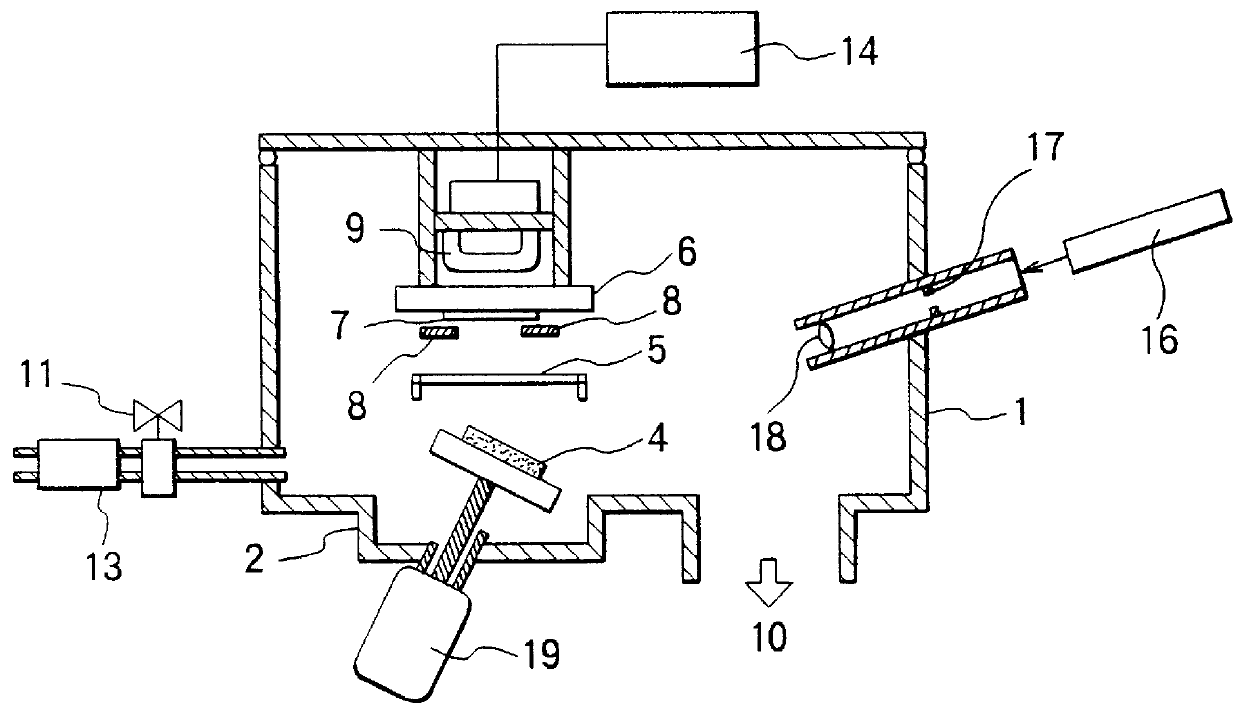
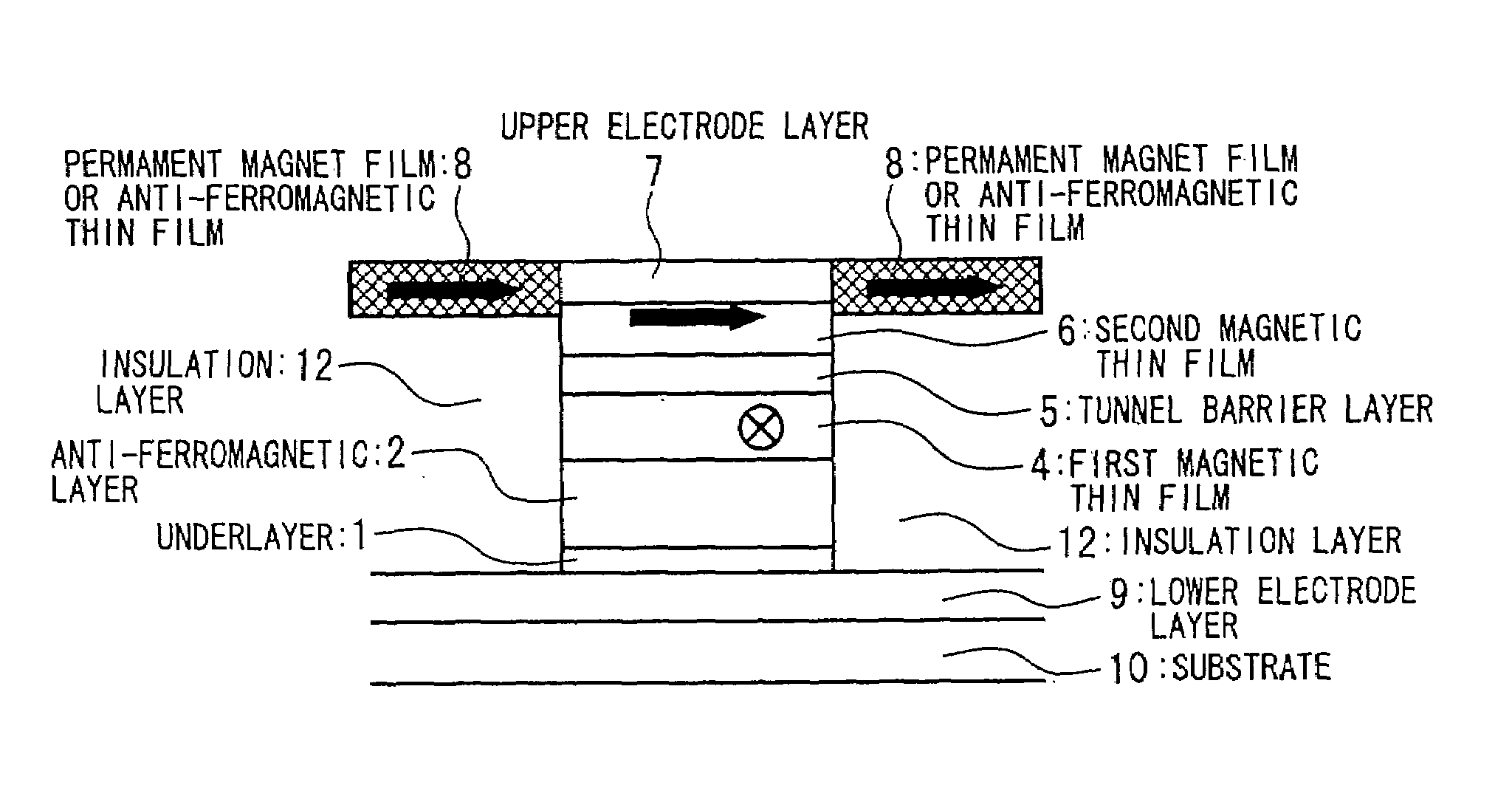
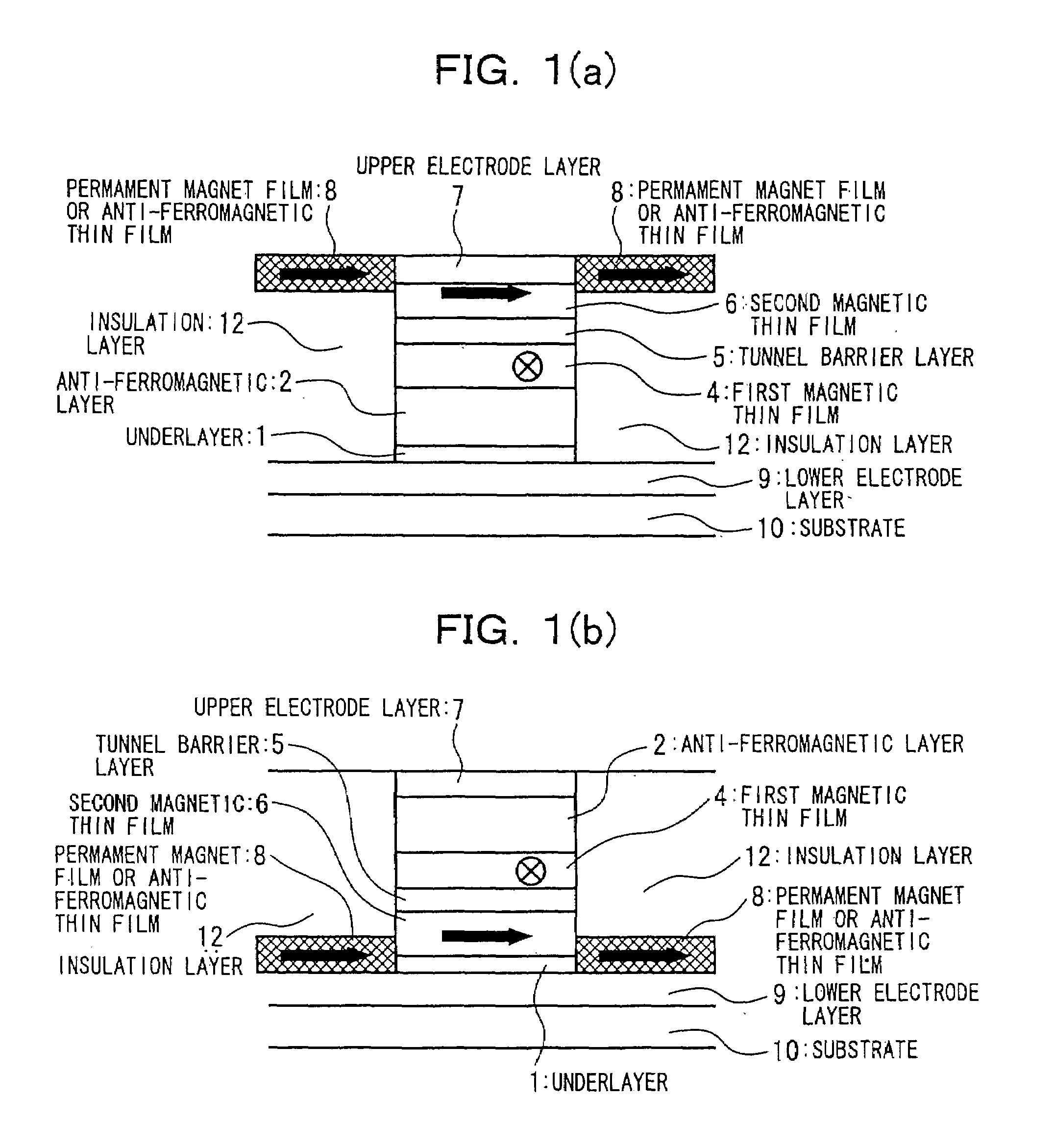
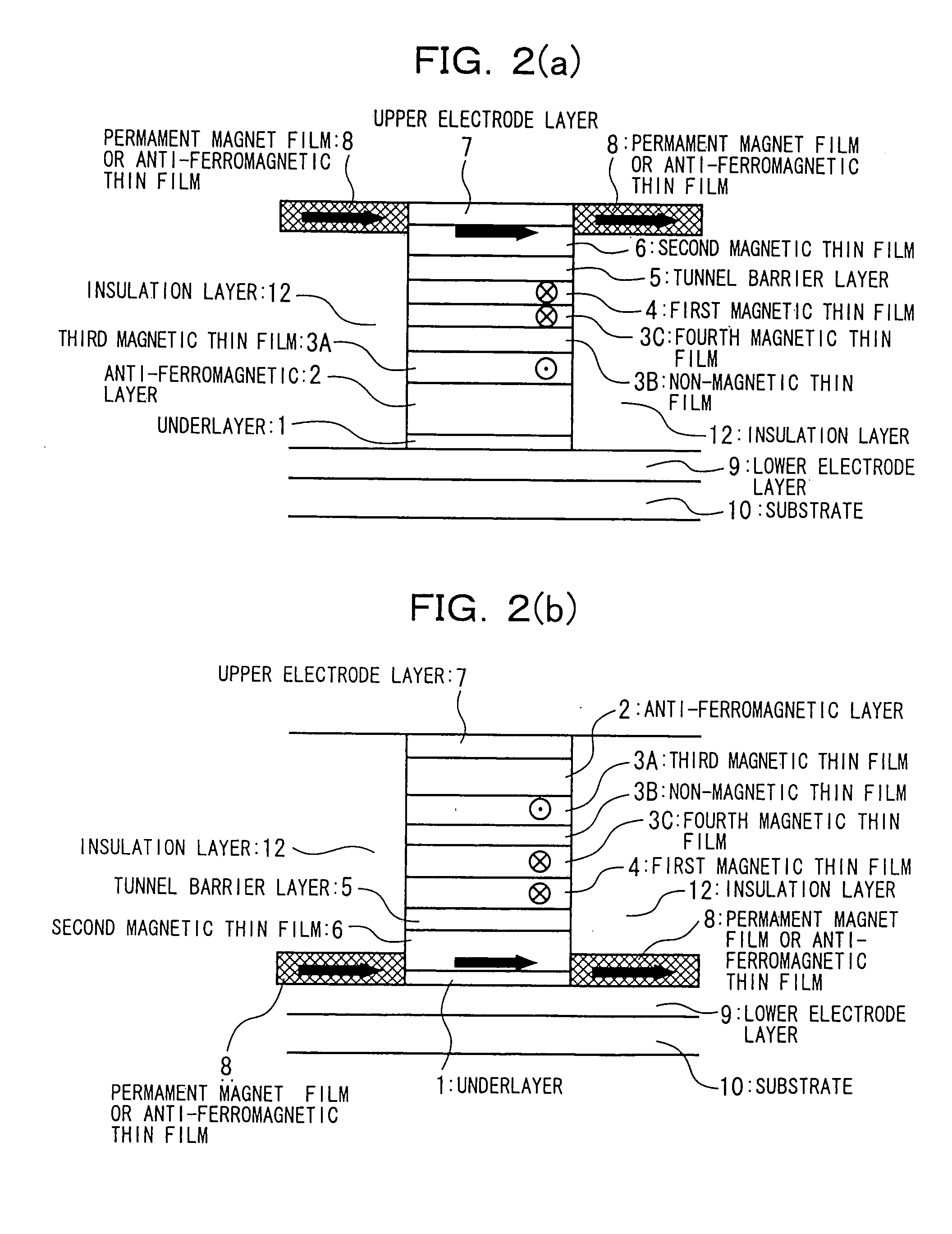
Patents
Literature
130 results about "Ferromagnetic thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
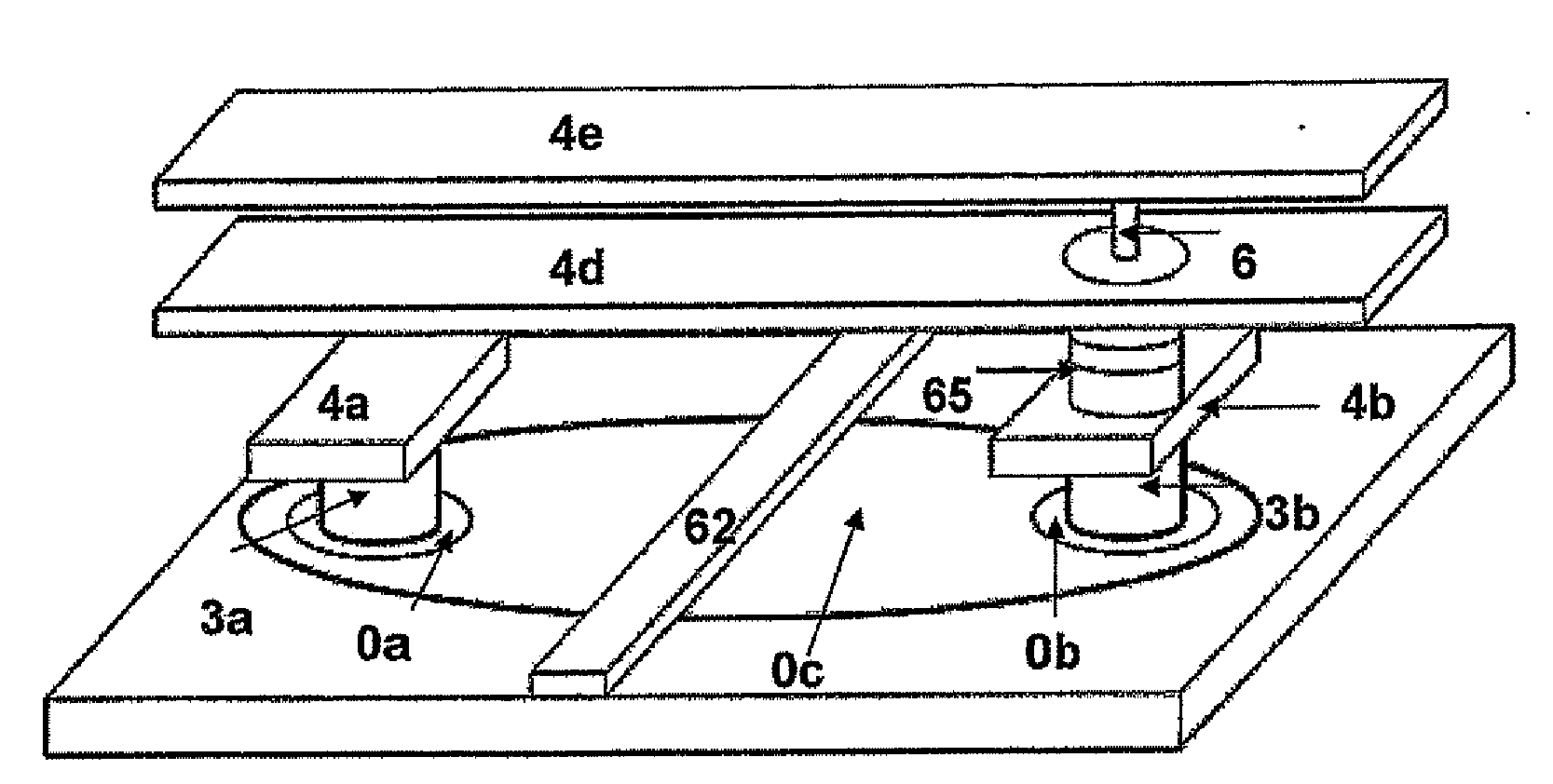
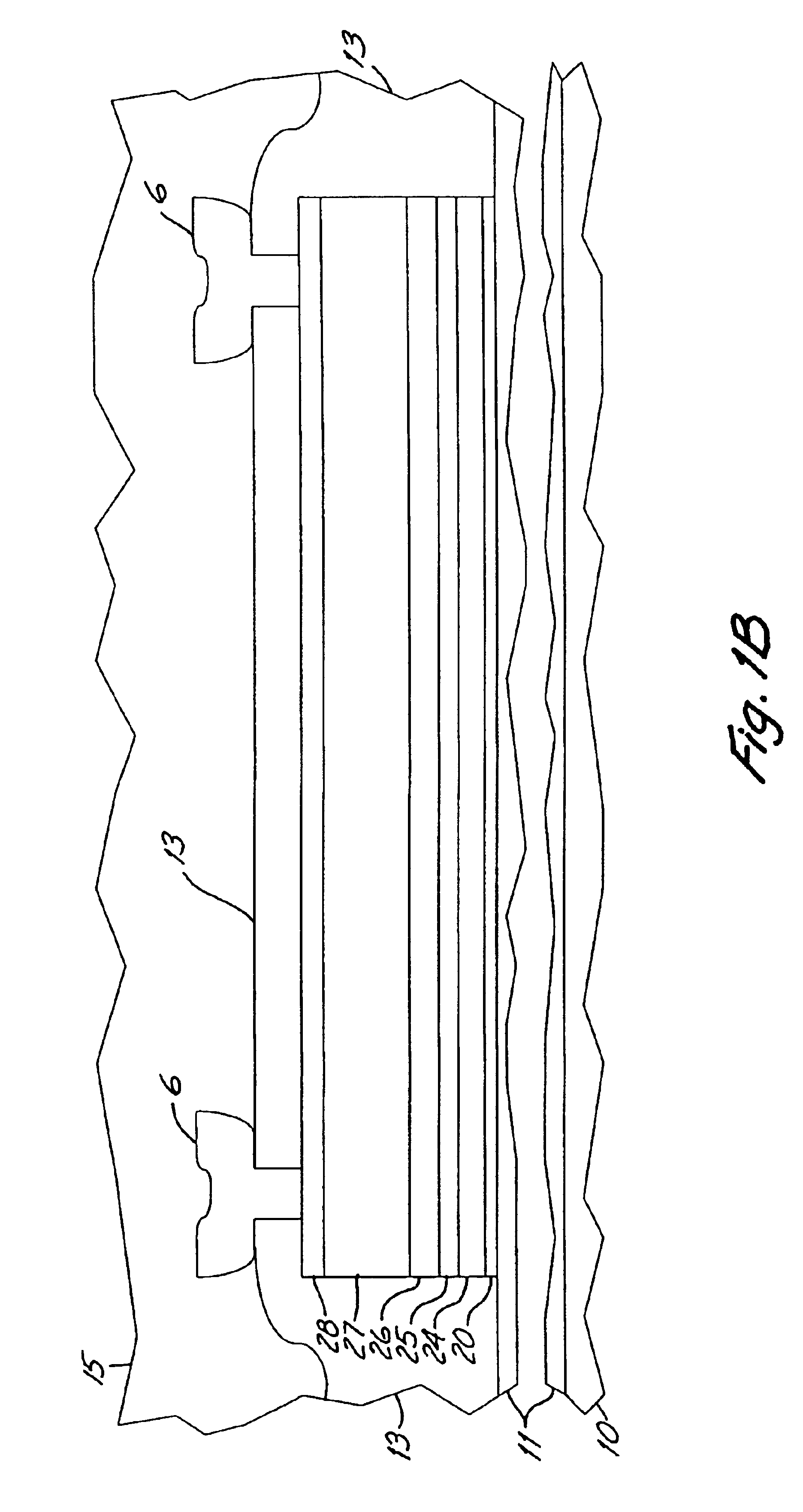
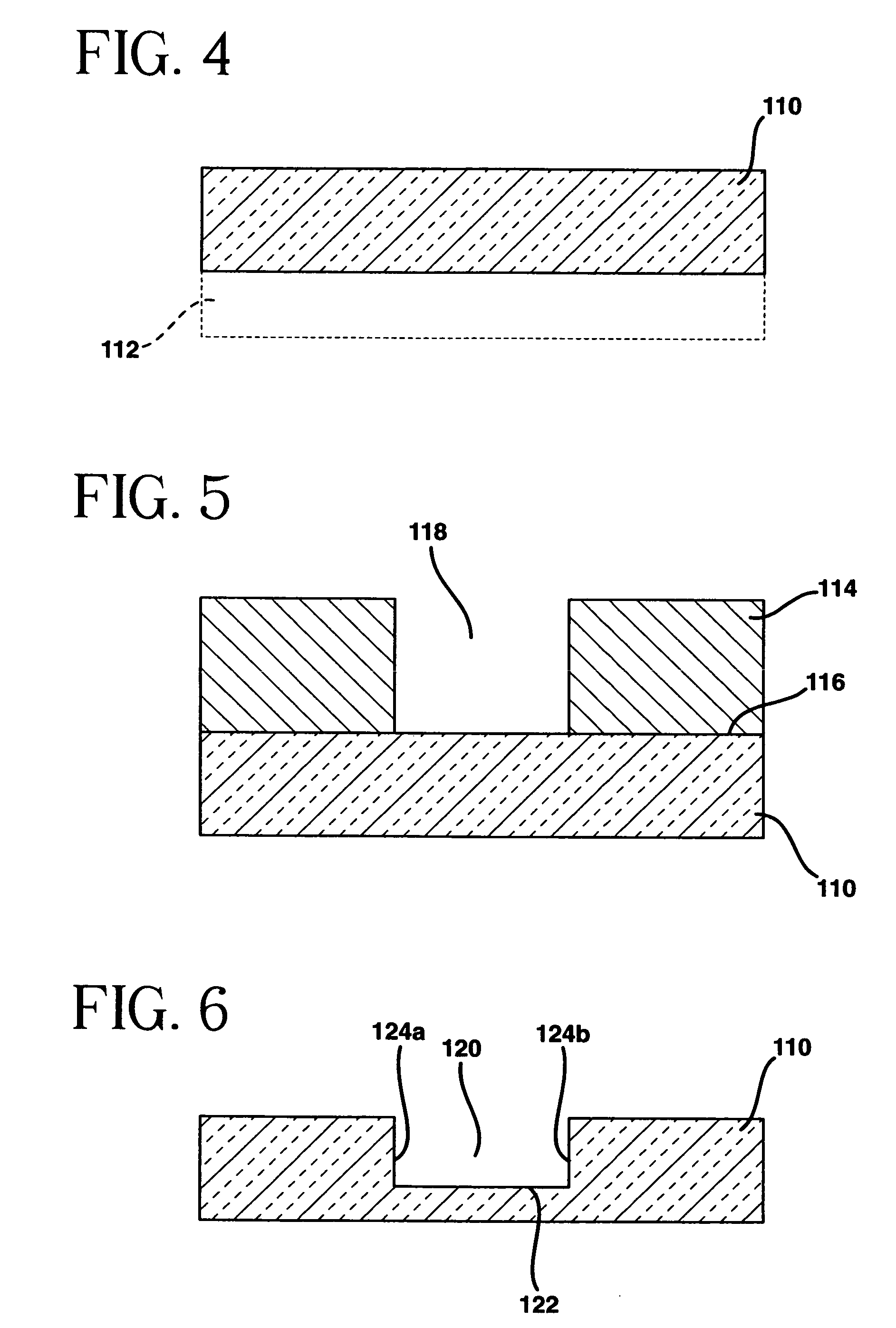
Close shaped magnetic multi-layer film comprising or not comprising a metal core and the manufacture method and the application of the same
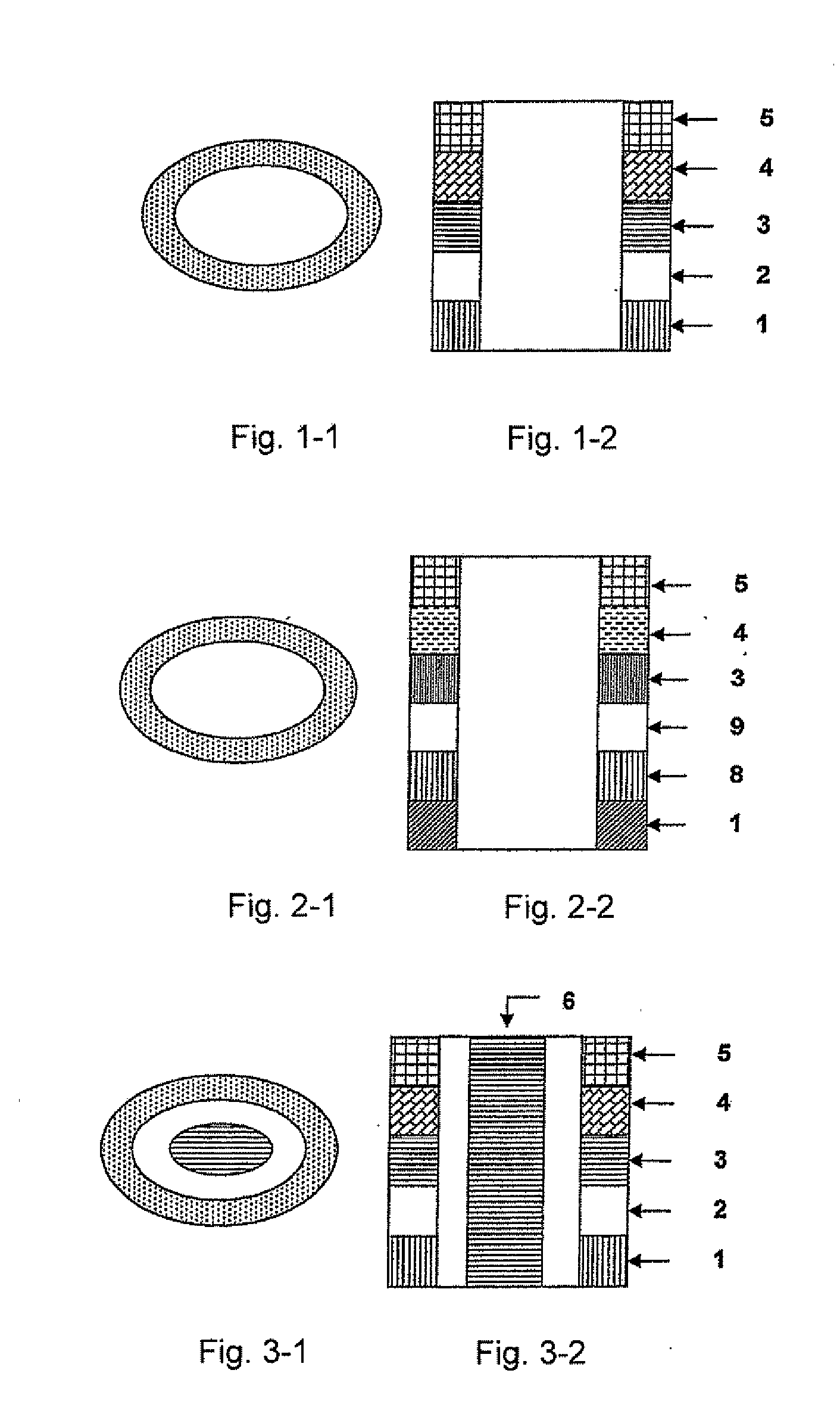
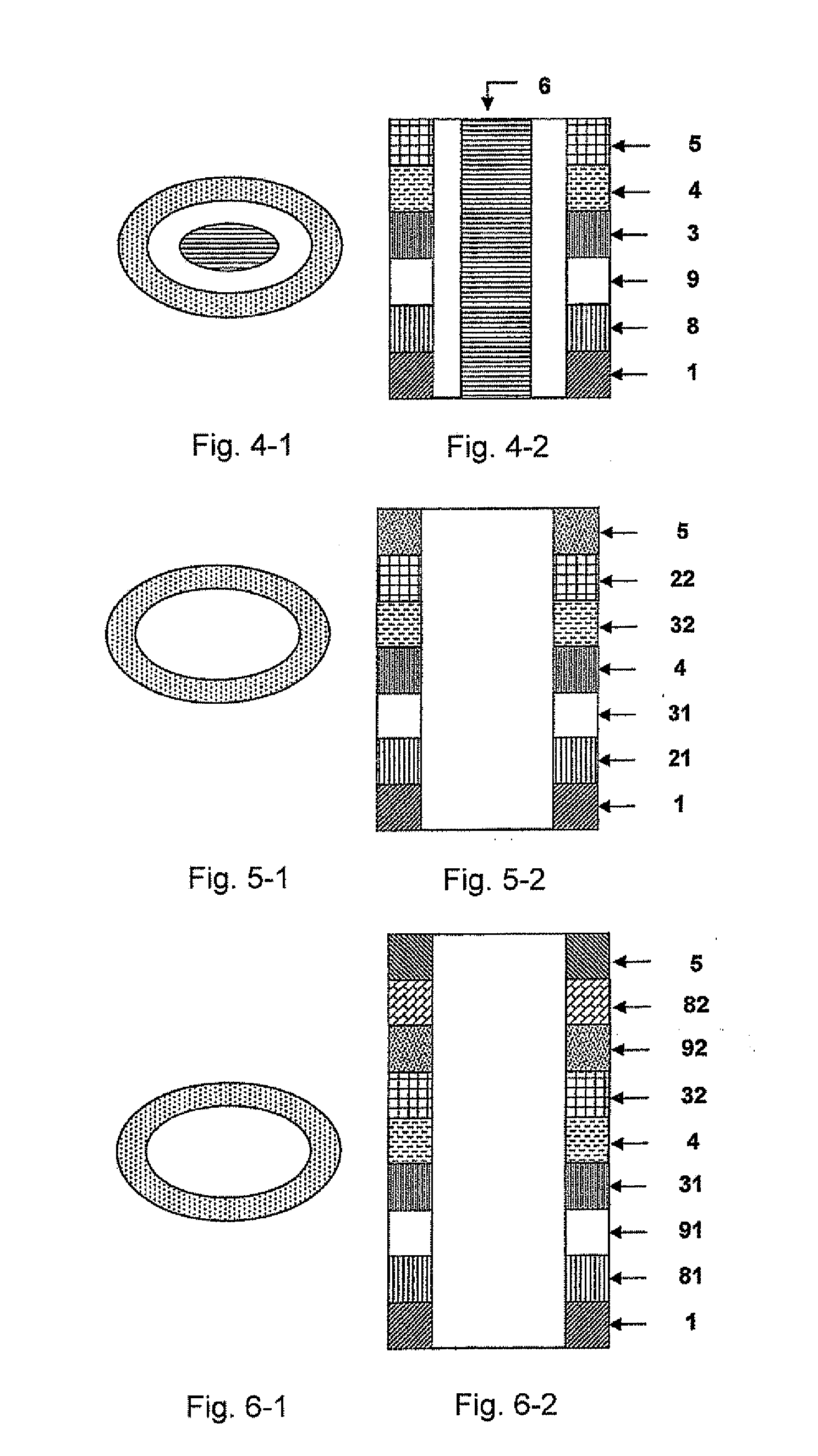
InactiveUS20090168506A1High densitySmall scaleNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic beadMagnetic logic
Each layer in the magnetic multilayer film is a closed ring or oval ring and the magnetic moment or flux of the ferromagnetic film in the magnetic unit is in close state either clockwise or counterclockwise. A metal core is put in the geometry center position in the close-shaped magnetic multilayer film. The cross section of the metal core is a corresponding circular or oval. A MRAM is made of the closed magnetic multilayer film with or without a metal core. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film is formed by micro process method. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film can be used broadly in a great variety of device that uses a magnetic multilayer film as the core, such as MRAM, magnetic bead in computer, magnetic sensitive sensor, magnetic logic device and spin transistor.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermomagnetically assisted spin-momentum-transfer switching memory
