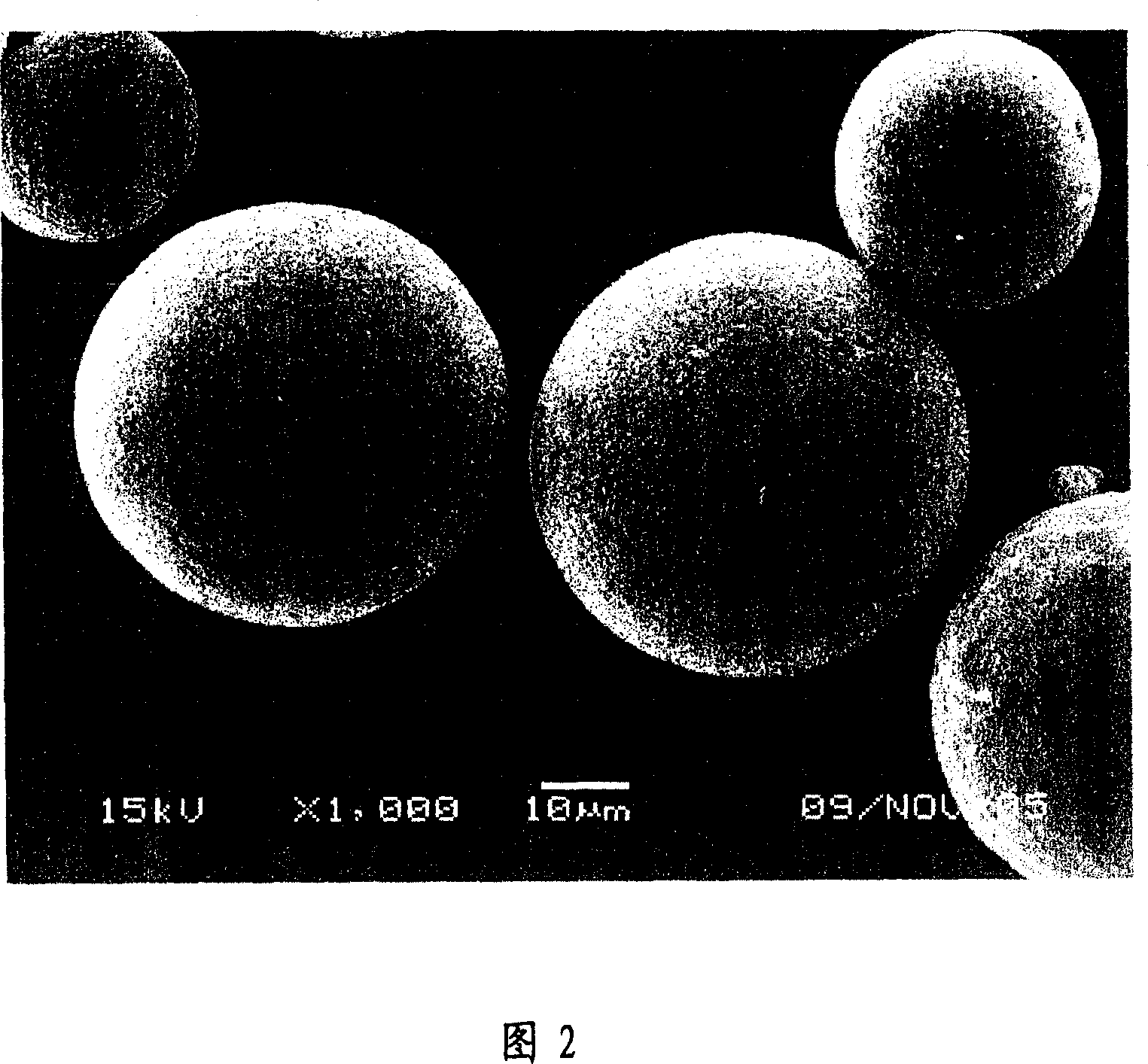
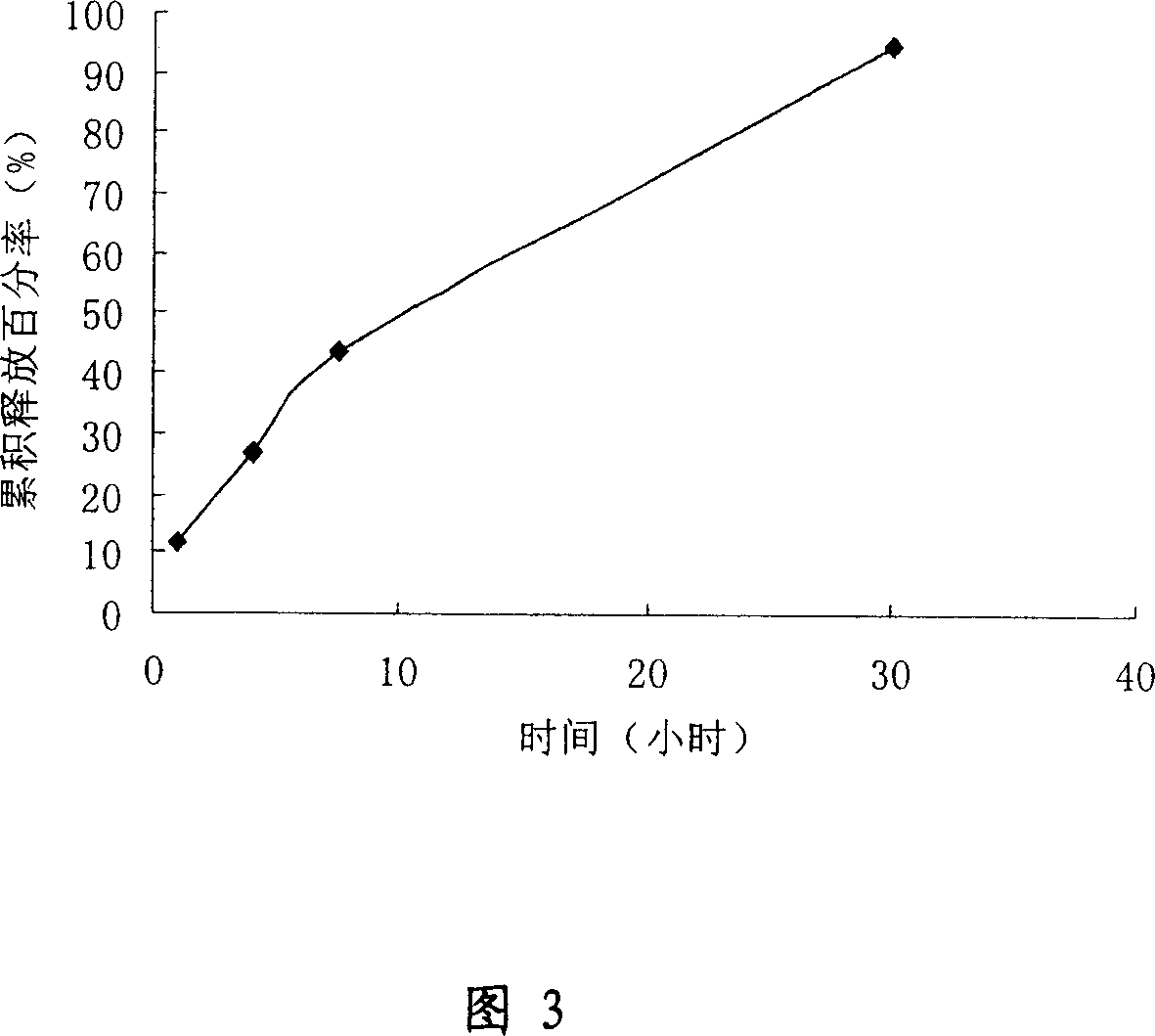
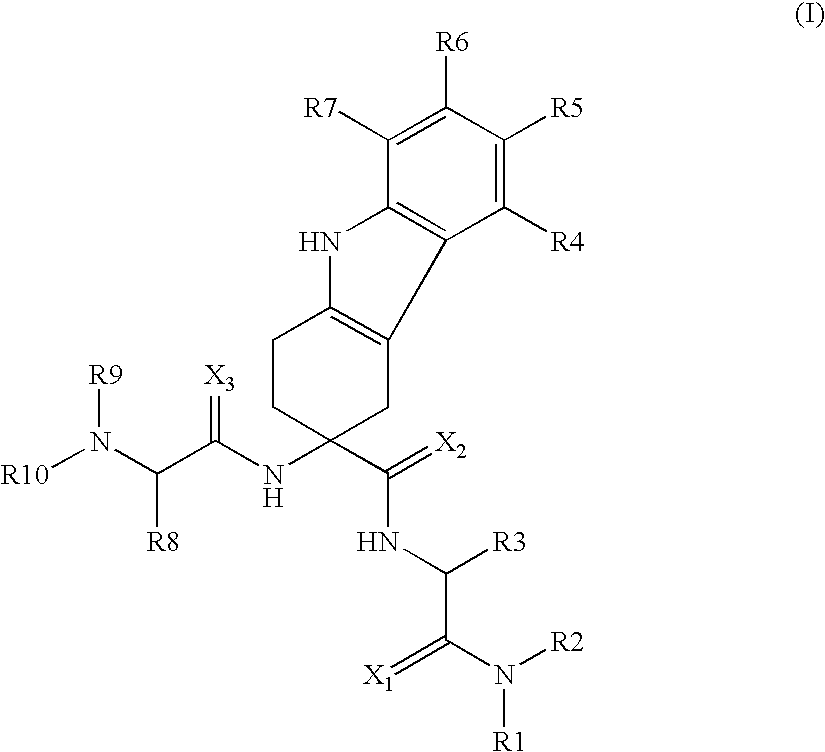
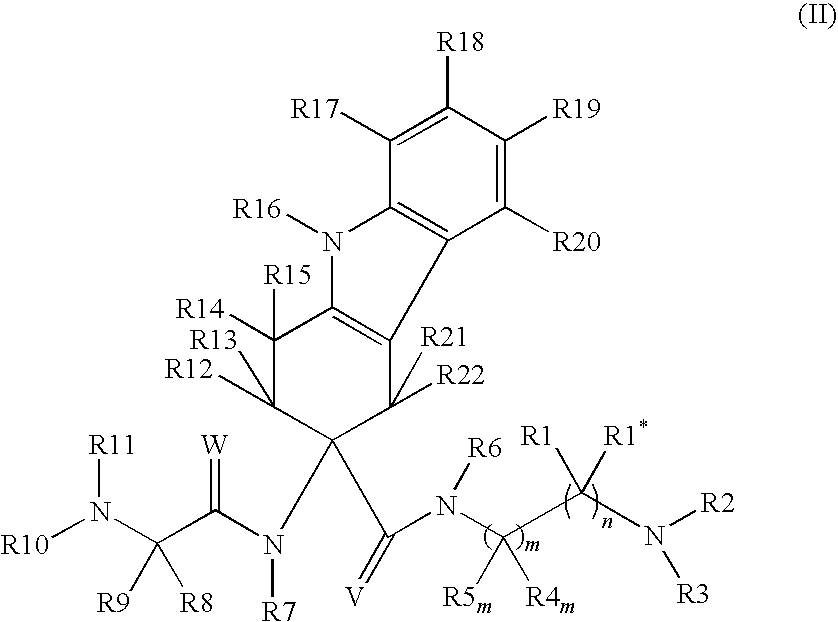
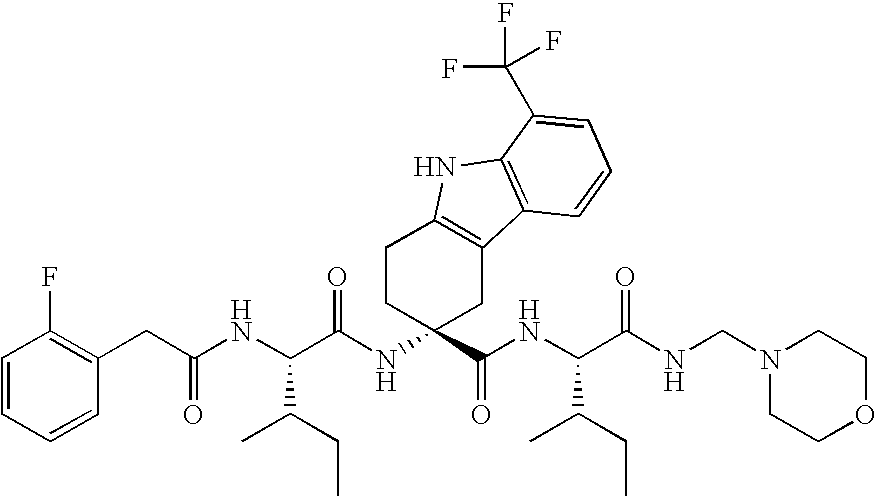
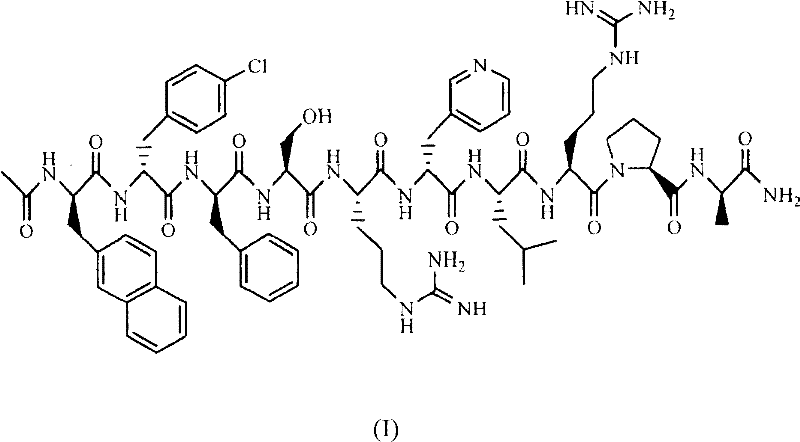
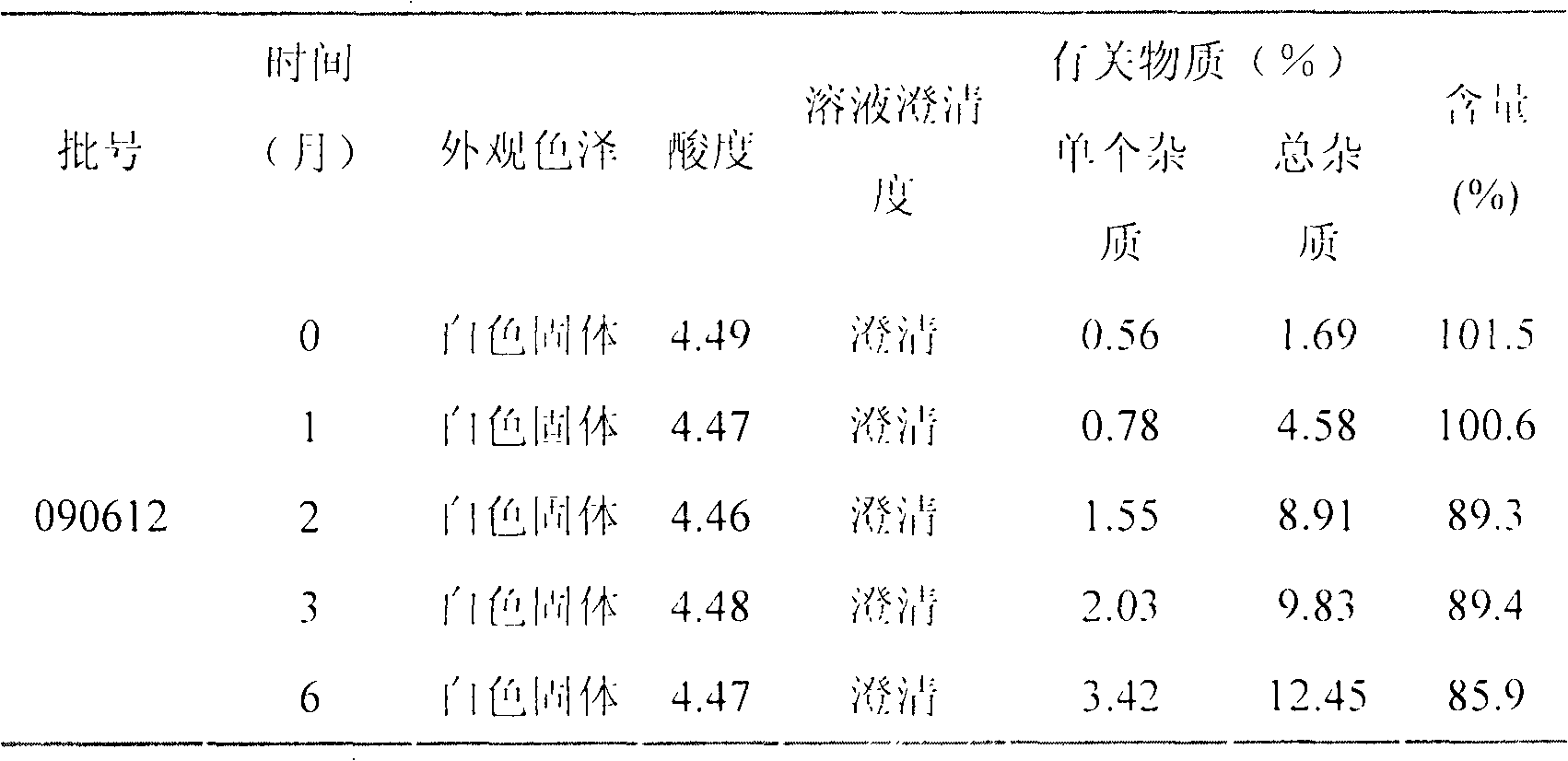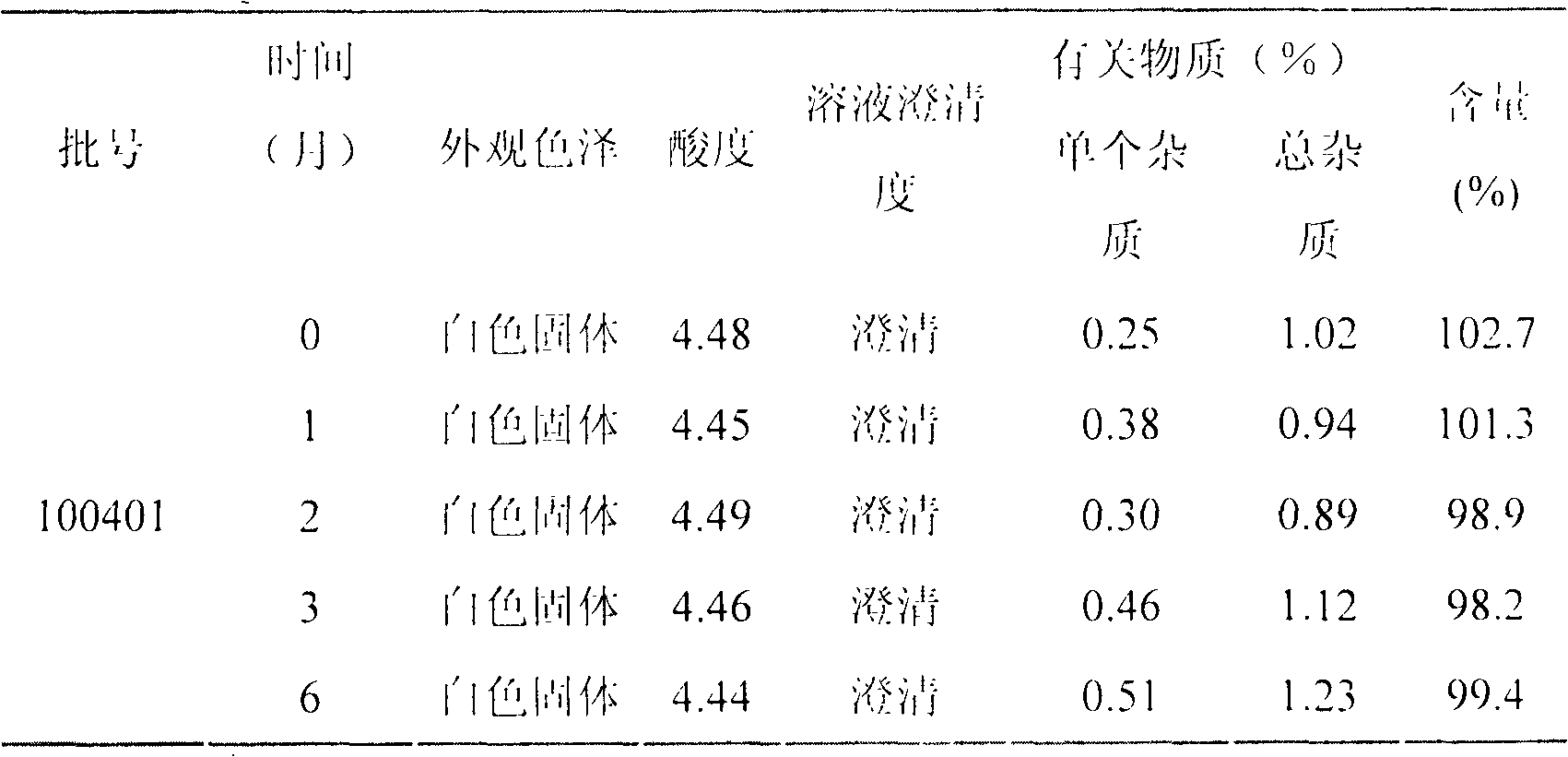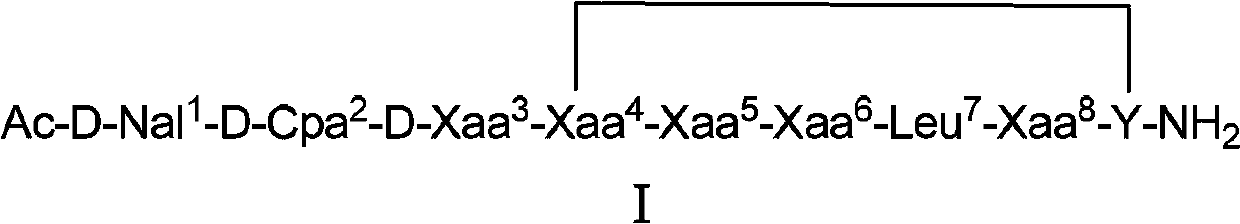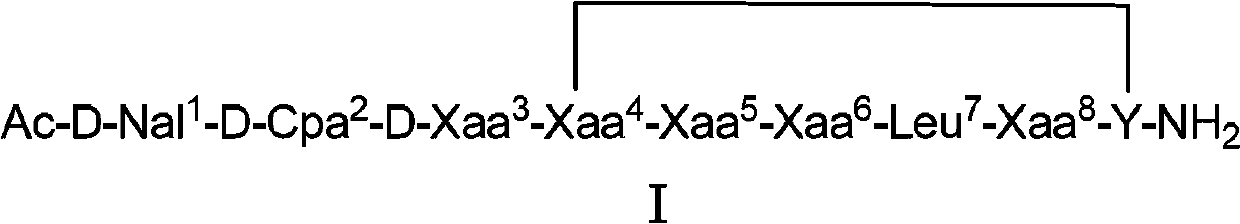Patents
Literature
42 results about "Lhrh antagonist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LHRH antagonist is a specific type of antagonist used in prostate cancer hormone therapy. LHRH antagonist mimics natural LHRH or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and plugs into the receptors of the pituitary gland.
