Patents
Literature
292 results about "Impact energy absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Light metal/CFRP structural member
InactiveUS6468613B1Prevent galvanic corrosionHigh structural reliabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusMetallic materialsRoom temperature
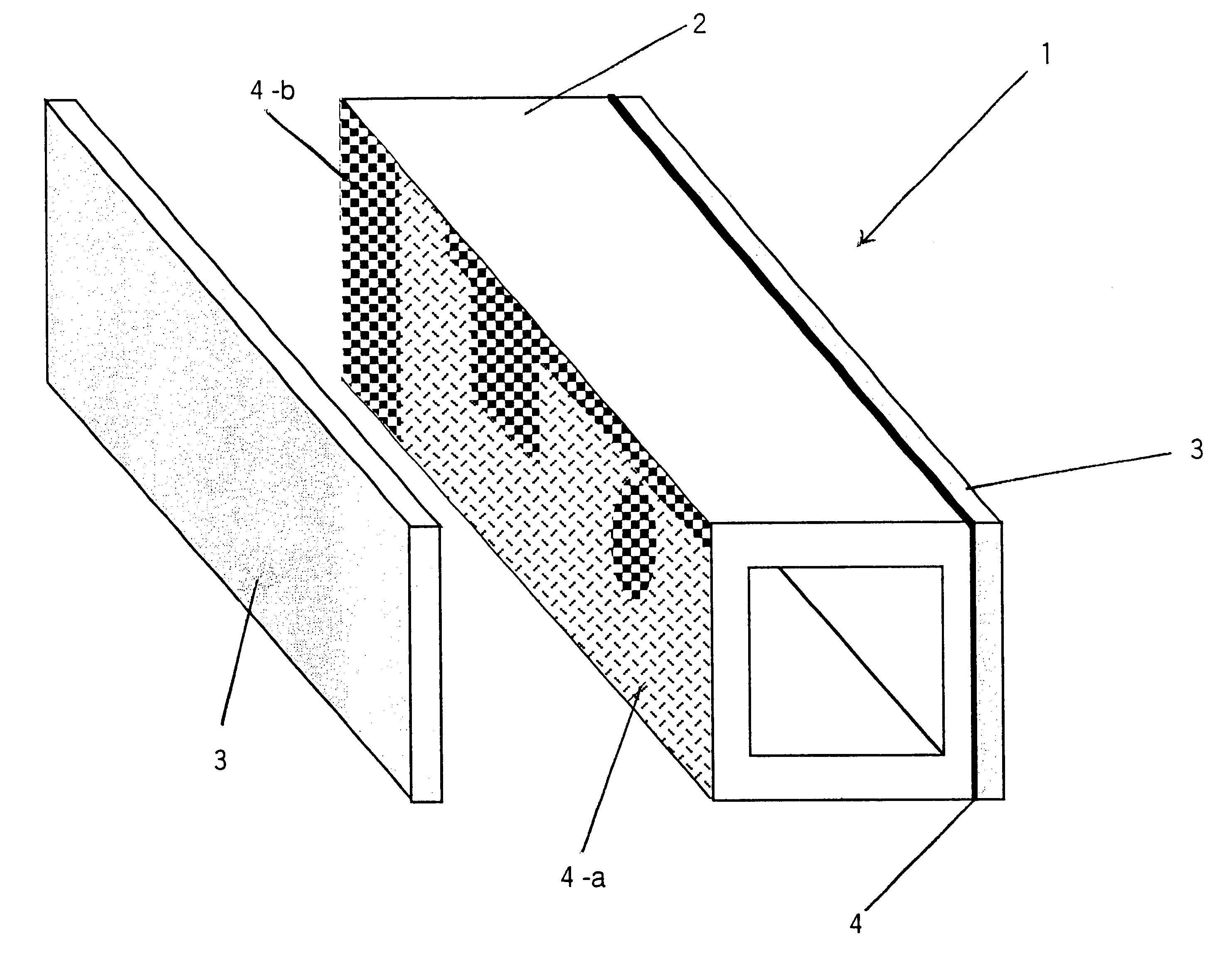
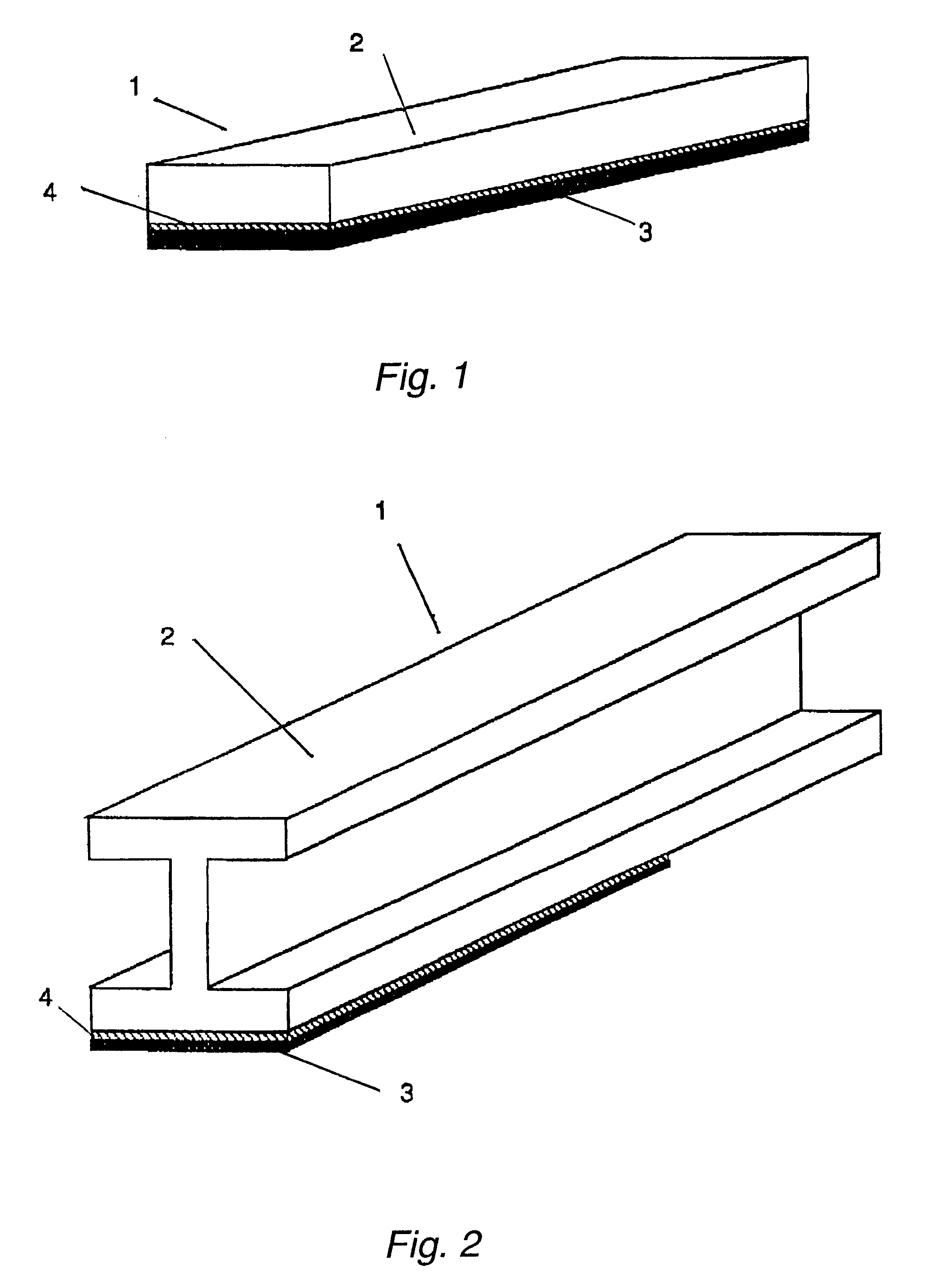
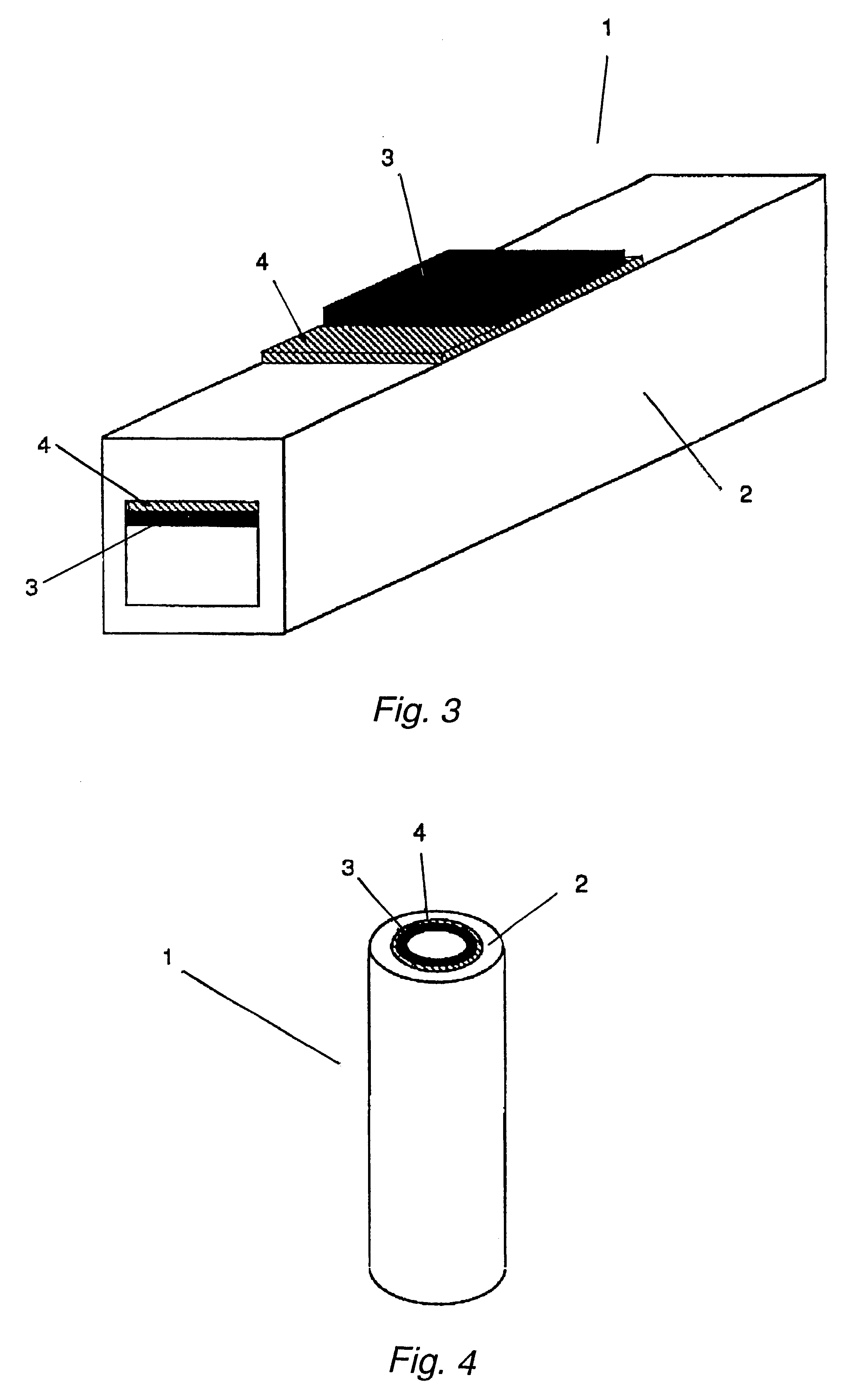
Light metal / CFRP-made structural members which are characterized in that they are structural materials in which a CFRP material is stuck to the surface of a light metal material via an adhesive agent layer of thickness at least 10 mum and up to 500 mum, and the volume resistivity of the adhesive agent layer between said metal material and said CFRP material is at least 1x1013 OMEGA.cm and, furthermore, the adhesive strength at room temperature is at least 15 MPa. In accordance with the present invention, since conventional light metal / CFRP structural materials can be made lighter and, furthermore, since the resistance to galvanic corrosion is outstanding and it is possible to markedly enhance the strength and the impact energy absorption performance, the development of applications and large-scale expansion into new fields becomes possible. Weight reduction and enhancing the durability and reliability of structures also makes a considerable contribution in terms of environmental protection.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
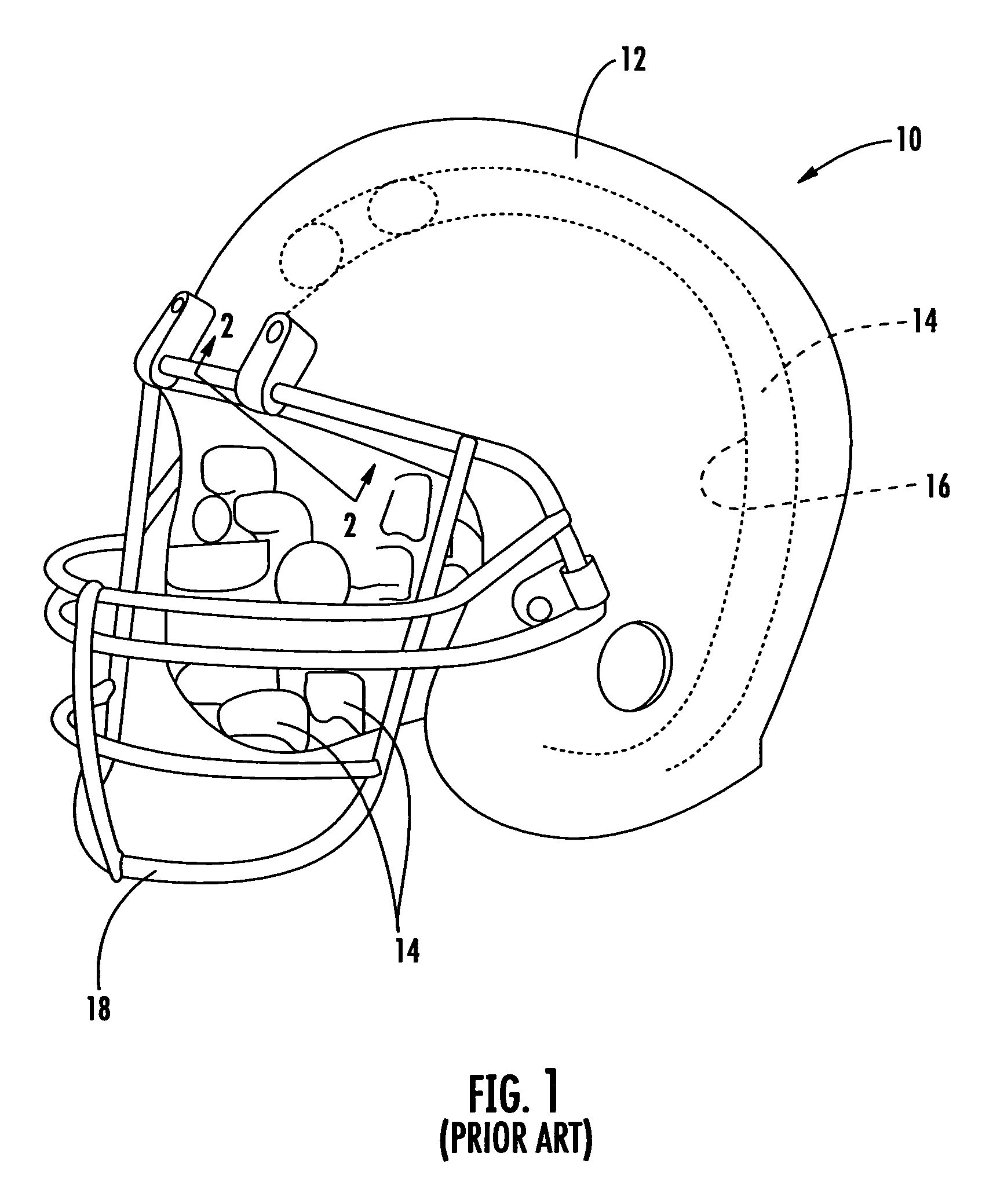
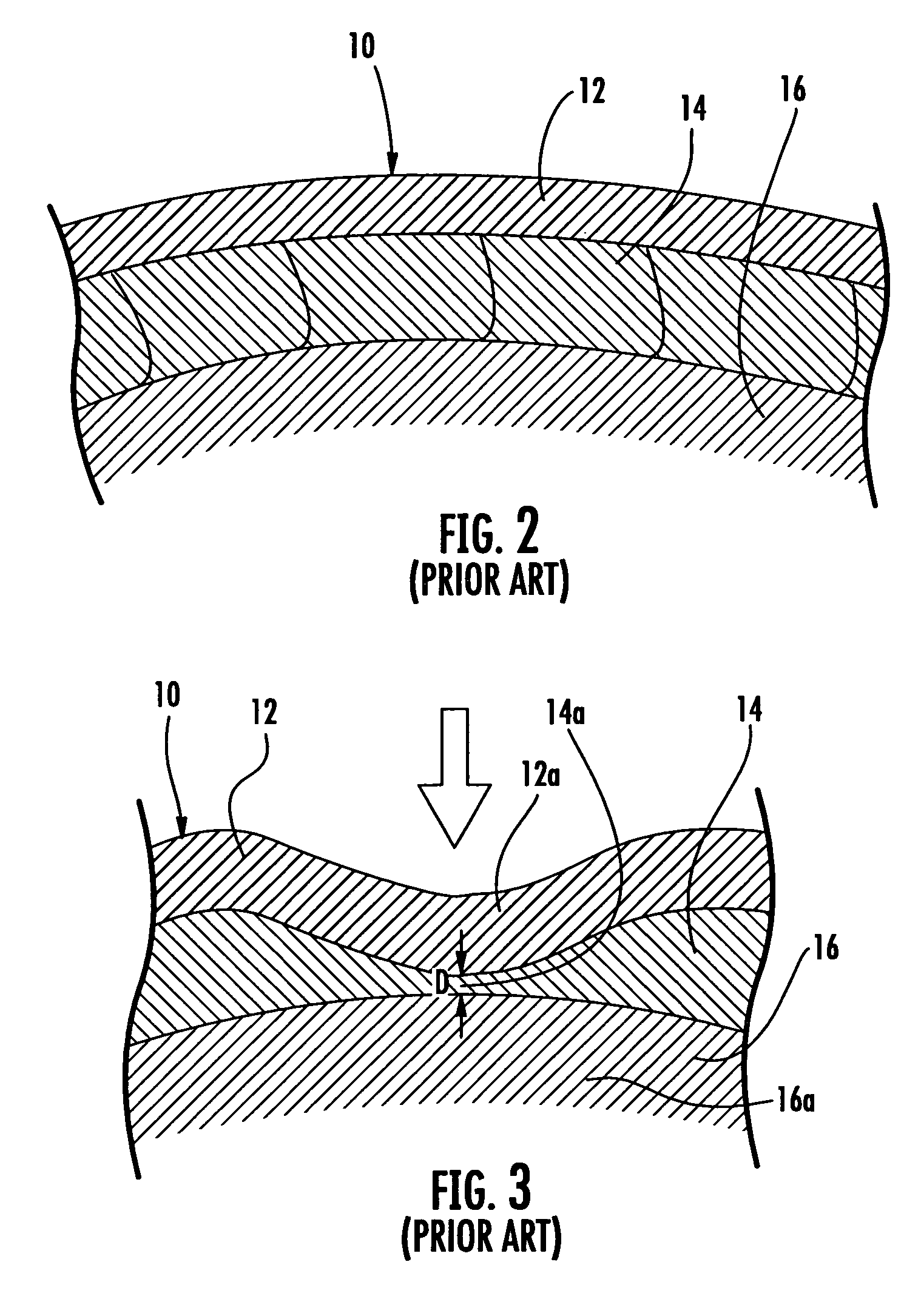
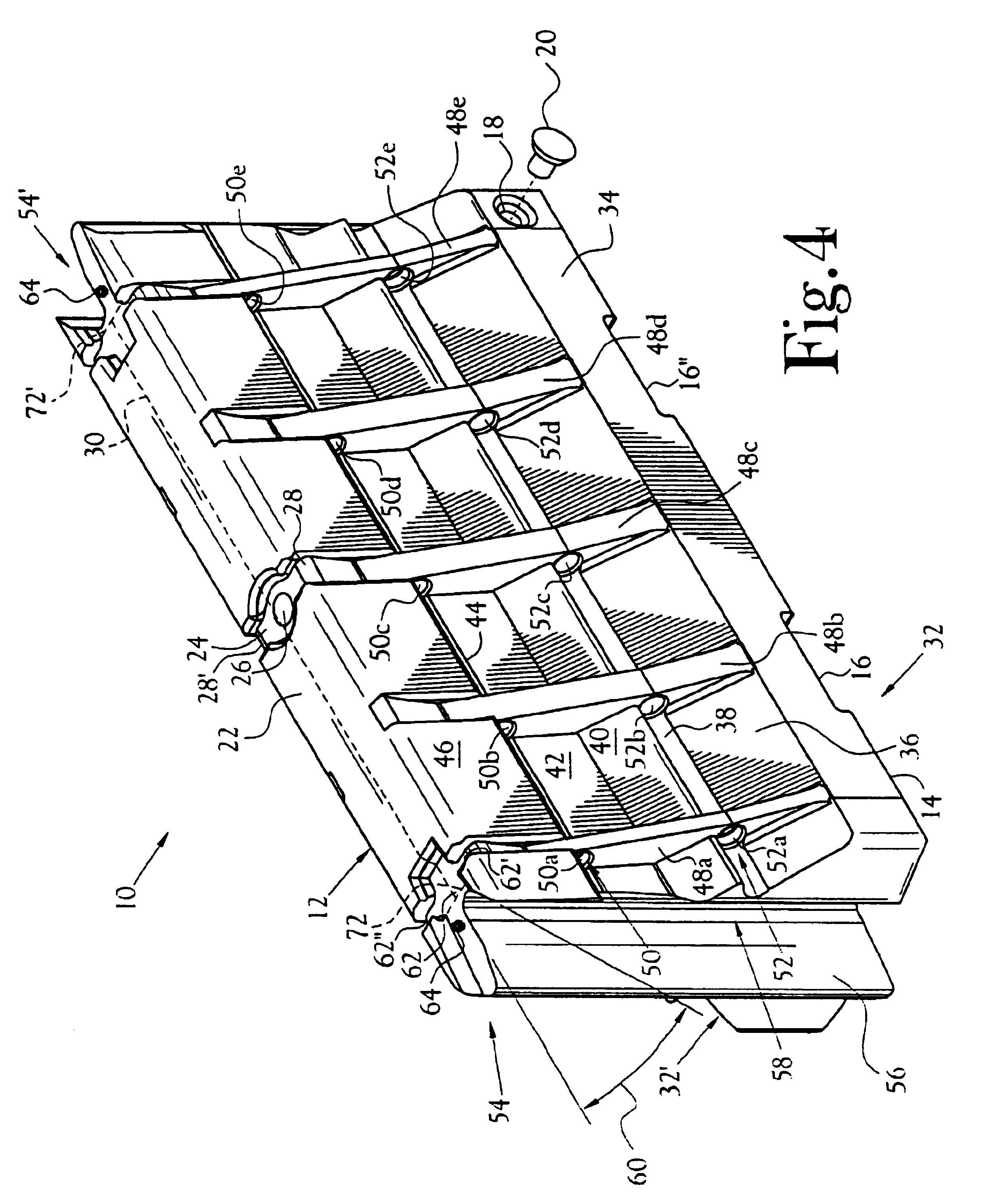
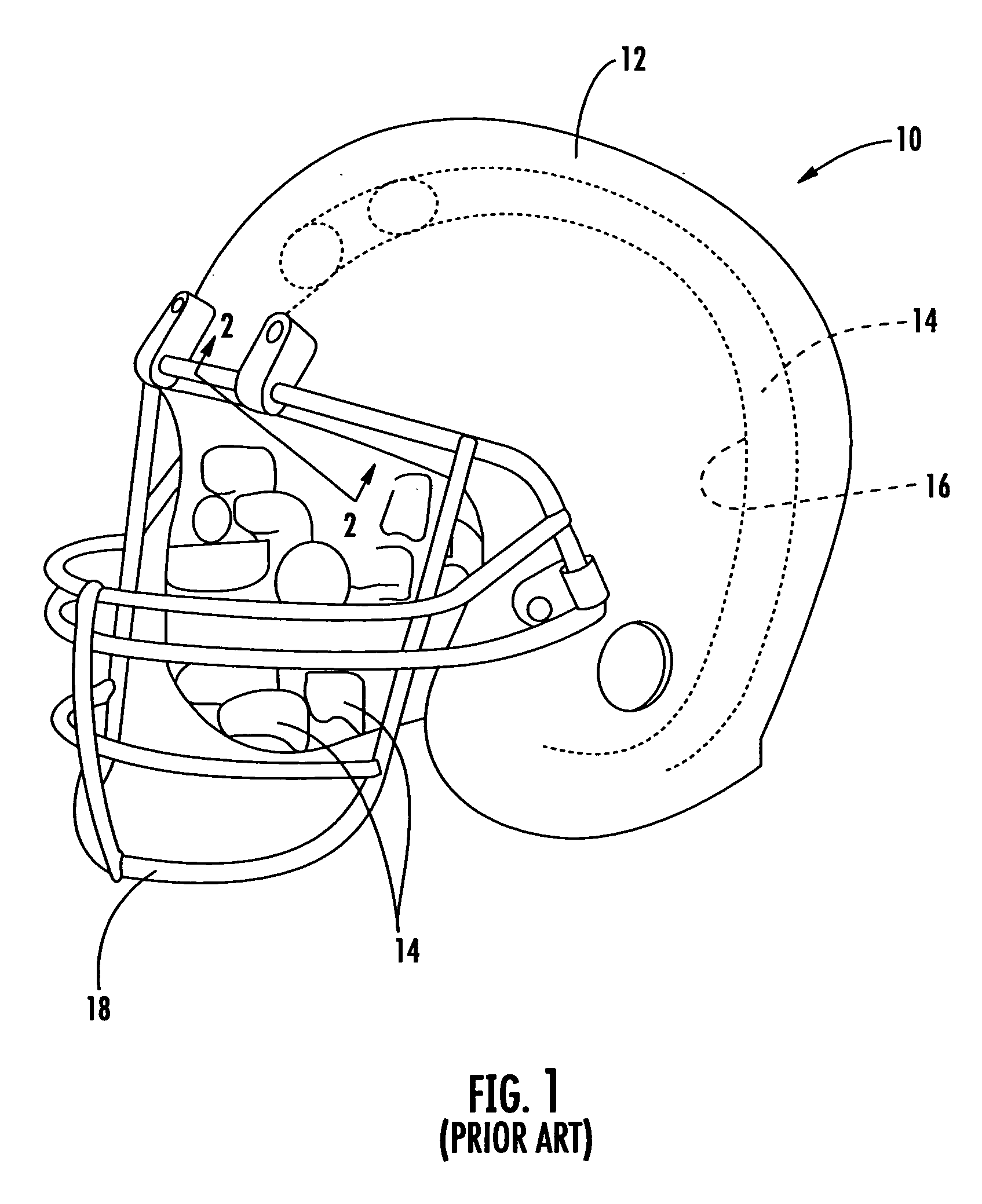
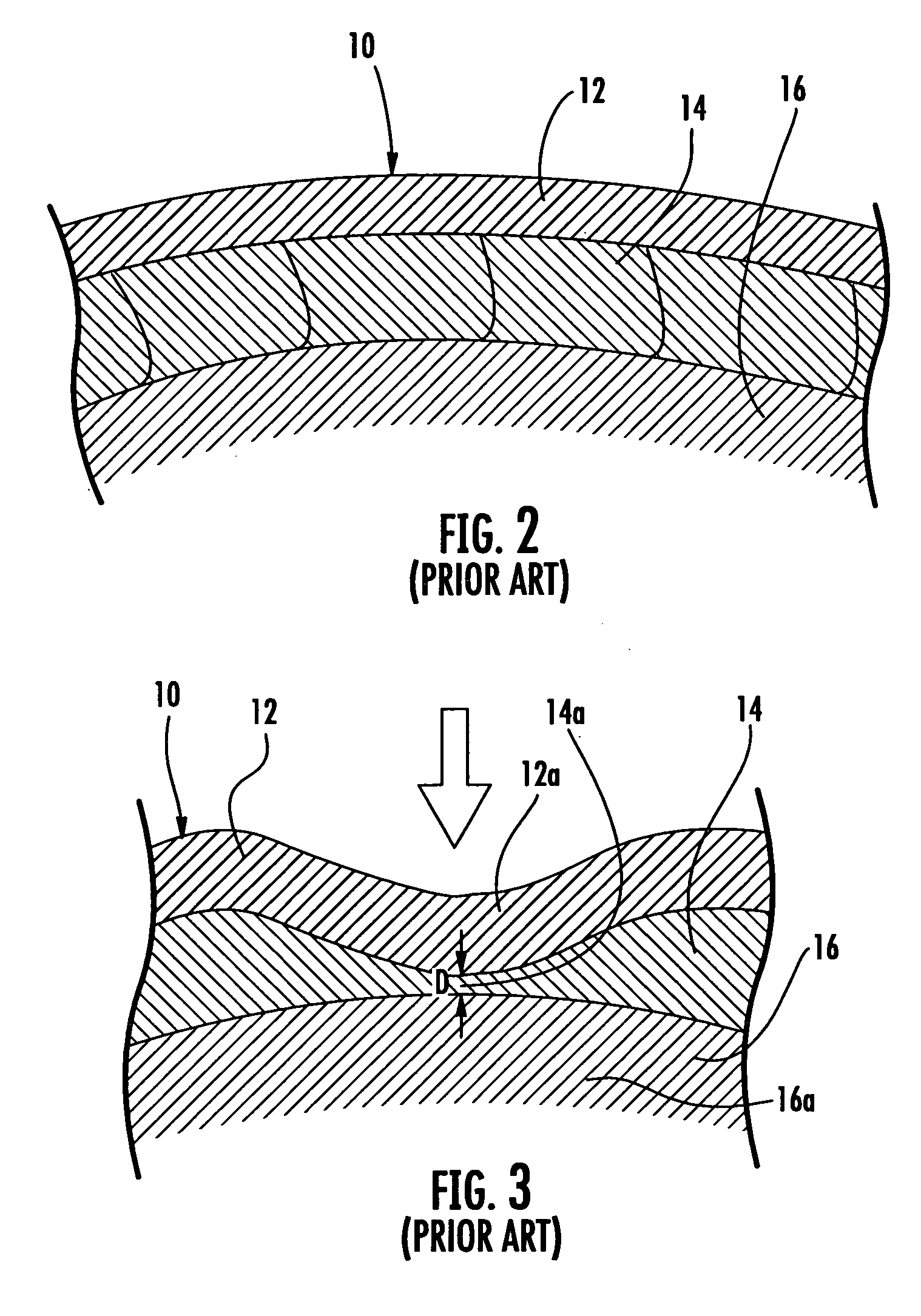
Protective headgear with improved shell construction
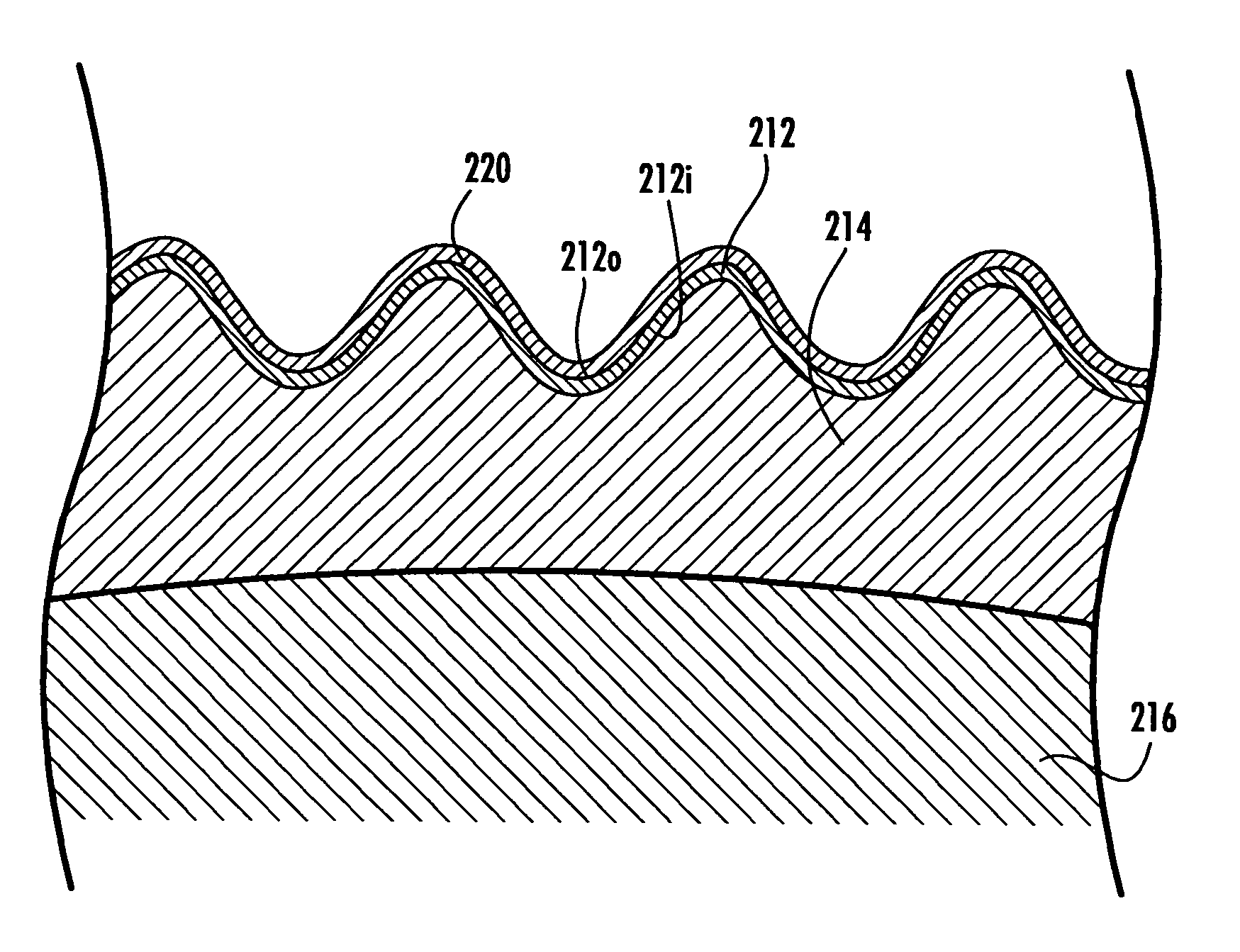
