Patents
Literature
279results about How to "Easy to separate from each other" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface cleaning device
A surface cleaning device comprises a suction nozzle, a water tank, a suction machine set, a suction pipeline and a negative pressure pipeline, wherein the suction nozzle is used for absorbing liquid on the surfaces of objects and outside air in the process of cleaning the surfaces of the objects; the water tank is provided with a cavity and used for collecting the absorbed liquid; the suction machine set is used for generating negative pressure and forming suction force; the suction pipeline is connected between the suction nozzle and the water tank and used for transporting the absorbed liquid and the outside air to the water tank; the negative pressure pipeline is connected between the suction machine set and the water tank and connected with an air path of the suction pipeline through the cavity inside the water tank. The surface cleaning device is characterized in that the suction nozzle, the suction pipeline, the water tank, the negative pipeline and the suction machine set are sequentially arranged from top to bottom; the liquid and the outside air absorbed by the suction nozzle enter the water tank along the same path through the suction pipeline from top to bottom; the liquid absorbed by the suction nozzle is collected by the water tank after entering the water tank; the outside air absorbed by the suction nozzle continues to flow along the path from top to bottom after entering the water tank and is exhausted by the suction machine set after passing through the negative pressure pipeline. The surface cleaning device is simple in structure, and can rapidly absorb the liquid on the surfaces of the objects and collect the liquid in the water tank.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN JINSHUN HOUSEHOLD WARES +1
Surface cleaning device capable of spraying mist or spraying water
ActiveCN103251347ALower purchase costWith cleaning suction functionDirt cleaningWindow cleanersSuction forceSurface cleaning
A surface cleaning device capable of spraying mist or spraying water is characterized by comprising a mist spraying or water spraying device, a suction nozzle, a first water tank and a suction unit. The mist spraying or water spraying device is used for spraying cleaning liquid or vaporific cleaning liquid to the surface of an object to be cleaned. The suction nozzle is used for sucking the liquid sprayed on the surface of the object and outside air when the object surface is cleaned. The first water tank is provided with a cavity and used for collecting the sucked liquid. The suction unit is used for generating negative pressure, forming suction force, enabling the sucked liquid to enter the first water tank and discharging the sucked outside air. The surface cleaning device capable of spraying mist or spraying water not only has the functions of cleaning and suction, but also has a function of spraying mist or spraying water, and is convenient to use due to the fact that an additional independent mist spraying or water spraying device does not need to be additionally purchased.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN JINSHUN HOUSEHOLD WARES +1
1E-grade reactor pile core temperature measurement equipment for nuclear power plant
ActiveCN105741894AFirmly connectedEasy to separate from each otherNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringElectricityNuclear power
