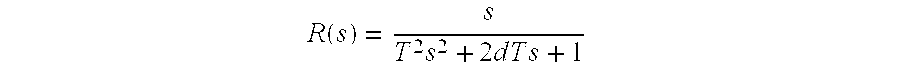Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Good vibes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
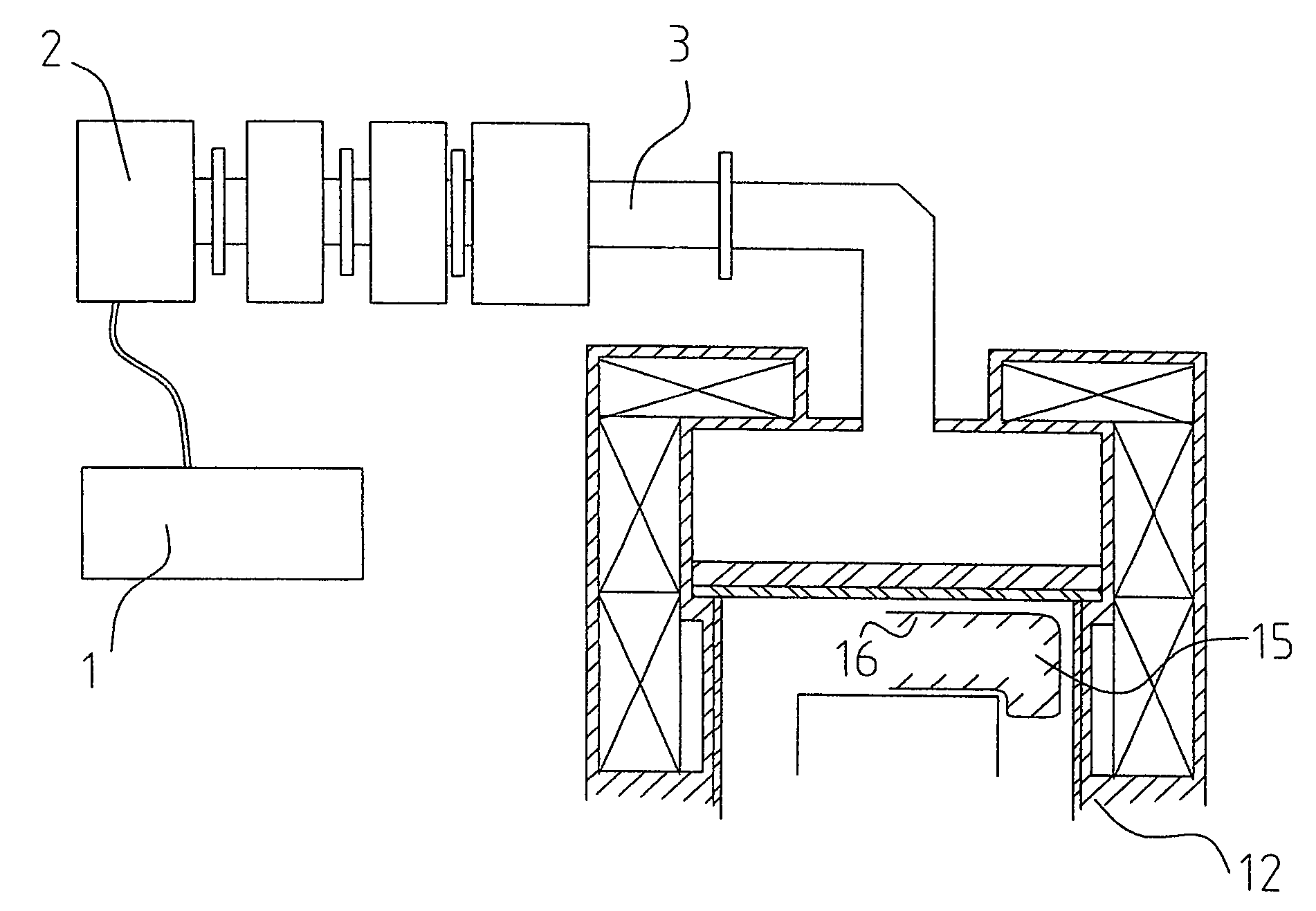
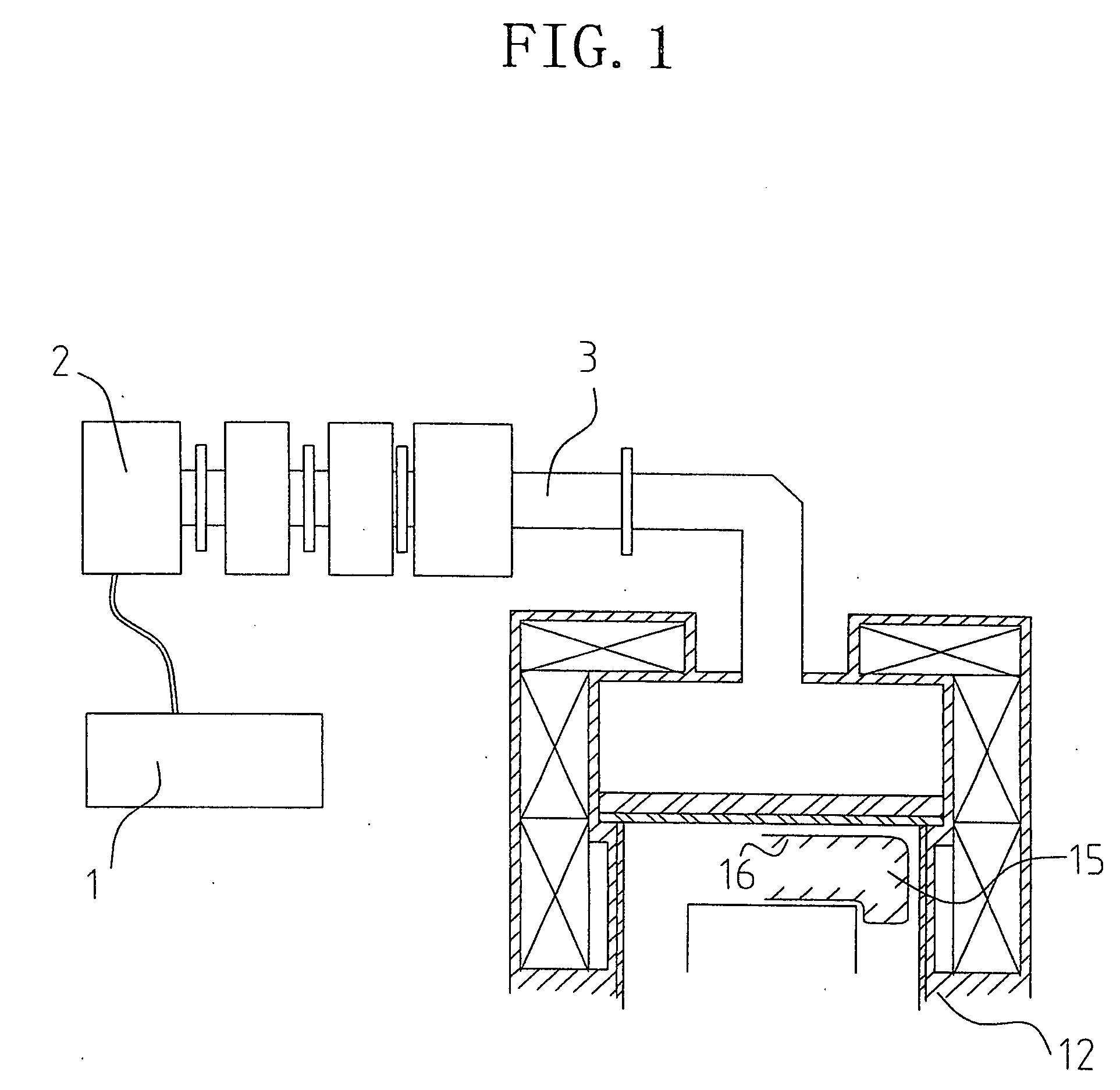
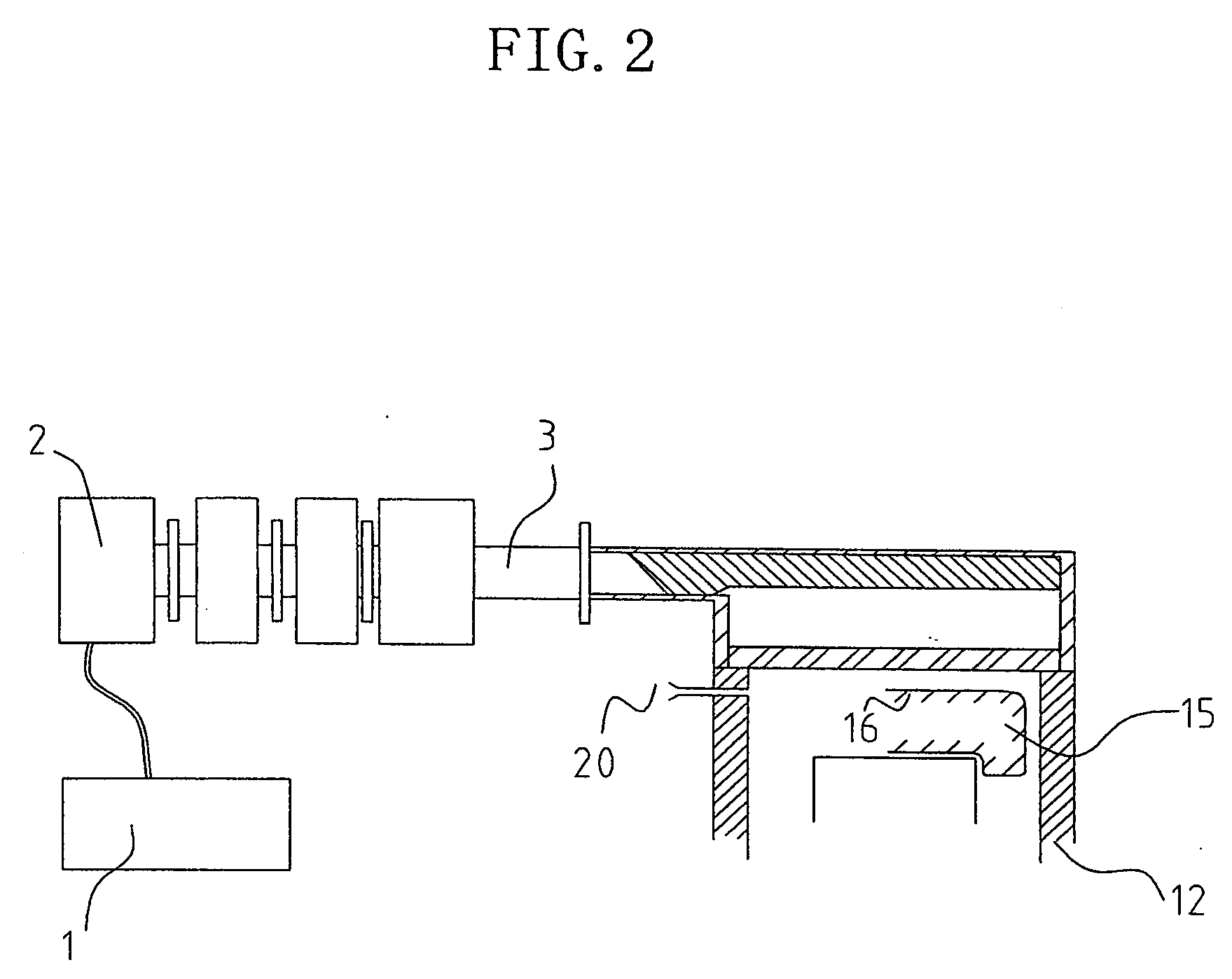
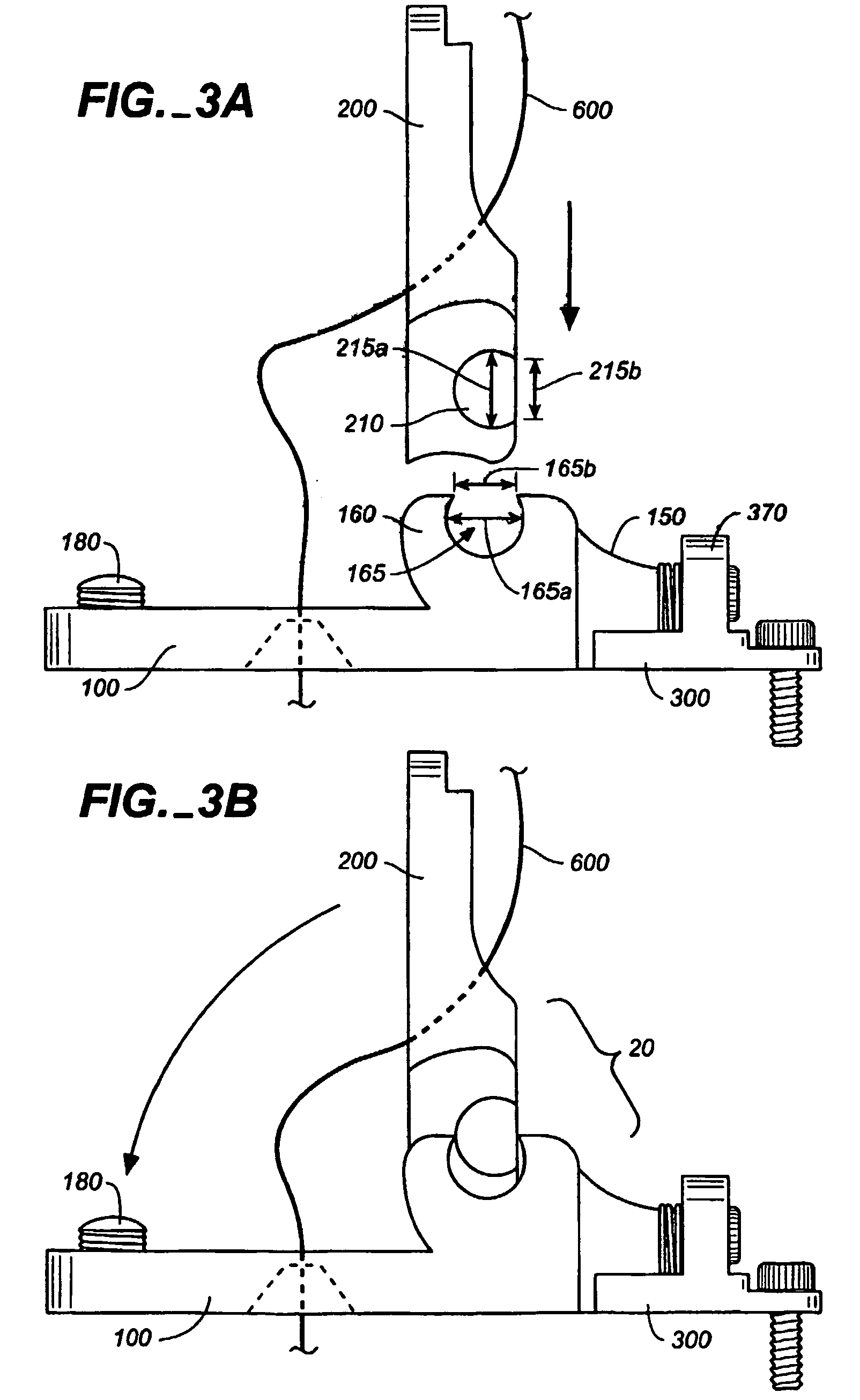
High frequency reaction processing system
InactiveUS20050212626A1Increase the areaImprove powerMicrowave heatingWaveguidesConductive materialsHandling system
A high frequency reaction processing system comprising an outer container (40) made of a dielictric material and having two end faces, which can close the inner cavity, one or more high frequency wave coupling portion (42) disposed at arbitrary position on the outer surface of the outer container (40), one or more inner container (41) made of a dielectric material and having two end faces, which can closeg the inner cavity, disposed at a position for receiving a high frequency wave guided through the high frequency wave coupling portion (42) without touching the inner side face of the outer container (40), and a covering portion (43) made of a conductive material, for covering the outer surface of the outer container except for the area occupied with the high frequency wave coupling portion (42) and sustaining the potential at a level equal to the ground potential of a waveguide line.
Owner:TAKAMATSU TOSHIYUKI
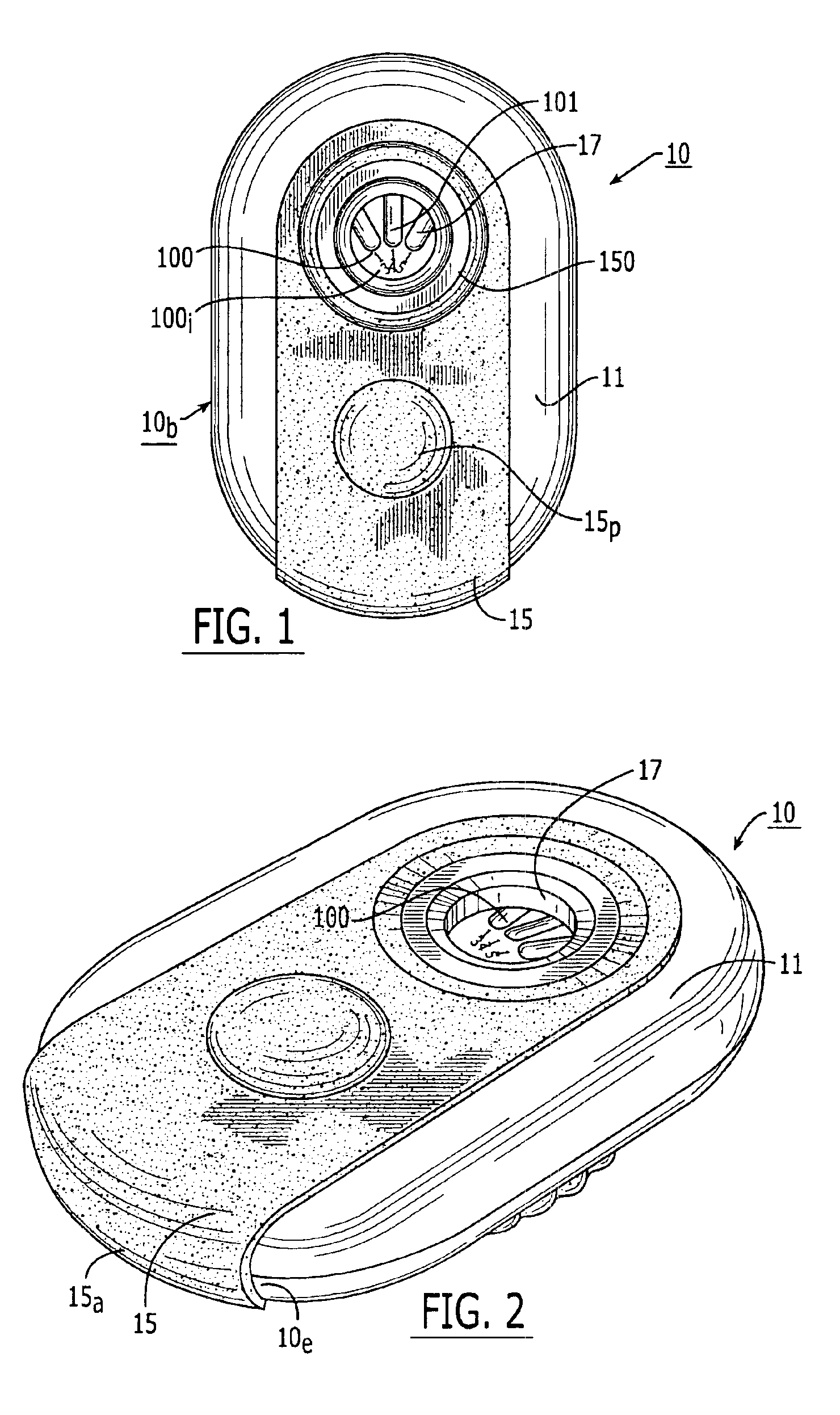
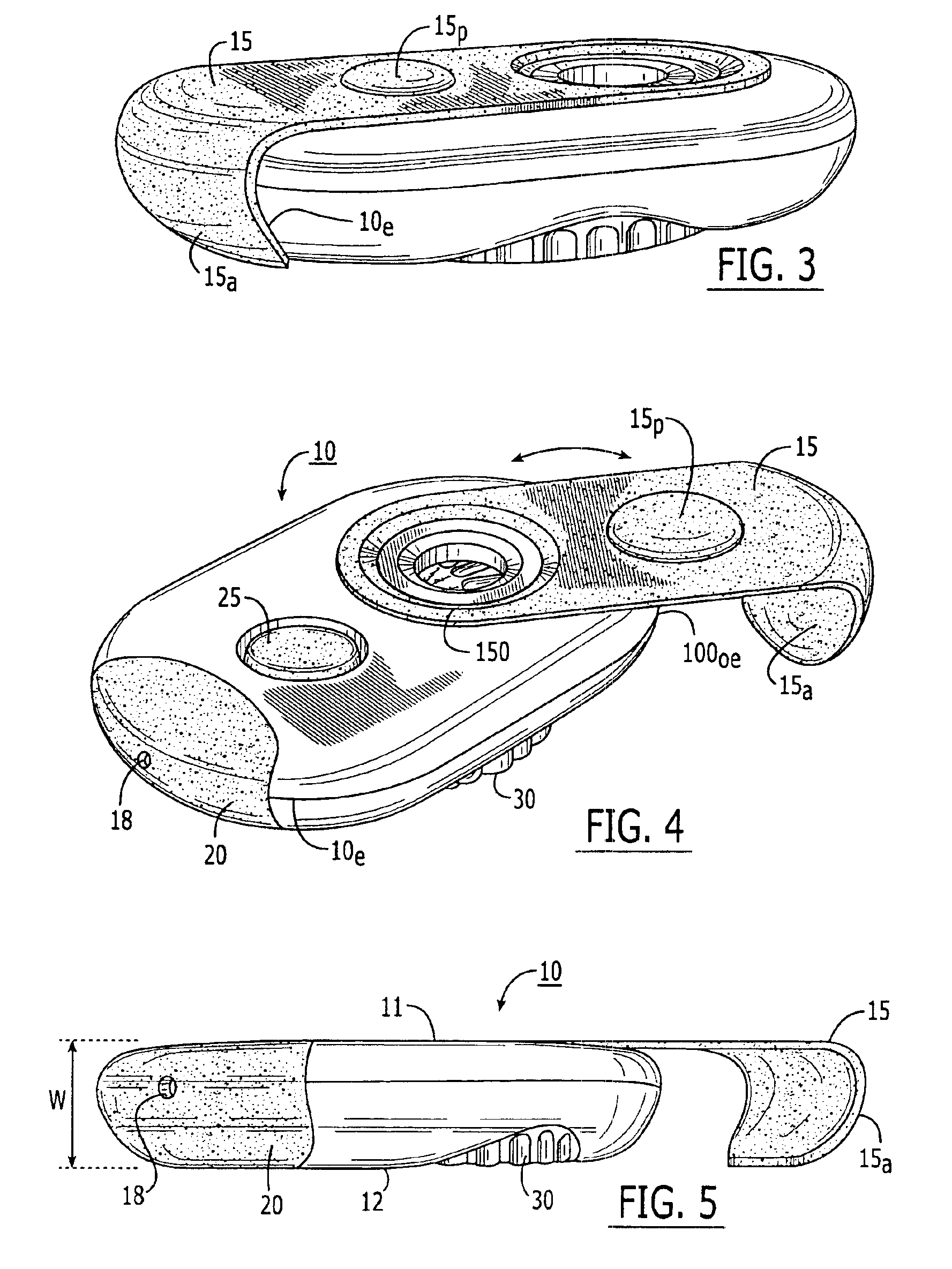
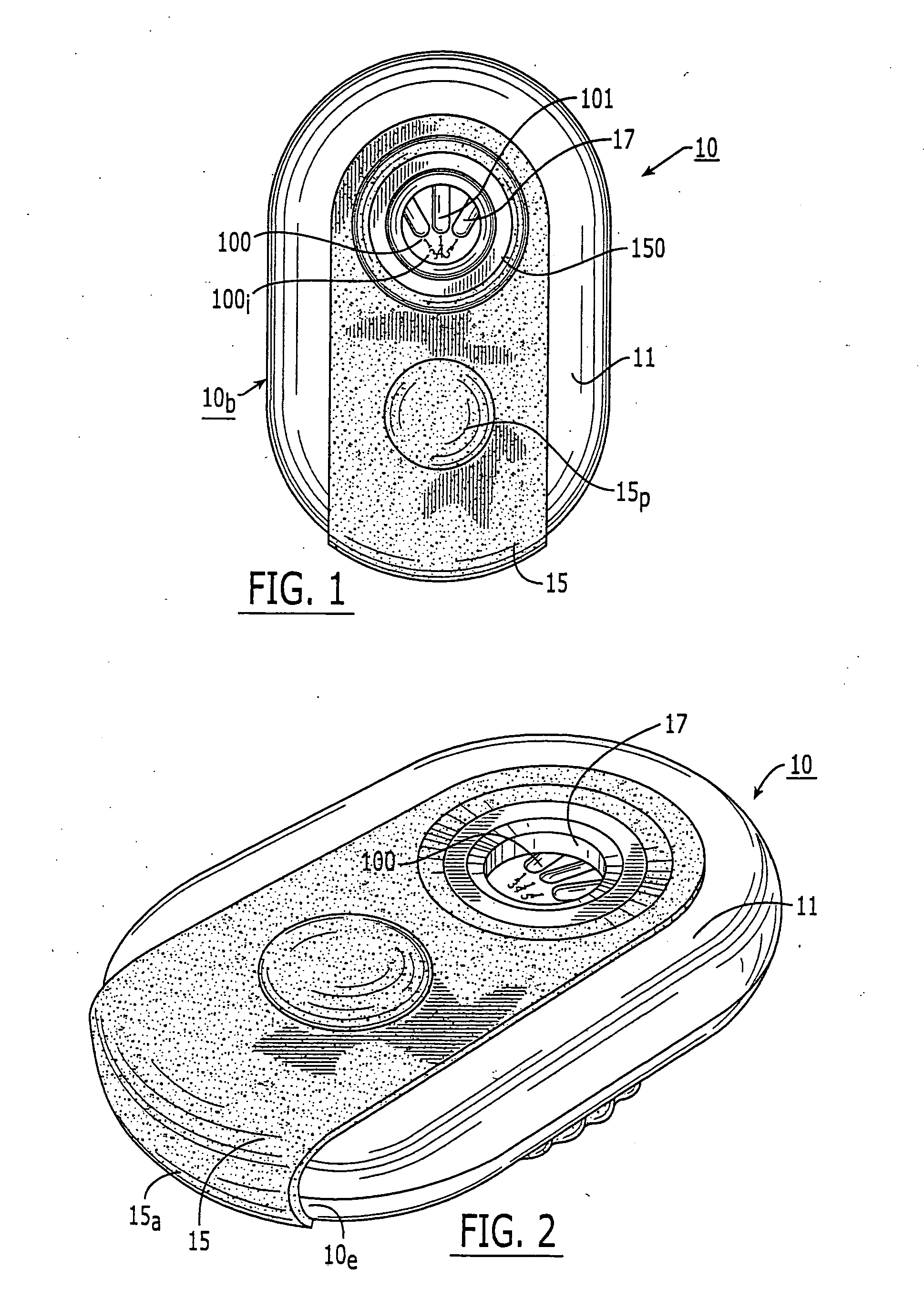
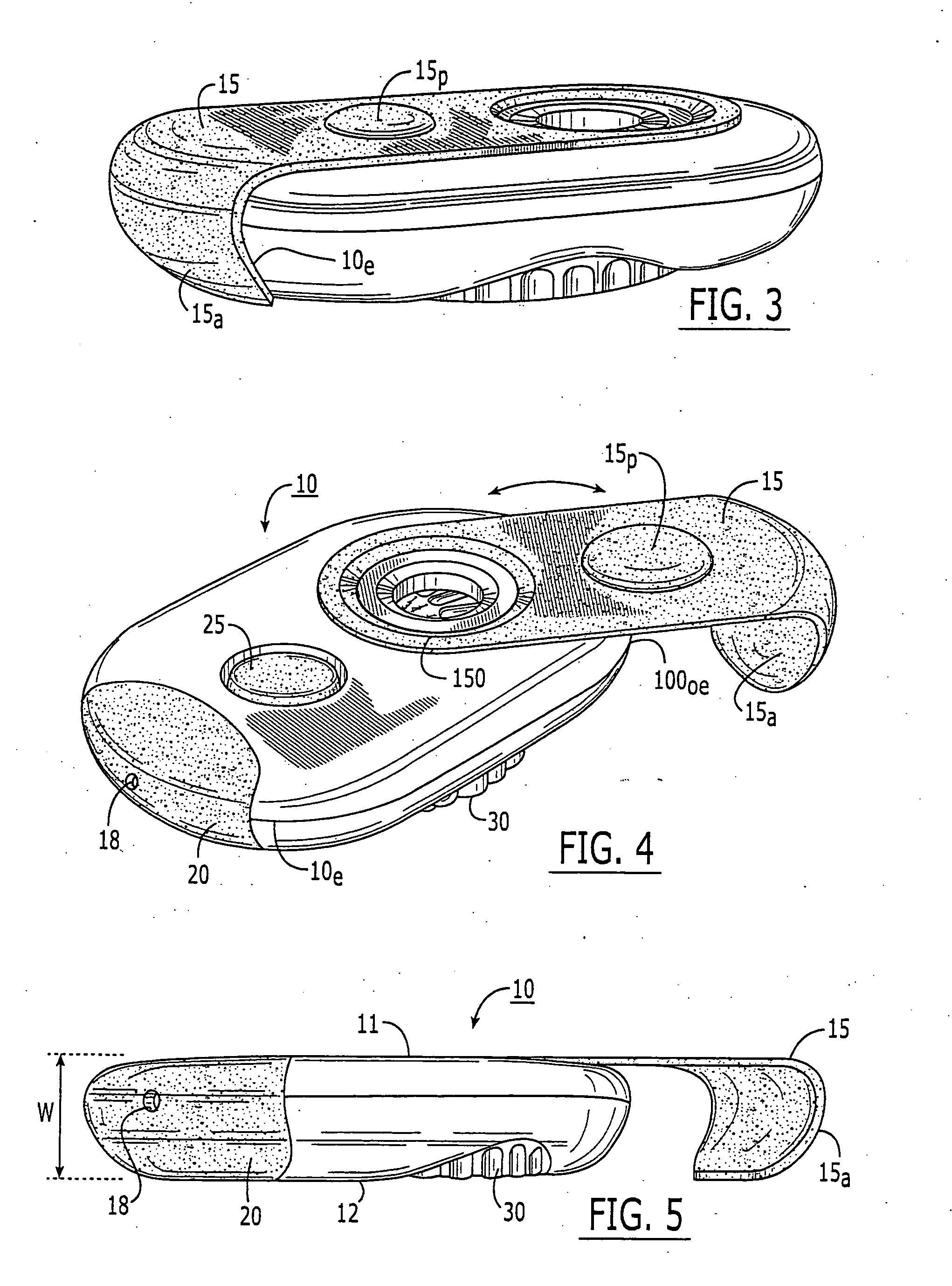
Dry powder inhalers, related blister devices, and associated methods of dispensing dry powder substances and fabricating blister packages
InactiveUS6889690B2Easy to optimizeLimit amount of resistanceSmall article dispensingLiquid surface applicatorsPowder InhalerInhalation
The present invention includes dry powder inhalers and associated multi-dose dry powder packages for holding inhalant formulated dry powder substances and associated fabrication and dispensing methods. The multi-dose package can include a platform body comprising at least one thin piezoelectric polymer material layer defining at least a portion of a plurality of spatially separated discrete elongate dry powder channels having an associated length, width and height; and a metallic material attached to selected portions of the piezoelectric polymer material including each of the regions corresponding to the elongate dry powder channels to, in operation, define active energy releasing vibratory channels. In operation, the elongate channels can be selectively individually activated to vibrate upon exposure to an electrical input.The dry powder inhaler includes an elongate body having opposing first and second outer primary surfaces with a cavity therebetween and having opposing top and bottom end portions and a multi-dose sealed blister package holding a plurality of discrete meted doses of a dry powder inhalable product located in the cavity of the elongate body. The inhaler also includes an inhalation port formed in the bottom end portion of