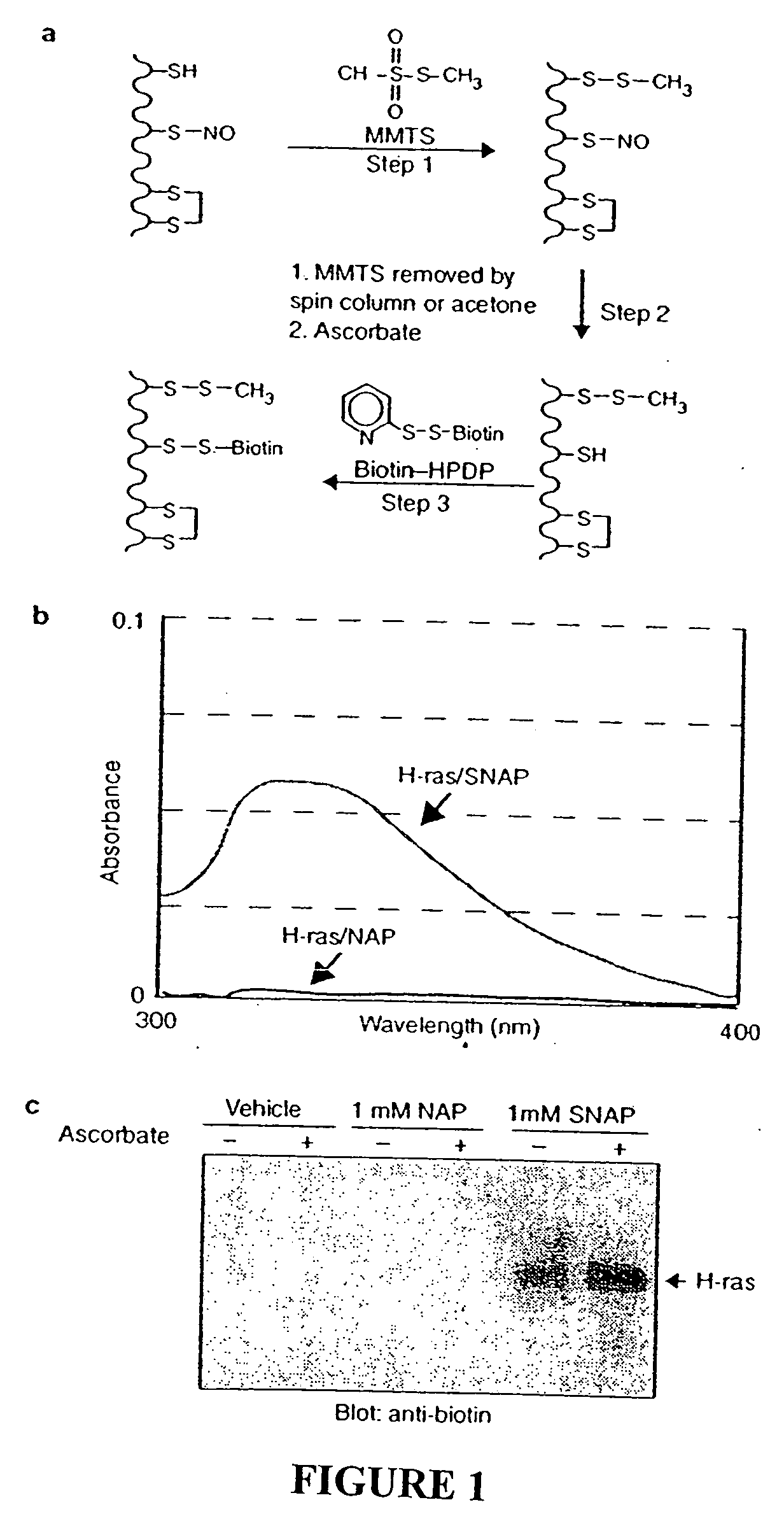
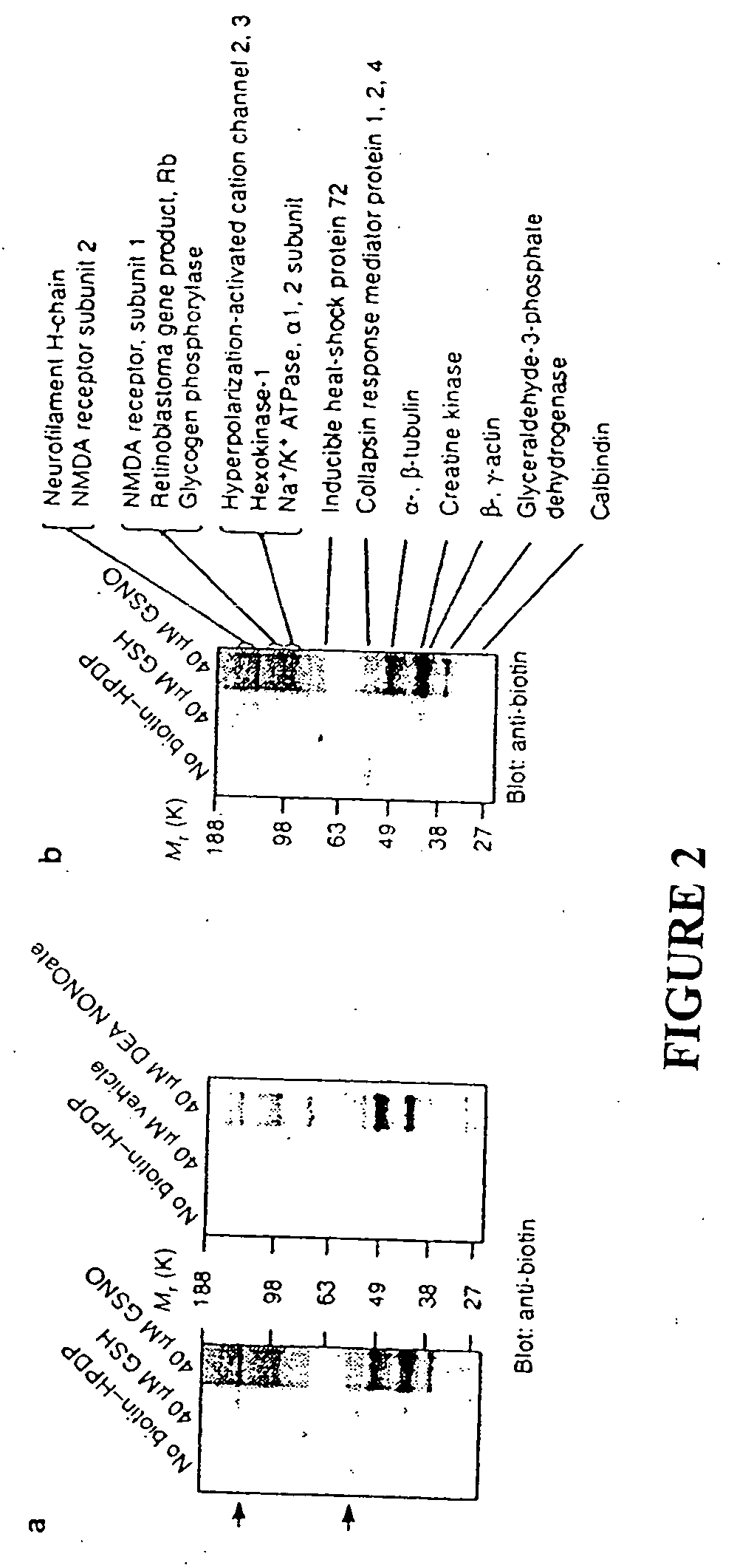
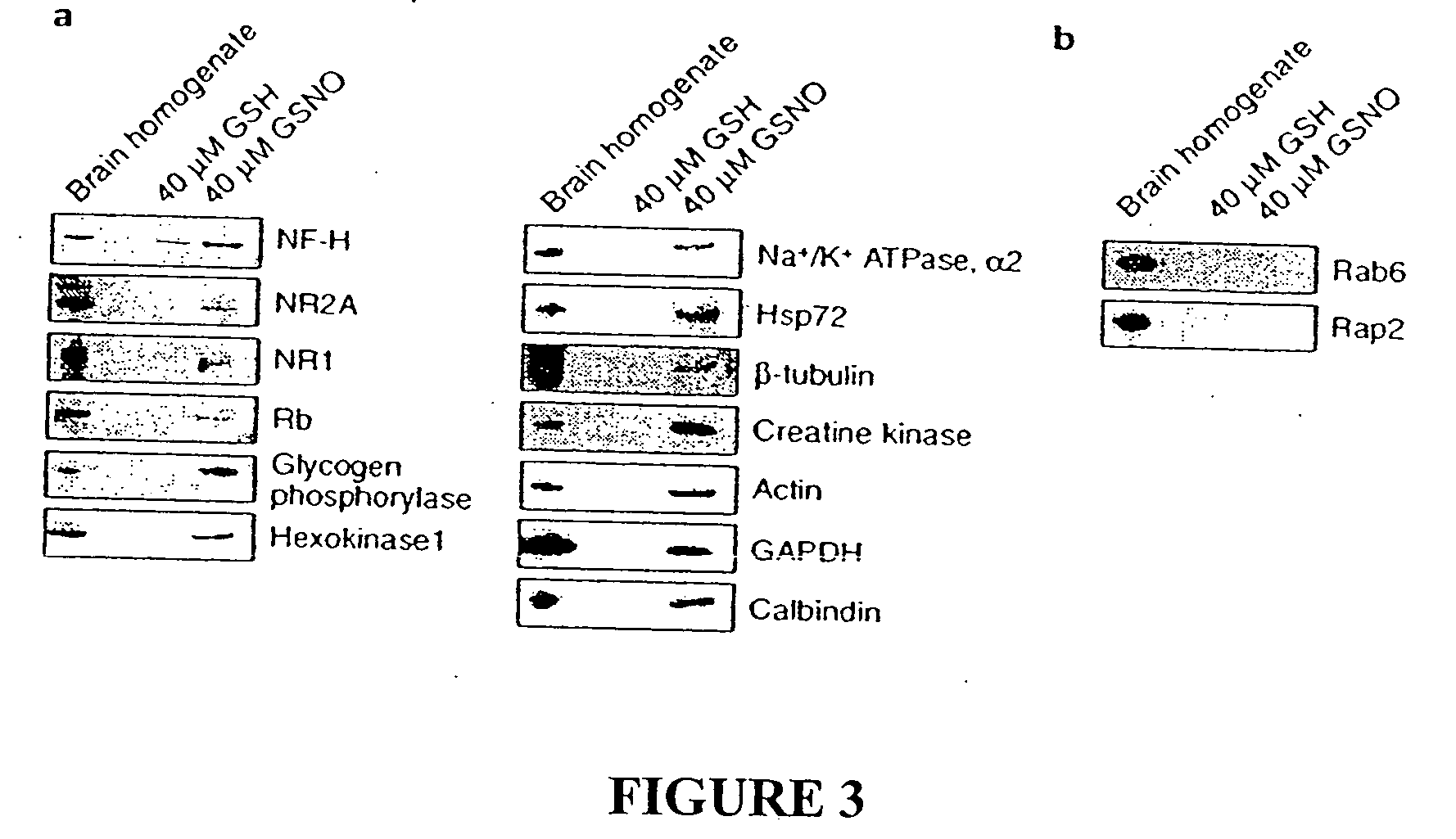
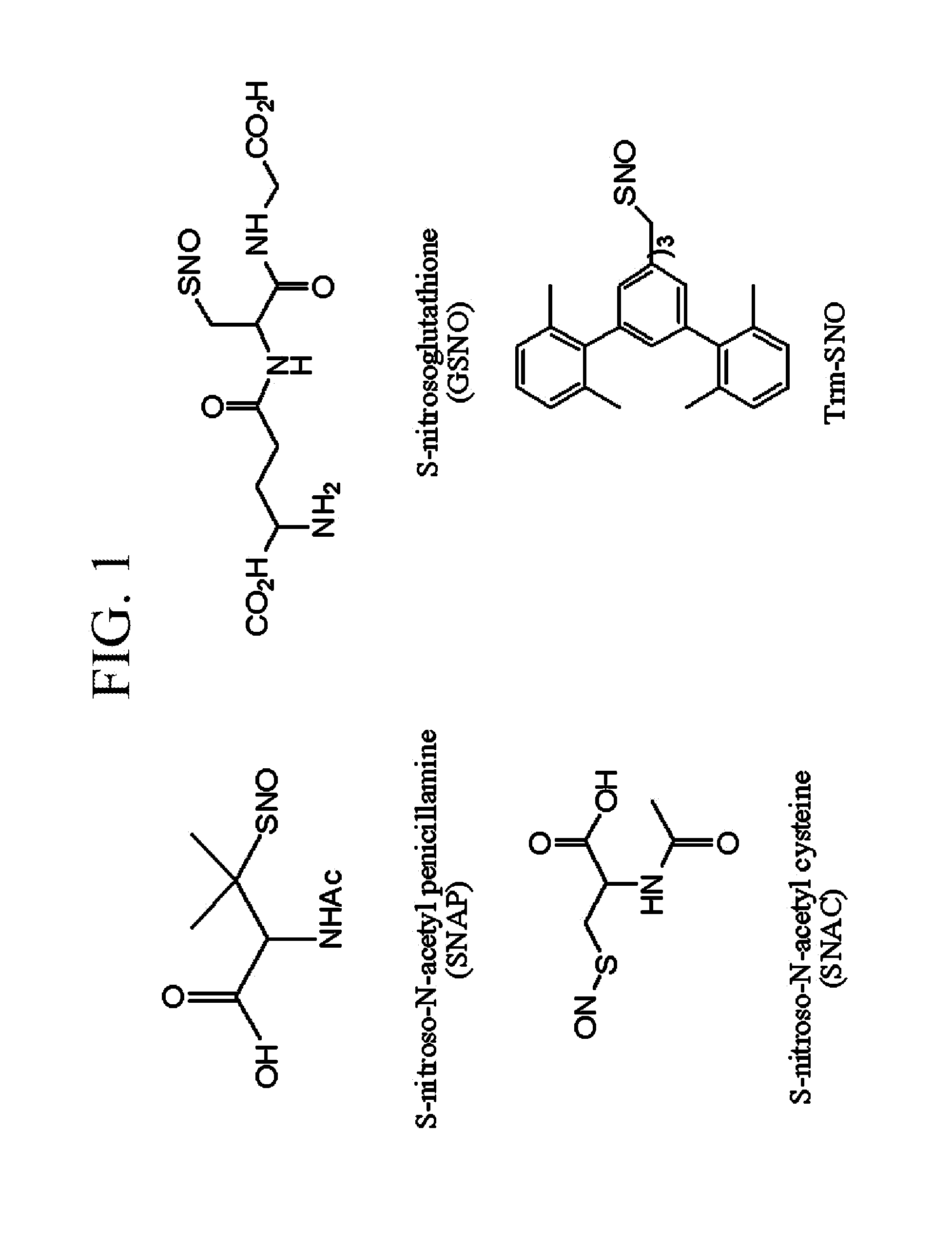
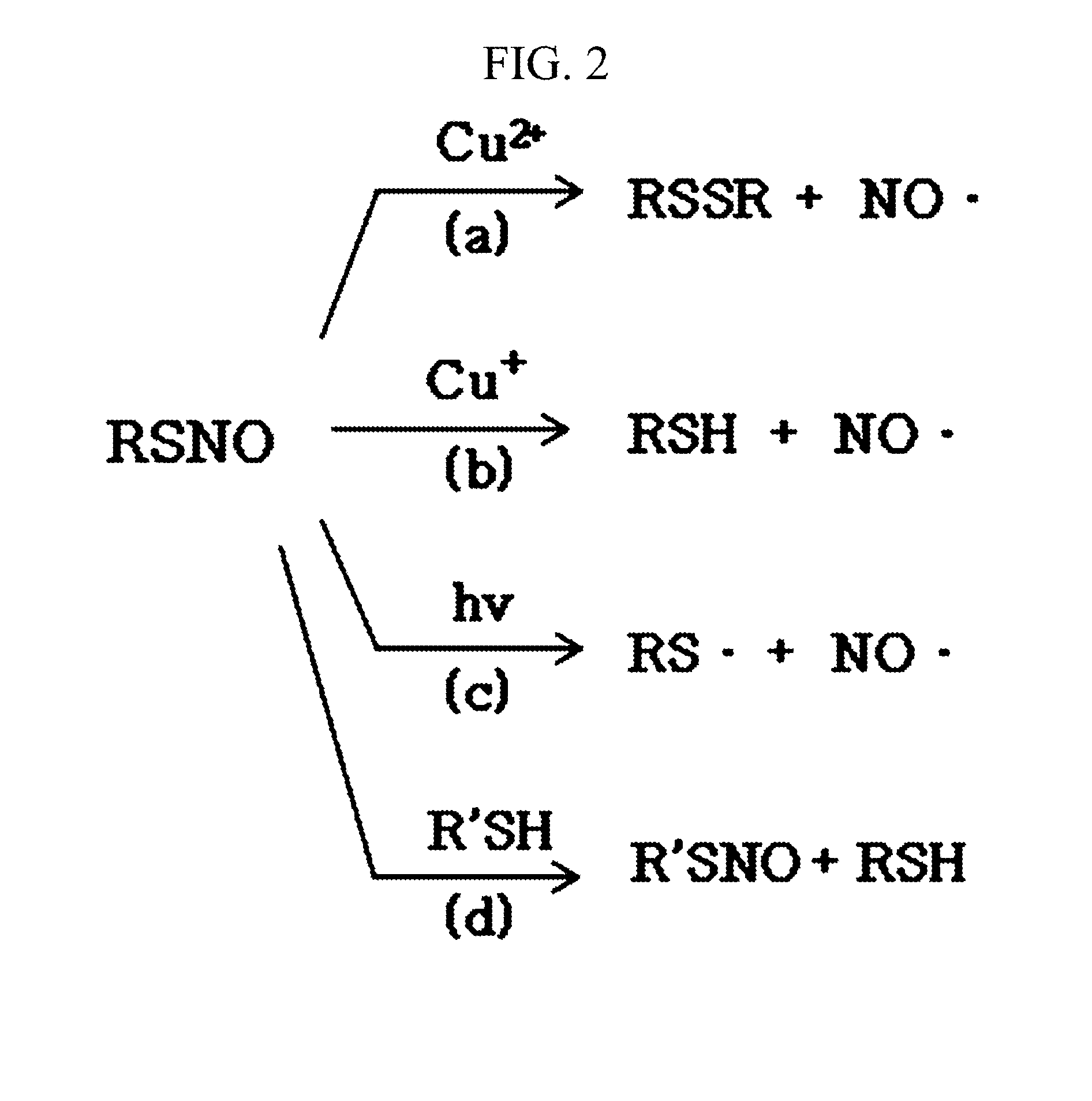
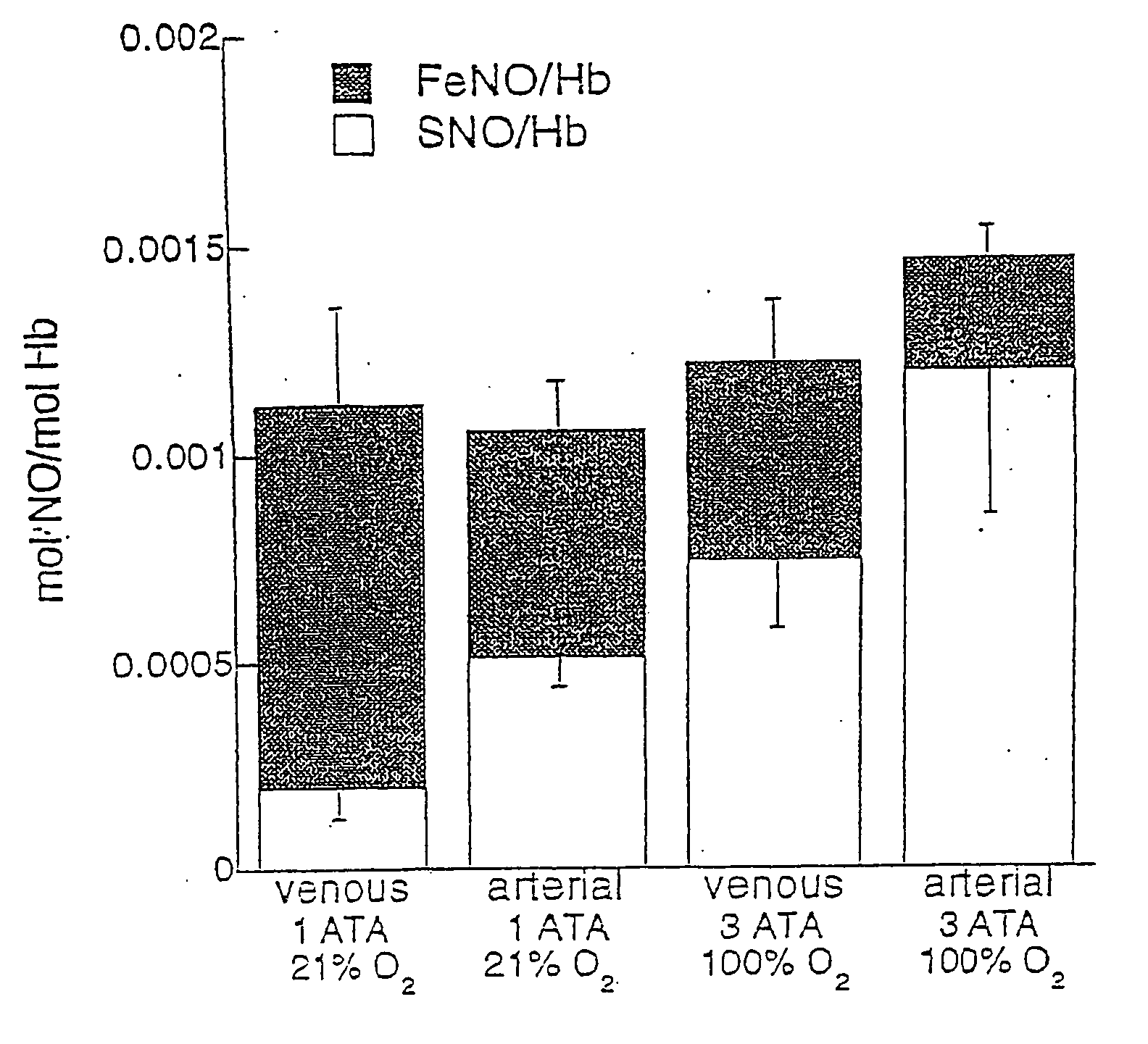
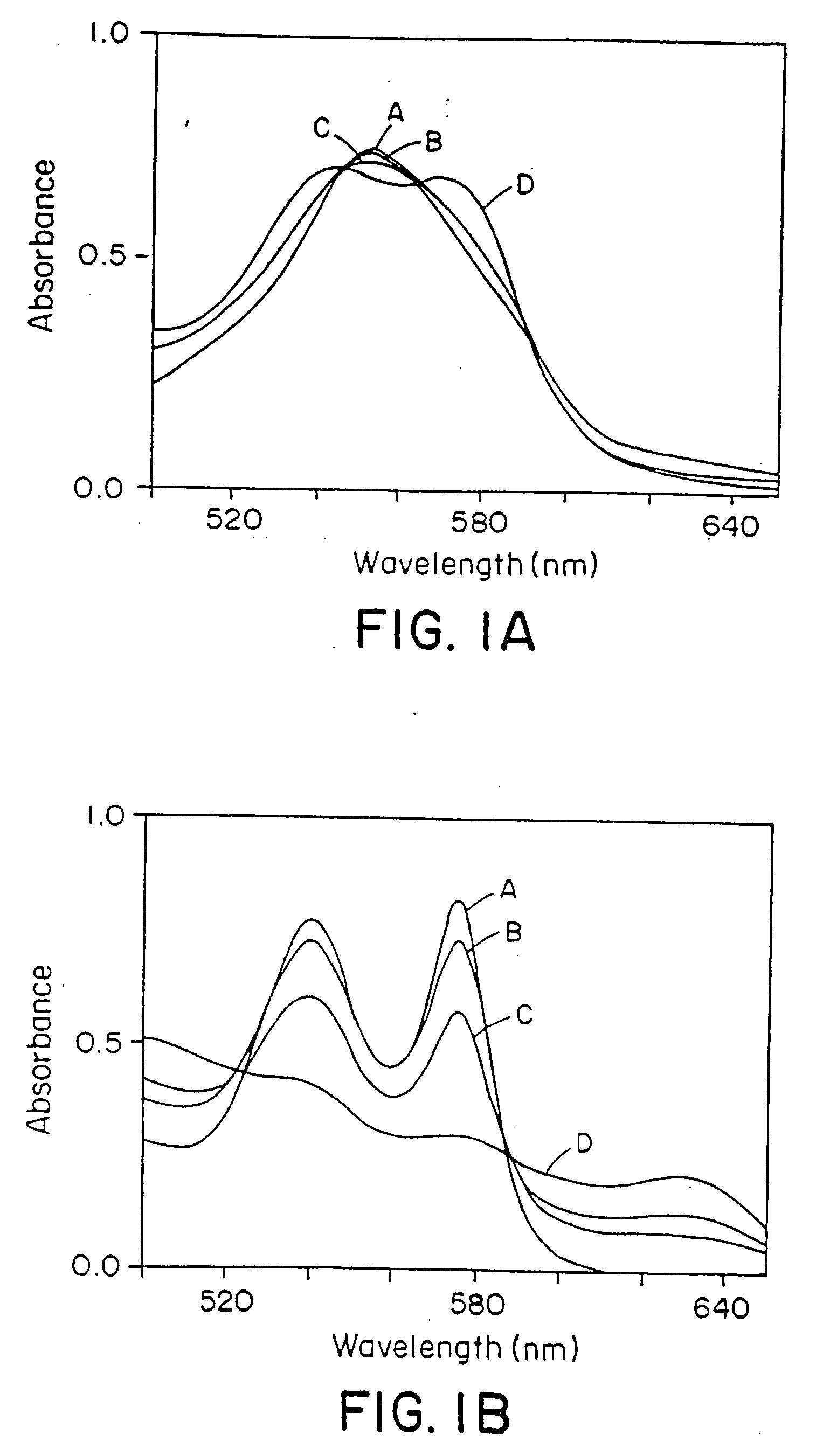
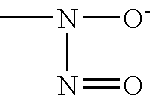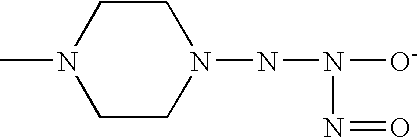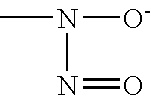Patents
Literature
52 results about "S-Nitrosothiols" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for modulating S-nitrosoglutathione reductase
InactiveUS20050014697A1High activityImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsNitrosoS-nitrosoglutathione reductase
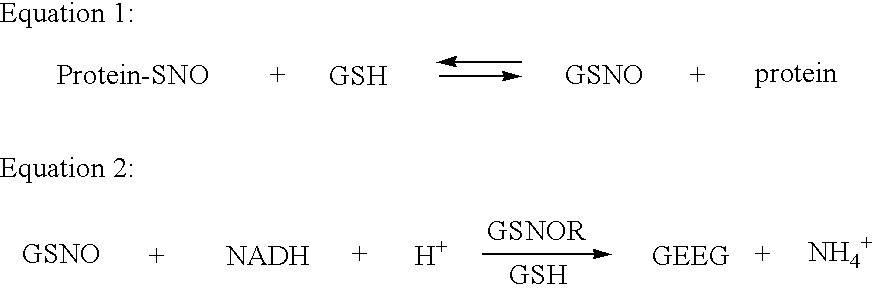
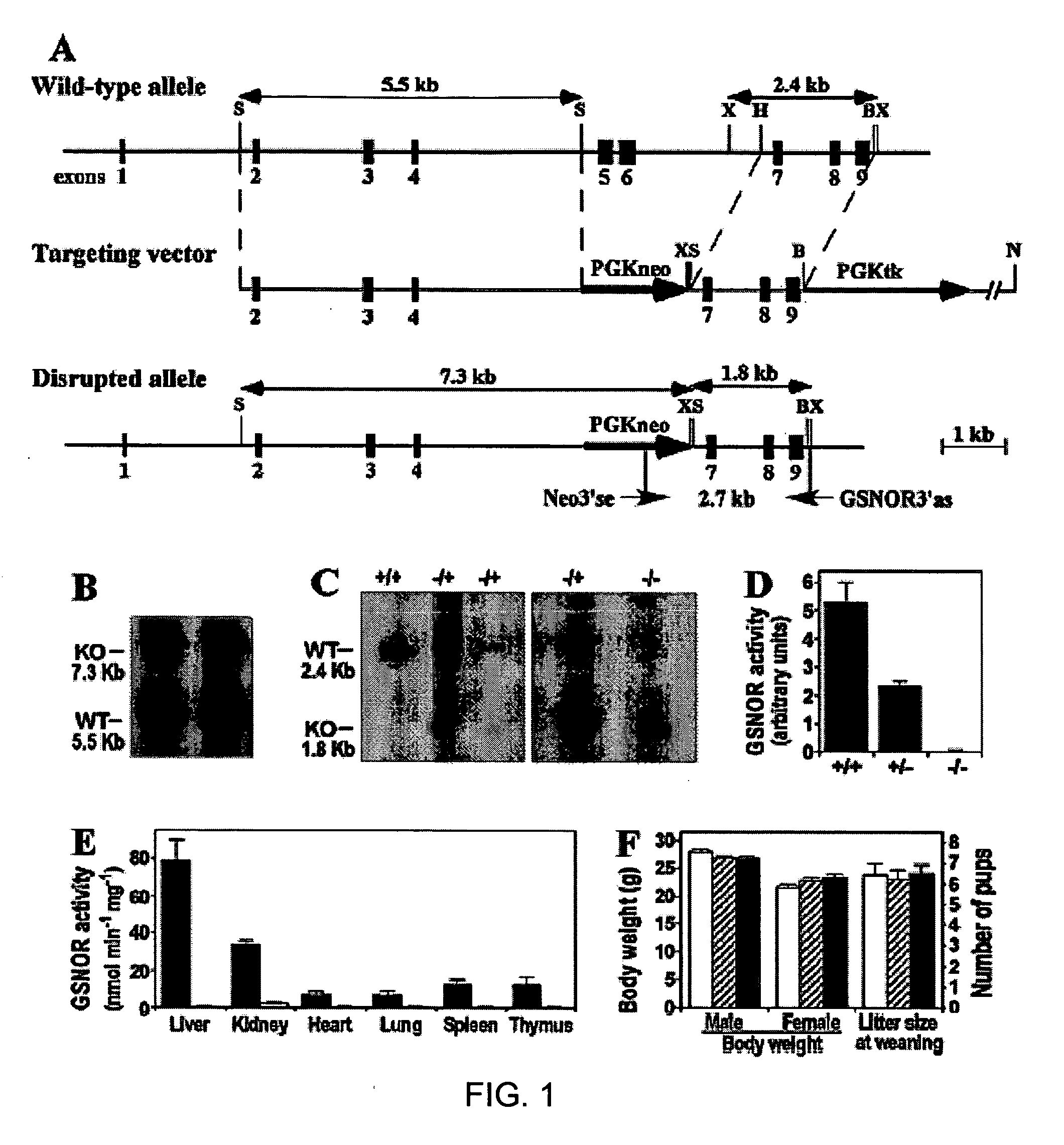
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for modulating the levels and / or activity of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNOR) in vivo or in vitro. Specifically disclosed are GSNOR deletion constructs, host cells and non-human mammals comprising GSNOR deletions, and methods of screening employing GSNOR deletion mutants. Also specifically disclosed are reagents and procedures for measuring, monitoring, or altering GSNOR levels or activity (as well as nitric oxide and S-nitrosothiol levels) in connection with various medical conditions.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
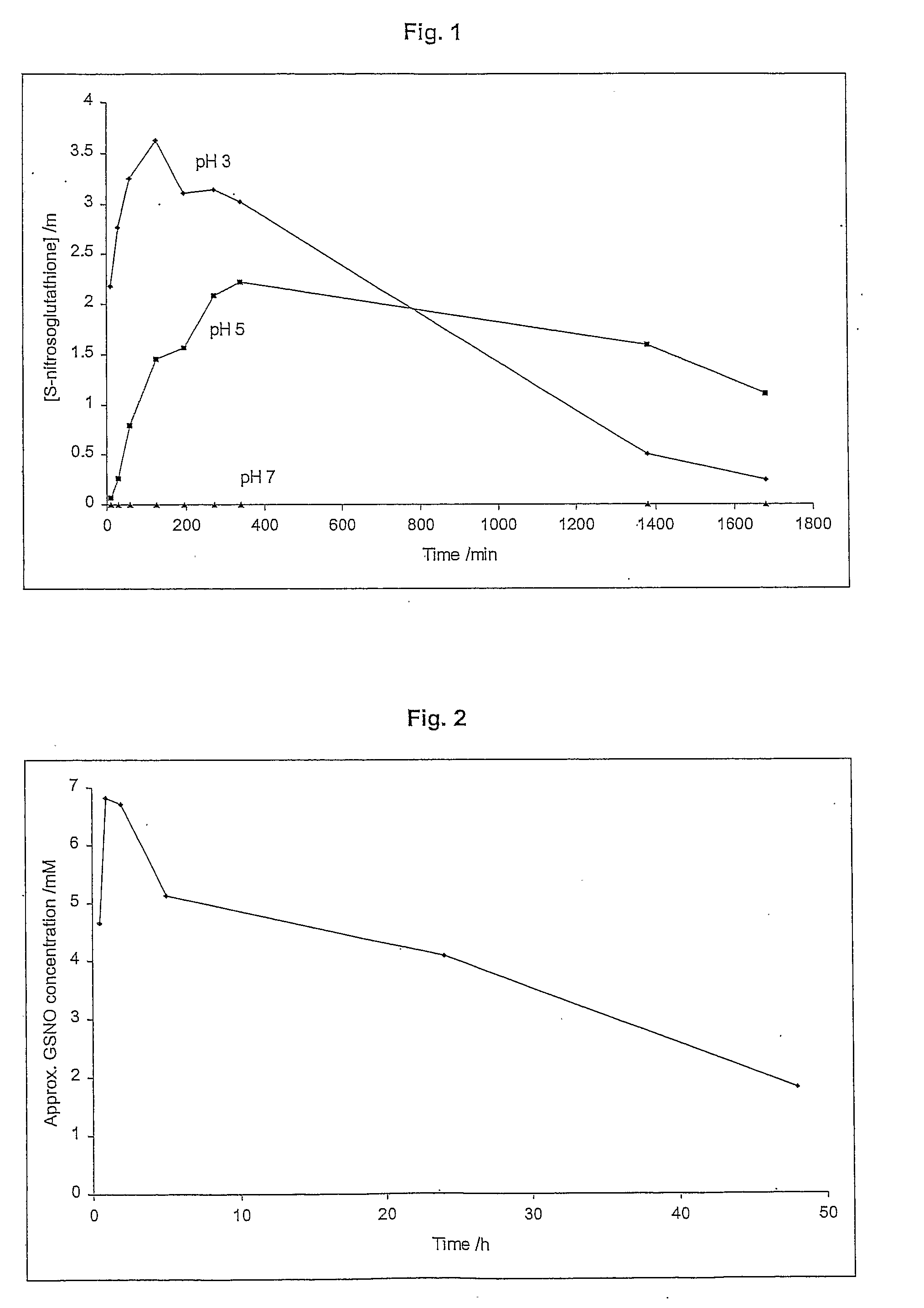
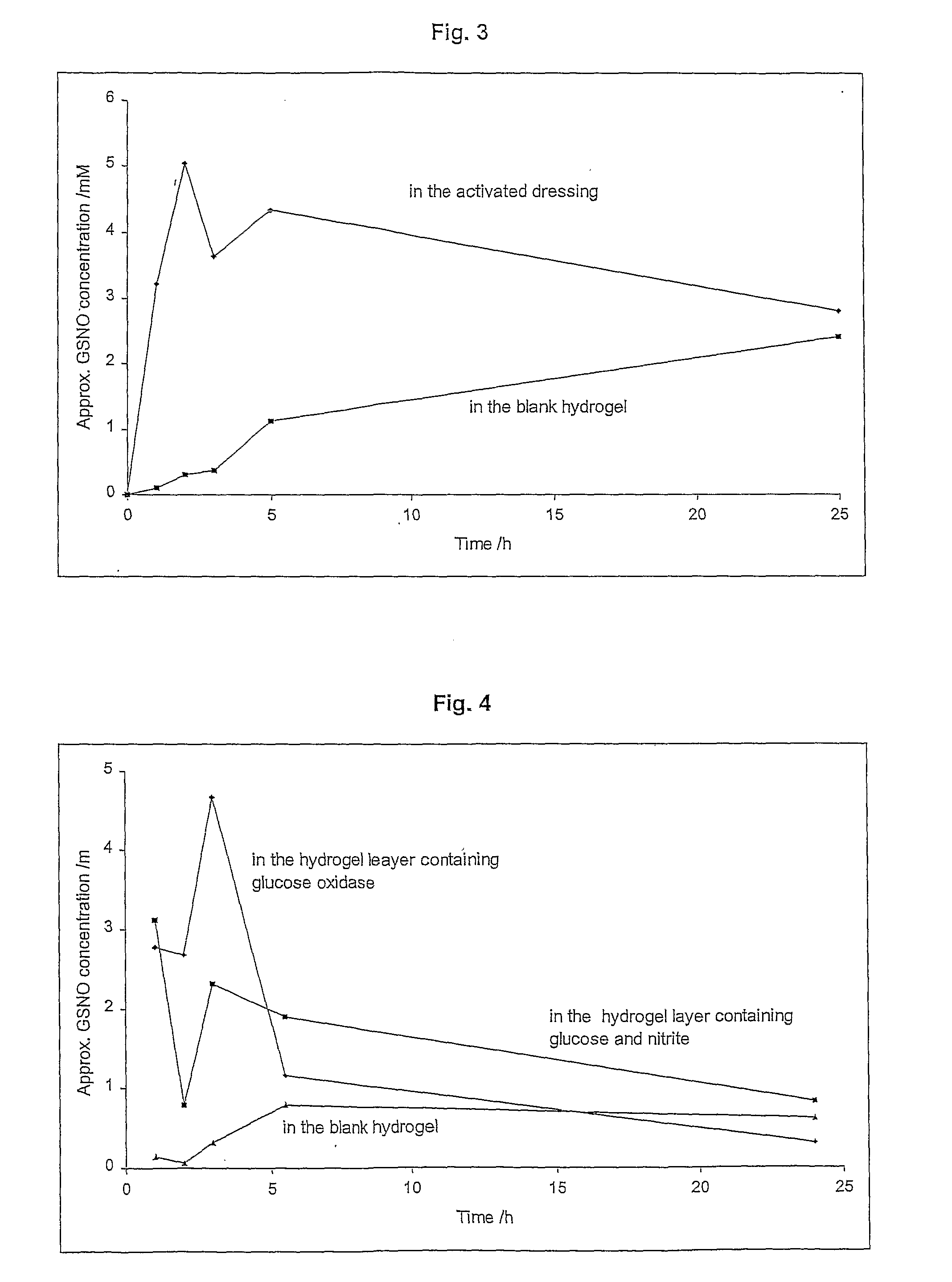
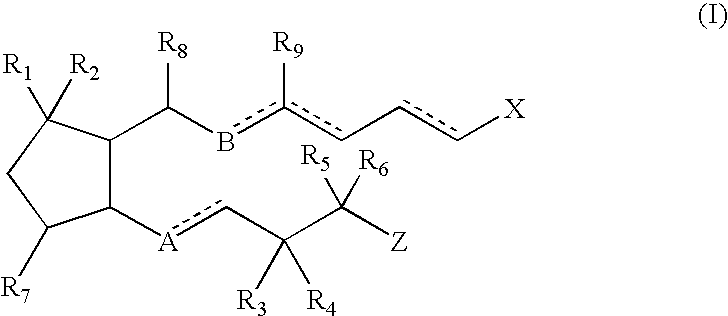
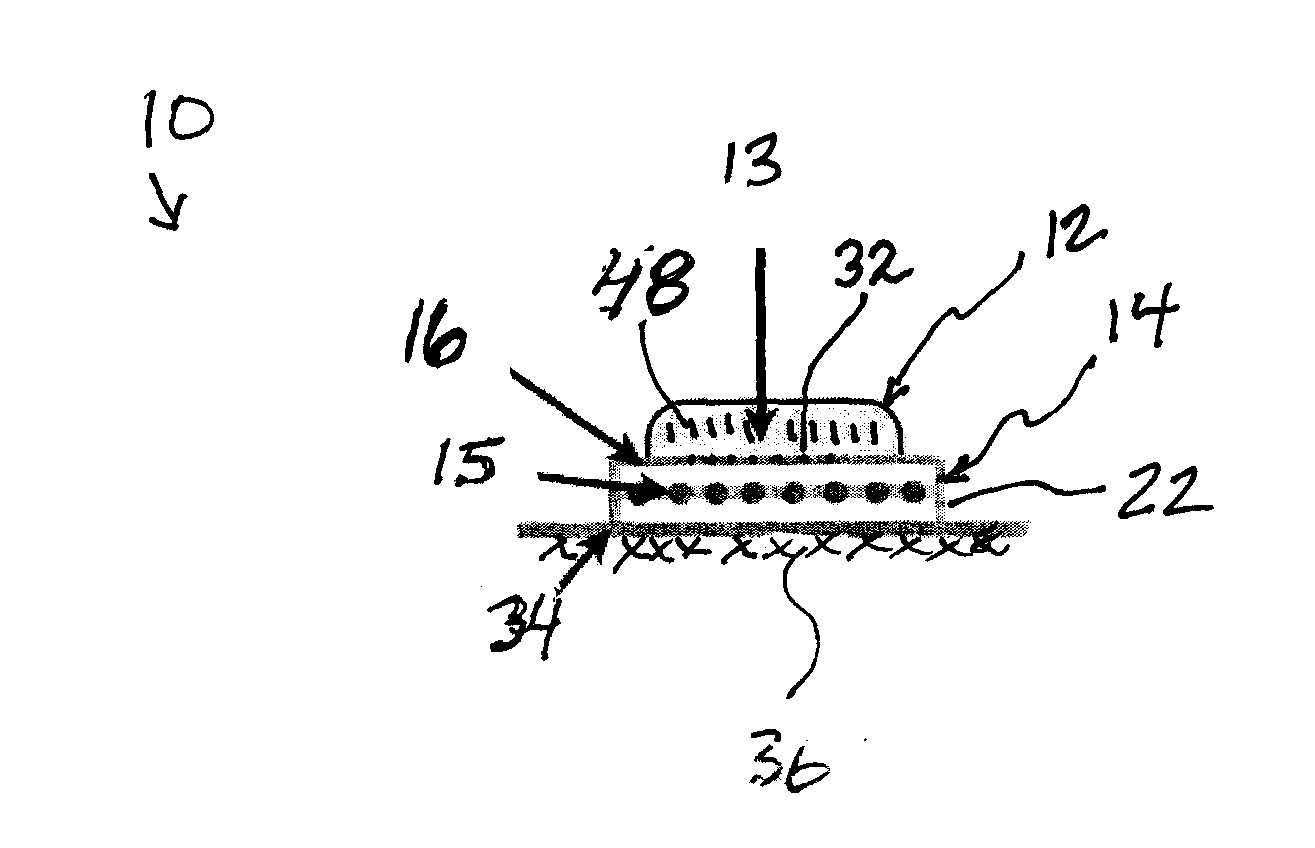
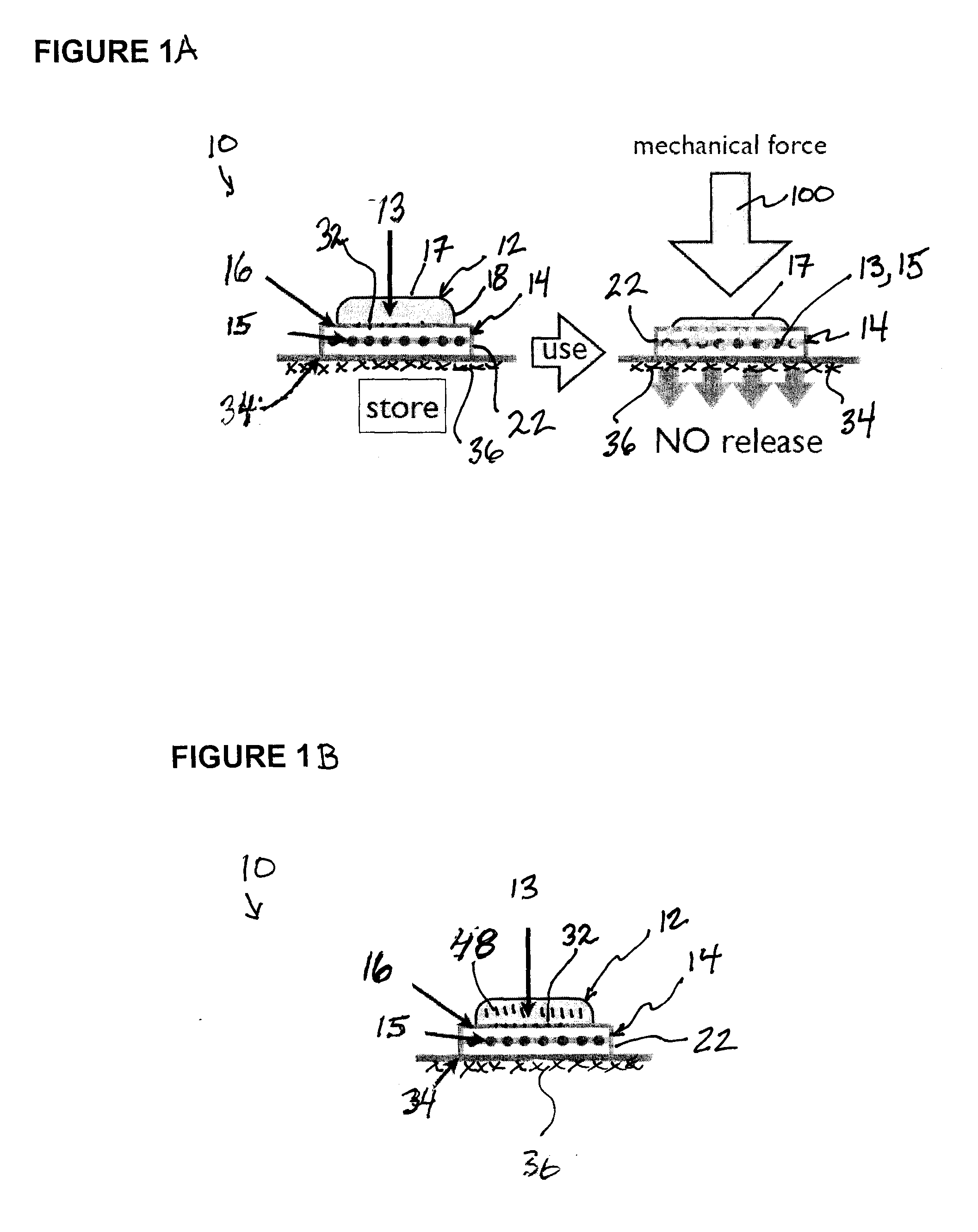
Skin Dressings
InactiveUS20090081279A1Increased collagen formationPromote cell differentiationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingNitroso
A skin dressing is adapted, on activation, to release one or more S-nitrosothiols, preferably S-nitroso-L-glutathione. S-nitrosothiols decompose spontaneously to produce nitric oxide, which has beneficial effects on tissues, particularly in wound healing.
Owner:INSENSE LIMITED
Nitrosated and nitrosylated prostaglandins, compositions and methods of use
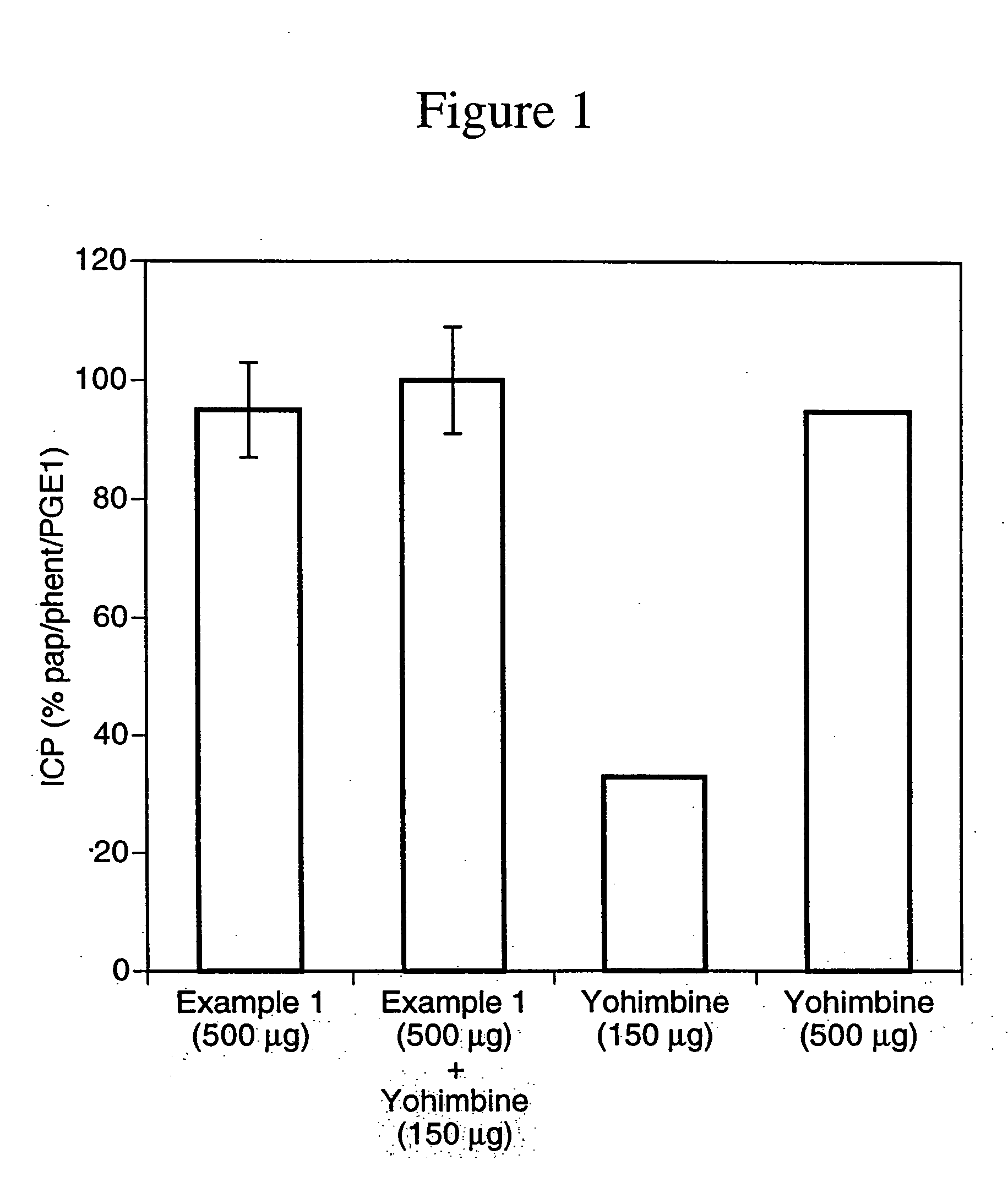
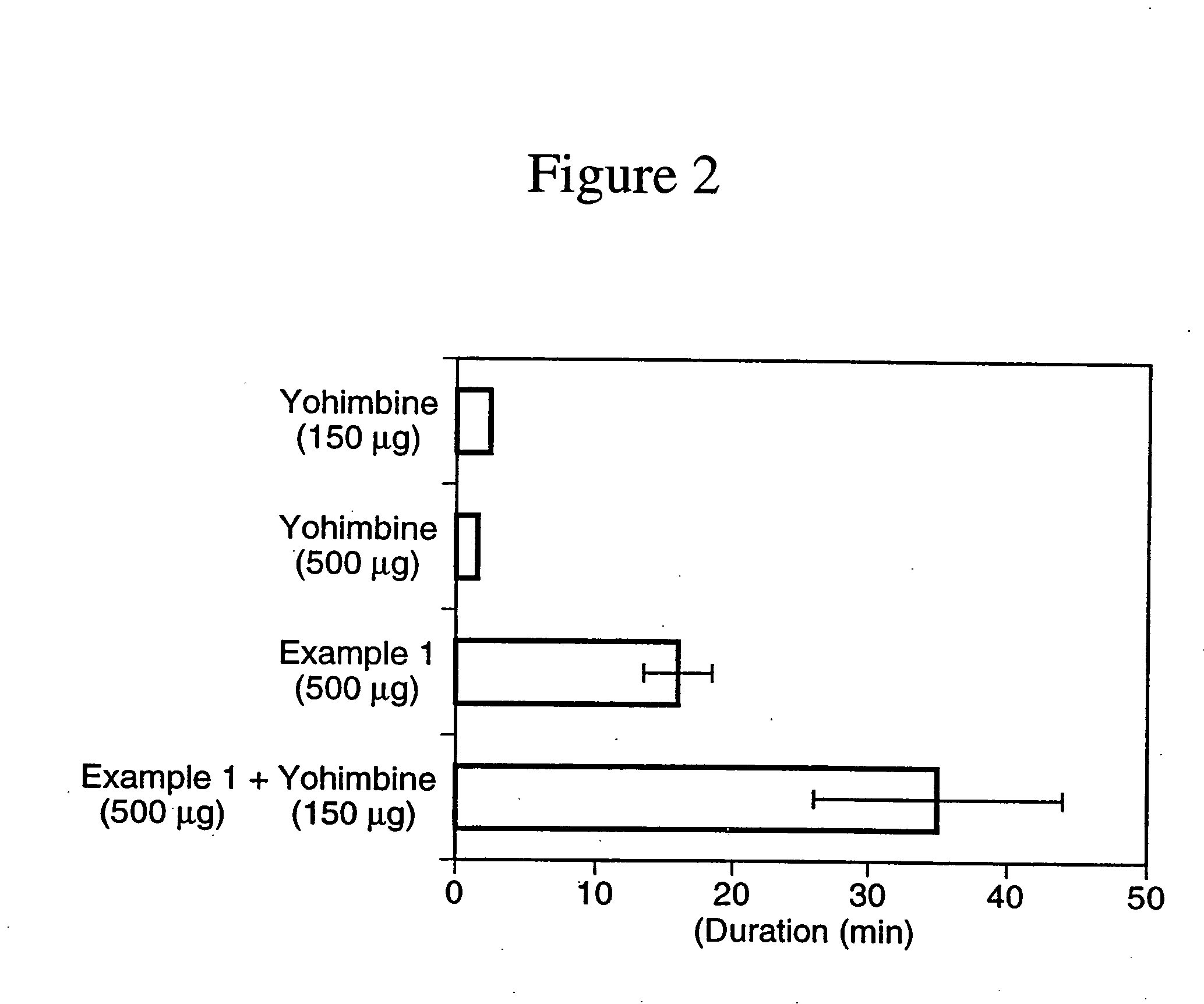
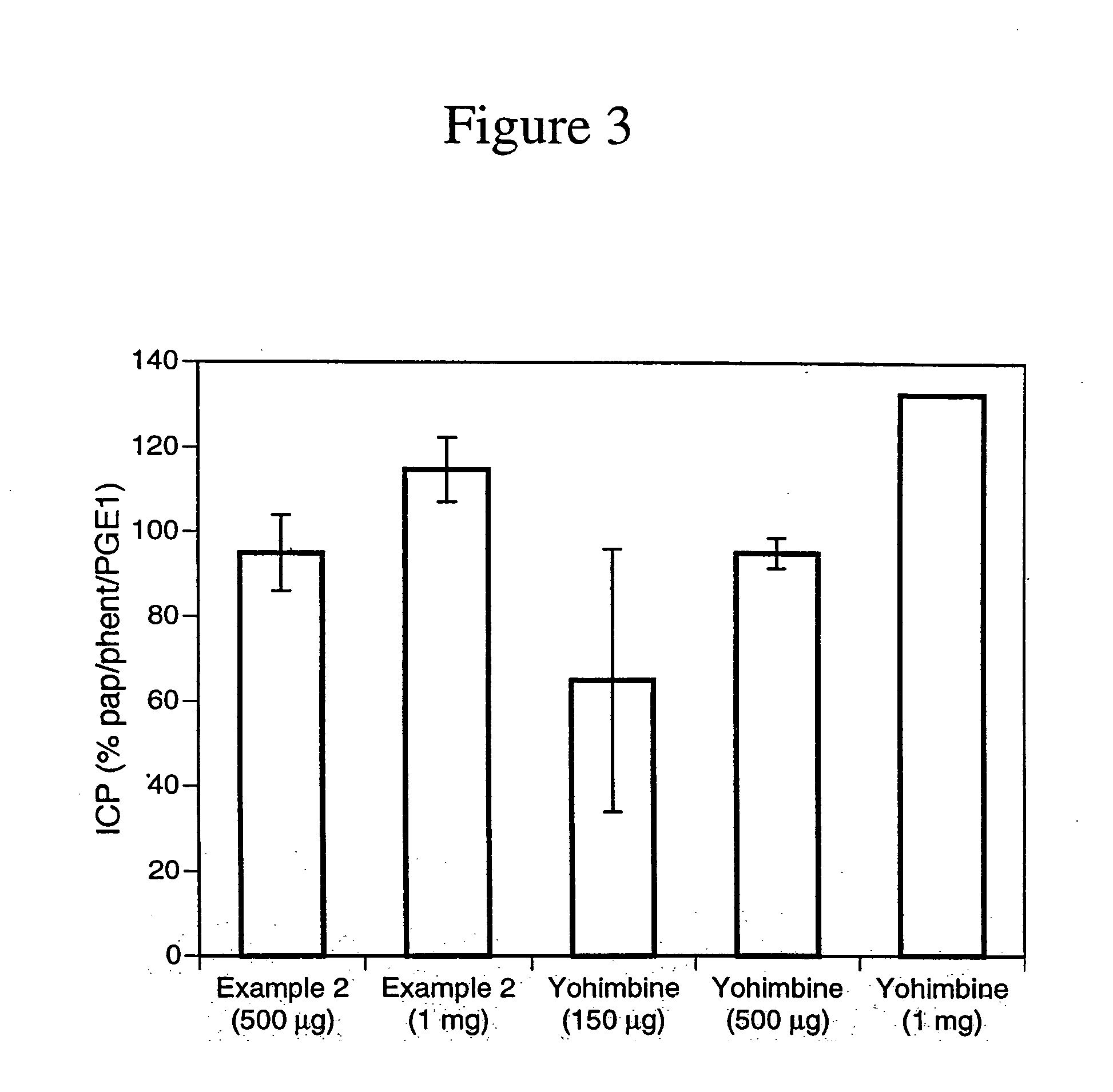
The invention describes novel nitrosated and / or nitrosylated prostaglandins, and novel compositions comprising at least one nitrosated and / or nitrosylated prostaglandin, and, optionally, at least one compound that donates, transfers or releases nitric oxide, elevates endogenous levels of endothelium-derived relaxing factor, stimulates endogenous synthesis of nitric oxide or is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase, and / or at least one vasoactive agent. The invention also provides novel compositions comprising at least one prostaglandin and at least one S-nitrosothiol compound, and, optionally, at least one vasoactive agent. The prostaglandin is preferably a prostaglandin E1 compound, more preferably alprostadil, and the S-nitrosothiol compound is preferably S-nitrosoglutathione. The invention also provides methods for treating or preventing sexual dysfunctions in males and females, for enhancing sexual responses in males and females, and for treating or preventing cerebrovascular disorders, cardiovascular disorders, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), glaucoma, peptic ulcers or for inducing abortions.
