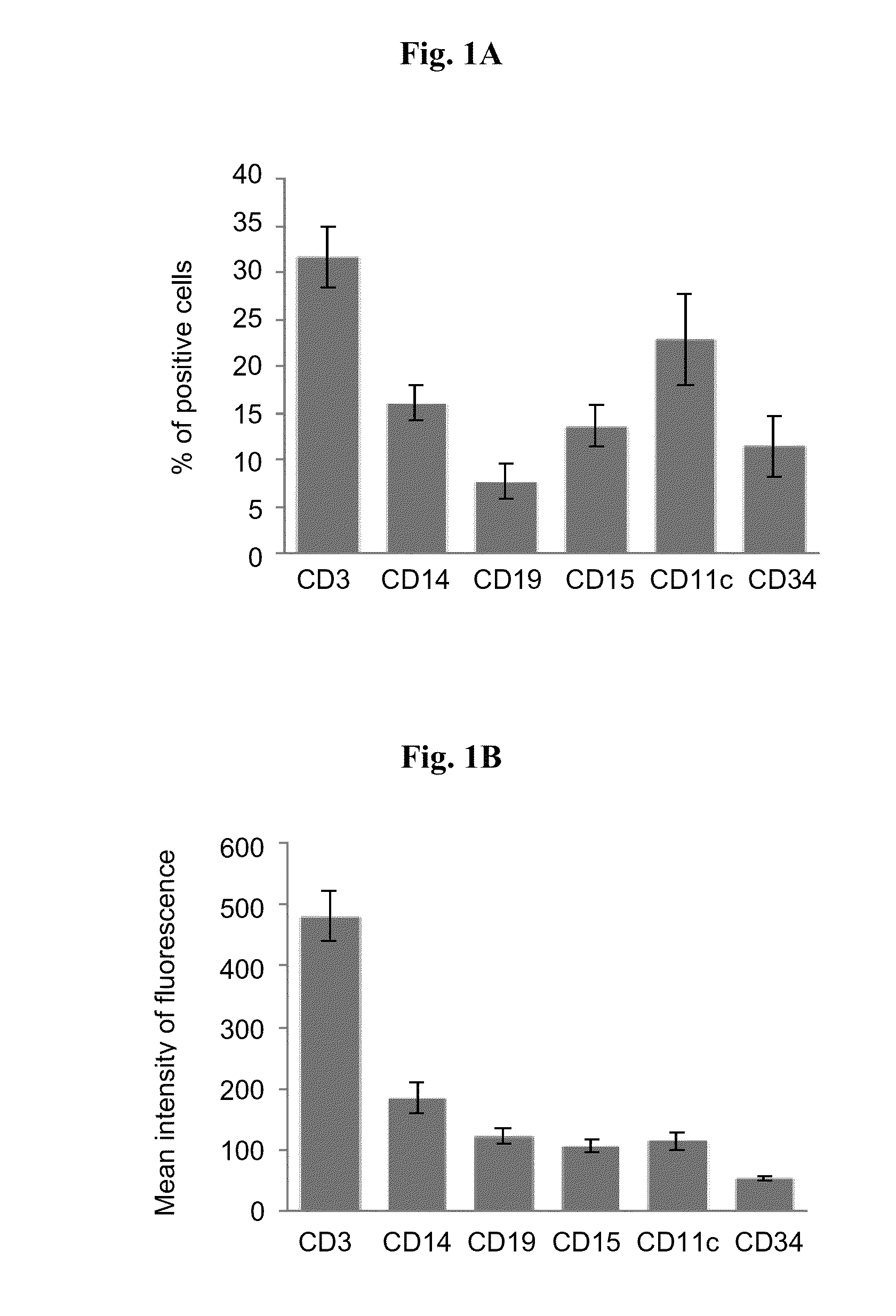
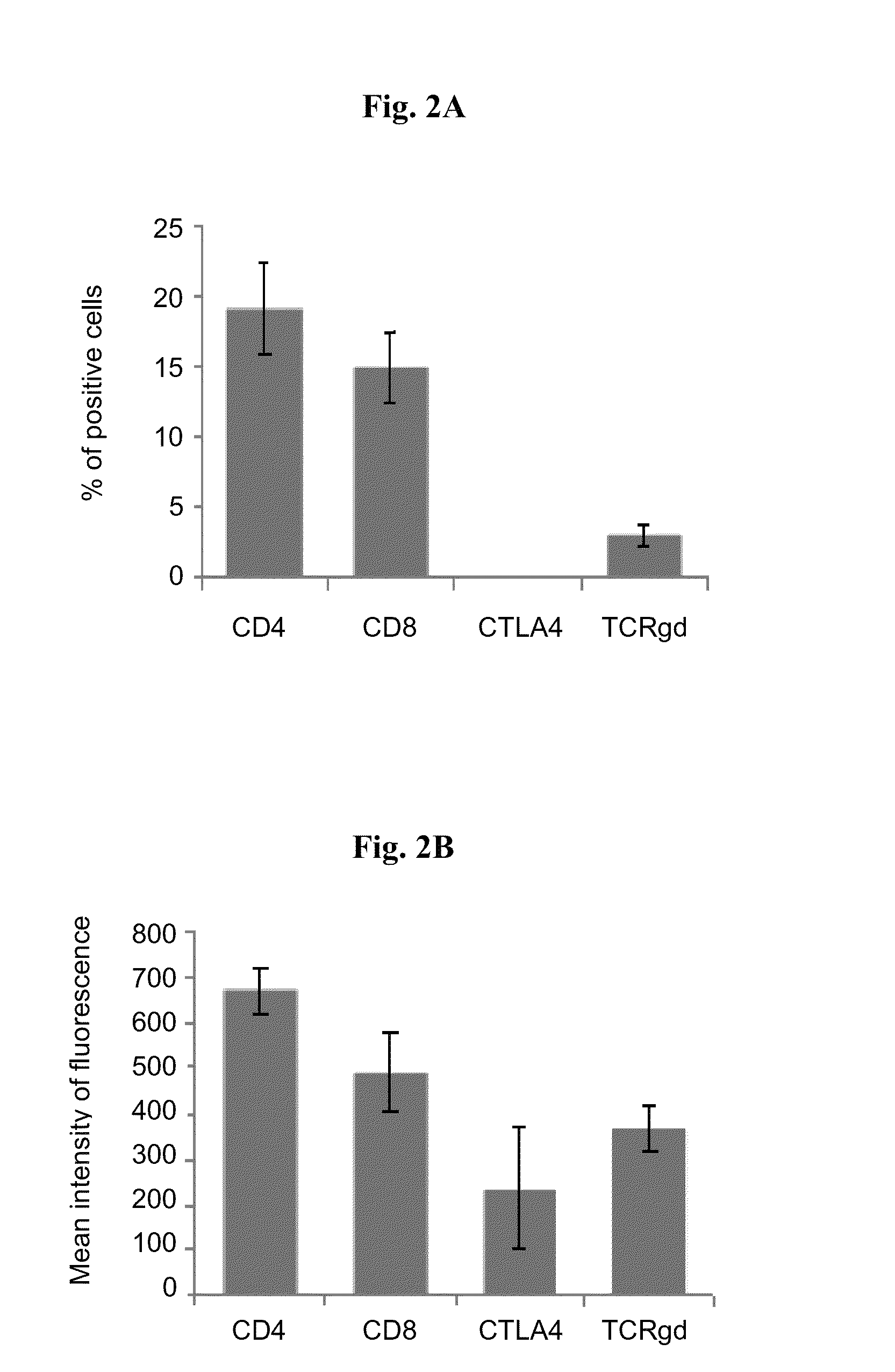
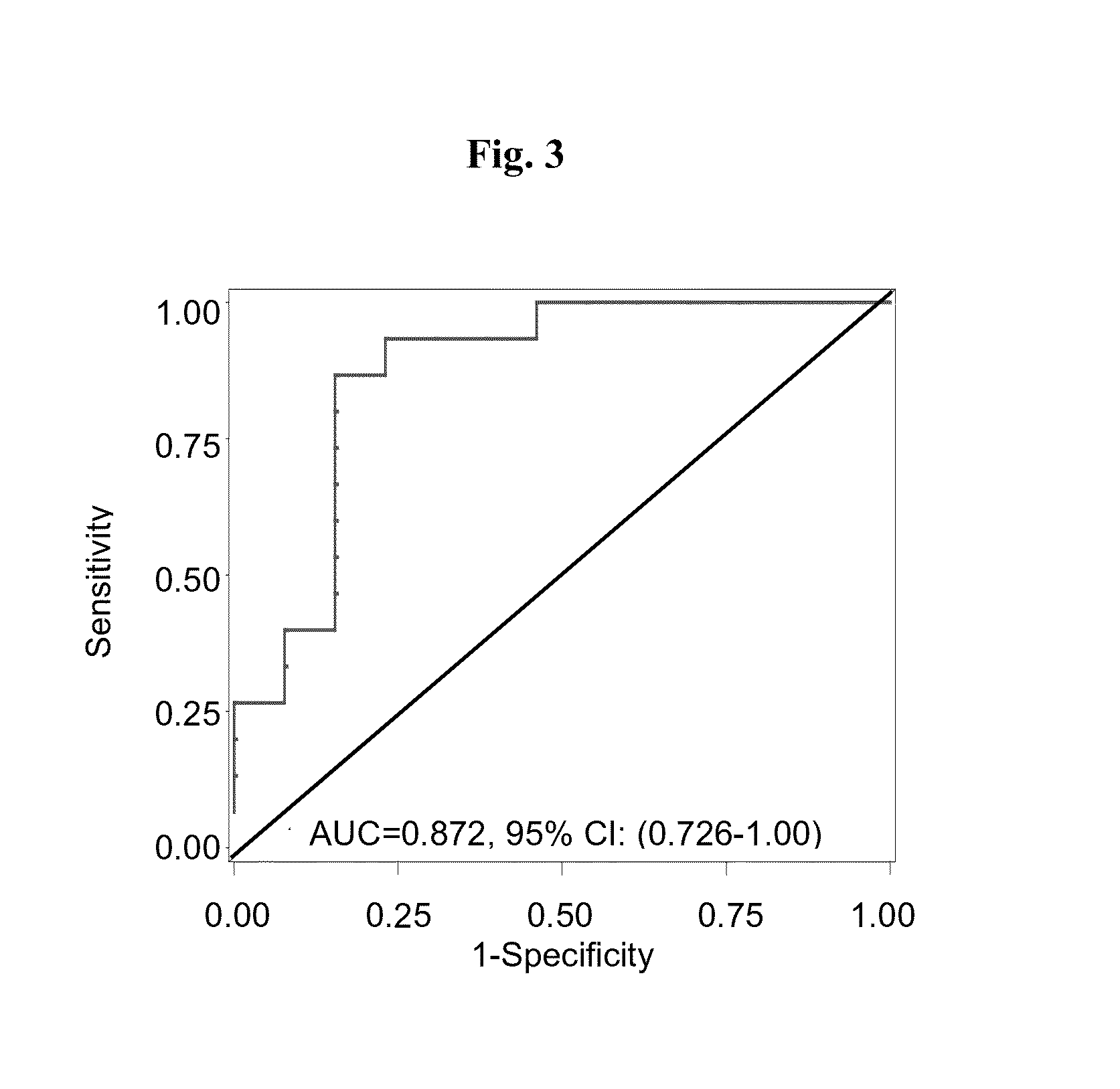
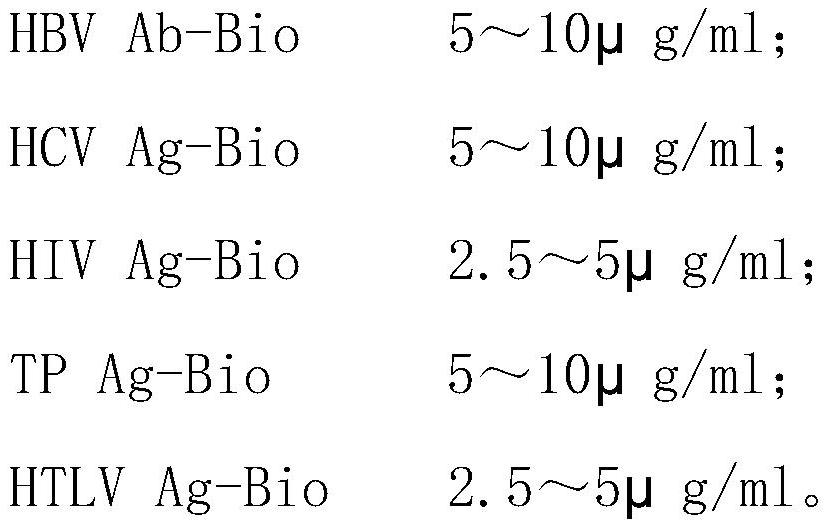Patents
Literature
42 results about "Blood marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen): a marker for the presence of colon, lung, and liver cancers. This marker may be used to determine if the breast cancer has traveled to other areas of the body. Circulating tumor cells: cells that break off from the cancer and move into the blood stream.
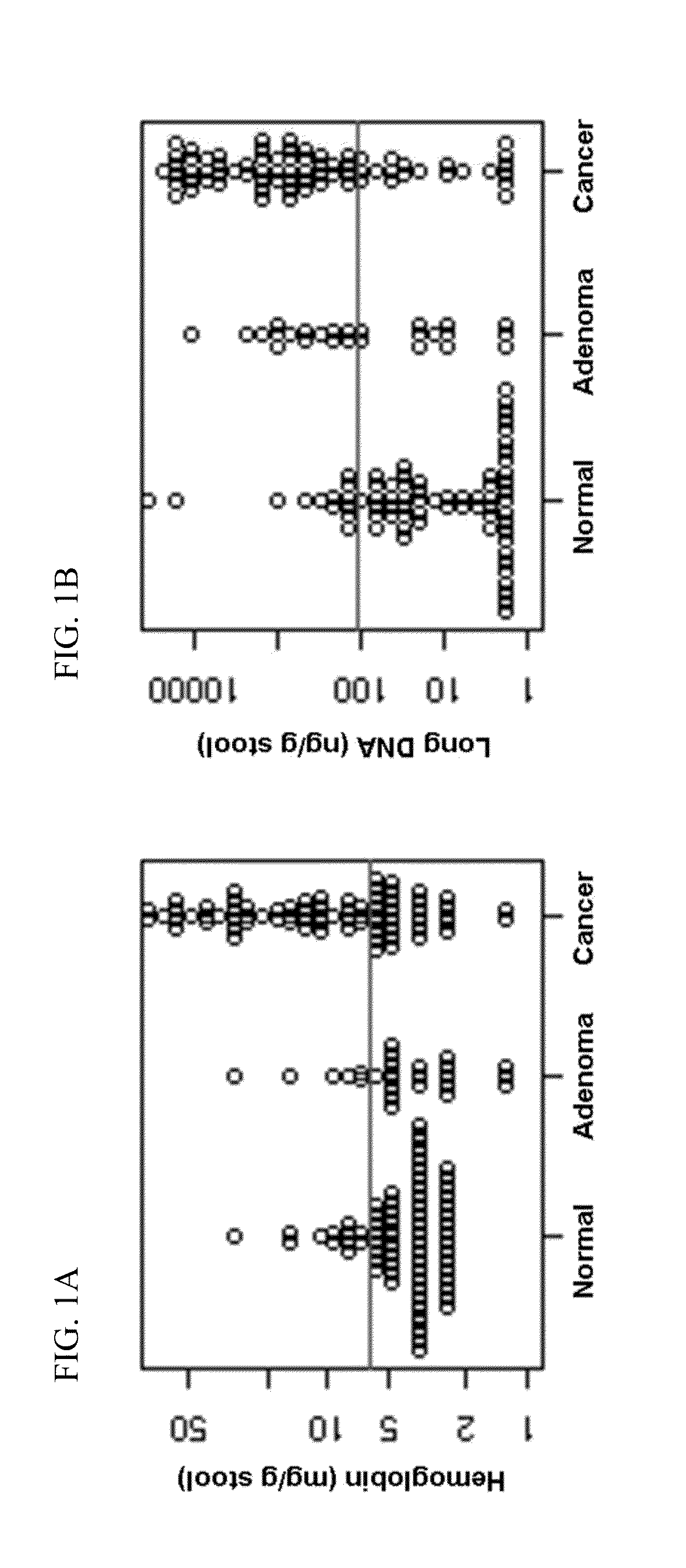
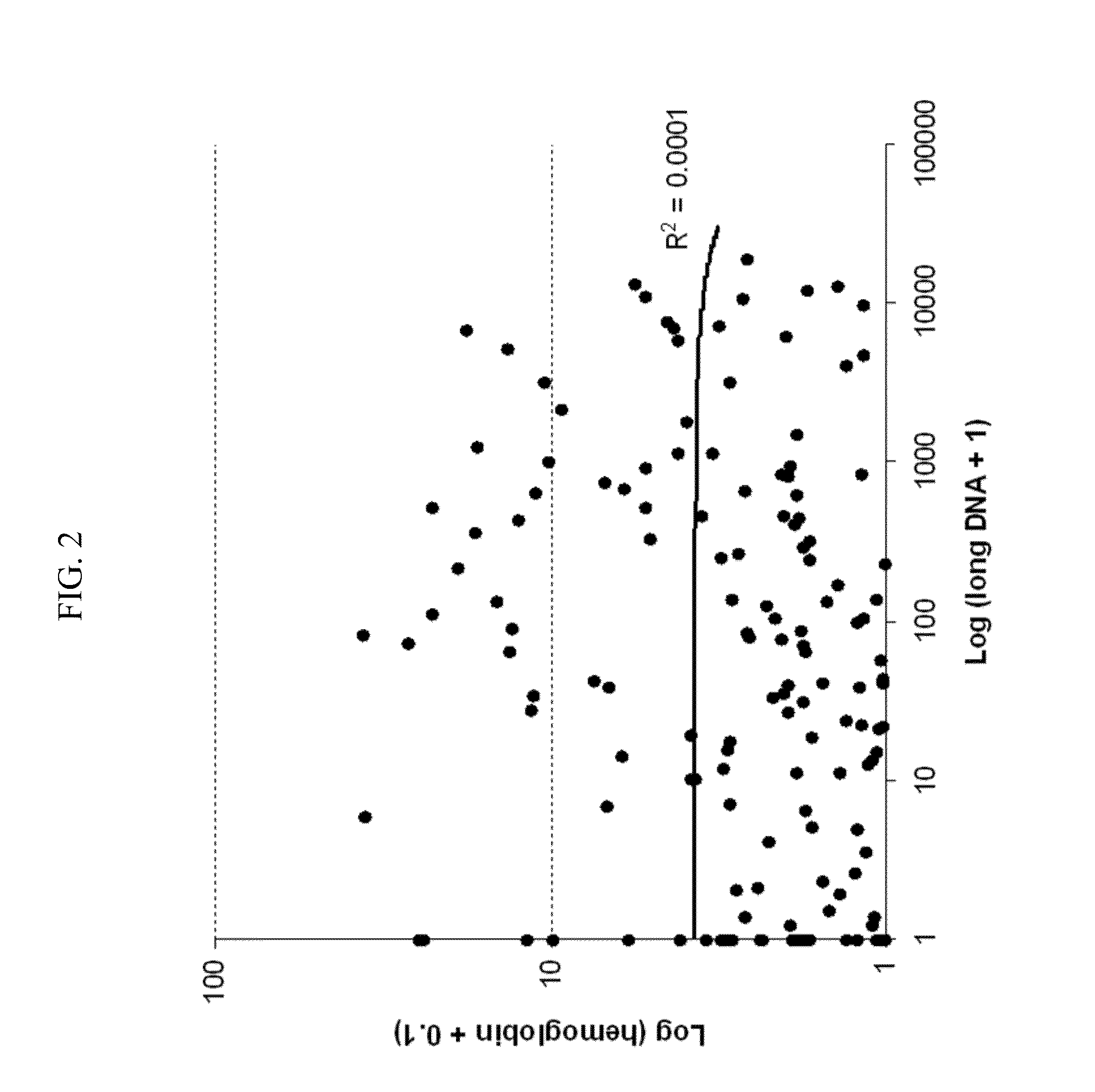
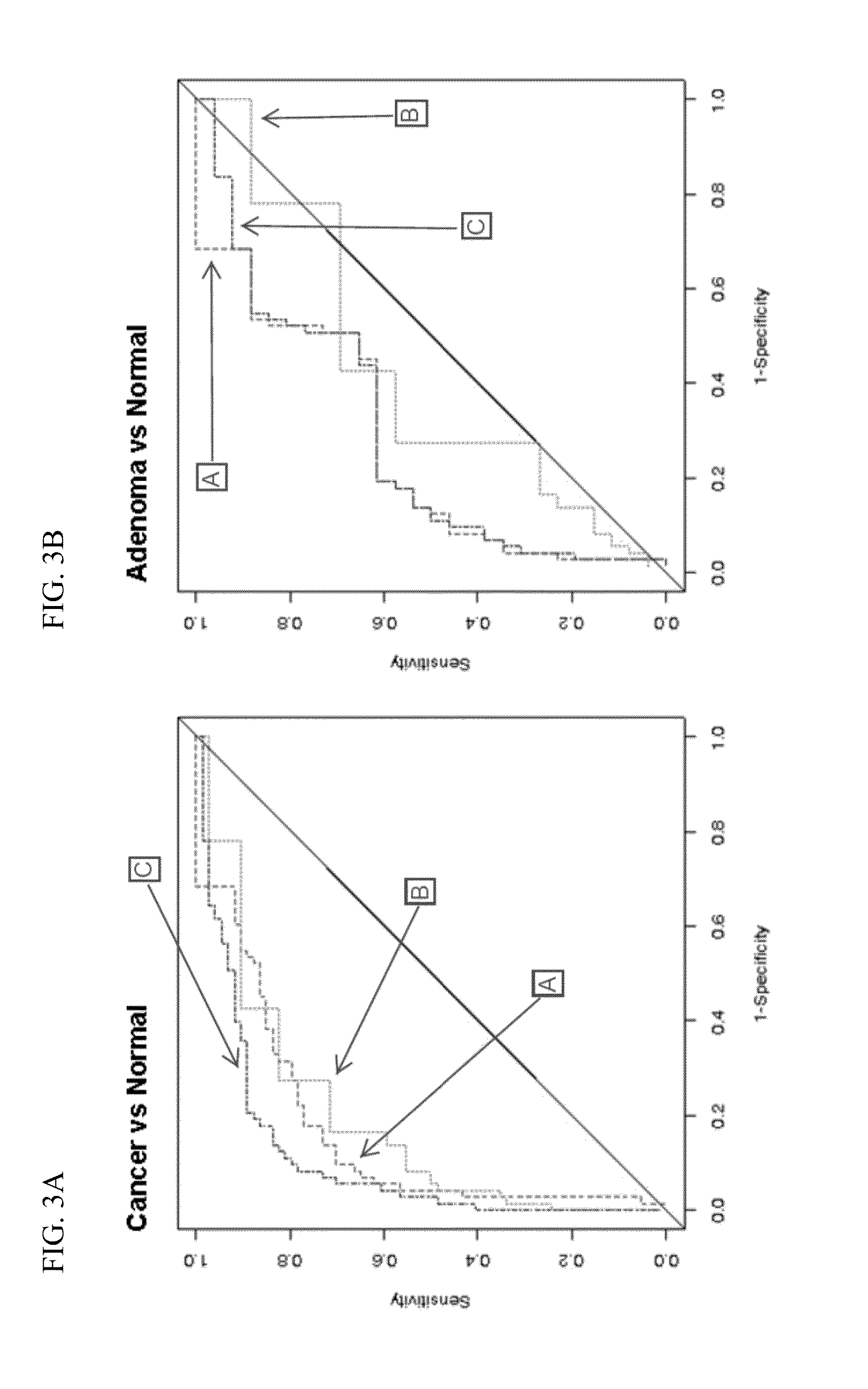
Methods and materials for detecting colorectal neoplasm
InactiveUS20110236916A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAbnormal tissue growthTumor-Related Protein
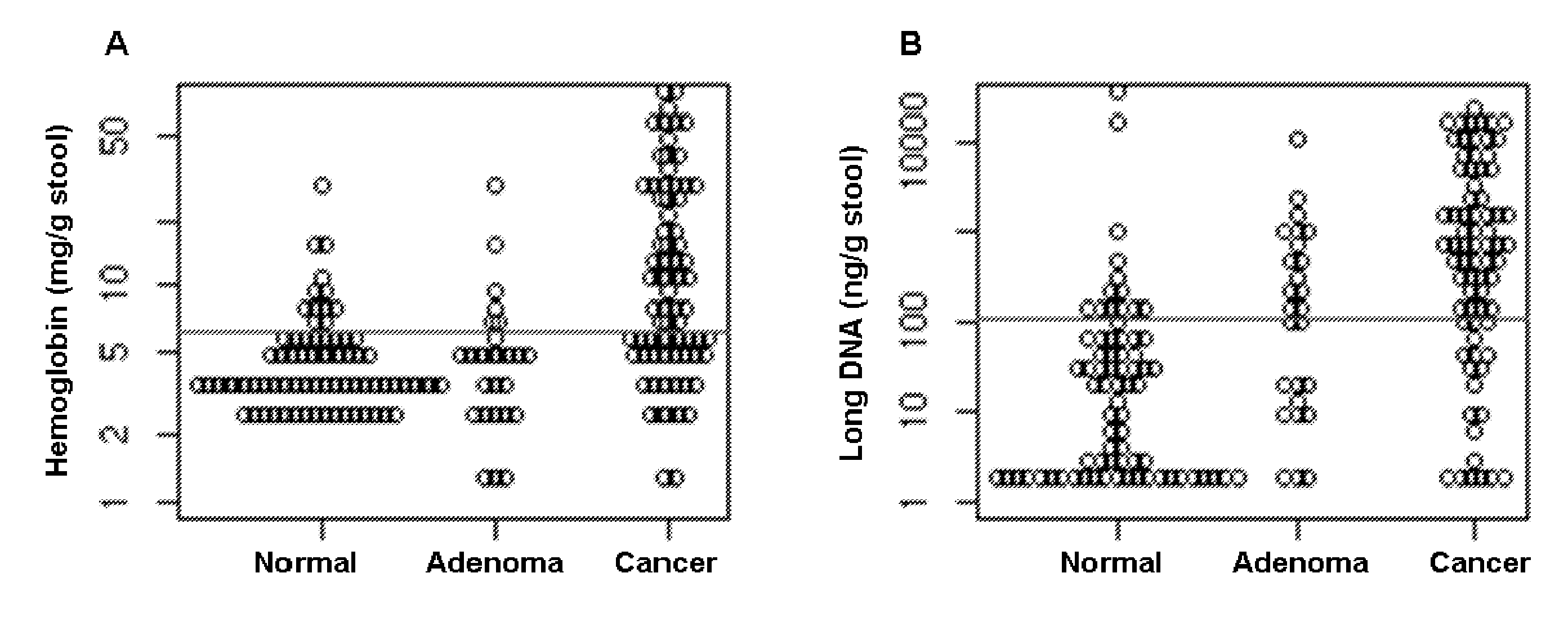
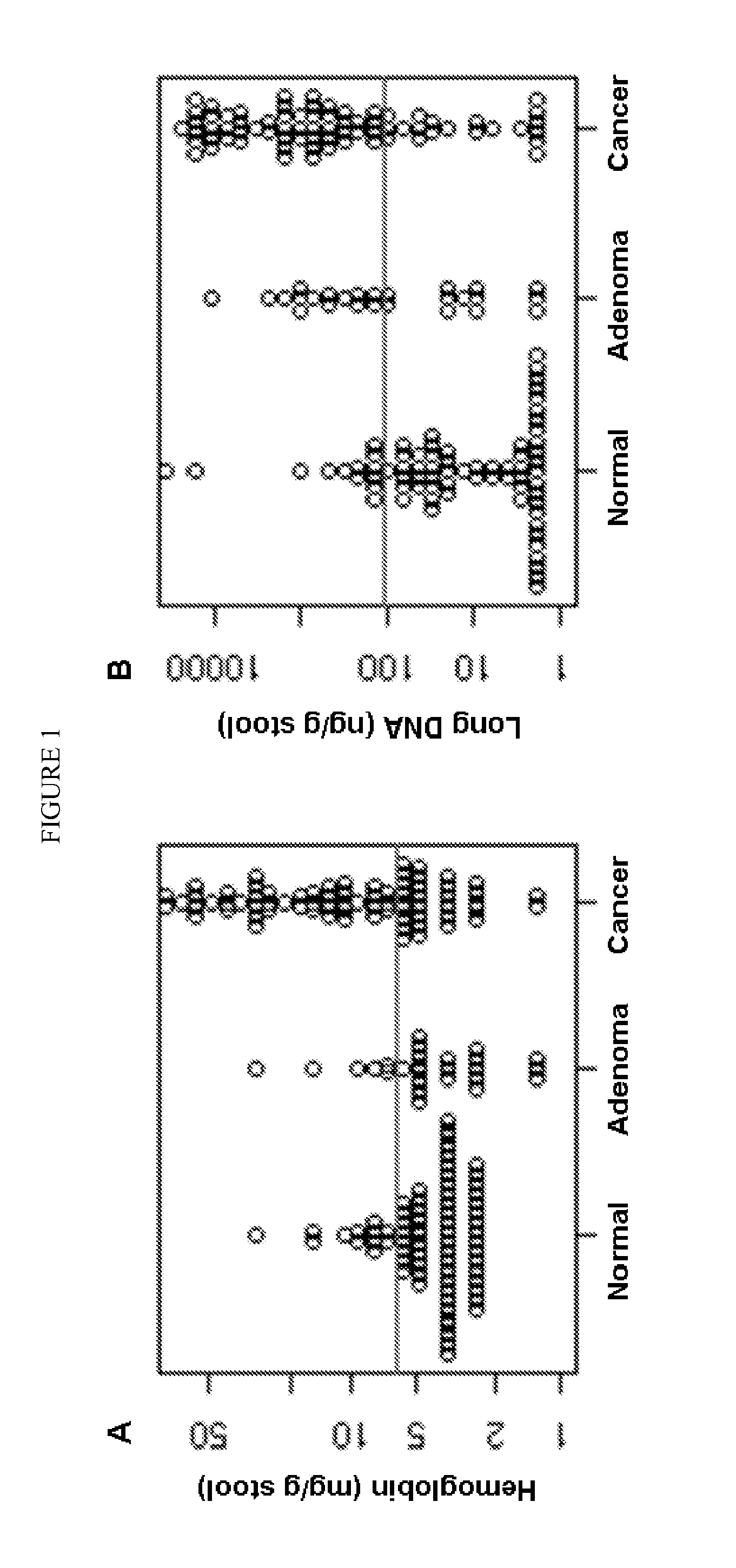
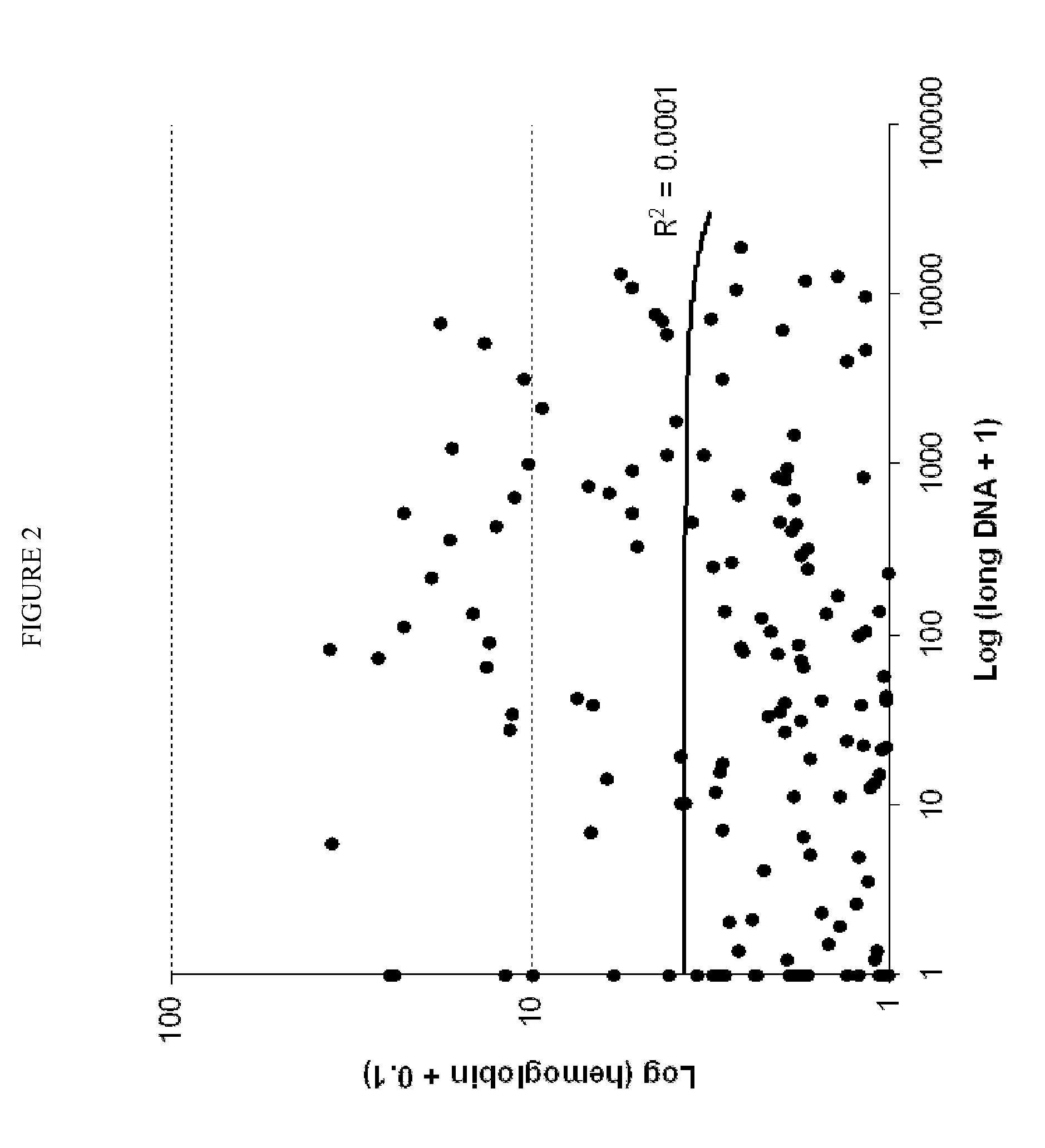
The present invention provides methods and materials related to the detection of colorectal neoplasm-specific markers in or associated with a subject's stool sample. In particular, the present invention provides methods and materials for identifying mammals having a colorectal neoplasm by