Patents
Literature
31 results about "Compliant substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
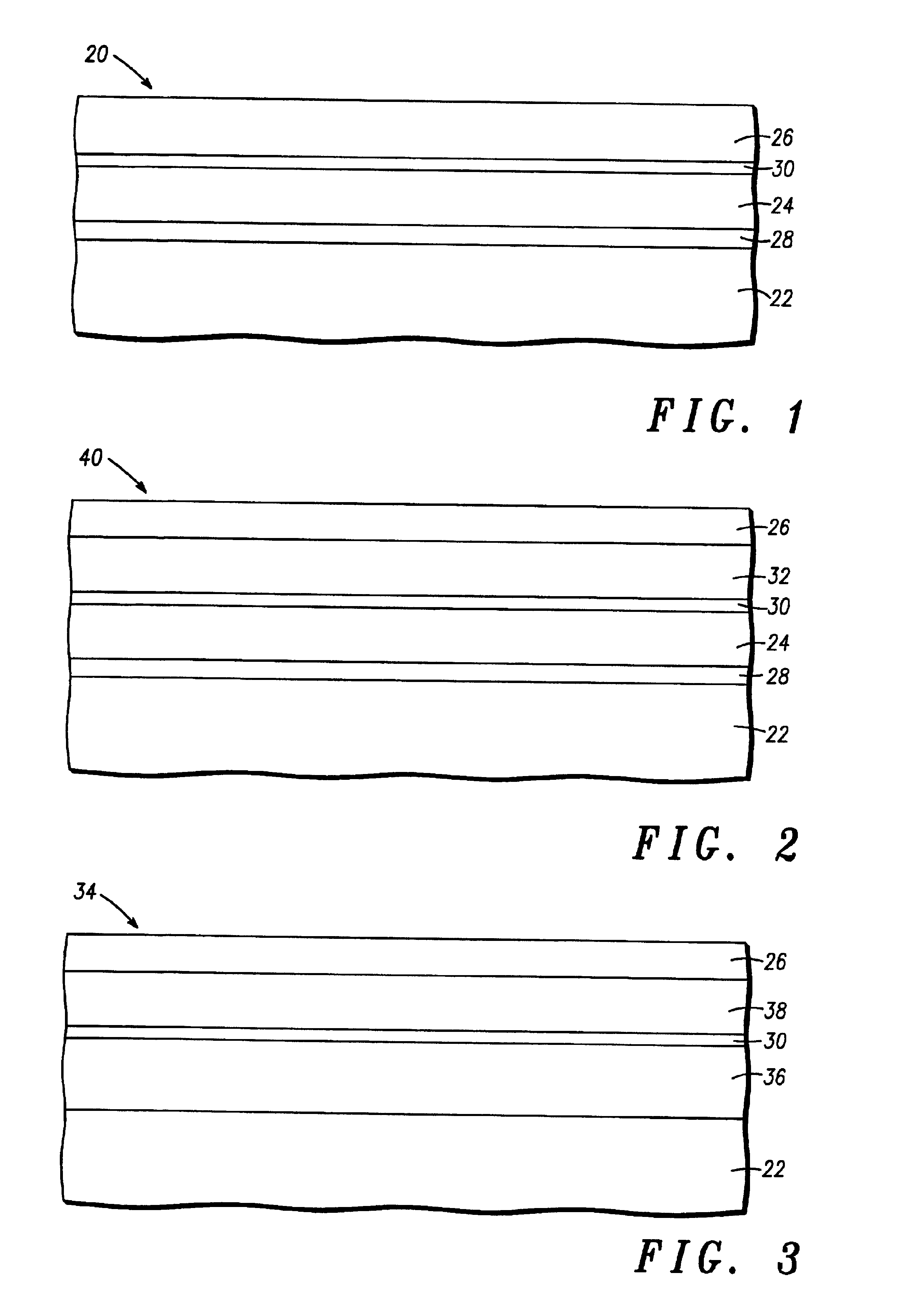
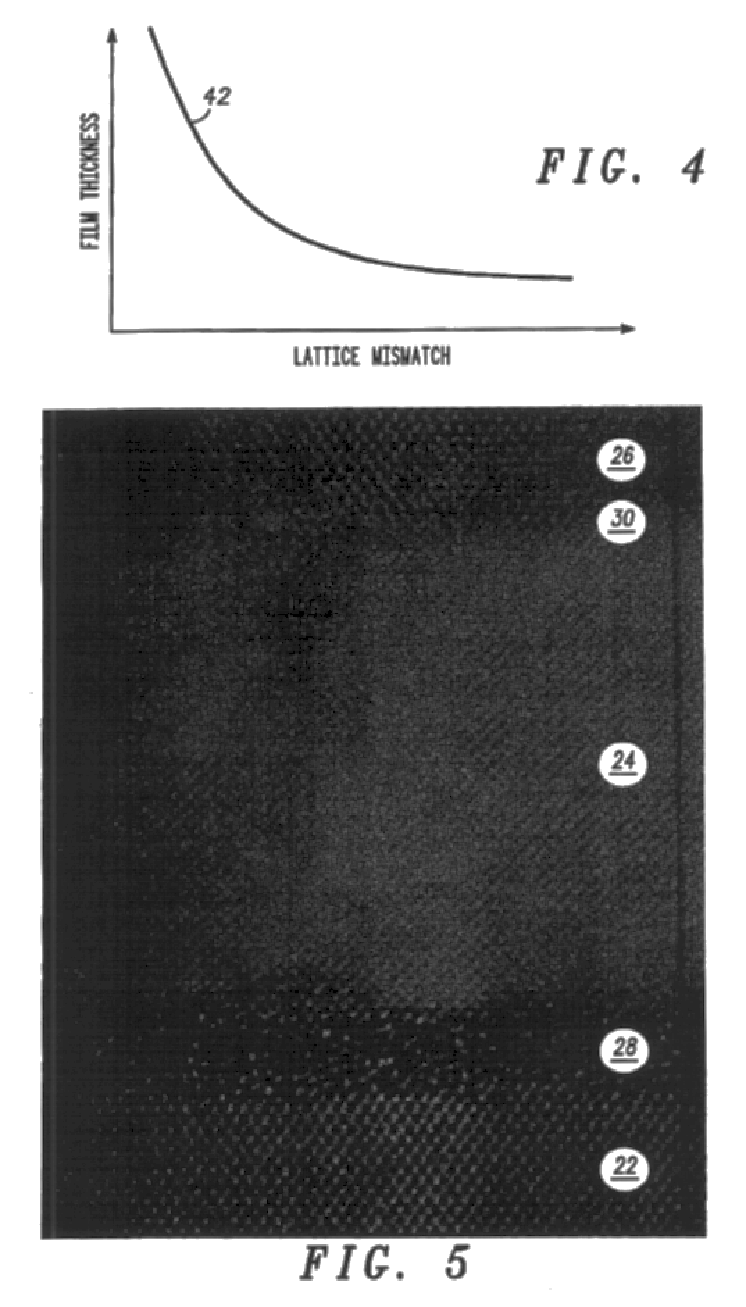
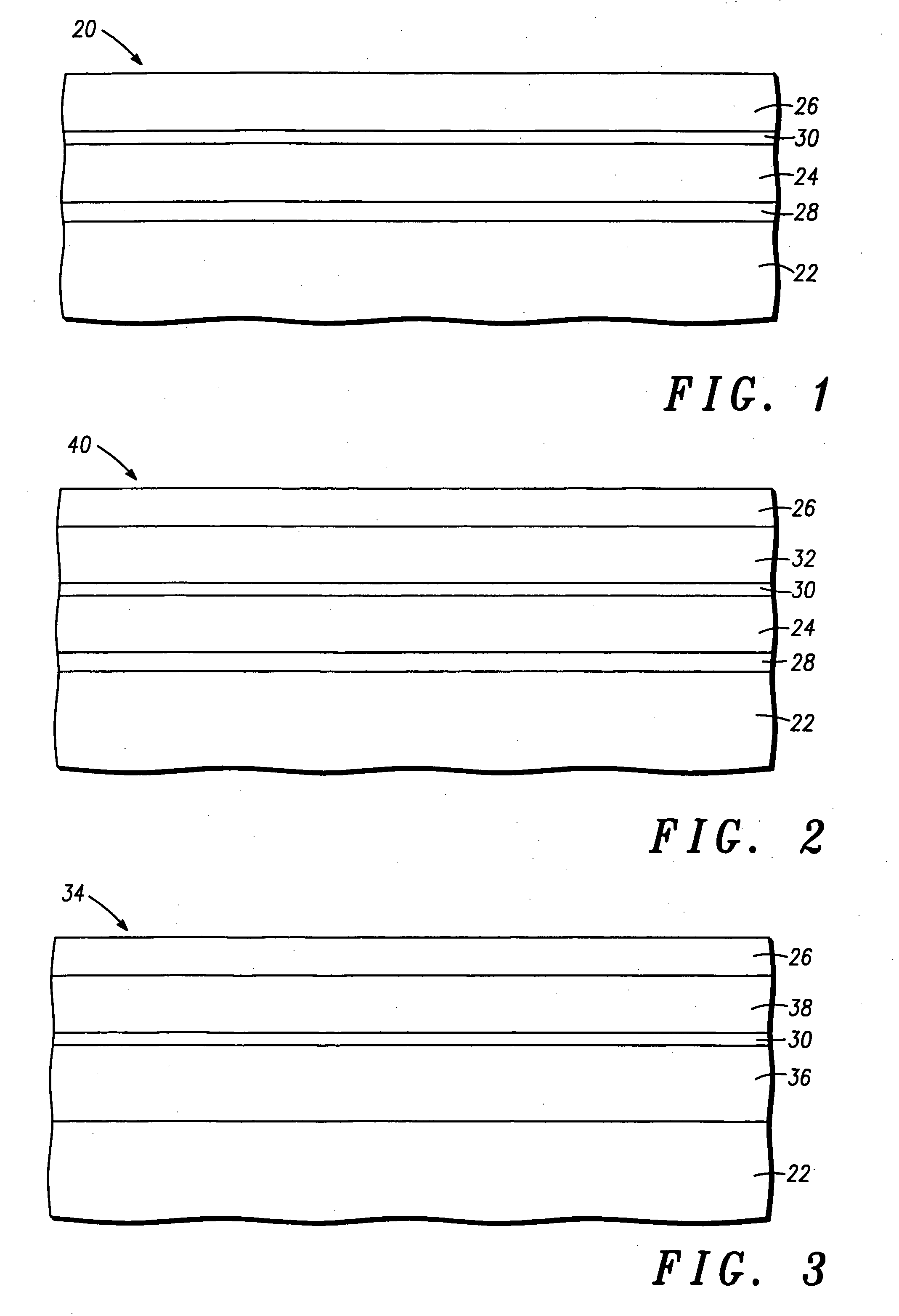
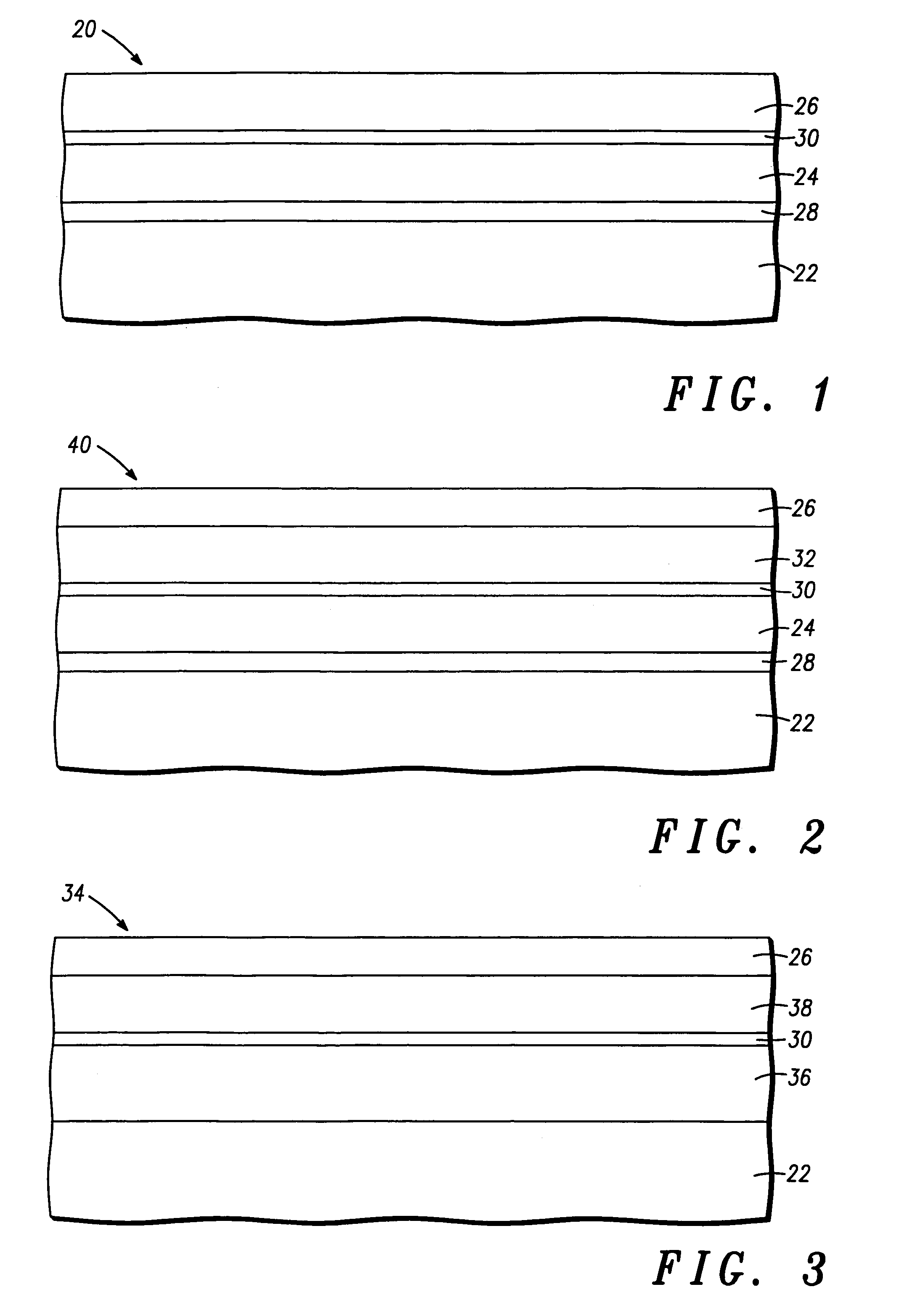
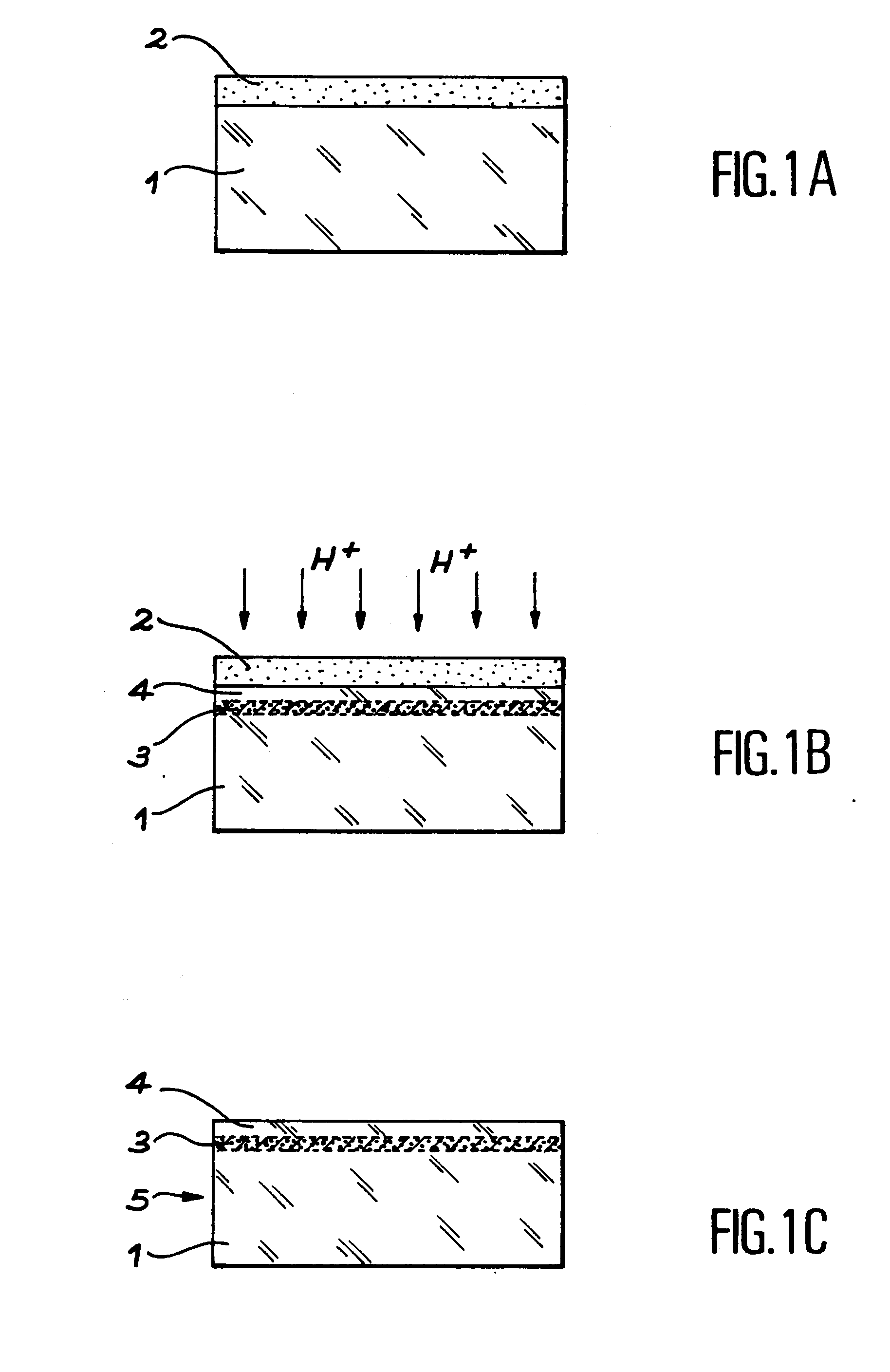
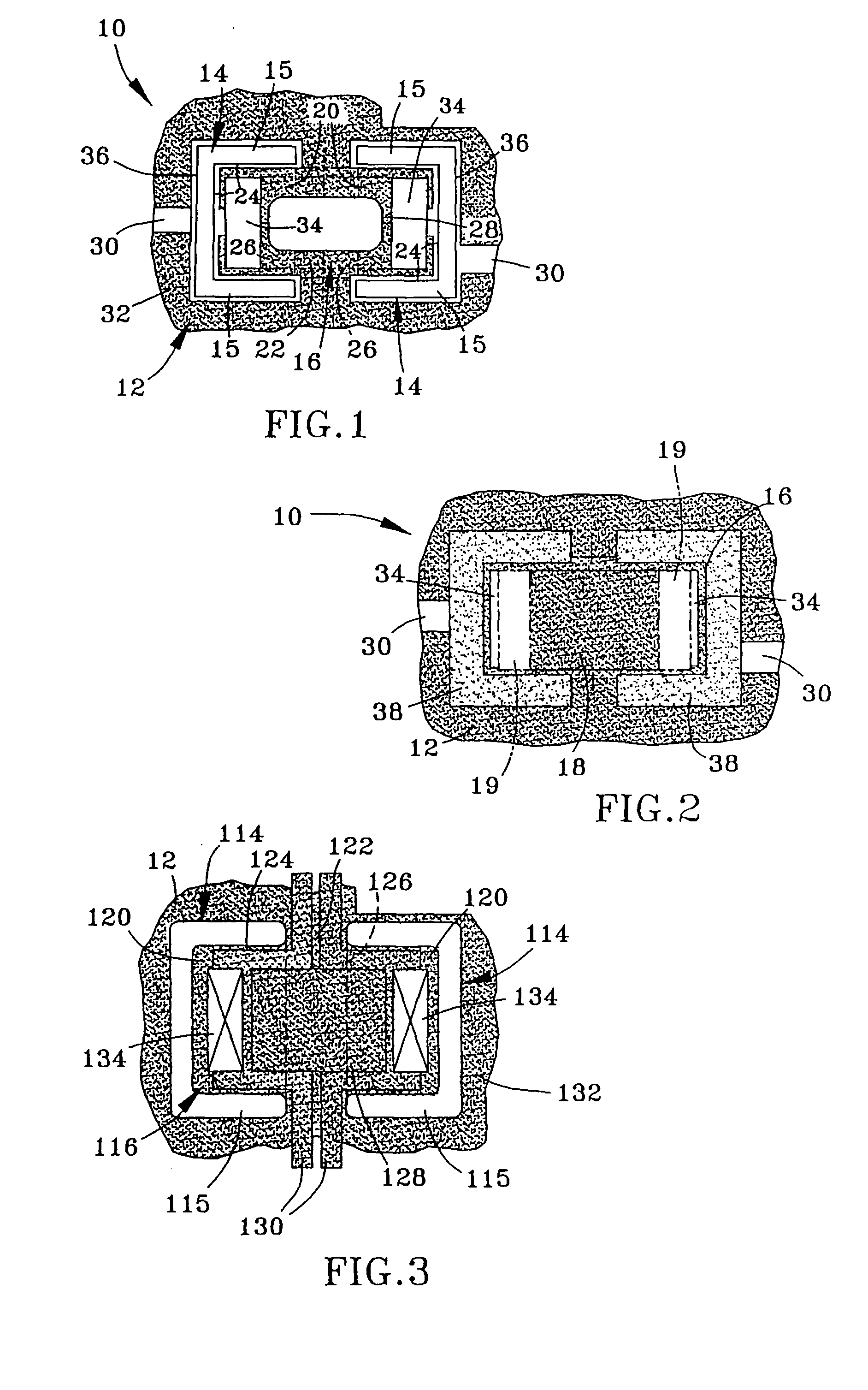
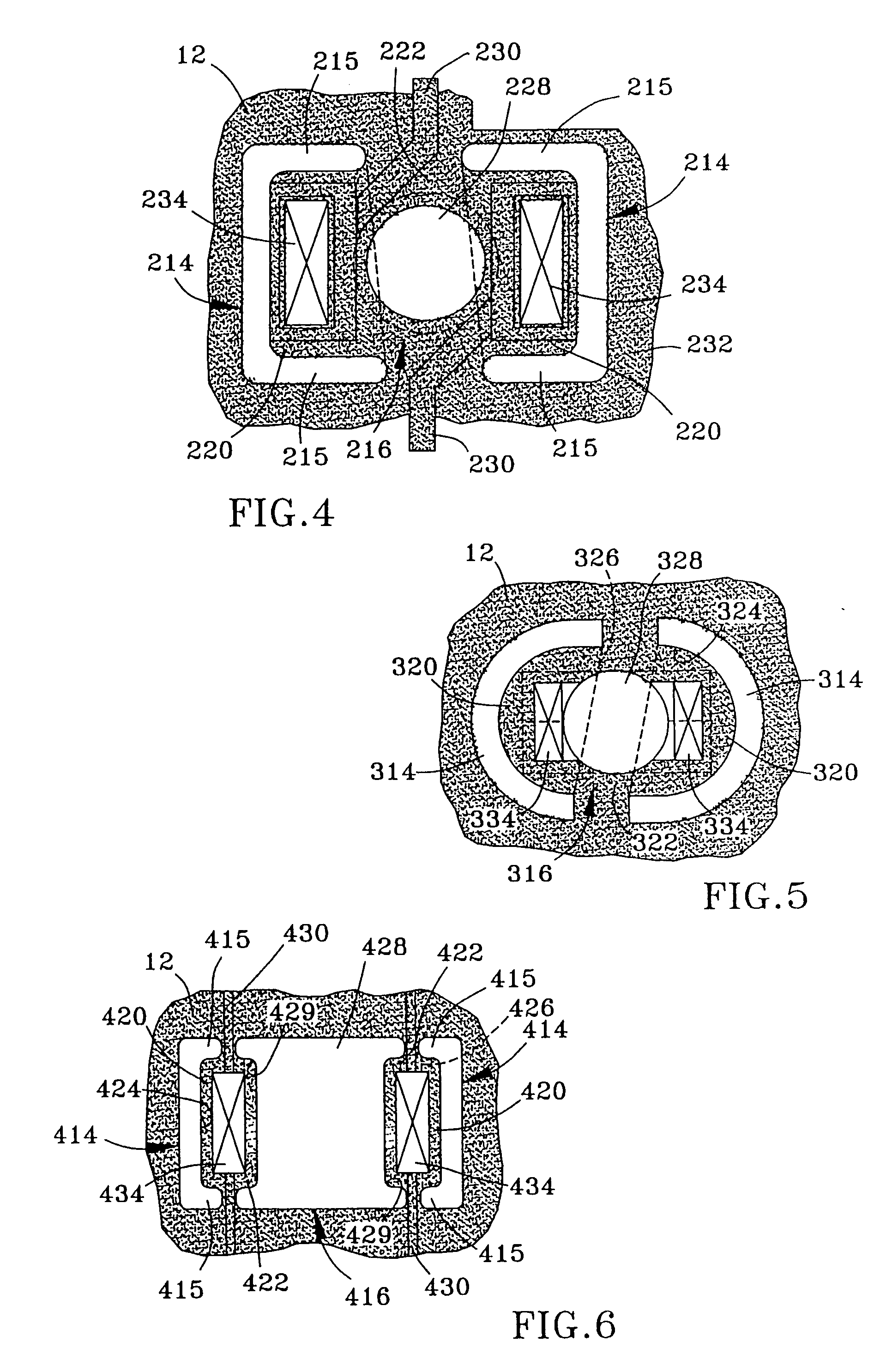
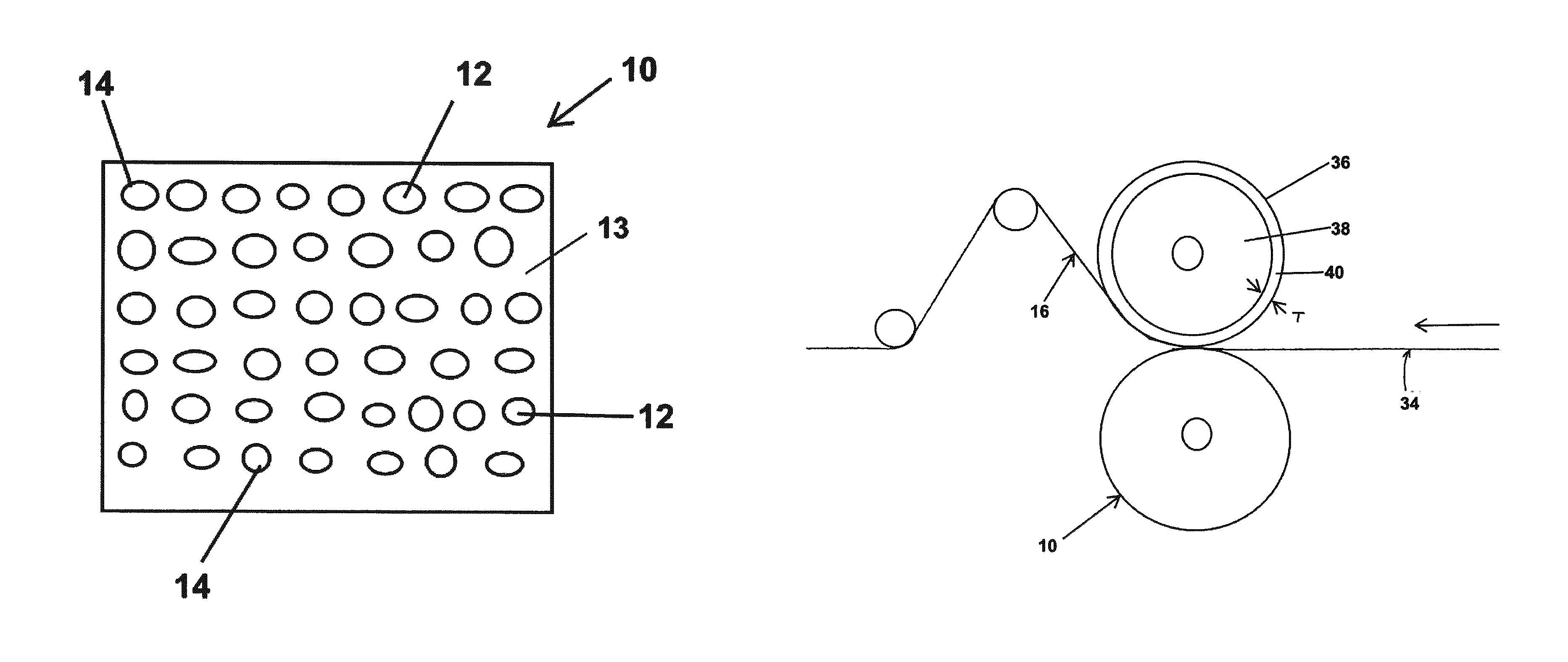
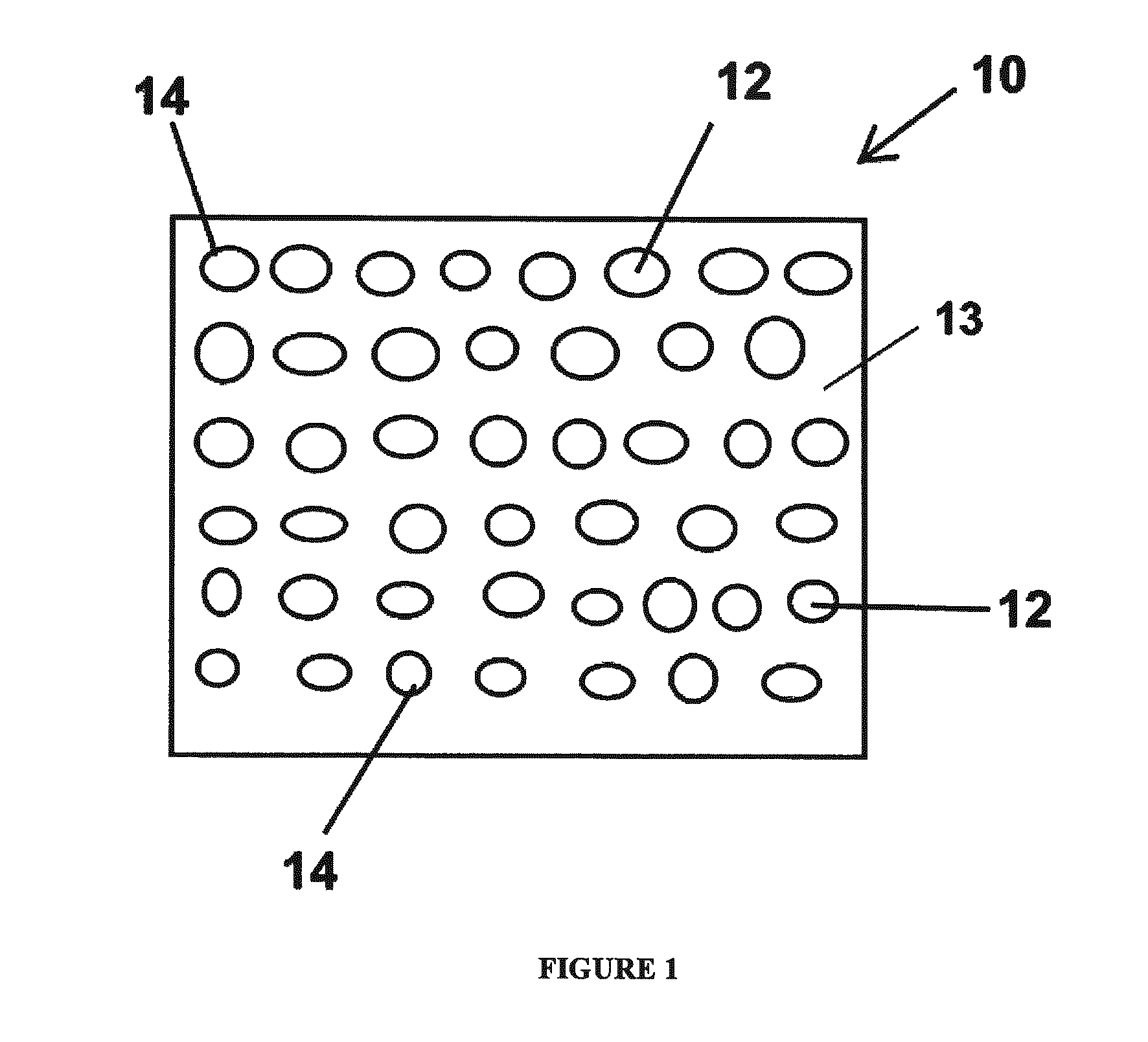
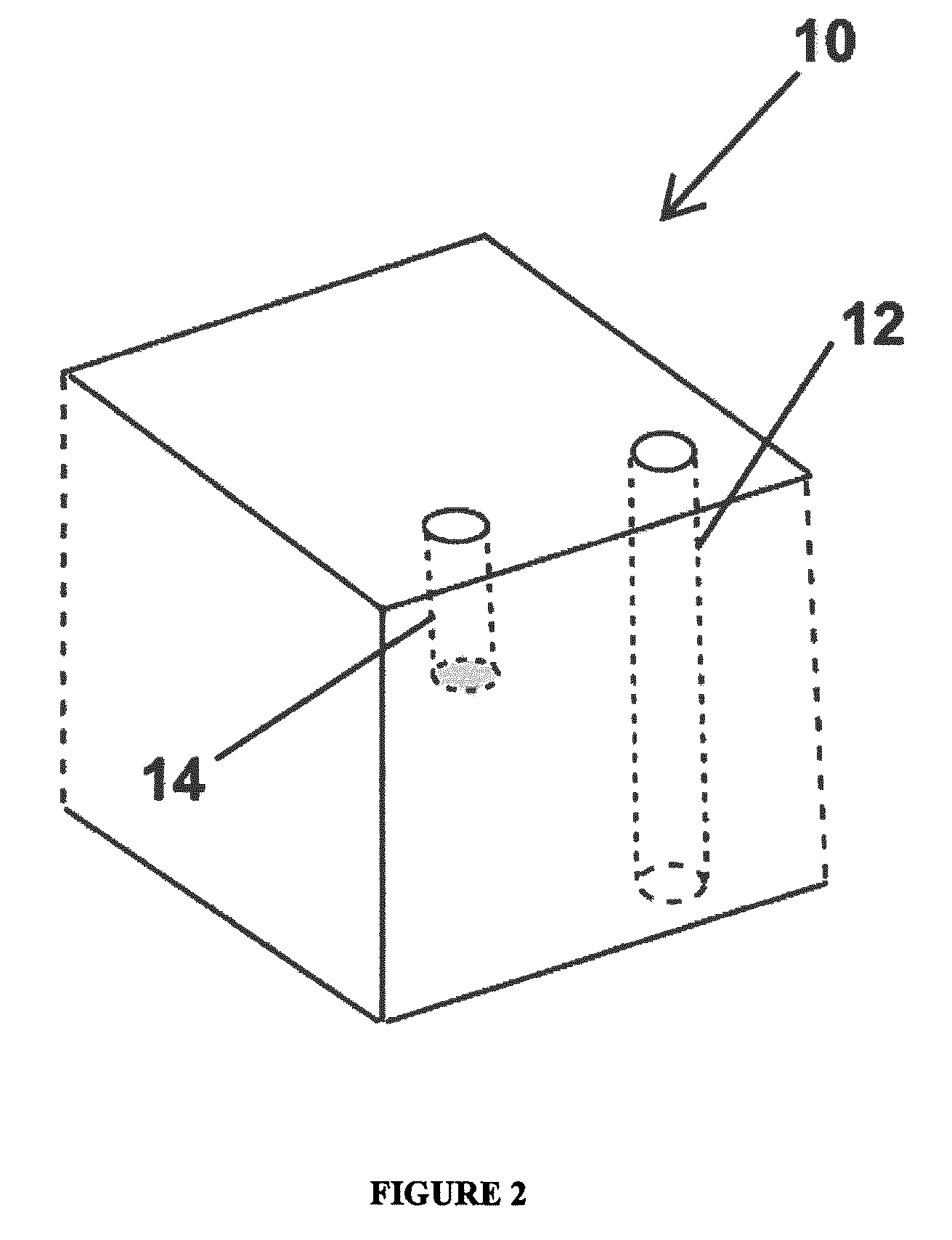
Monolithic photovoltaic energy conversion device
InactiveUS20070137698A1Solid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsEngineering
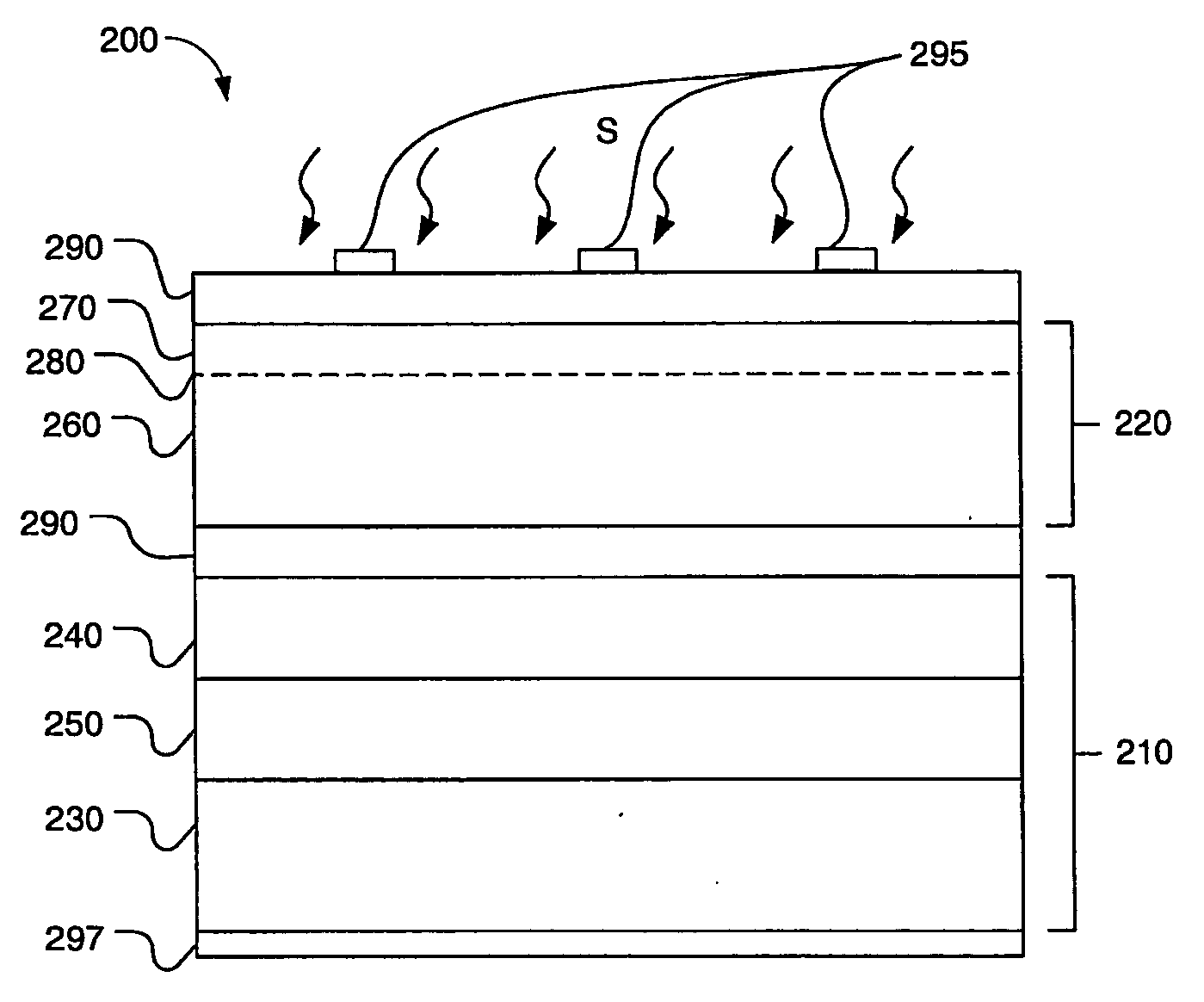
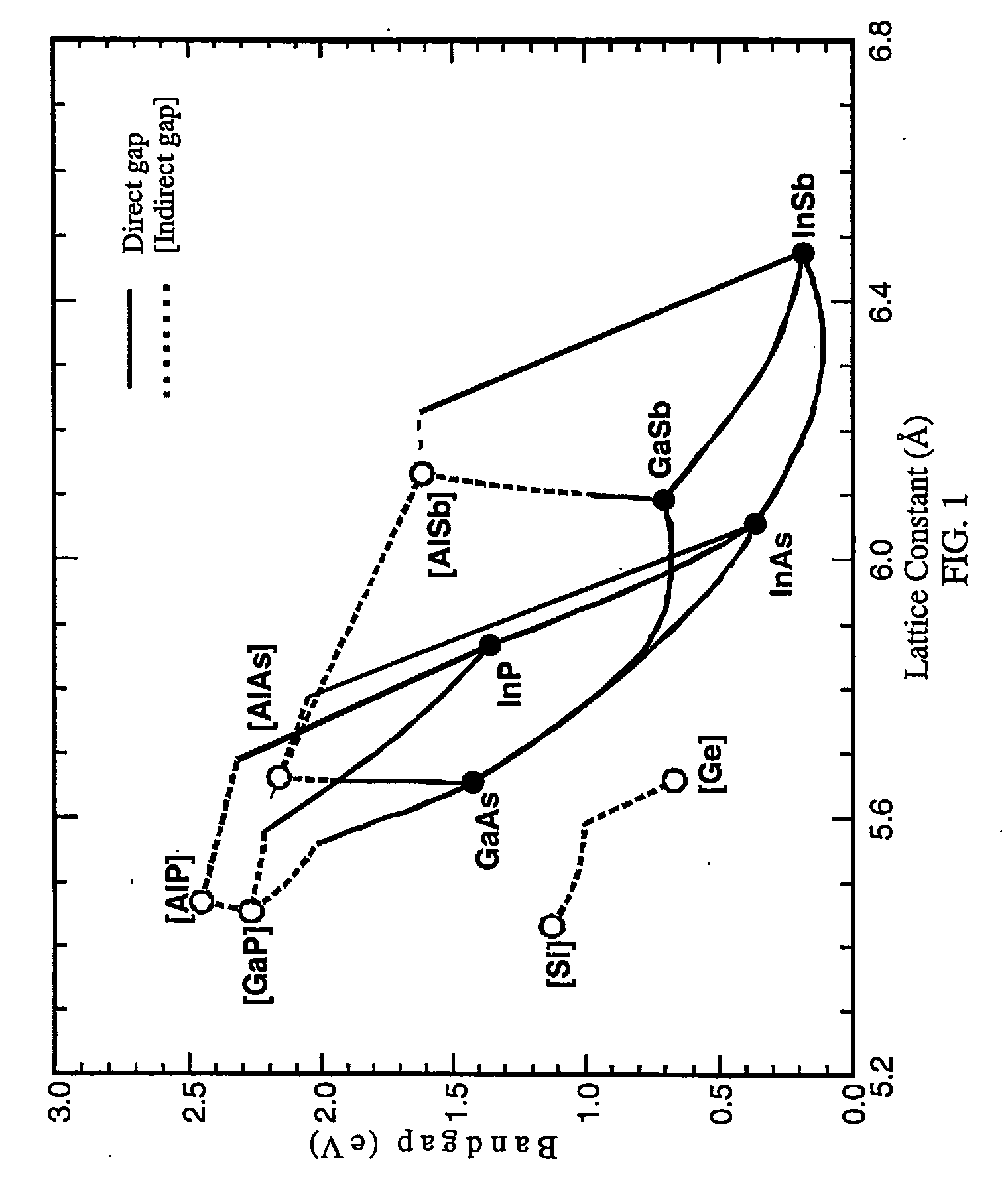
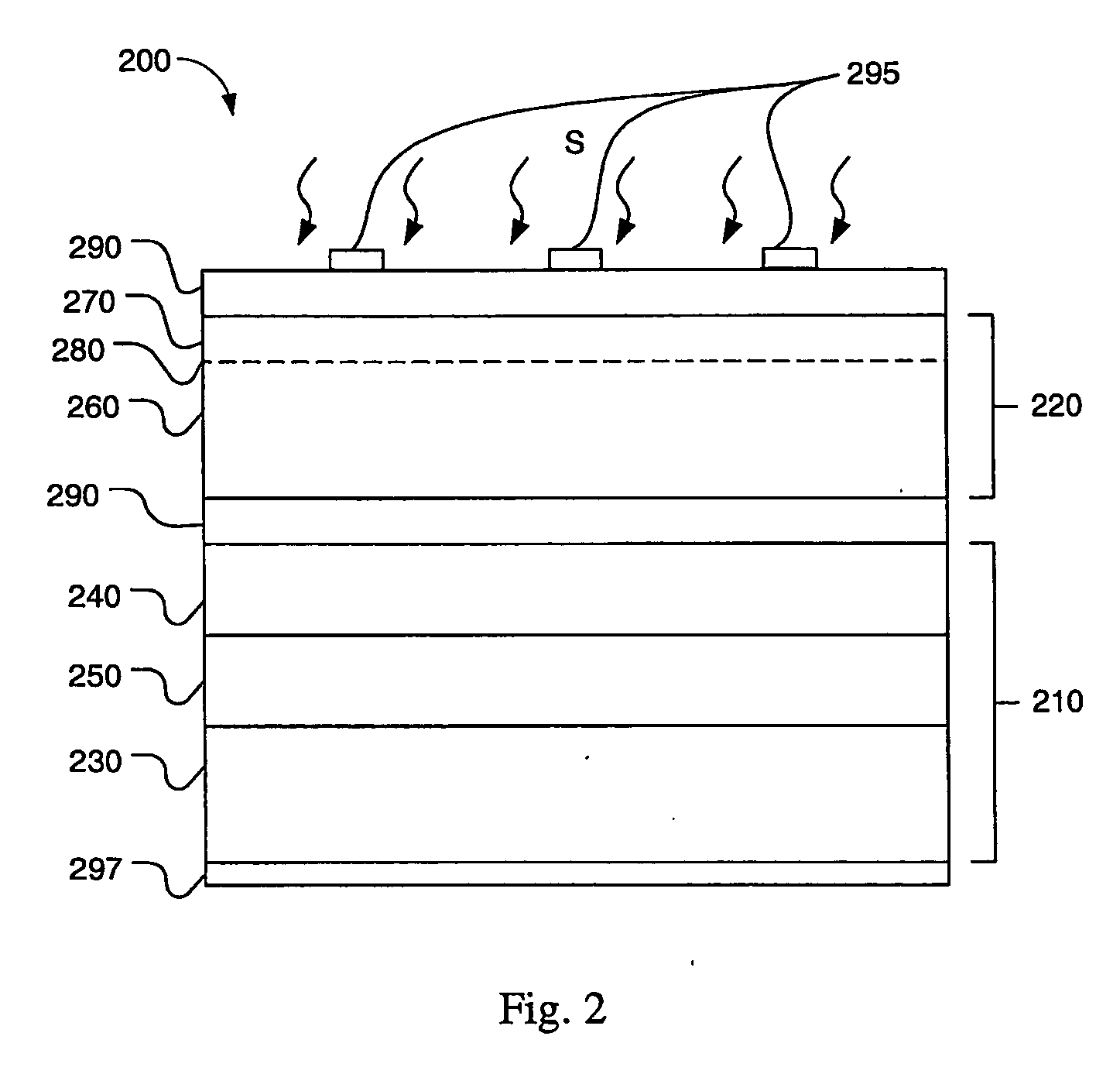
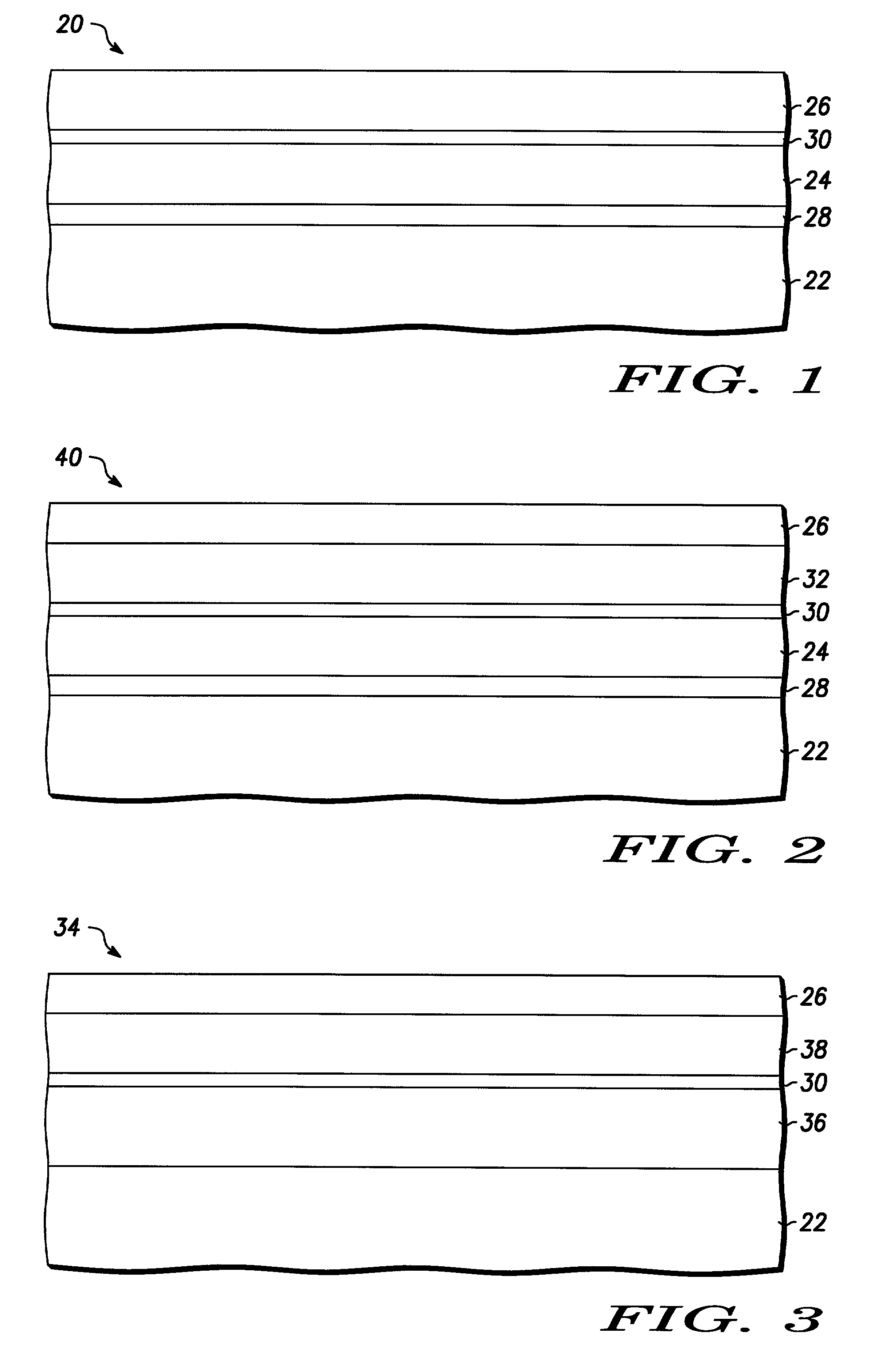
A multijunction, monolithic, photovoltaic (PV) cell and device (600) is provided for converting radiant energy to photocurrent and photovoltage with improved efficiency. The PV cell includes an array of subcells (602), i.e., active p / n junctions, grown on a compliant substrate, where the compliant substrate accommodates greater flexibility in matching lattice constants to adjacent semiconductor material. The lattice matched semiconductor materials are selected with appropriate band-gaps to efficiently create photovoltage from a larger portion of the solar spectrum. Subcell strings (601, 603) from multiple PV cells are voltage matched to provide high output PV devices. A light emitting cell and device is also provided having monolithically grown red-yellow and green emission subcells and a mechanically stacked blue emission subcell.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
LED illumination assembly with compliant foil construction
An illumination assembly includes a compliant substrate comprising a first and second electrically conductive foil separated by an electrically insulating layer. The insulating layer includes a polymer material loaded with particles that enhance thermal conductivity of the insulating layer. A plurality of LED dies are disposed on the first conductive foil.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Process for making an embossed web
A process for making an embossed web. A precursor web is provided between a forming structure and a compliant substrate. The forming structure has a plurality of discrete apertures or depressions. Pressure is provided between the compliant substrate and the forming structure to force the precursor web into the apertures or depressions of forming structure to form the embossed web. The resulting embossed web has a plurality of discrete extended elements.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
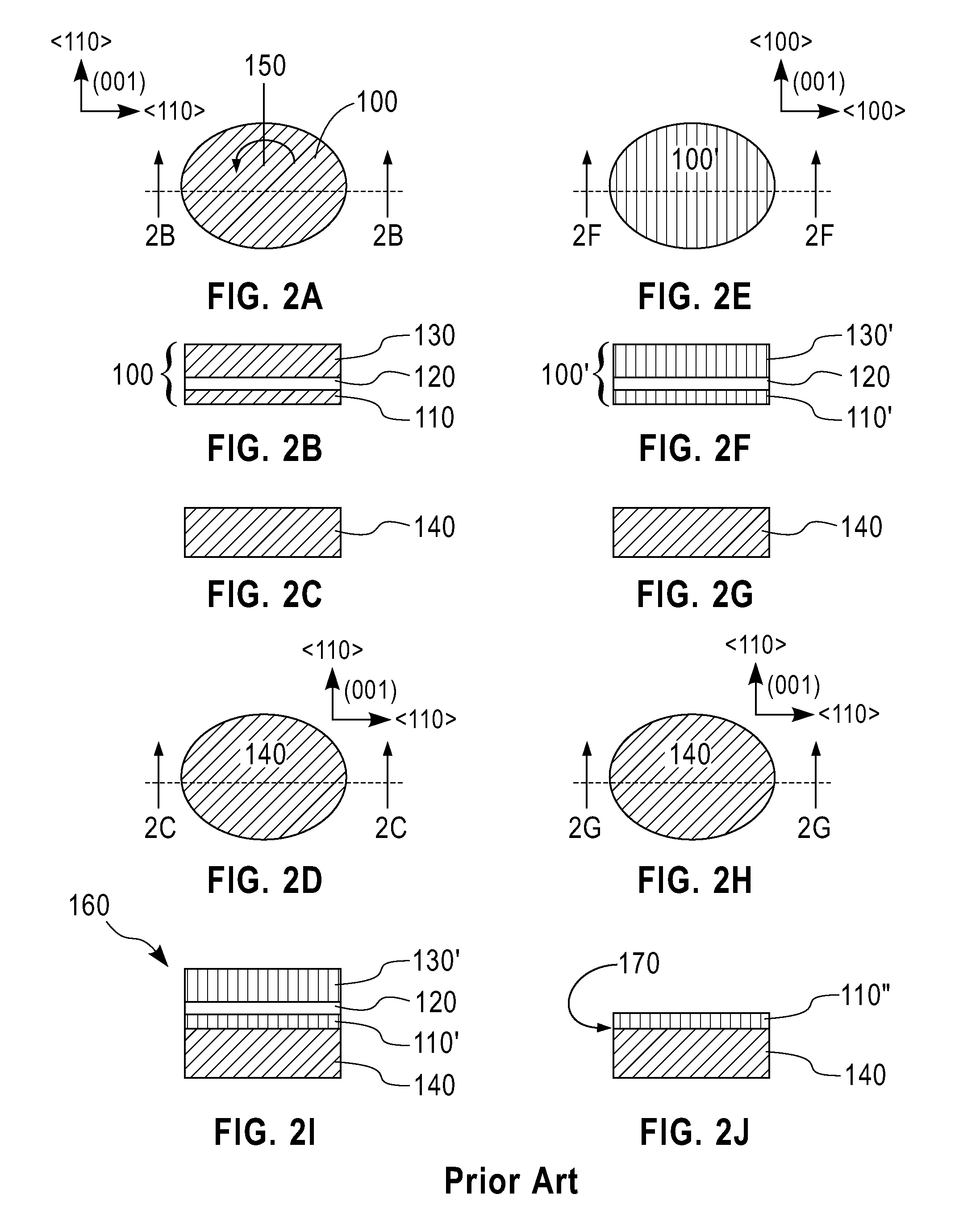
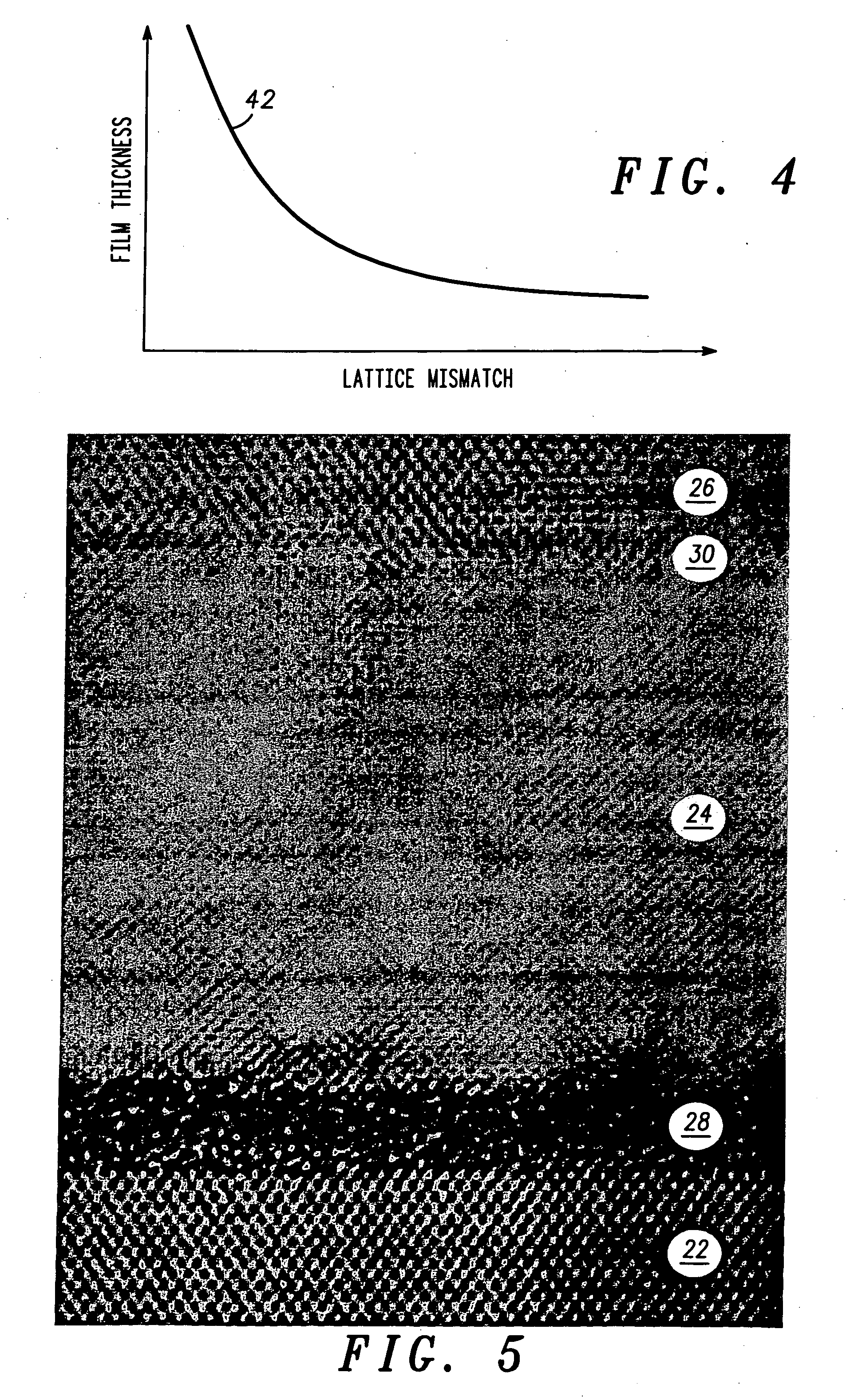
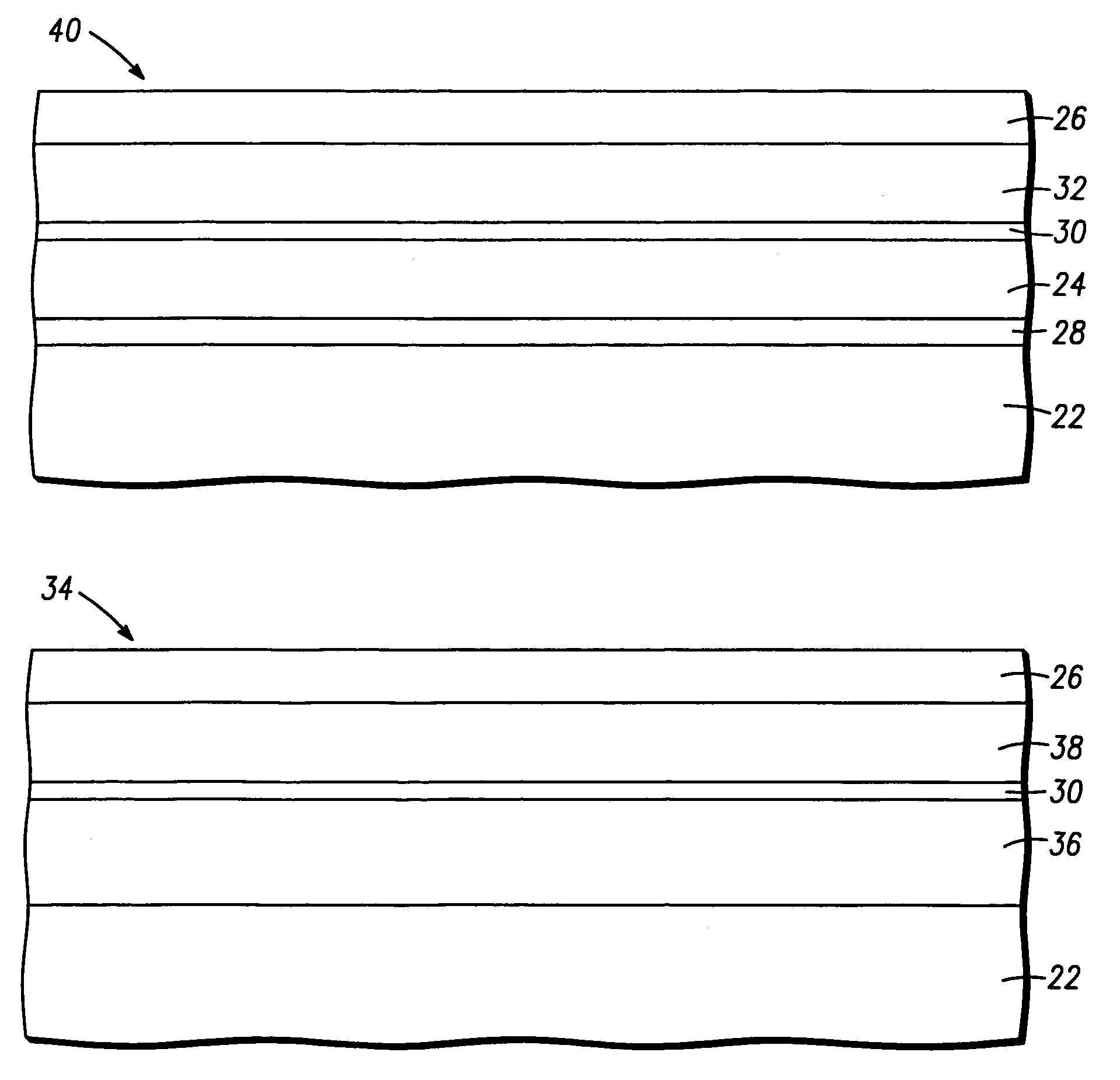
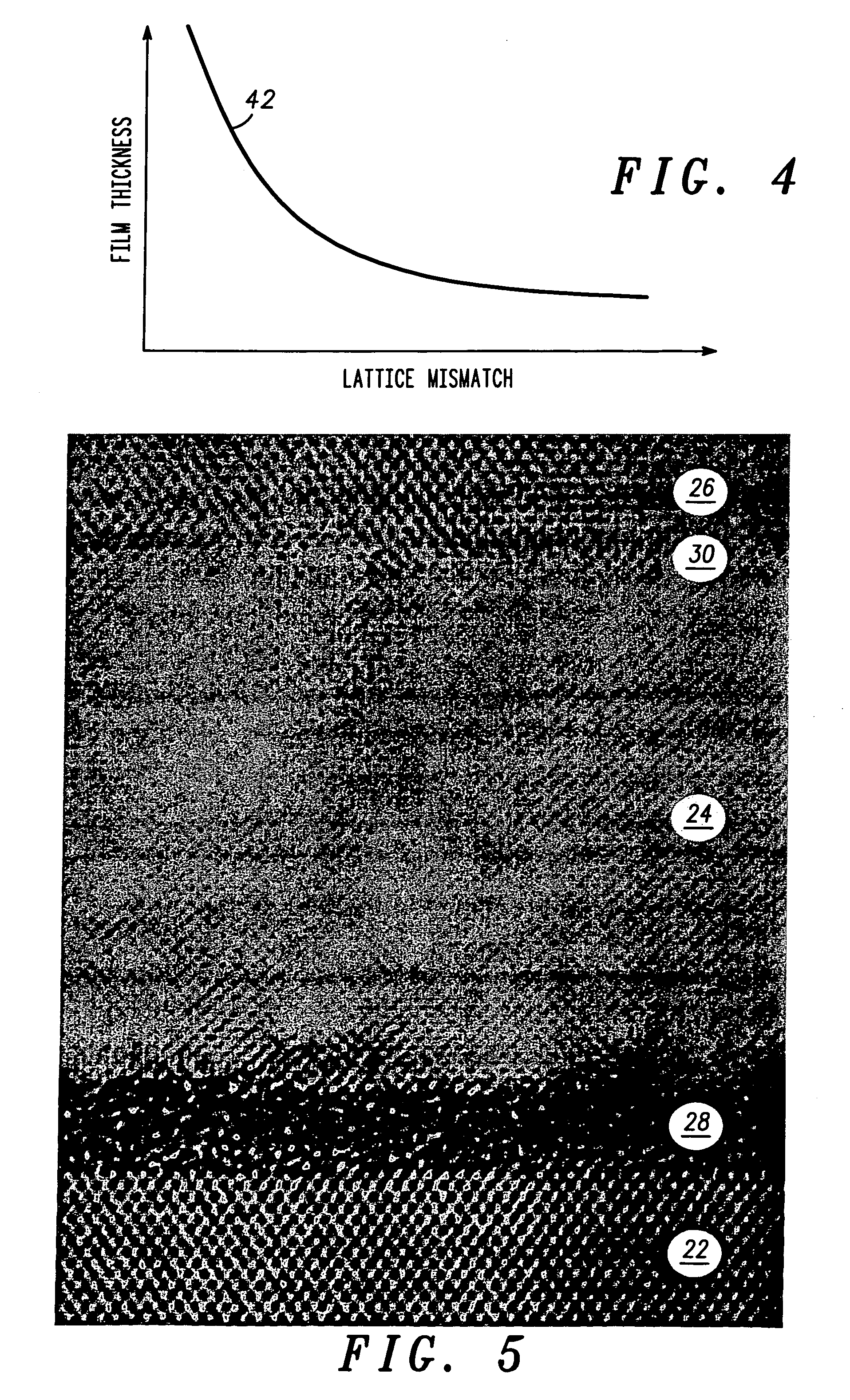
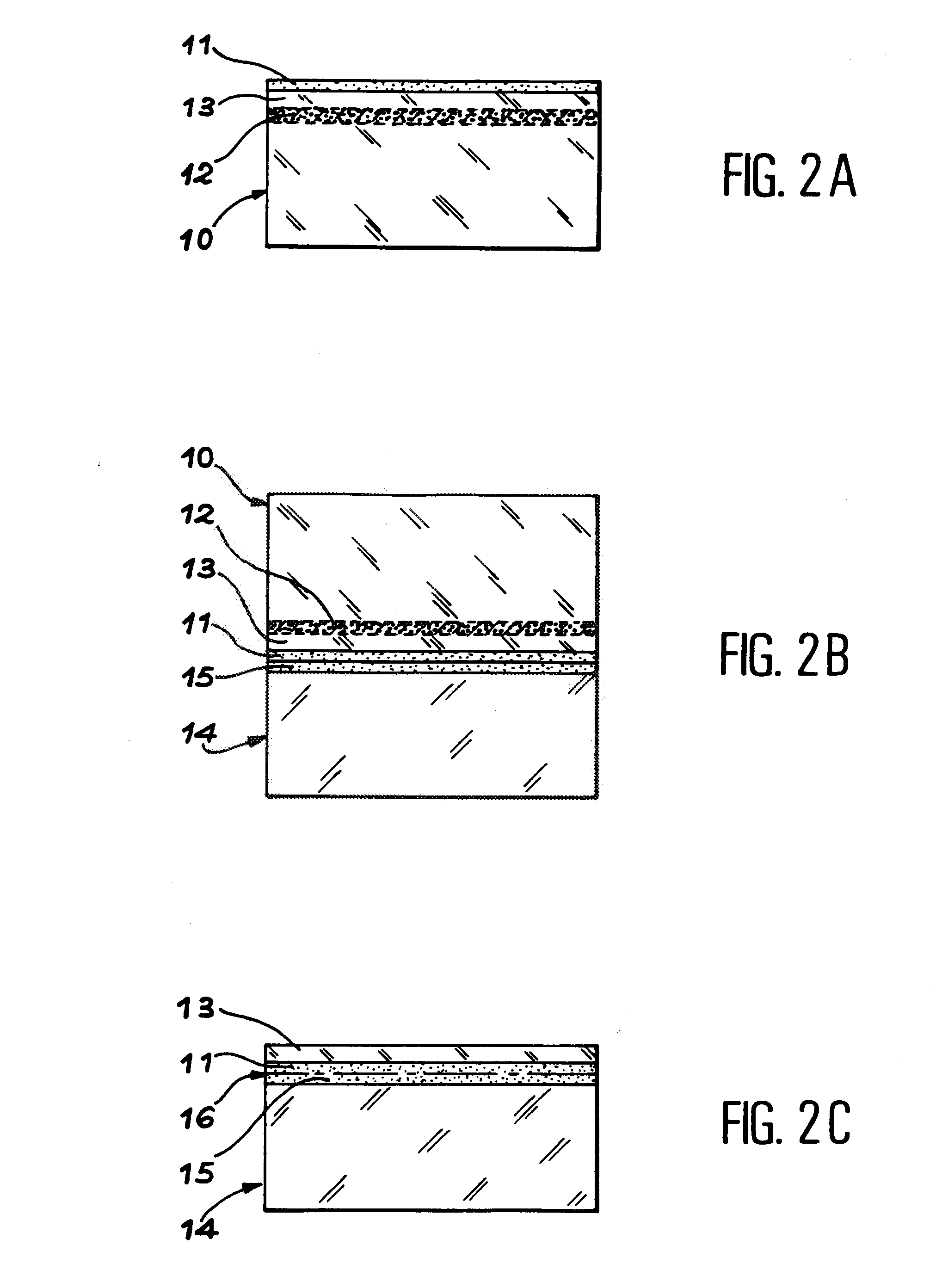
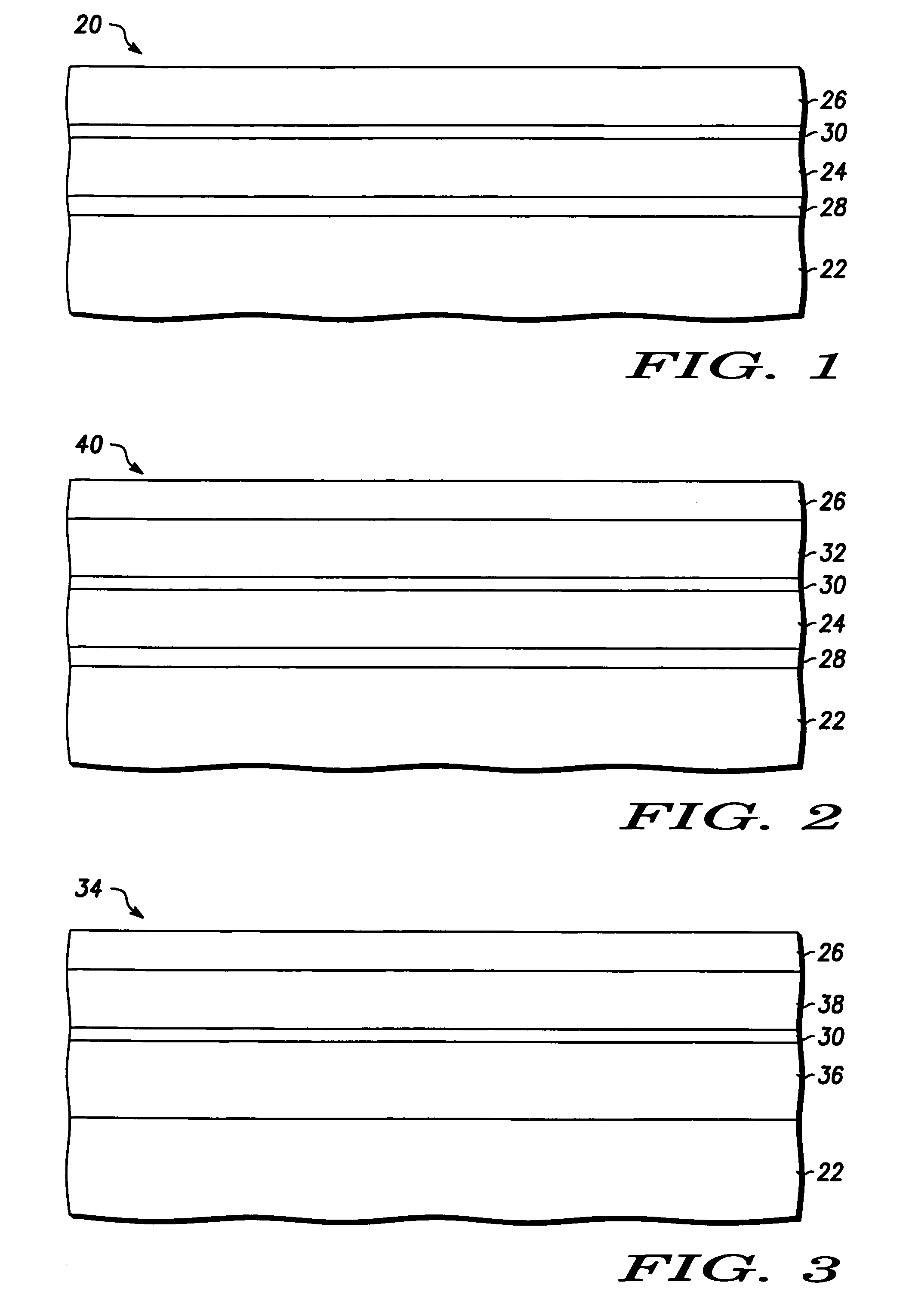
Structure and method for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices utilizing the formation of a compliant III-V arsenide nitride substrate used to form the same
InactiveUS20030013223A1Laser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsStrontium titanium oxideLattice mismatch
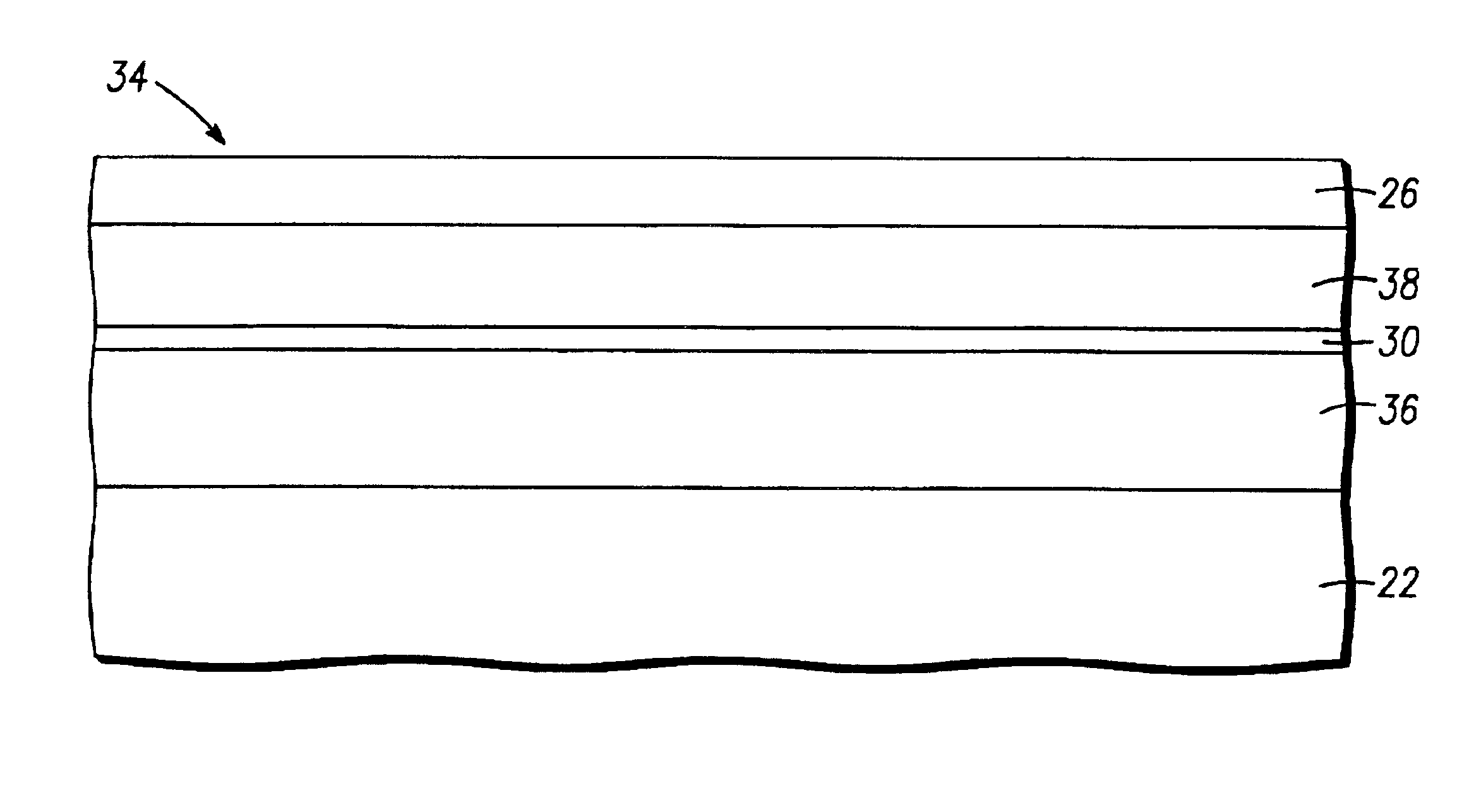
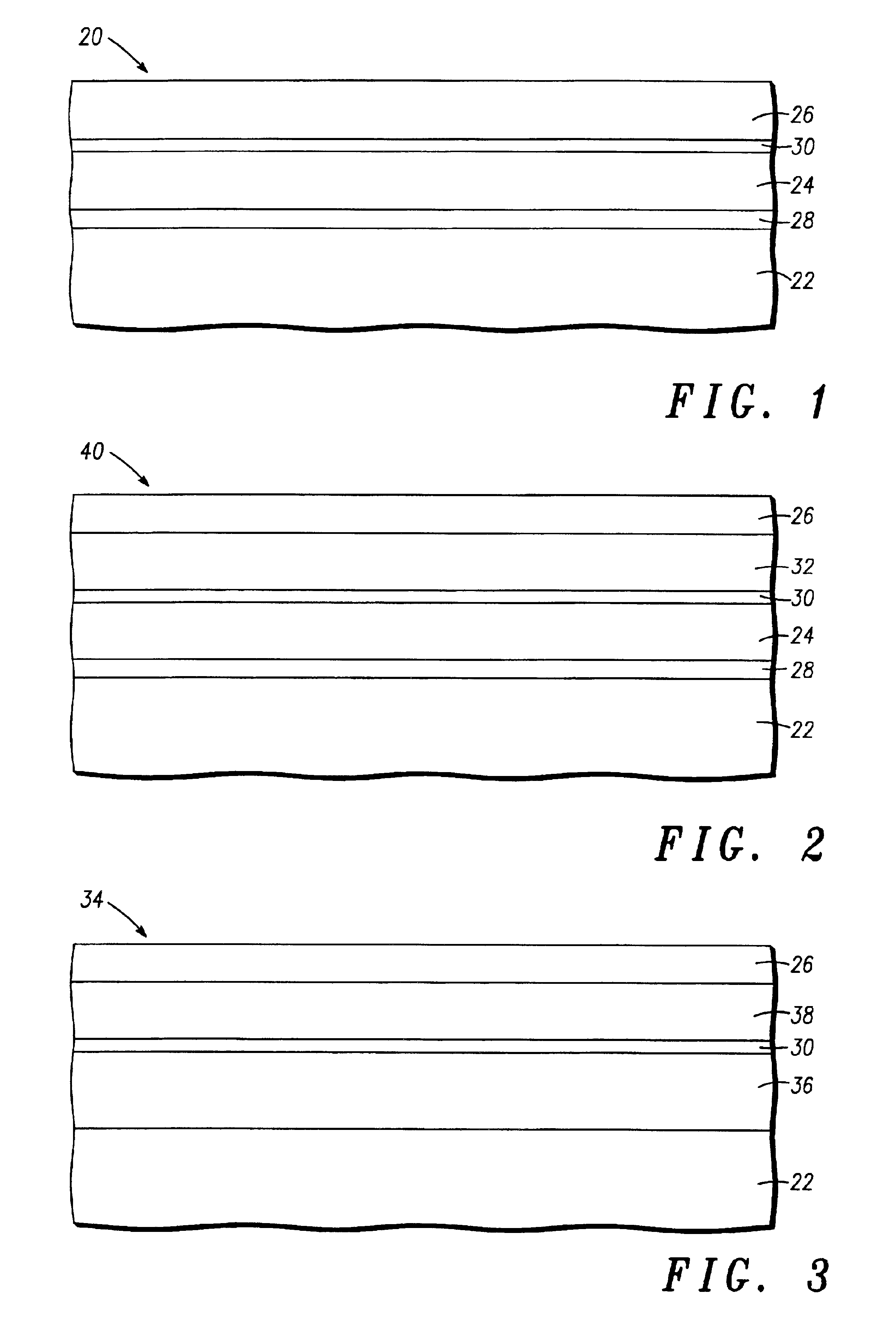
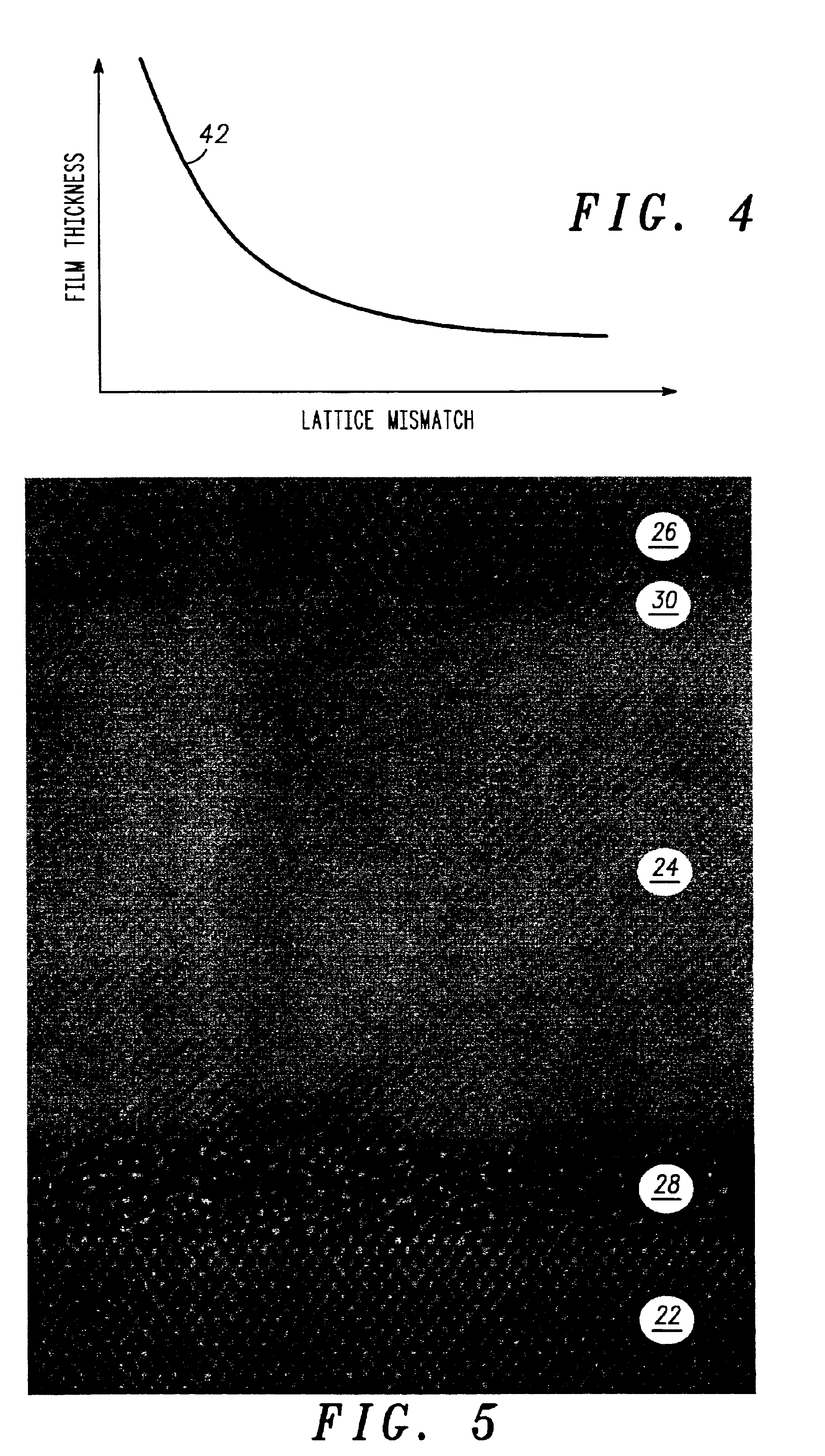
