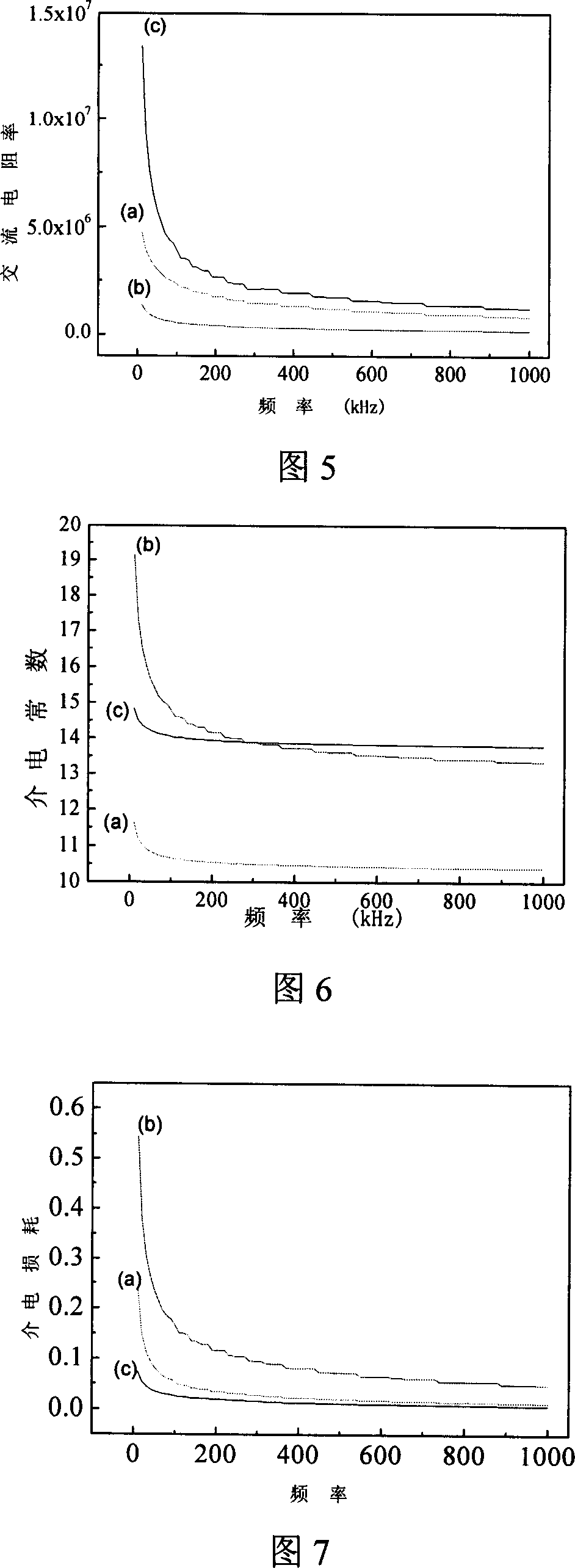
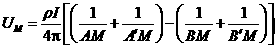Patents
Literature
64 results about "Dc resistivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DC Resistivity and Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) are surface geophysical methods in which an electrical current is injected into the ground through two electrodes and voltages on the surface are measured revealing the direction and amount of current flow in the subsurface. The data is used to image the subsurface resistivity.
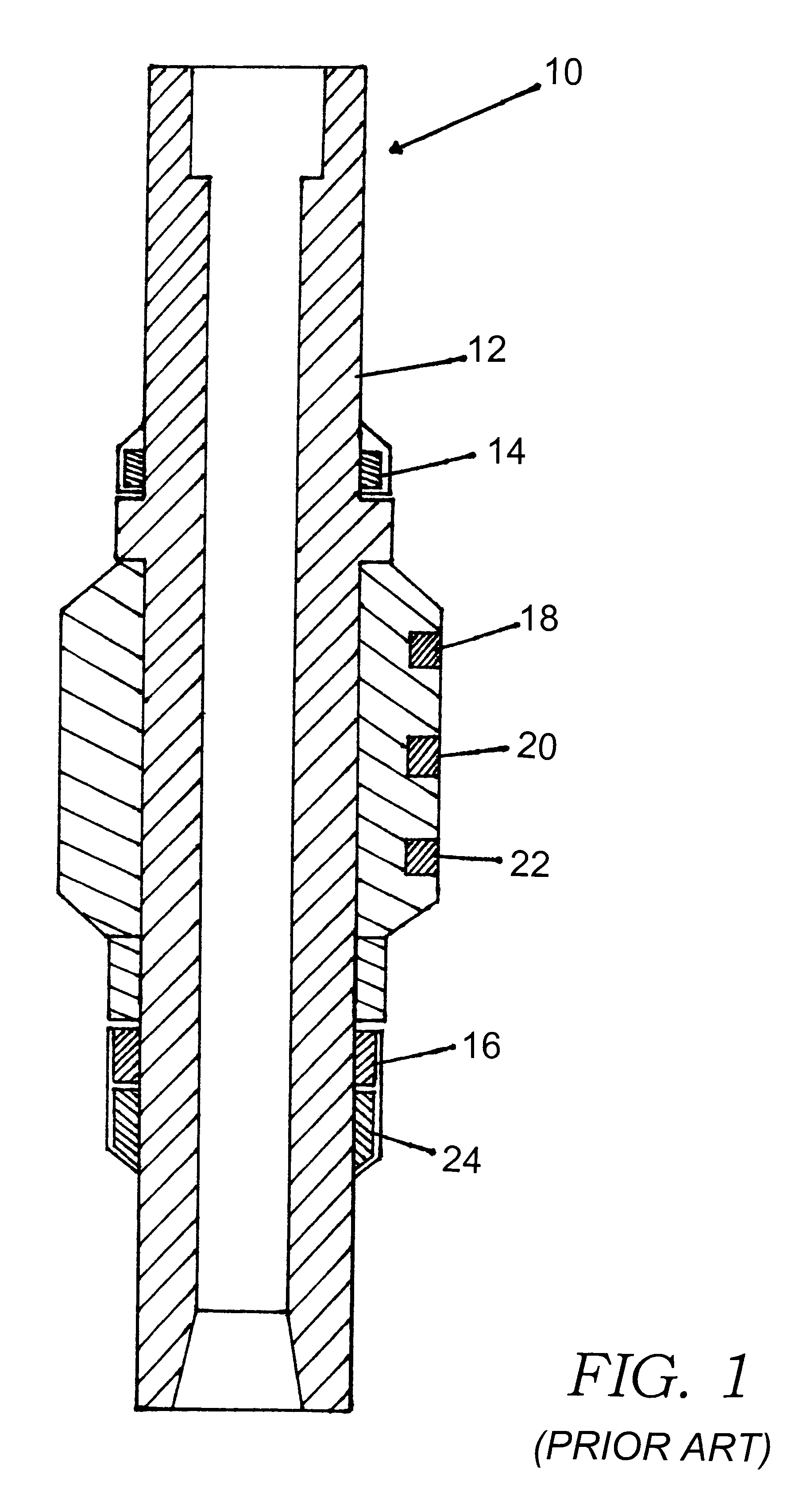
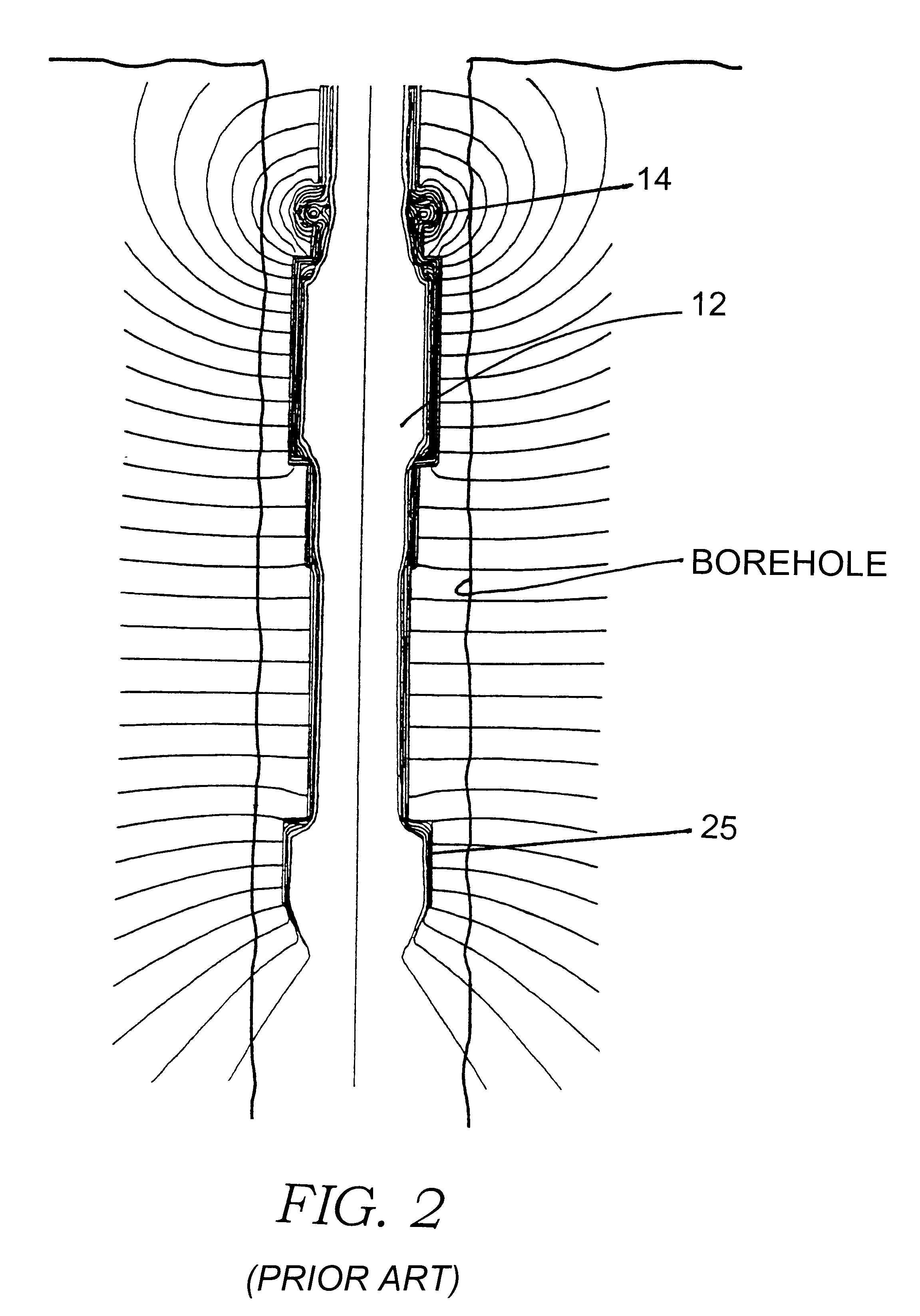
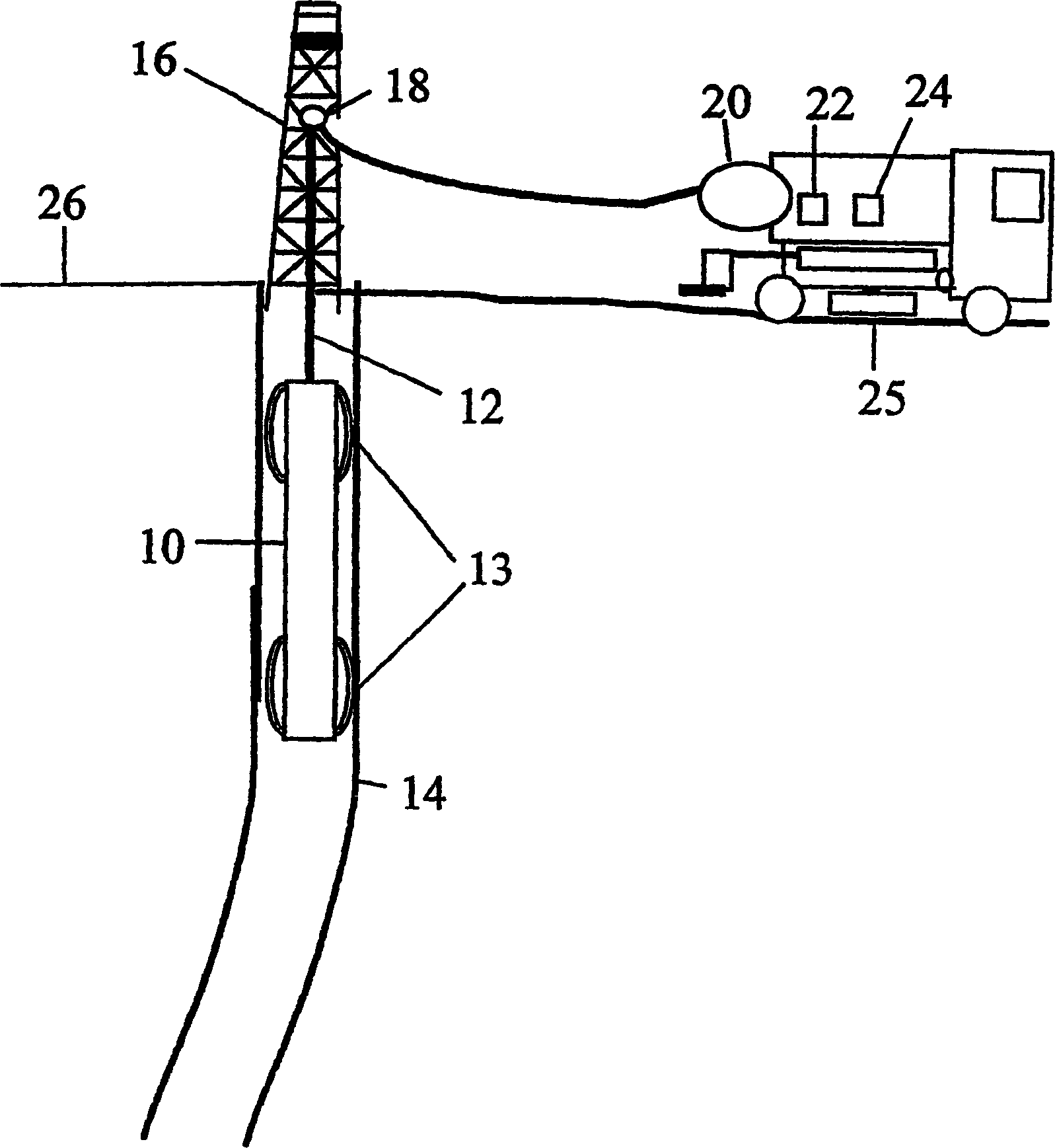
Method and apparatus for measurement of borehole size and the resistivity of surrounding earth formations
InactiveUS6384605B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsElectrical resistance and conductanceDc resistivity
A method and apparatus for determining the size or diameter of boreholes extending to a wide range of dimensions and / or the resistivity of the surrounding earth formations utilizing a well tool disposed in the borehole. The method involves generating model data representative of the well tool responses to different borehole diameters contrasted with formation and borehole fluid resistivity values, determining the borehole fluid resistivity, transmitting electromagnetic energy into the formation, measuring the energy shed back into the borehole at arbitrary sensor stations on the tool and generating resistivity signal data associated with the measured energy, and matching the signal data and the fluid resistivity against the modeled response data to determine the borehole caliper and / or formation resistivity. The apparatus forms part of a system for calculating a borehole caliper and / or the surrounding formation resistivity. The apparatus being coupled to a multi-sensor well tool and adapted to respond to signal data generated by the tool. The apparatus further adapted to receive the signal data; to receive a borehole fluid parameter; to store modeled well tool response data; and to process the signal data, the fluid parameter, and the modeled data to determine the borehole caliper and / or formation resistivity.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for positioning artificial wetland clogging area through resistivity curve
InactiveCN104049279AContinuous operationGuaranteed uptimeMaterial resistanceElectric/magnetic detectionDielectricConstructed wetland
The invention discloses a method for positioning an artificial wetland clogging area through a resistivity curve. The method includes the steps that first, a direct-current resistivity symmetrical four-pole sounding device is arranged above an artificial wetland, and the apparent resistivity is measured according to the mode that the electrode spacing becomes bigger and bigger; second, a power supply positive electrode A, a power supply negative electrode B, a measurement electrode M and a measurement electrode N of the direct-current resistivity symmetrical four-pole sounding device are all arranged symmetrical about a measurement point, and the apparent resistivity (please see the formula in the specification) of the electrode spacing is calculated every time the power supply electrode spacing is changed; third, the measured apparent resistivity is subjected to inversion, and the resistivity depth measurement curve is drawn according to the resistivity values obtained through inversion; fourth, the non-clogging area of the artificial wetland has the low resistivity characteristic, the clogging area of the artificial wetland has the high resistivity characteristic, and on the resistivity depth measurement curve, the vertical spatial position of the clogging area in the measurement point is determined according to the changing characteristic of the resistivity value. According to the method, on the basis of the conductivity difference of dielectric, the artificial wetland clogging area can be positioned through the resistivity difference.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
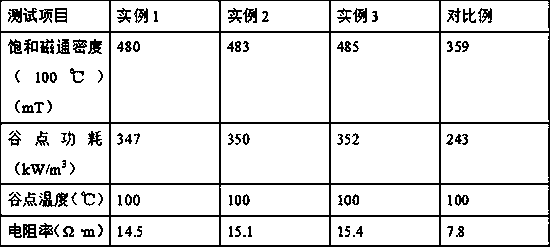
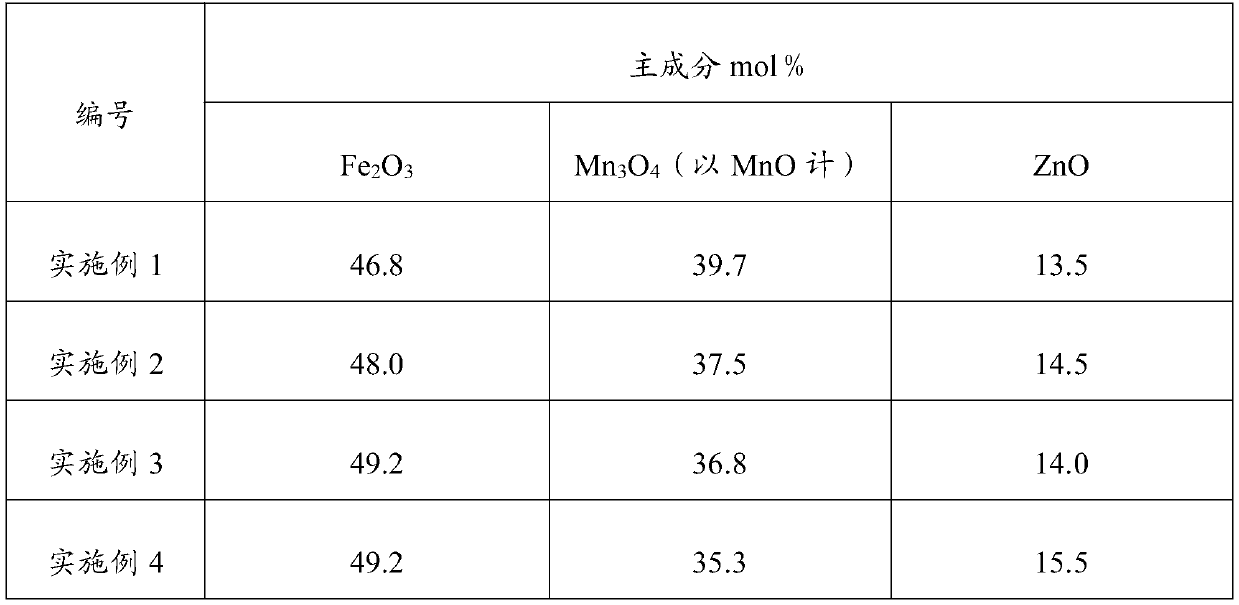
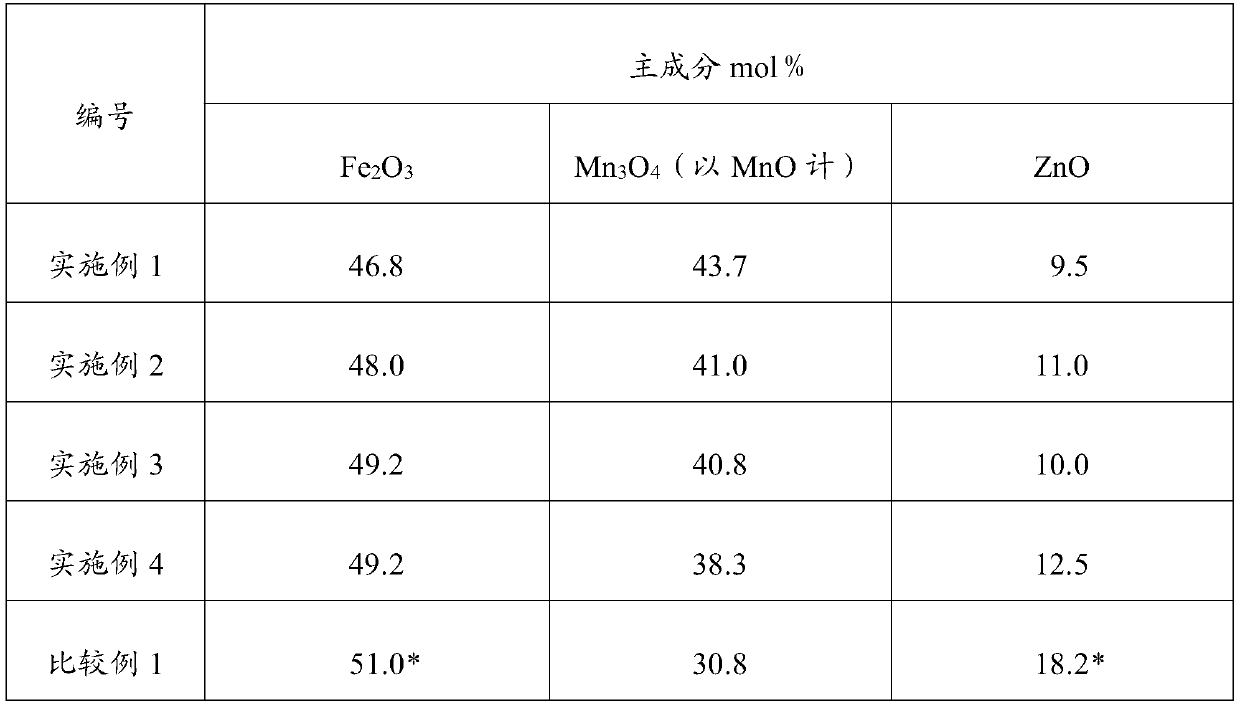
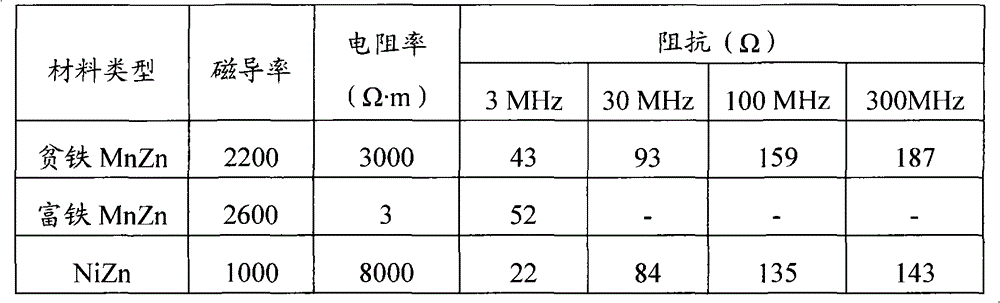
Broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material and manufacture method thereof
The invention provides a broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material, which comprises main components and assistant components. The main components comprise 47 to 50 mol percent of Fe203, 29 to 35 mol percent of Mn3O4 by MnO and 16 to 21 mol percent of ZnO. The assistant components are at least one kind from SiO2, CaCO3, V205 and Nb2O5. Total weight based on the main components is that SiO2 is0.002 to 0.01 wt percent, CaCO3 is 0.01 to 0.08 wt percent, V205 is 0.01 to 0.07 percent, and Nb2O5 is 0.01 to 0.07 percent. The broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material has DC resistivity larger than 103 omega meter, curie temperature higher than 115 degrees centigrade and 2000 plus or minus 20 percent initial permeability. Moreover, the low frequency impedance of the material is larger than the common NiZn ferrite material, the high frequency impedance thereof is equal to the common NiZn ferrite material and the material does not contain expensive raw material NiO. The invention further provides the manufacture method of the broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material, which comprises the steps of mixing, drying, preburning, ball-milling, granulation, molding, sintering and thelike.
Owner:江门江益磁材有限公司
