Patents
Literature
41 results about "Spontaneous magnetization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
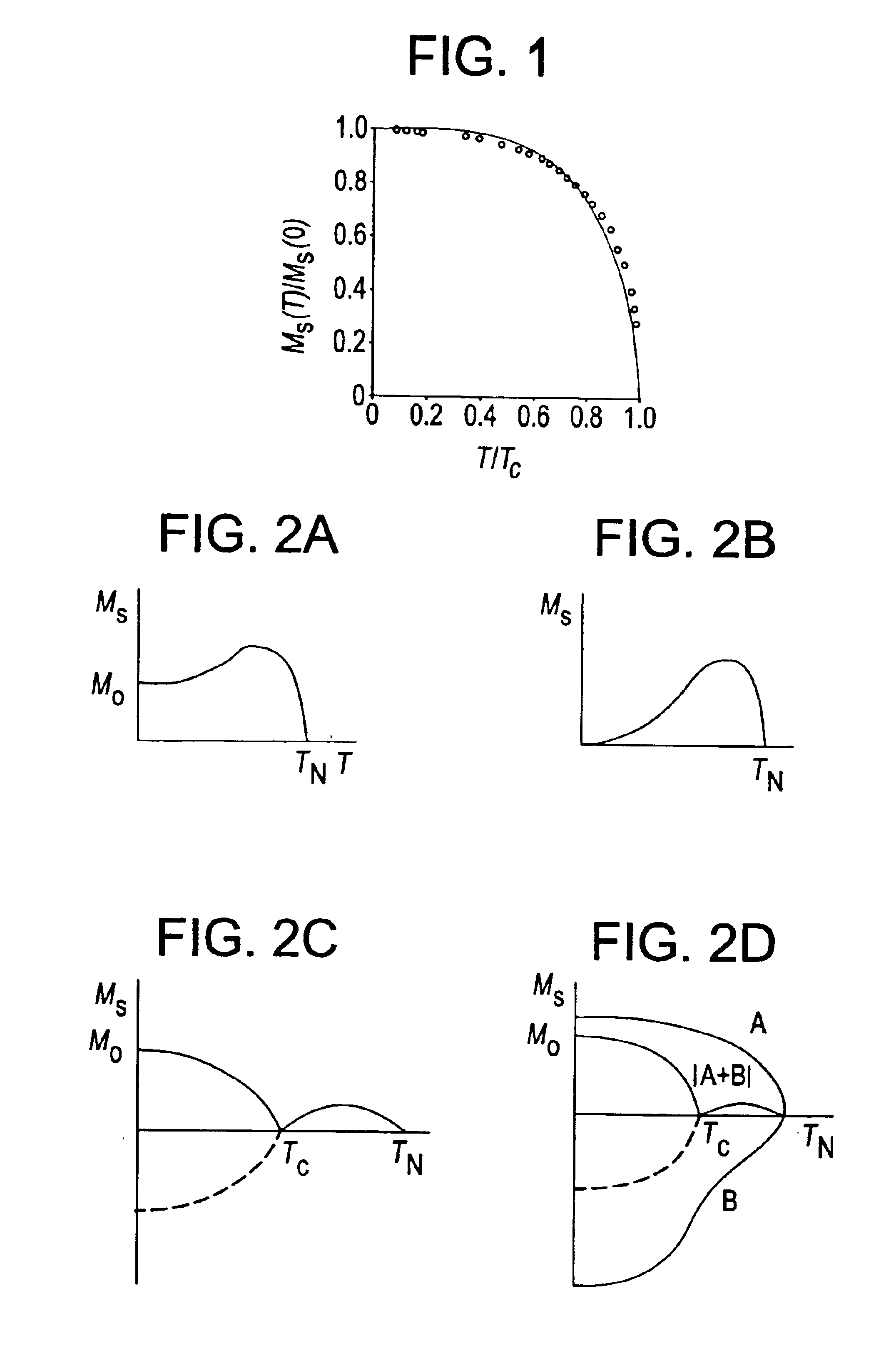
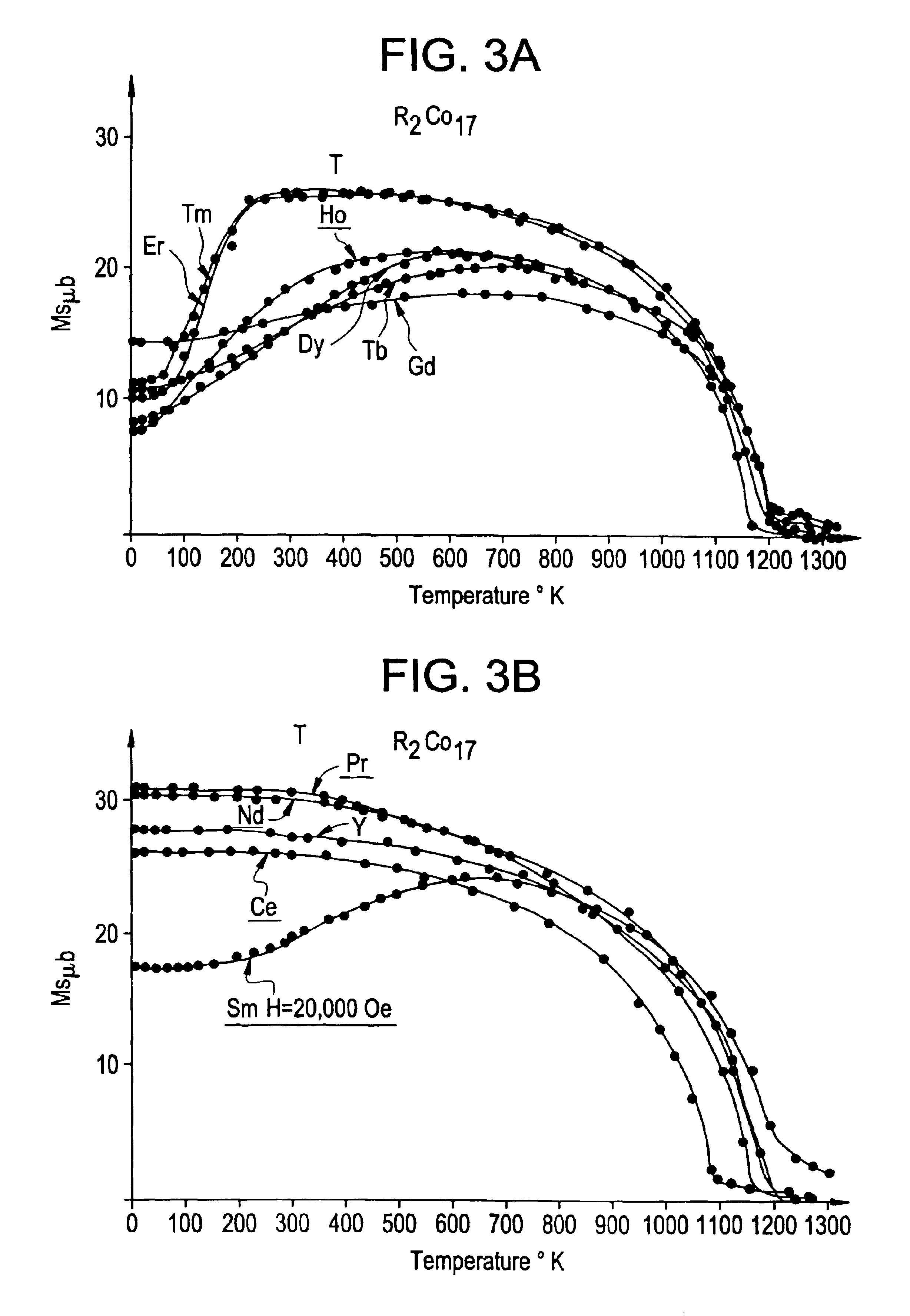
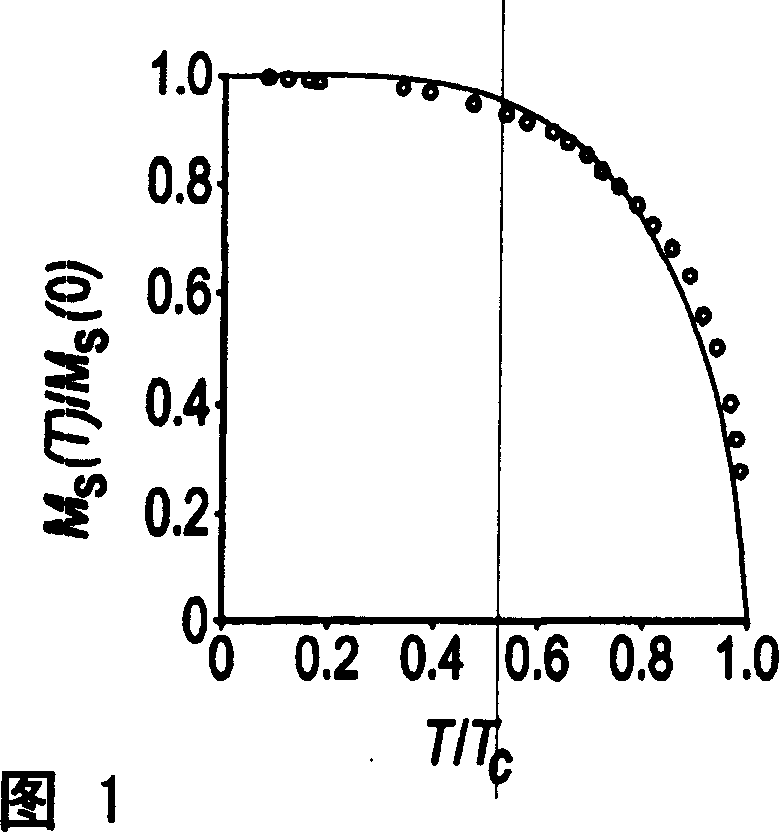
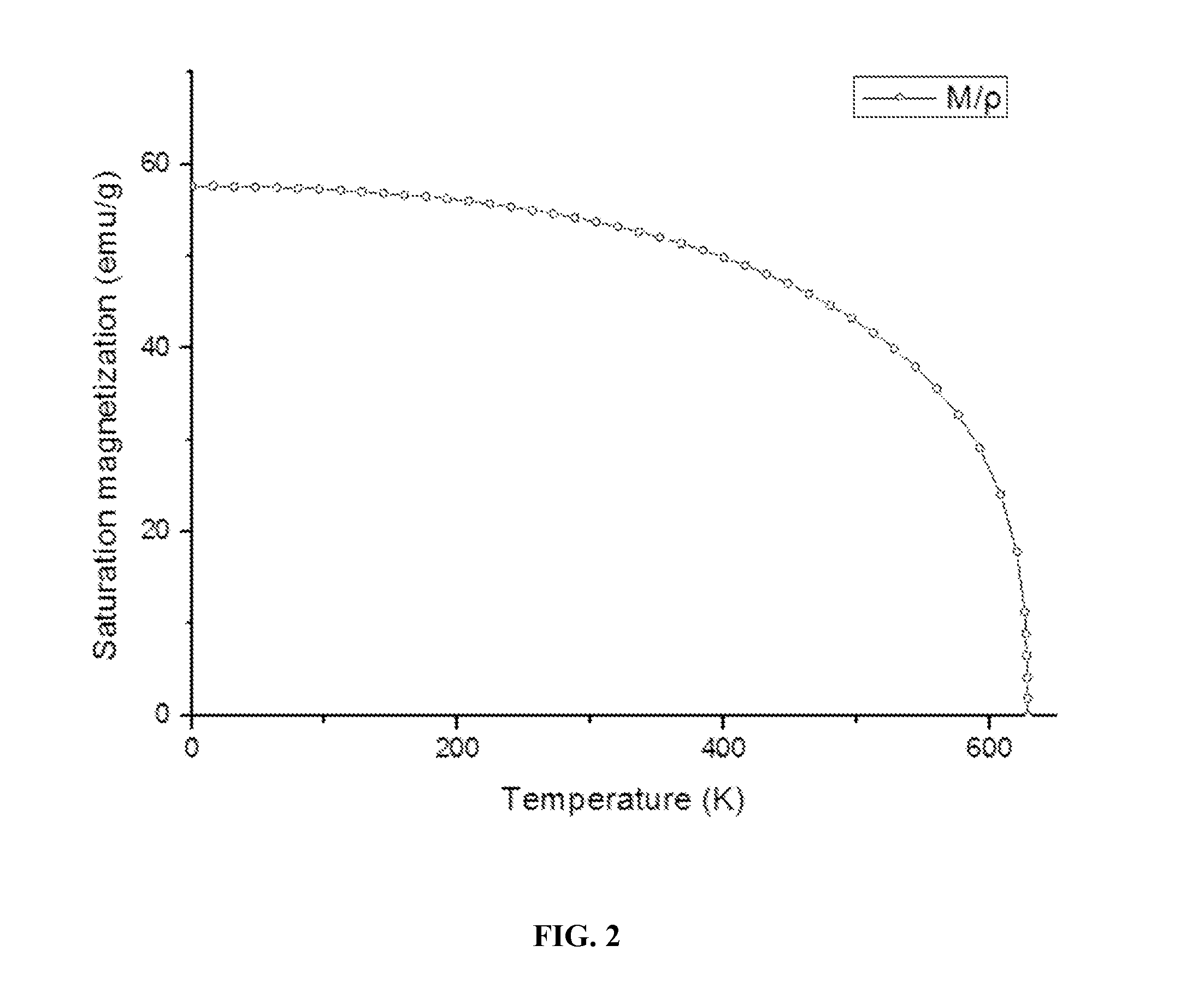
Spontaneous magnetization is the appearance of an ordered spin state (magnetization) at zero applied magnetic field in a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material below a critical point called the Curie temperature or TC.
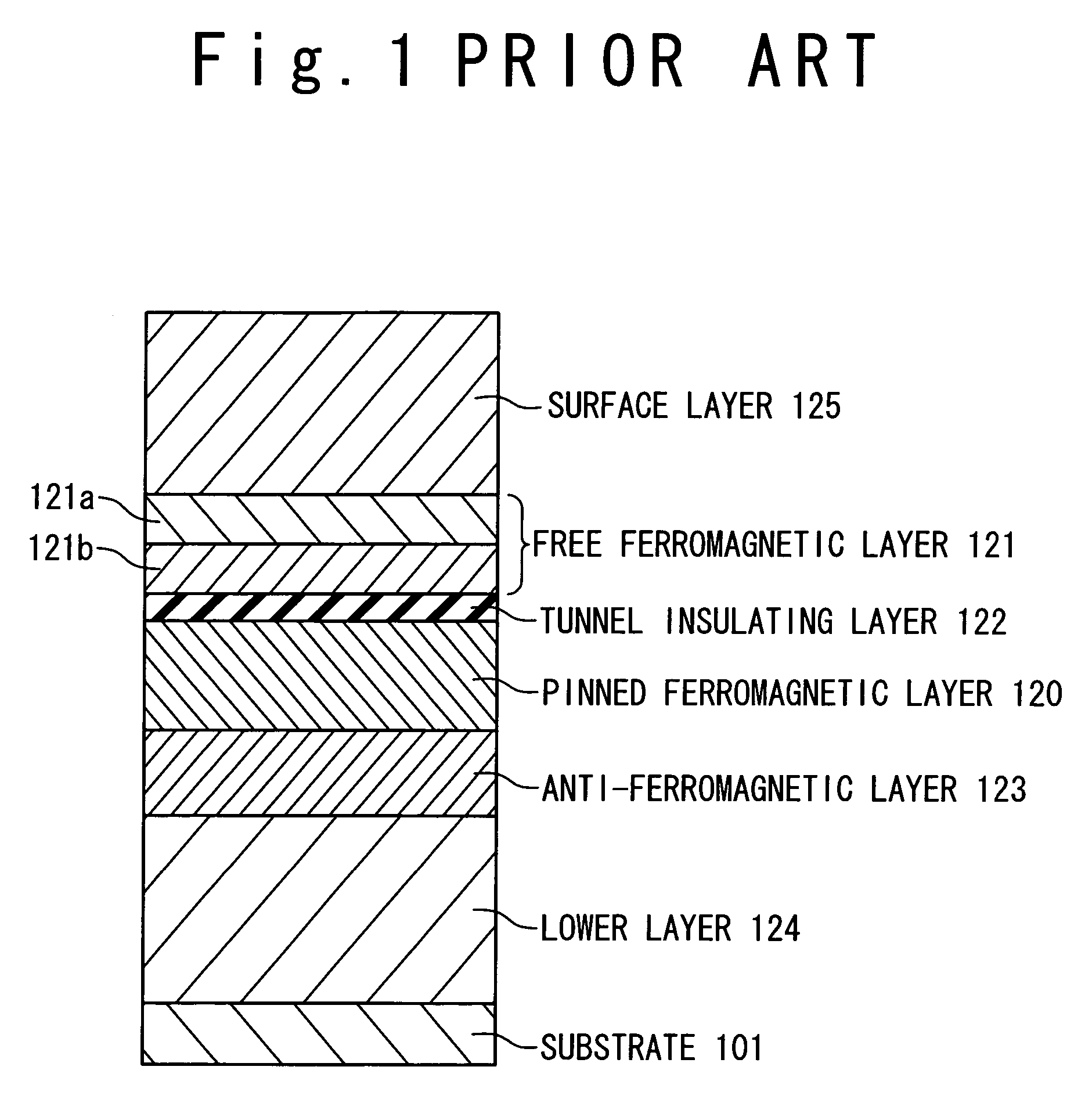
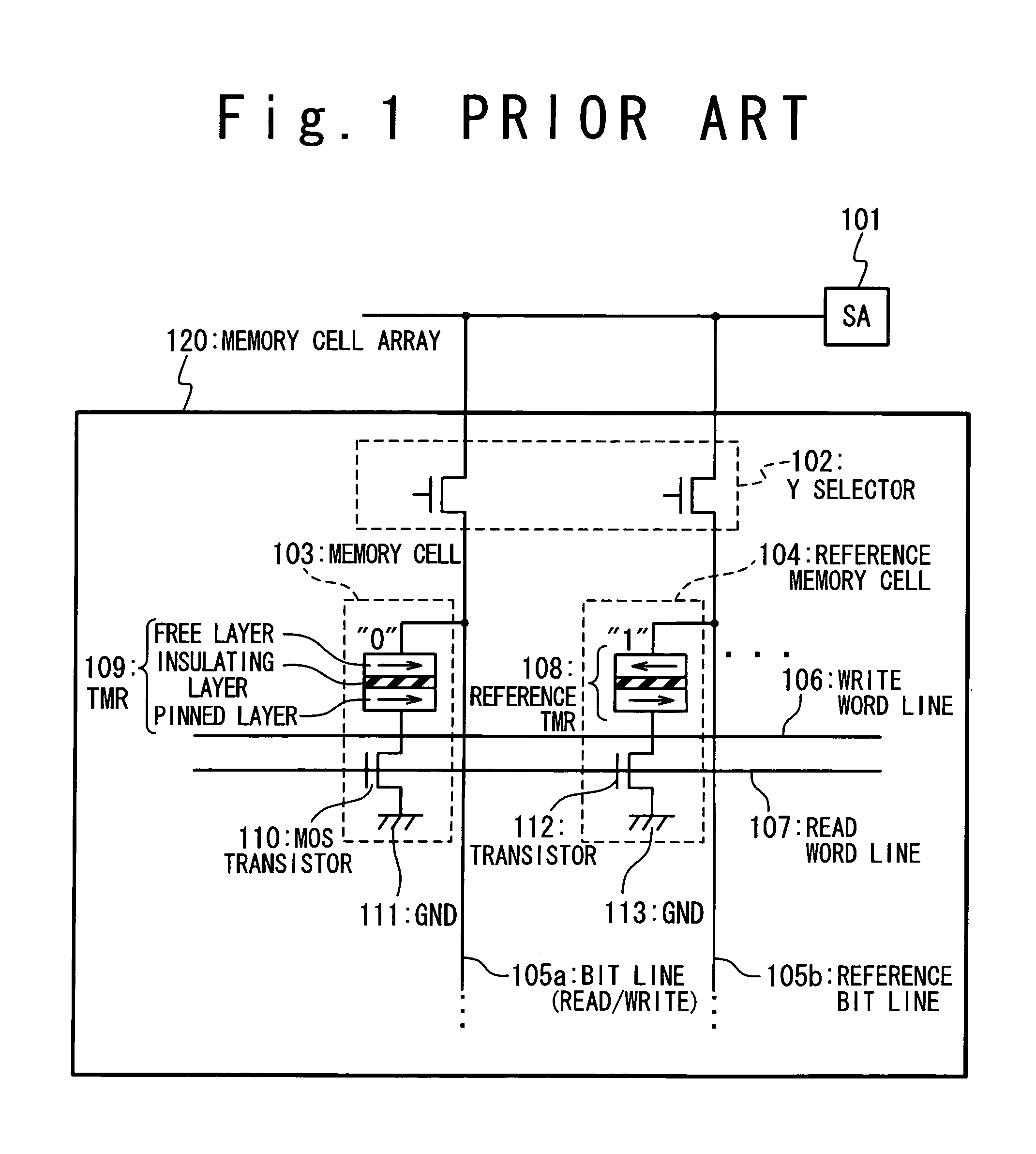
Magnetoresistance device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20040145850A1Nanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical conductorElectrical connection
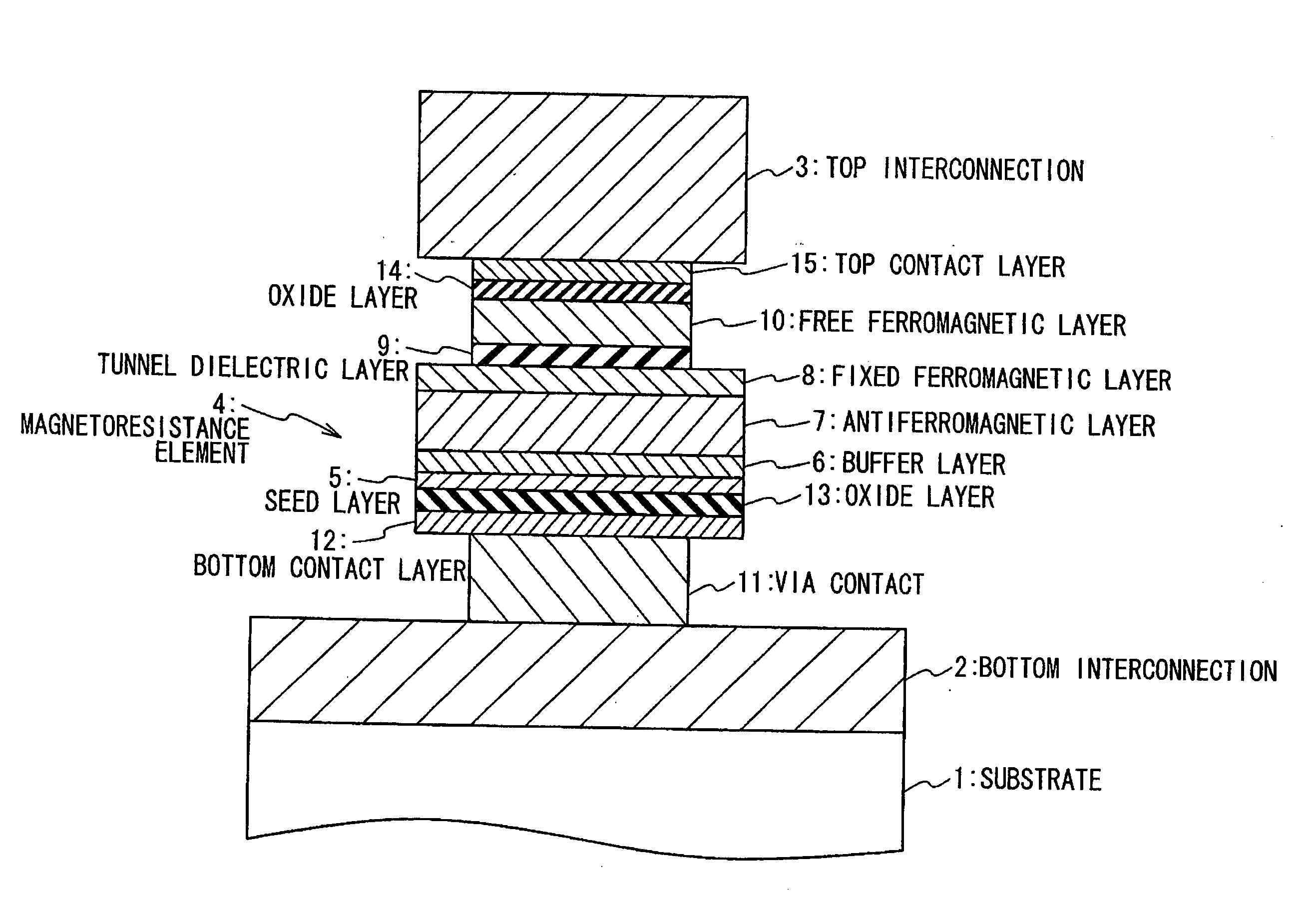
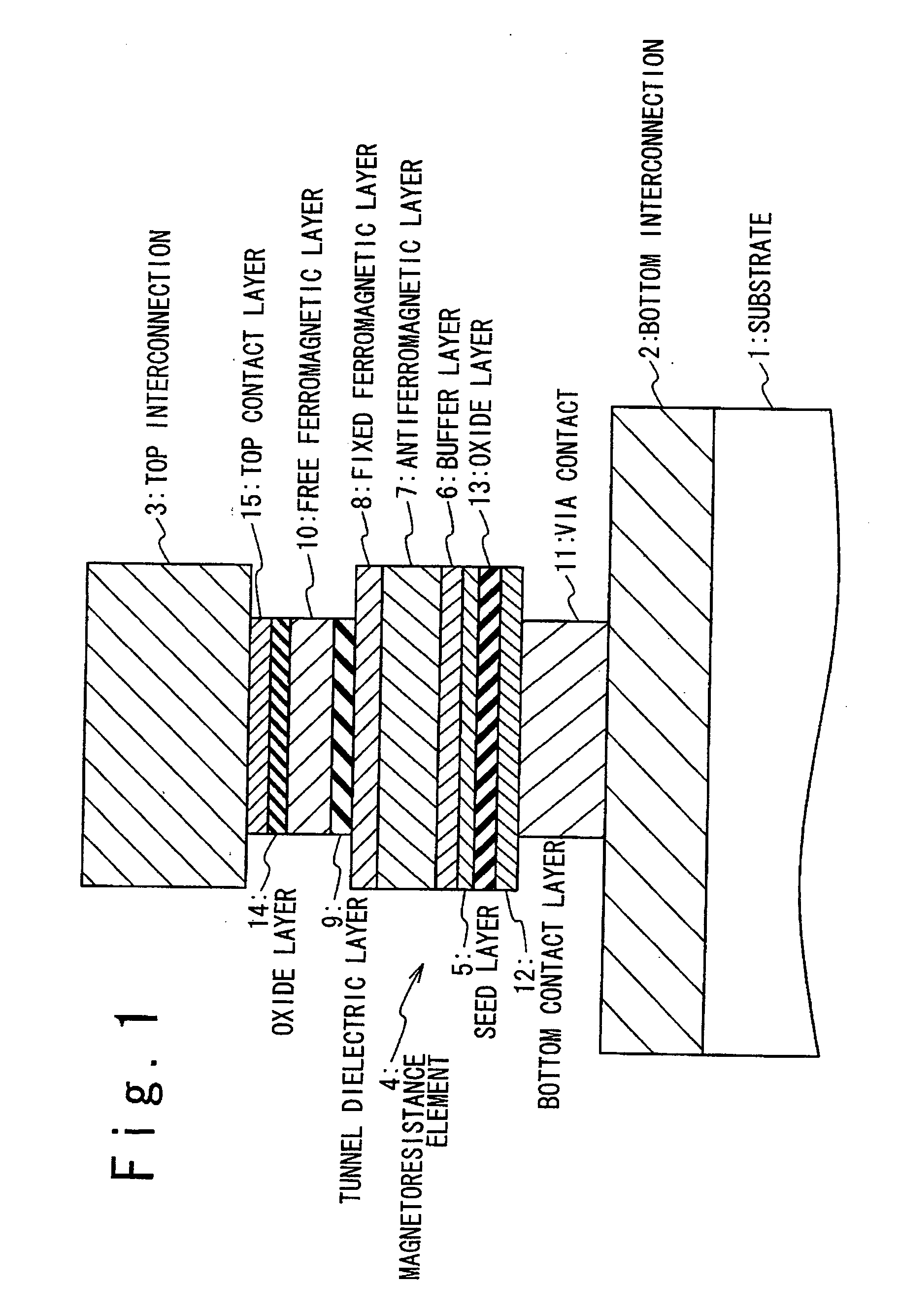
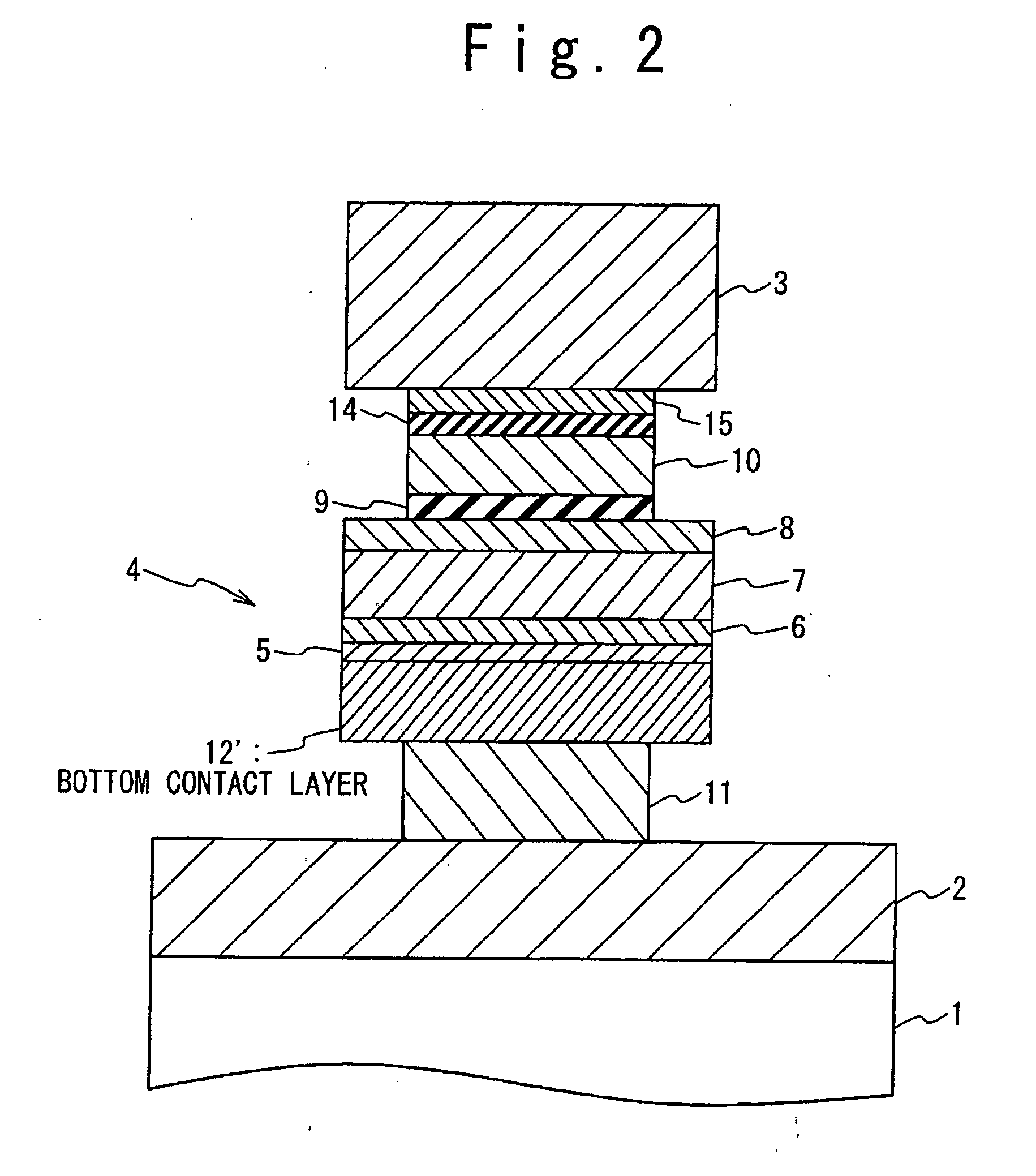
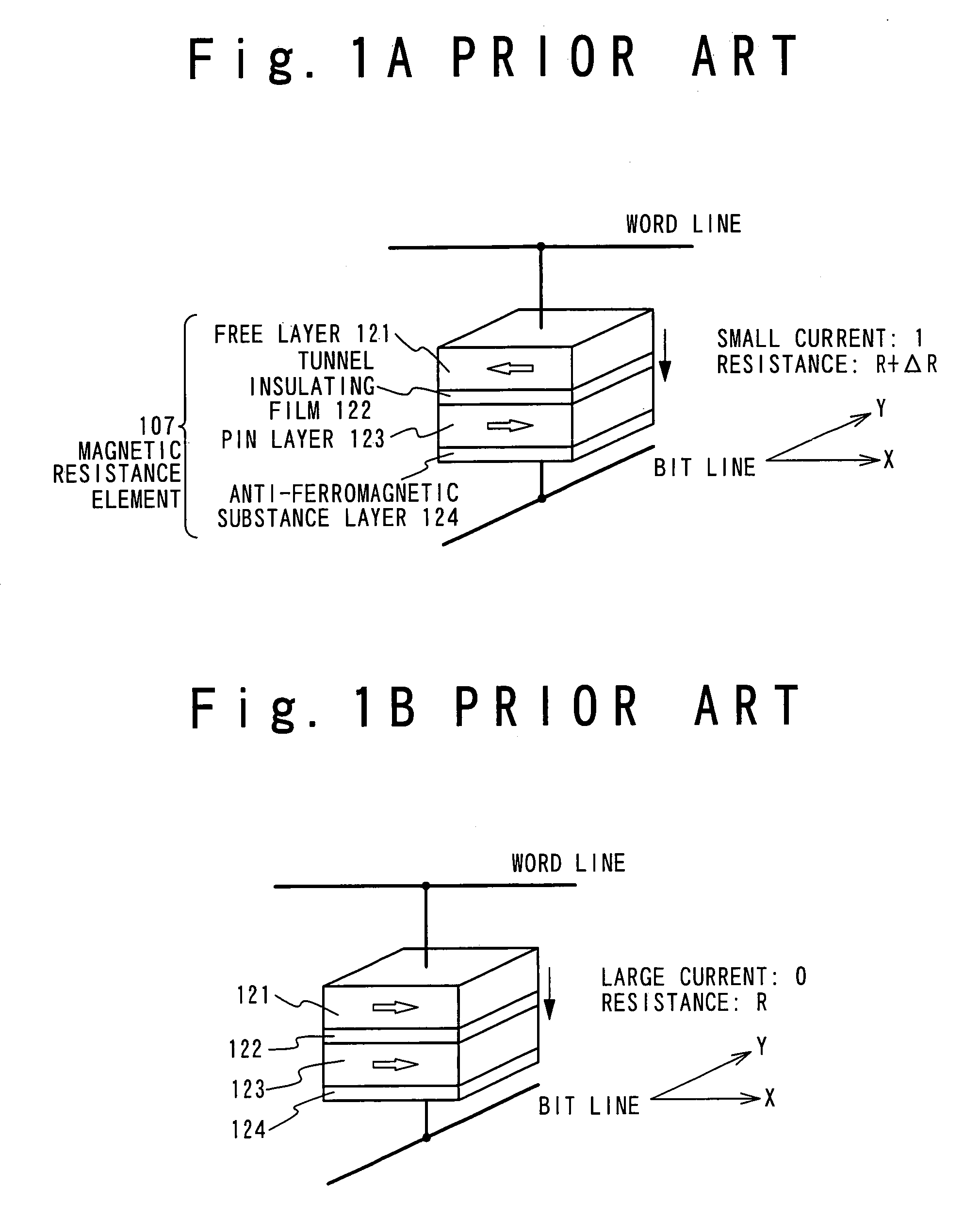
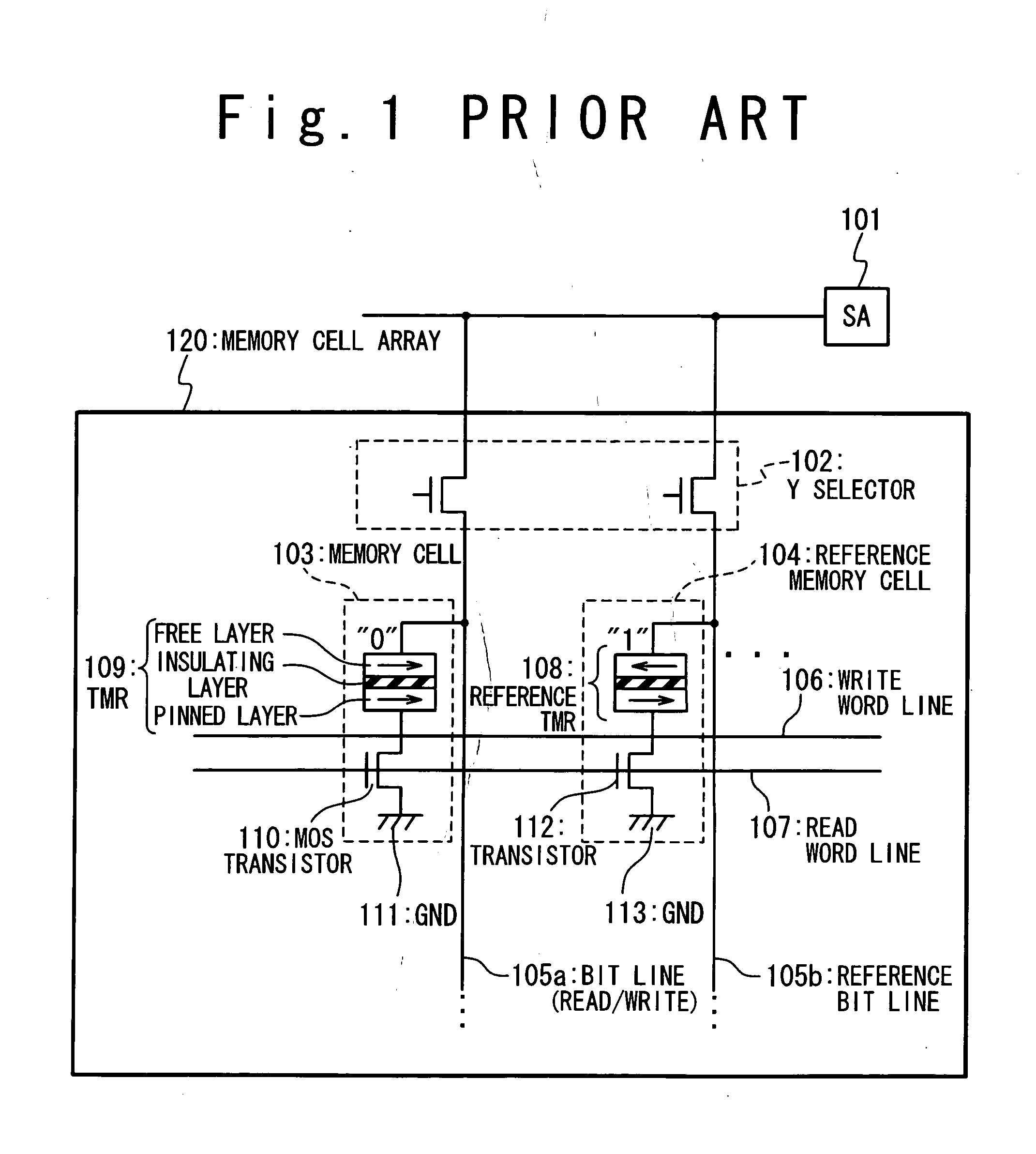
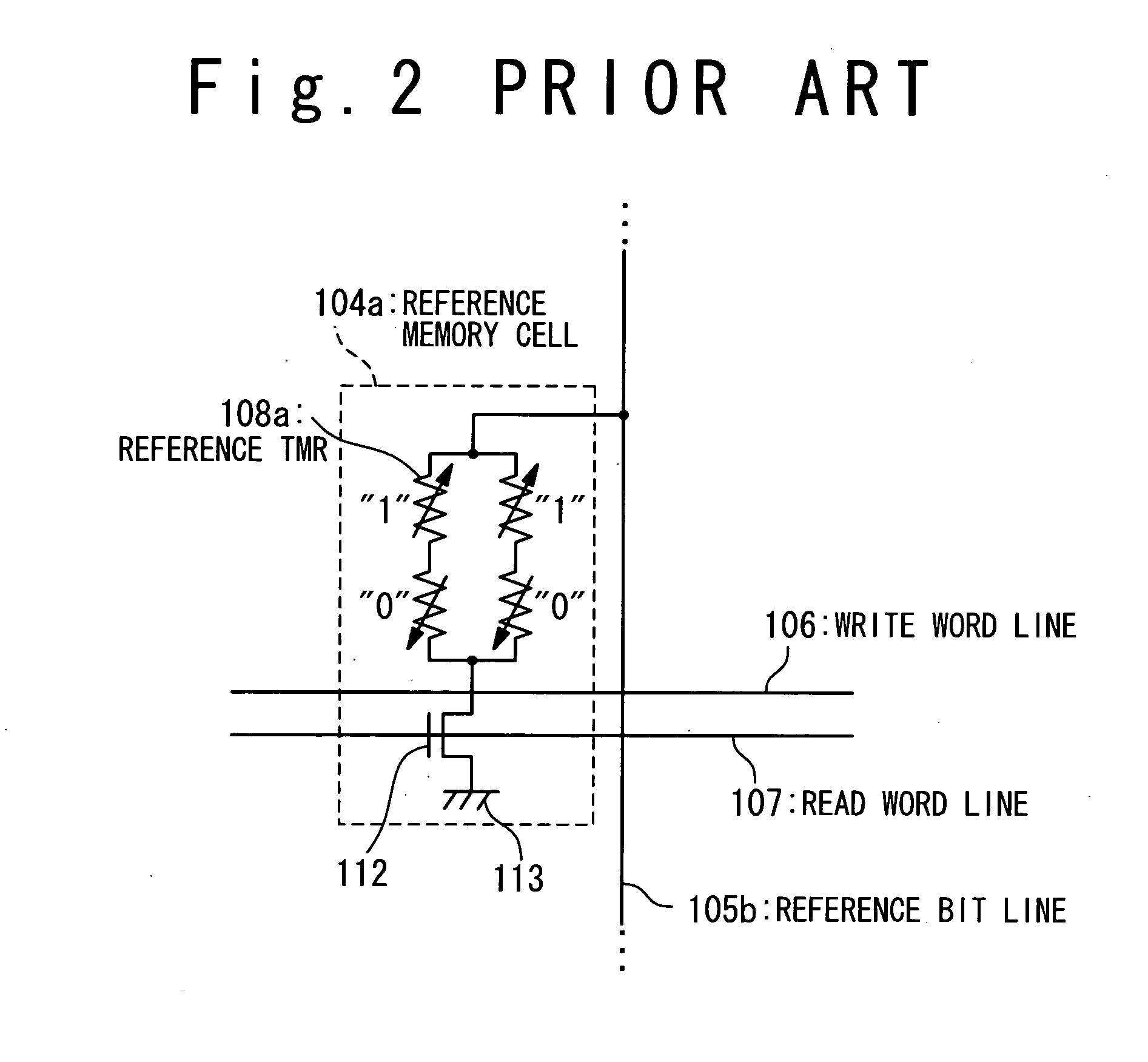
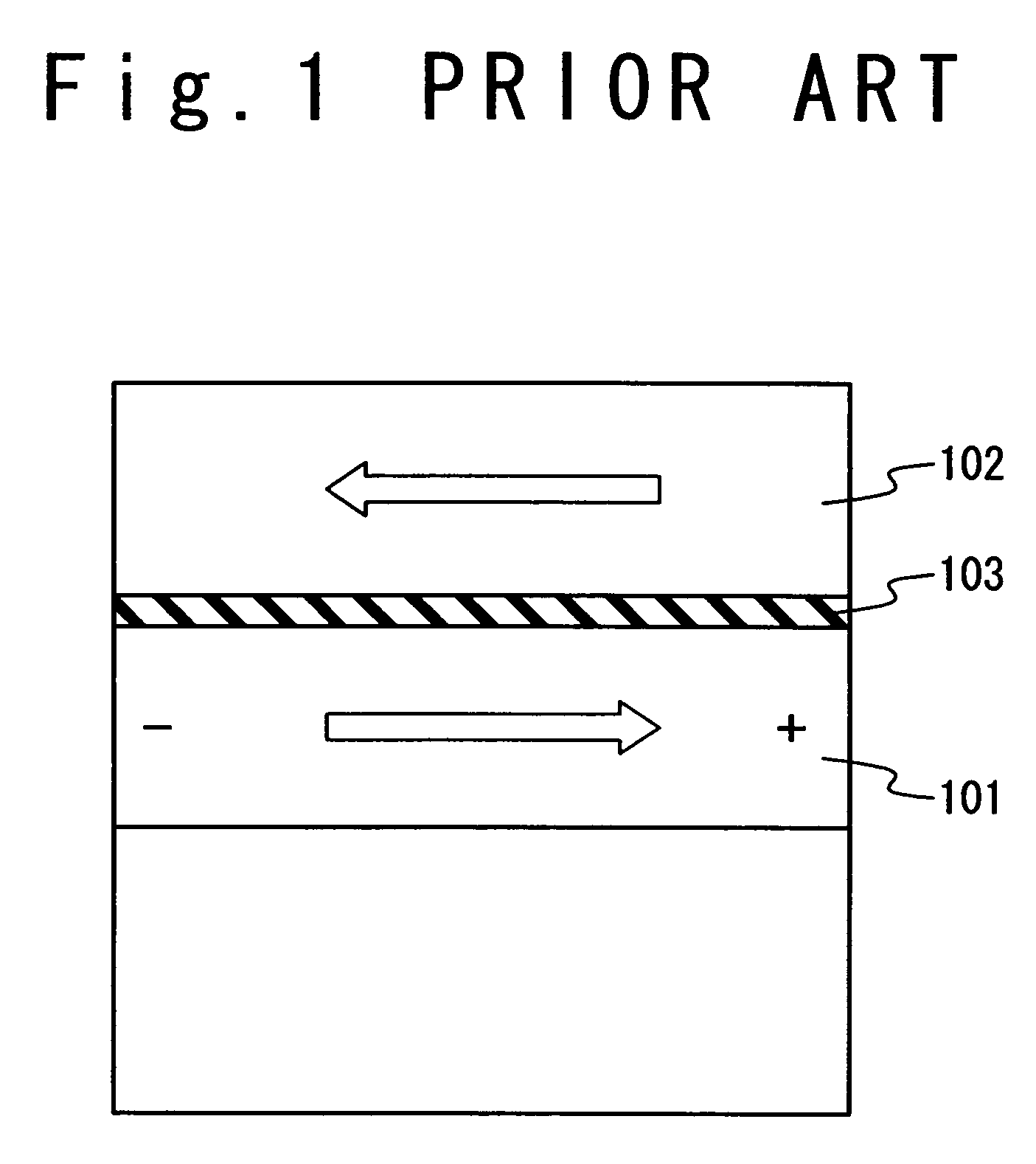