The invention discloses 1E-grade reactor pile core temperature measurement equipment for a nuclear power plant. The 1E-grade reactor pile core temperature measurement equipment comprises an armored thermocouple, an armored thermocouple compensation cable and a connector for connecting the thermocouple and the compensation cable, wherein the connector comprises a plug and a socket; the plug and the socket are connectors with a contact pin and a jack; the contact pin of the plug is inserted into the jack of the socket and the contact pin of the socket is inserted into the jack of the plug, so that electric connection is realized; the peripheries of the jacks are covered with insulating materials; shells of the plug and the socket are fixedly connected through threads, and an interface is sealed by adopting a sealing ring; two clamping sleeves, which are in overlapping joint, are arranged at inner hole parts in the tail ends of the plug and the socket; and a pressing part is in thread connection with the tail ends of the plug and the socket, is tightly pressed through the clamping sleeves and penetrates through a threading running cable at the tail end. The measurement equipment can reach nuclear safety-grade requirements and has the advantages of good insulating property, strong anti-interference capability and radiation resistance.
Owner:NINGBO AUQI AUTO INSTR EQUIP +2
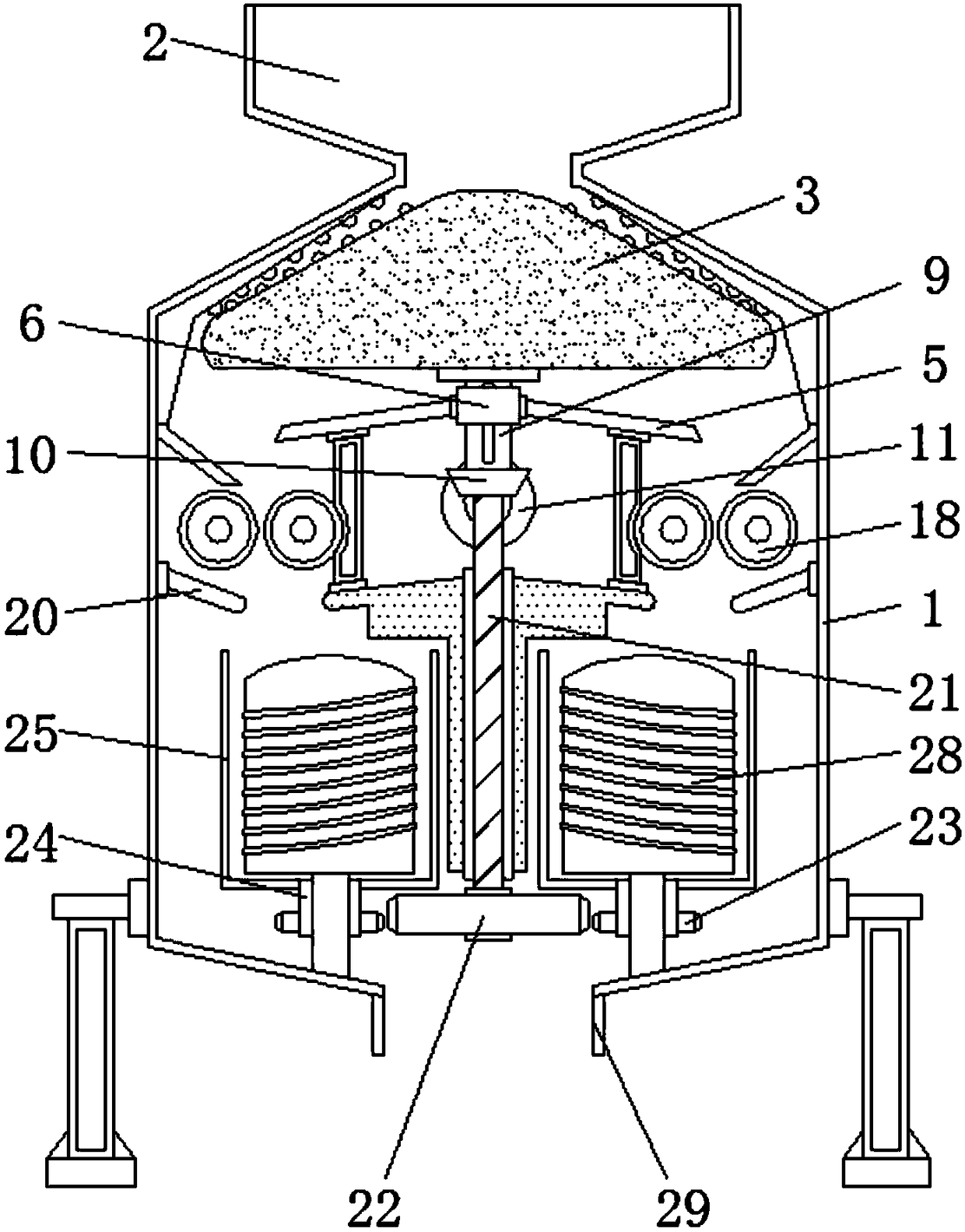
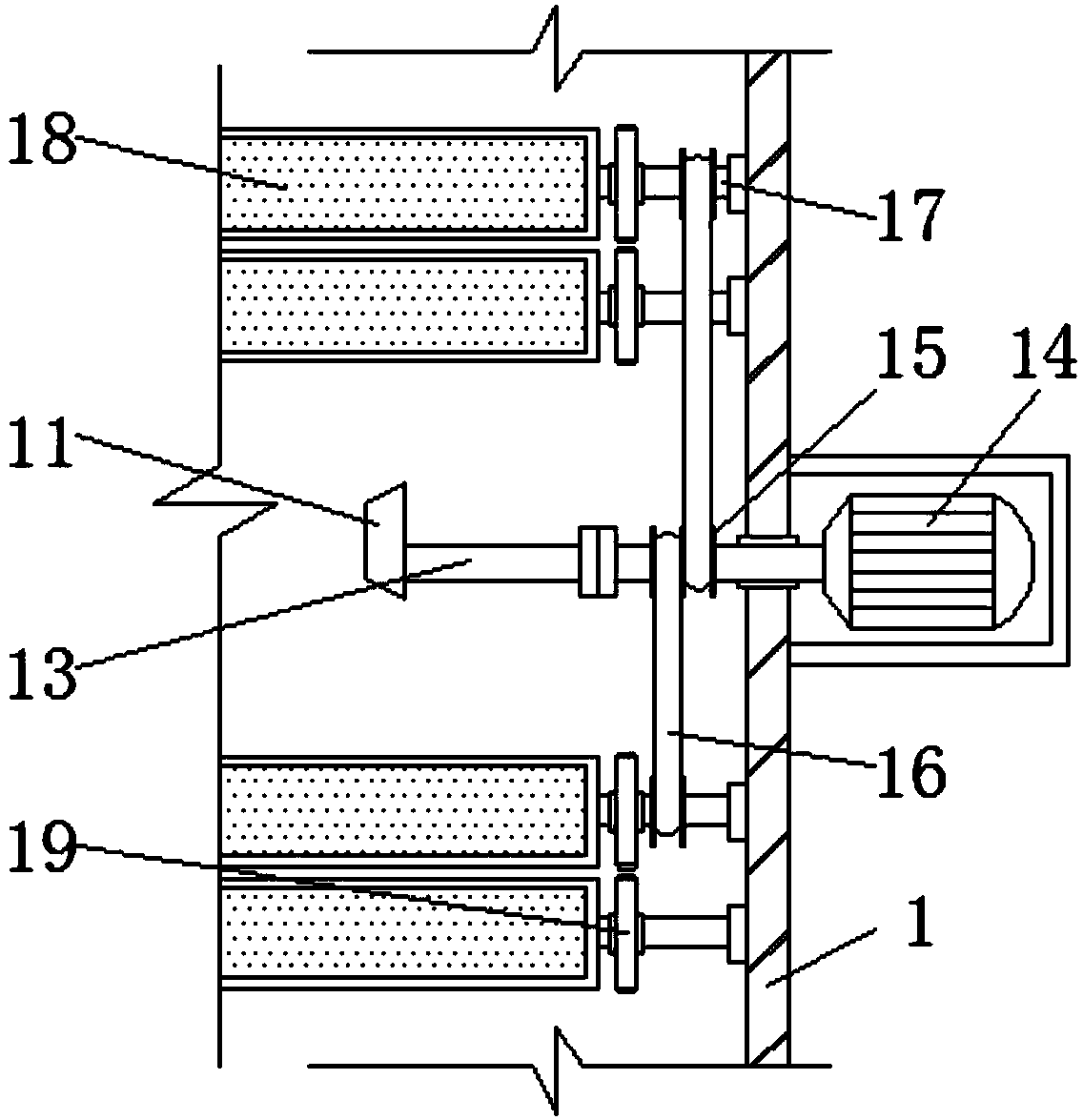
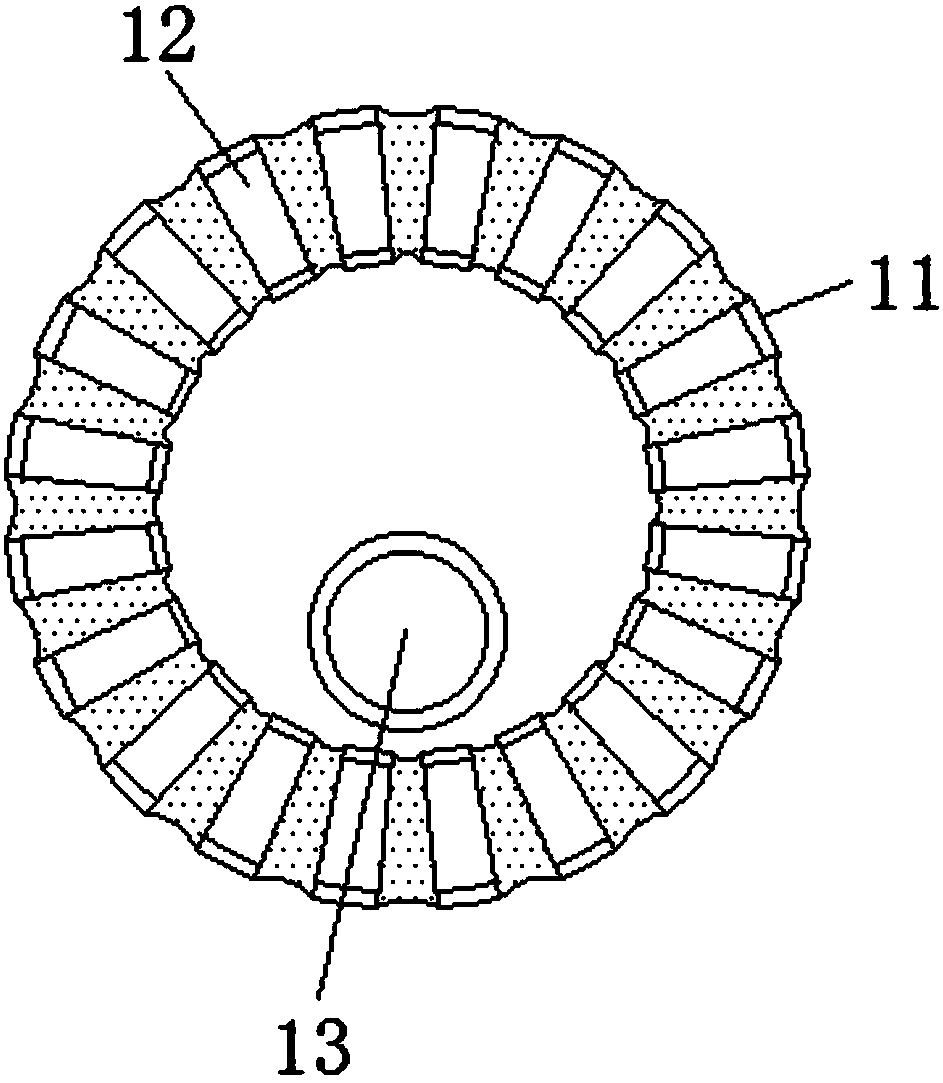
Screening device capable of conveniently crushing and screening mineral raw materials
InactiveCN108380299AEasy to crush and sieveHigh strengthCocoaGrain treatmentsEngineeringRaw material
The invention discloses a screening device capable of conveniently crushing and screening mineral raw materials. The screening device comprises a box body, a vertical bar and grinding tables. A material hopper is arranged above the box body, a crushing block is arranged below the material hopper, and the crushing block is arranged in the box body. Protruded blocks are fixed on the inner side of abearing. Loop bars are fixedly arranged on the inner sides of third gears and the loop bars are arranged below screening buckets. The screening buckets are provided with grinding ribs and screening holes. The grinding tables are arranged on the inner sides of the screening buckets, penetrate through the loop bars, and are fixedly connected with the box body. A discharging outlet is formed below the box body. According to the screening device capable of conveniently crushing and screening mineral raw materials, crushing processing is conveniently carried out on the hard mineral raw materials, rotating grinding and extruding grinding are carried out simultaneously, so that the crushing method is more abundant, the crushing effect of the mineral raw materials is improved, the need of multiplecrushing and grinding is avoided, and the beneficiation flowsheet is simplified.
Owner:潘建平
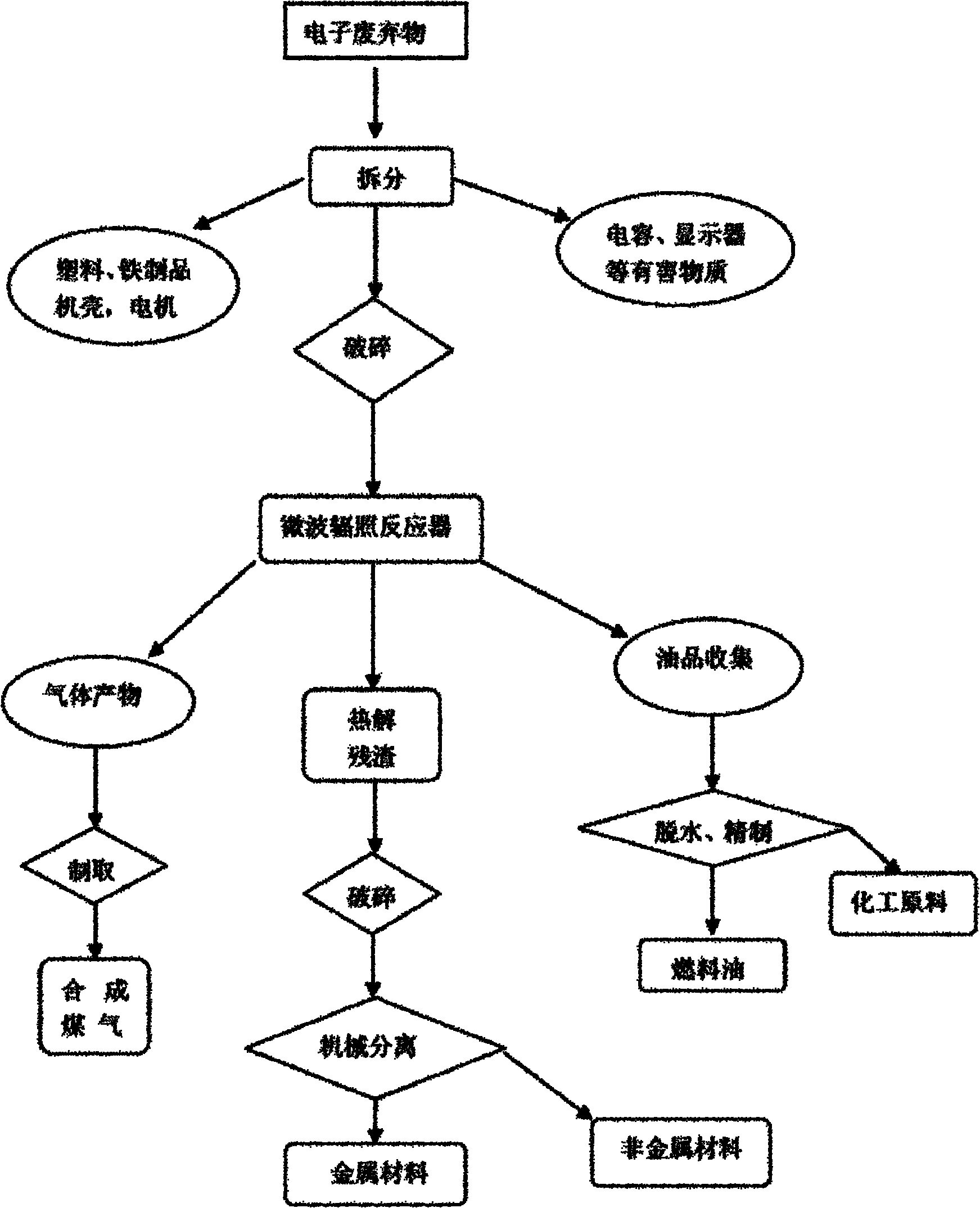
Method for reclaiming and treating electronic waste
InactiveCN102069086AFacilitate dissociationInhibition releaseSolid waste disposalSpecial form destructive distillationHazardous substanceHeat conducting
The invention relates to a method for reclaiming and treating electronic waste, which comprises the steps of crushing, sealing, nitrogen introduction, microwave radiation, separation and the like, wherein the microwave radiation is directly adopted for pyrolysis, and in the separation, solid residues are subjected to a mechanical crushing-physical separation process. The conventional external heating mode is replaced by adopting an 'internal heating' mode of coupling microwave heating and corona discharge, the corona discharge is excited by the microwave radiation, and the defect of low efficiency in conventional external heating due to the factors such as large material size, more pores, low heat conducting efficient and the like is overcome at the same time of promoting microwave heating by the discharge heat; therefore, the pyrolysis process is quickened, the utilization rate of energy is greatly improved, the metals in pyrolysis residues are separated and reclaimed by adopting a mechanical mode rather than a metallurgical mode, the energy consumption is relatively low, meanwhile, high temperature is avoided, and release of toxic or harmful substances is effectively suppressed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Combined 5G communication module assembly and assembling method thereof
