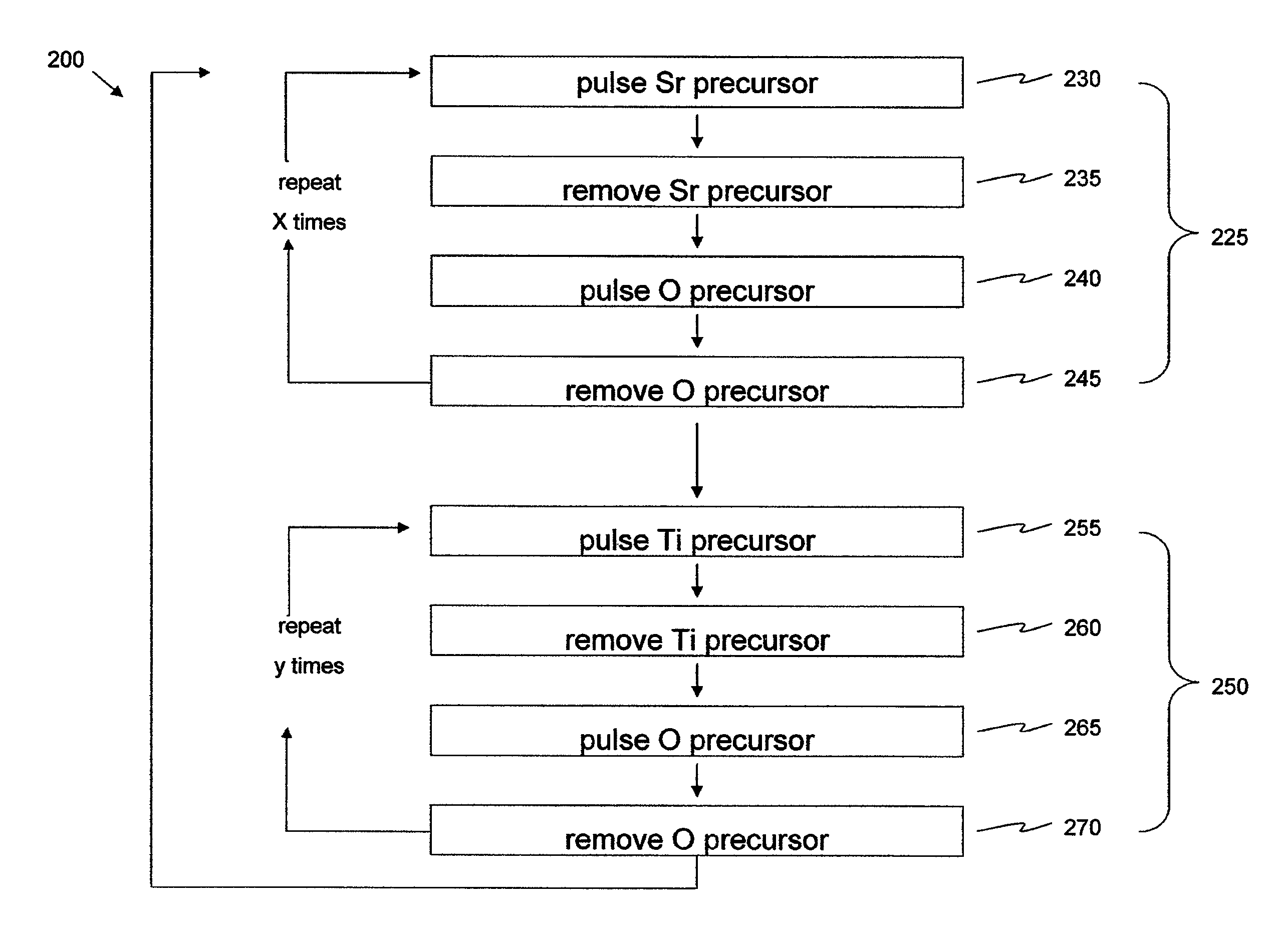
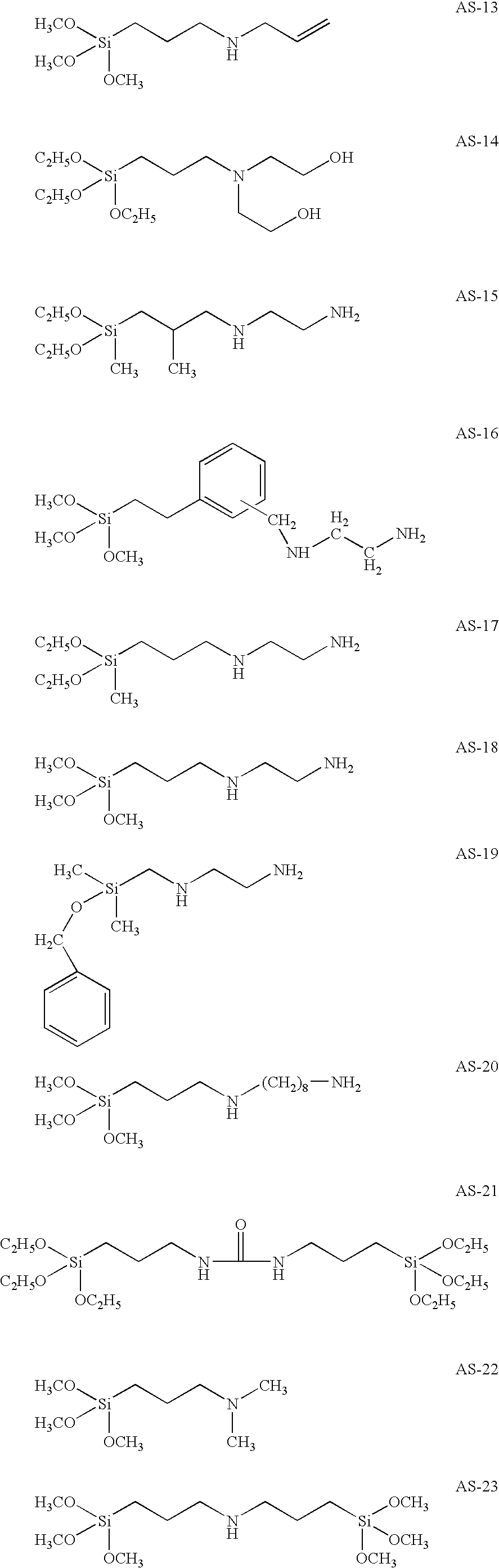
Patents
Literature
236 results about "Strontium titanium oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
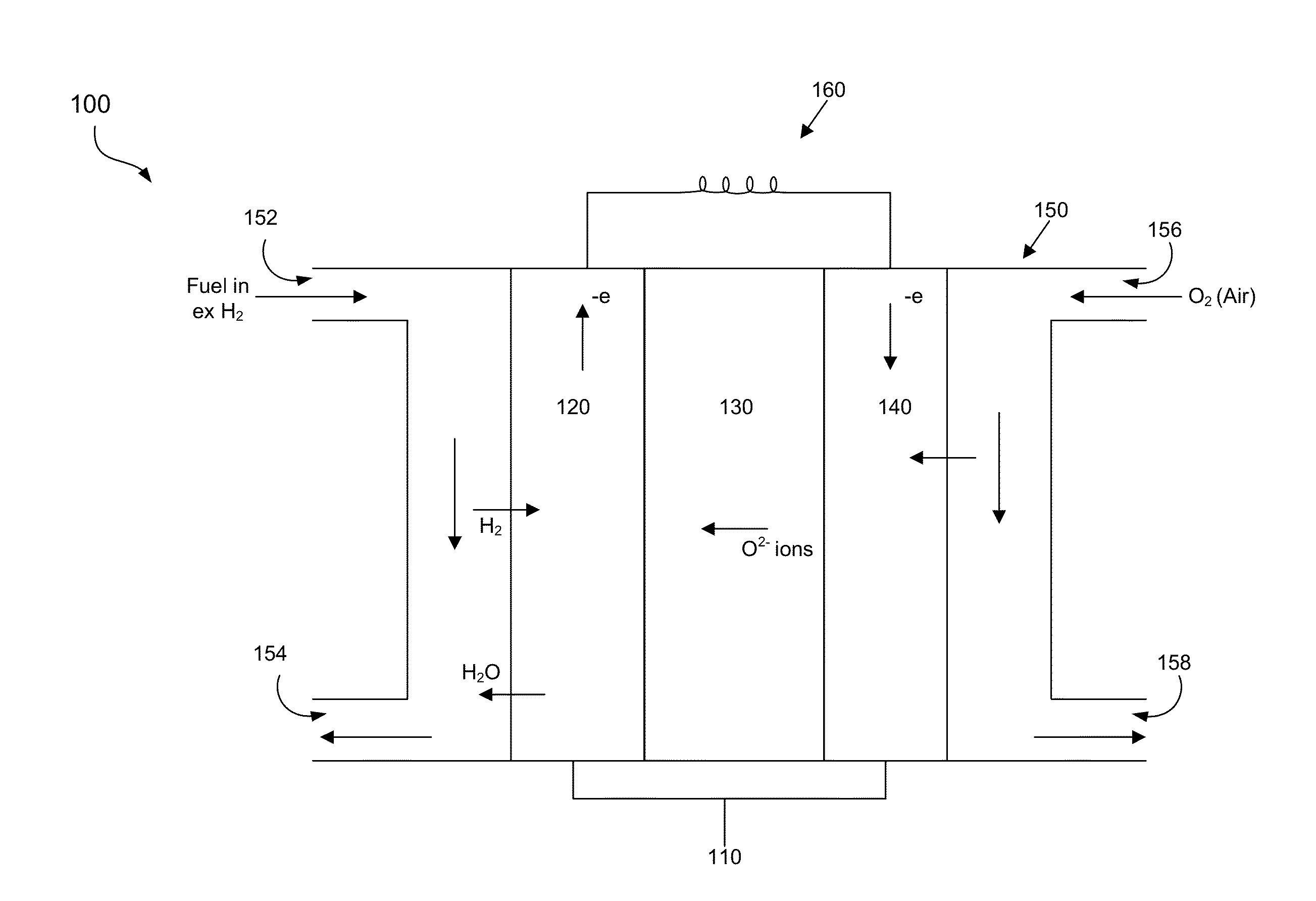
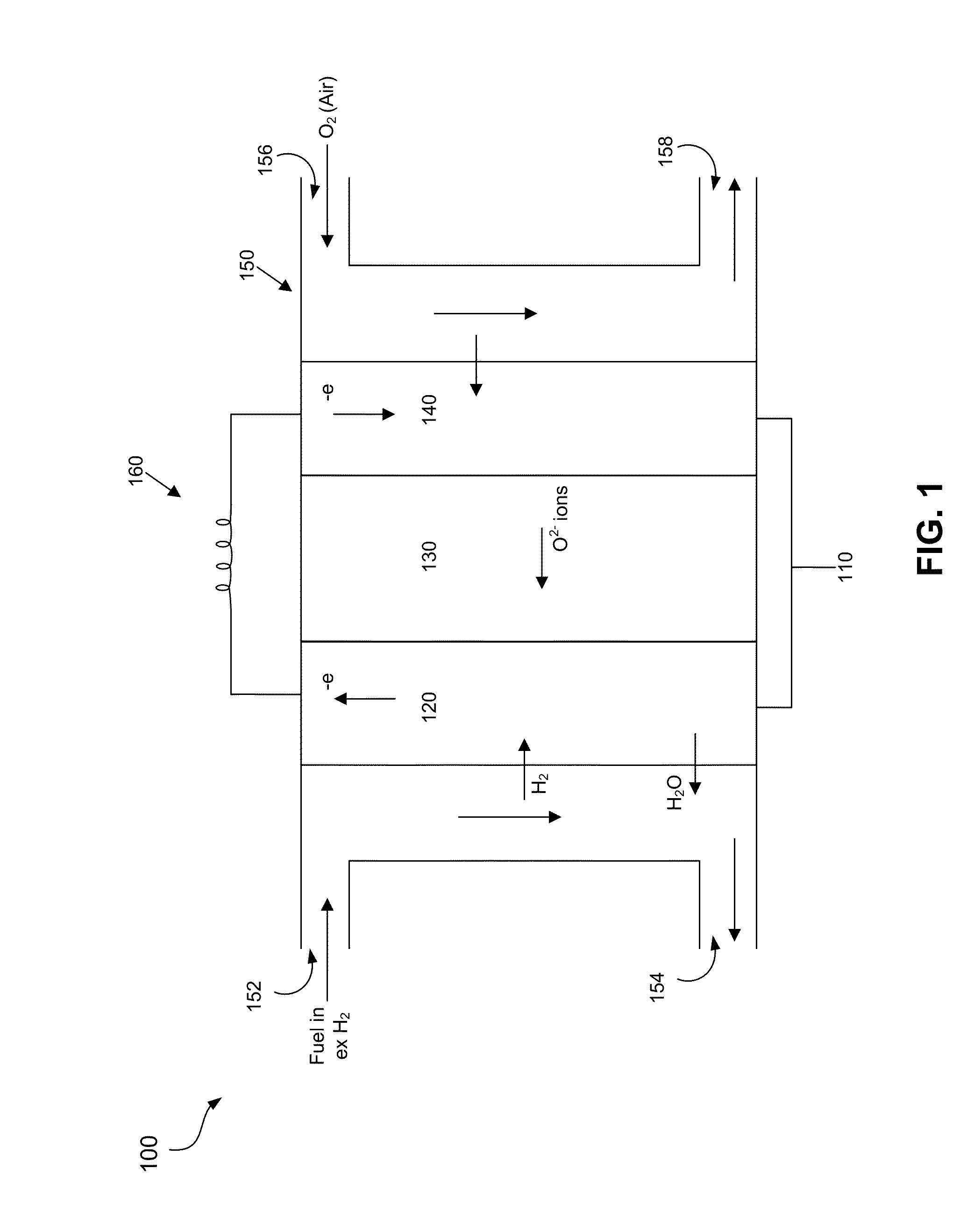
Strontium titanate is an oxide of strontium and titanium with the chemical formula SrTiO3. At room temperature, it is a centrosymmetric paraelectric material with a perovskite structure.
