Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Reduce sensor cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
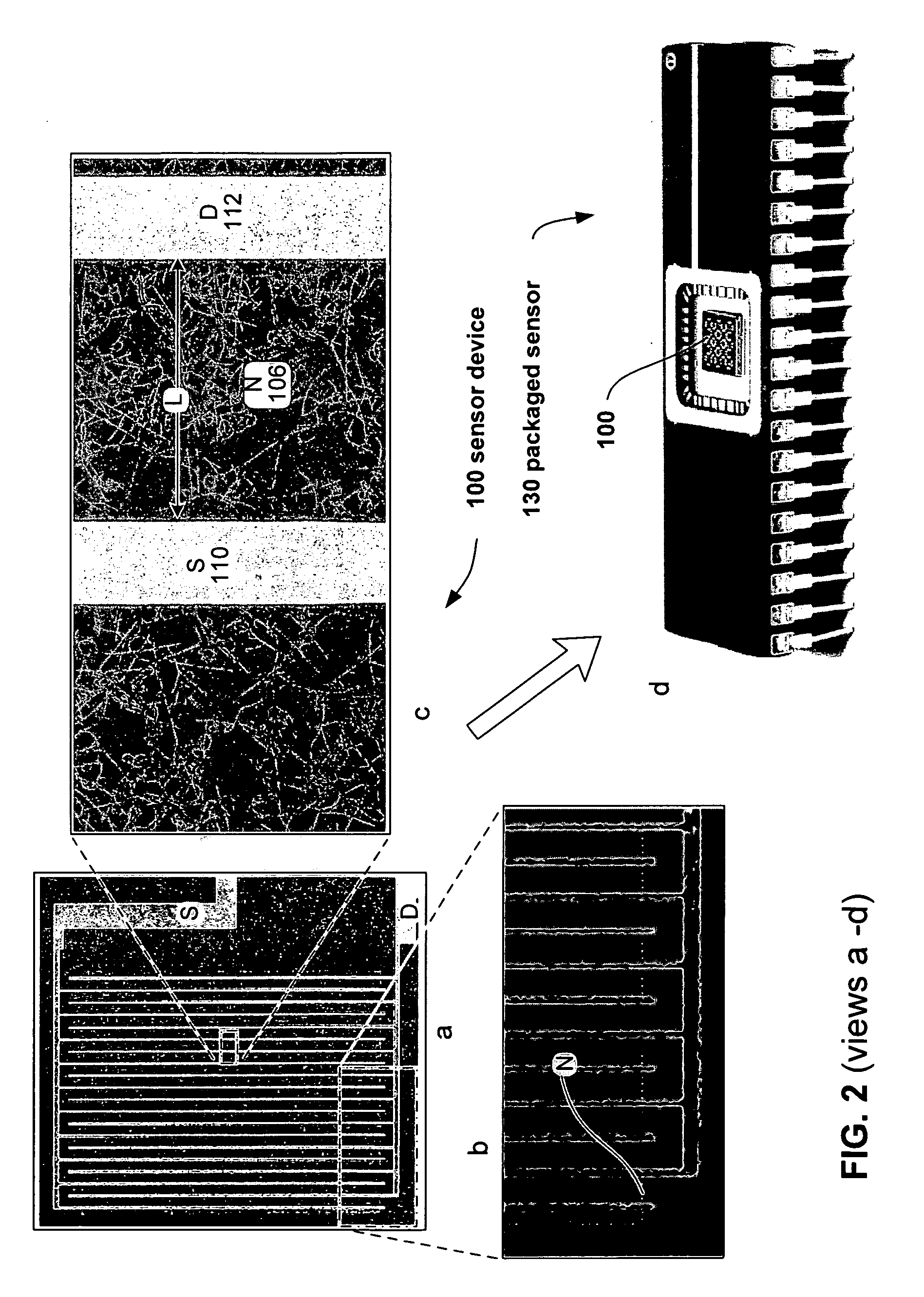
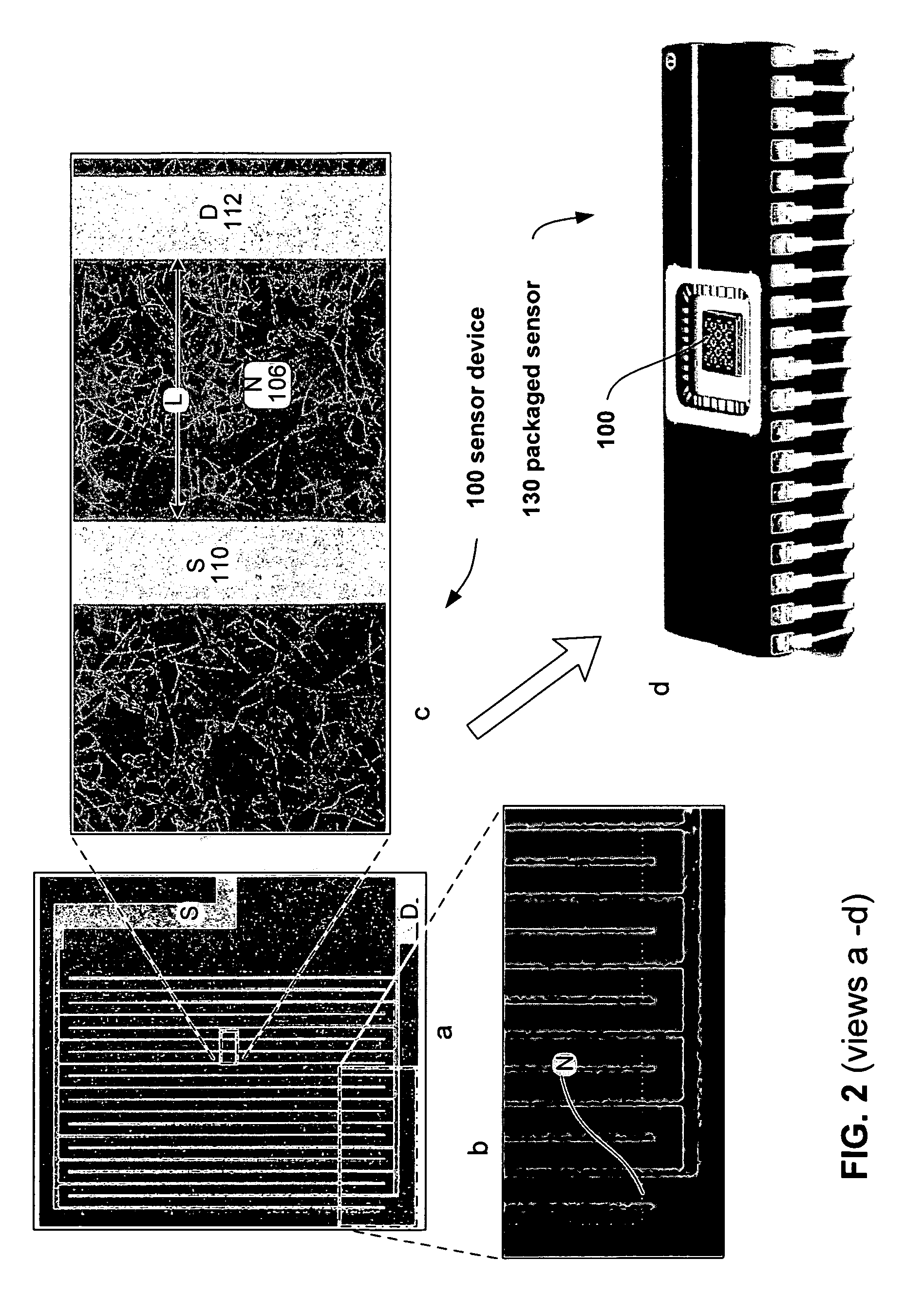
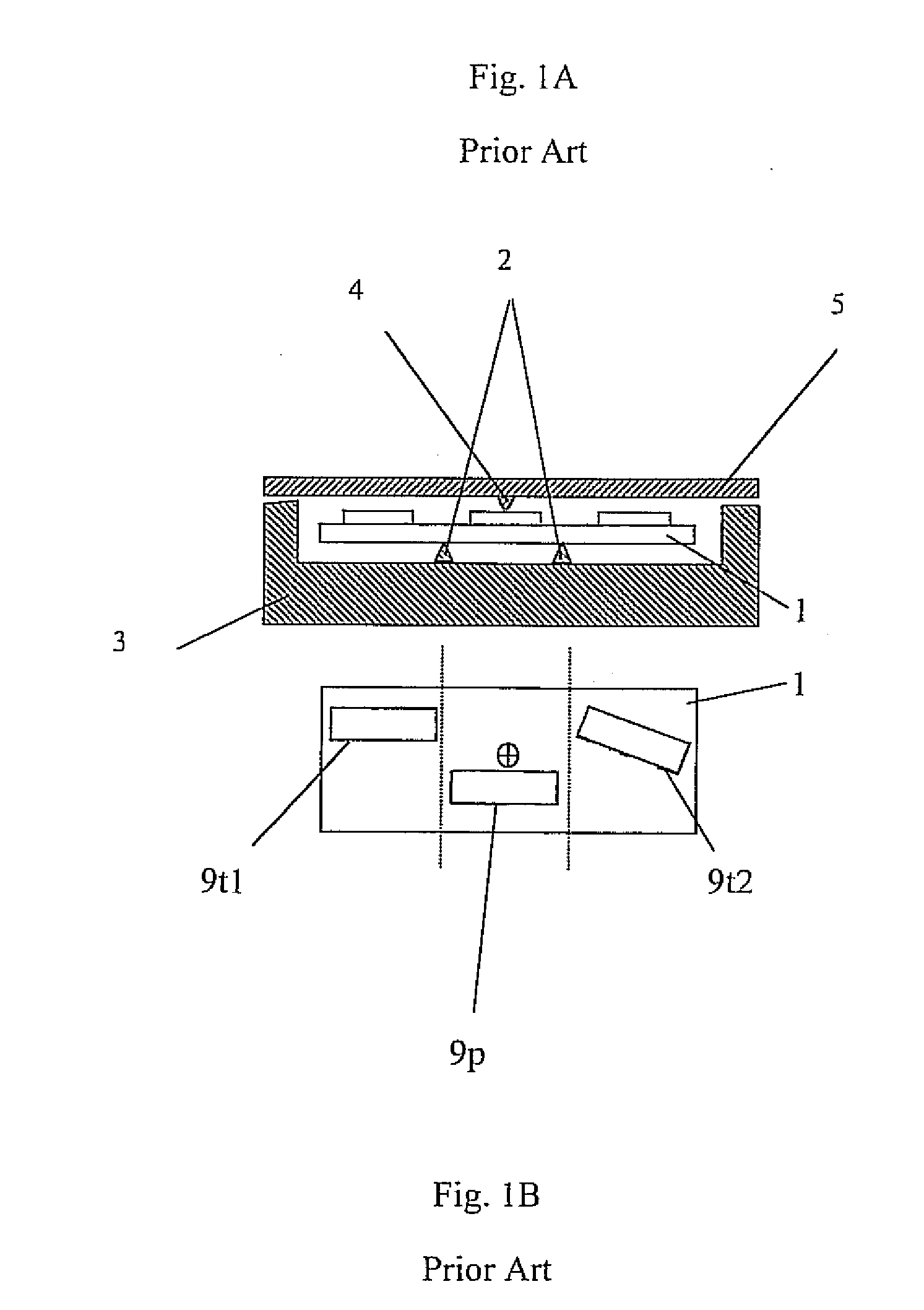
Sensor having a thin-film inhibition layer, nitric oxide converter and monitor
ActiveUS20080221806A1High sensitivityLarge dynamic rangeMaterial nanotechnologyTemperatue controlDiseaseVolatiles
Sensors and detection systems suitable for measuring analytes, such as biomolecule, organic and inorganic species, including environmentally and medically relevant volatiles and gases, such as NO, NO2, CO2, NH3, H2, CO and the like, are provided. Certain embodiments of nanostructured sensor systems are configured for measurement of medically important gases in breath. Applications include the measurement of endogenous nitric oxide (NO) in breath, such as for the monitoring or diagnosis of asthma and other pulmonary conditions.
Owner:NANOMIX
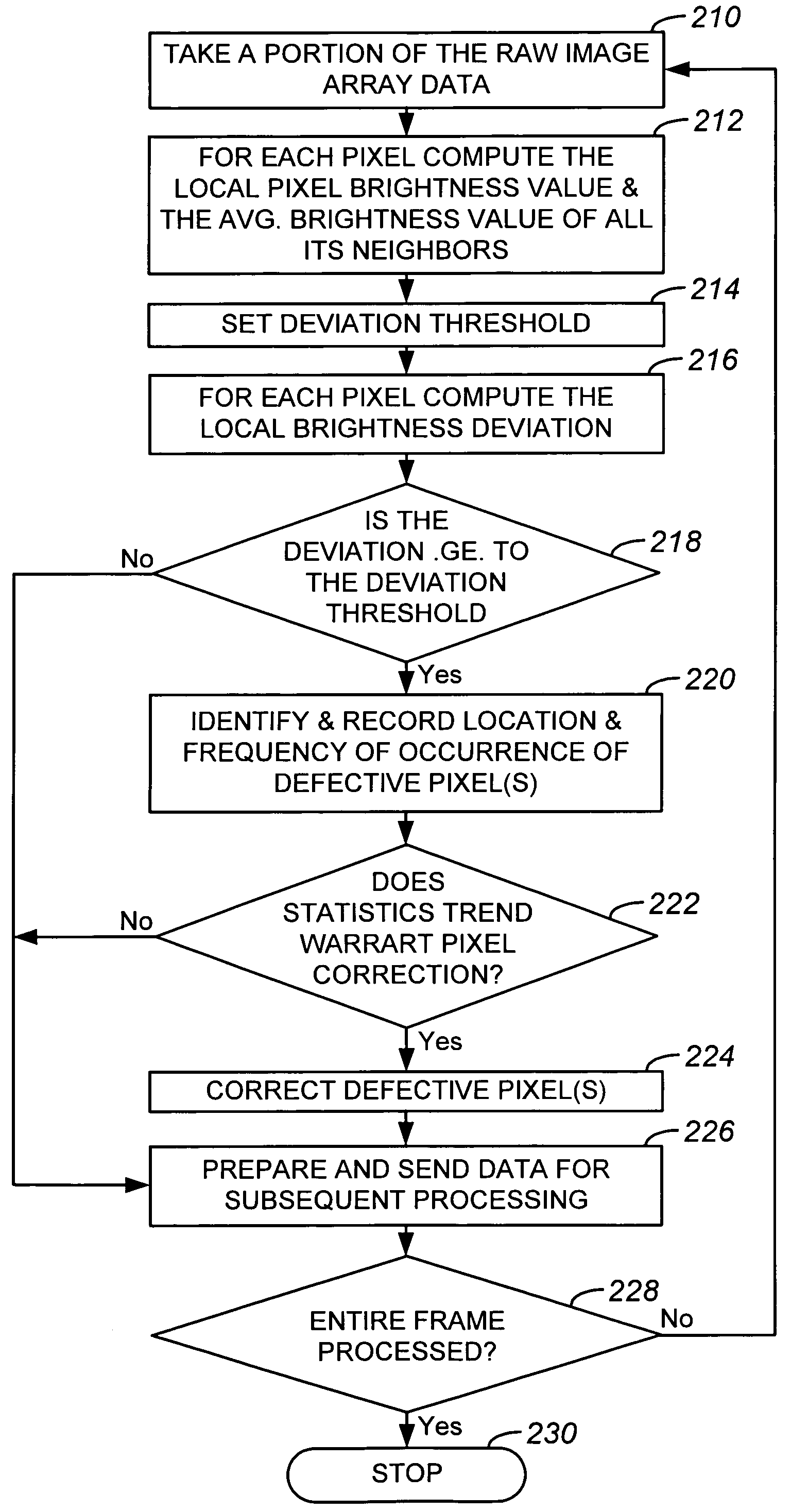
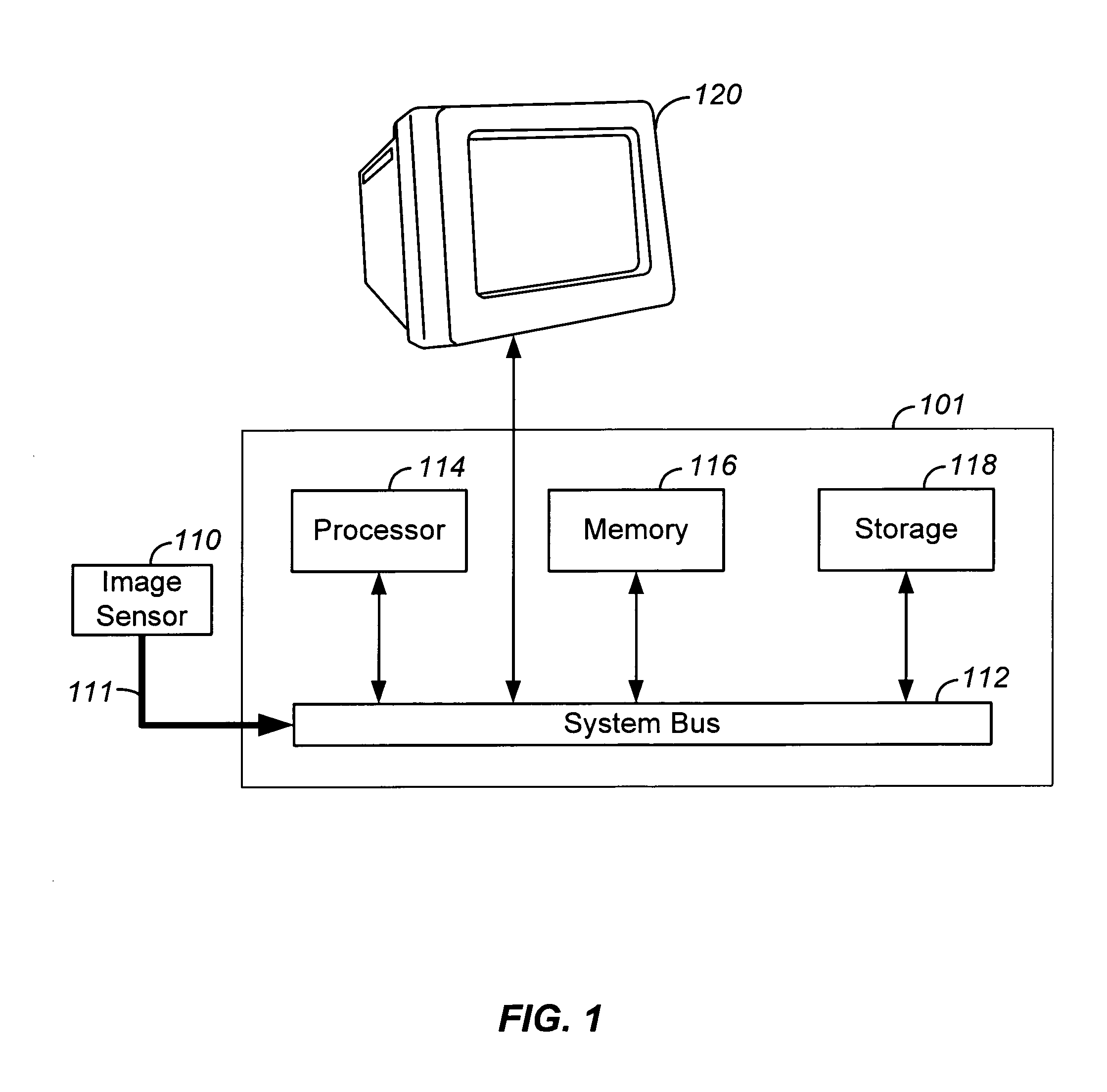
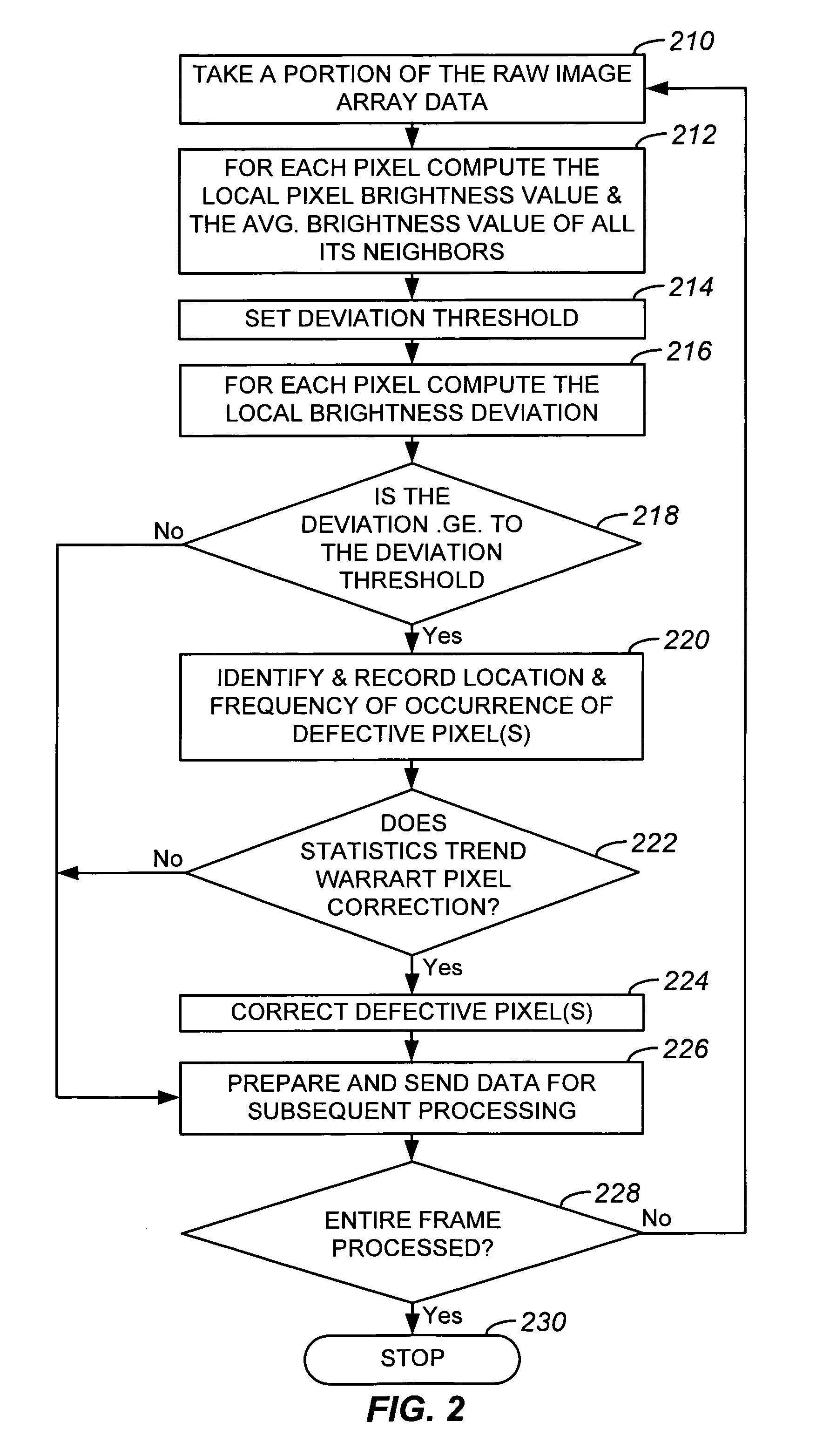
Dynamic anomalous pixel detection and correction
InactiveUS7009644B1Minimally affectedImpact rateTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionCMOS sensor
A method and a system for dynamically detecting and correcting anomalous pixels in the raw data taken from an image sensor array such as a CCD or a CMOS sensor array, thus allowing the use of dumb cameras to capture digital images for subsequent use by an intelligent host—such as being displayed on a computer monitor. This invention uses software algorithms running on an intelligent host processor to dynamically correct the anomalous pixels in the raw data taken from an image sensor array typical of those in a digital still or a video camera. Using the combination of a dumb camera which provides raw data to an intelligent host, which does all the subsequent image processing, the system works by scanning an image frame for pixels that vary more than a specified amount in their brightness value from their neighboring pixels and designating those as defective pixels. The location and frequency of the photosites sending the defective pixels are stored in a statistical database in the computer's memory. The brightness value of a defective pixel is then replaced by a local brightness value obtained from the defective pixel's neighboring pixels. The process includes video subsampling, meaning that the defective pixel detection is carried out and repeated at a pre-specified frame rate to ensure optimum detection and correction at a minimal level of scanning. A statistical database is kept so that truly anomalous pixels can over time be distinguished from false detection of true anomalies in the target image, lighting or other environmentally induced anomalies.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
