Patents
Literature
31 results about "Mass cytometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
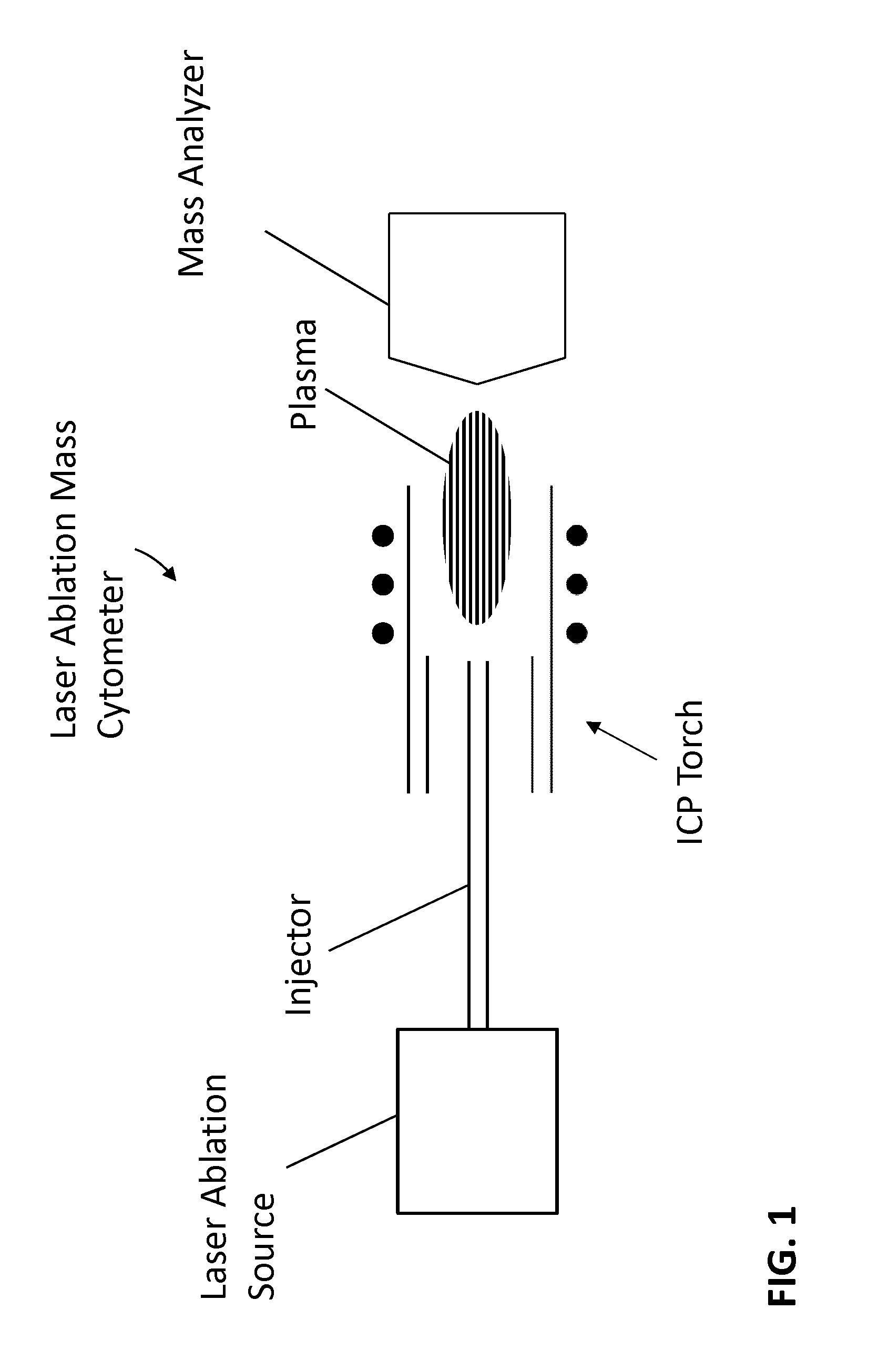
Mass cytometry is a mass spectrometry technique based on inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and time of flight mass spectrometry used for the determination of the properties of cells (cytometry). In this approach, antibodies are conjugated with isotopically pure elements, and these antibodies are used to label cellular proteins. Cells are nebulized and sent through an argon plasma, which ionizes the metal-conjugated antibodies. The metal signals are then analyzed by a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The approach overcomes limitations of spectral overlap in flow cytometry by utilizing discrete isotopes as a reporter system instead of traditional fluorophores which have broad emission spectra.
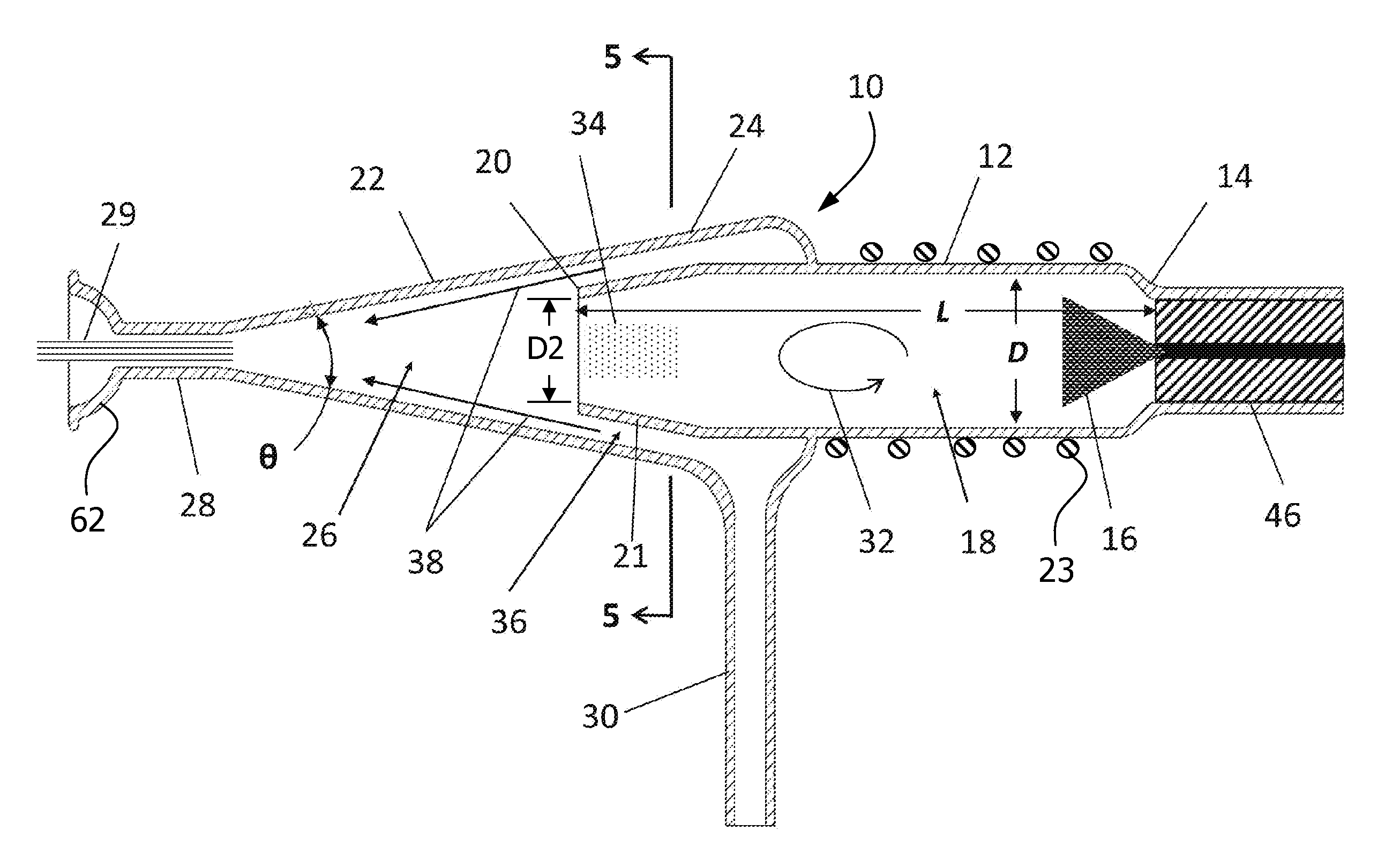
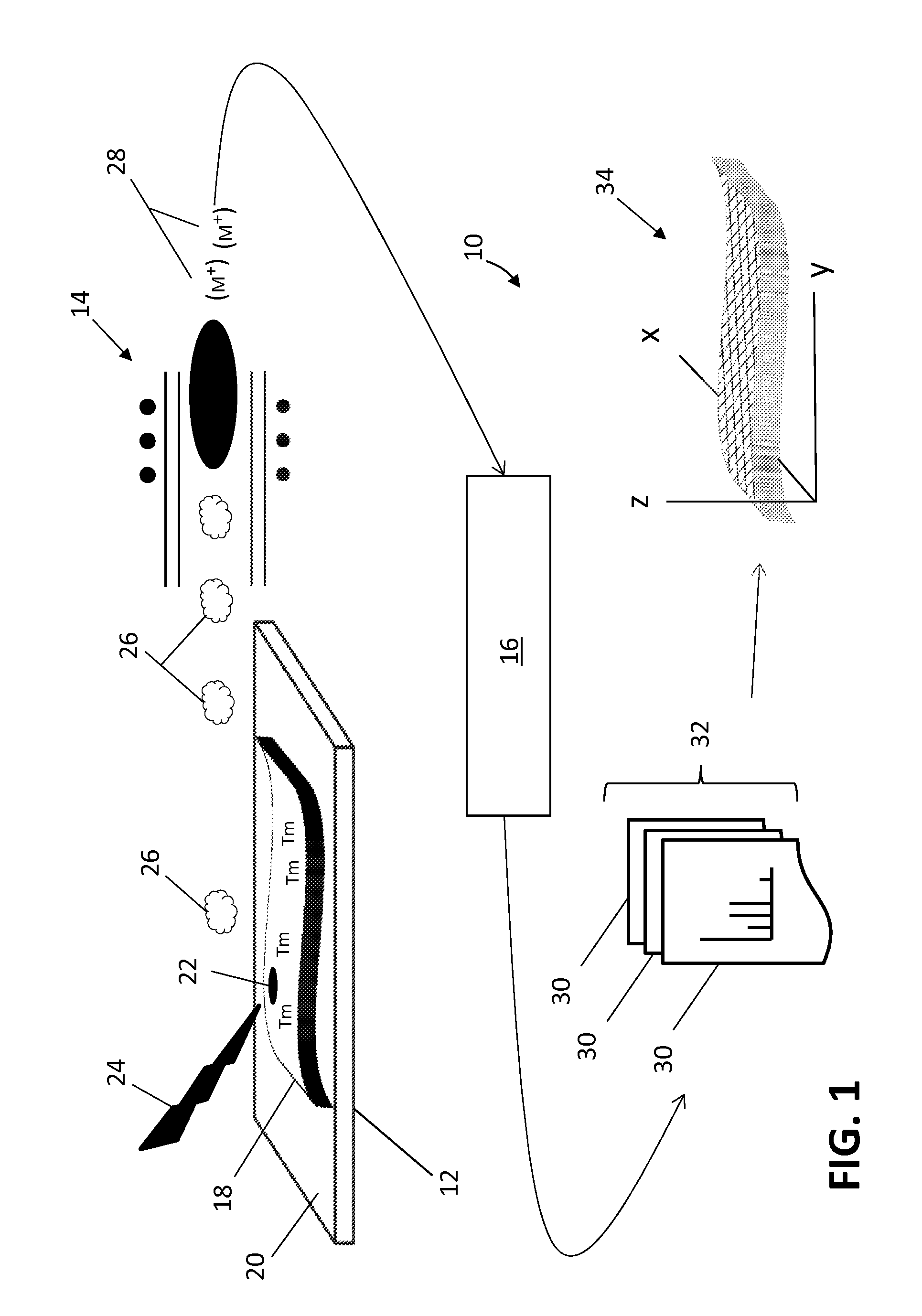
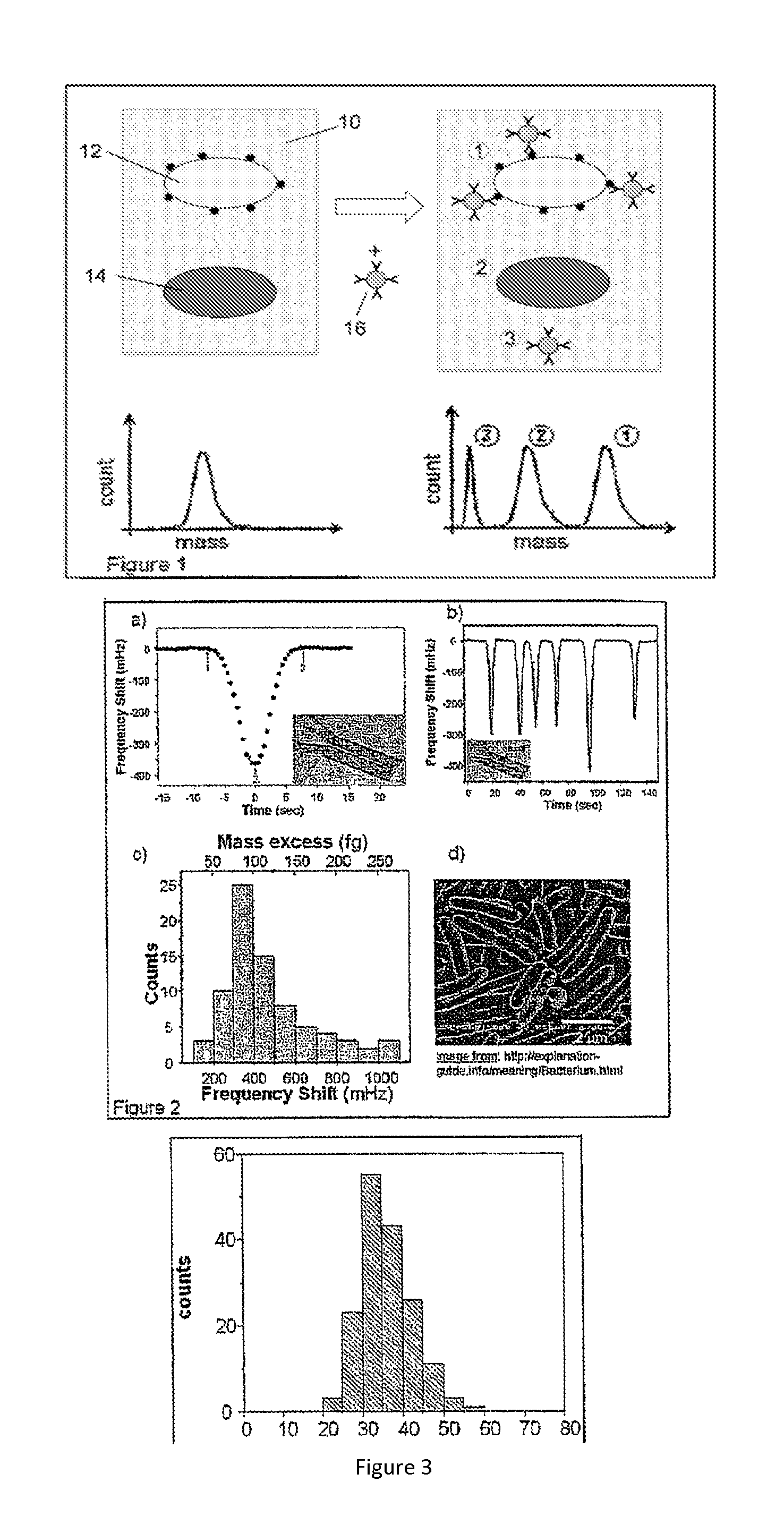
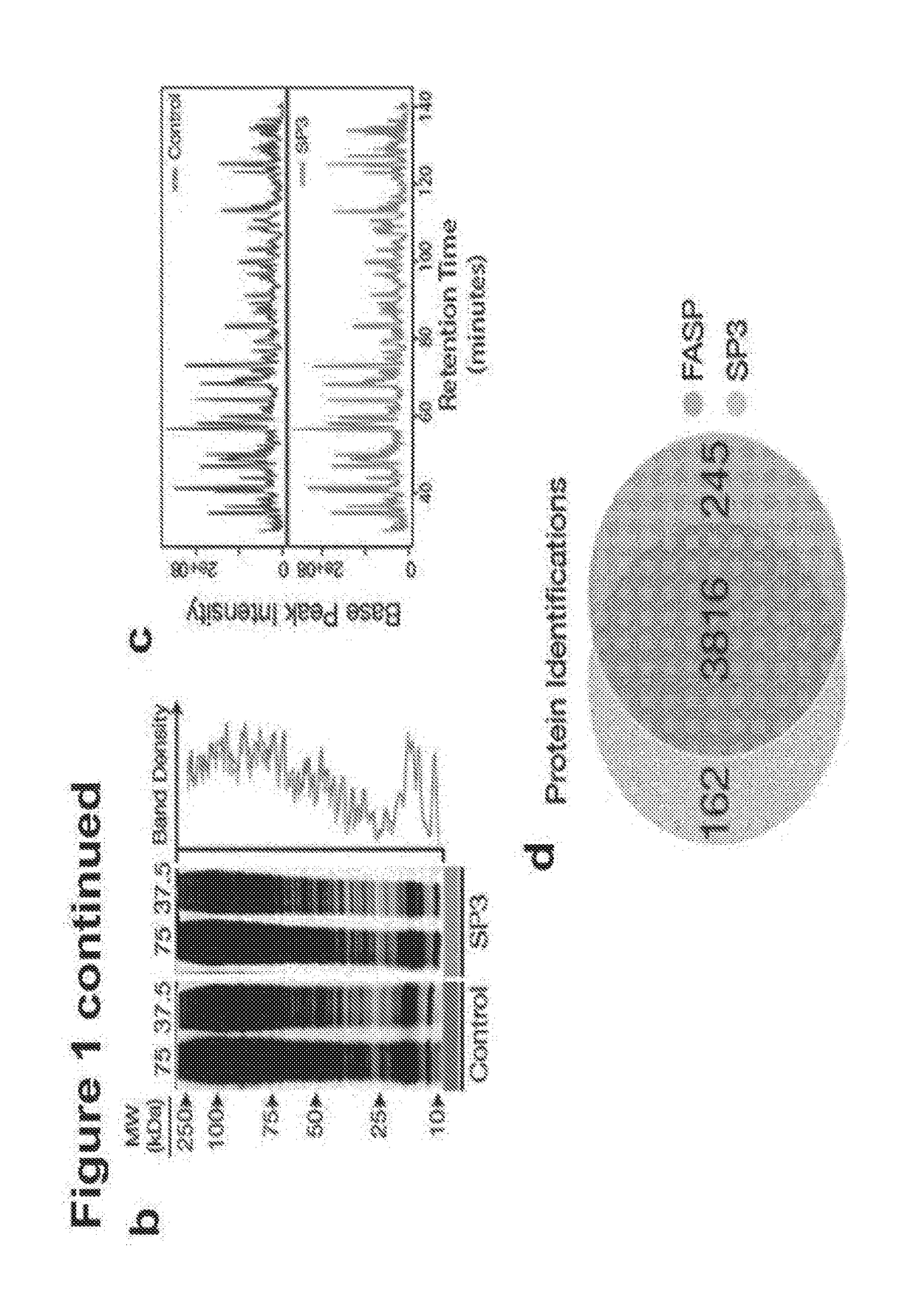
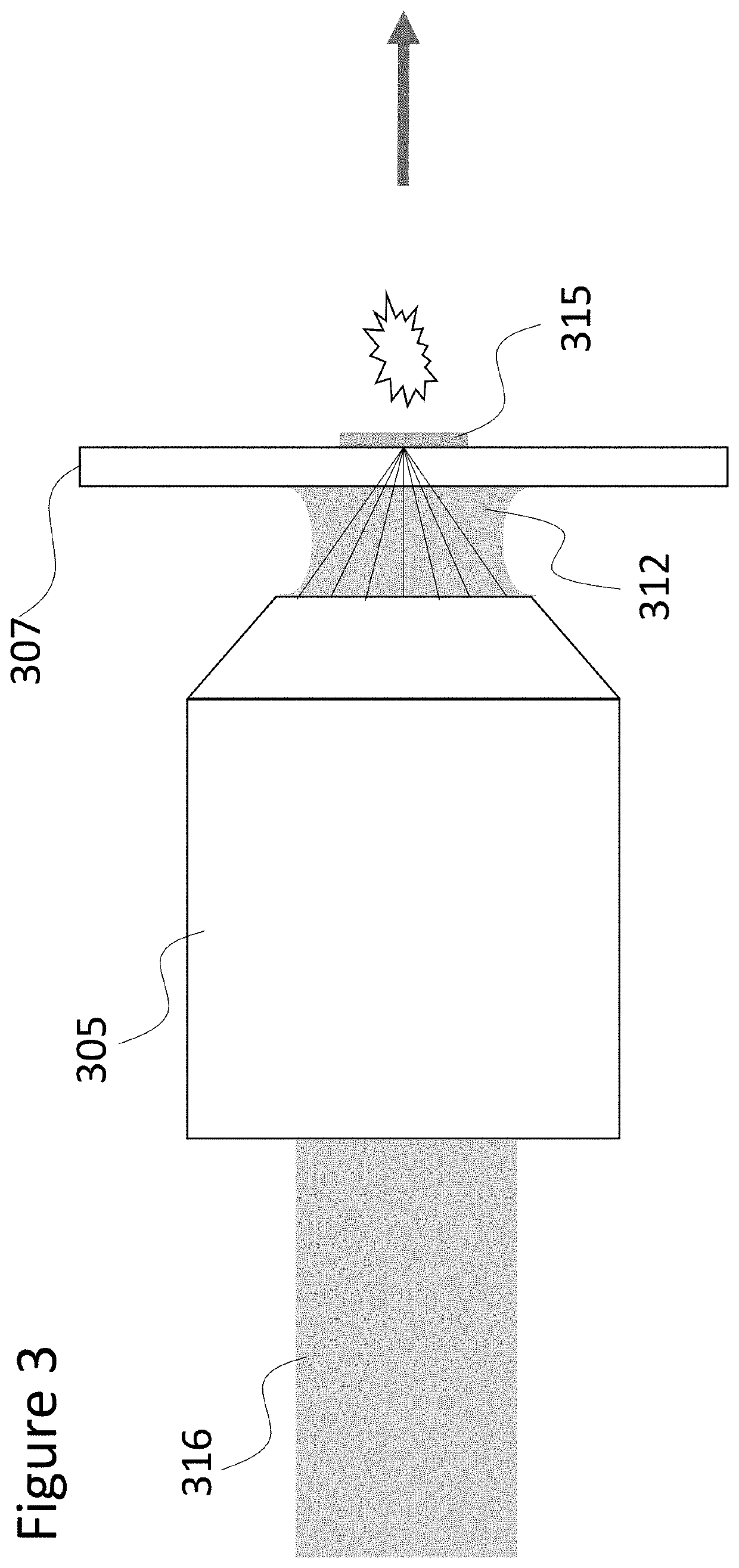
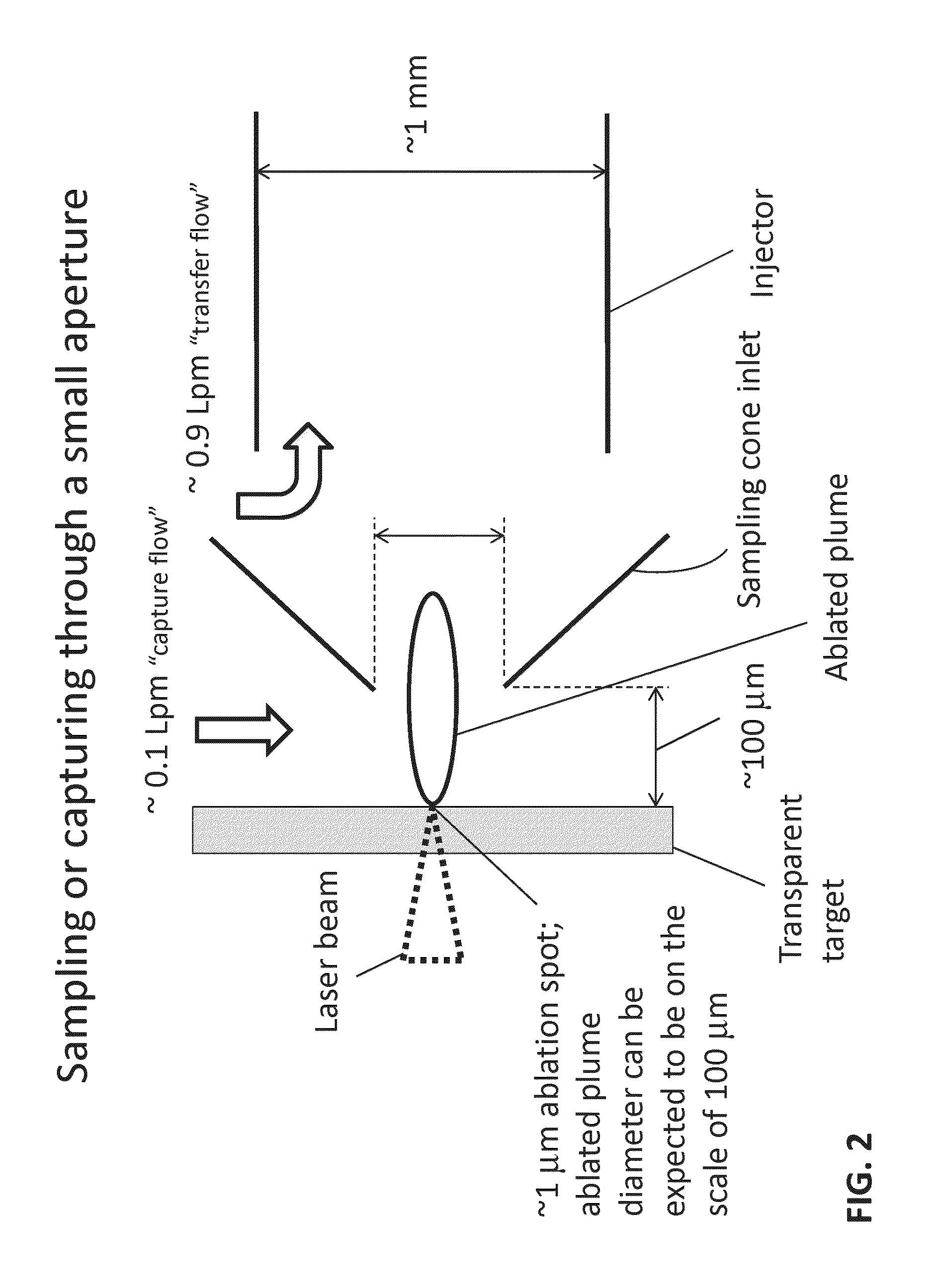
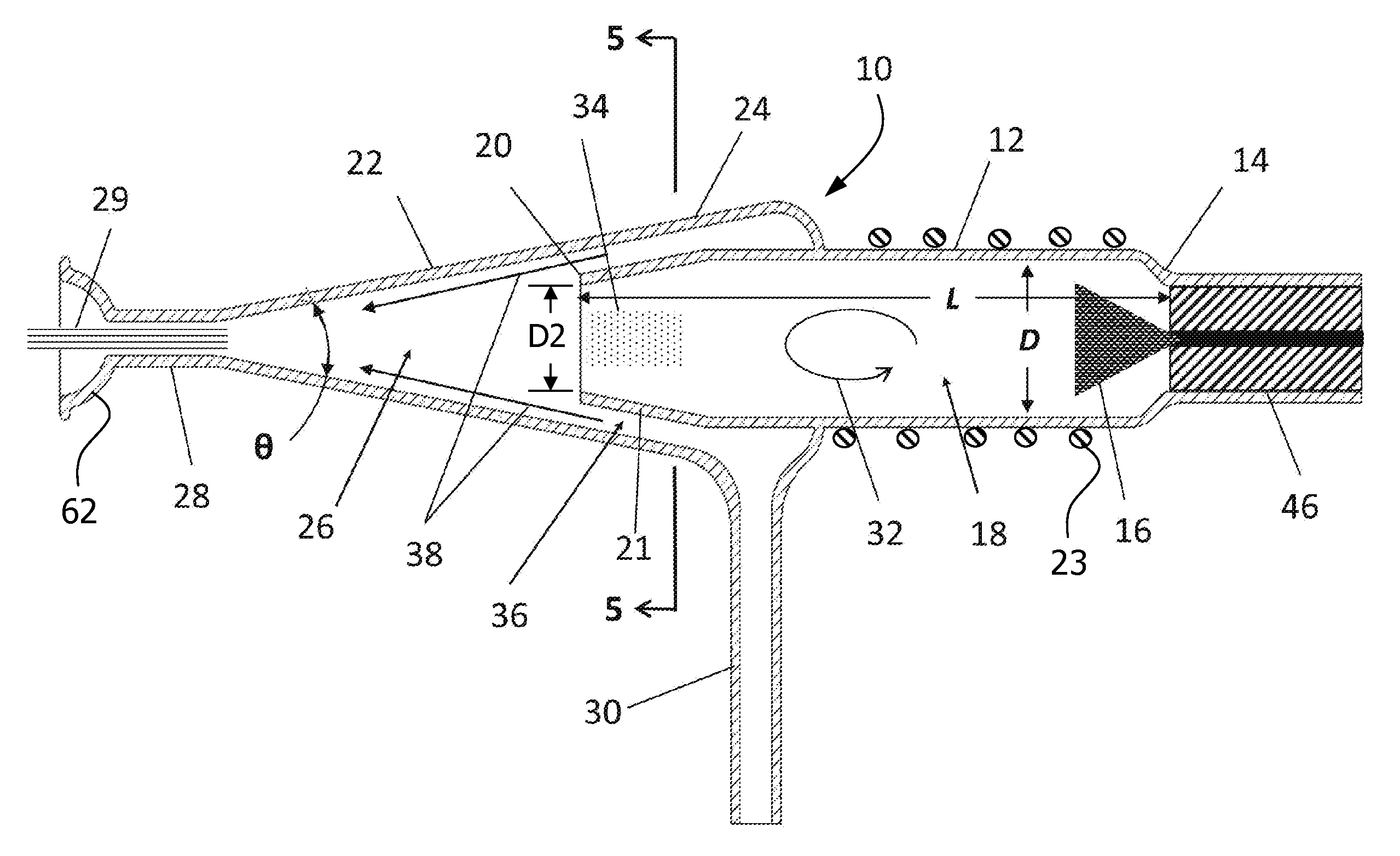
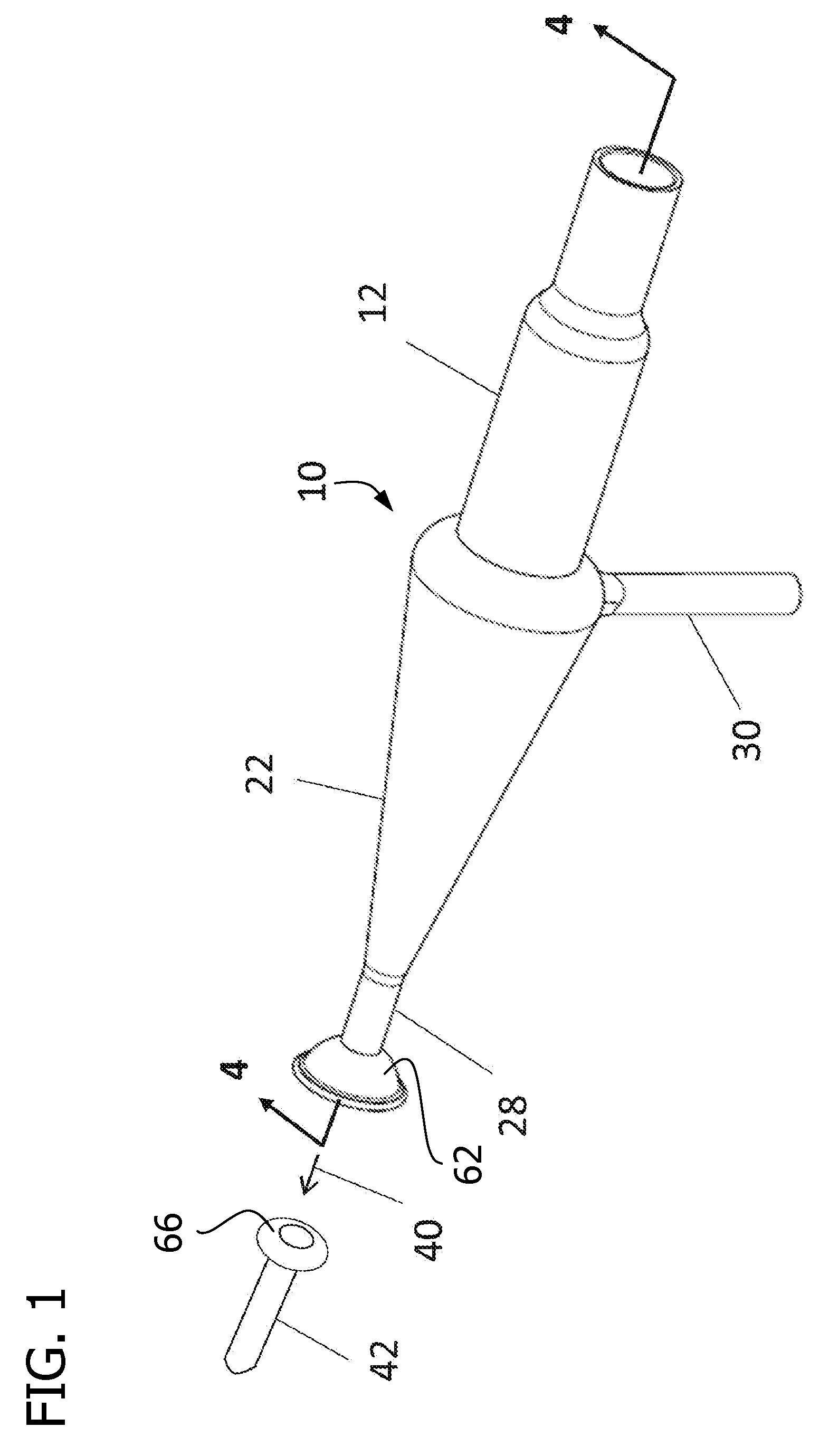
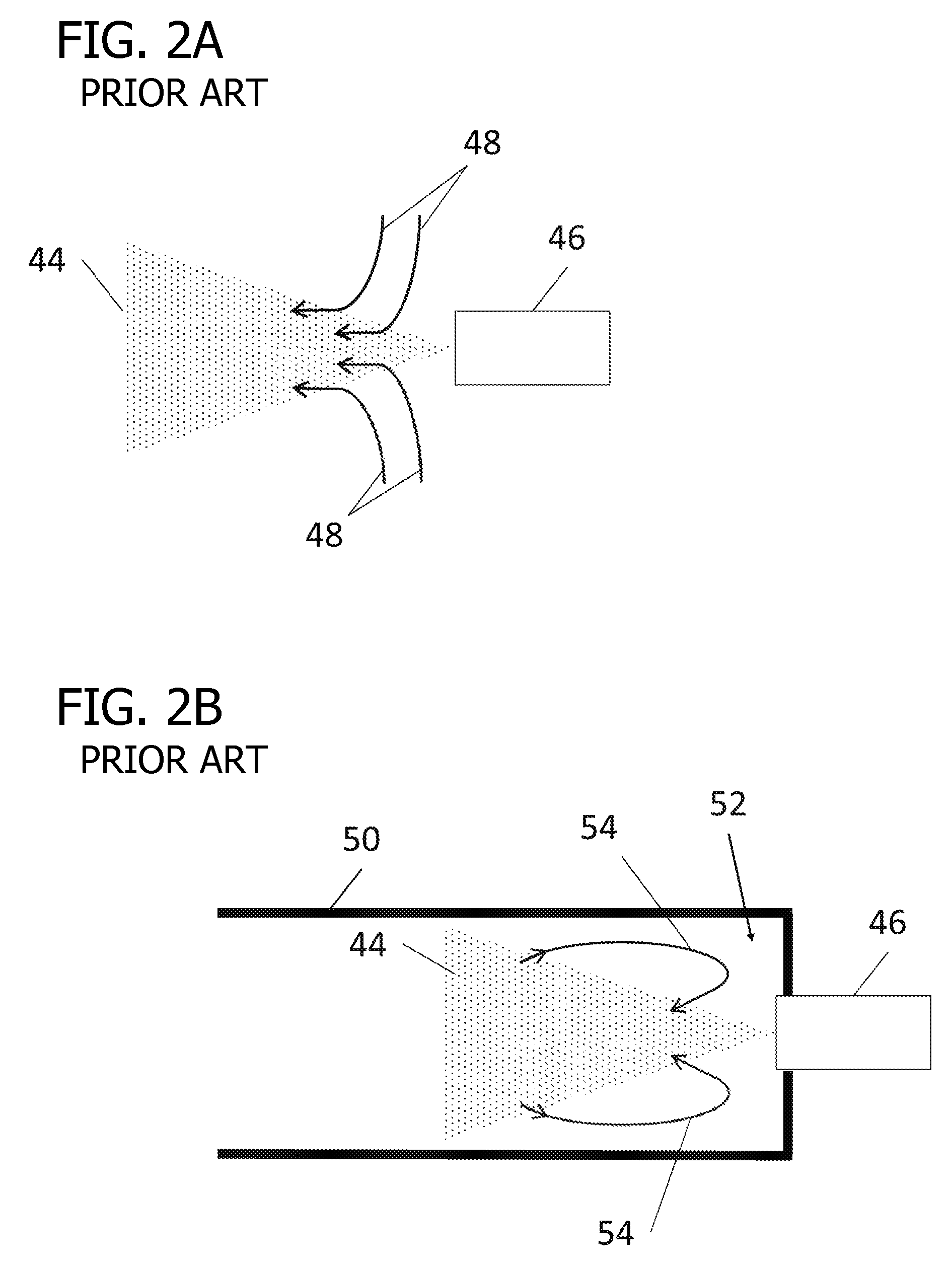
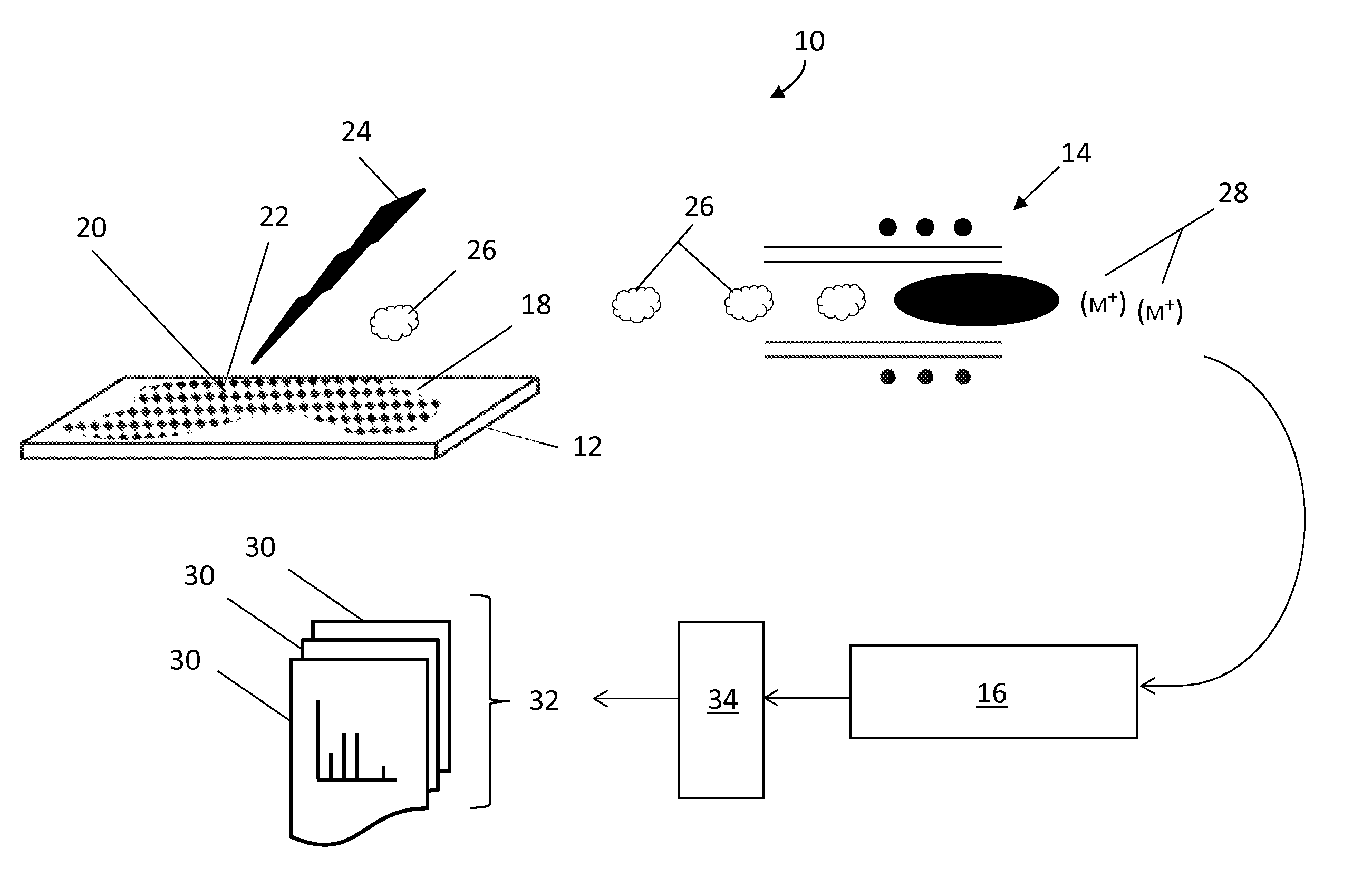
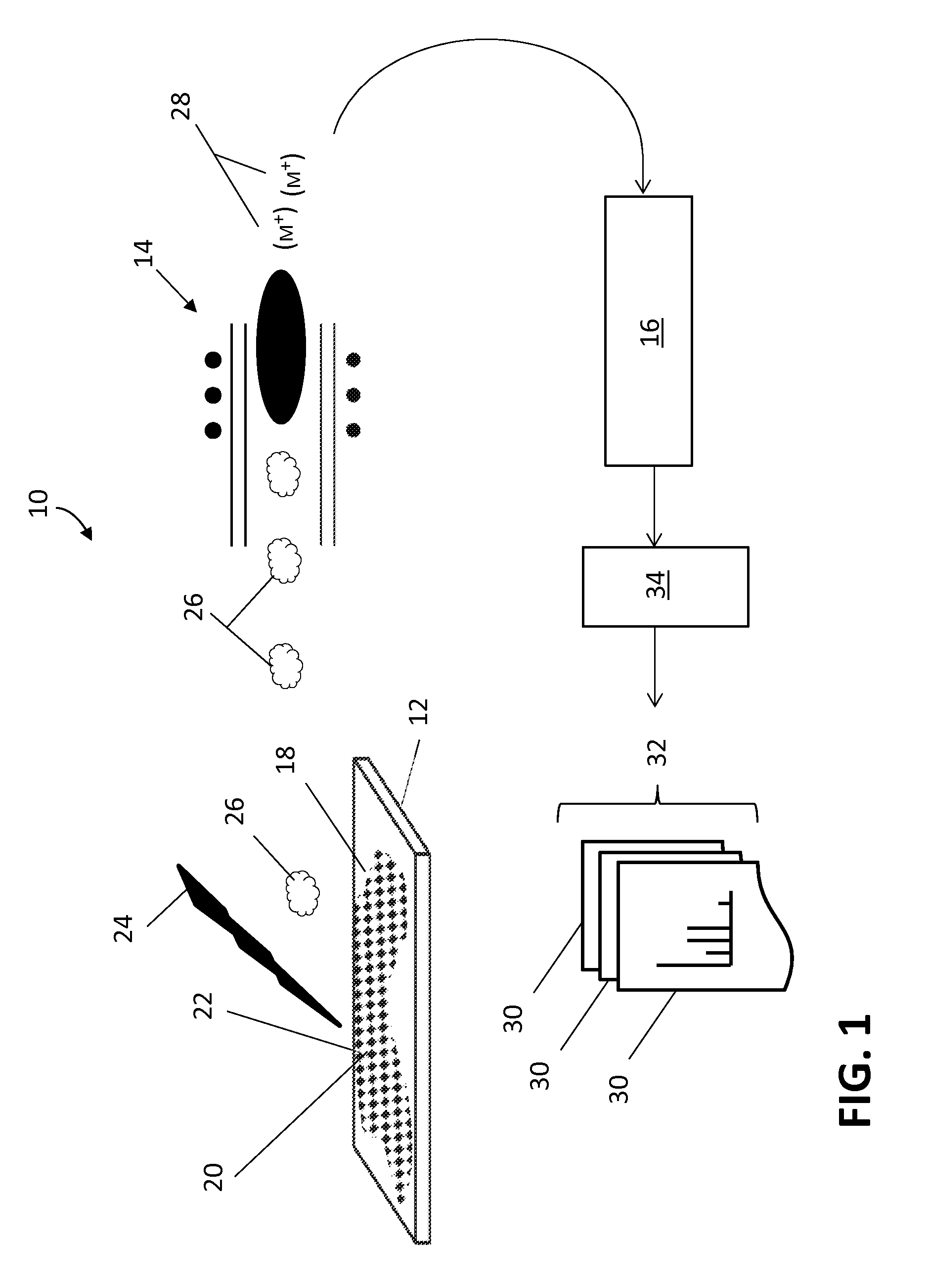
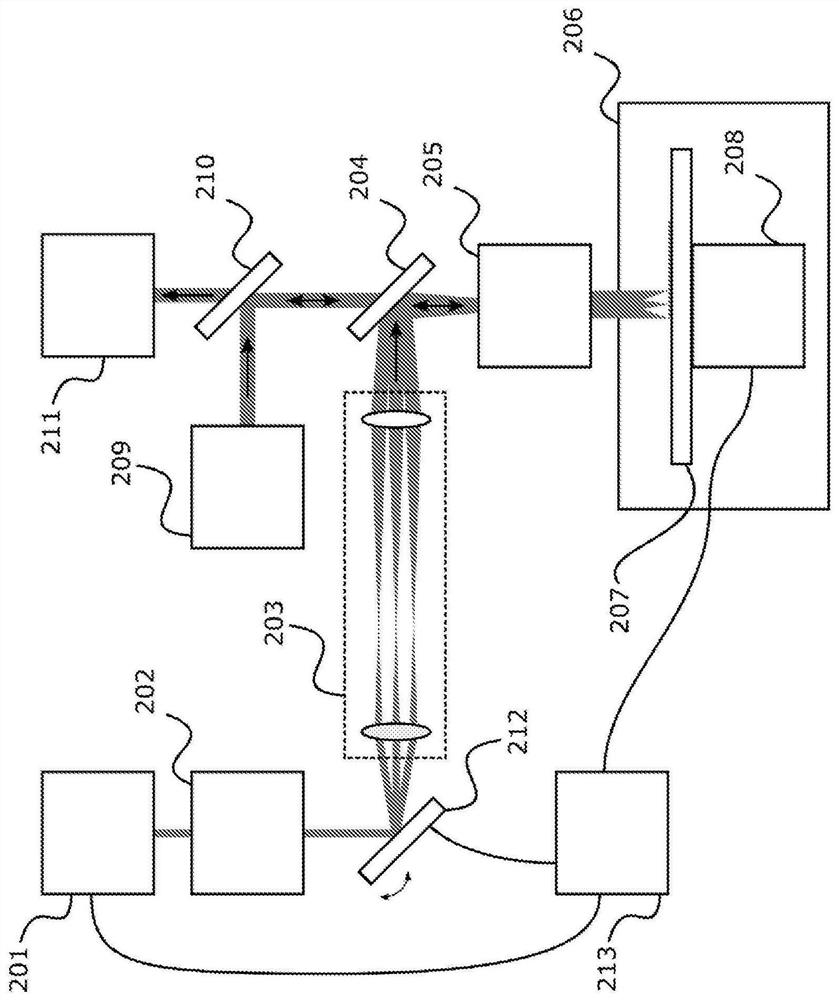
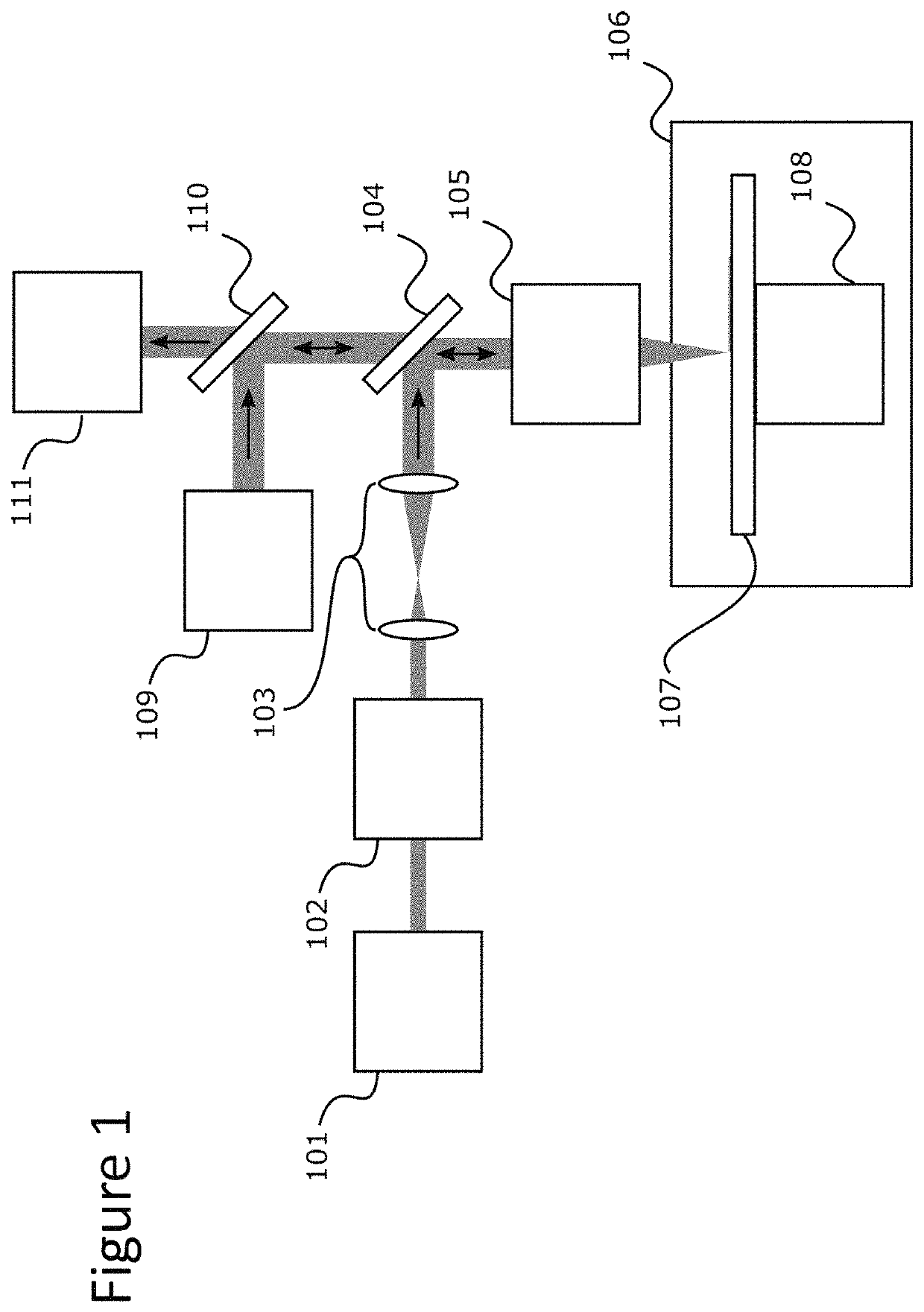
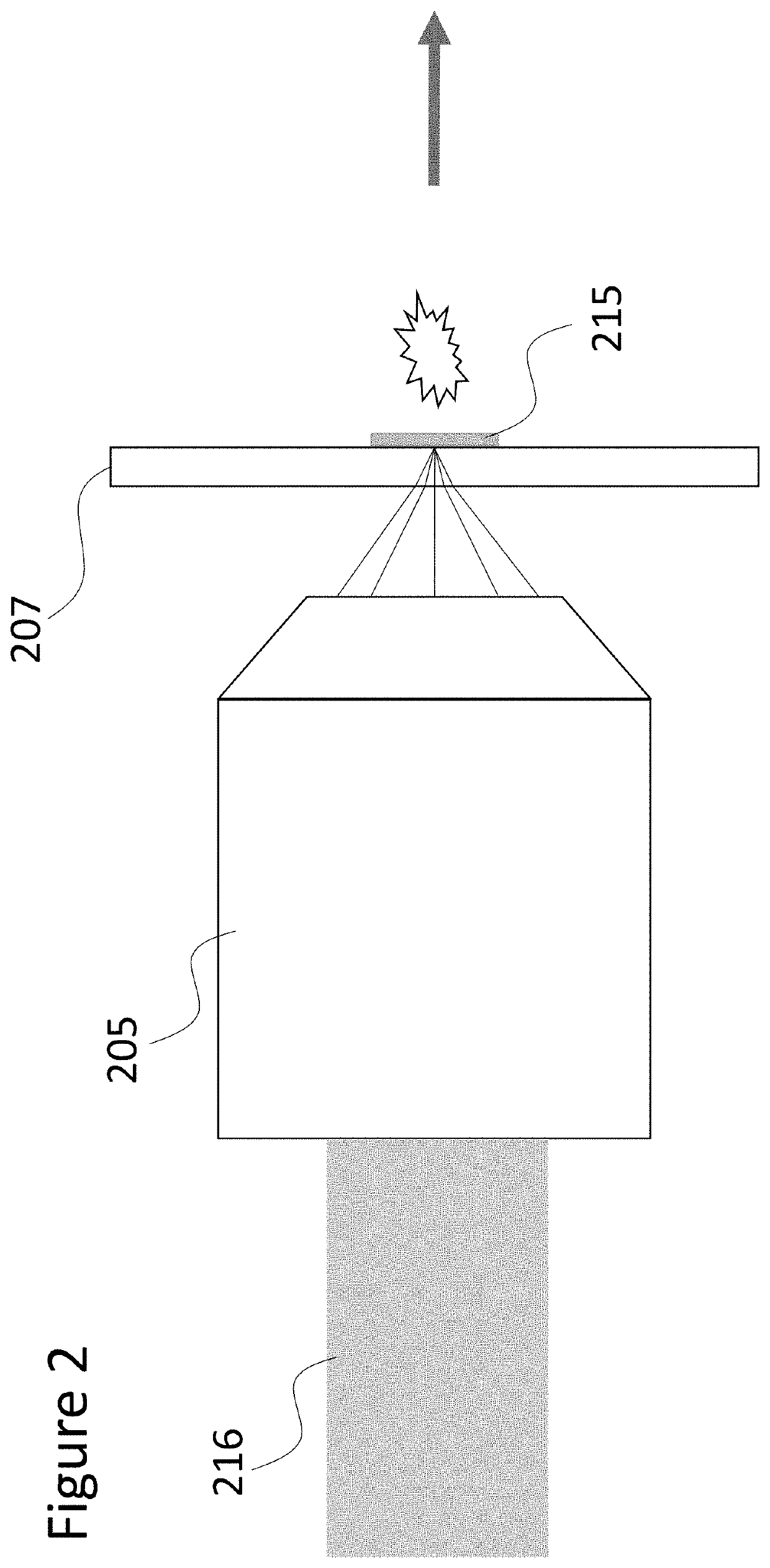
Sample Transferring Apparatus for Mass Cytometry
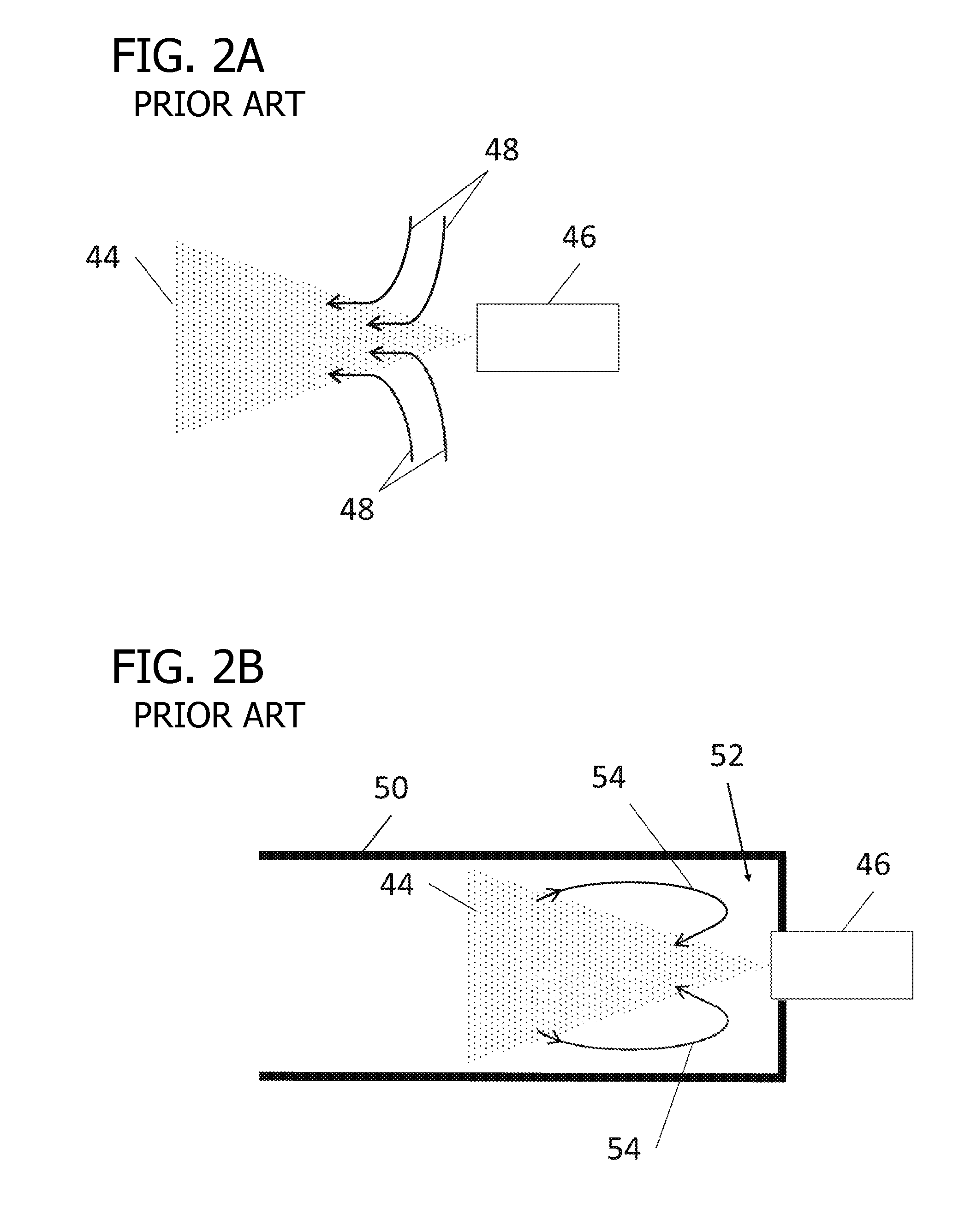
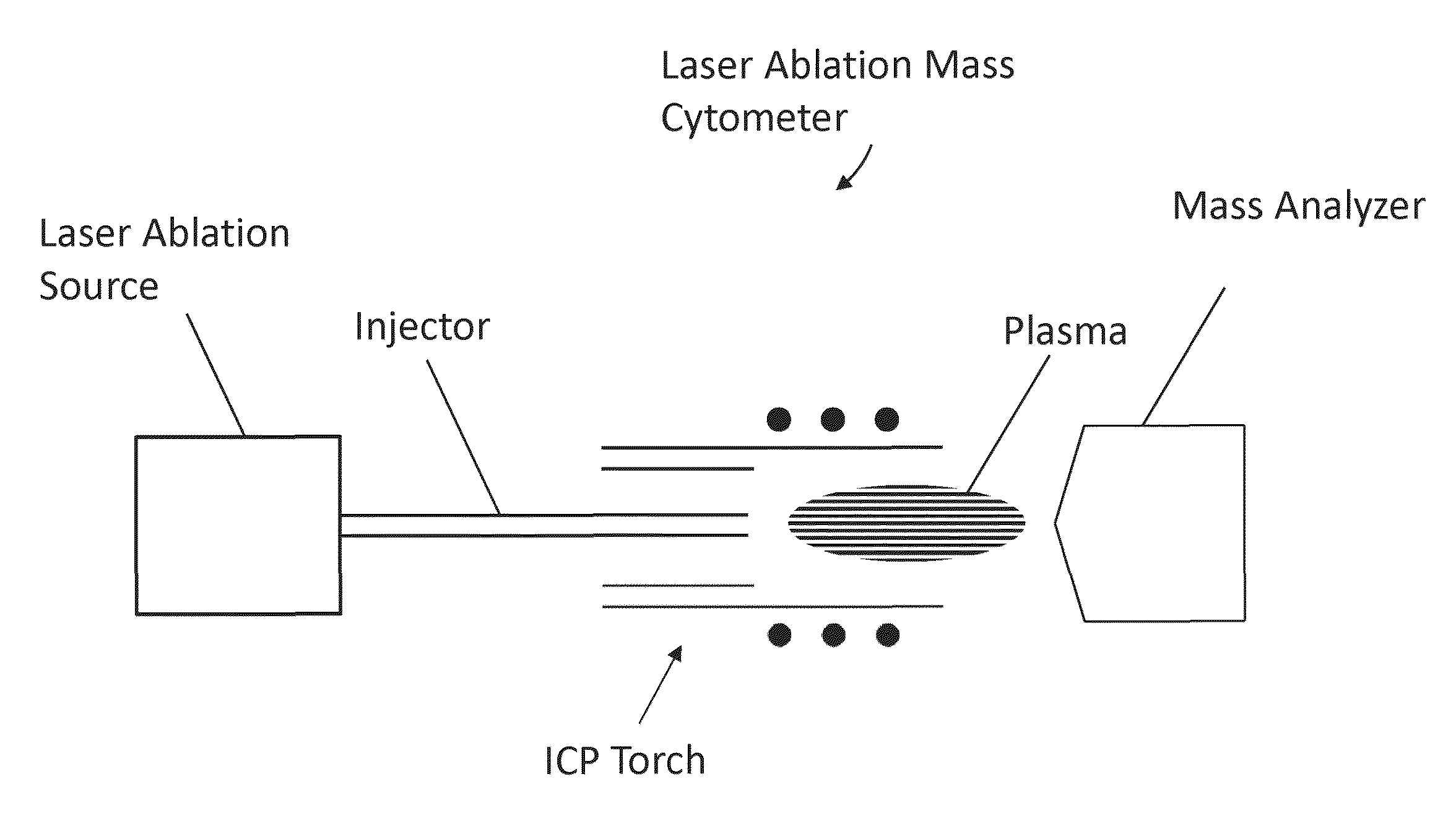
In a mass cytometer or mass spectrometer, a sample of elemental tagged particles is transferred from a dispersion to a gas flow through a carrier aerosol spray for atomization and ionization by inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source. The configuration of the sample transfer apparatus allow for total consumption of the sample by passing the sample spray through a deceleration stage to decelerate the spray of particles from its high velocity expansion. Following the deceleration stage, the decelerated sample of particles can be accelerated and focused through an acceleration stage for transferring into the ICP. This effectively improves the particle transfer between the sample spray and the ICP.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
Mass defect labeling for the determination of oligomer sequences
InactiveUS6962818B2Automatically filter out chemical noiseImproved absolute mass accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligomerChemical noise
Mass tagging methods are provided that lead to mass spectrometer detection sensitivities and molecular discriminations that are improved over other methods. In particular the methods are useful for discriminating tagged molecules and fragments of molecules from chemical noise in the mass spectrum. These mass tagging methods are useful for oligomer sequencing, determining the relative abundances of molecules from different samples, and identifying individual molecules or chemical processing steps in combinatorial chemical libraries. The methods provided are useful for the simultaneous analysis of multiple molecules and reaction mixtures by mass spectrometric methods.
