Patents
Literature
50 results about "Combustion front" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
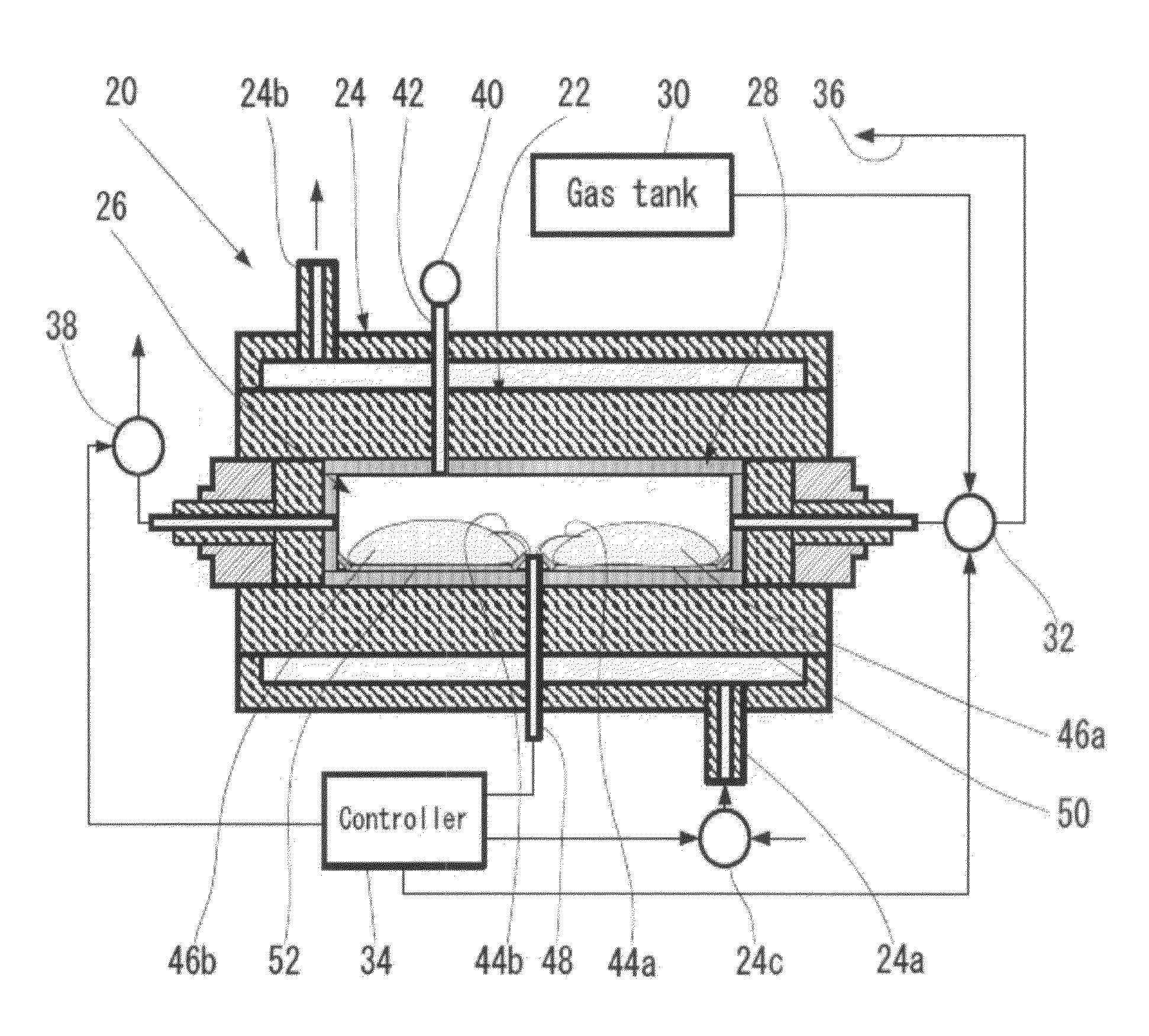
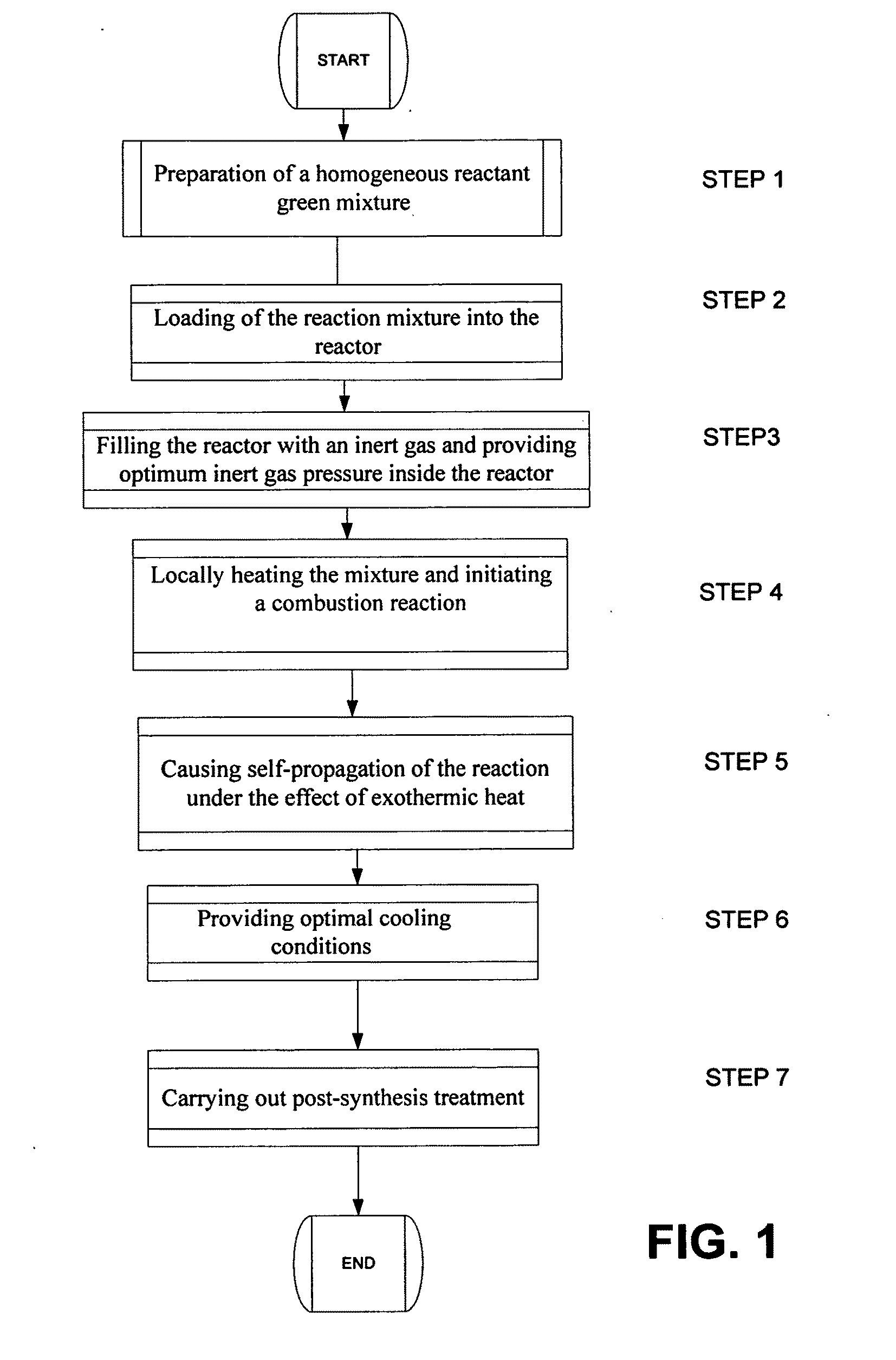
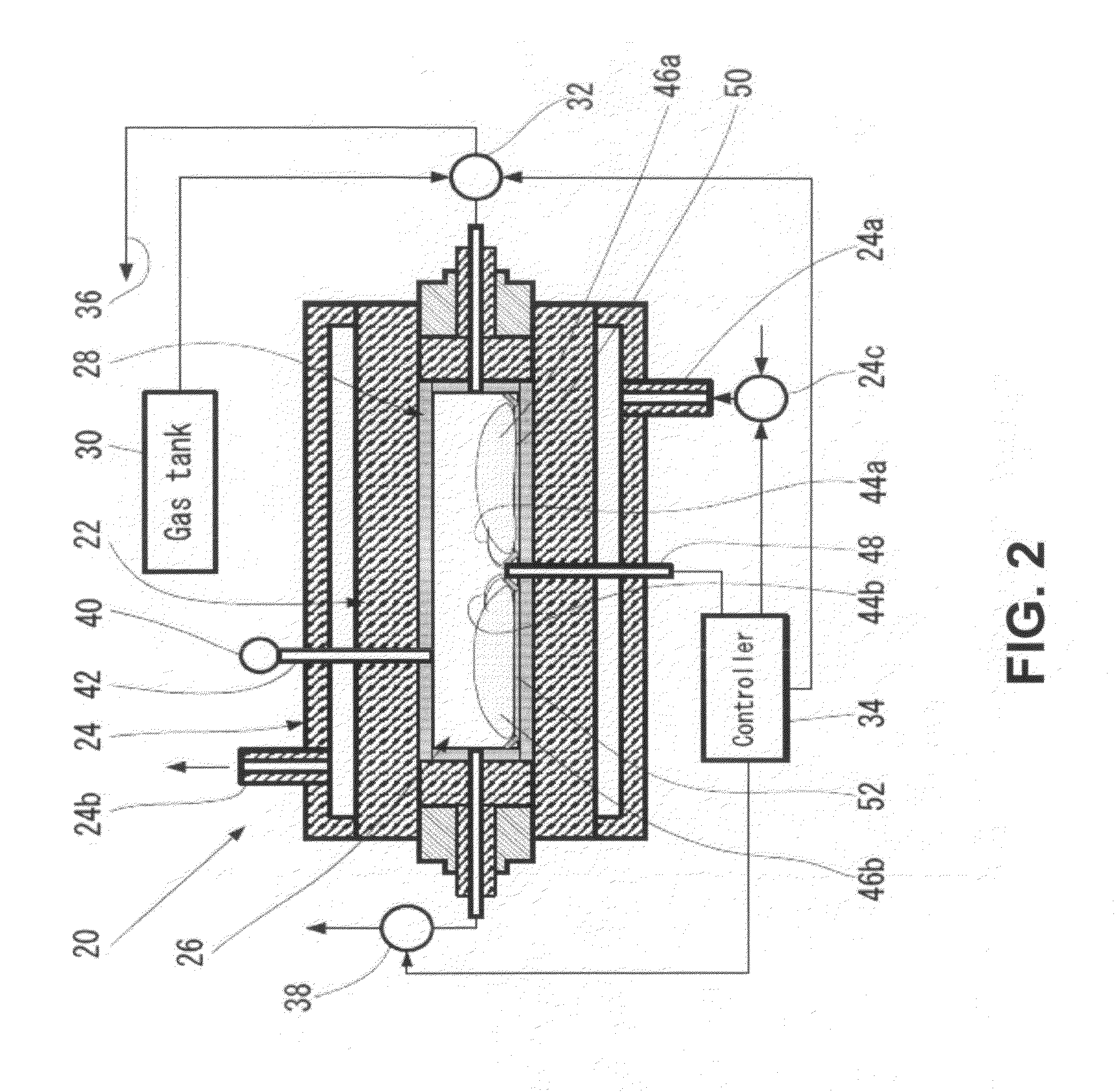
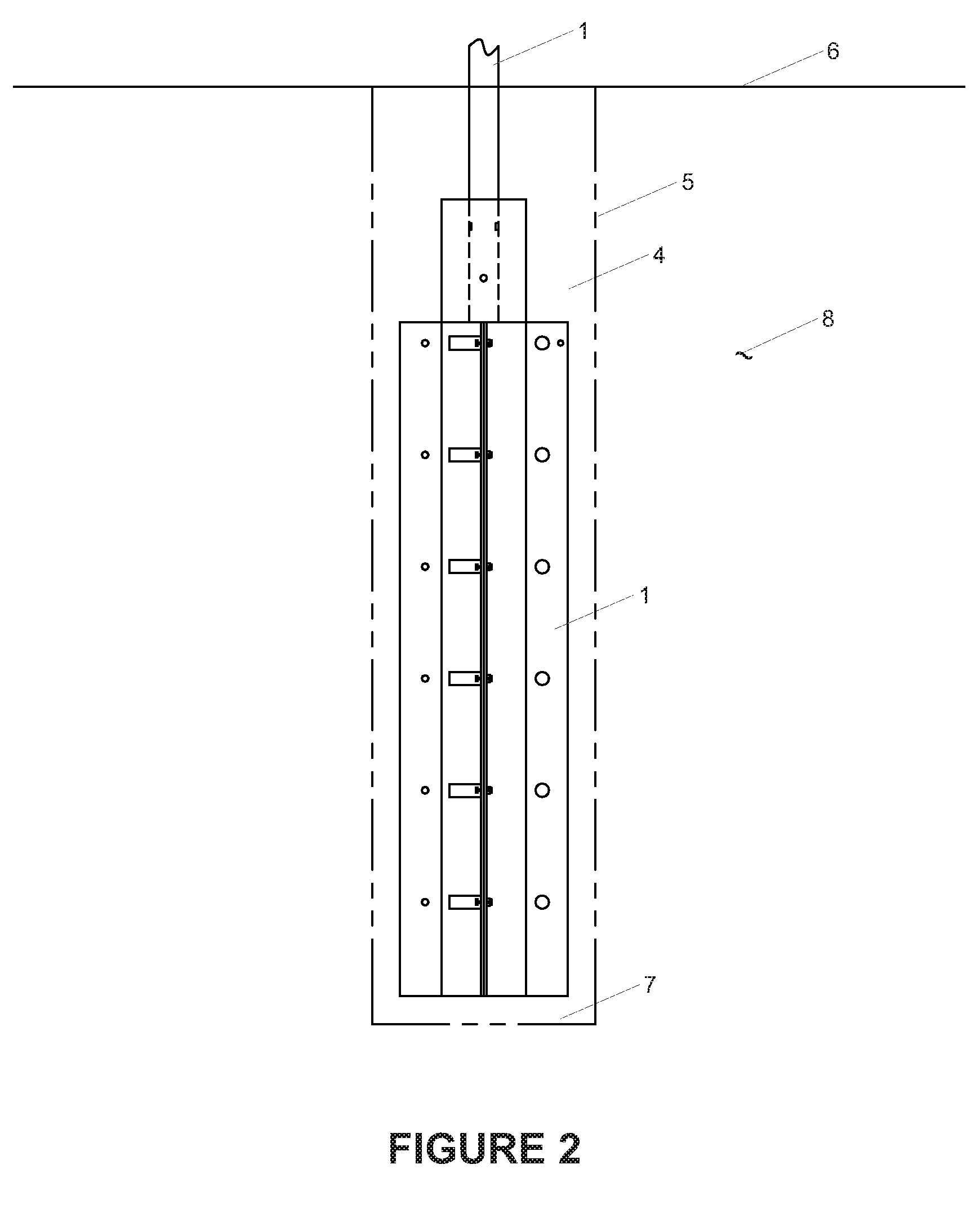
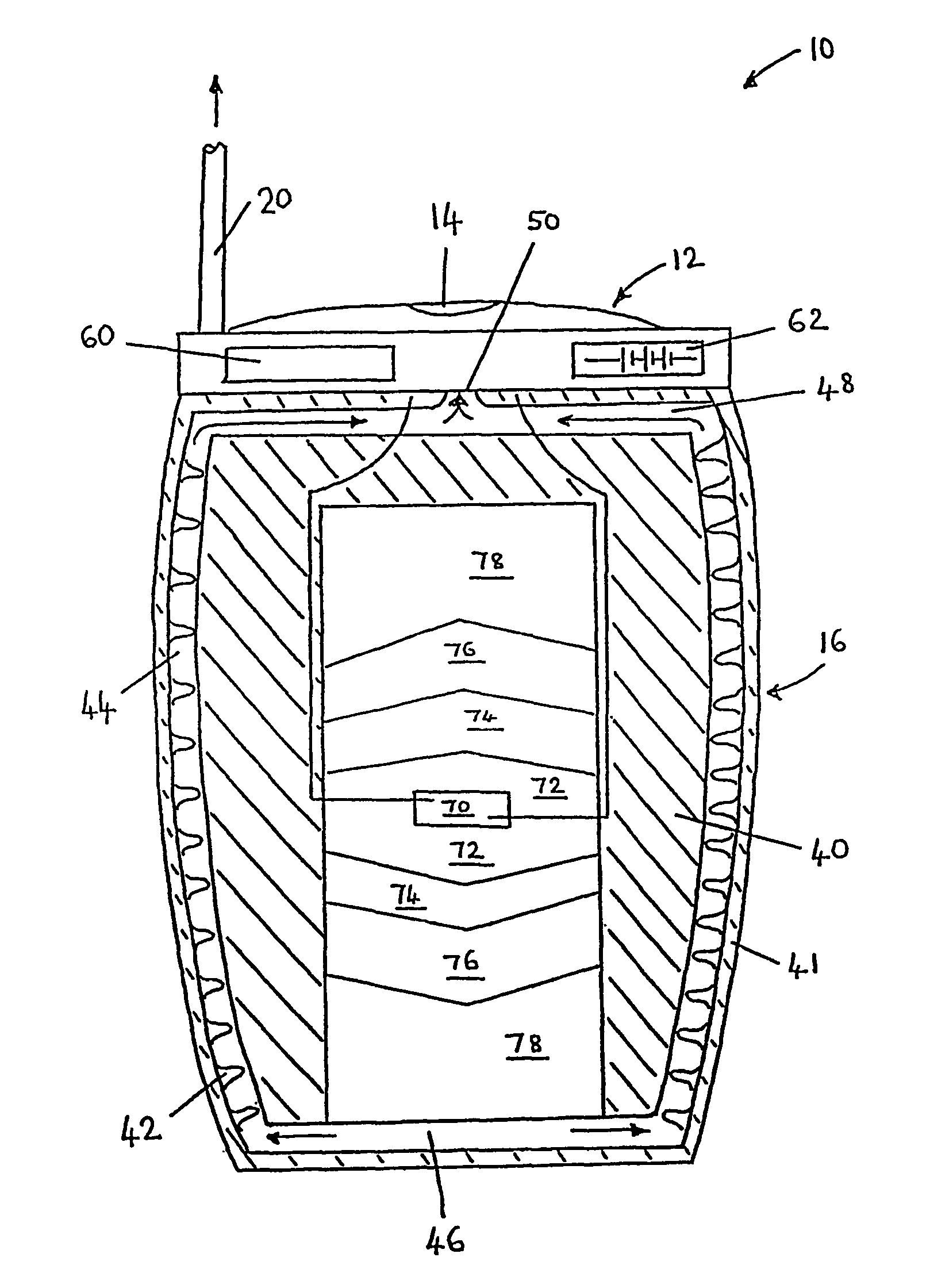
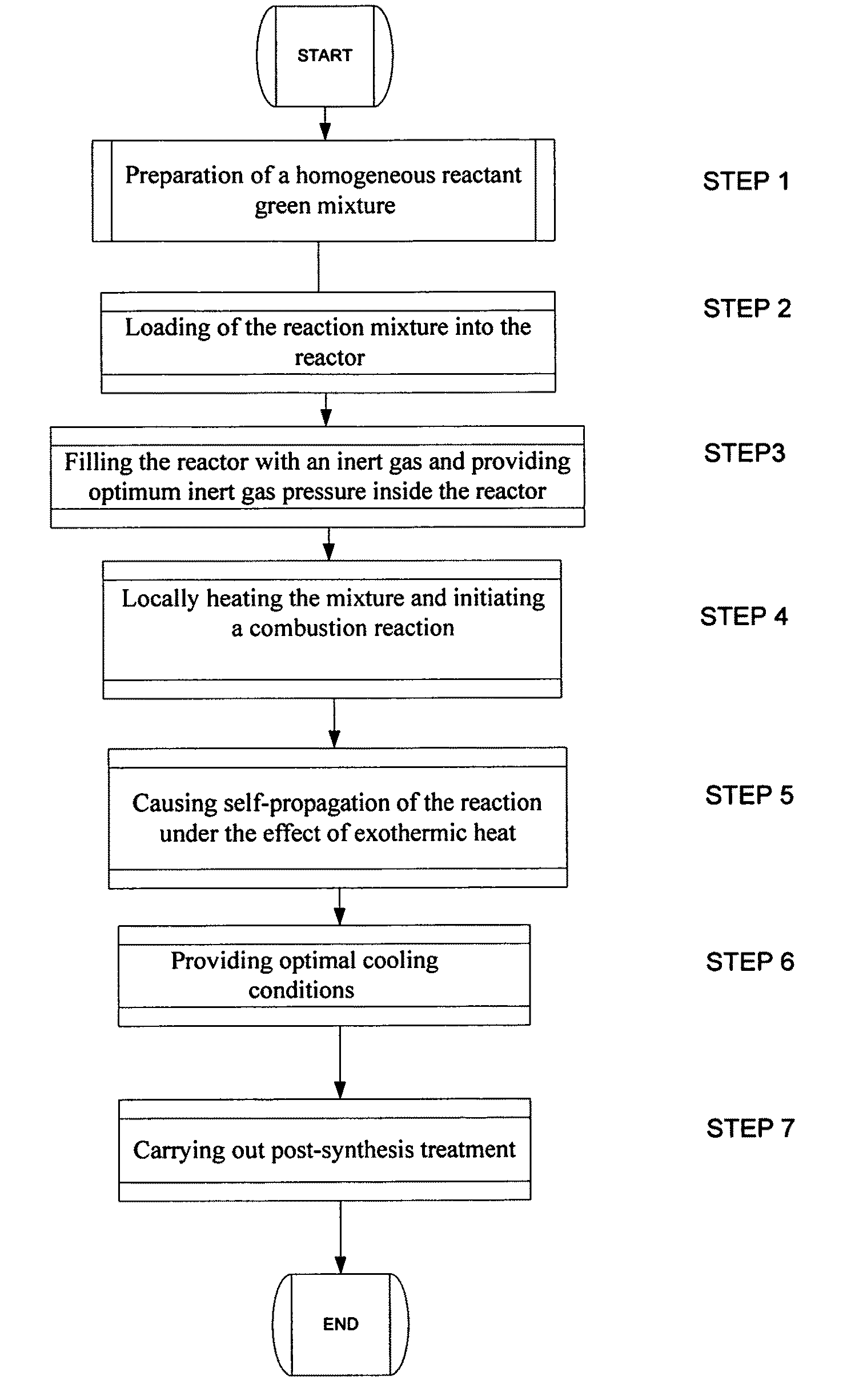
Method of manufacturing high-surface-area silicon
InactiveUS20110085960A1High purityReduce the amount requiredNanotechSiliconCombustion frontSilicon dioxide
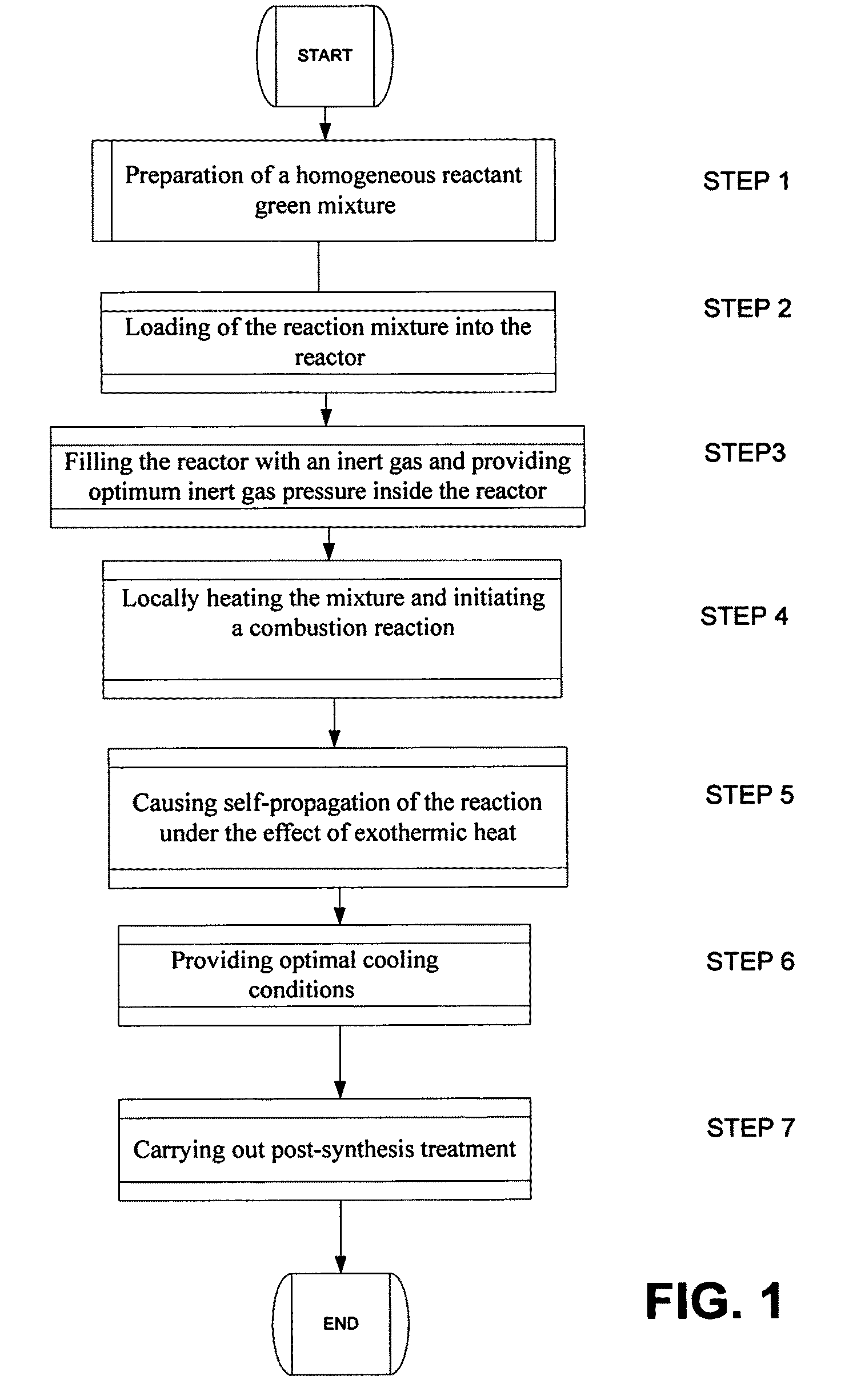
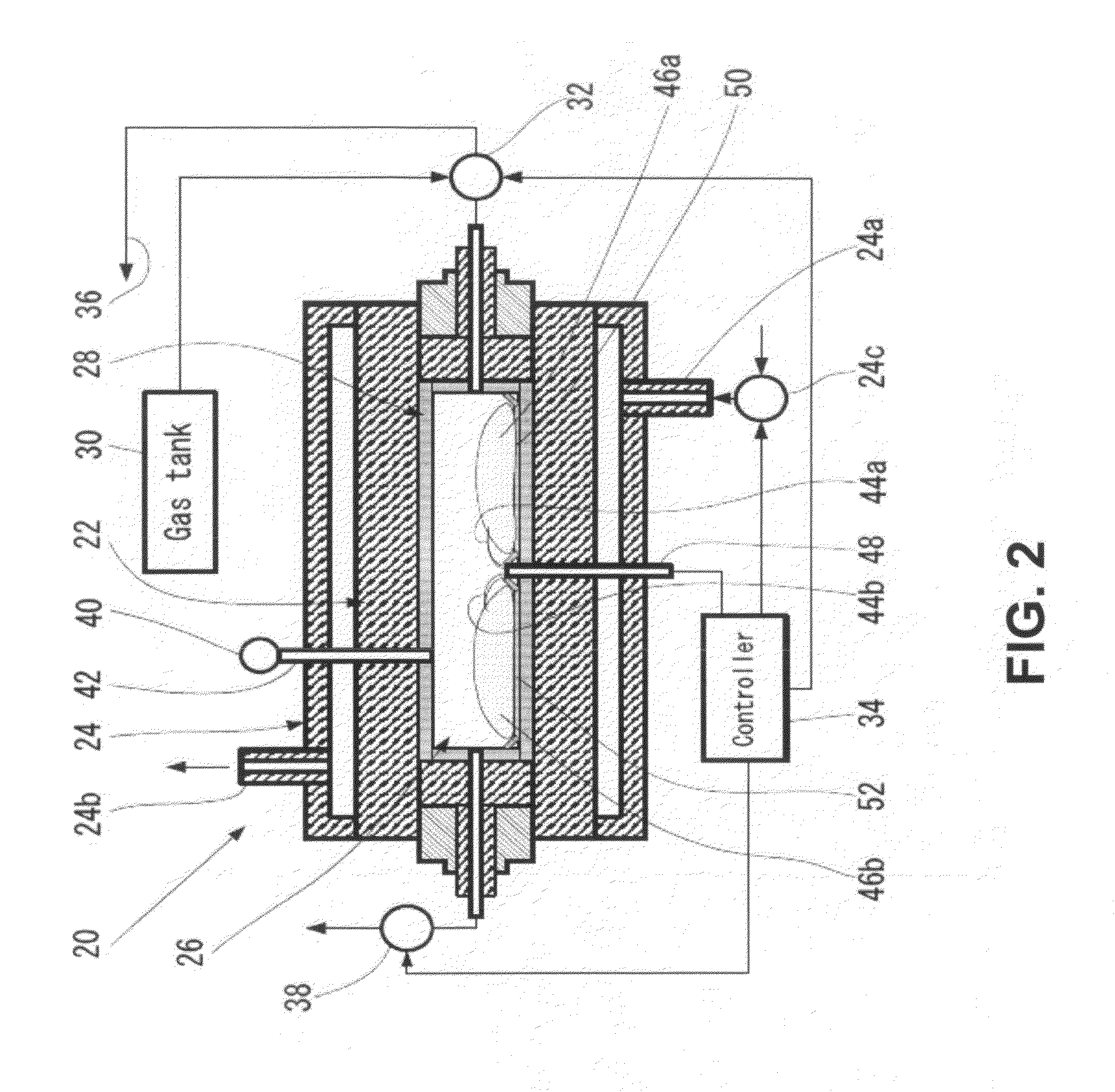
A method for synthesis of high surface-area (>100 m2 / g) and nanosized (≦100 nm) silicon powder by initiation of self-sustained combustion reaction in a mixture of silicon dioxide and magnesium powders in a sealed reactor chamber under pressurized inert gas atmosphere. A specific feature of the method is rapid cooling of the product at a rate of 100 K / s to 400 K / s in the area directly behind the combustion front.