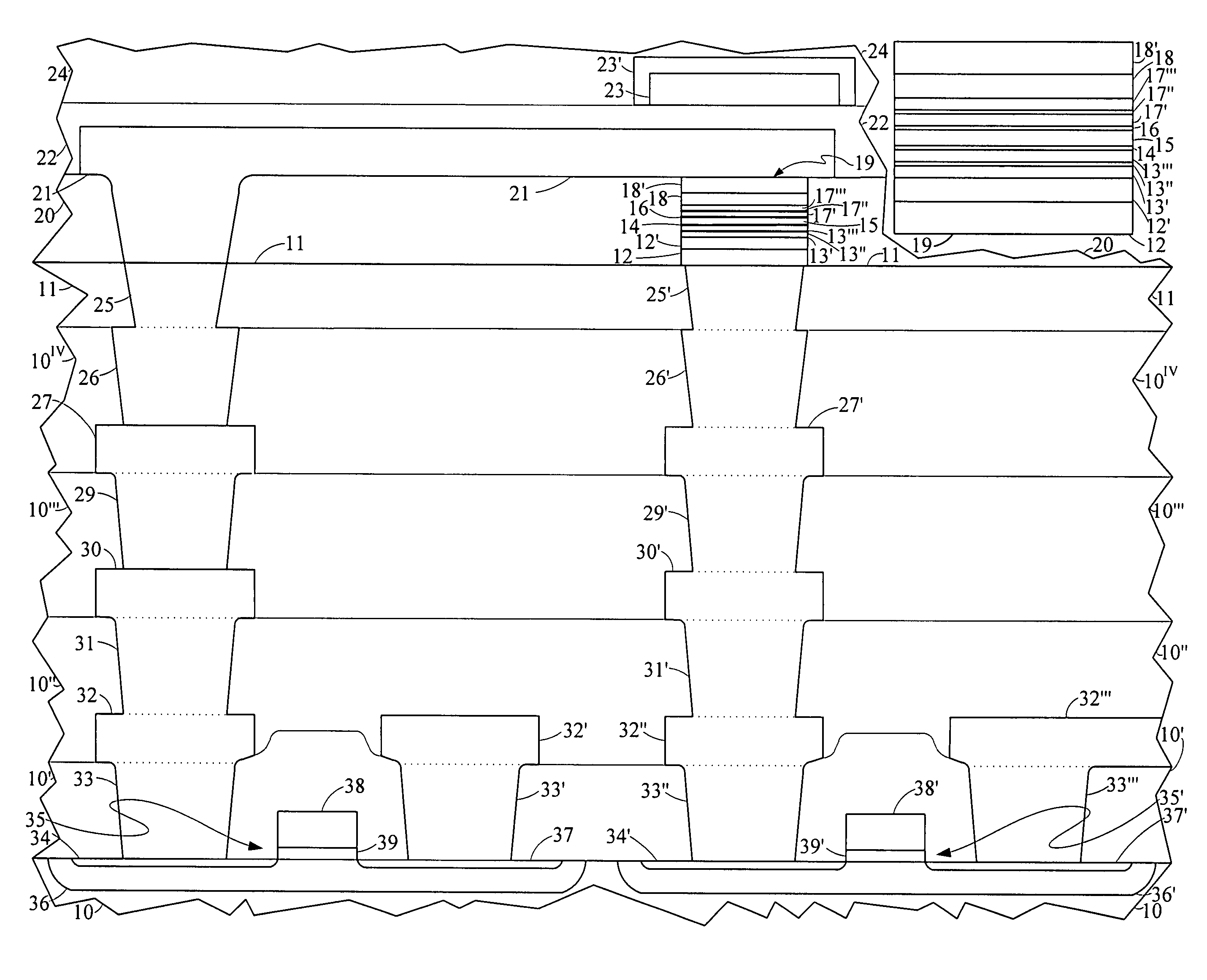
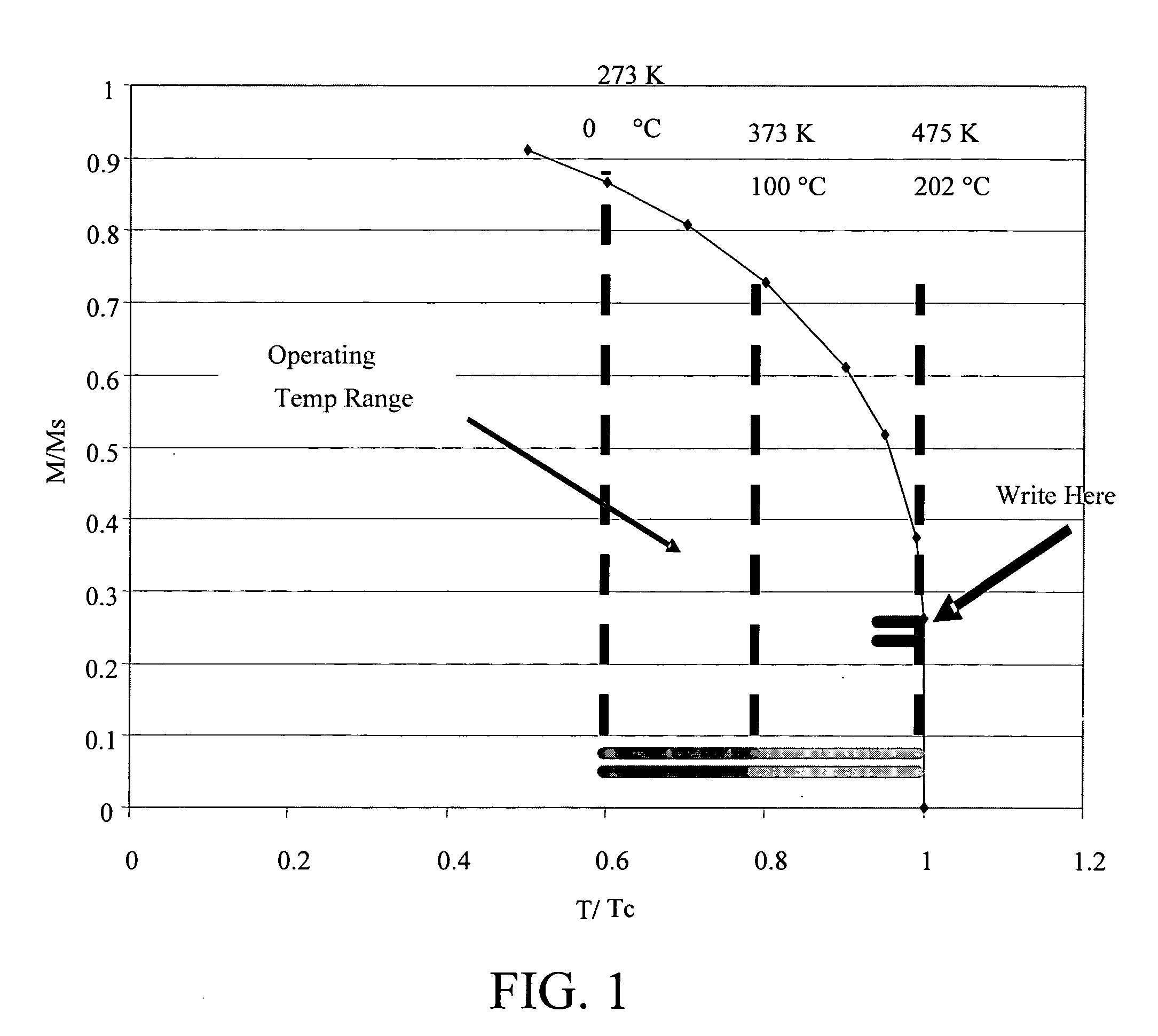
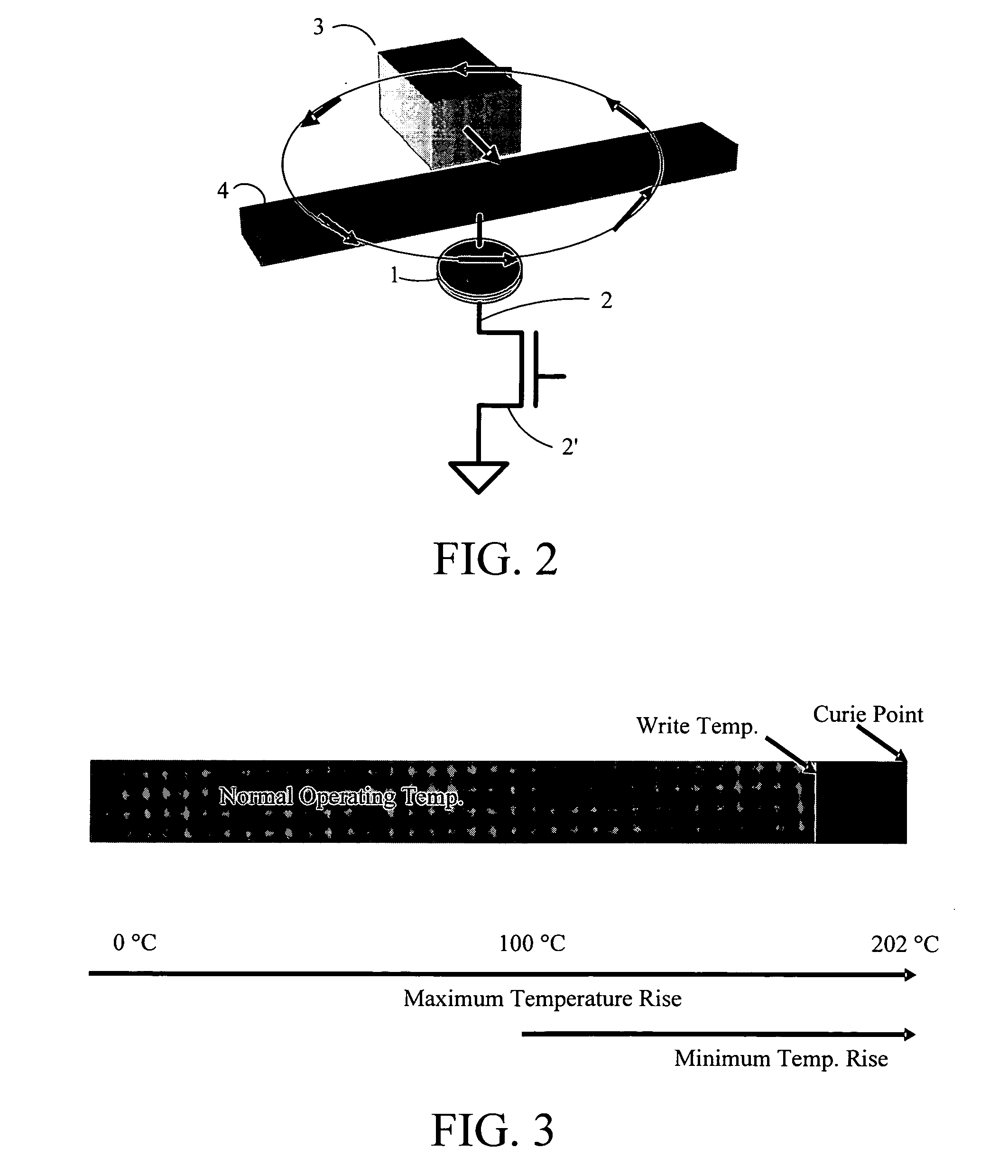
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a substrate supporting bit structures that are electrically interconnected with information storage and retrieval circuitry and having first and second oppositely oriented relatively fixed magnetization layers and a ferromagnetic material film in which a characteristic magnetic property is substantially maintained below an associated critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained. This ferromagnetic material film is separated from the first and second fixed magnetization films by corresponding layers of a nonmagnetic materials one being electrically insulative and that one remaining being electrically conductive. Each bit structure has an interconnection structure providing electrical contact thereto at a contact surface thereof substantially parallel to the intermediate layer positioned between the first contact surface and the substrate. A plurality of word line structures located across from a corresponding one of the bit structures on an opposite side. Electrical current selectively drawn through each of these bit structures and its interconnection structure can cause substantial heating of that bit structure to raise temperatures thereof while being above temperatures of at least an adjacent said bit structure because of sufficient thermal isolation.