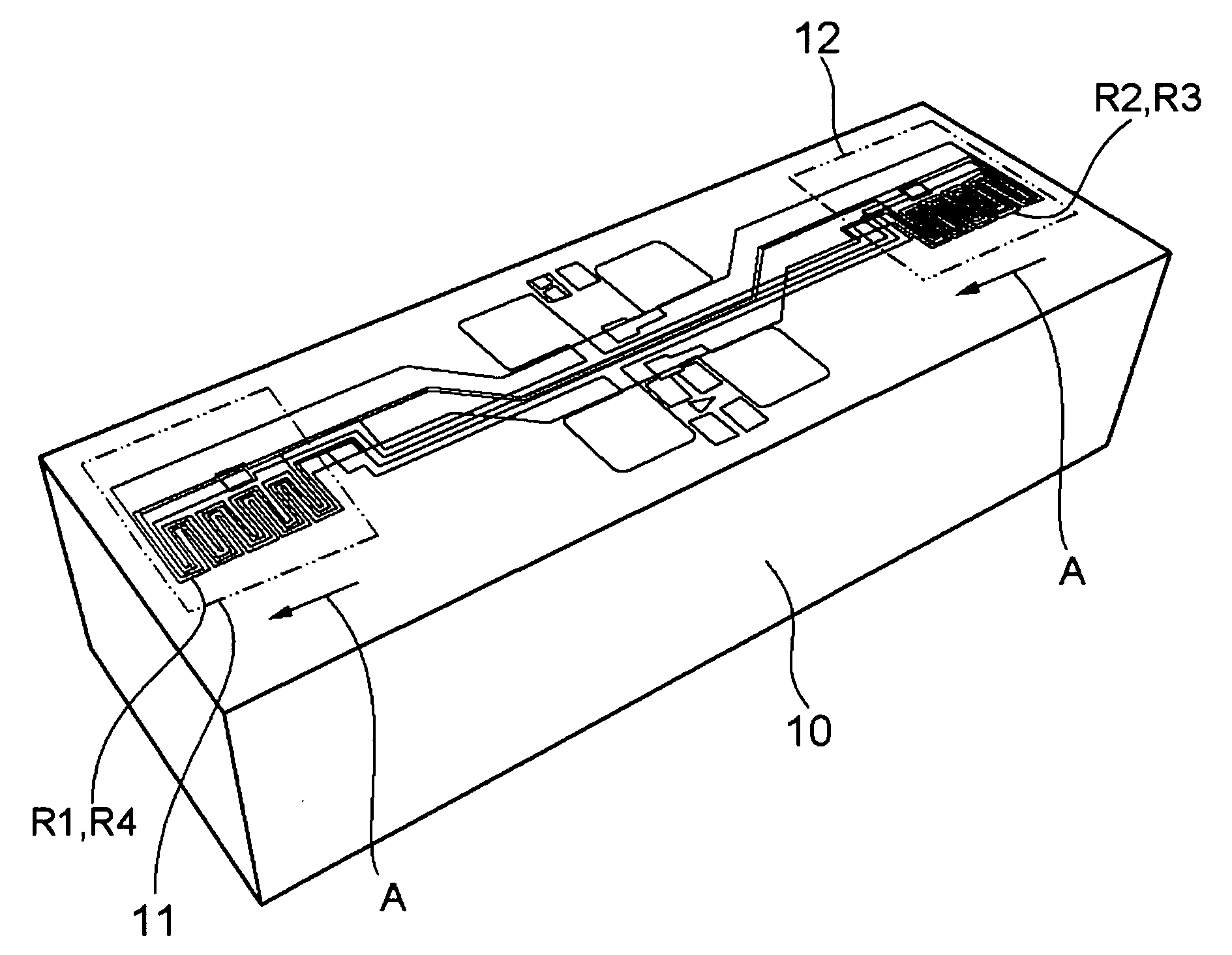
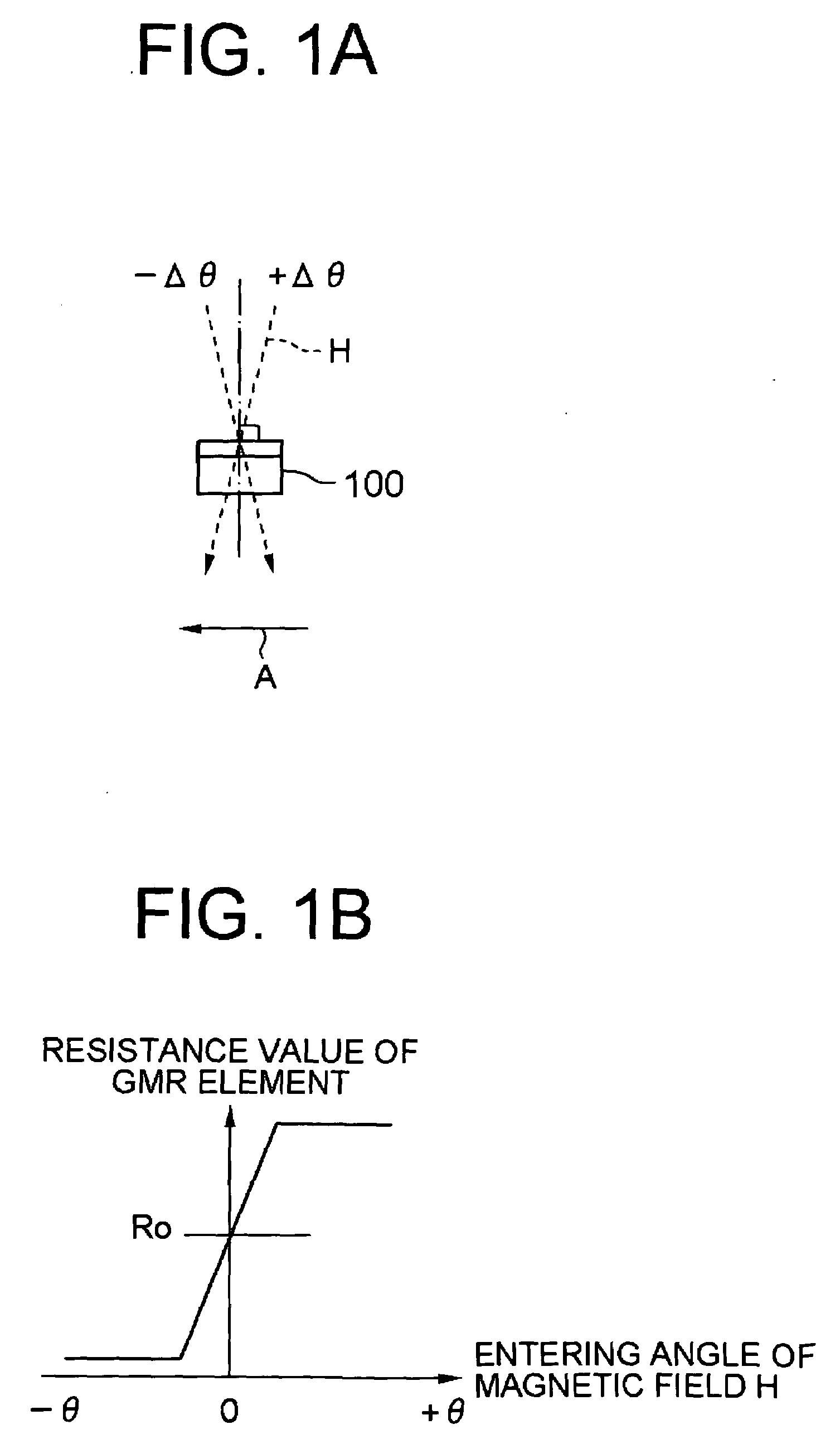
Magnetic sensor
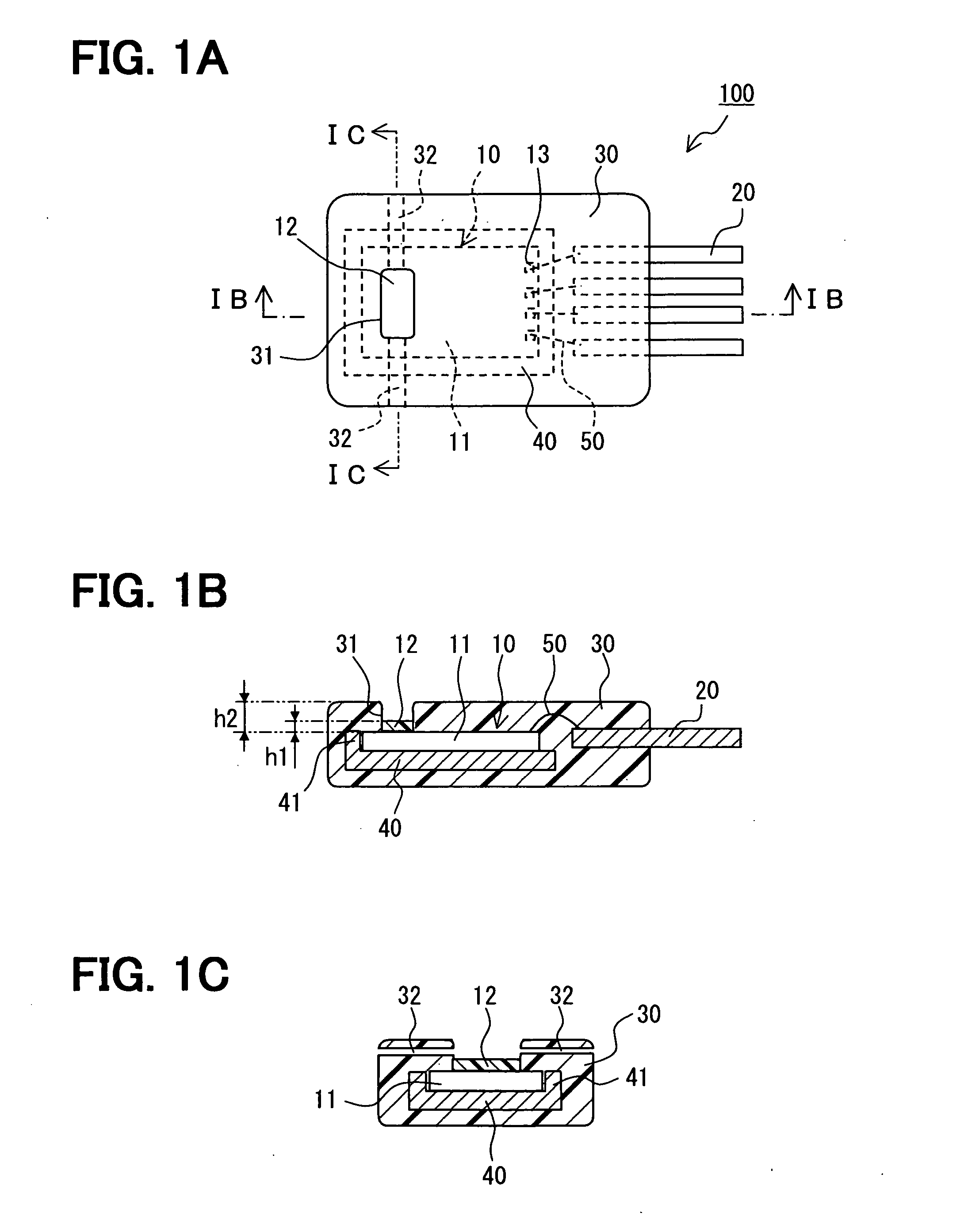
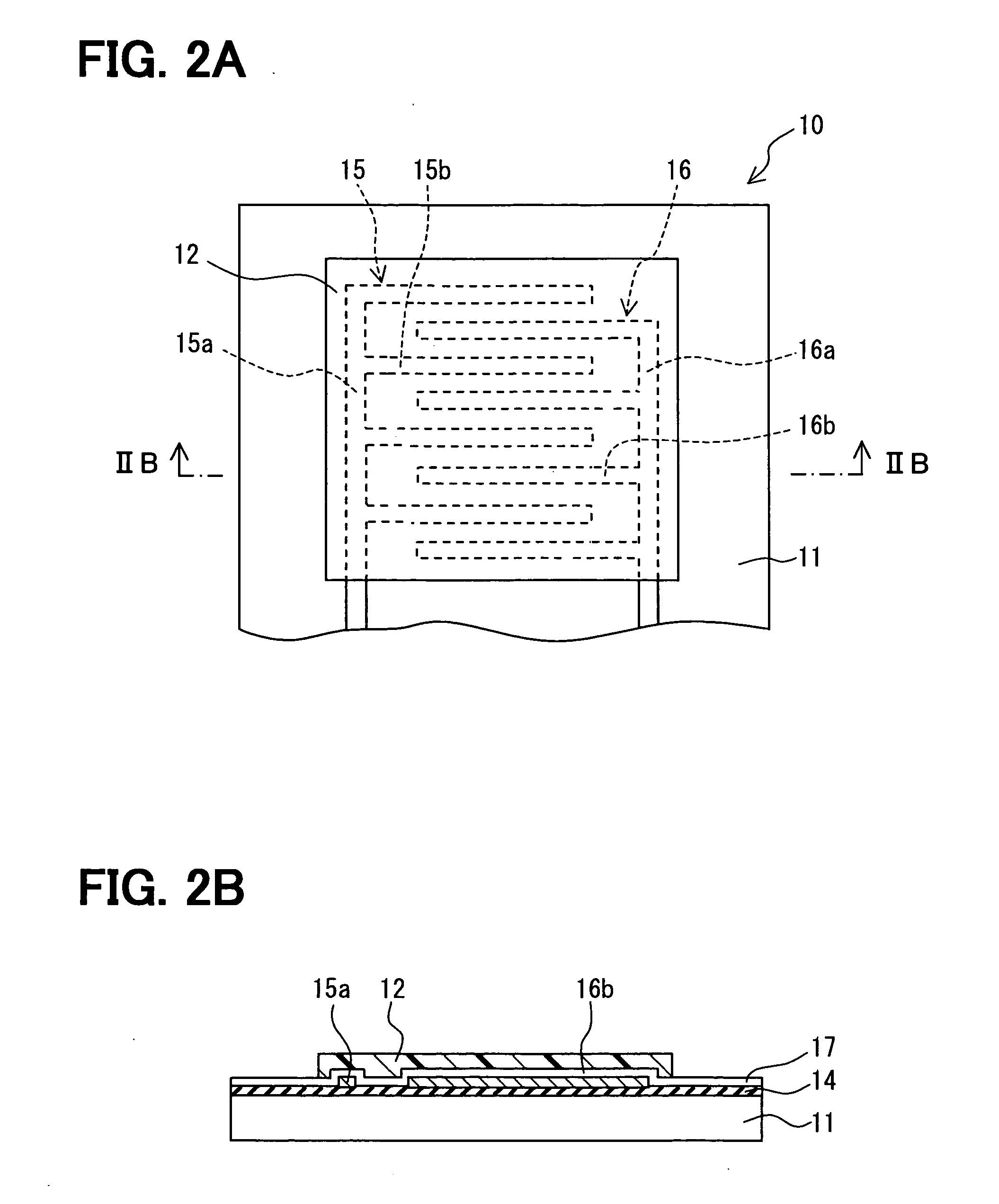
ActiveUS20090284254A1Improve detection accuracyLow costMeasurement using dc-ac conversionWave amplification devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A magnetic sensor capable of detecting a magnetic field with high sensitivity is provided. The magnetic sensor includes a bridge circuit having a plurality of magneto resistive effect elements connected with each other, and is capable of detecting a differential voltage between predetermined connecting points. The magneto resistive effect elements output resistance values which vary in accordance with a direction of a magnetic field to be input, and are arranged such that fixed magnetization directions of all magneto resistive effect elements are in the same direction. Further, a magnetic body which changes the direction of the magnetic field to be input to the magneto resistive effect elements is also provided in the vicinity of the bridge circuit.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Comparator circuit having latching behavior and digital output sensors therefrom
ActiveUS20100045268A1Lower power requirementCost reductionCurrent/voltage measurementSolid-state devicesComparators circuitsVoltage regulation
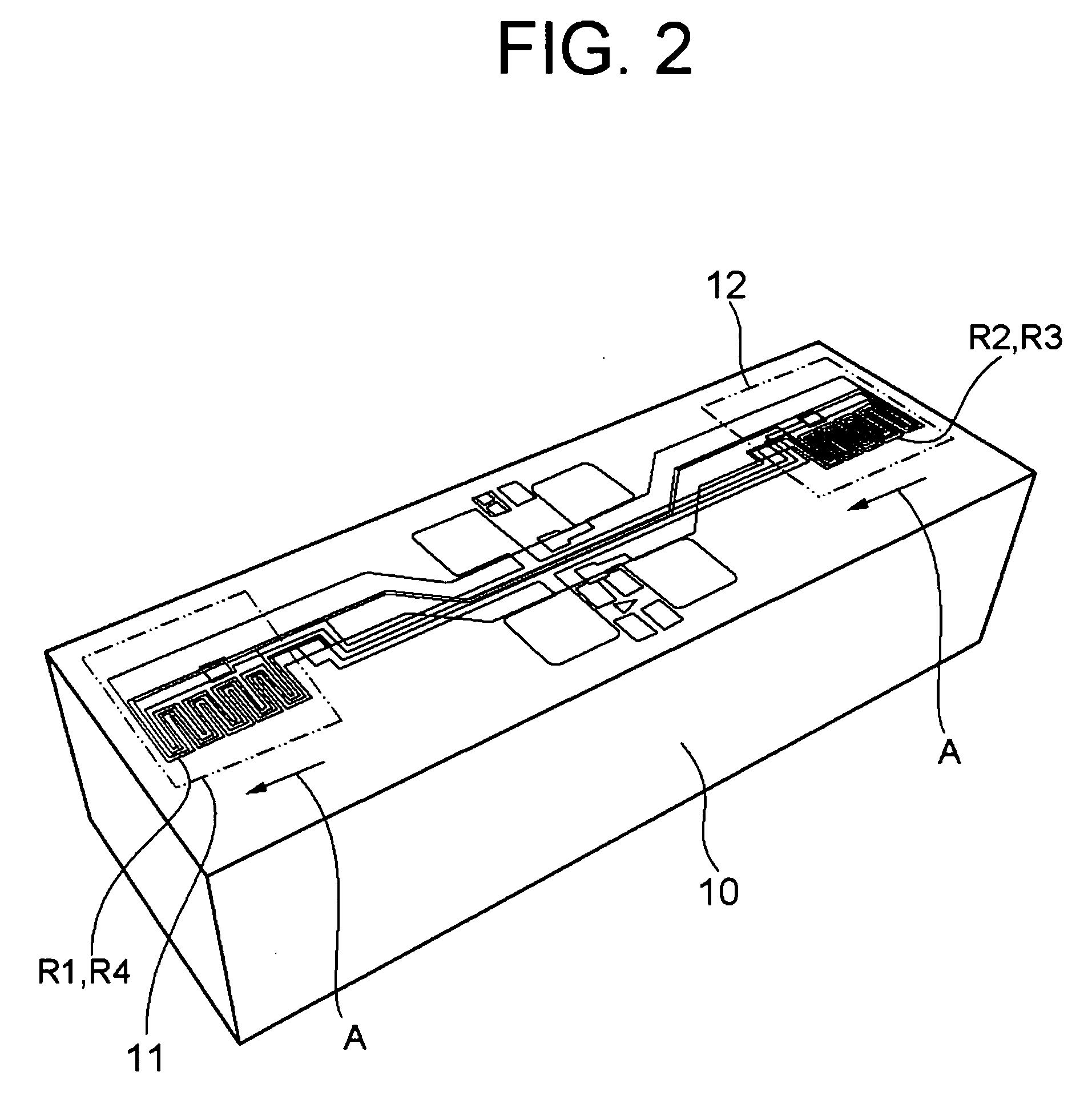
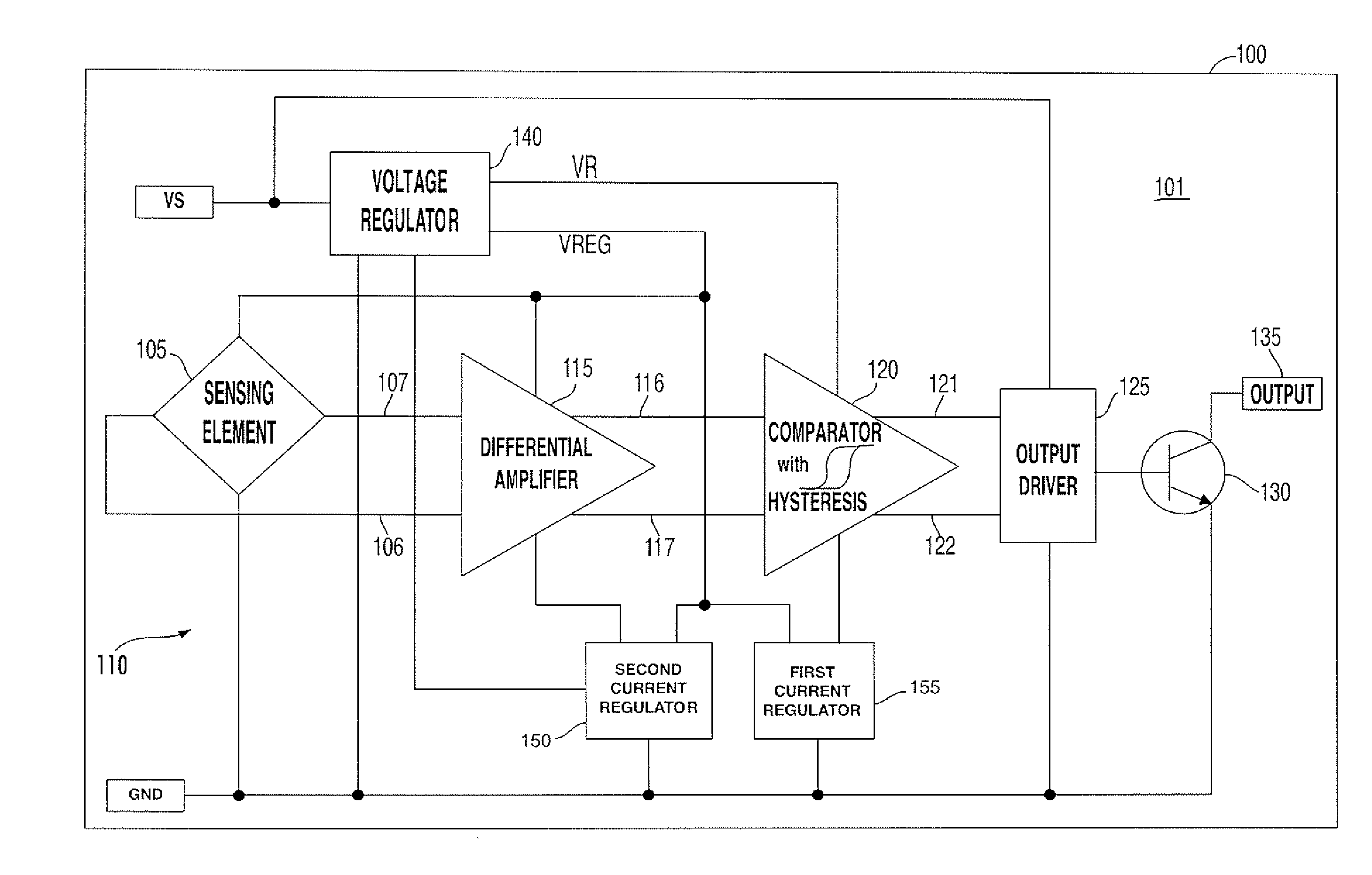
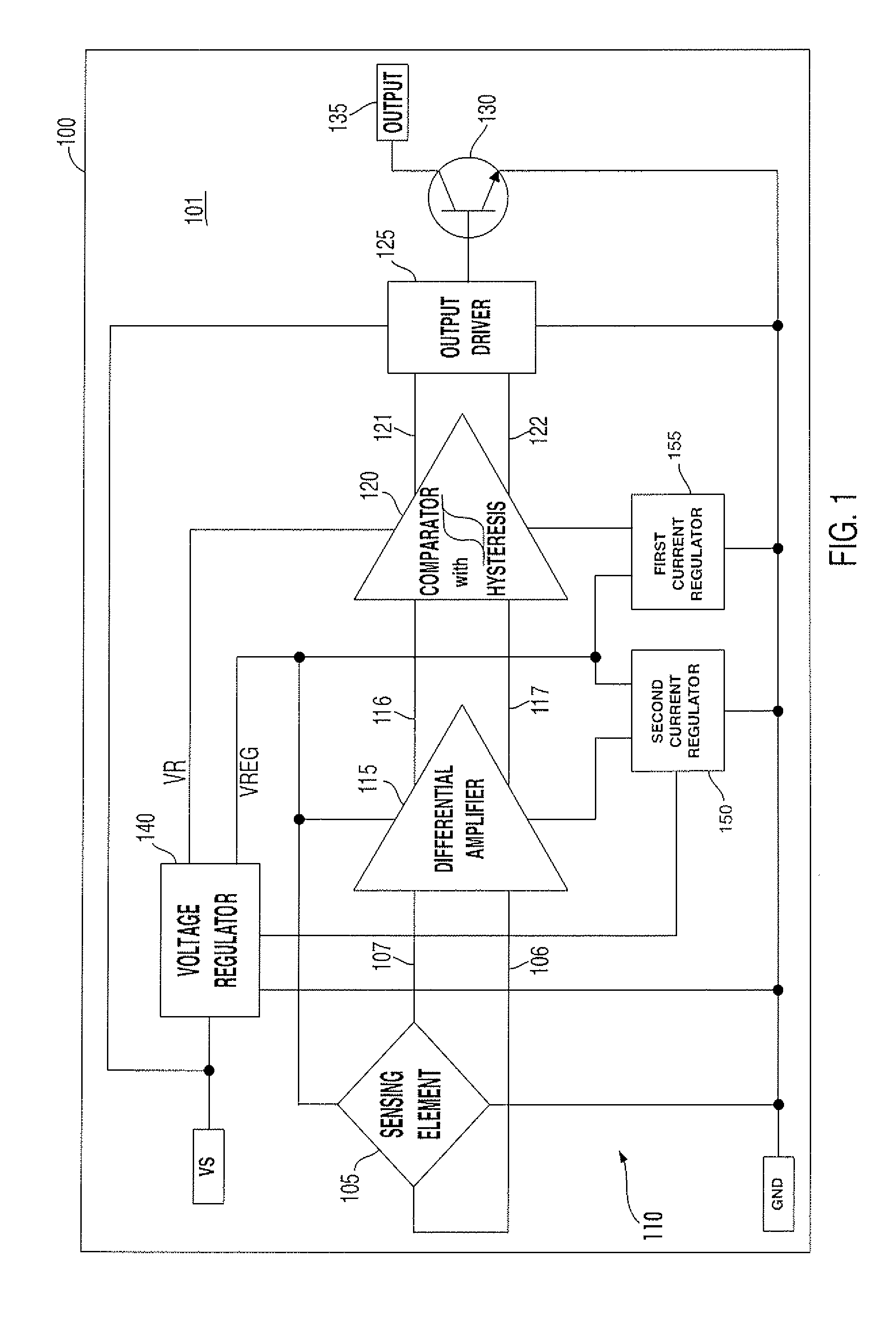
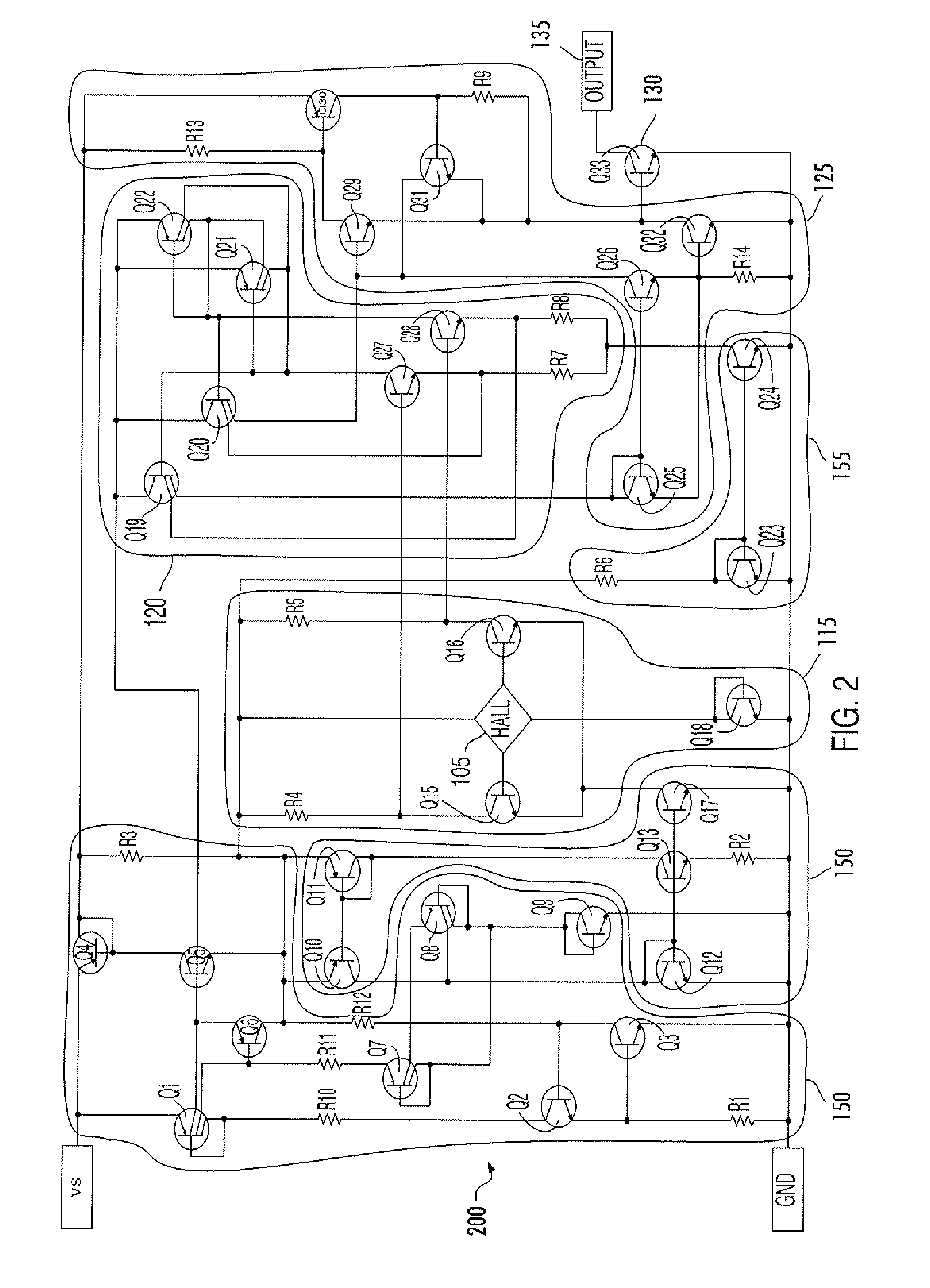
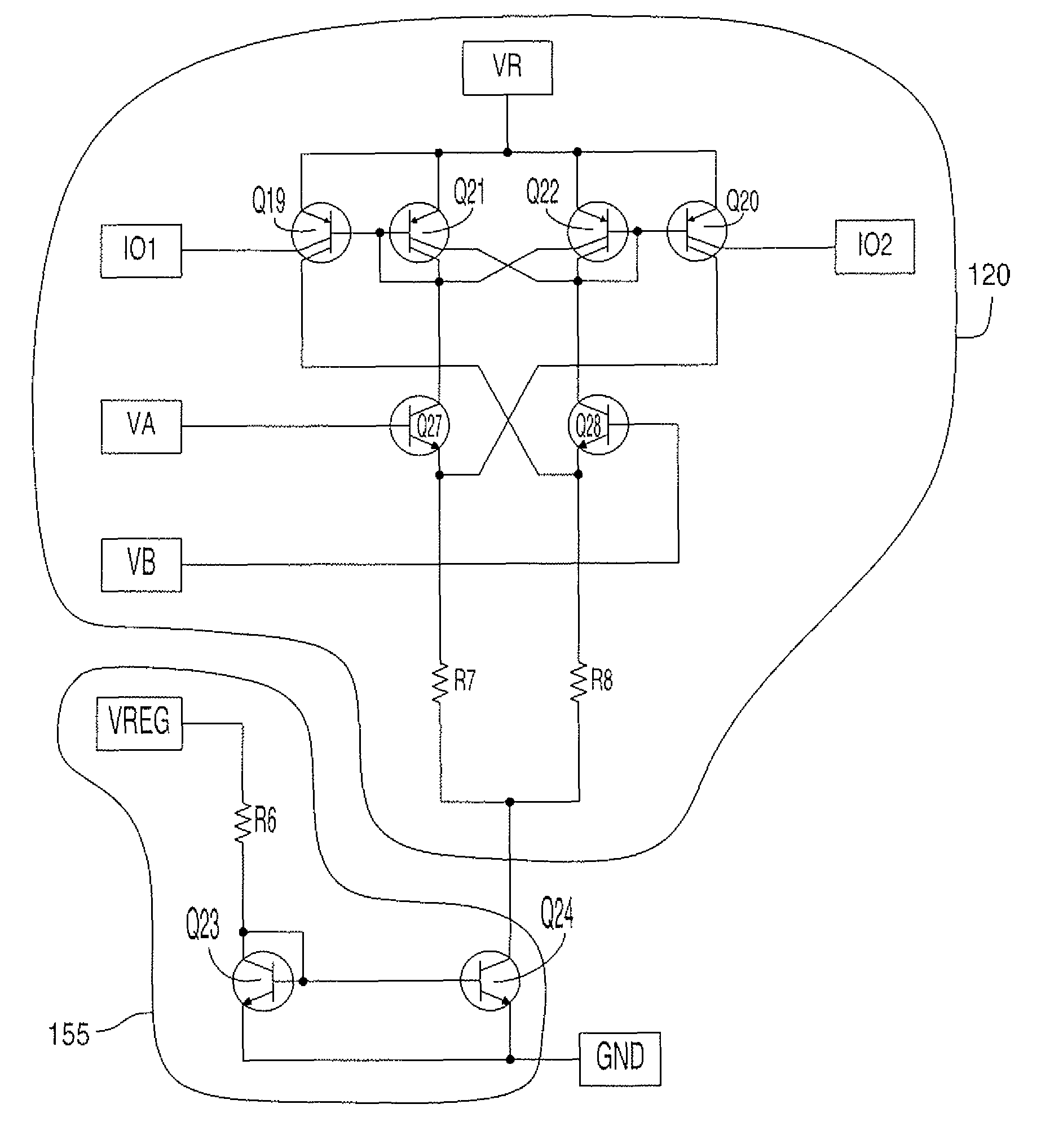
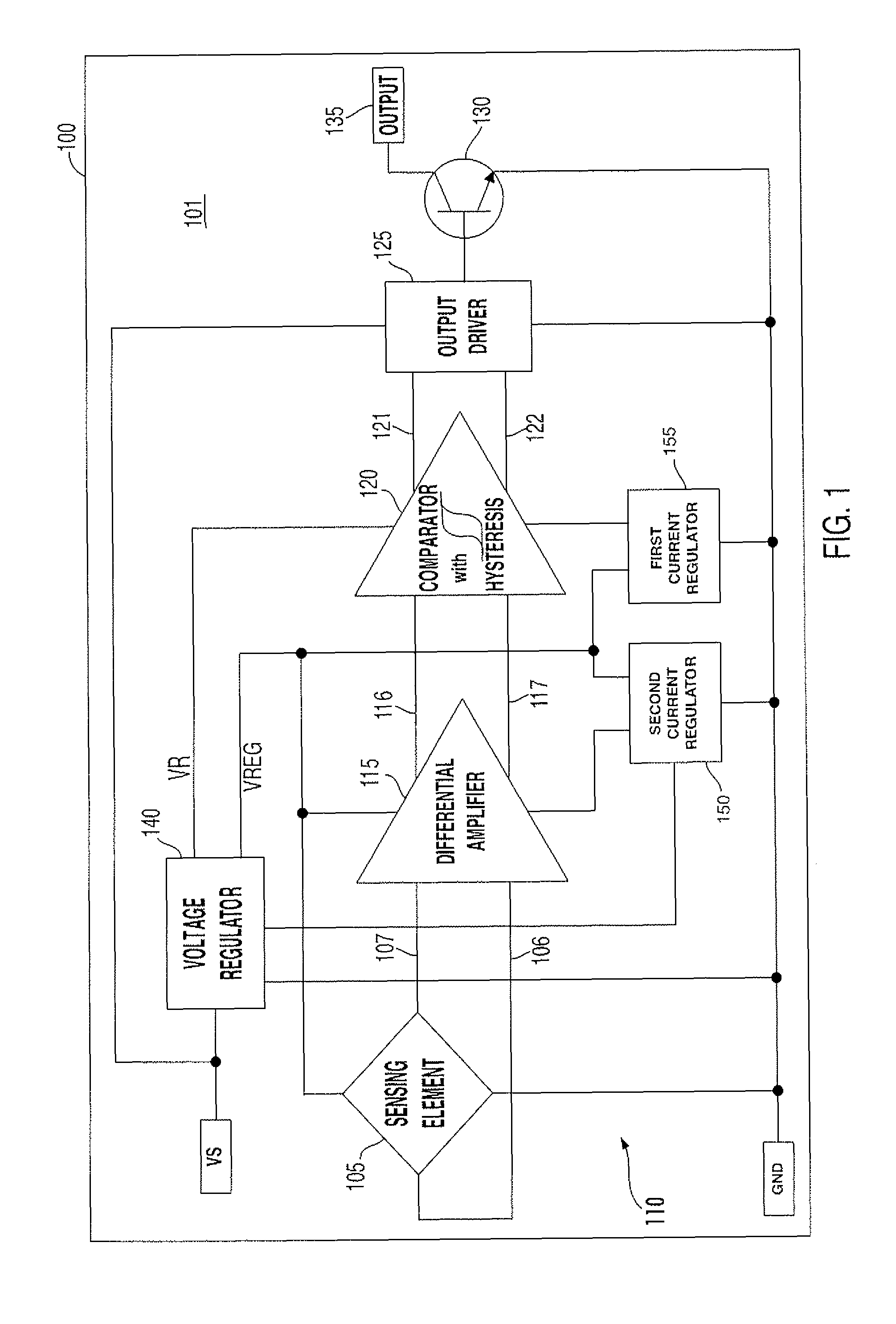
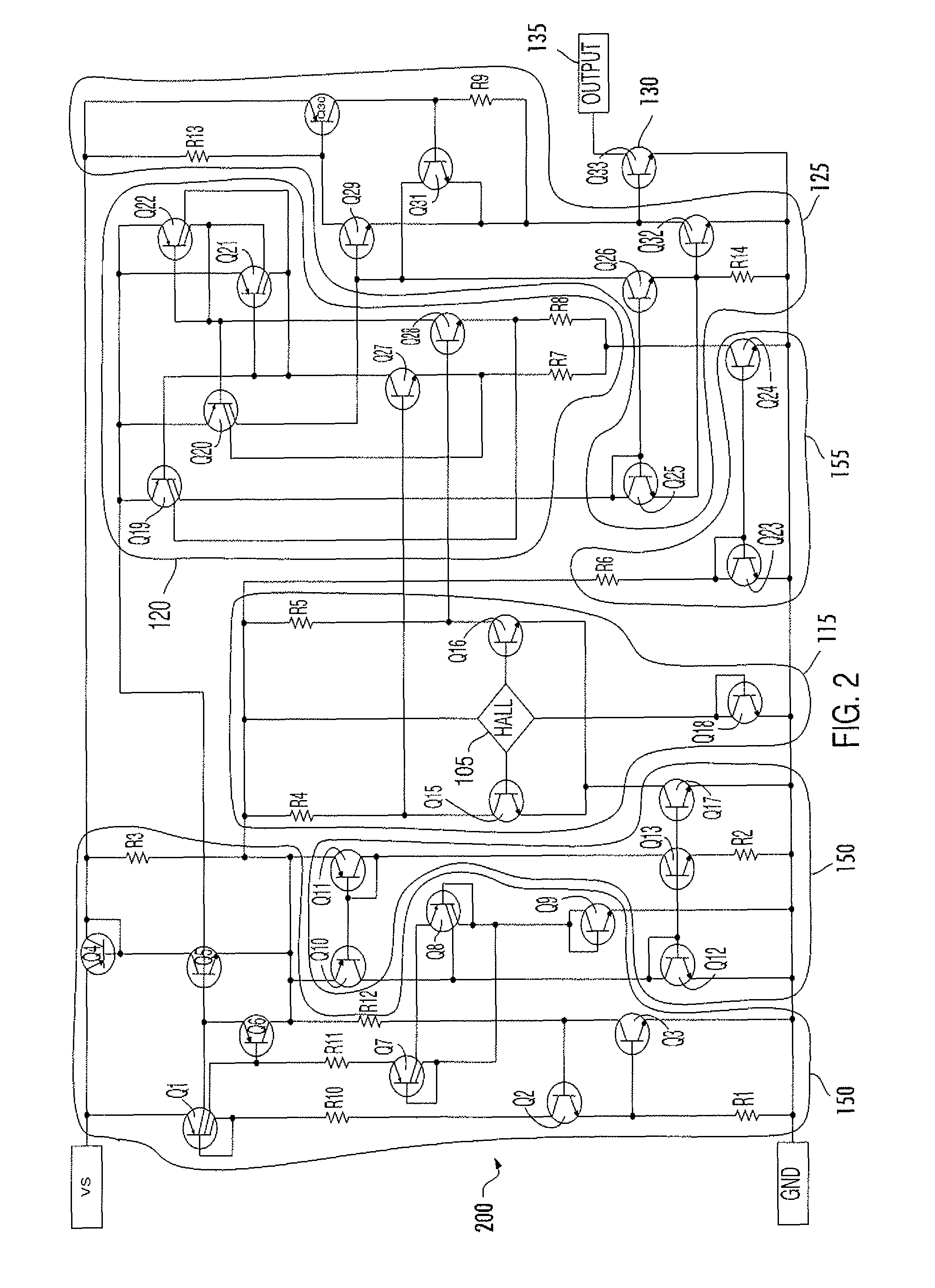
A digital output sensor (110) includes a sensing structure (105) including at least one sensing element. The sensing structure (105) outputs a differential sensing signal (106, 107). An integrated circuit (100) includes a substrate (101) including signal conditioning circuitry for conditioning the sensing signal (106, 107). The signal conditioning circuitry includes a differential amplifier (115) coupled to receive the sensing signal and provide first and second differential outputs (116, 117), and a comparator (120) having input transistors (Q27, Q28) coupled to receive outputs from the differential amplifier. The comparator (120) also includes first and second current-mirror loads (Q19 / Q21 and Q22 / Q20) coupled to the input transistors (Q27, Q28) in a cross coupled configuration to provide hysteresis, wherein the first and second current-mirror loads provide differential drive currents (121,122). An output driver (125) is coupled to receive the differential drive currents (121, 122). An output stage (130) includes at least one output transistor which is coupled to the output driver for providing a digital output for the sensor. A voltage regulator (140) is coupled to receive a supply voltage (VS) and output at least one regulated supply voltage (VREG), wherein the regulated supply voltage is coupled to the sensing structure (105), the differential amplifier (115) and the comparator (120).