Joint inversion method based on magnetotelluric and direct current resistivity data
ActiveCN111323830AImprove balanceSolve the disadvantages caused by fixed divisionDetection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationObservation dataComputational physics
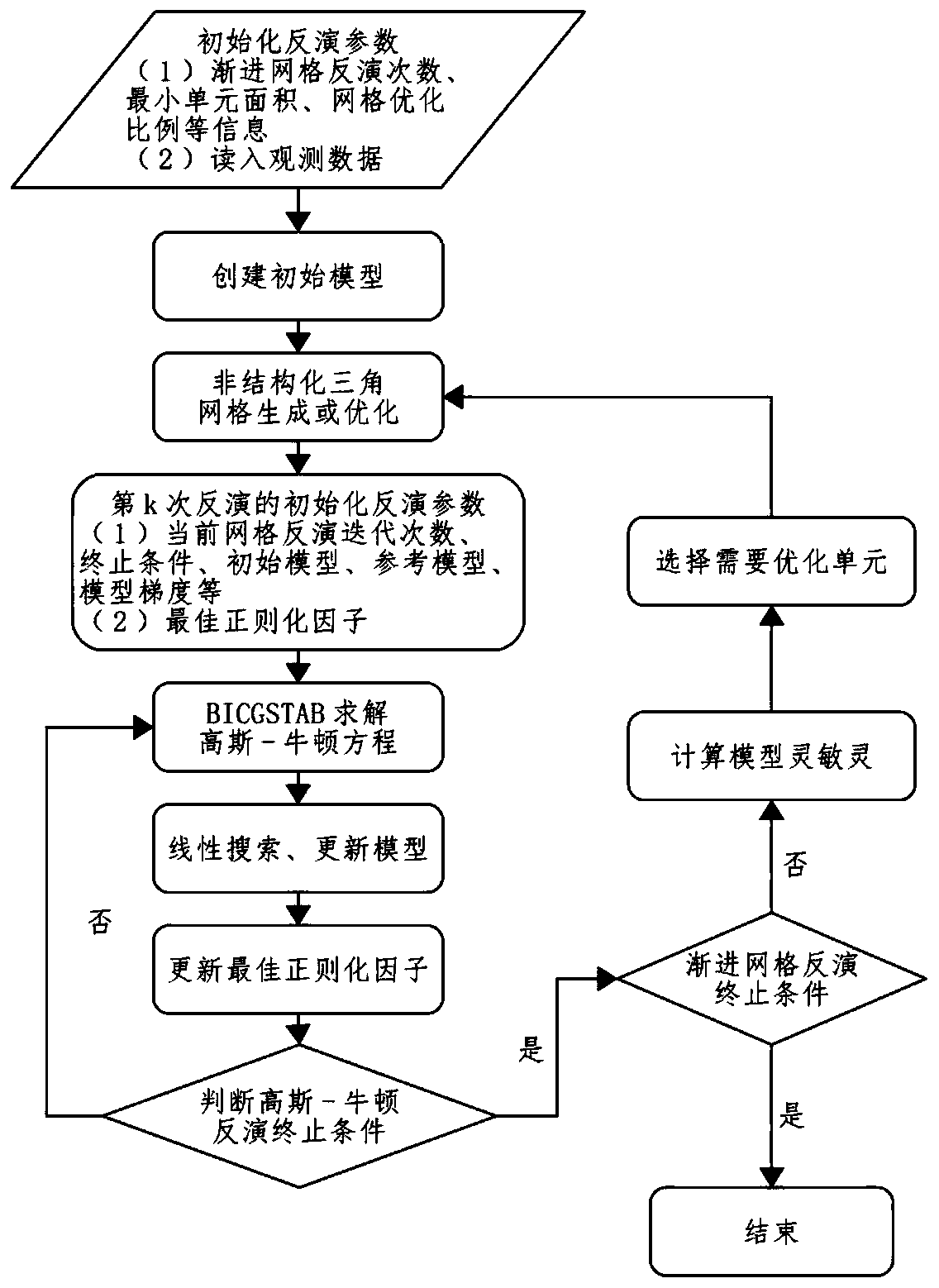
The invention discloses a joint inversion method based on magnetotelluric and DC resistivity data, and the method comprises the steps: determining an inversion region according to observation data, carrying out the subdivision to obtain an initial grid, and setting an initial value of an inversion parameter vector; performing Gaussian-Newton inversion iteration based on the current value of the inversion parameter vector to calculate a model change amount and a linear search step length, and then calculating an iterative update value of the inversion parameter vector; judging whether an inversion termination condition is met or not, and if not, carrying out next iteration; if so, judging whether a progressive grid inversion termination condition is reached or not, and if so, ending the inversion; and if not, carrying out refined subdivision on the grid cell, updating the inversion parameter vector value, and returning to carry out Gauss-Newton inversion iteration until inversion is finished. According to the invention, a joint inversion technology of inversion grid adaptive adjustment is researched and developed, the problem of multiplicity of solutions of joint inversion interpretation of a magnetotelluric method and direct current resistivity data is effectively reduced, and the joint interpretation accuracy is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low-temperature physical property measuring device of solid material
InactiveCN101957334AEfficient conductionAvoid enteringResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial heat developmentAviationMeasurement device
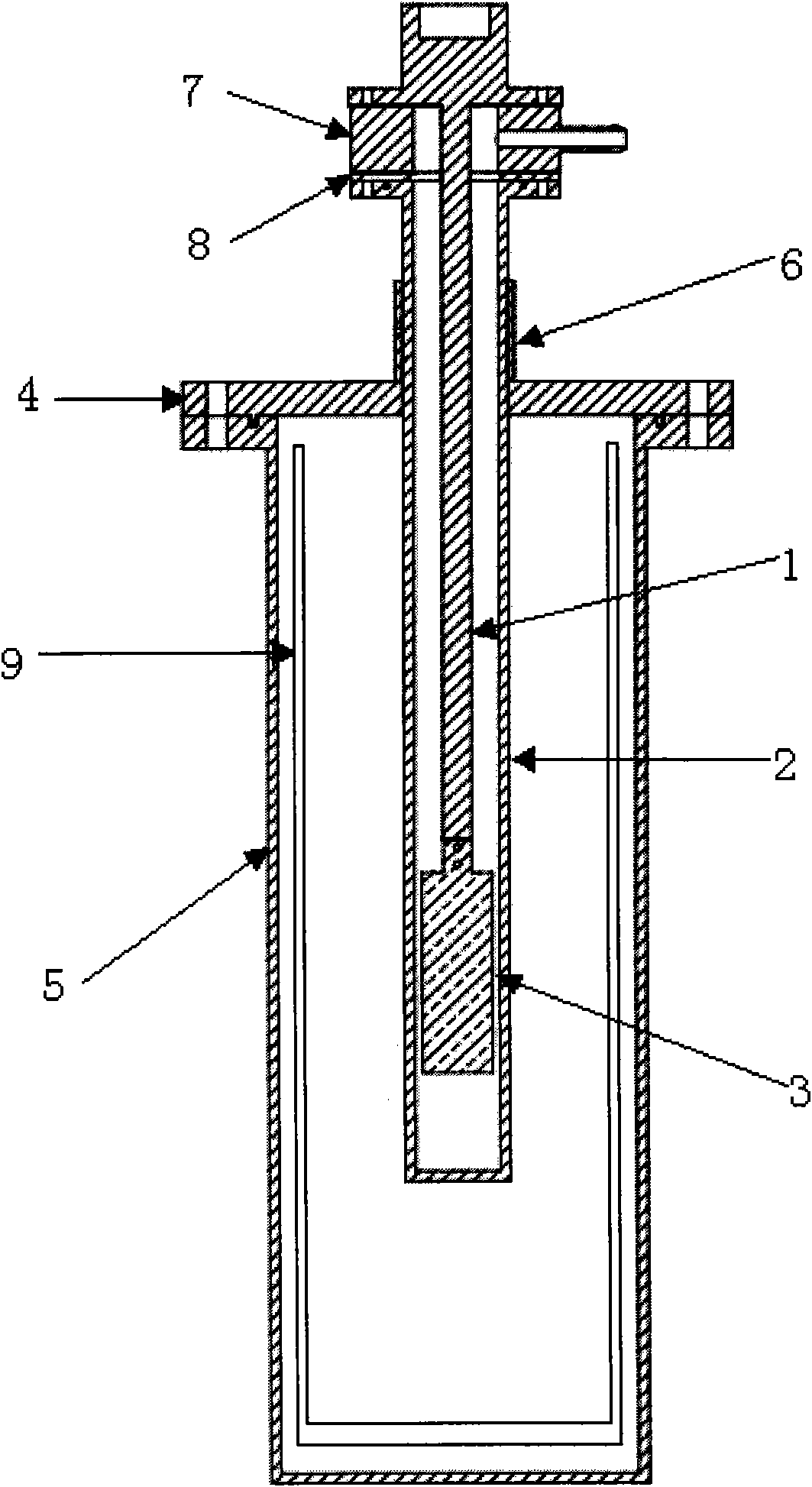
The invention relates to a low-temperature physical property measuring device of a solid material, which is used for measuring specific heat, alternating current and direct current resistivity, a heat conduction coefficient and a thermoelectric potential rate of a solid material at low temperature. The physical property measuring device comprises a sample carrying part and a refrigerating part, wherein the refrigerating part comprises a Dewar flask, a Dewar sleeve, a Dewar cover, a low-temperature chamber, a vacuum extracting module and an air leakage preventing module; the Dewar flask is arranged in the Dewar sleeve; the Dewar sleeve and the Dewar cover are fastened in a flange structure; the middle of the Dewar cover is provided with a hole in which the low-temperature chamber is inserted; and the middle of the low-temperature chamber is sleeved with a blocking sleeve for fixing the low-temperature chamber. The jointing position of a sample rod and the low-temperature chamber has a flange structure, and the air leakage preventing module and the vacuum extracting module are clamped between the sample rod and the low-temperature chamber from bottom to top and sealed by an O-shaped ring. An aviation plug is installed on the upper part of the sample rod, and an internal lead is connected to the aviation plug along a rod body of the sample rod. The invention has the advantages of less liquid nitrogen consumption, no indium wire consumption, short thermal relaxation time, stable low-temperature environment, relatively simple structure, low cost, and the like and can be applied to the physical property measurement of various solid materials in the teaching and researching process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
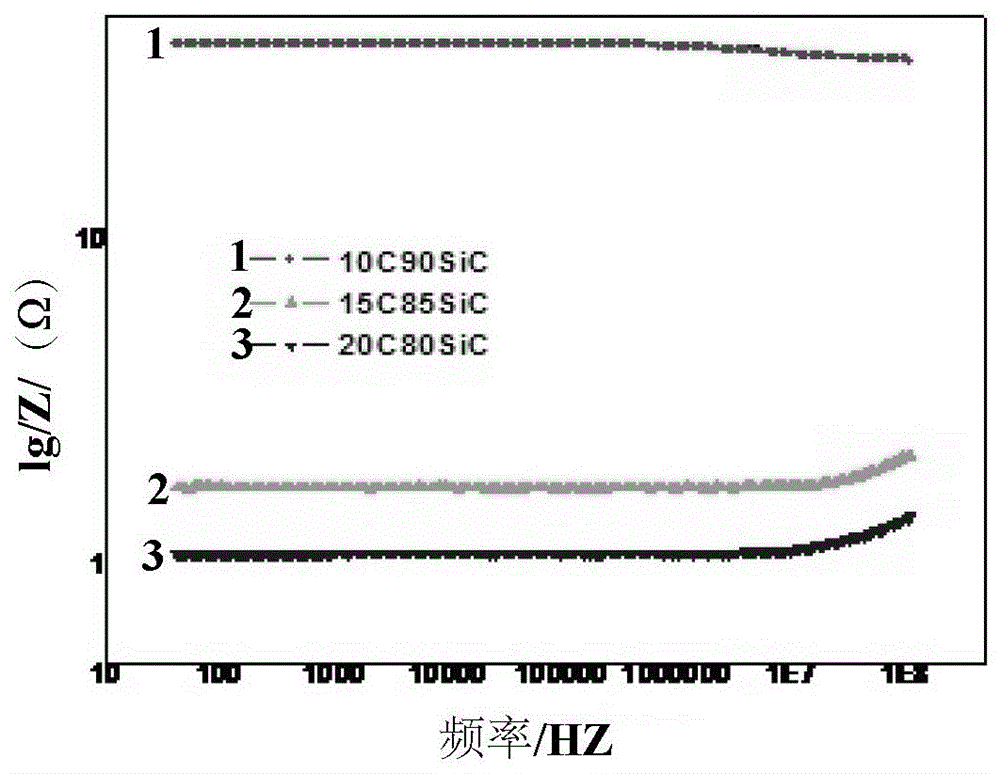
Low-resistivity linear-resistance silicon carbide and graphite composite and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low-resistivity linear-resistance silicon carbide and graphite composite and a preparation method thereof. The silicon carbide and graphite composite is composed of silicon carbide phase and a graphite phase converted from carbon phase during sintering and is free of third-phase substances, the graphite phase is 10-20% by weight, and the silicon carbide / graphite composite is 110-160 W / m<-1> / K<-1> in heat conductivity, 10-750 Omega / cm in direct-current resistivity that never changes with voltage, and 0.5-45 Omega in alternating-current resistivity modulus that never changes with frequency. The composite of the invention comprises only silicon carbide and graphite and is free of third-phase substances, and by adjusting the content of graphite, it is possible to obtain the silicon carbide / graphite composite with high heat conductivity, low resistance and linear resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
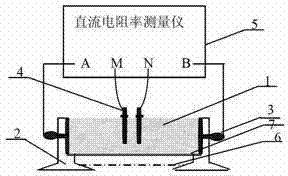
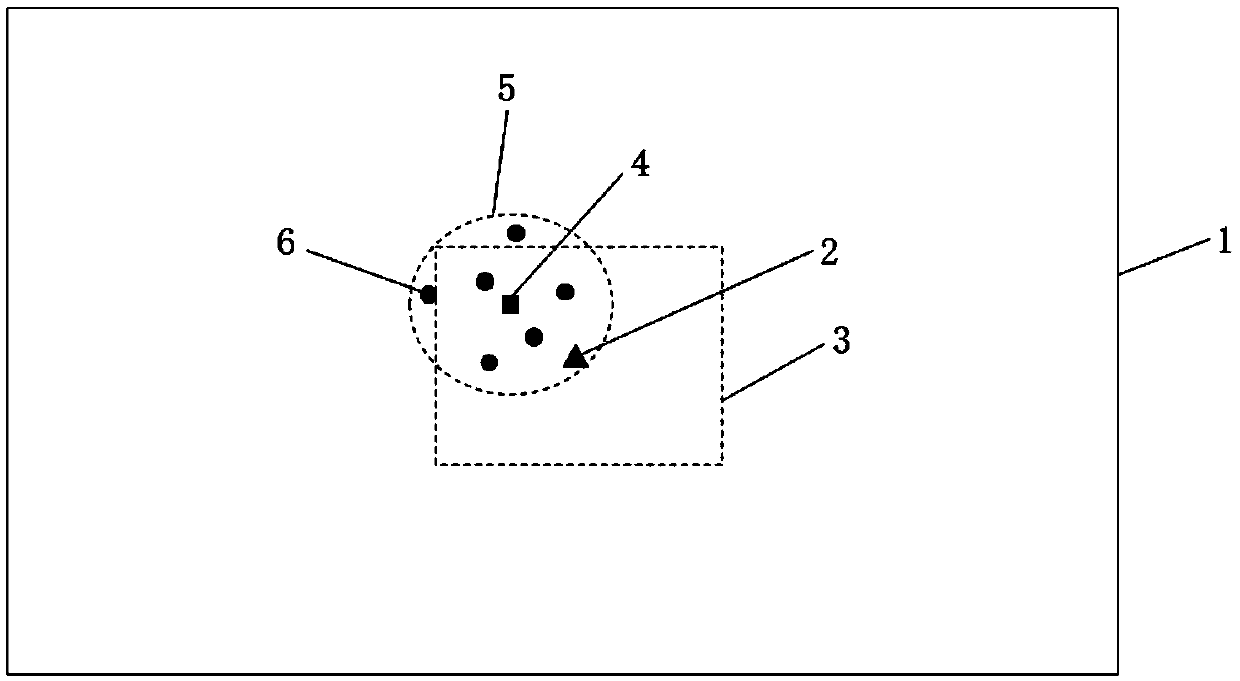
Method and device for measuring indoor resistivity of soil sample
InactiveCN102854392AReliable test resultsEasy to determineResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasuring instrumentDc resistivity
