Patents
Literature
206results about "Digital filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
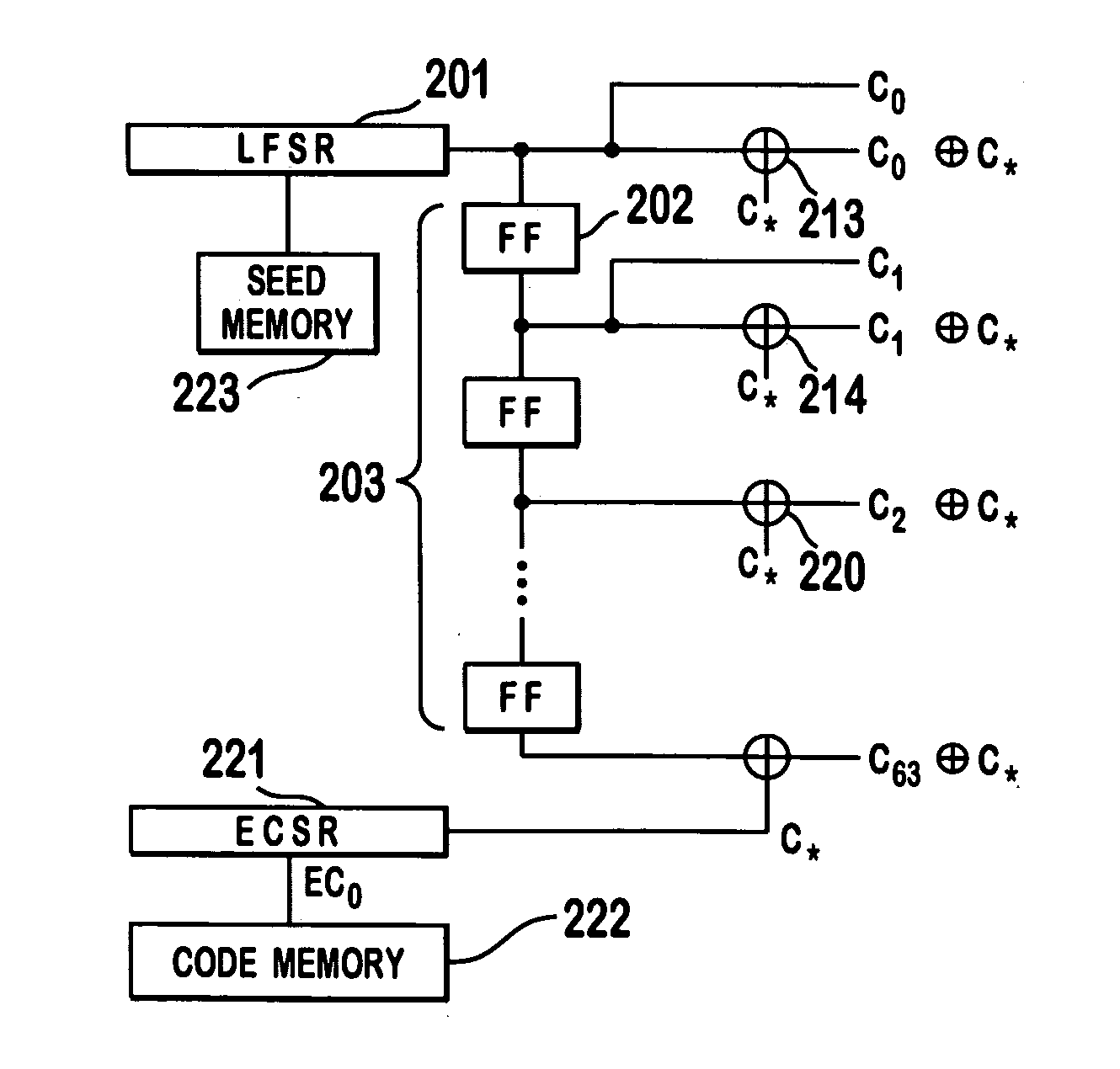
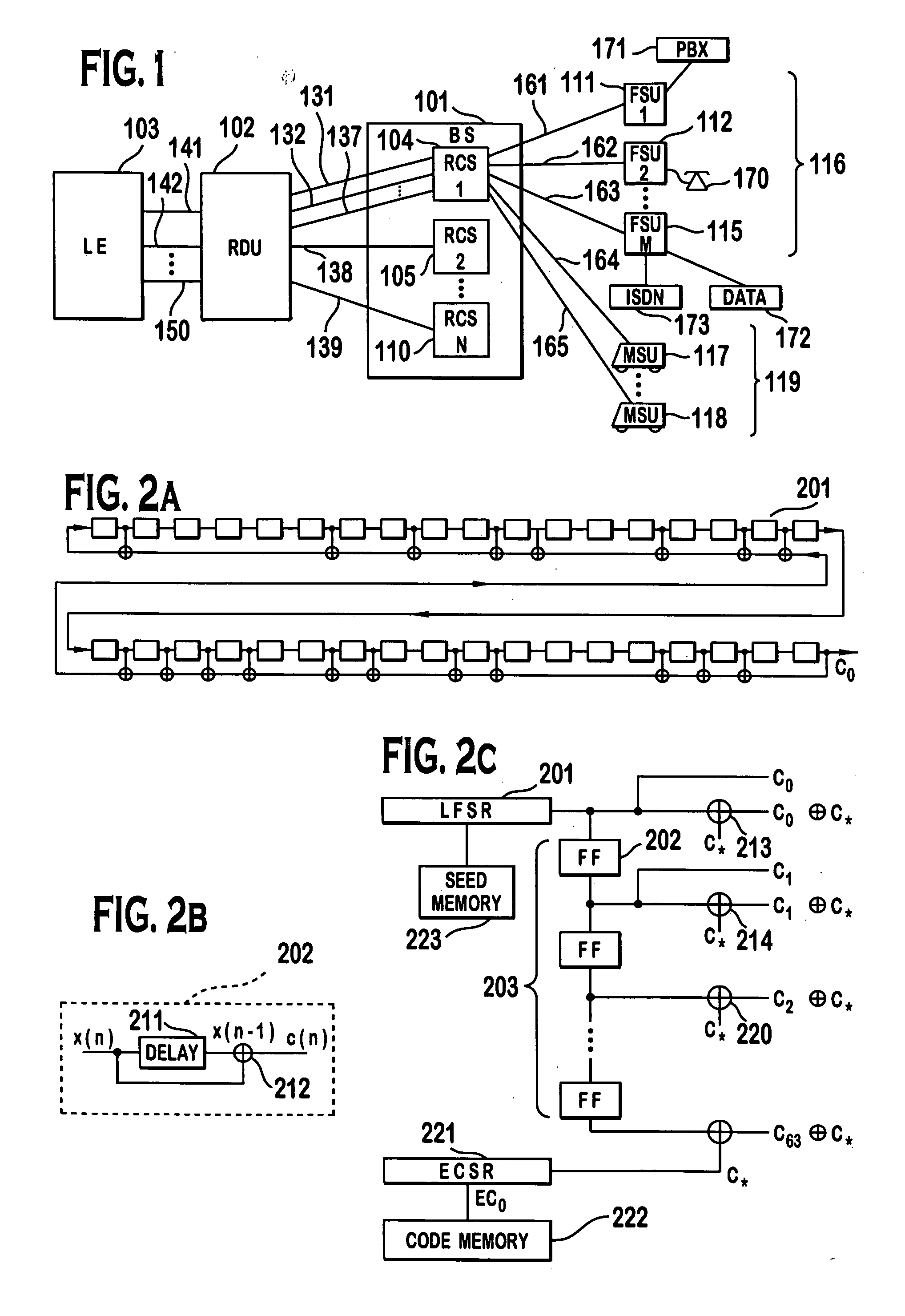
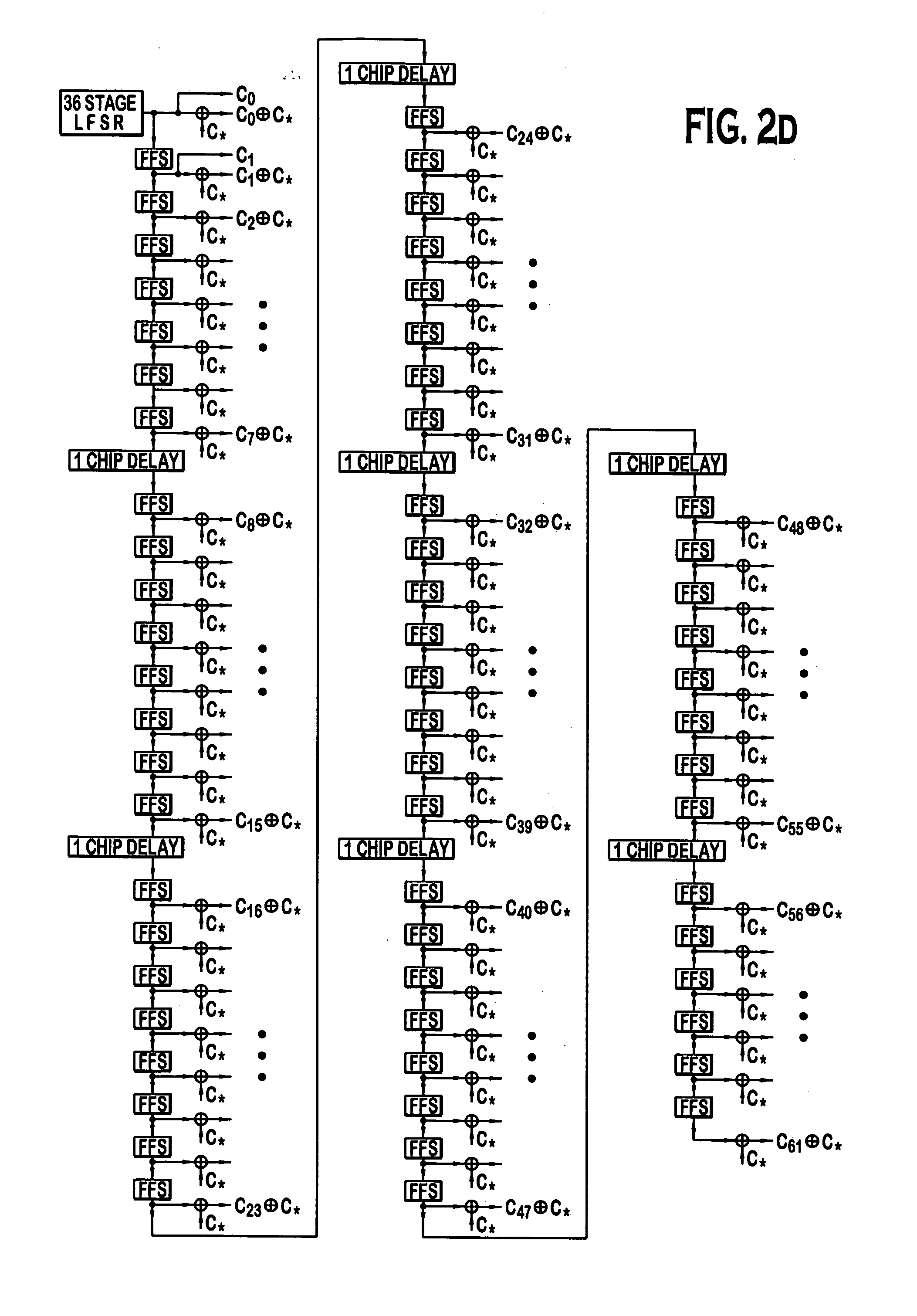
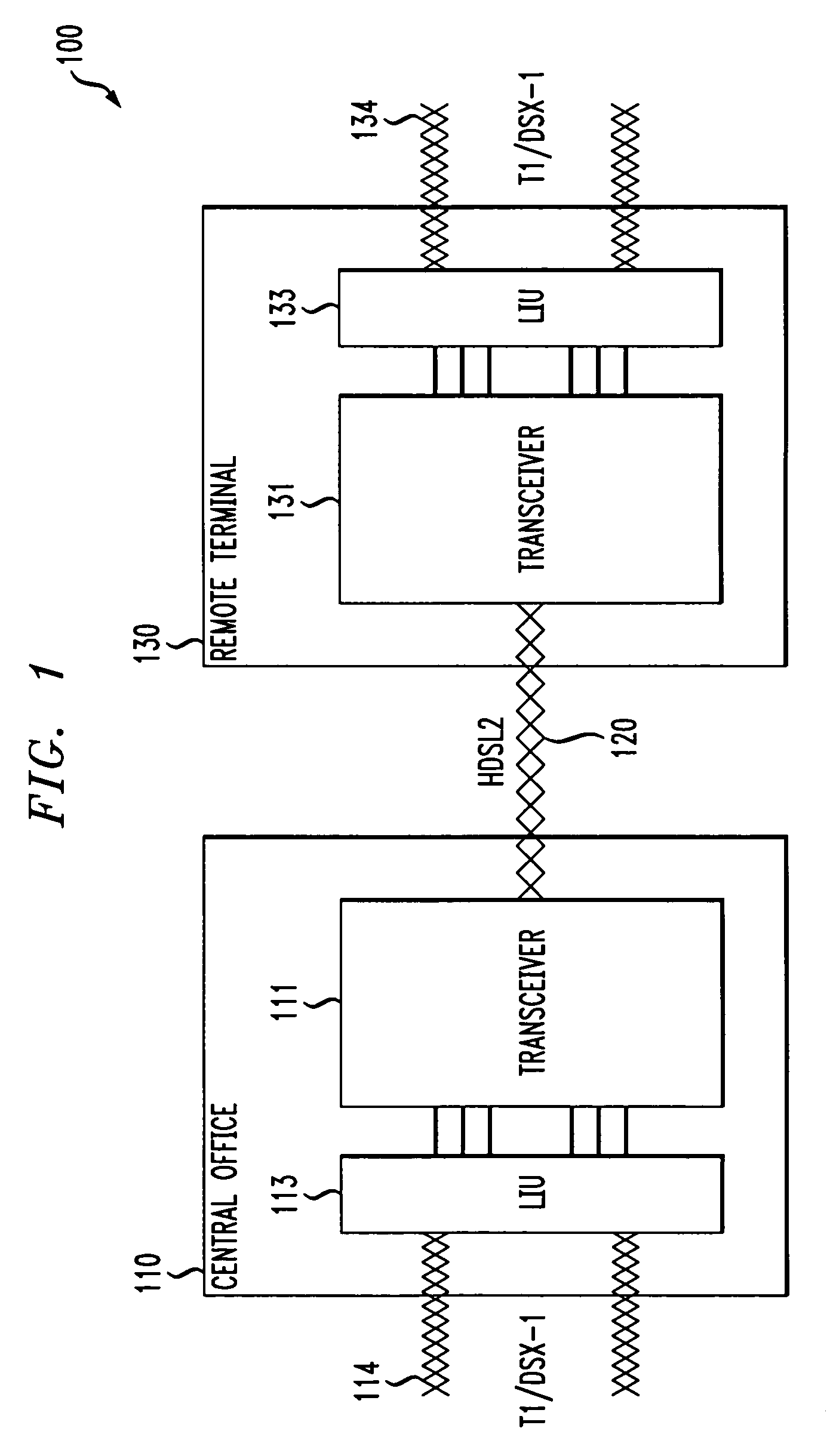
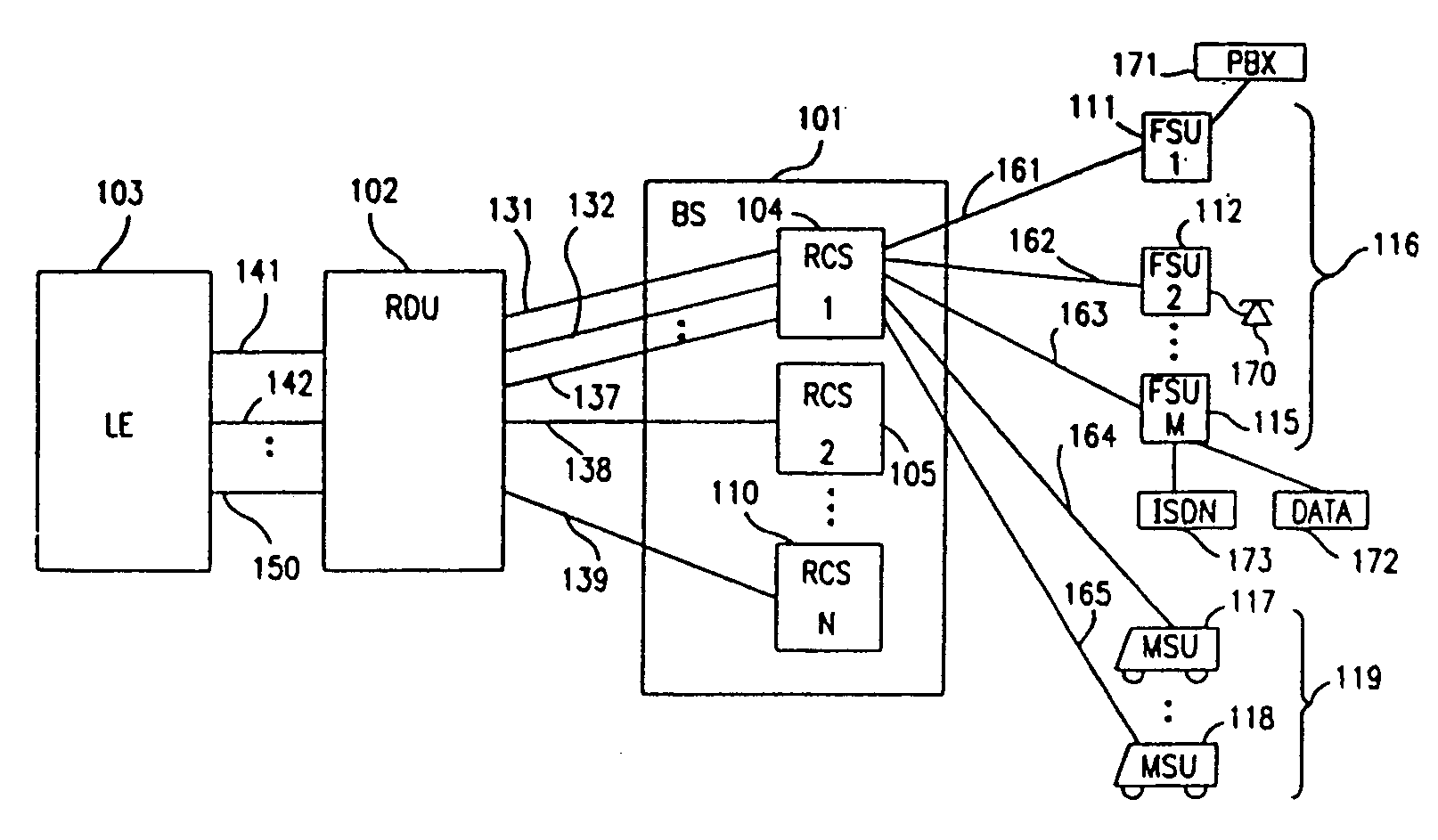
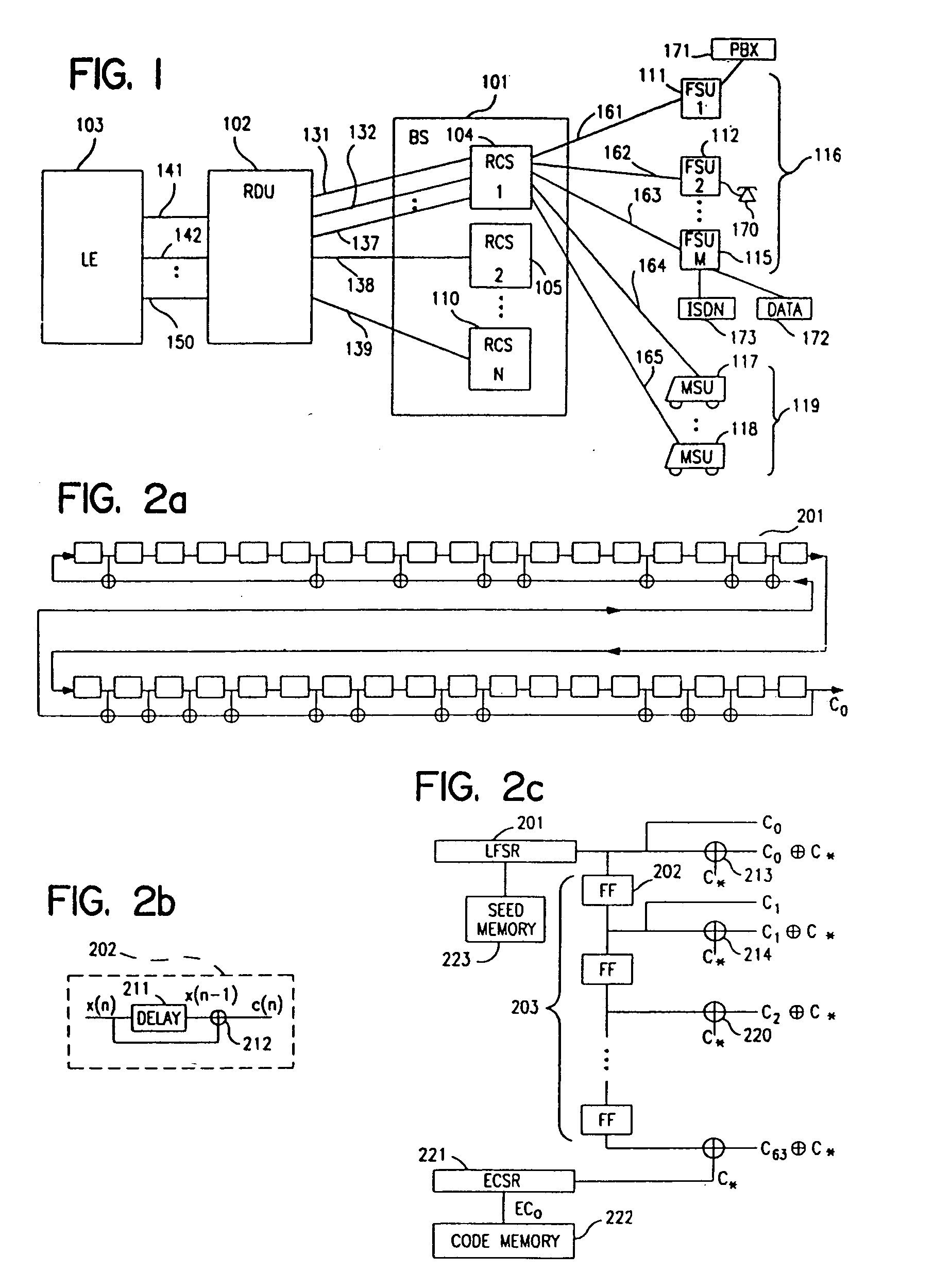
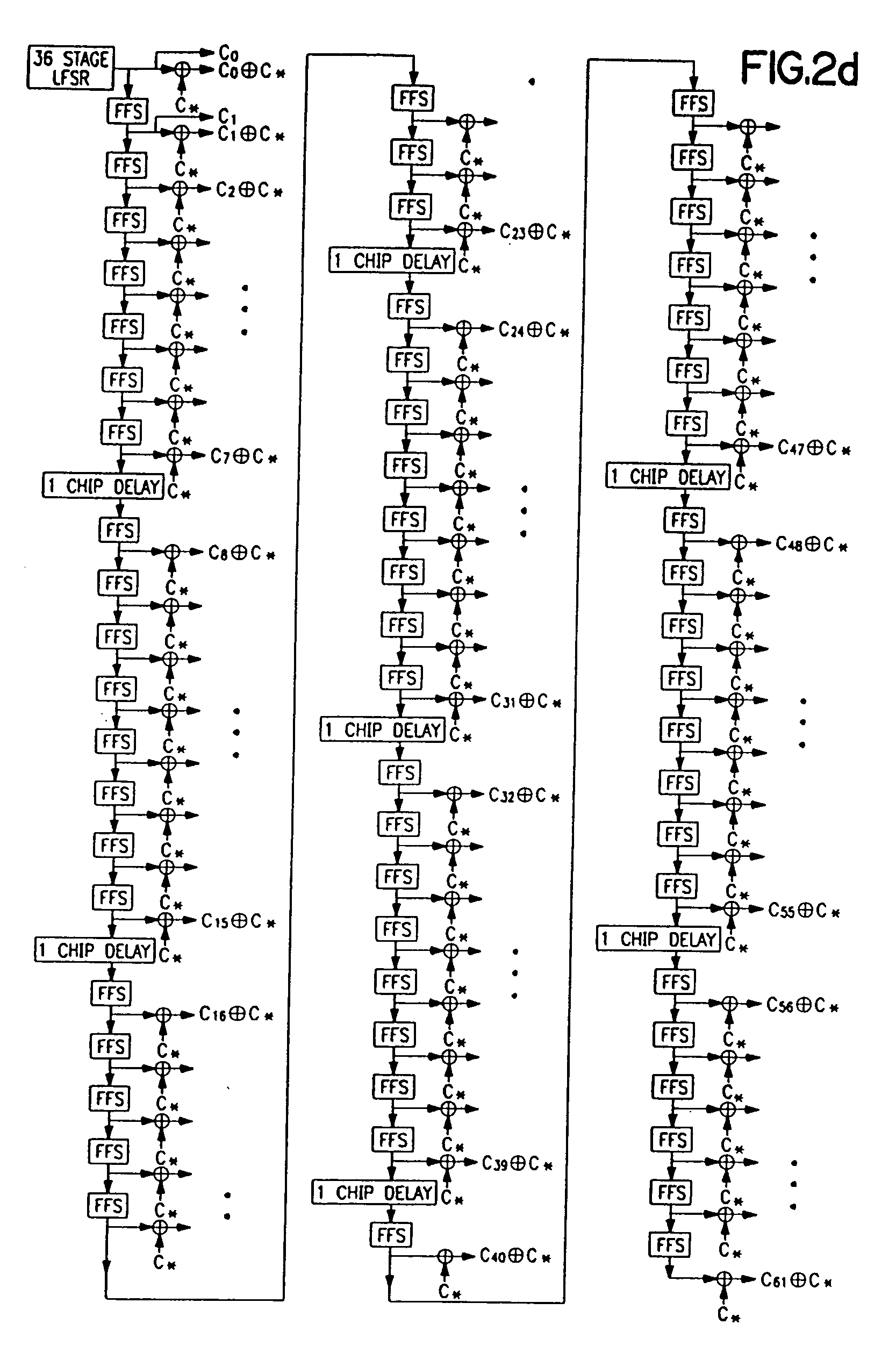
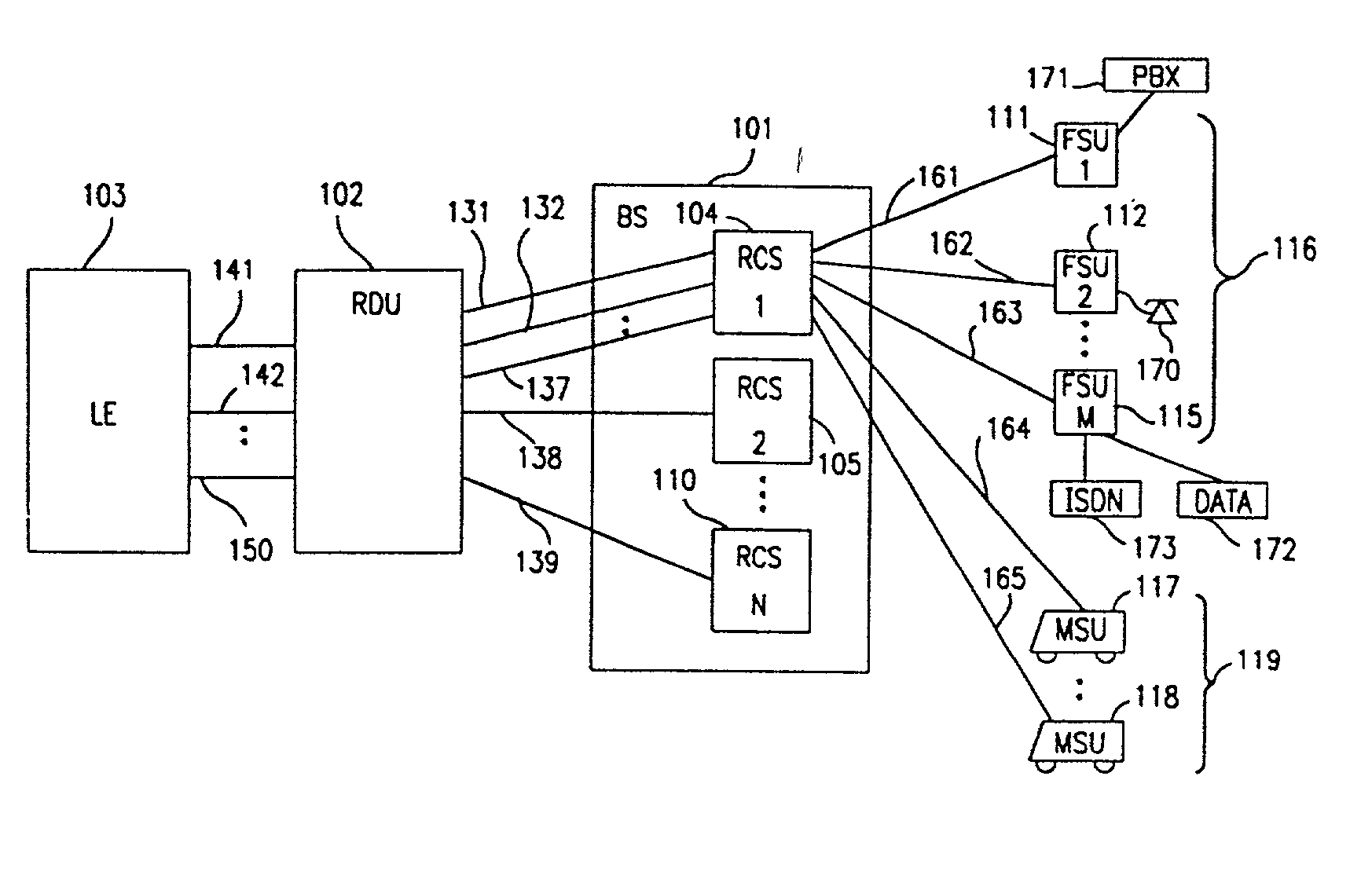
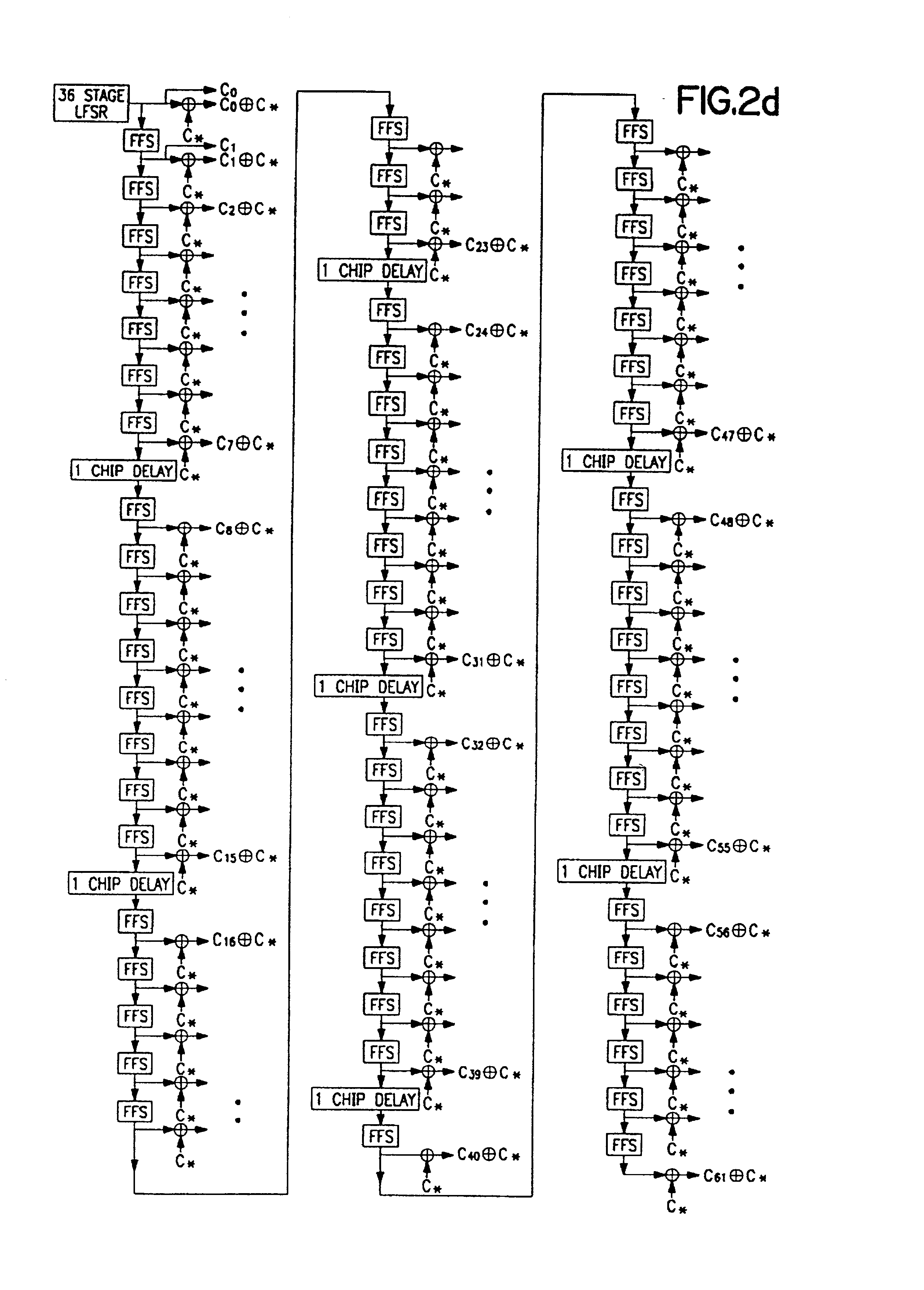
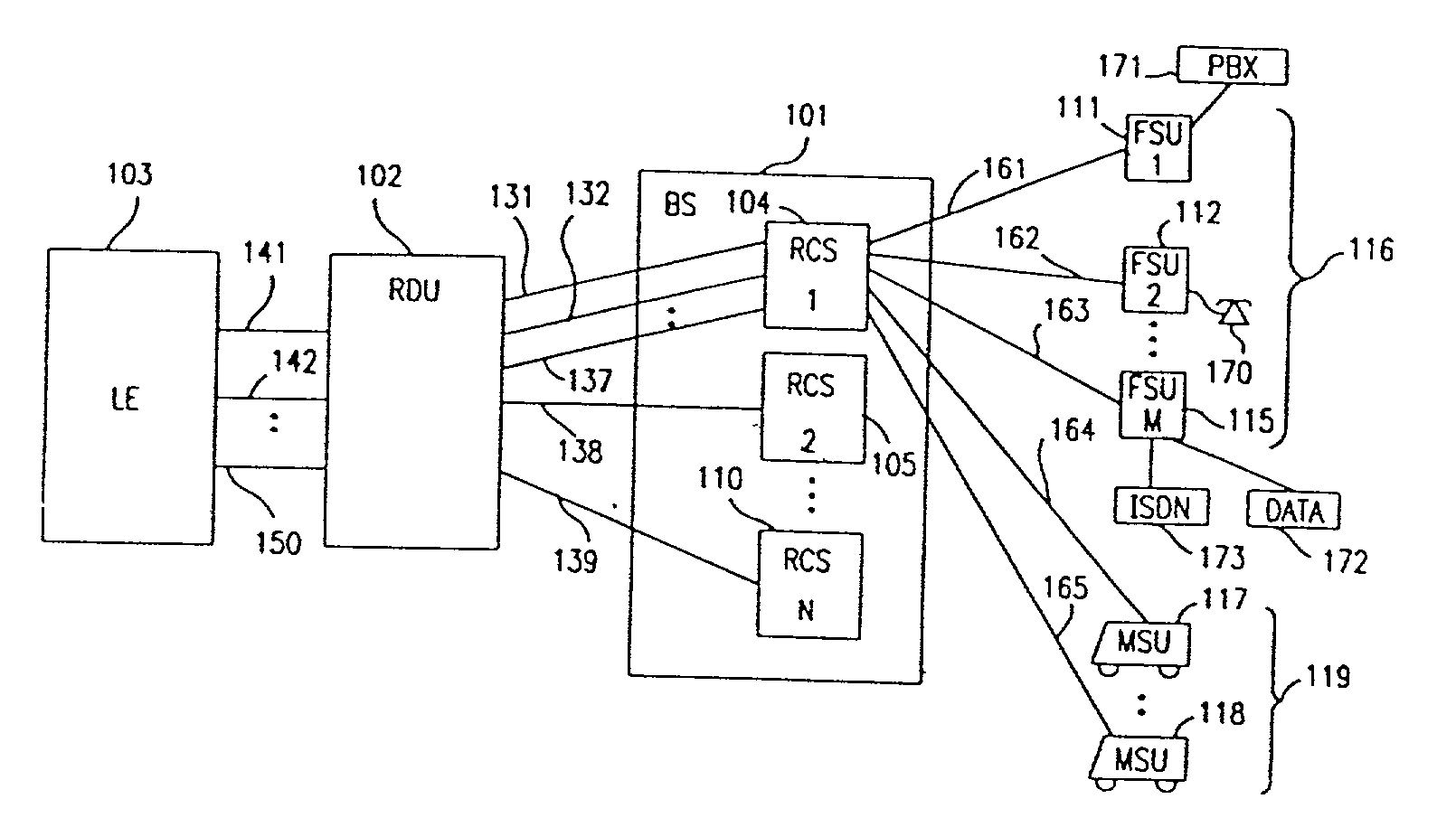
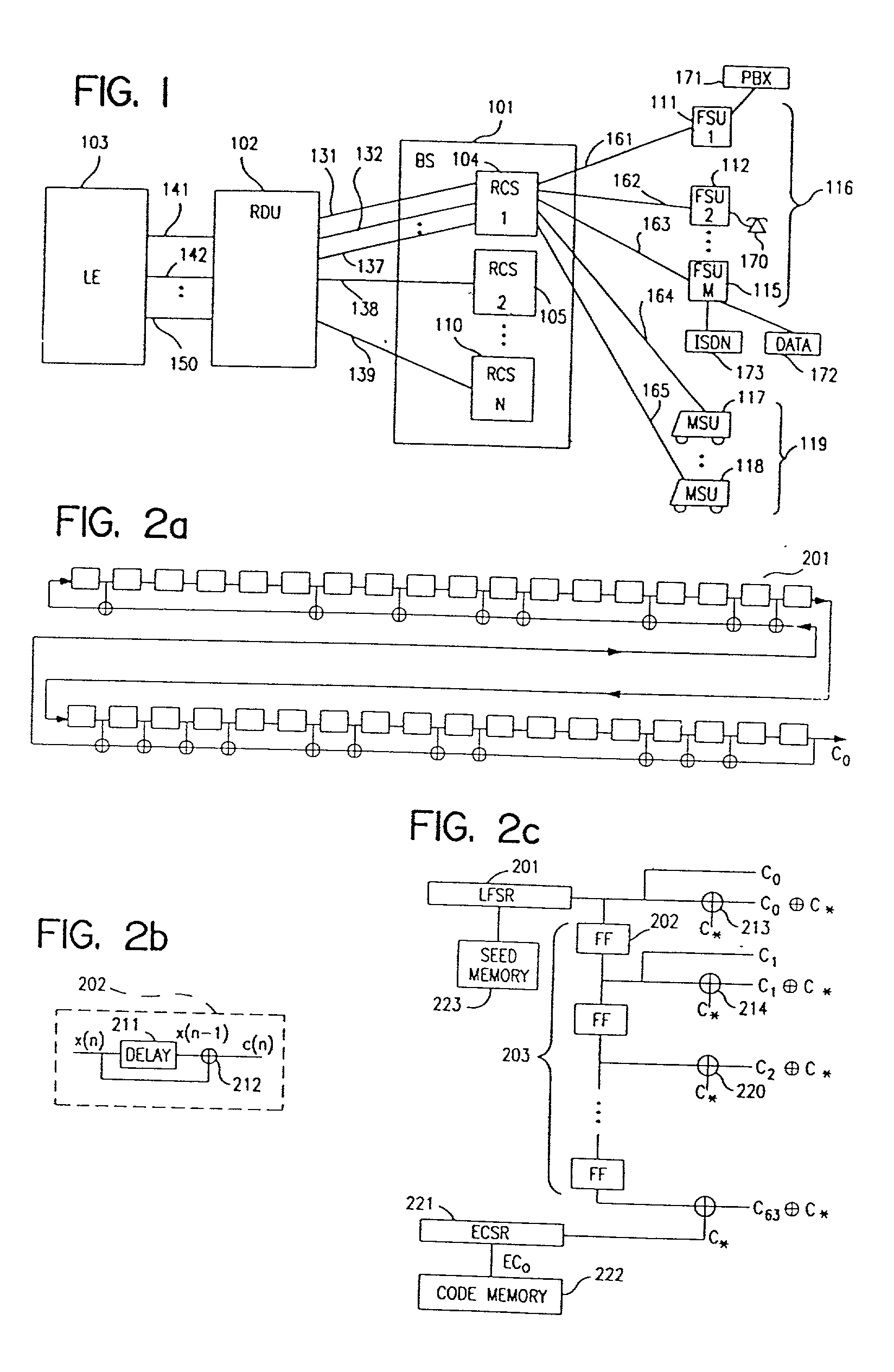
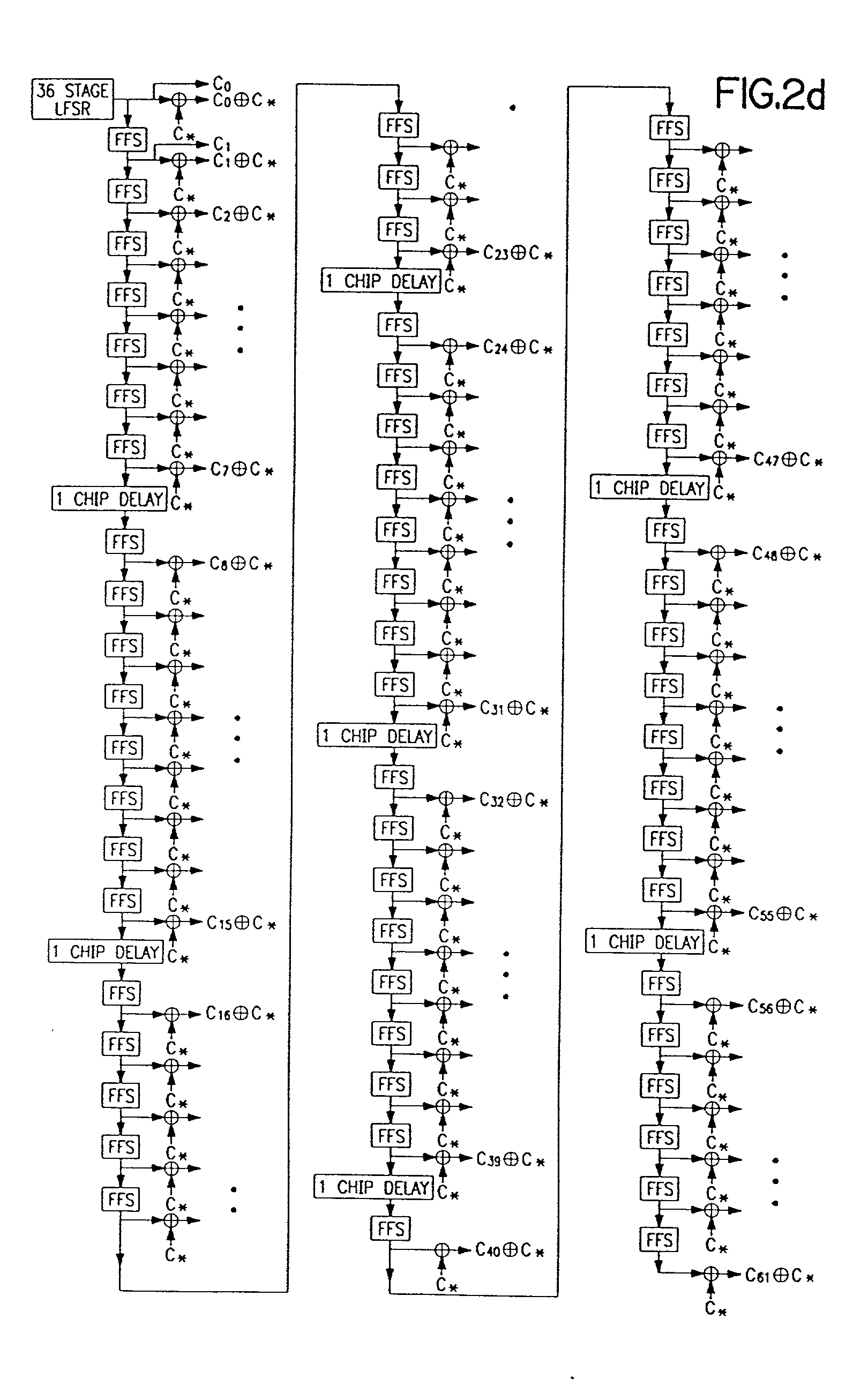
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050265430A1Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessCarrier signal
A system for rapidly acquiring a spreading code, used in a code division multiple access (CDMA) system, comprises a generator for generating a first long code and a second long code, with each long code having a length of N chips. The first long code is different from the second long code. A transmitter transmits the first long code and the second long code at a first phase angle and at a second phase angle, respectively, on a carrier signal over a communications channel using radio waves. The first long code and the second long code may be transmitted at an in-phase (I) angle and at a quadrature-phase (Q) angle, respectively, on the carrier signal. From the communications channel, an I acquisition circuit and a Q acquisition circuit may acquire, in parallel, the first long code and the second long code from the I angle and the Q angle, respectively, of the carrier signal by searching, in parallel, N / 2 chips of the first long code and the second long code.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