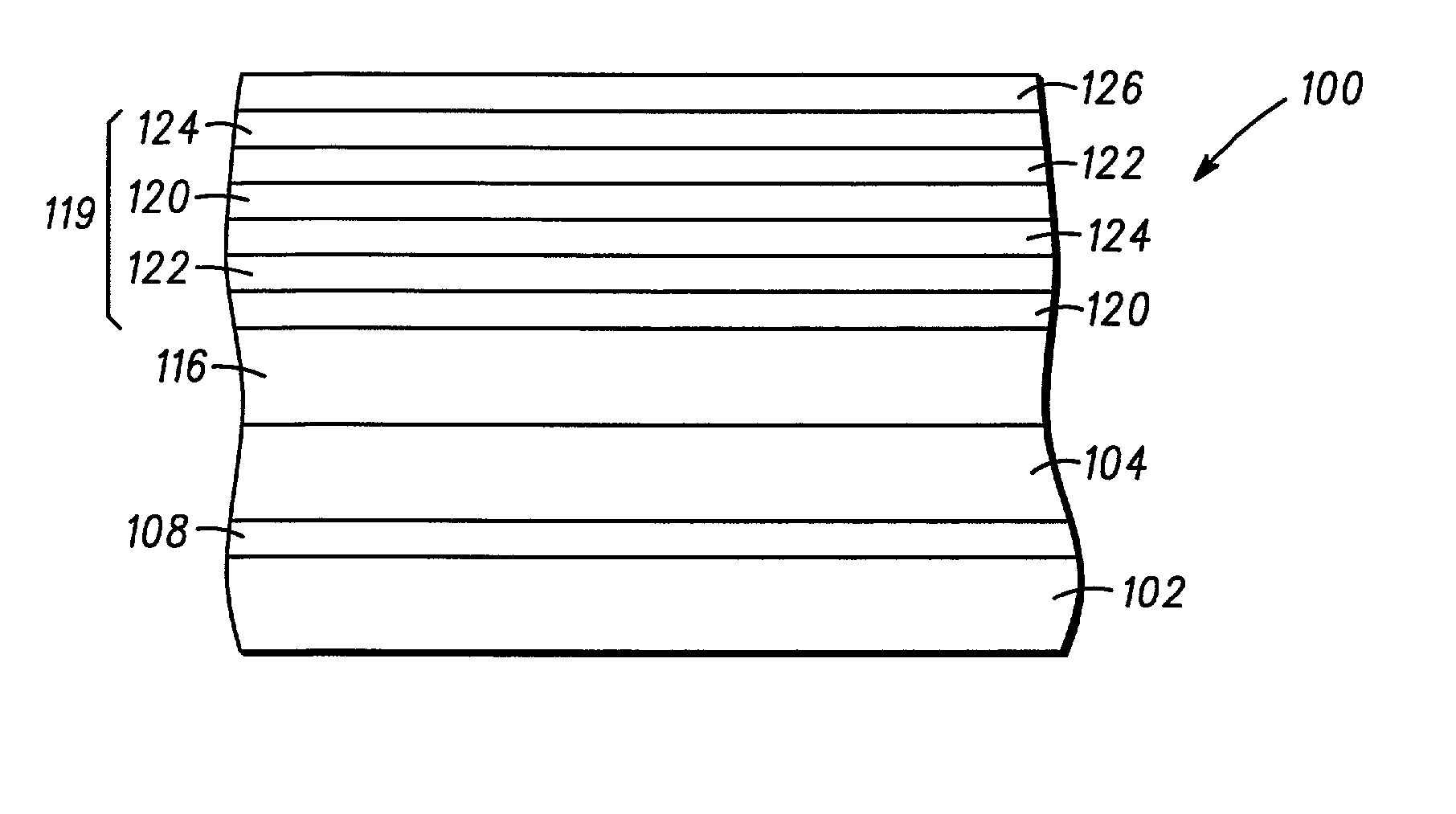
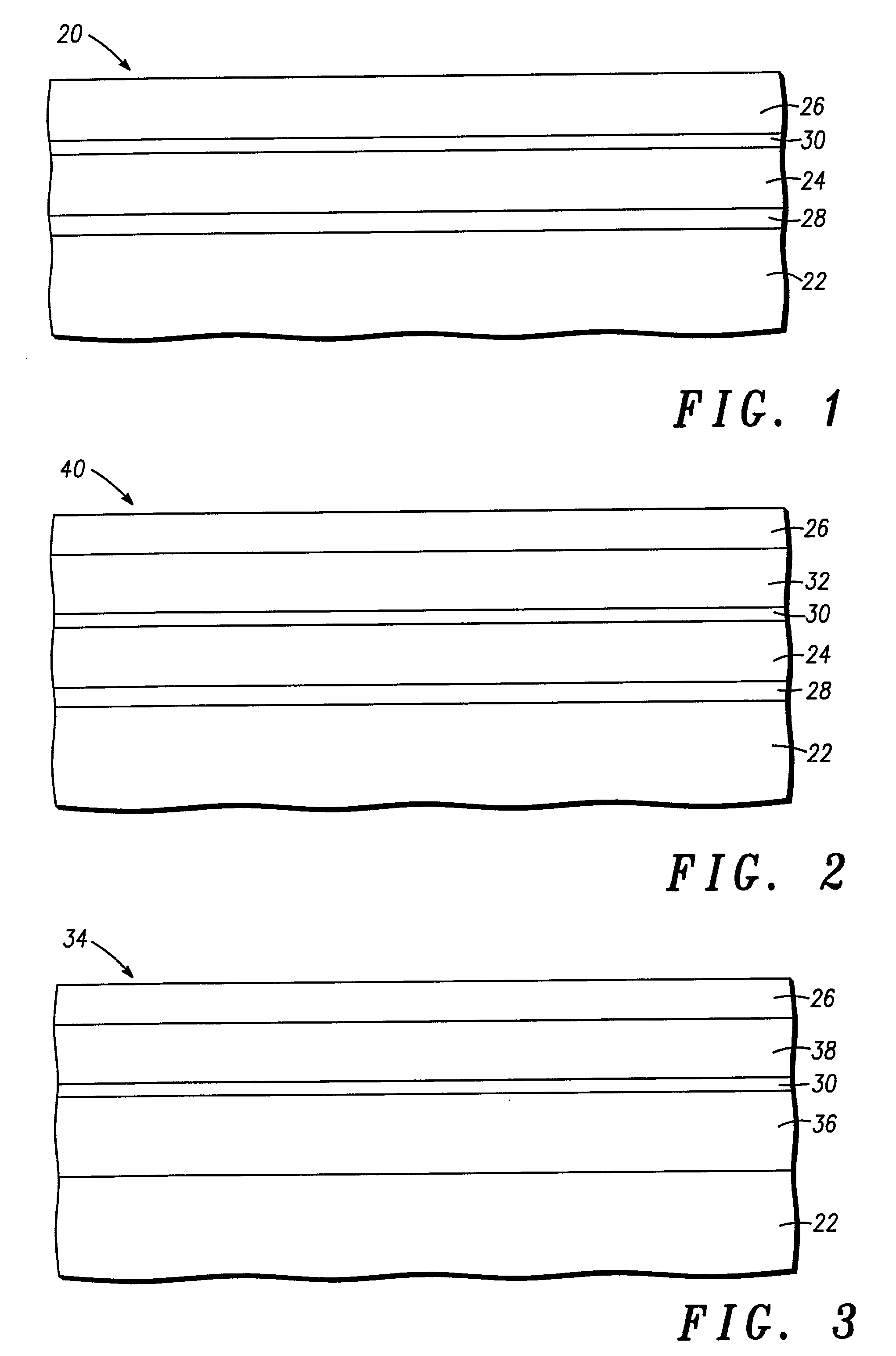
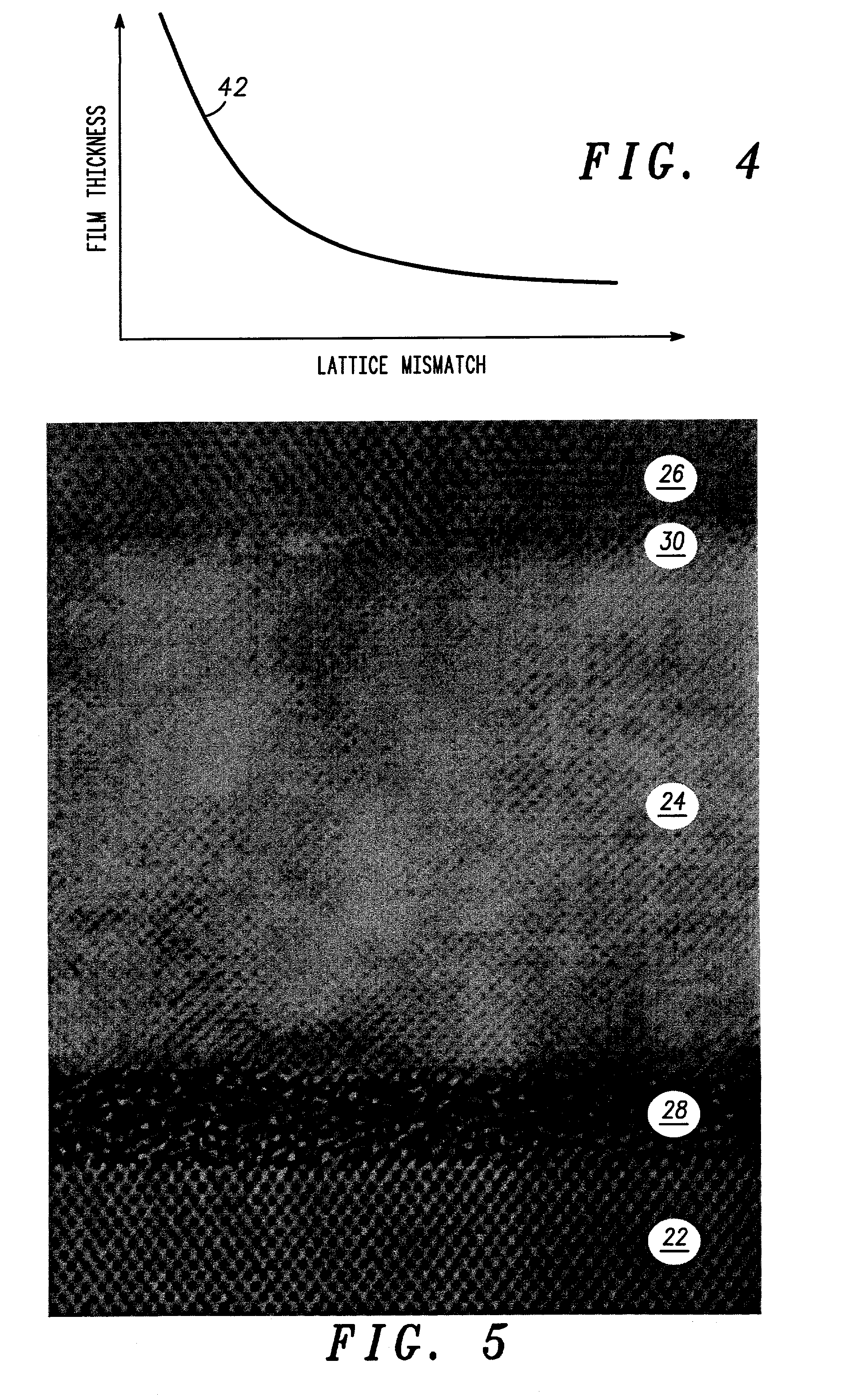
Structure and method for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices utilizing the formation of a compliant III-V arsenide nitride substrate used to form the same
InactiveUS20030013223A1Laser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsStrontium titanium oxideLattice mismatch
High quality epitaxial layers of monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride materials can be grown overlying monocrystalline substrates such as large silicon wafers by forming a compliant substrate for growing the monocrystalline layers. One way to achieve the formation of a compliant substrate includes first growing an accommodating buffer layer on a silicon wafer. The accommodating buffer layer is a layer of monocrystalline oxide spaced apart from the silicon wafer by an amorphous interface layer of silicon oxide. The amorphous interface layer dissipates strain and permits the growth of a high quality monocrystalline oxide accommodating buffer layer. The accommodating buffer layer is lattice matched to both the underlying silicon wafer and the overlying monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride material layer. Any lattice mismatch between the accommodating buffer layer and the underlying silicon substrate is taken care of by the amorphous interface layer. In addition, an accommodating buffer layer comprising a barium strontium titanium oxide and a monocrystalline III-V arsenide nitride layer, such as GaAsN, having a nitrogen concentration ranging from 1-5% function to further reduce any lattice mismatch between layers.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Hollow fiber membrane reactor for gaseous oxidation reaction, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101733048AImprove physicsImprove compatibilitySemi-permeable membranesHydrogenFiberComposite ceramic
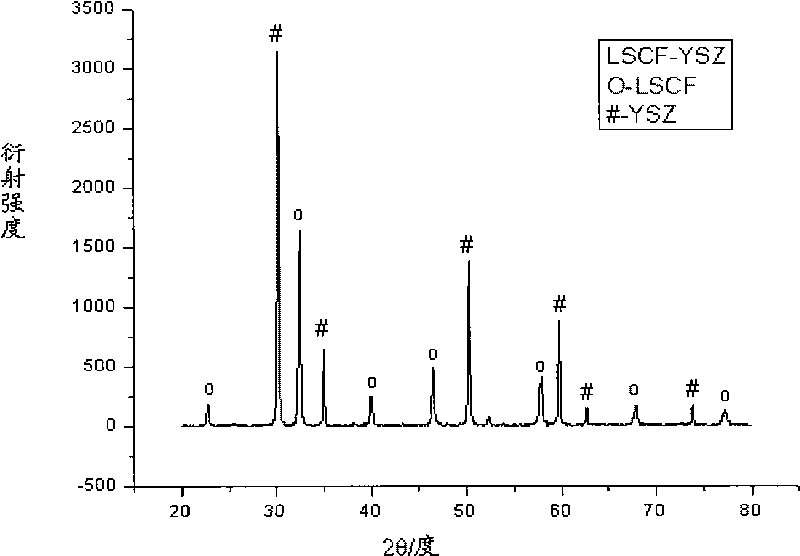
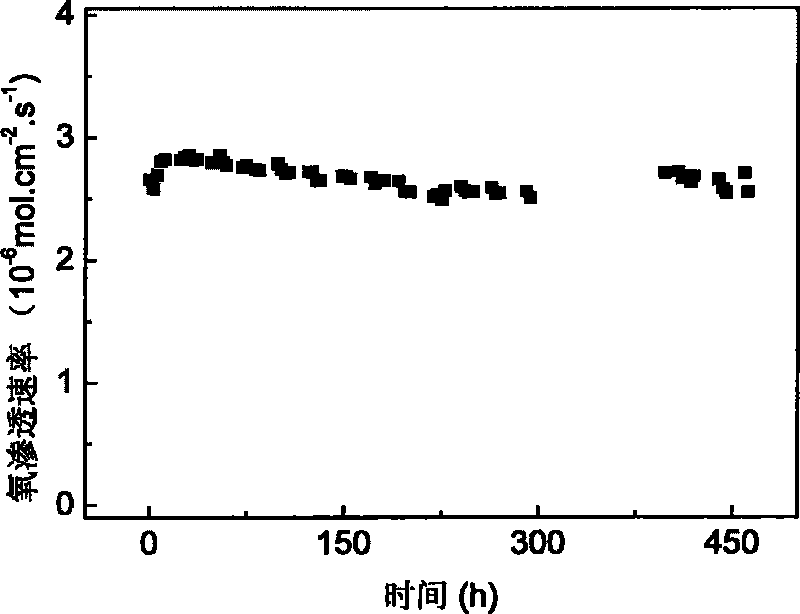
The invention discloses a hollow fiber membrane reactor for gaseous oxidation reaction, a preparation method and application thereof. The membrane reactor is made of a compact hollow fiber oxygen permeation membrane, wherein the wall thickness of a pipe is between 0.1 and 0.3mm, and the outer pipe diameter is between 1 and 3mm; the oxygen permeation membrane is made of a dual-phase composite ceramic oxygen permeation membrane material which is prepared by mixing an electron conductive phase material and an ion conductive phase material in a volume ratio of 0.43-1.5:1; the electron conductive phase material is provskite-type chromic lanthanum composite oxide (Ln1-xAx)1-zCr1-yByO3 and / or strontium titanate-based composite oxide (LnxSr1-x)1-zTi1-yByO3; and the ion conductive phase material is stabilized fluorite type zirconium dioxide Zr1-x1Rx1O2-delta, or doped cerium dioxide R'z1Ce1-z1O2-delta. The method for preparing the membrane reactor comprises the following steps: mixing the electron conductive phase material and the ion conductive phase material in the volume ratio of 0.43-1.5:1 to prepare a hollow fiber membrane blank by adopting a wet phase inversion method; and sintering the blank at the temperature of between 1,300 and 1,600 DEG C for 10 to 18 hours. The membrane reactor has high oxygen permeation performance, excellent high temperature reduction resistance and long-term stability and low production cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
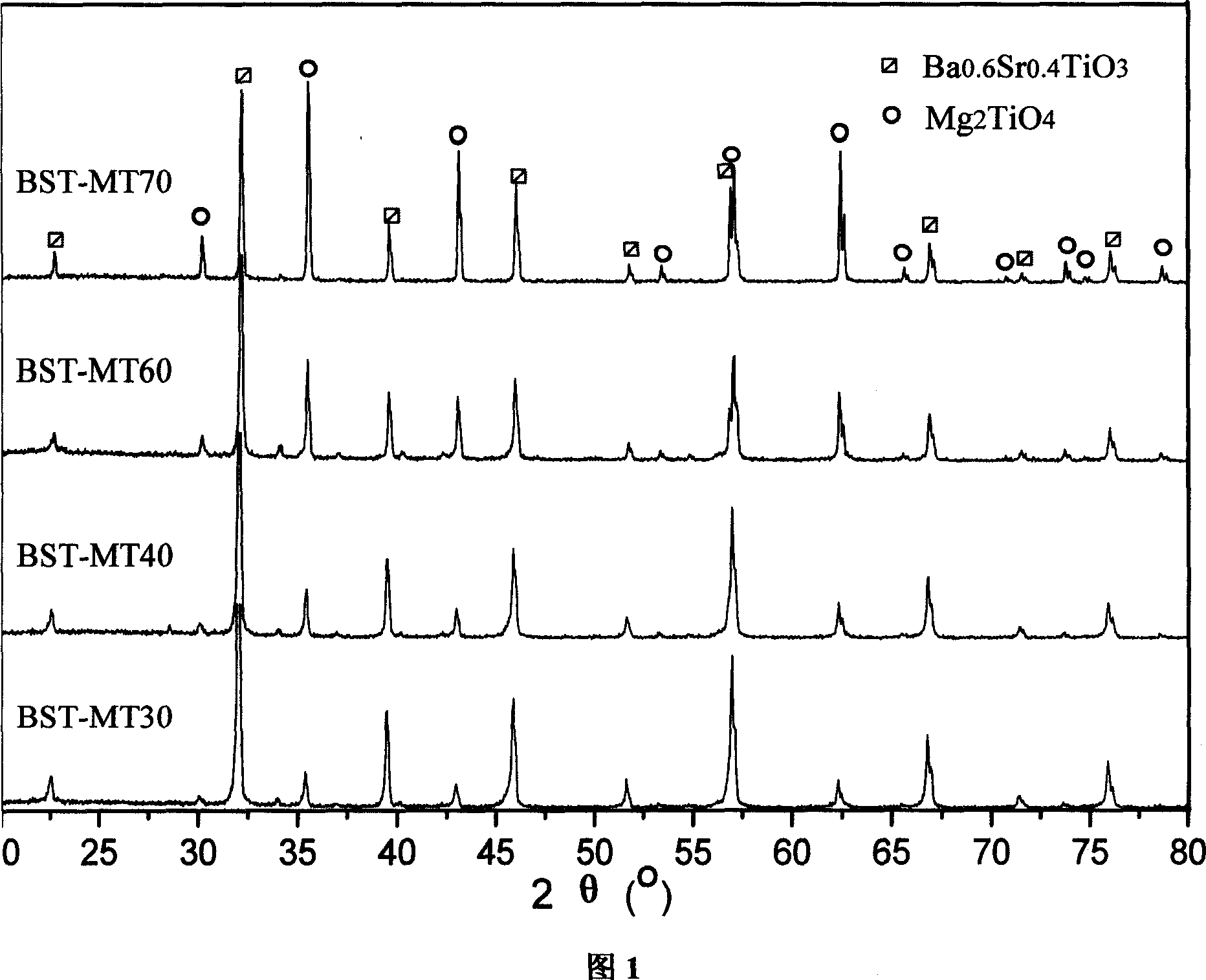
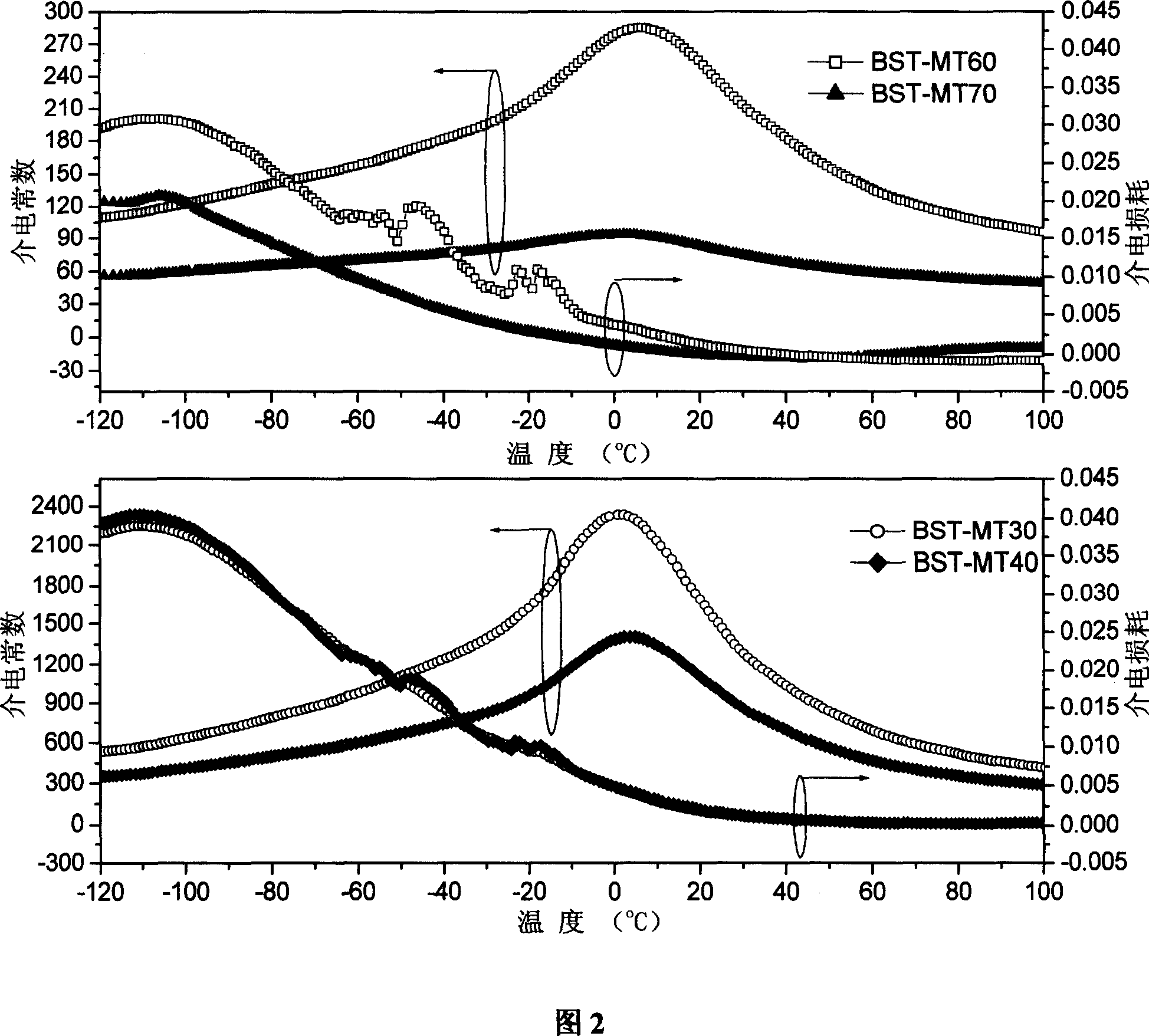
Ba1-xSrxTiO3-Mg2TiO4 two-phase composite ceramic material and its preparing process
InactiveCN101007736AExcellent dielectric propertiesHas dielectric tunable propertiesStrontium titanium oxideMicrowave