the elongate body, the inhalation port configured to be in fluid communication with at least one of the discrete meted doses during use and a cover member that is pivotably attached to the elongate body so that it remains attached to the body during normal operational periods of use and moves to a first closed position to overlie the inhalation port at the bottom end portion of the body during periods of non-use and moves to a second open position away from the inhalation port during periods of use to allow a user to access the inhalation port.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
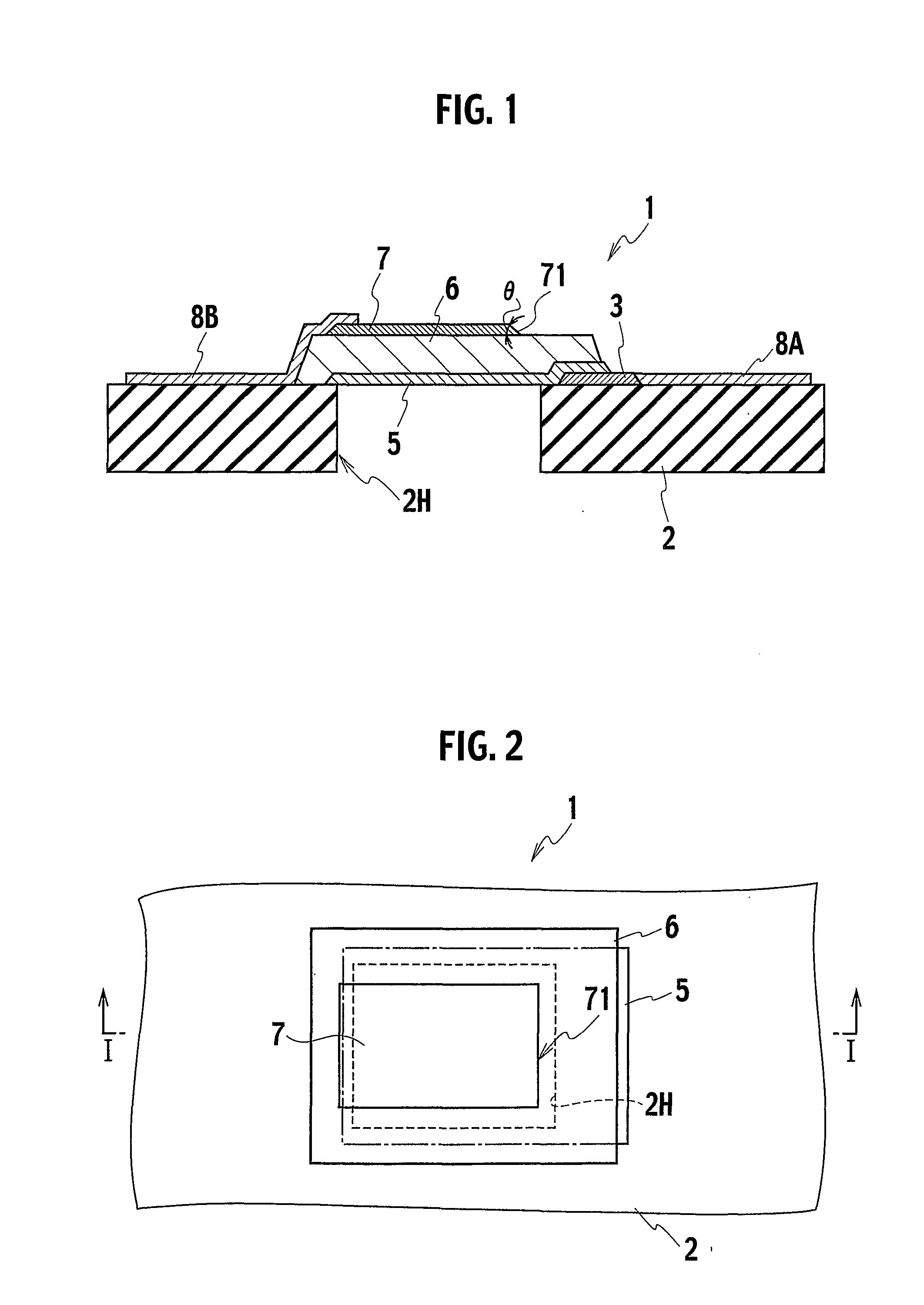
Thin film piezoelectric resonator and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090033177A1Good vibesOvercome problemsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksOptoelectronicsPiezoelectric thin films
A thin film piezoelectric resonator includes a substrate having a cavity; a first electrode extending over the cavity; a piezoelectric film placed on the first electrode; and a second electrode placed on the piezoelectric film, the second electrode having a periphery partially overlapping on the cavity and tapered to have an inner angle of 30 degrees or smaller defined by a part of the periphery thereof and a bottom thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
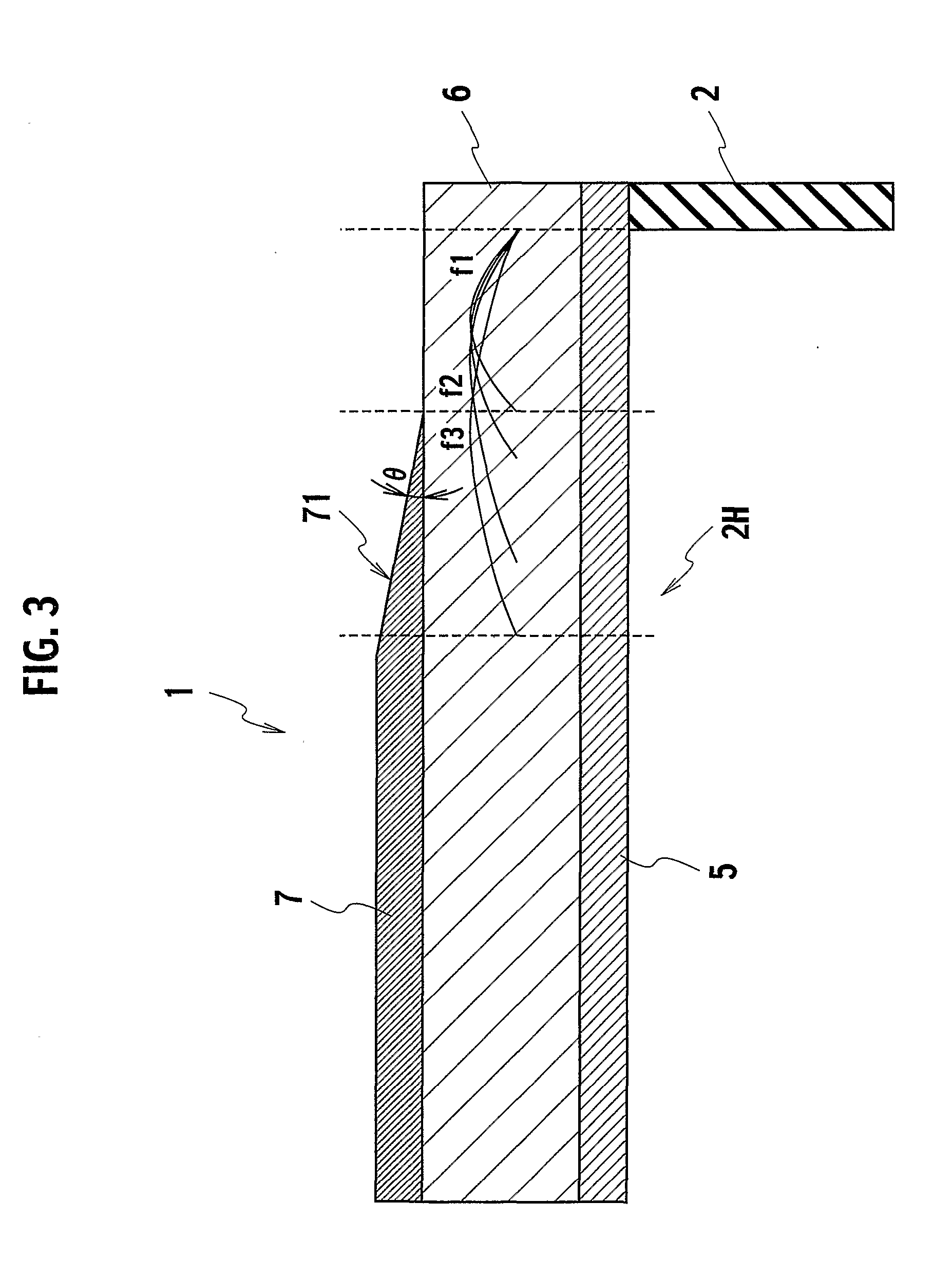
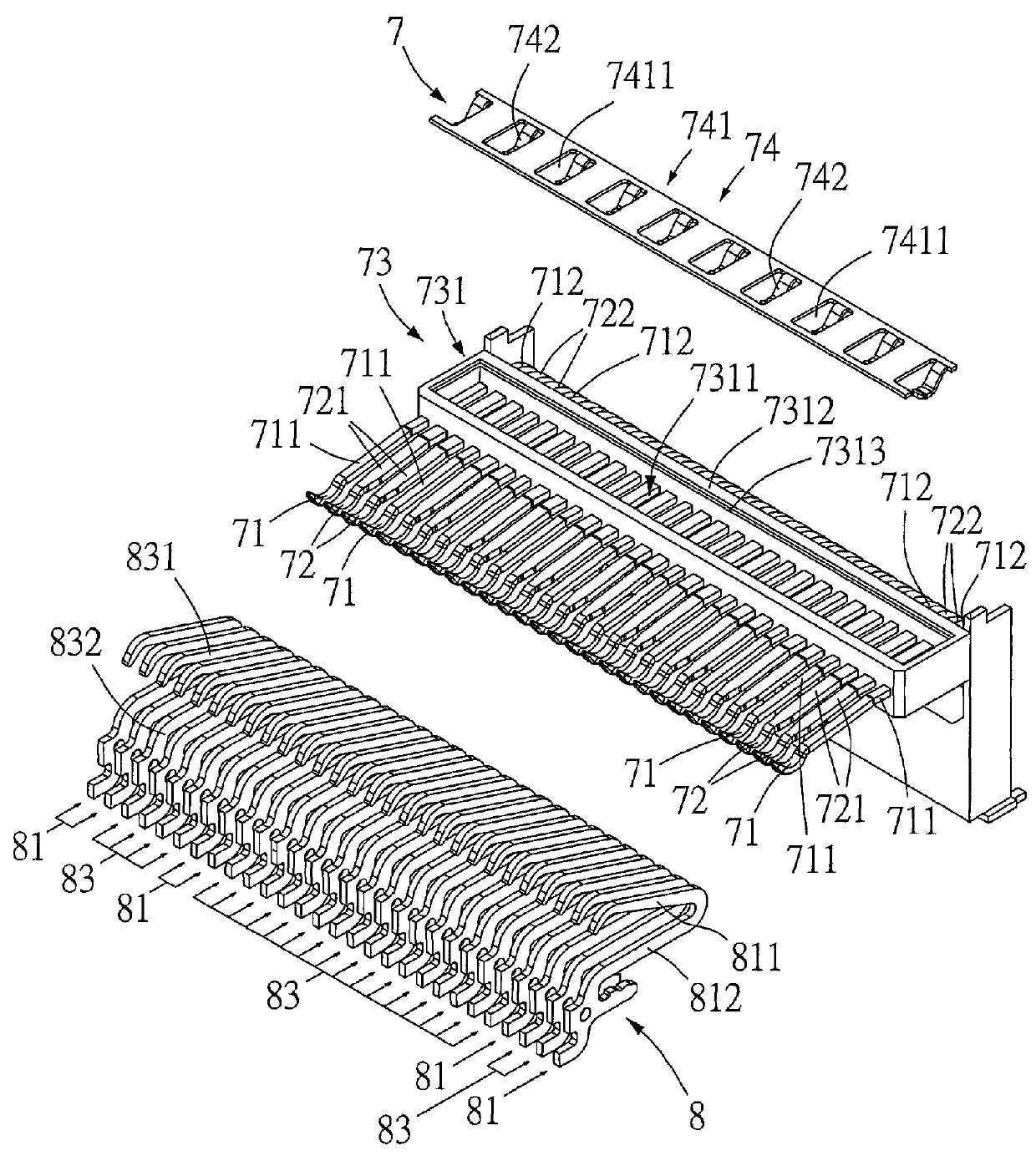
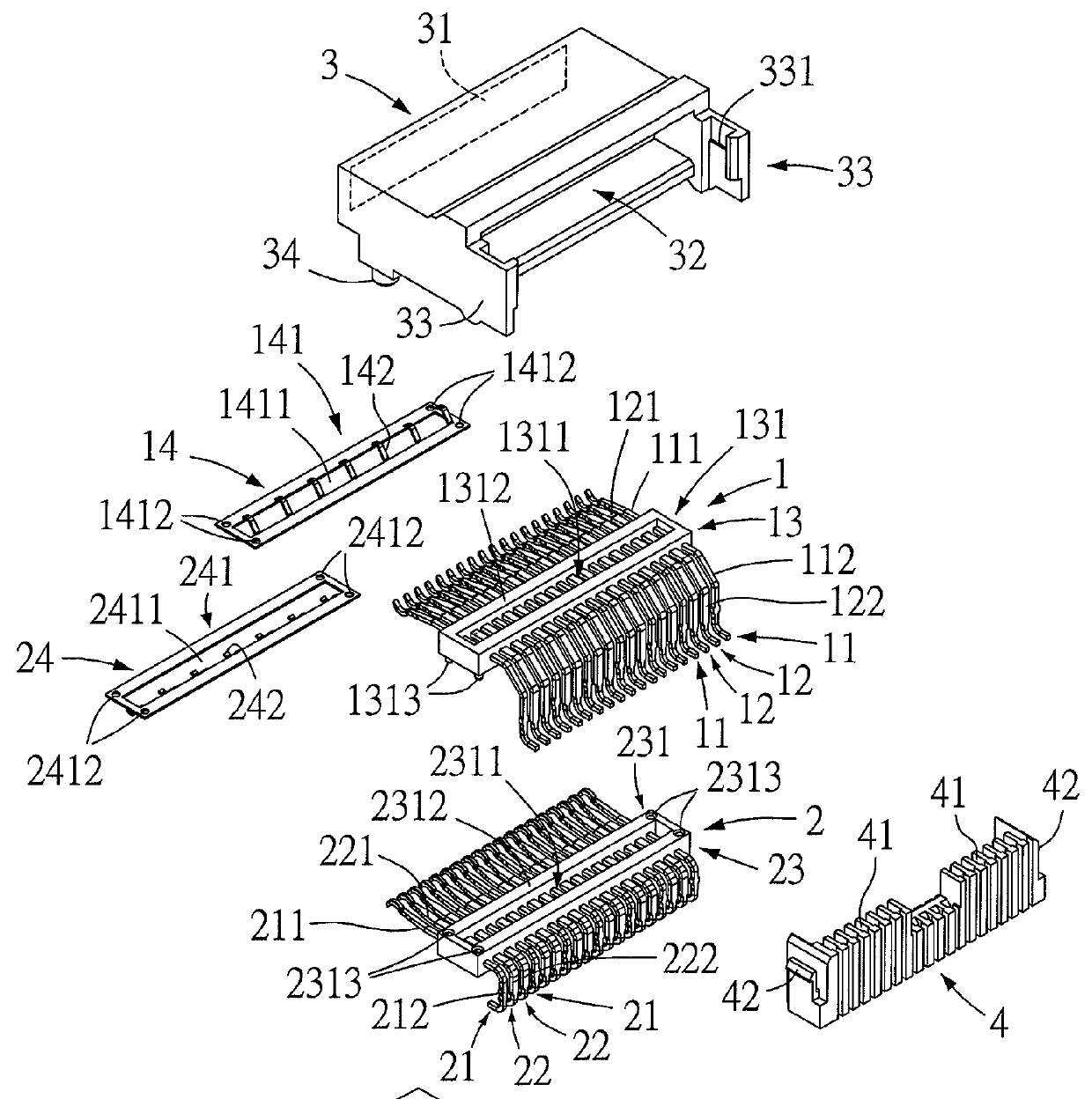
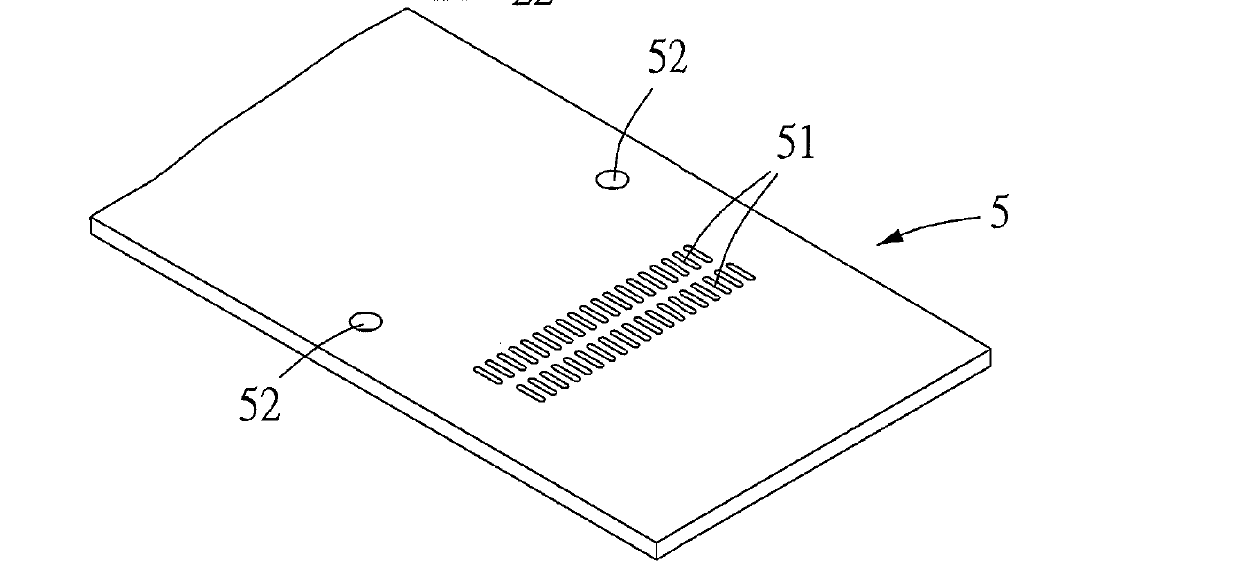
Terminal structure and electrical connector having the same
InactiveUS9337585B1Good vibesReduce signal lossCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityResonance
A terminal structure includes ground terminals, signal terminals, connection elements, and ground electrical connection elements. The connection elements connect the ground terminals to the signal terminals, respectively. The ground electrical connection elements are in connection with connection elements and in electrical contact with at least a ground terminal. An electrical connector includes two terminal structures and a casing. The connection elements are connected to each other. An insertion slot is disposed on the front side of the casing. The terminal structure is disposed at the casing. The resilient ground electrical contact segments and the resilient signal electrical contact segments face the insertion slot. The ends of the ground electrical connection segments and the ends of the signal electrical connection segments are exposed from the casing. The terminal structure and the electrical connector improve resonance, adjust impedance, reduce signal loss, simplify die structures, and extend service life of a die.
Owner:ALL BEST PRECISION TECH
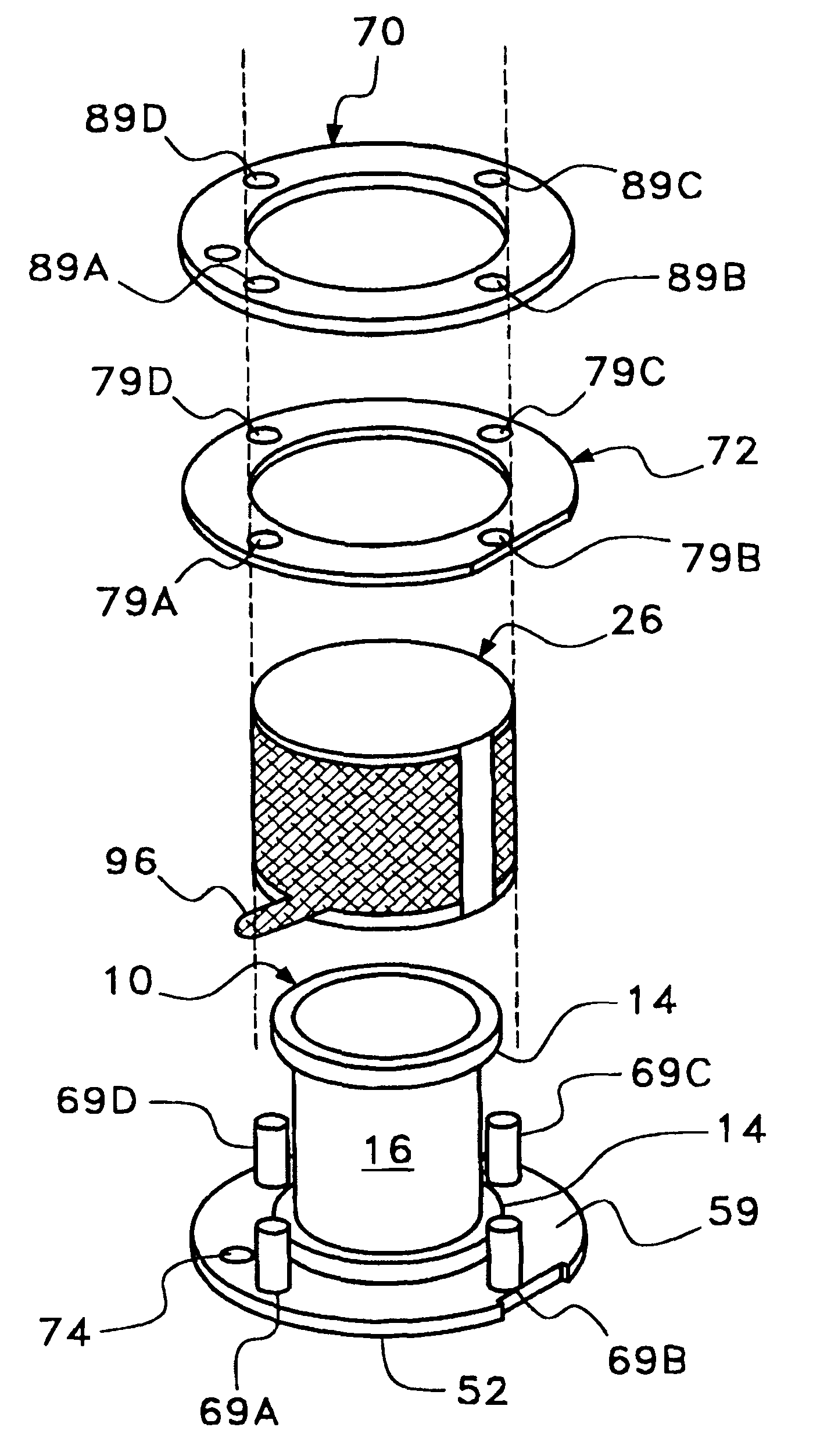
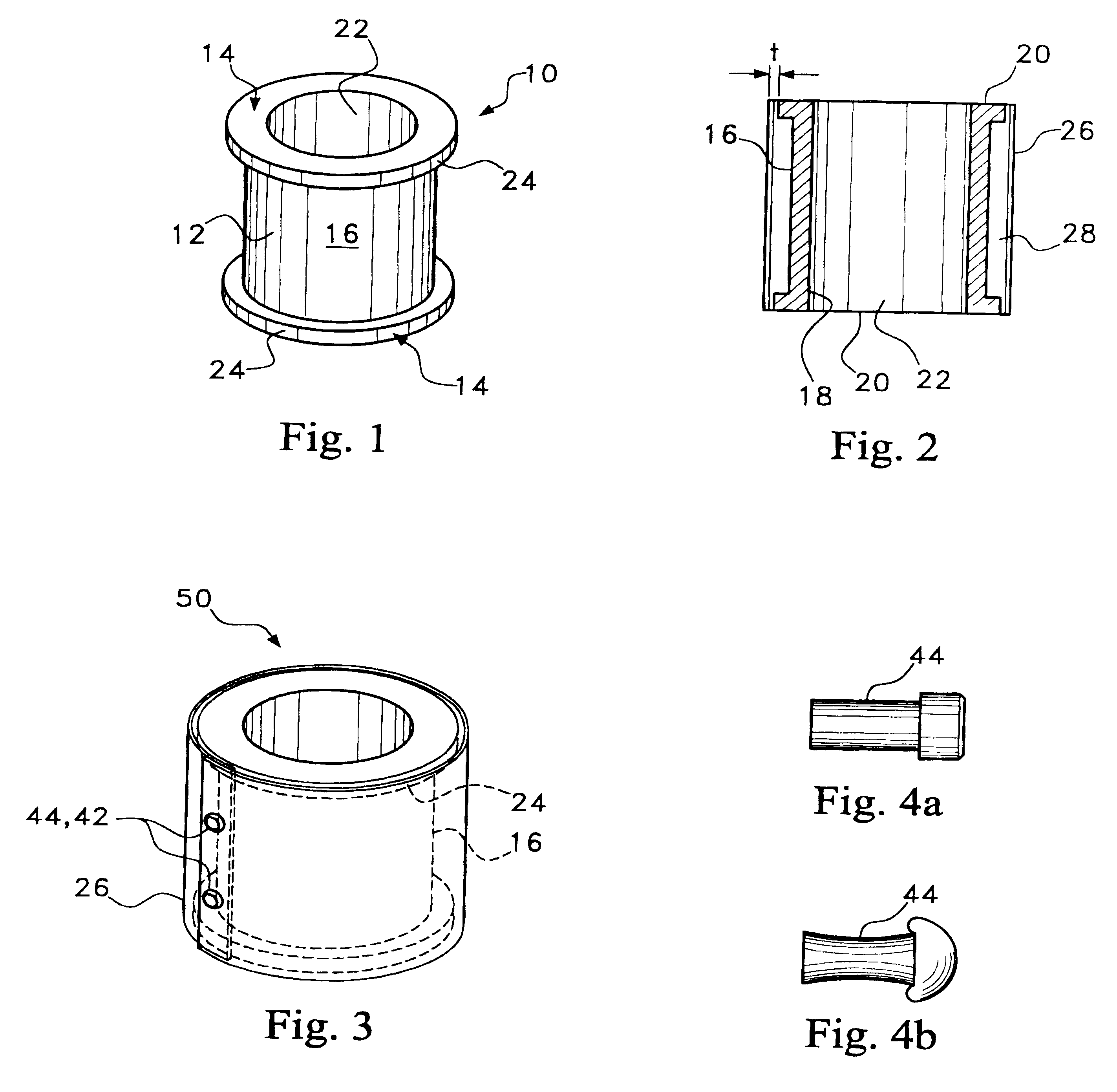
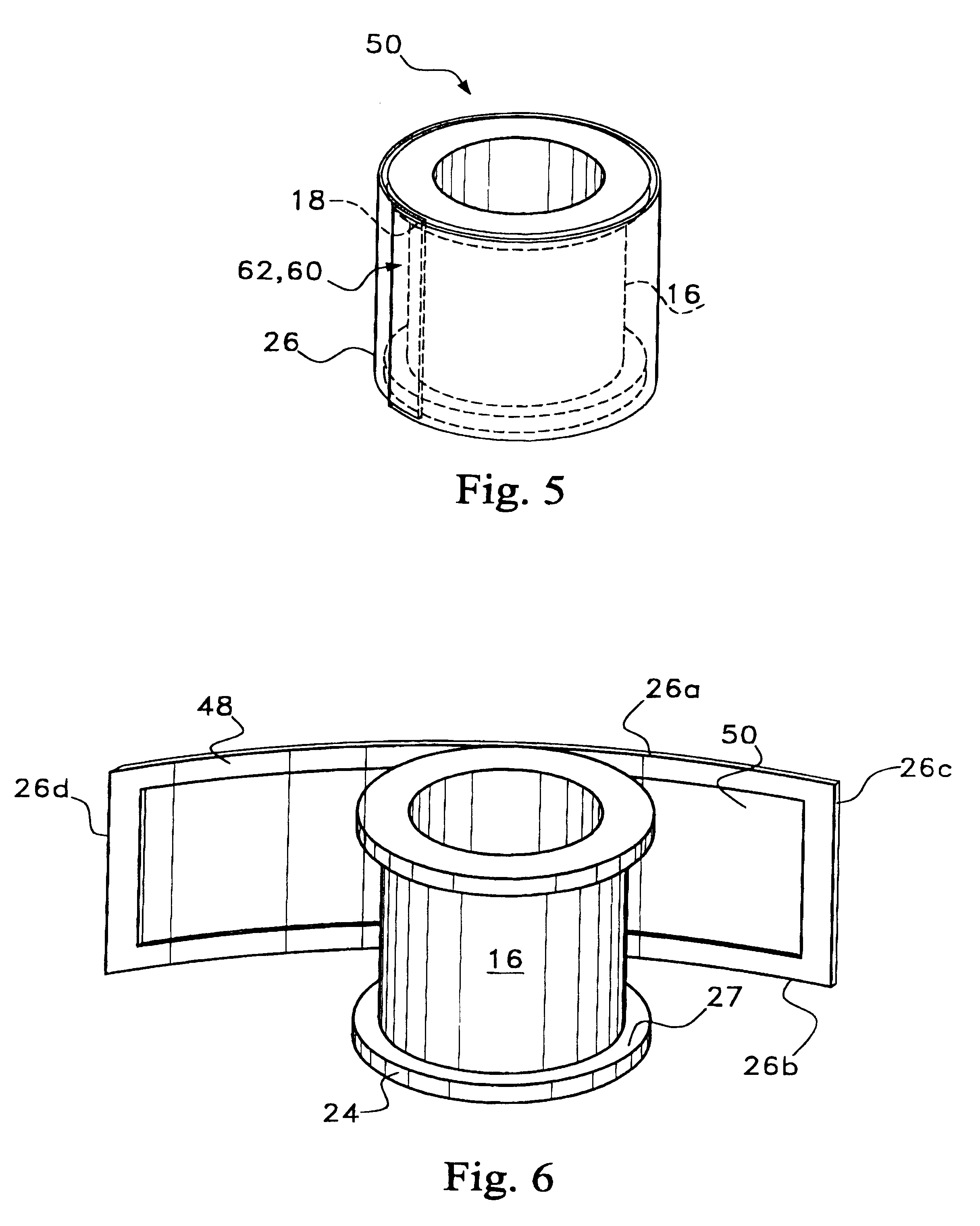
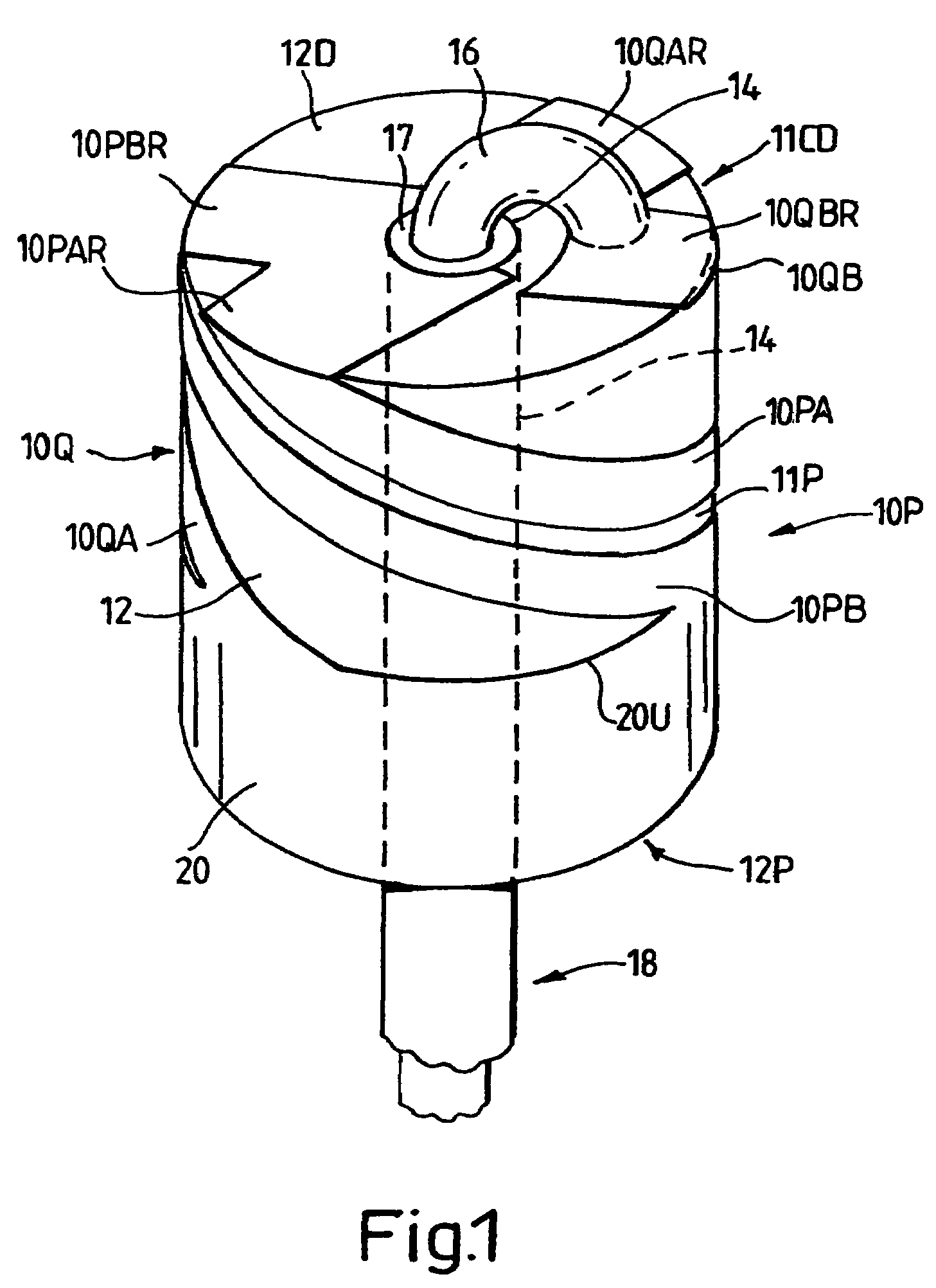
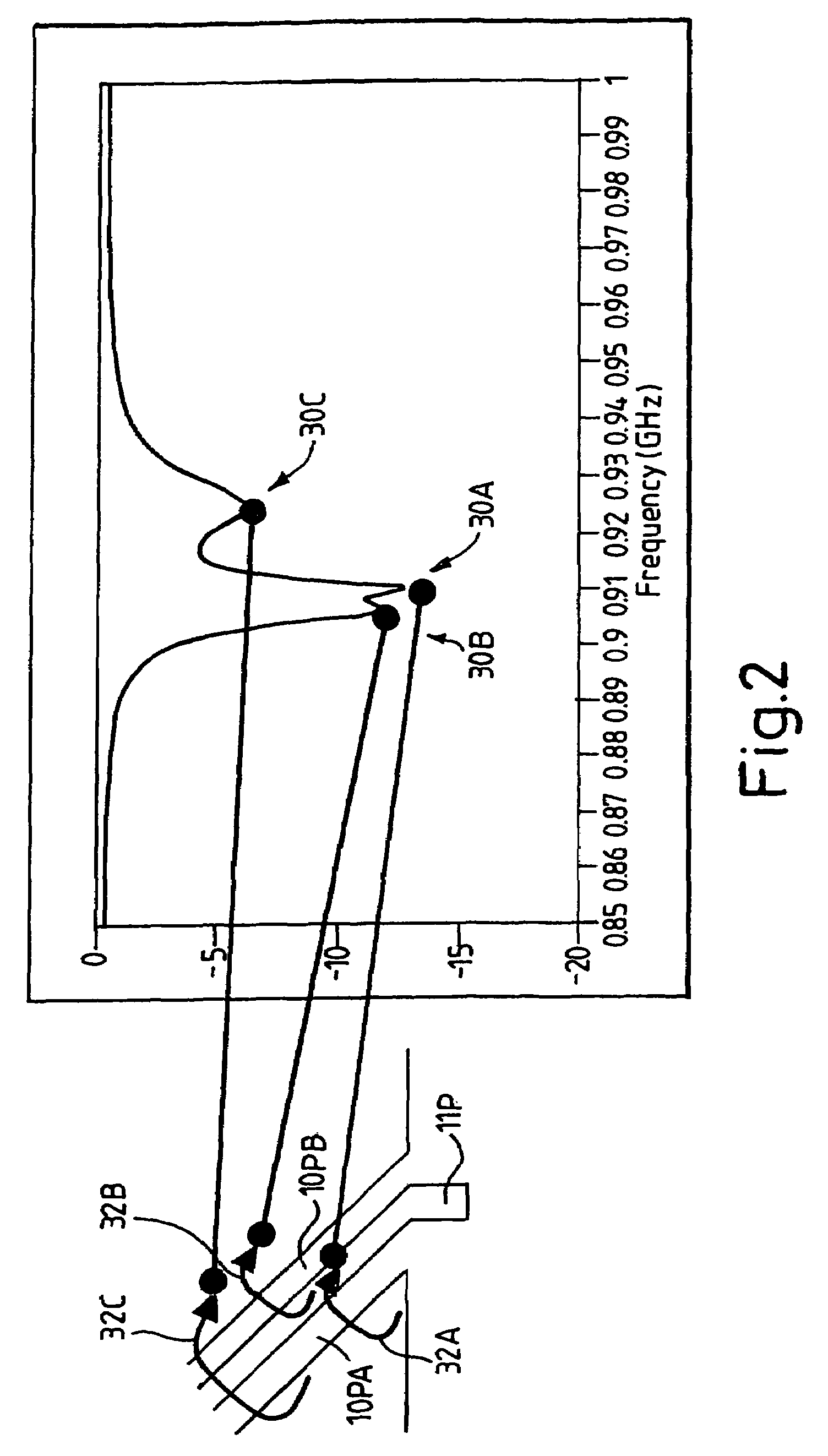
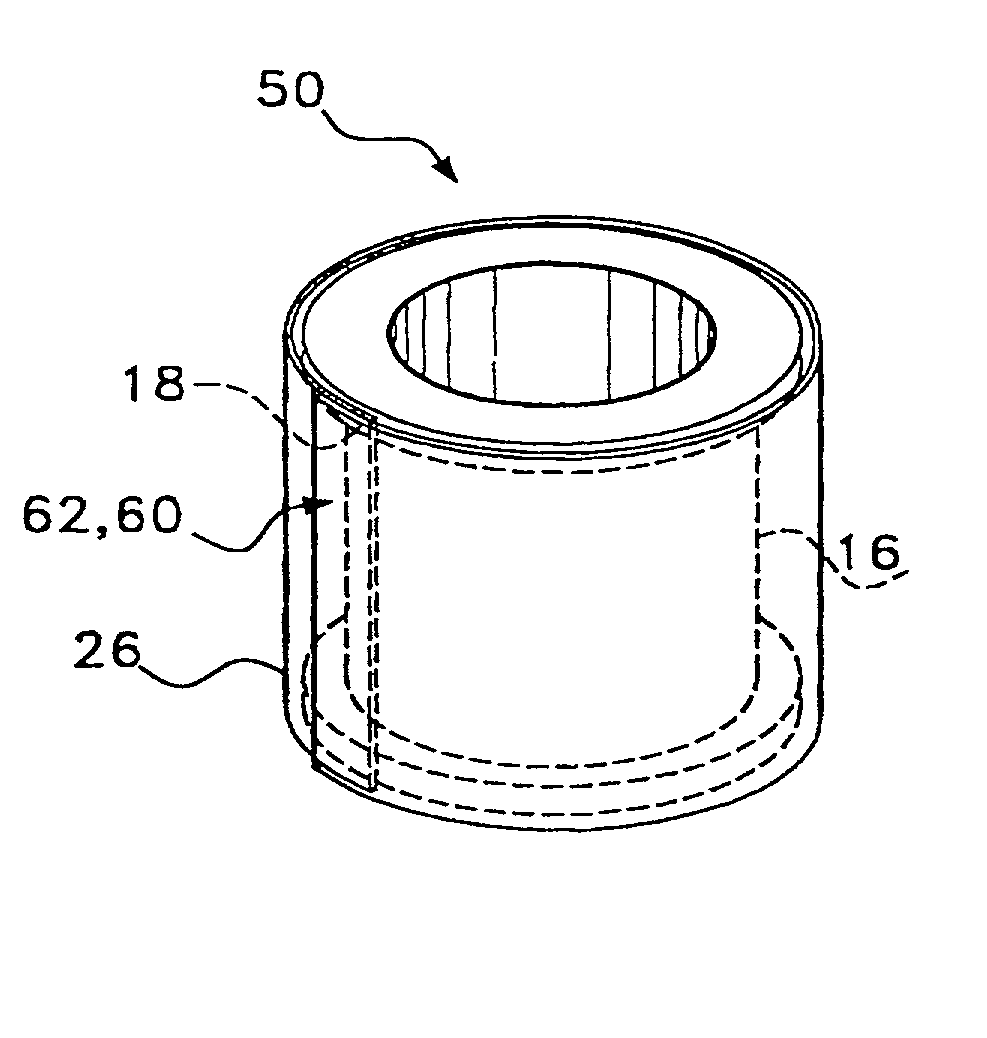
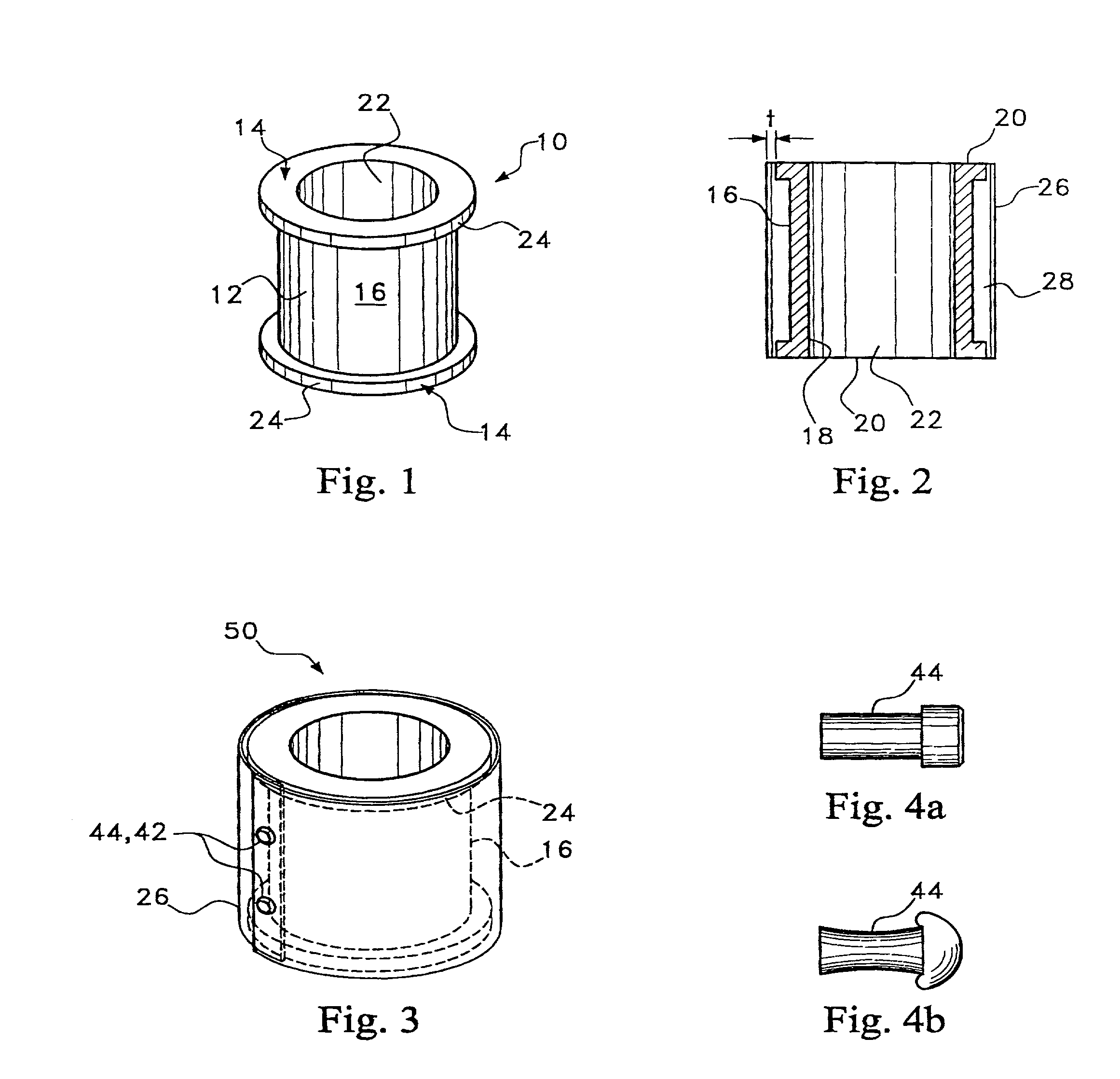
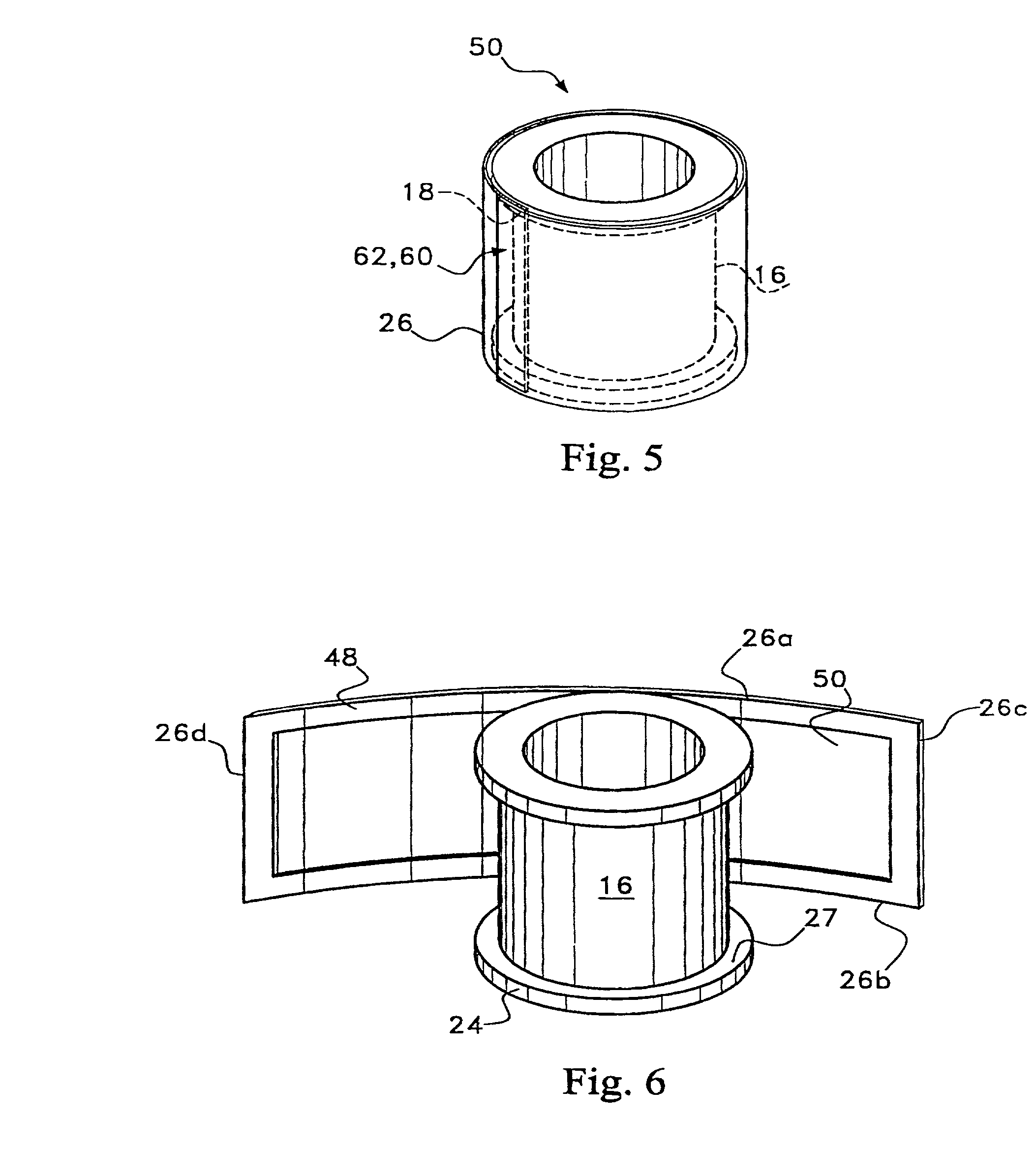