Owner:MUKASYAN ALEXANDER +2
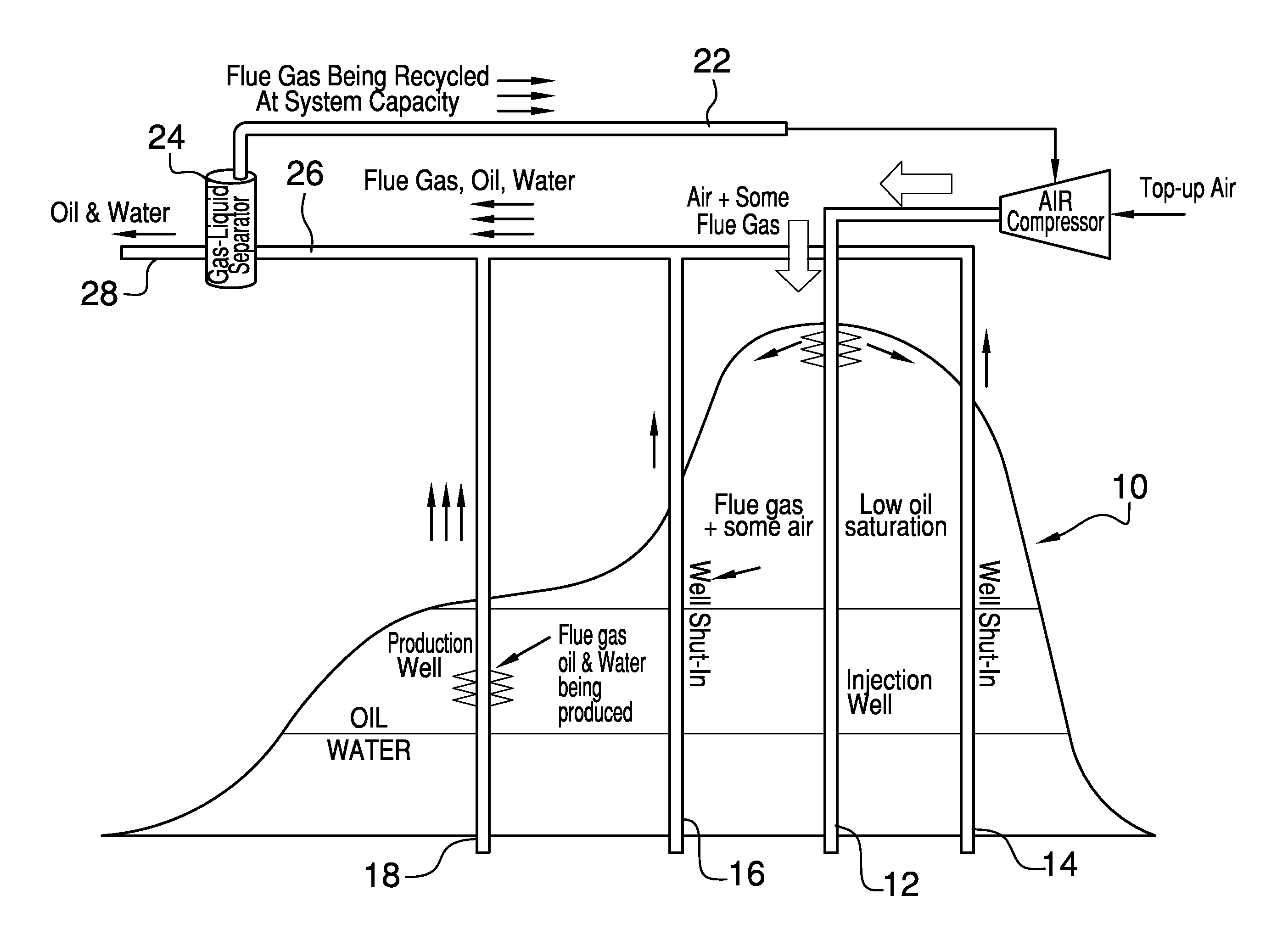
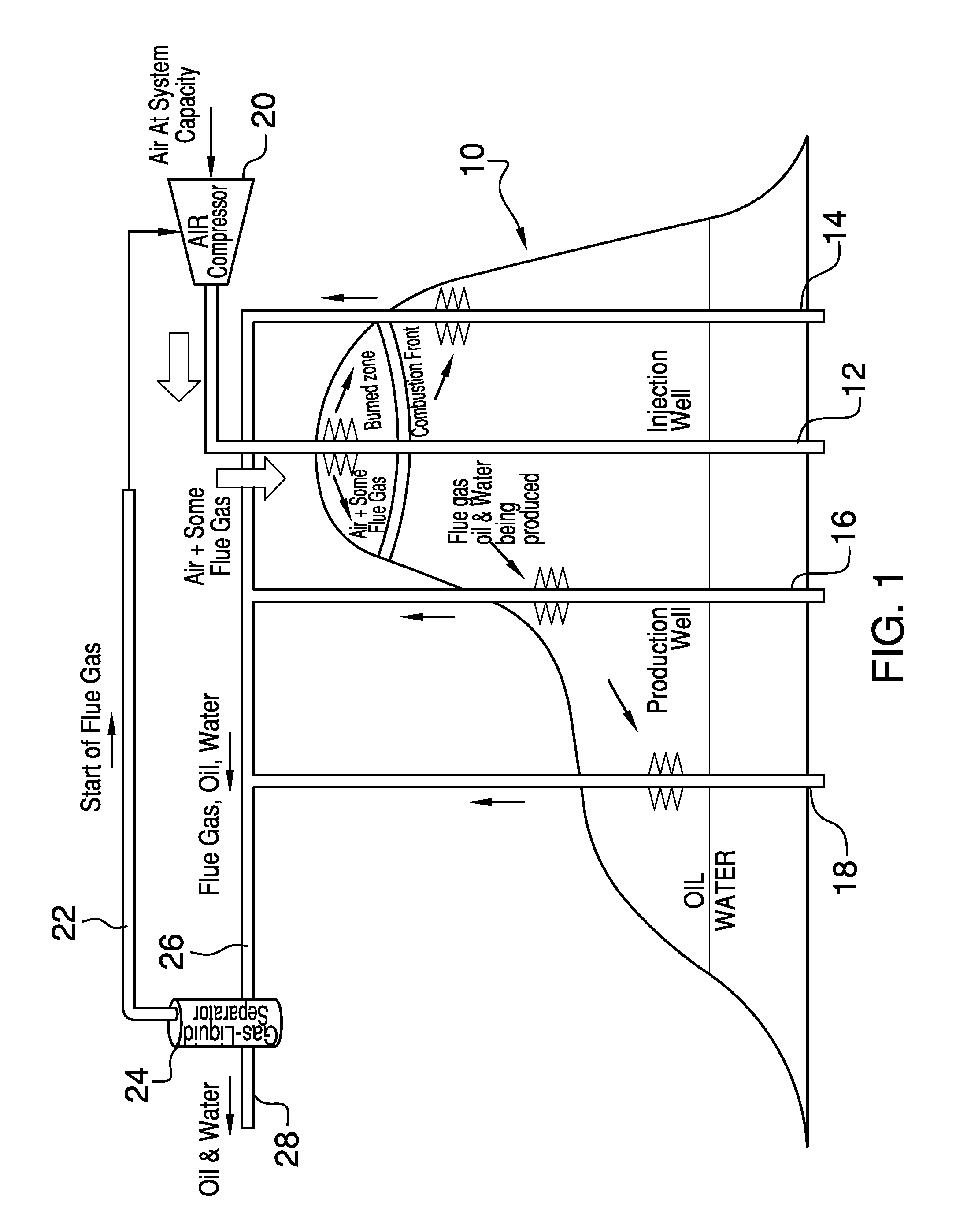
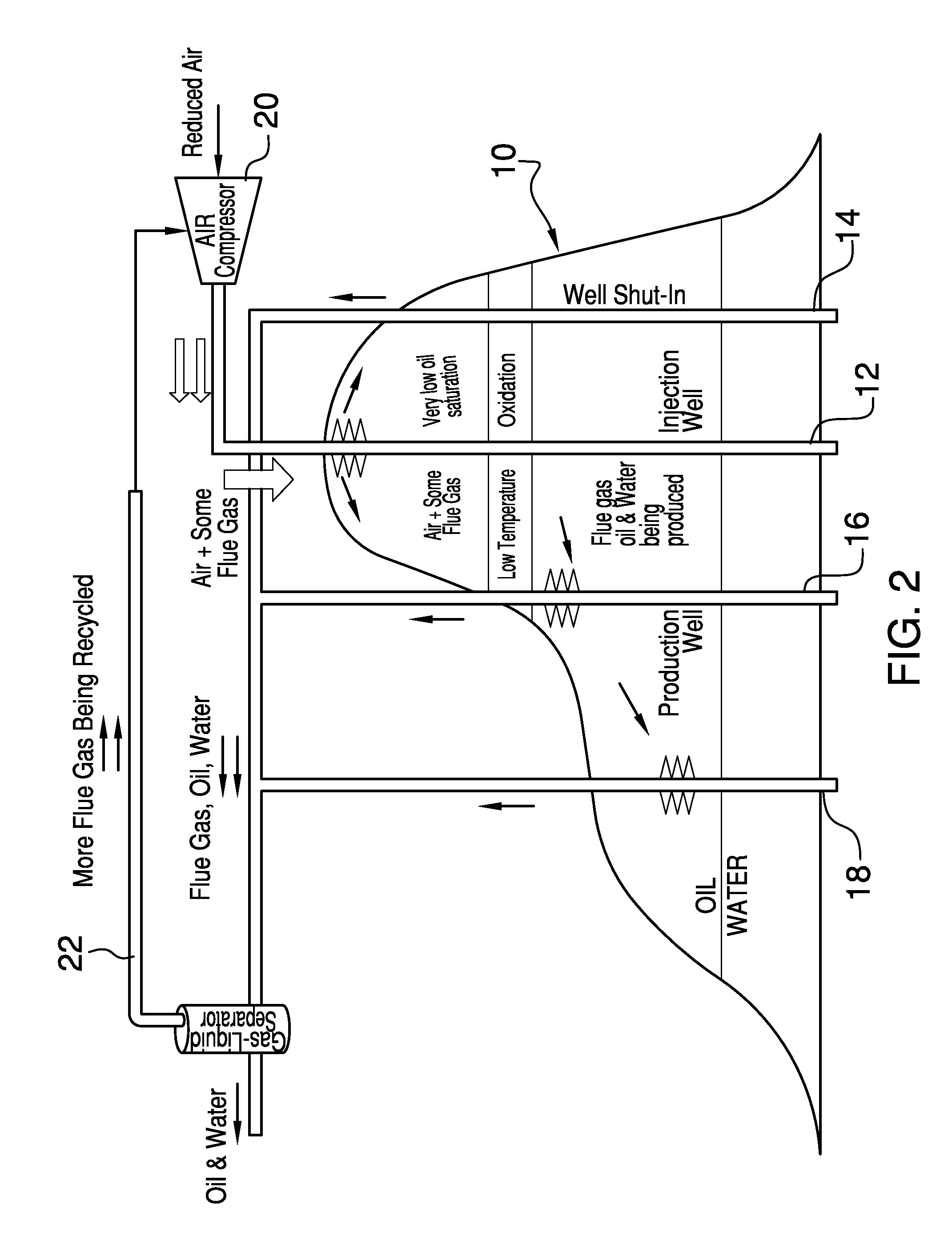
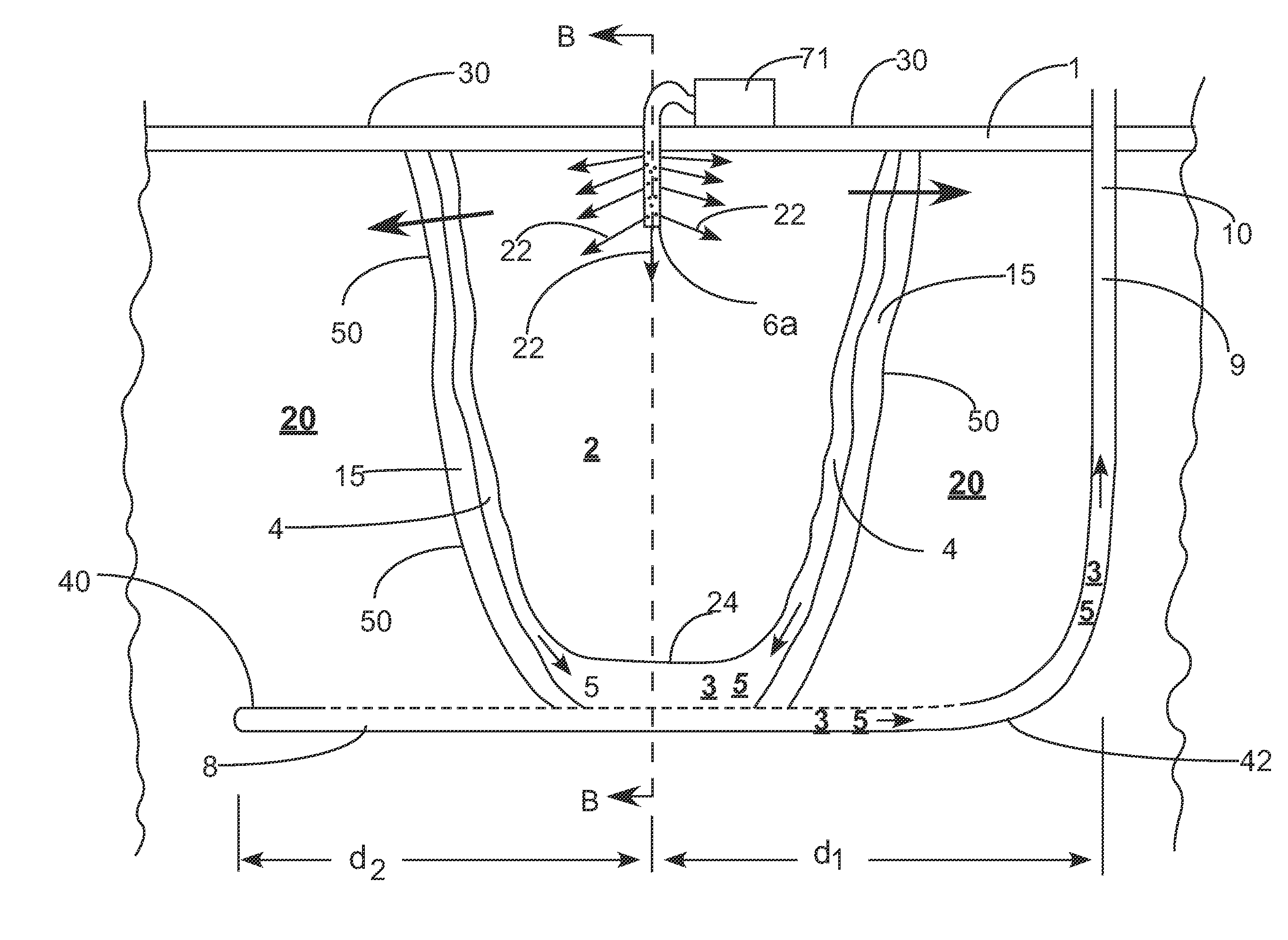
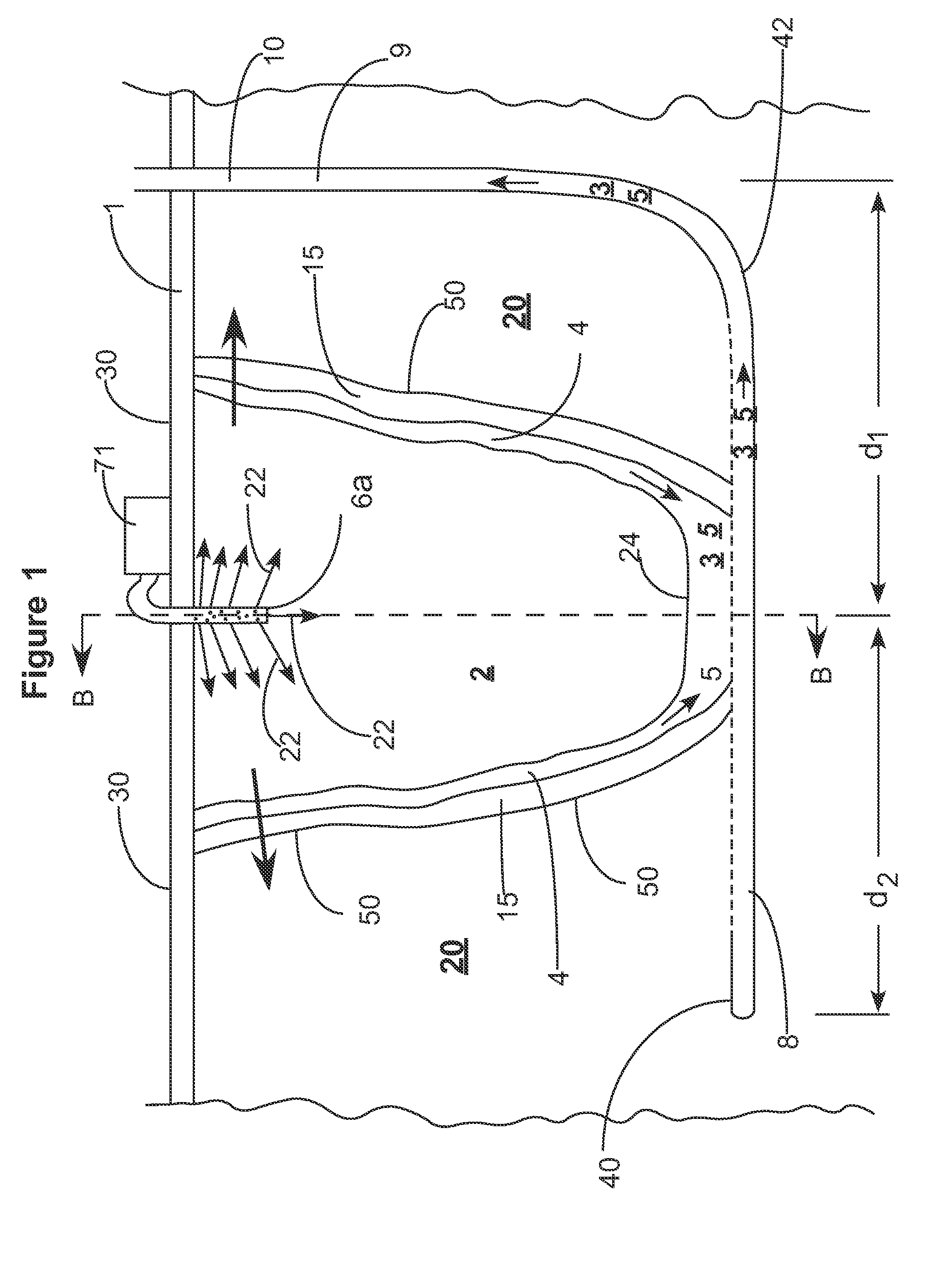
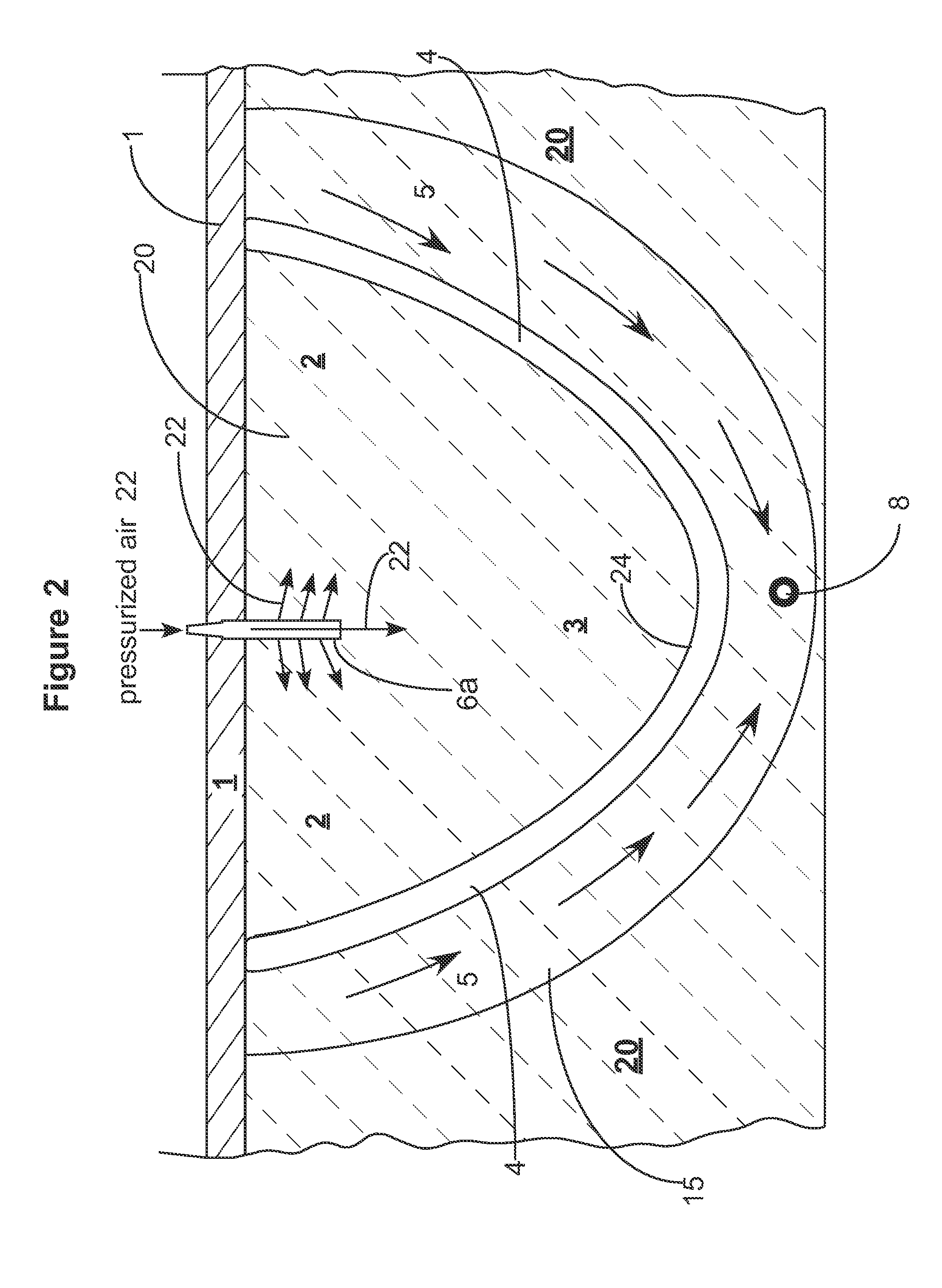
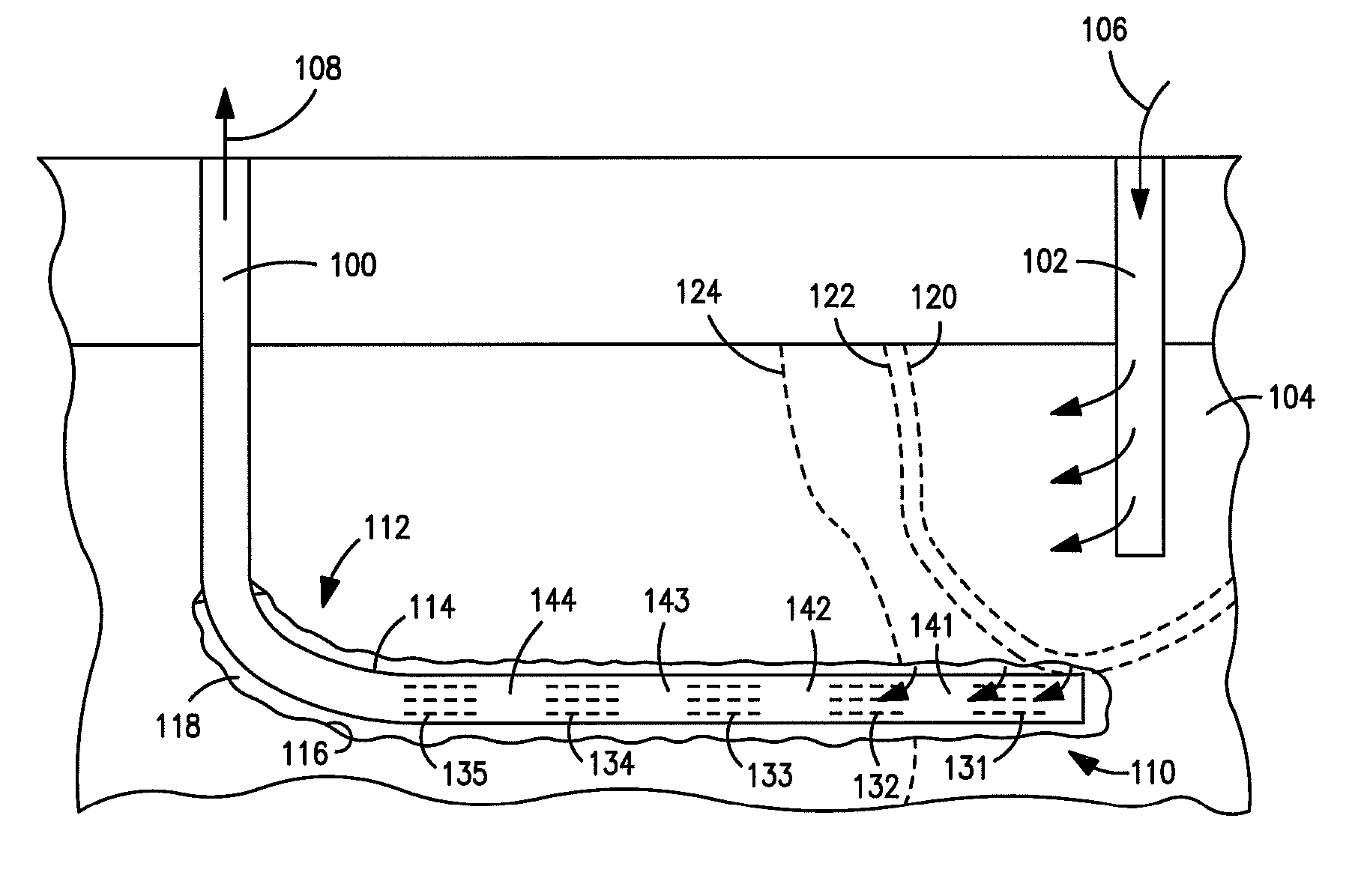
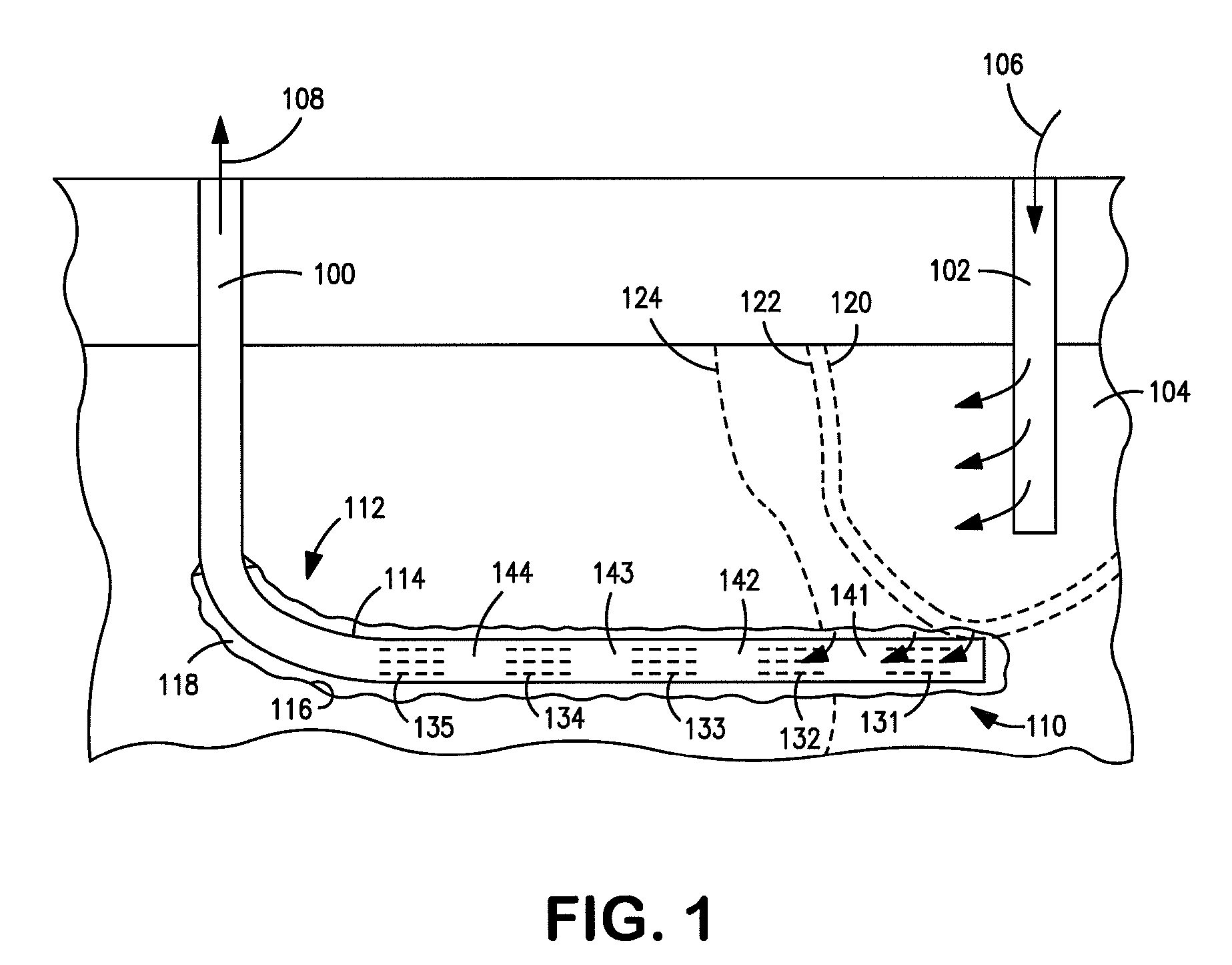
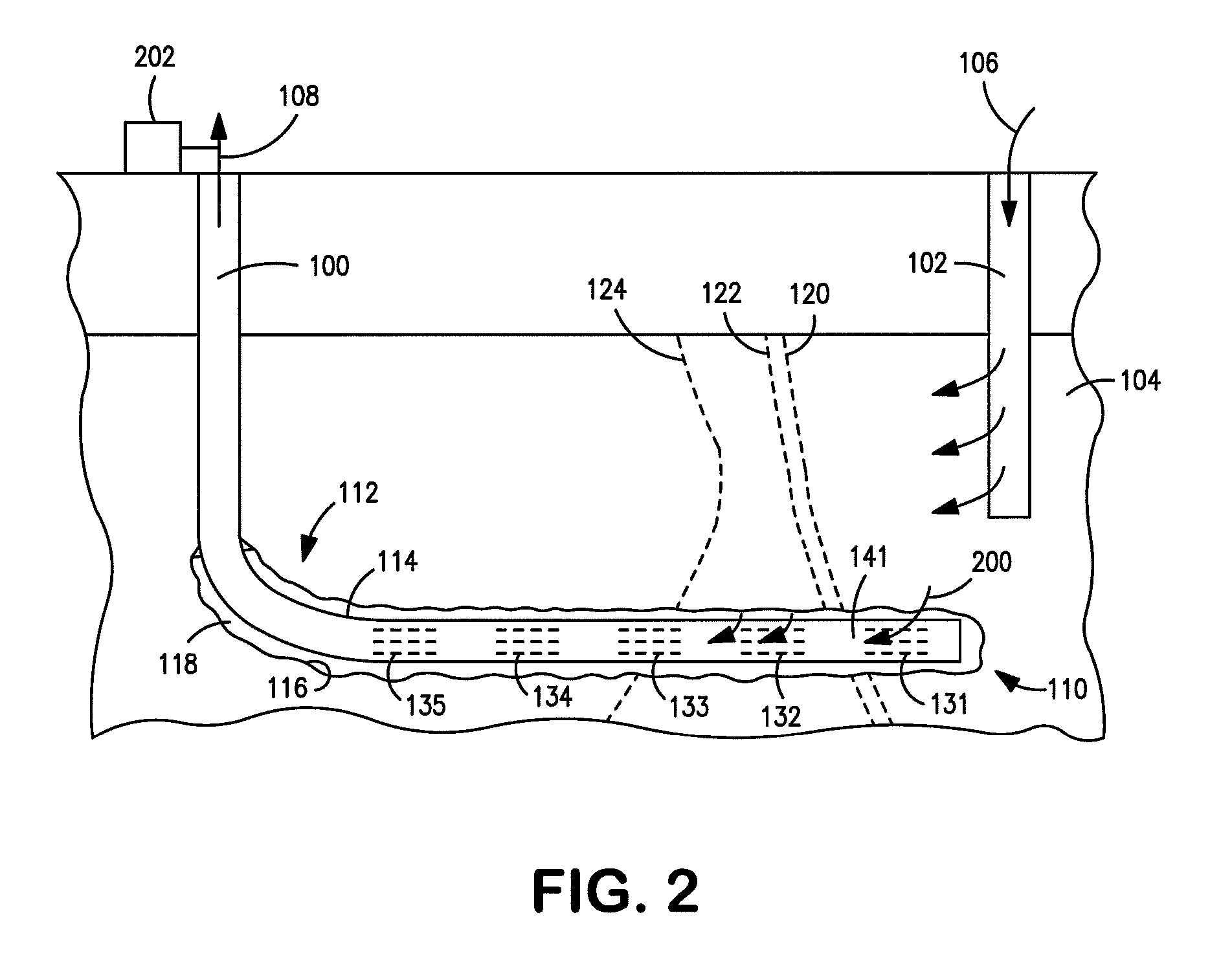
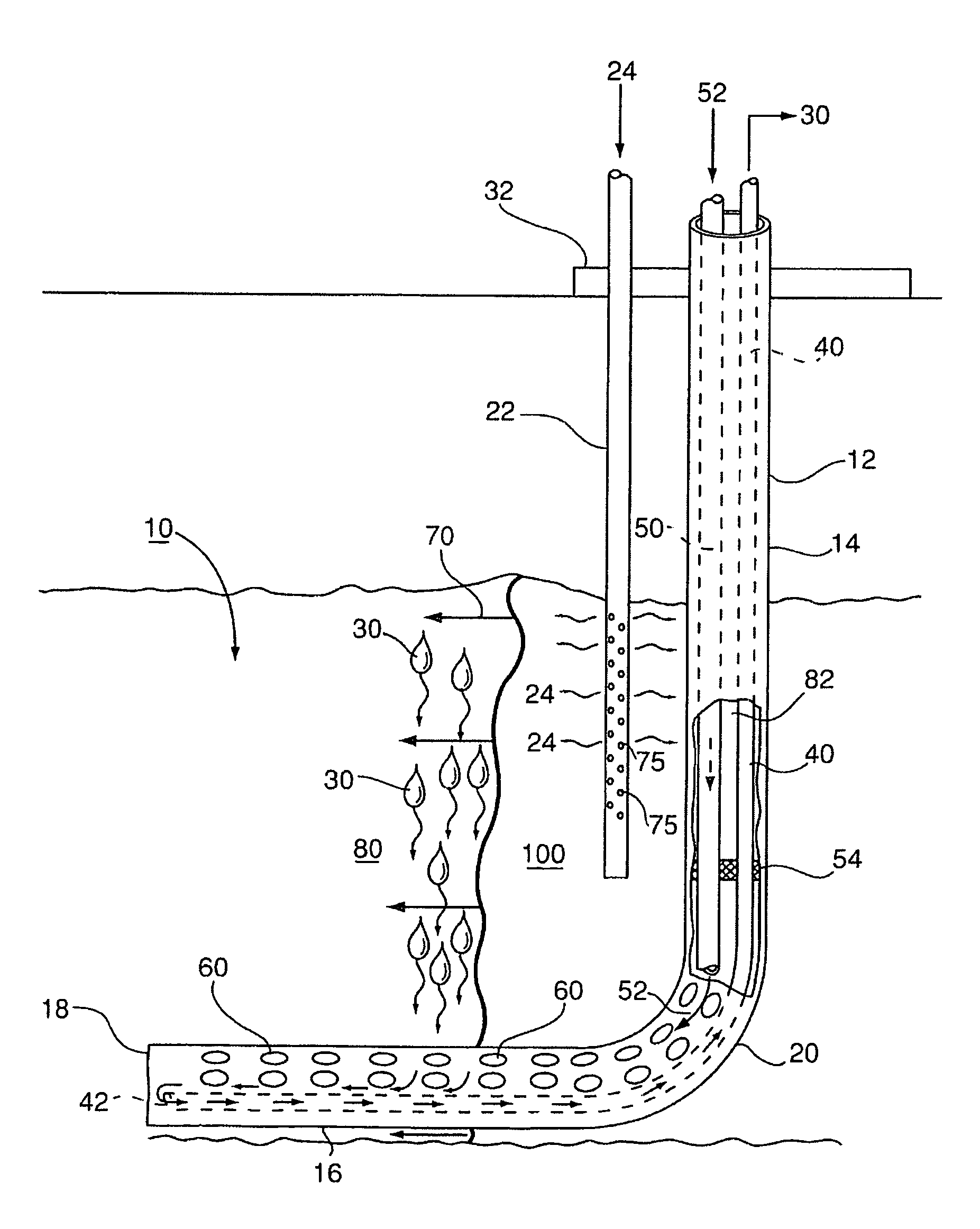
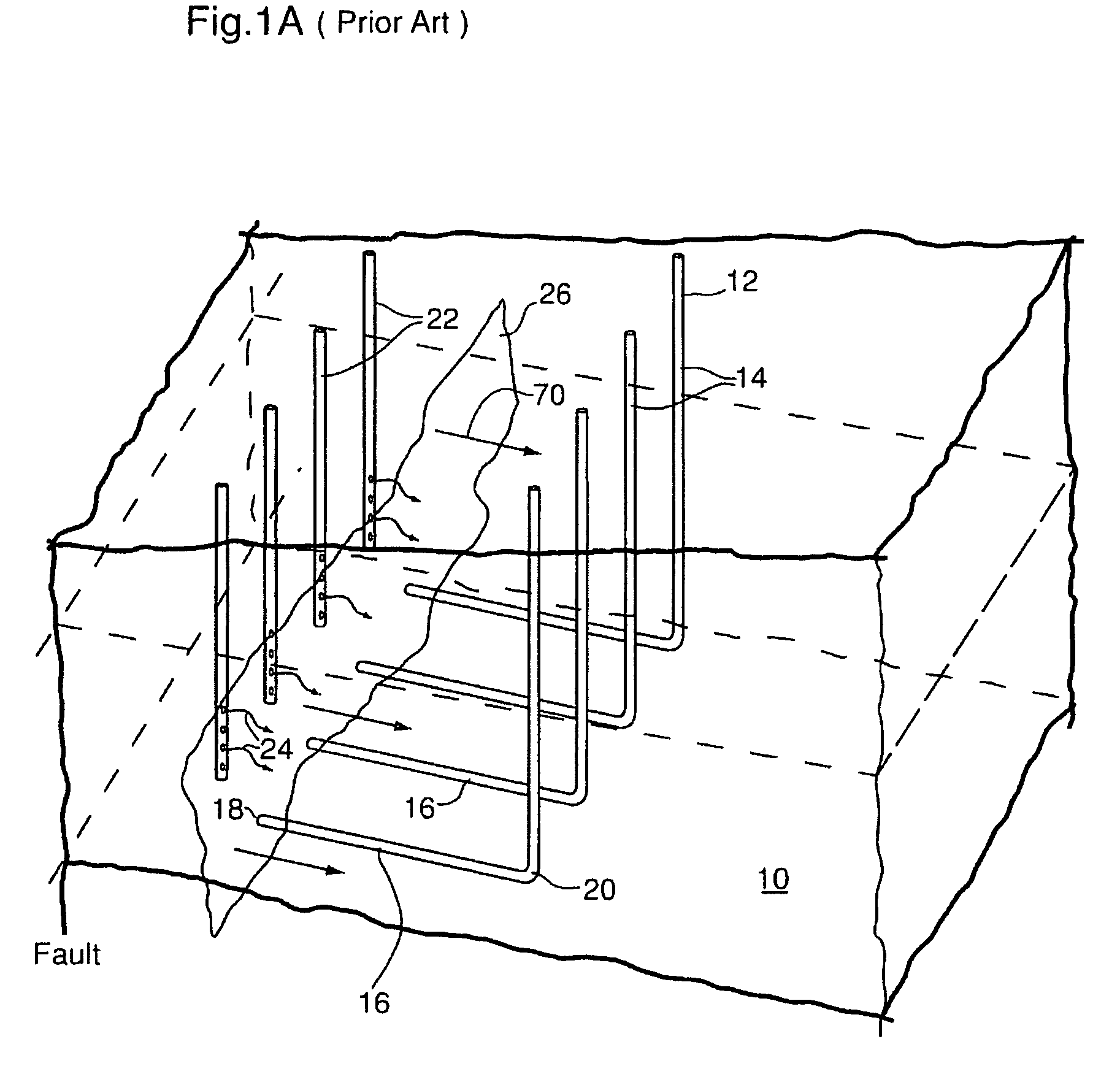
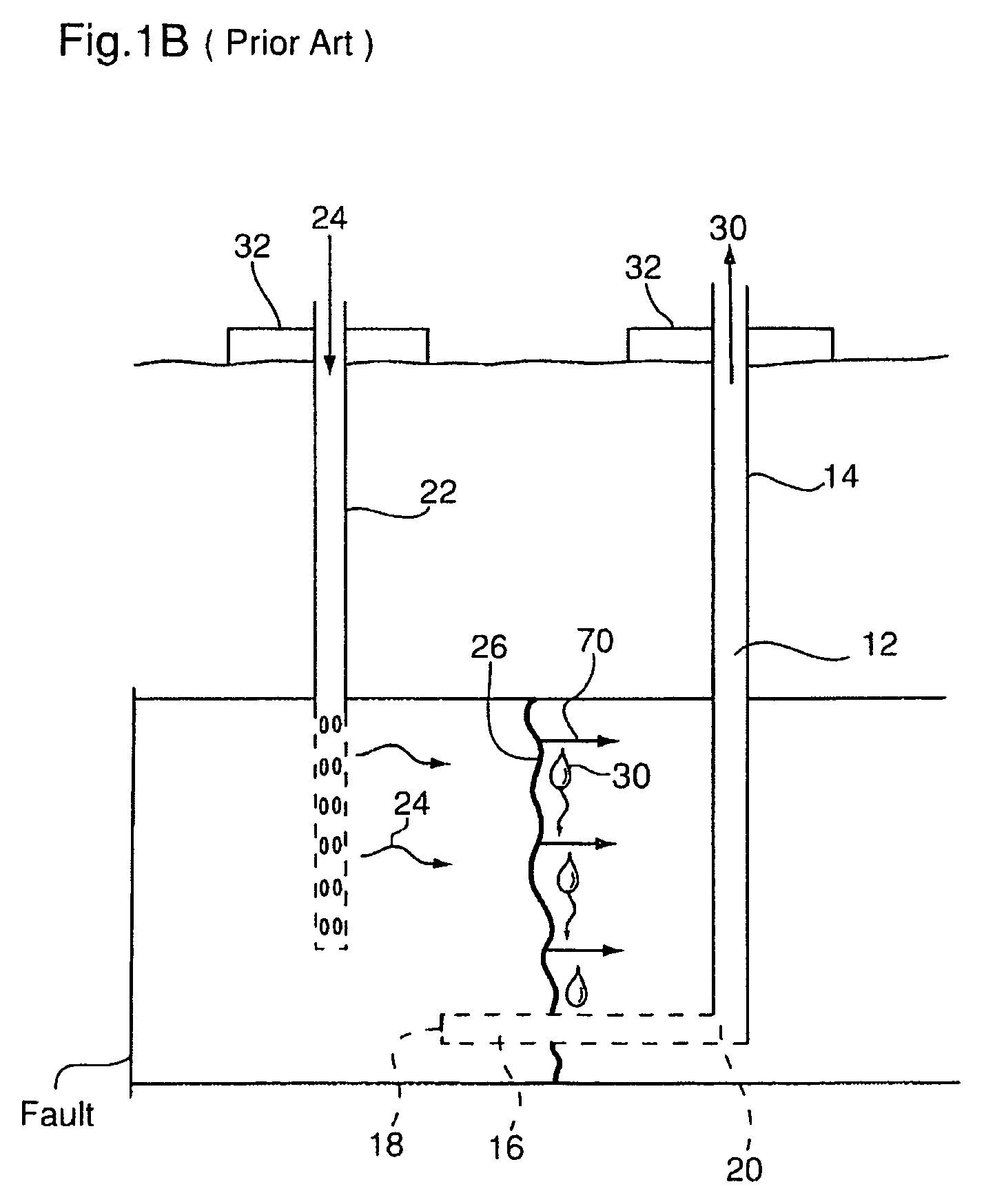
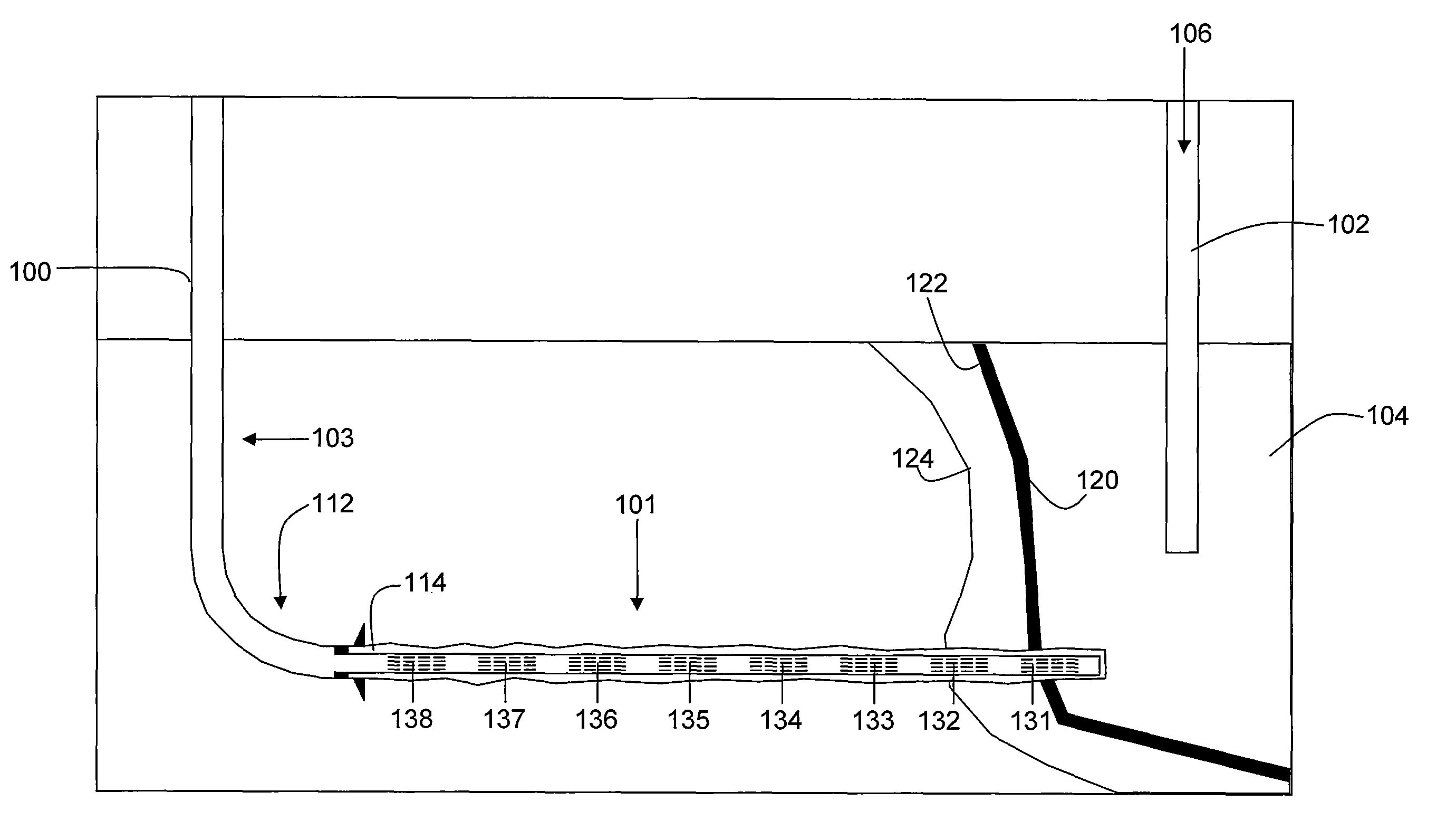
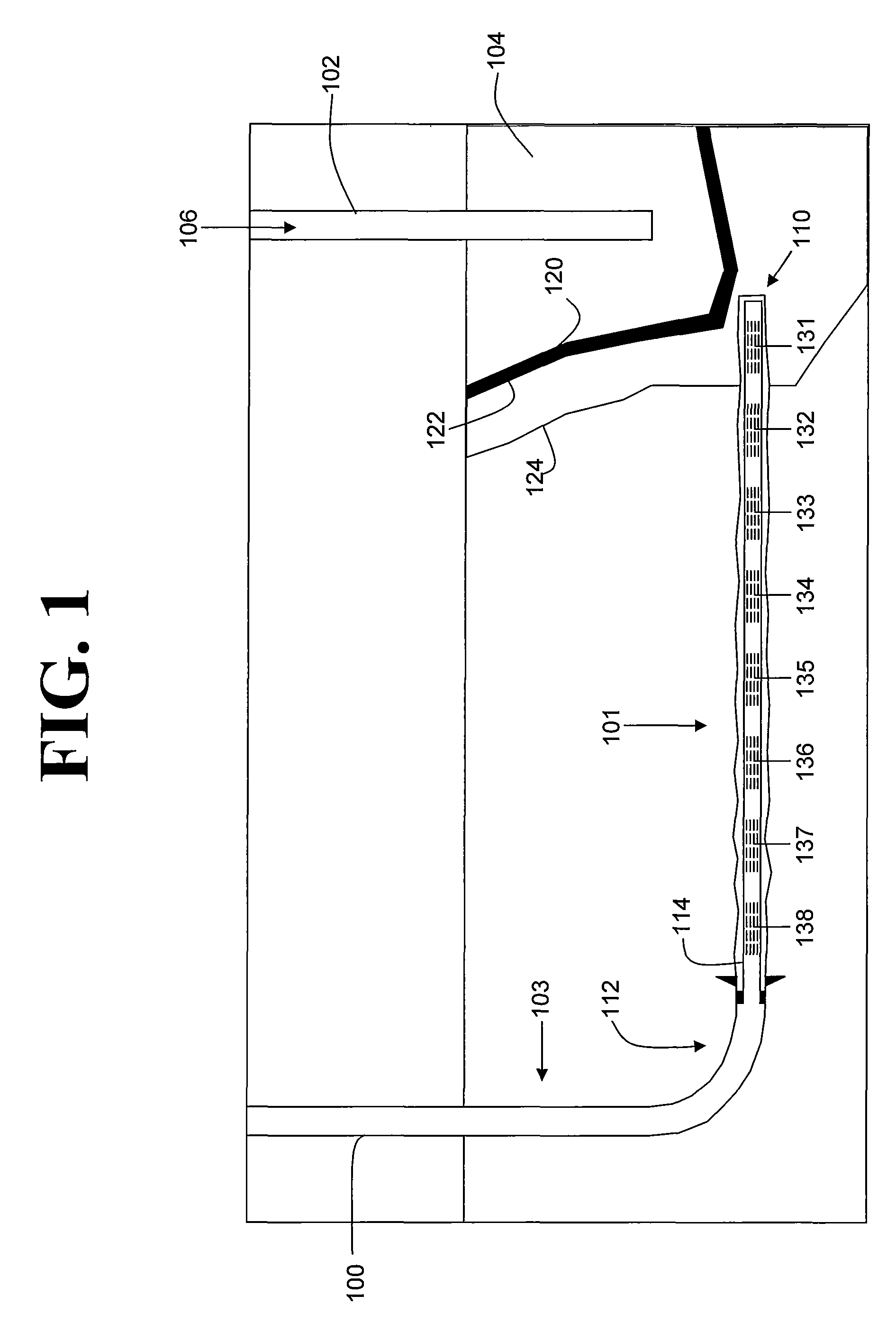
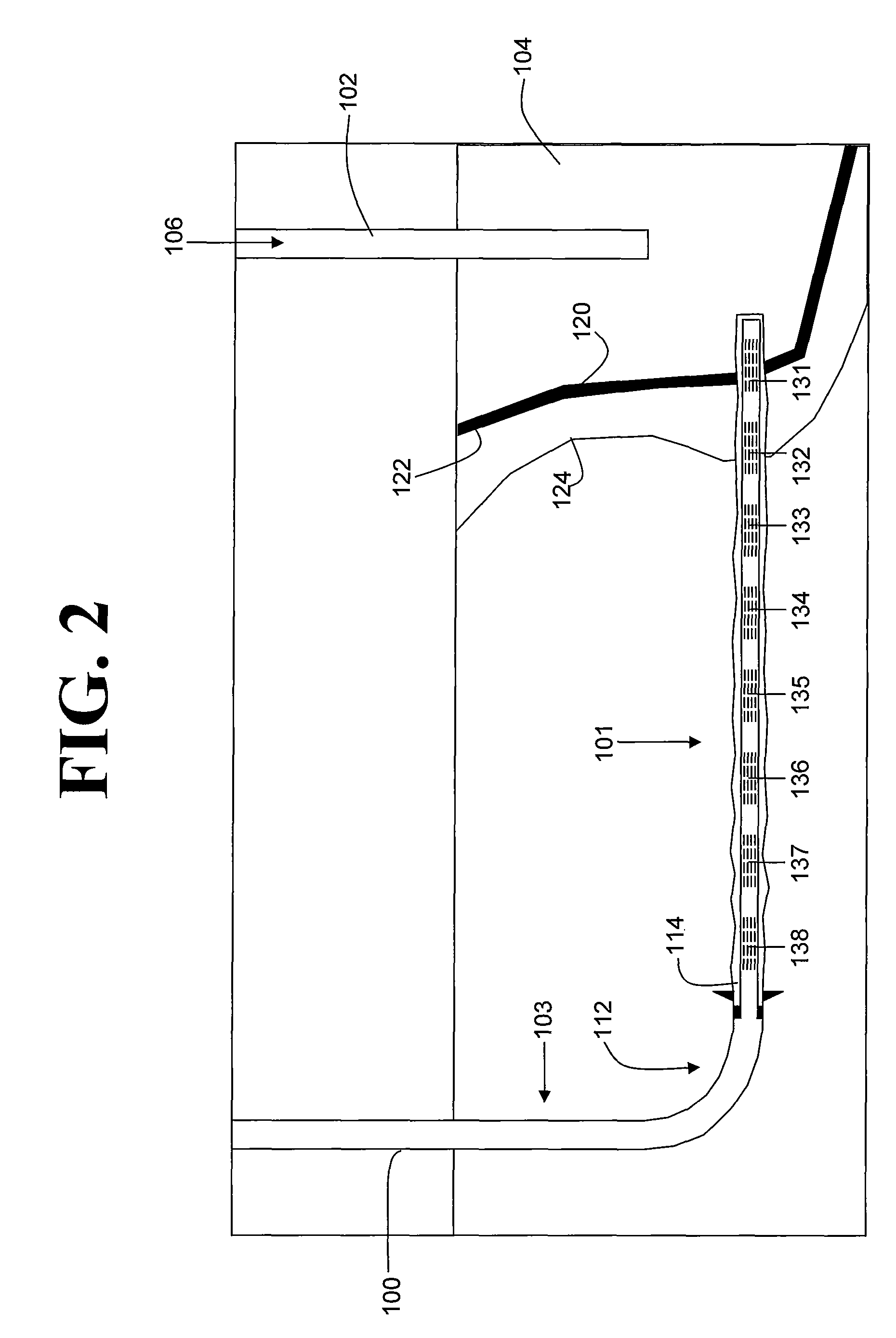
Enhanced hydrocarbon recovery by in situ combustion of oil sand formations
InactiveUS20070199700A1Upgrading in situ the quality of the produced hydrocarbon productEasy to pyrolyzeFluid removalCombustorHydrodesulfurization
The present invention is a method and apparatus for the enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by in situ combustion of the hydrocarbon deposit, from injection of an oxygen rich gas and drawing off a flue gas to control the rate and propagation of the combustion front to be predominantly vertical and propagating horizontally guided by the vertical highly permeable hydraulic fractures. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a highly permeable proppant containing hydrodesulfurization and thermal cracking catalysts. The oxygen rich gas is injected via the well bore into the top of the propped fractures, the in situ hydrocarbons are ignited by a downhole burner and the generated flue gas extracted from the bottom of the propped fractures through the well bore and mobile oil gravity drains through the propped fractures to the bottom of the well bore and pumped to the surface. The combustion front is predominantly upright, providing good vertical and lateral sweep, due to the flue gas exhaust control provided by the highly permeable propped fractures.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery By In Situ Combustion of Oil Sand Formations
InactiveUS20070199702A1Upgrade in situ the quality of the produced hydrocarbon productEasy to pyrolyzeInsulationFluid removalHydrodesulfurizationCombustion front