ActiveCN111970867AEasy maintenanceEasy to replaceScreening casingsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a combined 5G communication module assembly and an assembling method thereof and belongs to the technical field of 5G communication module assemblies. When a 5G communication module is connected and fixed, the 5G communication module is only simply inserted and exposed outside, and faults easily occur due to dust and moisture in air. With the combined 5G communication module assembly and the assembling method thereof of the invention adopted, the above problem can be solved. The combined 5G communication module assembly comprises a protective shell; a protective cover plate is movably installed above the protective shell; a filling bottom plate is movably installed at the bottom end of the protective shell; a lifting mechanism is installed between the filling bottomplate and the protective shell; the lifting mechanism comprises an installation bottom plate. With a communication module clamping mechanism and a communication module lifting mechanism installed, a5G communication module can be conveniently and rapidly clamped and fixed, the 5G communication module is comprehensively protected, the 5G communication module is prevented from breaking down due todust or moisture in air, and normal use of the 5G communication module is guaranteed.
Owner:江苏富联通讯技术股份有限公司
Novel medical glove processing device and use method therefor
ActiveCN111844642AConvenient automatic separationReduce laborDomestic articlesConveyor beltAutonomation
The invention discloses a novel medical glove processing device and a use method therefor, and relates to the technical field of medical glove production. The problems that when a medical glove is processed, demolding is inconvenient, manual operation is needed, the labor amount is large, and the efficiency is low are solved. The novel medical glove processing device and the use method therefor involve a fixing base, wherein two supporting side plates are uniformly and fixedly mounted on the upper surface of the fixing base, two conveyor belt side plates are uniformly mounted between the two supporting side plates, two guide rods are uniformly arranged above the two conveyor belt side plates, the ends of the guide rods are fixedly connected with the supporting side plates, a conveyor beltis movably mounted between the two conveyor belt side plates, and a processing mechanism is mounted above the conveyor belt. According to the device, by mounting the processing mechanism and the conveyor belt, the medical glove can be quickly formed and then stripped from a mold after forming, and thus automatic production and collection can be achieved, the labor intensity of workers is reduced,and the production efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:徐州华通手套有限公司
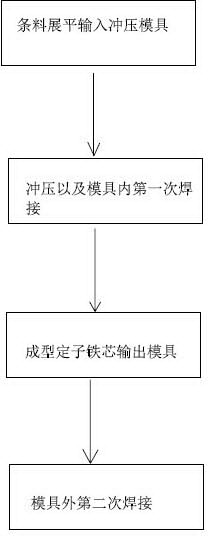
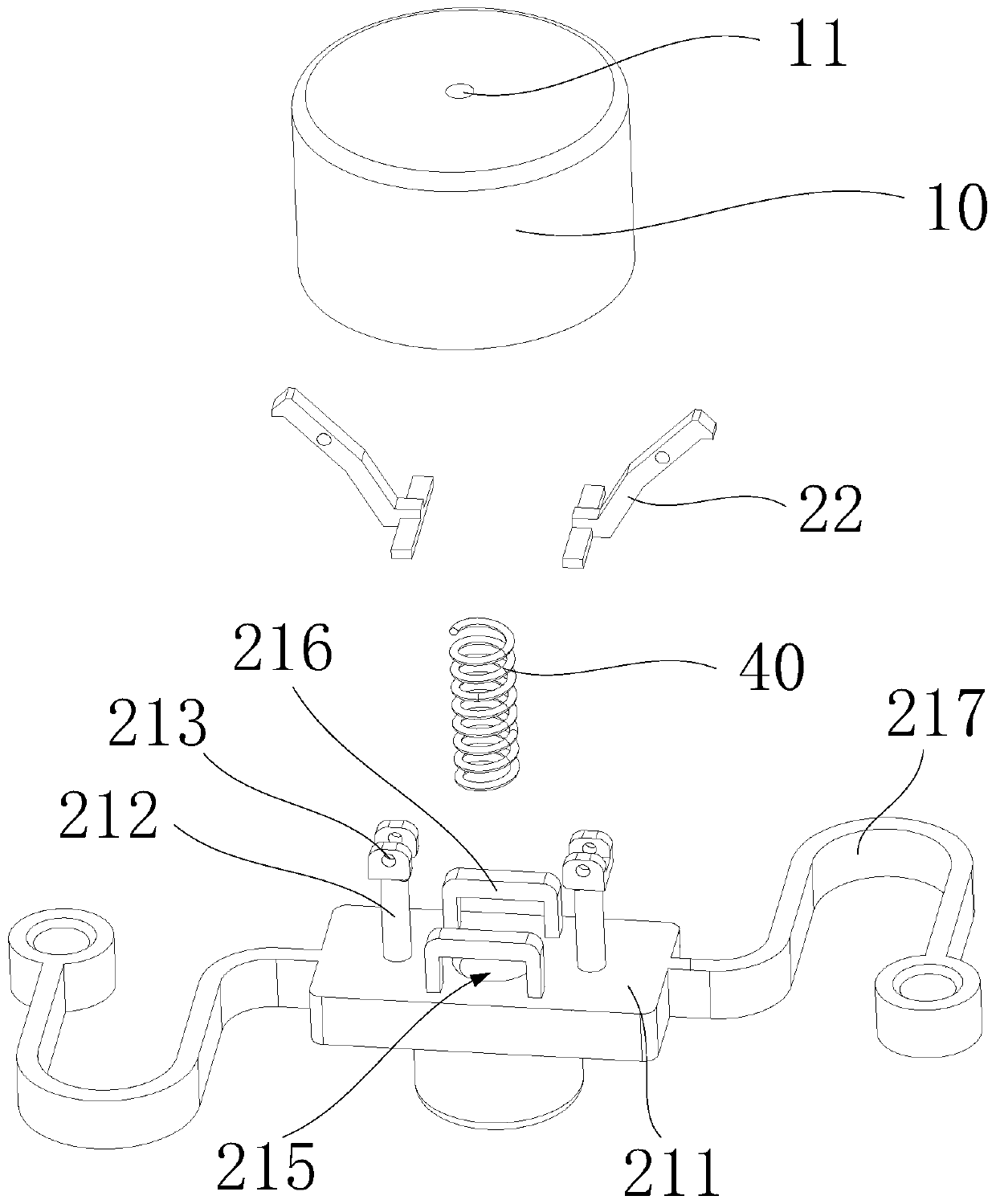
Process for manufacturing straight-bar stator cores
ActiveCN104348312AEasy to separate from each otherReduce processManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSingle plateEngineering
The invention discloses a process for manufacturing straight-bar stator cores. The process comprises the following steps of stamping a bar material into required stamped plates by using a progressive stamping die, and simultaneously welding the stamped plates into an iron core with certain thickness through laser in the die; welding the rest soldering points on the exterior of the die; finally forming the required products. Pre-welding is realized in the stamping die for the first time, and procedures are effectively reduced; in the stamping procedure, a welding groove gap of the (N+1)th plate is particularly stamped, so that the size of the welding groove of the plate is greater than the size of a welding groove of a conventional stator single plate, and the (N+1)th plate cannot be welded in the welding process in the die, so that stator cores welded in the die can be easily separated from each other, setting on laser welding equipment is not required, the welding yield is greatly improved and the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGYING XINZHI TECH CO LTD