Owner:NVE CORP
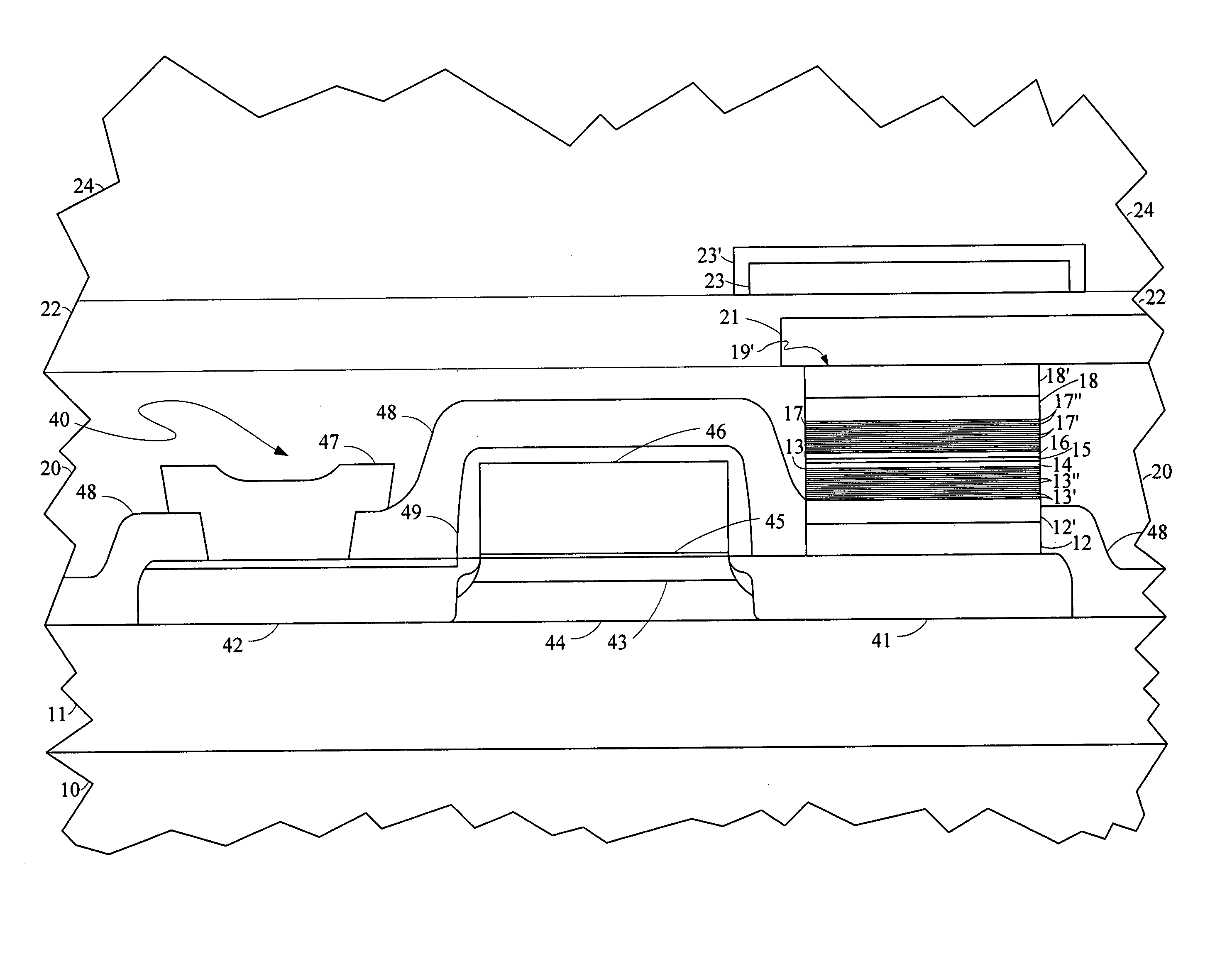
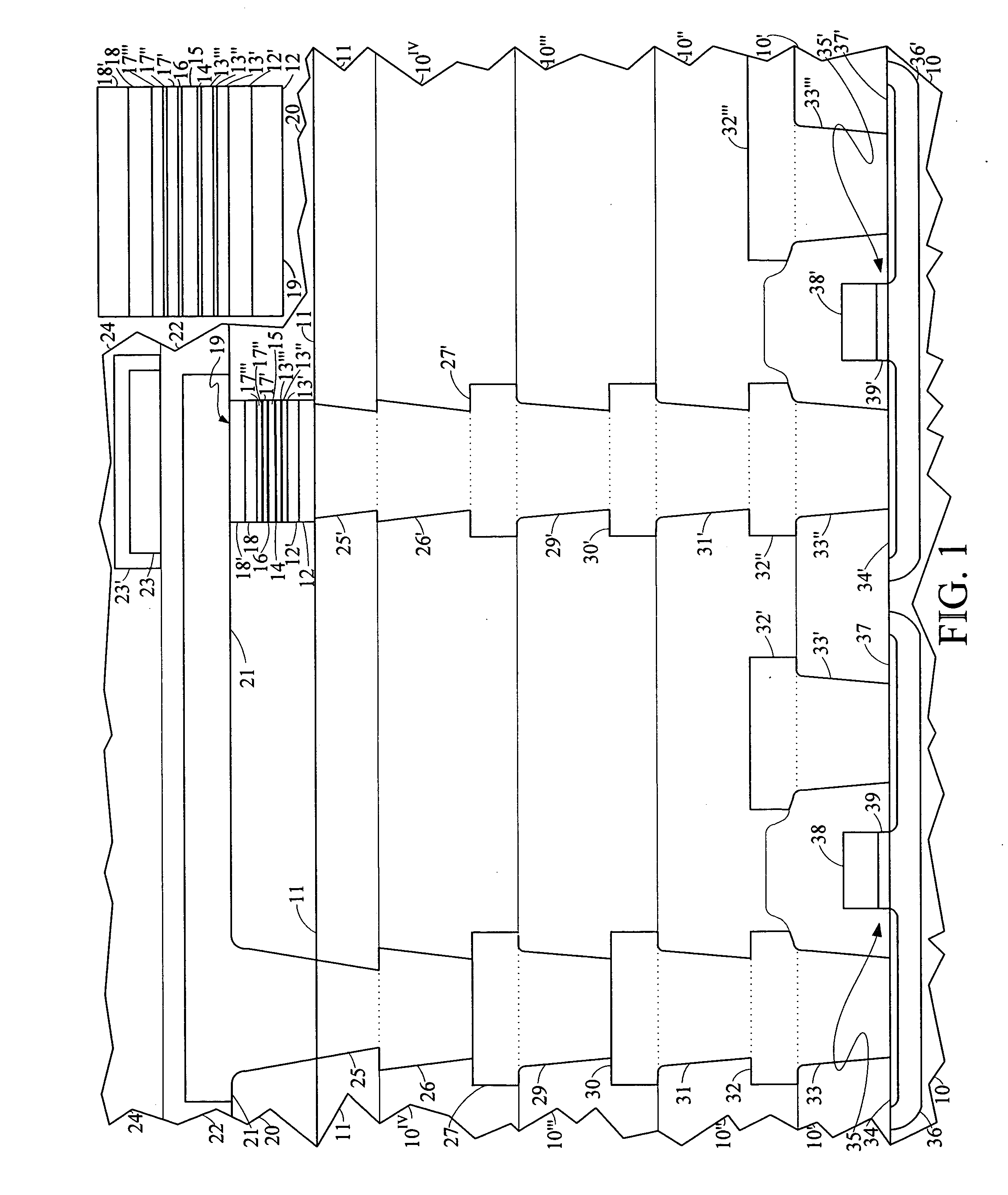
Stabilized shields for magnetic recording heads
ActiveUS20090279213A1Large reductions (or elimination) of the shield net momentGood pinningRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsThick plateAntiferromagnetic coupling
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Thermally operated switch control memory cell
Owner:NVE CORP
Structure and method for fabricating a magnetic thin film memory having a high field anisotropy
InactiveUS20120015099A1High magnetic materialLow critical currentNanomagnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureDiffusionHigh energy
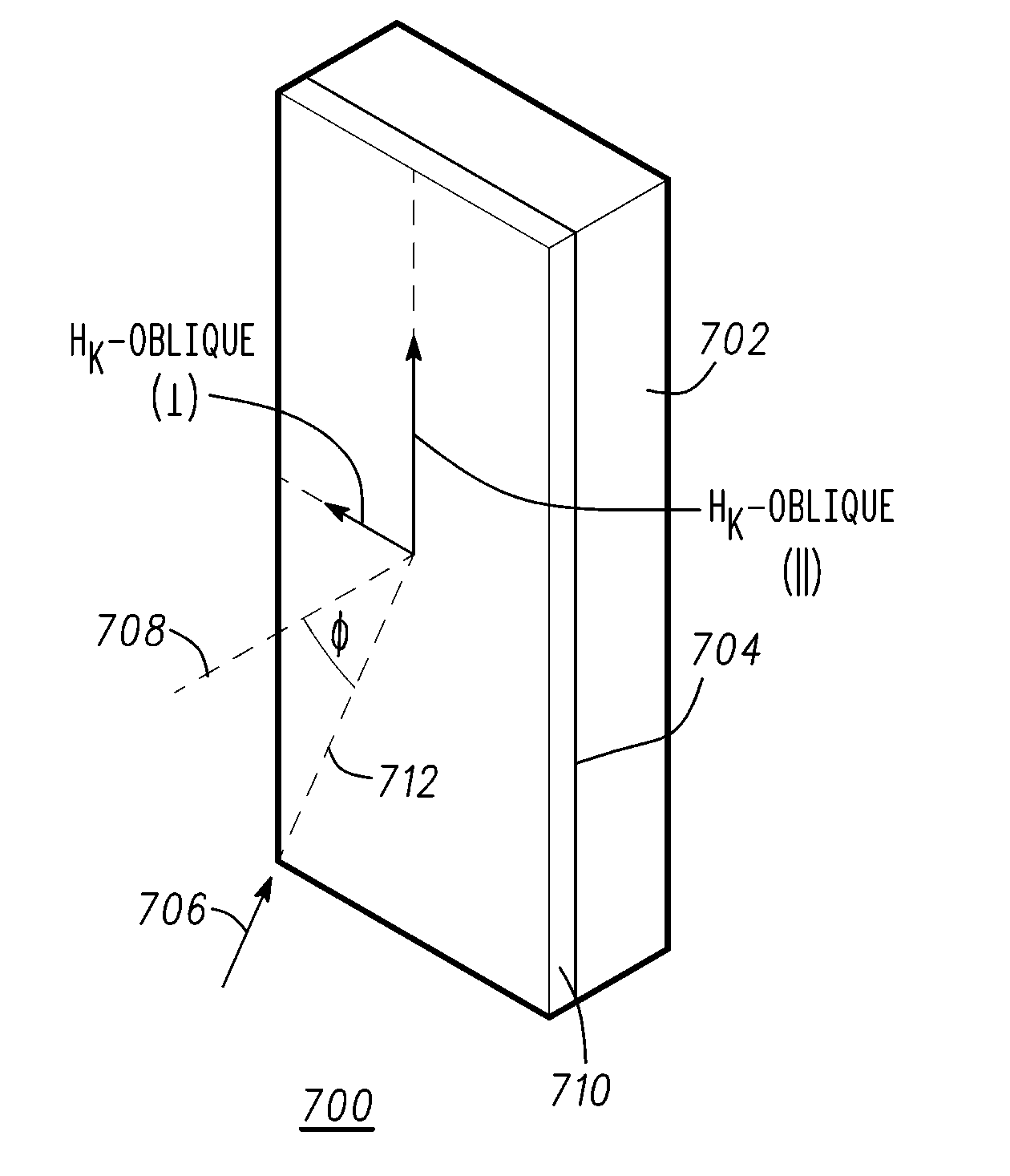
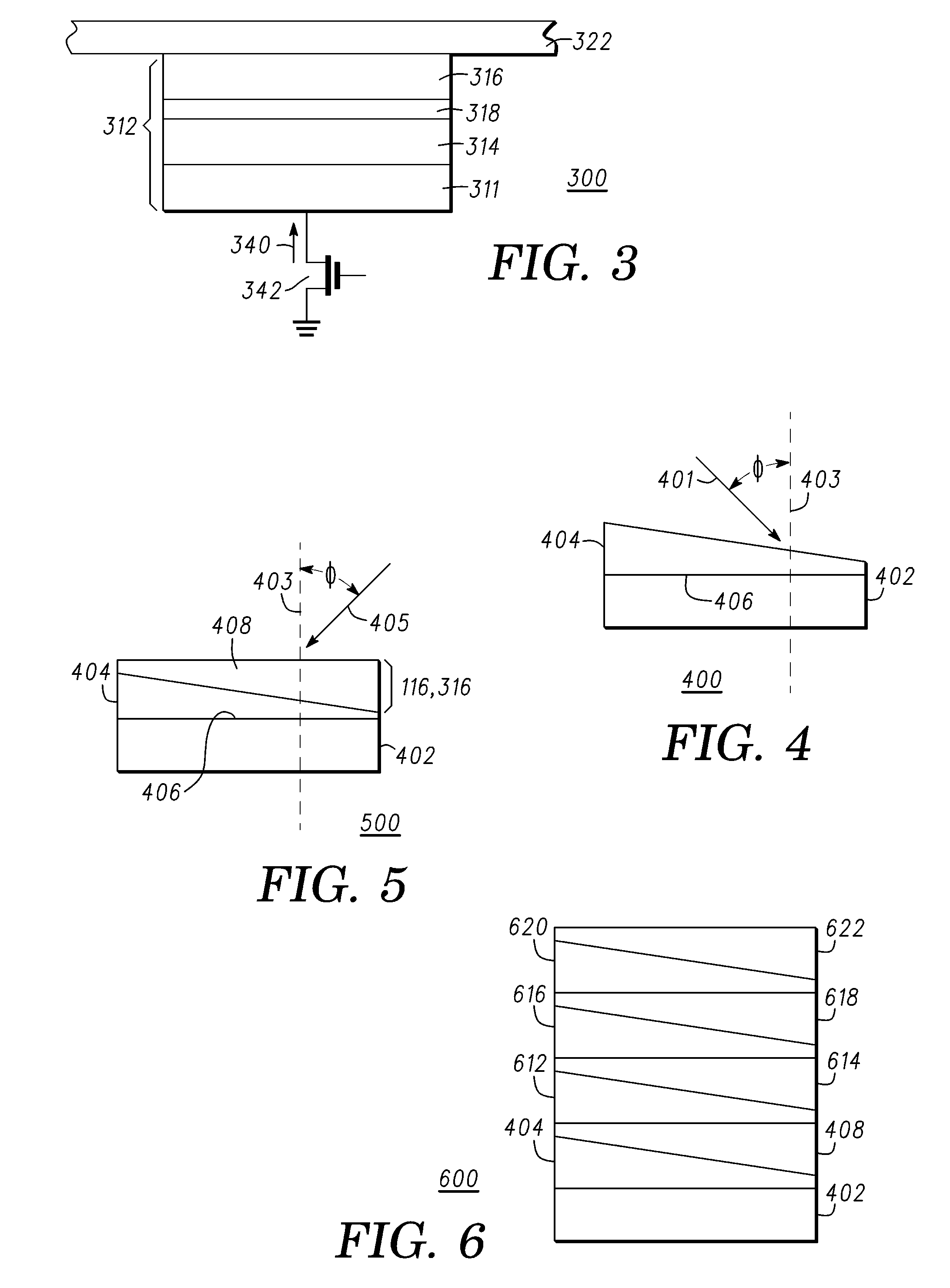
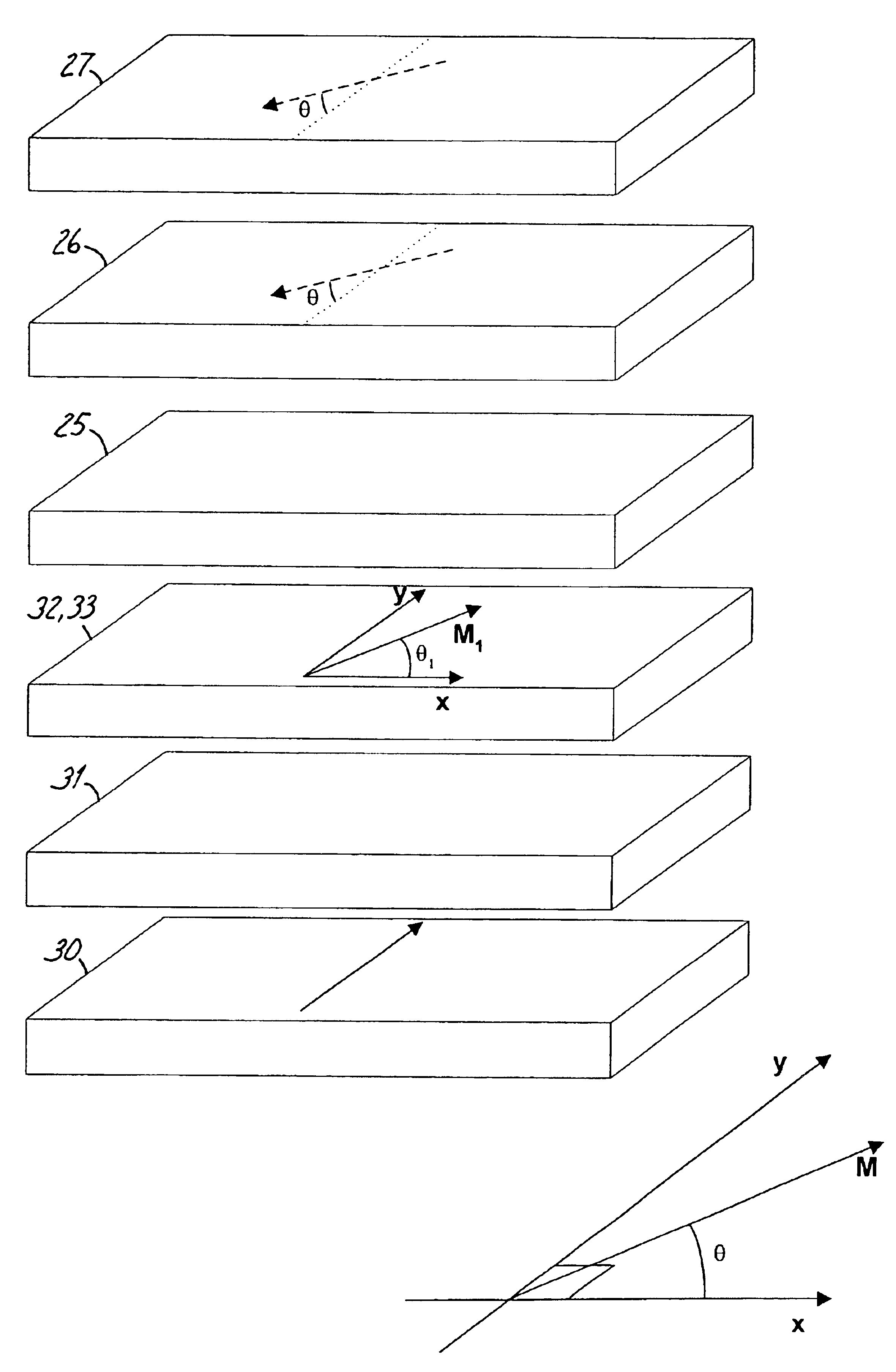
A method for depositing uniform and smooth ferromagnetic thin films with high deposition-induced microstructural anisotropy includes a magnetic material deposited in two or more static oblique deposition steps from opposed directions to form a free layer having a high kink Hk, a high energy barrier to thermal reversal, a low critical current in spin-torque switching embodiments, and improved resistance to diffusion of material from adjacent layers in the device. Nonmagnetic layers deposited by the static oblique deposition technique may be used as seed layers for a ferromagnetic free layer or to generate other types of anisotropy determined by the deposition-induced microstructural anisotropy. Additional magnetic or non-magnetic layers may be deposited by conventional methods adjacent to oblique layer to provide magnetic coupling control, reduction of surface roughness, and barriers to diffusion from additional adjacent layers in the device.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
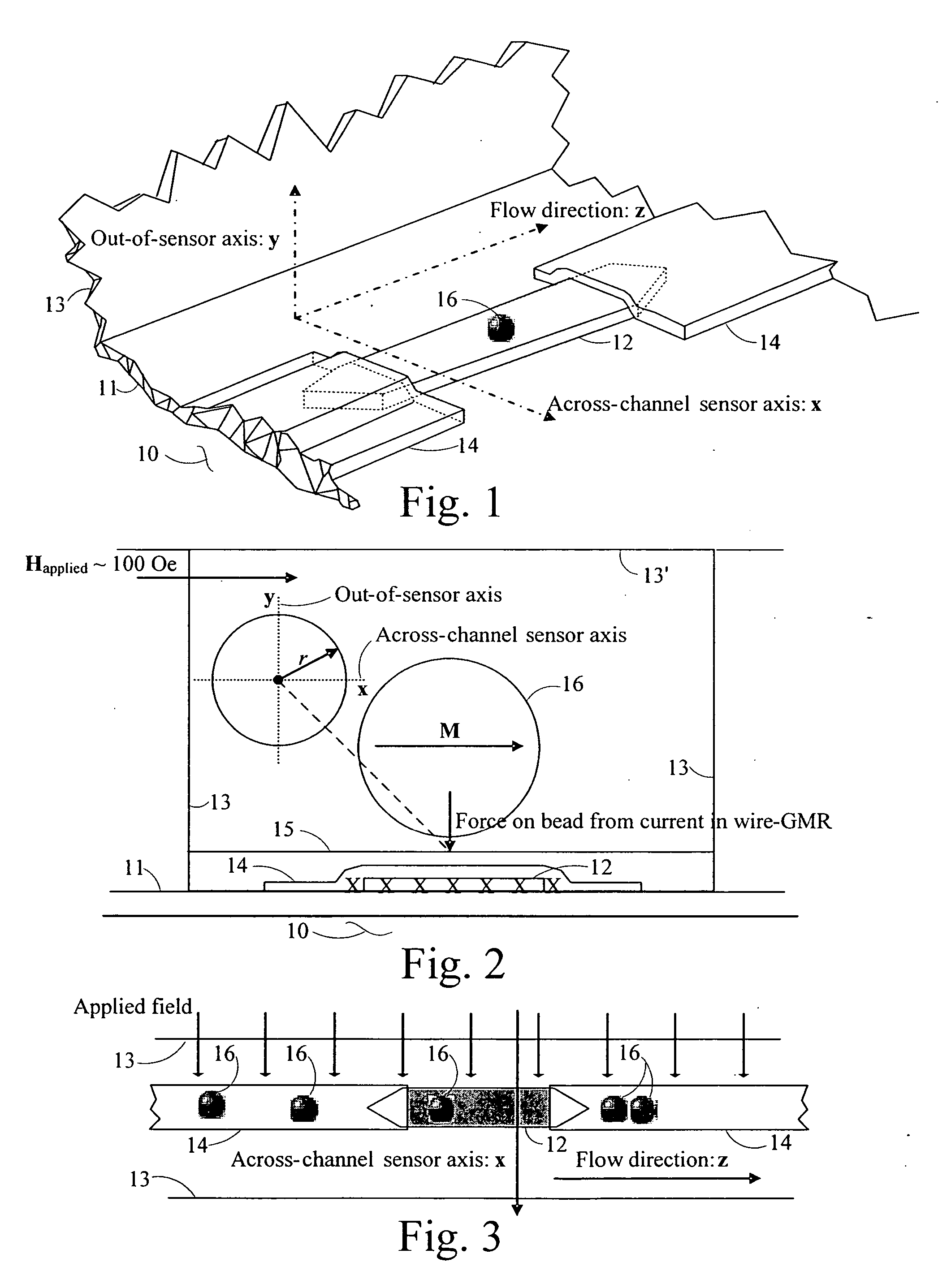
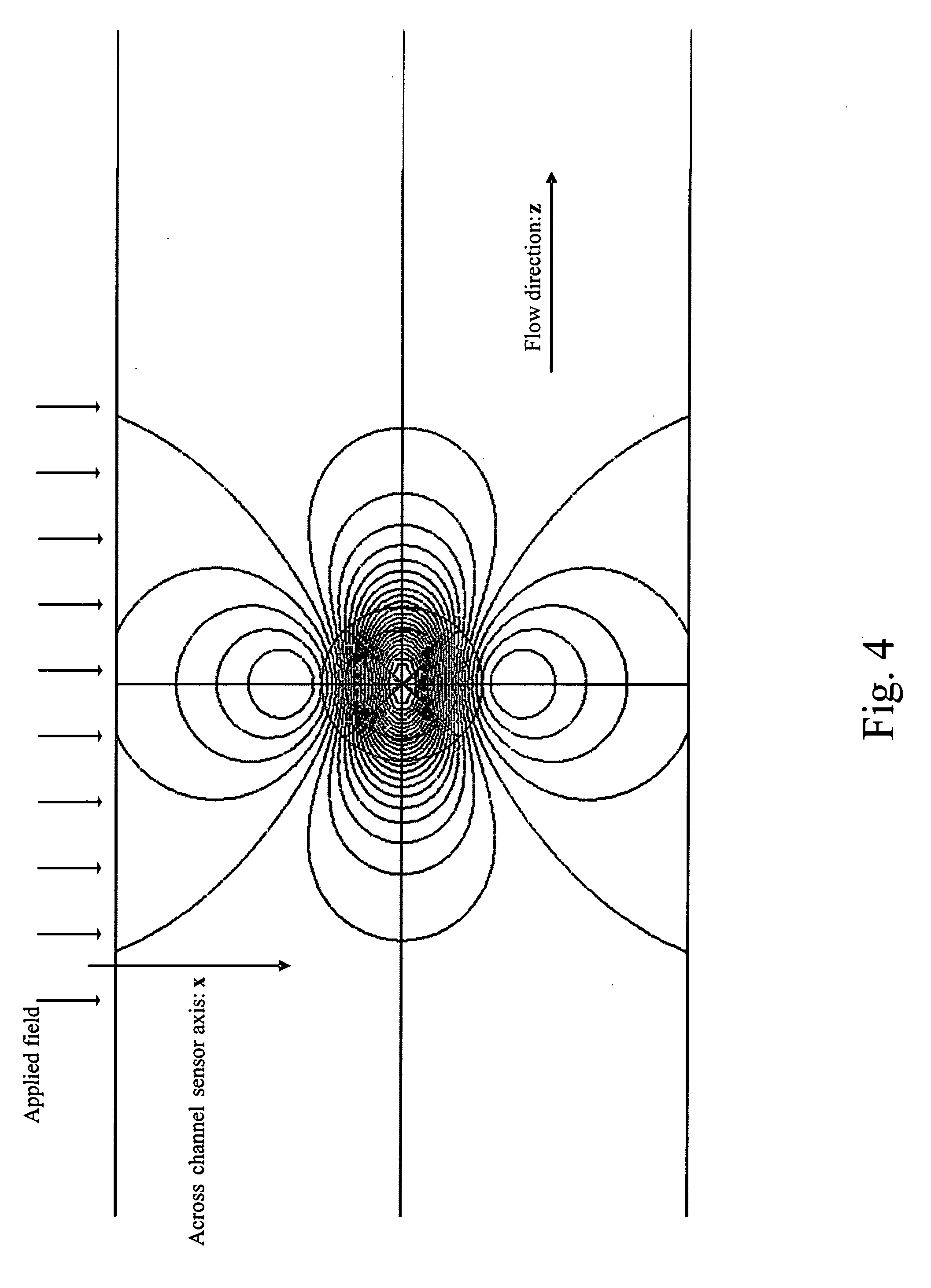
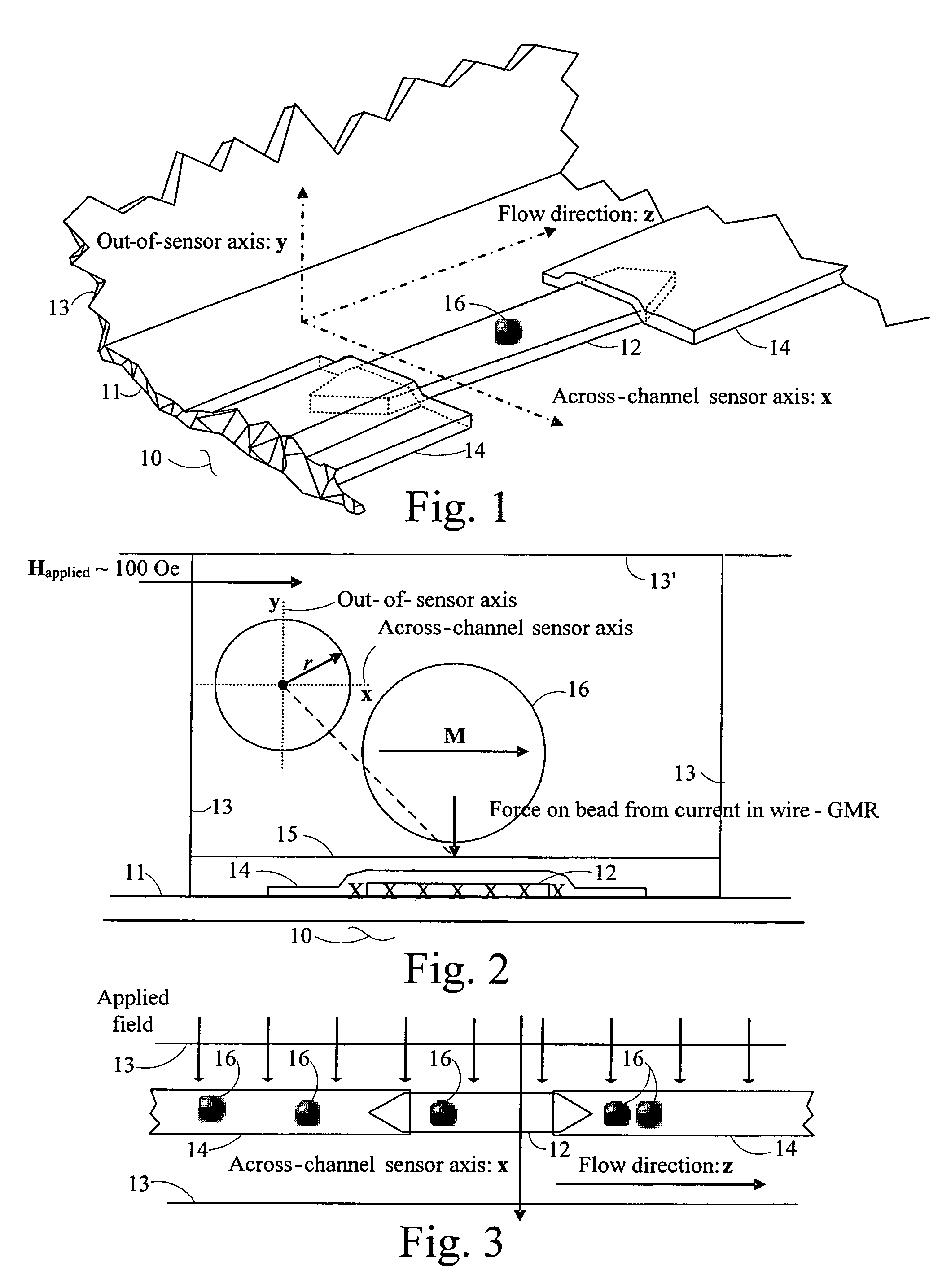
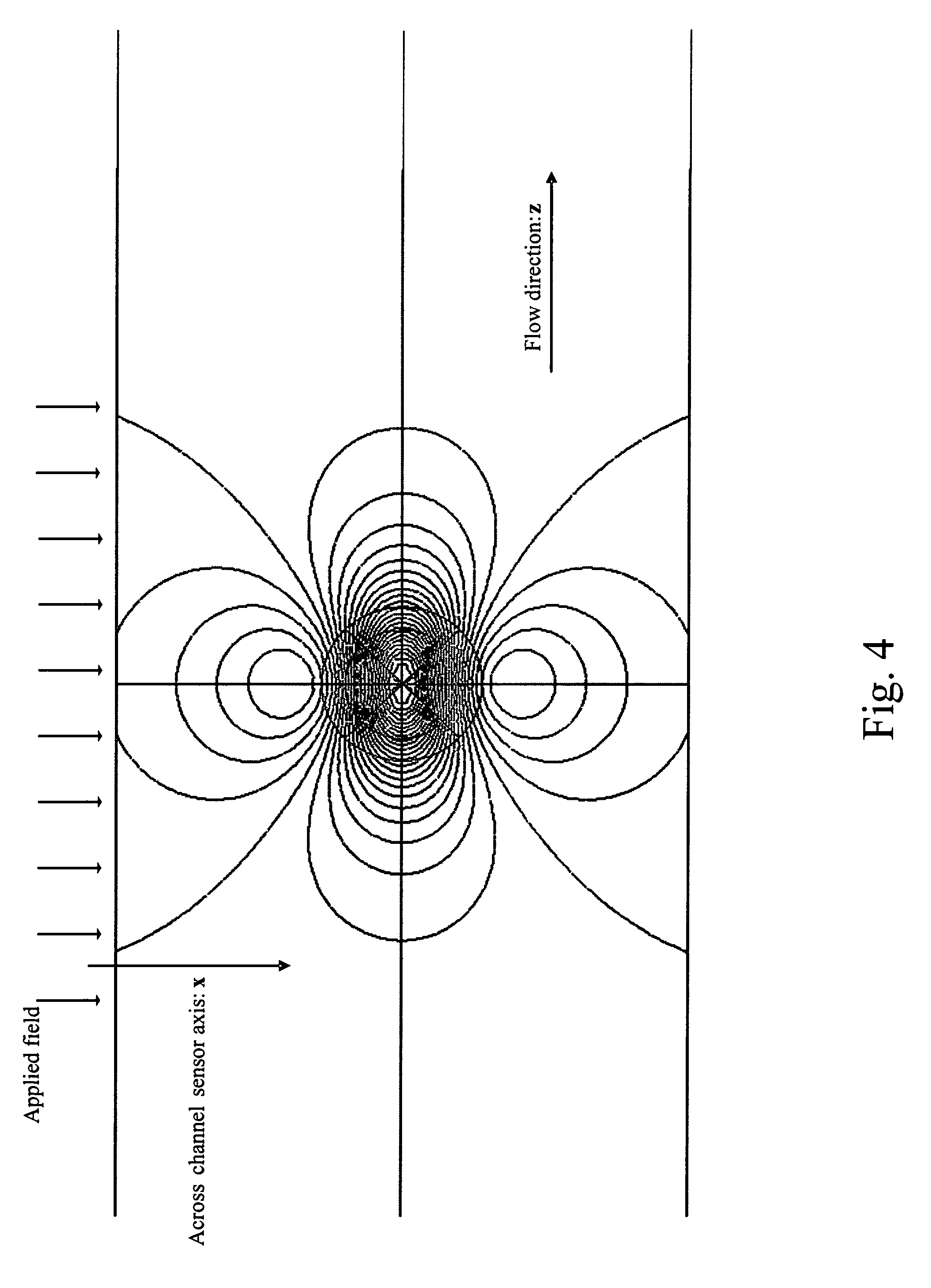
Magnetic particle flow detector
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field detection system having a substrate supporting a magnetic field sensor in a channel with a first electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap and in direct contact with at least some surface of the magnetic field sensor ands a second electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap in a region thereof adjacent to, but separated from, the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:NVE CORP
Two-axis magnetic field sensor
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field sensor with first and second sensitive direction sensing structures each having a nonmagnetic intermediate layer with two major surfaces on opposite sides thereof having a magnetization reference layer on one and an anisotropic ferromagnetic material sensing layer on the other having a length in a selected length direction and a smaller width perpendicular thereto and parallel to the relatively fixed magnetization direction. The relatively fixed magnetization direction of said magnetization reference layer in each is oriented in substantially parallel to the substrate but substantially perpendicular to that of the other. An annealing process is used to form the desired magnetization directions.
Owner:NVE CORP
Thermomagnetically assisted spin-momentum-transfer switching memory