The present invention is a method and apparatus for the enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by in situ combustion of the hydrocarbon deposit, from injection of an oxygen rich gas and drawing off a flue gas to control the rate and propagation of the combustion front to be predominantly horizontal and propagating vertically downwards guided by the vertical highly permeable hydraulic fractures. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a highly permeable proppant containing hydrodesulfurization and thermal cracking catalysts. The oxygen rich gas is injected via the well bore into the top of the propped fractures, the in situ hydrocarbons are ignited by a downhole burner, and the generated flue gas extracted from the bottom of the propped fractures through the well bore and mobile oil gravity drains through the propped fractures to the bottom of the well bore and pumped to the surface. The combustion front is predominantly horizontal, providing good vertical and lateral sweep, due to the flue gas exhaust control provided by the highly permeable propped fractures.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
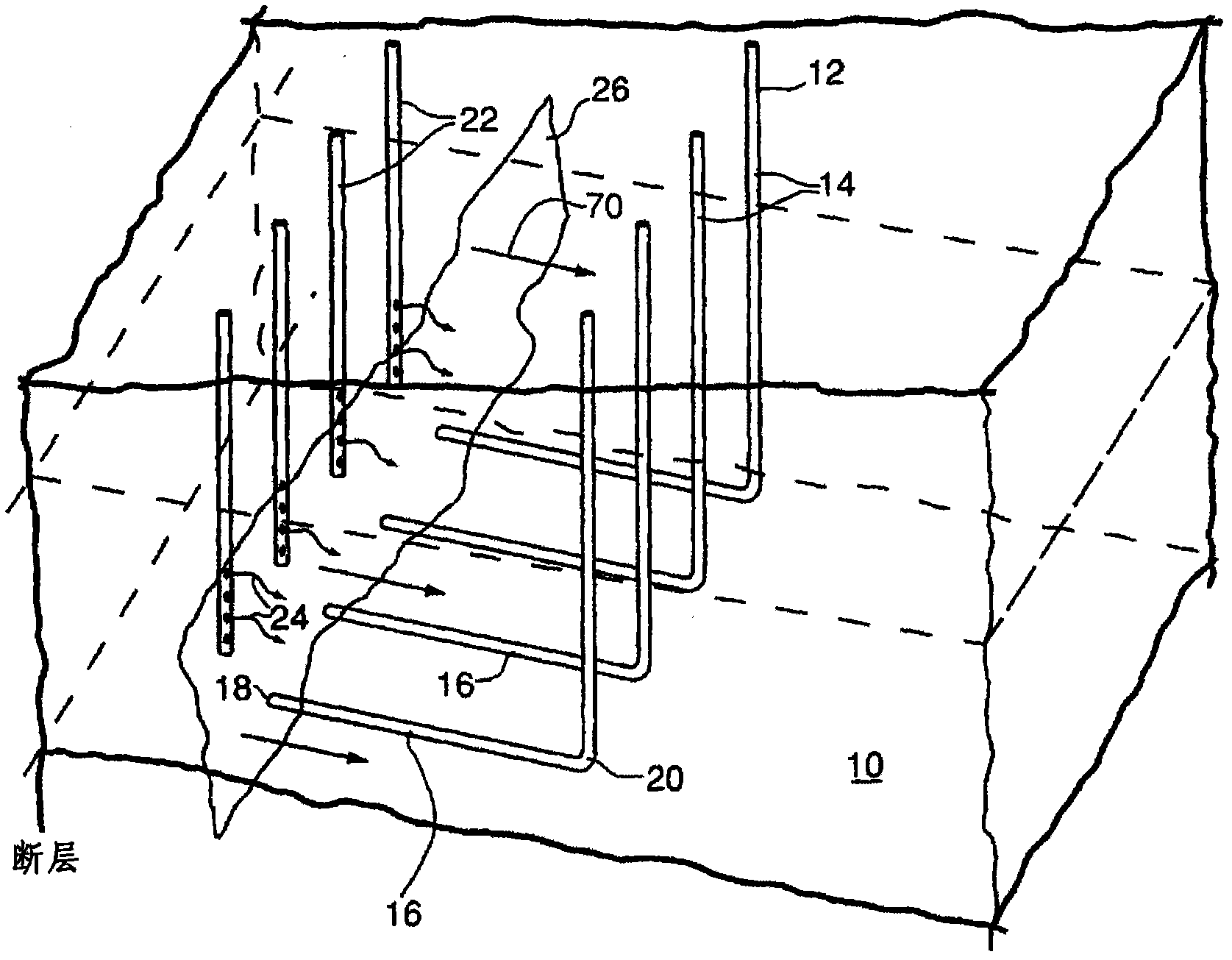
Fishbone well configuration for in situ combustion
An underground reservoir is provided comprising an injection well and a production well. The production well has a horizontal section oriented generally perpendicularly to a generally linear and laterally extending, upright combustion front propagated from the injection well.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Oxygen generator
Owner:MOLECULAR OXYGEN
Enhanced oil recovery initiated with zero emission in-situ combustion
InactiveUS20140041867A1Promote recoveryPromote gravity segregationFluid removalFlue gasCombustion front
The invention provides an enhanced oil recovery process that may be used in light oil reservoirs, and which is particularly beneficial in high-relief formations. The process includes an initial injection of air into the formation through an injection well to support the in-situ combustion and mobilize formation fluids. Produced flue gas is recovered and recycled into the formation by injection through an injection well. Initially, gas production is restricted for the purpose of increasing the gas injection to recovery ratio to pressurize the formation. With an increase in formation pressure, the rate of air injection is gradually reduced as the rate of recovered flue gas injection increases. Combustion front propagation in the formation is controlled by the rate of production at each actively producing well to ensure good horizontal sweep across the well and to prevent channeling to one or more production wells.
Owner:BELGRAVE JOHN
Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery by in Situ Combustion of Oil Sand Formations
InactiveUS20090159277A1Promote recoveryIncrease productionFluid removalCombustorHydrodesulfurization