Key and electronic equipment
PendingCN111048343AEasy to installEasy to disassembleElectric switchesKey pressingStructural engineering
The key comprises a key. The key comprises a key cap and a key main body; the key cap is provided with a hollow structure with a downward opening; a through hole is formed in the top wall of the key cap; the key main body is provided with a bracket and a buckle body; the bracket comprises a bracket body and a mounting part; the side, close to the bracket body, of the key cap abuts against the bracket body; a rotation hole is formed in the mounting part; the buckle body is provided with a rotating part; the rotating part is hinged to the rotation hole; the side wall of the key cap is inwards provided with a clamping boss; one end of the buckle body is provided with a buckling part; the buckling part is connected with the clamping boss in a clamping manner; a pressing part is arranged at theother end of the buckle body; the buckling part and the pressing part are arranged on the two sides of the rotating part; and the pressing part is arranged in the extending direction of the through hole. With the key and electronic equipment provided by the invention adopted, the problem that the key of the electronic equipment is not easy to disassemble in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:GEER TECH CO LTD
Syphilis diagnosis multi-channel apparatus with strongly-hydrophobic microfluidic chip substrate
InactiveCN107754874AEasy to disassembleEasy to separate from each otherLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesSilica particleSyphilis
The invention relates to a multi-channel device for syphilis diagnosis with a strongly hydrophobic substrate of a microfluidic chip, which belongs to the field of analysis and testing. It is a technical goal to use cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of the microfluidic chip for syphilis diagnosis. The gist of this case is that the substrate is selected from PDMS with an original ecological surface, and the hinged fixture with a micro-ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and positioned at the position adjacent to the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, so as to The ultrasonic wave induces the sample liquid flow to flow from the sample injection end of the chip along the pipe of the chip to the terminal. The pipe of the chip is filled with micron-sized silicon dioxide particle fillers. The function of the filler includes supporting the inner wall of the pipe, And, a collection of hydrophilic micro-channels is used to compensate the originally hydrophobic channels, and the inner wall of the channel is squeezed and covered to reduce the chance of biomacromolecules in contact with the inner wall.
Owner:葛光奇
Vaccum coating apparatus having the transmission roll for the transmission plate substrate
InactiveCN101092686AAvoid leak locationCost-effective manufacturingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringCoupling
The present invention relates to a vacuum covering equipment which is provided with a transmission system for the plate substrate that is transmitted through a vacuum chamber. The transmission system includes a plurality of parallel-arranged cylinders. It can provide one or a plurality of electric motors in the vacuum chamber or at the outside of the vacuum chamber as the driving mechanism of the cylinders. In any case it does the coupling between one or a plurality of motors and the cylinders by the magnetic coupling device. As there is no mechanical linking is found between the driving mechanism and the cylinders, they can easily separate from each other and it is allowed that the cylinder and the sputtering catelectrode is set can slide into or slide out the sliding element of the vacuum chamber. The cylinder coupled with the driving mechanism can be connected with other cylinder by the V-shaped strip unless each cylinder is provided with its respective driving mechanism.
Owner:アプライドマテリアルズゲーエムベーハーウントツェーオーカーゲー
Cable tower pole climbing assistance device
The invention discloses a cable tower pole climbing assistance device, and belongs to the field of cable tower poles. A cable tower pole climbing assistance device comprises an annular piece, a waistband and a pedal; a connecting plate is arranged at the end of the annular piece, and a connecting bolt penetrates through the interior of the connecting plate; a rotating shaft is arranged at the other end of the annular piece; a first spring is arranged on the inner side of the annular piece, and a sliding strip is connected to the end of the first spring; a fixing frame is arranged on the outer side of the sliding strip; a clamping block is connected to the interior of the fixing frame; a connecting belt is arranged at the end of the sliding strip; a clamping plate is connected to the end of the connecting belt; a limiting rod is arranged on the outer side of the clamping plate; and a rotating frame is arranged on the side of the limiting rod. By arranging the annular piece, sliding protection can be effectively conducted, and the situation of careless falling is prevented; and the pedal at the bottom is provided with a double-meshing structure, so that the situation that a user falls in the climbing process is effectively prevented, and the use safety is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER CO PINGYUAN POWER SUPPLY CO
Top skin adsorption device for autoclaved aerated concrete blocks
PendingCN111113541AEasy to separate from each otherAvoid cloggingCeramic shaping apparatusMetal working apparatusStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a top skin adsorption device for autoclaved aerated concrete blocks. The top skin adsorption device comprises a machine frame and an adsorption cover. Air cylinders separatelyconnected with both ends of the adsorption cover are arranged on both sides of the machine frame, and the adsorption cover is provided with a wind box. An adsorption plate is arranged on the bottom surface of the adsorption cover, and a cylindrical brush for cleaning the bottom surface of the adsorption plate is arranged on the surface, facing away from the adsorption cover, of the adsorption plate. The cylindrical brush is connected with a driving mechanism for driving the movement of the cylindrical brush, and the adsorption plate is provided with a plurality of through holes communicatingwith the adsorption cover. The adsorption cover is internally provided with a mesh frame, and the mesh frame is provided with a plurality of revolving columns extending into the through holes. The revolving columns are connected with the side walls of the through holes in an abutting mode, and a revolving mechanism which drives the revolving columns to move along the side walls of the through holes is connected to the mesh frame. The cylindrical brush is driven by the driving mechanism to move on the bottom surface of the adsorption plate, and debris on the bottom surface of the adsorption plate is swept down. The revolving mechanism drives the revolving columns to move along the side walls of the through holes, fragments in the through holes can be loosened and dropped, the blocking of the through holes is avoided, and the overall structure can improve the adsorption effect of the adsorption device.
