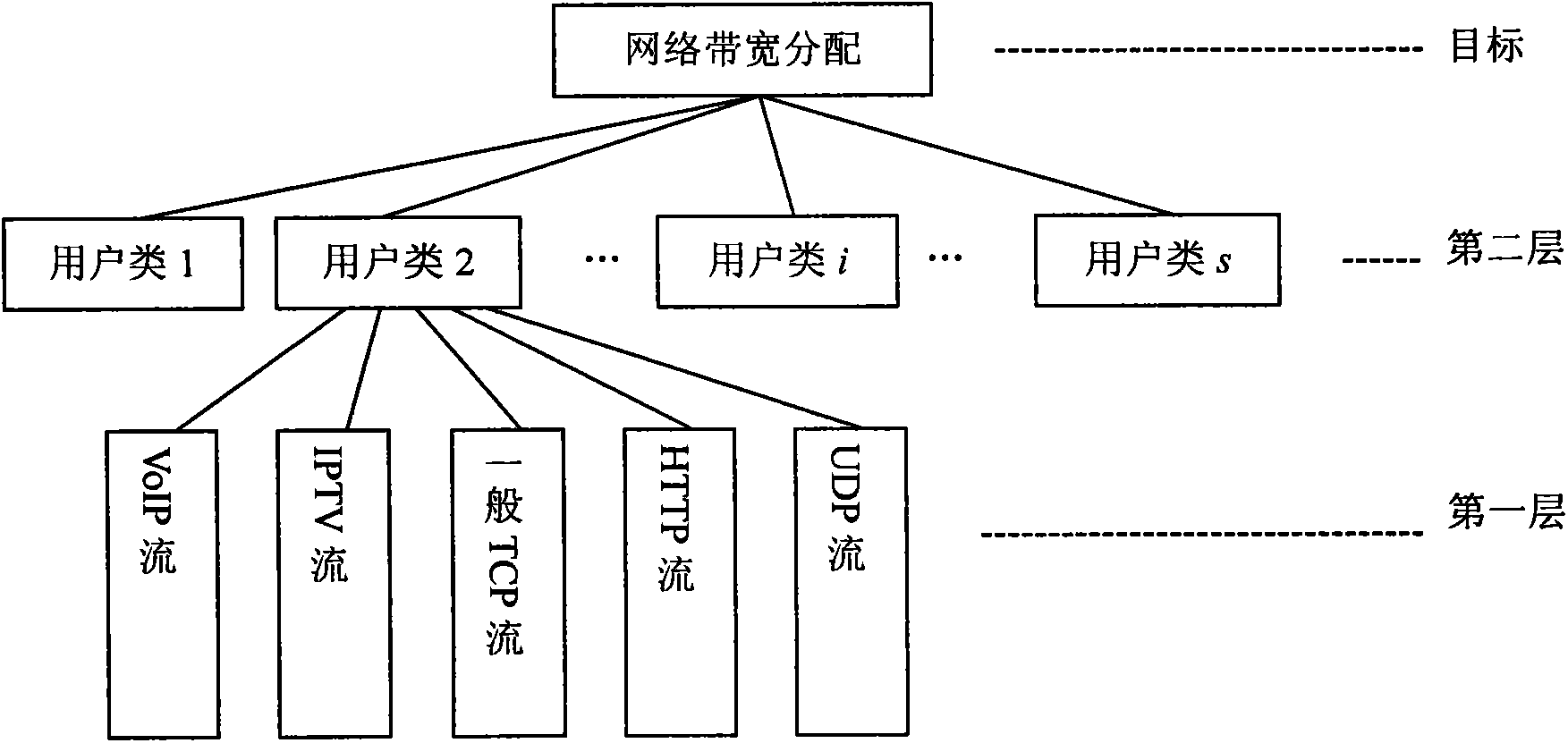
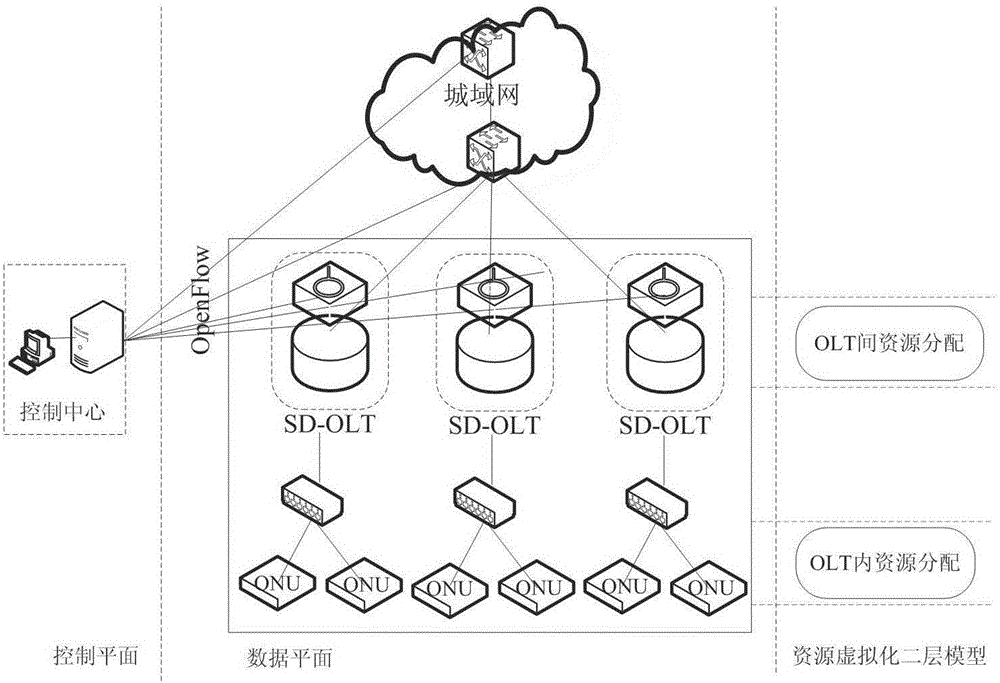
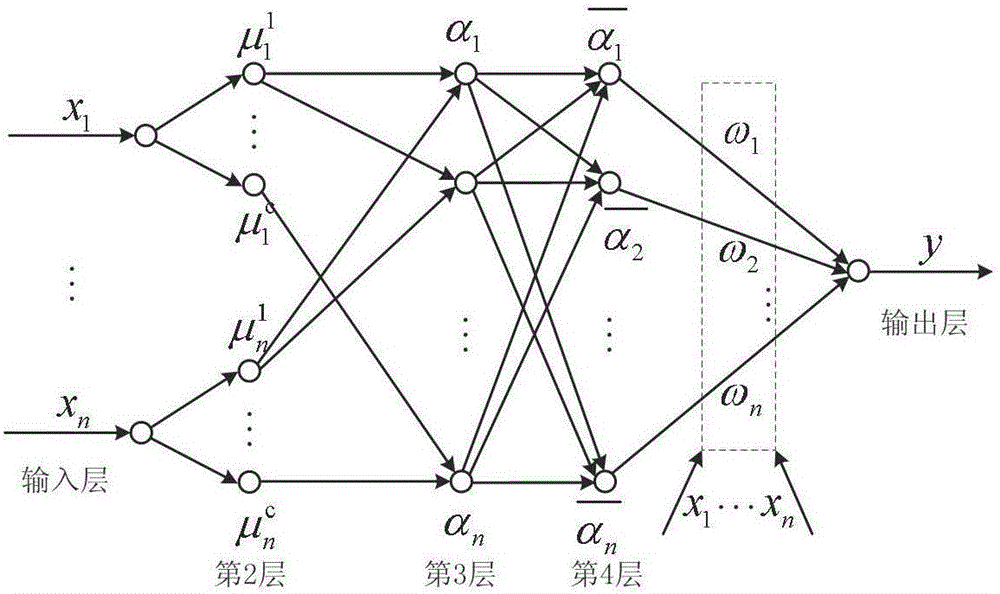
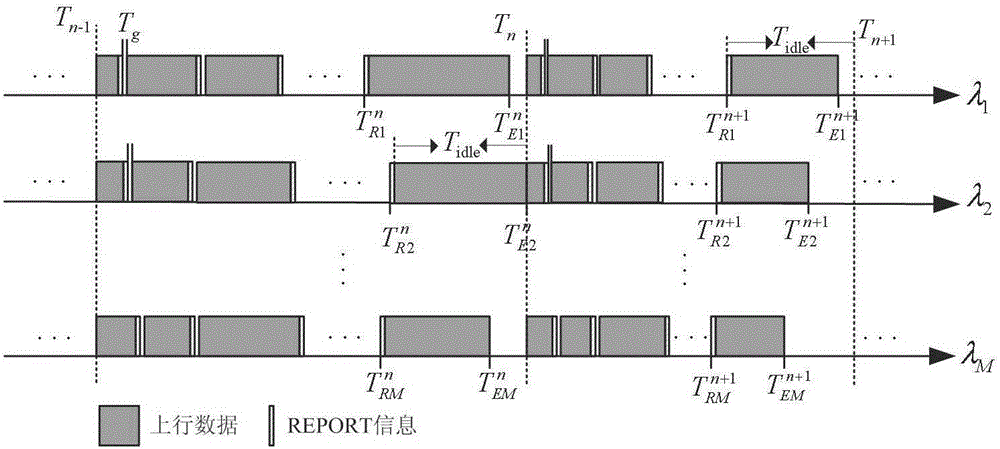
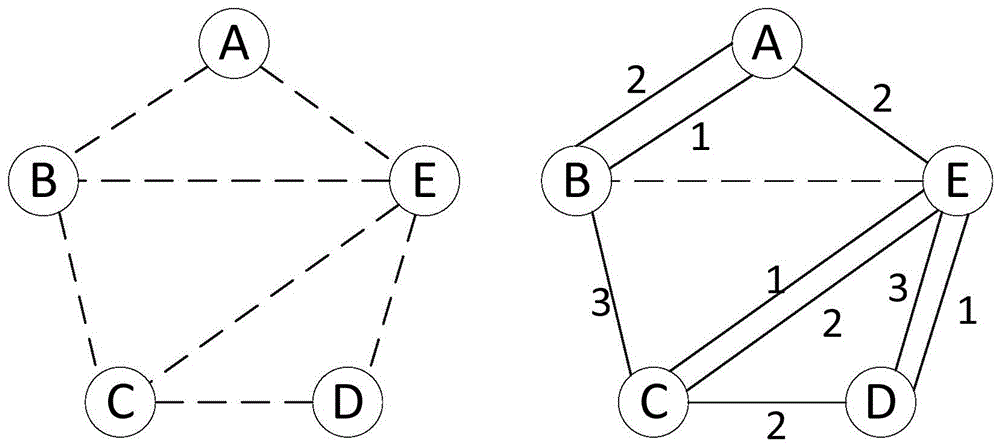
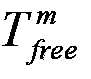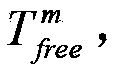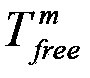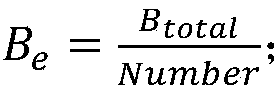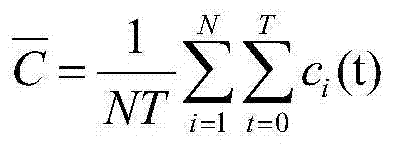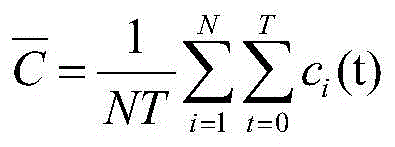Patents
Literature
48 results about "Bandwidth allocation algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
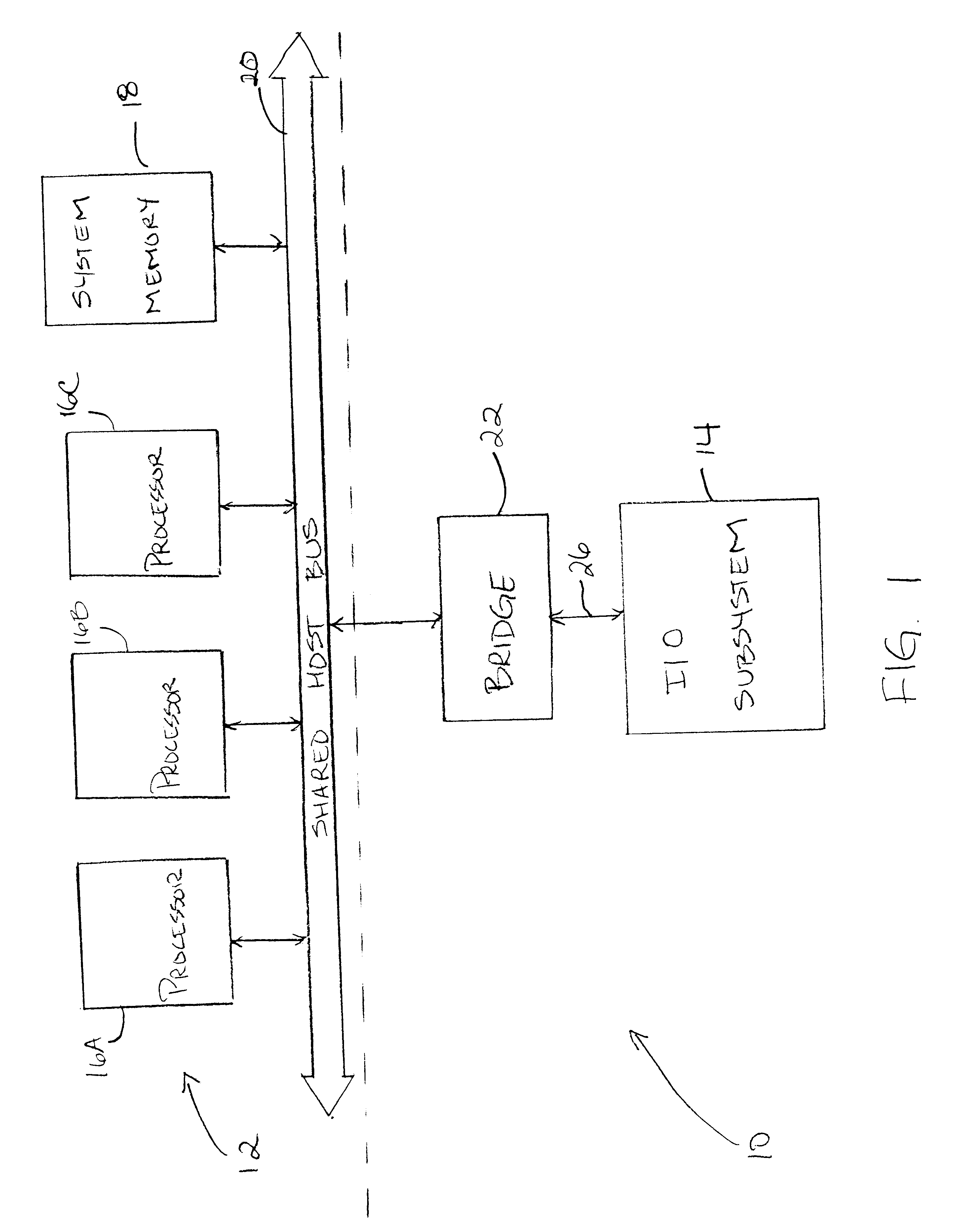
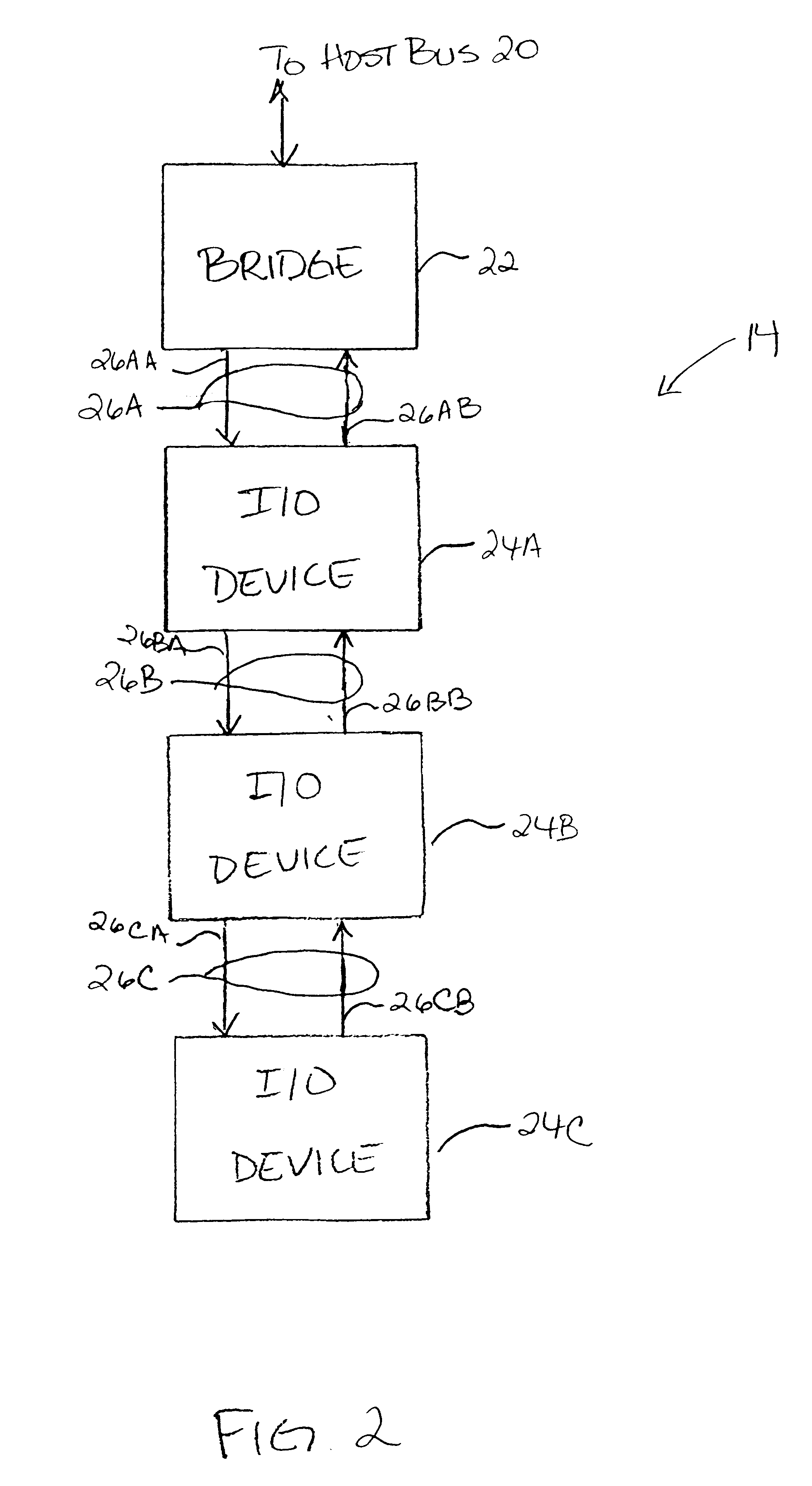
System and method of allocating bandwith to a plurality of devices interconnected by a plurality of point-to-point communication links
InactiveUS20020083233A1Data switching networksInput/output processes for data processingTelecommunications linkAllocation algorithm
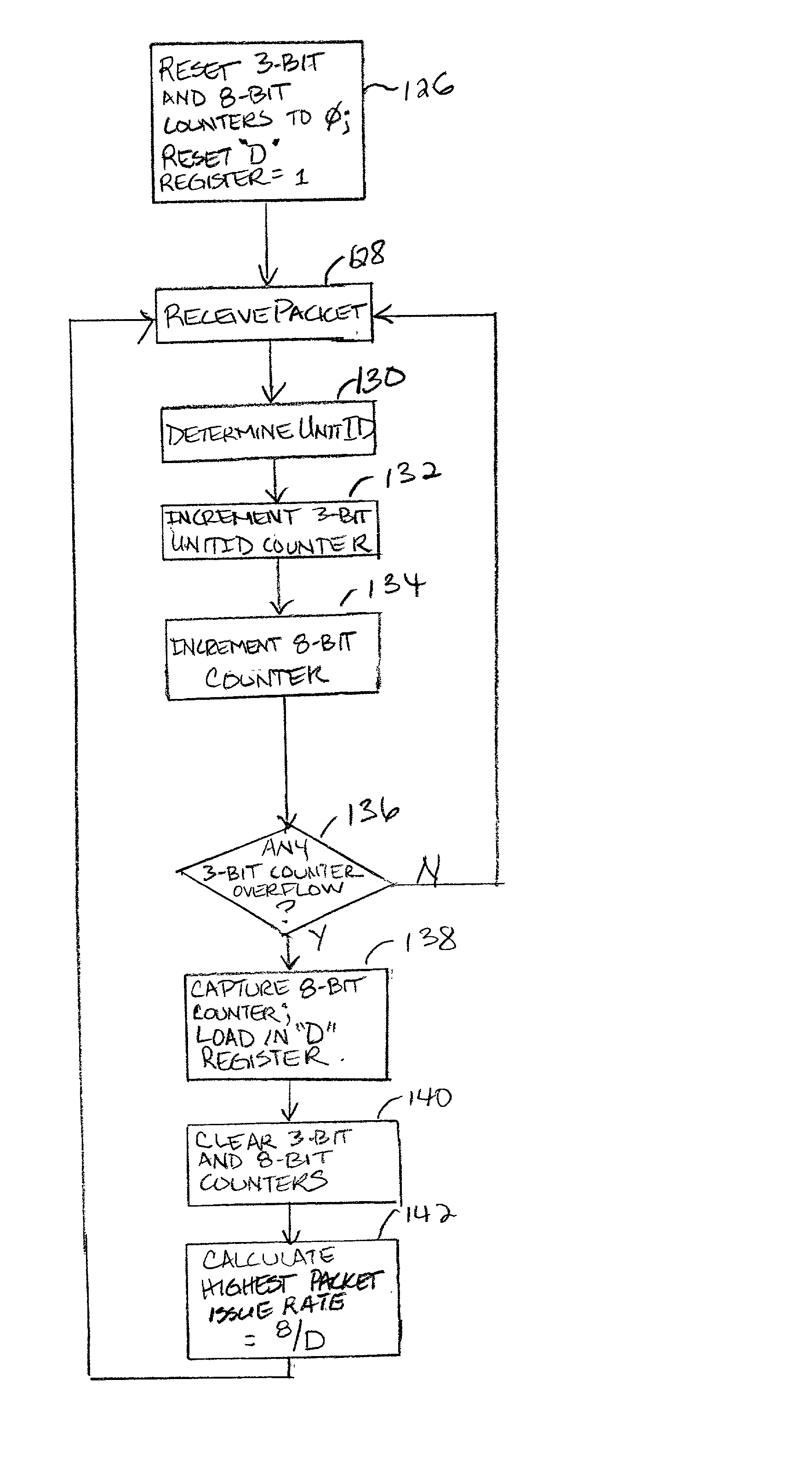
A method is provided for fairly allocating bandwidth to a plurality of devices connected to a communication link implemented as a plurality of point-to-point links. The point-to-point links interconnect the devices in a daisy chain fashion. Each device is configured to transmit locally generated packets and to forward packets received from downstream devices onto one of the point-to-point links. The rate at which each device transmits local packets relative to forwarding received packets is referred to as the device's insertion rate. A fair bandwidth allocation algorithm is implemented in each (upstream) device to determine the highest packet issue rate of the devices which are downstream of that (upstream) device. The packet issue rate of a downstream device is the number of local packets associated with the downstream device that are received at the upstream device relative to the total number of packets received at the upstream device. By monitoring the total flow of packets received at the upstream device, the highest packet issue rate of the respective packet issue rates of the downstream devices may be determined. Each upstream device then matches its insertion rate to the highest packet issue rate of its downstream devices. The determination of the highest packet issue rate may be performed dynamically such that the insertion rate of the upstream device can adapt to changes in communication traffic patterns. Further, the fair bandwidth allocation algorithm may include a priority algorithm to arbitrate between local and received packets transmitted at the insertion rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method of allocating bandwidth to a plurality of devices interconnected by a plurality of point-to-point communication links
InactiveUS6751684B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