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
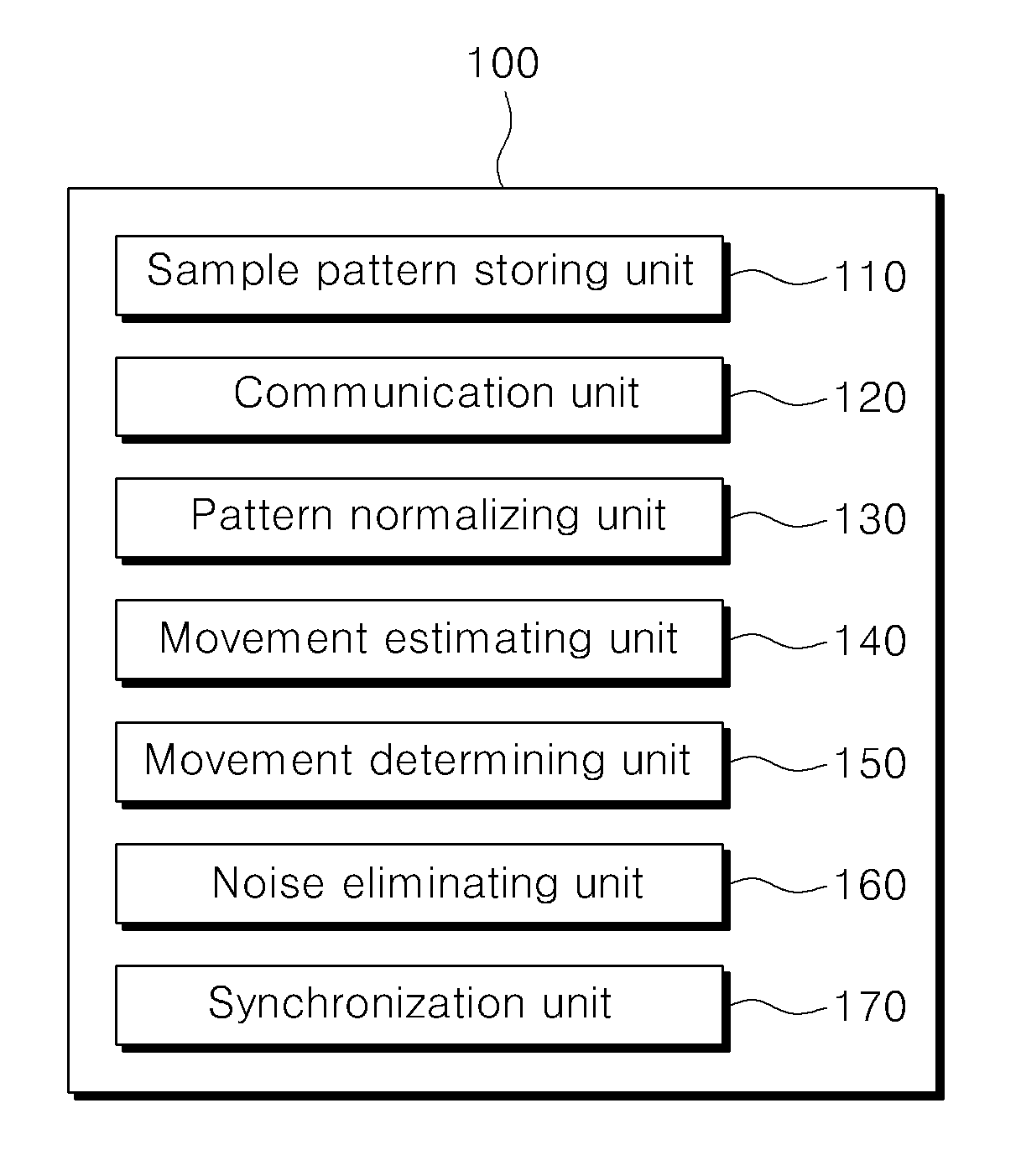
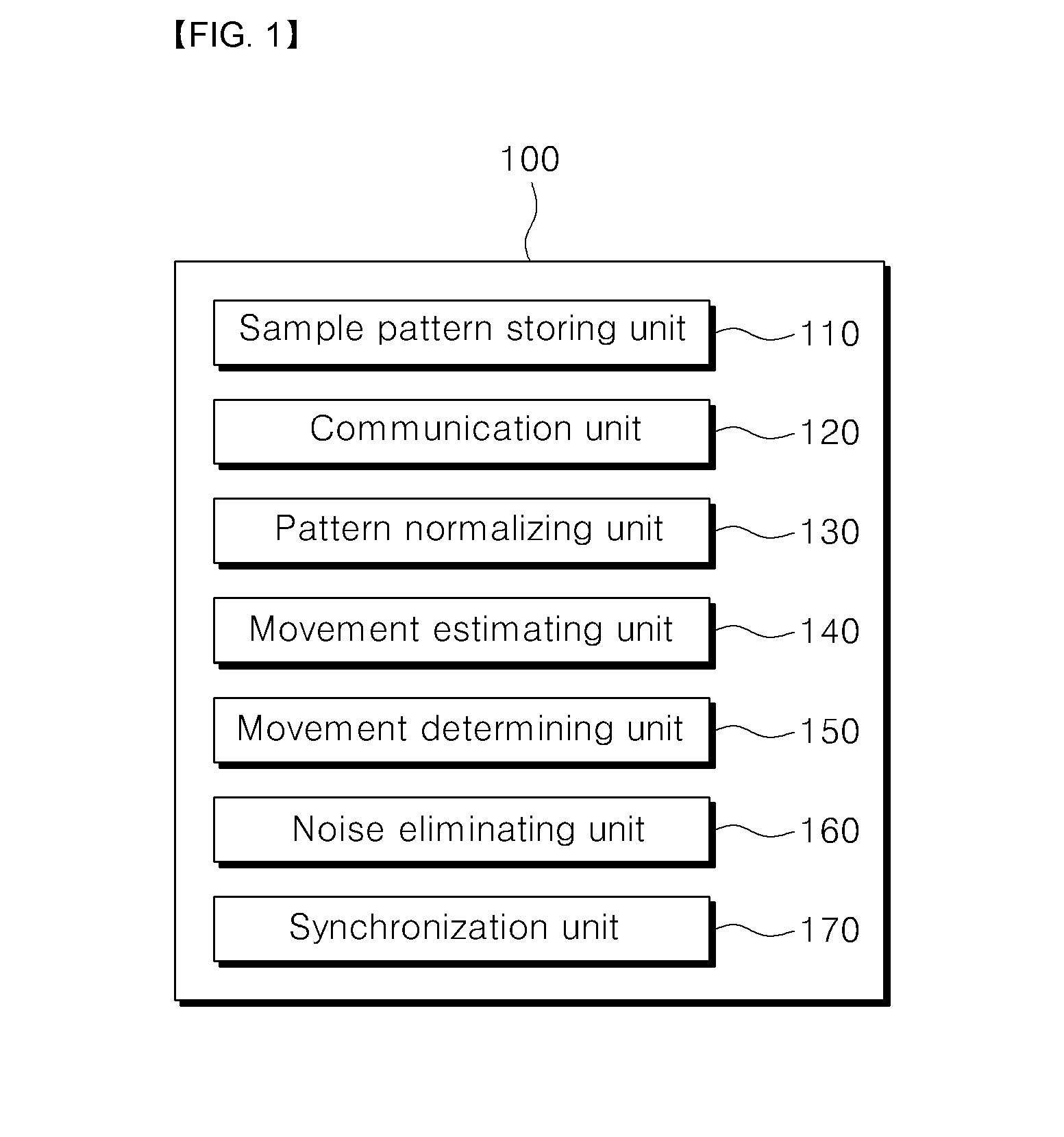
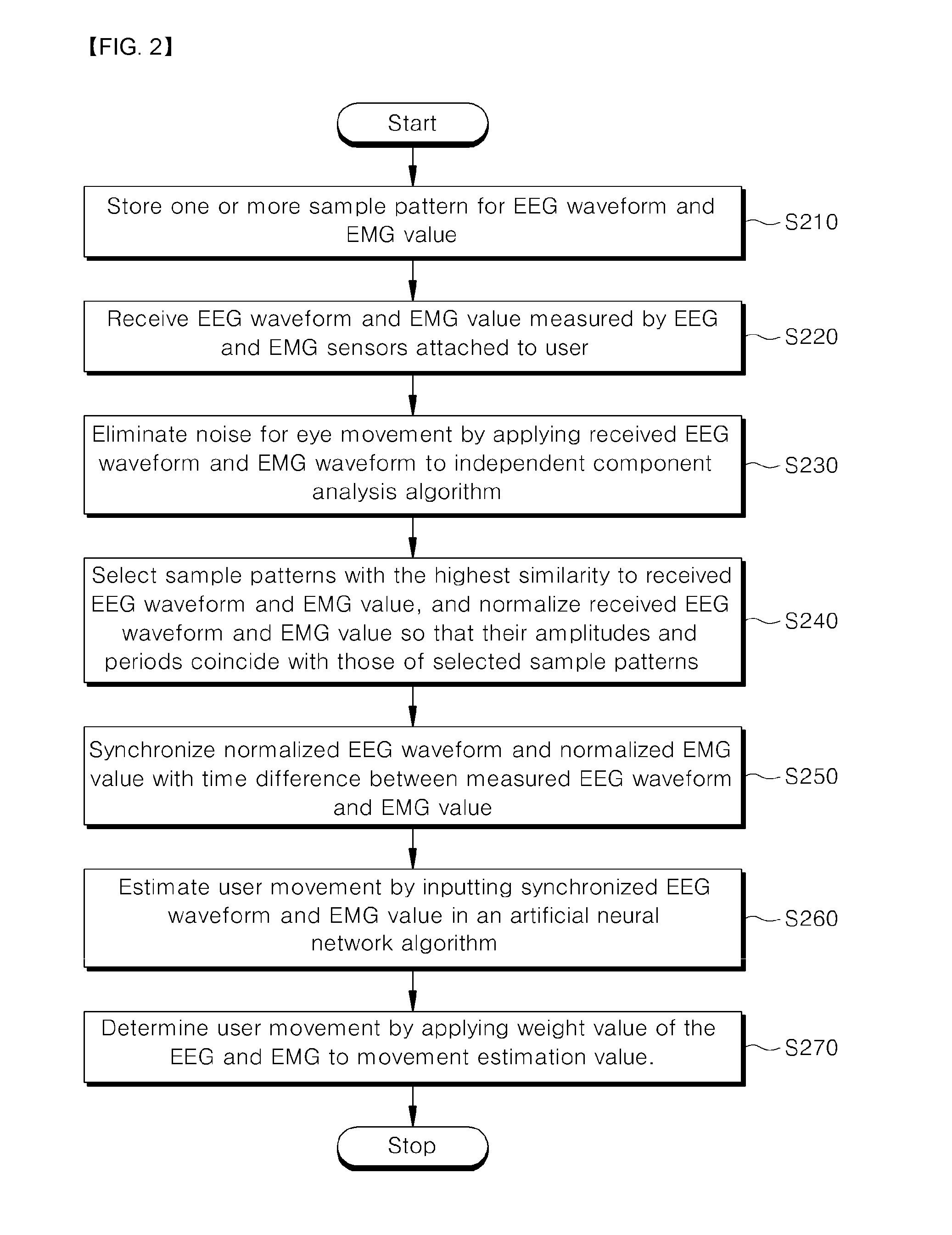
Movement pattern measuring apparatus using eeg and emg and method thereof
ActiveUS20170035313A1Accurate movement determinationAccurately determineElectroencephalographyElectromyographyCommunication unitElectroencephalography
Disclosed is an apparatus for measuring movements of a user, which may include: a sample pattern storing unit for storing one or more sample patterns which are obtained by patterning EEG waveforms and EMG values; a communication unit for receiving an EEG waveform and an EMG value of the user measured by the EEG and EMG sensors; a pattern normalizing unit for selecting sample patterns with the highest similarity to the received user's patterns among the stored sample patterns, and for normalizing the received user's patterns so that their amplitudes and periods coincide with those of the selected sample patterns; a movement estimating unit for estimating movement of the user by inputting the normalized EEG waveform and EMG value in an artificial neural network algorithm; and a movement determining unit for calculating the user's movement by applying each weight value of the EEG and EMG to each movement estimation value.
Owner:FOUND OF SOONGSIL UNIV IND COOP
Obstacle sensor having supersonic sensor
InactiveUS20080165620A1Small sizeReduce manufacturing costPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementElectromagnetic wave reradiationUltrasoundPhysics
Owner:DENSO CORP
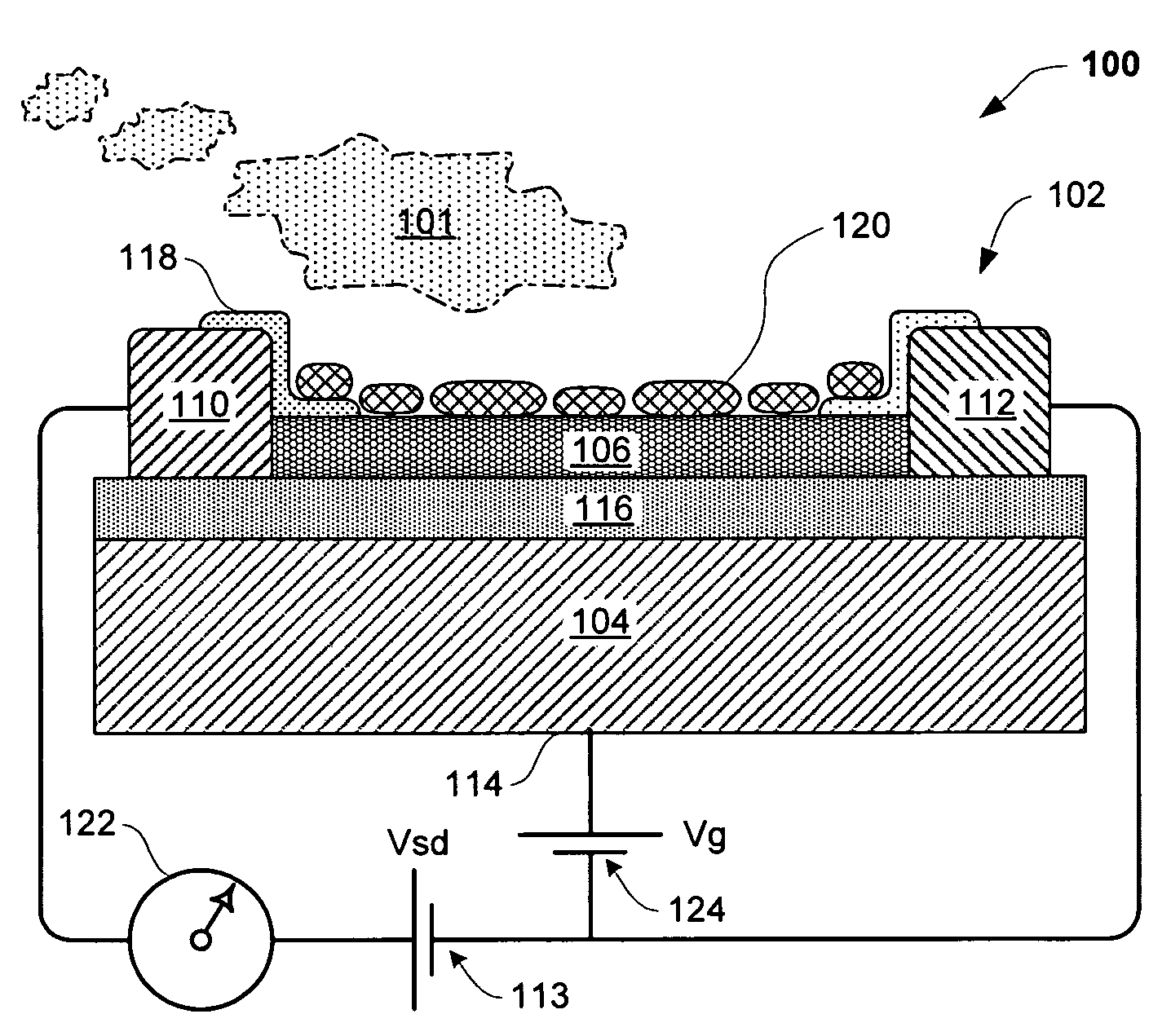
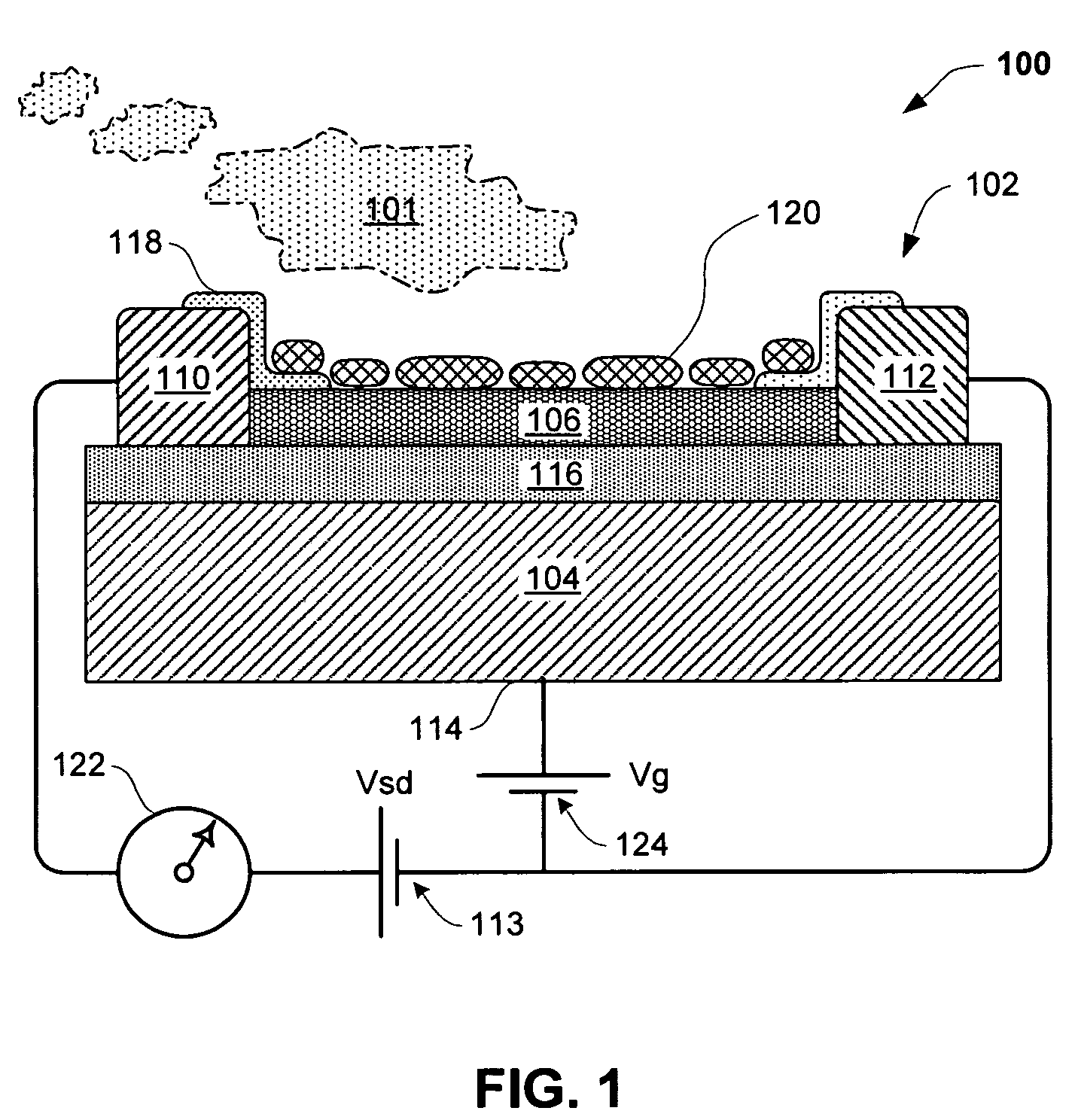
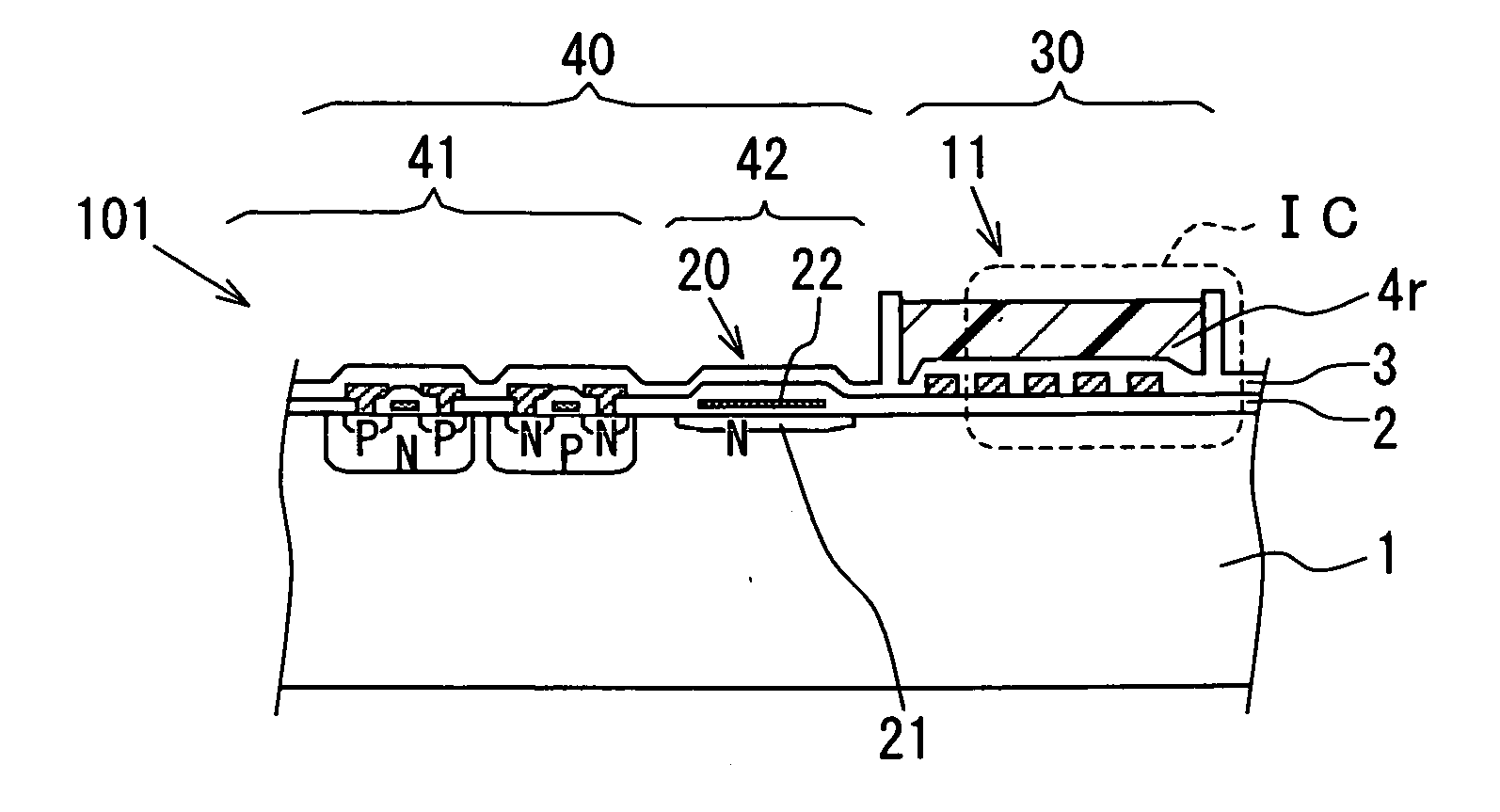
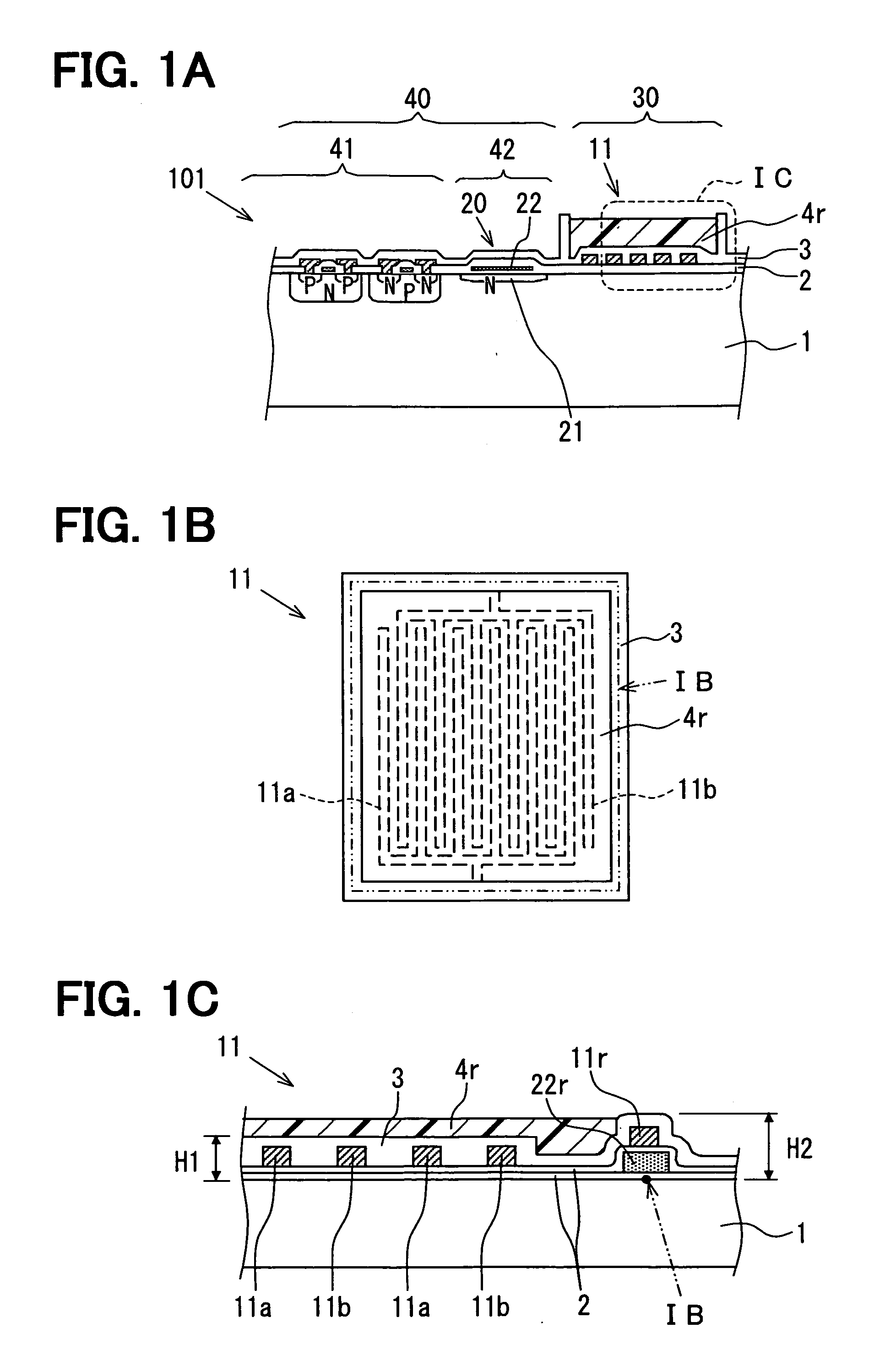
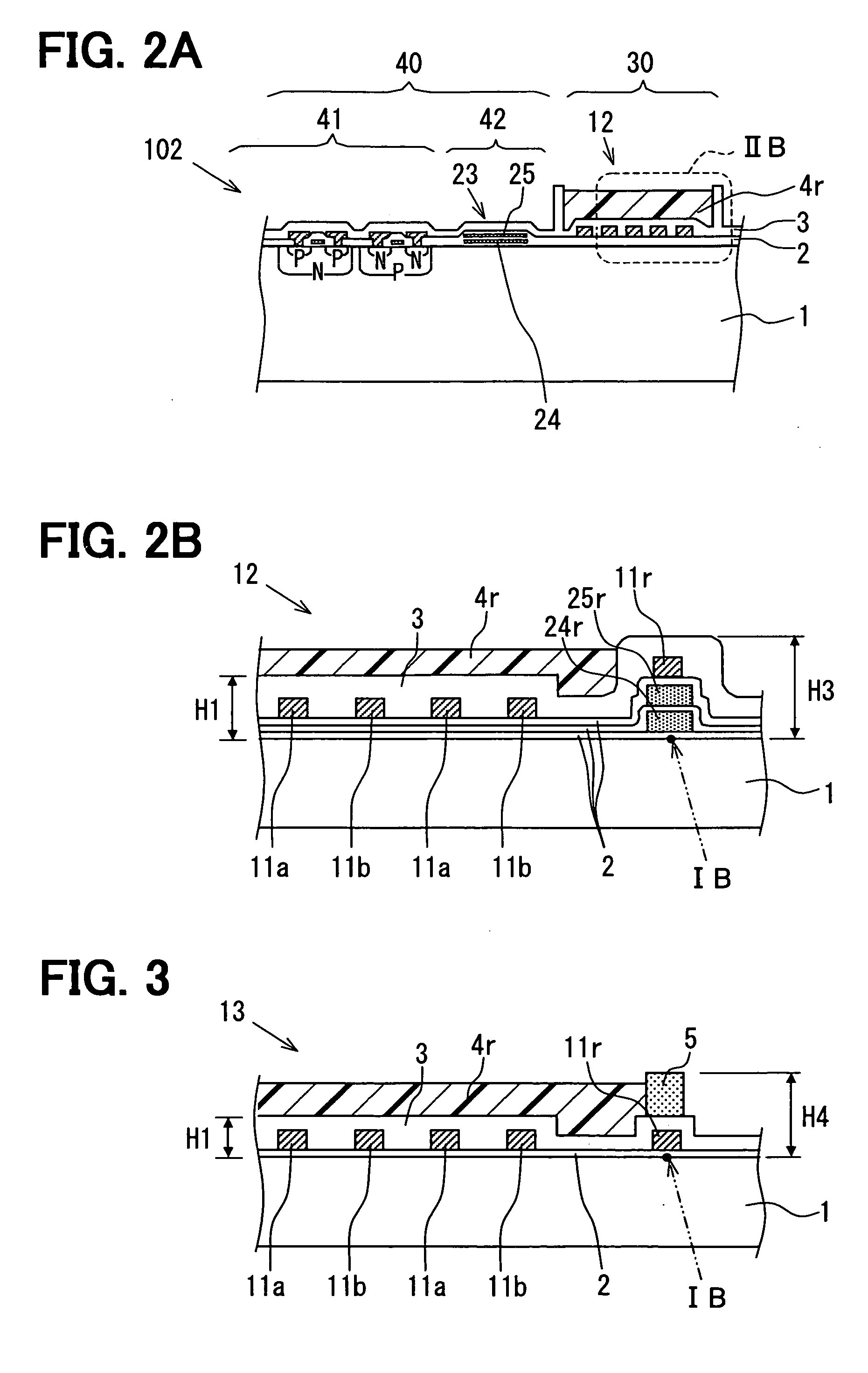
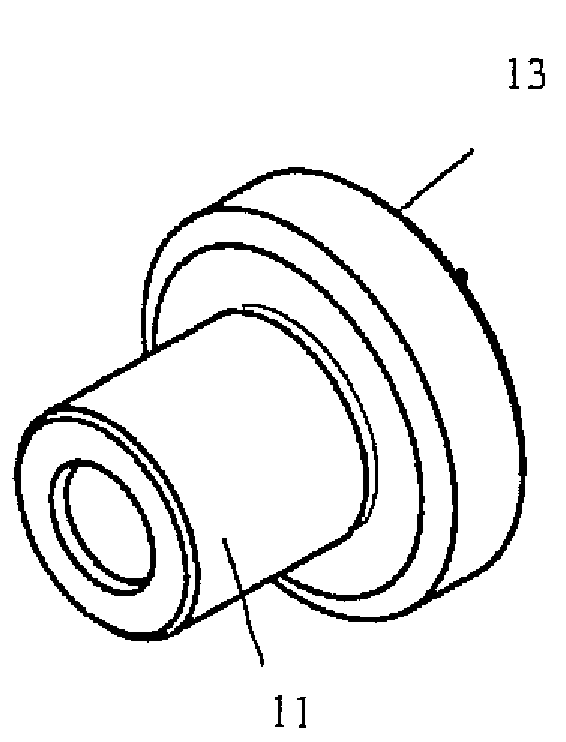
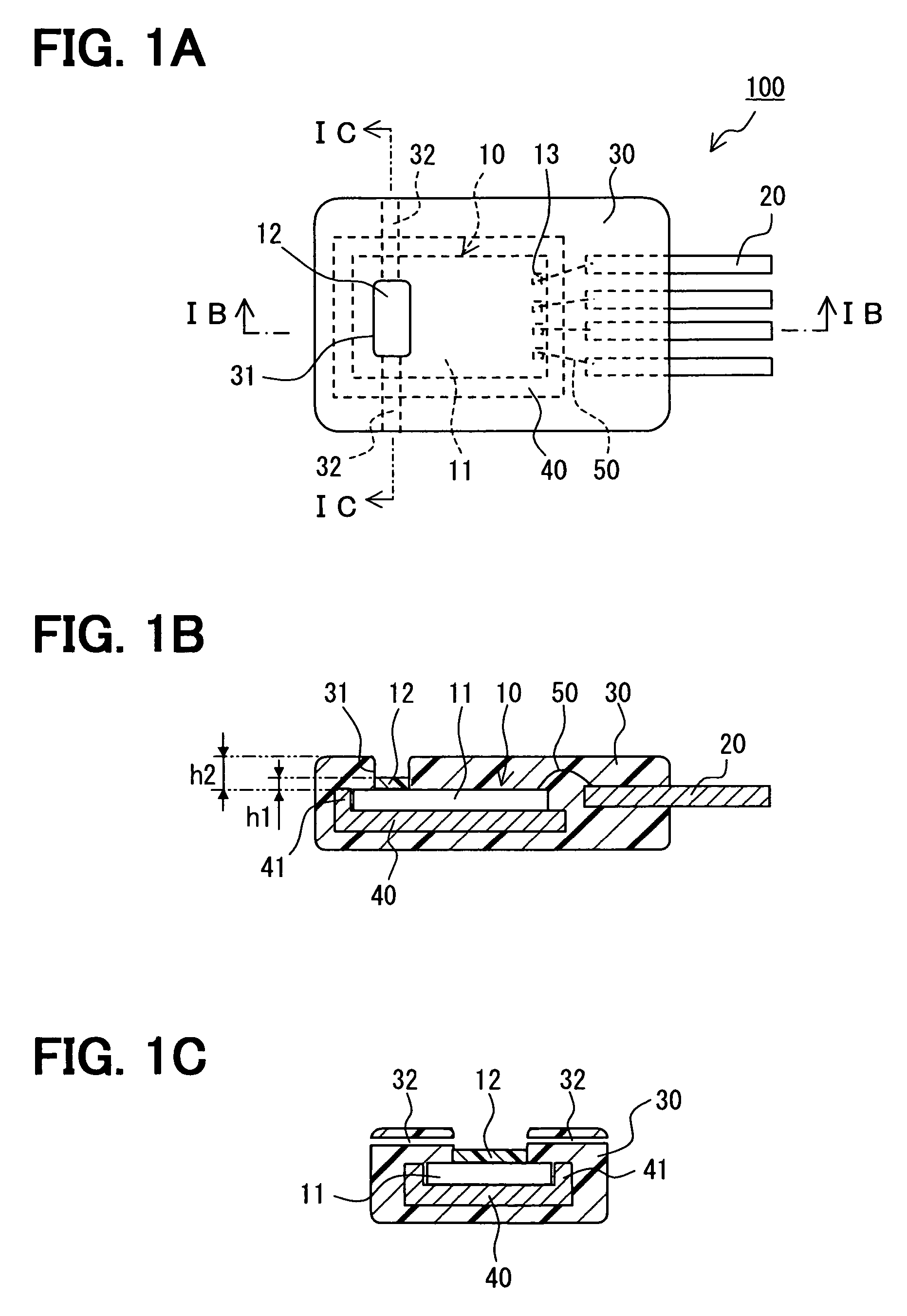
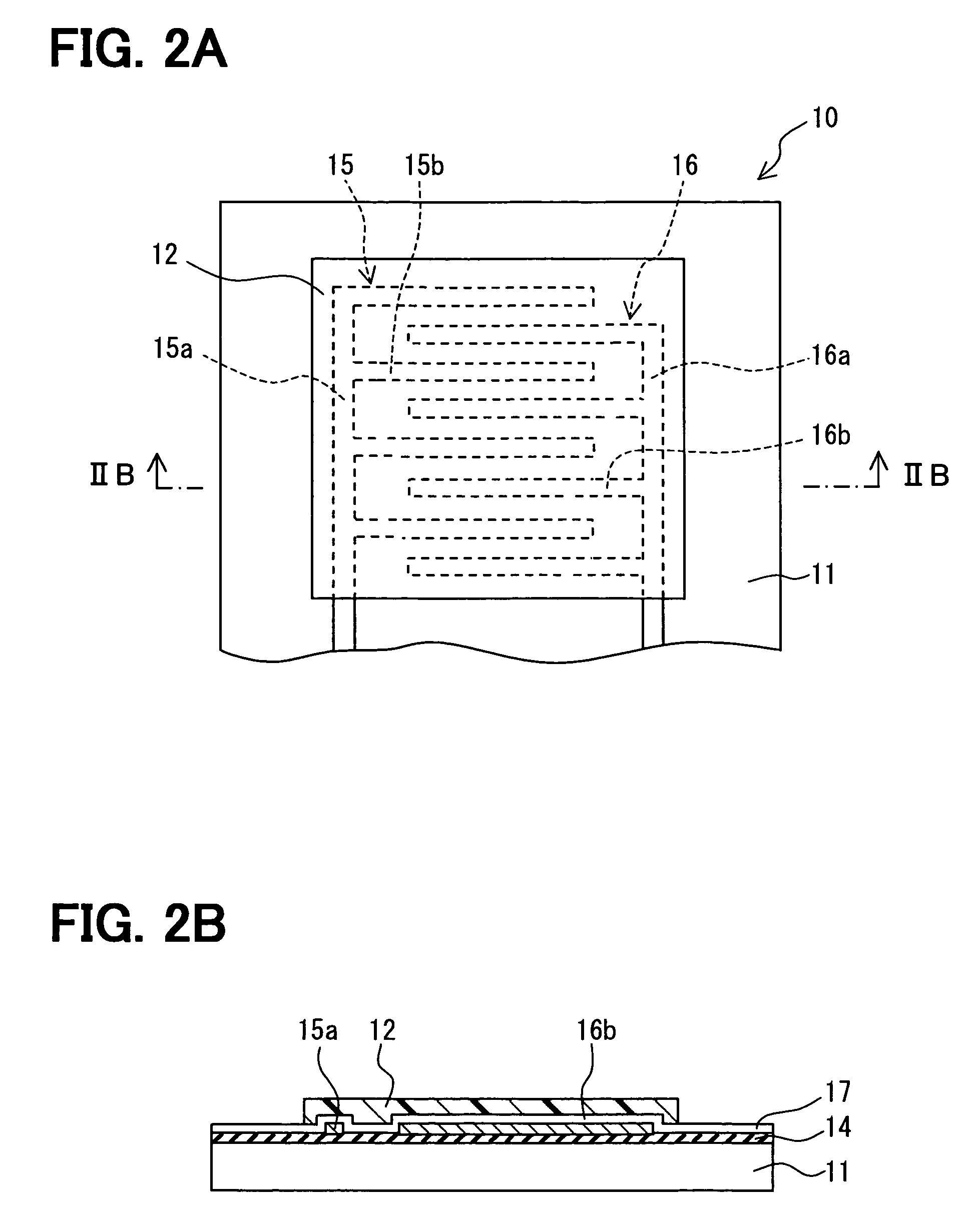
Sensor having a thin-film inhibition layer
ActiveUS7948041B2Small sizeReduce power consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyTemperatue controlAnalyteVolatiles
Owner:NANOMIX INC
Missing nozzle detection method and sensor for an ink jet printer
InactiveUS6843547B2Quality improvementReduce sensor costOther printing apparatusInk printerEngineering