The invention discloses a two-phase composite ceramic material of being used to microwave modulator, which comprises 80.0-20.0wt% Ba(1-x)SrxTiO3(x=0.3-0.6) and 20.0-80.0wt% Mg2TiO4. The invention is characterizes by the following: adopting traditional electronic ceramic preparing craft; selecting microwave dielectric material normal magnesium titanate with good dielectric property; proceeding two-phase gradient composition with strontium titanate barium ferroelectric materials different Ba / Sr ingredient; getting the product.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Touch screen cover plate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106033288AHigh glossImprove reflectivityInput/output processes for data processingZinc selenideBarium titanate
The invention relates to a touch screen cover plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The touch screen cover plate comprises a substrate, a reflecting layer, and an ink layer. The reflecting layer is formed on one surface of the substrate. The reflecting layer is arranged on the periphery of the edge of the substrate. The reflecting layer is a metal elemental film or a compound film. The compound film is one selected from an oxide film, a fluoride film, a zinc sulfide film, a zinc selenide film, a titanium nitride film, a silicon carbide film, a lanthanum titanate film, a barium titanate film, a strontium titanate film, a praseodymium titanate film, and a cadmium sulfide film. The ink layer is on the reflecting layer, and the ink layer can reflect light which passes through the reflecting layer back to the reflecting layer. The touch screen cover plate has relatively high reflectivity, so glossiness of the touch screen cover plate is good.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL TECH +3
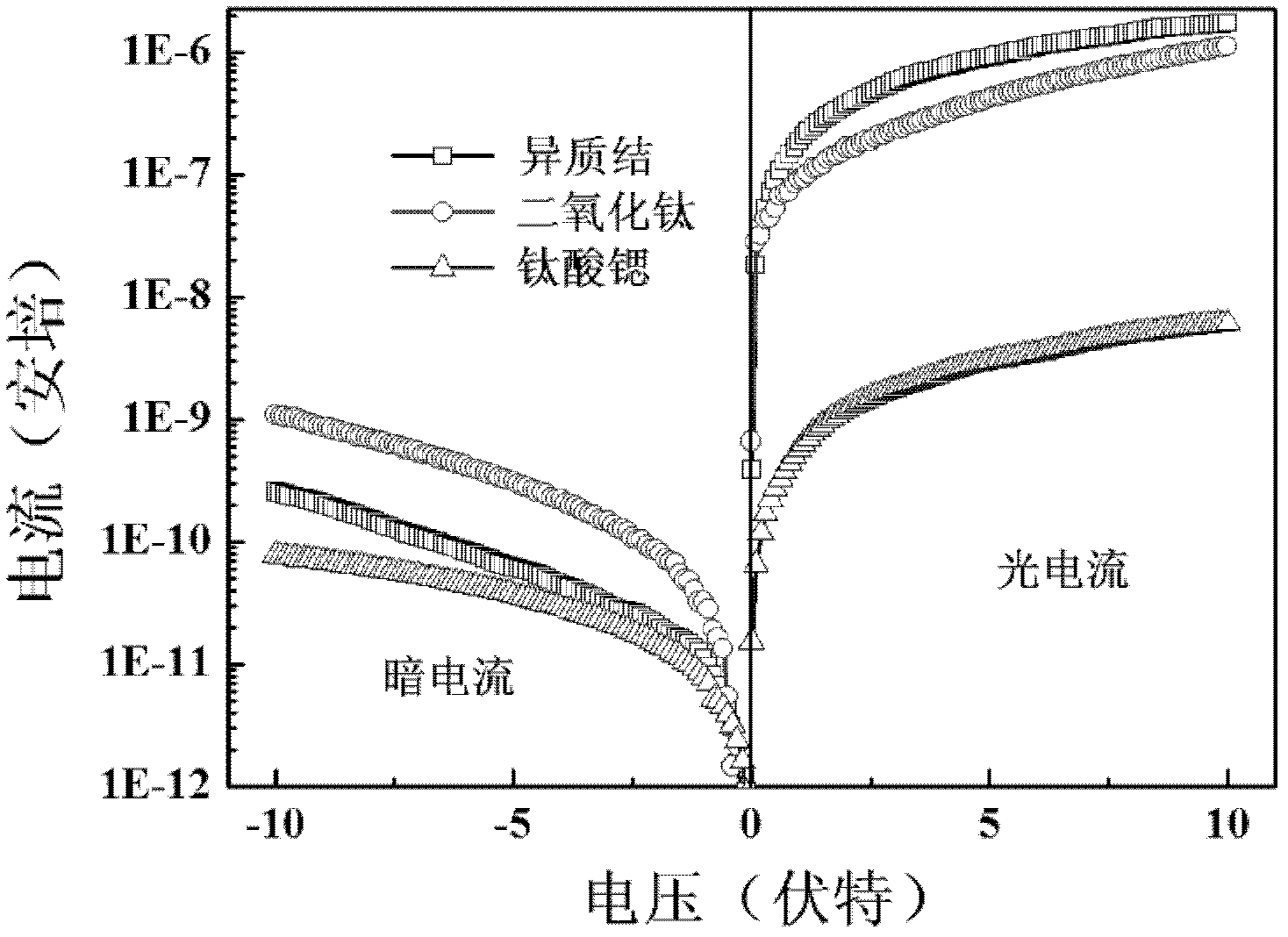
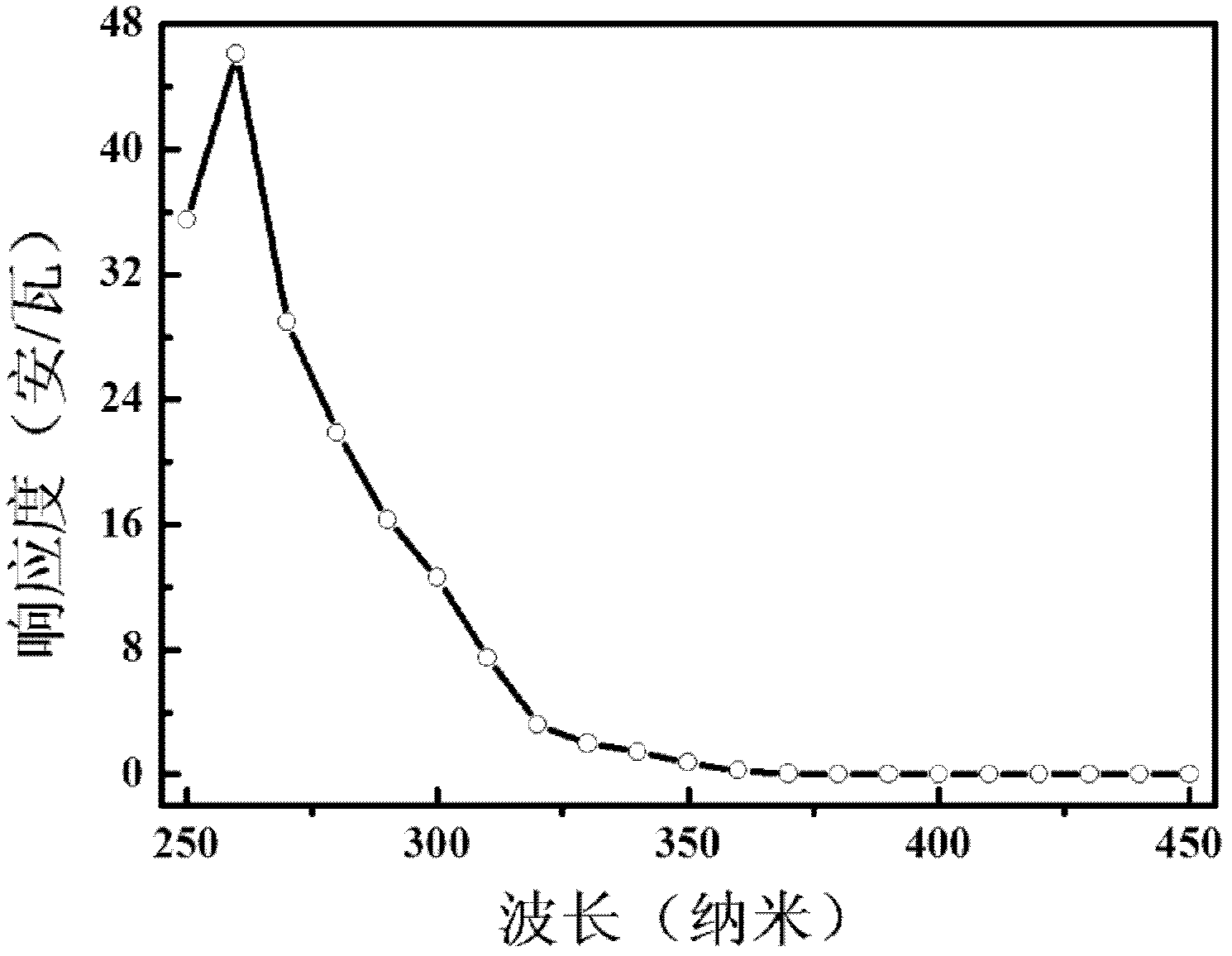
Ultraviolet detector based on titanium dioxide/strontium titanate heterojunction and preparation method
InactiveCN102509743AFree yourself from the lack of suitable substratesSimple processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionHYDROSOL
The invention particularly relates to a high-performance semiconductor ultraviolet photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof, wherein for the high-performance semiconductor ultraviolet photoelectric detector, an ultra-thin silicon chip is used as a substrate, a nano TiO2 / SrTiO3 heterojunction active layer is used as a base material, and Au is used as a metal interdigitated electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a TiO2 and SrTiO3 sol by adopting a sol-gel technology, and growing a compact nano SrTiO3 film and a compact TiO2 film in order on the ultra-thin silicon substrate; and preparing the Au interdigitated electrode with a certain shape on the surface of the films through adoption of a magnetron sputtering technology and a standard photoetching and stripping technology. The TiO2 / SrTiO3 heterojunction metal-semiconductor-metal ultraviolet detector prepared with the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simple preparation method, low cost and potentiality in large-scale production, and has a good detection performance for detecting ultraviolet rays of which the wavelength is 250-350 nm.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Barium titanate-based lead-free high-voltage ceramic capacitor material
The invention provides a barium titanate-based lead-free high-voltage ceramic capacitor material, which takes barium titanate, bismuth titanate, strontium titanate and calcium titanate as raw materials. After the materials are mixed, polyvinyl alcohol is added, the obtained mixture is pressed and formed, and the obtained product is sintered under about 1220 DEG C to obtain the high-pressure lead-free ceramic capacitor material. The voltage resistance of the capacitor material sintered by using the ceramic material formula is improved to 16.9kv / mm, the dielectric constant (Xir) is equal to 2089, and the dielectric loss (tan Delta) is equal to 0.0006 under 1MHz AC working current.