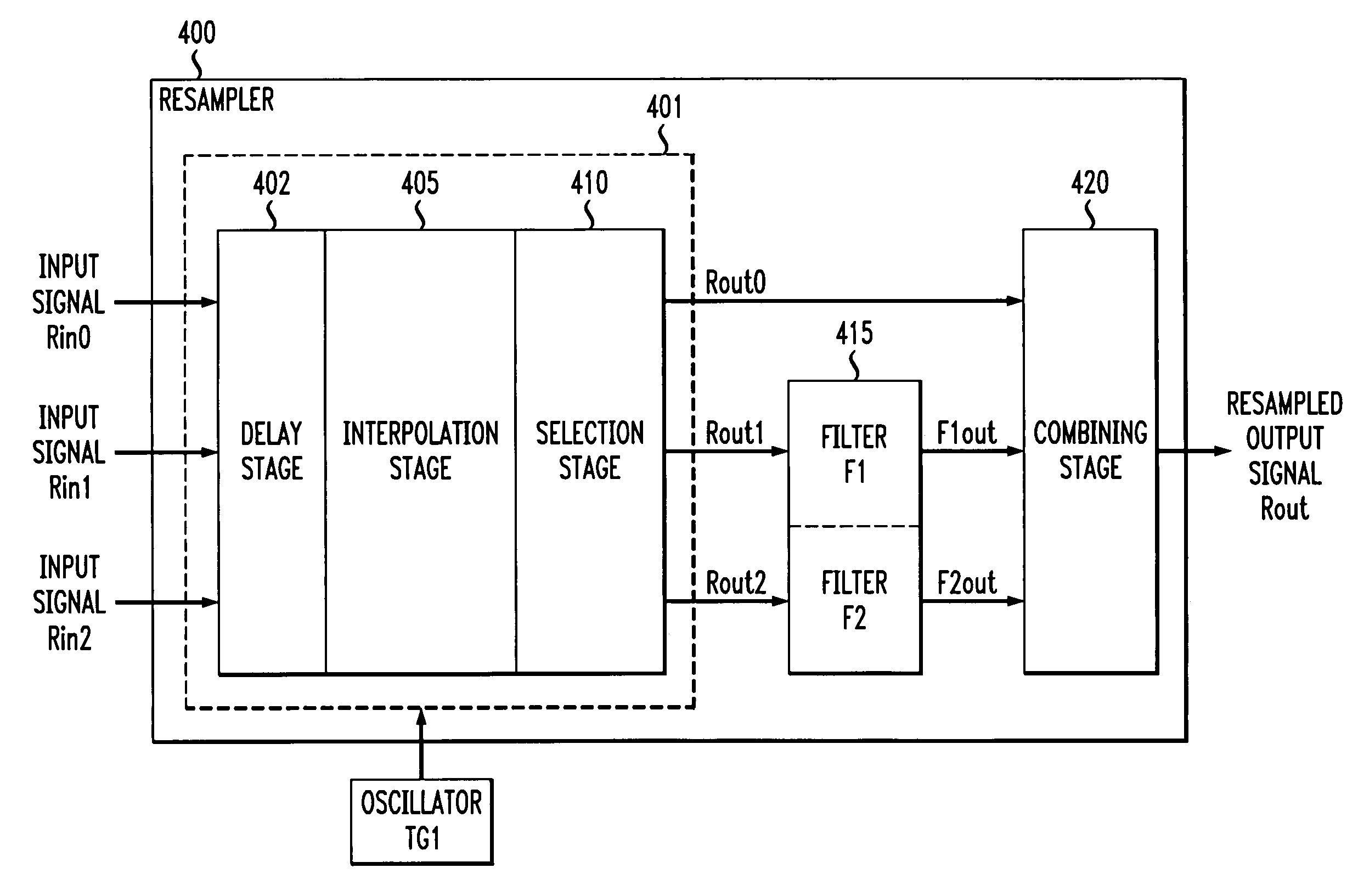
Interpolator, a resampler employing the interpolator and method of interpolating a signal associated therewith
InactiveUS6970511B1Adding significant additional complexityQuality improvementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSignal correlationComputer science
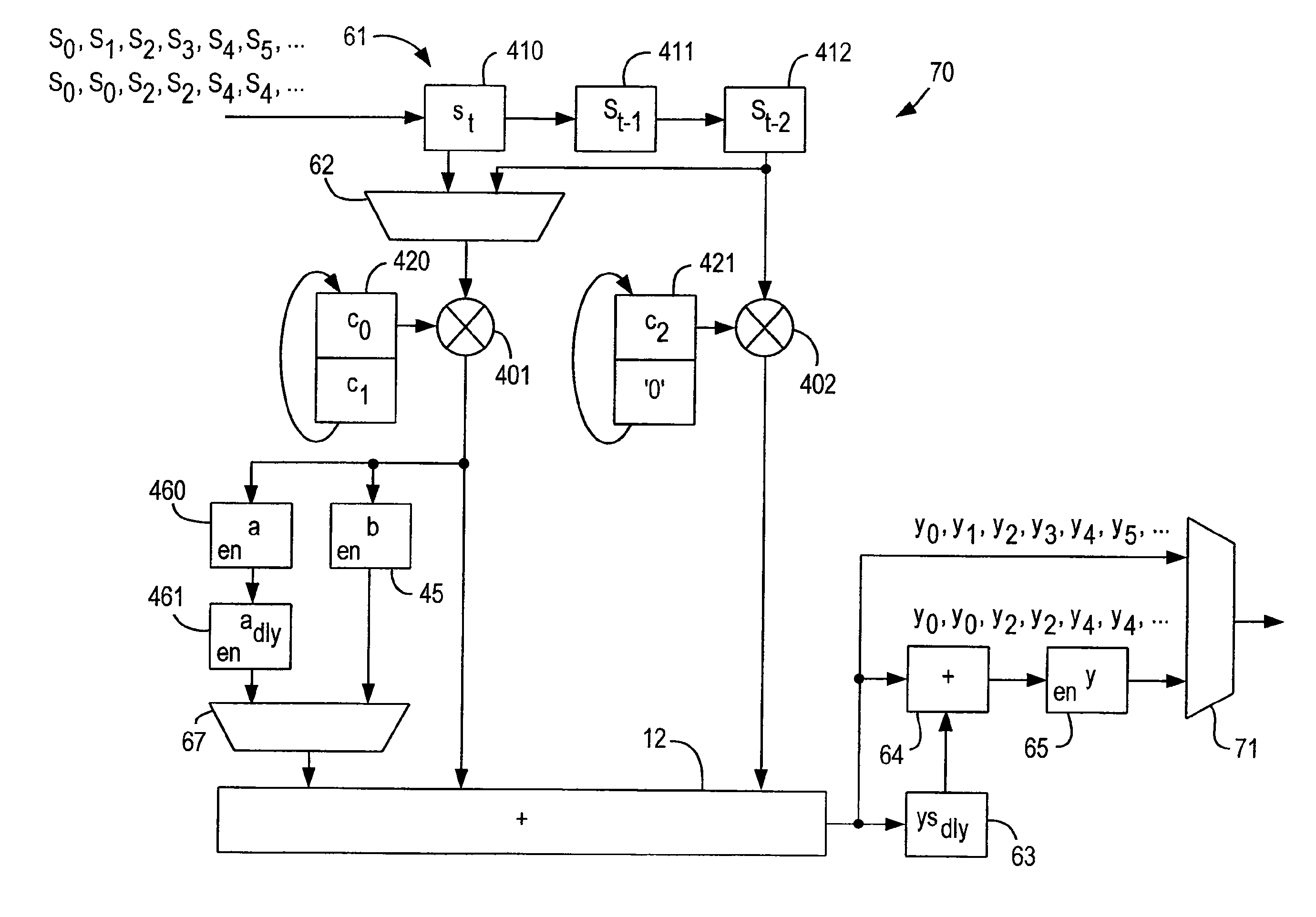
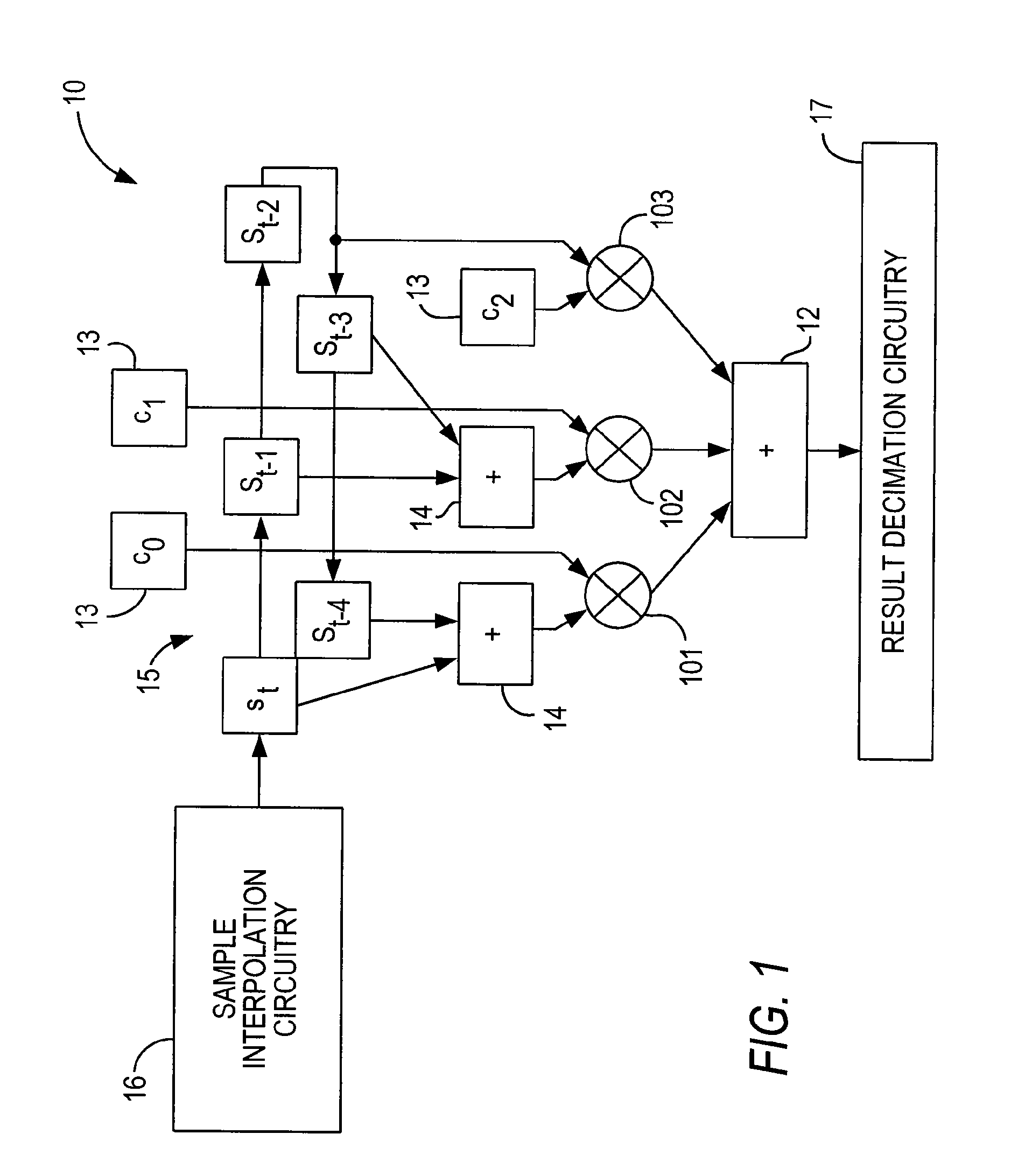
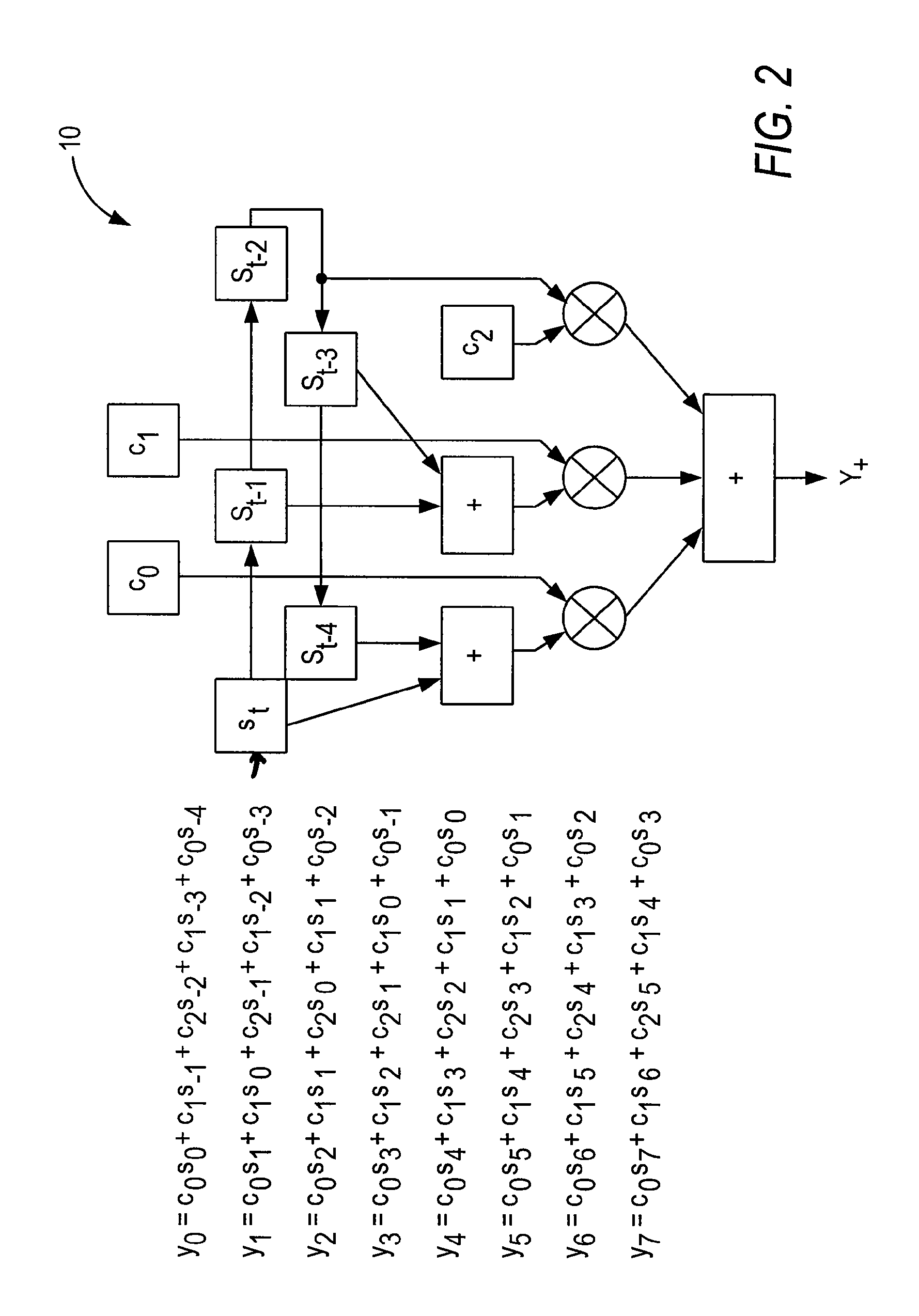
An interpolator, method of interpolating a one-bit signal and resampler employing the interpolator and method. The interpolator employs a cascaded architecture to interpolate a one-bit input signal received at an input thereof. In one embodiment, the interpolator includes a multiple order interpolation filter that generates a sample range from at least three input samples associated with the one-bit input signal. The interpolator further includes a linear interpolation filter, associated with the multiple order interpolation filter, that develops a plurality of samples within the sample range.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
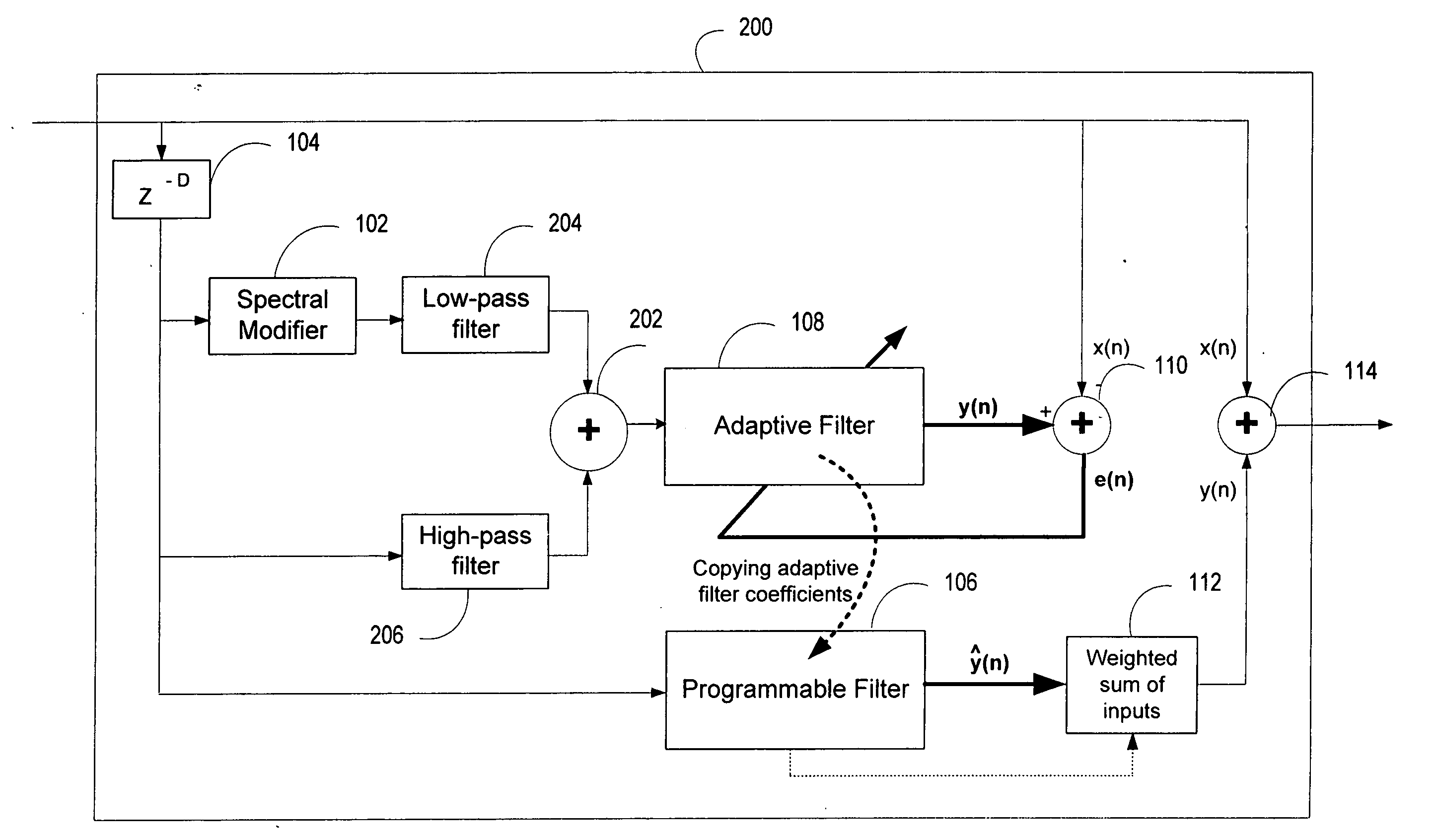
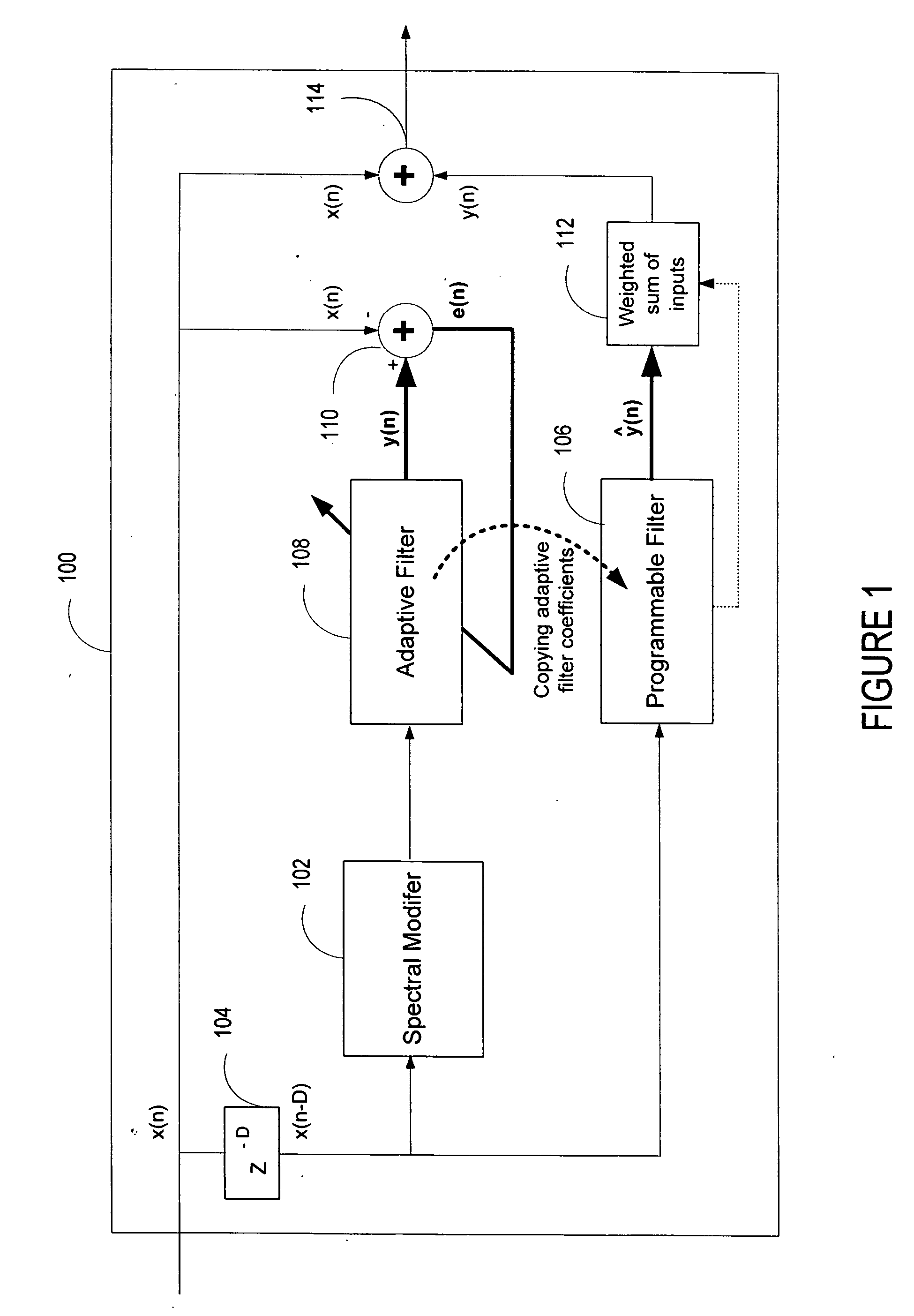
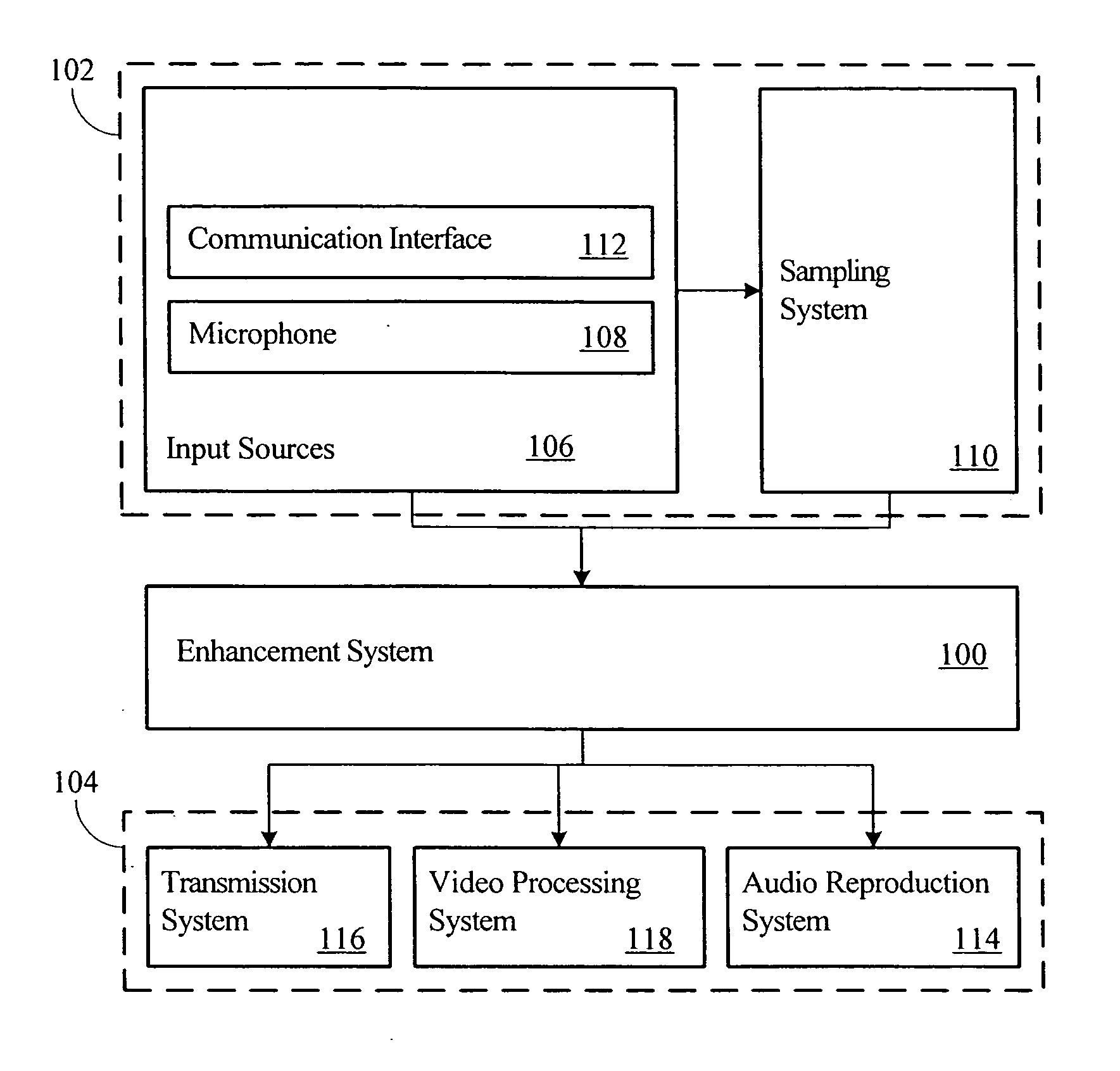
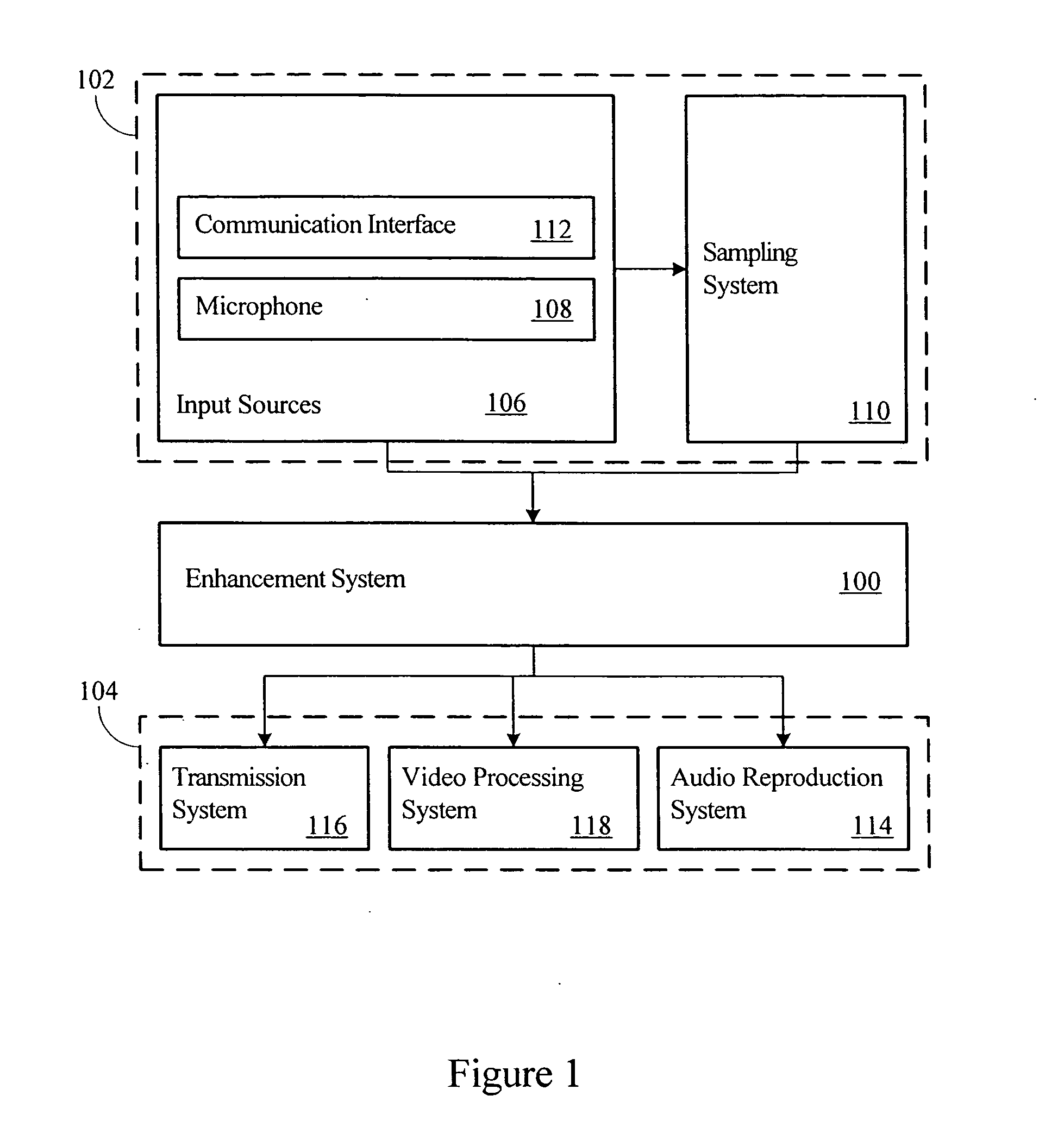
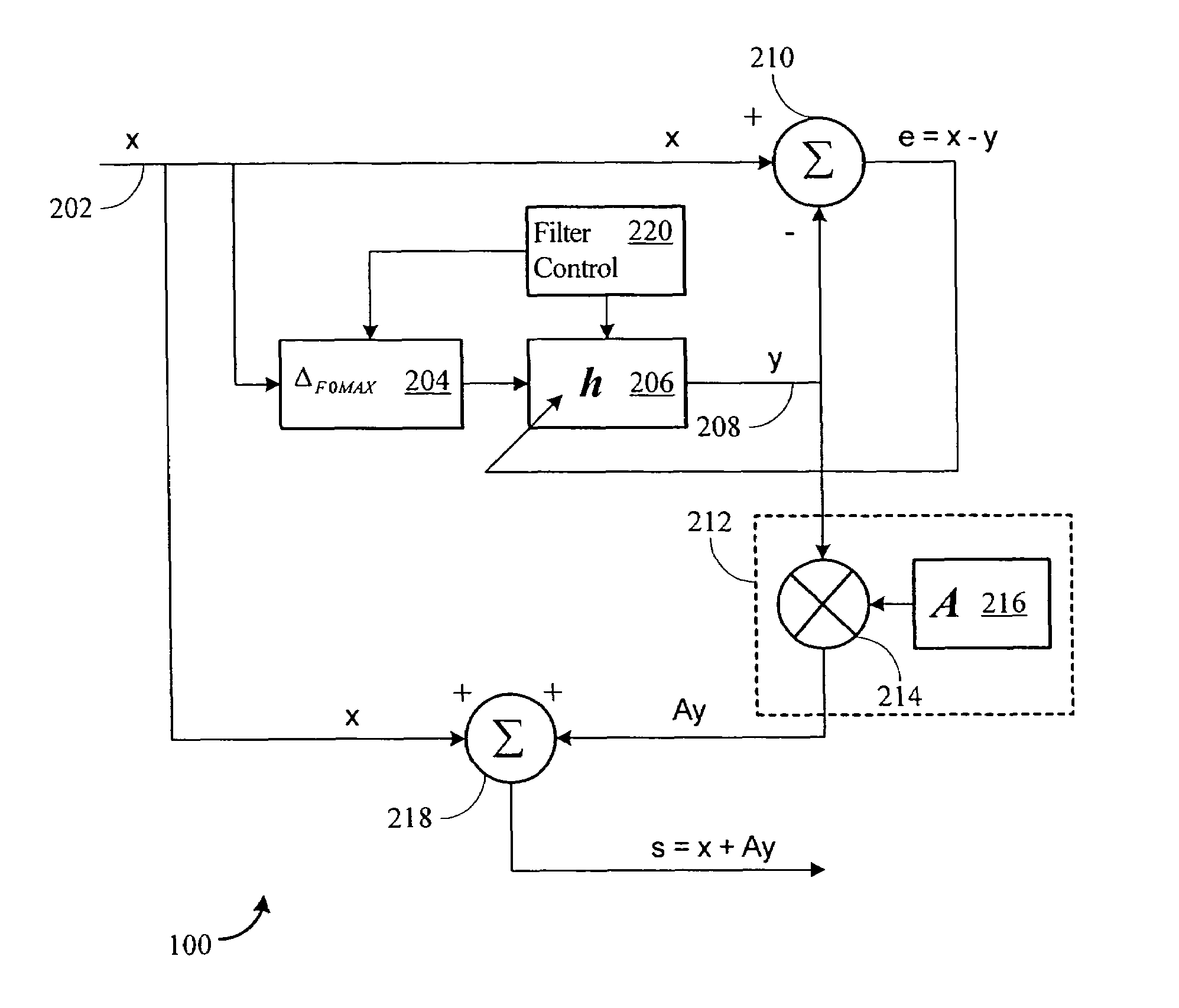
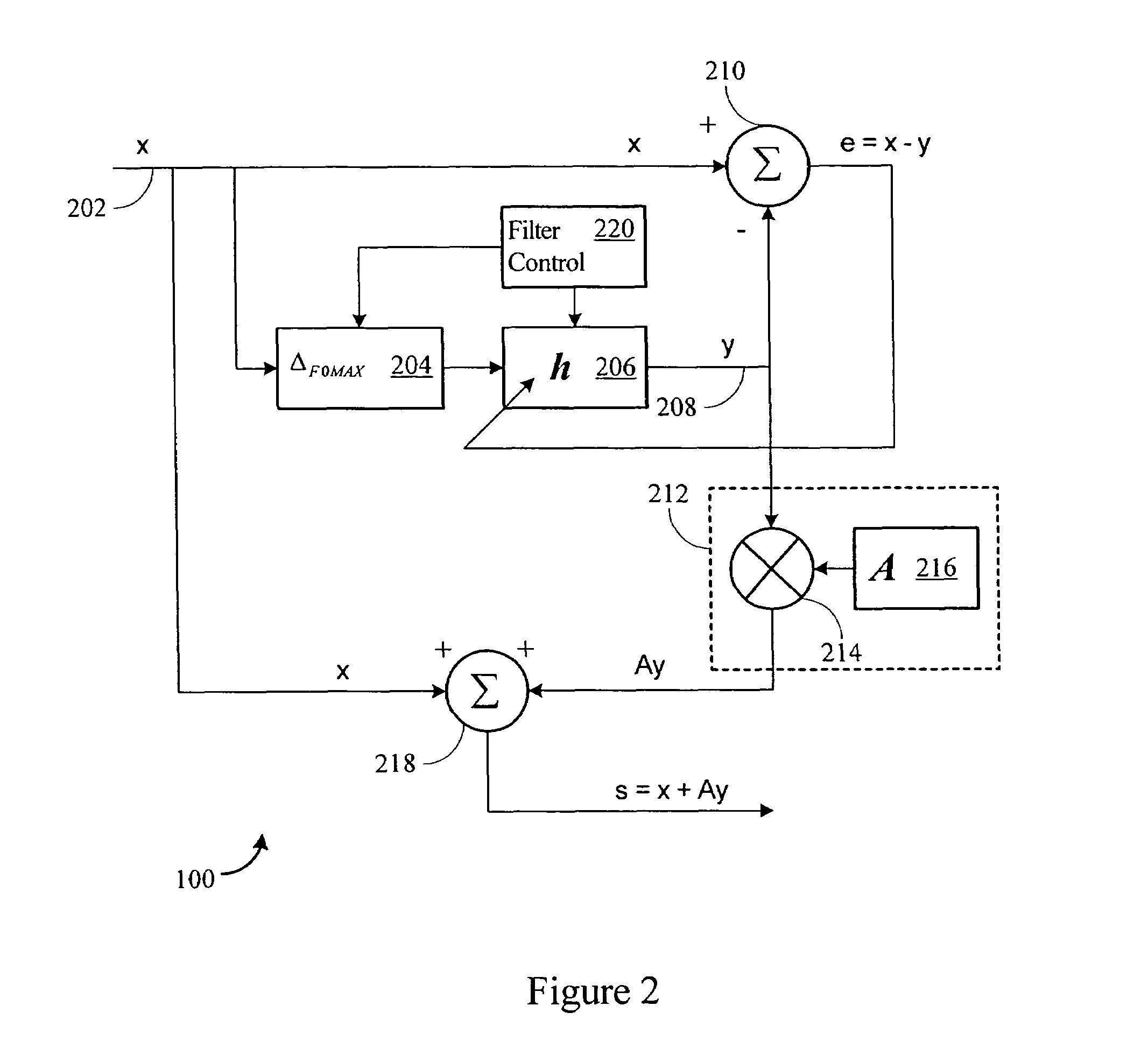