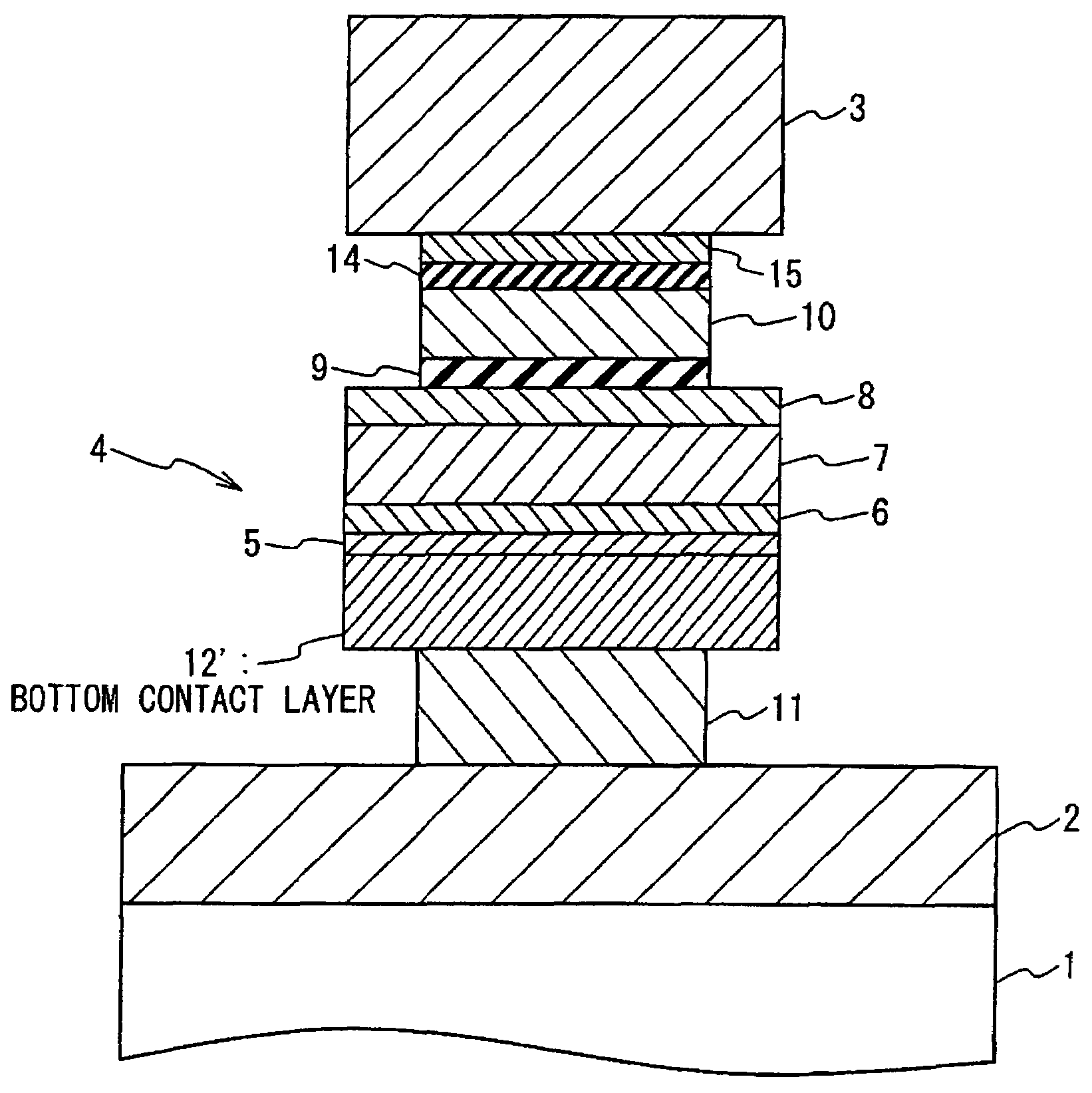
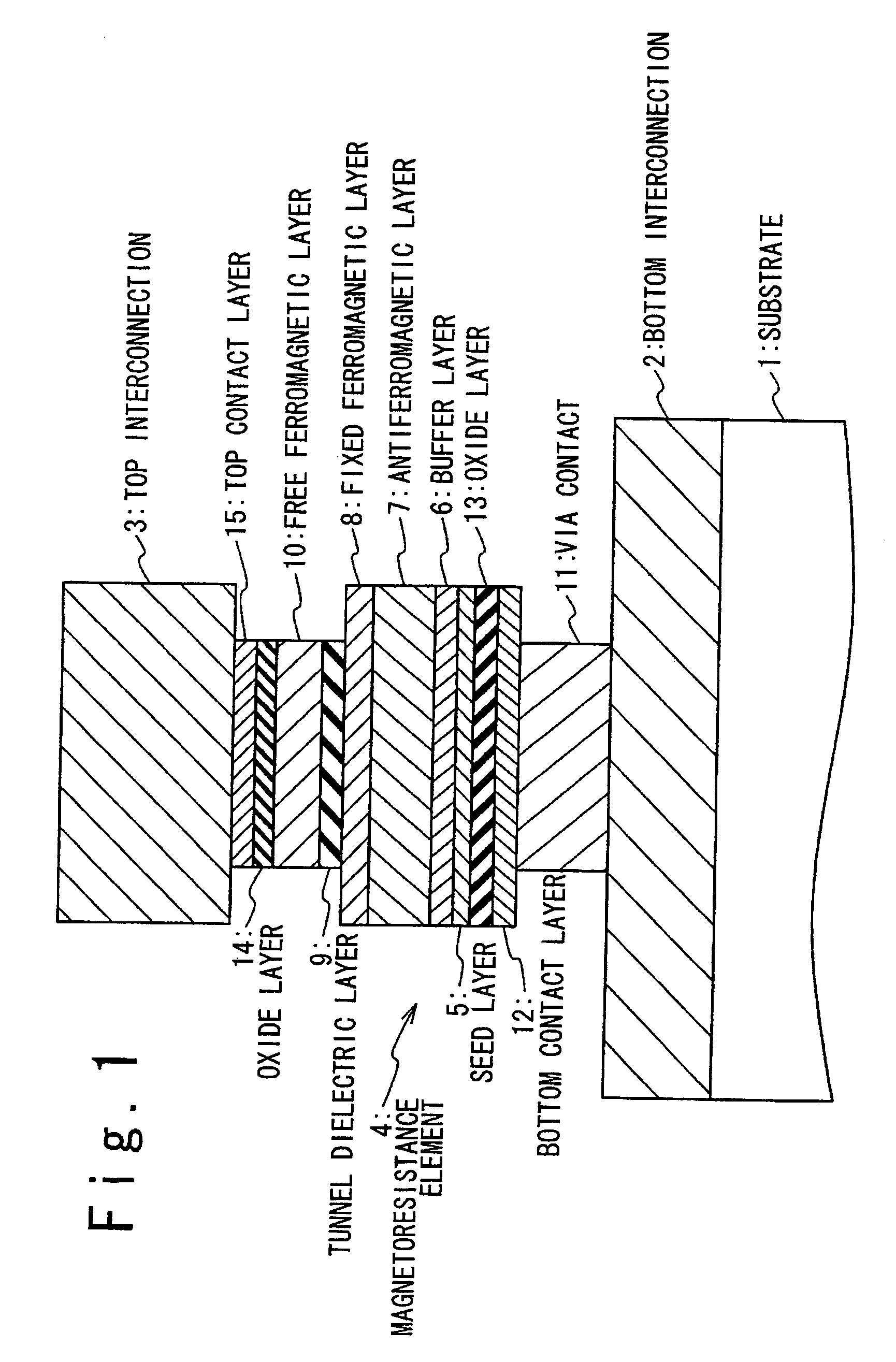
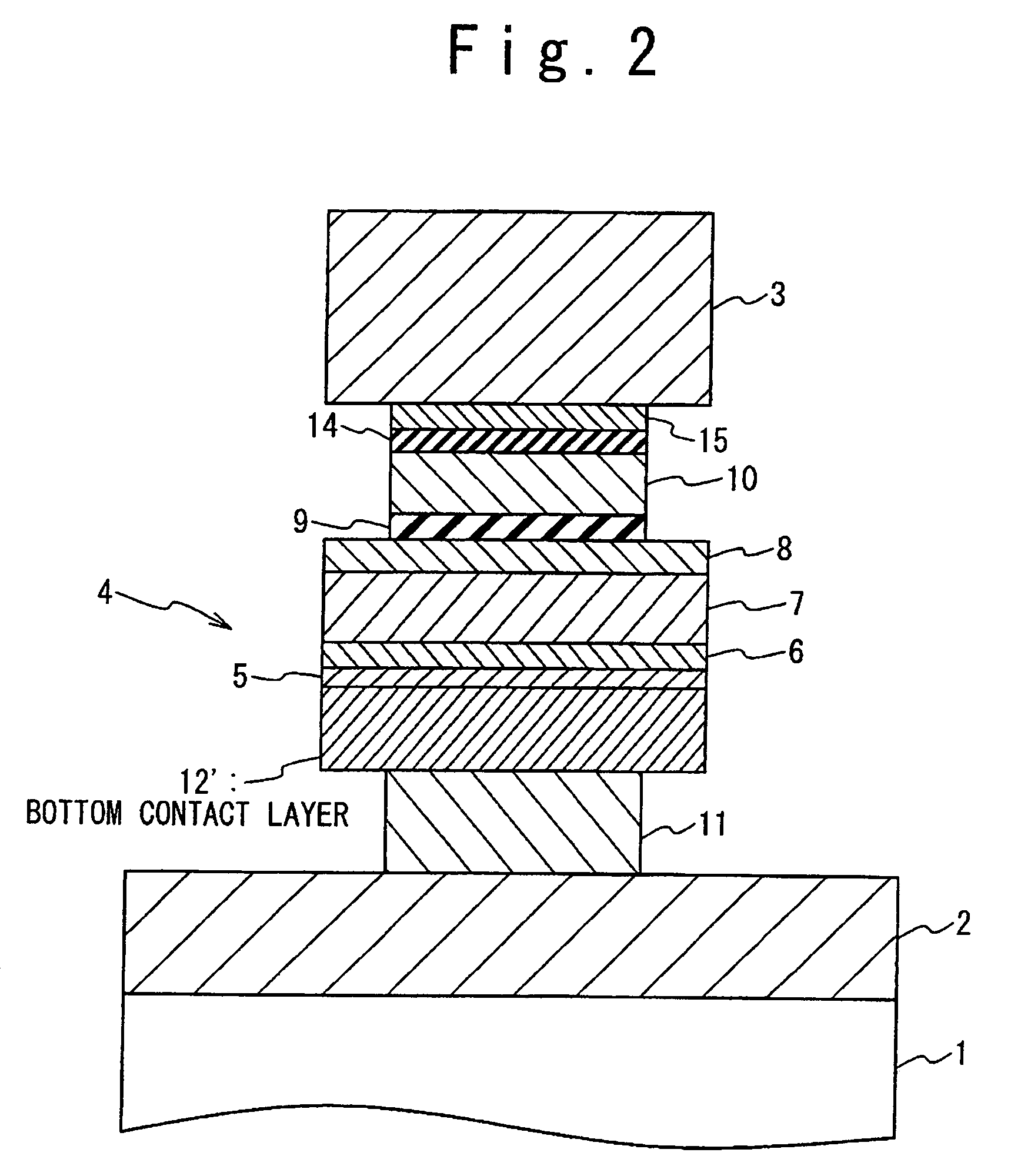
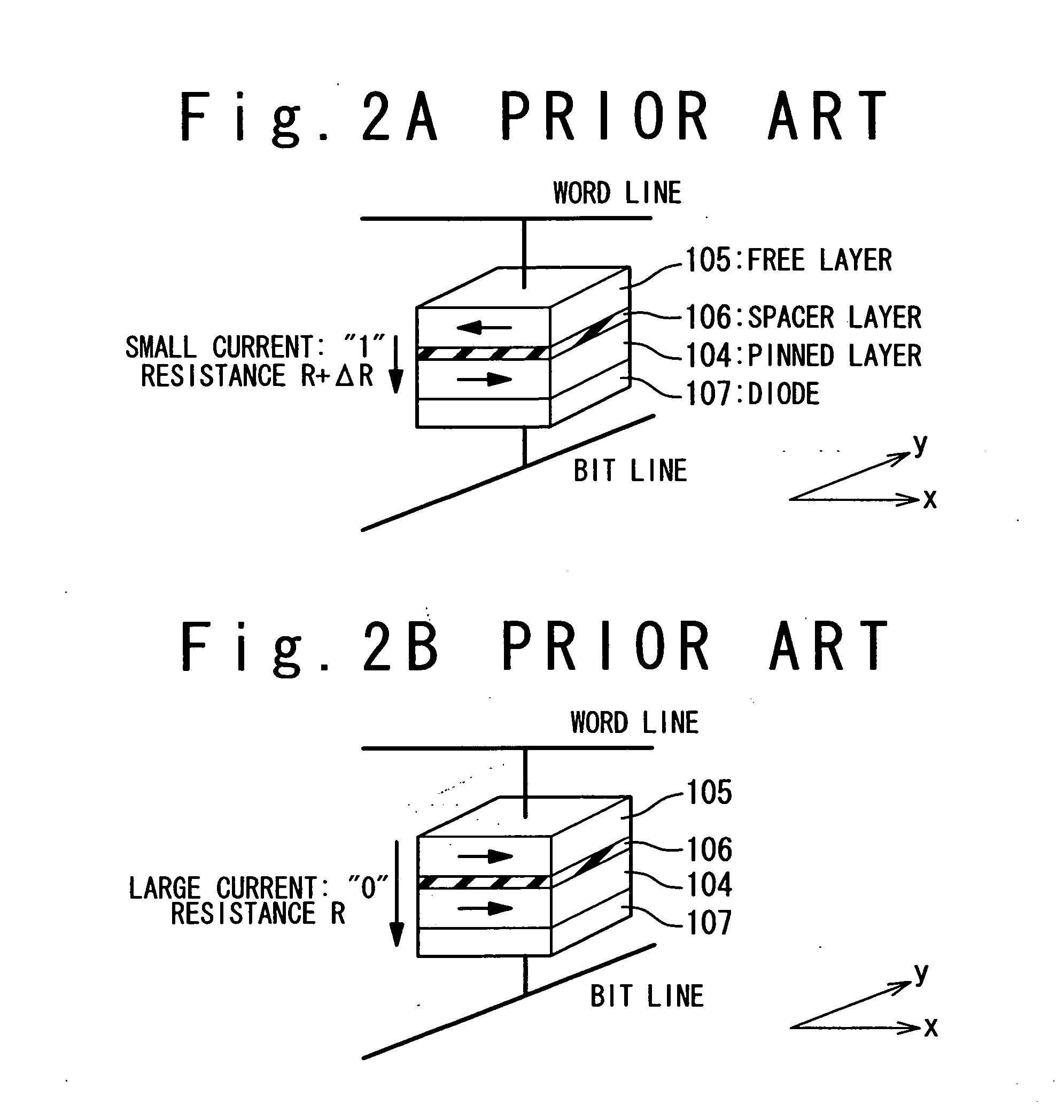
A magnetoresistance device is provided for improving thermal stability of a magnetoresistance element by preventing interdiffusion between a conductor (such as a via and an interconnection) for connecting the magnetoresistance element to another element and layers constituting the magnetoresistance element. A magnetoresistance device is composed of a magnetoresistance element, a non-magnetic conductor providing electrical connection between said magnetoresistance element to another element, and a diffusion barrier structure disposed between said conductor and said magnetoresistance element, the magnetoresistance element including a free ferromagnetic layer having reversible spontaneous magnetization, a fixed ferromagnetic layer having fixed spontaneous magnetization, and a tunnel dielectric layer disposed between said free and fixed ferroelectric layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
