Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Maximize response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
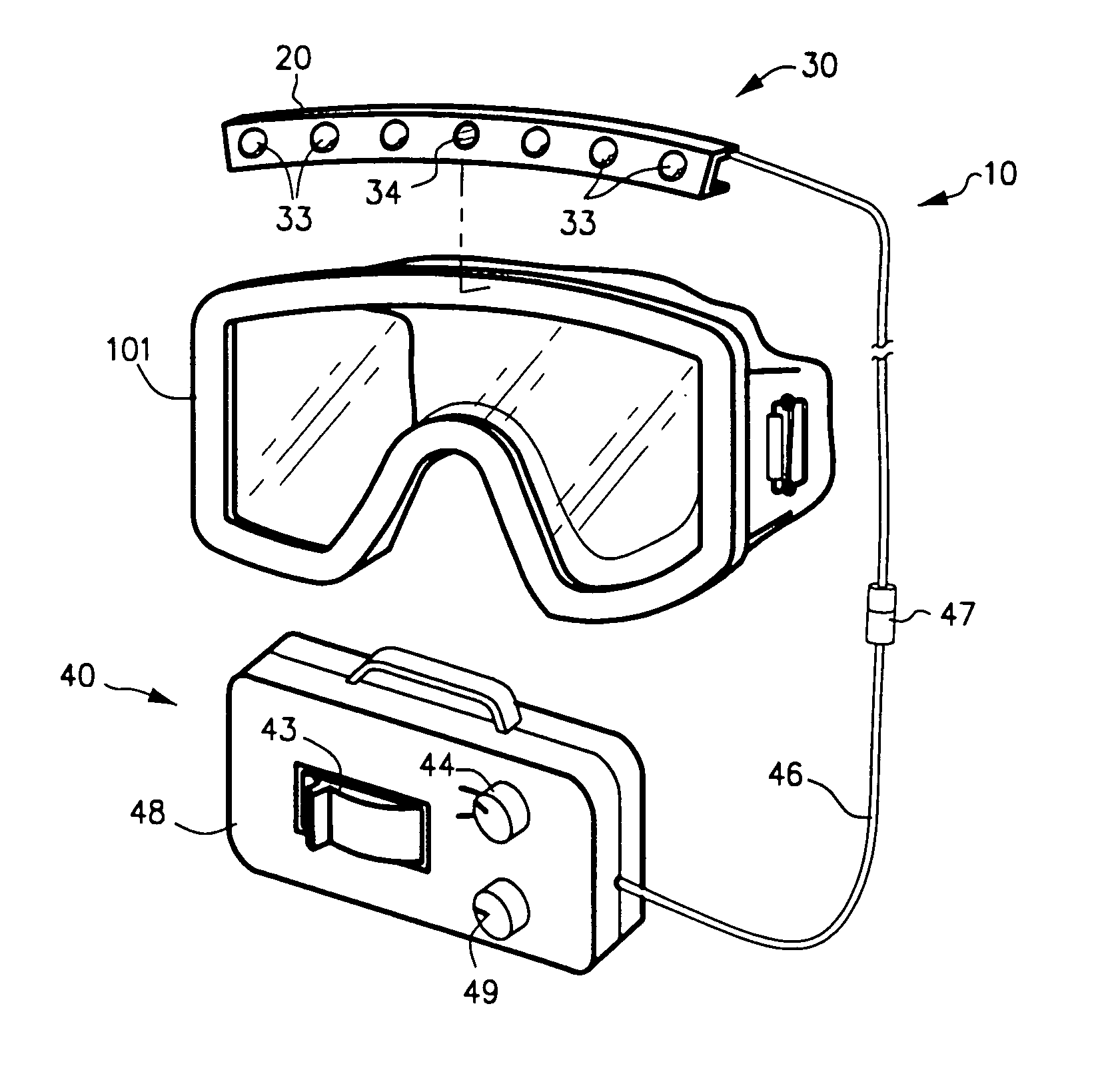
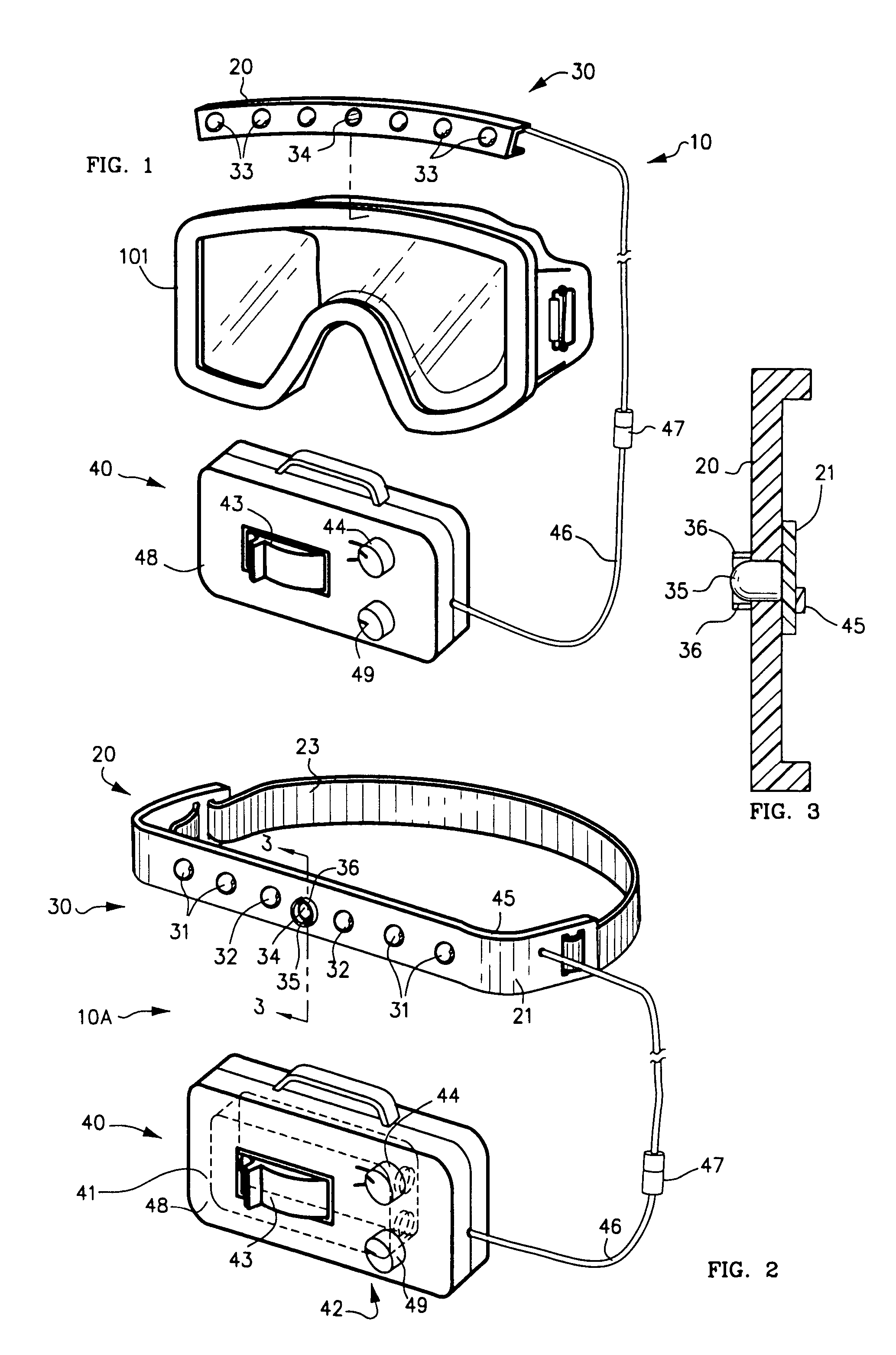
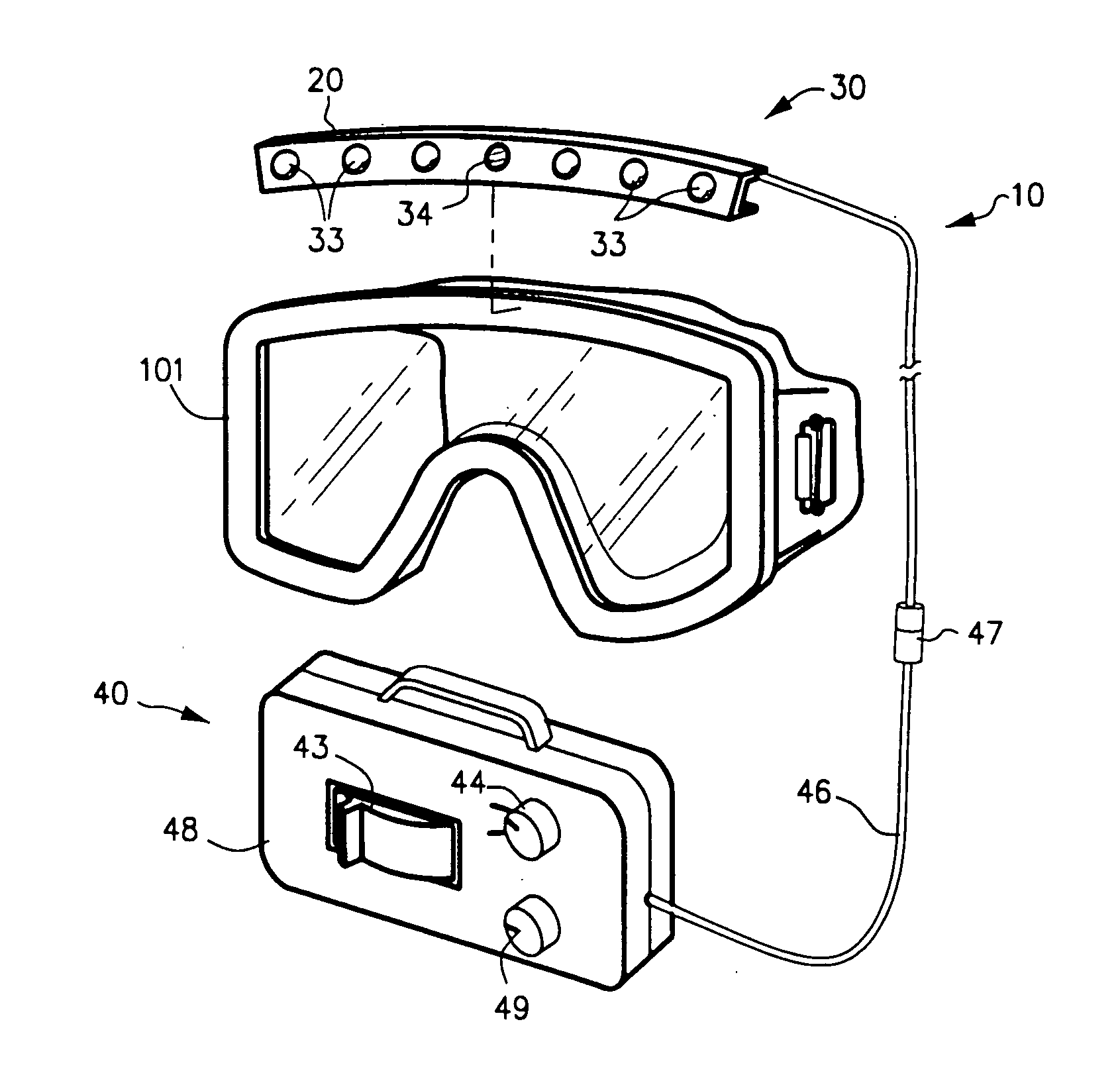
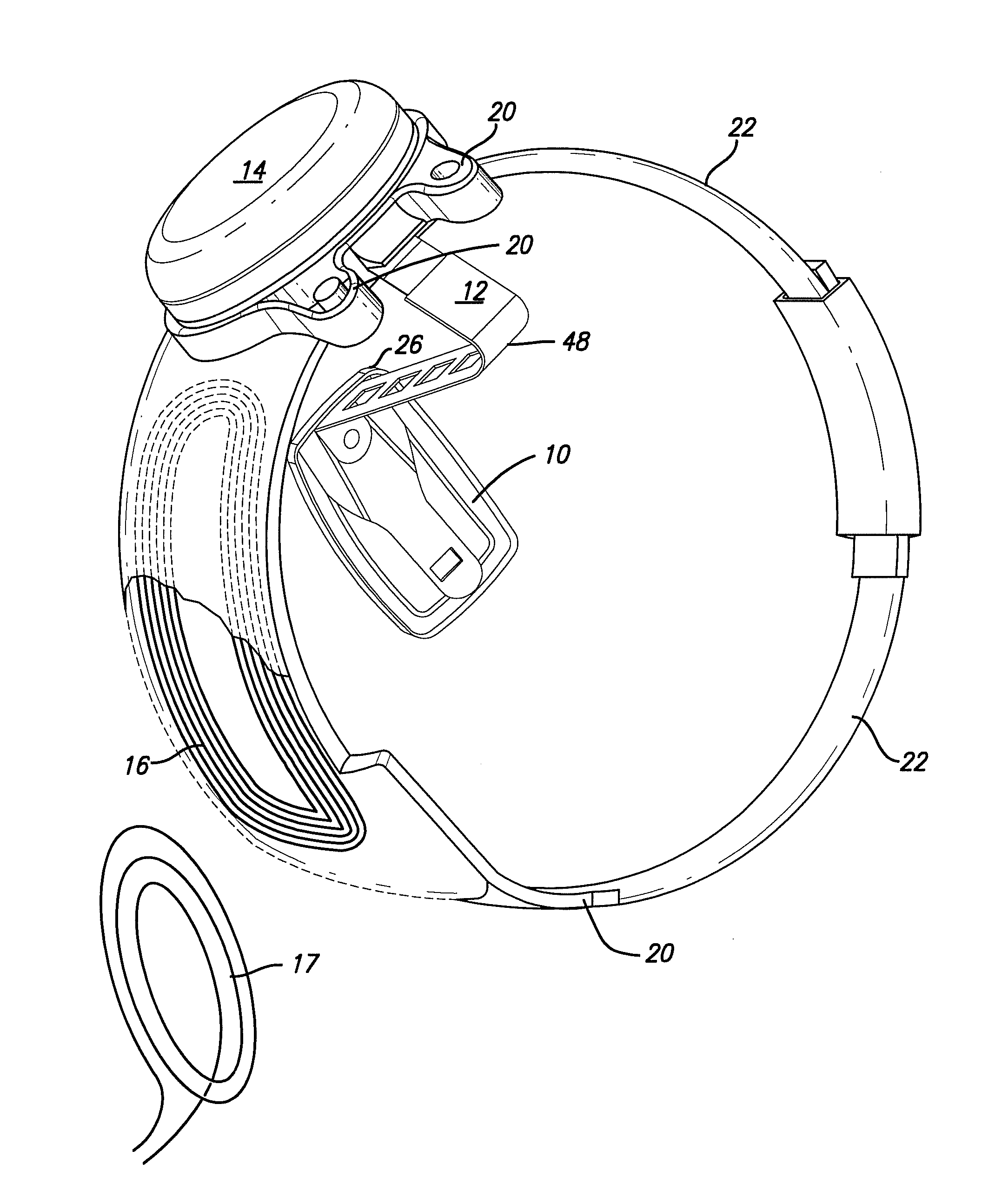
Wearable light device with optical sensor
ActiveUS6966668B2Improve eyesightPrevent glareElectrical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLighting systemControl circuit
Wearable light device for providing additional light for activities in low light includes a wearable mount (20) including a light system (30) and power source (40). Light system (30) includes one or more arrays of light sources such