Patents
Literature
268 results about "Glass cutter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
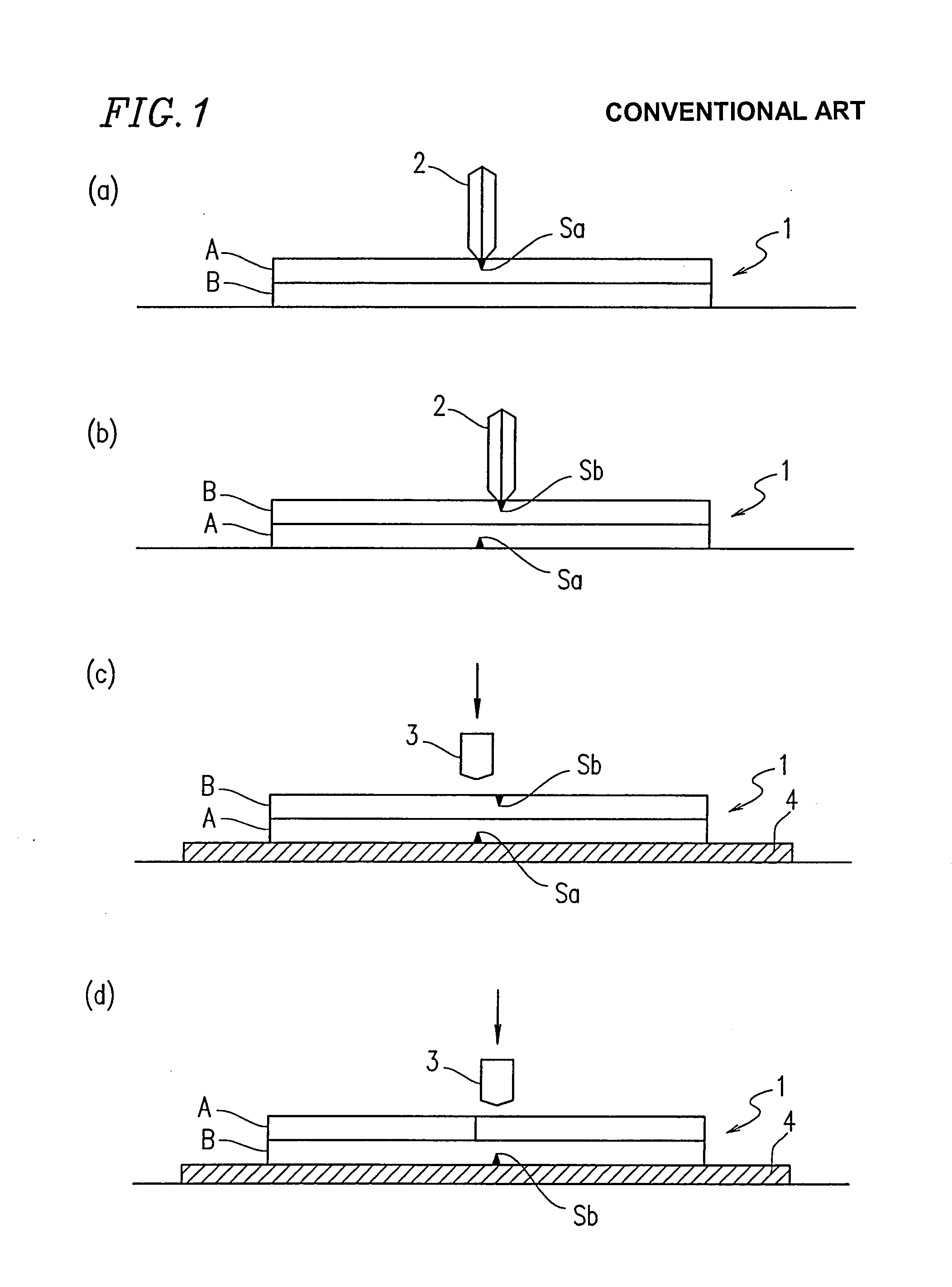
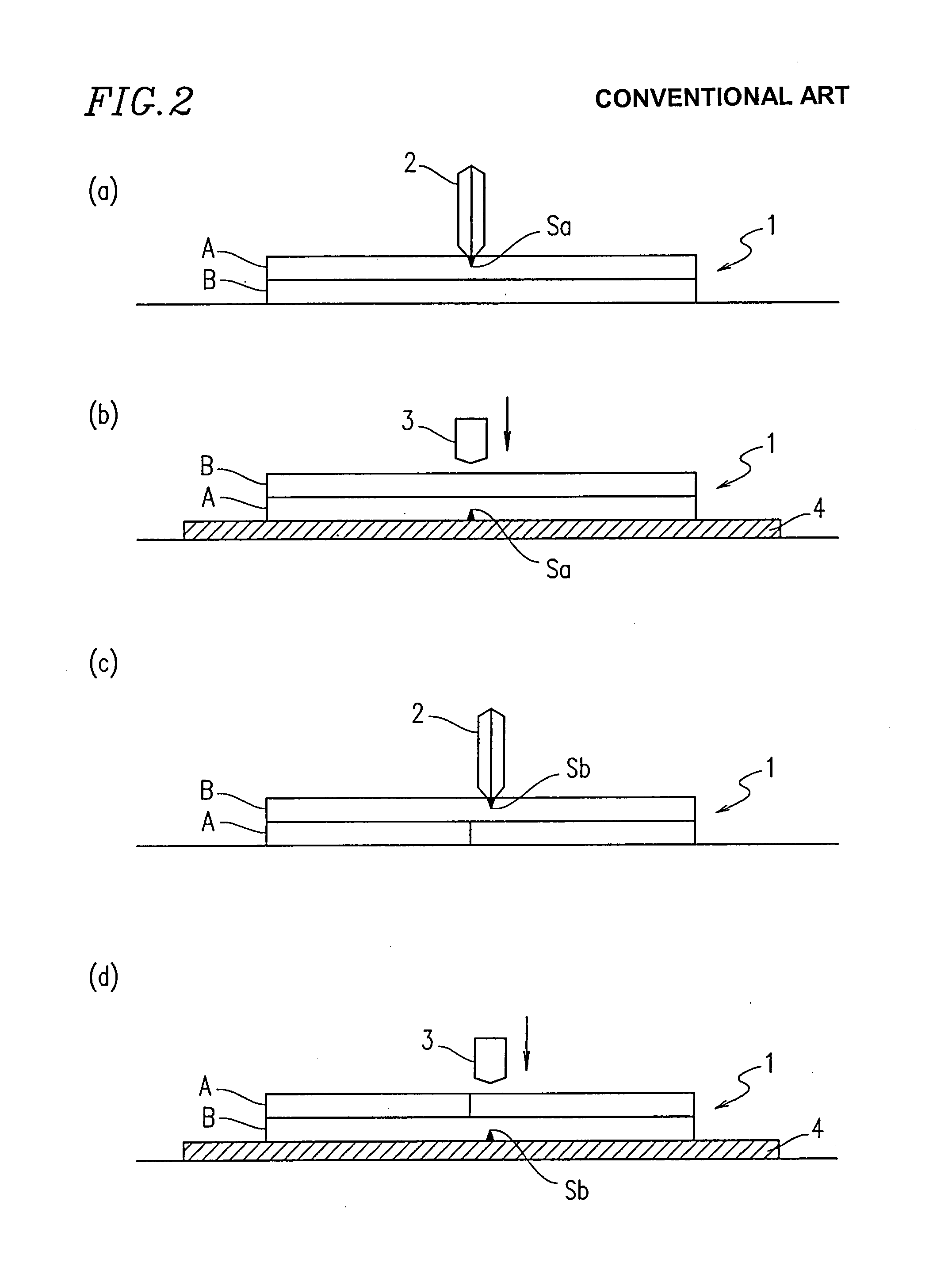
A glass cutter is a tool used to make a shallow score in one surface of a piece of glass that is to be broken in two pieces. The scoring makes a split in the surface of the glass which encourages the glass to break along the score. Regular, annealed glass can be broken apart this way but not tempered glass as the latter tends to shatter rather than breaking cleanly into two pieces.
Protective glass cutting machine
InactiveUS20200079678A1Quick cutImprove stabilityGlass severing apparatusMetal working apparatusCutting glassProtective glasses
The invention discloses a protective glass cutting machine, including a cutting body, a cutting cavity is arranged in the cutting body, a conveying device is arranged in the cutting cavity, and the conveying device comprises a vertically symmetric conveying The rotating wheel, the opposite direction of the conveying wheel can drive the glass tube to move to the left for cutting. The invention rotates along the glass tube by the heated cutting knife, and the glass tube is quickly cut, and the glass tube is cut. The left and right sides are respectively provided with an output device and a conveying device to ensure the stability of the glass tube and improve the stability of the glass tube cutting. Secondly, when the glass tube is input to the left, the cutting knife and the glass tube are not abutted by the telescopic device.
Owner:YAO JIANHUA
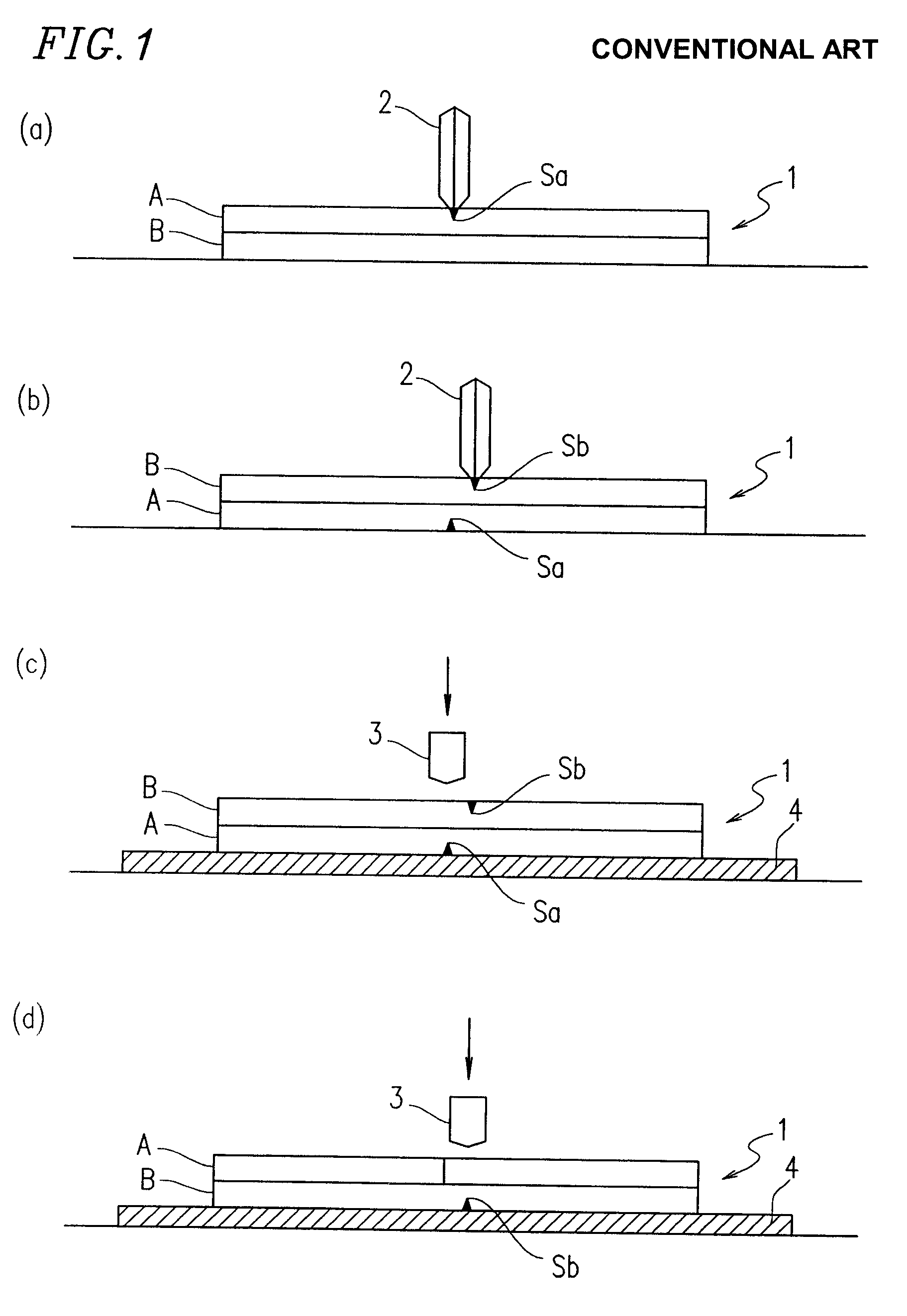
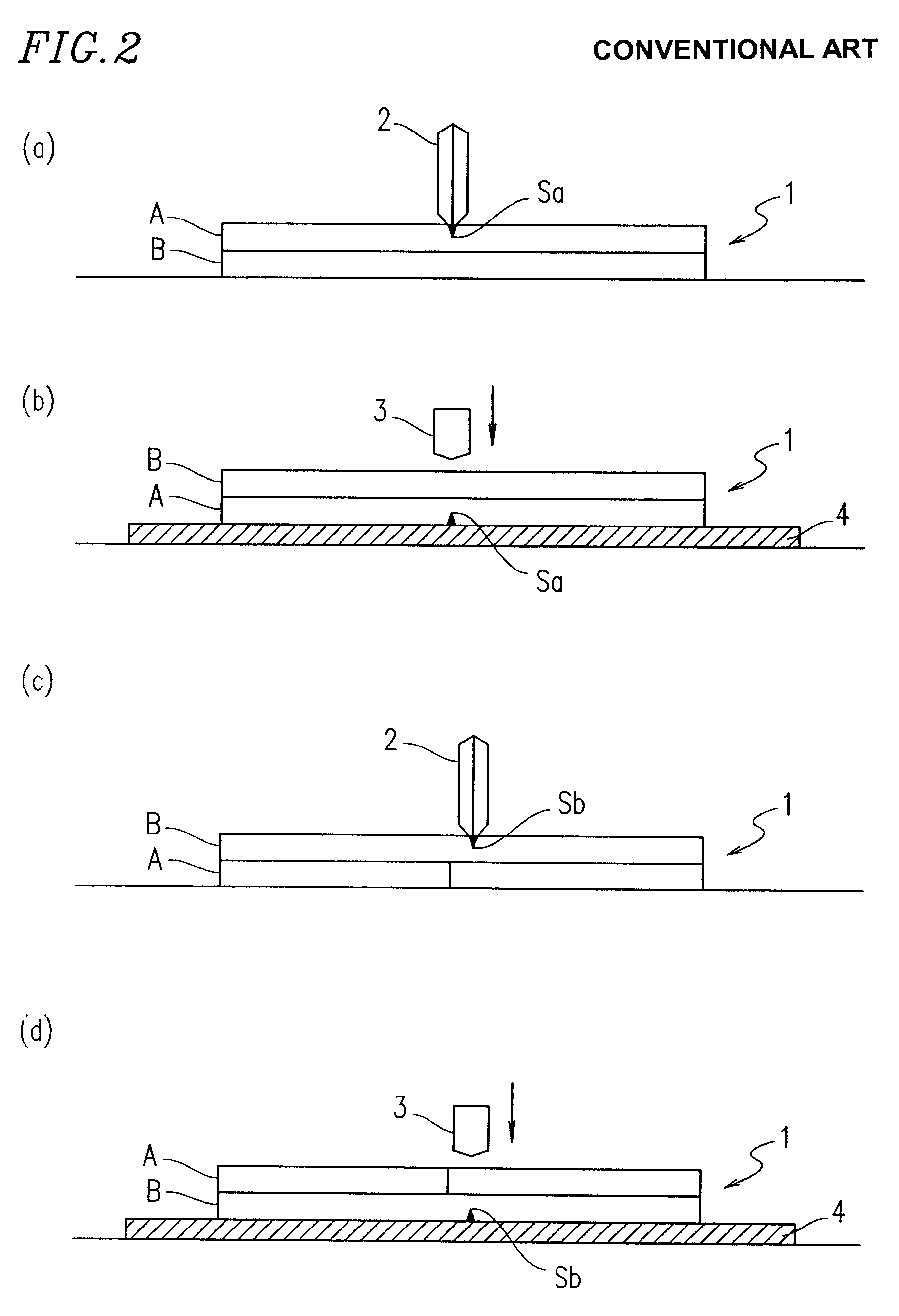
Scribing method, cutter wheel, scribing device using the cutter wheel, and cutter wheel manufacturing device for manufacturing the cutter wheel
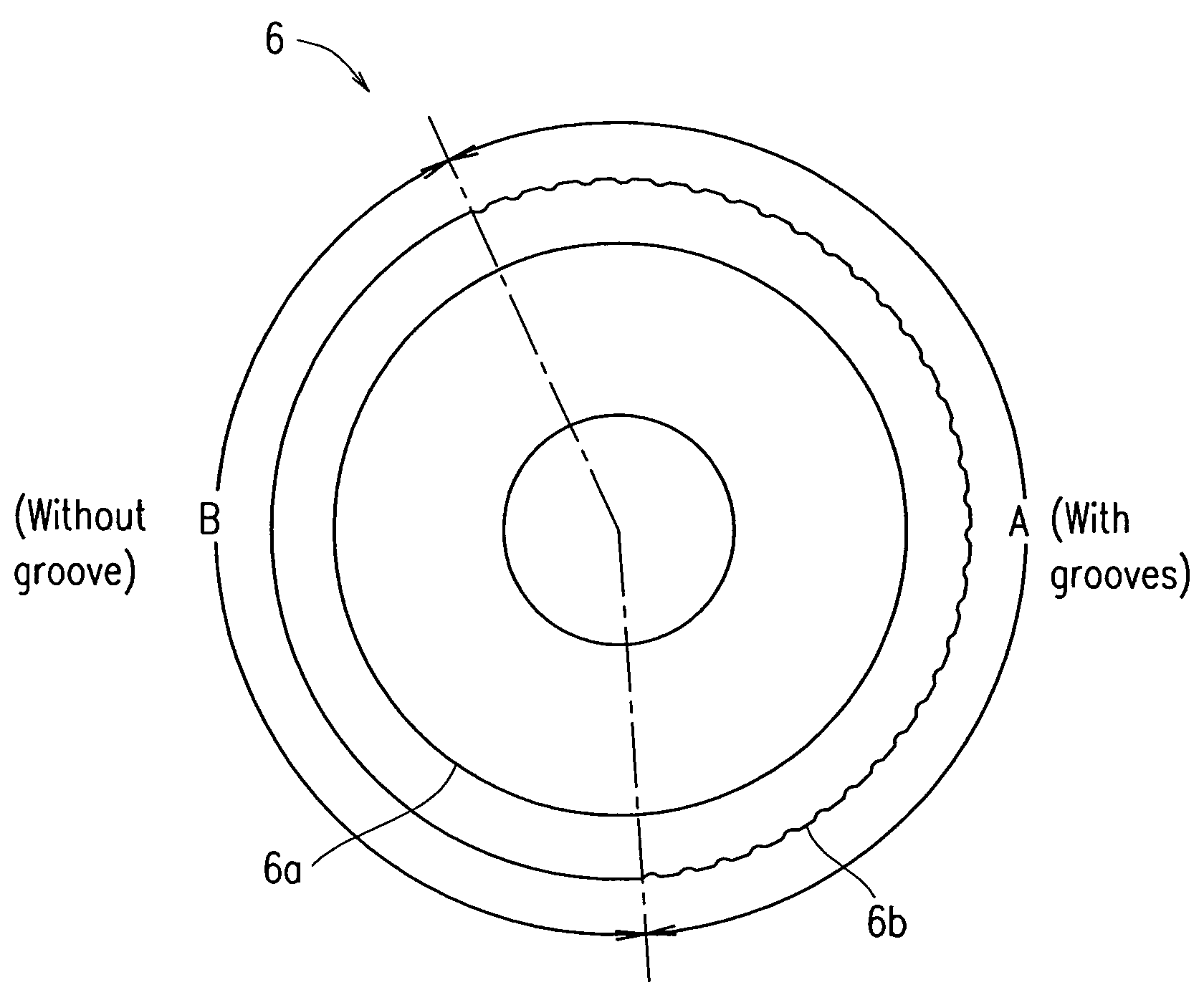
In a glass cutter wheel where a blade edge is formed on a disk-shaped wheel, grooves having a predetermined shape are formed at a predetermined pitch in a ¼ or smaller or ¾ or smaller blade edge line portion of the entire perimeter of the blade edge. The ratio of the groove portion to the entire perimeter, which largely contributes to a scribing characteristic, is changed such that a desired scribing characteristic can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Cutting roller for fragile material substrate and line drawer therewith