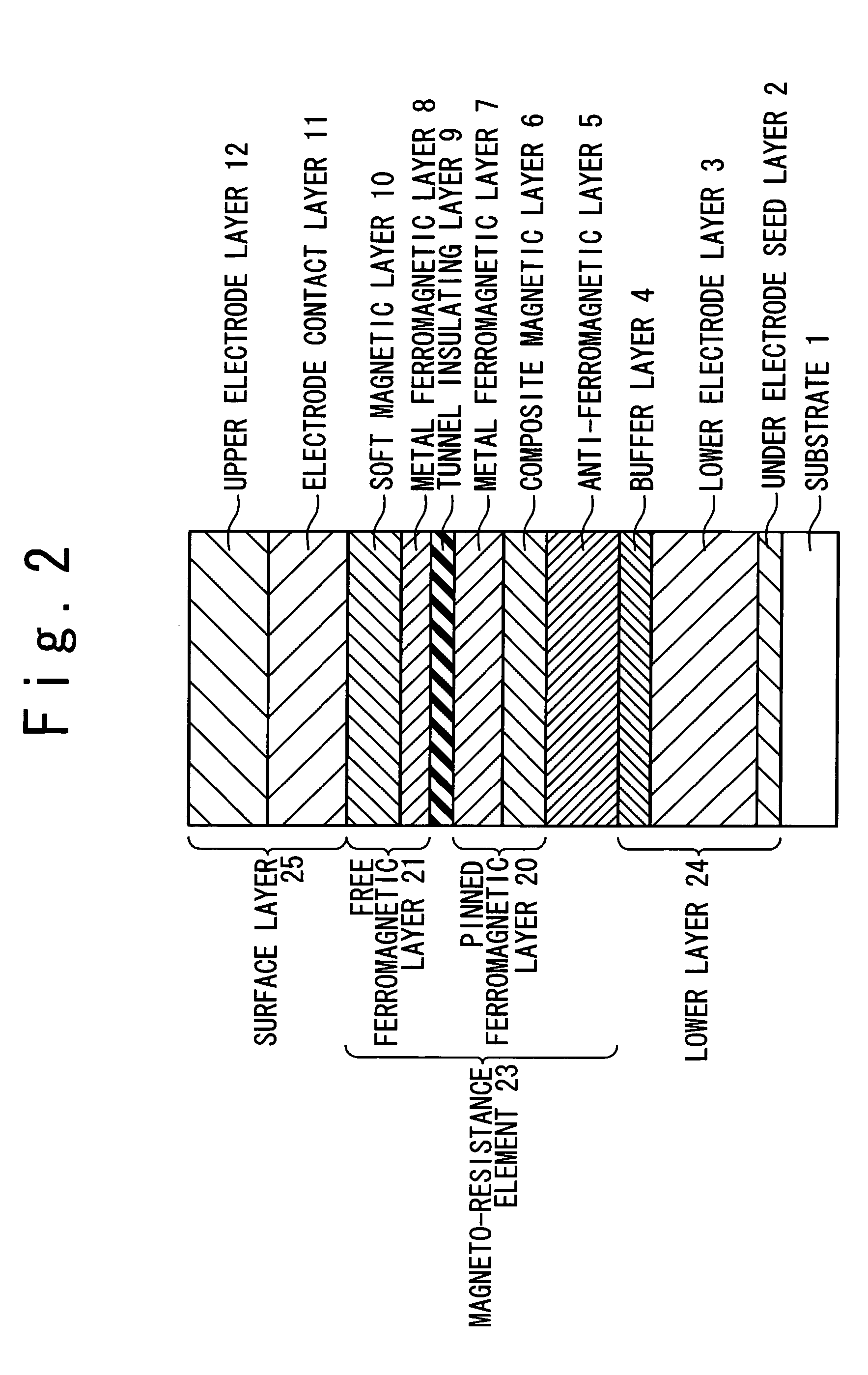
Magnetic tunnel magneto-resistance device and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7379280B2Thermal stability (thermal treatment resistance)Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic memoryMagnetic reluctance
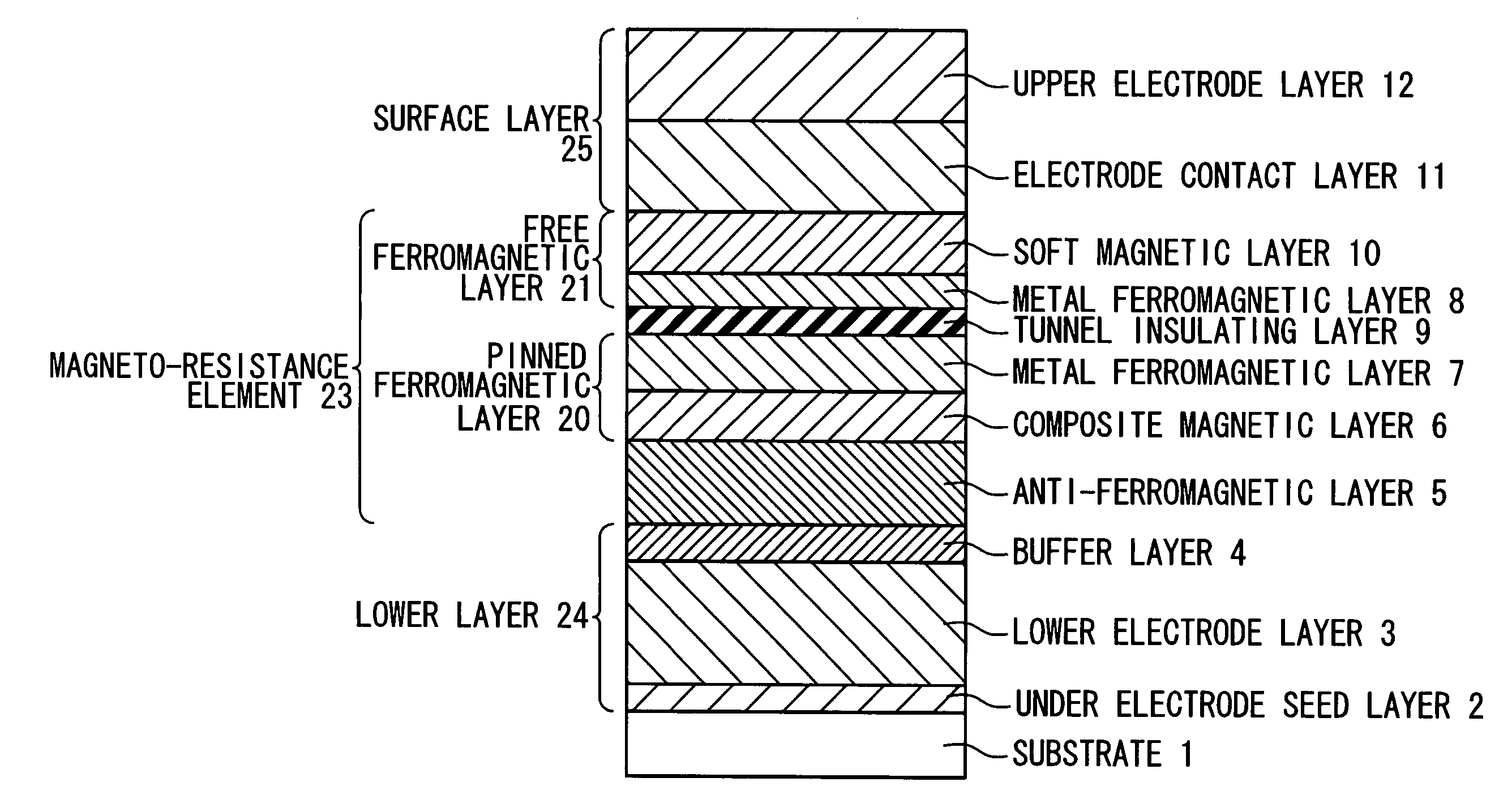
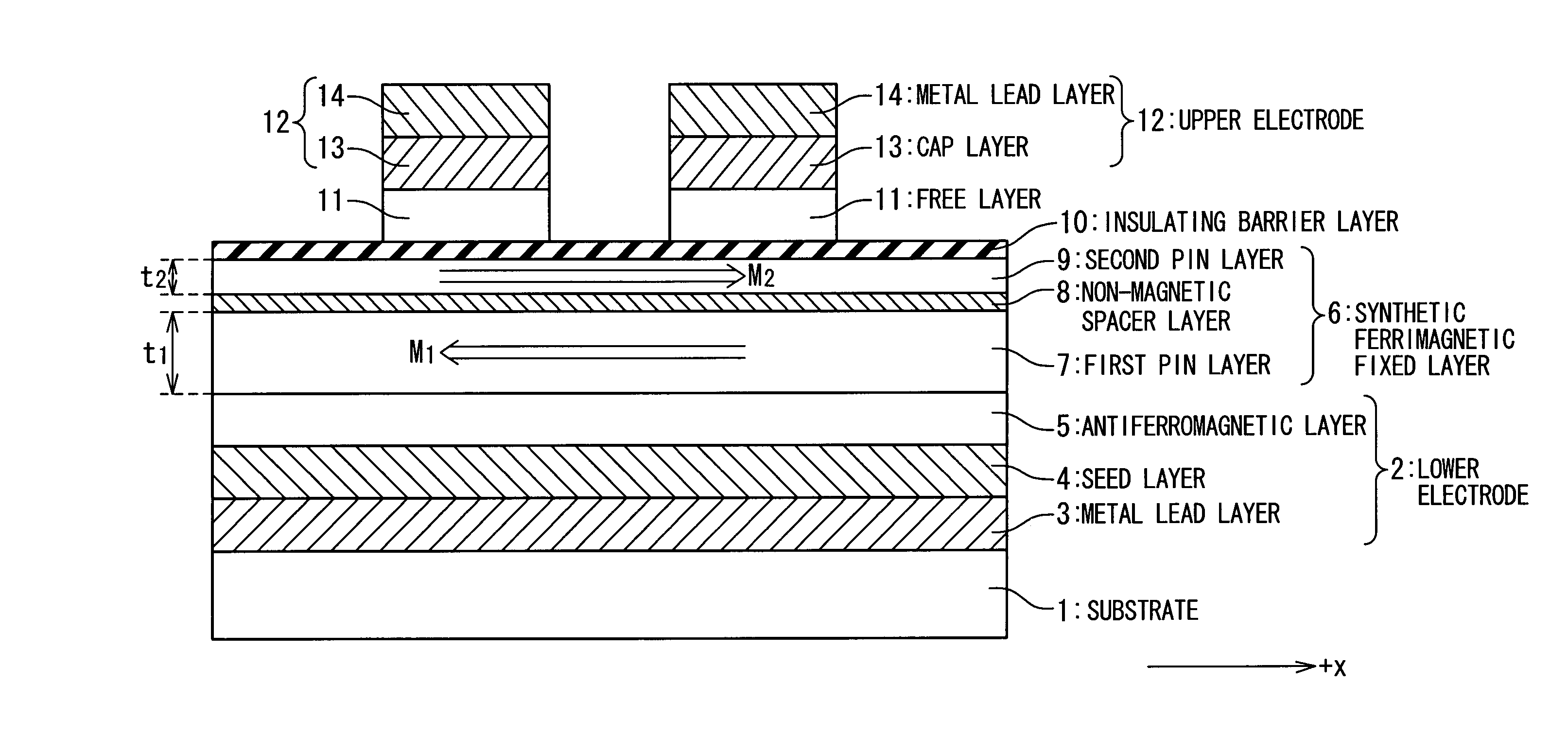
A magneto-resistance device is composed of an anti-ferromagnetic layer (5), a pinned ferromagnetic layer (20), a tunnel insulating layer (9) and a free ferromagnetic layer (21). The pinned ferromagnetic layer (20) is connected to the anti-ferromagnetic layer (5) and has a fixed spontaneous magnetization. The tunnel insulating layer (9) is connected to the pinned ferromagnetic layer (20) and is non-magnetic. The free ferromagnetic layer (21) is connected to the tunnel insulating layer (9) and has a reversible free spontaneous magnetization. The pinned ferromagnetic layer (20) has a first composite magnetic layer (6) to prevent at lest one component of the anti-ferromagnetic layer (5) from diffusing into tunnel insulating layer (9).