The protective helmet includes a rigid outer shell where the shell includes an undulating cross-sectional profile. A layer of impact-energy-absorbing material is positioned adjacent to the shell. The undulating profile of the shell can be any type of load spreading undulating profile, such as that of a sinusoidal or triangular wave configuration. The undulating load-spreading profile can be on the inner surface of the shell, on the outer surface of the shell or the entire cross-section of the shell may be undulating. The unique undulating profile makes the shell more rigid and spreads the impact load across the surface of the shell to thereby spread the deformation of the padding layer to prevent the shell from bottoming out of the impact-energy-absorbing material during an impact. As a result, a safer and more effective protective helmet is provided.
Owner:CRISCO JOSEPH J
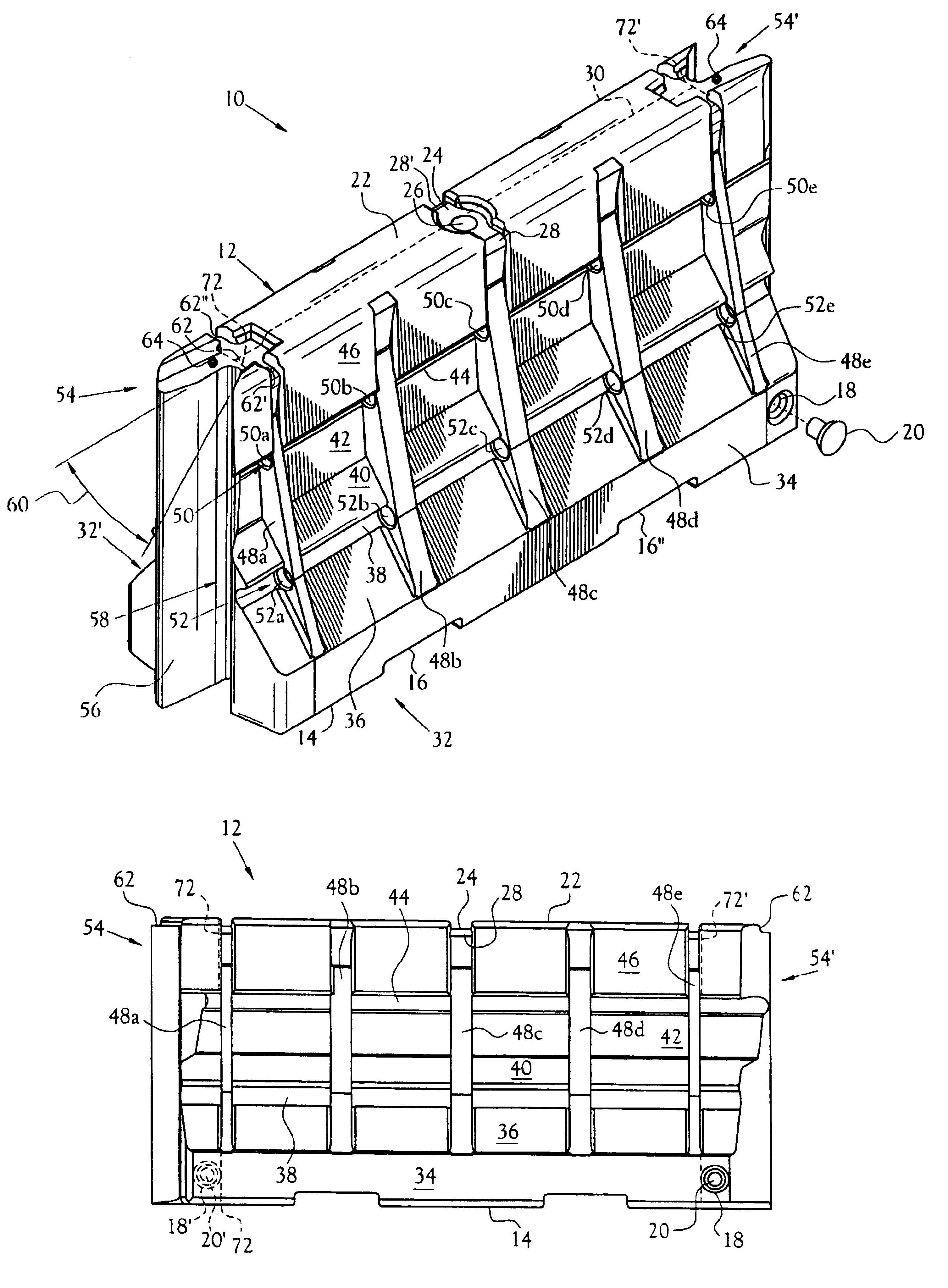
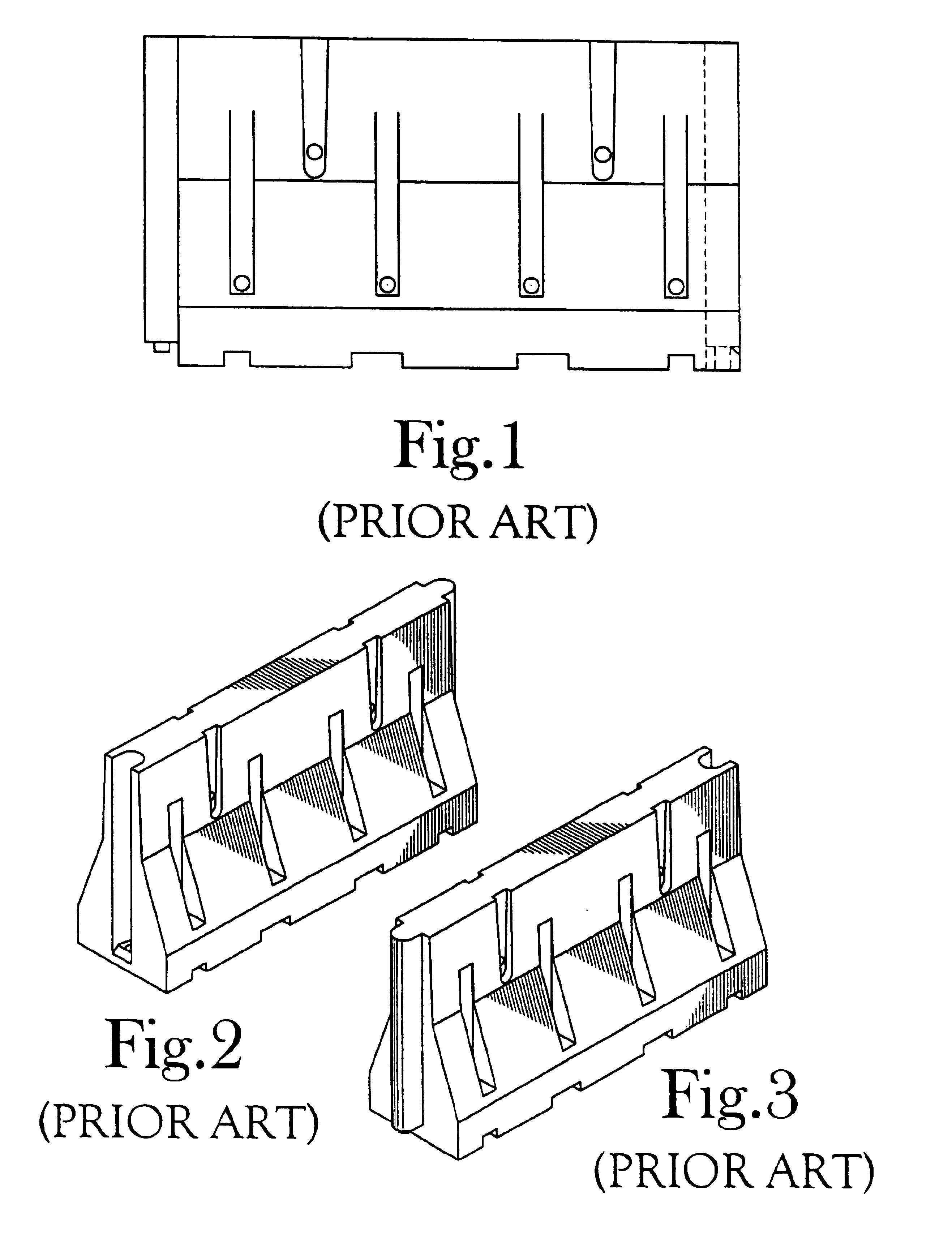
Protection barrier system
A protection barrier system for energy-absorption of impacts includes an elongated barrier defining a chamber therein. The barrier includes side walls having a plurality of connected non-vertical wall segments and a plurality of buttresses positioned vertically at spaced apart locations along each side wall. One or more guide channels are positioned on each side wall in horizontal alignment with similar guide channels on like-configured barriers. A coupling is disposed on each opposed end of the barrier for coupling of either barrier end juxtaposed in end-to-end nested arrangement with like barriers. A supplemental energy-absorbing system is connectable between opposed ends of end-to-end coupled barriers, providing energy-absorbing tubes removably inserted through each guide channel of each barrier. Cables are extendable through the tubes in the guide channels of the nested barriers, providing additional energy-absorption and deterrence from breaching of the barriers. A method of manufacture for the protection barrier is also disclosed.