Owner:NITROMED
Skin dressings
InactiveUS20100197802A1Increase ratingsQuick buildBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsNitrateDermal dressing
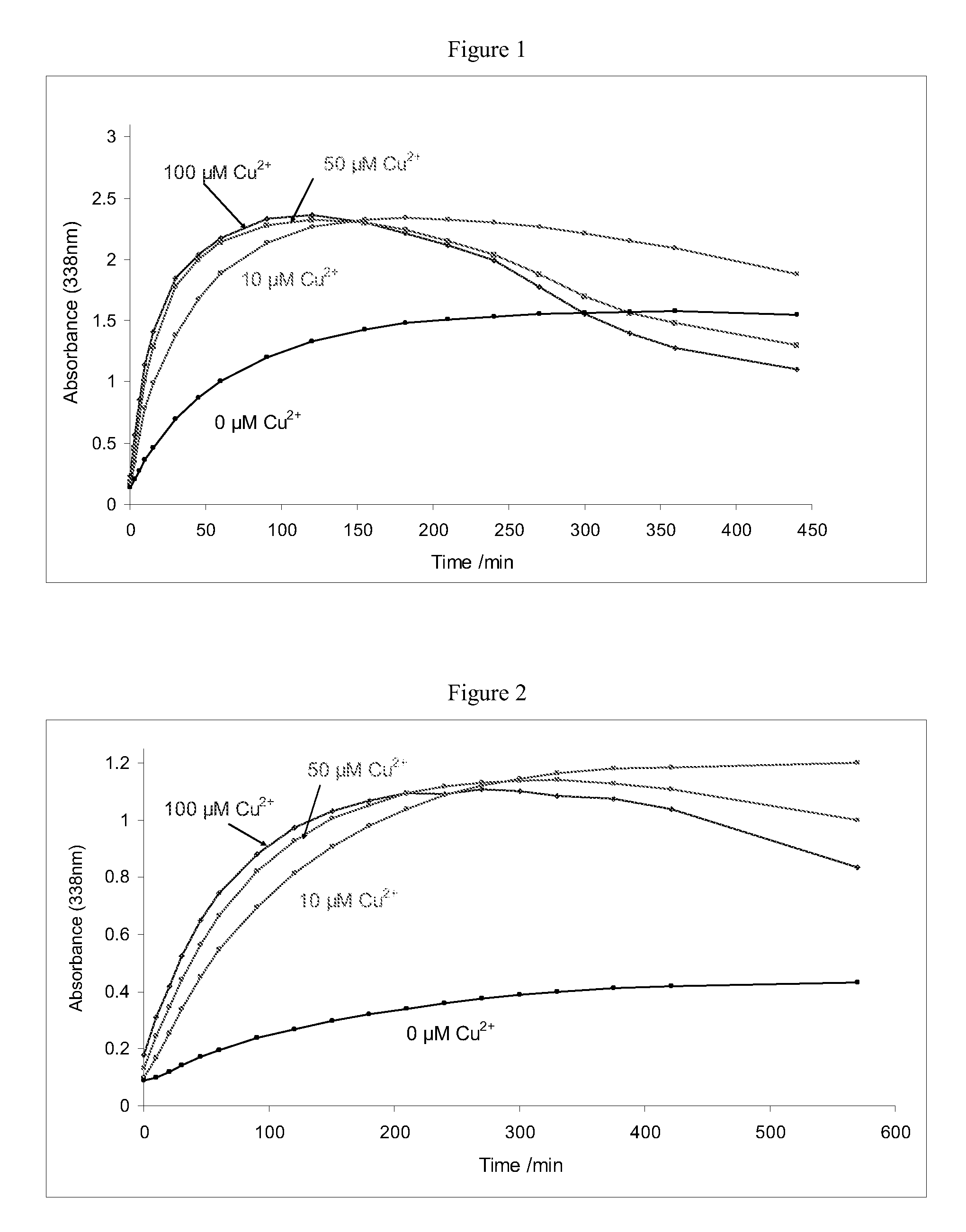
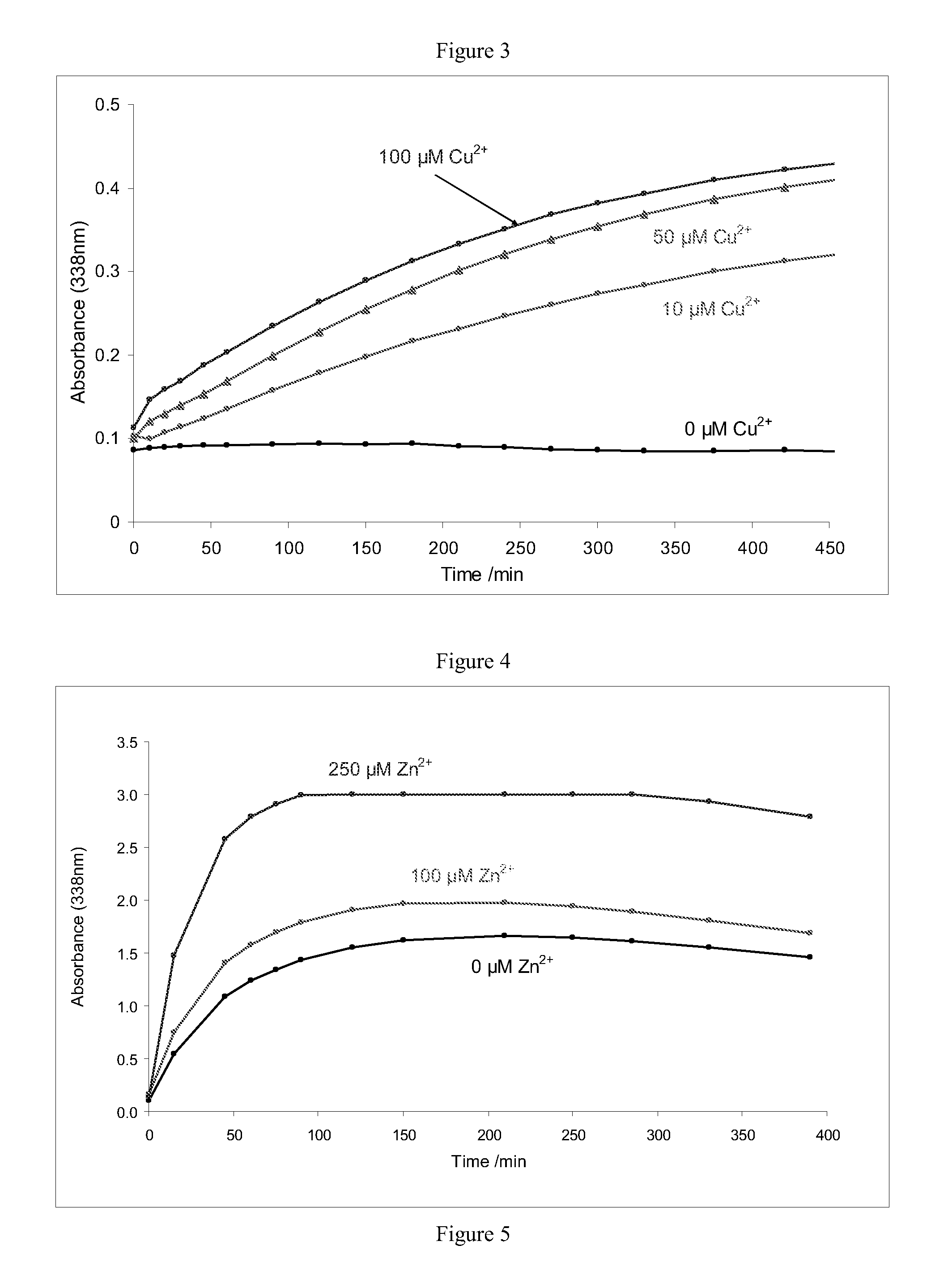
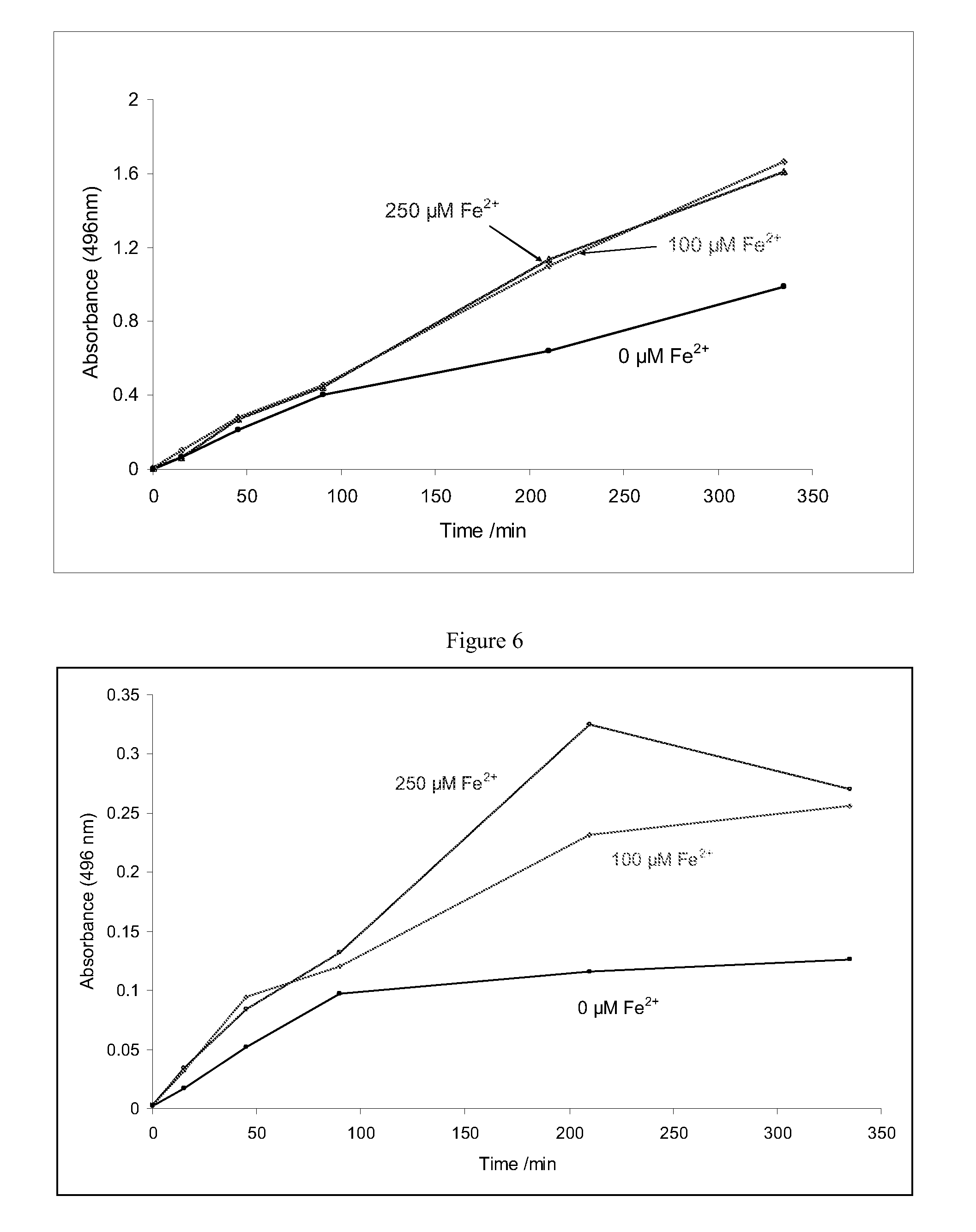
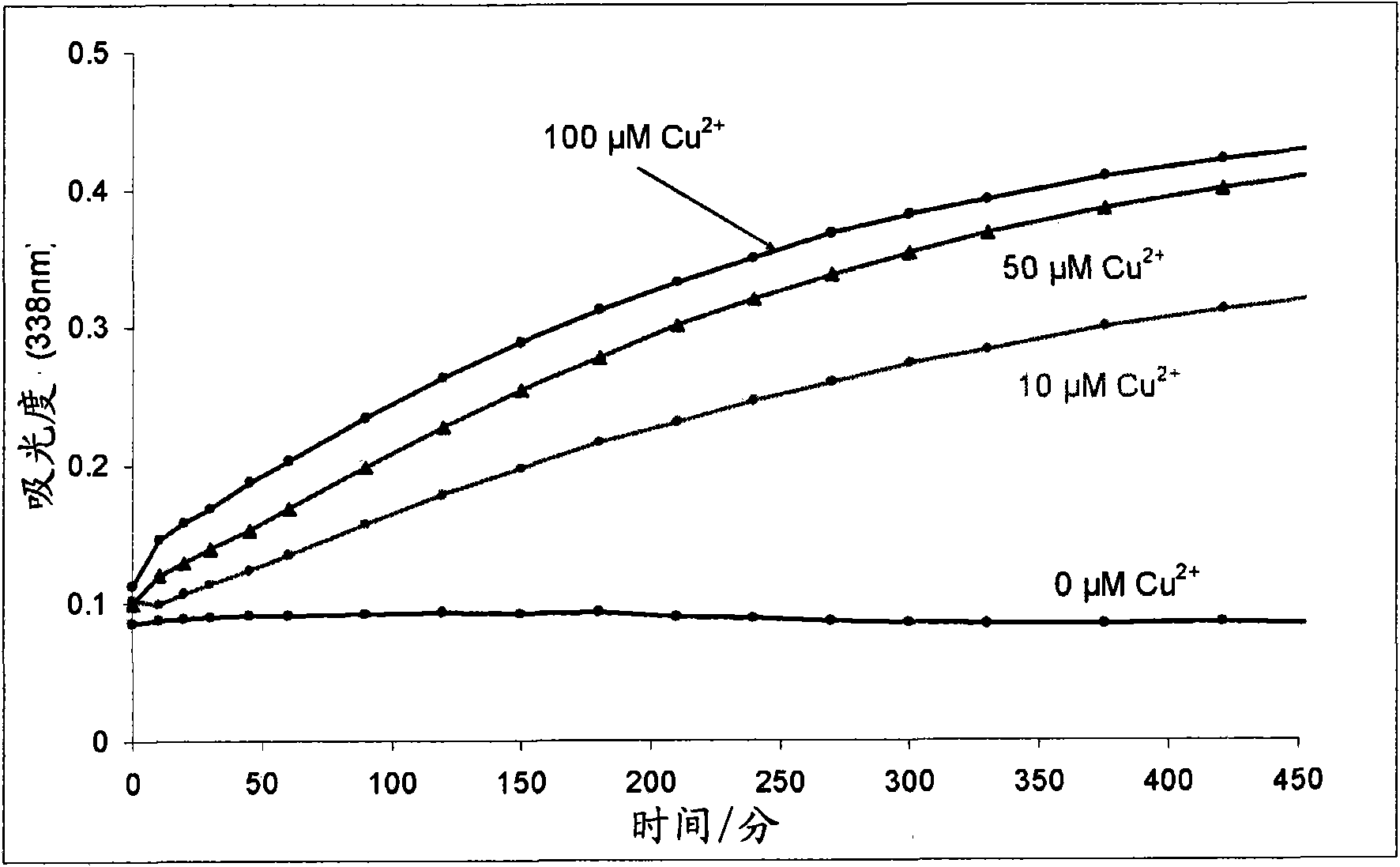
Improvements relating to skin dressing A skin dressing adapted, on activation, to generate one or more S-nitrosothiols by reaction between a thiol and a nitrate salt in the dressing, the skin dressing comprising a source of Cu2+, Zn2+ and / or Fe2+ ions for delivery of nitric oxide to a body site is provided.
Owner:INSENSE LIMITED
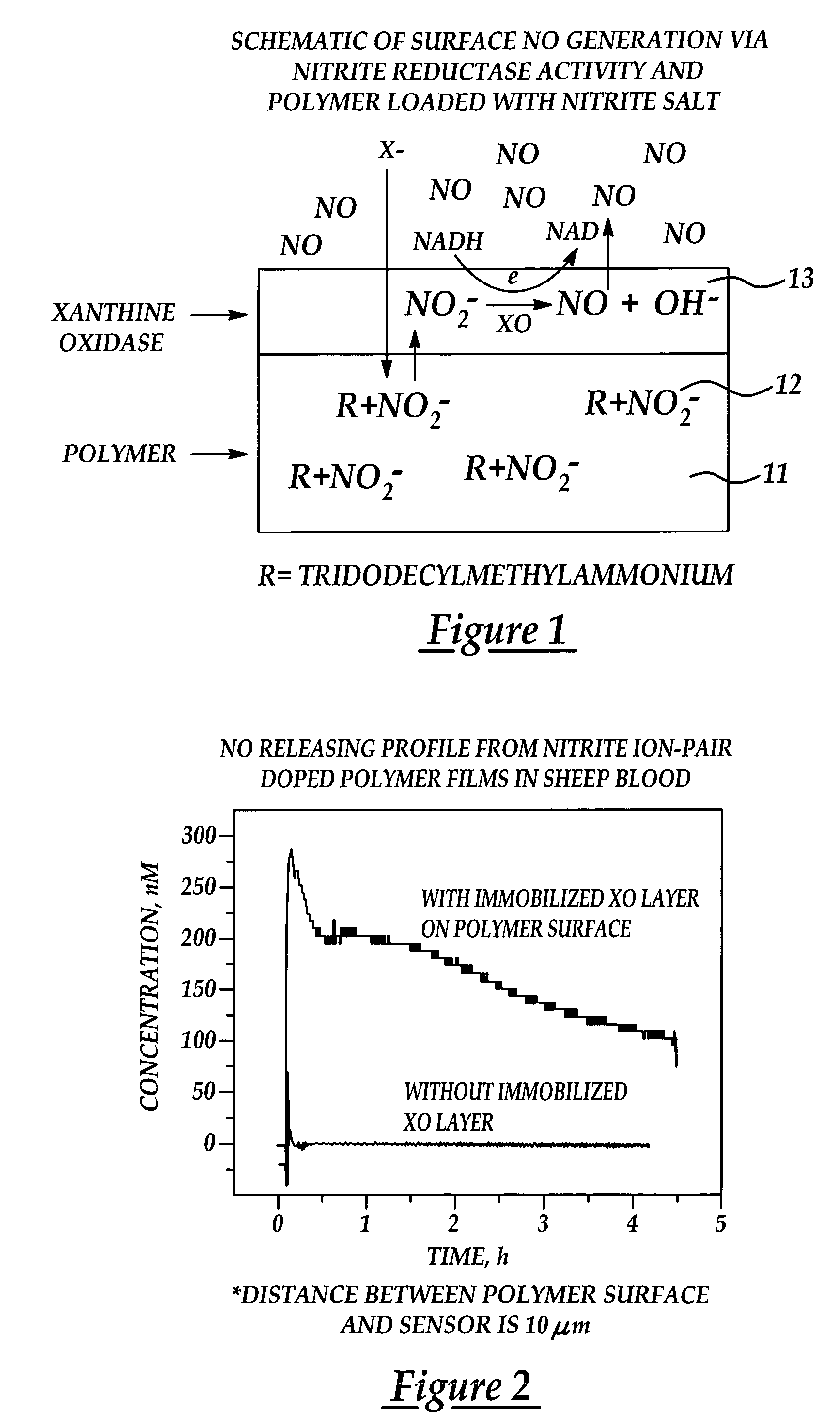
Generation of nitric oxide in vivo from nitrite, nitrate or nitrosothiols endogenous in blood
A material includes a surface and a reactive agent that is located at the surface of the material, covalently attached to a backbone of the material, and / or located within the material. The reactive agent has nitrite reductase activity, nitrate reductase activity, and / or nitrosothiol reductase activity. The reactive agent also converts at least one of nitrites, nitrates and nitrosothiols to nitric oxide when in contact with blood. A reproducible nitrosothiol sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICHIGAN CRITICAL CARE CONSULTANTS +1
Tertiary s-nitrosothiol-modified nitricoxide-releasing xerogels and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20140017121A1Reduce bacterial adhesionReduces and eliminates bacterial adhesionSilicon organic compoundsPharmaceutical containersNitrosoThiol
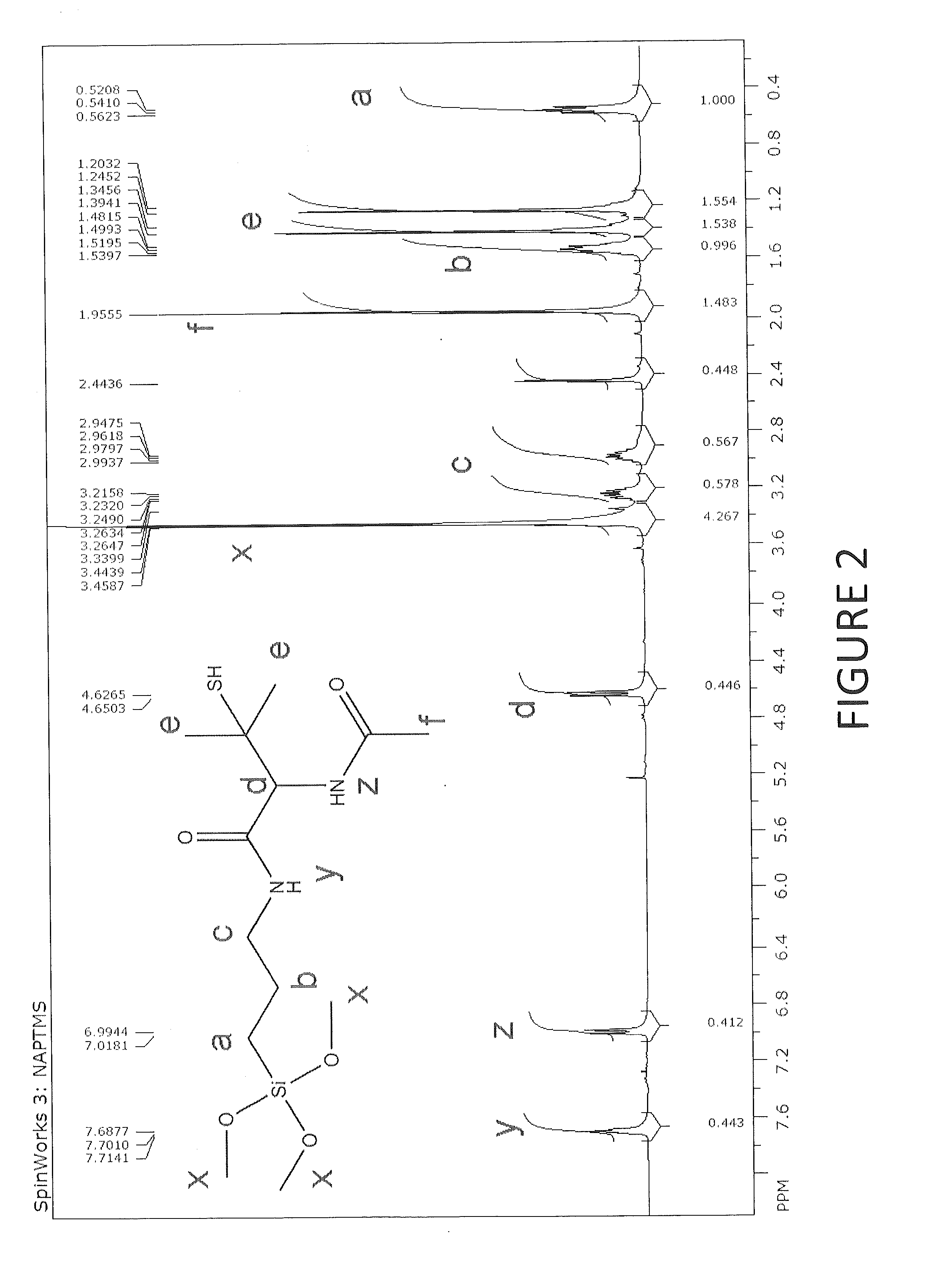
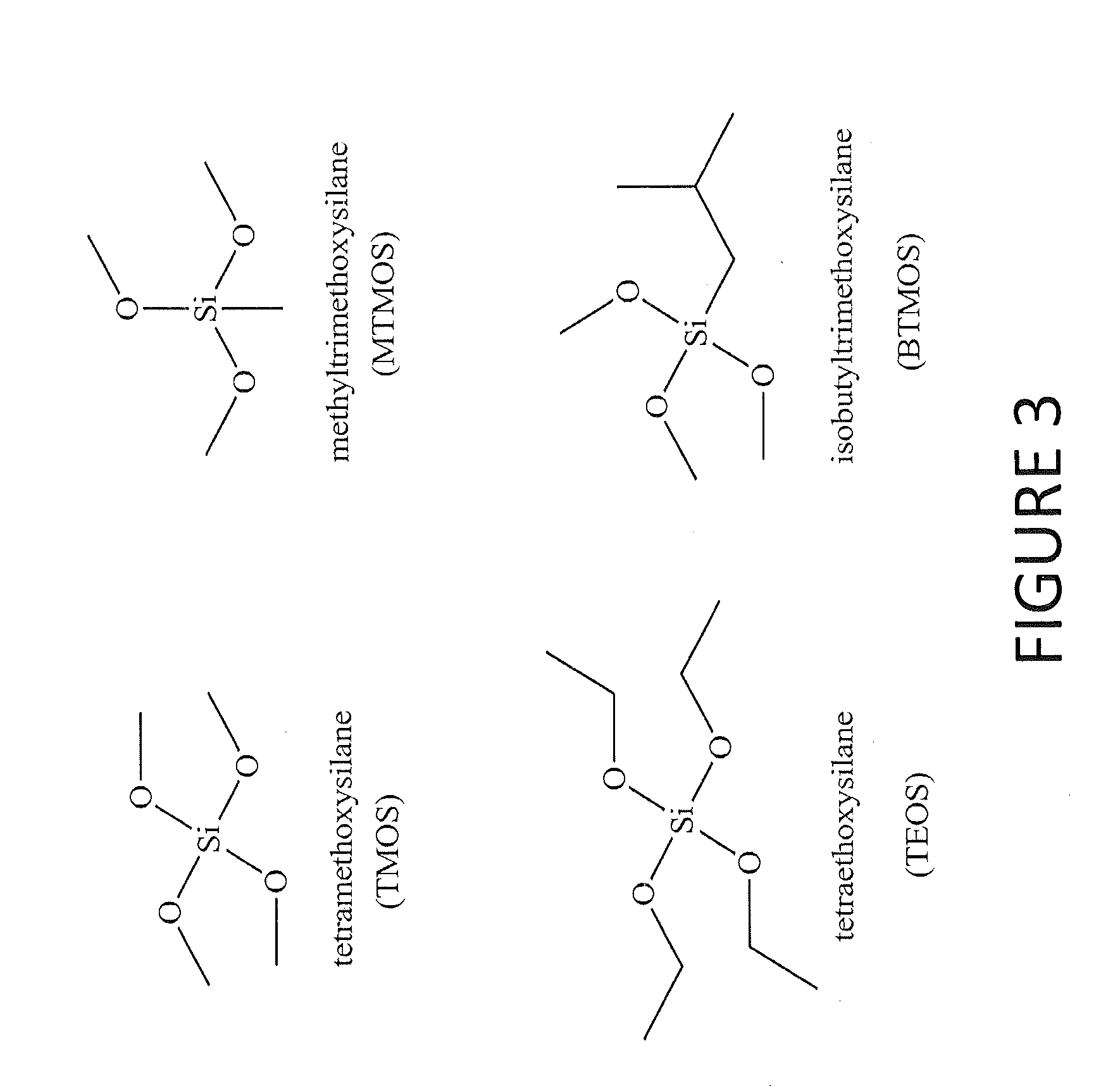
Provided according to embodiments of the invention are novel tertiary alkyl thiol compounds and novel tertiary alkyl nitrosothiol compounds. Further provided according to embodiments of the invention are methods of forming a nitric oxide (NO)-releasing xerogel coating that include (a) co-condensing a sol precursor solution comprising at least one backbone alkoxysilane and at least one tertiary thiol alkoxysilane in a solvent to form a sol; (b) coating a substrate with the sol; (c) optionally, drying the sol to form the xerogel coating; and (d) contacting the xerogel coating with a nitrosating agent. Methods of using xerogel coatings are also included.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Stents coated with no- and s-nitrosothiol-eluting hydrophlic polymeric blends
InactiveUS20100112033A1Efficient outcomeBiocideInorganic active ingredientsHydrophilic polymersPolyvinyl alcohol
This invention relates to stents coated with hydrophilic polymers containing S-nitrosothiols, which are able to provide local delivery of both nitric oxide and S-nitrosothiols by diffusion. This device is intended for coronary angioplasty applications with the purpose of inhibiting acute and chronic restenosis and refers to processes of stent coating with hydrophilic polymers containing incorporated S-nitrosothiols. This invention refers to an intracoronary implant device used in medical procedures, and introduces new S nitrosothiol-eluting stents coated with hydrophilic polymer multilayers. The hydrophilic polymers used for coating are polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylpirrolidone and polyvinyl alcohol / polyvinylpirrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol / polyethylene glycol, polyvinylpirrolidone / polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol / polyvinylpirrolidone / polyethylene glycol blends. The S-nitrosothiols incorporated to the polymer coatings are mainly primary S-nitrosothiols, characterized by the fact of the nitric oxide (NO) molecule being covalently bound to a sulfur (S) atom which, in turn, is linked to a primary carbon in the molecule's structure, thus constituting the S—NO chemical group. The coating processes include immersion of the stents in polymer solutions containing S-nitrosothiols and nebulization processes of the polymer solutions containing S-nitrosothiols onto the stent surface.
Owner:UNIV ESTADUAL DE CAMPINAS UNICAMP +1
Compositions and techniques for localized therapy
InactiveUS7947299B2Little effectOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesFibrinogenLocalized Therapy
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Apparatus for the controlled release of topical nitric oxide
ActiveUS20140296773A1Portability suitableSuitable shelf lifePeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsControl releaseMedicine
A stable delivery system for the therapeutic release and application of nitric oxide to a patient suffering from a cutaneous injury or wound includes a S-nitrosothiol and transition element nanoparticles. The transition metal nanoparticles are selected to react with the S-nitrosothiol to release and diffuse nitric oxide into the injury or wound.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
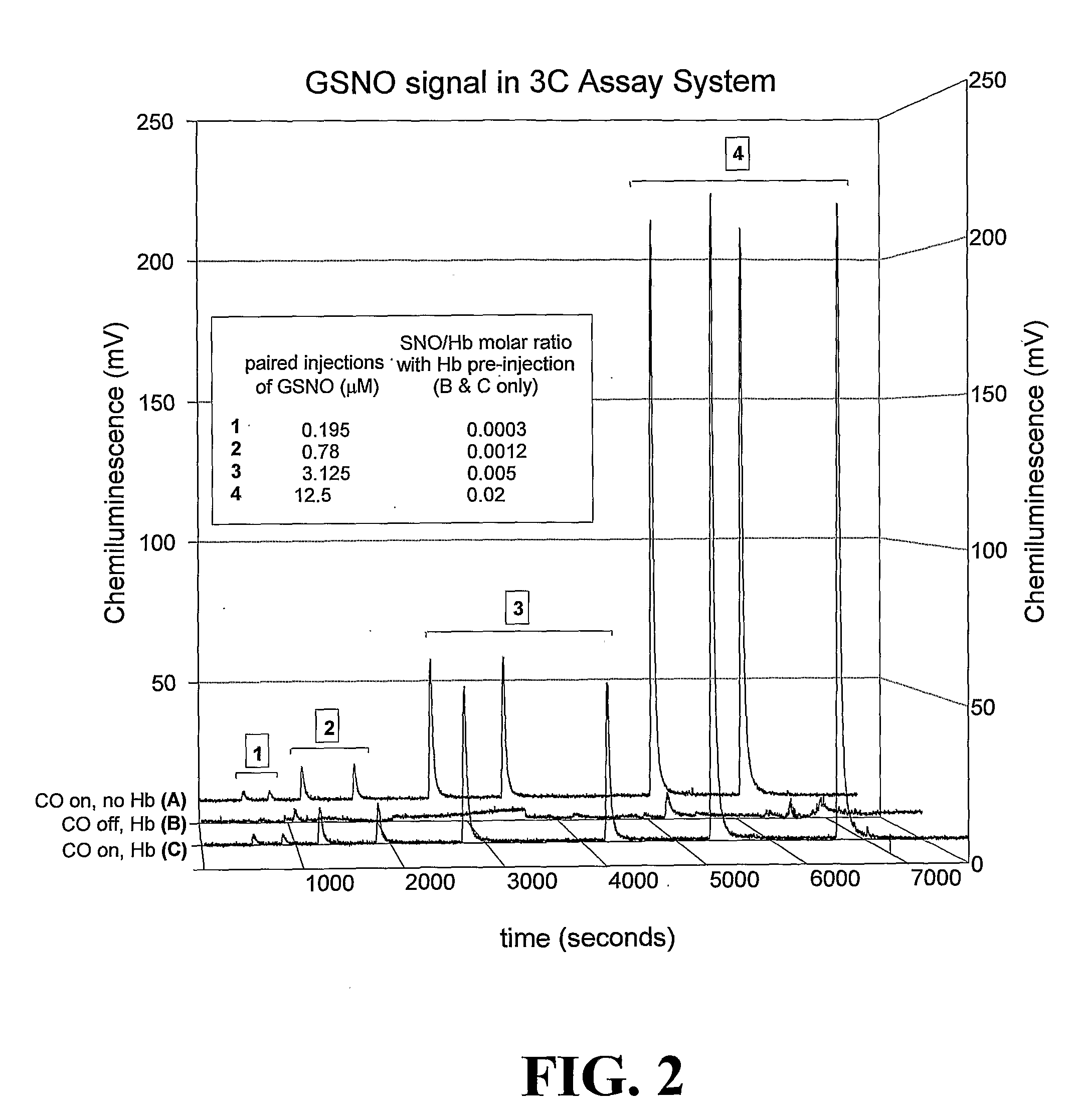
Methods For Identifying And Measuring S-Nitrosothiol Bonds In Heme-Containing Cells And Molecules
ActiveUS20070202605A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWithdrawing sample devicesCysteine thiolateHeme
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Nitrosated and nitrosylated alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonist compounds, compositions and their uses
InactiveUS20050065161A1Improve the level ofOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNitrosoSexual functioning
The invention is directed to nitrosated or nitrosylated alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists, compositions comprising alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists that are optionally substituted with at least one NO or NO2 moiety and compounds that donate, transfer or release nitric oxide or elevate levels of endogenous endothelium-derived relaxing factor, and methods for treating sexual dysfunctions in males and females. The invention also provides methods for treating female sexual dysfunctions by administering S-nitrosothiol compounds.