Owner:惠州市鑫业建材有限公司
Syphilis diagnosis chip device with substrate prepared from strong hydrophobic PDMS
InactiveCN106153910AEasy to disassembleEasy to separate from each otherMaterial analysisSyphilisUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a syphilis diagnosis chip device with a substrate prepared from strong hydrophobic PDMS, and belongs to the field of analysis testing. Problems exist when polydimethylsiloxane PDMS which is low in price and easy to process is adopted for manufacturing a substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for syphilis diagnosis. The surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic, the effect of targeted surface modification cannot be kept for a long time, and the scheme aims at solving the series of relevant problems. The device is characterized in that the PDMS with the original ecology surface is selected as the substrate, a hinge type clamp additionally provided with a minitype ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and positioned to the near position of a sample liquid flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, interface tension is reduced through ultrasonic waves, meanwhile, and rapid degression of ultrasonic wave strength in a short distance is achieved through the strong absorption ability of PDMS for ultrasonic waves, so that interface tension differences are formed at the two ends of the chip, and sample liquid flow is promoted to flow to the terminal along an originally hydrophobic capillary tube channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Easily-dismountable multichannel device for cholera diagnosis
InactiveCN107649217AGood compatibilityRapid reversible binding reactionLaboratory glasswaresDisease diagnosisTarget surfaceUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to an easily-dismountable multichannel device for cholera diagnosis and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. By using cheap and easily-processable polydimethylsiloxane,namely PDMS for manufacturing a substrate of a microfluidic chip for cholera diagnosis, a series of problems exist. The surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic. Through targeted surface modification, the effect is hard to last. The scheme aims to solve the series of related problems. According to main points of the scheme, PDMS with primitive surface is selected as the substrate, a chain-ring electromagnetic fixture attached with a miniature ultrasonic transducer is in cup joint to be positioned near the terminal of a sample liquid fluid of the microfluidic chip, interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and by PDMS's strong absorption of ultrasonic wave, ultrasonic intensity is rapidly decreased progressively in a short distance to form interfacial tension differencebetween two ends of the chip. Thereby, the sample liquid fluid is driven to flow along an originally hydrophobic capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:宋岳
An AIDS diagnosing device having an easily removably functional member used for driving an additionally added sample liquid
InactiveCN107045058AGood compatibilityRapid reversible binding reactionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesShortest distanceCapillary channel
The invention relates to an AIDS diagnosing device having an easily removably functional member used for driving an additionally added sample liquid, and belongs to the field of analysis testing. A technical objective is to prepare substrates of micro-fluidic chips used for AIDS diagnosis by utilizing polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS that is cheap and easy to process, but the PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface, and targeted surface modification or surface decoration fails to achieve durable effects. The objective of the device is to overcome the series of problems. The device is characterized in that PDMS having an original surface is adopted as a substrate, a chain-ring type electromagnetic clamp equipped with a minitype ultrasonic transducer is positioned at a position near a sample liquid stream terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in a sleeve joint manner, and an ultrasonic attenuator is mounted at a feeding end of the micro-fluidic chip to achieve rapid ultrasonic wave intensity attenuation in a short distance, and therefore an interfacial tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip, thus allowing the sample liquid stream to flow along originally hydrophobic capillary channels towards the terminal direction.
Owner:李榕生
Multichannel chip unit with PDMS as substrate and for AIDS diagnosis
InactiveCN107754953ASmall running resistanceNot prone to problems such as peeling offMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresStream flowMicropump
The invention relates to a multi-channel chip device for AIDS diagnosis using PDMS as a substrate, belonging to the field of analysis and testing. Using cheap and easy-to-process polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to make the substrate of the microfluidic chip for AIDS diagnosis has a series of problems. The gist of this case is that the substrate is selected from PDMS with an original ecological surface, and the hinged fixture with a micro-ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and positioned in the vicinity of the sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, so as to Ultrasound induces the driving force based on the difference in interfacial tension, and at the same time, it is coupled with the driving force of the micropump to drive the sample liquid to flow in the direction of the terminal. The pipe of the chip is filled with micron-sized silica particles. Its functions include supporting the inner wall of the pipeline, compensating the original hydrophobic pipeline with a collection of hydrophilic micro-channels, and squeezing and covering the inner wall of the pipeline to reduce the chance of biomacromolecules in contact with the inner wall.
Owner:葛宇杰
A combined 5g communication module assembly and assembly method thereof
ActiveCN111970867BEasy maintenanceEasy to replaceScreening casingsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a combined 5G communication module component and an assembly method thereof, relates to the technical field of 5G communication module components, and solves the problem that when the 5G communication module is connected and fixed, it is simply plugged in and exposed to the outside, which is easy to cause Dust and moisture in the air present malfunctioning problems. A combined 5G communication module assembly and an assembly method thereof, comprising a protective case, a protective cover plate is movably installed above the protective case, and a filling bottom plate is movably installed at the bottom of the protective case, and the filling bottom plate and An elevating mechanism is installed between the protective shells, and the elevating mechanism includes an installation base plate. The present invention can conveniently fast clamp and fix the 5G communication module by installing the communication module clamping mechanism and the lifting mechanism, fully protect the 5G communication module, avoid the 5G communication module from thinking that dust or moisture in the air fails, and ensure 5G Normal use of the communication module.