detecting the presence of exfoliated epithelial markers (e.g., human DNA, tumor associated gene alterations, tumor associated proteins) and blood markers (e.g., homoglobin, serum proteins) in a stool sample obtained from the mammal.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
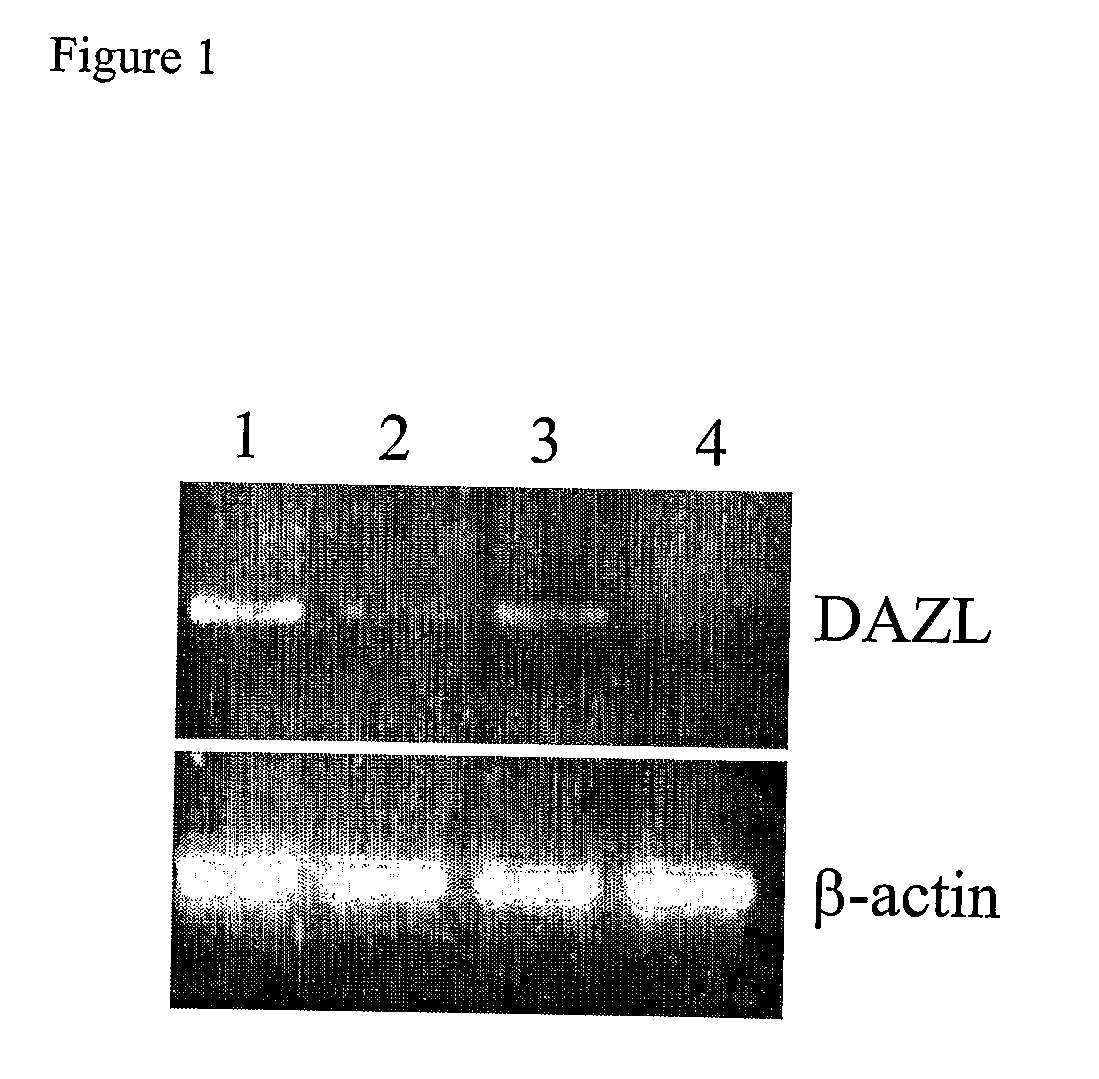
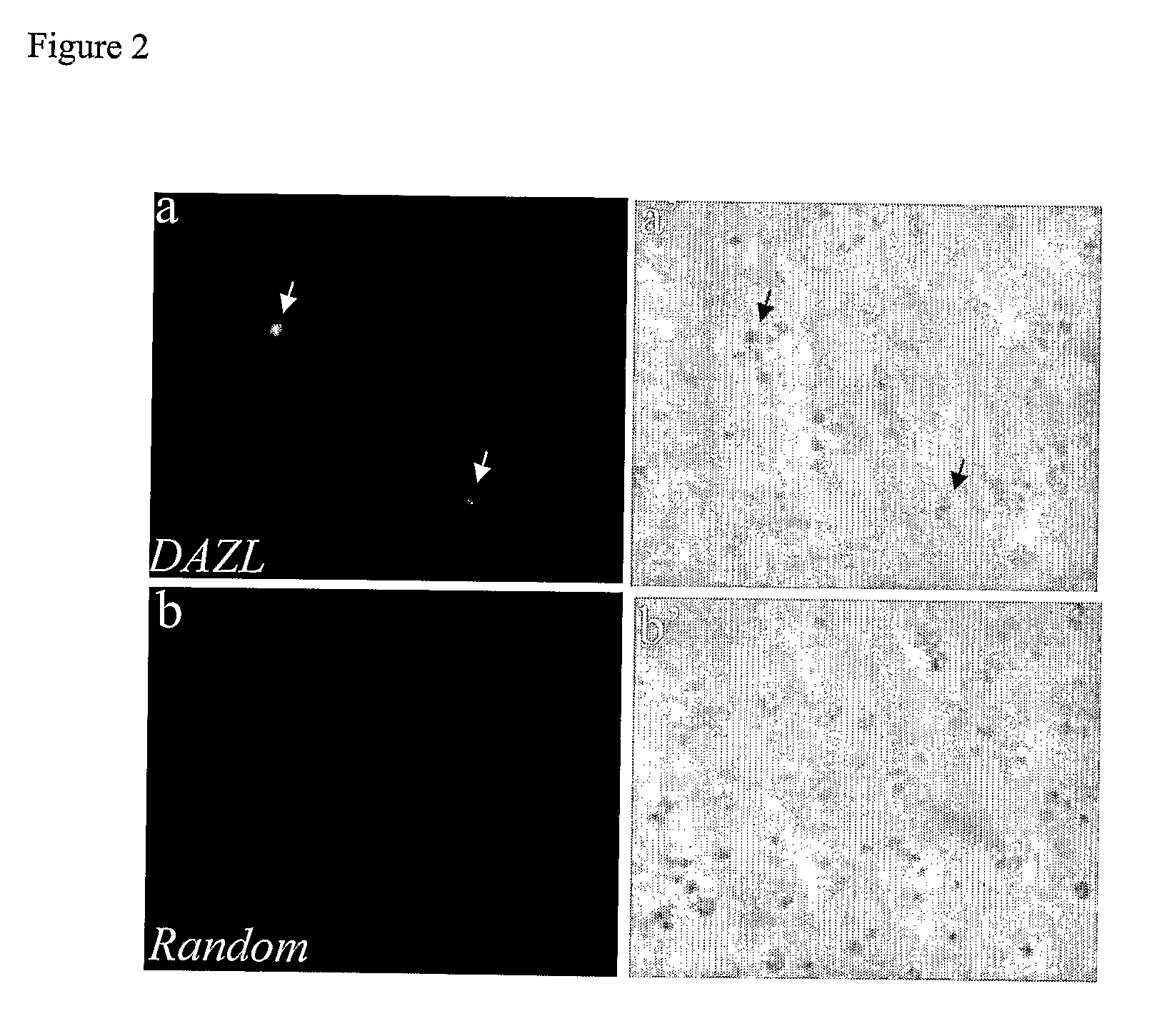
Stem cells characterized by expression of germline specific genes
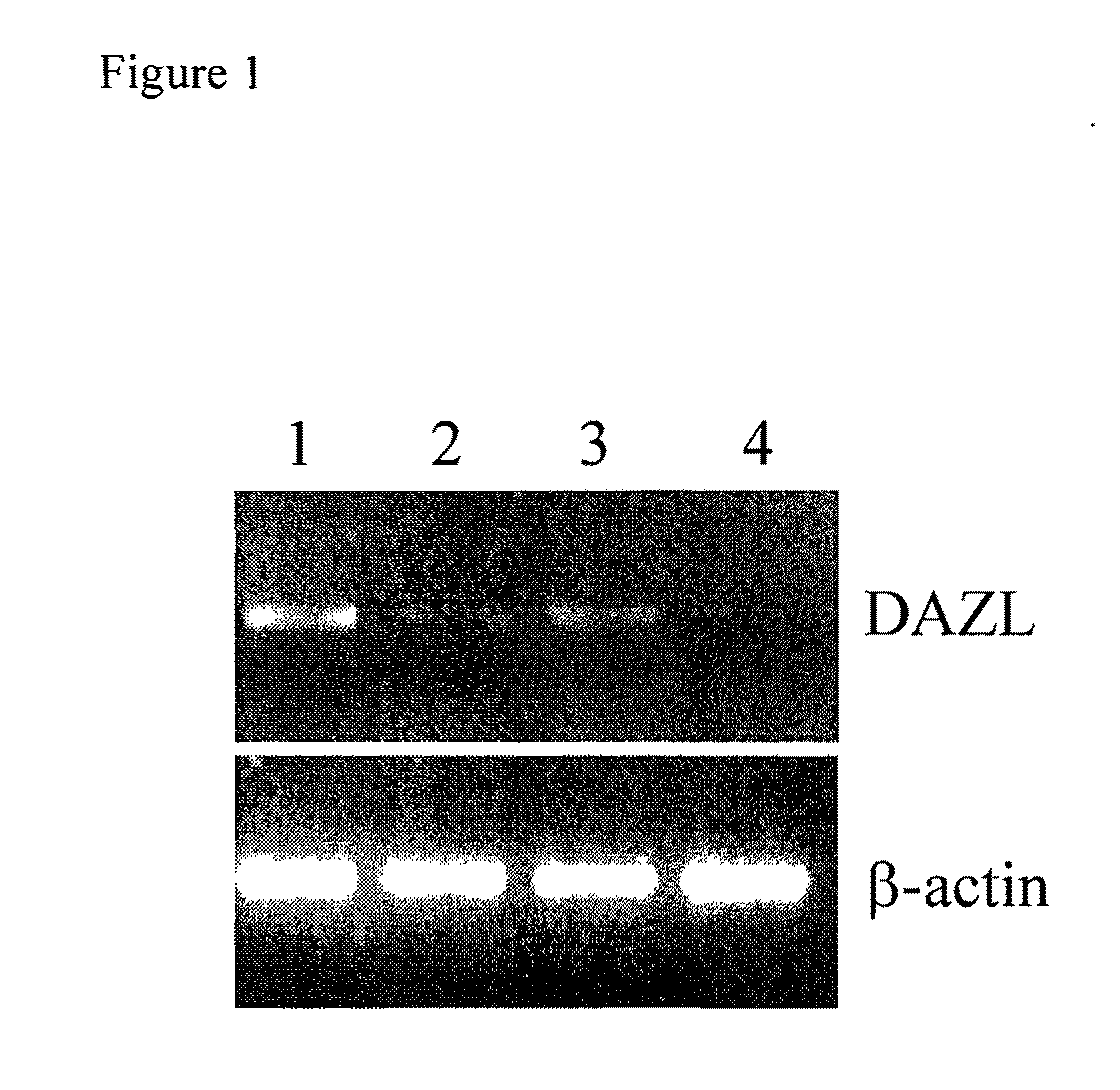
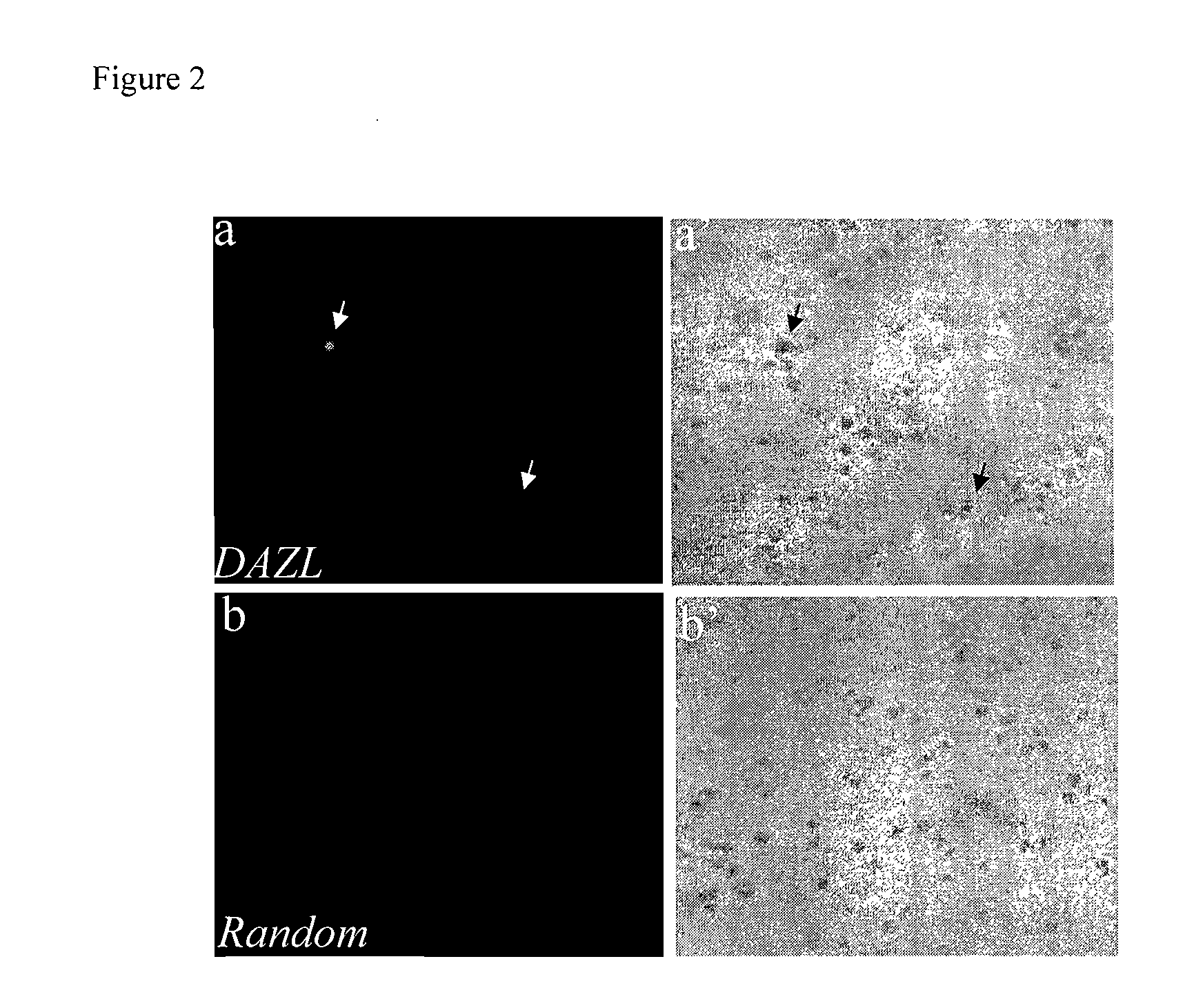
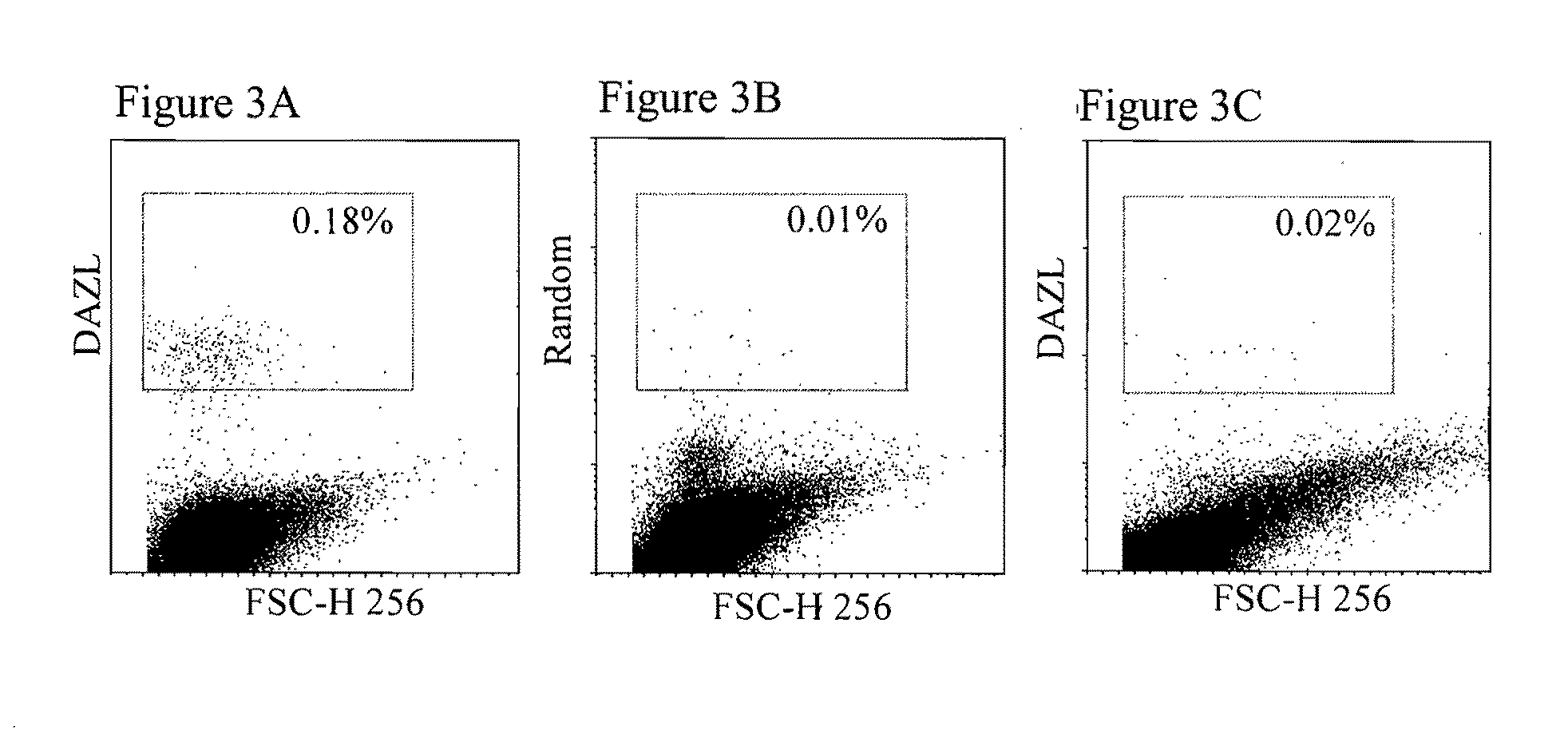
InactiveUS20110158966A1Efficiently identification and separationBiocideNervous disorderPlant Germ CellsBlood marker
The present invention relates to adult stem cells derived from somatic sources characterized by the expression of the germline specific gene, DAZL. The somatic stem cells expressing the DAZL marker are further characterized by expression of additional markers and absence of expression of certain blood markers. In particular, the present invention discloses therapeutic and diagnostic uses, other than the germ cell potential use, of the DAZL multipotent stem cells isolated from somatic sources such as peripheral blood, bone marrow or umbilical cord blood.