Owner:NEC CORP
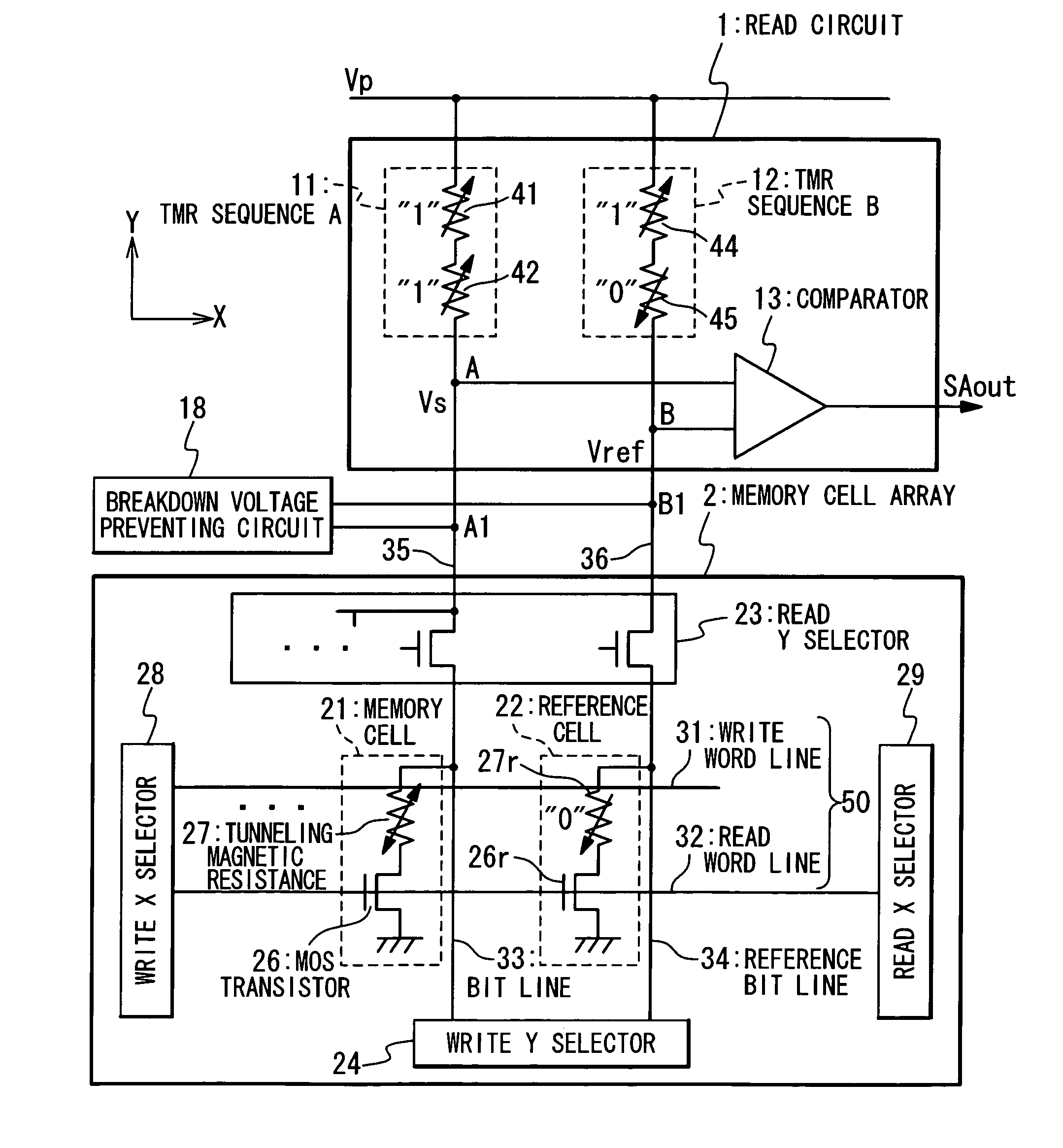
Magnetic random access memory with improved data reading method
ActiveUS7453719B2Improve reliabilityIncrease the areaDigital storageBit lineStatic random-access memory
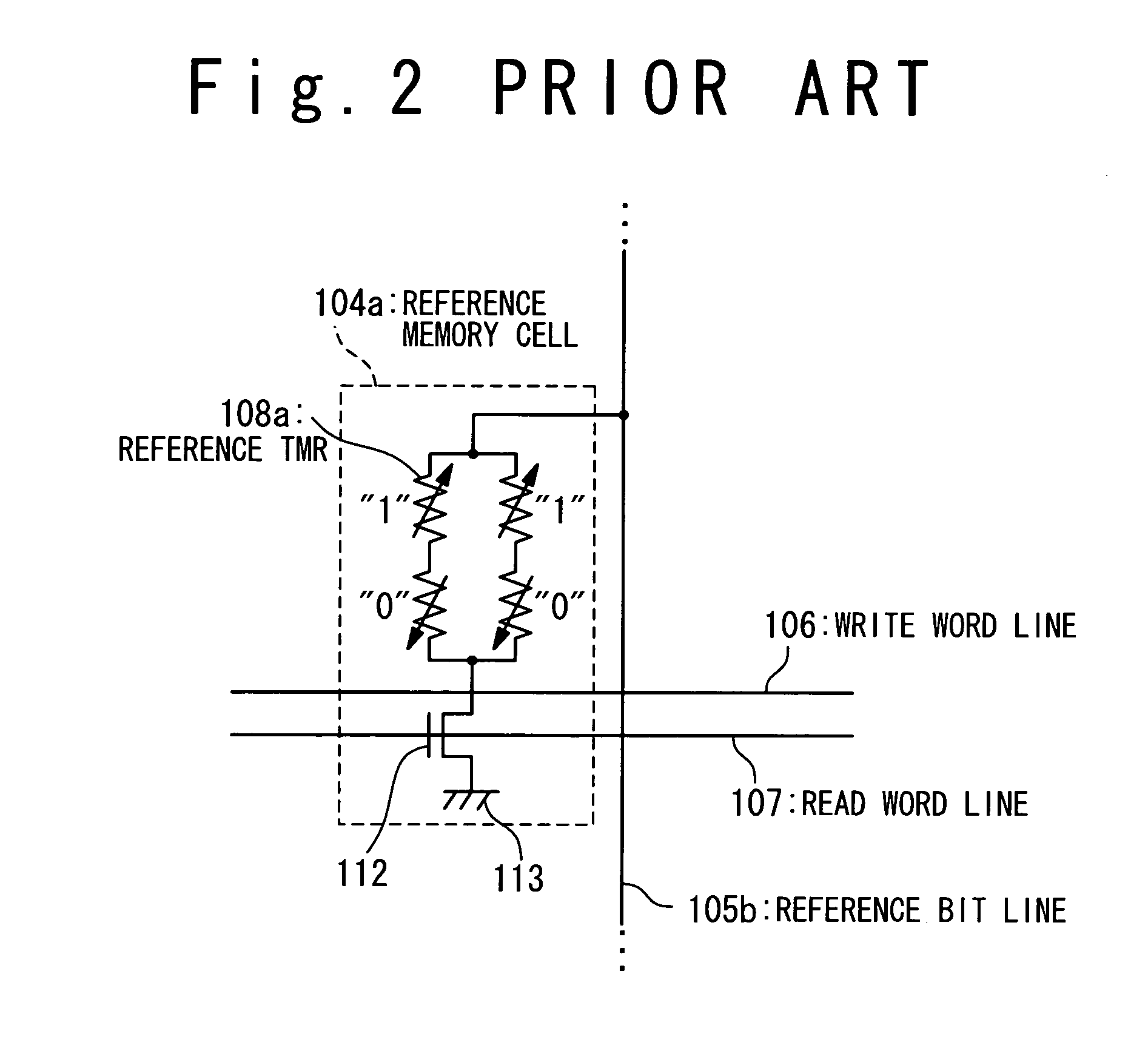
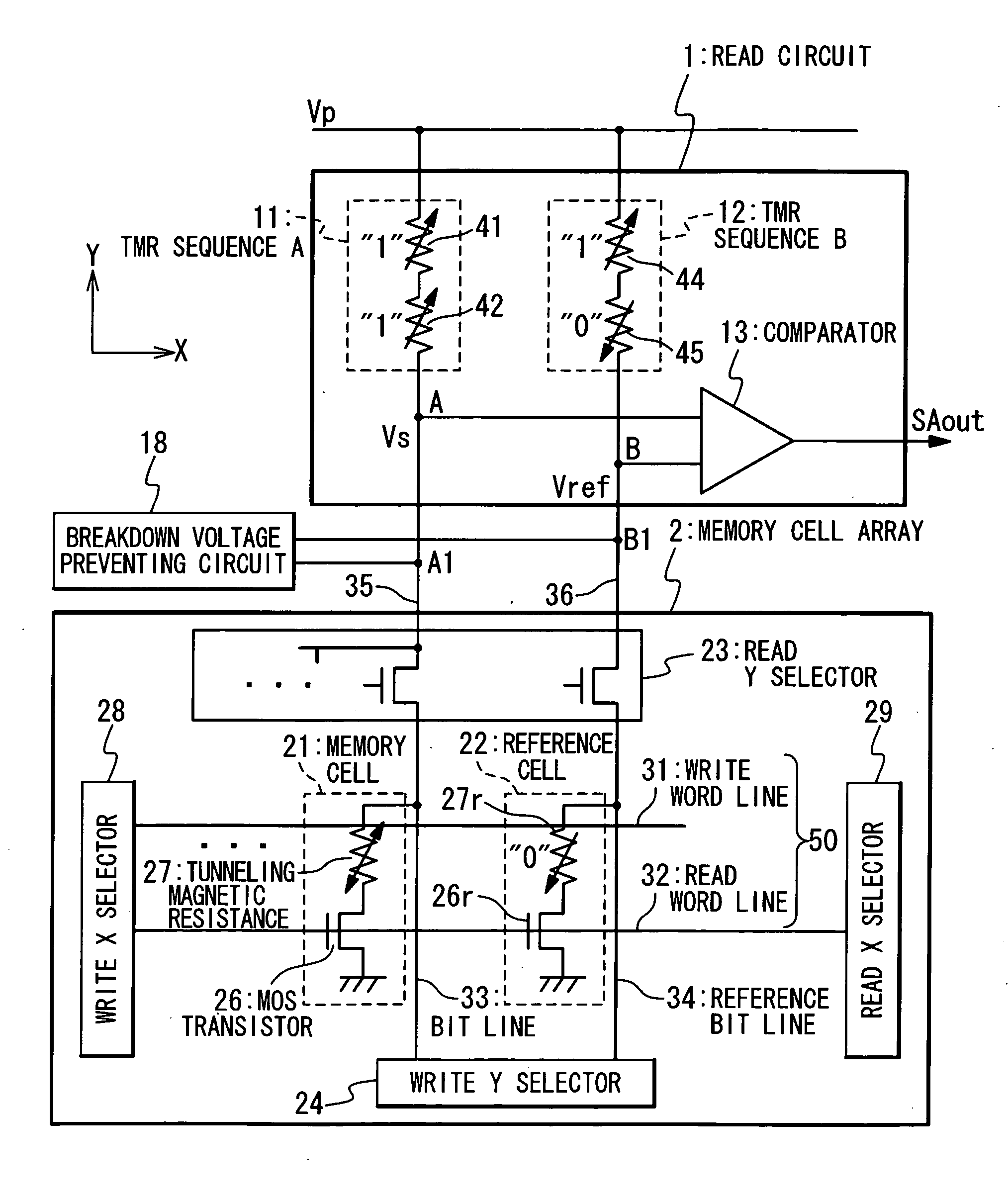
An MRAM has a plurality of bit lines, a reference bit line, a plurality of memory cells and reference cells and a read section. The memory cells are provided along the bit lines and the reference cells along the reference bit line. The memory cell and reference cell have a tunneling magnetic resistance and a reference tunneling magnetic resistance, each of which has a spontaneous magnetization whose direction is reversed in accordance with data stored therein. The read section has a first resistance section which contains a ninth terminal connected with a bit line and a tenth terminal connected with the first power supply, a second resistance section which contains an eleventh terminal connected with the reference bit line and a twelfth terminal connected with the first power supply, and a comparing section which compares a sense voltage on the ninth terminal and a reference voltage of the eleventh terminal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic memory cell and magnetic random access memory using the same
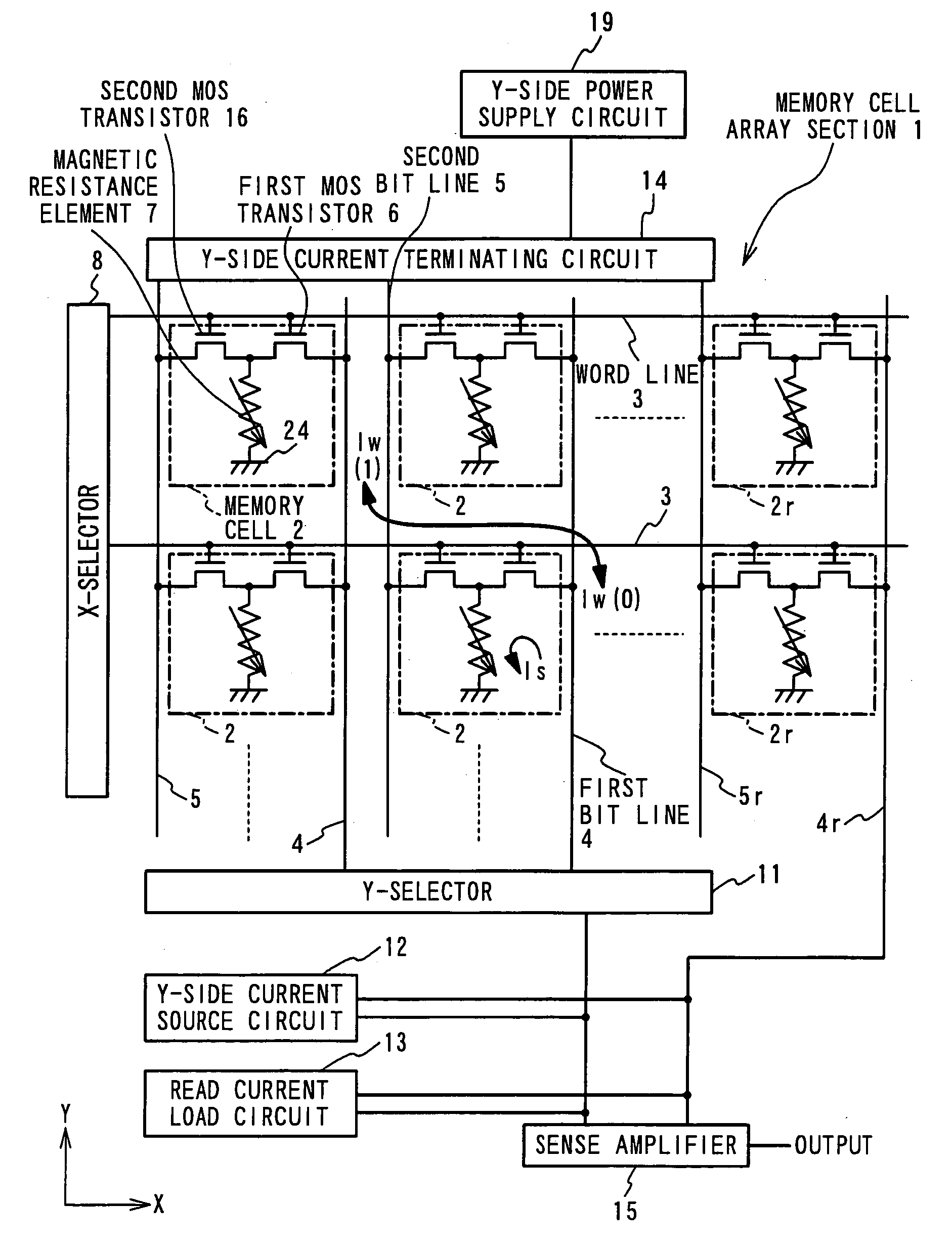
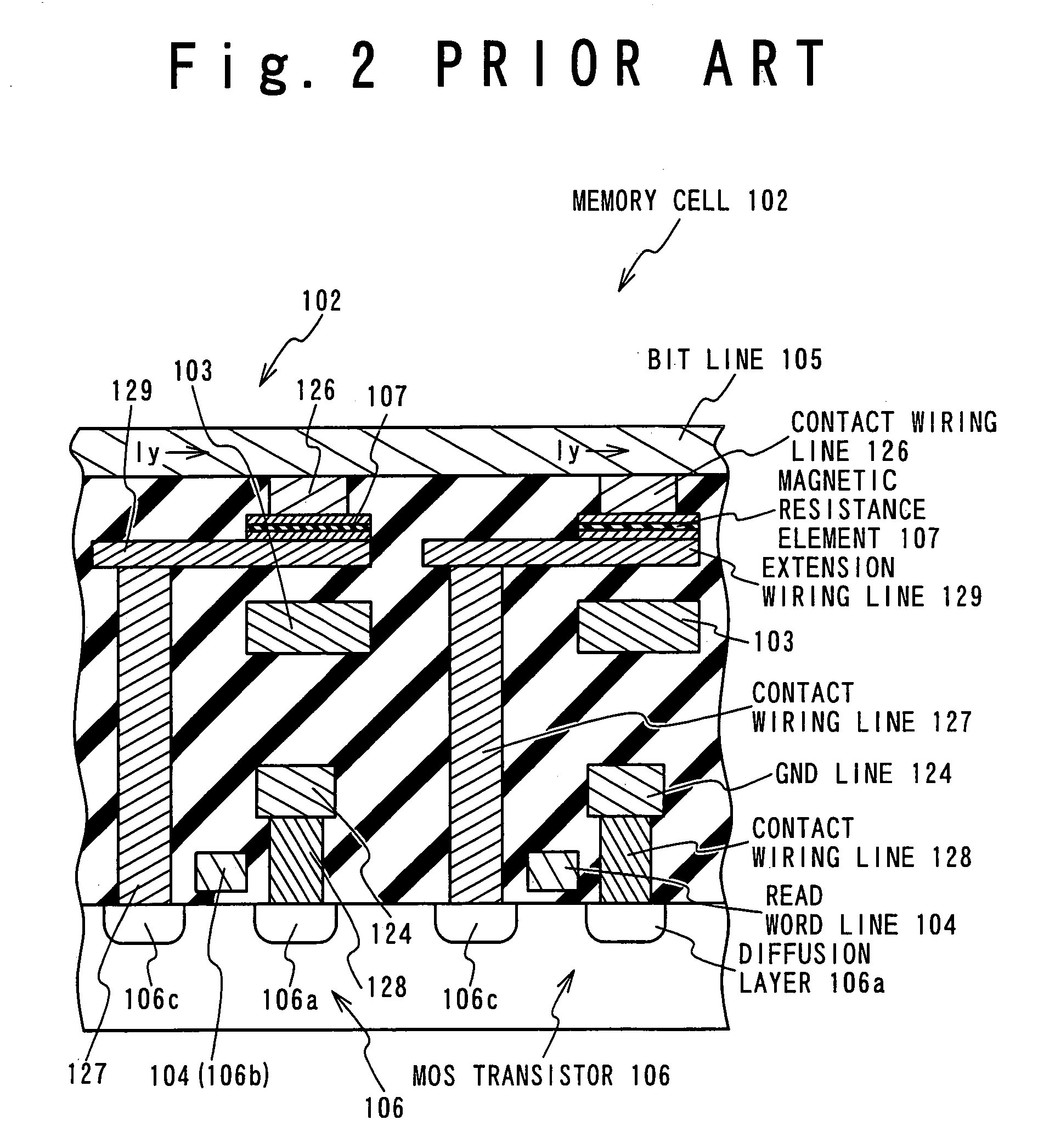
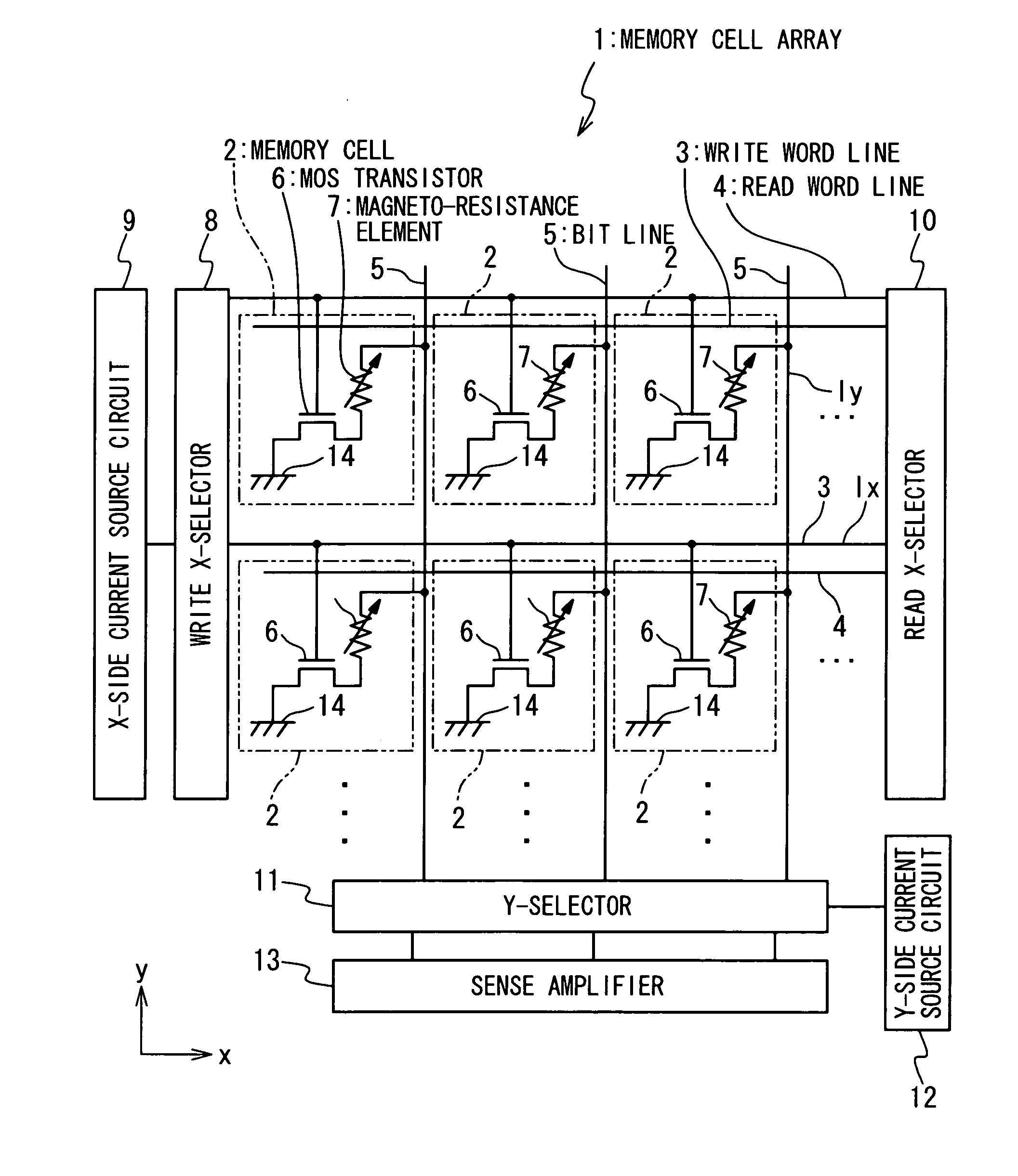
In a magnetic random access memory, a memory cell includes a magnetic field generating section having an extension wiring line, and connected with a first selected bit line, a conductive pattern, and a magnetic resistance element having a spontaneous magnetization, storing a data and connected between the extension wiring line and the conductive pattern. In a data write operation into the memory cell, a write data is written in the magnetic resistance element of the memory cell by a write electric current which flows through the extension wiring line of the magnetic field generating section of the memory cell, and a value of the write data is determined based on a direction of the write electric current. In a data read operation from the memory cell, a read electric current flows through the extension wiring line of the magnetic field generating section and the magnetic resistance element in the memory cell. A memory cell array section includes the memory cells arranged in a matrix, and each memory cell is connected with a first word line and a first bit line at least, the gate section.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic random access memory using improved data read out method