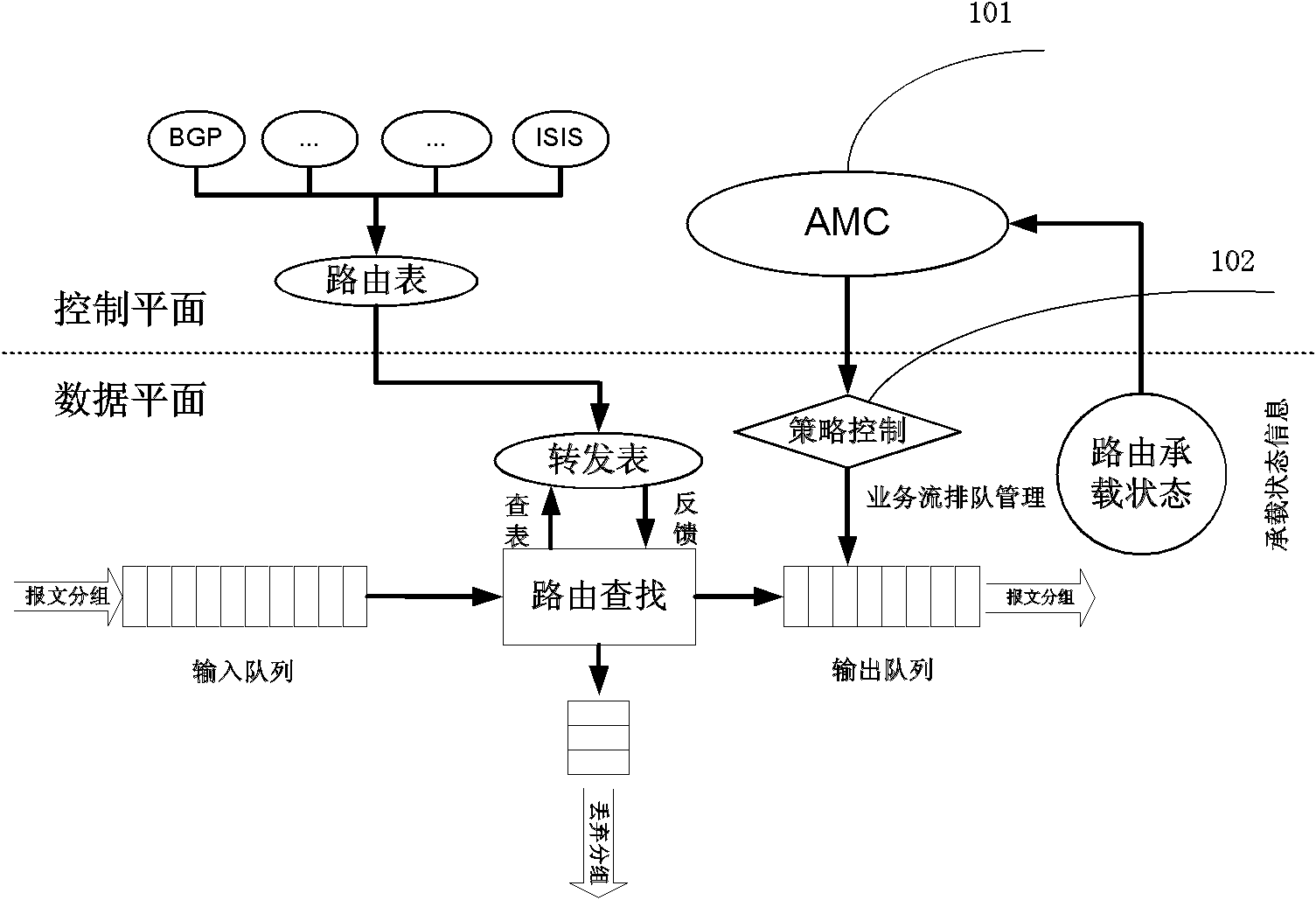
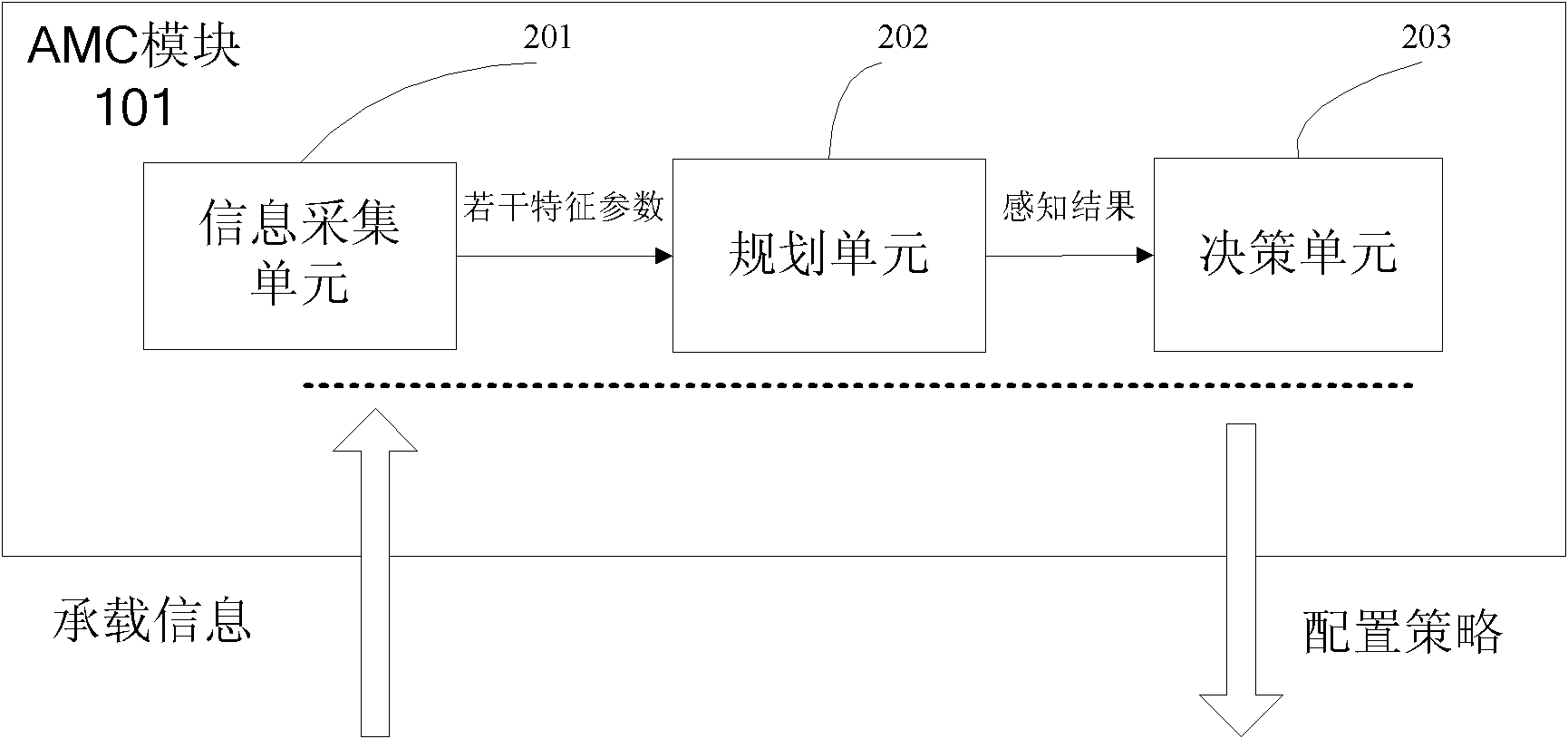
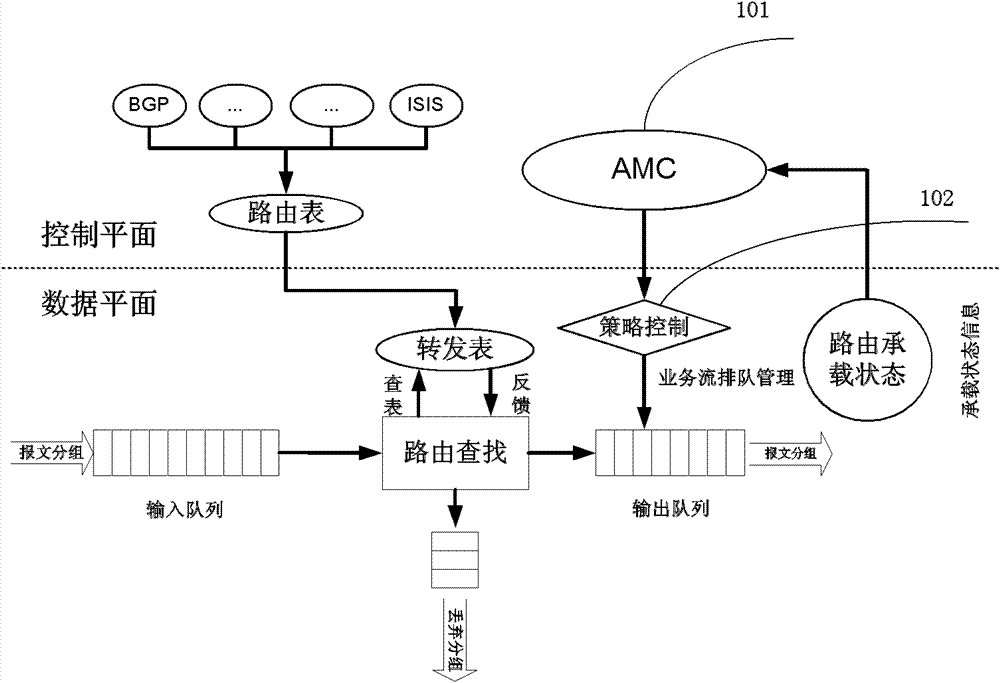
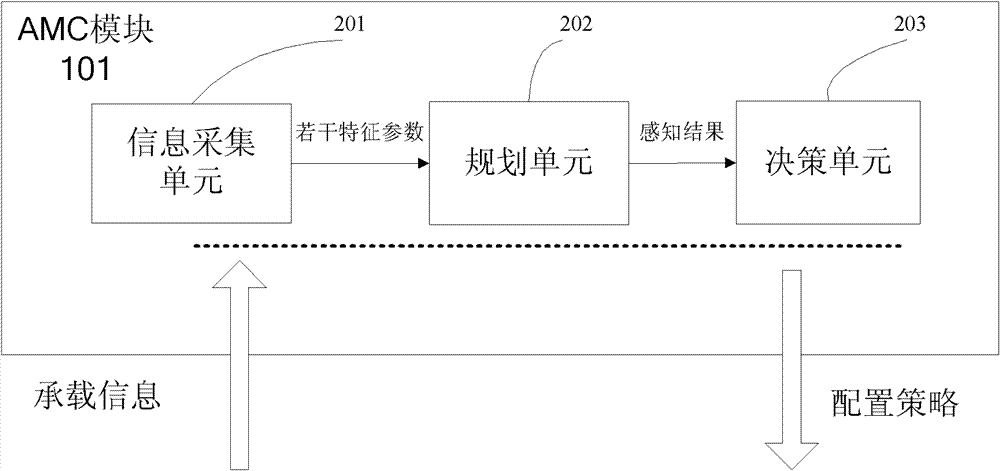
Router for sensing bearing state and service flow bandwidth distribution method thereof
InactiveCN102739507AFully consider the characteristics of dynamic changesIncrease flexibilityData switching networksService flowCognition Network Technology
The invention provides a router for sensing a bearing state and a service flow bandwidth distribution method thereof. The method comprises: a bandwidth distribution strategy generation step for all services; to be specific, collecting bearing state information of a router and quality of service (QoS) demand information of a service flow, employing bandwidth distribution algorithm that is provided based on a cognitive network technology to carry out analyzing and processing on the collected data, and integrating a plurality of set rules and using difference of QoS demands of various service flows for reference to generate a bandwidth distribution strategy for all the services; and a step for distributing bandwidths for all the service flows; to be specific, mapping the strategy into an operation instruction that can be identified by the router according to a requirement of configuration strategy and executing the operation to change router queue management so as to carry out bandwidth distribution on the service flows. According to the invention, the cognitive network technology is utilized to realize sensing of a network bearing state and a service flow state, so that network bandwidth distribution can fully consider a dynamic changing characteristic of the network to enable the distribution mode to become reasonable.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
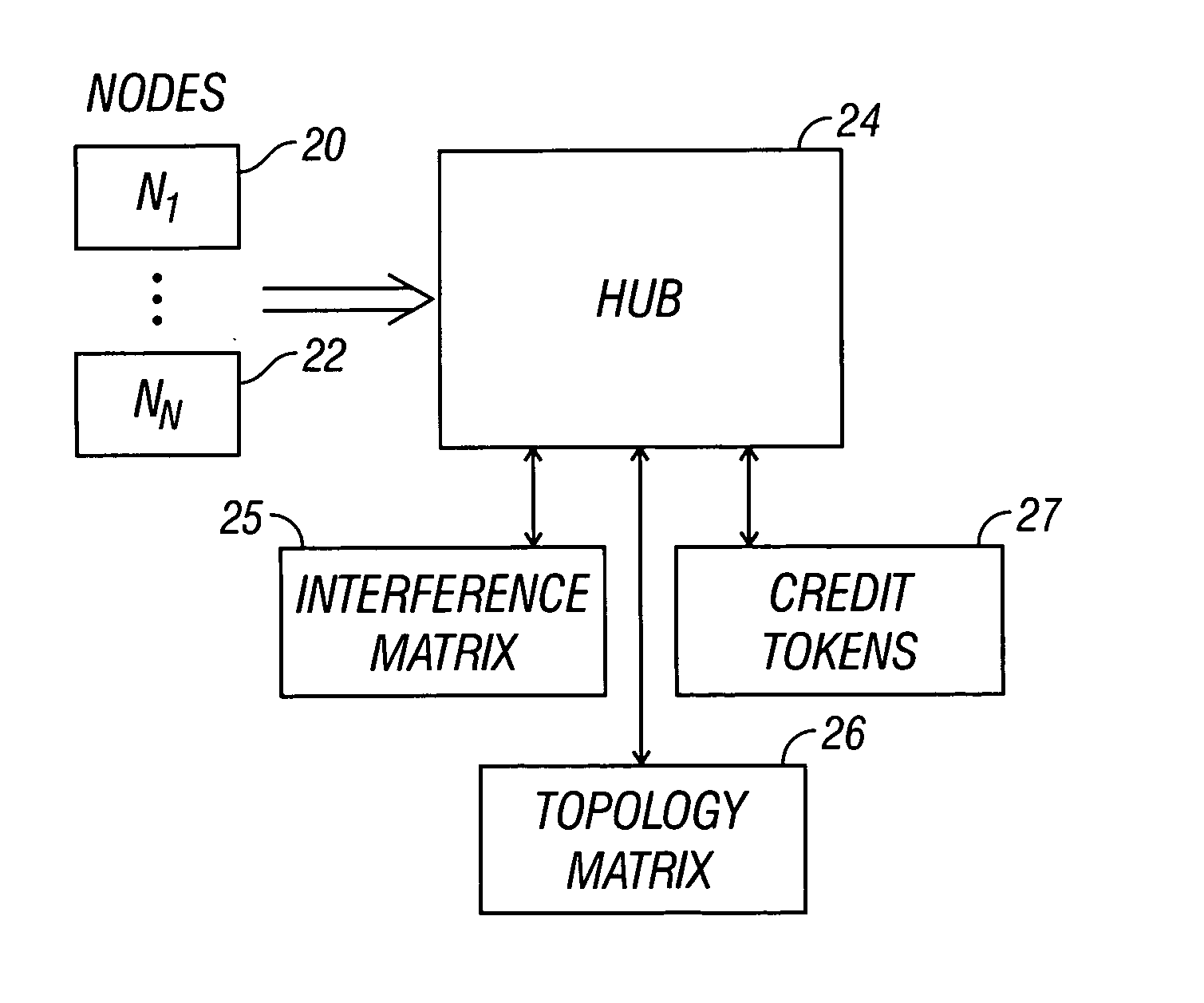
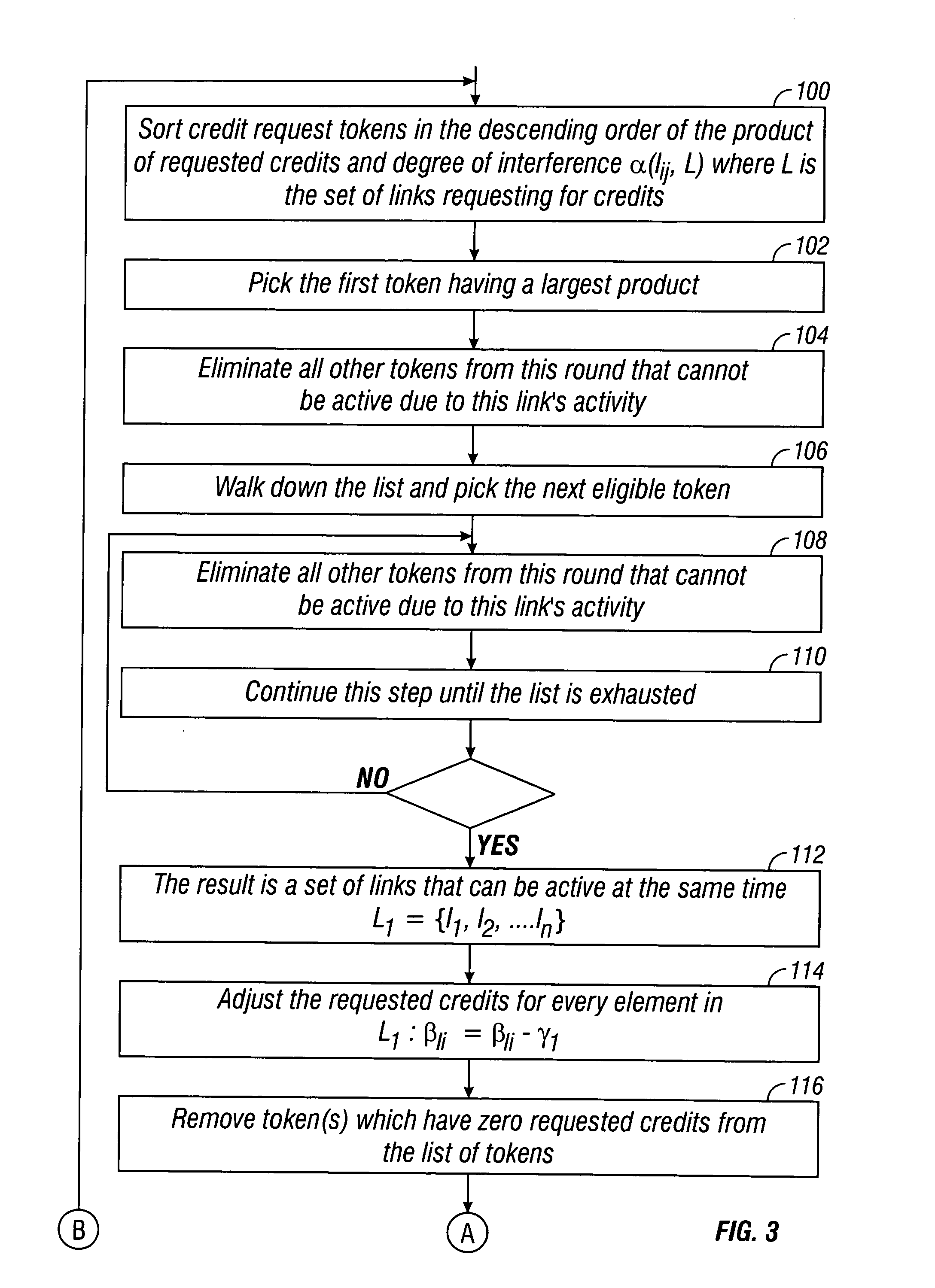
Bandwidth allocation method and apparatus for fixed wireless networks
InactiveUS20050007991A1Optimize bandwidth allocationFair and efficient and high-performance bandwidth allocation scheduleMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsTime-division multiplexWireless mesh networkNetwork topology
A simple, fair, good-performance bandwidth allocation algorithm for wireless networks is presented. Using a matrix of interlink interference and a list of links' bandwidth requests, the algorithm can schedule link activities to obtain non-collision transmissions. All bandwidth requests are served fairly and near-optimally based on the heuristic algorithm. Bandwidth granted for each link is prorated based on its requested bandwidth, total requested bandwidth in the network, and network capacity. The algorithm can be used for centralized bandwidth allocation and works with any network topology, including mesh networks.