Owner:NANODIAGNOSTICS
Blood marker for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and early cirrhosis
The invention discloses a blood marker for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and early cirrhosis. The blood marker refers to galectin 3. The concentration of the galectin 3 in the blood is analyzed by using the blood marker through enzyme linked immune reaction so as to analyze and evaluate hepatic fibrosis and early cirrhosis. By using the blood as the detection sample, early diagnosis on hepatic fibrosis and early cirrhosis can be achieved conveniently and rapidly.
Owner:ANHUI SIZHENG MEDICAL TECH
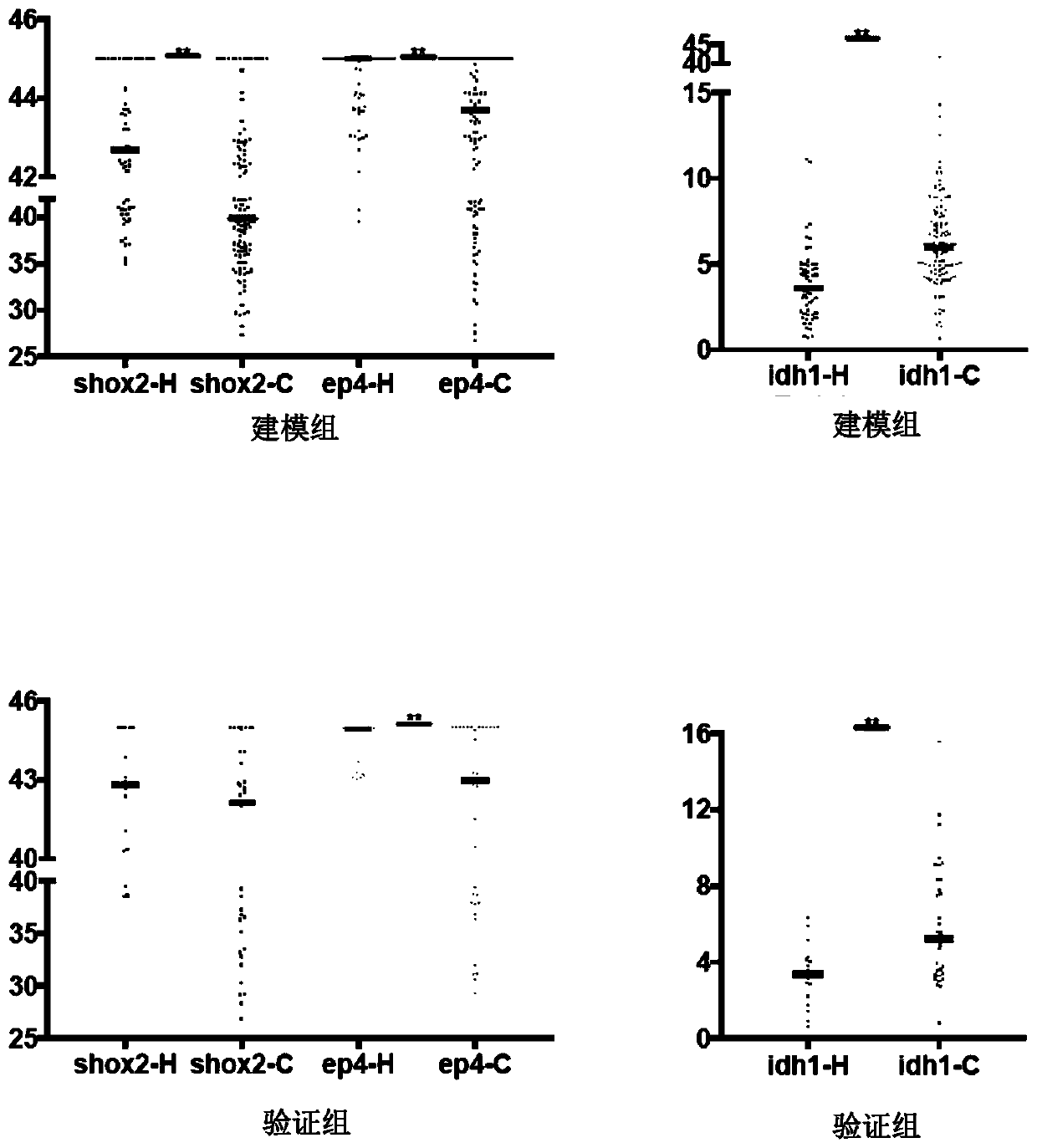
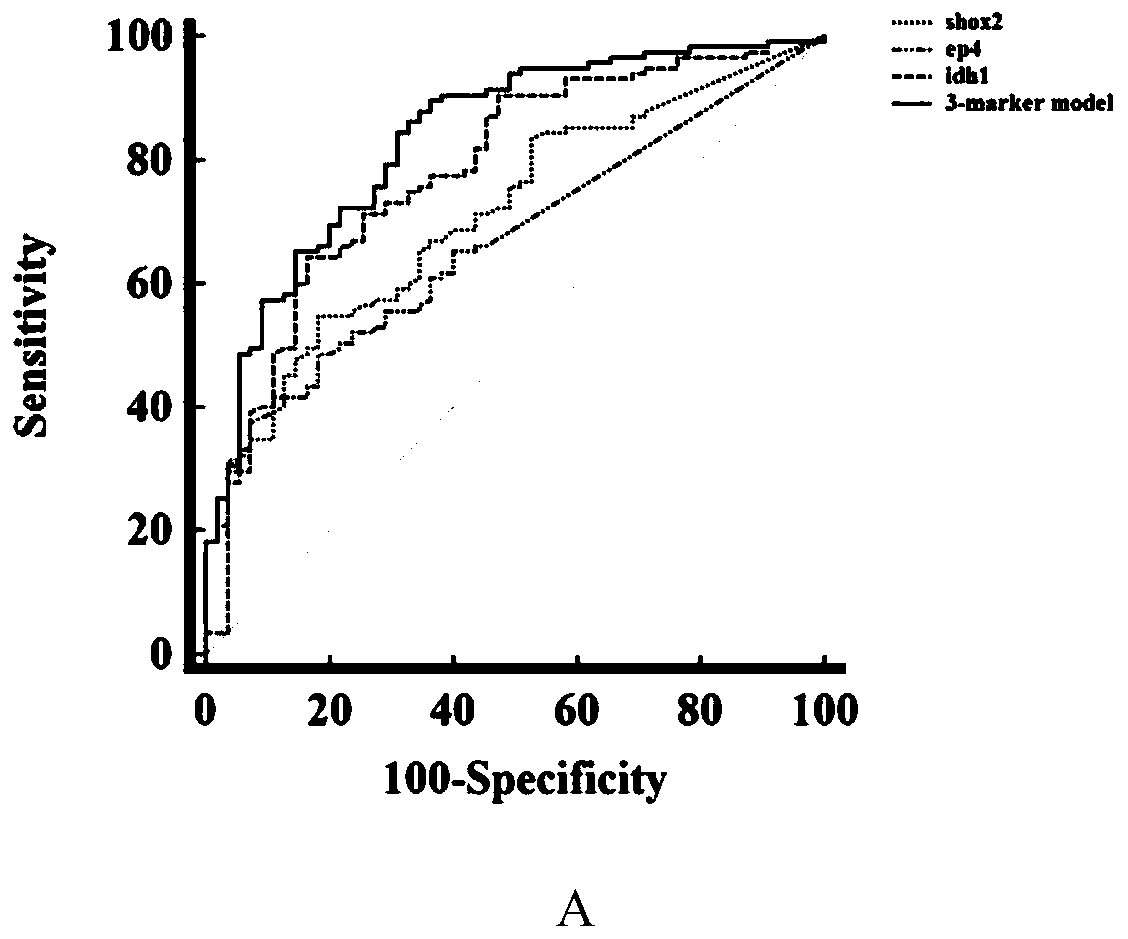
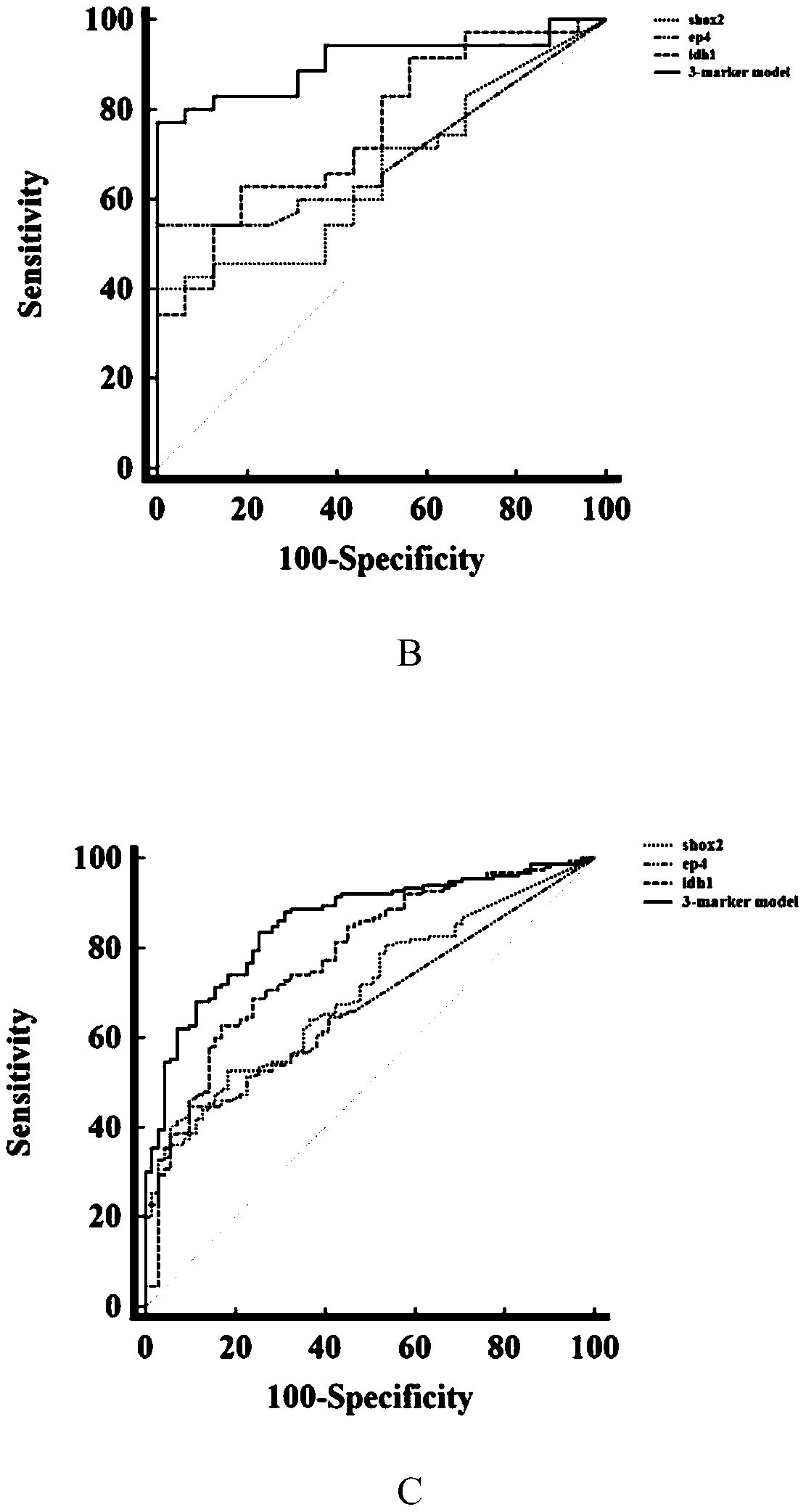
Peripheral blood methylation gene and IDH1 combined detection and diagnosis model for lung cancer
ActiveCN111172279AImprove diagnostic efficiencyWide coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisIDH1Blood markers
The invention discloses a peripheral blood methylation gene and IDH1 combined detection and diagnosis model for lung cancer. The invention provides application of methylated SHOX2 gene, methylated PTGER4 gene and IDH1 protein as markers in preparation of products for diagnosis or auxiliary diagnosis of lung cancer, and constructs a three-marker combined lung cancer diagnosis model. Experiments prove that: compared with an incorporated single factor, the diagnosis efficiency of the combined diagnosis model is remarkably enhanced. Therefore, the diagnosis efficiency of the lung cancer can be improved by combined detection blood markers.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
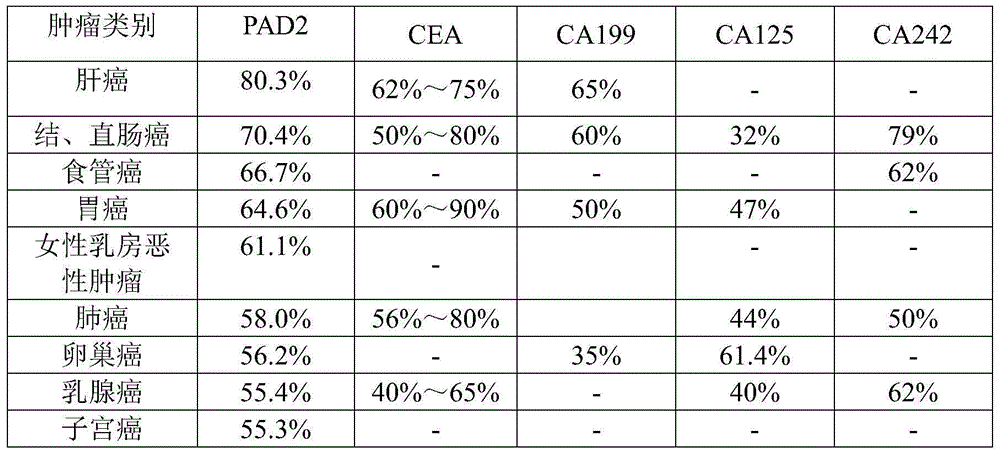
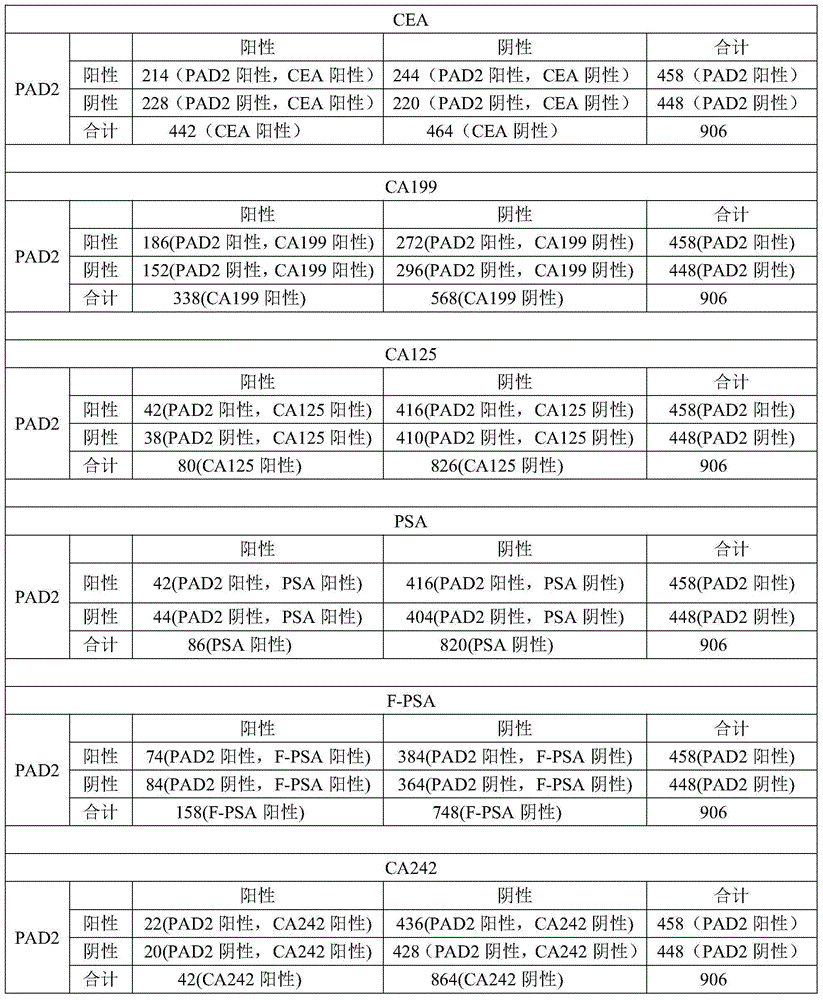
Application of peptidylarginine deiminase 2 (PAD2) to preparation of reagent for clinical diagnosis of tumors
The invention discloses an application of peptidylarginine deiminase 2 (PAD2) to preparation of a clinically diagnostic reagent or detection object for diagnosing tumors. The tumors are selected from liver cancers, gastric cancers, lung cancers, breast cancers, esophageal cancers, ovarian cancers, uterine cancers and colorectal cancers. When PAD2 is specially applied, an antibody against PAD2 is prepared by a conventional method, and a qualitative or quantitative method and a matching kit for detecting PAD2 are established. The invention also discloses a blood diagnosis reagent for diagnosing tumors. The blood diagnosis reagent comprises the PAD2 antibody, a horseradish peroxidase-immunoglobulin G (HRP-IgG) antibody and conventional reagents in the blood diagnosis reagent, wherein the conventional reagents in the blood diagnosis reagent include a carbonate buffer solution, a phosphate buffer solution-Tween (PBST) lotion, a blocking solution, developing solutions and a stop solution. PAD2 is found for the first time to be capable of being applied as a tumor blood marker. Experiments prove that PAD2 has feasibility as the tumor marker.
Owner:SHANDONG XINCHUANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
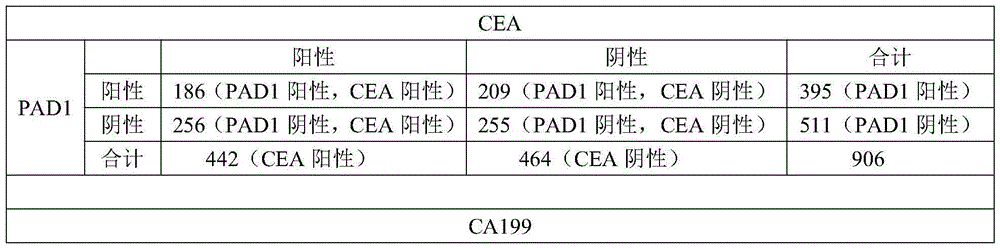
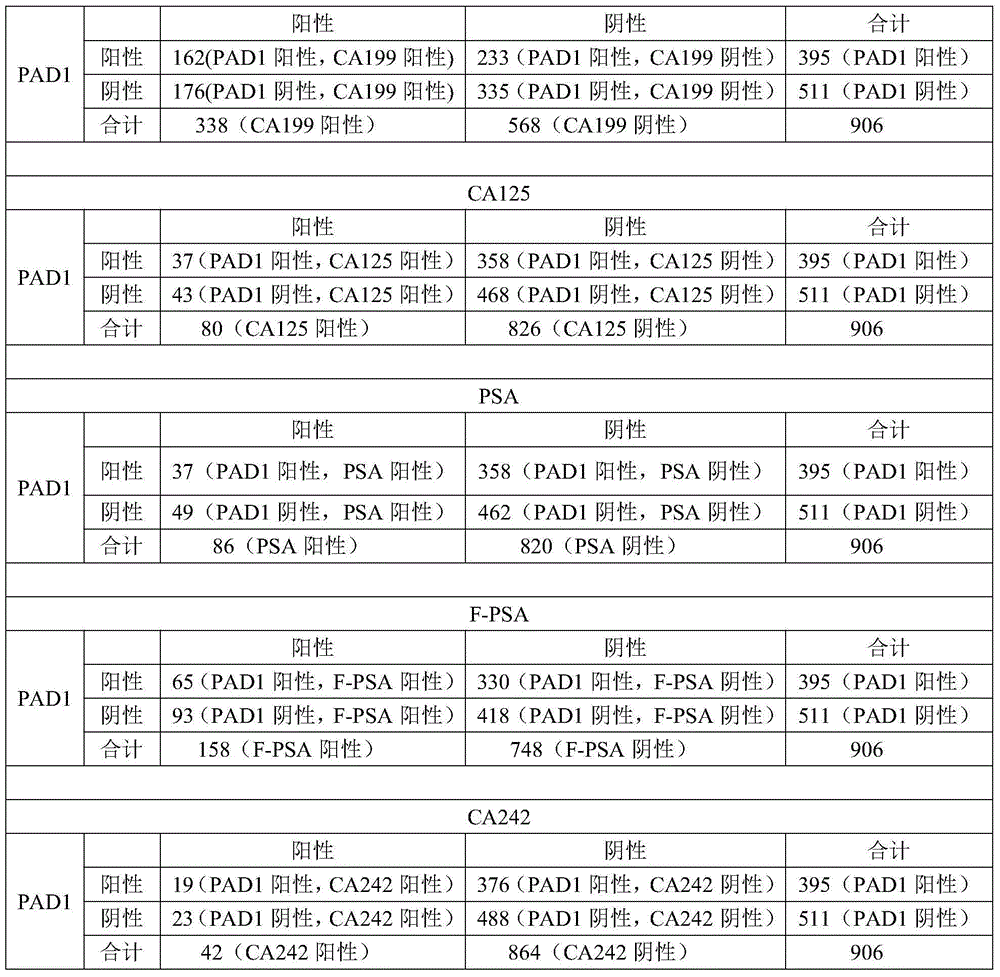
Application of peptidylarginine deiminase 1 (PAD1) to preparation of reagent for clinical diagnosis of tumors
The invention discloses an application of peptidylarginine deiminase 1 (PAD1) to preparation of a clinically diagnostic reagent or detection object for diagnosing tumors. The tumors are selected from uterine cancers, liver cancers, gastric cancers, esophageal cancers, ovarian cancers and lung cancers. When PAD1 is specially applied, an antibody against PAD1 is prepared by a conventional method, and a qualitative or quantitative method and a matching kit for detecting PAD1 are established. The invention also discloses a blood diagnosis reagent for diagnosing tumors. The blood diagnosis reagent comprises the PAD1 antibody, a horseradish peroxidase-immunoglobulin G (HRP-IgG) antibody and conventional reagents in the blood diagnosis reagent, wherein the conventional reagents in the blood diagnosis reagent include a carbonate buffer solution, a phosphate buffer solution-Tween (PBST) lotion, a blocking solution, developing solutions and a stop solution. PAD1 is found for the first time to be capable of being applied as a tumor blood marker. Experiments prove that PAD1 has feasibility as the tumor marker.