Owner:NITROMED
Stable S-nitrosothiol formulations
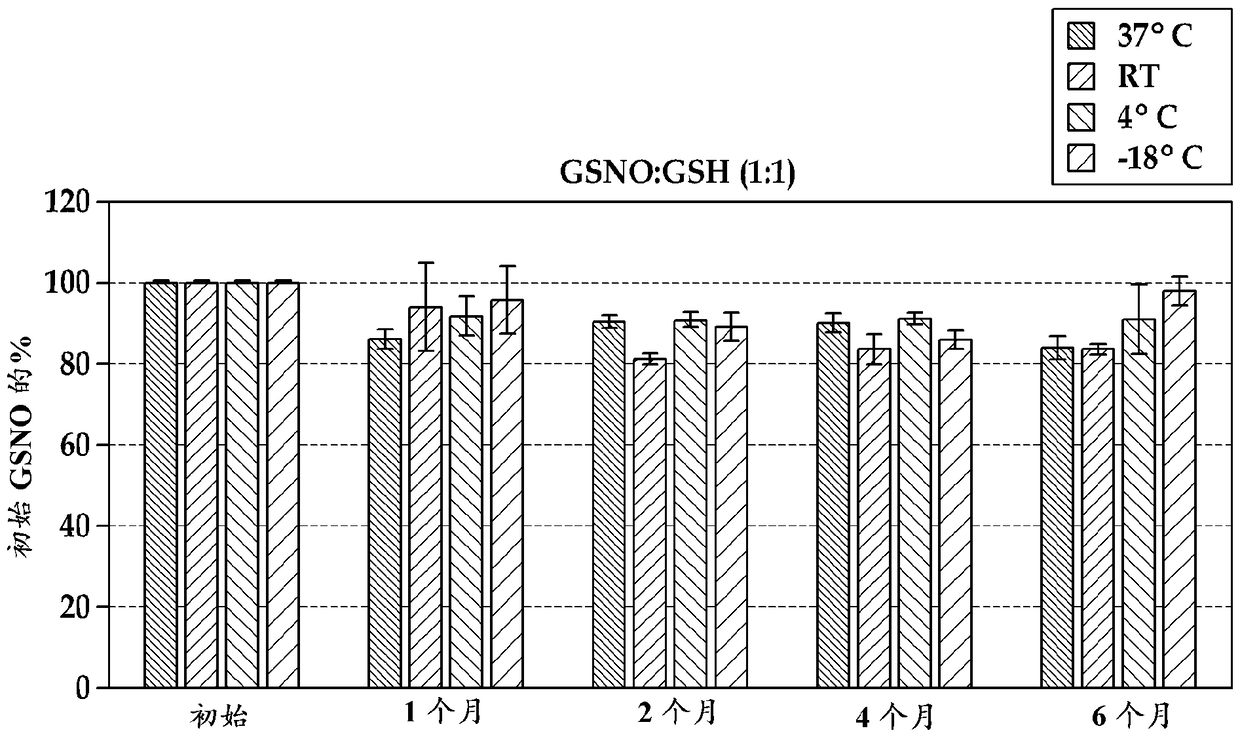
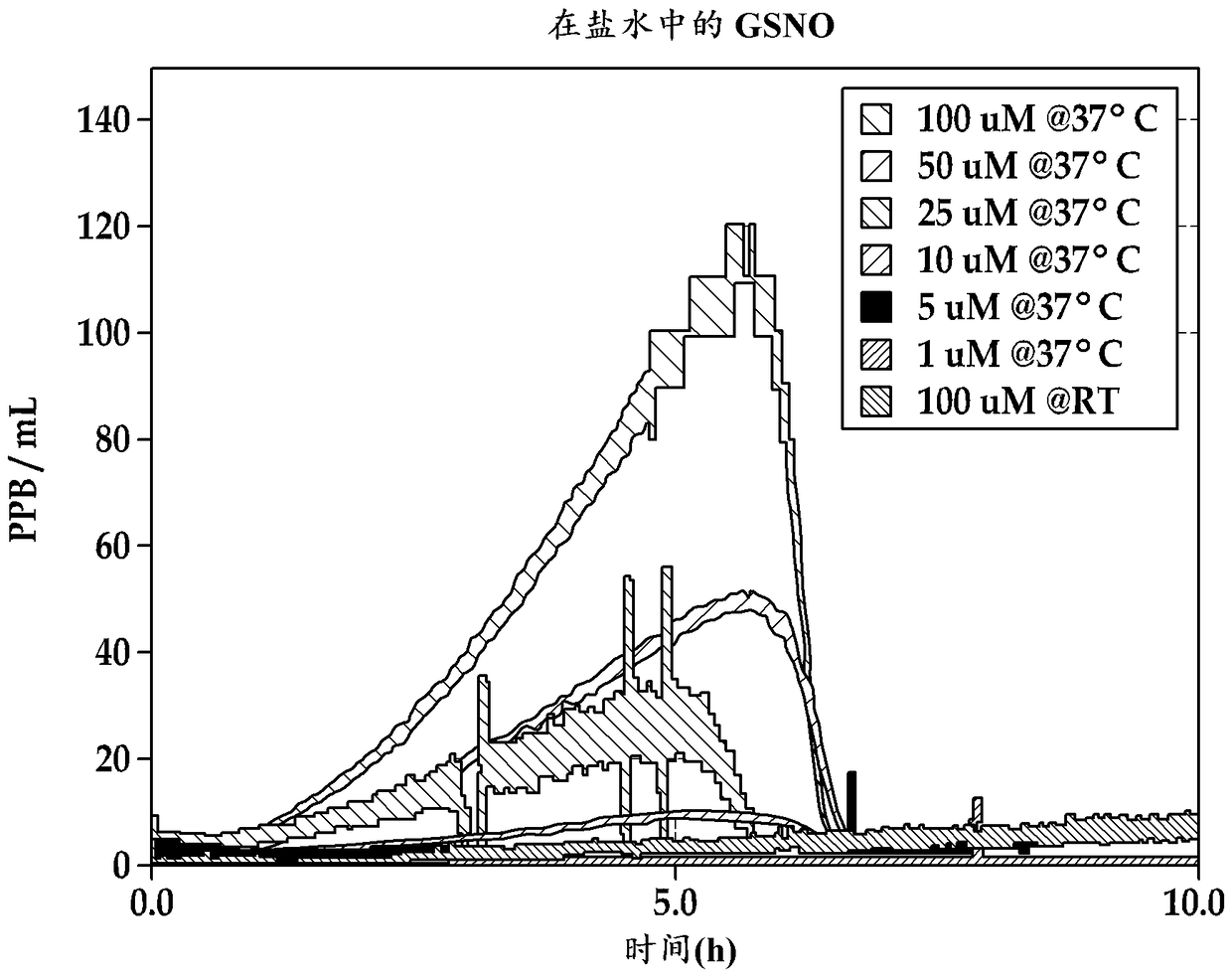
InactiveUS20070243262A1For long-term storageEffective meanPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryS-NitrosoglutathioneIn vivo
The invention provides stable S-nitrosothiol, such as S-nitrosoglutathione, formulations for long term storage and in vivo delivery of S-nitrosothiols. The invention provides stable aerosol formulations comprising S-nitrosothiol, such as S-nitrosoglutathione, and methods of treating patients in need of S-nitrosothiol, such as S-nitrosoglutathione, and / or nitric oxide treatment.
Owner:NITROX
S-Nitrosothiols Containing Composition for the Treatment of Fatty Liver Diseases, Obesity and Other Diseases Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome and the Use of Such Compositions
InactiveUS20100062059A1Avoid developmentEasy to returnAntibacterial agentsBiocideFatty liverRectal administration
The present invention refers to pharmaceutical compositions containing S-nitrosothiols as active principle. The referred compositions are intended for the treatment of the fatty liver disease and other diseases associated with the metabolic syndrome. The composition is administered either orally or rectally.
Owner:PROTAGEN
Methods and systems for indentifying and monitoring S-nitrosothiols in biological samples
InactiveUS20060154376A1Easy to modifyReduced activityEnzyme stabilisationTissue cultureFormazanBiology
The present invention describes methods and kits for determining the level of S-nitrosothiols in biological fluid samples. The method includes separating tissue or cellular matter from the biological fluid sample and then contacting the biological fluid sample with paraformaldehyde in an amount sufficient to fix free thiols thereby essentially eliminating diaphorase activity of the free thiols. The biological fluid sample is then contacted with NADPH and nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) wherein S-nitrosothiols in the biological fluid sample facilitate the reduction of NBT to NBT formazan or diformazan in the presence of paraformaldehyde. The amount of reduced NBT is measured and the determined levels correlate to the amount of S-nitrosothiols in the biological fluid sample.