Owner:TARGET DISCOVERY
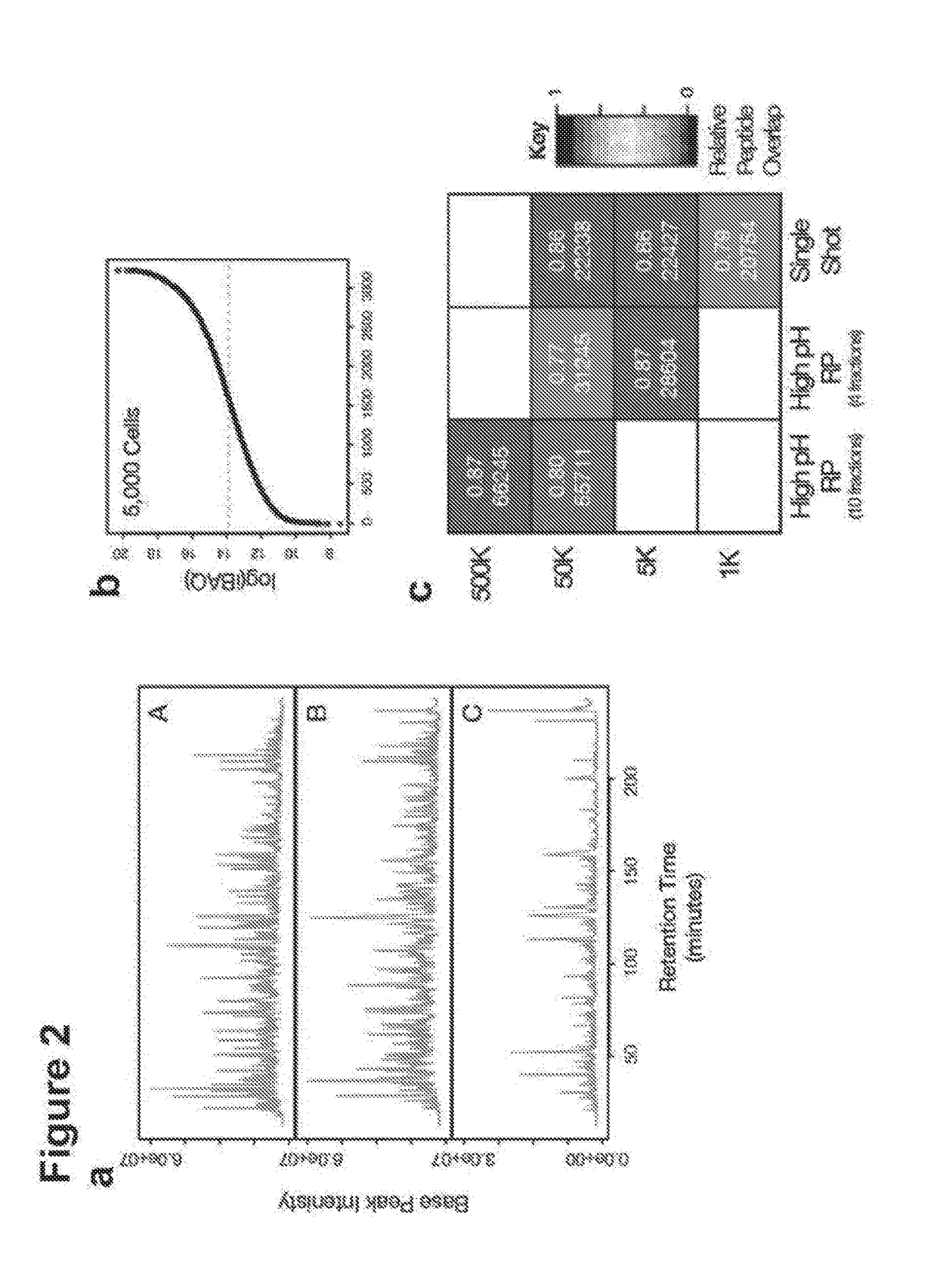
Sample analysis by mass cytometry
InactiveUS20140121117A1Particle separator tubesWithdrawing sample devicesTissue sampleMass cytometry
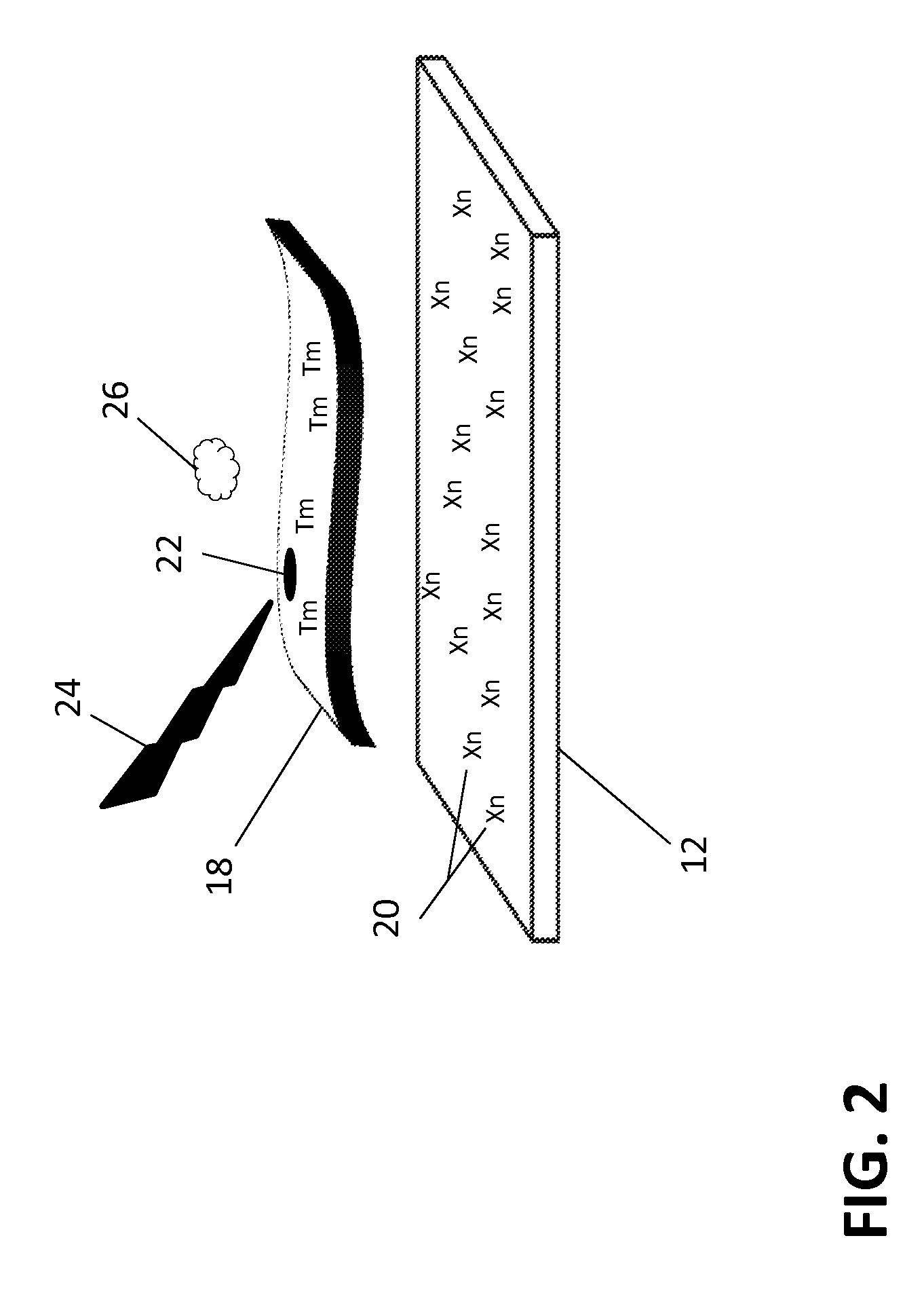
In a mass cytometer system, a tissue sample labeled with multiple metal tags is supported on an encoded substrate for distribution profile mapping by laser ablation. Groups of elemental ions from each plume generated by each laser pulse are detected by the mass cytometer and the data is mapped according to the encoded substrate. This configuration allows for the production of a 3-dimentional distribution profile of the multiple metal tags in the tissue sample.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CANADA INC
Flow cytometry methods and immunodiagnostics with mass sensitive readout
ActiveUS20100227310A1Packed tightlyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunodiagnosticsNanoparticle
Mass cytometry method. In one aspect, the method includes providing a sample having at least one cell type and mixing the sample with material such as nanoparticles functionalized with affinity molecules for the at least one cell type. The sample is transported through a suspended microchannel resonator to record a mass histogram and a cell count for the at least one cell type is determined from the histogram.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Flow cytometry methods and immunodiagnostics with mass sensitive readout
ActiveUS8722419B2Packed tightlyImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmunodiagnosticsNanoparticle
Mass cytometry method. In one aspect, the method includes providing a sample having at least one cell type and mixing the sample with material such as nanoparticles functionalized with affinity molecules for the at least one cell type. The sample is transported through a suspended microchannel resonator to record a mass histogram and a cell count for the at least one cell type is determined from the histogram.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Proteomic sample preparation using paramagnetic beads
InactiveUS20170074869A1Peptide preparation methodsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesMagnetic beadMass cytometry
The present invention relates to a method of reversibly binding polypeptides to a solid phase comprising a hydrophilic surface, preferably for the use in mass spectrometry based proteomics. Kits providing reagents for the method of the invention and uses of said kits.
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
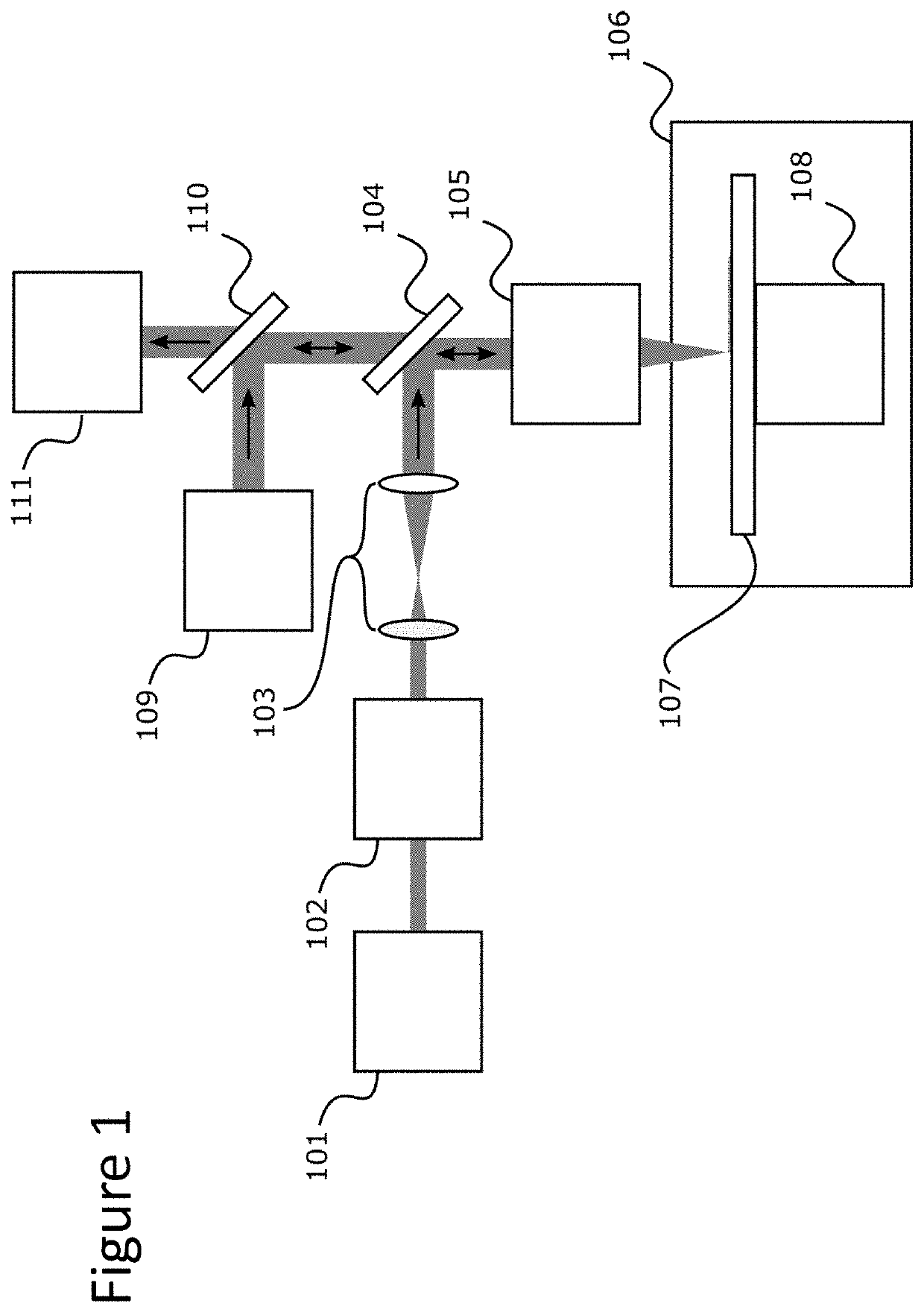
High resolution imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20210118661A1Increase speedSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersHigh resolution imagingMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to the high resolution imaging of samples using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) and to the imaging of biological samples by imaging mass cytometry (IMCTM) in which labelling atoms are detected by IMS. LA-ICP-MS (a form of IMS in which the sample is ablated by a laser, the ablated material is then ionised in an inductively coupled plasma before the ions are detected by mass spectrometry) has been used for analysis of various substances, such as mineral analysis of geological samples, analysis of archaeological samples, and imaging of biological substances. However, traditional LA-ICP-MS systems and methods may not provide high resolution. Described herein are methods and systems for high resolution IMS and IMC.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA +1
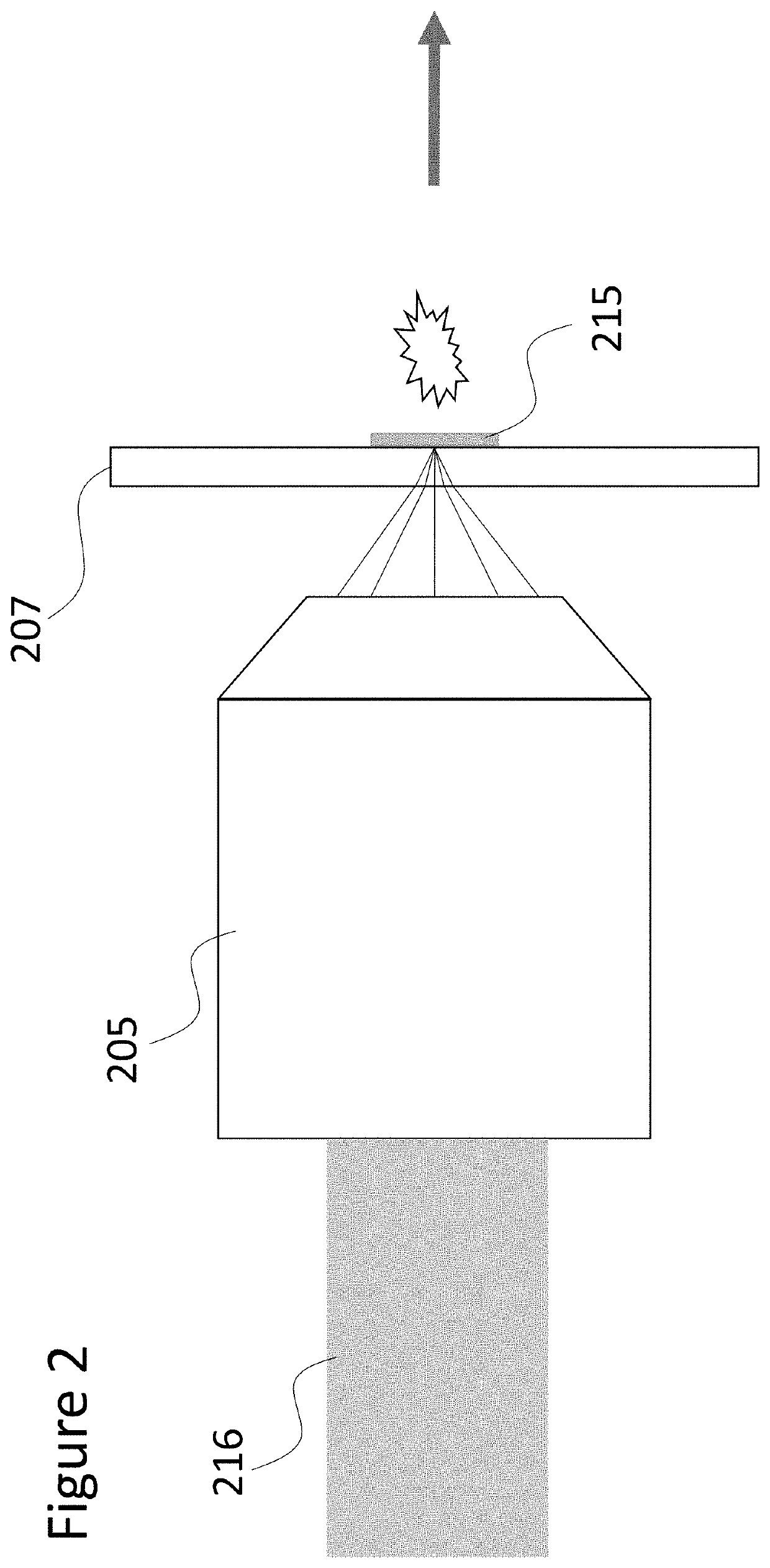
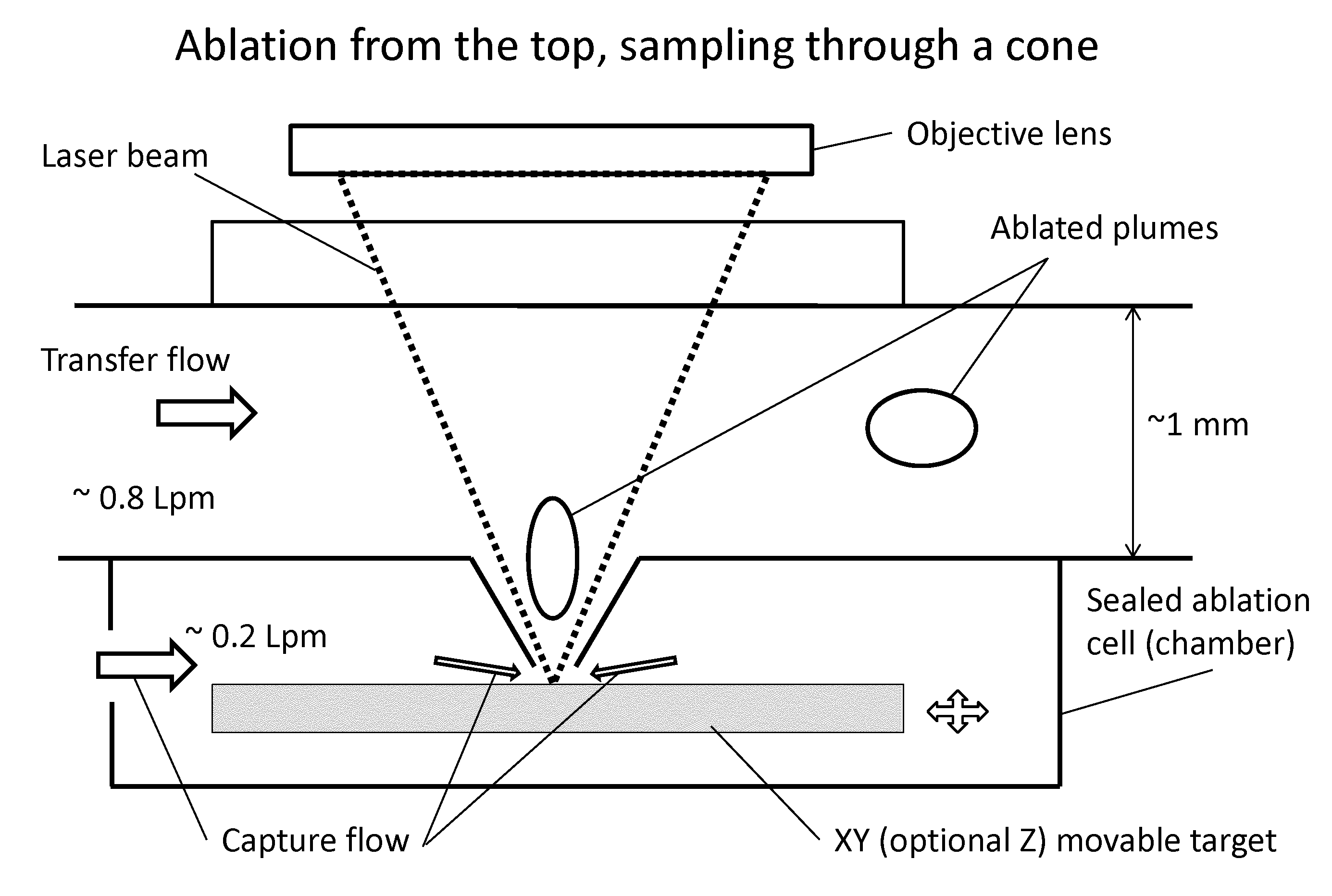
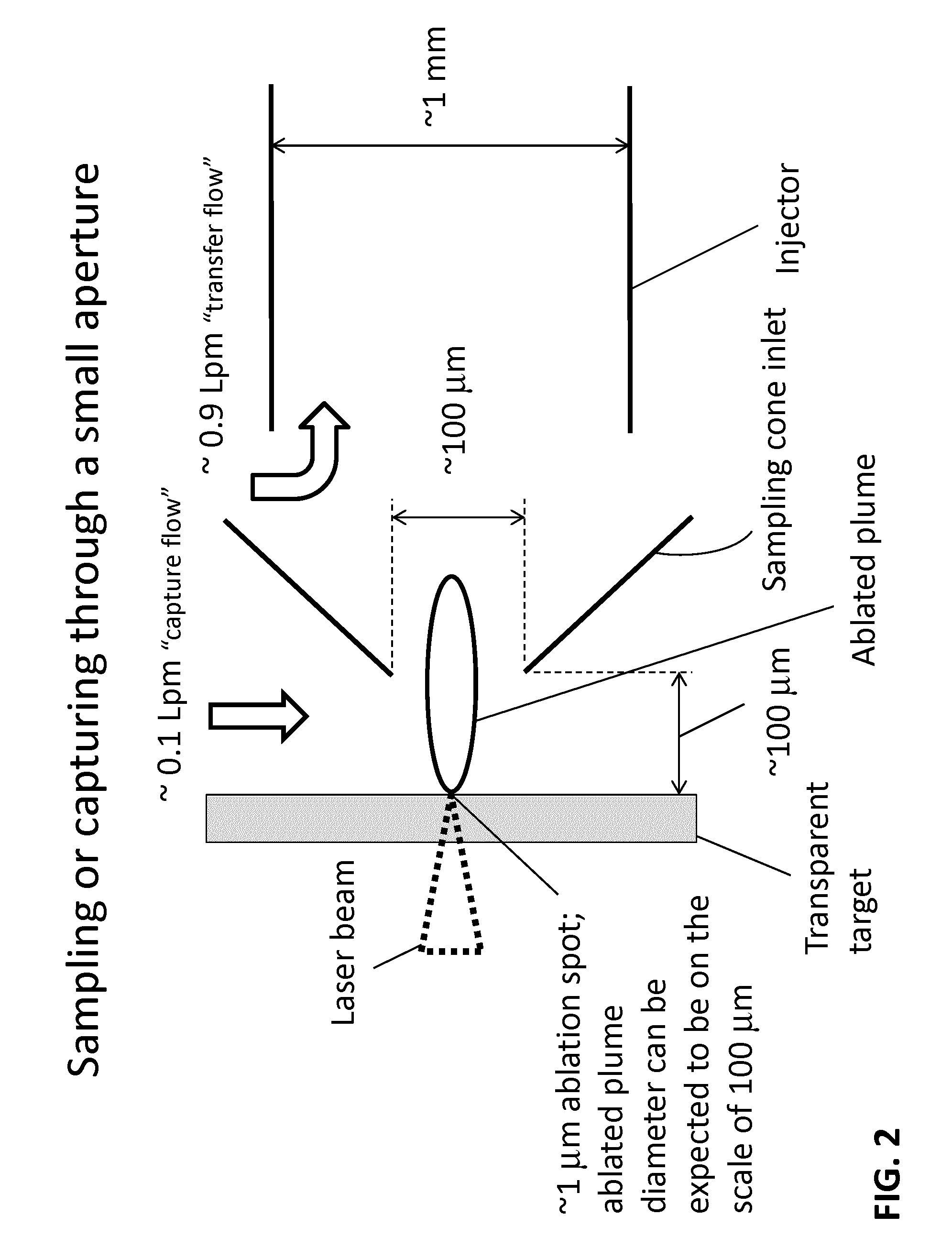
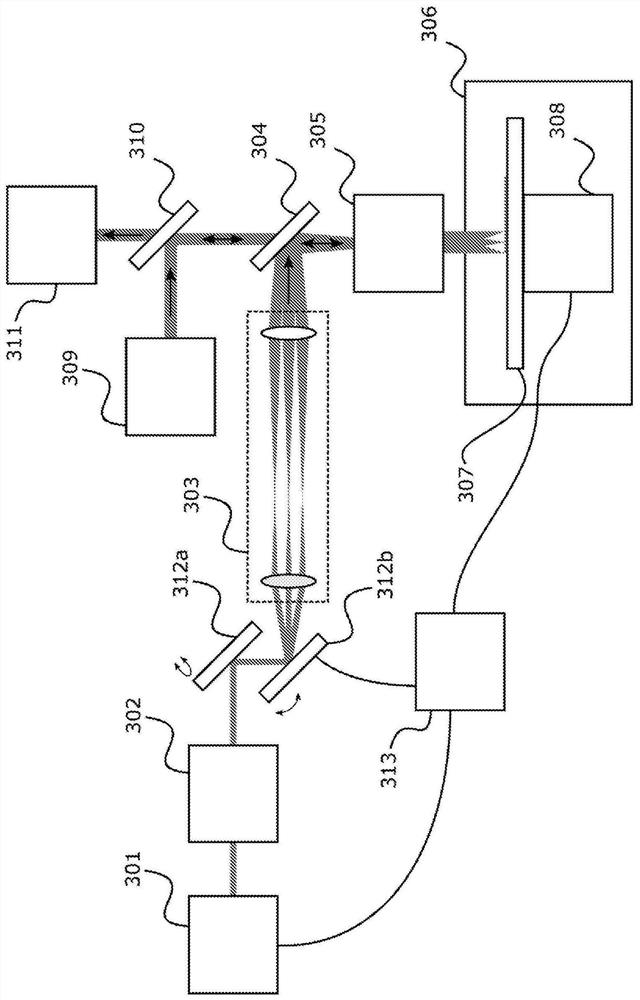
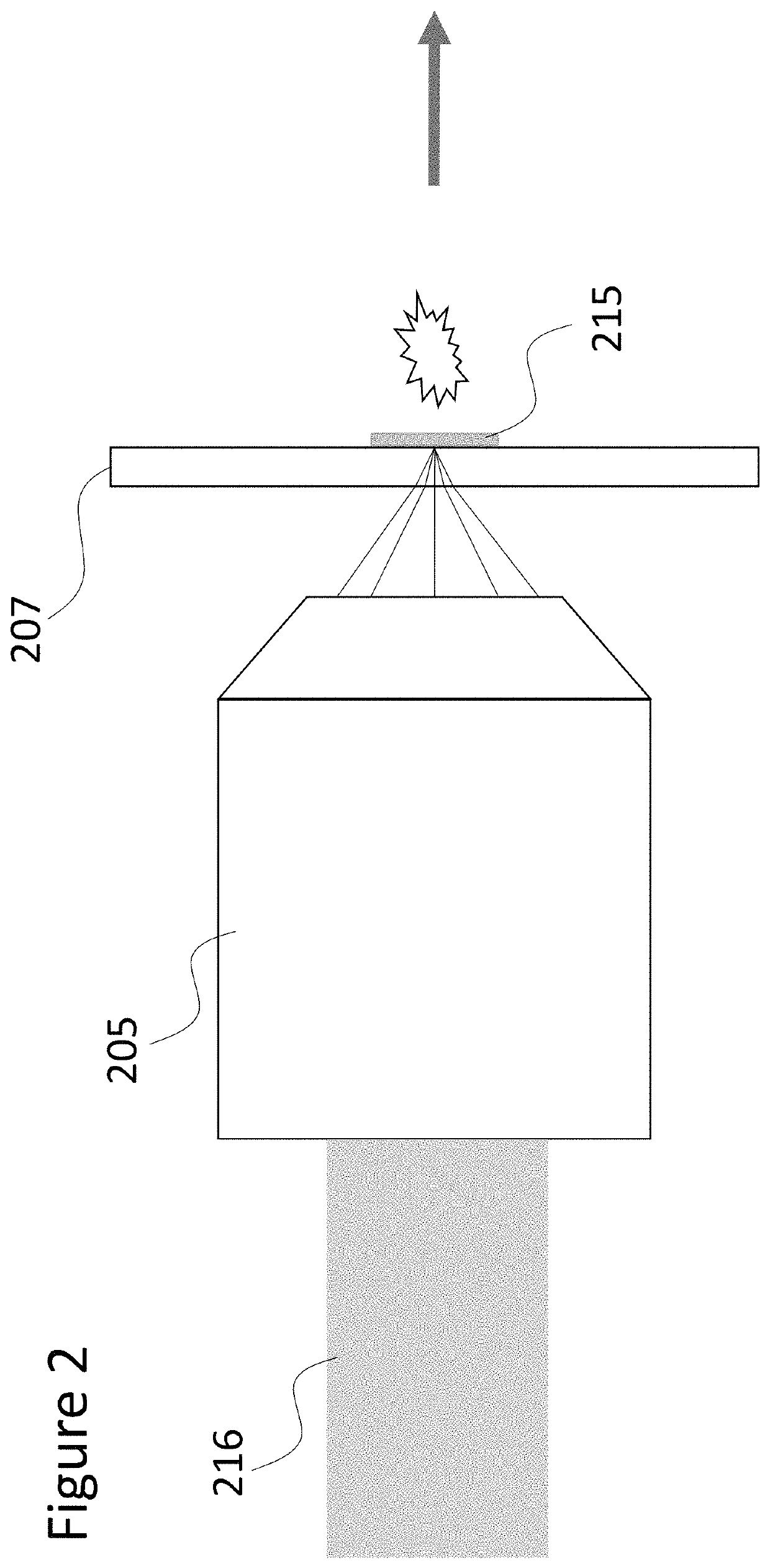
Sample analysis for mass cytometry
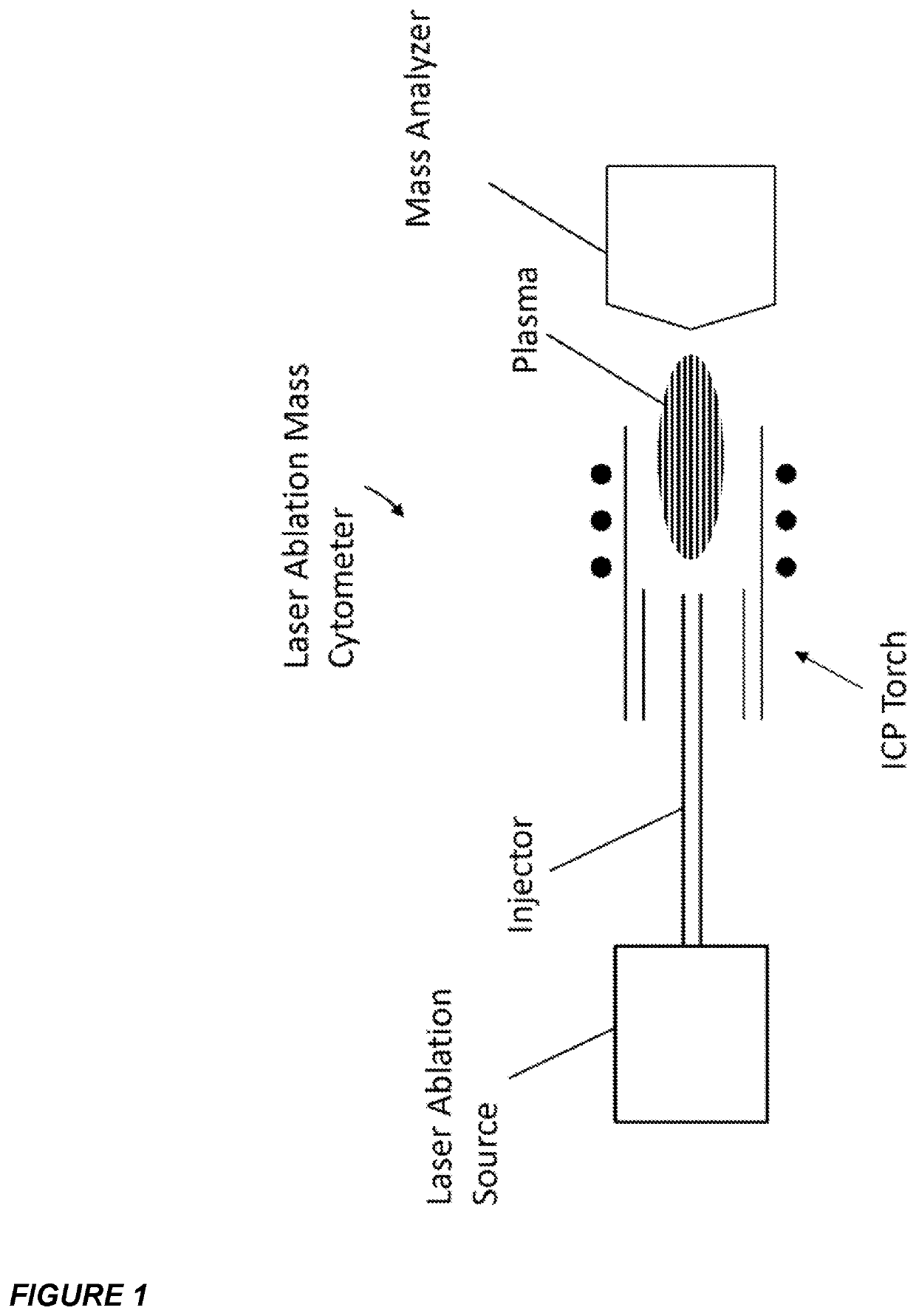
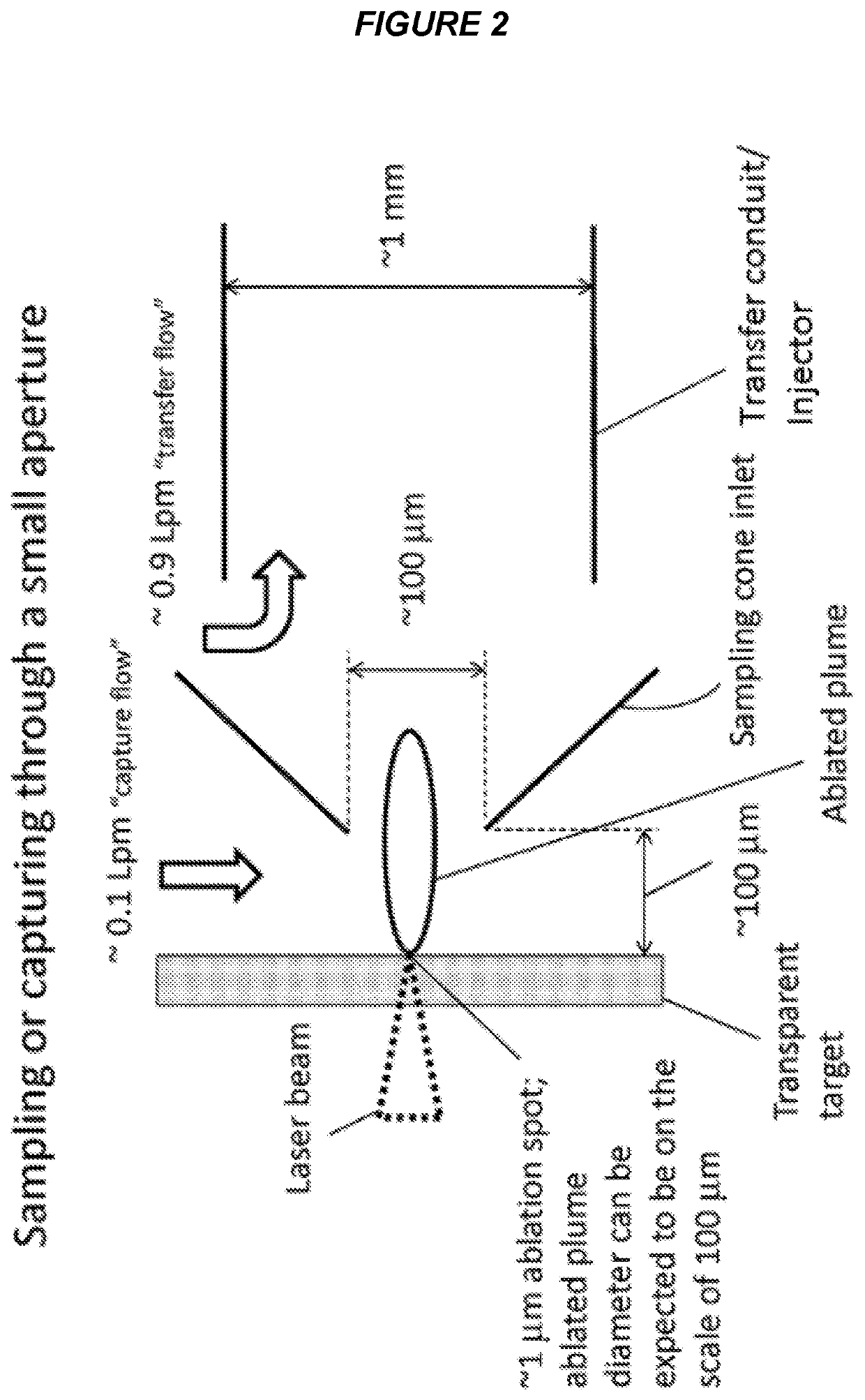
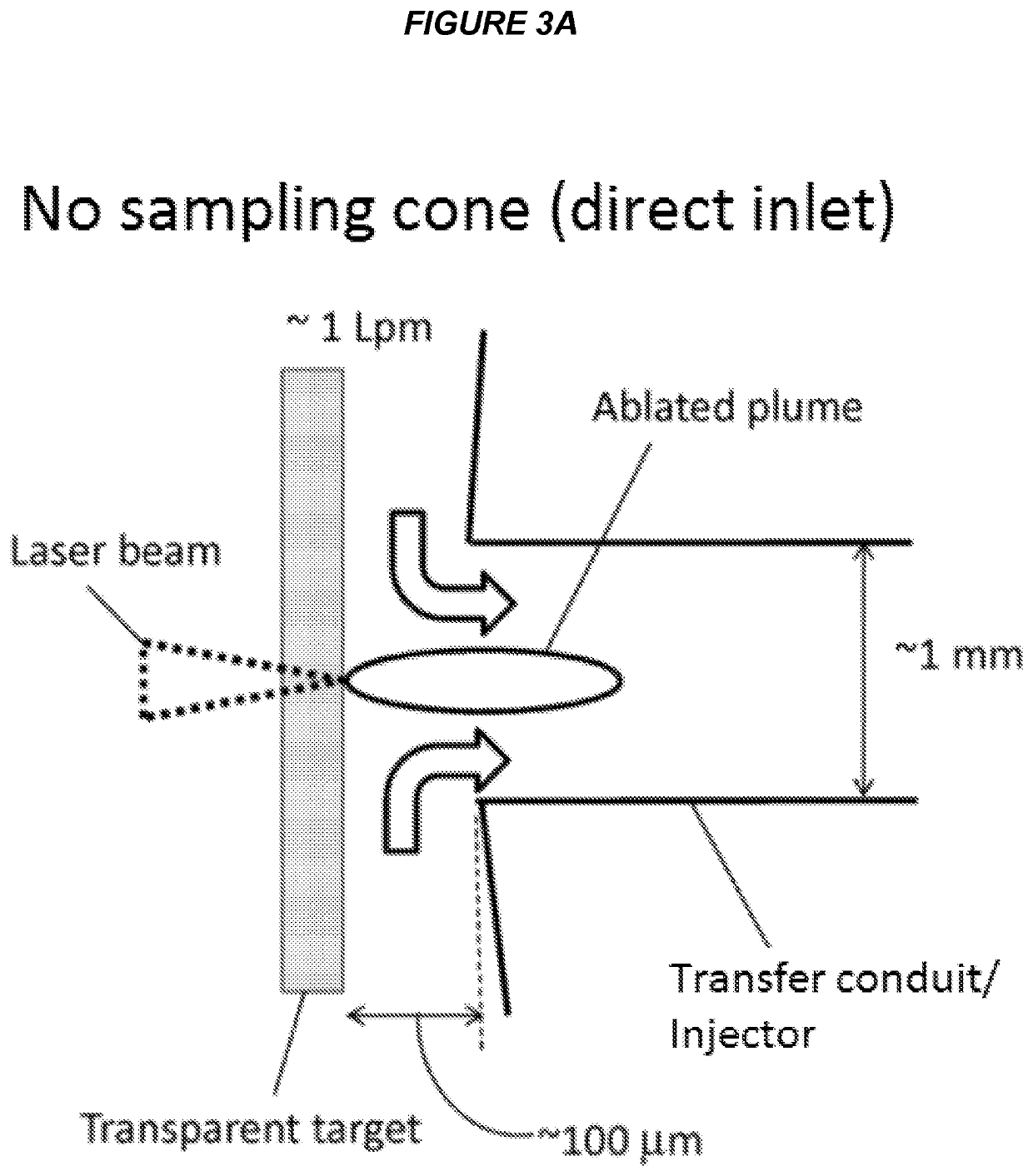
ActiveUS9589779B2Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionLaser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryMass analyzer