Owner:SHANDONG XINCHUANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
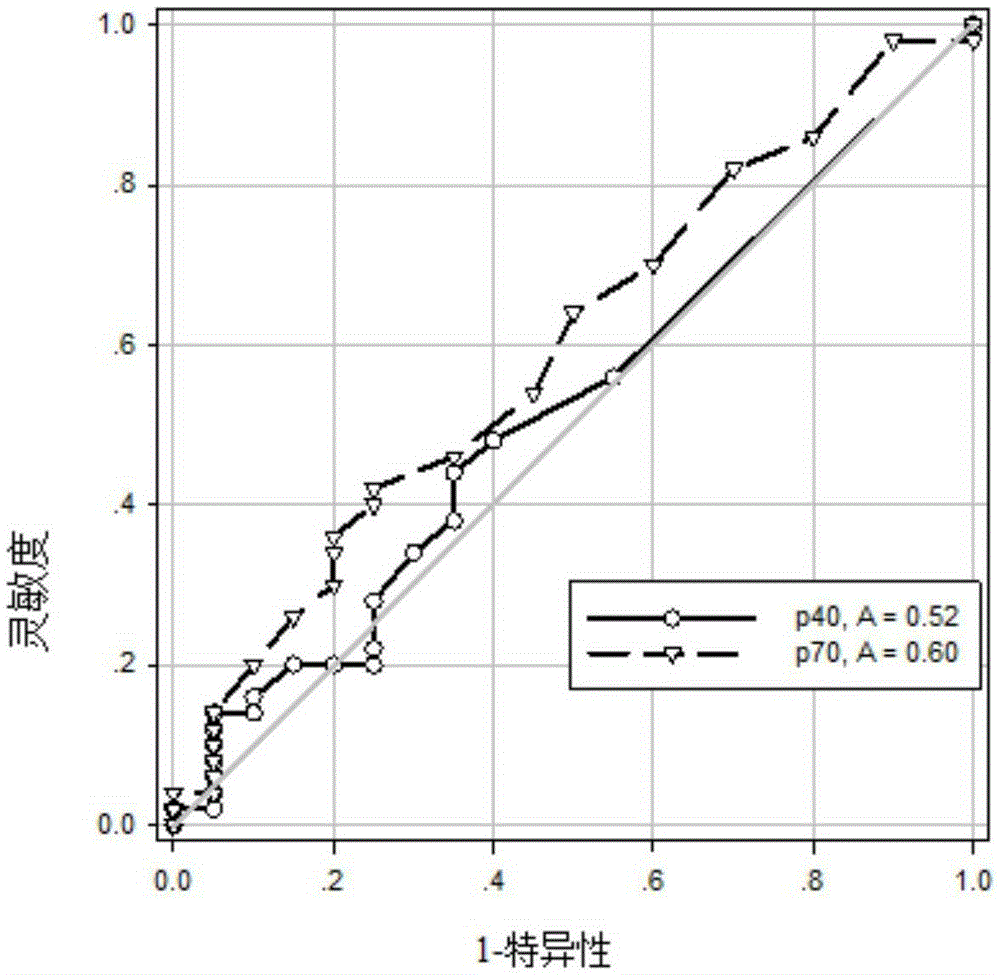
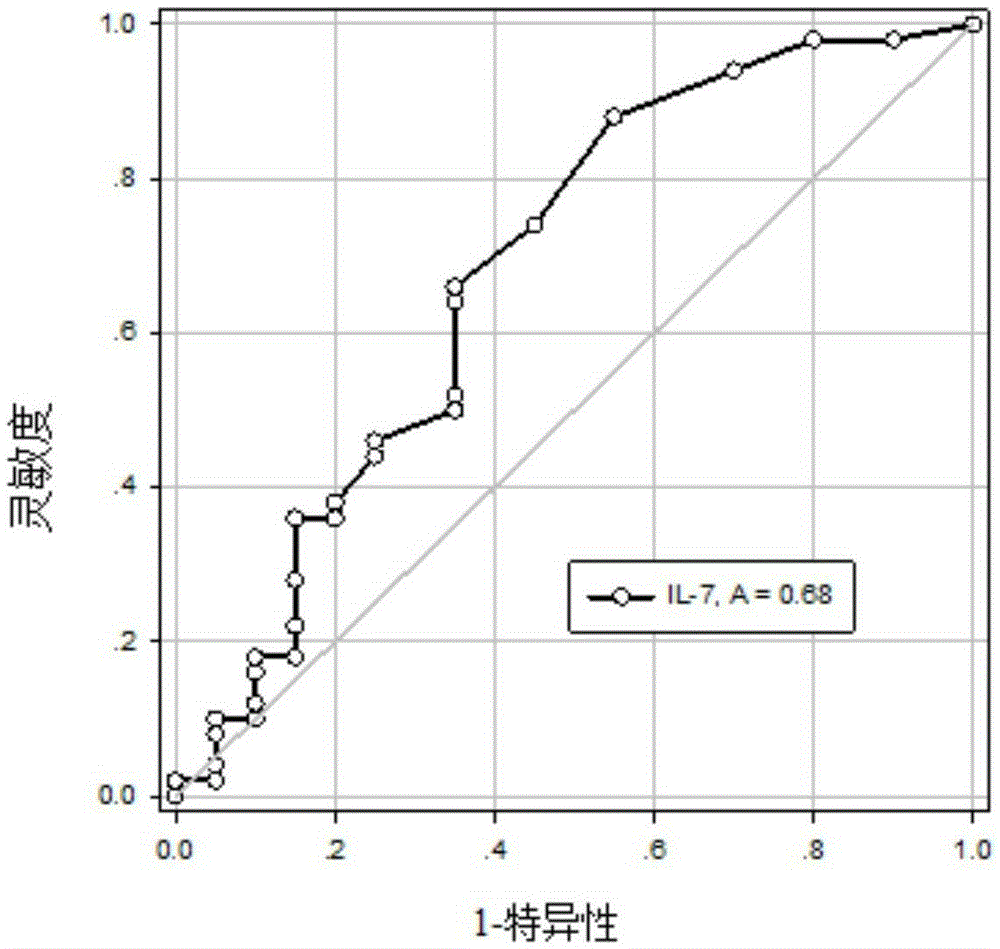
Use of Alzheimer's disease marker
InactiveCN105353135AEasy to sampleFlaws Addressing Limitations of Invasive Diagnostic SamplingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMedicine.hematologyBlood marker
The invention discloses a use of a reagent for measuring an Alzheimer's disease (AD) marker in preparation of a kit for detecting a tested object suffering from Alzheimer's disease, wherein the Alzheimer's disease marker is at least one of IL-12 (P40), IL-12 (P70), VEGF, sCD40L, GRO and IL-7, and a new blood marker is provided for diagnosis or differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides the kit for combined detection of the VEGF marker and the sCD40L marker; especially for senile patients, the kit is convenient to use, has the characteristics of no invassiveness and low test cost, can directly perform peripheral blood tests, has no need of collection of cerebrospinal fluid, relieves patient sampling pain, also has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity and good clinical diagnostic value, and lays a foundation for realization of hematology diagnosis of AD.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
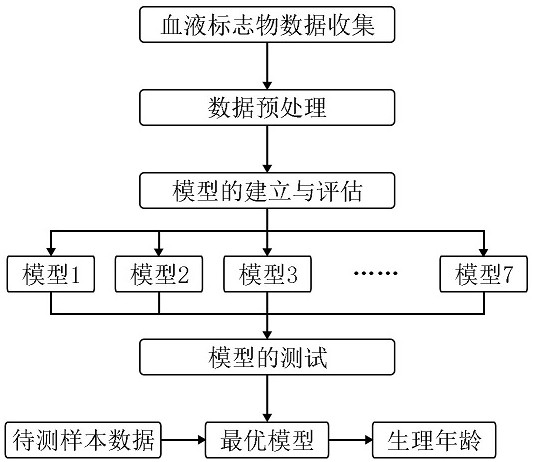
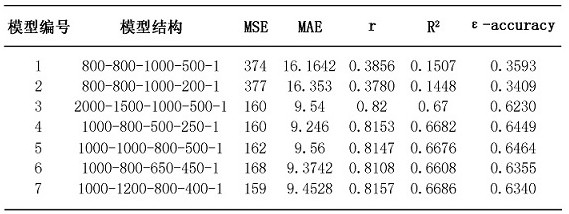
Method for predicting age by using blood marker
InactiveCN112466402AExplain aging levelsHigh calculationBiostatisticsNeural architecturesBlood markersHematological test
The invention relates to the field of biological information, and discloses a method for predicting age by using a blood marker, which comprises the following four steps of: collecting blood marker data, preprocessing the data, establishing and evaluating a model and testing the model. Compared with other methods and markers, the method has the advantages that the blood marker serves as an evaluation object of the physiological age, the individual aging condition can be reflected more comprehensively, the aging level can be explained more comprehensively, meanwhile, the selected blood marker is predicted through the machine learning model, the process is more intelligent, and the result is more accurate; the selected blood marker, namely a blood biochemical index, is the most common indexin clinical and physical examination institutions, and is low in acquisition difficulty, low in cost and high in interpretation degree.
Owner:天津奇云诺德生物医学有限公司
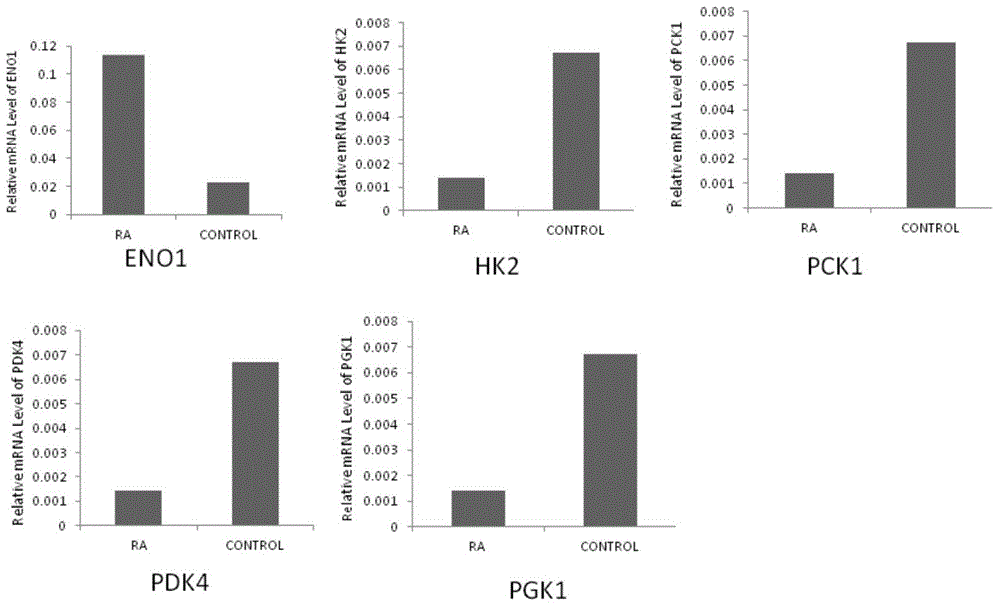
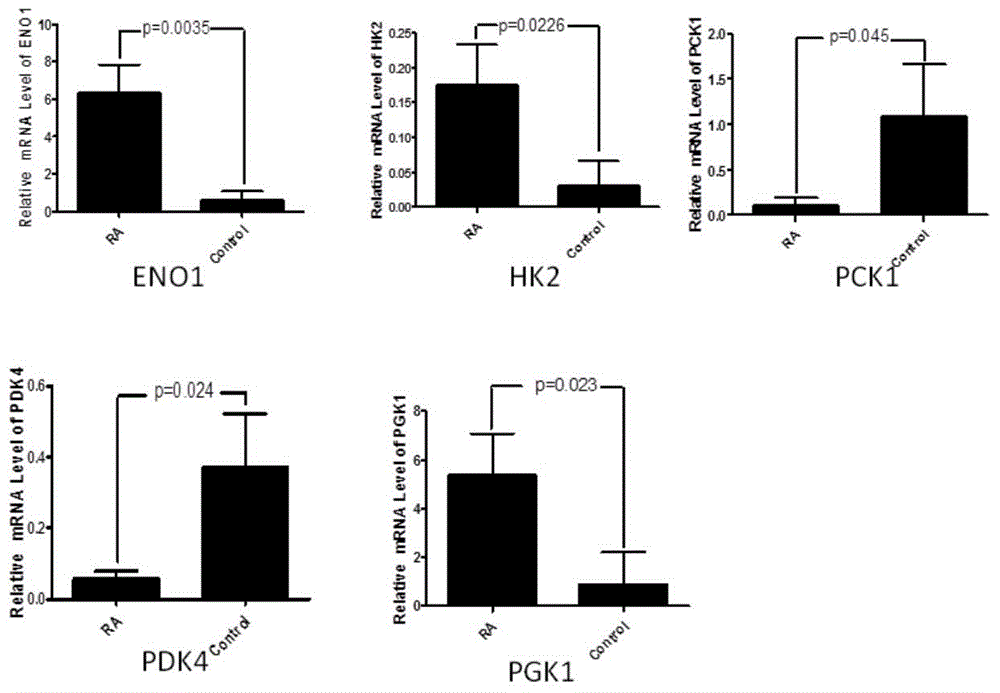
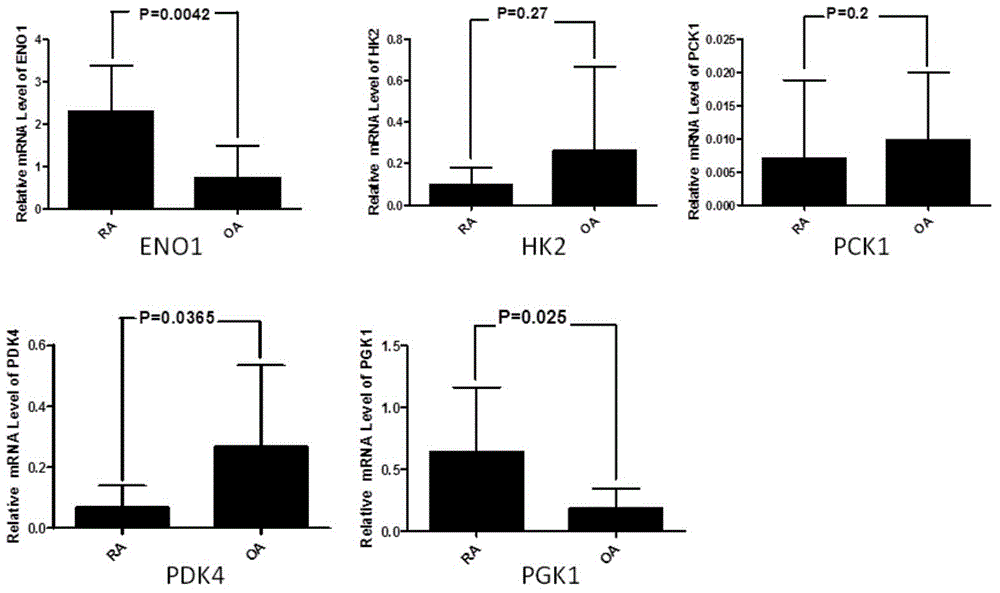
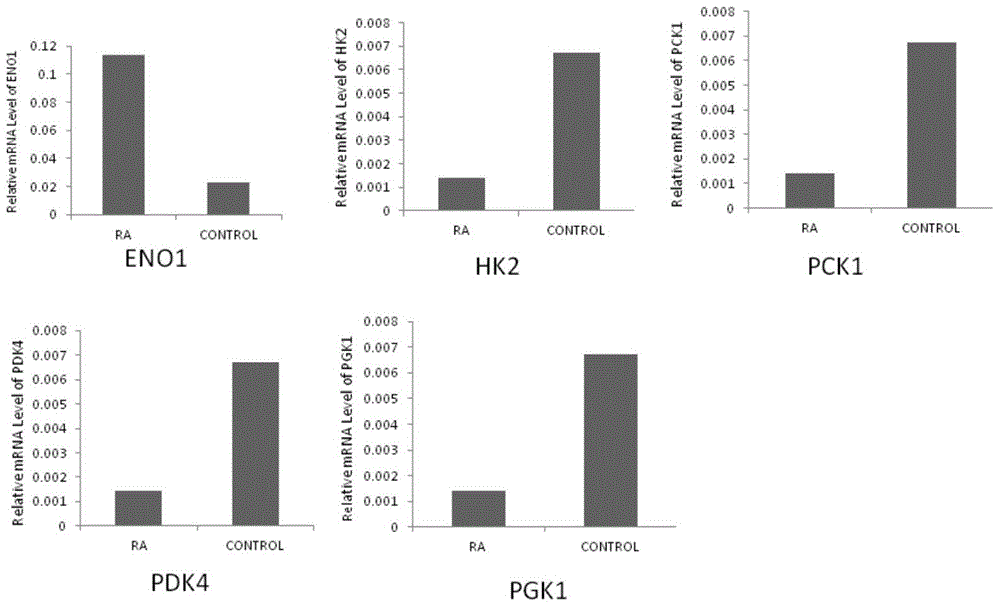
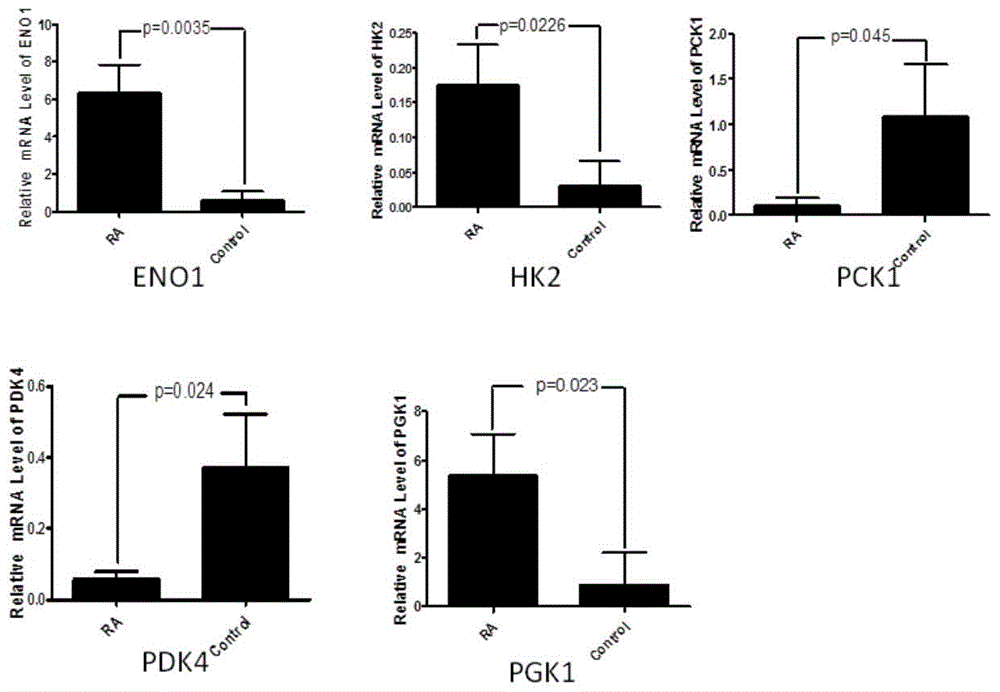
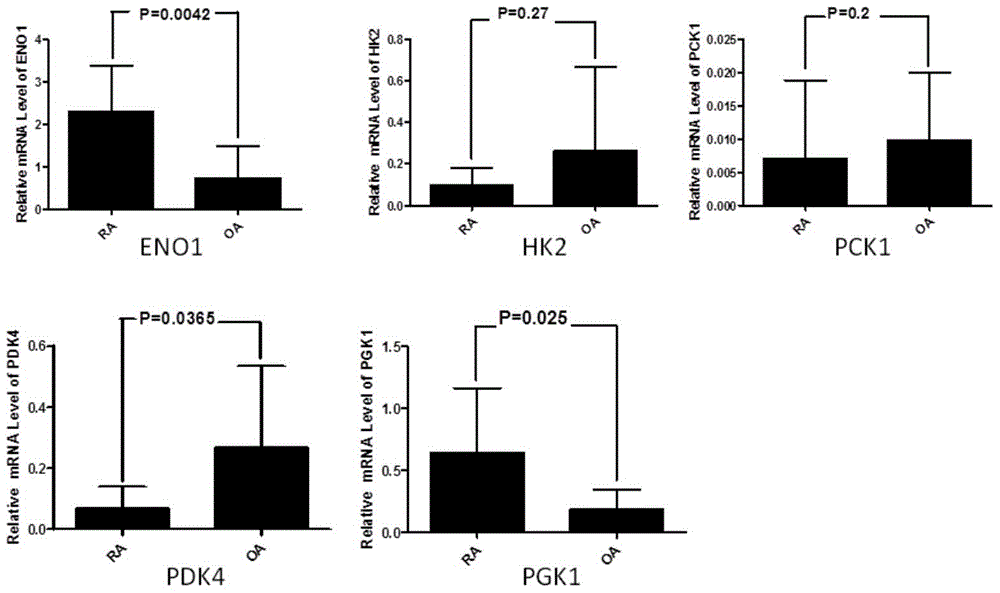
Application of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 to preparation of rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis reagent
InactiveCN104698194AImprove expression levelUnderstanding PathogenesisDisease diagnosisBiological testingPhosphoglycerate mutaseRheumatoide arthritis
The invention discloses a blood marker-PGK1 for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis, and discloses a reagent for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis. The reagent comprises a PGK1 antibody, an HRP-IgG antibody and a conventional reagent in a blood diagnosis reagent. The conventional reagent in the blood diagnosis reagent comprises a carbonate buffer solution, PBST washing liquor, confining liquid, a developing solution and a stop solution. The prepared detection reagent has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in specificity and the like and is capable of being widely applied to preliminary survey and health examination of clinical rheumatoid arthritis and providing a reliable basis for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:常晓天
Cellular markers for diagnosis of alzheimer's disease and for alzheimer's disease progression
The present invention provides methods for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and for determining the efficacy of a treatment for Alzheimer's disease in an Alzheimer's patient, i.e., monitoring Alzheimer's disease progression, utilizing cellular blood markers; as well as kits for carrying out these methods.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
Blood markers for lung cancer predisposition
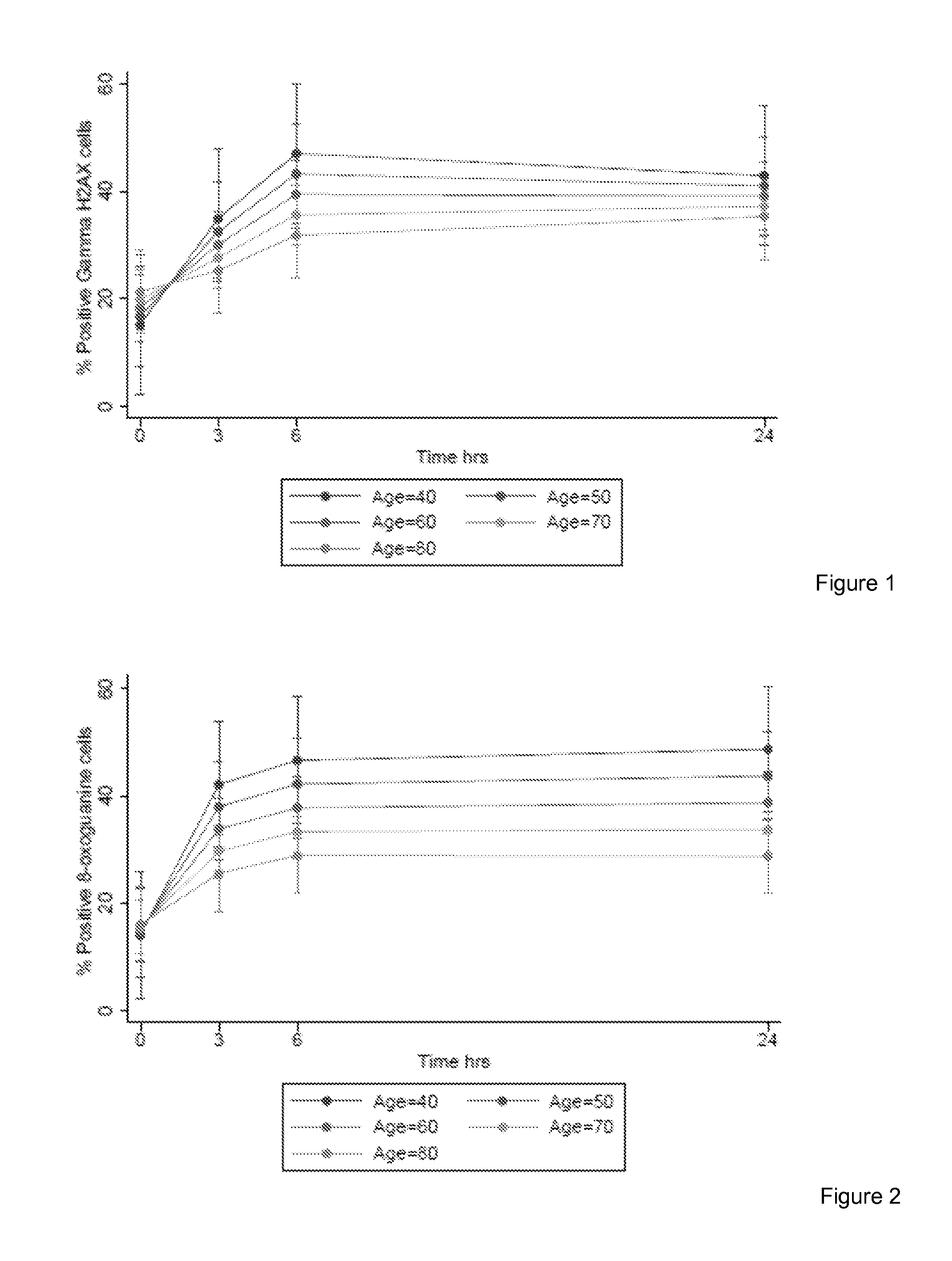
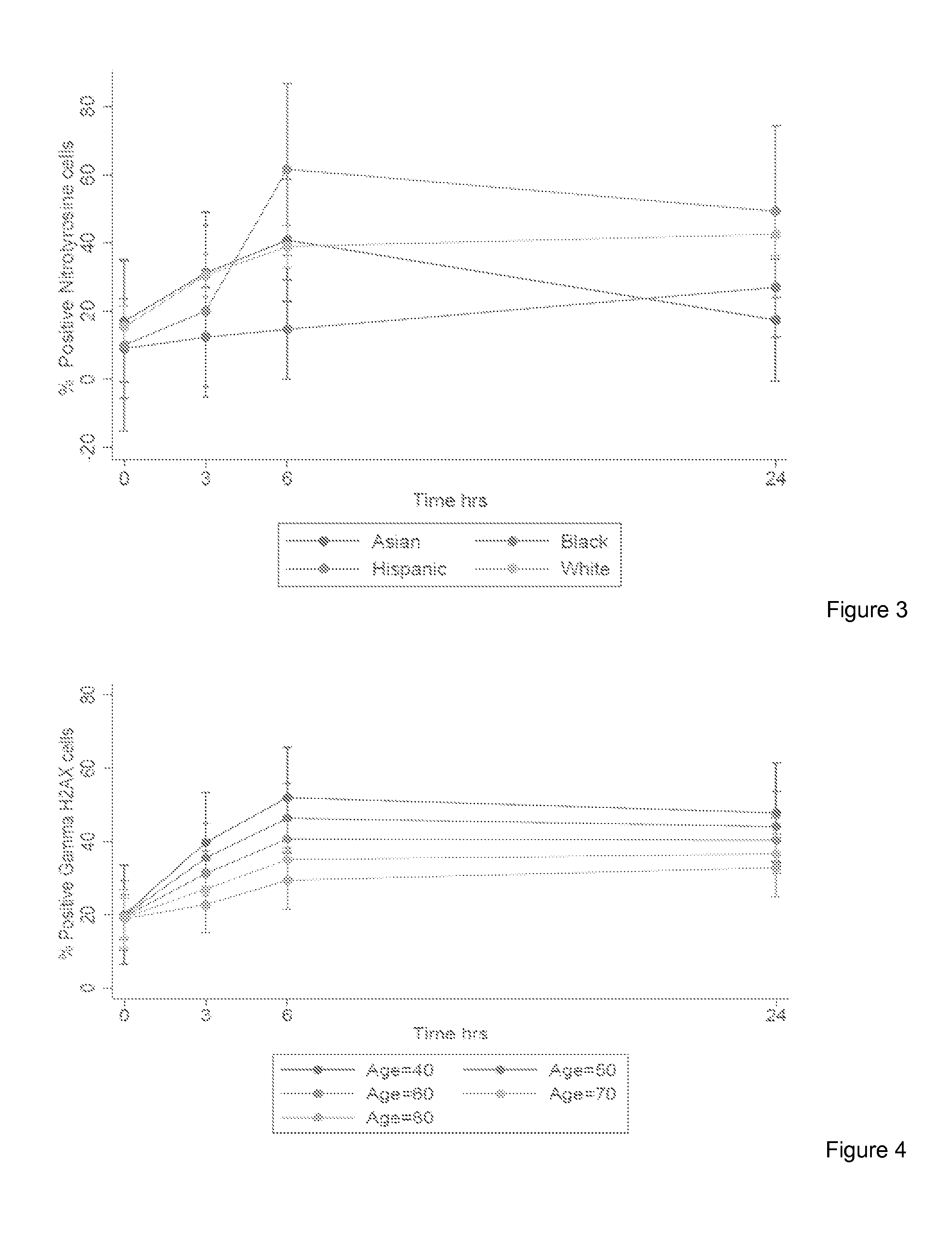
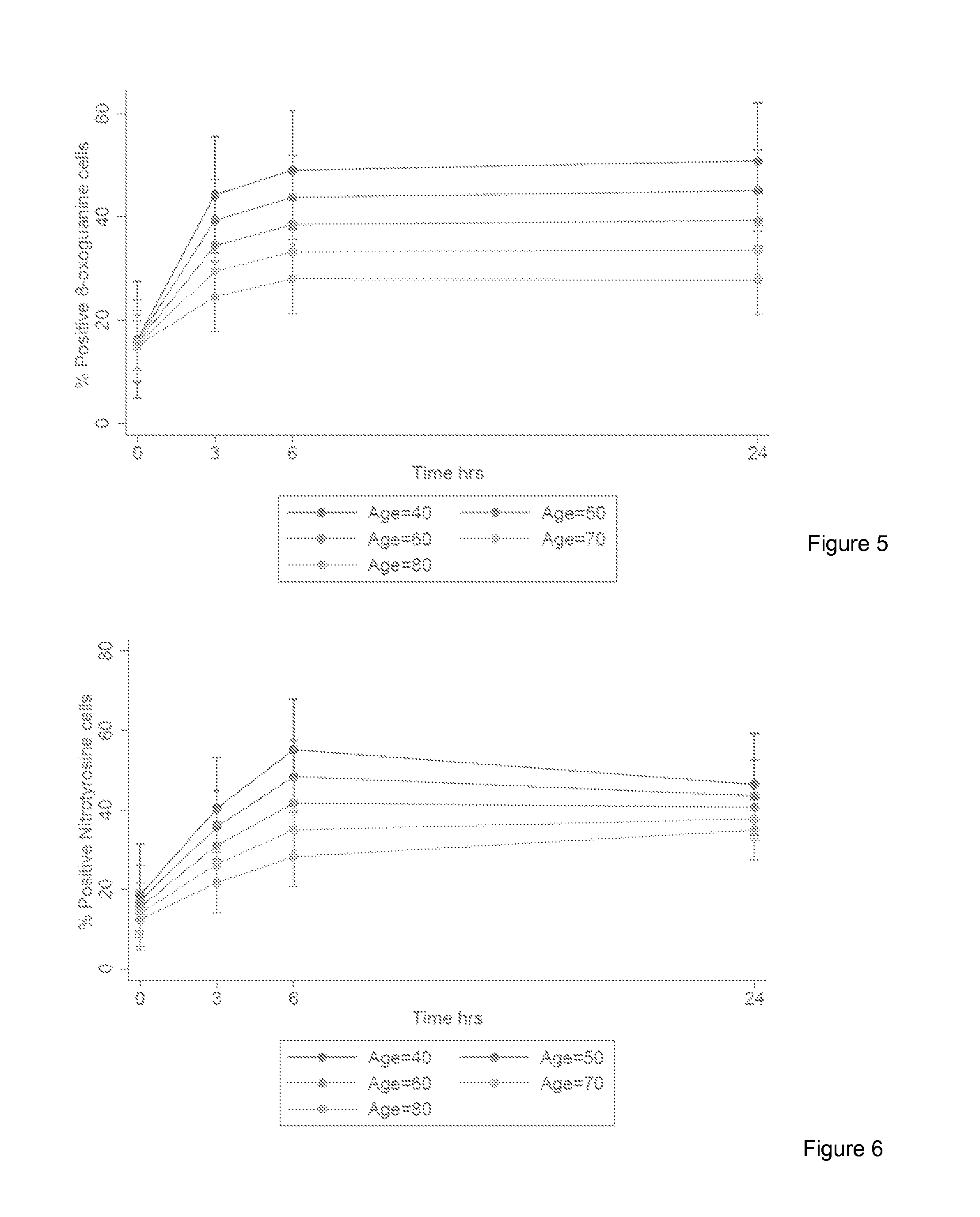
InactiveUS20150323539A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWhite blood cellWhole body