as light-emitting diodes (33). Photo sensor (34) detects ambient light or emitted light returned from a reflective surface and causes control circuit (45) to dim light emission.
Owner:FOXFURY
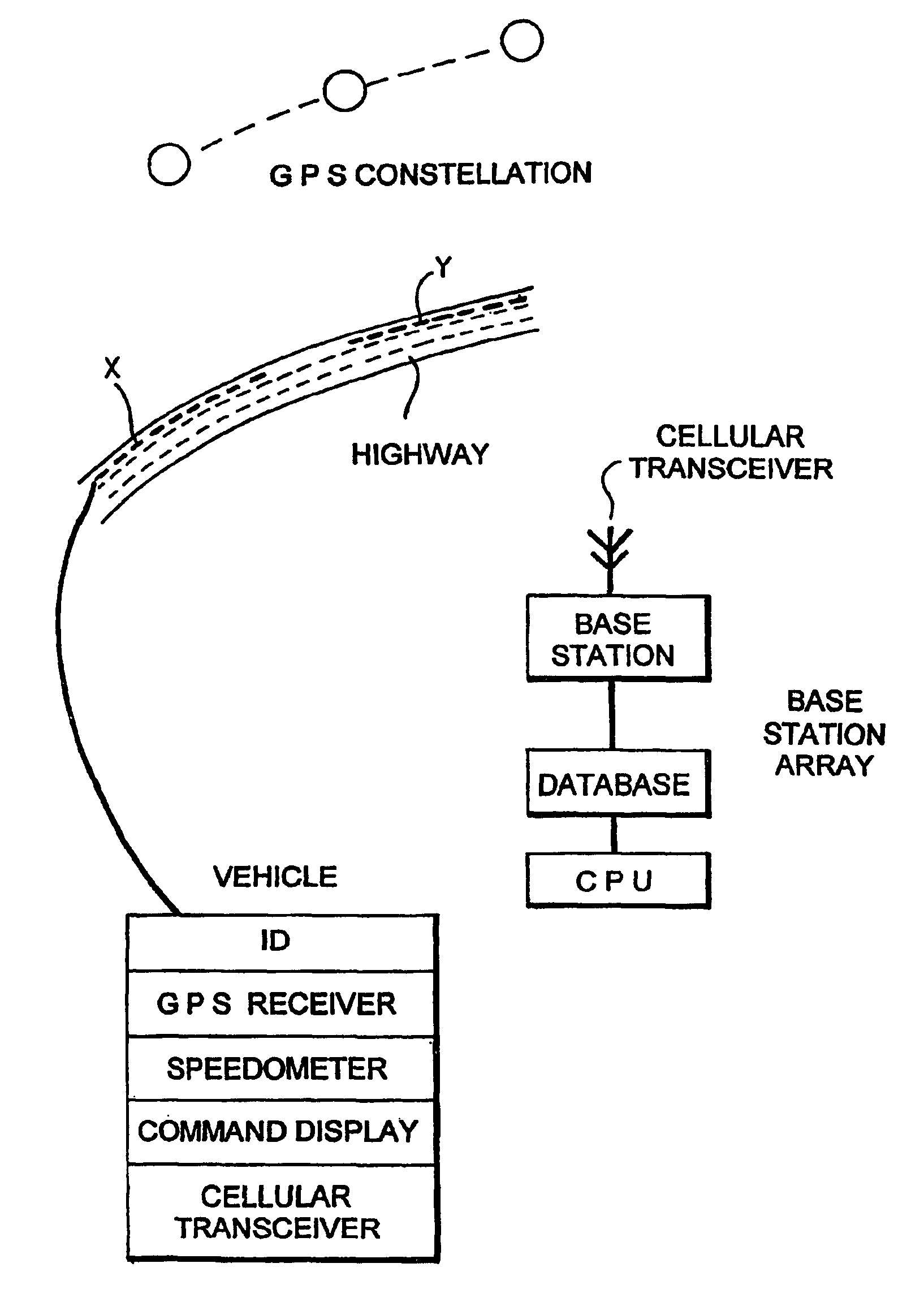
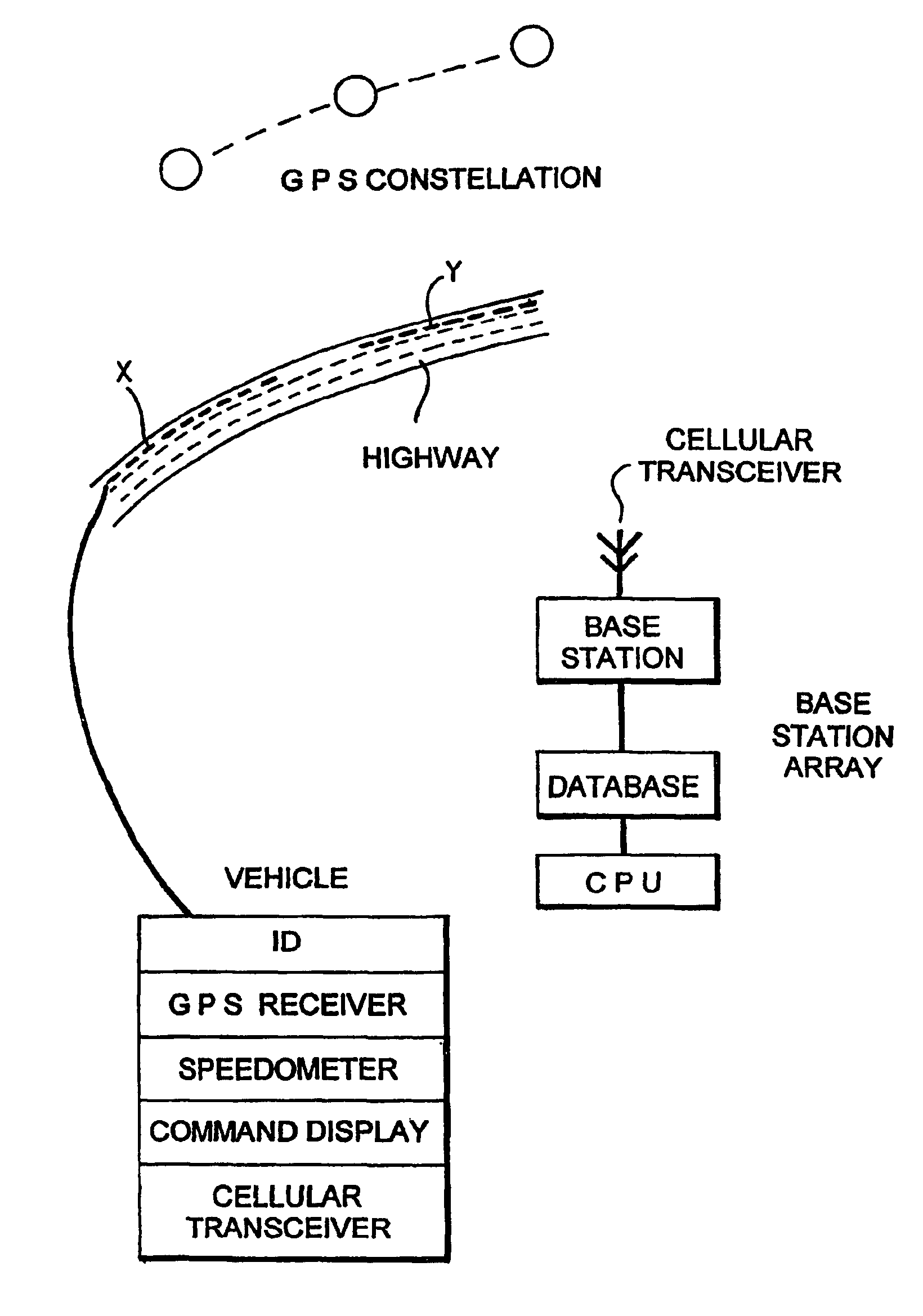
Highway vehicular traffic flow control
InactiveUS7002486B2High trafficEasy to useAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsTraffic capacityTraffic flow control
A base station receives signals from highway traffic and sends signals to selected vehicles on the highway to command them to increase / decrease speed or charge lane in order to more closely conform to a virtual model for vehicular use of the highway.