High quality epitaxial layers of monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride materials can be grown overlying monocrystalline substrates such as large silicon wafers by forming a compliant substrate for growing the monocrystalline layers. One way to achieve the formation of a compliant substrate includes first growing an accommodating buffer layer on a silicon wafer. The accommodating buffer layer is a layer of monocrystalline oxide spaced apart from the silicon wafer by an amorphous interface layer of silicon oxide. The amorphous interface layer dissipates strain and permits the growth of a high quality monocrystalline oxide accommodating buffer layer. The accommodating buffer layer is lattice matched to both the underlying silicon wafer and the overlying monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride material layer. Any lattice mismatch between the accommodating buffer layer and the underlying silicon substrate is taken care of by the amorphous interface layer. In addition, an accommodating buffer layer comprising a barium strontium titanium oxide and a monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride layer, such as GaAsN, having a nitrogen concentration ranging from 1-5% function to further reduce any lattice mismatch between layers.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Process for making an embossed web
ActiveUS20100230858A1Evenly distributedRubber hardnessMechanical working/deformationDecorative surface effectsEngineeringCompliant substrate
A process for making an embossed web. A precursor web is provided between a forming structure and a compliant substrate. The forming structure has a plurality of discrete protruded elements and lands completely surrounding them. Pressure is provided between the compliant substrate and the forming structure to conform the precursor web to the forming structure to form the embossed web. The resulting embossed web has a plurality of discrete extended elements completely surrounded by land areas.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Structure and method for fabricating configurable transistor devices utilizing the formation of a compliant substrate for materials used to form the same
InactiveUS6855992B2Laser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor structure includes a monocrystalline silicon substrate, an amorphous oxide material overlying the monocrystalline silicon substrate, a monocrystalline perovskite oxide material overlying the amorphous oxide material, and a monocrystalline compound semiconductor material overlying the monocrystalline perovskite oxide material. A composite transistor includes a first transistor having first active regions formed in the monocrystalline silicon substrate, a second transistor having second active regions formed in the monocrystalline compound semiconductor material, and a mode control terminal for controlling the first transistor and the second transistor.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Strained-channel fet comprising twist-bonded semiconductor layer
InactiveUS20090173967A1Increase critical thicknessImprove propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSLattice mismatch