Omni-directional ultrasonic transducer apparatus and staking method
InactiveUS6400065B1Good vibesCost effectivePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic weldingAdhesive
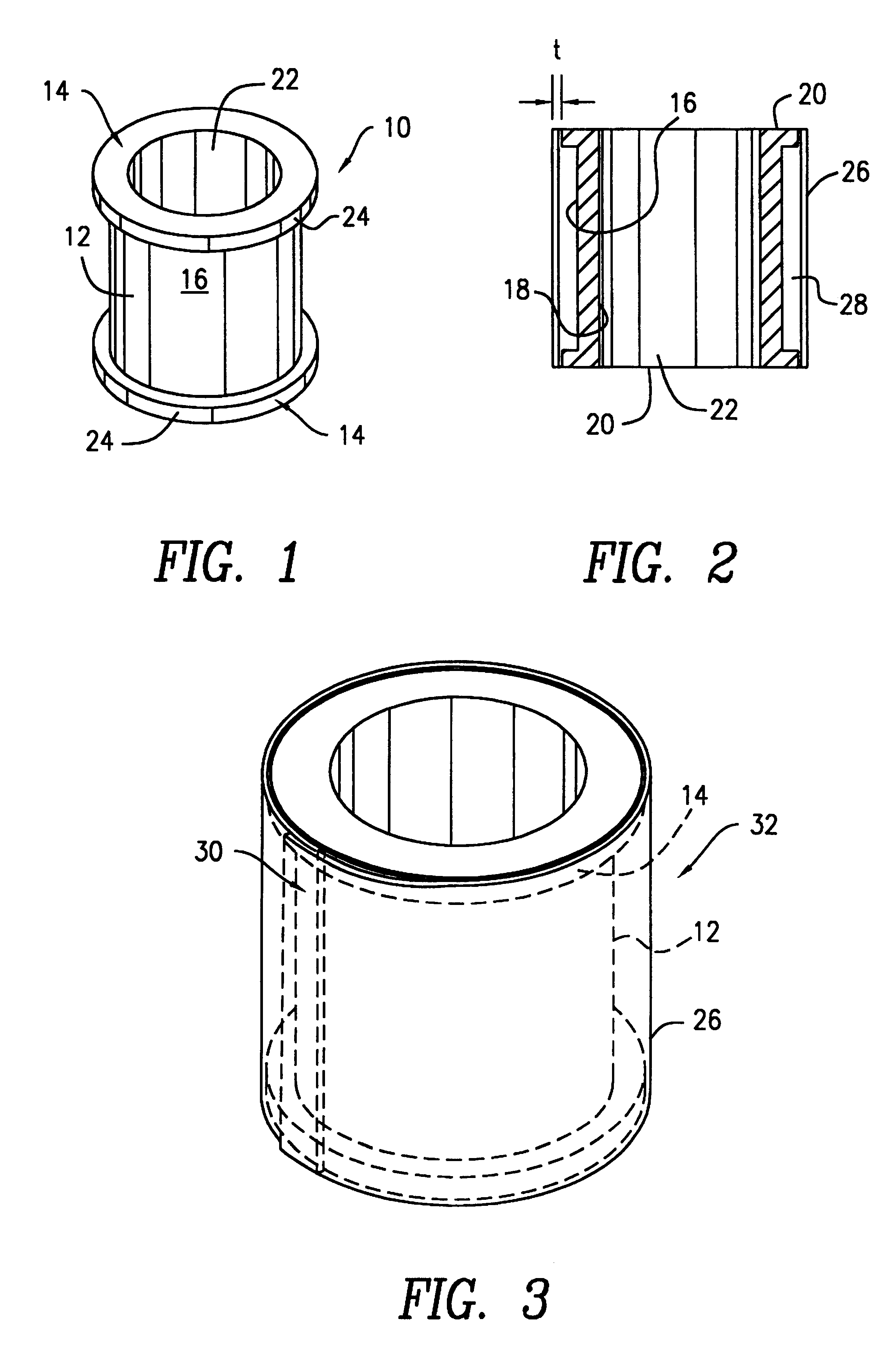
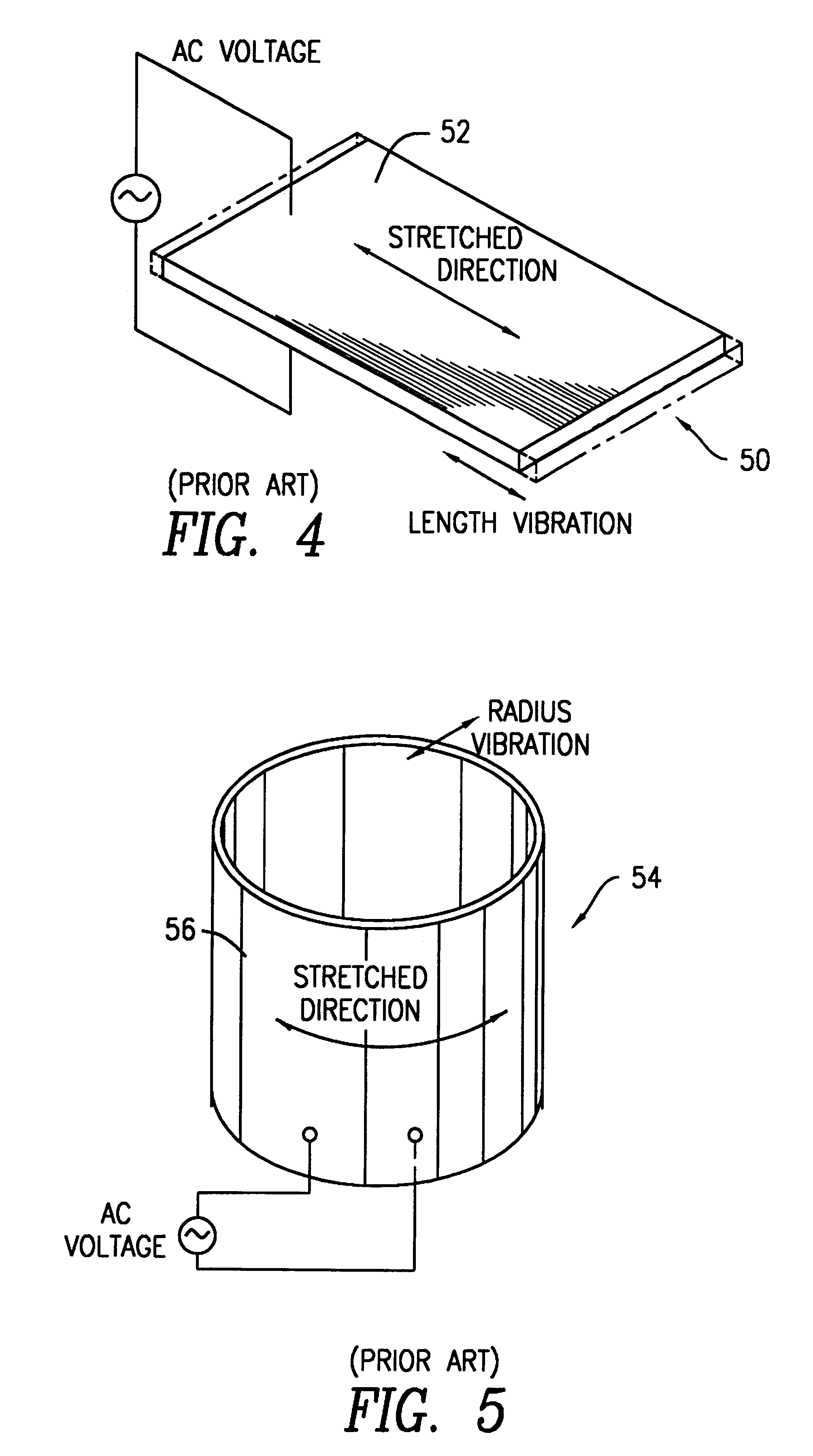
A transducer apparatus is disclosed having a spool member with a body portion and first and second elevated regions formed on the body portion. A PVDF film surrounds the spool member, the film including an inner surface facing the spool member and an outer surface opposite the inner surface. The film as surrounding the spool member has a predetermined frequency of resonance. Lateral ends of the film are secured together by a securing material. The securing material is such that the secured ends of the film will have substantially the same resonance frequency as a remainder of the film. The film includes a non-electrode area at a perimeter of the inner surface and an electrode material formed on a remainder of the inner surface. Upon securing the lateral edges of the film together, the securement is at overlapping non-electrode lateral edges of the film. The securing material may be any one of an adhesive in combination with screws or thermally deformable nails, adhesive alone, tape, or ultrasonic welding.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SPEC
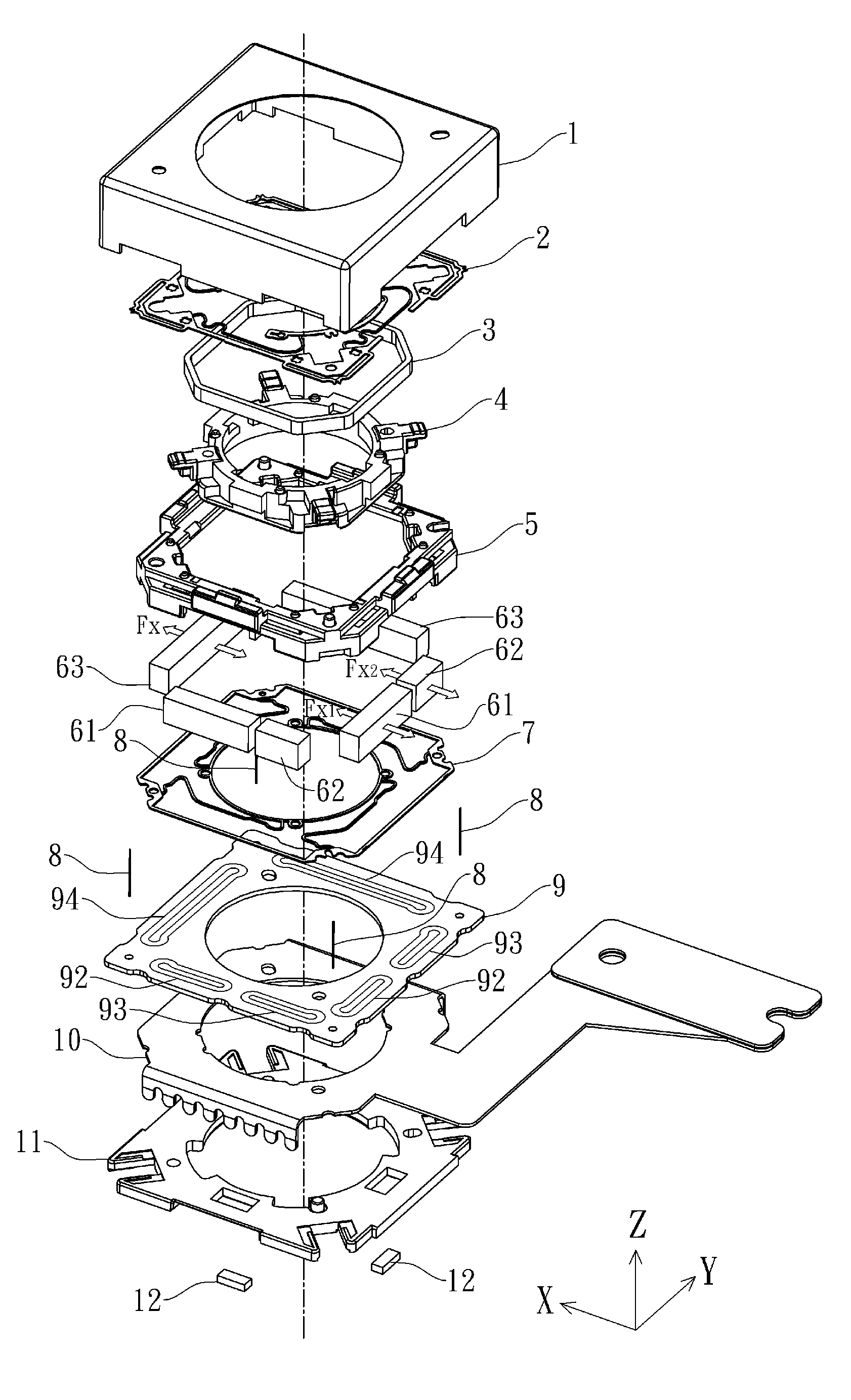
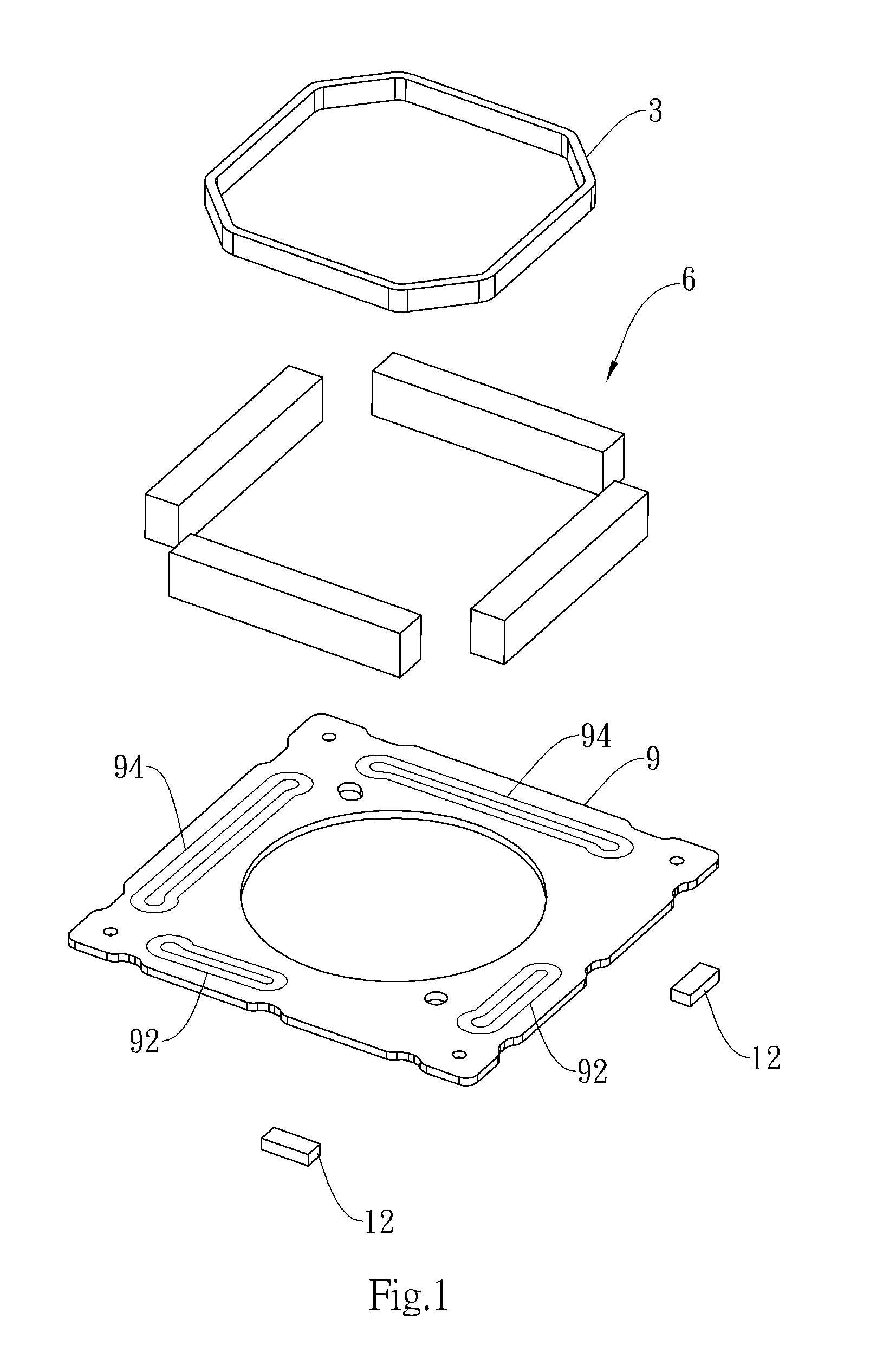
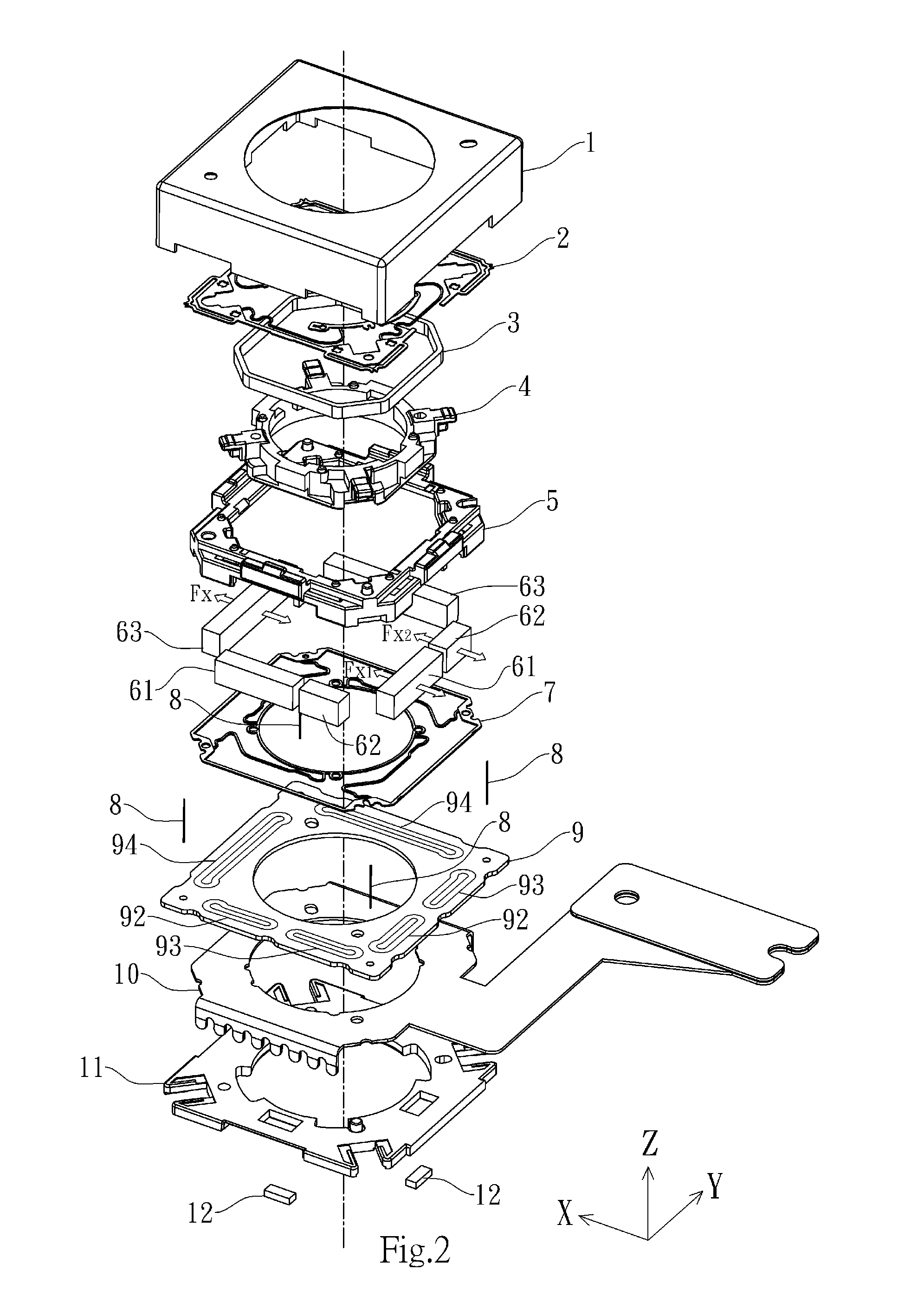
Lens driving device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150022891A1Improve yieldPrevent rotationManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesMountingsOptical axisMagnet
The present invention discloses a lens driving device and a method of manufacturing the same. In the present invention, there is provided a lens driving device comprising: a lens having an optical axis; a focusing coil disposed at a periphery of the lens with respect to the optical axis; a vibration correction coil set comprising a plurality of coils and disposed on a flat surface perpendicular to the optical axis; and a plurality of magnets disposed at the periphery of the lens with respect to the optical axis, each of which having a first surface facing the focusing coil and a second surface facing a corresponding one of respective coils of the vibration correction coil set; wherein the focusing coil acts on the first surface of each of the plurality of magnets to cause an assembly including the lens and the focusing coil to move in the optical axis direction with respect to the plurality of magnets; and wherein a direction in which one coil of the vibration correction coil set acts on the second surface of one of the plurality of magnets is the same as directions in which another two coils of the vibration correction coil set act respectively on the second surfaces of another two magnets of the plurality of magnets respectively so as to cause an assembly including the lens, the focusing coil and the plurality of magnets to move in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis with respect to the vibration correction coil set.