The invention relates to methods and devices for analysis of samples using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). The invention provides methods and devices in which individual ablation plumes are distinctively captured and transferred to the ICP, followed by analysis by mass cytometry.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
Lipid insertion for antigen capture and presentation and use as a sensor platform
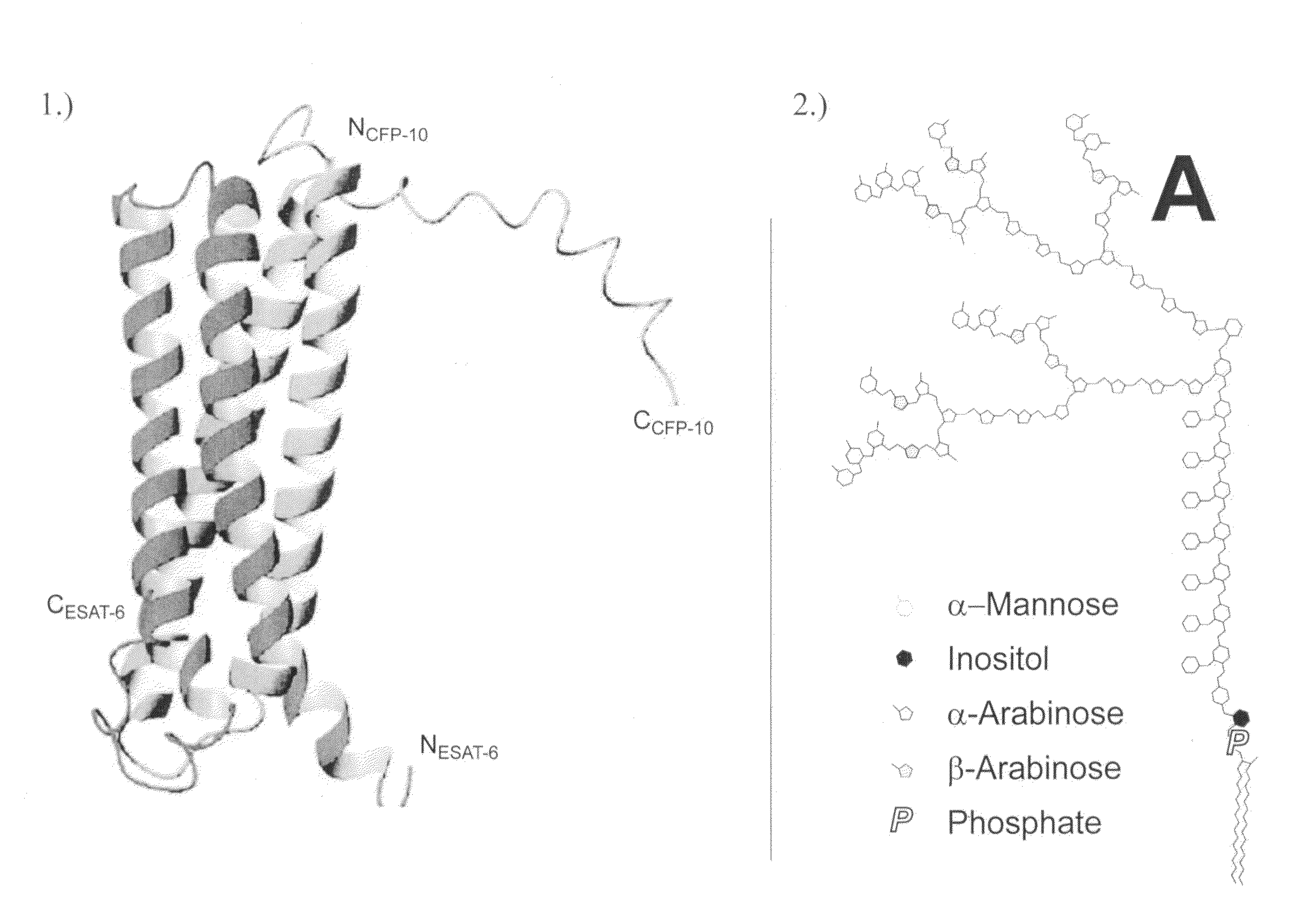
It has been found that moieties containing a lipophilic domain, e.g., lipophilic pathogen activated molecular patterns (PAMPs), insert into the lipid bilayer on a cell membrane to facilitate antigen recognition by the innate immune response receptors. This changes the basic understanding of antigen recognition by the innate immune system. A sensor platform for the ultra-sensitive and specific detection of moieties containing such a lipophilic domain, e.g., PAMPs, that are associated with a disease, has now been developed. To date, this approach has been validated with Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and lipopolysacharide (LPS), associated with gram-negative bacteria. This approach may be extendable to all lipophilic targets associated with pathogens and thus, is the basis of a very simple and specific sensing platform. In addition, novel applications for this technology in the selection of recognition ligands by mass spectroscopy have been identified.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
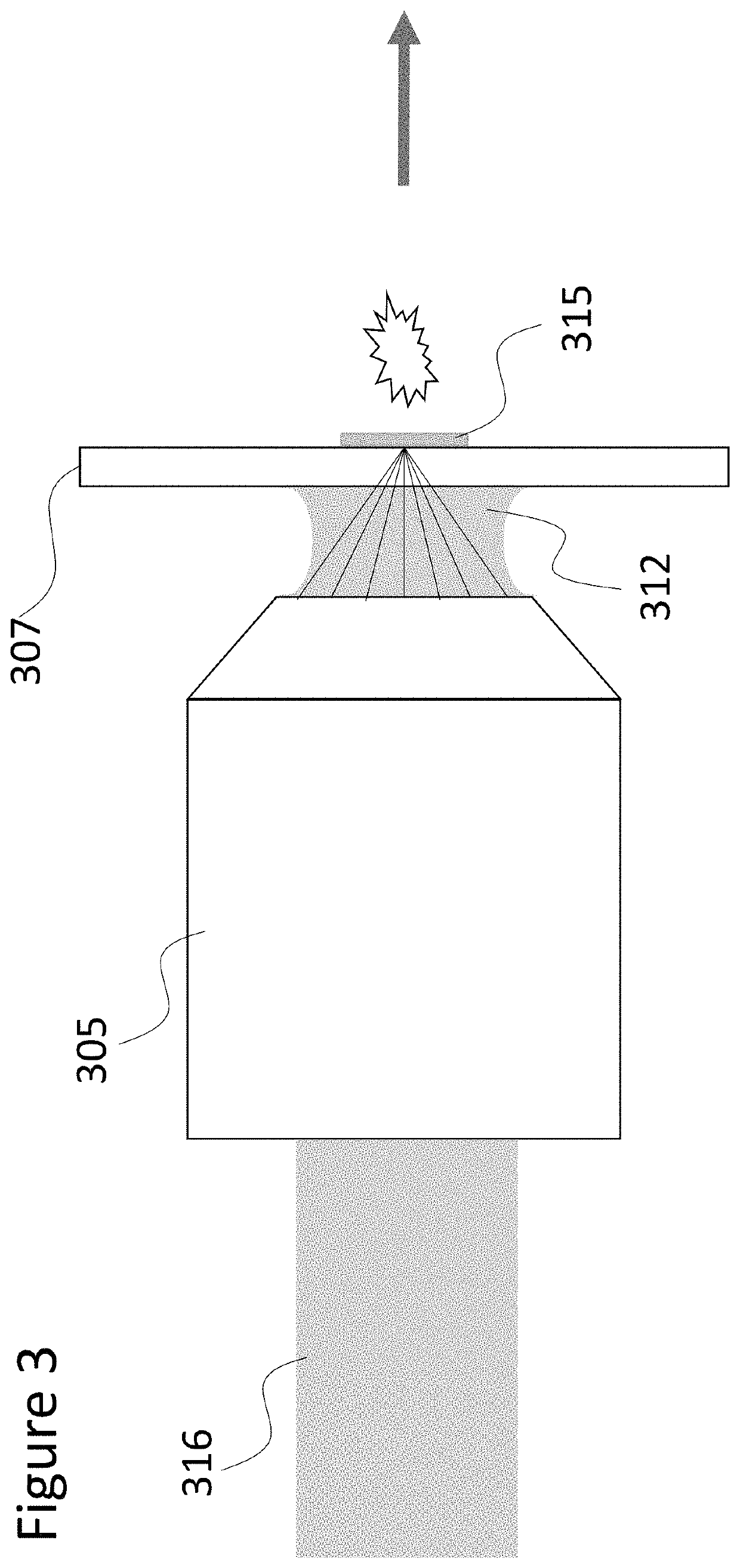
Laser enabled imaging mass cytometry
InactiveUS20160260598A1Samples introduction/extractionBiological particle analysisLaser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryLaser imaging
The invention relates to methods and devices for analysis of samples using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). The invention provides methods and devices in which individual ablation plumes are distinctively captured and transferred to the ICP, followed by analysis by mass cytometry.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CANADA INC
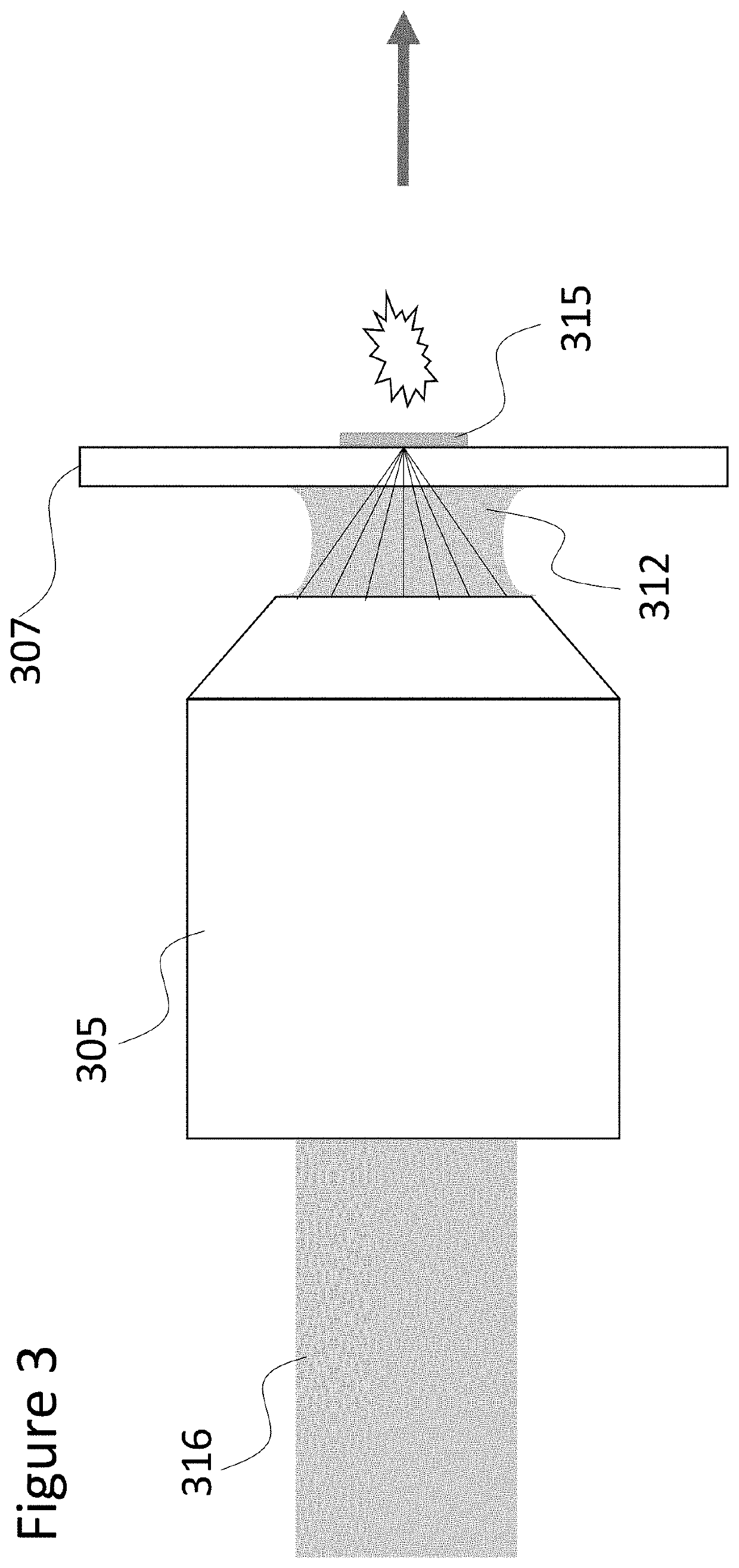
Sample transferring apparatus for mass cytometry
In a mass cytometer or mass spectrometer, a sample of elemental tagged particles is transferred from a dispersion to a gas flow through a carrier aerosol spray for atomization and ionization by inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source. The configuration of the sample transfer apparatus allow for total consumption of the sample by passing the sample spray through a deceleration stage to decelerate the spray of particles from its high velocity expansion. Following the deceleration stage, the decelerated sample of particles can be accelerated and focused through an acceleration stage for transferring into the ICP. This effectively improves the particle transfer between the sample spray and the ICP.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
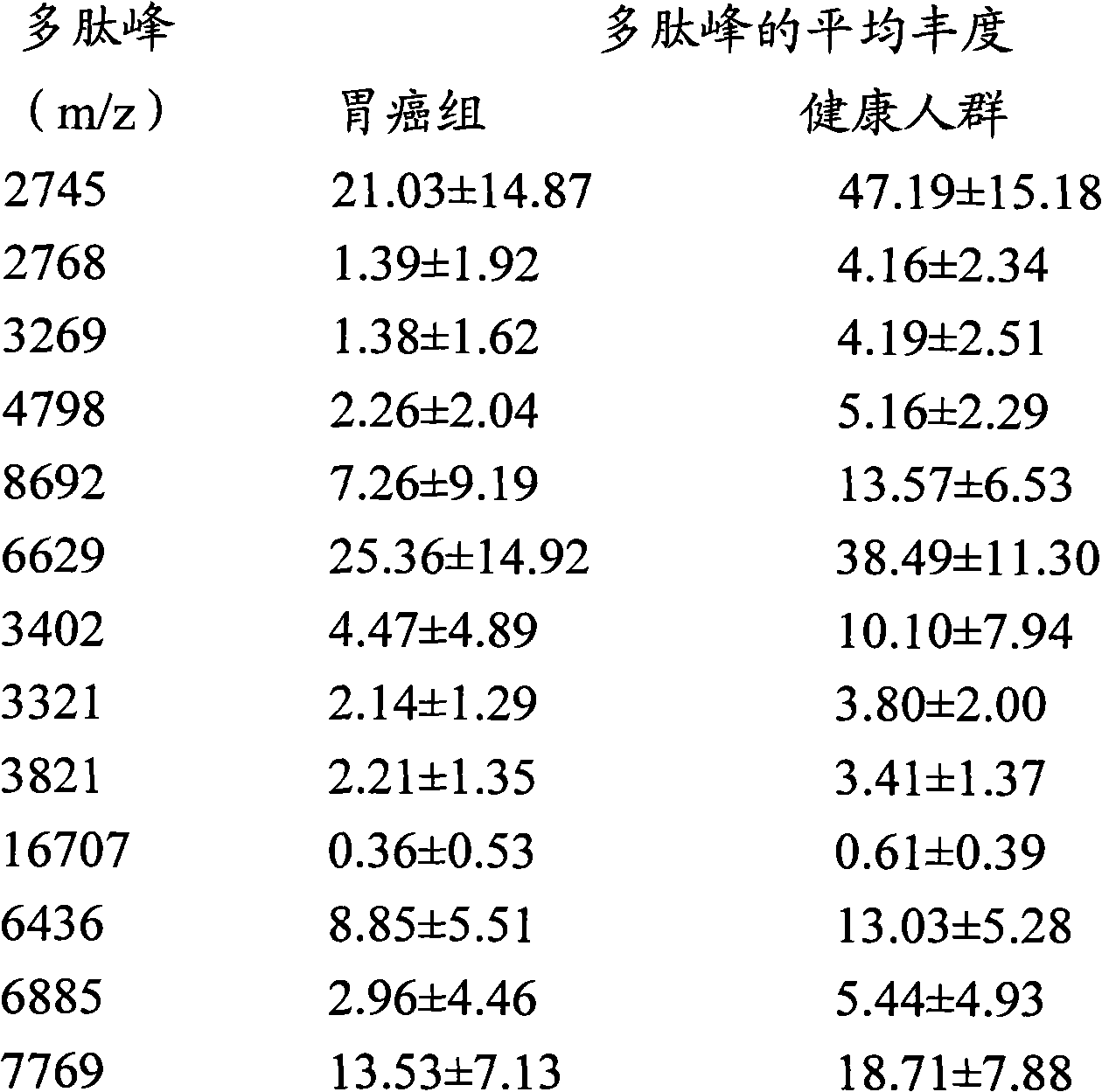
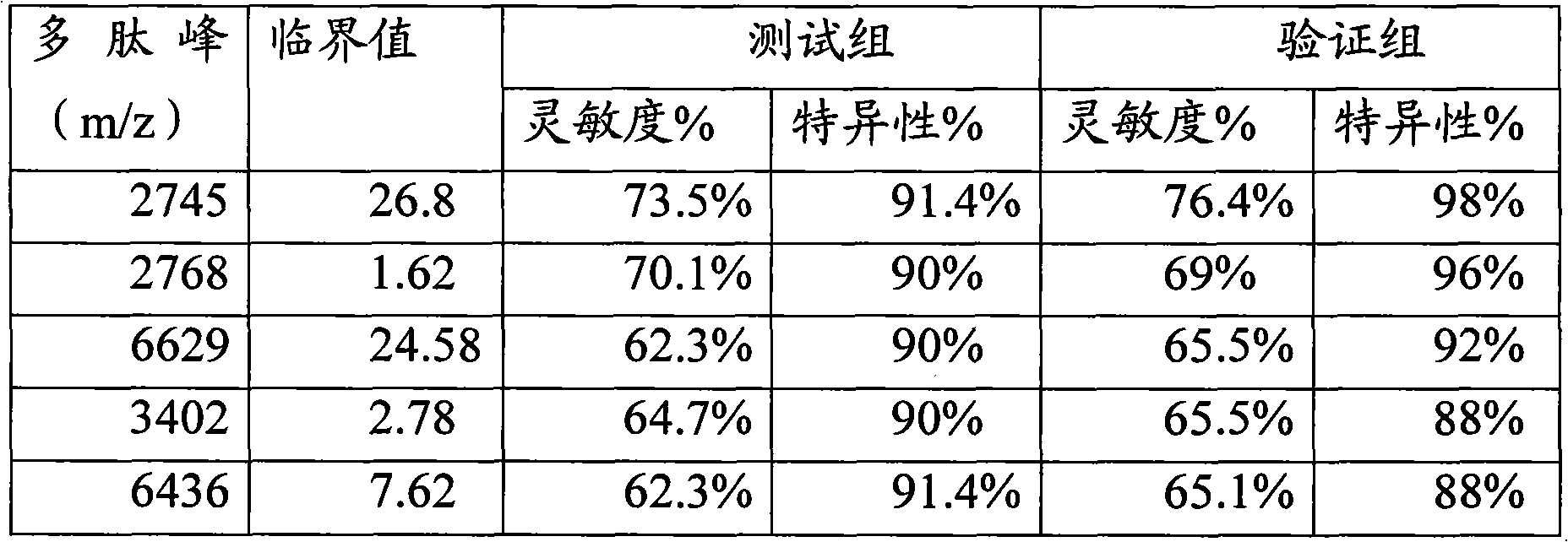
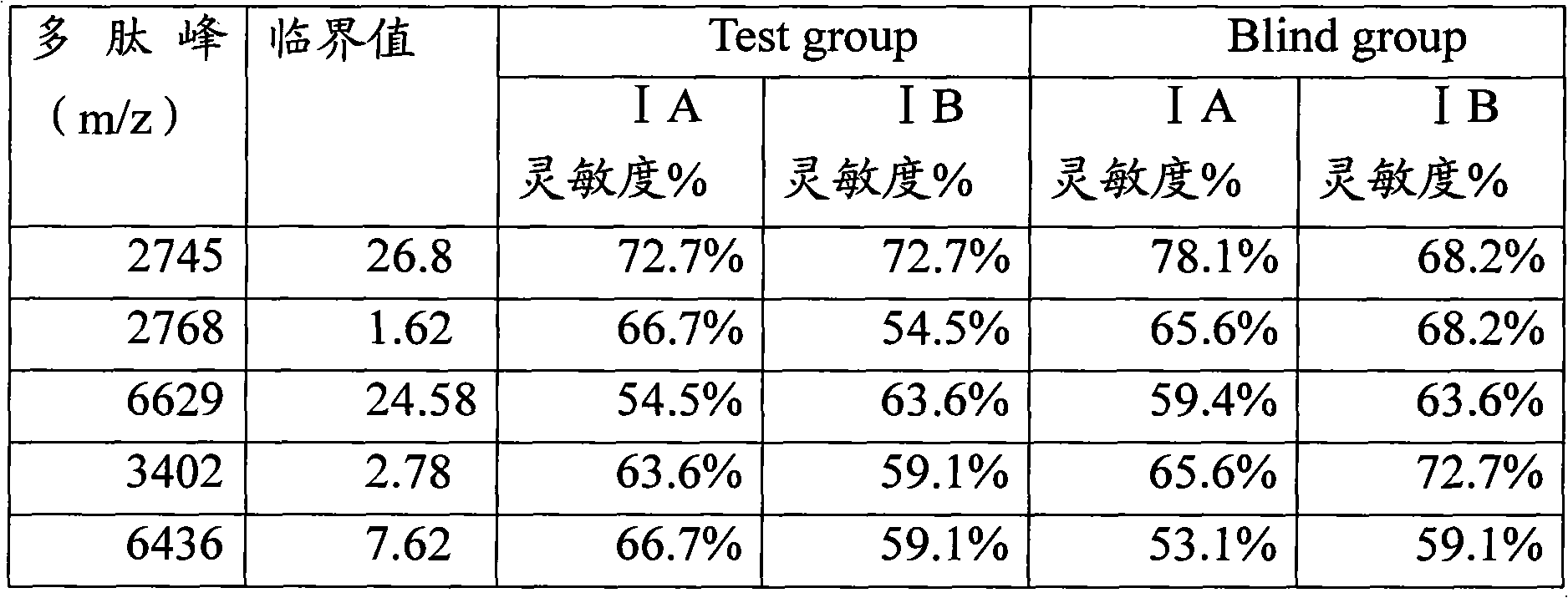
Mass spectrum detection method of serum polypeptide
InactiveCN101936948AImprove discovery ratePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSupport matrixSerum samples
The invention discloses a mass spectrum detection method of serum polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps: the magnetic bead supported matrix method is adopted to capture the gastric cancer peptidome in serum, a magnetic separator is used to separate magnetic beads and the sample without centrifuging the sample; and then the mass spectrum method is adopted to analyse the polypeptide spectrum. The method of the invention can be used to detect the serum samples of normal persons and patients with gastric cancer, and the detection result can be used as an important detection basis for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer. The detection method of the invention is accurate, convenient and fast.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CANCER HOSPITAL
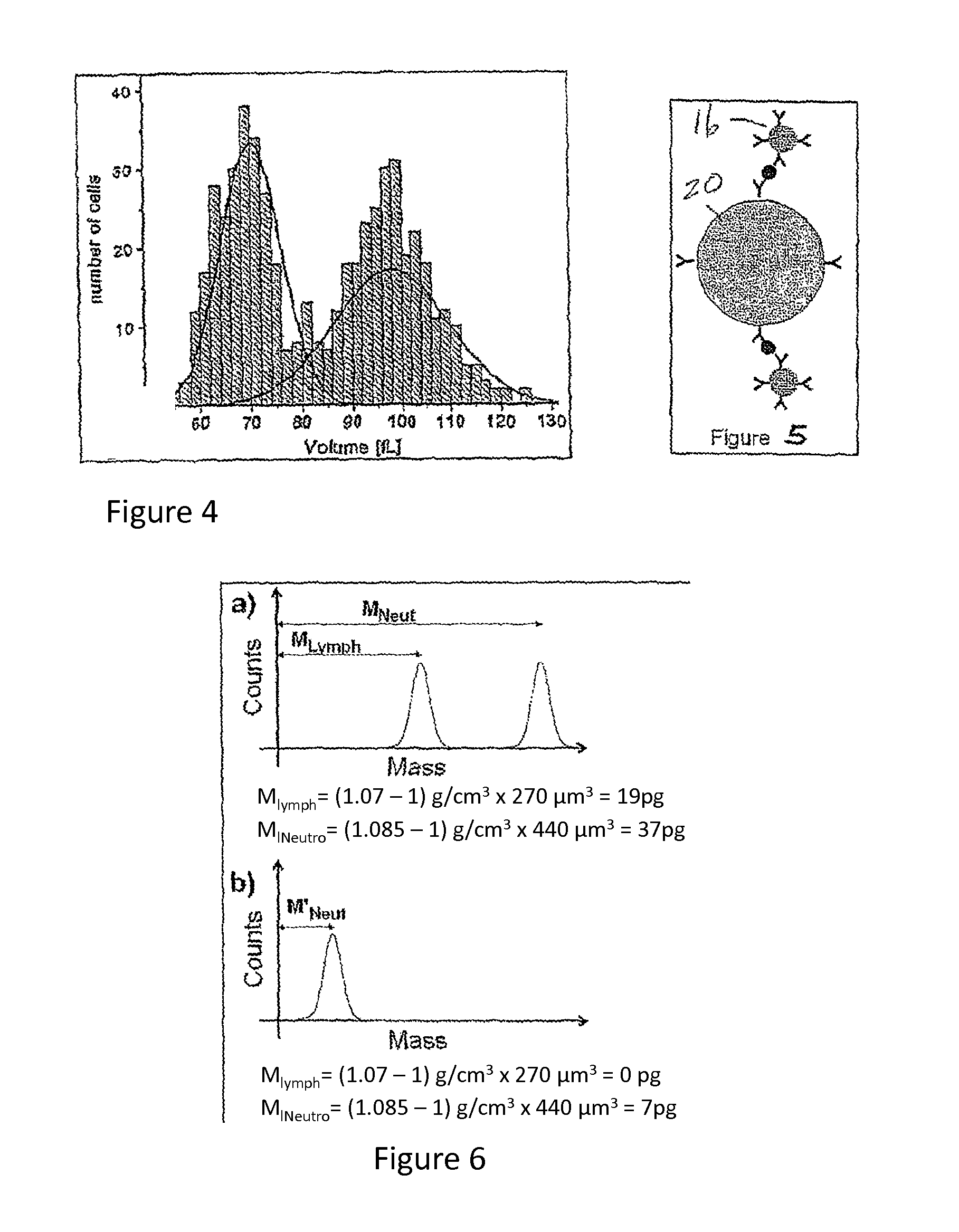
Cell analysis by mass cytometry
ActiveUS9261503B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage CytometryCell based