This invention provides a strained-channel field effect transistor (FET) in which the semiconductor of the channel of the FET is formed in a compliant substrate layer disposed over a twist-bonded semiconductor interface. This FET geometry increases the efficacy of local stress elements such as stress liners and embedded lattice-mismatched source / drain regions by mechanically decoupling the semiconductor of the channel region from the underlying rigid substrate. These strained-channel FETs may be incorporated into complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) circuits in various combinations. In one embodiment of this invention, both pFETs and nFETs are in a twist-bonded (001) silicon layer on a (001) silicon base layer. In another embodiment, pFETs are in a twist-bonded (011) silicon layer on a (001) silicon base layer and nFETs are in a conventional, non-twist-bonded (001) silicon base layer. This invention also provides a twist-bonded semiconductor layer on a polycrystalline base layer, as well as methods for fabricating the aforementioned FETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC +1
LED illumination assembly with compliant foil construction
An illumination assembly includes a compliant substrate comprising a first and second electrically conductive foil separated by an electrically insulating layer. The insulating layer includes a polymer material loaded with particles that enhance thermal conductivity of the insulating layer. A plurality of LED dies are disposed on the first conductive foil.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
LED illumination assembly with compliant foil construction
An illumination assembly includes a compliant substrate comprising a first and second electrically conductive foil separated by an electrically insulating layer. The insulating layer includes a polymer material loaded with particles that enhance thermal conductivity of the insulating layer. A plurality of LED dies are disposed on the first conductive foil.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Structure and method for fabricating GaN devices utilizing the formation of a compliant substrate
InactiveUS20050194593A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLattice mismatchSilicon
Owner:NXP USA INC
Structure and method for fabricating GaN devices utilizing the formation of a compliant substrate
InactiveUS7211852B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLattice mismatchSilicon
Owner:NXP USA INC
Process for making an embossed web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Structure and method for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices utilizing piezoelectric materials
InactiveUS6992321B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor structureInterface layer
High quality epitaxial layers of piezoelectric monocrystalline materials can be grown overlying monocrystalline substrates such as large silicon wafers by forming a compliant substrate for growing the piezoelectric monocrystalline layers. An accommodating buffer layer comprises a layer of monocrystalline oxide spaced apart from a silicon wafer by an amorphous interface layer of silicon oxide. The amorphous interface layer permits the growth of a high quality monocrystalline oxide accommodating buffer layer. The accommodating buffer layer is lattice matched to both the underlying silicon wafer and the overlying piezoelectric monocrystalline material layer.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
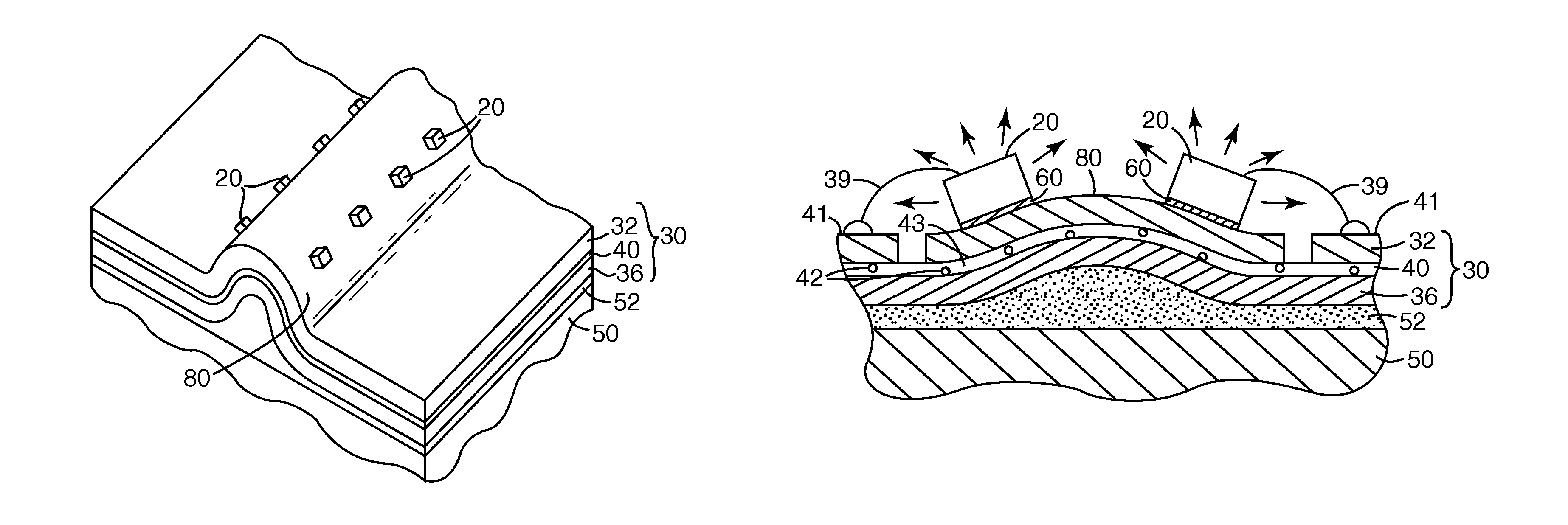
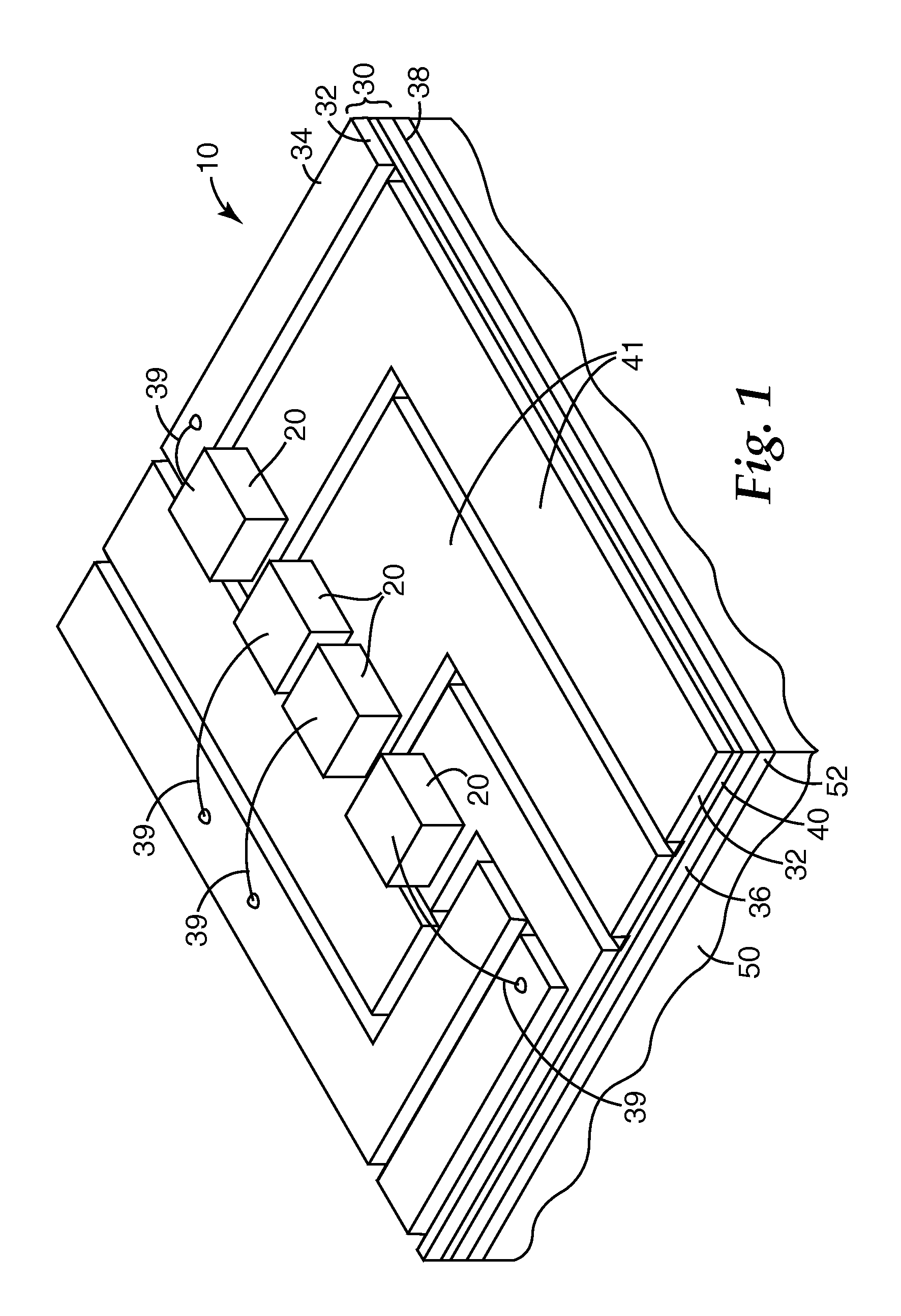
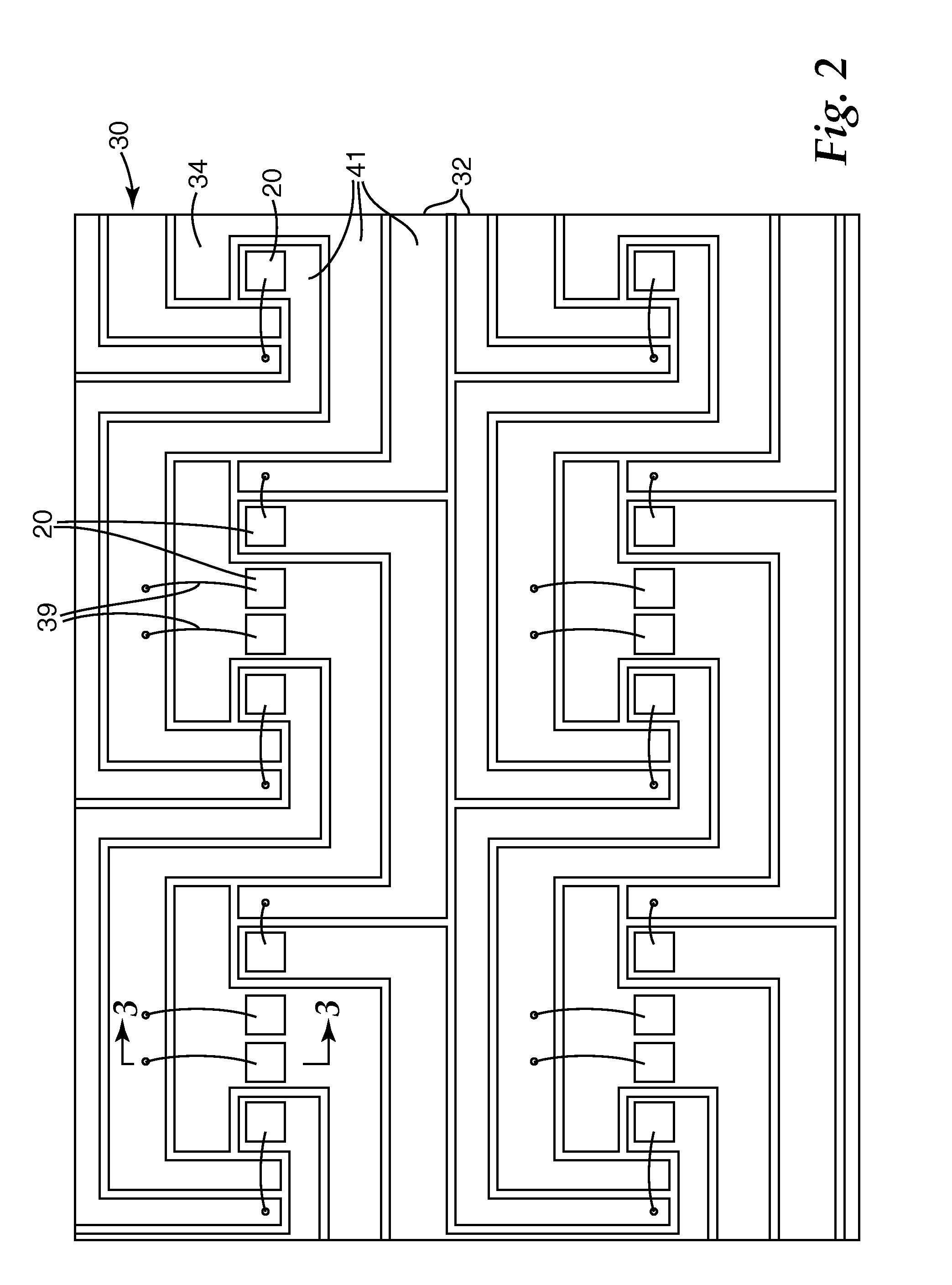
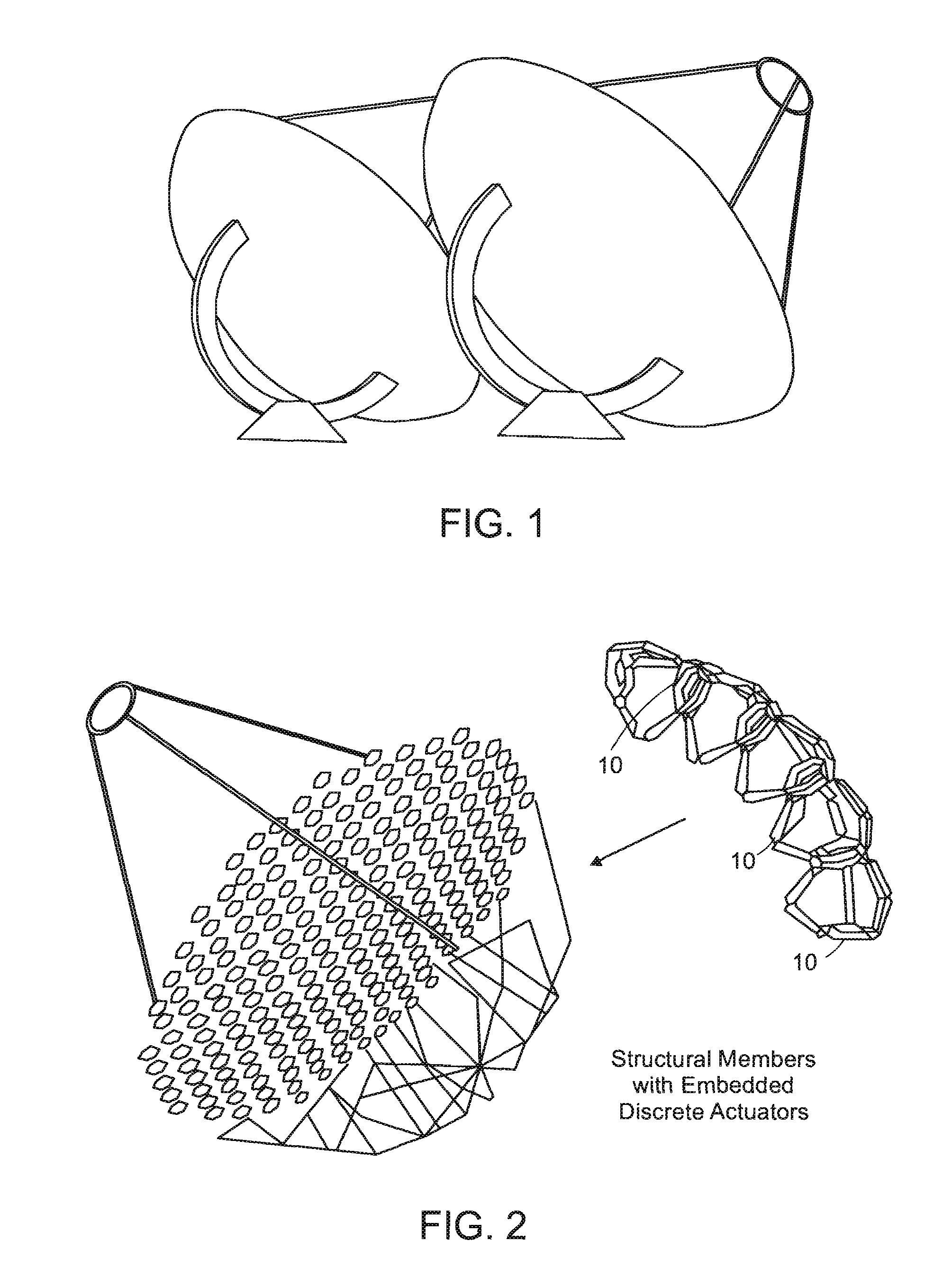
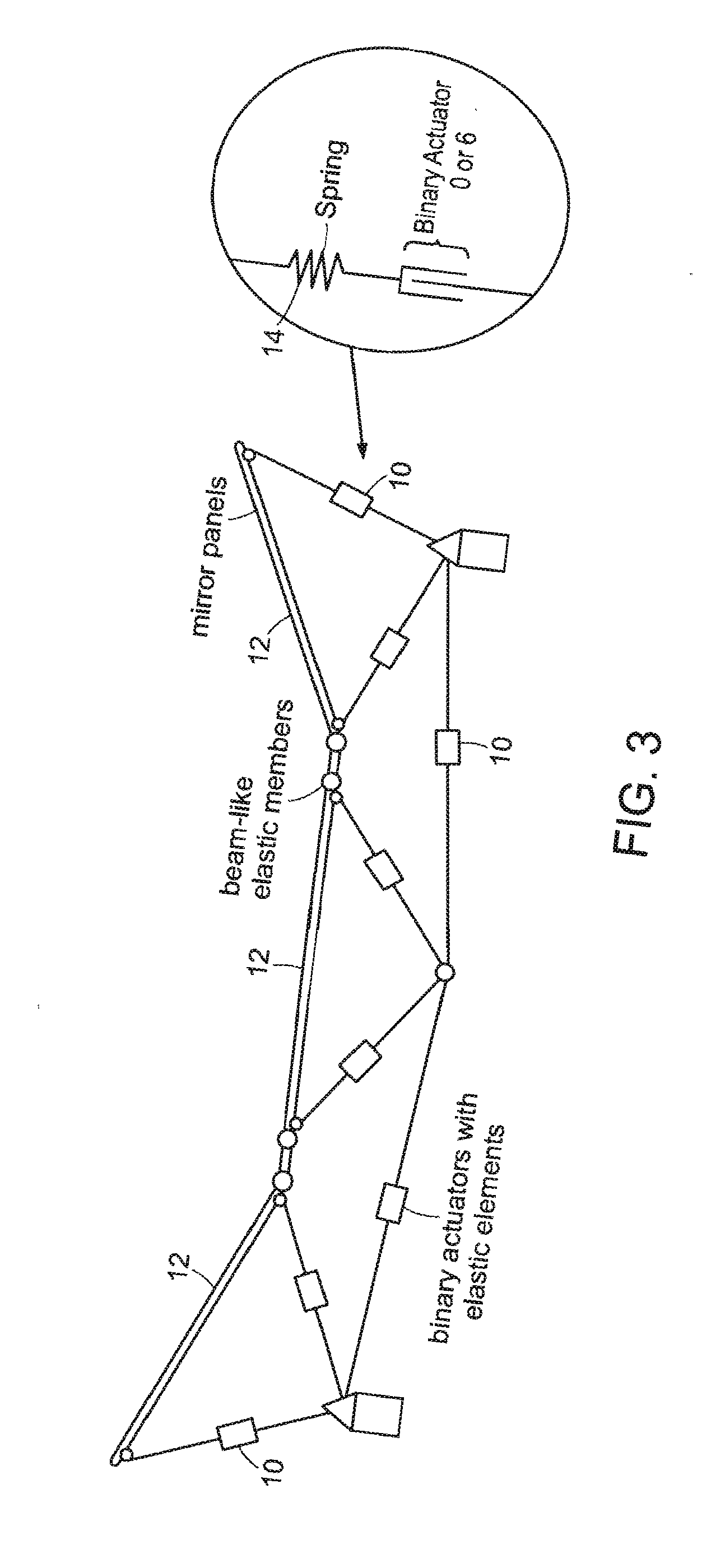
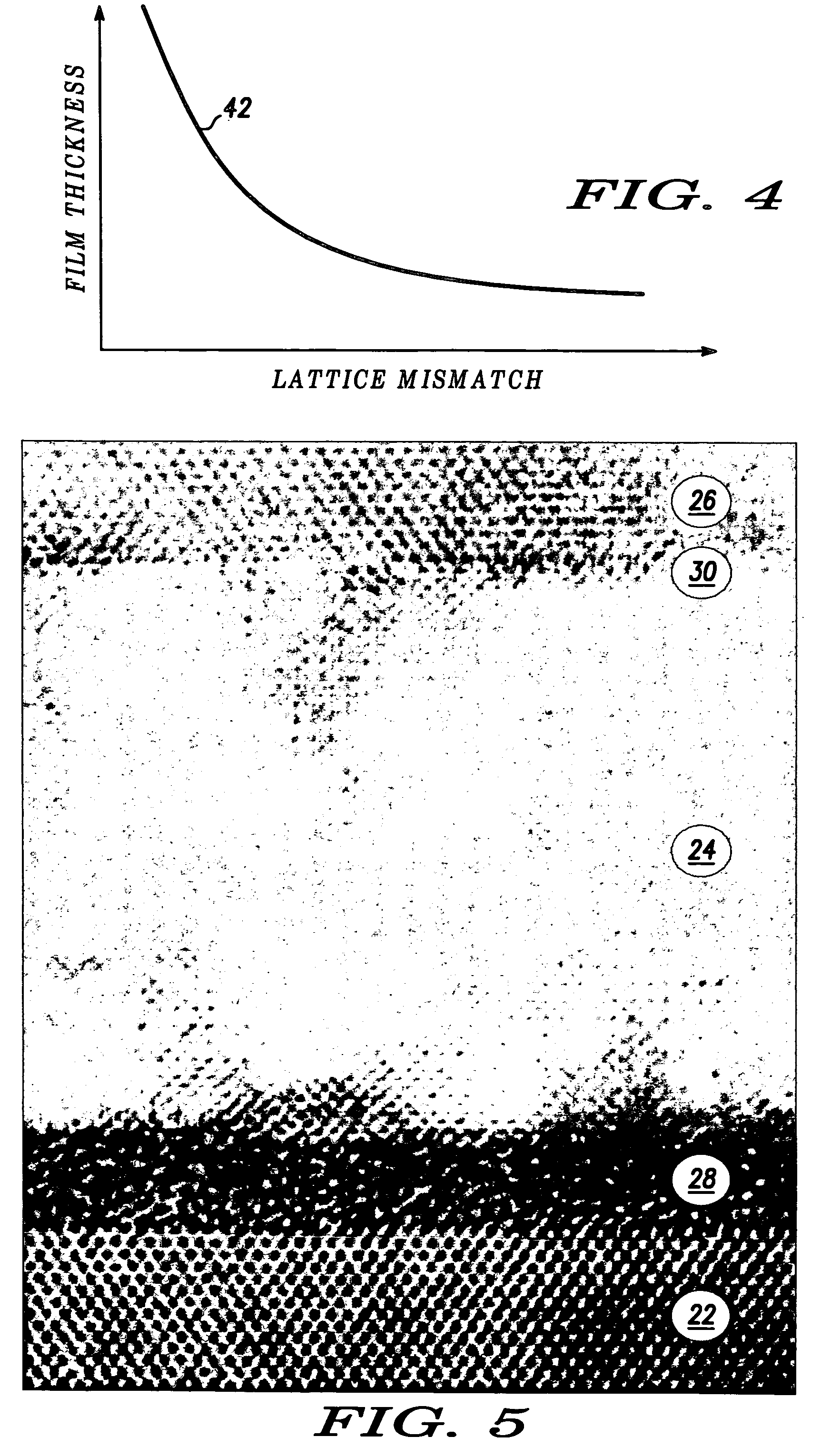
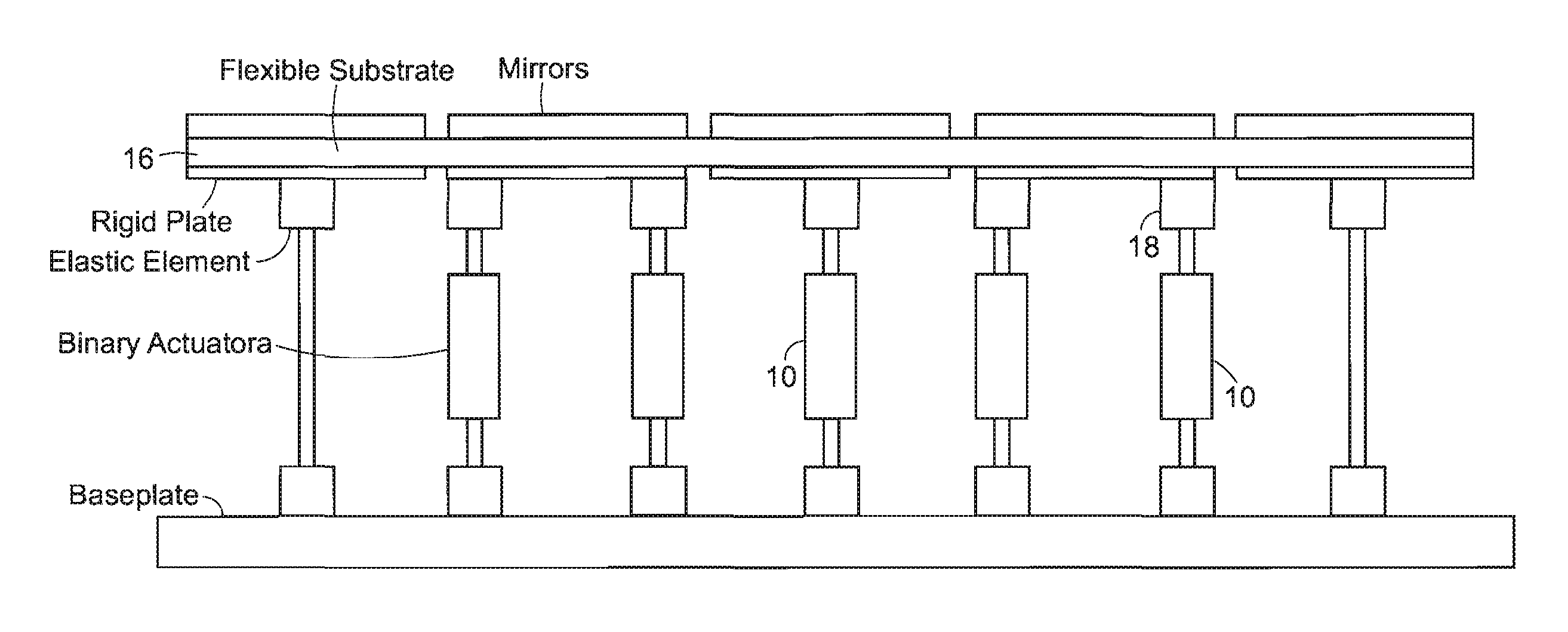
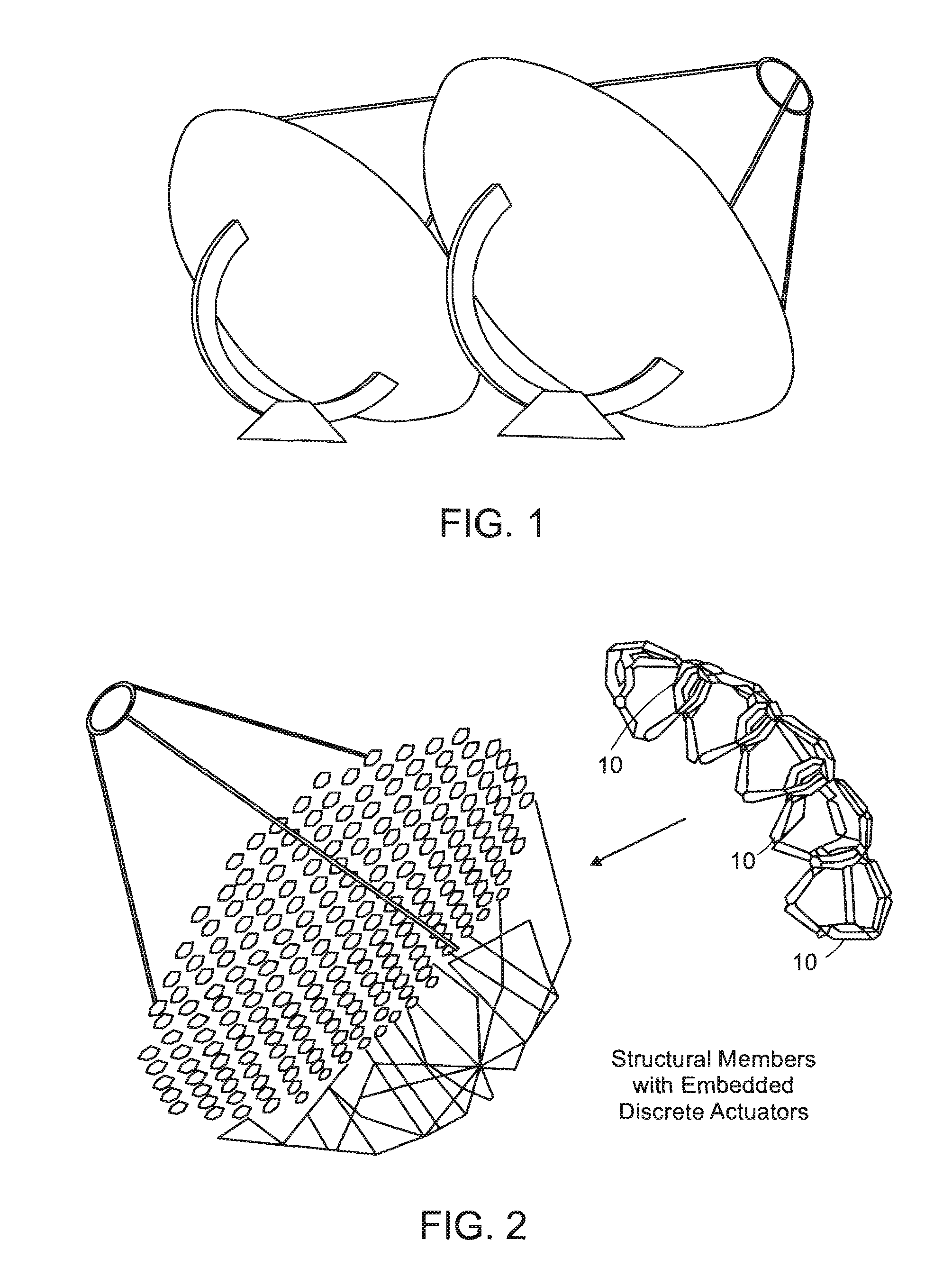