The present invention is a method and apparatus for the enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by in situ combustion of the hydrocarbon deposit, from injection of an oxygen rich gas and drawing off a flue gas to control the rate and propagation of the combustion front to be predominantly horizontal and propagating vertically downwards guided by the vertical highly permeable hydraulic fractures. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a highly permeable proppant containing hydrodesulfurization and thermal cracking catalysts. The oxygen rich gas is injected via the well bore into the top of the propped fractures, the in situ hydrocarbons are ignited by a downhole burner, and the generated flue gas extracted from the bottom of the propped fractures through the well bore and mobile oil gravity drains through the propped fractures to the bottom of the well bore and pumped to the surface. The combustion front is predominantly horizontal, providing good vertical and lateral sweep, due to the flue gas exhaust control provided by the highly permeable propped fractures.
Owner:HOCKING GRANT
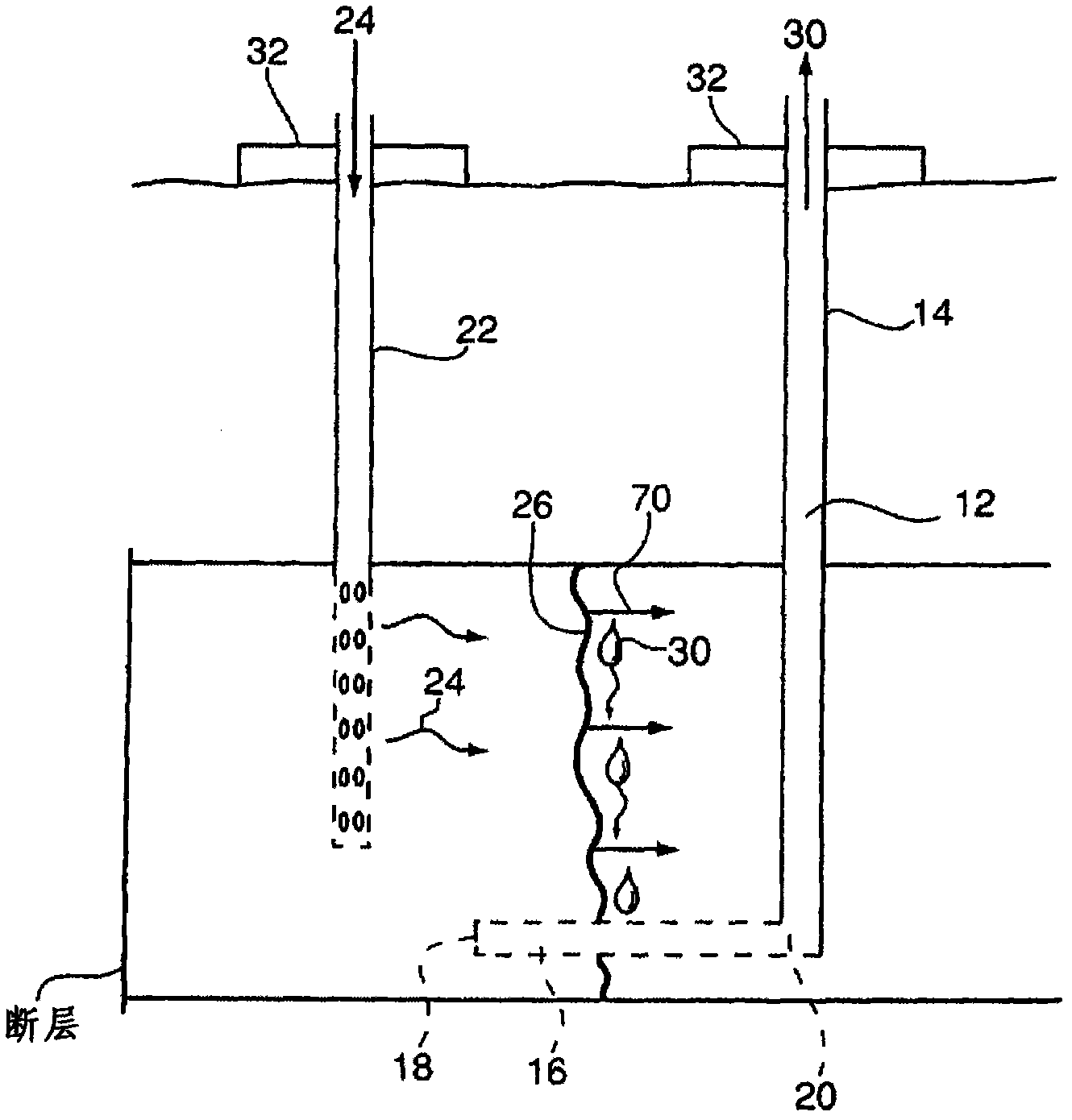
A modified process for hydrocarbon recovery using in situ combustion
The present invention provides a modified method of in situ recovery of hydrocarbon from an underground hydrocarbon-containing formation. An ''L'' shaped production well, having a vertical upper section, and a lower horizontally-extending leg which is positioned low in the hydrocarbon formation, is provided. The horizontal leg connects to the vertical section of the production well at a heel portion and has a toe portion at an opposite end thereof. An oxidizing gas is injected into the formation proximate the vertical section of the production well. A vertical combustion front is created which is caused to sweep outwardly therefrom and laterally within the formation above the horizontal leg, from the heel to the toe of the horizontal leg, causing hydrocarbons in the formation above the horizontal leg to be upgraded and liquify, and thereafter to drain downwardly into the horizontal leg which is permeable, where such liquified hydrocarbons are then delivered to surface via production tubing. A non-oxidizing gas is injected into the heel portion of the horizontal leg via injection tubing contained within the vertical section of the production well. Benefits of the modified method of in situ recovery include decreased costs and lessened environmental impact.