A combination of mutually exclusive cell-based analytical techniques can be applied to the same group of cells for analysis. The same group of cells can be prepared for analysis by each technique resulting with candidate cells targeted for mass cytometry analysis. This configuration allows for the correlation of the information between each technique to produce a matrix of multi dimension of cellular information with the same group of cells.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
Method for screening biomarker related to degree of fatigue in human body fluid by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveCN109425669AWide applicabilityAvoid missing detectionComponent separationHuman bodyScreening method
The invention relates to a method for screening a biomarker related to the degree of fatigue in human body fluid by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting human body fluid samples in different groups; step 2, pretreating the samples collected in step 1; step 3, detecting the samples pretreated in step 2 by the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; step 4, processing data obtained by detection in step 3 and setting threshold values, and screening out potential biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue; step 5, carrying out metabolic pathway retrieval on the potential biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue screened in step 4 and confirming the structure of the potential biomarker; and step 6, comparing structure-confirmed compounds in different groups in step 5, and confirming the biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue. The screening method is good in universality and high in accuracy and confidence level.
Owner:中国民用航空局民用航空医学中心
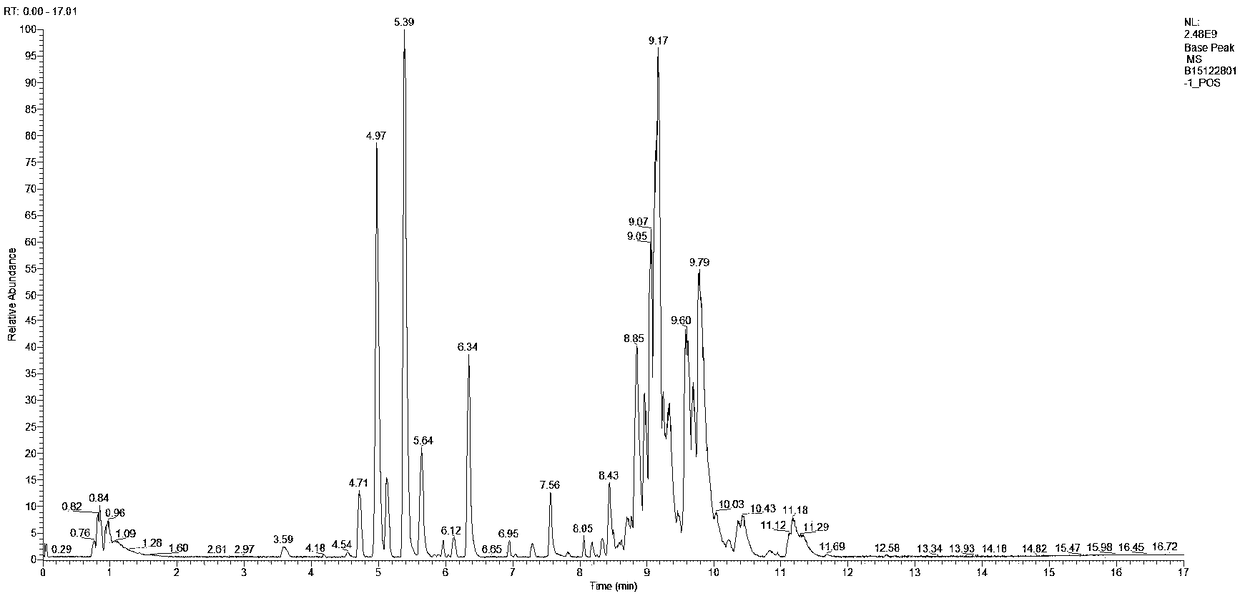
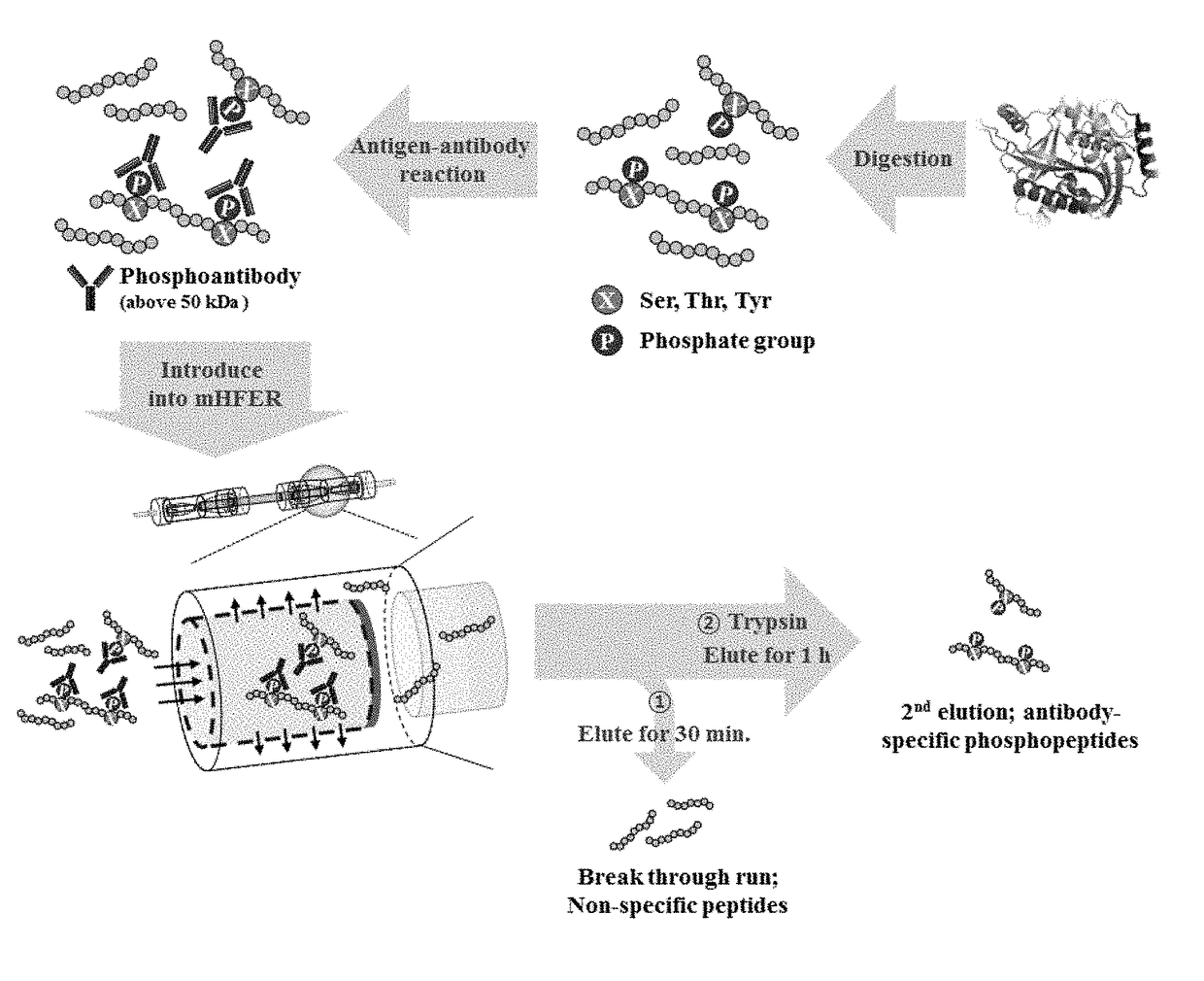
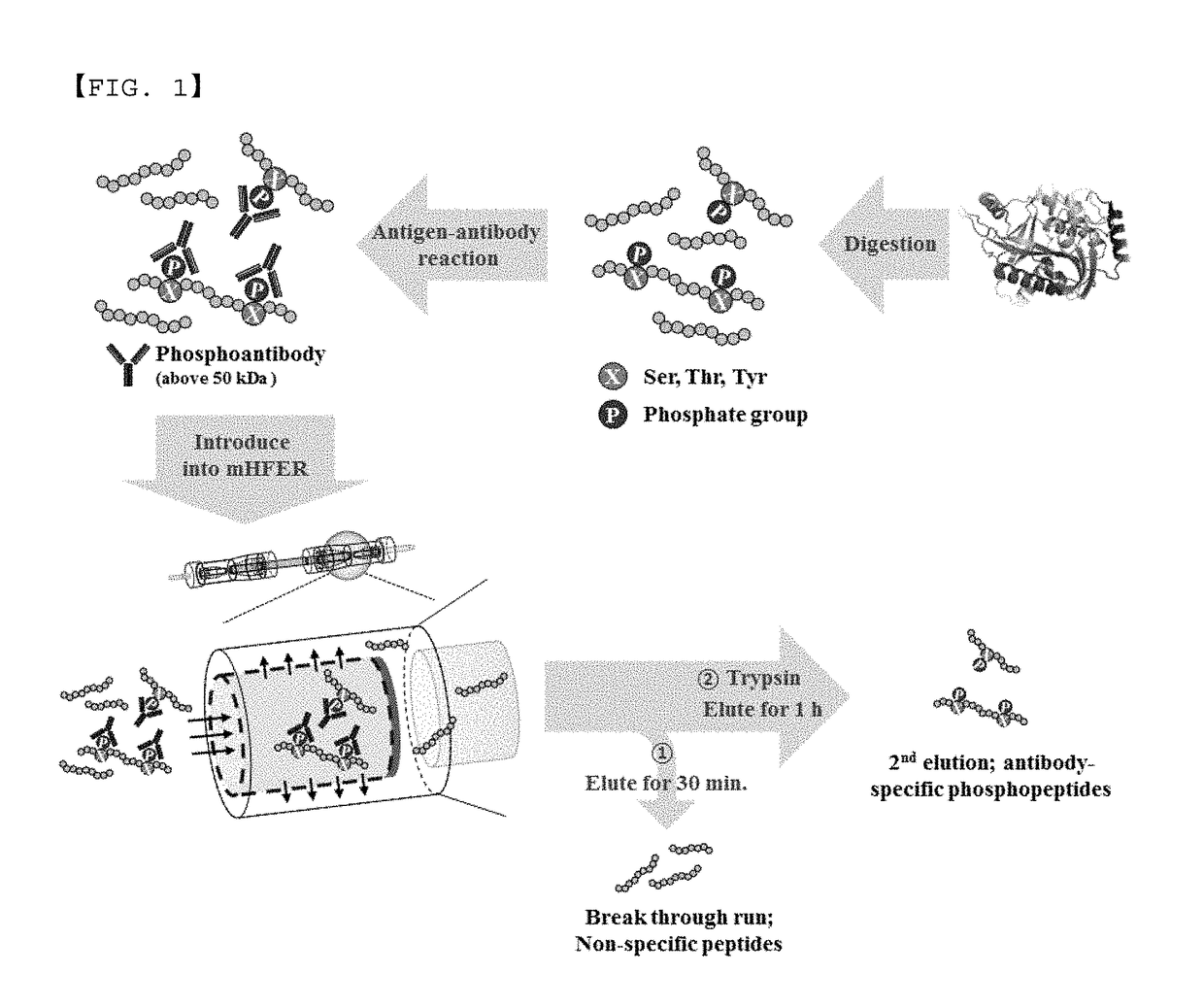
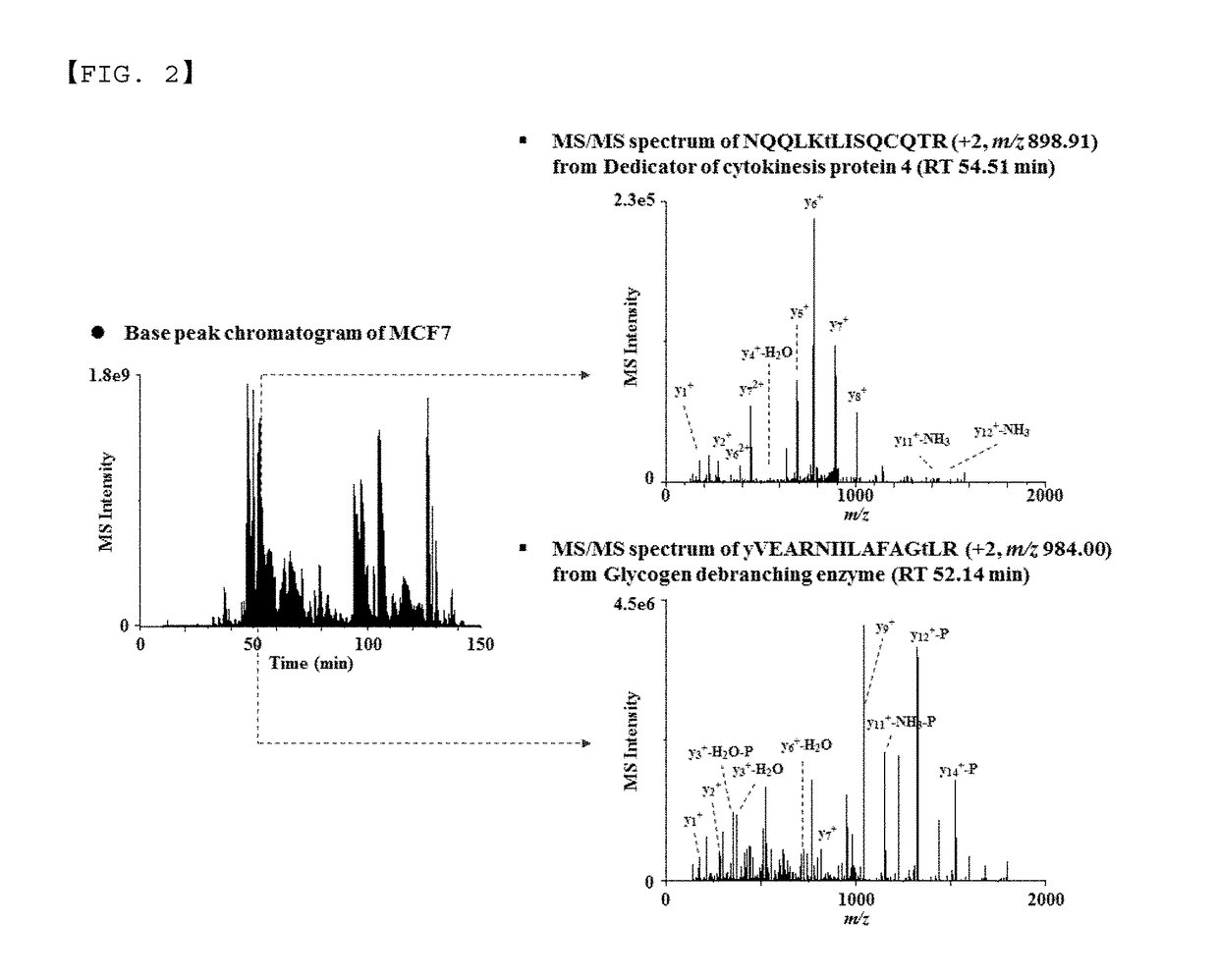
Monoclonal antibody based online phosphoprotein proteomics analysis method using microbore hollow fiber enzymatic reactor-tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20170261513A1Efficient extractionMinimizes problemHydrolasesParticle spectrometer methodsDiseaseProtein markers
A phosphoprotein extraction method and a mass spectrometric method using a microbore hollow fiber enzymatic reactor (mHFER) based antigen-antibody reaction and, specifically, to an extraction method and a mass spectrometric method, wherein phosphoproteins or phosphopeptides present in the body are extracted using phosphoserine-, phosphothreonine-, and phosphotyrosine-antibodies, and measured by a mass spectrometer, and thus biomarker phosphoproteins for diagnosis of diseases are found, contributing to early diagnosis of diseases. The mass spectrometric method using the antigen-antibody reaction based extraction method can: minimize temporal and economic burdens resulting from a low extraction rate and a complicated sample pre-treatment; increase the extraction efficiency by using a considerable number of phosphopeptides (or phosphoproteins) and antibodies with strong affinity; and allow the extraction of low-concentration phosphopeptides or phosphoproteins, and thus is expected to have high applicability in discovering disease diagnosis protein markers and identifying and studying mechanisms thereof.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Protein Expression Profile Database
InactiveUS20100137151A1Library screeningBiological testingSequence databaseProtein expression profile
This invention describes the use of peptide profiling to identify, characterize, and classify biological samples. In complex samples, many thousands of different peptides will be present at varying concentrations. The invention uses liquid chromatography and similar methods to separate peptides, which are then identified and quantified using mass spectrometry. By identification it is meant that the correct sequence of the peptide is established through comparisons with genome sequence databases, since the majority of peptides and proteins are unannotated and have no ascribed name or function. Quantification means an estimate of the absolute or relative abundance of the peptide species using mass spectrometry and related techniques including, but not limited to, pre- or post-experimental stable or unstable isotope incorporation, molecular mass tagging, is differential mass tagging, and amino acid analysis.