InactiveCN1338440AEliminate depth of cutReduce horizontal cracksGlass severing apparatusMetal working apparatusScriberEngineering
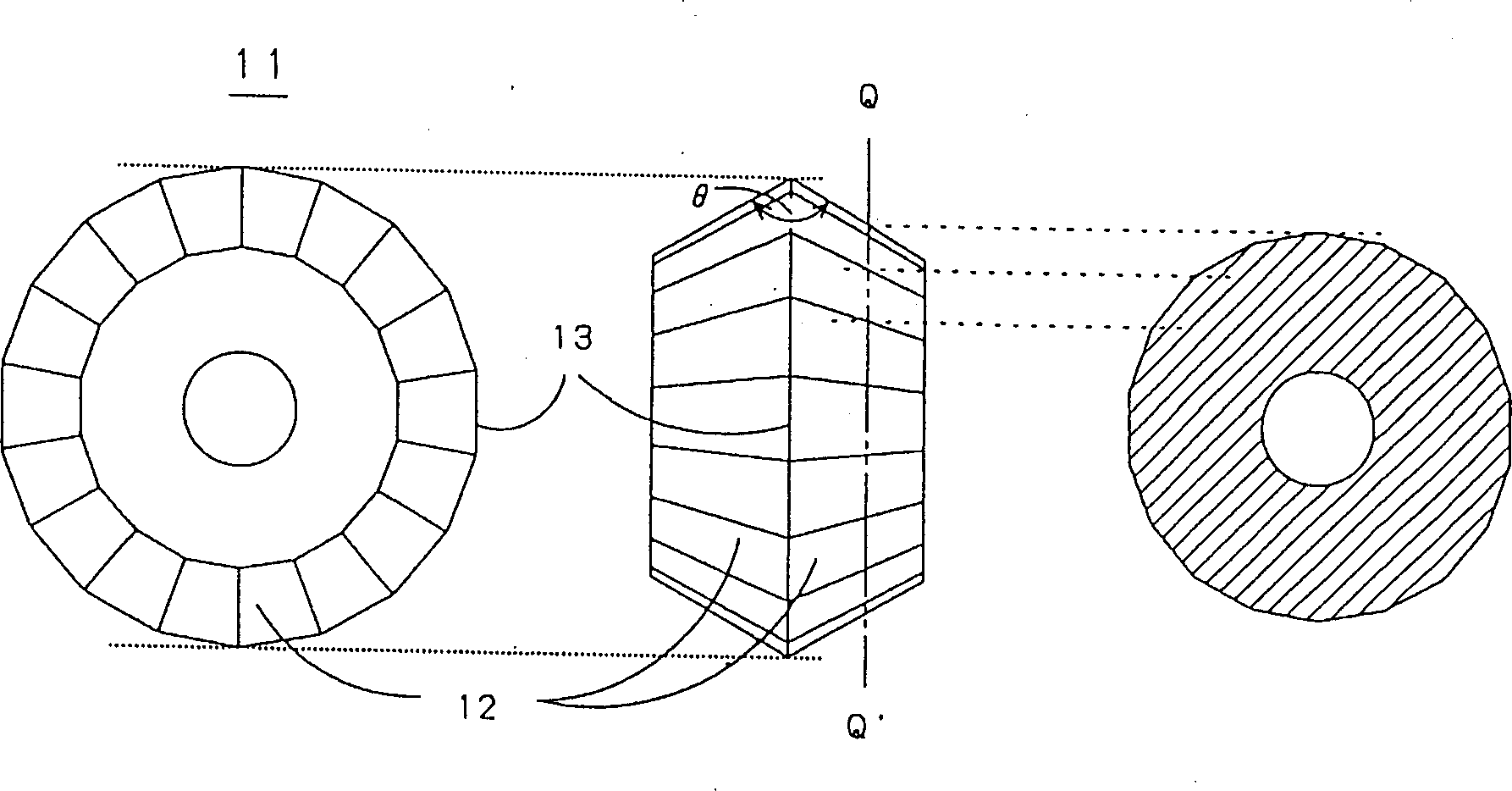
A cutter wheel for brittle material substrate. The glass cutter wheel having knife blades of a V shape along the circumferential part of a disk-shaped wheel is so formed that blade edges, for example, the ridgeline parts of the knife blades have a polygonal shape when viewed from sideways in forming the knife blades of the V shape. A scriber has a relatively moving unit moving in X-direction and Y-direction, campared to the glass cutter head arranged on the platform. The glass cutter head is provided with a cutter wheel for brittle material substrate. This inventive cutter wheel and scriber overcome effectively the problem such that a large quantity of horizontal cracks to degrade quality occur with the conventional glass cutter wheel.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Glass cutter
InactiveCN103755134ASimple structureEasy to useGlass severing apparatusCutting glassArchitectural engineering
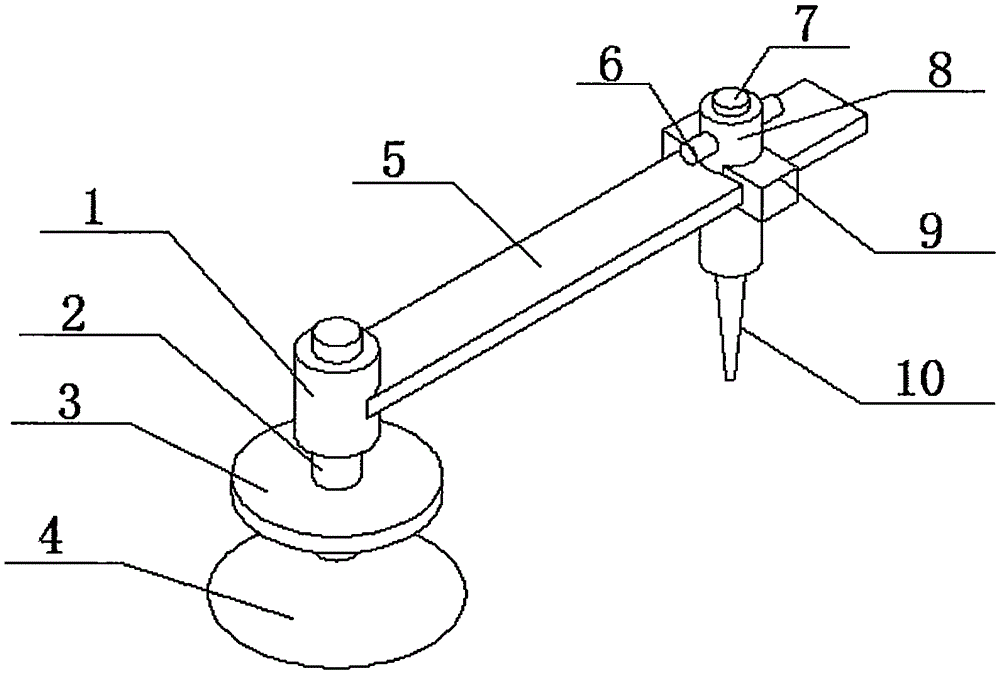
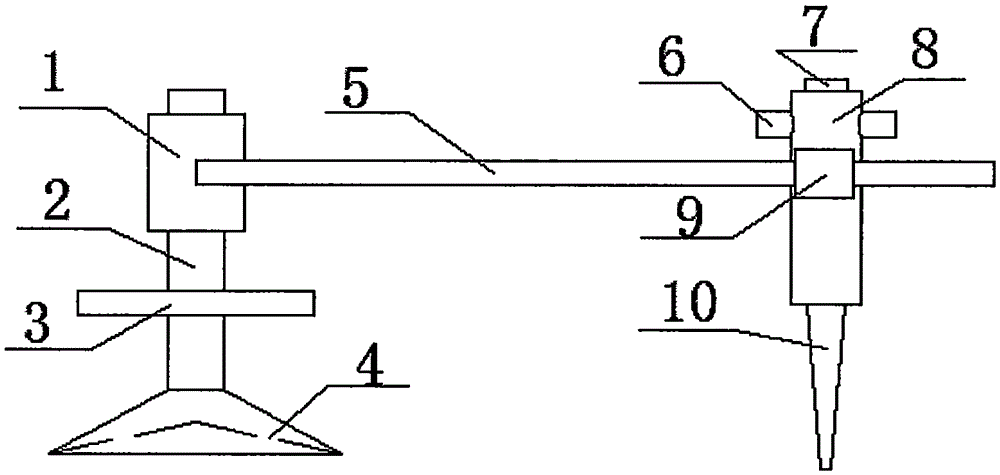
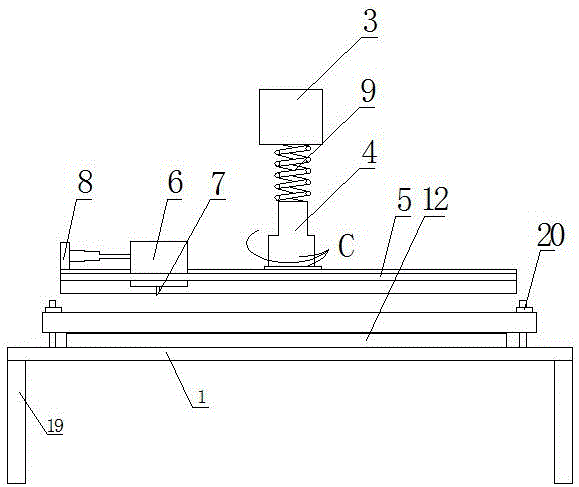
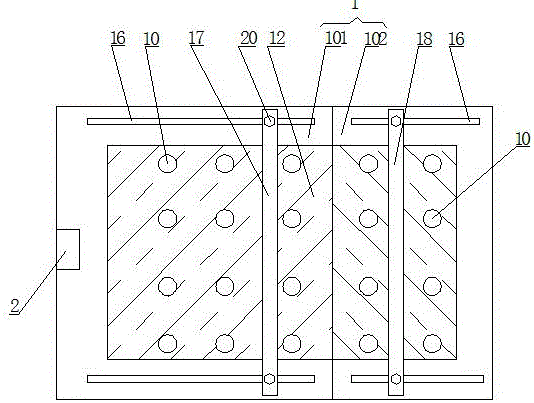
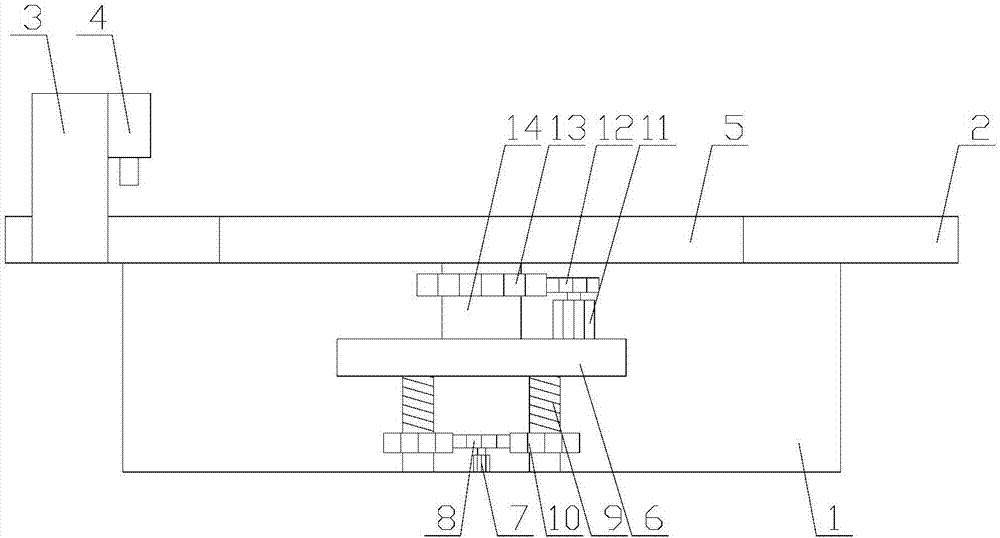
The invention relates to machinery used for cutting glass, specifically to a glass cutter. The glass cutter is characterized in that the glass cutter comprises a pedestal and a column fixed on the pedestal, wherein a first cantilever rotating with the column as an axle center is sleeved on the column, a second cantilever radially telescopic along the first cantilever is sleeved on the tail end of the first cantilever, a motor jacket is fixed on the tail end of the second cantilever, a motor is arranged in the motor, one side of the motor is provided with a tooth bar, a gear engaged with the tooth bar is mounted in the motor jacket, a handle used for controlling upward and downward movement of the motor is arranged at the outer side of the jacket, the end part of the handle passes through the motor jacket through a fixed axle and is connected with the gear in the motor jacket, and the bottom of the motor jacket is a cutter head connected with the output shaft of the motor. Compared with the prior art, the glass cutter provided by the invention can realize circular or arc cutting of glass, has a simple structure and is convenient to use.