ActiveUS20060227598A1Improve reliabilityIncrease the areaDigital storageBit lineRandom access memory
An MRAM has a plurality of bit lines, a reference bit line, a plurality of memory cells and reference cells and a read section. The memory cells are provided along the bit lines and the reference cells along the reference bit line. The memory cell and reference cell have a tunneling magnetic resistance and a reference tunneling magnetic resistance, each of which has a spontaneous magnetization whose direction is reversed in accordance with data stored therein. The read section has a first resistance section which contains a ninth terminal connected with a bit line and a tenth terminal connected with the first power supply, a second resistance section which contains an eleventh terminal connected with the reference bit line and a twelfth terminal connected with the first power supply, and a comparing section which compares a sense voltage on the ninth terminal and a reference voltage of the eleventh terminal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS7126201B2Efficient reductionUniformly reducingNanomagnetismSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
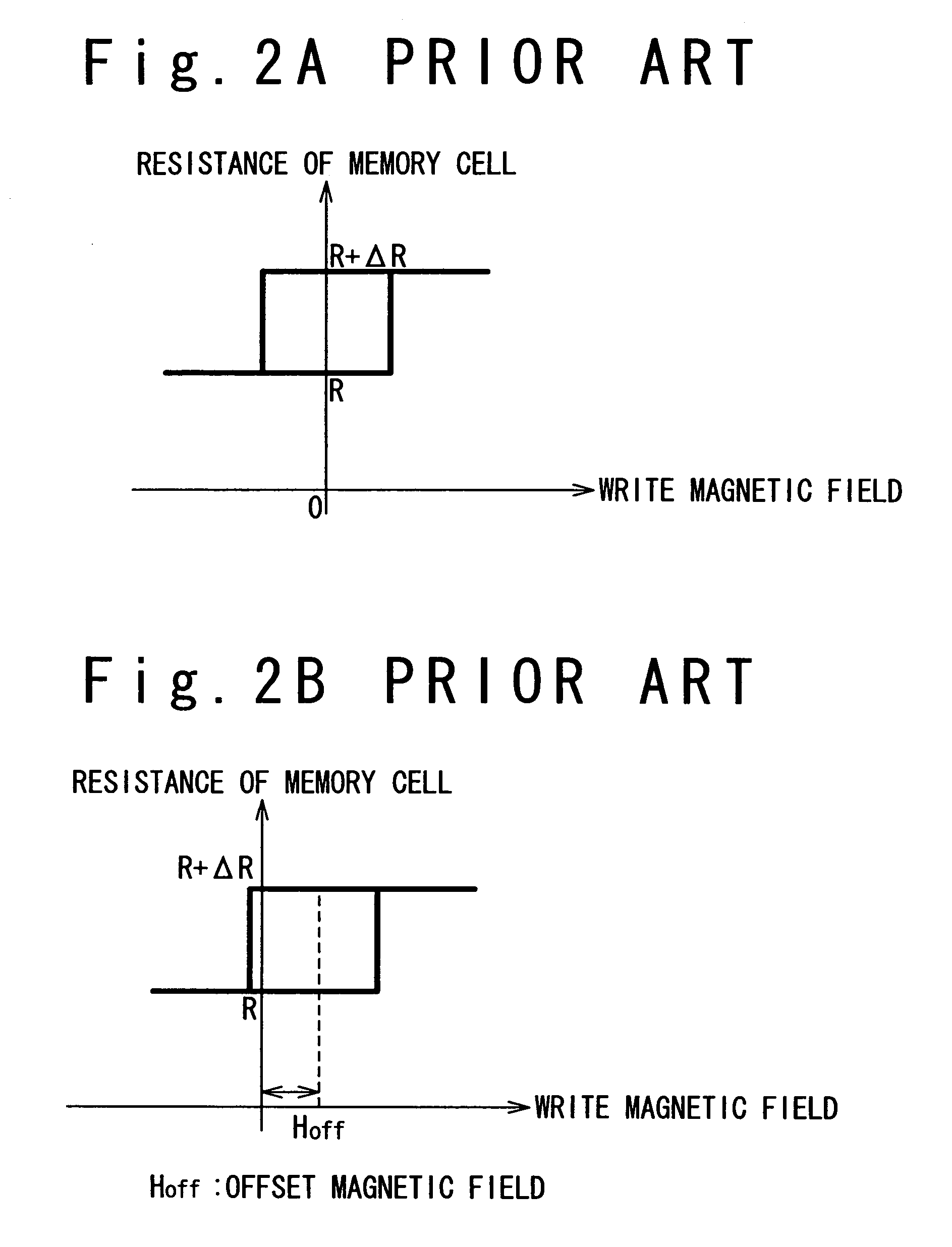
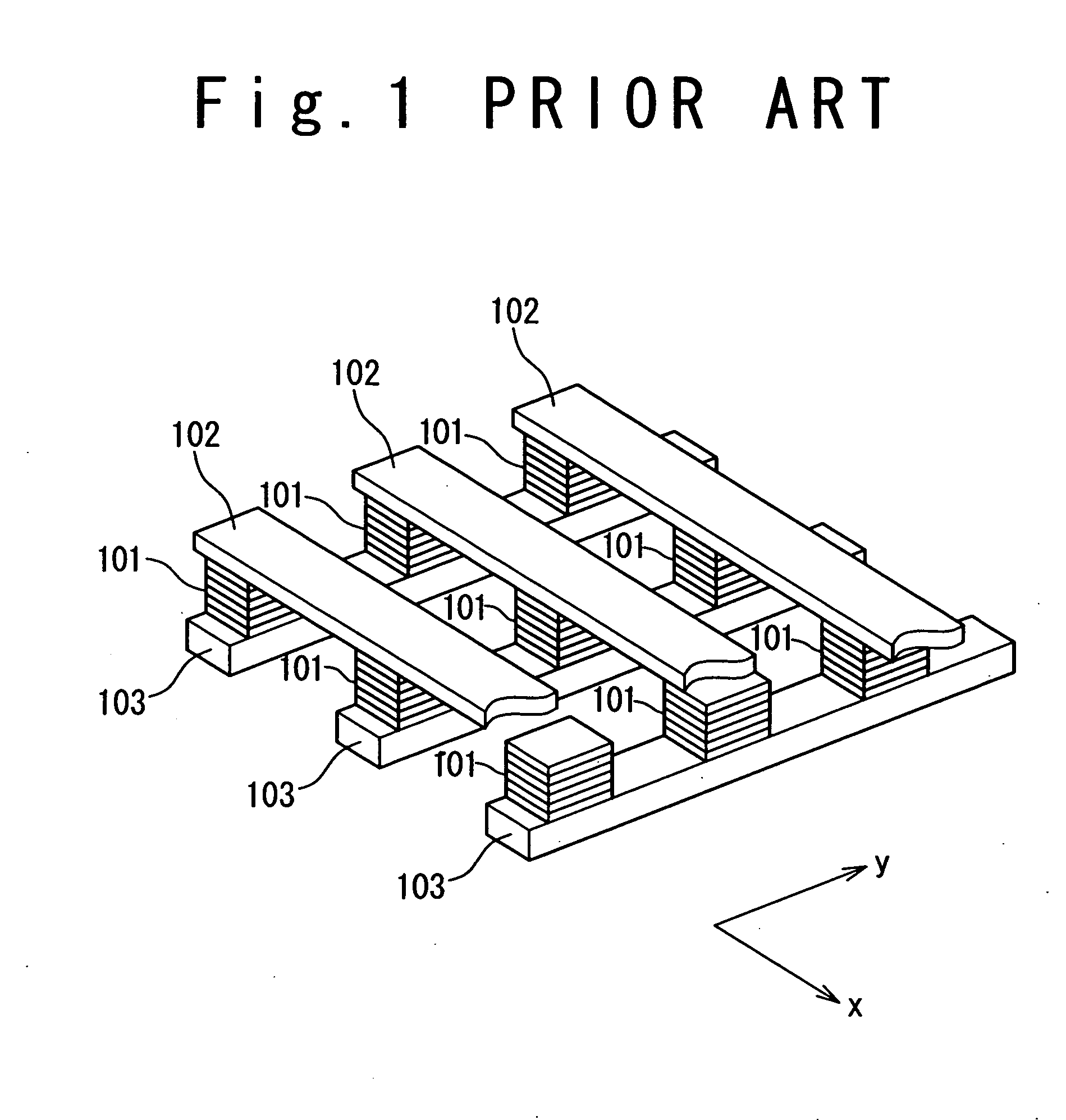
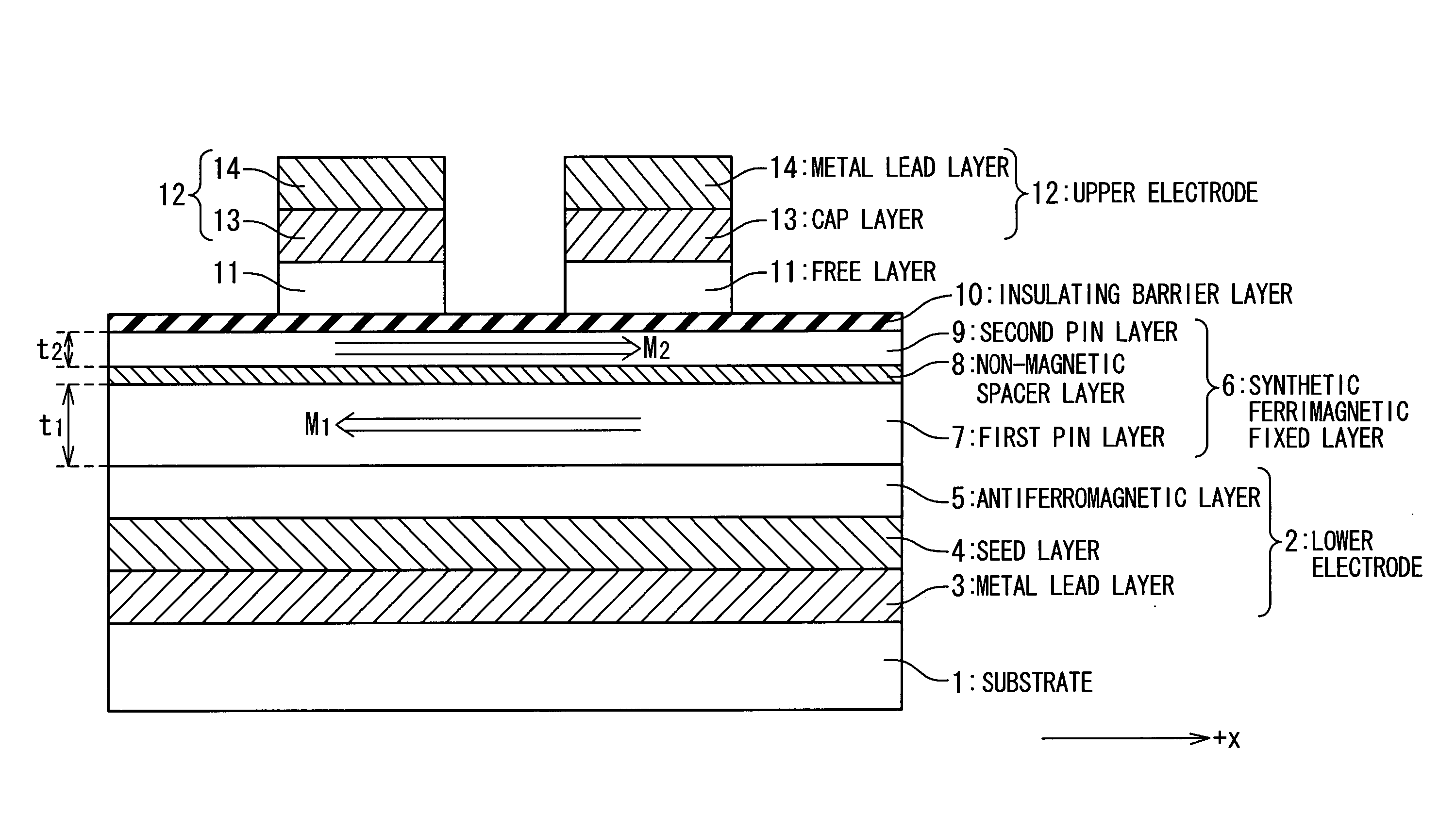
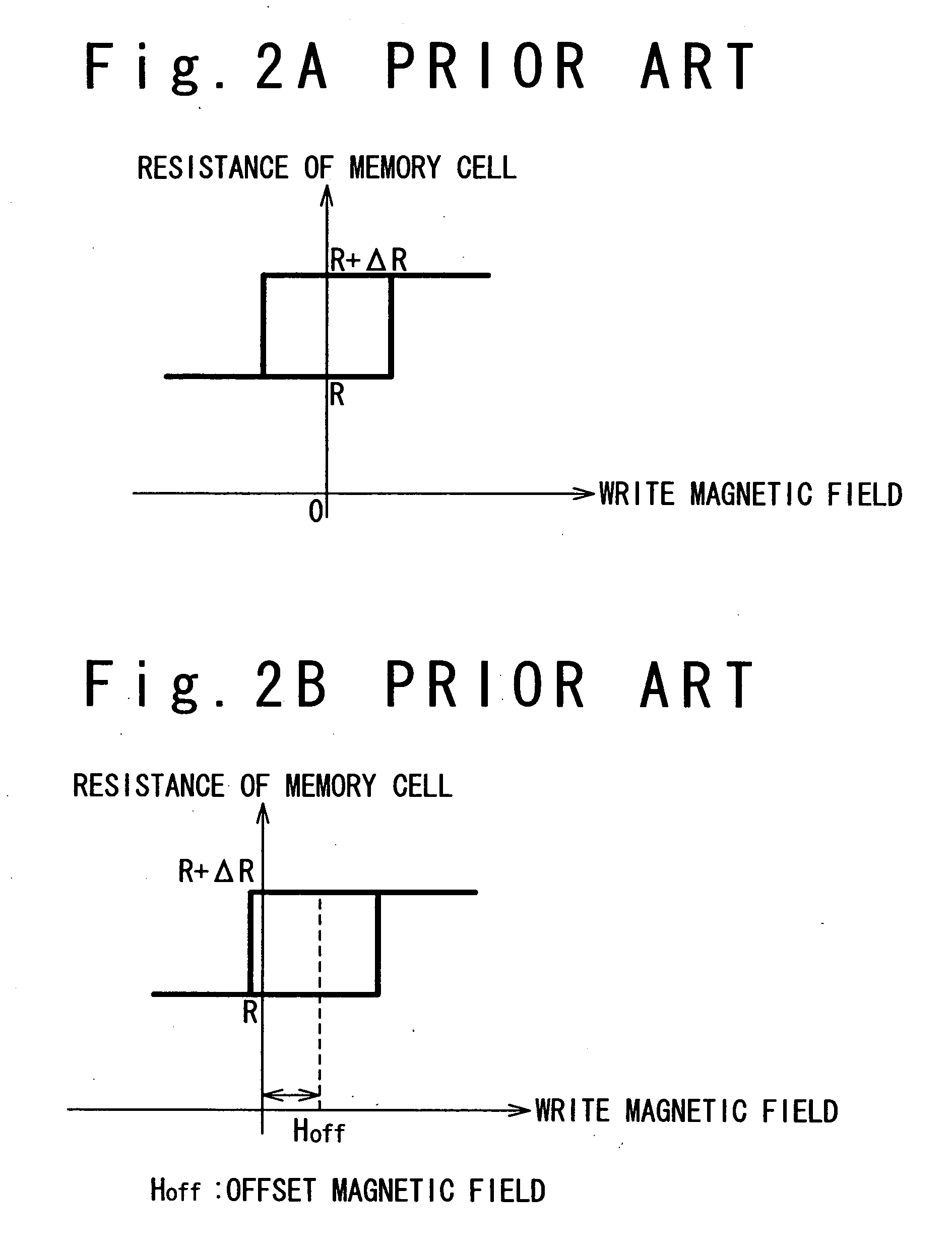
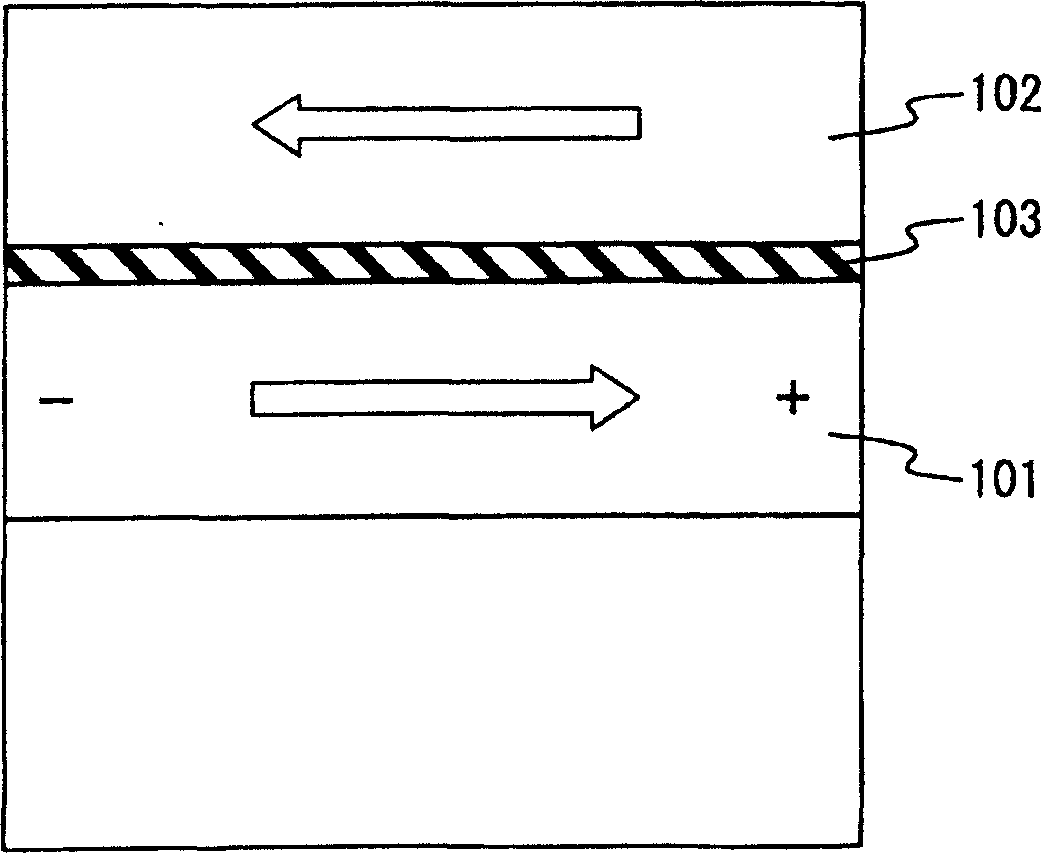
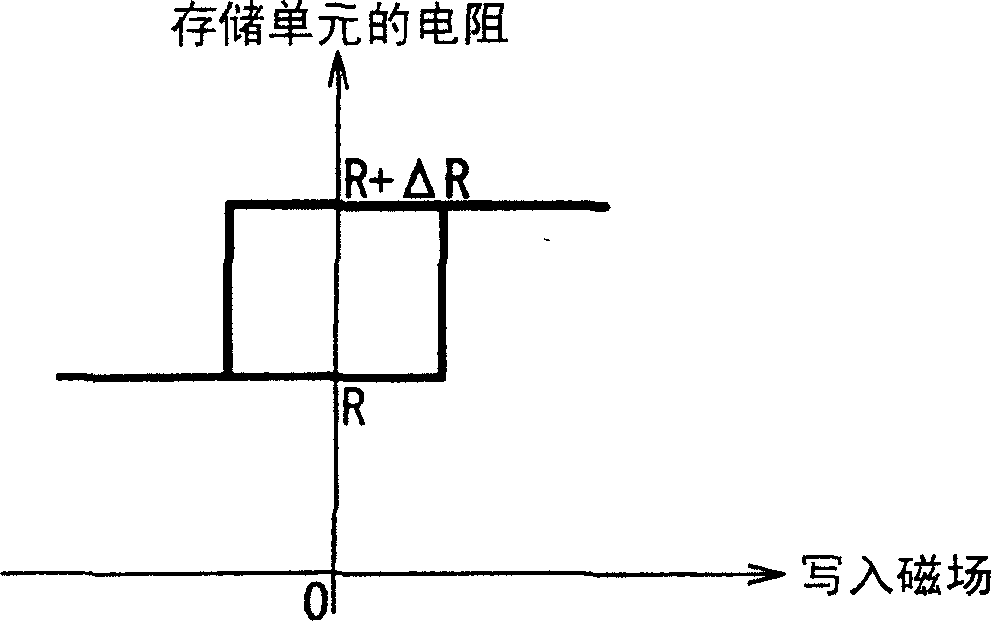
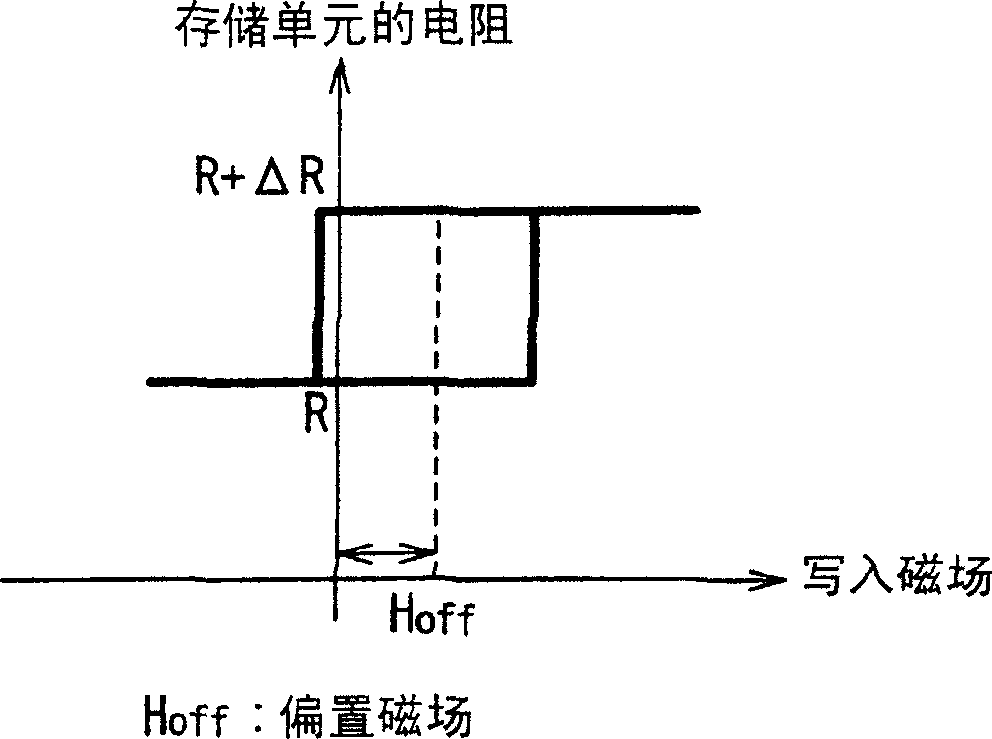
A technique is provided in which an offset magnetic field of a memory cell of a MRAM is reduced more effectively. The MRAM of the present invention is composed of a free layer (11) which has a reversible free spontaneous magnetization, a fixed layer (6) which has fixed spontaneous magnetization, and a spacer layer (10) formed of non-magnetic interposed between the free layer (11) and the fixed layer (6). The fixed layer (6) is formed such that orange peel effect and magneto-static coupling effect does not substantially influence on the free layer (11).