Owner:钱云春
Preparation method for strontium titanate lanthanum based powder material
InactiveCN102617139ASmall particle sizeHigh activityCell electrodesWater bathsSpontaneous combustion
A preparation method for a strontium titanate lanthanum based powder material belongs to the field of fuel cells. The method adopts a citric acid-nitrate spontaneous combustion method, using citric acid as a complexing agent and a reducing agent, using nitric acid as an oxidizing agent, introducing a sintering acid ammonium nitrate in-situ, dissolving with metal nitrate in deionized water, adding a tetrabutyl titanate citric acid solution to form an even transparent solution, heating in water bath, removing surplus water, forming even sol, and heating the sol in a muffle furnace till spontaneous combustion happens to form fluffy precursor powder. Then Grinding and calcining in an electric furnace to obtain single strontium lanthanum based anode powder. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple in synthesis process, low in cost, fine and even in powder particles and low in material phase forming temperature. The method is also applicable to synthesis preparation of strontium titanate based nanometer powder and can be used for laboratory synthesis and industrial production of a solid oxide fuel cell anode powder material.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
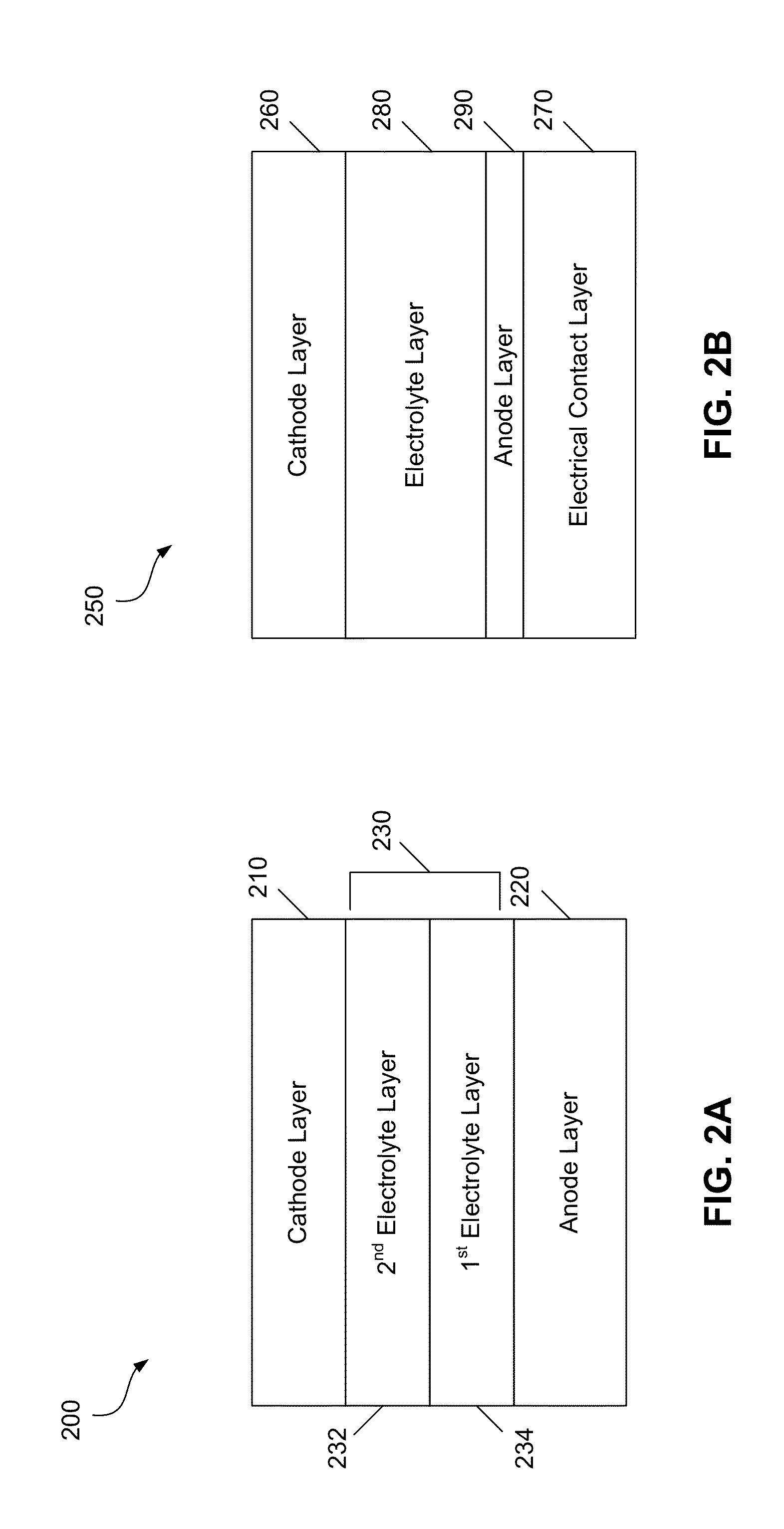
Insulation material, film, circuit board and method of producing them
ActiveUS7700185B2Increase volumeHigh dielectric constantPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsFixed capacitor dielectricStrontium titanium oxideBarium titanate
There is provided an insulation material having a dielectric constant of 10 or more, comprising a filler having a dielectric constant of 50 or more and having two peaks in different particle size ranges in a particle size distribution and an insulating resin combined with each other; an insulation material having a dielectric constant of 10 or more comprising, as essential components, 1) at least one filler selected from the group consisting of barium titanate, strontium titanate, potassium titanate, magnesium titanate, lead titanate, titanium dioxide, barium zirconate, calcium zirconate and lead zirconate, 2) an insulating resin and 3) a dispersant containing a carboxylic group; or an insulation material comprising a filler having a dielectric constant of 50 or more, a dispersant for dispersing the filler and an insulating resin as essential components, wherein an extract of a cured product of the insulation material obtained by extraction with water at 120° C. for 20 hours using a pressure vessel has a pH of 6 or higher.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Resistance memory element
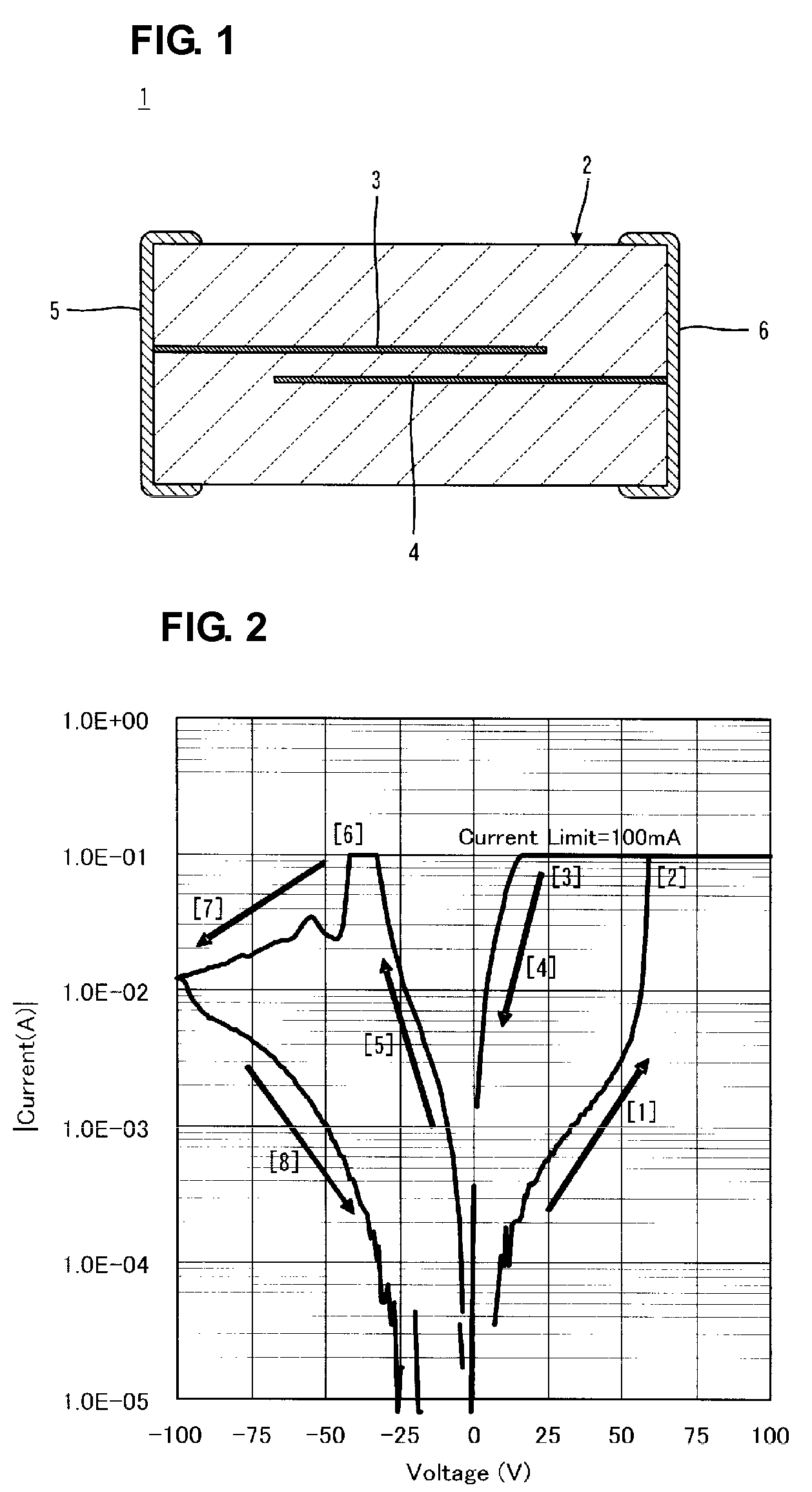
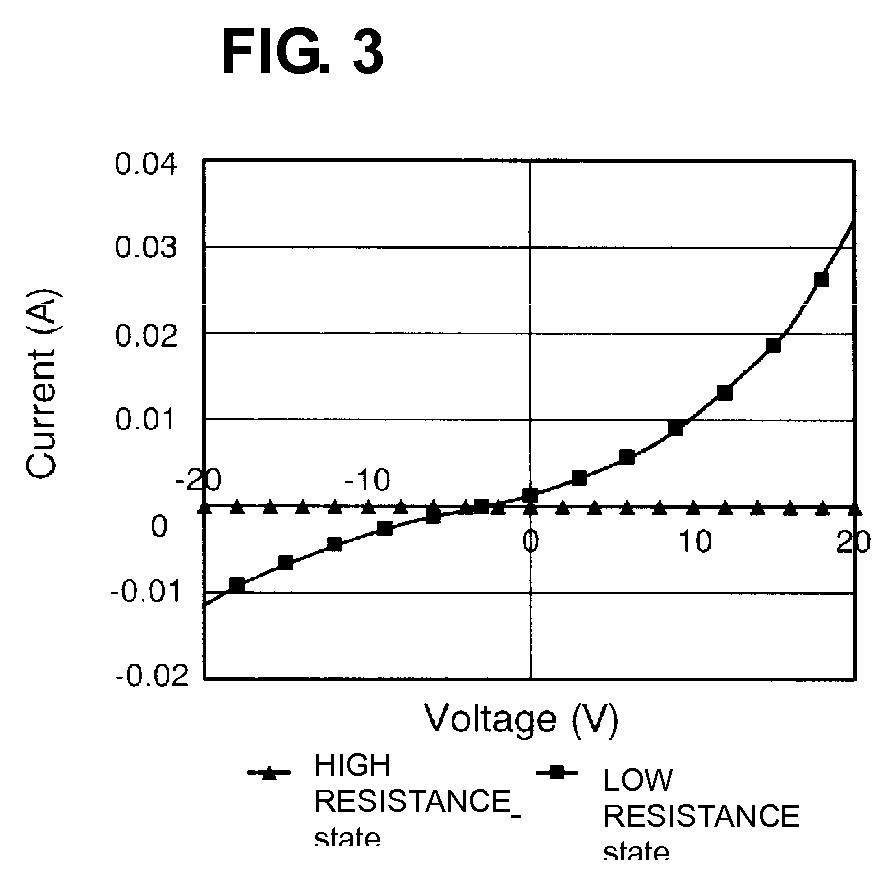
ActiveUS7649768B2High voltageIncrease chanceElectrical apparatusDigital storageStrontium titanium oxideRare-earth element
A resistance memory element includes an elementary body and opposing electrodes separated by at least a portion of the elementary body. The elementary body is preferably made of a strontium titanate-based semiconductor ceramic expressed by the formula: (Sr1−xAx)v(Ti1−yBy)wO3 (where A represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of Y and rare earth elements, and B represents at least one of Nb and Ta), and satisfies the relationships 0.001≦x+y≦0.02 (where 0≦x≦0.02 and 0≦y≦0.02) and 0.87≦v / W≦1.030. This semiconductor ceramic changes the switching voltage depending on, for example, the number of grain boundaries in the portion between the opposing electrodes.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Nano-composite organic spin valve
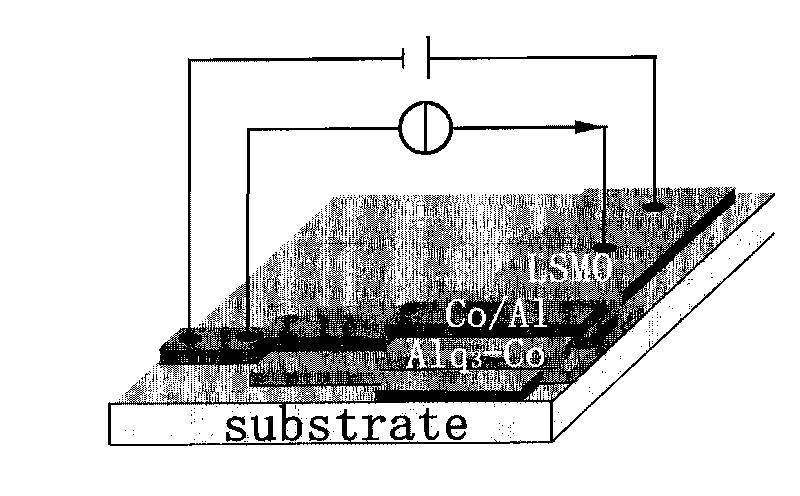
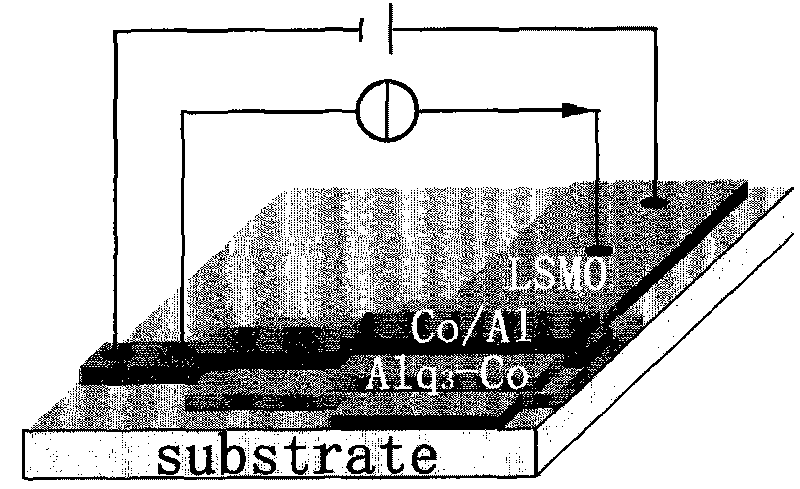
InactiveCN101710528ALarge magnetoresistance characteristicsAchieve transformationMagnetic film to substrate applicationSubstrate/intermediate layersEvaporationOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a nano-composite organic spin valve, belonging to technical field of spintronics. The spin valve comprises a sandwich structure; a top electrode is a transitional metallic cobalt thin film which is provided with an aluminum thin film as a protective layer; a bottom electrode is a La-Sr-Mn-O thin film; a middle transport layer is a nano-composite of the transitional metallic cobalt and organic micro-molecular 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum. The preparation method of the spin valve comprises the following steps of: preparing a La-Sr-Mn-O thin film bottom electrode of the spin valve on a strontium titanate substrate by using a laser pulse deposition method; preparing the middle transport layer of the transitional metallic cobalt and 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum by thermal evaporation; preparing the transitional metallic cobalt thin film as the top electrode on the middle transport layer of the nano-composite; and heating for evaporating the aluminum thin film as the protective layer on the top electrode of the transitional metallic cobalt thin film.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of high-performance doping strontium titanate oxide thermoelectric film
ActiveCN106784279AIncreased Seebeck coefficientImprove the Seebeck coefficientThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsSingle crystalFilm material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-performance doping strontium titanate perovskite oxide thermoelectric film. The method is characterized in that epitaxial coherent growth of a doping strontium titanate film material on the surface of an oxide monocrystal substrate which has the same lattice body structure and an unmatched parameter compared with the film material is realized by controlling a plasma property and a substrate condition; and an interfacial stress field is generated. A crystal structure property, an electronic structure property and a polarization characteristic of the film material, and an interfacial property between the film material and the substrate are adjusted by the stress field and the lattice distortion degree of the film material, so that thermoelectric transmission properties of the material such as conductivity and a seebeck coefficient are greatly improved. A room-temperature thermoelectric power factor of the prepared doping strontium titanate film material is 50-10000mnW / (cm*K<2>). The high-performance doping strontium titanate film material prepared by the method can be further applied to design and preparation of a thermoelectric device, so that the thermal and electric energy conversion efficiency of the prepared thermoelectric device during realization of functions such as temperature difference power generation, refrigeration and temperature sensing can be greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Method of preparing TiSrO3 coating on surface of titanium implant
ActiveCN104032291AImprove bindingLarge specific surface areaMetallic material coating processesHeat treatedMaterials science