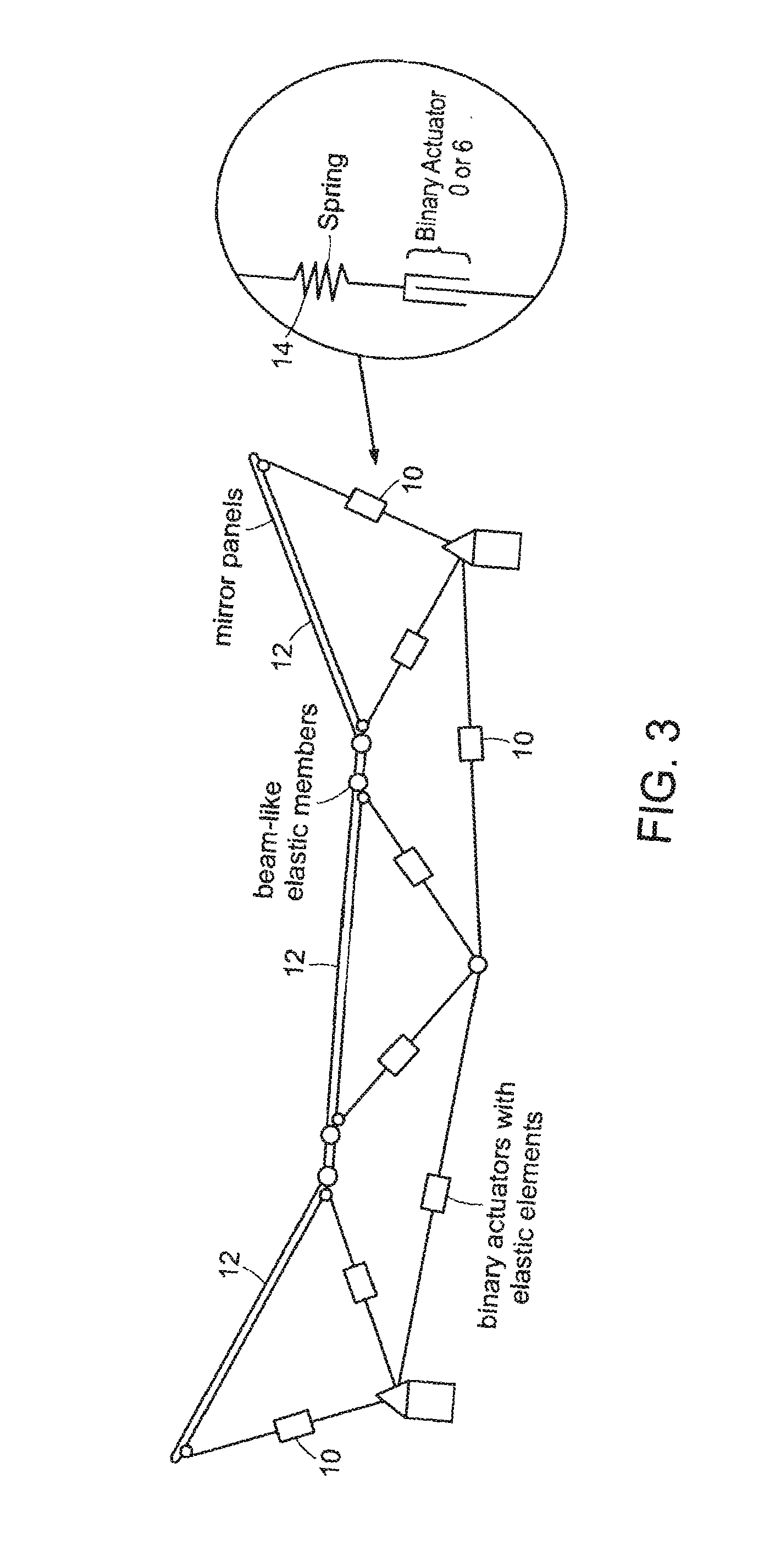
System for discretely actuated solar mirrors
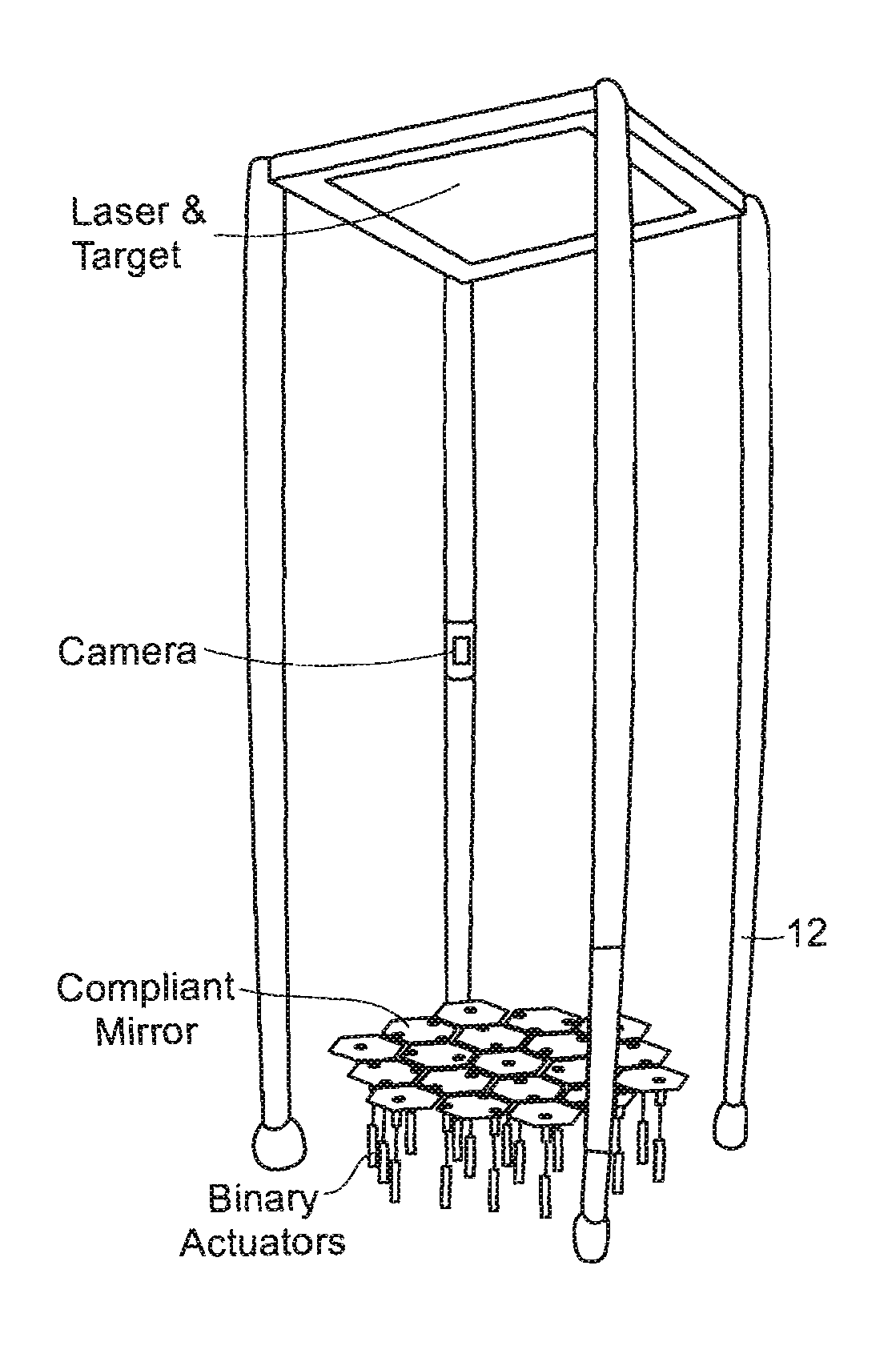
System for establishing a surface shape. The system includes a compliant substrate including the surface and having a reverse side, and a plurality of discrete actuators engaging the reverse side and arranged in a selected pattern to control the surface shape as individual discrete activators are activated. It is preferred that the actuators have multiple discrete stable states of elongation. A particularly preferred embodiment uses actuators that are binary with two stable states of elongation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
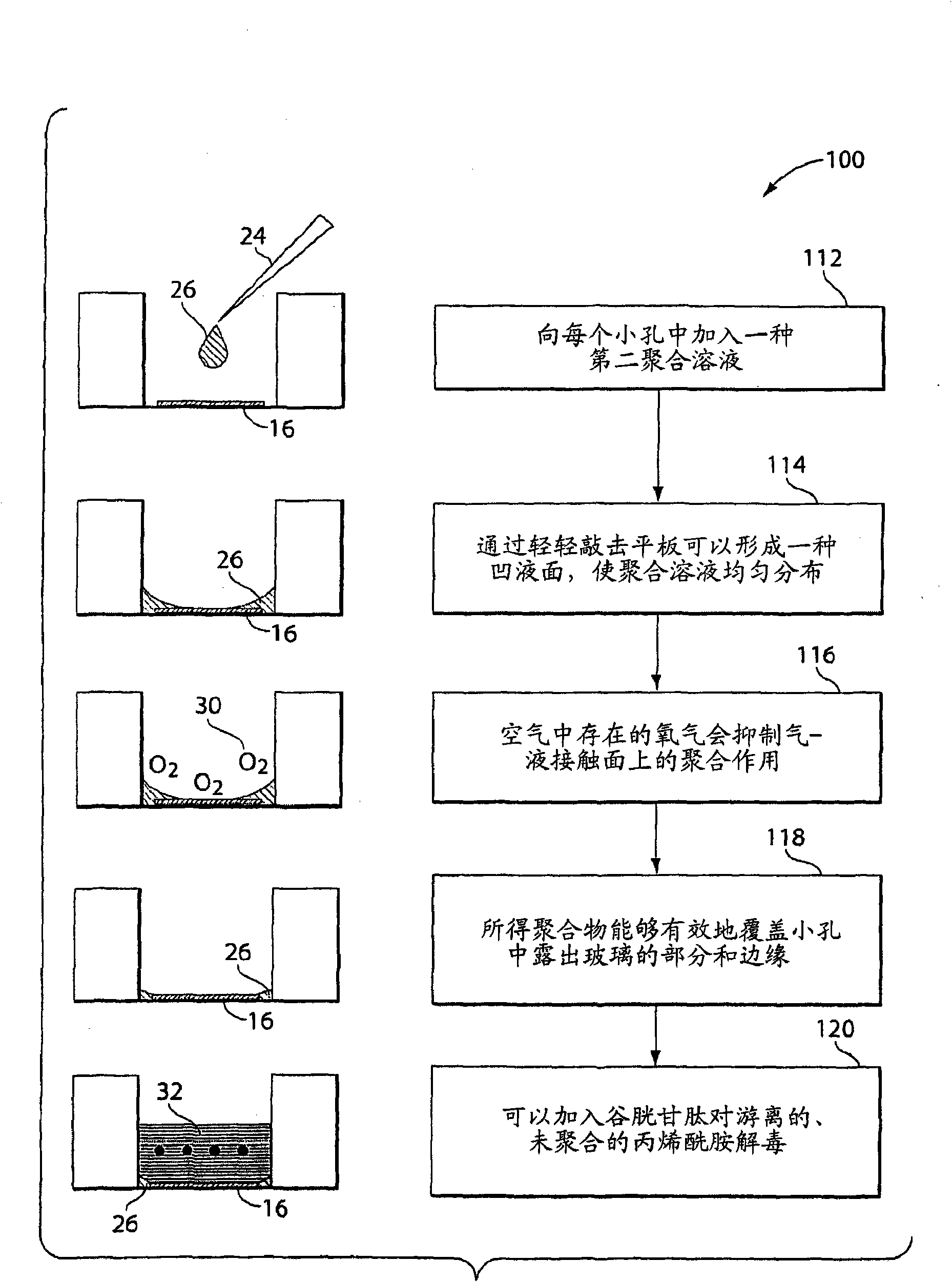
Compliant surface multi-well culture plate
InactiveCN101842474ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollagen iEngineering
A multi-well plate can be loaded with a range of compliant substrates. Commerically-available assays can be used to test cellular responses across a plate with shear modulus from 50 to 51200 Pascals. Cells can be grown in the plates, and can be manipulated and analyzed. Hydrogels can be attached to the bottom of a well. The plates can support the attachment and growth of different cell types and can be compatible with standard 96-well and 384-well plate assays. The mechanical properties of the hydrogels can be reproducible and stable to increase the shelf life of the substrate. The hydrogel can be compatible with growth of a variety of cell types, various attachment ligands such as collagen I, collagen IV, flbronectin, vitronectin, laminin, or RGD peptides and can be coupled to the gel surface.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
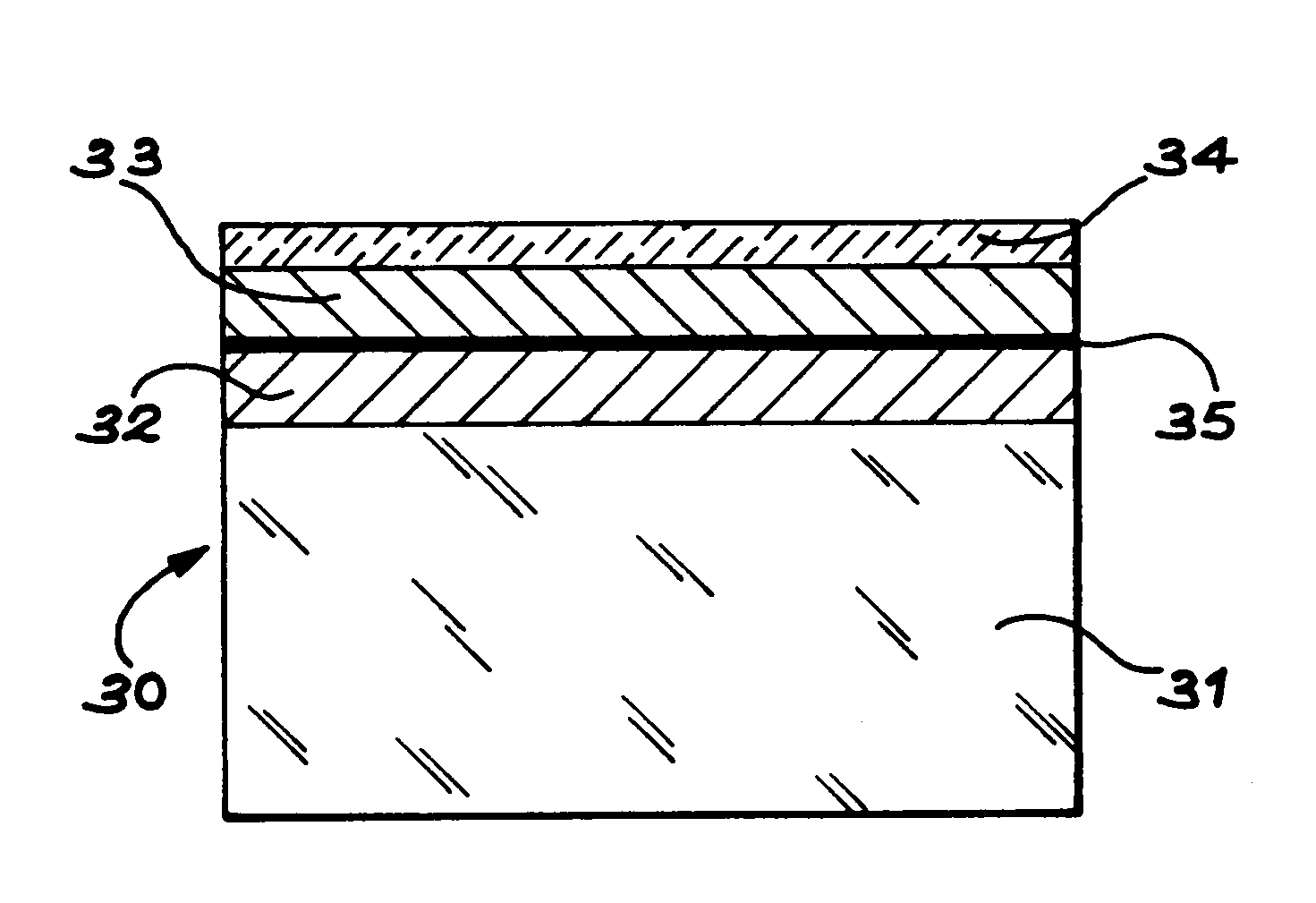
Compliant Substrate In Particular For Hetero-Epitaxial Depositing
InactiveUS20090311477A1Avoid it happening againSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond energyBond interface
The invention relates to a compliant substrate (5) comprising a carrier (1) and at least one thin layer (4), formed on the surface of the carrier and intended to receive, in integral manner, a stress-giving structure. The carrier (1) and the thin layer (4) are joined to one another by joining means (3) such that the stresses brought by said structure are absorbed in whole or in part by the thin layer (4) and / or by the joining means (3) which comprise at least one joining zone chosen from among the following joining zones: a layer of microcavities and / or a bonding interface whose bonding energy is controlled to permit absorption of said stresses.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
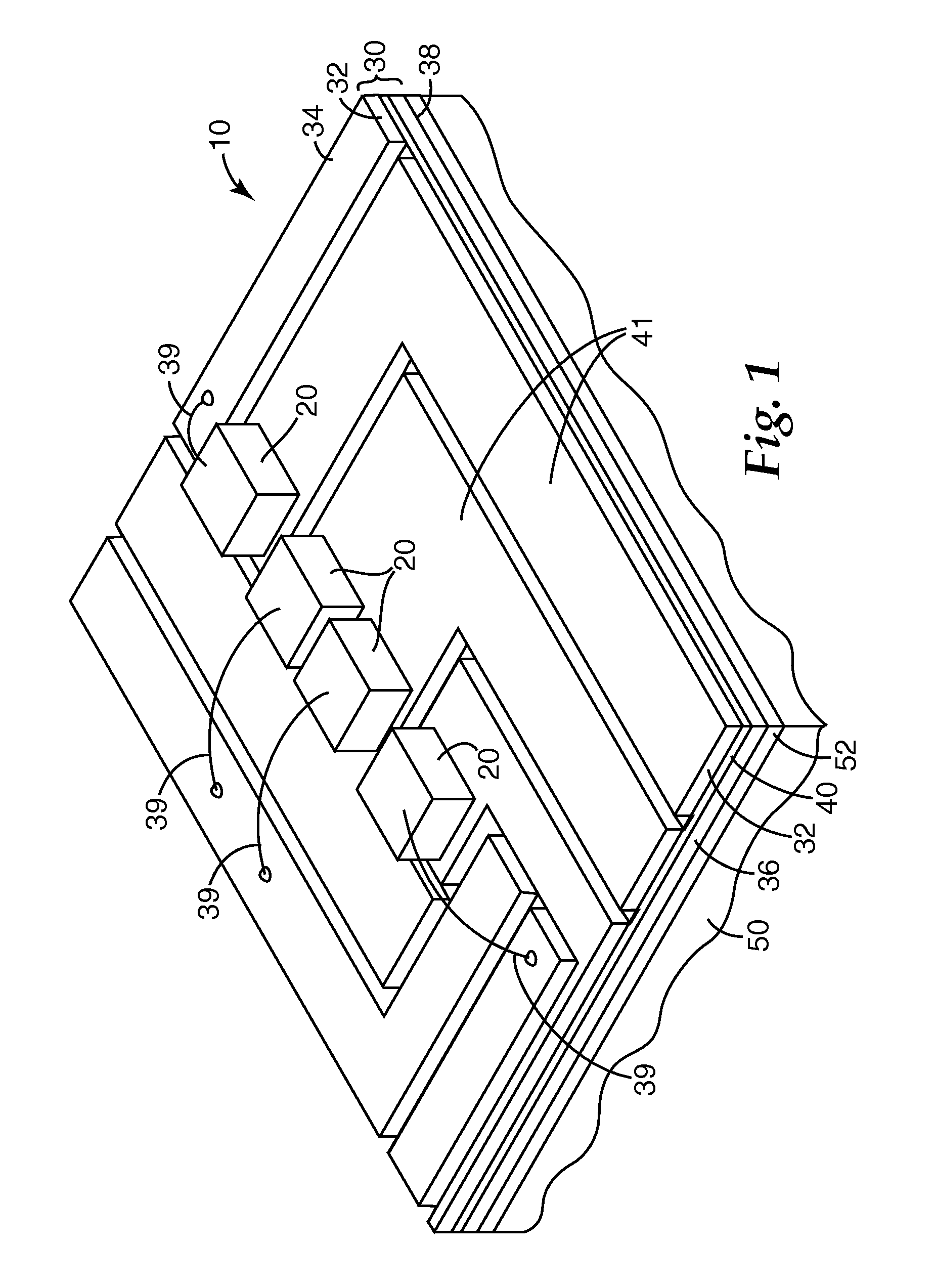
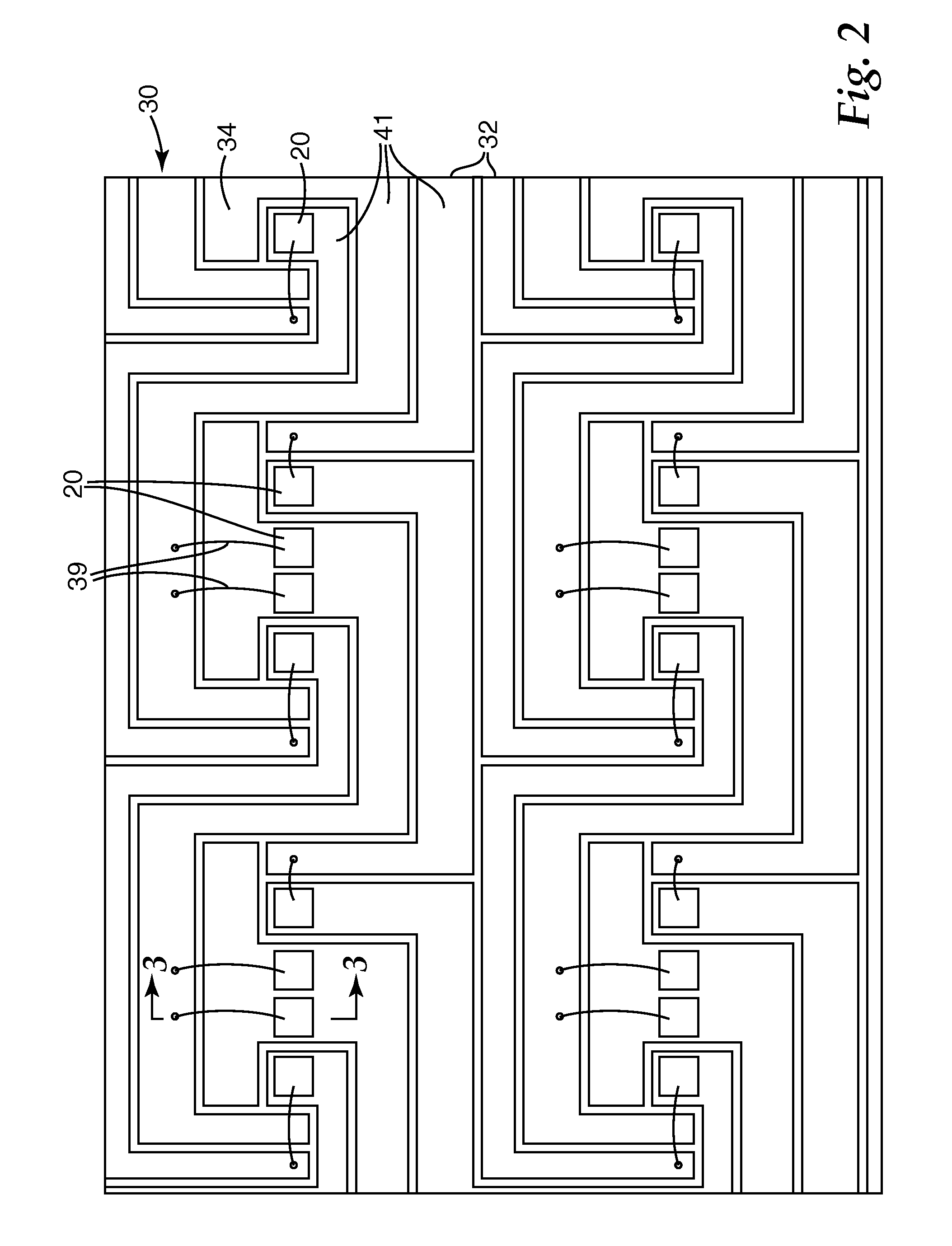
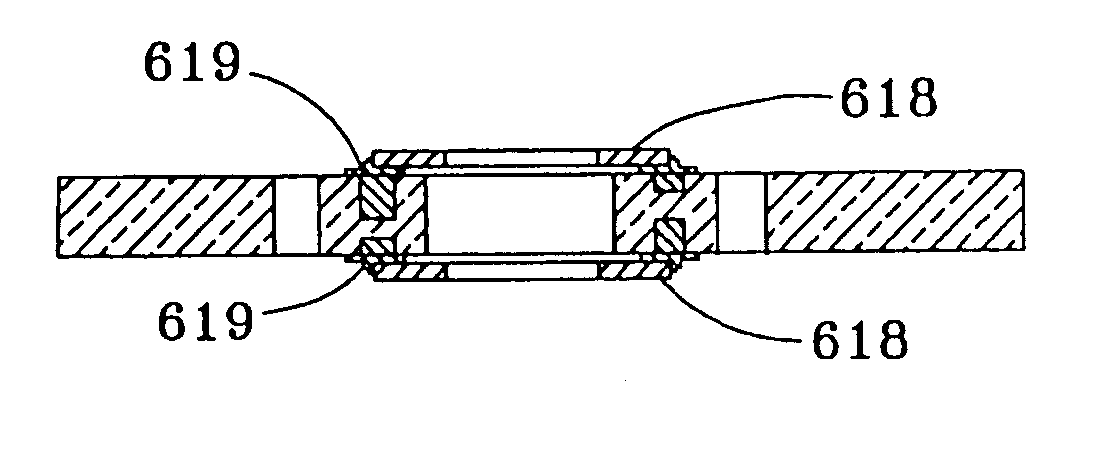
Circuit assembly having compliant substrate structures for mounting circuit devices
InactiveUS20050006141A1Reduce thermal stressWithout sacrificing reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSurface mountingEngineering
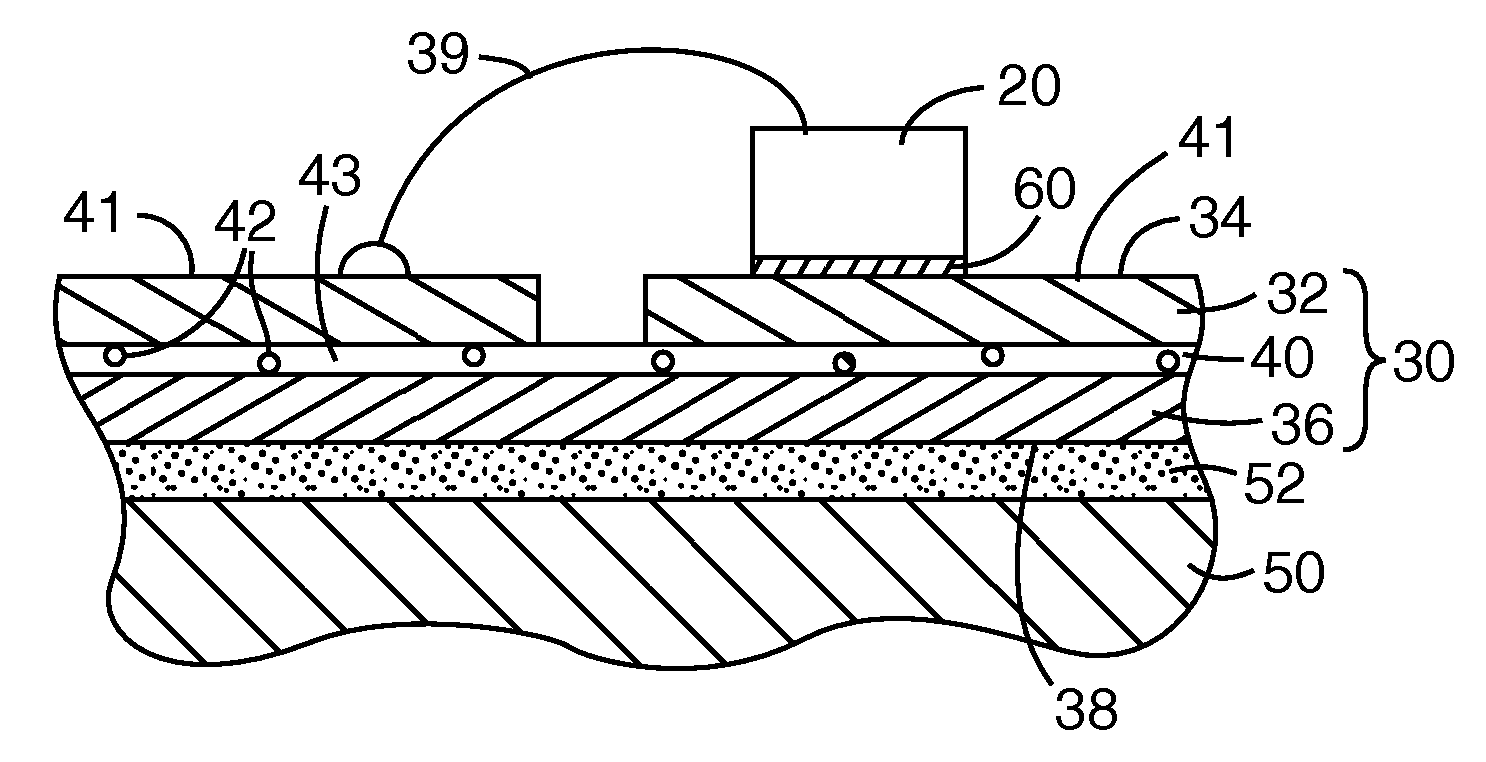
A circuit assembly comprising a substrate formed to have one or more apertures that define one or more compliant members in the substrate, and to which a circuit device can be attached so as to reduce thermally-induced stresses in the device and in solder joints securing the device to the substrate. The compliant members are sufficiently compliant to permit relatively large surface-mount devices to be attached to an organic substrate without sacrificing reliability.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Fabrication of a wavelength locker within a semiconductor structure