Owner:WHALEN ERIN J
Compositions and techniques for localized therapy
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
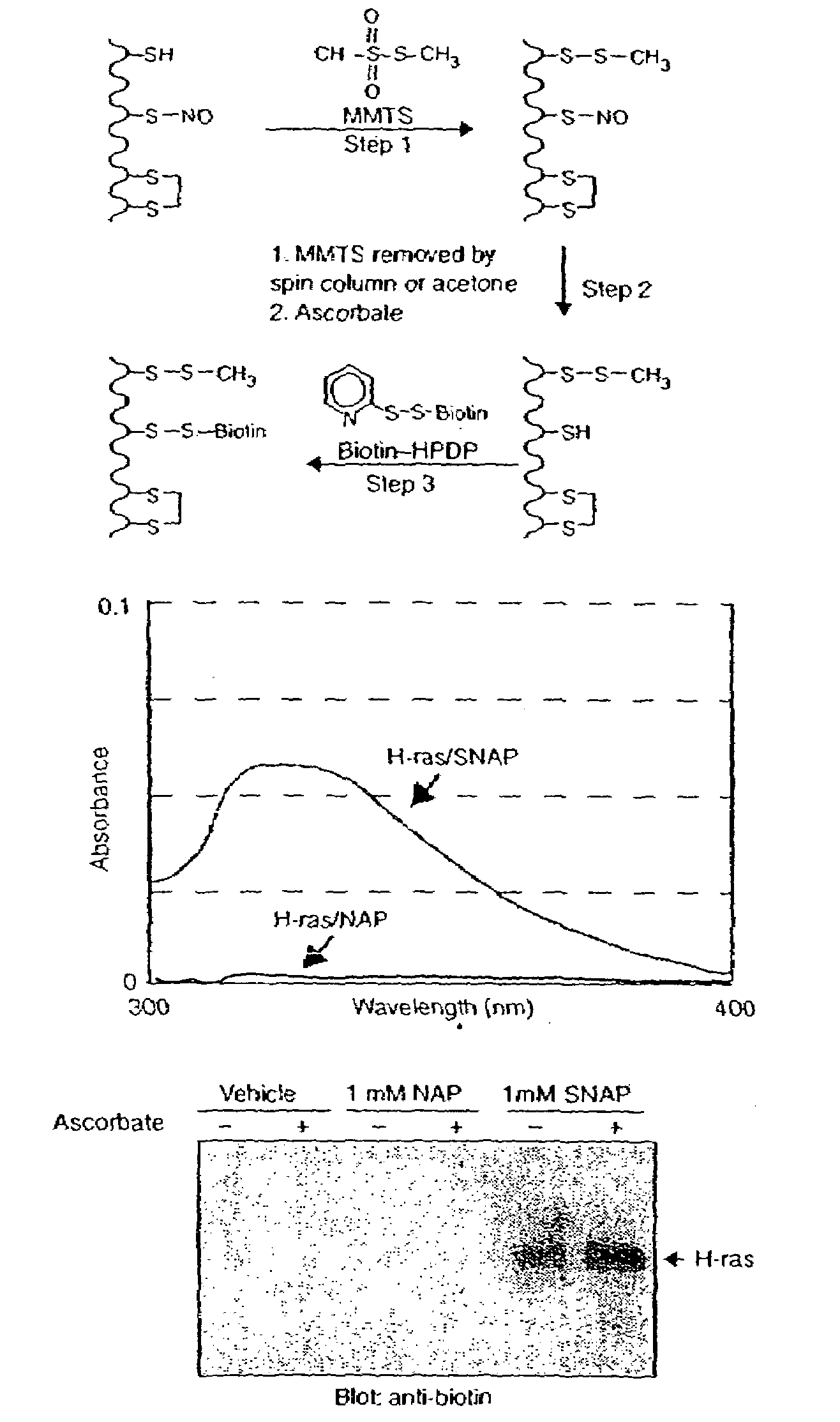
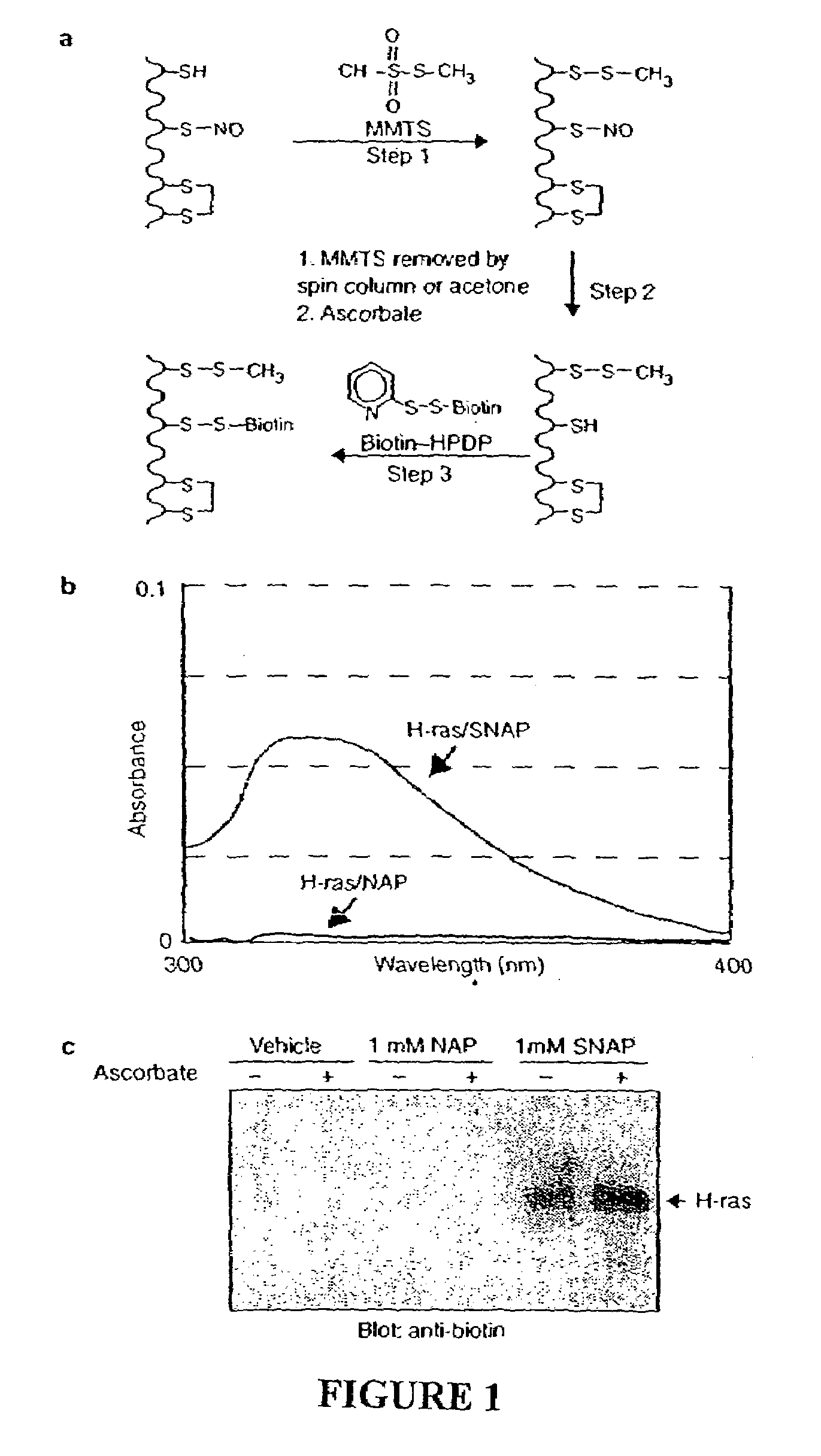
Method for assaying protein nitrosylation
Many of the effects of nitric oxide are mediated by the direct modification of cysteine residues resulting in an adduct called a nitrosothiol. A method to detect proteins which contain nitrosothiols involves several steps. Nitrosylated cysteines are converted to tagged cysteines. Tagged proteins can then be detected, for example, by immunoblotting and / or can be purified by affinity chromatography. The method is applicable to the detection of S-nitrosylated proteins in cell lysates following in vitro S-nitrosylation, as well as to the detection of endogenous S-nitrosothiols in selected protein substrates.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Improvements relating to skin dressings
A skin dressing is adapted, on activation, to release one or more S-nitrosothiols, preferably S-nitroso-L-glutathione. S-nitrosothiols decompose spontaneously to produce nitric oxide, which has beneficial effects on tissues, particularly in wound healing.
Owner:INSENSE LIMITED
Method for assaying protein nitrosylation
InactiveUS20050026227A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingCysteine thiolateS-Nitrosylation
Many of the effects of nitric oxide are mediated by the direct modification of cysteine residues resulting in an adduct called a nitrosothiol. A method to detect proteins which contain nitrosothiols involves several steps. Nitrosylated cysteines are converted to tagged cysteines. Tagged proteins can then be detected, for example, by immunoblotting and / or can be purified by affinity chromatography. The method is applicable to the detection of S-nitrosylated proteins in cell lysates following in vitro S-nitrosylation, as well as to the detection of endogenous S-nitrosothiols in selected protein substrates.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