Immobilized and activity-stabilized complexes of LHRH antagonists and processes for their preparation
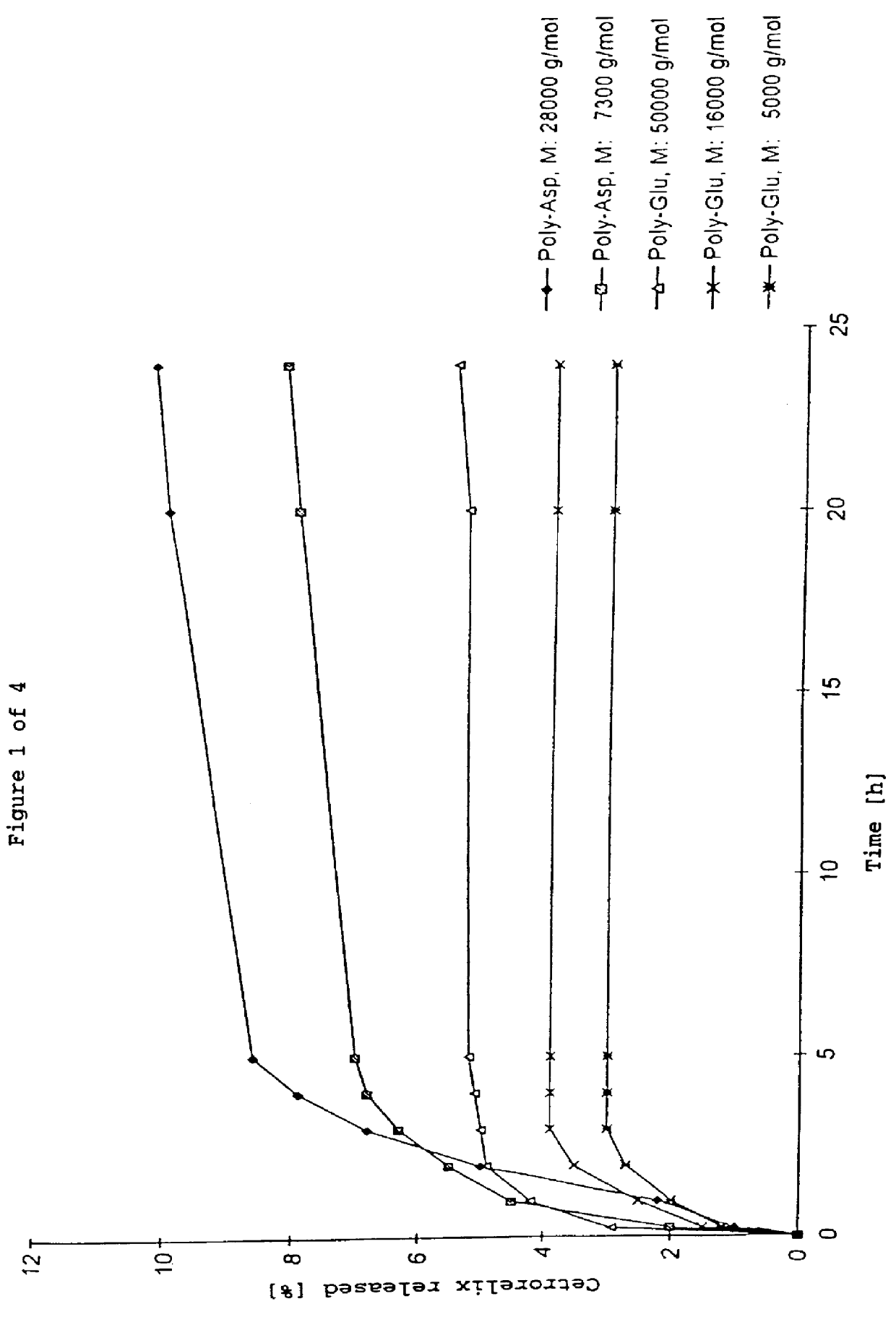
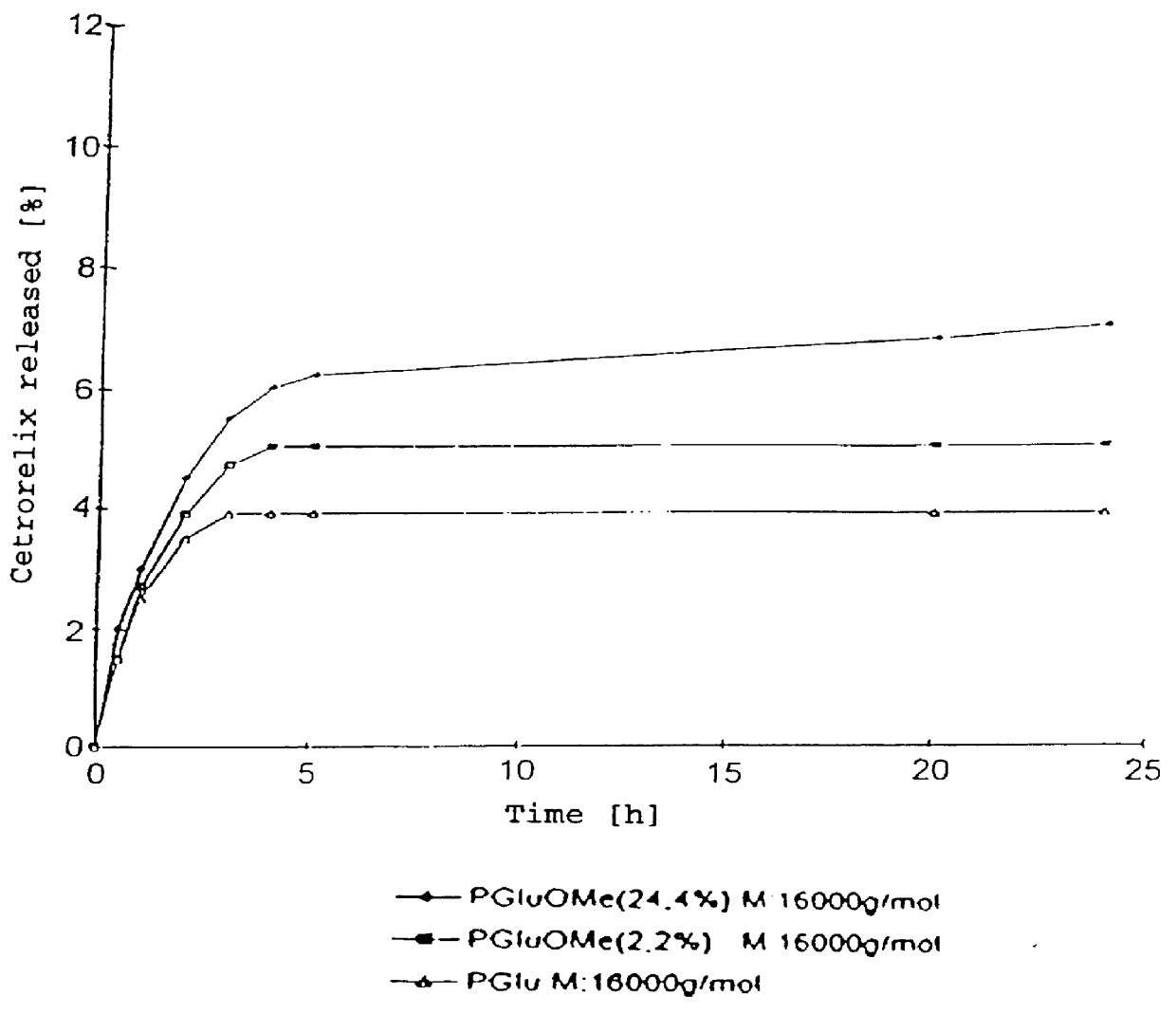
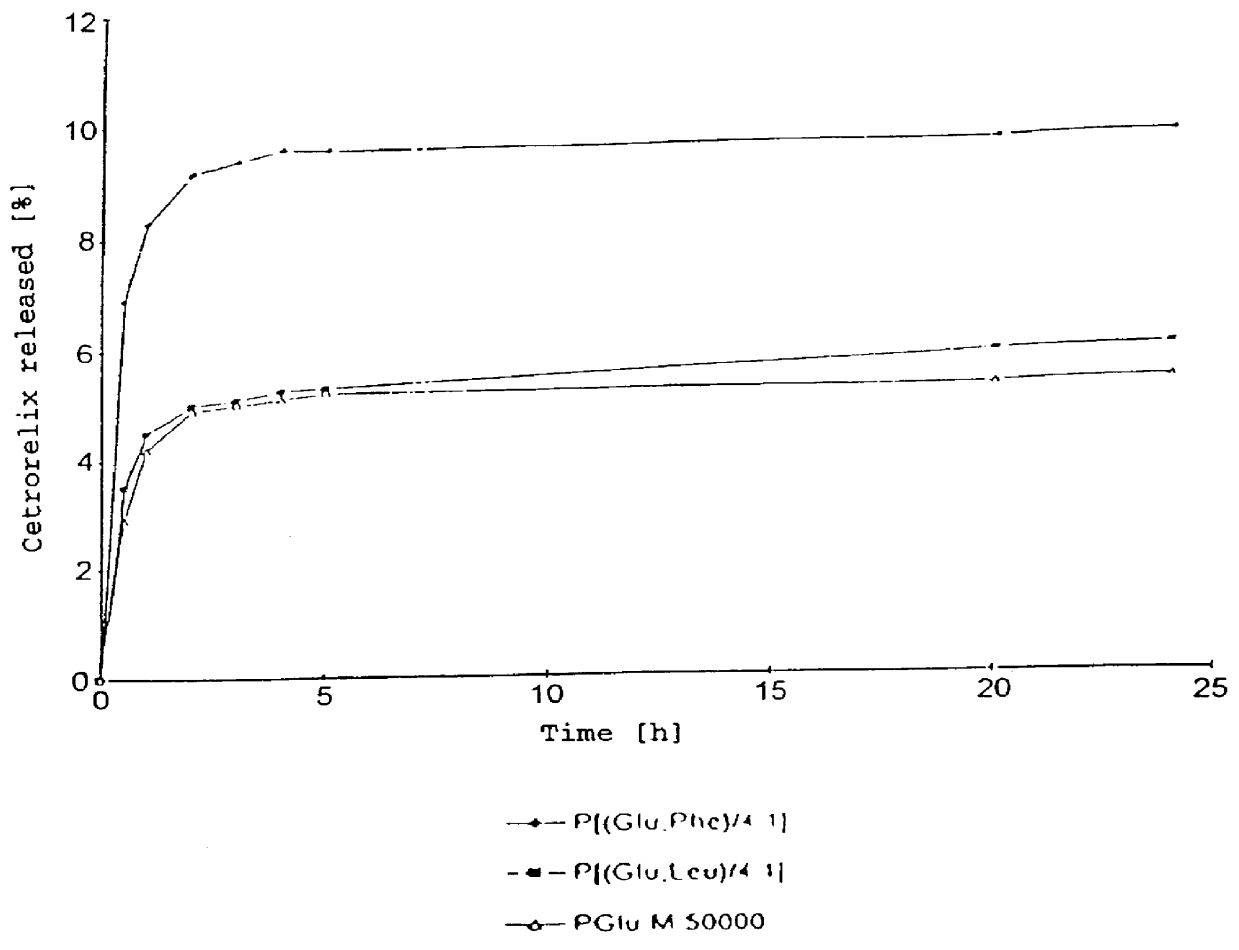
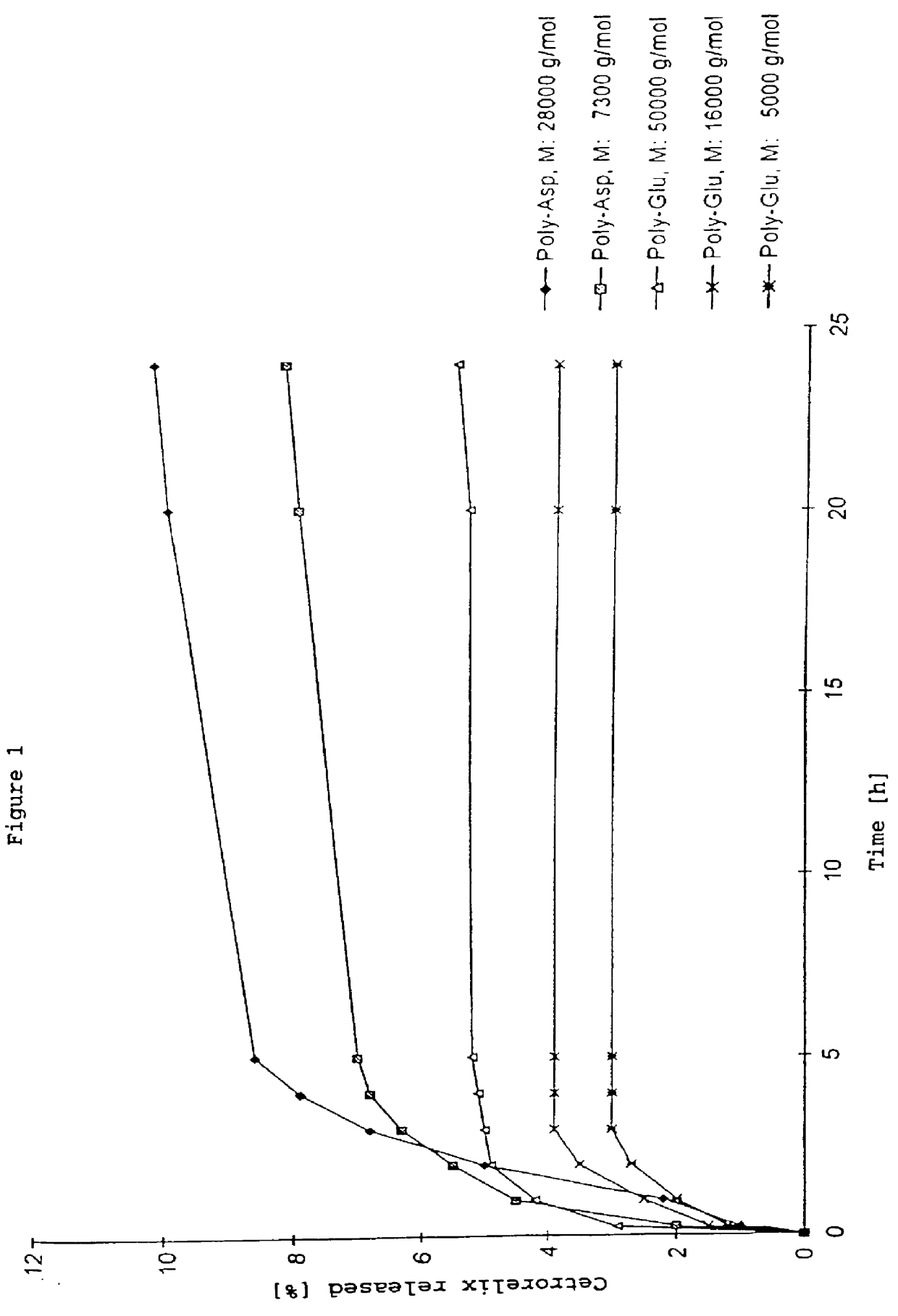
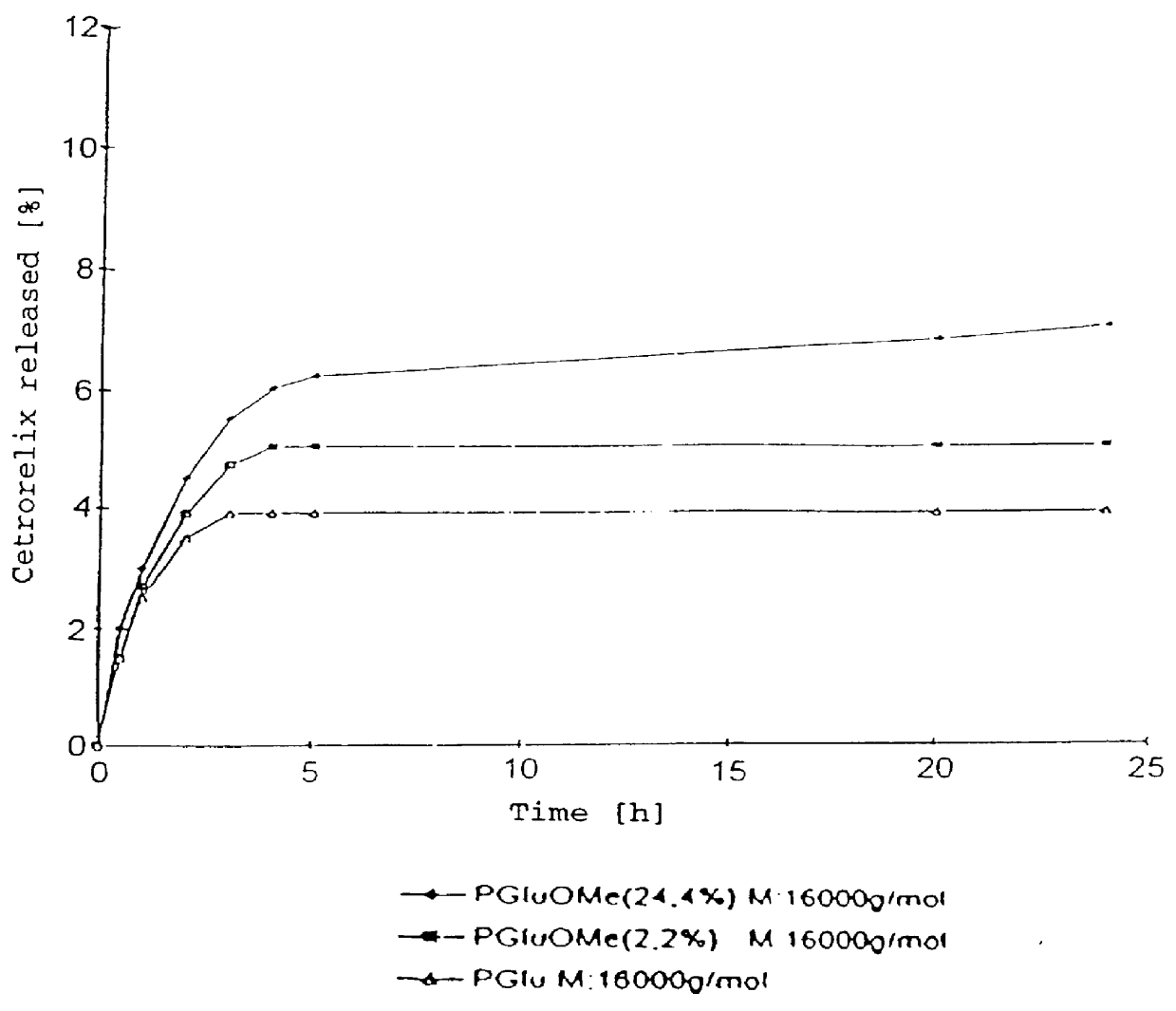
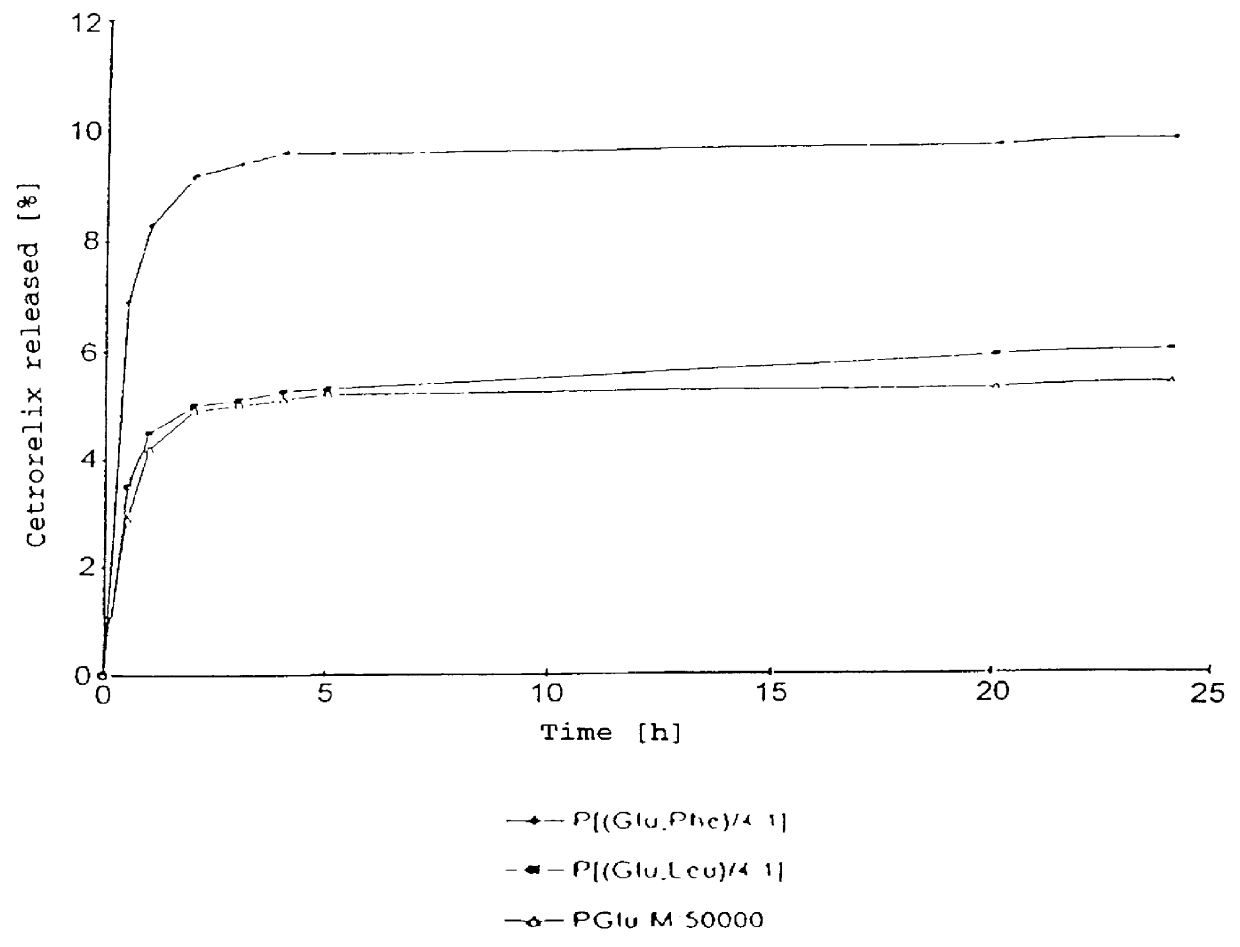
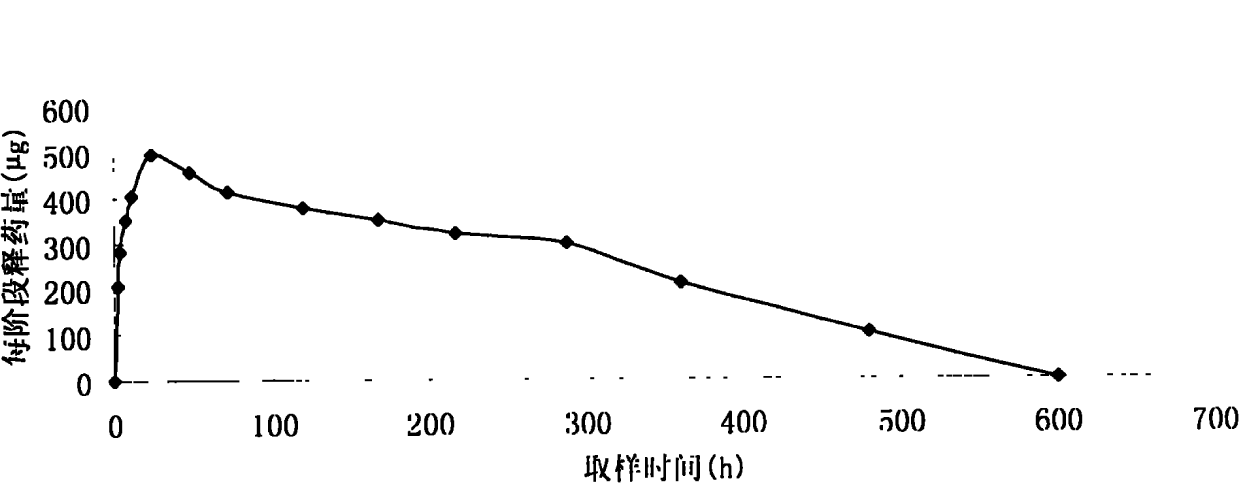
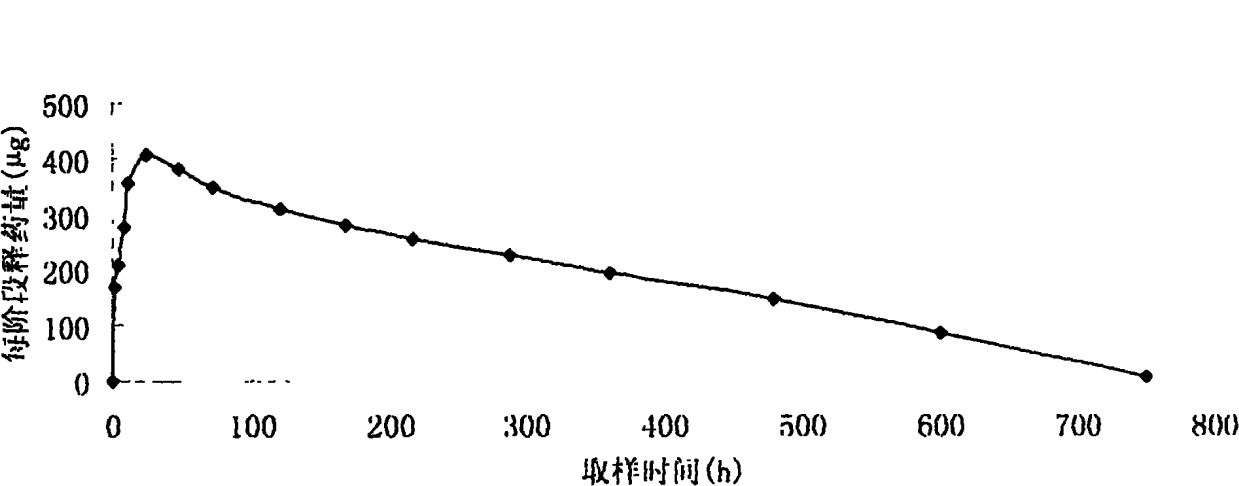
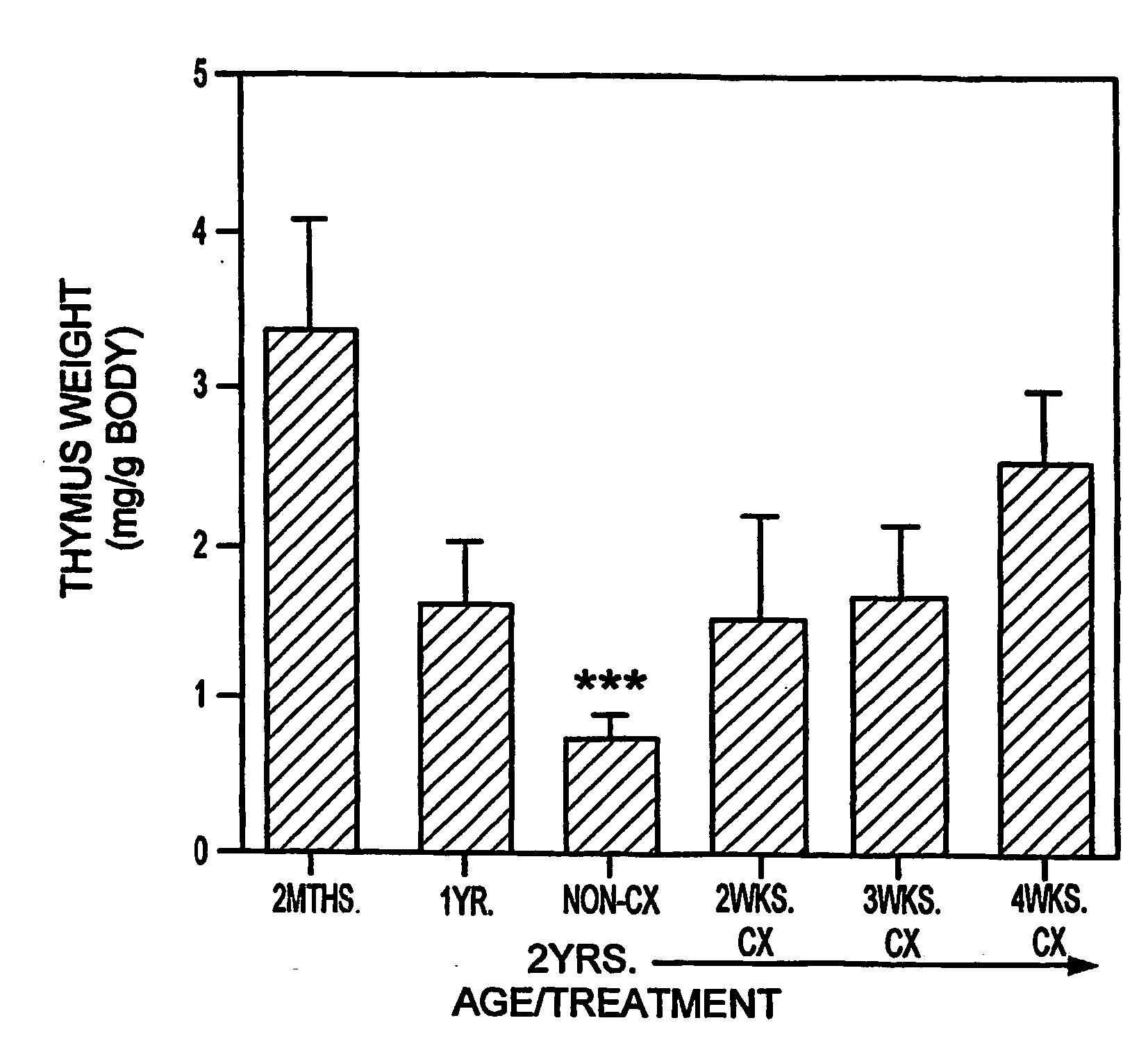
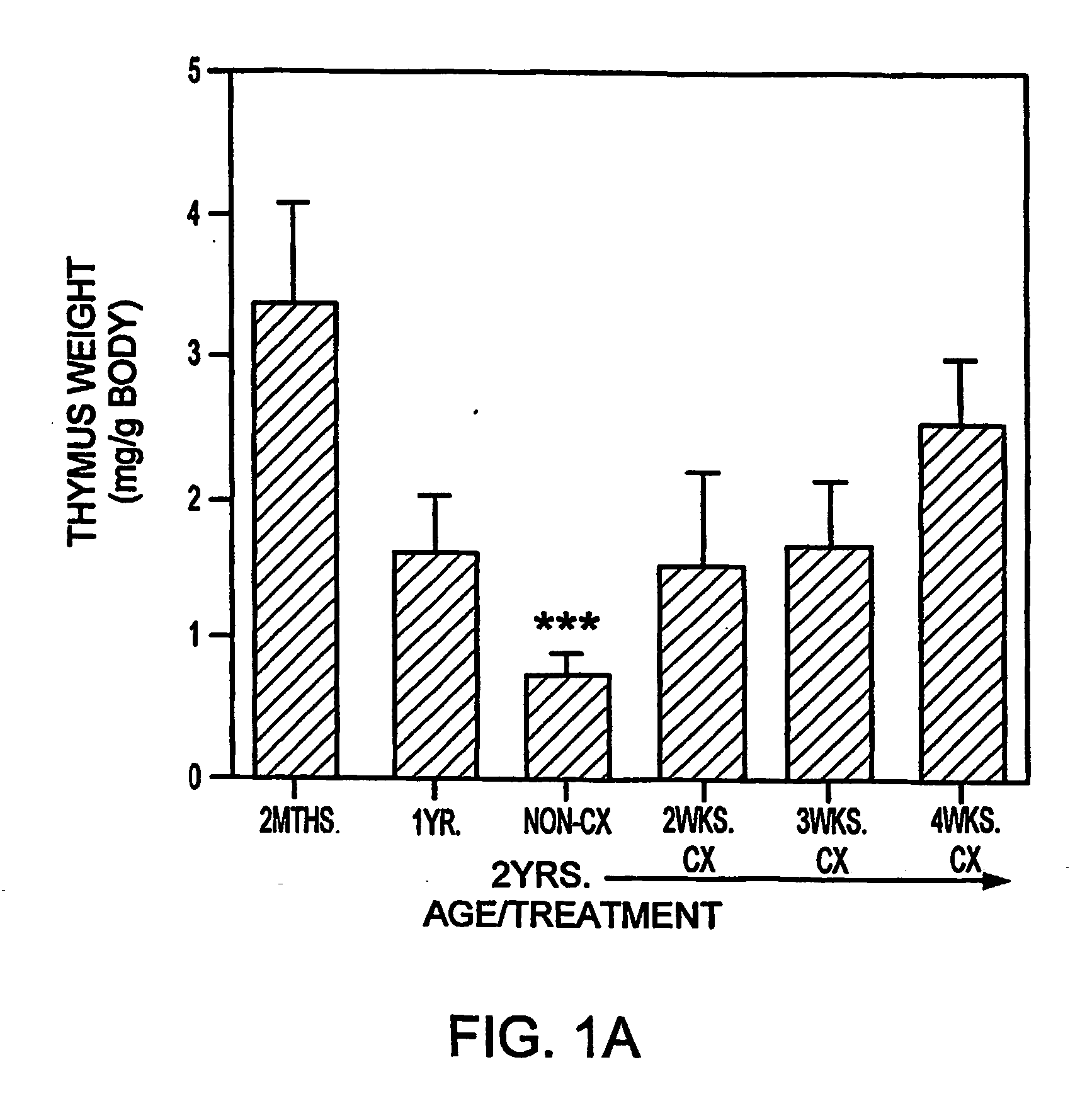
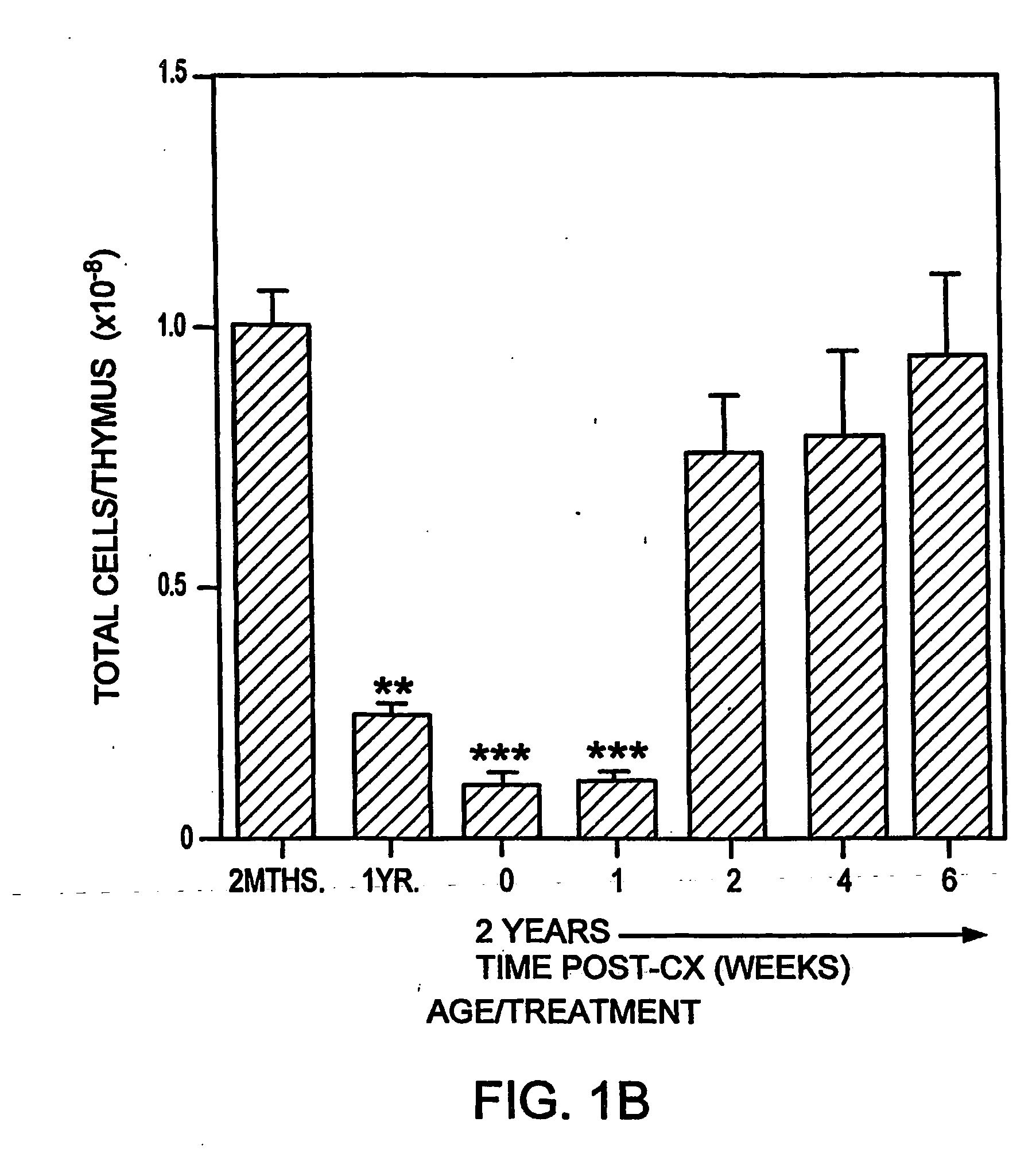
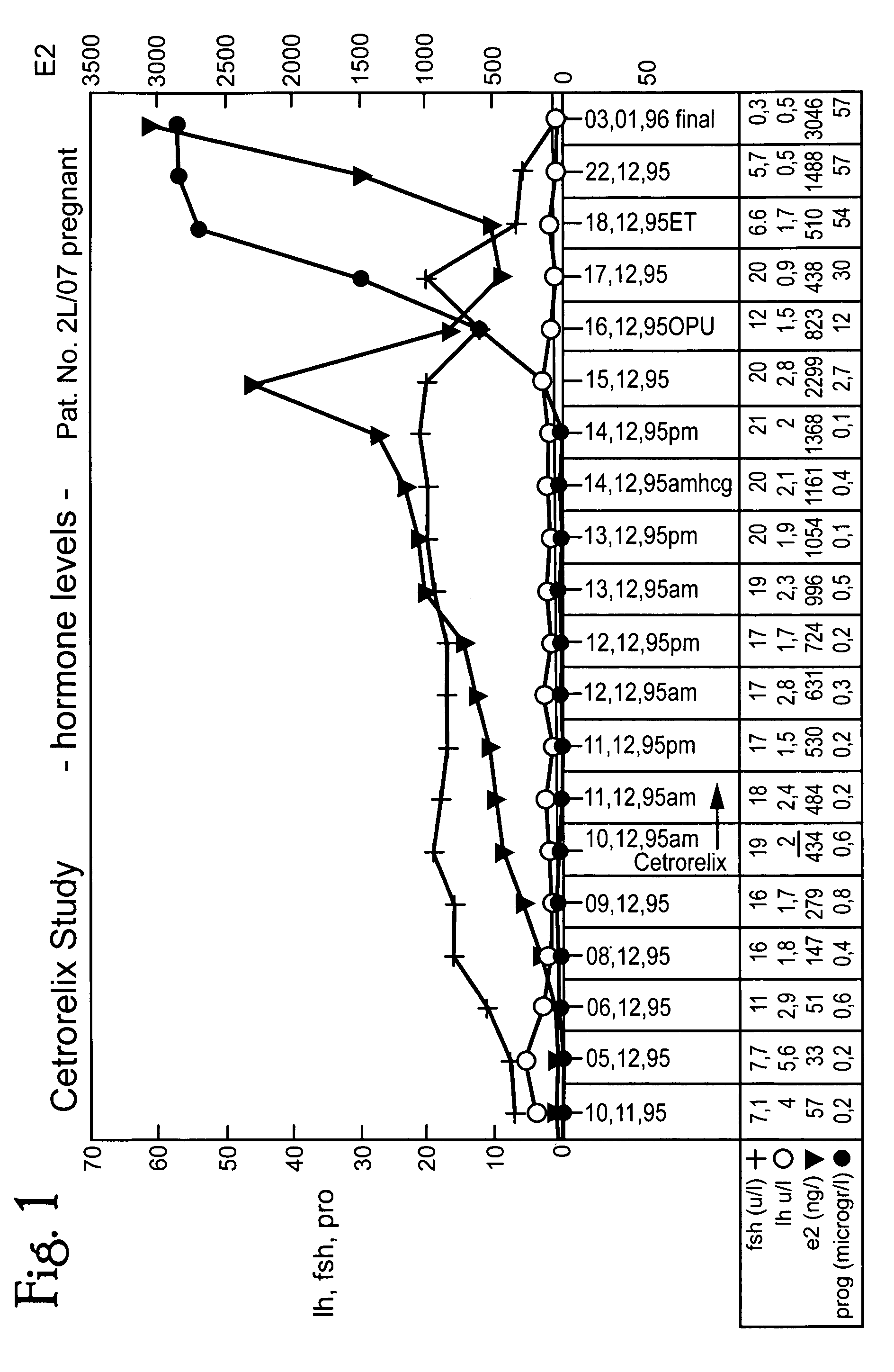
In this invention, a release-delaying system is to be developed for LHRH antagonists, in particular for cetrorelix, which allows the active compound to be released in a controlled manner over several weeks by complexation with suitable biophilic carriers. The acidic polyamino acids polyglutamic acid and polyaspartic acid were selected for complexation with cetrorelix. The cetrorelix polyamino acid complexes are prepared from aqueous solutions by combination of the solutions and precipitation of the complexes, which are subsequently centrifuged off and dried over P2O5 in vacuo. If complexes having a defined composition are to be obtained, lyophilization proves to be a suitable method. The cetrorelix-carboxylic acid complexes were also prepared from the aqueous solutions. In the random liberation system, the acidic polyamino acids poly-Glu and poly-Asp showed good release-delaying properties as a function