Owner:苏世杰
Cutter wheel for cutting glass
InactiveCN101121573AAvoid damagePromotes the growth of cracksGlass severing apparatusGlass productionBreaking strengthCutting glass
A glass cutter wheel includes a wheel body having a pair of inclined surfaces defining an annular cutting edge therebetween and extending obliquely radially inwardly from the cutting edge to the respective side surfaces of the wheel body. Each inclined surfaces is formed with ground lines that are spaced from the cutting edge by a distance of 2 to 100 mum. Because the cutting edge penetrates into a glass material by a distance of 3 to 7 mum without the need to form ribs on the cutting edge, the ground lines serve to form a large number of vertical cracks. This completely prevents discontinuous cutting lines and chipping of the glass material at intersections of cutting lines, and also serves to provide smooth cut surfaces, thereby increasing the breaking strength.
Owner:TOYO KOGYO CO LTD
Automatic ring cutting device for glass tube
InactiveCN101774756AImprove regularityImprove yieldGlass severing apparatusGlass productionEngineeringGlass cutter
The invention provides an automatic ring cutting device for a glass tube, which comprises a cylinder base, a cylinder, a guide rail base, guide rails, linear bearings, a bracket, a pinion gear, a rack wheel, a glass cutter, electric magnets I, electric magnets II, a cambered press plate, a stepping motor, a lower bracket, a bearing and the like, wherein two parallel polished rod guide rails are installed on a glass tube production line base through the guide rail base; two linear bearings are fixedly installed on the bracket and are in movable fit with the guide rails; the cylinder is installed on the glass tube production line base through the cylinder base; a piston of the cylinder is installed on the bracket; the stepping motor is installed on the bracket; the pinion gear is installed on the output shaft of the stepping motor; the rack wheel is installed on the bracket through the bearing and is meshed with the pinion gear; the electric magnets I are installed on the rack wheel; the glass cutter is installed on the shaft of the electric magnets I; the lower bracket is welded at one side of the bracket provided with the stepping motor; the two electric magnets II are installed on the lower bracket; and the cambered press plate is installed on the shafts of the electric magnets II. The invention can realize an automatic ring cutting function through a glass tube arranged at the center of the big gear of the device.
Owner:SHANDONG LIAOCHENG DAVID LASER SCI & TECH
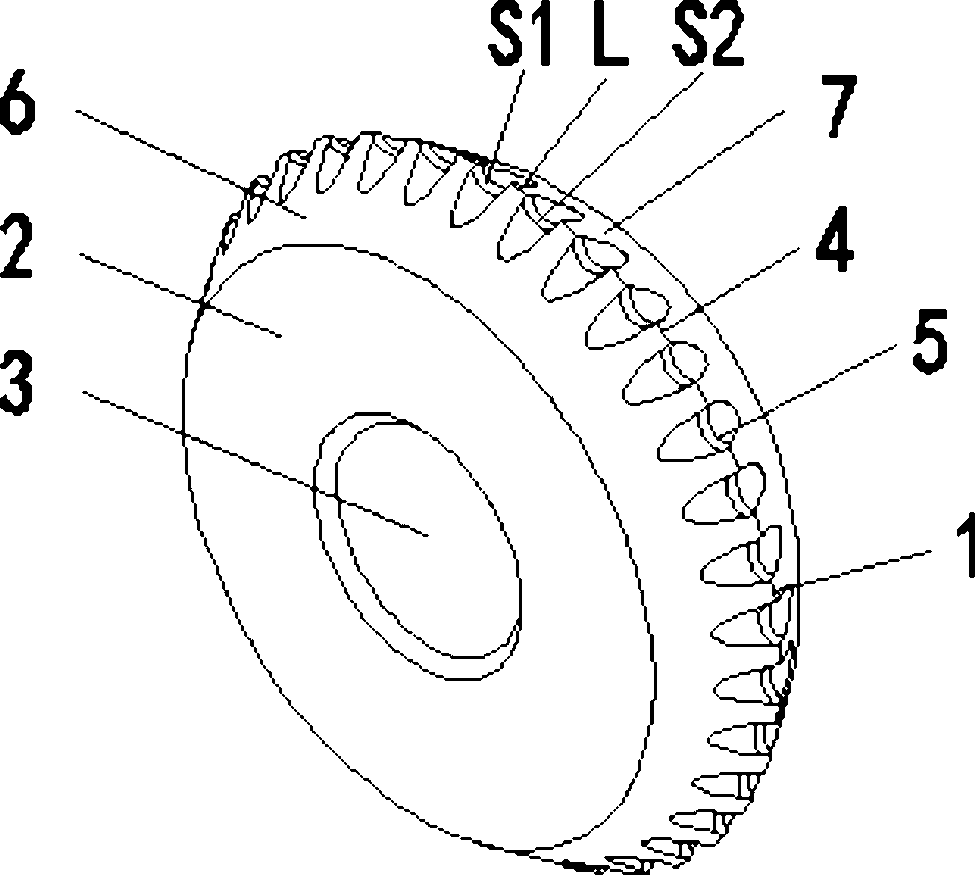
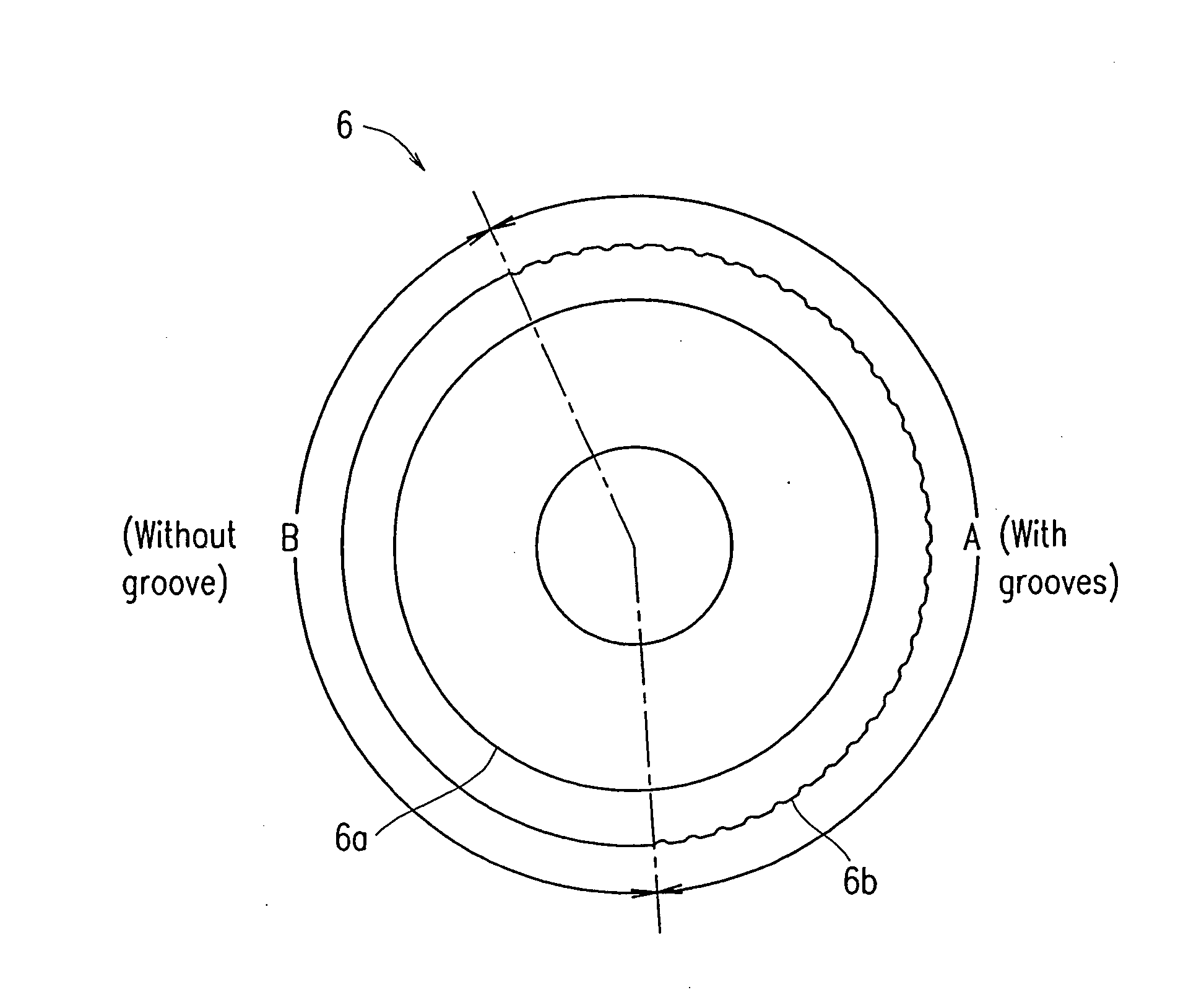
High-permeability glass cutter wheel with chamfer on side edge of concave part of cutting edge
ActiveCN102557424AGuaranteed impact strengthReduce areaGlass severing apparatusGlass chipEngineering
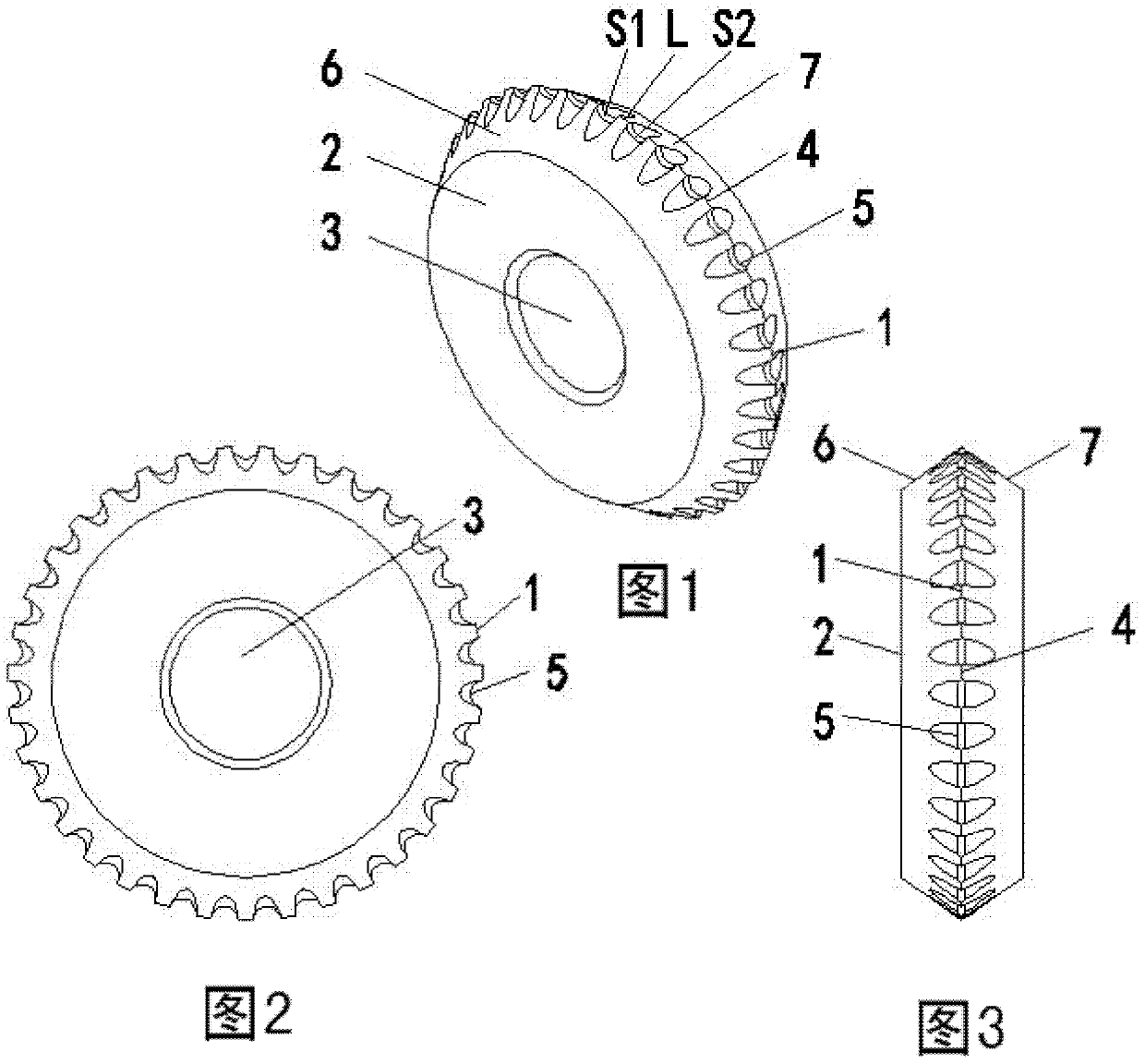
The invention relates to a high-permeability glass cutter wheel with a chamfer on the side edge of a concave part of a cutting edge. The cutter wheel is provided with a V-shaped cutting edge part, a disc surface and a shaft hole, wherein the V-shaped cutting edge part comprises a first curved surface S1, a second curved surface S2 and an outer edge ridge L. The cutting edge and the concave part are formed on the periphery of the outer edge ridge L of the V-shaped cutting edge part; and a first chambering oblique surface and a second chambering oblique surface which are symmetrical with each other are formed on the side edge of the concave part. Due to the adoption of the structure, the blockage of glass chips in the concave part of the cutter wheel can be avoided or reduced, the cutting pressure is reduced, and a destructive fracture line at the cutting edge of glass is reduced, so that the glass cutting quality is improved, and the service life of the cutter wheel for cutting the glass is improved.
Owner:JIAXING WORLDIA DIAMOND TOOLS CO LTD
Rounded glass cutting machine
ActiveCN110395897AReduce direct contactFor precise cuttingGlass severing apparatusGlass cutterGlass knife
The invention relates to a glass cutting machine, in particular to a rounded glass cutting machine. The rounded glass cutting machine can accurately conduct round cutting, saves manpower and is high in safety. The rounded glass cutting machine comprises a base, a platform, a rack, a first air cylinder, an N-shaped rod, an iron ring, a pressing block, a U-shaped frame, a first mounting plate, a motor, a first spring, a connecting plate and the like. The upper part of the base is connected with a platform; the right lower part of the base is connected with a rack; a first cylinder is mounted atthe top inside the rack. The rounded glass cutting machine is provided with the adjusting mechanism and the glass cutter, the position of the glass cutter is adjusted through the adjusting mechanism,rounded glass of a certain size can be accurately cut, and the accurate cutting effect is achieved; meanwhile, the motor arranged on the rounded glass cutting machine drives the glass cutter to rotatethrough related parts to conduct round cutting, and operation is convenient; the rounded glass cutting machine is further provided with a material box and related components, so that the equipment can move glass blanks more conveniently.
Owner:威海烟华安全玻璃有限公司
Glass cutting device
ActiveCN104829111AImprove cutting effectAnti-collision barGlass severing apparatusGlass cutterEngineering
The invention provides a glass cutting device. The glass cutting device comprises two fixing pedestals vertically and fixedly arranged on the two sides of a machine frame; the two fixing pedestals are connected with a horizontal screw rod; the horizontal screw rod and a sliding block are engaged in a movable manner; the top part of the sliding block is provided with a motor, and a guide bar is arranged below the horizontal screw rod; a cutting pedestal is fixedly arranged on the bottom of the sliding block; a telescopic cylinder is fixedly arranged on one side of the cutting pedestal via a fixing ring; a ring hole on the cutting pedestal is penetrated by a piston rod of the telescopic cylinder downward, and then the piston rod is connected with a glass cutter; a glass passage is formed by presetting a certain distance between the cutting edge of the glass cutter and a machine frame table surface; and the side wall of the inner side of the fixing pedestals are provided with limit sensors matching the cutting pedestal. The glass cutting device is simple in structure, high in automatic degree, low in labor intensity, and excellent in cutting effect.
Owner:江苏德佳玻璃科技有限公司
Processing technology of small-size camera ultrathin glass lens
InactiveCN107132593ADoes not affect light transmittanceImprove surface strengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensScreen printing
The invention relates to a processing technology of a small-size camera ultrathin glass lens. The technology comprises the steps that firstly glass raw material is cut by a glass cutting machine according to 15-20 times of the external contour size of the camera ultrathin glass lens and then chemical thinning and CNC formation are performed; and then cleaning and chemical toughened polishing are performed, and finally screen printing of the frame, laser cutting and FGAR film coating are performed. The beneficial effects are that application of the small-size ultrathin camera lens on the mobile phone, the tablet and the computer can be realized through the technology so that the product is enabled to be more exquisite and beautiful.