Owner:SAFETY BARRIERS
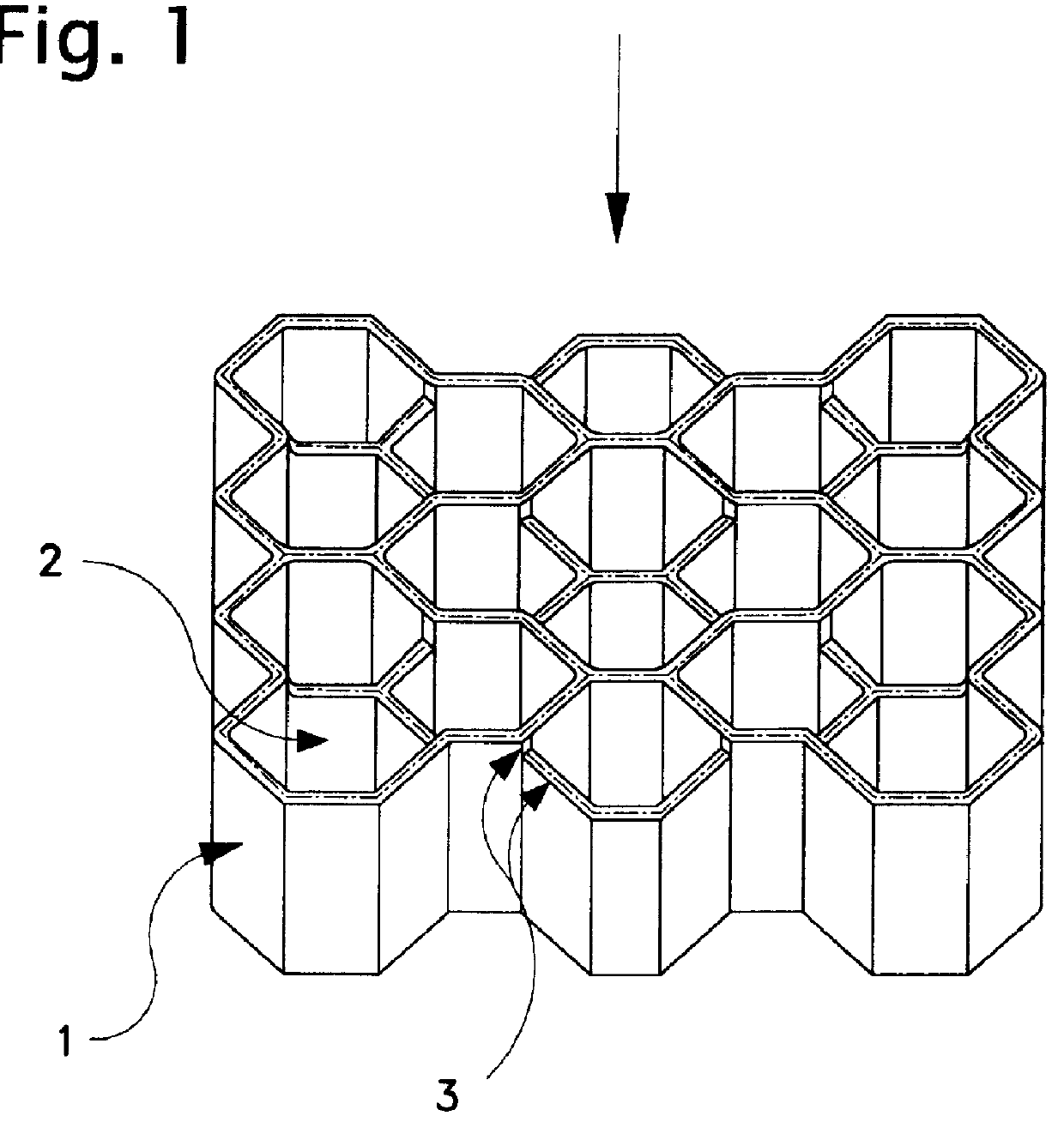
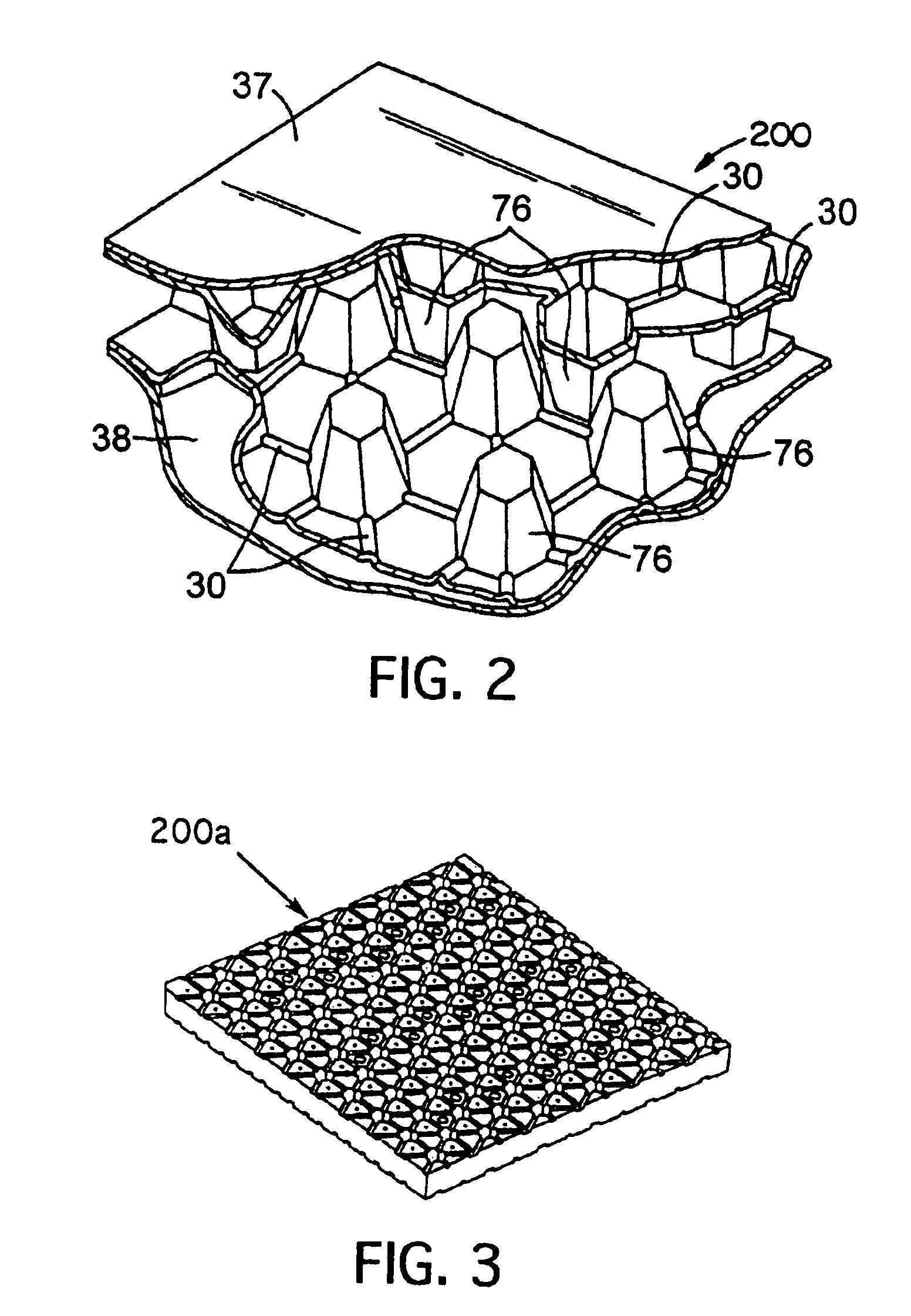
Impact absorber made of resin
InactiveUS6085878AImprove energy absorptionSmall sizeElastic dampersShock absorbersFlexural modulusHoneycomb
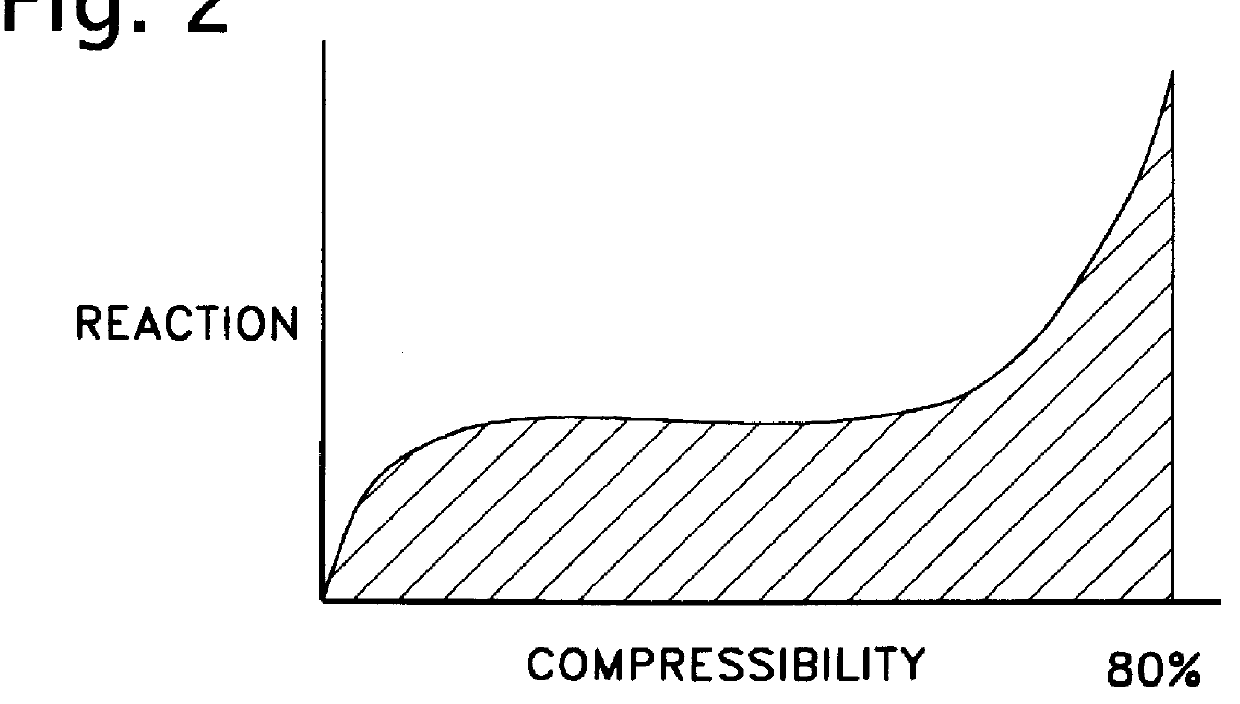
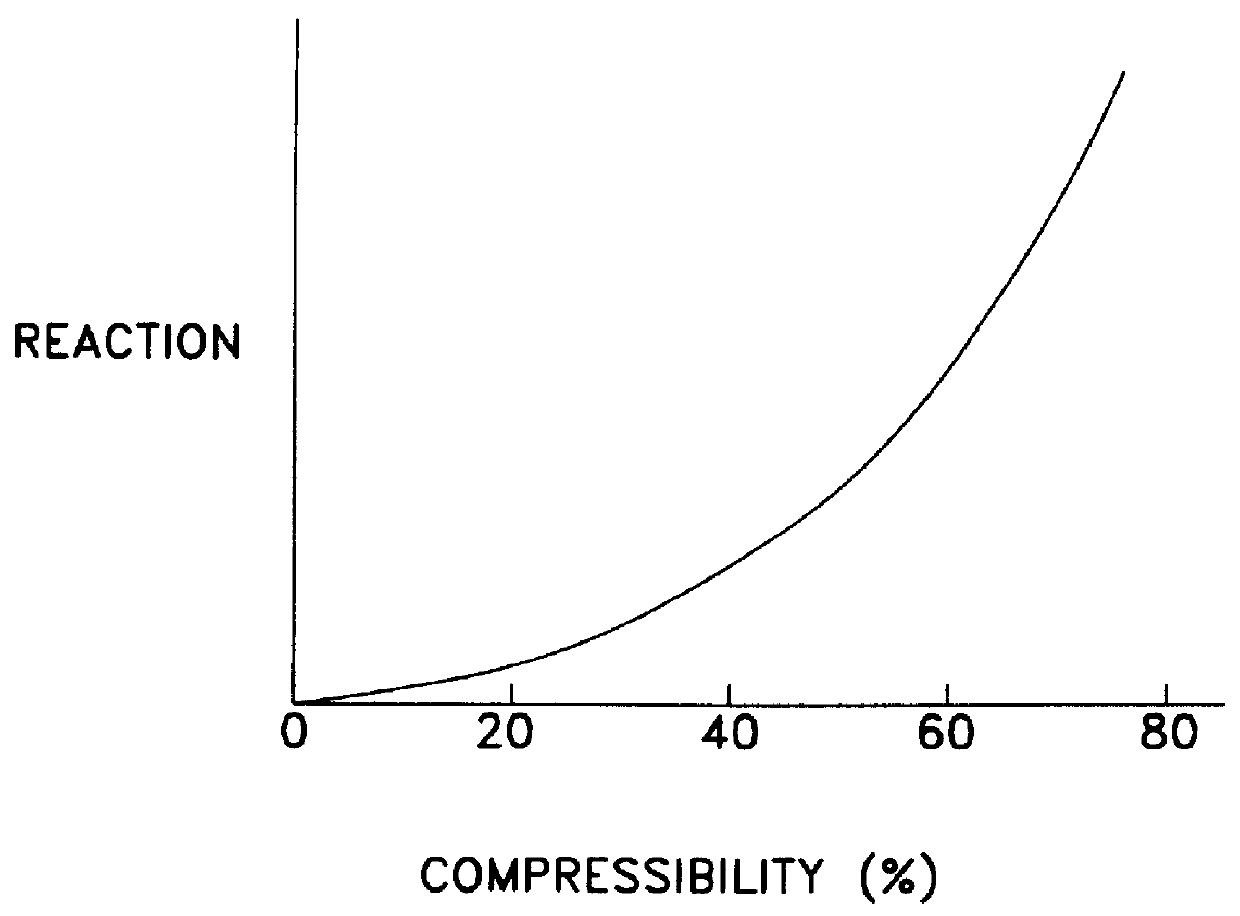
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 04596 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 26195 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 18, 1998A resin impact absorber comprising a hollow columnar body having a honeycomb section or a hollow columnar body having a cylindrical shape, the hollow columnar body being made of a resin with a flexural modulus of 500 to 5000 kgf / cm2, wherein a reaction-compressibility curve at the time of compression in the lengthwise direction of the columnar body satisfies the following conditions: (a) yield strength> / =100 Tf / m2 and (b) compression energy absorption> / =50 Tf.m / m3. The resin impact absorber of the present invention is small in size and light in weight and exhibits a high impact energy absorption capacity. A site or structure with an impact absorber of the present invention disposed therein can be prevented from remarkable damage or breakage when it receives a high impact force.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Impact energy absorbing device for a vehicle
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
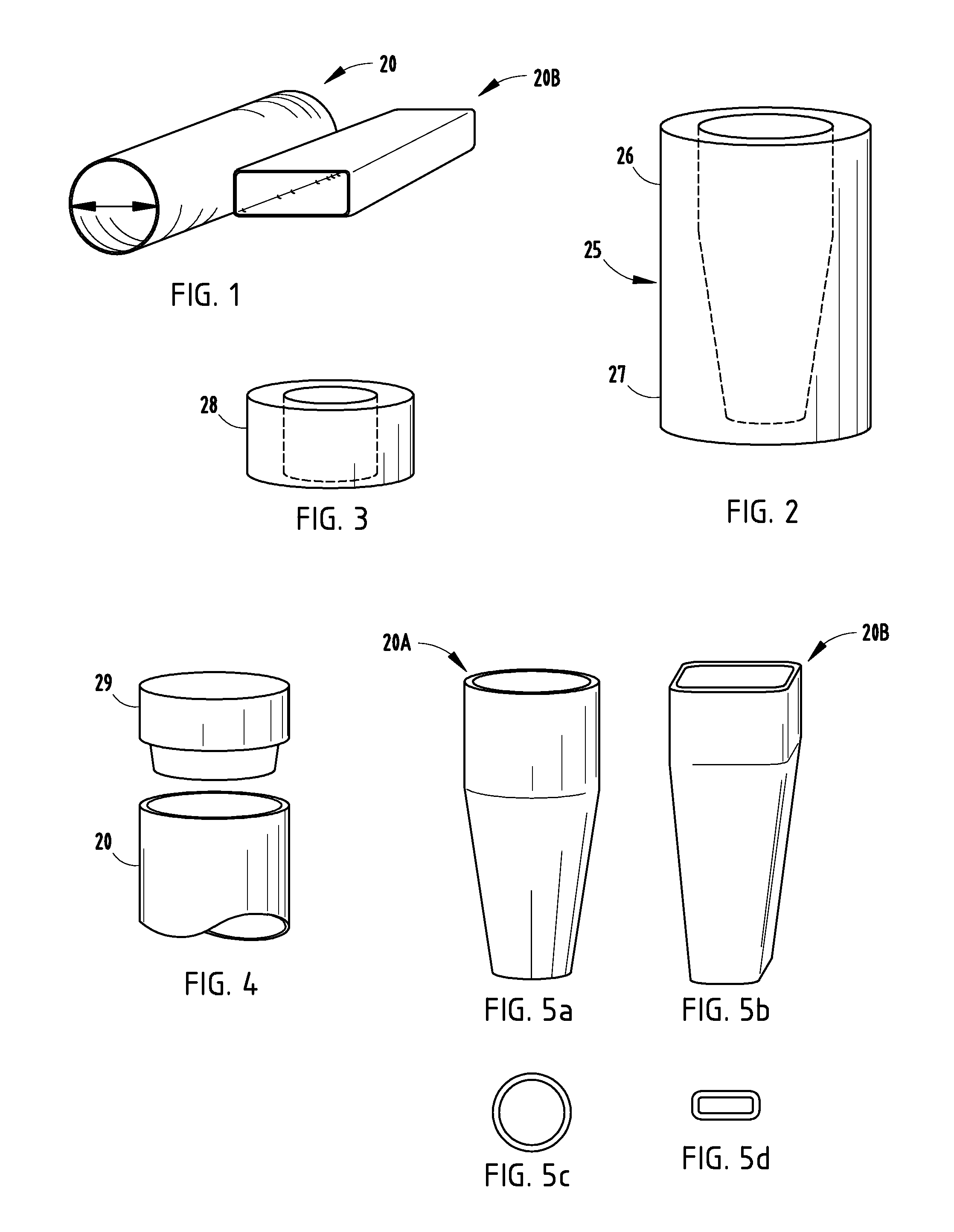
Tubular tapered crushable structures and manufacturing methods
A method includes steps of providing round tubing, providing a compression box and wedging dies, and reshaping the round tubing into a single or double-tapered rectangular tube including using the compression box to control an outside shape, while using the wedging dies to force material of the tubing outwardly toward the compression box. This arrangement minimizes material thinning. A tubular crushable structure is produced that is designed for longitudinal impact-energy-absorbing capability. The crushable structure includes a single or double-tapered rectangular tube made of material having a tensile strength of at least 40 KSI. In a narrower form the tensile strength is at least 80 KSI, though it can be 100 KSI or higher.
Owner:SHAPE CORP
Seat cushion
InactiveUS6938290B2Reduce harmReducing and eliminating damageDismountable chairsFoldable chairsFluid shiftingEngineering
Impact energy forces to the spine are reduced through the use of multiple overlying pliable impact energy absorbing layers. Each layer comprises a plurality of cells that are in fluid communication which provides for a valved transfer of fluid between the cells. Additionally, each layer has a different durometer.
Owner:MCKINNEY RICHARD A +2
Corrugated sandwich protective structure of battery box of electric vehicle
InactiveCN103730616AUndamagedFree from destructionElectric propulsion mountingVehicle sub-unit featuresAutomotive batteryEngineering
The invention discloses a corrugated sandwich protective structure of a battery box of an electric vehicle. The protective structure comprises a box body and a box cover, wherein the box body is not closed at top, is composed of a baseplate and a baseplate wallboard fixed around the baseplate and is used for accommodating batteries; the box cover comprises a top plate and a top-plate wallboard fixed around the top plate, and the box cover and the box body are buckled so as to form a closed space. The protective structure is characterized in that the baseplate and the baseplate wallboard are respectively made of a corrugated sandwich protective plate. According to the invention, the box body and the box cover are made of the corrugated sandwich protective plates, so that the batteries can be prevented from being damaged; the corrugated sandwich protective structure has the advantages of high specific stiffness, high specific strength, high fatigue life, strong impact resistance and shock resistance, good impacting energy absorption property, light weight, and the like, thereby facilitating the promotion and application of electric vehicles and passenger cars.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
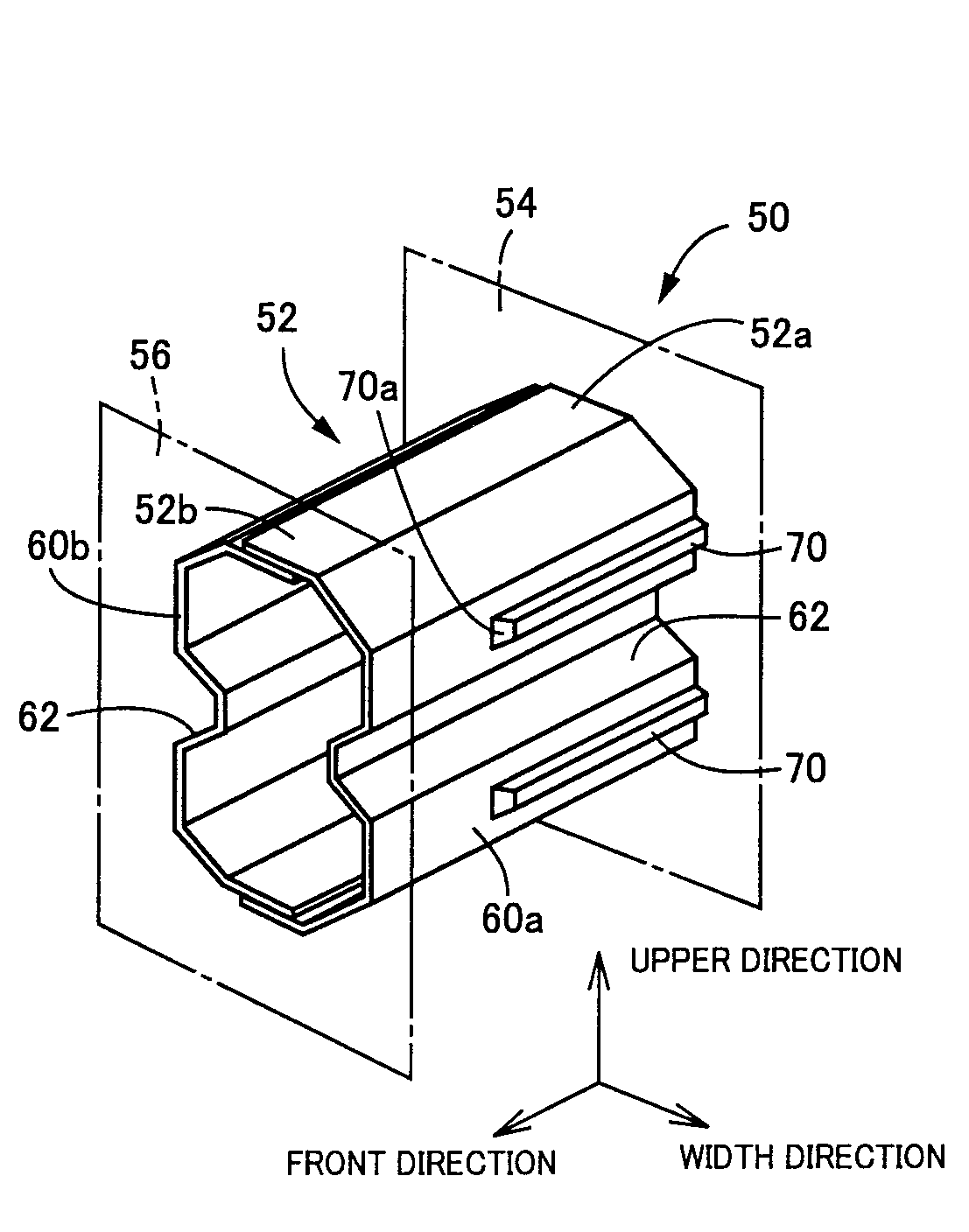
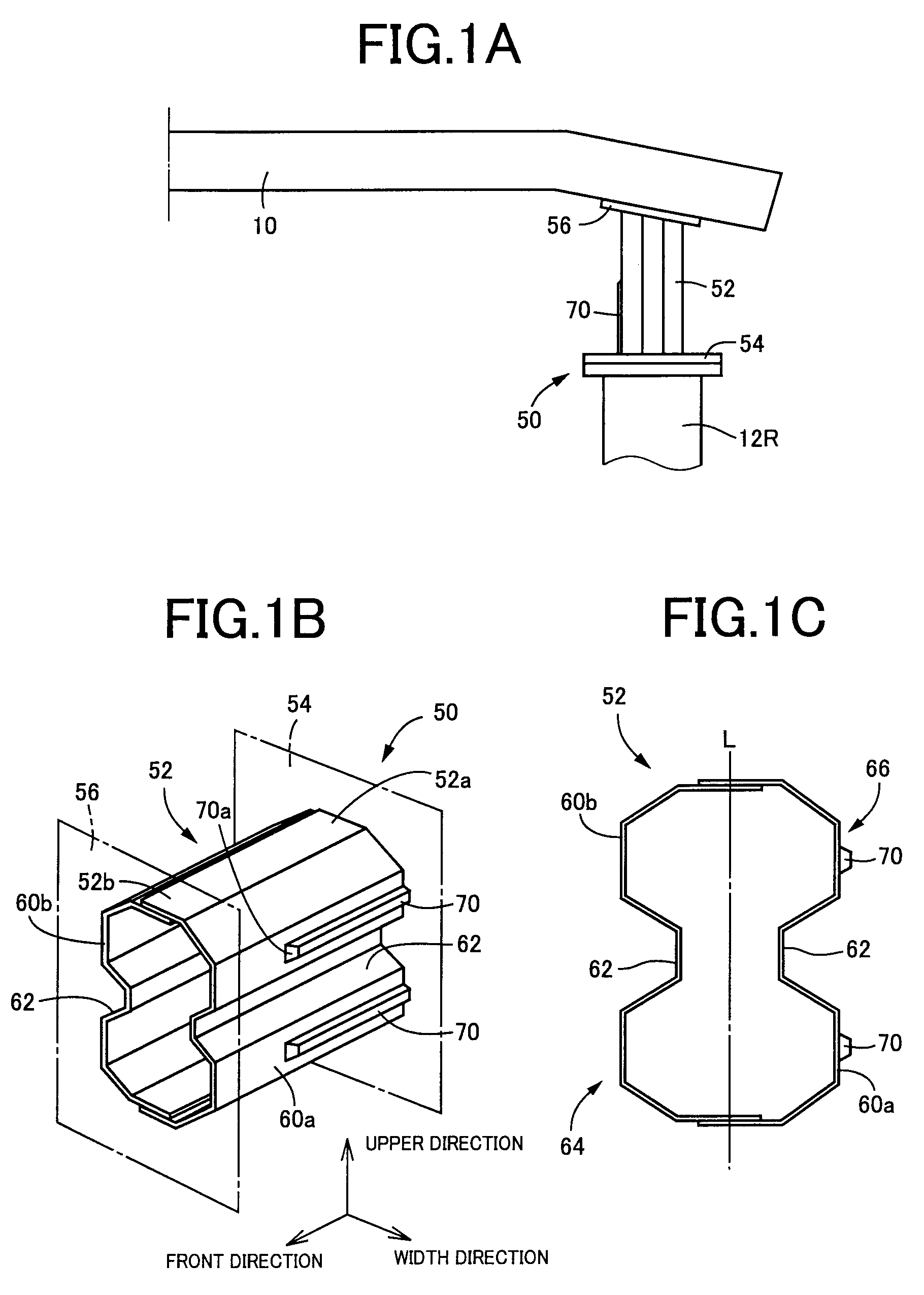
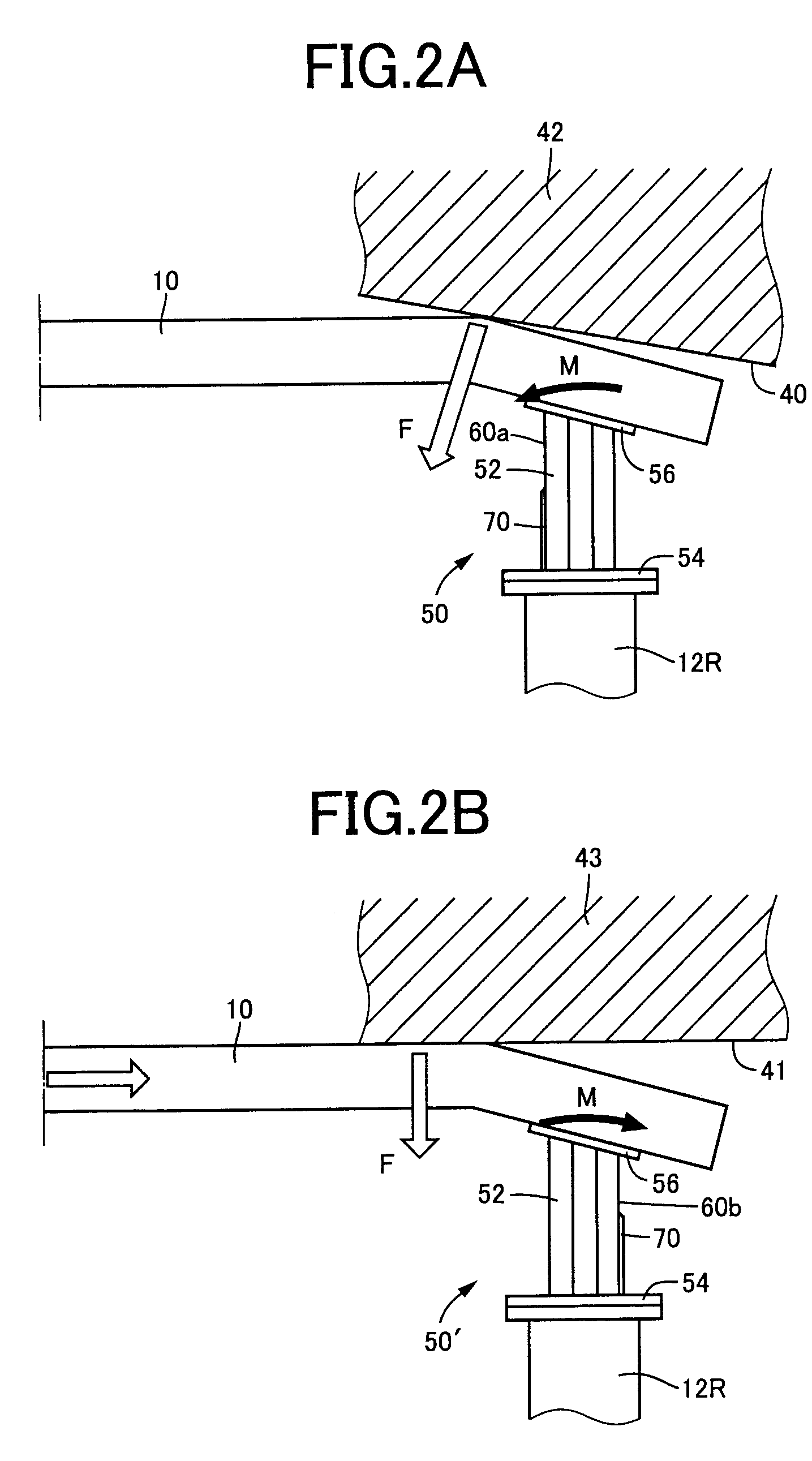
Impact absorbing member for vehicle
ActiveUS20110187135A1Improve impact absorption performanceIncrease supplyElastic dampersBumpersEngineeringMechanical engineering
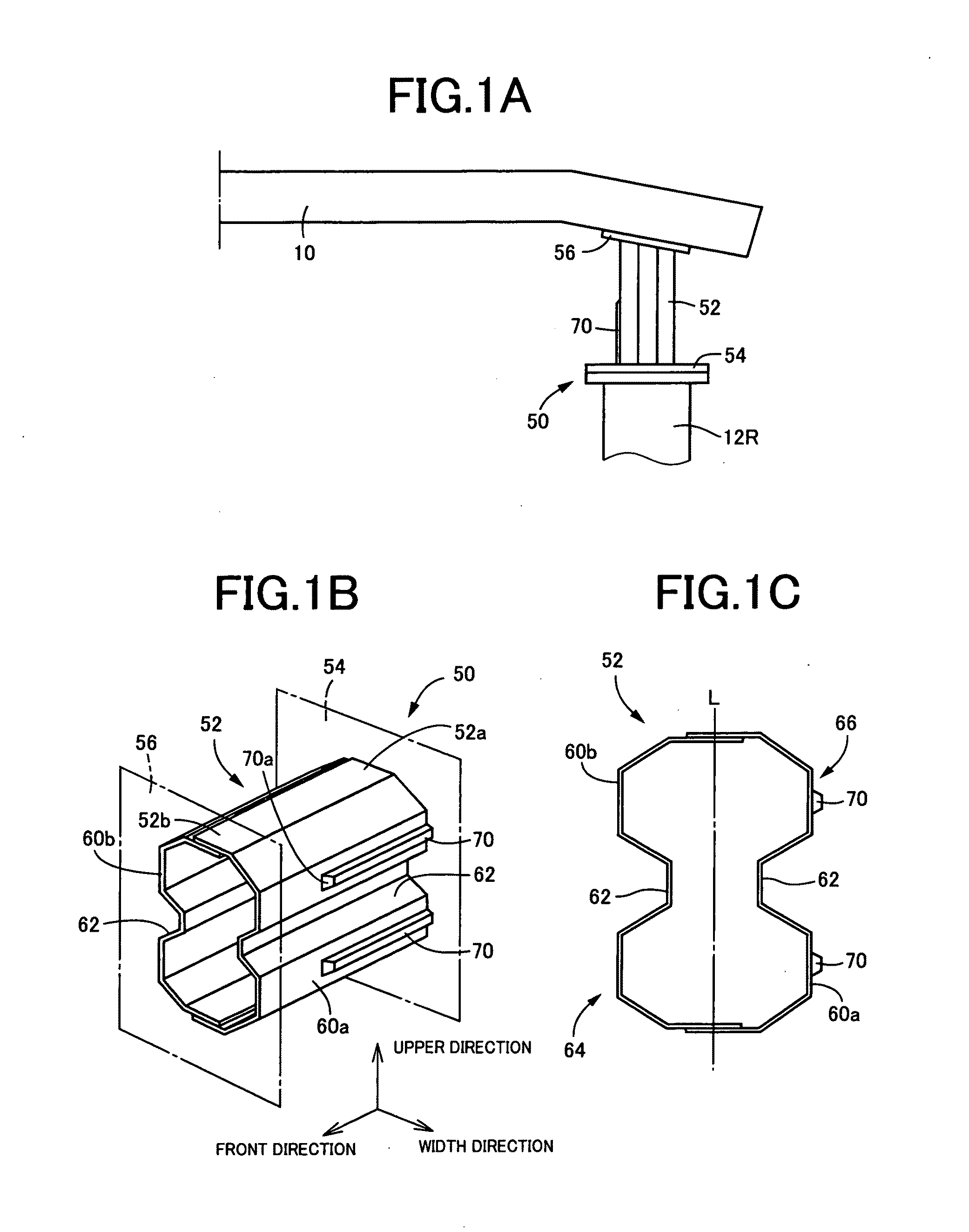
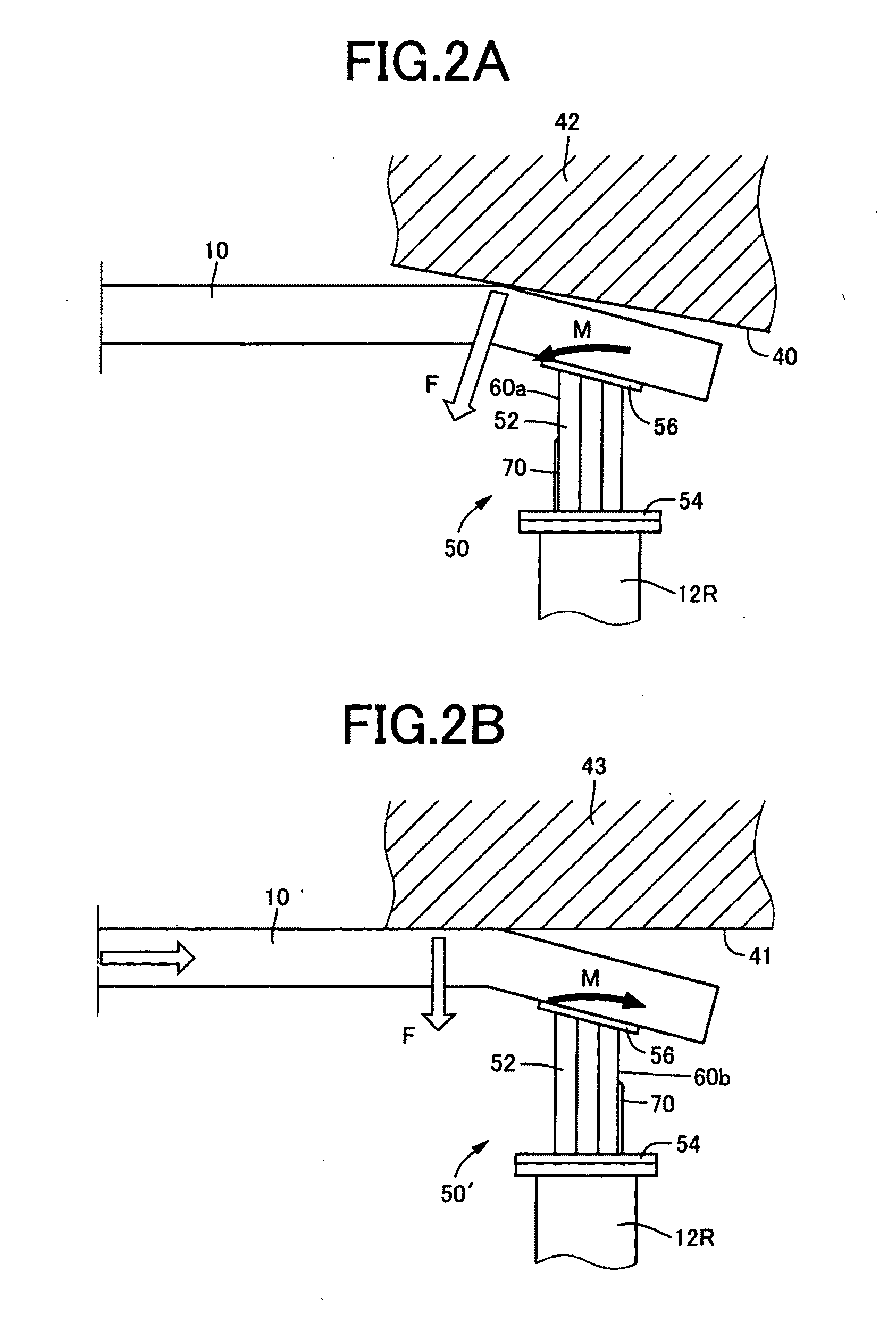
Of side wall portions (60a, 60b) of a tubular body portion (52) mainly constituting an impact absorbing member (50), a wider side wall portion (60a) on the vehicle inner side is provided with a projecting rib (70) projects outward in the direction perpendicular to the axis of the body portion. The projecting rib (70) extends from an axial end (52a) adjacent to a mounting plate (54) and parallel to the axial direction of the body portion. Therefore, even when an impact load is applied to the impact absorbing member (50) in an oblique direction with respect to the vehicle to generate a moment load, the existence of the projecting rib (70) prevents the impact absorbing member from falling down laterally. Accordingly, excellent impact-absorbing properties are stably obtained. The projecting rib (70) is formed not to reach the load input side, i.e., the axial end (52b) adjacent to a mounting plate (56), where collapse starts. Therefore, no load increase occurs in a crash initial stage to well maintain impact-energy-absorbing properties.