Owner:ARCHON TECH LTD
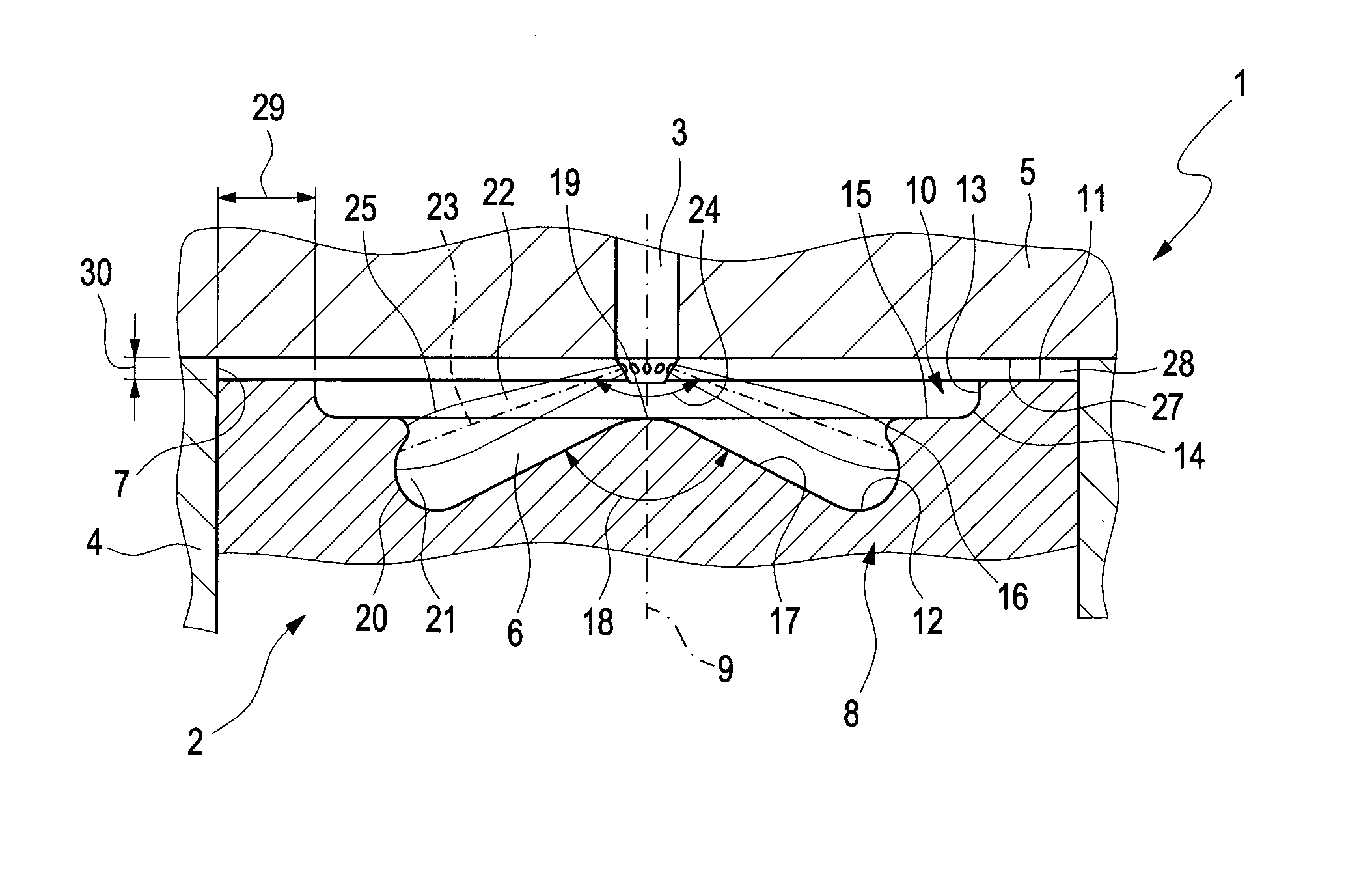
Combustion Method and Internal Combustion Engine
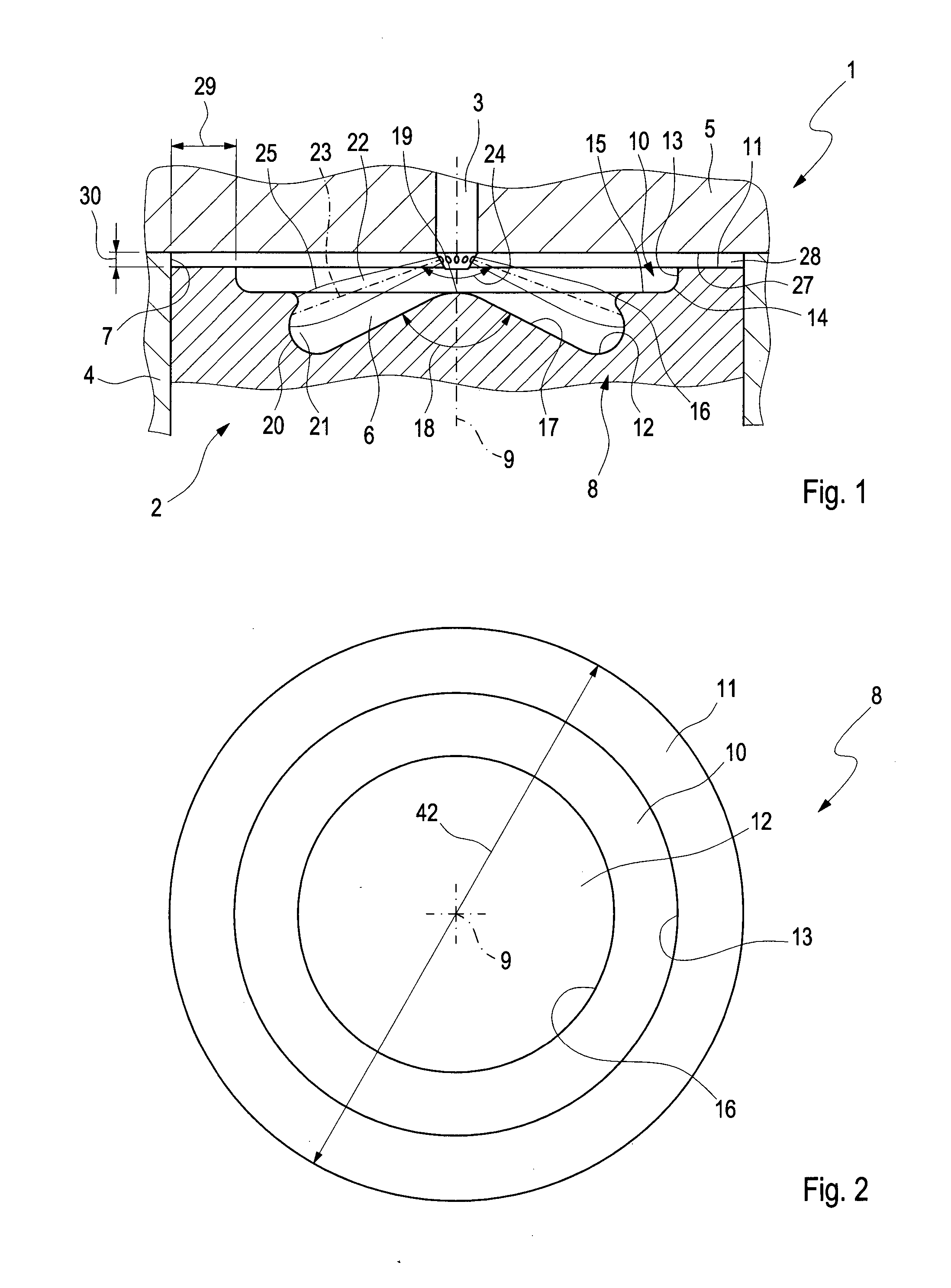
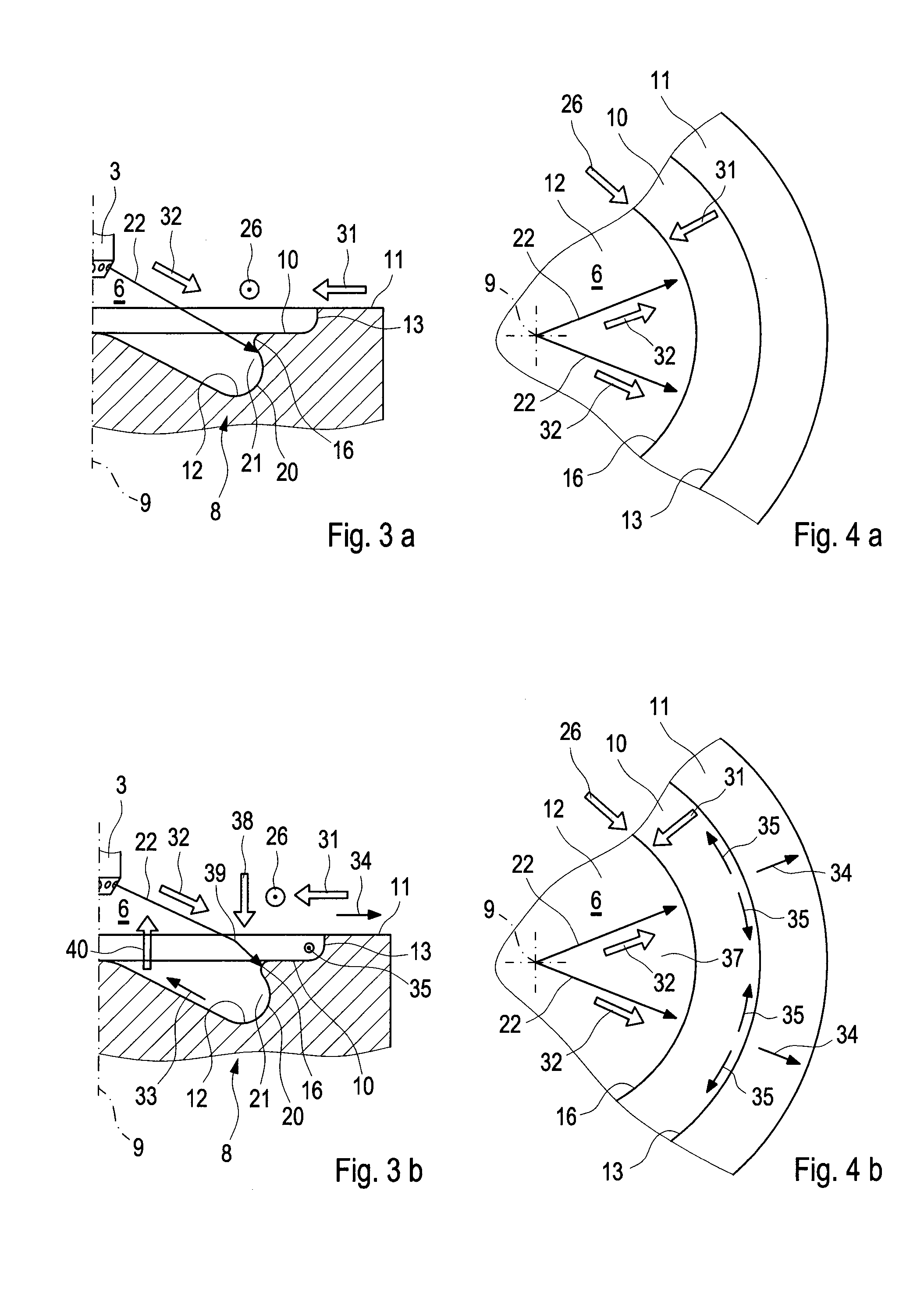
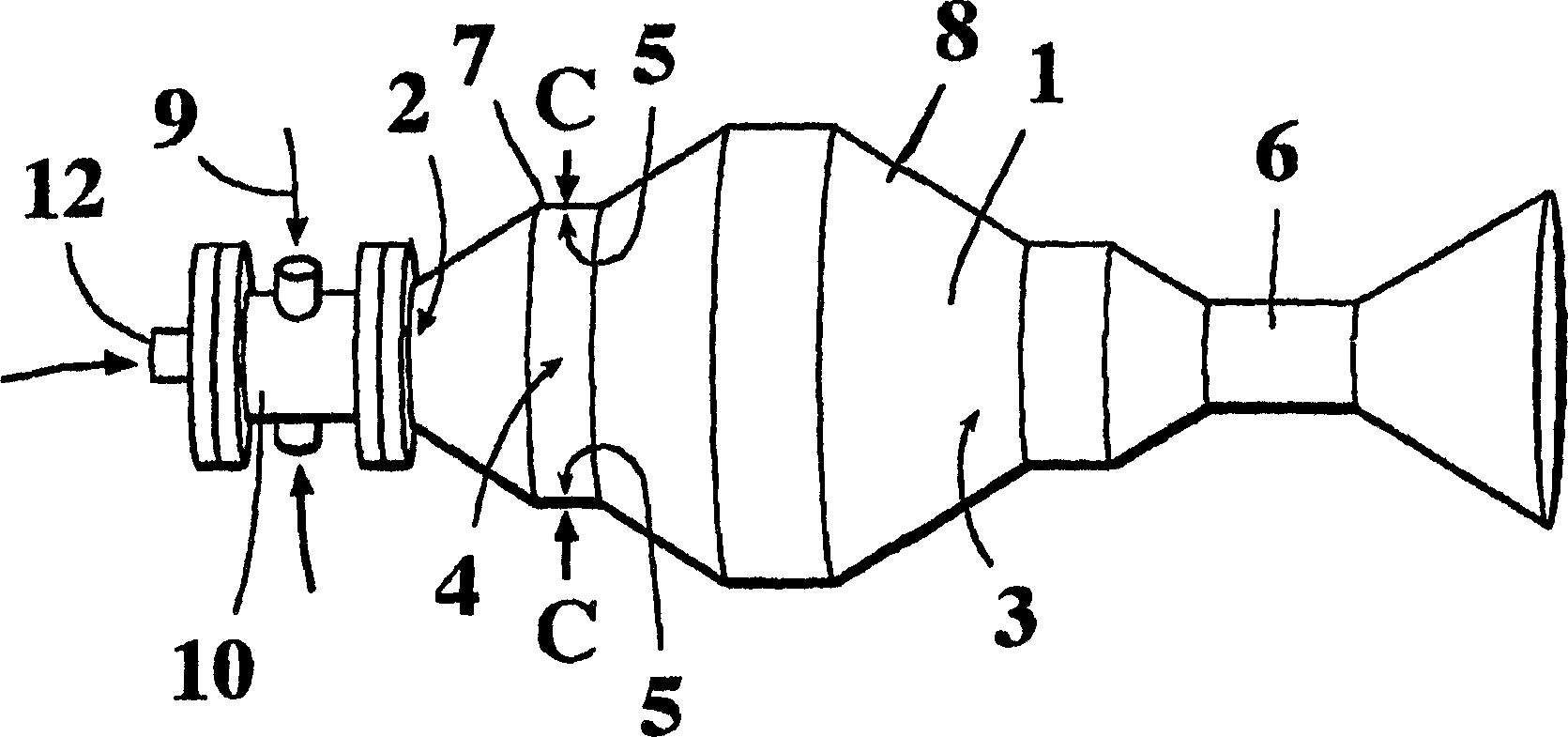
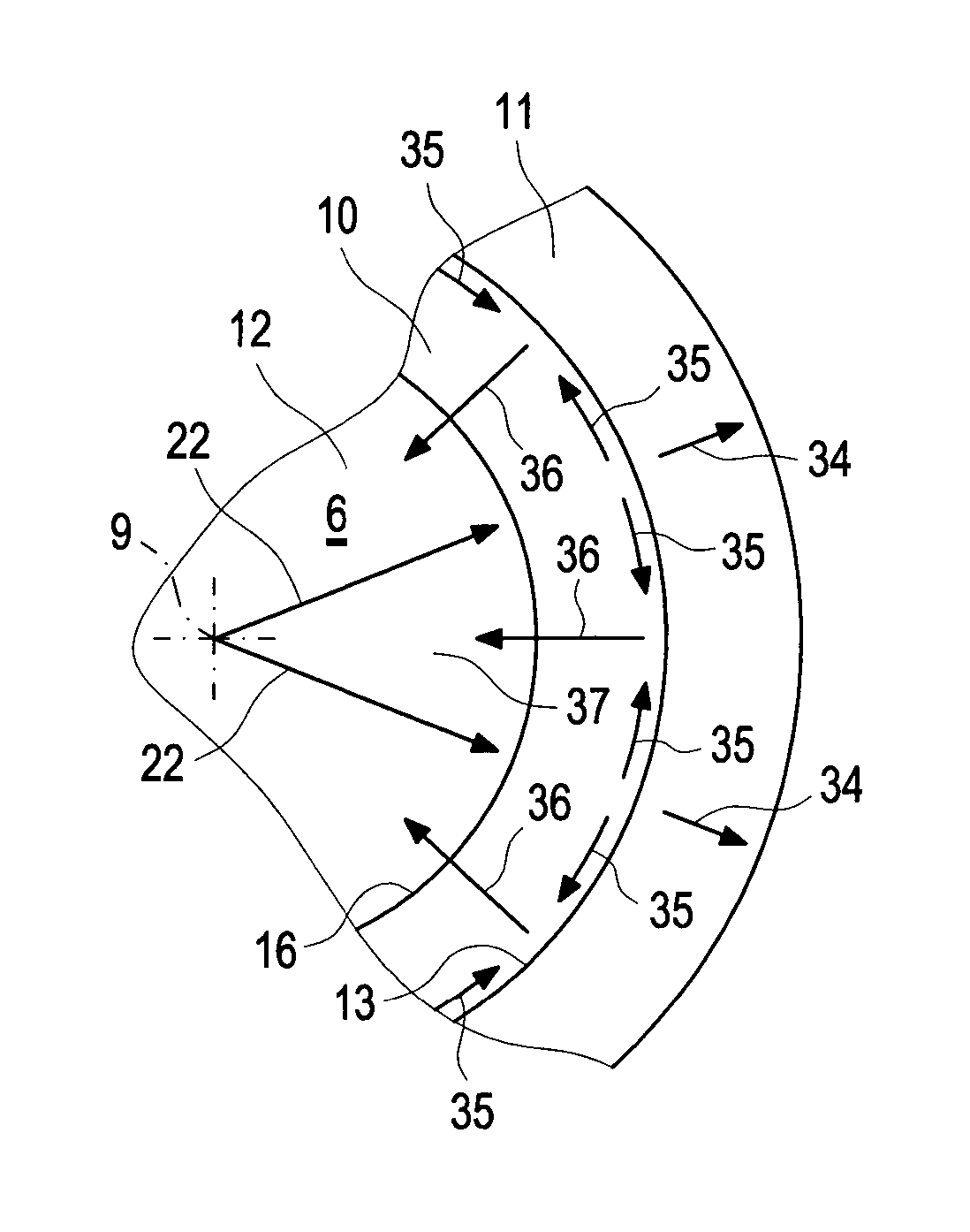
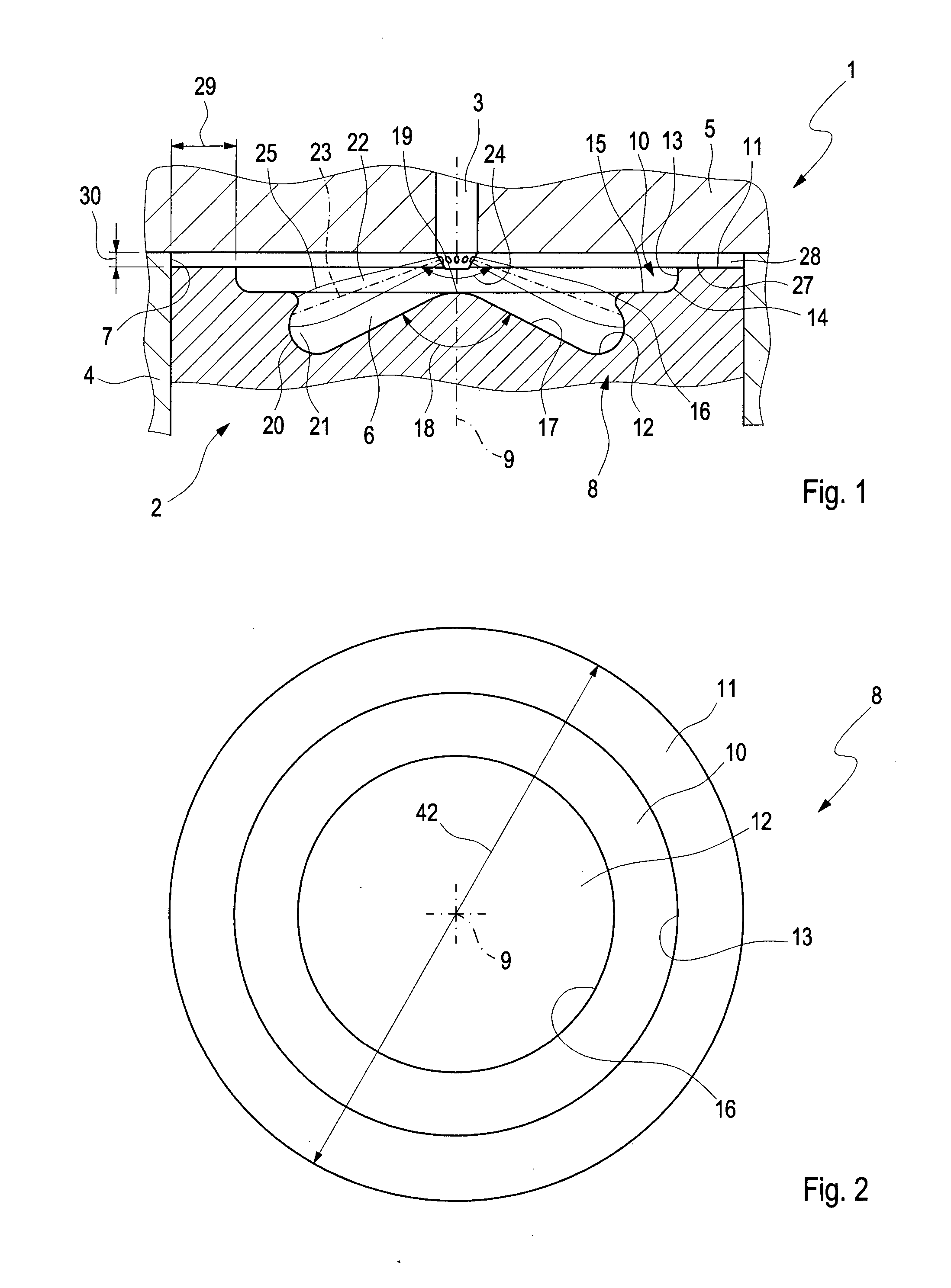
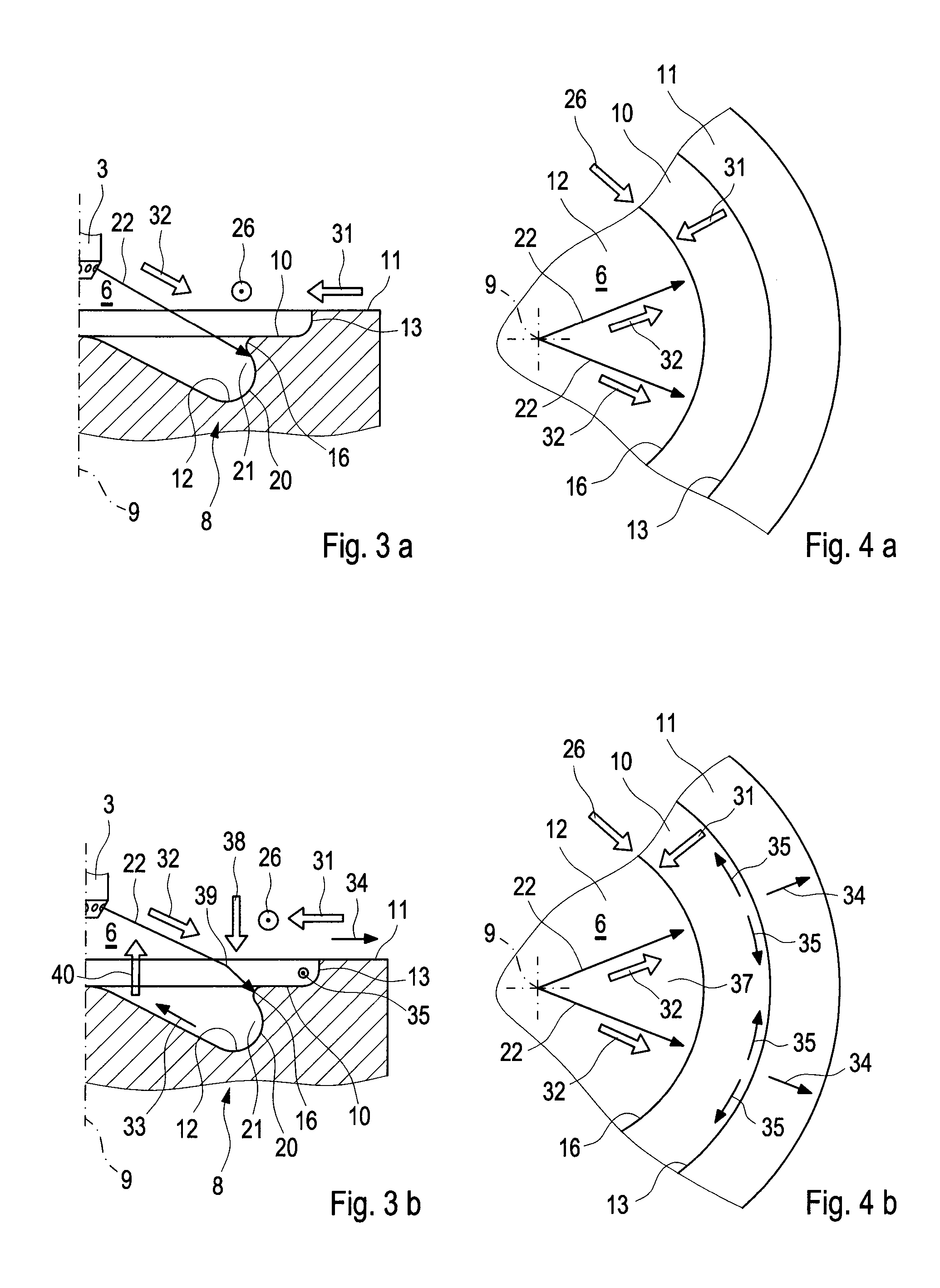
ActiveUS20140305402A1Reduce formationReduce the temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesJet flowCylinder head
A combustion process with auto-ignition for direct-injection internal combustion engines involves dividing injection jets at a jet divider contour into a first partial quantity, a second partial quantity, and third partial quantities. The first partial quantity enters into the piston cavity, the second partial quantity enters via the piston step into a region between the piston crown and the cylinder head, and the third partial quantities, starting from the respective injection jet, spread out on both sides in the peripheral direction in opposite directions along the piston step, and the respective third partial quantities collide with one another between two adjacent injection jets within the piston step and are deflected radially inwardly. The first partial quantity and the second partial quantity form a first combustion front and a second combustion front, and the partial quantities which in each case are jointly deflected inwardly form a third combustion front radially inwardly into a gap between the injection jets. The injection jets are deflected upstream from the jet divider contour in the direction of the piston by means of a resultant flow formed essentially from a swirl, a squish gap flow, and a jet flow.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Fishbone well configuration for in situ combustion
An underground reservoir is provided comprising an injection well and a production well. The production well has a horizontal section oriented generally perpendicularly to a generally linear and laterally extending, upright combustion front propagated from the injection well.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Hydrocarbon mobility and recovery through in-situ combustion with the addition of ammonia
ActiveUS20140224483A1Improve mobilityFluid removalDrilling compositionCombustion frontSURFACTANT BLEND
Air and ammonia gas are introduced into a subterranean formation during the in-situ combustion to increase the mobility of hydrocarbons in a subterranean formation and facilitate recovery of the hydrocarbons from the subterranean formation. The air supports in-situ combustion of a portion of the hydrocarbon within the subterranean formation to form water and establish a combustion front. The ammonia gas contacts the hydrocarbons ahead of the combustion front and reacts in-situ with naphthenic acid in the hydrocarbon to form a surfactant. The hydrocarbons, water and surfactant then form an oil-in-water emulsion that drains more freely through the formation. A production well, in fluid communication with the hydrocarbons ahead of the combustion front, may be used to remove the oil-in-water emulsion from the subterranean formation.