InactiveUS7019332B2Laser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsSemiconductor structureLattice mismatch
High quality epitaxial layers of monocrystalline materials can be grown overlying monocrystalline substrates such as large silicon wafers by forming a compliant substrate for growing the monocrystalline layers. An accommodating buffer layer comprises a layer of monocrystalline oxide spaced apart from a silicon wafer by an amorphous interface layer of silicon oxide. The amorphous interface layer dissipates strain and permits the growth of a high quality monocrystalline oxide accommodating buffer layer. The accommodating buffer layer is lattice matched to both the underlying silicon wafer and the overlying monocrystalline material layer. Any lattice mismatch between the accommodating buffer layer and the underlying silicon substrate is taken care of by the amorphous interface layer. In addition, formation of a compliant substrate may include utilizing surfactant enhanced epitaxy, epitaxial growth of single crystal silicon onto single crystal oxide, and epitaxial growth of Zintl phase materials. A wavelength locker for stabilizing a wavelength of an optical output signal from an optical transmitter is formed overlying the silicon wafer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Compliant substrate holding assembly
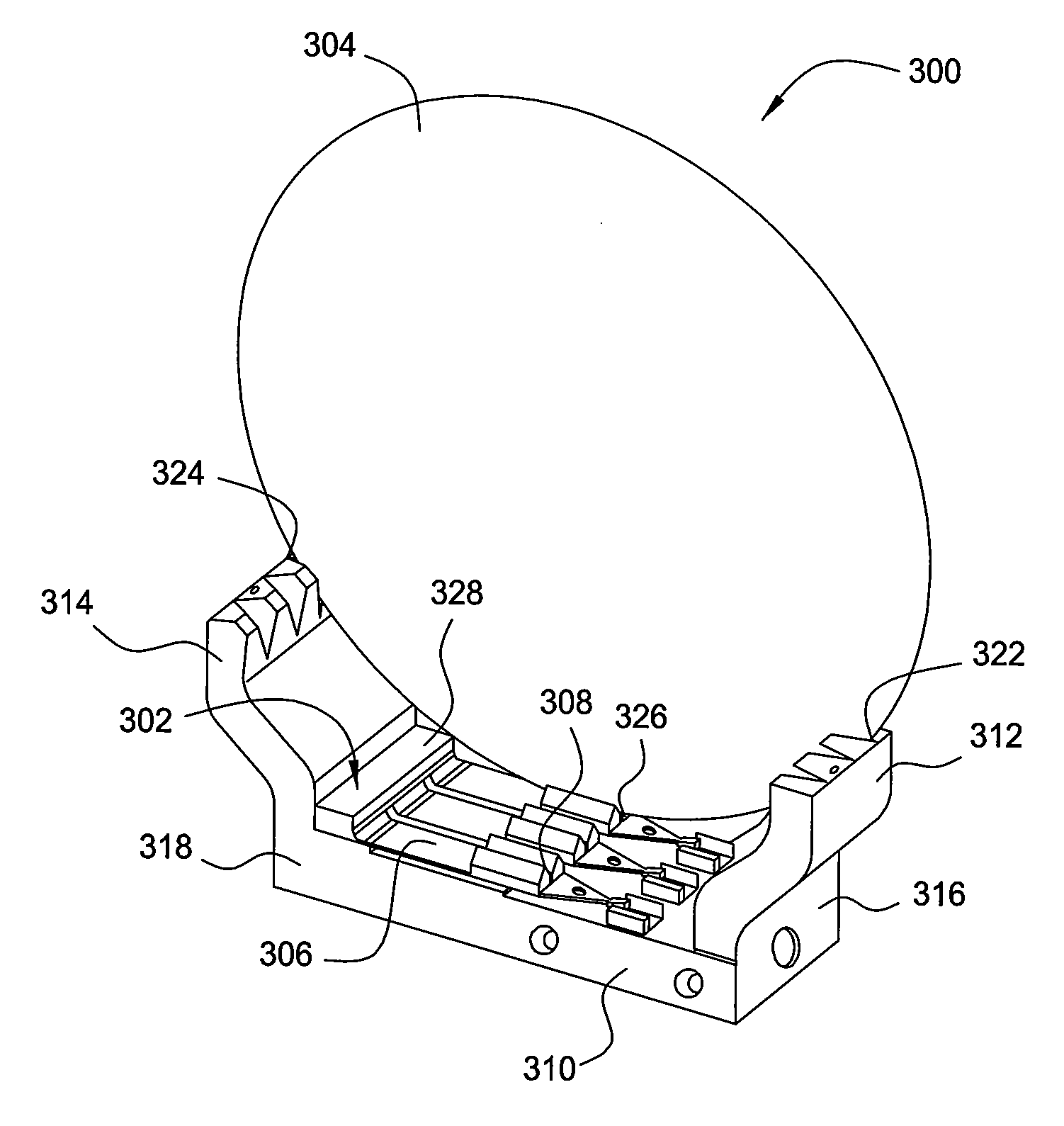
InactiveUS20080157455A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPositioning apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Methods and apparatus for holding substrate in a compliant substrate holding assembly are provided. In one embodiment, an apparatus for a compliant substrate holding assembly includes a base plate, a finger disposed on the base plate having a V-shaped slot formed thereon, and two arms disposed on opposite ends of the base plate and each arm having V-shaped slot formed therein. In another embodiment, a method for holding a substrate on a compliant substrate holding assembly includes inserting a substrate into a holding assembly having at least three substrate supporting members and detecting a change in position of one of the substrate supporting structures.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
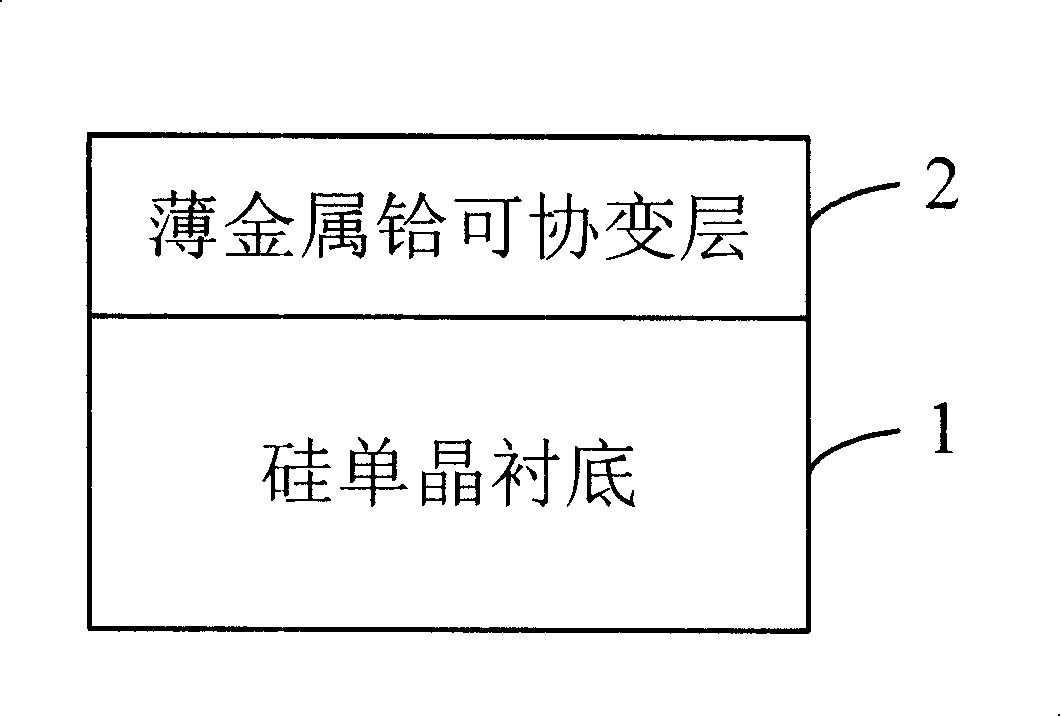
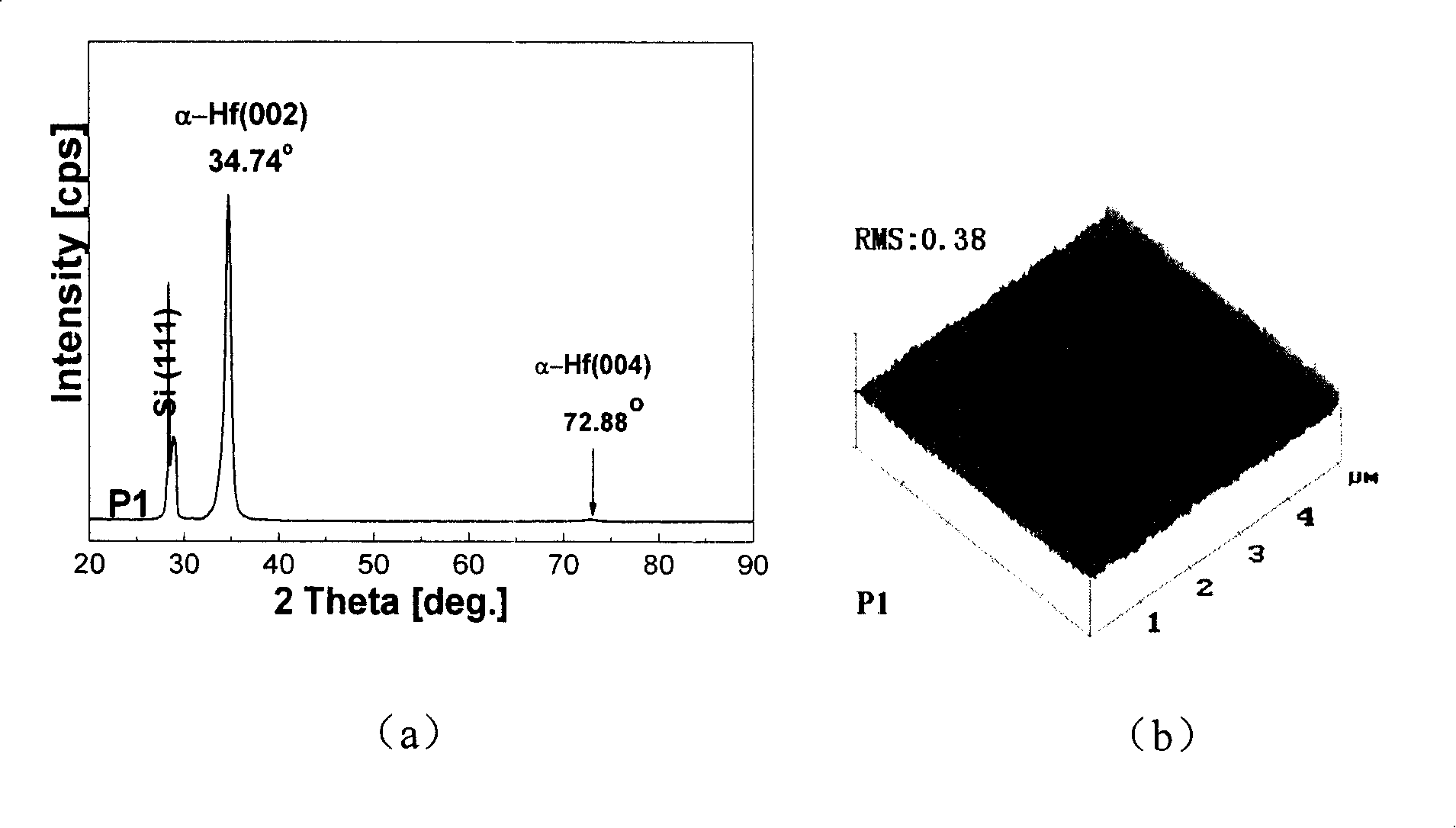
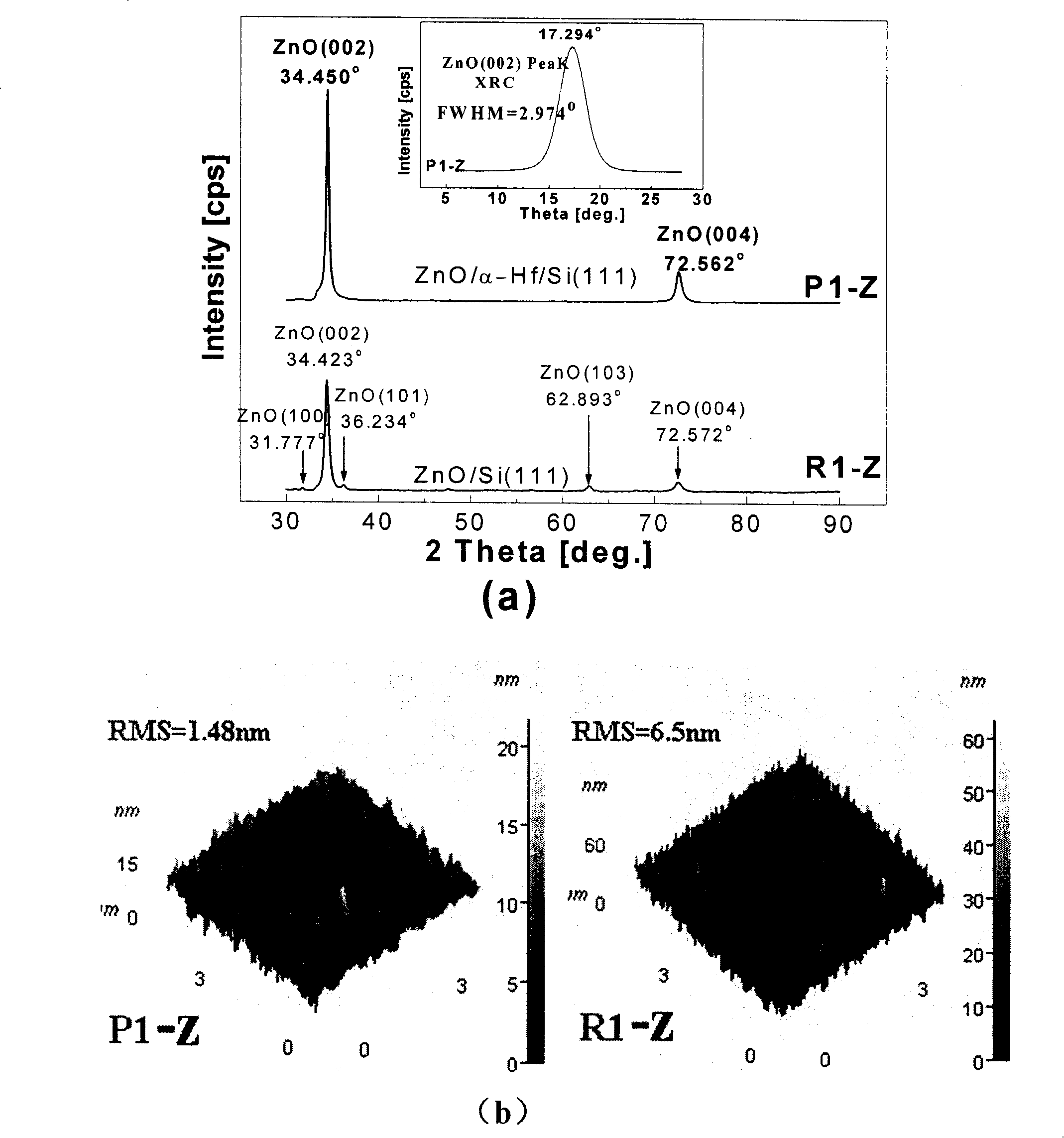
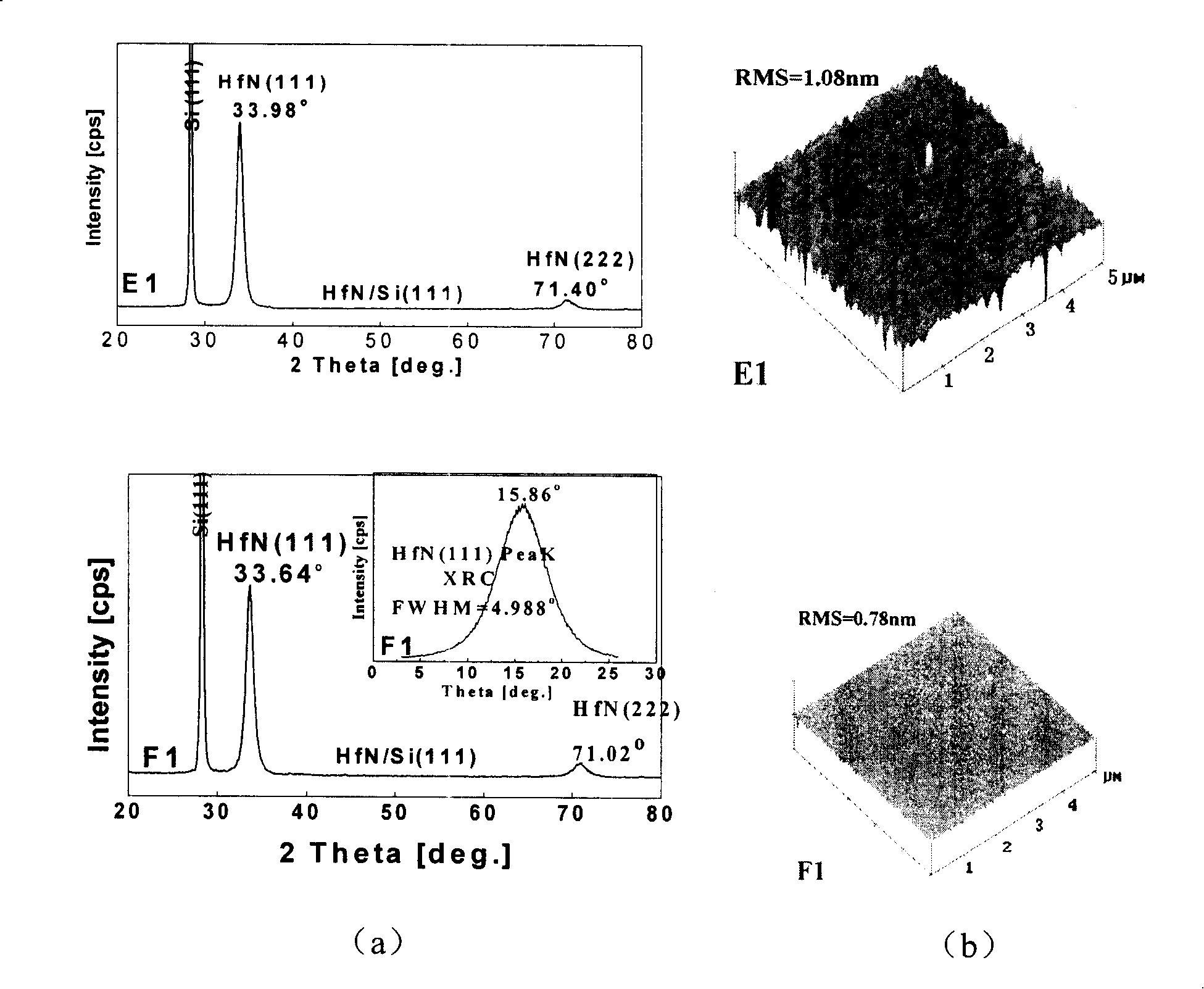
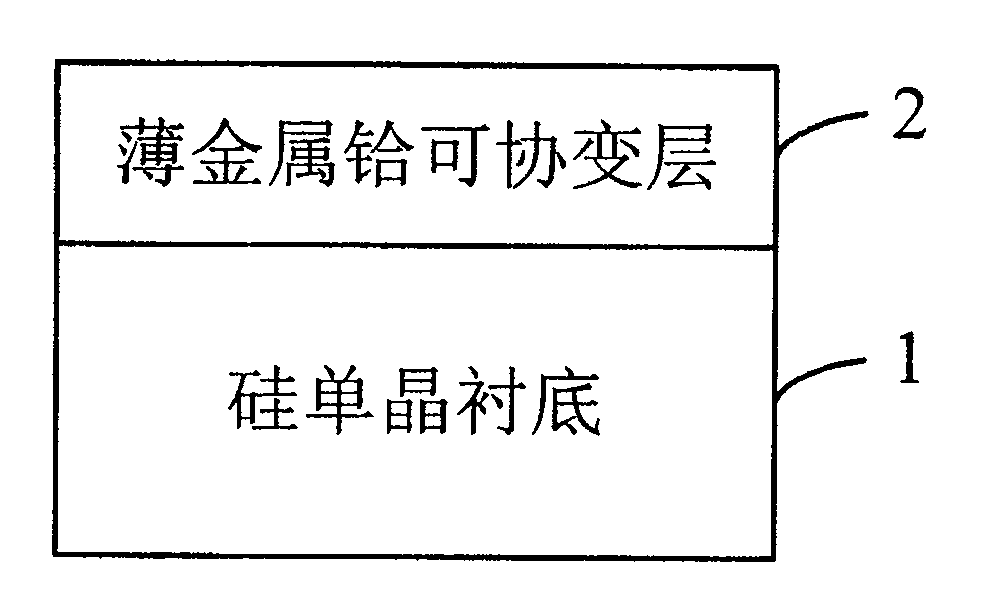
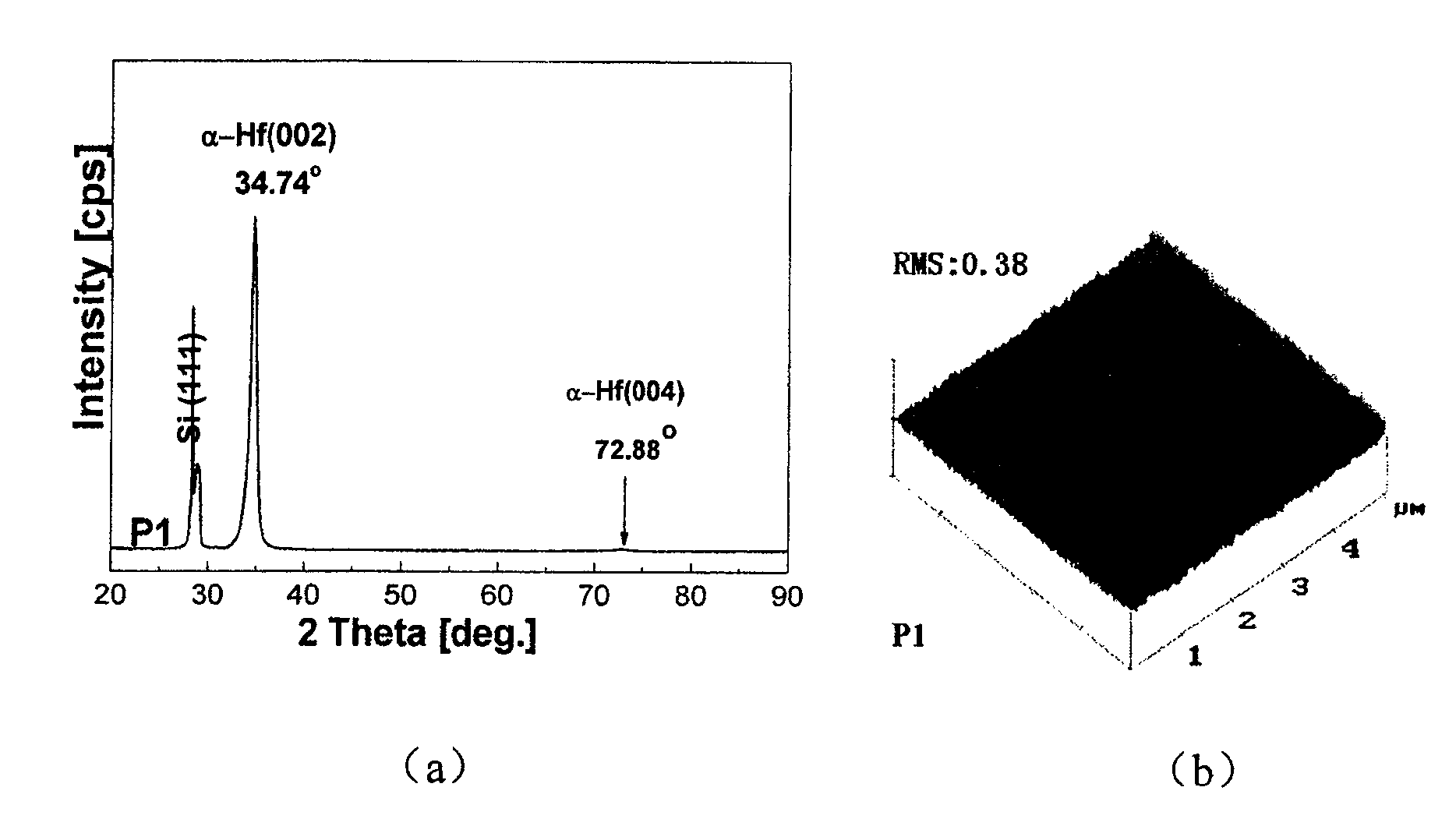
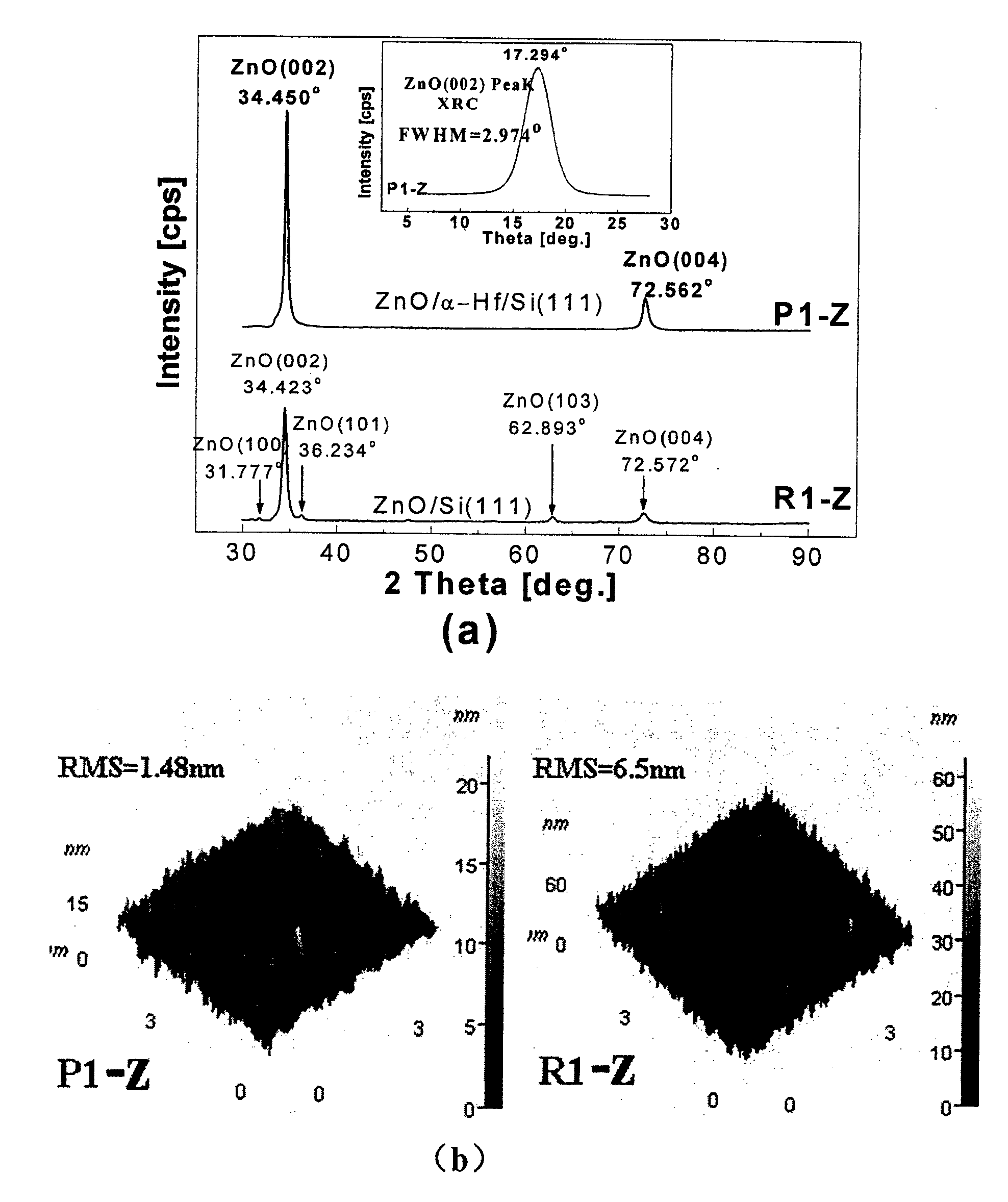
Silicon based compliant substrate material for zinc oxide epitaxial film growth
InactiveCN101211866ACoordination mismatch strainReduce residual stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMisfit strainThin metal
The invention relates to a technical field for making a zinc oxide epitaxial film in semiconductor material and discloses silicon-based covariant substrate material used for growing the zinc oxide epitaxial film, which comprises a silicon single crystal substrate used for supporting the whole silicon-based covariant substrate material; a thin metal hafnium covariant layer; the thin metal hafnium covariant layer is made on the silicon single crystal substrate used for coordinating misfit strain for the zinc oxide epitaxial film which epitaxial grows on the silicon single crystal substrate. By adopting the invention, the misfit strain of the zinc oxide epitaxial film grown on the silicon substrate is coordinated and residual stress is decreased thereby enhancing the crystal quality and improving the appearance of the surface, which lays a foundation for developing silicon based photoelectric devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