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring indoor resistivity of a soil sample. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of 1) preparing a sample placing device (2) and a direct-current resistivity measuring instrument (5) according to measurement requirements, fixing the soil sample (1) on the sample placing device (2), and connecting the sample placing device (2) with the direct-current resistivity measuring instrument (5) by a four-electrode method; 2) starting the device and setting parameters according to operation procedures of the direct-current resistivity measuring instrument; 3) beginning to acquire and record voltage, current and resistivity values Rho 1 after parameter setting is finished; 4) re-measuring the voltage, the current and the resistivity values Rho 1 after previous measurement is finished and two receiving electrodes are swapped, and recording measured voltage, current and resistivity values Rho 2; 5) further reducing a polarization effect by using a superposition averaging method, expressing superposition averaging by an expression of resistivity Rho=(Rho 1-Rho 2) / 2, and obtaining the indoor resistivity Rho=(Rho 1-Rho 2) / 2 of the measured soil sample. The method and the device for measuring the indoor resistivity of the soil sample have the advantages of accuracy in measurement and simple measurement method, and are applicable to measuring the indoor resistivity of marine soil samples, land soil samples or manufactured sample soil.
Owner:CHINA ENERGY ENG GRP GUANGDONG ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST CO LTD
Background grid adaptive segmenting method in DC resistivity no-unit method
InactiveCN108287371AImprove computing efficiencyImprove numerical stabilityElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationElectricityNumerical stability
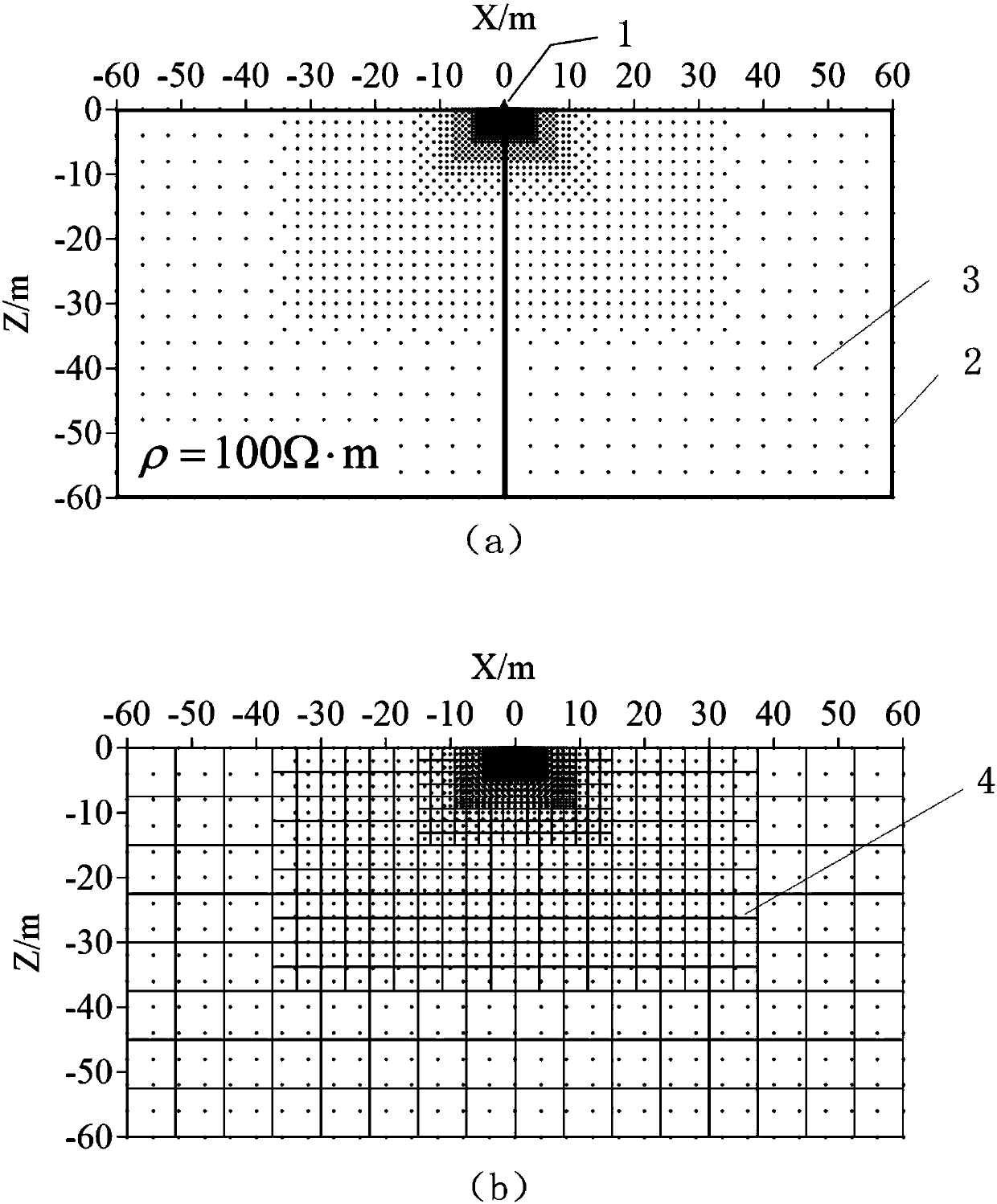
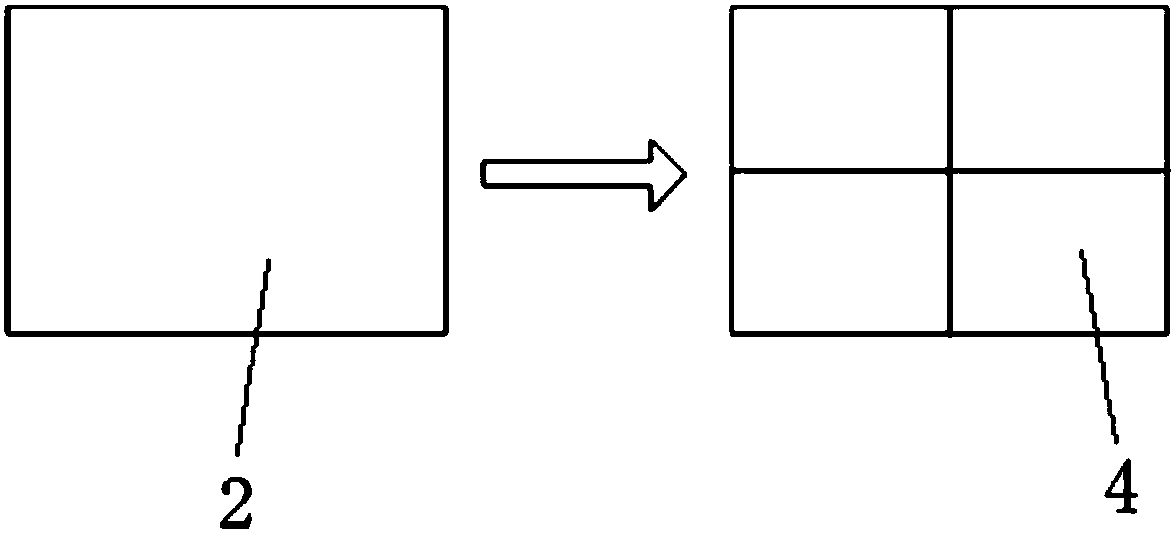
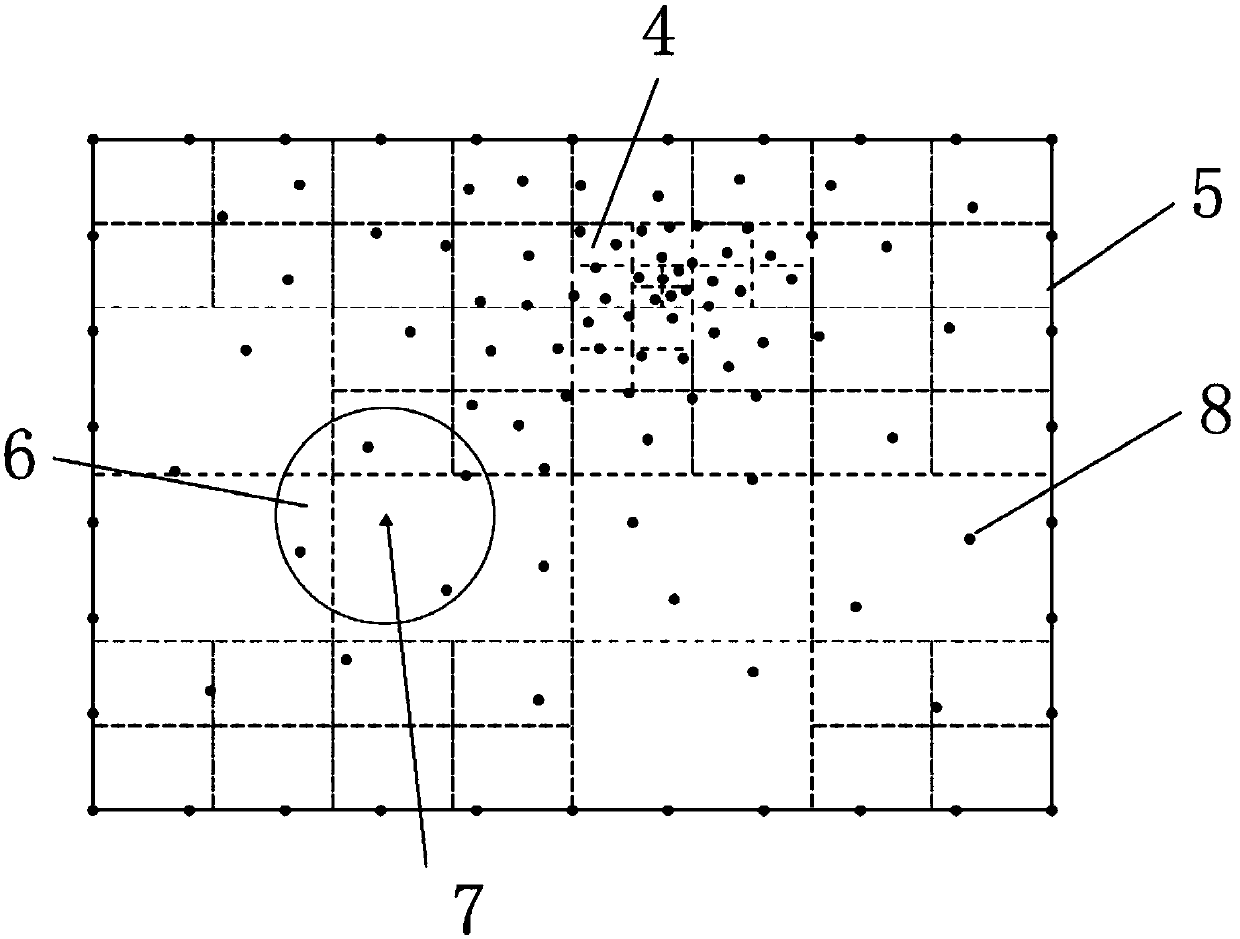
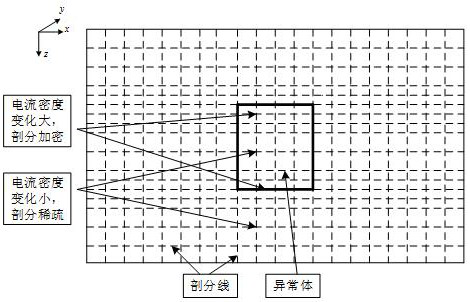
The invention provides a background grid adaptive segmenting method in a DC resistivity no-unit method. The method comprises the following steps of determining distribution condition of medium, abnormal member, landform, electrode and the like in a two-dimensional ground electric model, establishing a DC resistivity no-unit method calculating domain, and utilizing an irregularly distributed node discrete ground electric model; covering the calculating domain by means of a small number of rough and simple initial quadrangular grids, setting a control value which guides adaptive segmentation, and performing adaptive segmentation by the background grid according to the control value and a node distribution condition; arranging ng Gaussian integration points xg in each background grid, and obtaining a no-unit method equation set of the region; solving the equation set for obtaining a node electric field value, and calculating the vision resistivity parameter of a viewing point. The methodcan be based on any node distribution discrete model. High adaptability for any complicated ground electric model is realized. The background grid adaptive segmenting method improves value stability and computing efficiency in routine DC resistivity no-unit method forward calculation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for eliminating influence of roadways and terrains on apparent resistivity in direct-current exploration
ActiveCN103278855AAvoid difficultiesGuaranteed accuracyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTerrainDc resistivity
The invention discloses a method for eliminating the influence of roadways and terrains on the apparent resistivity in direct-current exploration. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a model according to a roadway shape, the roadway cutting depth, topographic relief elevation and the like; taking the minimum value of the formation resistivity of an exploration area as the resistivity of a uniform half-space containing the roadways and the terrains; putting a power supply electrode at a corresponding position in the model according to the type of the adopted device for direct-current exploration and the electrode distribution mode; performing one-time three-dimensional numerical simulation every time the power supply electrode moves, obtaining potential response of a background field, and interpolating to obtain potential difference between receiving electrodes as potential difference of the background field; deducing an apparent resistivity formula from a potential formula of a point current source in the horizontal uniform self-space; and subtracting the potential difference of the background field from the measured potential difference to obtain potential different without the influence of the roadways and the terrains, and substituting the potential difference into an apparent resistivity formula of a current source in an underground self-space to obtain the relative apparent resistivity. The method can be widely applied to direct-current resistivity exploration projects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of manganese zinc soft magnetic ferrite
InactiveCN107827448AFine and uniform particlesHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismPyrolusiteCurie temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a manganese zinc soft magnetic ferrite, and belongs to the technical field of ferrite material preparation. Orange peels and iron powder are reduced ina sulfuric acid solution for reduction leaching to form manganese dioxide in pyrolusite so as to obtain a leaching agent containing manganese ions, and manganese dioxide is added into the leaching agent, and the manganese zinc soft magnetic ferrite is obtained through ball-milling, mold pressing and sintering, so that the direct current electrical resistance is extremely high, the generation of aneddy current can be reduced, the loss of a magnetic core is reduced, and the saturation flux density of the soft magnetic ferrite is improved; during sintering, the sintering temperature is raised toa relatively high temperature, and then the sintering temperature is deceased to a relatively low temperature, the temperature is preserved for a period of time, in the period, crystal particles arefree of obvious growth, the sintered and obtained soft magnetic ferrite has uniformer and finer particles and relatively high density by controlling the change of the temperature, and the Curie temperature of the soft magnetic ferrite is increased, so that the manganese zinc soft magnetic ferrite has high saturation flux density and abroad application prospects.