Owner:江苏富联通讯技术股份有限公司
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome diagnosis apparatus adopting hydrophobic material as substrate of microfluidic chip
InactiveCN106153706AGood compatibilityRapid reversible binding reactionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesAbsorption capacityShortest distance
The invention relates to an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome diagnosis apparatus adopting a hydrophobic material as the substrate of a microfluidic chip, and belongs to the field of analysis testing. According to the present invention, the use of inexpensive and easily-processed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) to produce the substrate of a microfluidic chip for diagnosing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a technical target, but the surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic and the effect of the targeted surface modification or surface modifying is difficult to lasting, and a purpose of the present invention is to solve the series of the related problems; and the apparatus is characterized in that the substrate selects the PDMS having an original ecological surface, a hinge type fixture provided with a miniature ultrasonic wave transducer is manually fastened and positioned at a position close to the sample liquid fluid terminal end of the microfluidic chip so as to reduce the interfacial tension through the ultrasonic wave, and the strong absorption capacity of the PDMS on the ultrasonic wave is used to rapidly decrease the intensity of the ultrasonic wave within a short distance, such that the interfacial tension difference is formed on both ends of the chip so as to promote the sample liquid fluid to flow to the terminal direction along the originally-hydrophobic capillary channel.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Dual-drive tumor marker joint inspection chip device with PDMS as substrate
InactiveCN106610429AEasy to processEasy to disassembleMaterial analysisUltrasonic sensorShortest distance
The invention relates to a dual-drive tumor marker joint inspection chip device with PDMS as a substrate and belongs to the field of analysis test. Utilizing polydimethyl siloxane, namely PDMS, to prepare the substrate of a typical tumor marker multichannel joint inspection micro-fluidic chip has advantages and also has problems; aiming at the problems, the dual-drive tumor marker joint inspection chip device is characterized in that the substrate is chosen from the PDMS with the original surface, a hinge type clamp additionally provided with a minitype ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and located to the neighbor position of a sample fluid terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, the interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and the rapid decreasing of the ultrasonic wave strength in a short distance is achieved through the strong absorption ability of the PDMS to the ultrasonic wave; thus the interfacial tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip, the difference can provide the force for driving the sample fluid to flow in the direction from a drainage capillary channel to the terminal, and the force is also coupled with and in collaborative operation with the mechanical pumping force of a micro pump contained in the structure of dual-drive tumor marker joint inspection chip device.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Micro-fluidic chip device with various driving mechanism and synergistic operation for syphilis diagnosis
InactiveCN106268988AEasy to disassembleEasy to separate from each otherMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresUltrasonic sensorSyphilis
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic chip device with various driving mechanism and synergistic operation for syphilis diagnosis, belongs to the field of analysis testing, and aims at solving series of problems exist by adopting polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is low in price and extremely easy to process as the substrate of a micro-fluidic chip for syphilis diagnosis. According to the key point of the device, PDMS with an original ecological surface is selected for the substrate, and a chain-ring type electromagnetic clamp with a miniature ultrasonic transducer is sheathed and positioned at the position adjacent to the sample flow terminal of the micro-fluidic chip, so that the interfacial tension is reduced with ultrasonic wave, the strength of ultrasonic wave is quickly decreased in a short distance by utilizing the strong absorbability of PDMS for ultrasonic wave, an interfacial tension difference is formed between two ends of the chip and supplies a force for driving the sample flow to flow along the hydrophobic capillary channel toward the terminal direction, and the force is coupled and synergistically runs with the mechanical pumping force of a micro-pump in the structure at the same time.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microfluidic chip device with polydimethylsiloxane as substrate material
InactiveCN107649207AGood compatibilityEliminate surface chemical modificationLaboratory glasswaresMicrofluidic chipPhysics
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip device with polydimethylsiloxane as a substrate material and belongs to the field of analysis and testing. By using cheap and easily-processable polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS for manufacturing a substrate of a microfluidic chip, there exist some problems. The surface of the PDMS material is strongly hydrophobic. Through targeted surface modification, the effect is hard to last. The scheme aims to solve the series of related problems. According to main points of the scheme, PDMS with primitive surface is selected as the substrate, a hinge-type fixture attached with a miniature ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and positioned near the terminal of a sample liquid fluid of the microfluidic chip, interfacial tension is reduced by ultrasonic wave, and by PDMS's strong absorption of ultrasonic wave, ultrasonic intensity is rapidly decreased progressively in a short distance so as to form interfacial tension difference between two endsof the chip. Thereby, the sample liquid fluid is driven to flow along an originally hydrophobic capillary channel towards the terminal.
Owner:洪小女
Drying device for plastic granules
ActiveCN113623979BSpeed up dryingQuick changeDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsDrive wheelThermal fatigue
Owner:赛纬精密电子科技江苏有限公司
Syphilis diagnosis multi-channel device with double-drive coupling operation function for hydrophobic substrate
InactiveCN107159323AEasy to processEasy to disassembleMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresUltrasonic sensorSyphilis
The invention relates to a syphilis diagnosis multi-channel device with a double-drive coupling operation function for a hydrophobic substrate, and belongs to the field of analysis and tests. By the aid of the syphilis diagnosis multi-channel device, the series difficult problems of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is inexpensive and is extremely easy to process when the polydimethylsiloxane is used for manufacturing syphilis diagnosis micro-fluidic chips can be solved. The scheme mainly includes that PDMS with original ecological surfaces is selected for the substrate, a chain-ring electromagnetic fixture with a miniature ultrasonic transducer sleeves a location adjacent a test sample liquid flow end point of a micro-fluidic chip and is positioned at the location adjacent to the test sample liquid flow end point of the micro-fluidic chip, and ultrasonic reduction machines are arranged at a sample injection end of the micro-fluidic chip, so that the ultrasonic wave intensity can be quickly reduced in short distances. The syphilis diagnosis multi-channel device has the advantages that interfacial tension difference can be formed at two ends of the chip, and force for driving test sample liquid flow to flow towards the end point along hydrophobic capillary channels can be provided by the difference, is coupled with mechanical pumping force of a micro-pump in the syphilis diagnosis multi-channel device and can be collaboratively operated with the mechanical pumping force.