The invention discloses a method of preparing TiSrO3 coating on the surface of a titanium implant. The method comprises the following steps: after carrying out sand blasting and double acid treatment on a pure titanium implant, putting the titanium implant in a hydrothermal solution containing strontium ions for hydrothermal treatment and surface modification; and forming a nanoscale protruding structure with multiple holes on the surface of the implant, wherein the protruding layer on the surface is a strontium titanate crystal structure and an anatase crystal structure and has the effects of promoting osteoblast and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. Meanwhile, the coating has good wettability and has a wide application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
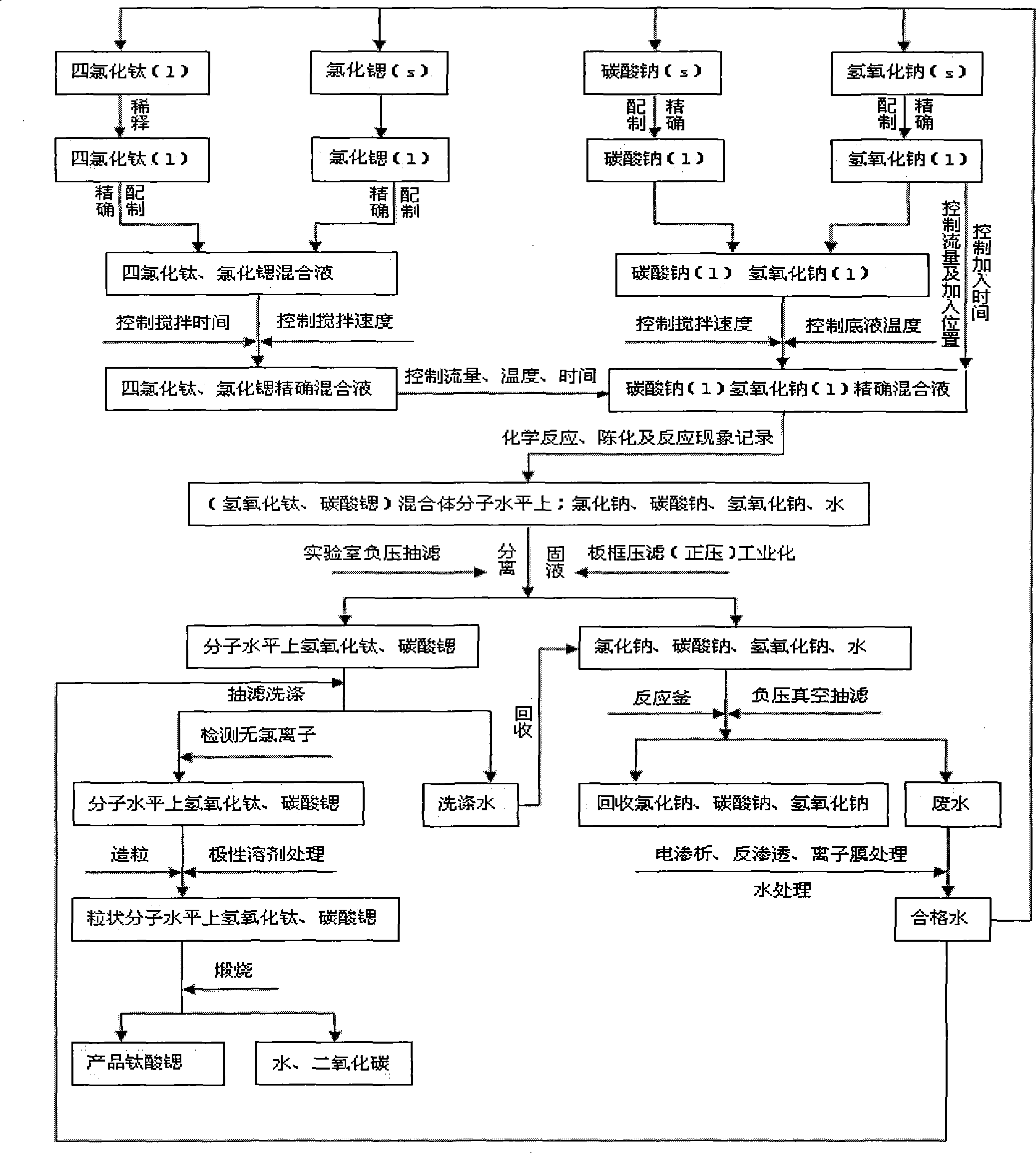
Method for preparing strontium titanate powder
ActiveCN103011807AImprove performance consistencyQuality improvementStrontium titanium oxideTetrachloride
The invention provides a method for preparing strontium titanate powder. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: adopting a titanium tetrachloride solution and a strontium chloride solution as the raw materials, and a sodium carbonate solution and a sodium hydroxide solution as precipitators; carrying out liquid-phase chemical coprecipitation reaction on the raw materials and the precipitators, so as to obtain a precursor precipitate of the strontium titanate; separating the precipitate from the reaction solution system; washing; drying; and dynamically roasting at a high temperature in a rotating way, so as to obtain the strontium titanate powder. The method is environment-friendly, simple in technological process, and convenient for industrial production; and the prepared strontium titanate powder is stable in quality, and high in purity and uniformity.
Owner:内蒙古科学技术研究院
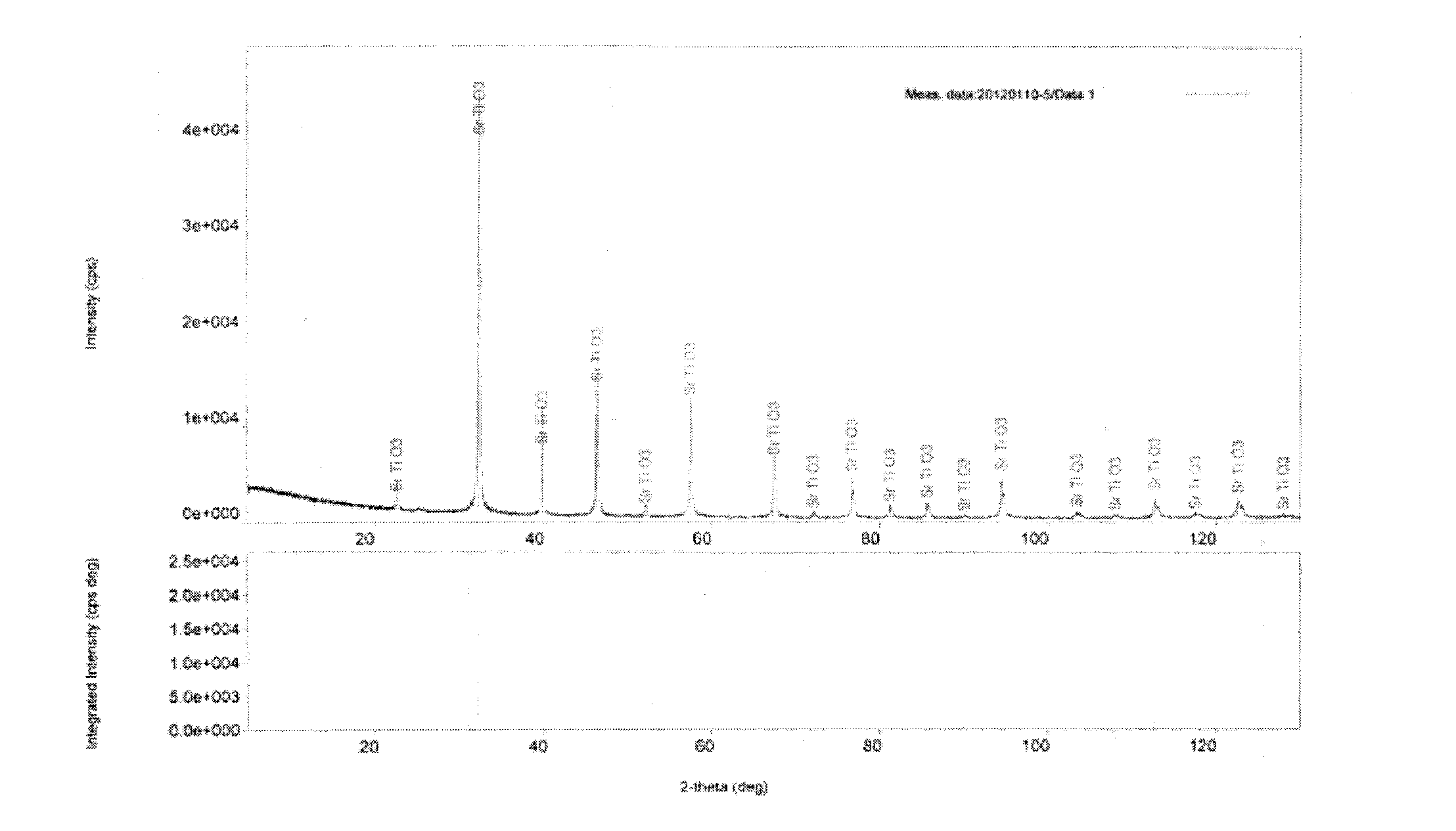
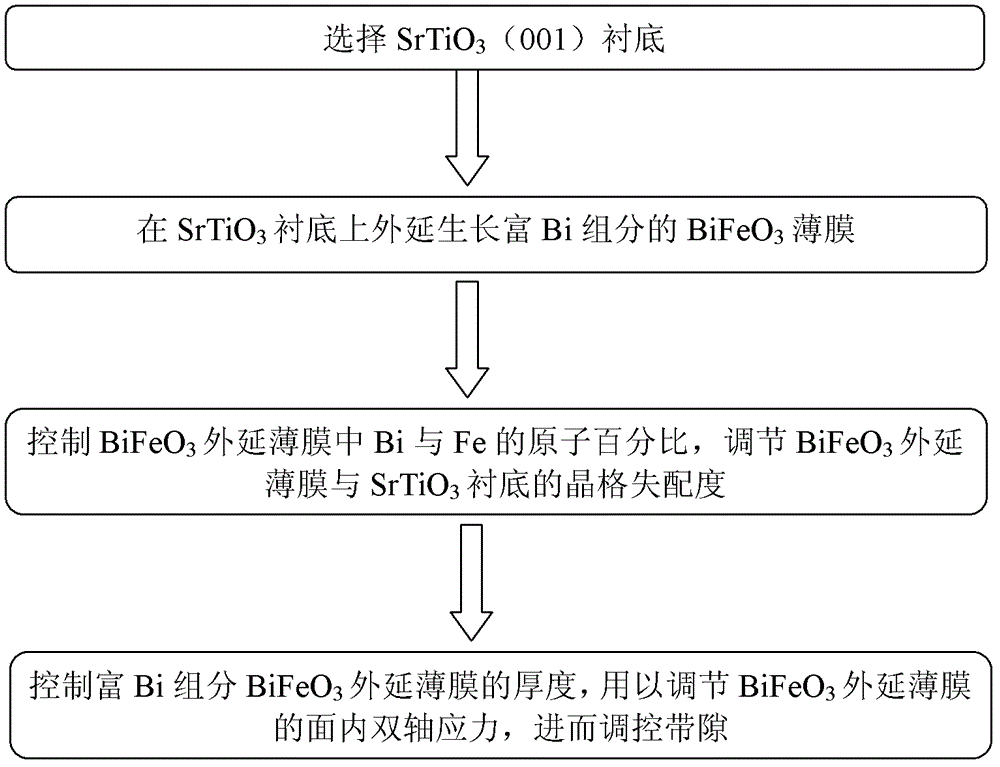
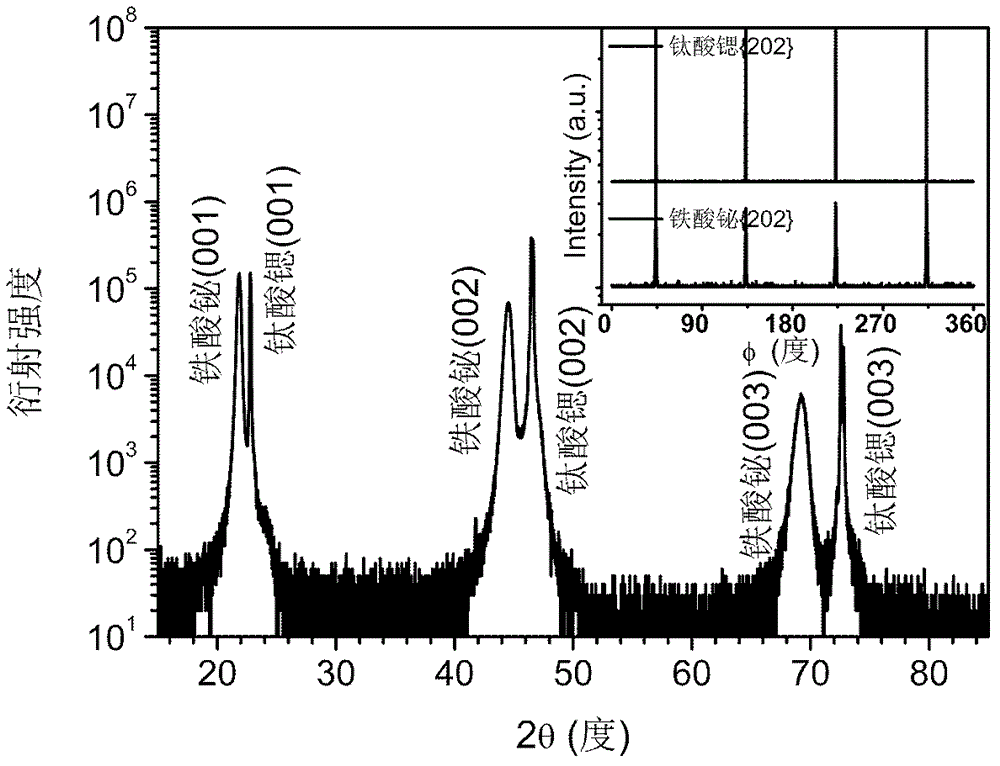
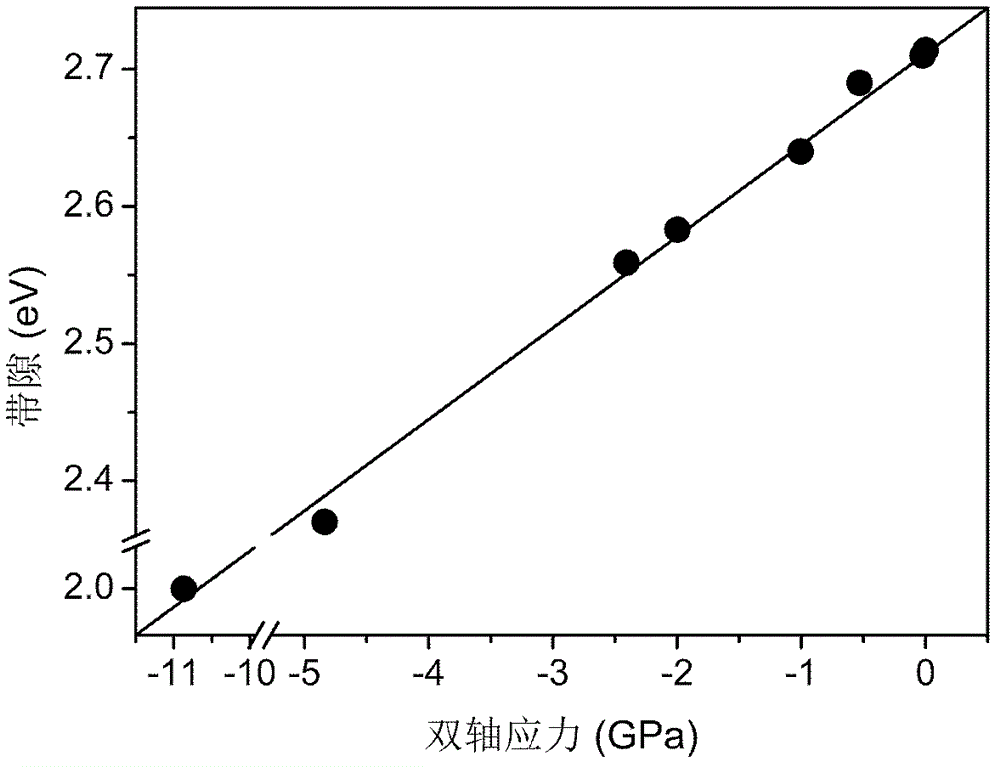
Method for regulating and controlling multiferroic BiFeO3 epitaxial film band gap on SrTiO3 substrate
InactiveCN102723400APrecisely control the magnitude of biaxial compressive stressFlexible and adjustable bandgapFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesStrontium titanium oxideIn plane
A method for regulating and controlling a multiferroic BiFeO3 epitaxial film band gap on a SrTiO3 substrate comprises the following steps: 1) Selecting a strontium titanate substrate; 2) Making a BiFeO3 epitaxial film rich in Bi component grow on the SrTiO3 substrate; 3) Controlling an atomic percent of the Bi and Fe in the BiFeO3 epitaxial film and regulating crystal lattice mismatching of the BiFeO3 epitaxial film and the SrTiO3 substrate; 4) Controlling thickness of the grown BiFeO3 epitaxial film rich in Bi component and regulating an in-plane bi-axis stress of the BiFeO3 epitaxial film.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ceramic Anode Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Novel anode materials including various compositions of vanadium-doped strontium titanate (SVT), and various compositions of vanadium- and sodium-doped strontium niobate (SNNV) for low- or intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell (SOFCs). These materials offer high conductivity achievable at intermediate and low temperatures and can be used as the structural support of the SOFC anode and / or as the conductive phase of an anode. A method of making a low- or intermediate-temperature SOFC having an anode layer including SVT or SNNV is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
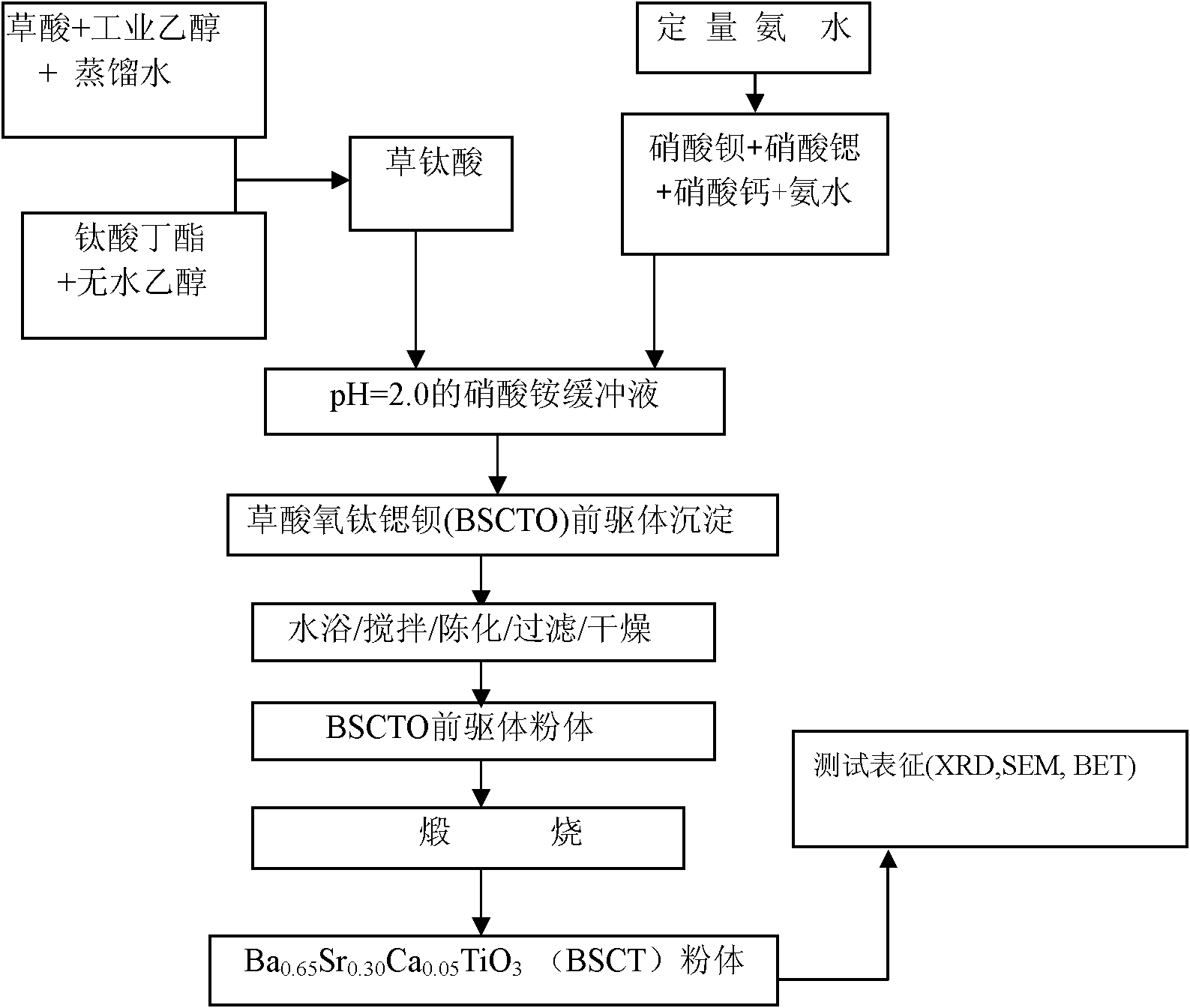
Barium strontium titanate-based superfine powder and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to barium strontium titanate-based superfine powder and a preparation method thereof. The powder is Ba1-xSrxTiO3, wherein x=0.2-0.8; or the powder is Ca2+ doped Ba1-z-ySrxCayTiO3, wherein z=0.2-0.7 and y=0-0.2. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing salt solution, buffer solution of ammonium nitrate, oxalic acid solution, ethanol solution of titanium butoxide and acid solution of titanyl oxalate monohydrate; performing coprecipitation reaction; and ageing, drying and calcining to obtain barium strontium calcium titanate powder. The barium strontium titanate-based superfine powder with the advantages of a little agglomeration, high dispersability, and high chemical activity is prepared by the chemical copercipitation method, accords with a stoichiometric ratio, has the advantages of small grain size, high uniformity, a little agglomeration, large specific surface area, and high chemical activity, and contributes to the compactness and sintering performance of the prepared ceramic capacitor materials.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Lithium-sulfur battery composite positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106532016ASimple methodNo complicated operationsCell electrodesLead zirconate titanateBarium titanate
The invention discloses a lithium-sulfur battery composite positive electrode material. Graphene oxide is used as a matrix of the battery positive electrode material, a graphene / ferroelectric composite material is obtained after the graphene oxide and a ferroelectric material are compounded, and then the graphene / ferroelectric composite material is mixed with nano sulfur according to a mass ratio of 3:7 to prepare the lithium-sulfur battery composite positive electrode material; and the ferroelectric material is one of barium titanate, lead titanate, potassium niobate, strontium titanate, lithium niobate or lead zirconate titanate. According to the lithium-sulfur battery composite positive electrode material disclosed by the invention, excellent electrical conductivity and structural stability of the graphene oxide are utilized, and the graphene oxide is used as an excellent conductive network and the positive electrode matrix, so that electrical conductivity of the positive electrode material is improved; and by utilizing strong adsorption of ferroelectricity of the ferroelectric material on polar polysulfide, dissolution and shuttling of the polysulfide in electrolyte are inhibited, so that loss of active substances is reduced, coulombic efficiency of a lithium-sulfur battery is improved and a cycle life of the lithium-sulfur battery is prolonged.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Strontium titanate dielectric layer based meta-material wave absorbing device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN110085996AActive adjustable frequencyActive adjustable intensityMagnetic/electric field screeningAntennasStrontium titanium oxideResonance