Owner:ARCOWV WIRELESS +1
Multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management method
The invention discloses a multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management method, which comprises the following steps of: A10, configuring CIR (Committed Information Rate) and PIR (peak Information Rate) (or EIR (Excess Information Rate)) of each stage of scheduling node according to a business model, wherein the CIR of the node is set according to the bandwidth purchased by a user in the first stage, the bandwidth distribution principle of each node from the second stage of scheduling is shown in the description, EIRni=PIRni-CIRni, and n is not less than 2; and A20, respectively marking messages as green, yellow or red by using MEF (Managed Extensibility Framework), RFC2697 (Request for Comments 2697) or RFC2698 algorithms in the first stage, configuring each node into a color sensitive mode and a coupling mode from the second stage, and shaping the traffic according to the MEF algorithm. By using the invention, the multi-stage hierarchical bandwidth management is realized on an exchanging chip supporting the MEF Traffic Shaping algorithm without need of special ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuits) or hardware; and the requirements are satisfied through updating software under the situation of changing or updating the business so that considerable hardware cost is saved; and the bandwidth distribution algorithm of the hierarchical business model is simple and convenient for web masters to configure.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Novel bandwidth allocation algorithm based on OFDM-PON
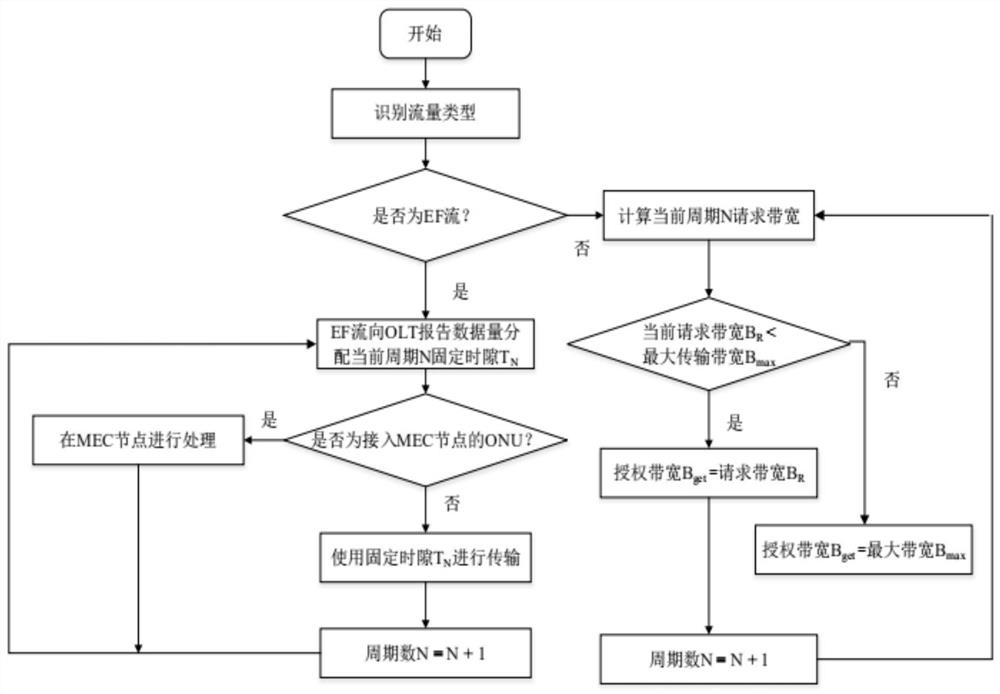
InactiveCN102395060AMeet basic needsGuaranteed low latency requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsMulti-frequency code systemsService flowResponse method
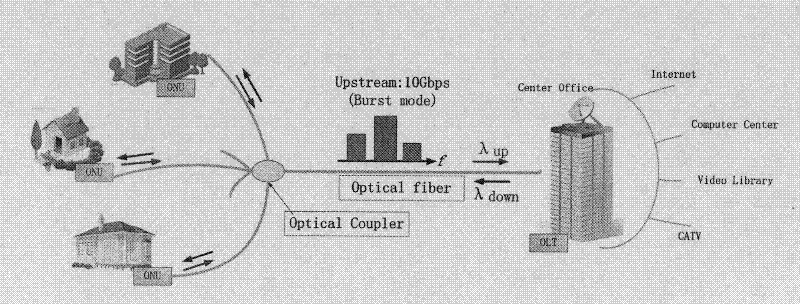
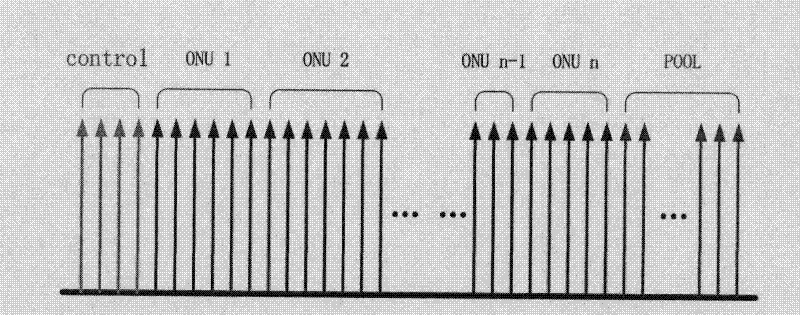
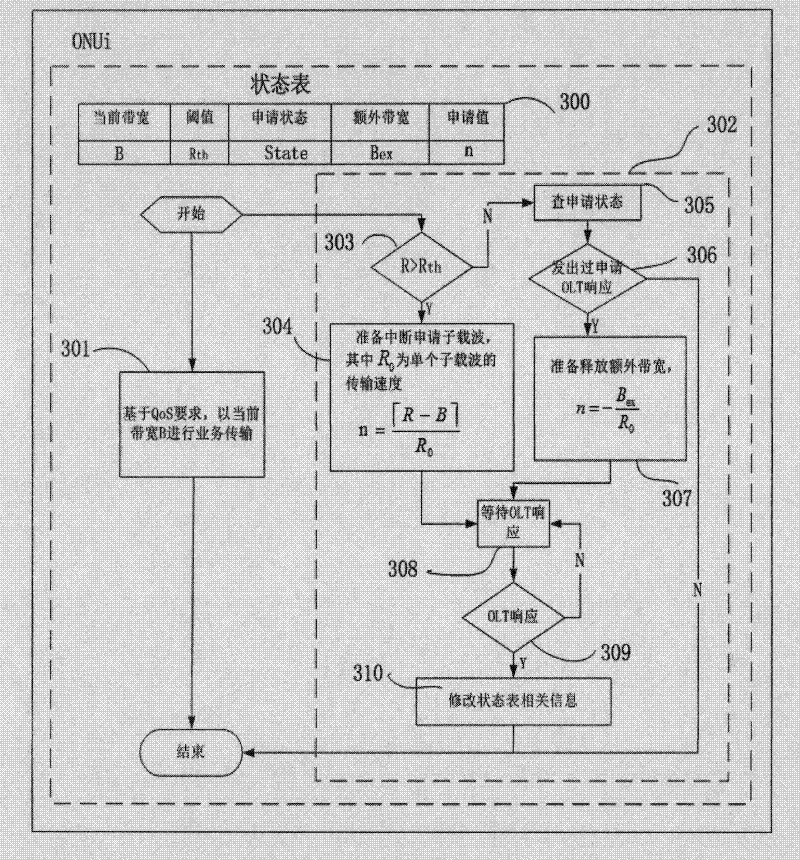
The invention discloses a dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm applied to an OFDM-PON (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network) system and belongs to optical fiber communication systems. The invention utilizes an interruption application response method to realize the bandwidth request and allocation; a plurality of subcarriers in the system are divided into three parts, namely, a communication channel control part, an ONU (Optical Network Unit) default bandwidth part and a part stored in a dynamic pool; when the load on the link is light, each ONU compares respective local flow with local threshold value so as to decide whether an interruption application for extra bandwidth is started; and when the load on the link is heavy, an OLT (Optical Line Terminal) allocates the surplus subcarriers based on the requiring ratio of the ONUs under the condition that the rated bandwidth of the ONUs is met firstly, so as to realize dynamic allocation. The invention ensures low time delay and low package loss rate of a high priority service, also performs bandwidth allocation as required, and can meet the equal allocation between the ONUs and the equal-level priority service when the load of link service flow is heavy.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Large request first-fair excess allocation dynamic wave length bandwidth allocation method
InactiveCN103401632AImprove resource utilizationReduce latencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAccess networkAllocation algorithm
The invention discloses a large request first-fair excess (LRF-FE) allocation dynamic wave length bandwidth allocation method which is suitable for a time-and wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWDM-PON), and belongs to the technical field of optical access networks. According to the method, optical network units (ONU) transmit request bandwidths to an optical line terminal (OLT); the OLT adopts an LRF-FE algorithm to authorize all the ONUs, i.e. all the ONUs are ordered from large to small according to the request, wavelengths which are firstly not occupied are sequentially allocated to the ONUs according to the sequence, and available wavelength communication channels and initial using times of the ONUs are designated; and the OLT allocates the available bandwidths to the ONUs according to an excess quota bandwidth fair excess (FE) algorithm and designates the transmission data window for the ONUs. After an LRF wavelength allocation algorithm is applied, time fragments on wavelength communication channels can be reduced, wavelength resources can be effectively utilized, the time delay of a system can be reduced, and the resource utilization rate of the system is improved; and after an FE bandwidth allocation algorithm is applied, the system can fairly allocate resources, so that the fairness of the ONUs is realized. Consequently, an LRF-FE is an efficient and fair dynamic wavelength and bandwidth allocation algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
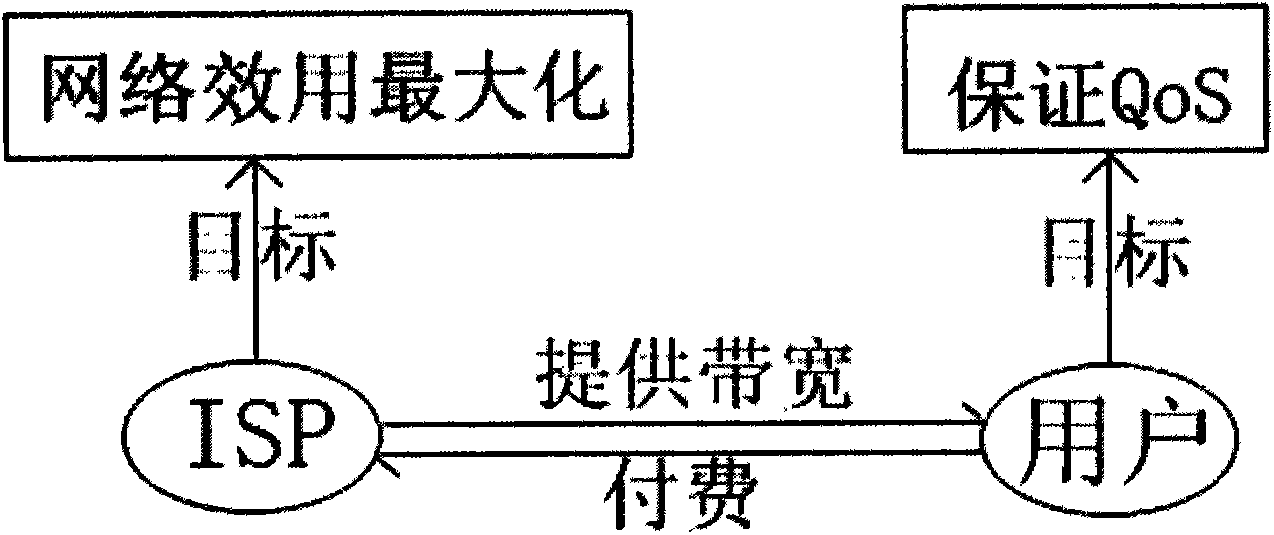
Novel bandwidth allocation algorithm supporting QoS
The invention discloses a novel bandwidth allocation algorithm supporting QoS. According to the algorithm, based on utility functions, a user demand factor and a service demand factor are considered comprehensively. According to the utility functions of all kinds of services in a network, influences on all kinds of service utilities by bandwidth are analyzed, so that weights are allocated to all kinds of services. According to a toll strategy made by an Internet provider, weights of all kinds of users are obtained when the bandwidth is allocated. By the utilization of an analytic hierarchy process, the service weights and the user weights are unified to be weights of specific users and specific services to serve as a basis when the network bandwidth is allocated. In order to provide better service quality, according to the method, the network load balancing problem is also researched so that influences on service quality caused by network load unbalancing can be reduced.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Hybrid multiplexing passive optical network (PON) overall resource efficient allocation method
ActiveCN106209687ARealize centralized controlAchieve optimal distributionData switching networksResource utilizationWeight coefficient
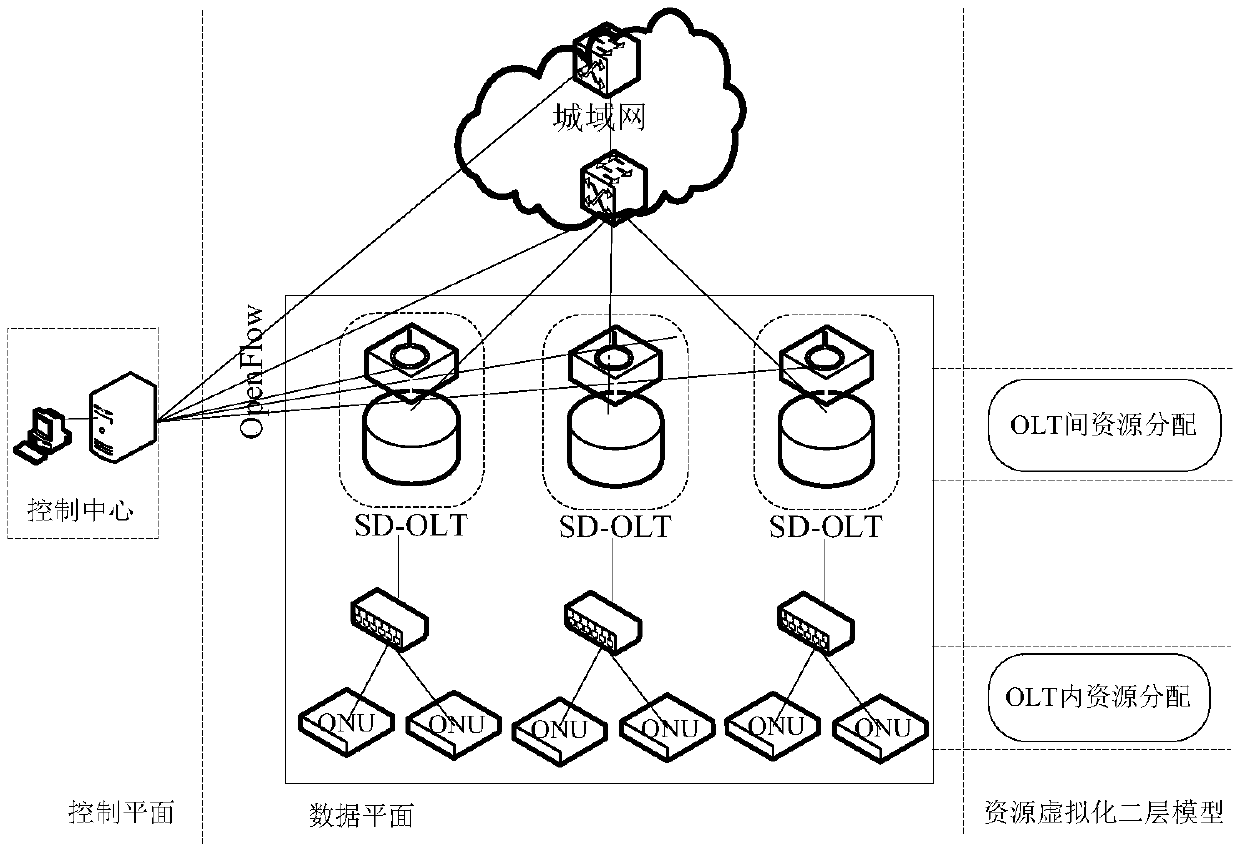
The invention relates to a hybrid multiplexing passive optical network (PON) overall resource efficient allocation method, and belongs to the technical field of optical communication. The method comprises the steps of firstly introducing a software defined network (SDN) with a concentrated control capacity into a PON to achieve concentrated control and optimization on allocation of multiple optical line terminal (OLT) resources; then using a fuzzy neural network prediction model to reduce time delay generated by information interaction between the OLTs and a controller, and then allocating the resources with reasonable sizes to the OLTs according to self-adaptive elastic weight coefficients allocated to the OLTs, thus improving a resource utilization rate among the OLTs; and at last, improving the resource utilization rate in each OLT by changing an information sending position of the last optical network unit report (ONU REPORT) on each wavelength, and by using a light-load ONU residual bandwidth and cycle idle time slot dual residual bandwidth re-allocation dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm. According to the method of the invention, the PON overall resource efficient allocation is achieved, the network time delay is reduced, and the resource utilization rate is improved by controlling the overall resources in a concentrated manner, and optimizing resource configuration among the OLTs and in the OLTs in a united manner.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
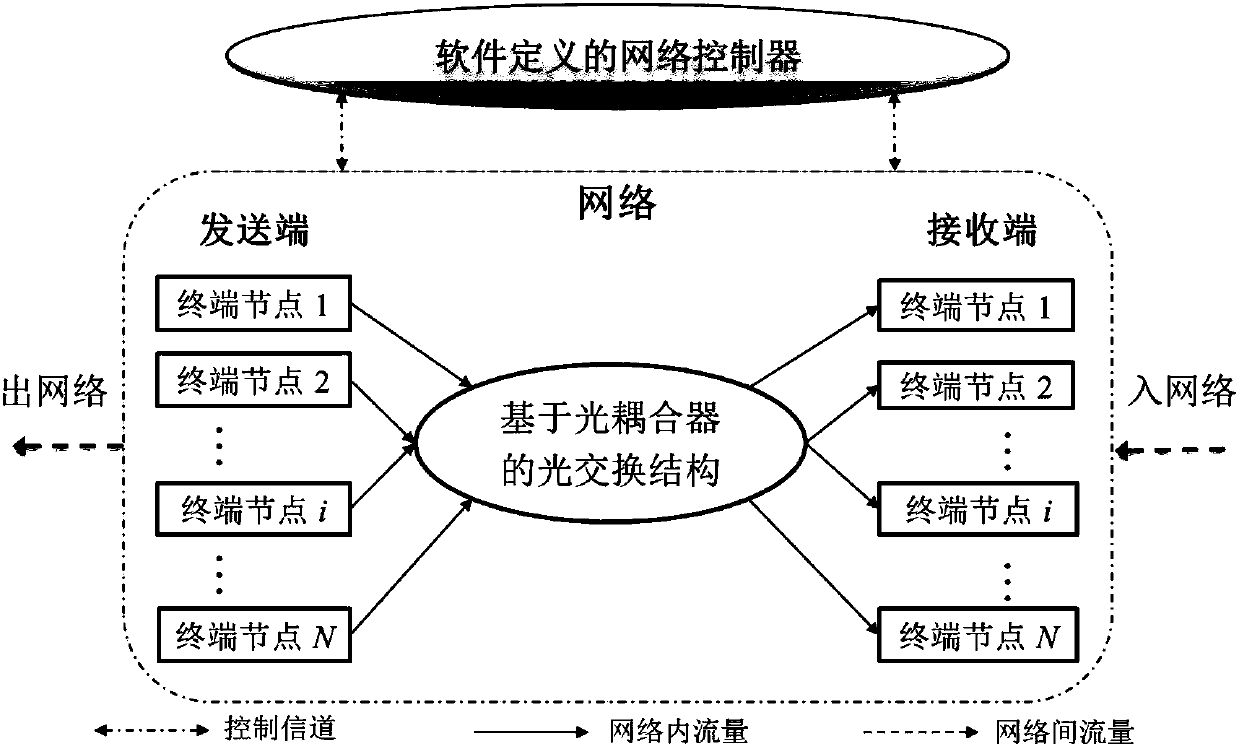
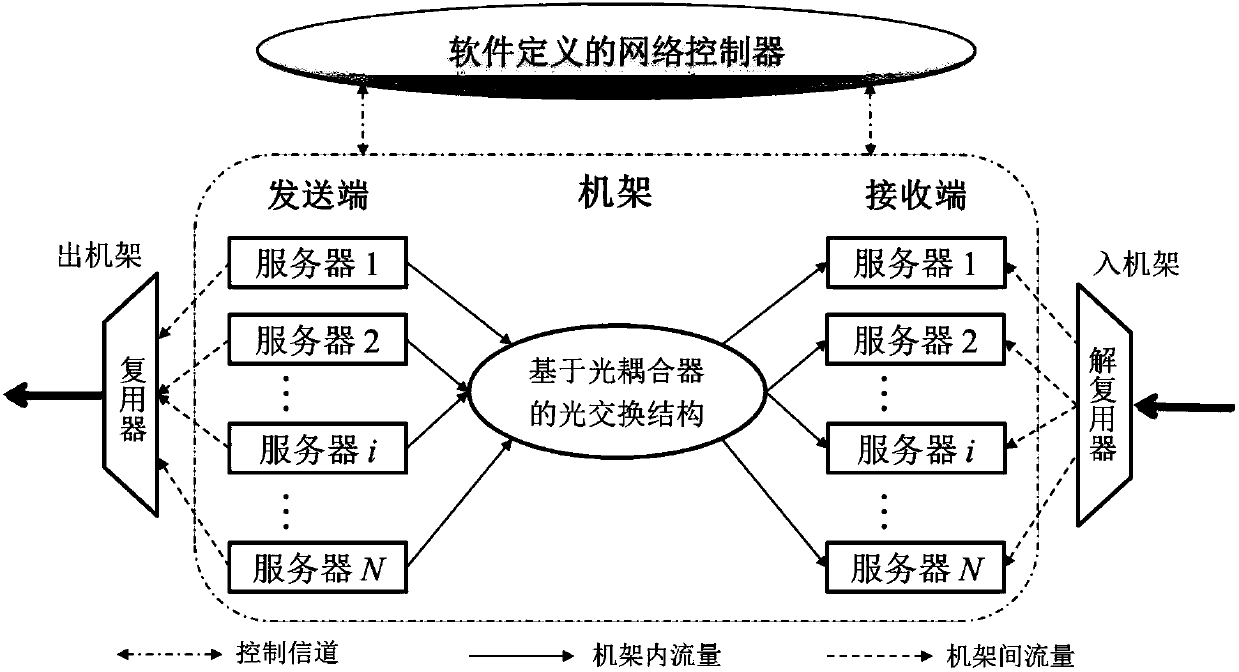
Passive optical interconnection network structure based on software definition and data communication method
InactiveCN105959163ALow costReduce energy consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksComputer hardwareStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a passive optical interconnection network structure based on software definition. The structure comprises terminal nodes, a switching structure based on an optical coupler and a software defined network controller. The switching structure based on the optical coupler is interconnected with the terminal nodes, thereby forming an optical data channel. The software defined network controller is connected with each terminal node, thereby forming an electric control channel. The software defined network controller collects network state information and allocates network resources to the terminal nodes dynamically. The network controller coordinates communication among the nodes through adoption of a software defined medium access control SD-MAC mechanism, collisions occurring in the network are avoided, and the network throughput is improved. According to the SD-MAC mechanism, the bandwidth resources are allocated to the terminal nodes through adoption of a maximum-minimum fair shared bandwidth allocation algorithm, and the fair and order data communication among the terminal nodes is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
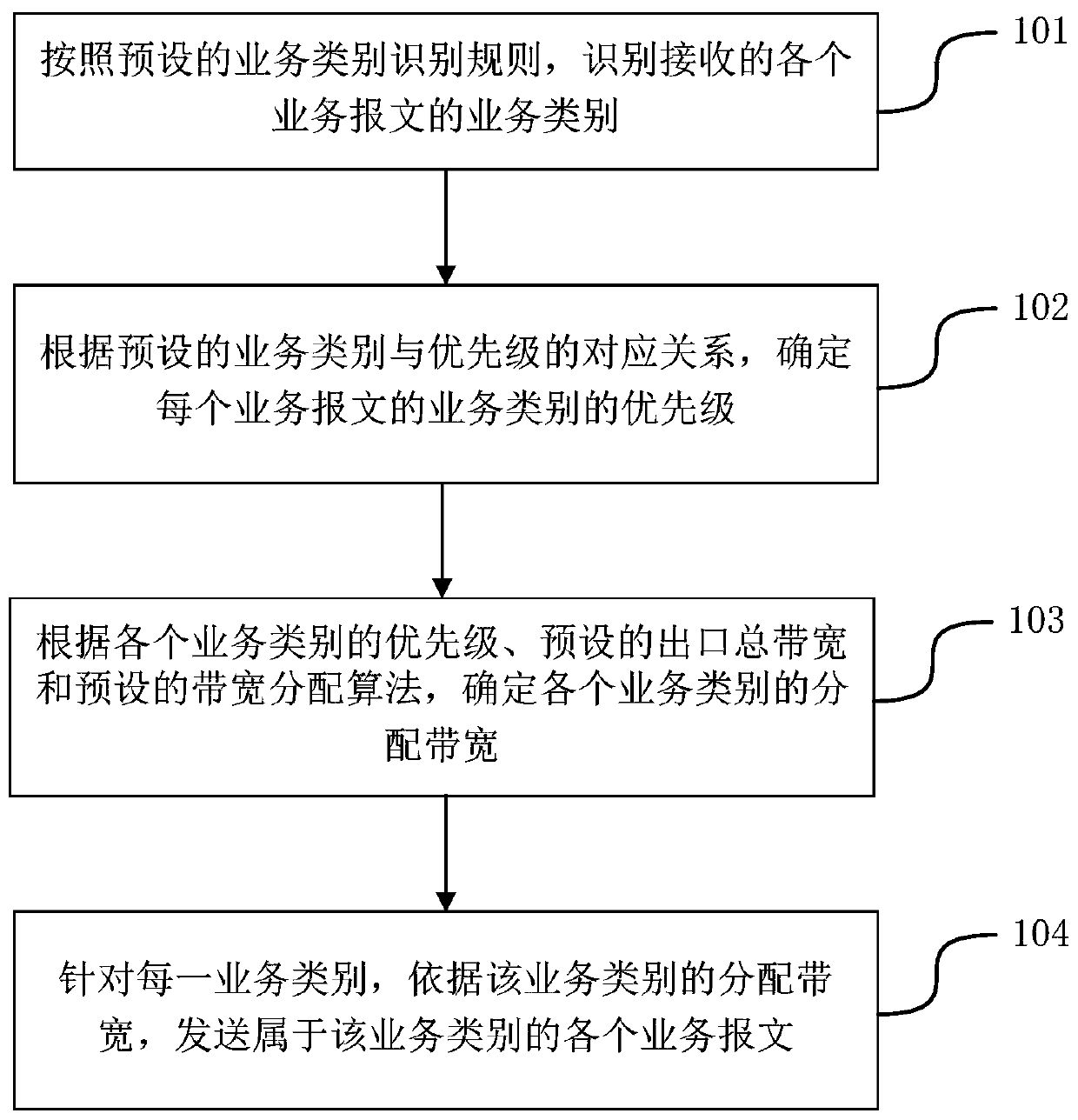
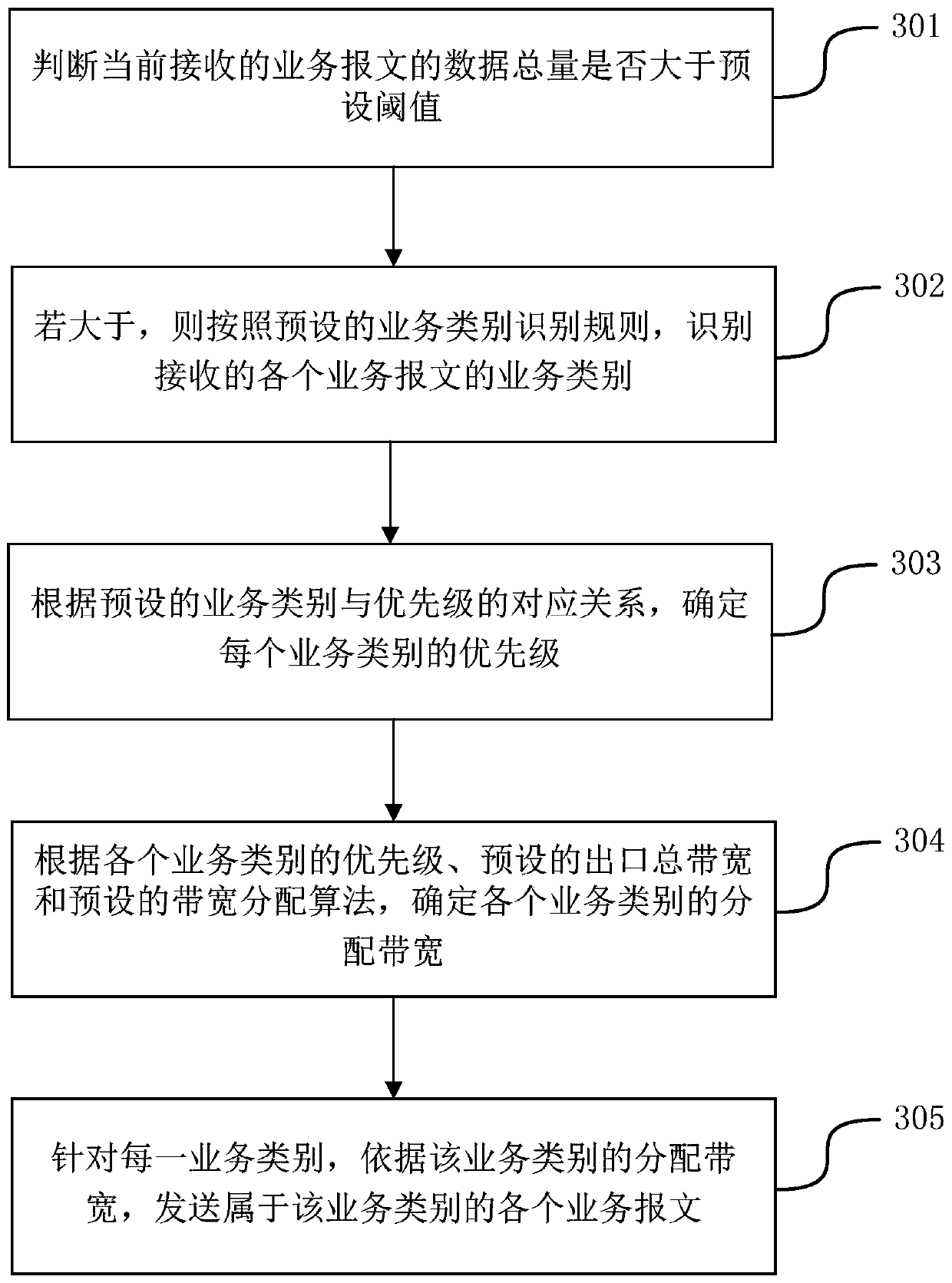
Service message sending method and device
ActiveCN110138610AMeet transfer requirementsData switching networksBandwidth allocation algorithmDistributed computing
The embodiment of the invention provides a service message sending method and device, and relates to the technical field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: identifying the service category of each received service message according to a preset service category identification rule; determining the priority of each service category according to a preset corresponding relation between the service categories and the priorities; according to the priority of each service category, a preset exit total bandwidth and a preset bandwidth allocation algorithm, determining an allocation bandwidth of each service category; and for each service category, sending each service message belonging to the service category according to the distribution bandwidth of the service category.According to the invention, the transmission requirement of the service message can be met.
