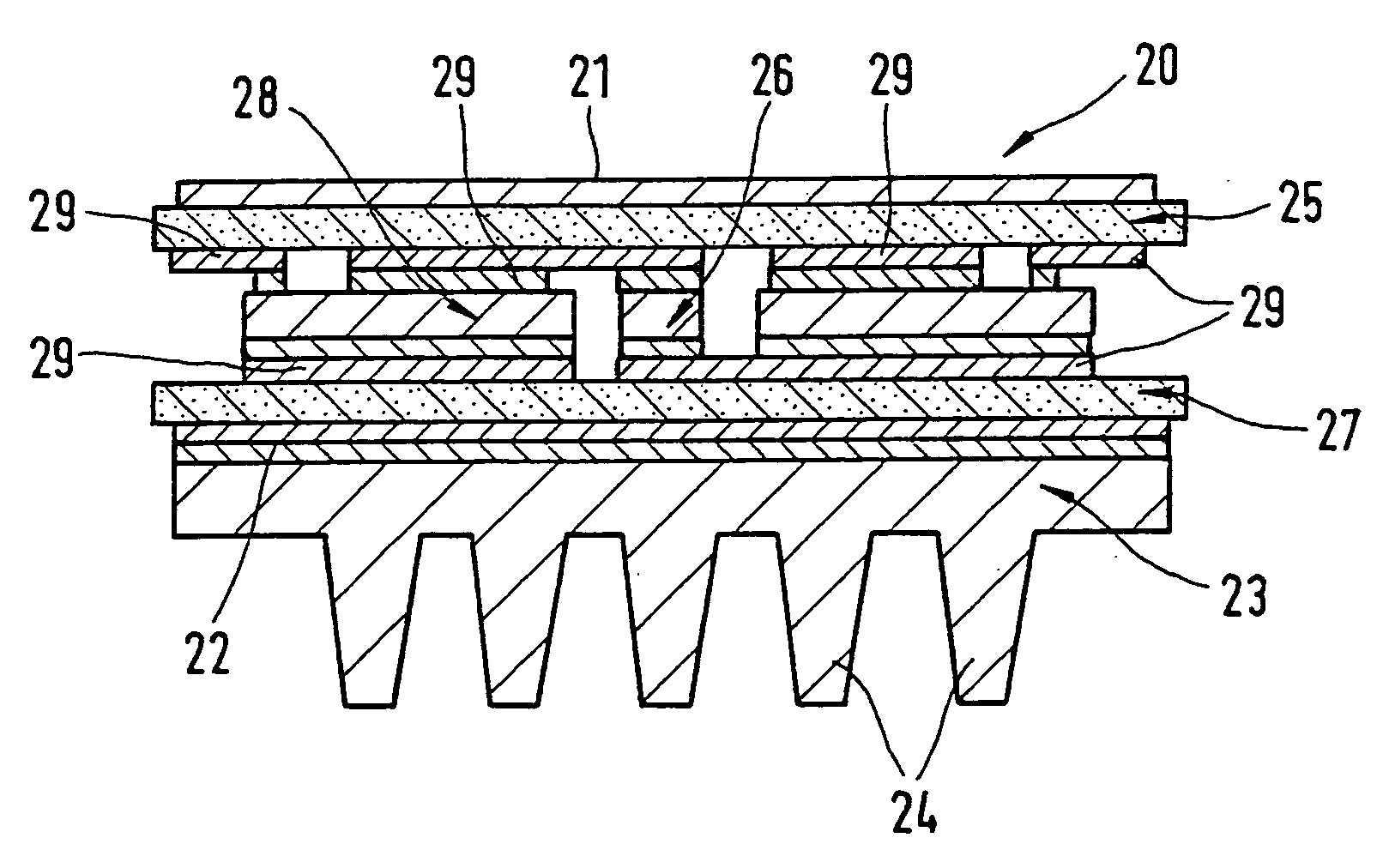
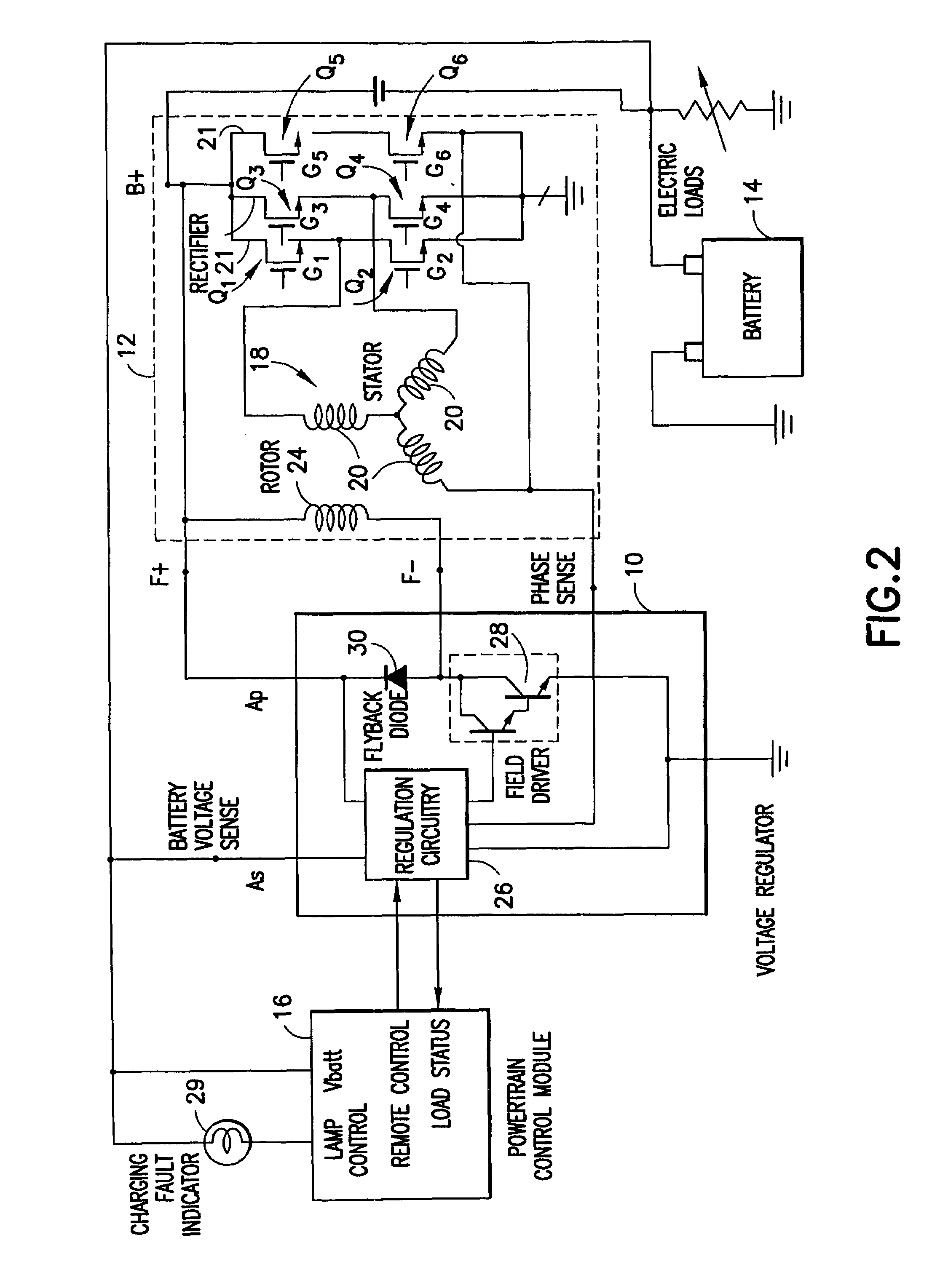
InactiveUS7292445B2Increase power generationNegative charging of batteryBatteries circuit arrangementsConversion constructional detailsCharge currentAutomotive battery
An active integrated rectifier and regulator module for providing charging current to a battery of an automobile including a stacked structure comprising two lead frames disposed above on another, the module including a voltage regulator and elements for active rectification of alternating current from a stator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS MOTION SYST HLDG
Power converters
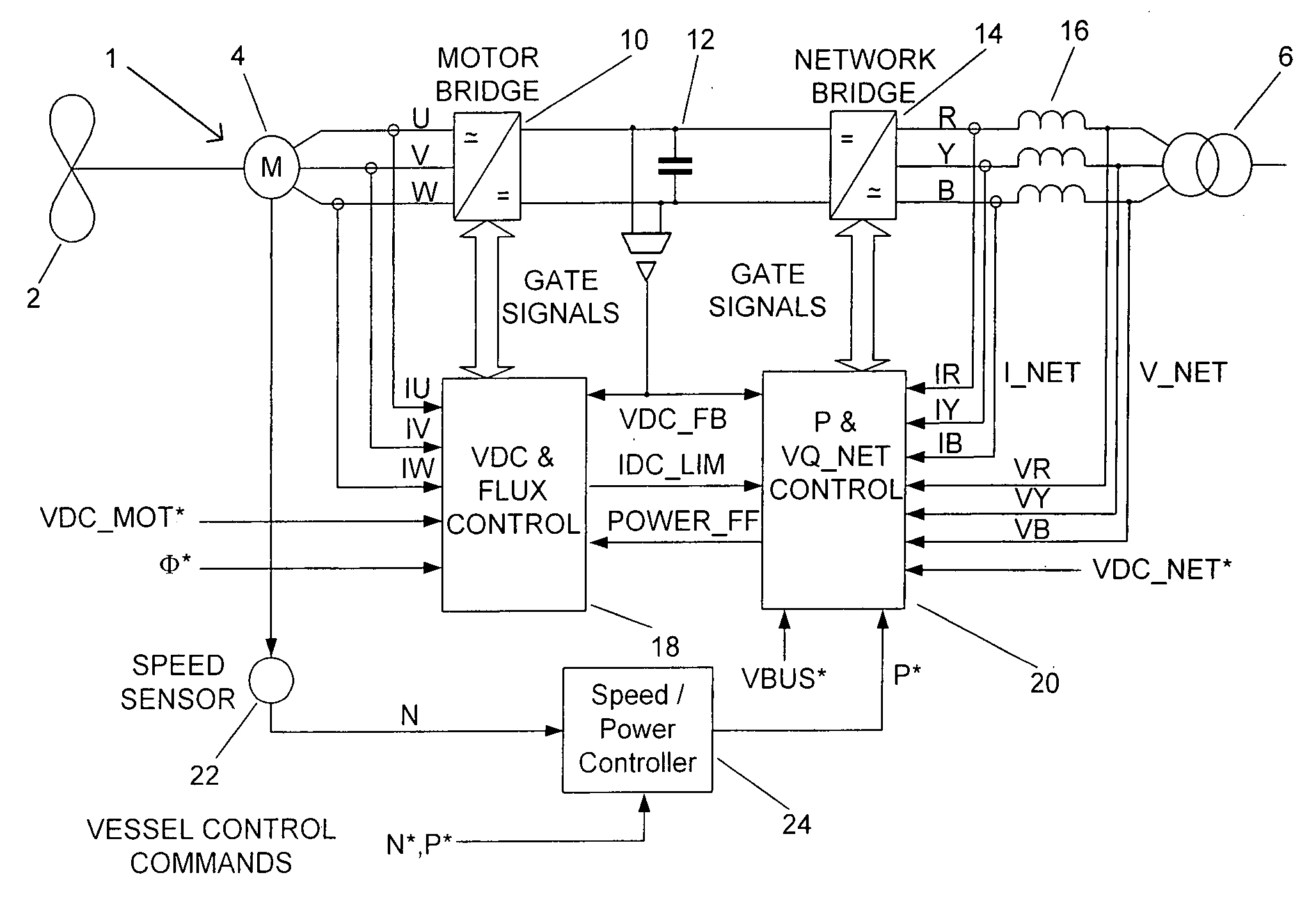
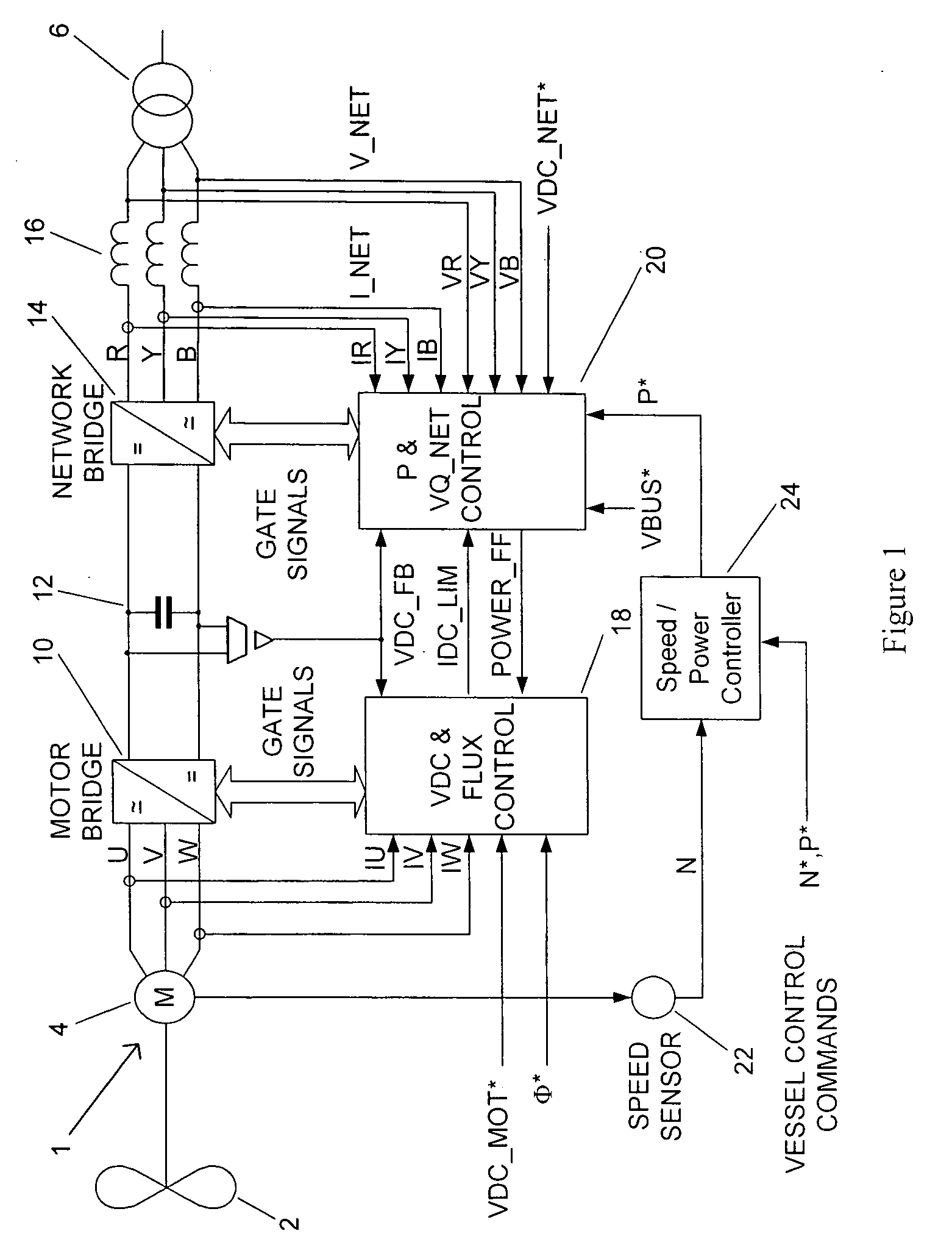
ActiveUS20080284369A1Restrict levelAvoid powerSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlElectricityMarine propulsion
The present invention is directed to a power converter that can be used to interface a motor 4 that requires variable voltage at variable frequency to a supply network (bus) providing a nominally fixed voltage and nominally fixed frequency. The power converter includes a first active rectifier / inverter 10 electrically connected to the stator of the motor 4 and a second active rectifier / inverter 14. Both the first and second active rectifier / inverters include a plurality of semiconductor power switching devices. A dc link 12 is connected between the first active rectifier / inverter and the second active rectifier / inverter. A filter 16 is connected between the second active rectifier / inverter and the supply network and includes network terminals. The power converter includes a first controller 18 for the first active rectifier / inverter and a second controller 20 for the second active rectifier / inverter. The first controller 18 uses a dc link voltage demand signal VDC_MOT* indicative of a desired dc link voltage to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the first active rectifier / inverter 10 to achieve the desired level of dc link voltage that corresponds to the dc link voltage demand signal. The second controller 20 uses a power demand signal P* indicative of the level of power to be transferred to the dc link 12 from the supply network (bus) through the second active rectifier / inverter 14, and a voltage demand signal VBUS* indicative of the voltage to be achieved at the network terminals of the filter 16 to control the semiconductor power switching devices of the second active rectifier / inverter 14 to achieve the desired levels of power and voltage that correspond to the power and voltage demand signals. The power converter can be employed in a marine propulsion system where the rotor of the motor 4 is used to drive a propeller assembly 2.