Advanced periodic signal enhancement
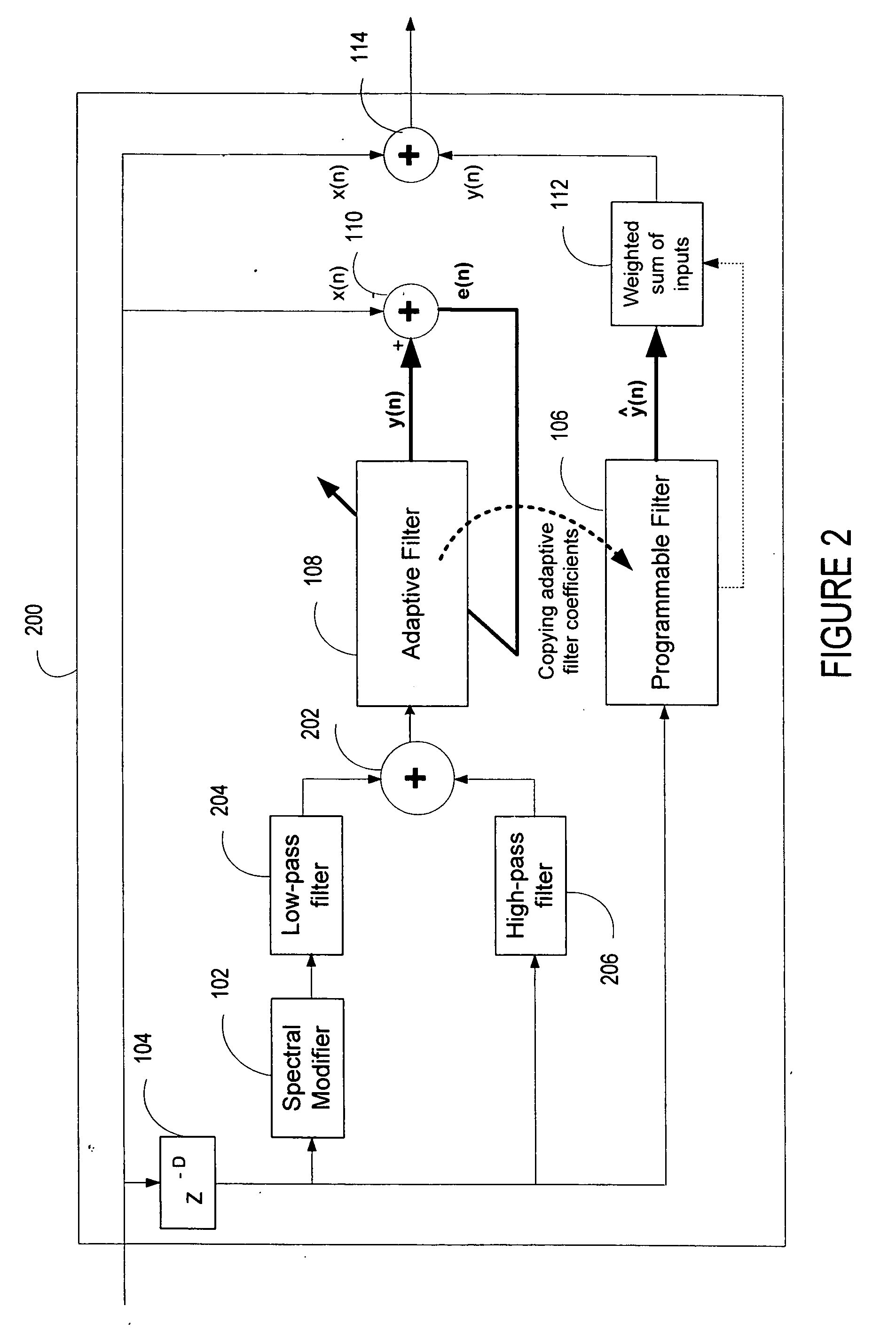
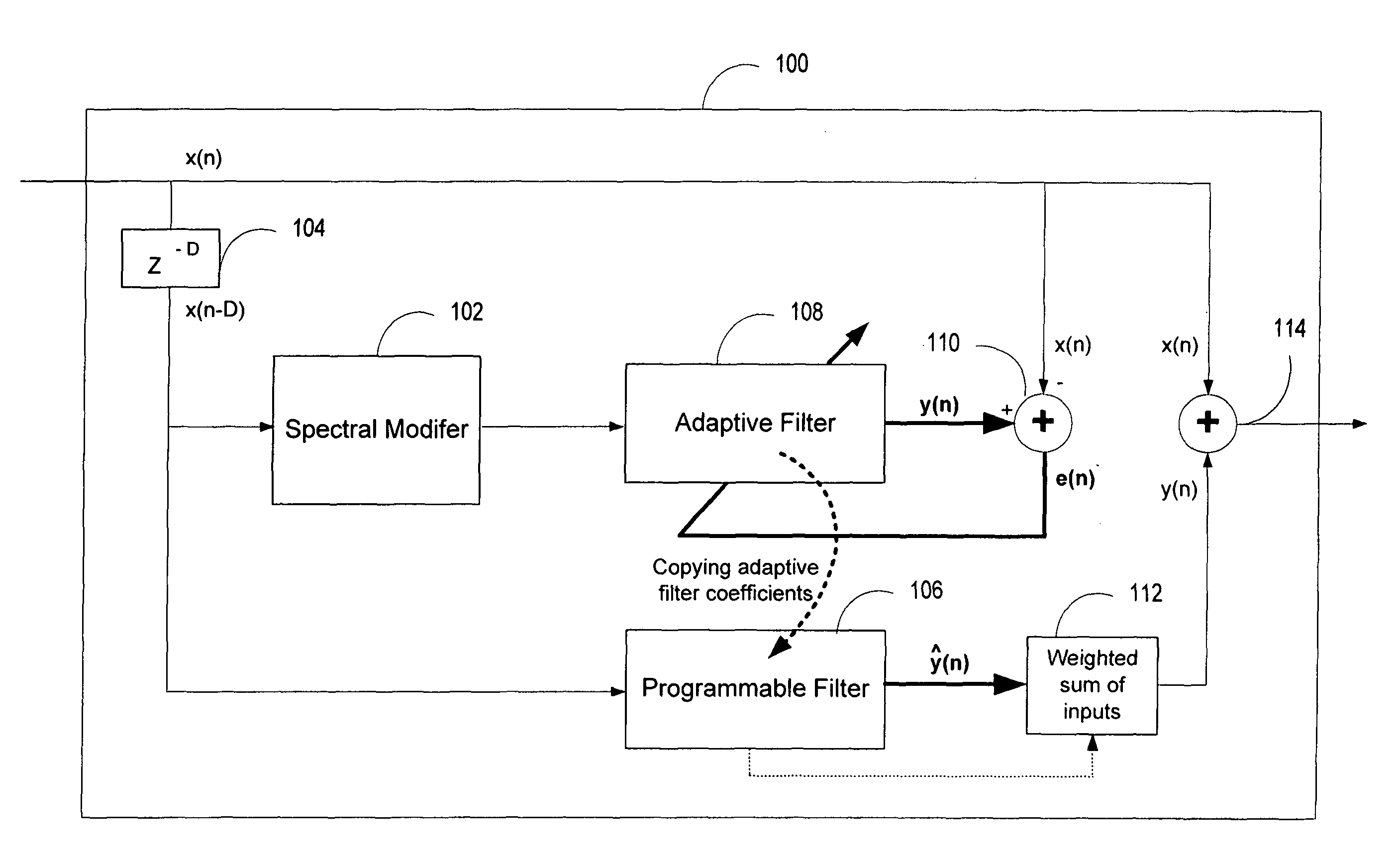
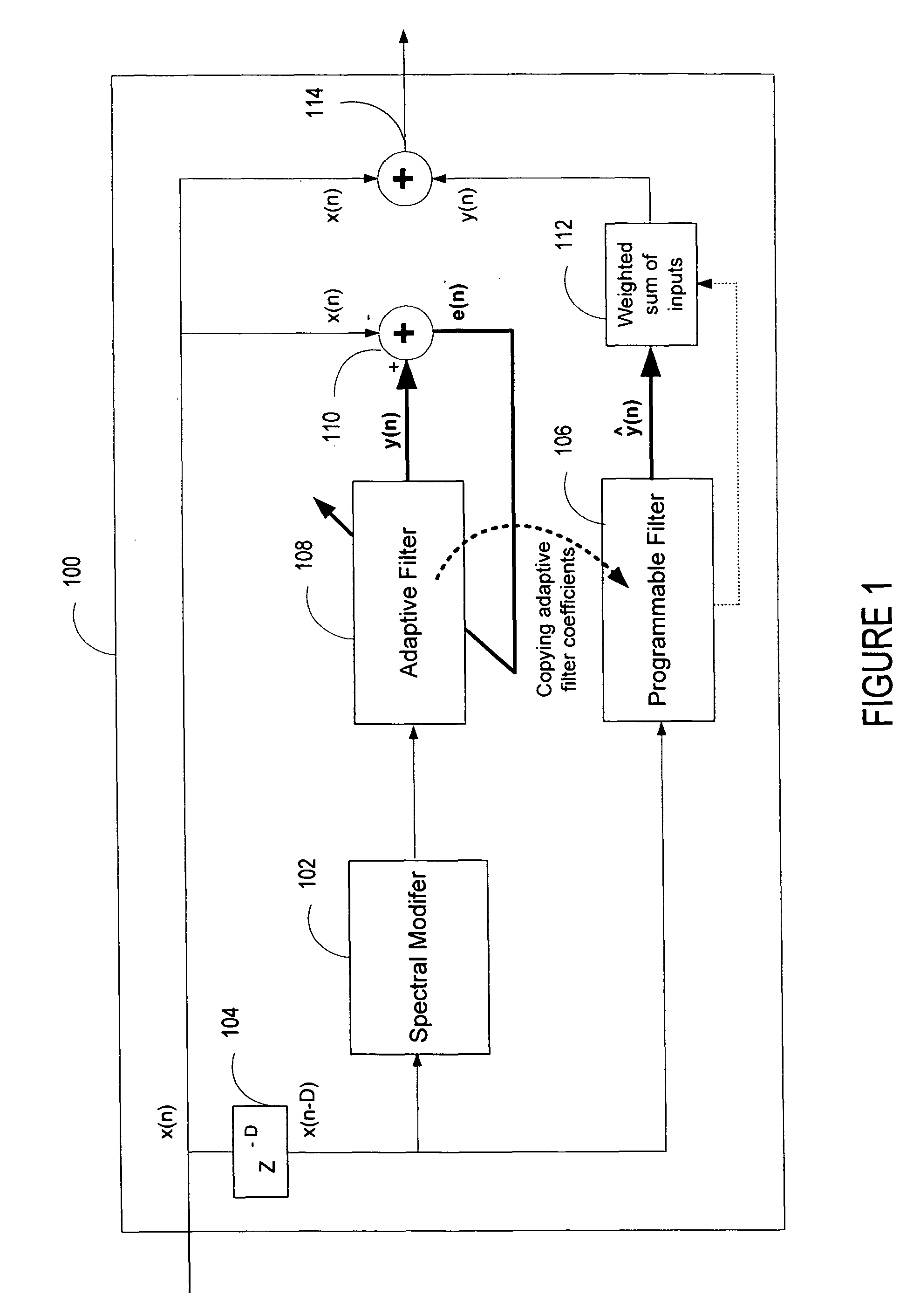
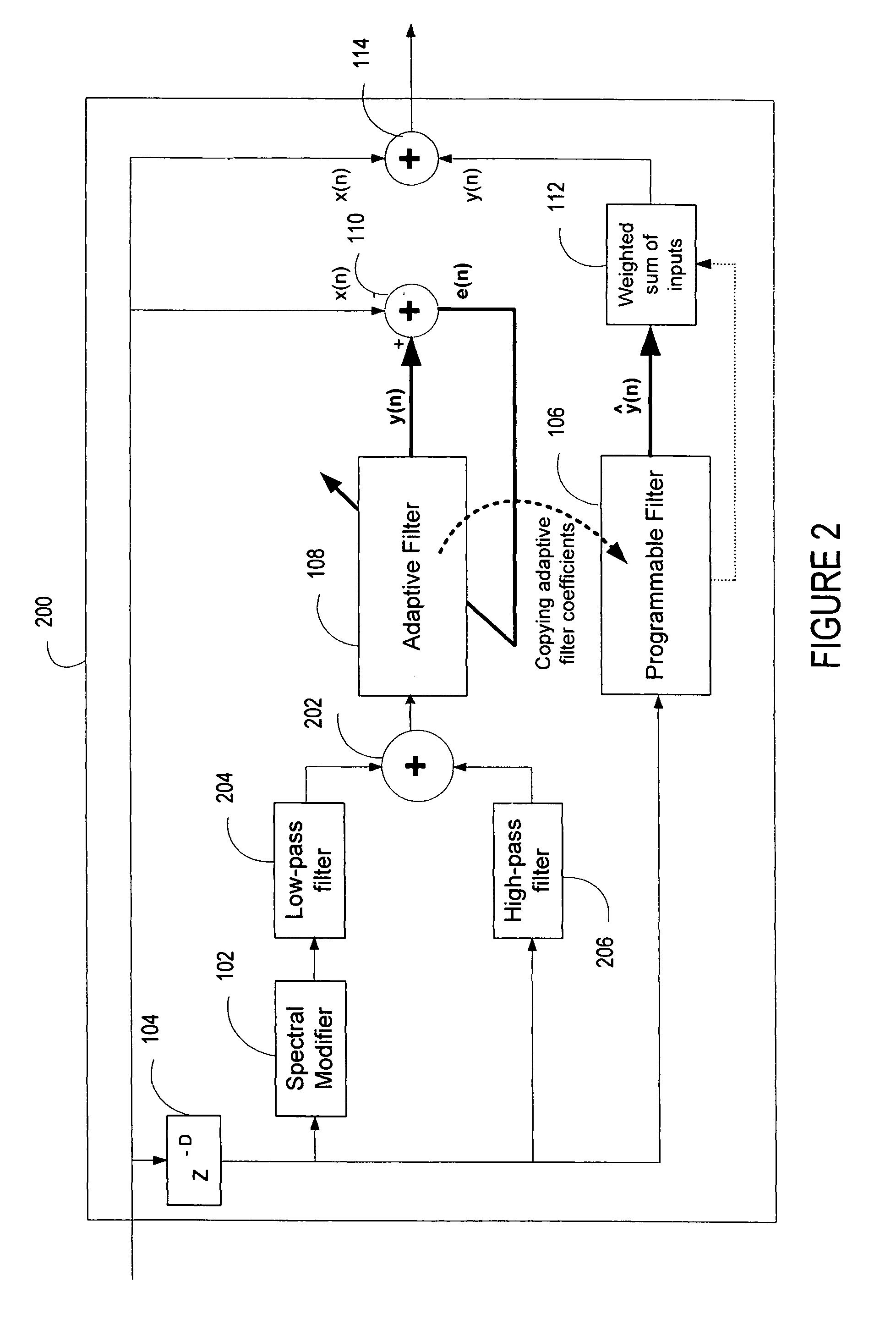
ActiveUS20060136199A1Improve processing qualityFlatten spectral character of background noiseAdaptive networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumProgrammable filters
An enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed speech. The system includes a delay unit that delays a signal received through a discrete input. A spectral modifier linked to the delay unit is programmed to substantially flatten the spectral character of a background noise. An adaptive filter linked to the spectral modifier adapts filter characteristics to match a response of a non-delayed signal. A programmable filter is linked to the delay unit. The programmable filter has a transfer function functionally related to a transfer function of the adaptive filter.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
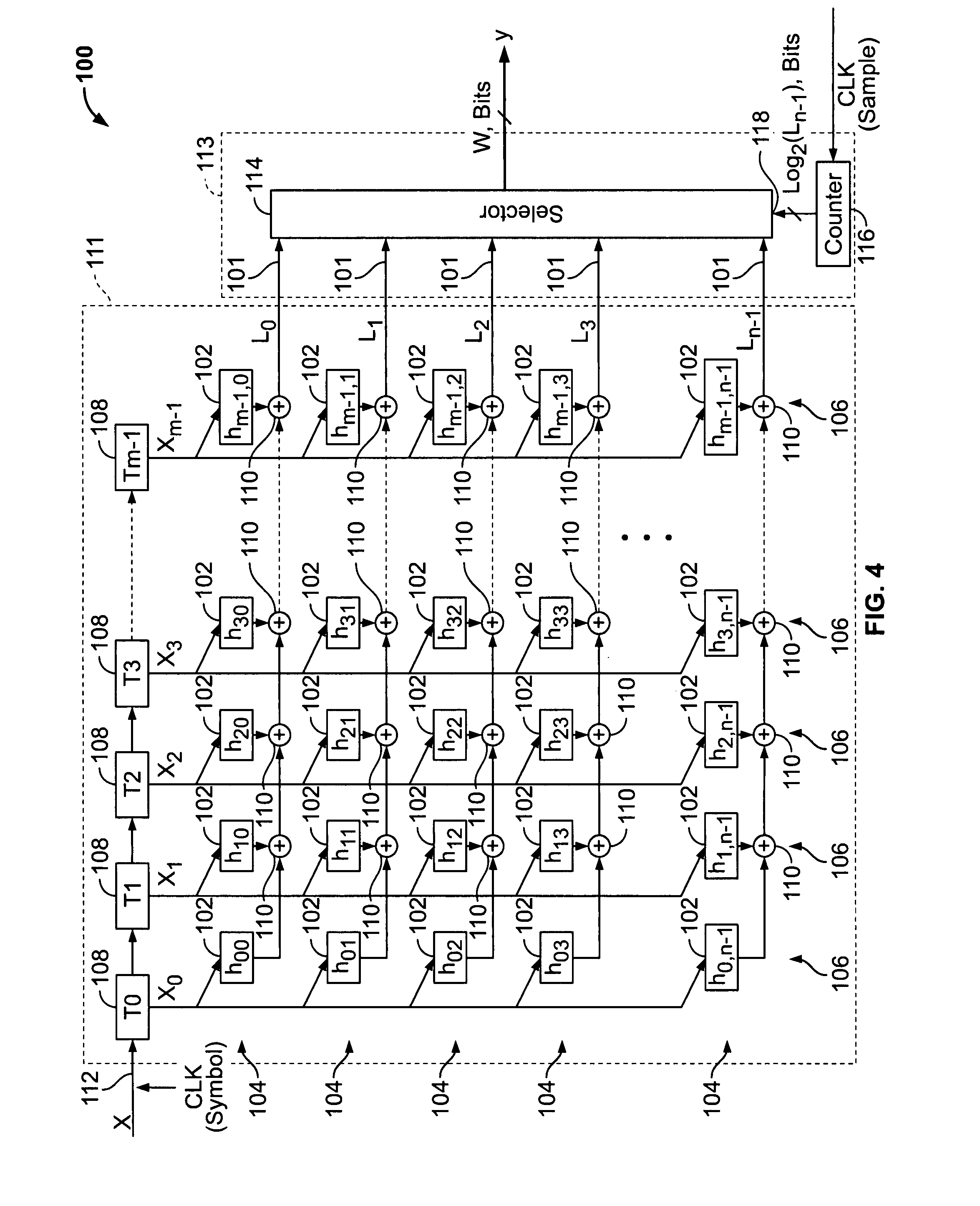
Method and architecture for digital pulse shaping and rate conversion
A method and architecture for pulse shaping are provided. The architecture includes a pulse shaping filter having a plurality of memory elements and a plurality of taps connected to the plurality of memory elements wherein a total number of the plurality of taps is independent of a sampling rate. The pulse shaping filter further includes a selector configured to select outputs from the plurality of taps to define a pulse shaped output.