of the hydrophobicity and the molecular mass of the polyamino acid. In animal experiments, it was possible to confirm the activity of the cetrorelix-polyamino acid complexes as a depot system in principle. It is thus possible by complexation of cetrorelix with polyamino acids to achieve testosterone suppression in male rats over 600 hours. The release of active compound here can be controlled by the nature and the molecular mass of the polymers.
Owner:ZENTARIS GMBH
Application of initial doses of LHRH analogues and maintenance doses of LHRH antagonists for the treatment of hormone-dependent cancers and corresponding pharmaceutical kits
ActiveUS20080032935A1Negative hormone withdrawal symptomsPeptide/protein ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneGynecologyInitial dose
LHRH analogues and LHRH antagonists for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of hormone-dependent cancers, in particular prostate cancer, prostate carcinoma and / or advanced prostate carcinoma, by administering an initial dose of an LHRH analogue over a first period sufficient to effect hormonal castration, then administering a maintenance dose of an LHRH antagonist over a second period, the dose being insufficient to achieve and / or maintain hormonal castration.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy
InactiveUS20050020524A1Avoid infectionHigh activityBiocideUnknown materialsLhrh antagonistCell resistance
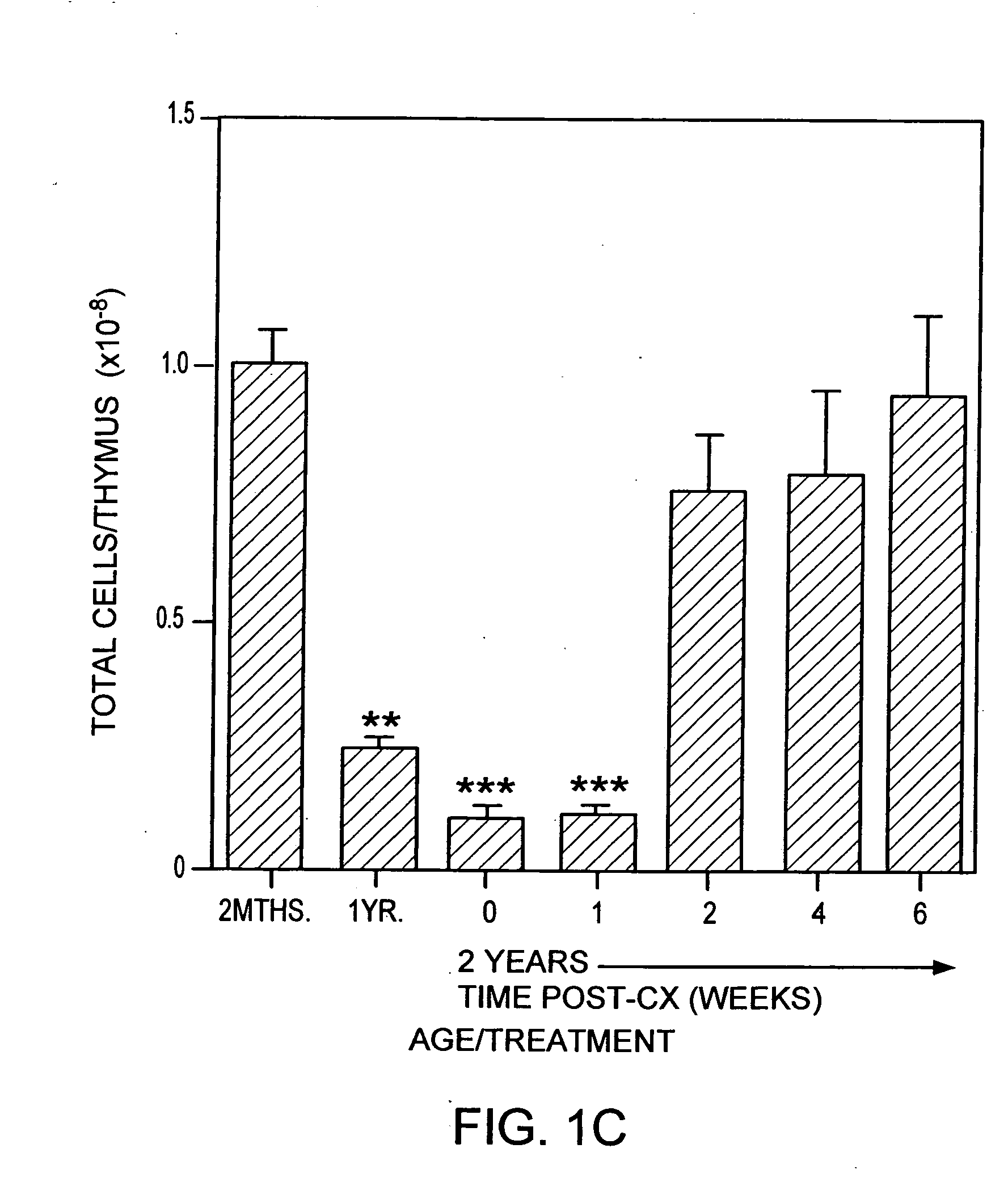
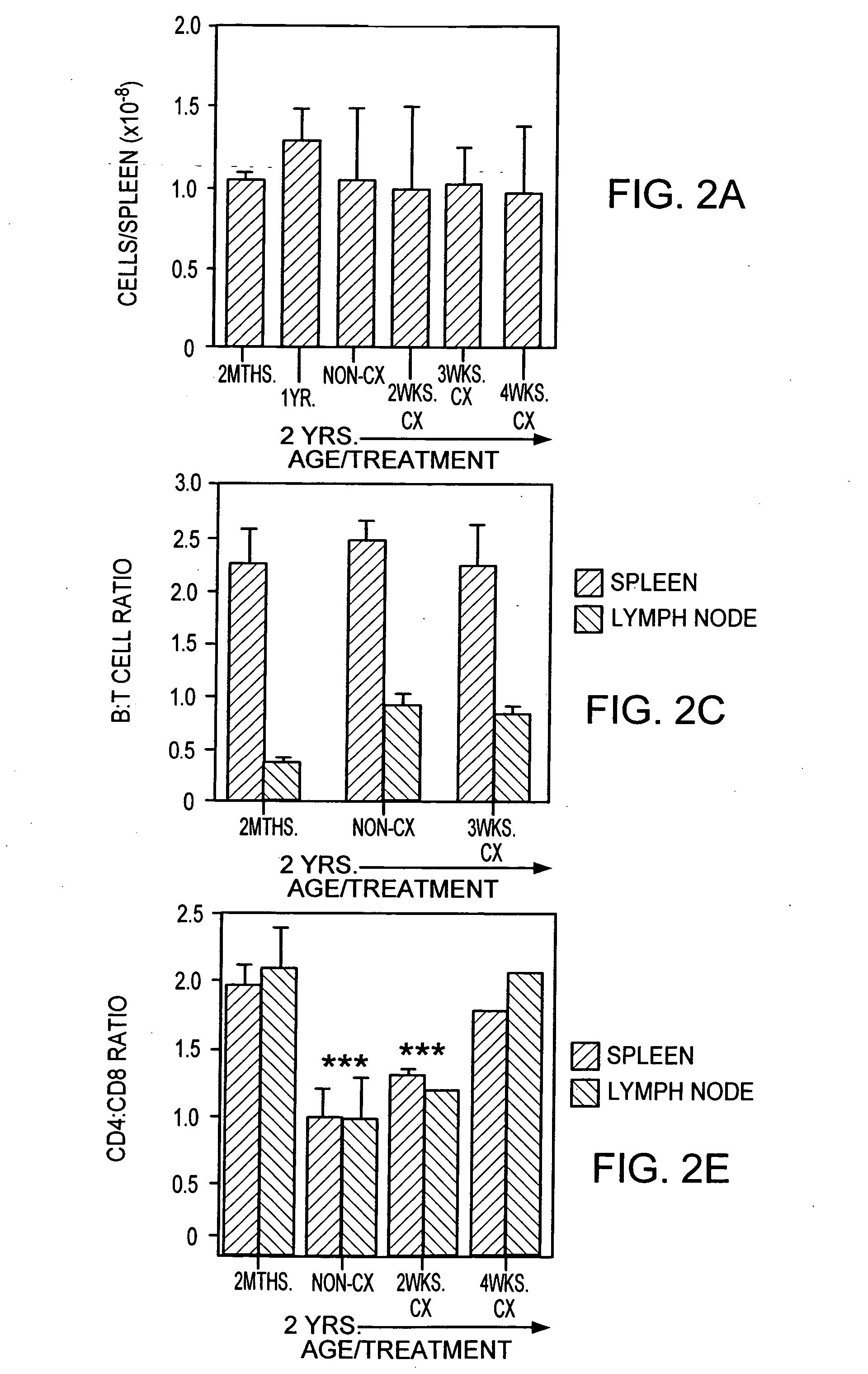