Owner:TOYODA IRON WORKS CO LTD
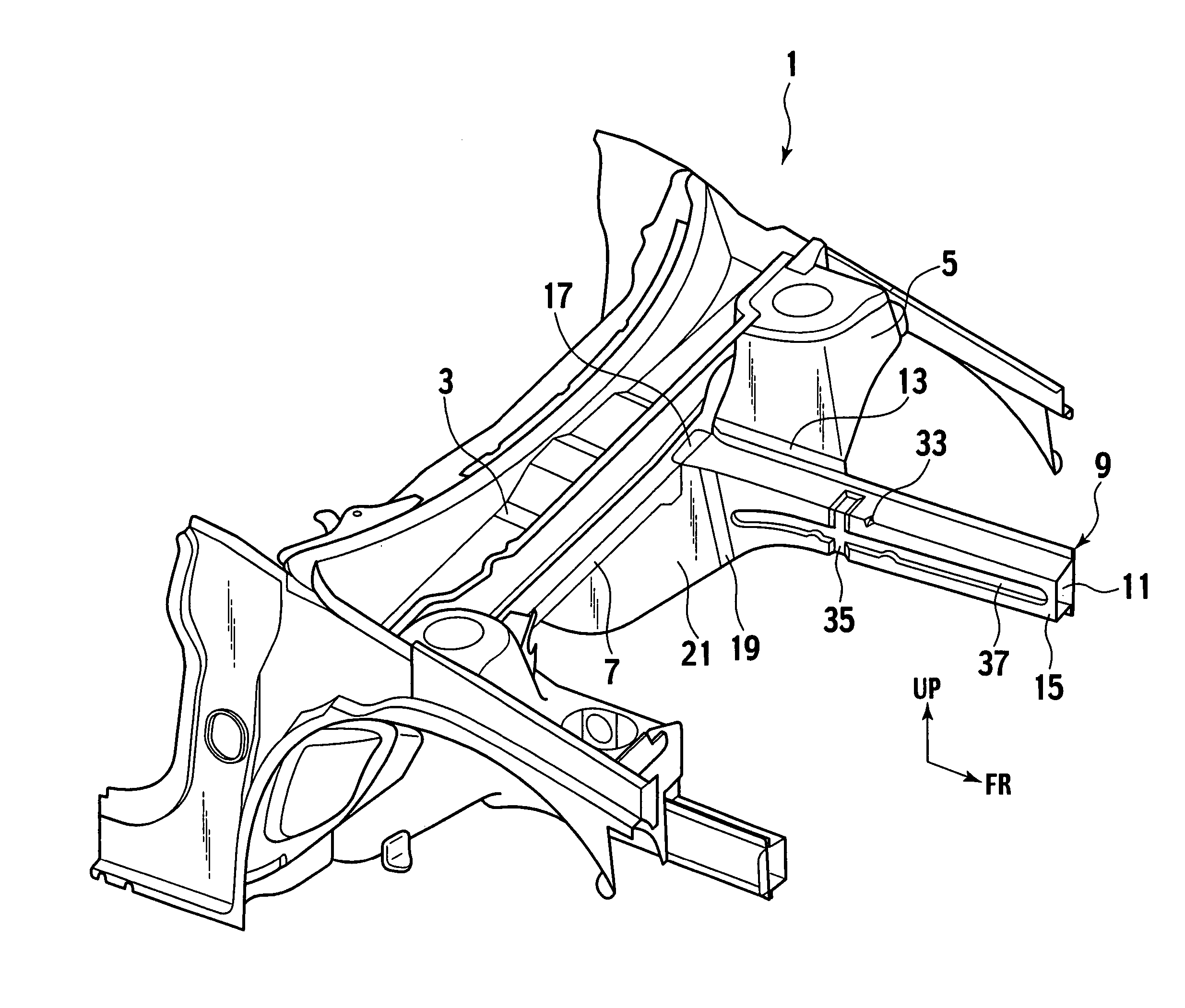
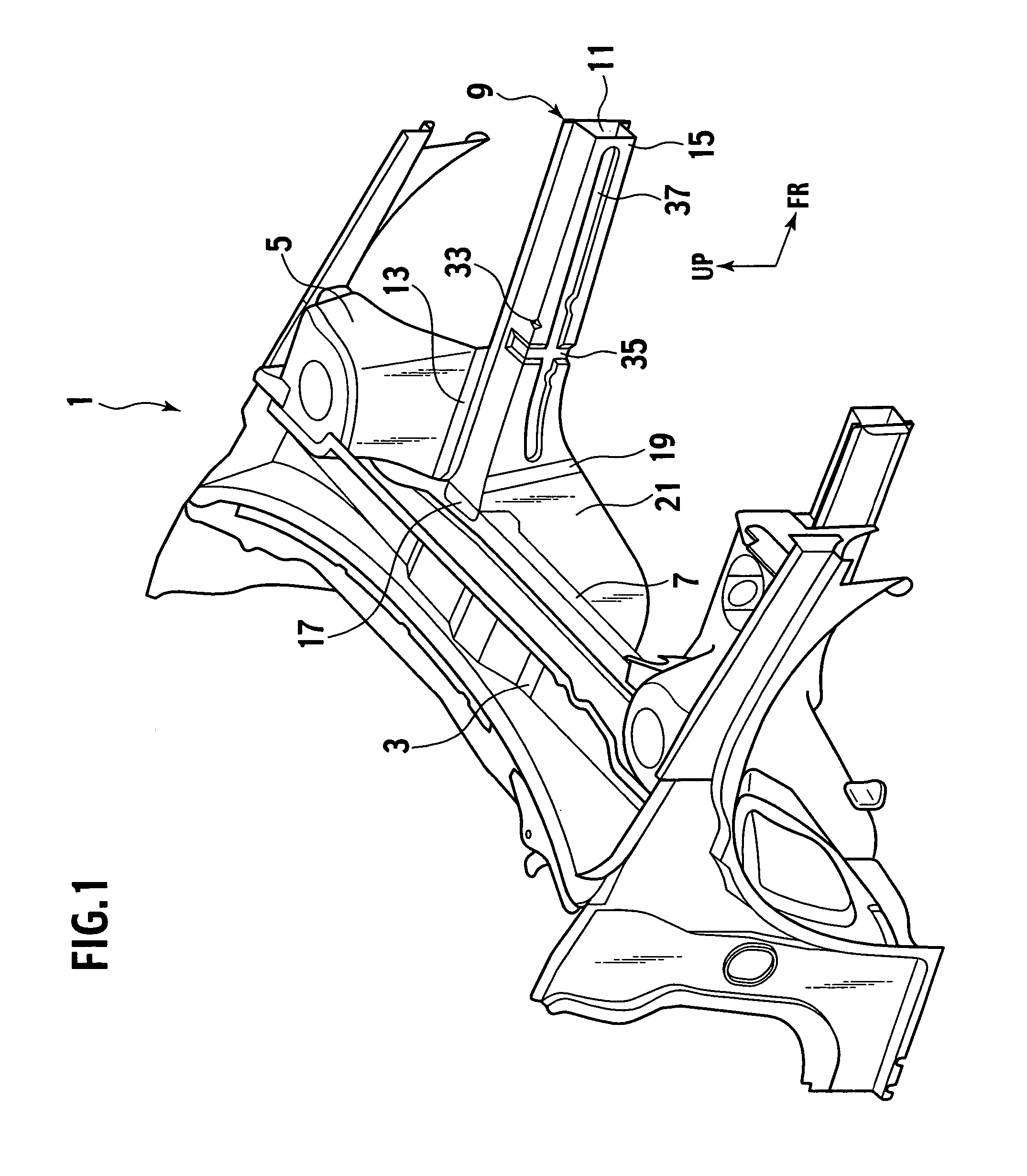
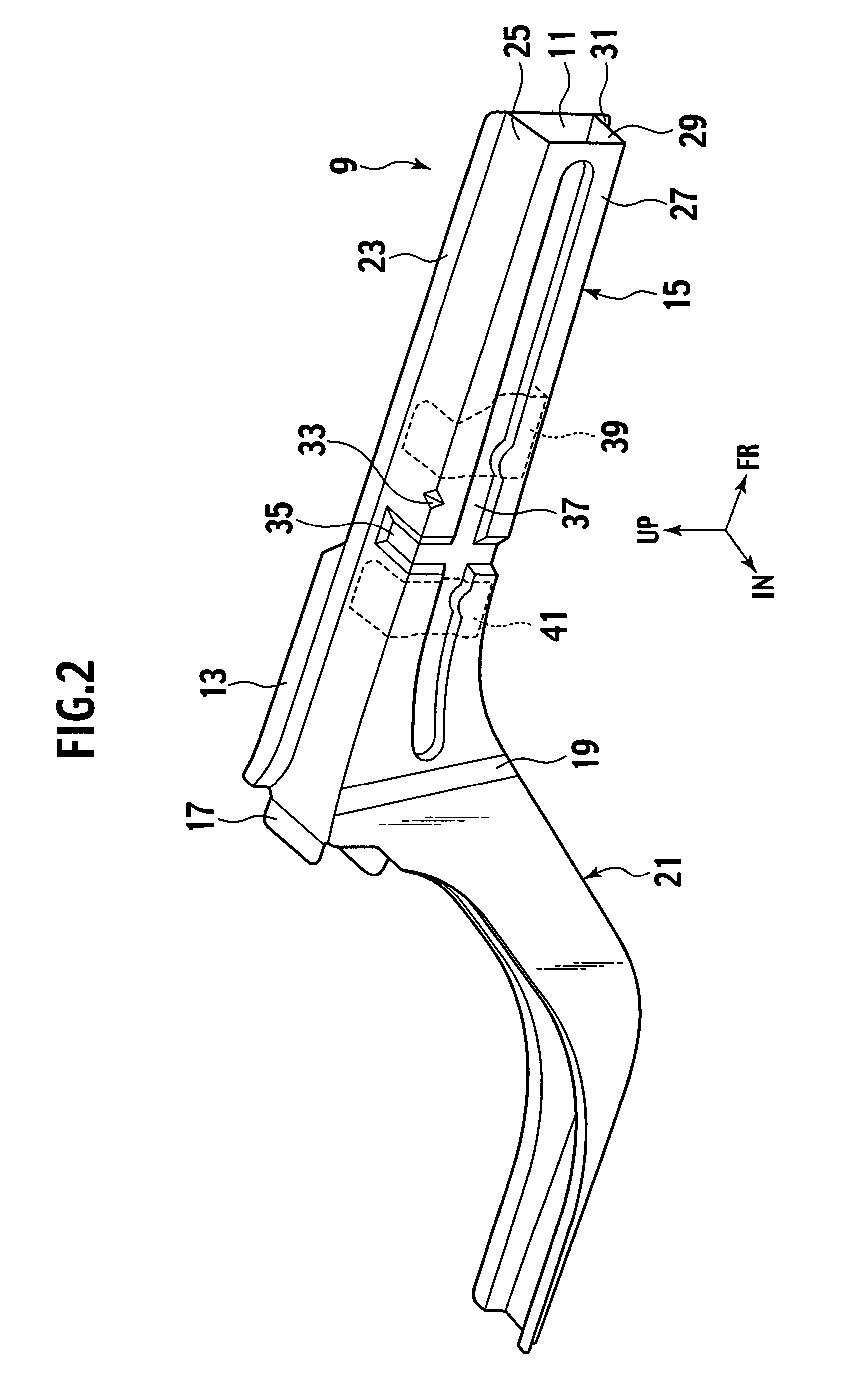
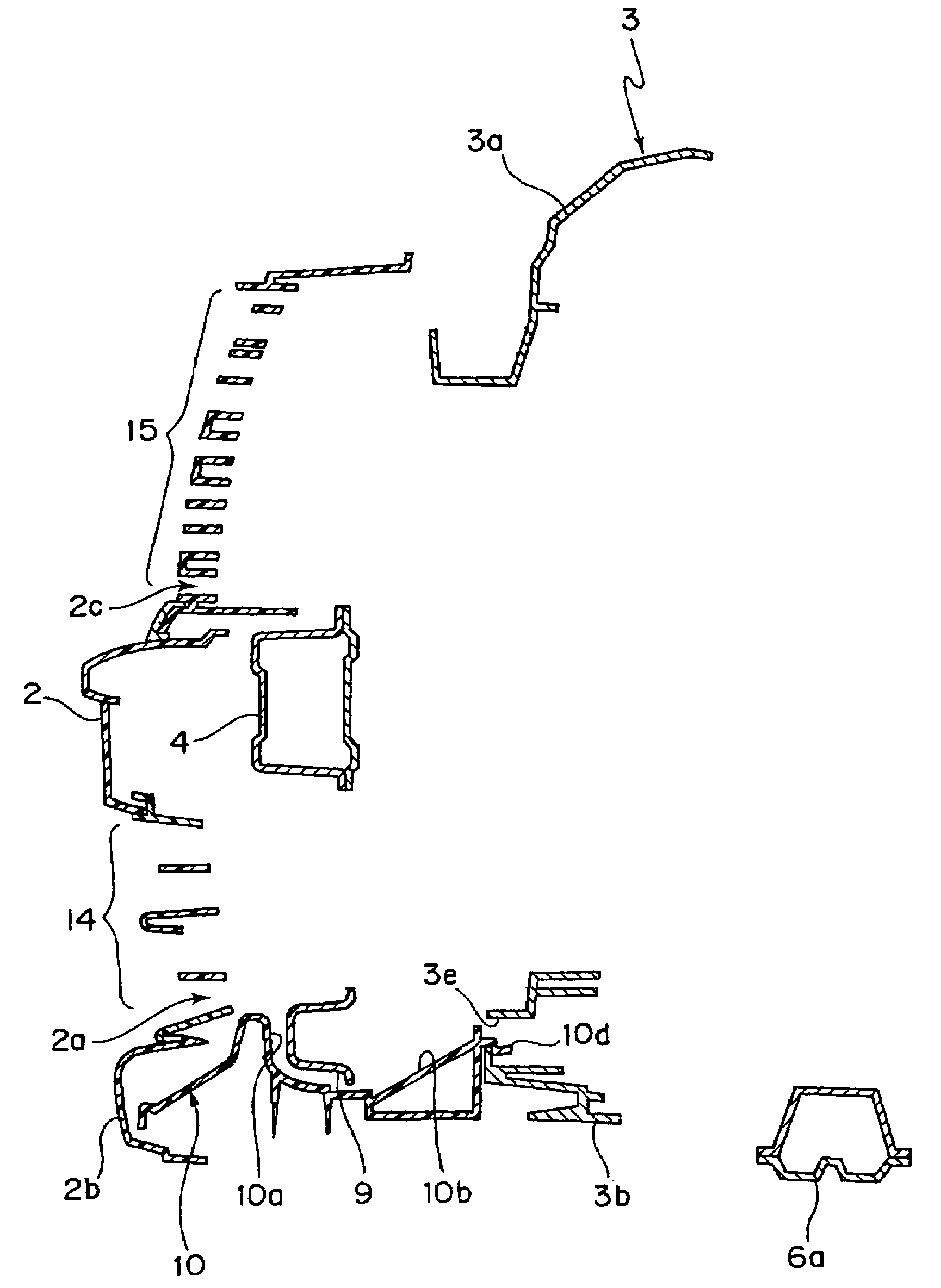
Impact energy absorbing structure for upper part of body of motor vehicle and energy absorber
InactiveUS6302477B1Easy to manufactureEasy to installVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMobile vehicleCoupling
In an impact energy absorbing structure for an upper part of a body of a motor vehicle having a structural member that extends in a longitudinal direction and an inner trim member that is disposed toward an interior of a cabin and spaced apart from the structural member by a certain distance, an energy absorber is disposed within the distance. The energy absorber has two hollow tubular body portions whose axes extend in the longitudinal direction and a coupling portion for coupling the tubular body portions to each other. The two tubular body portions are formed integrally with the coupling portion, and the energy absorber is fixed to the structural member by the coupling portion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Front longitudinal beam structure for automobiles
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Impact absorbing member for vehicle
ActiveUS7896411B2Maintain good propertiesIncrease supplyVehicle seatsElastic dampersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NASA +1
Deployable rigid system for crash energy management
A deployable cellular structure providing impact energy absorption capability is disclosed. The structure may be packed when not in use and deployed automatically or manually to provide impact protection. The structure is useful in a variety of situations including vehicular protection of occupants, deployable highway safety barriers, and aviation emergency safety devices.