Owner:CHAMPIONX LLC +1
Method for exploiting thickened oil or asphalt
The invention provides a method for exploiting thickened oil or asphalt. The method for exploiting the thickened oil or asphalt comprises the steps that steam is injected into a stratum, and then air and an alkali compound are injected so that the air and the alkali compound can enter an underground reservoir stratum. According to the method for exploiting the thickened oil or asphalt, flowing of the thickened oil or asphalt in the reservoir stratum can be promoted. The method for exploiting the thickened oil or asphalt further comprises the steps that a combustion front is established in part of the thickened oil or asphalt in the reservoir stratum through combustion of oil in-situ, air and the alkali compound are injected into the stratum during combustion of oil in-situ, and the alkali compound makes contact with hydrocarbons at the position of the combustion front and reacts with naphthenic acid in the hydrocarbons so that a surface active agent can be formed.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Enhanced hydrocarbon recovery by in situ combustion of oil sand formations
InactiveUS7520325B2Upgrade in situ the quality of the produced hydrocarbon productEasy to pyrolyzeInsulationFluid removalCombustorHydrodesulfurization
The present invention is a method and apparatus for the enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by in situ combustion of the hydrocarbon deposit, from injection of an oxygen rich gas and drawing off a flue gas to control the rate and propagation of the combustion front to be predominantly horizontal and propagating vertically downwards guided by the vertical highly permeable hydraulic fractures. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a highly permeable proppant containing hydrodesulfurization and thermal cracking catalysts. The oxygen rich gas is injected via the well bore into the top of the propped fractures, the in situ hydrocarbons are ignited by a downhole burner, and the generated flue gas extracted from the bottom of the propped fractures through the well bore and mobile oil gravity drains through the propped fractures to the bottom of the well bore and pumped to the surface. The combustion front is predominantly horizontal, providing good vertical and lateral sweep, due to the flue gas exhaust control provided by the highly permeable propped fractures.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
Method and apparatus for generating gas pulses
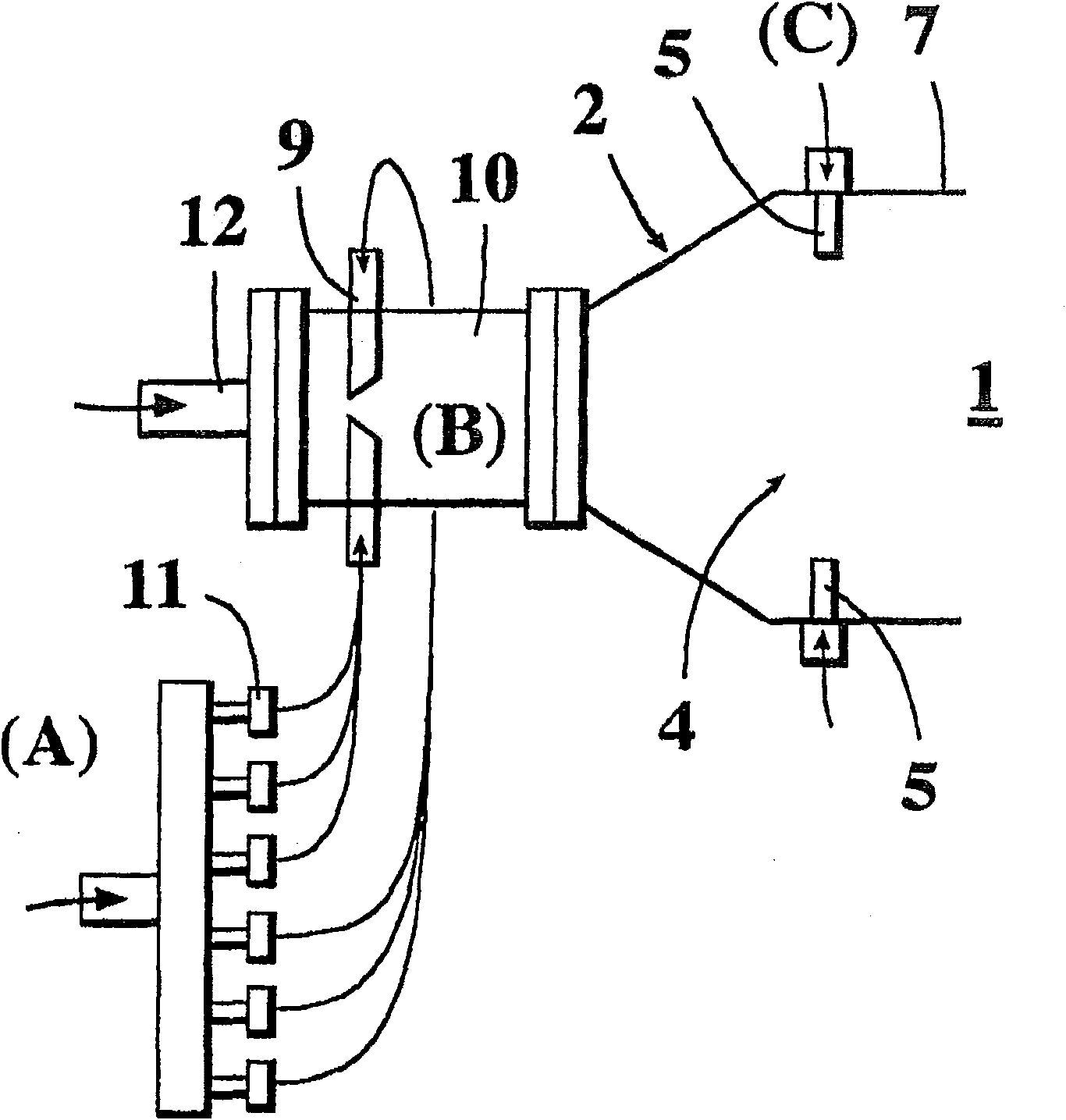
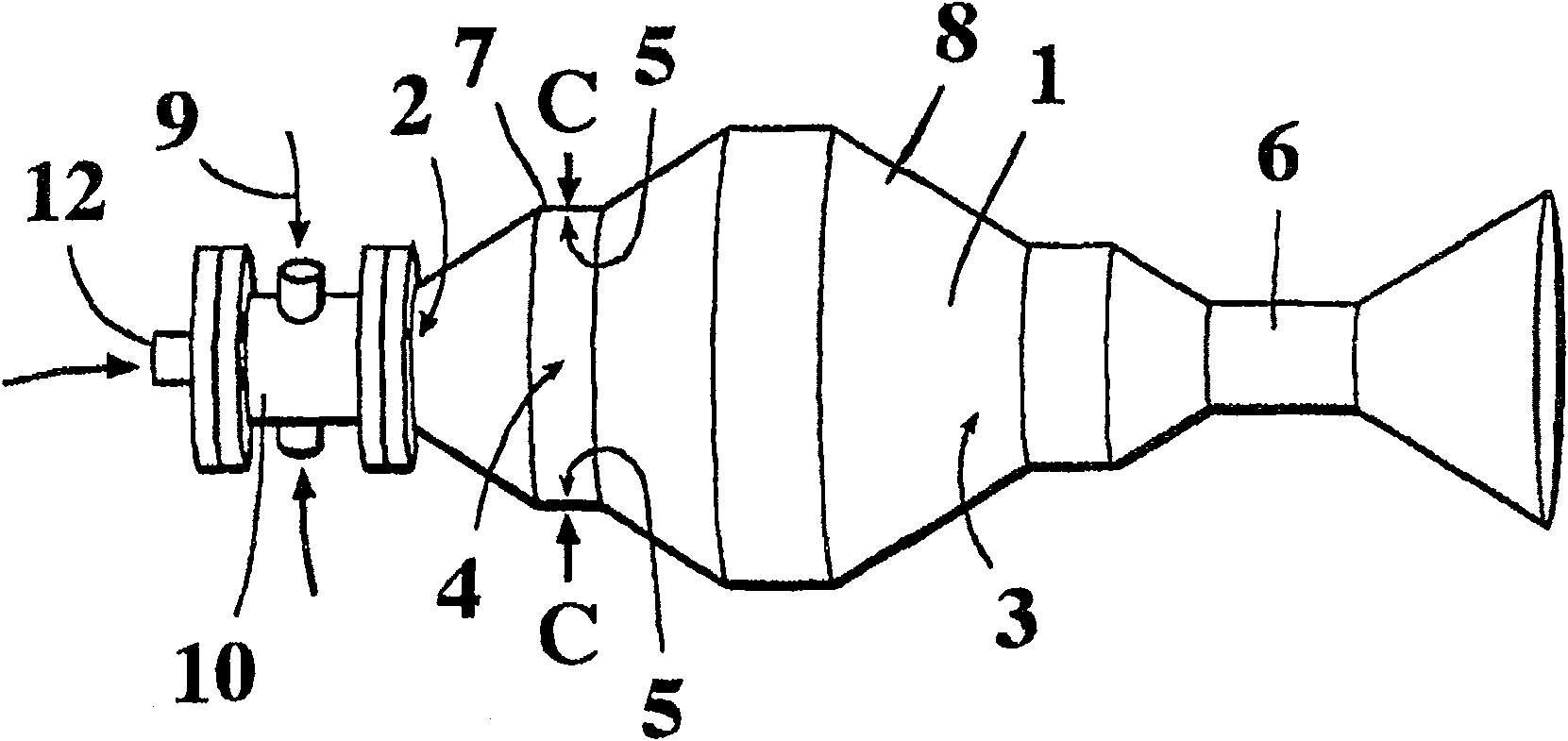
ActiveCN1839001AReduce consumptionPulsating combustionVibration cleaningDetonationCombustion chamber
Method and apparatus of producing gas pressure pulses in a dust-deposit cleaning apparatus. The apparatus comprises a combustion chamber and an amplifying horn. According to the method a combustible gas and oxygen is fed into the combustion chamber, which has a generally elongated shape, the gas mixture is ignited for generating a pressure pulse, and the pressure pulse is released from the chamber and conducted to the amplifying horn. The gas mixture is ignited to generate an initial explosion which causes a pressure wave, which is reflected from the inner walls of the chamber end to form a collision zone, in which the initial explosion is at least partially transformed into a detonation. The combustion front is reflected from the gas inlet end and compressed at the other end of the chamber and released to the amplifying horn. By means of the invention, sound levels of about 165-170 dB can be produced at low fuel consumption.
Owner:NIRAFON OY
Combustion method and internal combustion engine
ActiveUS9476346B2Reduce formationReduce the temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesPistonsCylinder headExternal combustion engine
A combustion process with auto-ignition for direct-injection internal combustion engines involves dividing injection jets at a jet divider contour into a first partial quantity, a second partial quantity, and third partial quantities. The first partial quantity enters into the piston cavity, the second partial quantity enters via the piston step into a region between the piston crown and the cylinder head, and the third partial quantities, starting from the respective injection jet, spread out on both sides in the peripheral direction in opposite directions along the piston step, and the respective third partial quantities collide with one another between two adjacent injection jets within the piston step and are deflected radially inwardly. The first partial quantity and the second partial quantity form a first combustion front and a second combustion front, and the partial quantities which in each case are jointly deflected inwardly form a third combustion front radially inwardly into a gap between the injection jets. The injection jets are deflected upstream from the jet divider contour in the direction of the piston by means of a resultant flow formed essentially from a swirl, a squish gap flow, and a jet flow.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Double-point control method of 450 m<2> sintering machine
ActiveCN103225955AImprove product qualityReduced guiding run timeFurnace typesCombustion frontRunning time
The invention discloses a double-point control method of a 450 m<2> sintering machine, and belongs to iron making methods. The method comprises a method for controlling a burning through point and is characterized in that parameter control for a combustion front point is added, that is, 6 exhaust gas temperature detection facilities are arranged in width directions of bellows ranging from 11# to 18# of the 450 m<2> sintering machine; at the same time, temperatures at the bellow 11# and a bellow 12# are set to be temperatures of the exhaust gas at the combustion front point during sintering; and an actual detection temperature change trend curve is compared with a set temperature, and corresponding measurements are taken. According to the method, the parameter of the burning through point can be known within 15 minutes after ignition, and deviation rectifying operation can be performed in 25 minutes after a deviation rectifying parameter is issued, so that the deviation rectifying operation time is reduced, and the product quality of a sinter is improved.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
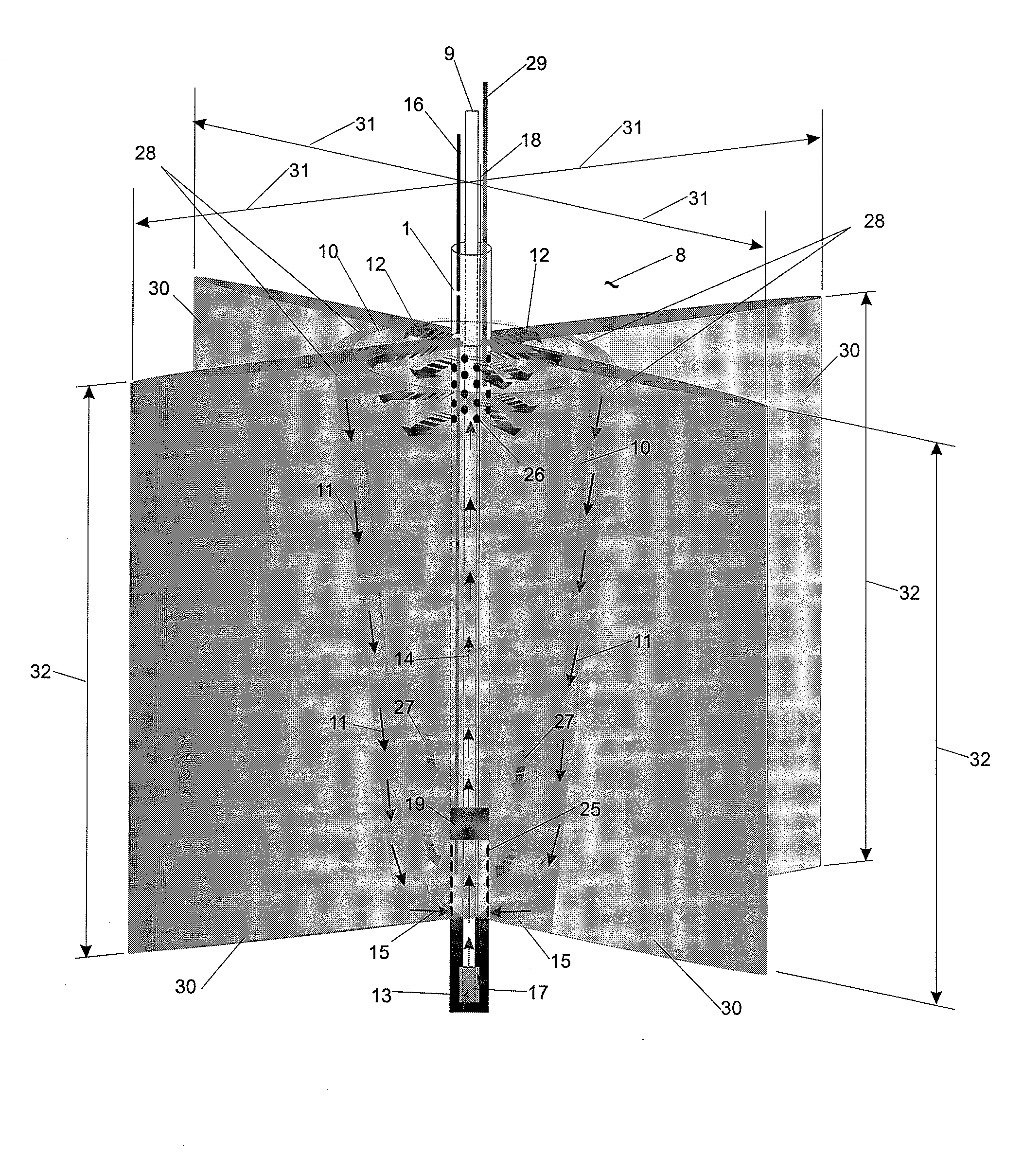
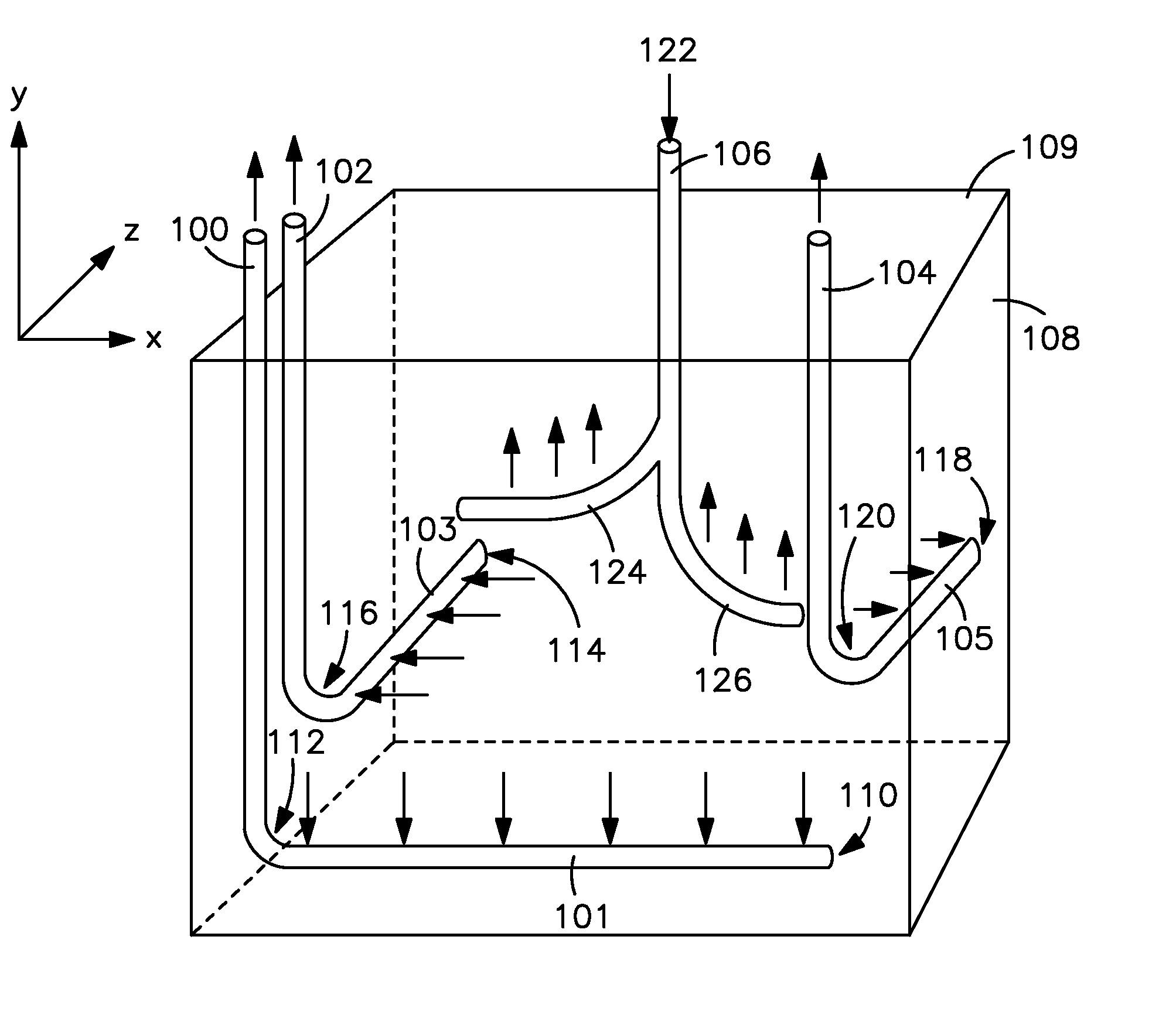
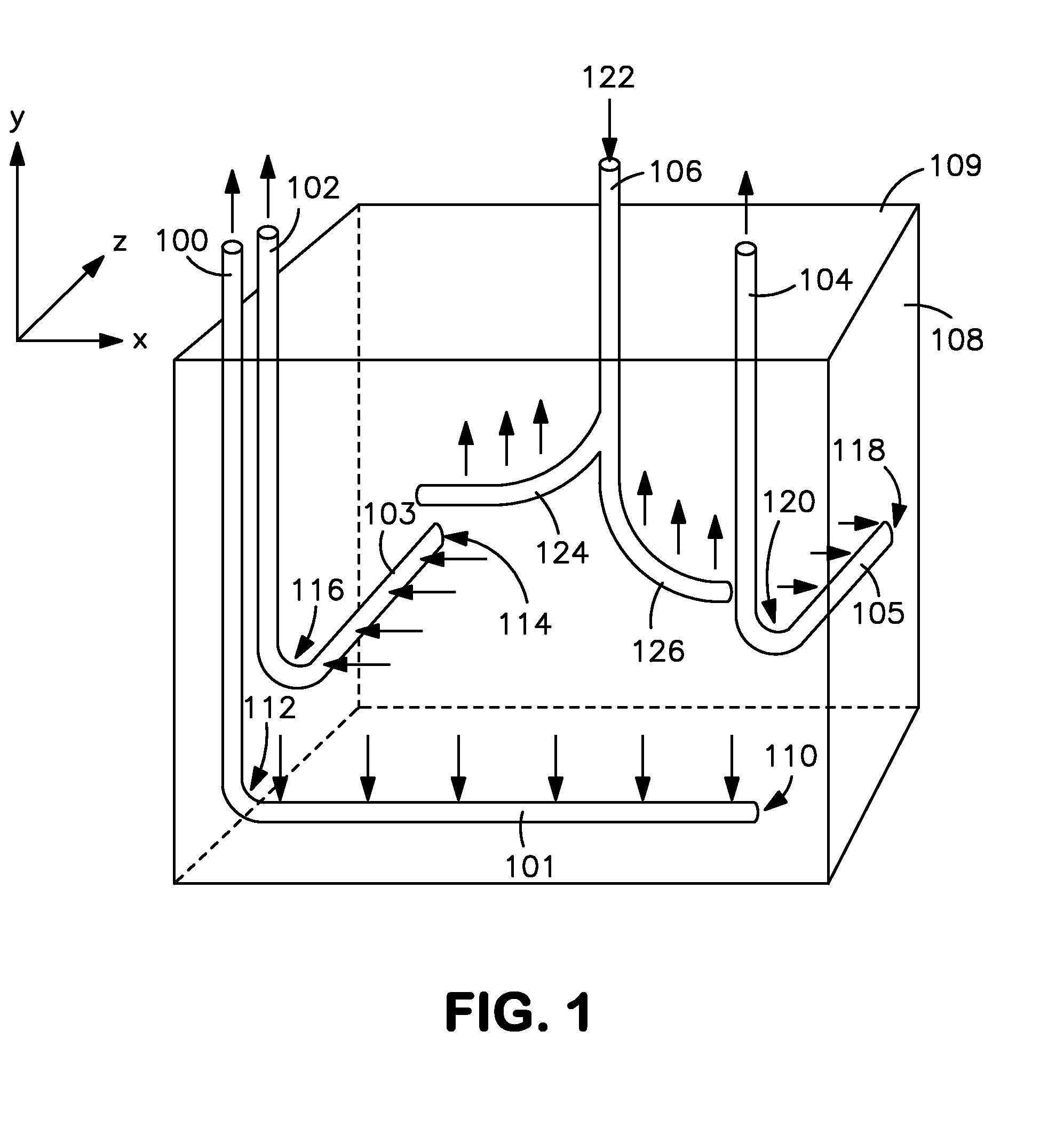
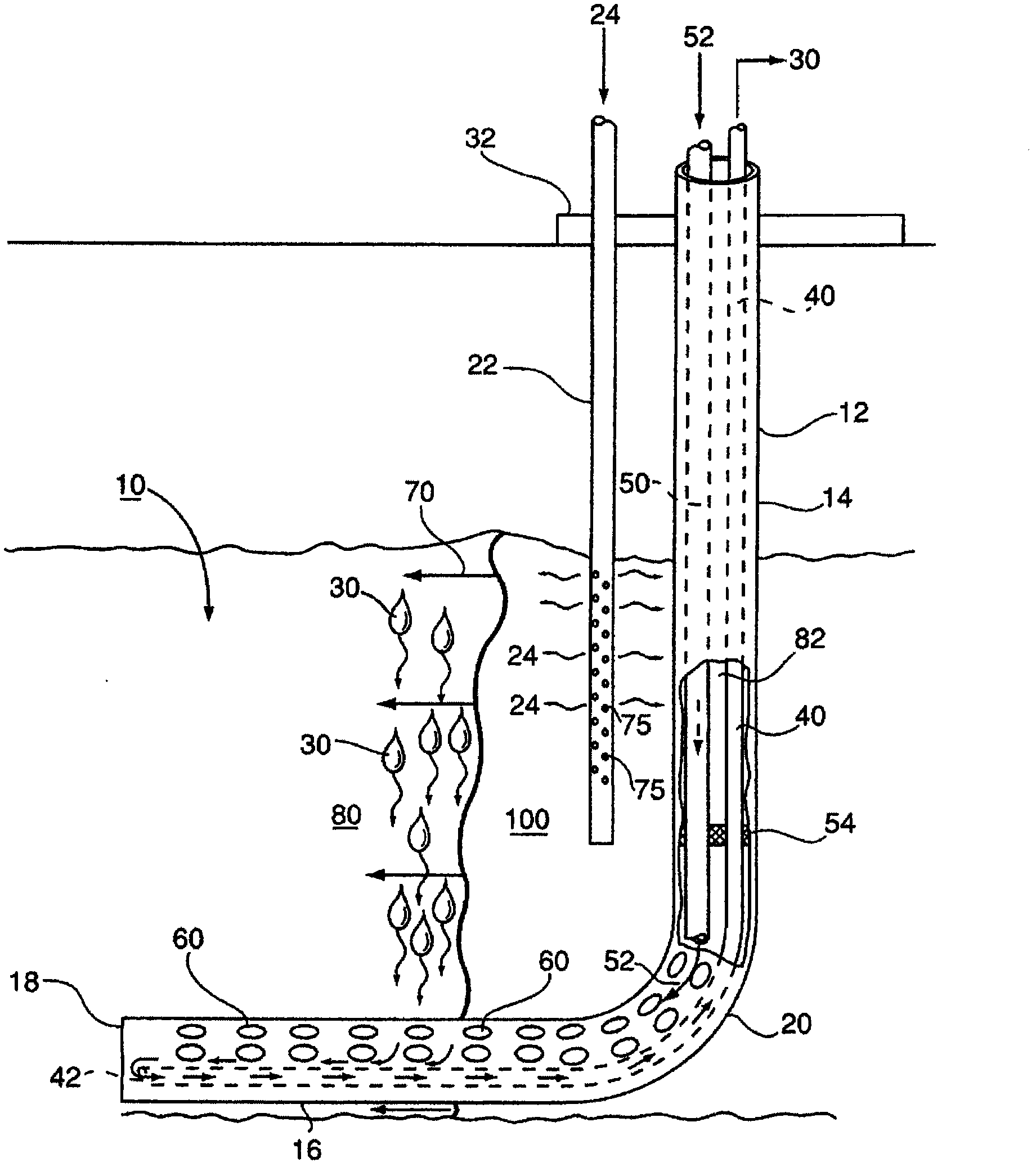