Owner:LAWRENCE MALCOLM G
Devices and methods for optimizing electrode placement for anti-inflamatory stimulation
ActiveUS8412338B2Maximize responseMinimize responseElectrotherapyElectrode placementInflammatory reflex
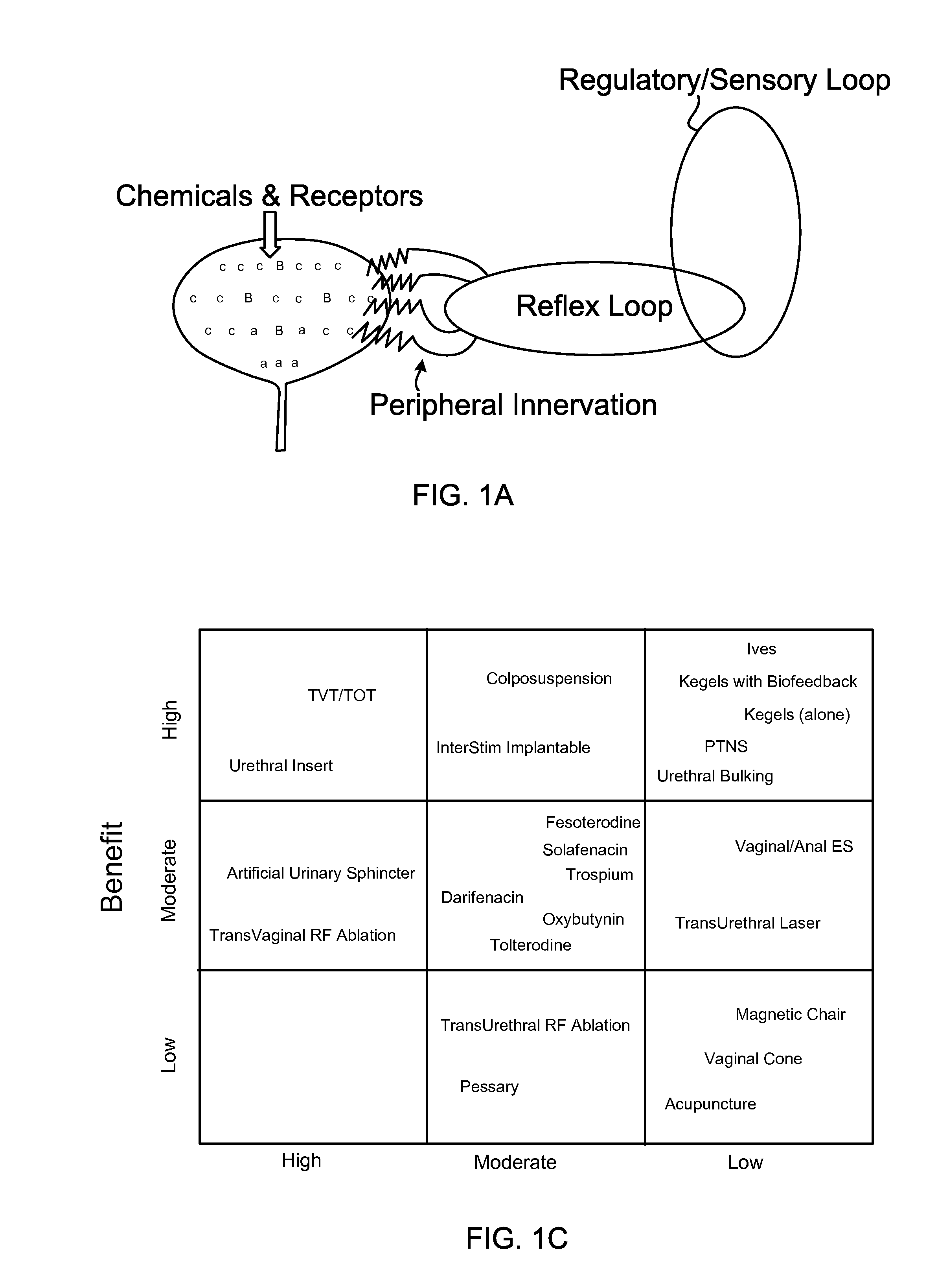
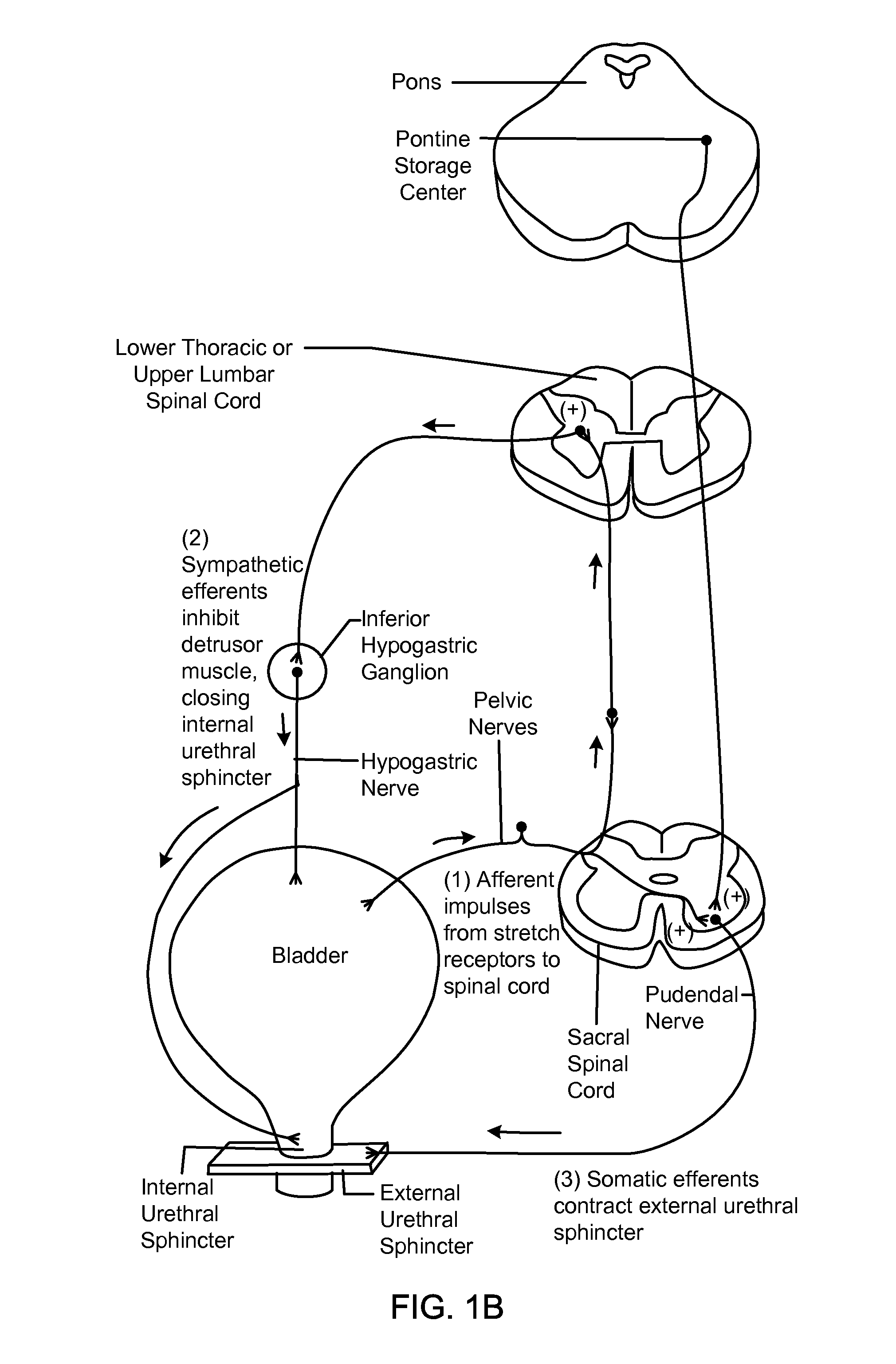
Described herein are methods, devices and system for selecting an optimum position of a stimulation electrode, and particularly methods, devices and systems for optimizing the position of a stimulation electrode for stimulating the inflammatory reflex and thereby inhibiting inflammation. The methods, devices and systems described herein may generally include the analysis of one or more artifact modalities arising after the application of a stimulation pulse. One or more of these artifact modalities (e.g., EMG, ECG, etc.) may be detected and used to generate a comparable indicator of the fitness of the position of the electrode relative to a target, such as a portion of the inflammatory reflex like the vagus nerve.