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a substrate supporting bit structures that are electrically interconnected with information storage and retrieval circuitry and having first and second oppositely oriented relatively fixed magnetization layers and a ferromagnetic material film in which a characteristic magnetic property is substantially maintained below an associated critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained. This ferromagnetic material film is separated from the first and second fixed magnetization films by corresponding layers of a nonmagnetic materials one being electrically insulative and that one remaining being electrically conductive. Each bit structure has an interconnection structure providing electrical contact thereto at a contact surface thereof substantially parallel to the intermediate layer positioned between the first contact surface and the substrate. A plurality of word line structures located across from a corresponding one of the bit structures on an opposite side. Electrical current selectively drawn through each of these bit structures and its interconnection structure can cause substantial heating of that bit structure to raise temperatures thereof while being above temperatures of at least an adjacent said bit structure because of sufficient thermal isolation.
Owner:NVE CORP
Inverted magnetic isolator
ActiveUS20060061350A1Measurement using dc-ac conversionSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical conductor
A current determiner comprising a first input conductor and a first current sensor, formed of a plurality of magnetoresistive, anisotropic, ferromagnetic thin-film layers at least two of which are separated from one another by a nonmagnetic layer positioned therebetween, and both supported on a substrate adjacent to and spaced apart from one another so they are electrically isolated with the first current sensor positioned in those magnetic fields arising from any input currents. A first shield / concentrator of a material exhibiting a substantial magnetic permeability is positioned between the substrate and the first input conductor. The substrate can include a monolithic integrated circuit structure containing electronic circuit components of which at least one is electrically connected to the first input conductor. A similar second current sensor can be individually formed, but can also be in the current determiner structure that is supported on the substrate along with a second input conductor supported on the substrate suited for conducting input currents therethrough. This second input conductor is positioned at that side of the second current sensor opposite to that side thereof facing the substrate so as to be adjacent to, yet spaced apart from, the second current sensor to thereby be electrically isolated from any direct circuit interconnection therewith on the substrate but to have the second current sensor positioned in those magnetic fields arising from the input currents in the second input conductor. In addition, a second shield / concentrator layer of material exhibiting a substantial magnetic permeability to serve as a magnetic field concentrator is positioned at that side of the second input conductor opposite to that side thereof facing the substrate. In the first instance, the second shield / concentrator layer is electrically connected to the second input conductor, and can be so connected in the second instance.