The invention discloses a strontium titanate dielectric layer based meta-material wave absorbing device and a manufacturing method thereof. The wave absorbing device comprises a bottom structure, a middle dielectric layer and a top resonance structure, the bottom structure comprises at least a metal film layer, and the middle dielectric layer is fixed on the bottom structure. The top resonance structure is fixed on the middle dielectric layer, and comprises metal resonance structures arranged in an array. The metal resonance structures are all fixed in the end surface, far from the bottom structure, of the middle dielectric layer. The metal film and metal resonance structures are made of copper, and the middle dielectric layer is made of a SrTiO3 material. The SrTiO3 material serves as themiddle dielectric layer of the meta-material wave absorbing device, the outside ambient temperature can be changed to adjust the wave absorbing frequency and intensity actively, further the application field of the meta-material wave absorbing device is widened, incident electromagnetic waves in the terahertz frequency is controlled effectively, and development and application of terahertz science and technology are facilitated.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of energy storage tungsten trioxide/strontium titanate/titanium dioxide nanometer composite film photoanode
ActiveCN106894024AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyInhibitory complexElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingComposite filmTio2 nanotube
The invention discloses a preparation method of an energy storage tungsten trioxide / strontium titanate / titanium dioxide nanometer composite film photoanode, and relates to a photoanode. A titanium foil is used as a basal body for ultrasonic operation in acetone, anhydrous ethanol and de-ionized water; a titanium basal body sample is used as an anode; a platinum piece is used as a cathode; after the anode is oxidized, a prepared sample is cleaned and dried to obtain a TiO2 nanotube array film; the TiO2 nanotube array film is put in a polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle; mixed solution containing Sr(COOH)2 and KOH is added for hydrothermal reaction; the sample is taken out to dip in HCl solution for cleaning, drying and calcining; and a SrTiO3 / TiO2 composite film is obtained. The SrTiO3 / TiO2 composite film is used as a working electrode; the platinum piece and a saturated calomel electrode are used as an auxiliary electrode and a reference electrode; constant potential is applied to an electrolytic cell for electric deposition to prepare WO3 on the surface of the SrTiO3 / TiO2 composite film; and the sample is flushed by de-ionized water, and is calcined after drying to obtain the photoanode.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
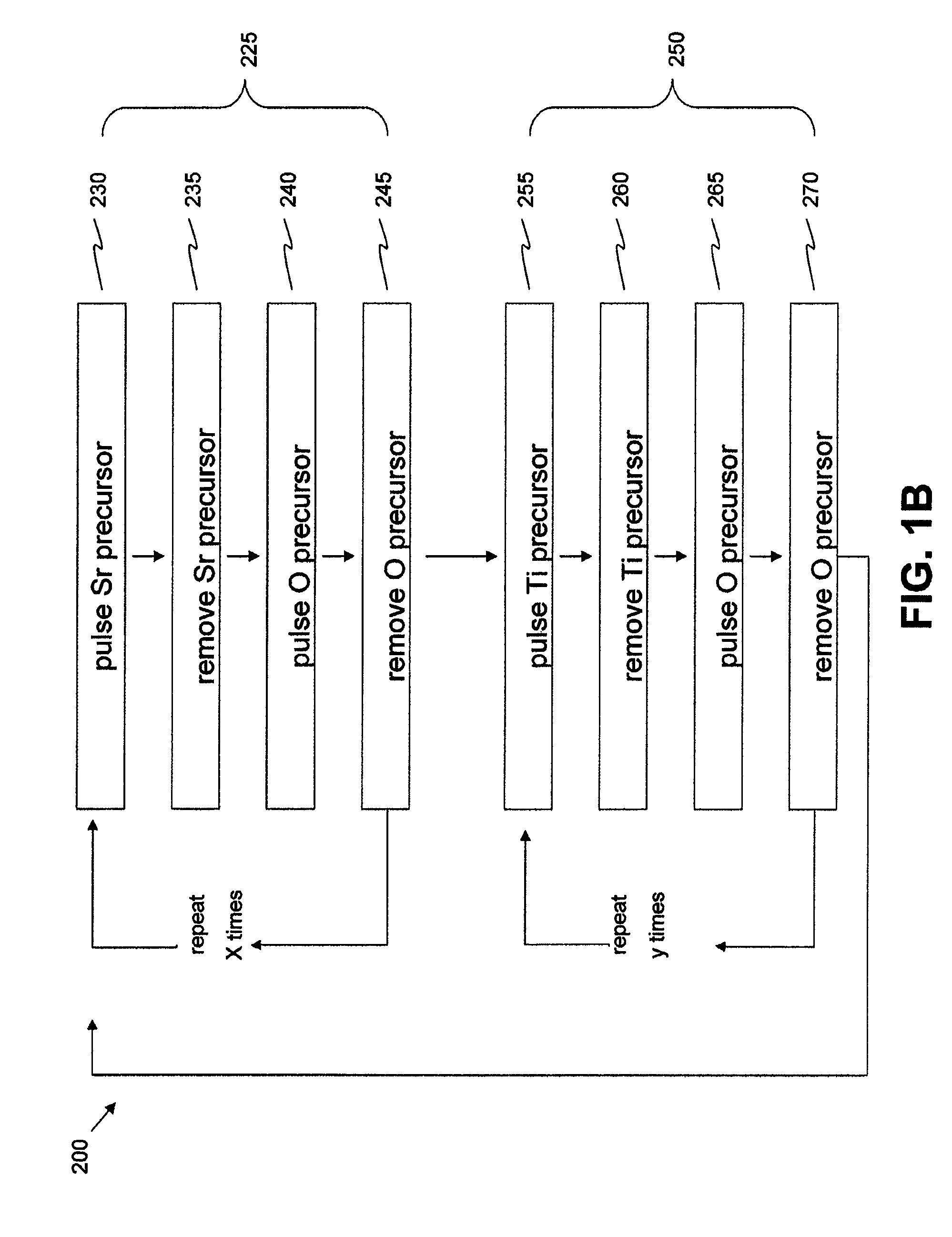
Crystalline strontium titanate and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS9062390B2From gel statePolycrystalline material growthStrontium titanium oxideSingle crystal
Methods of forming a crystalline strontium titanate layer may include providing a substrate with a crystal enhancement surface (e.g., Pt), depositing strontium titanate by atomic layer deposition, and conducting a post-deposition anneal to crystallize the strontium titanate. Large single crystal domains may be formed, laterally extending greater distances than the thickness of the strontium titanate and demonstrating greater ordering than the underlying crystal enhancement surface provided to initiate ALD. Functional oxides, particularly perovskite complex oxides, can be heteroepitaxially deposited over the crystallized STO.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for preparing strontium titanate nanoparticles
InactiveCN102139916ASimple processEasy to controlNanotechnologyTitanium compoundsStrontium titanium oxideNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method for preparing strontium titanate nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a mineralizing agent, namely potassium hydroxide, with proper concentration, into hydrothermal reaction materials, namely titanium hydroxide coprecipitate and deionized water solution of strontium nitrate; introducing solution obtained by hydrothermally decomposing glucose into a hydrothermal system to influence nucleation and control the particle size of products; and synthesizing the strontium titanate nanoparticles of which the diameter is 20 to 50nm by hydrothermal reaction. The process is simple and is easy to control; the method is environment-friendly and low in cost; and the products are easy to produce.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of bismuth vanadate/strontium titanate composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN106390986AGood ability to photolyze water to produce hydrogenIncrease migration rateEnergy inputHydrogen productionWater bathsHeterojunction
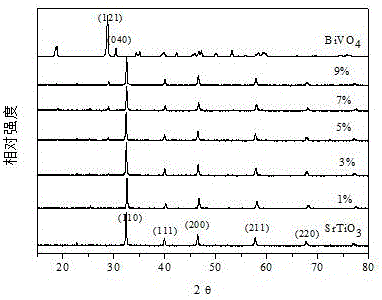
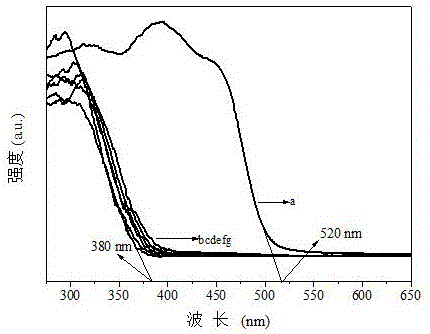
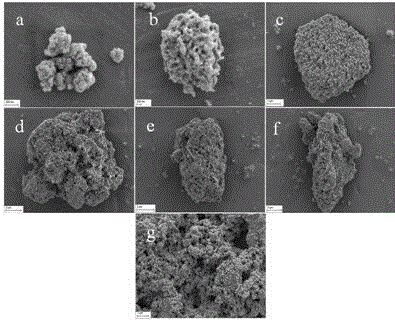
The invention discloses preparation of a BiVO4 / SrTiO3 composite photocatalyst, and is mainly applied to the technology of photocatalytic hydrogen production from water decomposition. A preparation method of the BiVO4 / SrTiO3 composite photocatalyst disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: stirring BiVO4 and dispersing the BiVO4 in distilled water in an ultrasonic manner, then adding SrTiO3, stirring and processing in an ultrasonic manner; evaporating to dry the mixture in a water bath at a constant temperature of 40-60 DEG C; finally transferring into a muffle furnace, and calcining for 1-2 hours at a temperature of 450-500 DEG C to obtain the BiVO4 / SrTiO3 composite photocatalyst. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a hydrogen producing material SrTiO3 serves as a main body, and a heterojunction composite material is formed by compositing the SrTiO3 with the SrTiO3, so as to increase the migration rate of photoinduced electrons on a semiconductor BiVO4 interface, meanwhile the absorption range of the SrTiO3 in solar energy spectrum is widened, and therefore the performance of the SrTiO3 on photocatalytic hydrogen production from water decomposition is improved. Experimental results show that hydrogen production of the photocatalyst can reach 611.6mu mol / g in the process of hydrogen production from water decomposition.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Heat-resisting sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104376947AImprove performanceImprove thermal stabilityInorganic material magnetismStrontium titanium oxideIron powder
The invention relates to a heat-resisting sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material and a preparation method thereof. Neodymium iron boron powder is composed of 18.6-23.1% of Nd, 0.73-0.81% of B, 0.44-0.53% of Cu, 0.95-1.03% of Co, 0.41-0.46% of Ga, 0.67-0.73% of Nb, 0.67-0.73% of Nb, 2.6-3.1% of Dy, 0.23-0.29% of Al and the balance Fe. The heat-resisting sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material is prepared by adding nano-iron powder, nano strontium titanate and nano vanadium nitride into the neodymium iron boron powder with uniform mixing prior to sintering. The heat-resisting sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material has the advantages that an optimal ingredient formula is adopted, appropriate nano elements are added, and through a special mixing manufacturing technique, a neodymium iron boron magnet which is high in performance and and heat stability can be produced; the neodymium iron boron magnet is small in size of grain boundary angle pair, more regular in shape and homogenized, refined and regular in crystalline grain, and the magnet has higher corrosion resistance and heat resistance.