Owner:TDK TAIWAN
Antenna element
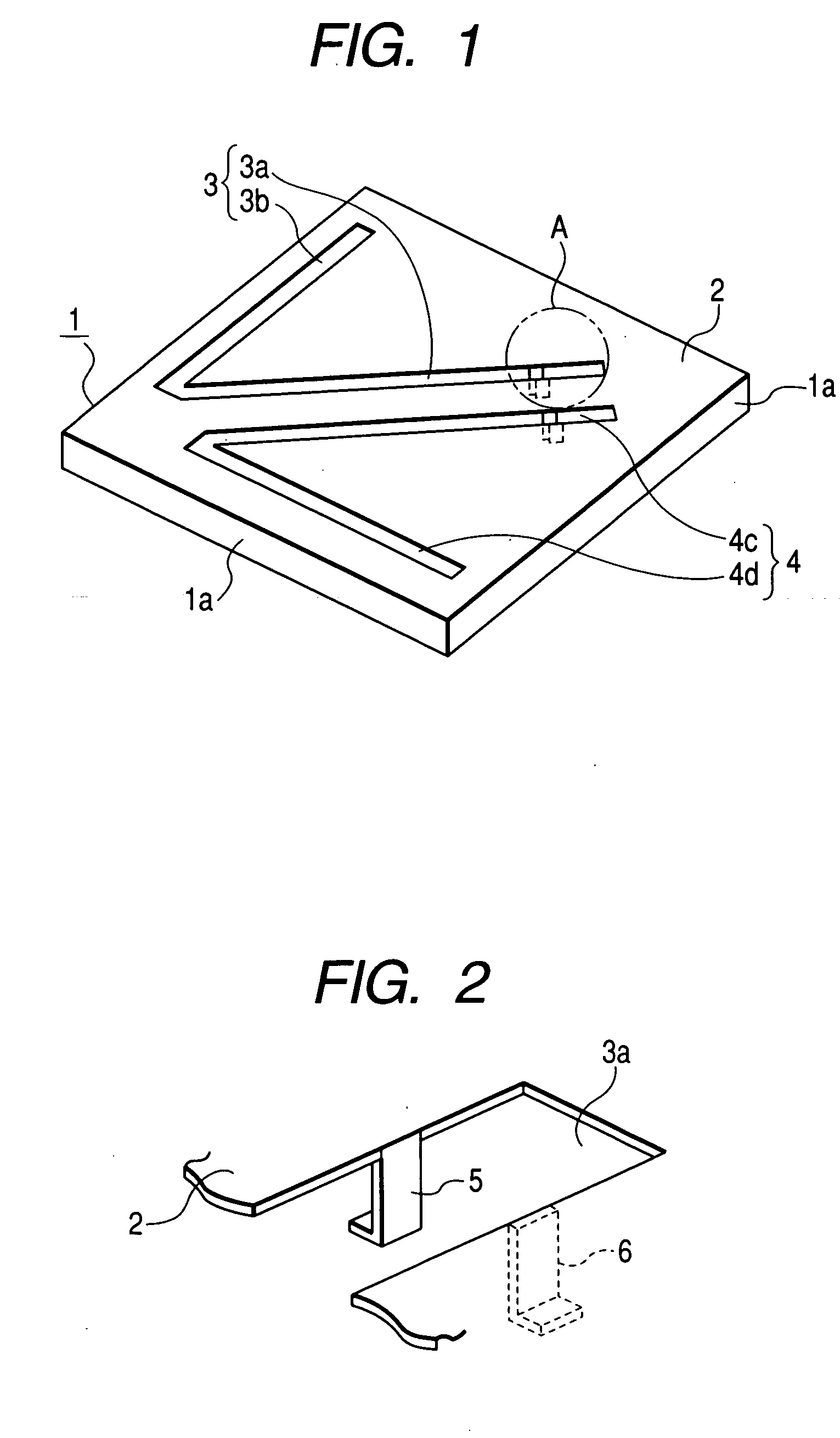
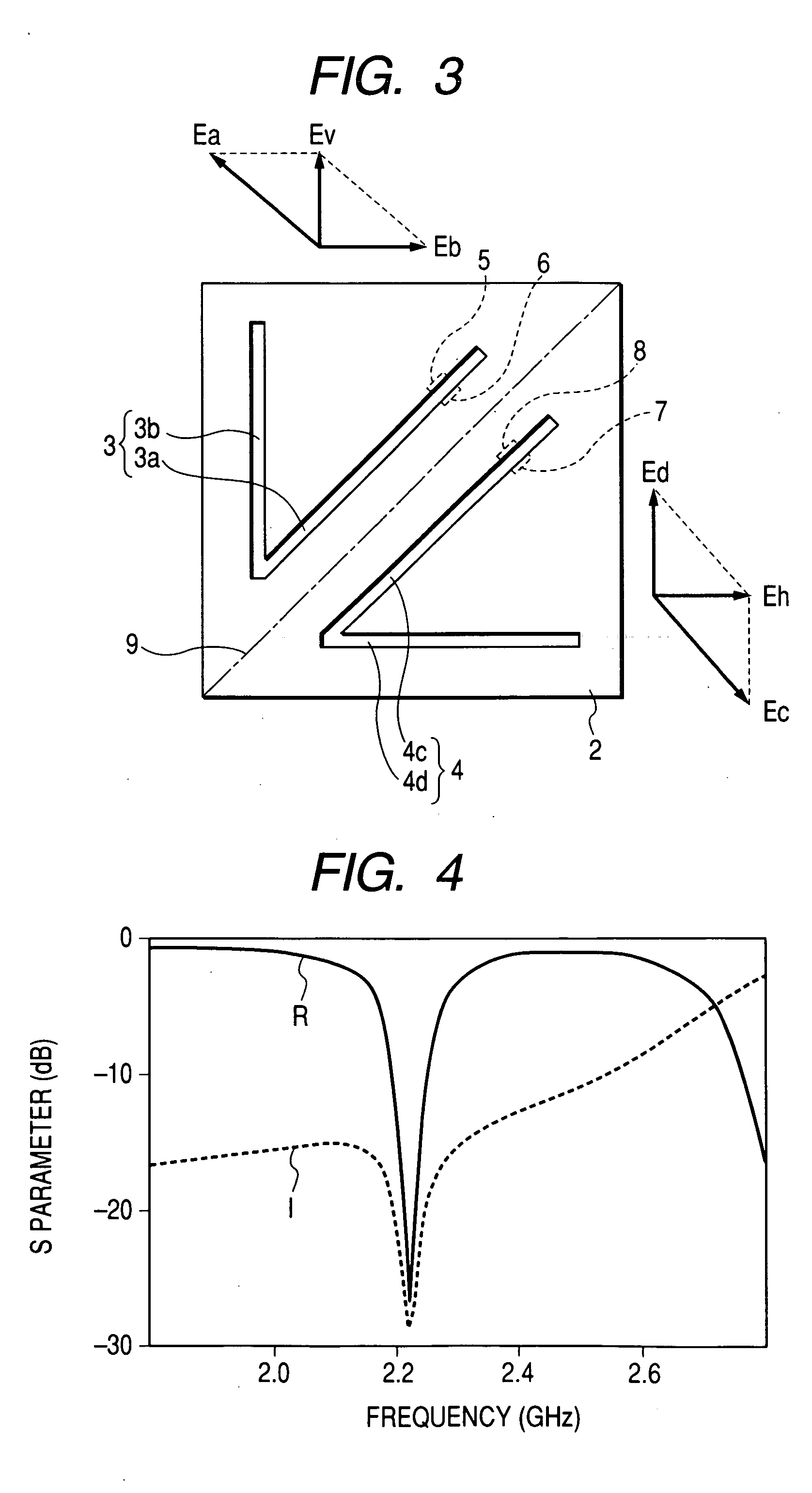
InactiveUS20020126049A1Stable characteristicsHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorResonance
To provide an antenna element having a radiation electrode formed mainly on one surface of a dielectric substrate. The radiation electrode is substantially symmetric in form with respect to the center thereof, and has a first half and a second half with the same direction of main polarization of radiation emitted therefrom. Each of the halves of the radiation electrode may be a quarter-wave antenna for a wavelength of the emitted radiation. A power supply conductor to be connected to a high frequency signal source is connected to the first half of the radiation electrode, and a ground conductor to be connected to a ground is connected to the second half. A total impedance of the first half of the radiation electrode and the power supply conductor and a total impedance of the second half of the radiation electrode and the ground conductor can substantially match to one another, so that resonance between the halves of the radiation electrode can be enhanced and a wider bandwidth can be realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Acoustic Drum With Resonators Disposed Therein
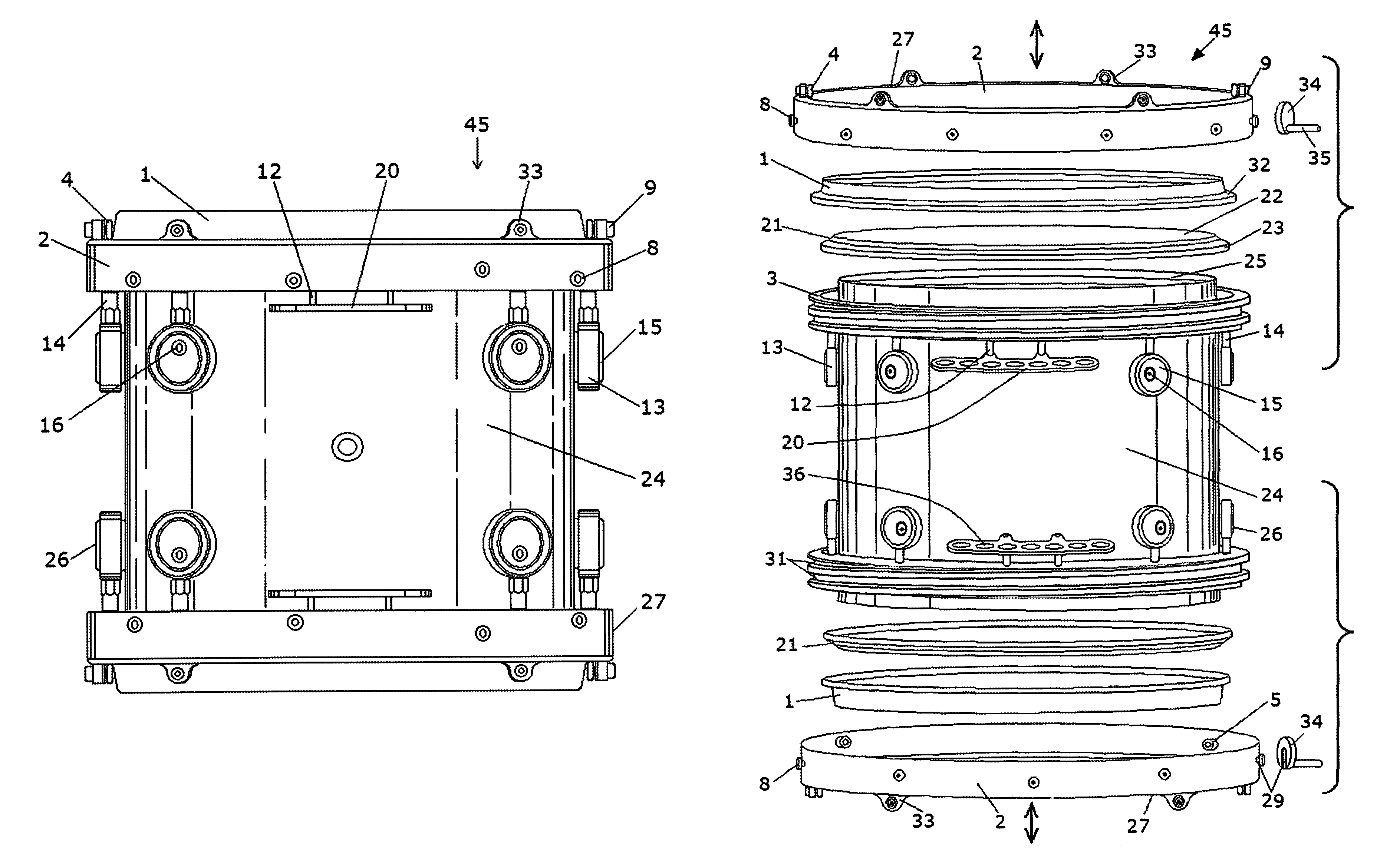
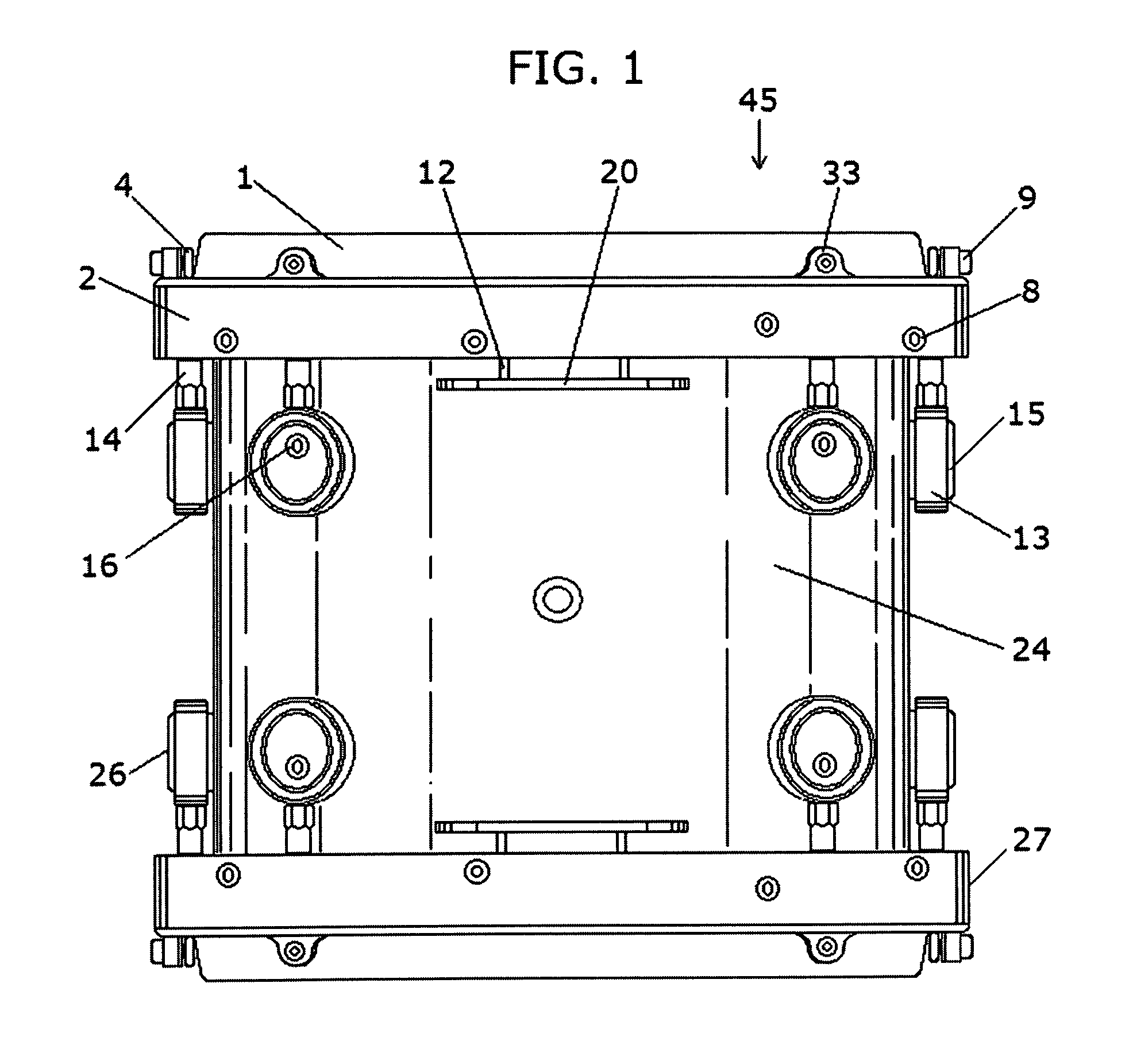
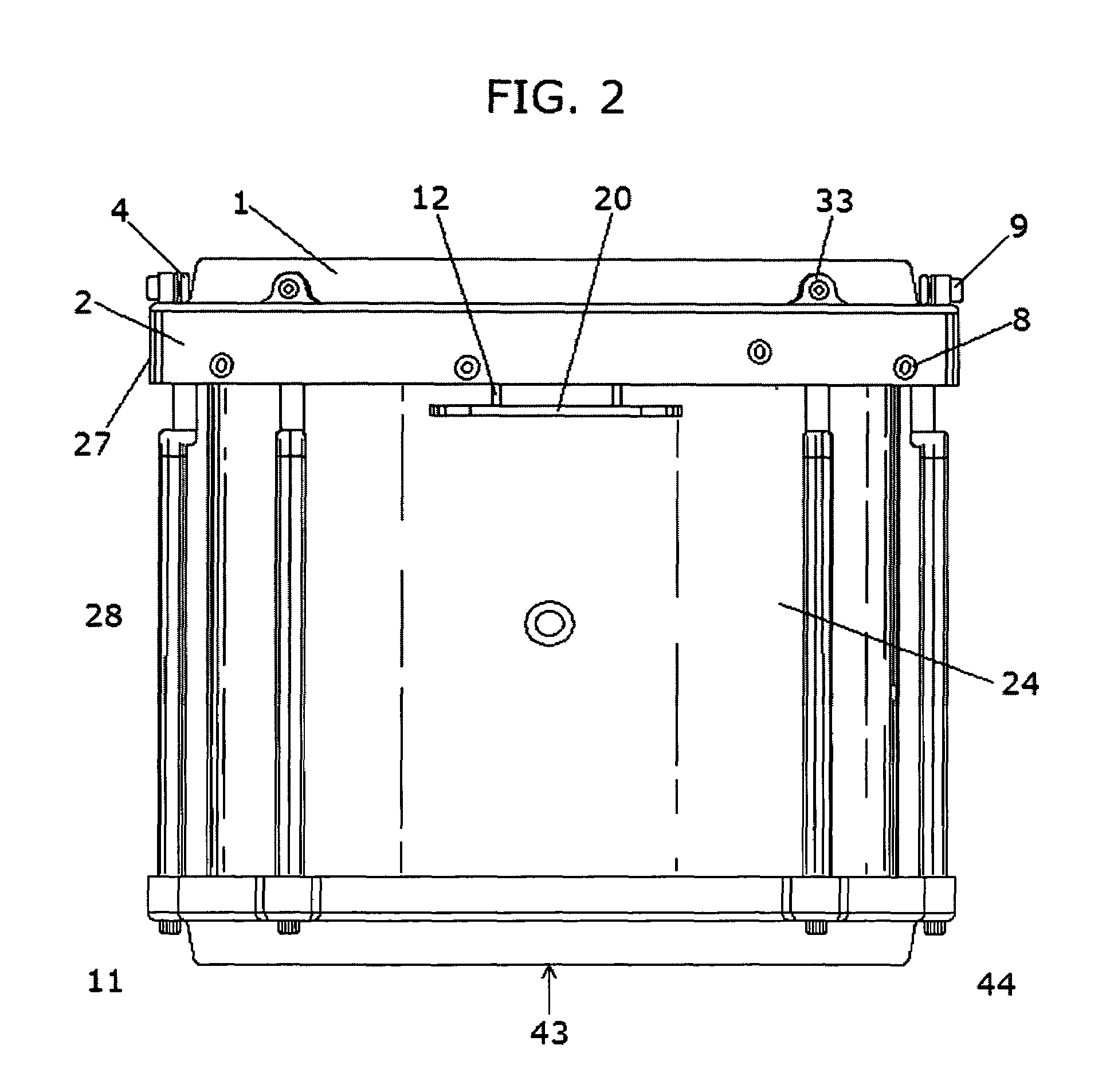
InactiveUS20100083812A1Improve resonance characteristicsImprove featuresPercussion musical instrumentsResonatorEngineering
An acoustic drum includes: a shell having first and second, spaced apart ends, and an interior surface defining an interior volume; a drumhead stretched over the first end of the shell; and at least one resonator coupled at one edge in lever fashion to the interior surface of the shell, the at least one resonator being sized and shaped to resonate at a frequency proximate to a peak resonant frequency of the drum.
Owner:PEAVEY ELECTRONICS
Rotation activated drum tuning system
ActiveUS7501567B1Increased mechanical advantageMinimized contact areaPercussion musical instrumentsBearing downEngineering
A drum tuning system which rotates clockwise or counterclockwise to adjust the tension of a drum head fitted over the open end of a drum body. It utilizes a rotating ring having numerous opposing equally spaced vertically projecting tabs along the top of the body's diameter, each with inward facing wheels that ride on the horizontal surface of a separate inner hoop bearing down on the drum head. The rotating actuator ring is fitted with multiple radial cleats projecting from its outside diameter for grasping it. A radius plate having horizontal holes extends from the drum body, and a tool engages the radial cleats on the rotating actuator ring to facilitate rotation. Multiple adjustable eccentric lugs are used to raise and lower the drum camming mechanism in relation to the open end of the drum body where attached. Horizontal projecting links support the drum attached to suspension mounting systems.
Owner:SPINAZZOLA DAVID MICHAEL
Antenna device with improved isolation characteristic
ActiveUS20060132373A1Without sacrificing isolation characteristicSmall sizeAntenna arraysSlot antennasGround lineFeed line
A pair of radiating slots open in a flat metal plate having a square shape to be line-symmetrically arranged with respect to a symmetry axis, and power feeding lines and ground lines are provided at power feeding positions of the respective radiating slots. The respective radiating slots have first slot portions and second slot portions that contact at 45 degrees and linearly extend, respectively. Both the radiating slots are arranged in a back-to-back manner that edges of the first slot portions face each other, and the second slot portions extend in a direction to be separated from each other along two sides of the flat metal plate. Further, a polarization direction of an electric wave to be generated by one radiating slot and a polarization direction of an electric wave to be generated by the other radiating slot are set to be perpendicular to each other.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Resonance enhanced rotary drilling
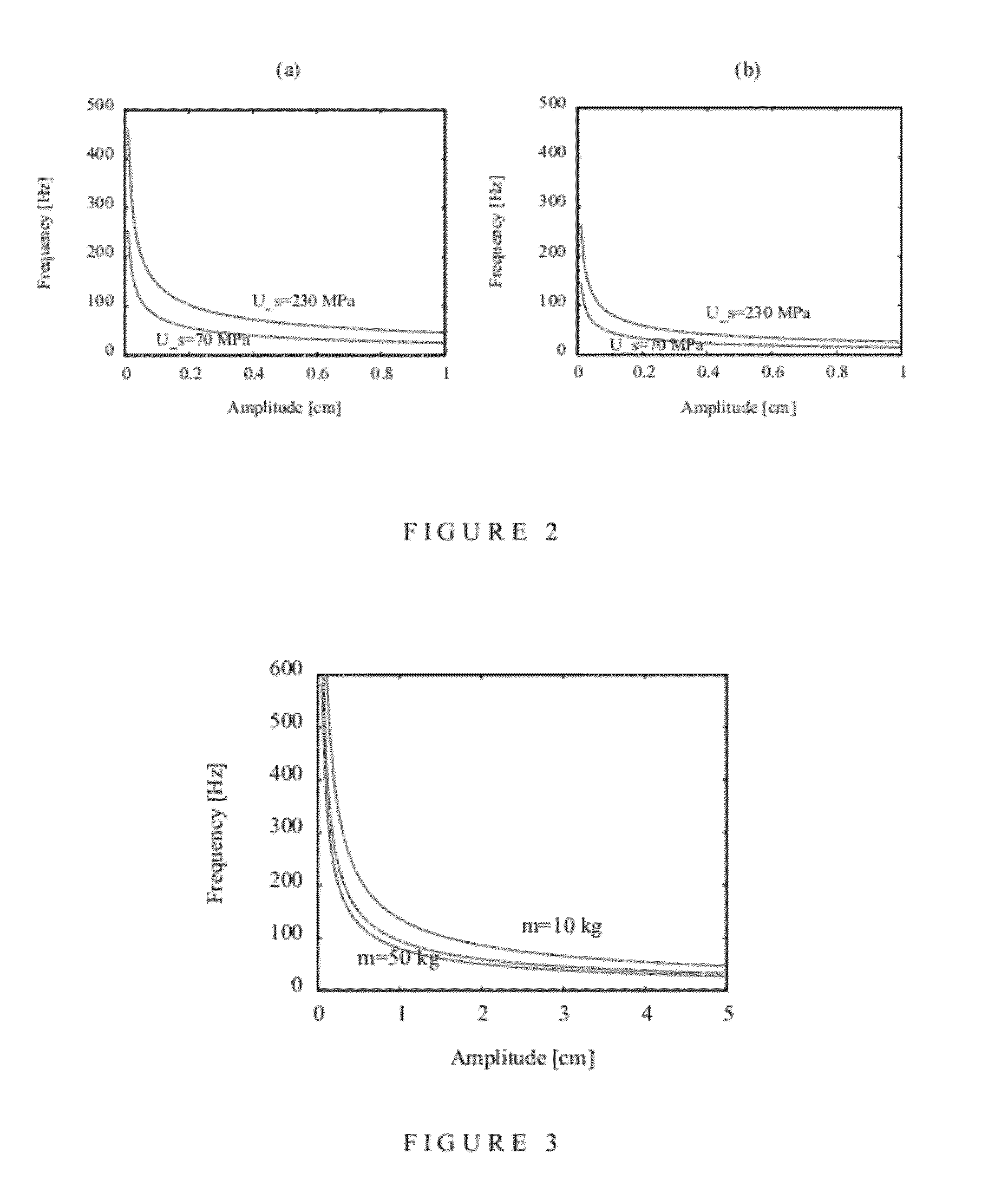
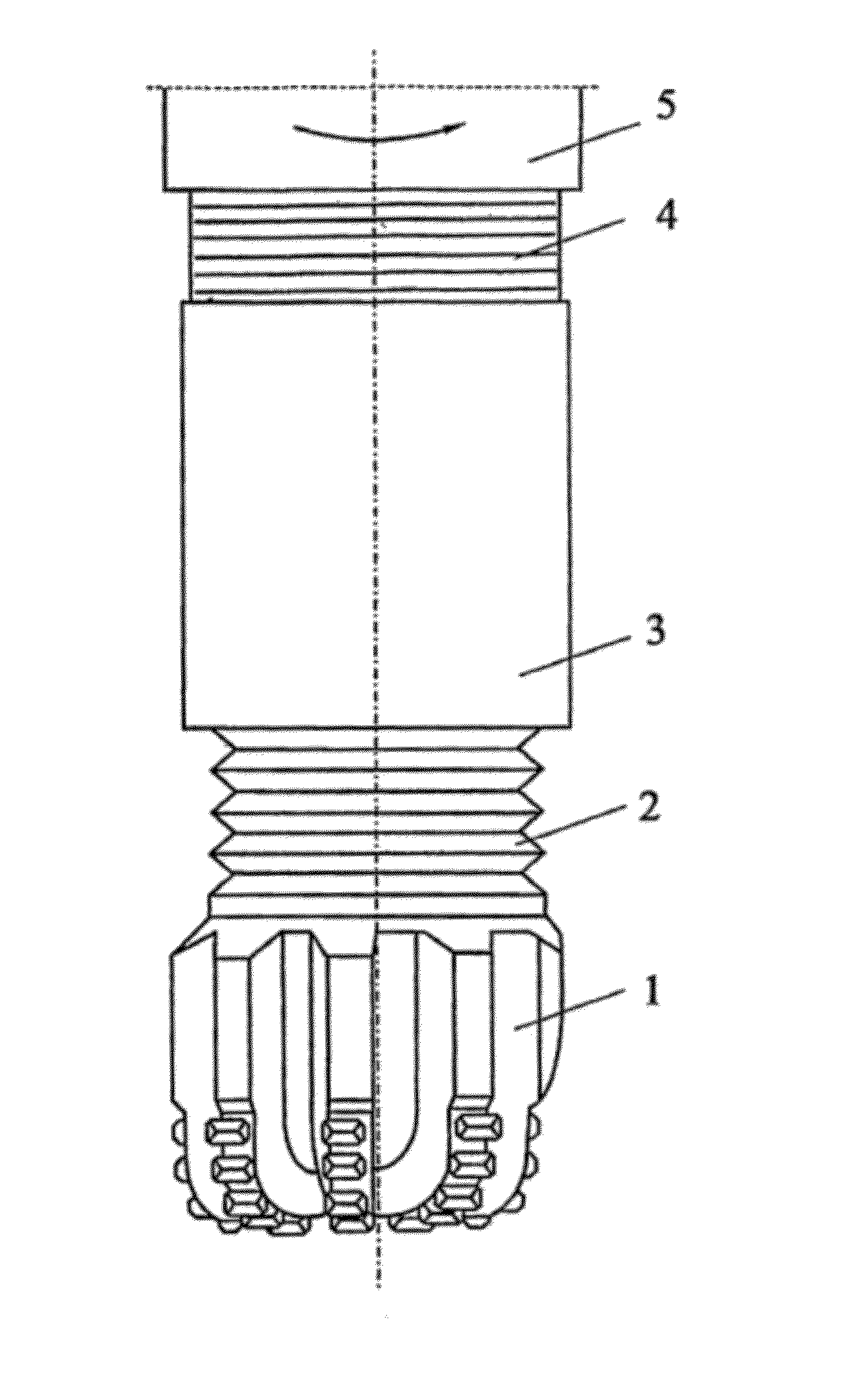
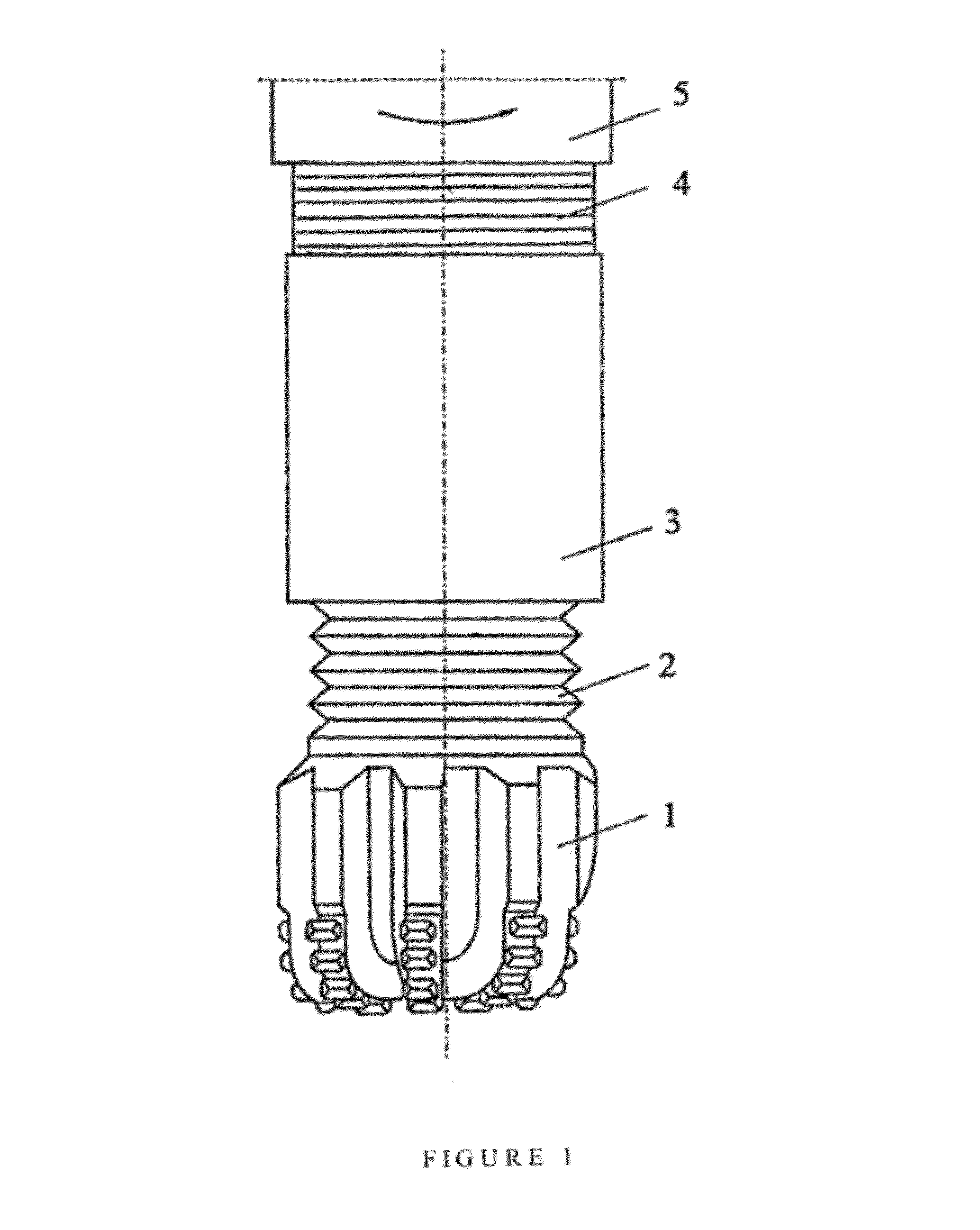
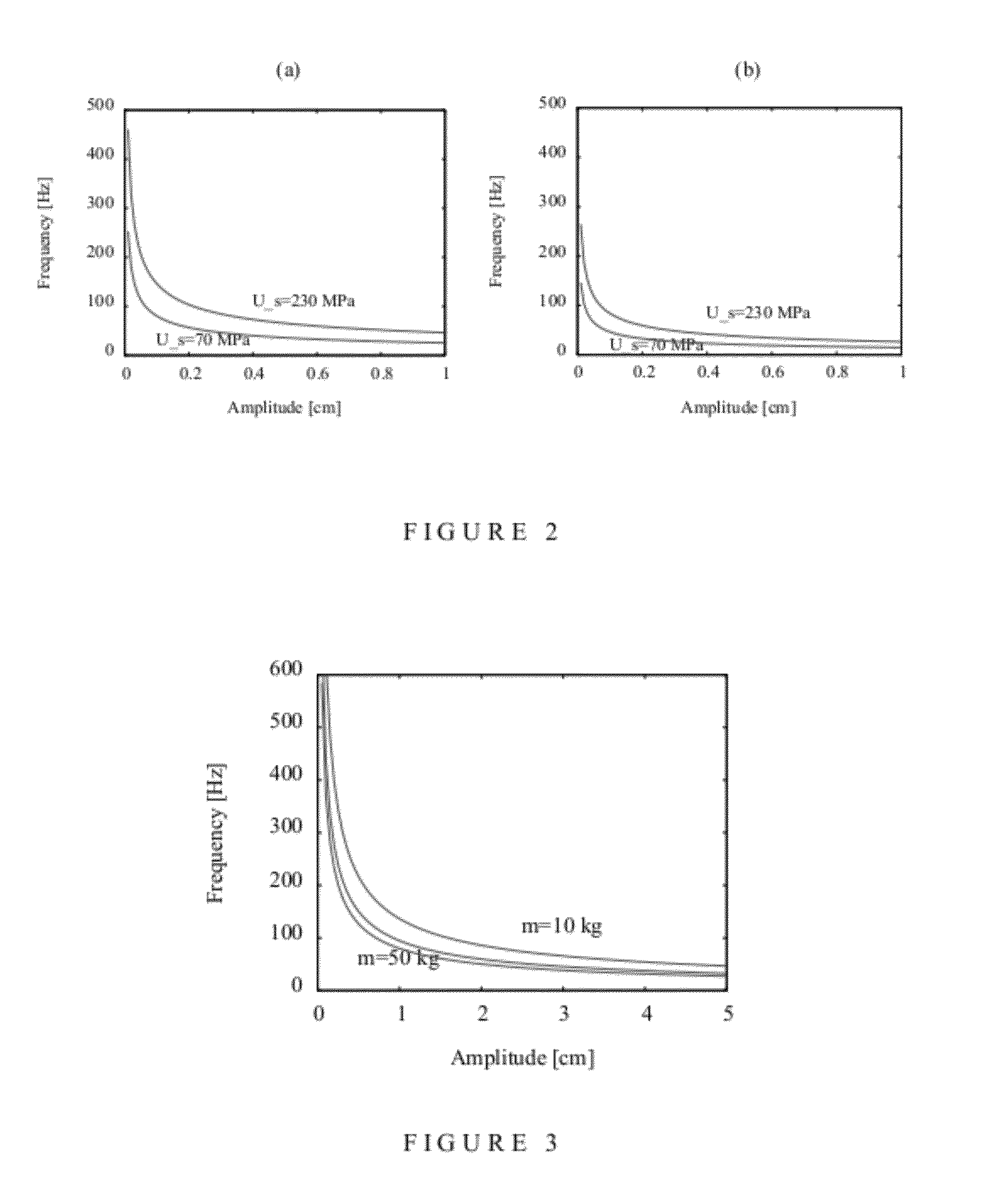
ActiveUS20120241219A1Improve high performanceHigh drilling performanceDirectional drillingVibration devicesEffective diameterDrill bit
A method for controlling a resonance enhanced rotary drill comprising a rotary drill bit and an oscillator for applying axial oscillatory loading to the rotary drill bit, the method comprising:controlling frequency (f) of the oscillator in the resonance enhanced rotary drill whereby the frequency (f) is maintained in the range(D2 Us / (8000 πAm))1 / 2≦f≦Sf(D2 Us / (8000 πAm))1 / 2 where D is diameter of the rotary drill bit, Us is compressive strength of material being drilled, A is amplitude of vibration, m is vibrating mass, and Sf is a scaling factor greater than 1; andcontrolling dynamic force (Fd) of the oscillator in the resonance enhanced rotary drill whereby the dynamic force (Fd) is maintained in the range[(π / 4)D2effUs]≦Fd≦SFd[(π / 4)D2effUs]where Deff is an effective diameter of the rotary drill bit, Us is a compressive strength of material being drilled, and SFd is a scaling factor greater than 1,wherein the frequency (f) and the dynamic force (Fd) of the oscillator are controlled by monitoring signals representing the compressive strength (Us) of the material being drilled and adjusting the frequency (f) and the dynamic force (Fd) of the oscillator using a closed loop real-time feedback mechanism according to changes in the compressive strength (Us) of the material being drilled.