Owner:CONVERTEAM TECH LTD
Active rectifier and method for energy harvesting power management circuit
ActiveUS8284581B2Efficient rectificationLow powerEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionElectrical conductorAudio power amplifier
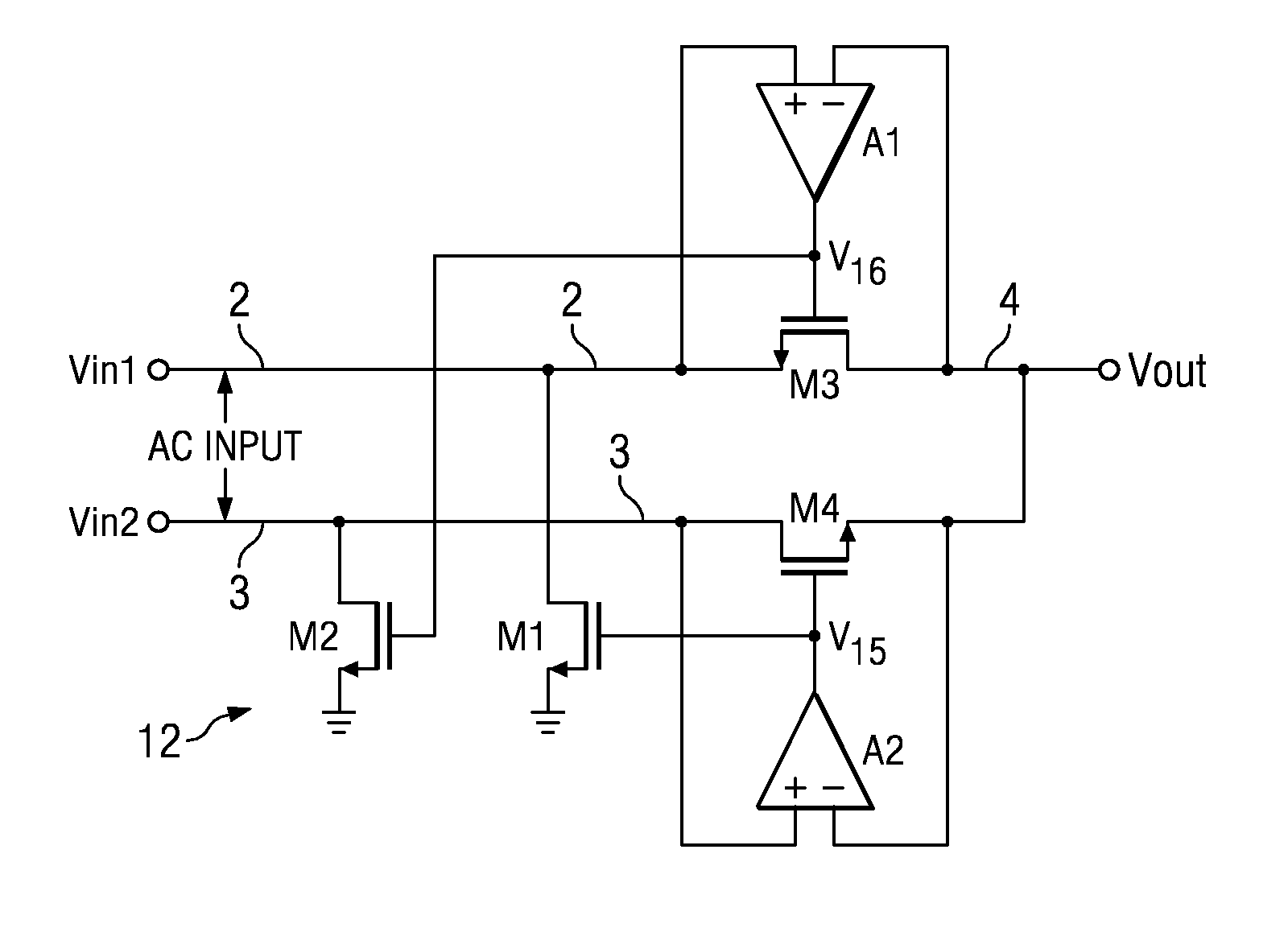
An active rectifier (12) couples a first input voltage (Vin1) to a first electrode of a first transistor (M3) having a second electrode coupled to an output (4) conducting an output voltage (Vout), and couples a second input voltage (Vin2) to a first electrode of a second transistor (M4) having a second electrode coupled to the output conductor. A first amplifier (A1) controls a voltage (V16) of a gate of the first transistor to maintain an input offset of the first amplifier between the first input voltage and the output voltage while the first input voltage exceeds the output voltage, and a second amplifier (A2) controls a voltage (V15) on a gate of the second transistor to maintain an input offset between the second input voltage and the output voltage while the first input voltage exceeds the output voltage. The input offsets prevent backflow of current from the output to either of the first electrodes when the first or second input is nearly equal to the output voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Clean input ups with fast rectifier control and improved battery life
InactiveUS20080219036A1Enhance response control performanceReduce power consumptionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc link voltageControl theory