Owner:东阳市亿力磁业有限公司
Quick-response photo-thermal induced voltage thin-film material and application
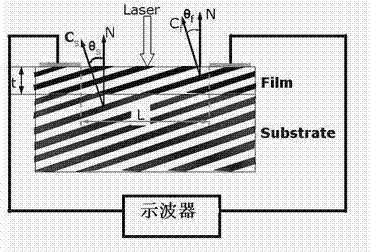
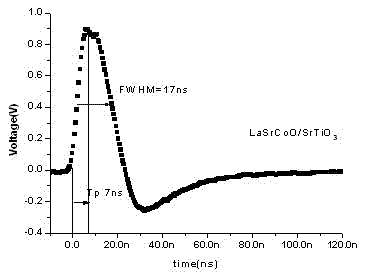
InactiveCN102544347AQuick responseThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsMeasuring instrumentFull width at half maximum
The invention discloses a photo-thermal induced voltage thin-film material having response time of less than 10 ns, and the application of the material. Lal-xSrxCoO3 serves as a quick-response induced voltage material, wherein x is equal to 0.1 to 0.6. A thin film is grown on an inclined strontium titanate (SrTiO3) single-crystal substrate by using a pulse laser deposit technology and has photo-thermal radiation induced voltage effects. Pulse laser light of which the pulse width is 28 ns and the wavelength is 248 nm is irradiated to the thin film, a quick-response large voltage signal of which the response time is 7 ns and the full width at half maximum is 17ns is obtained in the inclination direction of the thin film, and the voltage signal is acquired by a high-frequency oscilloscope. The photo-thermal induced voltage thin-film material is characterized in that: the response time is short; the material can operate at a wide optical spectrum of 0.19 to 11 mu m; the operation flow is easy, and energy sources are saved; the material can be used for manufacturing quick-response photo-thermal induced voltage detector devices; the response speed of a photo-thermal measuring instrument is increased; and the material is applicable to sensitive detection and tracking of pulse photo-thermal signals and military targets in the technical field of industry and the field of life.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-temperature structural material, structural body for solid electrolyte fuel cell, and solid electrolyte fuel cell
InactiveUS20130071770A1Increase manufacturing costAvoid mechanical strengthFuel cells groupingBuilding constructionsStrontium titanium oxideFuel cells
A high-temperature structural material which not only has a coefficient of thermal expansion close to the coefficient of thermal expansion of an electrolyte material, but also undergoes no decrease in mechanical strength even in a reducing atmosphere, and can be sintered at relatively low temperatures just by adding a predetermined sintering aid, a structural body for a solid electrolyte fuel cell, which is formed with the use of the high-temperature structural material, and a solid electrolyte fuel cell including the structural body. The high-temperature structural material contains strontium titanate and aluminum, wherein the aluminum is in an amount of 10 parts by mol or more and 60 parts by mol or less with respect to 100 parts by mol of the strontium titanate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electrophotographic developing agent
InactiveUS20060110673A1Avoid problemsLength of timeElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersStrontium titanium oxideParticulates
Provided is an electrophotographic developing agent including: toner particles including a binder resin, a colorant, and a charge control agent; and an external additive added to the surface of the toner particles, wherein the external additive includes at least one inorganic particulate component and at least two types of strontium titanate particulate component having different mean primary particle diameters. Typically, the inorganic particulate component is not strontium titanate. Also, an electrophotographic image forming apparatus using the electrophotographic developing agent is provided. The strontium titanate particulate component having different mean primary particle diameters are used as an external additive to maintain uniform charging characteristics and to prevent fog in a non-image area, thereby obtaining good image quality. In addition, the external additives prevent deposition of the developing agent on a developing agent regulating blade due to stress when the developing agent is used for a long time.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Toner, electrophotographic apparatus and process cartridge
InactiveUS20070281232A1Improve stabilityMinimize image deletionDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusStrontium titanium oxideInorganic particle
A toner, and an electrophotographic apparatus and an electrophotographic process cartridge using the toner are provided having excellent charge stability without adversely affecting electric properties of the toner even when used for a long period of time and having excellent image density stability without bringing about image deletion and blurring. The toner includes colored particles containing at least a binder resin and a colorant, and two or more external additives. At least one of the external additives includes hydrophobic treated mesoporous particles, and the mesoporous particles are inorganic particles of at least one type selected from the group consisting of silica, titanium oxide, alumina, cerium oxide, and strontium titanate.
Owner:CANON KK
Dielectric ceramic material with high-temperature stability and preparation method thereof
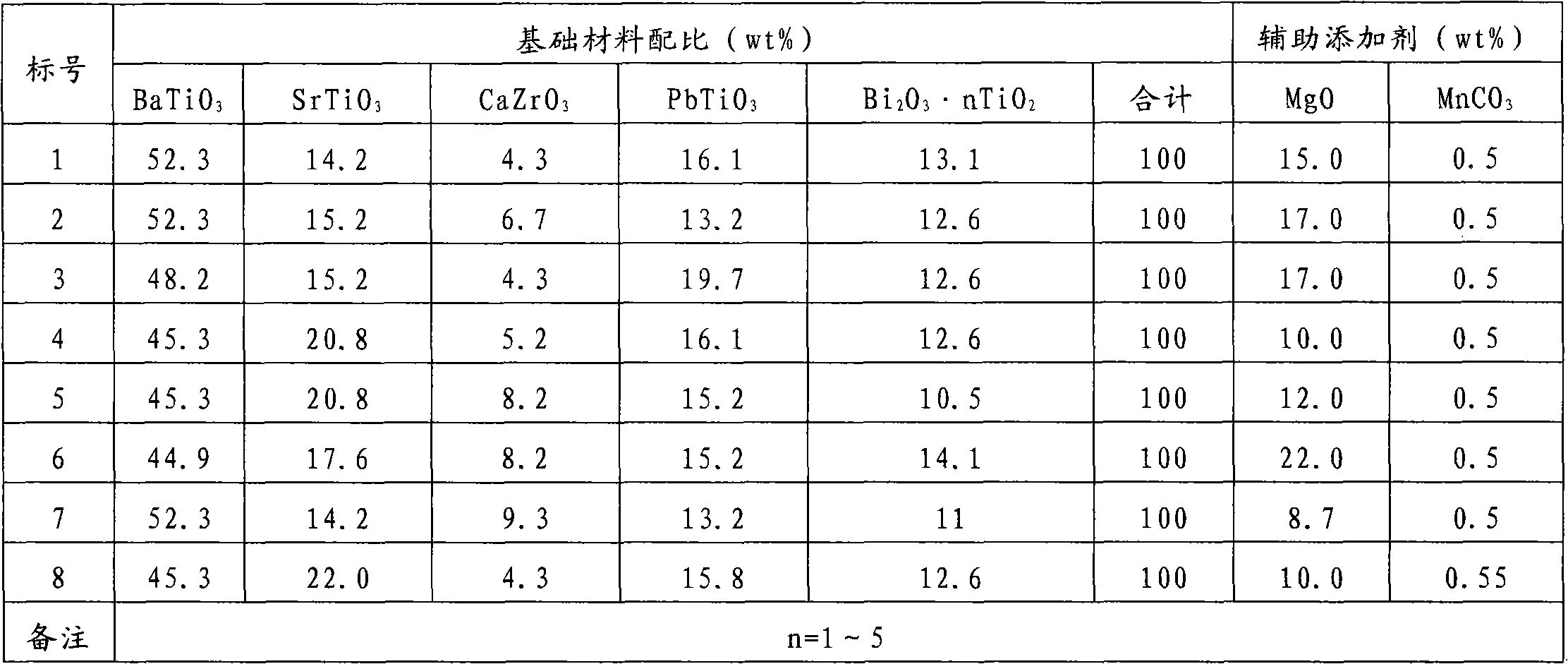
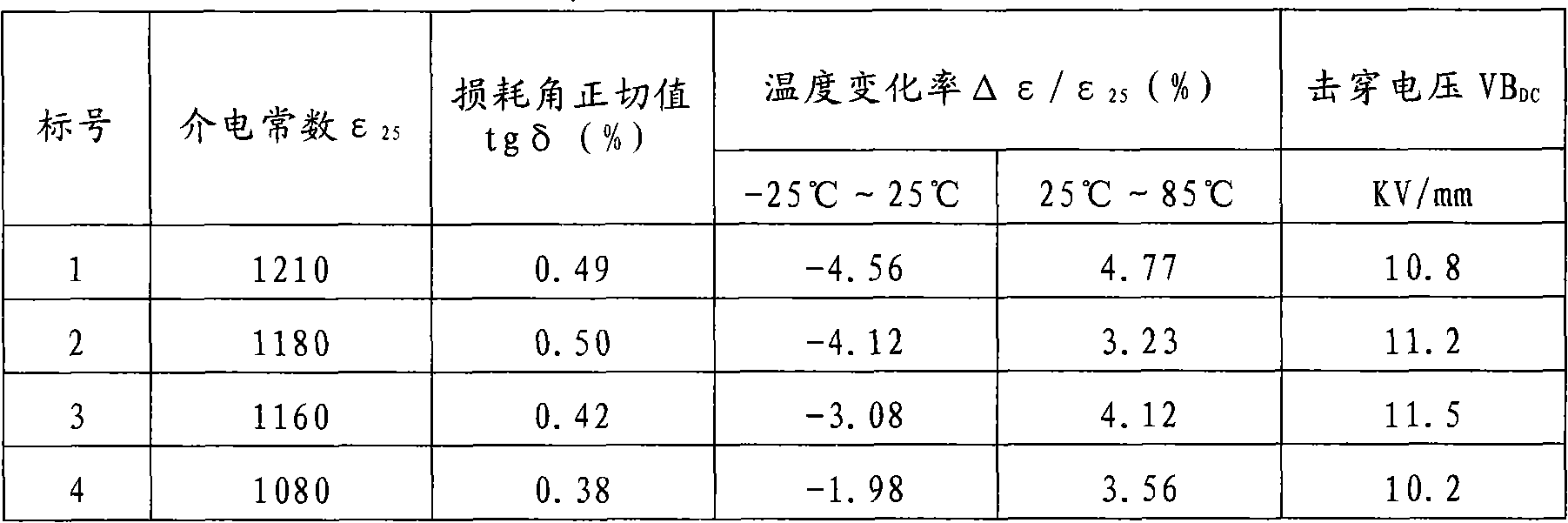
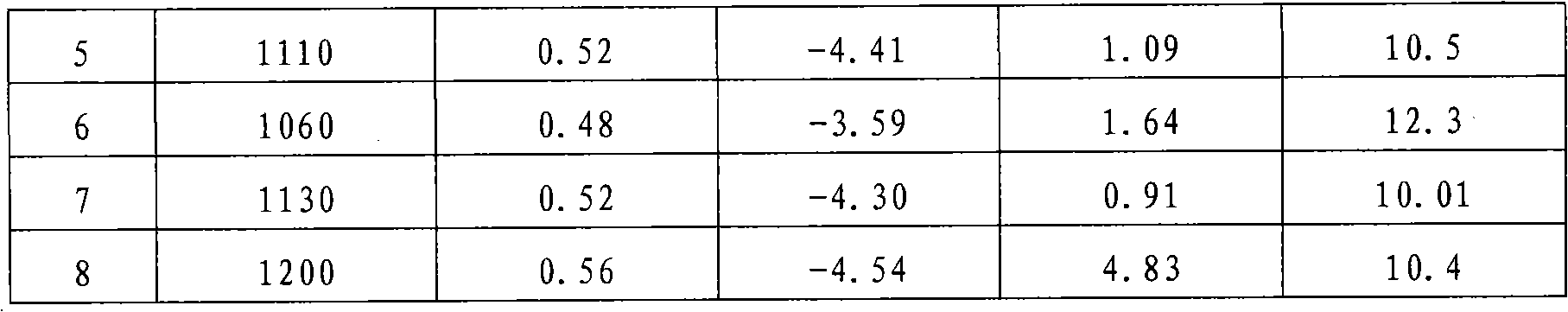
The invention belongs to the field of capacitor dielectric material preparation and relates to a dielectric ceramic material with high-temperature stability and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: pre-synthesizing base materials including barium titanate (BaTiO3), strontium titanate (SrTiO3), lead titanate (PbTiO3), calcium zirconate (CaZrO3) andBi2O3.nTiO2 by using barium carbonate (BaCO3), strontium carbonate (SrCO3), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), lead oxide (PbO), bismuth trioxide (Bi2O3), zirconium oxide (ZrO2) and titanium oxide (TiO2) as raw materials and by a solid-phase synthesis process, wherein n is 1 to 5; according to a proportioning requirement, mixing the base materials and auxiliary additives including magnesium oxide (MgO) and manganese carbonate (MnCO3) and performing resynthesis by the solid-phase synthesis process; and then preparing the dielectric ceramic material with high-temperature stability by the preparation process of the conventional dielectric ceramic material. According to detection, a ceramic capacitor manufactured by the dielectric ceramic material has the electrical characteristics that: the temperature change rate, namely absolute value of delta epsilon / epsilon25, is less than or equal to 5 percent (between 25 DEG C below zero and 85 DEG C); the dielectric constant epsilon25 is more than or equal to 1,000; the tangent tg delta of a loss angle is less than or equal to 1 percent; and the breakdown voltage VBDC is more than or equal to 10 KV / mm.