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetoresistance device with a diffusion barrier between a conductor and a magnetoresistance element and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7394626B2Improve thermal stabilityPrevent interdiffusionNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical conductorMagnetic reluctance
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods of manipulating the relaxation rate in magnetic materials and devices for using the same
InactiveUS20070242395A1Reduced dampingLow intrinsic damping rateNanomagnetismImpedence networksManganeseThin membrane
In accordance with the present invention, ferromagnetic thin films of iron that have reduced relaxation rates and methods of making the same are provided. It should be noted that pure iron is a ferromagnet (i.e., has a spontaneous magnetization alignment) with the lowest intrinsic damping rate of all of the ferromagnets. The present invention provides a ferromagnetic structure comprising a substrate and a ferromagnetic thin film of iron (Fe) formed on the substrate. An element selected from the group consisting of titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), and manganese (Mn) (i.e., a lower-Z transition metal element) is alloyed with the ferromagnetic thin film of iron to reduce the relaxation rate of the ferromagnetic thin film.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Magnetic materials, passive shims and magnetic resonance imaging systems
ActiveUS20050077899A1Increase in spontaneous magnetizationIncrease temperatureMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSpontaneous magnetizationUltimate tensile strength
A shim adapted for altering a magnetic field of a magnet includes a first material which exhibits an increase in spontaneous magnetization with an increase in temperature for a predetermined temperature range.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic materials, passive shims and magnetic resonance imaging systems
InactiveUS6906606B2Enhanced magnetizationIncrease temperatureMagnetsInorganic material magnetismSpontaneous magnetizationUltimate tensile strength
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tetrazolyl cobalt (II) complex magnetic material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103087111AHigh yieldGood reproducibilityCobalt organic compoundsRecord information storagePolymer scienceTetrazole
The invention relates to a 5-methyl-1H-tetrazole and isophthalic acid mixed ligand cobalt (II) coordination polymer magnetic material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the coordination polymer magnetic material provided by the invention is {[Co7(H2O)2(mu3-OH)4(mtz)2(ip)4].13 / 4H2O}, wherein mtz is the 5-methyl tetrazole anion with valence of -1, and ip is the isophthalic acid anion with valence of -2. The coordination polymer magnetic material is prepared by solvothermal synthesis, and is high in productivity and good in reproducibility. The coordination polymer magnetic material is the three-dimensional cobalt (II) compound simultaneously including 5-methyl-1H-tetrazole and isophthalic acid mixed ligand, presents continuous two-step field-induced metamagnetic transition and spin-flop transition, which are from antiferromagnetic order to week spontaneous magnetization, in different external magnetic fields, and can be used as molecular-based magnetic material to have great application value in the field of material science.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Mixed valence copper (I/II) complex containing a mixed ligand as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102659822AHigh yieldImprove thermal stabilityCopper organic compoundsOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismPhysical chemistrySpontaneous magnetization
The invention relates to a mixed valence copper (I / II) complex magnetic material containing a 1, 2, 4-triazole and 5-isophthalic acid mixing ligand as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical formula of the complex magnetic material is [CuI0.5CuII1.5(H2O) (trz)2(H0.5nip)], wherein trz is a 1, 2, 4-triazole-valence anion, and H0.5nip is a 5-isophthalic acid-1.5 valence anion. The complex magnetic material is prepared by adopting a hydrothermal method and has higher yield and good repeatability. The complex magnetic material is a mixed valence copper (I / II) complex simultaneously containing the 1, 2, 4-triazole and 5-isophthalic acid ligand, has the remarkable spontaneous magnetization behavior at a low temperature, can be taken as a molecule-based magnetic material and has huge application value in the field of materials science.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic materials, passive shims and magnetic resonance imaging systems
InactiveCN1606100ASpontaneous increase in magnetizationMagnetsMagnetic property measurementsSpontaneous magnetizationRise over thermal
The present invention provides a magnetic material, a passive gasket and a magnetic resonance imaging system. A shim (24, 34, 54) adapted for altering a magnetic field of a magnet (12, 14, 36) includes a first material which exhibits an increase in spontaneous magnetization with an increase in temperature for a predetermined temperature range.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
5-methyl-1H-tetrazole cobalt (II) complex magnetic material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102690296AHigh yieldImprove thermal stabilityCobalt organic compoundsOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismPolymer scienceTetrazole
The invention relates to a 5-methyl-1H-tetrazole / 1,2,3-trimesic acid mixed ligand cobalt (II) complex magnetic material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the complex magnetic material is [Co2(H2O)(mtz)(btc)], wherein mtz is a 5-methyltetrazole -1-valent anion, and btc is a 1,2,3-trimesic acid -3-valent anion. The complex magnetic material is prepared by a hydrothermal method, and has the advantages of high yield and favorable repeatability. The complex magnetic material is a cobalt (II) complex simultaneously containing 5-methyl-1H-tetrazole 1,2,3-trimesic acid mixed ligand; and the complex magnetic material has obvious spontaneous magnetization behavior at low temperature, and has huge application value as a molecule-base magnetic material in the field of material science.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
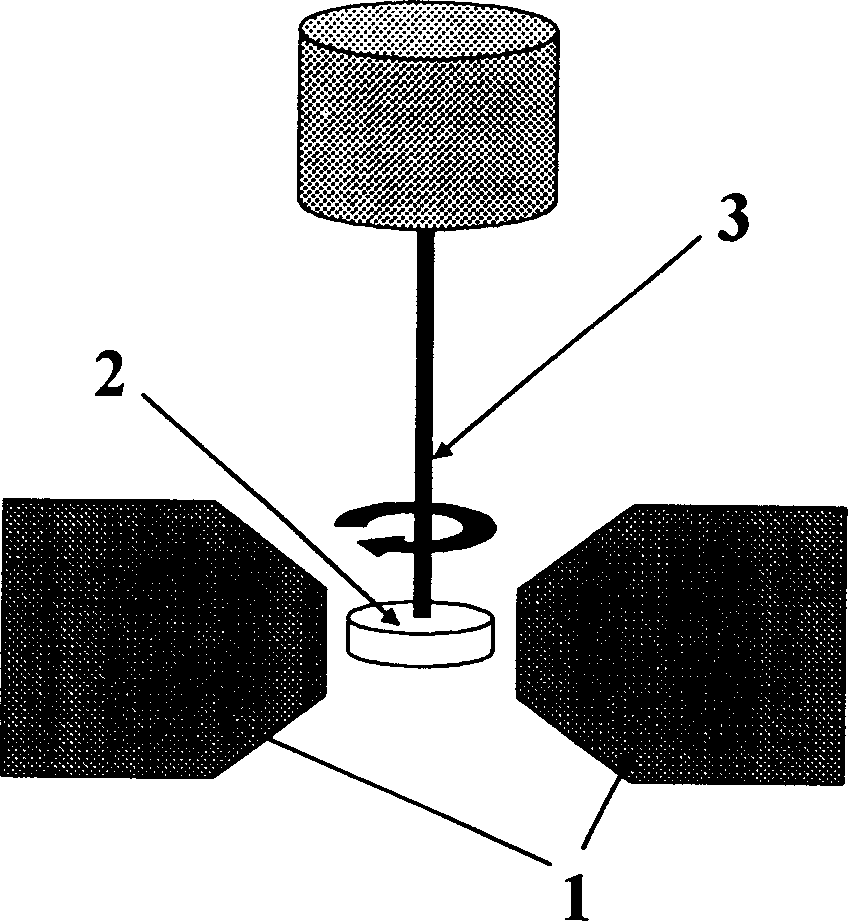
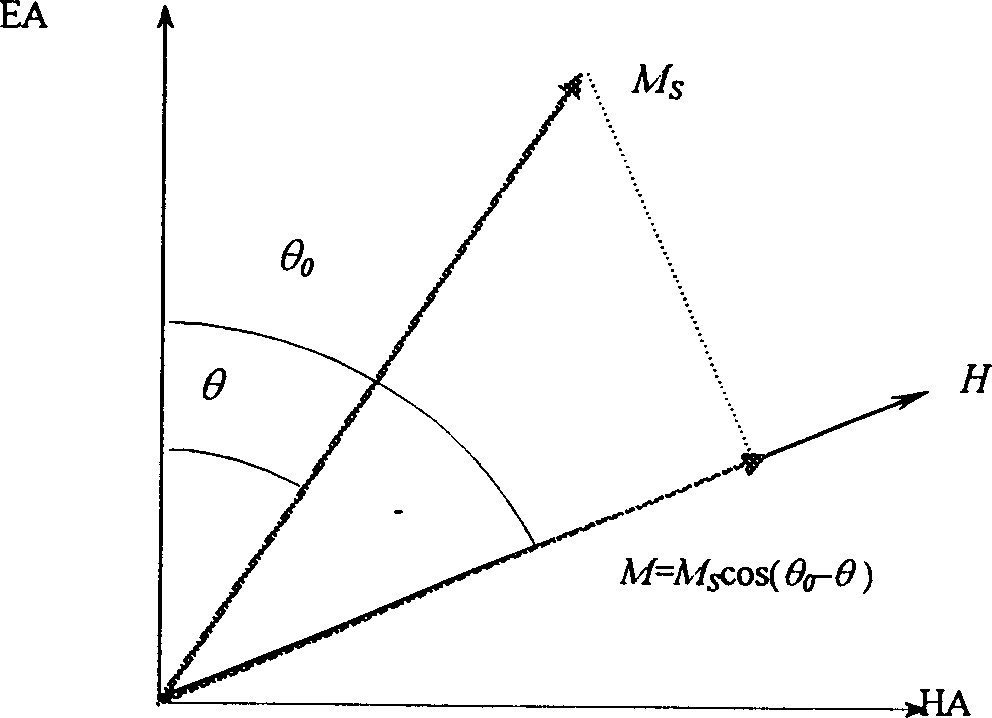
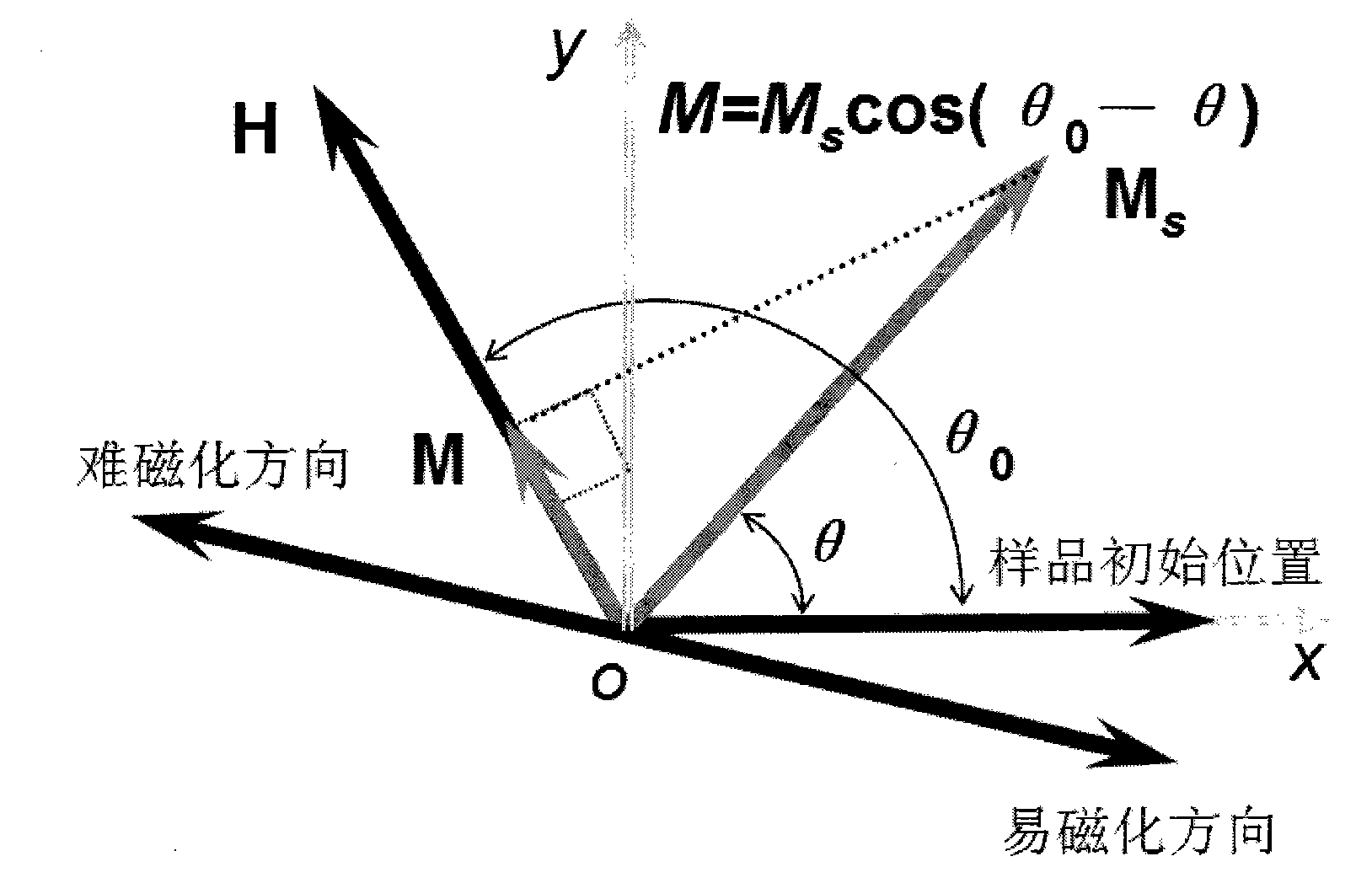
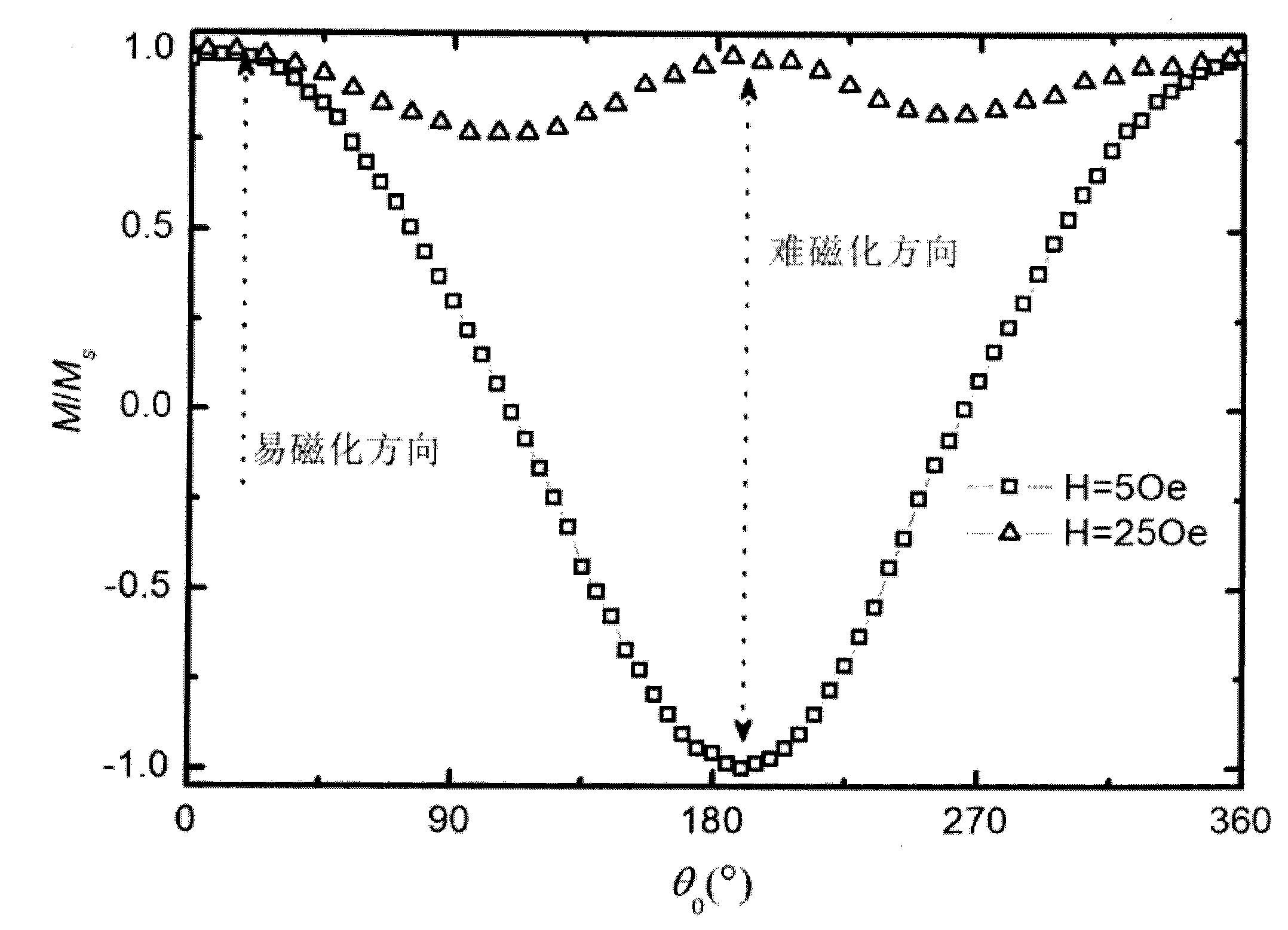
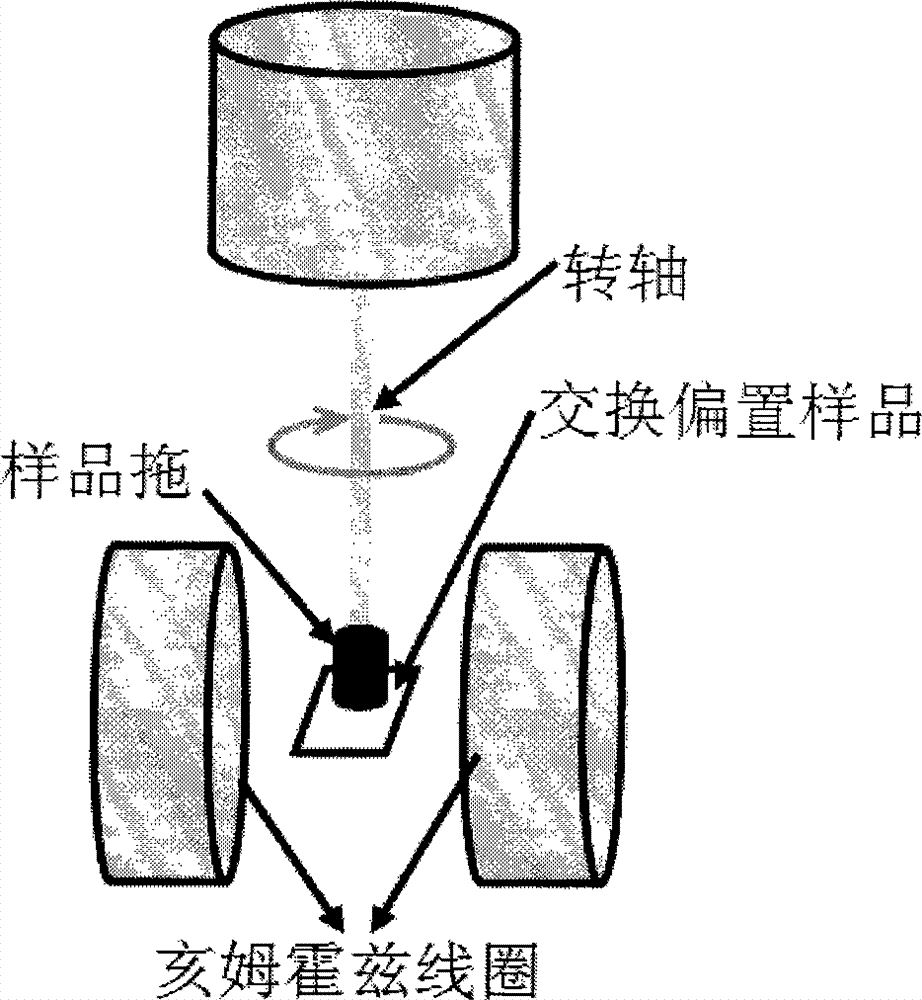
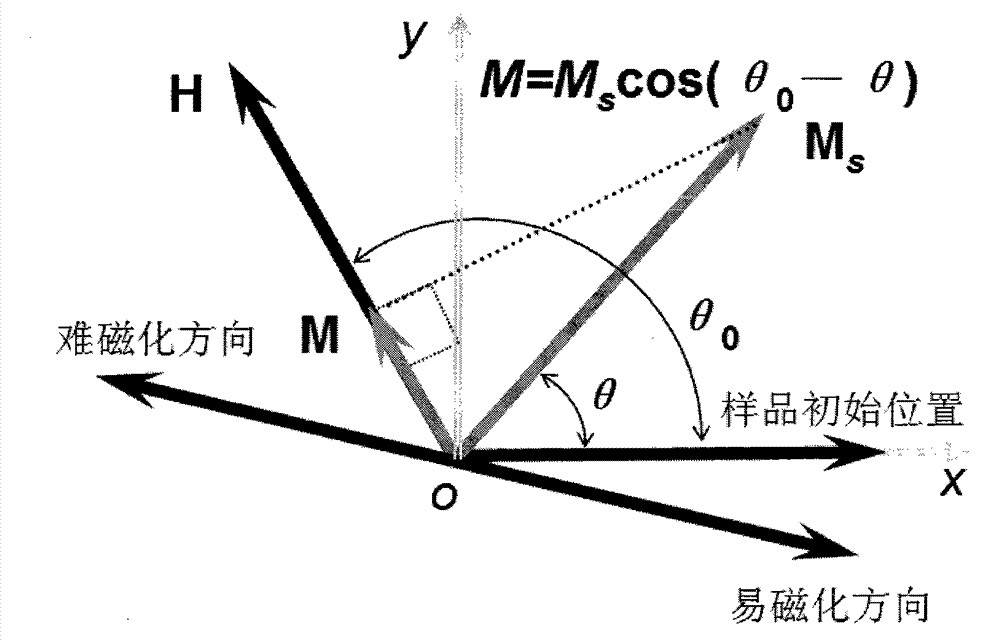
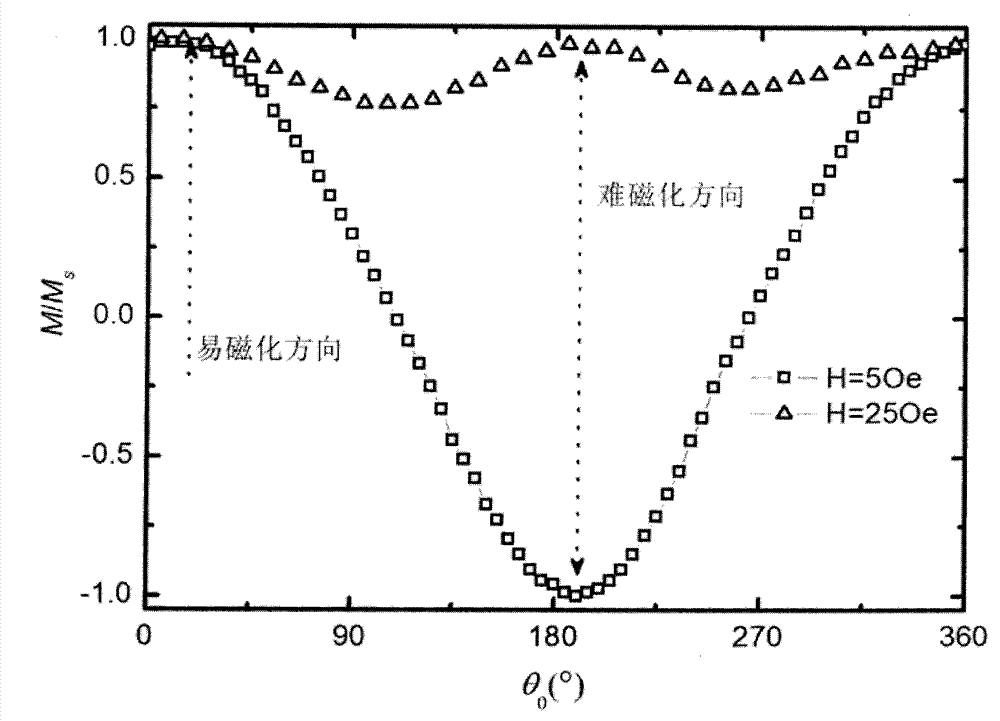
In-plane mono-axial anisotropy test method for magnetic film material
InactiveCN1790005ADistinguishing the direction of hard and easy magnetizationSimple test methodMaterial magnetic variablesIn planeFilm plane
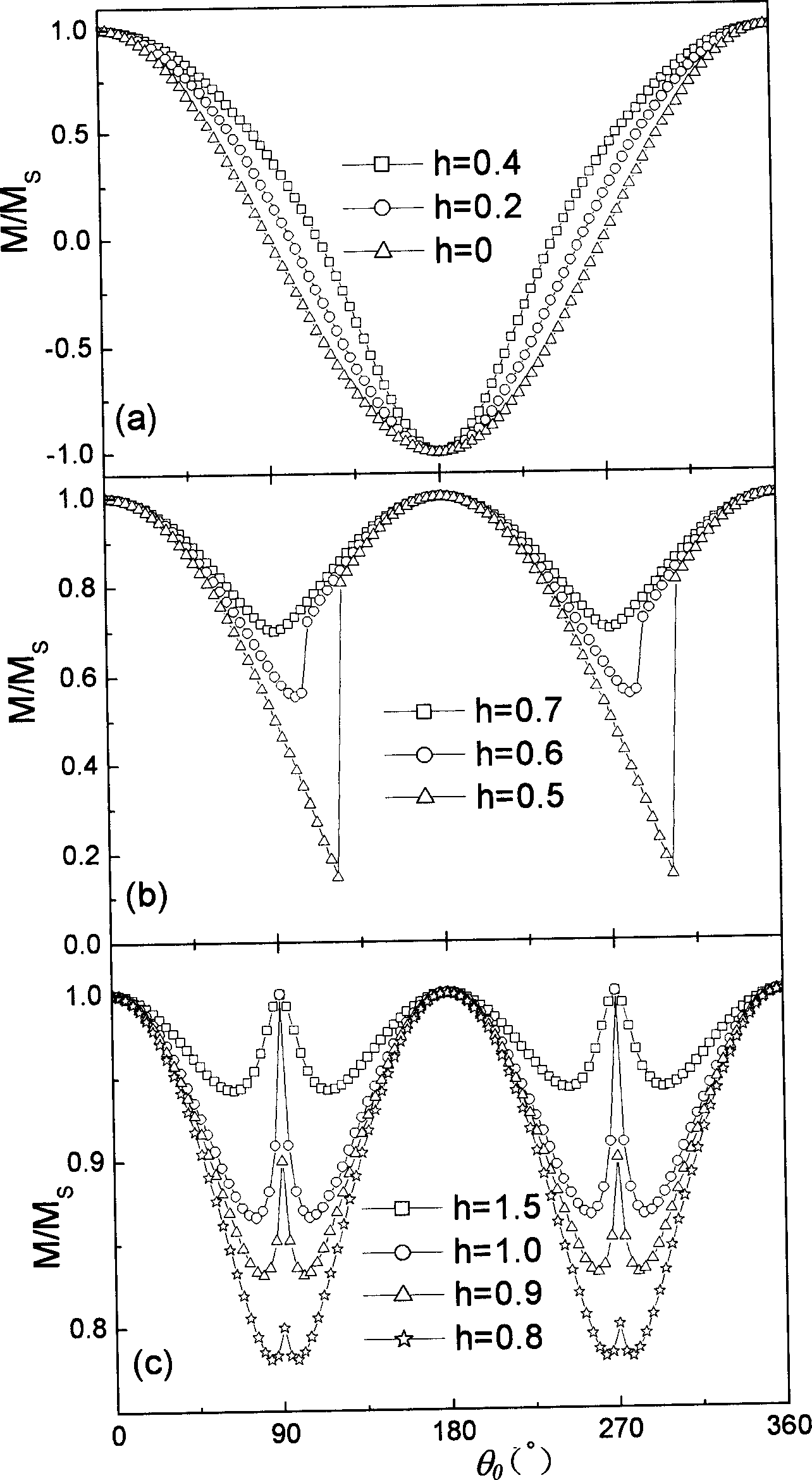
The invention discloses a test technique of magnetic material, which is characterized by the following: placing the detected sample film in the extra DC magnetic field; paralleling the detected sample film plane to the extra magnetic field direction; rotating the detected sample film around the vertical axle of plane; making the detected film reach magnet saturation and extra magnet field between saturated field and coercive field; keeping the magnet field; rotating the detected sample at certain angle; measuring the spontaneous magnetization strength MS and corresponding projection value M in the ª’0 condition; calculating the M value function corresponding to different ª’0.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
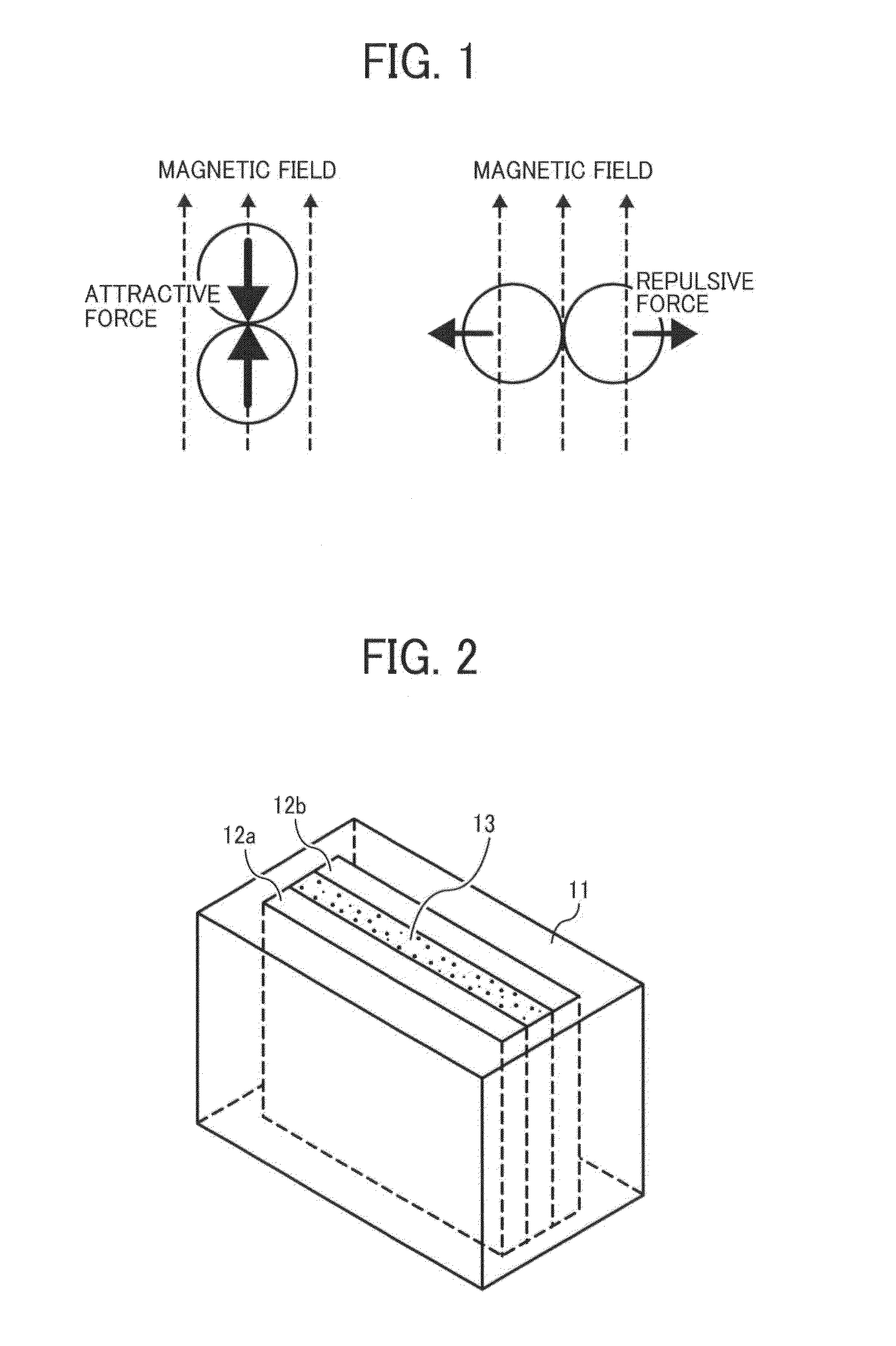
Substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) H-plane self-bias isolator based on soft magnetic nano wire array
InactiveCN105914439AReduce volumeSimple structureWaveguide type devicesDielectric substrateSpontaneous magnetization
The invention discloses a substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) H-plane self-bias isolator based on a soft magnetic nano wire array, which relates to a microwave device. The substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) H-plane self-bias isolator based on the soft magnetic nano wire array comprises an SIW transmission line and four orderly soft magnetic nano wire array bars arranged inside the transmission line, wherein the SIW transmission line comprises a dielectric substrate; the dielectric constant of the dielectric substrate material is between 8 and 16; metal layers are arranged on the upper surface and the lower surface of the dielectric substrate respectively; two rows of parallel conductive through holes arranged in the dielectric substrate form two through hole edges of the waveguide; each orderly soft magnetic nano wire array bar is long strip-shaped and is arranged between the substrate and the surface metal layer and attached to the metal layers on the upper surface and the lower surface, the long edge of the orderly soft magnetic nano wire array bar is parallel to the two through hole edges of the waveguide, spontaneous magnetization directions of two orderly soft magnetic nano wire array bars close to one side of the waveguide are upward, and spontaneous magnetization directions of two orderly soft magnetic nano wire array bars close to the other side of the waveguide are downward. The substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) H-plane self-bias isolator based on soft magnetic nano wire array is small in size, simple in structure, simple in processing and is easily integrated with a planar microwave circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Noninvasive measuring method for rapid temperature variation under DC excitation magnetic field