Owner:EAGLE TECH LLC
Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050094604A1Increase profitRadio transmission for post communicationDuplex signal operationSequence signalEngineering
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station, and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The system and method transmits from the base station, a synchronization channel having a chip-sequence signal used by the plurality of subscriber units for synchronization. A first subscriber unit receives the synchronization channel, and determines timing from the synchronization channel. In order to initiate communications with the base station, the first subscriber unit transmits an access signal. The access signal has a plurality of power levels, which typically ramp up. The base station receives the access signal at a particular-power level. The base station then transmits to the first subscriber unit an acknowledgment signal. The first subscriber unit receives the acknowledgment signal, and transmits to the base station, a spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020036996A1Easy to liftShortens channel acquisition timeRadio transmission for post communicationDuplex signal operationSequence signalCdma systems
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station, and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The system and method transmits from the base station, a synchronization channel having a chip-sequence signal used by the plurality of subscriber units for synchronization. A first subscriber unit receives the synchronization channel, and determines timing from the synchronization channel. In order to initiate communications with the base station, the first subscriber unit transmits an access signal. The access signal has a plurality of power levels, which typically ramp up. The base station receives the access signal at a particular-power level. The base station then transmits to the first subscriber unit an acknowledgment signal. The first subscriber unit receives the acknowledgment signal, and transmits to the base station, a spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
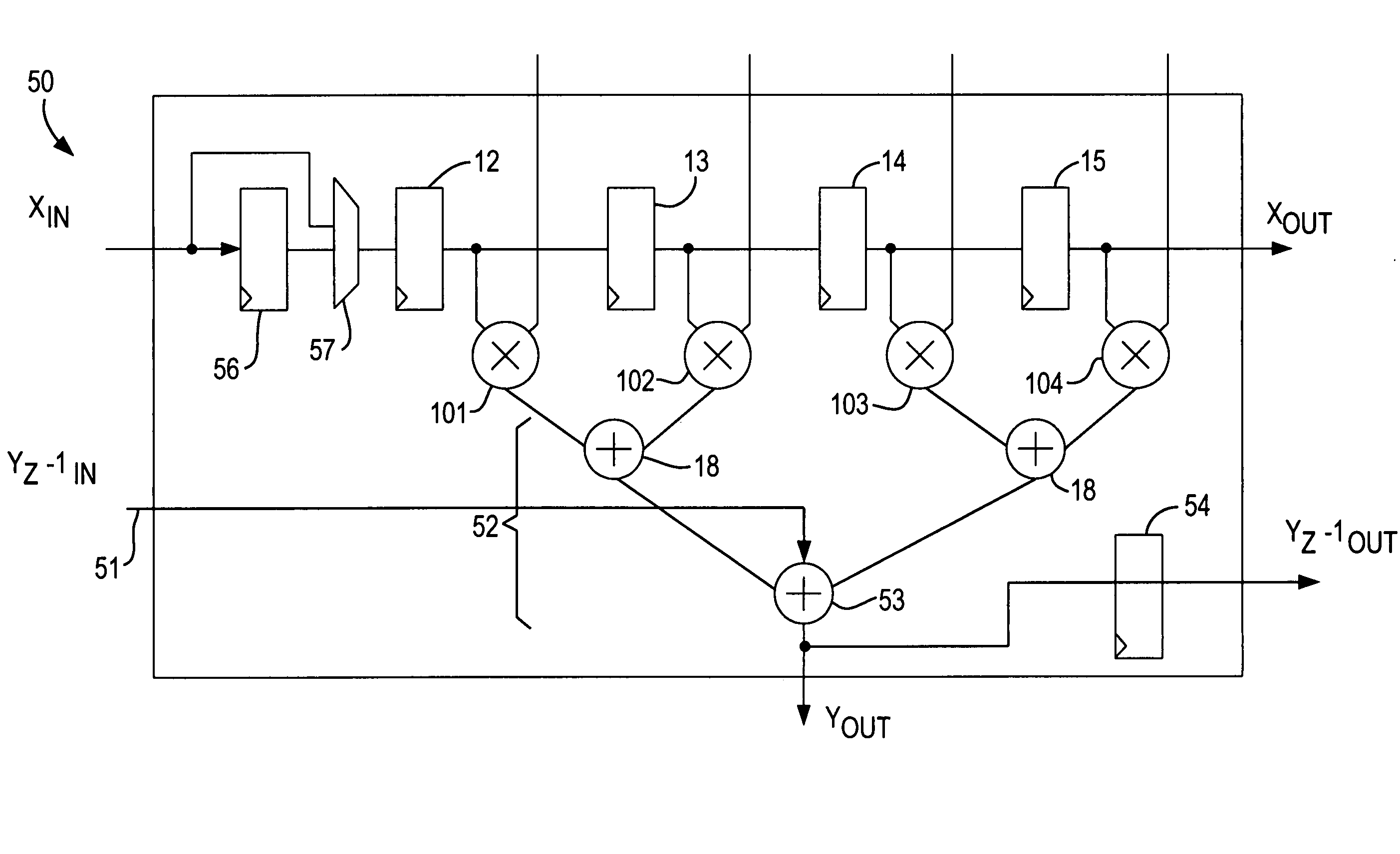
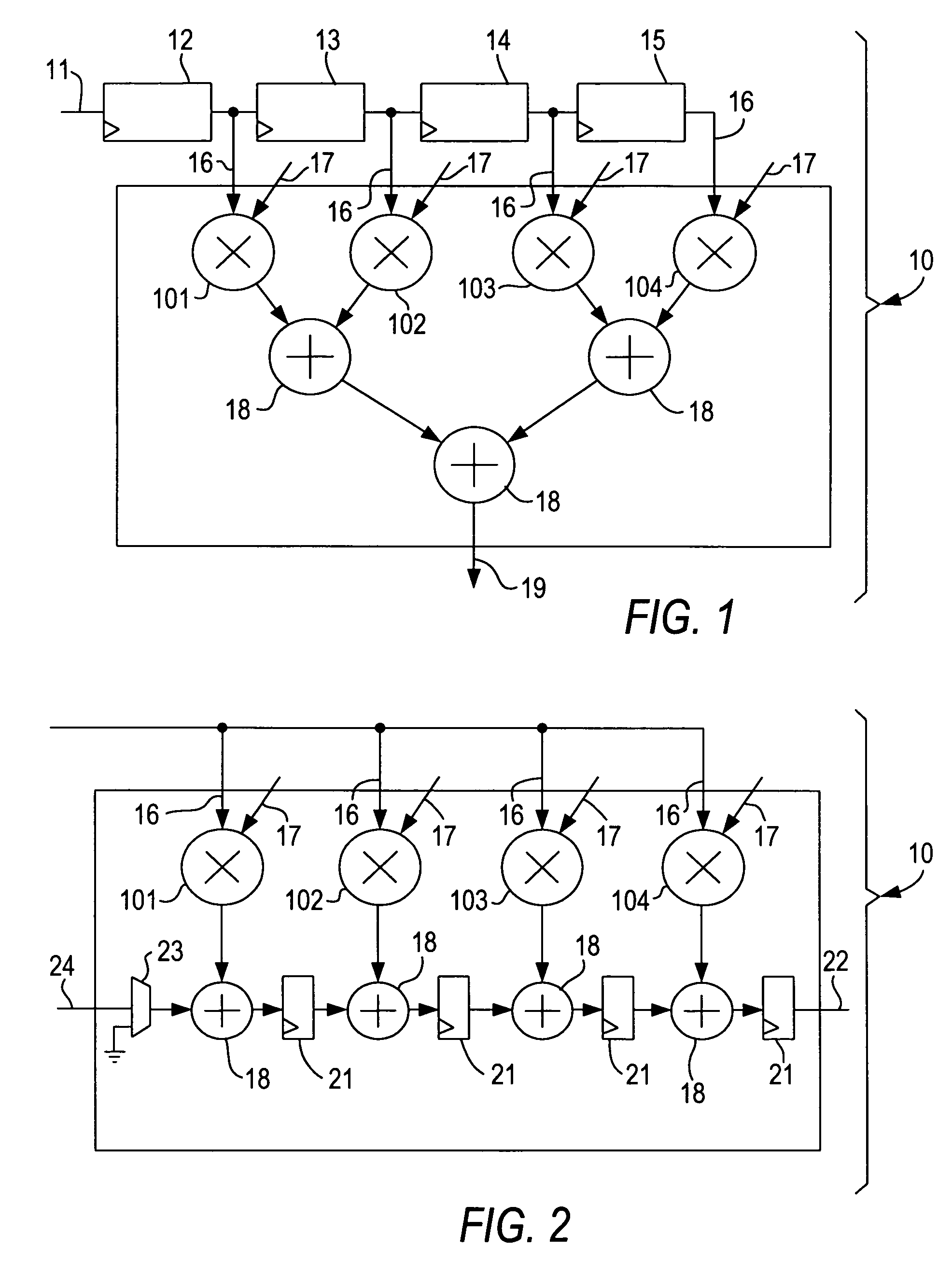
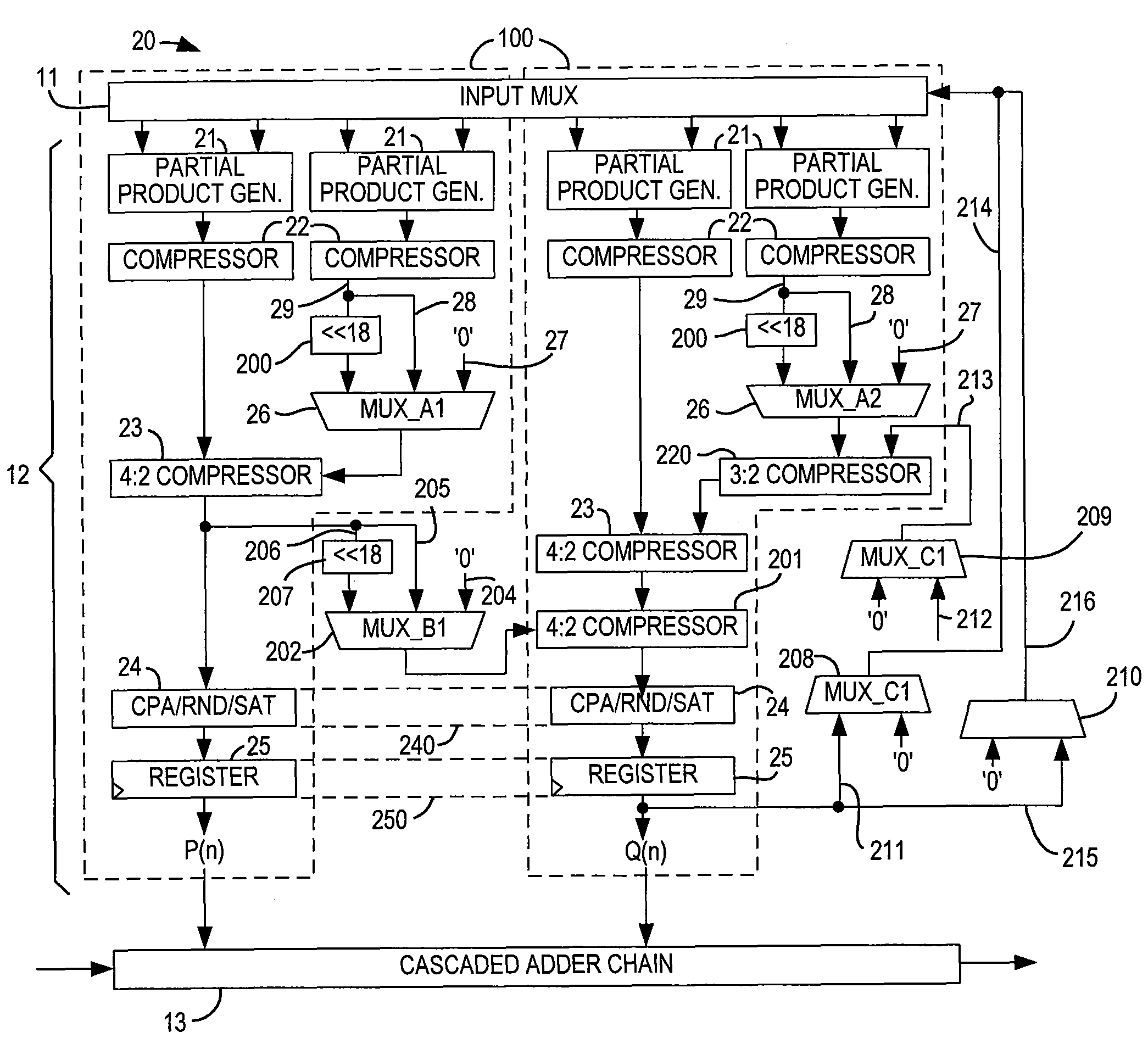
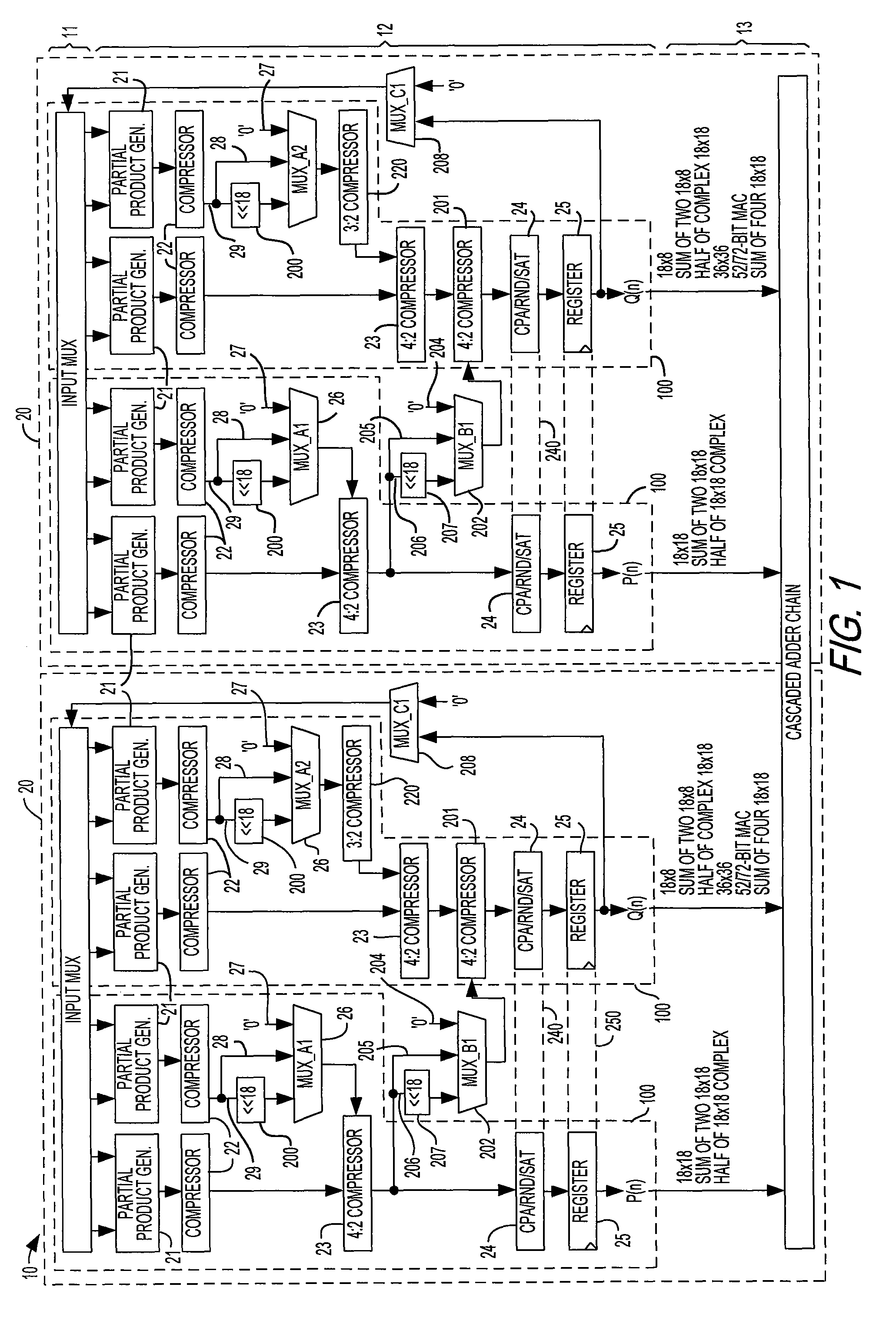
Programmable logic device with specialized multiplier blocks
InactiveUS7590676B1Good flexibilityDigital technique networkDigital data processing detailsFinite impulse responseBinary multiplier
A specialized multiplier block in a programmable logic device incorporates multipliers and adders, and is configurable as one or more types of finite impulse response (FIR) filter including a Direct Form II FIR filter. The specialized multiplier block further includes input and output registers to allow chaining of Direct Form II FIR filters into longer Direct Form II FIR filters. An output accumulator also allows the specialized multiplier block to operate as a time-division multiplexed FIR filter, performing several filtering operations during each clock cycle of the programmable logic device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Advanced periodic signal enhancement
ActiveUS7716046B2Improve processing qualityFlatten spectral character of background noiseAdaptive networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumProgrammable filters
An enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed speech. The system includes a delay unit that delays a signal received through a discrete input. A spectral modifier linked to the delay unit is programmed to substantially flatten the spectral character of a background noise. An adaptive filter linked to the spectral modifier adapts filter characteristics to match a response of a non-delayed signal. A programmable filter is linked to the delay unit. The programmable filter has a transfer function functionally related to a transfer function of the adaptive filter.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Combined interpolation and decimation filter for programmable logic device
InactiveUS7814137B1Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseMultiplexing
A programmable logic device can be configured as a finite impulse response (FIR) filter capable of operating in either interpolation mode or decimation mode and of switching between those modes at run time. The FIR filter structure can be mapped onto a specialized processing block of the programmable logic device that includes multipliers and adders for adding the products of the multipliers. The FIR filter structure minimizes the number of multipliers used by reusing various calculations that are repeated as a result of the interpolation or decimation operation, using multiplexers or other run-time-controllable selectors to select which current or stored multiplier outputs to use.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Initial power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS7123600B2Increase profitRadio transmission for post communicationDuplex signal operationSequence signalCdma systems