A method of detecting malfunctioning ones of a plurality of nozzles of a printhead in an ink jet printer includes providing a sensor having at least two terminals defining at least one gap therebetween. An attempt is made to jet ink from a first of the nozzles into the at least one gap. A resistance between at least two of the terminals is measured to determine whether the ink has been jetted into the at least one gap. The attempting and measuring steps are repeated for each remaining nozzle.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Modular rotary multi-sensor sensor ring
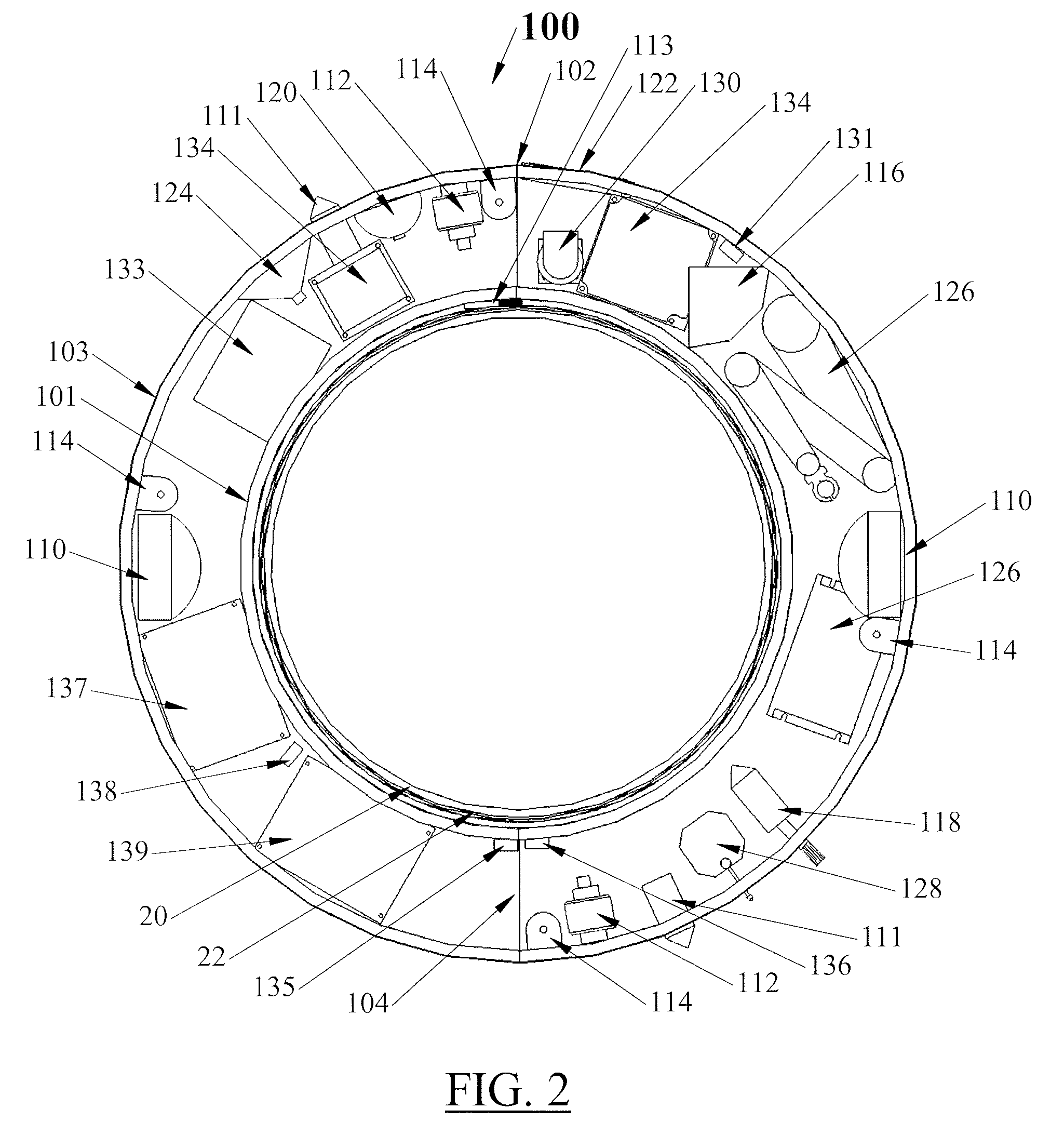
ActiveUS20090088896A1Large volumeReduce sensor costProgramme controlElectronic commutation motor controlEngineeringCost savings
An intelligent modular rotary multi-sensor sensor ring platform for such uses as in mobile robotics allows a few sensors to scan the local area and environment, provides a cost saving, volume and a power savings as well as reducing calibration and maintenance costs. The sensor ring platform has a large internal diameter allowing a maximum area for the chassis structural elements as well as other equipment located in the chassis. Local sensor signal processing is combined with time, rotation speed and position data stamps to allow processed data to be used locally as well as to be transferred to other systems or subsystems or for data logging purposes.
Owner:CYCOGS
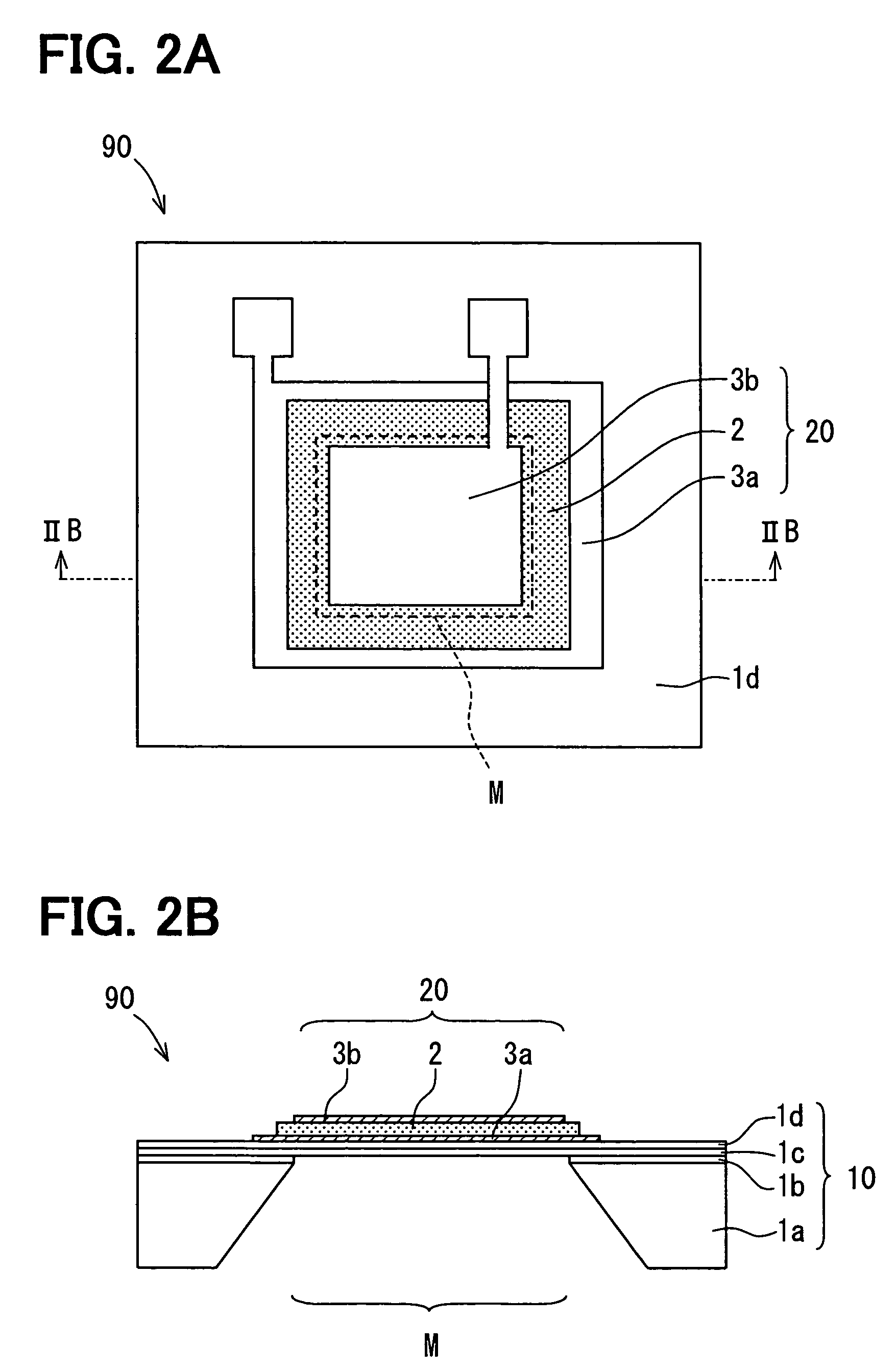
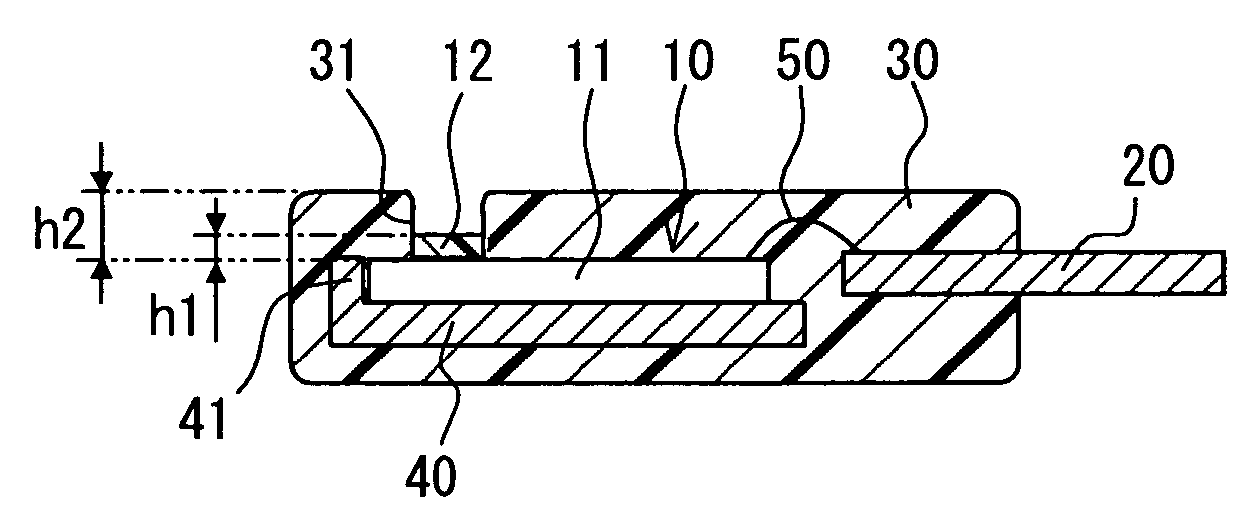
Humidity sensor having humidity sensitive film and method for manufacturing the same
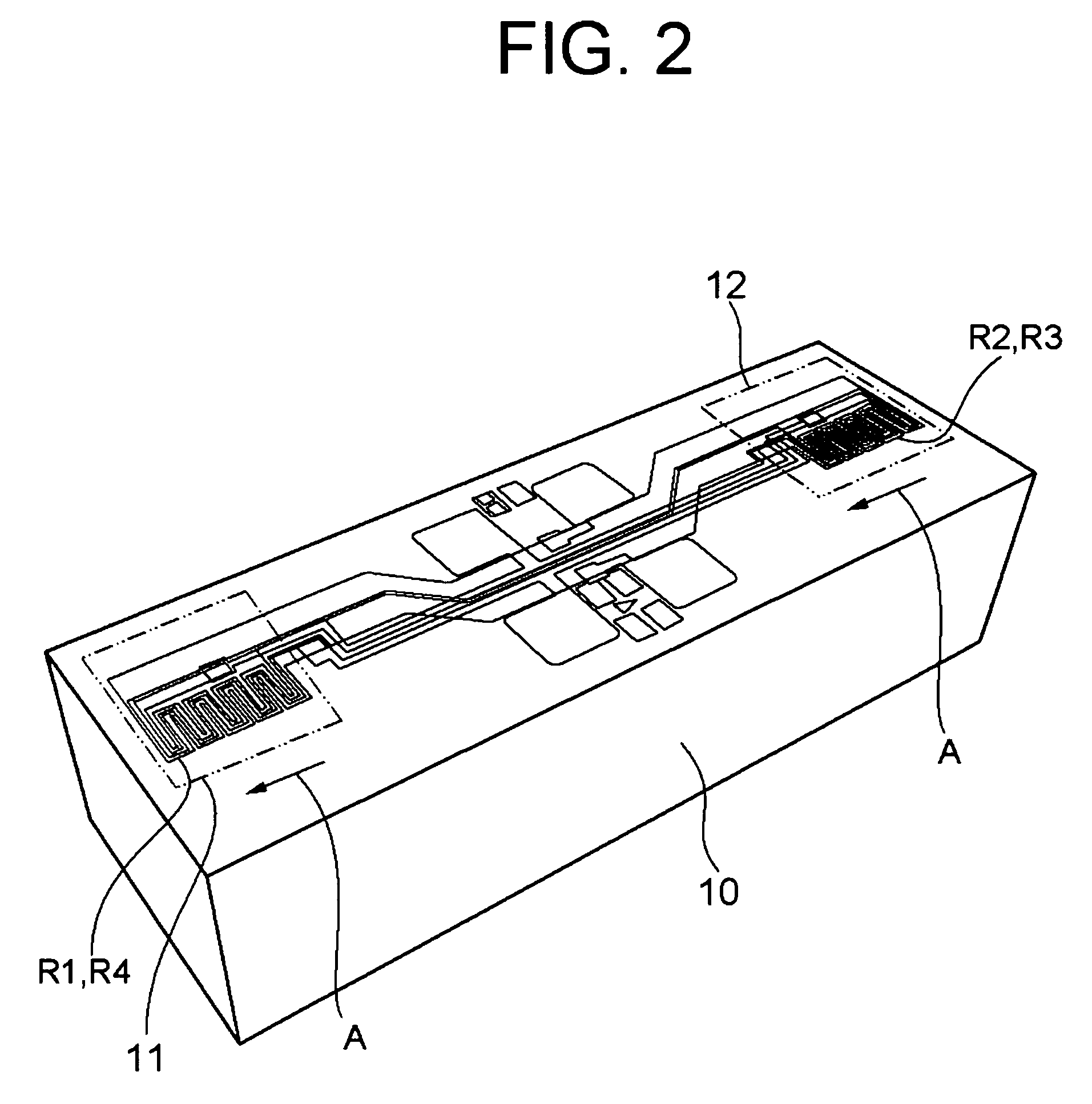
InactiveUS20070113648A1Reduce variationReduce sensor costSolid-state devicesUsing mechanical meansMoisture sensorRelative permittivity
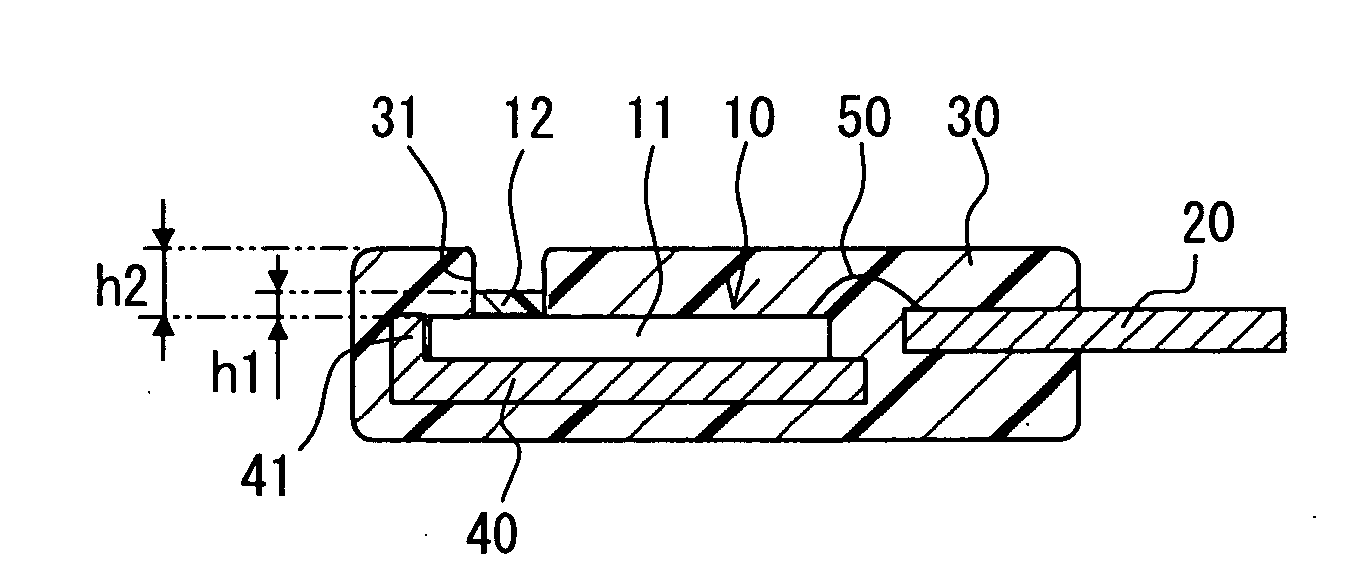
A humidity sensor includes: a sensor chip including a capacitive humidity sensor element and a connection electrode, wherein the capacitive humidity sensor element includes a humidity sensitive film having relative permittivity changeable in accordance with humidity, and wherein the connection electrode is electrically connected to the humidity sensor element; a lead plate electrically connected to the connection electrode; and a mold for covering a connection portion between the connection electrode and the lead plate. The mold is disposed on the sensor chip and includes a groove. The humidity sensitive film is disposed in the groove. The humidity sensitive film has a height in the groove, the height equal to or lower than a surface of the mold. The height of the humidity sensitive film in the groove is homogeneous.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS8193805B2Improving accuracy in detecting magnetic fieldReduce variationWave amplification devicesMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetoHemt circuits
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Ultrasonic sensor having transmission device and reception device of ultrasonic wave