Owner:苏州市智诚光学科技有限公司
Glass cutting machine, glass cutter, and glass cutting method
InactiveUS8997619B2Avoid layeringInhibition formationGlass severing apparatusMetal working apparatusCutting glassGlass cutter
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
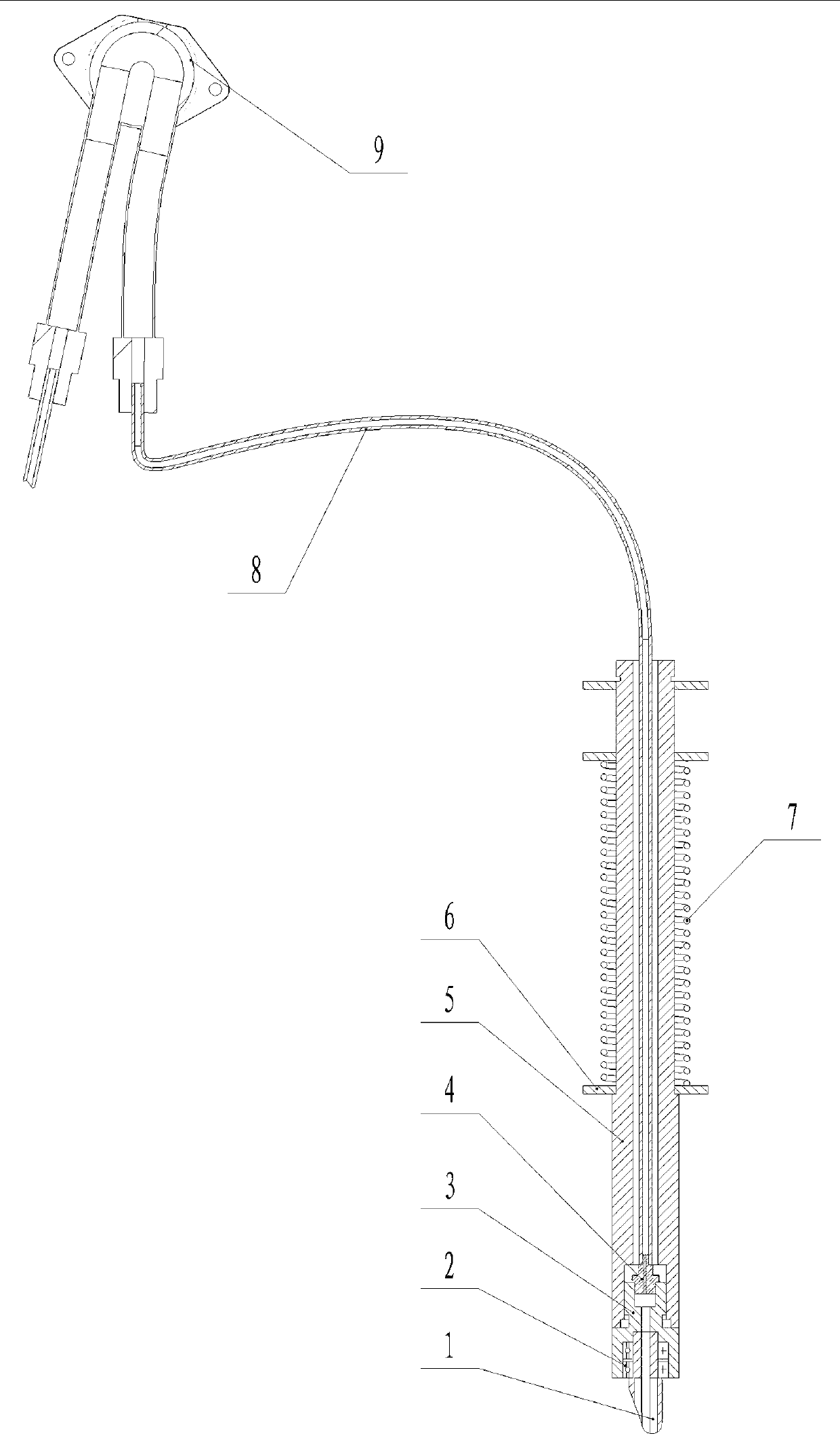
Tool bit of glass cutter
ActiveCN103342458ANot easy to damageSimple structureGlass severing apparatusTool bitPeristaltic pump
The invention discloses a tool bit of a glass cutter. The tool bit of the glass cutter comprises a tool grain, a tool front head link, a tool bar, an oil conveying pipe, an oil pipe joint as well as a tool bit control circuit, wherein the tool front head link is arranged on the front end of the tool bar; the tool grain is arranged on the tool front head link; and the oil pipe joint is arranged above the tool grain in the tool bar, and is communicated with the oil conveying pipe. The tool bit of the glass cutter is characterized by also comprising a bearing and a peristaltic pump, wherein the tool grain and the tool front head link are rotatably connected through the bearing; a pump pipe of the peristaltic pump is communicated with the oil conveying pipe; a driver of the peristaltic pump is connected with the tool bit control circuit; the tool bit of the glass cutter is also provided with a tool bit protection device comprising a photoelectric sensor and a distance sensor which are arranged on a steering engine; the steering engine, the photoelectric sensor and the distance sensor are connected with a sensor servo control circuit; the sensor servo control circuit is connected with the tool bit control circuit; and the steering engine is arranged on the tool bar. The tool bit disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the tool grain rotates flexibly; glass after being cut is even to crack; and the tool grain is difficult to be damaged.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Glass cutter cleaning apparatus
InactiveCN104108870APrevent splashSimple structureGlass severing apparatusCleaning using liquidsCutting glassGlass cutter
The invention discloses a glass cutter cleaning apparatus. The apparatus is composed of a fixed bracket, a workbench, a crossbar, a cutter, a water sprinkling head and a sliding bar. The workbench is horizontally fixed on the fixed bracket, the sliding bar is arranged on the cross bar, the cutter is arranged at the lower end of the sliding bar, and the sprinkling head suspends above the cutter, and is connected with the sliding bar. The apparatus has the advantages of simple structure, cutting of the cutter by rapid steam ejected by the sprinkling head after glass cutting in work, decrease of dusts near the edge of the cutter, and prevention of the splashing of glass particles to human bodies.
Owner:ANHUI HUAQIANG GLASS TECH