Owner:VERIDIAN SYST DIV
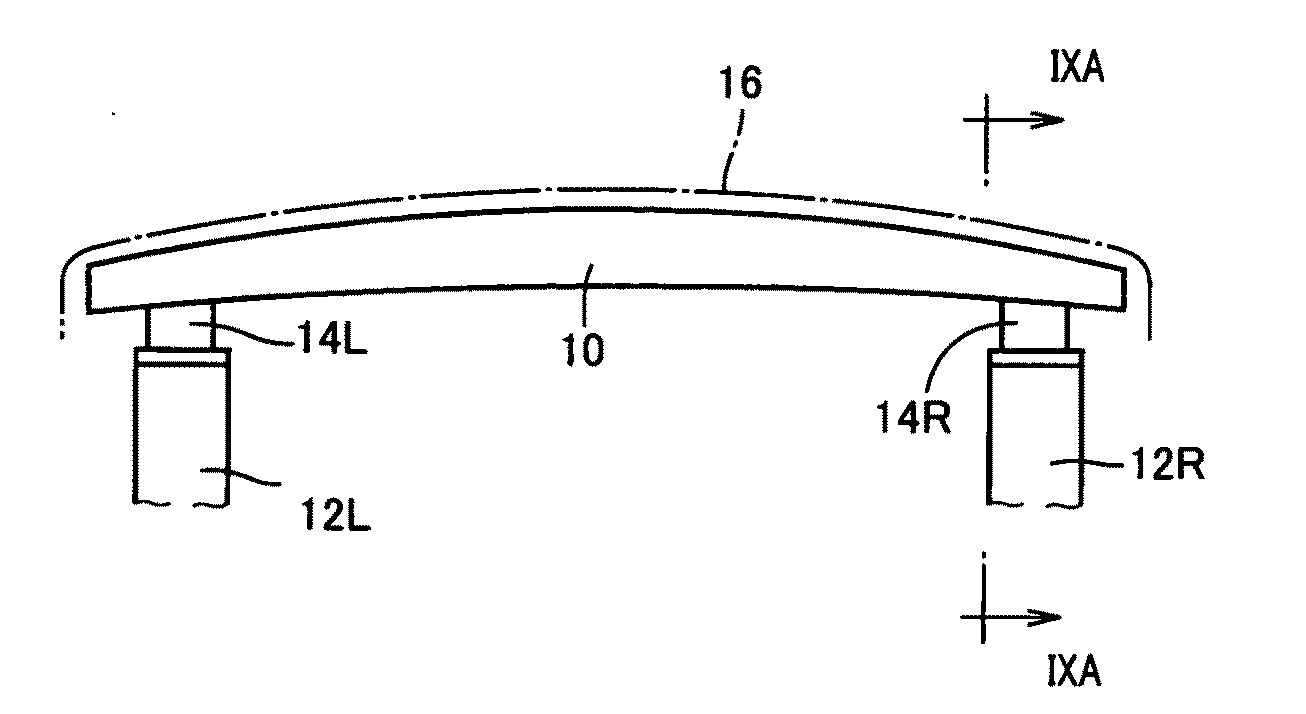
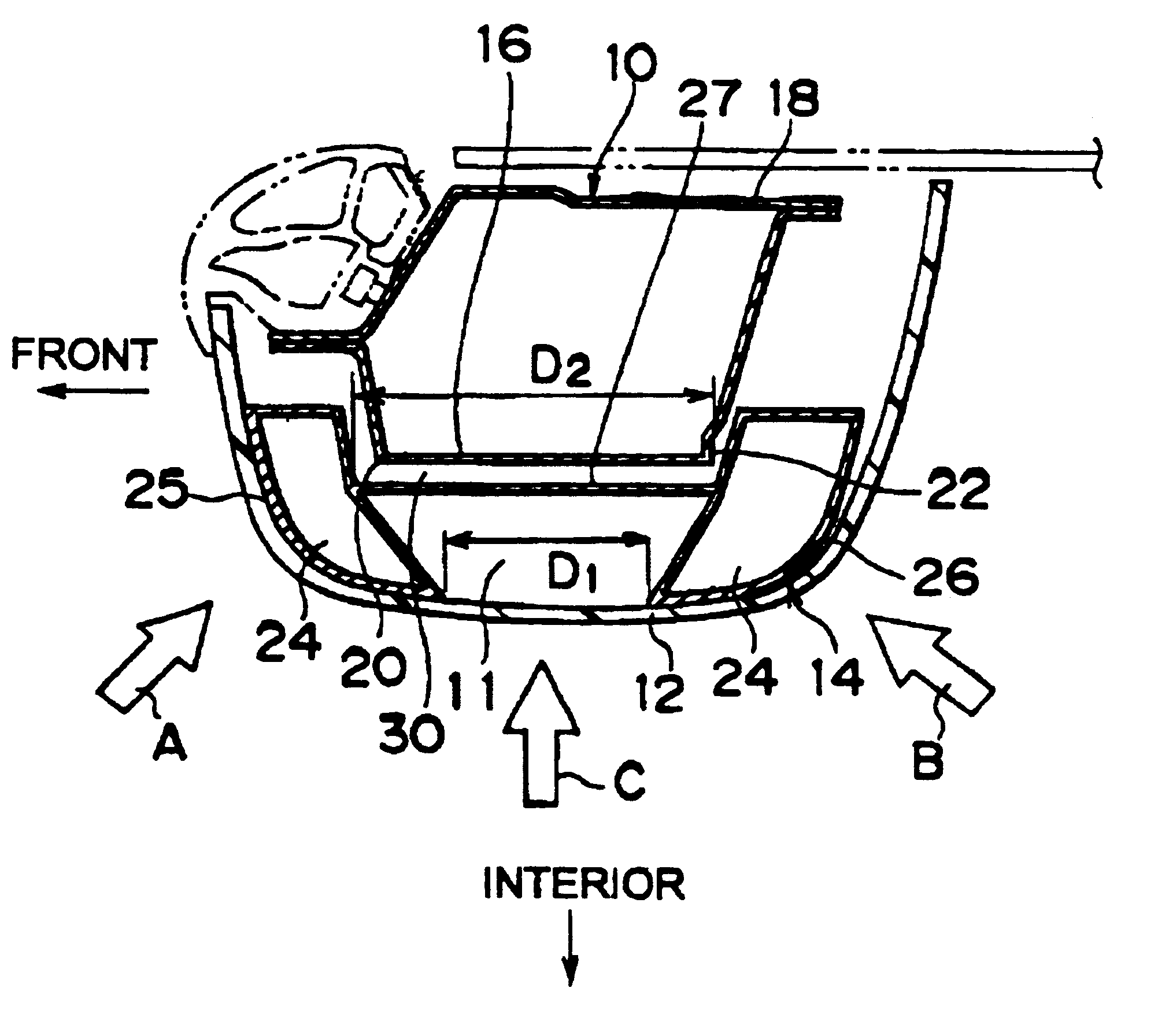
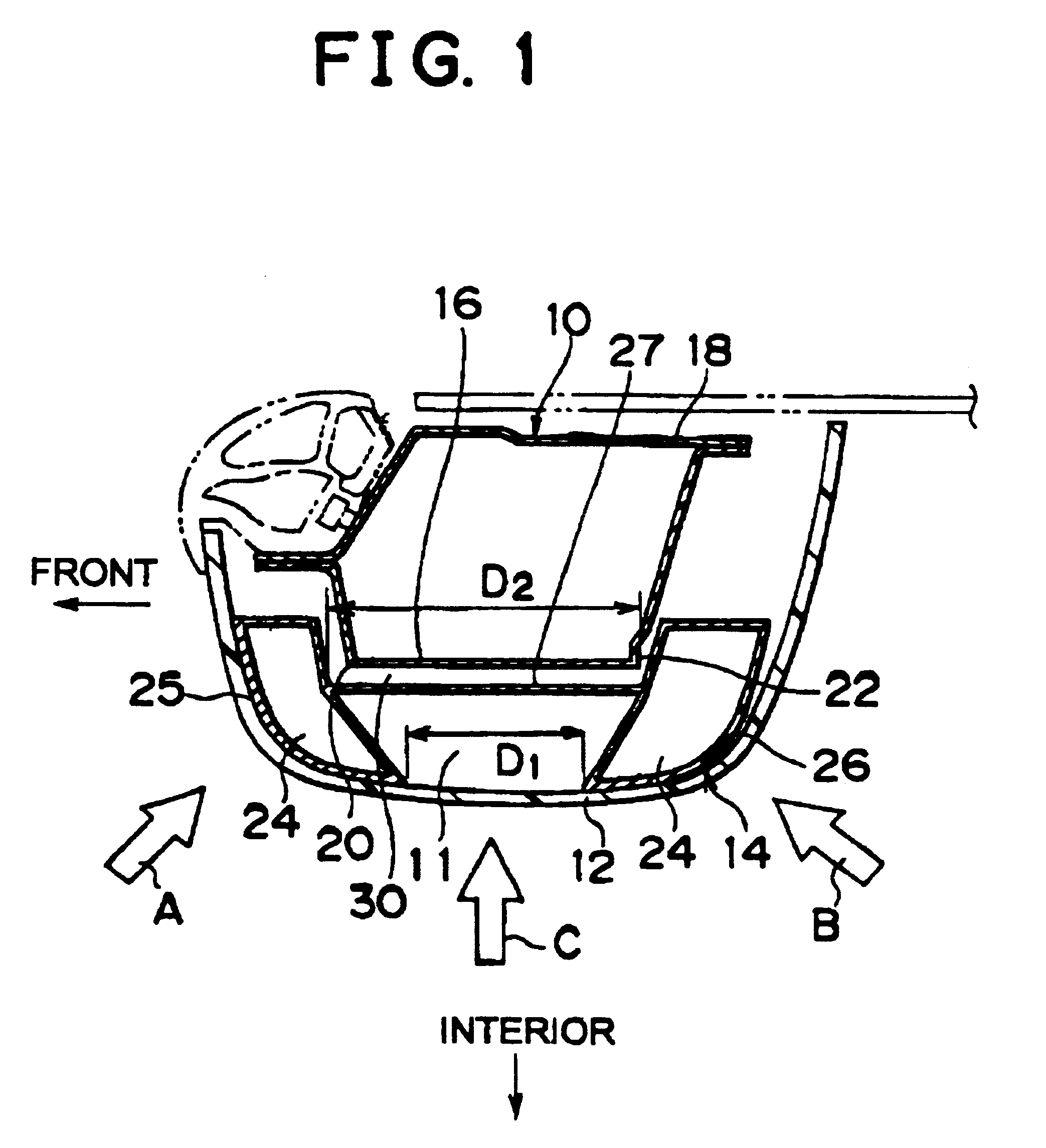
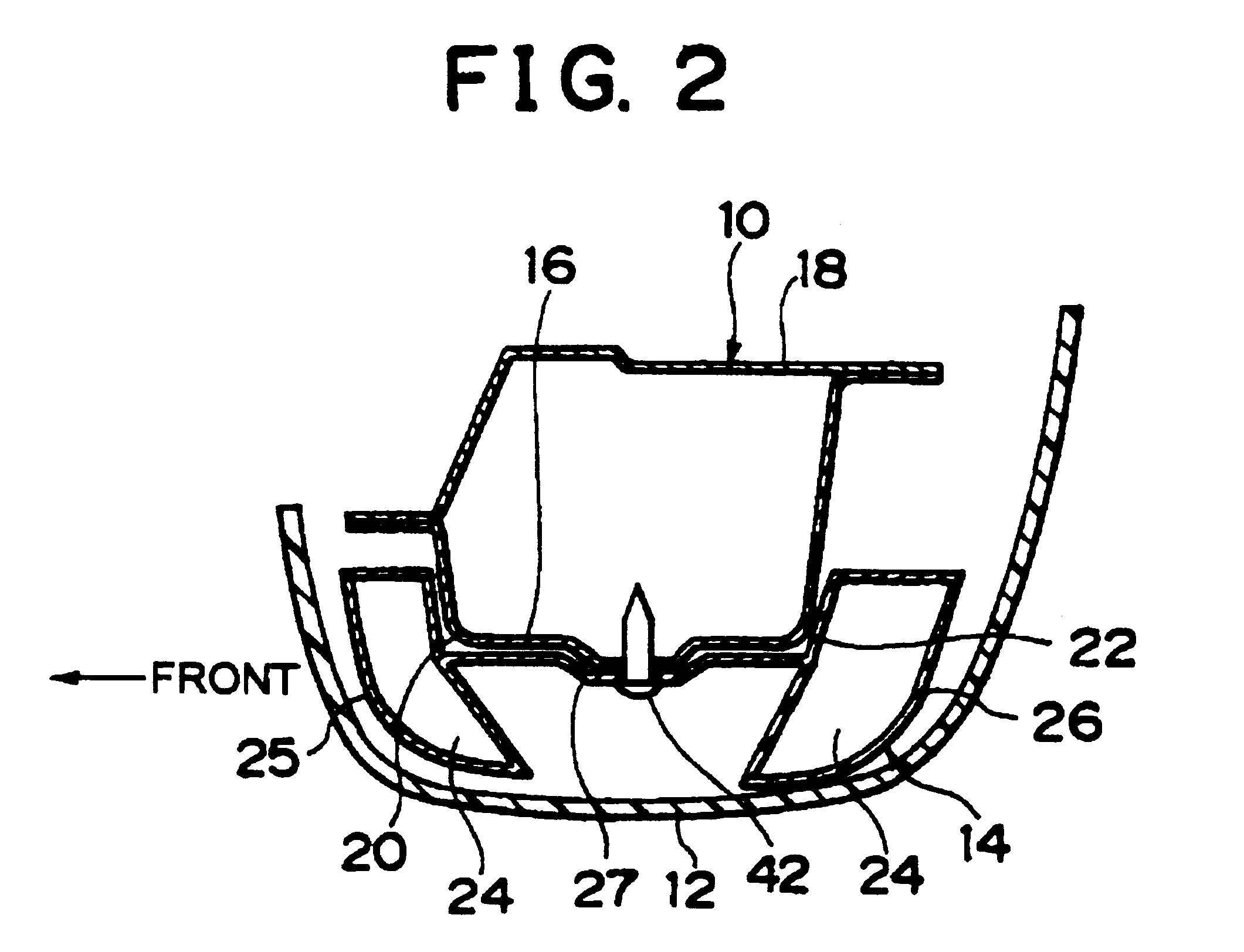
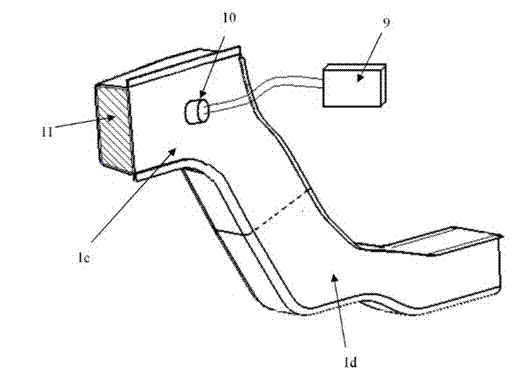
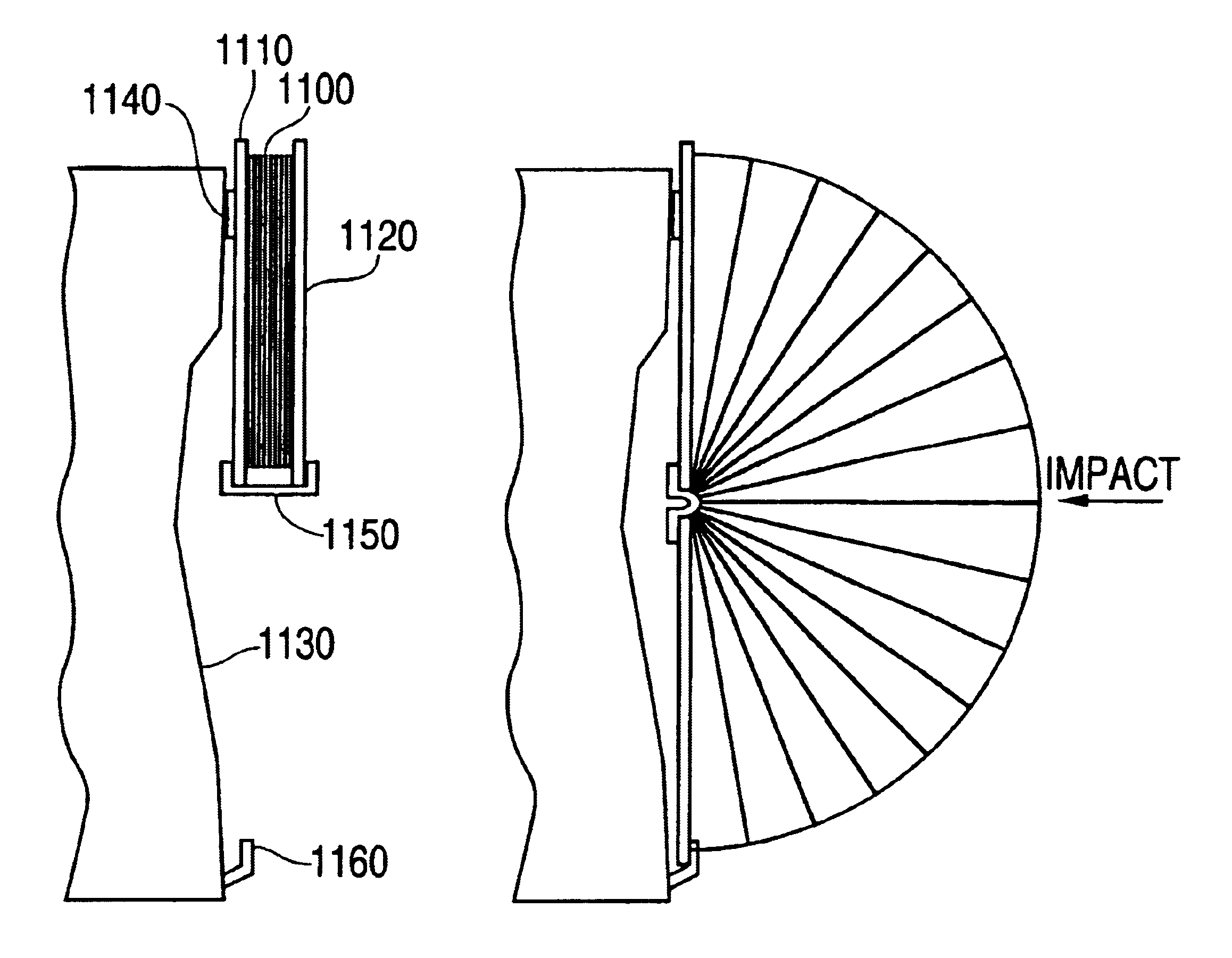
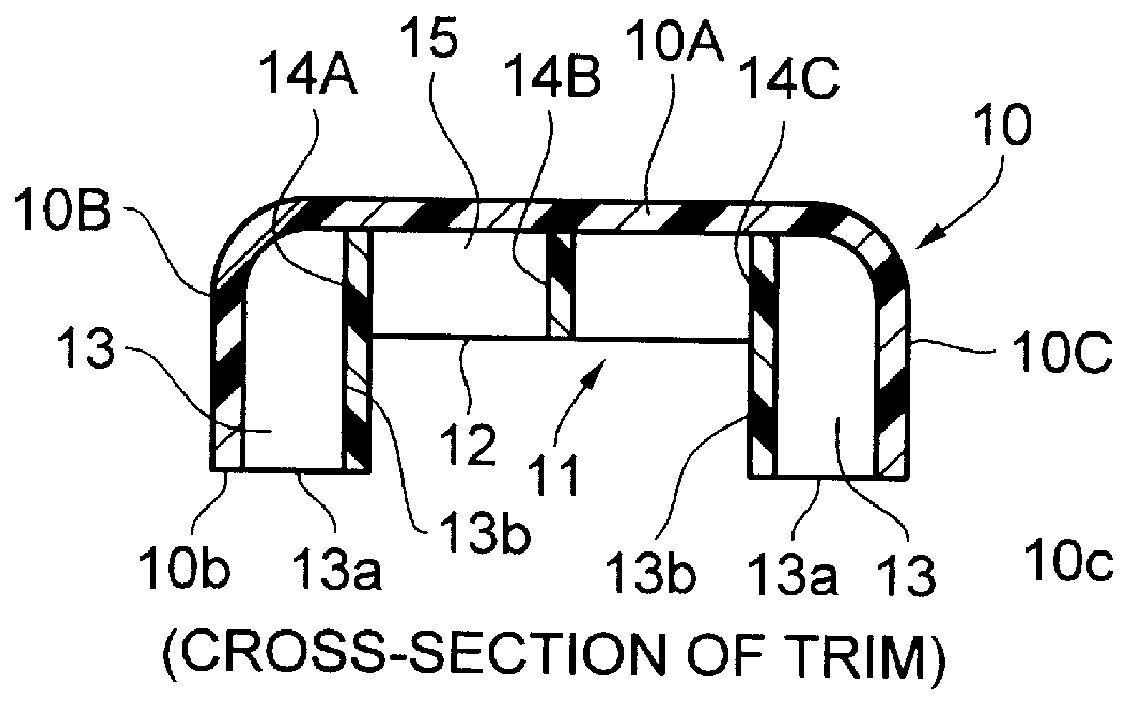
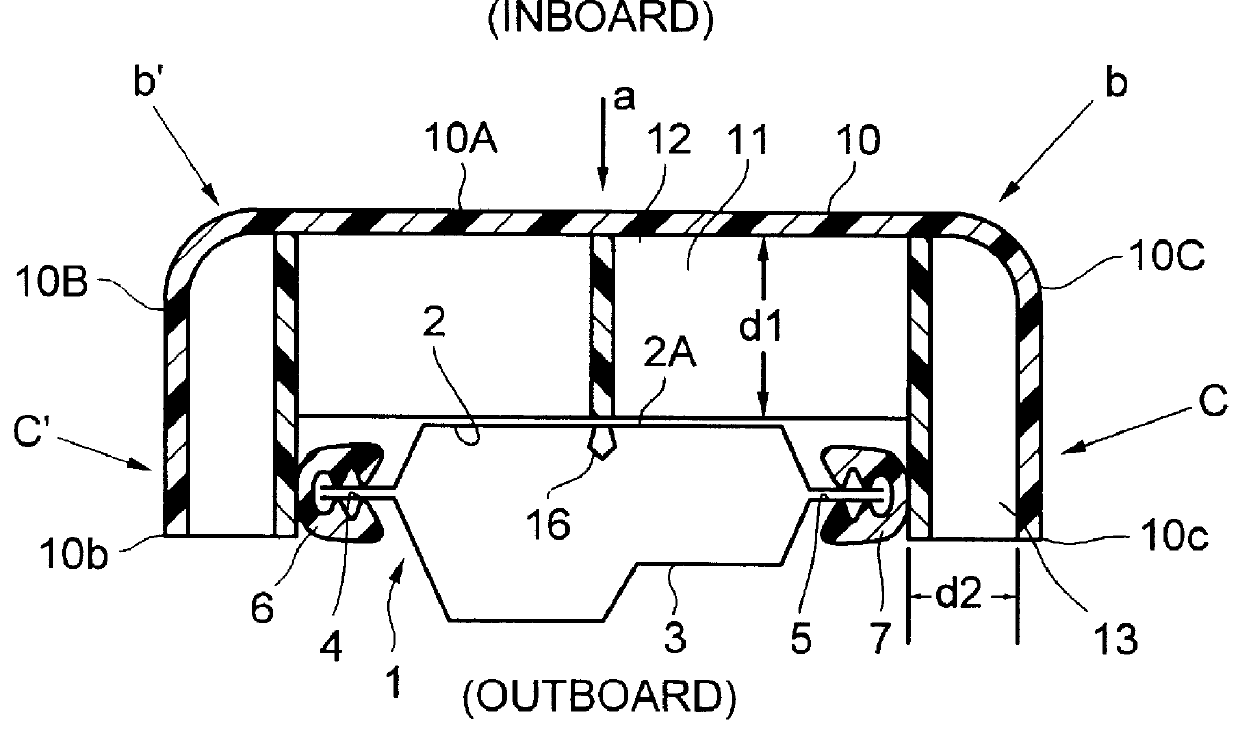
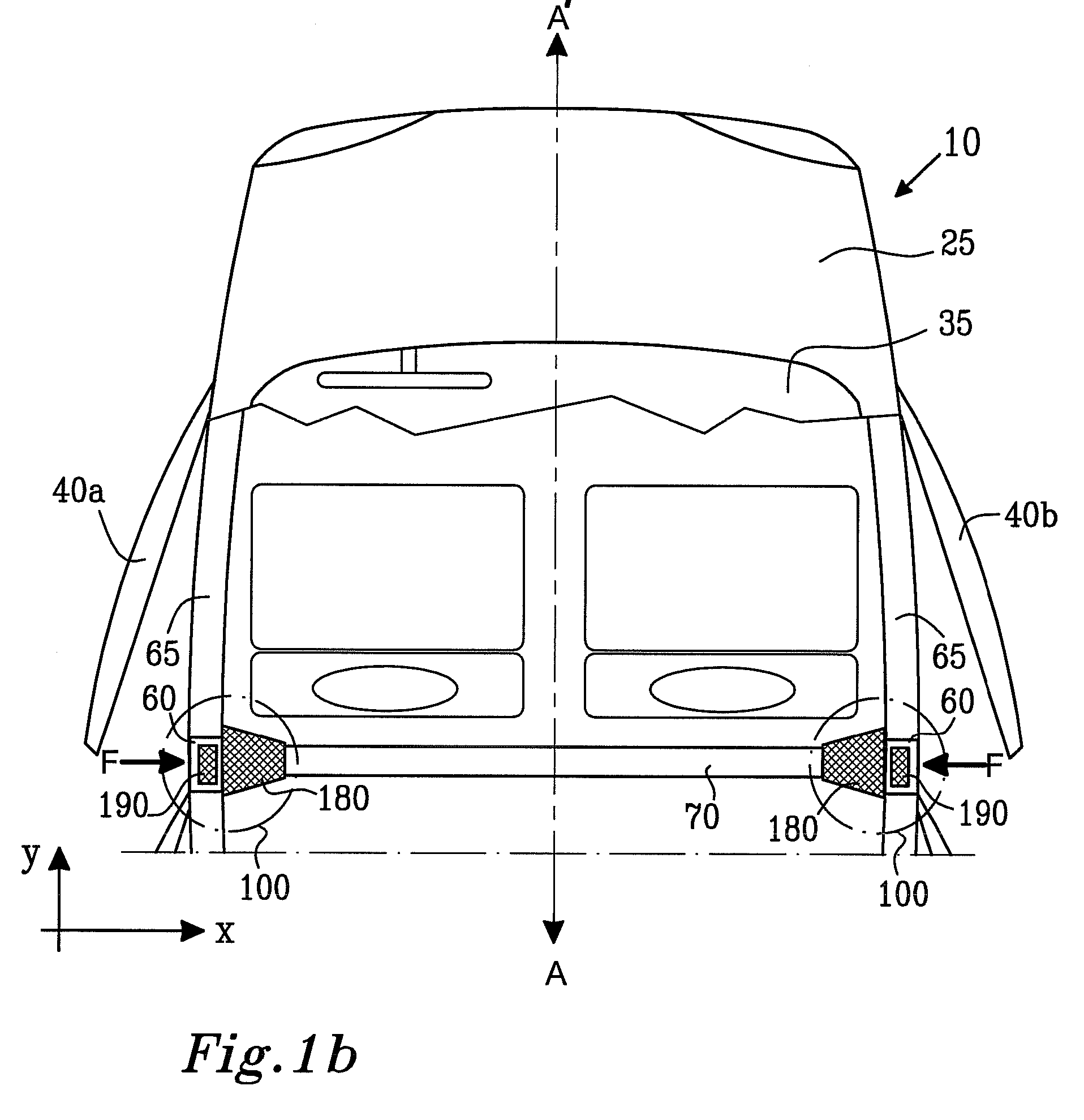
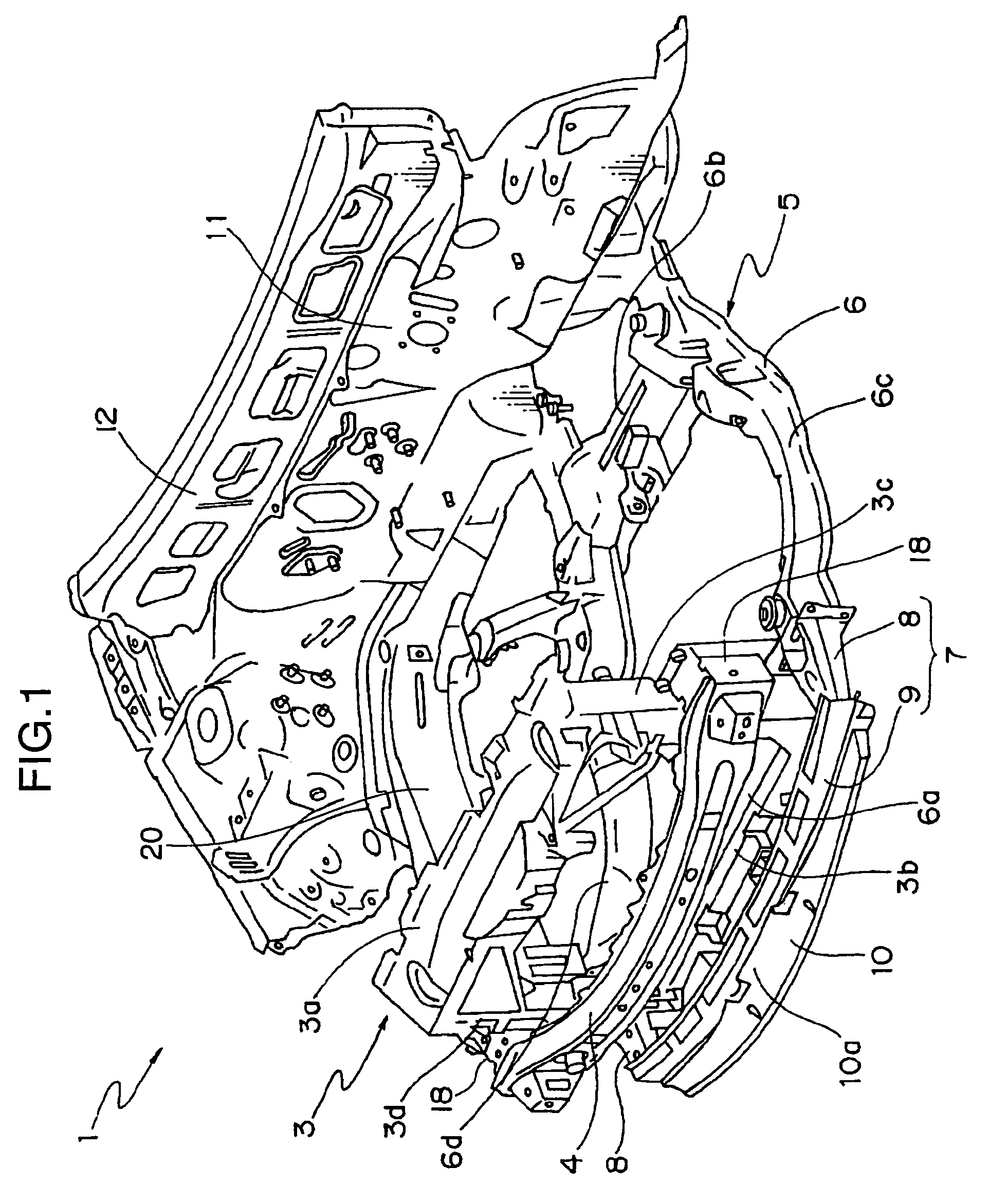
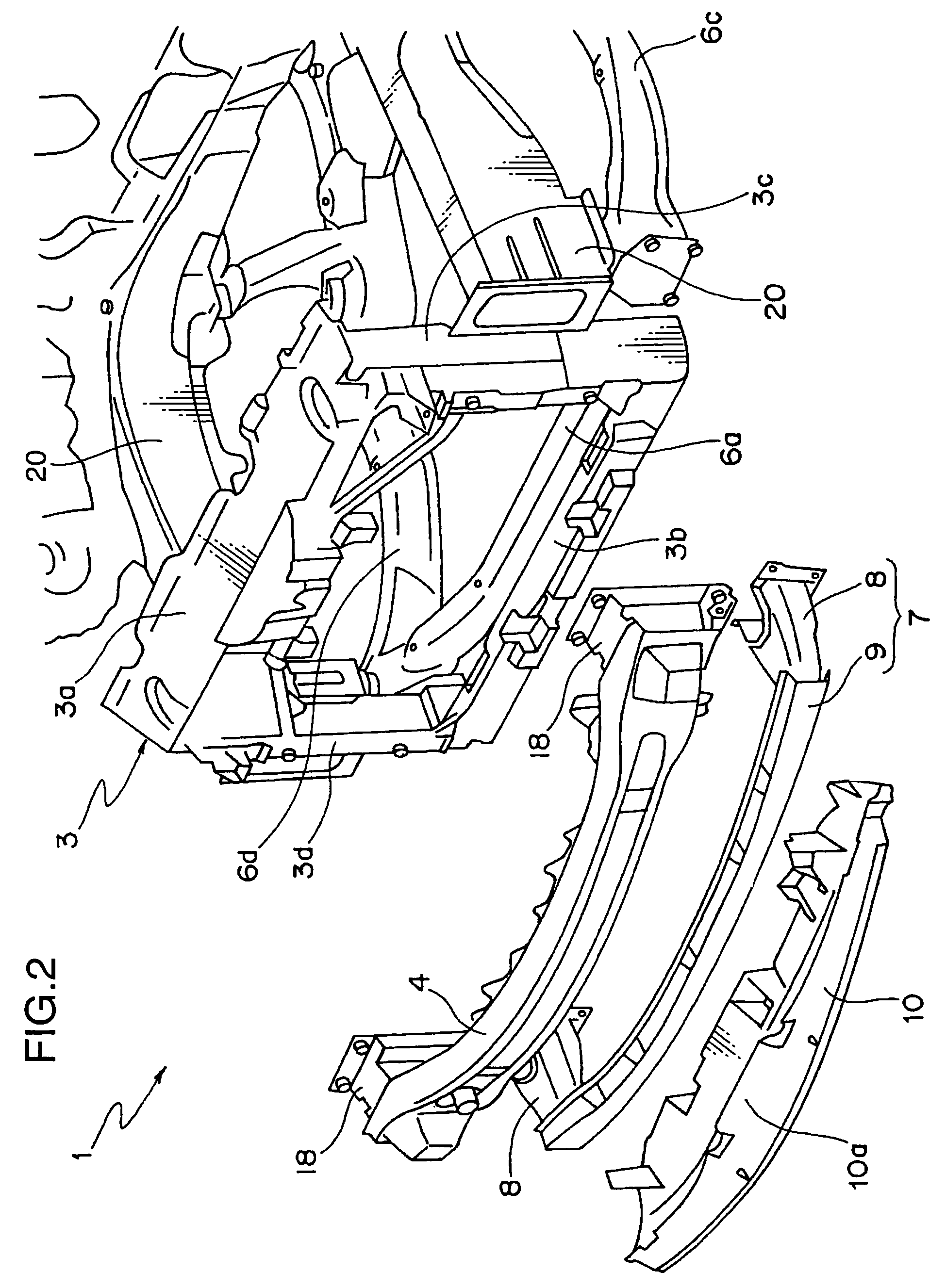
Impact energy absorbing structure for vehicle cabin
This invention relates to an impact energy absorbing structure for a cabin of an automotive vehicle. The impact energy absorbing structure is provided with a trim member (10) covering an inboard side of a structural member, which constitutes the cabin of the automotive vehicle. An impact absorbing member is interposed between the inboard side of the structural member and the trim member (10), so that impact energy directed from a surface of the trim member (10) toward the structural member can be absorbed. When an occupant of the cabin is about to hit the structural member, impact energy is damped so that the occupant can be protected. The structural member includes a pillar (1) or the like, which constitutes the cabin of the automotive vehicle. The trim member (10) is arranged to cover an inboard side of the pillar (1) or the like. Resin-made ribs (11) or the like can be mentioned as the impact absorbing member. It is possible to design the structure so that impact energy directed from the surface of the trim member (10) toward the pillar (1) or the like can be absorbed through deformation or destruction of these resin-made ribs (11).
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Impact Protection Structure
ActiveUS20070063543A1Improved side impact energy absorptionIncreased passengerVehicle seatsUnderstructuresDriver/operatorEngineering
There is provided an impact protection structure for providing impact energy absorption at a region substantially between a first transverse strengthening member and a second substantially upright strengthening member of a road vehicle. In operation, the first and second members are disposed substantially mutually perpendicularly. The impact protection structure comprises an energy absorbing block arrangement and a cover arrangement for maintaining the absorbing block arrangement substantially in position during impact. In operation, the impact protection structure is susceptible to reducing lateral damage to the road vehicle in crash or impact situations, thereby potentially increasing passenger and driver safety.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
Impact energy absorbing structure of vehicle frame member
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Bulletproof lightweight metal matrix macrocomposites with controlled structure and manufacture the same
InactiveUS20030161750A1Stop crack propagationPromote reproductionMilitary adjustmentWelding/cutting media/materialsPorosityGeometric pattern