Owner:NEW H3C SECURITY TECH CO LTD
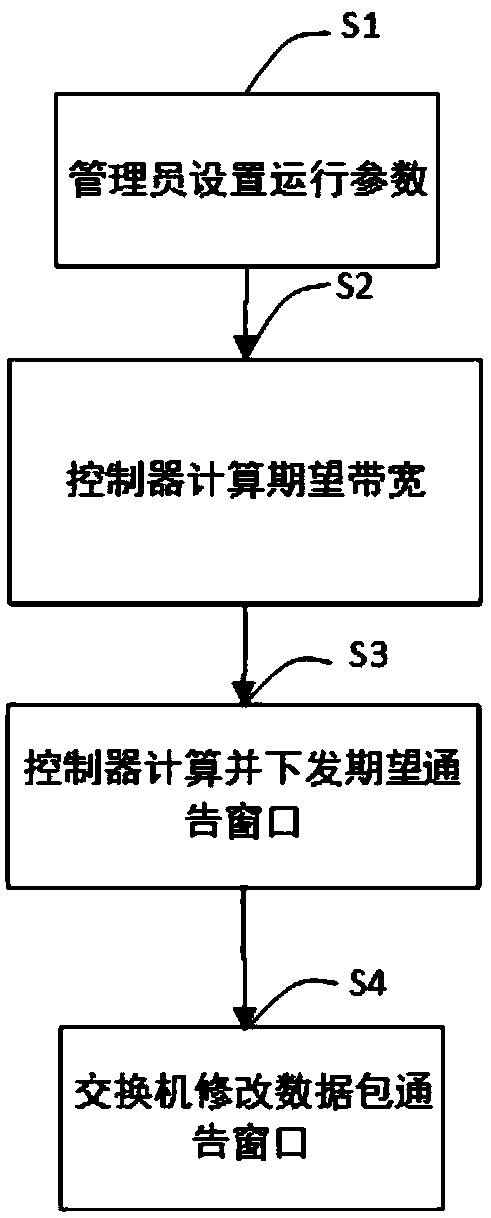
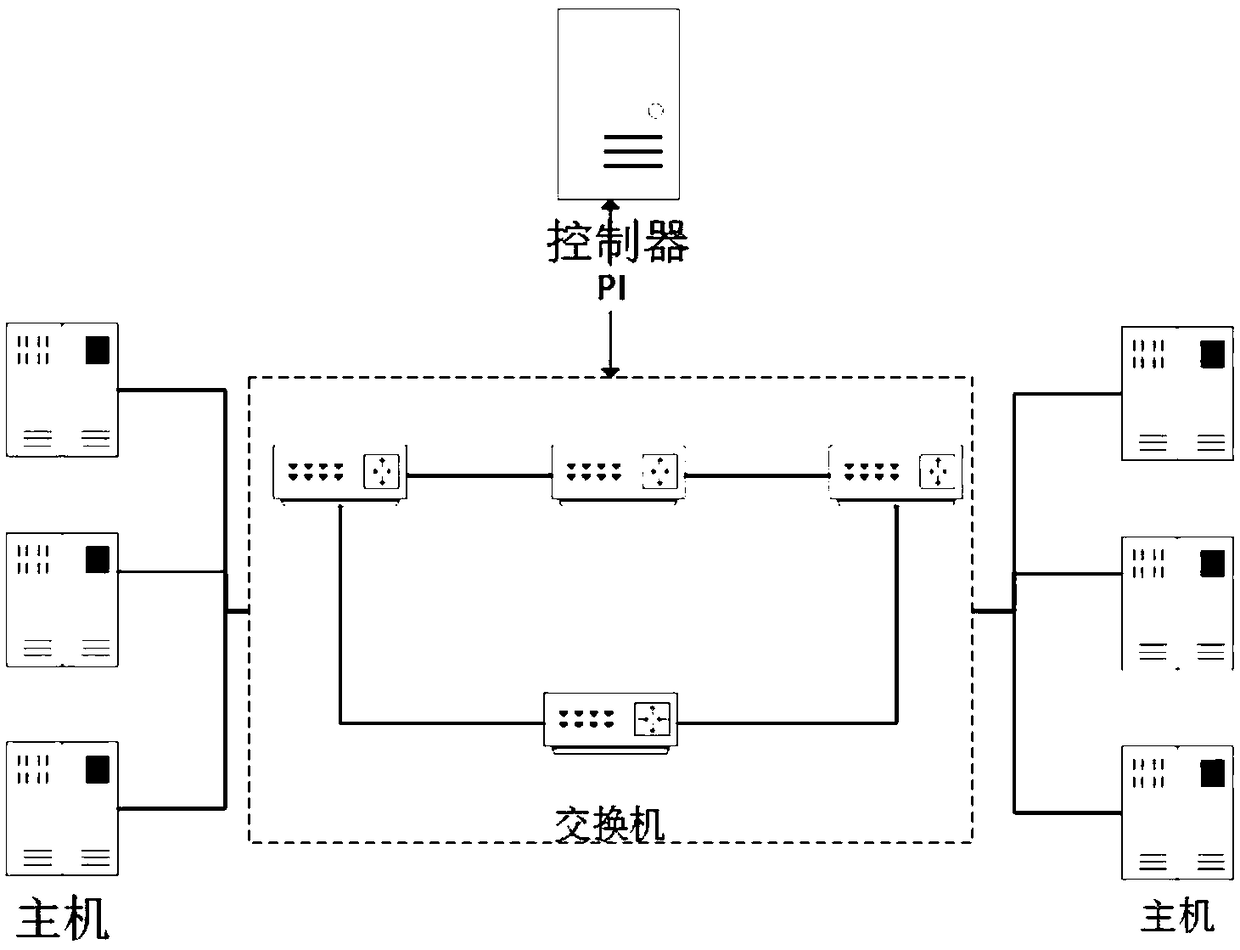
Congestion control mechanism based on advertisement window adjusting method under SDN environment
ActiveCN108768880ASave bandwidthRemove complexityData switching networksRelevant informationResource utilization
The invention relates to the field of the SDN and the computer network, and realizes a congestion control mechanism based on an advertisement window adjusting method under SDN environment. The methodcomprises the following steps: a manager sets a parameter related to the system operation, and assigns a corresponding bandwidth distribution algorithm for a service stream in controller management range; the controller dynamically collects related information of various nodes in a network, computes the corresponding expected bandwidth for the service stream according to the bandwidth distributionalgorithm; the controller computes and issues an expected advertisement window value to a switch according to the computed expected bandwidth value; the switch transmits the actual bearing capacity of the network to a source-end node by using the advertisement window adjusting method; and the source-end node precisely adjusts a data packet sending rate according to a network status, thereby better adapting the network change and improving the network resource utilization rate. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the existing congestion control mechanism of the source-end node is unnecessary to modify, the method can be compatible with the existing network congestion control method, and can well solve the unfairness problem when the ECN and the non-ECN are coexistent.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
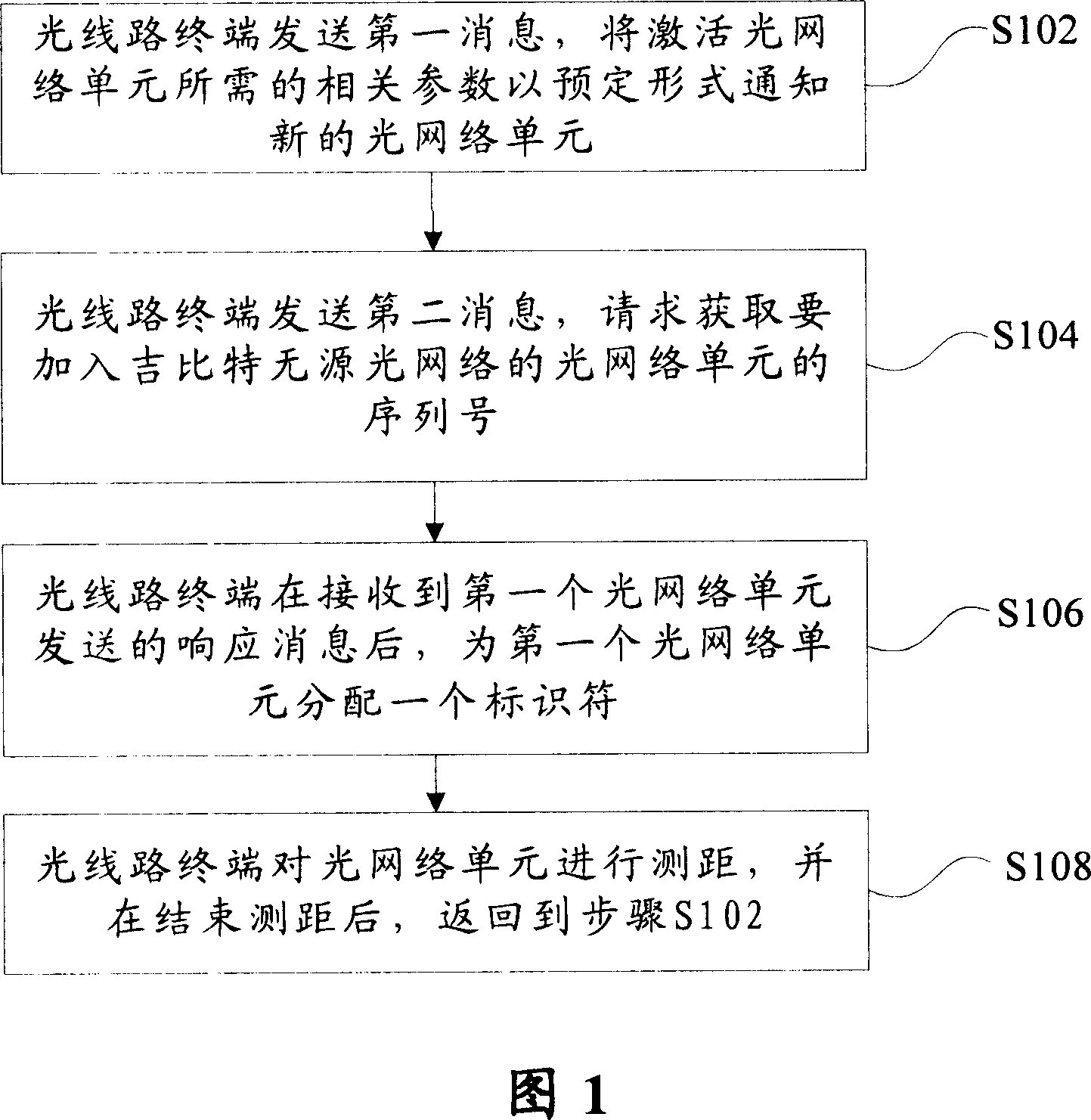
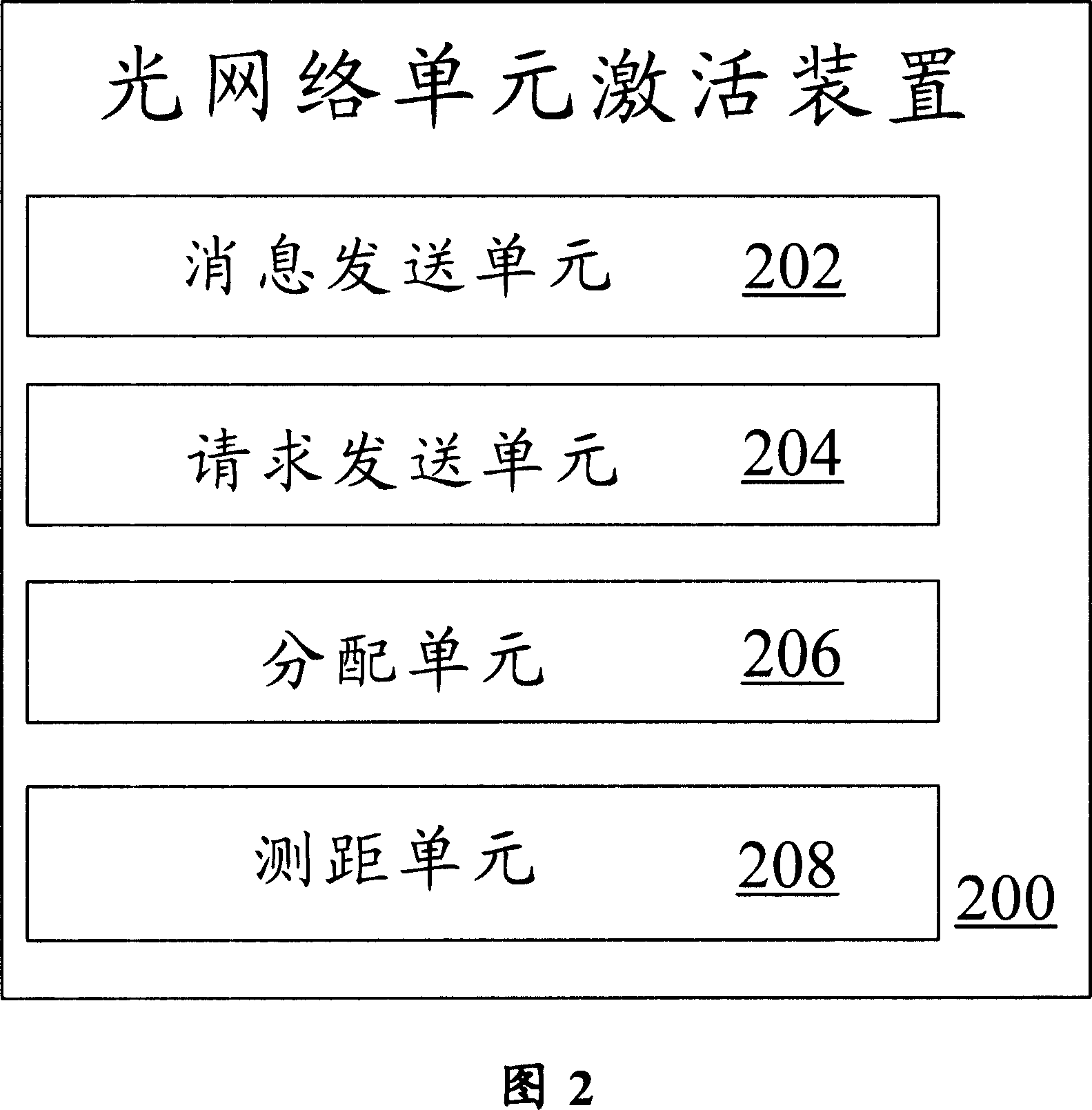
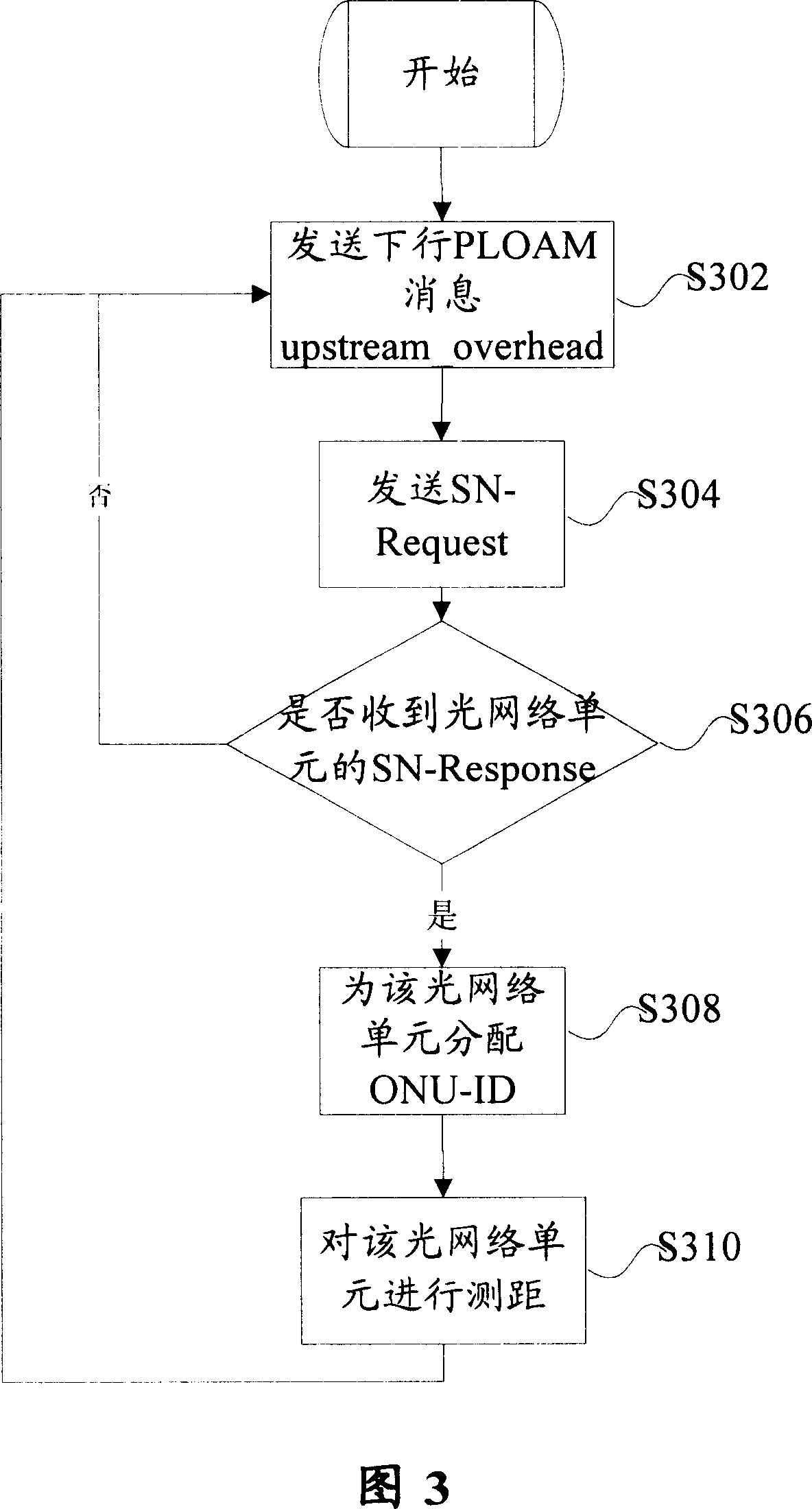
Optical network unit activating method and device
ActiveCN101026474AImprove activation abilityReduce waiting timeSubstation remote connection/disconnectionGigabitOptical network unit
The method includes following steps: S102 step, optical line terminal (OLT) sends first message to inform new optical network unit (ONU) the relevant parameters in prearranged format needed for activating ONU; S104 step, OLT sends out second message to request obtaining sequence number of ONU demanding to enter to passive optical network in giga bit; step S106, after receiving first response message sent from ONU, OLT assigns a ID for first ONU; S108 step, OLT measures distance to ONU, and returns back to S102 after completing measurement. The invention shortens waiting time for obtaining sequence number of ONU, and simplifies complex degree of algorithm for assigning dynamic bandwidth for OLT in procedure of distance measurement.
Owner:ZTE CORP
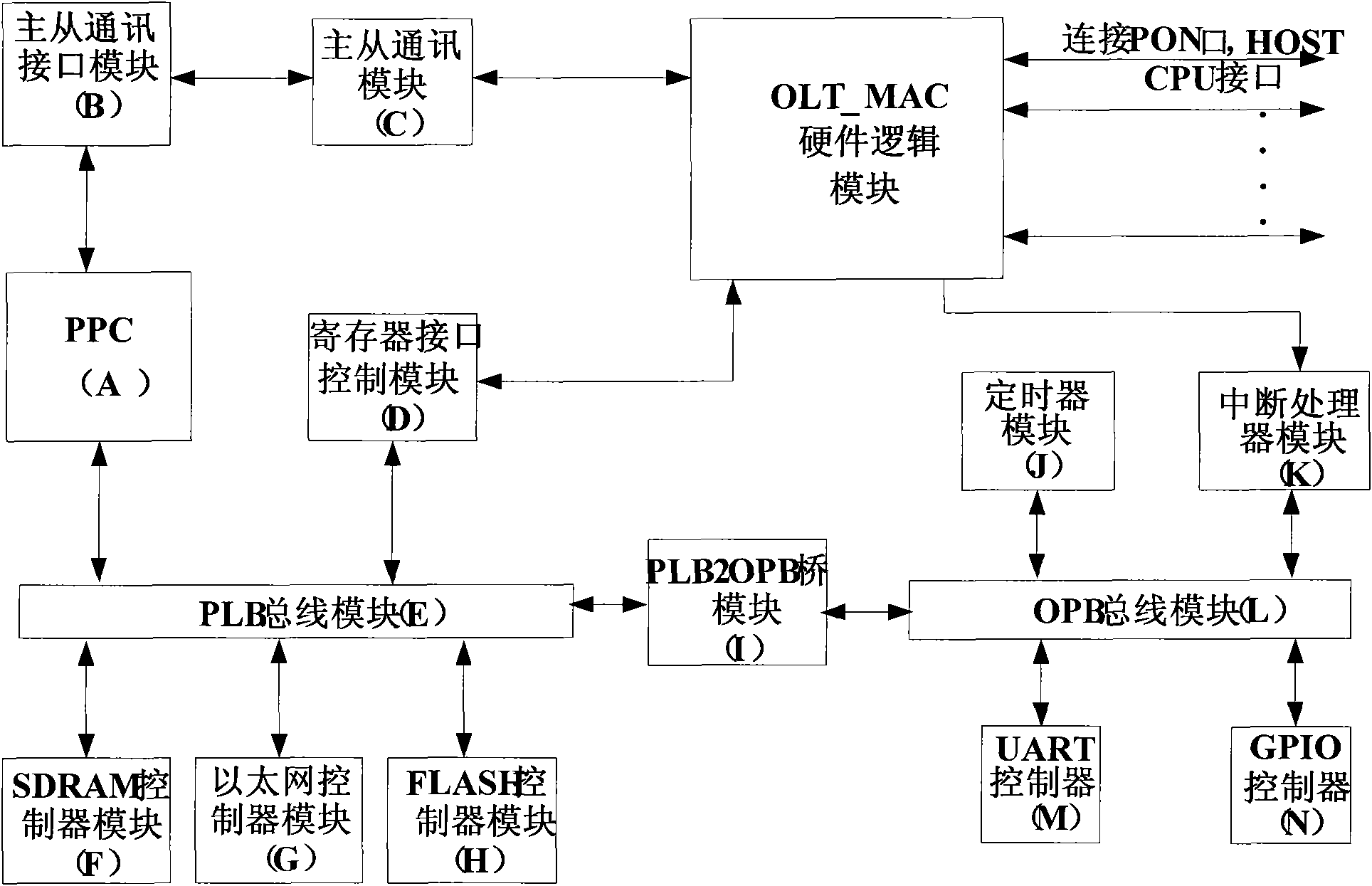
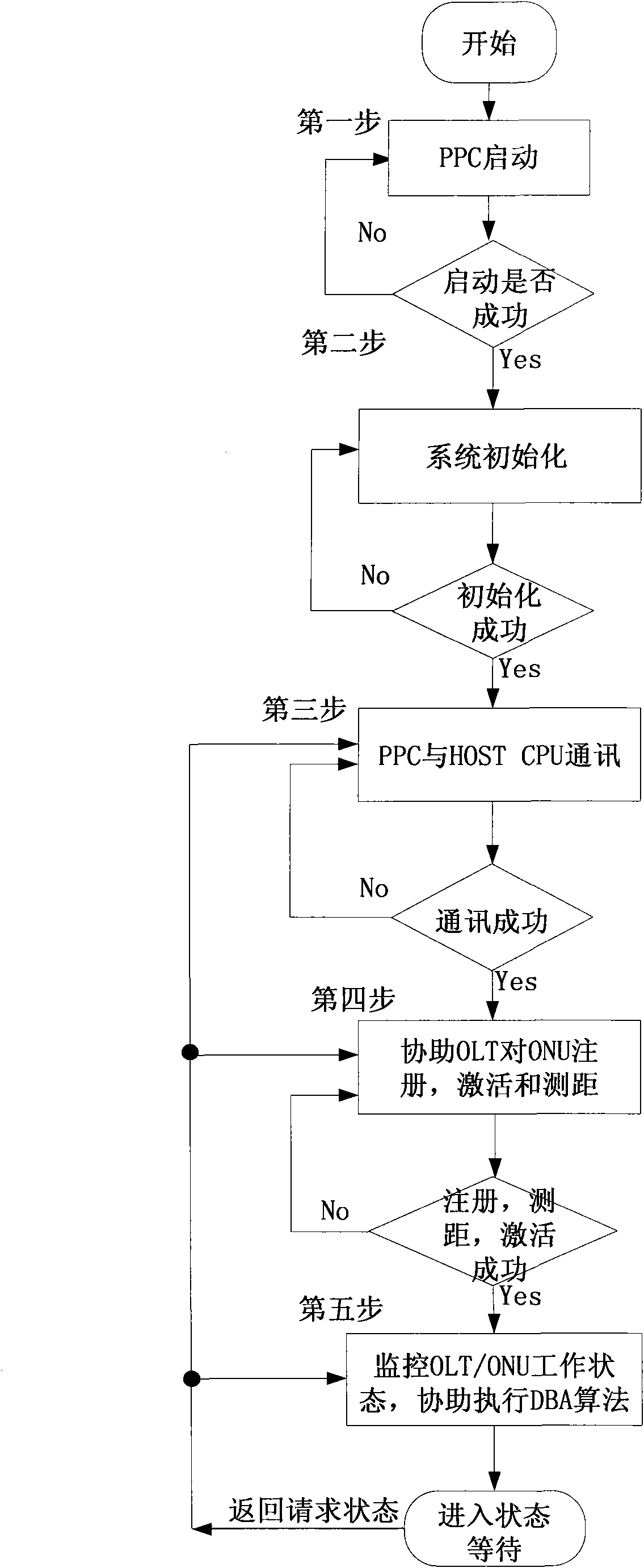
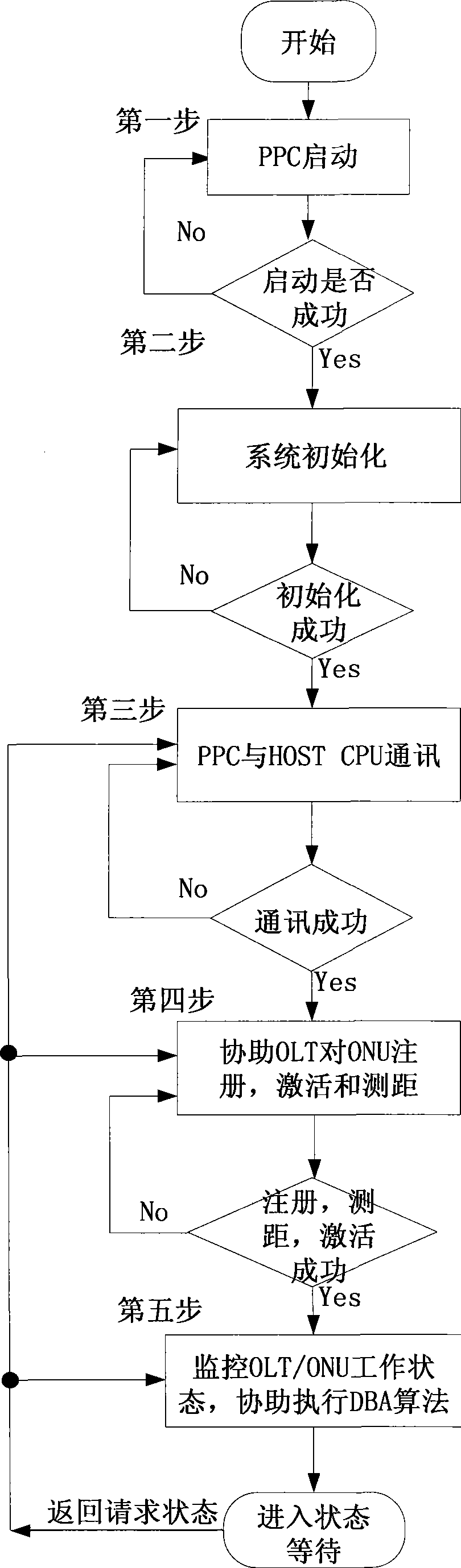
Hardware device and method for assisting in processing dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm
ActiveCN101668233AIncrease flexibilityImprove practicalityMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionProcess dynamicsCommunication interface
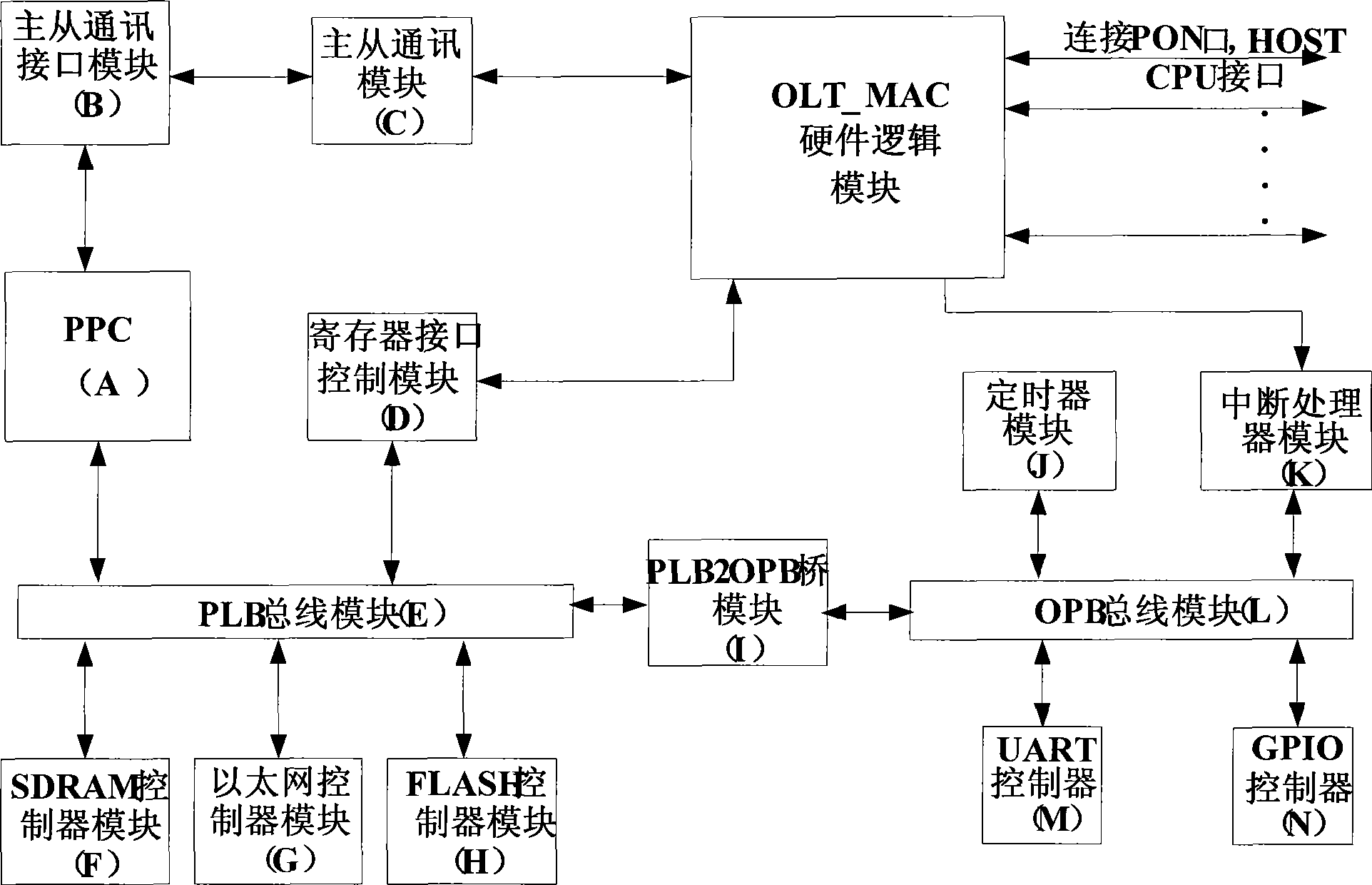
The invention discloses a hardware device and a method for assisting in processing a dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) algorithm. The hardware device comprises a hardware logic module, a register interface control module, a synchronous dynamic RAM controller module, a FLASH controller module, an interrupt processor module, a universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter controller module, and a master-slave communication module, a master-slave communication interface module, a PowerPc CPU module, a processor bus module, a processor bus-to-on-chip- peripheral-bus bridge module and an on chip peripheral bus module which are orderly connected, wherein the PowerPc CPU module is used for processing and controlling data acquired by the hardware logic module, is connected with a master CPU interface in the hardware logic module through the master-slave communication module to finish communications between an embedded CPU and a master CPU, and controls and configures a register in the hardwarelogic module and the report and the allocation of the dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm through a register interface module. The hardware device and the method for assisting in processing the dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm can flexibly process the DBA core algorithm and save the cost.