In-situ combustion recovery process using single horizontal well to produce oil and combustion gases to surface
InactiveUS20130074470A1Quick collectionReduce chanceCombustion enginesFluid removalCombustion frontInjection well
An in-situ combustion process which process does not employ one or more separate gas venting wells. At least one vertical production well having a substantially vertical portion extending downwardly into the reservoir and a horizontal leg portion extending horizontally outwardly therefrom completed relatively low in the reservoir is provided. At least one vertical oxidizing gas injection well, positioned above and in spaced relation to the horizontal well, is positioned laterally along the horizontal well approximately midsection thereof. Oxidizing gas is injected therein and combustion fronts are caused to progress outwardly from such injection well in mutually opposite directions along the horizontal well. Preferably a plurality of injection wells are provided along the direction of the horizontal well, and oxidizing gas is injected in each and combustion fronts caused to progress outwardly and in opposite directions from each, and oil is caused to drain down into the horizontal well, which oil along with hot combustion gases is produced to surface.
Owner:ARCHON TECH LTD
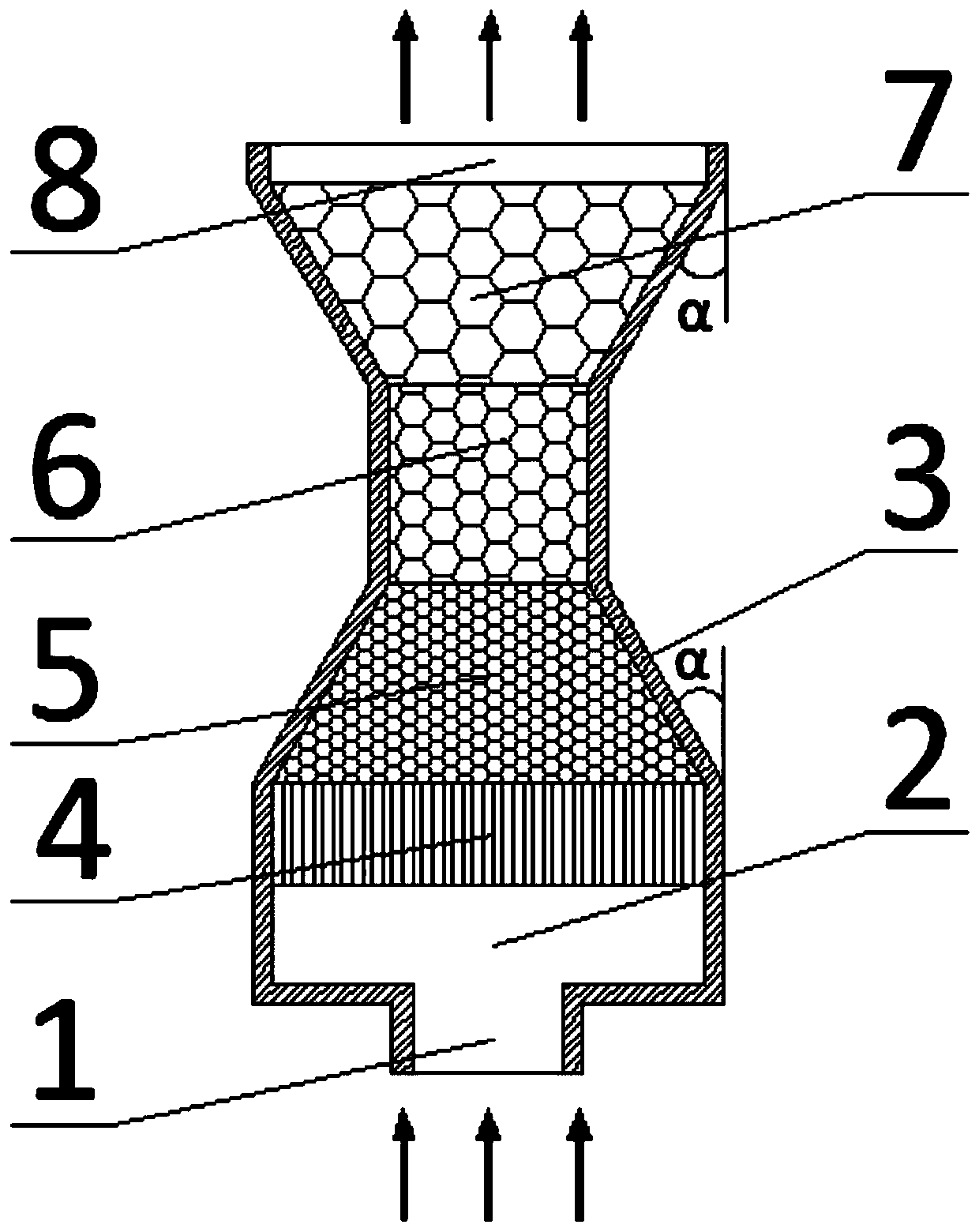
Angle type porous medium burner
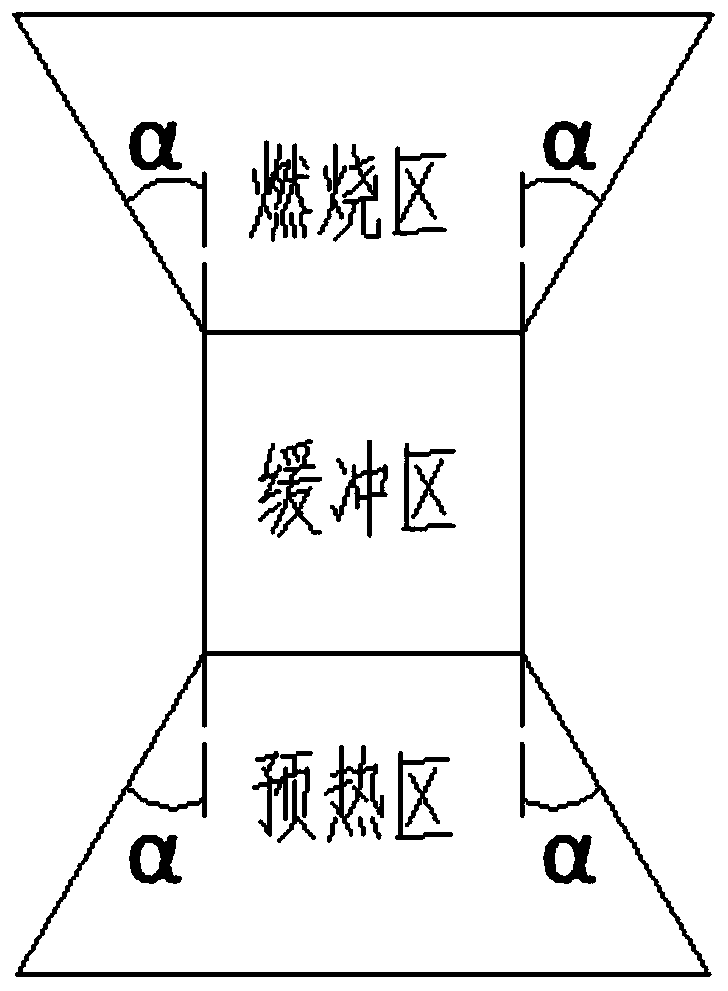
ActiveCN110425536AHigh speedShorten speedIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationGaseous fuel burnerCombustorFlue gas
The invention relates to an angle type porous medium burner. The angle type porous medium burner comprises a gas inlet, a combustion front chamber, a burner shell, a protection zone, a preheating zone, a buffer zone, a combustion zone and a flue gas outlet; the preheating zone, the buffer zone and the combustion zone are collectively called as porous medium zones and are filled with porous mediummaterials; and the preheating zone and the combustion zone are respectively and gradually expanded inwards and outwards by a certain angle alpha, and meanwhile, the buffer zone is arranged in the preheating zone and the combustion zone, so that the air flow speed is reduced, and the flame inclination phenomenon is prevented. The limit range of the flame stabilizing speed can be obviously widened,flame tempering and fire dropping are effectively prevented, the outlet radiation efficiency is improved, and meanwhile, the occurrence of thermal shock damage of the porous medium is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for exploiting heavy oil reservoir with edge water invasion in final huff and puff stage
ActiveCN113494285APrevent intrusionImprove heat utilizationFluid removalCombustion frontVaporization
The invention discloses a method for exploiting a heavy oil reservoir with edge water invasion at a final huff and puff stage. The exploiting method includes the steps that a steam flooding well pattern is deployed in a main body non-water-invasion area, and a fire flooding well pattern is deployed in an edge water invasion area; the joint of the steam flooding well pattern and the fire flooding well pattern is separated by a production well row; and steam flooding and fire flooding development are carried out at the same time. According to the method for exploiting the heavy oil reservoir with the edge water invasion at the final huff and puff stage, the edge water invasion area can be effectively utilized, the edge water invasion can be inhibited by utilizing the plugging effect of a fire flooding high-temperature combustion front edge on a high-permeability layer and the vaporization effect of the high-temperature combustion front edge on water, and the main body steam flooding heat utilization rate is improved, so that the steam flooding development effect is improved, the overall development level of a block is improved, and the problem that continuous development is difficult due to the fact that no effective conversion mode exists when edge water invades into the heavy oil reservoir in the final huff and puff stage is solved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Oxygen generator
ActiveUS7371350B2Easy to controlEvenly distributedOxygen respiratorsFire rescueCombustion frontCandle
Owner:MOLECULAR OXYGEN
In situ combustion for steam recovery infill
Methods and systems produce petroleum products from a formation by a steam assisted process followed by an in situ combustion process. The steam assisted process utilizes an injector and first producer to form a steam chamber within the formation as the products are recovered. The in situ combustion then starts by injecting an oxidant into the formation and ignition of residual products. A combustion front advances toward a second producer that may be offset in a lateral direction from the first producer. Heat and pressure from the in situ combustion sweeps the products ahead of the combustion front to the second producer for recovery.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method and apparatus for generating gas pulses
ActiveCN100544841CReduce consumptionPulsating combustionVibration cleaningCombustion chamberCombustion front
Owner:NIRAFON OY
Producer well plugging for in situ combustion processes
Methods and apparatus relate to controlling location of inflow into a production well during in situ combustion. The production well includes intervals closable to the inflow at identified times. Once a combustion front from the in situ combustion passes one of the intervals, a blockage conveyed from surface into the production well forms a barrier to the inflow at the interval that has been passed by the combustion front. An example of the blockage includes a cement plug delivered through coiled tubing into the production well, which may include production tubing that defines the intervals based on at least two consecutive alternating lengths of solid wall sections and slotted or perforated sections of the production tubing.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method of manufacturing high-surface-area silicon
InactiveUS7964172B2High purityReduce the amount requiredNanotechSiliconCombustion frontSilicon dioxide
A method for synthesis of high surface-area (>100 m2 / g) and nanosized (≦100 nm) silicon powder by initiation of self-sustained combustion reaction in a mixture of silicon dioxide and magnesium powders in a sealed reactor chamber under pressurized inert gas atmosphere. A specific feature of the method is rapid cooling of the product at a rate of 100 K / s to 400 K / s in the area directly behind the combustion front.