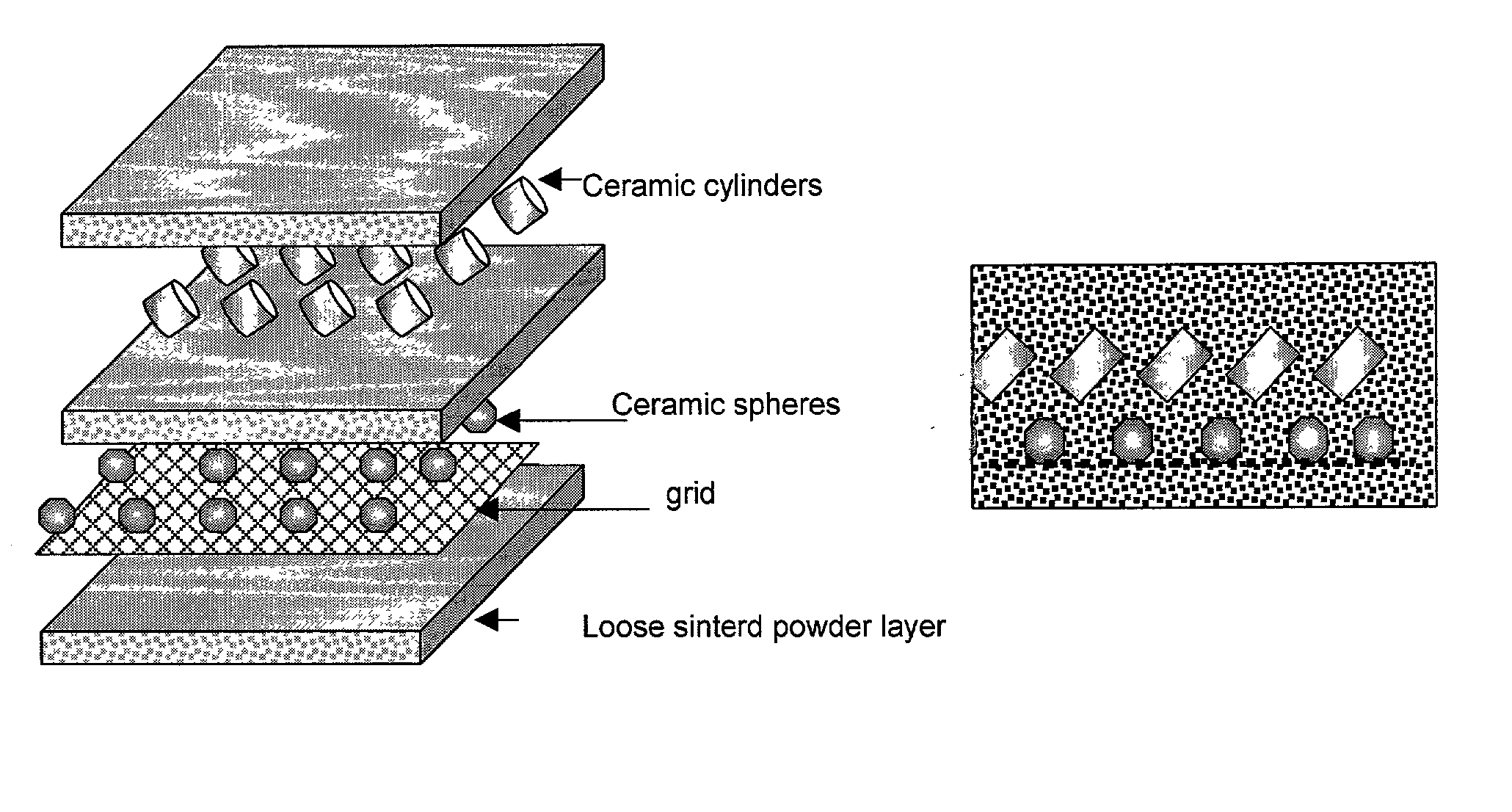
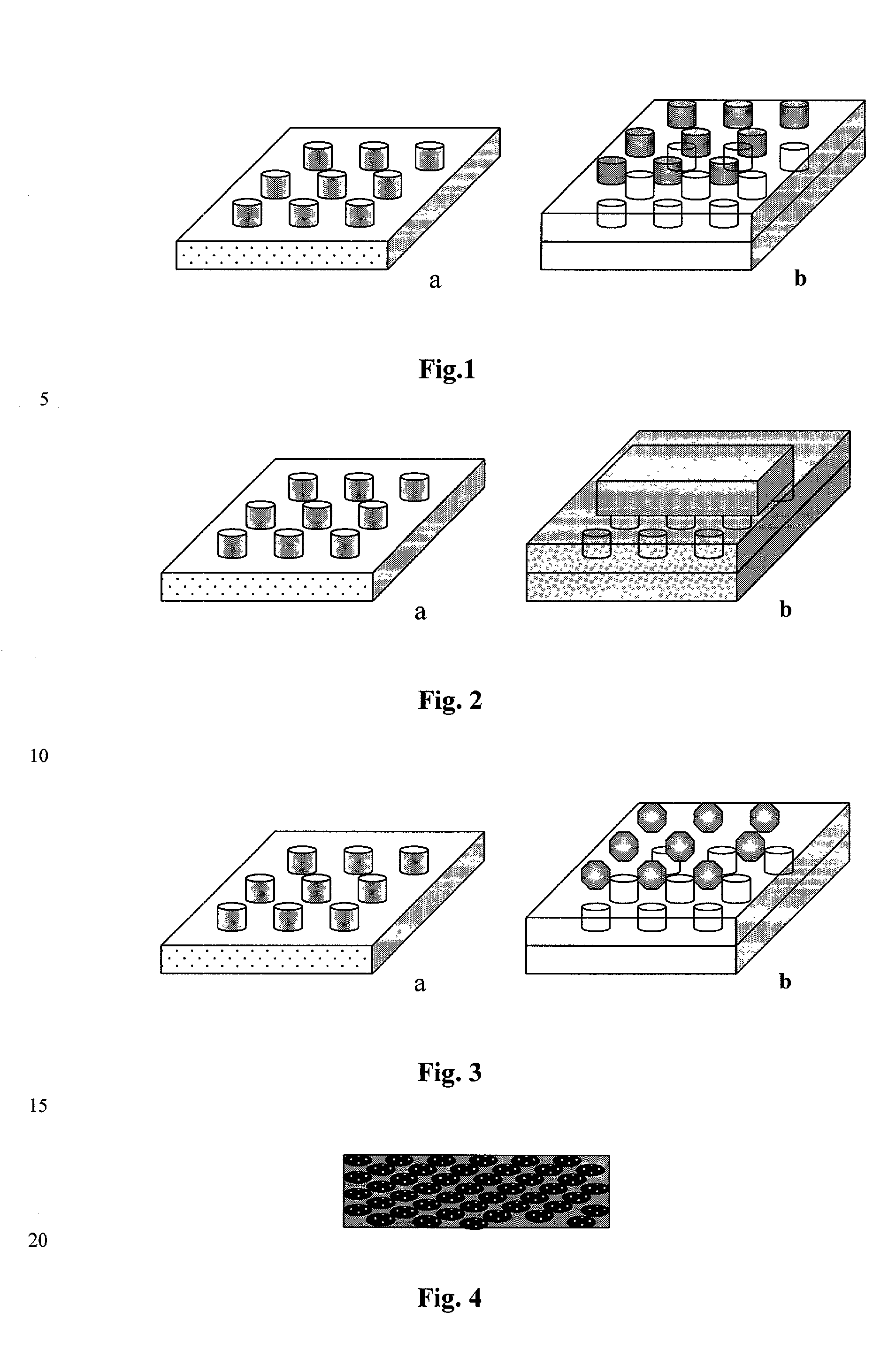
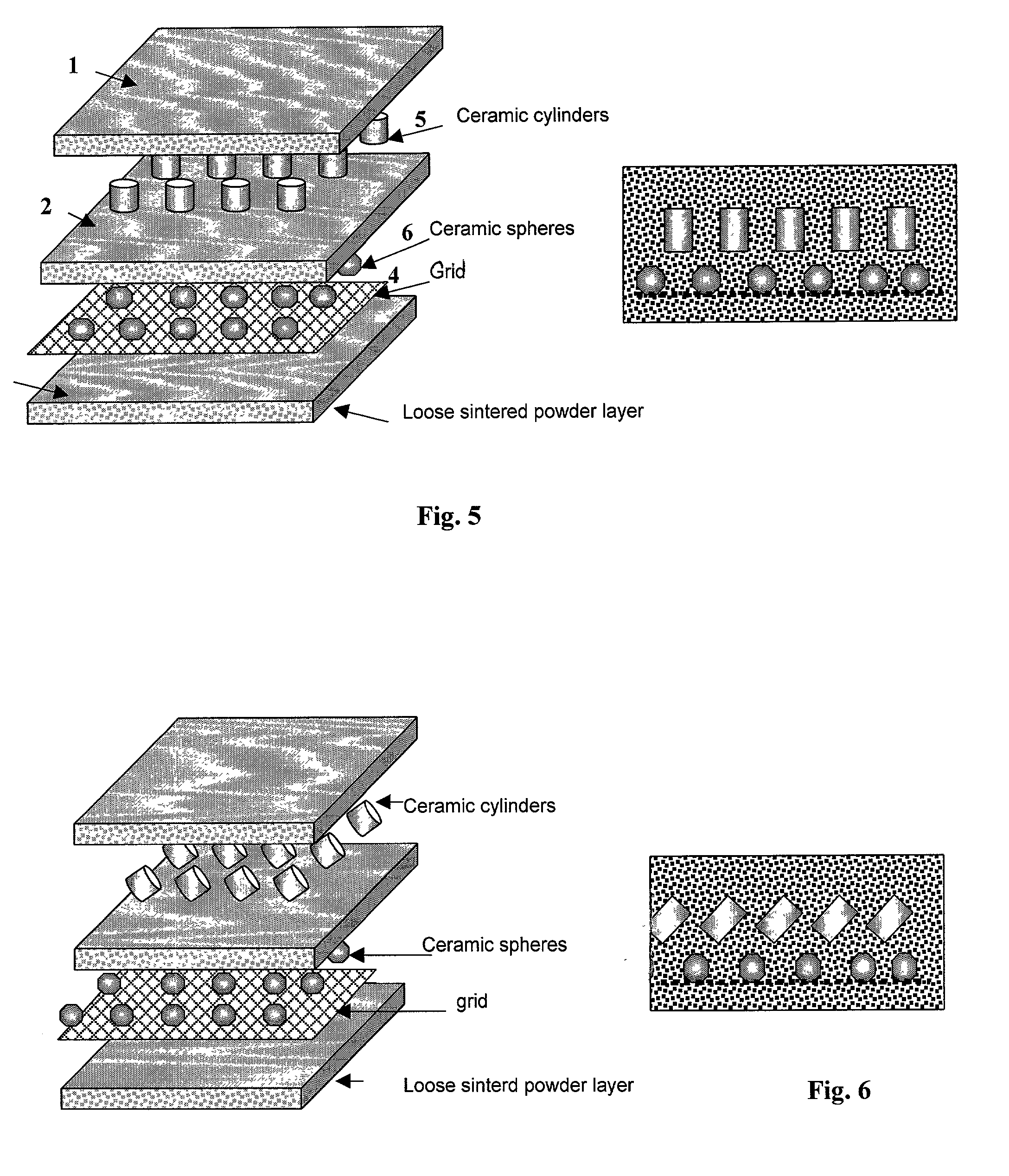
The lightweight bulletproof metal matrix macrocomposites (MMMC) contain (a) 10-99 vol. % of permeable skeleton structure of titanium, titanium aluminide, Ti-based alloys, and / or mixtures thereof infiltrated with low-melting metal selected from Al, Mg, or their alloys, and (b) 1-90 vol. % of ceramic and / or metal inserts positioned within said skeleton, whereby a normal projection area of each of said inserts is equal to or larger than the cross-section area of a bullet or a projectile body. The MMMC are manufactured as flat or solid-shaped, double-layer, or multi-layer articles containing the same inserts or different inserts in each layer, whereby insert projections of each layer cover spaces between inserts of the underlying layer. The infiltrated metal contains 1-70 wt. % of Al and Mg in the balance, optionally, alloyed with Ti, Si, Zr, Nb, V, as well as with 0-3 wt. % of TiB2, SiC, or Si3N4 sub-micron powders, to promote infiltrating and wetting by Al-containing alloys. The manufacture includes (a) forming the permeable metal powder and inserts into the skeleton-structured preform by positioning inserts in the powder followed by loose sintering in vacuum to provide the average porosity of 20-70%, (b) heating and infiltrating the porous preform with molten infiltrating metal for 10-40 min at 450-750° C., (c) hot isostatic pressing of the infiltrated composite, and (d) re-sintering or diffusion annealing. The positioning of the ceramic inserts in Ti-based powder is carried out by using a metal grid aiding the placement of inserts in a predetermined geometric pattern, and said grid becomes the integral part of the macrocomposite material. The technology is suitable for the manufacture of flat or shaped metal matrix macrocomposites having improved ductility and impact energy absorption such as lightweight bulletproof plates and sheets for airplane, helicopter, and automotive applications.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Protective headgear with improved shell construction
The protective helmet includes a rigid outer shell where the shell includes an undulating cross-sectional profile. A layer of impact-energy-absorbing material is positioned adjacent to the shell. The undulating profile of the shell can be any type of load spreading undulating profile, such as that of a sinusoidal or triangular wave configuration. The undulating load-spreading profile can be on the inner surface of the shell, on the outer surface of the shell or the entire cross-section of the shell may be undulating. The unique undulating profile makes the shell more rigid and spreads the impact load across the surface of the shell to thereby spread the deformation of the padding layer to prevent the shell from bottoming out of the impact-energy-absorbing material during an impact. As a result, a safer and more effective protective helmet is provided.