Owner:ITI SCOTLAND
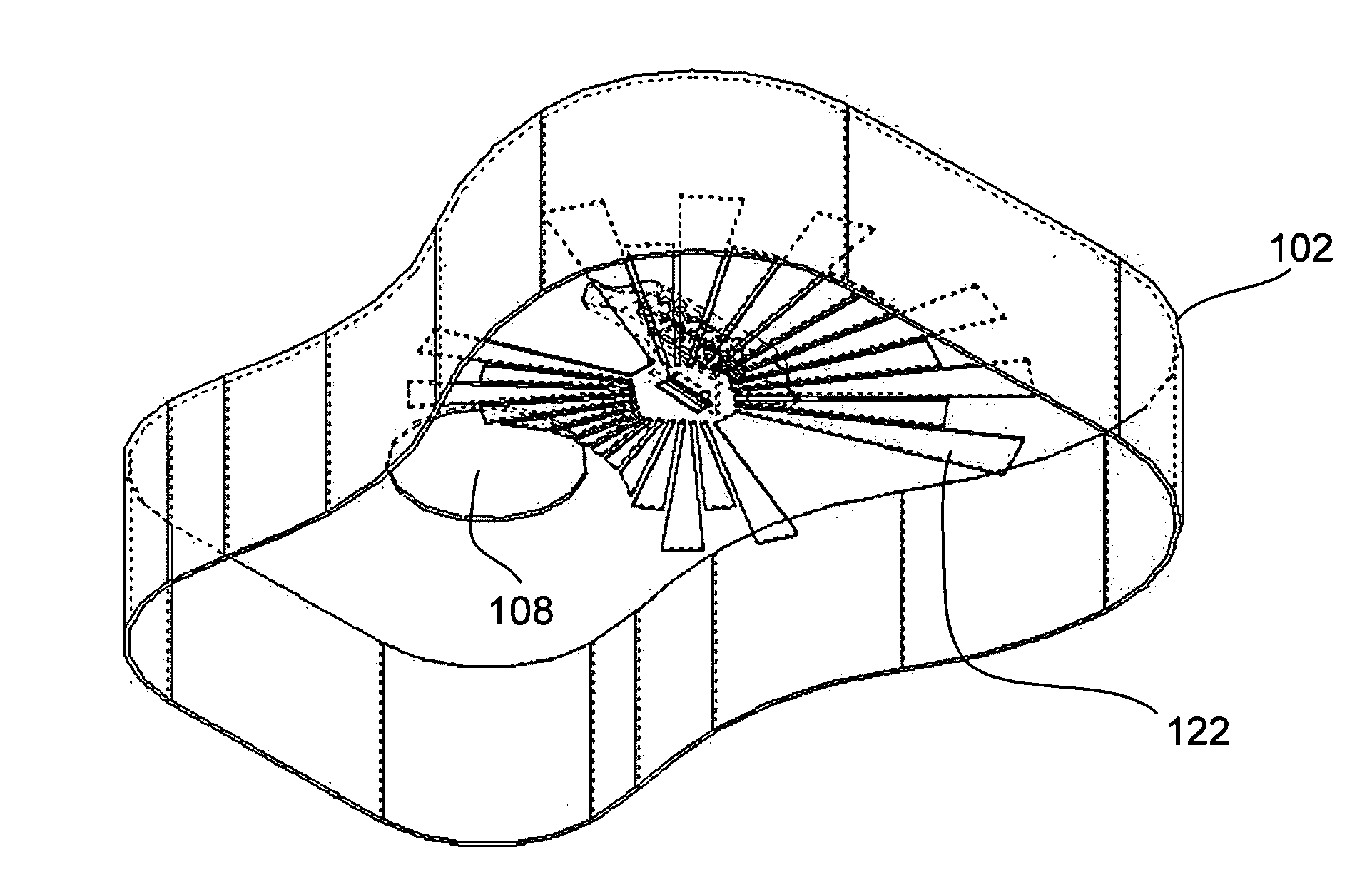
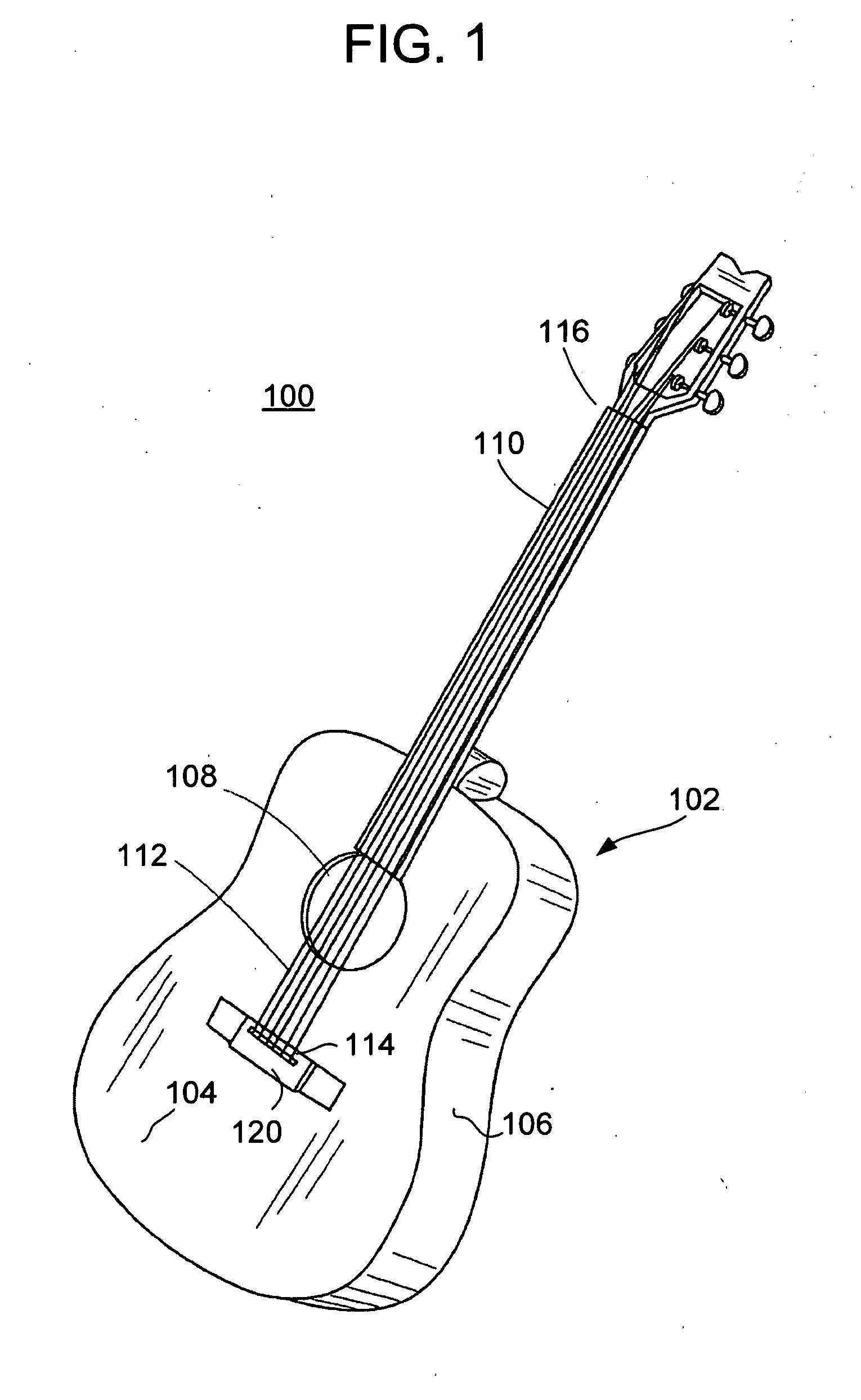
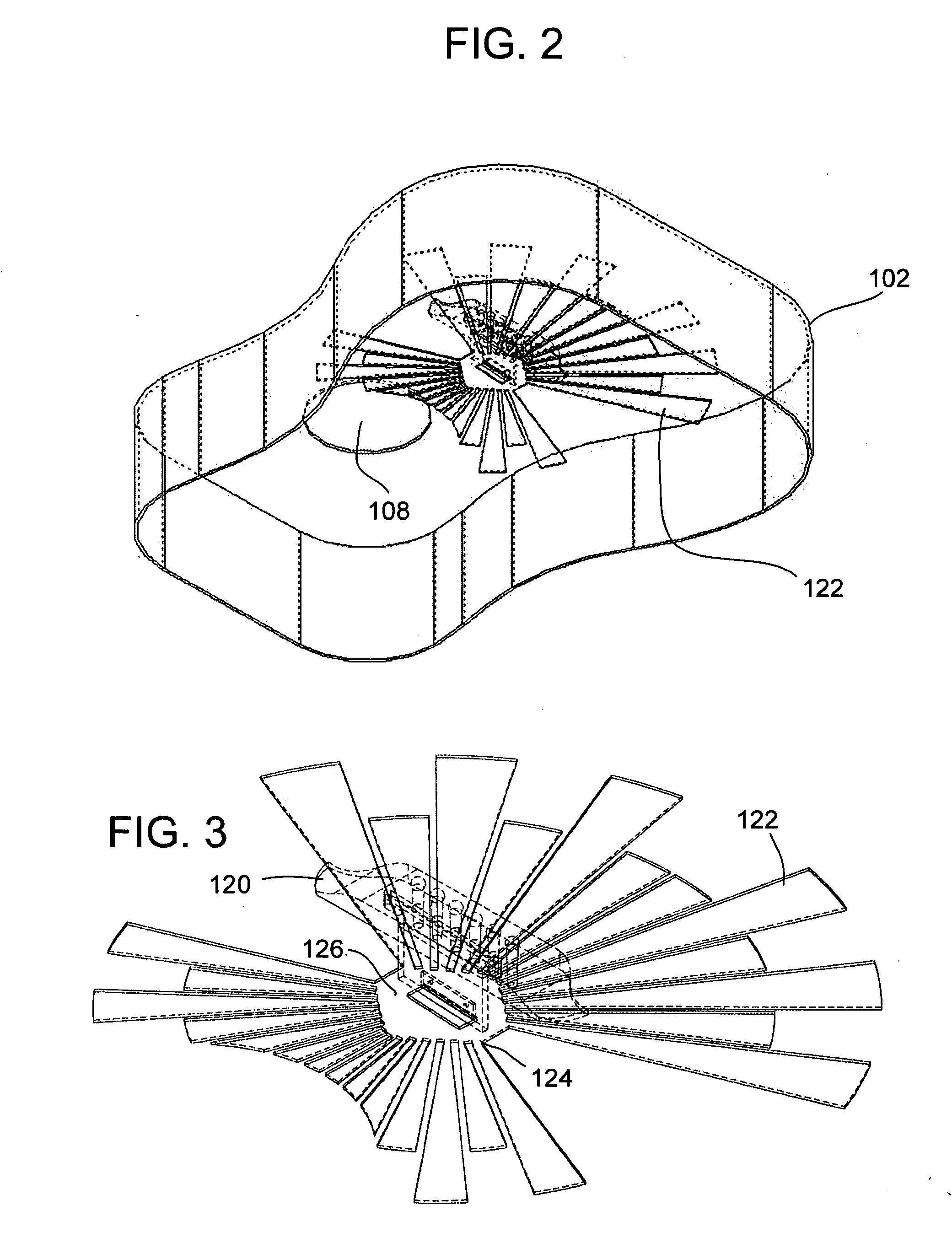
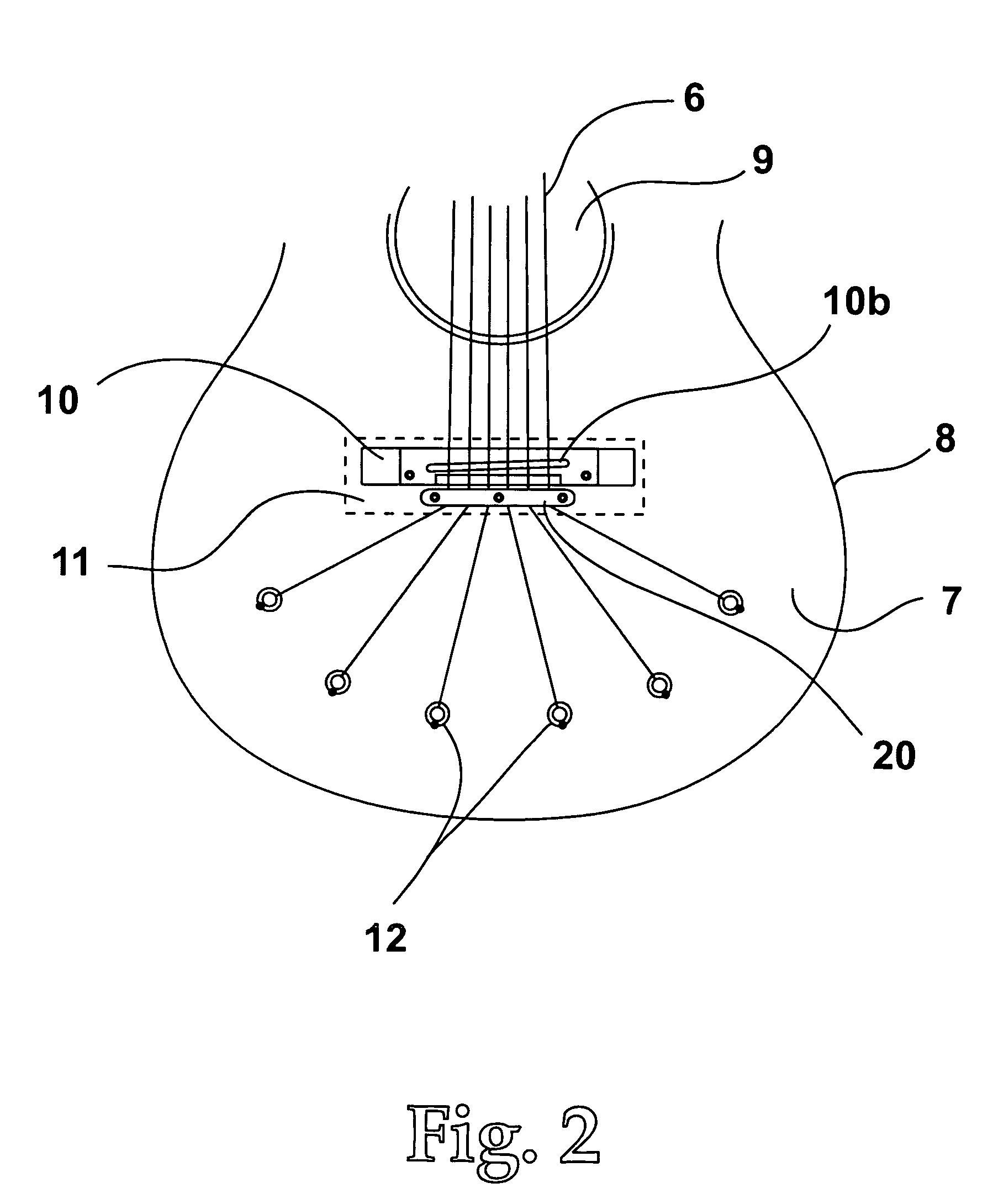
Acoustic Guitar With Resonators Augmenters Disposed Therein
InactiveUS20100083806A1Good vibesIncrease surface areaStringed musical instrumentsEngineeringFundamental frequency
An acoustic guitar includes: a body having a soundboard, a back, and sides defining an interior volume thereof; a neck extending away from the body; a plurality of strings, each stretched from a first end at the body to a second end at a terminal end of the neck; and a plurality of resonant augmenters disposed within the interior volume of the body, each resonant augmenter being coupled at one edge in lever fashion to a mounting plate, the mounting plate being coupled to the soundboard, wherein one or more of the resonant augmenters are sized and shaped to resonate at one or more respective fundamental frequencies.
Owner:PEAVEY ELECTRONICS
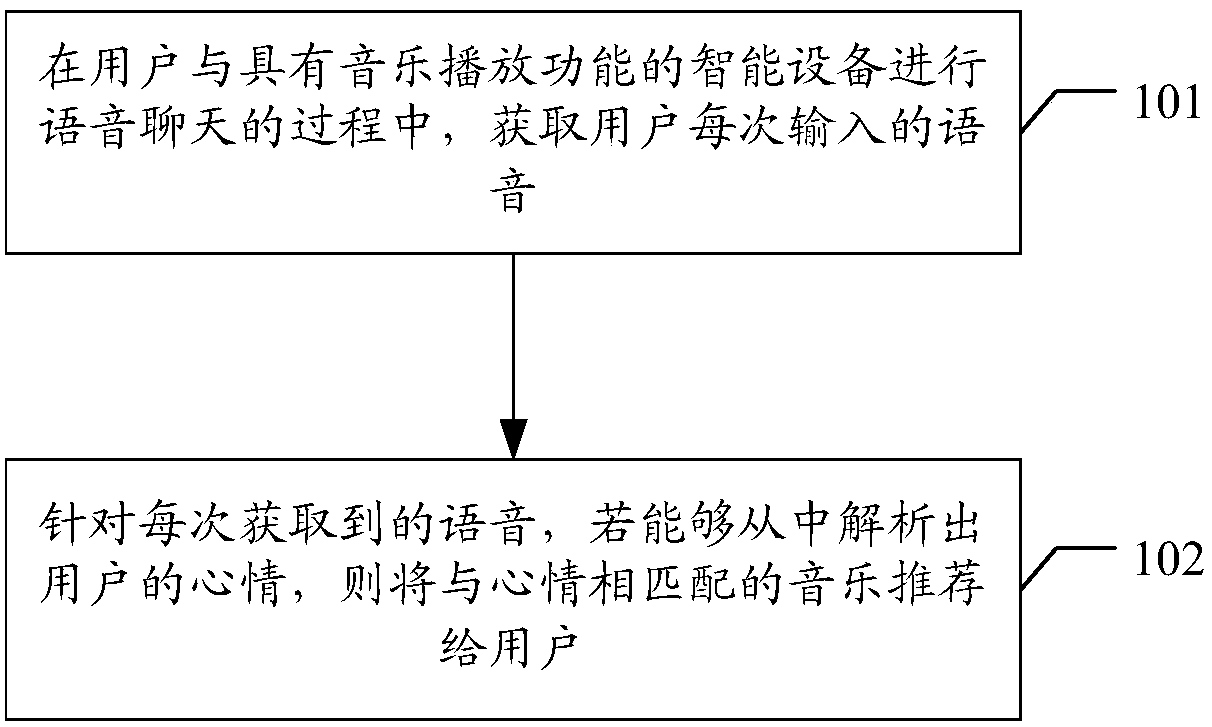
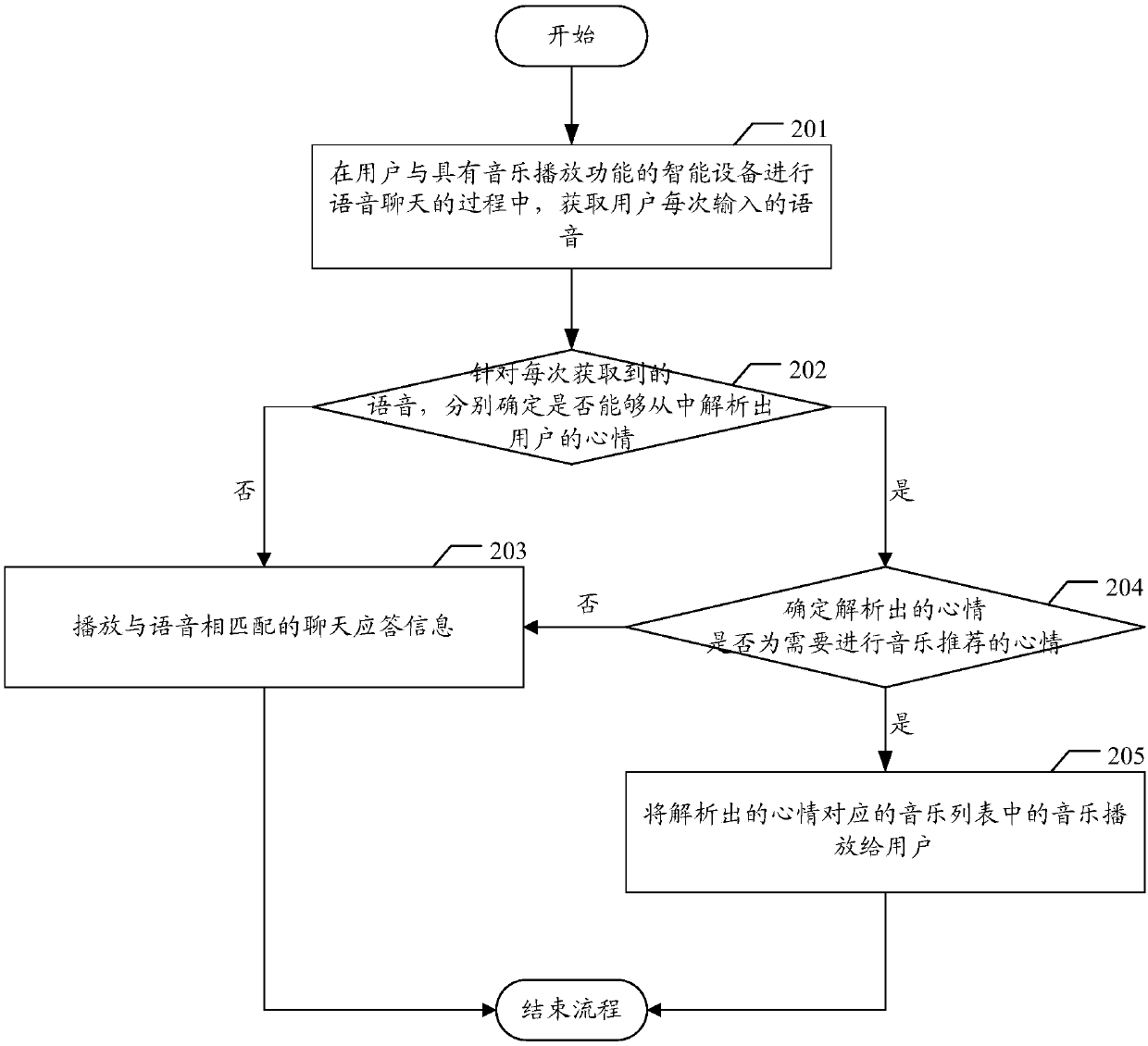
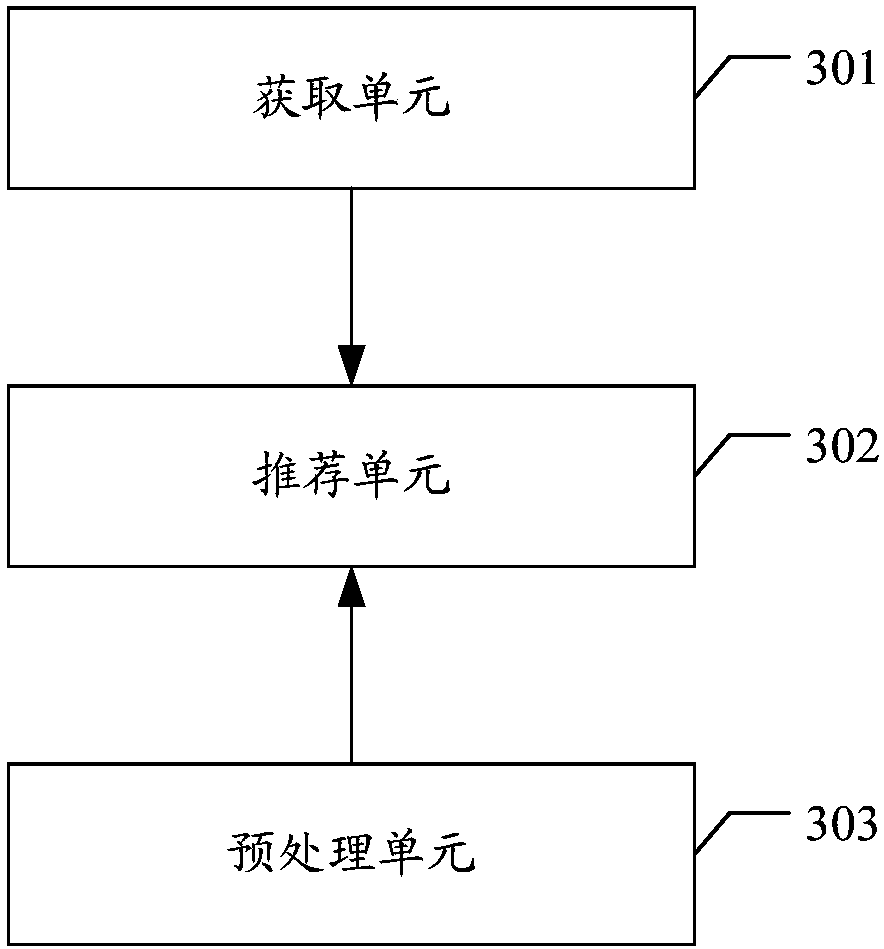
Music recommendation method and apparatus, device and storage medium
PendingCN107562850AFor music needsGood vibesSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpeech soundVoice chat
The invention discloses a music recommendation method and apparatus, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a voice input by a user each time in a process that theuser performs voice chat with an intelligent device with a music playing function; and for the voice obtained each time, if the voice can be analyzed to obtain the mood of the user, recommending musicmatched with the mood obtained by analysis to the user. By applying the scheme, the intelligence of the device can be improved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD +1
Omni-directional ultrasonic transducer apparatus having controlled frequency response
InactiveUS6239535B1Good vibesReducing spring effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorResonance
A transducer apparatus is disclosed including a spool member having a body portion and first and second elevated regions formed on the body portion. A piezoelectric film such as a PVDF film surrounds the spool member and is spaced apart from the body portion of the spool member by an elevation of the elevated region, thereby forming a predetermined gap between the piezoelectric film and the body portion of the spool member. The predetermined gap is at least 0.1 mm and enables a predetermined resonance frequency in the piezoelectric film to control the resonance frequency of the transducer. Opposite lateral ends of the piezoelectric film are secured together such that secured ends of the piezoelectric film have substantially the same resonance frequency as a remainder of the piezoelectric film.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SPEC
String instrument
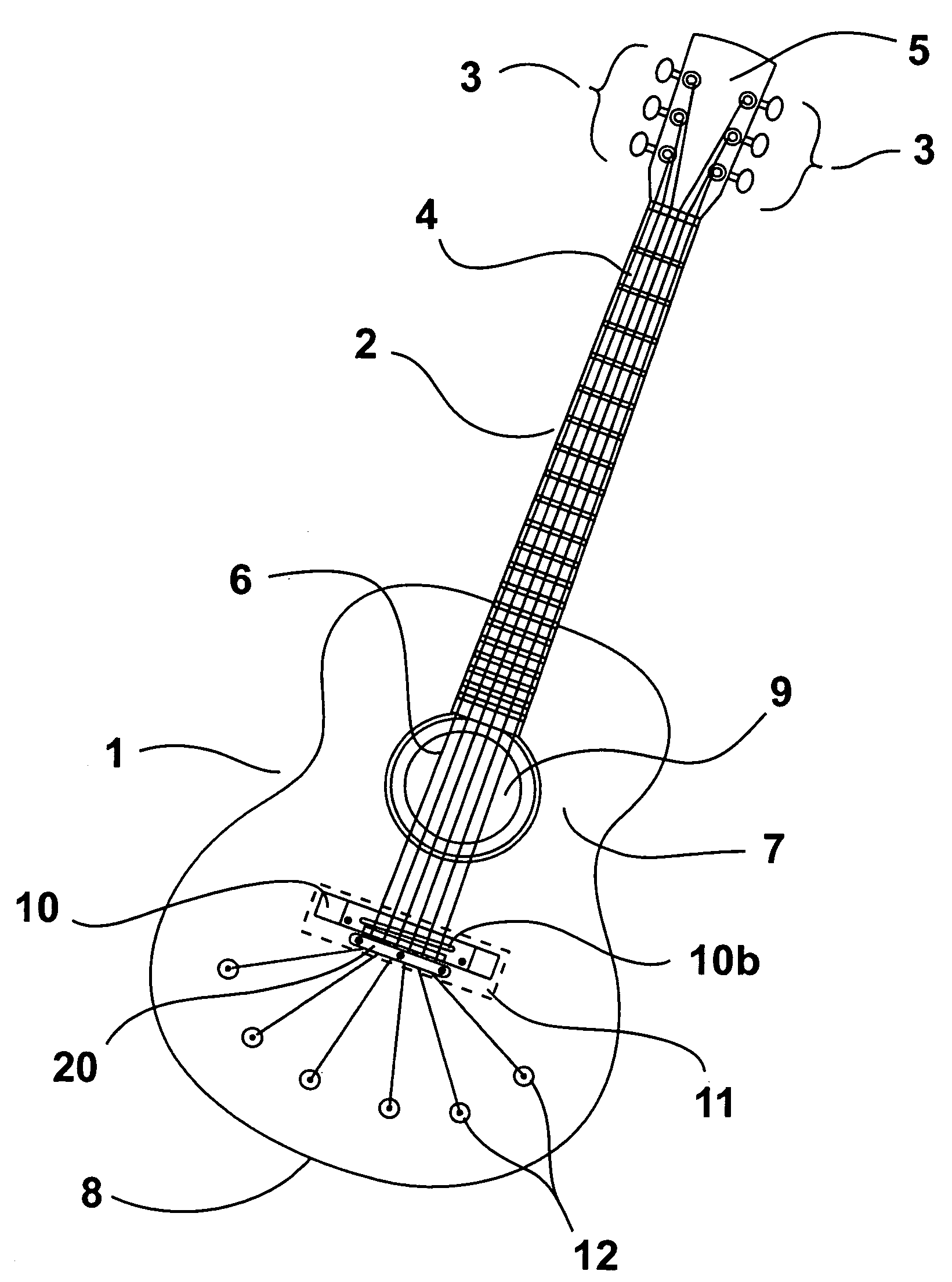
A stringed musical instrument, such as a guitar, whereby the lower end of the strings are anchored to the soundboard itself with one or more of the string anchors being positioned past the bridge. This arrangement provides an offset of the lateral compressive forces to the entire soundboard, therefore allowing the soundboard to vibrate more freely in response to the string vibration, and creating an acoustical perpetuating effect. Due to the inherent strength to this design, internal soundboard bracing can be minimized in weight and size as well, which offers a fuller and louder sound, with an increase in sonic balance and sustain.