Owner:吴刚
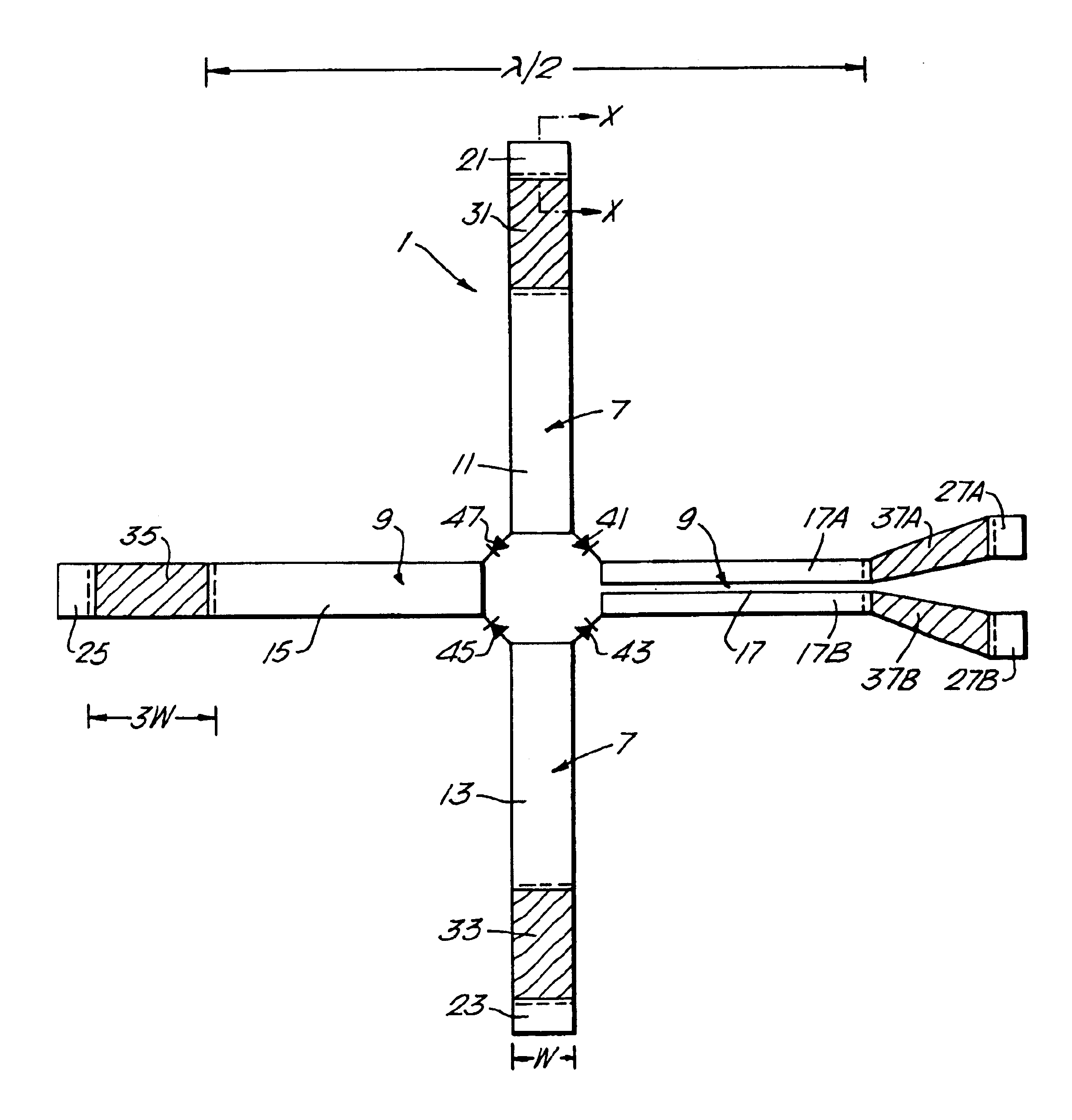
Integrated antenna device with resistive connection
InactiveUS6989790B1Low resistivityAdvantage of reproduceabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsIntermediate frequencyIntegrated antenna
A planar metal antenna mounted on a semiconductor body and incorporating an active circuit element, for example a diode, integrated in the path of the antenna. Connection between the antenna metal and a peripheral contact is provided by a connecting link of resistive sheet material sub-divided, by voids or by inclusions of high resistive material, into a number of conductive tracks each of width and spacing of dimension small compared with the width of the antenna. The link thus exhibits an effectively high sheet resistivity at high frequency—i.e. at a frequency at or near to the frequency of antenna resonance and thus affords effective hf isolation between the antenna and the contact. At the same time, at dc and at intermediate frequency, a relatively low resistance path is afforded for bias and for extraction of IF signal. The number, width and spacing of the tracks may be varied with distance from the antenna metal to minimize the dc resistivity. Thus the track density may be graded; the link may be comprised of several sections each of different track density. Alternatively, the track density may be made a tapered function of distance from the antenna metal by variation of the size and density of voids or high resistivity inclusions. The connection may be formed of material overlying the semiconductor body. Alternatively, it may be defined in the semiconductor body by dopant implant.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD +1
Nickel zinc ferrite material and its preparation method
The invention discloses a Ni-Zn-Fe oxide material with expressive formula as Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4, which comprises the following steps: weighing pure ferric citrate, zinc nitrate and nickel nitrate; dissolving zinc nitrate and nickel nitrate into deionized water; blending to add ferric citrate; stirring evenly to obtain clear former solution; heating the former solution; evaporating solvent to form black red foaming material; producing self-combustion; bulking the foaming material to obtain the loose brown powder; compressing the brown powder; sintering to obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Functional network characteristic analysis method based on breast cancer diseases
ActiveCN109375271AReduce the influence of the inversion effectElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationData acquisitionDc resistivity
The invention provides a functional network characteristic analysis method based on breast cancer diseases. The method comprises the following steps: step one, integrating various relationship networks including a drug-disease network, a drug-drug network, a drug-target network, and a target-target network and carrying out a series of network topology structure analyses on the networks; step two,on the basis of the e topological structure relation of breast cancer functional networks, digging 11 kinds of pieces of characteristic information capable of describing the drug-target mutual interaction relationship; and step three developing a related breast cancer functional network feature extraction tool. According to the invention, a functional network analysis method for characteristics ofbreast cancer diseases is established to solve a problem of relocation of the drugs; and the potential targets and new drug uses are predicted by using the method, so that the good prediction effectis obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
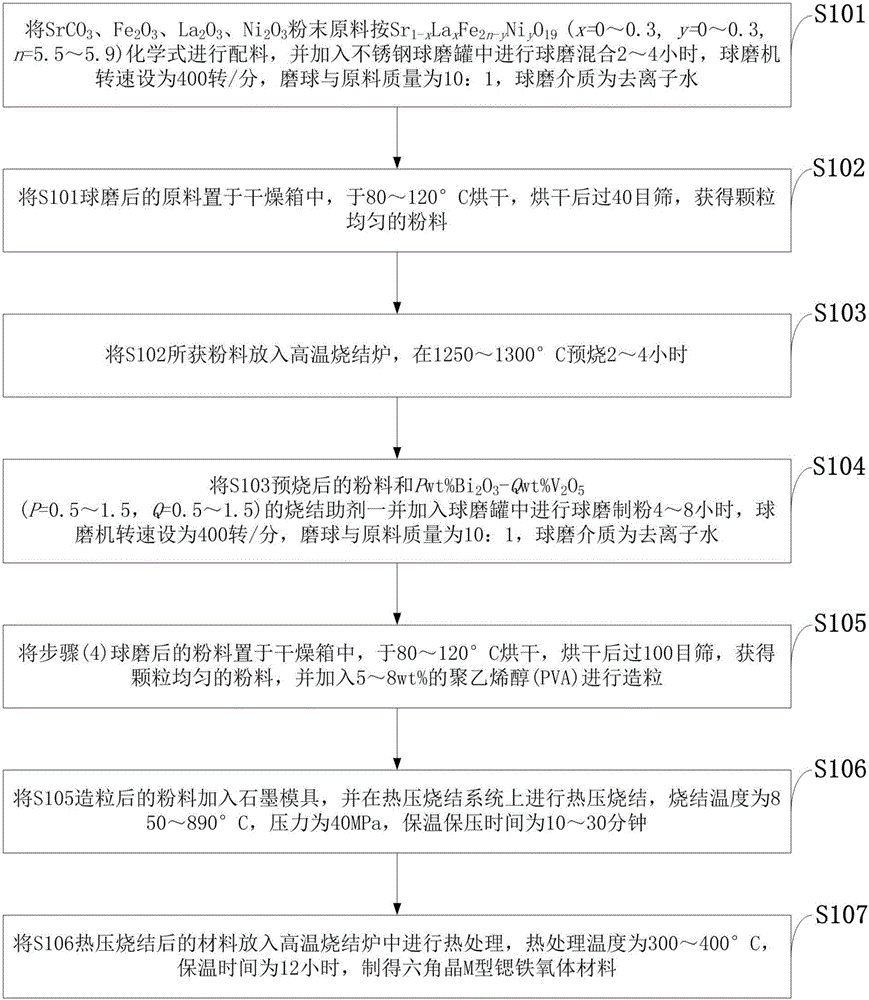
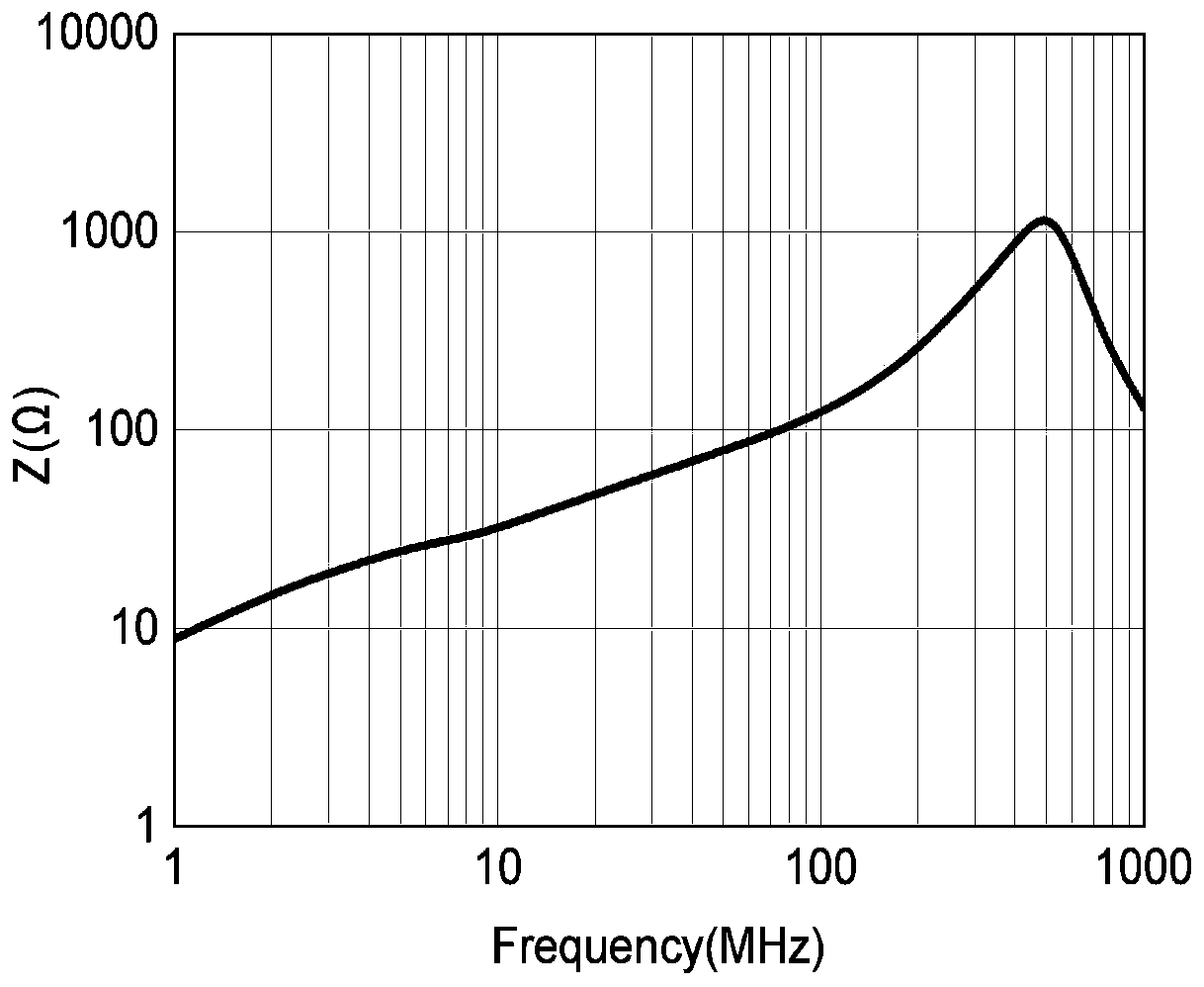
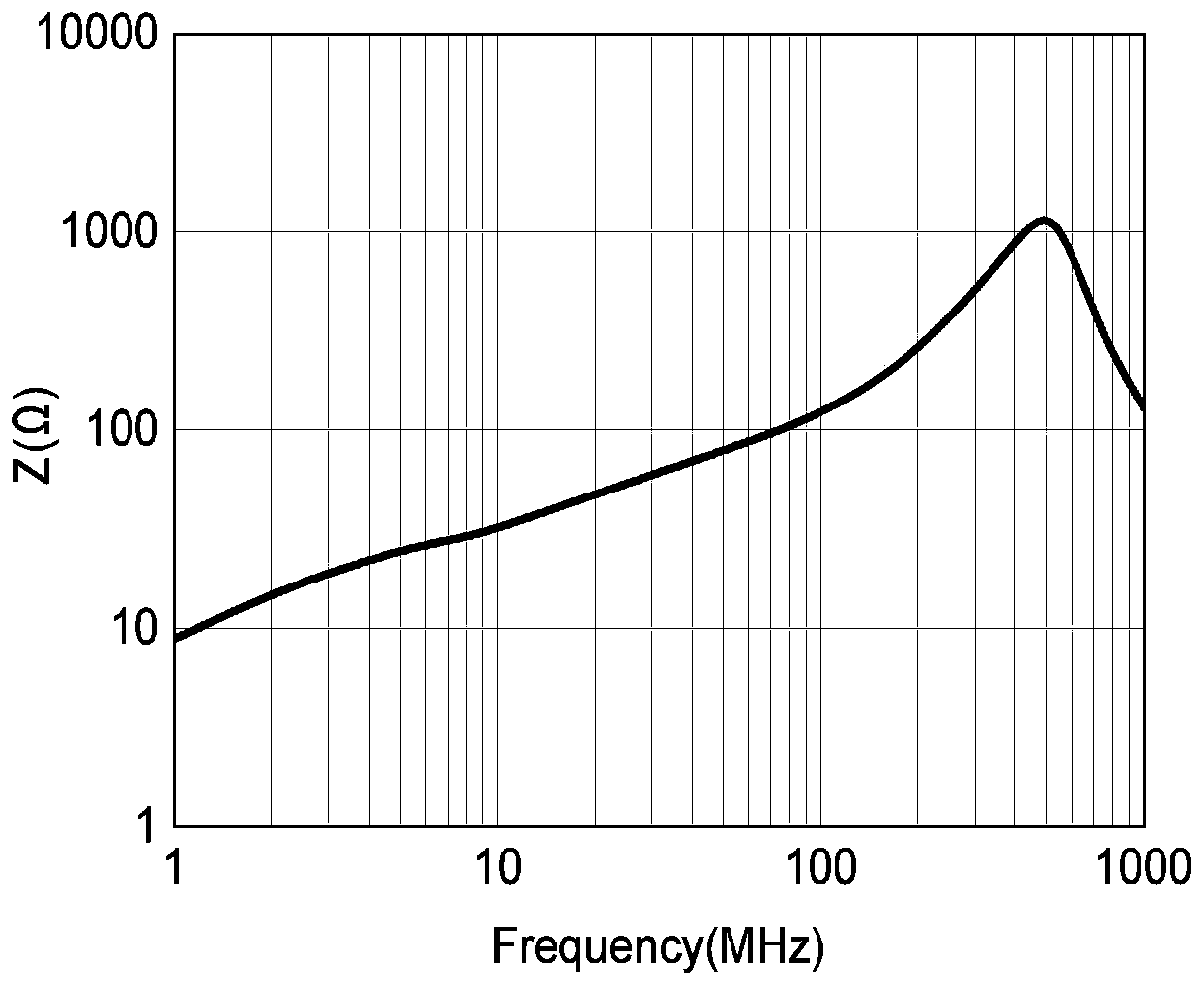
High performance low temperature sintered hexagonal M-type strontium ferrite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high performance low temperature sintered hexagonal M-type strontium ferrite and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, based on SrFe12O19 ferrite, deficient iron and La<3+> replace Sr<2+>, Ni<2+> replaces Fe<3+>, SrCO3, Fe2O3, La2O3 and Ni2O3 powdery raw materials are blended according to a chemical formula of Sr1-xLaxFe2n-yNiyO19, x represents 0-0.3, y represents 0-0.3, n represents 5.5-5.9, Bi2O3 and V2O5 are used as sintering aids and a hot pressing sintering process and sintering aids such as Bi2O3 and V2O5 are combined. The preparation method has simple processes and does not produce pollution in the process. The produced strontium ferrite has high sintering density, saturation magnetization, intrinsic coercivity and DC resistivity and has a great meaning and value of solving the prominent problem of deficiency of a key substrate material in the existing LTCC circulator.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH +1
Manufacturing method of high-conductivity high-strength aluminum alloy wire for smart power grid