Owner:EMILI ANDREW +1
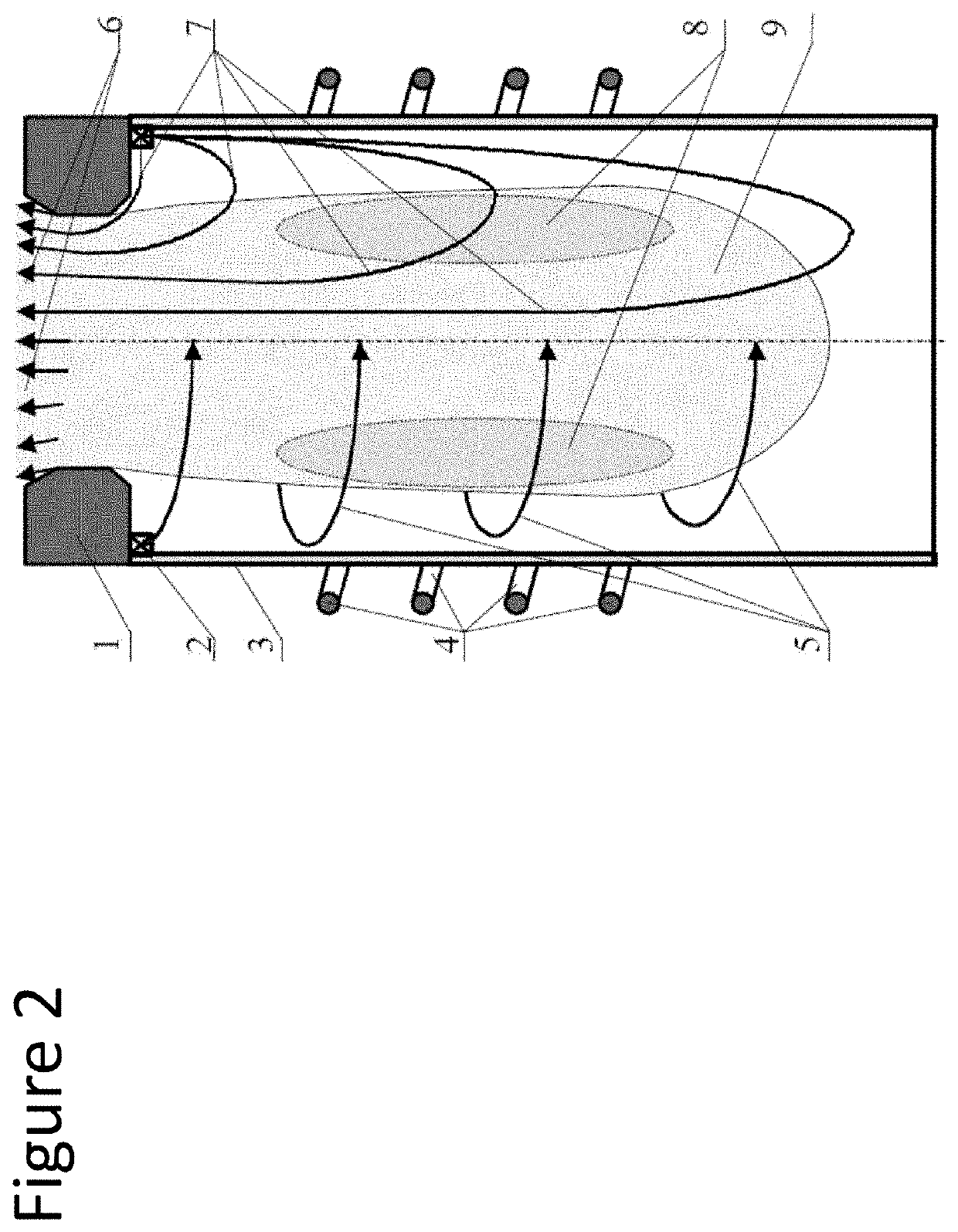
High speed modulation sample imaging apparatus and method
PendingCN112970092ASamples introduction/extractionWithdrawing sample devicesFemto second laserImaging quality
This disclosure relates to systems and methods for high speed modulation sample imaging. Disclosed herein are systems and methods for performing imaging mass cytometry, including analysis of labelling atoms by elemental (e.g., atomic) mass spectrometry. Aspects include a sampling system having, and method of using, a femtosecond (fs) laser and / or laser scanning. Alternatively or in addition, aspects include systems and methods for co-registering other imaging modalities with imaging mass cytometry.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CANADA INC
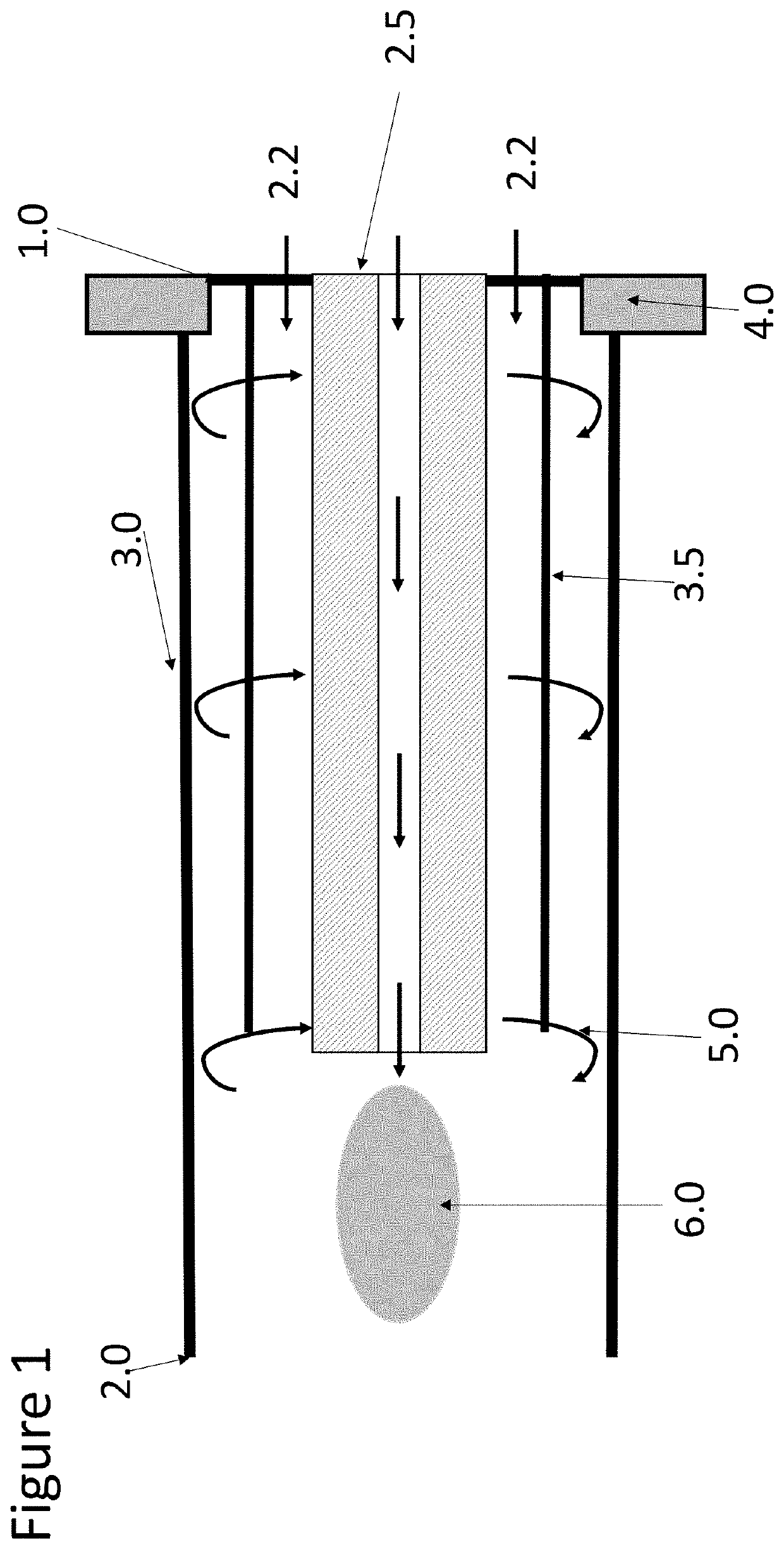
Inductively coupled plasma torch with reverse vortex flow and method of operation
PendingUS20210404968A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce widthAnalysis by electrical excitationIon sources/gunsPhysical chemistryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
We describe in this application the analysis of samples using elemental or mass spectrometry and the analysis of samples, such as biological samples by suspension mass cytometry or imaging mass cytometry and an inductively coupled plasma torch with reverse vortex flow for elemental analysis and a method of operating an ICP torch configured to interface with a spectrometer.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
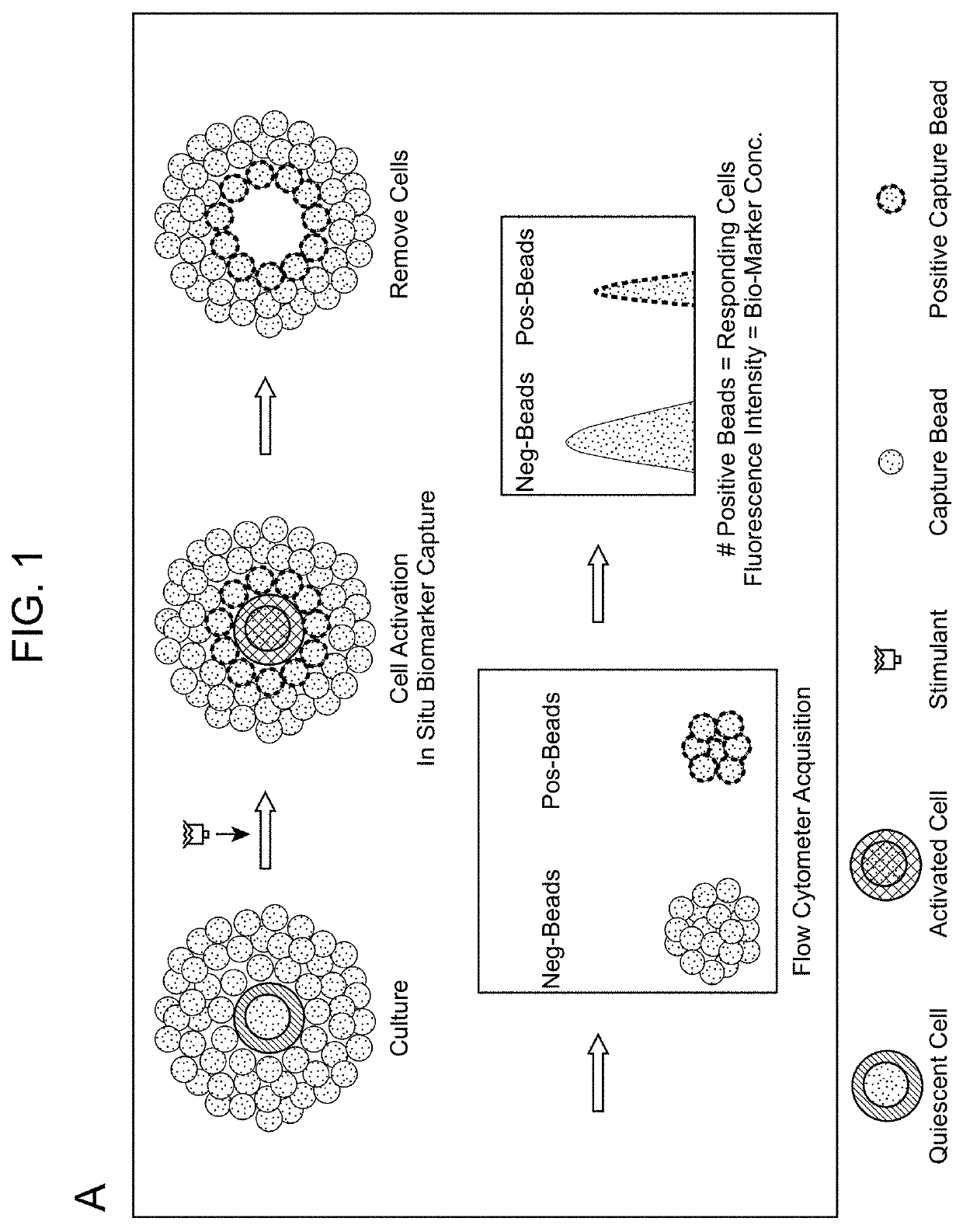
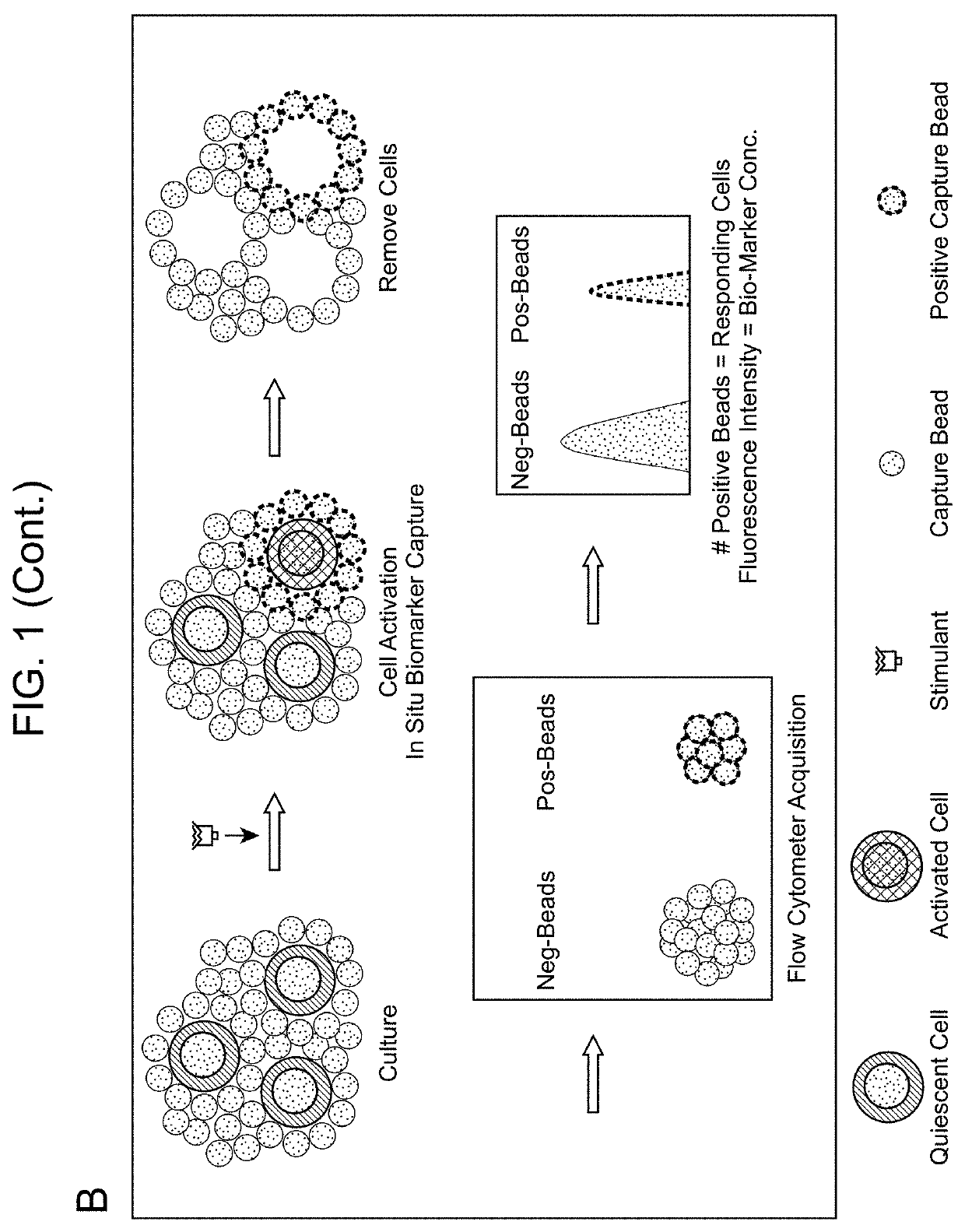
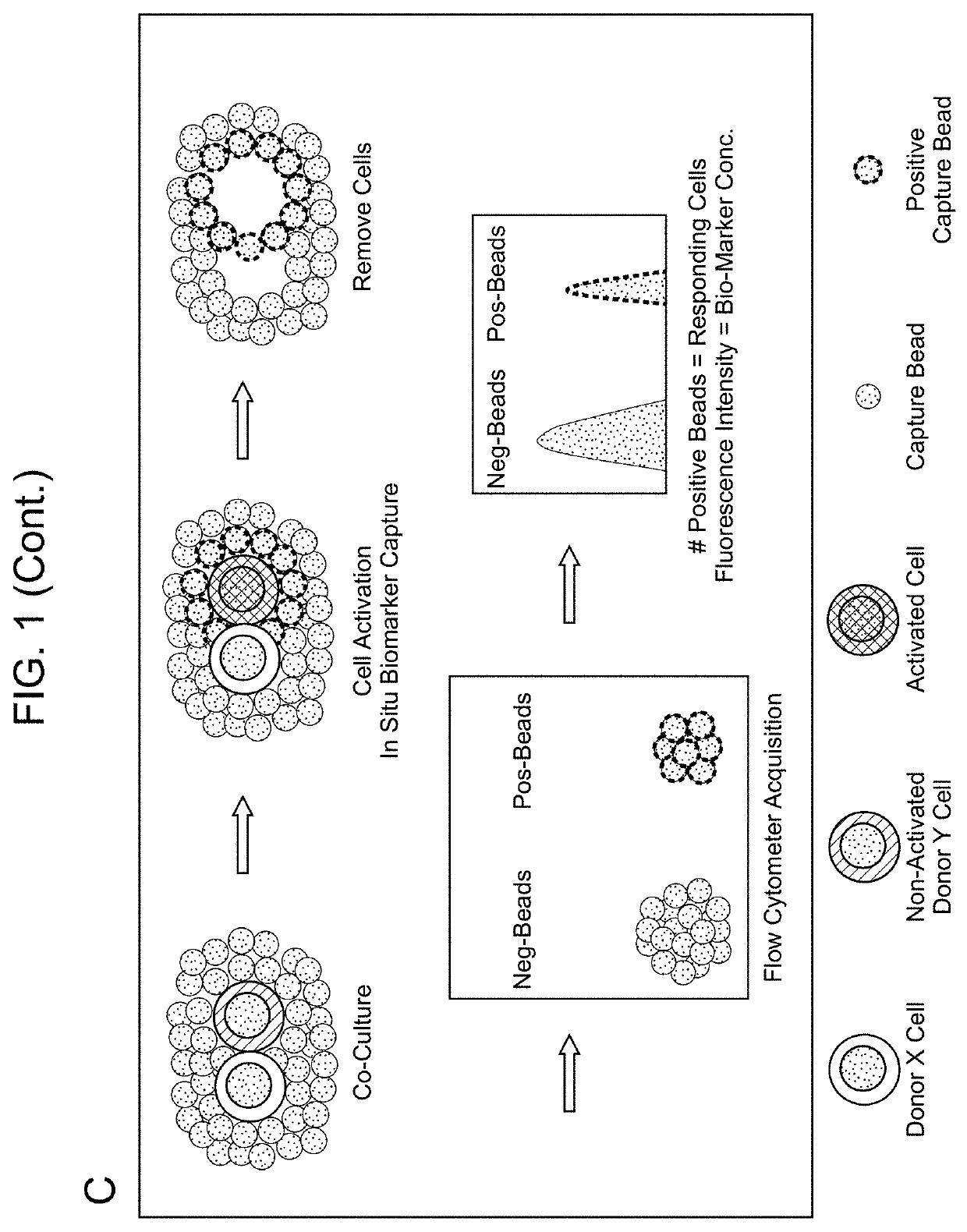
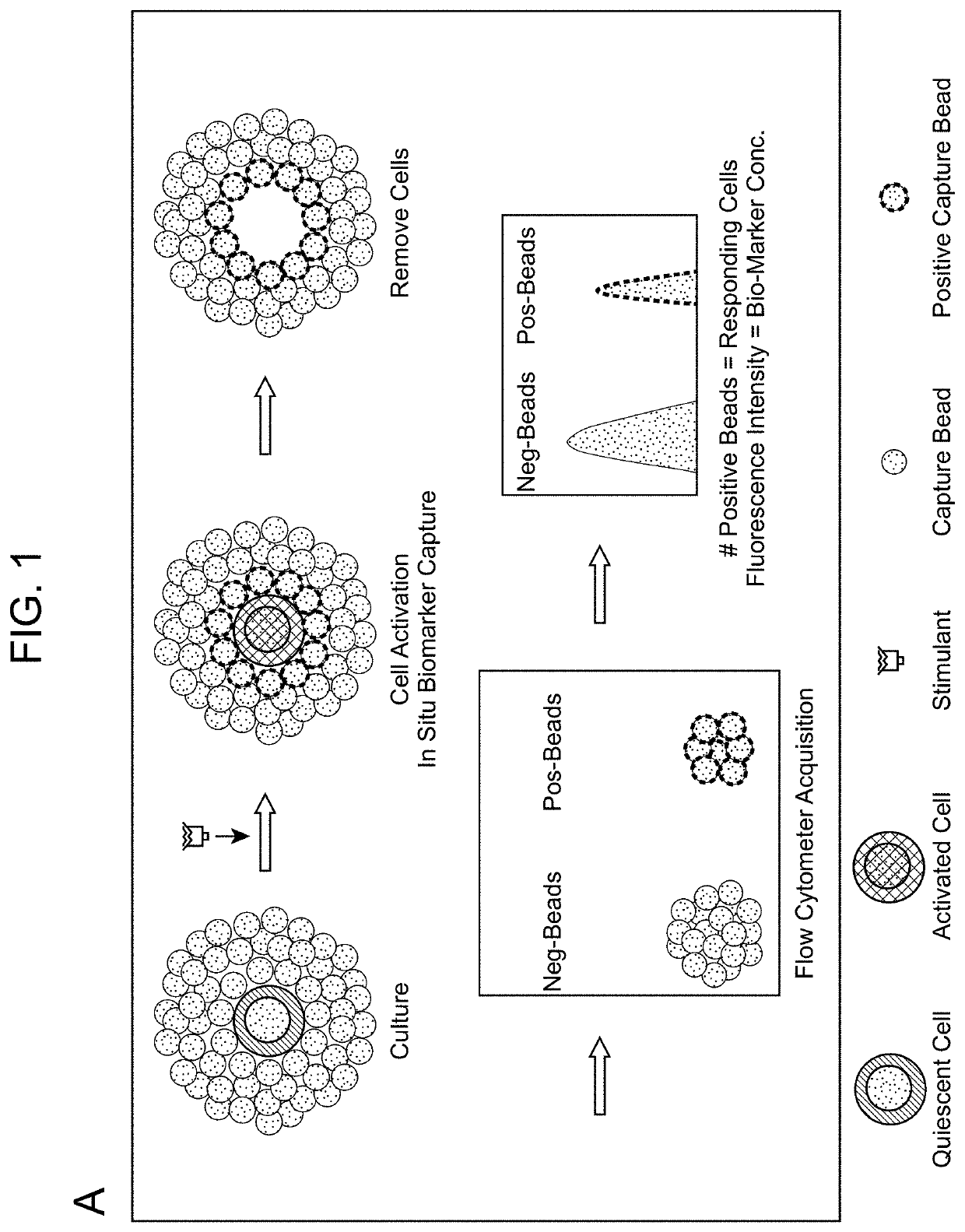
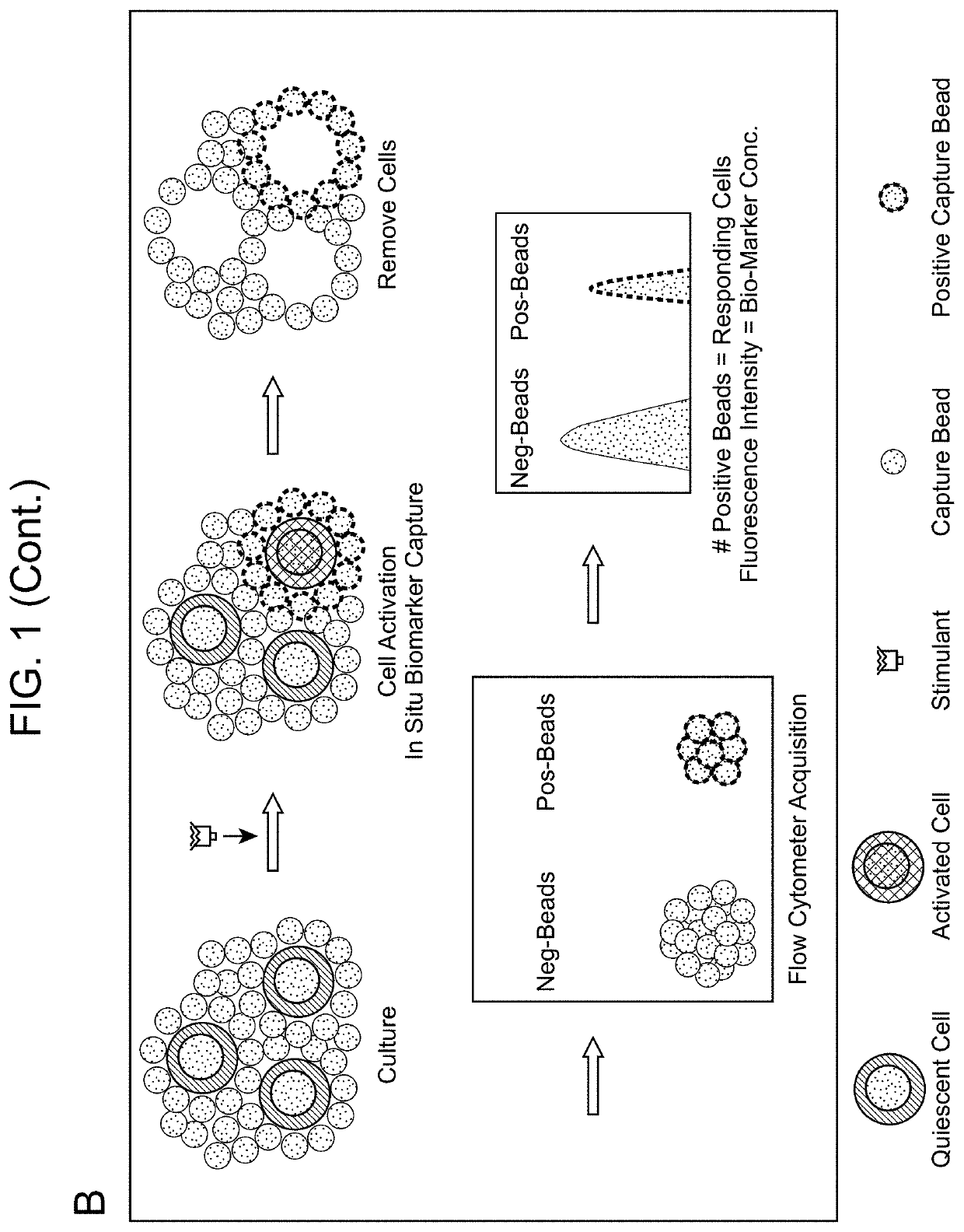
Biomarker Detection Methods and Systems and Kits for Practicing Same
ActiveUS20170131268A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroparticleBiomarker (petroleum)
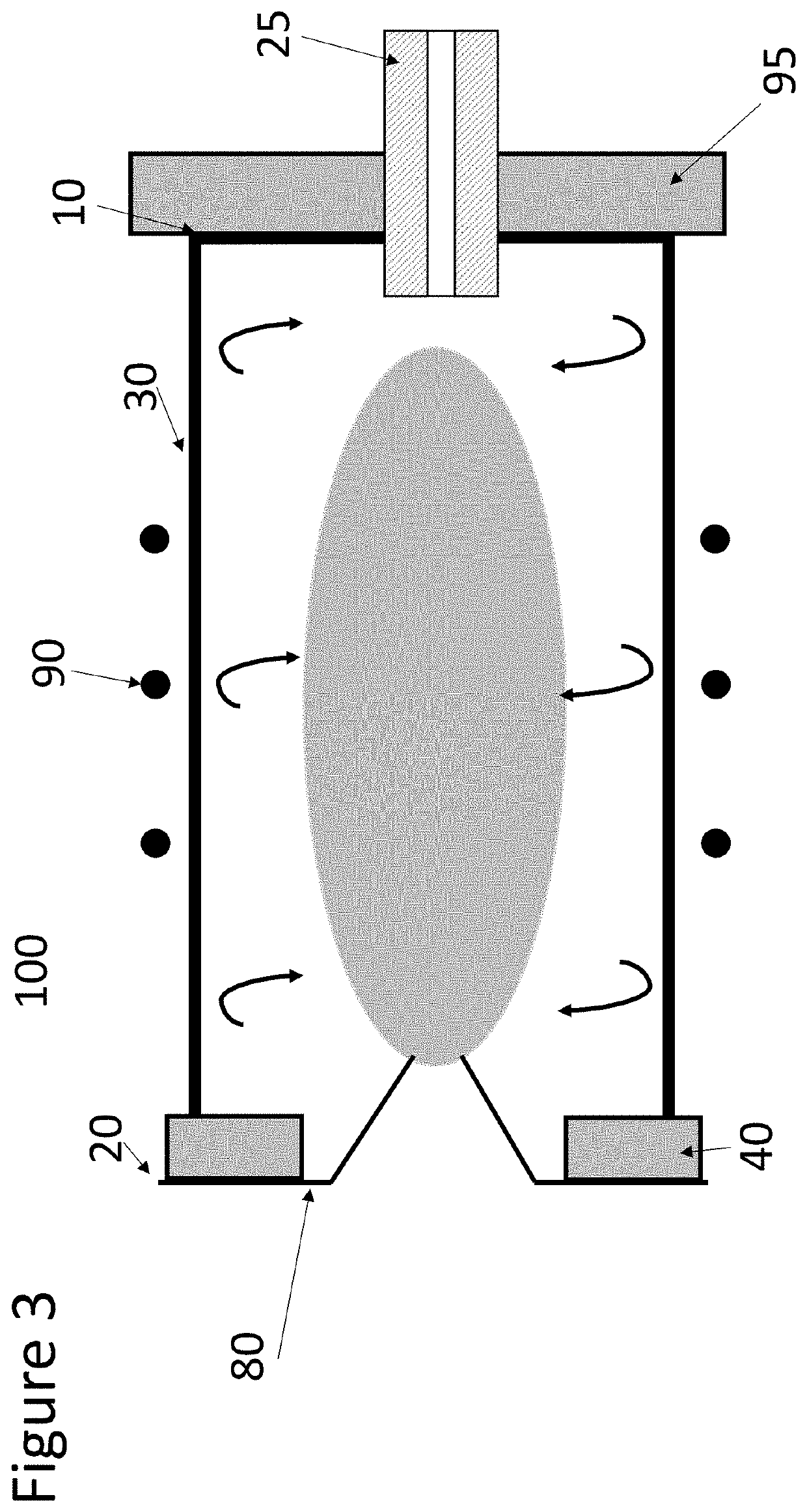
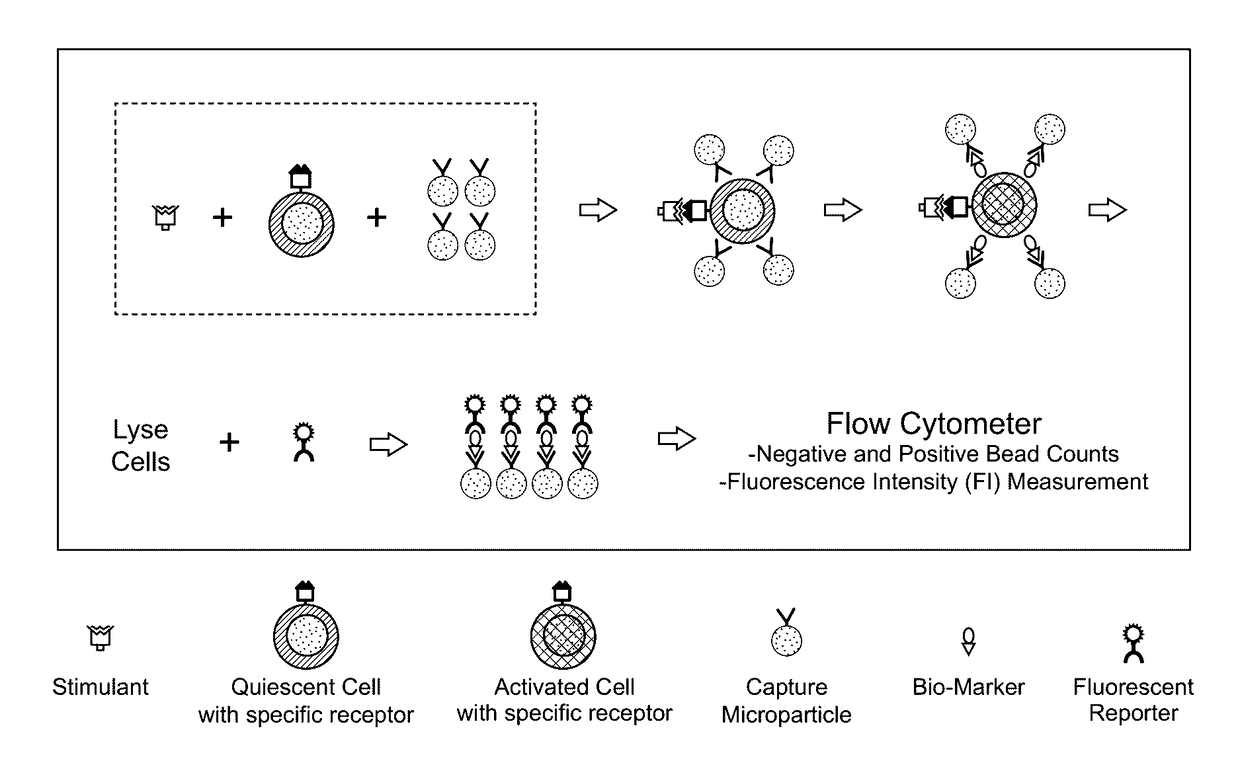
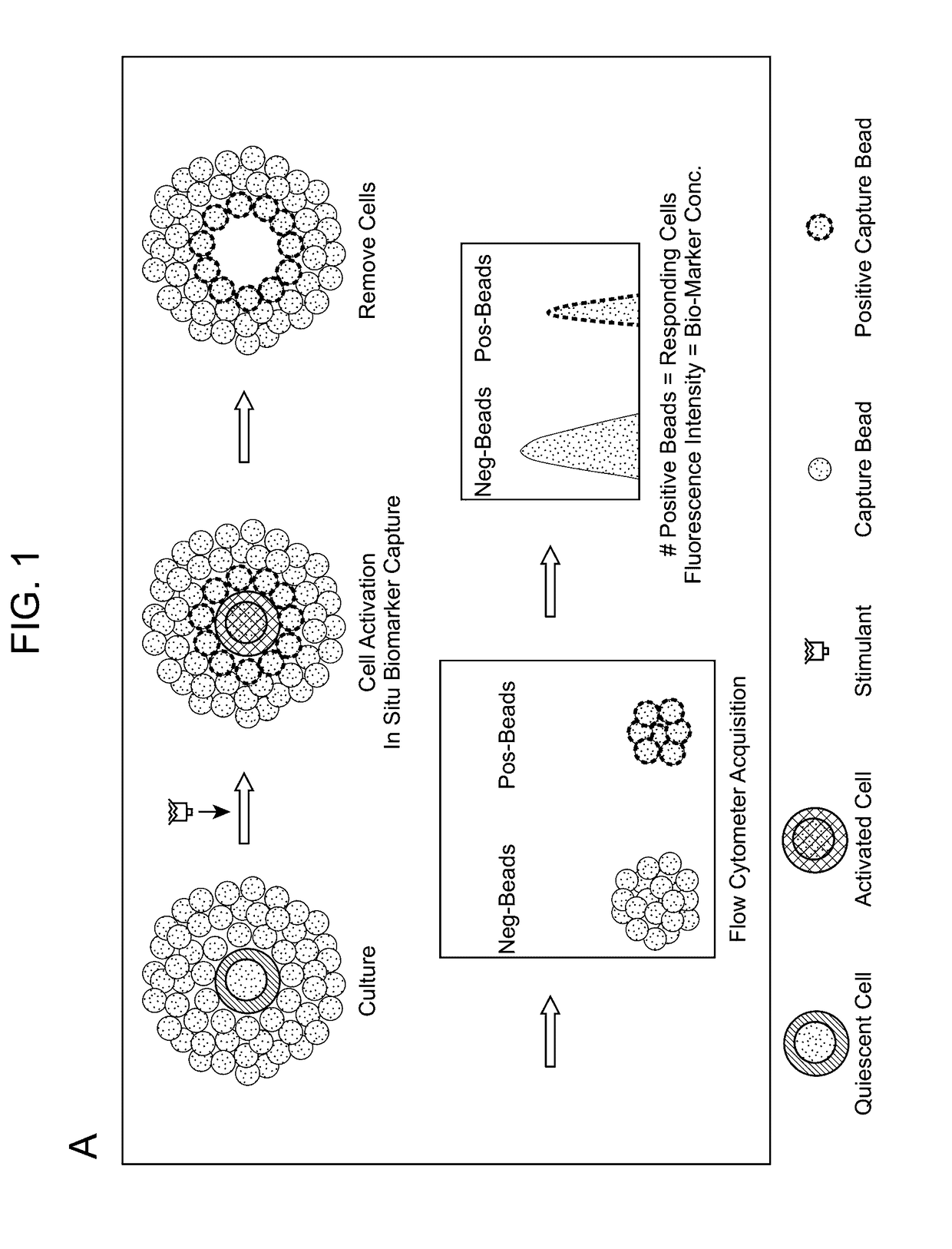