The invention provides a method for detection of lung cancer, or predisposition to lung cancer, in a subject that comprises assaying a test sample of peripheral blood from the subject for a marker of DNA damage. An elevated amount of marker present in the test sample compared to control sample is indicative of lung cancer, or predisposition to lung cancer. The method can be adapted for quantitatively monitoring the efficacy of treatment of lung cancer in a subject. Markers of DNA damage include single- and / or double-stranded breaks in leukocytes, oxidative DNA damage in leukocytes, or a marker of nitrotyrosine oxidative activity (protein nitrosylation in leukocytes). This unexpected discovery of markers of systemic genotoxicity that can be tested using circulating leukocytes enables detection of lung cancer, or predisposition to lung cancer, with a relatively simple and minimally invasive assay using peripheral blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
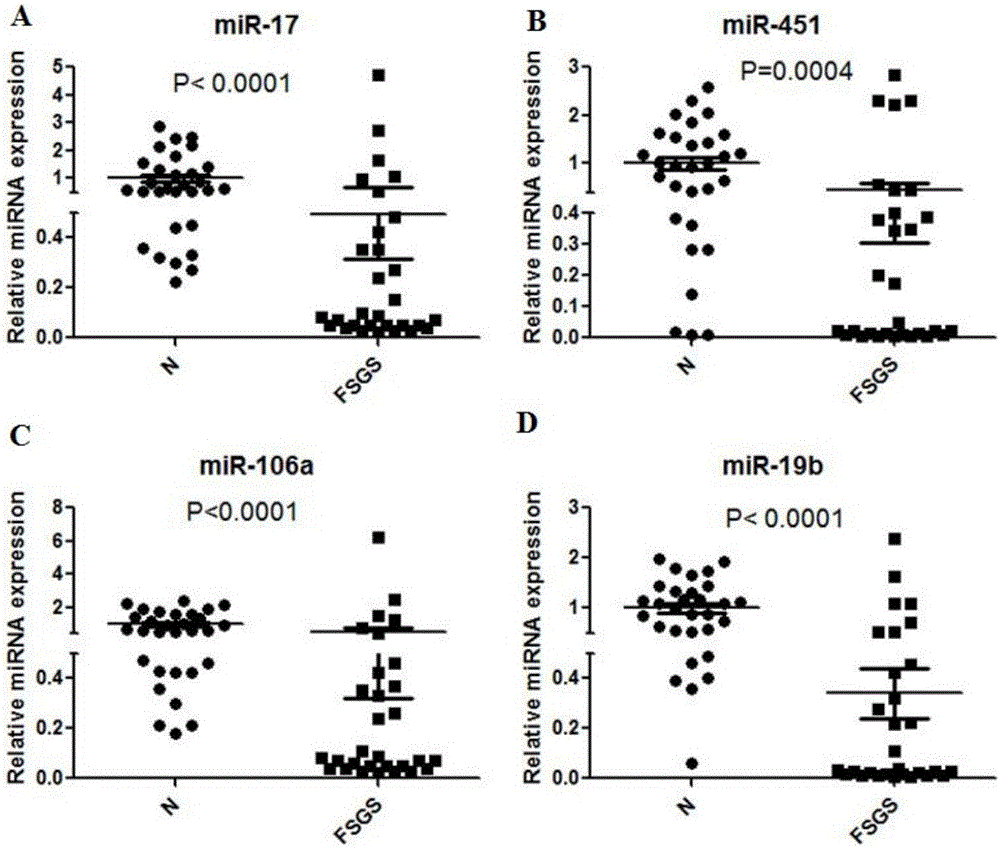
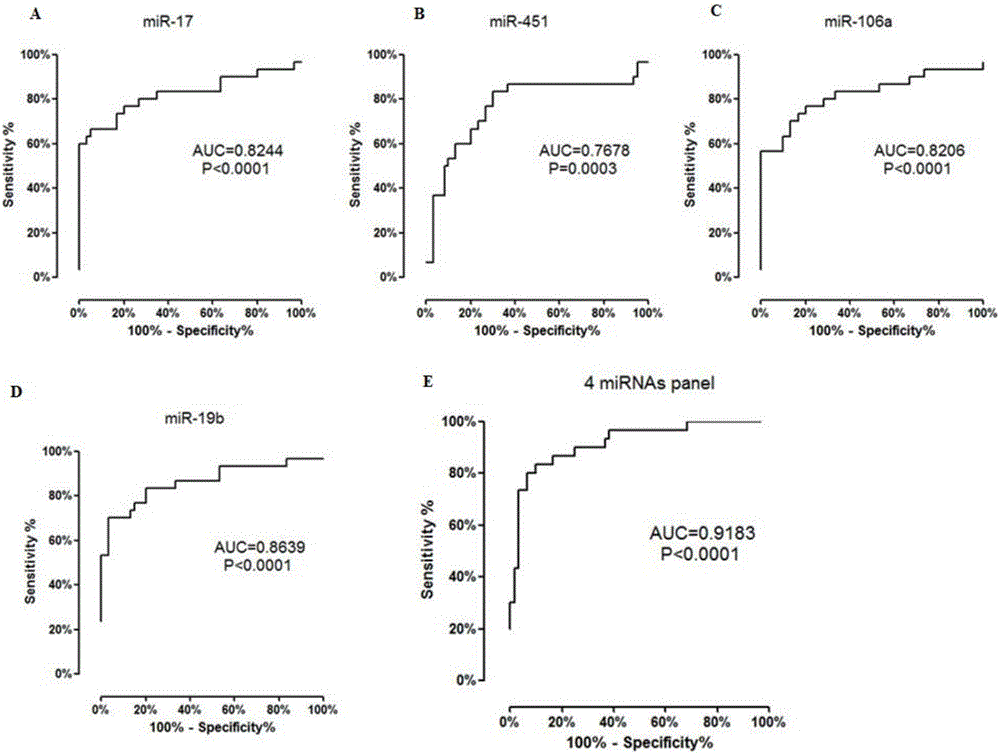
Markers for diagnosing and predicating focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
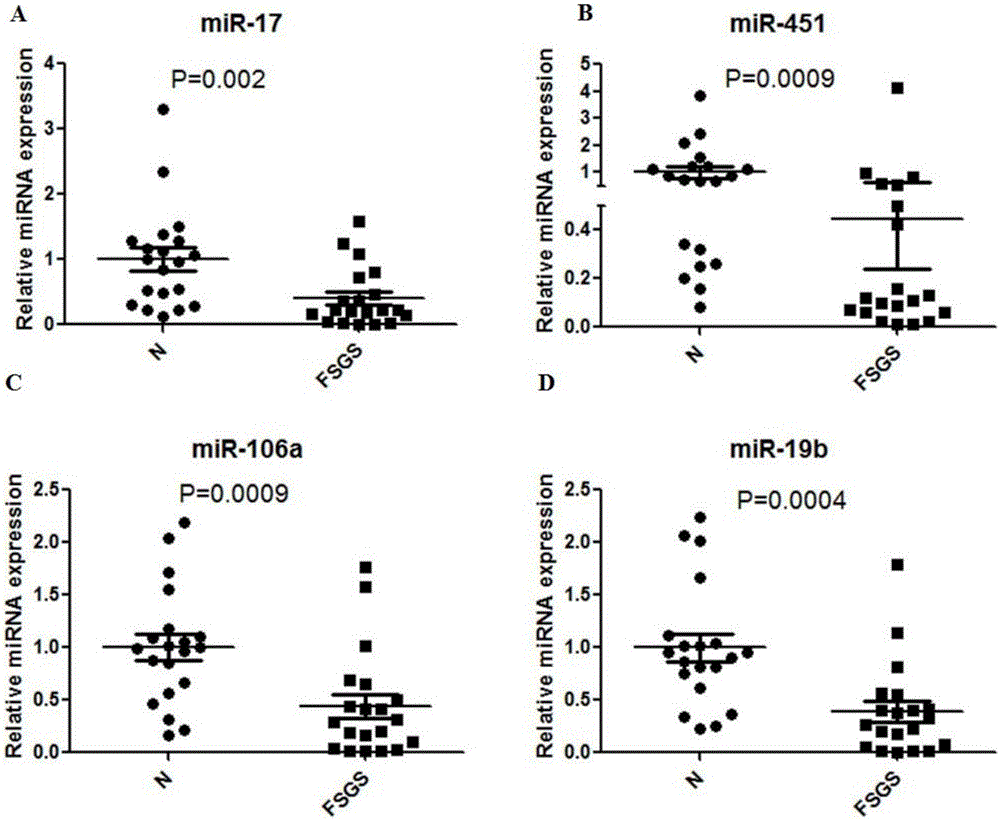
InactiveCN105779606AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicine.hematologyBlood marker
The invention discloses application of reagent of markers for detecting focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) to preparation of a kit for diagnosing and predicating focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, the focal segmental glomerulosclerosis markers are one or more of miR-17, miR-451, miR-106a and miR-19B, By means of the markers for diagnosing and predicating focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, new blood markers are provided for clinical diagnosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, peripheral blood testing can be directly conducted, and the markers have the advantages of being good in specificity and high in sensitivity, have good clinical diagnosis value and lay a foundation for implementation of hematology diagnosis of FSGS.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
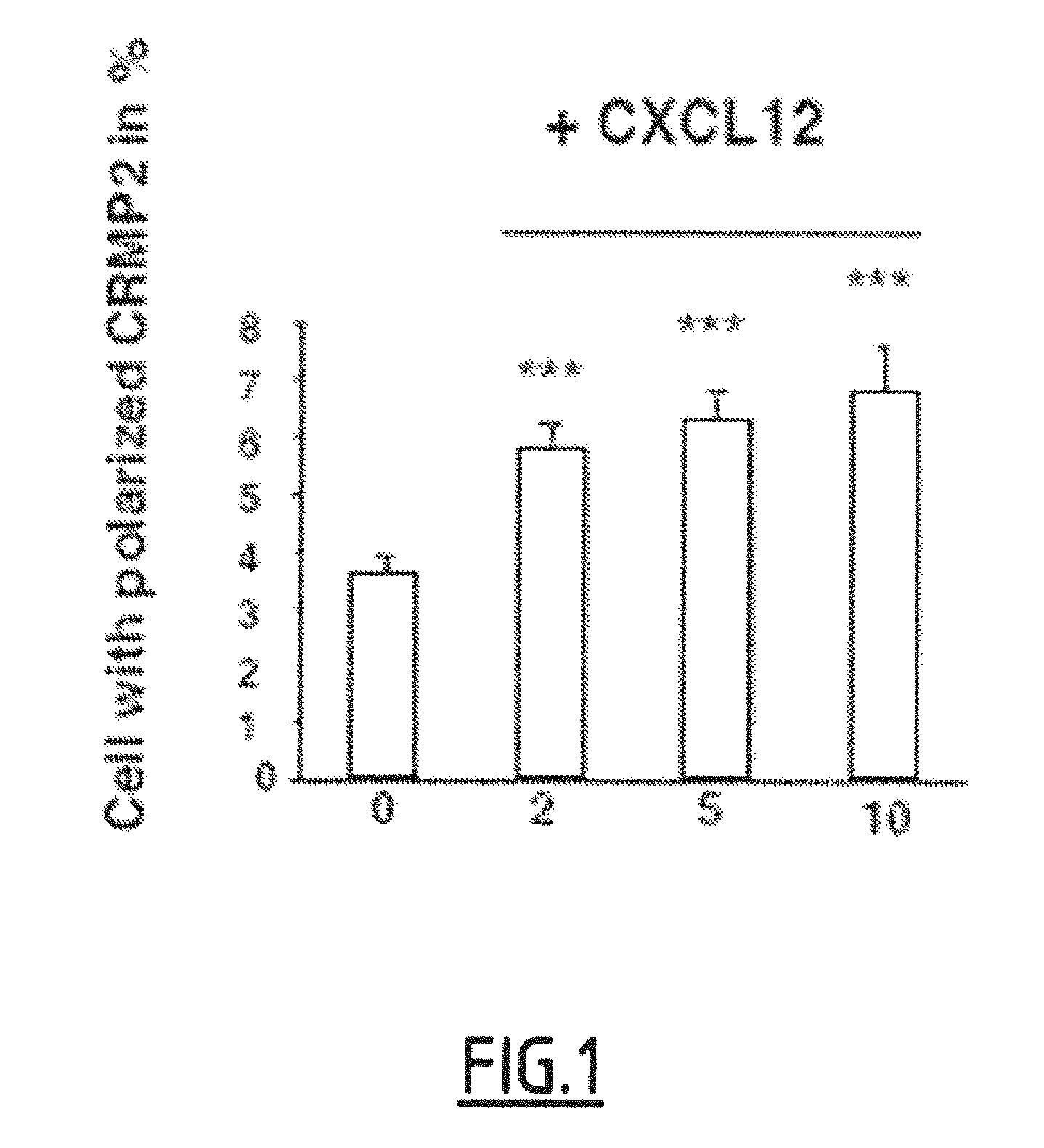
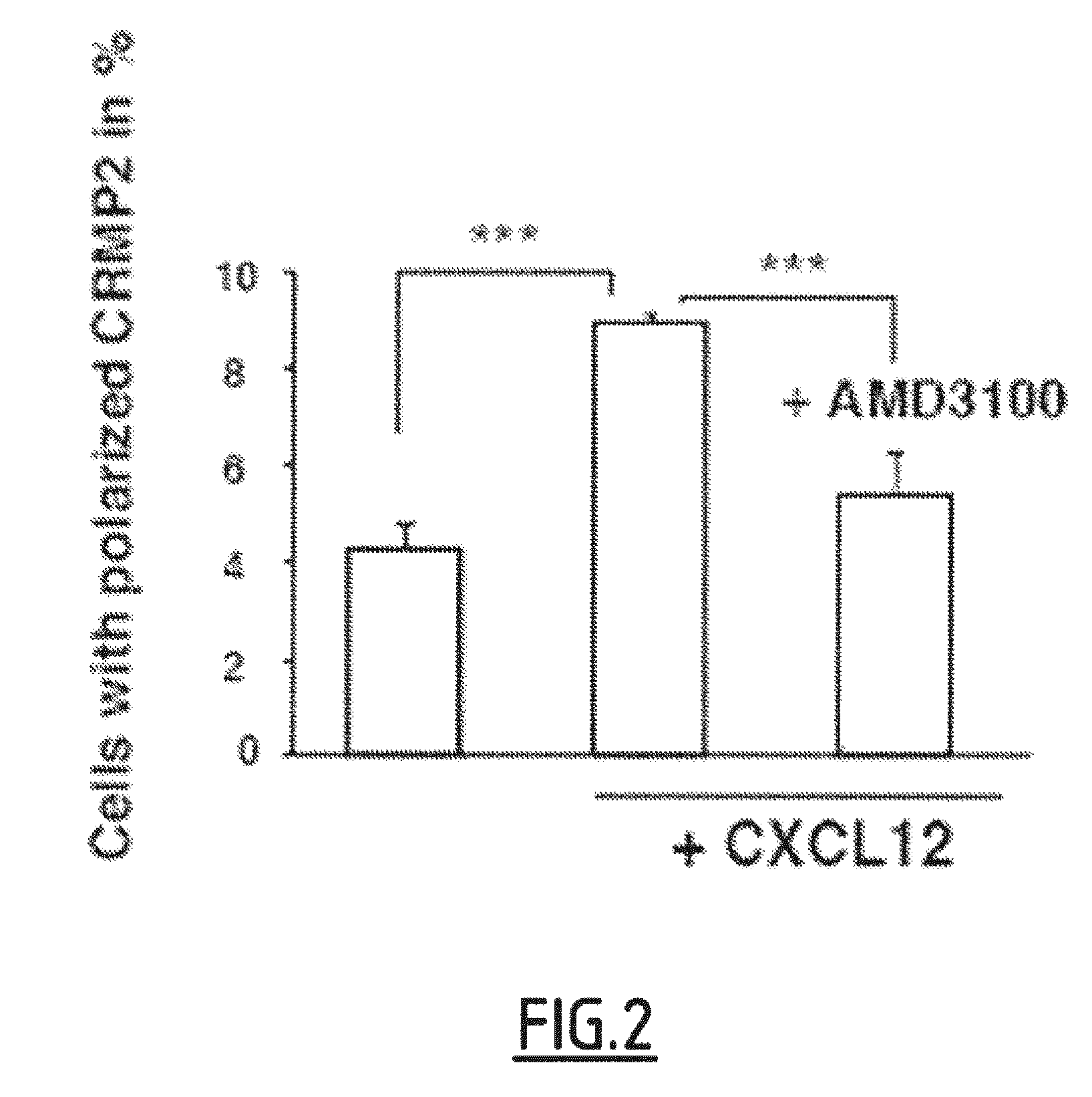
Cleaved and Phosphorylated CRMP2 as Blood Marker of Inflammatory Diseases of the Central Nervous System
InactiveUS20120135009A1Reduce decreaseEasy to detectAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderAnserinePhosphorylation
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro prognosis, diagnosis and / or monitoring of an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system in a subject, said method comprising detecting, in a sample of cells of the immune system from the subject, the presence of a Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 2 (CRMP2) which is phosphorylated on tyrosine 479 (Y479), and optionally further phosphorylated on serine 465 (S465), wherein the detection of the presence of Y479-phosphorylated CRMP2, which is optionally further phosphorylated on serine 465, is indicative of an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Liver disease-related methods and systems
InactiveUS7668661B2Easy diagnosisFacilitates pointMicrobiological testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsDiseaseHepatic Diseases
The invention provides diagnostic methods, kits, and systems, and related computer-readable media, which use multiple blood marker values, including serum and plasma marker values, to aid in the diagnosis of the status or progress of a liver disease in a patient.The invention also provides methods and systems, and related computer-readable media, that use blood marker values, including serum and plasma marker values: (1) to screen for active ingredients useful in the treatment of a liver disease; (2) to aid in the selection of treatment regimens for patients that are predisposed to, or suffer from, liver disease; and (3) to aid in the design of clinical programs useful in monitoring the status or progress of liver disease in one or more patients.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methods and materials for detecting colorectal neoplasm
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Pluripotent stem cells characterized by expression of germline specific genes
InactiveUS20100297087A1Efficient identificationEffective isolationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementInduced pluripotent stem cellPlant Germ Cells
The present invention relates to pluripotent or multipotent somatic stem cells characterized by the expression of the germline specific gene, DAZL. The somatic stem cells expressing the DAZL marker are further characterized by expression of additional markers and absence of expression of certain blood markers. In particular, the present invention discloses therapeutic and diagnostic uses, other than the germ cell potential use, of the DAZL pluripotent or multipotent stem cells isolated from adult or peripheral somatic sources such as peripheral blood, bone marrow or umbilical cord blood.