Owner:NVE CORP
Magnetic memory layers thermal pulse transitions
InactiveUS20060083056A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryDigital storage
Owner:NVE CORP
Microwave oscillator tuned with a ferromagnetic thin film
InactiveUS7528663B2High Q tunedPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsSustained oscillationsResonance
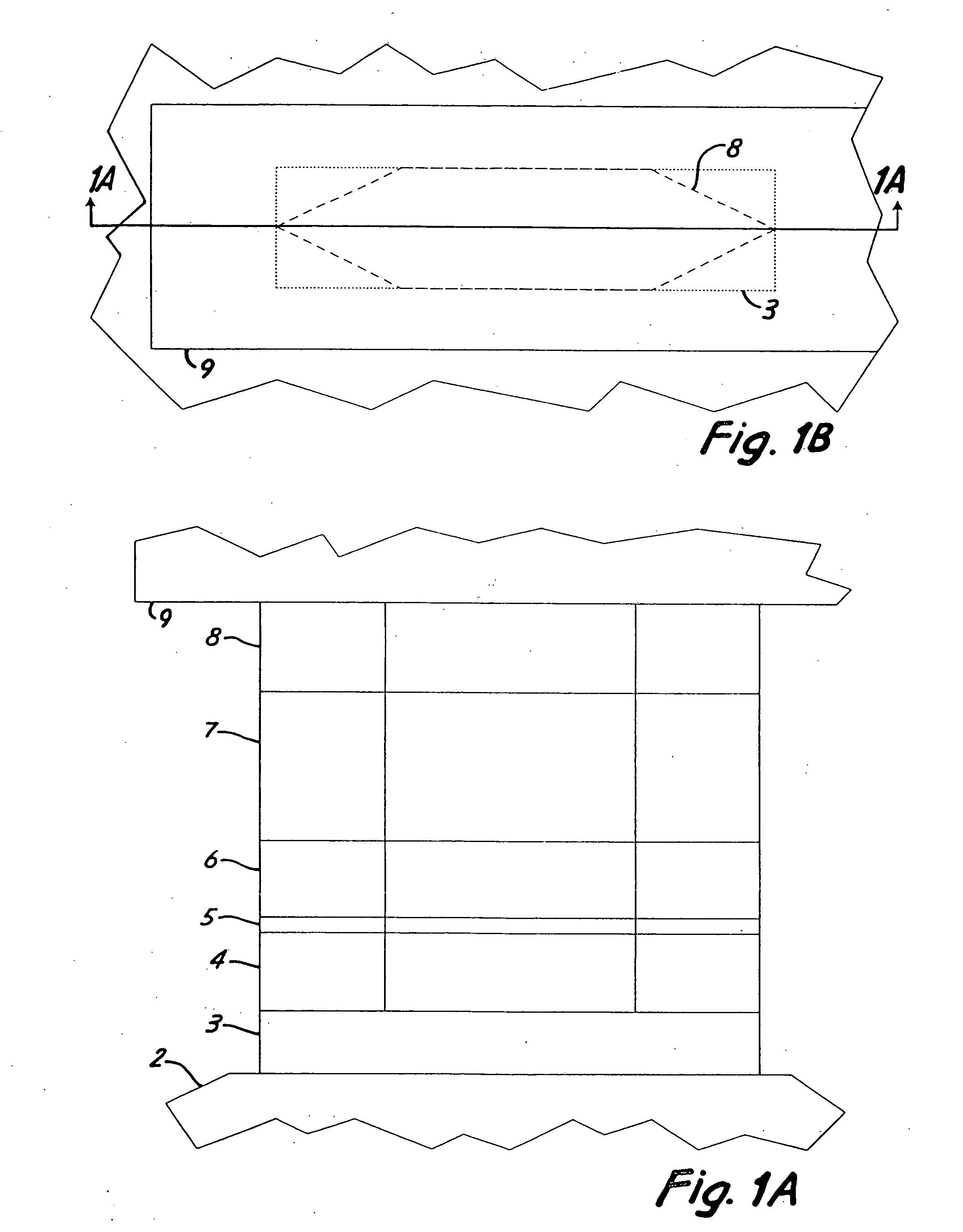
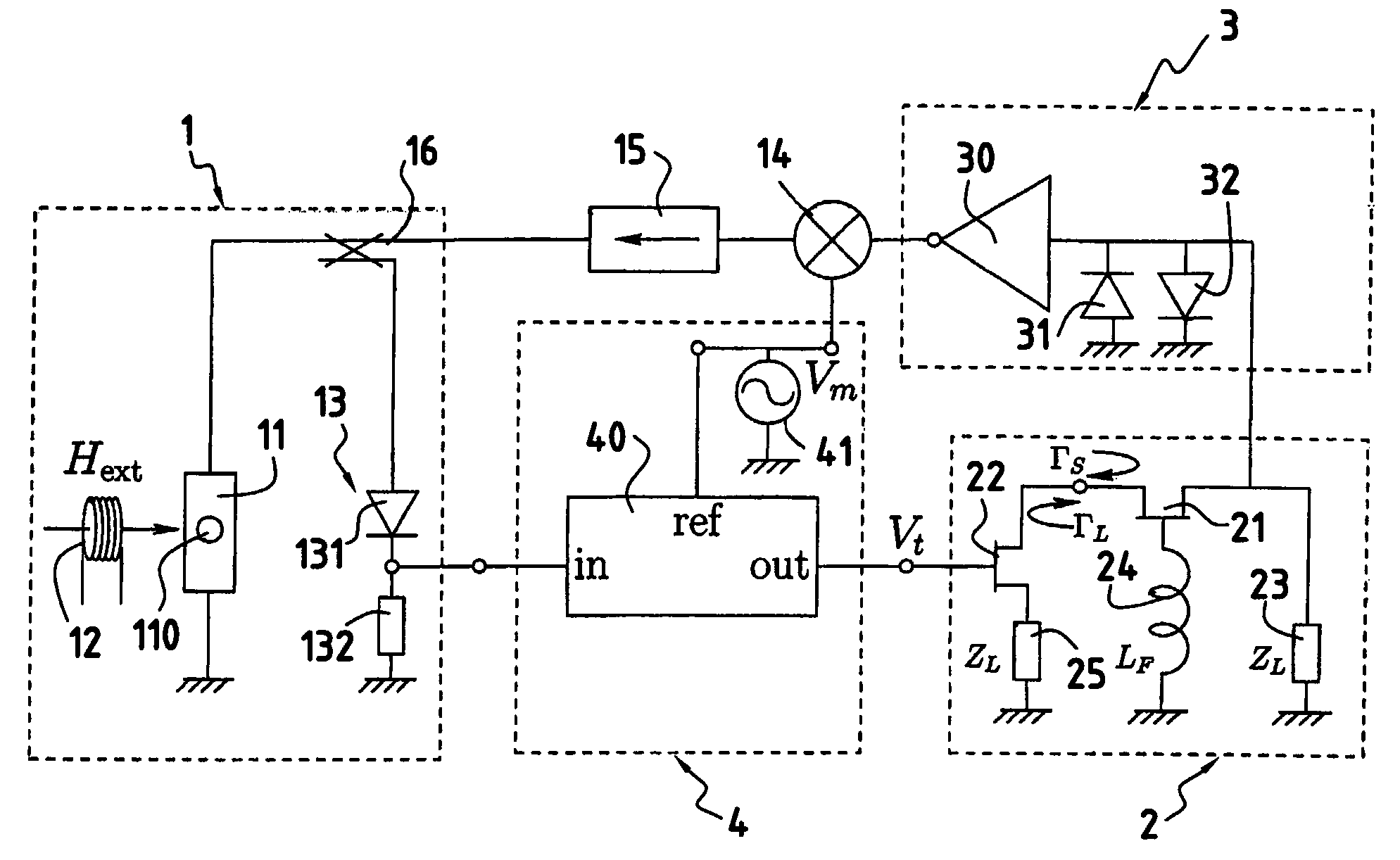
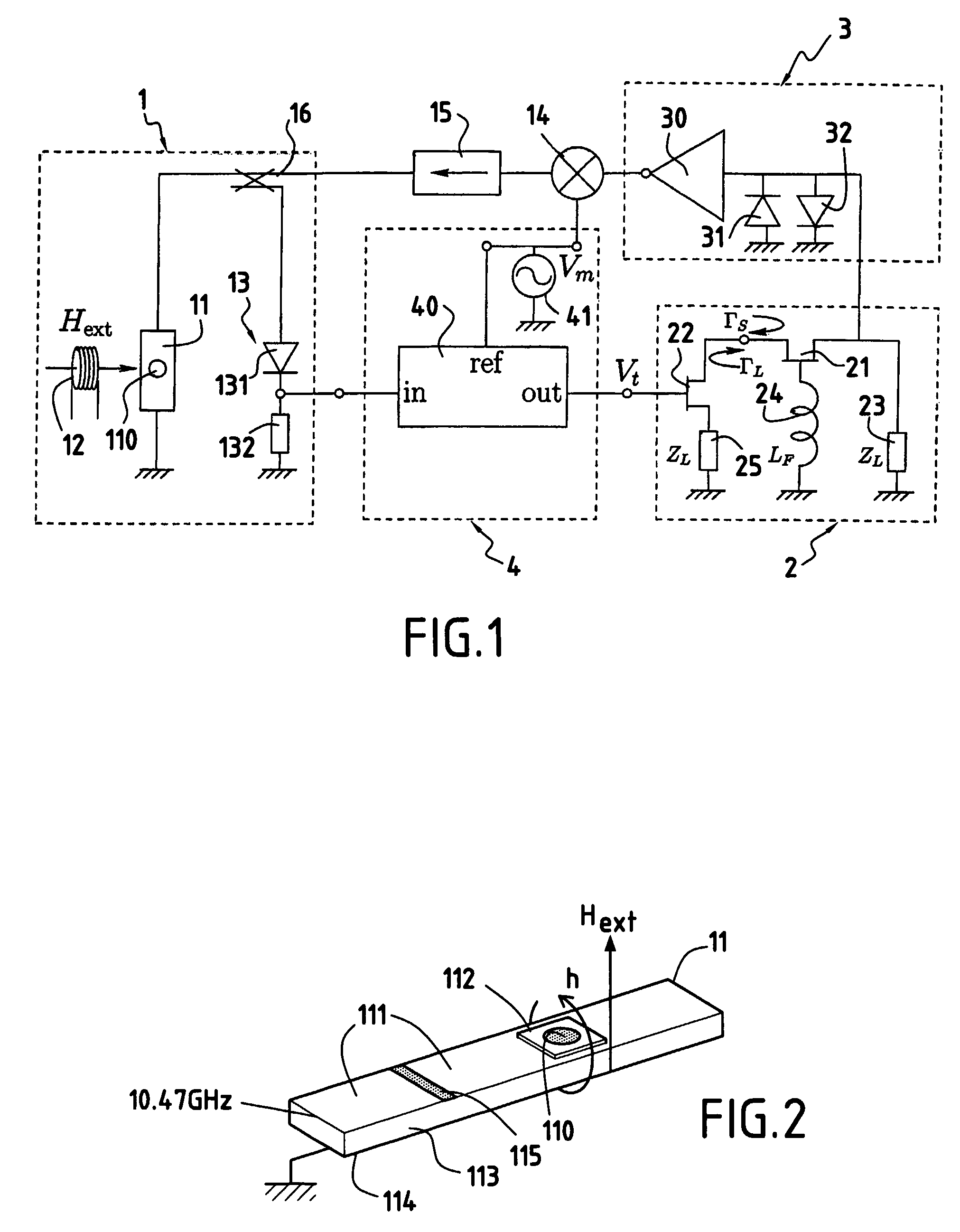
A microwave tuned oscillator utilizing a ferromagnetic thin film resonator comprises: a) a microwave resonator (1) comprising a ferromagnetic thin film resonance plate (110) such as a disc-shaped YIG crystal placed on a microwave integrated circuit (11), such as a half-wavelength strip-line resonator, b) bias magnetic field means (12) for applying a bias magnetic field perpendicular to the ferromagnetic thin film resonance plate (110), c) an active element for oscillation (21), a reactive feedback element (24) and a load (23, 25) controlled by the microwave properties of the ferromagnetic thin film resonance plate (110) through a load feedback loop (4), and d) an overall positive feedback loop (3, 14, 15) connected between the active element for oscillation (21) and the microwave resonator (1) to cause a sustained oscillation to build up at one of parametrically excited resonances of the ferromagnetic thin film resonance plate (110).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
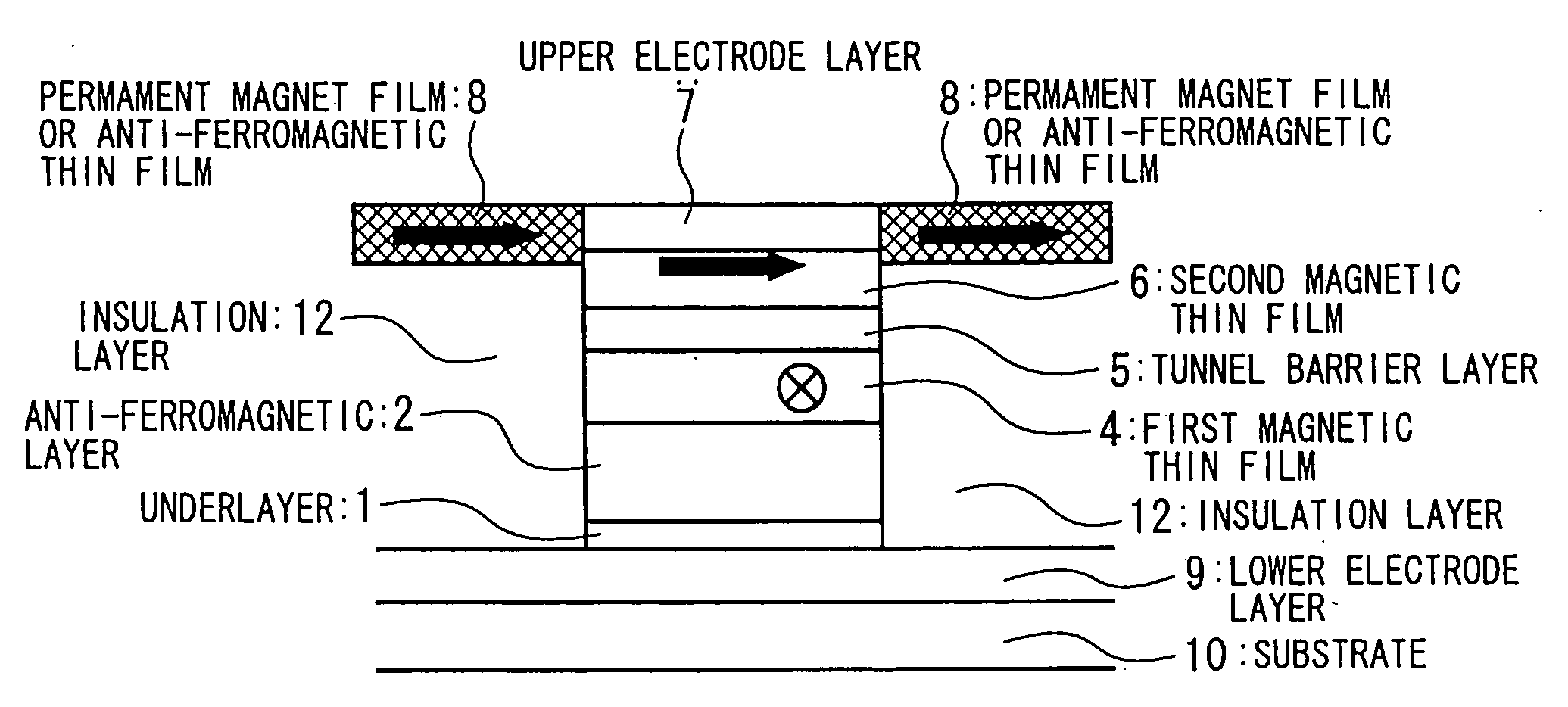
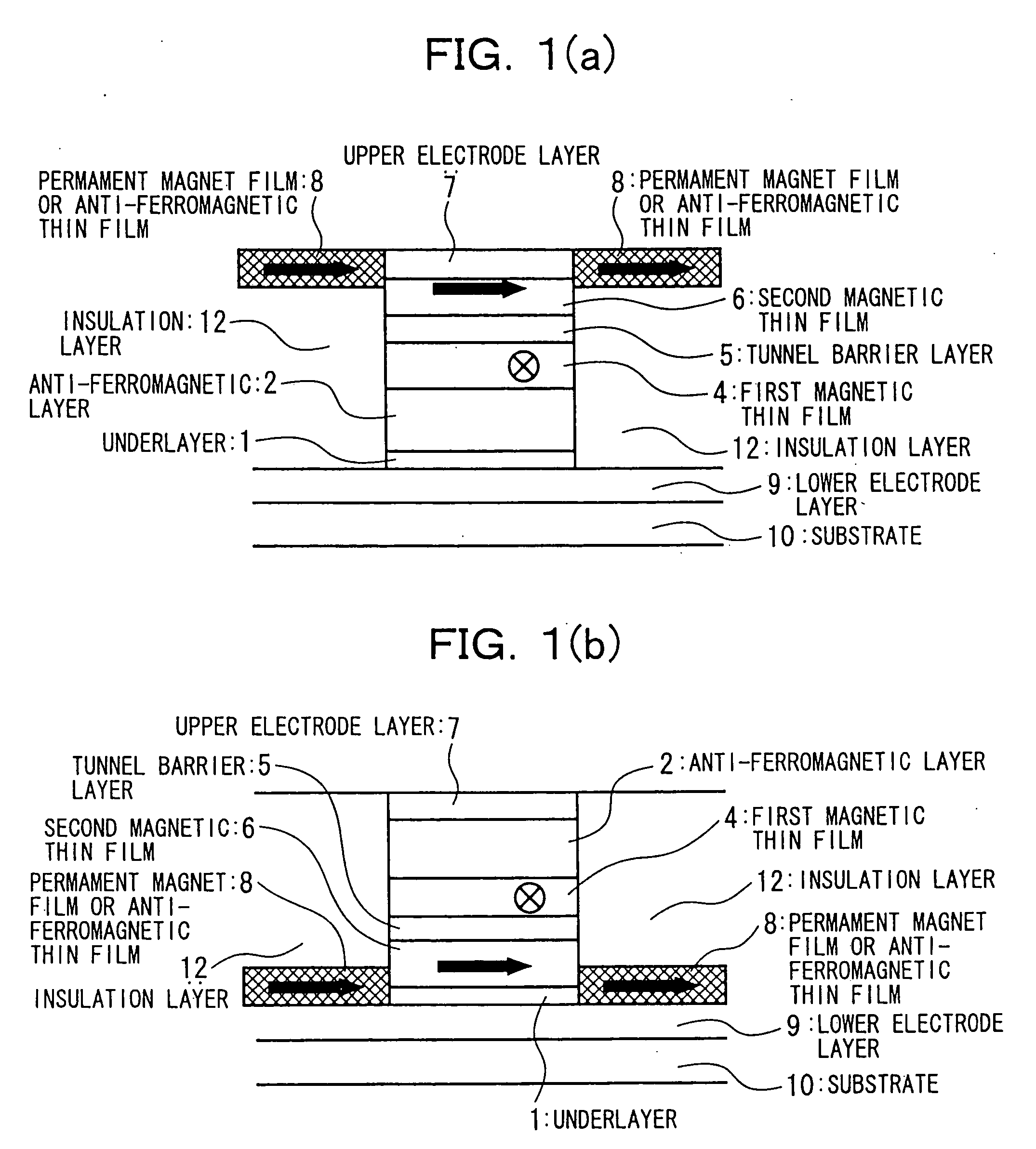
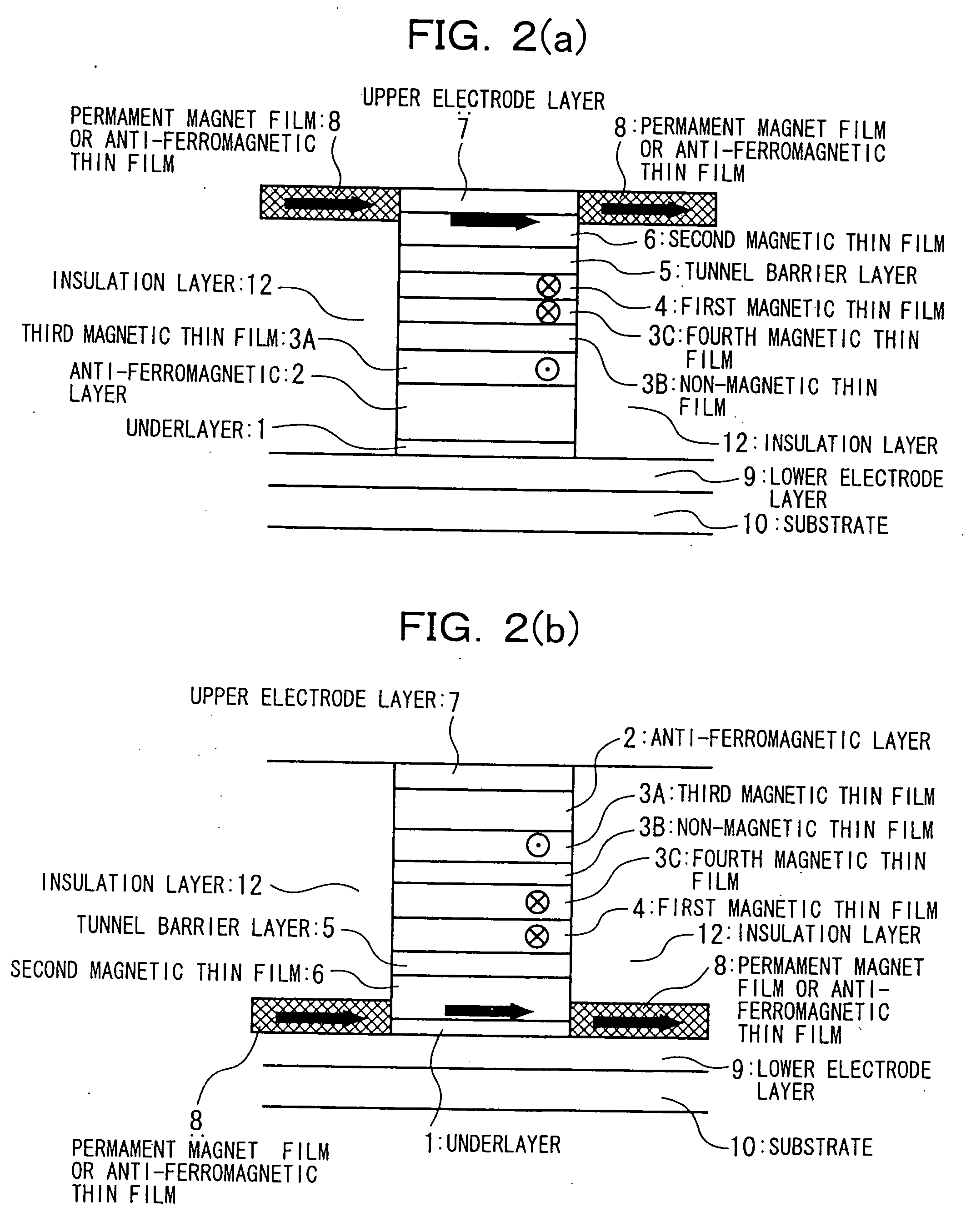
Ferromagnetic Film, Magneto-Resistance Element And Magnetic Random Access Memory
InactiveUS20080008908A1Reduce variationImprove operating profitNanomagnetismSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical resistance and conductanceRandom access memory
A ferromagnetic film according to the present invention includes ferromagnetic element and nonmagnetic element and has a first portion and a second portion. Concentration of the nonmagnetic element in the first portion is lower than an average concentration of the nonmagnetic element in the ferromagnetic film. On the other hand, concentration of the nonmagnetic element in the second portion is higher than the average concentration of the nonmagnetic element in the ferromagnetic film. The nonmagnetic element includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Zr, Ti, Nb, Ta, Hf, Mo and W. The ferromagnetic film is applied to a magnetic free layer of a magneto-resistance element in an MRAM.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Magnetoresistive memory SOI cell
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a substrate formed of a base supporting an electrically insulating material primary substrate layer in turn supporting a plurality of current control devices each having an interconnection arrangement with each of said plurality of current control devices being separated from one another by spacer material therebetween and being electrically interconnected with information storage and retrieval circuitry. A plurality of bit structures are each supported on and electrically connected to a said interconnection arrangement of a corresponding one of said plurality of current control devices and have magnetic material films in which a characteristic magnetic property is substantially maintained below an associated critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained of which two are separated by at least one intermediate layer of a nonmagnetic material having two major surfaces on opposite sides thereof. A plurality of word line structures located across from a corresponding one of the bit structures on an opposite side of the intermediate layer of a corresponding one of said bit structures from its interconnection arrangement supporting that bit structure. Sufficient electrical current selectively drawn through each of these bit structures as interconnected can cause substantial heating of that bit structure to raise temperatures thereof to have at least one of the magnetic material films therein at least approach its corresponding associated critical temperature while being substantially above temperatures of at least an adjacent said bit structure because of sufficient thermal isolation.