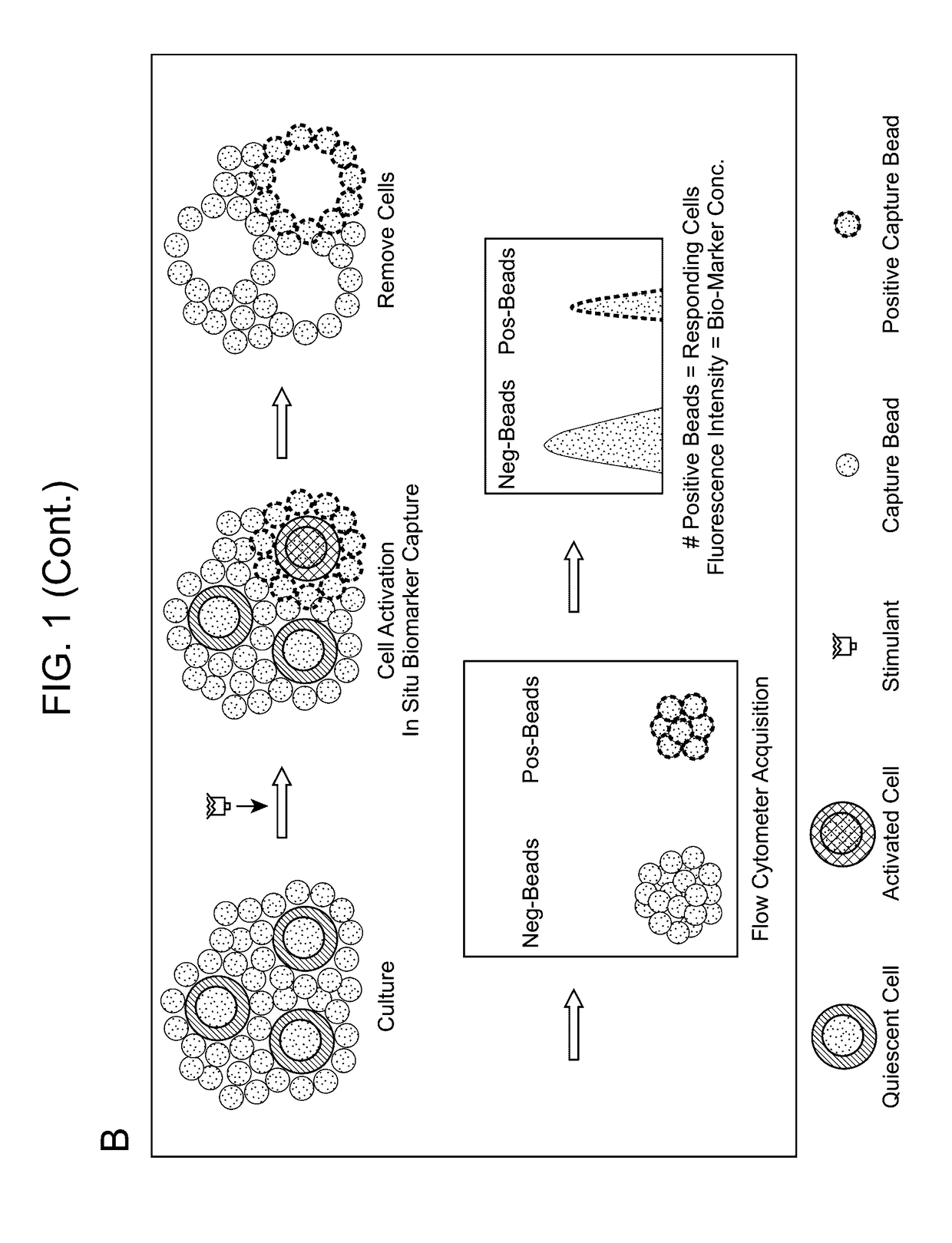
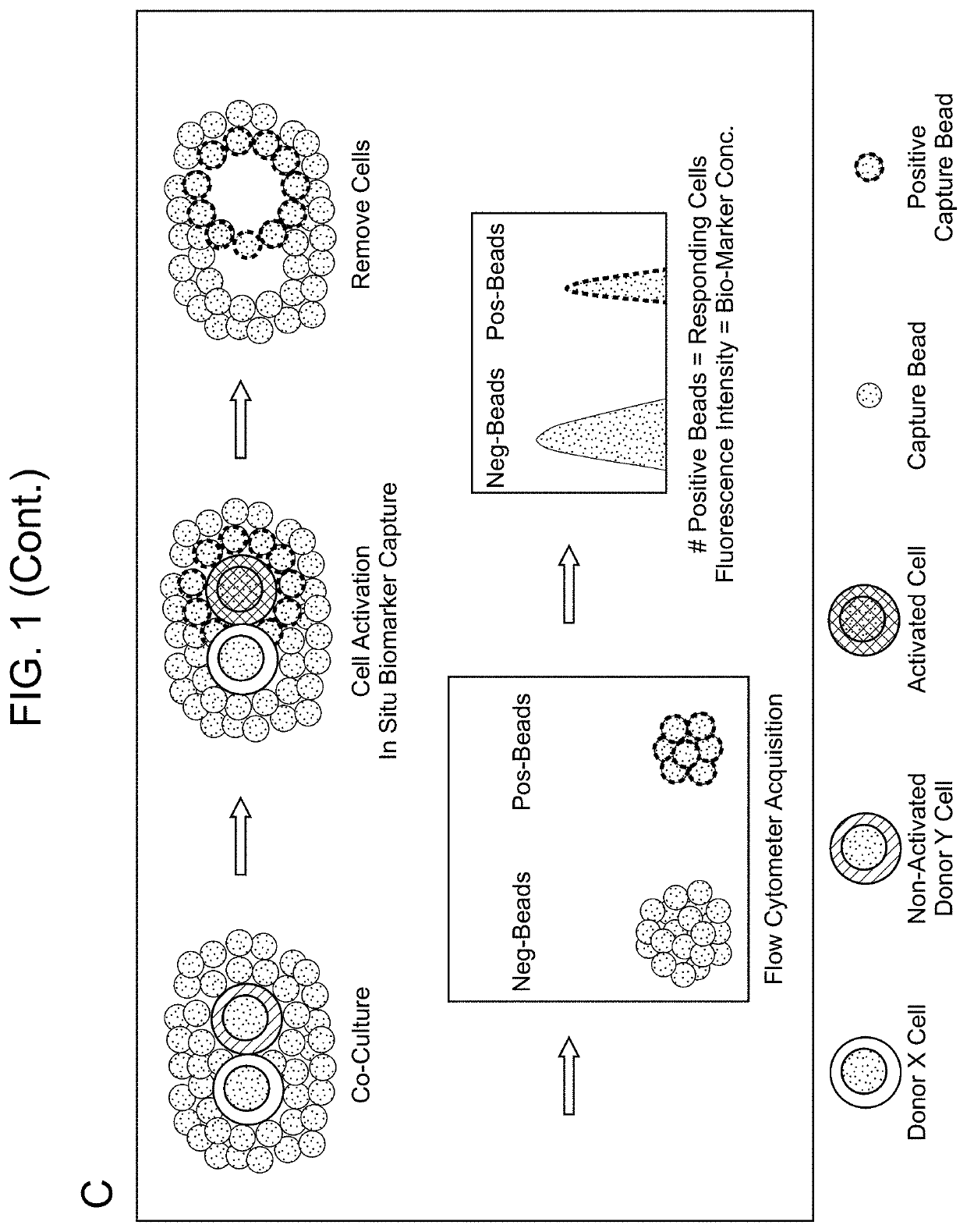
Aspects of the present disclosure include methods that include co-culturing a cell and a microparticle that includes a capture ligand, in a culture medium under conditions in which a biomarker produced by the cell is bound by the capture ligand. Such methods may further include detecting (e.g., by flow or mass cytometry) complexes that include the microparticle, the capture ligand, the biomarker, and a detection reagent. The methods may further include determining the proportion or number of cells among a heterogeneous cell population that produced the biomarker and / or the level of biomarker secreted by such cells. Compositions, systems and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
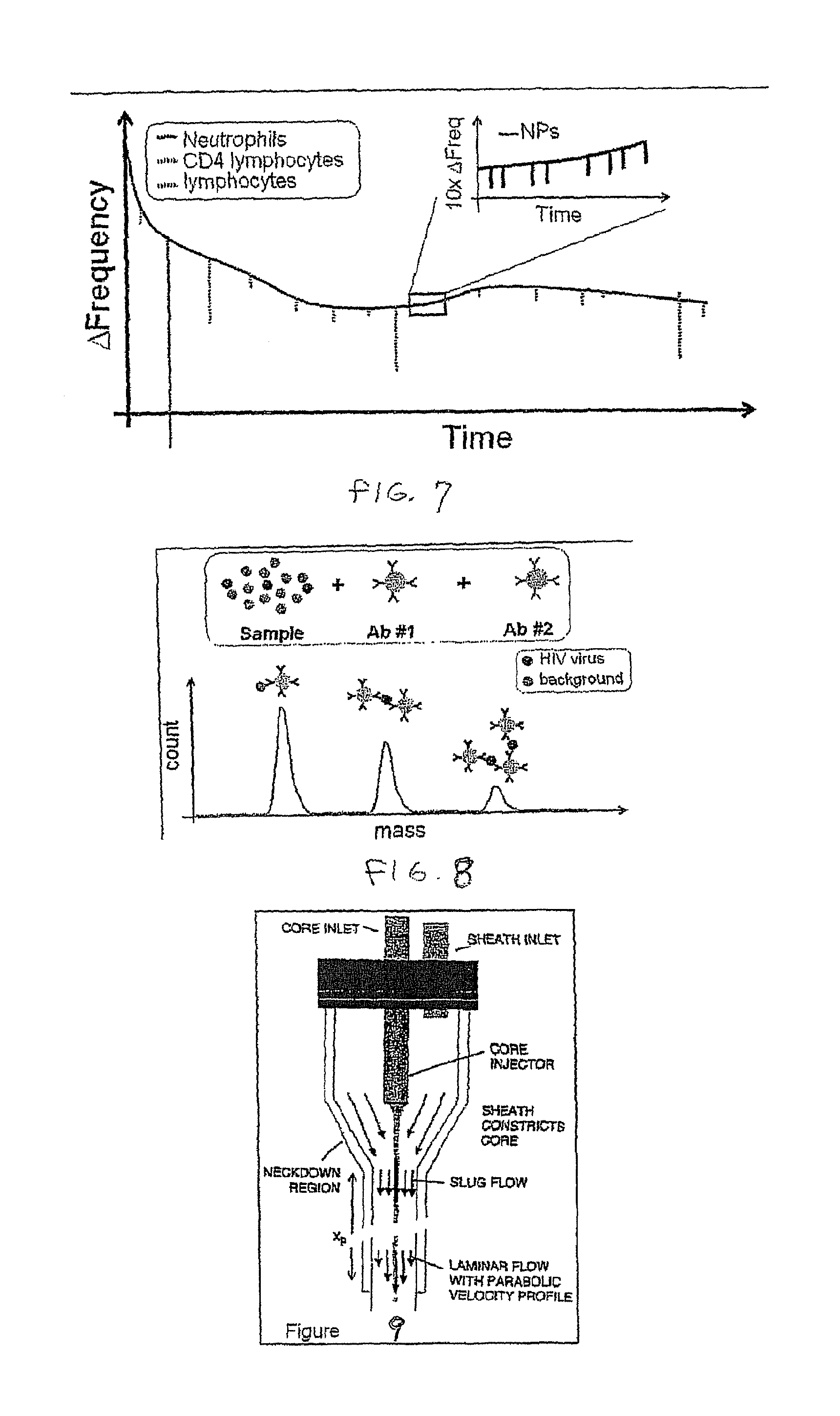
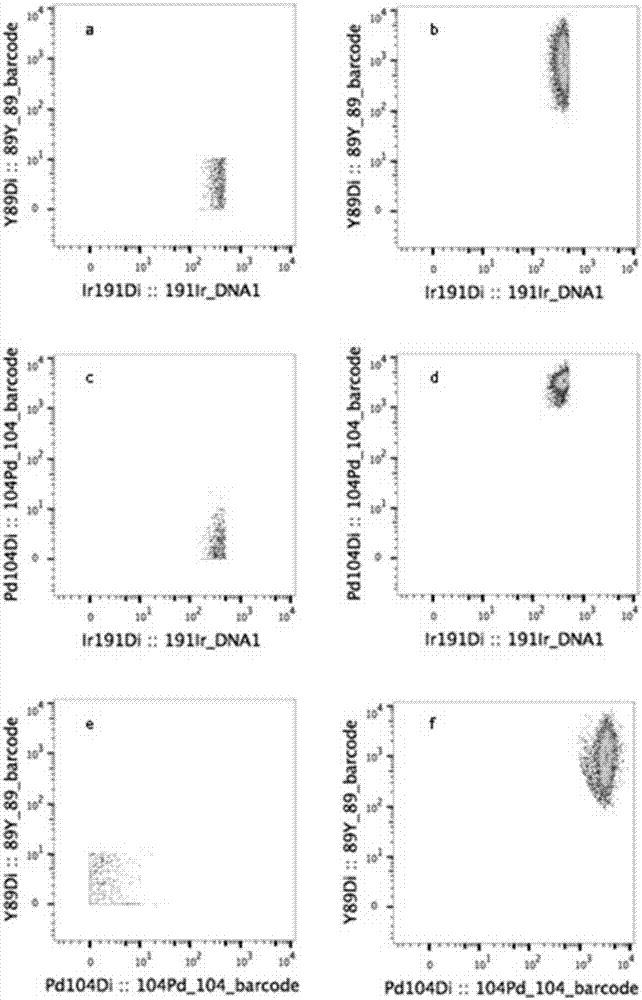
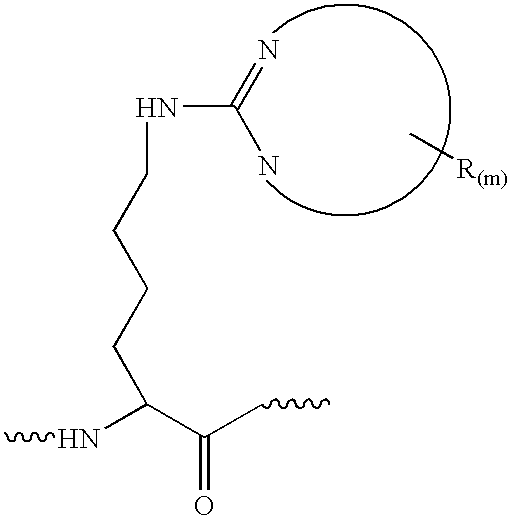
Novel Barcoding 89Y reagent for mass cytometry
InactiveCN107505252AExtended barcoding channelIndividual particle analysisUltrafiltrationCentrifugation
The invention discloses a novel Barcoding 89Y reagent for mass cytometry. The reagent is prepared through the following steps: firstly, adding 39-195 mu L L of buffer to a tube of X8 polymer, blowing and beating the mixture uniformly to fully dissolve the X8 polymer, then adding 1-5 mu L of a 100 mM yttrium (III) chloride hexahydrate solution, and performing uniform stirring and incubation; secondly, transferring all the solution to a 3 kd ultrafiltration tube after incubation, performing centrifugation, removing a supernatant, collecting a liquid in the ultrafilter tube to a centrifugal tube, cleaning the ultrafiltration tube with 40-200 mu L L of buffer, collecting all the liquid in the centrifugal tube, and fully mixing the liquid uniformly to obtain the Barcoding 89Y reagent. Cells can be labeled, and accordingly, screening work of increased flux of flow cytometry can be performed, and the barcoding channel applicable to mass cytometry is extended.