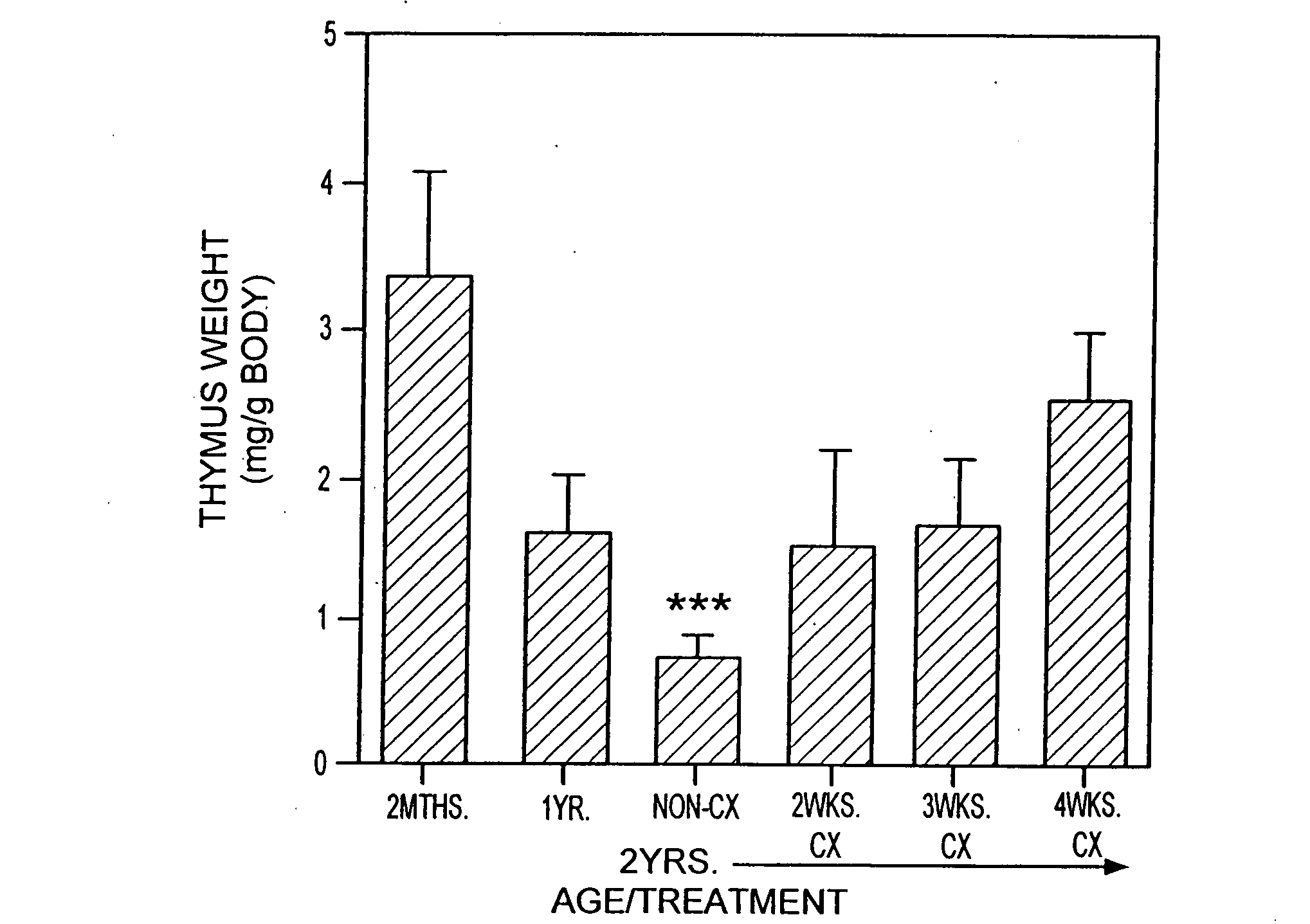
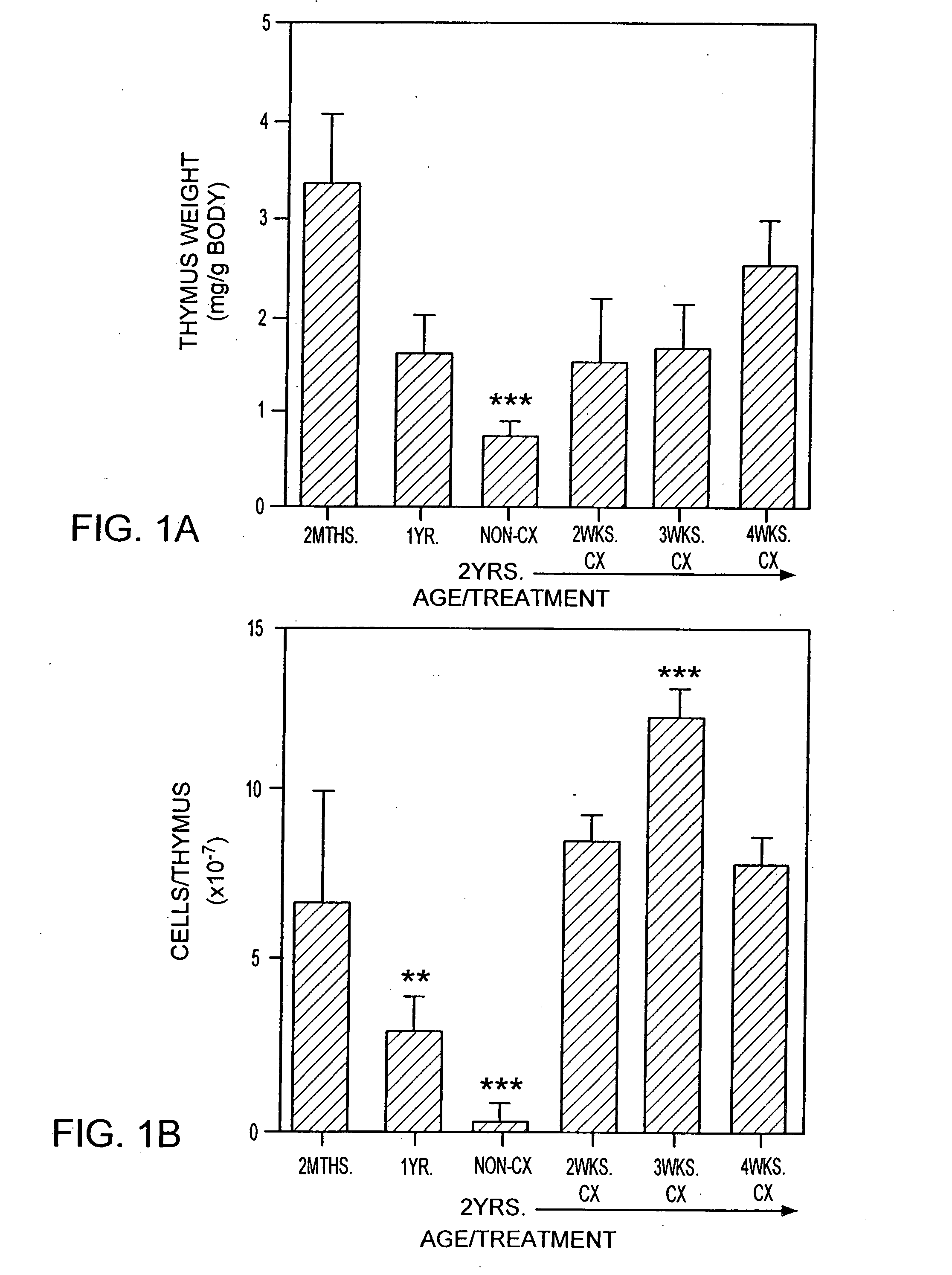
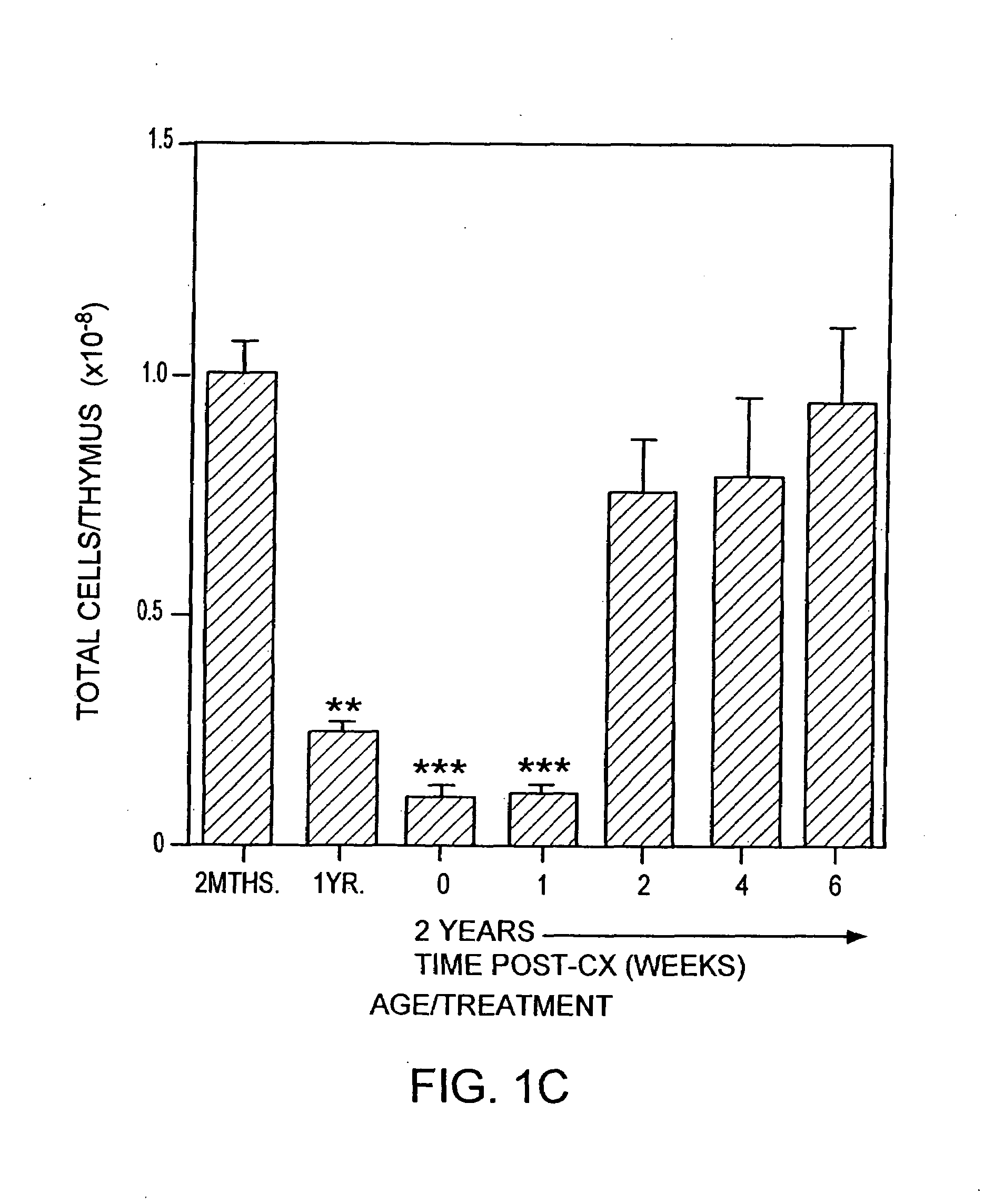
The present disclosure provides methods for gene therapy utilizing hematopoietic stem cells, lymphoid progenitor cells, and / or myeloid progenitor cells. The cells are genetically modified to provide a gene that is expressed in these cells and their progeny after differentiation. In one embodiment the cells contain a gene or gene fragment that confers to the cells resistance to HIV infection and / or replication. The cells are administered to a patient in conjunction with treatment to reactivate the patient's thymus. The cells may be autologous, syngeneic, allogeneic or xenogeneic, as tolerance to foreign cells is created in the patient during reactivation of the thymus. In one embodiment the hematopoietic stem cells are CD34+. The patient's thymus is reactivated by disruption of sex steroid mediated signaling to the thymus. In another embodiment, this disruption is created by administration of LHRH agonists, LHRH antagonists, anti-LHRH receptor antibodies, anti-LHRH vaccines or combinations thereof.
Owner:NORWOOD IMMUNOLOGY
Method for the treatment of fertility disorders
InactiveUS6319192B1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsObstetricsHormones regulation
An improvement to the method of intrauterine insemination by the administration of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonists (LHRH antagonists).
Owner:ZENTARIS IVF