The present invention relates to the control of active rectifiers for UPS systems. Aspects of the present invention relate to a control algorithm that is implemented to realize a fast rectifier control operation that results in the improved life of a battery that is linked to the active rectifier of the UPS system. Within aspects of the present invention under unbalanced load conditions, it is possible to select (he desired behavior between the two possible extreme conditions, i.e. implement a clean power input that results in the reduced life of the battery or implement a non-clean power input resulting in the improved life of the battery. Additionally, the present invention utilizes fast rectifier control and specific feed-forward action to make it possible to obtain the very rigid control of a dc link voltage, even under extreme step load variations.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High voltage DC power generation
InactiveUS20120126758A1AC motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityLow speed
A DC power system includes a permanent magnet generator (PMG), and an active rectifier in electrical communication with the PMG. The active rectifier is adapted to actively rectify power output from the PMG if the PMG is operating at low speed, and the active rectifier is further adapted to passively rectify power output from the PMG if the PMG is operating at high speed.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Active rectifier module for three-phase generators of vehicles
InactiveUS7420224B2Improve efficiencyGuaranteed usageBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalThree-phaseAlternating current
A rectifier for rectifying alternating current into direct current is described, in which a three-phase generator includes a three-phase stator winding. The phases of the stator winding are triggered via switching elements of a power circuit. The power circuit is controlled via a control