Owner:CRISCO JOSEPH J
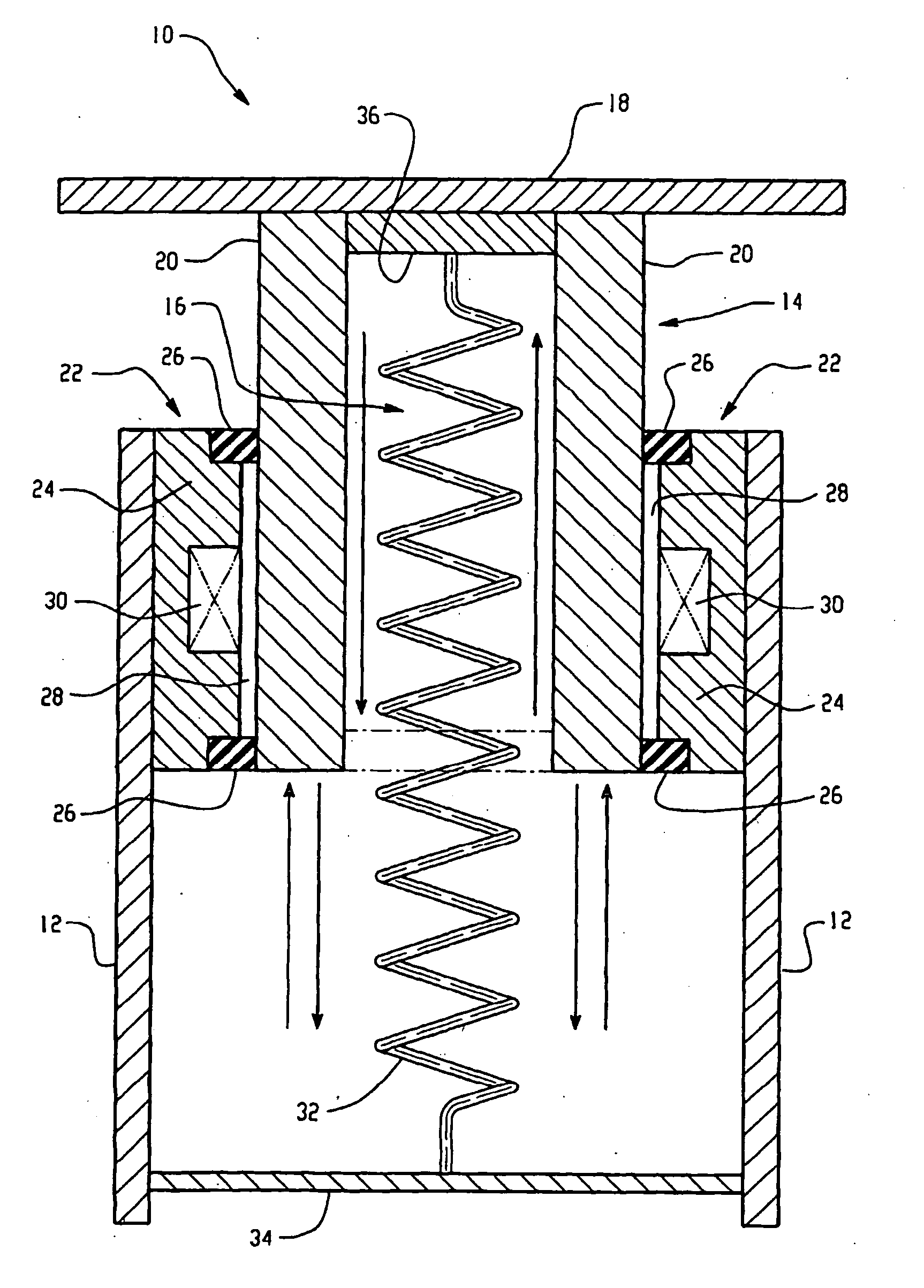
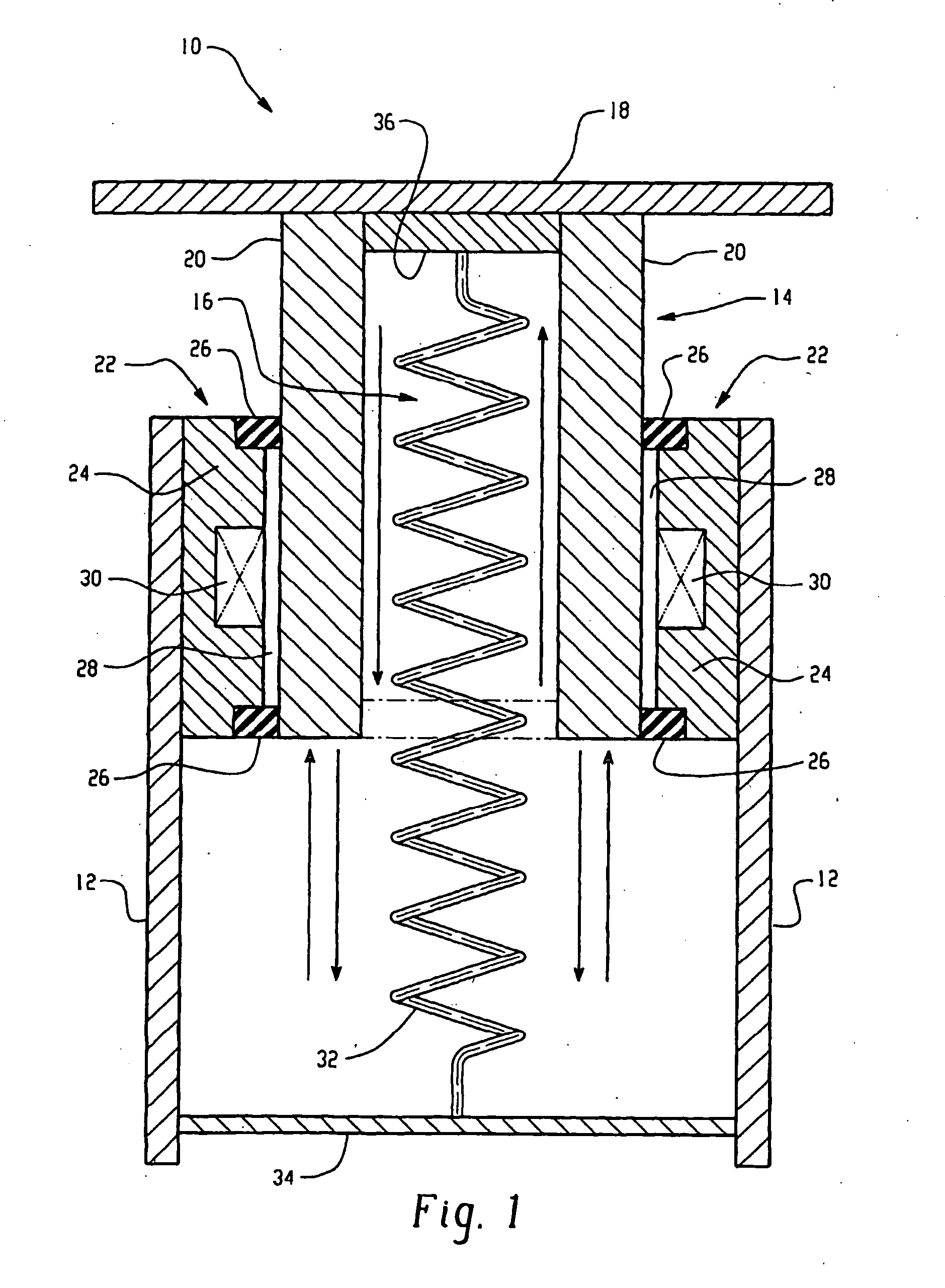
Impact energy absorber and process
ActiveUS20050087410A1SpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic currentMagnetorheological fluid
A tunable and reusable impact energy absorbing system and process includes a control structure comprising a sleeve having an outer surface fixedly attached to a chassis, a seal at each end of the sleeve, a magnetorheological fluid disposed between the seals, and a coil in proximity to the magnetorheological fluid, wherein the seal and the magnetorheological fluid are in sliding engagement with a support member, wherein the impact surface is fixedly attached to a support member. Varying the current to the coil alters the magnetic field upon the magnetorheological fluid, which can be used to tune the yield stress of the sliding engagement.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
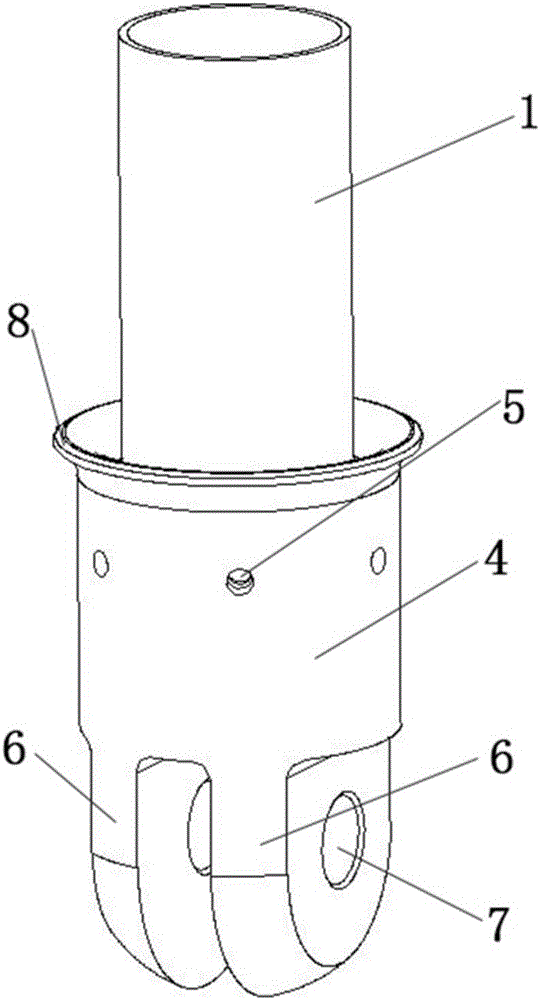
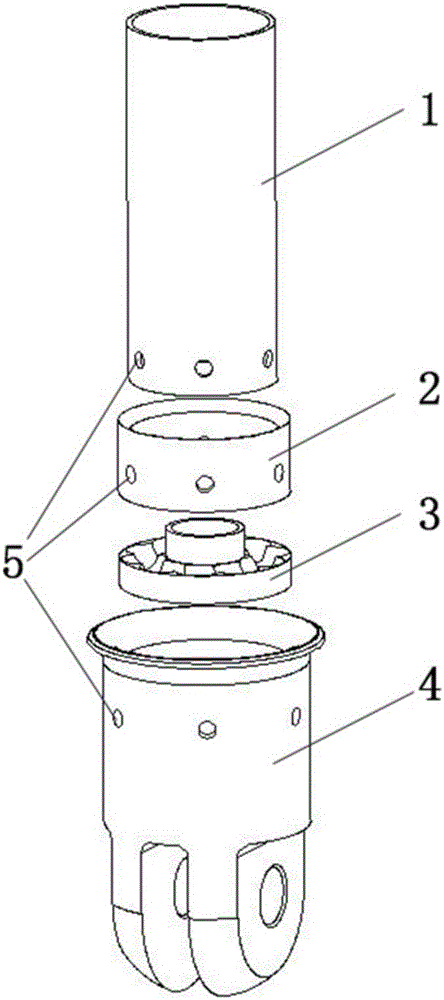
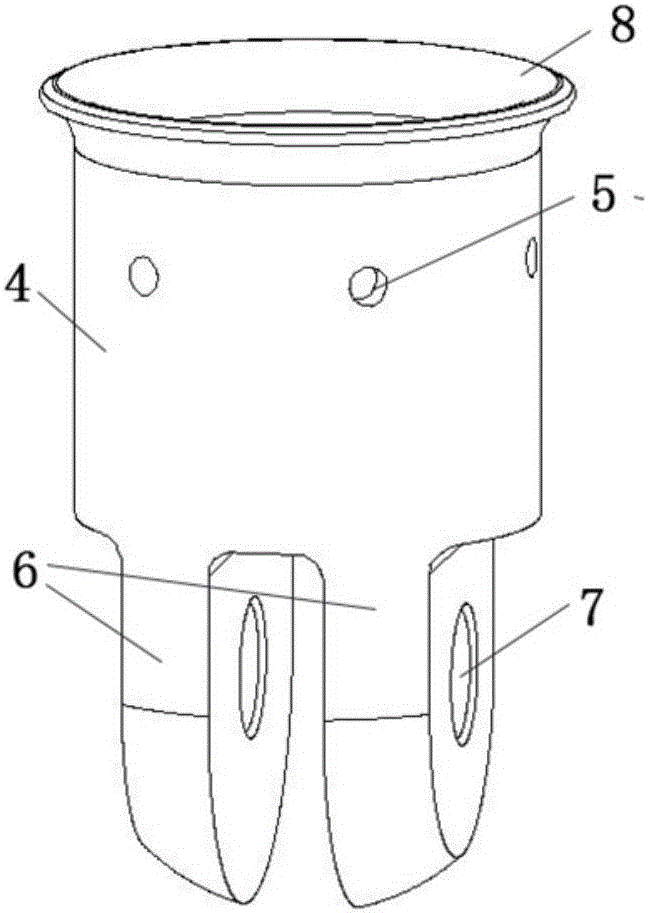
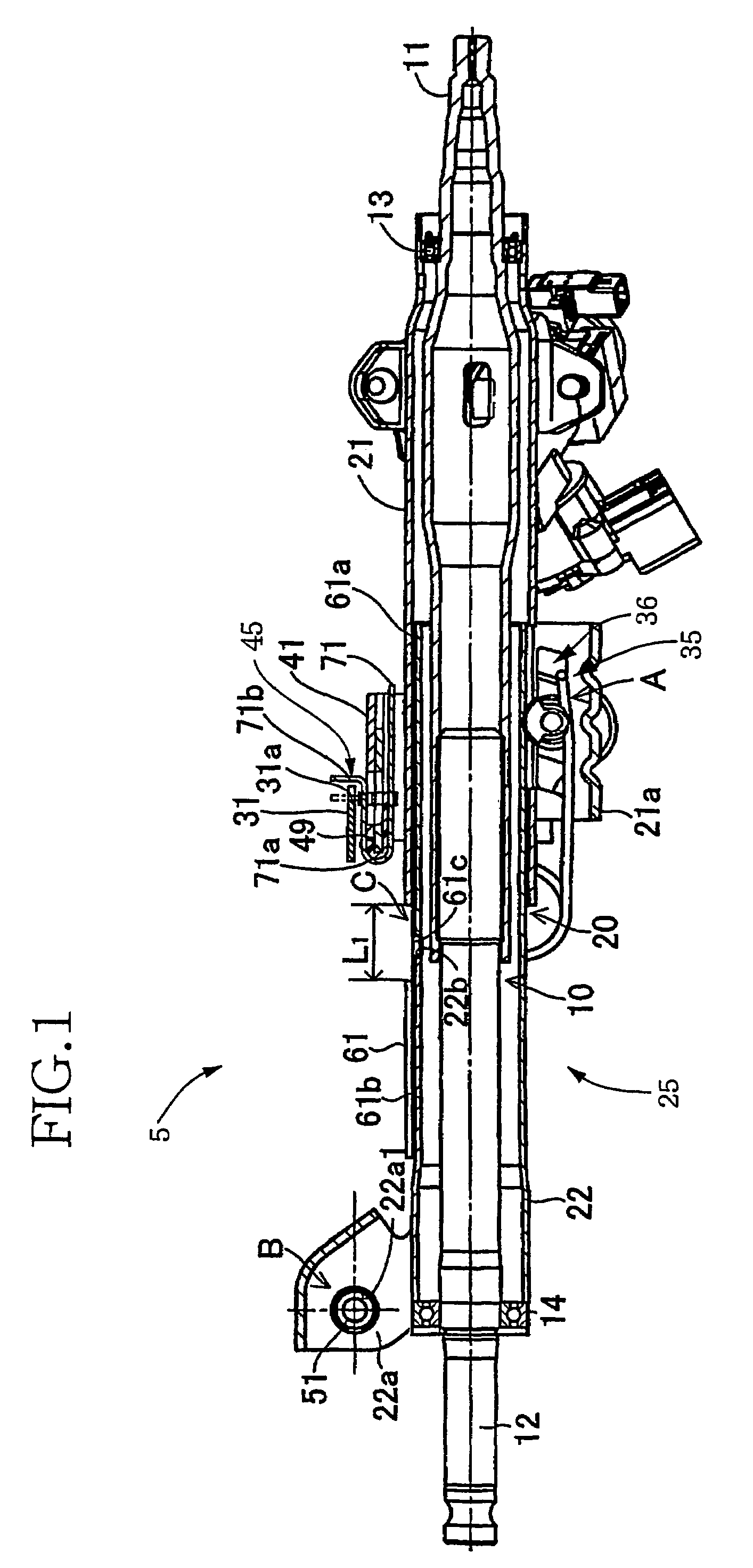
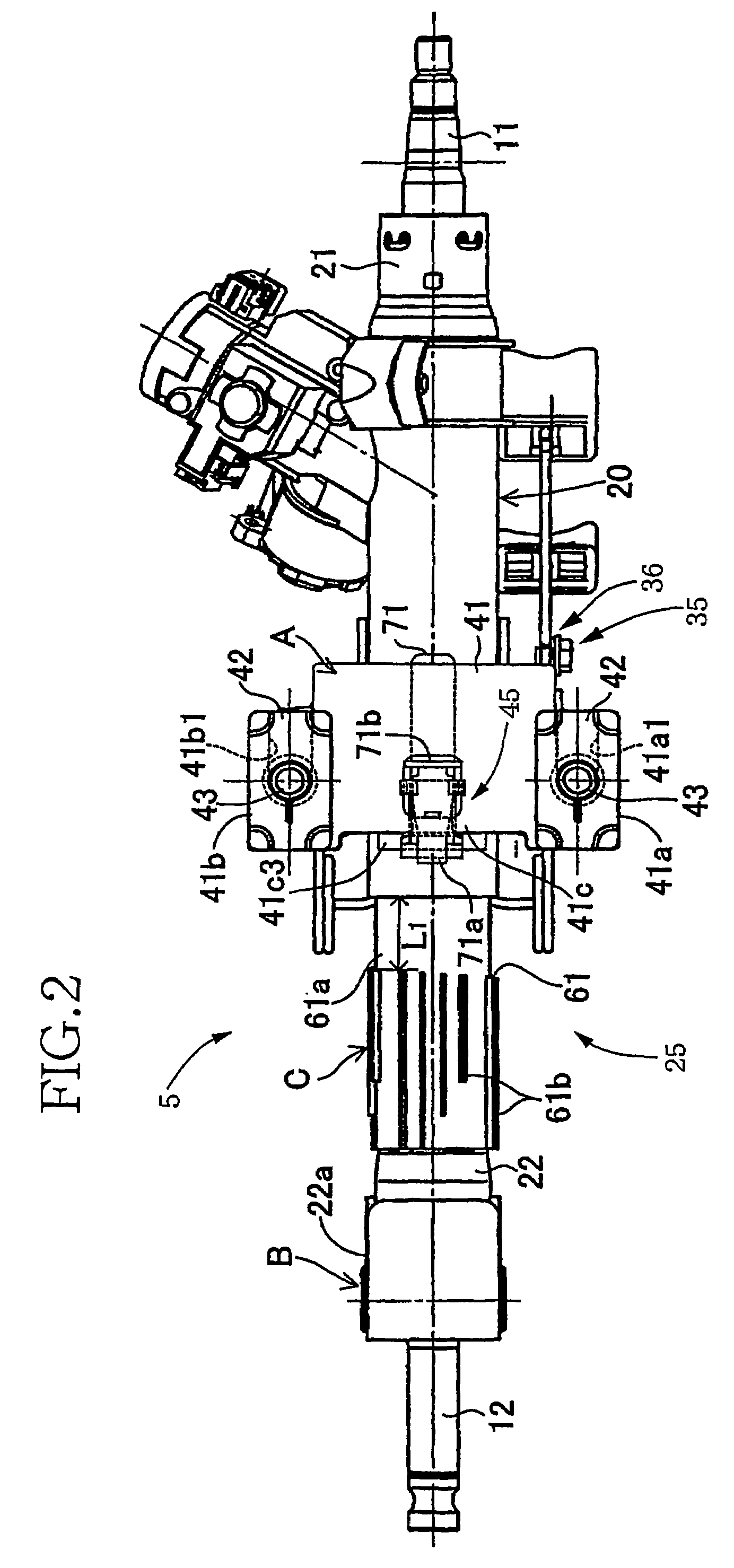
Steering column of vehicle having collision energy absorbing apparatus
InactiveCN101274638ALow costStrong impactPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSteering columnsSteering columnEngineering
Disclosed is a steering column of a vehicle having a collision energy absorbing apparatus. The steering column includes: a hollow tube having a steering shaft disposed in the hollow tube; a plate bracket surrounding an outer peripheral surface of the tube and having guide grooves formed on a top part of the plate bracket; a reinforcing member for reinforcing and supporting the plate bracket, the reinforcing member being coupled to the tube and being provided within the plate bracket; and a mounting bracket having impact-absorbing guide members inserted in the guide grooves and fixing holes formed on both sides of the mounting bracket for fixing the mounting bracket to a chassis.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Vehicle front structure
InactiveUS7438348B2Sufficient pedestrian protection performanceImpact capacityVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVehicle framePedestrian
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Impact energy absorbing crash cushion
A crash cushion including a cushion filled with material; and a back plate including at least one recess communicating with a back of the cushion such that material from the cushion fills the recess; wherein the back plate is configured so that when a force is applied to said cushion, the material within the at least one recess breaks a portion of the bumper plate and exits the recess. A crash cushion including a cushion filled with material; a back plate, including at least one opening communicating with a back of the cushion such that the material from the cushion is capable of filling the recess; and at least one valve; wherein the at least one valve is configured so that when a force is applied to the cushion, a portion of the material within the cushion opens the valve and exits the cushion.