ActiveCN106623478AImprove conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesCable/conductor manufactureSmart gridEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a high-conductivity high-strength aluminum alloy wire for a smart power grid. The method includes the steps that firstly, an aluminum alloy continuous casting and continuous rolling unit with an on-line purification system is used for conducting machining to obtain a supersaturated aluminum alloy rod; secondly, natural aging is conducted on the supersaturated aluminum alloy rod; thirdly, cold drawing is conducted on the aluminum alloy rod obtained in the second step to form an aluminum alloy wire; fourthly, the aluminum alloy wire is placed into a continuous aging oven for manual aging strengthening treatment; and fifthly, multiple wires obtained through the fourth step are concentrically twisted, and the performance of the twisted high-strength aluminum alloy wire meets the conditions that the tensile strength is not smaller than 340 MPa, the elongation is not smaller than 5.0%, the 20 DEG C direct current resistant rate is not higher than 0.031927 ohm.mm2 / m, and the electric conductivity is not smaller than 54.0%IACS. The wire obtained through the manufacturing method has the characteristics of being high in tension-weight ratio, good in electric conductivity and high in overload resistance; the process is simple; and the method is suitable for industrial production, can greatly save line construction cost and operation cost when applied to the smart power grid field, and has excellent economic benefits.
Owner:FAR EAST CABLE +2
Broadband high-impedance manganese-zinc ferrite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111138181AHigh DC resistivityHigh impedance characteristicInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureInitial permeabilityManganese
The invention discloses a broadband high-impedance manganese-zinc ferrite material. The material comprises a main component and an auxiliary component, the main component comprises Fe2O3, ZnO and Mn3O4 (in terms of MnO), and the auxiliary component is selected from at least one of SiO2, CaCO3, Nb2O5, Co2O3 and TiO2. The manganese-zinc ferrite material has the direct-current resistivity of above 1000 ohm.m, the Curie temperature of above 150 DEG C, the normal-temperature saturation flux density of above 420 mT and the initial permeability of above 2000, and also has the characteristic of high impedance in a broadband range of 0.01-700 MHz.
Owner:江门安磁电子有限公司
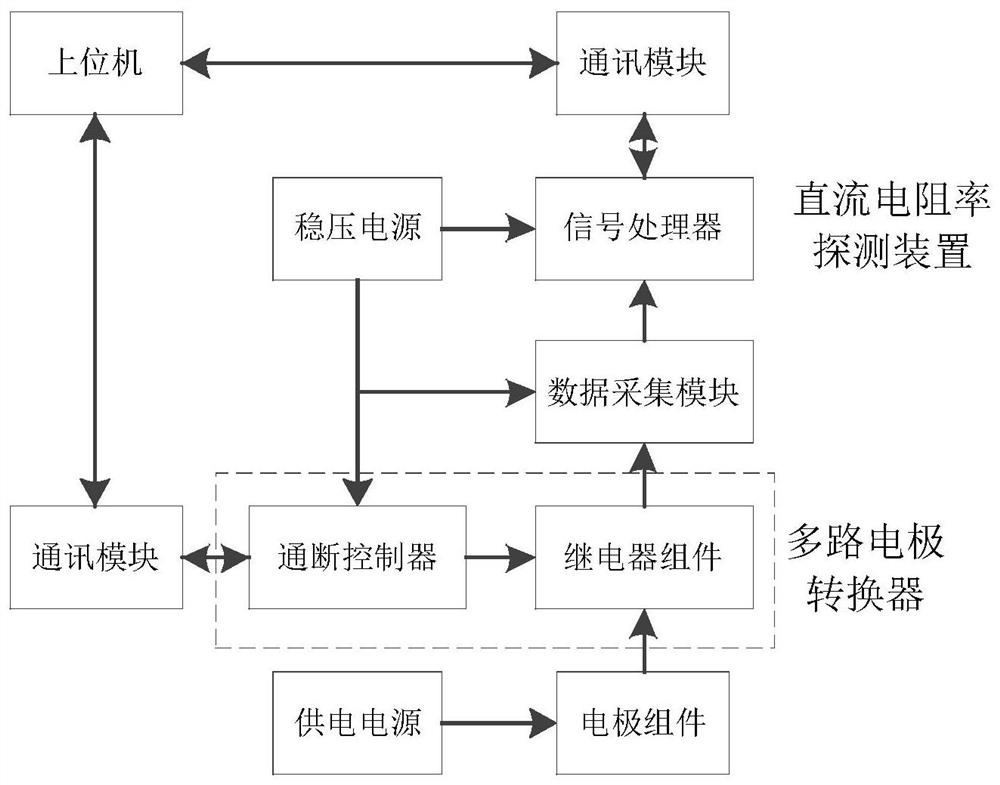
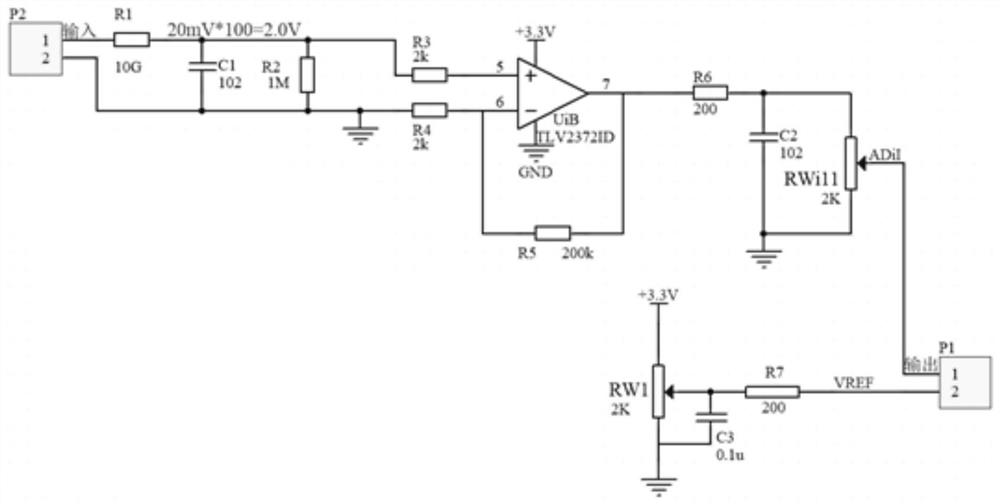
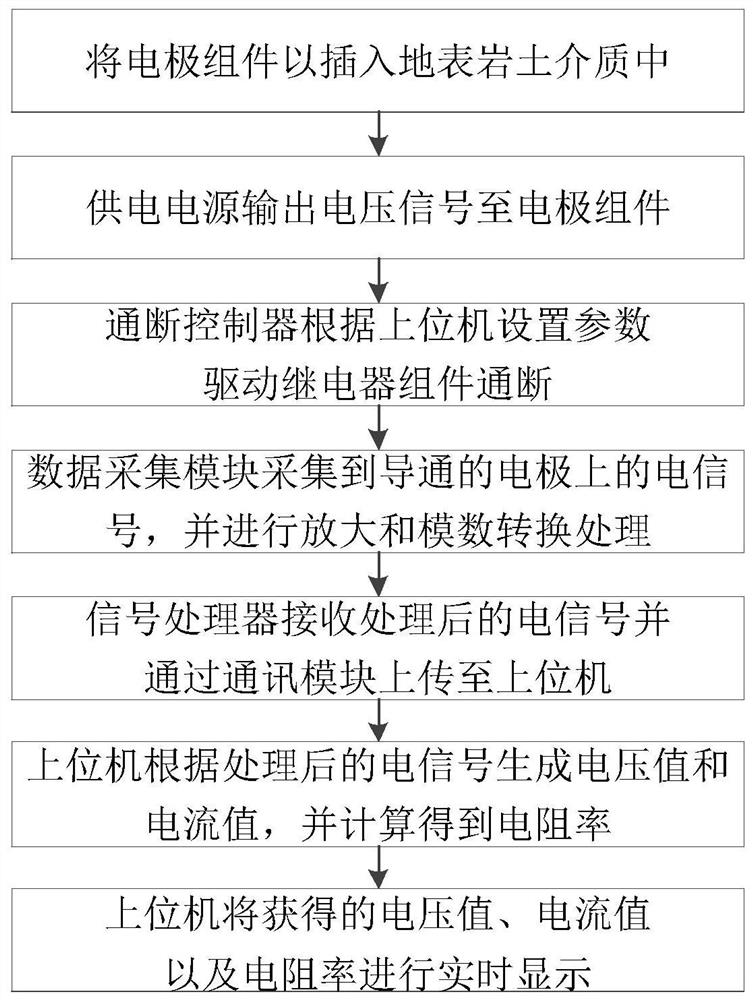
Resistivity monitoring system and monitoring method for underground three-dimensional migration process of pollutants
The invention provides a resistivity monitoring system for the underground three-dimensional migration process of pollutants. The system is characterized in that the system comprises a direct-current resistivity detection device and a multipath electrode converter; the direct-current resistivity detection device comprises a power supply, a voltage-stabilized source, an electrode assembly, a data acquisition module and a signal processor; the multipath electrode converter comprises a relay assembly and an on-off controller; and the signal processor and the on-off controller are respectively provided with communication modules, and are externally connected with an upper computer through the communication modules. The system is simple in structure, convenient to operate and high in test repeatability, can achieve automatic monitoring, improve monitoring efficiency, and achieve the transmission of monitoring data.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Integrated borehole system for reservoir detection and monitoring
InactiveCN1575425AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismologyElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasuring instrument
A method is disclosed for generating an image of earth formations penetrated by a wellbore. The method includes generating an initial model of the earth formations using formation resistivity measured by a direct current signal. A response to the initial model of an instrument used to make the direct current resistivity measurements is calculated. The calculated response is compared to the measurements of resistivity. The model is adjusted, and the calculating and comparing are repeated until a difference between the calculated response and measurements reaches a minimum. The adjusted model is refined based on resistivity measurements made using an electromagnetic measuring instrument, and the refined model is constrained using acoustic velocity measurements.
Owner:KJT ENTPR
Composite metal wire and manufacturing method
InactiveCN103943165ALow DC resistivityReduce lossNon-insulated conductorsMetal/alloy conductorsDc resistivityAlloy
The invention relates to a composite metal wire and a manufacturing method. The composite metal wire is formed by compositing a core body and a coating layer, and the coating layer is made of copper and particularly the copper with the weight purity ranging from 99.90% to 99.98%; the core body is an iron alloy comprising, by weight, 35% of copper, 55% of iron and 10% of aluminum; the thickness of the coating layer is from one fourth to one second the radius of the wire. The direct-current resistivity of the composite wire made of the copper-coated iron alloy is lower than that of a copper-coated steel wire, signal transmission is ensured, the requirement for the carrying capacity when the composite metal wire is applied to the electron industry is met, and the loss of the composite metal wire is smaller than that of the copper-coated steel wire.