part, which includes a controller component. The rectifier includes a control part (control module) having control terminals and a power circuit (power module) controlled by the control module and optionally provided with a cooling device, in which all the power-conducting components are designed as power MOS components and integrated in a stacked construction.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
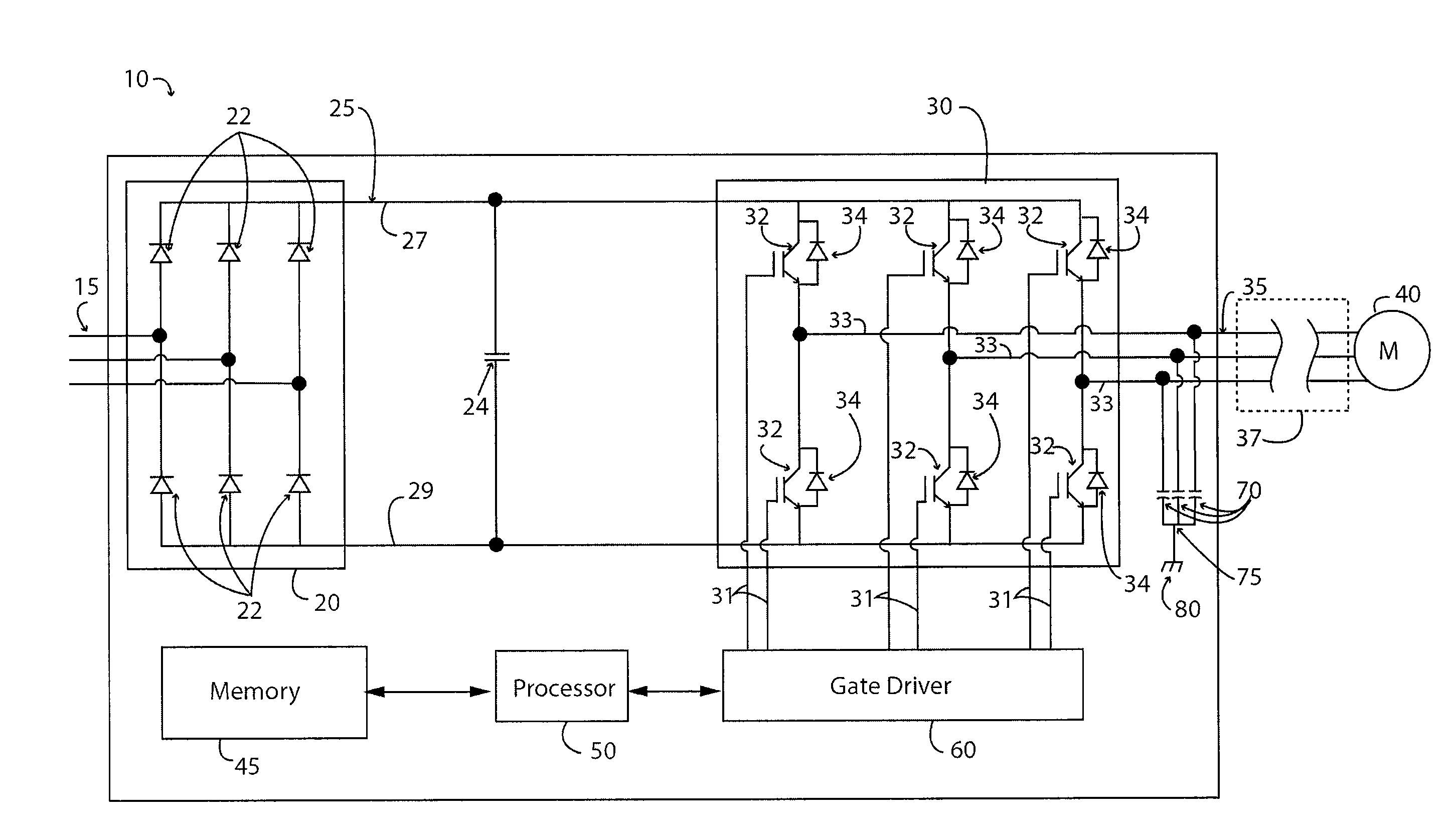
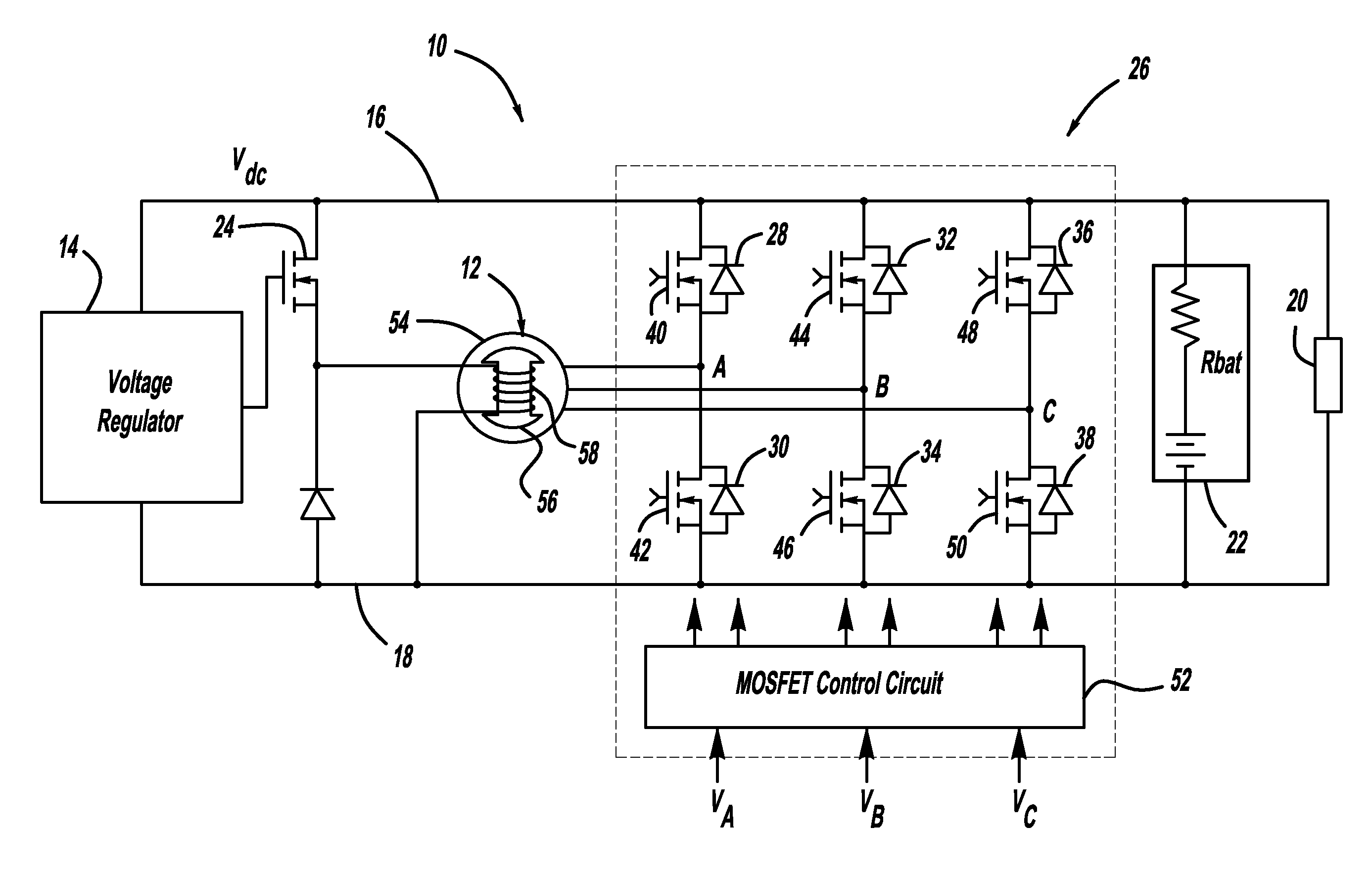
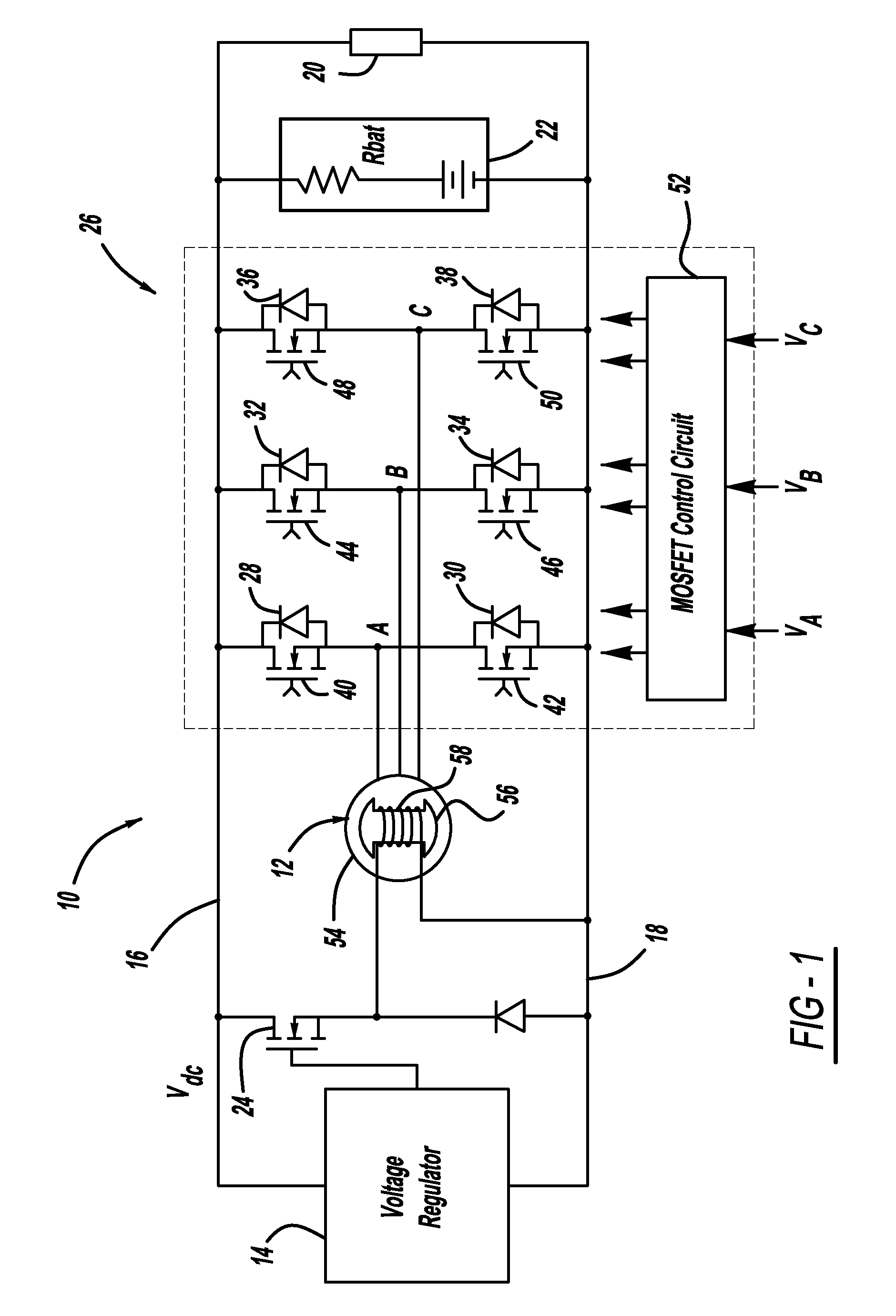
High efficiency generator
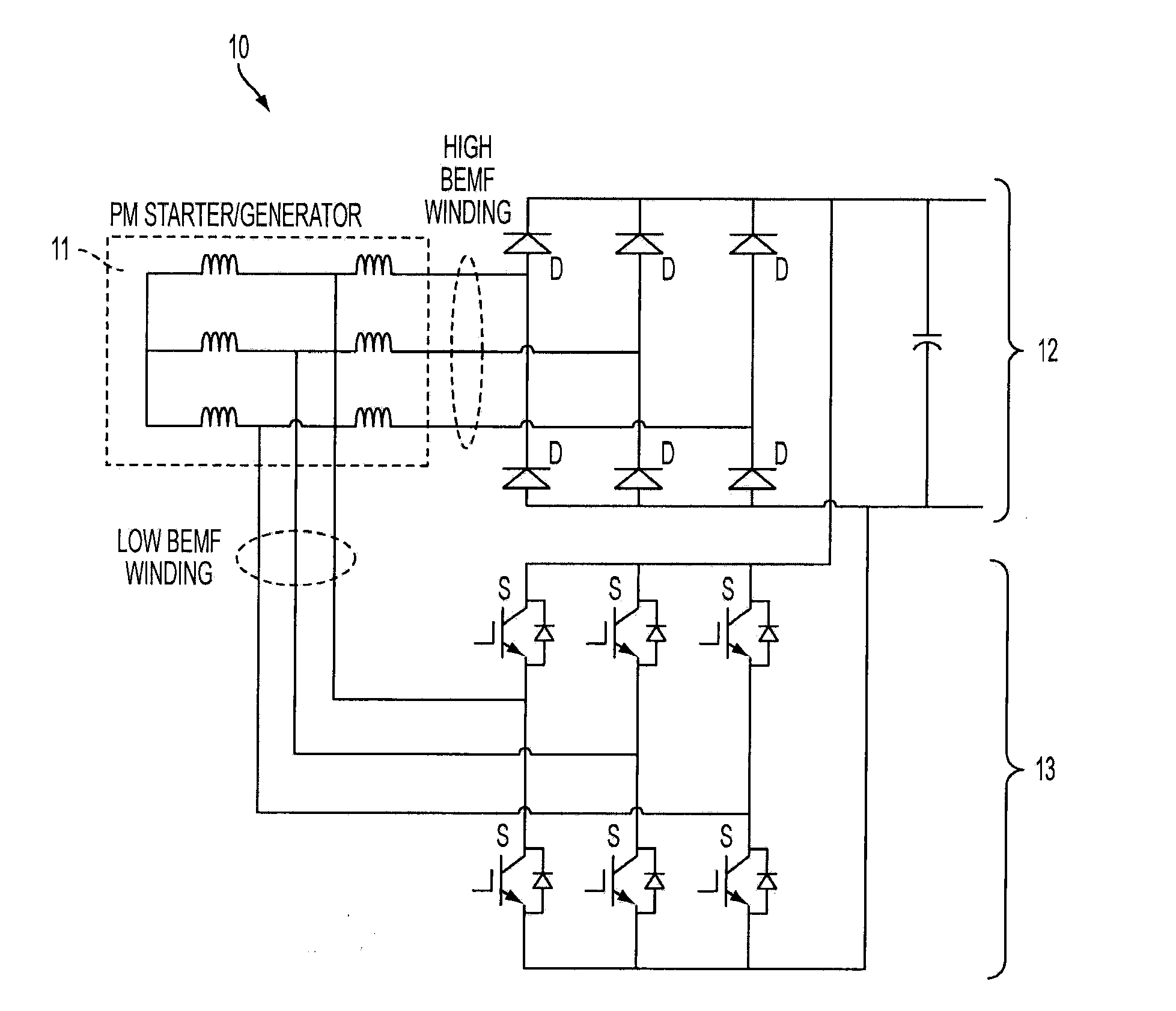
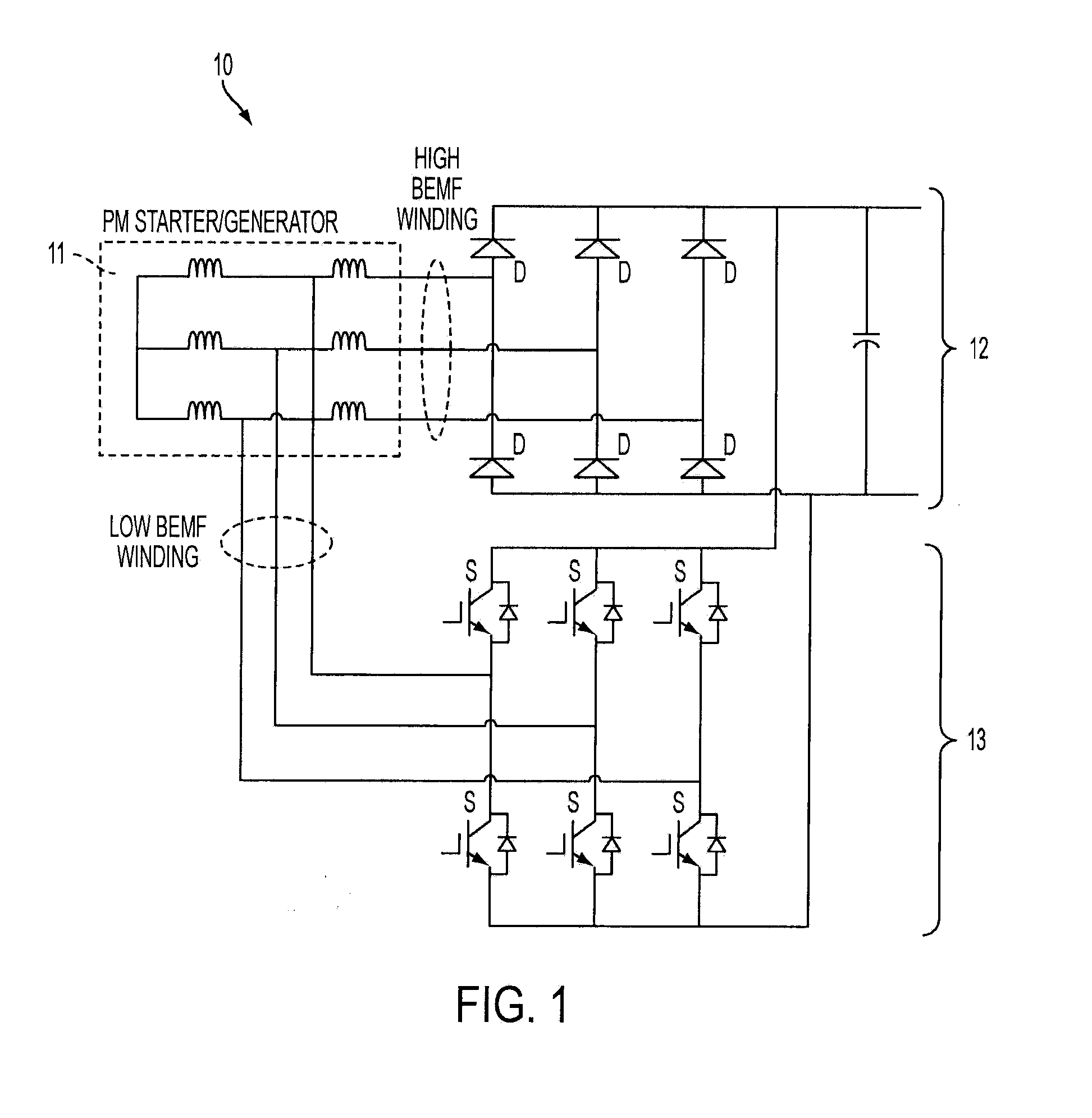
InactiveUS20080284385A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsMOSFETThree-phase
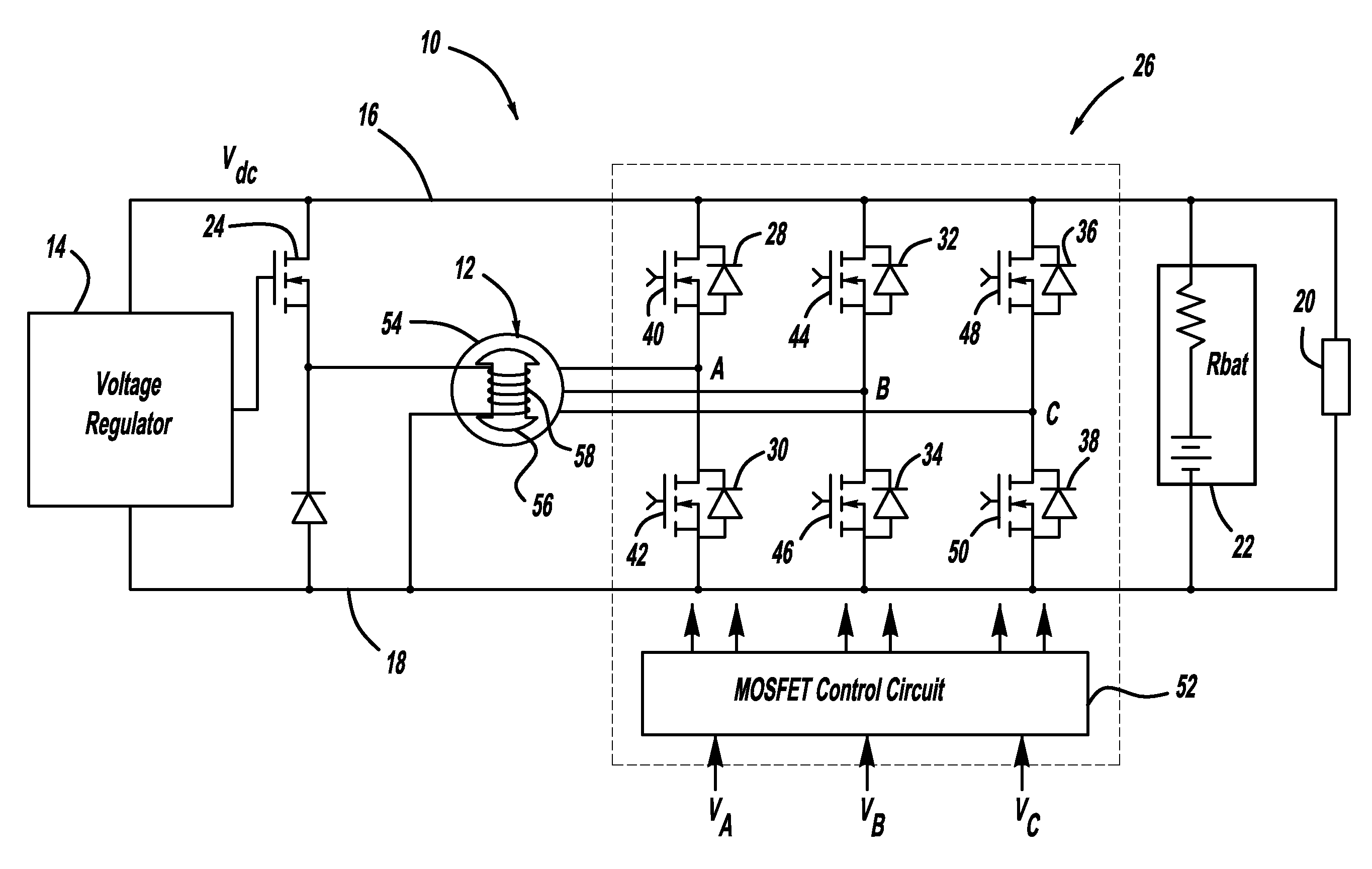
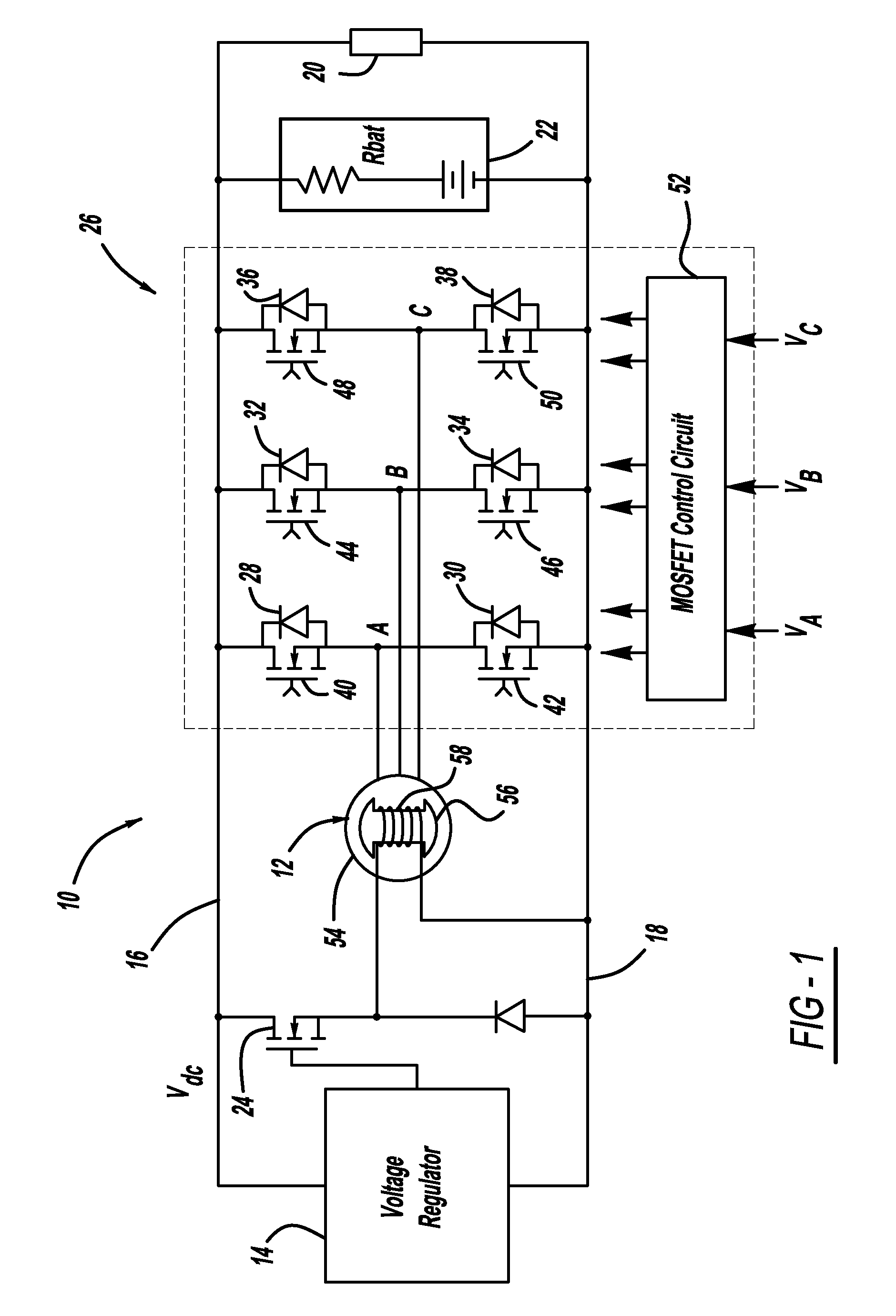
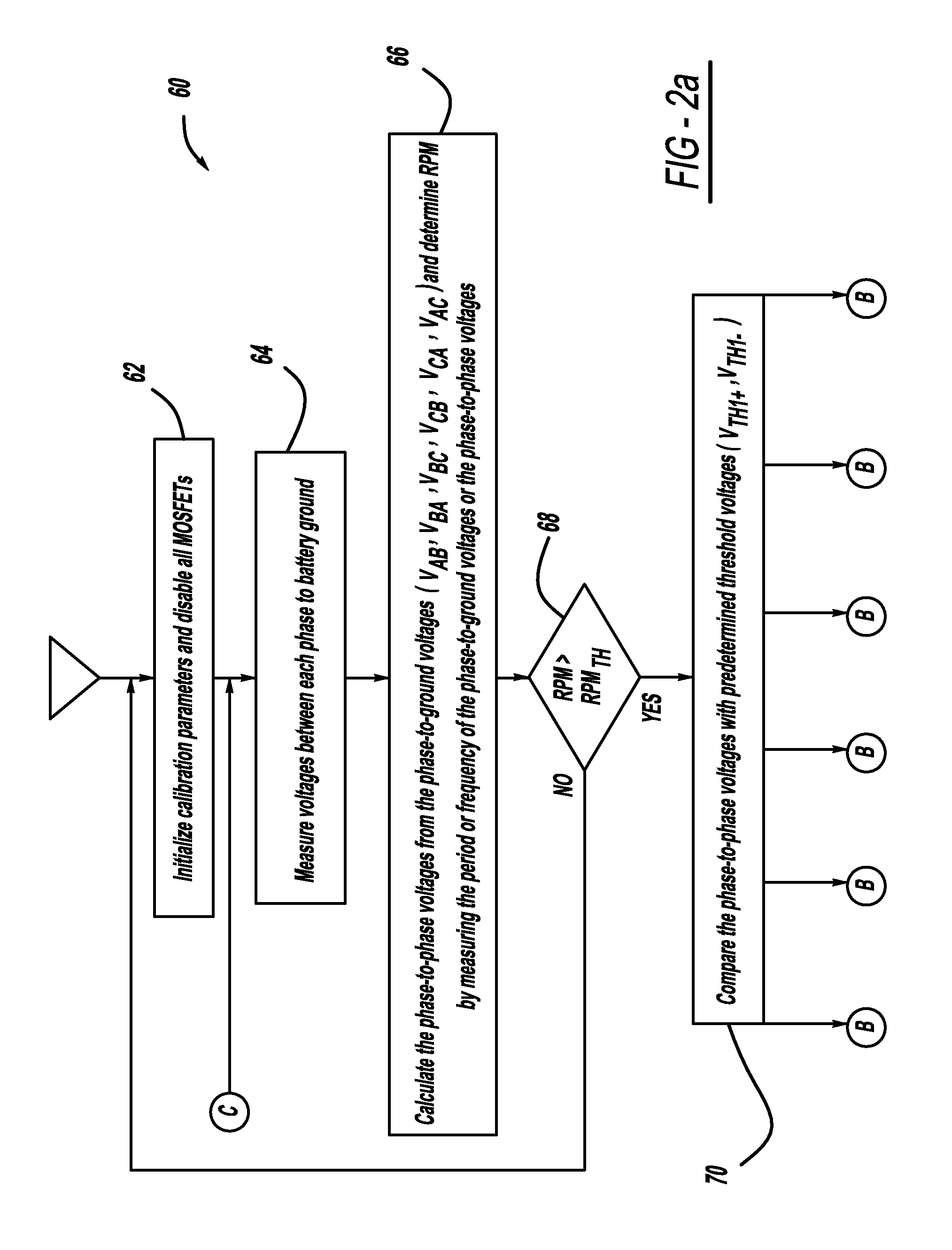
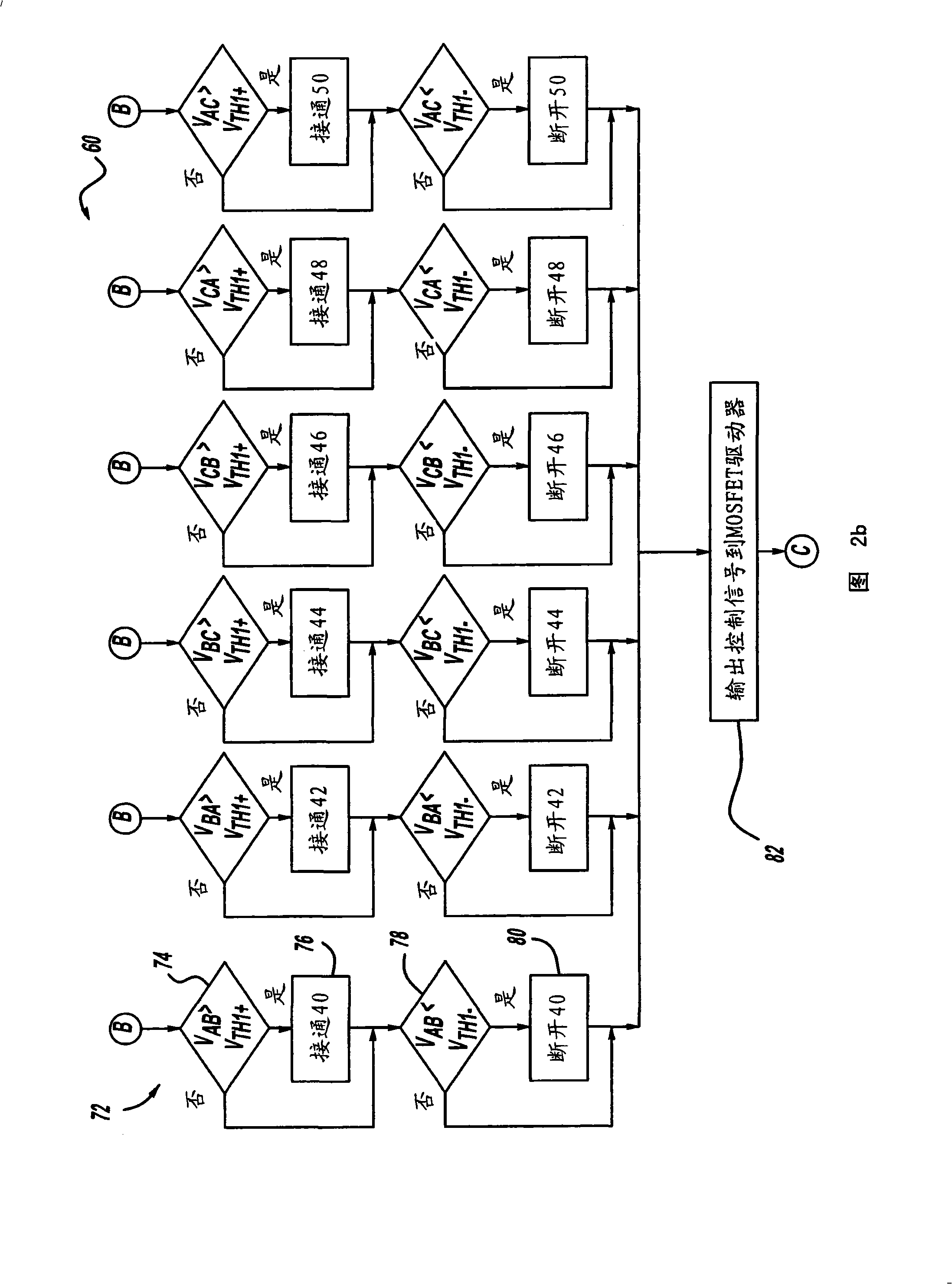
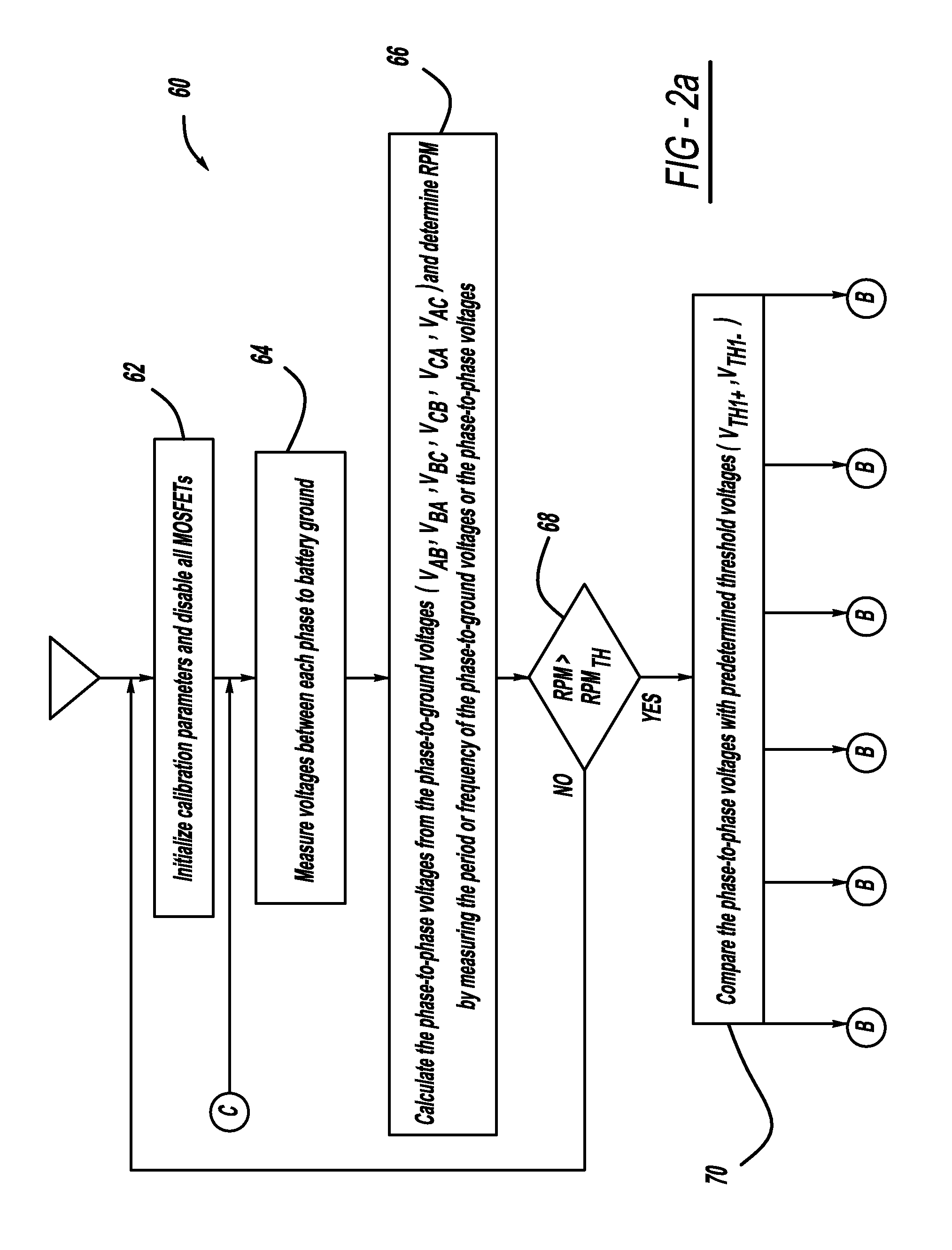
A generator system that includes a three-phase AC machine and an active rectifier bridge employing low on-resistance MOSFET switches for converting the AC current from the machine to a DC current. The system also includes a switch control circuit to switch the MOSFET switches in synchronization with the three-phase current flow. The system determines the phase-to-ground voltages of the machine as inputs to the switch control circuit. The control circuit calculates the phase-to-phase voltages from the phase-to-ground voltages. The control circuit then determines if each of the phase-to-phase voltages is above or below first and second predetermined threshold voltages, where if the phase-to-phase voltage is above the first threshold voltage, the control circuit closes the switch, and if the phase-to-phase voltage is below the second threshold voltage, the control circuit opens the switch.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Resonant converter and control method thereof