Cutting device for glass processing
InactiveCN110963690ASimple structureEasy to useGlass severing apparatusMachine partsElectric machine
The invention particularly relates to a cutting device for glass processing. The device comprises a base, supporting columns and a top plate. A first air cylinder and a second air cylinder are arranged in the supporting columns. An asynchronous motor is arranged on a left side of an upper end of a lifting rod; a sliding sleeve is arranged on the sliding rod; a moving cylinder is mounted on a frontend surface of the sliding sleeve; a first belt pulley is mounted on a left side of a rotating roller rotating shaft; a second belt pulley is mounted on a rotating shaft of a rotating motor; a bottomplate is arranged on a right side of the base; and an auxiliary air cylinder is arranged at an upper end of a joint of the bottom plate and the base. A sliding plate is arranged at an upper end of the bottom plate; and a machined part placing plate is horizontally arranged at top ends of a supporting rod and a first supporting air cylinder. A fixed plate drives a glass cutter to rotate through adriving motor, and the rotating roller plays a supporting role, so that the glass is cut, the glass is convenient to cut, the glass is sucked through a suction cup to move up and down after cutting iscompleted, a redundant part is separated from round glass, and the use requirements of people can be met.
Owner:闫凤杰
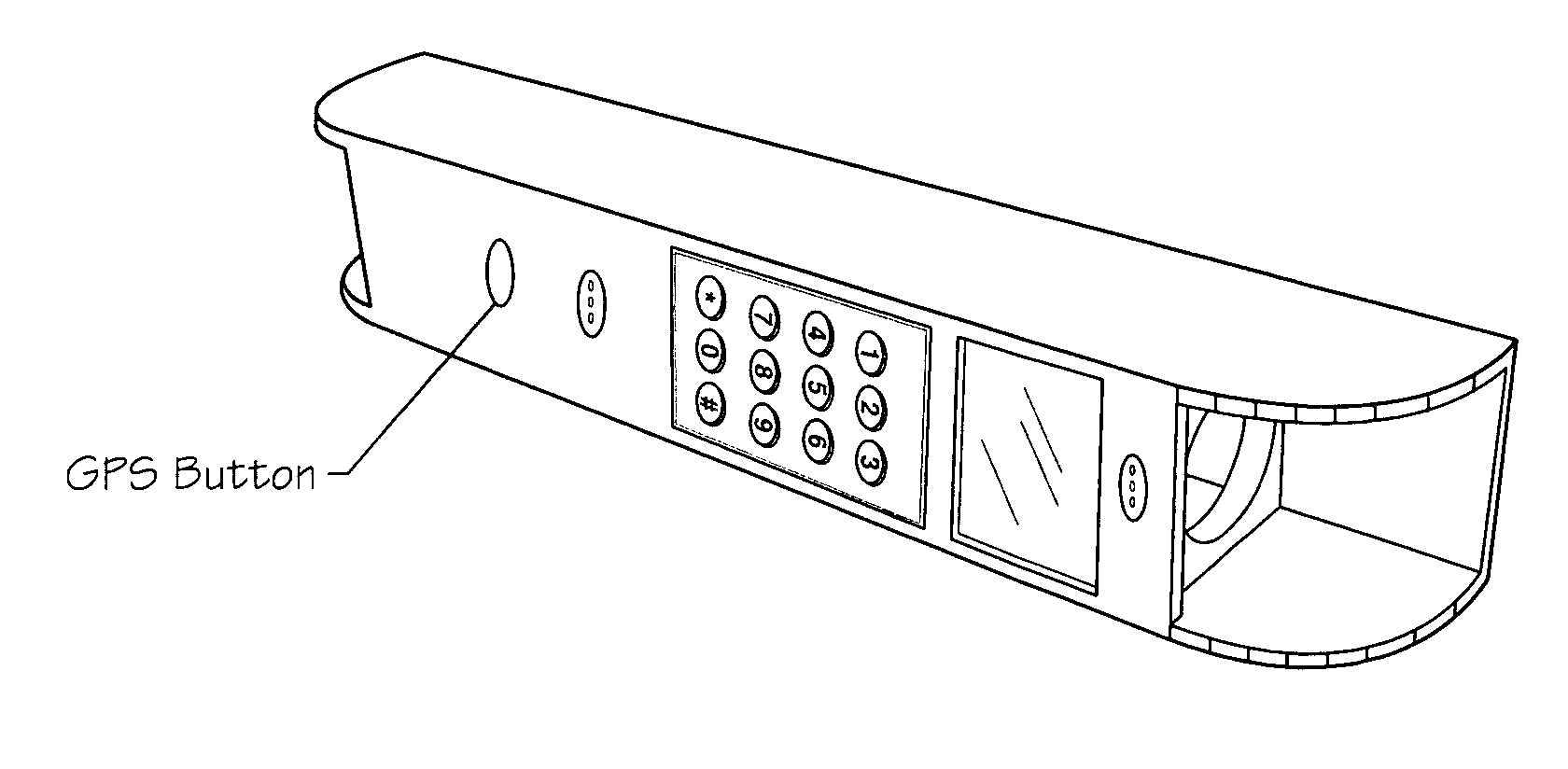
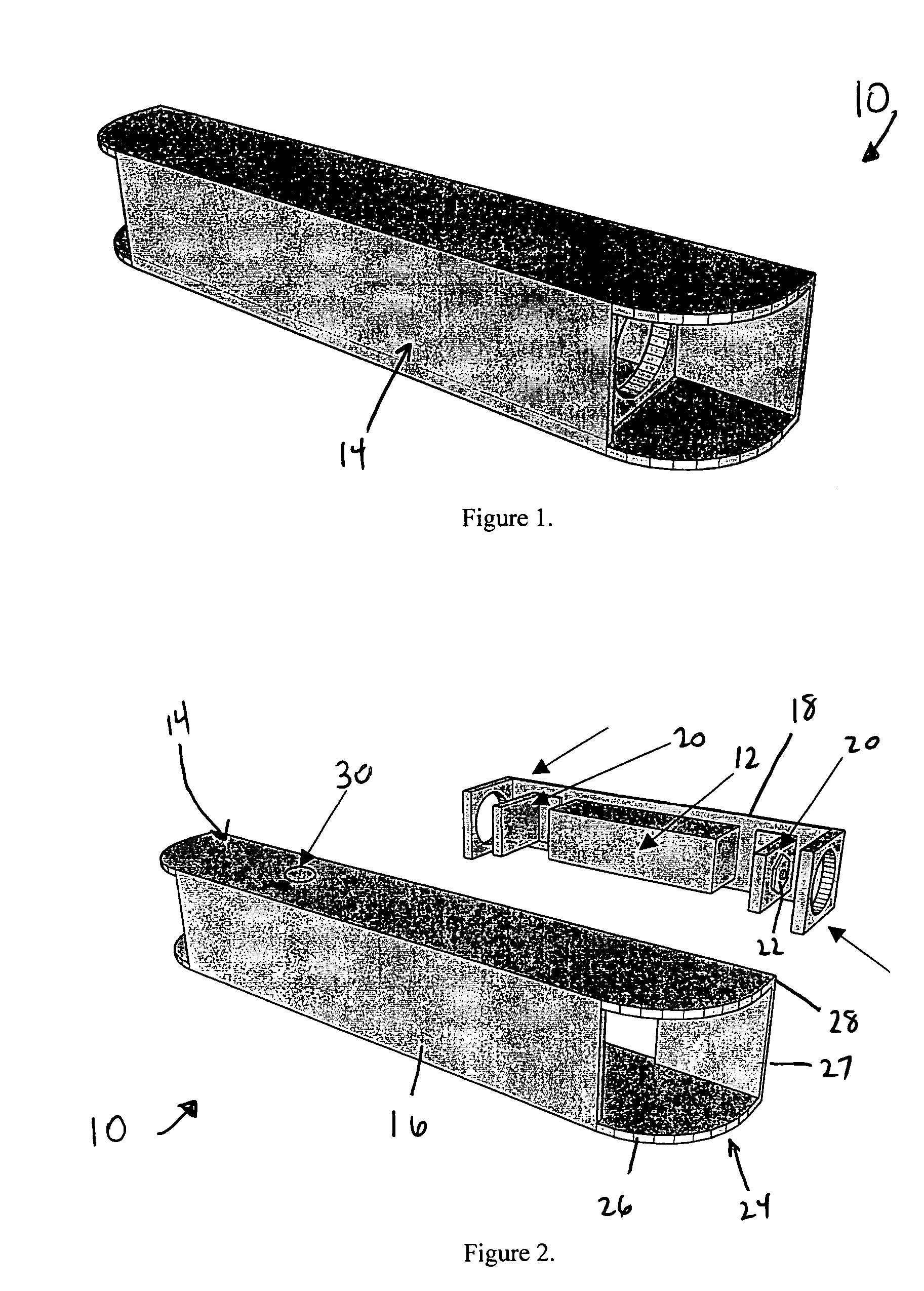
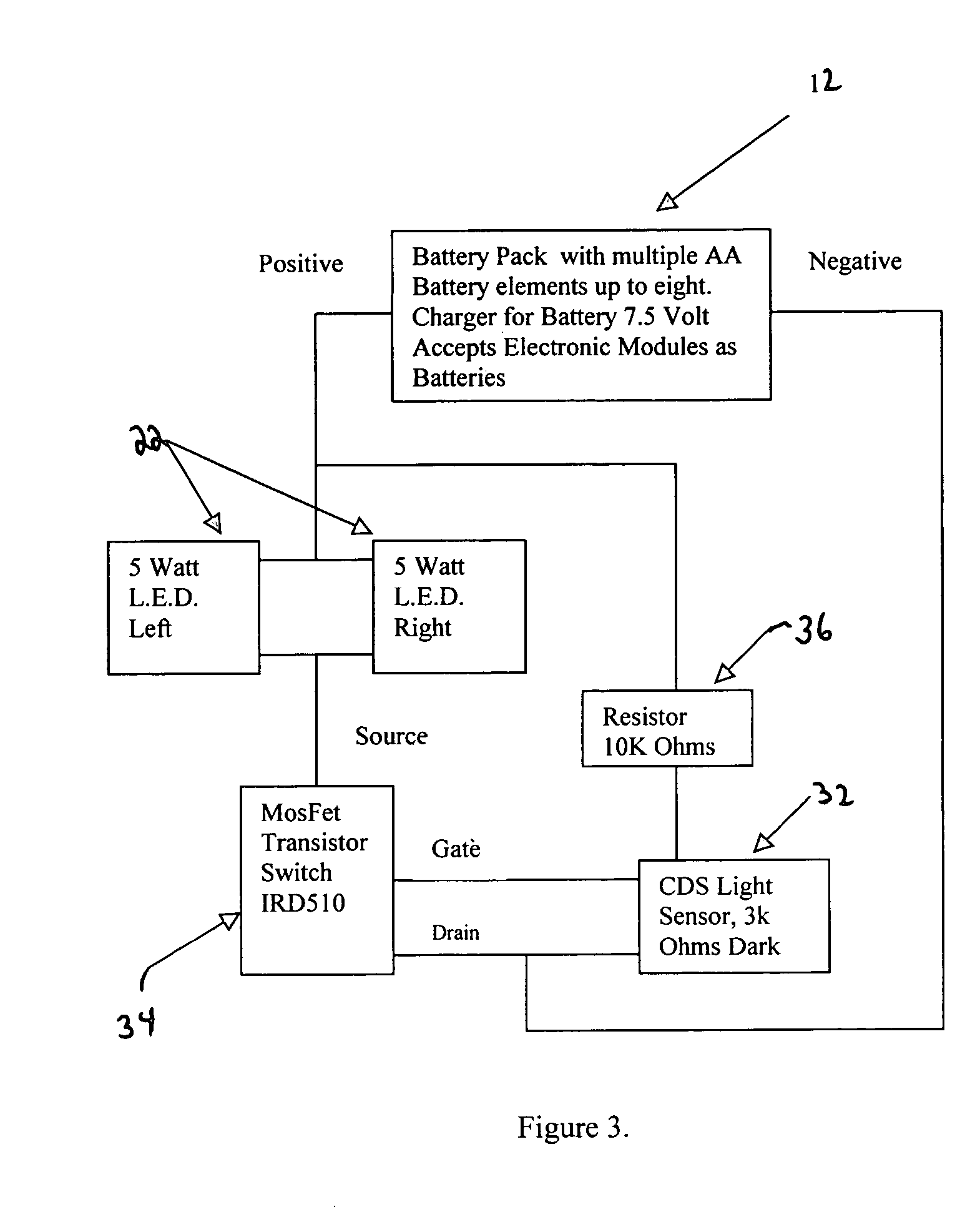
Combination L.E.D. emergency lamp, glass cutter hammer pick with smoke triggered power on
Owner:BOLTA CHARLES
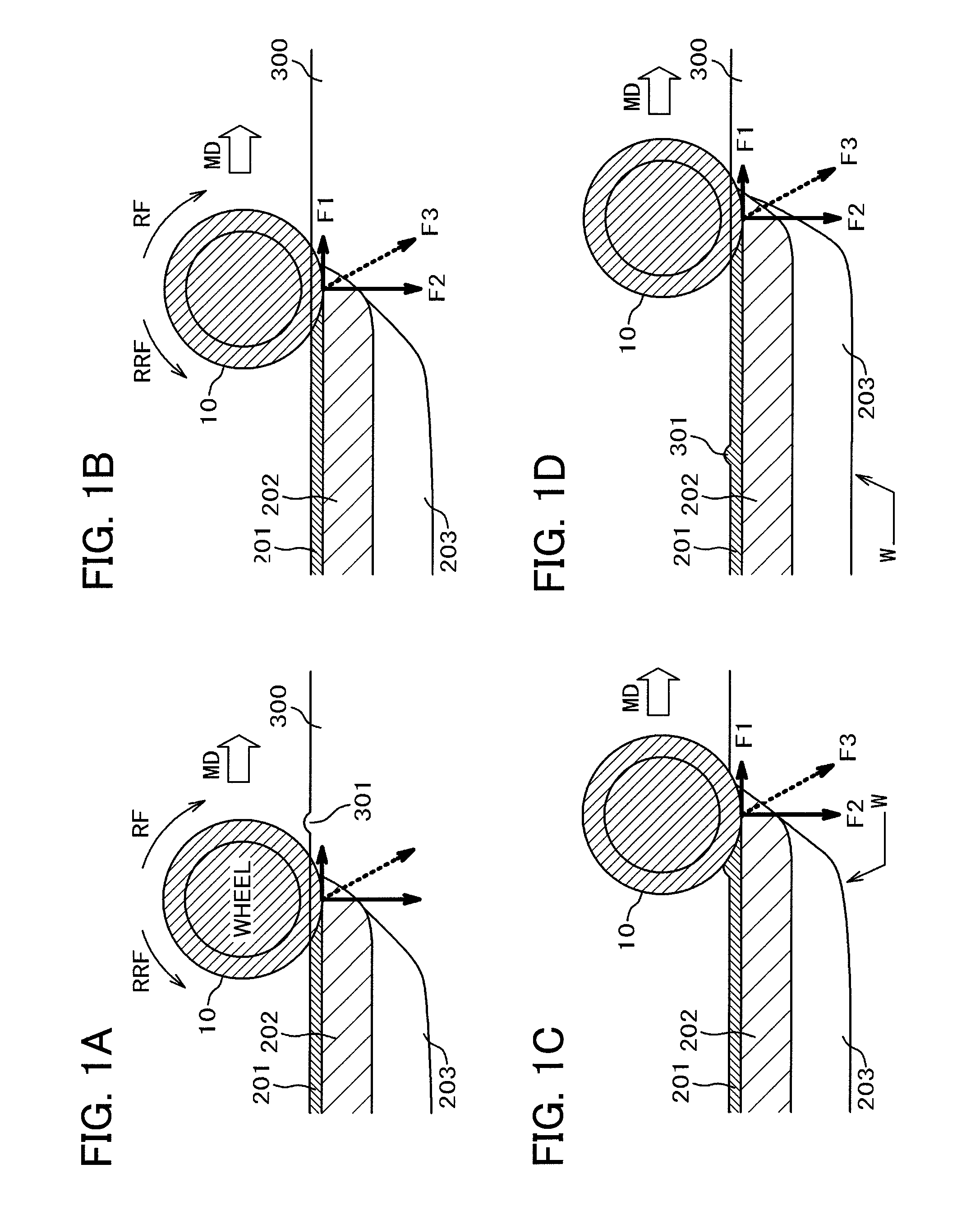
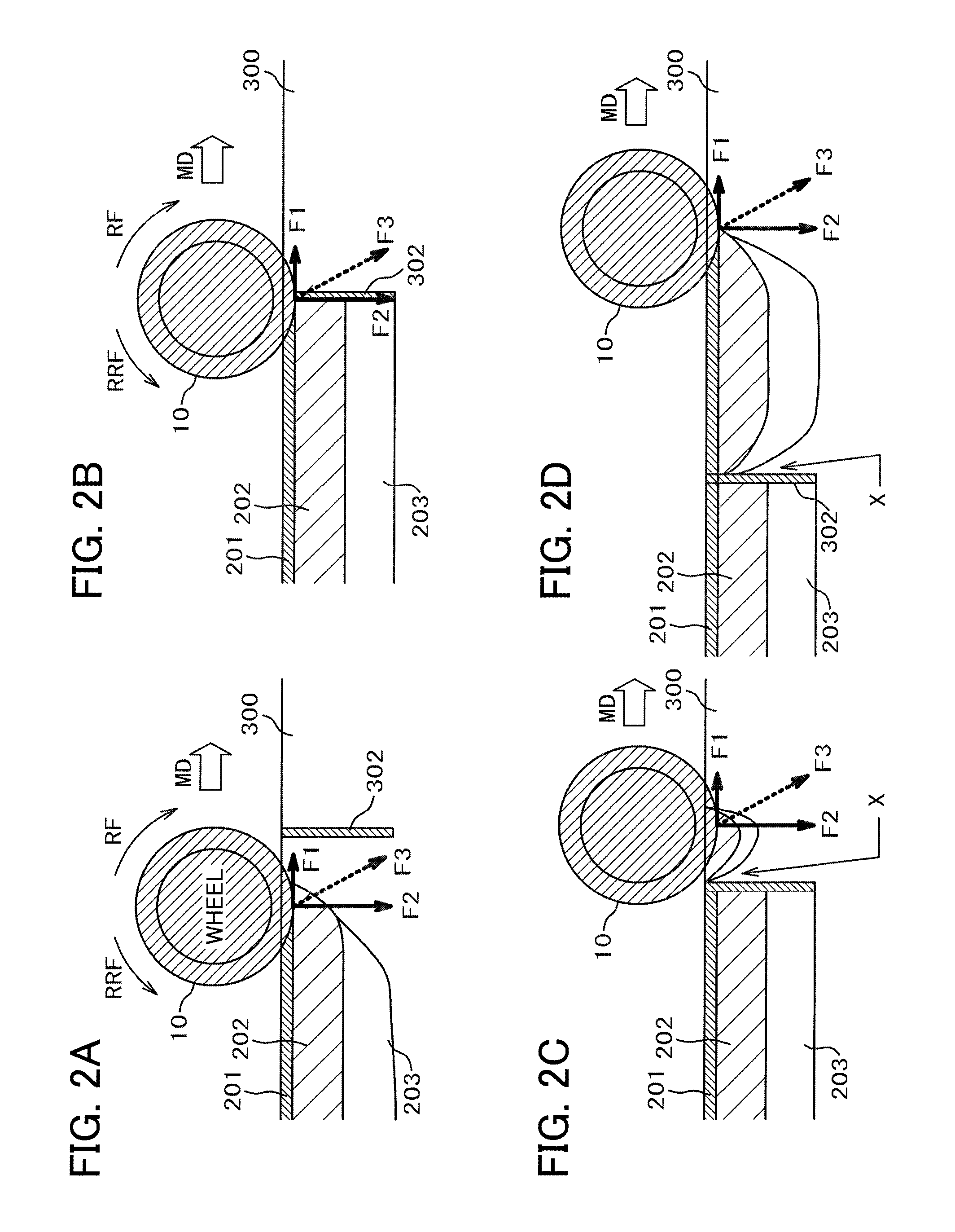
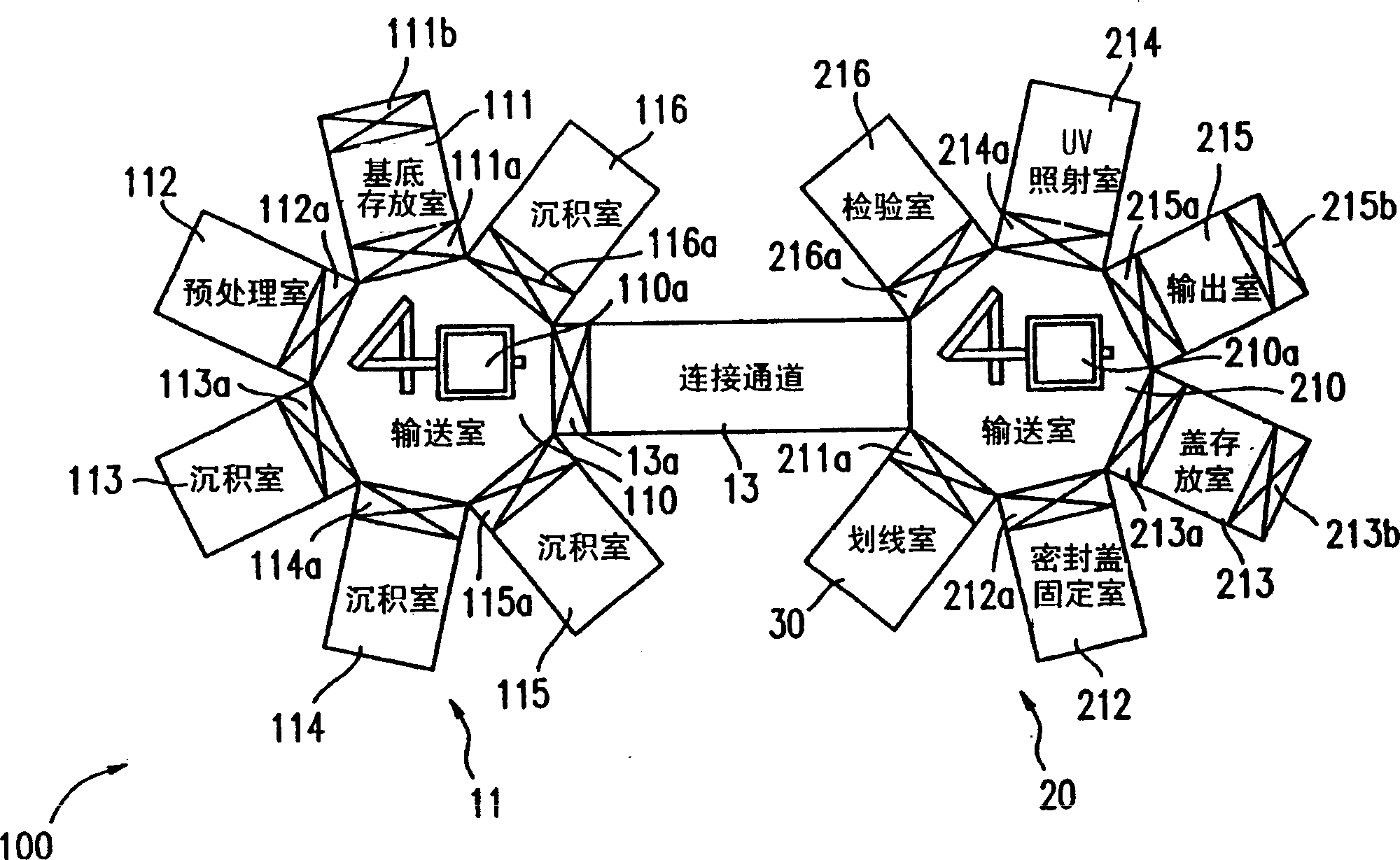
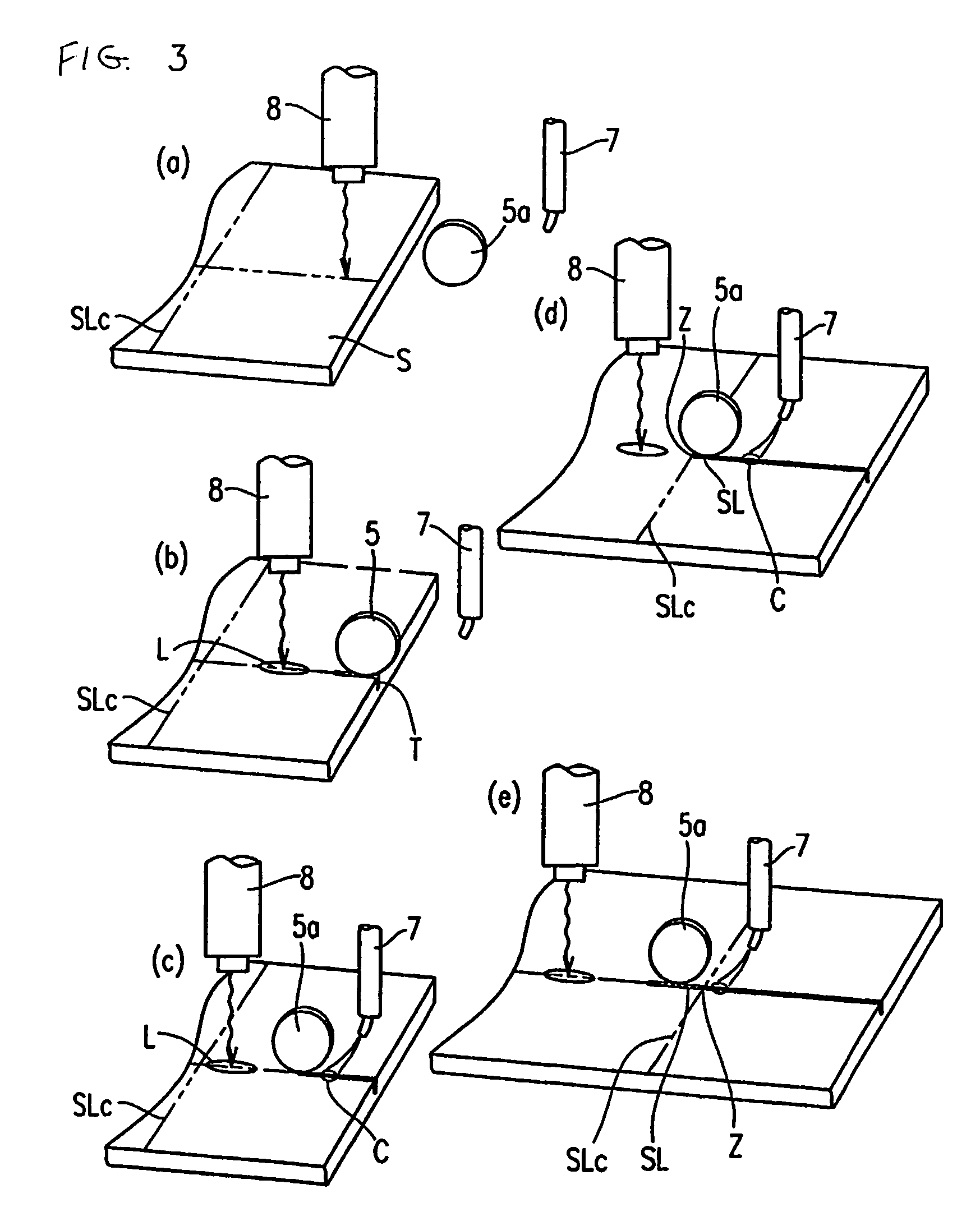
Production device and production method for organic EL dispaly
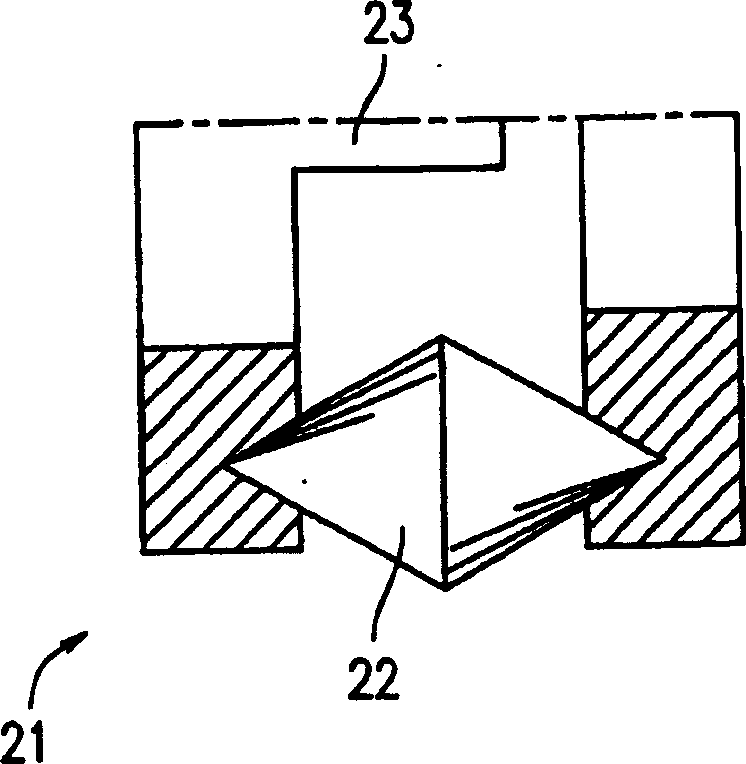
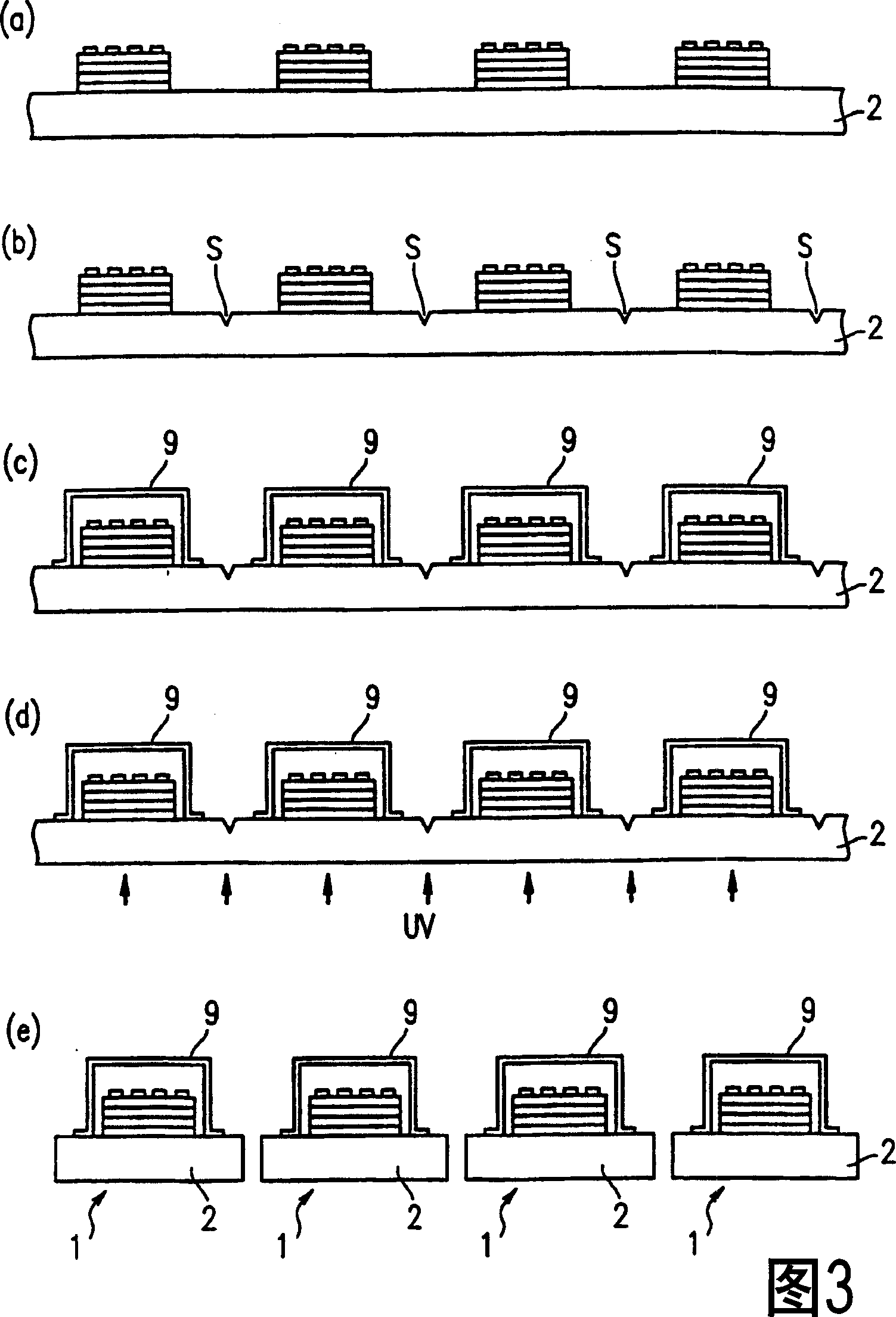
A scribe line (S) is formed, for each area that is a potential organic EL display, on a glass substrate (2) prior to attaching a sealing cap (9). This can prevent the contact between a sealing cap (9) and a glass cutter (21) that poses a problem when a scribe line (S) is formed on a glass substrate (2) after a sealing cap (9) is set, and at the same time can eliminate a faulty segmentation by the effect of a residual stress caused by a pasted sealing cap (9).
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Glass cutting machine
The invention provides a glass cutting machine. The glass cutting machine comprises a tool apron, a tool rest and a glass cutter, wherein the tool apron is fixed on glass to be cut; the tool rest is mounted on the tool apron in a sliding manner; the glass cutter is mounted on the tool apron is a manner of being adjusted up and down; a cutting end of the glass cutter penetrates through the tool apron. By adopting the glass cutting machine provided by the invention, the cutting strength of the glass cutter on the glass to be cut can be adjusted and the glass is uniformly cut by utilizing the strength, so that the success rate of glass cutting is remarkably improved.