Owner:SETPOINT MEDICAL CORP
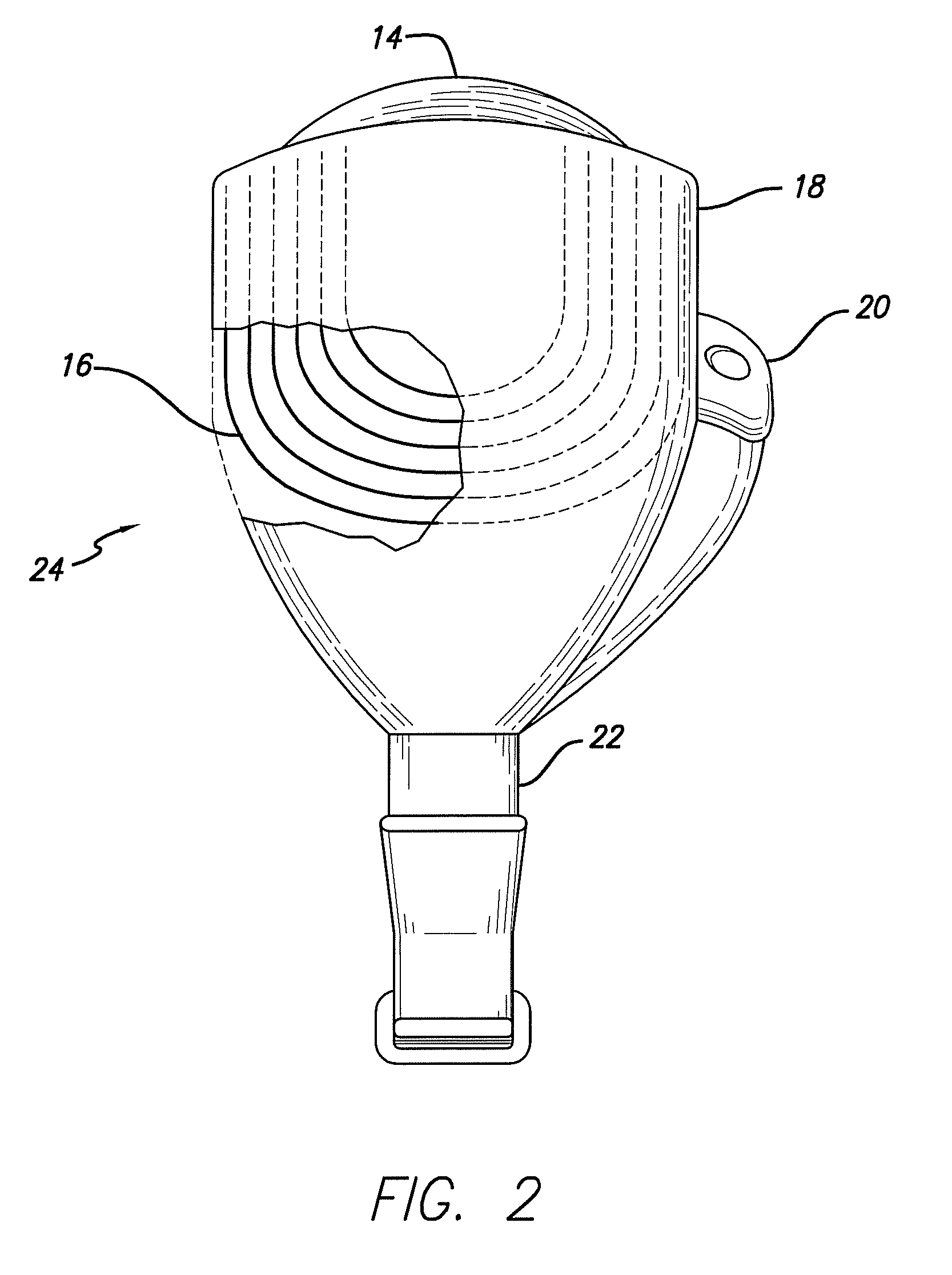
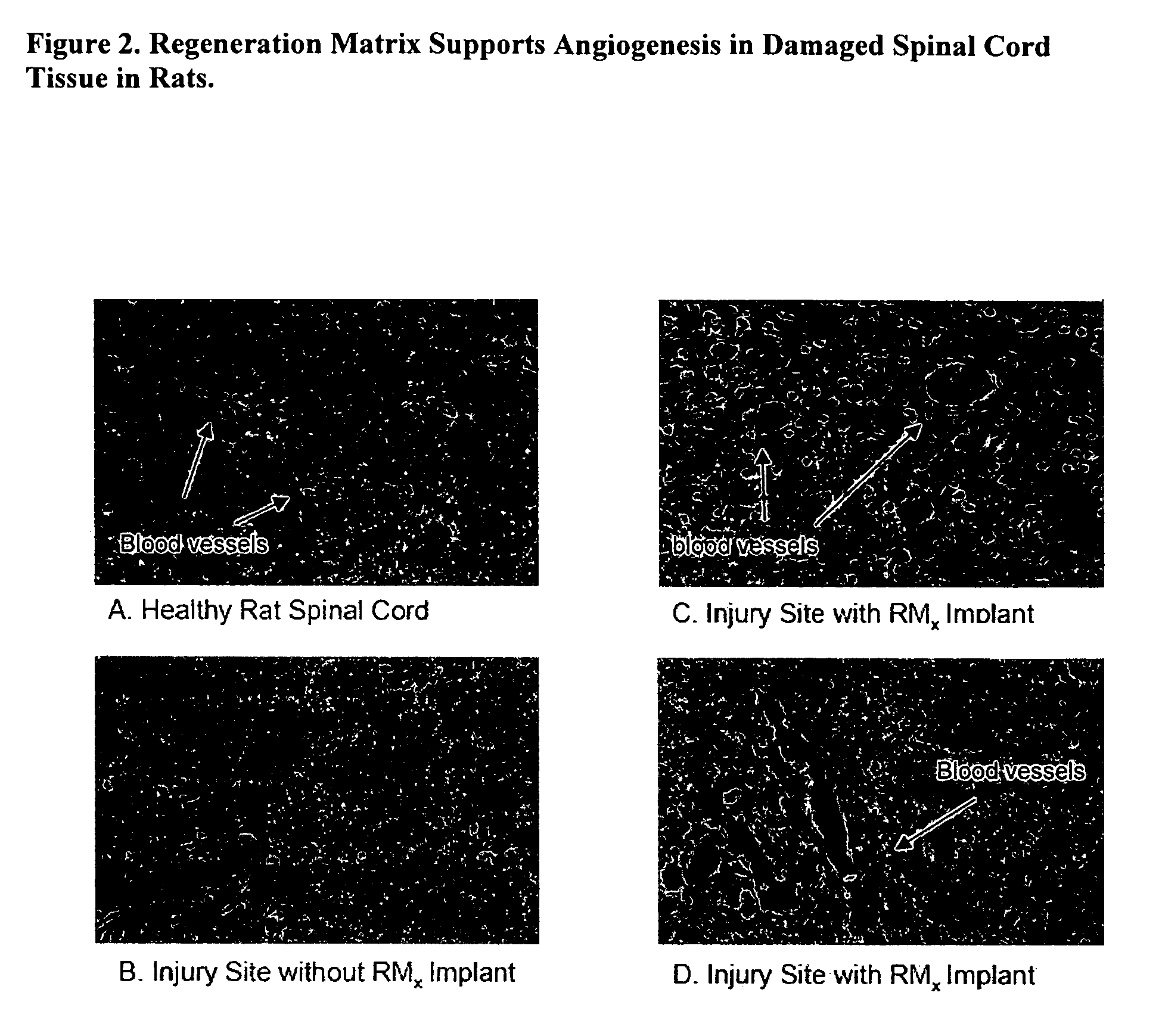
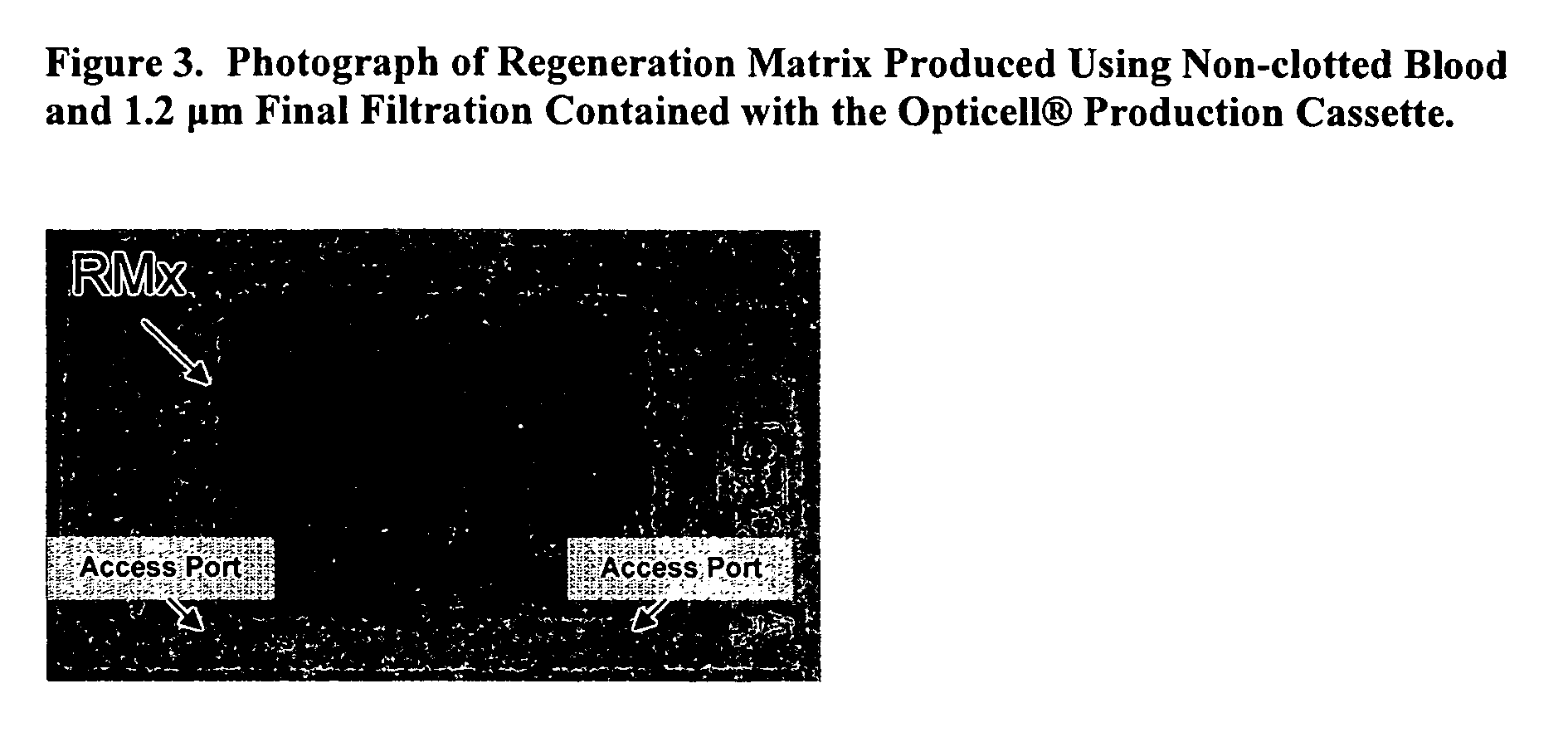
Acellular bioabsorbable tissue regeneration matrices
ActiveUS20070202189A1Lightweight productionPromote regenerationBiocideNervous disorderNerves tissuePathology
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
Simplified water-bag technique for magnetic susceptibility measurements on the human body and other specimens
InactiveUS7047059B2Less-expensive fabricationLess-expensive useMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHuman bodyMagnetic susceptibility
A probe instrument using room-temperature sensor(s) that can measure variations in magnetic susceptibilities. The instrument has sufficient resolution to monitor paramagnetic materials in a human body, such as iron in a human liver, by noninvasively examining patients with iron-overload diseases. The instrument includes room temperature magnetic sensors, and detects the sample, that is, the tissue response to an alternating current field applied by an applied field coil. The applied field coil dimensions are chosen so that the applied field is optimized for maximum response from the liver while minimizing the effects due to the overlying abdominal tissue and at the same time not unduly increasing the sensitivity of the instrument to the lung. To overcome variations in the sensor output due to fluctuations in the applied field, change in the ambient temperature and mechanical relaxation of the instrument, the sensor-sample distance is modulated. The detector assembly is oscillated while the examined patient remains stationary. An improved water-bag technique is employed to eliminate background tissue response. The detector assembly forms part of a probe instrument for performing noninvasively the paramagnetic concentration of a patient.