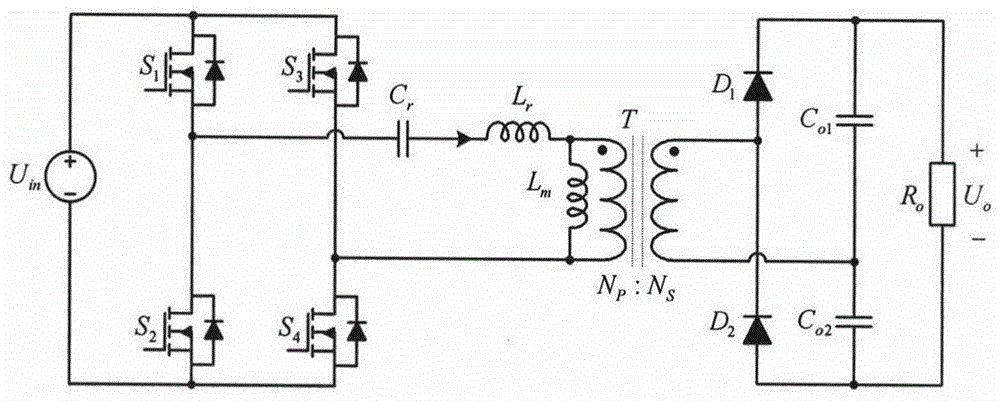
InactiveCN105896986ASimple designWide voltage gain rangeDc-dc conversionEnergy industryResonant converterPower electronics converters
The present invention discloses a resonant converter and a control method thereof, belonging to the field of the power electronic converter technology. The resonant converter and control method thereof are composed of an input source, an original edge LLC resonance circuit, a transformer, a secondary active Boost rectification circuit and an output load. Based on the traditional LLC resonance converter, the secondary active Boost rectification circuit is substituted for the active Boost rectification circuit so as to realize the fixed frequency phase-shifting control of a converter, the frequency conversion control of the converter and the frequency conversion and fixed frequency phase-shifting combined control to facilitate the design of magnetic elements, reduce the voltage stress of the original edge switch tube and the secondary rectifier tube so as to realize the soft switch of each power semiconductor device, improve the voltage gain range, the efficiency and the power density of the converter and satisfy the requirement of a wide voltage gain margin conversion occasion.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High efficiency generator
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
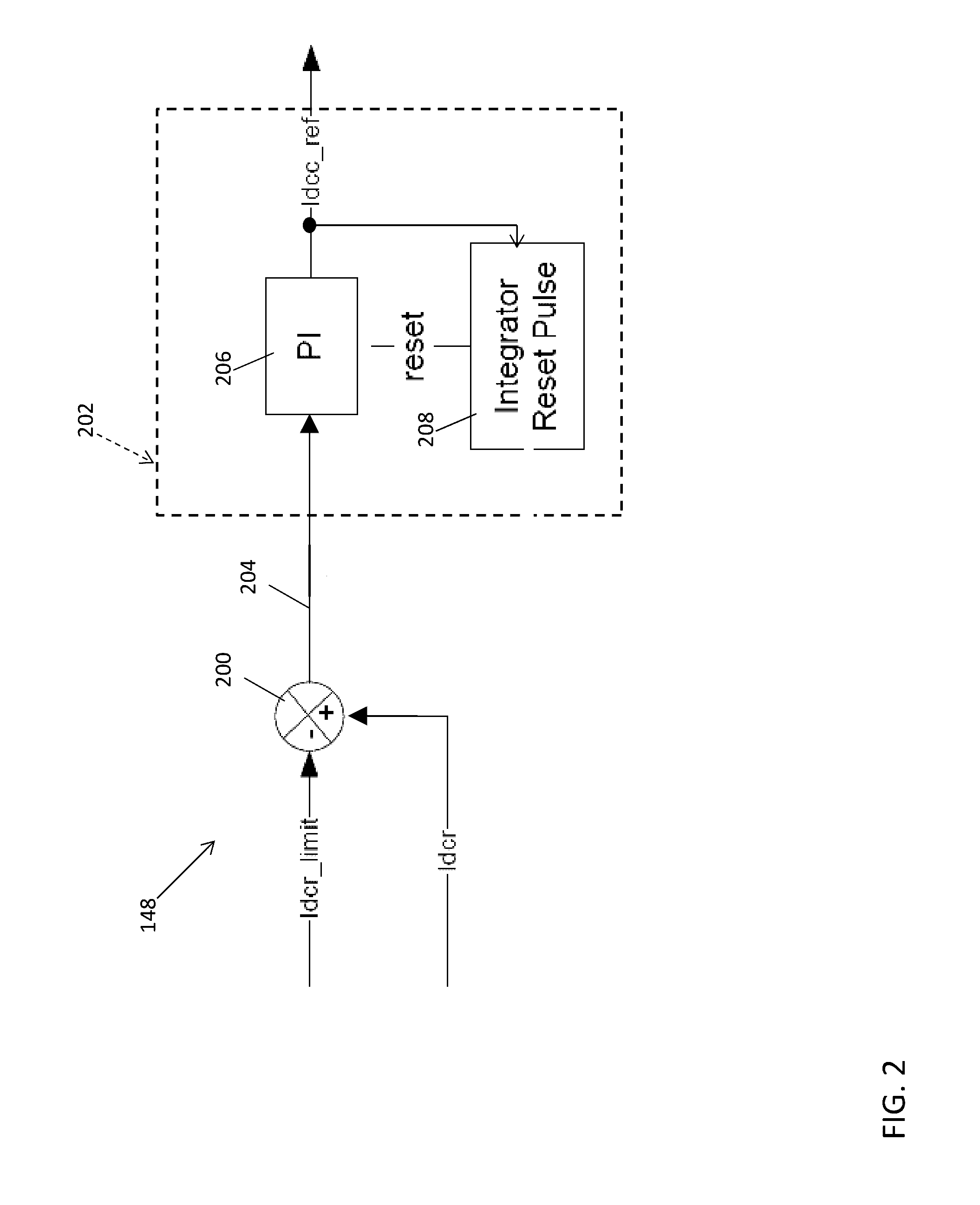
Method of reducing input current distortion in a rectifier
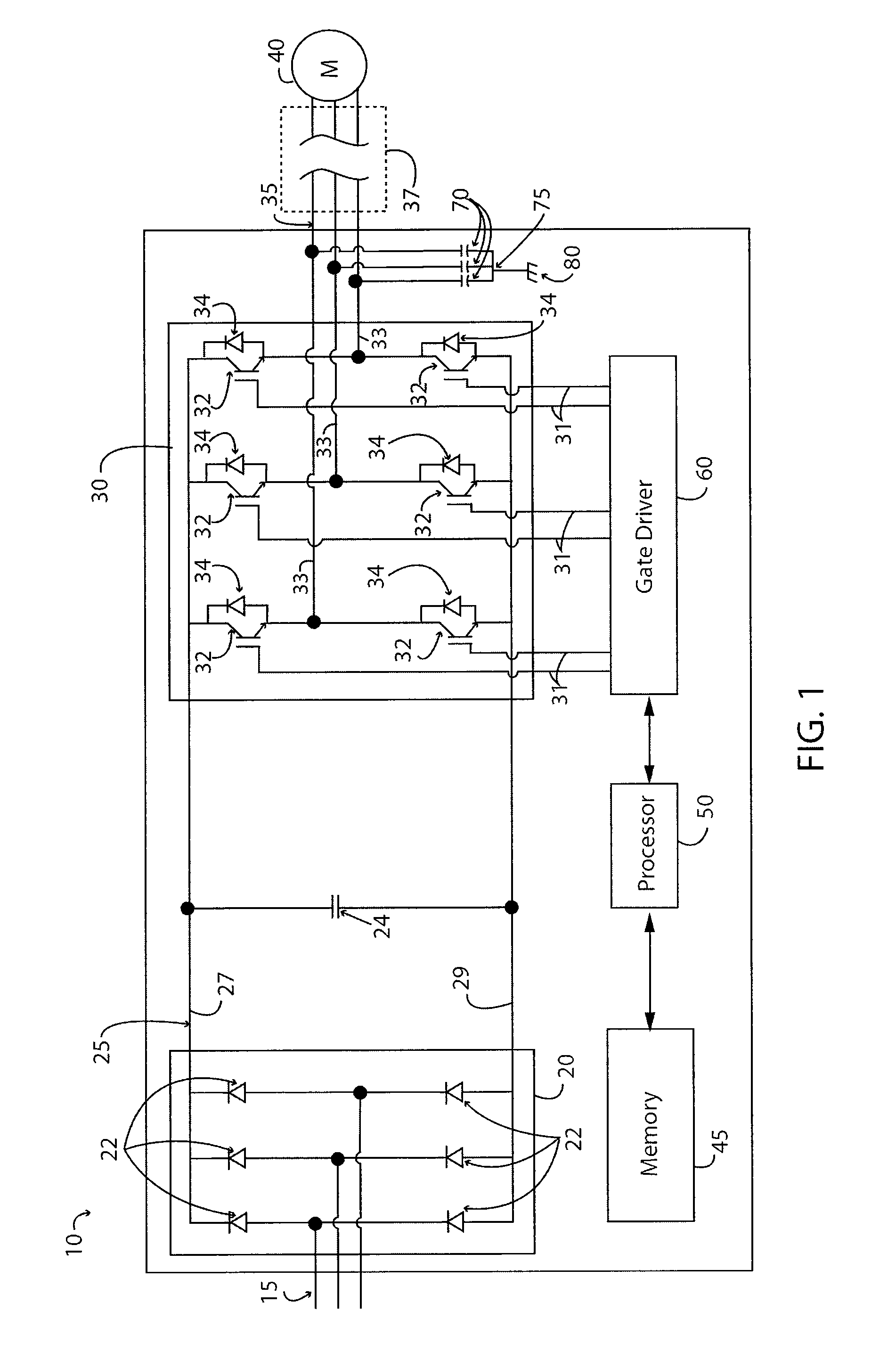
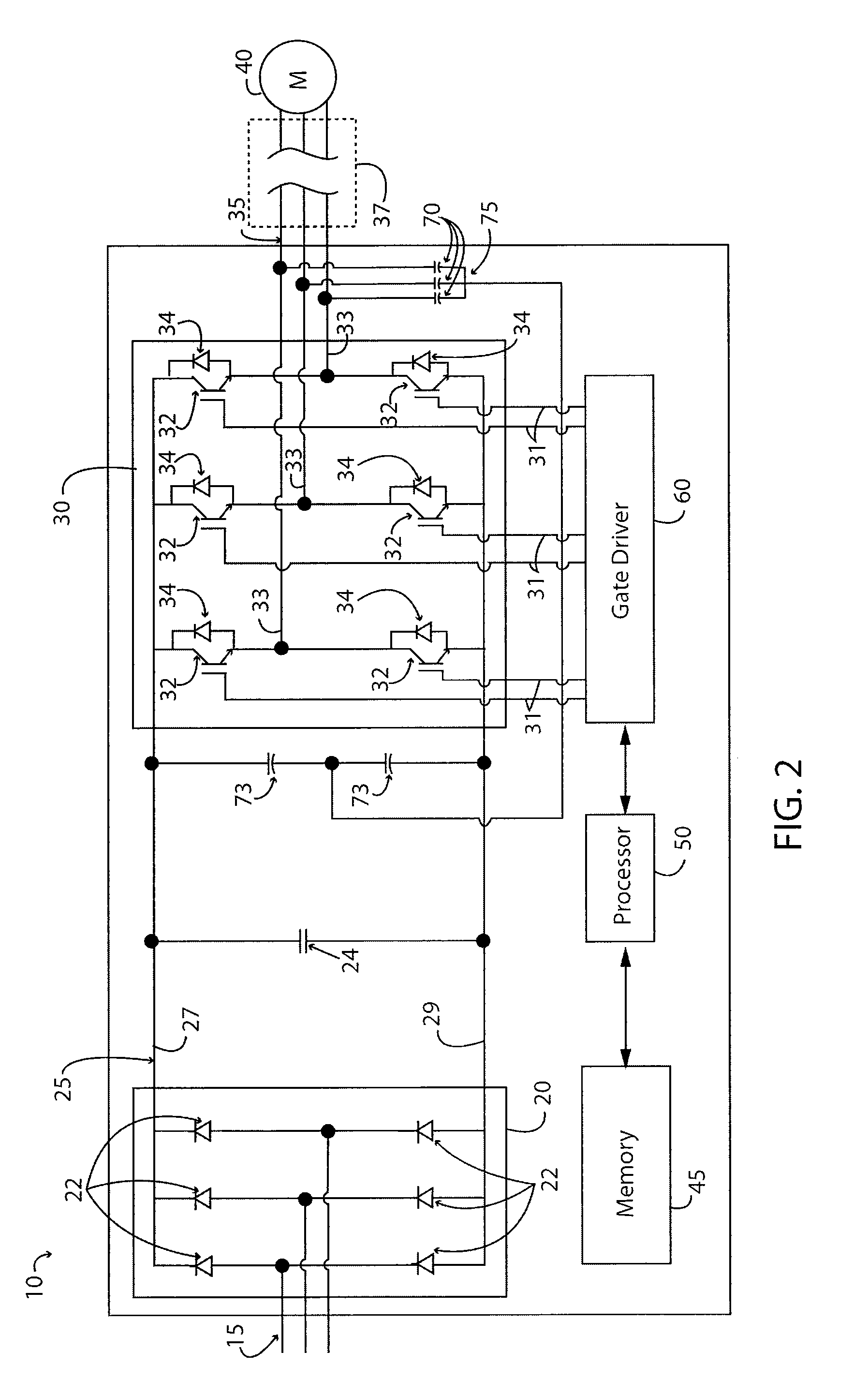