Owner:重庆艺美玻璃有限公司
Multifunctional glass cutter
The invention discloses a multifunctional glass cutter which comprises a vacuum suction cup. A rotating shaft is arranged on the vacuum suction cup. A sleeve is connected with the rotating shaft and connected with a caliper. A sliding block is arranged on the caliper and connected with a cutter handle. A cutter bit is connected to the cutter handle. A divided disc is arranged on the rotating shaft. A pressure handle is arranged on the cutter handle. A pressure gauge is arranged on the top of the cutter handle. The multifunctional glass cutter has the advantages that circular glass of different radiuses or sector glass of different radiuses and different angles can be cut out precisely, more labor can be saved when the glass is cut, the pressure adopted when the glass is cut can be measured, and the phenomena that a workbench and a cutter are damaged due to the fact that excessive force is exerted or cutting is not complete due to the fact that exerted force is not large enough are avoided.
Owner:ANHUI HUAGUANG PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIAL TECH GRP CO LTD
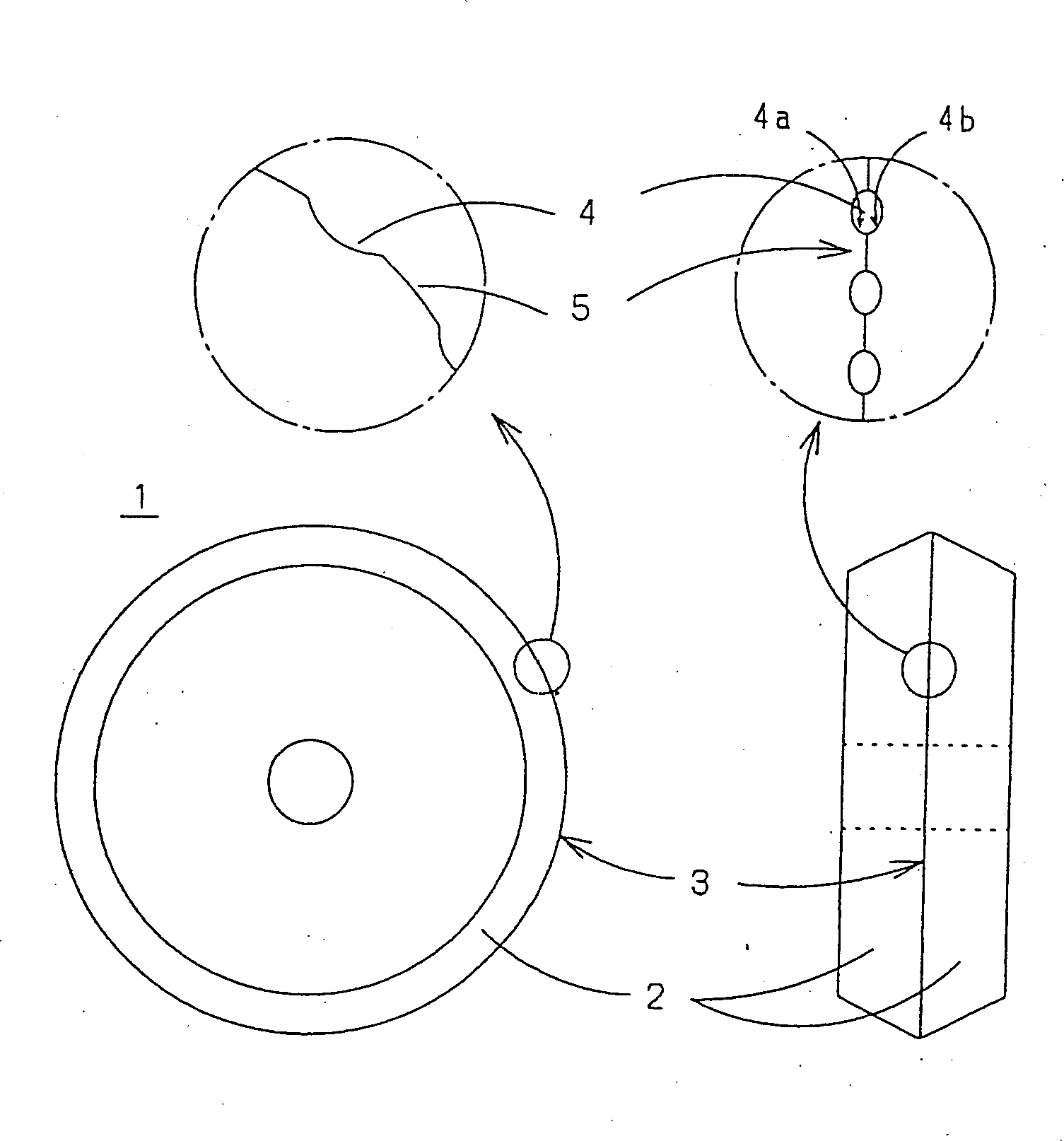
Scribe line forming device and scribe line forming method
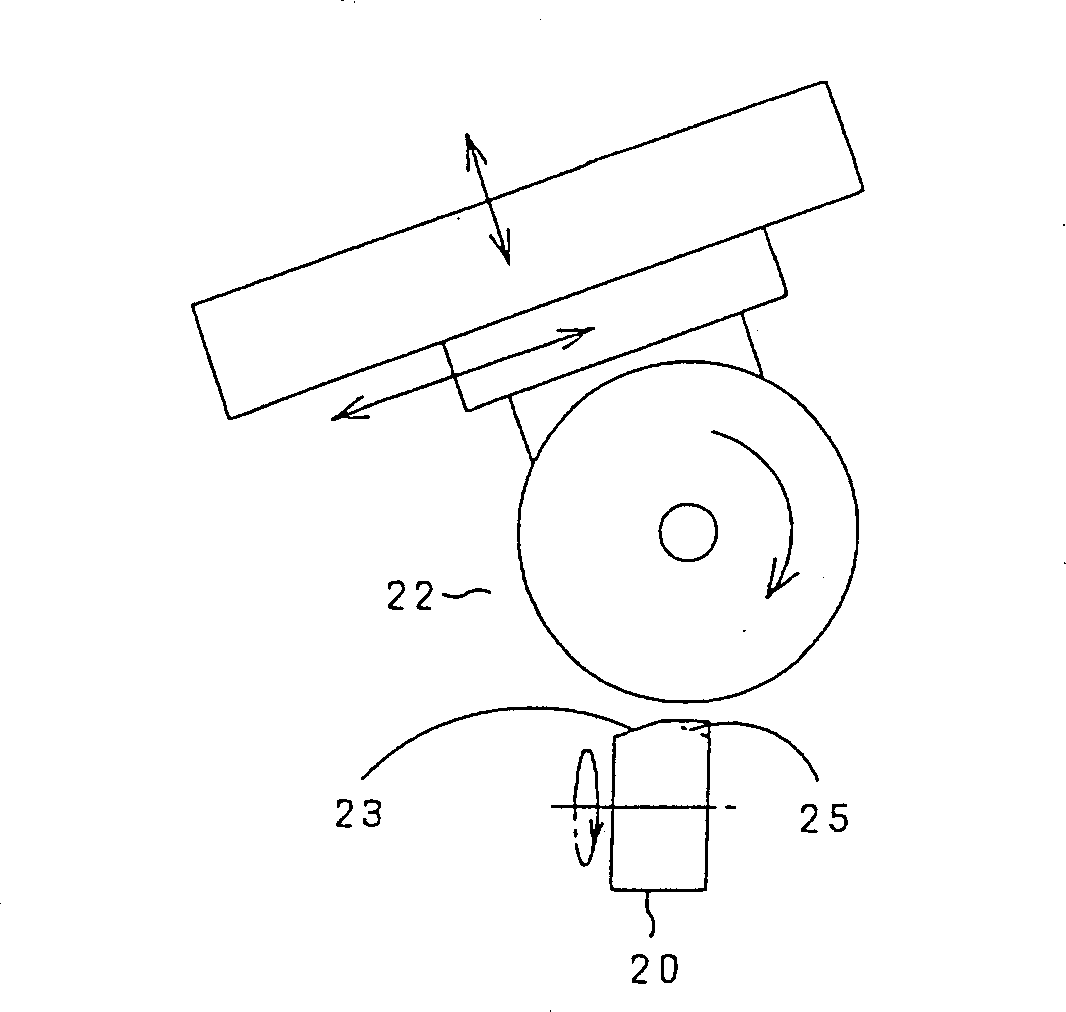
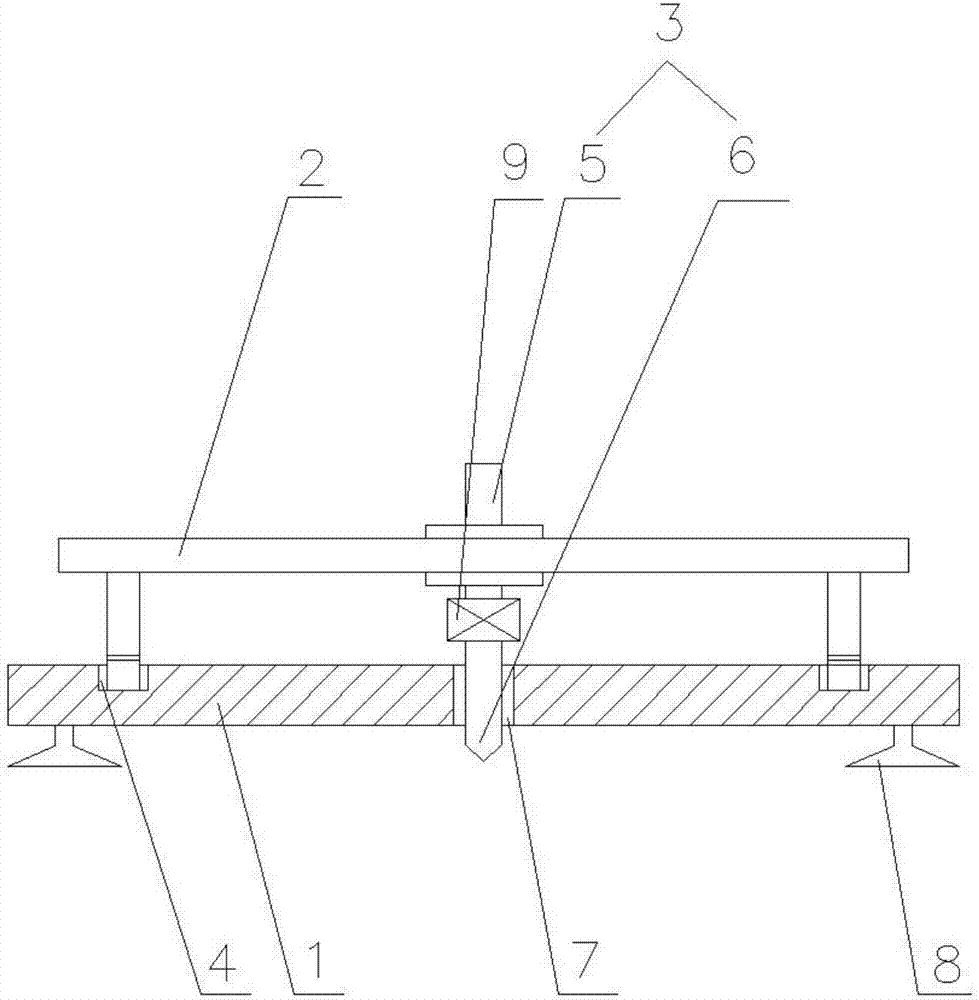
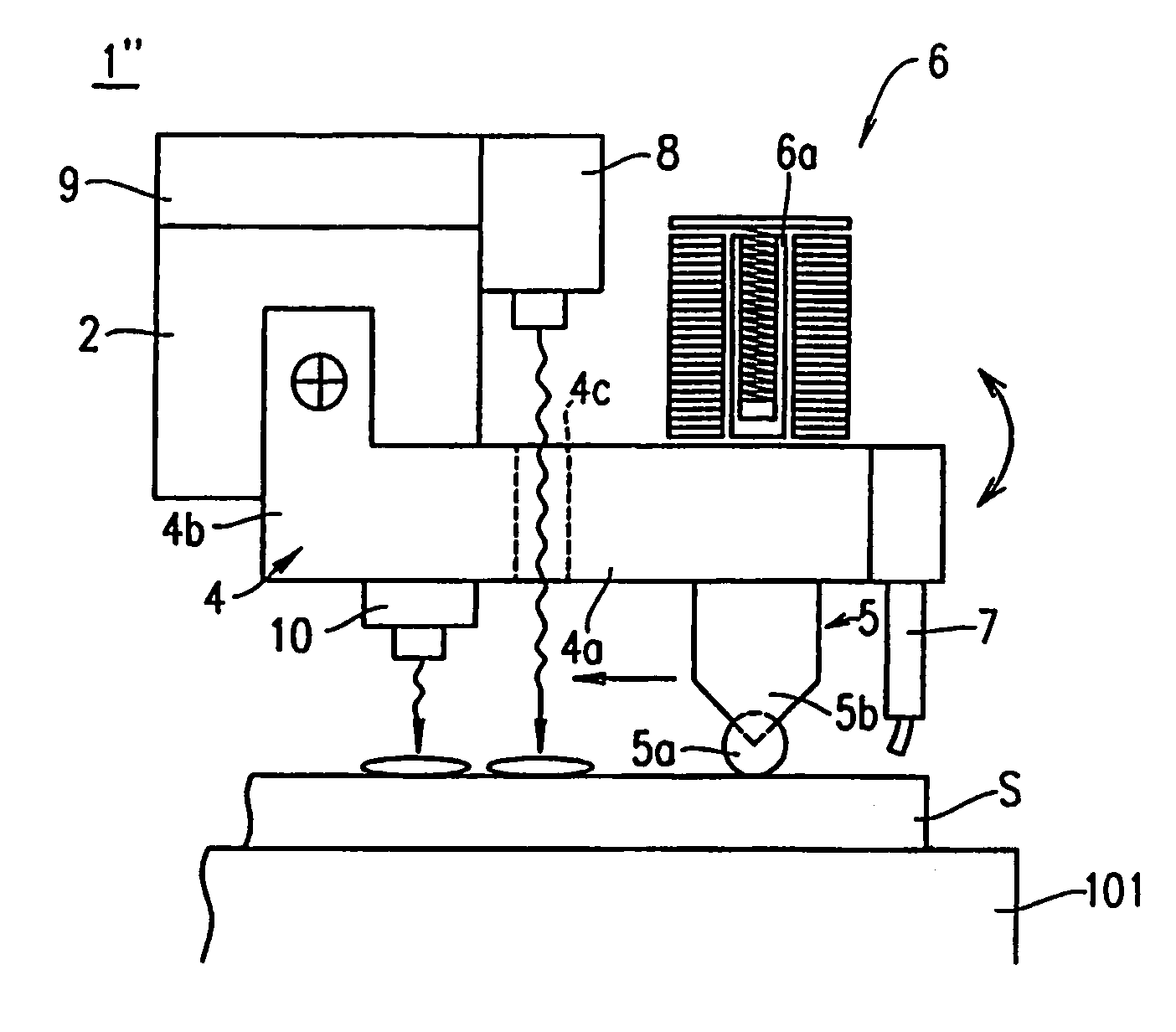
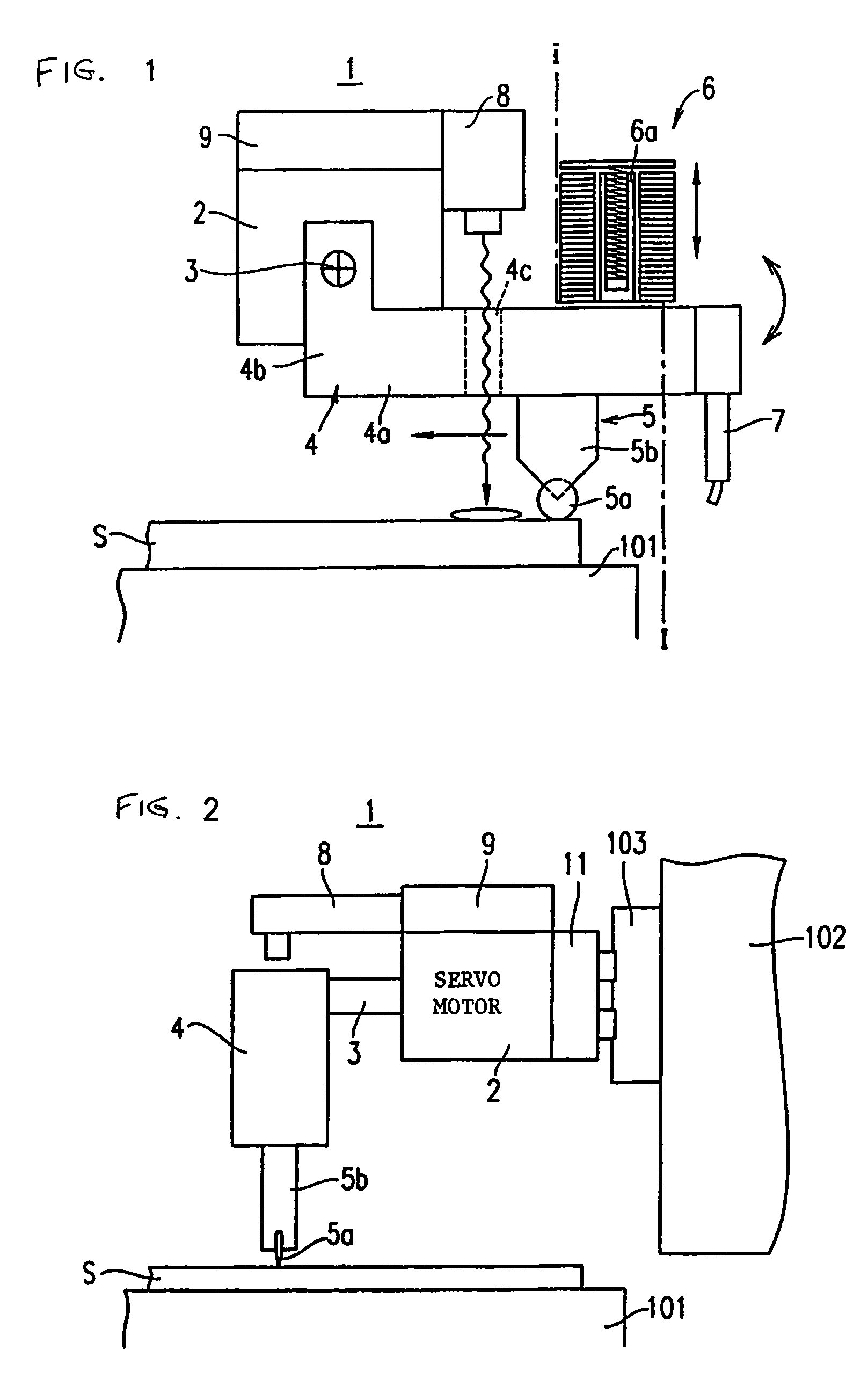
A vertical crack is generated at a desired position on a brittle material substrate S by making a wheel tip 5a of a glass cutter 5 move while being in contact with the substrate surface by a load which does not allow the wheel tip 5a to damage the surface, using an armature 6 applying an abrupt impact force for generating the vertical crack having a predetermined depth, to the glass cutter 5 moving on the substrate. A scribe line is formed as the vertical crack is urged to extend along a planned scribe line, due to a stress gradient exerted onto the vertical crack and occurring between a compressive stress in an irradiation area on the substrate at which a laser beam is irradiated from a laser beam oscillator 8 and a tensile stress in a cooling area made by a cooling medium released from a cooling nozzle 7.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Method for drawing dual cones on preformed rod
InactiveCN107056041AHorizontal tension controllableThe magnitude of the horizontal tension is controllableGlass making apparatusBlow torchGlass cutter