Owner:NVE CORP
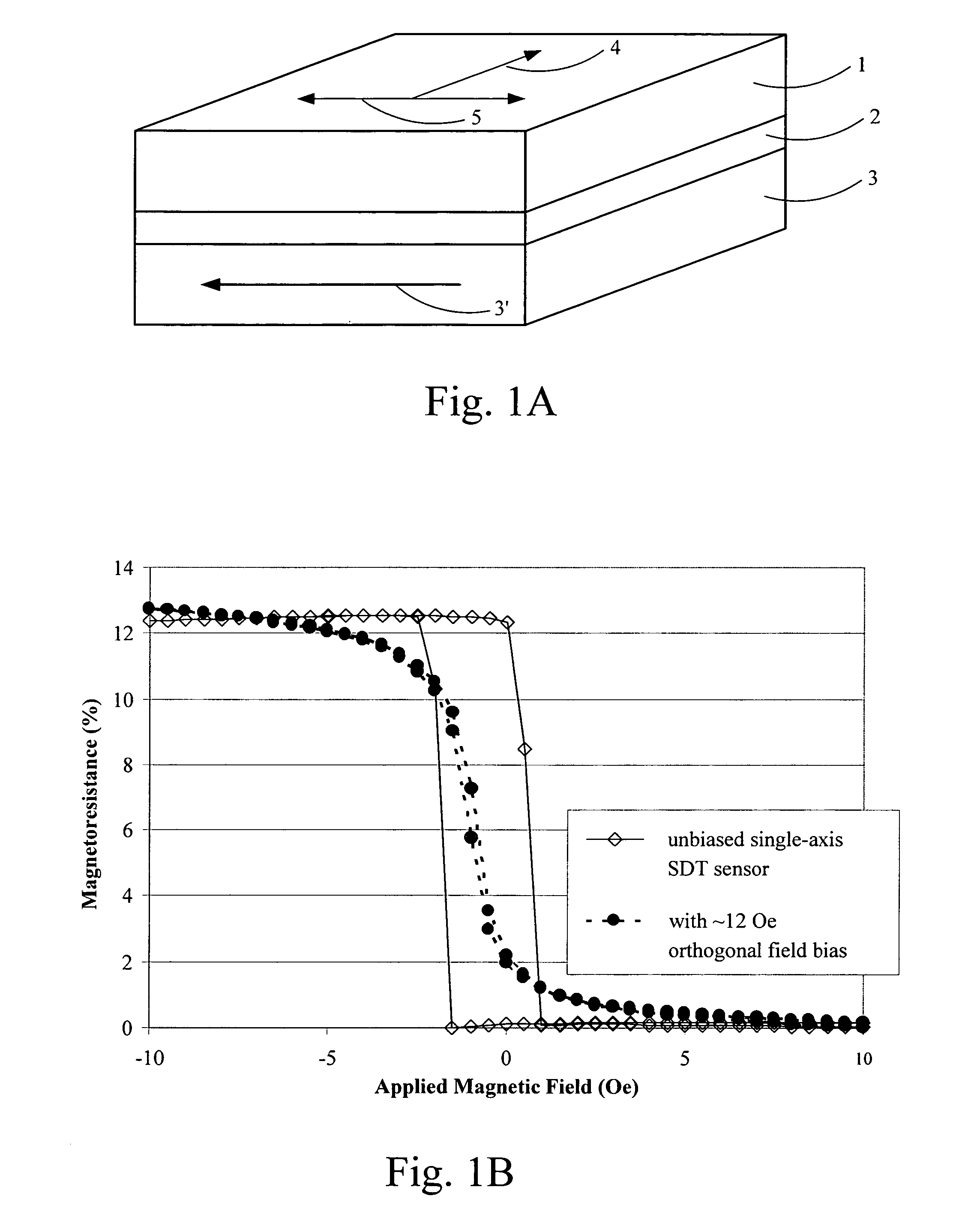
Magnetic field sensor with augmented magnetoresistive sensing layer
ActiveUS6872467B2Reduce and eliminate topological couplingNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsInter layerCoupling
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field sensor having a nonmagnetic intermediate layer with two major surfaces on opposite sides thereof upon one of which a magnetization reference layer is provided and upon the other there being provided a sensing layer. A spacer layer is provided on the sensing film to separate this sensing film from an augmenting film with the spacer layer being sufficiently thick so as to significantly reduce or eliminate topological coupling between the sensing and augmenting films, and to significantly randomize spin states of emerging electrons traversing therethrough.
Owner:NVE CORP
Spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film and element, magnetoresistive sensor using same, magnetic apparatus, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050019610A1Reduced effectivenessPrevent oxidationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsNon magneticOxygen
In a spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film in which a magnetic thin film to which an exchange bias is applied by exchange coupling via an anti-ferromagnetic thin film and a magnetic thin film that detects a magnetic field are laminated, a magnetic thin film or an anti-ferromagnetic thin film (PtMn, PdMn, NiMn) is laminated onto an underlayer (Ta, Zr, Hf), the surface roughness thereof being in the range from 0.1 to 5 Angstroms. A means used to control the surface roughness introduces into the film growing chamber oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, or a gas mixture thereof into a vacuum of 10−6 Torr to 10−9 Torr, reduces the substrate temperature to 0° C. or lower during film growth, or oxidizes an underlayer. The lower electrode layer material used is a film laminate of a high-permeability amorphous magnetic material and a non-magnetic metallic layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetoresistive memory SOI cell
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a substrate formed of a base supporting an electrically insulating material primary substrate layer in turn supporting a plurality of current control devices each having an interconnection arrangement with each of said plurality of current control devices being separated from one another by spacer material therebetween and being electrically interconnected with information storage and retrieval circuitry. A plurality of bit structures are each supported on and electrically connected to a said interconnection arrangement of a corresponding one of said plurality of current control devices and have magnetic material films in which a characteristic magnetic property is substantially maintained below an associated critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained of which two are separated by at least one intermediate layer of a nonmagnetic material having two major surfaces on opposite sides thereof. A plurality of word line structures located across from a corresponding one of the bit structures on an opposite side of the intermediate layer of a corresponding one of said bit structures from its interconnection arrangement supporting that bit structure. Sufficient electrical current selectively drawn through each of these bit structures as interconnected can cause substantial heating of that bit structure to raise temperatures thereof to have at least one of the magnetic material films therein at least approach its corresponding associated critical temperature while being substantially above temperatures of at least an adjacent said bit structure because of sufficient thermal isolation.
Owner:NVE CORP
Magnetic particle flow detector
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic field detection system having a substrate supporting a magnetic field sensor in a channel with a first electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap and in direct contact with at least some surface of the magnetic field sensor ands a second electrical conductor supported on the substrate positioned at least in part along the channel gap in a region thereof adjacent to, but separated from, the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:NVE CORP
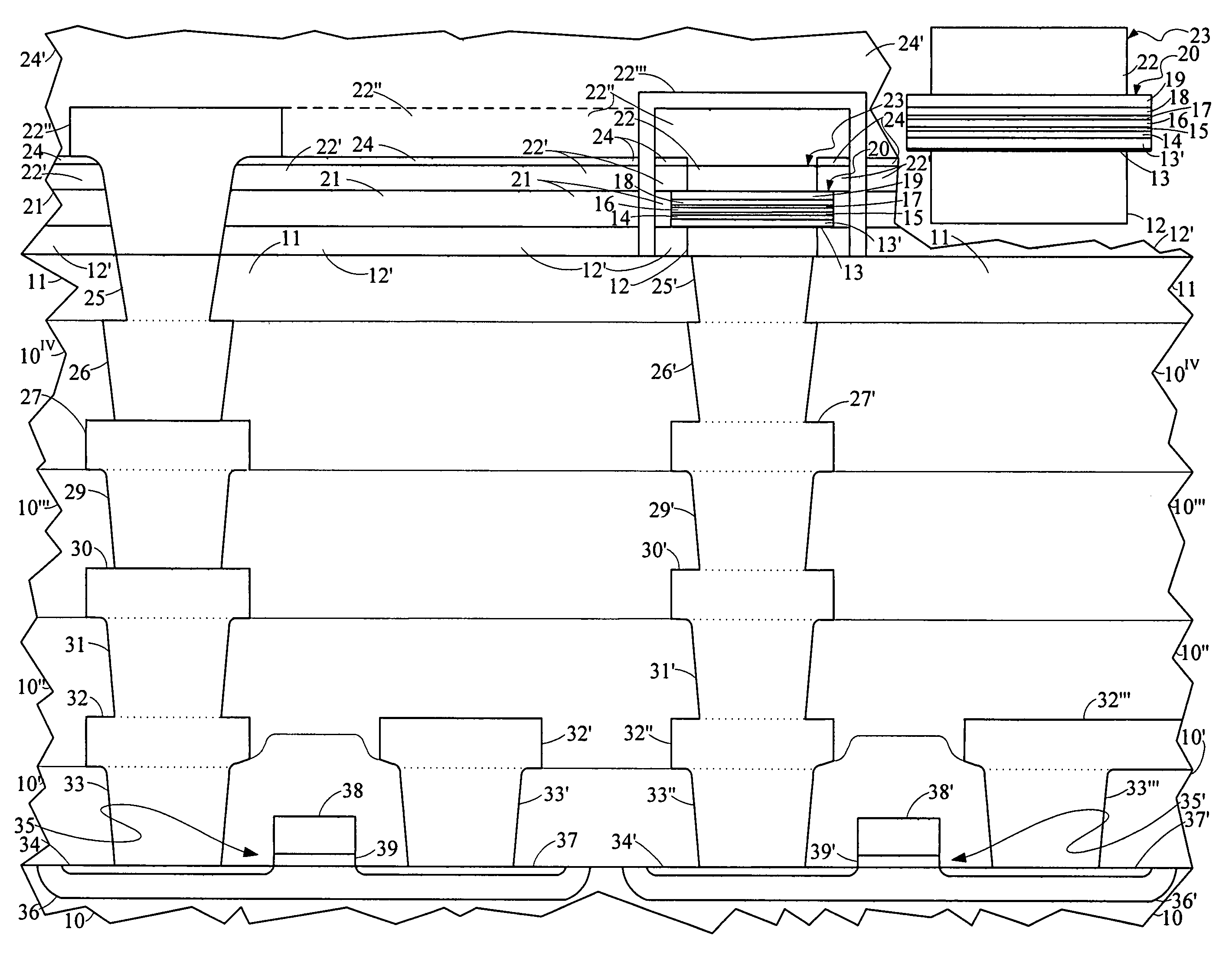
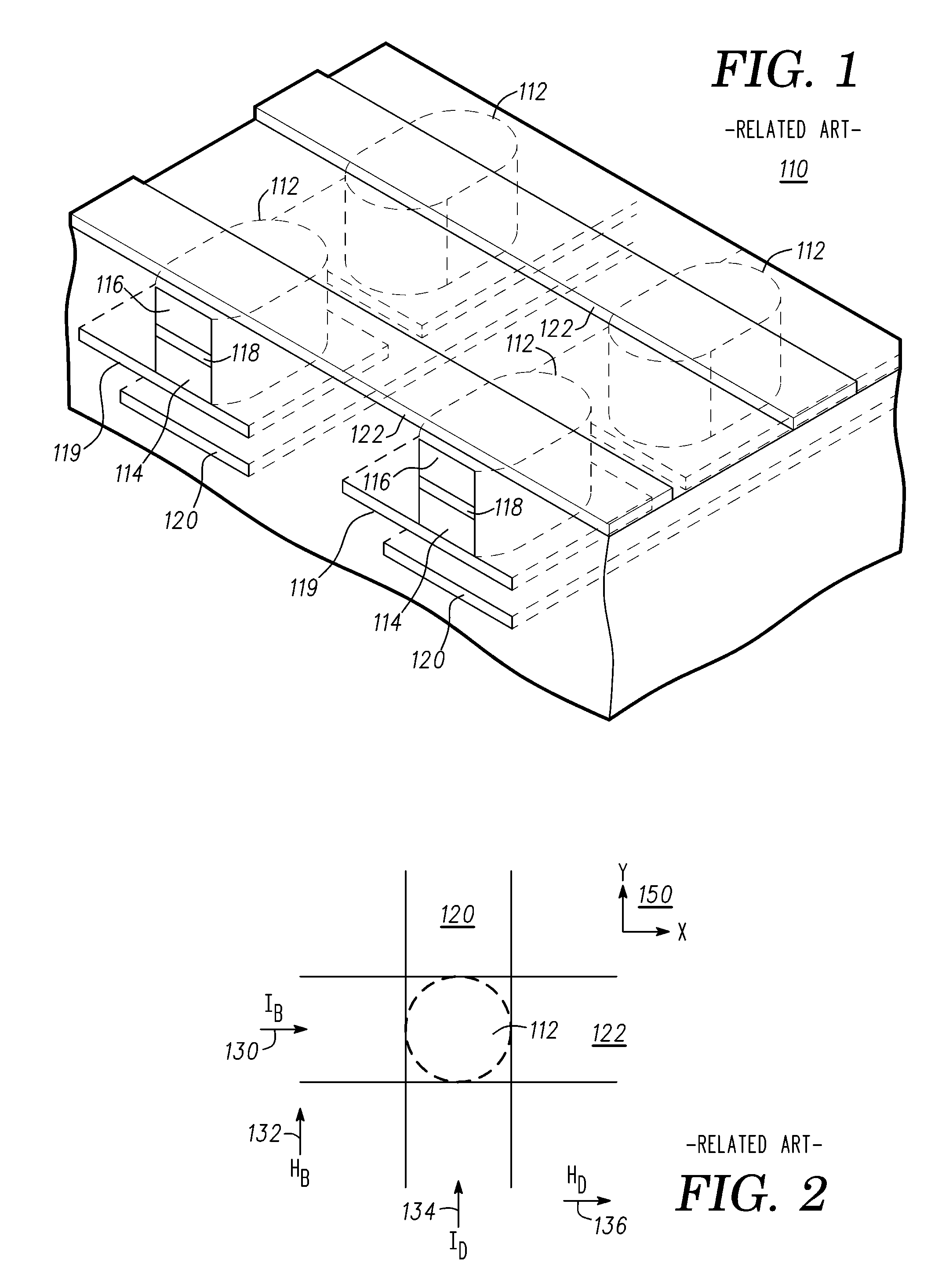
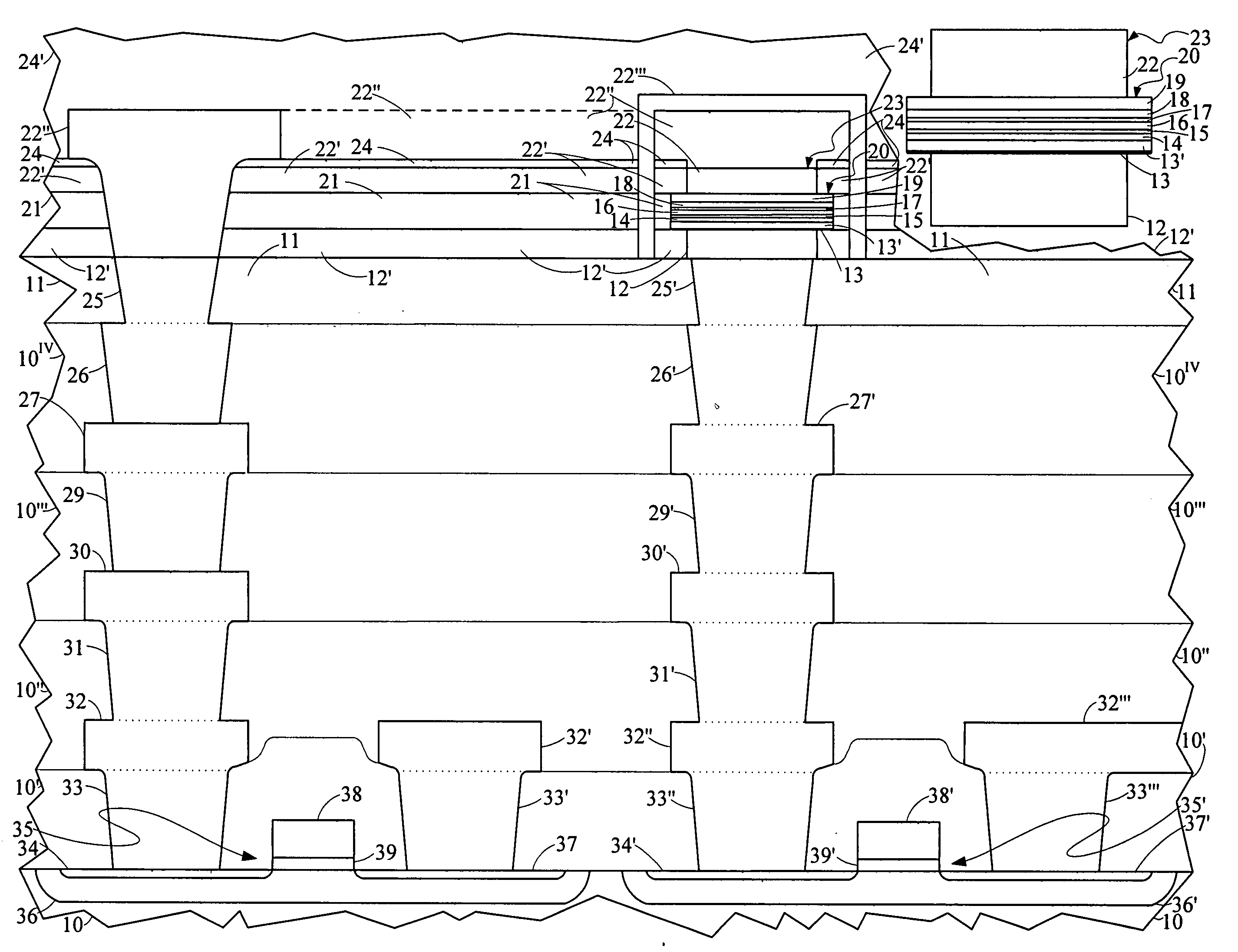
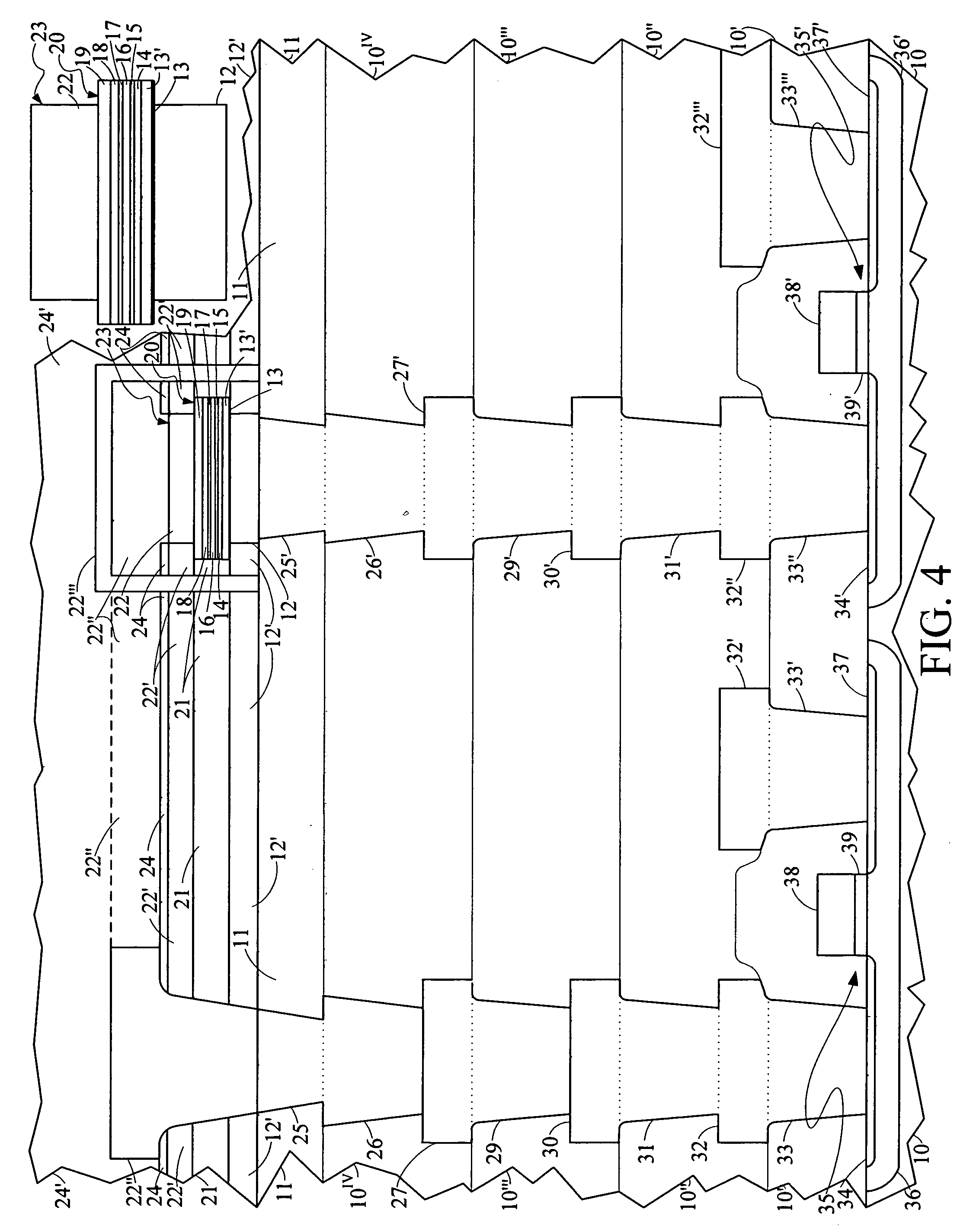
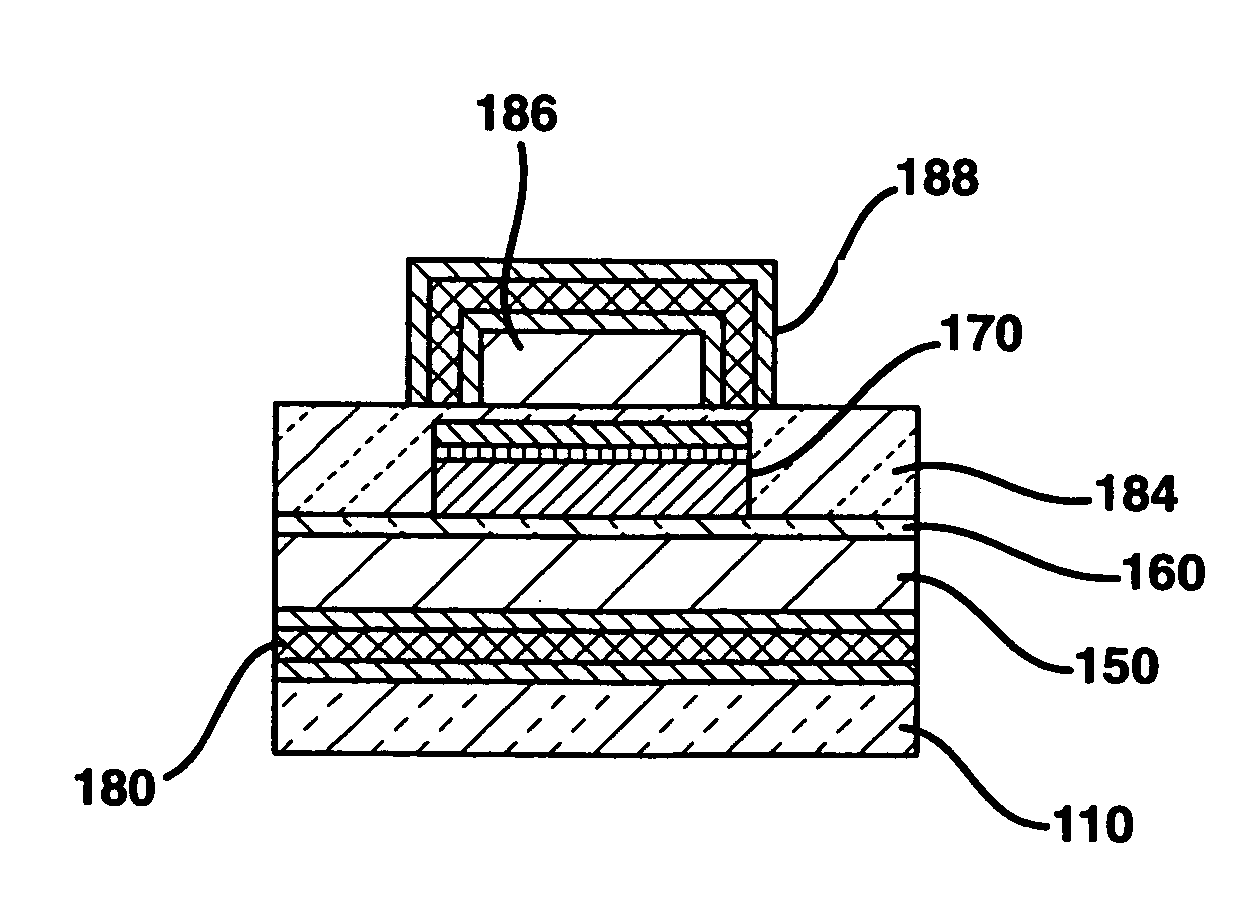
Methods of forming magnetic shielding for a thin-film memory element
InactiveUS7166479B2Reduce undesirable fieldsEnhance the desirable magnetic fieldsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin-film memoryMagnetic memory
A monolithically formed ferromagnetic thin-film memory is disclosed that has local shielding on at least two sides of selected magnetic storage elements. The local shielding preferably extends along the back and side surfaces of a word line and / or digital lines of a conventional magnetic memory. In this configuration, the local shielding not only may help reduce externally generated EMI, internally generated cross-talk and other unwanted fields in the magnetic bit region, but may also help enhance the desired magnetic fields in the bit region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