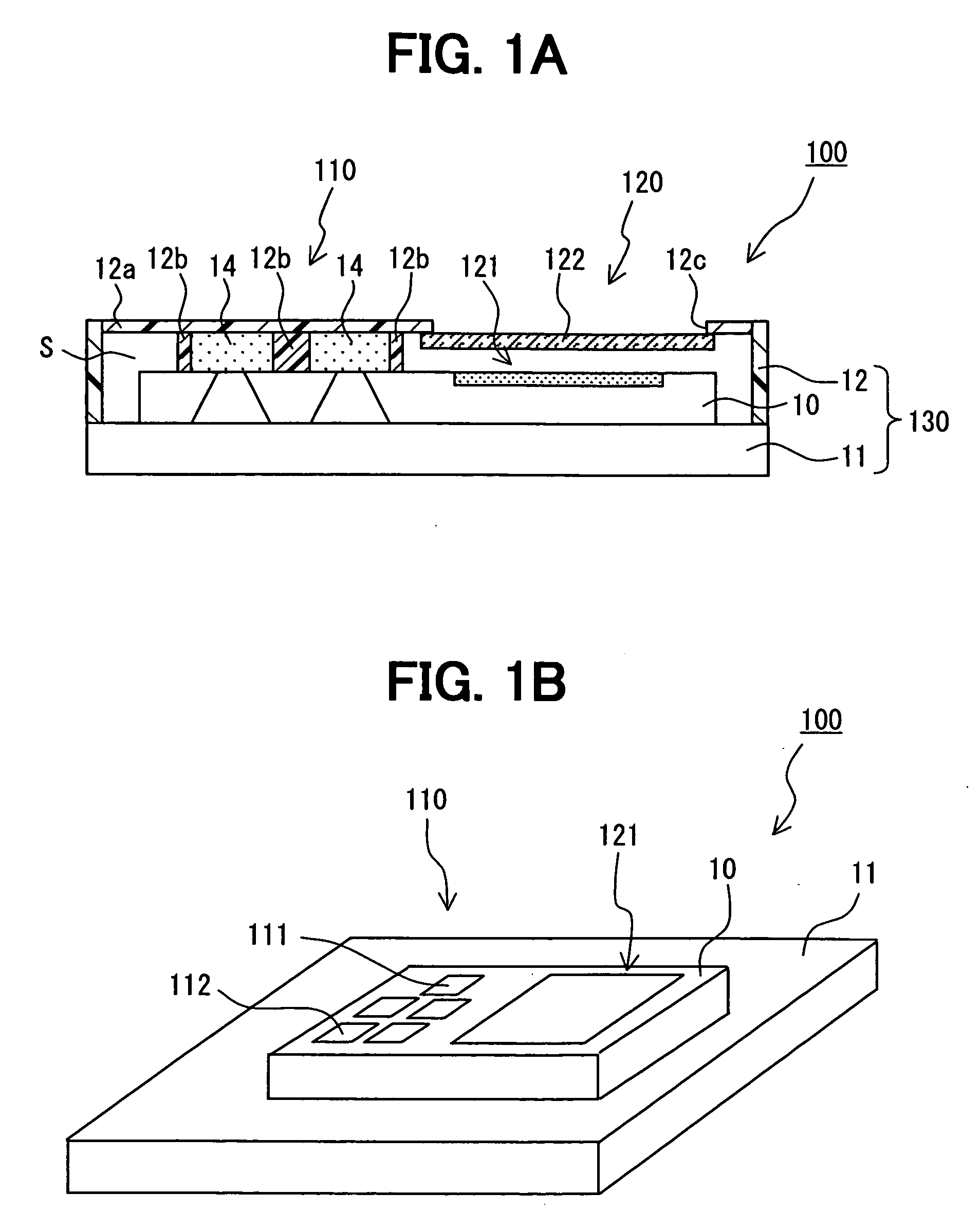
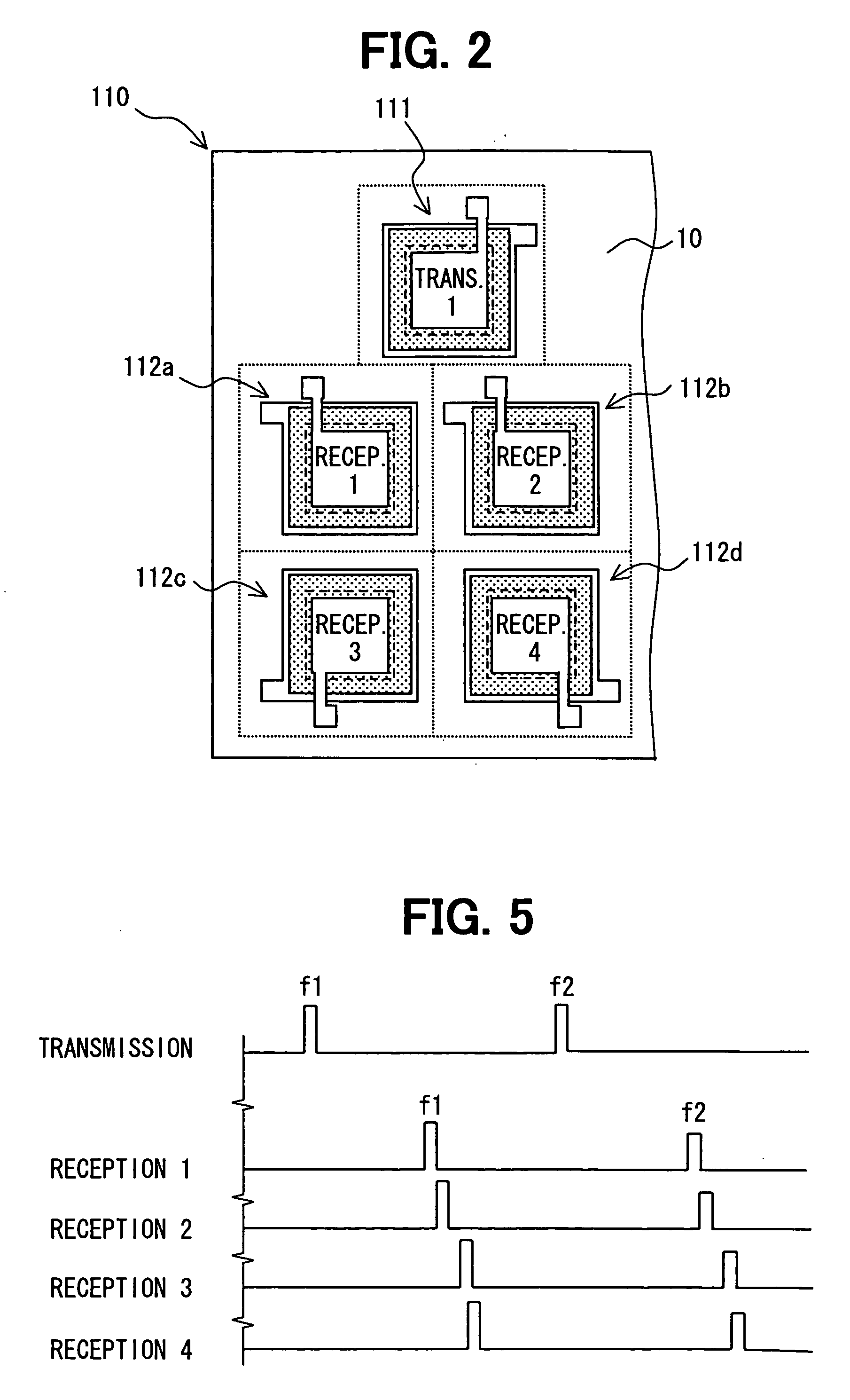
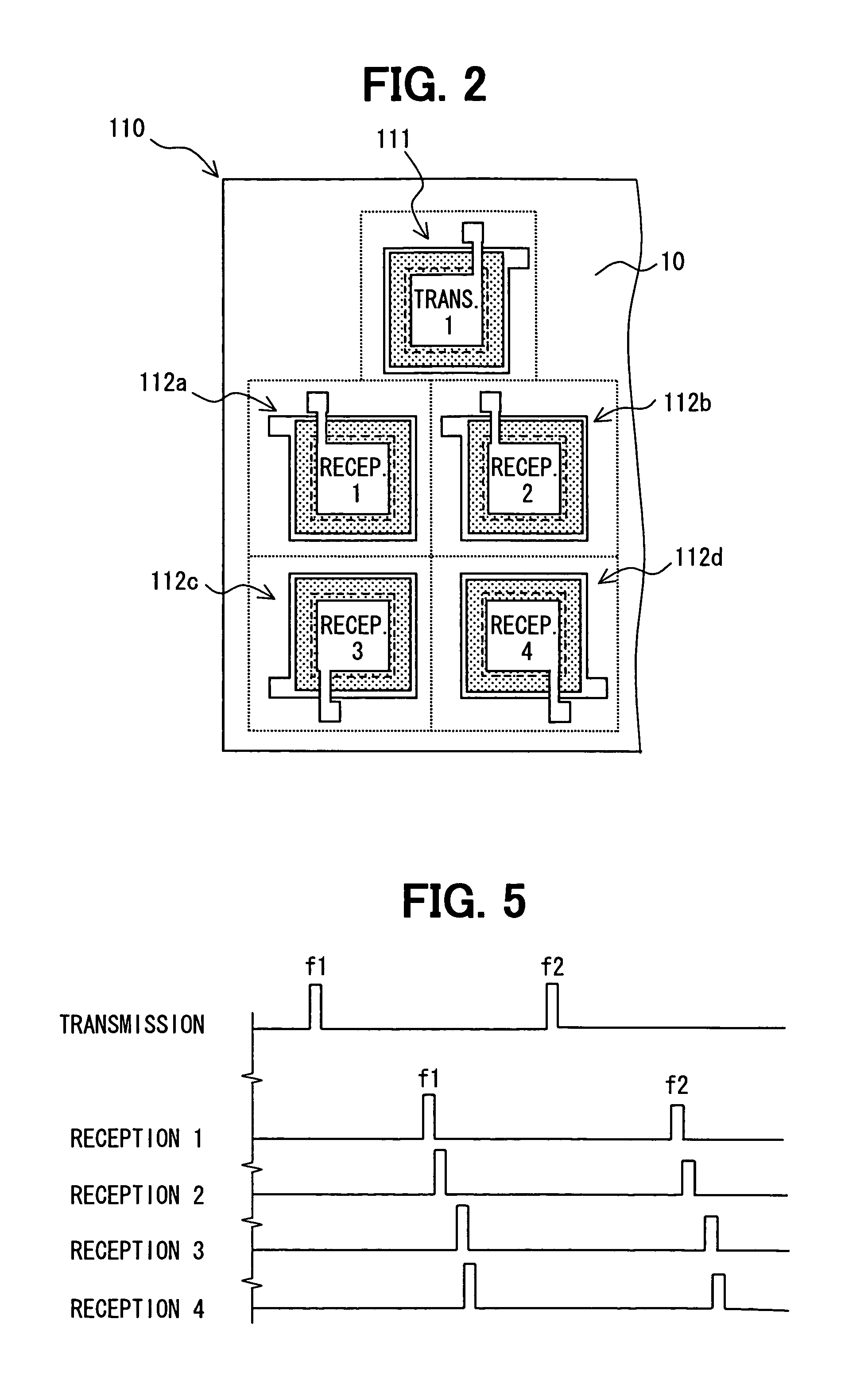
InactiveUS20090107243A1Accurately determineReduce sensor costAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersUltrasonic sensorUltrasound
An ultrasonic sensor for detecting an object includes: a substrate; a transmission device for transmitting an ultrasonic wave; a plurality of reception devices for receiving the ultrasonic wave; and a circuit for processing received ultrasonic waves, which are received by the reception devices after the ultrasonic wave transmitted from the transmission device is reflected by the object. The transmission device and the reception devices are integrated into the substrate. The dimensions of the sensor are minimized, and detection accuracy of the sensor is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
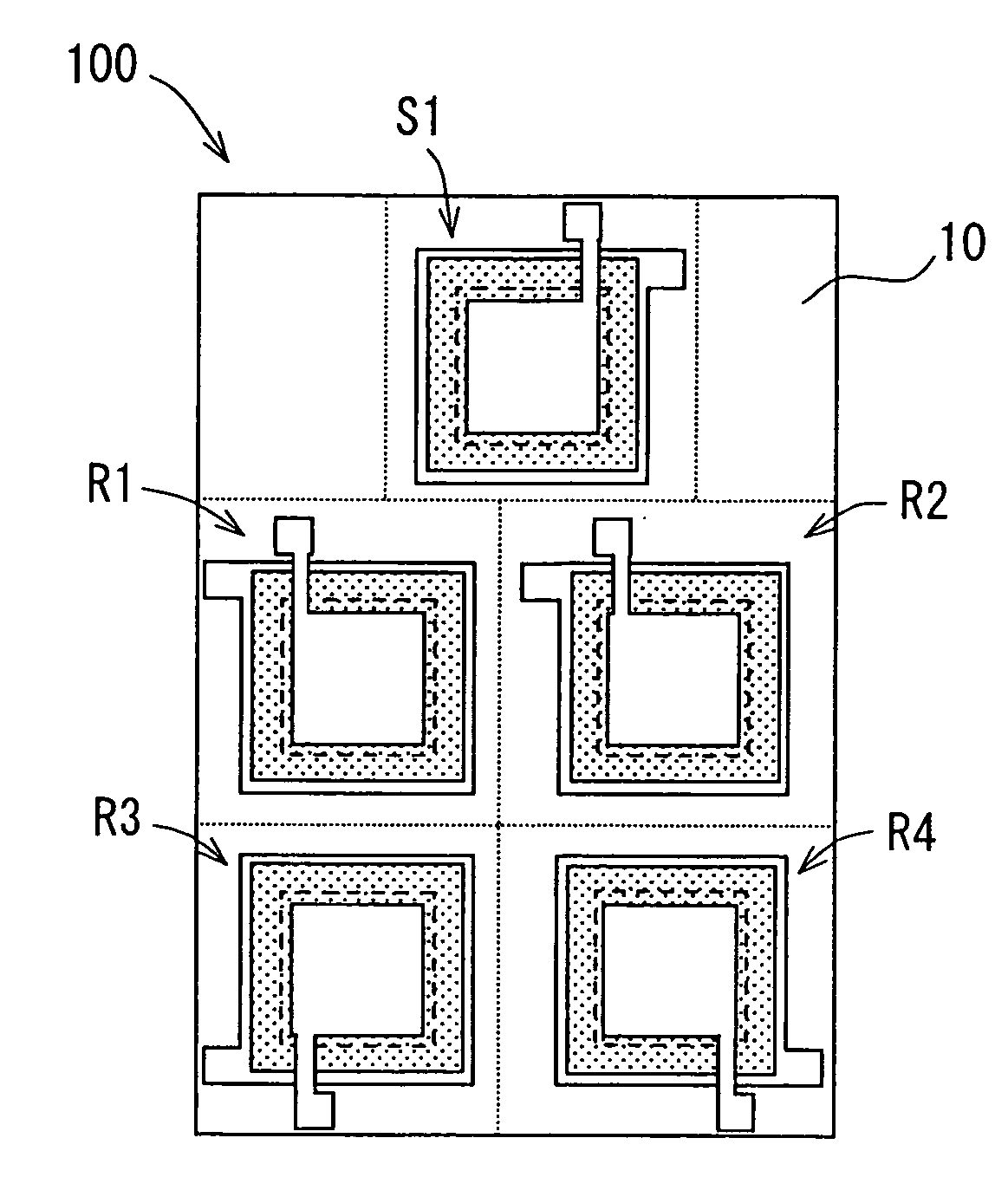
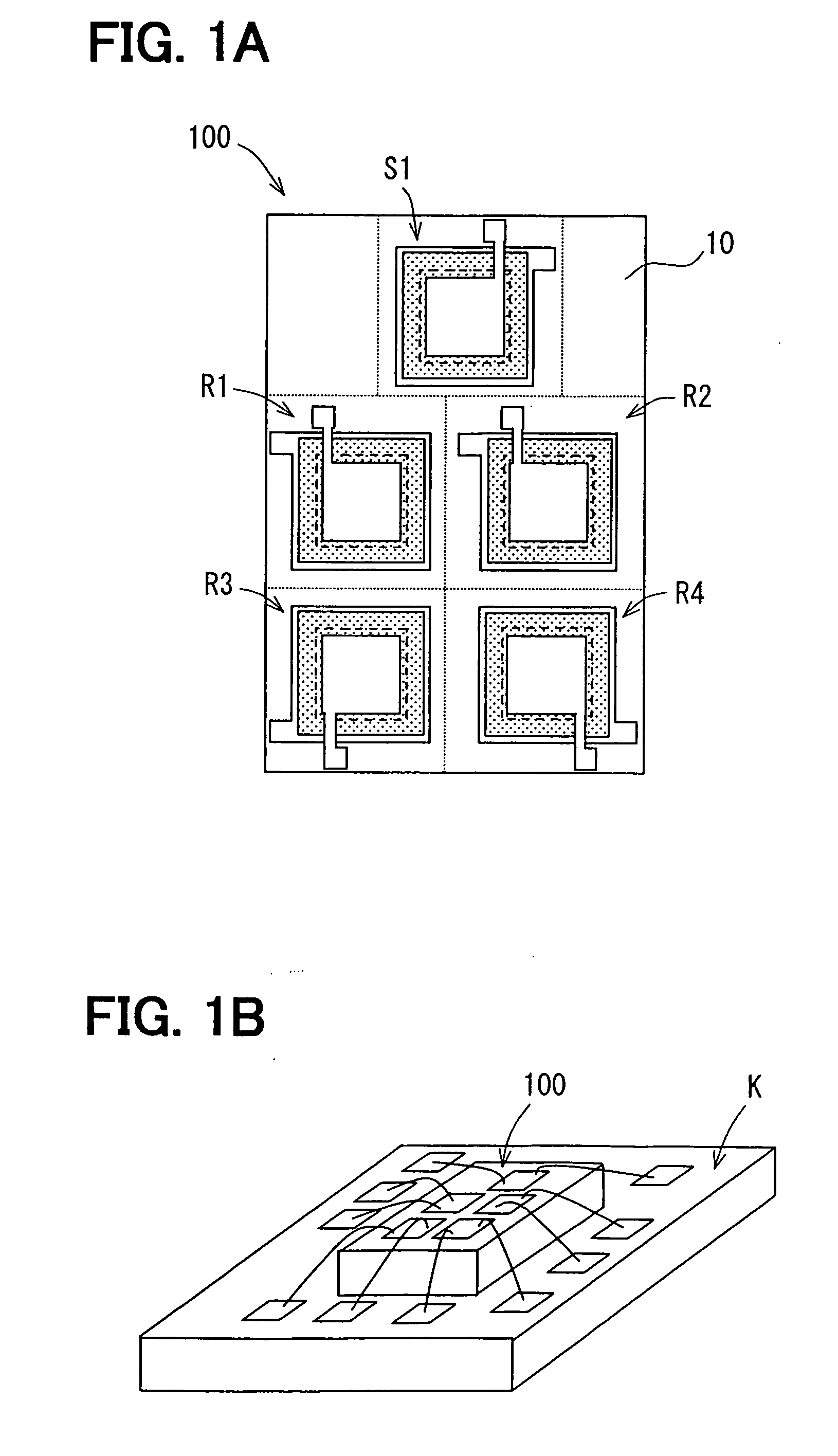
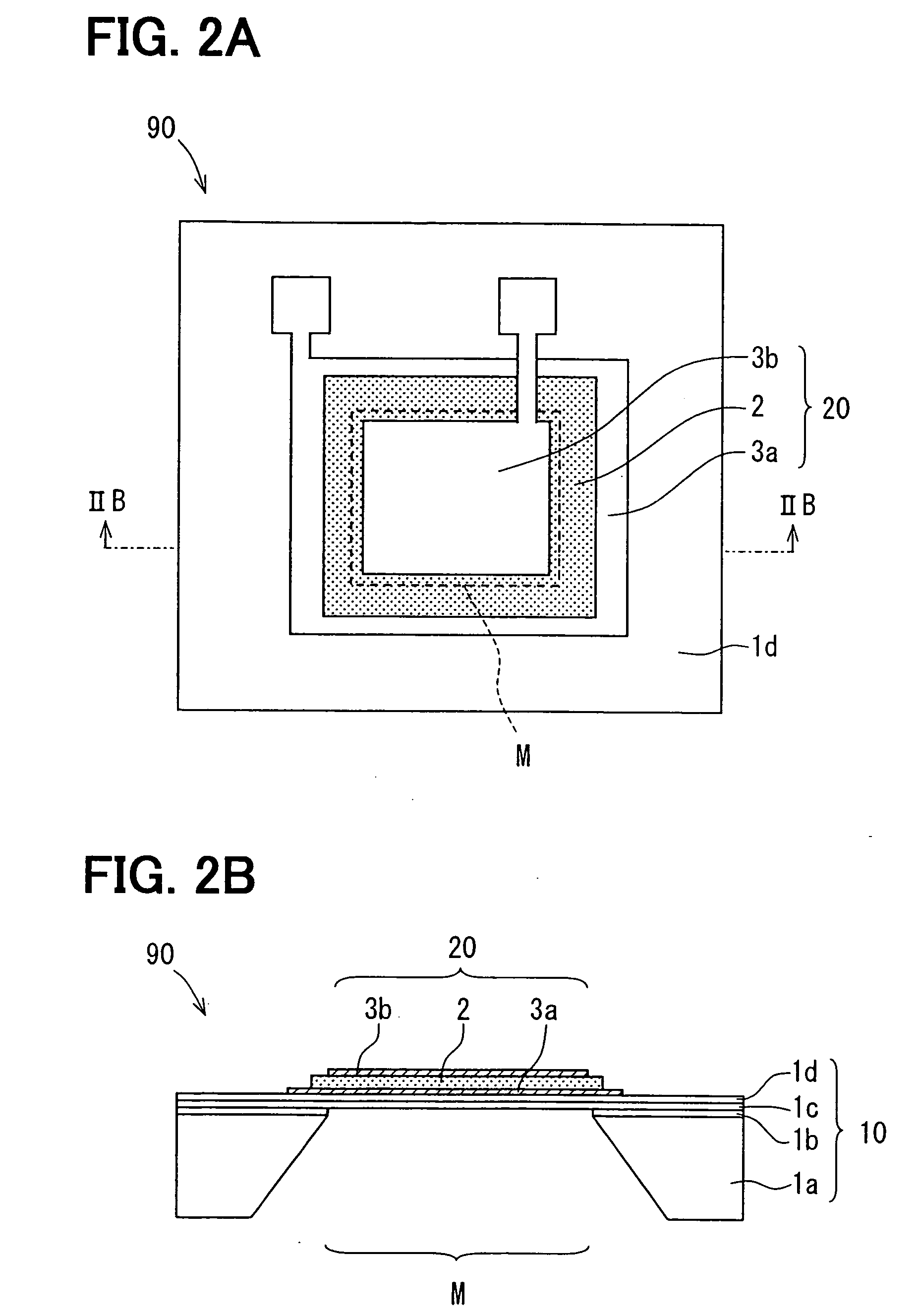
Capacitive humidity sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060238290A1Improve detection accuracyWell formedElectrolytic capacitorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRing patternMoisture sensor
A capacitive humidity sensor includes: a humidity sensing element; a substrate; and an insulation film. The humidity sensing element includes a pair of comb-shape electrodes and a humidity sensitive film. The comb-shape electrodes are surrounded by a dam provided by a part of the insulation film. The insulation film on the comb-shape electrodes has a first height. The part of the insulation film on the dam has a second height higher than the first height. The humidity sensitive film has a height equal to or lower than the second height, and is disposed inside of the dam. The dam further includes a first ring pattern made of a same material as the comb-shape electrodes.
Owner:DENSO CORP
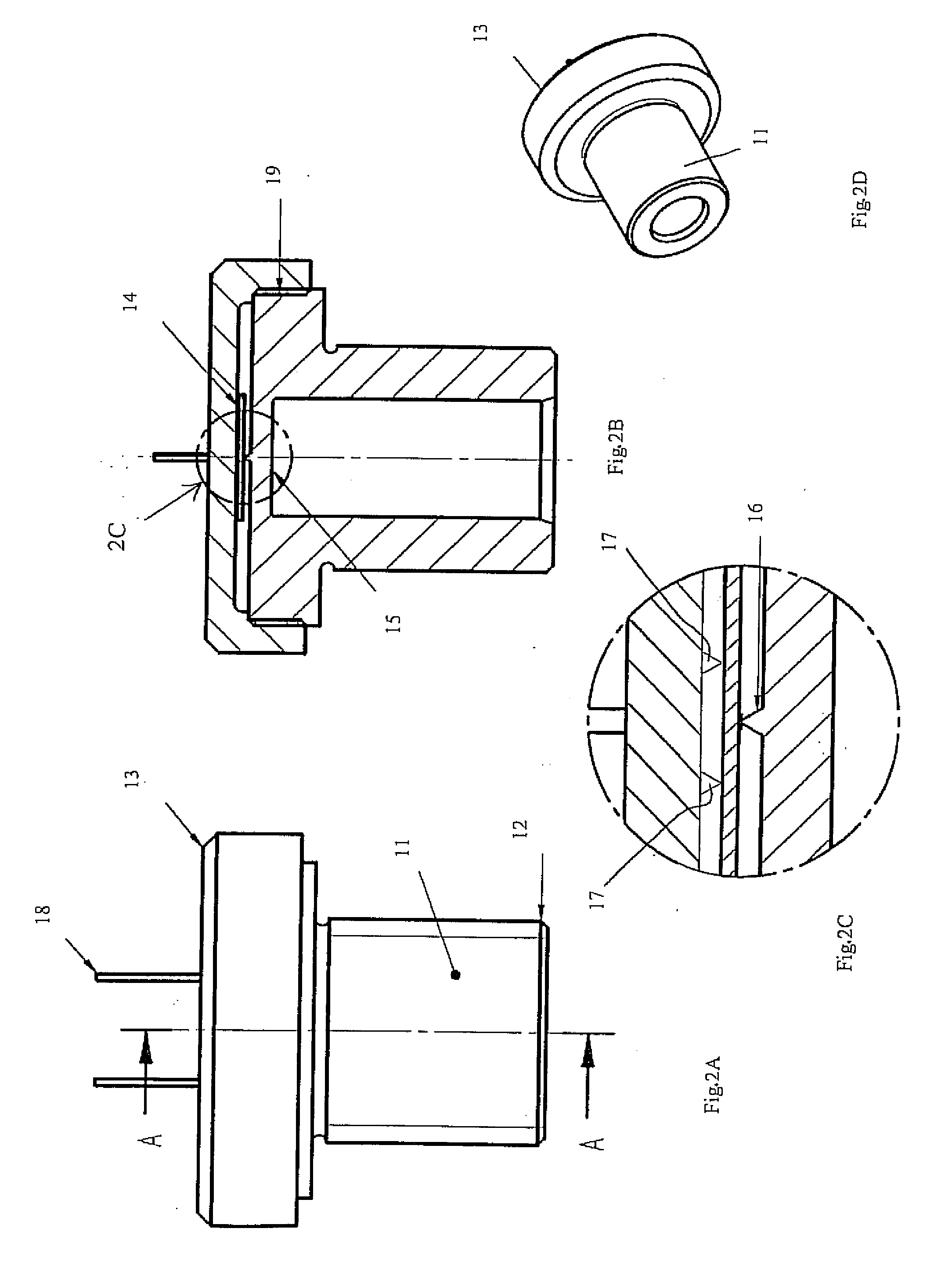
Saw sensor with adjustable preload
InactiveUS20090001850A1Less deformationSimplify the assembly processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMeasurement apparatus componentsEngineeringInternal cavity
A SAW based sensor having a base and a lid engageable with the base to form an internal cavity therewith. A substrate is supported in the cavity on either tile base or the lid 13 and a dimple 16 is formed on the other which extends towards the substrate so as to engage against the substrate and apply a preload thereto. The base and lid include complementary threads by means of which they are attachable to each other. The preload applied to the substrate by the dimple 16 is adjustable by varying the rotational position of the lid relative to the base.