Owner:ZTE CORP +1
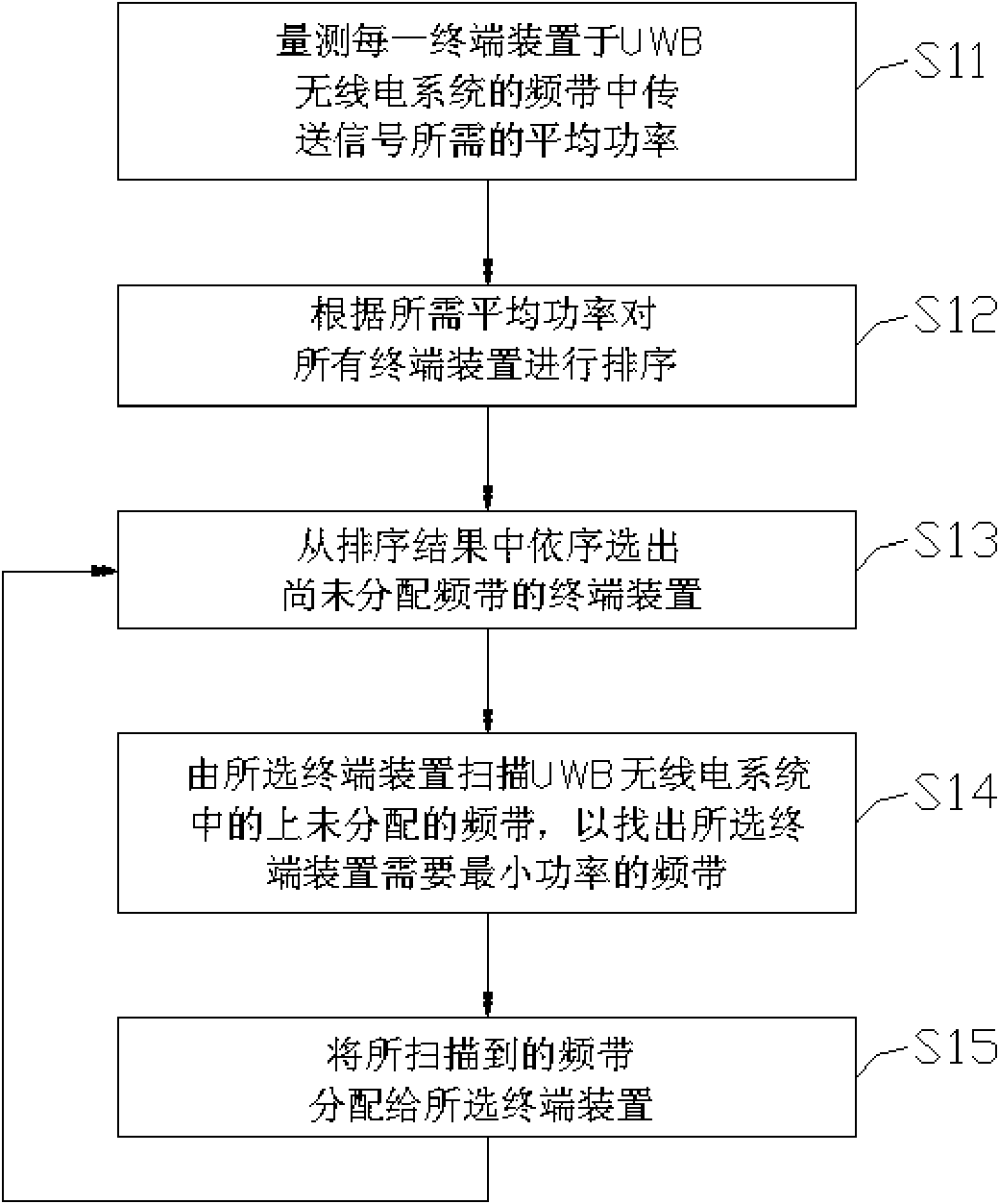
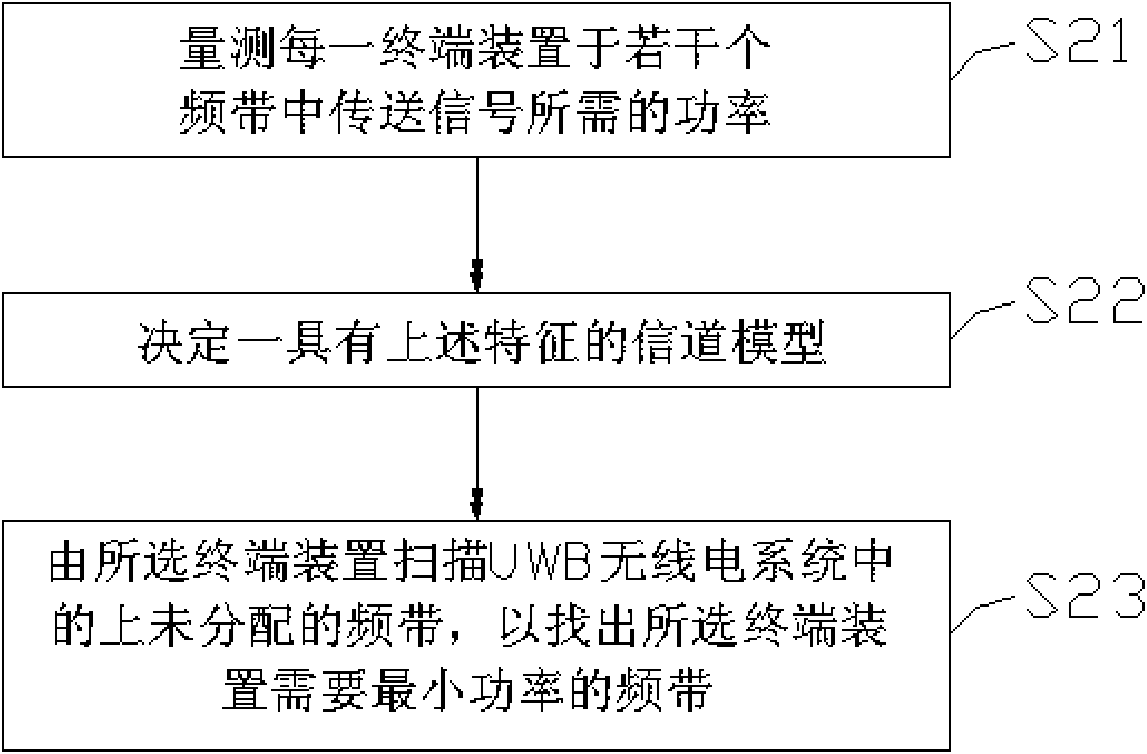
Bandwidth allocation method of UWB (Ultrawideband) wireless network
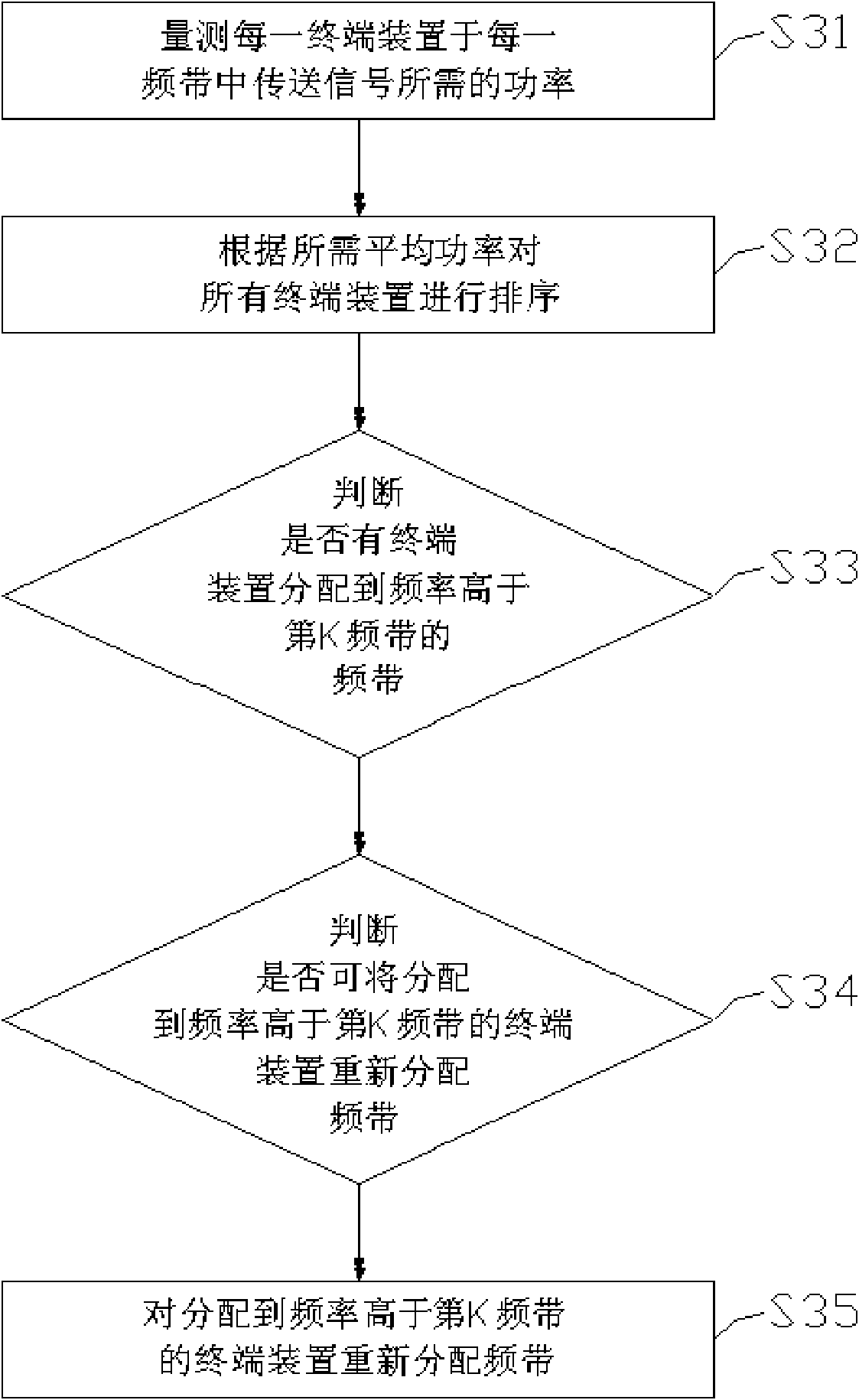
InactiveCN101902748AThe amount of computation to solve increases with the number of terminal devicesSolve the shortcomings of rapid increaseNetwork planningUltrasound attenuationTerminal equipment
The invention discloses a bandwidth allocation method of a UWB (Ultrawideband) wireless network used for allocating a plurality of bandwidths of the UWB wireless network to a plurality of terminal devices. The bandwidth allocation method of the UWB wireless network comprises the following steps of: firstly, measuring power needed by each terminal device for transferring a signal in the plurality of bandwidths; and allocating at least one of the plurality of bandwidths to each terminal device according to a channel model, a bandwidth allocation algorithm and a power measuring value corresponding to each terminal device, wherein the channel model has the characteristic that the average bandwidth gain decreases along with frequency increase. In an embodiment, the channel model comprises an SV (Stochastic Volatility) model and a path attenuation model, the bandwidth allocation method is an algorithm with the computational complexity O (KS), K is the number of the plurality of terminal devices, and S is the number of the plurality of bandwidths.
Owner:MITAC COMP (SHUN DE) LTD
Dynamic bandwidth allocation method based on non-fixation multithreading polling
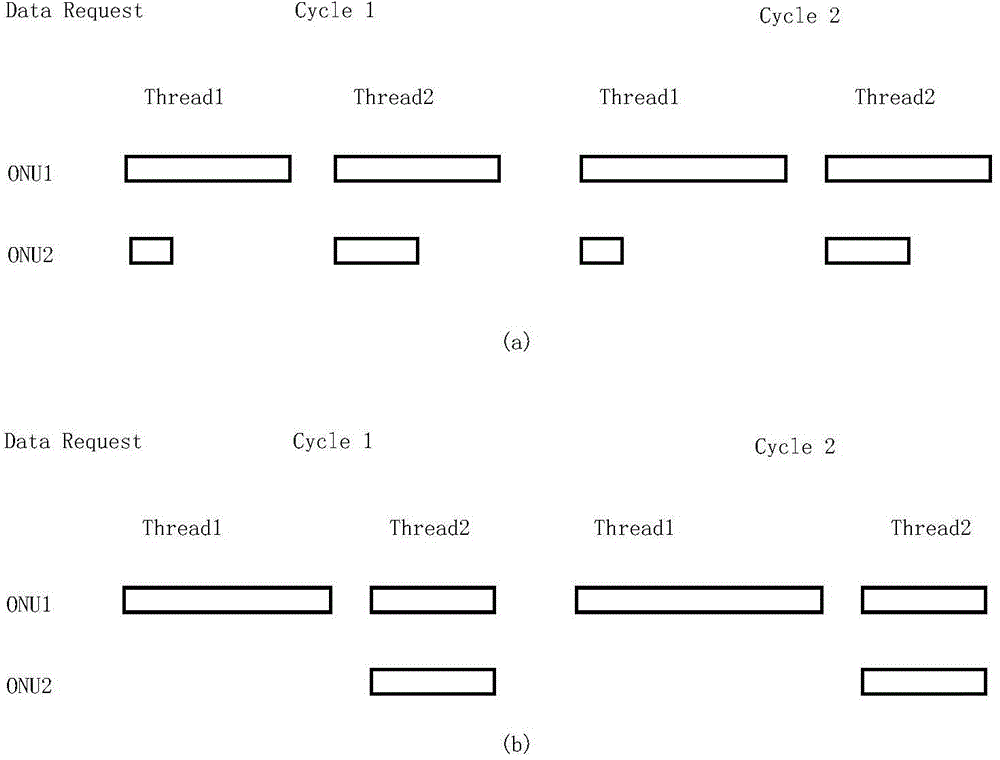
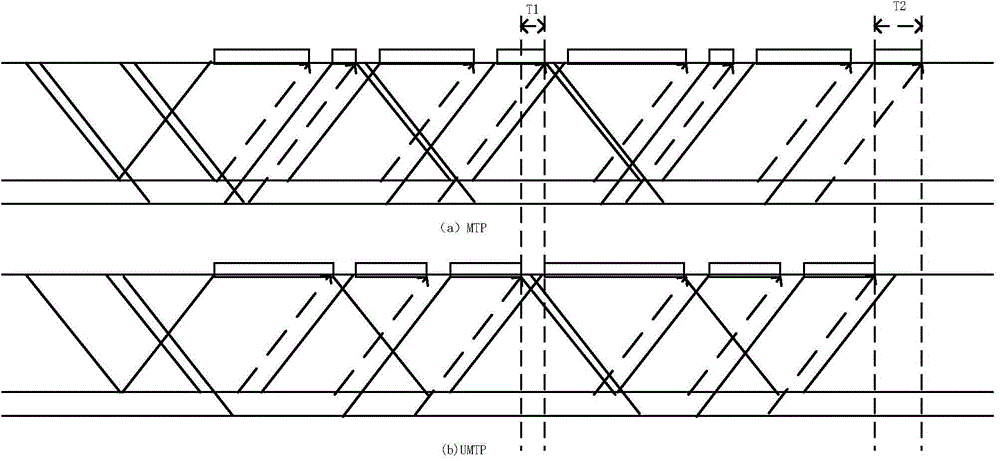
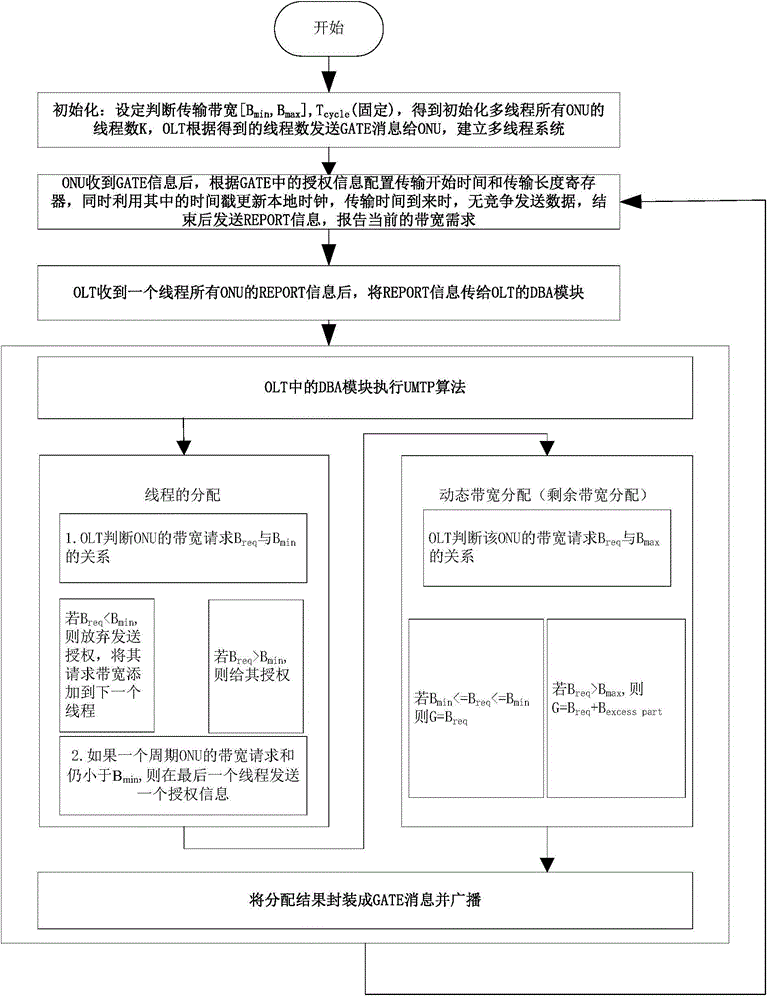
ActiveCN104468409AImprove resource utilizationReduced latency for heavily loaded ONUsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksAccess networkTime delays
The invention discloses a non-fixation multithreading polling dynamic bandwidth allocation (UMTP) method suitable for the long distance optical access network (LR-PON). The method includes the steps that optical network units (ONUs) initiate service requests, and the service requests are transmitted to optical line terminals (OLTs); the UMTP algorithm is adopted in the OLTs to conduct threading polling on all the ONUs, fewer threads are distributed by the OLTs to the ONUs with the small bandwidth requests, more threads are distributed by the OLTs to the ONUs with the large bandwidth requests, and the unequal-number threading polling is completed; the OLTs distribute the available bandwidth to the ONUs according to the residue bandwidth allocation algorithm, and transmission data windows are specified. Through application of the UMTP algorithm, the number of threads of the ONUs can be flexibly distributed, the number of the threads of the light-load ONUs is decreased, the working efficiency of the OLTs is decreased, the resource using rate of the system is improved, and time delay of the heavy-load ONUs is reduced. In short, the UMTP applied to the LR-PON is a relatively-efficient dynamic bandwidth allocation method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
P2P file sharing network bandwidth allocation algorithm based on price mechanism
ActiveCN105450738AAchieve fair distributionClose to actual needsTransmissionComplete dataResource Provider
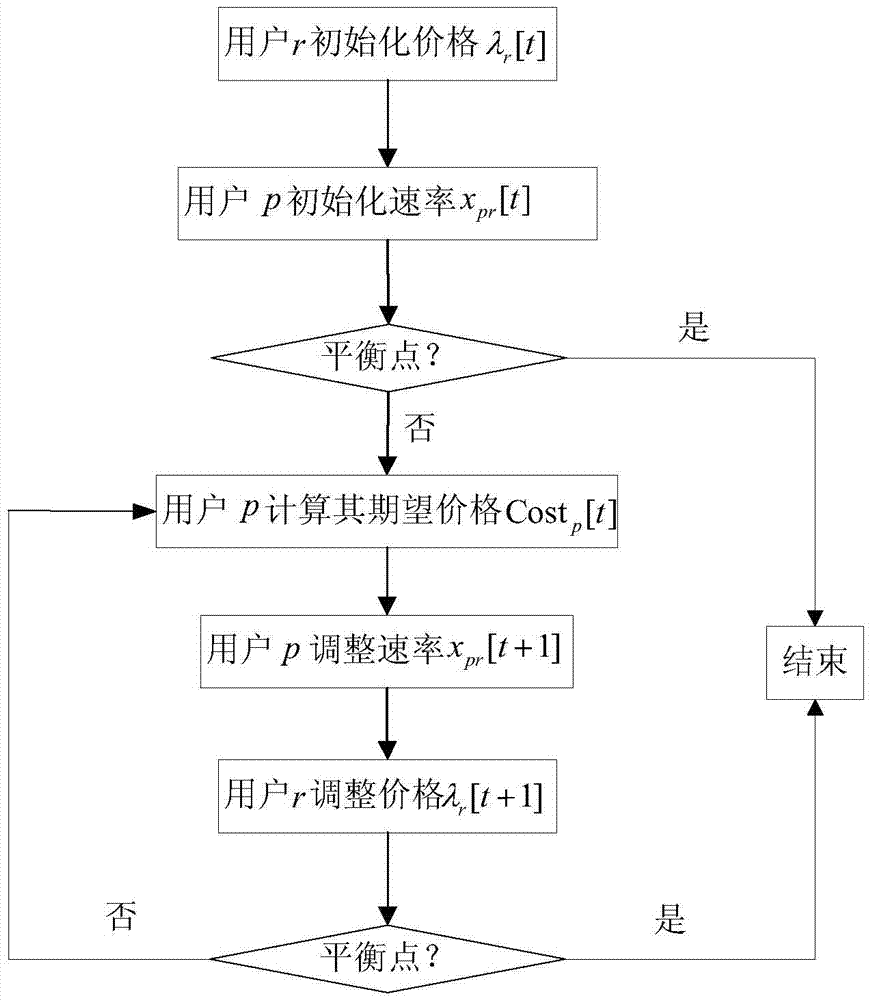
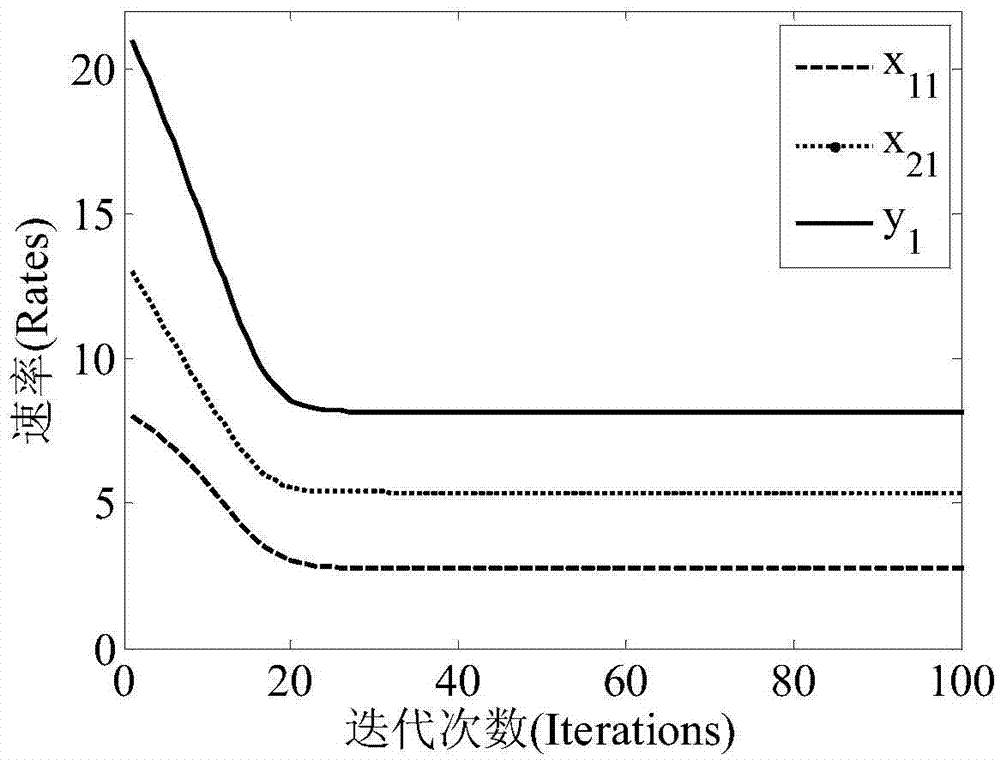
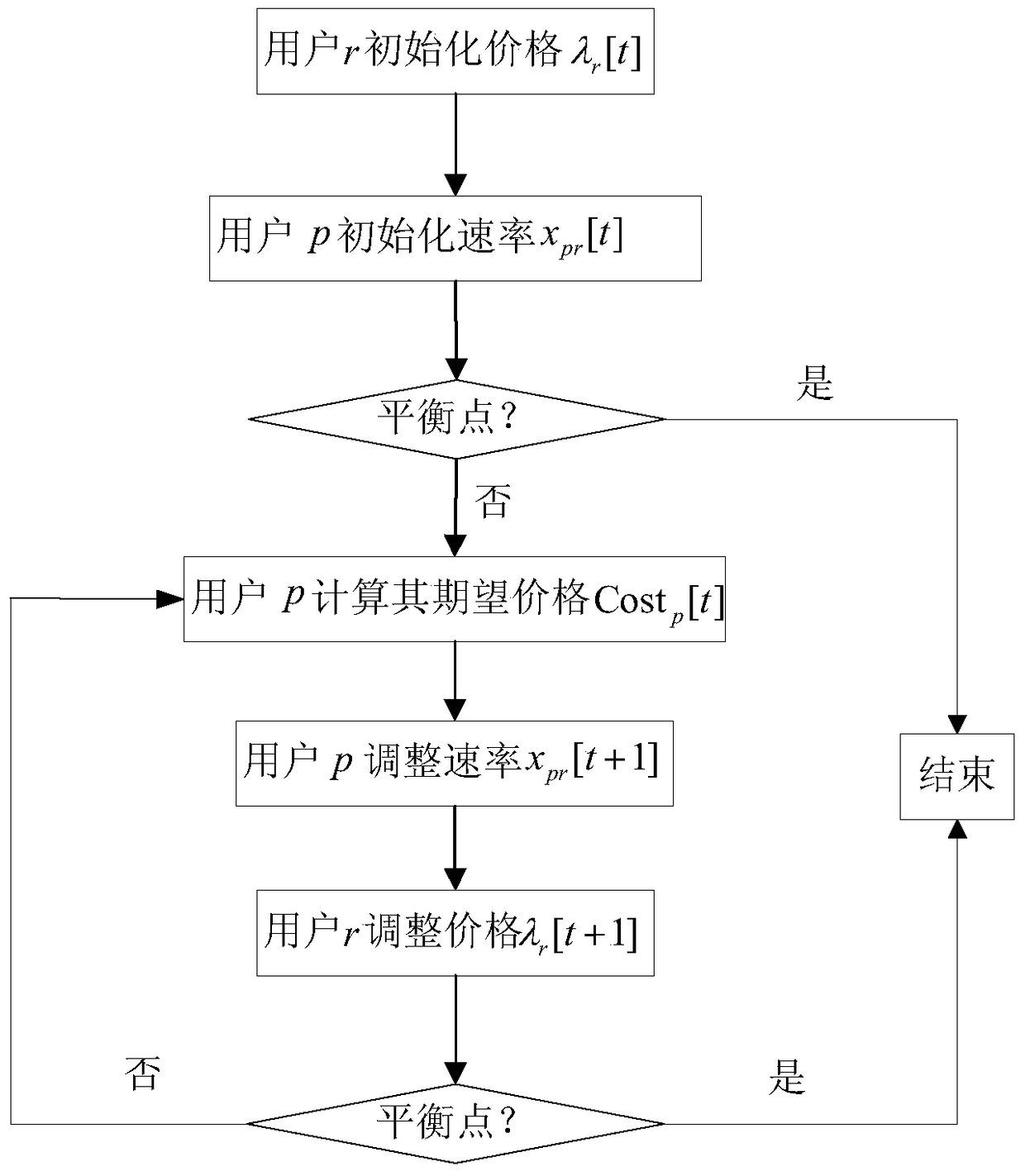
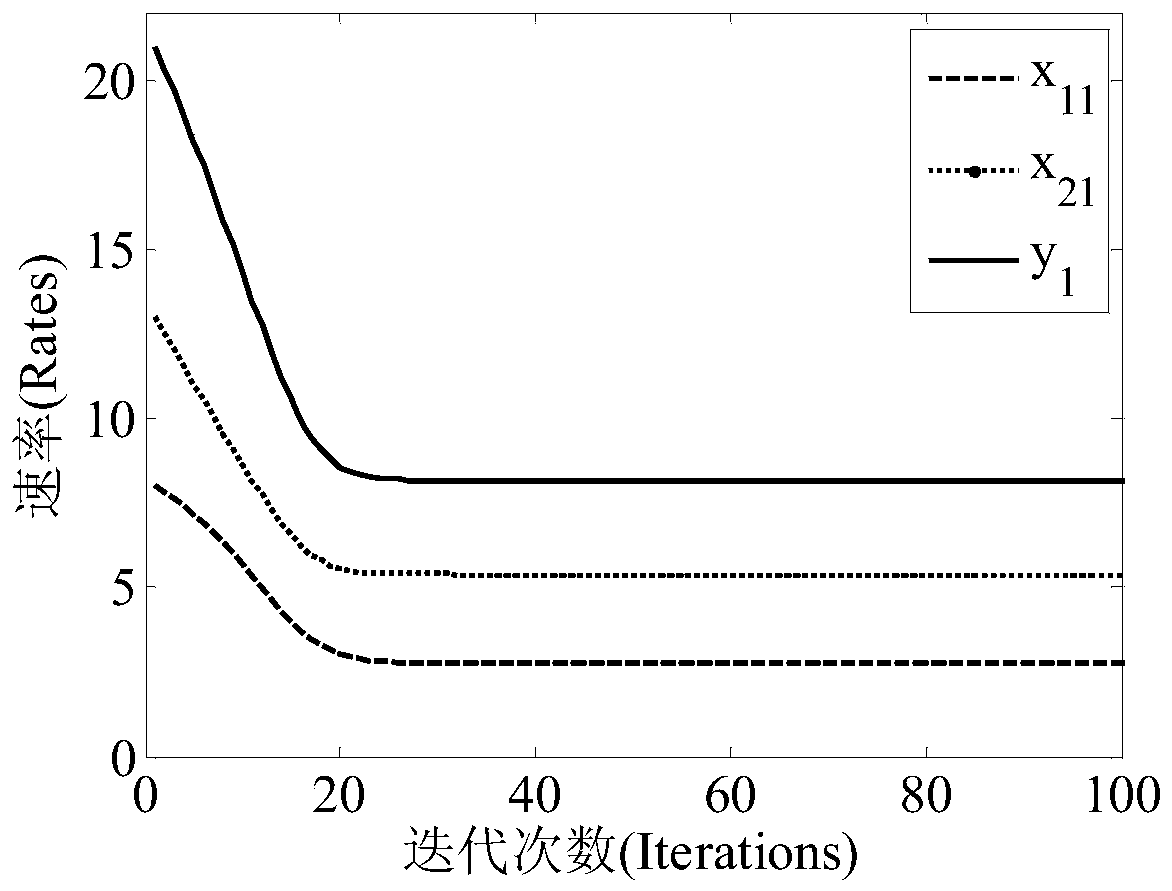
Provided is a P2P file sharing network bandwidth allocation algorithm based on a price mechanism, comprising the following steps: each resource requestor r initializes a price Lambda(r)[t] which can be provided thereby; resource providers p initialize an allocated bandwidth xpr[t] for each resource requestor r; the resource providers p work out an expected price Costp[t] for the initialized allocated bandwidth xpr[t] of each resource requestor r and the price Lambda(r)[t] provided by the resource requestor r according to the upload bandwidth Cp thereof; the resource providers p adjust the bandwidth xpr[t+1] allocated for the resource requestors r according to the expected price Costp[t] and the price Lambda(r)[t] provided by the resource requestors r; the resource requestors r adjust the price Lambda(r)[t+1] according to the acquired bandwidth; all the resource providers p carry out iteration according to the steps to achieve a balance, namely, the resource providers p upload optimal bandwidth allocation; the resource providers and the resource requestors complete data transmission according to the optimal bandwidth allocation; and if there is a new node joining or an original node exiting, the iteration process is repeated until a new balance is achieved. The P2P file sharing network bandwidth allocation algorithm of the invention has the advantages of fair allocation and simple calculation.
Owner:宅人桥(南京)网络科技有限公司
Implementation method of spatial information network large-scale link simulator
ActiveCN110535764AGuarantee authenticityFlexibleData switching networksBandwidth extensionInformation networks
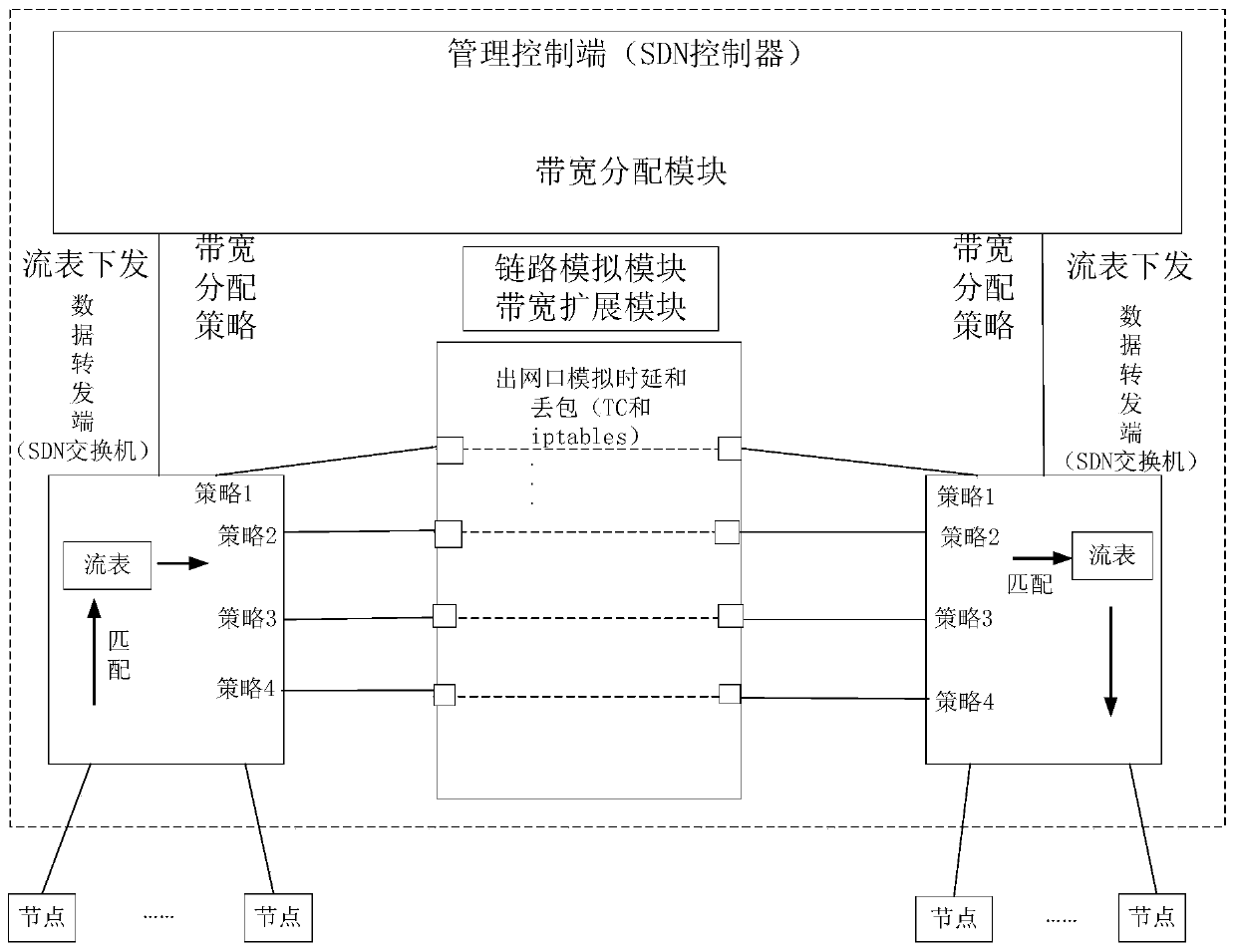
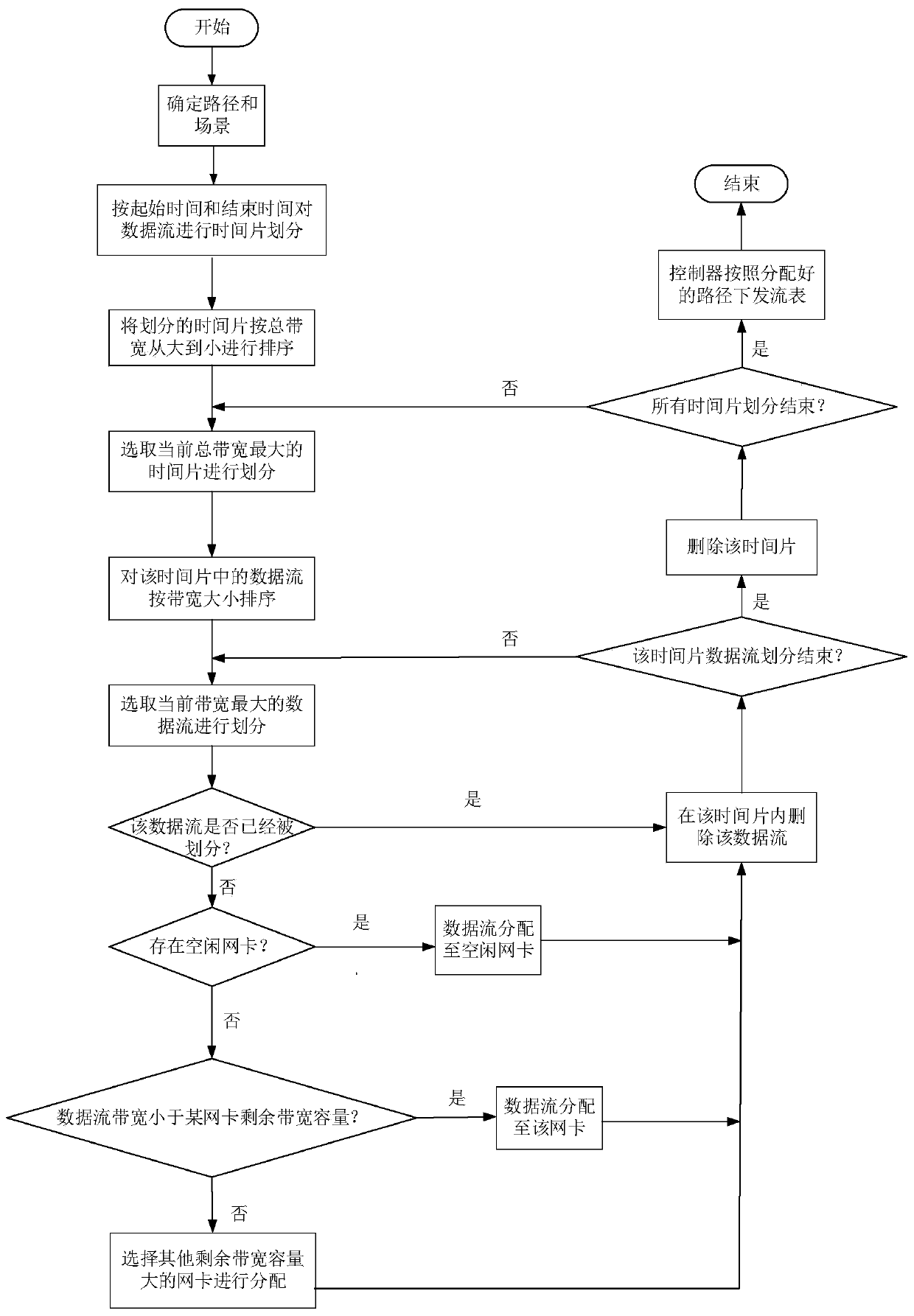
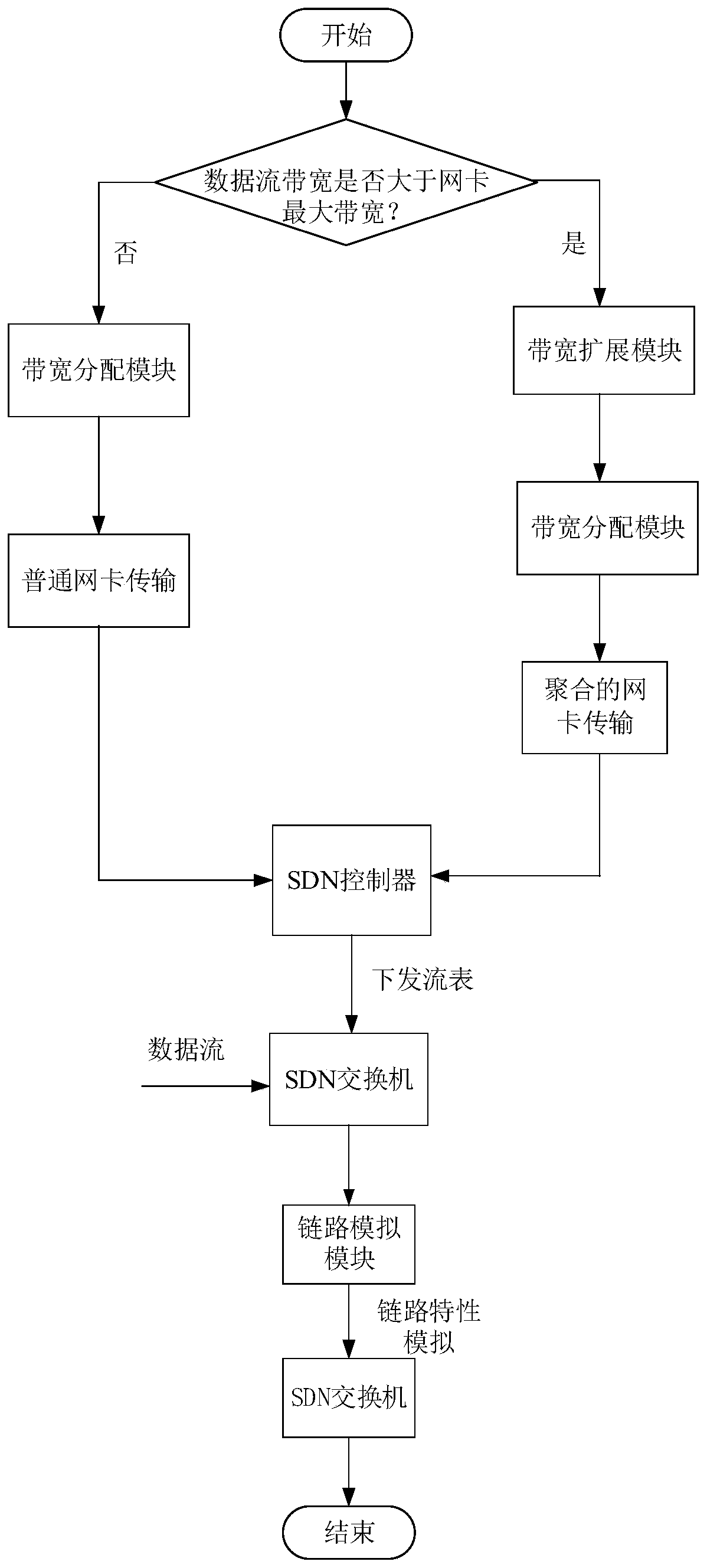