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station, and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The system and method transmits from the base station, a synchronization channel having a chip-sequence signal used by the plurality of subscriber units for synchronization. A first subscriber unit receives the synchronization channel, and determines timing from the synchronization channel. In order to initiate communications with the base station, the first subscriber unit transmits an access signal. The access signal has a plurality of power levels, which typically ramp up. The base station receives the access signal at a particular-power level. The base station then transmits to the first subscriber unit an acknowledgment signal. The first subscriber unit receives the acknowledgment signal, and transmits to the base station, a spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
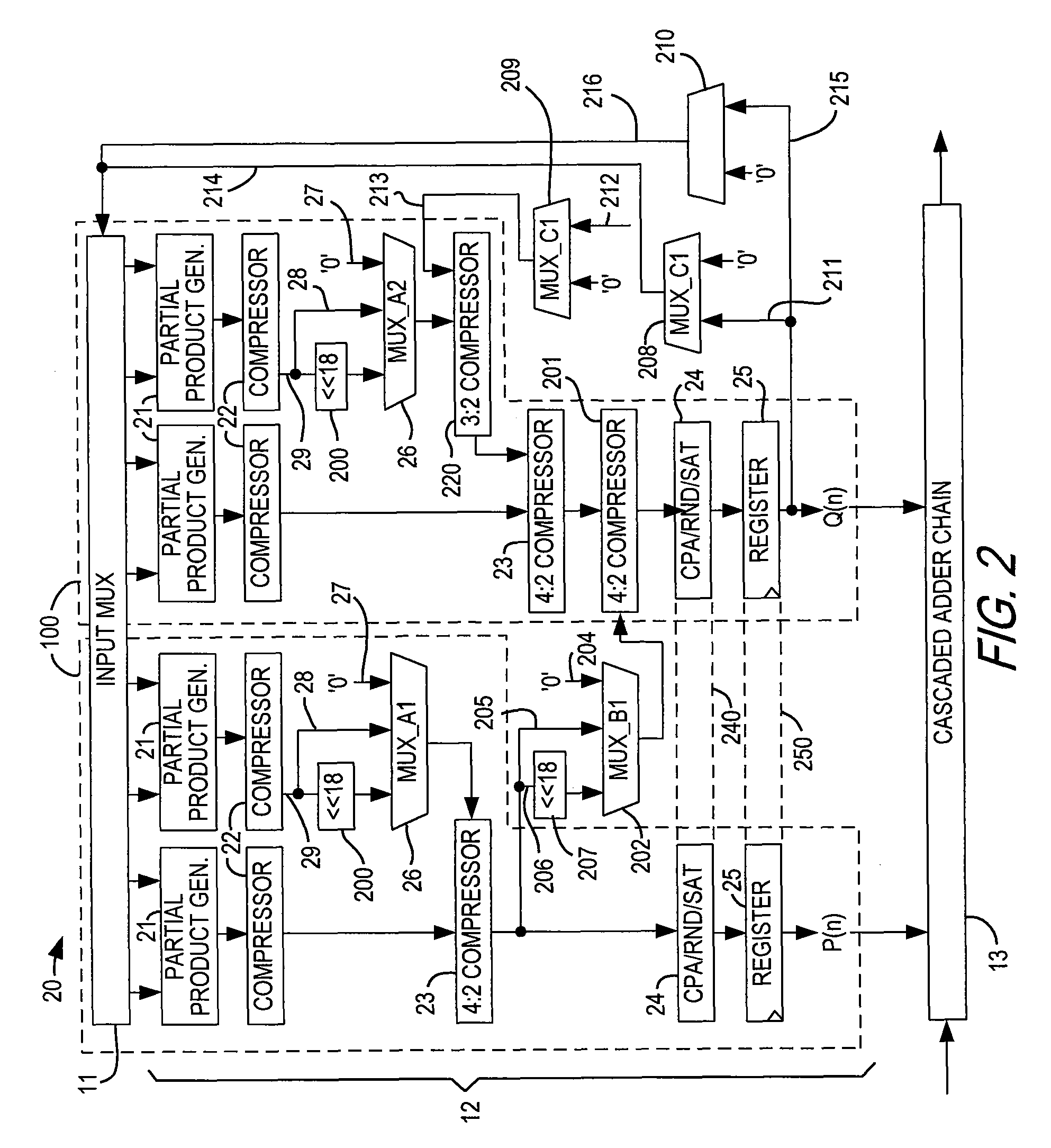
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
InactiveUS7836117B1Reduce areaImprove efficiencyDigital technique networkDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingComputer architecture
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device incorporates a fundamental processing unit that performs a sum of two multiplications, adding the partial products of both multiplications without computing the individual multiplications. Such fundamental processing units consume less area than conventional separate multipliers and adders. The specialized processing block further has input and output stages, as well as a loopback function, to allow the block to be configured for various digital signal processing operations.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
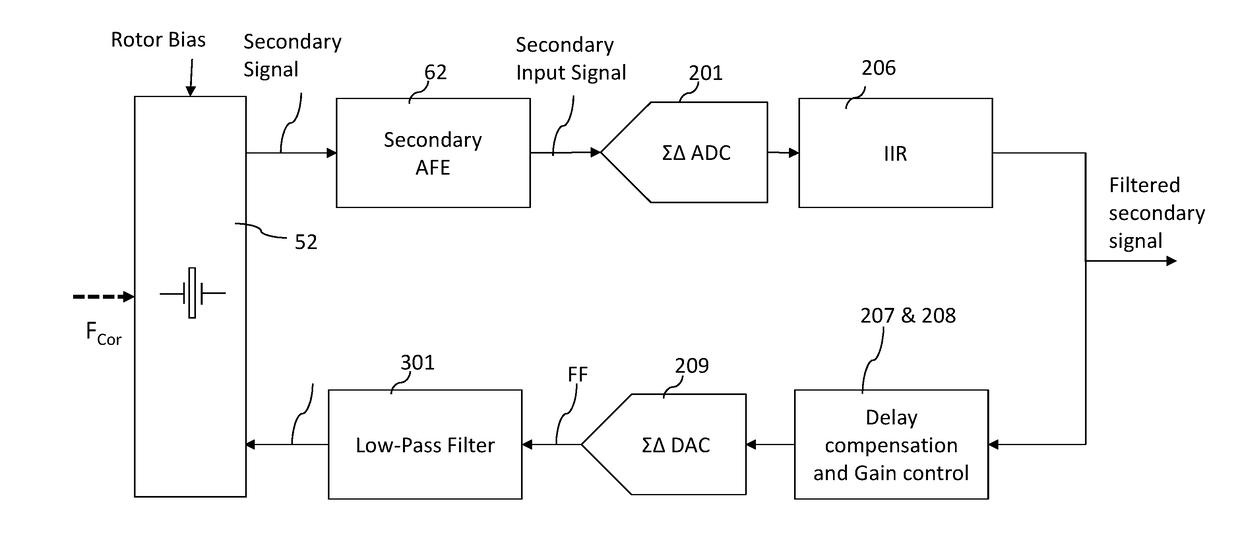
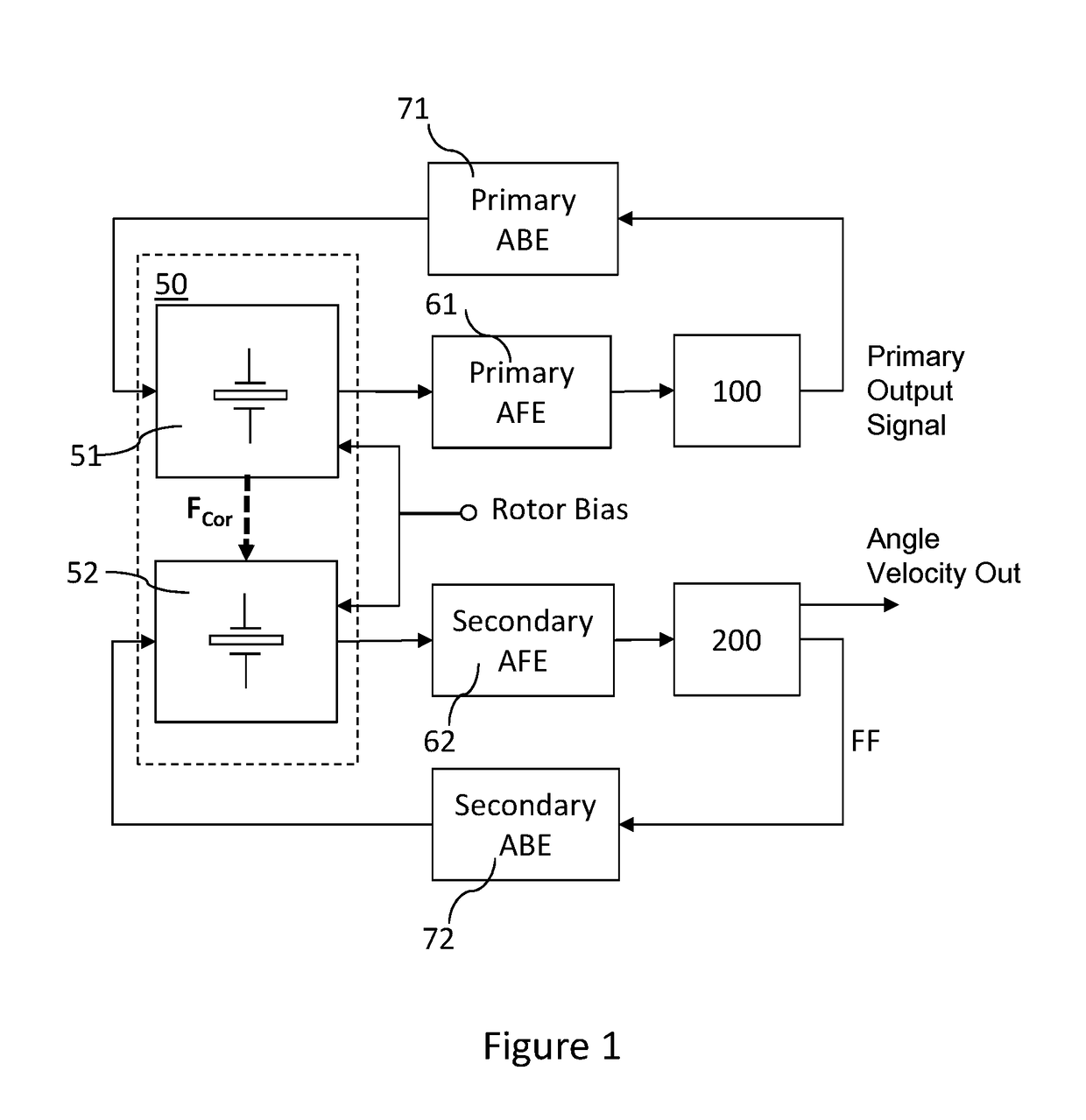
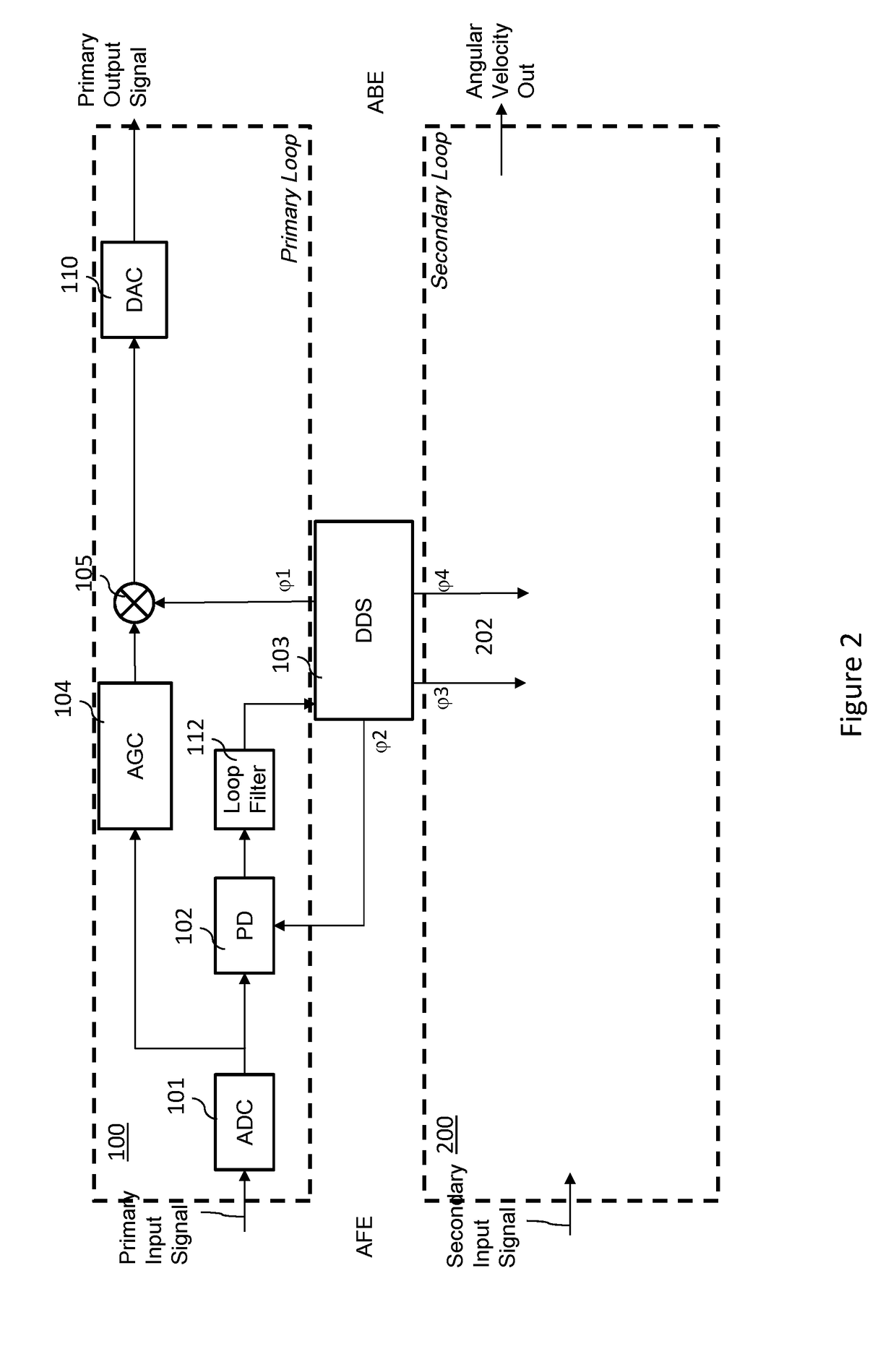
Digital controller for a MEMS gyroscope
ActiveUS20170328712A1Good compensationEasy to detectModulation transferenceDigital technique networkGyroscopePhase shifted
A digital control circuitry for a MEMS gyroscope is provided. The digital control circuitry comprises a digital primary loop circuitry configured to process a digitized primary signal, a digital secondary loop circuitry configured to process a digitized secondary signal and a digital phase shifting filter circuitry configured to generate two phase shifted demodulation signals from the digitized primary signal. The digital secondary loop is configured to demodulate the digitized secondary signal using the two phase shifted demodulation signals.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
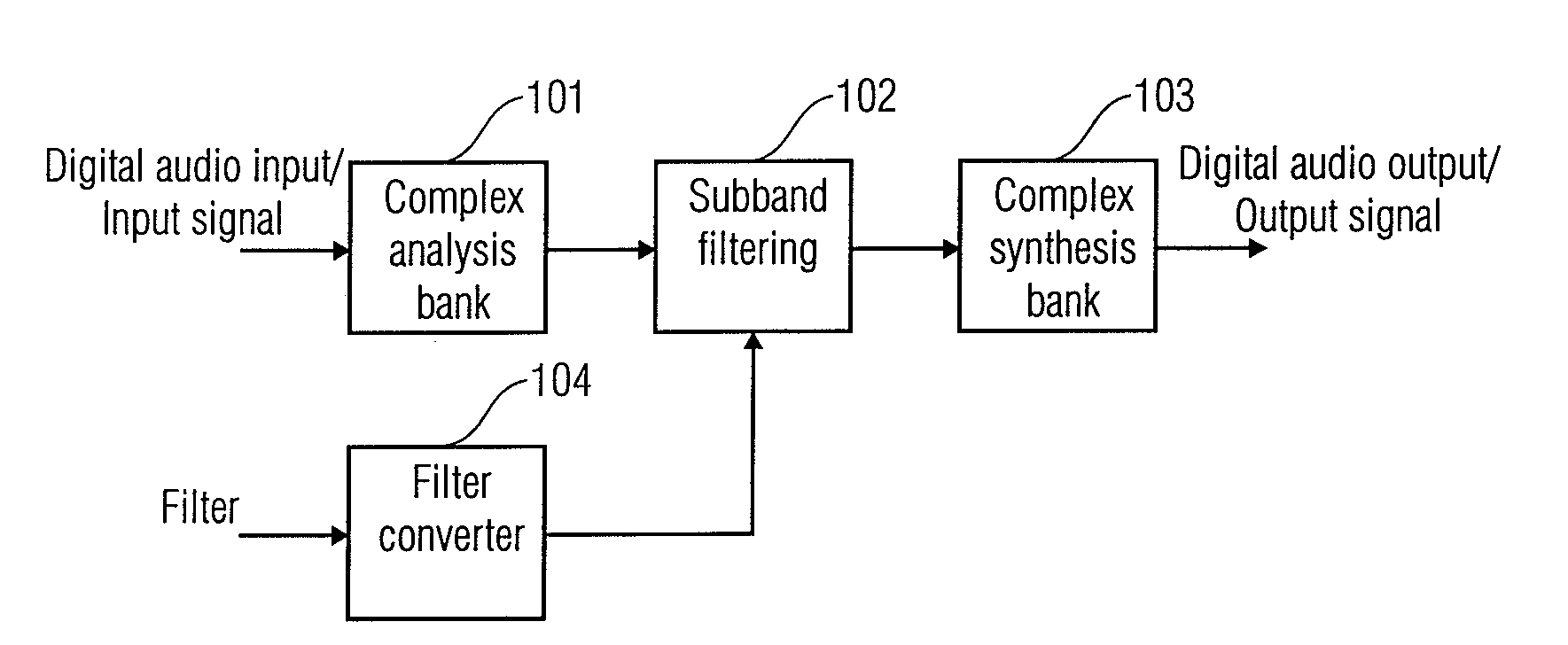
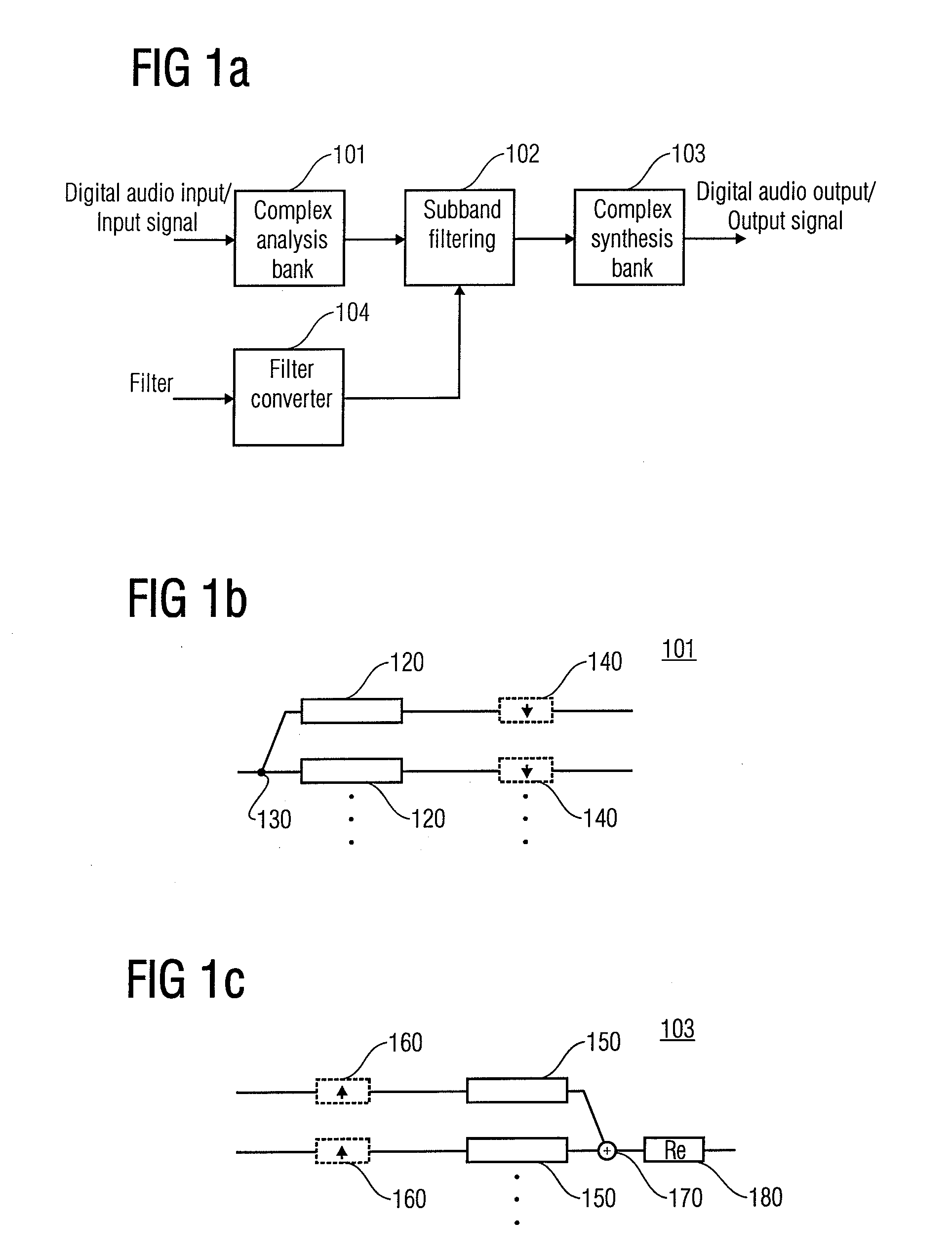
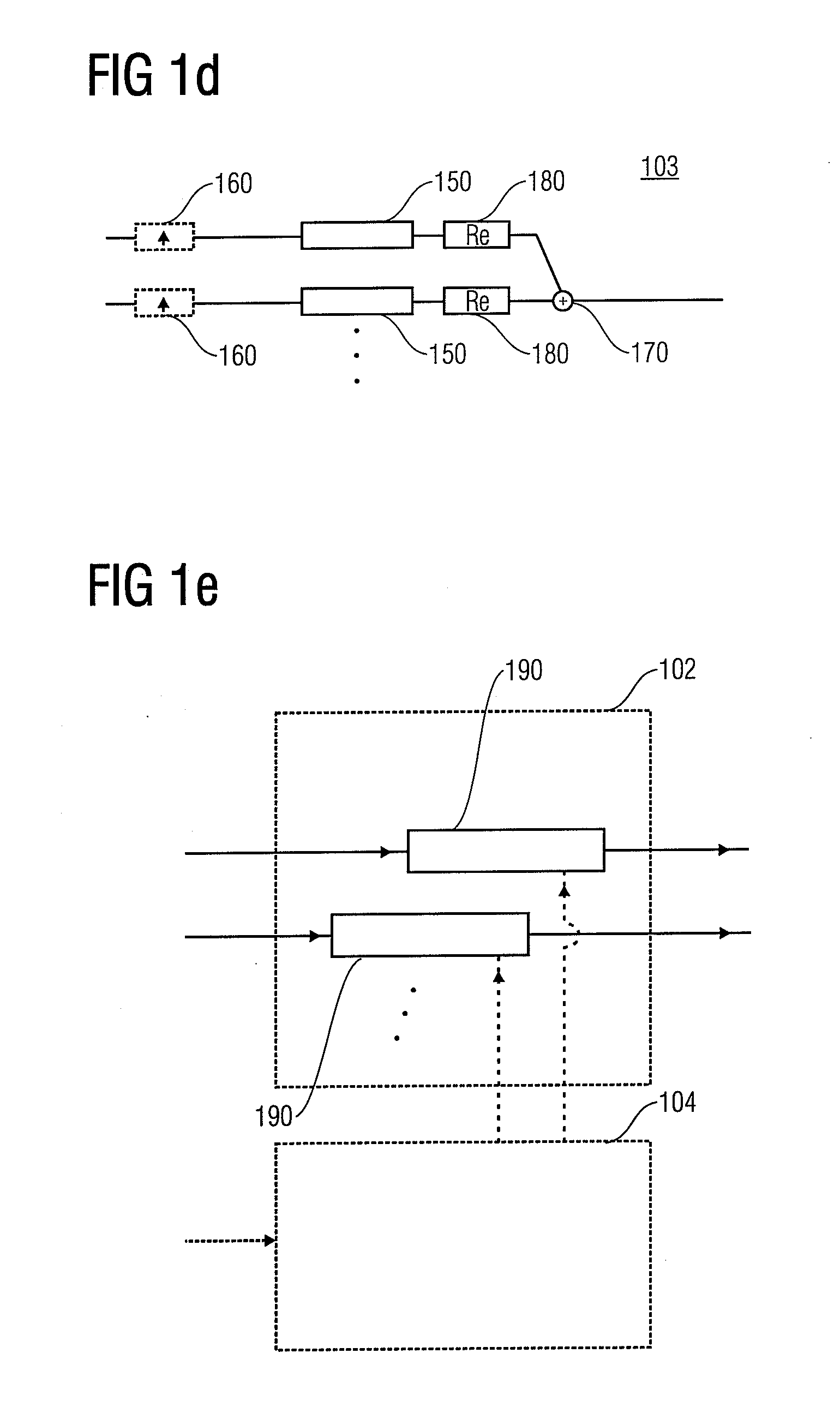
Efficient filtering with a complex modulated filterbank
ActiveUS20070179781A1Fast and efficient parallel computationEfficient memory usageDigital technique networkSpeech analysisTime domainFrequency characteristic
A filter apparatus for filtering a time domain input signal to obtain a time domain output signal, which is a representation of the time domain input signal filtered using a filter characteristic having an non-uniform amplitude / frequency characteristic, comprises a complex analysis filter bank for generating a plurality of complex subband signals from the time domain input signals, a plurality of intermediate filters, wherein at least one of the intermediate filters of the plurality of the intermediate filters has a non-uniform amplitude / frequency characteristic, wherein the plurality of intermediate filters have a shorter impulse response compared to an impulse response of a filter having the filter characteristic, and wherein the non-uniform amplitude / frequency characteristics of the plurality of intermediate filters together represent the non-uniform filter characteristic, and a complex synthesis filter bank for synthesizing the output of the intermediate filters to obtain the time domain output signal.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Polyphase filter with low-pass response
ActiveUS20030186671A1Reduce the impactNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDigital technique networkLow-pass filterTransfer function
A complex low-pass filter that reduces the influence of component mismatch. The filter includes a first filter section for effecting a first single pole transfer function and a second filter section for effecting a second single pole transfer function, where the first and the second single pole transfer functions collectively define a conjugate pair of poles. In higher order low-pass filters, an optimal cascade order follows a shoestring pattern.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
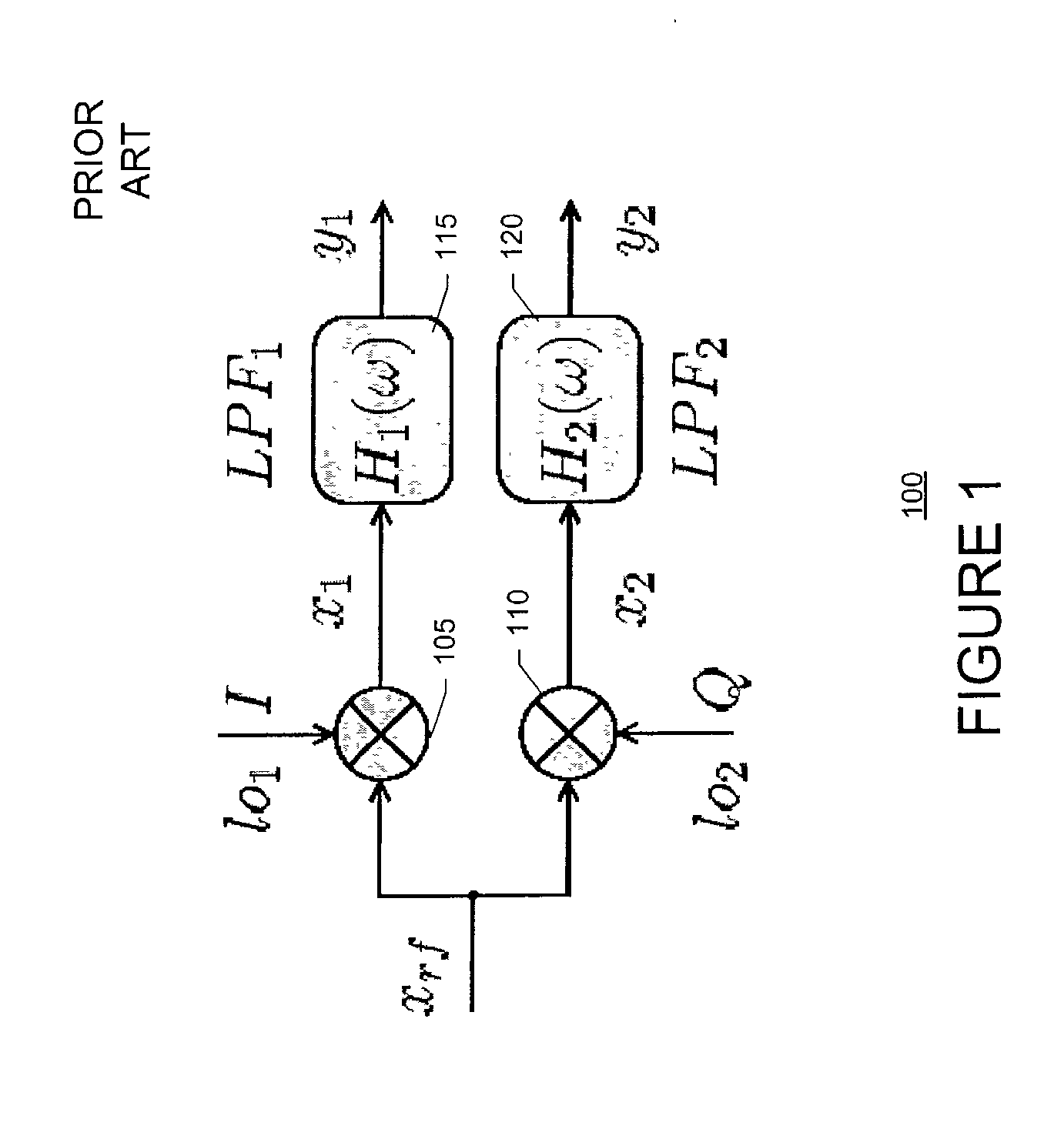
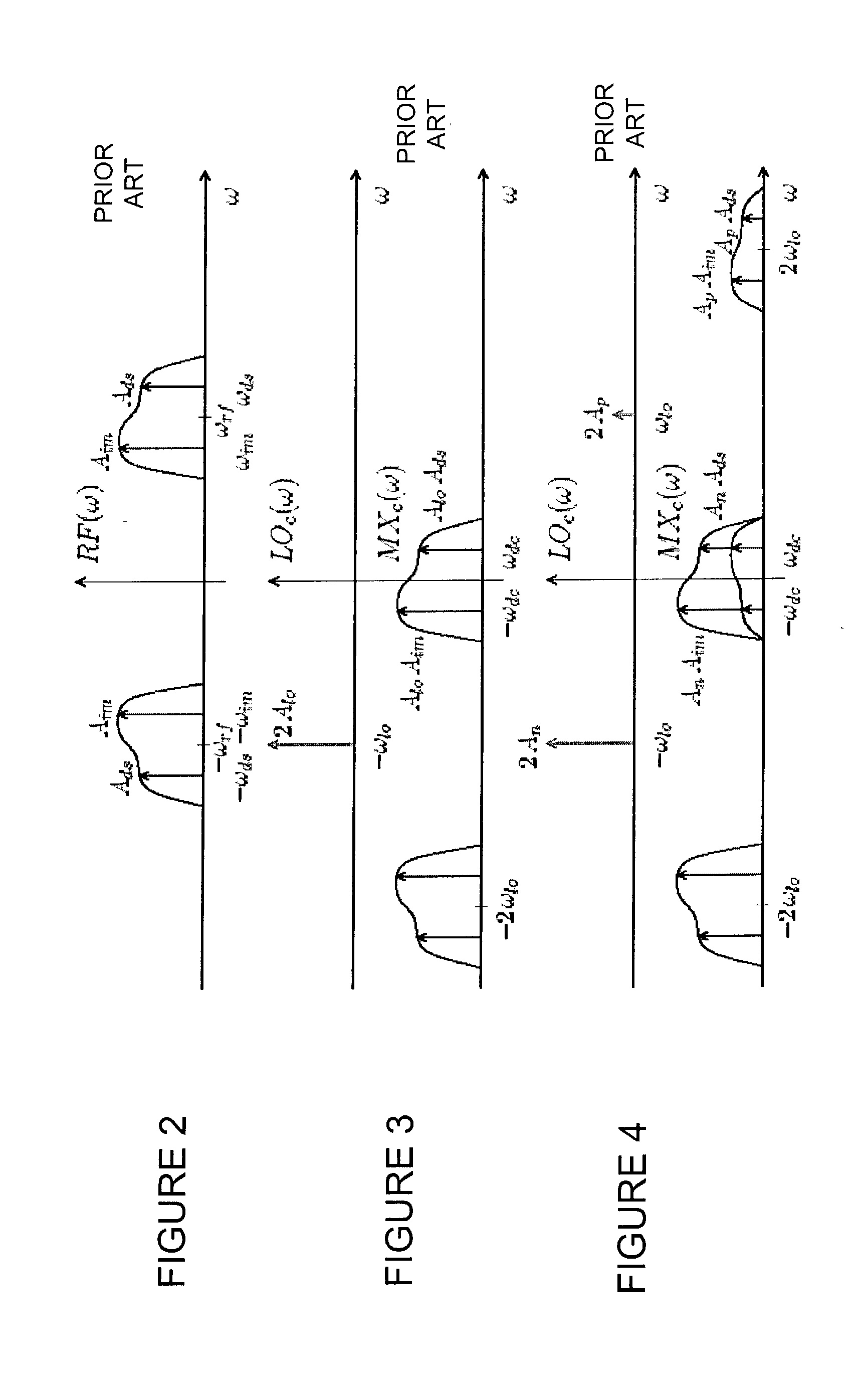
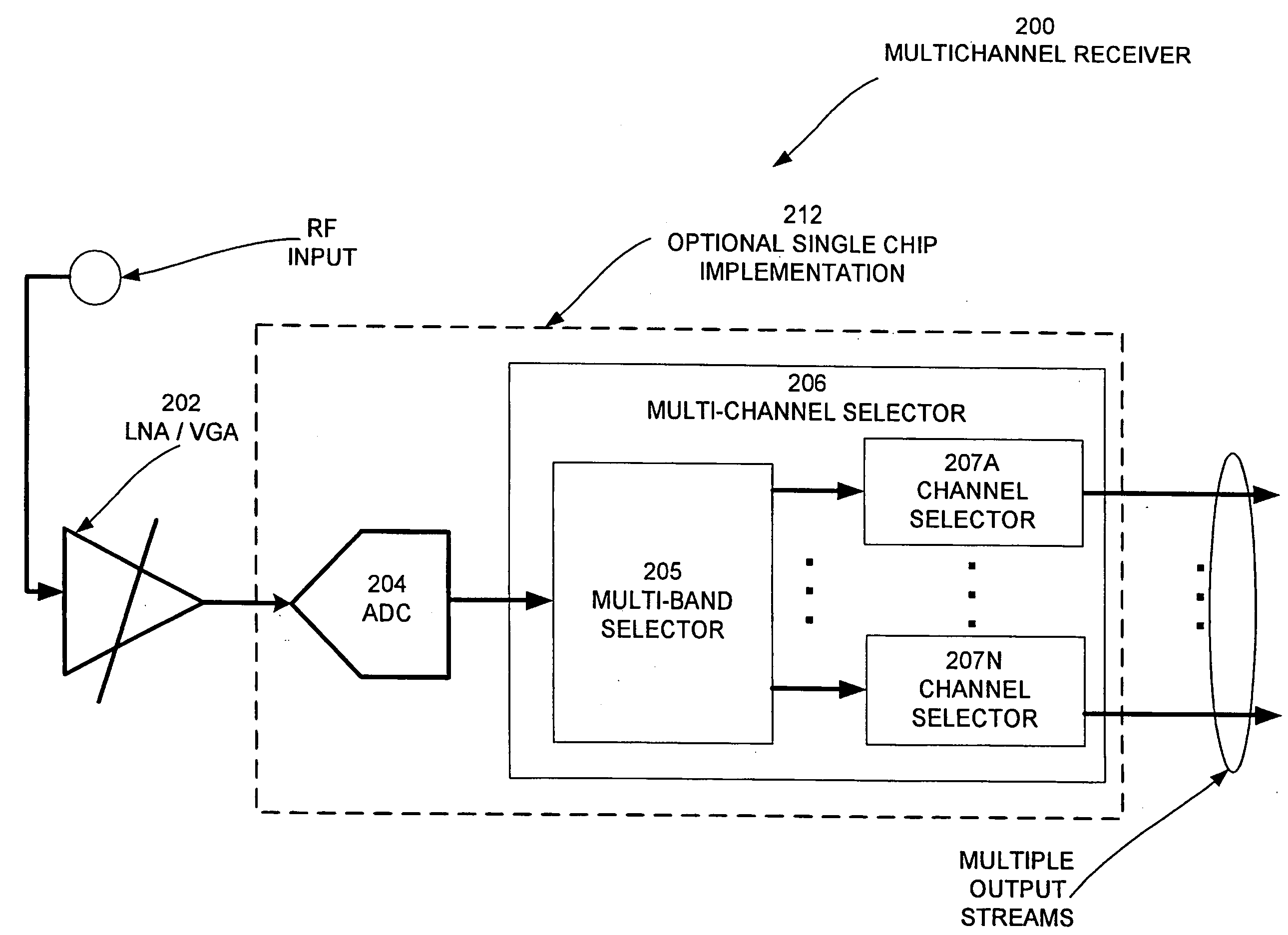
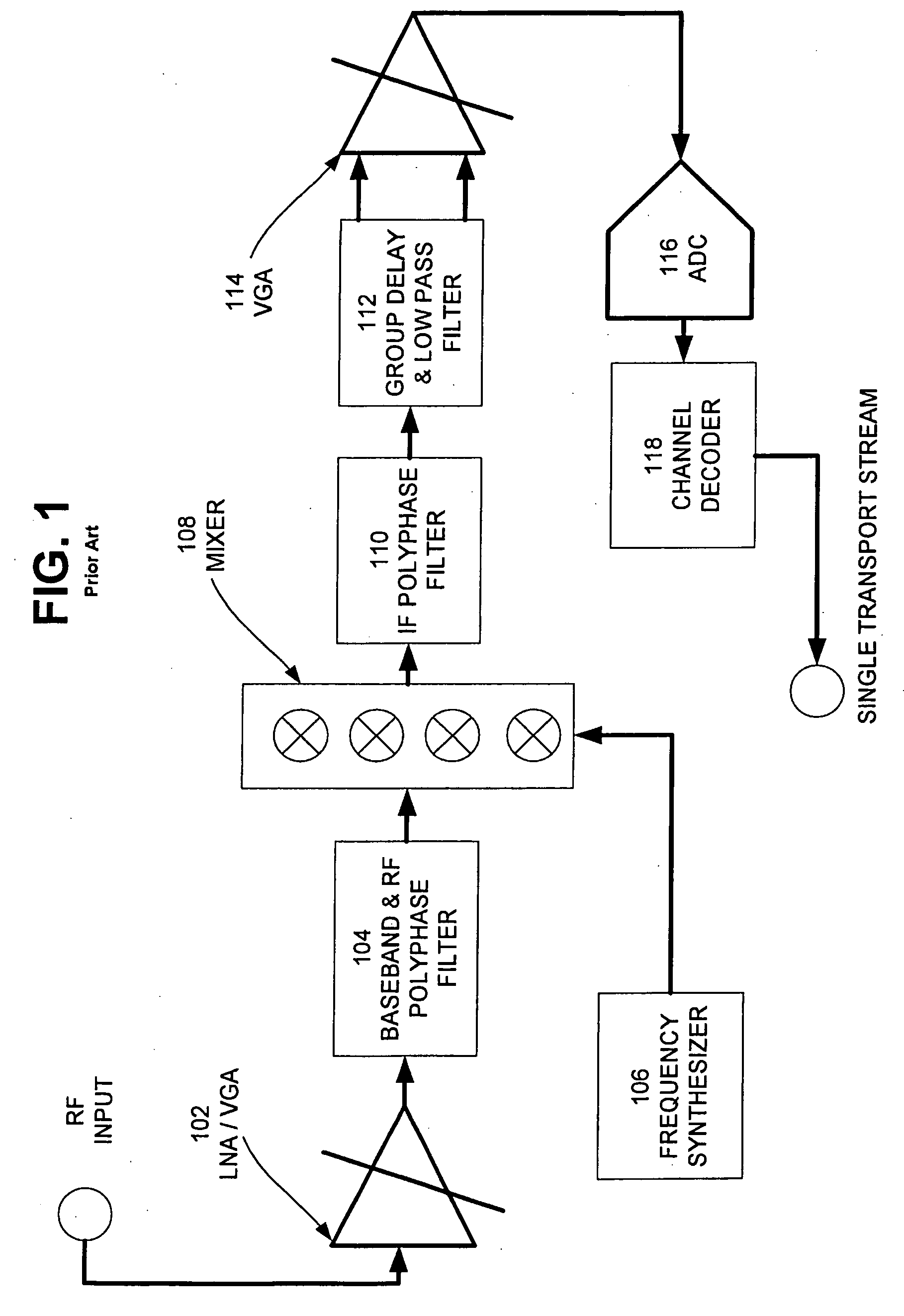
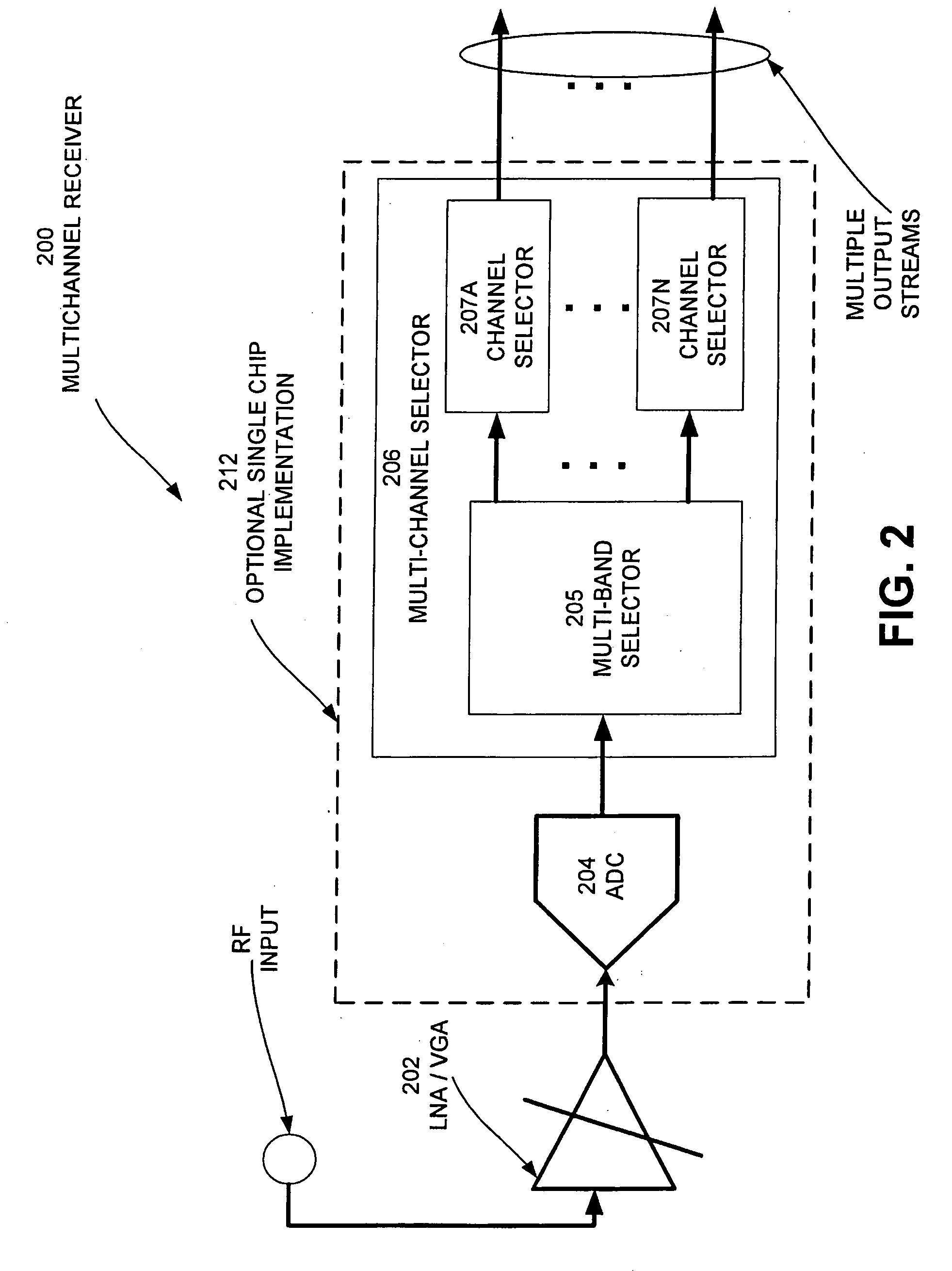
Multi-Channel Receiver Architecture and Reception Method
ActiveUS20100120386A1Easy to receiveTelevision system detailsDigital technique networkMulti bandWideband
A multi-channel receiver comprising an ADC and a multi-band, multi-channel selector. The ADC converts a broad-band multi-channel signal into a digital signal. The digital signal is then broken into sub-bands each containing a plurality of channels. A channel selector selects desired channels from the appropriate sub-band. The multi-channel receiver may deliver simultaneous channels equal to the number of channel selectors that have been implemented. The multi-channel receiver may be implemented on a single integrated circuit.