Owner:TRANSENSE TECH
Ultrasonic sensor having transmission device and reception device of ultrasonic wave
InactiveUS7540194B2Accurately determineReduce sensor costMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUltrasonic sensorUltrasound
An ultrasonic sensor for detecting an object includes: a substrate; a transmission device for transmitting an ultrasonic wave; a plurality of reception devices for receiving the ultrasonic wave; and a circuit for processing received ultrasonic waves, which are received by the reception devices after the ultrasonic wave transmitted from the transmission device is reflected by the object. The transmission device and the reception devices are integrated into the substrate. The dimensions of the sensor are minimized, and detection accuracy of the sensor is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and device for demodulation of signals
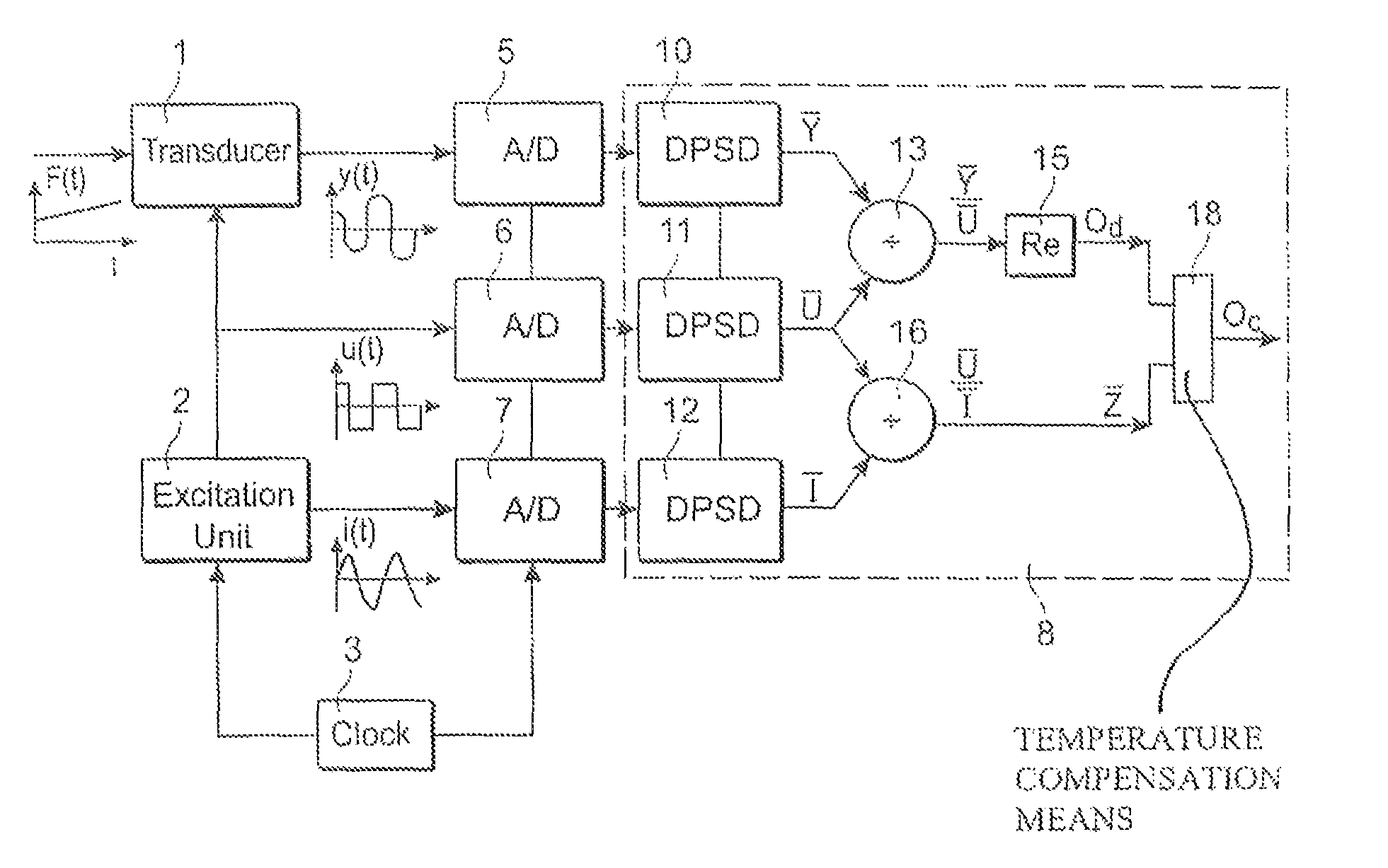
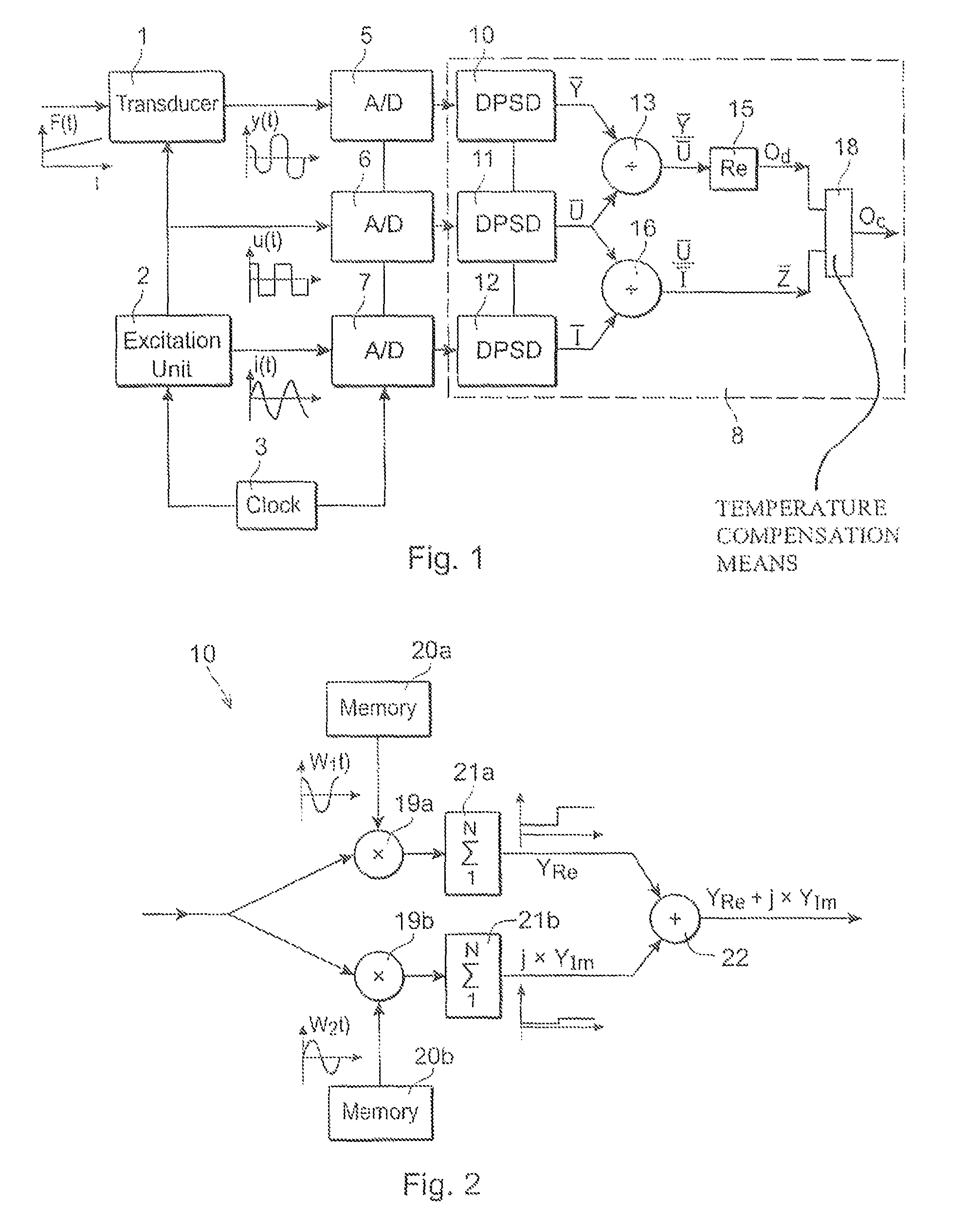
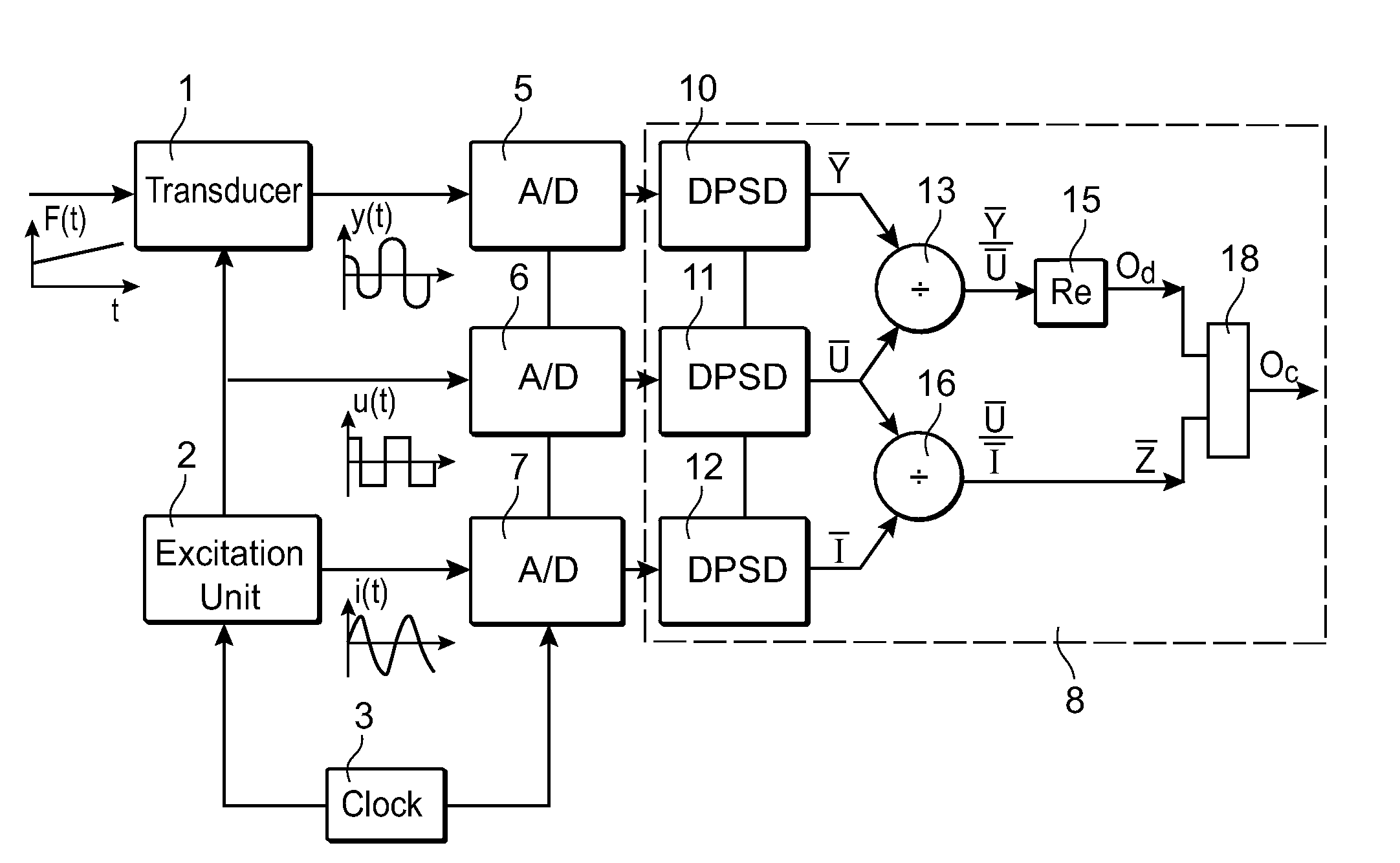
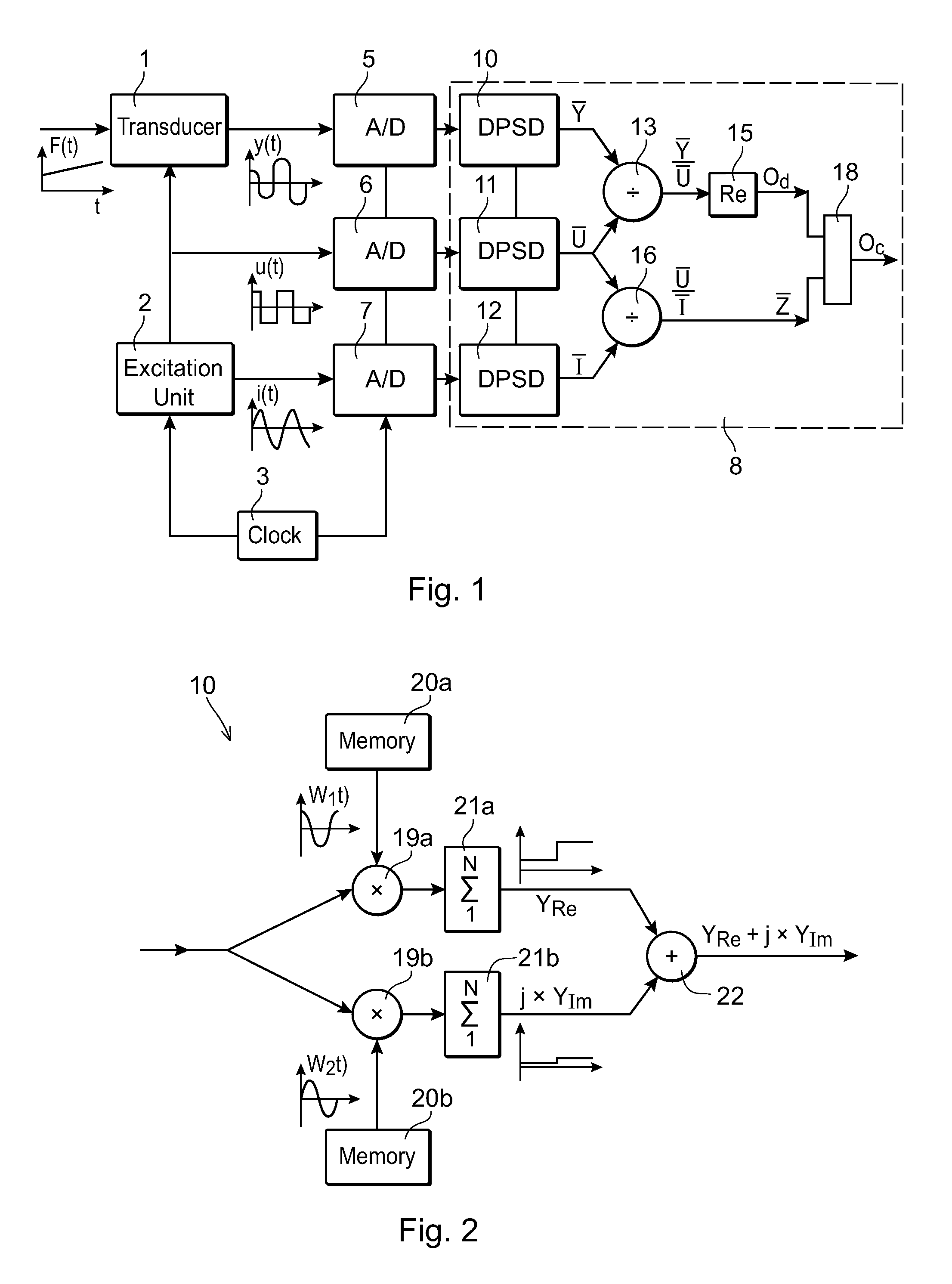
ActiveUS8063648B2Enhance demodulationReduce sensor costResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementTransducerExcitation signal
A method and device are provided for demodulation of an output signal from a transducer (1) driven by an alternating excitation signal having an excitation frequency. The transducer produces an amplitude-modulated output signal (y(t)) containing the quantity to be measured. The device has sampling units (5,6,7) to sample the output signal from the transducer and the output signal from the excitation unit, and a computation unit (8) to compute a first complex valued quantity ( Y) including information on the amplitude and phase of the output signal at the excitation frequency based on sampled values of the output signal from the transducer, compute a second complex valued quantity (Ū, Ī) including information on the amplitude and phase of the excitation signal at the excitation frequency based on sampled values of the excitation signal, forming a complex valued output quotient between the first and second complex valued quantities, and compute the demodulated output signal (Od) based on the output quotient.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Humidity sensor having humidity sensitive film and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7644615B2Reduce variationReduce sensor costSolid-state devicesUsing mechanical meansMoisture sensorRelative permittivity
A humidity sensor includes: a sensor chip including a capacitive humidity sensor element and a connection electrode, wherein the capacitive humidity sensor element includes a humidity sensitive film having relative permittivity changeable in accordance with humidity, and wherein the connection electrode is electrically connected to the humidity sensor element; a lead plate electrically connected to the connection electrode; and a mold for covering a connection portion between the connection electrode and the lead plate. The mold is disposed on the sensor chip and includes a groove. The humidity sensitive film is disposed in the groove. The humidity sensitive film has a height in the groove, the height equal to or lower than a surface of the mold. The height of the humidity sensitive film in the groove is homogeneous.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Obstacle sensor having supersonic sensor
InactiveUS7420876B2Small sizeWide detection rangeVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound
Owner:DENSO CORP
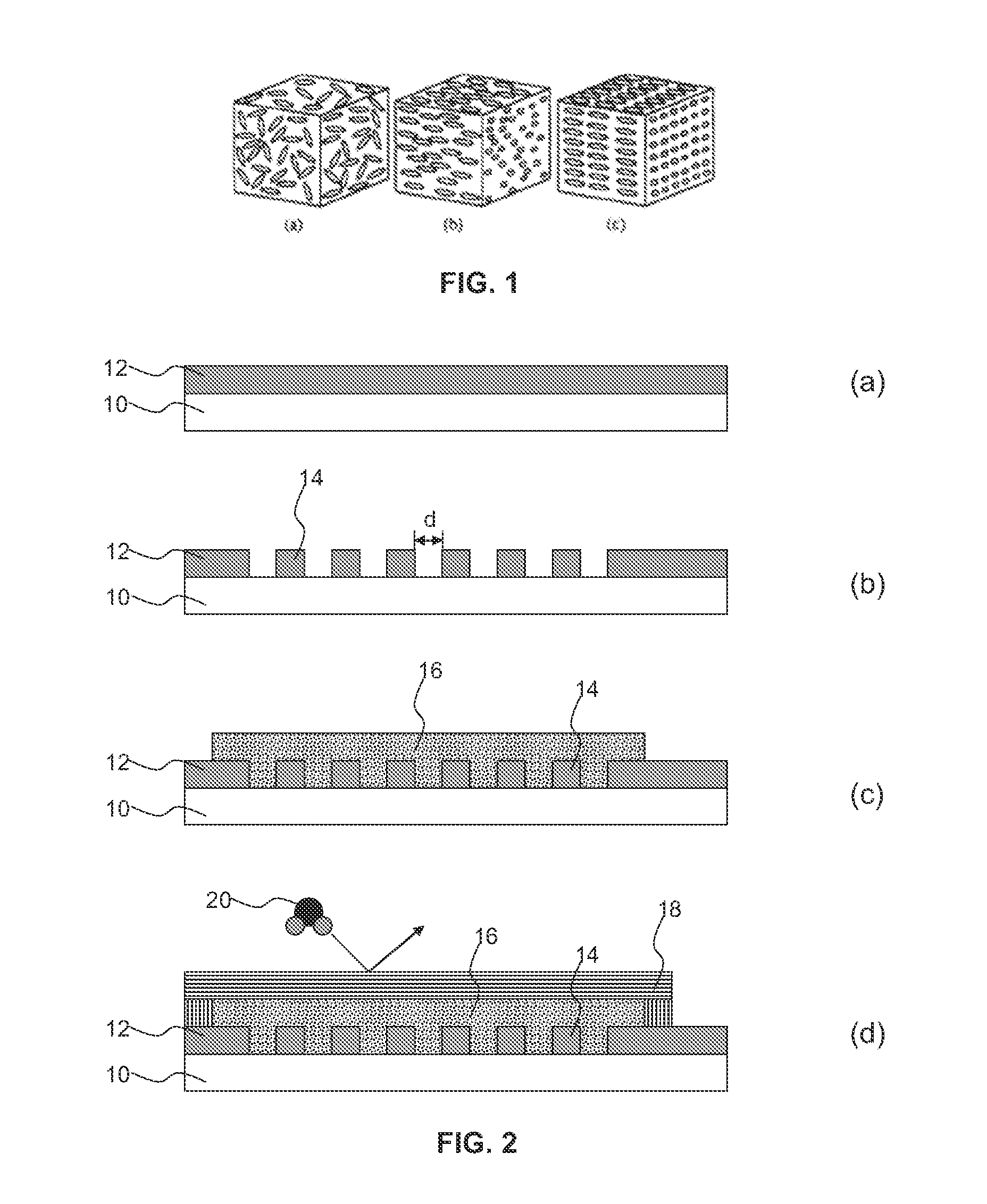
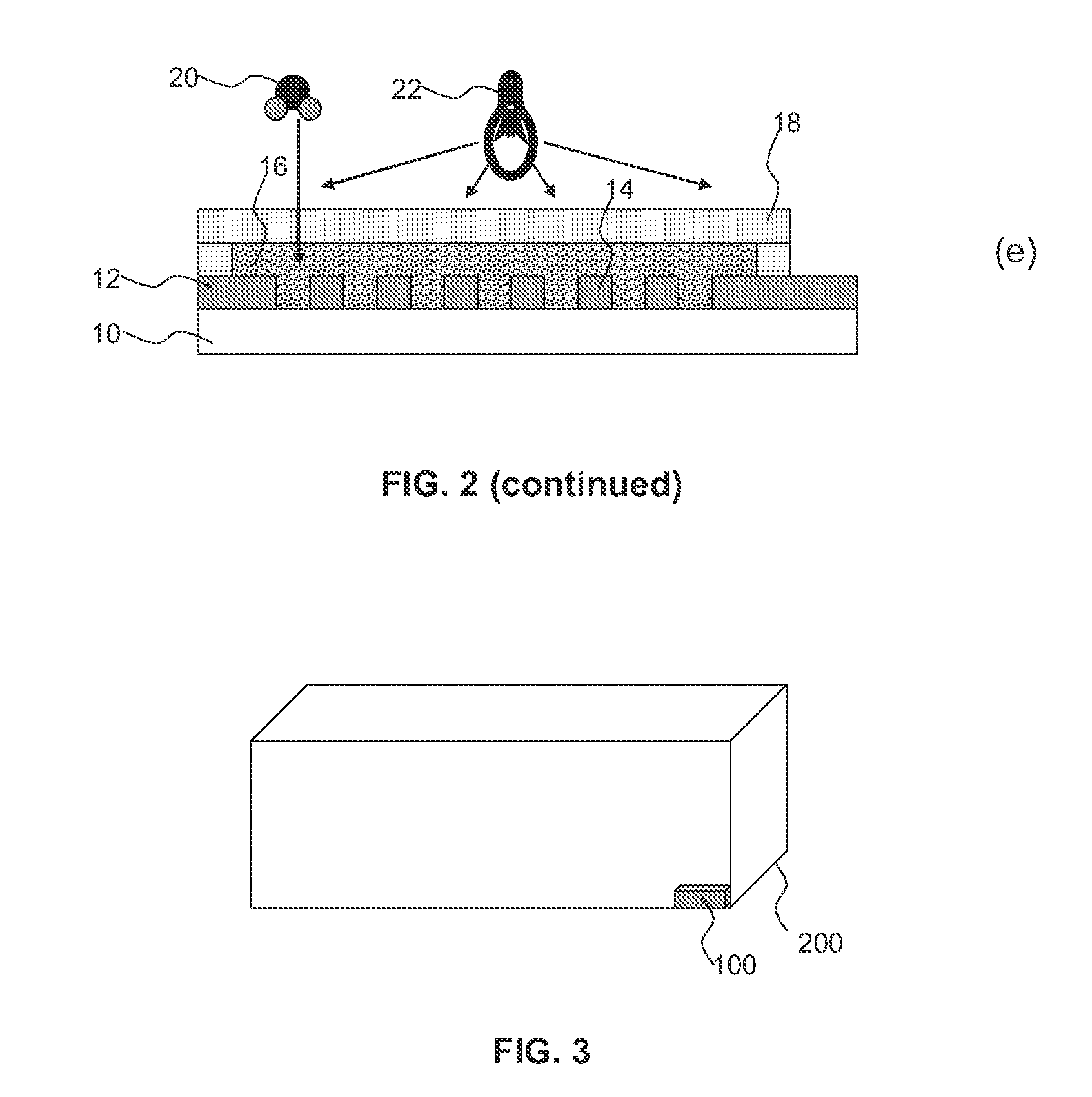
Atmospheric Sensor, NFC Device, Package and Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20120234079A1Increase exposureProtection elementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUsing mechanical meansEngineeringAtmosphere
Disclosed is a sensor for detecting a component (20) of an atmosphere, the sensor comprising a sensing surface (14, 16) covered by a barrier layer (18) of a material switchable between respective layer orientations that have permeability to the component. A NFC device comprising such a sensor, a package incorporating the NFC device and a method of manufacturing the sensor are also disclosed.