Process for the preparation of immobilized and activity-stabilized complexes of LHRH antagonists
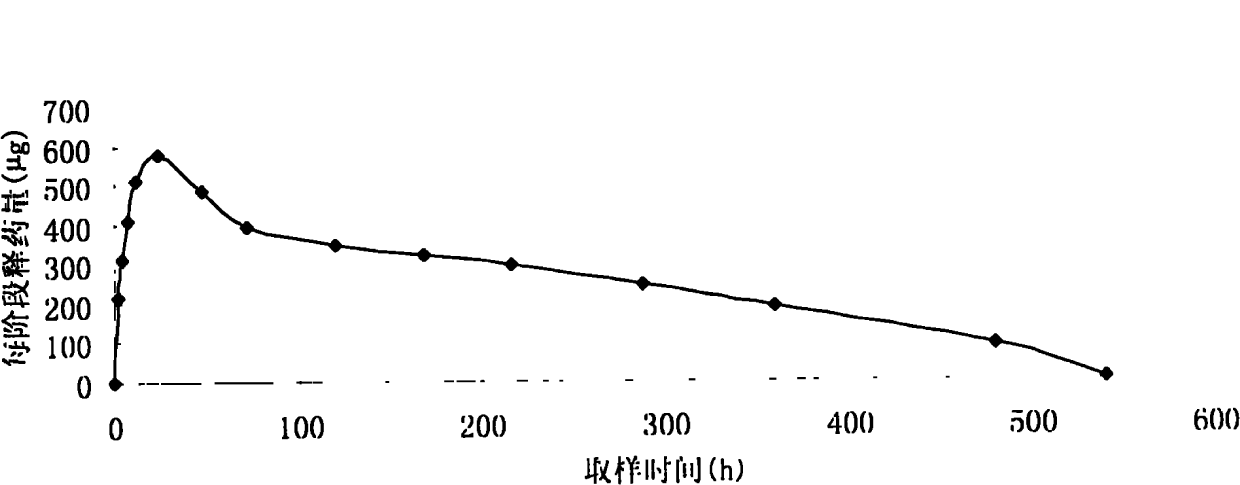
In this invention, a release-delaying system is to be developed for LHRH antagonists, in particular for cetrorelix, which allows the active compound to be released in a controlled manner over several weeks by complexation with suitable biophilic carriers. The acidic polyamino acids polyglutamic acid and polyaspartic acid were selected for complexation with cetrorelix. The cetrorelix polyamino acid complexes are prepared from aqueous solutions by combination of the solutions and precipitation of the complexes, which are subsequently centrifuged off and dried over P2O5 in vacuo. If complexes having a defined composition are to be obtained, lyophilization proves to be a suitable method. The cetrorelix-carboxylic acid complexes were also prepared from the aqueous solutions. In the random liberation system, the acidic polyamino acids poly-Glu and poly-Asp showed good release-delaying properties as a function of the hydrophobicity and the molecular mass of the polyamino acid. In animal experiments, it was possible to confirm the activity of the cetrorelix-polyamino acid complexes as a depot system in principle. It is thus possible by complexation of cetrorelix with polyamino acids to achieve testosterone suppression in male rats over 600 hours. The release of active compound here can be controlled by the nature and the molecular mass of the polymers.