Owner:黄忠波
Broadband high-impedance manganese-zinc ferrite material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111138180AHigh DC resistivityHigh impedance characteristicInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureManganeseDc resistivity
The invention discloses a broadband high-impedance manganese-zinc ferrite material. The material comprises a main component and an auxiliary component, the main component comprises Fe2O3, ZnO and Mn3O4 (in terms of MnO), and the auxiliary component is selected from at least one of SiO2, CaCO3, Nb2O5, Co2O3 and TiO2. The manganese-zinc ferrite material has the direct-current resistivity of above 2,000 ohm.m, the Curie temperature of above 180 DEG C, the normal-temperature saturation magnetic induction intensity of above 430mT and the initial magnetic conductivity of above 1000, and also has thecharacteristic of high impedance in a broadband range of 0.01-700 MHz.
Owner:江门安磁电子有限公司
DC resistivity element-free forward modelling method based on partition of unity quadrature (PUQ)
ActiveCN108873084AForward simpleReduce dependenceElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationNODALDc resistivity
The invention provides a DC resistivity element-free forward modelling method based on partition of unity quadrature (PUQ); the method comprises the following steps: building a computational domain according to the medium resistivity distribution in a 2D earth electricity model, and geometrical morphology and hypsography form of a resistivity anomalous body, and using irregularly distributed nodesto disperse the earth electricity model; using the partition of unity quadrature (PUQ) convert a global computational domain integral equation of the DC resistivity method into a node local domain integral equation; building node local integral domains, and employing a Gauss integral to compute an integral formula in each node local integral domain, thus obtaining a computational domain disperseequation; solving the disperse equation to as to obtain a node electric field value, and calculating to obtain an apparent resistivity parameter of an observation point. Based on the random node distribution disperse model, the method uses the partition of unity quadrature (PUQ) to convert the global domain integral into the node local domain integral without needing inter-node connection information and unit, and removing grid constraints; the method has a strong adaptation and flexibility on a random complex earth electricity model.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Carrier for electrostatic latent image developer, electrostatic latent image developer formed of carrier and toner, and process cartridge using the developer
InactiveUS20130101930A1Increased durabilityThe total amount is stableDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusParticulatesLatent image
A carrier for developing an electrostatic latent image, including a particulate core material having a magnetism having developed spontaneous magnetization; and a covering layer comprising an electroconductive material, covering the surface of the particulate core material, wherein the carrier has an electrical resistivity Log R [Ωcm] of from 8.0 to 12.0 when measured by a method, including filling the carrier in a cell containing a pair of facing electrodes, each having a surface area of 2×4 [cm2] with a gap of 2 [mm] therebetween; and applying a DC voltage of 1,000 [V] therebetween to measure a DC resistivity, and a weight-average particle diameter (Dw) of from 25 to 45
Owner:RICOH KK
Broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101857426BLow Curie temperatureHigh resistivityInorganic material magnetismInitial permeabilityMetallurgy
The invention provides a broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material, which comprises main components and assistant components. The main components comprise 47 to 50 mol percent of Fe203, 29 to 35 mol percent of Mn3O4 by MnO and 16 to 21 mol percent of ZnO. The assistant components are at least one kind from SiO2, CaCO3, V205 and Nb2O5. Total weight based on the main components is that SiO2 is0.002 to 0.01 wt percent, CaCO3 is 0.01 to 0.08 wt percent, V205 is 0.01 to 0.07 percent, and Nb2O5 is 0.01 to 0.07 percent. The broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material has DC resistivity larger than 103 omega meter, curie temperature higher than 115 degrees centigrade and 2000 plus or minus 20 percent initial permeability. Moreover, the low frequency impedance of the material is larger than the common NiZn ferrite material, the high frequency impedance thereof is equal to the common NiZn ferrite material and the material does not contain expensive raw material NiO. The invention further provides the manufacture method of the broadband high impedance MnZn ferrite material, which comprises the steps of mixing, drying, preburning, ball-milling, granulation, molding, sintering and thelike.
Owner:江门江益磁材有限公司
MnZn ferrite material with high frequency and high impedance and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a MnZn ferrite material with high frequency and high impedance. The MnZn ferrite material is composed of main components and auxiliary components. The MnZn ferrite material is characterized in that counted by oxides according to molar percentage, the main components comprise 46.0-54.0mol% of Fe2O3, 25.0-27.0mol% of MnO and 19.0-21.0mol% of ZnO; counted by oxides according to percentage by weight, based on the total weight of the main components, the auxiliary components comprise at least one of 0.03-0.08wt% of TiO3, 0.03-0.08wt% of CaCO3 and 0.03-0.08wt% of V2O5. At 100MHz, the MnZn ferrite material has direct current resistivity greater than 200.Omega m, a Curie temperature of 25 DEG C and initial magnetic conductivity greater than or equal to 7000.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHUNHUI COMPOSITE MATERIAL
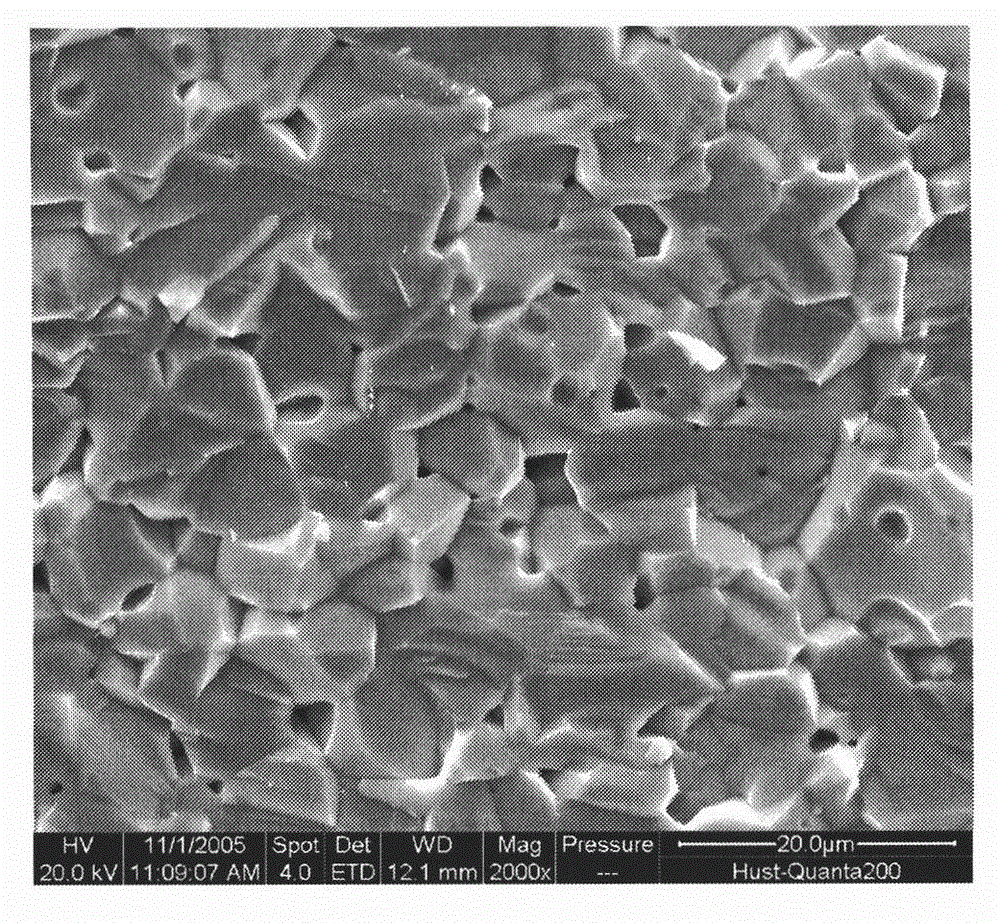
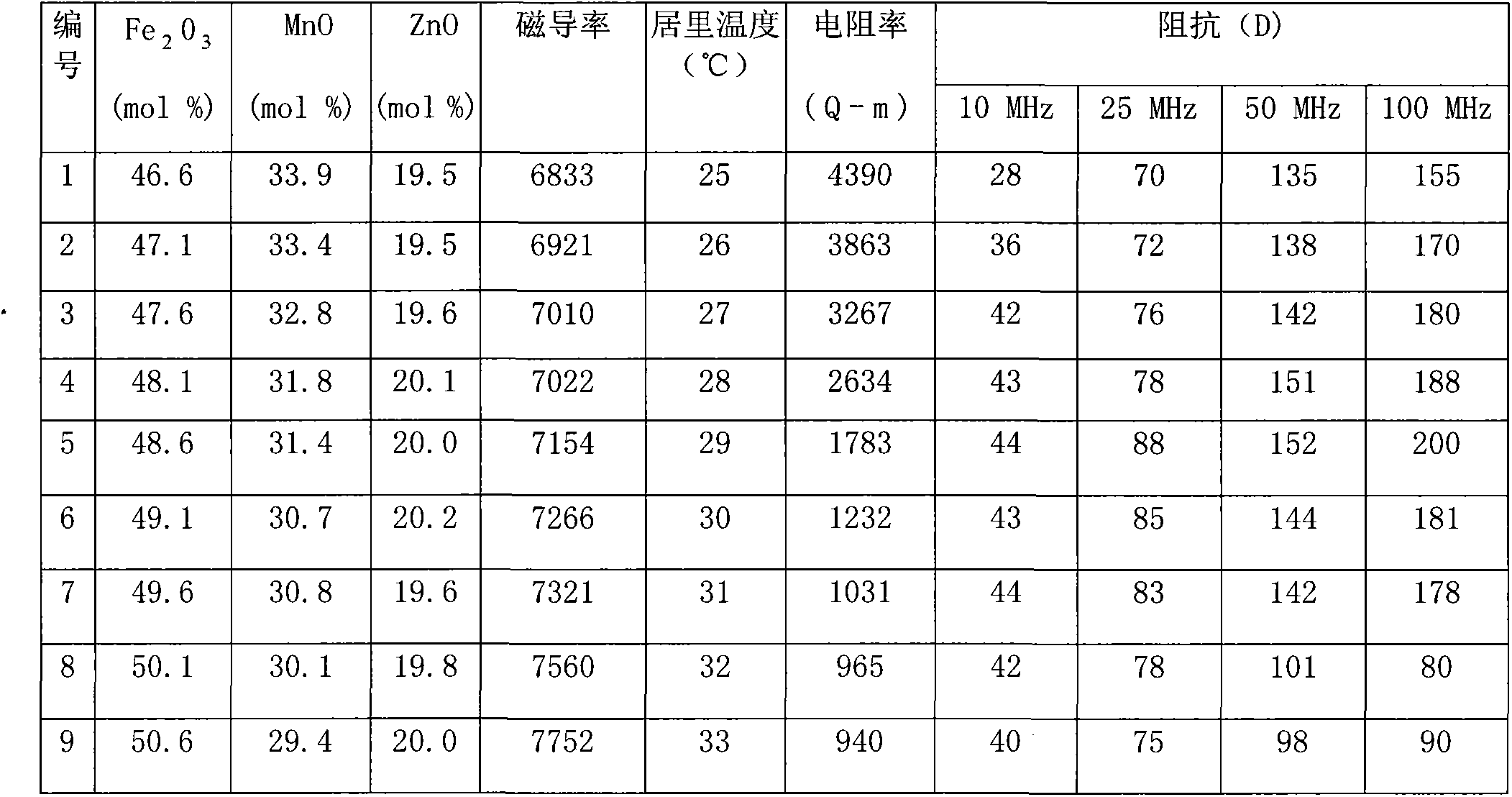
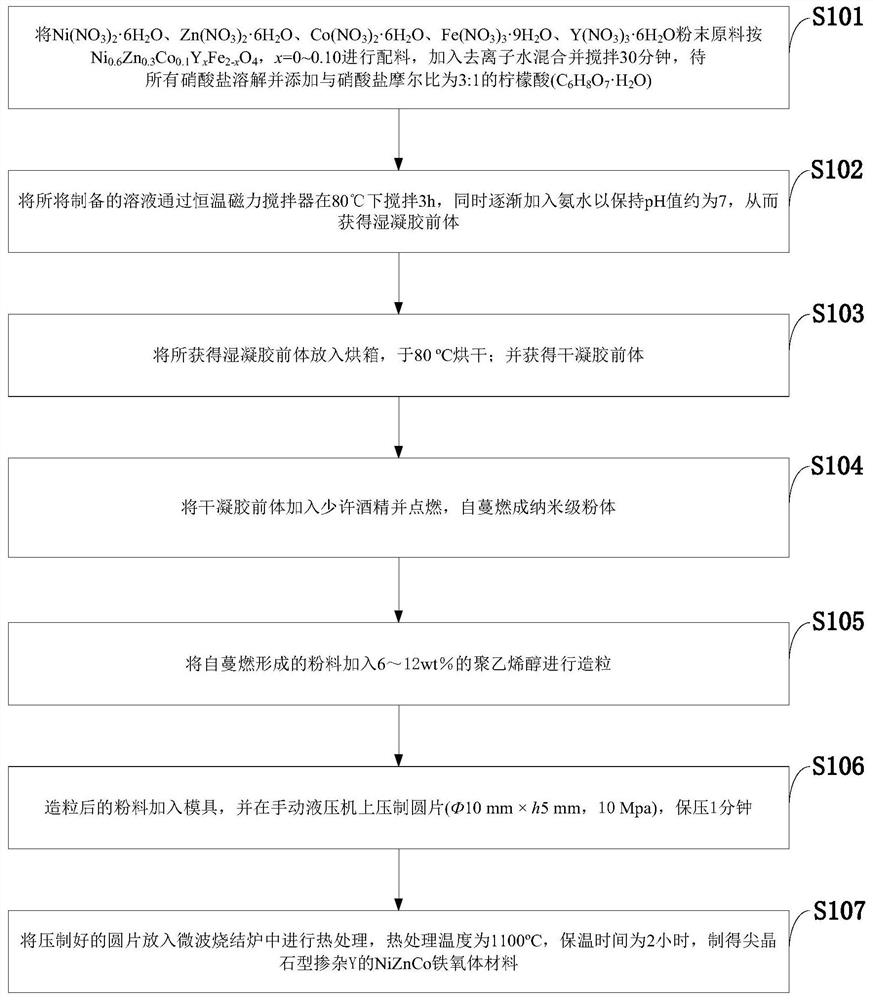
Yttrium-doped nickel-zinc-cobalt ferrite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112159219AImprove electromagnetic performanceHigh initial permeabilityWeak currentDc resistivity