Owner:QUANTUM MAGNETICS
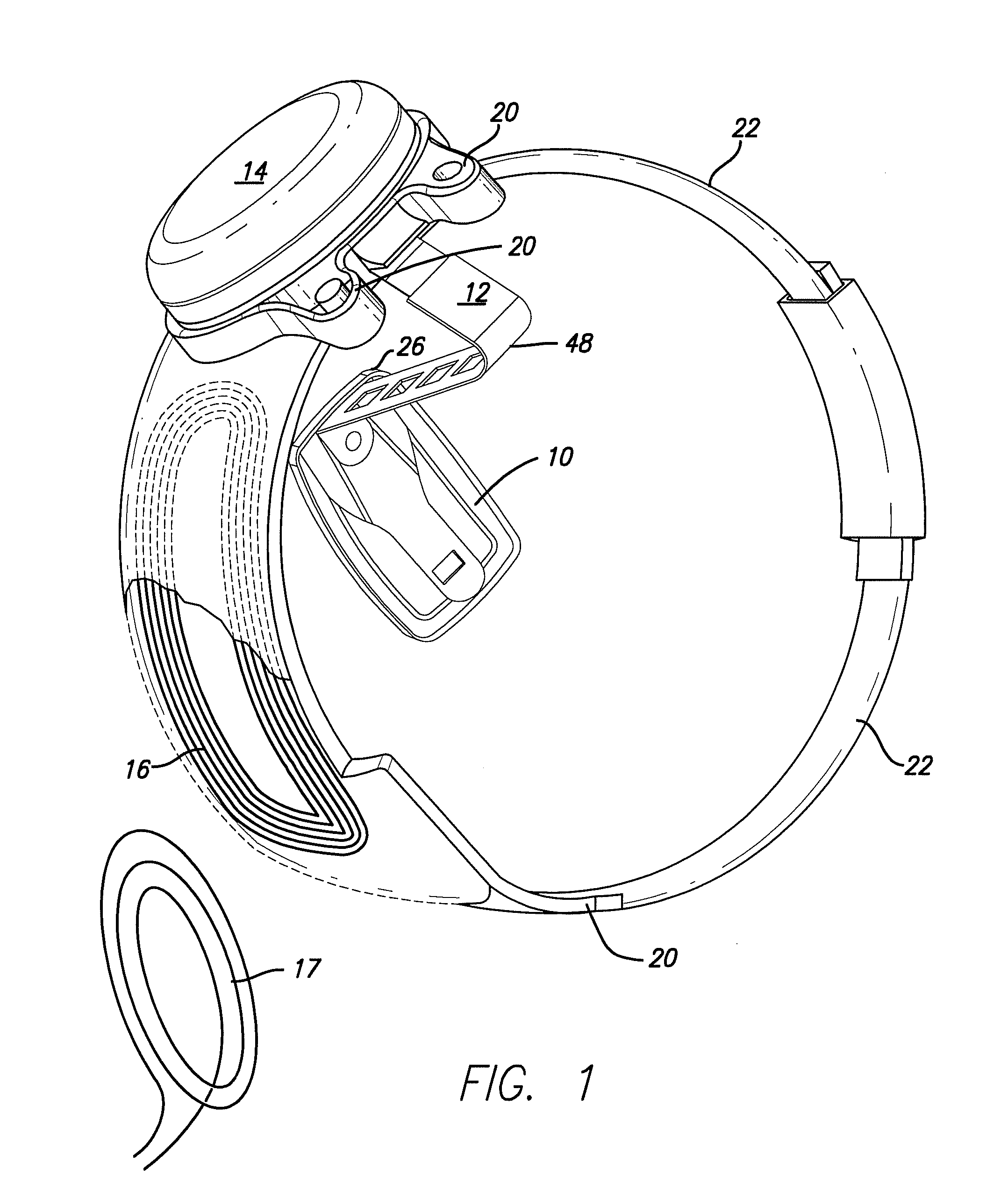
Wearable light device with optical sensor
ActiveUS20050099798A1Improve eyesightPrevent glarePoint-like light sourceElectrical apparatusLighting systemControl circuit
Wearable light device for providing additional light for activities in low light includes a wearable mount (20) including a light system (30) and power source (40). Light system (30) includes one or more arrays of light sources such as light-emitting diodes (33). Photo sensor (34) detects ambient light or emitted light returned from a reflective surface and causes control circuit (45) to dim light emission.
Owner:FOXFURY
Cup waveguide antenna with integrated polarizer and OMT
InactiveUS8077103B1Compact structureGood radiation characteristicsWaveguide type devicesAntenna detailsPolarizerOrthomode transducer
A cup waveguide antenna with integrated polarizer and OMT for simultaneously communicating left and right hand circularly polarized electromagnetic waves is adjustable to obtain efficient propagation and reception of electromagnetic waves. The antenna includes a circular waveguide having an orthomode transducer utilizing first and second pins longitudinally spaced apart and oriented orthogonally with respect to each other. Six radially-oriented adjustable polarizer screws extend from the exterior to the interior of the waveguide. A septum intermediate the first and second pins is aligned with the first pin. Adjustment of the polarizer screws enables maximized propagation of and / or response to left hand circularly polarized electromagnetic waves by the first pin while simultaneously enabling maximized propagation of and / or response to right hand circularly polarized electromagnetic waves by the second pin.
Owner:NASA
Electrical neuromodulation stimulation system and method for treating urinary incontinence
InactiveUS20150328454A1Enhance patient resultImprove therapeutic efficacyExternal electrodesDigestive electrodesElectricityProtection mechanism
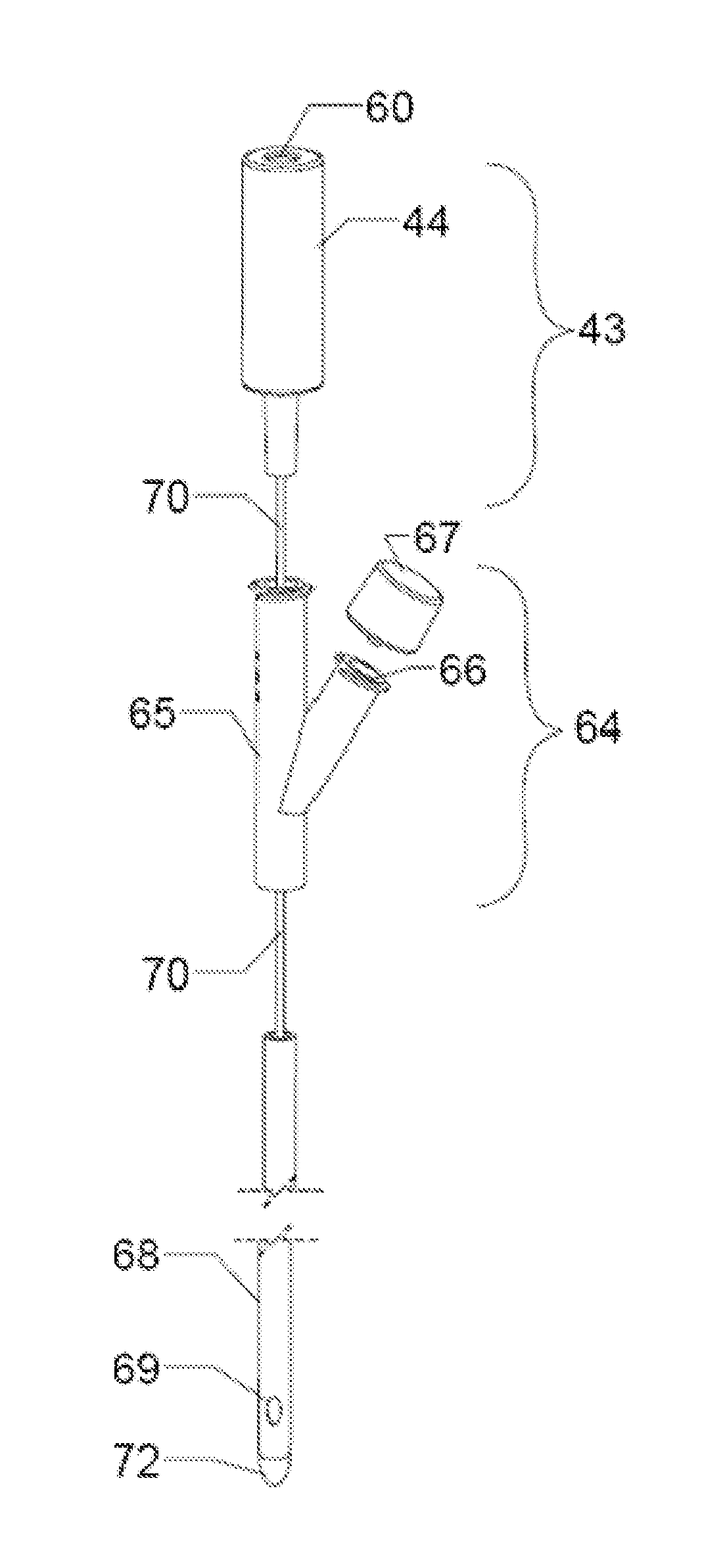
A system and method are provided for using neuromodulation techniques and intravesical electrical stimulation to treat Urinary Incontinence and related bladder-system conditions. The system uses an electrical stimulation module, stimulation electrodes and catheters, and / or a measurement and feedback system to determine an electrical stimulation therapy program as a function of a pre-programmed library and, optionally, measured and patient-provided response data. IVES and other electrical stimulation signals are generated and conveyed to the patient via catheter electrodes placed in and around the bladder system and related nerves, nodes and motor control points. The system employs a variety of safety mechanisms, including safety algorithms, a one-time use catheter connection, and catheter electrical-shock protection mechanisms.