The invention discloses an implementation method of a spatial information network large-scale link simulator. The system comprises a basic link simulator, an SDN controller and an SDN switch, whereinthe SDN controller comprises a bandwidth allocation module, the basic link simulator comprises a link simulation module and a bandwidth expansion module, and the link simulation module is used for realizing the most basic function of simulating link characteristics and simultaneously realizing accurate simulation of a plurality of spatial links so as to meet the basic requirements of simulation ofa plurality of links among spatial information network nodes; the bandwidth extension module effectively breaks through the bandwidth upper limit of a single link originally simulated by a link simulator through an SDN group table and a link aggregation technology; a bandwidth allocation algorithm is integrated in the bandwidth allocation module, the number of links supported by the link simulator is effectively increased through the algorithm, and the link simulator has the advantages of being authentic, flexible, extensible and the like and can be well applied to a spatial information network.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for allocating bandwidths in multi-user single relay communication system
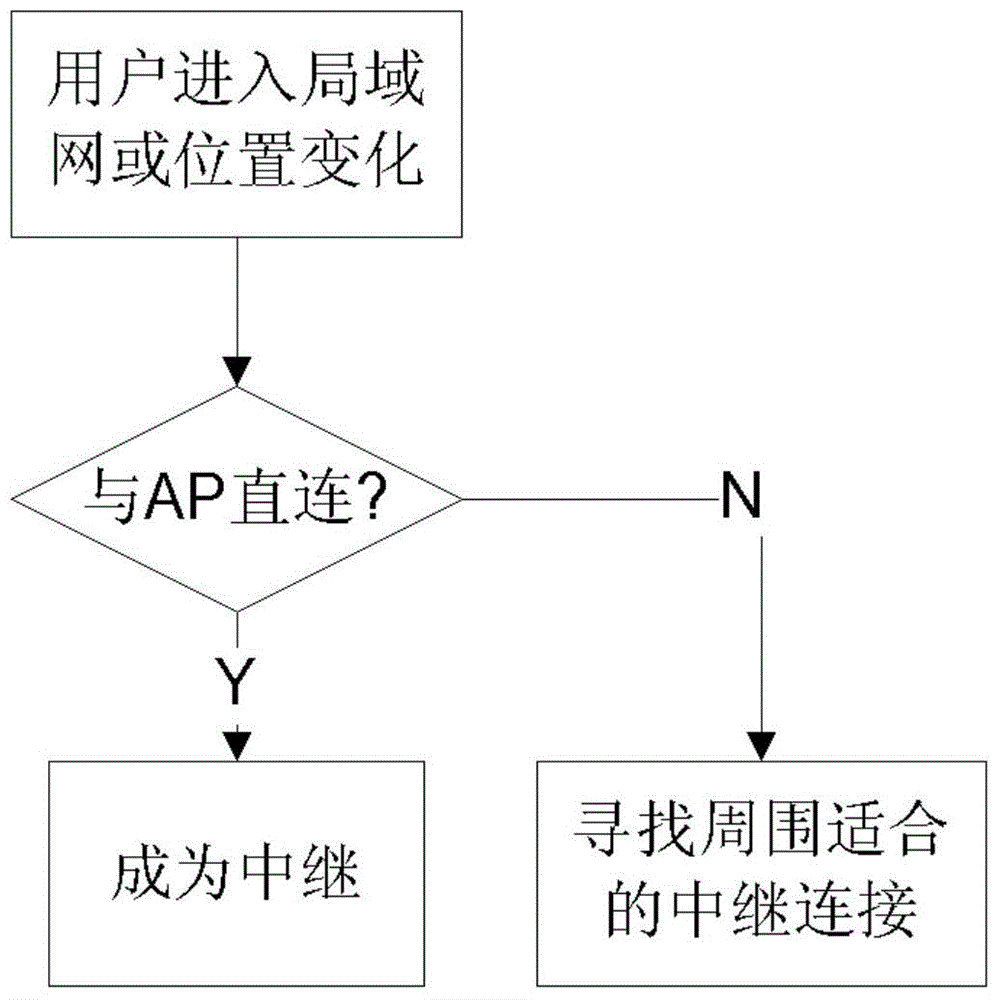
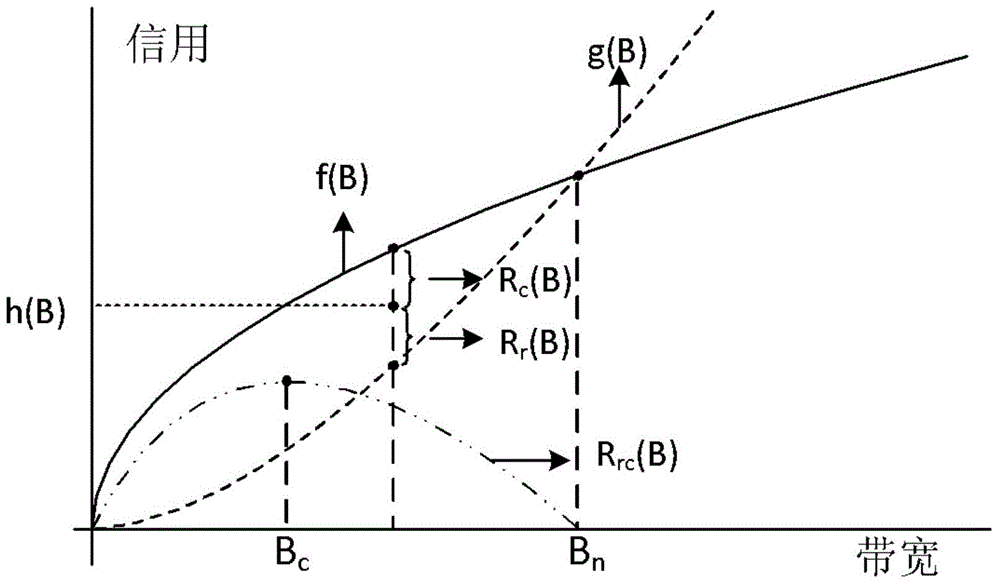
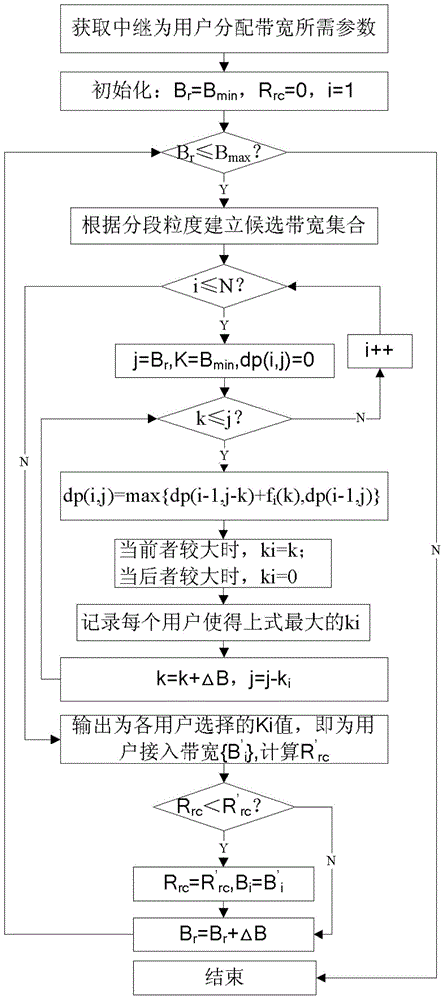
ActiveCN103561471AMaximize service benefitsReduce overheadNetwork topologiesUser needsCommunications system
The invention provides a method for allocating bandwidths in a multi-user single relay communication system. The method includes the steps that when multiple users exist in a region, part of users can be directly connected with APs to become a relay, and part of the users need to be connected with relay users to acquire data services; when the users enter a common local area network region, user revenue functions are discretized according to the user revenue functions and relay consumption functions, and a bandwidth allocation algorithm is utilized to select an optimum bandwidth allocation strategy to allocate the bandwidths; meanwhile, the limitation of the maximum service bandwidth of the relay and the minimum required bandwidth of the users is considered, the users who have little benefit to a network are removed under the appropriate condition, new users who have higher benefits are connected, and bandwidth allocation of a whole cluster is updated; when the users leave, the bandwidths are released, and the bandwidth allocation is updated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
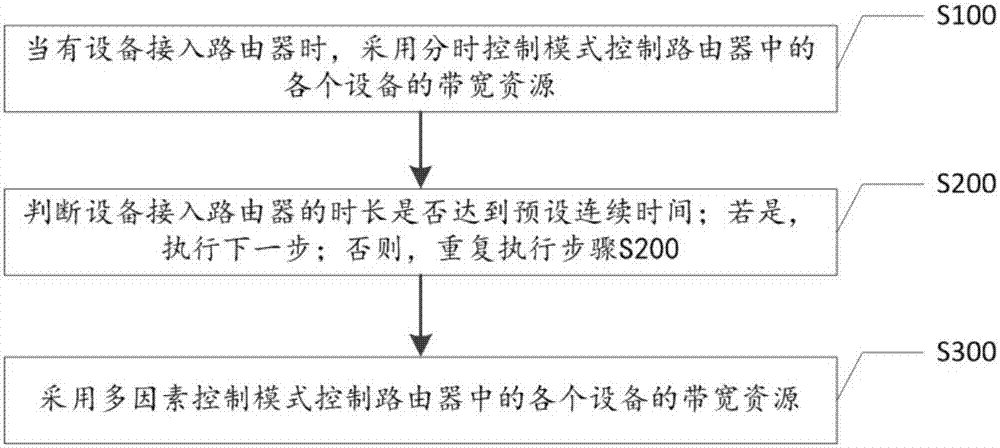
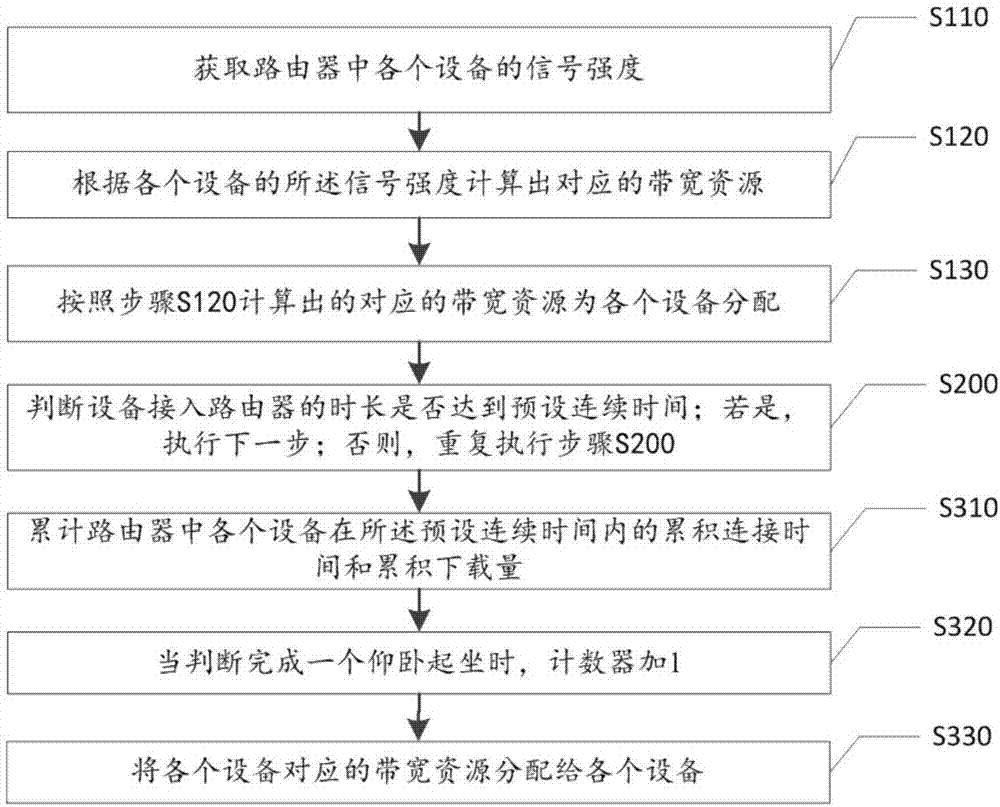
Multi-mode bandwidth control method and apparatus
The invention discloses a multi-mode bandwidth control method. The multi-mode bandwidth control method comprises the following steps: S100, when a device accesses a router, controlling the bandwidth resources of devices in the router by adopting a time division control mode; S200, judging whether the time length of the device accessing the router reaches a preset continuous time; if so, executing a next step; and otherwise, repeatedly executing step S200; and S300, controlling the bandwidth resources of devices in the router by adopting multi-factor control mode. According to the multi-mode bandwidth control method, factors of integrated flux and cumulative time are added to a bandwidth allocation algorithm, the bandwidth is automatically allocated, whether the device is a network rubbing device is not judged just depending on the signal strength, and the router has the function of identifying own devices and network rubbing devices.
Owner:HARBIN YULONG AUTOMATION
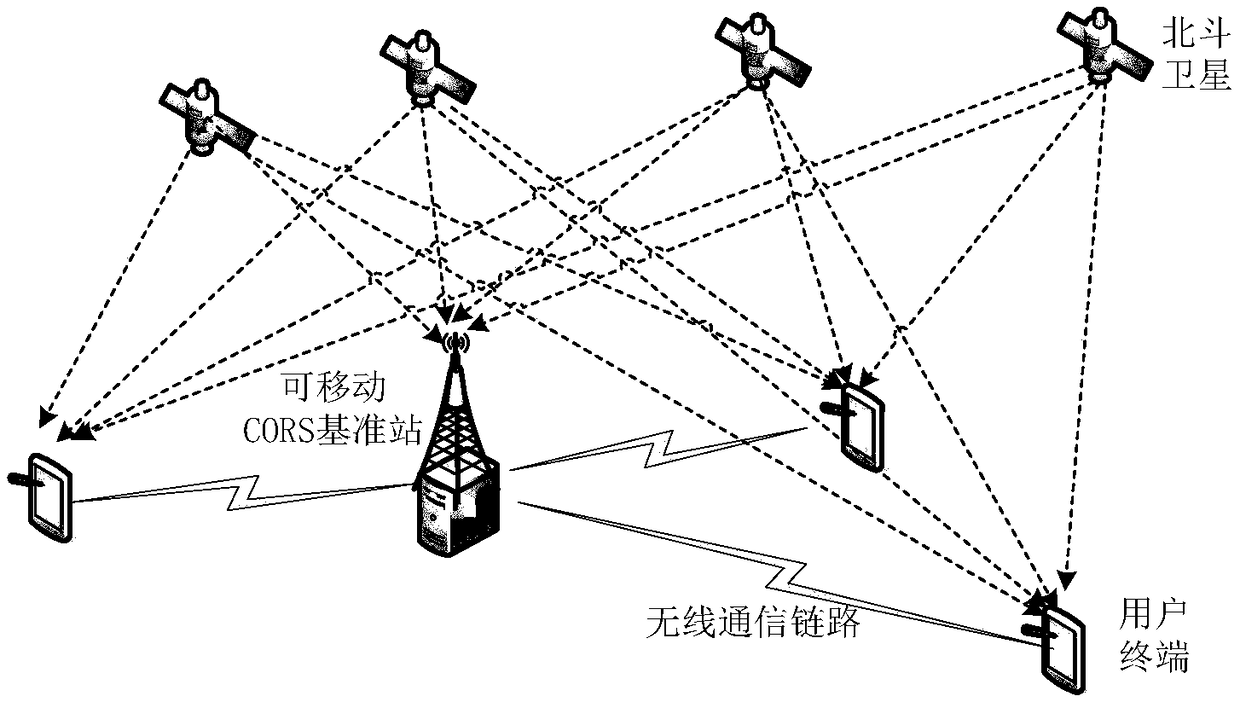
Differential positioning data transmission method, device and system of differential positioning system
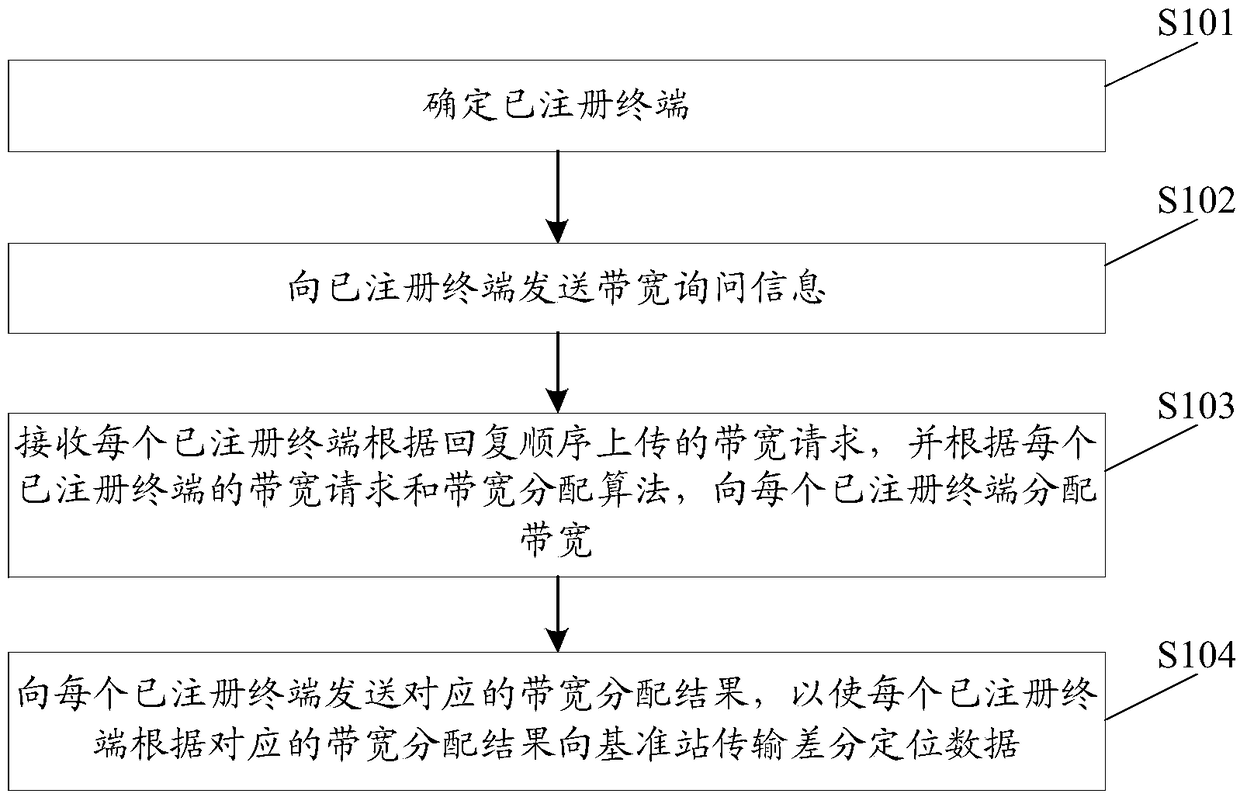
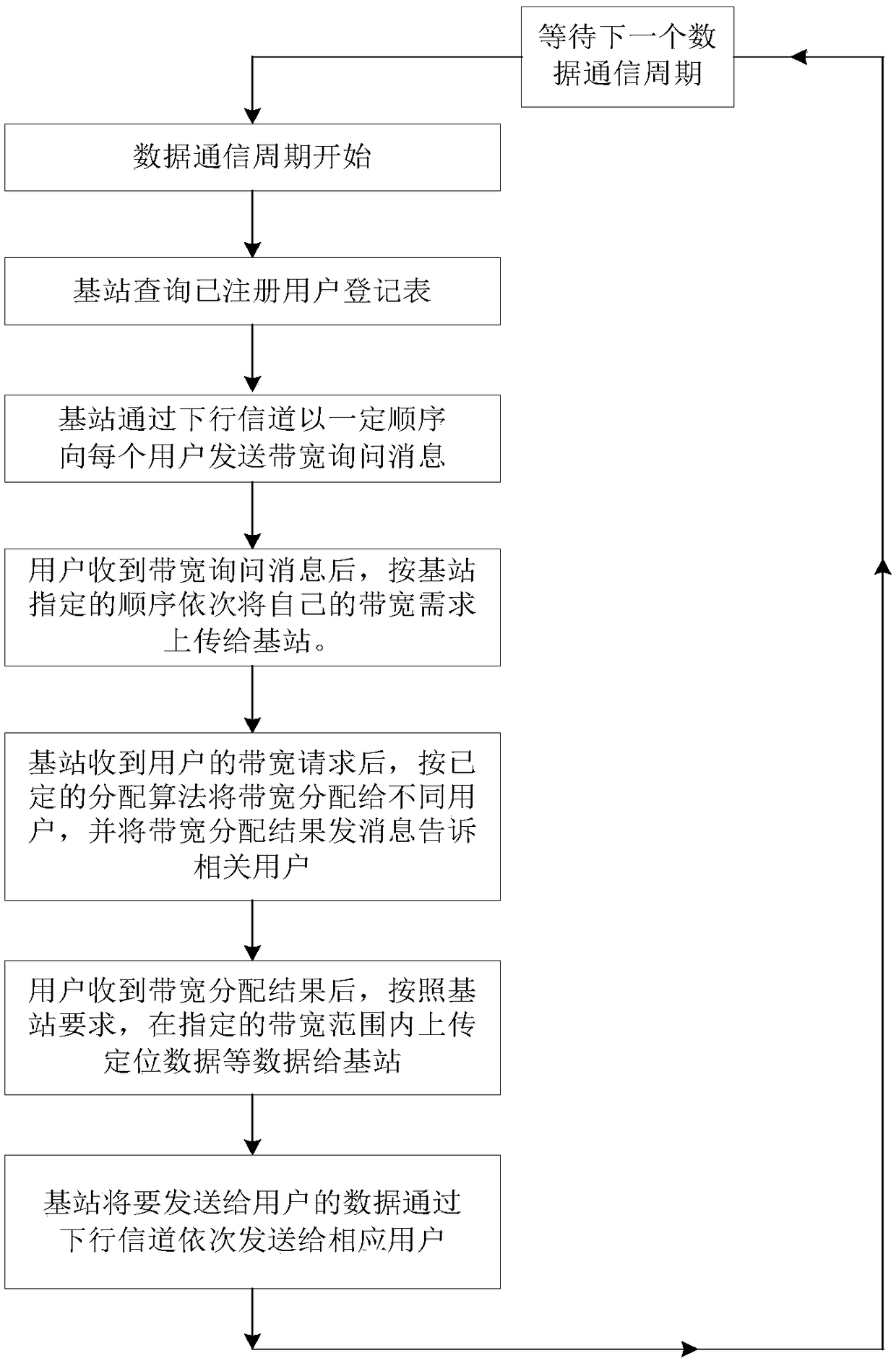
PendingCN109041235AAccurate transmissionAvoid confictWireless communicationAllocation algorithmData transmission
The invention discloses a differential positioning data transmission method of a differential positioning system. The method comprises: determining a registered terminal; sending bandwidth inquiry information to the registered terminal; receiving a bandwidth request uploaded by each registered terminal according to a reply sequence, and allocating bandwidth to the registered terminal according tothe bandwidth request and the bandwidth allocation algorithm of each registered terminal; transmitting a corresponding bandwidth allocation result to each registered terminal so that each registered terminal transmits differential positioning data to a reference station according to the corresponding bandwidth allocation result. Thus, in this scheme, the reference station allocates the respectivebandwidth to the registered terminals, so that the registered terminals and the reference station carry out the orderly communication within the respective allocated bandwidth, so as to realize the accurate transmission of the differential positioning data, avoid the collision of uploading signals of different terminals, and improve the bandwidth utilization rate. The invention also discloses a differential positioning data transmission device, a device and a system of the differential positioning system, which can also realize the technical effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
A method for efficient allocation of global resources for hybrid multiplexing
ActiveCN106209687BRealize centralized controlEnsure fair distributionData switching networksWeight coefficientTime delays
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
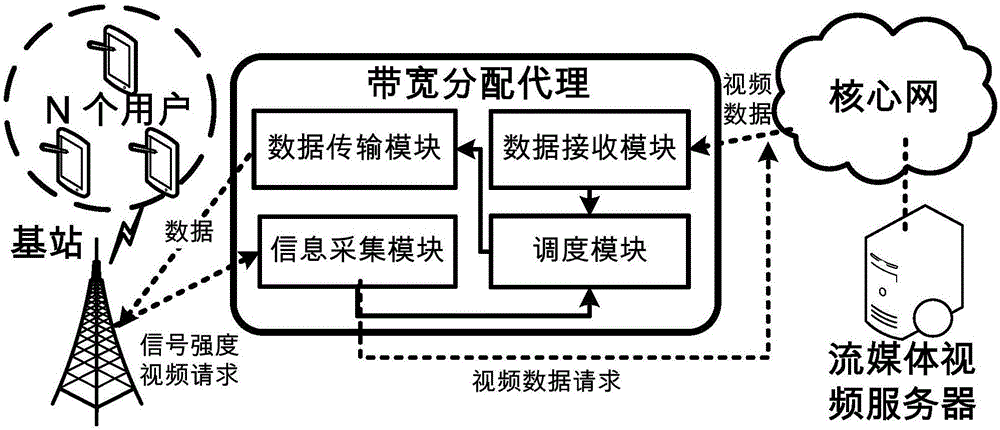
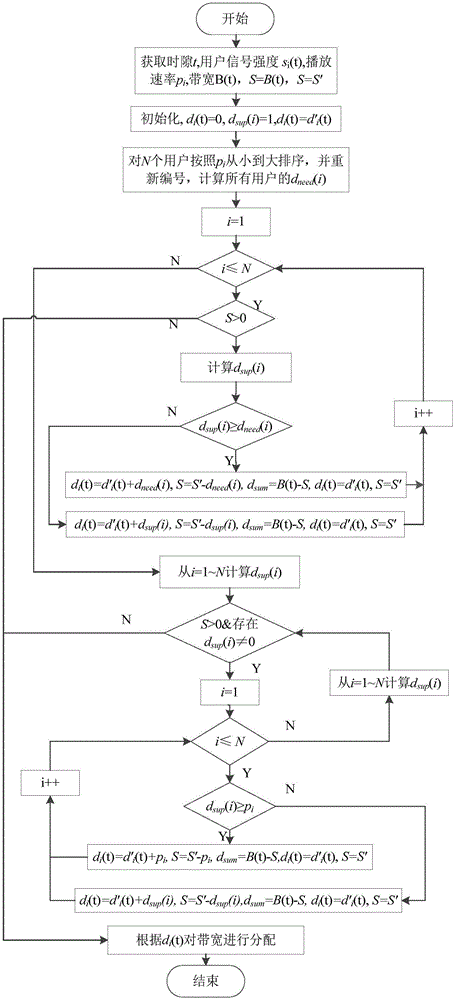
Bandwidth allocation method for stream media application rapid buffering
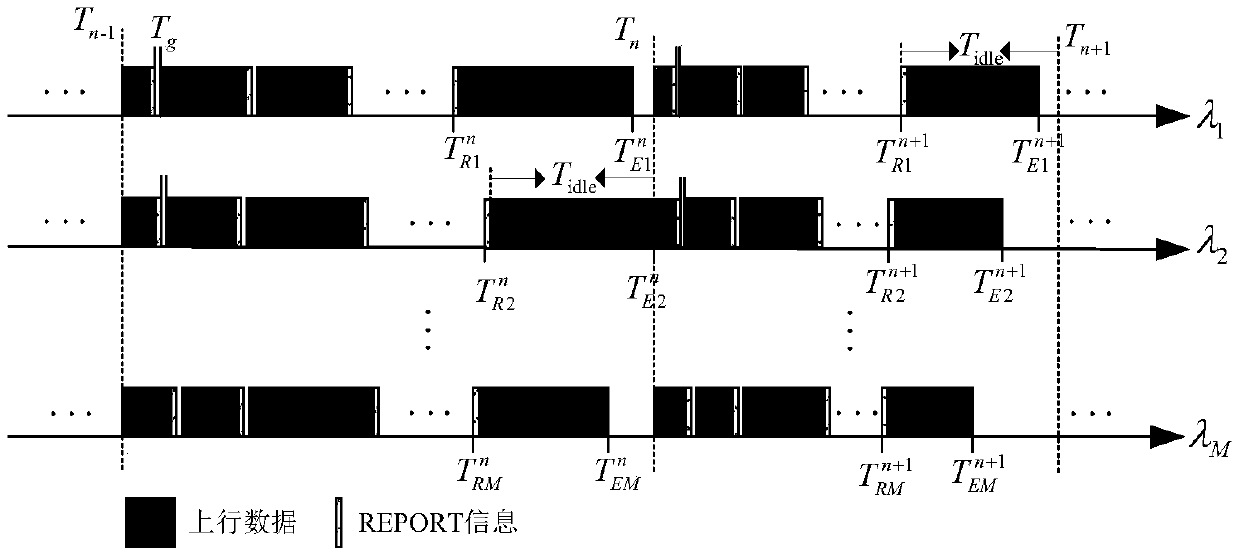
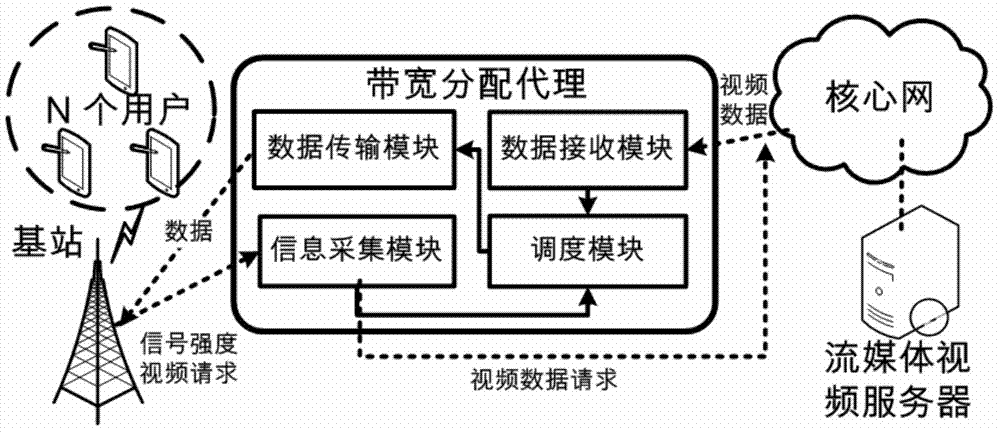
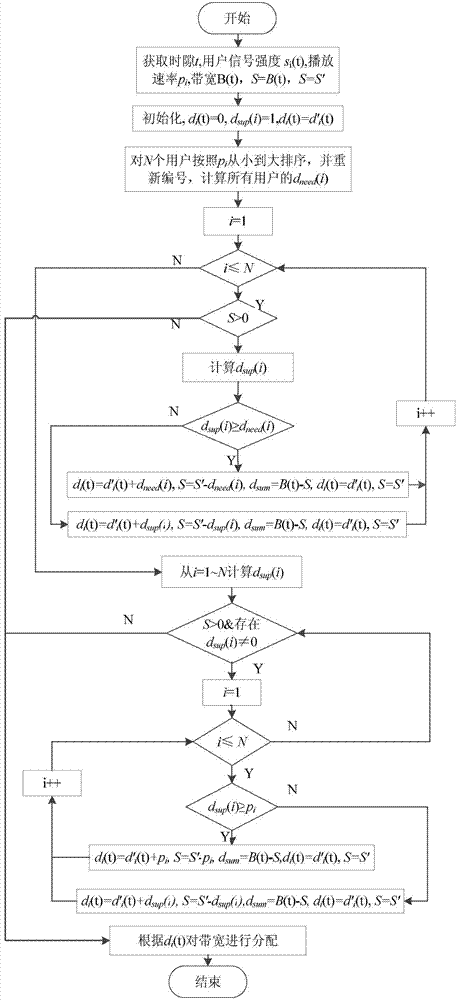
ActiveCN104333779AImprove experienceTroubleshoot bandwidth allocation issuesSelective content distributionData transmissionBandwidth allocation algorithm