ActiveUS20140369092A1Minimize impactEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionHarmonicEngineering
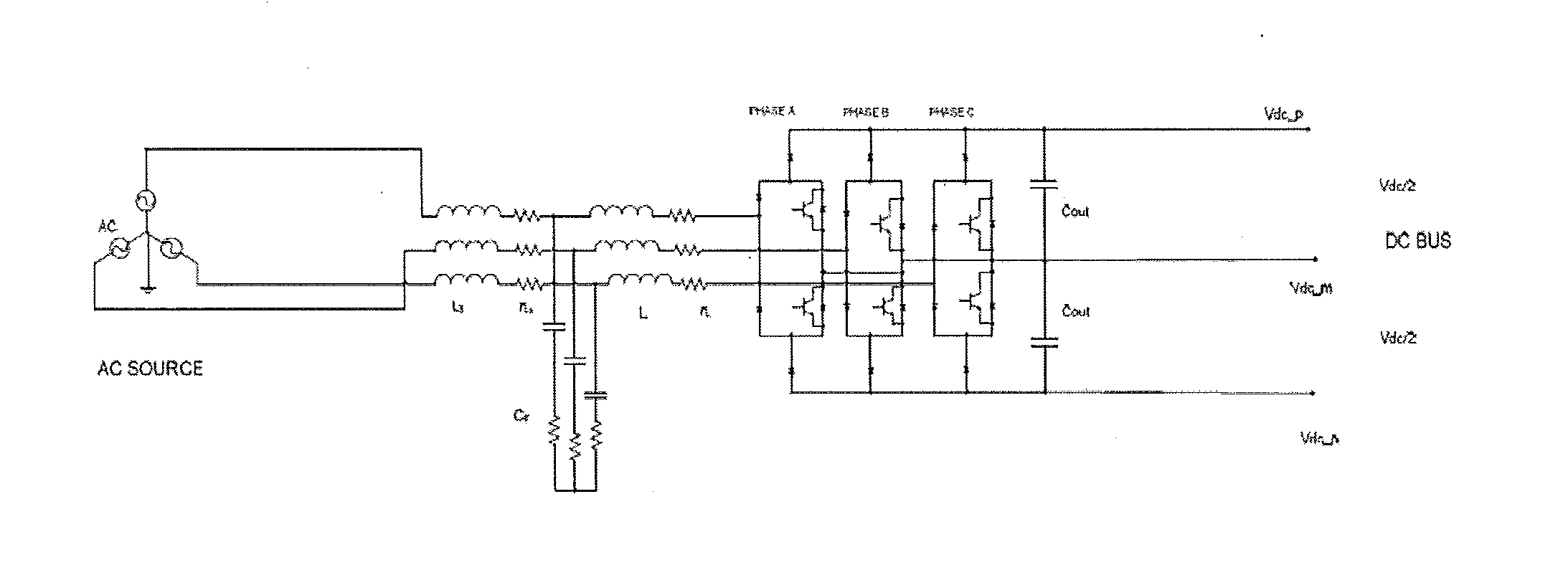
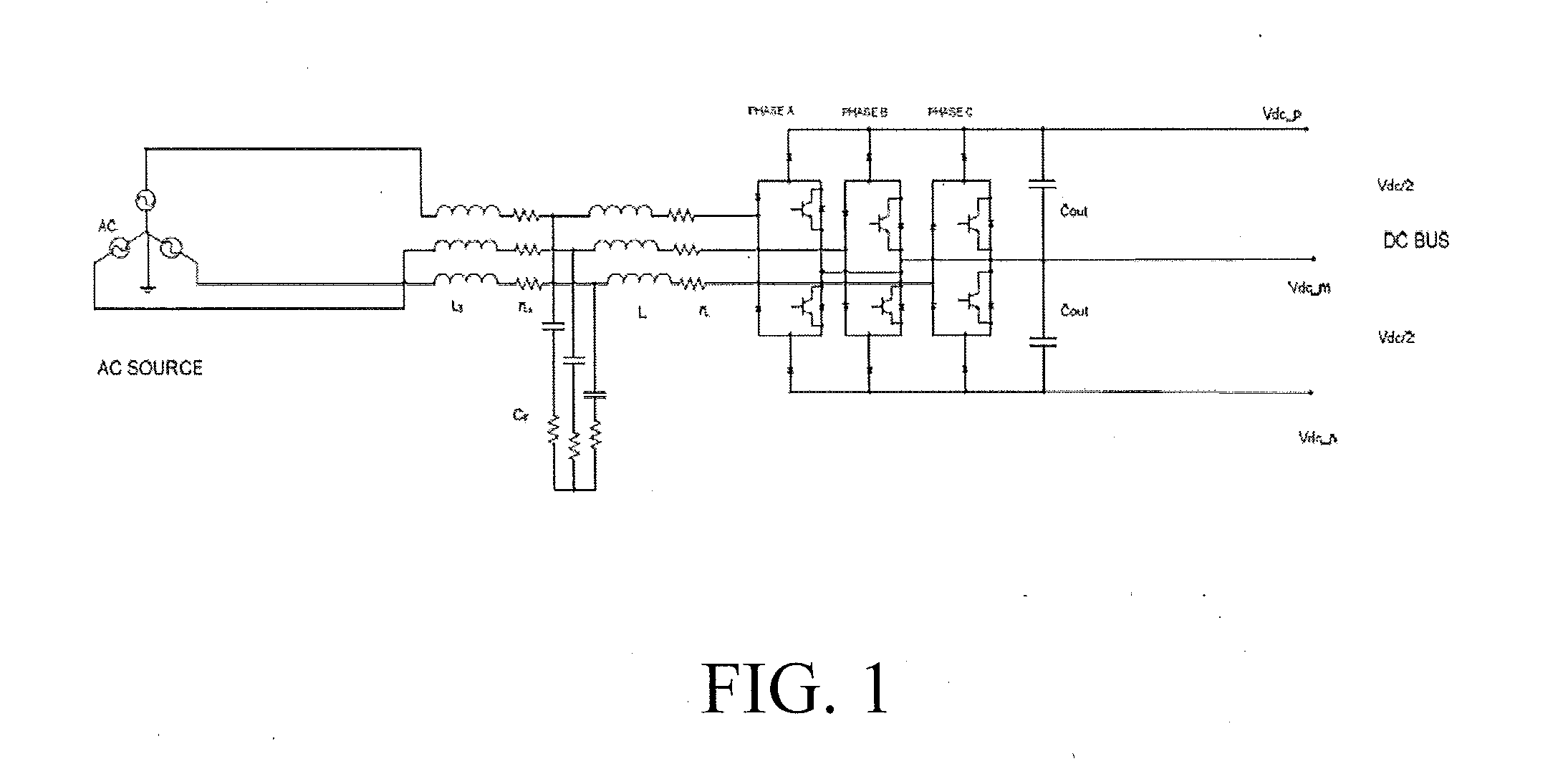
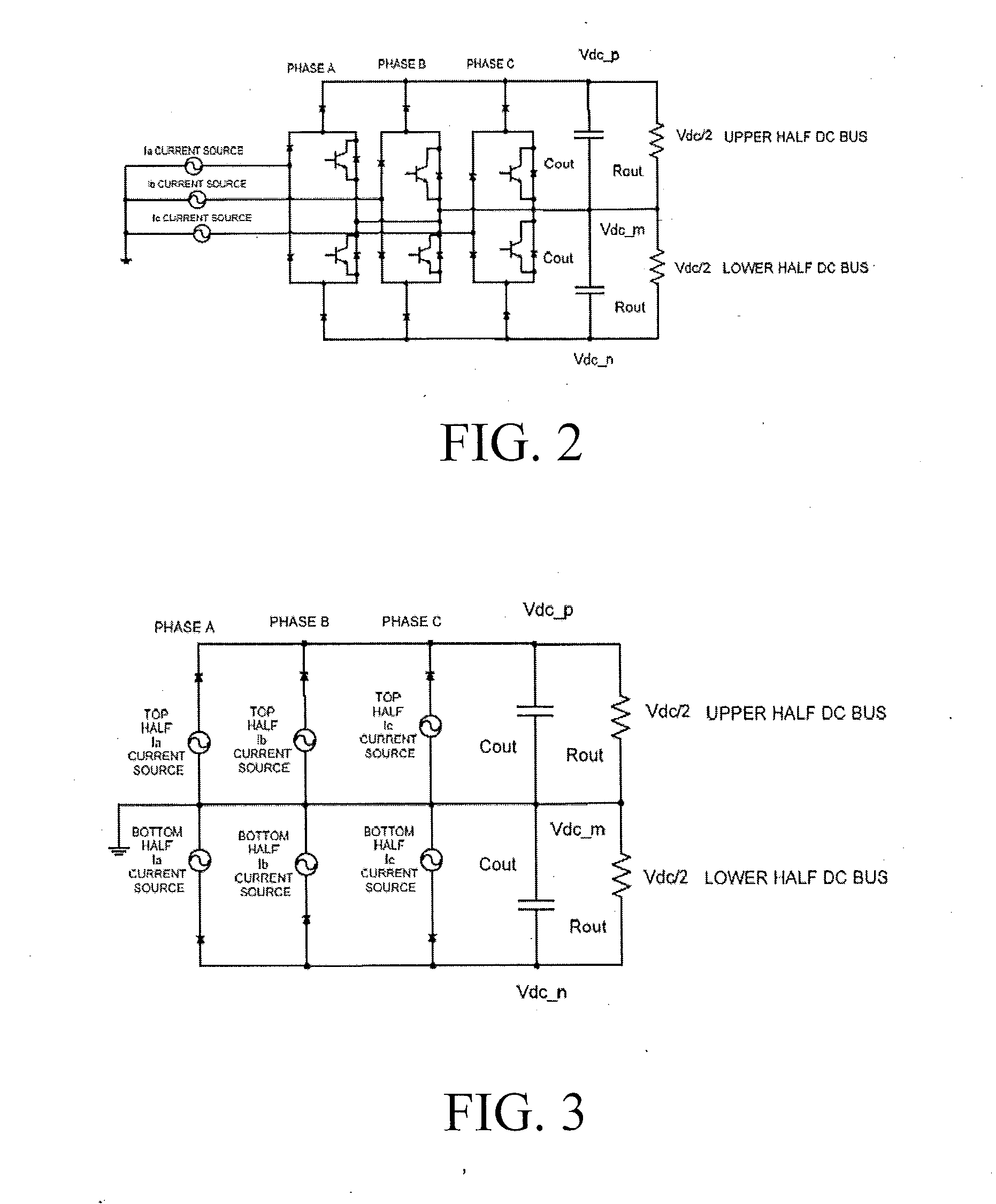
A method is disclosed for reducing input current harmonic distortion in a Vienna-type active rectifier that includes the steps of sensing voltage values from upper and lower halves of a DC bus associated with the rectifier, determining an average of the sensed voltage values, calculating upper and lower scale factors by dividing the sensed voltage values with the averaged sensed voltage value, rescaling a reference signal from a controller using the upper and lower calculated scale factors, and forward feeding the rescaled reference signal from the controller to a pulse width modulator to obtain a gate driver signal for power semiconductor switches of the rectifier.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
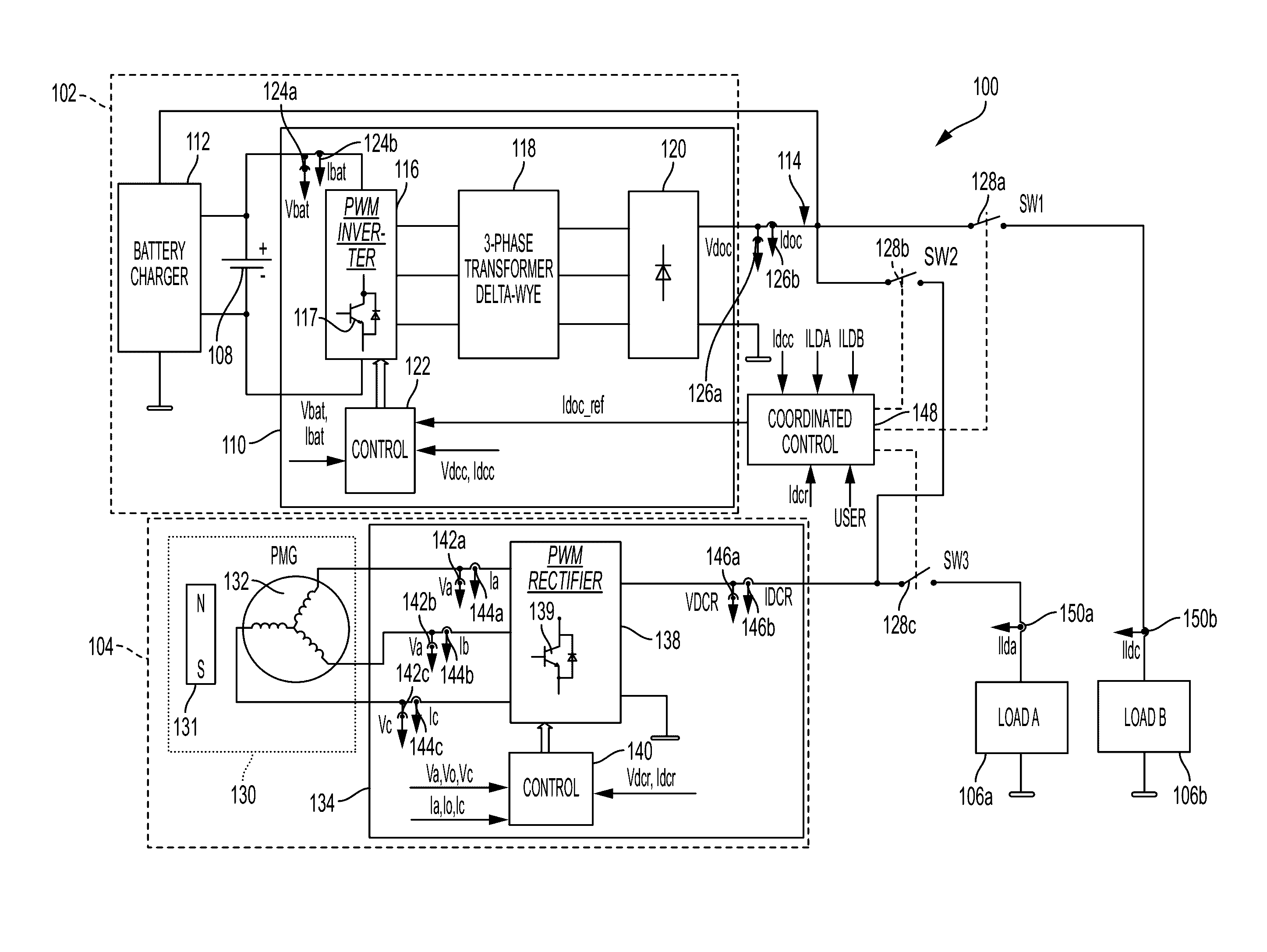
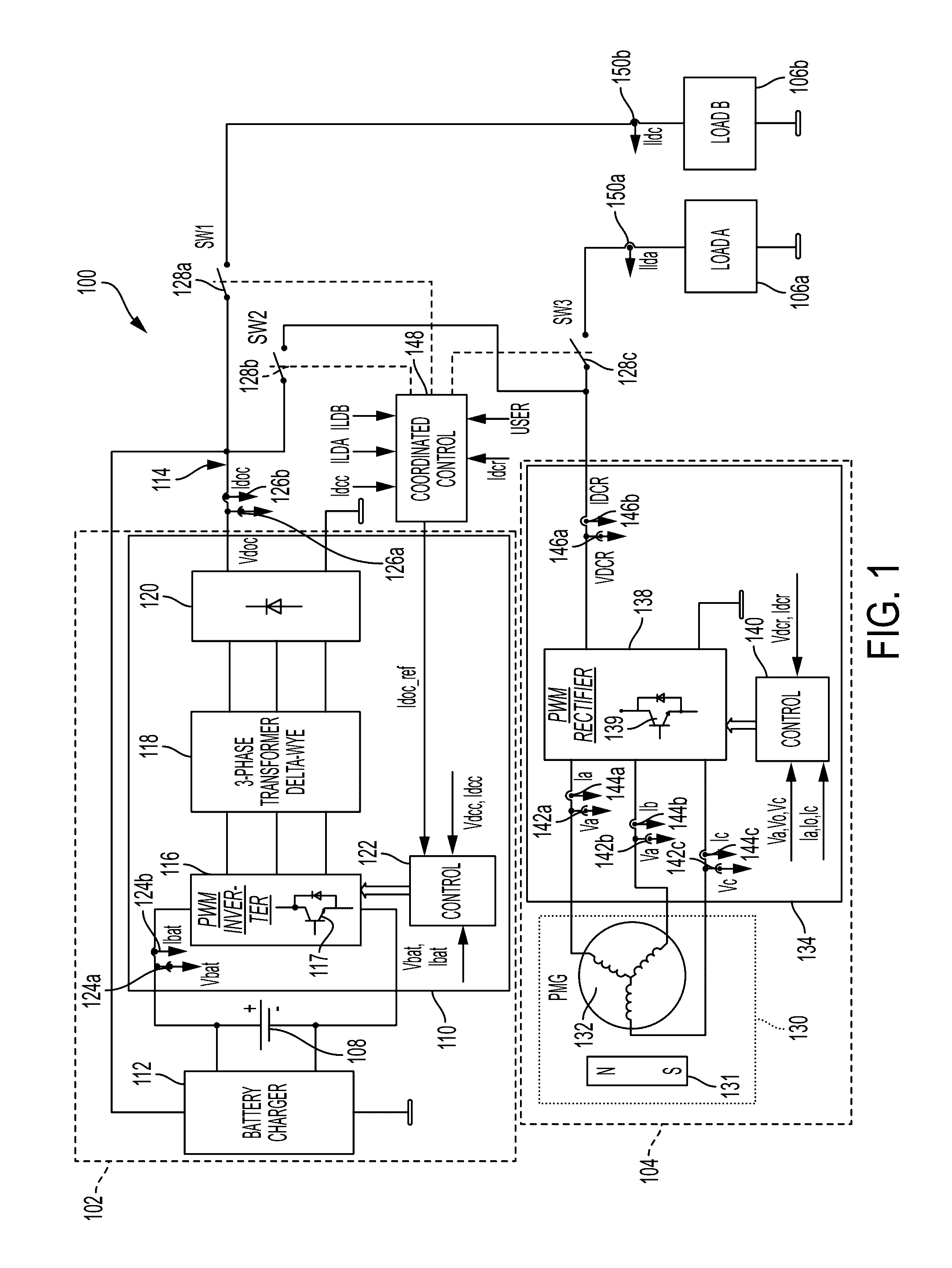
Dual-source multi-mode vehicle power supply
ActiveUS20170033594A1Satisfy loadingAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric devicesDc dc converterElectrical battery
A dual-source multi-mode power supply system includes a battery power supply, a first DC bus, an electric power generating system and a second DC bus. The battery power supply includes a DC-DC converter circuit configured to convert a first DC voltage into a second DC voltage for supplying power to the first DC bus. The electric power generating system includes a permanent magnet generator and an active rectifier circuit configured to convert a variable-voltage / variable-frequency output into a constant high-voltage direct current (HVDC) to supply power to a second DC bus. An electronic coordinated control module determines a load request, and controls one or more switch such that the power from the first DC bus and power from the second DC bus are delivered to the loads to satisfy the load request.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Method and Apparatus for Reducing Radiated Emissions in Switching Power Converters
ActiveUS20140035497A1Reduce radiationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPower inverterMotor drive
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
High efficiency generator
InactiveUS7919949B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsMOSFETDc current
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Regenerative variable frequency drive with auxiliary power supply
ActiveUS20170170743A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionBipolar voltageThree-phase
A regenerative variable frequency drive includes an active converter connected to a DC bus that is connected to a first inverter that converts DC power to variable frequency, three phase AC power, and variable frequency, three phase AC power to DC power, and to a second inverter that converts DC power to three phase AC sine wave power. The converter converts single phase AC power to DC power and DC power to single phase AC power, and maintains a selected voltage on the DC bus. The converter has an active rectifier and a controller that drives the rectifier with a pulse width modulation according to a hybrid voltage switching scheme that switches the rectifier according to a unipolar voltage switching scheme through most of each cycle and switches the rectifier according to a bipolar voltage switching scheme around each zero crossing.