Owner:BABICZ JEFFREY T
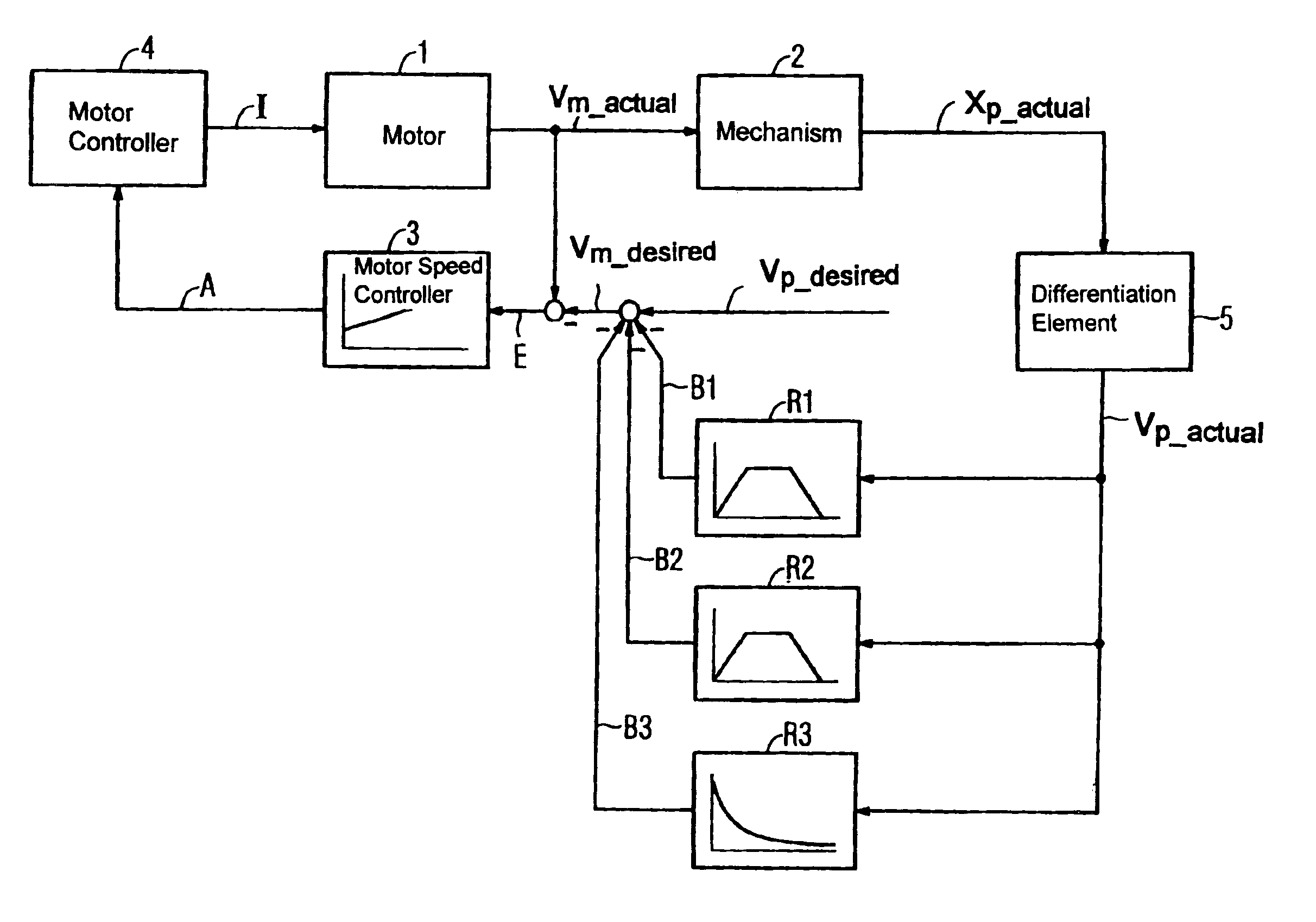
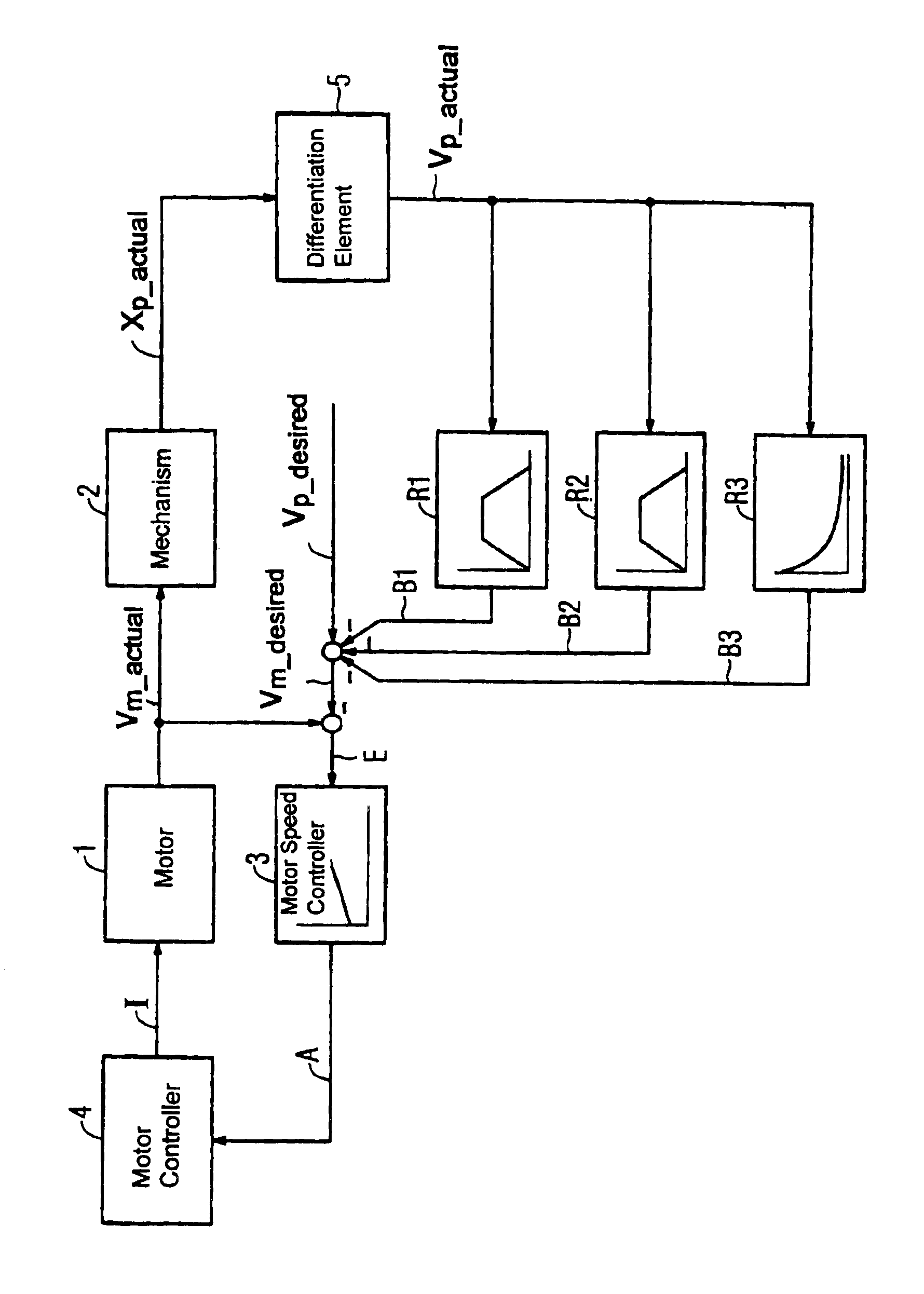
Method and apparatus for damping mechanical oscillations of a shaft in machine tools, manufacturing machines and robots
ActiveUS6903529B2Increase dampingEnsure stabilityProgramme controlComputer controlMotor speedElectric machine
Damping of mechanical oscillation in a shaft that is provided by feedback wherein the output signals of multiple feedback devices are negatively coupled and added to a desired speed signal of a motor speed controller of the driving motor is disclosed. At least one sensor and / or measuring system can be provided for measuring an actual position value. The actual speed of the shaft can be determined by differentiation from the shaft position value measurements or by integration from shaft acceleration measurements. The measured or actual speed of the shaft can be supplied as an input signal to each feedback element. Each feedback element is specifically tuned to an oscillation frequency range of the shaft that is to be damped. The invention provides an easy and cost-effective way of damping mechanical oscillations that have limited frequency ranges.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
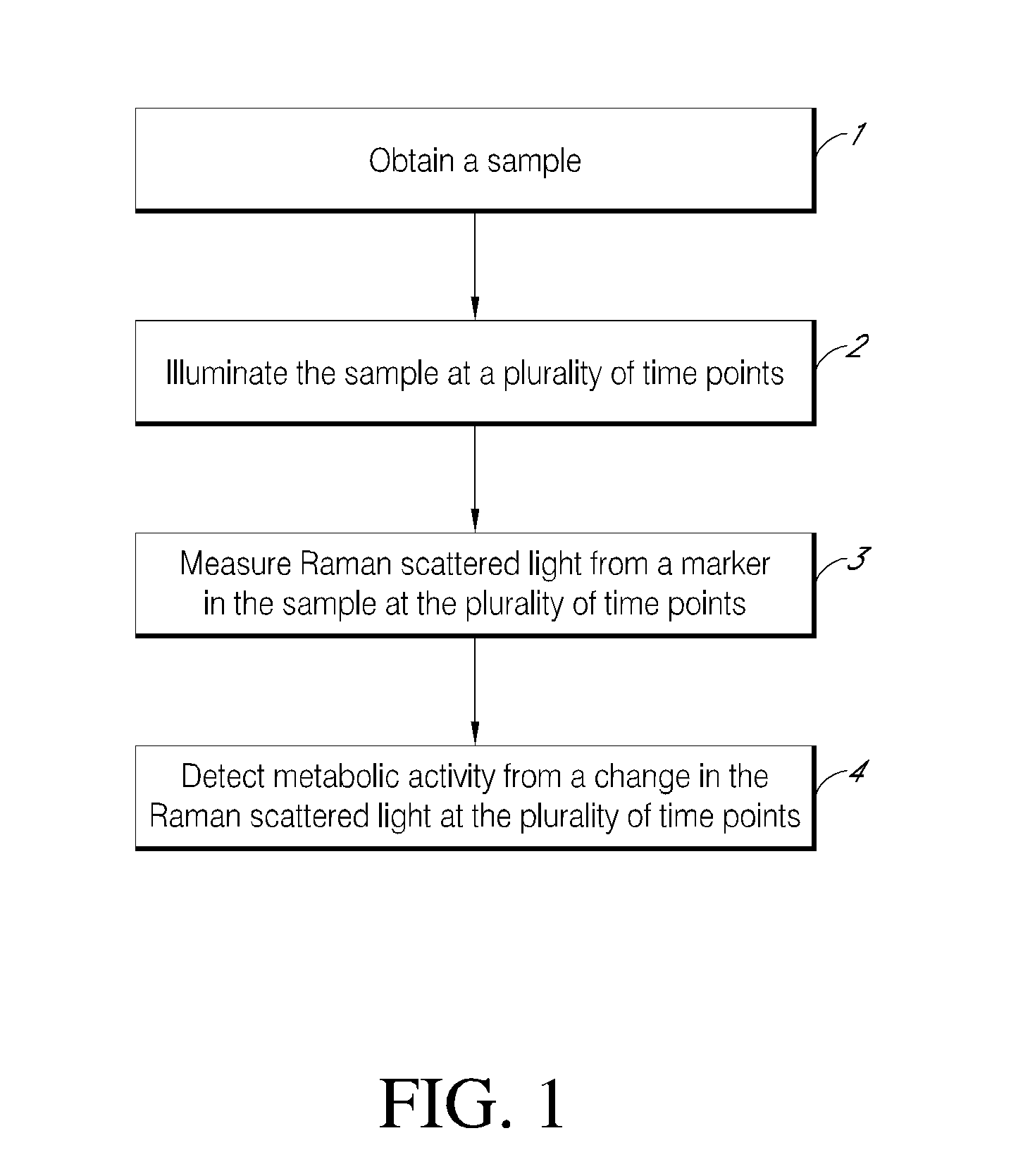
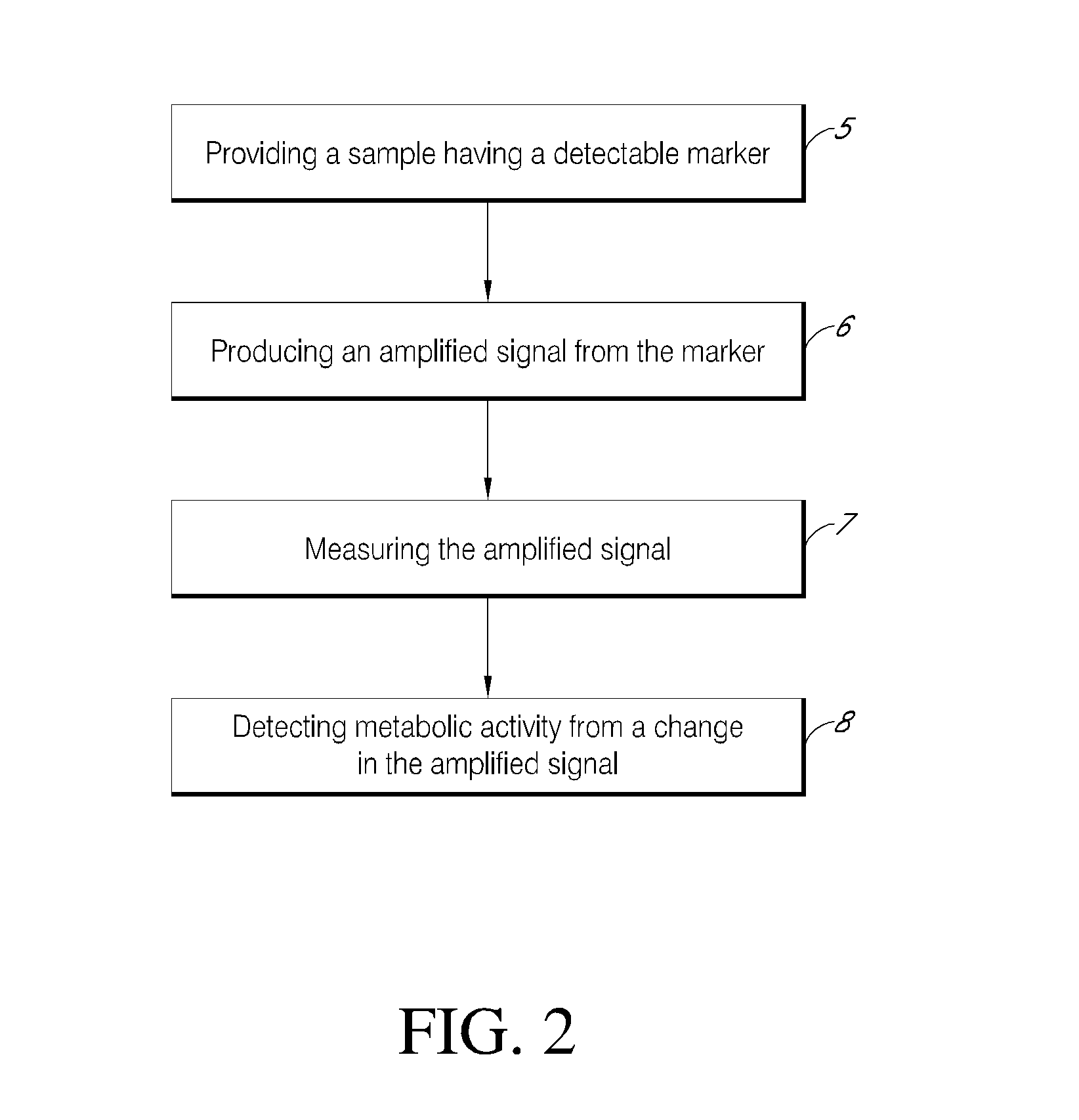
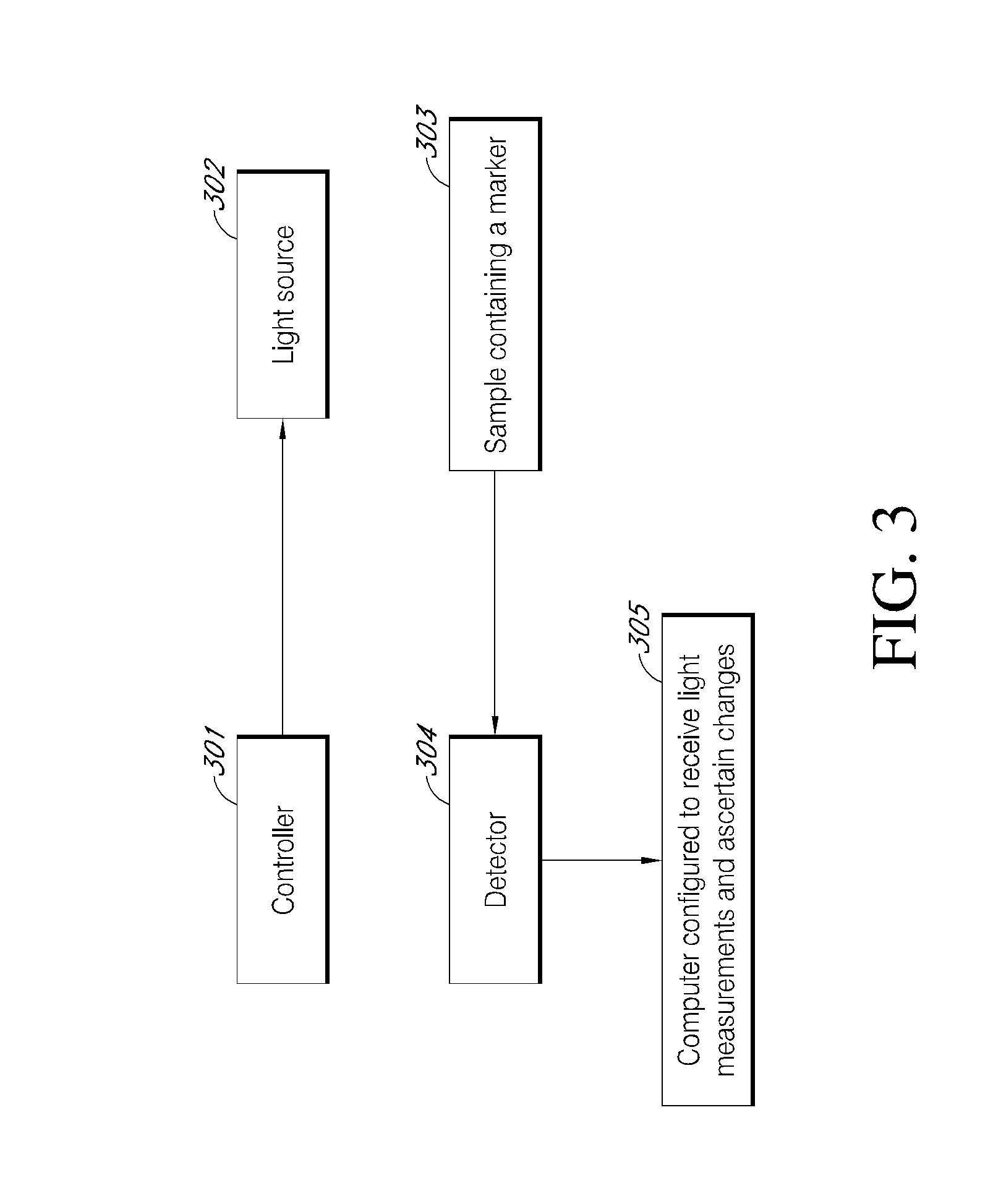
Rapid detection of metabolic activity
InactiveUS20130052636A1High light transmittanceGood vibesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyTransmitted light
Some aspects of the invention provide for a method for detecting metabolic activity in a sample by obtaining a sample, illuminating the sample at a plurality of time points, measuring transmitted light from a marker of metabolic activity in the sample at the plurality of time points, and detecting the presence or absence of metabolic activity from a change in the transmitted light at the plurality of time points. Other aspects of the invention provide for a method for detecting metabolic activity in a sample by providing a sample have a detectable marker therein that is reflective of metabolic activity in the sample, producing an amplified signal from the marker, measuring the amplified signal at a plurality of time points, and detecting metabolic activity from a change in the signal. Additional aspects provide for a system for detecting metabolic activity in a sample.
Owner:SPECTRAL PLATFORMS
Dielectrically-loaded antenna
InactiveUS7372427B2Reduced insertion lossShorten the lengthRadiating elements structural formsHelical antennasEngineeringComposite element
In a dielectrically-loaded quadrifilar antenna for operation with circularly polarised signals, four coextensive composite helical elements are plated on the outer surface of a cylindrical dielectric core, each composite element comprising two mutually adjacent conductive tracks defining between them an elongate channel or slit. The track edges bounding each channel are longer than the opposite edges of the respective tracks in that they follow parallel meandered paths, with the result that each channel deviates from a mean helical path and is longer than the corresponding portion of the mean helical path. At a frequency within the operating band of the antenna, the channels have respective electrical lengths equivalent to a half wavelength. The bandwidth of the antenna is greater than the bandwidth of a correspondingly dimensioned antenna having single-track helical elements.
Owner:SARANTEL LTD
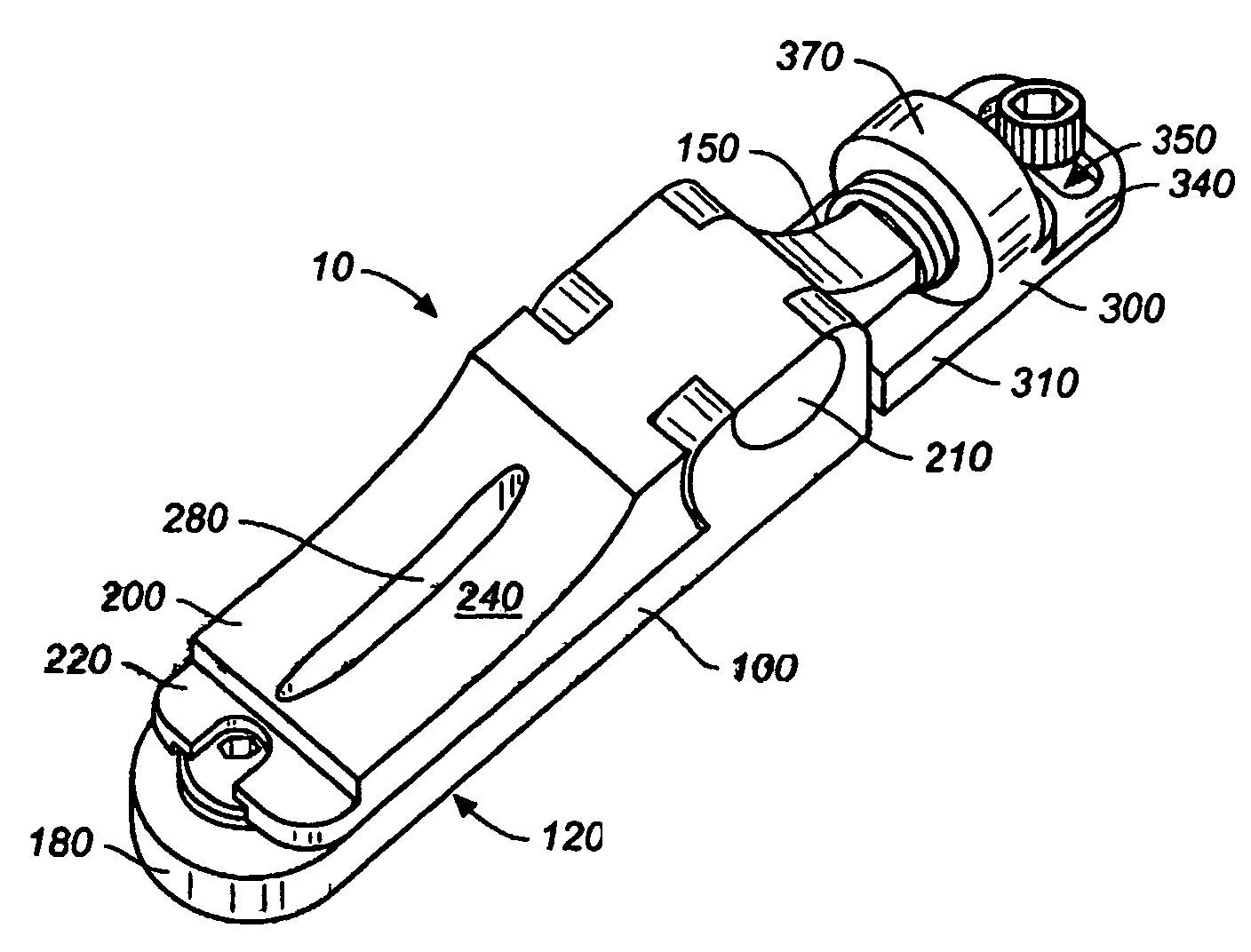
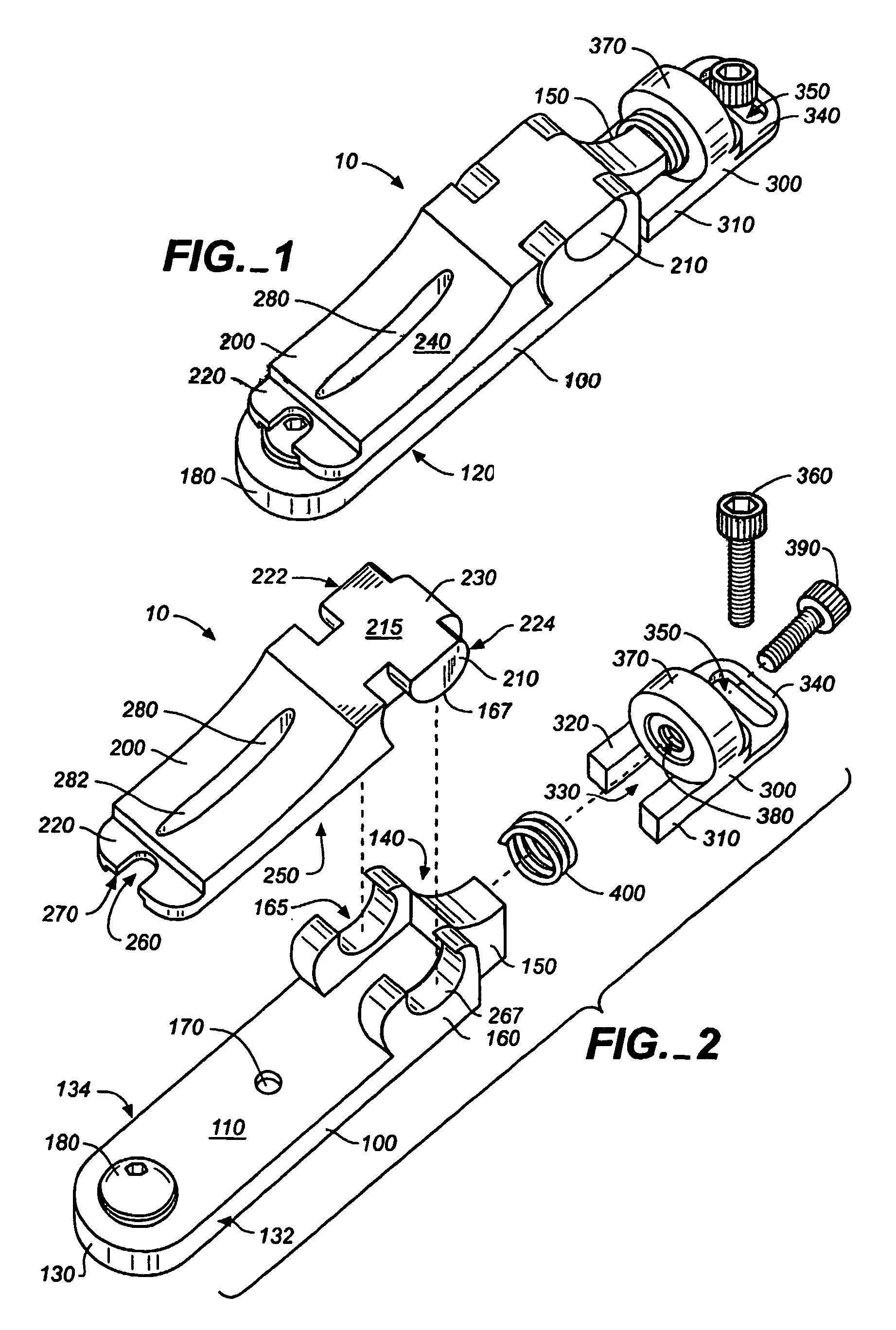
Adjustable bridge system for a stringed instrument
Owner:HANNES ROLAND R
Antenna device with improved isolation characteristic
ActiveUS7271777B2Small sizeFavorable isolationAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsEngineeringGround line
A pair of radiating slots open in a flat metal plate having a square shape to be line-symmetrically arranged with respect to a symmetry axis, and power feeding lines and ground lines are provided at power feeding positions of the respective radiating slots. The respective radiating slots have first slot portions and second slot portions that contact at 45 degrees and linearly extend, respectively. Both the radiating slots are arranged in a back-to-back manner that edges of the first slot portions face each other, and the second slot portions extend in a direction to be separated from each other along two sides of the flat metal plate. Further, a polarization direction of an electric wave to be generated by one radiating slot and a polarization direction of an electric wave to be generated by the other radiating slot are set to be perpendicular to each other.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Earpiece
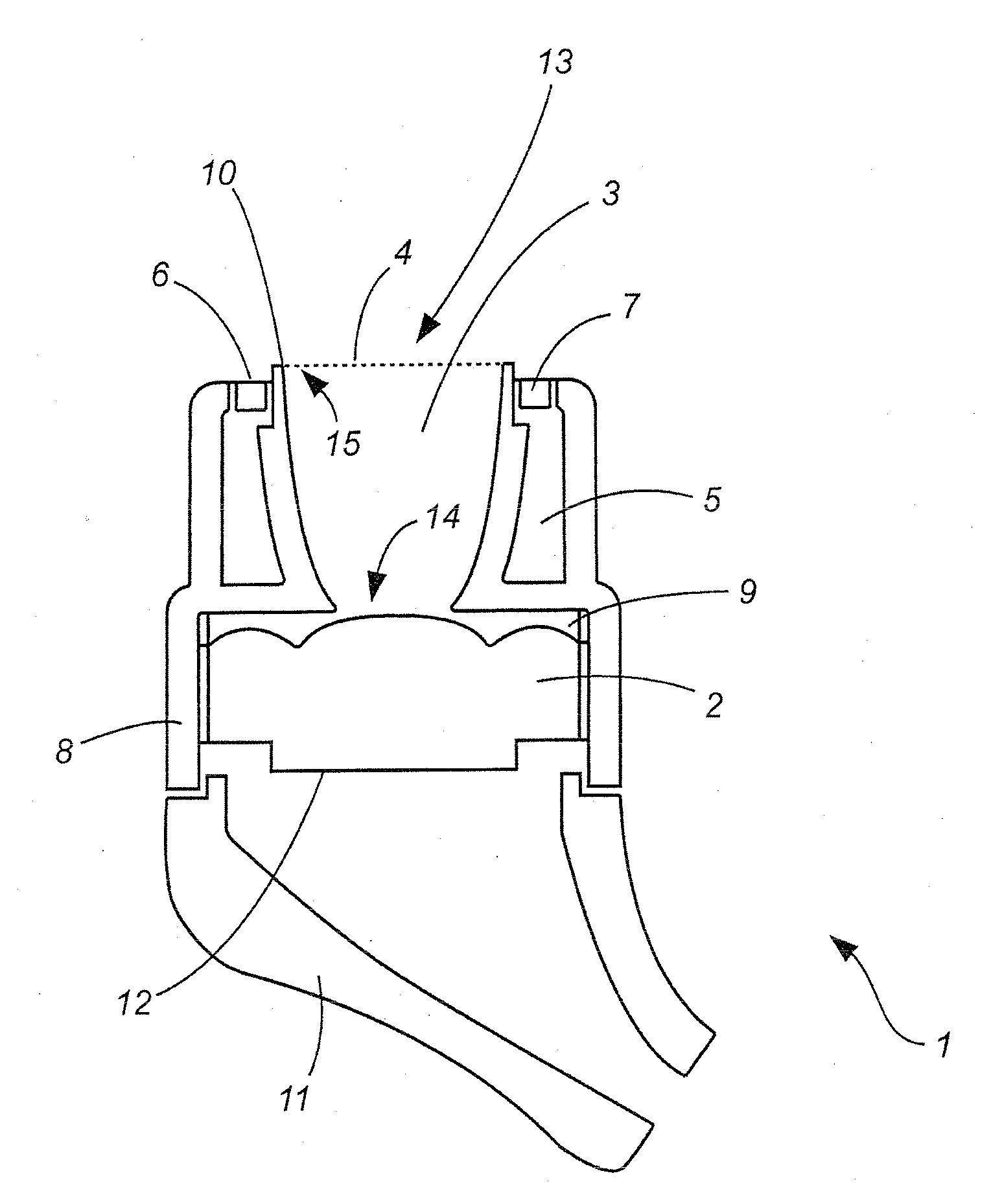
ActiveUS20110311070A1Improve sound qualityReduce an excessive increase in ear canal resonanceIn the ear hearing aidsIntra aural earpiecesTransducerEngineering
There is provided an earpiece having a first side towards the ear, an acoustic transducer for outputting a sound signal and a sound guide element having a first end and a second end. In that case the first end faces the acoustic transducer and the second end faces the first end of the (ear canal) earpiece. The sound guide element serves for guiding the sound signal to an ear canal of a user. The sound guide element has a first opening at its second end. The (ear canal) earpiece also has at least one volume element which delimits a volume and which has at least one second opening for connecting the volume to the first end of the ear canal earpiece.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
Dry powder inhalers, related blister devices, and associated methods of dispensing dry powder substances and fabricating blister packages
InactiveUS20050126569A1Limit amount of resistanceMore hygienic productRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsElastomerBlisters
The present invention includes dry powder inhalers for dispensing and / or holding inhalant formulated dry powder substances and associated fabrication and dispensing methods that can employ an amplitude modulated non-linear signal comprising a plurality of superimposed frequencies, the frequencies corresponding to a priori flow characteristic frequencies of the dry powder being dispensed. The present invention also includes pocket-sized inhalers with an elastomeric flexible pivoting cover.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
Omni-directional ultrasonic transducer apparatus and staking method
InactiveUS20020148088A1Good vibesCost effectivePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAdhesiveResonance
A transducer apparatus is disclosed having a spool member with a body portion and first and second elevated regions formed on the body portion. A PVDF film surrounds the spool member, the film including an inner surface facing the spool member and an outer surface opposite the inner surface. The film as surrounding the spool member has a predetermined frequency of resonance. Lateral ends of the film are secured together by a securing material. The securing material is such that the secured ends of the film will have substantially the same resonance frequency as a remainder of the film. The film includes a non-electrode area at a perimeter of the inner surface and an electrode material formed on a remainder of the inner surface. Upon securing the lateral edges of the film together, the securement is at overlapping non-electrode lateral edges of the film. The securing material may be any one of an adhesive in combination with screws or thermally deformable nails, adhesive alone, tape, or ultrasonic welding.