The invention discloses a bandwidth allocation method for stream media application rapid buffering, which is used for a scene with a single base station and multiple users in a mobile cellular network. In the scene, channel competition occurs among multiple users to result in data transmission waiting and video standstill. According to the invention, a bandwidth allocation agency is deployed between the base station and a core network of the cellular network, and the bandwidth allocation agency collects information periodically such as service bandwidth of the network stream media application, signal intensity information of each user, video playing speed of each user and stream media data size requested by users; when mobile users in the network request for stream media data, the agency runs a bandwidth allocation algorithm of the stream media application rapid buffering, and performs allocation of the stream media bandwidth for stream media users in the cellular network. Therefore, all the users can play videos smoothly, buffering time and standstill of the videos is reduced, and user experience is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Router for sensing bearing state and service flow bandwidth distribution method thereof
InactiveCN102739507BFully consider the characteristics of dynamic changesIncrease flexibilityData switching networksService flowCognition Network Technology
The invention provides a router for sensing a bearing state and a service flow bandwidth distribution method thereof. The method comprises: a bandwidth distribution strategy generation step for all services; to be specific, collecting bearing state information of a router and quality of service (QoS) demand information of a service flow, employing bandwidth distribution algorithm that is provided based on a cognitive network technology to carry out analyzing and processing on the collected data, and integrating a plurality of set rules and using difference of QoS demands of various service flows for reference to generate a bandwidth distribution strategy for all the services; and a step for distributing bandwidths for all the service flows; to be specific, mapping the strategy into an operation instruction that can be identified by the router according to a requirement of configuration strategy and executing the operation to change router queue management so as to carry out bandwidth distribution on the service flows. According to the invention, the cognitive network technology is utilized to realize sensing of a network bearing state and a service flow state, so that network bandwidth distribution can fully consider a dynamic changing characteristic of the network to enable the distribution mode to become reasonable.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
FIWI network media access control system and method based on edge computing
ActiveCN112261667AReduce end-to-end latencyImprove load balancingNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionEdge computingControl system
The invention relates to an FIWI network media access control system and method based on edge computing, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The system comprises a TDM-PON optical network, a wireless access system and an edge computing server, the TDM-PON optical network and the wireless access system are integrated into a new wireless access node, and the edge computing server isconnected with the integrated wireless access node and processes data with high time delay requirements. According to the method, a static bandwidth allocation mode and a dynamic bandwidth allocationmode are adopted at the same time according to flow types, bandwidth resources are allocated to each access node by adopting a maximum and minimum bandwidth allocation algorithm, and ordered communication of data among the access nodes is realized. According to the invention, the performances of time delay, packet loss rate and the like of the FIWI network can be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
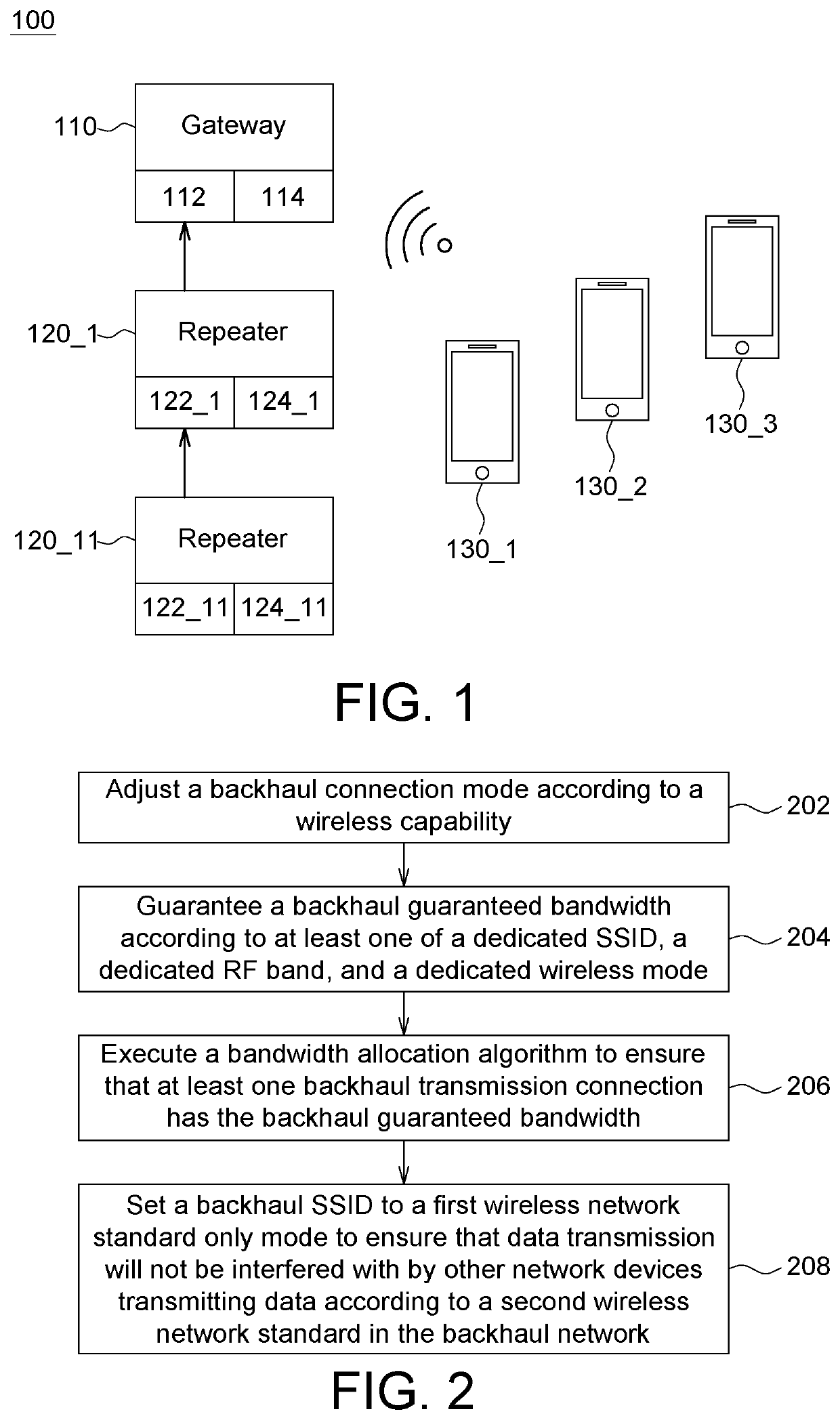
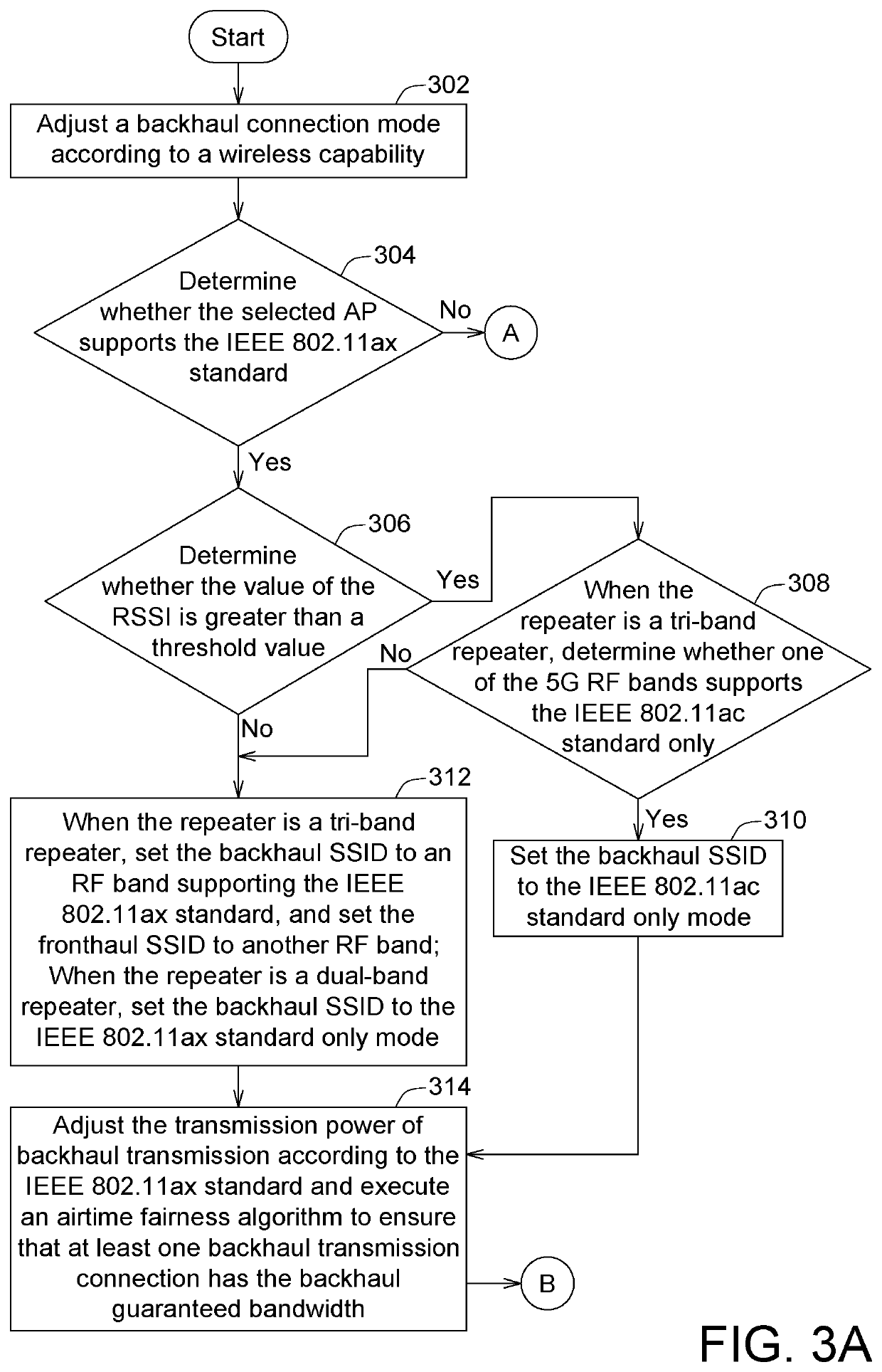
Backhaul bandwidth management method and system for wireless network
ActiveUS20200359266A1Efficiently allocate bandwidthGuaranteed transmission speedNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionRadio frequencyData transmission
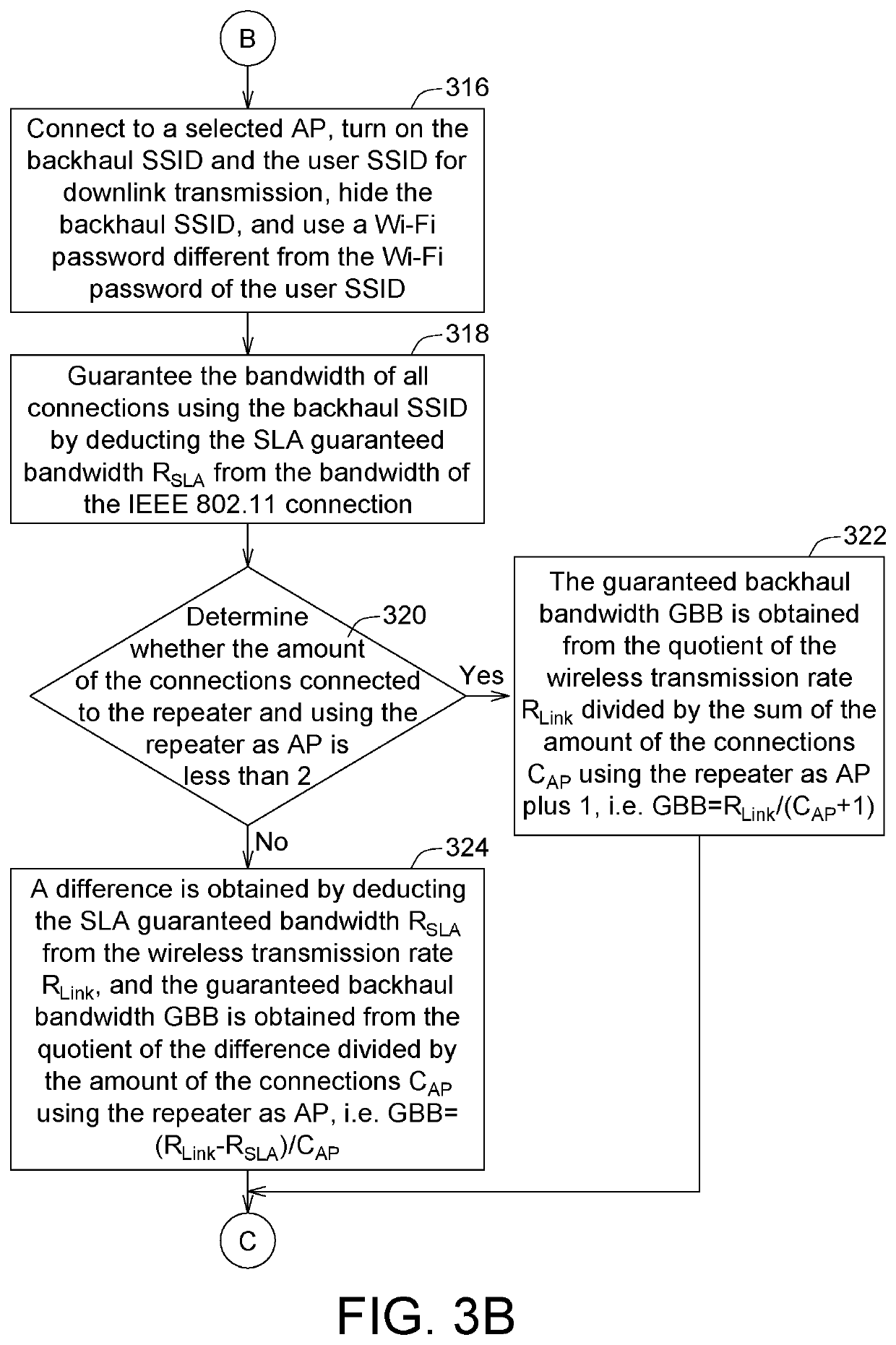
A backhaul bandwidth management method for a wireless network is provided. Firstly, a backhaul connection mode is adjusted by a network device in a backhaul network according to a wireless capability. Then, a backhaul guaranteed bandwidth is guaranteed by the network device according to at least one of a dedicated service set identifier (SSID), a dedicated radio frequency (RF) band and a dedicated wireless mode. Then, a bandwidth allocation algorithm is executed by the network device to ensure that at least one backhaul transmission connection has the backhaul guaranteed bandwidth. Finally, a backhaul SSID is set to a first wireless network standard only mode by the network device to ensure that data transmission will not be interfered with by other network devices transmitting data according to a second wireless network standard in the backhaul network.
Owner:ARCADYAN
A Method of Bandwidth Allocation in P2P File Sharing Network Based on Price Mechanism
ActiveCN105450738BAchieve fair distributionClose to actual needsTransmissionComplete dataResource Provider