Owner:ZENTARIS GMBH
Stimulation of thymus for vaccination development
InactiveUS20080199495A1Recovery functionBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsVaccinationLhrh antagonist
The present disclosure provides methods for enhancing the response of a patient's immune system to vaccination. This is accomplished by reactivating the thymus. Optionally, hematopoietic stem cells, autologous, syngeneic, allogeneic or xenogeneic, are delivered to increase the speed of regeneration of the patient's immune system. In one embodiment the hematopoietic stem cells are CD34+. The patient's thymus is reactivated by disruption of sex steroid mediated signaling to the thymus. In one embodiment, this disruption is created by administration of LHRH agonists, LHRH antagonists, anti-LHRH receptor antibodies, anti-LHRH vaccines or combinations thereof.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Controlled-release implanting preparation used for injecting LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) antagonist
InactiveCN102145160AIncrease concentrationIncrease and prolong concentrationPeptide/protein ingredientsGranular deliveryControl releaseLhrh antagonist
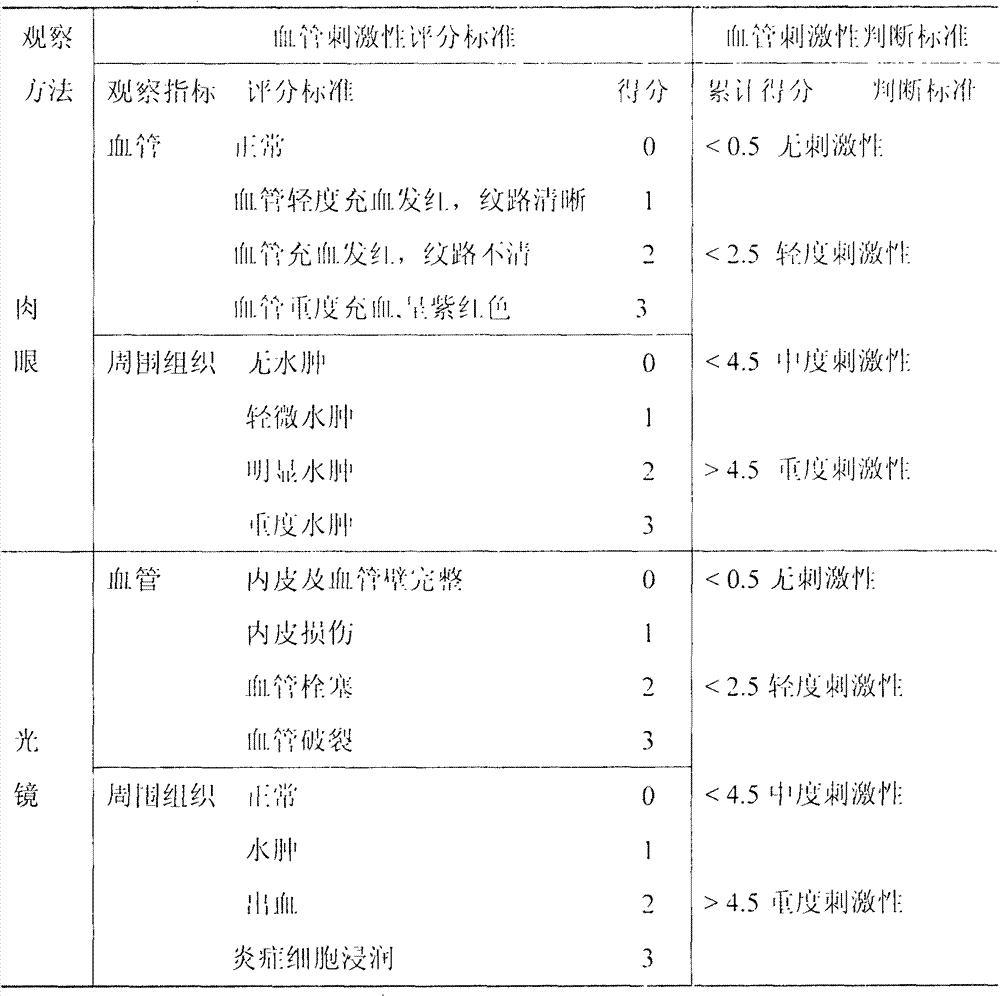
The invention relates to a controlled-release implanting preparation used for injecting an LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) antagonist. The invention is characterized in that the LHRH antagonist, namely cetrorelix acetate is loaded into a high polymer material carrier in a certain proportion, and then compressed into an implanting preparation of a certain shape so as to be used for implanting injection, thereby achieving the effect of long-acting controlled release. The controlled-release implanting preparation consists of the cetrorelix acetate with the effective dose for cancer resisting and controlled-release auxiliary materials, and the controlled-release auxiliary materials mainly comprise a biodegradable and biocompatible macromolecule copolymer; and the controlled-release implanting preparation is injected into tumors or around tumors, thereby being favorable for the effective diffusion of the medicament in the solid tumors, selectively improving the local medicament concentration of the tumors, reducing the injection times and the medicament tolerance, enhancing the compliance of patients and facilitating the clinical use and the medication for the patients.
Owner:SHENZHEN JYMED TECH
Methods for treating hormone associated conditions using a combination of LHRH antagonists and specific estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS20070066536A1Avoid side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHormone Receptor ModulatorsTherapeutic Hormone
Methods for treating hormone associated conditions, such as endometriosis, uterine leiomata, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, or vaginal bleeding, using LHRH antagonists and selective estrogen receptor modulators are disclosed. The methods include administering to a subject a combination of an LHRH antagonist and a selective estrogen receptor modulator. Pharmaceutical compositions and kits for use in the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:PRAECIS PHARM INC
Sustained-release microsphere of LHRH antagonist for injection and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1965809APeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectEmulsion
The invention relates to an injection slow-release micro ball of LHRH antagonist material, wherein its average diameter is 0.5-100 mum, with high package ratio. And it comprises LHRH antagonist material, degradable macromolecule findings, and other acceptable findings. The invention uses emulsion-liquid drying method, single-emulsion-liquid drying method, S / O / O method, atomization drying method, etc. Said micro ball can prolong drug function time, improve utilization of LHRH antagonist material, and reduce side effect.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
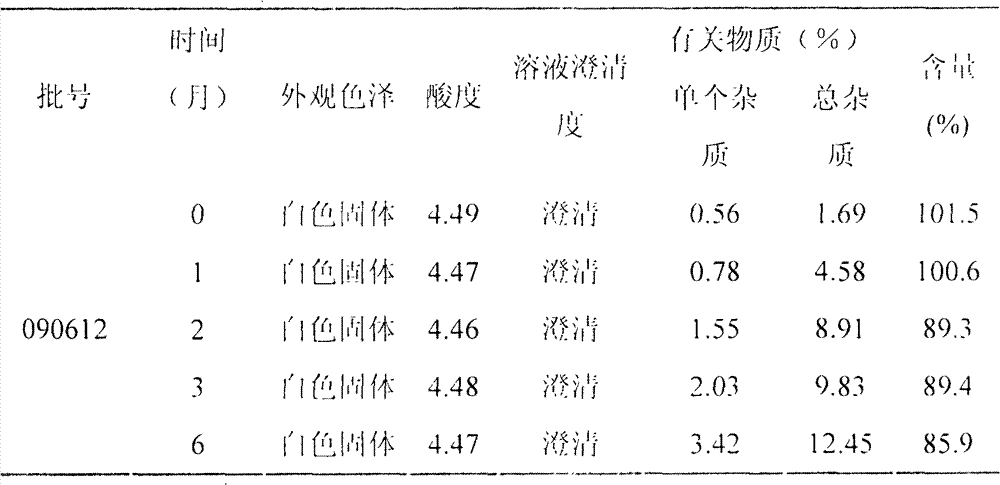
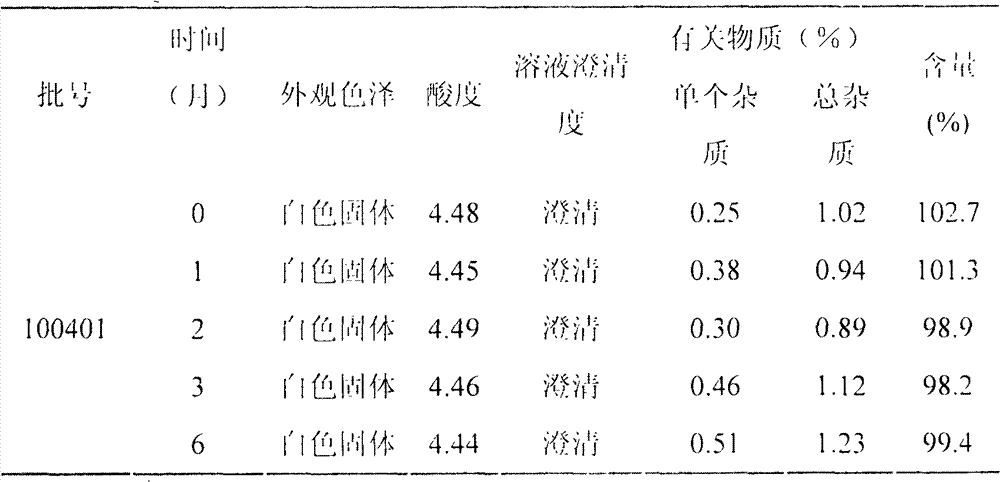
LHRH (luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonist) lyophilized powder injection with improved stability
ActiveCN102144980AQuality improvementDefinite curative effectPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPatient complianceAntioxidant
The invention relates to an LHRH (luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonist) lyophilized powder injection with improved stability. The preparation mainly comprises cetrorelix as an active ingredient, an excipient, a pH regulator, an antioxidant and a local analgesic agent, wherein the addition of the antioxidant can improve the stability of the preparation, and the addition of the local analgesic agent can relieve the pains of patients while having no impact on the active ingredient. The preparation process of the preparation mainly comprises weighing, dissolving, adsorbing pyrogen with activated carbon, filtering, final filtering, subpackaging, vacuum drying, plugging, and covering. The LHRH lyophilized powder injection provided by the invention can control the stimulatory function of an ovary, prevent early release of immature ovarian follicles, and help become pregnant. The LHRH lyophilized powder injection has the advantages of stable quality, definite therapeutic effect, and good patient compliance.
Owner:深圳市健翔生物制药有限公司
LHRH antagonist with low-histamine releasing function