The invention relates to nickel-zinc-cobalt ferrite and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soft magnetic ferrite materials. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide the yttrium-doped nickel-zinc-cobalt ferrite prepared by high-performance microwave sintering. The molecular formula of the yttrium-doped nickel-zinc-cobalt ferrite is Ni < m >Zn < n > Co < 1 > m < n > Y < x > Fe < 2 > x < O4 >, and the electromagnetic performance of the material is improved by combining microwave sintering and sol-gel self-propagating on the basis of Ni <m > Zn < n > Co < 1 > m < n > Fe < 2 > O < 4 > ferrite. Iron deficiency and Y < 3 + > are used for replacing Fe < 3 + > to improve the magnetic performance and the electrical performance of the material, the preparation process is simple, the process is pollution-free, the obtained material simultaneously obtains high sintering density, initial permeability and direct-current resistivity and low coercive force and dielectric loss, a key material can be provided for high-frequency inductors and capacitors. The current situation that related electronic components in the field of high-frequency weak current do not exist in China is solved, the core competitiveness of miniaturization and integration of high-frequency and even ultrahigh-frequency electronic devices in China is expected to be improved, and foreign technical blockage is broken through.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Numerical simulation method for three-dimensional direct current resistivity method
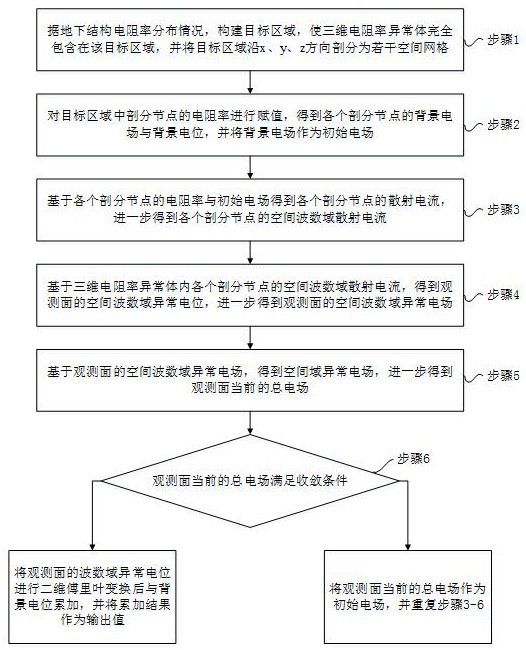
ActiveCN113051779AReduce the amount of calculationReduce storage needsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScale modelCurrent electric
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method for a three-dimensional direct current resistivity method, which comprises the following steps of: setting direct current method exploration area and background resistivity parameters, three-dimensional anomalous body distribution range and resistivity parameters, calculating current density, performing two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform, calculating wave number domain abnormal potential, performing two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform, performing iterative convergence judgment and the like. And efficient and high-precision numerical simulation of three-dimensional direct current electric method exploration is realized. The problem that fine inversion of large-scale direct-current electric method data cannot be met due to the fact that the data size is large, the storage requirement is high and the calculation time is slow when a large-scale model is calculated in current direct-current electric method exploration numerical simulation is solved, and fine inversion and explanation of direct-current electric method measured data under field complex terrains or underground complex structures can be achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Boundary treatment method of coupling direct-current resistivity element-free method with finite element method
ActiveCN108108579AImprove computing efficiencyHigh simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary knot methodMixed finite element method
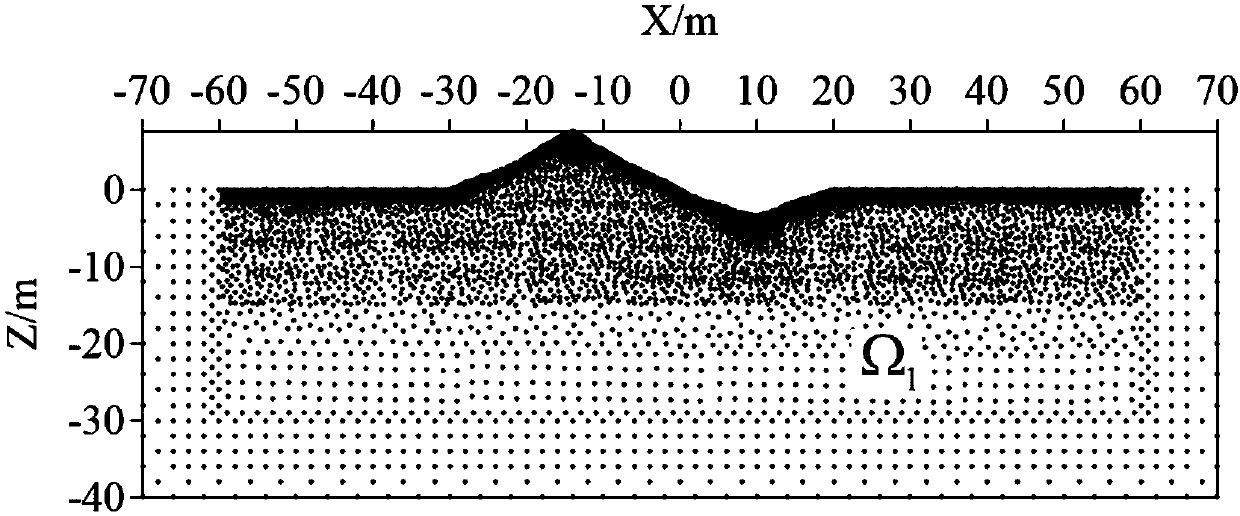
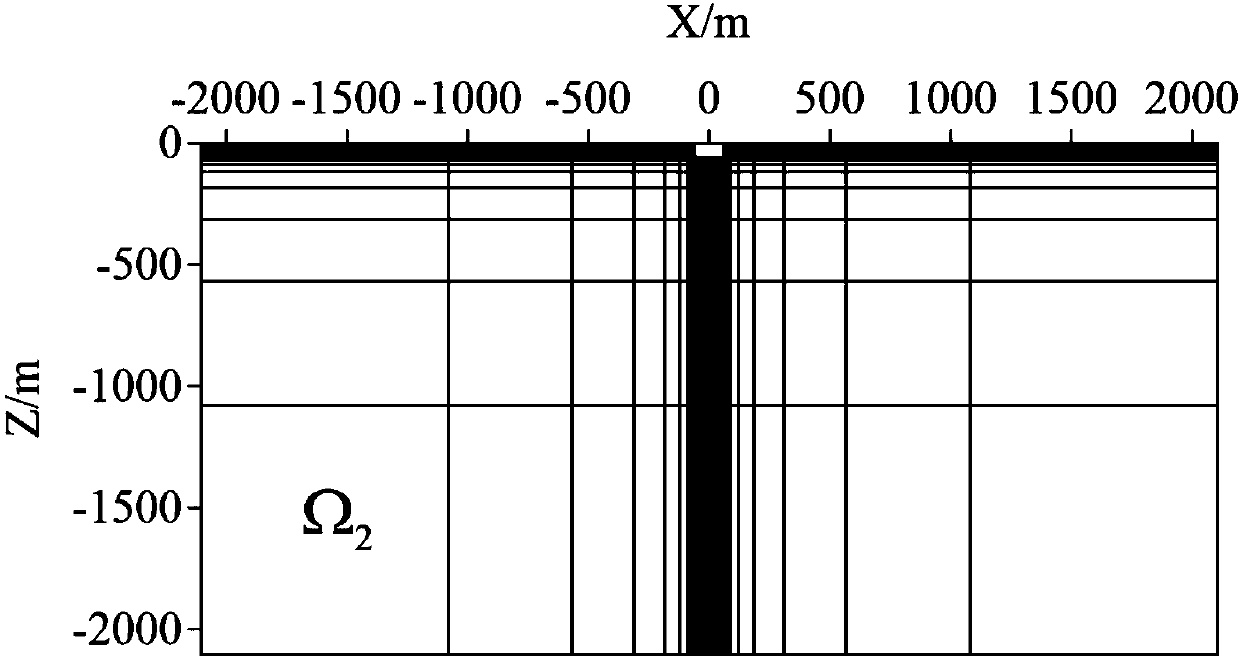
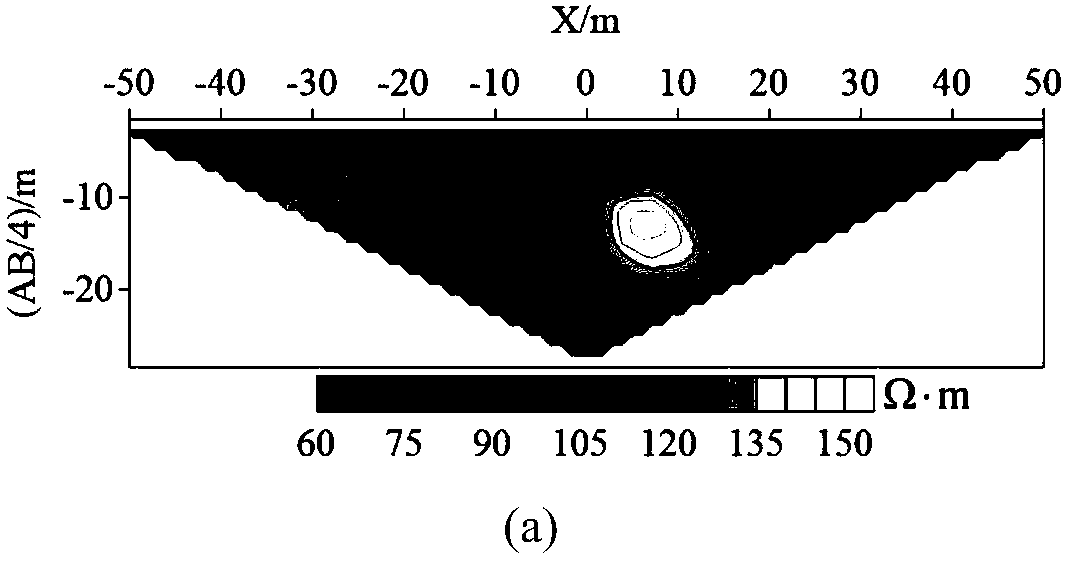
The invention provides a boundary treatment method of coupling a direct-current resistivity element-free method with a finite element method. The boundary treatment method includes the steps of building a small-range element-free method area omega 1 to a two-dimension geoelectric model, calculating by the element-free method for the area, covering the element-free method area omega 1 with regularly distributed rectangular or parallelogram background grid to obtain an element-free method equation set of the area; subdividing the periphery of the element-free method area omega 1 by finite element method grid which is capable of rapid expansion, building a large-enough finite element method area omega 2 which meets requirements of first class of boundary conditions, calculating by the finiteelement method to obtain a finite element equation set of the area; combing the equation sets of the two areas and solving to obtain parameter of the apparent resistivity of an observation point. Themodels can be discrete on the basis of arbitrary node distribution by the method, the boundary treatment method has high adaptability to any complex geoelectric models, and calculation efficiency of forward modeling in the conventional direct-current resistivity element-free method is improved since boundary treatment is carried out by means of the finite element method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Direct current electrical resistivity imaging device and distributed measurement station
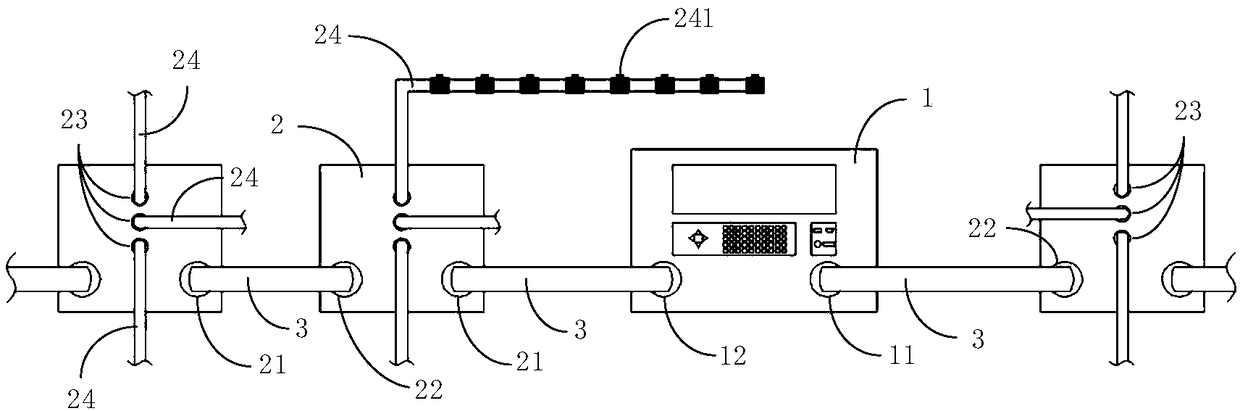
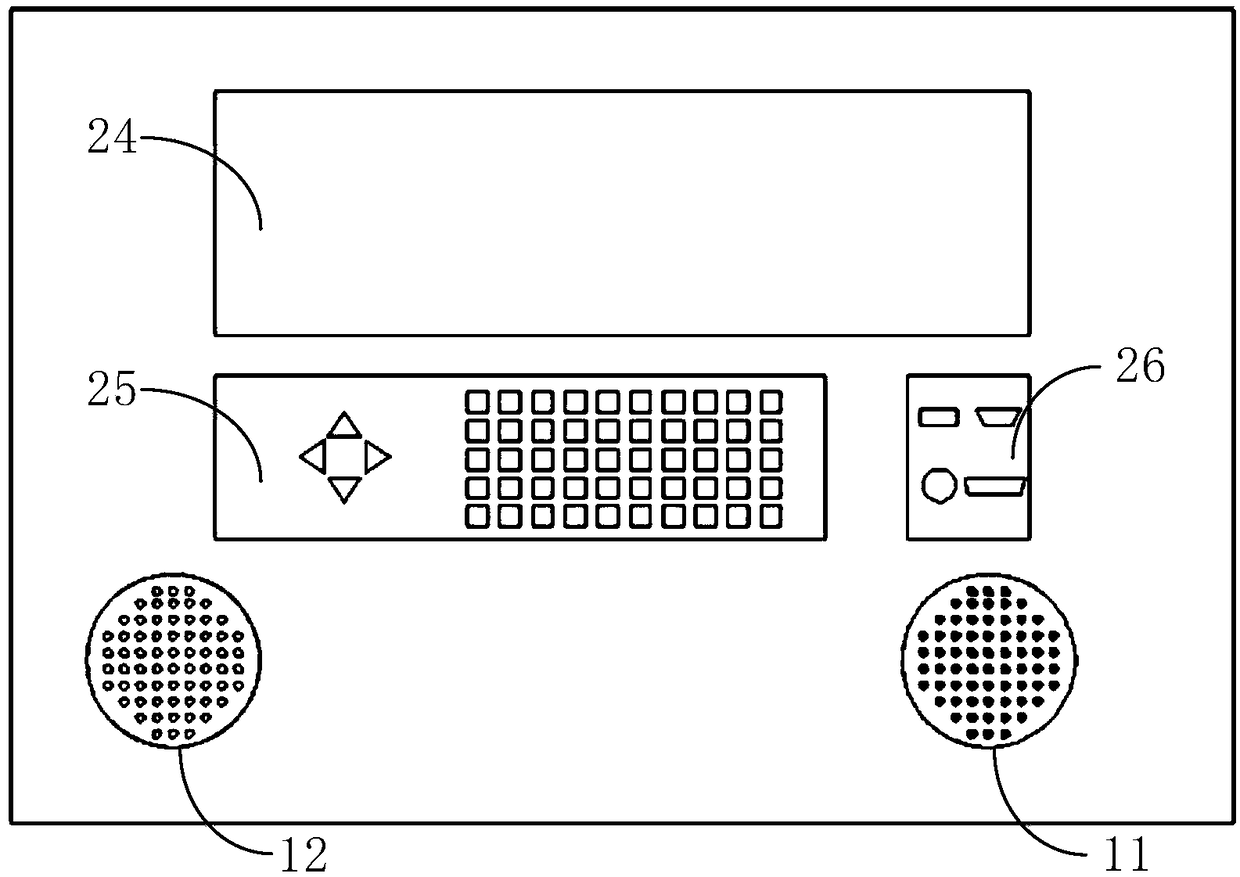
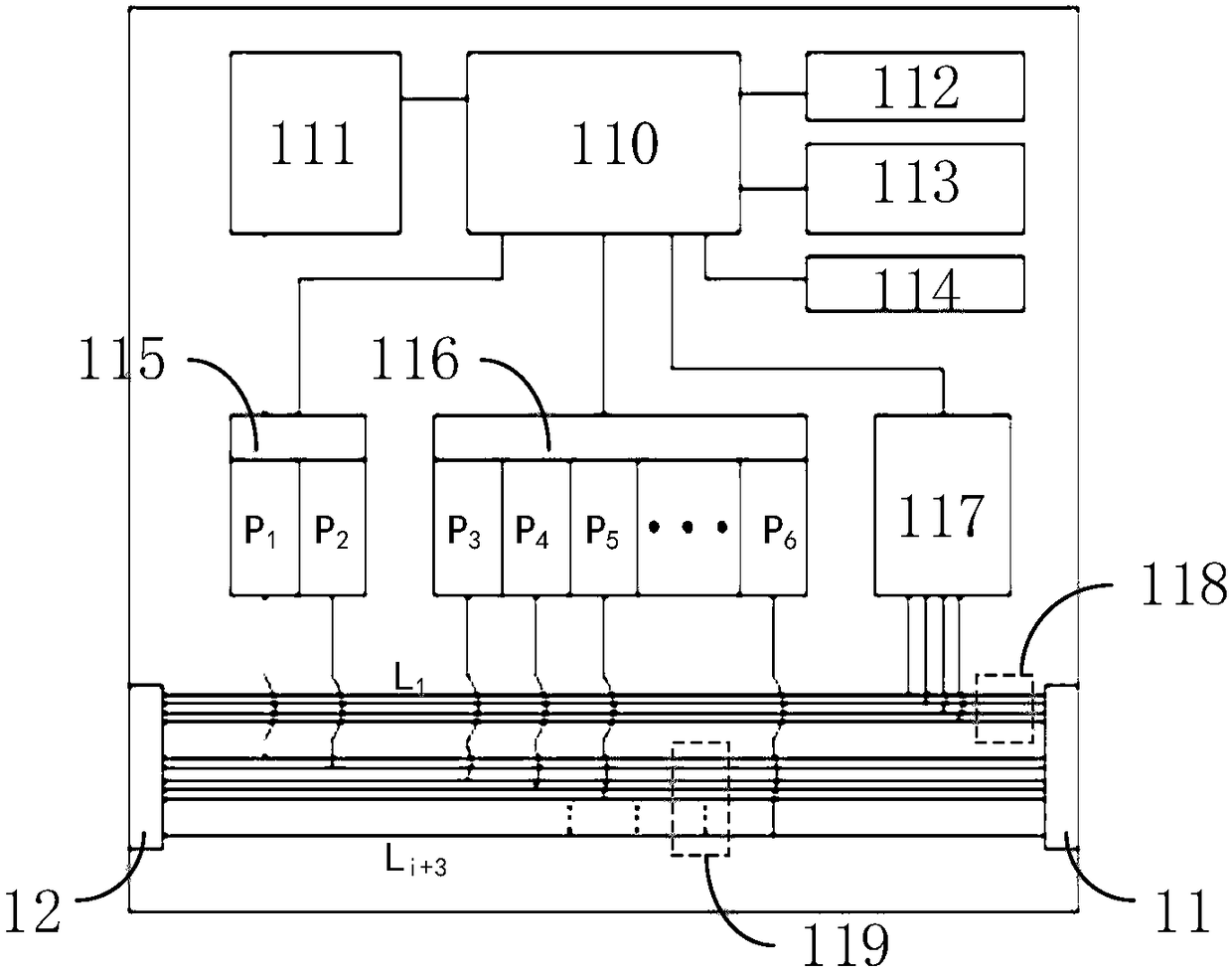
ActiveCN108614300AUniqueness guaranteedEasy to set upElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationPrimary stationDc resistivity
The invention relates to a direct current electrical resistivity imaging device and a distributed measurement station. The imaging device comprises a host, multiple distributed measurement stations and a main cable. The host and the distributed measurement stations are connected together through the main cable. Each distributed measurement station comprises multiple electrode cables. Multiple electrode joints are arranged on the electrode cables. According to the invention, by use of the combination scheme of mixing the distributed scheme and the centralized scheme, the host and the measurement stations are connected in a distributed manner and communicate with each other in a bus manner; one main station can be serially connected with and control multiple measurement stations, so expandability of the whole set of the device is ensured; centralized control is achieved between the measurement stations and the electrodes, so efficiency of the measurement work is improved; and in the system, common electrodes are used as grounding bodies, and no electronic parts are arranged on the electrodes, so cost is remarkably reduced and working reliability is improved.