Owner:NANODIAGNOSTICS ISRAEL LTD
Method of predicting gender by using blood marker
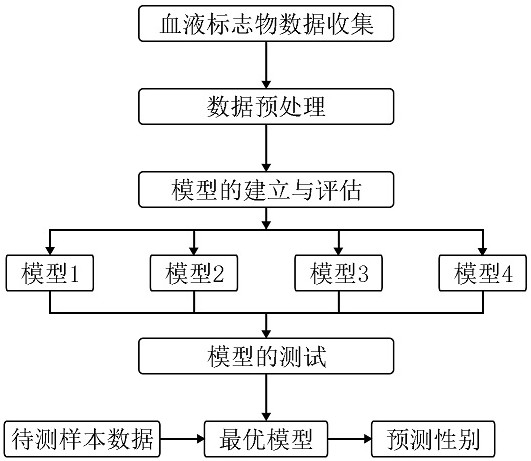
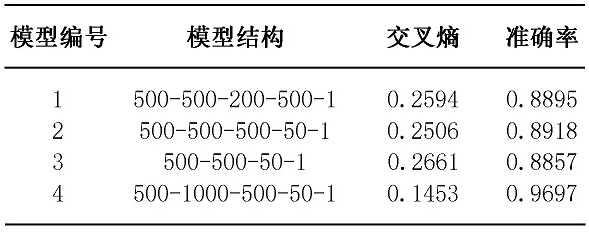
InactiveCN112485162ALow costMake it easier to getBiological particle analysisBiological testingBlood markersHematological test
The invention relates to the field of biological information, and discloses a method for predicting gender by using a blood marker. The method comprises the following four steps of: collecting blood marker data, preprocessing the data, establishing and evaluating a model and testing the model. Compared with other methods and markers, the selected blood marker, namely a blood biochemical index, isthe most common index in clinical and physical examination institutions, the acquisition difficulty is low, the cost is low, and meanwhile, a machine learning model is used for calculating the selected blood marker, so that the process is more intelligent, and the result is more accurate.
Owner:天津奇云诺德生物医学有限公司
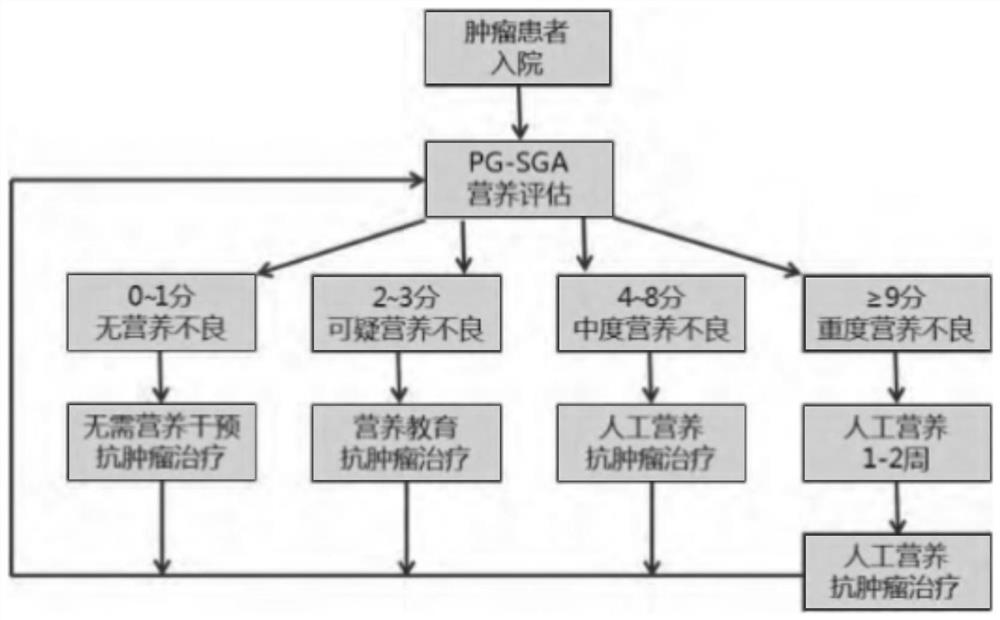
P16-based lung cancer postoperative comprehensive rehabilitation management method
PendingCN114520049AImprove prognostic quality of lifePrognosis Quality of Life AssuranceMedical communicationHealth-index calculationBlood markersNutrition
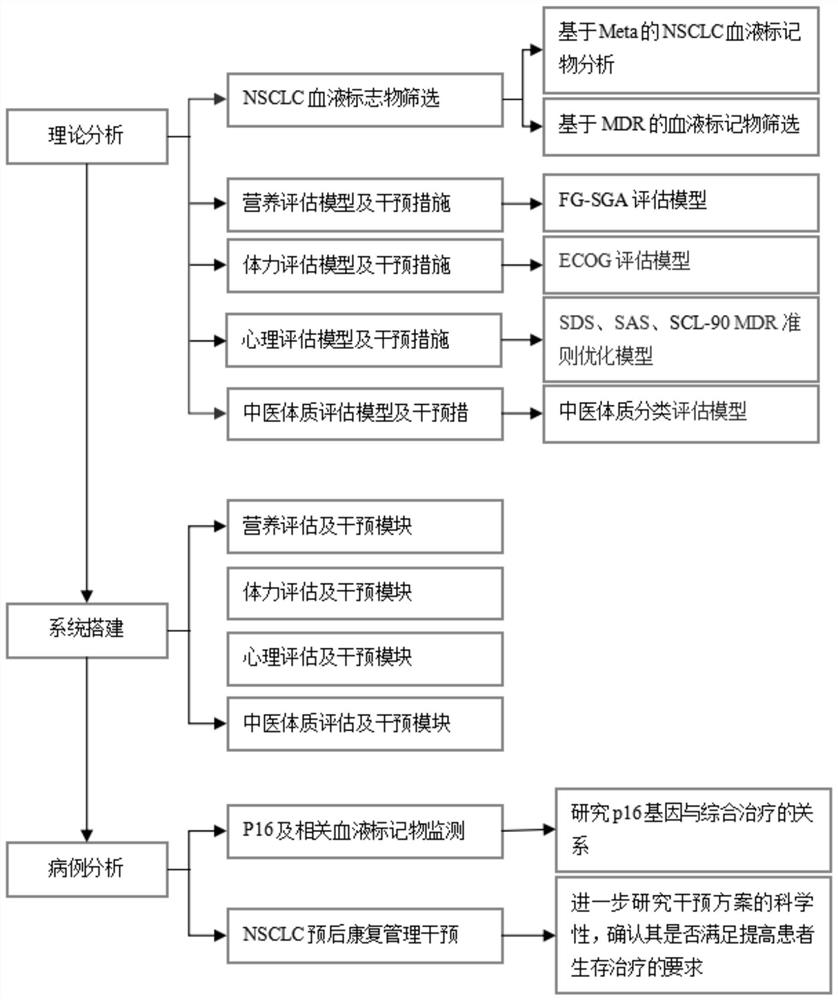
The invention discloses a P16-based lung cancer postoperative comprehensive rehabilitation management method, which comprises a theoretical analysis module, a system establishment module, a case analysis module and PG-SGA nutrition assessment. The theoretical analysis module comprises NSCLC blood marker screening, a nutrition evaluation model and intervention measures, a physical strength evaluation model and intervention measures, a psychological evaluation model and intervention measures, and a traditional Chinese medicine constitution evaluation model and intervention measures, and the NSCLC blood marker screening comprises Meta-based NSCLC blood marker analysis and MDR-based blood marker screening. The nutrition evaluation model and the intervention measure adopt an FG-SGA evaluation model, and the physical power evaluation model and the intervention measure adopt an ECOG evaluation model. According to the P16-based lung cancer postoperative comprehensive rehabilitation management method, after a patient is discharged from a hospital, the patient can evaluate personal nutrition, psychology, physical strength and other conditions anytime and anywhere through a mobile phone APP, and professional and normative intervention measures are obtained according to personal evaluation results without extra expenditure.
Owner:SHENZHEN HENGTAIKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Tumor blood marker and application thereof
The invention provides a tumor blood marker and an application thereof and particularly provides an application of a reagent for detecting GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) in a blood sample to preparation of composition for tumor screening, tumor risk assessment of a subject, tumor progression stage division, tumor curative effect identification and / or detection of tumor progression risk analysis. The invention further provides a kit and a detection method for GAPDH concentration of the blood sample.
Owner:SHANDONG ZEJI BIOTECH CO LTD
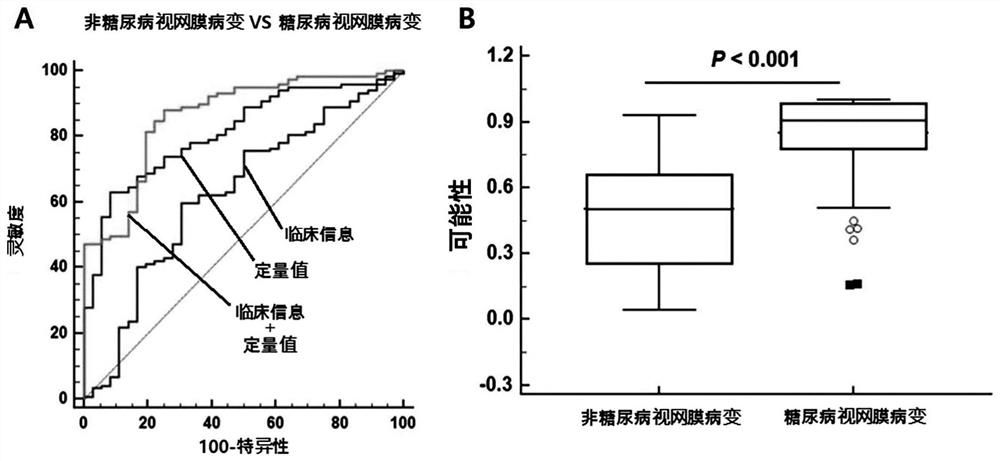
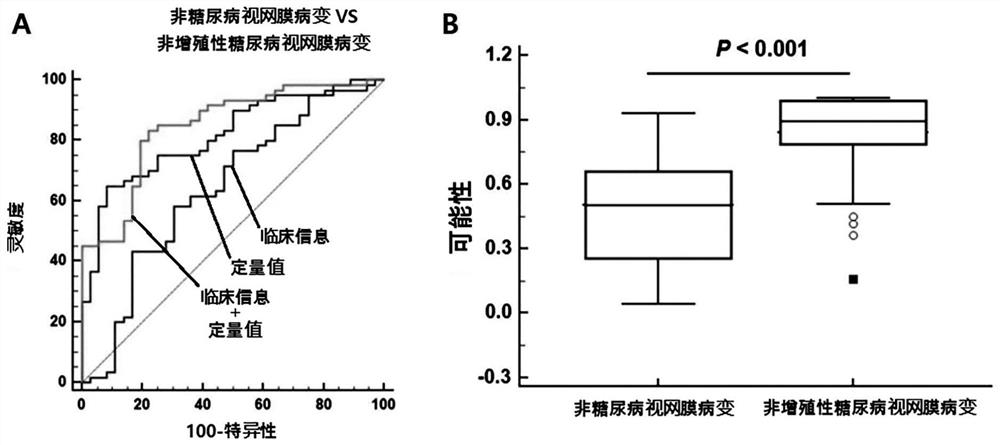
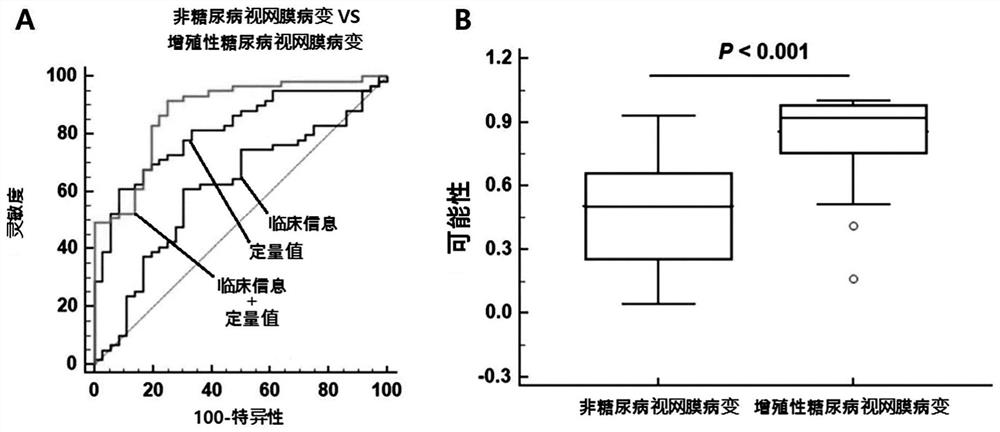
Composite marker for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and use thereof
PendingCN113544513AHigh sensitivityEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiabetes retinopathyBlood markers
The present invention relates to a composite marker for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and a use thereof and, more particularly, to a composite marker, for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy, comprising two or more blood markers specific for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and thus having an improved diagnostic performance. In addition, the present invention relates to a composition for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy, a diagnostic kit, and a method for providing information necessary for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, each of which uses the composite marker. The composite marker for diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy of the present invention was found to be superior to combinations of other markers in terms of sensitivity and diagnosis performance and to exhibit a high diagnostic potential for initial diabetic retinopathy, as analyzed for combinations between protein quantitation values of the composite marker and fundamental clinical information. In addition, the composite biomarker of the present invention does not use blood proteins for biopsy, but can conveniently perform analysis by means of patient plasma and thus can be advantageously applied to the early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy.
Owner:RETI MARK CO LTD
Multiplex detection kit for neonatal disease screening and preparation method and use method thereof
PendingCN113655227AEasy to detectAvoid quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMultiplexImmune profiling
The invention discloses a multiplex detection kit for neonatal disease screening and a preparation method and a use method thereof. The multiplex detection kit comprises a buffer solution, at least two reaction cups, acridinium ester marker microspheres, a calibration product, a quality control product, an excitation solution, a concentrated washing solution and a hemolytic agent, the reaction cup is a micropore of which the inner surface is coated with a target antibody or antigen conjugate; the target antibody or antigen conjugate is an anti-TSH antibody protein, thyroxine T4 coupled bovine serum albumin, 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone coupled bovine serum albumin and an anti-GAA antibody protein. According to the invention, one kit is used for combined screening of multiple (2-8) blood markers, so that the preparation work is greatly simplified, errors caused by manual operation are reduced, and the working efficiency is improved; the high performance of quantitative detection is ensured by applying a chemiluminescence labeling immunoassay technology and a fluorescence analysis method which take acridinium ester as a marker.
Owner:广州俊通生物科技有限公司
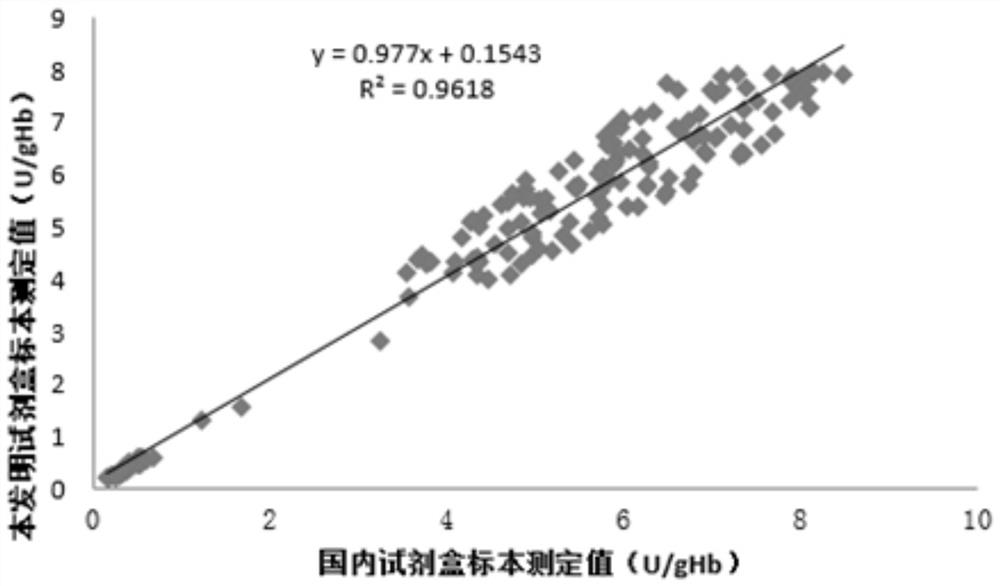
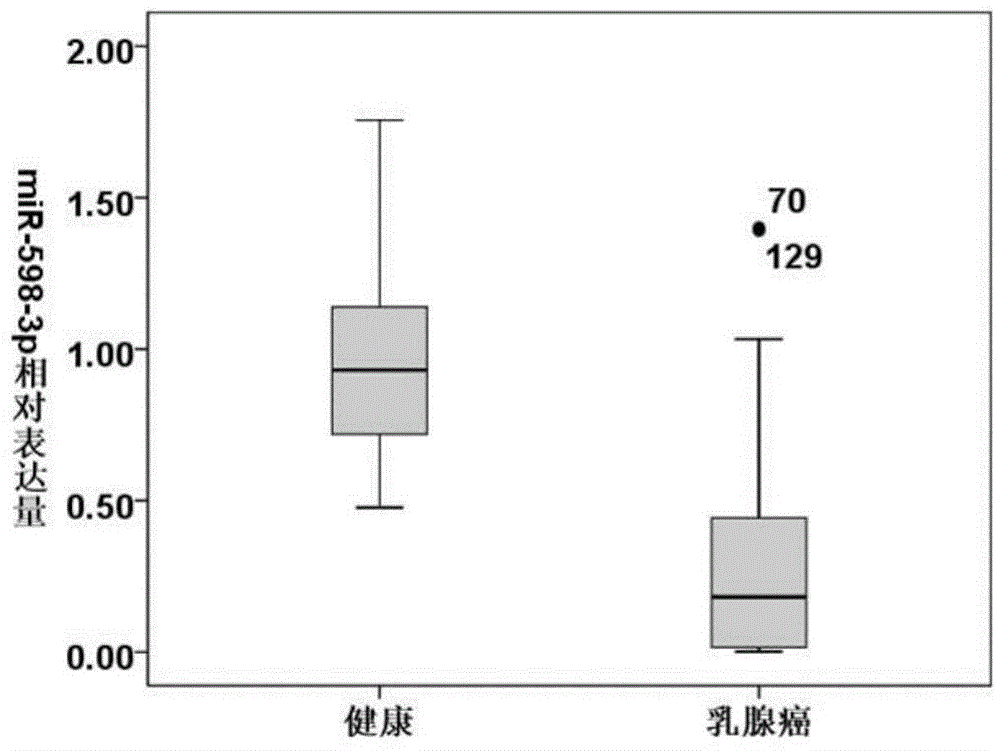
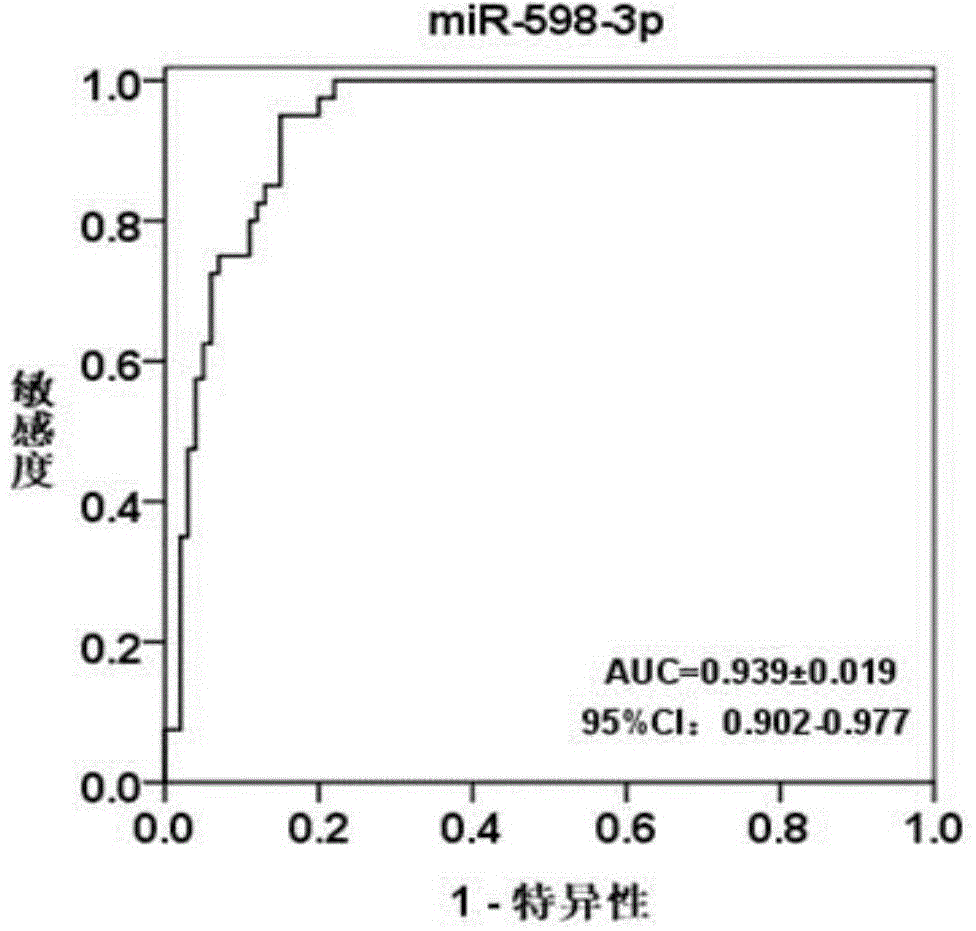
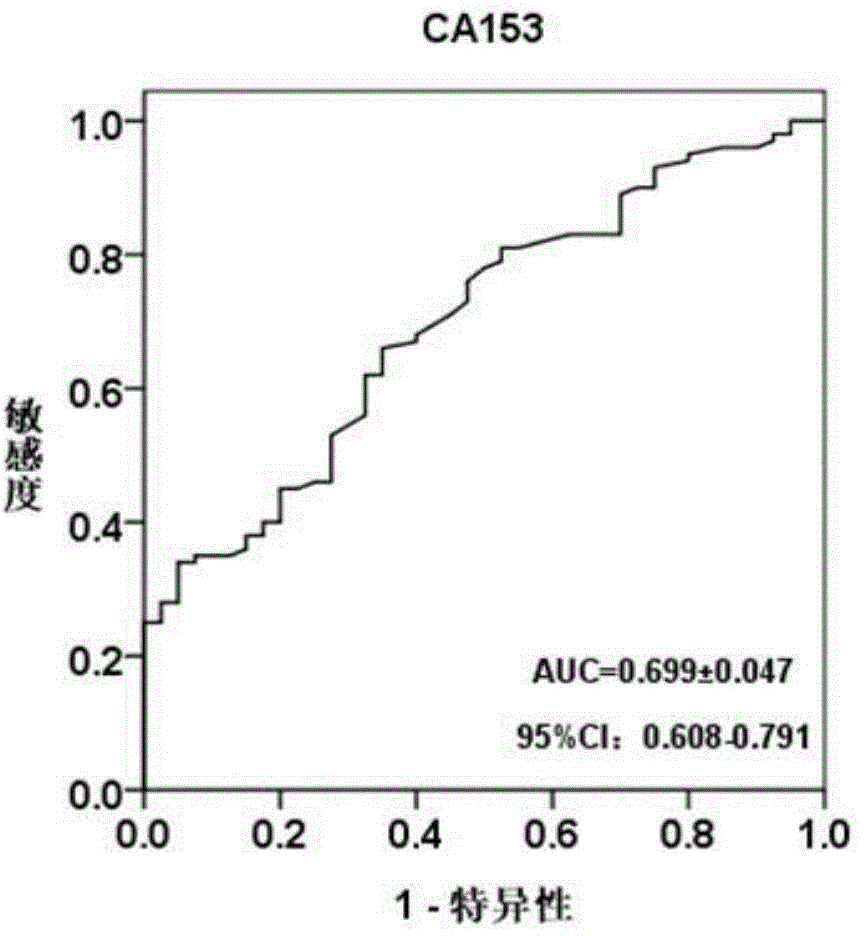
Blood serum marker related to human breast cancer and application of blood serum marker
InactiveCN104673921AIncrease contentStable in natureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSerum markersBlood marker
The invention discloses a blood serum miRNA (Micro Ribonucleic Acid) marker related to a breast cancer and an application of the marker. The marker is a combination of miR-598-3p or miR-598-3p and CA153. The marker and a primer of the marker can be used for preparing a diagnostic kit for early diagnosis of the human breast cancer.