ActiveUS20160252405A1High definitionSolve technical problemsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansLow speedRoom temperature
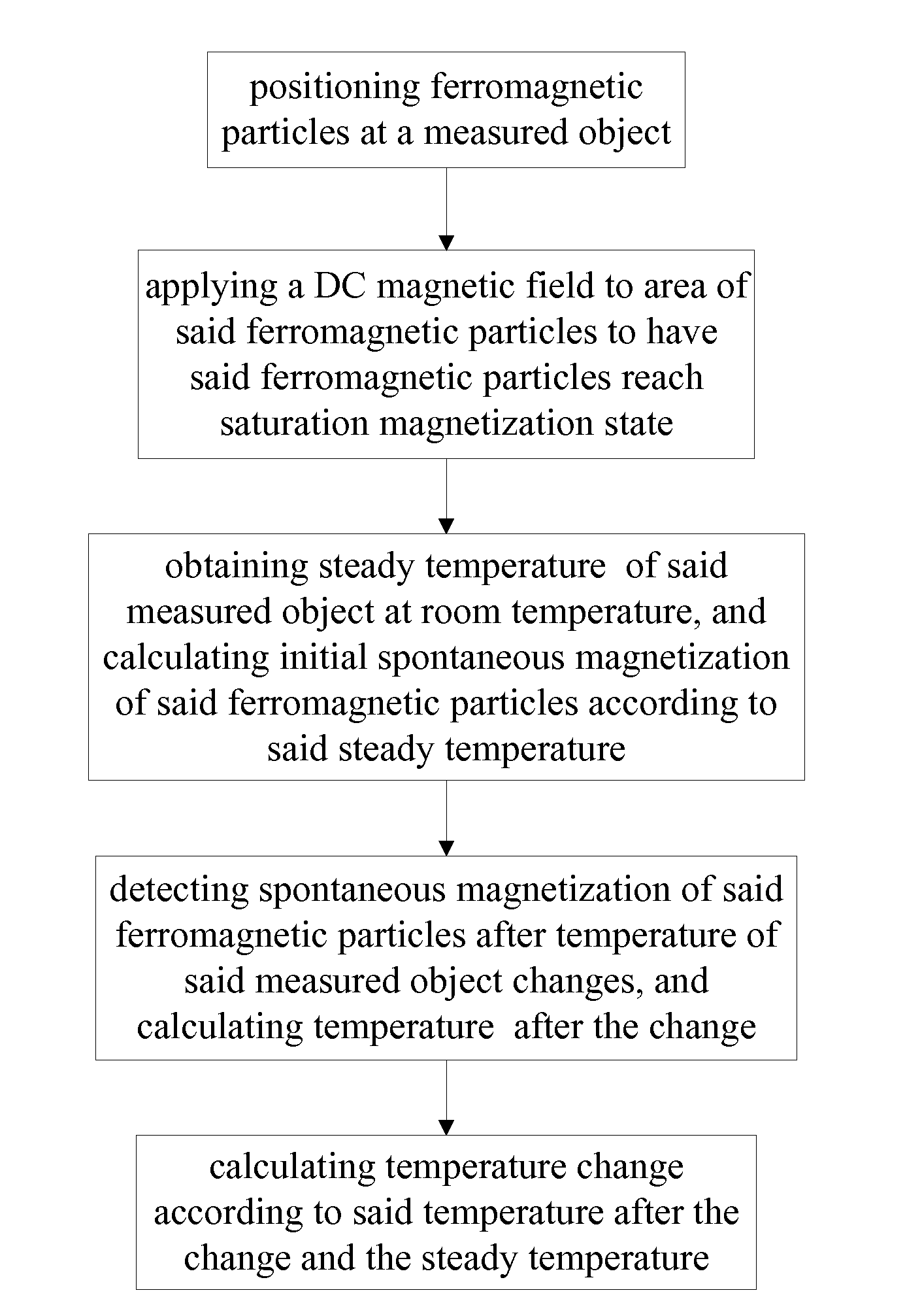
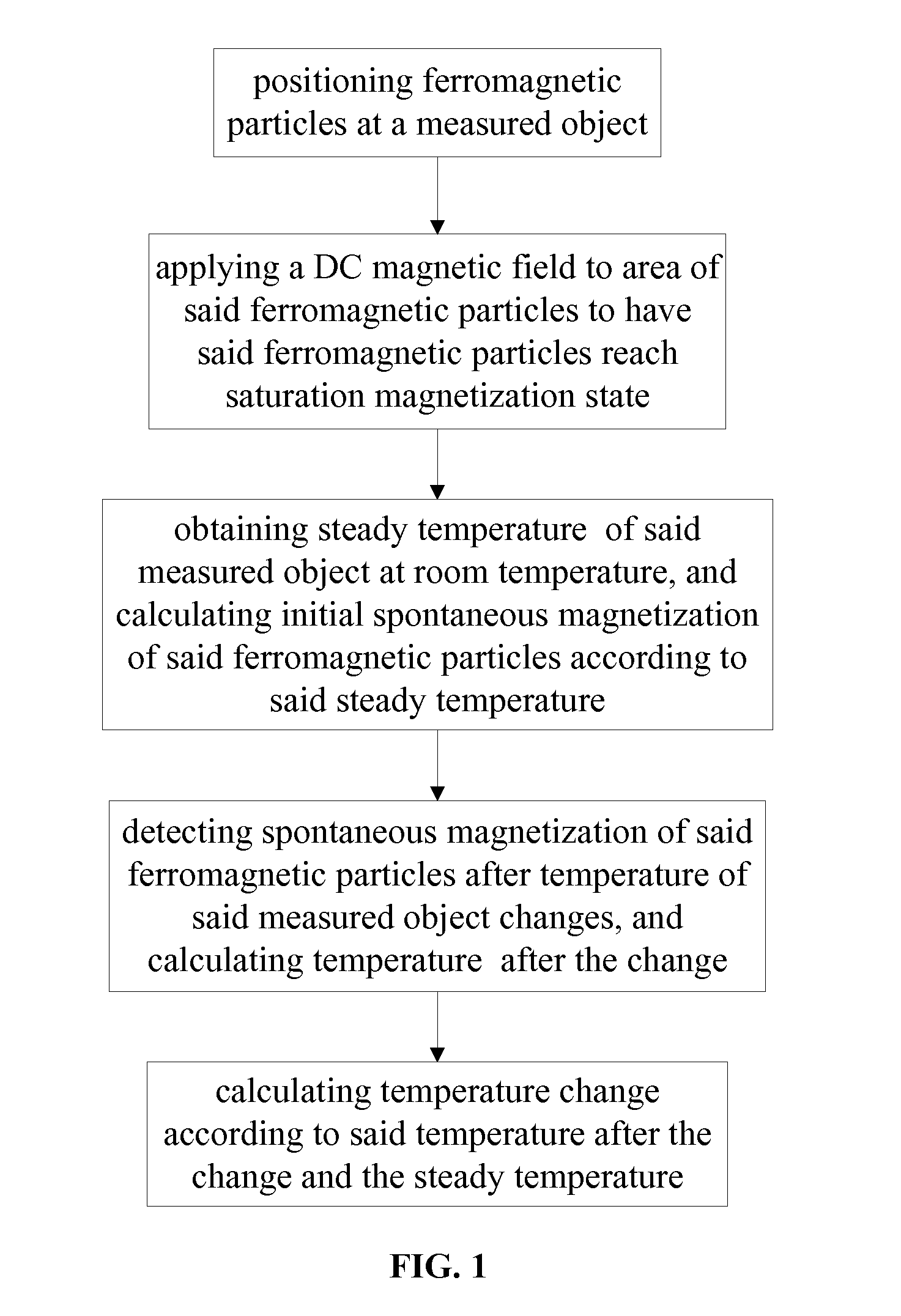
Provided is a noninvasive measuring method for rapid temperature variation under a DC excitation magnetic field, comprising: (1) positioning ferromagnetic particles at a measured object; (2) applying a DC magnetic field to area of the ferromagnetic particles enabling the ferromagnetic particles to reach saturation magnetization state; (3) obtaining steady temperature T1 of the measured object at room temperature, and calculating initial spontaneous magnetization M1, of the ferromagnetic particles according to the steady temperature T1; (4) detecting amplitude A of a magnetization variation signal of the ferromagnetic particles after temperature of the measured object varies, and calculating temperature T2 after change according to the amplitude A of the magnetization variation signal; and (5) calculating temperature variation ΔT=T2-T1 according to the temperature T2 after change and the steady temperature T1. The present invention can realize noninvasive temperature measurement with high speed and high accuracy so as to resolve technical problems of low speed and low precision.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Carrier for electrostatic latent image developer, electrostatic latent image developer formed of carrier and toner, and process cartridge using the developer
InactiveUS20130101930A1Increased durabilityThe total amount is stableDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusParticulatesLatent image
A carrier for developing an electrostatic latent image, including a particulate core material having a magnetism having developed spontaneous magnetization; and a covering layer comprising an electroconductive material, covering the surface of the particulate core material, wherein the carrier has an electrical resistivity Log R [Ωcm] of from 8.0 to 12.0 when measured by a method, including filling the carrier in a cell containing a pair of facing electrodes, each having a surface area of 2×4 [cm2] with a gap of 2 [mm] therebetween; and applying a DC voltage of 1,000 [V] therebetween to measure a DC resistivity, and a weight-average particle diameter (Dw) of from 25 to 45
Owner:RICOH KK
Three-dimensional planar magnetic sensor
InactiveCN103543414AIncrease production capacityImprove yieldMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSpontaneous magnetizationMagnetic insulation
A three-dimensional planar magnetic sensor comprises a first magnetic sensor, a second magnetic sensor, a third magnetic sensor and a circuit. The first magnetic sensor, the second magnetic sensor and the third magnetic sensor are arrange on the same plane and respectively measure component of a magnetic field in the first, second and third directions, and the third direction is perpendicular to the first direction and the second direction. The third magnetic sensor comprises a third fixed layer, a third magnetic insulation layer and a third free layer, wherein the magnetization direction of the third fixed layer is the third direction or the reverse direction, the spontaneous magnetization of the third free layer is the first direction and the second direction or inclines to the third direction by 0-180 degrees, the magnetic resistance value is an intermediate value in the spontaneous magnetization direction and changes along with the magnetic field. The three-dimensional planar magnetic sensor is manufactured by the semiconductor processing technology without vertical binding, output and durability are improved, and cost and time are saved.
Owner:ISENTEK INC
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS20060098477A1High selectivityGuaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storageRandom access memoryEngineering
A magnetic random access memory is composed of a plurality of first signal lines provided to extend in a first direction, a plurality of second signal lines provided to extend in a second direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction, a plurality of memory cells respectively provided at the intersections of the plurality of first signal lines and the plurality of second signal lines, and a plurality of magnetic structures respectively provided to the plurality of memory cells. Each of the plurality of memory cells has a magneto-resistance element containing a spontaneous magnetization layer which has a first threshold function, and the direction of the spontaneous magnetization of the spontaneous magnetization layer is reversed when an element applied magnetic field having the intensity equal to or larger than a first threshold function value is applied. Each of the plurality of magnetic structures has a second threshold function, and generates a magnetic structure magnetic field in response to a structure-applied magnetic field. When the structure-applied magnetic field has the intensity equal to or larger than the second threshold function value, a third magnetic field is generated as the magnetic structure magnetic field. When the structure applied magnetic field has the intensity less than the second threshold function value, a fourth magnetic field is generated which is weaker than the third magnetic field as the magnetic structure magnetic field. A first write current supplied to one of the plurality of first signal lines as a first selected signal line, and a first magnetic field is generated. A second write current is supplied to one of the plurality of second signal lines as a second selected signal line, and a second magnetic field is generated. A first synthetic magnetic field of the first magnetic field and the second magnetic field is applied to the magnetic structure as the structure applied magnetic field. The element applied magnetic field having the intensity equal to or larger than the first threshold function value is applied to the selected memory cell provided at the intersection of the first selected signal line and the second selected signal line. A second synthetic magnetic field of the first synthetic magnetic field and the magnetic structure magnetic field is generated as the element applied magnetic field such that the element applied magnetic field having the intensity less than the first threshold function value is applied to each of non-selected memory cells other than the selected memory cell.
Owner:NEC CORP
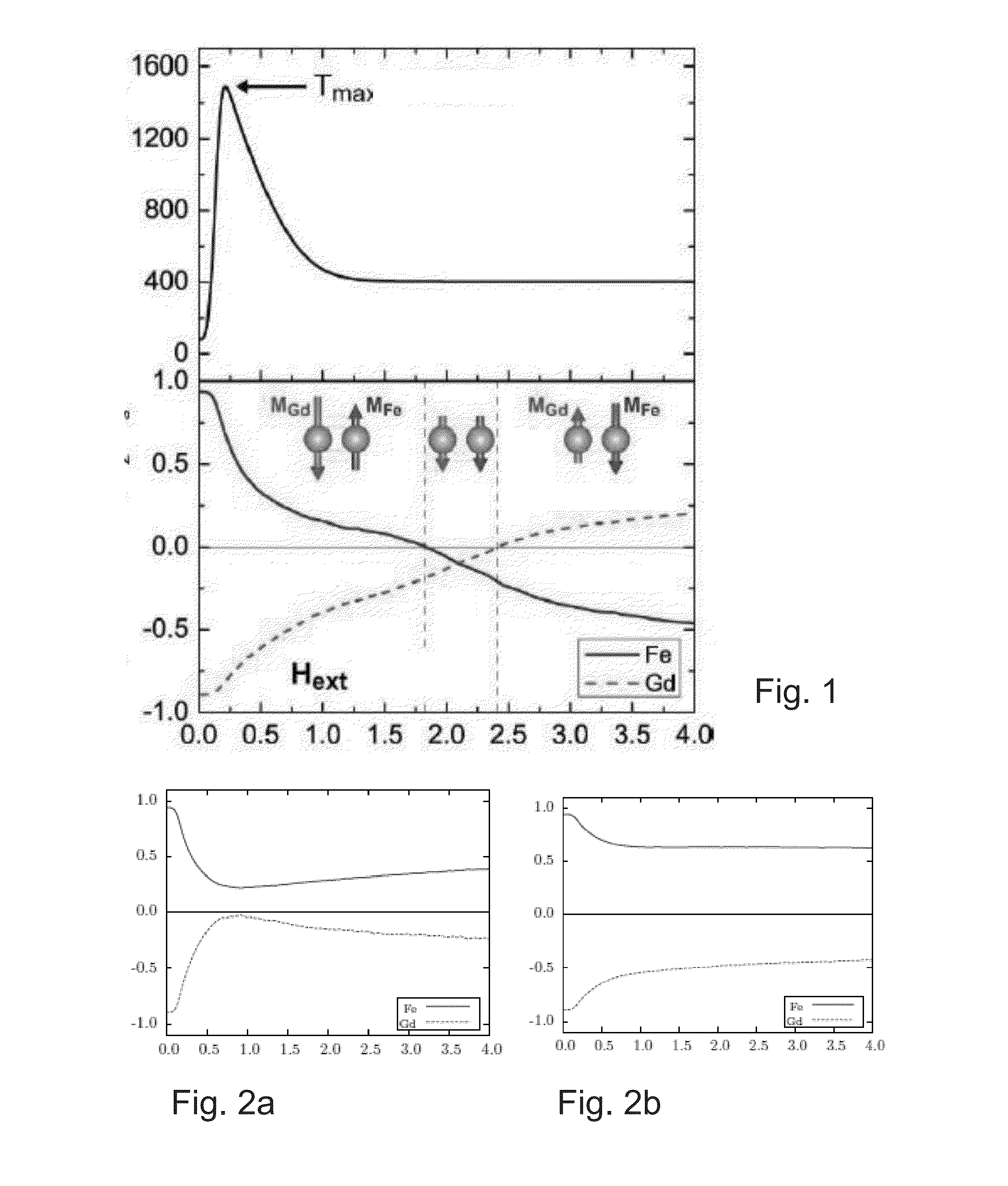
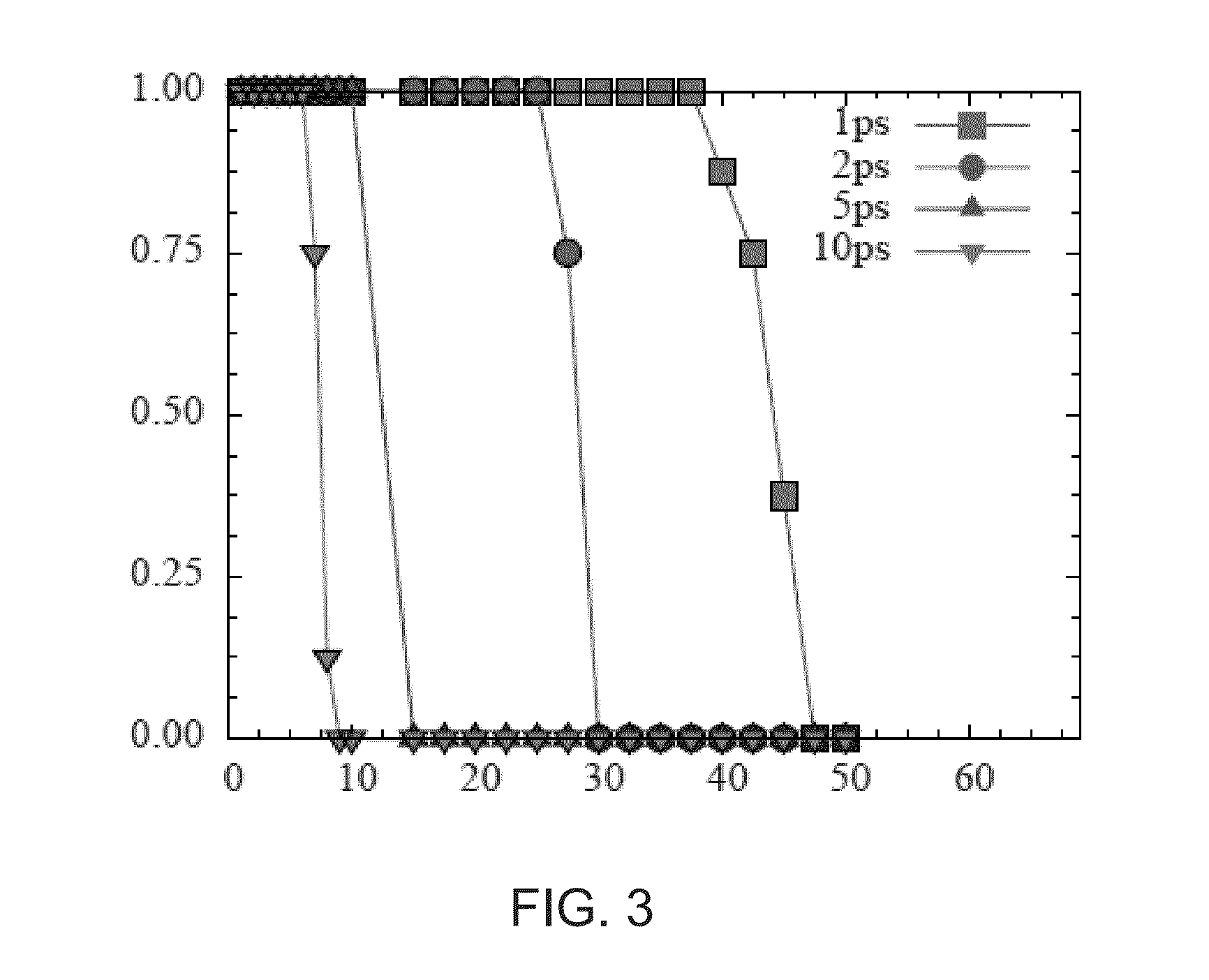
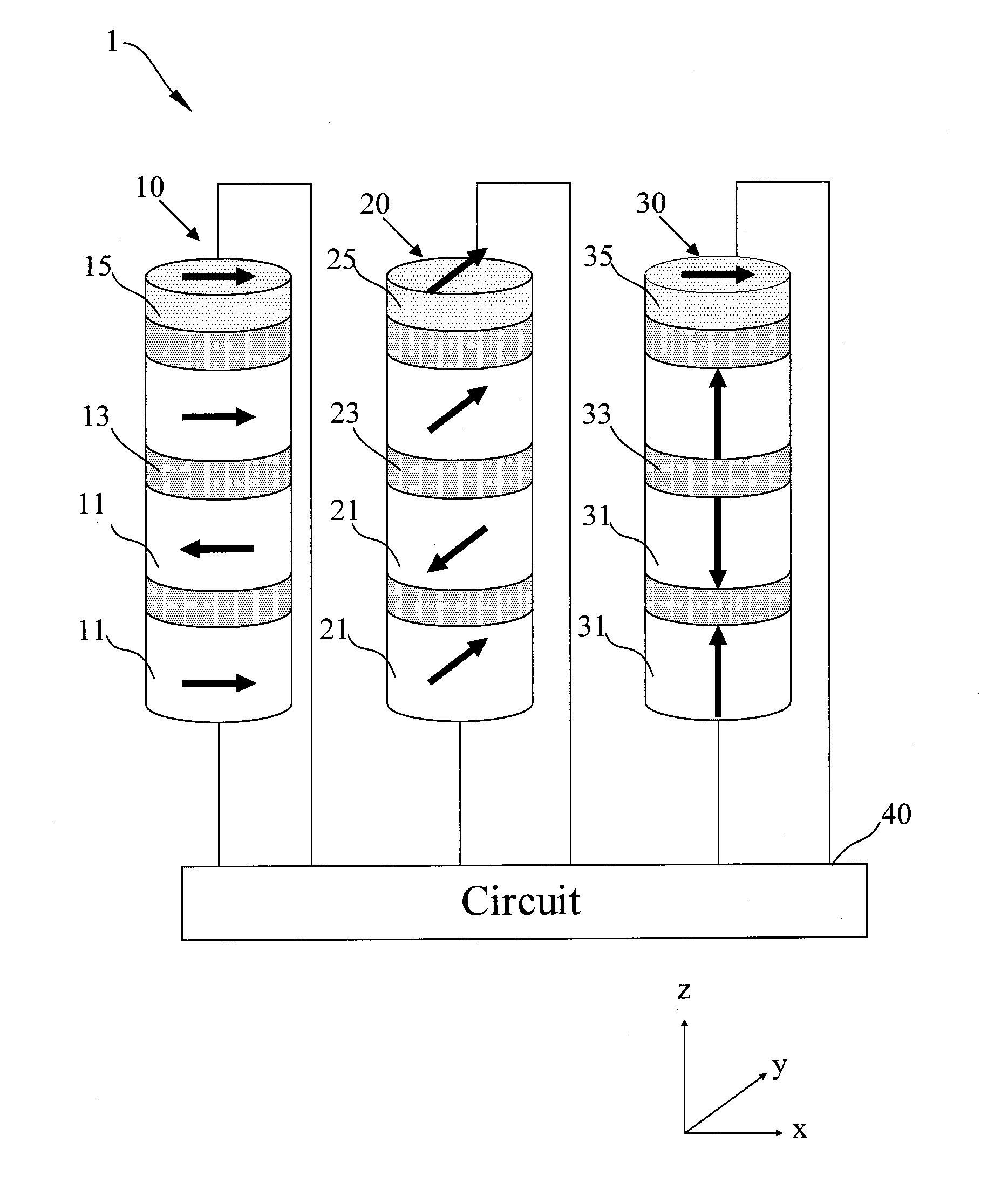
Magnetization Reversal
ActiveUS20140368303A1Time stableIncrease magnetic densityElectromagnets without armaturesDigital storageA domainSpontaneous magnetization
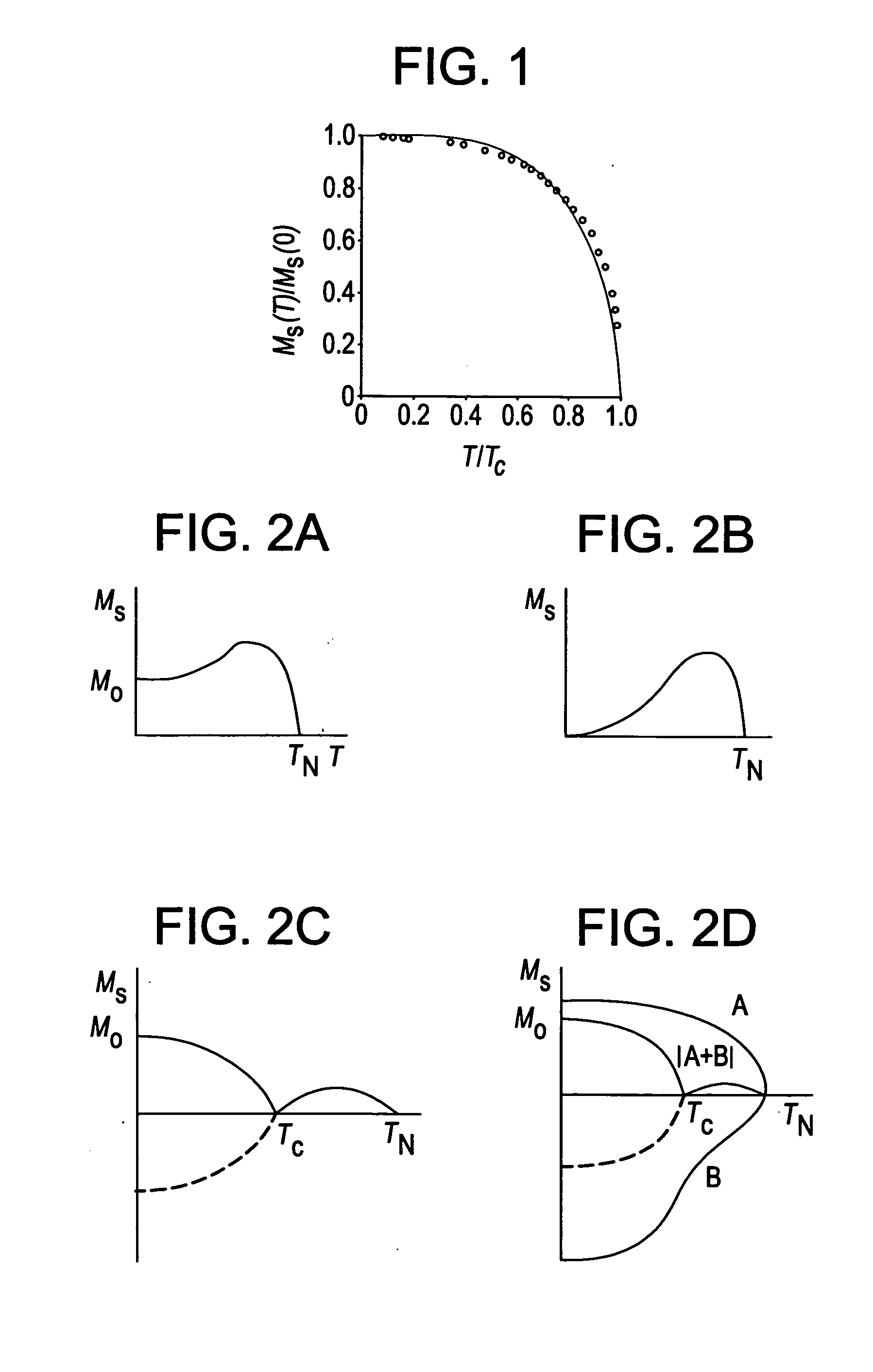
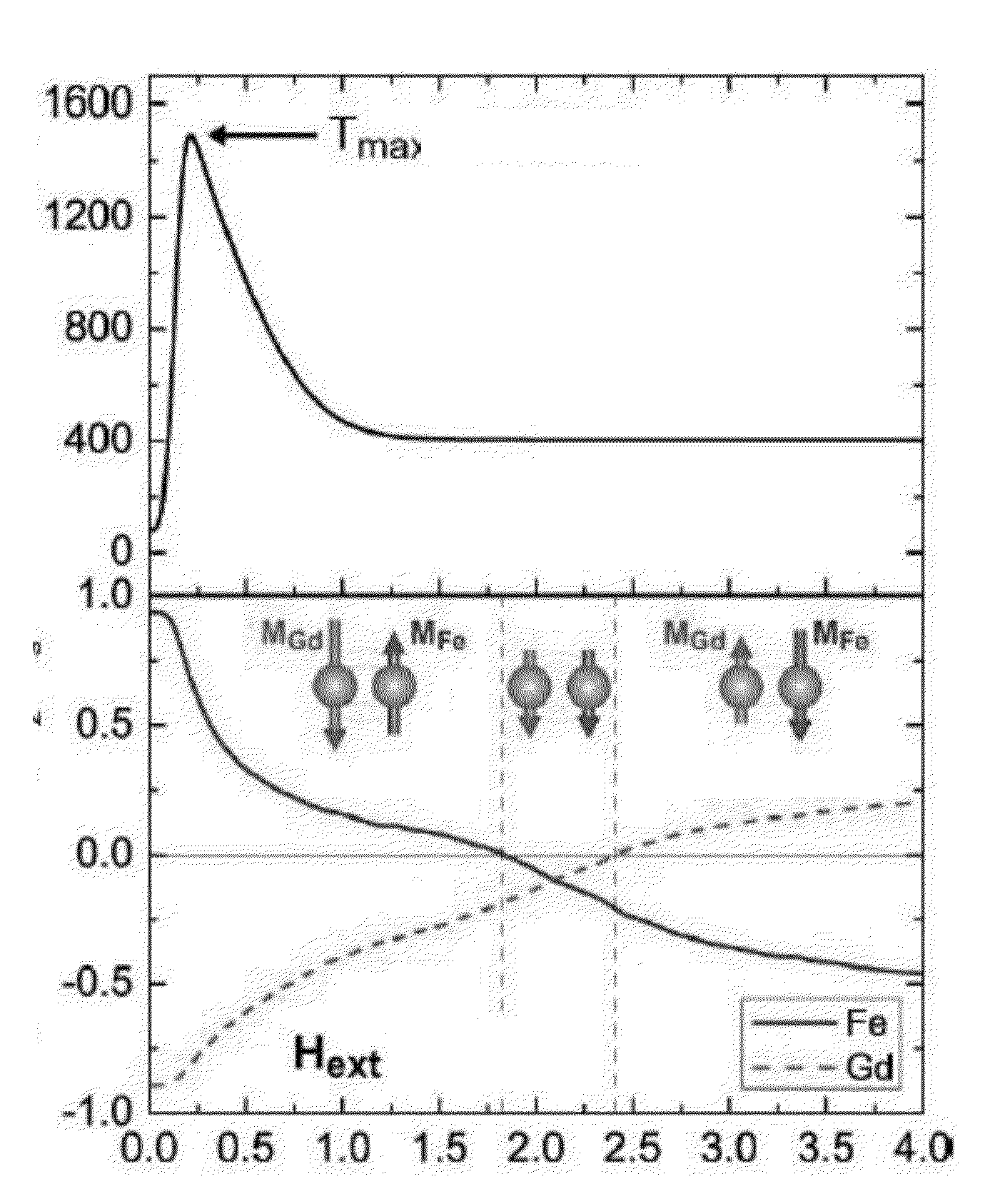
A method of magnetization reversal, time stable ferrimagnetic material, a product and a domain comprising said material, a system for magnetization reversal, and information storage. Therein, a ferrimagnetic material is one in which magnetic moments of the atoms on different sublattices are opposed, as in antiferromagnetism; however, in ferrimagnetic materials, the opposing moments are unequal and a spontaneous magnetization remains.
Owner:RADBOUD UNIVERSITY NIJMEGEN
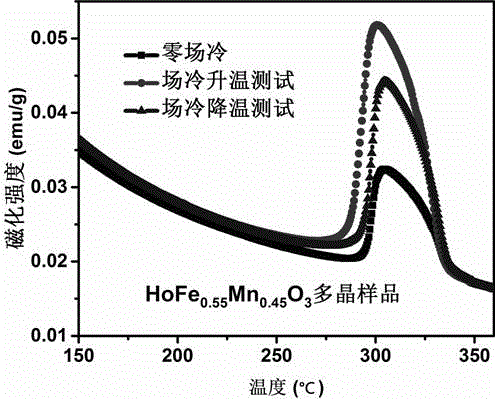
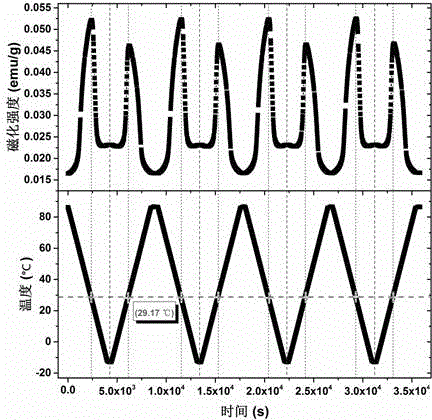
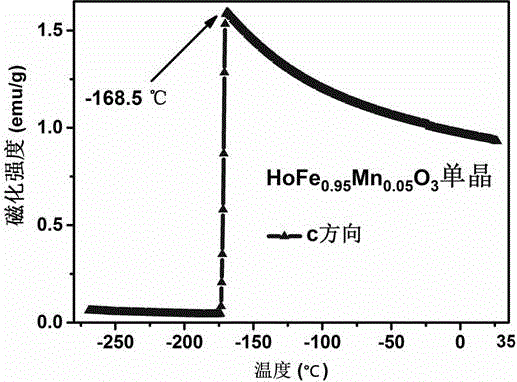
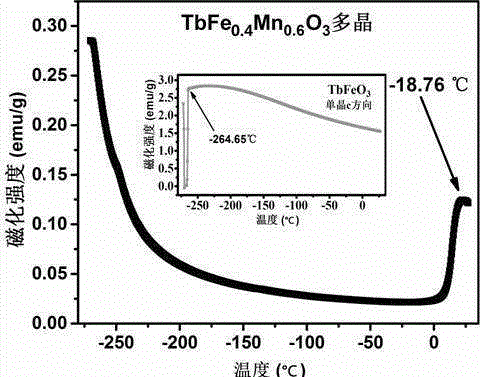
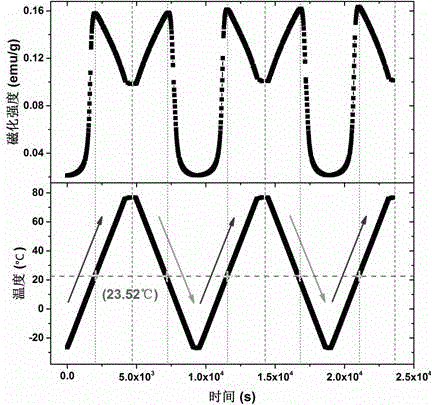
Magnetic thermosensitive material manganese-doped holmium iron oxide as well as preparation methods of monocrystalline and polycrystalline thereof
InactiveCN105483822ARaise the transition temperatureAdjustable transition temperaturePolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsMagnetic transitionsDevice material