Owner:NXP BV
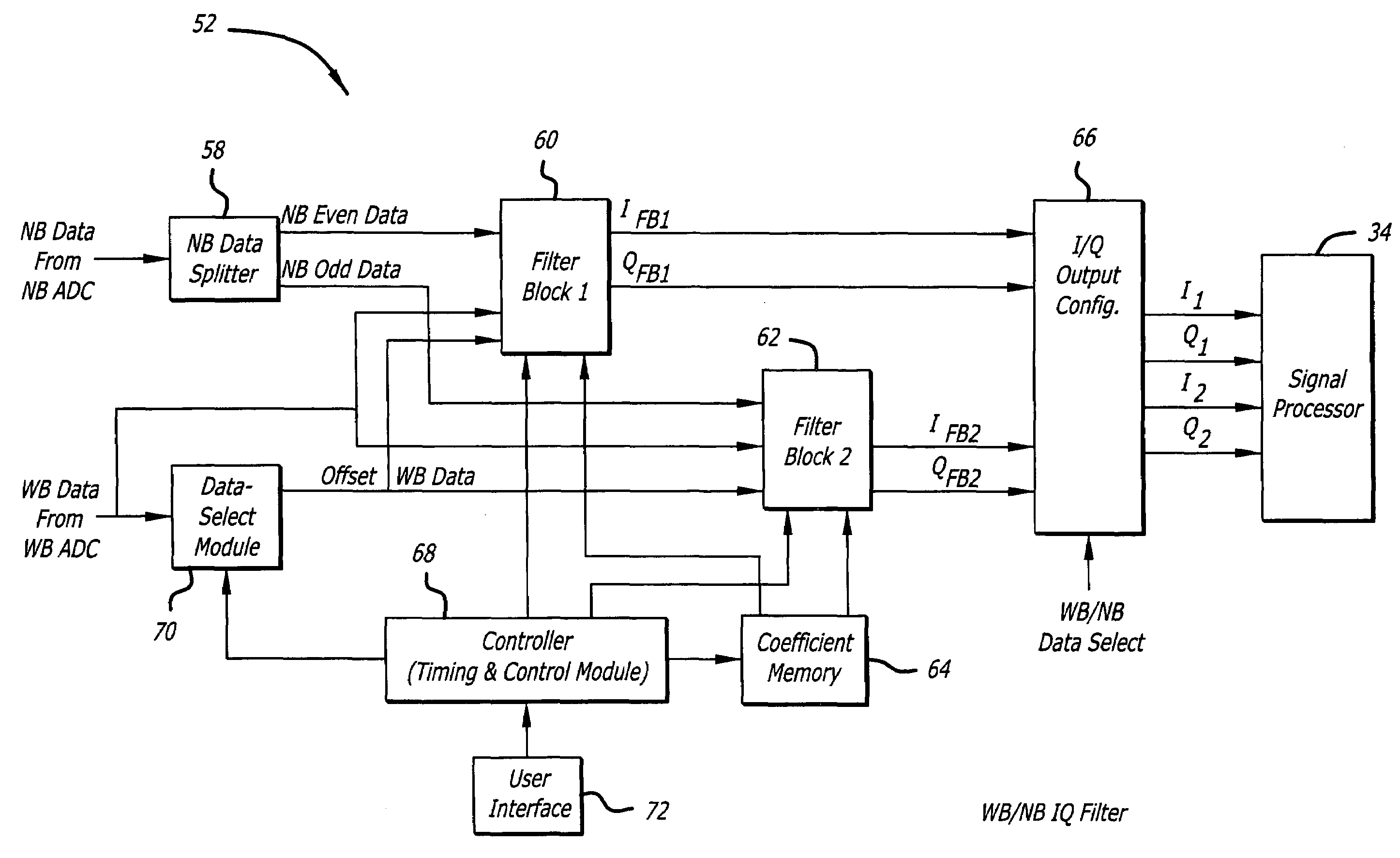
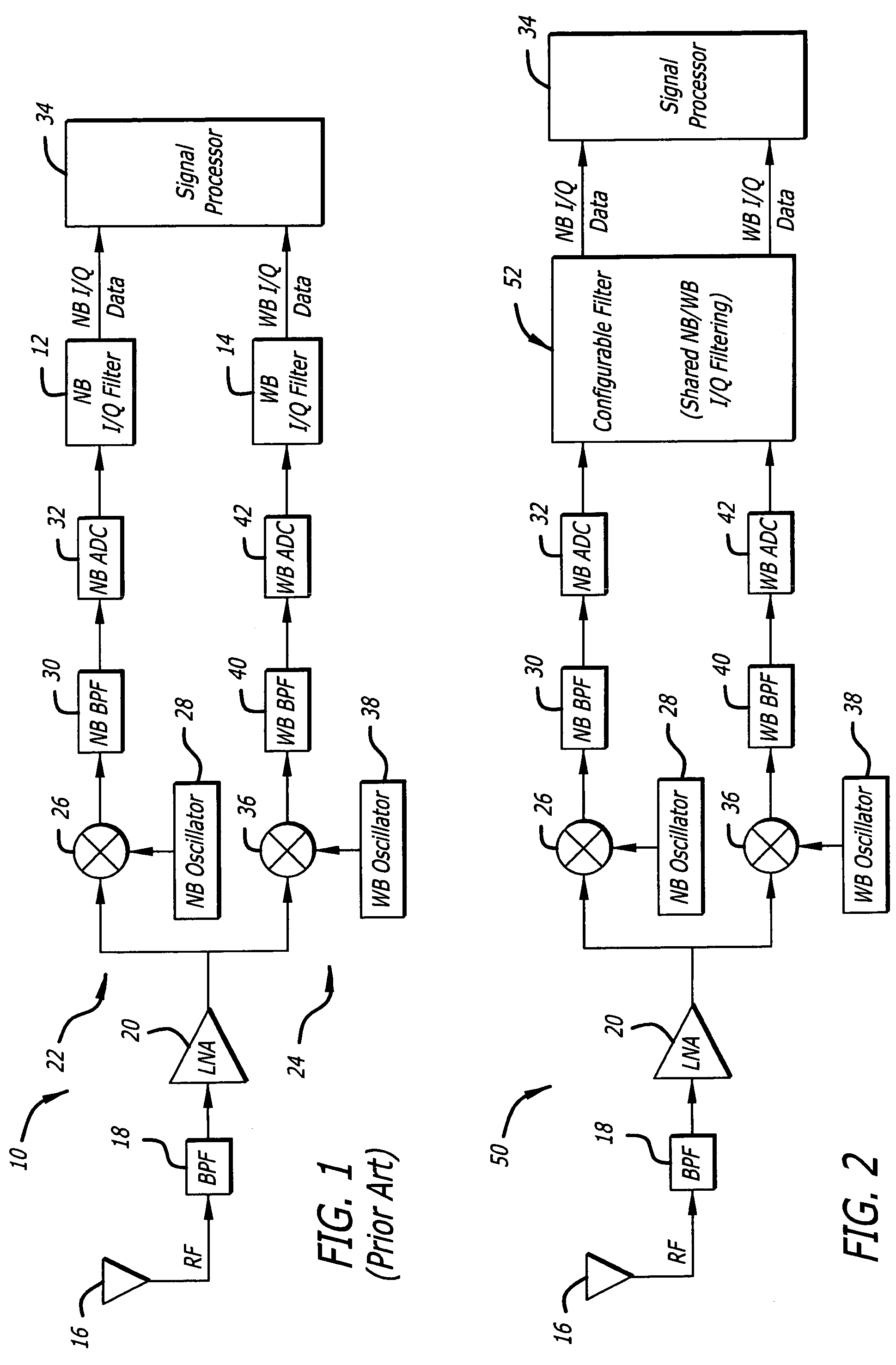
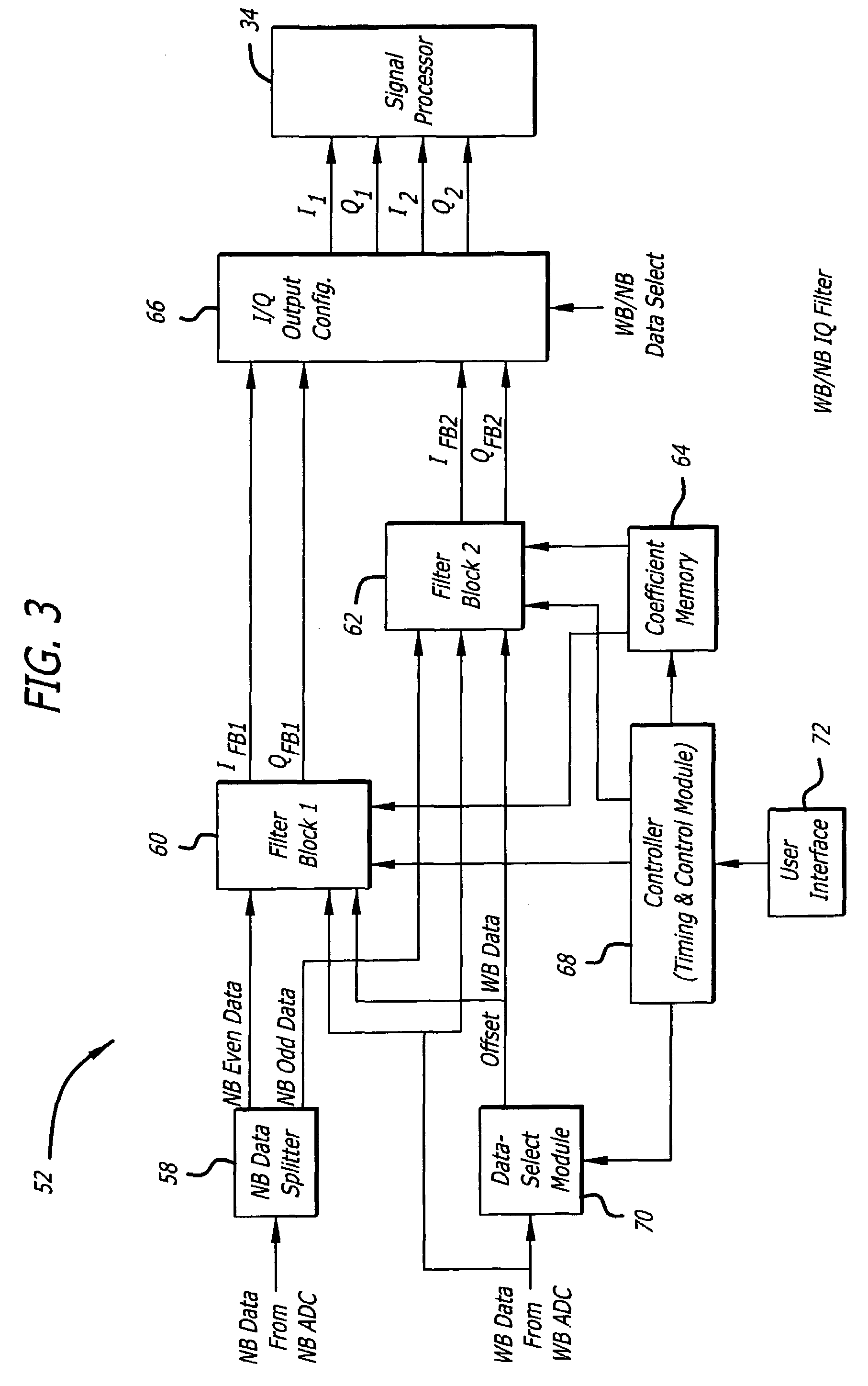
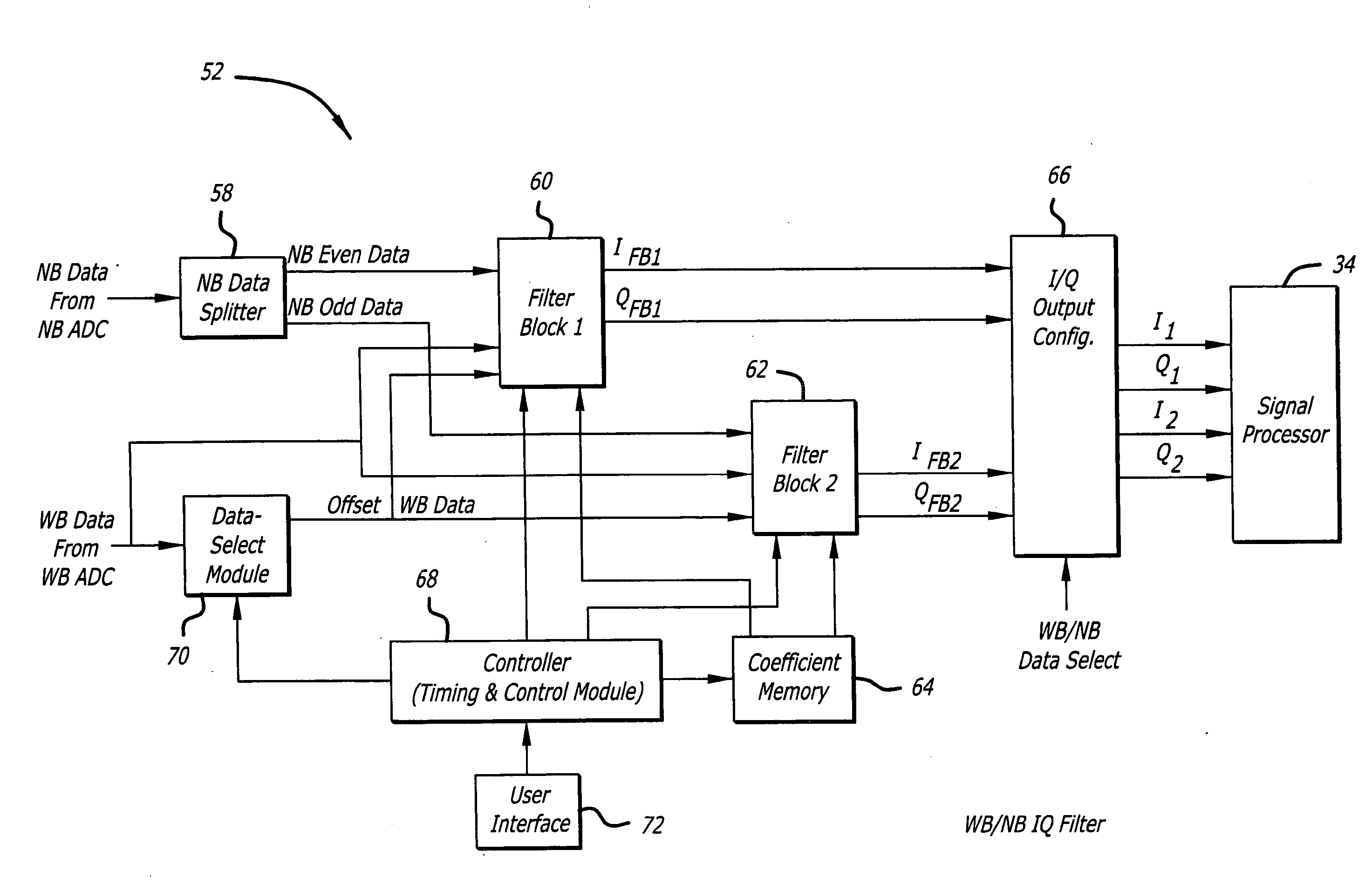
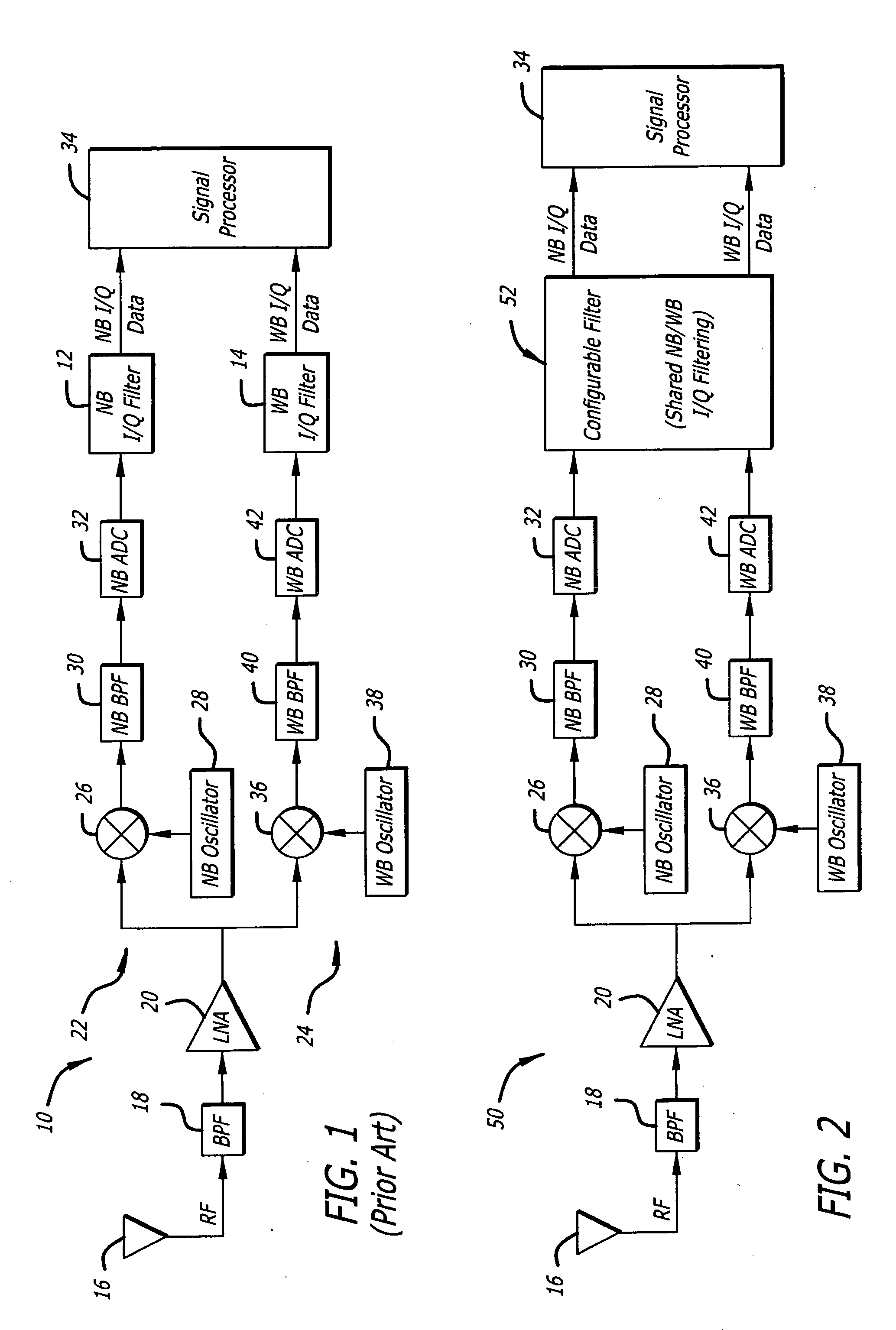
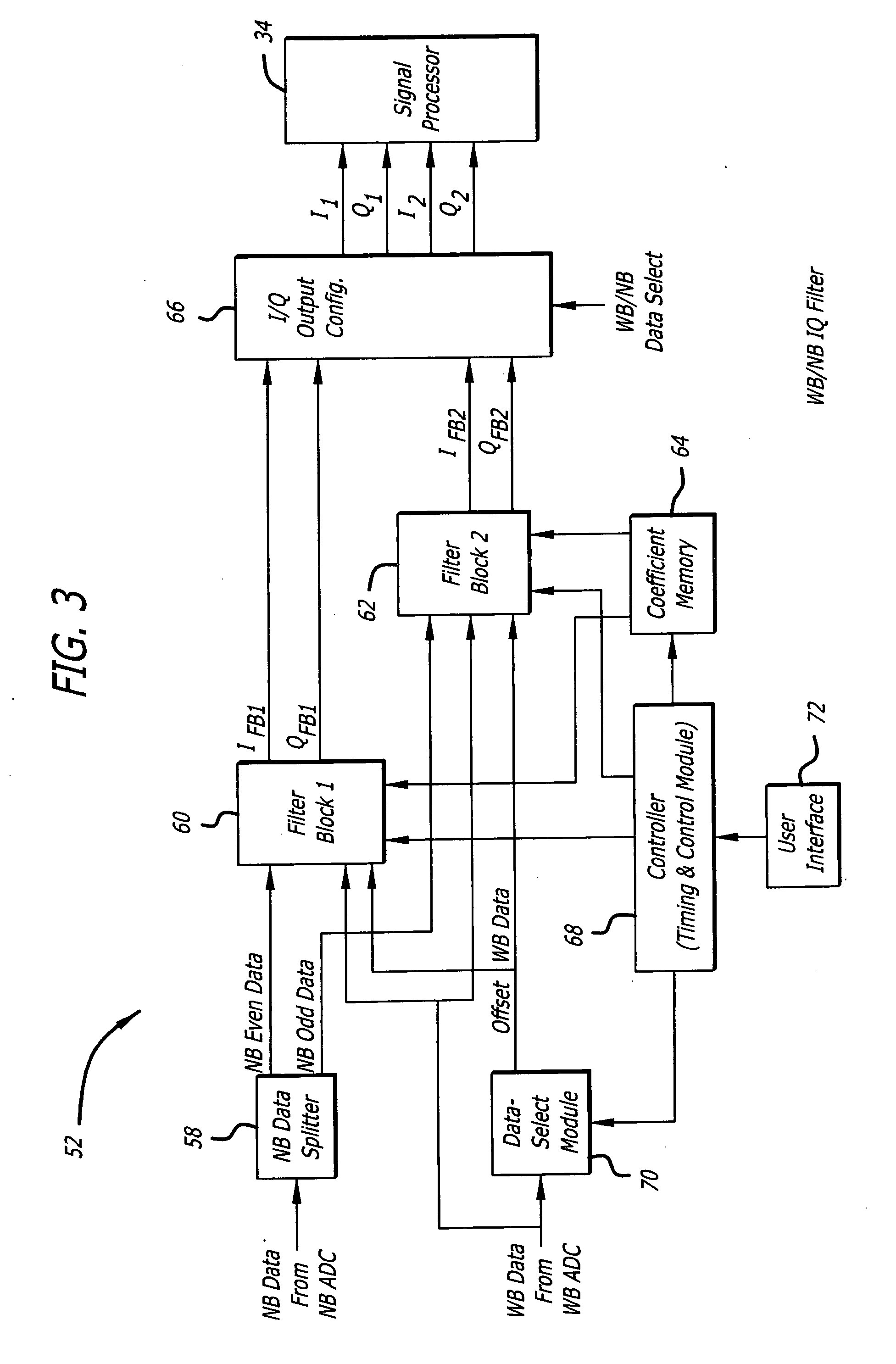
Configurable filter and receiver incorporating same
ActiveUS7526052B2Selectively affecting filter responseFacilitates coefficientModulated-carrier systemsSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMultiplexerControl signal
An efficient configurable signal filter. The filter includes a first mechanism for receiving a first signal of a first type and a second signal of a second type. A second mechanism selectively filters the first signal during a first mode of operation, and filters the second signal during a second mode of operation. A third mechanism generates control signals. A fourth mechanism automatically configures the second mechanism to operate in the first mode of operation or the second mode of operation based on the control signals. In a specific embodiment, the first type of signal is characterized by a first rate, and the second type of signal is characterized by a second rate. The first signal and the second signal are digital ADC outputs. The second mechanism includes plural filter blocks, each having one or more Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) pipes. Each of the one or more MAC pipes include one or more MAC blocks that are each associated with a coefficient memory data structure of a coefficient memory. The third mechanism or a user selects coefficients from each memory data structure to apply to each MAC block, thereby selectively affecting filter response. The control signals direct multiplexers or switches to configure the MAC pipes in a serial configuration or a parallel configuration corresponding to the first mode of operation or the second mode of operation, respectively.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
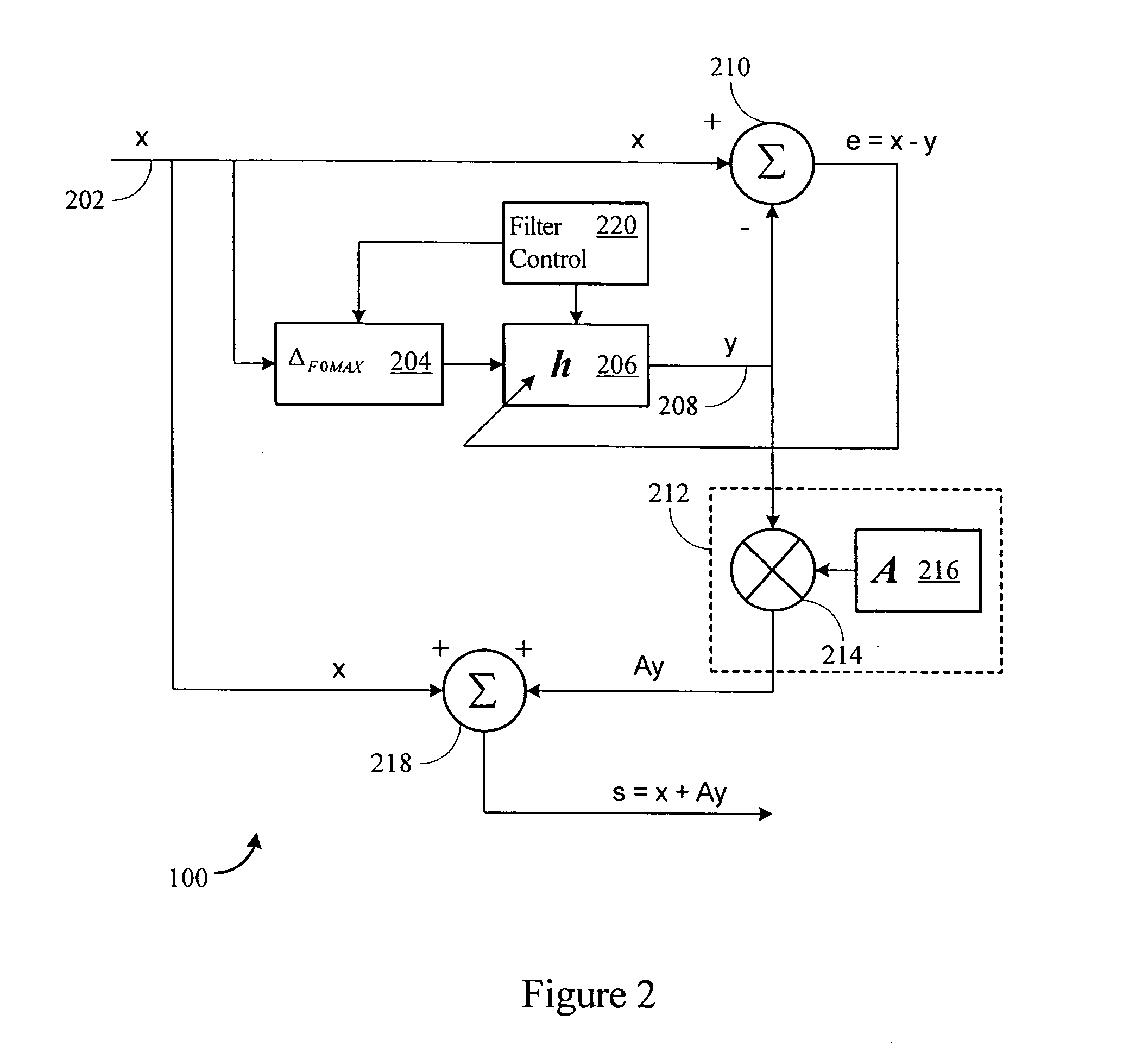
Periodic signal enhancement system
ActiveUS20060089958A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease contentAdaptive networkEar treatmentAdaptive filterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A signal enhancement system improves the understandability of speech or other audio signals. The system reinforces selected parts of the signal, may attenuate selected parts of the signal, and may increase SNR. The system includes delay logic, an adaptive filter, and signal reinforcement logic. The adaptive filter may track one or more fundamental frequencies in the input signal and outputs a filtered signal. The filtered signal may approximately reproduce the input signal approximately delayed by an integer multiple of the signal's fundamental frequencies. The reinforcement logic combines the input signal and the filtered signal output to produce an enhanced signal output.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Configurable filter and receiver incorporating same
ActiveUS20060133551A1Enhances filter versatilityImprove programmabilitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexerControl signal
An efficient configurable signal filter. The filter includes a first mechanism for receiving a first signal of a first type and a second signal of a second type. A second mechanism selectively filters the first signal during a first mode of operation, and filters the second signal during a second mode of operation. A third mechanism generates control signals. A fourth mechanism automatically configures the second mechanism to operate in the first mode of operation or the second mode of operation based on the control signals. In a specific embodiment, the first type of signal is characterized by a first rate, and the second type of signal is characterized by a second rate. The first signal and the second signal are digital ADC outputs. The second mechanism includes plural filter blocks, each having one or more Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) pipes. Each of the one or more MAC pipes include one or more MAC blocks that are each associated with a coefficient memory data structure of a coefficient memory. The third mechanism or a user selects coefficients from each memory data structure to apply to each MAC block, thereby selectively affecting filter response. The control signals direct multiplexers or switches to configure the MAC pipes in a serial configuration or a parallel configuration corresponding to the first mode of operation or the second mode of operation, respectively.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
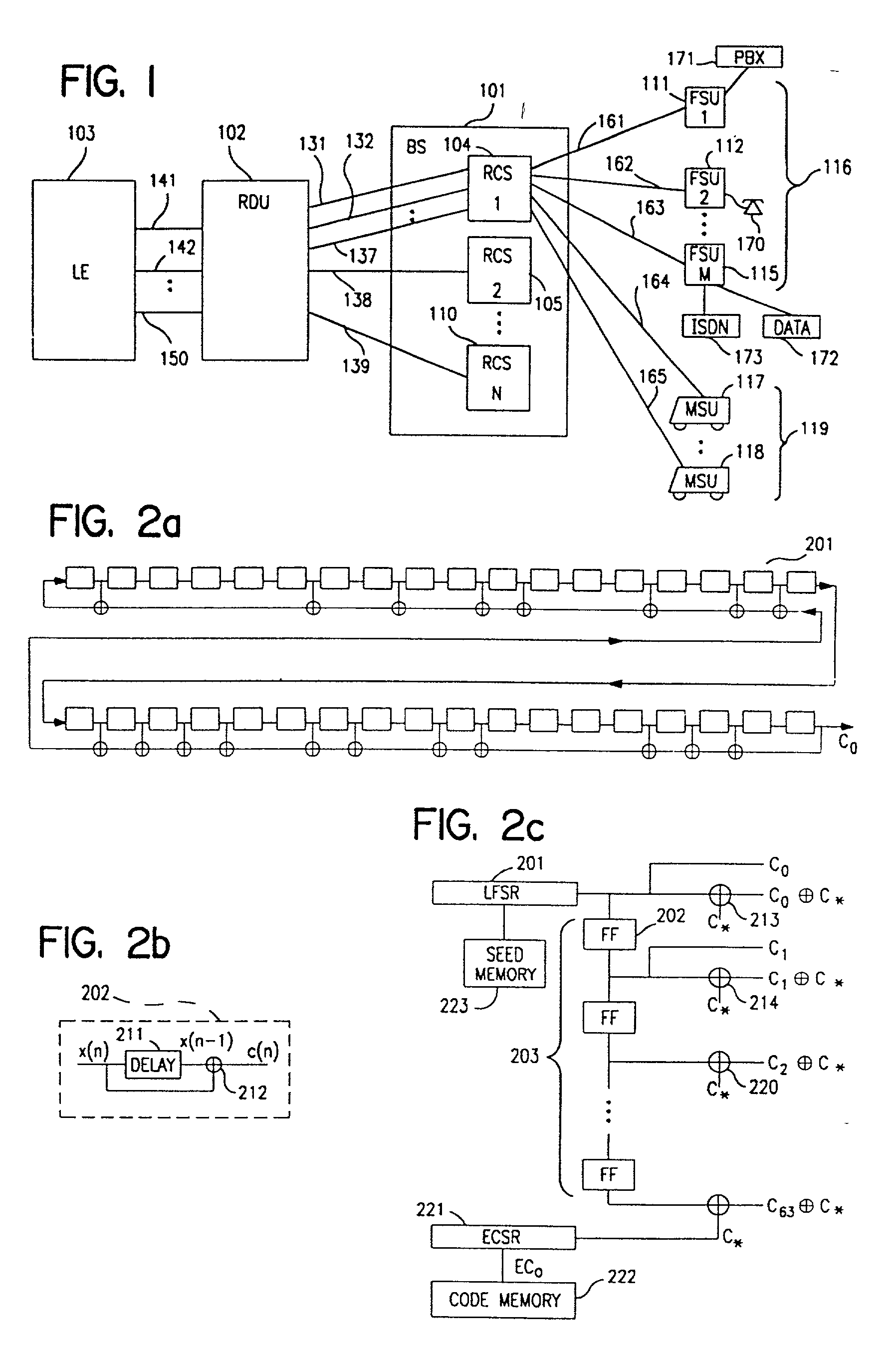
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020021686A1Easy to liftShortens channel acquisition timeEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationSystem capacityModem device
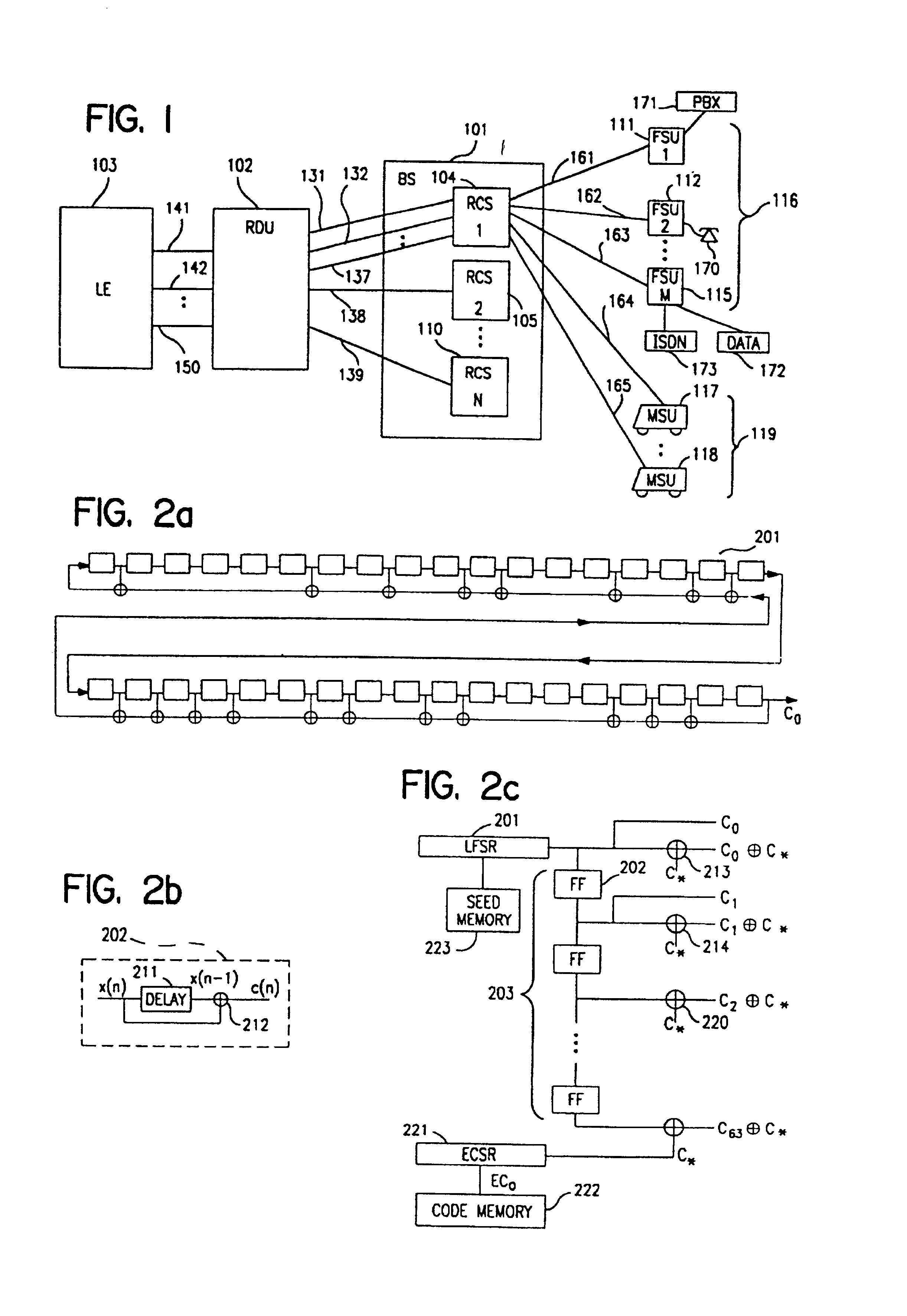
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
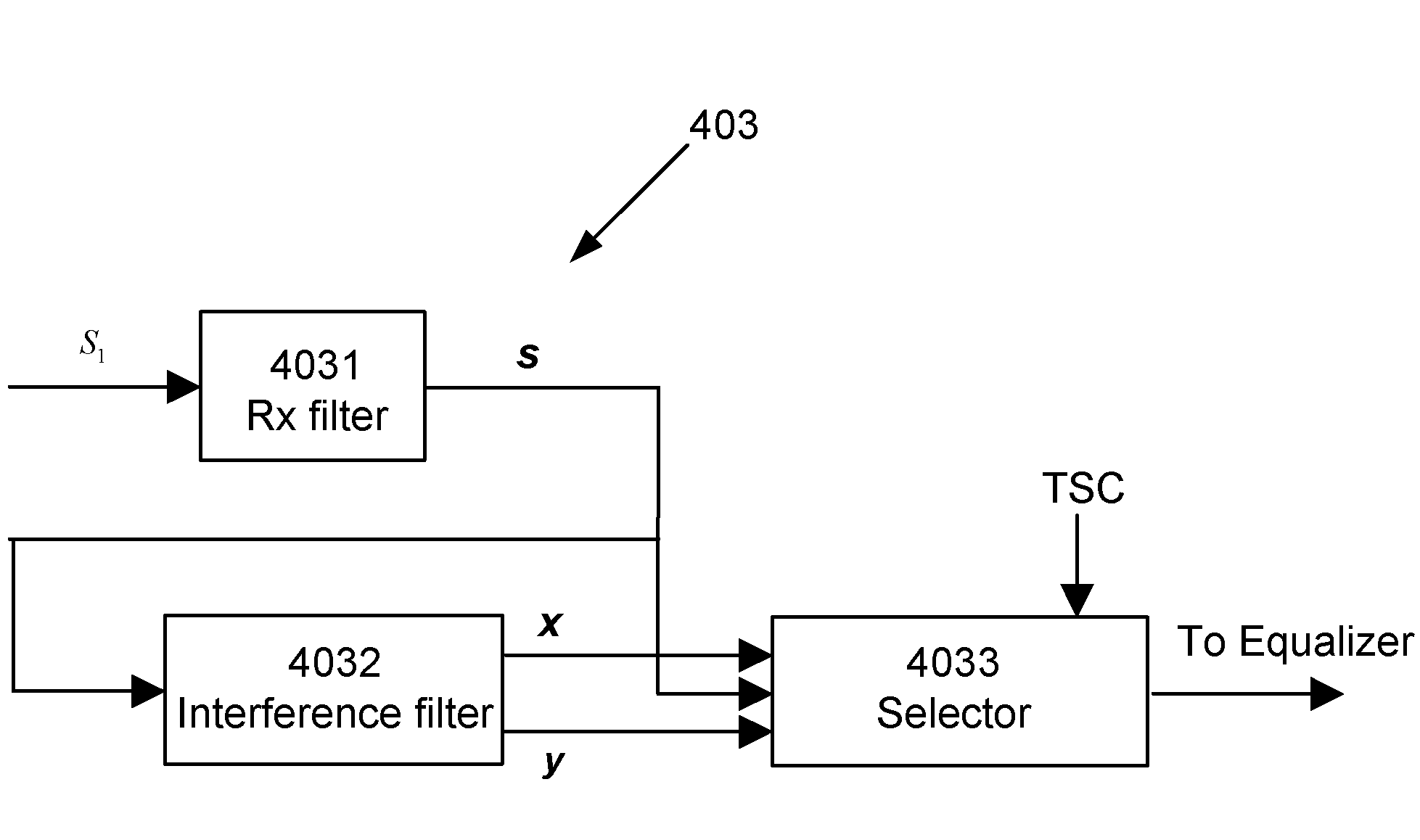
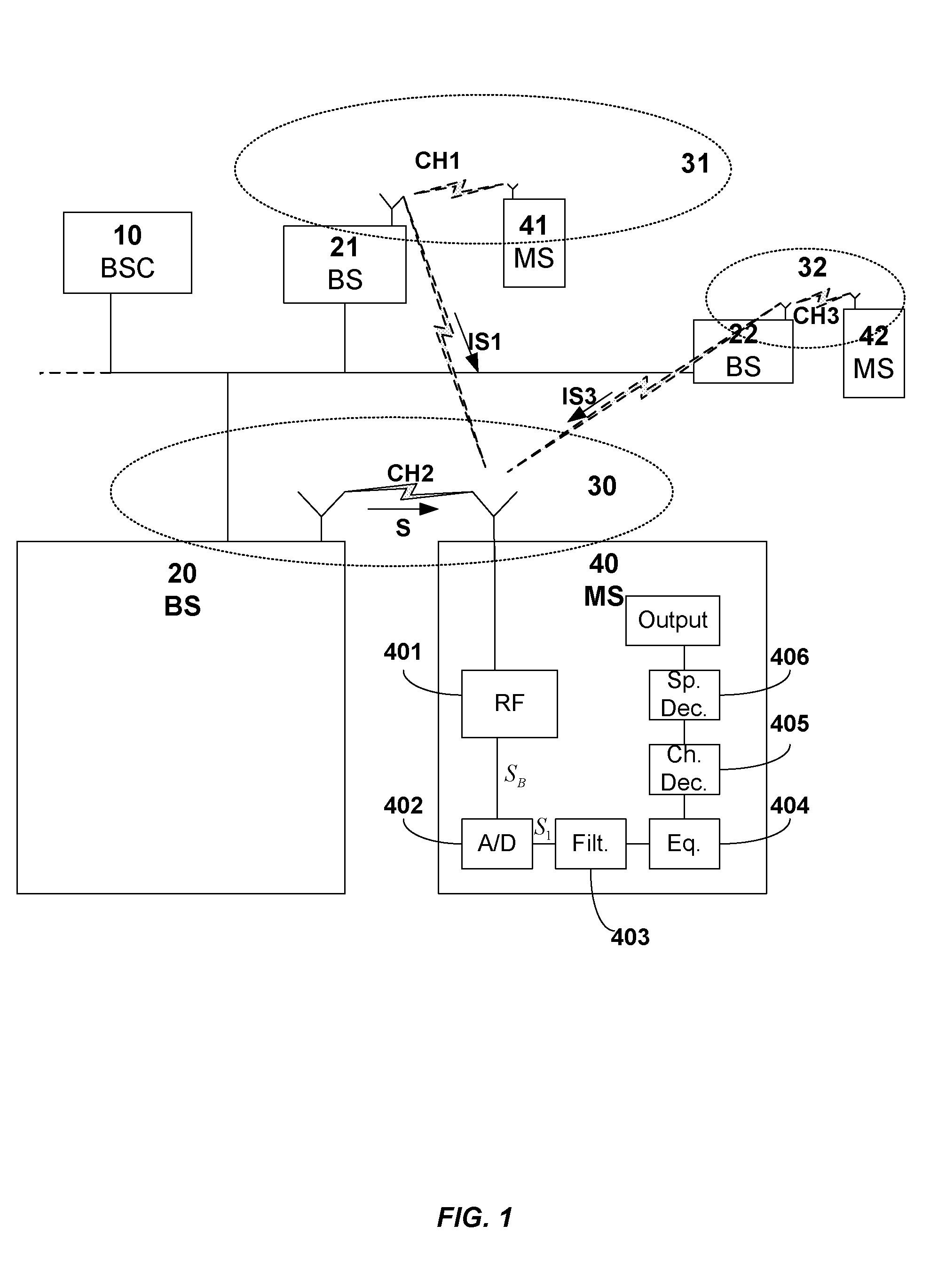
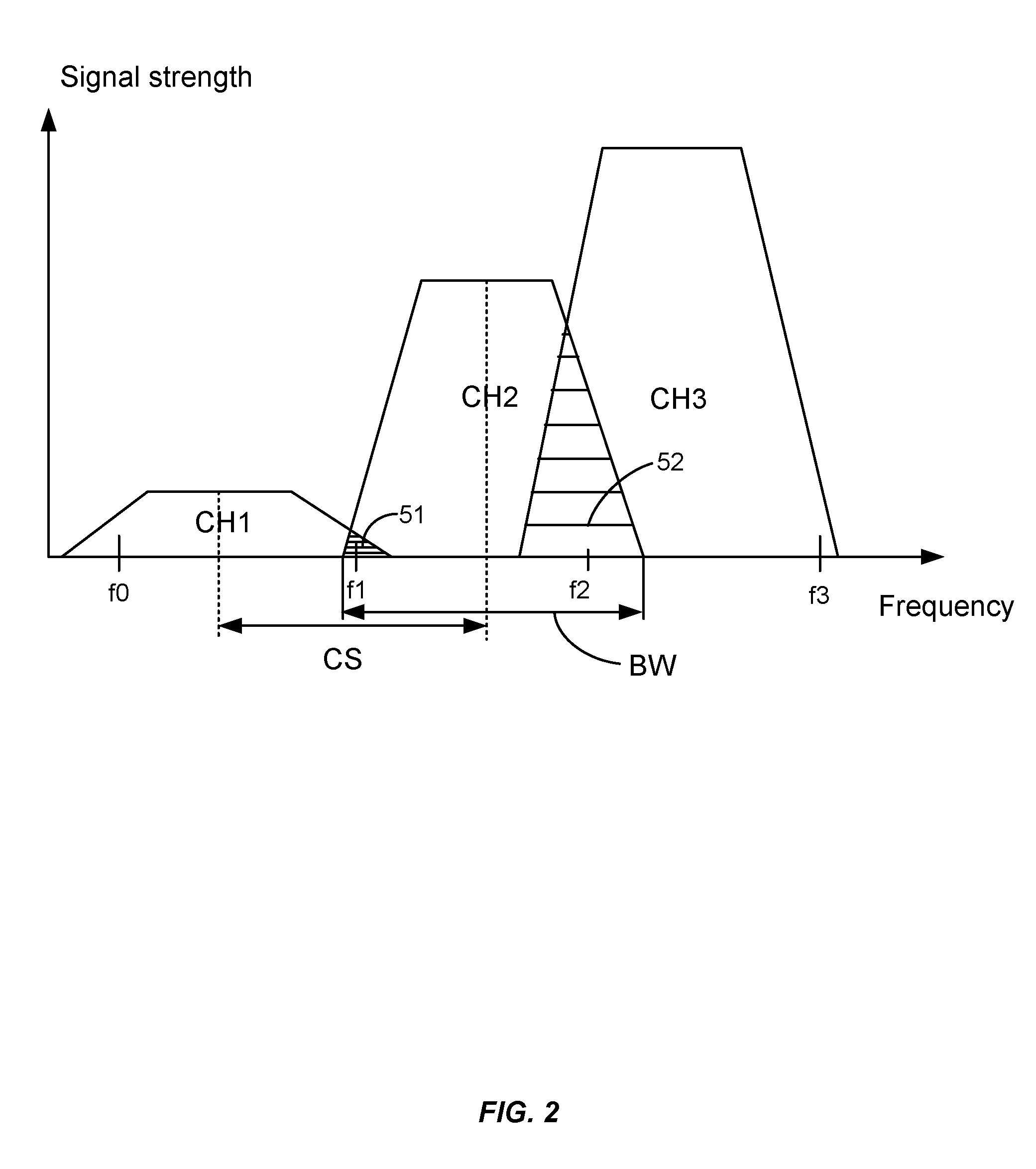
Filter and Method for Suppressing Effects of Adjacent-Channel Interference