Provided is a P2P file sharing network bandwidth allocation algorithm based on a price mechanism, comprising the following steps: each resource requestor r initializes a price Lambda(r)[t] which can be provided thereby; resource providers p initialize an allocated bandwidth xpr[t] for each resource requestor r; the resource providers p work out an expected price Costp[t] for the initialized allocated bandwidth xpr[t] of each resource requestor r and the price Lambda(r)[t] provided by the resource requestor r according to the upload bandwidth Cp thereof; the resource providers p adjust the bandwidth xpr[t+1] allocated for the resource requestors r according to the expected price Costp[t] and the price Lambda(r)[t] provided by the resource requestors r; the resource requestors r adjust the price Lambda(r)[t+1] according to the acquired bandwidth; all the resource providers p carry out iteration according to the steps to achieve a balance, namely, the resource providers p upload optimal bandwidth allocation; the resource providers and the resource requestors complete data transmission according to the optimal bandwidth allocation; and if there is a new node joining or an original node exiting, the iteration process is repeated until a new balance is achieved. The P2P file sharing network bandwidth allocation algorithm of the invention has the advantages of fair allocation and simple calculation.
Owner:宅人桥(南京)网络科技有限公司
Spectrum Resource Allocation Method Based on Topology Control in Cognitive Radio Networks
InactiveCN103596181BConnectivity is not brokenReduce the possibility of interferenceNetwork planningFrequency spectrumNetwork topology
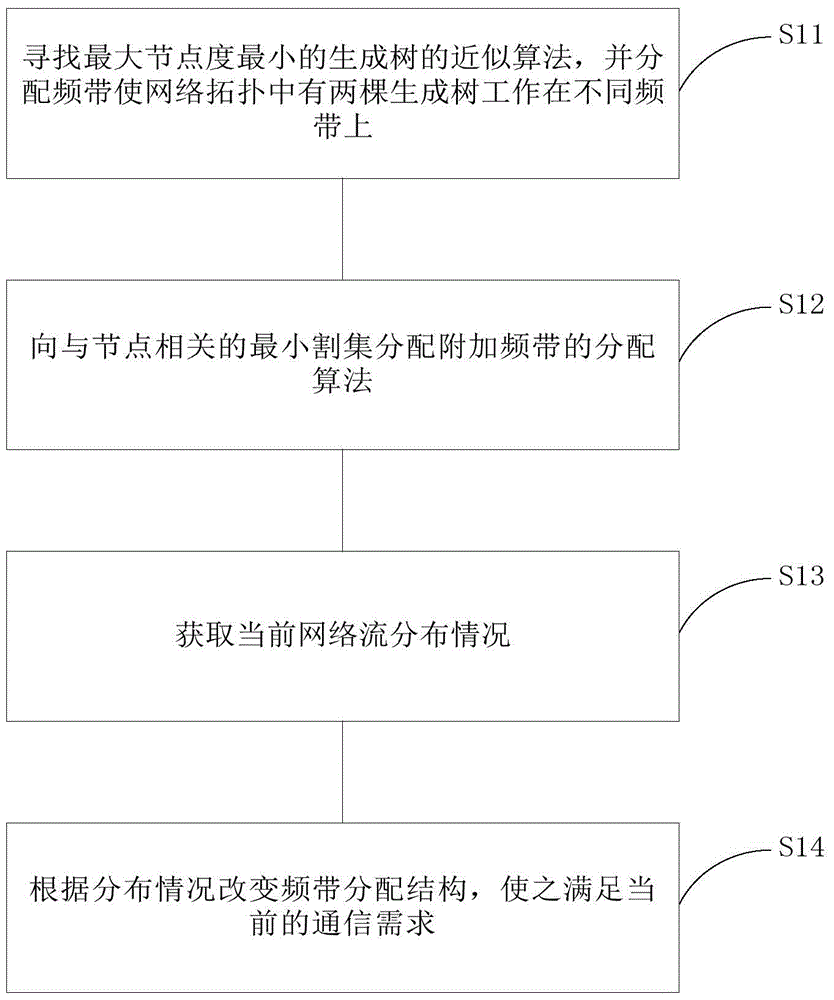
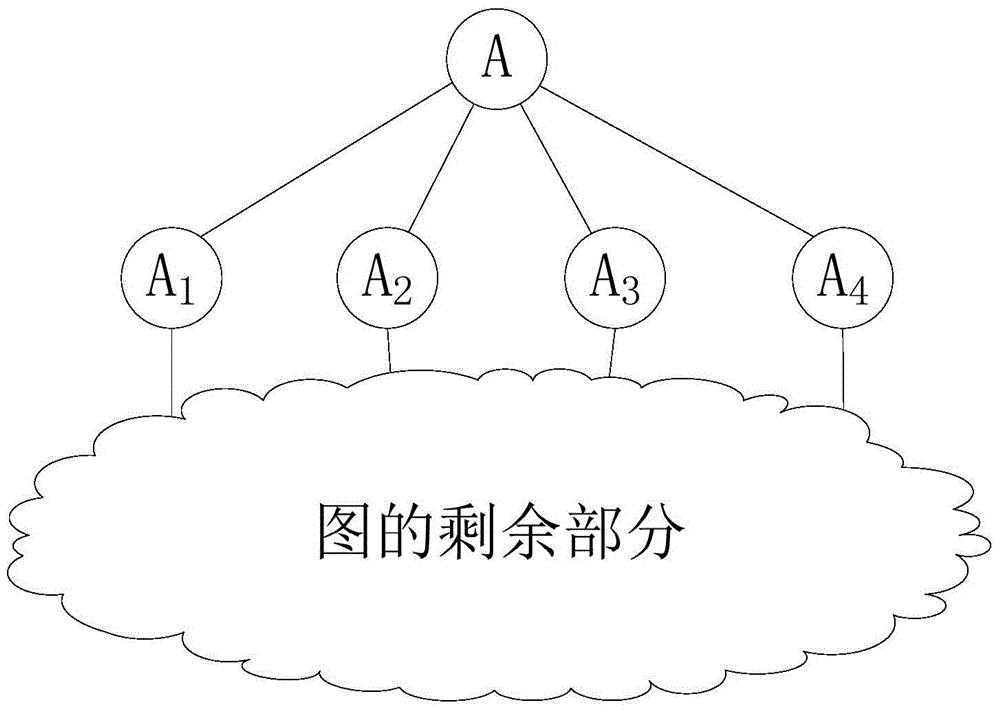
The present invention provides a spectrum resource allocation method based on topology control in a cognitive radio network, including: a static allocation method with a long execution period, the static allocation method includes: an approximate algorithm for finding a spanning tree with the smallest maximum node degree, Allocate frequency bands to links in the network according to the spanning tree; an allocation algorithm for allocating additional frequency bands to the minimum cut set related to nodes; a dynamic allocation algorithm with a short execution cycle, the dynamic allocation algorithm includes: obtaining the current network flow distribution ; Change the frequency band allocation structure according to the distribution to meet the current communication needs. The method provided by the invention can improve the robustness and capacity of the secondary user network, has low computational complexity, and optimizes the performance of the cognitive radio secondary user network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Hardware device and method for assisting in processing dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm
ActiveCN101668233BIncrease flexibilityImprove practicalityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksProcess dynamicsCommunication interface
The invention discloses a hardware device and a method for assisting in processing a dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) algorithm. The hardware device comprises a hardware logic module, a register interface control module, a synchronous dynamic RAM controller module, a FLASH controller module, an interrupt processor module, a universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter controller module, and a master-slave communication module, a master-slave communication interface module, a PowerPc CPU module, a processor bus module, a processor bus-to-on-chip- peripheral-bus bridge module and an on chip peripheral bus module which are orderly connected, wherein the PowerPc CPU module is used for processing and controlling data acquired by the hardware logic module, is connected with a master CPU interface in the hardware logic module through the master-slave communication module to finish communications between an embedded CPU and a master CPU, and controls and configures a register in the hardwarelogic module and the report and the allocation of the dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm through a register interface module. The hardware device and the method for assisting in processing the dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm can flexibly process the DBA core algorithm and save the cost.
Owner:ZTE CORP +1
A Bandwidth Allocation Method for Fast Buffering in Streaming Media Applications
ActiveCN104333779BImprove experienceTroubleshoot bandwidth allocation issuesSelective content distributionData transmissionBandwidth allocation algorithm
The invention discloses a bandwidth allocation method for stream media application rapid buffering, which is used for a scene with a single base station and multiple users in a mobile cellular network. In the scene, channel competition occurs among multiple users to result in data transmission waiting and video standstill. According to the invention, a bandwidth allocation agency is deployed between the base station and a core network of the cellular network, and the bandwidth allocation agency collects information periodically such as service bandwidth of the network stream media application, signal intensity information of each user, video playing speed of each user and stream media data size requested by users; when mobile users in the network request for stream media data, the agency runs a bandwidth allocation algorithm of the stream media application rapid buffering, and performs allocation of the stream media bandwidth for stream media users in the cellular network. Therefore, all the users can play videos smoothly, buffering time and standstill of the videos is reduced, and user experience is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com