Owner:李招云
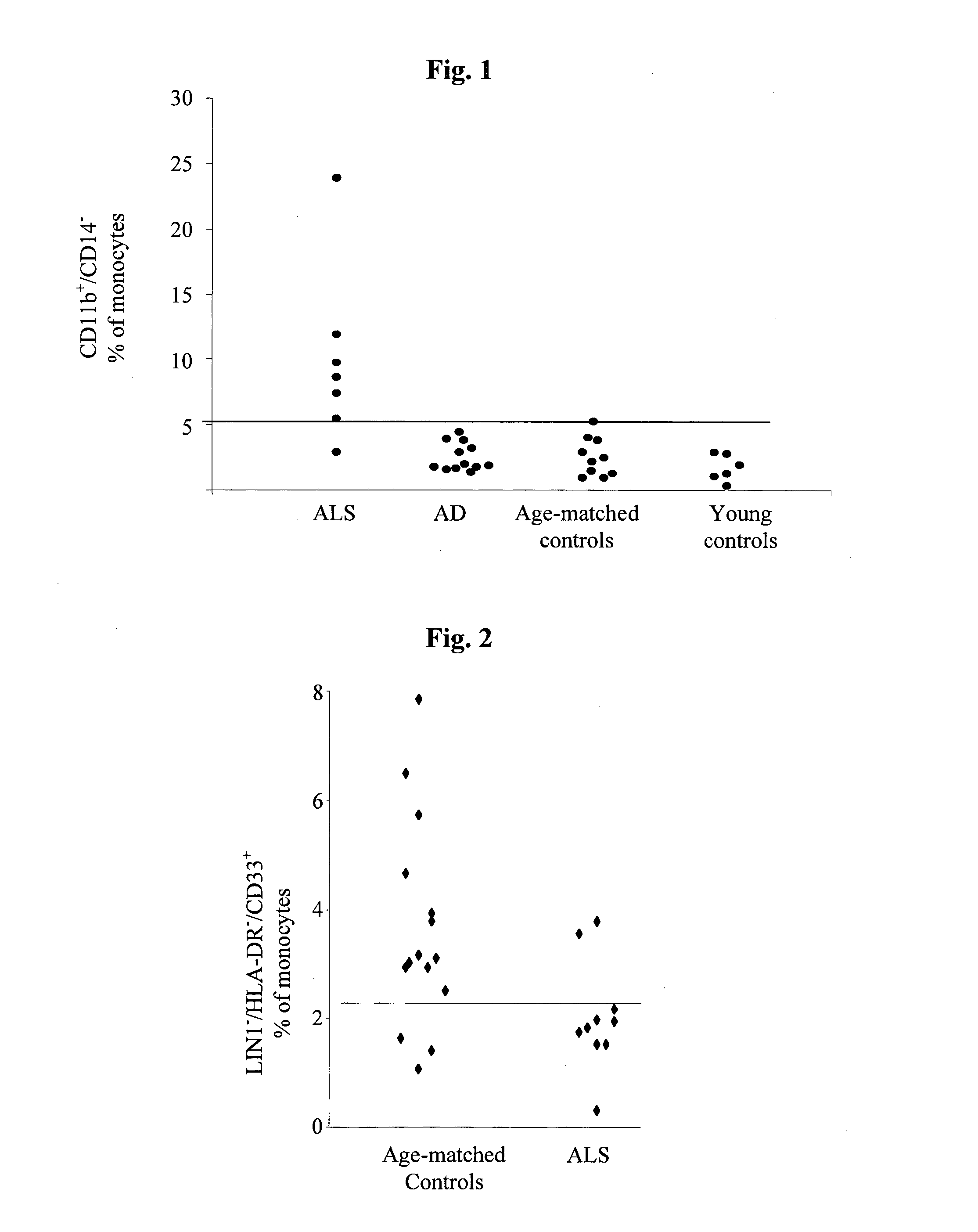
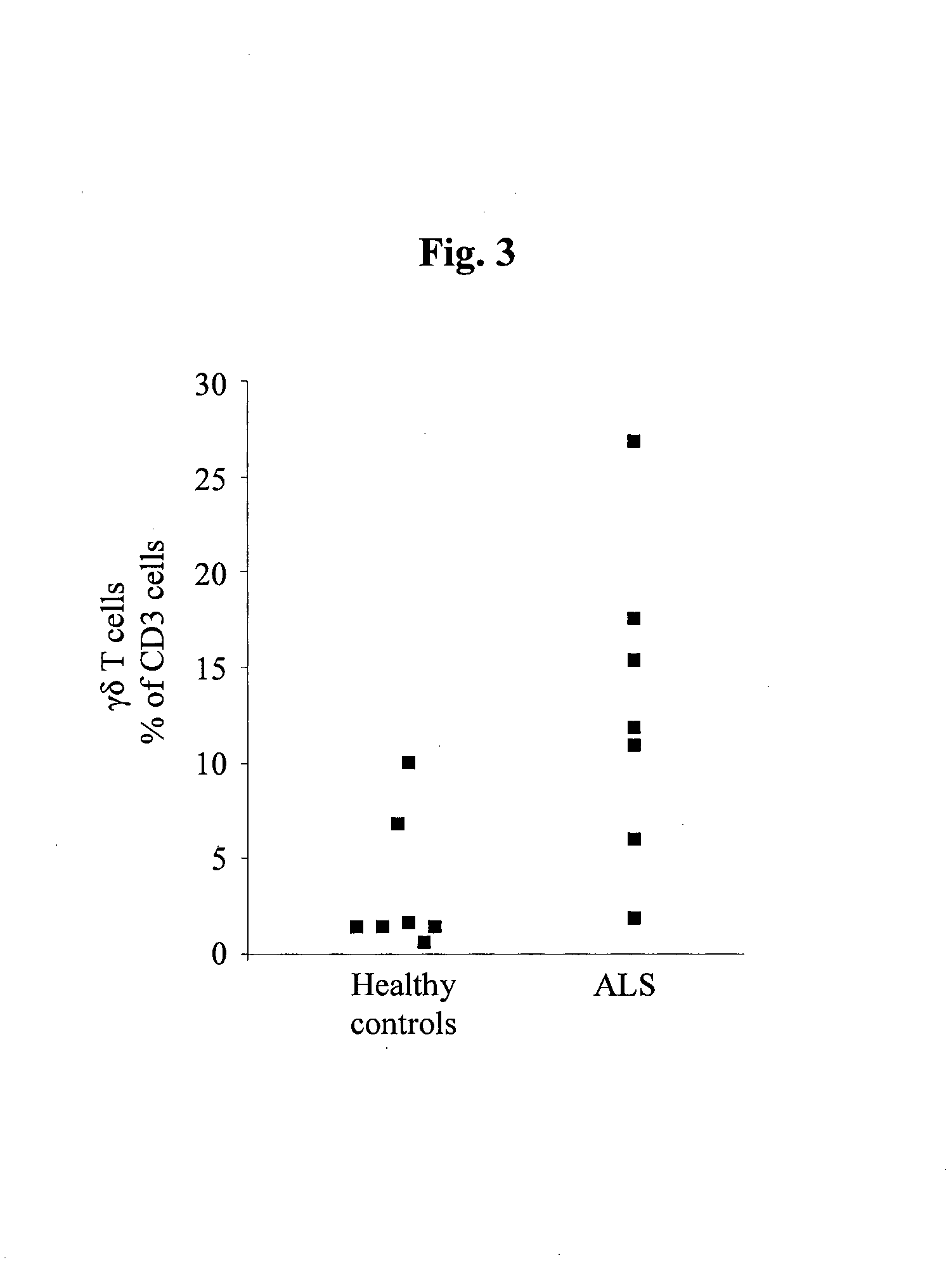
Cellular blood markers for early diagnosis of als and for als progression
InactiveUS20130230499A1Reducing myeloid derived suppressor cell levelBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsDiagnosis earlyBlood markers
The present invention provides methods for early diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and for determining the efficacy of a treatment for ALS in an ALS patient, i.e., monitoring ALS progression, utilizing cellular blood markers; as well as kits for carrying out these methods.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
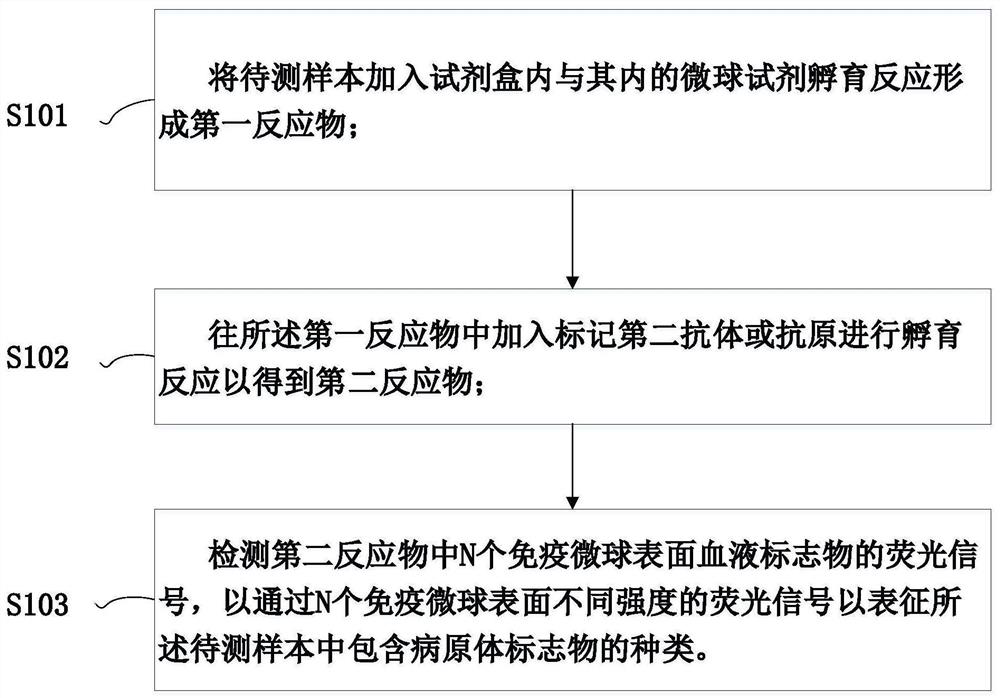
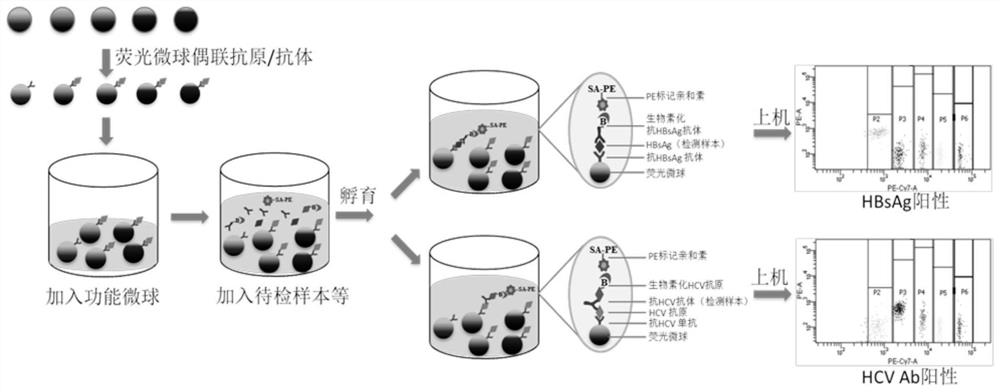
Kit and method for joint detection based on microspheres with different fluorescence intensities
PendingCN112763709AAdequate responseUniform responseBiological material analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigenBlood markers
The invention provides a kit for joint detection based on microspheres with different fluorescence intensities. The kit comprises a microsphere reagent, and a labeled second antibody or antigen; the microsphere reagent is N microspheres with the same diameter and different fluorescence intensity codes, the surfaces of the N microspheres are correspondingly coated with first antibodies or antigens of N blood markers, and N is an integer between 2 and 5; and the labeled second antibody or antigen comprises N second antibodies or antigens of blood markers, fluorescein is labeled on the second antibodies or antigens, and the binding sites of the first antibody or antigen and the corresponding antigens or antibodies and the binding sites of the second antibodies or antigens and the corresponding antigens or antibodies are different. The invention also relates to a method for joint detection based on microspheres with different fluorescence intensities. The kit provided by the invention can realize specific detection of five pathogen antigens / antibodies in blood transfusion through one-time reaction, and the detection process is simple, convenient and accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cellular markers for diagnosis of alzheimer's disease and for alzheimer's disease progression
InactiveUS20150057176A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTherapeutic effectBlood marker
The present invention provides methods for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and for determining the efficacy of a treatment for Alzheimer's disease in an Alzheimer's patient, i.e., monitoring Alzheimer's disease progression, utilizing cellular blood markers; as well as kits for carrying out these methods.
Owner:NEUROQUEST LTD +1
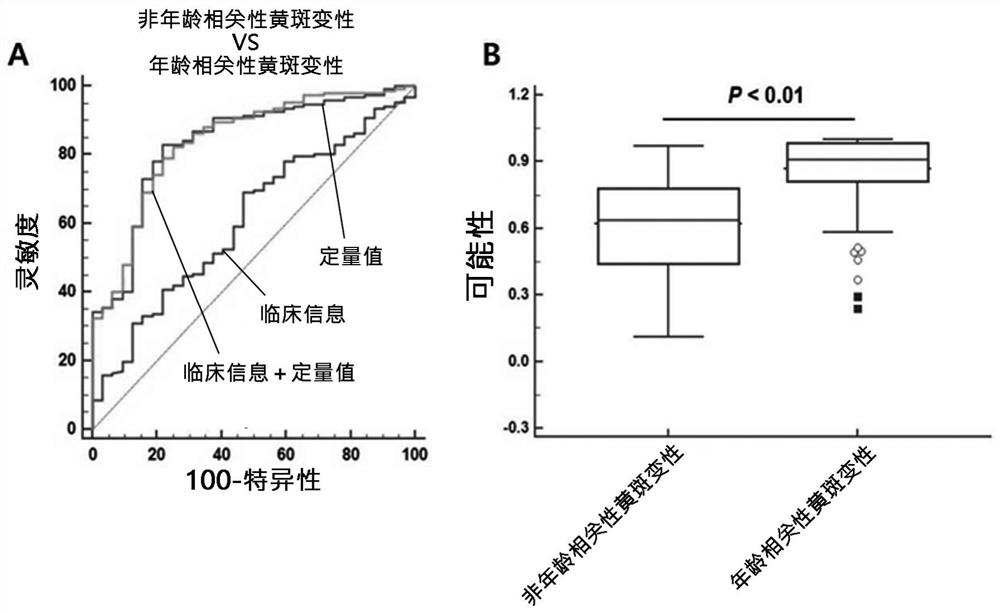
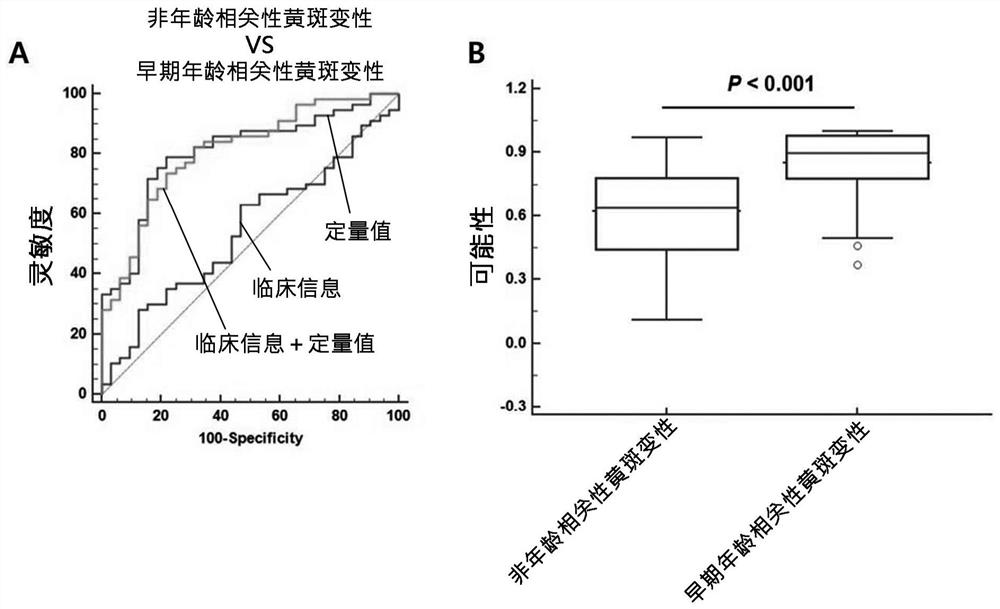
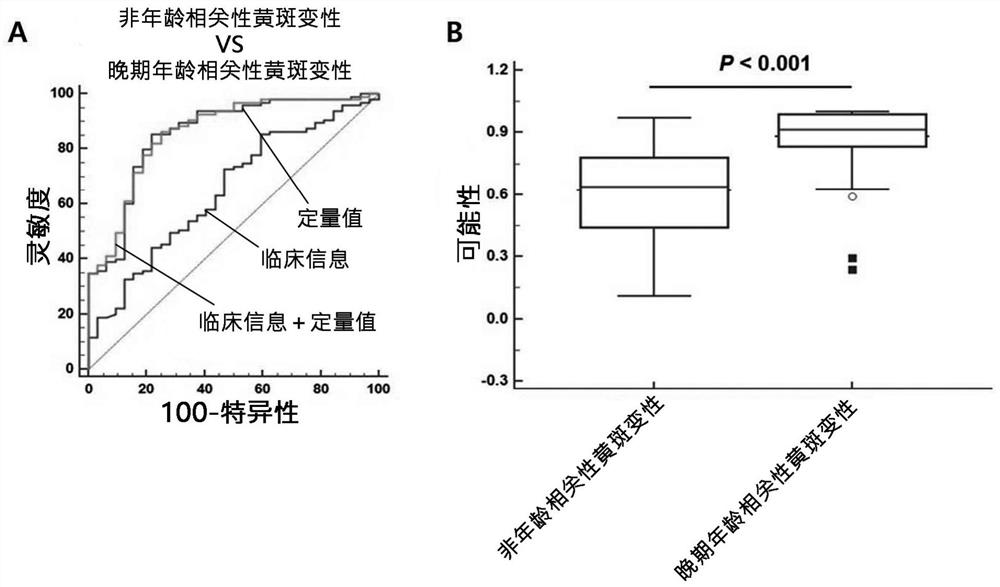
Composite marker for diagnosis of age related macular degeneration and use thereof
PendingCN113544286AHigh sensitivityEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBlood markersBlood plasma
The present invention relates to a composite marker for diagnosis of age related macular degeneration (AMD) and a use of same and, more specifically, to a composite markers for diagnosis of age related macular degeneration, which consists of two or more blood markers specific to diagnosis of age related macular degeneration and has improved diagnostic performance. In addition, the present invention relates to a composition for diagnosis of age related macular degeneration, a diagnostic kit, and a method for providing information necessary for diagnosing age related macular degeneration, each of which uses the composite marker. The composite marker for diagnosis of age related macular degeneration of the present invention was found to be superior to combinations of other markers in terms of sensitivity and diagnosis performance and to exhibit a high diagnostic potential for both initial and late macular degeneration, as analyzed for combinations between protein quantitation values of the composite marker and fundamental clinical information. In addition, the composite marker of the present invention does not use blood proteins for biopsy, but can conveniently perform analysis using patient plasma and as such, can be advantageously applied to the early diagnosis of age related macular degeneration.