ActiveUS20090135973A1Reduced processing power requirementsReduced Power RequirementsDigital technique networkModulated-carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceLow frequency band
A filter device and method for suppressing effects of Adjacent-Channel Interference of a received signal in a Frequency-Division-Multiple-Access system by filtering a baseband signal of the received signal. The filter device comprises an interference filter, which is a complex digital Single-Input-Multiple-Output, SIMO, filter that is adapted to simultaneously generate a first signal filtered at an upper-frequency-band and a second signal filtered at a lower-frequency-band, wherein the first signal is separate from the second signal. The filter device also comprises a selector adapted to select one of the signals as the output from the filter device.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Periodic signal enhancement system
ActiveUS7680652B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease contentEar treatmentAdaptive networkAdaptive filterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
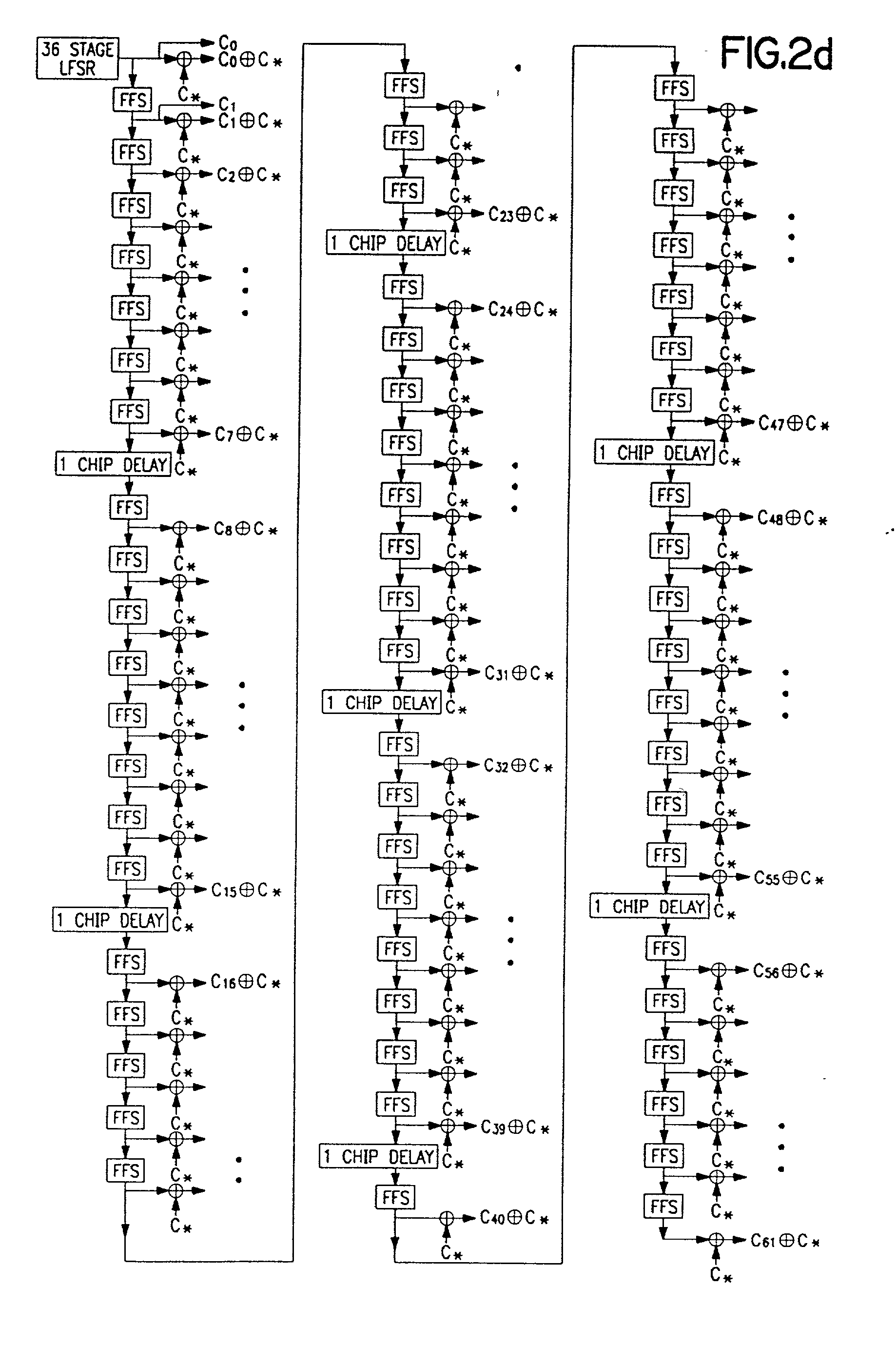
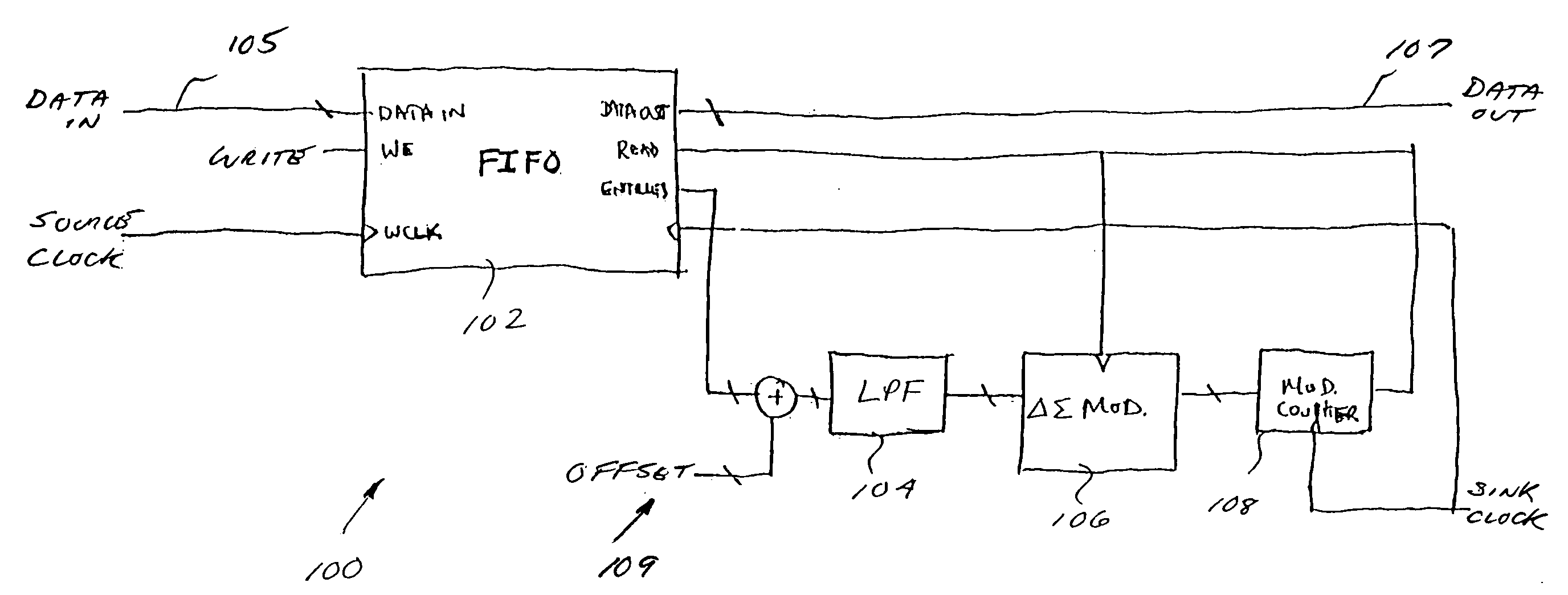
Noise shaped interpolator and decimator apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050207480A1Suppress phase noiseReduce presenceSynchronisation information channelsDigital technique networkNoise shapingEngineering
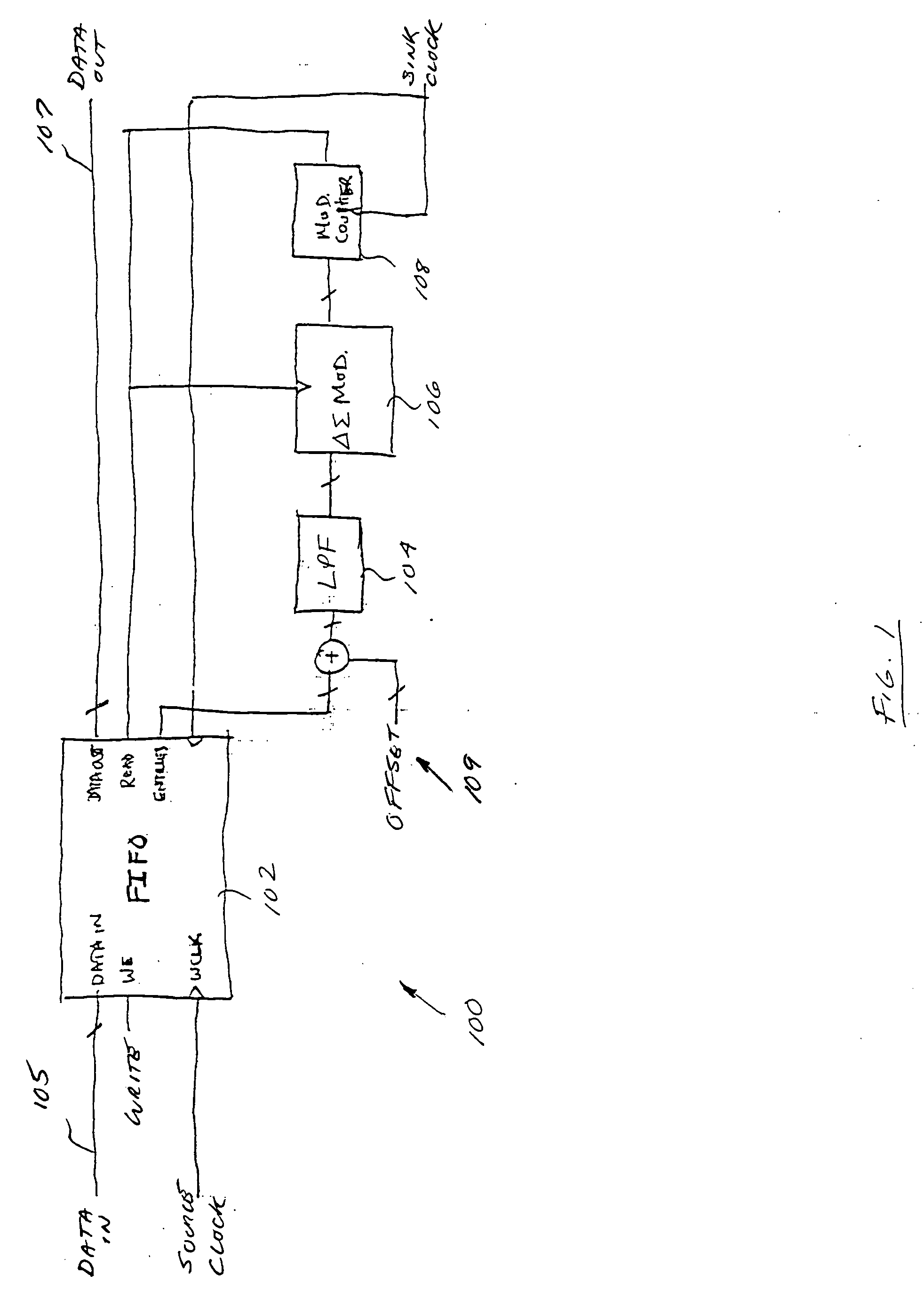
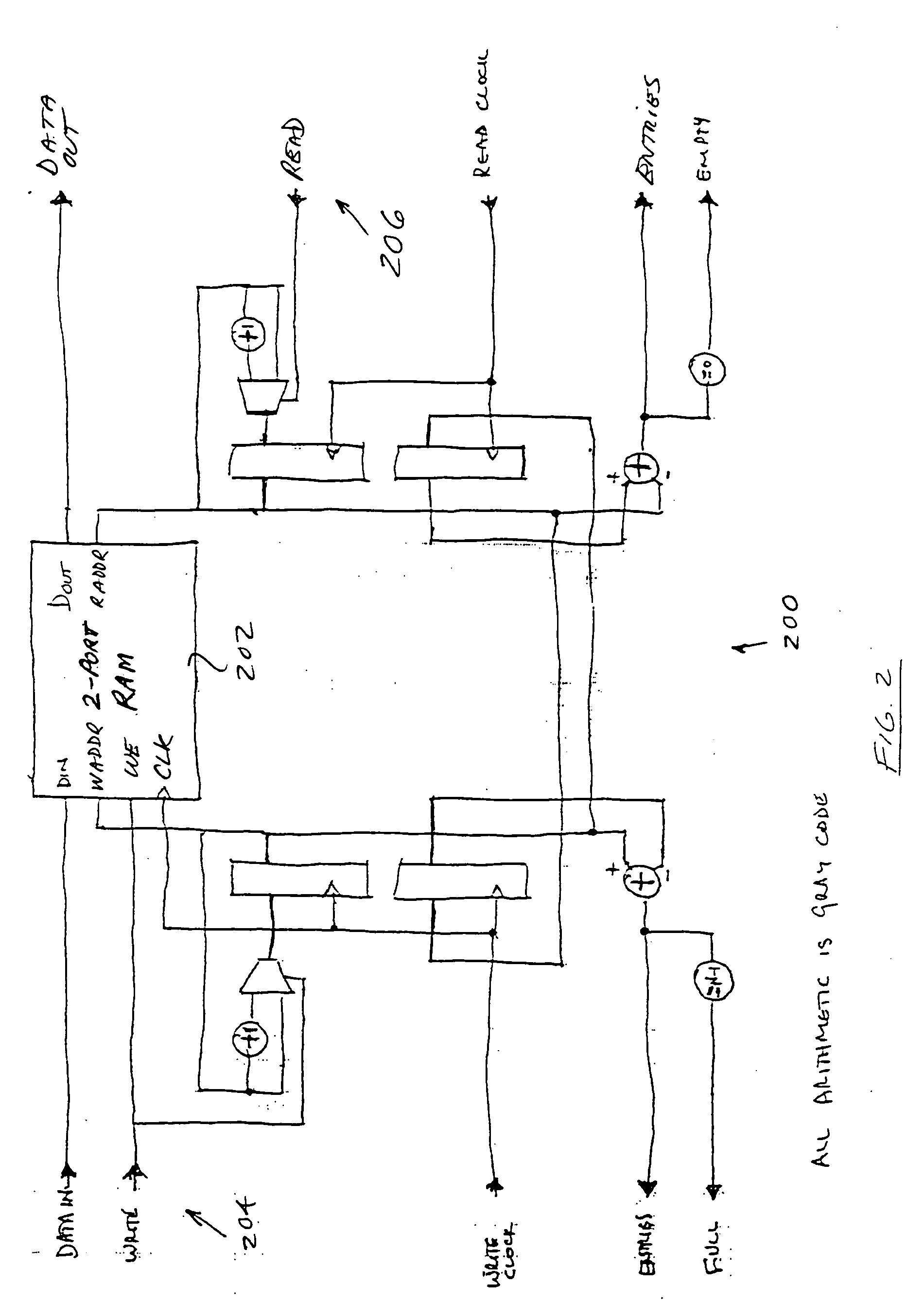
Improved interpolator and decimator apparatus and methods, including the addition of an elastic storage element in the signal path. In one exemplary embodiment, the elastic element comprises a FIFO which advantageously allows short term variation in sample clocks to be absorbed, and also provides a feedback mechanism for controlling a delta-sigma modulated modulo-N counter based sample clock generator. The elastic element combined with a delta-sigma modulator and counter creates a noise-shaped frequency lock loop without additional components, resulting in a much simplified interpolator and decimator.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
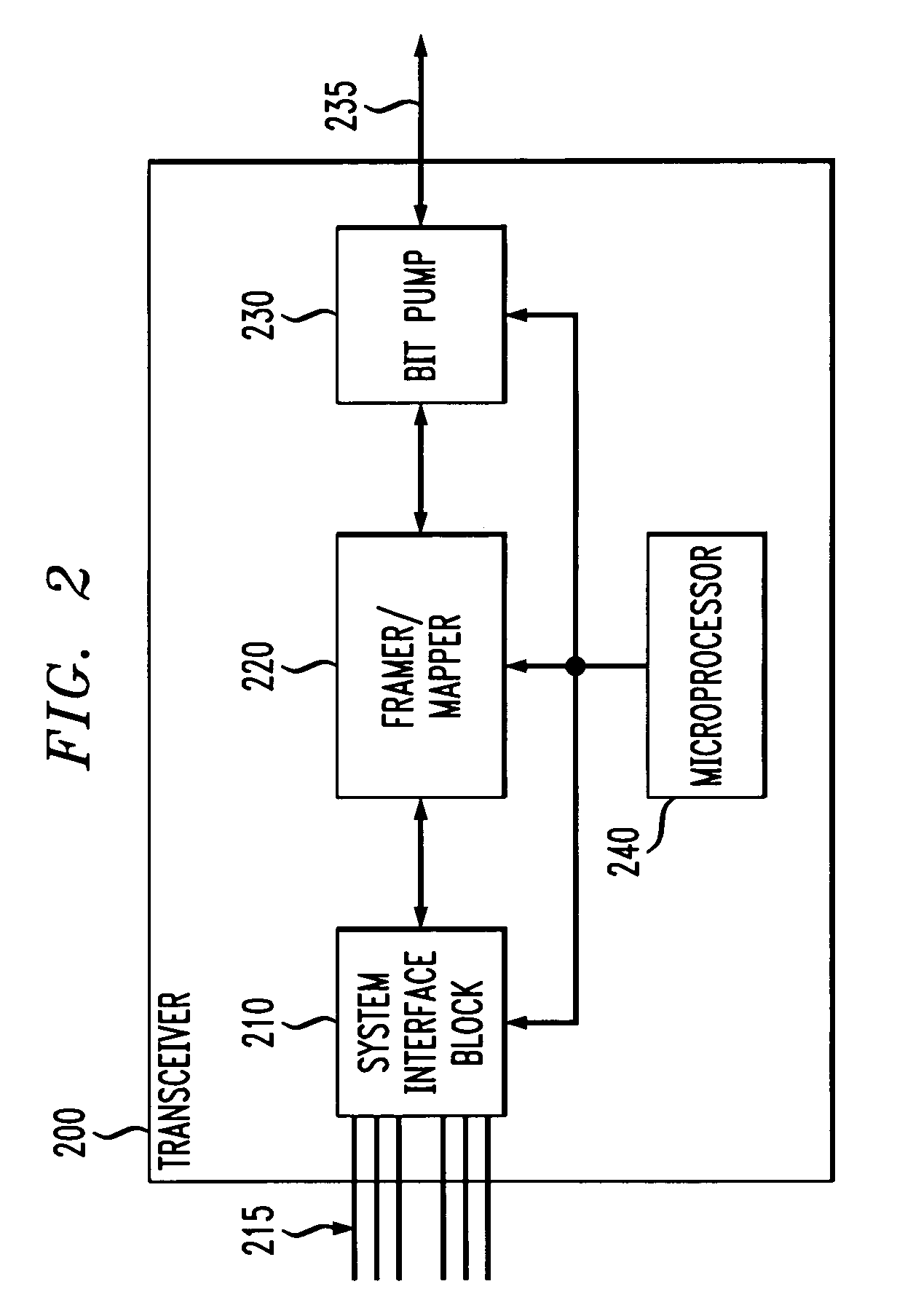
Low-current sample rate converter
InactiveUS6347123B1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital technique networkCurrent sampleTransceiver
A low power sample rate converter adapted for use with a telecommunications system transceiver. The sample rate converter includes a first circuit that provides an input signal characterized by a first sample rate and a delayed version of the input signal. A second circuit periodically multiplies, at a second sample rate, samples in the input signal by a first predetermined coefficient in accordance with a predetermined transfer function and provides a first signal in response thereto. A third circuit periodically multiplies, at the second sample rate, samples in the delayed version of the input signal by a second predetermined coefficient in accordance with the predetermined transfer function and provides a second signal in response thereto. A fourth circuit combines the first signal and second signal providing a rate-converted version of the input signal as an output signal in response thereto. In a specific embodiment, the delayed version of the input signal is delayed by one sample with respect to the input signal. The sample rate converter further includes a counter that is clocked by a first periodic signal. The first periodic signal has a frequency related to the first sample rate by a predetermined fraction. The counter is cleared by a second periodic signal having a second frequency equivalent to the first sample rate. The counter produces a counter output at the first frequency. In the preferred embodiment, the predetermined fraction is ⅓ and the first predetermined coefficient is equivalent to the sum of 1 and the counter output. The second predetermined coefficient is equivalent to the difference of 2 and the counter output. The fourth circuit includes an adder for adding the first signal and the second signal and providing the output signal in response thereto. The predetermined transfer function is represented by the following coefficient sequence: [1 2 3 2 1].
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
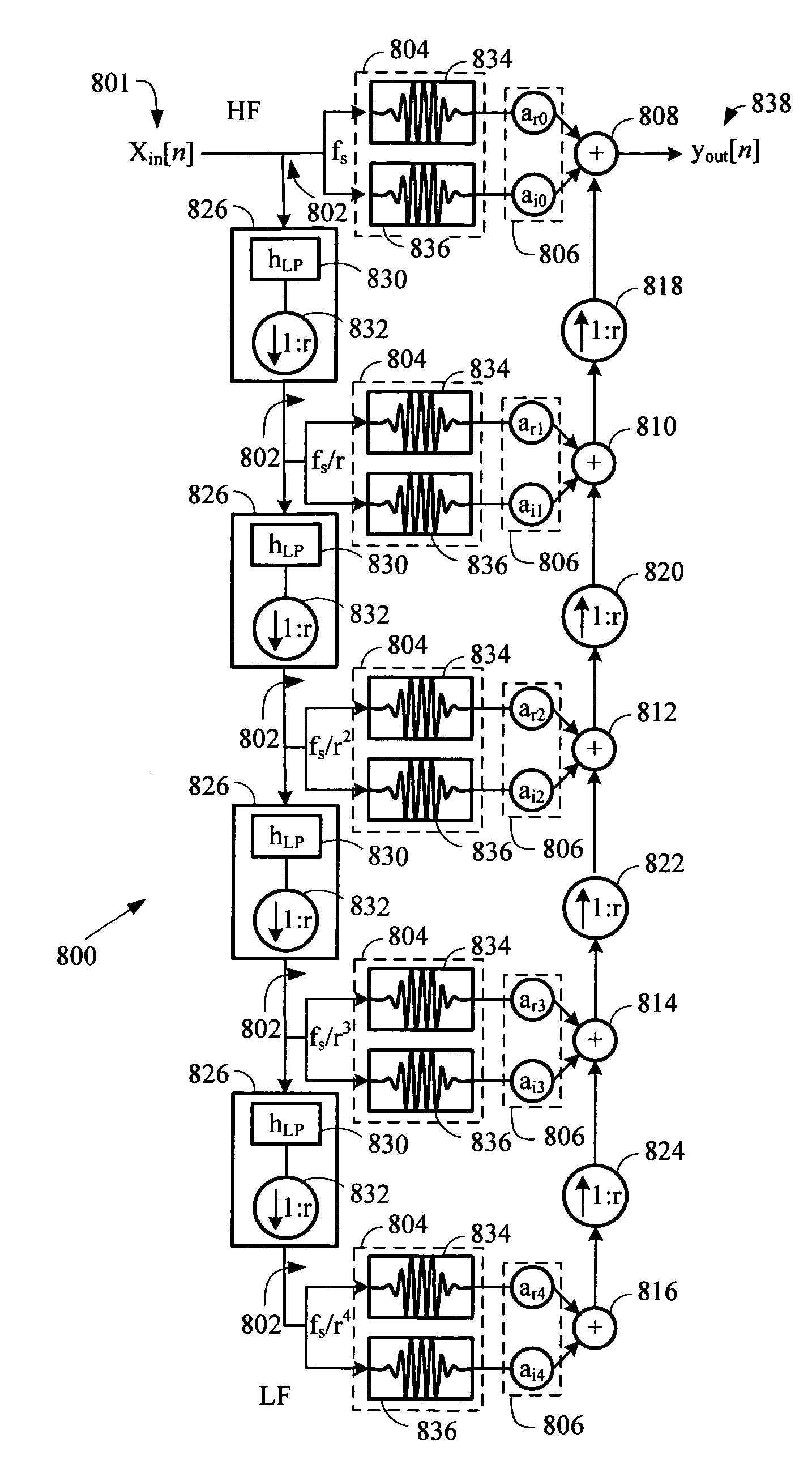
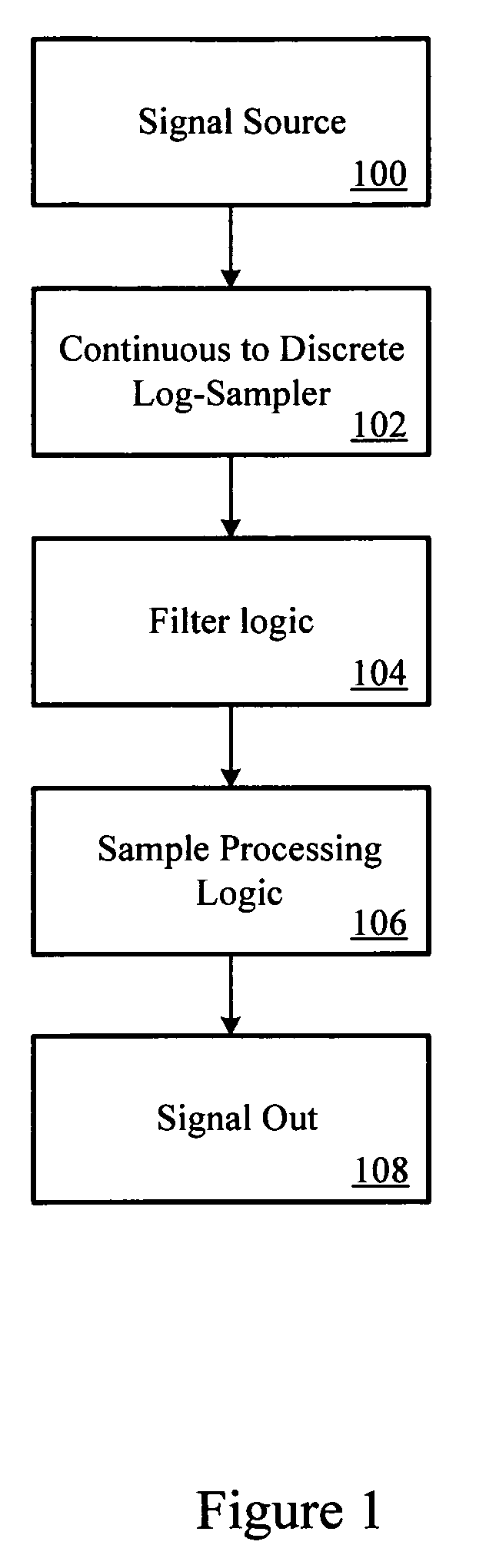
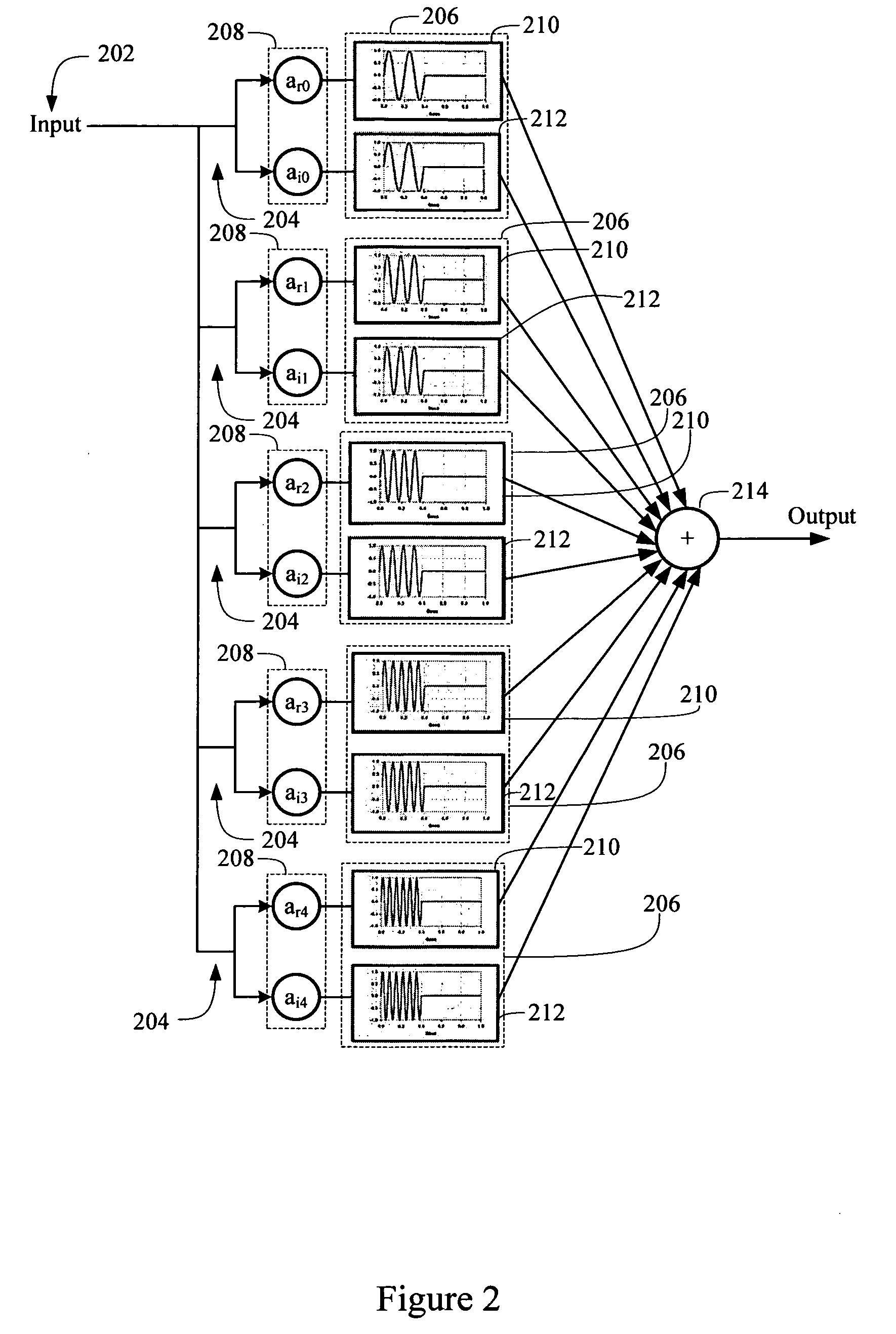
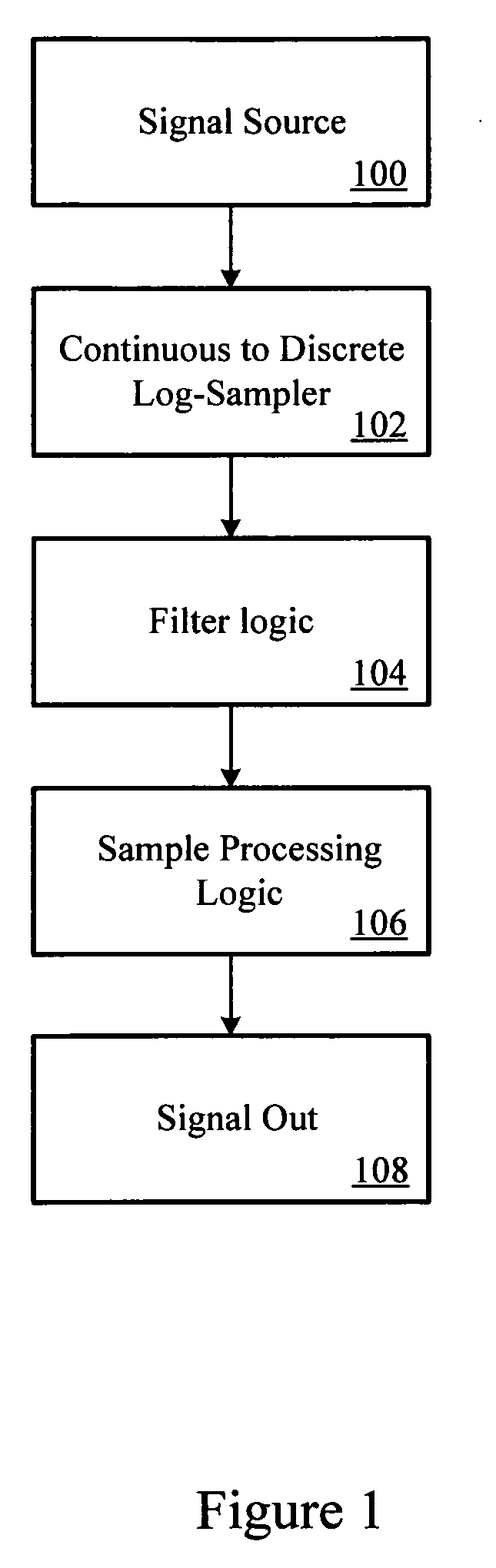
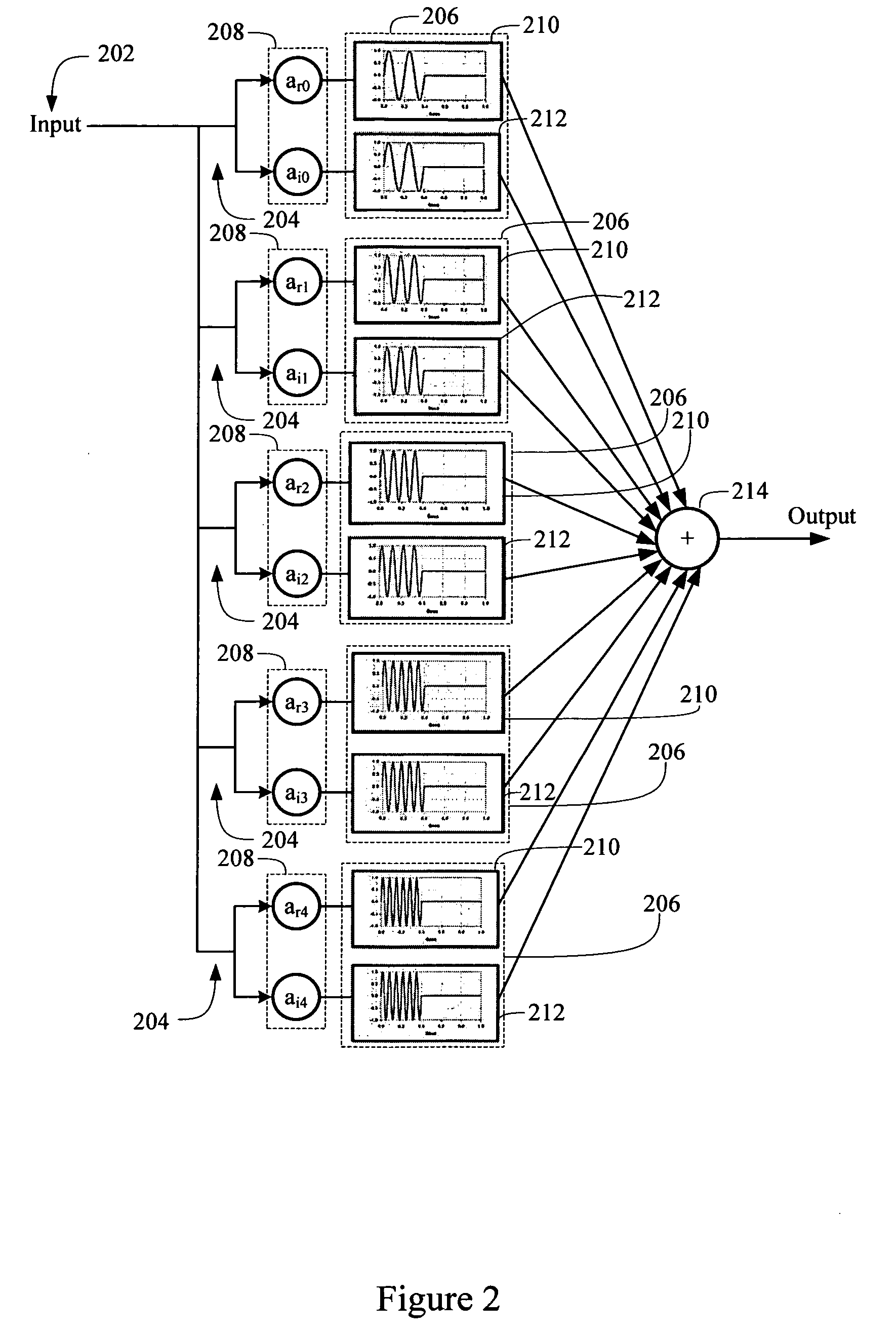
Log-sampled filter system
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
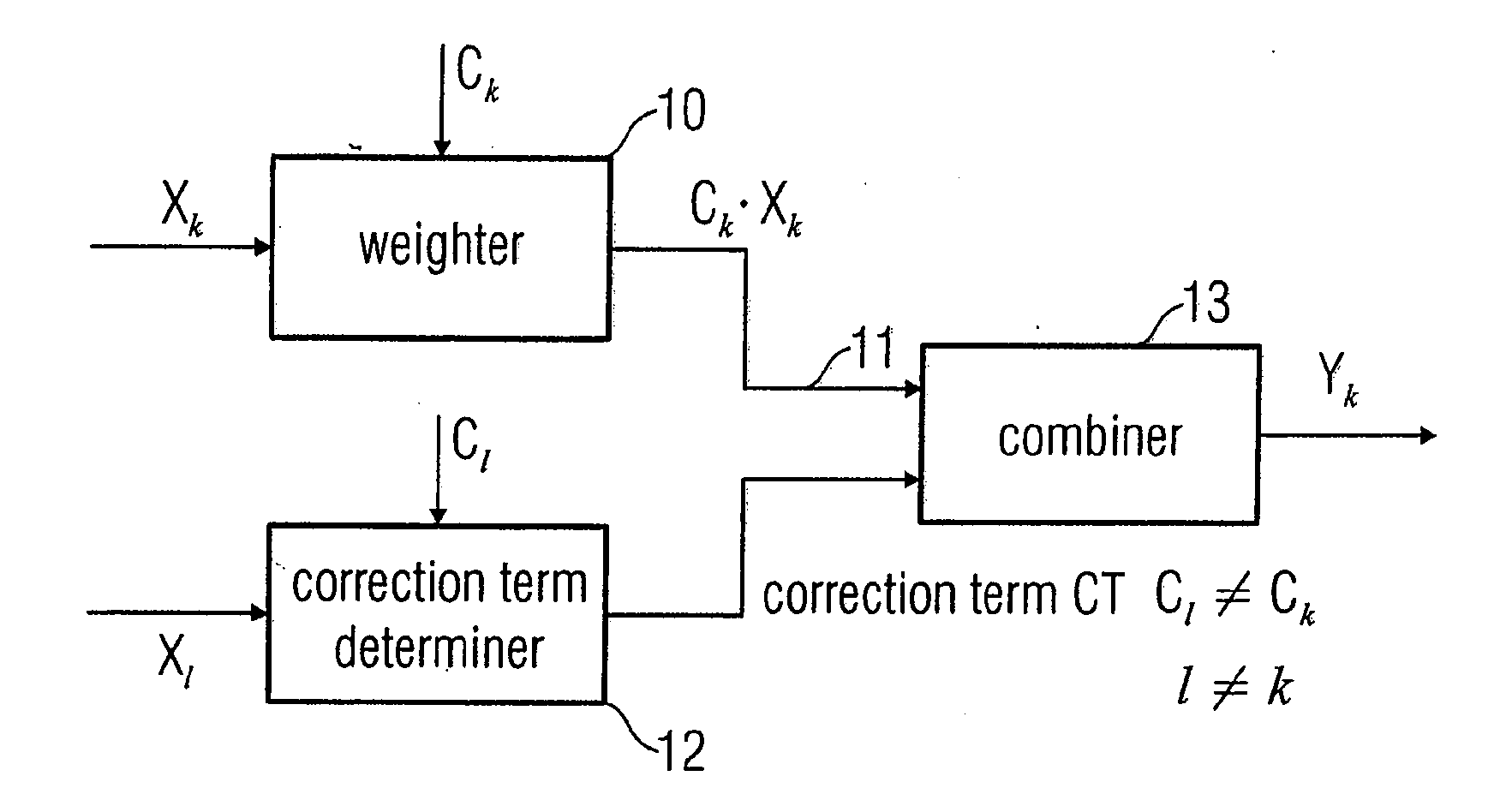
Device and Method for Processing a Real Subband Signal for Reducing Aliasing Effects
ActiveUS20100013987A1Great filter lengthReduce aliasingMultiple-port networksGain controlDiscrete-time signalComputer science
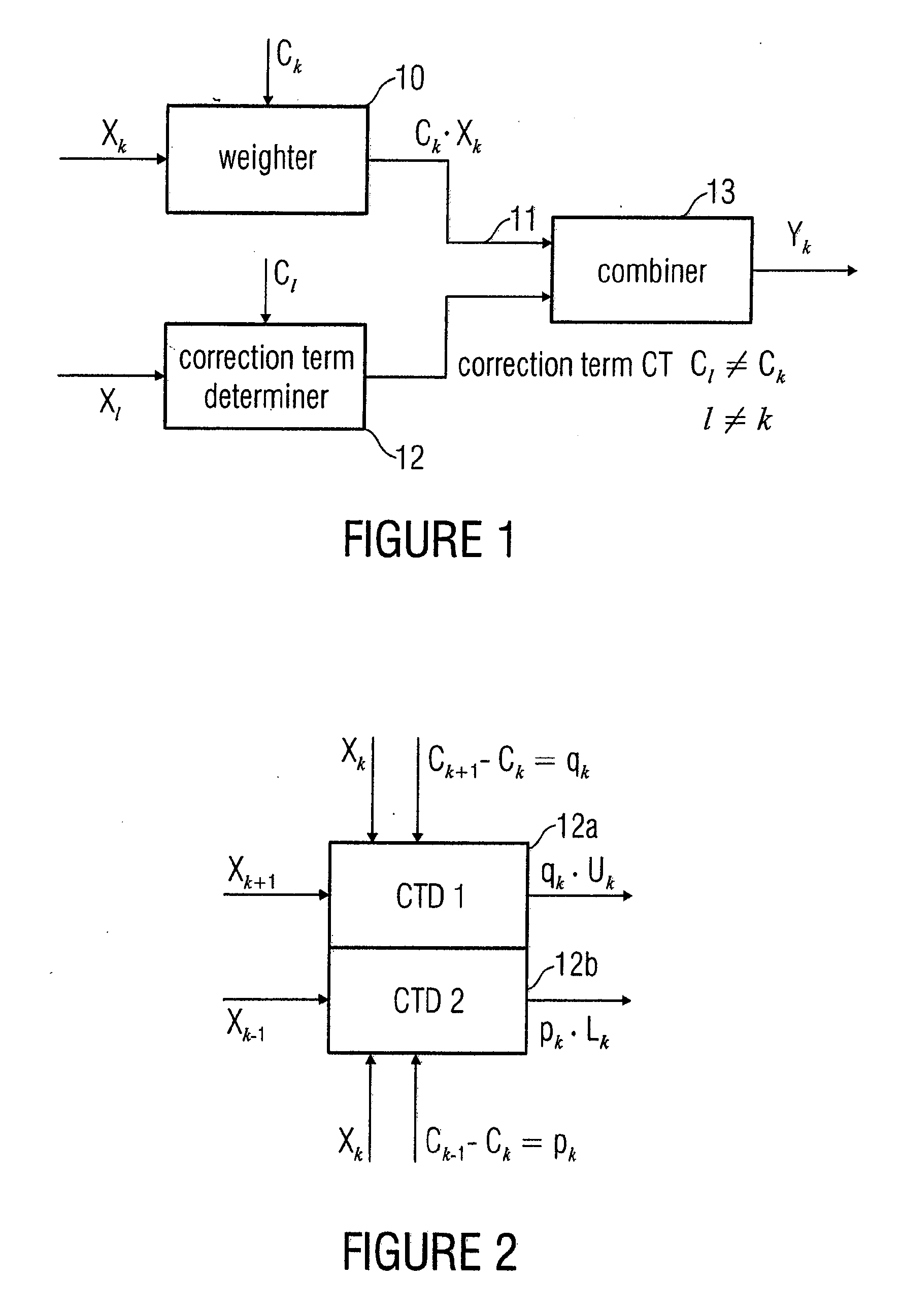
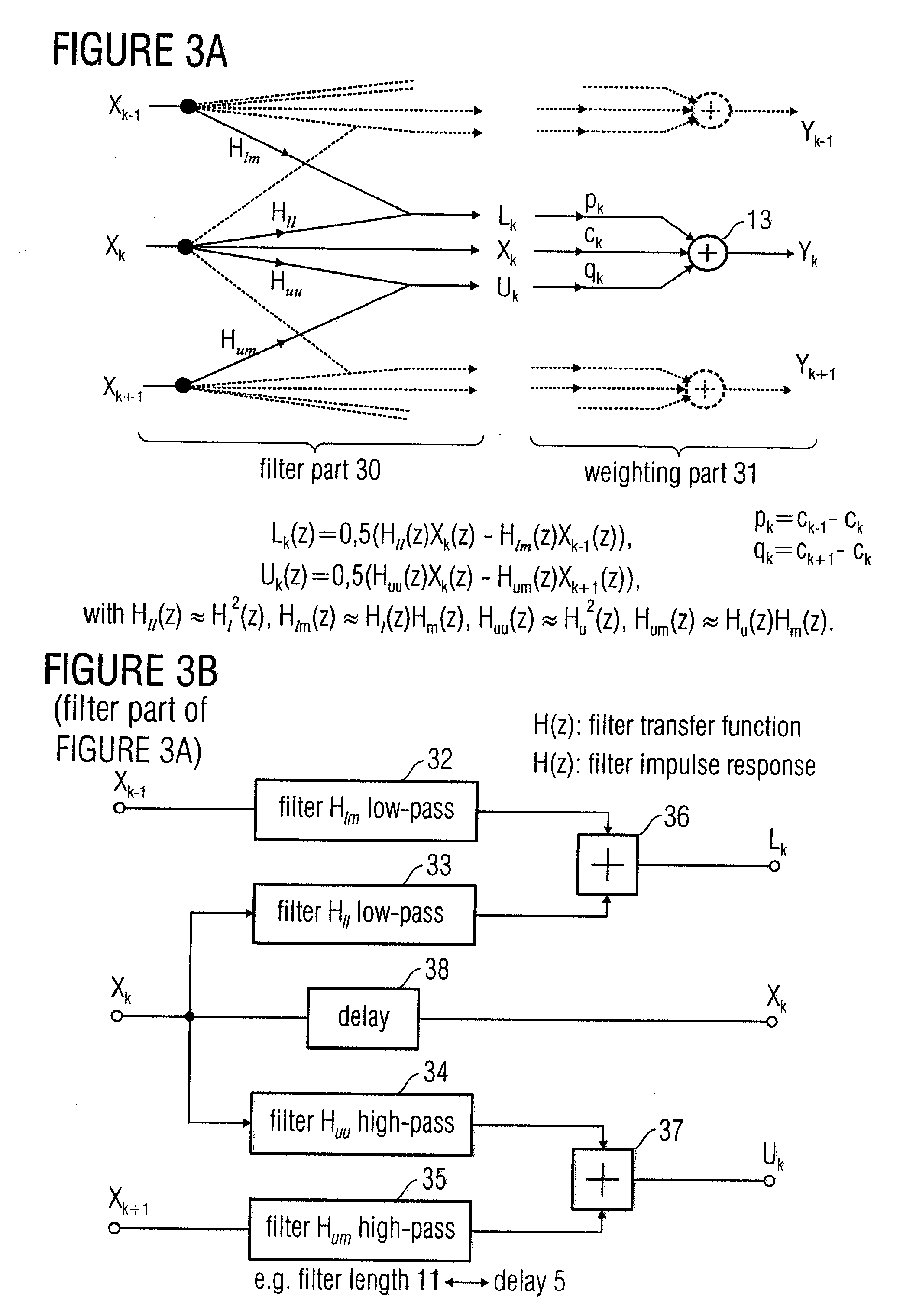