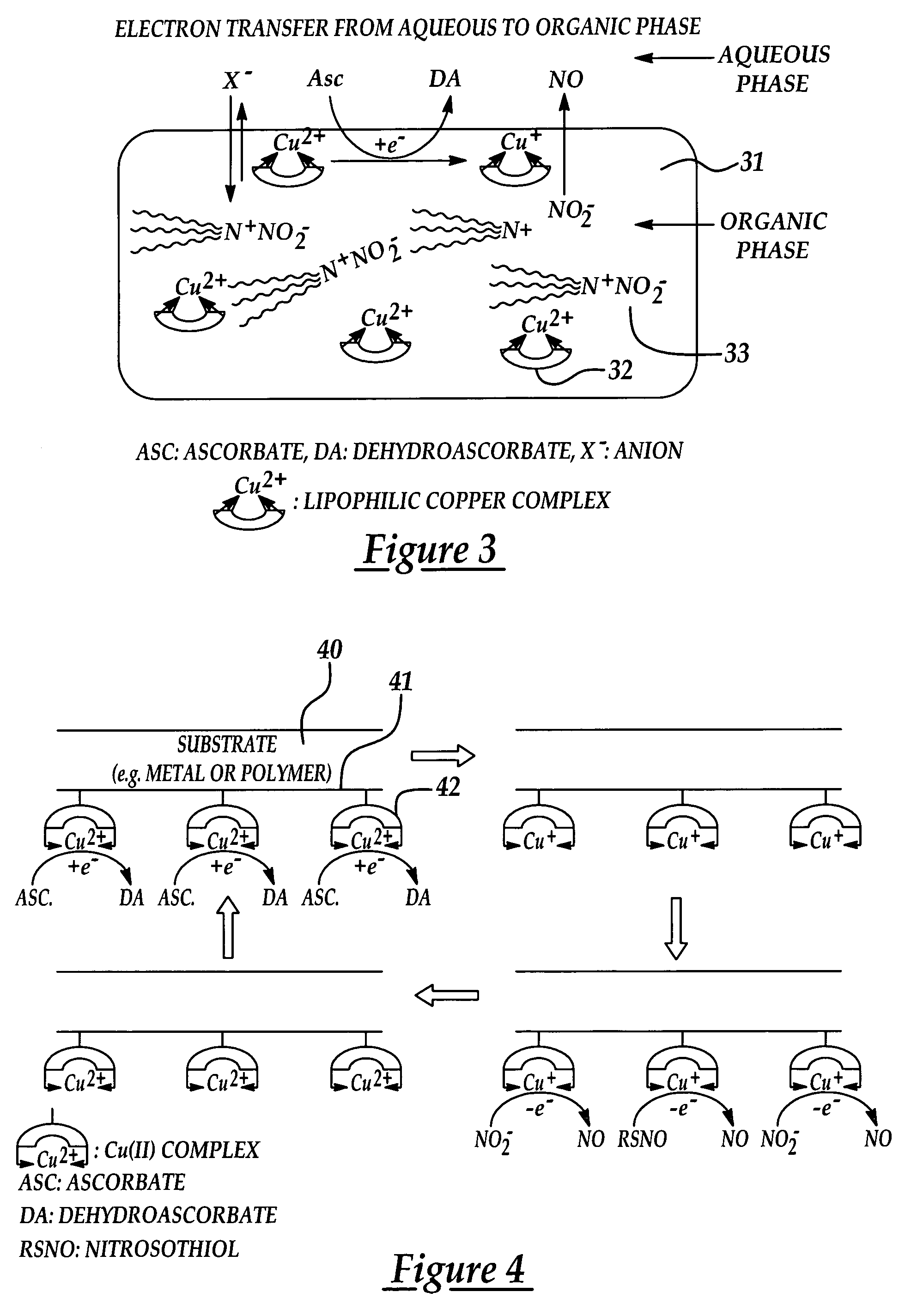
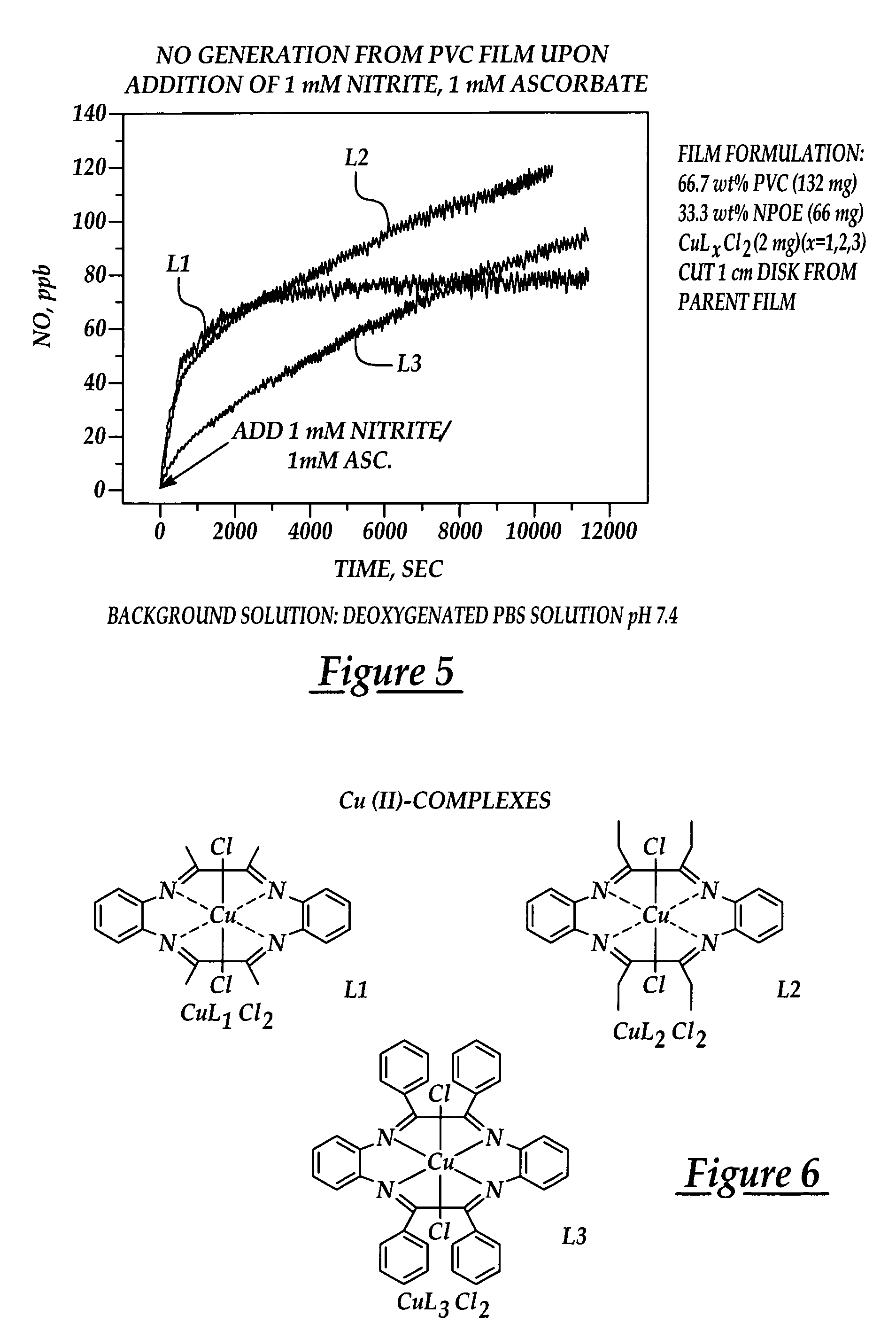
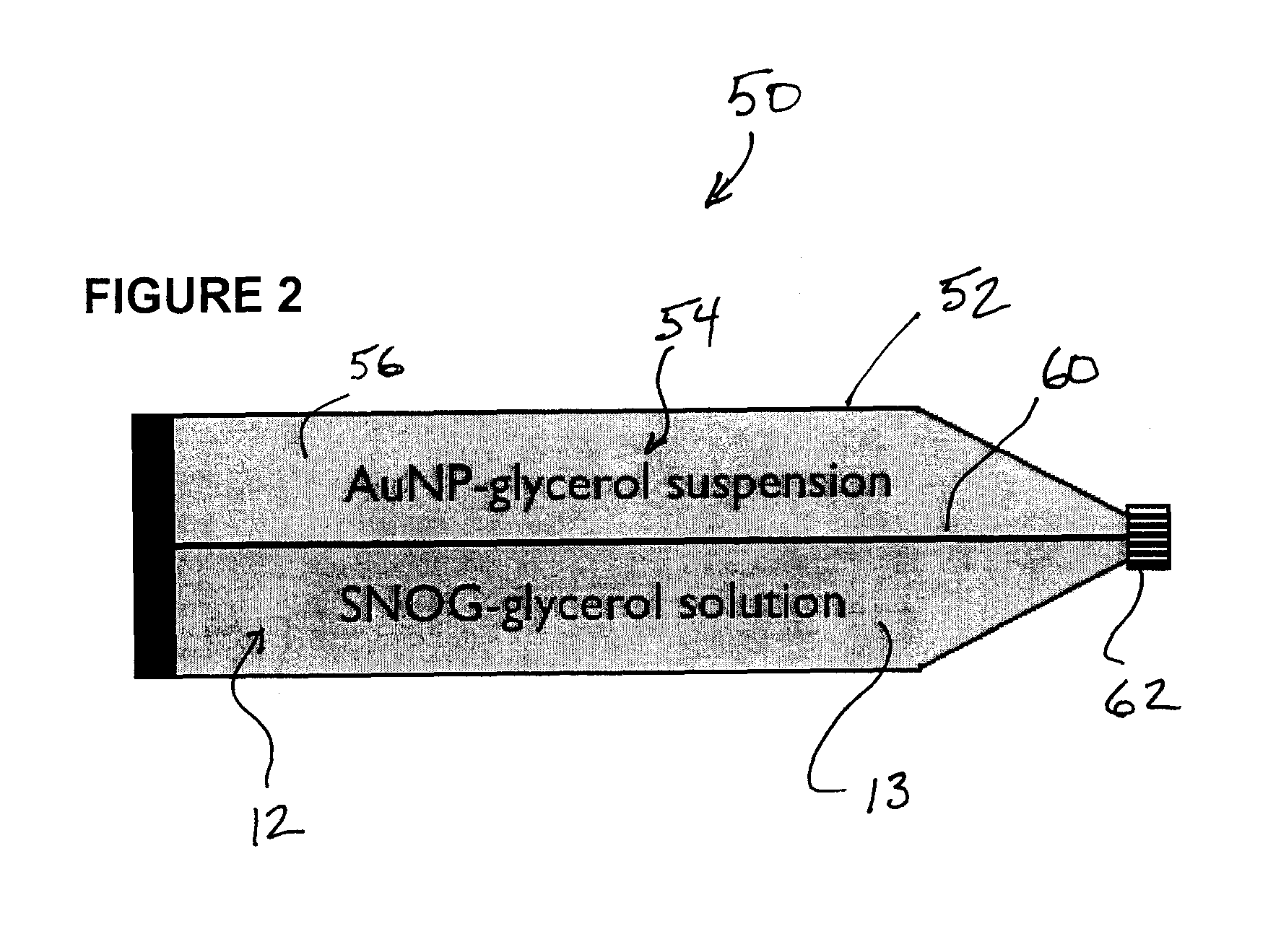
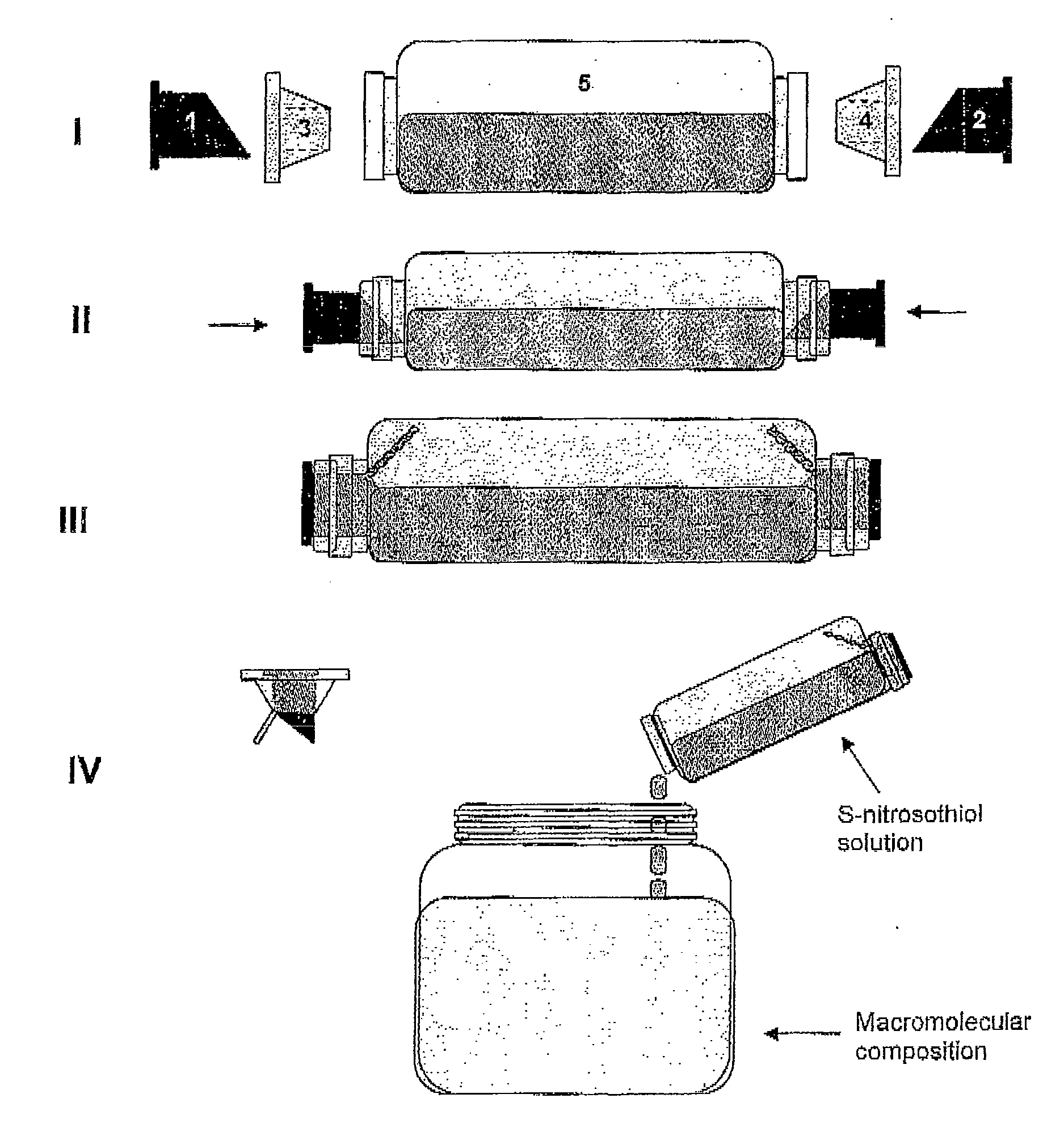
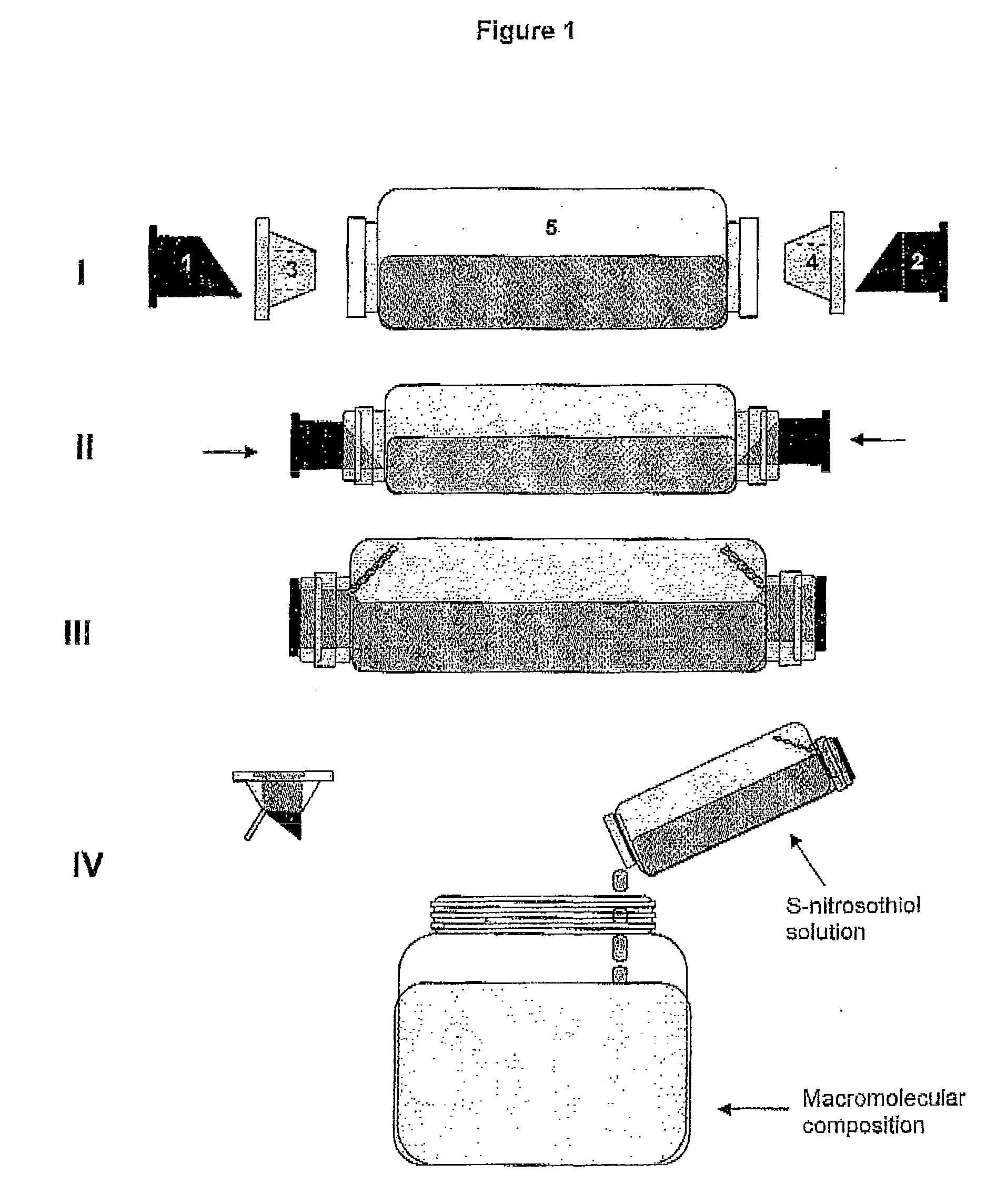
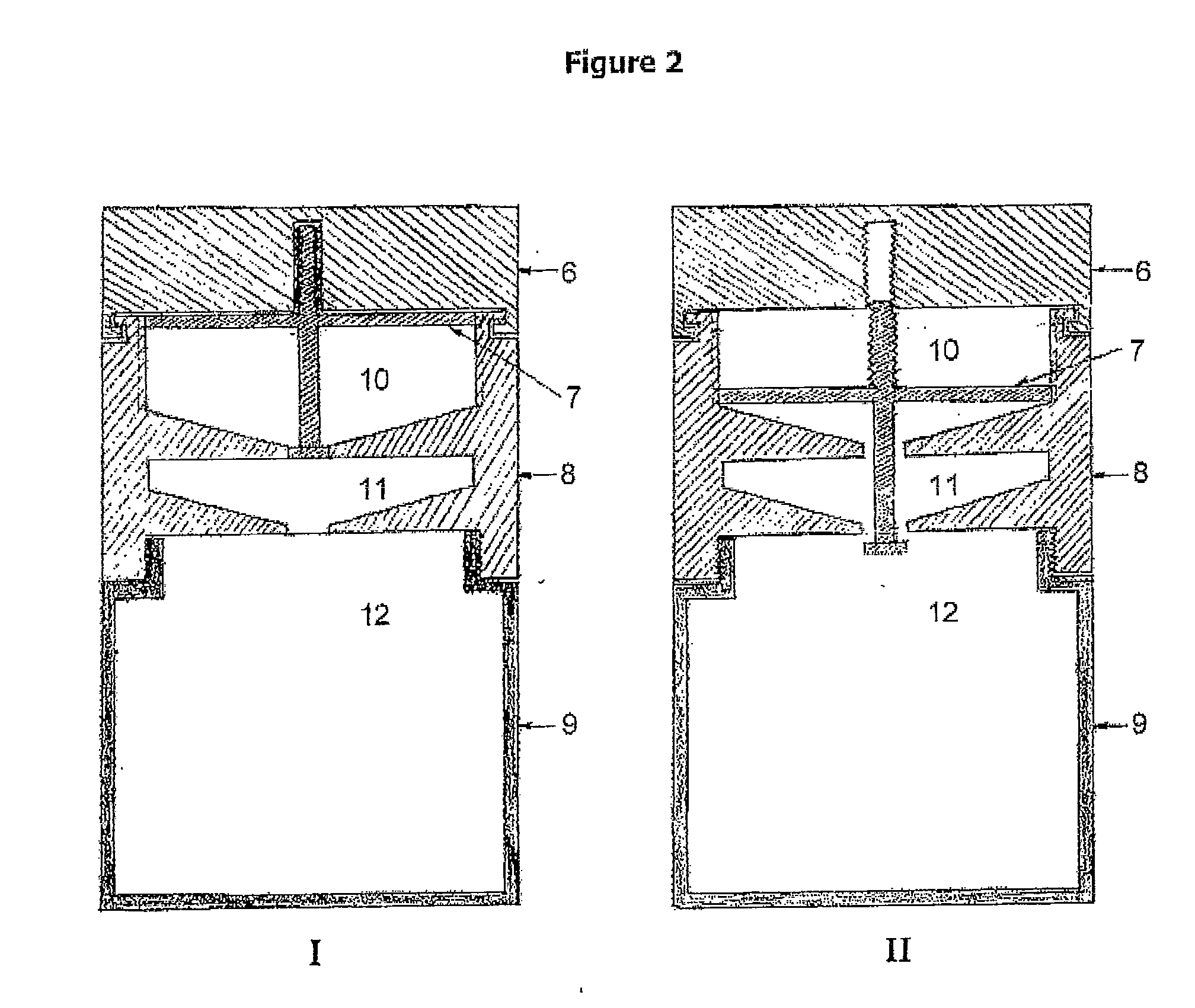
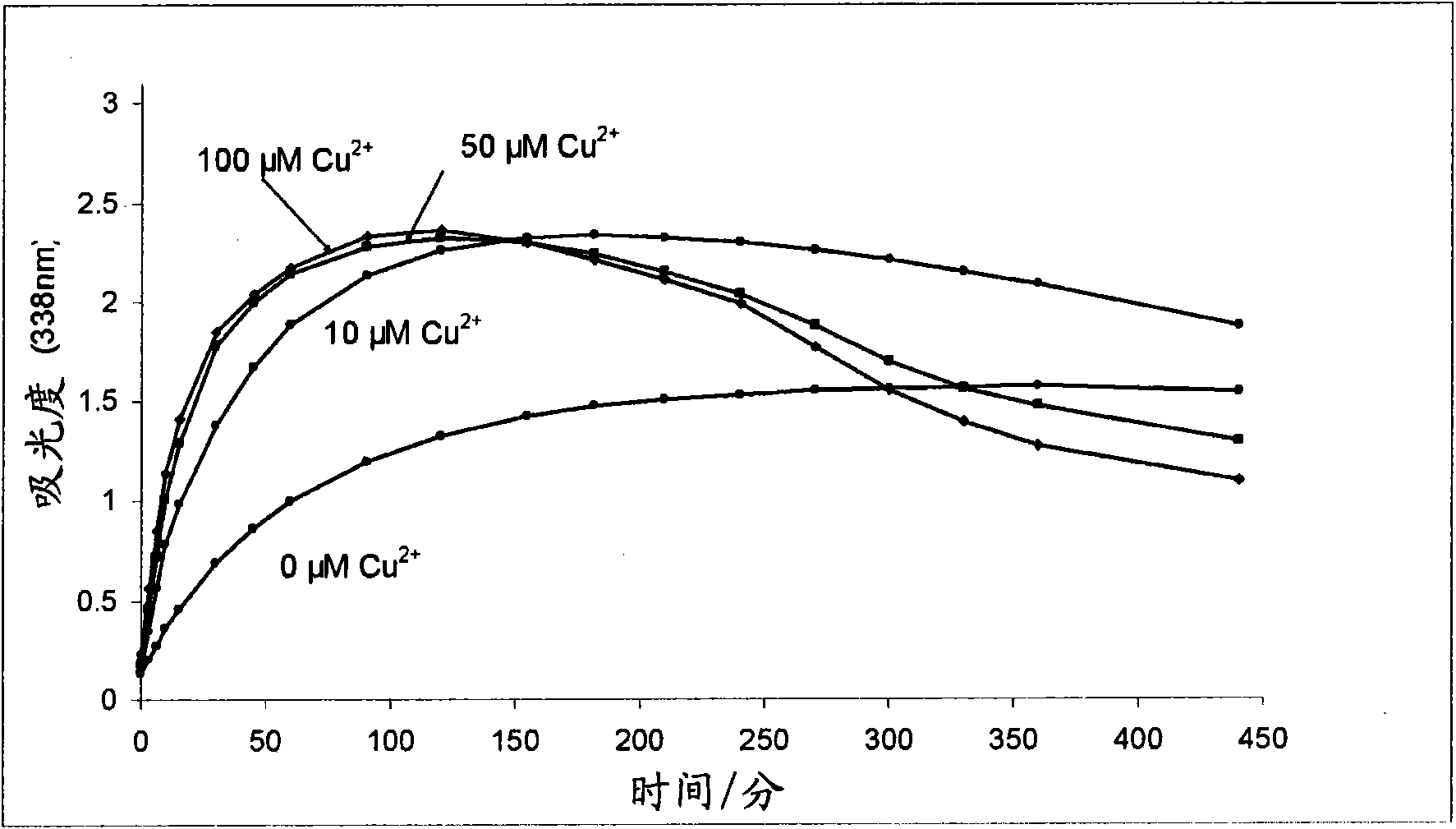
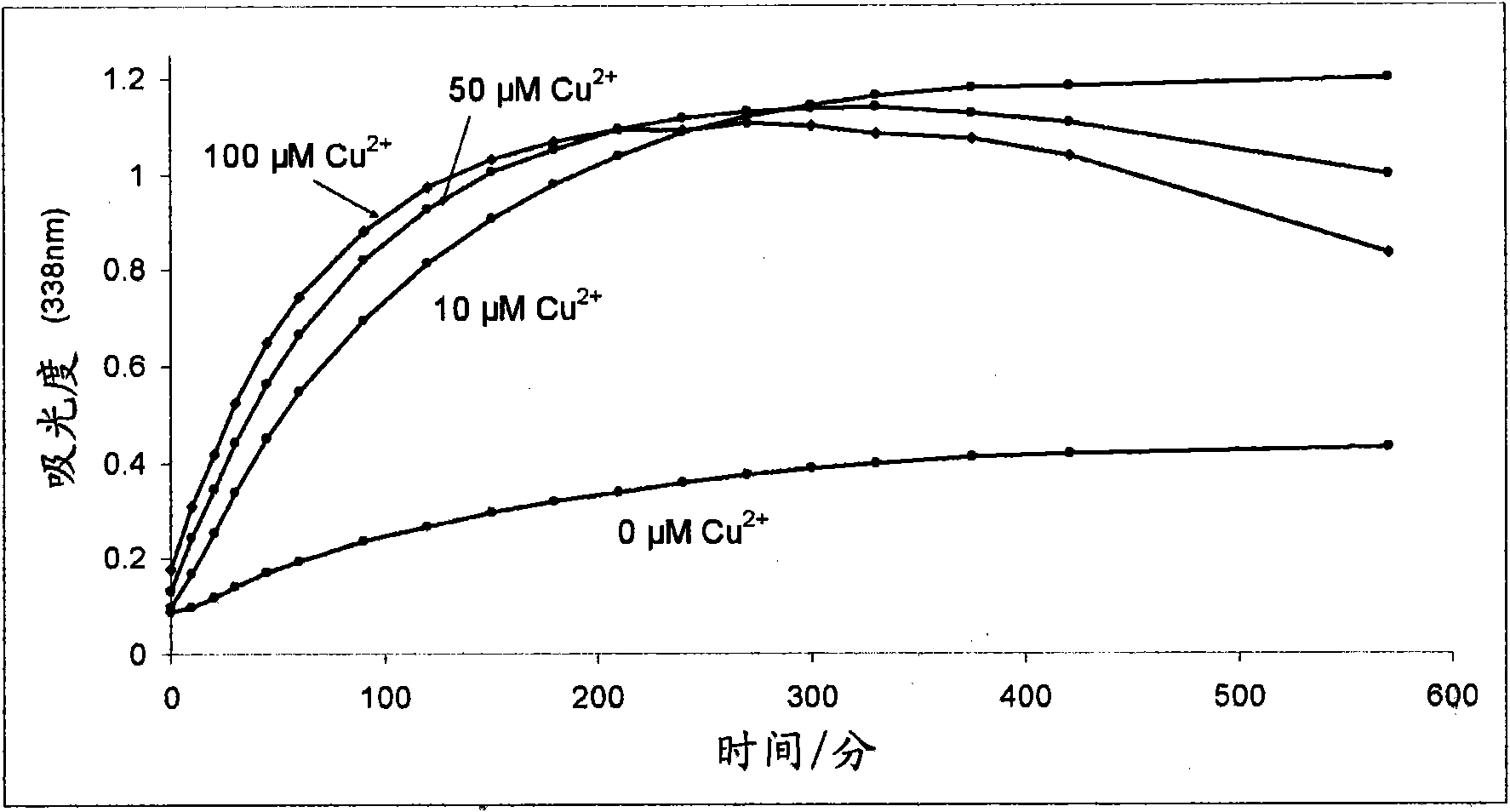
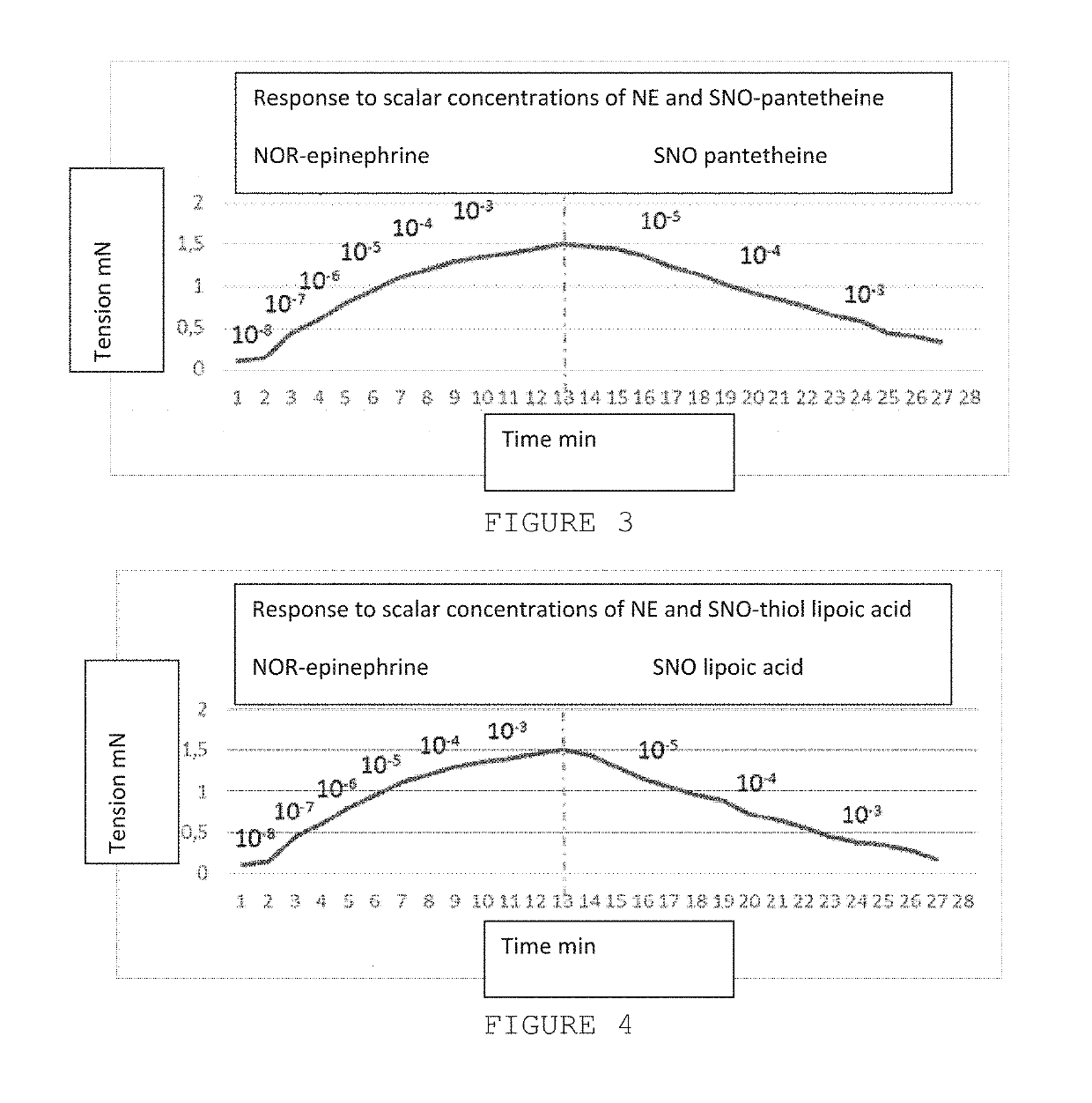
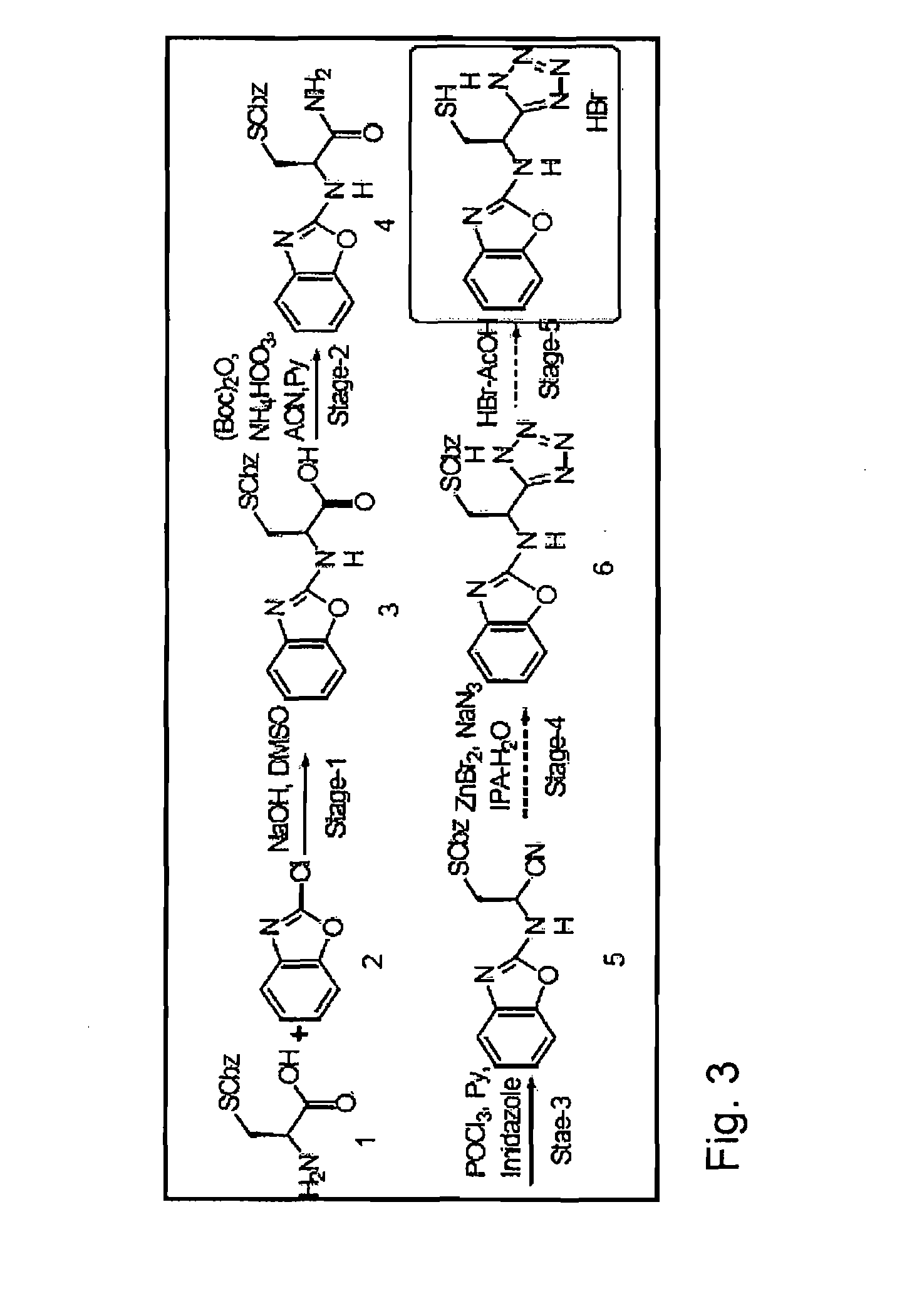
Process for synthesis and incorporation of nitric oxide donors in macromolecular compositions
InactiveUS20090311292A1Improve thermal stabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTripeptide ingredientsSufficient timeDelivery vehicle
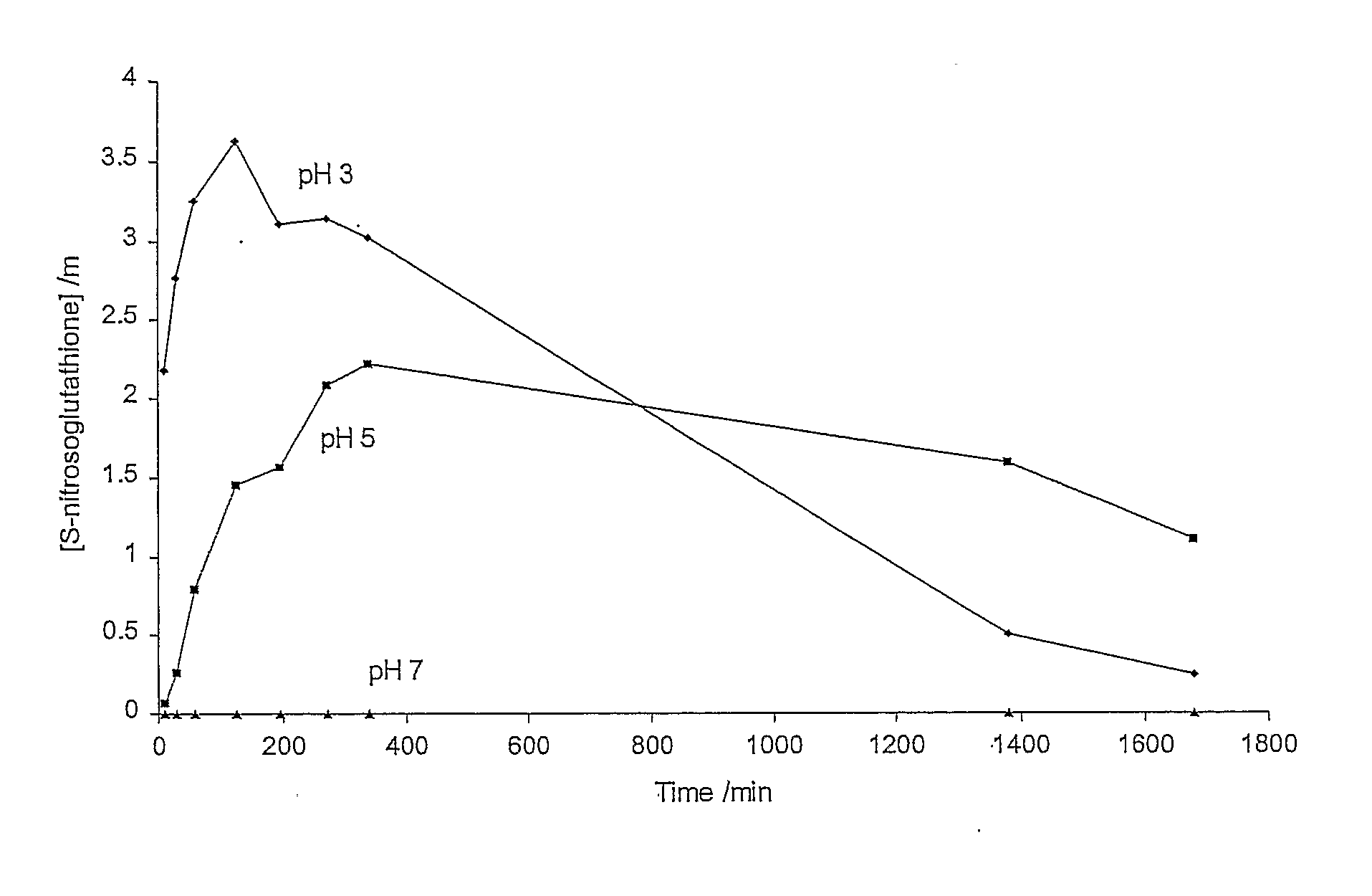
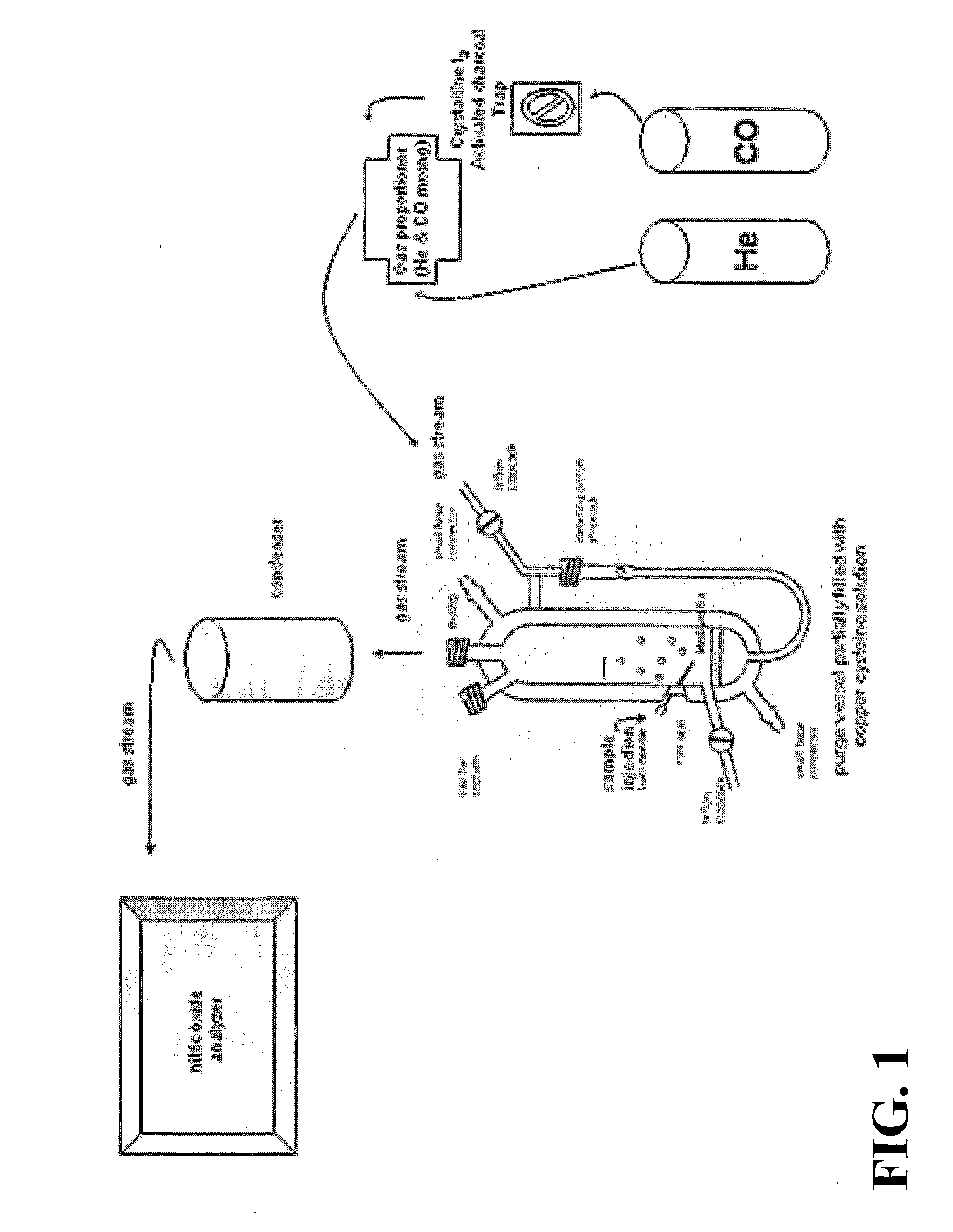
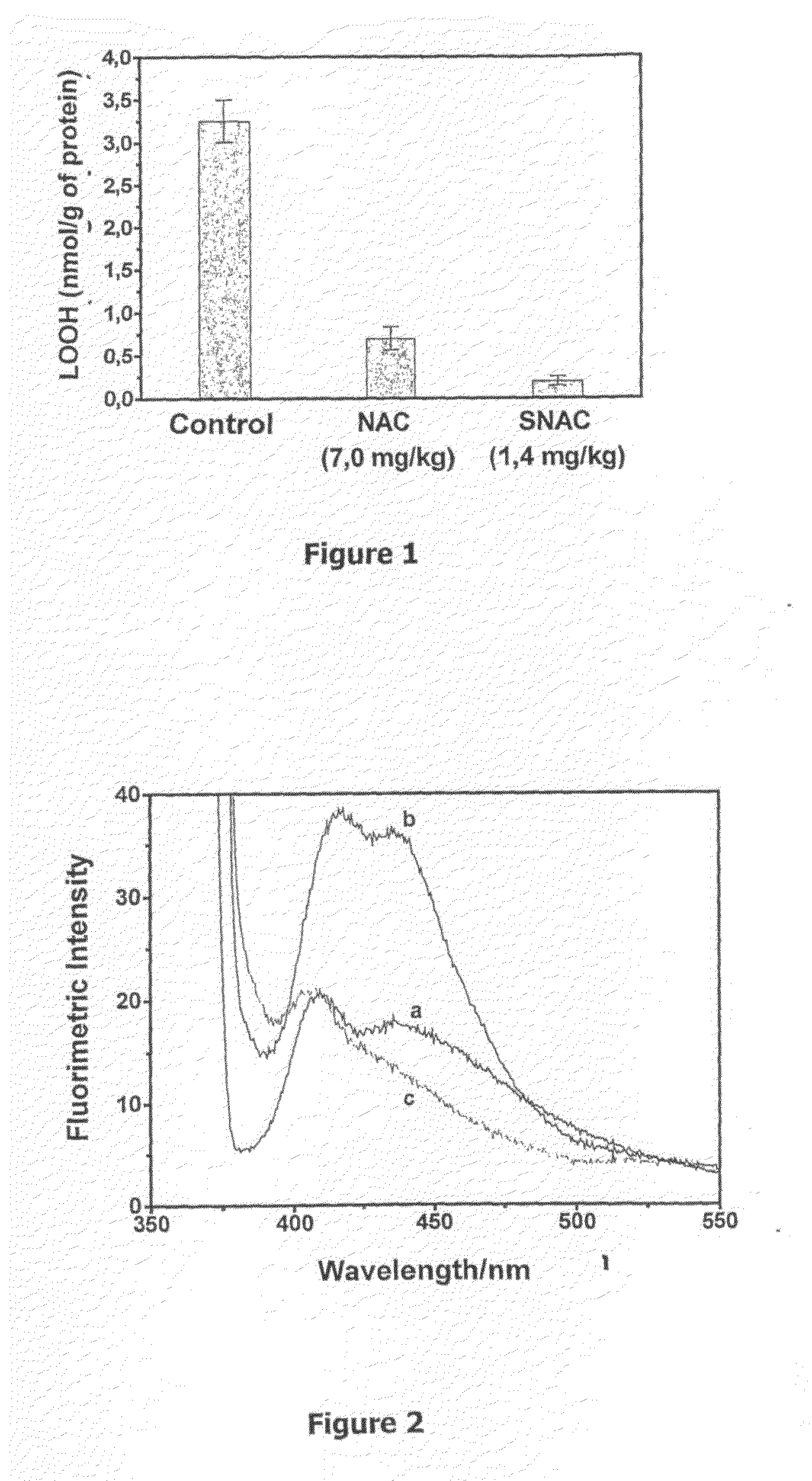
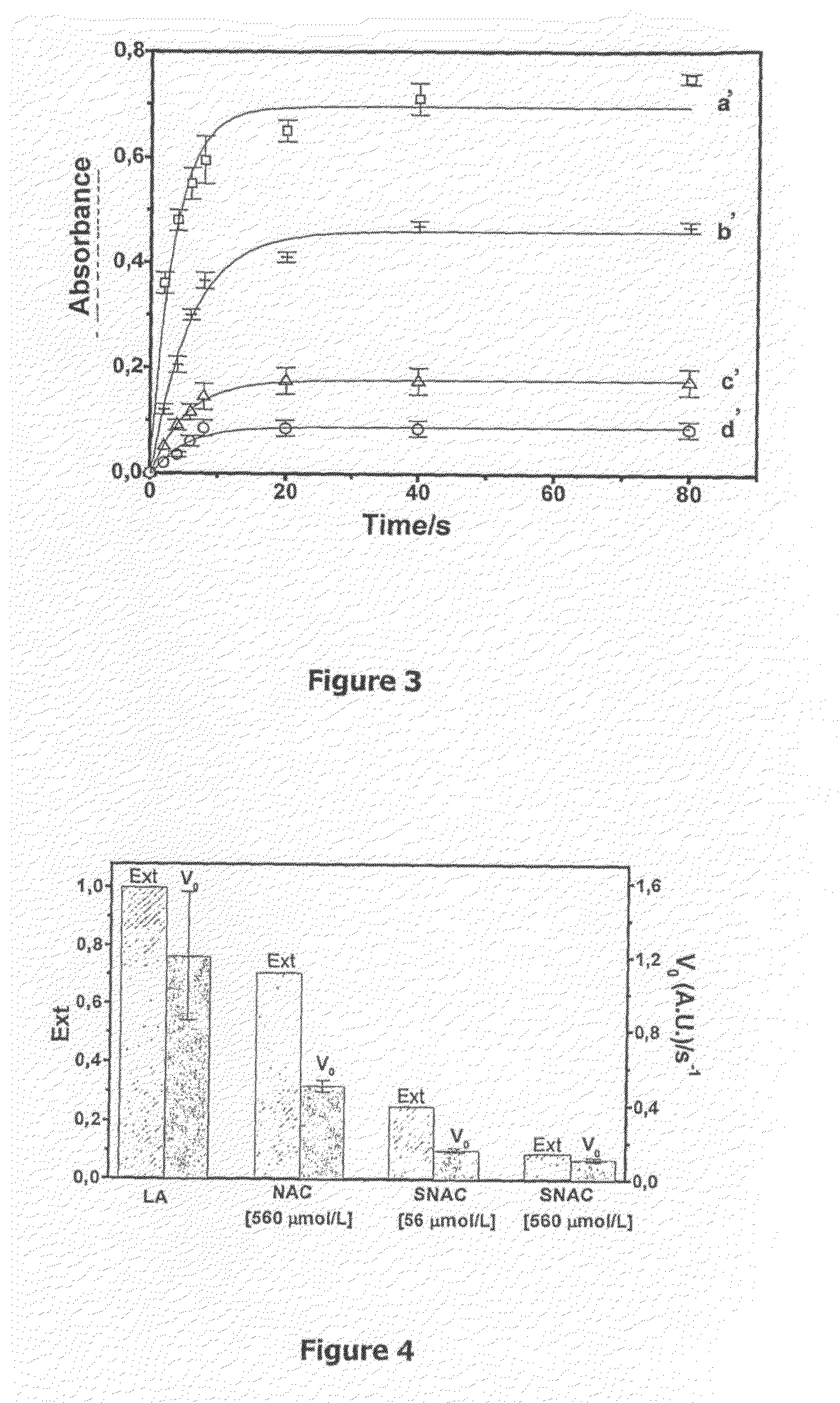
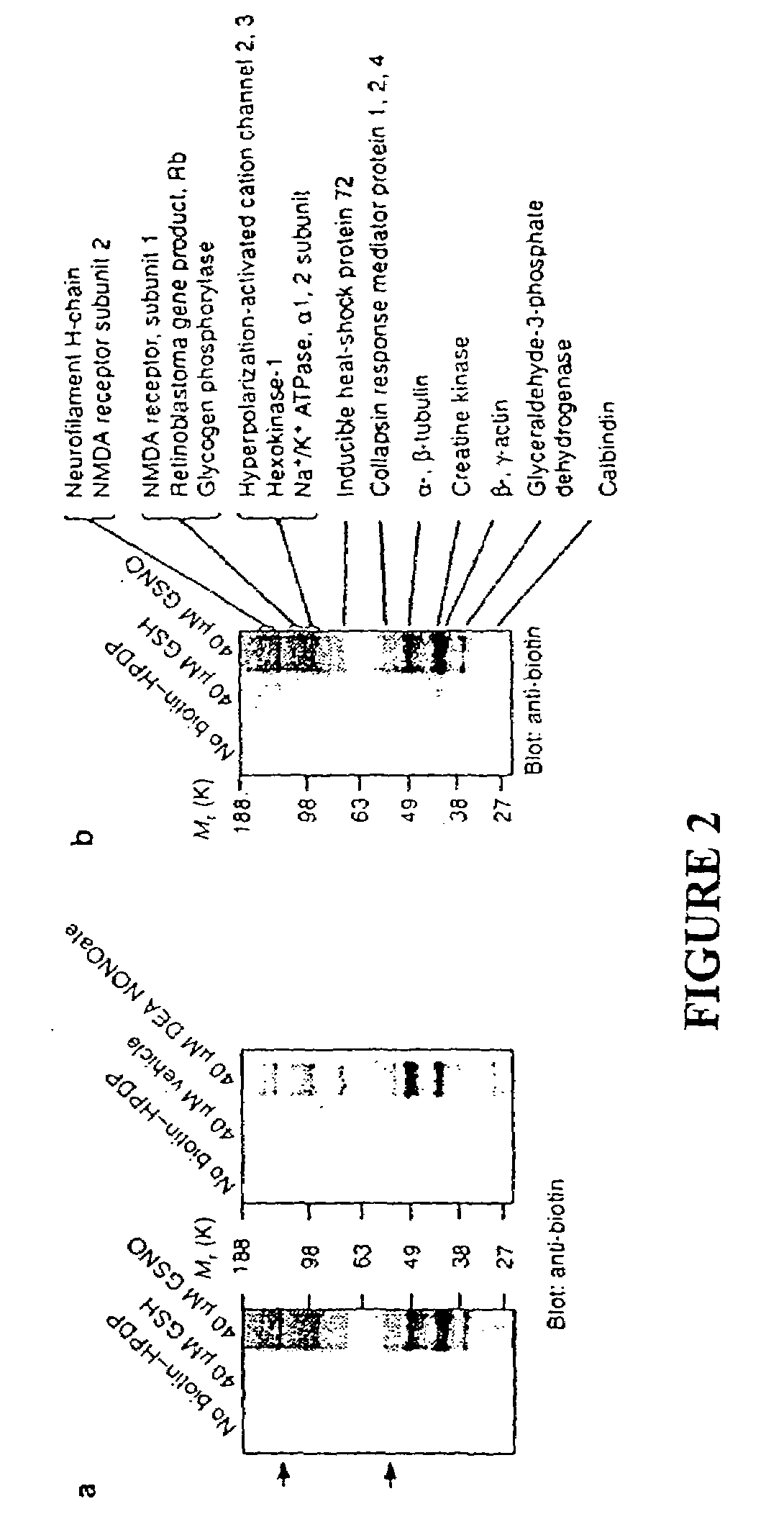
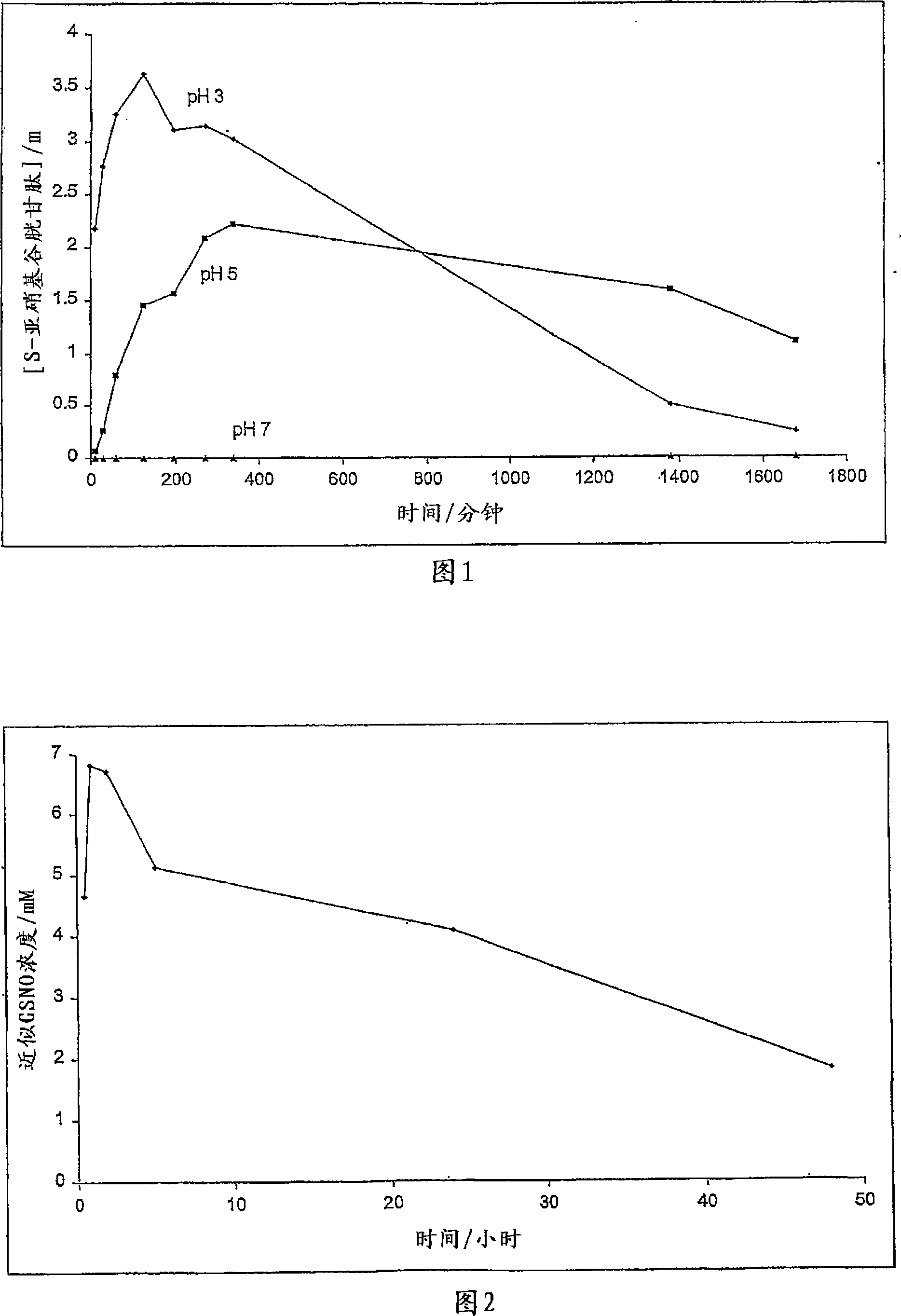
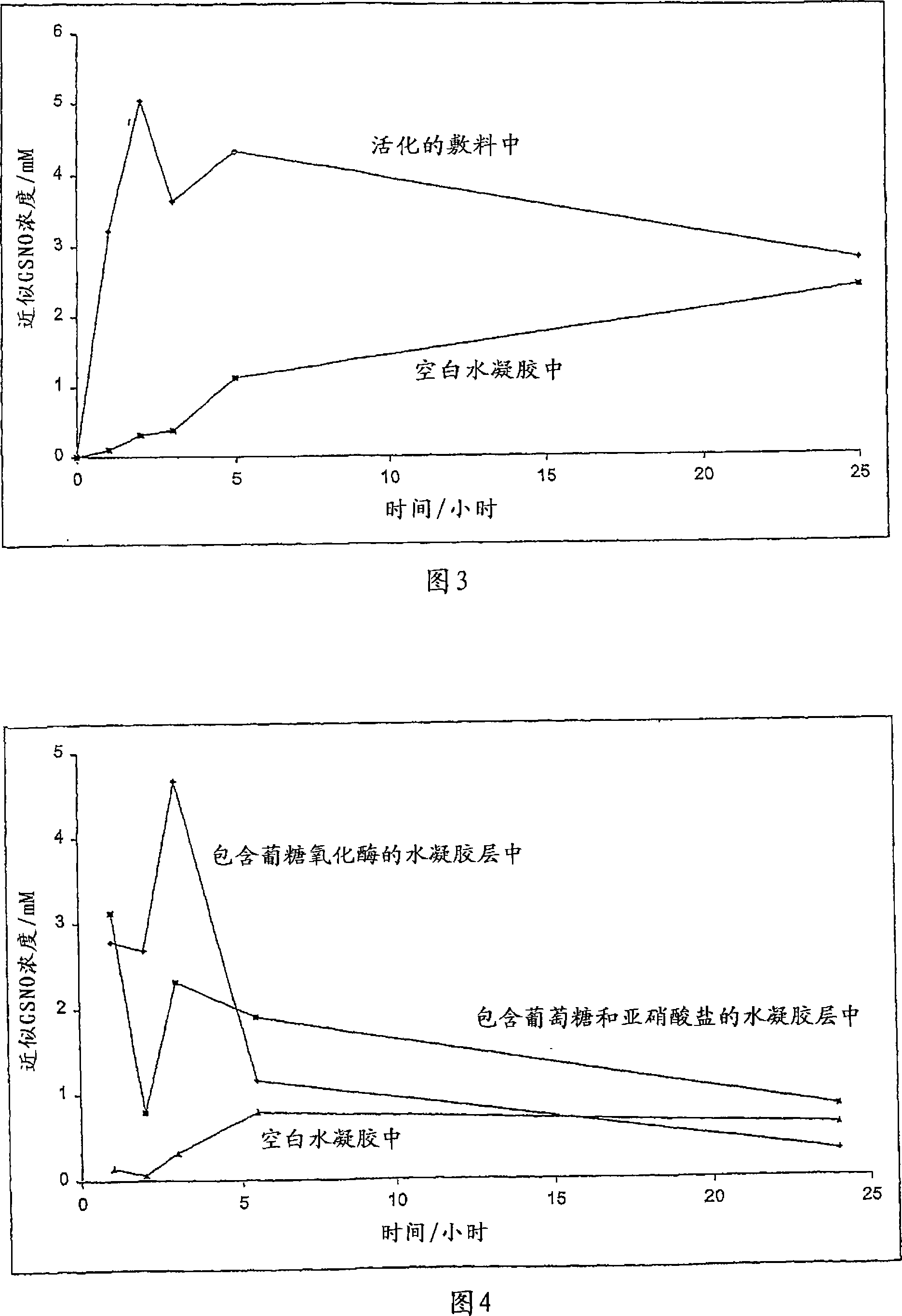
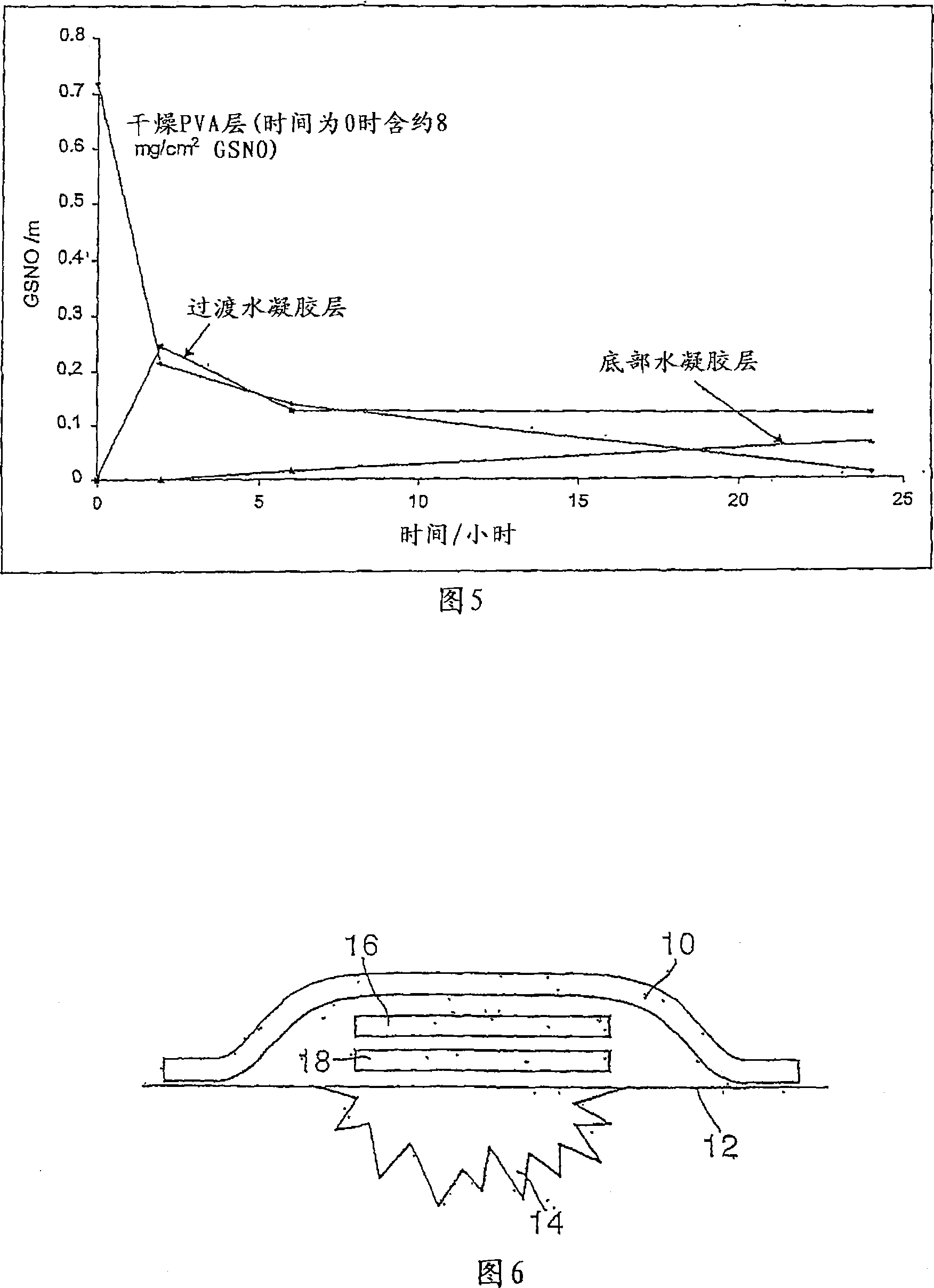
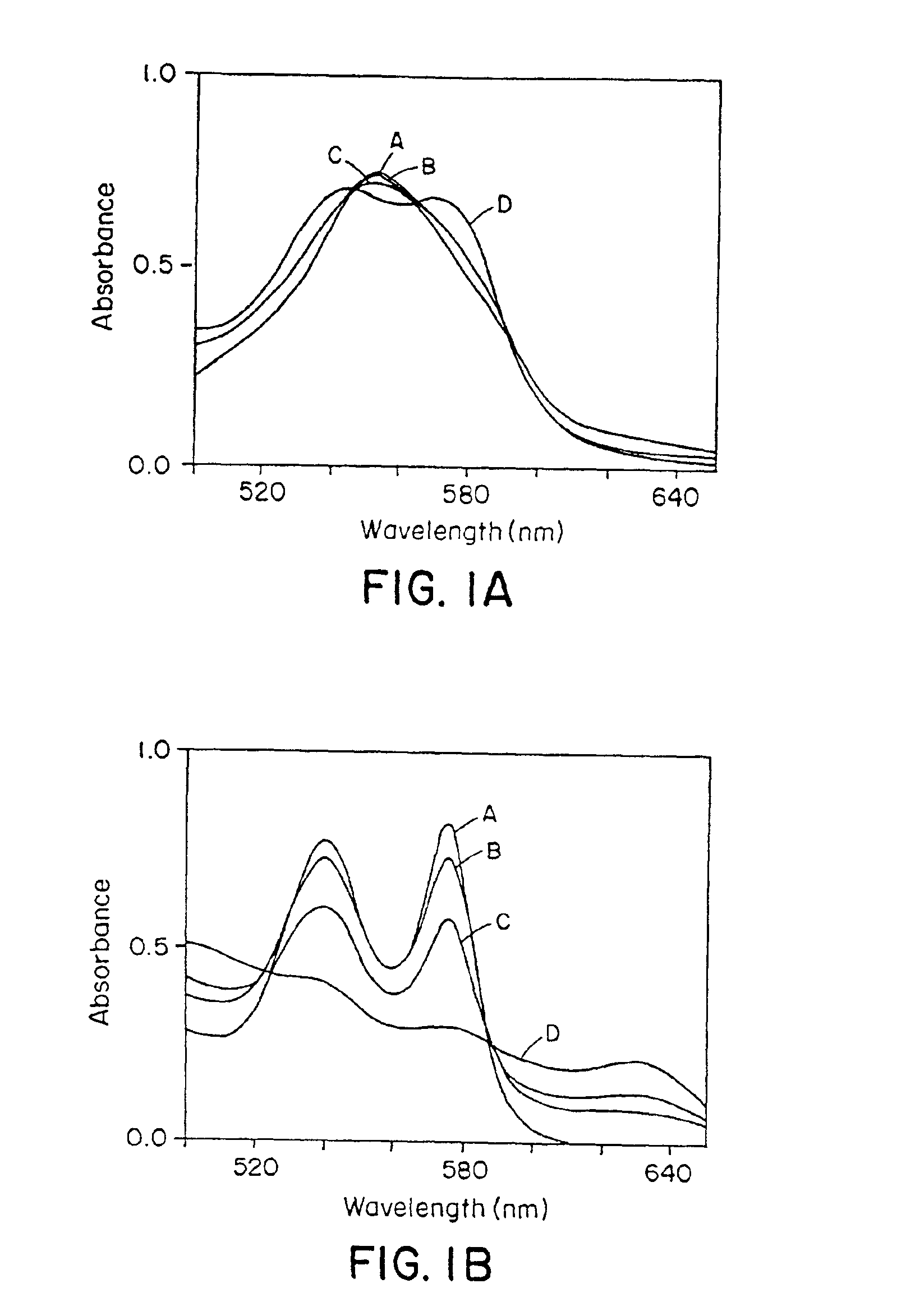
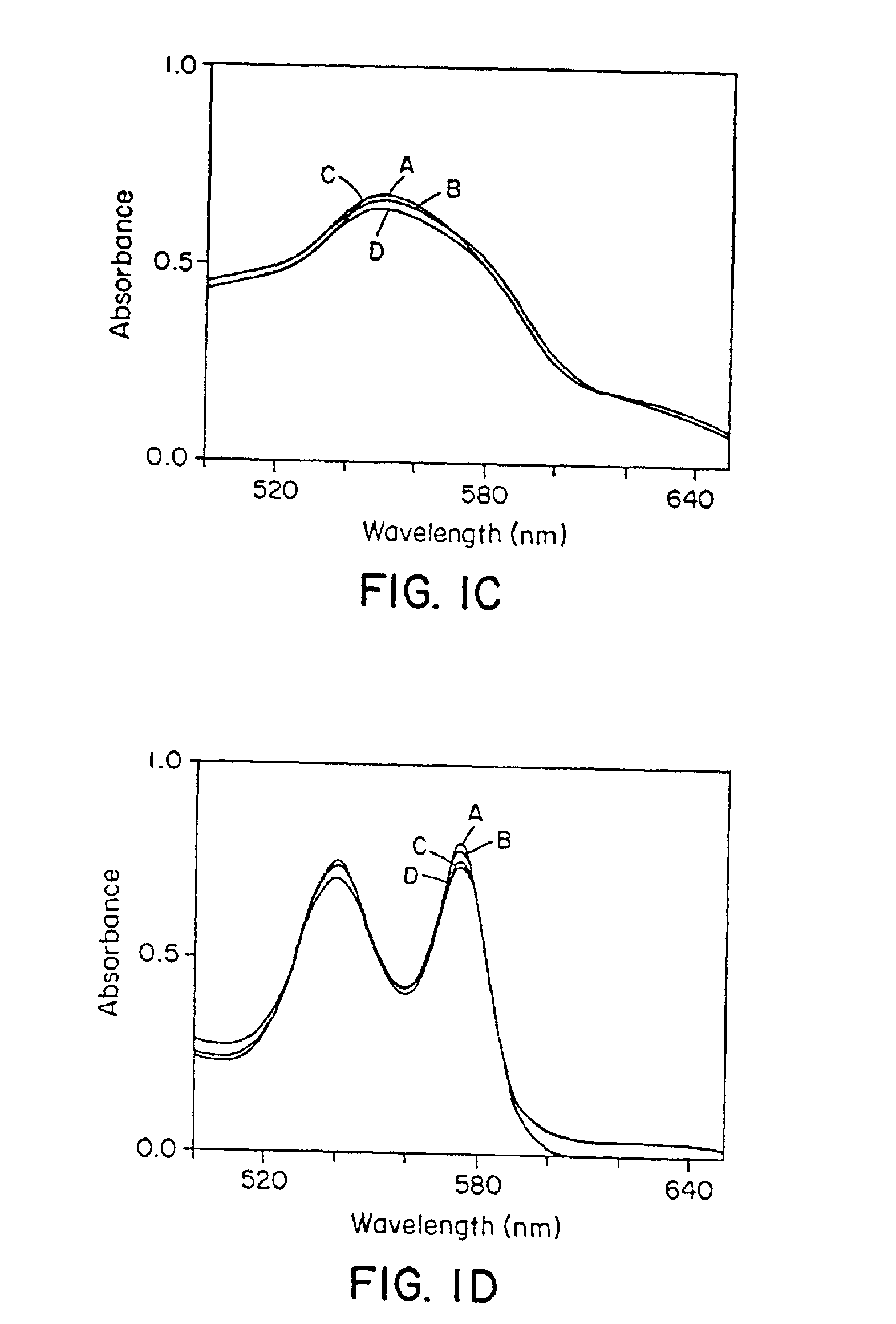
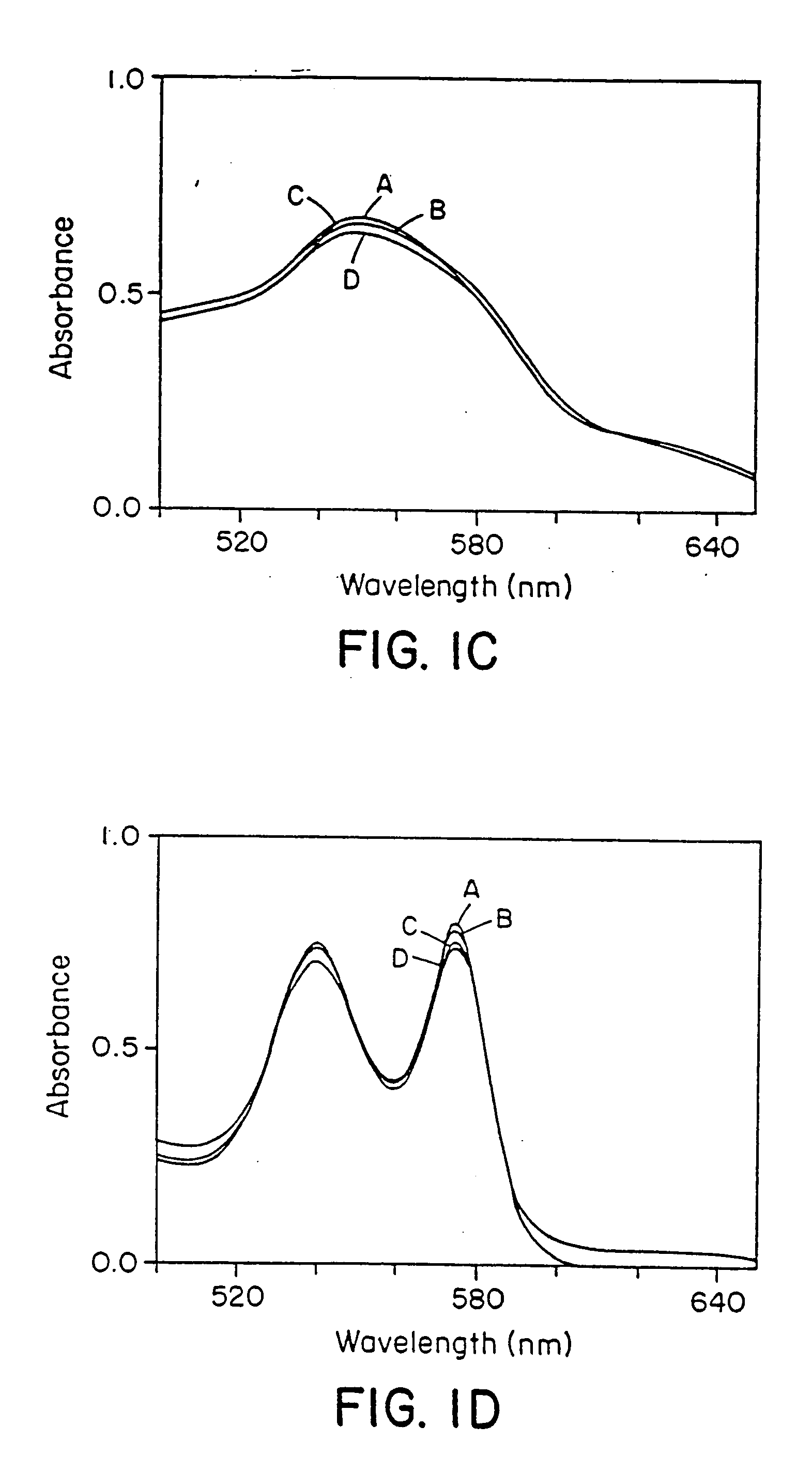
The present invention describes a process for the synthesis of S-nitrosothiols and the subsequent incorporation of these compounds in hydrophilic macromolecular compositions. By the process described herein, the S-nitrosothiols are synthesized in a device (FIG. 2) in a first step from the S-nitrosation reaction of their respective precursor thiols (A), promoted by a mechanical action that puts the thiols in contact with the nitrous acid formed from nitrite anions in acidic medium (B), and in a second mechanical operation, the freshly formed S-nitrosothiols are incorporated in an application vehicle (C) based on hydrophilic macromolecular compositions that increases their thermal stability. Therefore, the process under consideration combine the pre-application synthesis of S-nitrosothiols with their subsequent incorporation in delivery vehicles, with provide a relative stabilization of the S-nitrosothiols for sufficient periods so that the formulations prepared by this process may be stored in a domestic refrigerator during its time of use in its several possible applications.