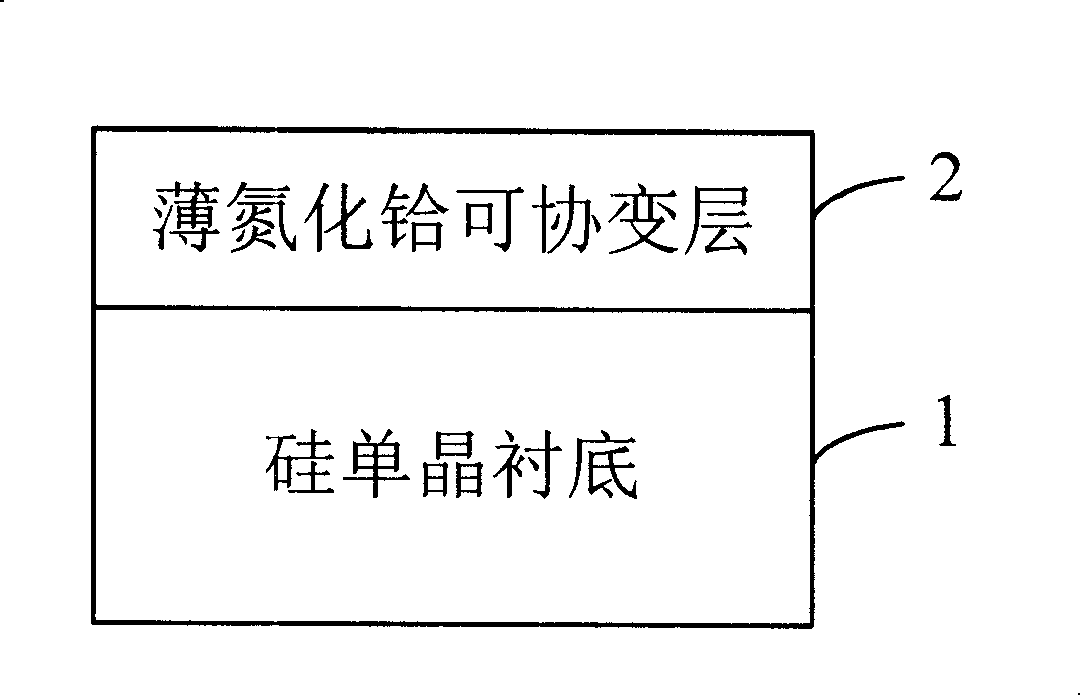
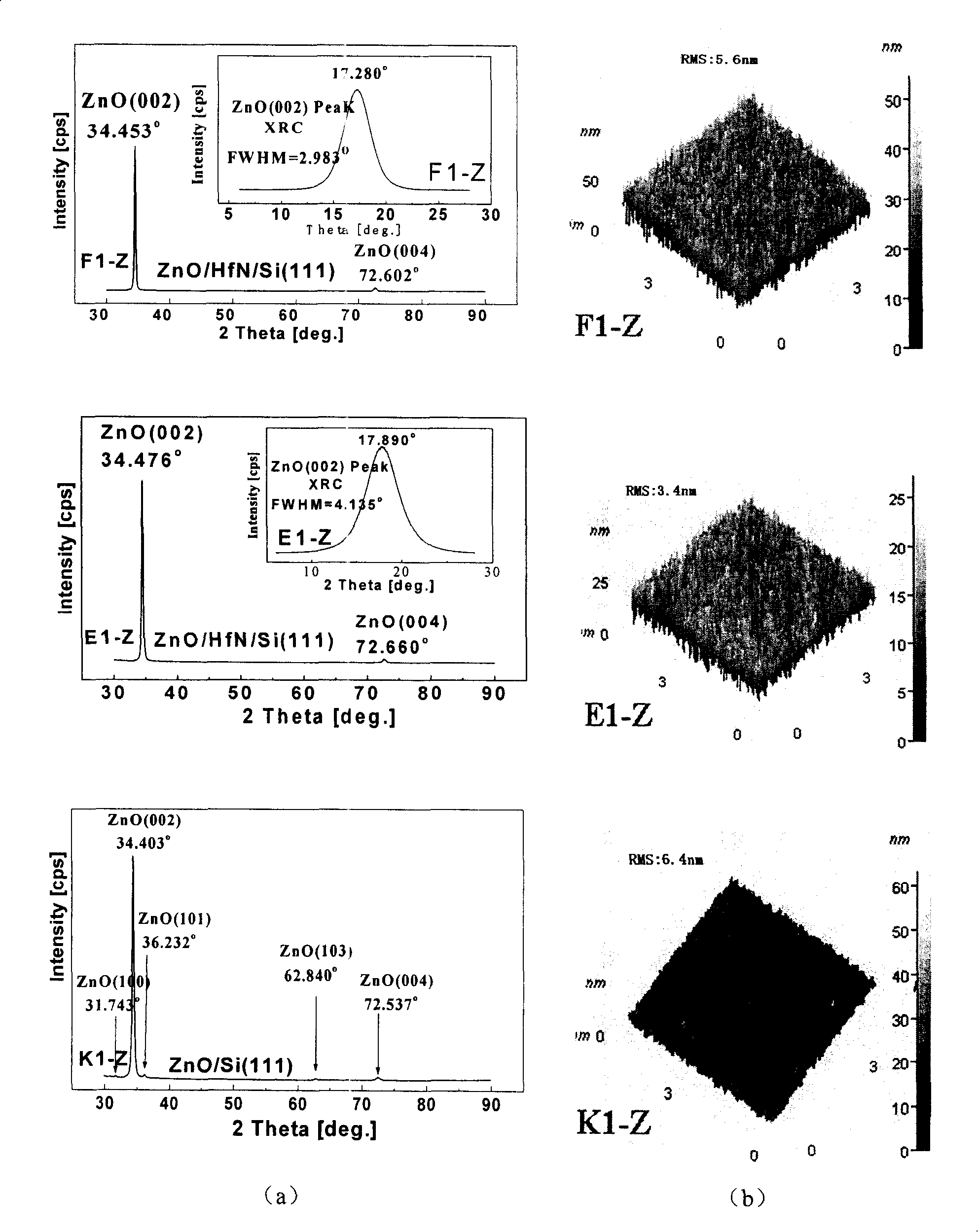
Silicon based compliant substrate material possessing thin hafnium nitride compliant layer
InactiveCN101211989ACoordination mismatch strainGood chemical and thermal stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor materialsGrown film
The invention relates to the technical field of epitaxial film preparation of zinc oxide of semiconductor materials and discloses a silicon-based compliant substrate material with thin hafnium nitride compliant layer. The material includes the following components: a single crystal silicon substrate which is used for supporting the whole silicon-based compliant substrate material; a thin hafnium nitride compliant layer, whose preparation is on the single crystal silicon substrate and is used for adjusting mismatch strain of epitaxial grown film of zinc oxide. By adopting the invention, mismatch strain of epitaxial film of zinc oxide on silicon substrate can be adjusted and residual stress be reduced, thus improving the crystal quality and surface appearance and laying a foundation for research of silicon-based optoelectronic devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
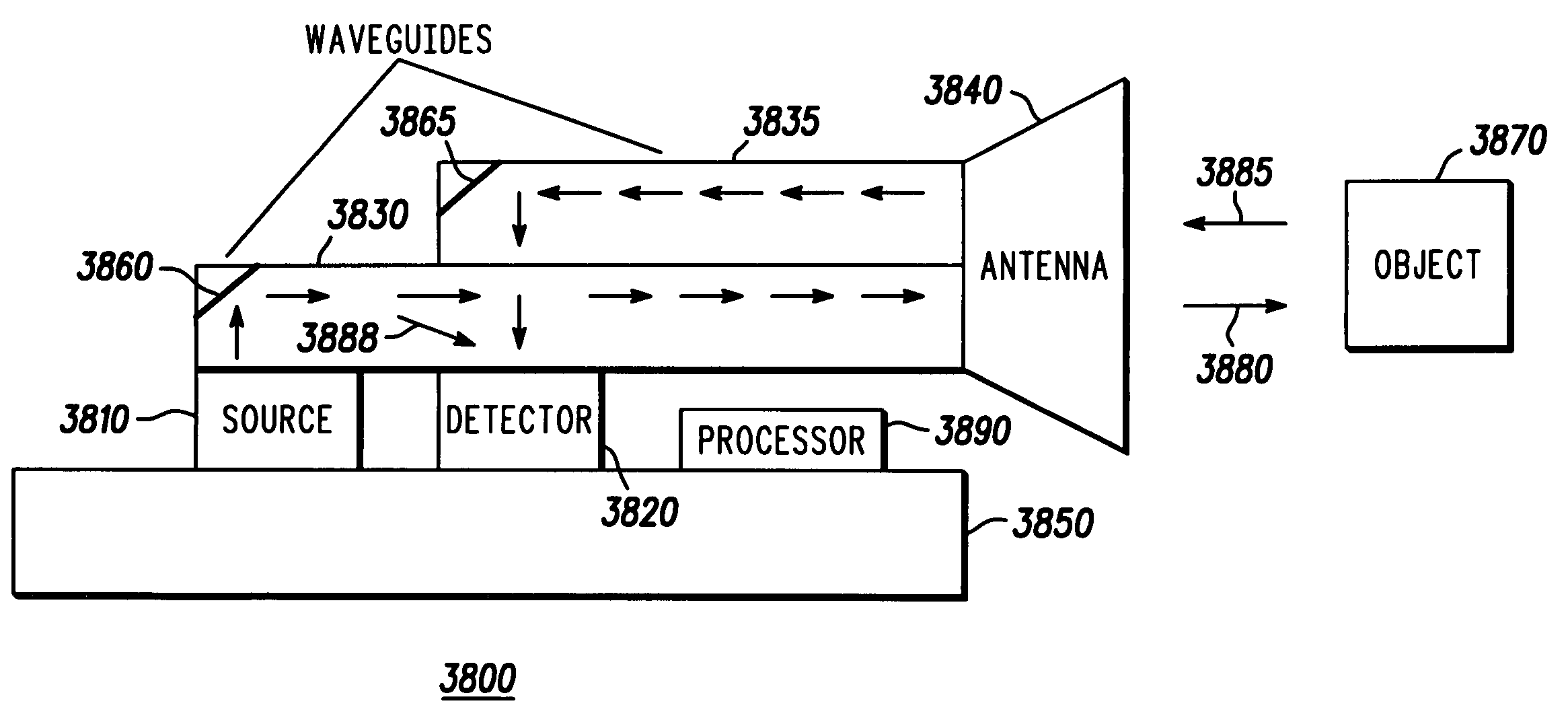
Structure and method for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices for detecting an object
InactiveUS7161227B2Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor structureLattice mismatch
High quality epitaxial layers of monocrystalline materials can be grown overlying monocrystalline substrates such as large silicon wafers by forming a compliant substrate for growing the monocrystalline layers. An accommodating buffer layer comprises a layer of monocrystalline oxide spaced apart from a silicon wafer by an amorphous interface layer of silicon oxide. The amorphous interface layer dissipates strain and permits the growth of a high quality monocrystalline oxide accommodating buffer layer. The accommodating buffer layer is lattice matched to both the underlying silicon wafer and the overlying monocrystalline material layer. Any lattice mismatch between the accommodating buffer layer and the underlying silicon substrate is taken care of by the amorphous interface layer. In addition, formation of a compliant substrate may include utilizing surfactant enhanced epitaxy, epitaxial growth of single crystal silicon onto single crystal oxide, and epitaxial growth of Zintl phase materials. A high quality layer of compound semiconductor material is used to form a source component and a receiver component that are interconnected with an antenna and each other within a semiconductor structure that can detect a parameter, such as the speed, of an object.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System for discretely actuated solar mirrors
System for establishing a surface shape. The system includes a compliant substrate including the surface and having a reverse side, and a plurality of discrete actuators engaging the reverse side and arranged in a selected pattern to control the surface shape as individual discrete activators are activated. It is preferred that the actuators have multiple discrete stable states of elongation. A particularly preferred embodiment uses actuators that are binary with two stable states of elongation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Process for making an embossed web