In order to process a subband signal of a plurality of real subband signals which are a representation of a real discrete-time signal generated by an analysis filter bank, a weighter for weighting a subband signal by a weighting factor determined for the subband signal is provided to obtain a weighted subband signal. In addition, a correction term is calculated by a correction term determiner, the correction term determiner being implemented to calculate the correction term using at least one other subband signal and using another weighting factor provided for the other subband signal, the two weighting factors differing. The correction term is then combined with the weighted subband signal to obtain a corrected subband signal, resulting in reduced aliasing, even if subband signals are weighted to a different extent.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Multi-channel sample rate conversion method
InactiveUS20060212503A1Valid conversionProvides computational efficiencyDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsSample rate conversionComputer science
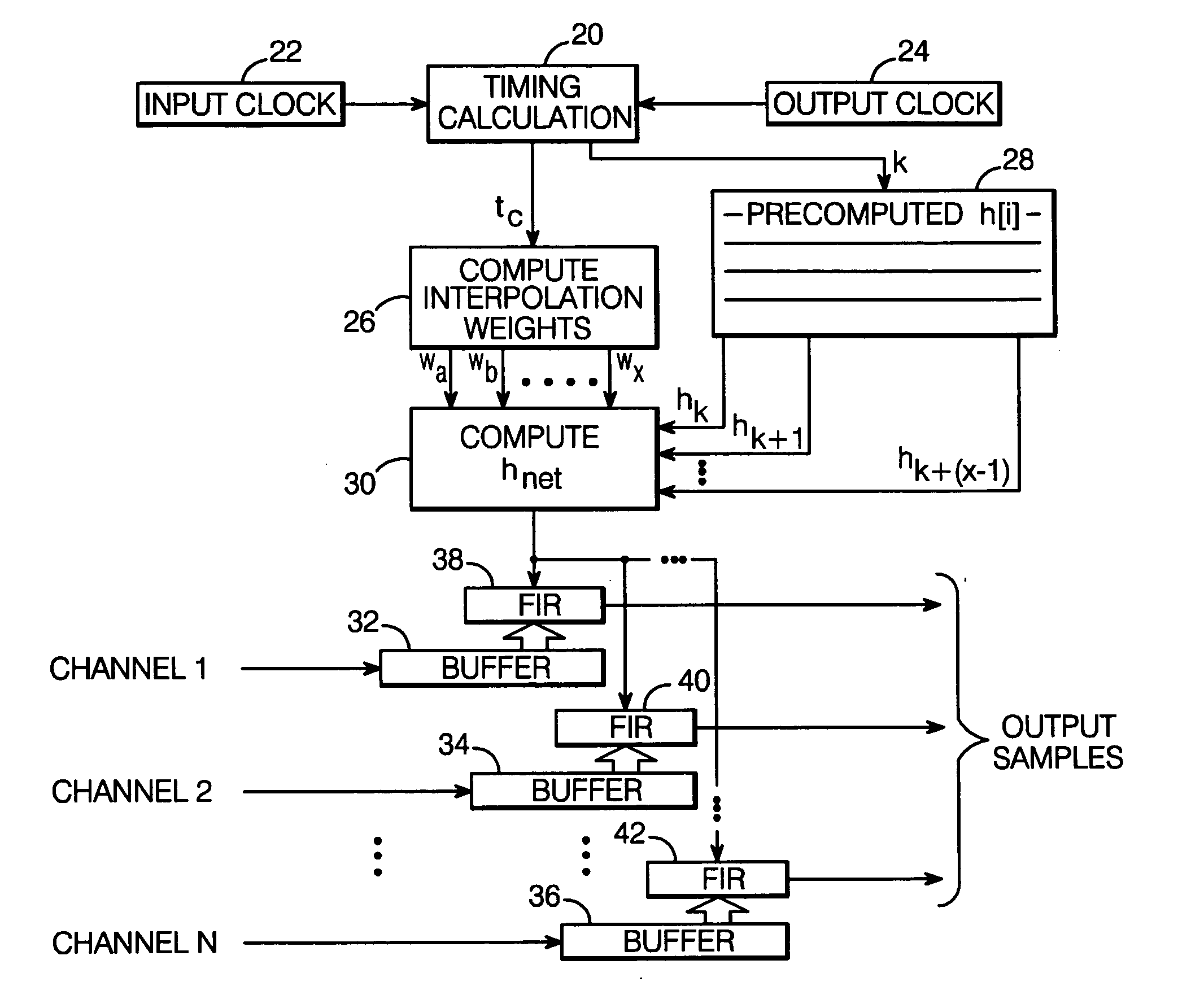
A sampling-rate conversion method receives N input channels which have been digitized at an input sampling rate, and converts the sampling rate of each input channel to produce N output channels at an output sampling rate. The method comprises computing a common FIR interpolating function which depends upon the input and output sample clocks and the instantaneous output time, and applying the common FIR interpolating function to all N input channels to compute all N output channels.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Implementation of decimation filter in integrated circuit device using ram-based data storage
ActiveUS7949699B1Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseShift register
A programmable integrated circuit device such as a programmable logic device can be configured as a finite impulse response (FIR) filter capable of operating in decimation mode. The device includes at least one user-configurable random access memory block, and that user-configurable random access memory is configured as coefficient memories and data sample memories. The memories are large enough to hold up to all of the coefficients of the filter and a plurality of data samples at one time. Because the data samples and coefficients need not be shifted through the filter at the programmable logic device clock rate, overclocking of the filter is not necessary. The filter can run at a clock rate which is the same as the input data rate, while taking advantage of the available random access memory to mimic a shift register.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
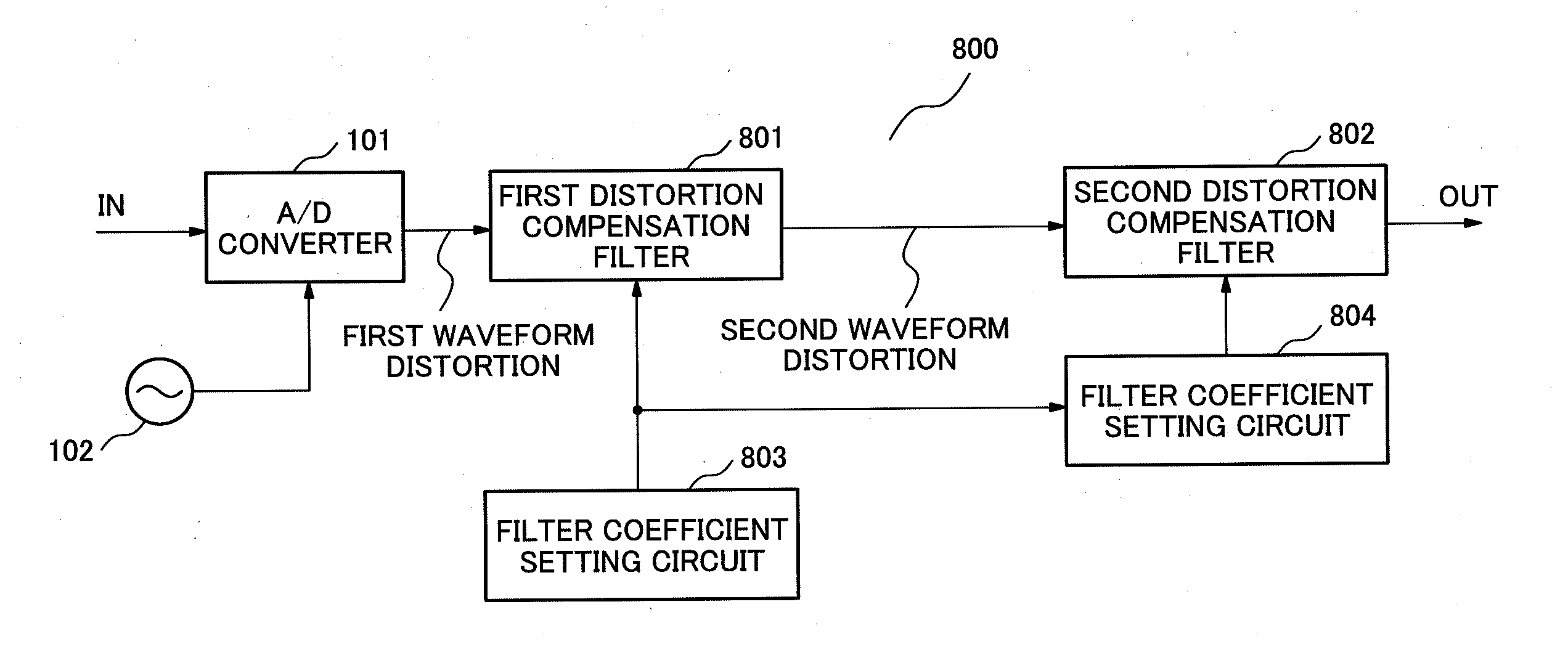
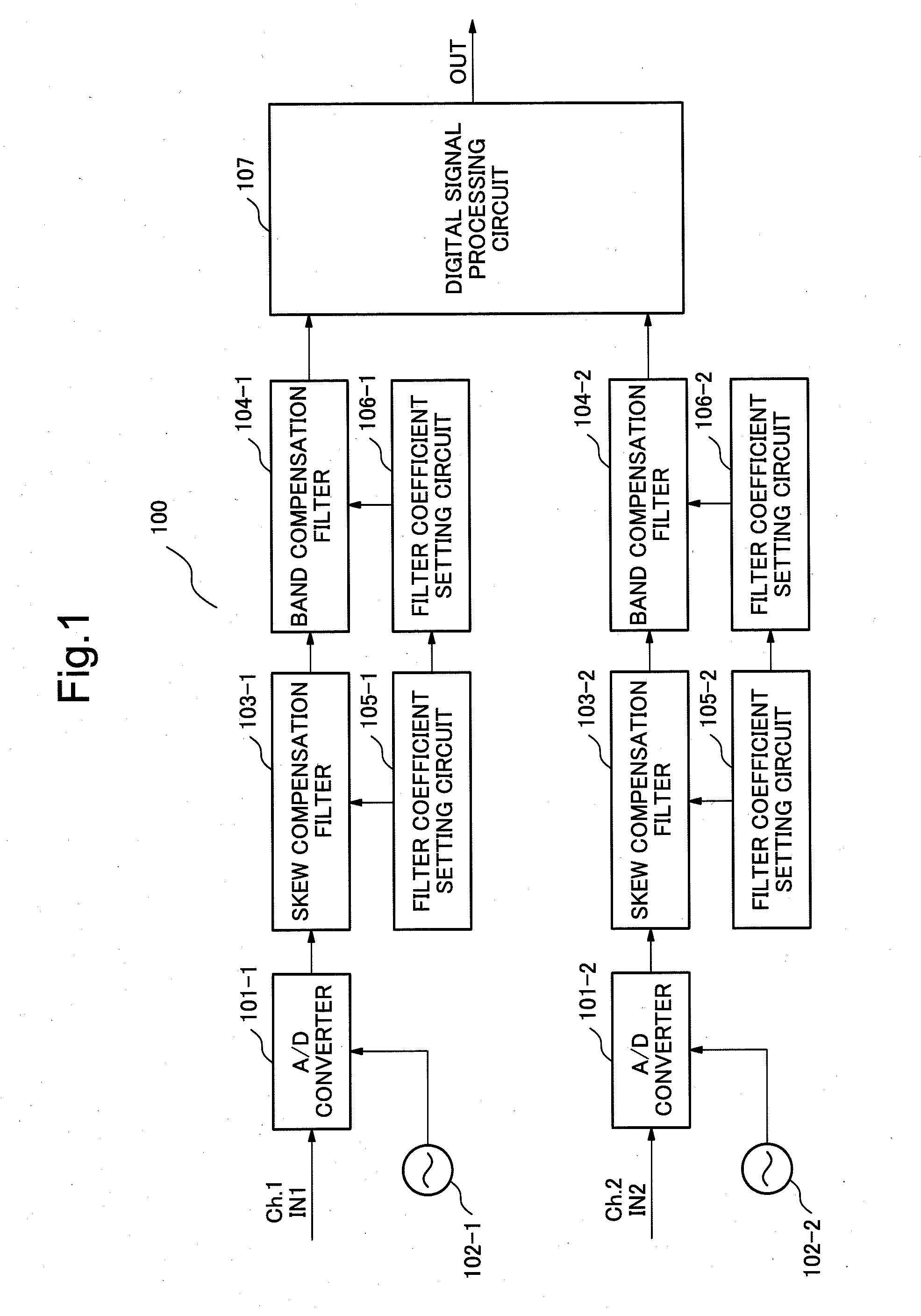
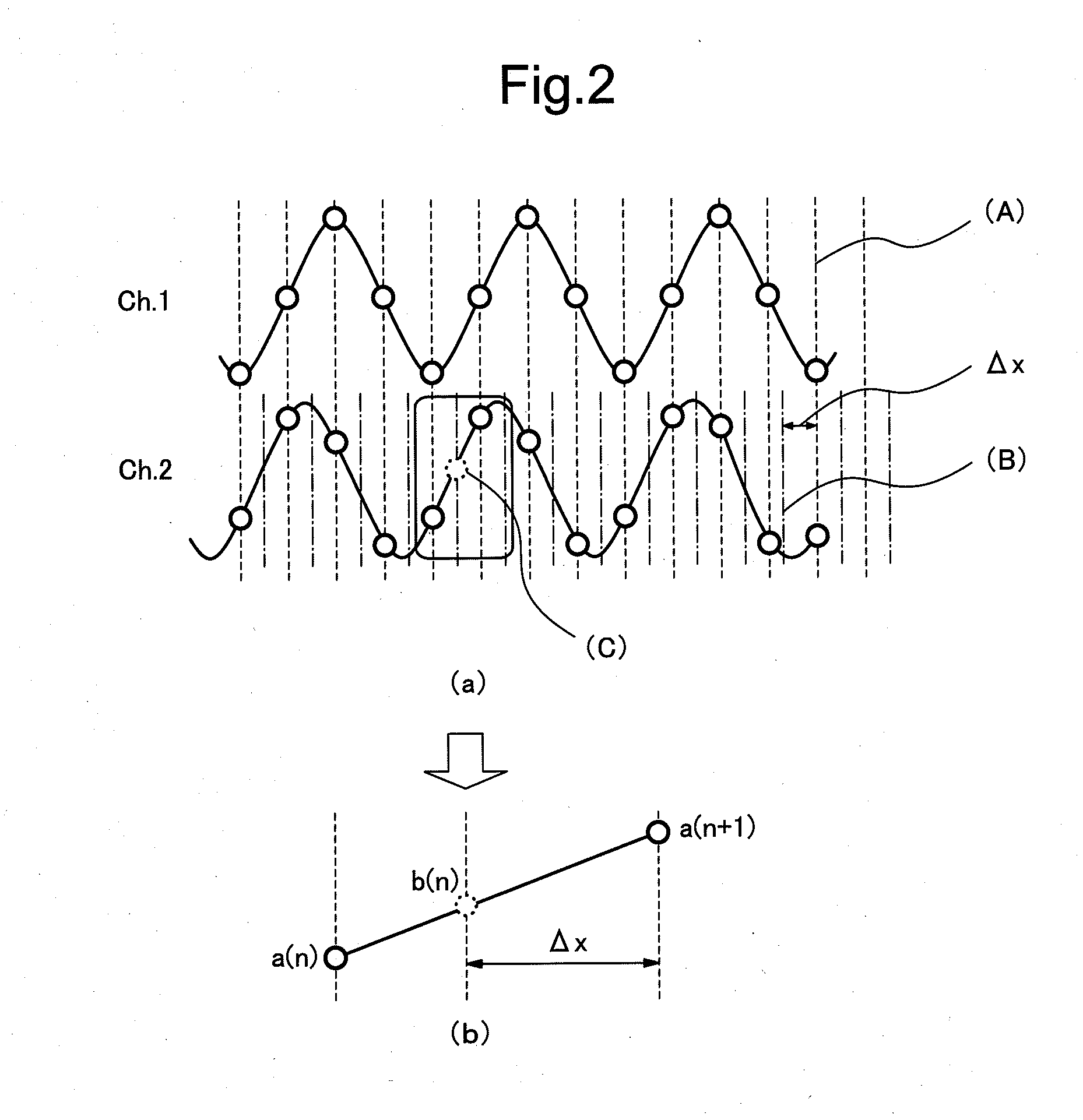
Digital filter device, digital filtering method and control program for the digital filter device
ActiveUS20130287390A1Improve controllabilityImprove performanceDigital technique networkTransmission monitoringDigital signal processingDigital filter
In order to solve a problem of achieving distortion compensation with high accuracy, a digital filter device includes a first distortion compensation filter unit for conducting distortion compensation of first waveform distortion included in an inputted signal through digital signal processing, a first filter coefficient setting unit for setting a filter coefficient of the first distortion compensation filter unit, a second distortion compensation filter unit for compensating second waveform distortion included in a signal outputted from the first distortion compensation filter unit, and a second filter coefficient setting unit for setting a filter coefficient of the second distortion compensation filter unit based on the filter coefficient set by the first filter coefficient setting unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Log-sampled filter system
This invention provides a filter system which may be implemented with less hardware and software resources than traditional filters. In addition, the filter system structure reduces the complexities typically associated with filter design by permitting direct specification of the filter frequency response. Thus, the filter system may adaptively change the filter frequency response on the fly without incurring excessive time or computational costs. The filter system may provide a filtered signal output to any subsequent processing system, such as a voice recognition system or audio reproduction system.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
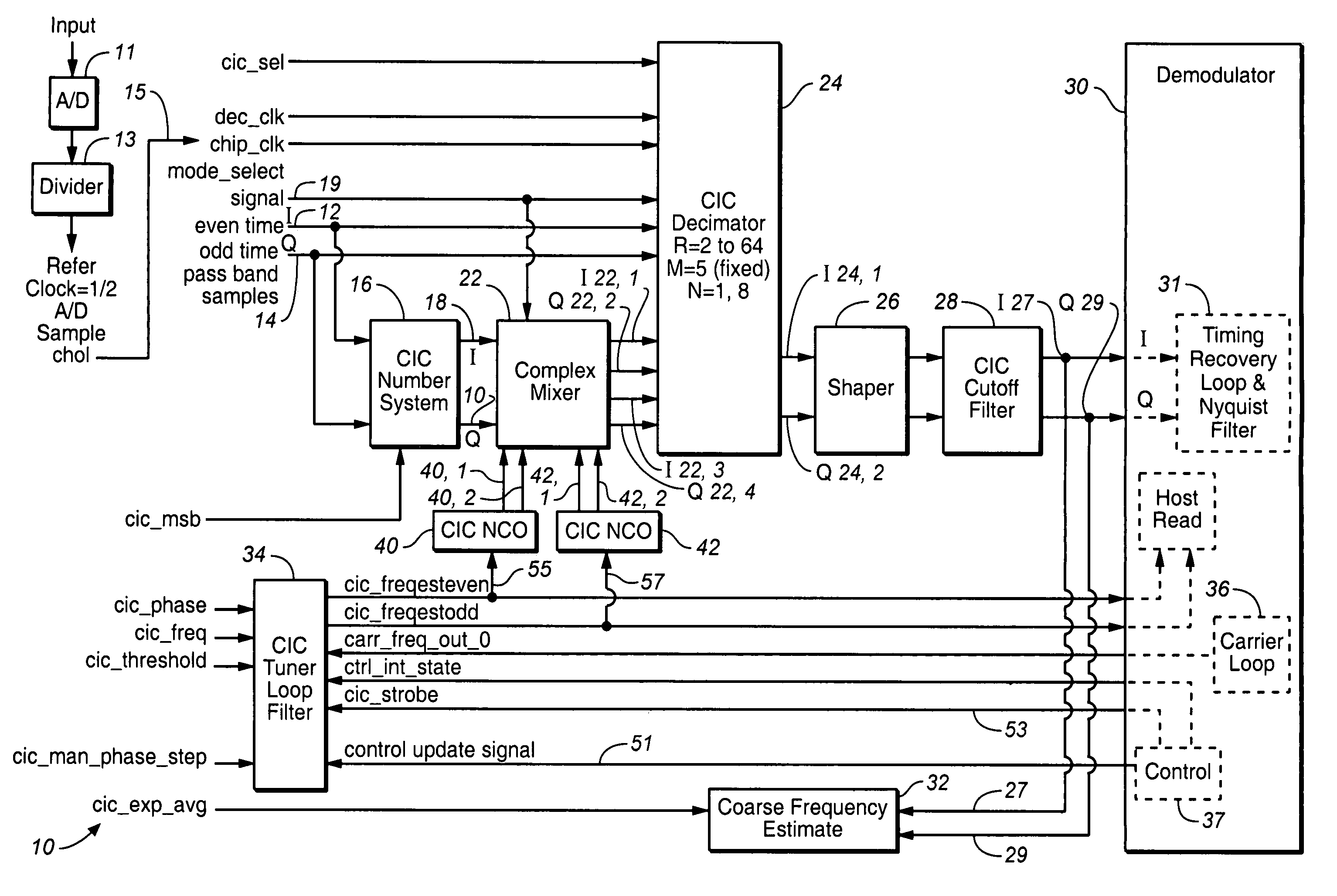
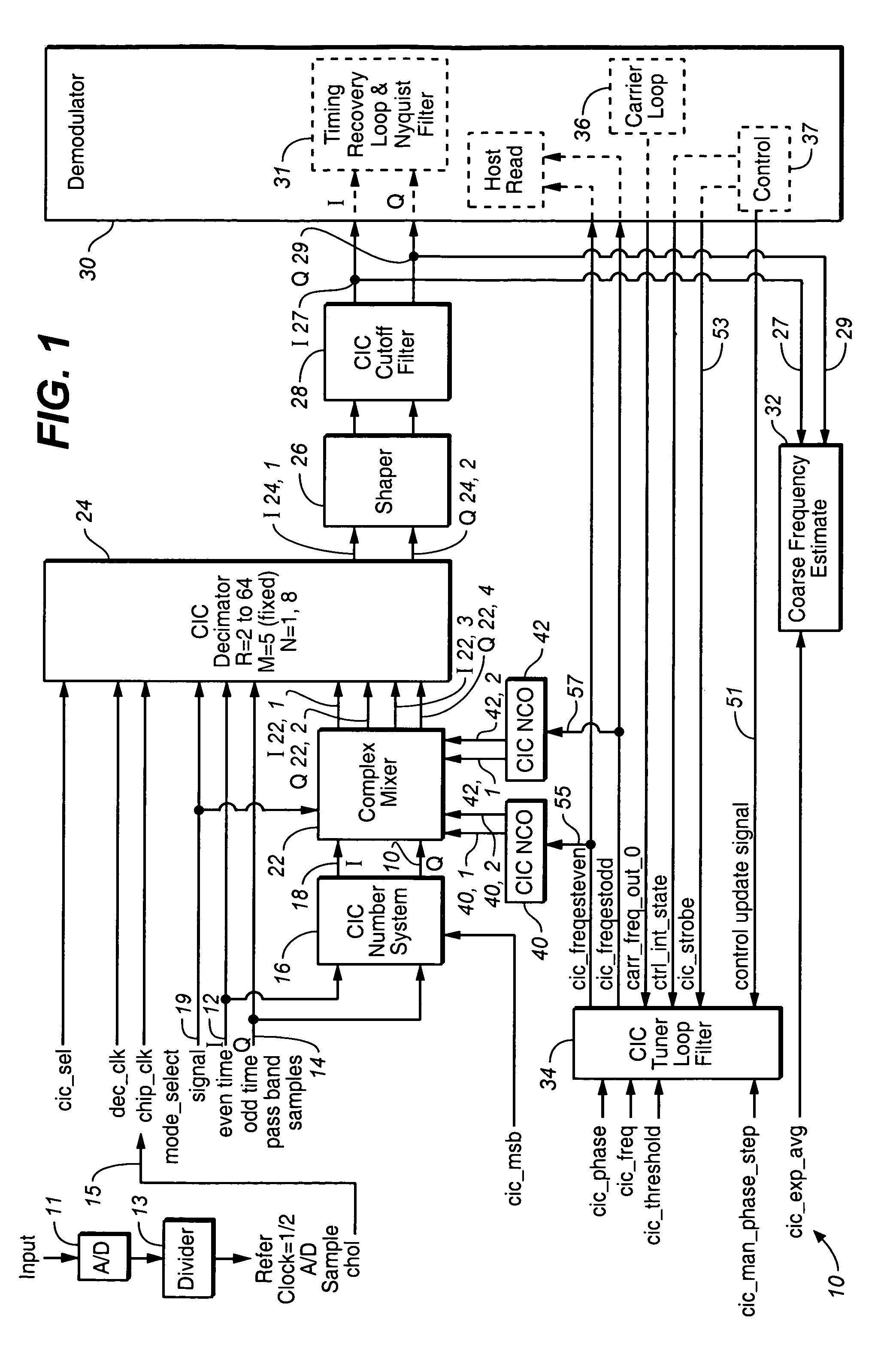
Frequency agile tuner and variable rate decimator for digital demodulator
InactiveUS7170956B1High speedDelay minimizationDigital technique networkSynchronisation error detectionSingle sampleLoop filter
An apparatus for demodulating a digital input signal having a pre-assigned symbol rate by using a single sample clock signal is disclosed. The pre-assigned symbol rate is selected from the group consisting of a plurality of symbol rates. The apparatus comprises: a Cascaded Integrated Comb (CIC) Decimator filter configured to perform a filtering-decimation operation to isolate the down converted digital signal having the pre-assigned symbol rate; a Shaper configured to restore an original spectrum of the I and Q components of the CIC output signal; and a CIC tuner loop filter configured to insert the estimated by the Coarse Frequency estimation block frequency offset into a carrier loop in order to complete a carrier recovery of the pre-assigned input digital signal.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com