Owner:YELLOW RIVER INST OF HYDRAULIC RES YELLOW RIVER CONSERVANCY COMMISSION
Piezoelectric ceramic material applied to high-temperature environment and preparation method of piezoelectric ceramic material
ActiveCN108546125AIncreased tetragonalityImprove electrical performanceDc resistivityCurie temperature
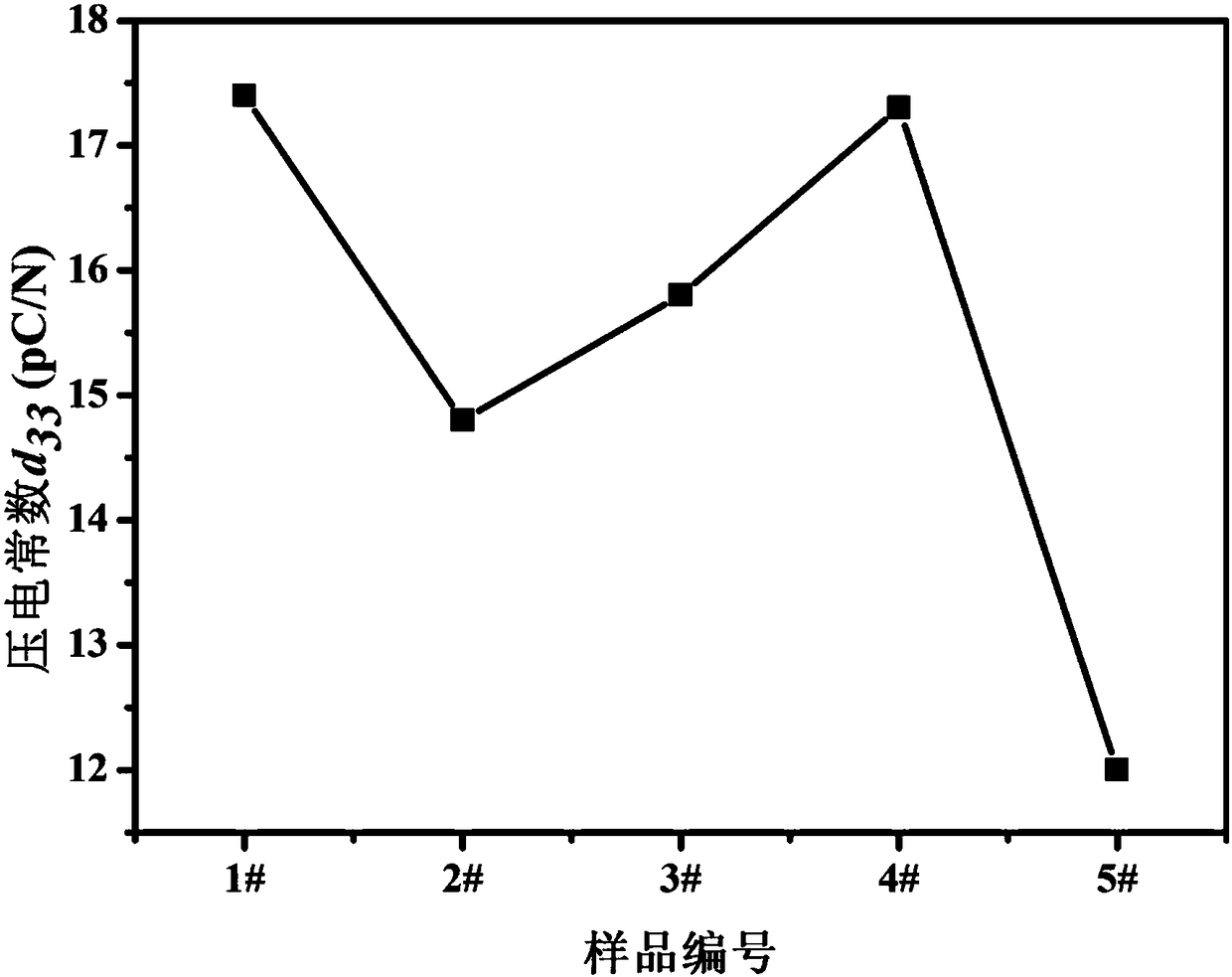
The invention provides a piezoelectric ceramic material applied to a high-temperature environment and a preparation method of the piezoelectric ceramic material. A chemical ratio formula of the ceramic material is as follows: Ca0.8-deltaSrdeltaBi2Nb2-x-yTaxWyO9 + z wt% Li2CO3 + w wt% Bi2O3 + q wt% M, wherein M is a metal oxide, and in the formula, value ranges of delta, x, y, z, w and q satisfy the relationships of 0 <= delta <= 0.2, 0 < x <= 1, 0 < y <= 0.5, 0 < z < 2, 0 < w < 10, and 0 < q <= 5. The piezoelectric ceramic material provided by the inventions has the advantages of high Curie temperature, high high-temperature direct-current electrical resistivity, good piezoelectric activity and good thermal stability.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Tunnel advanced exploration method of long-electrode source direct current electric field
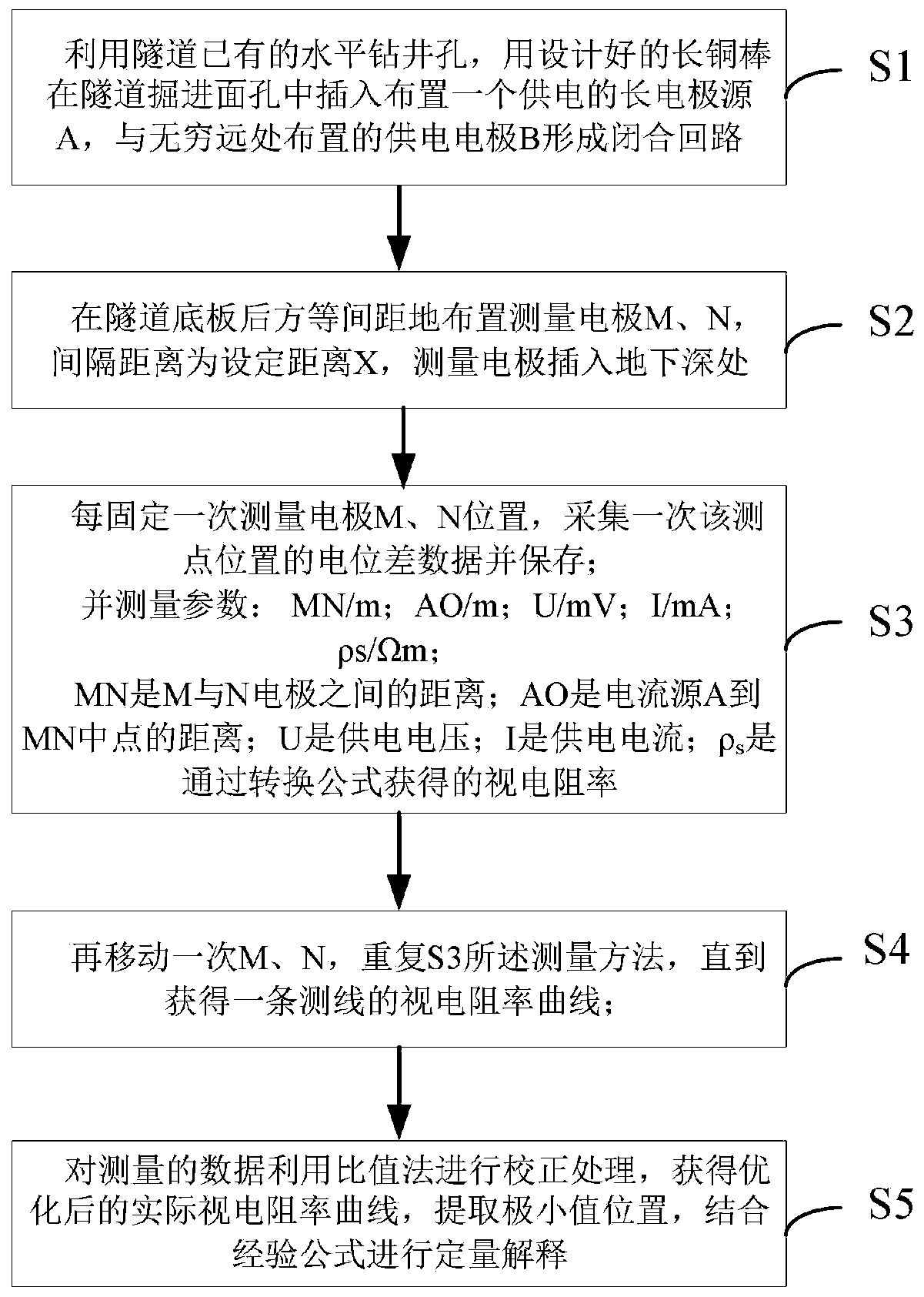
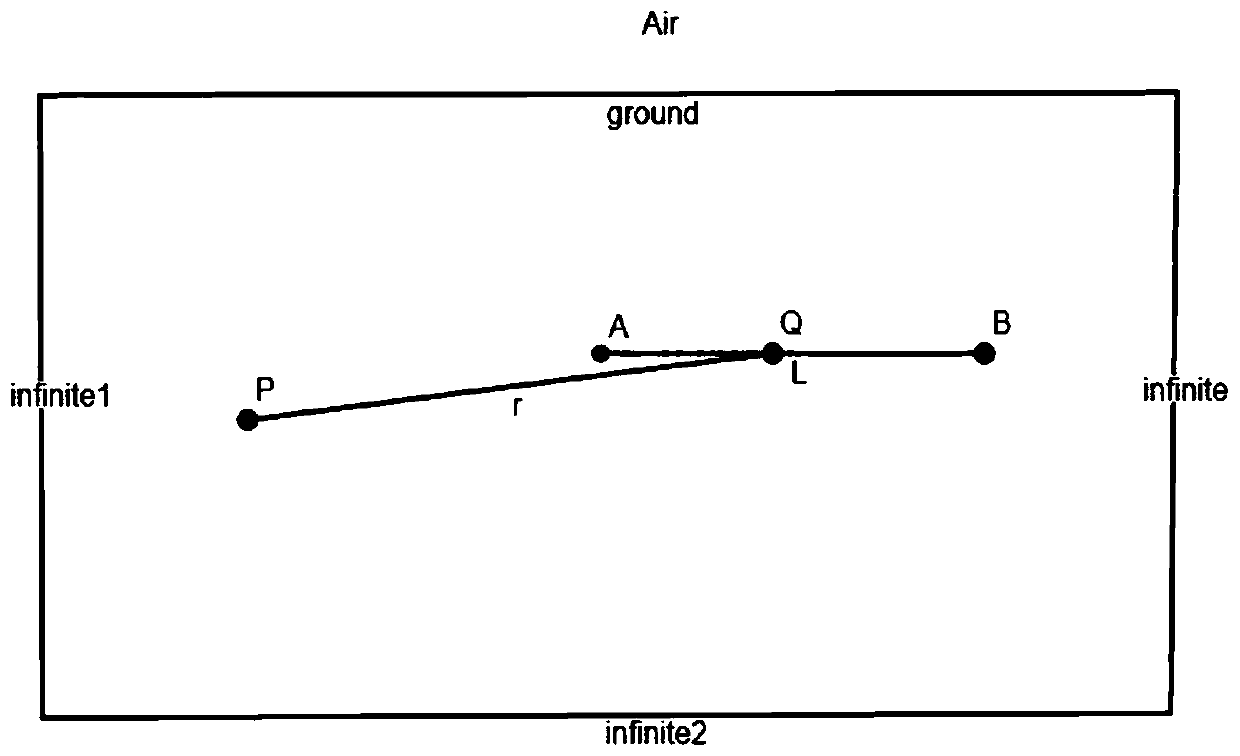
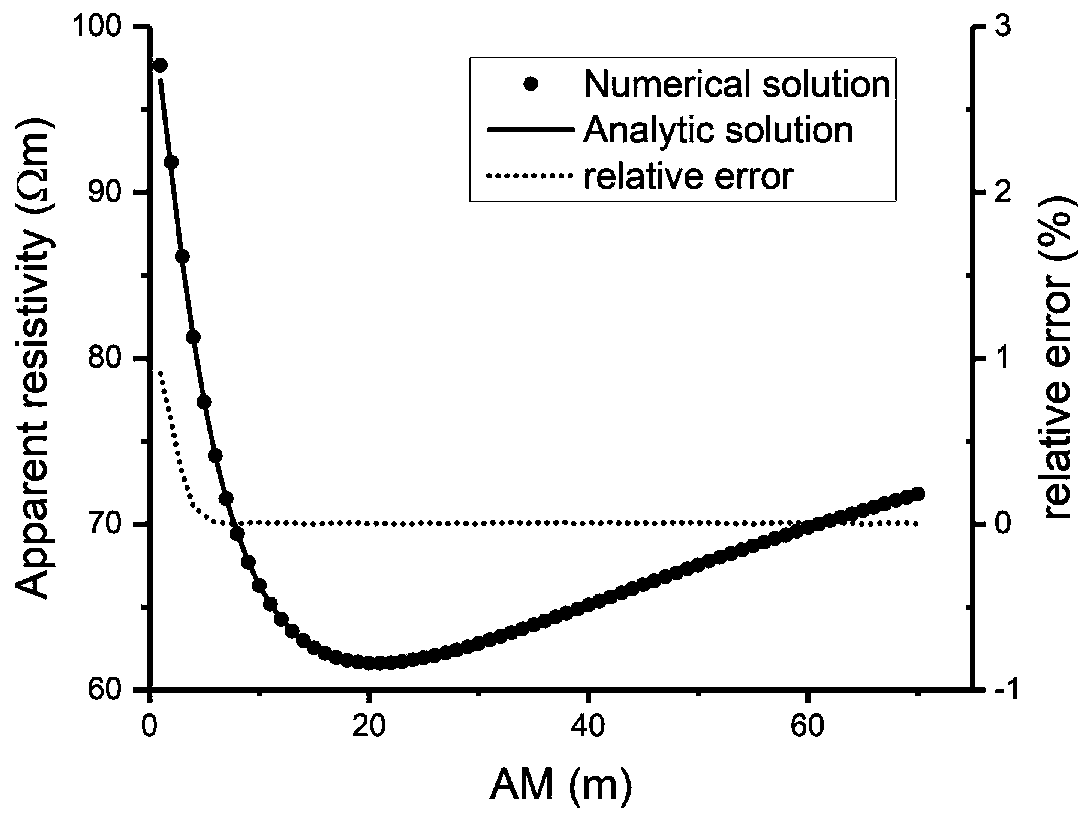
InactiveCN110333542AAddressing vulnerability to floating coalResolve interferenceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentPotential differenceDc resistivity
A tunnel advanced exploration method of a long-electrode source direct current electric field is disclosed. In actual exploration applications, by using a traditional direct current resistivity method, an induced electric field signal is relatively weak and is easily interfered by tunnel conditions such as float coal, a metal orbit and the like. By using the method of the invention, the above problems can be solved. The method comprises the following steps of arranging a long electrode source A for providing power in a center of a tunneling heading face, and providing a large current to the ground to form a stable artificial electric field; and using a potential or a potential difference observed by a dipolar device and a tripolar device to obtain a minimum position of a curve through an apparent resistivity conversion formula, and combining an empirical formula to quantitatively explain position information of a front abnormal body in full-space formation. In the invention, a detection ability of predicting a water-bearing abnormality is increased, and an application effect of a long-electrode source resistivity method in many fields such as urban subway detection, highway tunnelmonitoring, mine disaster detection and the like can be promoted.
Owner:安徽国科骄辉科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com