Owner:浙江普罗亭健康科技有限公司
Biomarker detection methods and systems and kits for practicing same
ActiveUS10527613B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiologic markerMicroparticle
Aspects of the present disclosure include methods that include co-culturing a cell and a microparticle that includes a capture ligand, in a culture medium under conditions in which a biomarker produced by the cell is bound by the capture ligand. Such methods may further include detecting (e.g., by flow or mass cytometry) complexes that include the microparticle, the capture ligand, the biomarker, and a detection reagent. The methods may further include determining the proportion or number of cells among a heterogeneous cell population that produced the biomarker and / or the level of biomarker secreted by such cells. Compositions, systems and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
High resolution imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS11264221B2Increase speedSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersHigh resolution imagingImaging quality
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA +1
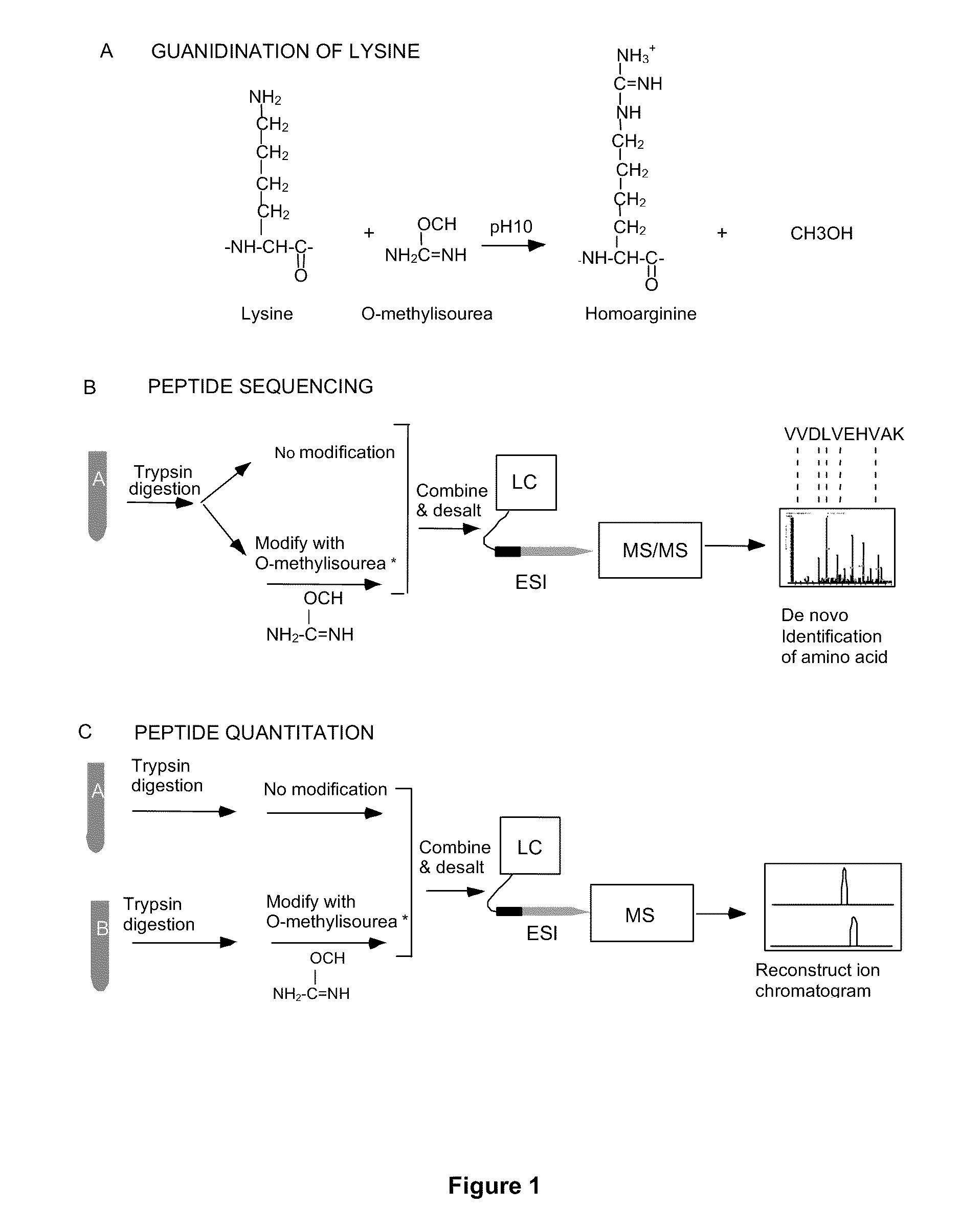
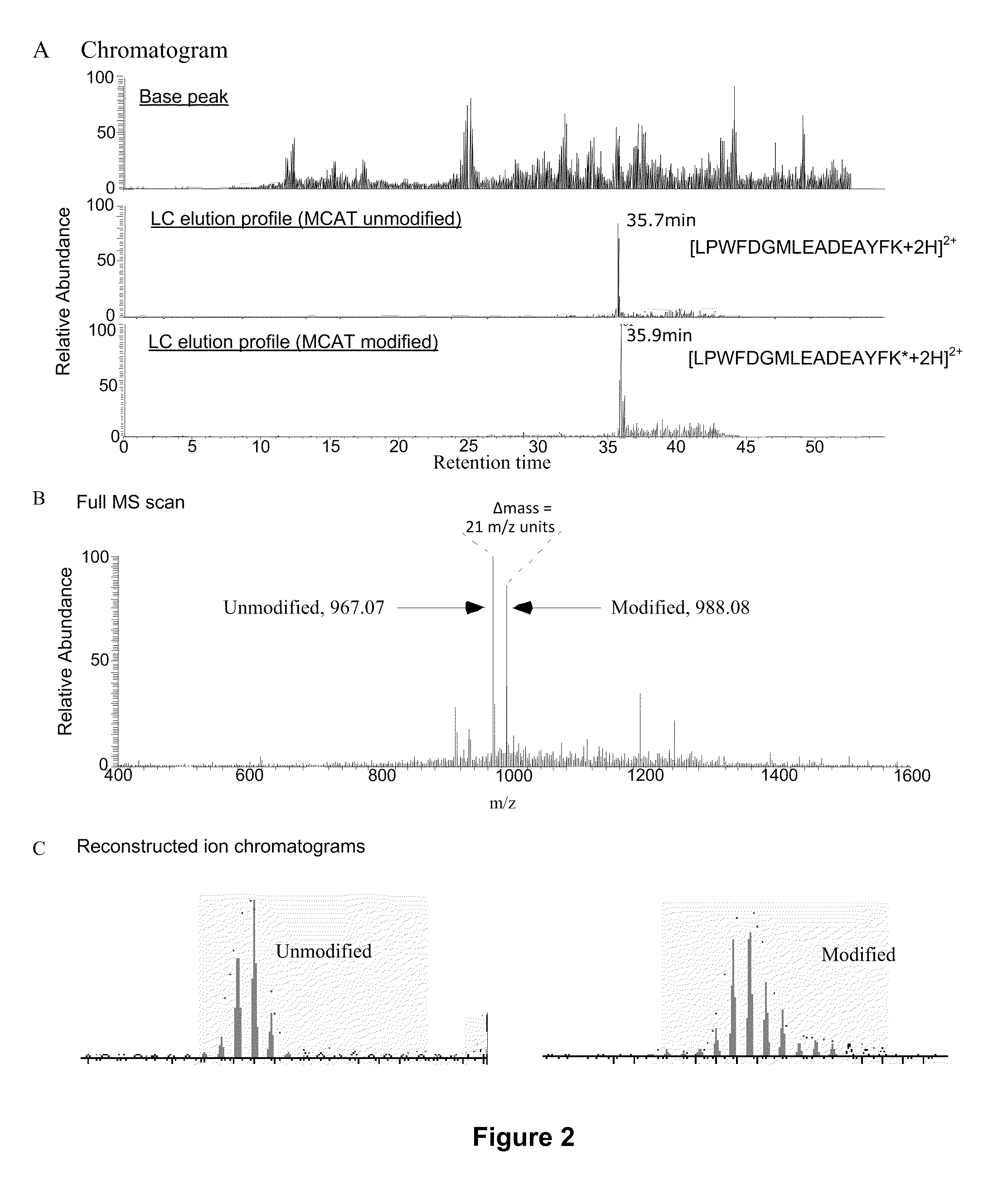
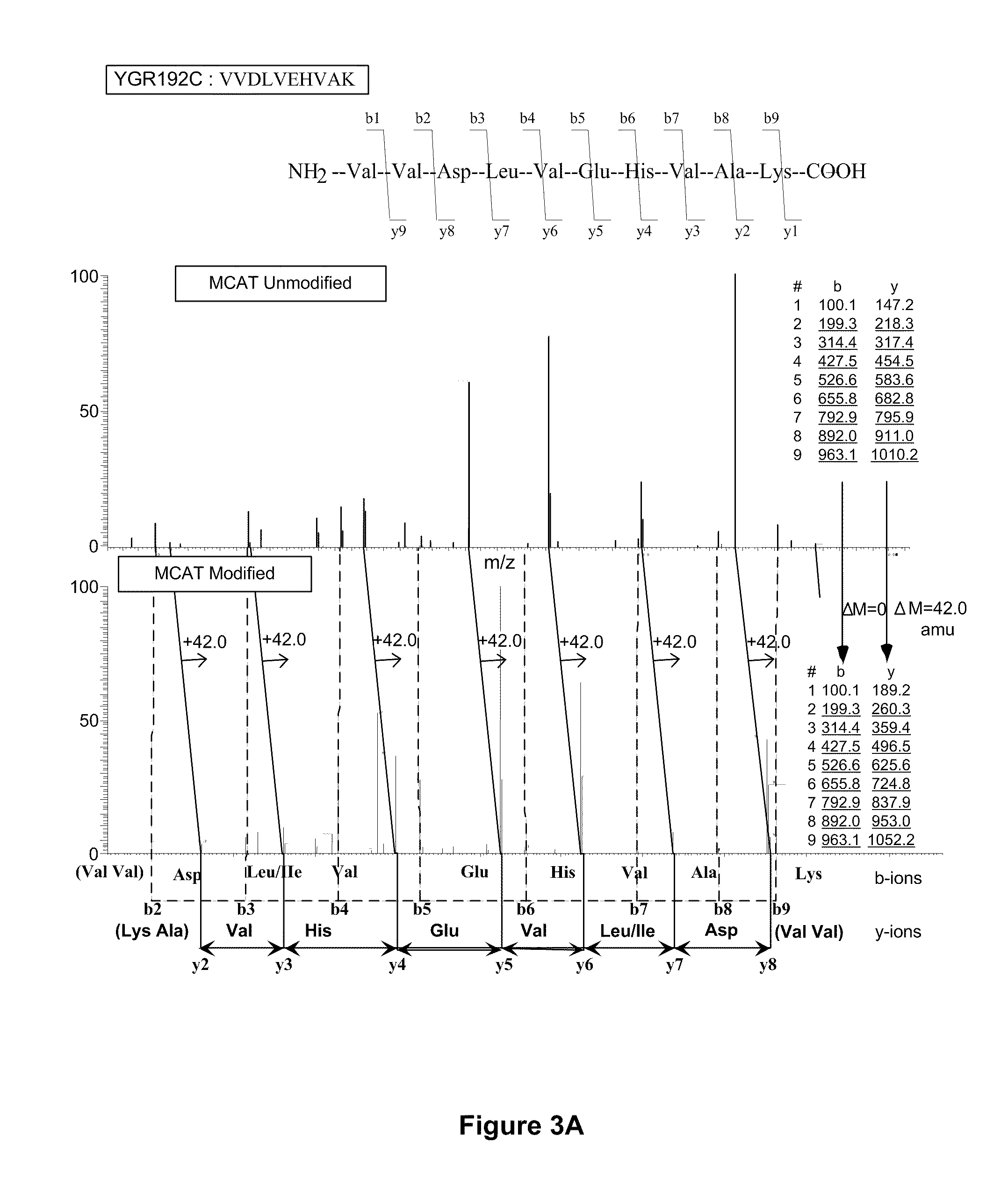
Serial derivatization of peptides for de novo sequencing using tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060014210A1Improve spectral qualityQuality improvementPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reactionAnalyte
Serial derivatization by chemical reactions of analytes for mass spectrometry is disclosed. The derivatizations enhance the use of MS techniques for analyzing protein samples, particularly when the sequence of a polypeptide is determined by tandem MS / MS. Accurate mass analysis techniques are described for use in sequencing polypeptides, together with the use of sequencing data in protein analysis.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Reagents and methods for elemental mass spectrometry of biological samples
PendingUS20210239707A1Increase capacityReduce non-specific adsorption of analytesWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
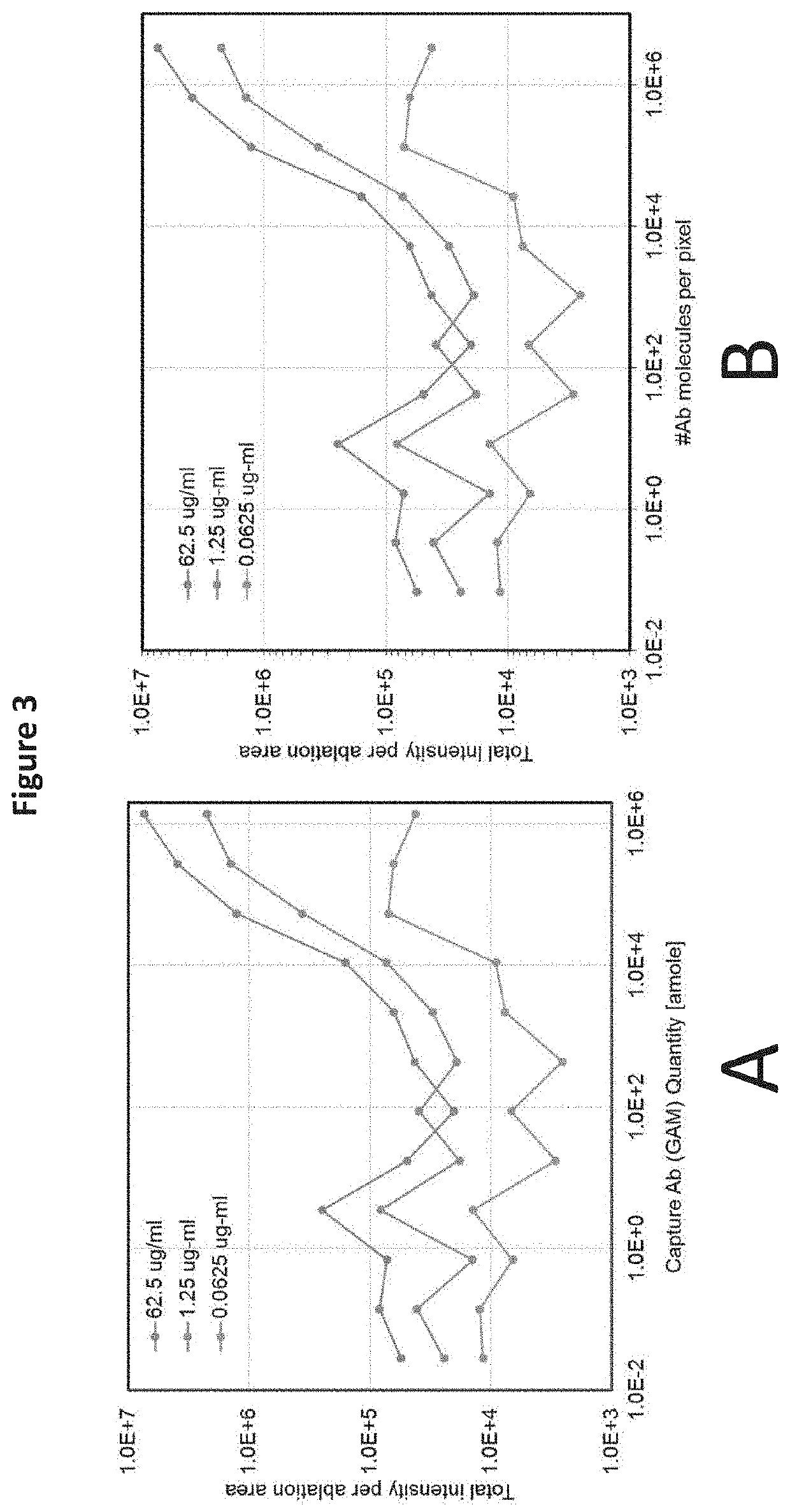
Embodiments of the present invention relate to reagents and their use for elemental imaging mass spectrometry of biological samples. The embodiments comprising methods for quantifying one or more analytes within a sample, comprising the steps of: (a) providing the sample, wherein the one or more analytes are immobilized to a sample carrier, wherein the sample has been labelled with one or more mass tags comprising one or more labelling atoms, (b) performing mass cytometry on the sample to determine the level of the one or more labelling atoms, wherein the level of the one or more labelling atoms corresponds to the copy number of the one or more analytes.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
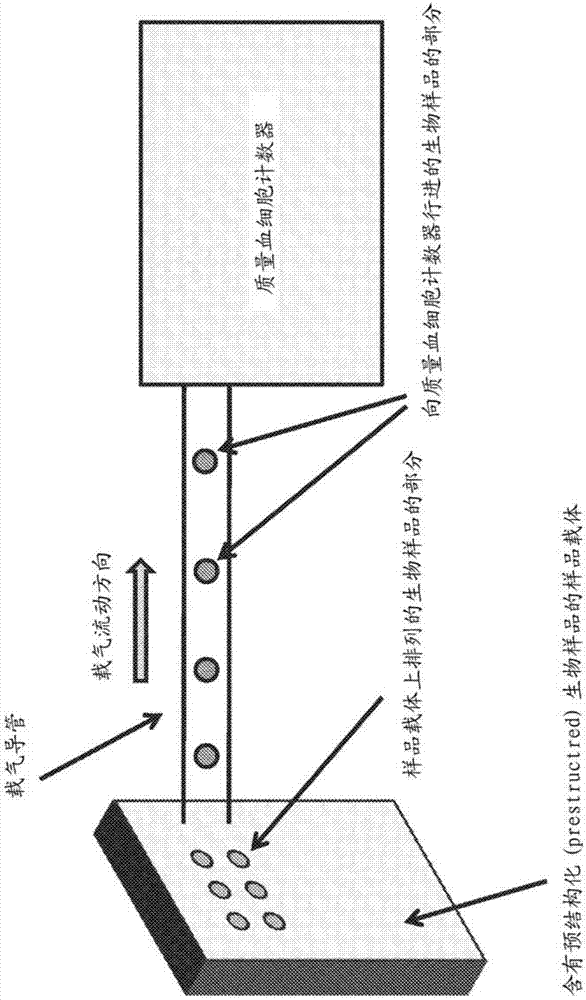
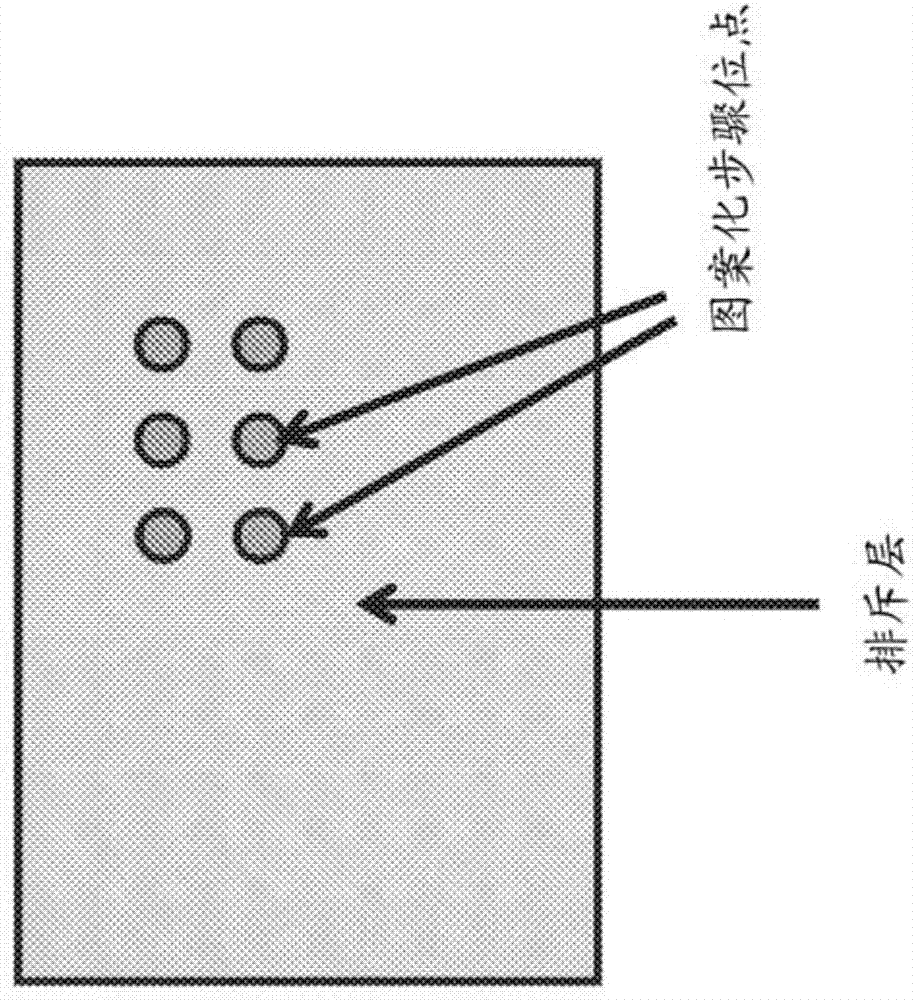
Structured biological samples for analysis by mass cytometry
PendingCN107429214ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMass cytometryBiological materials
Apparatus and methods for delivering biological samples to an ICP source of a mass cytometer are disclosed. Biological material is disposed on a plurality of discrete sites on a carrier. The plurality of discrete sites are configured to retain biological material and to release the biological material upon application of energy. The carrier is positioned in proximity to a gas conduit and upon release from the discrete sites, the biological material becomes entrained in a gas flow, which delivers discrete portions of biological material through the conduit to the ICP source for analysis by mass cytometry. The apparatus and methods can provide a continuous stream of discrete portions of biological material to a mass cytometer.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CANADA INC
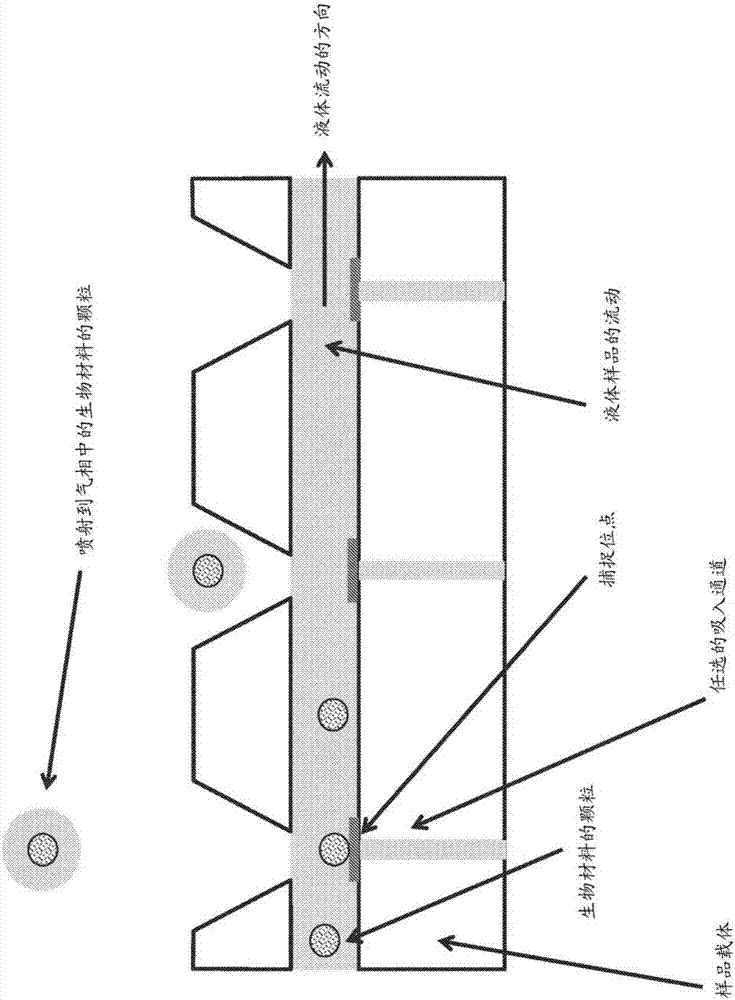
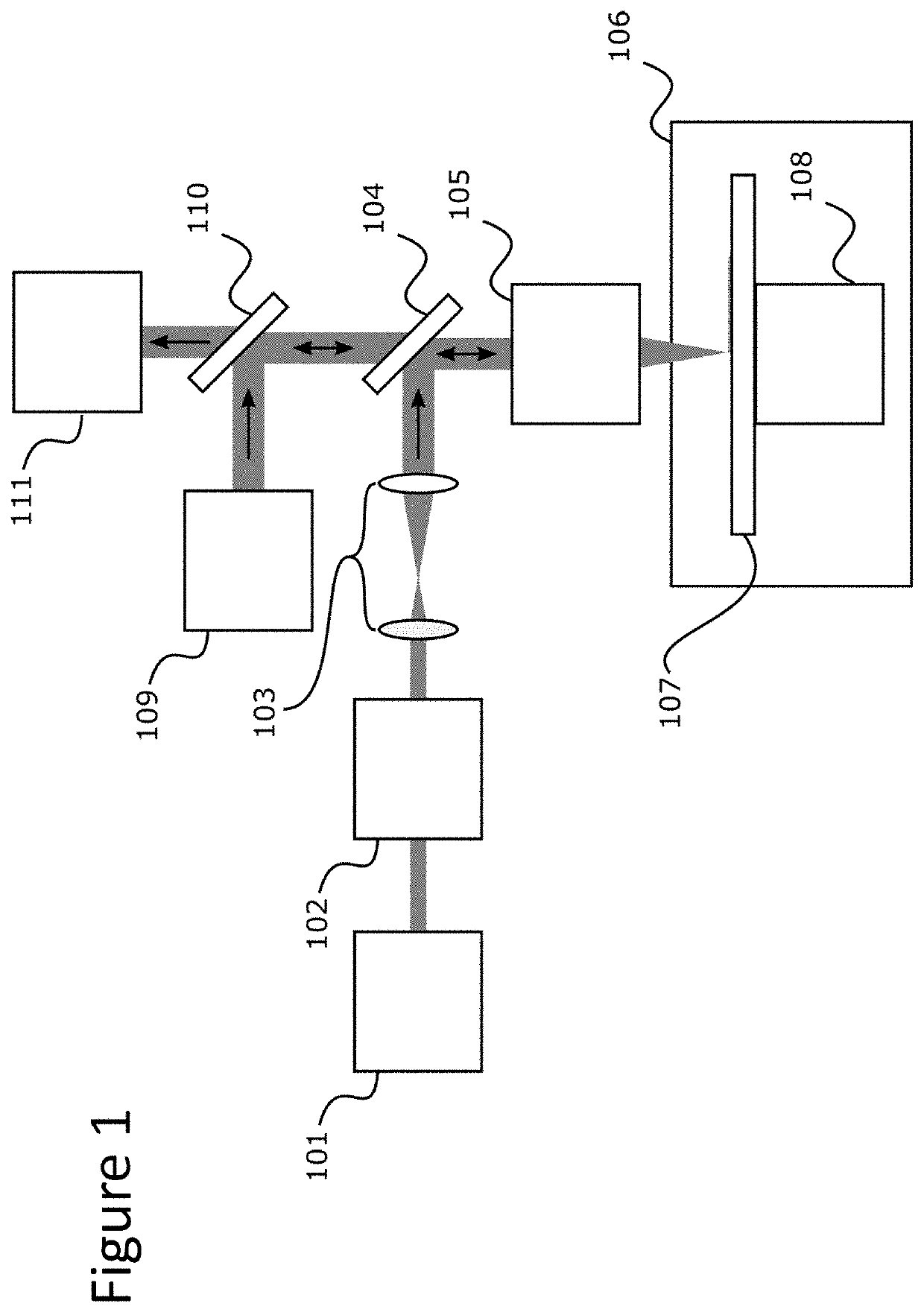
Laser ablation system
ActiveUS10622199B2Minimize timeSamples introduction/extractionWithdrawing sample devicesMedicineExAblate
The invention relates to methods and devices for analysis of samples using laser ablation imaging mass cytometry and mass spectrometry. The invention provides methods and devices in which individual ablation plumes are distinctively captured and rapidly transferred to the ionization system, followed by analysis by mass spectrometry. A transfer conduit can be used to convey ablation plumes to an ionization system. The transfer conduit can include an asymmetric cone. The transfer conduit can be tapered. A flow sacrificing system can be adapted to divert a part of the sheath flow out a sacrificial outlet while the core of the sheath flow containing ablation plumes enters the ionization system.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC
Mass spectrometric determination of blood enzyme activity
ActiveUS8142996B2Avoid reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseMass spectrometry measurement
The invention relates to the determination of the nature and strength of enzymatic activity in blood using mass spectrometric measurement of a profile of the reaction products. The determination of the enzymatic activity can be used for medical diagnostics, for example, and also to check the effectiveness of medication. The invention provides a method whereby adding probe substances usually not present in blood offers standardized substrates for measuring the enzymatic activity. The probe substances may be added to whole blood, plasma, or serum. The mass spectrometric measurement of the reaction products, after their reversible immobilization on actively binding surfaces of solids, for example, can deliver biomarker patterns of the reaction products which may be indicators for metabolic anomalies or diseases, since these are often accompanied by the formation or activation of characteristic enzymes.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
High resolution imaging apparatus and method
PendingUS20220223398A1Increase speedTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsHigh resolution imagingMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention relates to the high resolution imaging of samples using imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) and to the imaging of biological samples by imaging mass cytometry (IMC™) in which labelling atoms are detected by IMS. LA-ICP-MS (a form of IMS in which the sample is ablated by a laser, the ablated material is then ionised in an inductively coupled plasma before the ions are detected by mass spectrometry) has been used for analysis of various substances, such as mineral analysis of geological samples, analysis of archaeological samples, and imaging of biological substances. However, traditional LA-ICP-MS systems and methods may not provide high resolution. Described herein are methods and systems for high resolution IMS and IMC.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS CANADA INC +1
Biomarker Detection Methods and Systems and Kits for Practicing Same
ActiveUS20200333335A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiologic markerMicroparticle
Aspects of the present disclosure include methods that include co-culturing a cell and a microparticle that includes a capture ligand, in a culture medium under conditions in which a biomarker produced by the cell is bound by the capture ligand. Such methods may further include detecting (e.g., by flow or mass cytometry) complexes that include the microparticle, the capture ligand, the biomarker, and a detection reagent. The methods may further include determining the proportion or number of cells among a heterogeneous cell population that produced the biomarker and / or the level of biomarker secreted by such cells. Compositions, systems and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
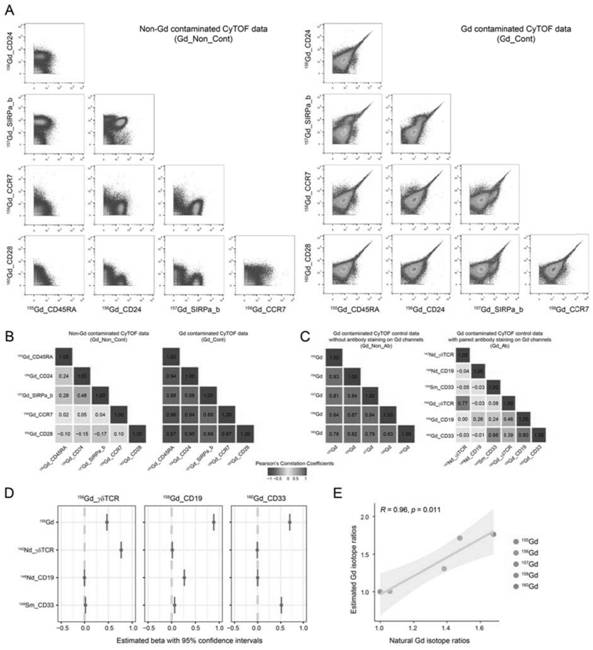
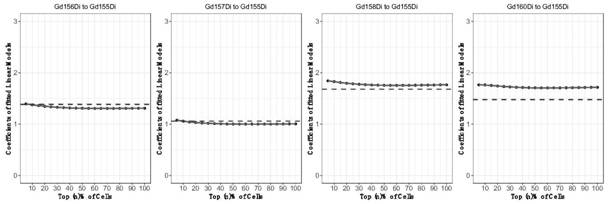
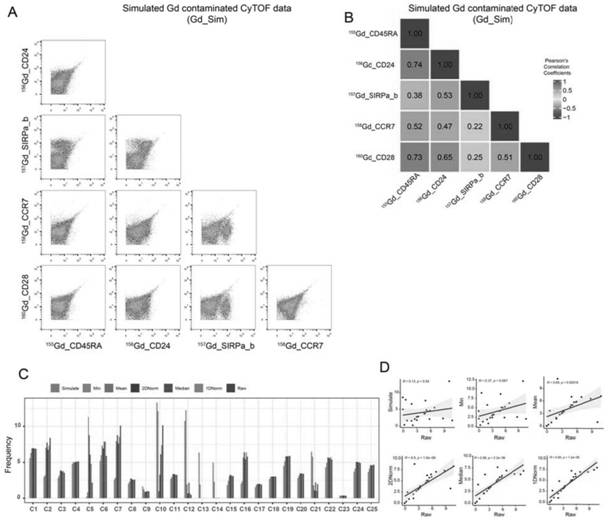
A Method for Removing Gadolinium Isotope Channel Contamination in Mass Cytometry Data
ActiveCN113588524BQuality improvementPrevent deviationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGadolinium isotopePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for removing gadolinium isotope channel pollution in mass spectrometry data. By using the gadolinium isotope channel ( 155 Gd~ 158 Gd, 160 Gd) Contamination signals have collinear characteristics, and under the condition that pre-designed gadolinium isotope-coupled antibody-specific labeled biomarkers cannot be co-expressed on a single cell at the same time, calculate the estimation of contamination signal of a single cell in the gadolinium isotope channel value, and obtain data corrected to remove gadolinium isotope channel contamination. The present invention provides a method for estimating and removing the pollution signal of the gadolinium isotope channel in the mass spectrometry flow data, which avoids the deviation caused by the artificial change of the cell components of the tested sample brought about by directly removing the polluted cells, It has important application value for improving the quality of mass spectrometry flow detection data and subsequent data analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com