Owner:TODA MINORU +3
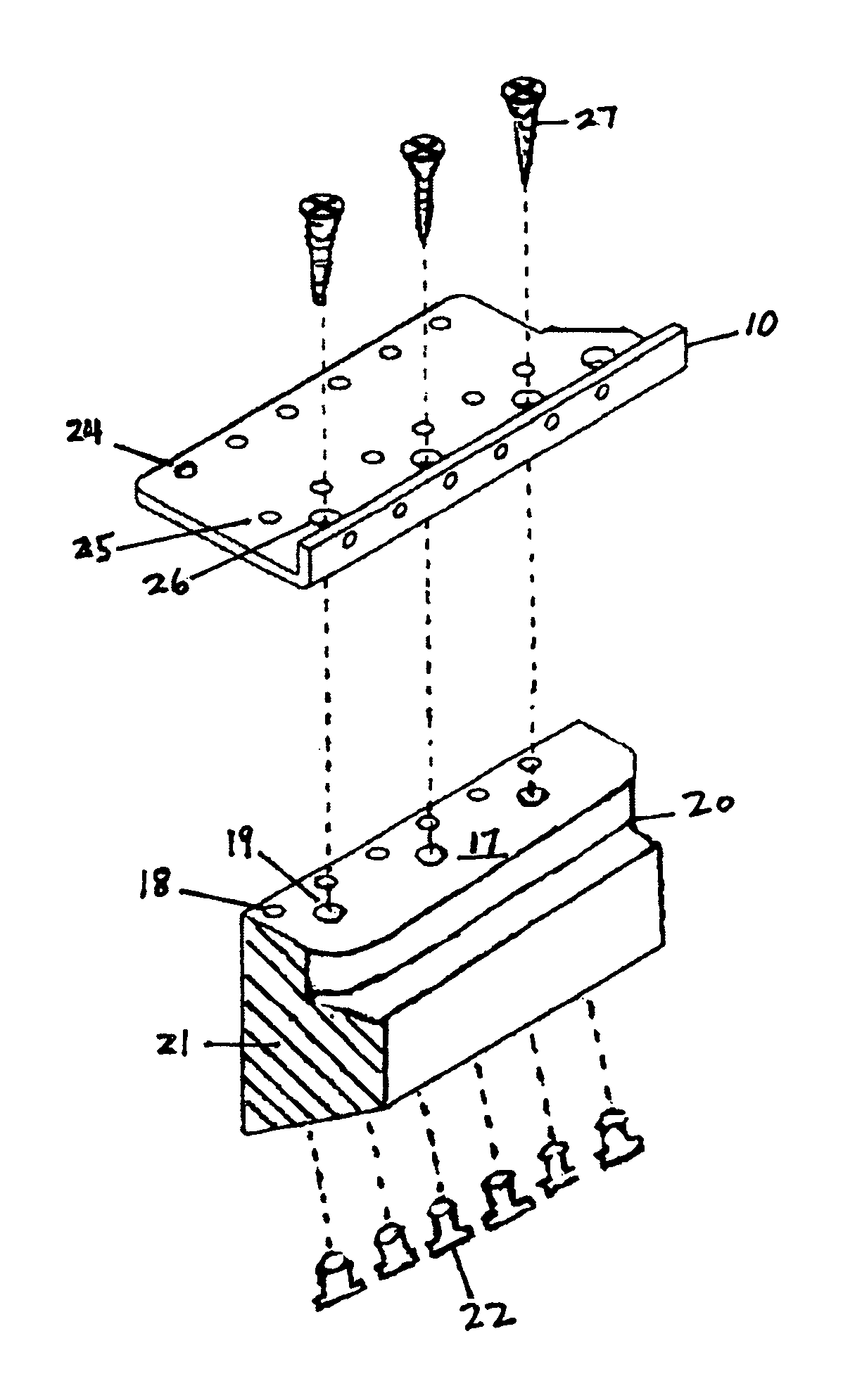
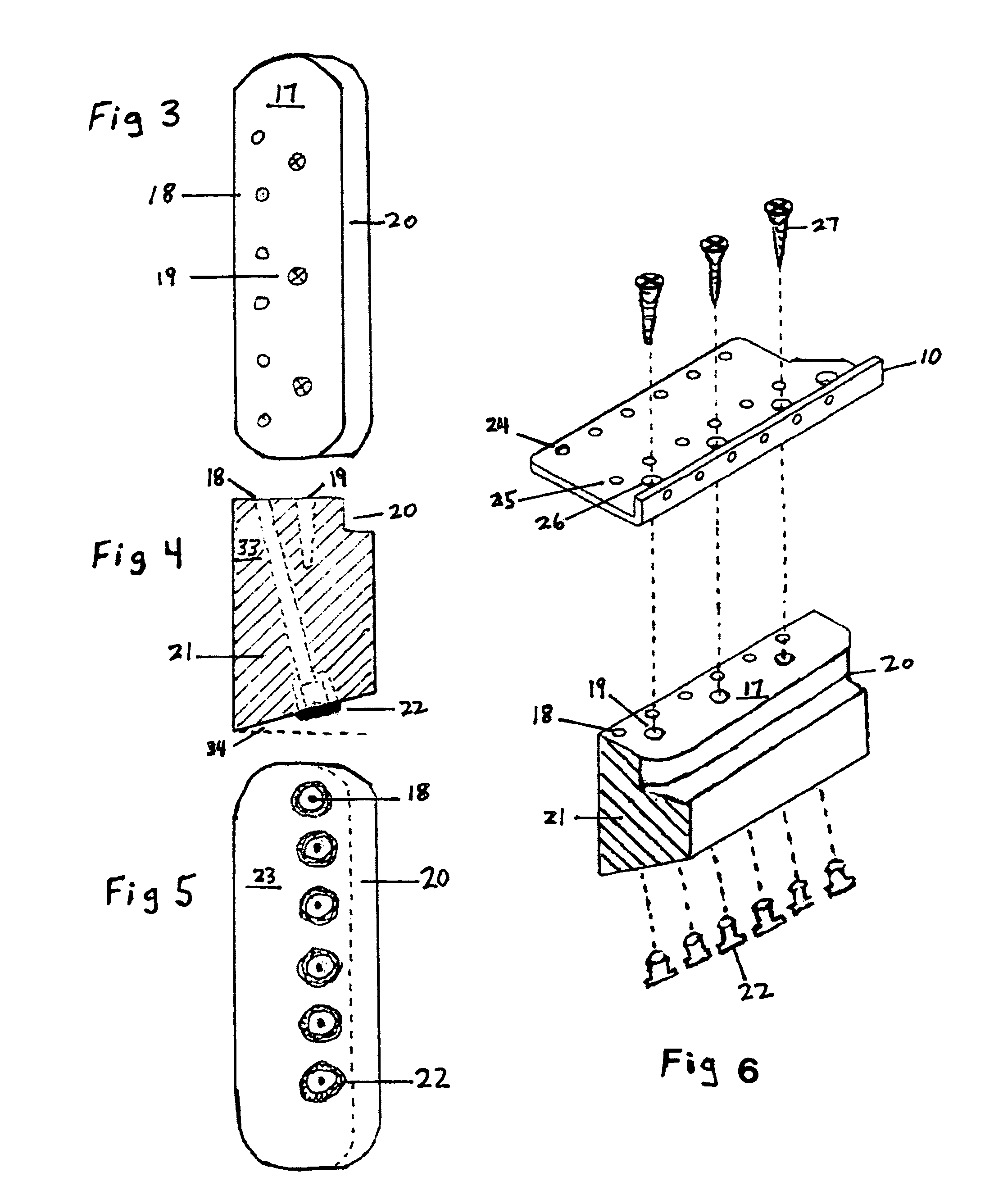
Hardtail converter block for a tremolo equipped guitar
InactiveUS7557282B2Eliminating intonation and tuning problemGood vibesStringed musical instrumentsEngineeringTremolo
A converter block for a Stratocaster.®. style tremolo system that effectively changes it to a hardtail configuration. Players who do not use the tremolo can benefit from the ease and stability in tuning, reduced weight, improved tonal characteristics and the reduction in string breakage that this novel design offers.
Owner:HOLDWAY DAVID ALLAN
Two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and optical reflector using interference between point defects
InactiveUS6996319B2Low refractive indexImprove the level ofLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical reflectionLinear region
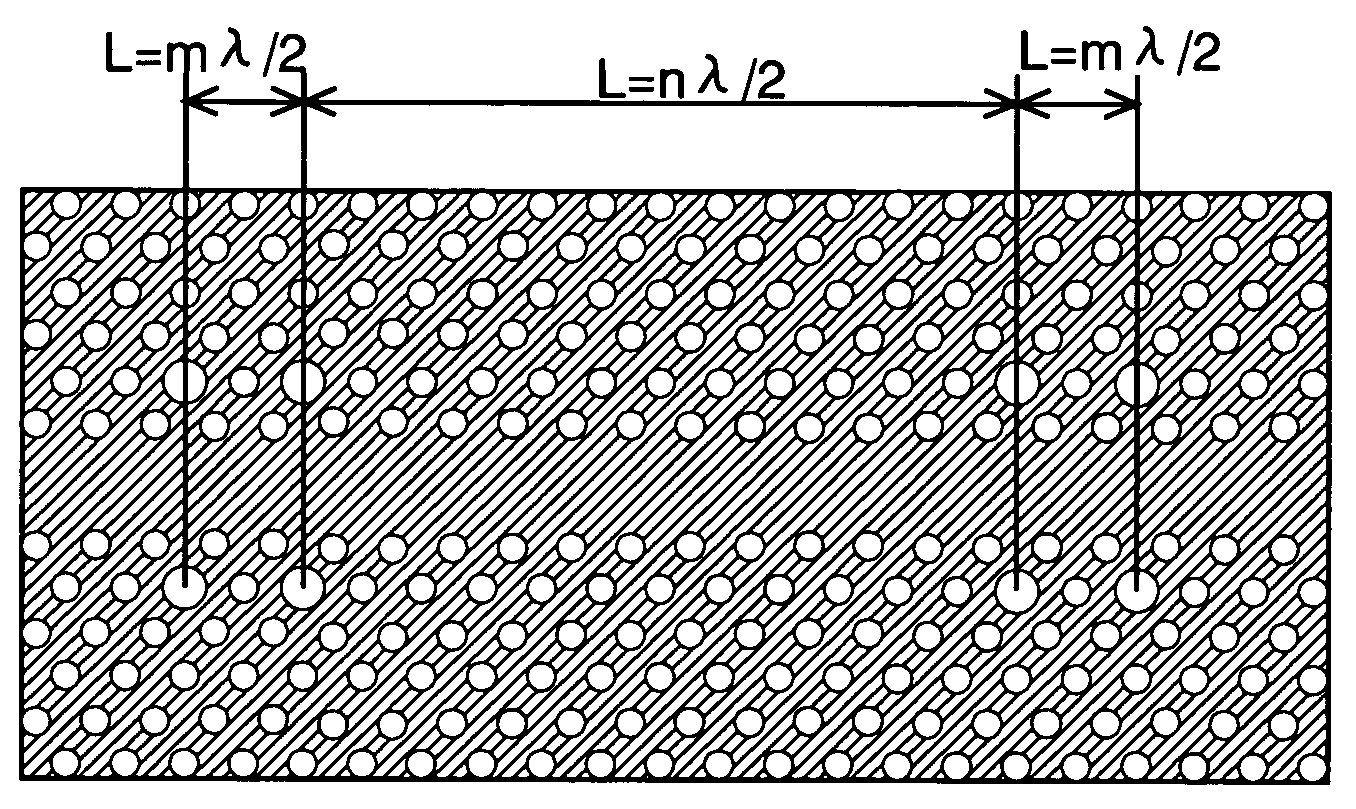
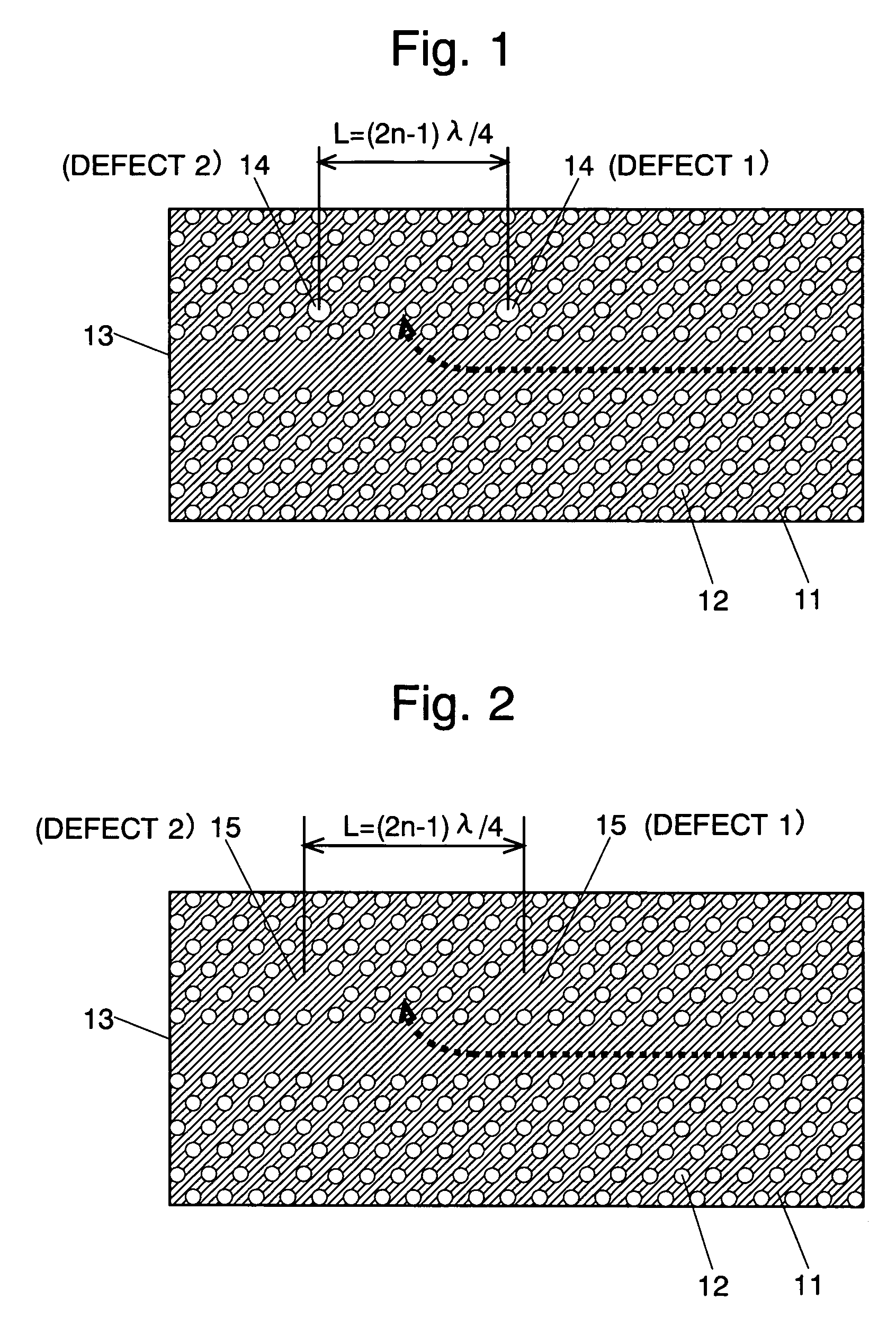
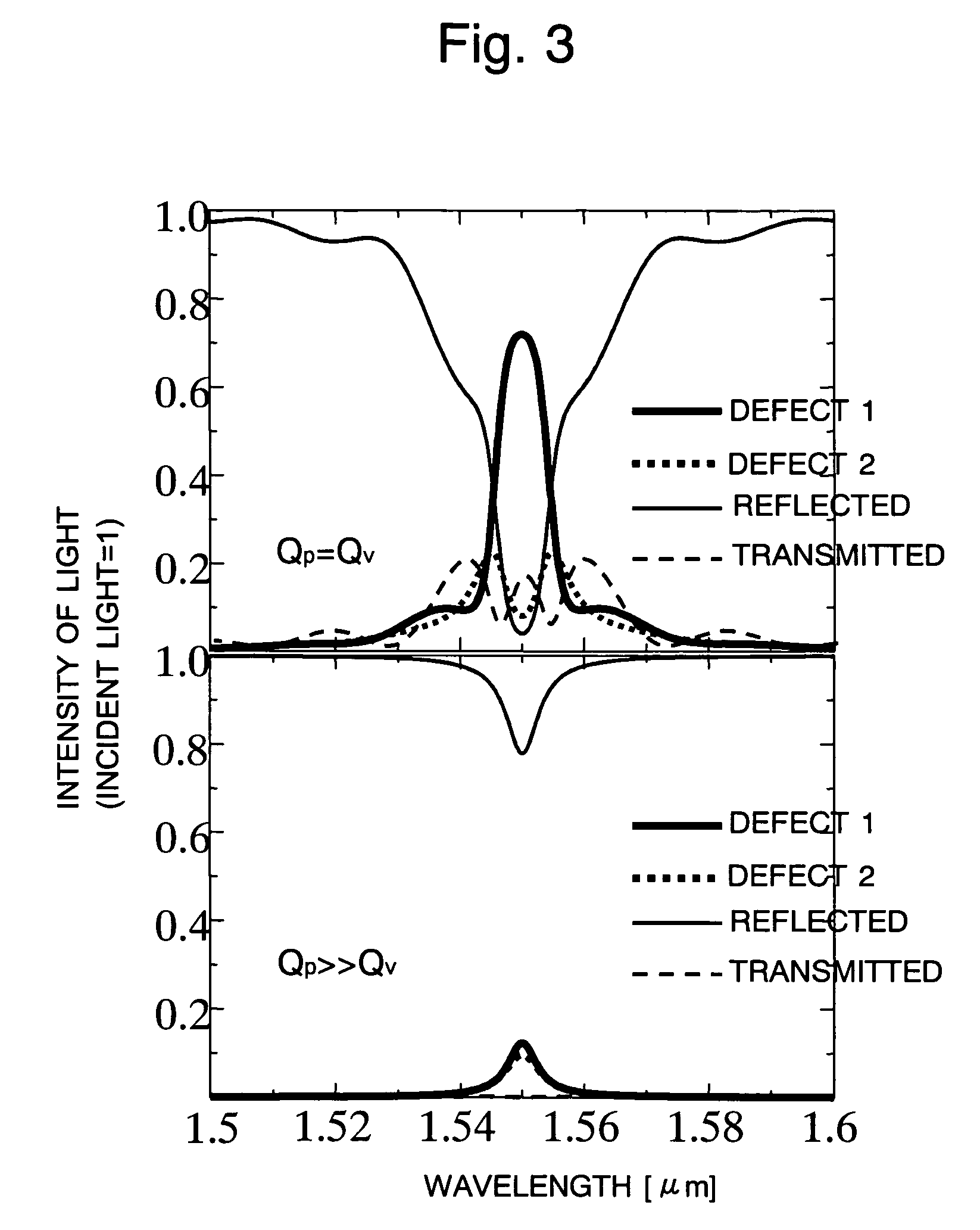
The present invention provides a two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and reflector having high light-extracting efficiency. A two-dimensional photonic crystal consisting of a slab-shaped body is created by periodically arranging holes having a refractive index different from that of the body. A waveguide is formed by providing a linear zone where no hole is bored. Two acceptor type point defects are formed by enlarging two holes spaced apart from each other by a distance L in the longitudinal direction of the waveguide. An appropriate selection of the distance L suppresses or increases the reflection and transmission of light at the point defects, allowing an efficient extraction of light resonating at the point defects. This allows the body to be used as an optical resonator for producing a resonance of light between the two point defects or optical reflector for reflecting light at the two point defects.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Adjustable bridge system for a stringed instrument
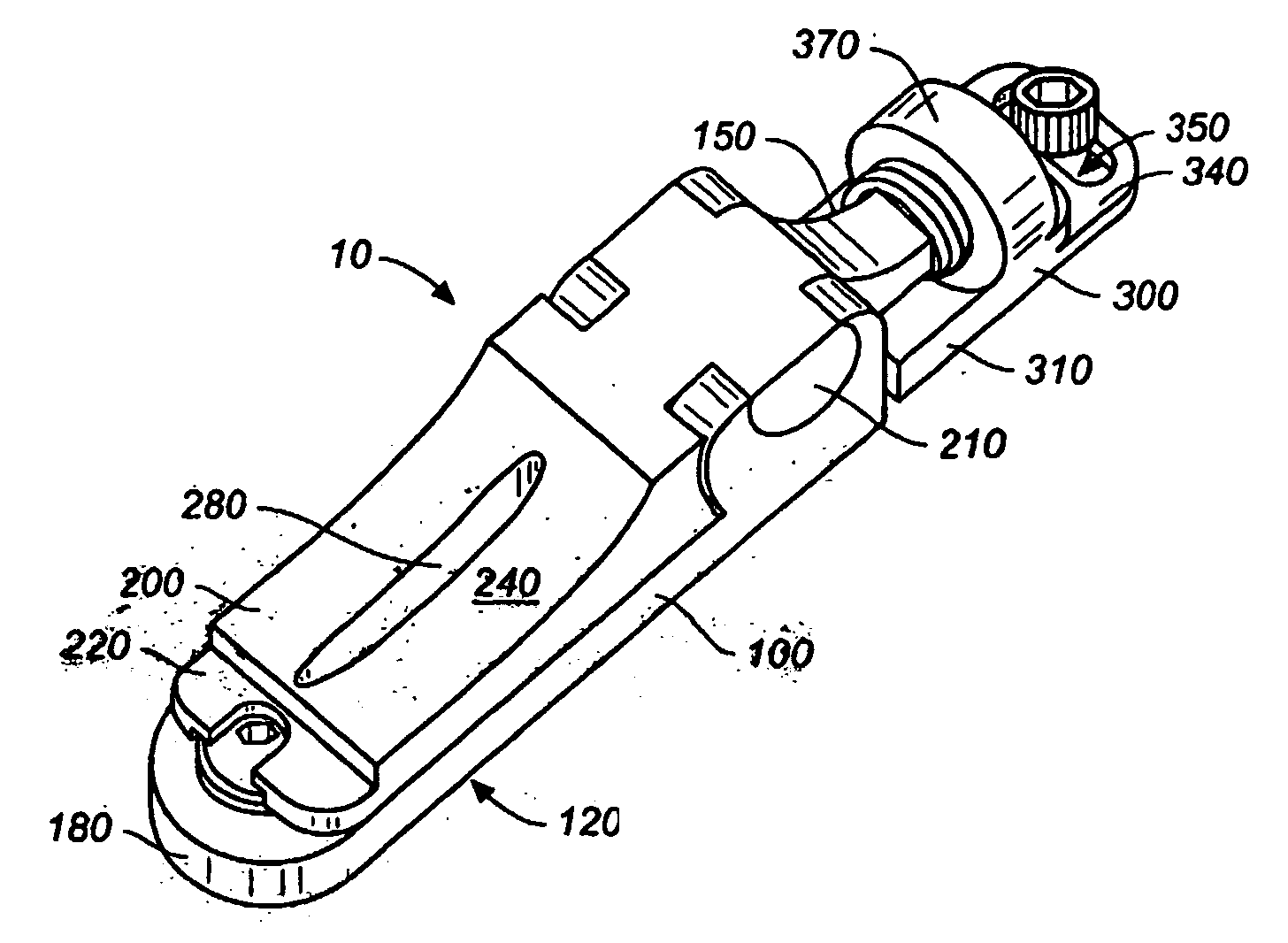
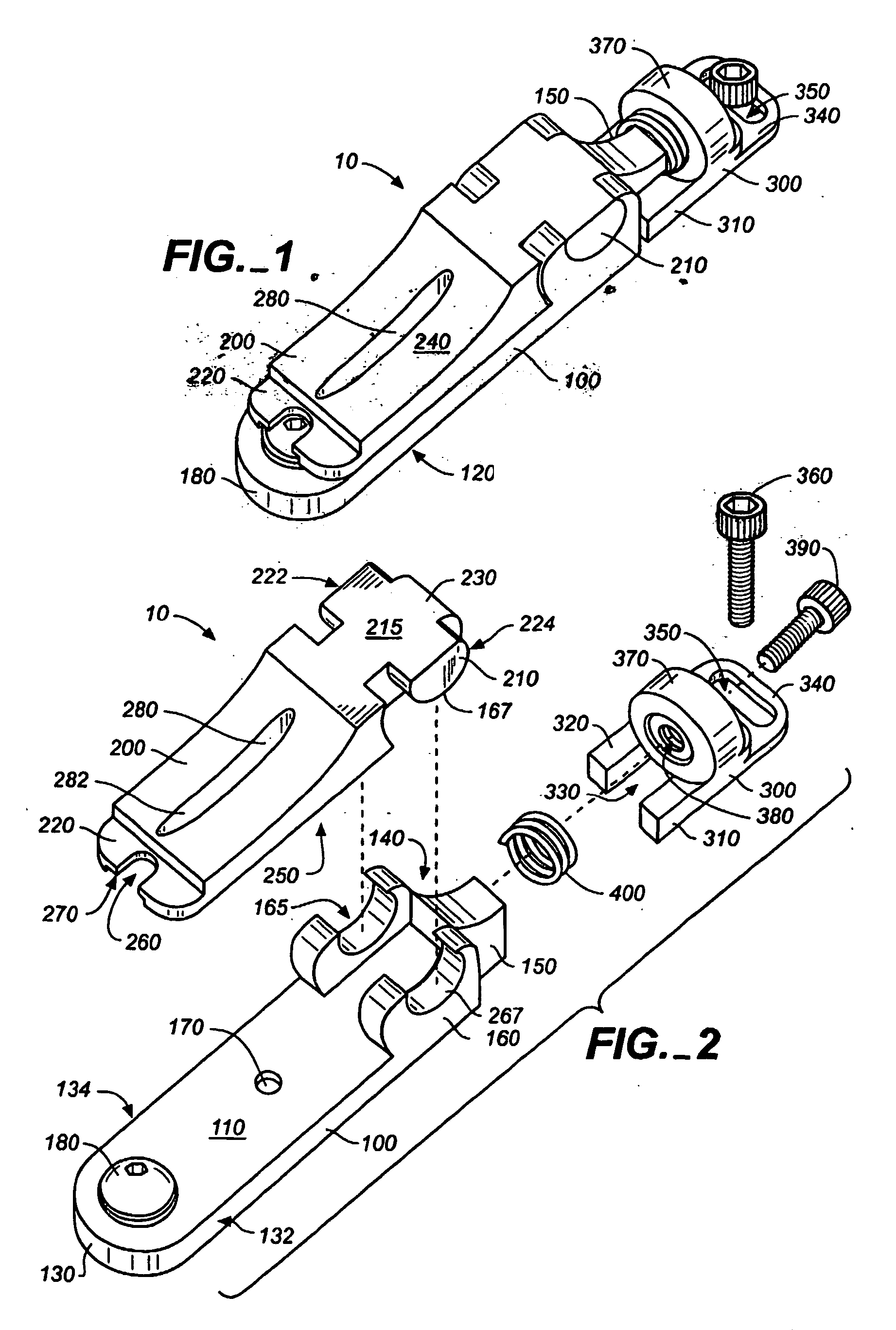
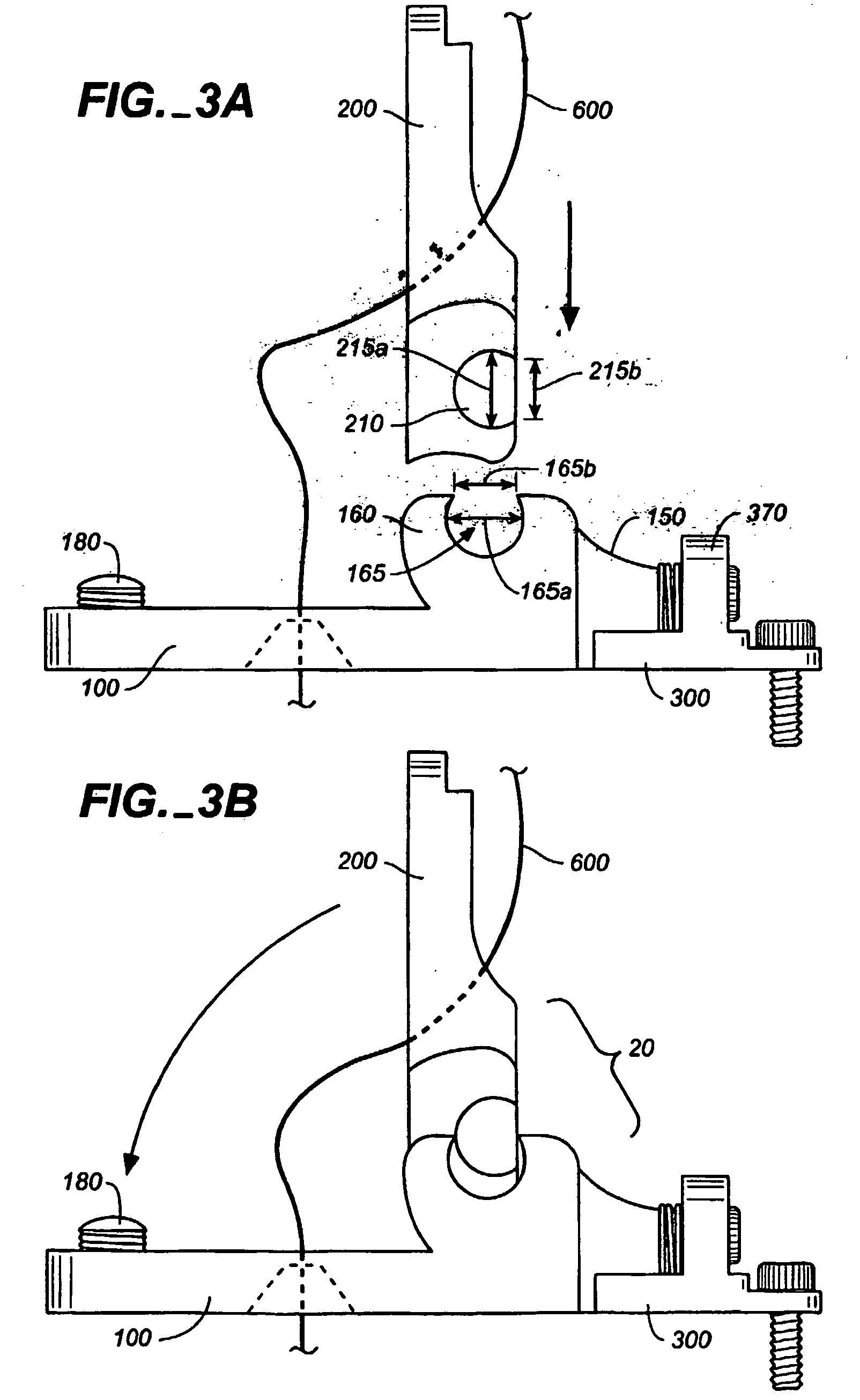
A bridge system (10) for a stringed instrument having means to adjust independent bridge elements longitudinally, vertically, and laterally. The bridge (10) elements include a unit (20), a control anchor (300) having a ring (340) and bolted to the instrument body through an elongate opening in the ring (340). A longitudinal adjustment screw (390) connects the control anchor (300) to the saddle / base unit (20), and the structural base (100) includes a height adjustment screw (180) that engages the saddle (200). Multidimensional adjustments can be made with a single tool.