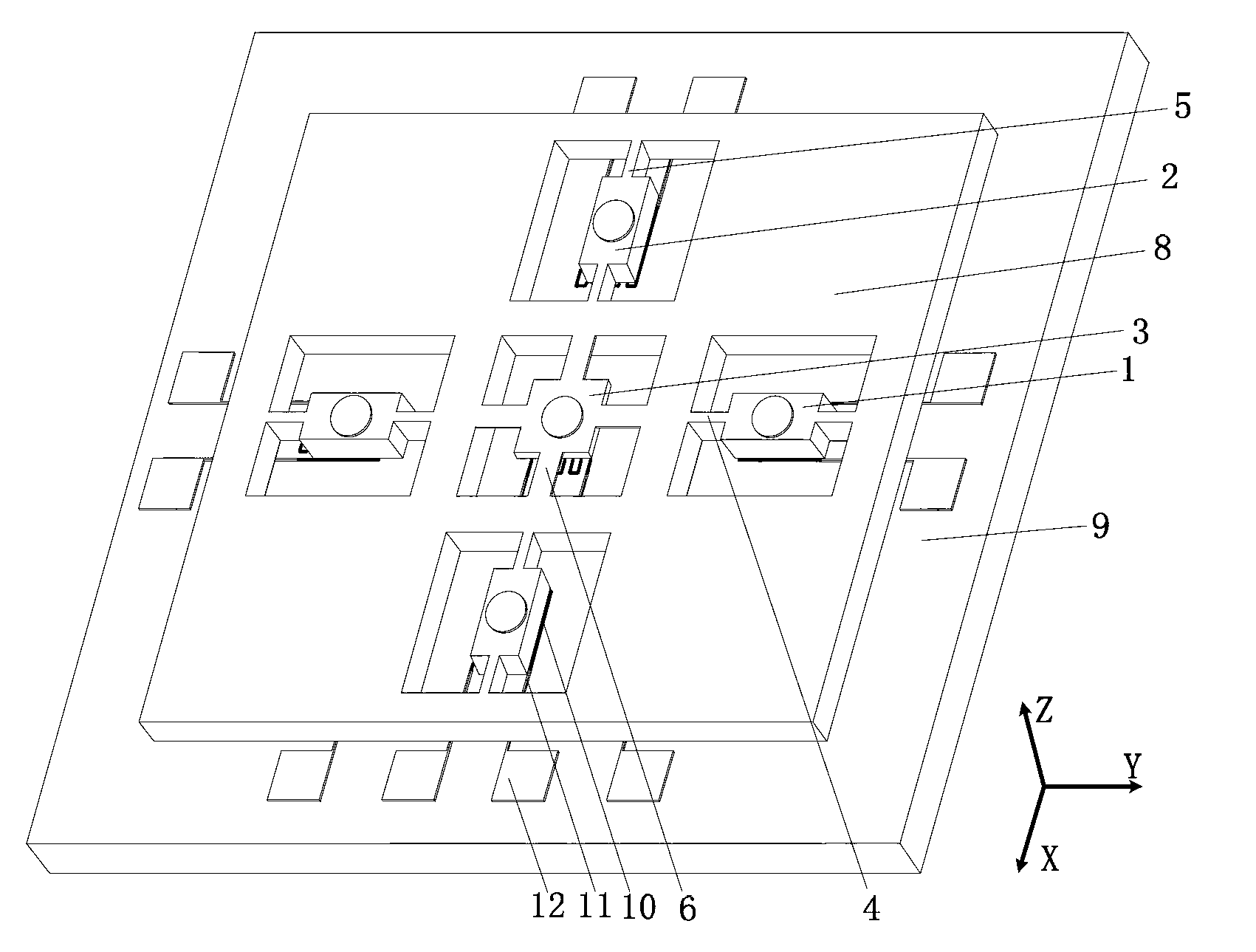
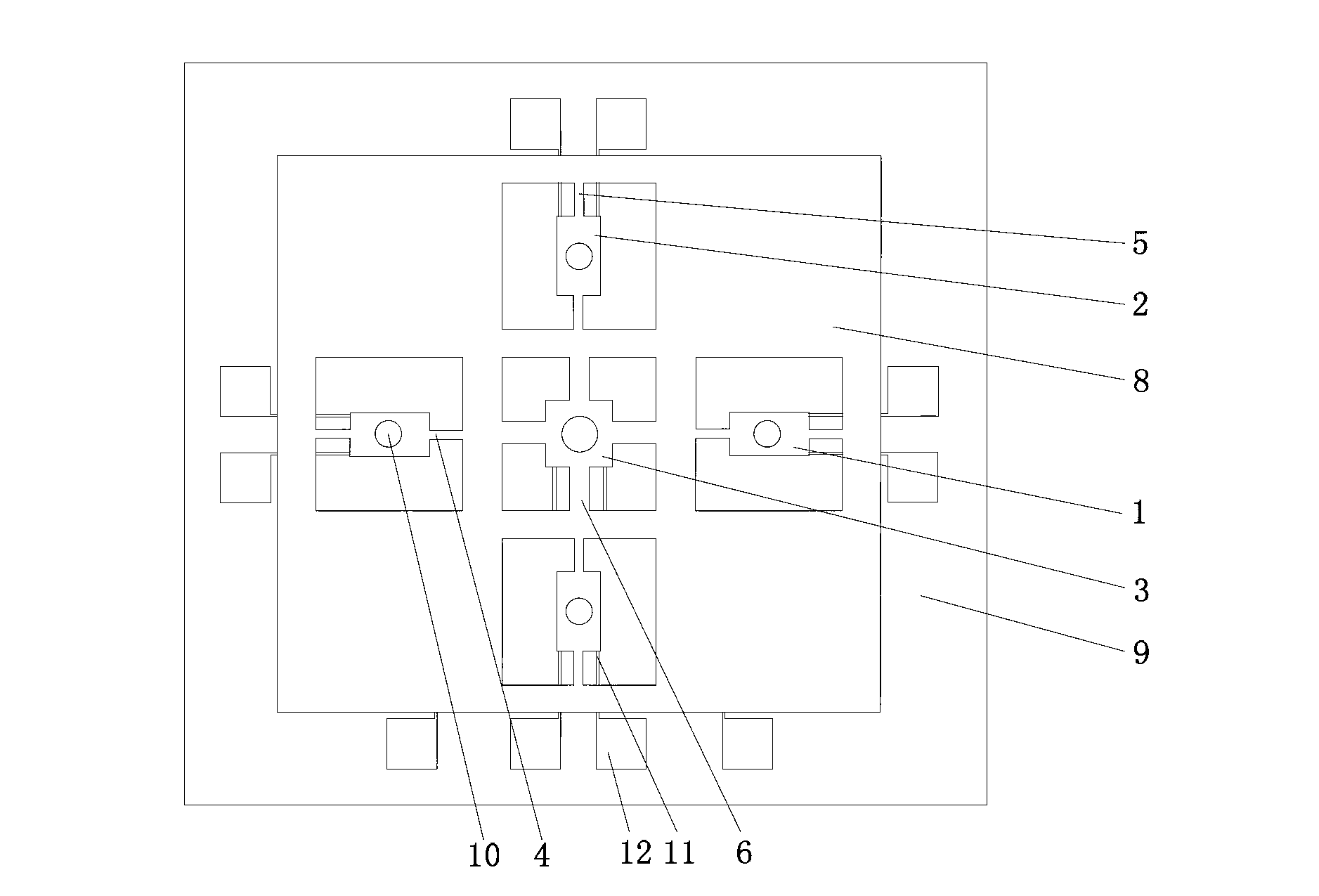
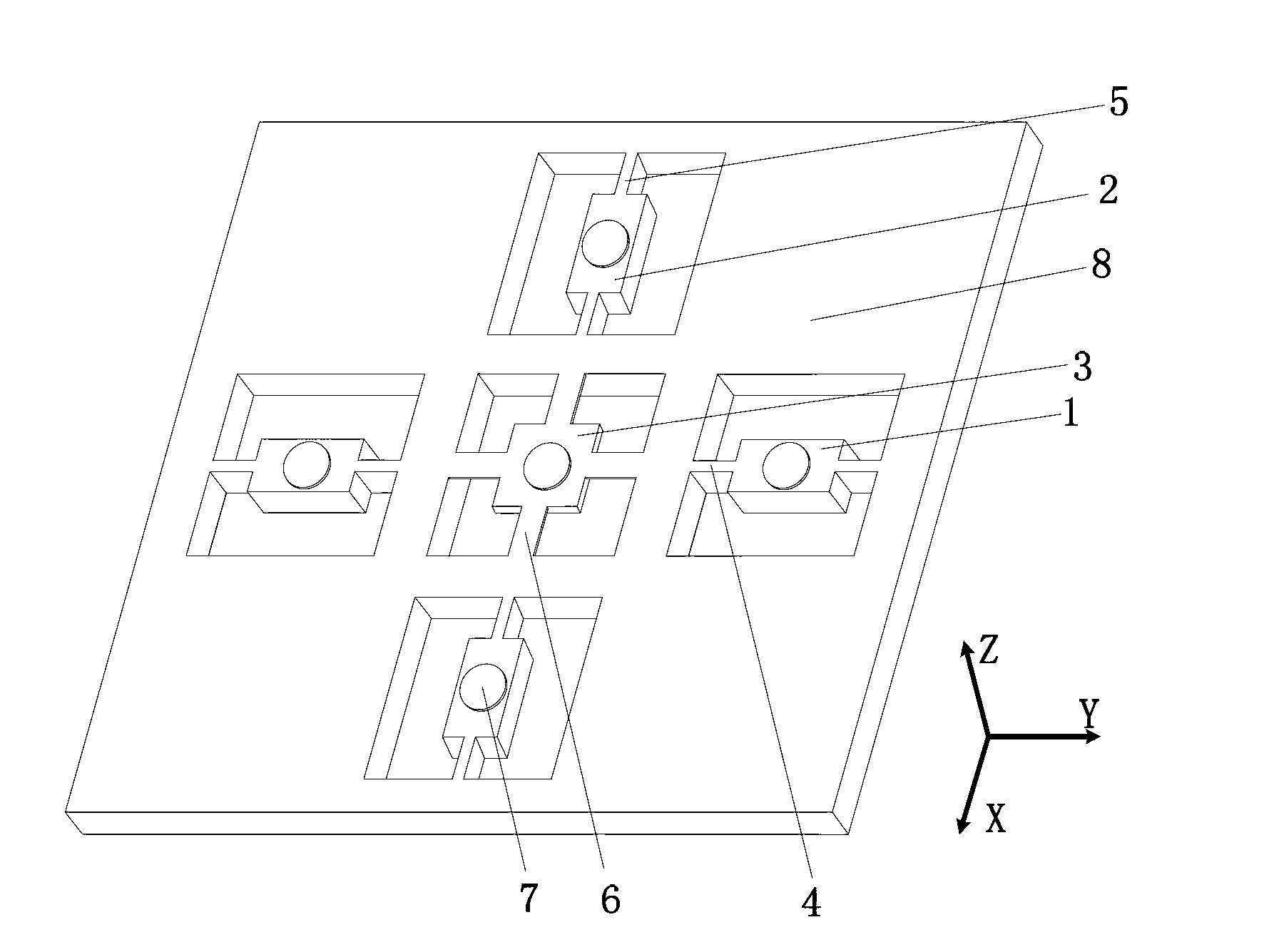
Tri-axial accelerometer with giant magneto-resistance effect
InactiveCN102841217AHigh sensitivitySimple designAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsGiant magnetoresistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a tri-axial accelerometer with giant magneto-resistance effect. The tri-axial accelerometer comprises a bonding substrate, giant magneto-sensitive resistors and micro accelerators, wherein the giant magneto-sensitive resistors are arranged on the upper surface of the bonding substrate, and are in positional correspondence to giant magneto-sensitive resistors on the upper surface of a sensitive mass block of the accelerator in each detection direction; the micro-accelerators are arranged above the bonding substrate and are connected with the bonding substrate; and each of the micro-accelerators comprises the sensitive mass block, a ferromagnetic thin film and a cantilever beam. According to the tri-axial micro-mechanical accelerator disclosed by the invention, an overall structural design is adopted, and three accelerators for detection in different directions are integrally manufactured on the same frame, therefore, the tri-axial accelerometer is reasonable in structure, simple in detection circuit, convenient to use, good in reliability and suitable for microminiaturization.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Thermally operated switch control memory cell
ActiveUS20050002267A1Stay magneticSufficient currentSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionThermal isolationEngineering
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a substrate supporting bit structures that are electrically interconnected with information storage and retrieval circuitry and having magnetic material films in which a characteristic magnetic property is substantially maintained below an associated critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained separated by at least one layer of a nonmagnetic material with each bit structure having an interconnection structure providing electrical contact thereto at a contact surface thereof substantially parallel to the intermediate layer positioned between the first contact surface and the substrate. A plurality of word line structures located across from a corresponding one of the bit structures on an opposite side of the intermediate layer of a corresponding one of said bit structures from its interconnection structure provides electrical contact thereto. Sufficient electrical current selectively drawn through each of these bit structures and its interconnection structure can cause substantial heating of that bit structure to raise temperatures thereof to have at least one of the magnetic material films therein at least approach its corresponding associated critical temperature while being substantially above temperatures of at least an adjacent said bit structure because of sufficient thermal isolation.
Owner:NVE CORP
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head, magnetic head assembly, magnetic storage system
InactiveUS20050030676A1Increase contactEffectively applying the bias magnetic fieldNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic storageCoupling
Disclosed are a high-sensitivity and high-reliability magnetoresistance effect device (MR device) in which bias point designing is easy, and also a magnetic head, a magnetic head assembly and a magnetic recording / reproducing system incorporating the MR device. In the MR device incorporating a spin valve film, the magnetization direction of the free layer is at a certain angle to the magnetization direction of a second ferromagnetic layer therein when the applied magnetic field is zero. In this, the pinned magnetic layer comprises a pair of ferromagnetic films as antiferromagnetically coupled to each other via a coupling film existing therebetween. The device is provided with a means of keeping the magnetization direction of either one of the pair of ferromagnetic films constituting the pinned magnetic layer, and with a nonmagnetic high-conductivity layer as disposed adjacent to a first ferromagnetic layer on the side opposite to the side on which the first ferromagnetic layer is contacted with a nonmagnetic spacer layer. With that constitution, the device has extremely high sensitivity, and the bias point in the device is well controlled.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Spin dependent tunneling devices having reduced topological coupling
A ferromagnetic thin-film based magnetic device with internal film coupling compensation including a nonmagnetic material intermediate layer with an initial thin-film of an anisotropic ferromagnetic material on one side. A compensation thin-film of an anisotropic ferromagnetic material is provided on the opposite side with an antiparallel coupling layer thereon and a subsequent thin-film of an anisotropic ferromagnetic material on the antiparallel coupling layer with the compensation thin-film being less thick than the subsequent thin-film. A antiferromagnetic layer can be supported by the layers on either side of the intermediate layer.