Owner:CRISTALIA PROD QUI FARM LTDA +1
Improvements relating to skin dressings
InactiveCN101878046AIncrease spawn rateIncrease speedAbsorbent padsDermatological disorderMedicineBiological activation
Owner:INSENSE LIMITED
Red blood cells loaded with S-nitrosothiol and uses therefor
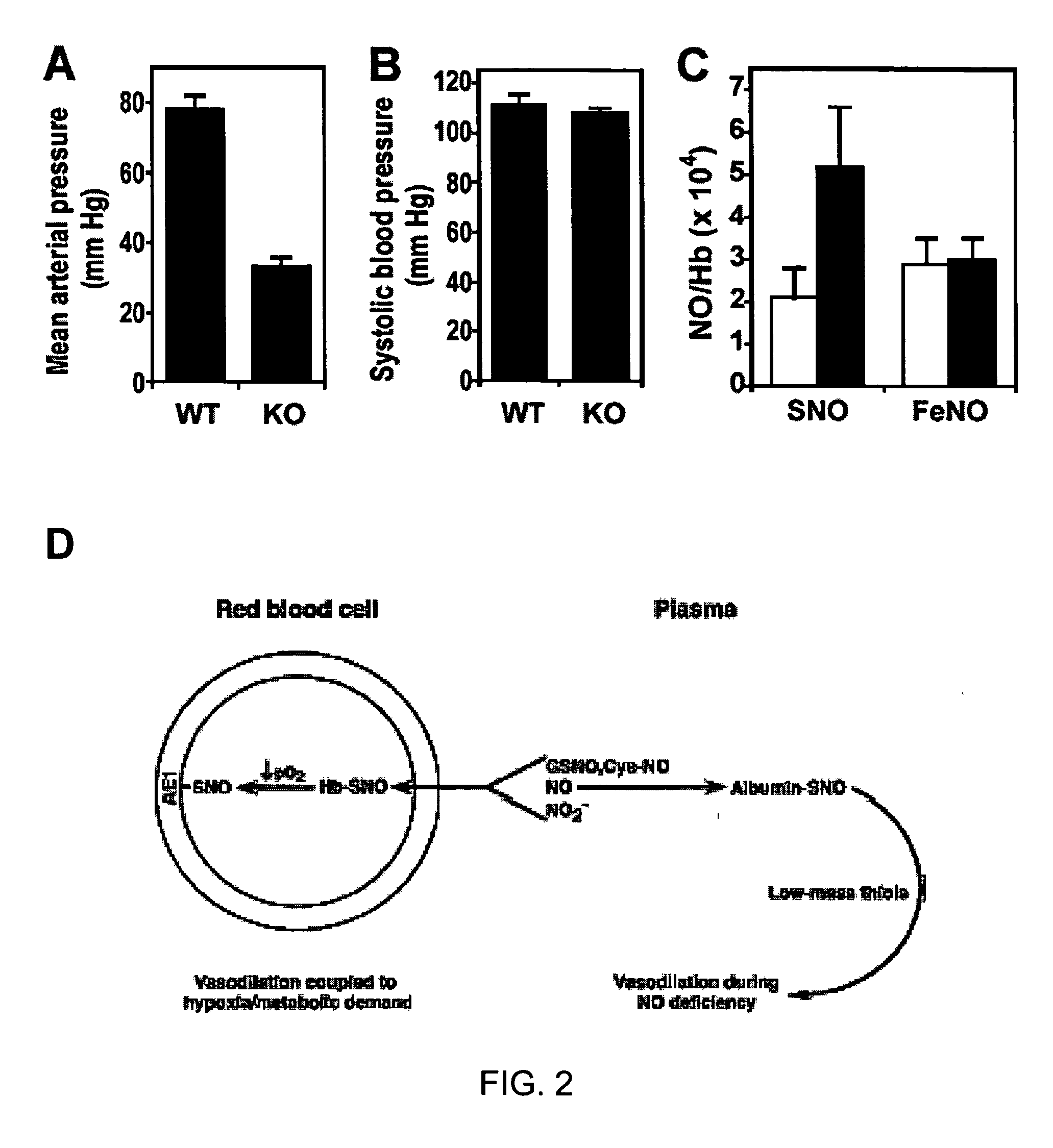
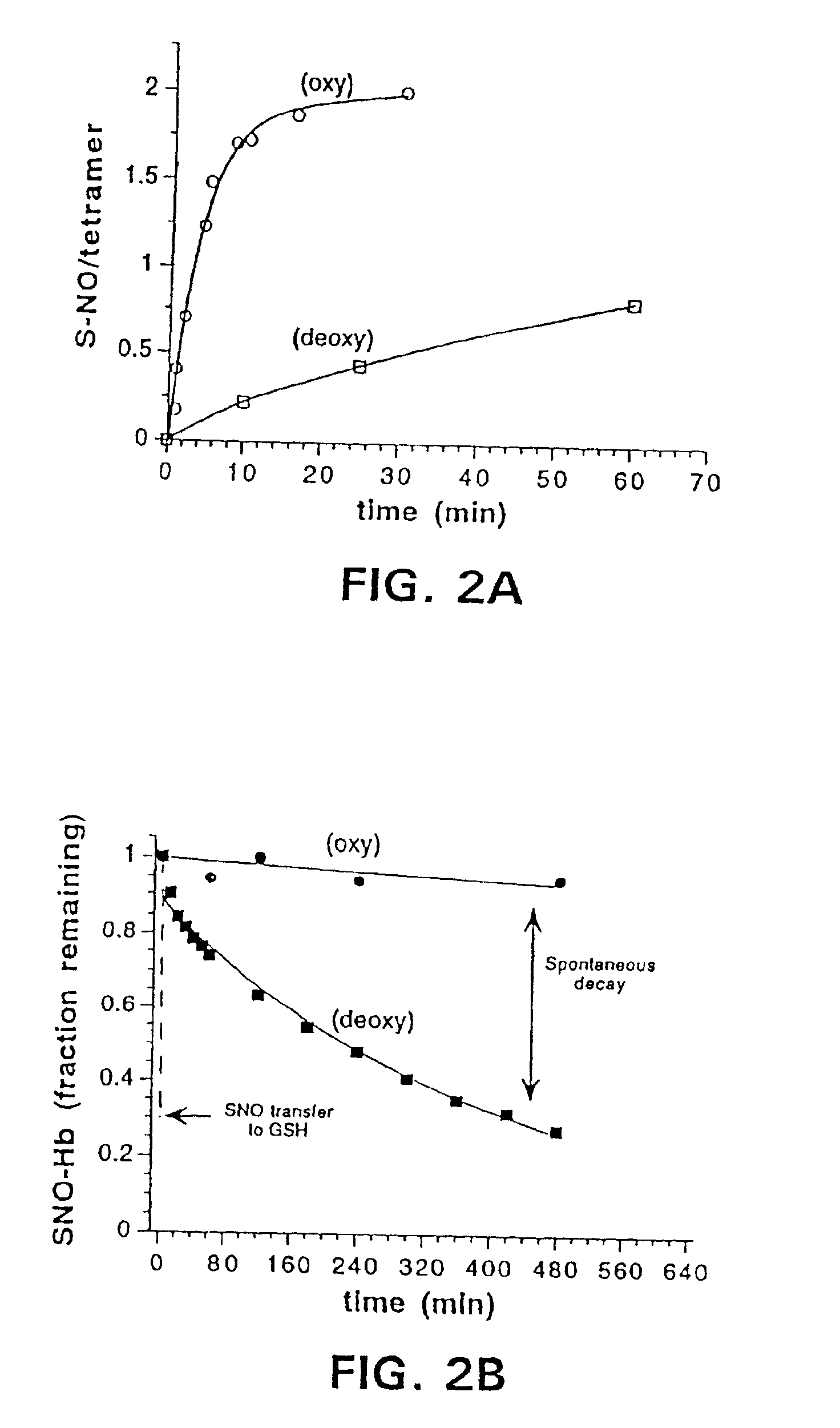
Red blood cells can be loaded with low molecular weight nitrosylating agents, such as S-nitrosothiols, to act as a delivery system for NO+ groups to tissues. Loaded red blood cells can be used in methods of therapy for conditions which are characterized by abnormal O2 metabolism of tissues, oxygen-related toxicity, abnormal vascular tone, abnormal red blood cell adhesion, or abnormal O2 delivery by red blood cells. Such treatment of red blood cells can be extended to in vivo therapies, with the object to achieve an increase in the ratio of red blood cell S-nitrosothiol to hemoglobin.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Formulation For Release Of Nitric Oxide
ActiveUS20190282610A1Facilitates inversionImprove microcirculationInorganic active ingredientsSexual disorderSolventReducing agent
A composition for releasing nitric oxide which provides a rapid release of nitrogen monoxide, and also allows formation of S-nitrosothiol compounds which provide a slower extended release of nitrogen monoxide. A composition kit includes two components that are mixed together to initiate nitric oxide release. The kit includes: a liquid phase comprising a solvent and at least one reducing agent; and a solid phase comprising a nitrate and / or nitrite salt, copper ions and at least one thiol. A method of treating sexual dysfunction involves topically applying the composition to an area of the subject to be treated.
Owner:GLANOTECH LTD
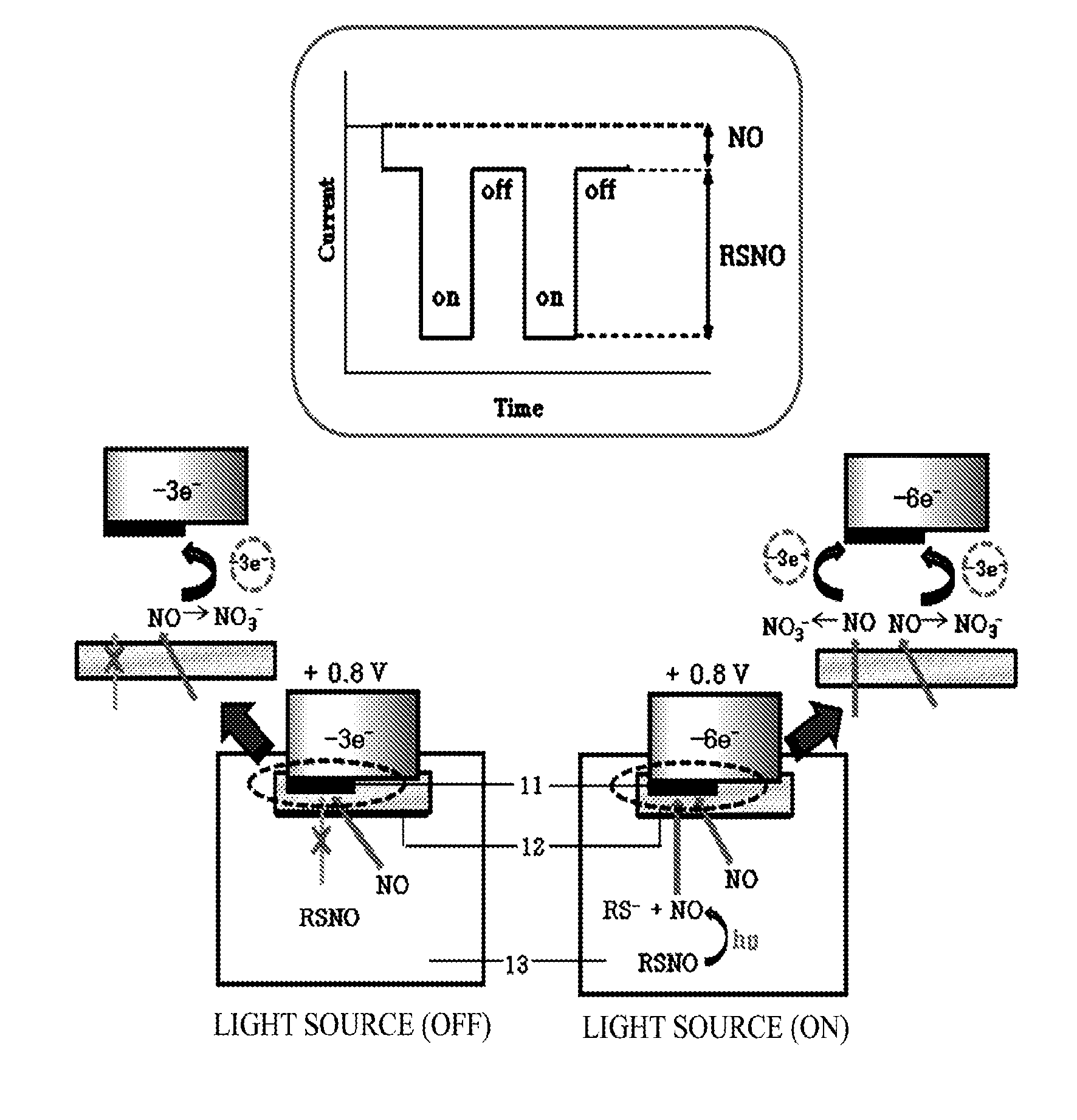
Amperometric sensors and devices for measuring concentration of s-nitrosothiols based on photo-induced decomposition of s-nitrosothiols
ActiveUS20140014512A1Reliably measureEasy to manufactureCurrent/voltage measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesDecompositionCurrent sensor
Provided are an amperometric sensor and device for electrochemically quantifying nitrosothiol (RSNO), which is associated with storage and delivery of nitric oxide (NO) in the human body. The amperometric sensor for measuring a concentration of RSNO includes an electrode configured to measure an electric current generated by an oxidation reaction of NO, and a means configured to start and stop photo-induced decomposition of RSNO. Here, the electric current is measured by the oxidation reaction of NO before and after the photo-induced decomposition of RSNO. The amperometric sensor may measure separate signals of RSNO and NO, which are present in the sample at the same time, using one electrode, thereby preventing an inhibition action caused by NO during the measurement of RSNO. Also, the amperometric sensor is simple in structure and easy to manufacture and may be applied to manufacture of a small electrode, and thus may be developed as a sensor for in vivo measurements.
Owner:I SENS INC
Red blood cells loaded with s-nitrosothiol and uses therefor
Red blood cells can be loaded with low molecular weight nitrosylating agents, such as S-nitrosothiols, to act as a delivery system for NO+ groups to tissues. Loaded red blood cells can be used in methods of therapy for conditions which are characterized by abnormal O2 metabolism of tissues, oxygen-related toxicity, abnormal vascular tone, abnormal red blood cell adhesion, or abnormal O2 delivery by red blood cells. Such treatment of red blood cells can be extended to in vivo therapies, with the object to achieve an increase in the ratio of red blood cell S-nitrosothiol to hemoglobin.
Owner:STAMLER JONATHAN S +3
Nitric oxide generating formulations and kits
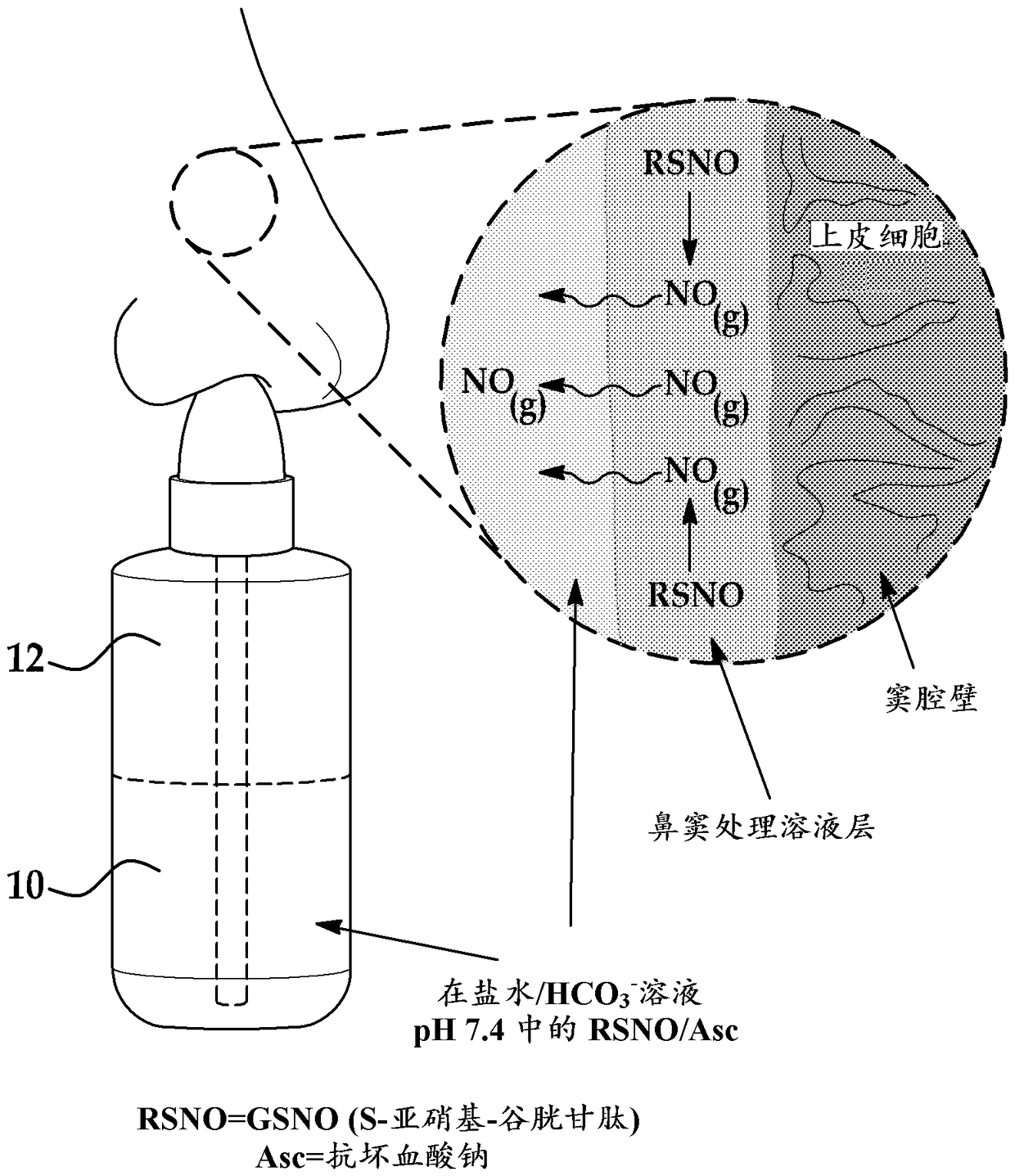
An example of a nitric oxide generating formulation includes an S-nitrosothiol (RSNO) powder, a salt, and an additive. The additive is to control or accelerate a rate of release of nitric oxide (NO) from RSNO after the RSNO powder, the salt, and additive are dissolved into a liquid carrier. The nitric oxide generating formulation may be part of a kit that includes a container for dissolving the components into a liquid carrier. One of the kits may be used to prevent and / or treat sinonasal infections and another of the kits may be used to create antimicrobial lock solutions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and systems for indentifying and monitoring S-nitrosothiols in biological samples
InactiveUS7507585B2Reduced activityHigh activityEnzyme stabilisationTissue cultureFormazanParaformaldehyde
The present invention describes methods and kits for determining the level of S-nitrosothiols in biological fluid samples. The method includes separating tissue or cellular matter from the biological fluid sample and then contacting the biological fluid sample with paraformaldehyde in an amount sufficient to fix free thiols thereby essentially eliminating diaphorase activity of the free thiols. The biological fluid sample is then contacted with NADPH and nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) wherein S-nitrosothiols in the biological fluid sample facilitate the reduction of NBT to NBT formazan or diformazan in the presence of paraformaldehyde. The amount of reduced NBT is measured and the determined levels correlate to the amount of S-nitrosothiols in the biological fluid sample.
Owner:WHALEN ERIN J
S-Nitrosothiol Compounds and Related Derivatives
InactiveUS20100105685A1Stabilizing breathing rhythm of a mammalConvenient and smoothBiocideOrganic chemistryS-NitrosylationMedicine
The present invention is directed to a method of treating a lack of normal breathing control including the treatment of apnea and hypoventilation associated with sleep, obesity, certain medicines and other medical conditions. In an aspect, the invention is directed to treating disordered control of breathing by administering an composition comprising a single compound which treats lack of normal breathing. In another aspect, the invention is directed to treating disordered control of breathing by administering an composition comprising a combination of two or more compounds, at least one of which treats lack of normal breathing. In an aspect, a compound is an S-nitrosylating agent.