Owner:HANNES ROLAND R
Headphone structure for extending and enhancing resonance
ActiveUS20200228890A1Extending and enhancing resonanceIncrease stroke displacementSupra/circum aural earpiecesFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsHeadphonesLoudspeaker
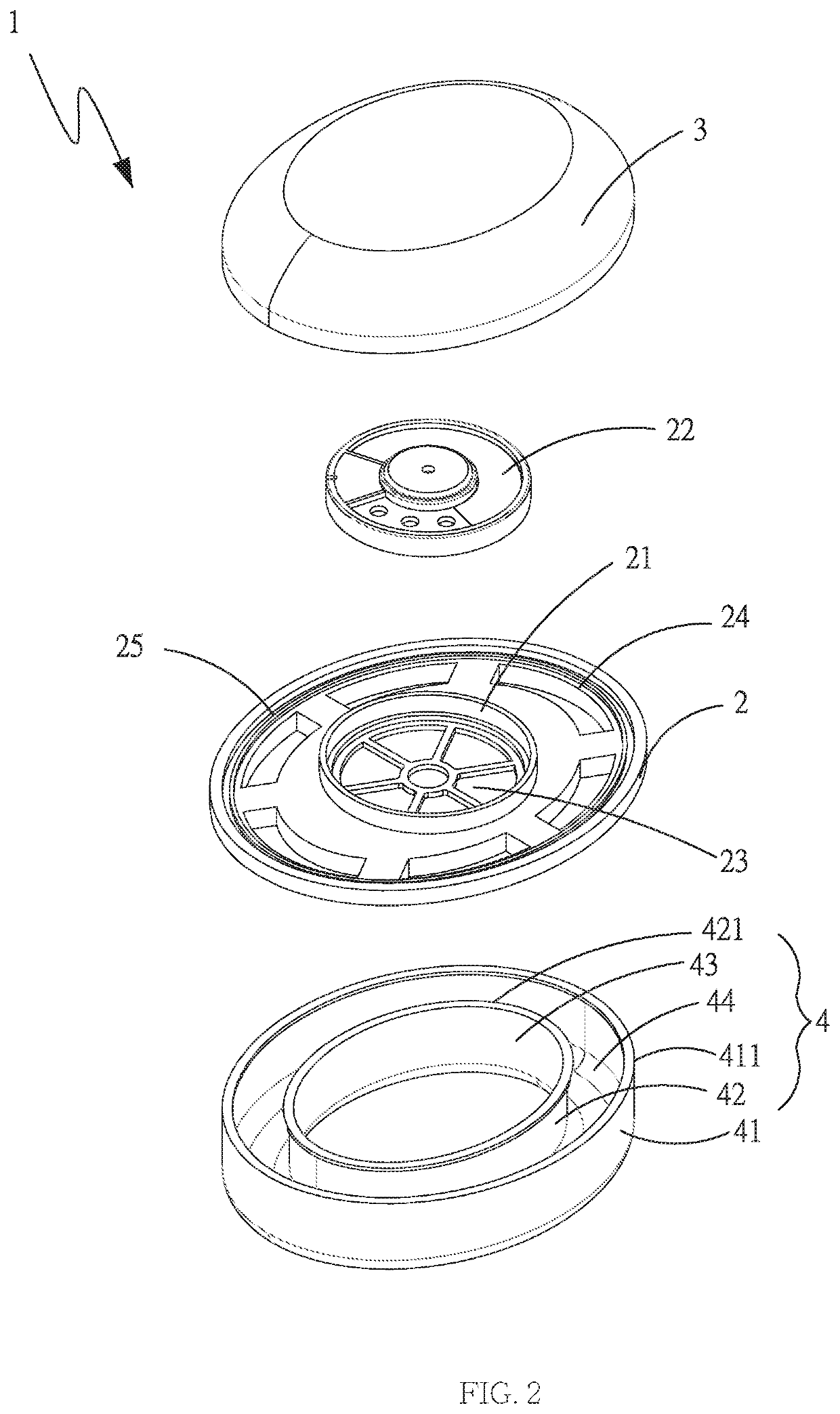
The present invention provides a headphone structure for extending and enhancing resonance comprising a main body, a cover and a shield. The main body has an accommodating portion for accommodating a speaker, a plurality of master sound guiding holes are penetrated in the accommodating portion and a plurality of side sound guiding holes are penetrated in the main body. A rear cavity space is formed between the cover and the main body, and the shield forms a rear cavity extending space to communicate with the side sound guiding holes and the rear cavity space. Thereby, the headphone structure can reduce air damping through the rear cavity extending space communicating with the rear cavity space, so as to achieve effects of increasing stroke displacement of the speaker and reducing air suppression of sound.
Owner:EVGA CORPORATION
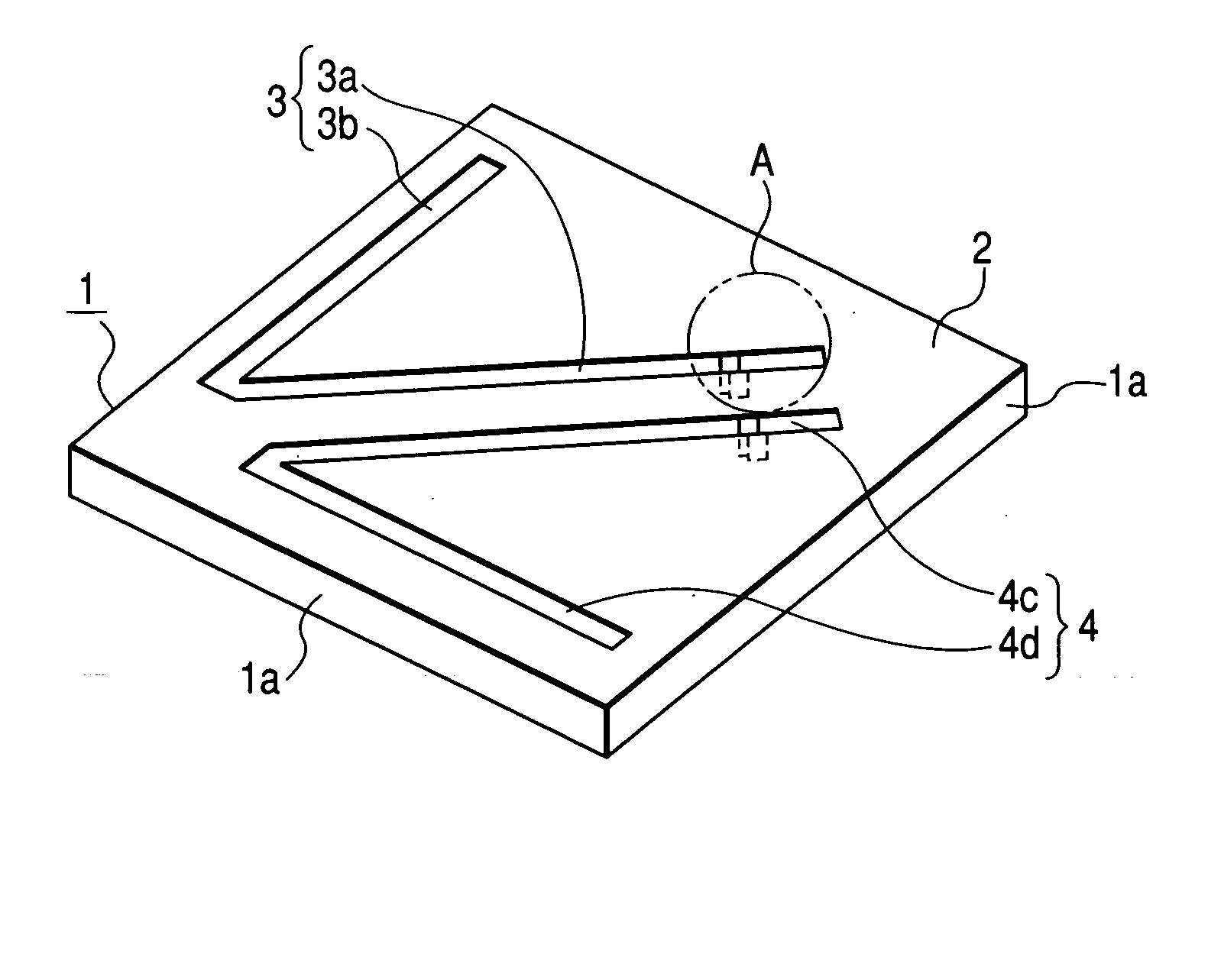
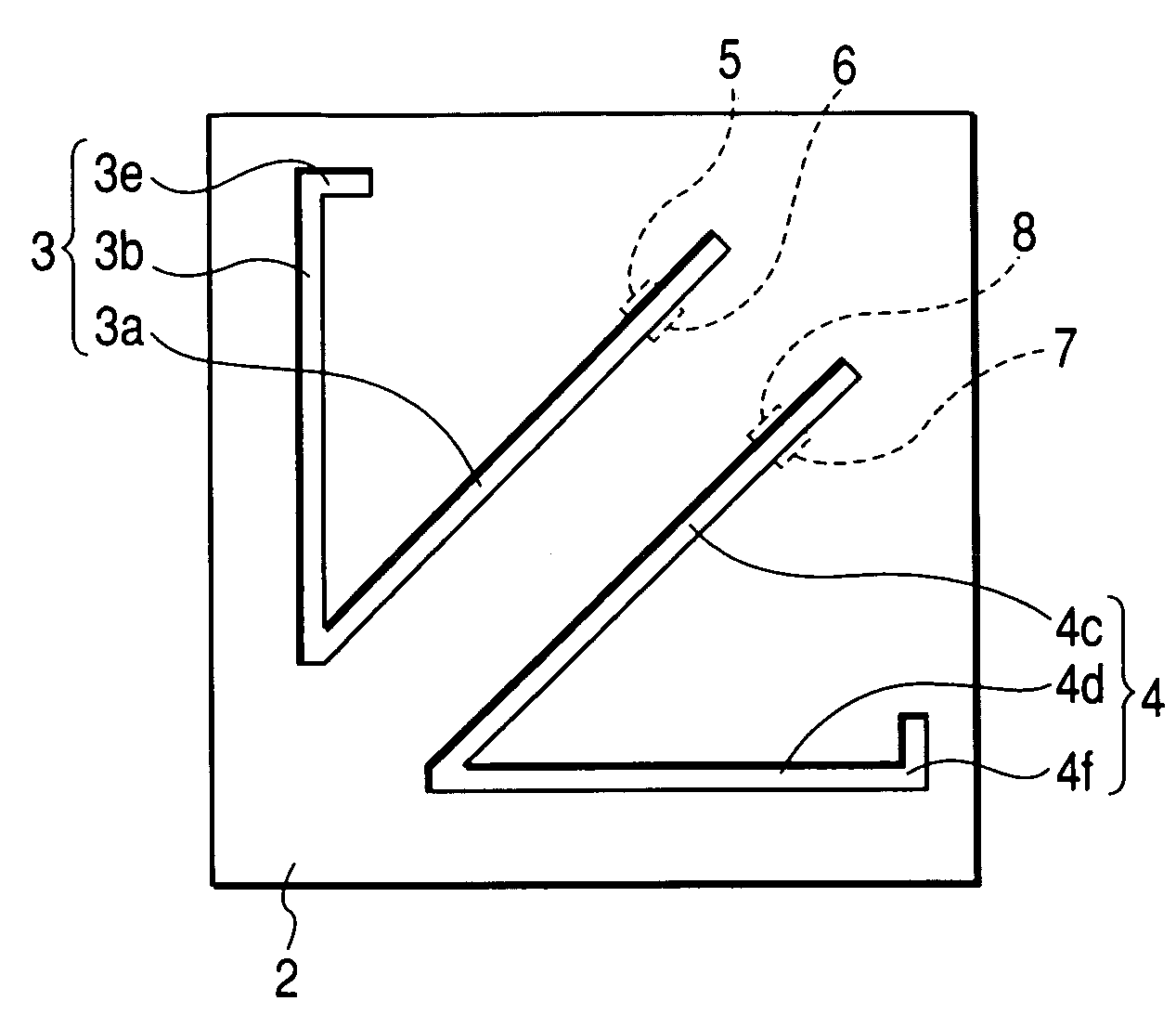
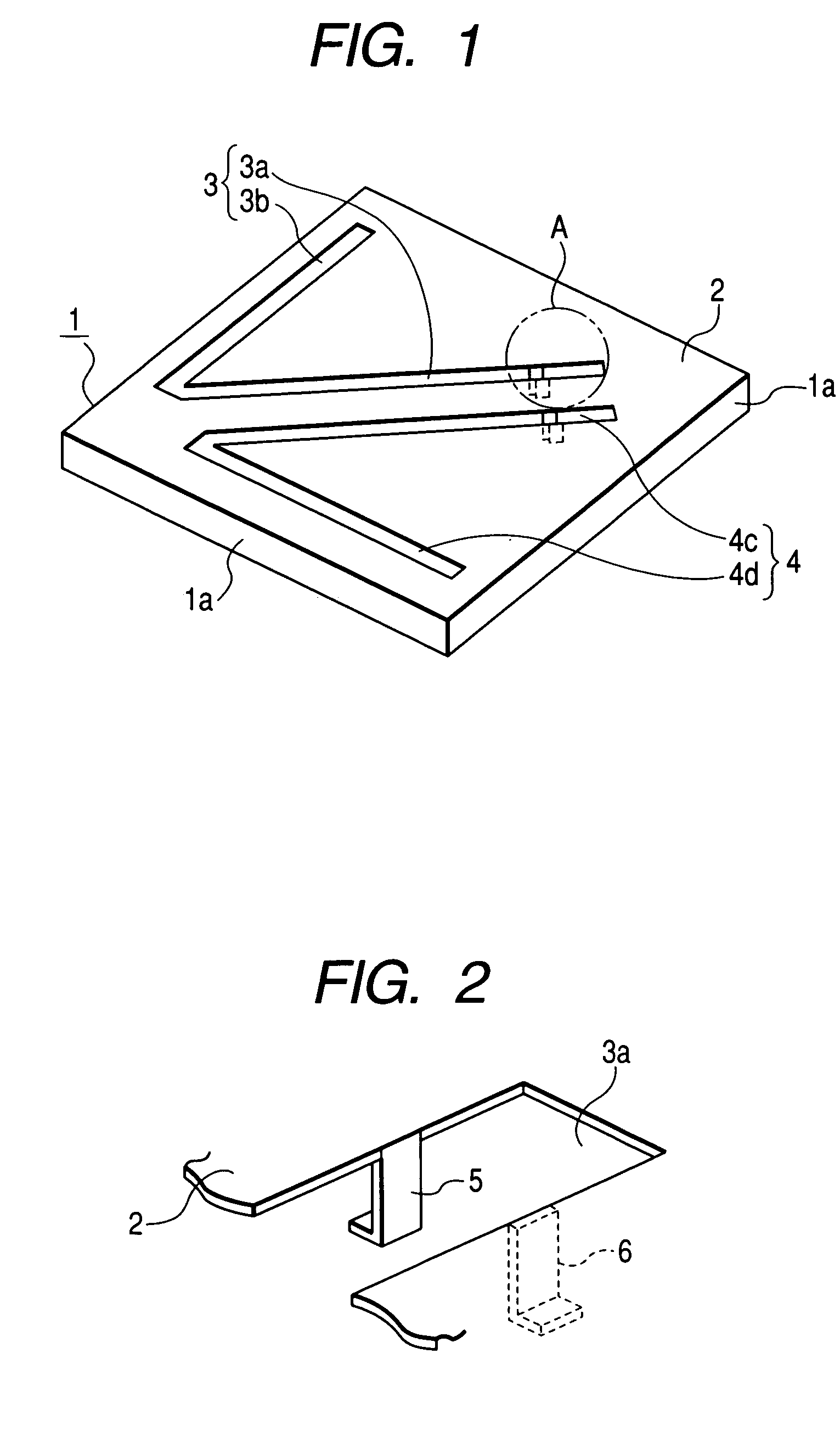
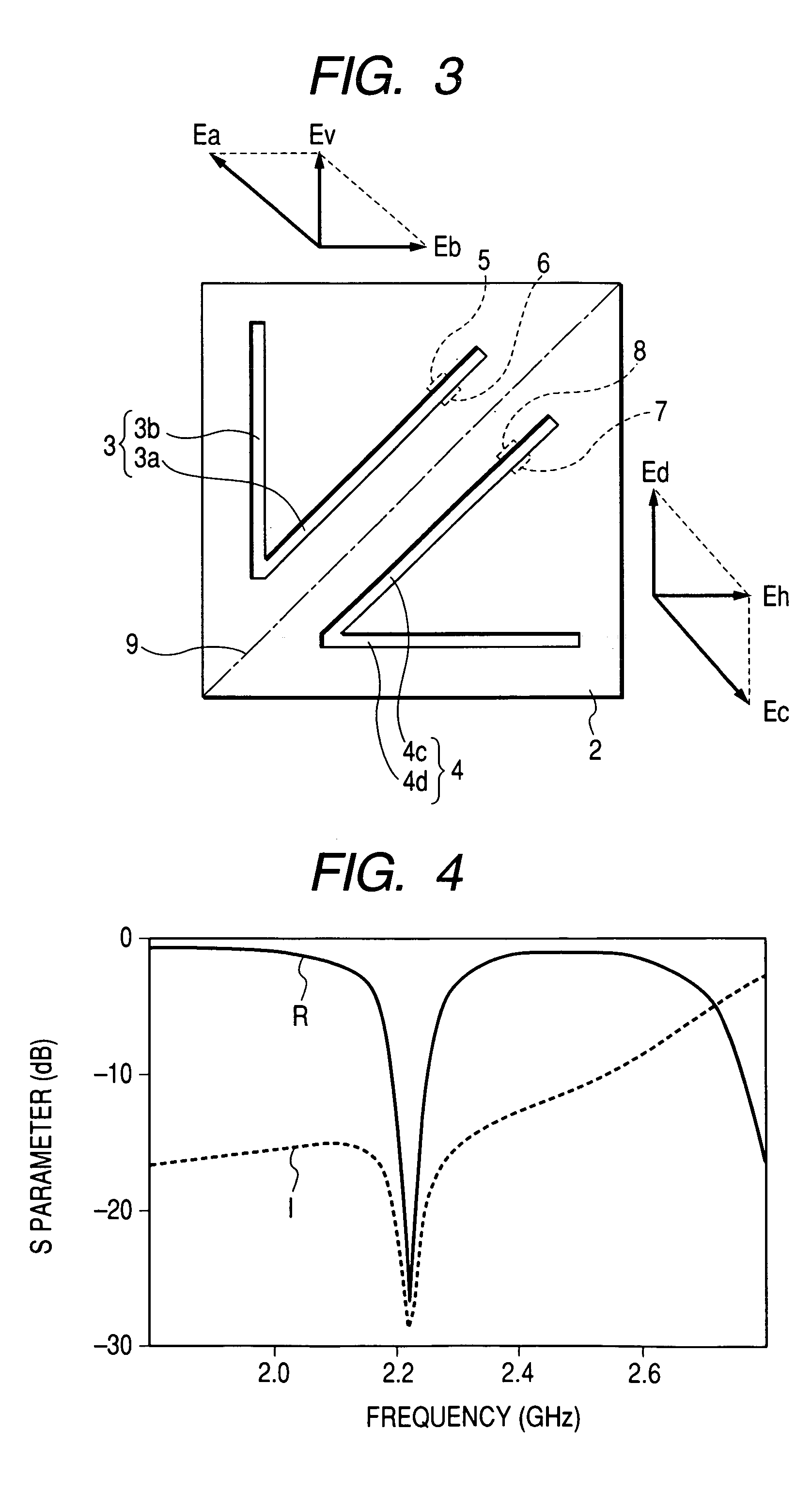
Antenna structure
ActiveUS20180342808A1Good vibesLower overall heightSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPlanar inverted f antennaResonance
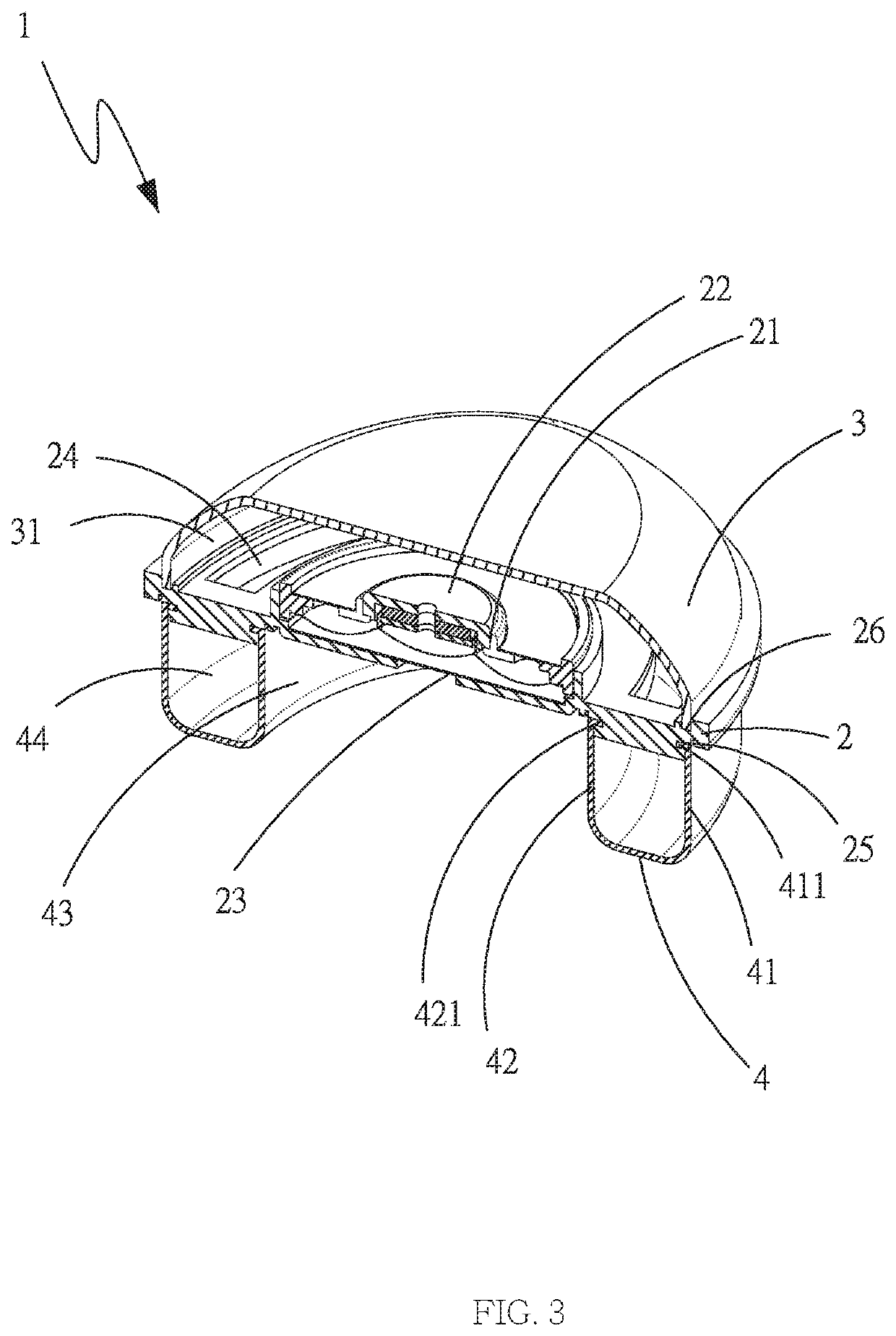
An antenna structure (10) includes an antenna feed-in element (1), a first antenna trace element (2), a second antenna trace element (3), a supporting element (4), a grounded-short-circuit element (5), a third antenna trace element (6) and a fourth antenna trace element (7). The first antenna trace element (2), the second antenna trace element (3), the third antenna trace element (6) and the fourth antenna trace element (7) which have vertical segments in different lengths form a multi-trace planar inverted-F antenna to obtain the best bandwidth covering the full band, so that the height of the antenna structure (10) is lower, the length is shorter and the structure is denser. The impedance matching of the antenna structure (10) is controlled easily. No external matching element is required. With the multi-trace and grounded-short-circuit design of the antenna structure (10), the better resonance in the LTE full band is obtained.
Owner:TAOGLAS GROUP HLDG LTD
Resonance enhanced rotary drilling
ActiveUS9068400B2Downhole apparatus more compactImprove acceleration performanceDrilling drivesBorehole drivesResonanceClosed loop
Owner:ITI SCOTLAND
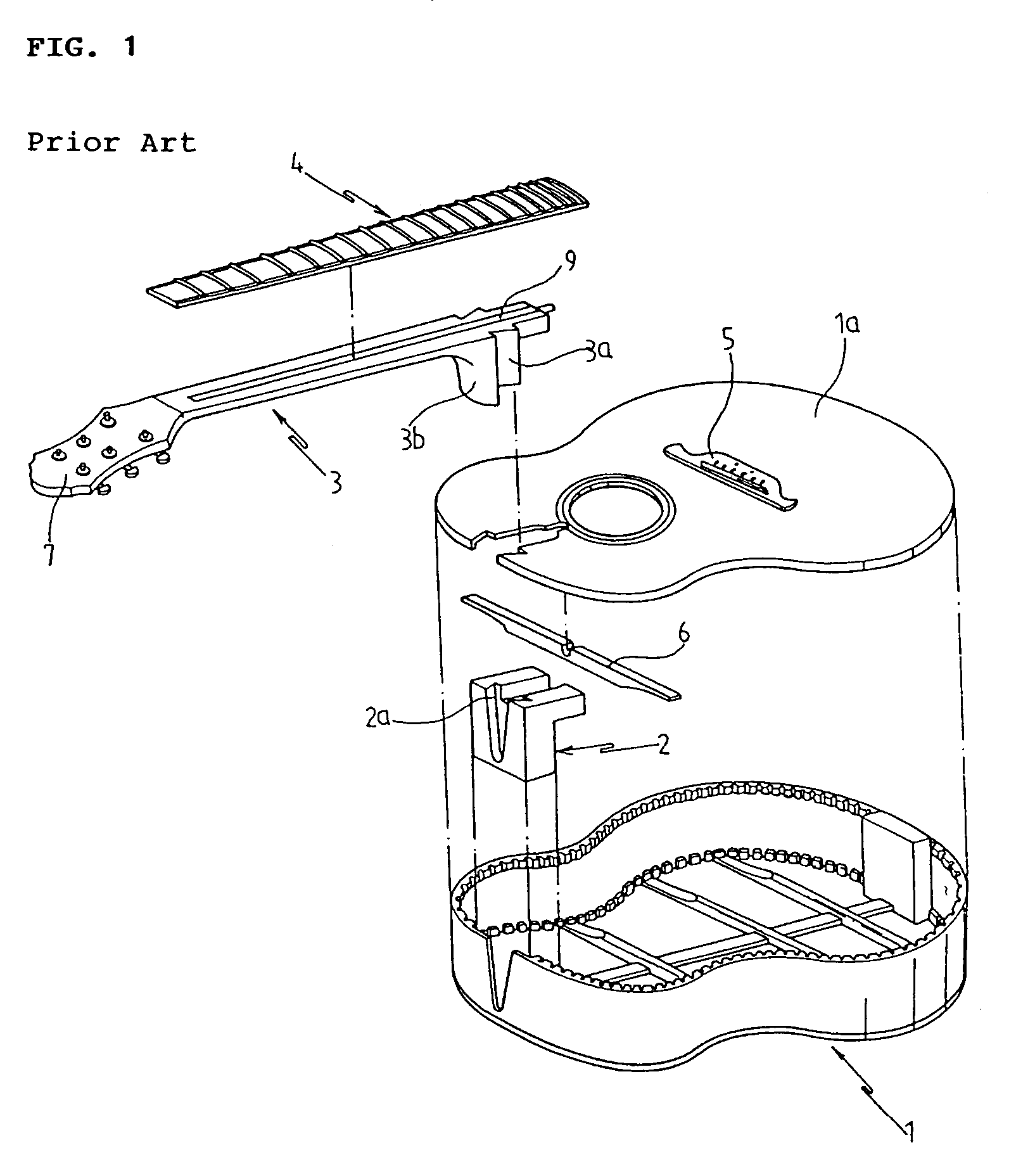
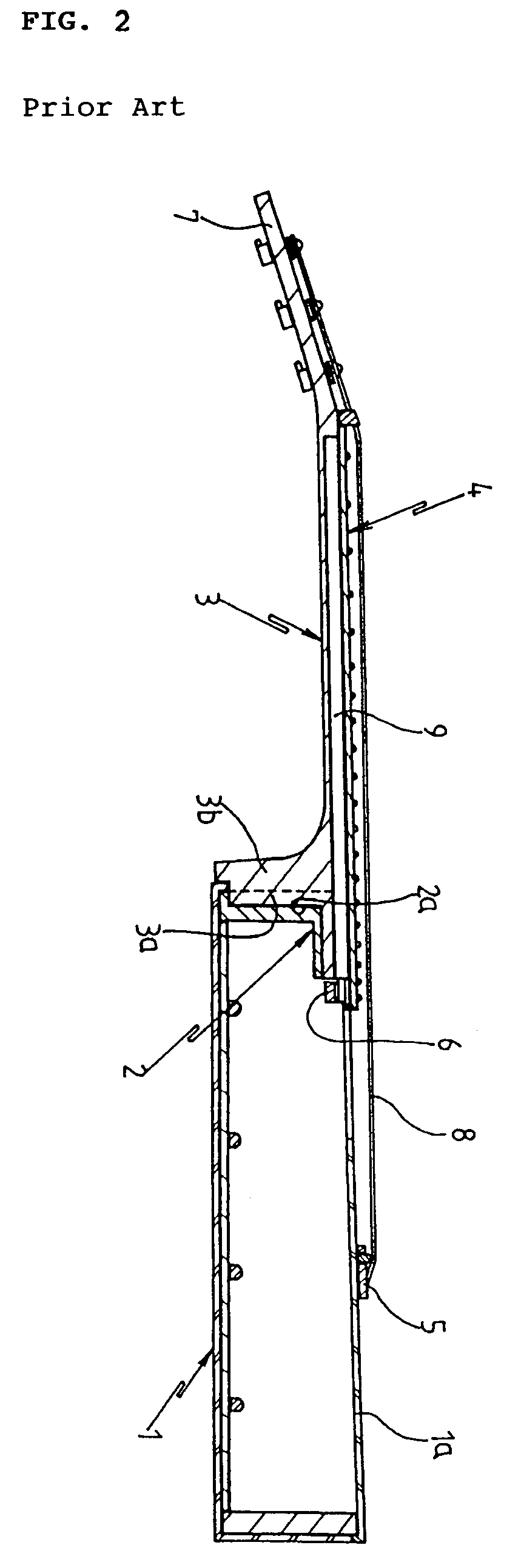
Brace bar for sound board of guitar
Disclosed is a brace bar attached to an inner surface of a sound board of a guitar to prevent the sound board from being distorted, which has a modified shape to improve the flexibility of the sound board while maintaining the strength of the sound board, thus improving the resonance of the sound board and reducing a weight of the sound board. The brace bar includes a narrow portion having a cross-section with a profile of which at least one side extends vertically upward to a position of a predetermined height, thus forming a lower base part, and is bent inward at the position toward a center of the brace bar, and, thereafter, extends upward while being inclined at a predetermined inclination angle to form a tapered upper part.
Owner:SUNGEUM MUSIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com