Owner:BIO HEALTH FRONTIERS
Methods and compositions for immunization against virus
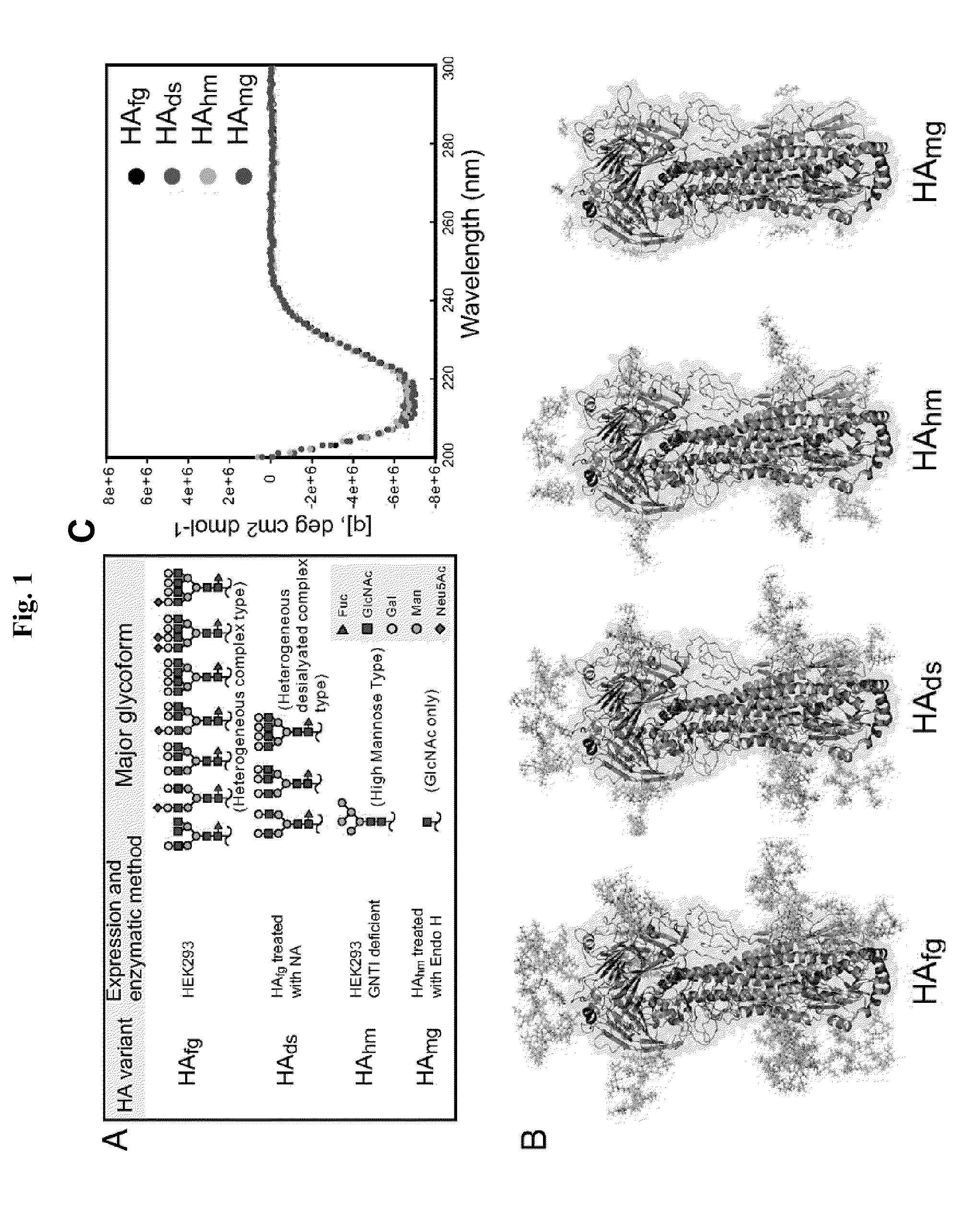
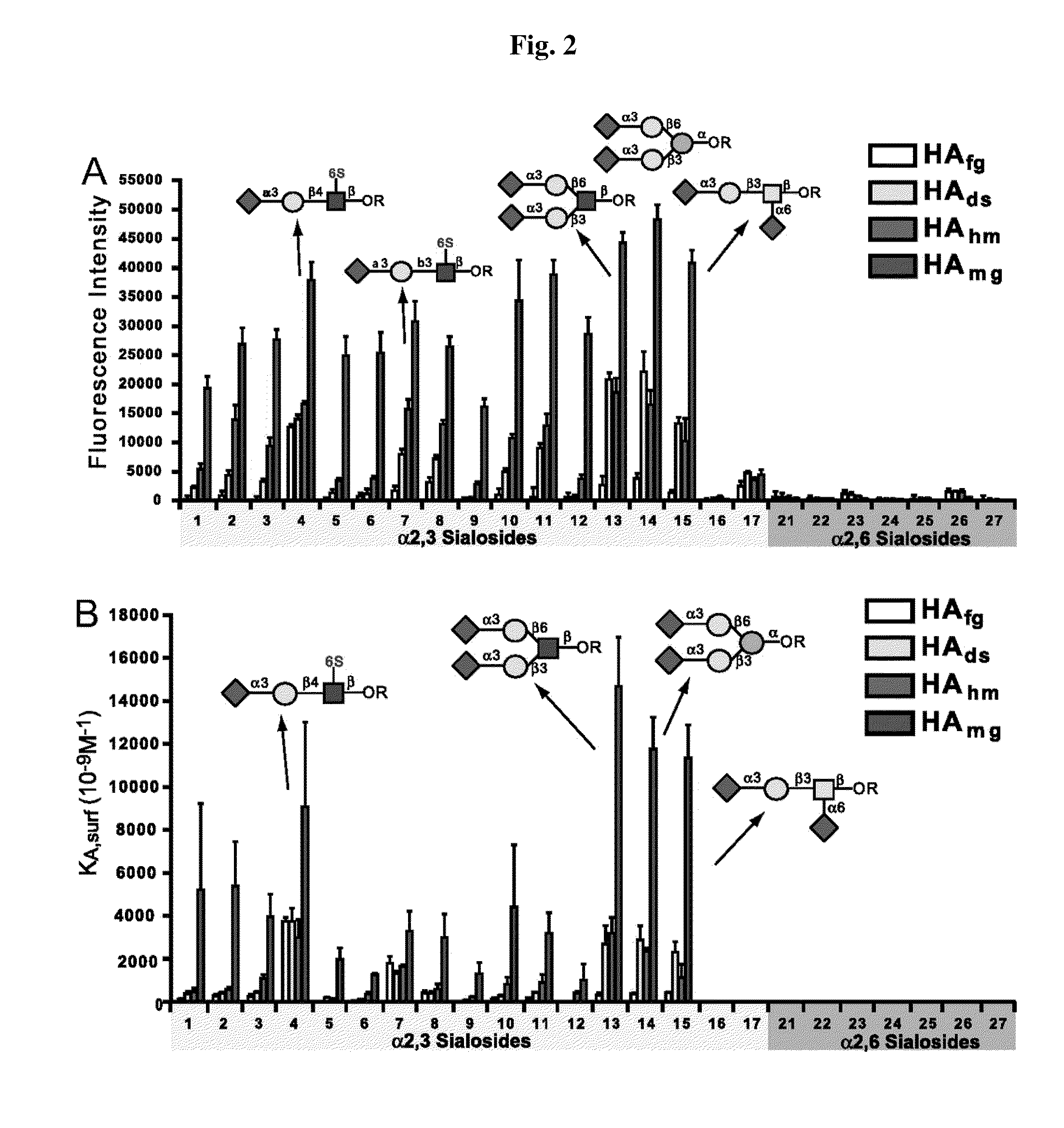
ActiveUS20100247571A1Increase immunogenicityMaximize responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseImmunogenicityViral glycoprotein
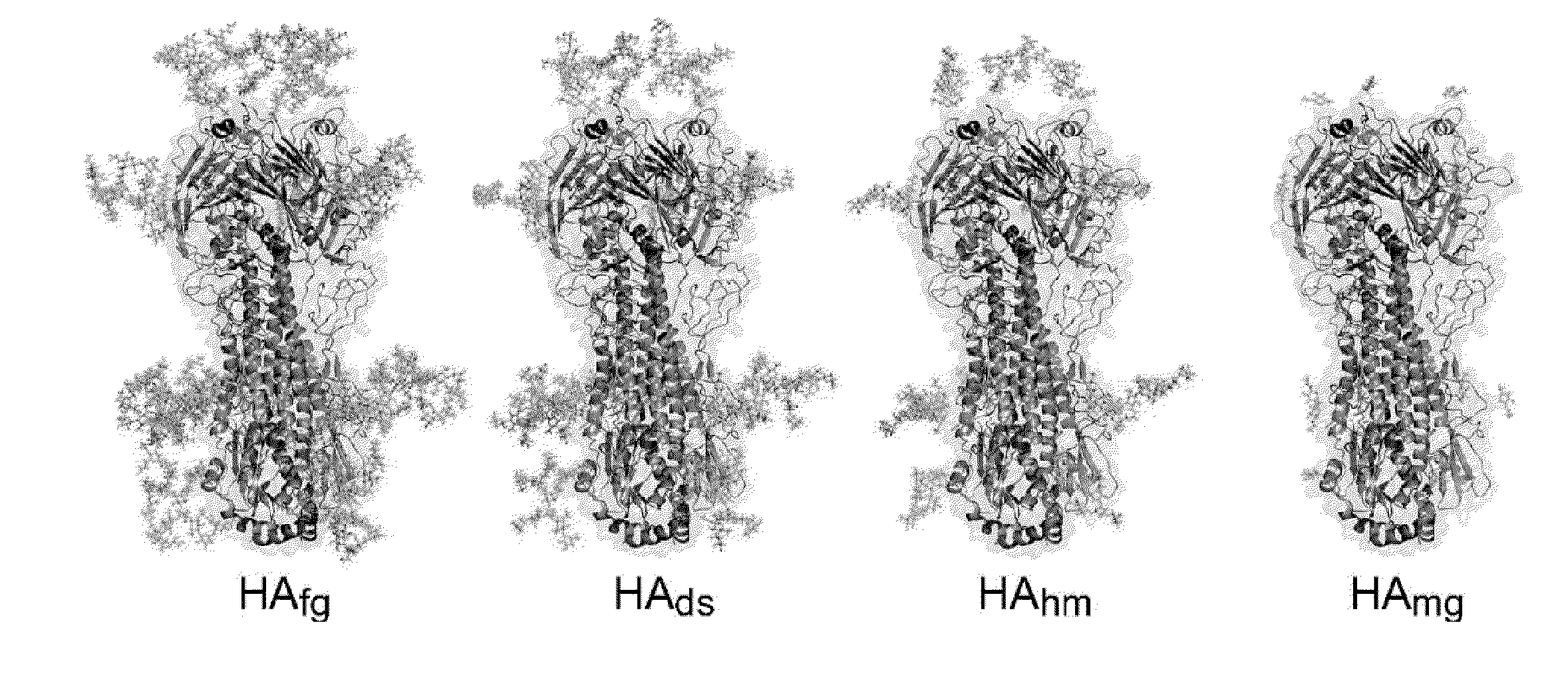
Immunogenic compositions comprising partially glycosylated viral glycoproteins for use as vaccines against viruses are provided. Vaccines formulated using mono-, di-, or tri-glycosylated viral surface glycoproteins and polypeptides provide potent and broad protection against viruses, even across strains. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising monoglycosylated hemagglutinin polypeptides and vaccines generated therefrom and methods of their use for prophylaxis or treatment of viral infections are disclosed. Methods and compositions are disclosed for influenza virus HA, NA and M2, RSV proteins F, G and SH, Dengue virus glycoproteins M or E, hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E1 or E2 and HIV glycoproteins gp120 and gp41.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Multitone harmonic radar and method of use
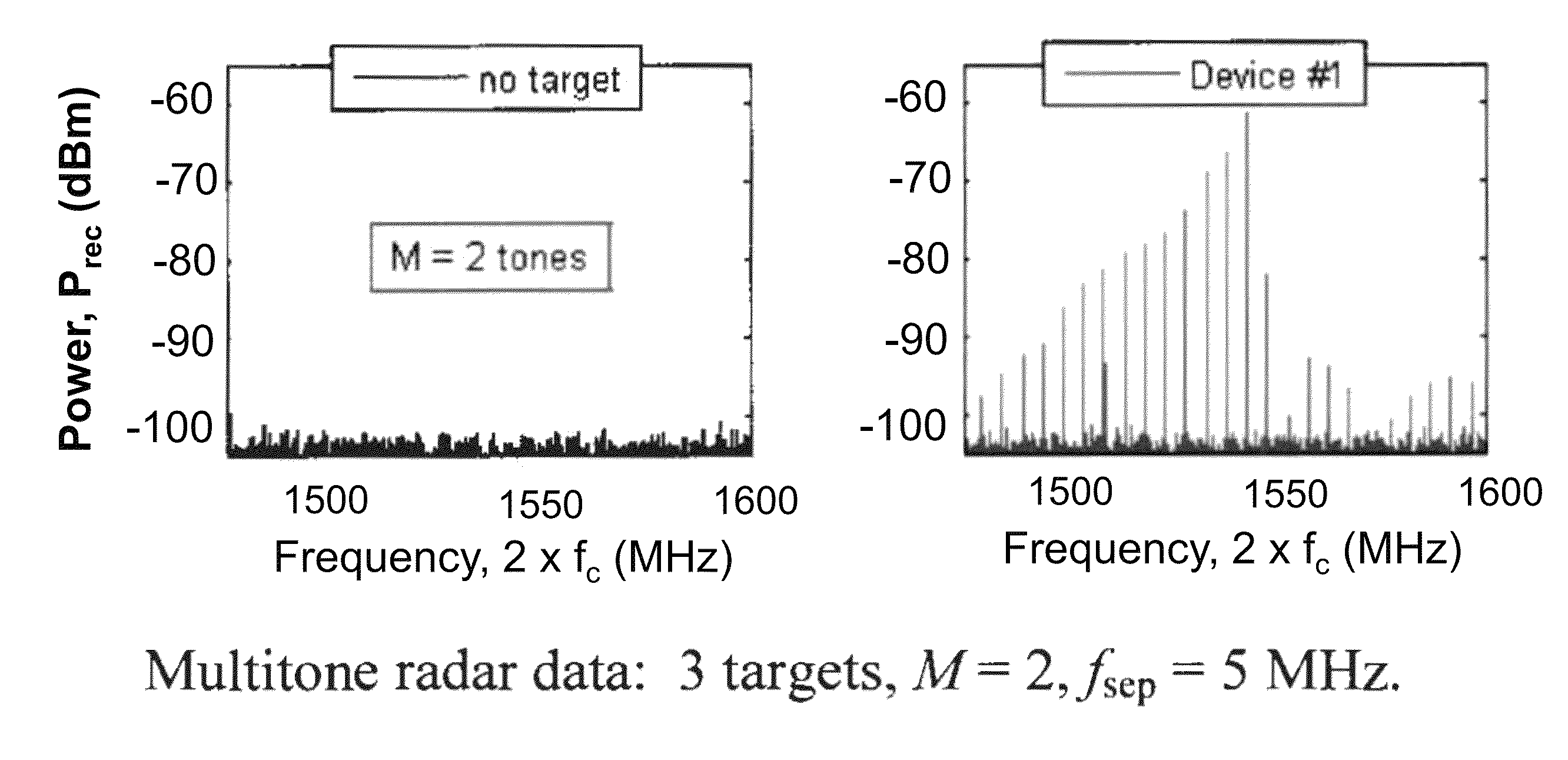
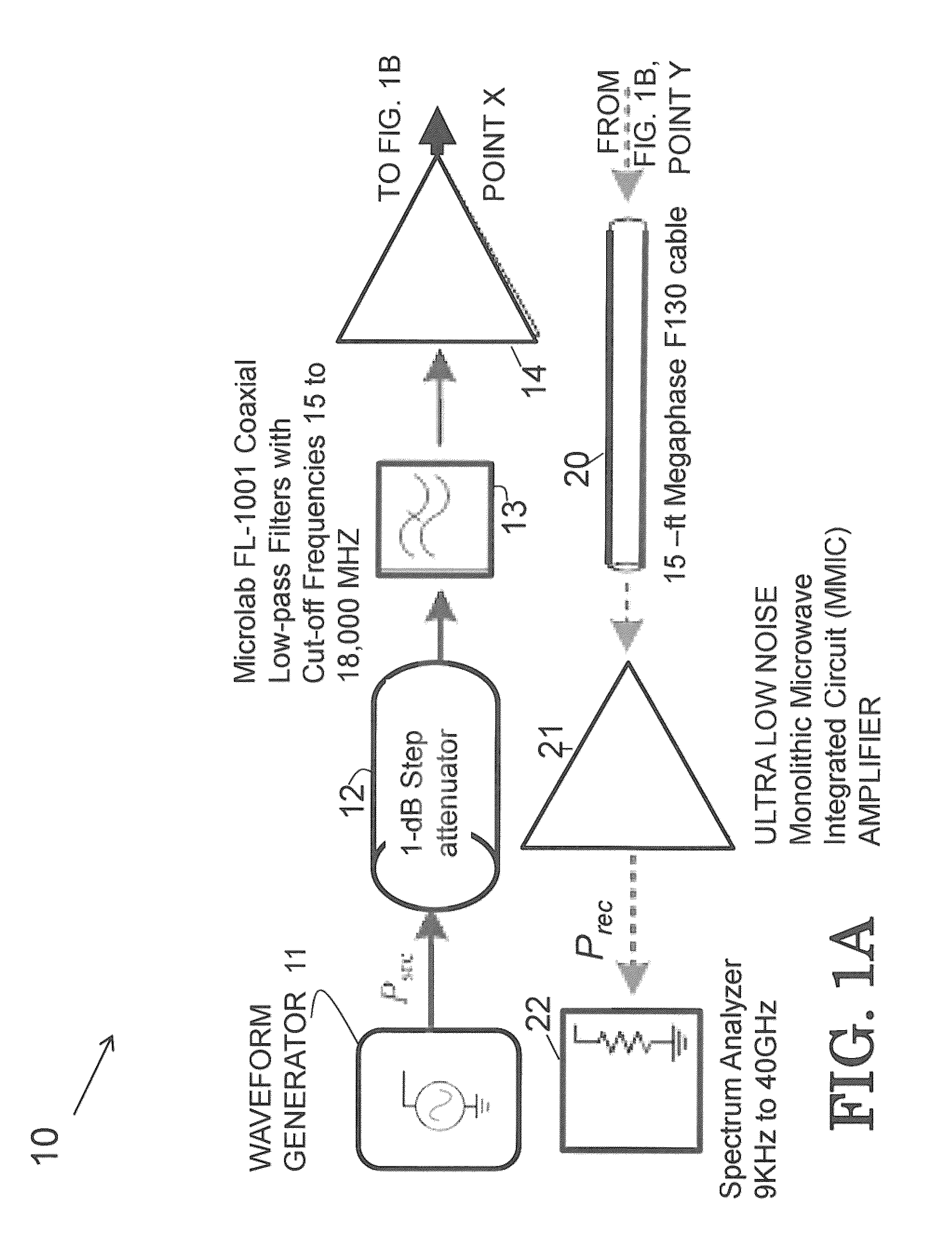
ActiveUS9395434B2Minimize or eliminate system-generated nonlinear productsRaise the ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsHarmonic radar
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Coaching and training system and method for integrated monitoring, managing, supporting, scheduling and prompting of clients