The invention discloses a magnetic thermosensitive material manganese-doped holmium iron oxide as well as preparation methods of monocrystalline and polycrystalline thereof. A solid reaction method is carried out with Ho2O3, MnO2 and Fe2O3 powder for synthesis of a HoFe1-xMnxO3 polycrystalline material, and the polycrystalline material grows into a monocrystalline material by an optical-floating-zone furnace method. Applied magnetic fields are not needed for assisting the magnetic thermosensitive material, magnetic transition temperature has a high susceptibility, the magnetic transition critical temperature can be adjusted for usage of the material at room temperature, and the material can be applied to a magnetic thermosensitive device. Ratio of the magnetic thermosensitive material can be changed, in order to obtain different materials whose magnetic transition critical temperature range is between -213.15 to 29.17 DEG C, so that the magnetic transition speed of the material is higher than the magnetic transition speed of the traditional material whose magnetic transition critical temperature is around the Curie temperature, and spontaneous magnetization happens at the temperature above the critical temperature, so that applied magnetic fields are not needed for induction before and after transition. The magnetic thermosensitive material is better than the traditional magnetic thermosensitive device material whose magnetic transition depends on the Curie temperature.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS20050242407A1Reduce offset magnetic fieldSuppress offset magnetic fieldNanomagnetismSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A technique is provided in which an offset magnetic field of a memory cell of a MRAM is reduced more effectively. The MRAM of the present invention is composed of a free layer (11) which has a reversible free spontaneous magnetization, a fixed layer (6) which has fixed spontaneous magnetization, and a spacer layer (10) formed of non-magnetic interposed between the free layer (11) and the fixed layer (6). The fixed layer (6) is formed such that orange peel effect and magneto-static coupling effect does not substantially influence on the free layer (11).
Owner:NEC CORP
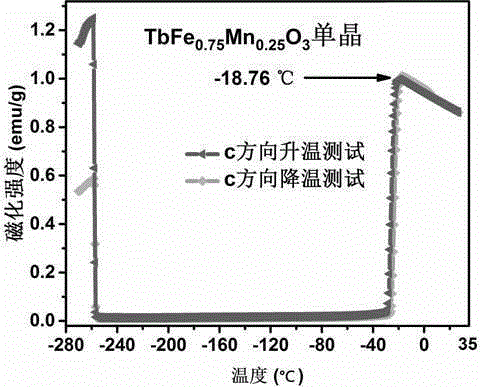
Magnetic temperature sensitive material of manganese doped terbium iron oxide and preparation method of monocrystal and polycrystal of magnetic temperature sensitive material
InactiveCN105332055AHigh temperature sensitivity of magnetic transitionIncreased sensitivityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsMagnetic transitionsDevice material
The invention discloses a magnetic temperature sensitive material of manganese doped terbium iron oxide and a preparation method of monocrystal and polycrystal of the magnetic temperature sensitive material. Tb4O7, MnO2 and Fe2O3 powder are synthesized into a TbFe1-xMnxO3 polycrystalline material by using a solid reaction process, and the polycrystalline material grows into a monocrystal material by using an optical floating zone furnace method. According to the magnetic temperature sensitive material, an external magnetic field is not needed, the magnetic transition temperature sensitivity is high, the magnetic transition critical temperature can be adjusted and can reach the room temperature, and the magnetic temperature sensitive material is applied to magnetic temperature sensitive devices. According to the magnetic temperature sensitive material, different materials of which the magnetic transition critical temperature is between -264.65 DEG C and 25.85 DEG C can be obtained by changing the proportion, the magnetic transition speed is higher than the traditional magnetic transition speed near the Curie temperature due to the phase change, spontaneous magnetization occurs at more than critical temperature, and therefore, the external magnetic field is not needed to induce before and after transition. The material is better than a traditional magnetic sensitive temperature device material depending on the magnetic transition near the Curie temperature.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
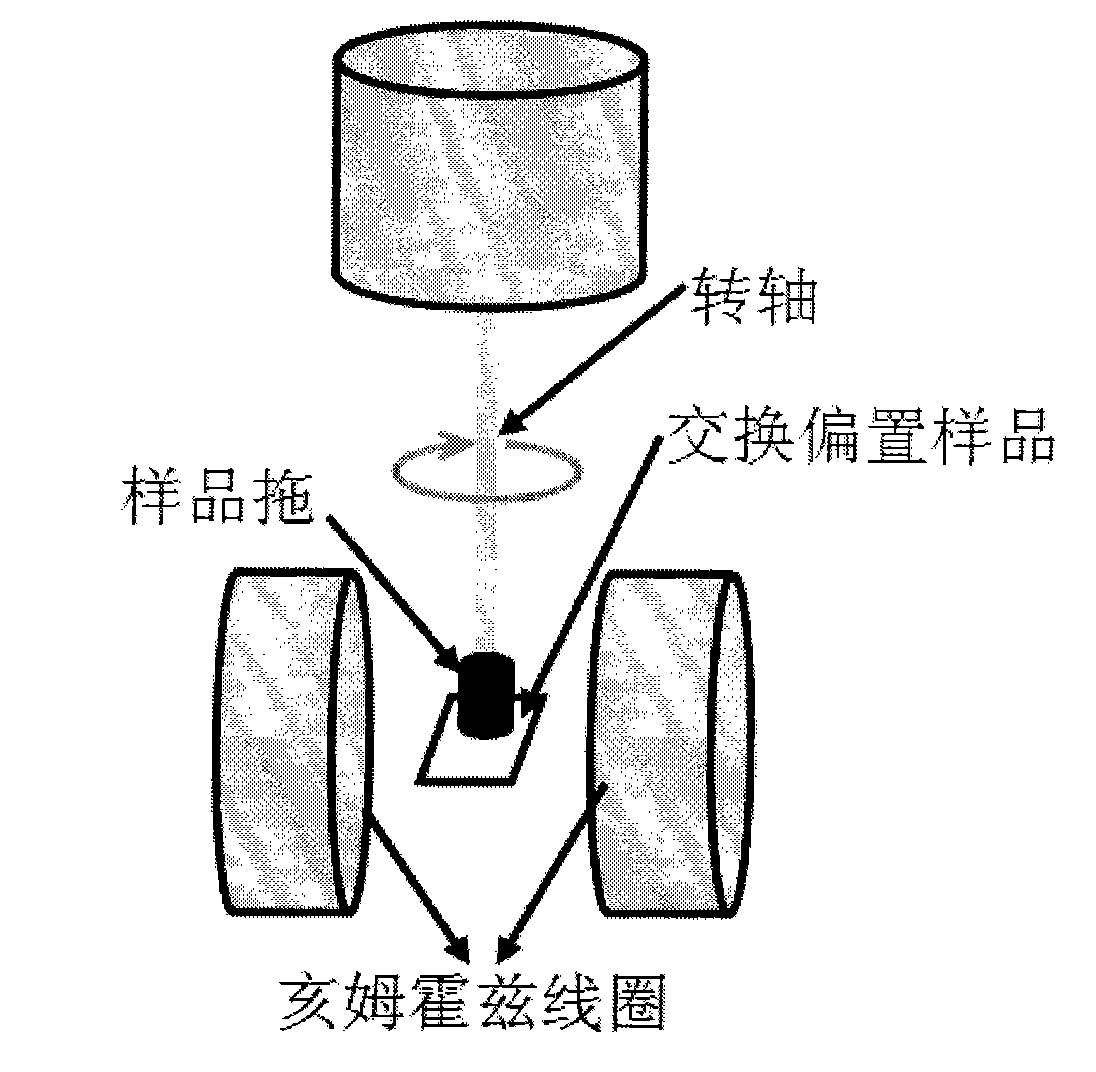
Method for testing hard and easy magnetization direction of exchange bias film
InactiveCN102253351ASimple test methodImprove test accuracyMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic measurementsSpontaneous magnetization
The invention relates to a magnetic measurement method, in particular to a method for testing a hard and easy magnetization direction of a magnetic film material with exchange bias. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging a sample film to be tested in an external direct current magnetic field, so that a plane of the sample film to be tested is parallel to the direction of the external magnetic field; rotating the sample film to be tested around an axis vertical to the plane; during test, optionally applying a given external magnetic field, keeping the magnetic field invariable, and recording an initial position of the sample and magnetization at the moment; rotating the sample film to be tested at an angle, and measuring a corresponding projection value M of spontaneous magnetization MS of the film to be tested in the direction of the external magnetic field at the angle theta0 so as to obtain a function of the sample film to be tested at different rotating angles theta0 and corresponding M values; and determining an easy magnetization axis or a hard magnetization axis of the exchange bias film according to a measured M-theta0 curve.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for testing hard and easy magnetization direction of exchange bias film
InactiveCN102253351BSimple test methodImprove test accuracyMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic measurementsSpontaneous magnetization
The invention relates to a magnetic measurement method, in particular to a method for testing a hard and easy magnetization direction of a magnetic film material with exchange bias. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging a sample film to be tested in an external direct current magnetic field, so that a plane of the sample film to be tested is parallel to the direction of the external magnetic field; rotating the sample film to be tested around an axis vertical to the plane; during test, optionally applying a given external magnetic field, keeping the magnetic field invariable, and recording an initial position of the sample and magnetization at the moment; rotating the sample film to be tested at an angle, and measuring a corresponding projection value M of spontaneous magnetization MS of the film to be tested in the direction of the external magnetic field at the angle theta0 so as to obtain a function of the sample film to be tested at different rotating angles theta0 and corresponding M values; and determining an easy magnetization axis or a hard magnetization axis of the exchange bias film according to a measured M-theta0 curve.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional in-plane magnetic sensor
InactiveUS20140062470A1Increase capacityImprove yield rateMagnetic sensor geometrical arrangementsThree-component magnetometersIn planeManufacturing cost reduction
A three-dimensional (3D) in-plane magnetic sensor includes a first magnetic sensor, a second magnetic sensor, a third magnetic sensor and a circuit. The first magnetic sensor, second magnetic sensor and third magnetic sensor are installed on a same plane to measure the magnetic field component of first direction, second direction and third direction, where the third direction is perpendicular to the first and second direction. The third magnetic sensor includes a third fixed layer, a third magnetic insulating layer and a third free layer. The magnetoresistance of the third free layer is an intermediate value in the spontaneous magnetization direction, and is varied when interfered by an external magnetic field. In short, the 3D in-plane magnetic sensor is manufactured with semiconductor processing which does not require vertical adhesion, and also bring the benefits of improved production capacity, prolonged product life, reduced manufacturing cost and time.
Owner:ISENTEK INC +1
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveCN1669147AThe bias magnetic field decreasesReduce bias magnetic fieldNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A technique is provided in which an offset magnetic field of a memory cell of a MRAM is reduced more effectively. The MRAM of the present invention is composed of a free layer ( 11 ) which has a reversible free spontaneous magnetization, a fixed layer ( 6 ) which has fixed spontaneous magnetization, and a spacer layer ( 10 ) formed of non-magnetic interposed between the free layer ( 11 ) and the fixed layer ( 6 ). The fixed layer ( 6 ) is formed such that orange peel effect and magneto-static coupling effect does not substantially influence on the free layer ( 11 ).
Owner:NEC CORP
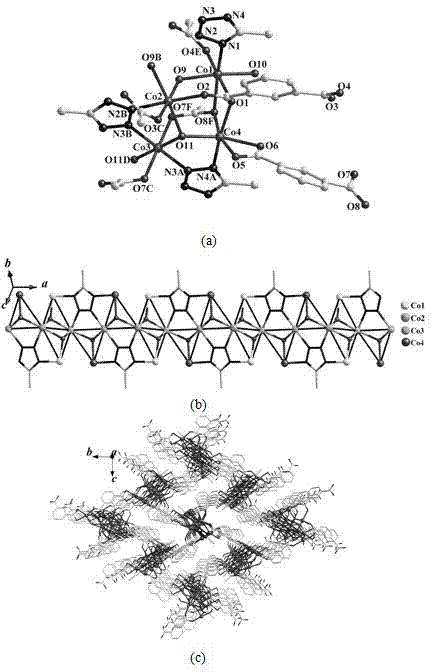
MOFs material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an MOFs (Metal Organic Frameworks) material. The chemical formula of the MOFs material is Co3RE4(TZI) 6.9H2O, RE comprises at least one of Gd, Sm, Eu, Tb and Dy, and TZI3- in the Co3RE4 (TZI) 6.9H2O is a trivalent anion of 5-(1-H-tetrazole)-isophthalic acid. Co and 4f rare earth metals are used as magnetic center atoms; the MOFs material obtained by taking 5-(1-H-tetrazole)-isophthalic acid as a ligand has a porous structure in a three-dimensional space; an asymmetric unit of the crystal is hourglass-shaped; Co ions and adjacent rare earth metal ions act to spontaneouslymagnetize, electronic magnetic moments are arranged in the same direction, and the spontaneous magnetization intensity of the other asymmetric unit in the same unit cell is equal to that of the former and opposite to that of the former, so that the net magnetic moment of the whole unit cell is zero, and the magnetic moment of the whole crystal is in an ordered state and is anti-ferromagnetic.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Substrate-integrated waveguide h-plane self-biased isolator based on soft magnetic nanowire array
InactiveCN105914439BReduce volumeSimple structureWaveguide type devicesDielectric substrateMagnetic nanowires
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com