Owner:AKAD OSMAN E
Filling structure
InactiveUS20050058787A1Speed up the flowIncrease volumeEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsFilling materialsEngineering
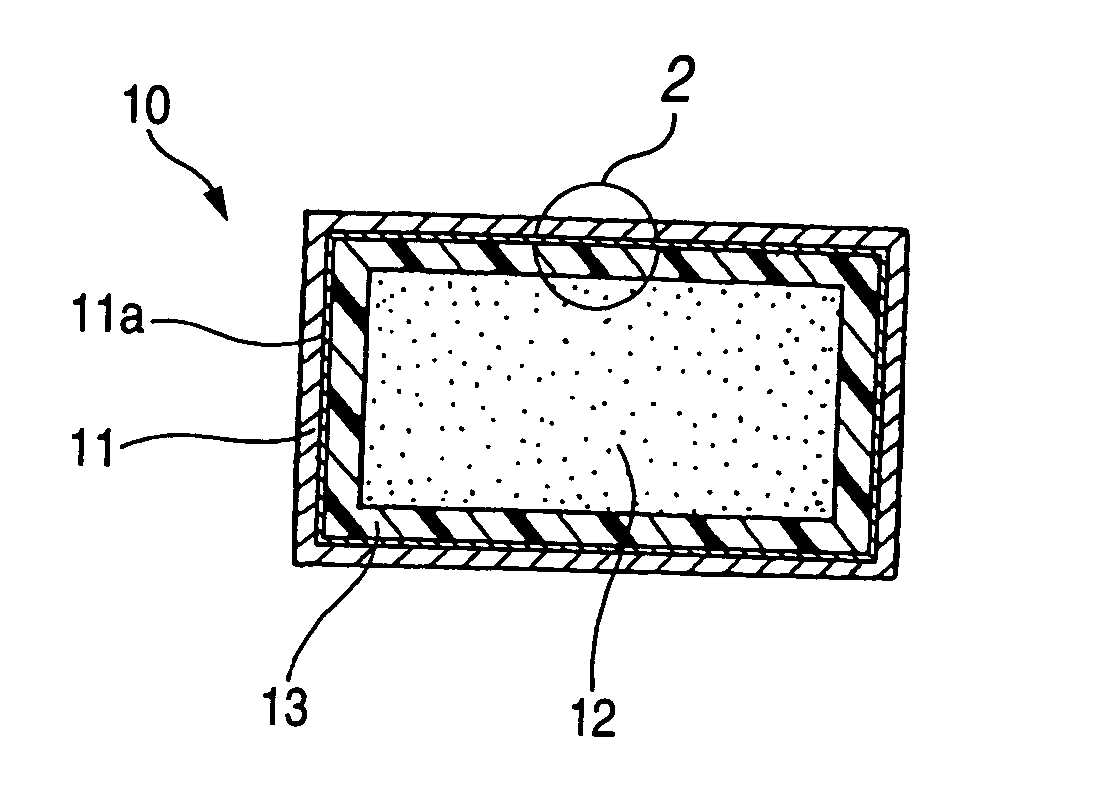
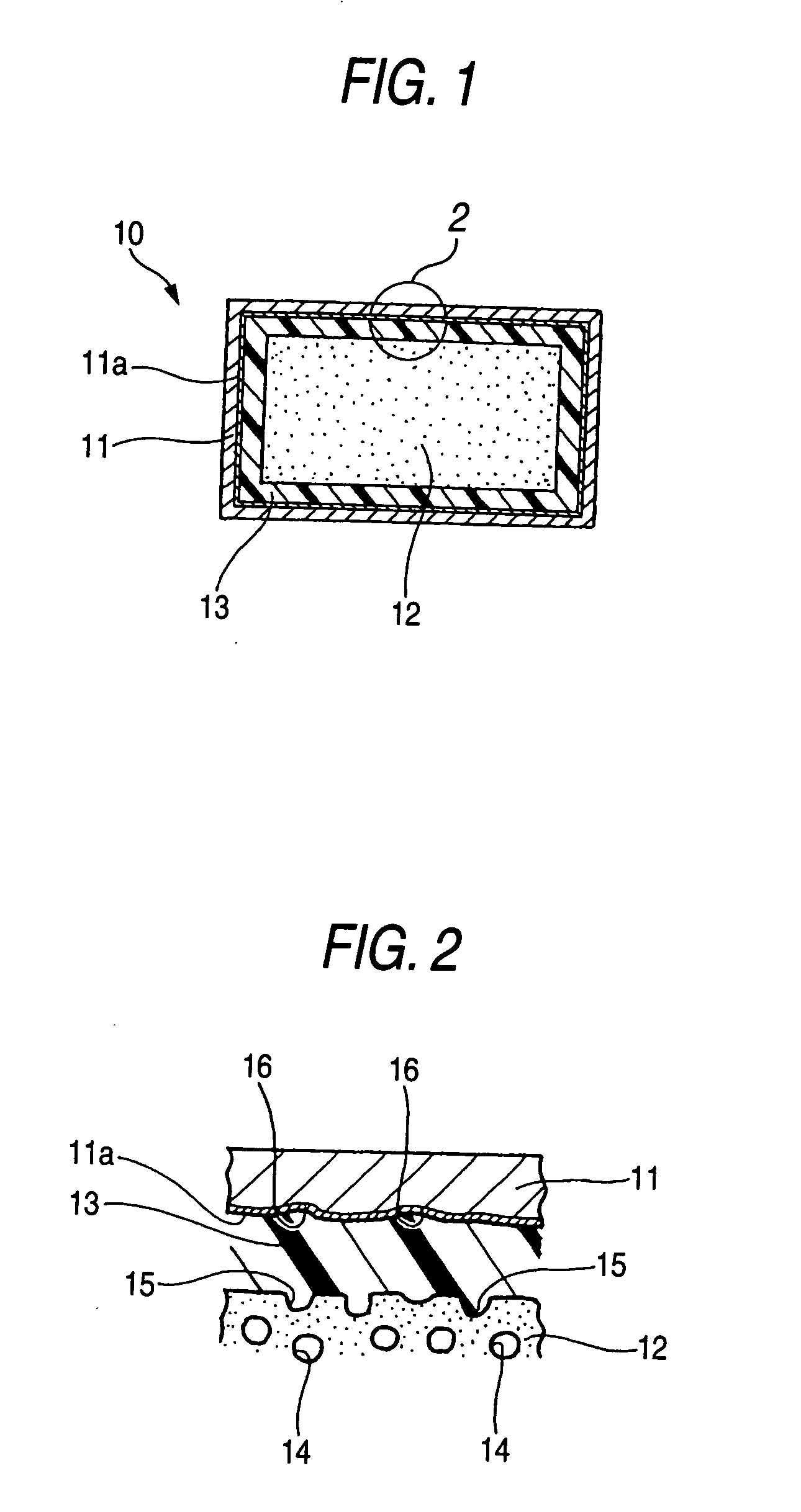
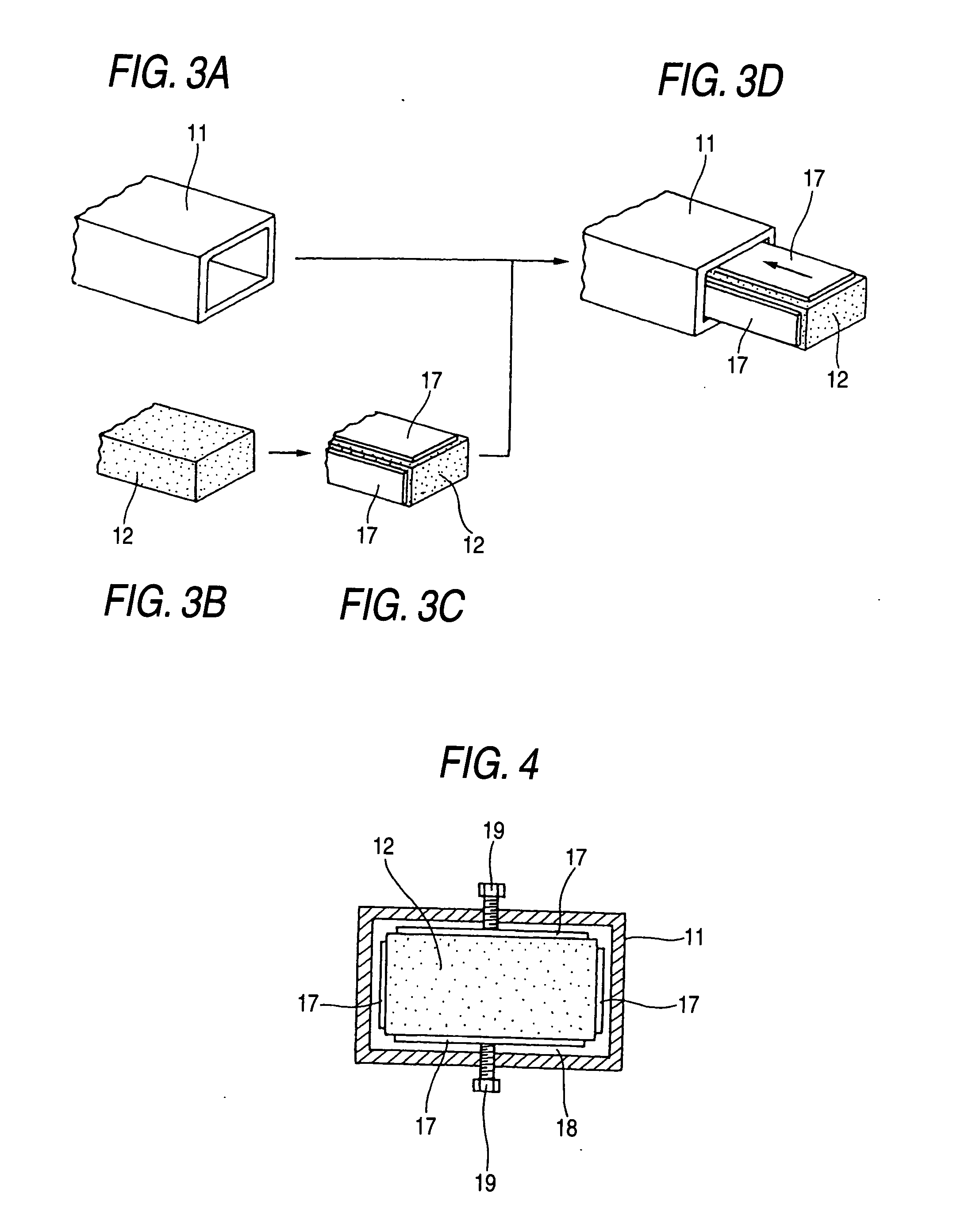
A filling structure 10 is a structure in which a filling material 12 having a higher impact energy absorbing performance is inserted into the inner part of a hollow member 11, and the filling material 12 so inserted is fixed to the hollow member 11 with an adhesive layer 13 resulting when the filling material 12 is heated to expand and is cooled to set thereafter.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Shock absorber for vehicles
InactiveUS20040084820A1High shock-energy absorbing characteristicIncrease volumeNon-rotating vibration suppressionPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringHollow form
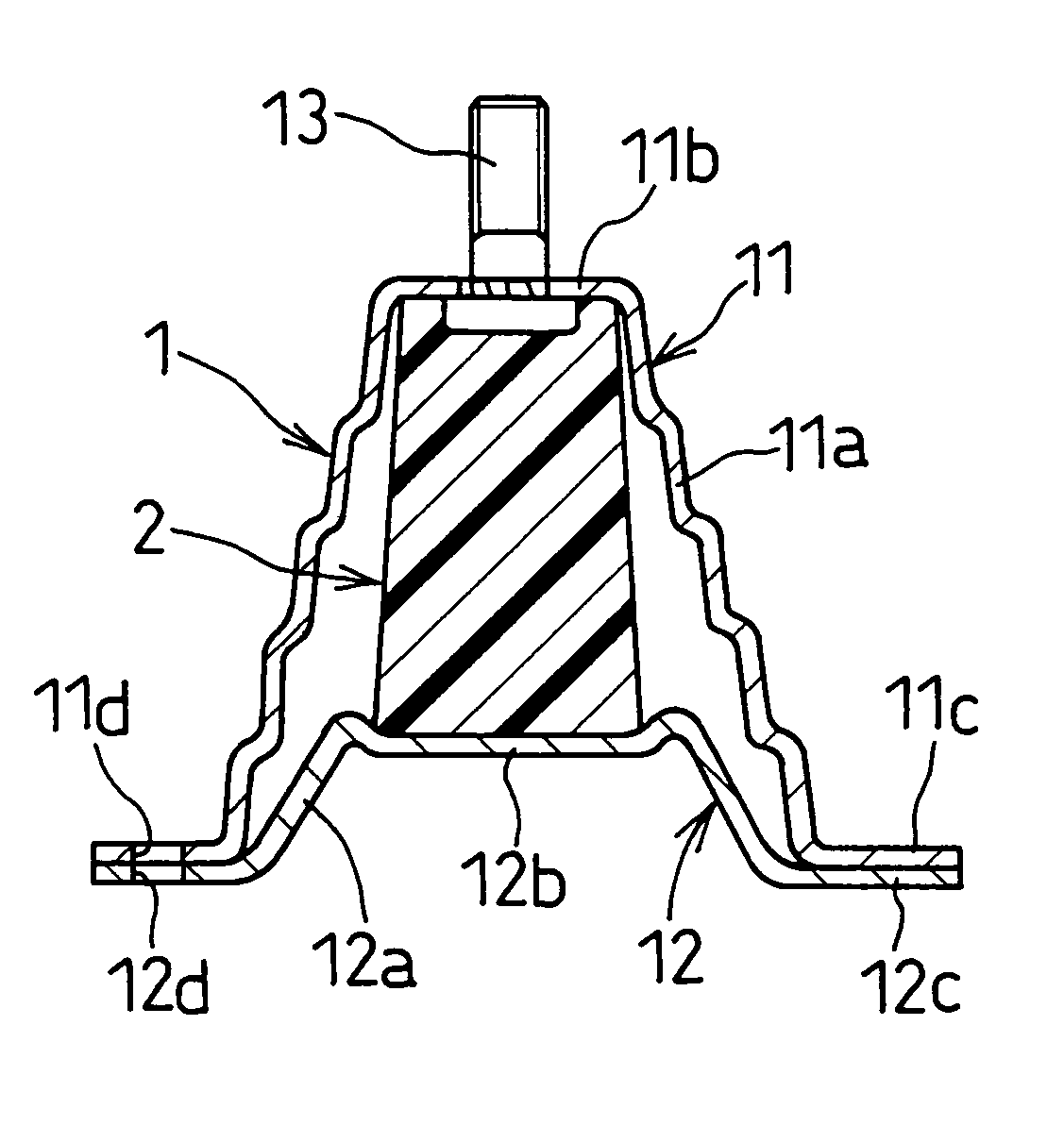
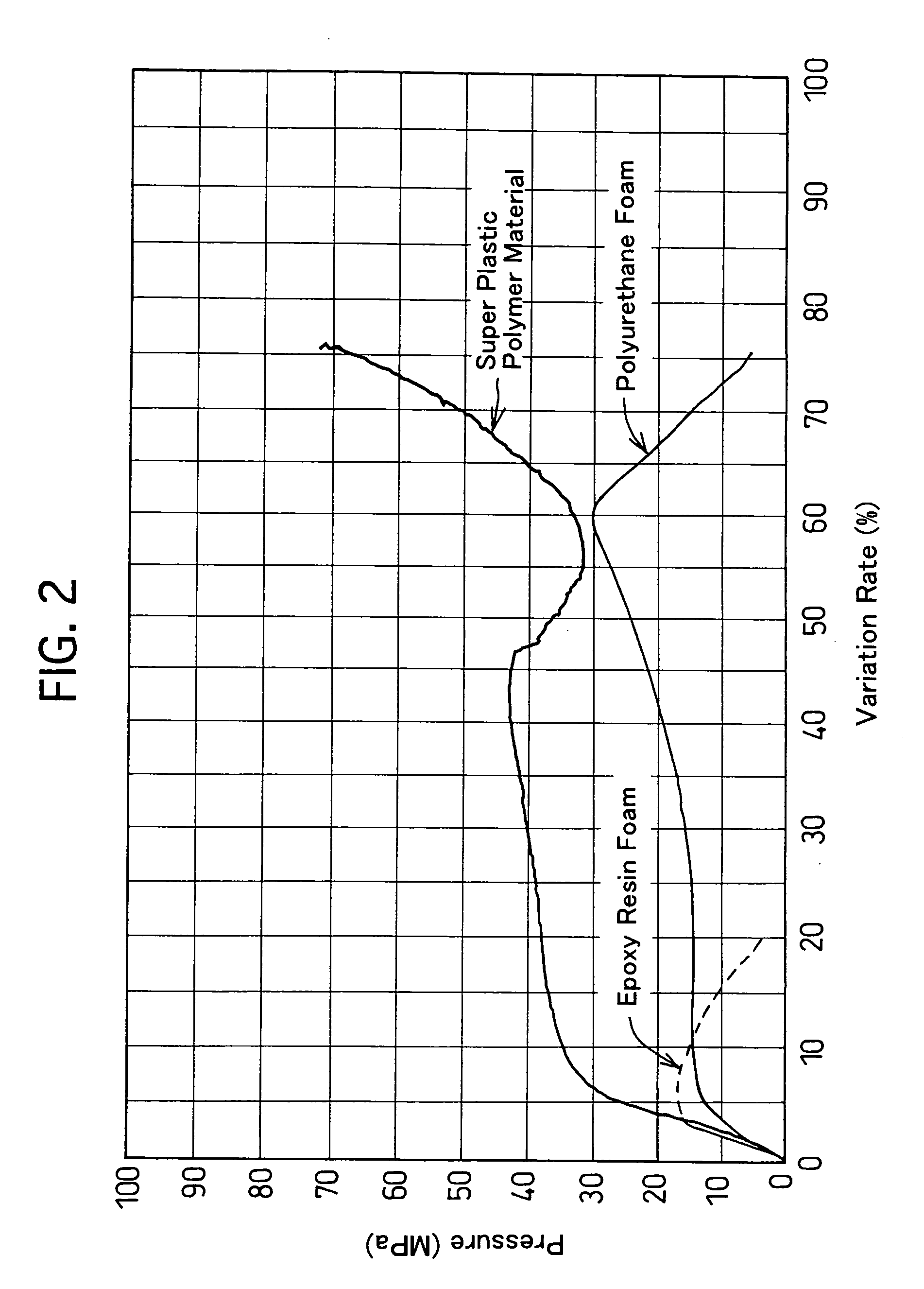
A vehicle shock absorber includes a housing, and a shock-absorbing member. The housing has at least one hollow formed therein, is formed of a rigid material, and is fixed to a bone structural member of vehicles. The shock-energy absorbing member is disposed in the hollow of the housing at least, and is formed of a super plastic polymer material. The super plastic polymer material exhibits a tensile breaking elongation of 200% or more, a yield strength of 20 MPa or more with respect to a predetermined strain, and a tensile elastic modulus of 400 MPa or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
Method for machining high-strength steel hot stamping formed parts
ActiveCN103878237AFlexible controlFlexible trimmingIncreasing energy efficiencyHot stampingHigh intensity
The invention discloses a method for machining high-strength steel hot stamping formed parts. The main principle of the machining method is that partial tempering or annealing processing is carried out on the hot stamping formed parts with the uniform performance, gradient changes of the tempering or annealing temperature are achieved through heat conduction of a board, gradient changes of the performance are achieved, and the partial trimming and hole punching performance and the impact performance of the parts are improved on the premise that the high strength is kept on other portions. The method includes the implementation steps of according to three-dimensional structures of a trimming and hole punching region and an impact energy absorption region, designing corresponding high-frequency induction heating coils, partially tempering or annealing the trimming and hole punching region and the impact energy absorption region to enable the trimming and hole punching region and the impact energy absorption region to be at certain temperature, achieving the gradient changes of the tempering or annealing temperature, carrying out air cooling on the partially-tempered or partially-annealed parts to enable the partially-tempered or partially-annealed parts to be at certain temperature, and finally and rapidly moving the air-cooled hot stamping formed parts to a trimming and hole punching mold to carry out mold trimming and hole punching.
Owner:吉林省正轩车架有限公司
1000 MPa-level high-strength high-plasticity aluminum-containing medium manganese steel and manufacturing method thereof
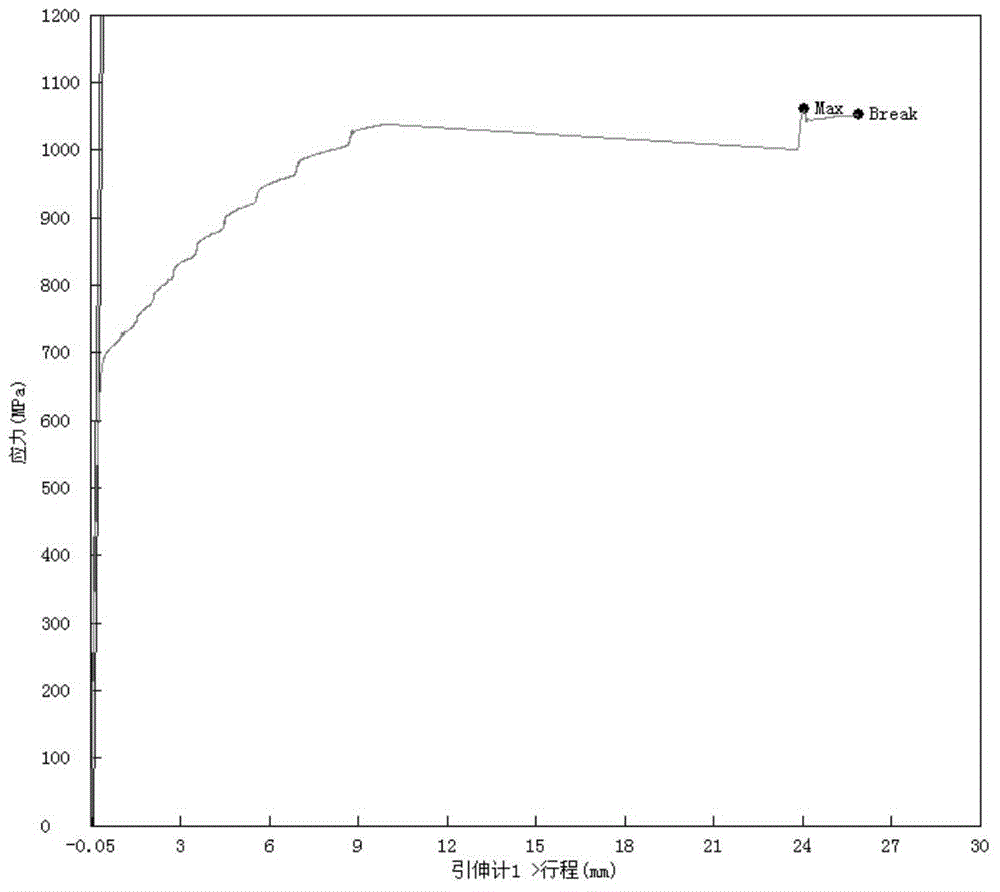
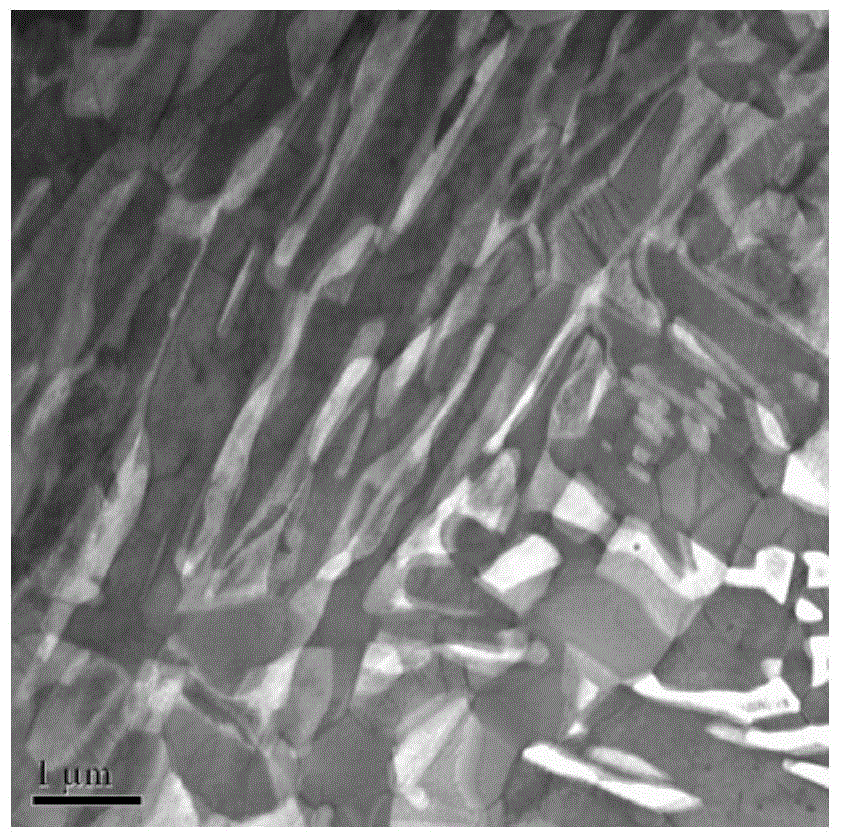
The invention discloses 1000 MPa-level high-strength high-plasticity aluminum-containing medium manganese steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical components by mass percent: 0.05-0.25% of C, 0.02-0.40% of Si, 7.0-11% of Mn, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of S, 1.50-3.50% of Al, 0.02-0.60% of Cr, smaller than or equal to 0.50% of Cu, smaller than or equal to 0.40% of Mo, smaller than or equal to 0.10% of Nb, smaller than or equal to 0.010% of N and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The manufacturing method of the steel comprises the steps of smelting, continuous casting, hot continuous rolling, cover annealing, acid pickling cold rolling, cover annealing or continuous annealing and finishing packing. The steel disclosed by the invention has high strength, excellent cold stamping forming performance and impacting energy absorption performance.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
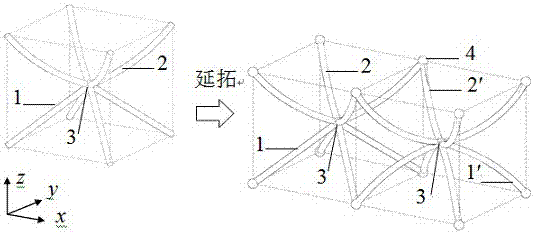
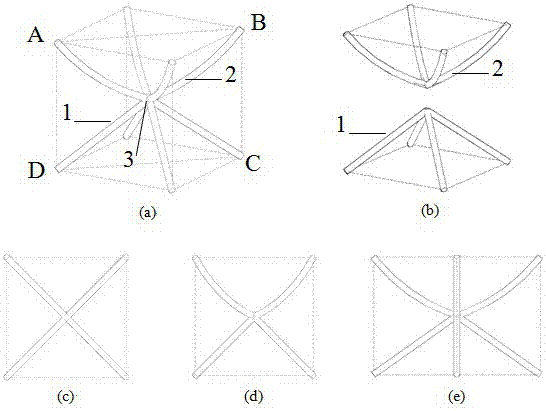
Space lattice material based on curved bar base cells
ActiveCN107100268AImprove absorption rateImprove deformation abilityConstruction materialShock proofingThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The invention discloses a space lattice material based on curved bar base cells. The material comprises N base cells, each base cell is formed by connecting two sets of curved bars through a base cell inner node, every two adjacent base cells are connected through inter-base-cell nodes, and the three-dimensional space lattice material is formed through extension and expansion of the base cells in x, y and z directions. The curvatures of the both sets of curved bars in each base cell are different, and the curvatures of all the sets of curved bars in every two adjacent base cells in the x, y and z directions are also different, so that rigidity (deformation characteristic) of different directions is changed according to the required gradient. The space lattice material is small in weight and high in strength and has a large impacting deformation capacity and high impacting energy absorption rate, and the excellent impacting resistance characteristic is taken on; and the material is simple in structure, low in production cost, high in applicability and wide in application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
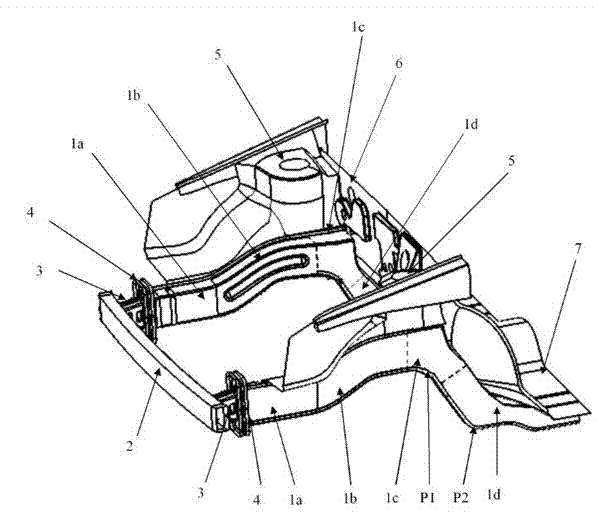
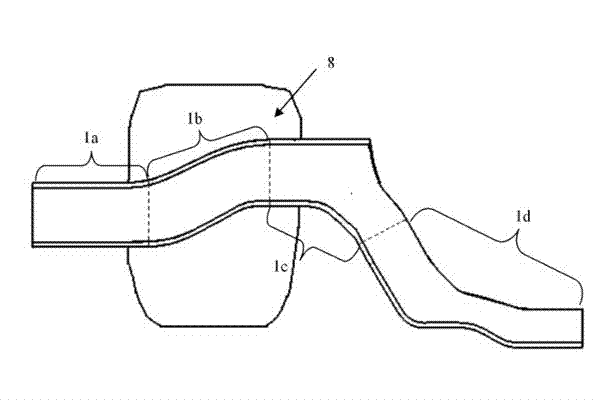
One-piece shotgun with impact energy absorber
A one-piece shotgun is configured to absorb impact energy when a front of the vehicle is impacted. The shotgun comprises an upper portion, a mid portion, and a lower portion, the upper portion having an end configured to connect to a hinge pillar; and a Z-trigger formed by two indentations and being located adjacent the upper portion end. The indentations of the Z-trigger are located on an outer side and an inner side of the shotgun to cause substantially lateral bending when sufficient force is applied to the shotgun.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Impacting energy absorption device based on composite pipe cutting inward-turning crushing
ActiveCN105905056AExquisite structure designHigh strengthSpringsSprings/dampers design characteristicsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to an impacting energy absorption device based on composite pipe cutting inward-turning crushing. The impacting energy absorption device comprises an outer sleeve, a cutter and a positioning pipe. The cutter is located inside the outer sleeve, the lower end of the cutter is connected with an inner flange of the outer sleeve, and the upper end of the cutter is connected with the positioning pipe. The positioning pipe is located inside the outer sleeve and closely connected with the inner wall of the outer sleeve, and the lower surface of the positioning pipe makes contact with the cutter. The outer sleeve, the positioning pipe and a composite pipe are provided with pin holes capable of coinciding, and the outer sleeve, the positioning pipe and the composite pipe are closely combined together through pins. Compared with the prior art, the impacting energy absorption device has the advantages that the overall structure is simple, the material utilization rate is high, and the surrounding structure is not affected while the pipe strength is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Shock absorbing steering apparatus
InactiveUS7455320B2Reduces ease of assemblingAccelerated programSteering columnsSteering columnEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com