Owner:GALLEON PHARMA INC
Compositions and methods for enhancing red blood cell storage time and survivability using nitric oxide releasing hybrid hydrogel nanoparticles
InactiveUS20170105407A1Pollution suppressionReduce processing stepsDead animal preservationBiological bodySurvivability
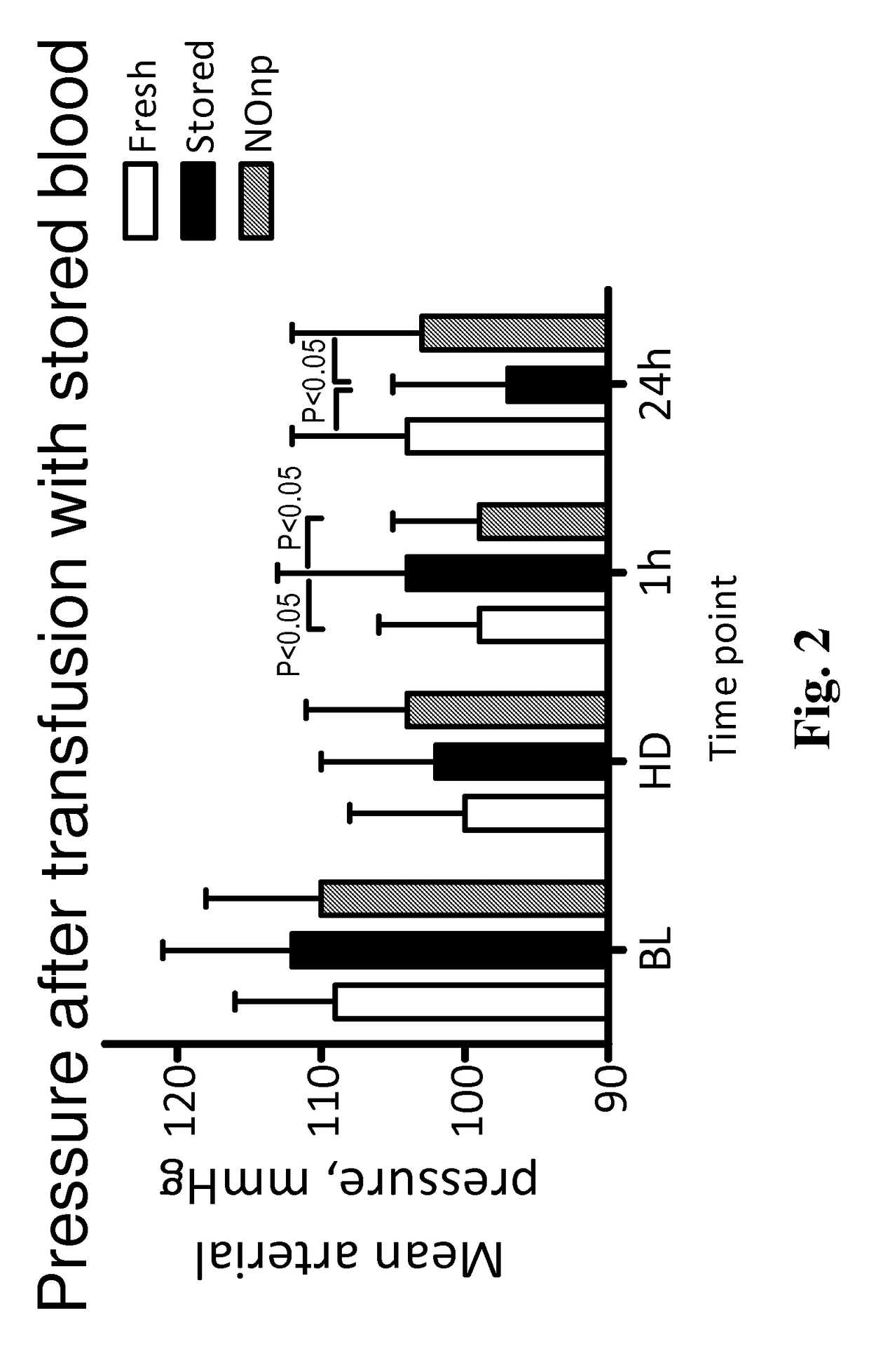
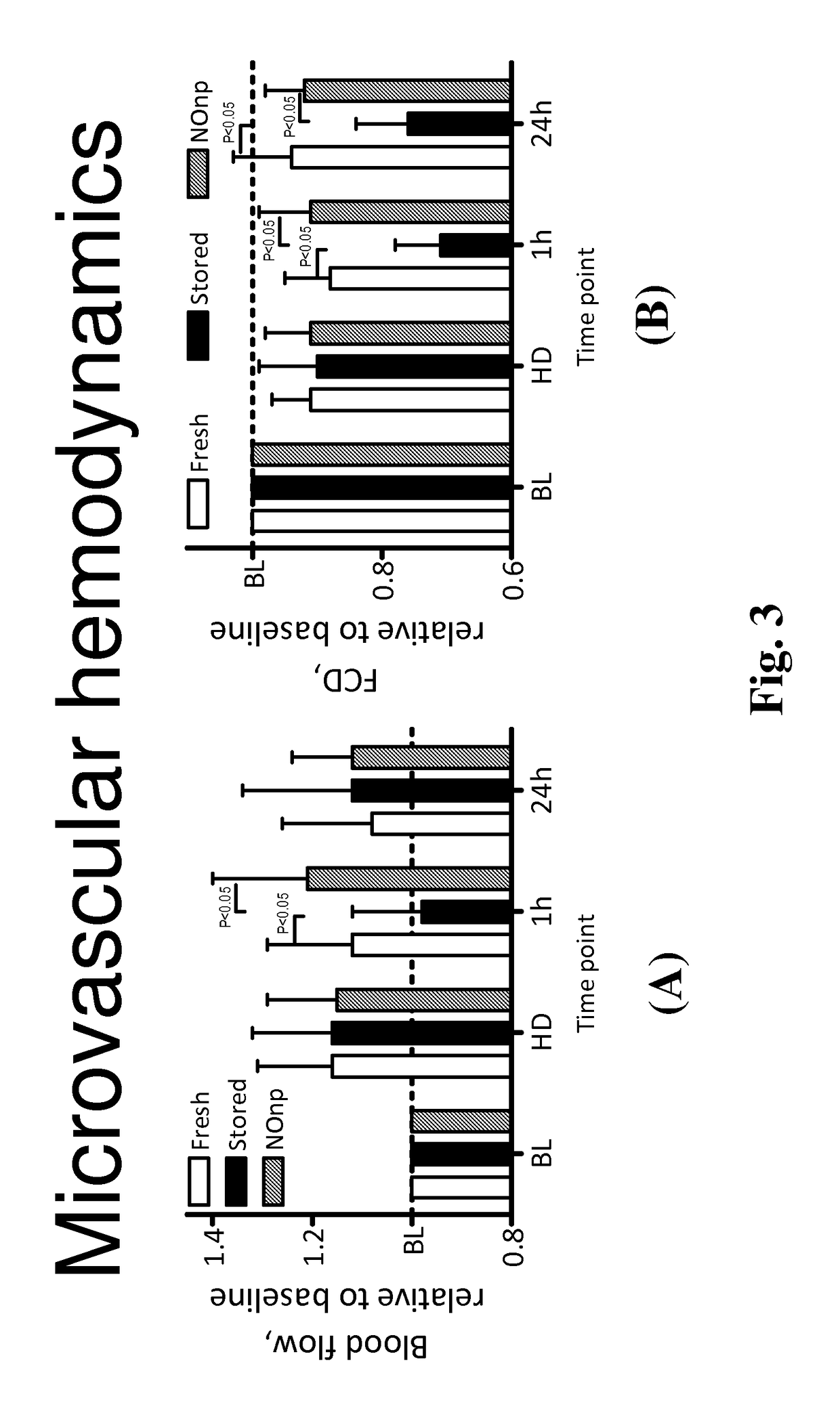
Described herein are hydrogel-based nanoparticles which release nitric oxide (NO) or other bioactive forms of NO including nitrosothiols, nitrofatty acids and dinitrogen trioxide into stored red blood cells (RBCs). Also provided herein is a method for using hydrogel-based nanoparticles to supplement stored RBCs with NO to enhance red blood cell (RBC) storage time, improve survivability in circulation, minimize toxicity associated with transfusion, and improve transfusion safety by eliminating infective organisms in stored blood.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE INC +1
S-nitrosothiol-mediated hyperbranched polyesters
ActiveCN109937234AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsInorganic active ingredientsHyperbranched polyesterBiodegradable polymer
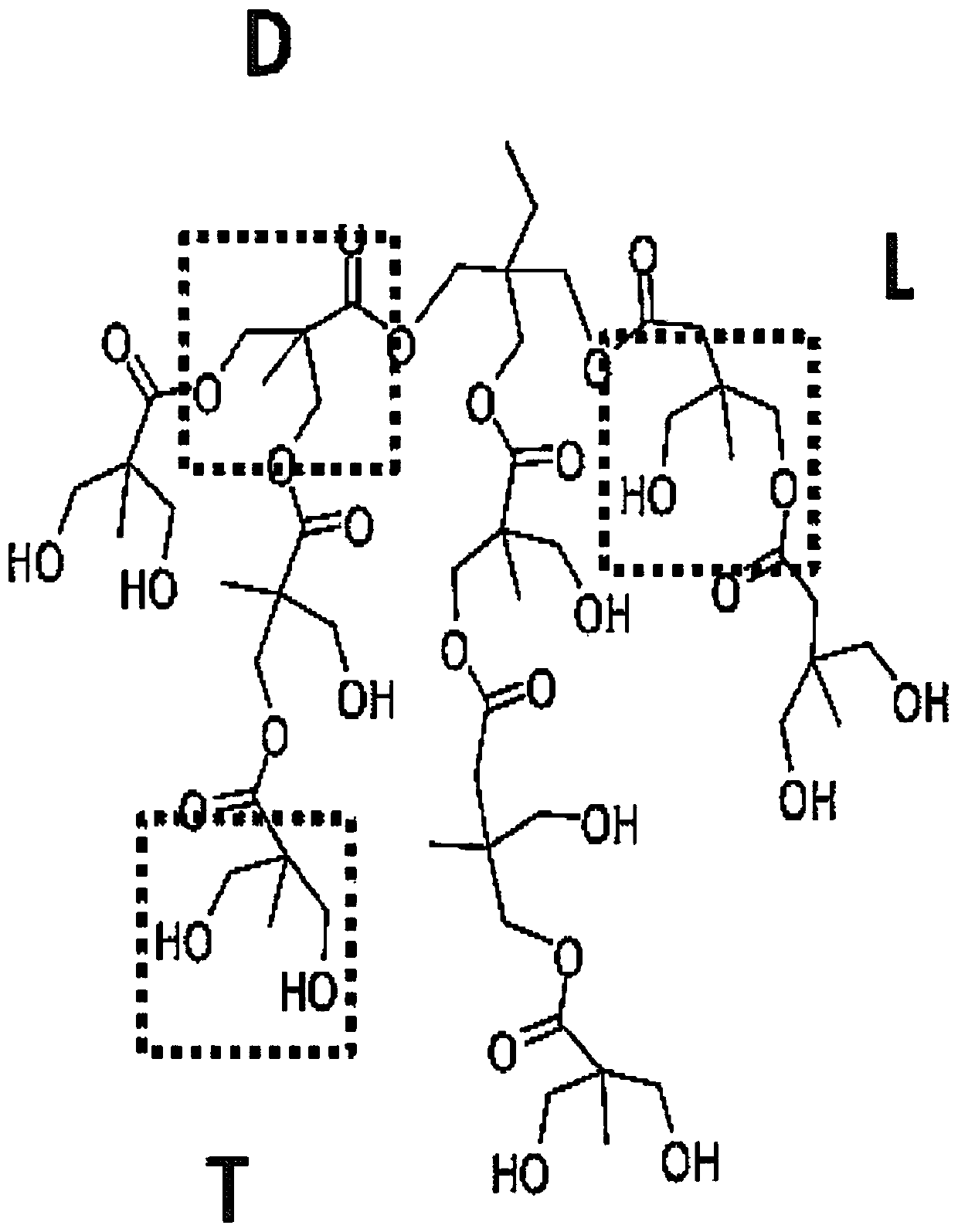
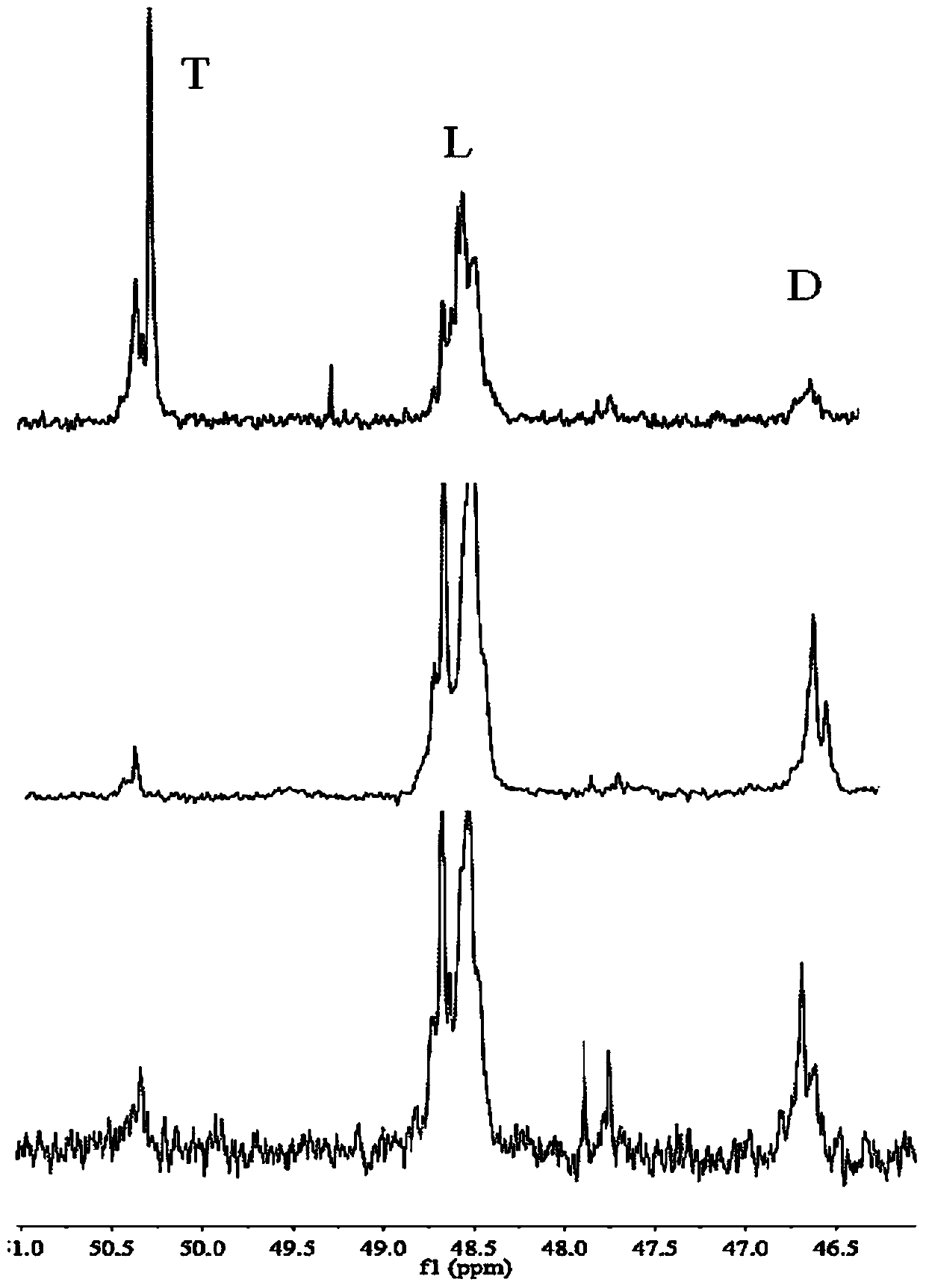
The invention generally relates to compositions comprising degradable polymers and methods of making degradable polymers. Specifically, the disclosed degradable polymers comprise a biodegradable polymer backbone, a nitric oxide linker moiety, and a nitric oxide molecule. This abstract is intended as a scanning tool for purposes of searching in the particular art and is not intended to be limitingof the present invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
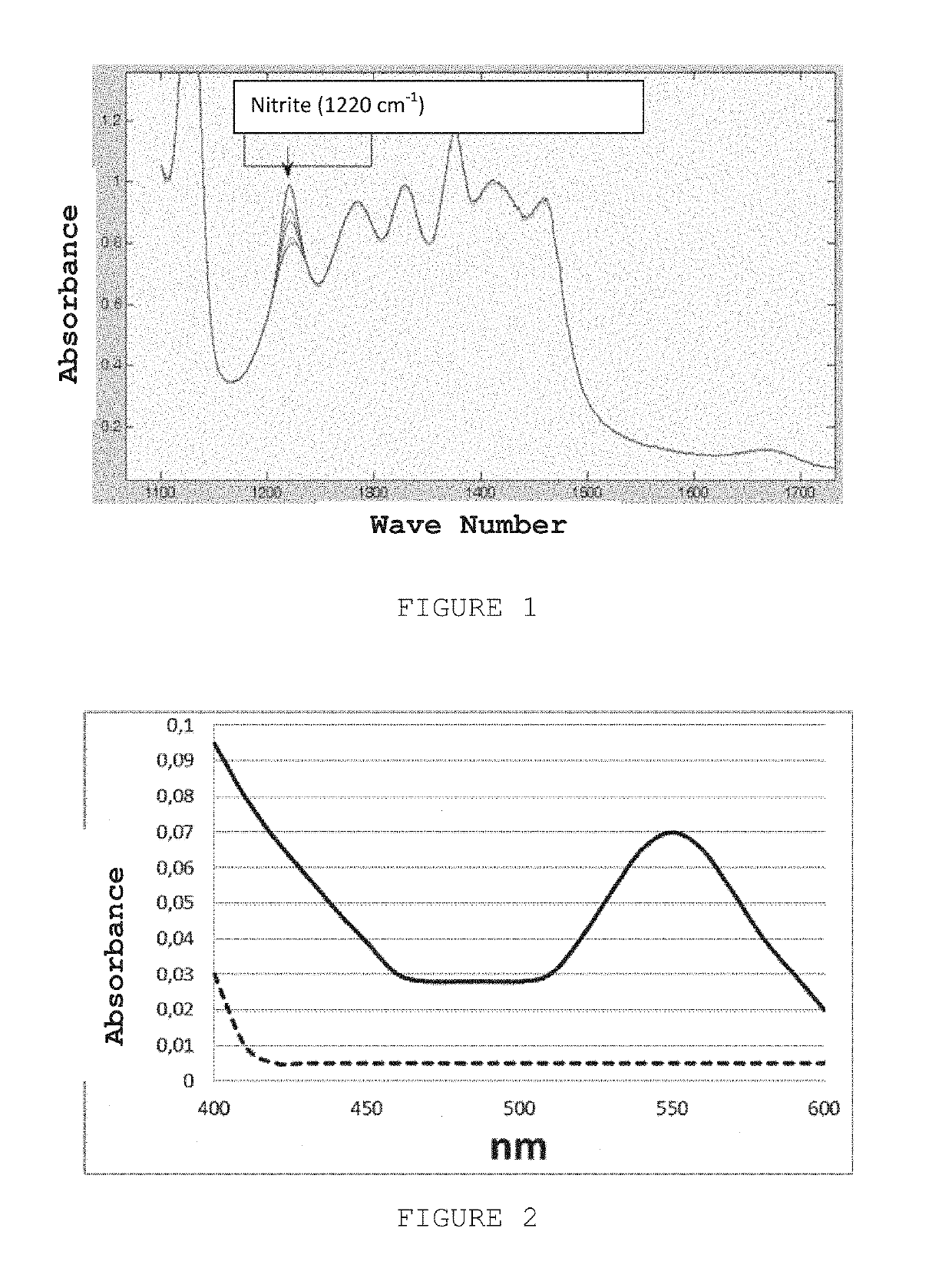
Process for determining S-nitrosothiols in biological fluids
InactiveUS8148099B2Cheaply and easilyLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisNitrosoDecomposition
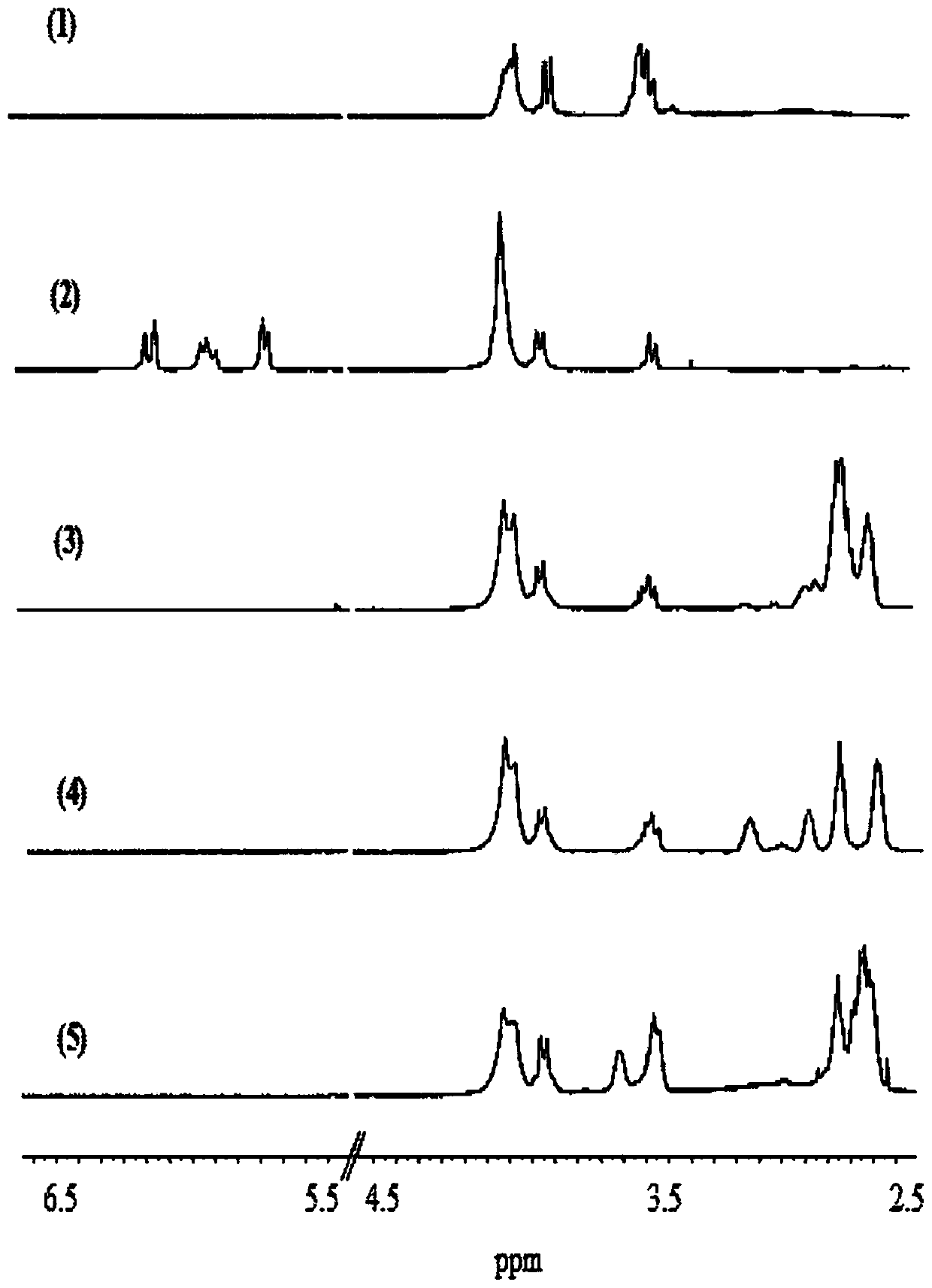
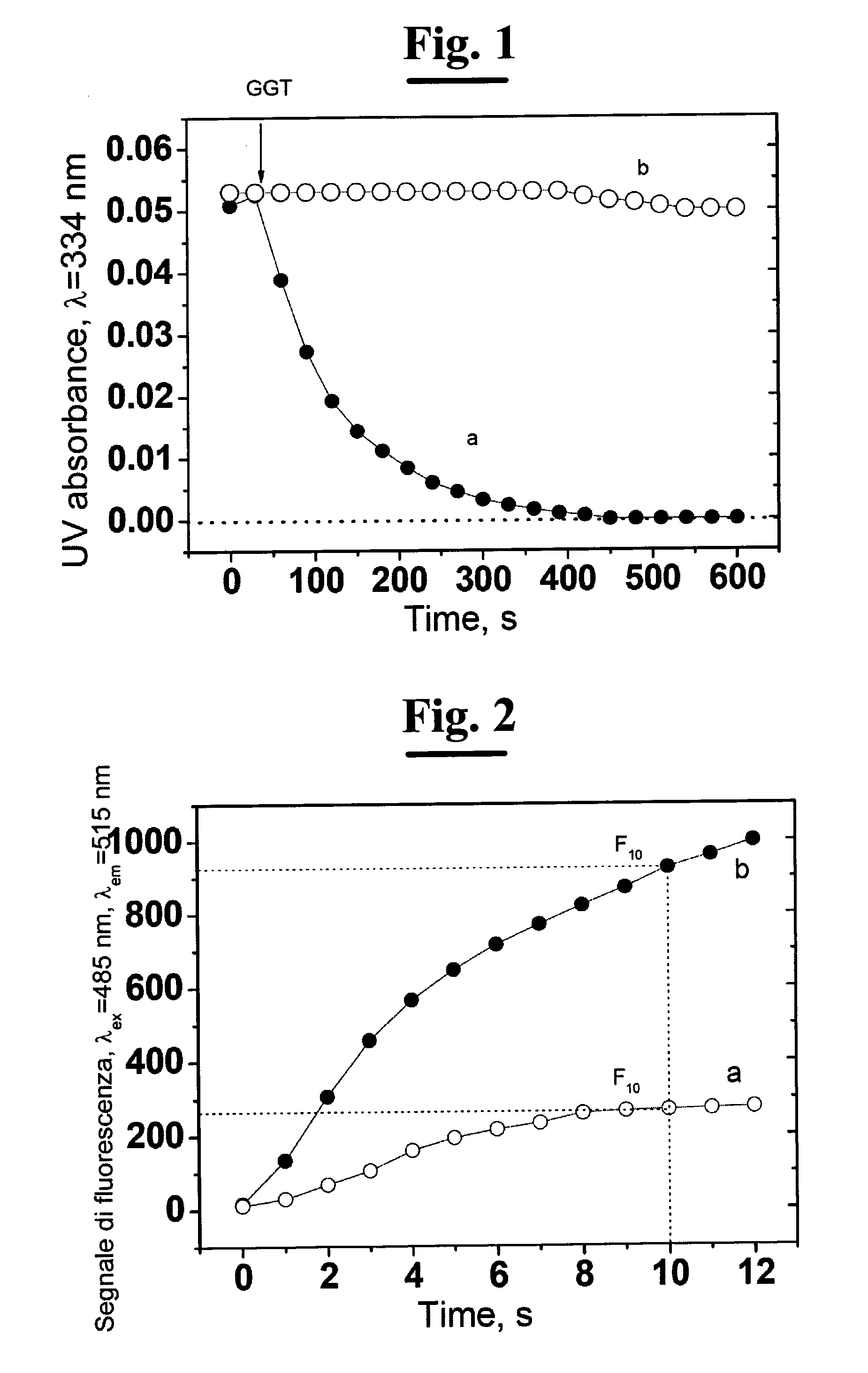
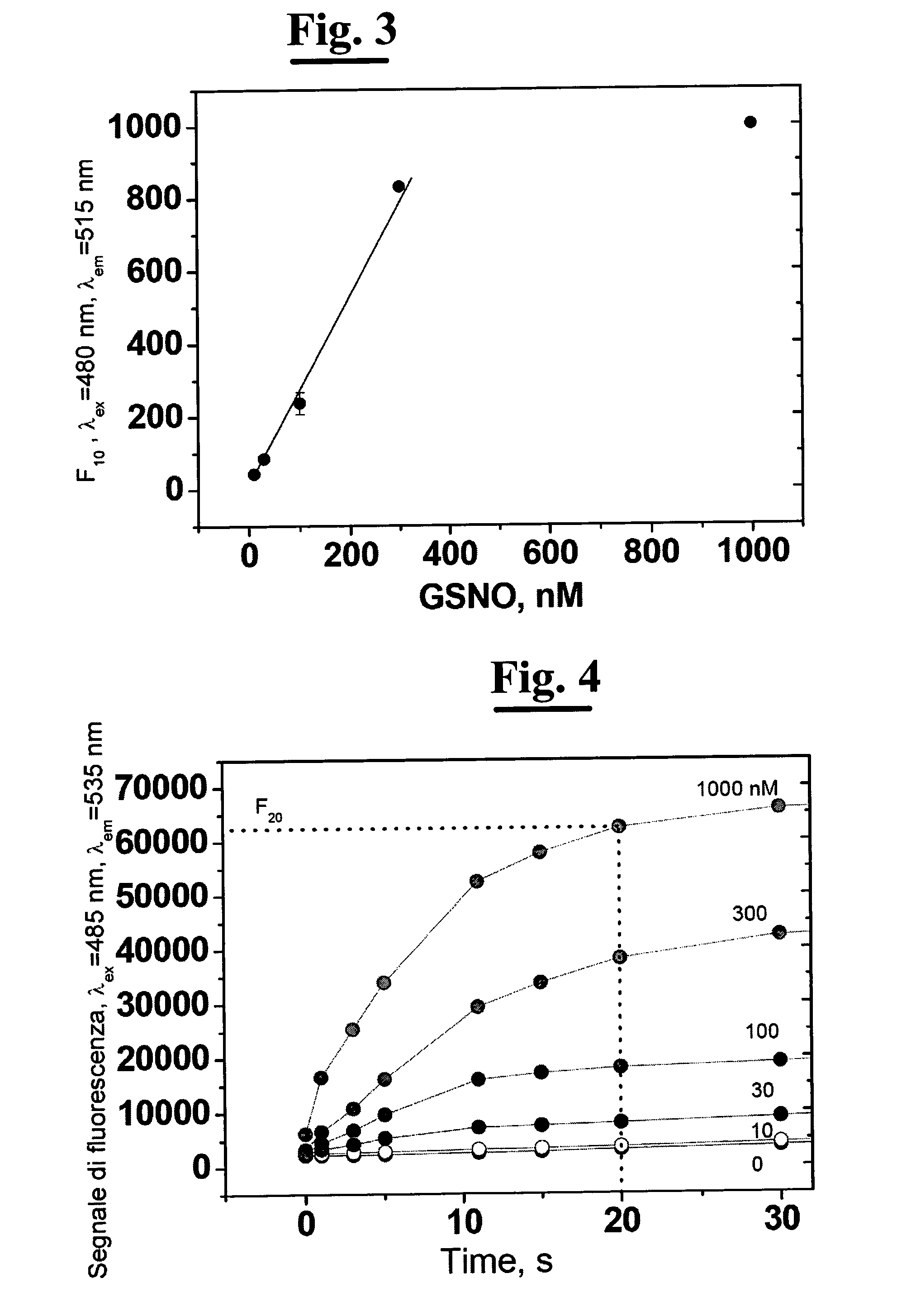
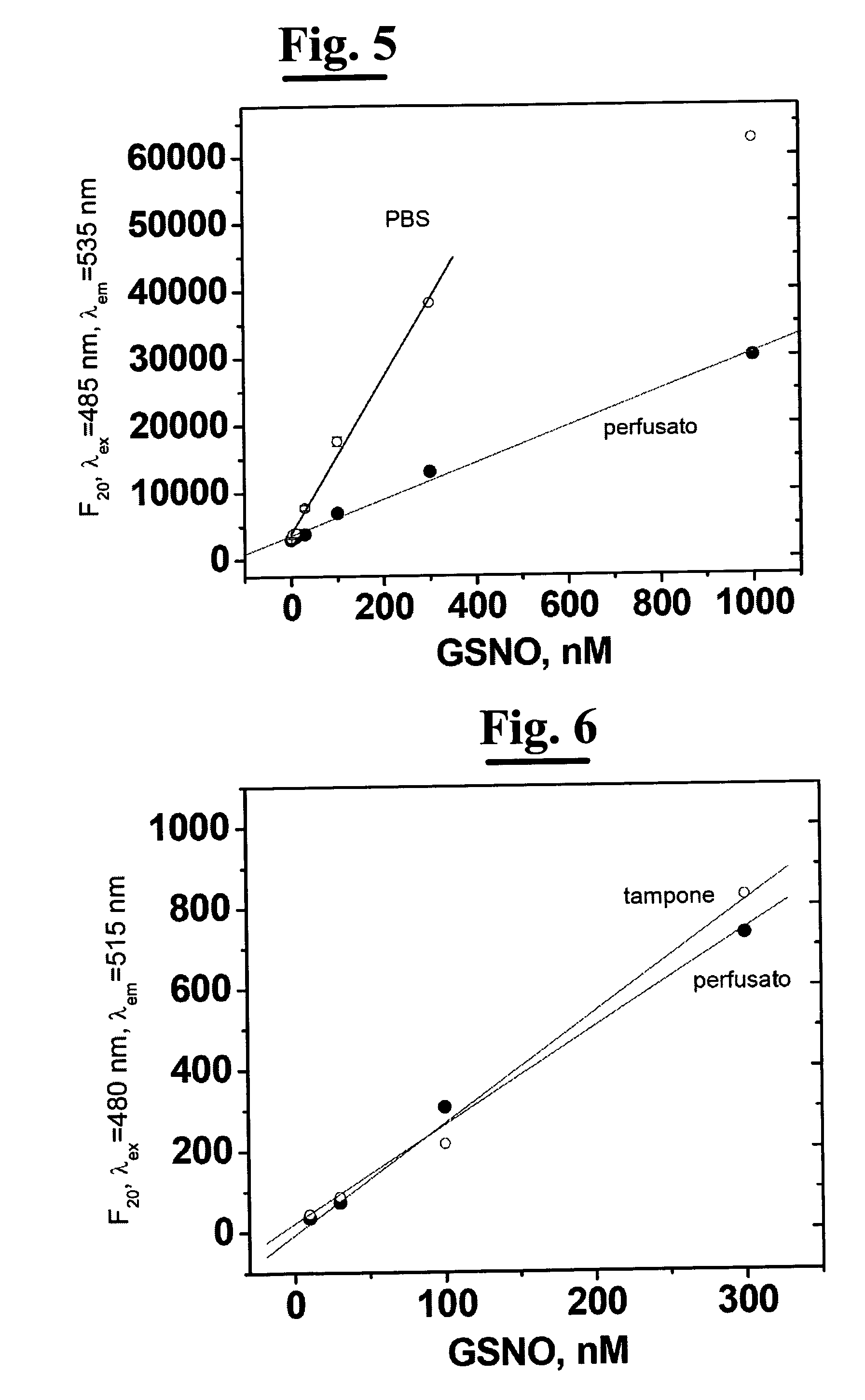
A process for determining S-nitrosothiols, in particular S-nitrosoglutathione, in biological fluids that is easy, selective, cheap with respect to the prior art, which requires the use of equipment commonly available in laboratories, at low cost, which can be used by not qualified operators. The process is based on the hydrolysis of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) by an enzyme, in particular γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT). This enzyme hydrolizes the residual γ-glutamyl of GSNO for giving glutamate (GIu) and S-nitroso-cysteinylglycine (GIyCySNO). In the presence of ions of transition metals GGT speeds up the release of NO since the intermediate that is formed, the GIyCySNO, is much more sensitive to a metal-dependent decomposition. Advantageously, the amount of nitric oxide present in the sample is measured through a reaction thereof with 4,5 diaminof luorescein (DAF-2), said reaction creating a fluorescent compound in an amount proportional to the S-nitrosothiol amount present in the sample. Alternatively, the amount of released NO can be measured by a chemiluminescence analyser, commercially available. In the presence of biological fluids having complex matrix, the introduction of the enzyme is done after separation of the S-nitrosothiol from the other components of the fluid.
Owner:UNIV DI PISA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com