InactiveCN101037472AGood LHRH antagonistic activityLow histamine release side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisLhrh antagonistLhrh receptor
The invention relates to decapeptide derivative which has LHRH receptor antagonism activity, an effect of inhibiting pituitary to excrete gonadotrophic hormone, an effect of inhibiting the gonad to excrete steroid hormone and has a lower histamine releasing effect, its producing method, the drug combination and its drug applications for treating the sex hormone correlated disease such as prostatecancer and the disease correlated to the anti-histamine or reducing histamine release.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Lhrh antagonists for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms
InactiveUS20090075937A1Low urinary tract symptomNegative hormone withdrawal symptoms are minimized and/or preventedBiocideOrganic chemistryMammalLhrh antagonist
The present invention provides at least one LHRH antagonist for the treatment or prophylaxis of at least one lower urinary tract symptom in mammals which is to be administered in an intermediate dose, which does not cause chemical (hormonal) castration.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
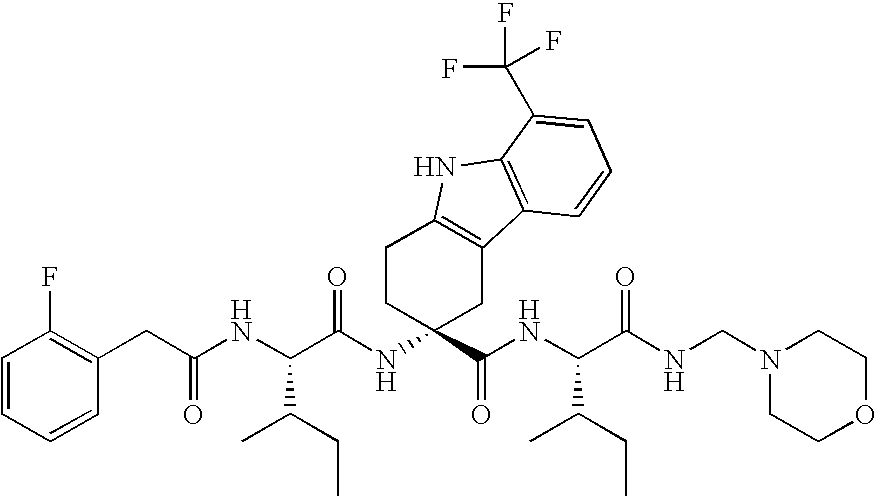
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonist derivative, preparation method of LHRH antagonist derivative and application of LHRH antagonist derivative
InactiveCN102675418AGood LHRH antagonist activityLow histamine releasing activityPeptide/protein ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneDiseaseSexual hormones
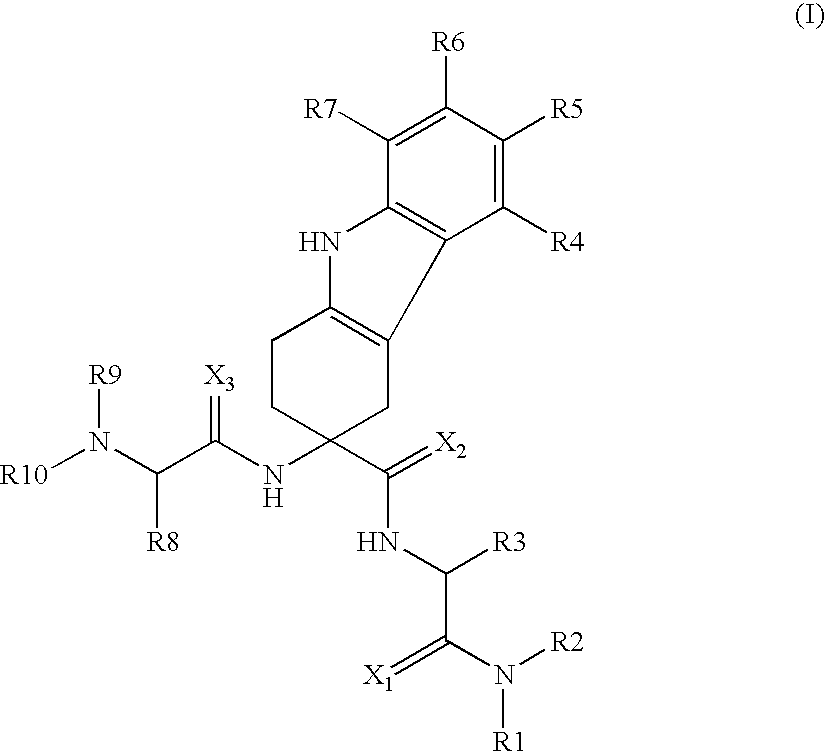
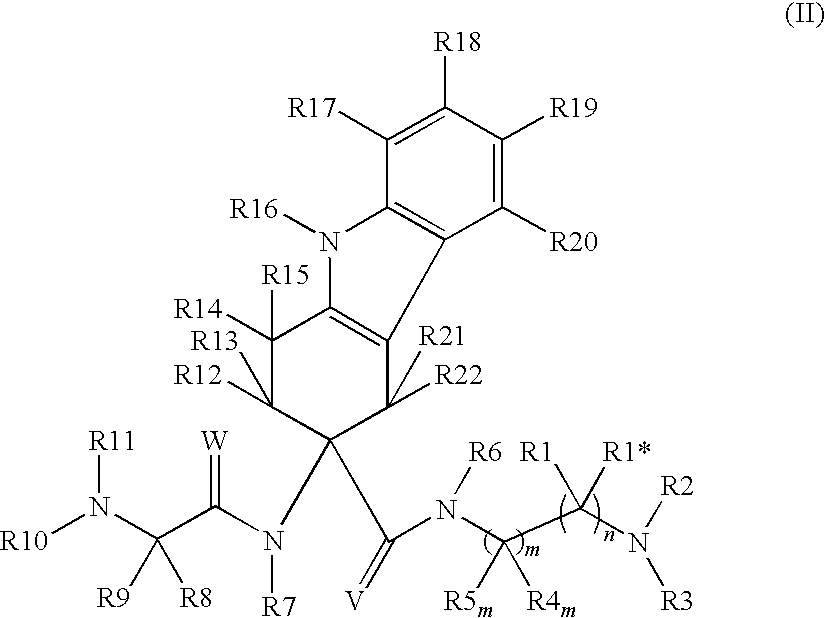
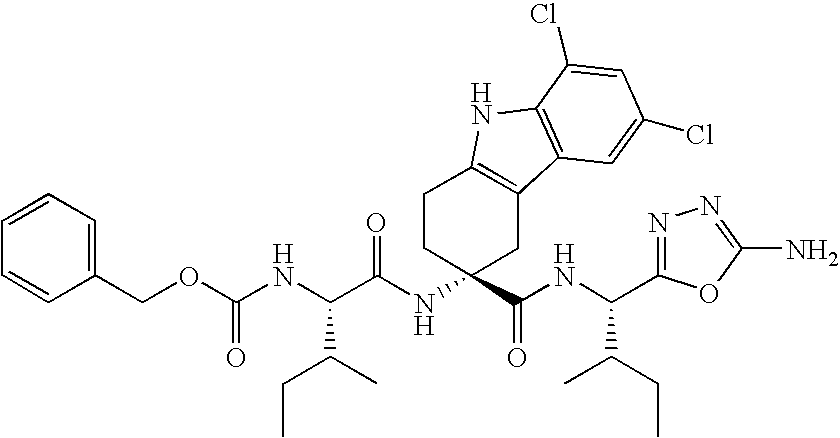
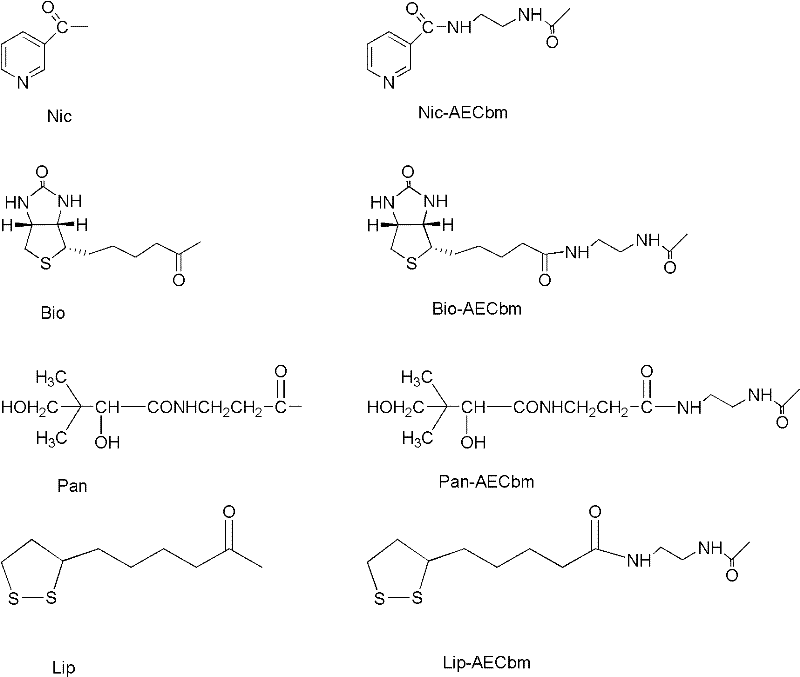
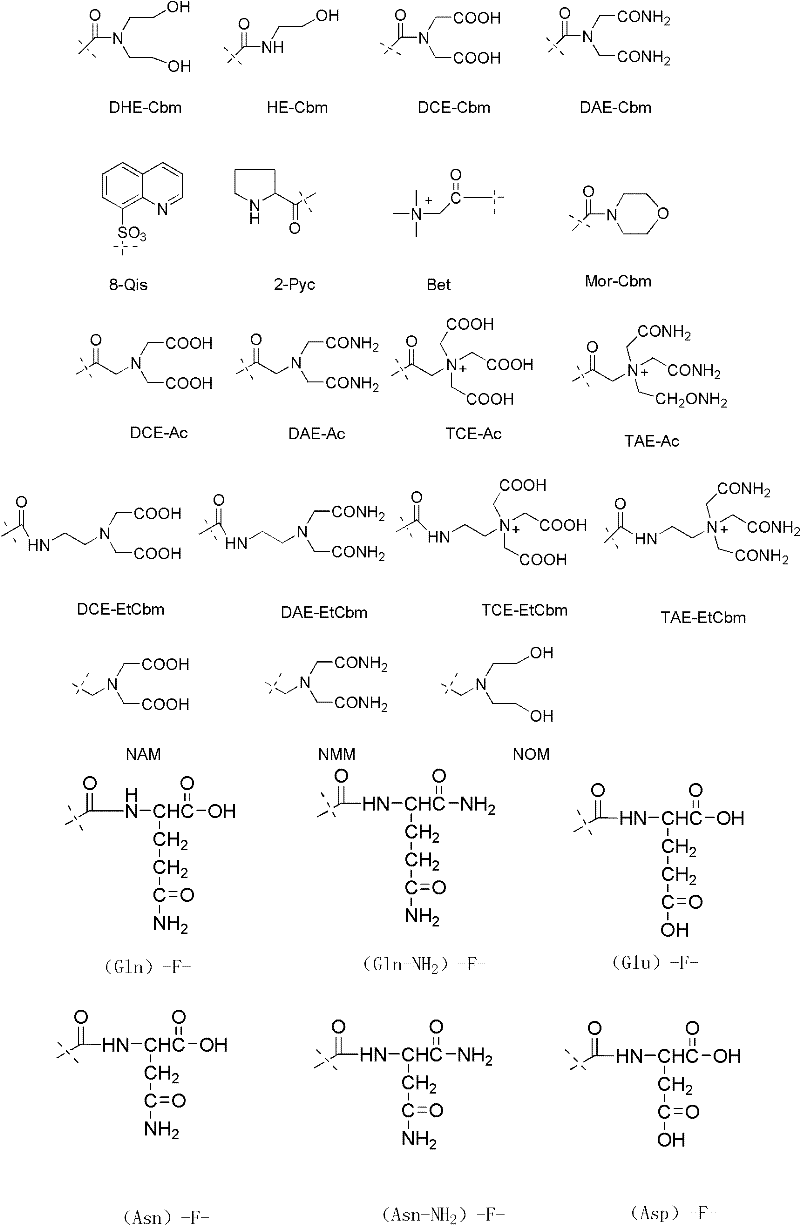
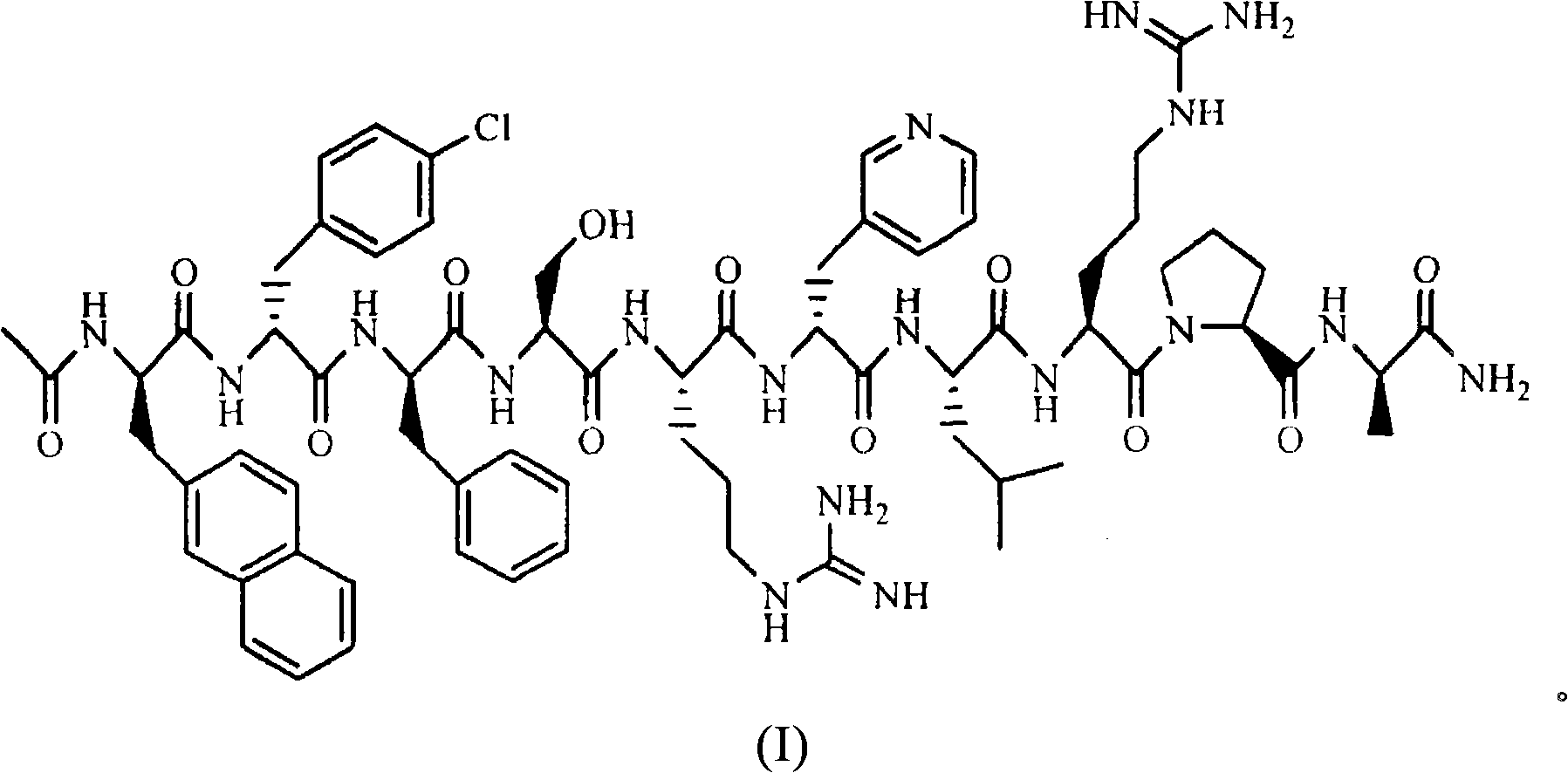
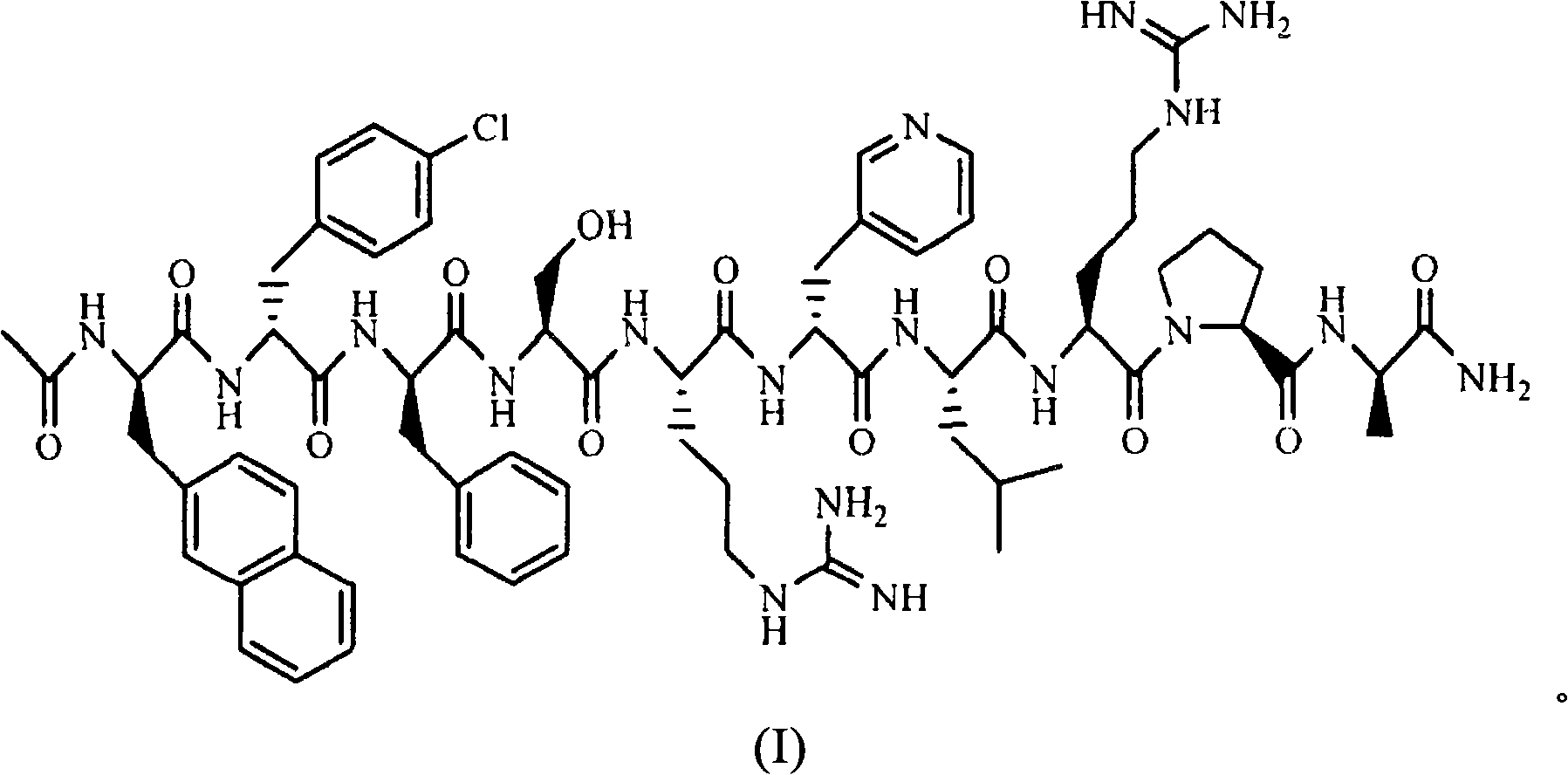
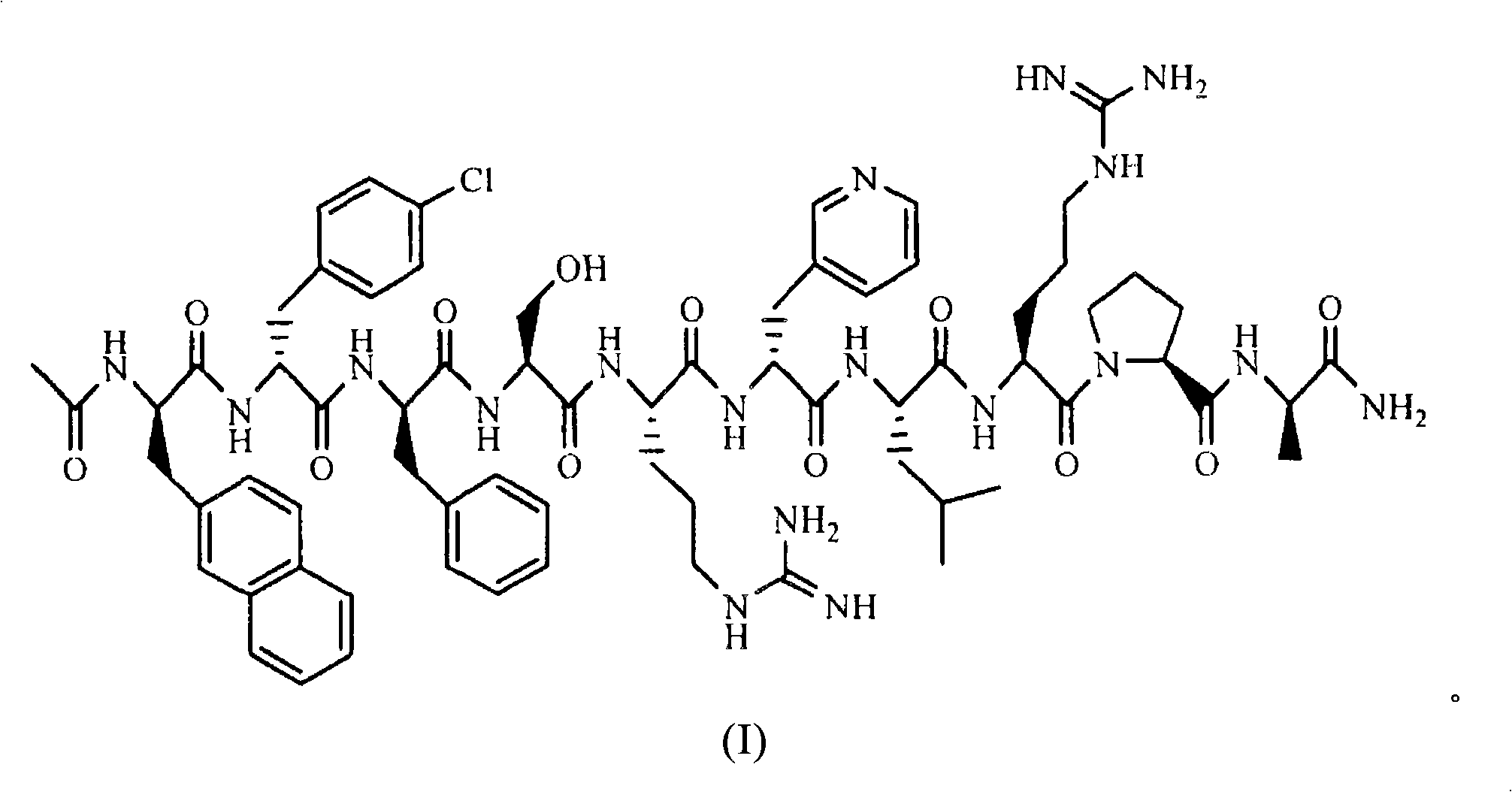
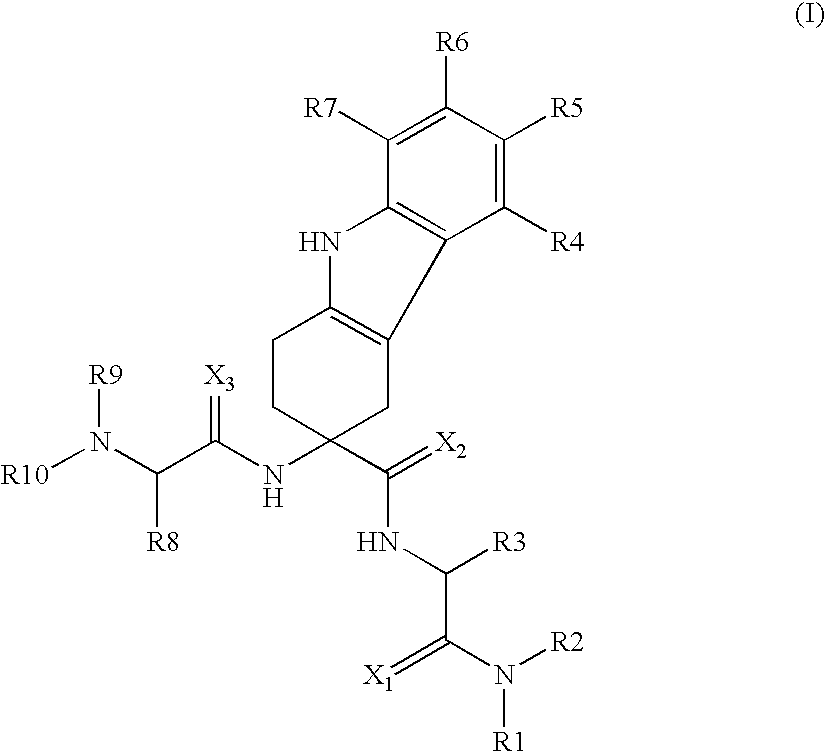
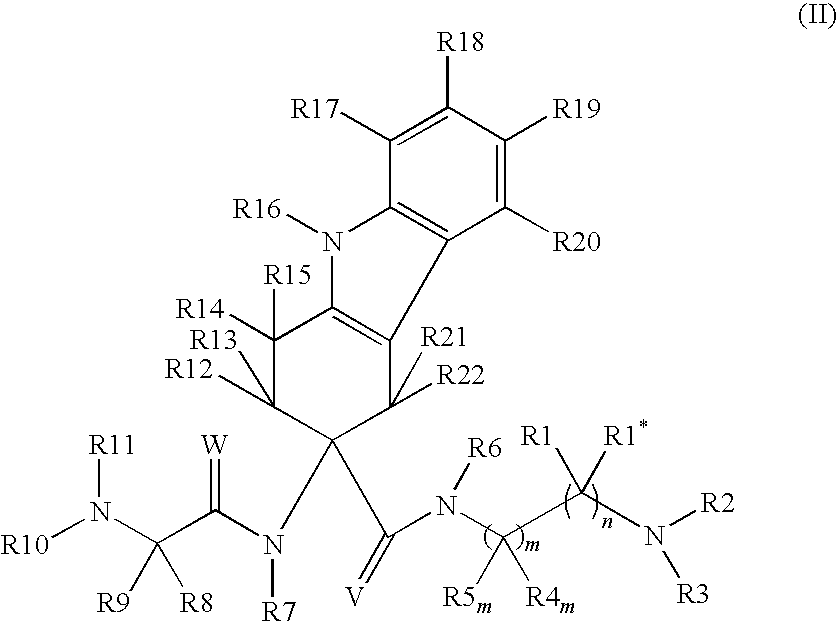
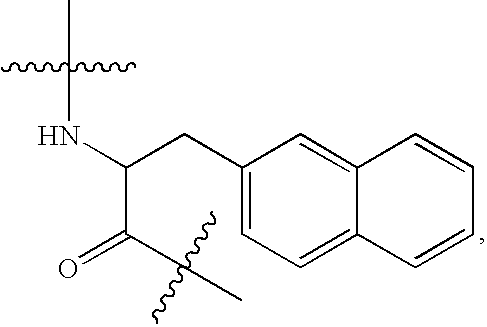
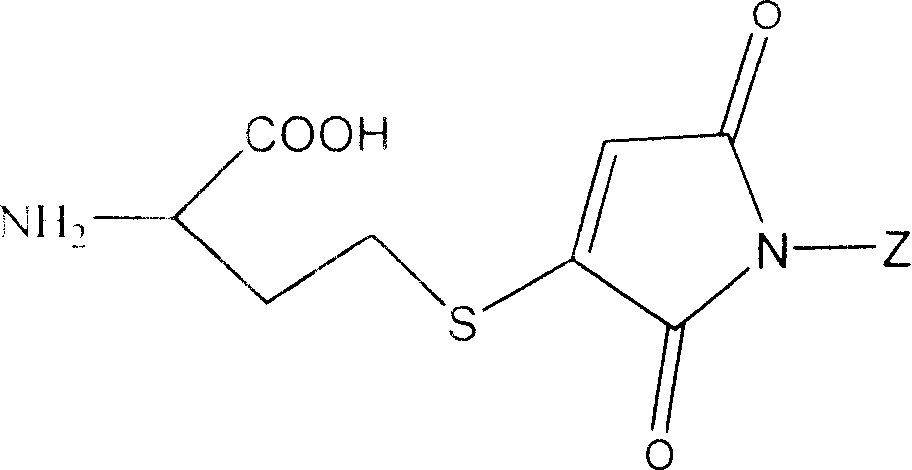
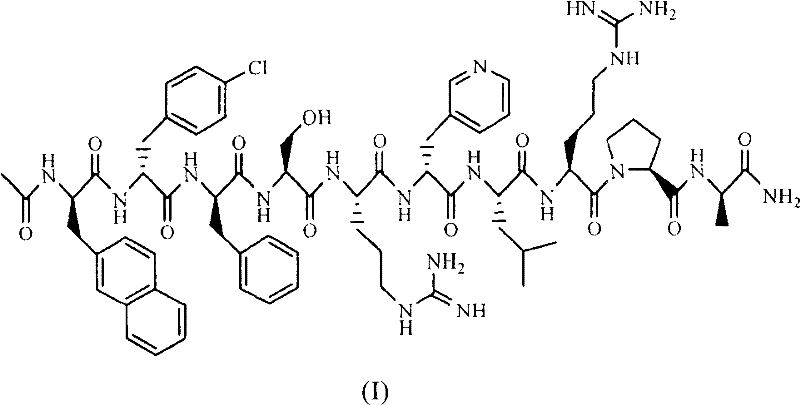
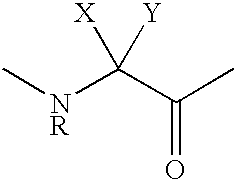
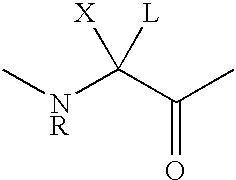
The invention belongs to the field of medicine and chemistry and particularly relates to a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) antagonist derivative which is represented as formula (I), a preparation method of the LHRH antagonist derivative and application for preparation of drugs curing related sex hormone diseases or contraceptives. The invention also relates to a stereoisomeride of the LHRH antagonist derivative which is represented as the formula (I), a solvate of the LHRH antagonist derivative which is represented as the formula (I), or physio-toxicity-free salt of the LHRH antagonist derivative which is represented as the formula (I) and a pharmaceutical composition which contains compounds such as the LHRH antagonist derivative, the stereoisomeride, the solvate or the salt. An LHRH antagonist is modified with a water soluble group and a water soluble vitamin structure, the obtained LHRH antagonist derivative can maintain the activity of original antagonists, has low histamine-releasing activity and is beneficial to the clinic application and the water solubility is increased. The formula (I) is R-D-NAI-D-Cpa-D-Aaa3-Ser-Aaa5-Aaa6-Leu-Aaa8-Pro-D-Ala-B.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Sustained release preparation for injection of LHRH antagonist substances and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a sustained release preparation for injection of LHRH antagonist substances and a preparation method thereof. The sustained release preparation comprises a therapeutic effective dose of an active component in a structure of a formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs thereof, and oily solvent.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
LHRH antagonist with long-acting low-histamine release side effect
The invention relates to a decapeptide derivative with LHRH receptor antagonism activity and actions of restricting a pituitarium to secrete gonadotrophins and restricting a gonad to secrete steroid hormones, a preparation method thereof, a medicine composition containing the decapeptide derivative and the application of the medicine composition on treating prostatic cancer, endometrial cancer, interrelated sex hormone dependence diseases relative to reproduction, contraception, and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Tolerance to Graft Prior to Thymic Reactivation
InactiveUS20070274946A1Enhanced graft acceptanceFunction increaseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTolerabilitySterol
The present disclosure provides methods for inducing tolerance in a recipient to a mismatched graft of an organ, tissue, and / or cells, by disrupting sex steroid signaling in the patient, wherein the bone marrow and other immune cell functionality is improved without, prior to, or concurrently with, thymic regeneration. In some embodiments, sex steroid signaling in the patient, is interrupted or ablated by the administration of LHRH agonists, LHRH antagonists, anti-LHRH receptor antibodies, anti-LHRH vaccines, anti-androgens, anti-estrogens, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), selective progesterone response modulators (SPRMs), ERDs, aromatase inhibitors, or various combinations thereof.