Owner:PHASE TECH
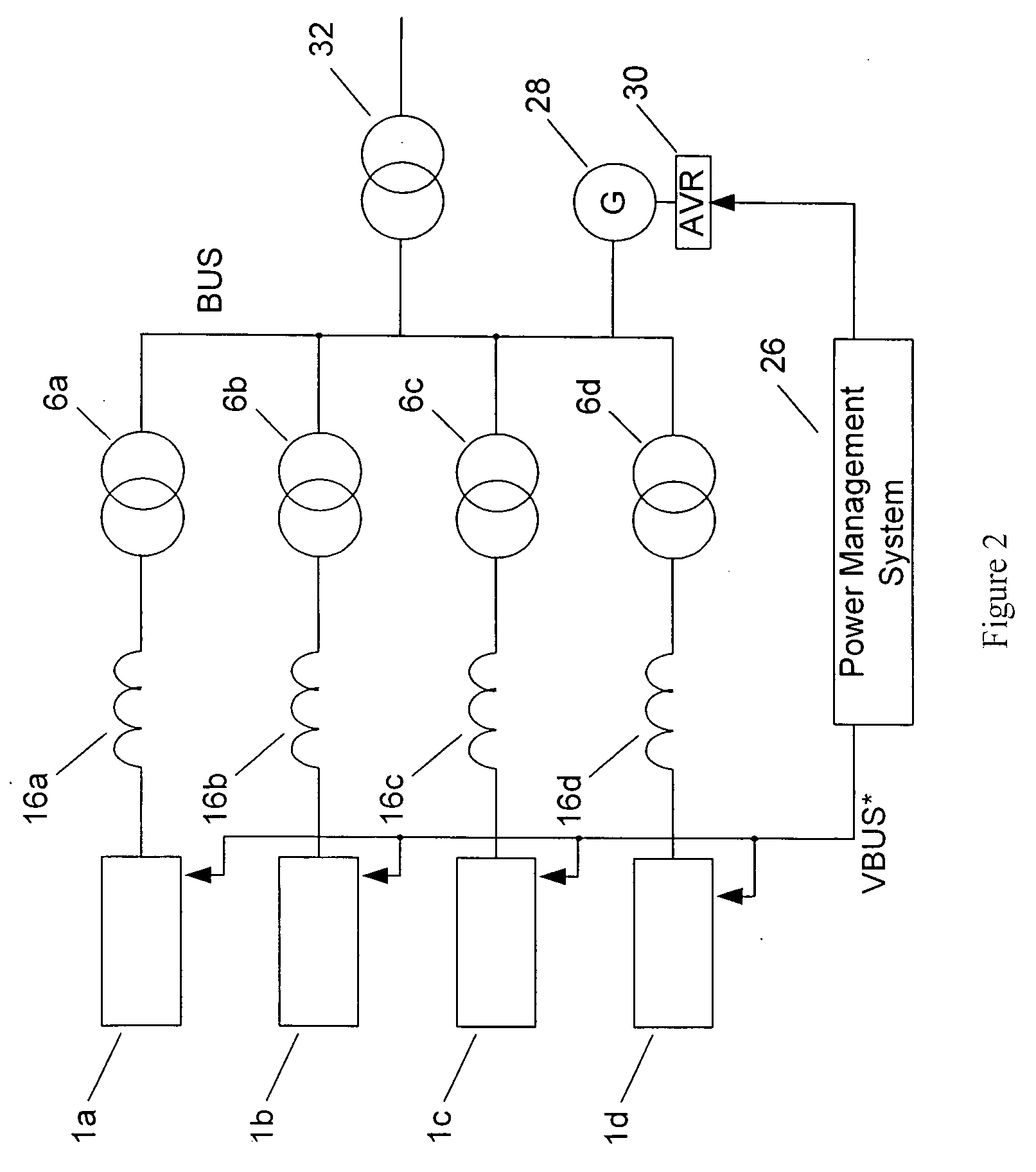
Direct current generating, management and distribution system
ActiveUS8699251B2Electric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsDistribution systemCell controller
A direct current generating, management and distribution system includes a first armature winding, a first active rectifier having a first controller and coupled to the first armature winding, a first direct current bus coupled to the first active rectifier, a second armature winding, a second active rectifier having a second controller and coupled to the second armature winding, a second direct current bus coupled to the second active rectifier, a unit controller coupled to the first and second controllers, a first set of switches coupled to the first direct current bus and to the unit controller, a second set of switches coupled to the second direct current bus and to the unit controller, a third switch coupled to the first direct current bus and to the unit controller and a fourth switch coupled to the second direct current bus and the unit controller.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Three-phase power supply and system of leds with three-phase power supply
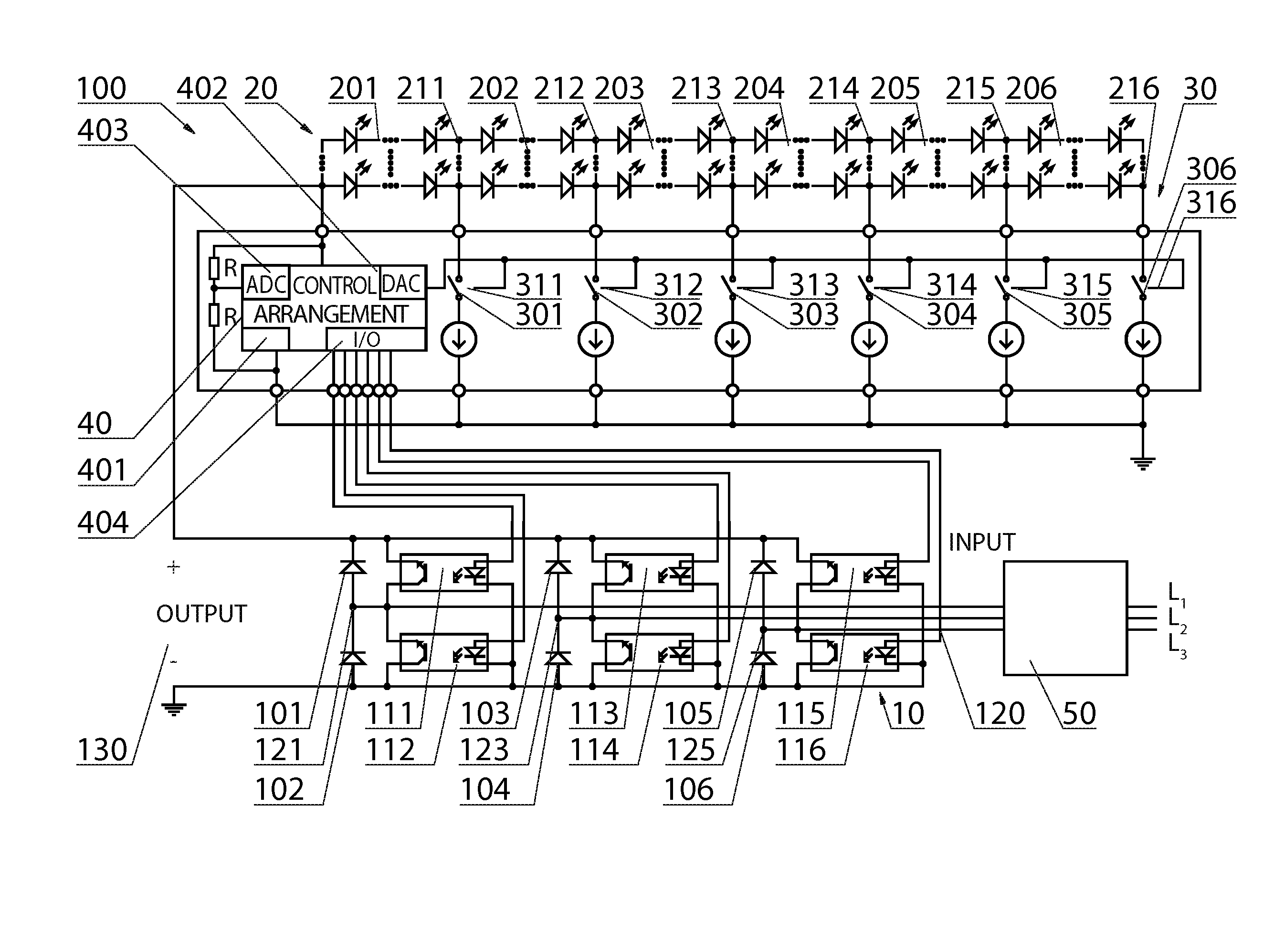
ActiveUS20150054408A1Reduce power consumptionReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesMicrocontrollerDiode bridge rectifier
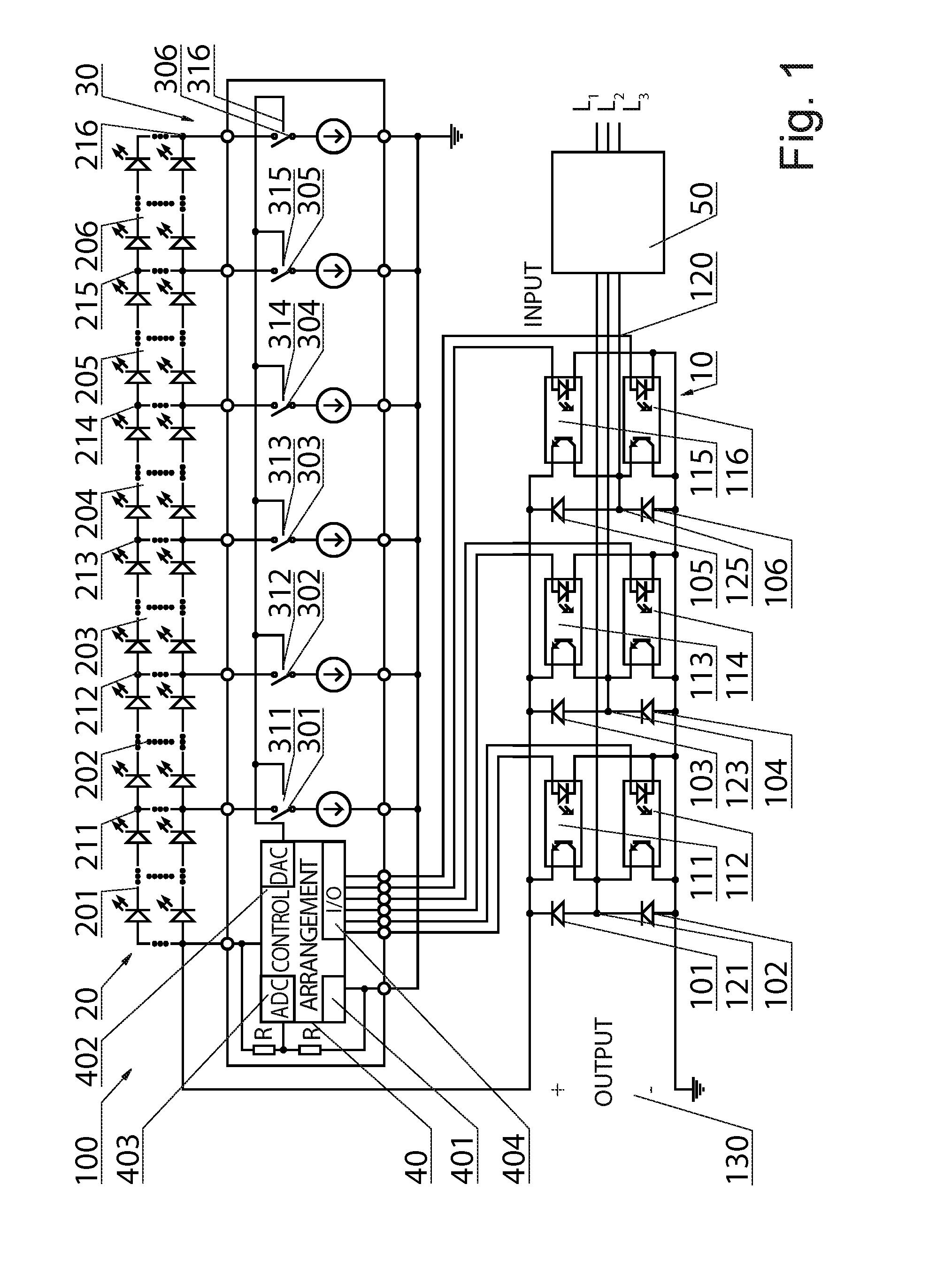
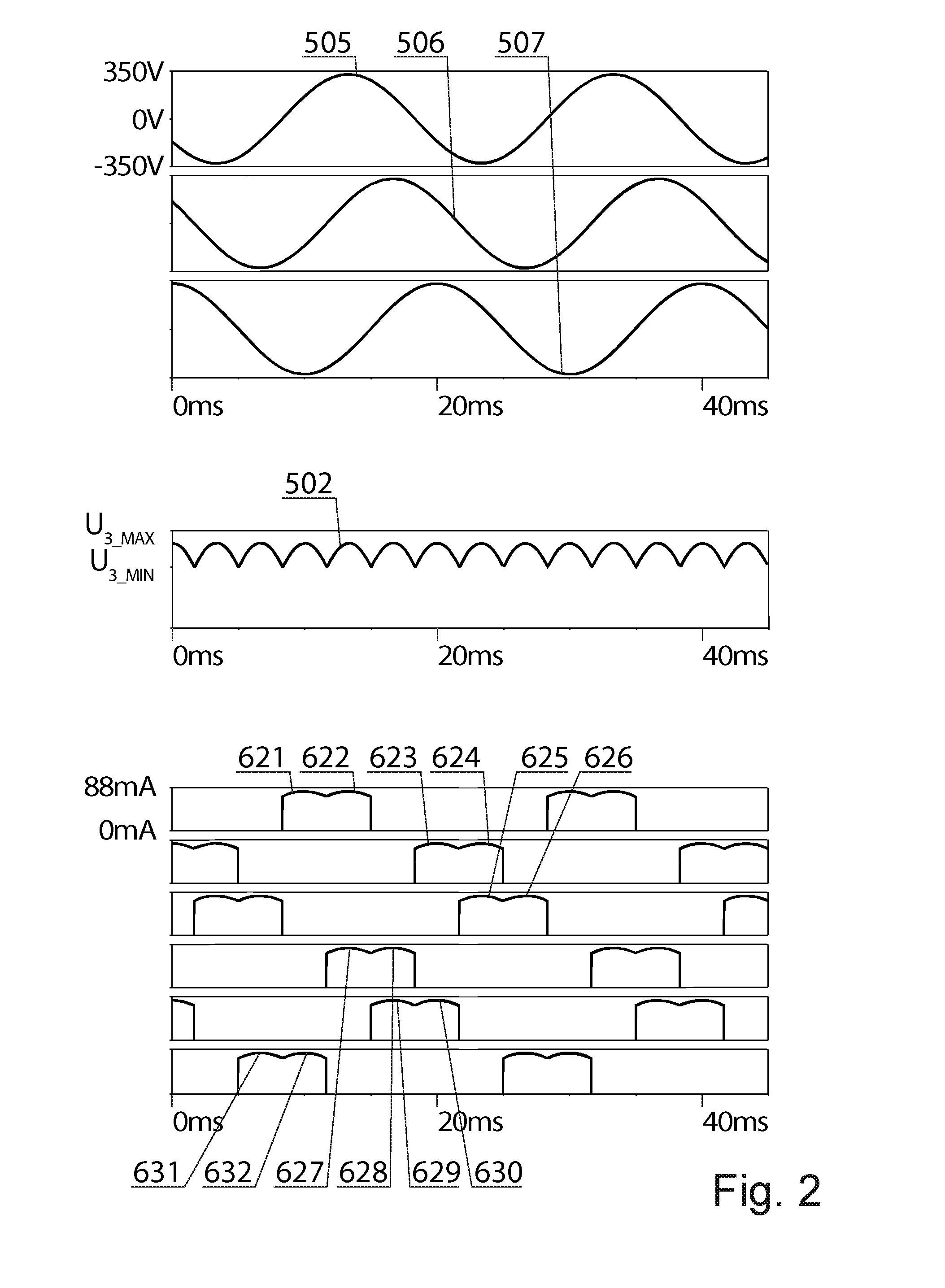
A three-phase power supply (10), intended especially to supply LEDs system (20), has a system of a diode bridge rectifier which comprises rectifying diodes (101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106). The three-phase power supply (10) is additionally equipped with FETs and each of the rectifying diodes is bypassed by an FET of a rectifying unit (111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116), respectively, which is controlled by a control system (40), comprising en anglogue-to-digital converter ADC 403, a digital-to-analogue converter (402), a microcontroller (401), which provides a control signal to a gate of the appropriate FET through the input / output (404). Once the control system (40), in particular the microcontroller (401), detects stable power supply conditions and starts operation of elements of an LED sequencer (30), it starts at the same time to control over the FETs in the active rectifier.
Owner:MILOO ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com