Owner:NXP BV
Comparator circuit having latching behavior and digital output sensors therefrom
ActiveUS8098062B2Reduce sensor costReduced Power RequirementsCurrent/voltage measurementSolid-state devicesHysteresisEngineering
A digital output sensor (110) includes a sensing structure (105) including at least one sensing element. The sensing structure (105) outputs a differential sensing signal (106, 107). An integrated circuit (100) includes a substrate (101) including signal conditioning circuitry for conditioning the sensing signal (106, 107). The signal conditioning circuitry includes a differential amplifier (115) coupled to receive the sensing signal and provide first and second differential outputs (116, 117), and a comparator (120) having input transistors (Q27, Q28) coupled to receive outputs from the differential amplifier. The comparator (120) also includes first and second current-mirror loads (Q19 / Q21 and Q22 / Q20) coupled to the input transistors (Q27, Q28) in a cross coupled configuration to provide hysteresis, wherein the first and second current-mirror loads provide differential drive currents (121,122). An output driver (125) is coupled to receive the differential drive currents (121, 122). An output stage (130) includes at least one output transistor which is coupled to the output driver for providing a digital output for the sensor. A voltage regulator (140) is coupled to receive a supply voltage (VS) and output at least one regulated supply voltage (VREG), wherein the regulated supply voltage is coupled to the sensing structure (105), the differential amplifier (115) and the comparator (120).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
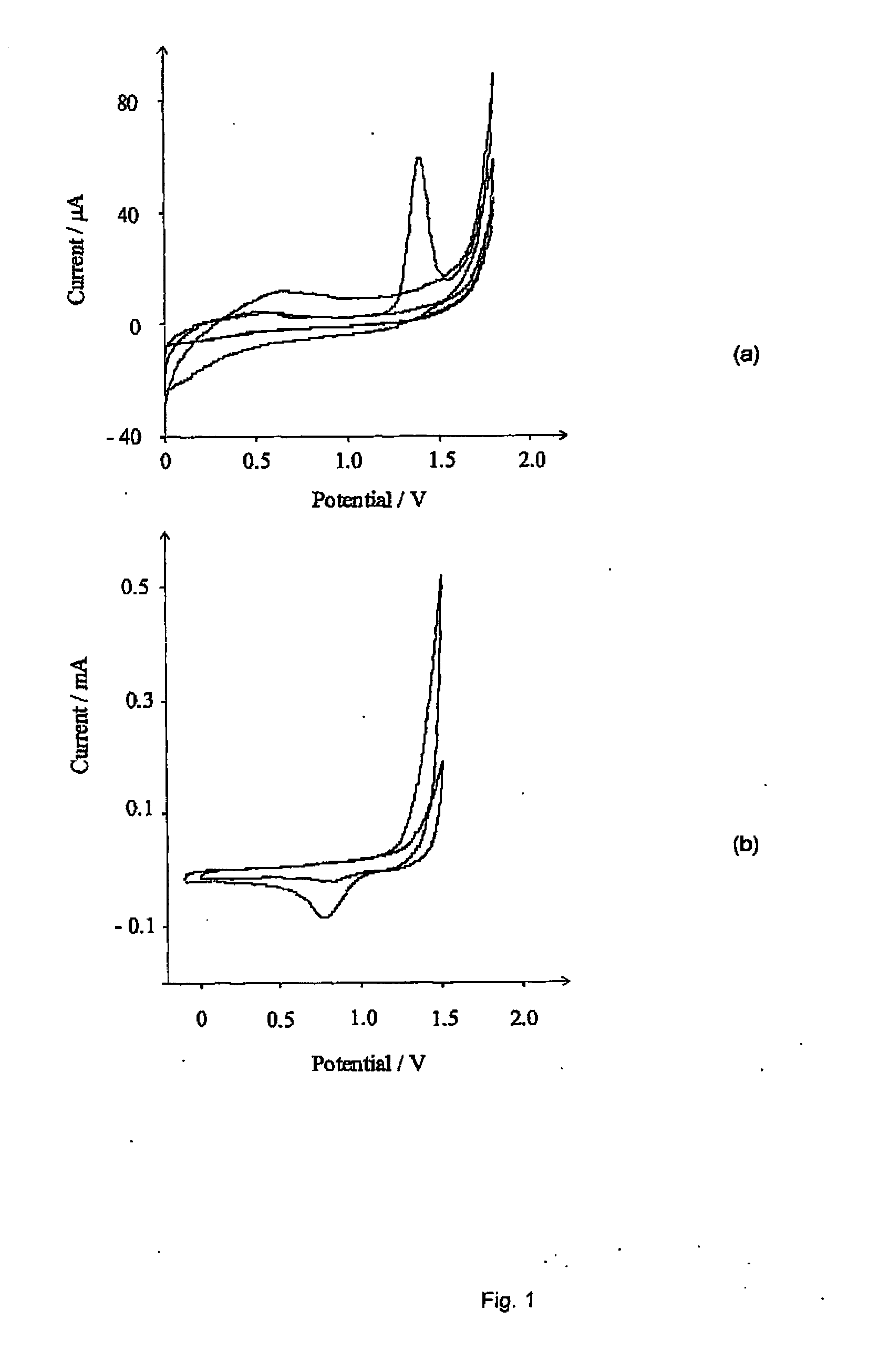
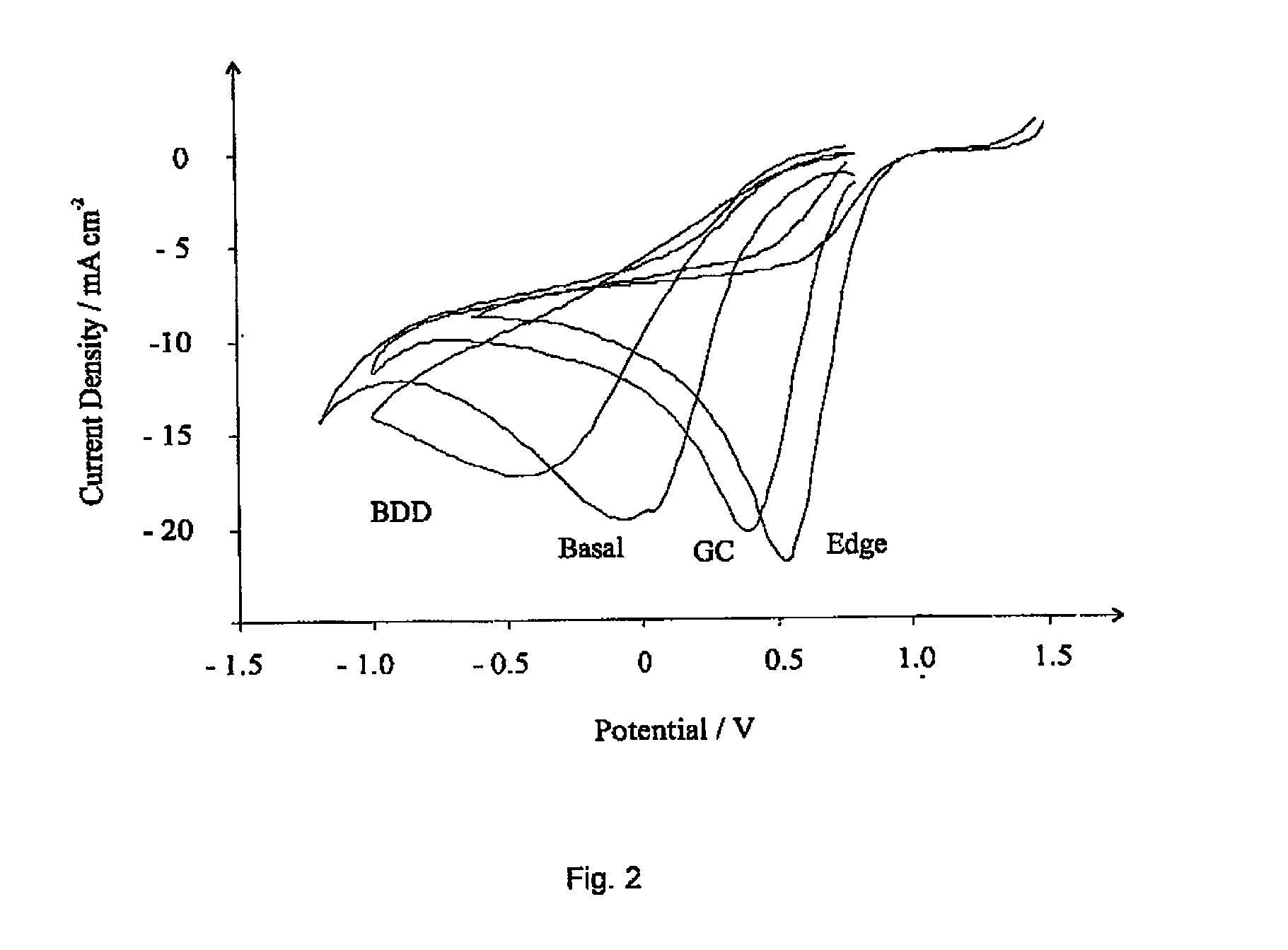
Amperometric Sensor and Method for the Detection of Gaseous Analytes Comprising A Working Electrode Comprising Edge Plane Pyrolytic Graphite
InactiveUS20100147705A1Cost reductionExcellent signalWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementEnvironmental chemistryWorking electrode
An electrochemical sensor and method of detecting gaseous analytes are provided, which involve the use of a working electrode comprising edge plane pyrolytic graphite.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Sensor device, particularly for controlling lighting devices of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS7214918B2Not restrict visual rangeEasy to controlVehicle headlampsRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile vehicleEffect light
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
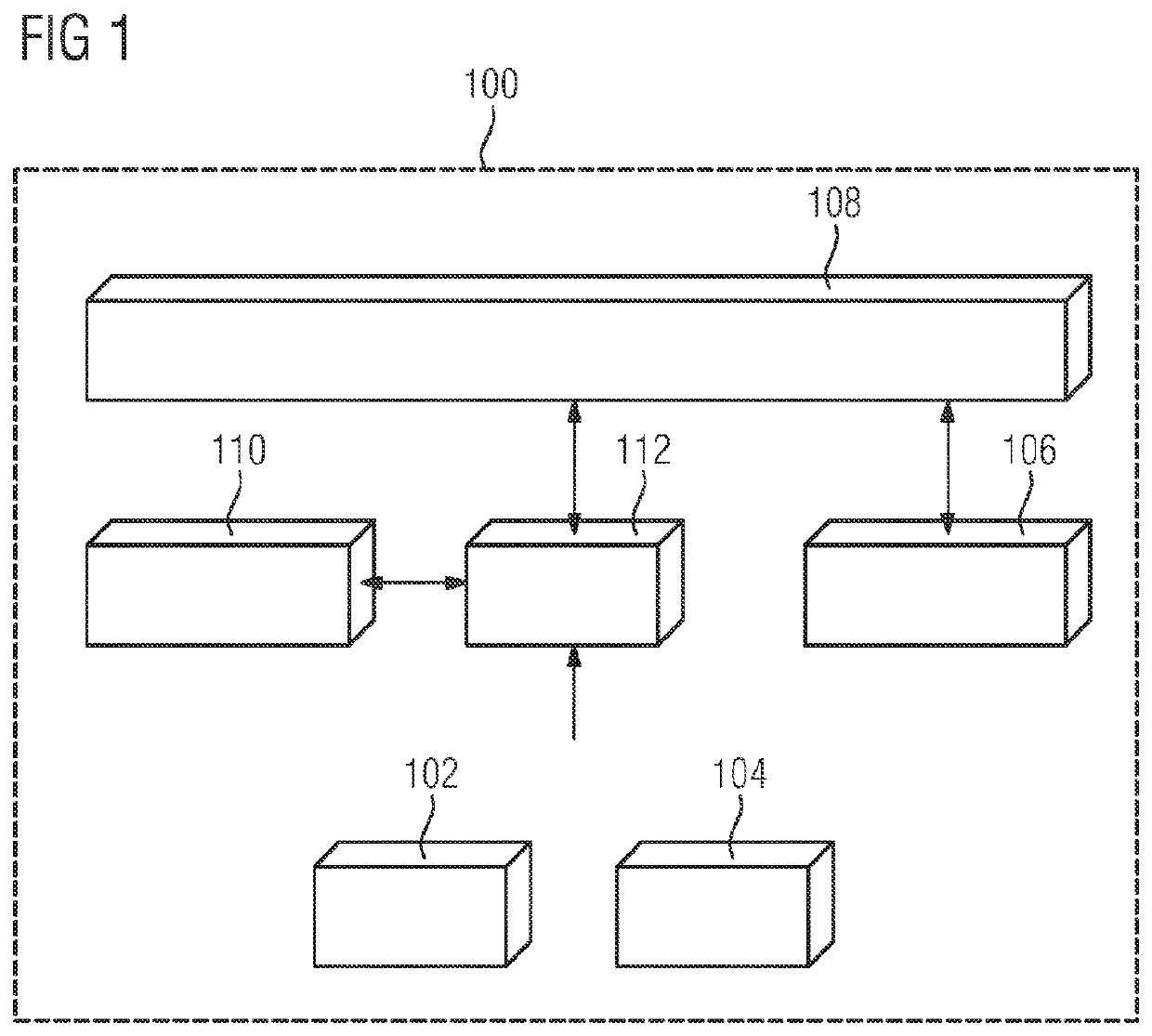
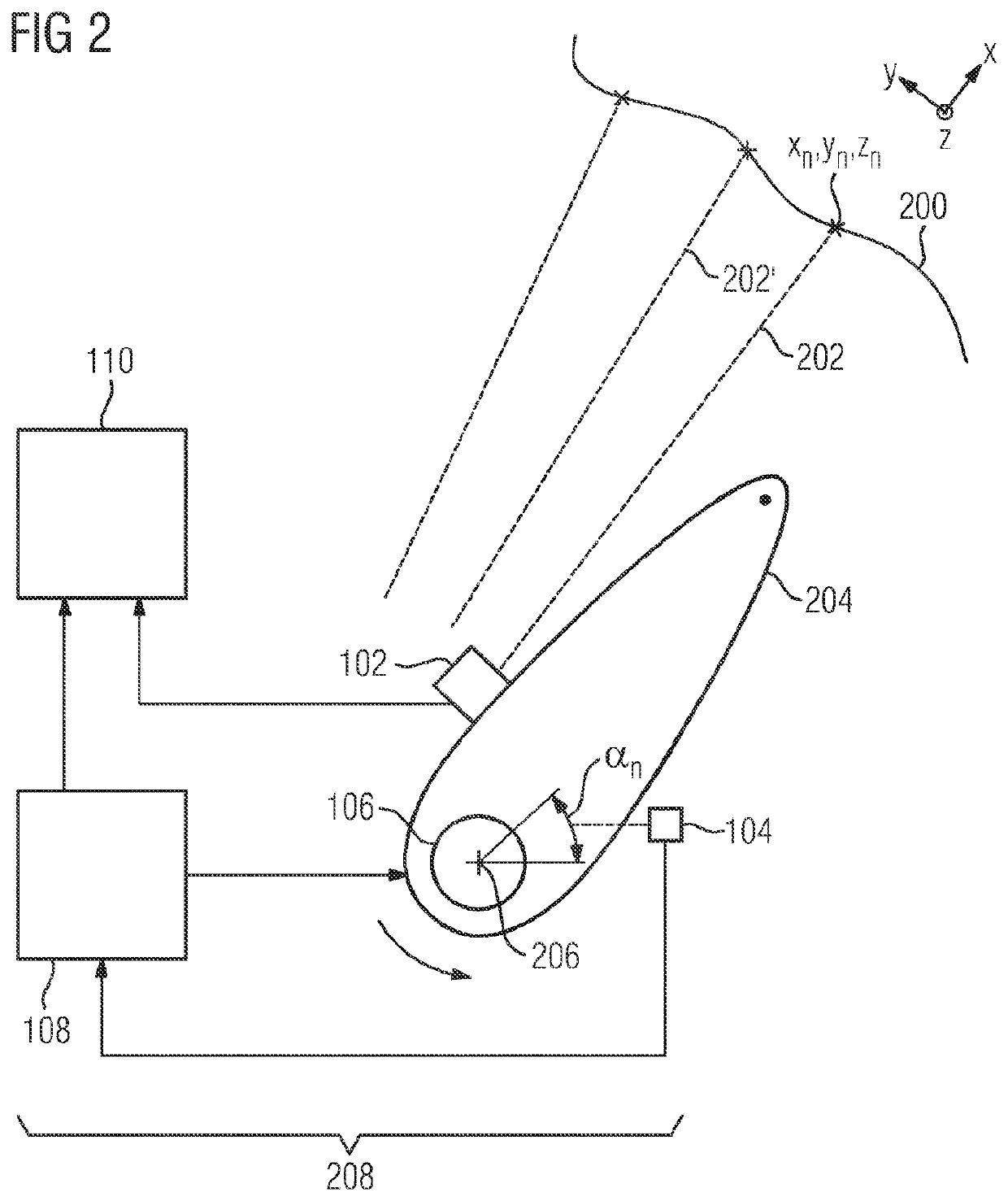
Method and device for determining an N+1-dimensional environment model and mining apparatus
ActiveUS10570589B2Quickly updateReduce automation costsGeometric CADMechanical machines/dredgersEngineeringEnvironmental model
A method for determining an N+1-dimensional environmental model is provided. According to the method, environmental information in N dimensions is determined using a sensor. In a further step, position and / or orientation of the sensor is / are determined. Then, the N+1-dimensional environmental model is determined based on the determined environmental information in N dimensions and the determined position and / or orientation of the sensor. Further, a device and a mining apparatus are provided.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Method and Device for Demodulation of Signals
ActiveUS20100109766A1Enhance demodulationReduce decreaseResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementTransducerExcitation signal
A method and device are provided for demodulation of an output signal from a transducer (1) driven by an alternating excitation signal having an excitation frequency. The transducer produces an amplitude-modulated output signal (y(t)) containing the quantity to be measured. The device has sampling units (5,6,7) to sample the output signal from the transducer and the output signal from the excitation unit, and a computation unit (8) to compute a first complex valued quantity ( Y) including information on the amplitude and phase of the output signal at the excitation frequency based on sampled values of the output signal from the transducer, compute a second complex valued quantity (Ū, Ī) including information on the amplitude and phase of the excitation signal at the excitation frequency based on sampled values of the excitation signal, forming a complex valued output quotient between the first and second complex valued quantities, and compute the demodulated output signal (Od) based on the output quotient.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Voltage sensor for high and medium voltage use and a method of making the same
InactiveUS20150346238A1Reduce effortShorten the timeBase element modificationsManufacture of electrical instrumentsEngineeringHigh pressure