A process for making an embossed web. A precursor web is provided between a forming structure and a compliant substrate. The forming structure has a plurality of discrete apertures or depressions. Pressure is provided between the compliant substrate and the forming structure to force the precursor web into the apertures or depressions of forming structure to form the embossed web. The resulting embossed web has a plurality of discrete extended elements.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
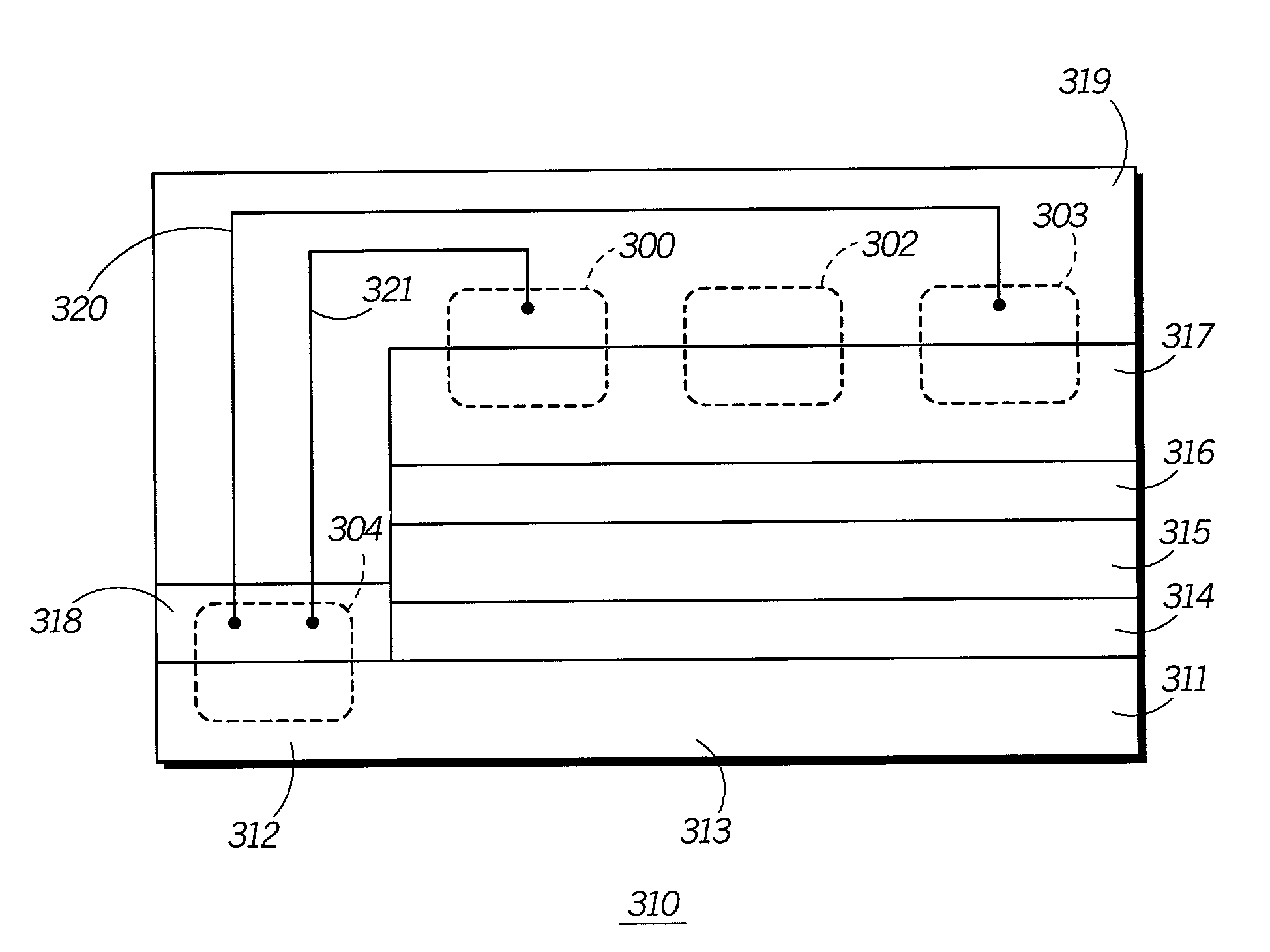
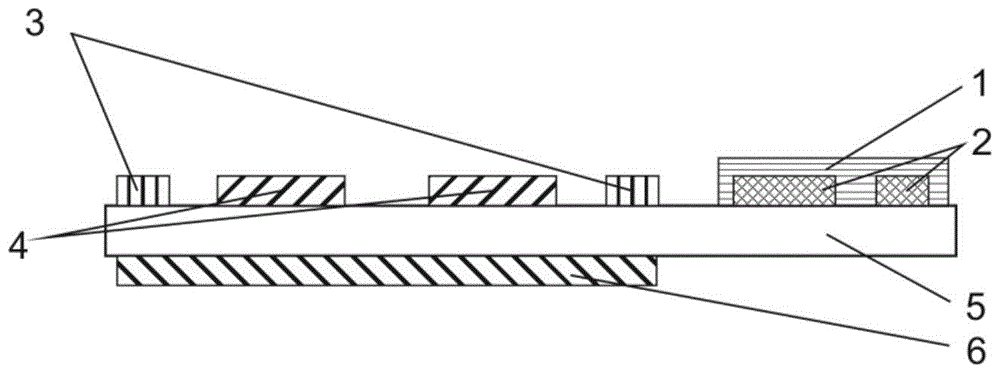
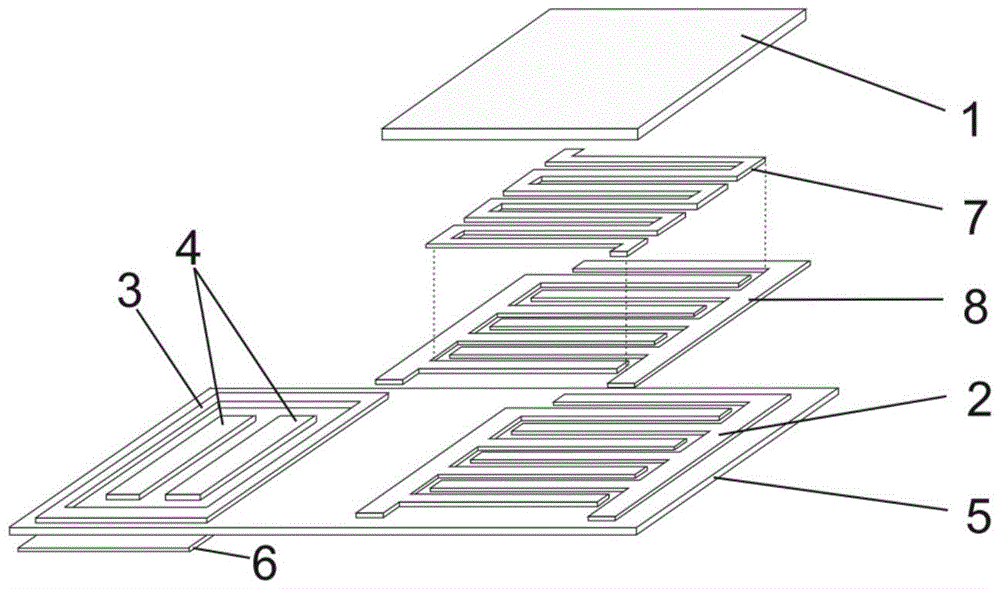
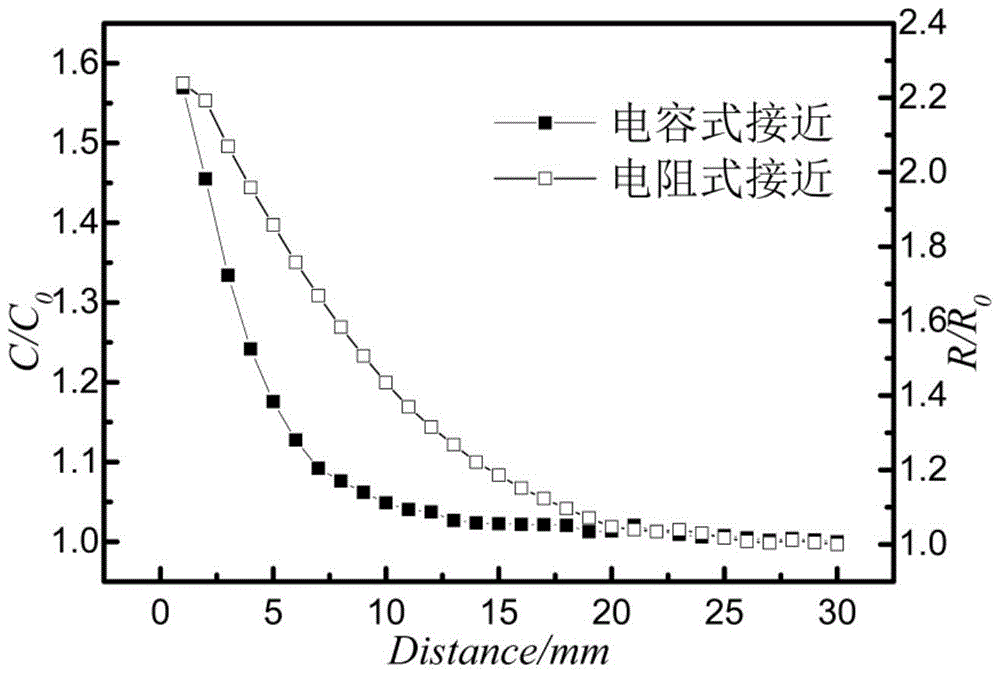
A fully flexible capacitive-resistive dual-mode proximity sensor
InactiveCN104764481BFlexible Electrode RoutingFacilitate array structure designMeasurement devicesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a full-compliancy capacitance and resistance dual mode proximate sense transducer. The full-compliancy capacitance and resistance dual mode proximate sense transducer is characterized in that a capacitance type proximate sense transducer body and a resistance type proximate sense transducer body are arranged on a compliant substrate in a spaced mode, and the capacitance type proximate sense transducer body and the resistance type proximate sense transducer body cooperate to perceive object proximity information in a segmented mode. According to the full-compliancy capacitance and resistance dual mode proximate sense transducer, the capacitance and resistance dual mode is utilized to cooperatively detect the object proximity information in a segmented mode, and therefore the accuracy of the transducer can be improved; all structures of the transducer have the compliancy, all leads are led to the same compliant substrate, and therefore the problems that the leads are tedious, not beautiful and not easy to maintain during array structure design are solved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
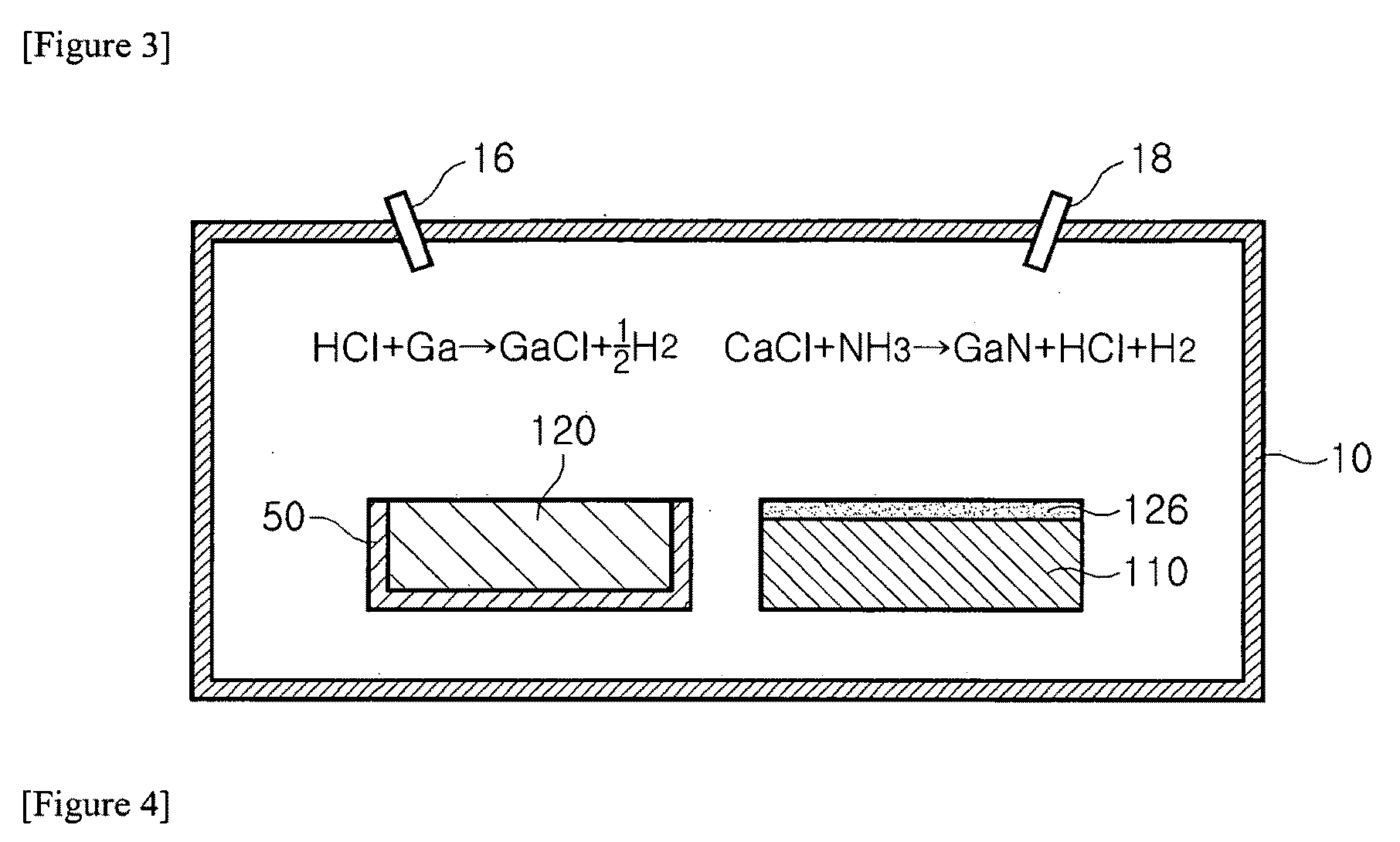
Gallium nitride based compound semiconductor device including compliant substrate and method for manufacturing the same
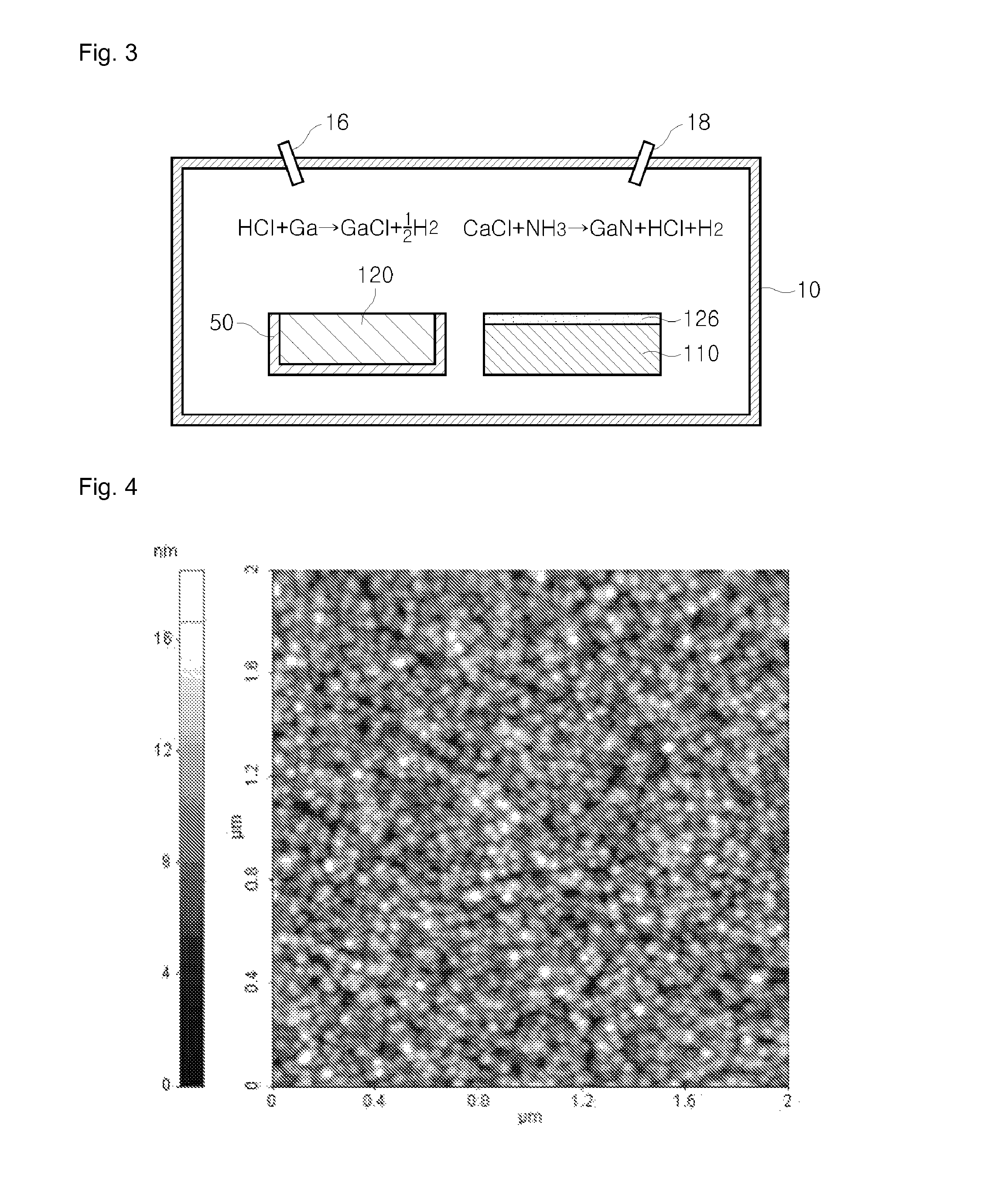
InactiveUS7795118B2Reduce processing timeQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumWafering
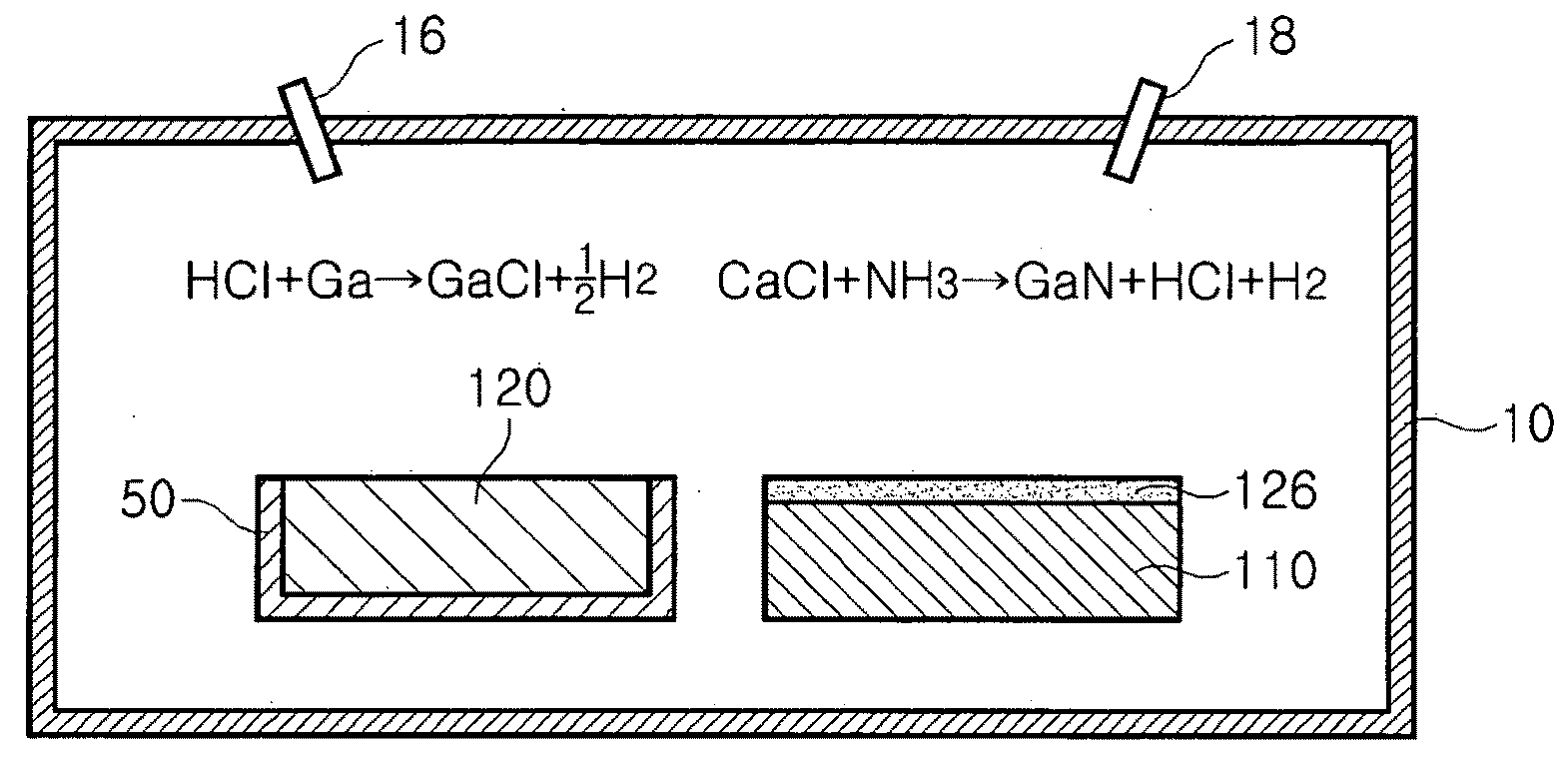
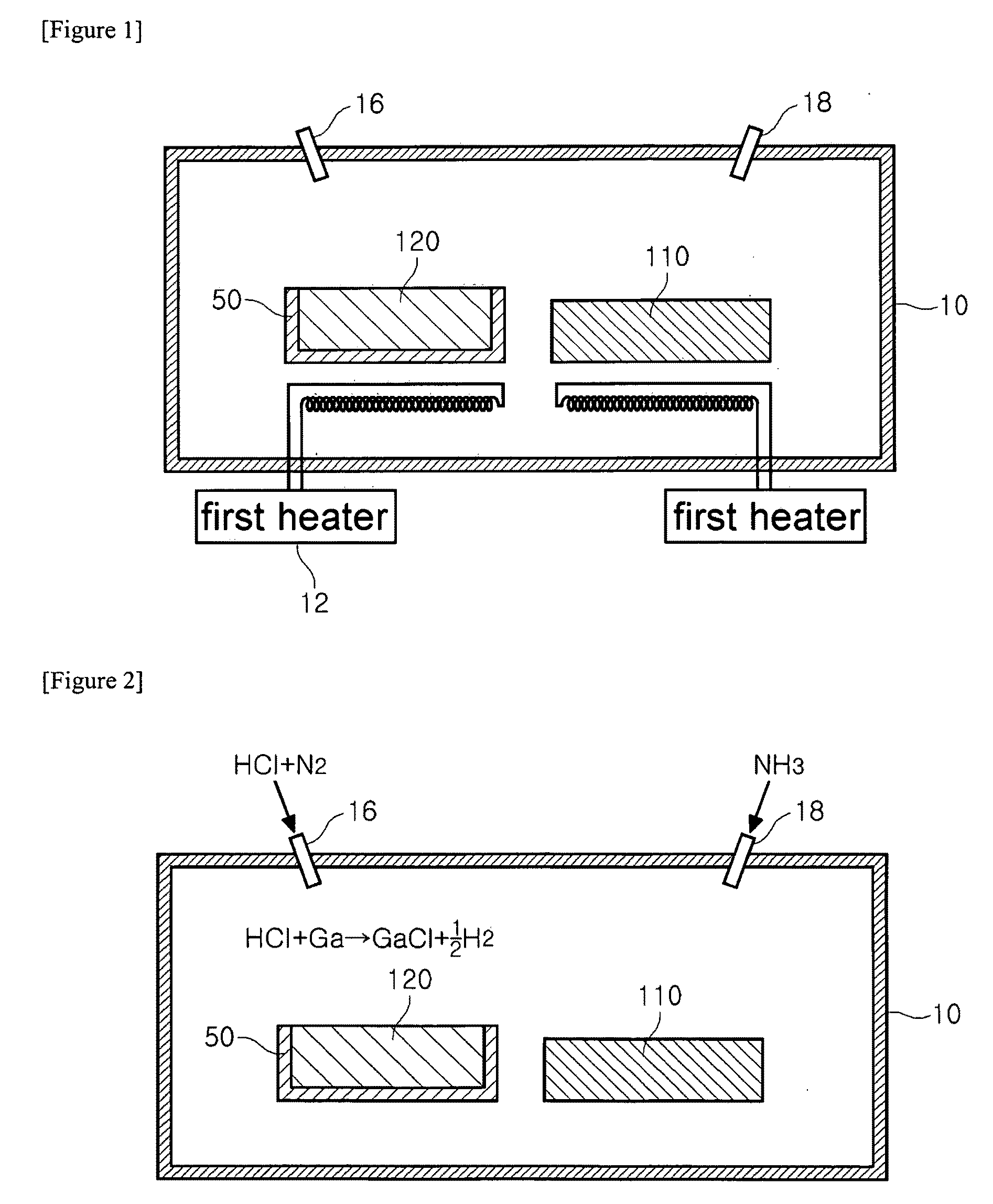
A gallium nitride based compound semiconductor device including a compliant substrate having a reduced stress and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The compliant substrate included in the gallium nitride based compound semiconductor device is manufactured by heating a substrate and a group III metal including at least one of an aluminum, a gallium and an indium, and a chloride based compound generated by introducing a HCl gas to the melted group III metal reacts with a NH3 gas to form a nitride based thin film on the wafer.
Owner:THELEDS
Compliant substrate for a heteroepitaxial structure and method for making same
InactiveUS20060030087A1Promote growthPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSingle crystal