Owner:无锡隆傲电子有限公司
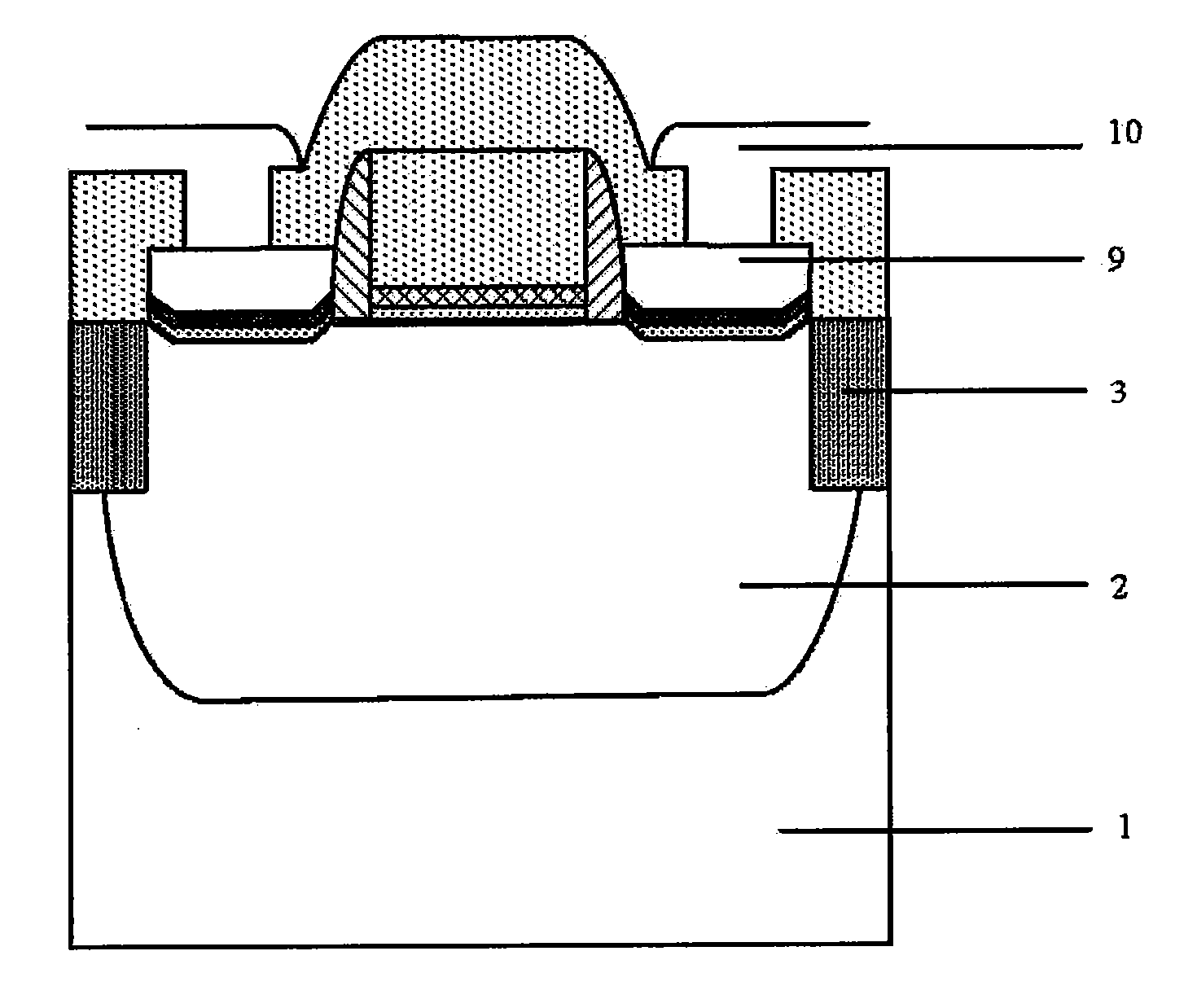
Germanium-based nmos device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20130069126A1On-off ratio can be increasedLittle resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideHafnium
An embodiment of the invention provides a germanium-based NMOS device and a method for fabricating the same, which relates to fabrication process technology of an ultra-large-scale-integrated (ULSI) circuit. The germanium-based NMOS device has two dielectric layer interposed between a metal source / drain and a substrate. The bottom dielectric layer includes a dielectric material having a high pinning coefficient S such as hafnium oxide, silicon nitride, hafnium silicon oxide or the like, and the top dielectric layer includes a dielectric material having a low conduction band offset ΔEC such as titanium oxide, gallium oxide, strontium titanium oxide or the like. According to the method, Fermi level pinning effect can be alleviated, electron barrier height can be lowered, and thus performance of the germanium-based Schottky NMOS device can be improved. Compared with a conventional single dielectric layer such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), Schottky barrier height can be lowered while low source / drain resistances can be maintained, and thus performance of the device can be significantly improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Semiconductor gallium arsenide compatible epitaxial ferroelectric devices for microwave tunable application
ActiveUS20150054037A1Improve temperature stabilityHigh dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricStrontium titanium oxideBarium strontium titanate
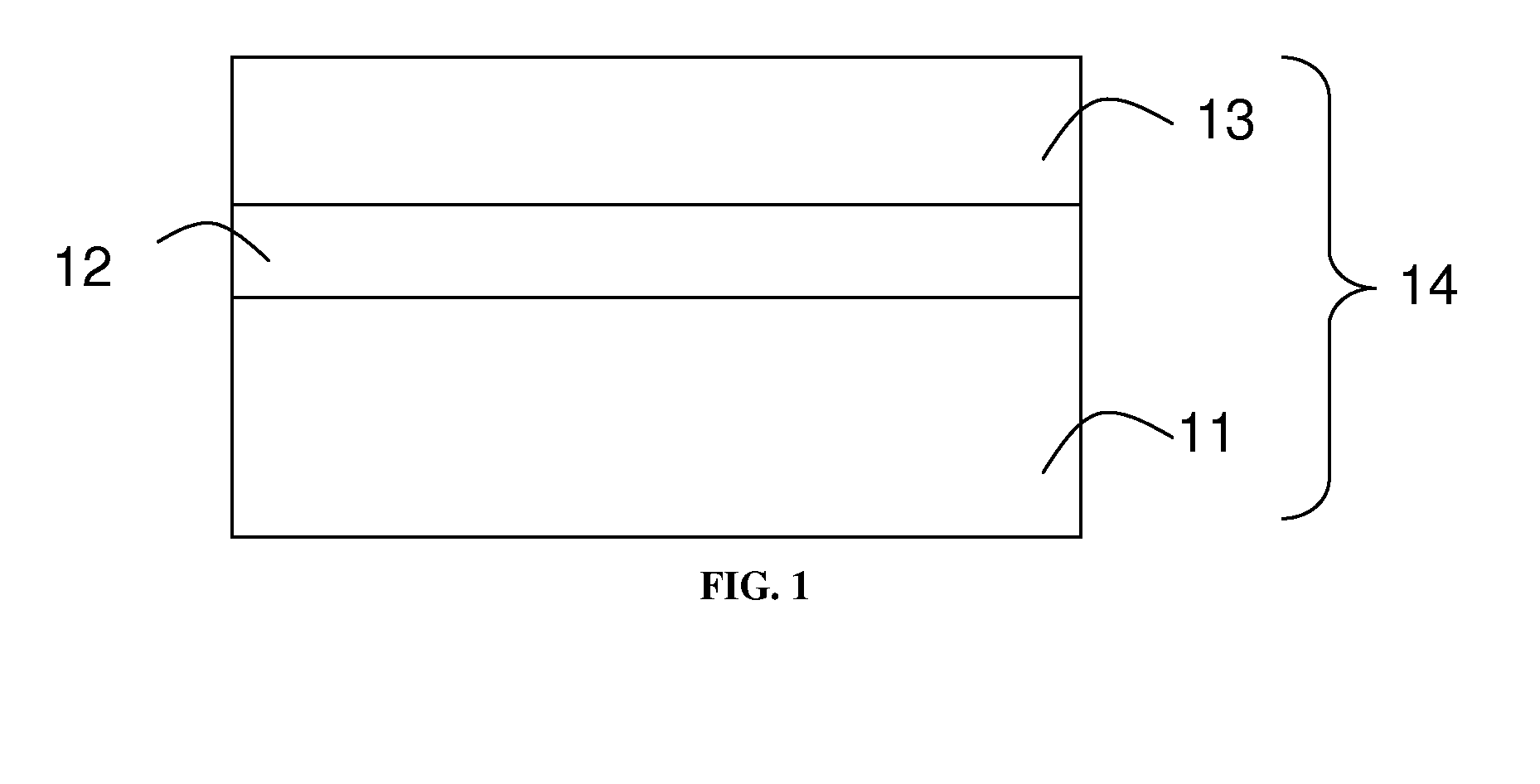
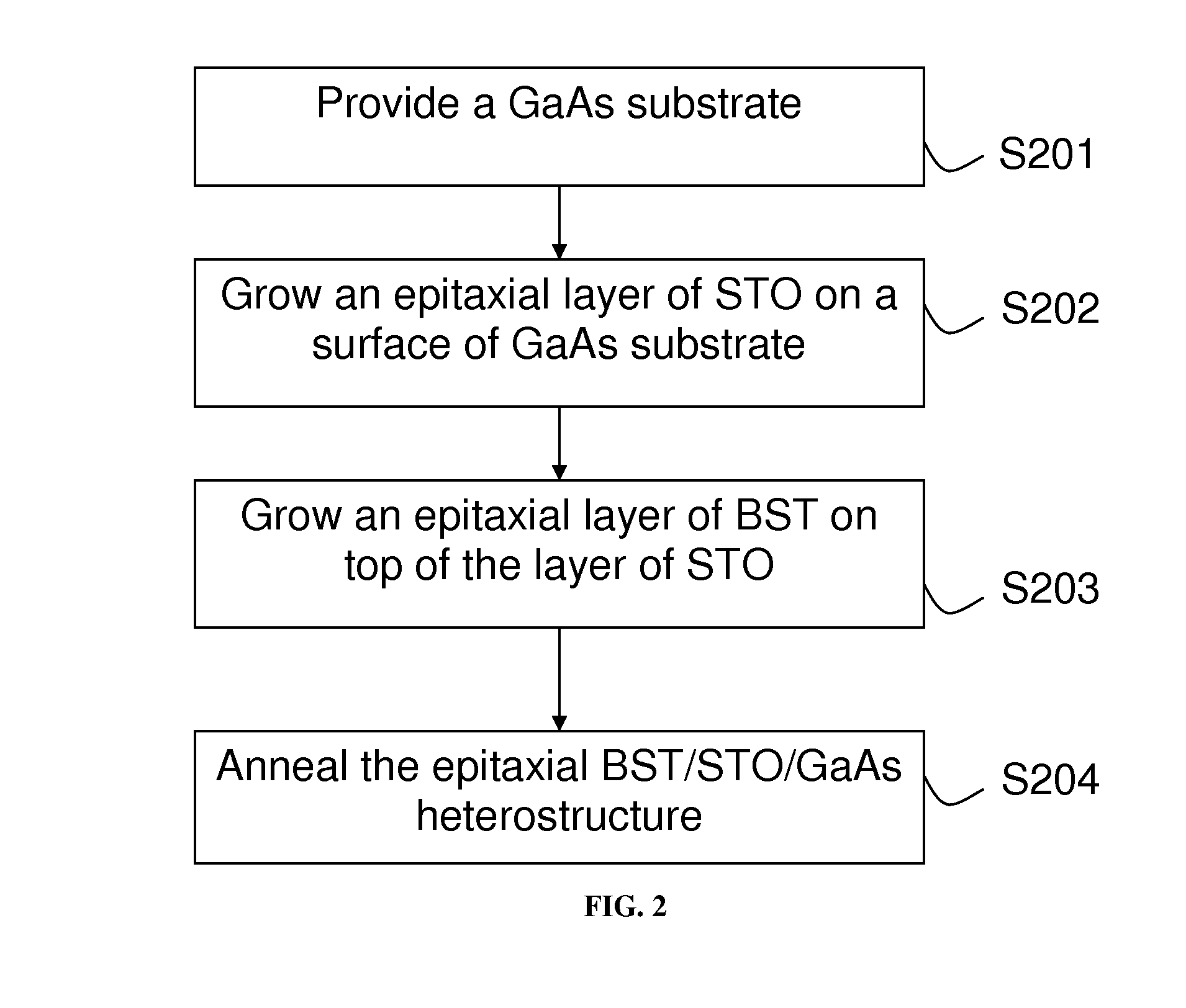
The presently claimed invention provides a barium strontium titanate / strontium titanate / gallium arsenide (BST / STO / GaAs) heterostructure comprising a gallium arsenide (GaAs) substrate, at least one strontium titanate (STO) layer, and at least one barium strontium titanate (BST) layer. The BST / STO / GaAs heterostructure of the present invention has a good temperature stability, high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss, which enable to fabricate tunable ferroelectric devices. A method for fabricating the BST / STO / GaAs heterostructure is also disclosed in the present invention, which comprises formation of at least one STO layer on the GaAs substrate by a first laser molecular beam epitaxial system, and formation of at least one BST layer on the STO layer by a second laser molecular beam epitaxial system.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com