A voltage sensor is disclosed for high and medium voltage use, wherein a voltage divider is arranged in a housing with external creepage distance enlarging ribs. To implement structures for creepage path enlargement to a sensor housing in a very effective and easy way, the voltage divider is arranged in a housing or in housing modules which is or are covered at least partly by at least one shrinking tube of insulating material such that the shrinking creepage enlarging structures are implemented at least at outer surface of the shrinking tube.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Capacitive humidity sensor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7332995B2Improve detection accuracyWell formedElectrolytic capacitorsUsing mechanical meansRing patternEngineering
A capacitive humidity sensor includes: a humidity sensing element; a substrate; and an insulation film. The humidity sensing element includes a pair of comb-shape electrodes and a humidity sensitive film. The comb-shape electrodes are surrounded by a dam provided by a part of the insulation film. The insulation film on the comb-shape electrodes has a first height. The part of the insulation film on the dam has a second height higher than the first height. The humidity sensitive film has a height equal to or lower than the second height, and is disposed inside of the dam. The dam further includes a first ring pattern made of a same material as the comb-shape electrodes.
Owner:DENSO CORP
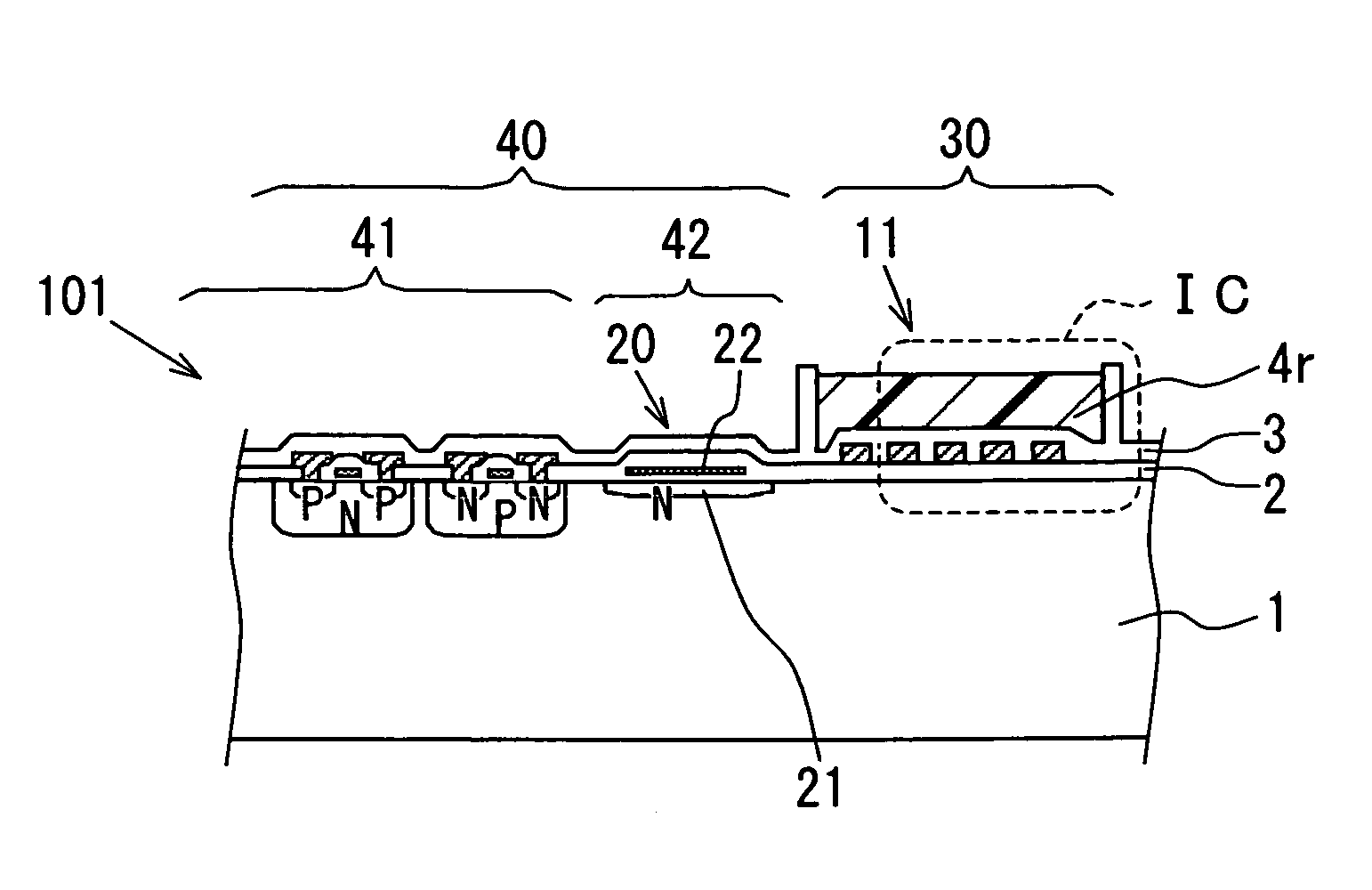
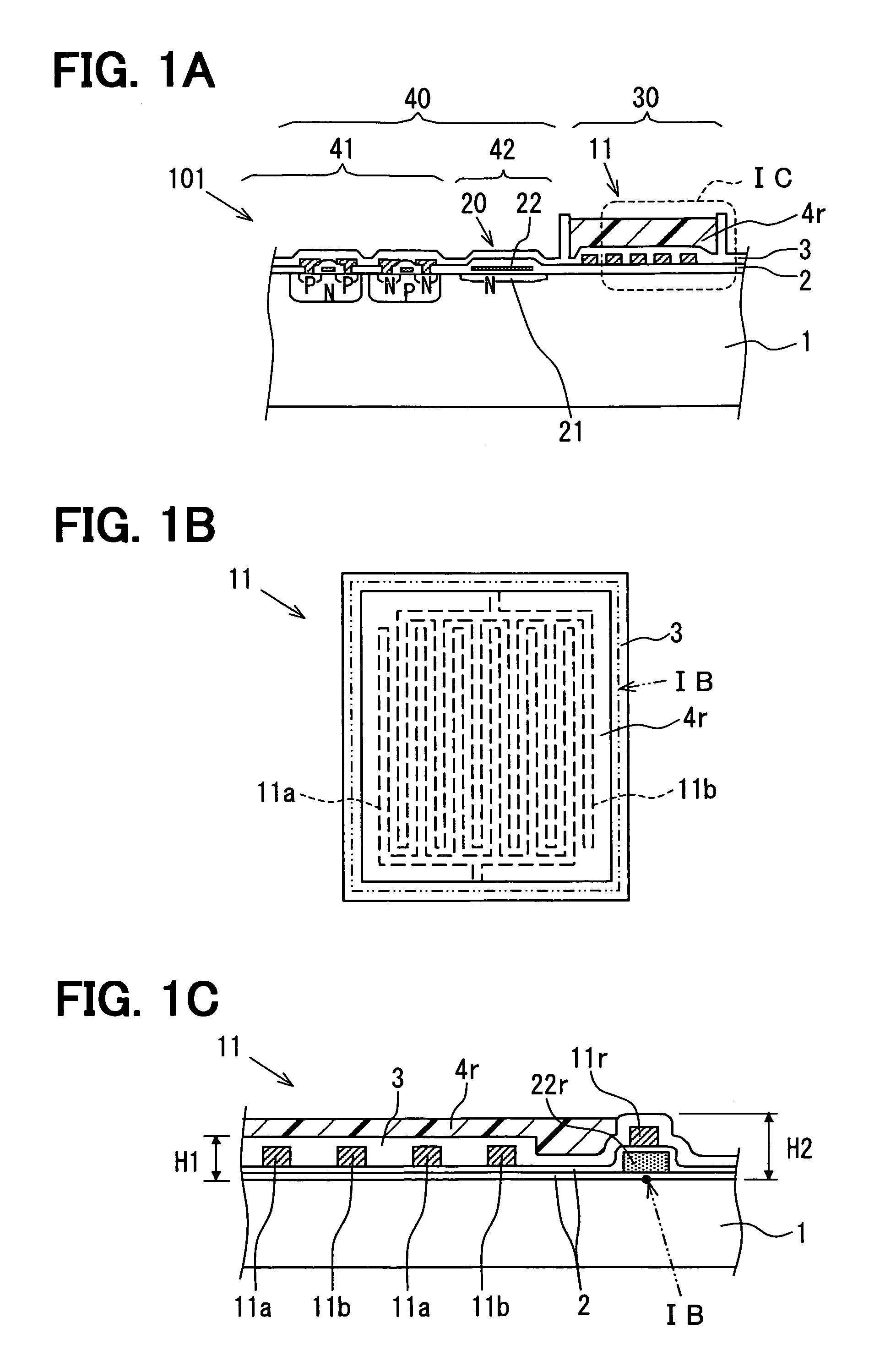
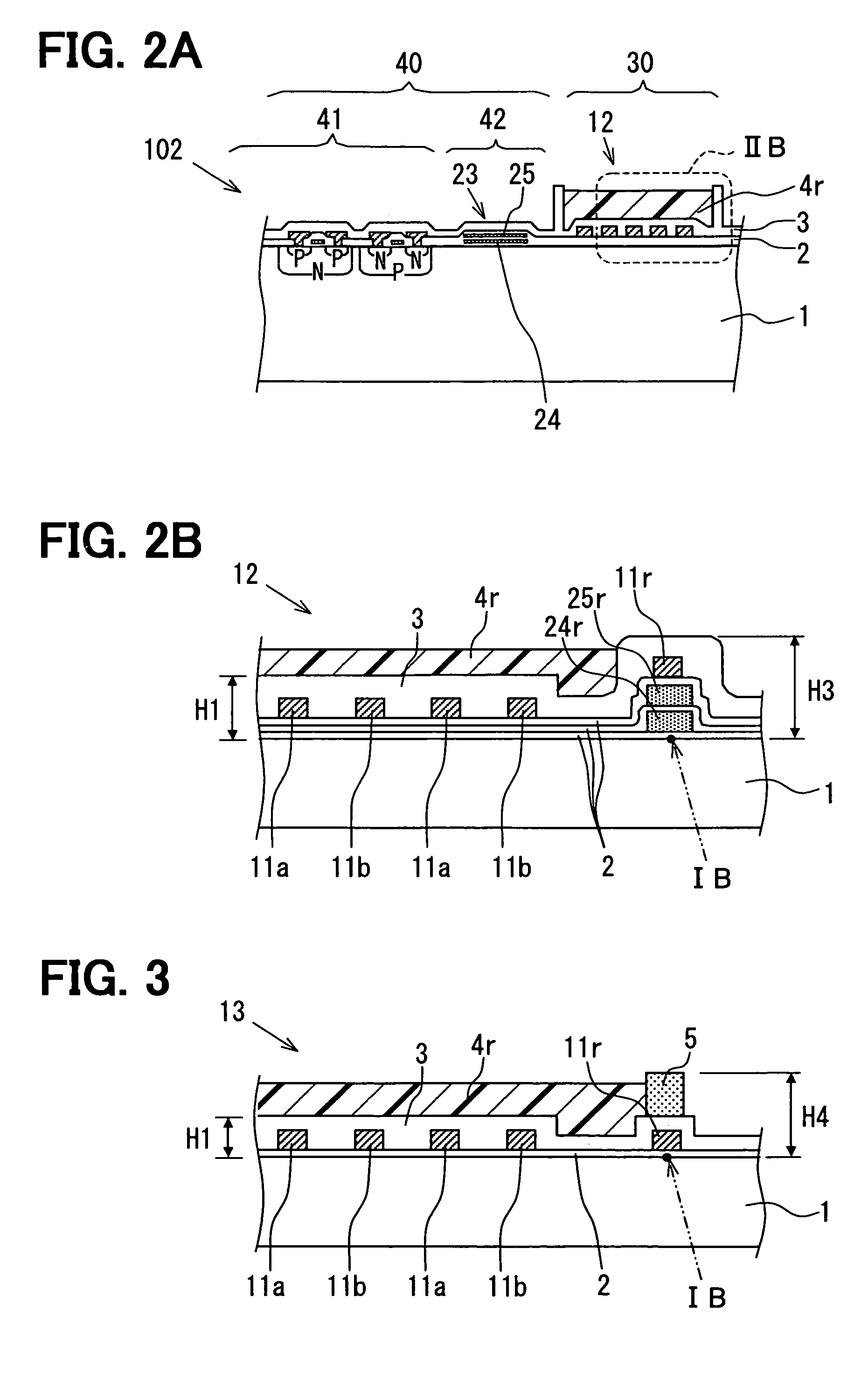
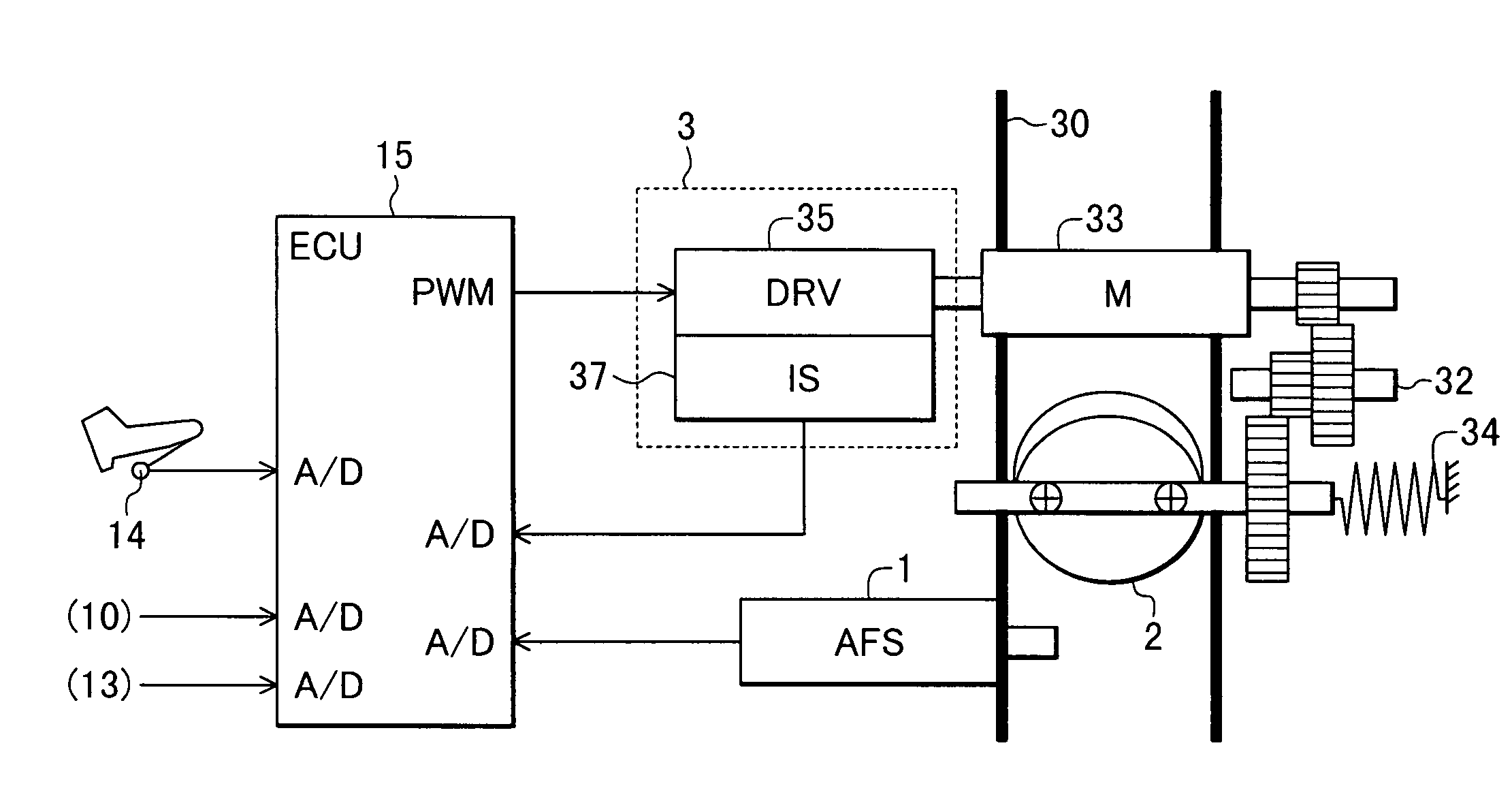
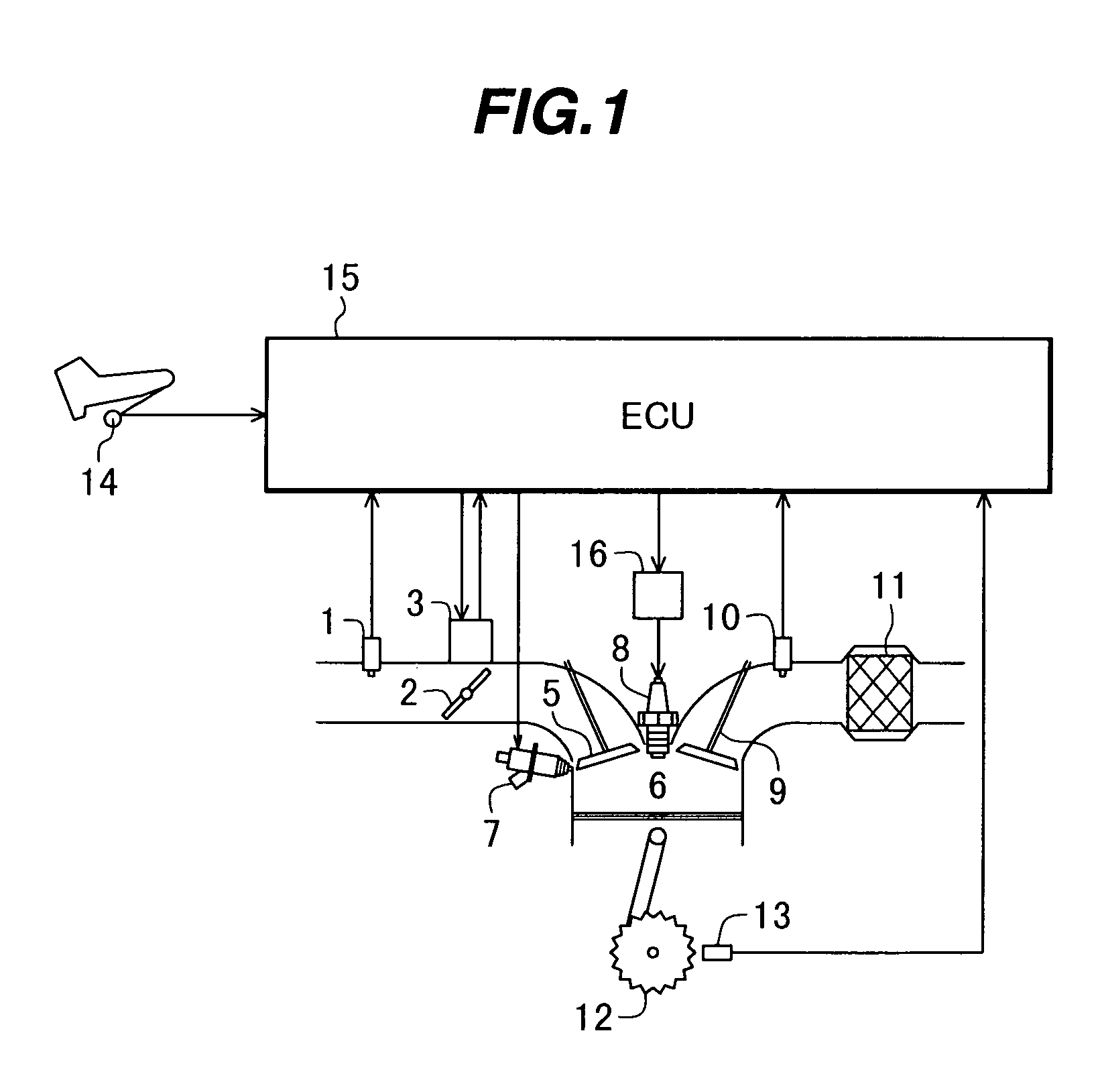
Device for controlling throttle valve
InactiveUS6976470B2Increased durabilityLow costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl delayInternal combustion engine
A control device for a throttle valve, by dispensing a position sensor for the throttle valve, can reduce a cost of the sensor and which is excellent in durability and reliability and is reduced in its control delay. The control device includes an air flow sensor 1 for detecting an air flow rate flowing through a intake pipe of an internal combustion engine, a motor 33 for driving the throttle valve 2 disposed in the intake pipe and an ECU 15 for controlling the driving operation of the motor. The ECU 100 feedback-controls the output of the air flow sensor so that a difference between the output of the air flow sensor 1 and an air flow rate required for the engine reduces.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Device for processing a flat material web, and method for processing a flat material web
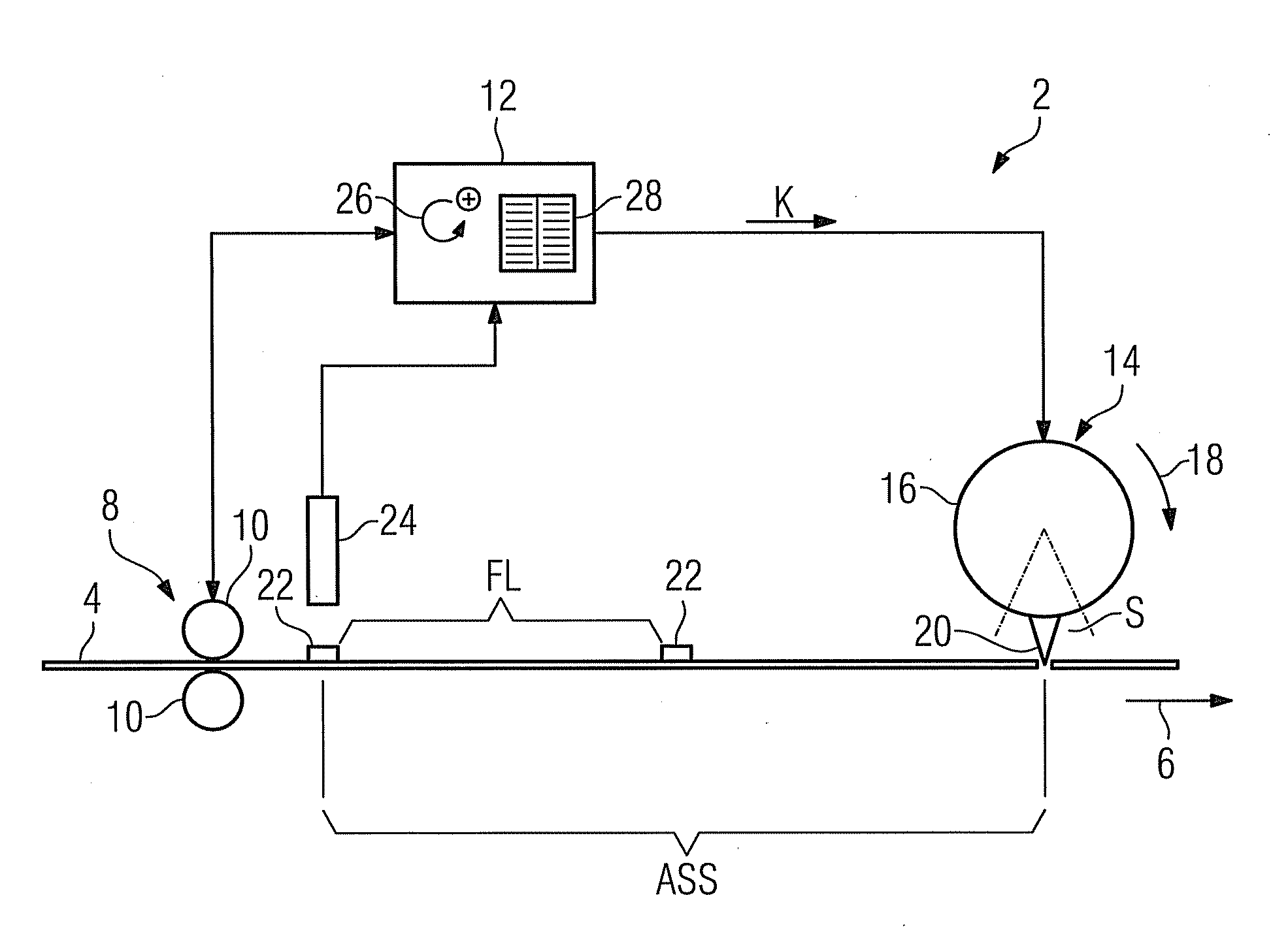
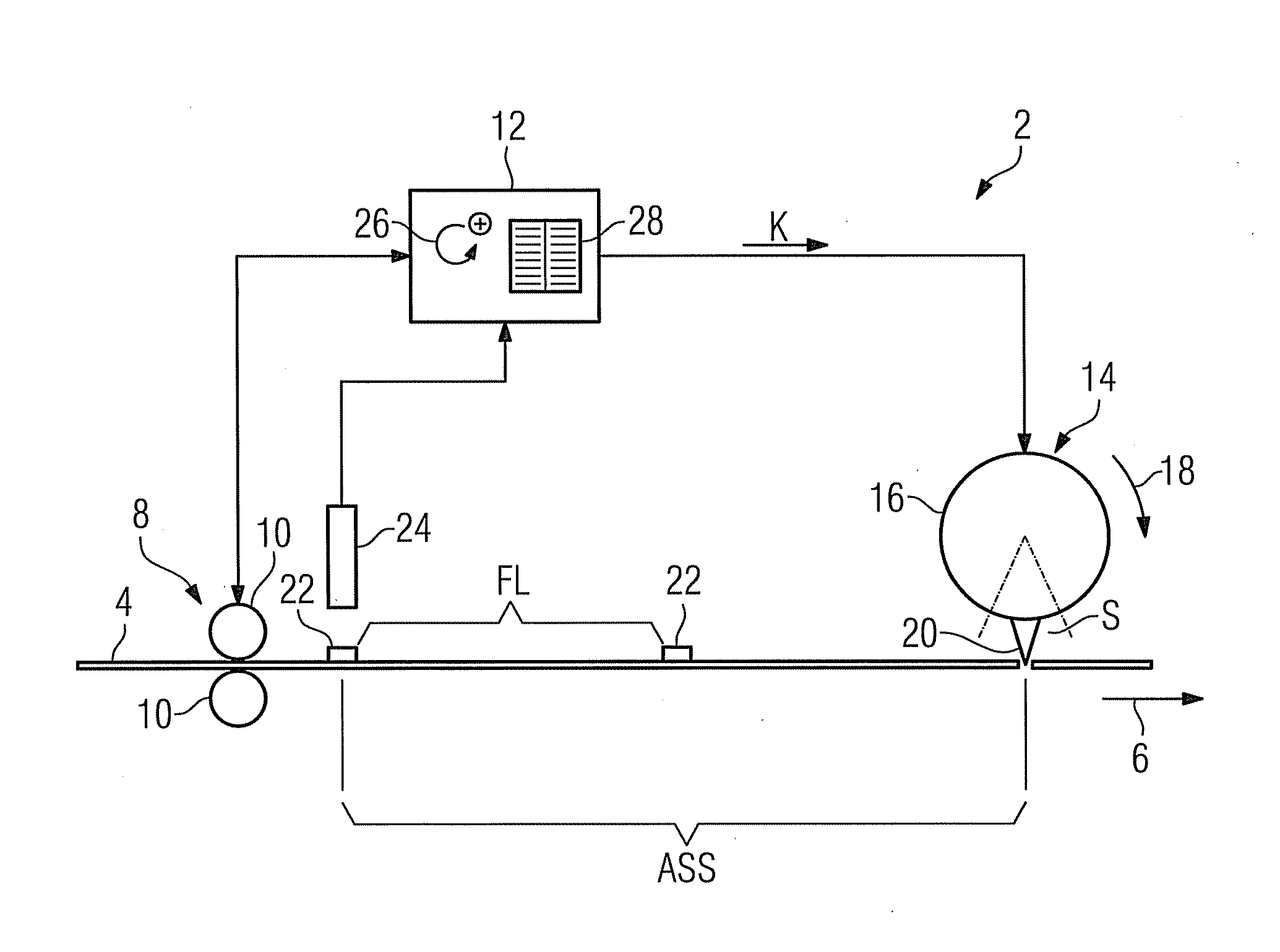
InactiveUS20100120593A1Simple mean of correcting positioningAutomatic detectionBox making operationsPaper-makingEngineeringComputer science
A device for processing a flat material web including a sensor for detecting processing marks of the material web is provided. A control unit assigns a first location information to each detected processing mark. Furthermore, the control unit and a processing unit assign a second location information to the time of processing of the processing mark. Both pieces of location information are calculated together by the control unit to determine a correcting value. A processing position of the material web is corrected by the correcting value.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Positioning control device of actuator provided with strain wave gearing using h-infinity control
ActiveUS20180239327A1Easily loses stabilityImprove stabilityToothed gearingsSpeed/accelaration controlControl systemPosition response
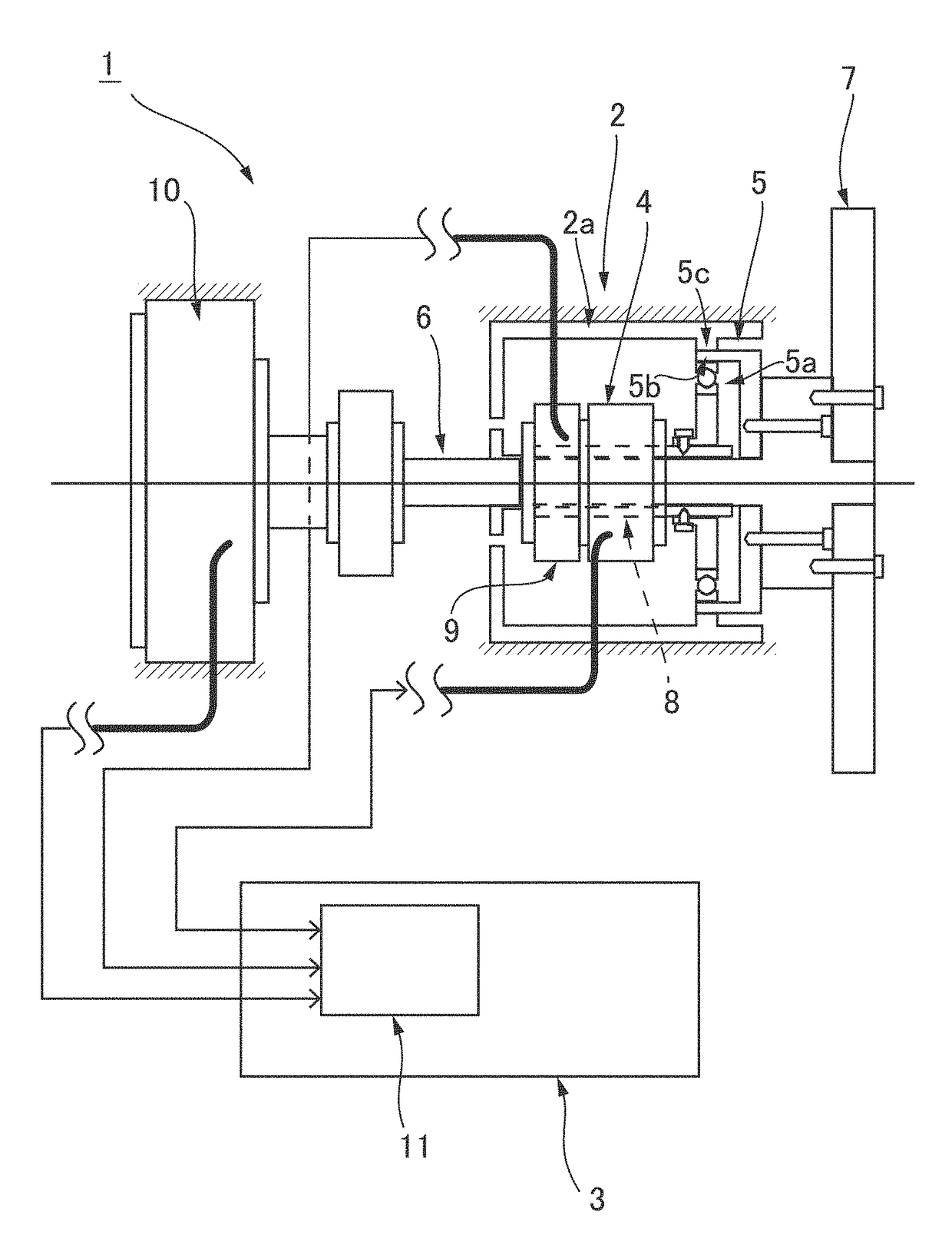
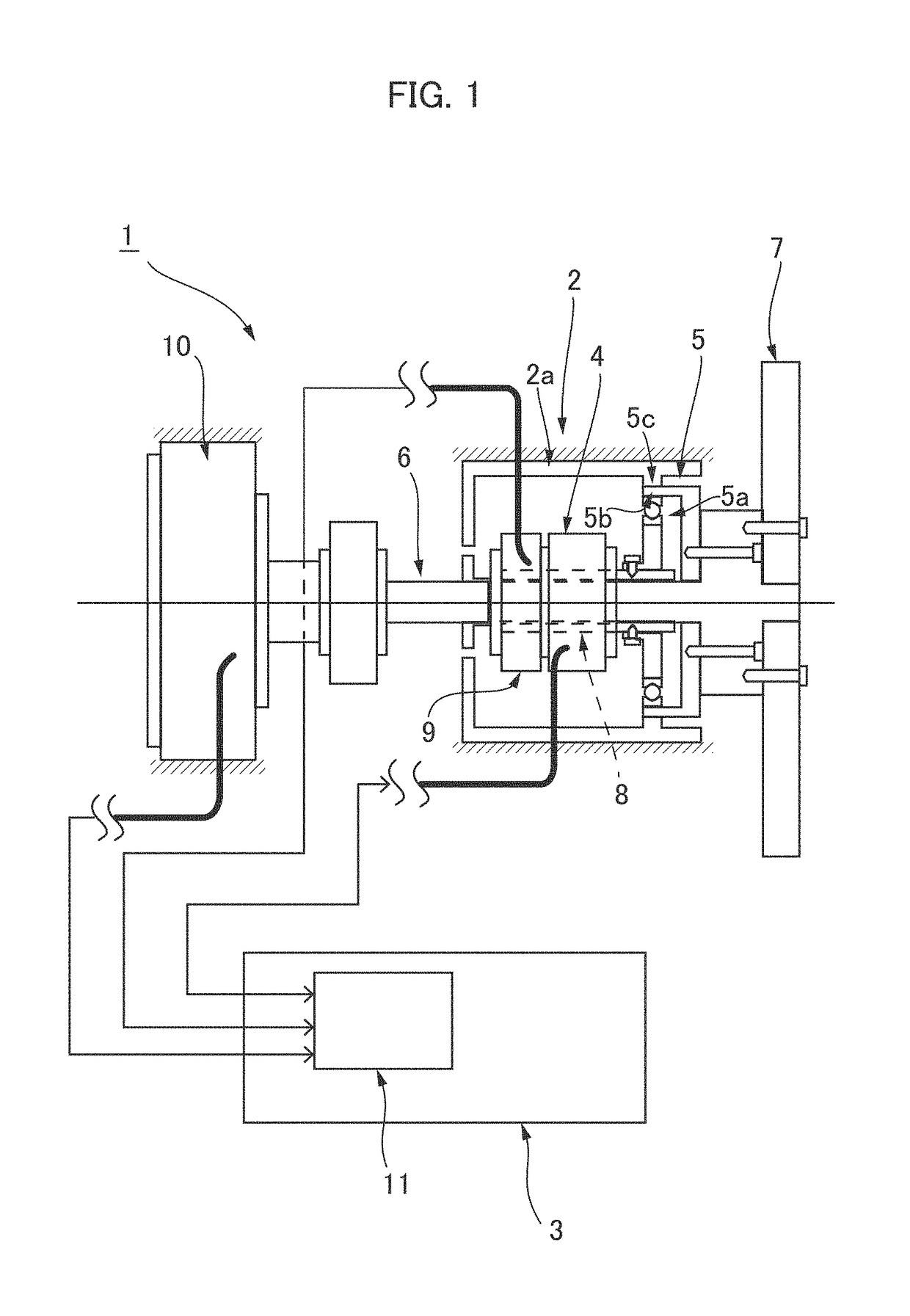
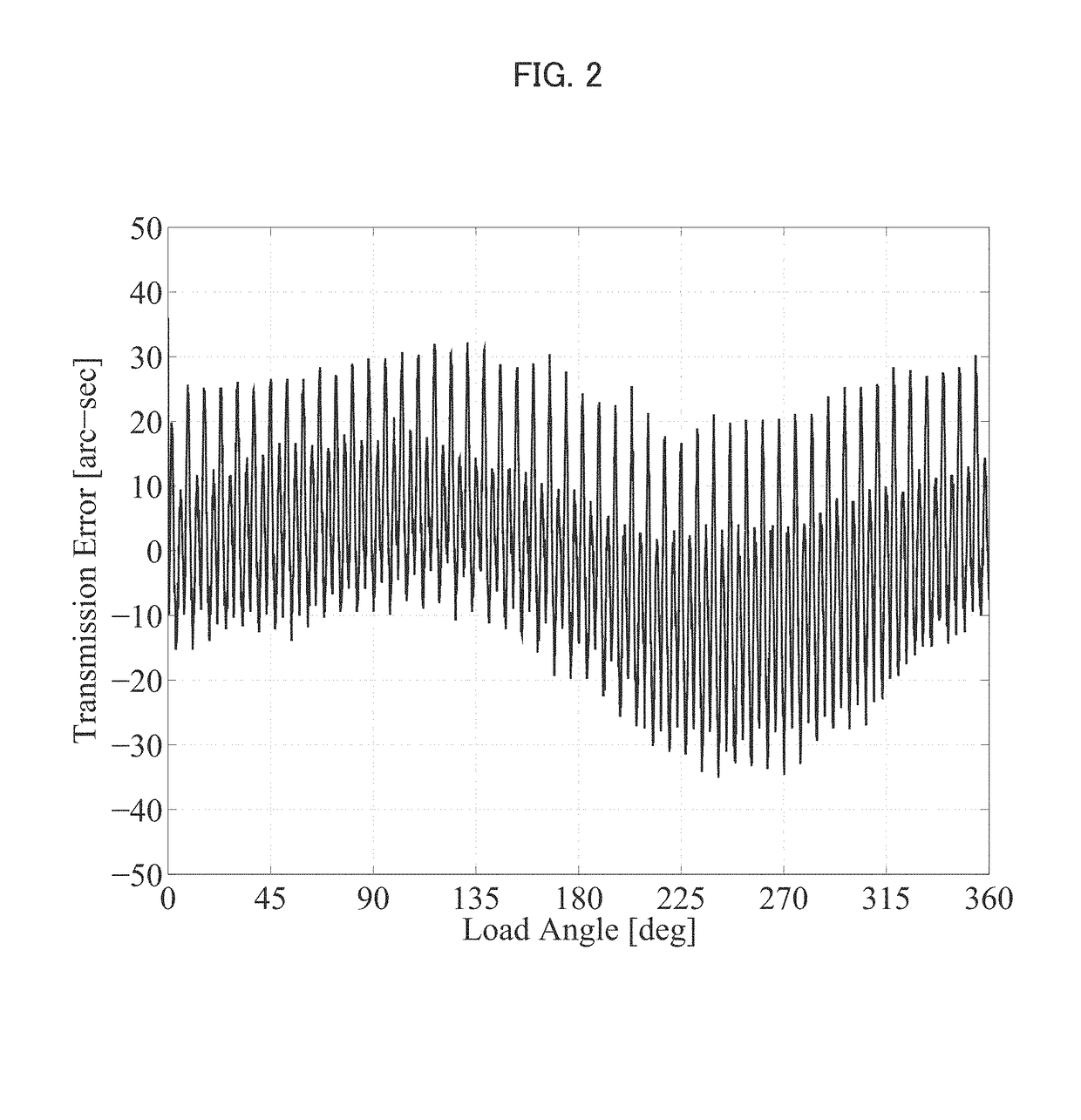
A positioning control device of an actuator provided with a strain wave gearing has a full-closed control system for feeding back a position of a load shaft, and driving and controlling a motor so as to position the load shaft at a target position. The full-closed control system has an H∞ compensator designed so that, when a generalized plant having angular transmission error in the strain wave gearing as a disturbance input is assumed, an H∞ norm of a transfer function from the disturbance input of the generalized plant to an evaluation output is a predetermined value or less. Mechanical vibration during positioning response caused by angular transmission error in the strain wave gearing can be reliably suppressed.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
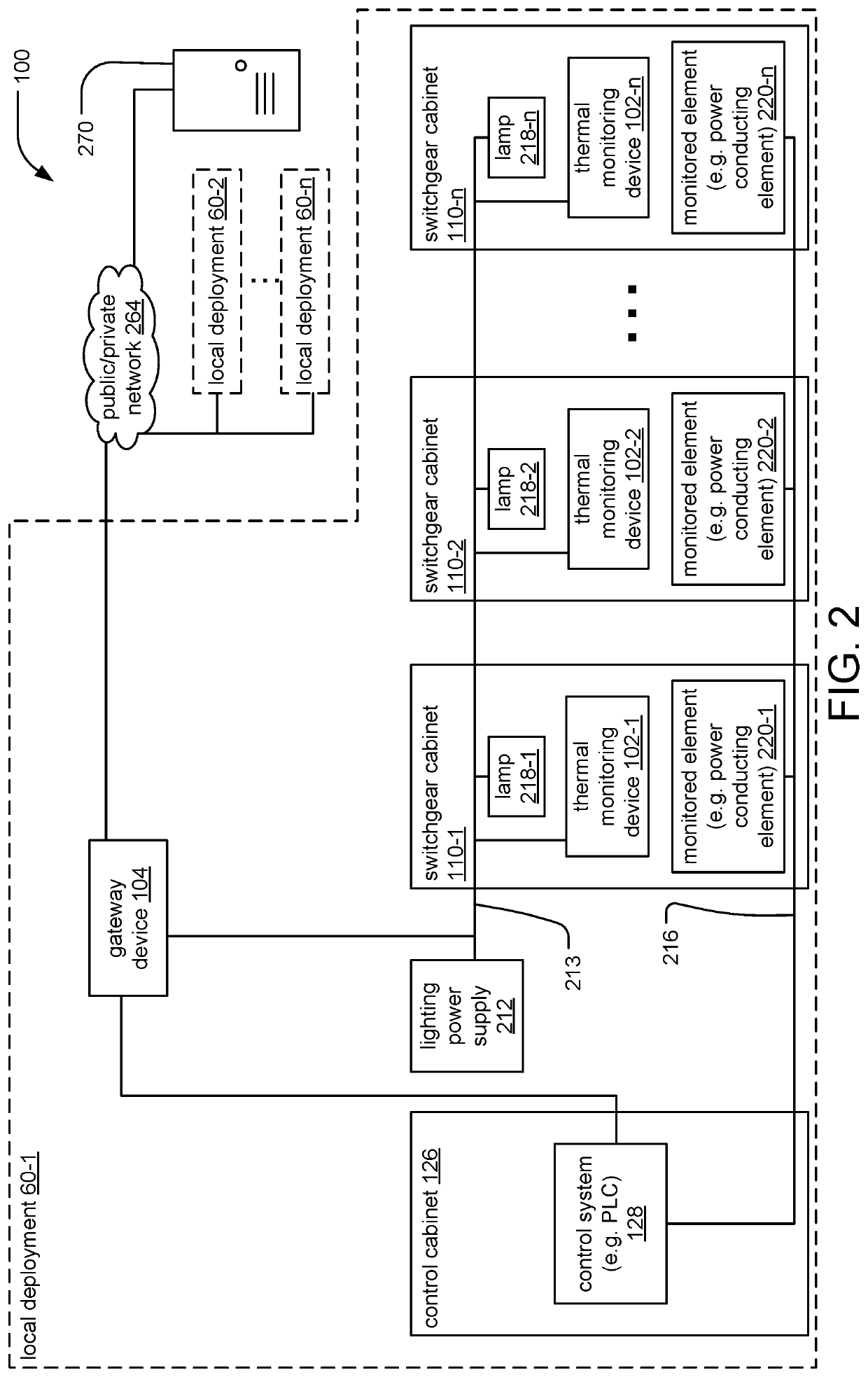
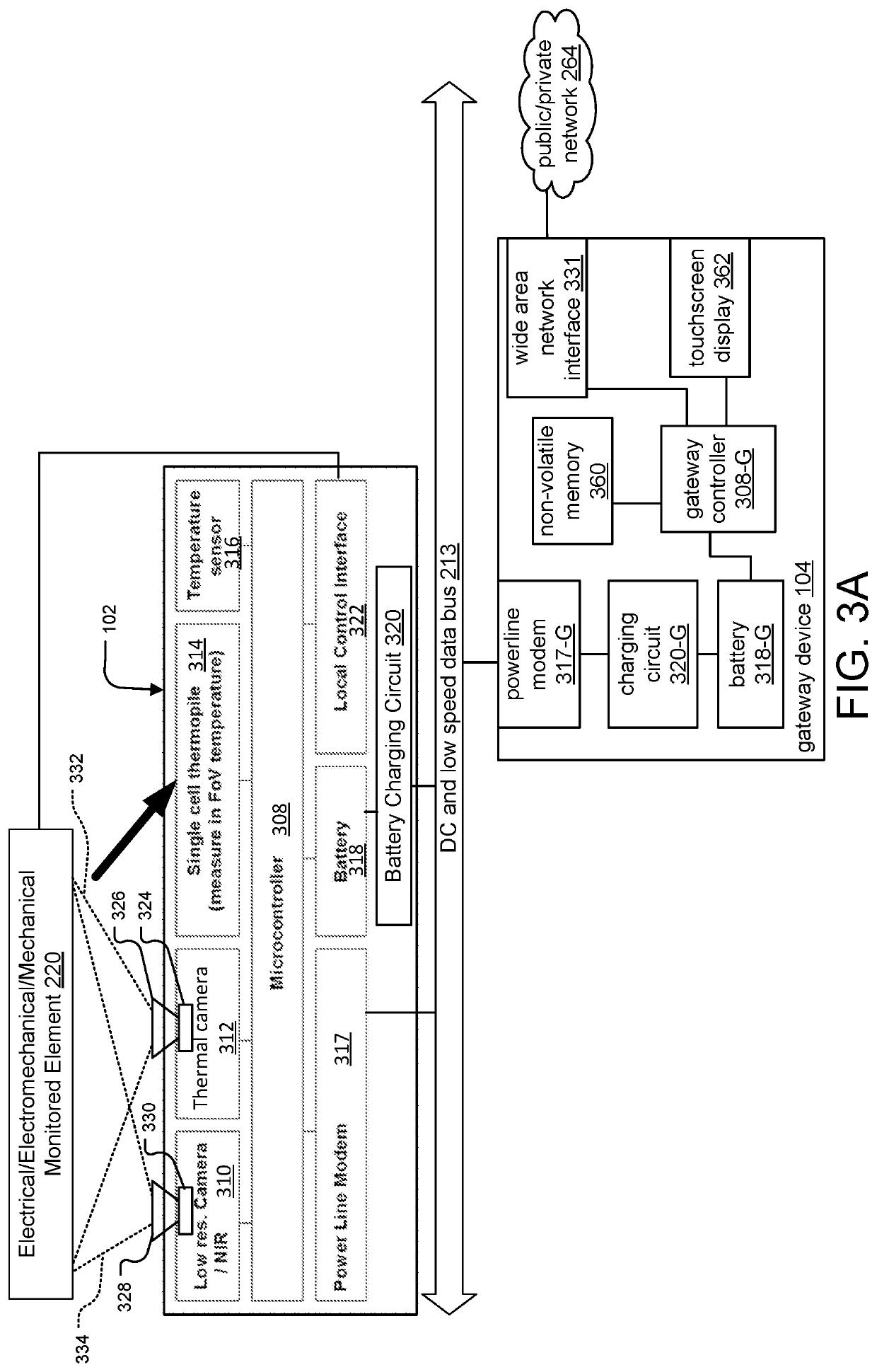
Infrared thermal monitoring system for industrial application
ActiveUS11415464B2Improve detection accuracyReduce sensor costTelevision system detailsSwitchgear arrangementsThermal monitoringData pack
Owner:ADVANCETREX SENSOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com