Owner:葛宇杰
AIDS diagnosis device with easily-detachable component used for driving to-be-tested sample liquid
InactiveCN107649190AGood compatibilityRapid reversible binding reactionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesUltrasonic sensorAbsorption capacity
The invention relates to an AIDS diagnosis device with an easily-detachable component used for driving a to-be-tested sample liquid, belonging to the fields of analysis and testing. The invention aimsto solve a series of related problems that manufacturing of a substrate of a microfluidic chip used for AIDS diagnosis from cheap and easily-processed polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has a technical obstacle; and the PDMS material has highly-hydrophobic surface and is difficult to obtain lasting effects through targeted surface modification or surface decoration. The invention has the following mainpoints: PDMS with original ecological surface is selected as the substrate; a link type electromagnetic fixture equipped with a miniature ultrasonic transducer is in sleeve connection with and is positioned at a position close to the terminal of a sample liquid flow of the microfluidic chip; ultrasonic wave is used to reduce the interfacial tension; meanwhile, strong absorption capacity of the PDMS to the ultrasonic wave is utilized, so rapid decrease of ultrasonic intensity in a short distance is realized, and an interfacial tension difference between two terminals of the chip is formed; thus, the sample liquid flow is driven to flow to the terminal direction along original hydrophobic capillary channels.
Owner:宋岳
A micro-fluidic chip apparatus adopting a substrate made of a PDMS material
InactiveCN107042126AGood compatibilityEliminate surface chemical modificationLaboratory glasswaresShortest distanceCapillary channel
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic chip apparatus adopting a substrate made of a PDMS material, and belongs to the field of analysis testing. Preparation of substrates of micro-fluidic chips by utilizing polydimethylsiloxane, namely PDMS that is cheap and easy to process, has difficult problems actually. The PDMS material has a strongly hydrophobic surface, and targeted surface modification or surface decoration fails to achieve durable effects. The objective of the apparatus is to overcome the series of problems. The apparatus is characterized in that PDMS having an original surface is adopted as a substrate, a chain-ring type electromagnetic clamp equipped with a minitype ultrasonic transducer is positioned at a position near a sample liquid stream terminal of a micro-fluidic chip in a sleeve joint manner, and an ultrasonic attenuator is mounted at a feeding end of the micro-fluidic chip to achieve rapid ultrasonic wave intensity attenuation in a short distance, and therefore an interfacial tension difference is formed between the two ends of the chip, thus allowing the sample liquid stream to flow along originally hydrophobic capillary channels towards the terminal direction.
Owner:李榕生
Microfluidic chip apparatus adopting high hydrophobic substrate for detecting subtype swine influenza
InactiveCN106290935AGood compatibilityEasy to processMaterial electrochemical variablesHigh absorptionUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip apparatus adopting a high hydrophobic substrate for detecting subtype swine influenza, which belongs to the field of analysis and test. The application of a substrate which is used for the microfluidic chip for diagnosing subtype swine influenza and made of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) low in price and easy to process has a series of difficulties. The invention provides a scheme for solving the series of difficulties. A key point of the scheme is that the substrate is made of the PDMS with an original ecological surface, a hinge-type clamp with a micro ultrasonic transducer is manually tightened and positioned at a position nearby a test sample liquid flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, the interface tension is reduced by virtue of the ultrasonic waves; meanwhile, by utilizing the high absorption capacity of the PDMS for the ultrasonic waves, the ultrasonic intensity is rapidly attenuated in a short distance, so that interface tension difference is formed at two ends of the chip, the difference provides power for driving the test sample liquid flow to flow to the terminal along a hydrophobic capillary passage, and the power is synergistic with mechanical pumping power of a micro-pump contained in the structure.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Robot ejection connecting structure with stable butt joint function for storage and freight transport
ActiveCN111017461AStable ejection connection structureConvenient positioning workStorage devicesButt jointControl engineering
The invention discloses a robot ejection connecting structure with a stable butt joint function for storage and freight transport. The robot ejection connecting structure comprises a storage robot main body, a goods shelf main body, a lifting column and bolts, a bottom plate is arranged over the storage robot main body, the bottom plate is welded and fixed to the outer surface of the bottom end ofthe goods shelf main body, the lifting column is arranged in the center of the storage robot main body, the top surface of the lifting column is fixedly connected with the center of the bottom surface of a supporting plate, and the supporting plate is located in a first connecting groove. According to the robot ejection connecting structure with the stable butt joint function for storage and freight transport, the storage robot main body controls the supporting plate and a top plate to ascend and descend through the lifting column, so that the supporting plate conveniently pushes the top plate to slide into a positioning hole for clamping, meanwhile, a limiting shaft can slide into a limiting groove for clamping connection through pushing of elastic force of a connecting spring, the overall positioning work of the goods shelf main body is facilitated, and therefore the goods shelf main body is prevented from shaking during subsequent transportation.
Owner:南京荣达物流设备有限公司
Chip device adopting PDMS as substrate material for subtype swine flu detection
InactiveCN106153694AEasy to disassembleEasy to separate from each otherMaterial electrochemical variablesUltrasonic sensorHigh absorption
The invention relates to a chip device adopting PDMS as a substrate material for subtype swine flue detection, and belongs to the field of analytical tests. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) which is low in price and extremely easy to process is used for making the substrate of a microfluidic chip for subtype swine flue diagnosis, and some problems actually exist; the surface of PDMS is strongly lyophobic, the effect of specific surface modification or surface decoration has difficulty in being lasting, and the invention aims at solving the series of related problems. The chip device adopting PDMS as the substrate material for subtype swine flue detection is characterized in that a substrate adopts PDMS with an original surface, a hinge type fixture additionally provided with a miniature ultrasonic transducer is manually fastened and positioned on a nearest location of a sample flow terminal of the microfluidic chip, the interfacial tension is reduced through ultrasonic waves, and meanwhile by means of a high absorption capacity of PDMS for the ultrasonic waves, the ultrasonic wave intensity is decreased progressively and rapidly within a short distance; an interfacial tension difference is formed at the two ends of the chip, and therefore a sample flow is promoted to flow along an original hydrophobic capillary channel in the terminal direction.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Separator and method for firing plurality of green sheet units using same
ActiveCN110315631AEconomical and reliable manufactureEasy to handleLamination ancillary operationsLaminationEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present disclosure relates to a separator and a method for firing a plurality of green sheet units using the same, the method enabling thin green sheets to be stacked and fired at a time. According to the method, after a green sheet assembly is formed by pressing a carbon separator having a protruding portion formed on one surface thereof so that the protruding portion comes into contact withboth surfaces of a green sheet, a plurality of green sheet assemblies are mounted on a firing setting member, the carbon separator is thermally decomposed at a set temperature and evaporated, and thenthe green sheet is fired and unit ceramic sheets are separated.
Owner:JOINSET
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com