Owner:MUKASYAN ALEXANDER +2
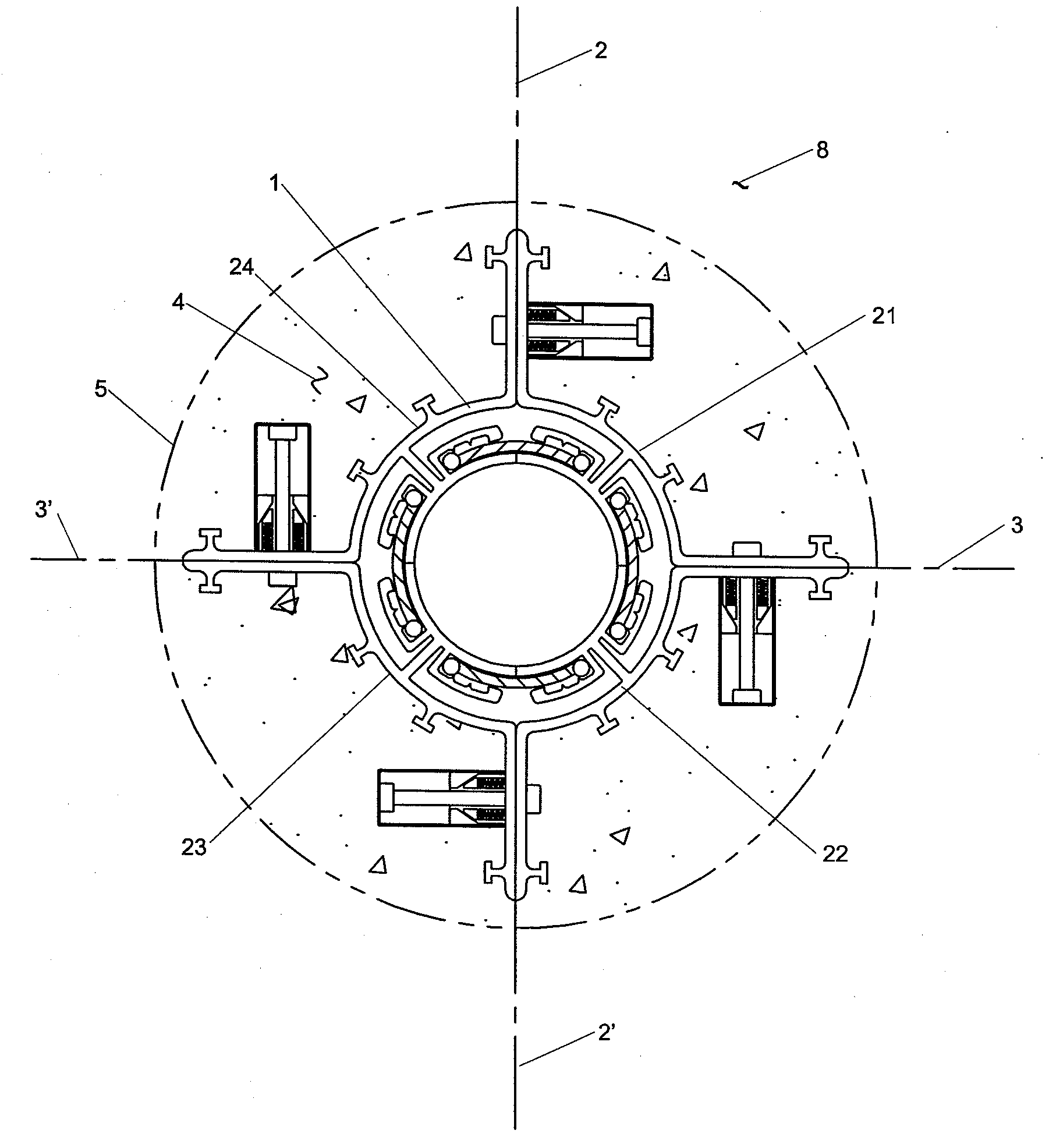
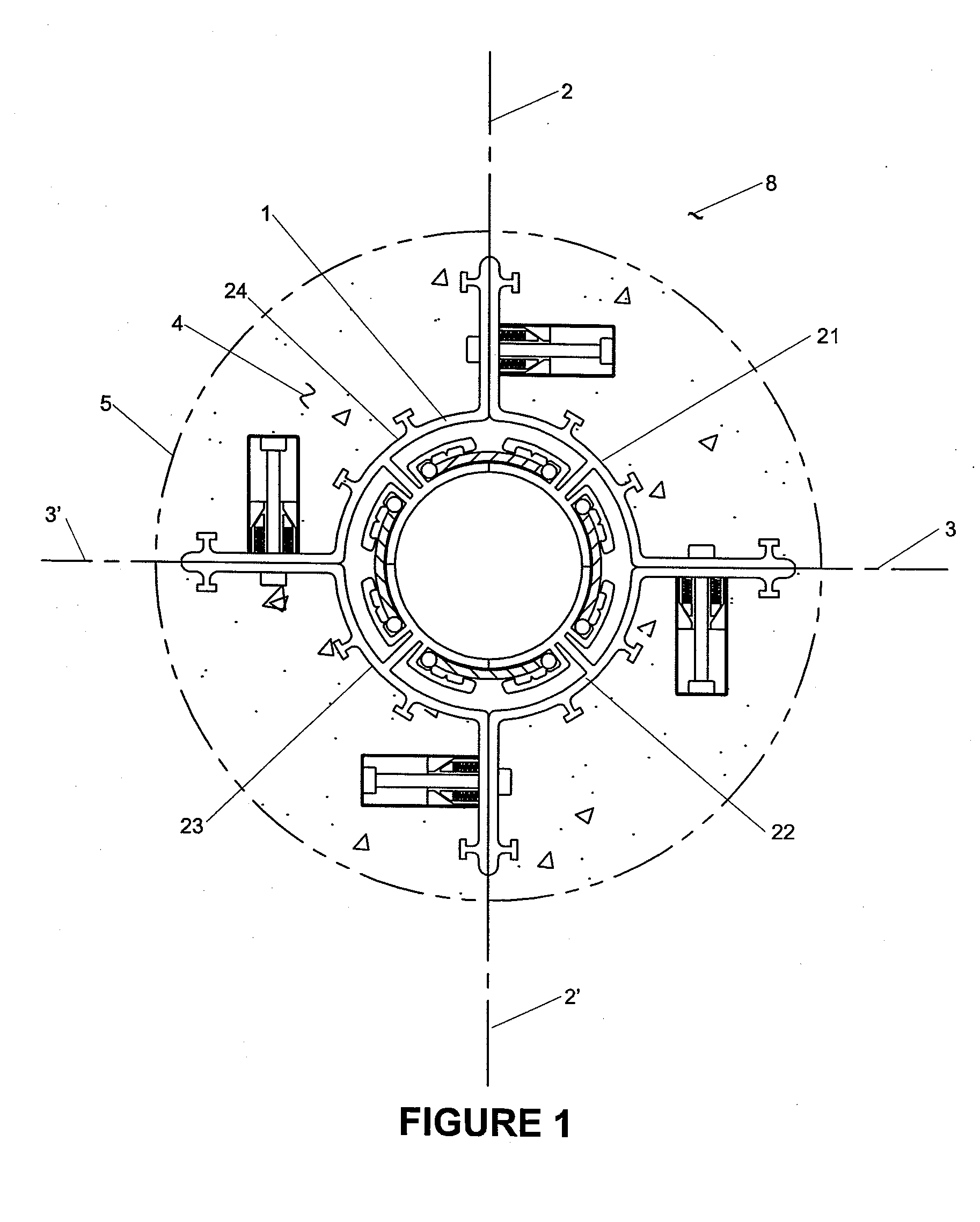
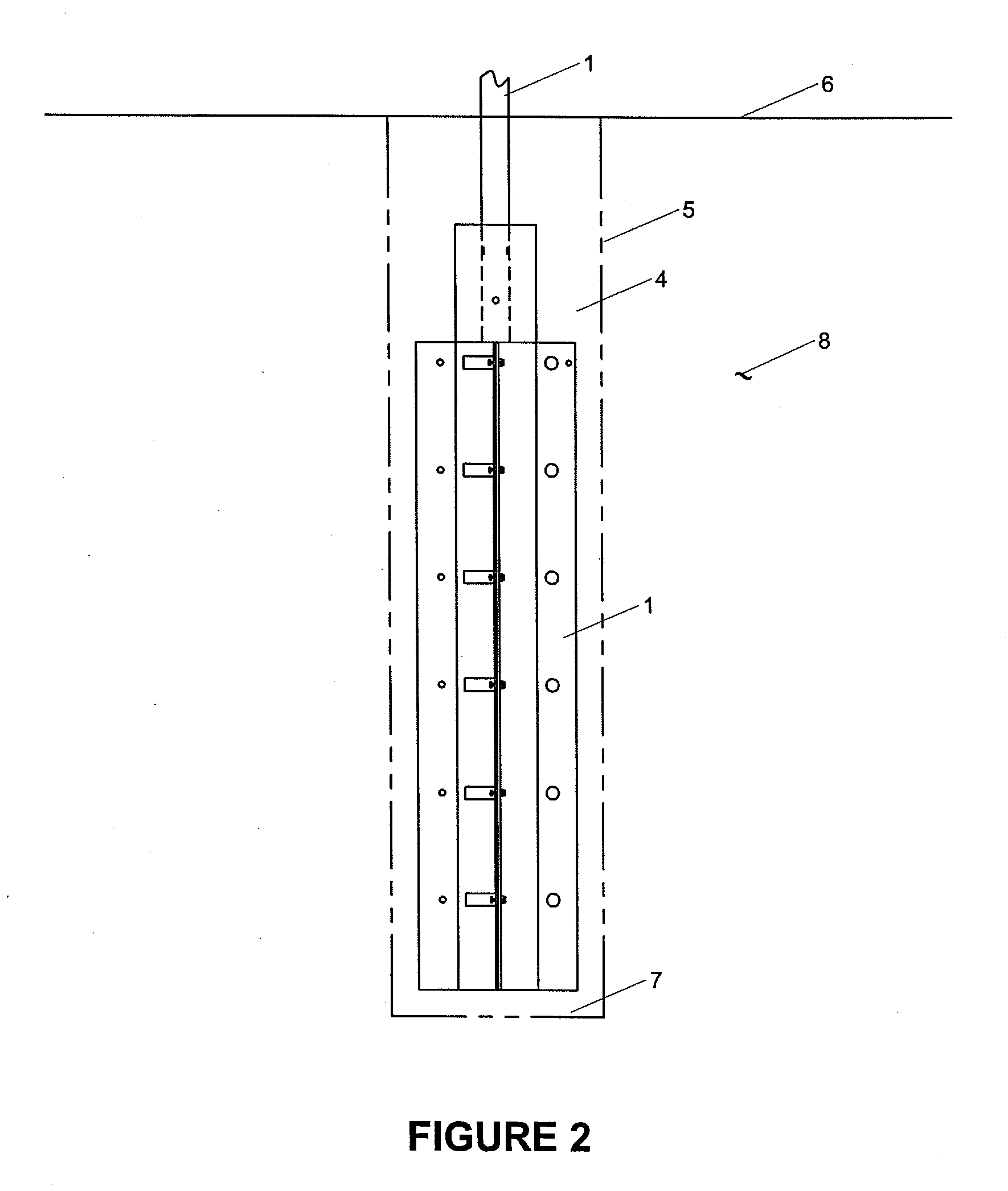
Middle block fire grate sheet
The invention relates to a medium-sized lumps fire grate segment, a framework of which is provided with three adapter sleeves, wherein, one adapter sleeve is arranged in the middle at one side of the framework, and the other two adapter sleeves are arranged at the two ends of the other side of the framework, and the three adapter sleeves on the back of the framework of the fire grate segment are connected with each other by a fixing bracket which is moulded together with the ramework of the fire grate segment into a whole; a plurality of fire grate segments are connected in series to form a hearth through a long pin through connection sleeve hole, so that the whole structure has high strength, difficult burnout, long service life, little wastage and low cost; a combustion front of the fire grate segment is provided with 2-4 lines of ventilating slots, a reinforcing rib is arranged in the middle of each line of ventilating slots, coal is paved on a combustion front of the hearth, and air in a draught chamber enters the coal through the ventilating slots, thus the ventilation effect is good, and the coal is fully burnt.
Owner:李立华
Modified process for hydrocarbon recovery using in situ combustion
InactiveUS7841404B2Decreasing detrimental environmental impactLow costFluid removalDrinking water installationCombustion frontProduct gas
A modified method for in situ recovery of hydrocarbon from an underground hydrocarbon-containing formation. An “L” shaped production well, having a vertical section, and a lower horizontal leg positioned low in the formation, is provided. The horizontal leg connects to the vertical section at a heel portion, and has a toe portion at an opposite end thereof. Oxidizing gas is injected into the formation in or proximate the vertical section. A combustion front sweeps outwardly from the vertical section and laterally within the formation above the horizontal leg, from the heel to the toe, causing hydrocarbons in the formation above the horizontal leg to drain downwardly into the horizontal leg, which are then delivered to surface via production tubing. A non-oxidizing gas is injected into at least the heel portion and preferably additional portions of the horizontal leg via injection tubing contained within the vertical section of the production well.
Owner:ARCHON TECH LTD
Method for improving shale oil reservoir recovery efficiency by cracking reservoir through catalytic oxidation combustion
ActiveCN113216918AImprove combustion efficiencyImprove combustion stabilityFluid removalPtru catalystThermodynamics
The invention discloses a method for improving shale oil reservoir recovery efficiency by cracking a reservoir through catalytic oxidation combustion. The method comprises the following steps that a catalyst is selected; a mixture slug of a catalyst and an organic solvent is injected into a shale oil reservoir subjected to staged fracturing of a horizontal well, and the well is soaked for a period of time; and then air is injected into the shale oil reservoir, the shale reservoir is fractured through catalytic oxidation / combustion, and the flow conductivity of shale oil is enhanced. By means of the method for improving the shale oil reservoir recovery efficiency by cracking the reservoir through catalytic oxidation combustion, the shale oil reservoir ignition difficulty can be obviously reduced, the combustion efficiency and the combustion front edge stability can be improved, the shale is fractured by fully utilizing the oxidation / combustion chemical effect, the synergistic effect is generated with an existing hydraulic fracturing method, the reservoir pore-fracture structure is improved, and the recovery efficiency is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
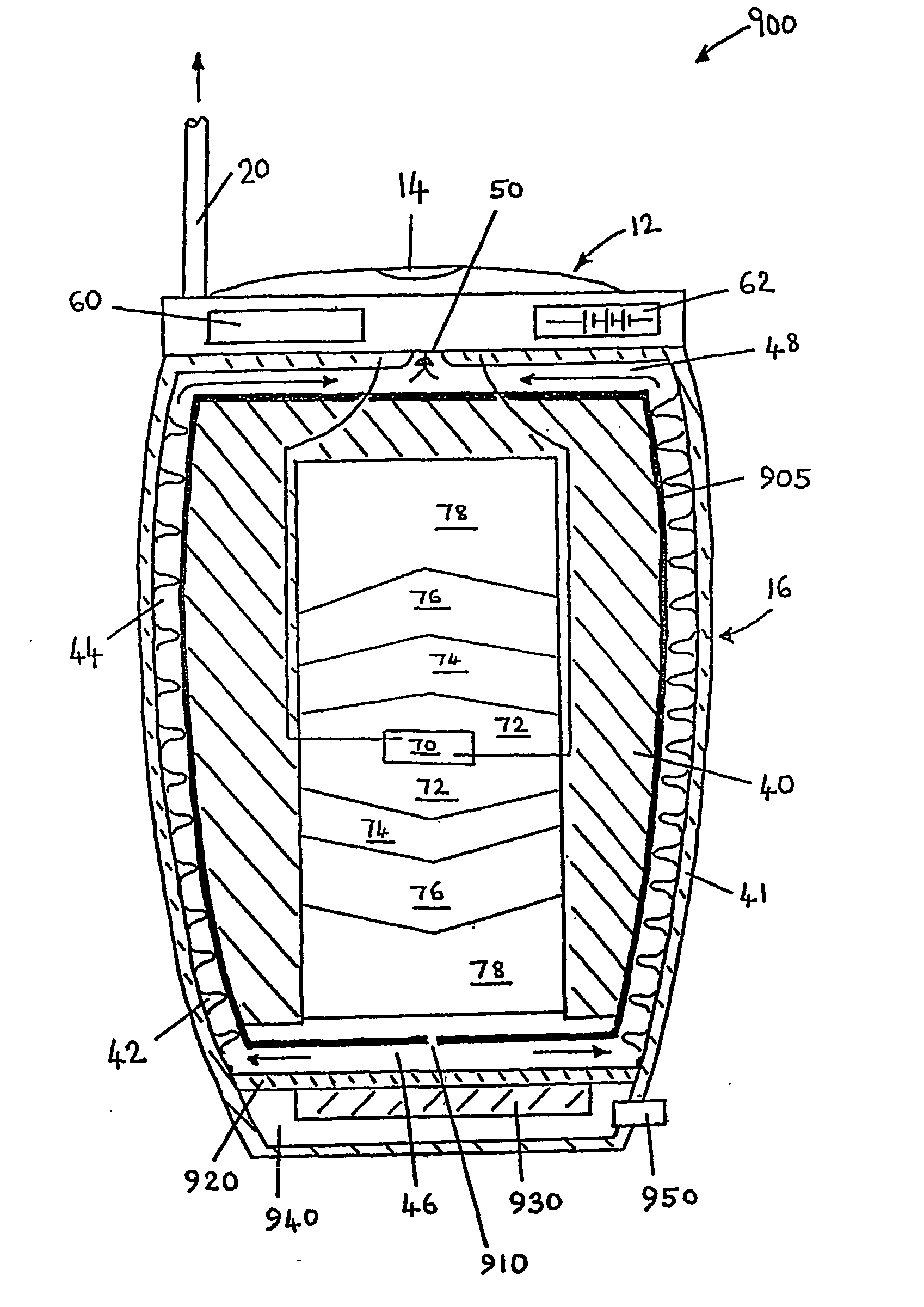
Flame vessel
The invention discloses a flame vessel. The flame vessel comprises an outer-ring-flame base, an outer-ring-flame large shell, an outer-ring-flame small shell, an outer perforated mesh, an outer combustion front, an inner-ring-flame base, an inner-ring-flame shell, an inner perforated mesh and an inner combustion front. The outer-ring-flame base is provided with first air inlets, a first flow-guiding air distributing plate is arranged above every first air inlet, a second air inlet is formed in the middle of the inner-ring-flame base, a second flow-guiding air distributing plate is arranged above the second air inlet, a first ejector mixing pipe is welded below every first air inlet, and a second ejector mixing pipe is welded below the second air inlet. The flame vessel adopts an outer flame and inner flame combustion heating structure, a plurality of evenly distributed first ejector mixing pipes are arranged on the outer-ring-flame base, the second ejector mixing pipe is arranged in the middle of the inner-ring-flame base, and the first flow-guiding air distributing plates and the second flow-guiding air distributing plate are mounted above the first ejector mixing pipe and the second ejector mixing pipe respectively, so that a heating mode is added and usability is improved.
Owner:广州威旭环保科技有限公司
Completion method for horizontal wells in in situ combustion
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
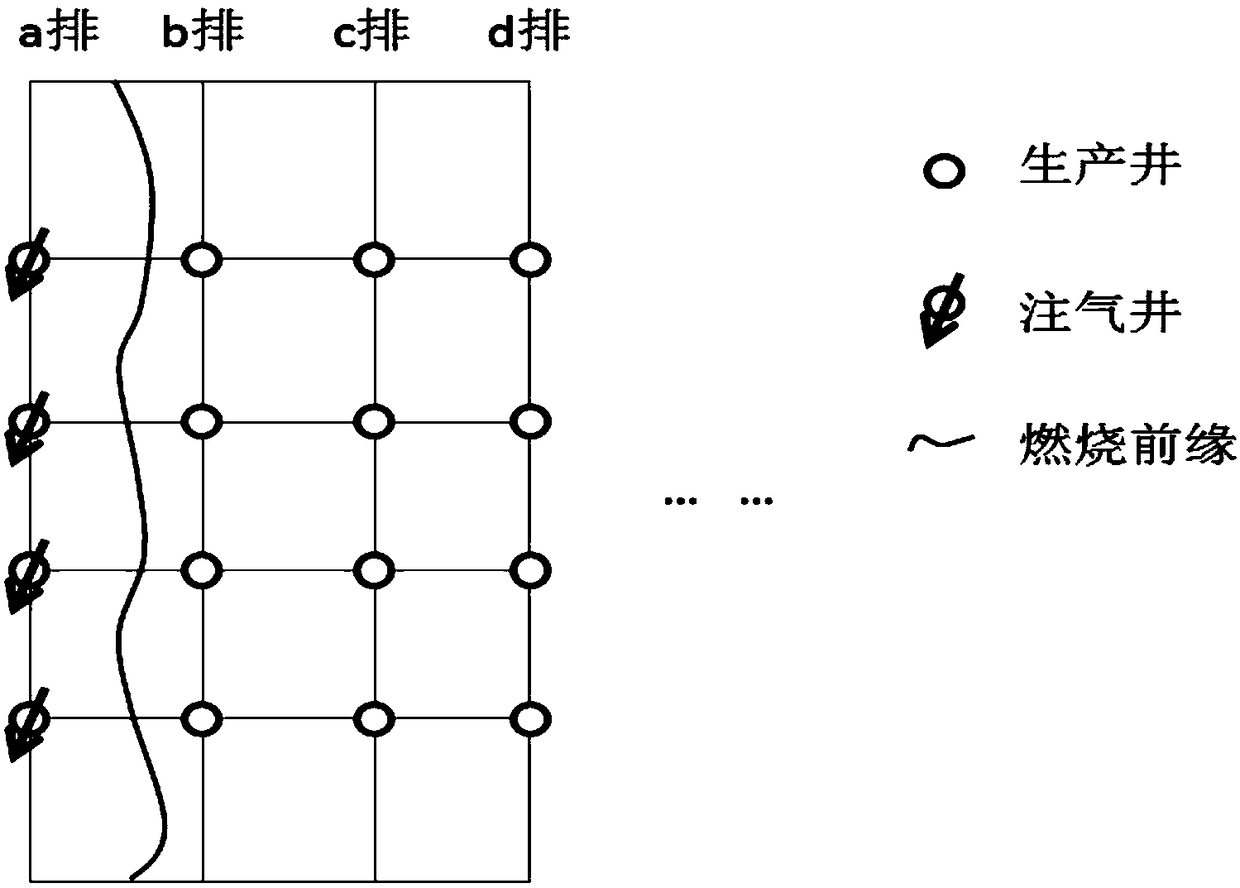
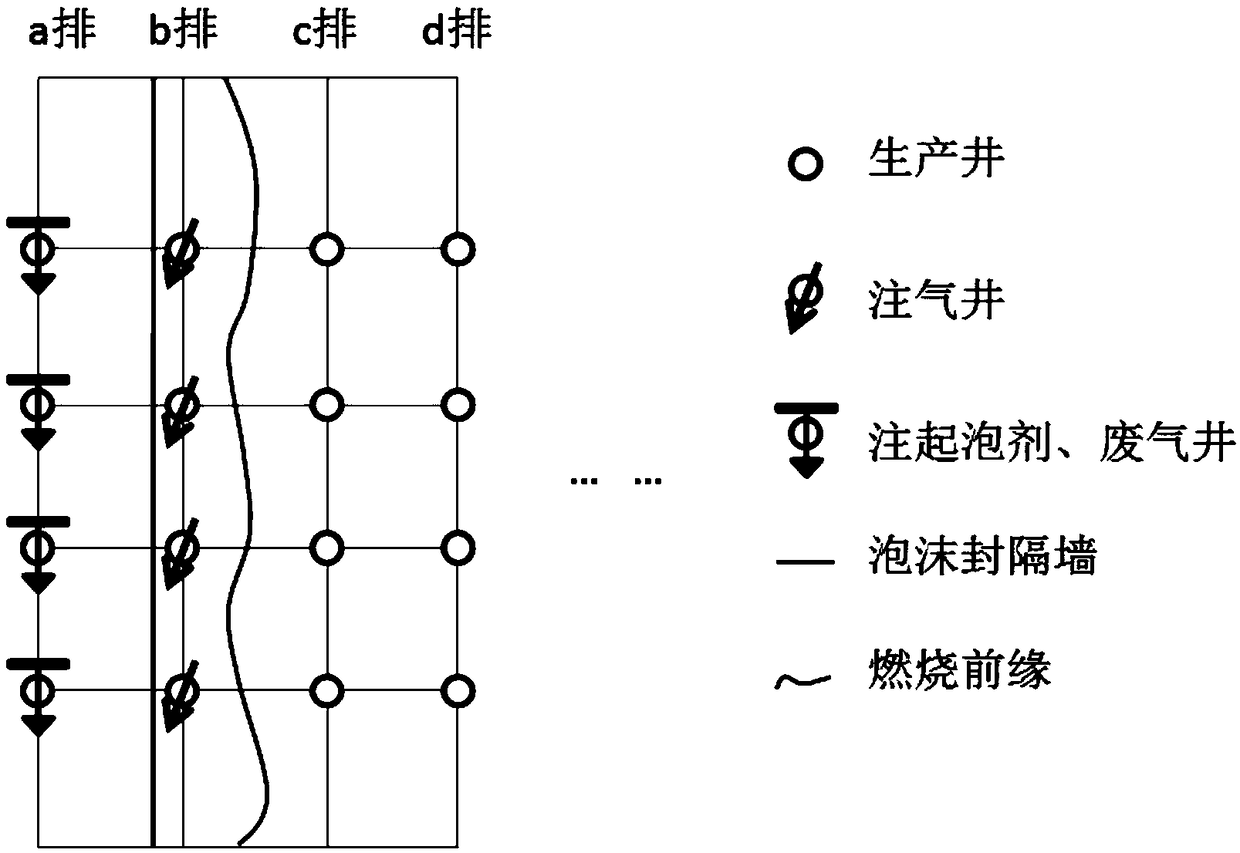
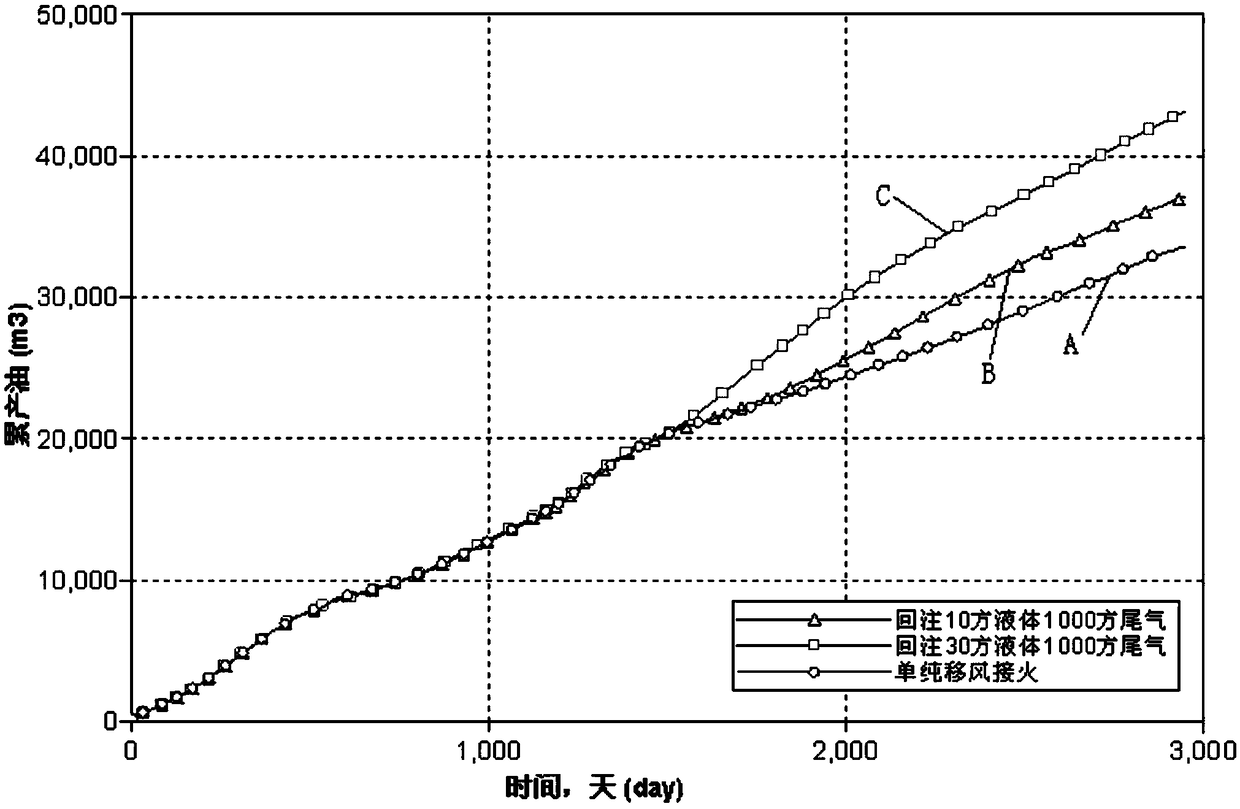
Method for adopting linear fireflood for producing tail gas for burying and utilization
The invention discloses a method for adopting linear fireflood for producing tail gas for burying and utilization. According to the method, a row of well drains in a well pattern is divided into gas-injection well drain bodies, other rows of well drains are divided into producing well drain bodies, ignition and gas injection are conducted on the first row of gas-injection well drain bodies, afterthe combustion front crosses the first row of producing well drain bodies, the first row of producing drain bodies are changed into the second row of gas-injection well drain bodies, and the first rowof gas-injection well drain bodies are changed into reinjection wells in which foam liquid and fireflood tail gas are injected; the foam liquid and the fireflood tail gas are injected into the reinjection wells, the injected foam liquid forms a foam blocking wall between the first row of gas-injection well drain bodies and the first row of producing well drain bodies, and the foam blocking well blocks the injected fireflood tail gas and the second row of gas-injection well drain bodies; meanwhile, the fireflood tail gas is buried under the wells; when the combustion front crosses the second row of producing well drain bodies, the second row of producing well drain bodies are changed into the third row of gas-injection well drain bodies, and the second row of gas-injection well drain bodies are changed into reinjection wells in which the foam liquid and the fireflood tail gas are injected; analogy is conducted gradually until the combustion front crosses the N th row of producing welldrain bodies.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com