The invention provides a method for drawing dual cones on a preformed rod. The method is characterized by including the steps of firstly, preheating, to be specific, fixing the preformed rod by two clamps on an operating platform to ensure that the preformed rod is arranged at the horizontal plane, and turning on a blow torch to burn positions where the cones are drawn out until surface glass is in a melting state; secondly, carrying out N drawing stages, to be specific, a first drawing stage, namely, slowly moving the clamps when the surface glass of the preformed rod is in the melting state and then stopping until the distance between the left clamp and the right clamp is increased to a set distance, a second drawing stage, namely continuing heating the positions, with the maximum reducing, of the preformed rod by the blow torch, and then moving the clamps to repeat the operation of the first step, repeating the previous steps until completing drawing of the Nth stage; further, turning off the blow torch, placing the position, to be drawn, of the preformed rod, in a holding furnace, cooling slowly for a certain time, cutting off from the finest drawing position by a glass cutter, moving the two sections of preformed rod with the cones formed by drawing out of the holding furnace, and cooling the same for stand-by application.
Owner:JIANGSU STERLITE TONGGUANG FIBER
Automatic cutting machining machine and method for tempered glass
InactiveCN113173698AAvoid misalignmentAvoid scratchesGlass severing apparatusReciprocating motionGlass cutter
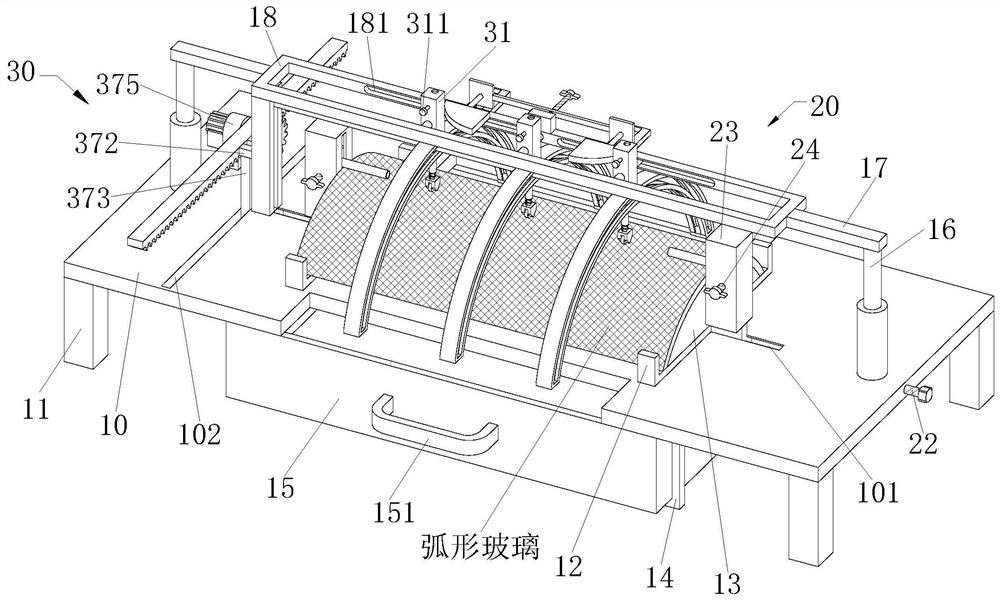
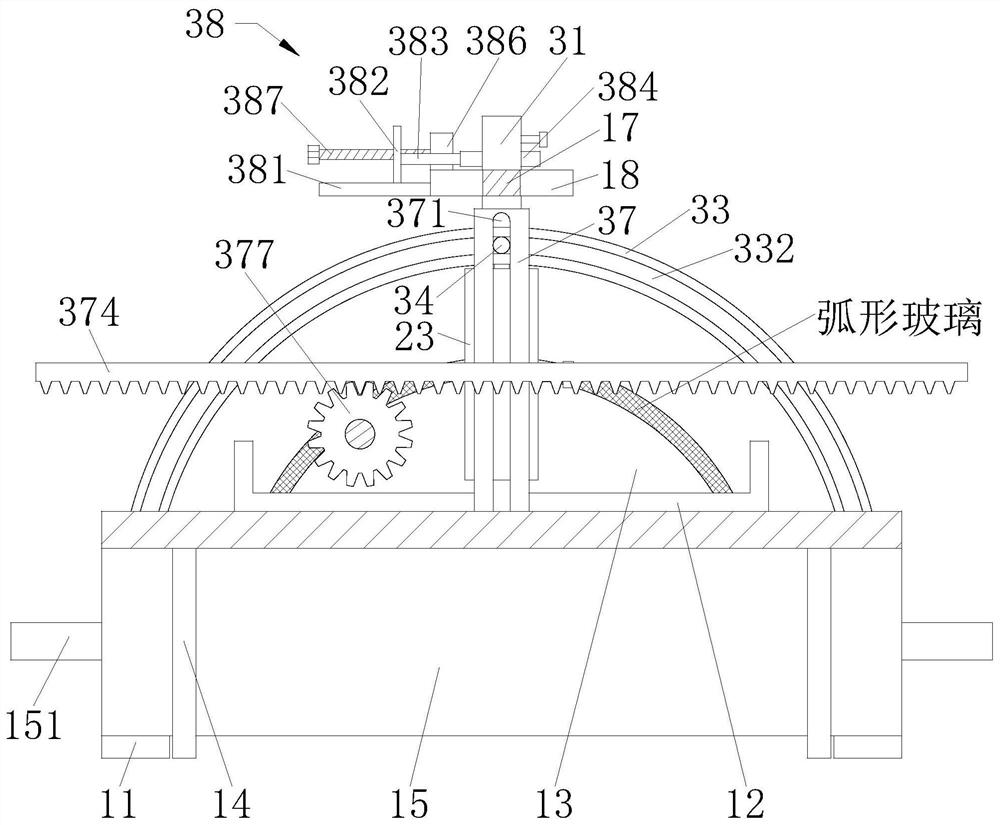
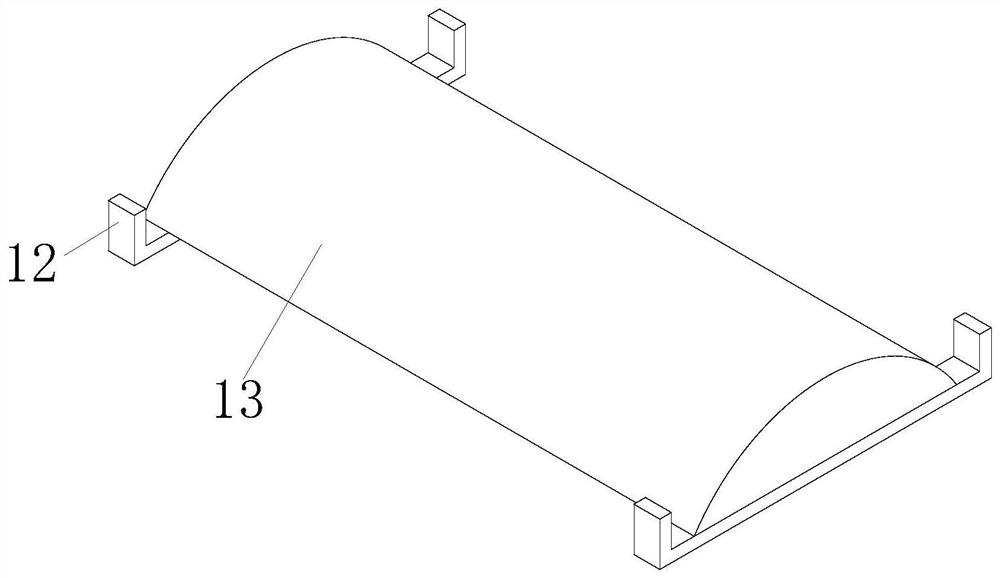
The invention relates to an automatic cutting machining machine and method for tempered glass. The machine comprises a workbench and a fixing device arranged above the workbench, wherein a cutting device is arranged above a curved base. According to the invention, a lifting rack is driven by a rotating gear to reciprocate up and down, so the lifting rack can drive an extrusion rod and a rubber sleeve to move to the topmost end of to-be-processed arc-shaped glass, the to-be-processed arc-shaped glass is fixed, and the phenomenon that the processing position of the to-be-processed arc-shaped glass is misplaced in the cutting process is prevented; a rubber sleeve is made of a flexible material, has compression performance and prevents the phenomenon that a hard material directly makes contact with the surface of glass to cause scratches; and the cutting position can be rapidly and accurately cooled through a water tank, and broken glass obtained after cutting is cleaned so as to prevent the cutting edge of the glass cutter from being abraded, so grinding force and friction heat are reduced, and the wear resistance and the cutting quality of the to-be-processed arc-shaped glass are improved.