The present invention relates to a compliant substrate having a top surface for receiving a heteroepitaxial structure or heteroepitaxial layer. This substrate comprises a carrier substrate, a top single-crystalline layer, a buried layer located between the carrier substrate and the top layer, and a weakened region located in the top layer or between the top layer and the buried layer such that the compliant substrate facilitates relaxed growth of a heteroepitaxial layer or structure upon the top surface. The invention also relates to the combination of the compliant substrate and a heteroepitaxial layer provided thereon, as well as to a method of making the compliant substrate and combination.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Silicon based compliant substrate material for zinc oxide epitaxial film growth
InactiveCN100546017CCoordination mismatch strainReduce residual stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMisfit strainThin metal
The invention relates to a technical field for making a zinc oxide epitaxial film in semiconductor material and discloses silicon-based covariant substrate material used for growing the zinc oxide epitaxial film, which comprises a silicon single crystal substrate used for supporting the whole silicon-based covariant substrate material; a thin metal hafnium covariant layer; the thin metal hafnium covariant layer is made on the silicon single crystal substrate used for coordinating misfit strain for the zinc oxide epitaxial film which epitaxial grows on the silicon single crystal substrate. By adopting the invention, the misfit strain of the zinc oxide epitaxial film grown on the silicon substrate is coordinated and residual stress is decreased thereby enhancing the crystal quality and improving the appearance of the surface, which lays a foundation for developing silicon based photoelectric devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and Apparatus for Comparing Colors
A Method and Apparatus for Comparing Colors have been disclosed. In one implementation a compliant membrane which is substantially transparent with an area having a shade / color is placed on the user's skin to see what the shade / color will look like on the skin. In one implementation a compliant substrate which is largely transparent with an area having a shade / color is placed on an inanimate object to see how the shade / color will appear on the inanimate object without the substrate itself causing an unnecessary barrier between the inanimate object and the shade / color.
Owner:KAPLAN LEE
Method for manufacturing compliant substrate, compliant substrate manufactured thereby, gallium nitride based compound semiconductor device having the compliant substrate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090261345A1Reduce processing timeQuality improvementVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumChloride
A compliant substrate having a reduced stress, a method for manufacturing the same having a reduced manufacturing time, a gallium nitride based compound semiconductor device including the compliant substrate and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The compliant substrate is manufactured by heating a substrate and a group III metal including at least one of an aluminum, a gallium and an indium, and a chloride based compound generated by introducing a HCl gas to the melted group III metal reacts with a NH3 gas to form a nitride based thin film on the wafer.
Owner:THELEDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com