Owner:NORWOOD IMMUNOLOGY
Use of lhrh antagonists for intermittent treatments
The invention relates to methods of treatment or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathological conditions with at least one LHRH antagonist, in particular at least one peptidomimetic LHRH antagonistsuch that the at least one LHRH antagonist is administered in a dose, which does not cause chemical (hormonal) castration.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
LHRH-antagonists in the treatment of fertility disorders
InactiveUS7393834B2Reduces the severe adverse eventsPatient compliance is goodBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMenstrual cycleLhrh antagonist
Owner:ZENTARIS IVF
Method of preparing peptide
InactiveUS7569548B2Few stepsHigh yieldTetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsCombinatorial chemistryLhrh antagonist
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Intermediates for lhrh antagonist synthesis, process for their production, and process for lhrh antagonist production
InactiveUS20050124788A1High purityHigh yieldTripeptide ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneSynthetic analogueCombinatorial chemistry
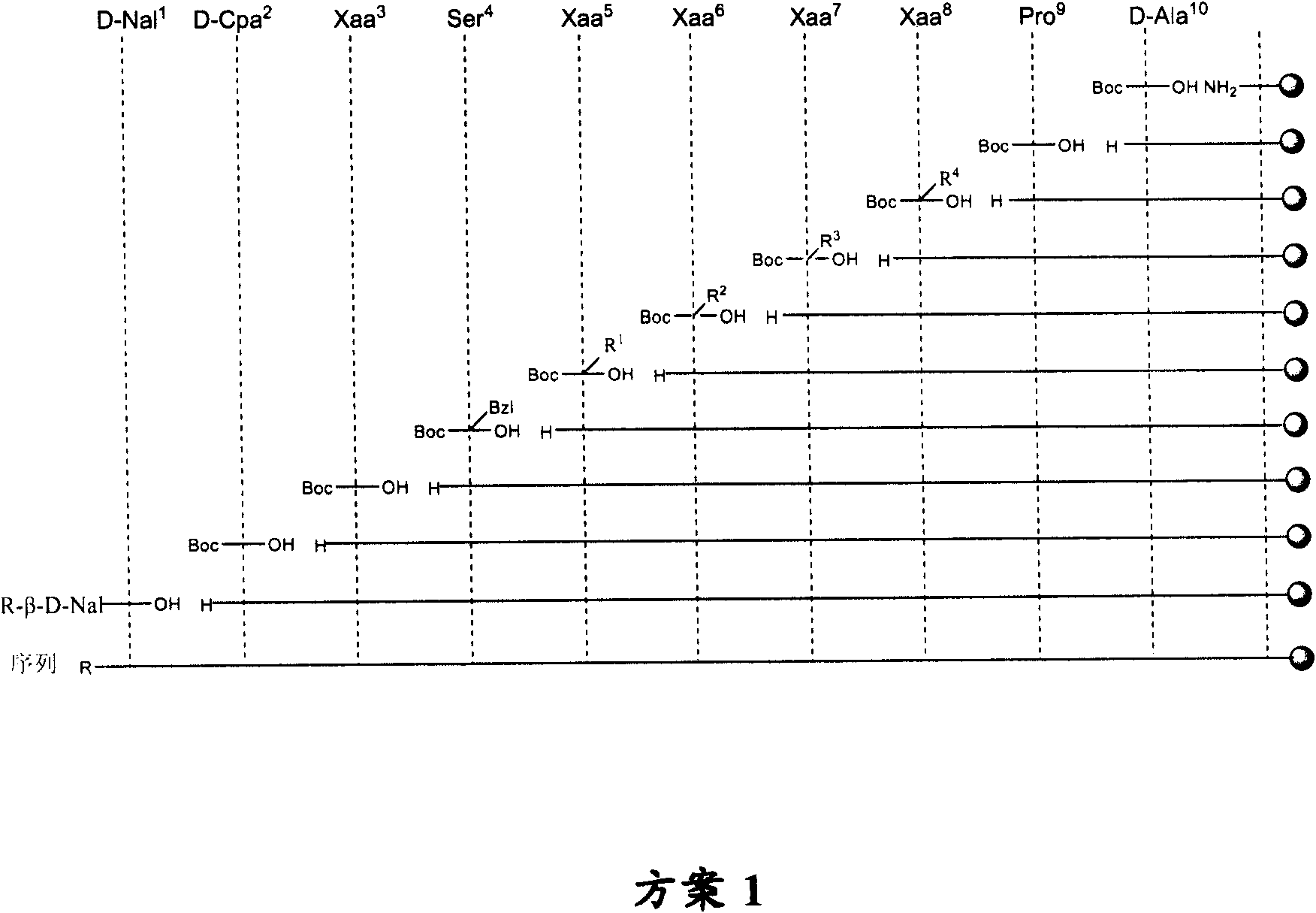
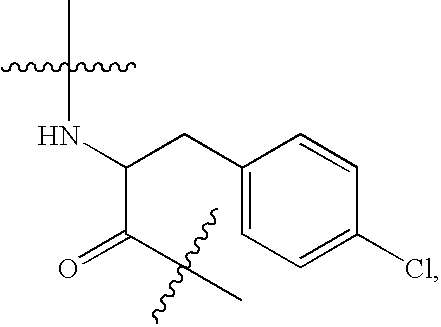
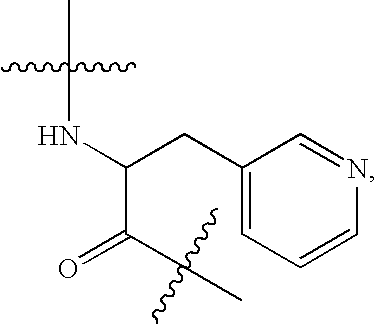
The novel tripeptides Ac-D-2Nal-D-4ClPhe-D-3Pal-OH and Boc-D-2Nal-D-4ClPhe-D-3Pal-OH are intermediates useful in the synthesis of LHRH analogs by coupling with suitable heptapeptides, in particular with the heptapeptides P1-Ser(P2)-NMeTyr(P3)-D-Lys(Nic)-Leu-Lys(iPr, P4)-Pro-D-AlaNH2 and P1-Ser(P2)-NMeTyr(P3)-D-Asn-Leu-Lys(iPr, P4)-Pro-D-AlaNH2.
Owner:POLYPEPTIDE LAB AS
Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy
InactiveUS20050002913A1High activityImprove functional statusBiocideGenetic material ingredientsLhrh antagonistBiology
The present disclosure provides methods for gene therapy utilizing hematopoictic stem cells, lymphoid progenitor cells, and / or myeloid progenitor cells. The cells are genetically modified to provide a gene that is expressed in these cells and their progeny after differentiation. In one embodiment the cells contain a gene or gene fragment that confers to the cells resistance to HIV infection and / or replication. The cells are administered to a patient in conjunction with treatment to reactivate the patient's thymus. The cells may be autologous, syngeneic, allogeneic or xenogeneic, as tolerance to foreign cells is created in the patient during reactivation of the thymus. In one embodiment the hematopoietic stem cells are CD34+. The patient's thymus is reactivated by disruption of sex steroid mediated signaling to the thymus. In another embodiment, this disruption is created by administration of LHRH agonists, LHRH antagonists, anti-LHRH receptor antibodies, anti-LHRH vaccines or combinations thereof.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
LHRH-antagonists in the treatment of fertility disorders
InactiveUS20050049200A1Patient compliance is goodLow costBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOvulation timesMenstrual cycle
A method of treating infertility disorders by 1) administering an LH-RH antagonist, preferably Cetrorelix, in amounts to selectively suppress endogenous LH but not FSH secretion and 2) inducing follicle growth by administration of exogenous gonadotropin. The selective suppression OF LH allows FSH secretion to be at natural levelS thereby not affecting individual estrogen development. The LH-RH antagonist can be given as a single or dual subcutaneous dose in the range of 1 mg to 10 mg, preferably 2 mg-6 mg. In multiple dosing-posology, LH-RH antagonist can be administered subcutaneously in an amount in the range of 0.1 to 0.5 mg of LH-RH antagonist / day. LH-RH antagonist is applied starting cycle day 1 to 10, preferably on day 4 to 8, and ovulation can be induced between day 9 and 20 of the menstruation cycle by administering rec. LH, native LH-RH, LH-RH agonist or by HCG. In addition rec. LH, native LH-RH or LH-RH agonist can be given to avoid hyperstimulation syndrome and native LH-RH or a LH-RH agonist can be administered to avoid luteal phase stimulation by neutralizing the negative effects of HCG.
Owner:ZENTARIS IVF
Application of initial doses of LHRH analogues and maintenance doses of LHRH antagonists for the treatment of hormone-dependent cancers and corresponding pharmaceutical kits
ActiveUS8921318B2Negative hormone withdrawal symptomsPeptide/protein ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneGynecologyInitial dose
LHRH analogs and LHRH antagonists for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of hormone-dependent cancers, in particular prostate cancer, prostate carcinoma and / or advanced prostate carcinoma, by administering an initial dose of an LHRH analog over a first period sufficient to effect hormonal castration, then administering a maintenance dose of an LHRH antagonist over a second period, the dose being insufficient to achieve and / or maintain hormonal castration.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
Novel LHRH antagonist
The present invention relates to decapeptide derivatives with LHRH receptor antagonistic activity, the function of inhibiting pituitary gland secretion of gonadotropin and gonadal secretion of steroid hormones, their preparation method, their pharmaceutical composition and their role in the treatment of prostate cancer and Use for sex hormone dependence-related diseases related to reproduction.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
LHRH (luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonist) lyophilized powder injection with improved stability
ActiveCN102144980BQuality improvementDefinite curative effectPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntioxidantPatient compliance
The invention relates to an LHRH (luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone antagonist) lyophilized powder injection with improved stability. The preparation mainly comprises cetrorelix as an active ingredient, an excipient, a pH regulator, an antioxidant and a local analgesic agent, wherein the addition of the antioxidant can improve the stability of the preparation, and the addition of the local analgesic agent can relieve the pains of patients while having no impact on the active ingredient. The preparation process of the preparation mainly comprises weighing, dissolving, adsorbing pyrogen with activated carbon, filtering, final filtering, subpackaging, vacuum drying, plugging, and covering. The LHRH lyophilized powder injection provided by the invention can control the stimulatory function of an ovary, prevent early release of immature ovarian follicles, and help become pregnant. The LHRH lyophilized powder injection has the advantages of stable quality, definite therapeutic effect, and good patient compliance.
Owner:深圳市健翔生物制药有限公司
Use of LHRH antagonists for intermittent treatments
The invention relates to methods of treatment or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathological conditions with at least one LHRH antagonist, in particular at least one peptidomimetic LHRH antagonist such that the at least one LHRH antagonist is administered in a dose, which does not cause chemical (hormonal) castration.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
Injection sustained-release preparation of LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) antagonist substance and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102525914APeptide/protein ingredientsSolution deliveryAntagonist substanceHormones regulation
The invention provides an injection sustained-release preparation containing an LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) antagonist substance or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Lhrh antagonist peptides
The present invention is directed to a method for essentially complete oxidation of a concentrated liquor containing oxidizable organic matter. Each step of the method is performed under substantially superatmospheric pressure. Initially, the liquor is preheated to a temperature higher than about 10° C. below the boiling point of water at the substantially superatmospheric pressure. A feed formed of the concentrated liquor is then essentially completely oxidized at a temperature of at least 800° C. in the presence of a gas comprising at least sixty percent by volume of oxygen to form a suspension of a hot gas and a molten slag. The molten slag is separated from the hot gas before the slag is dissolved in water to form a brine. The separated hot gas is then cooled to a temperature below 250° C. by quenching with an aqueous liquid. Finally, the aqueous liquid is separated from the hot gas.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
3',3'-N-substituted macrolide LHRH antagonists
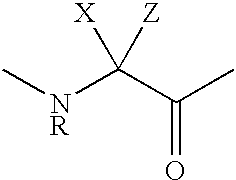
Disclosed are 3',3'-N-bisdesmethyl-3',3'-N-bis-substituted-6-O-methyl-11-deoxy-11,12 -cyclic carbamate erythromycin A derivatives of formula (I) which are antagonists of lutenizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH). Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, methods of using the compounds and the process of making the same.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Cyclic peptide lhrh antagonist derivatives and their pharmaceutical use
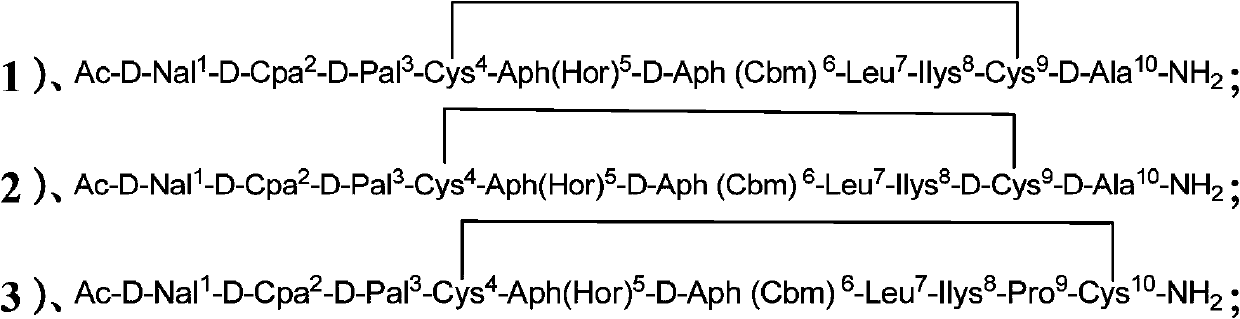
InactiveCN103524599BGood effectImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormoneCyclic peptideDisease
Disclosed in the present invention are cyclopeptide derivatives with LHRH acceptor antagonistic activity of general formula I, the preparation method thereof, the pharmaceutical composition containing them and uses thereof in the preparation of medicines for treating prostate cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer and other sexual hormone dependent diseases related to reproduction, and of contraceptives.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com