Owner:NVE CORP
Device and method for detecting force thermal magnetic coupling action of ferromagnetic thin film
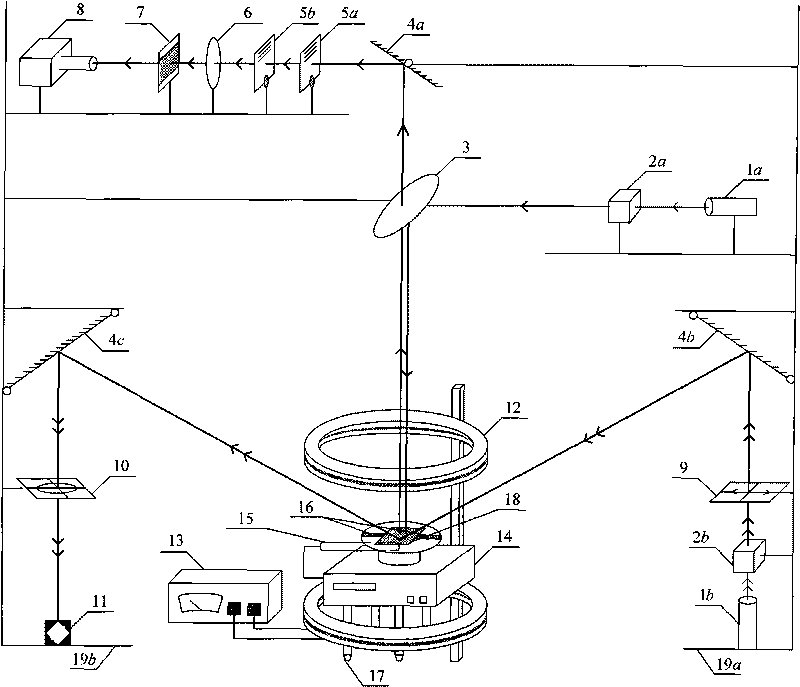
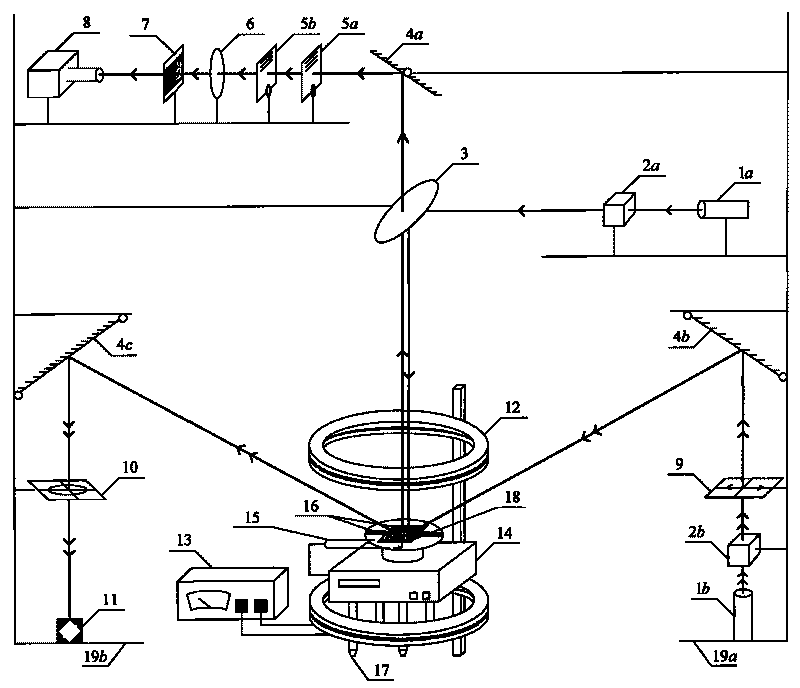
ActiveCN101706427ARealize onlineRealize non-contactPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansGratingHelmholtz coil
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting a force thermal magnetic coupling action of a ferromagnetic thin film, and belongs to the technical fields of engineering materials, structure deformation and mechanical experiments. The device comprises a ferromagnetic thin film uneven stress measuring optical circuit, a film magnetic hystersis loop measuring optical circuit, a Helmholtz coil and a power supply thereof, a test piece heating table, a thermocoupler, a force loading structure and an adjusting bracket. The film uneven stress measuring optical circuit comprises a laser, a beam expander, a spectroscope, a reflector, a raster, a lens, a filtering screen and a CCD camera; and the film magnetic hystersis loop measuring optical circuit comprises a laser, a beam expander, a reflector, a polarizer, a polarization analyzer and a photodetector. The method utilizes the Helmholtz coil to provide an even magnetic field for the ferromagnetic thin film, utilizes the test piece heating table to heat the film, utilizes the force loading structure to carry out force loading on the film, utilizes shearing interference to measure uneven curvature of the surface of the film and further obtain the stress of the film through the curvature, and utilizes Kerr magnetooptical effect on the surface of the ferromagnetic thin film to measure a magnetic hystersis loop of the film.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Thin film memory device having local and external magnetic shielding
InactiveUS6872993B1Reduce undesirable fieldOvercome disadvantagesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThin-film memoryMagnetic memory
A monolithically formed ferromagnetic thin-film memory is disclosed that has local shielding on at least two sides of selected magnetic storage elements. The local shielding preferably extends along the back and side surfaces of a word line and / or digital lines of a conventional magnetic memory. In this configuration, the local shielding not only may help reduce externally generated EMI, internally generated cross-talk and other unwanted fields in the magnetic bit region, but may also help enhance the desired magnetic fields in the bit region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
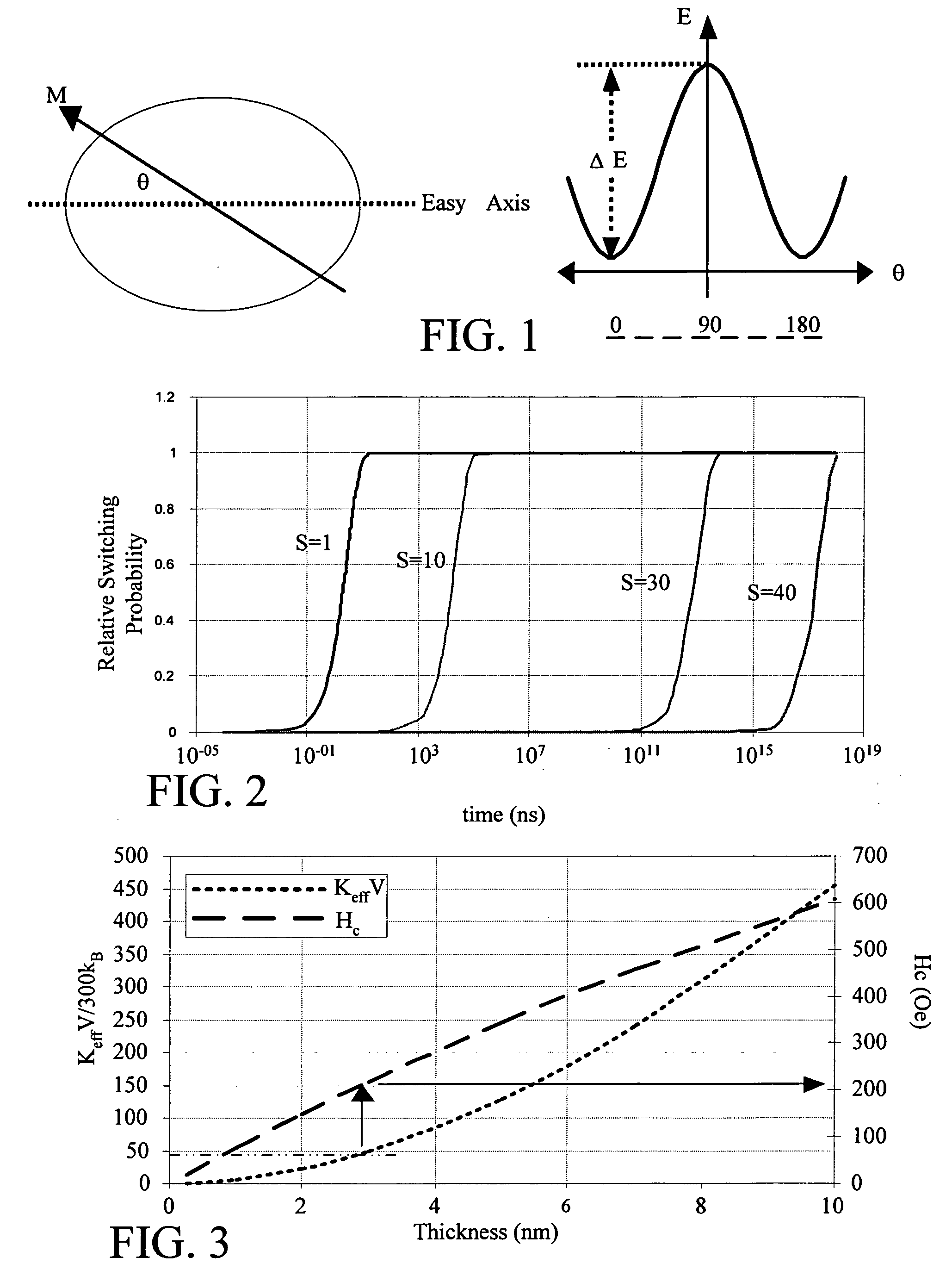
Methods of manipulating the relaxation rate in magnetic materials and devices for using the same
InactiveUS20070242395A1Reduced dampingLow intrinsic damping rateNanomagnetismImpedence networksManganeseThin membrane
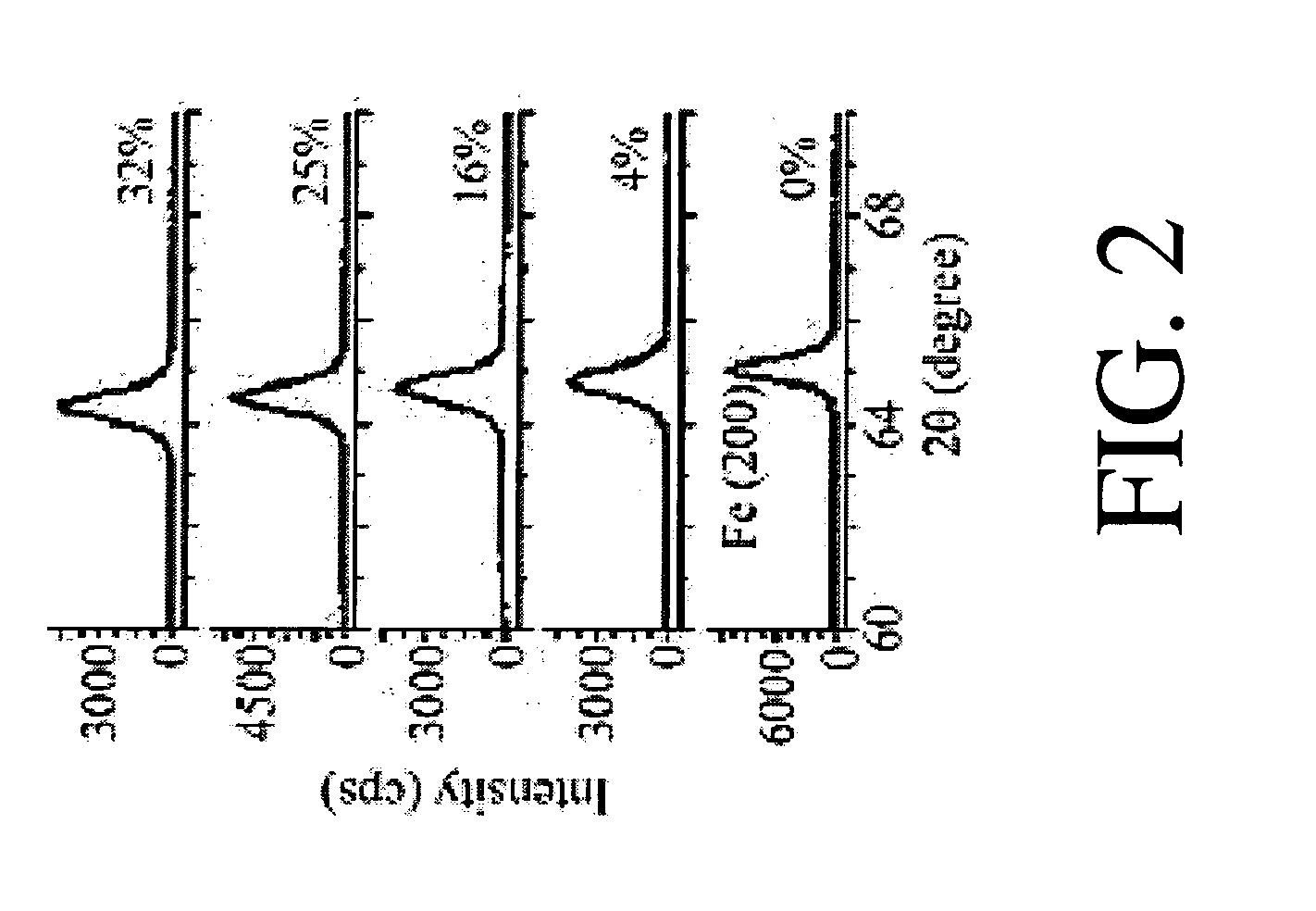
In accordance with the present invention, ferromagnetic thin films of iron that have reduced relaxation rates and methods of making the same are provided. It should be noted that pure iron is a ferromagnet (i.e., has a spontaneous magnetization alignment) with the lowest intrinsic damping rate of all of the ferromagnets. The present invention provides a ferromagnetic structure comprising a substrate and a ferromagnetic thin film of iron (Fe) formed on the substrate. An element selected from the group consisting of titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), and manganese (Mn) (i.e., a lower-Z transition metal element) is alloyed with the ferromagnetic thin film of iron to reduce the relaxation rate of the ferromagnetic thin film.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Thin film magnet, cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film and production method thereof
InactiveUSRE36517E1Improve magnetic propertiesSmall sizeFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementPerpendicular magnetizationGas phase
A thin film magnet and a cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film having a high maximum energy product (greater than 120 kJ / m3) and thus suitable for use in miniature high performance devices are provided. The thin film magnet is produced by means of physical vapor deposition. The thin film magnet is an (Nd1-xRx)yM1-y-zBz alloy having a ferromagnetic compound of the Nd2Fe14B type as its main phase, wherein R is Tb, Ho, and Dy and M is Fe metal or an Fe-based alloy including at least one of Co and Ni, 0.04< / =x< / =0.10,0.11< / =y< / =0.15, and 0.08< / =z< / =0.15. A perpendicular magnetization film having such a composition is deposited on the side wall of a substrate in the columnar (or cylindrical) form thereby obtaining a cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film having radial anisotropy.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film and element, magnetoresistive sensor using same, magnetic apparatus, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7160572B2Reduced effectivenessPrevent oxidationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsNitrogen gasOxygen
In a spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film in which a magnetic thin film to which an exchange bias is applied by exchange coupling via an anti-ferromagnetic thin film and a magnetic thin film that detects a magnetic field are laminated, a magnetic thin film or an anti-ferromagnetic thin film (PtMn, PdMn, NiMn) is laminated onto an underlayer (Ta, Zr, Hf), the surface roughness thereof being in the range from 0.1 to 5 Angstroms. A means used to control the surface roughness introduces into the film growing chamber oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, or a gas mixture thereof into a vacuum of 10−6 Torr to 10−9 Torr, reduces the substrate temperature to 0° C. or lower during film growth, or oxidizes an underlayer. The lower electrode layer material used is a film laminate of a high-permeability amorphous magnetic material and a non-magnetic metallic layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
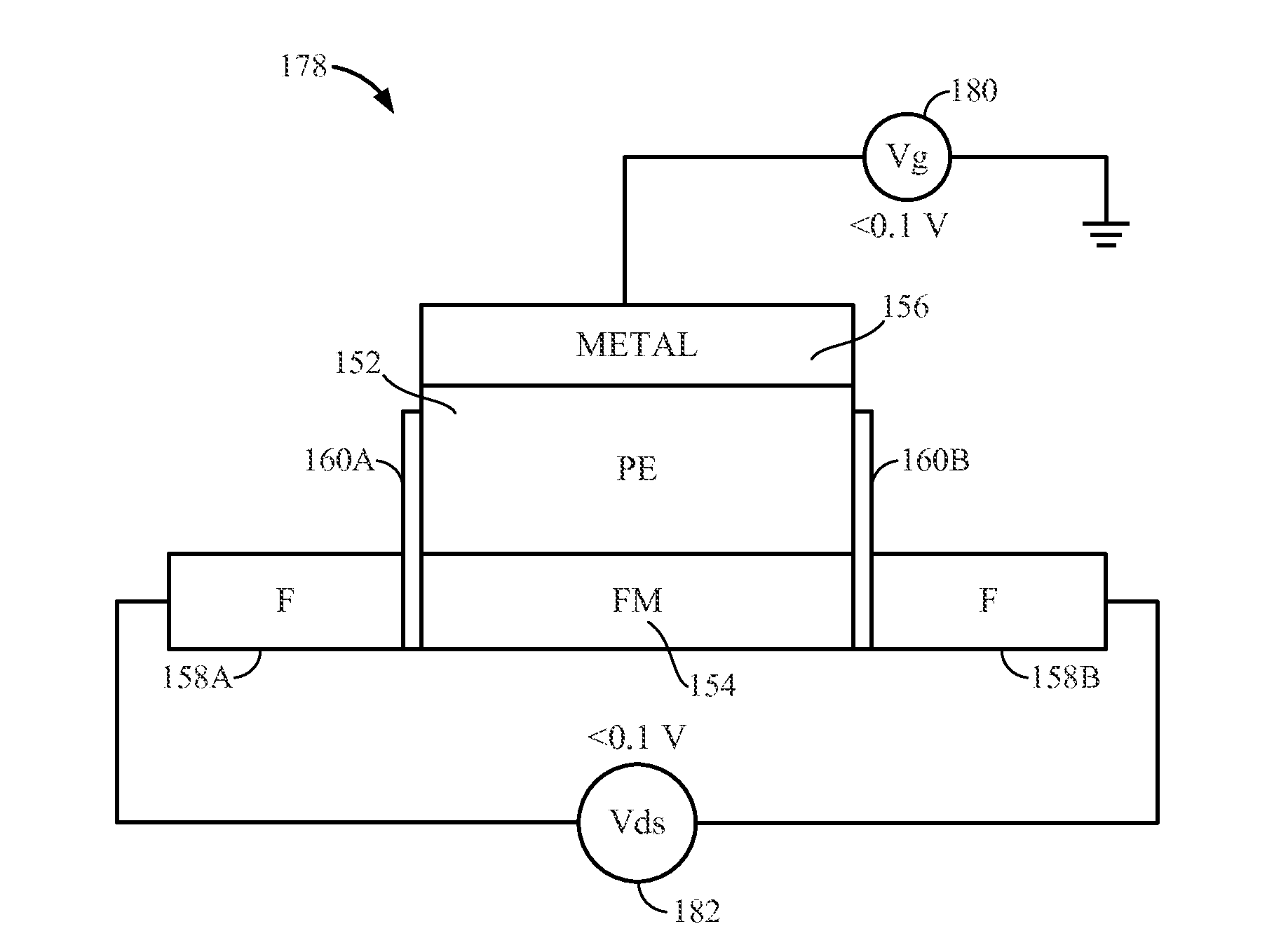
Spin Transistors Employing a Piezoelectric Layer and Related Memory, Memory Systems, and Methods
ActiveUS20130299880A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsSpin transitionSpin channel
Spin transistors and related memory, memory systems, and methods are disclosed. A spin transistor is provided by at least two magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) with a shared multiferroic layer. The multiferroic layer is formed from a piezoelectric (PE) thin film over a ferromagnetic thin film (FM channel) with a metal electrode (metal). The ferromagnetic layer functions as the spin channel and the piezoelectric layer is used for transferring piezoelectric stress to control the spin state of the channel. The MTJ on one side of the shared layer forms a source and the MTJ on the other side is a drain for the spin transistor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Stabilized shields for magnetic recording heads
ActiveUS8514524B2Large reductions (or elimination) of the shield net momentGood pinningRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsThick plateAntiferromagnetic coupling
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic memory layers thermal pulse transitions
ActiveUS7023723B2Stay magneticMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesDigital storageMagnetic memory
A ferromagnetic thin-film based digital memory having a bit structures therein a magnetic material film in which a magnetic property thereof is maintained below a critical temperature above which such magnetic property is not maintained, and may also have a plurality of word line structures each with heating sections located across from the magnetic material film in a corresponding one of the bit structures. These bit structures are sufficiently thermally isolated to allow selected currents in the adjacent word lines or in the bit structure, or both, to selectively heat the bit structure to approach the critical temperature. Such bit structures may have three magnetic material layers each with its own critical temperature for maintaining versus not maintaining a magnetic property thereof.
Owner:NVE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com