Owner:王春红
Preparation method of graphene thin films
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene thin films. The preparation method comprises the steps: firstly, taking conductive glass, cutting into a plurality of pieces of small glass with the size of 3 cm*1 cm by a glass cutter, laying on filter paper, and cleaning; then allowing graphite oxide to form a graphite oxide colloid or suspension in water by utilizing an ultrasonic effect, selecting and using an N,N-dimethyl formamide (DMF) solution, preparing a DMF solution with the concentration of 1 mg graphite oxide / mL, and carrying out sealed preservation; followed by dripping the prepared solution on the prepared glass conductive surfaces, performing left and right rotation and uniformly shaking, then placing in a glass ware, drying for half an hour in a dryer, and storing for standby application; and finally connecting the conductive glass through a working electrode, with an electrolytic solution of a KCl solution, electrolyzing under a constant potential, and thus obtaining the graphene thin films. With adopting of the technical scheme of the invention, the graphene thin films have a certain hindrance function to light, and have the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and environmental friendly, and are also suitable for production.
Owner:SUZHOU SHIYOUJIA ELECTRONICS TECH
LCD glass cutting system
InactiveCN110981177AAvoid chippingAvoid compromising qualityCleaning using toolsCleaning using gasesForeign matterEngineering
The invention discloses an LCD glass cutting system which structurally comprises a glass cutting machine, a machine door, an electric controller, a vertical sliding rail, a sliding mechanism and a workbench, the sliding mechanism is composed of a sliding frame, a guide cutting frame, a drag chain, a transverse sliding rail and a sliding plate, and the glass cutting machine provides moving workingpower for a cutting device through the sliding mechanism. The guide cutting frame generates airflow through a miniature air pump to blow away particles or small stones below the periphery of a cuttingtool, a sweeping mechanism is used for cleaning foreign matters on the surface of LCD glass, the working efficiency is improved, and the problem that the quality is affected due to the fact that theLCD glass is scratched by the particles when the cutting device works is solved. A separating mechanism is used for slightly striking the cut part of the LCD glass to separate the cut part of the LCDglass, so that the glass is prevented from being broken due to overlarge force caused by non-uniform force of an operator.
Owner:范建华
Glass segmentation processing device
InactiveCN106587588AEasy to operateReduce labor intensityGlass severing apparatusSlide plateGlass cutter
The invention relates to equipment in the field of glass segmentation technologies, and the name of the equipment is a glass segmentation processing device, comprising a platform for placing glass, wherein a support frame is below the platform; an upright rod is arranged on a side surface of a platform body; a cross beam is hinged on the upright rod; a downward plumbing arm is arranged at one end of the cross beam; a horizontal slideway is connected blow the plumbing arm and is parallel to the platform; a sliding plate is arranged on the slideway; a glass cutter with a downward cutting edge is arranged below the sliding plate; the sliding plate is connected with a motor; when the motor runs, the sliding plate moves back and forth on the sideway; the plumbing arm is a cylinder; a spring is arranged between the cylinder and the cross beam; the platform body is provided with a plurality of sucking discs in uniform distribution, an air extracting device connected with the sucking discs, and a control device connected with the air extracting device. The glass segmentation device has the advantages of simple operation, small labor intensity, and convenience in use.
Owner:CHANGGE JIQING MACHINERY PLANT
Glass cutter for cutting round workpiece conveniently
InactiveCN106986532AHigh precisionHigh speedGlass severing apparatusGlass productionEngineeringGlass cutter
The invention relates to a glass cutter for cutting a round workpiece conveniently. The glass cutter comprises a base, a first cutting table, a cutting bridge and a cutting head, wherein the base further comprises a second cutting table, a driving device and a fixing device; the driving device comprises a lifting mechanism and a rotating mechanism; the fixing mechanism comprises two fixing mechanisms; each fixing mechanism comprises a third motor, a second screw rod, a sliding rod, a sliding block, an air cylinder and a fixing groove. In the glass cutter for cutting the round workpiece conveniently, the second cutting table is embedded in the middle of the first cutting table; when the round workpiece needs to be cut, the driving device is used for driving the second cutting table to be higher than the first cutting table; after glass is placed on the second cutting table, the glass is fixed by the fixing device; the driving device is used for driving the second cutting table to rotate to drive the glass to rotate; the cutting head is used for cutting the glass in place on one side of the rotating center; therefore, the accuracy and speed of cutting the round workpiece are improved, and the production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:泉州泉港润美环保科技有限公司
Glass machining device and method
The invention relates to a glass machining device and method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the left and right ends of glass are placed at the upper ends of two lower clamping plates,so that two upper clamping plates press at the left and right ends of the glass to clamp the glass; (2) lines are marked at the middle parts of the glass by using a glass cutter; (3) two electric extension rods synchronously shrink to drive lifting rods to descend, and meanwhile, drive outer ends of two groove rods to synchronously rotate down; and (4) the two groove rods drive two thread columnsto rotate along with the groove rods; and two compression springs I are compressed, and drive outer ends of two rotating plates to rotate down so as to drive the two lower clamping plates to rotate tobreak off the glass.
Owner:江门市江海区金颖钢化玻璃有限公司
Glass cutter
InactiveCN104496163AConvenience for gluing workAvoid the hassle of frequently changing the position of the cutterGlass severing apparatusCutting glassGlass cutter
The invention provides a glass cutter. The glass cutter comprises a machine body, wherein the lower end of the machine body is provided with a rail, the machine body is provided with a slide rail, and the slide rail is internally provided with a slidable glass knife, and the slide rail is provided with a glass knife fixing block, the glass knife is fixedly arranged on the slide rail by virtue of the glass knife fixing block; the bottom end of the slide rail is provided with a telescopic cylinder, the left and right ends of the machine body are provided with clamping devices, and the glass knife moves on the slide rail by virtue of a moving motor at the bottom; the glass is transported by virtue of the slide rail, the glass is fixed by virtue of the clamping devices, the glass knife moves in the slide rail, and the work of the cutting the glass is carried out; manual cutting is replaced by mechanical cutting, so that the working efficiency is improved; as long as the moving track of the glass knife is changed so as to change the specification of cutting glass, the trouble of frequently changing the position of a cutter of a simple glass cutting machine is avoided, rejects caused by human errors are prevented, a glue brush is used for conveniently performing glue brushing operation on the cut glass, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:WUHU POWER TECH
Novel medical ampoule bottle opening device
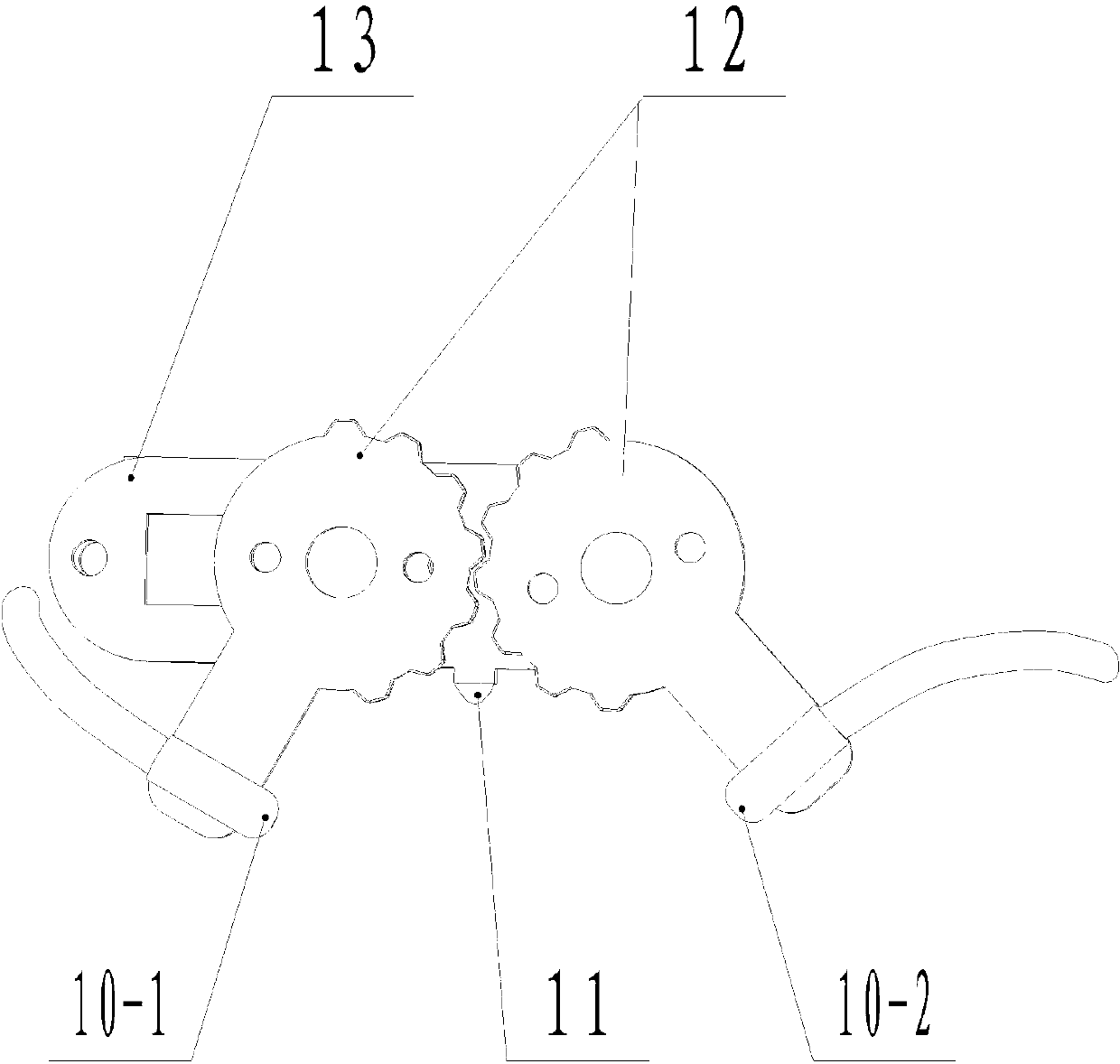
InactiveCN109502525AImplement the open functionEasy to take outBottle/container closurePower operated devicesGear driveEngineering
The invention discloses a novel medical ampoule bottle opening device. The novel medical ampoule bottle opening device comprises a shell and an installation plate. According to the novel medical ampoule bottle opening device, an internal-tooth gear and a half-tooth gear are arranged, the half-tooth gear drives the internal-tooth gear to intermittently rotate, and therefore the time difference is provided for the operation of ampoule bottles. Due to the fact that a cam mechanism, springs and a glass cutter are arranged, when the ampoule bottles move to the space below a transverse plate, a camenables the transverse plate to move downwards, scratches are marked on the ampoule bottles by the glass cutter, then the springs enable a rotating shell and a circular plate to be bounced and reset,and the ampoule bottles are opened in the follow-up process advantageously. Due to the fact that limiting blocks are arranged, the springs can be fixed, and fixing rods can be effectively prevented from sliding down. Due to the fact that a baffle is arranged, when the bottle heads of the ampoule bottles which are marked by the glass cutter collide with the baffle, the bottle heads can be opened, and the function of opening the ampoule bottles is fulfilled. Due to the fact that rectangular openings are formed in the shell, the ampoule bottles are conveniently placed and taken out, and the bottle heads of the ampoule bottles conveniently drop down. The novel medical ampoule bottle opening device has the advantages of being easy and convenient to operate and high in bottle opening efficiency.
Owner:徐州易途医疗器械有限公司
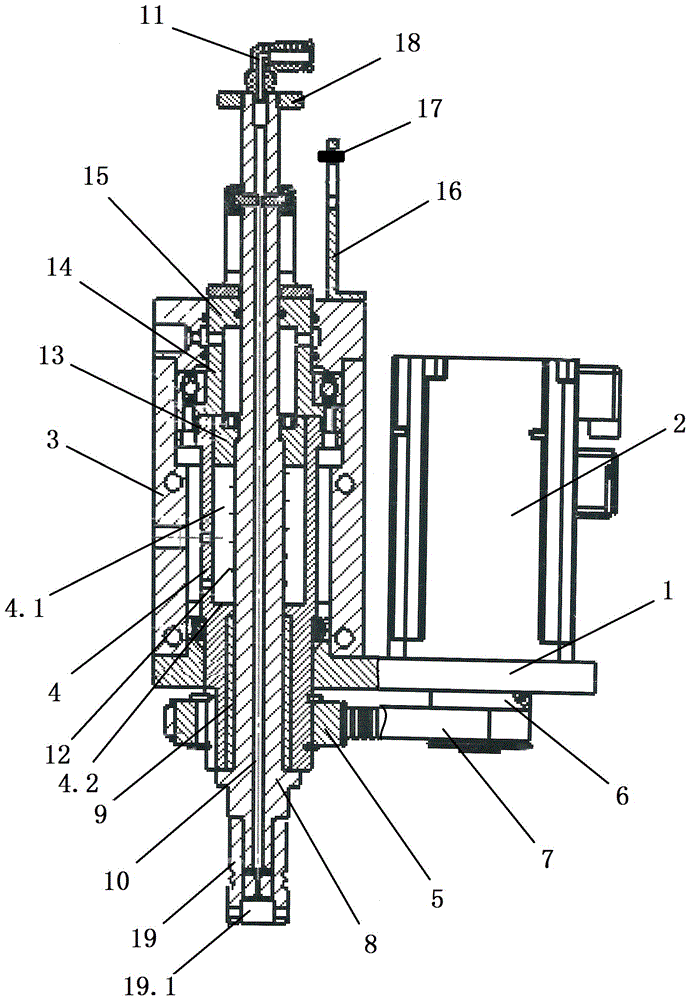
Glass cutter box
ActiveCN105859114AImprove cutting accuracyIncrease productivityGlass severing apparatusGlass productionDrive wheelTransmission belt
The invention discloses a glass cutter box which comprises a support plate, wherein a motor and a cutter box are mounted on the support plate; a rotating cylinder is arranged inside the cutter box; a driven wheel is connected with the rotating cylinder in a sleeving manner; the motor is connected with a driving wheel; the driving wheel is connected with the driven wheel through a transmission belt; a cutter rod is mounted inside the rotating cylinder; a return spring is connected with the cutter rod in a sleeving manner; a piston is connected in match inside a step through hole in the upper side of the rotating cylinder; the piston is fixed on the cutter rod in a sleeving manner; a cutter is fixedly connected at the lower end of the cutter rod; a first oil hole is formed inside the cutter rod; a second oil hole which is communicated with the first oil hole is formed inside the cutter; a rotating connector is connected to the upper end of the cutter rod; the rotating connector is communicated with the first oil hole; a pneumatic sleeve is further connected with the cutter rod inside the cutter box in a sleeving manner; the pneumatic sleeve is correspondingly matched with the piston; and a proportional valve is connected with the pneumatic sleeve. The glass cutter box has the advantages that glass of which the thickness is within 2-25mm can be cut, the cutting precision, production efficiency and product quality of ultra-thin glass can be improved, the rejection rate of a raw material can be reduced, and the production cost can be lowered.
Owner:ANHUI ZHICHENG NC TECH CO LTD
Scribing method, a cutter wheel, a scribing apparatus using the cutter wheel, and an apparatus for producing the cutter wheel
In a glass cutter wheel where a blade edge is formed on a disk-shaped wheel, grooves having a predetermined shape are formed at a predetermined pitch in a 1 / 4 or smaller or 3 / 4 or smaller blade edge line portion of the entire perimeter of the blade edge. The ratio of the groove portion to the entire perimeter, which largely contributes to a scribing characteristic, is changed such that a desired scribing characteristic can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com