Owner:RETI MARK CO LTD
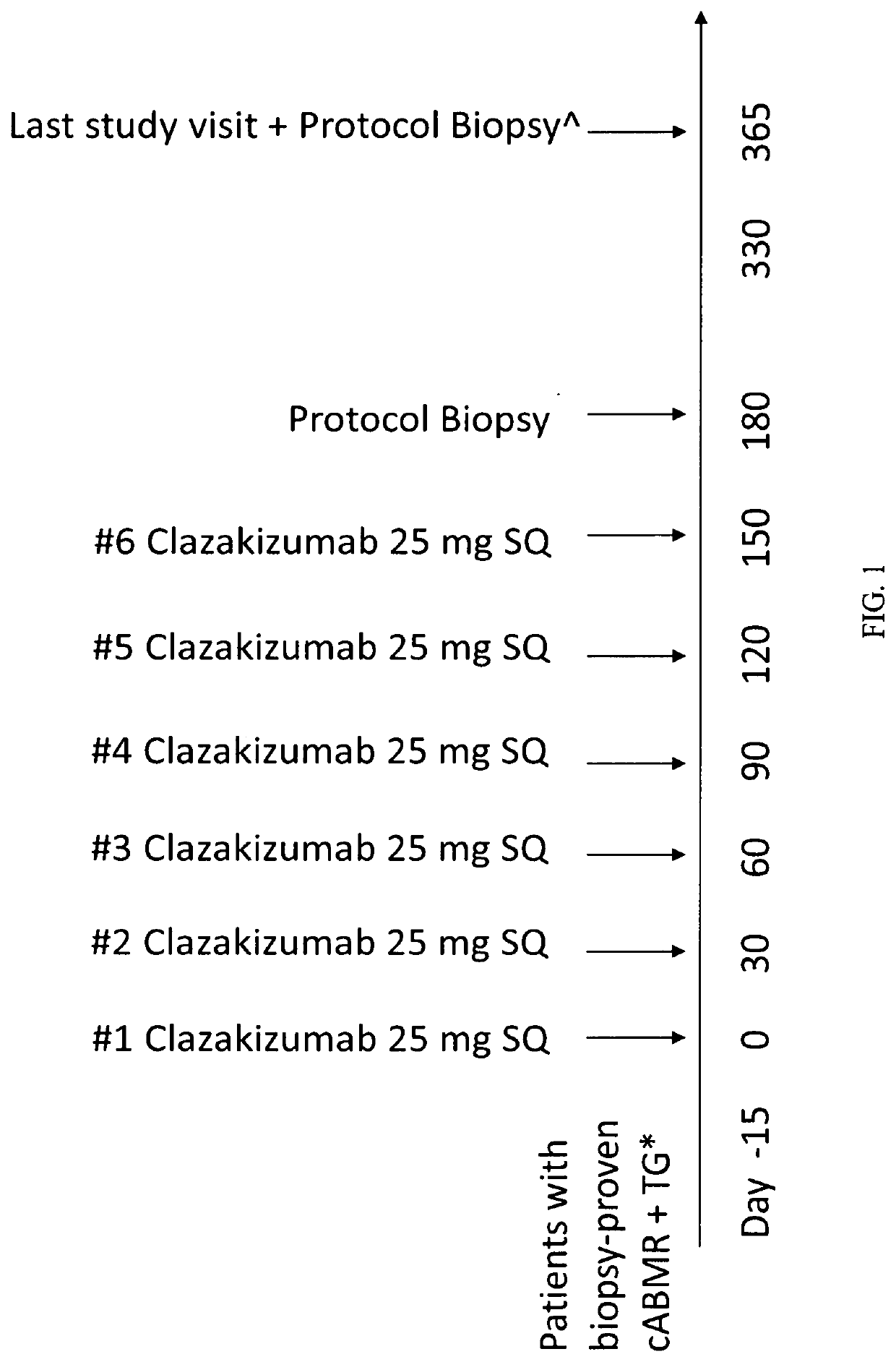
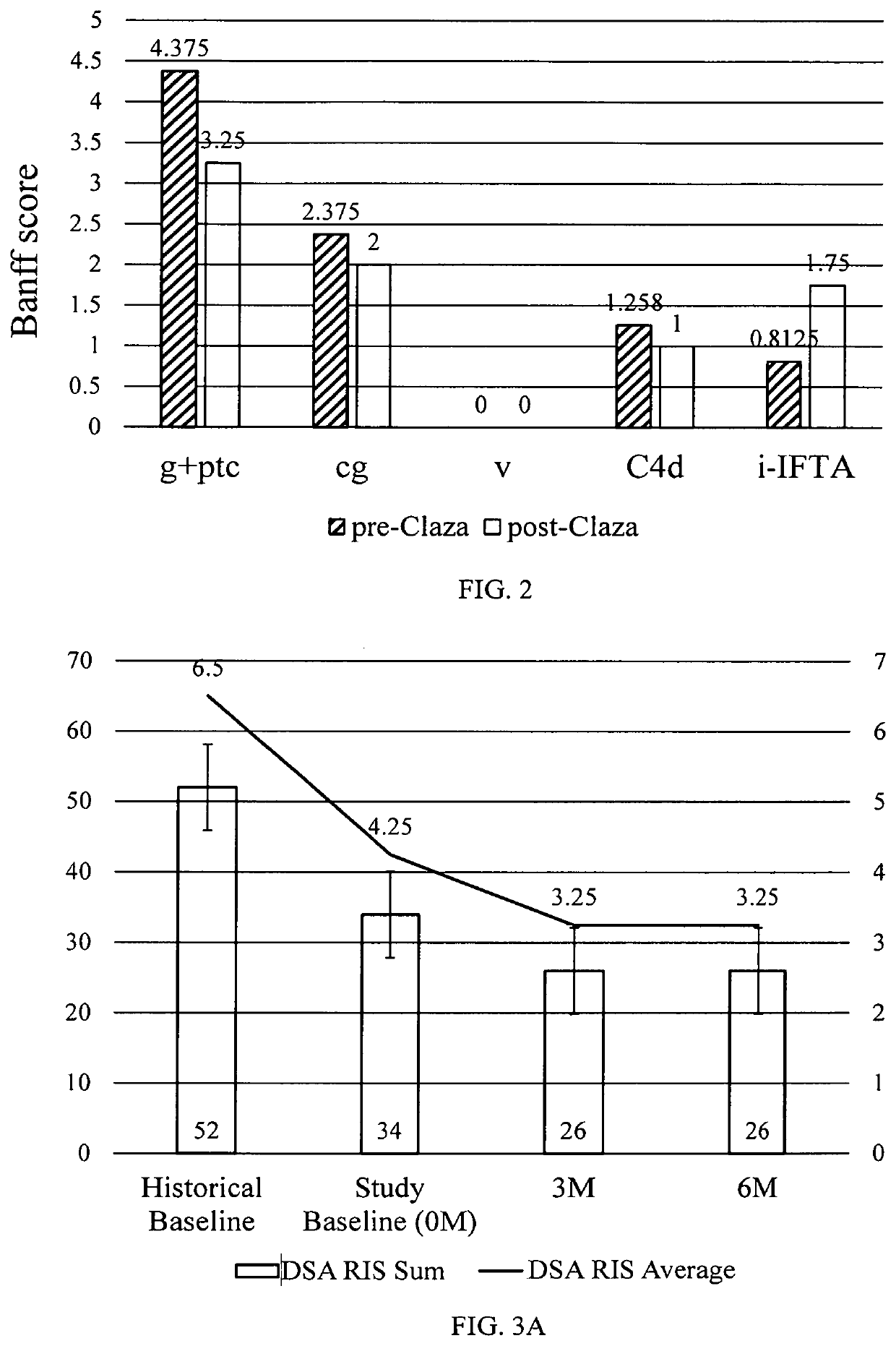
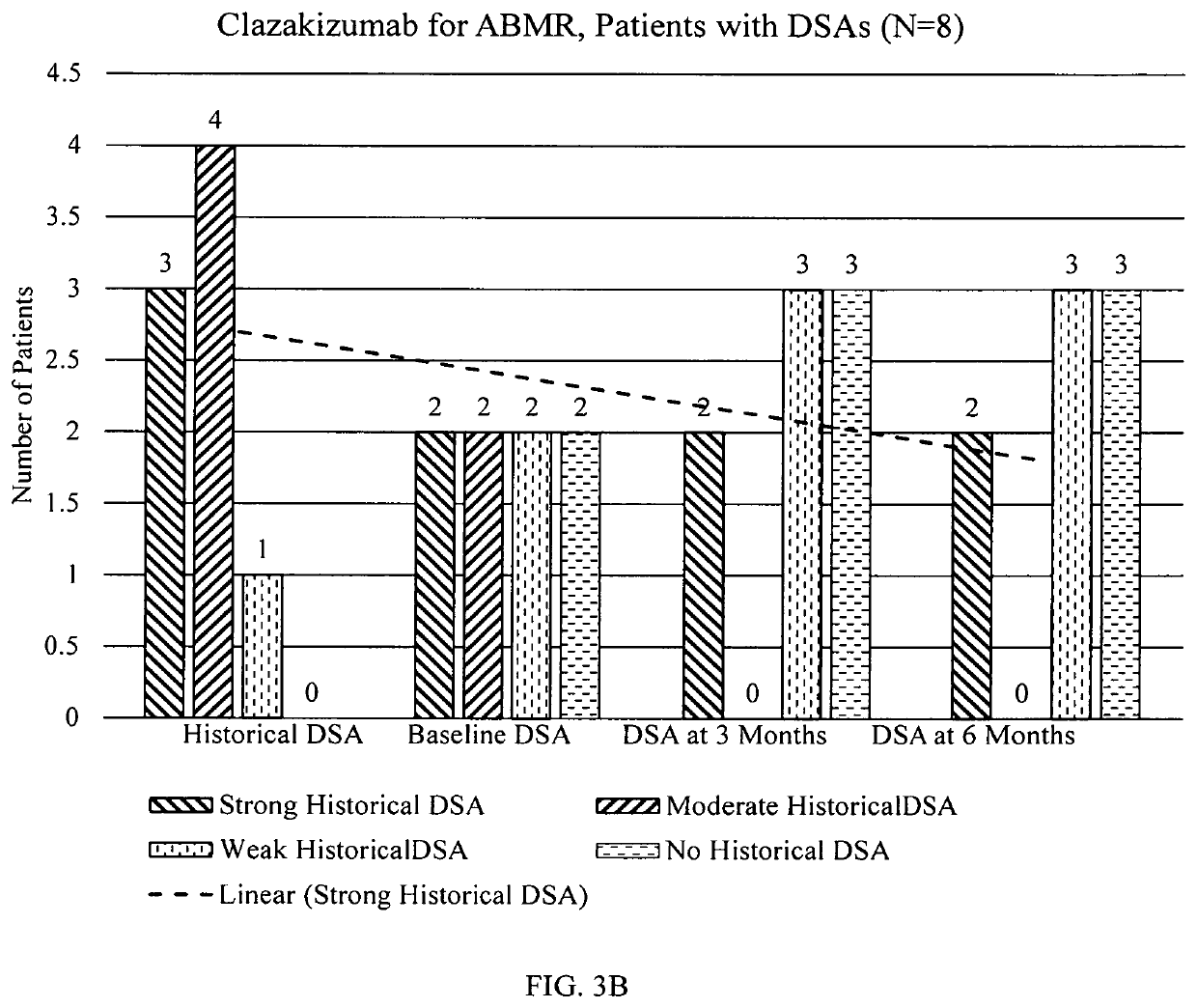
Clazakizumab in the treatment of chronic antibody-mediated rejection of organ transplant
PendingUS20220073605A1Increase ratingsTreating and inhibiting and reducing severityImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntibody ingredientsRenal glomerulusAntiendomysial antibodies
Described herein are methods for treating antibody mediated rejection (ABMR), especially chronic active ABMR (cABMR), of transplanted organs using clazakizumab Human kidney transplant recipients with biopsy-proven cABMR, transplant glomerulopathy and who are donor-specific antibody positive showed stabilization of renal function and lowered DSA levels following clazakizumab treatment. The estimated glomerular filtration rate of the patients at six, 12 or even 18 months were stabilized, inflammatory markers of cABMR were reduced or stabilized, and inflammatory blood markers were reduced, since clazakizumab treatment.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
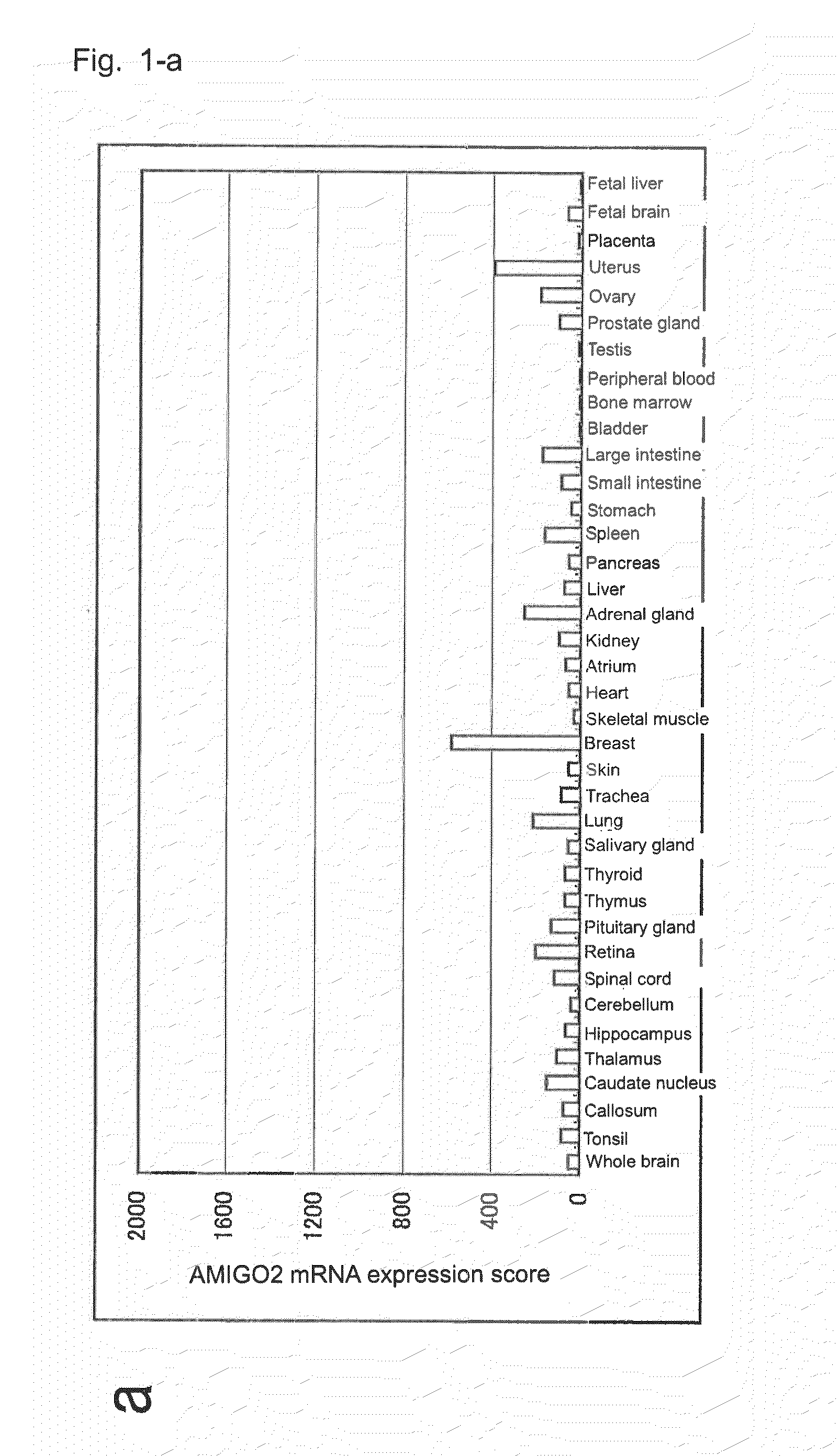
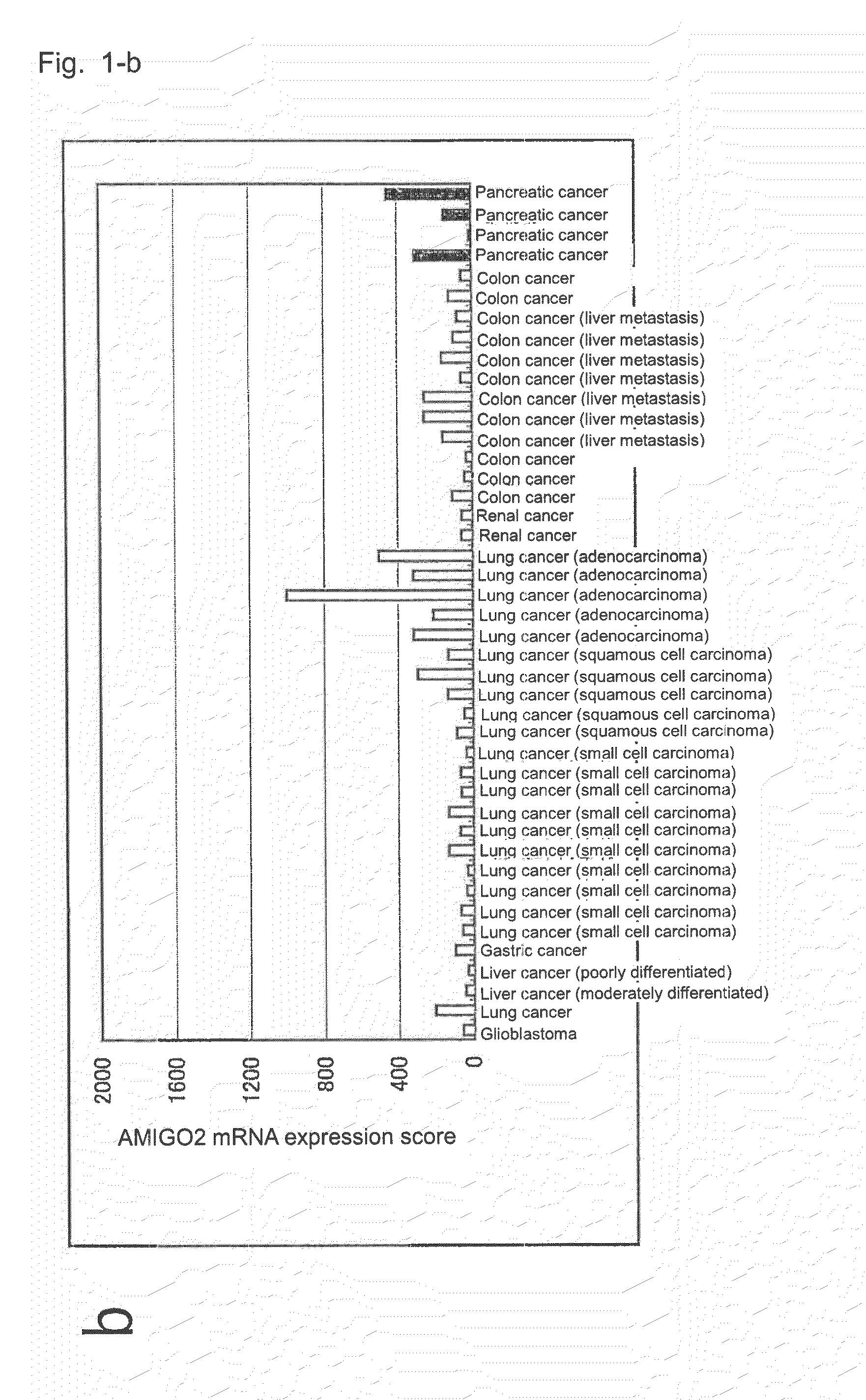
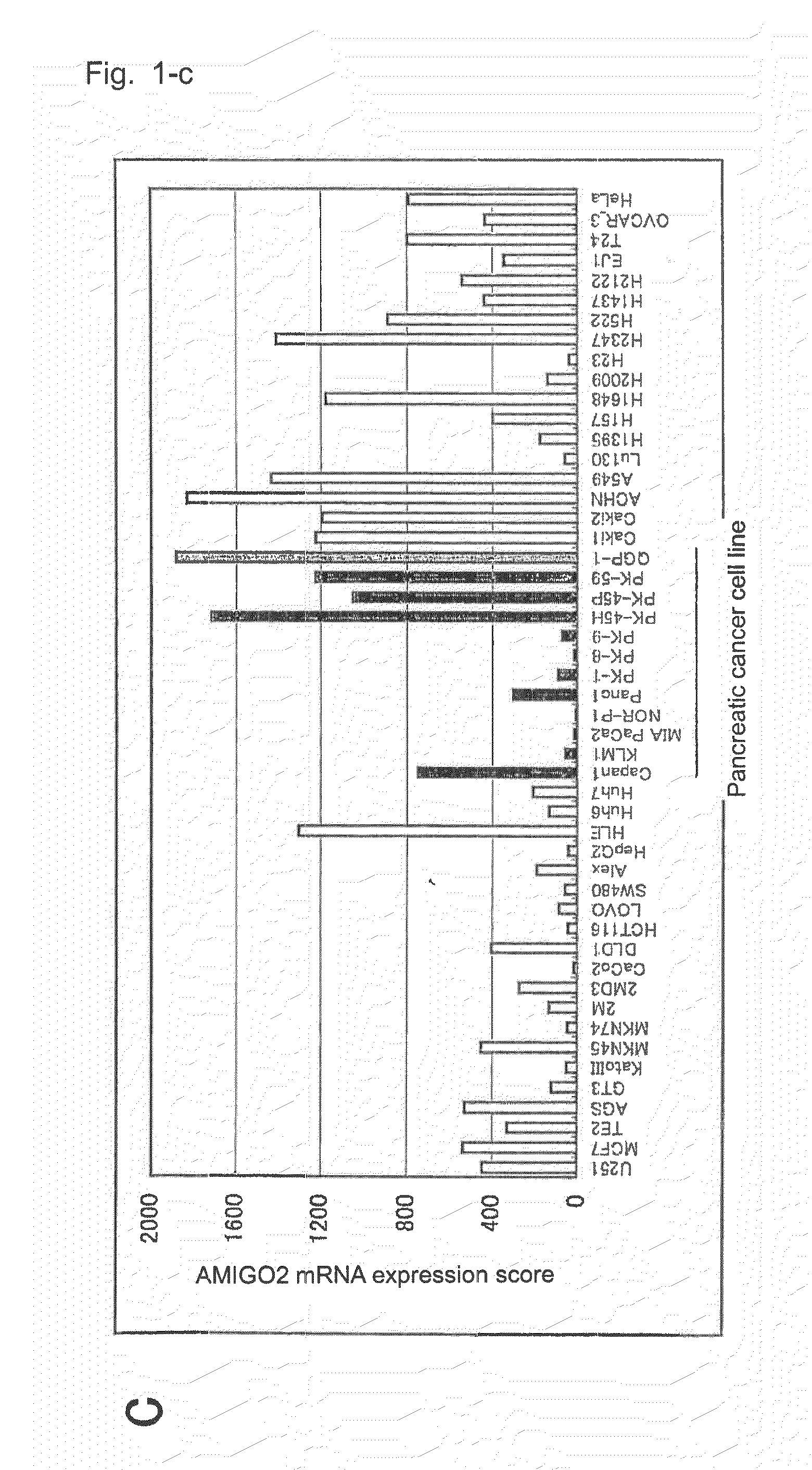
Diagnostic agent and therapeutic agent for pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS20110288278A1Reduce the burden onIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDigestive systemDiagnostic agentBlood marker
The present invention provides a novel diagnostic or therapeutic method for pancreatic cancer employing a blood marker. The present invention provides a diagnostic or therapeutic drug for pancreatic cancer containing an anti-AMIGO2 antibody.
Owner:PERSEUS PROTEOMICS INC +1
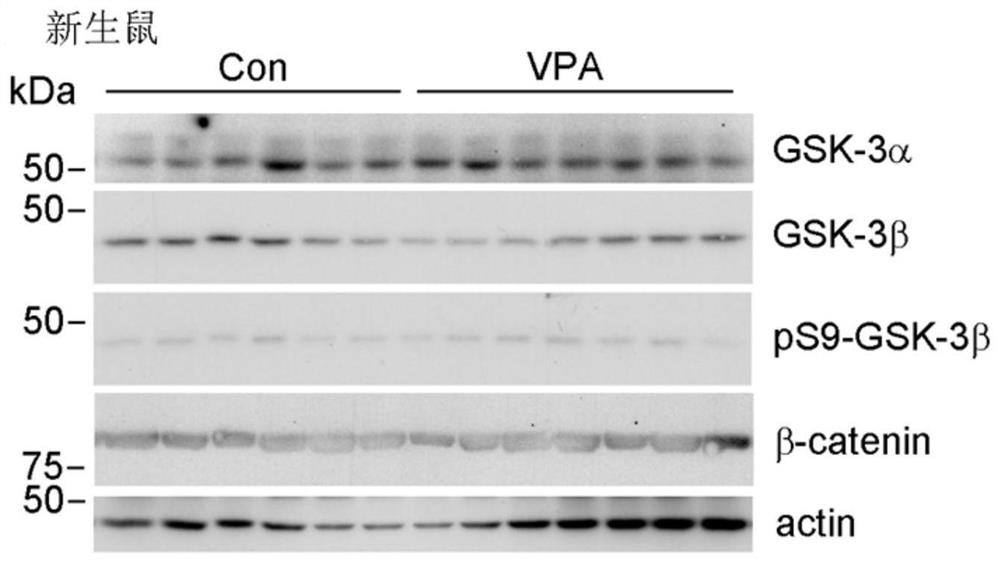
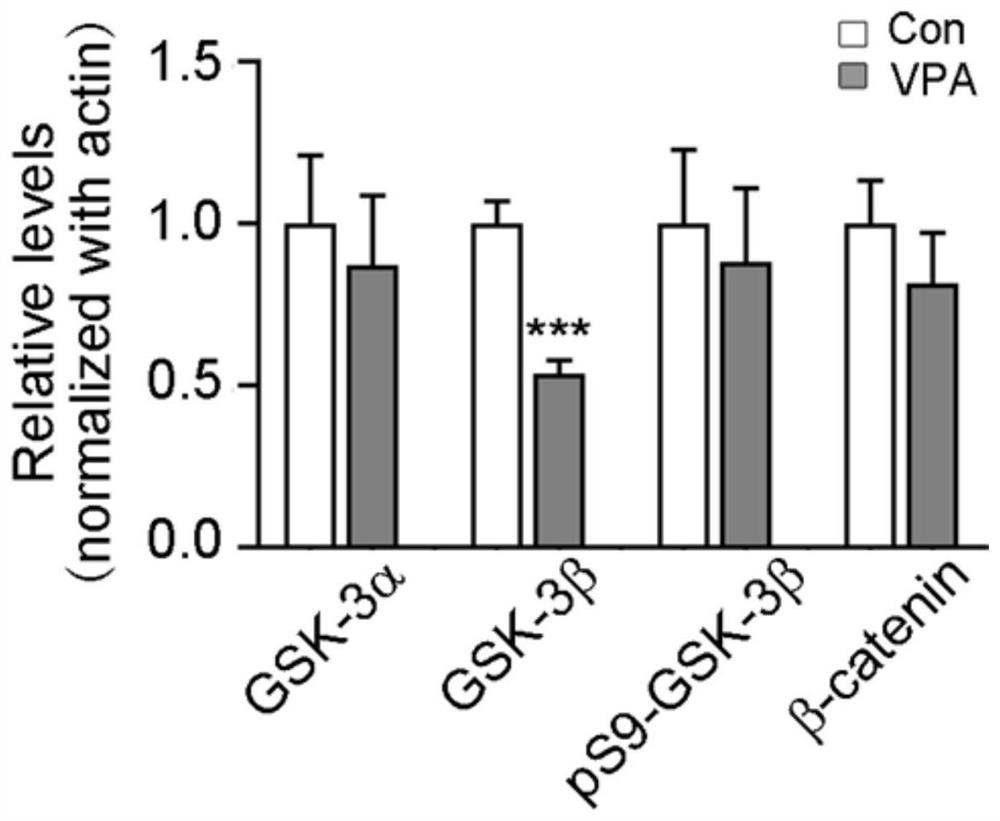
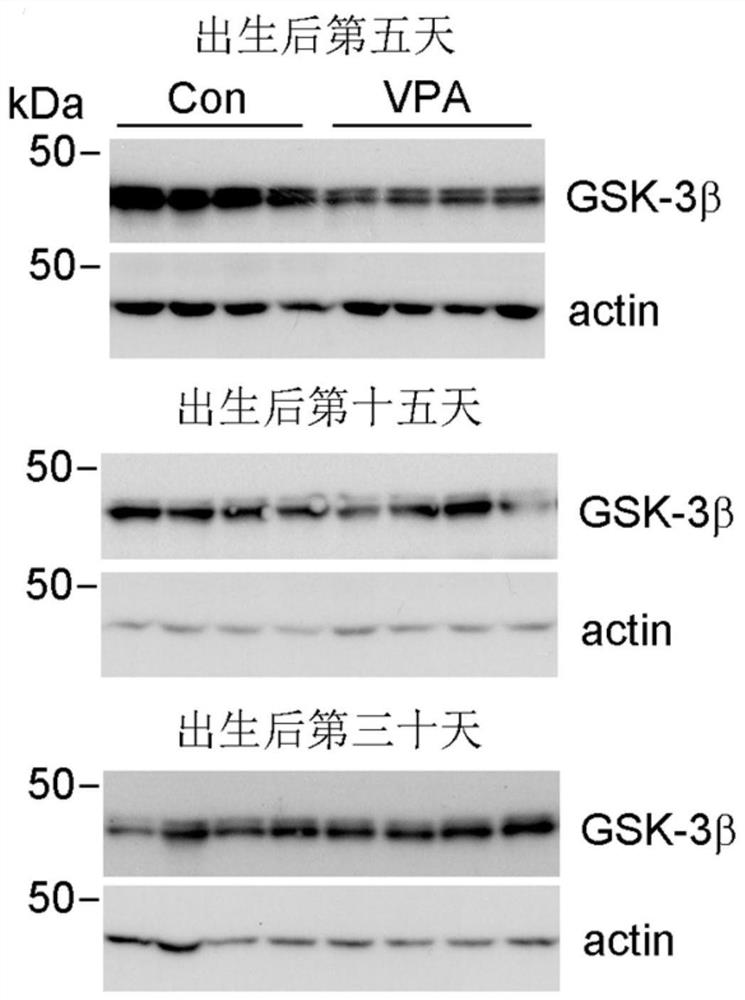
Application of GSK-3beta as a blood marker in preparation of mental disorder early-diagnosis reagent
ActiveCN111690732AFacilitate early detectionFacilitate early interventionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBlood markersFull Term Neonate
The invention discloses an application of GSK-3beta as a blood marker in the preparation of a diagnostic reagent for mental disorders, especially autism spectrum disorders (ASD). GSK-3beta can be usedas an ASD early-diagnosis reagent, and a detection time window is 0-3 months for newborns. The non-invasive auxiliary diagnosis of ASD can be carried out by only using a small amount of blood sample,the large-scale infant ASD screening is facilitated, and early discovery, early intervention and early treatment of ASD are facilitated.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Application of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 in the preparation of diagnostic reagents for rheumatoid arthritis
InactiveCN104698194BStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingPhosphoglycerate mutaseEarly rheumatoid arthritis
The invention discloses a blood marker-PGK1 for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis, and discloses a reagent for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis. The reagent comprises a PGK1 antibody, an HRP-IgG antibody and a conventional reagent in a blood diagnosis reagent. The conventional reagent in the blood diagnosis reagent comprises a carbonate buffer solution, PBST washing liquor, confining liquid, a developing solution and a stop solution. The prepared detection reagent has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in specificity and the like and is capable of being widely applied to preliminary survey and health examination of clinical rheumatoid arthritis and providing a reliable basis for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:常晓天
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com