InactiveUS20150379891A1Maximize effectivenessMaximize responseTransmissionElectrical appliancesIntegrated monitoringComputer science
An integrated system and method to permit coaches, trainers and other life enhancement entities and individuals to monitor, manage, support, schedule, prompt and otherwise motivate clients to achieve set goals, establish new goals and continue routines during times of non-personal interaction between the coach, trainer or enhancement entity or person and the client.
Owner:MINICUCCI ALEX
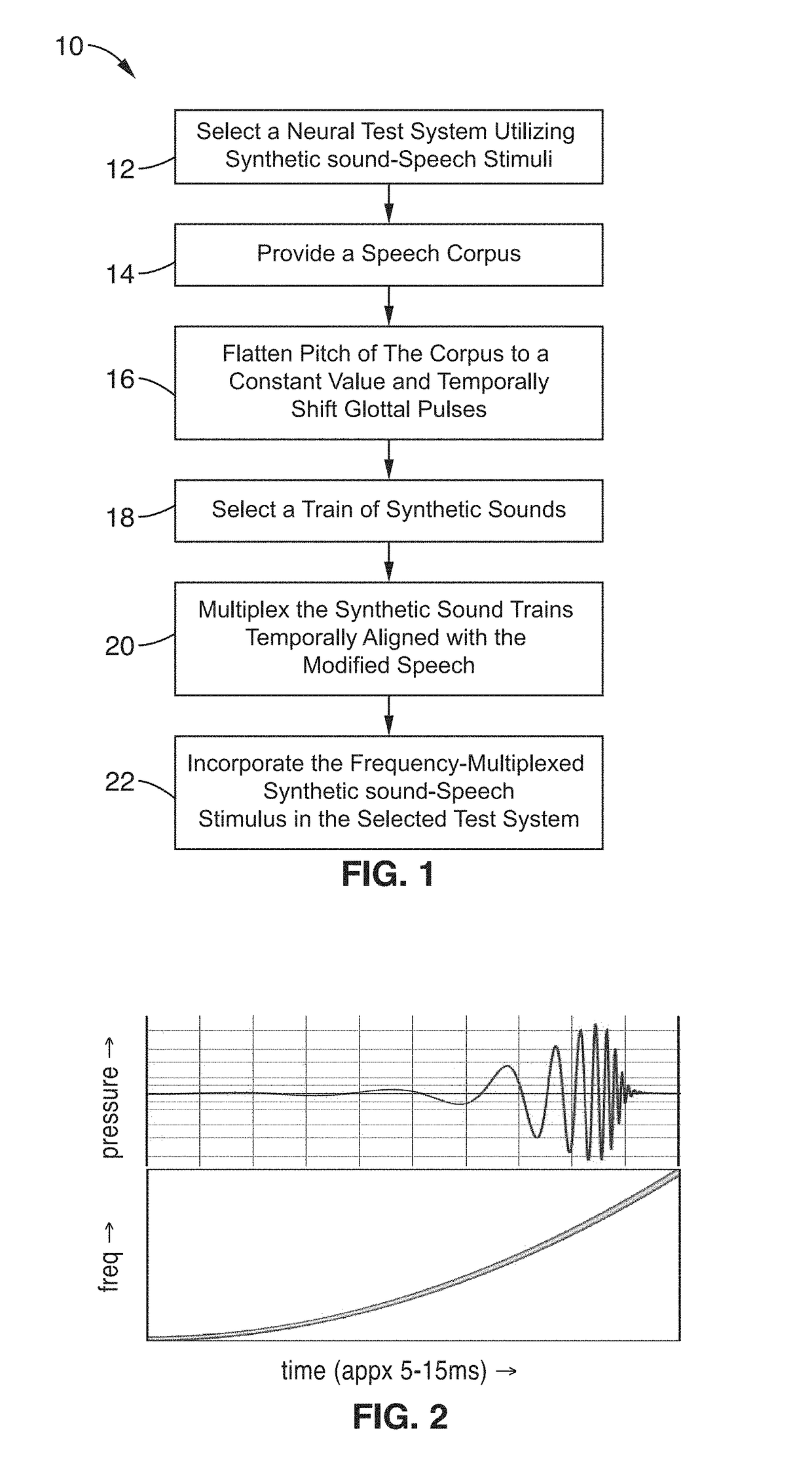
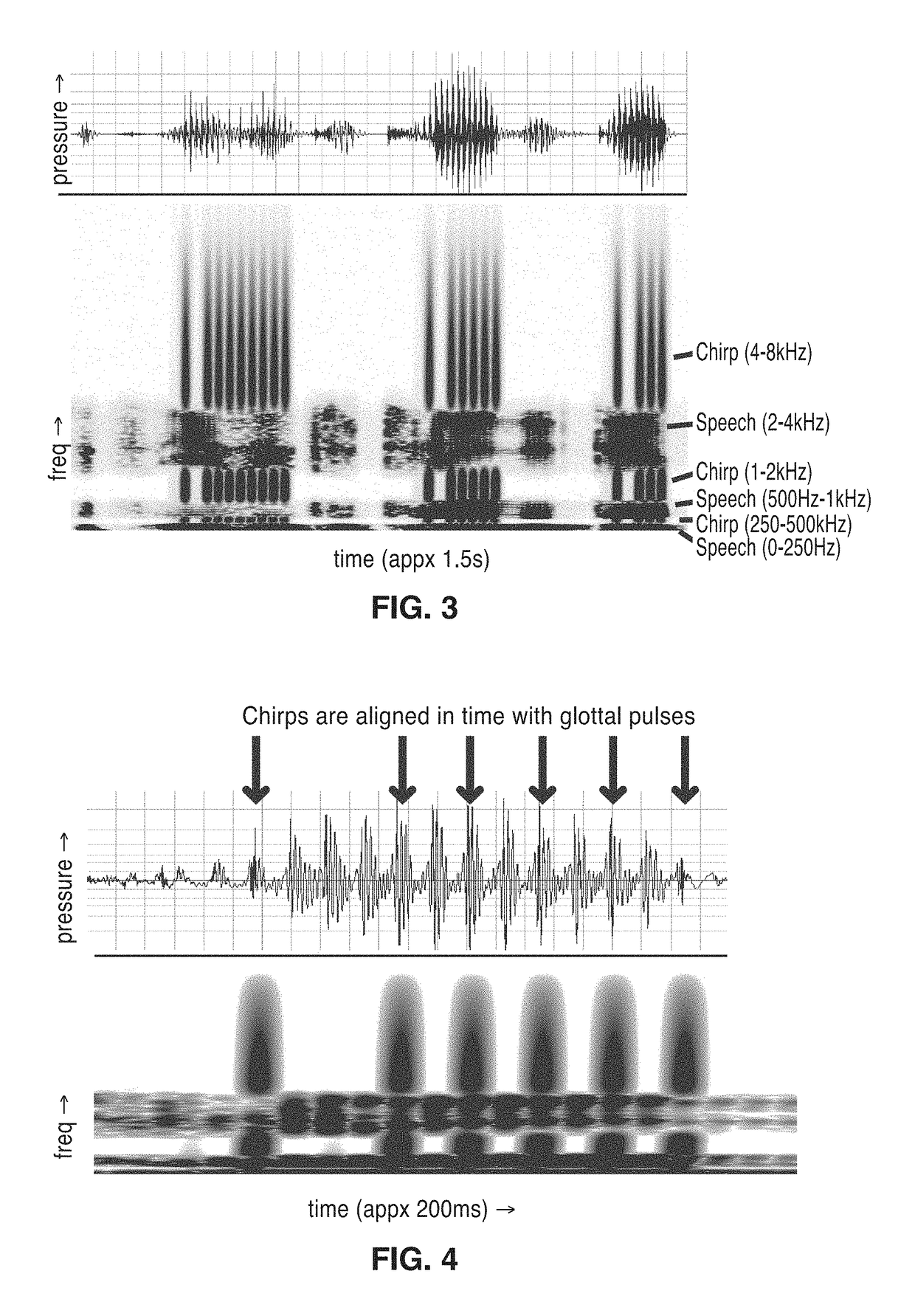
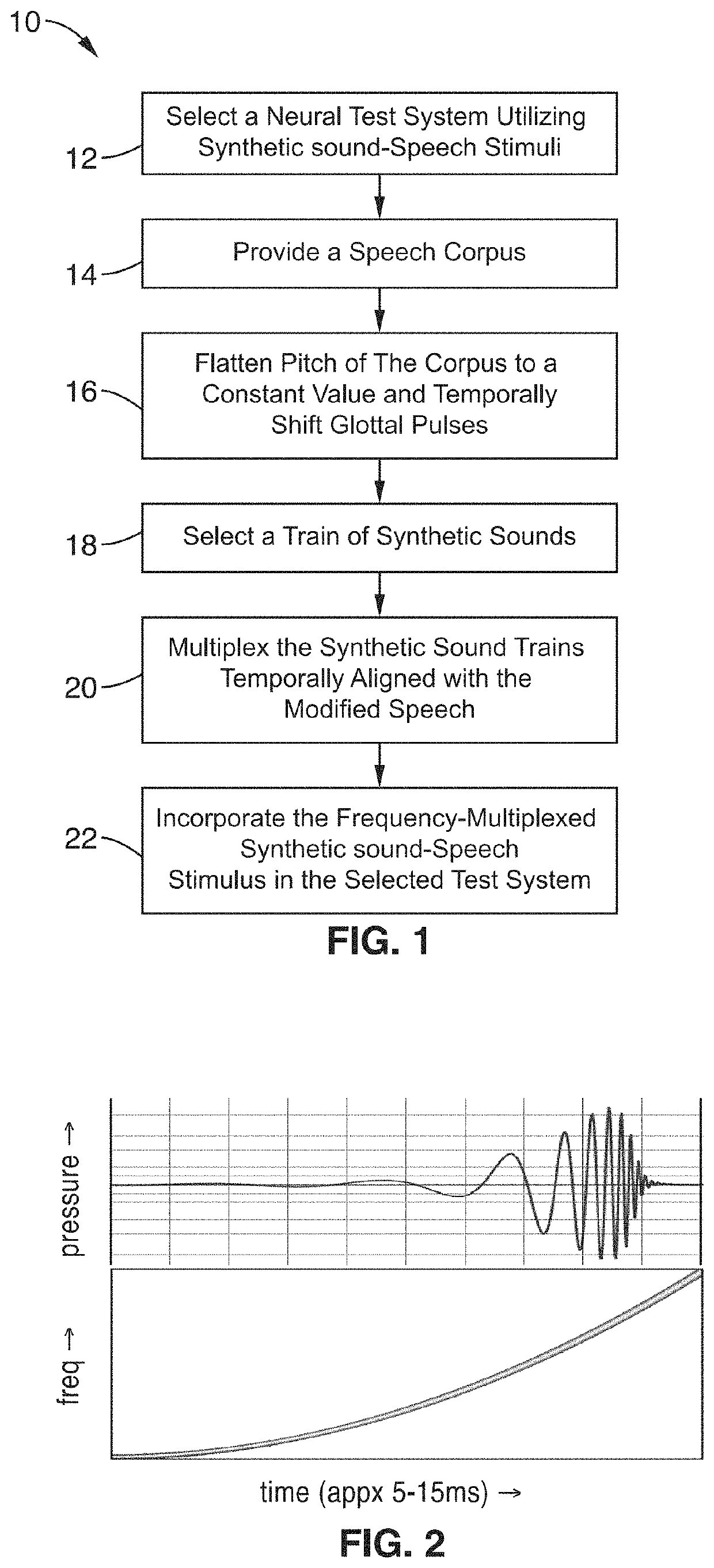
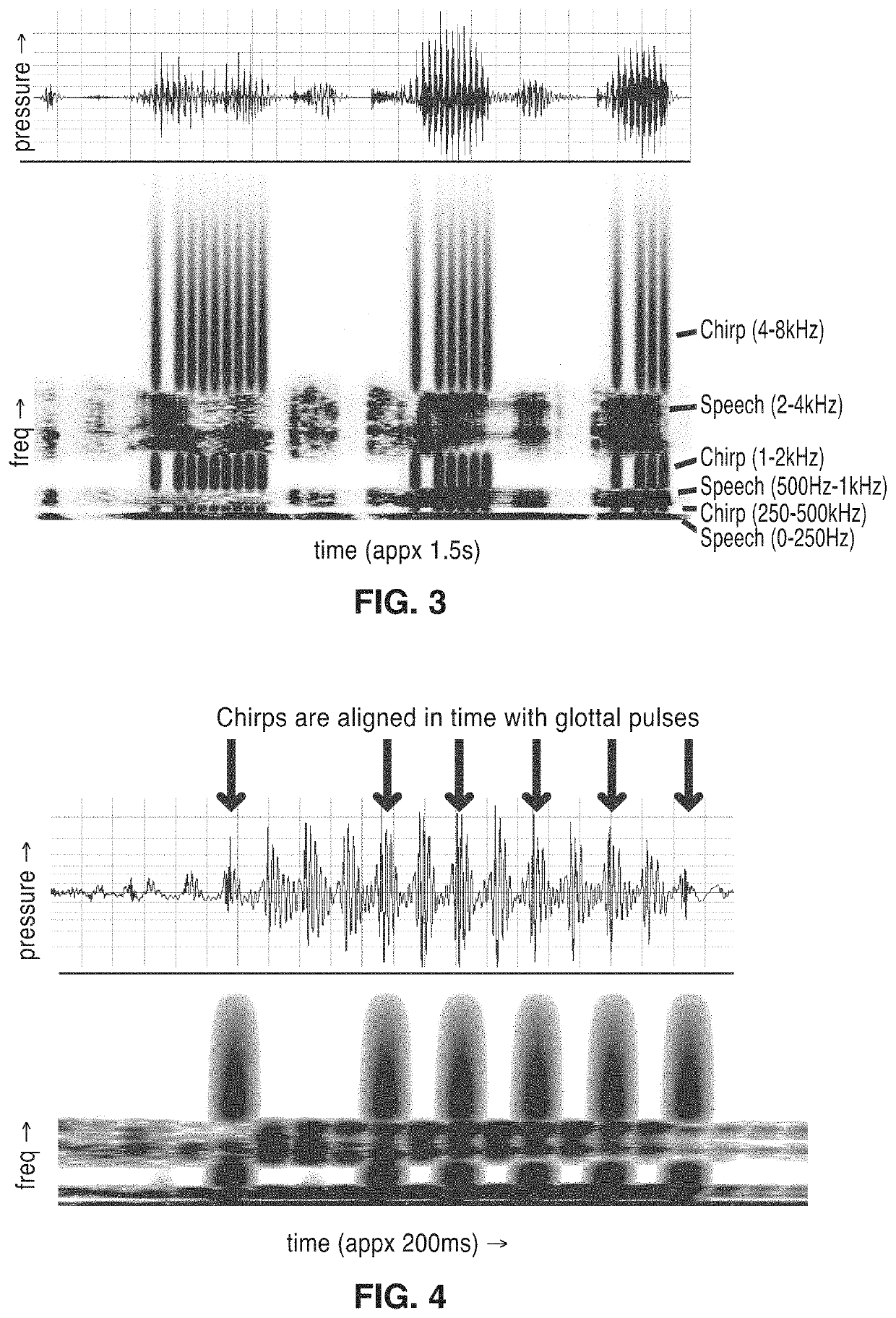
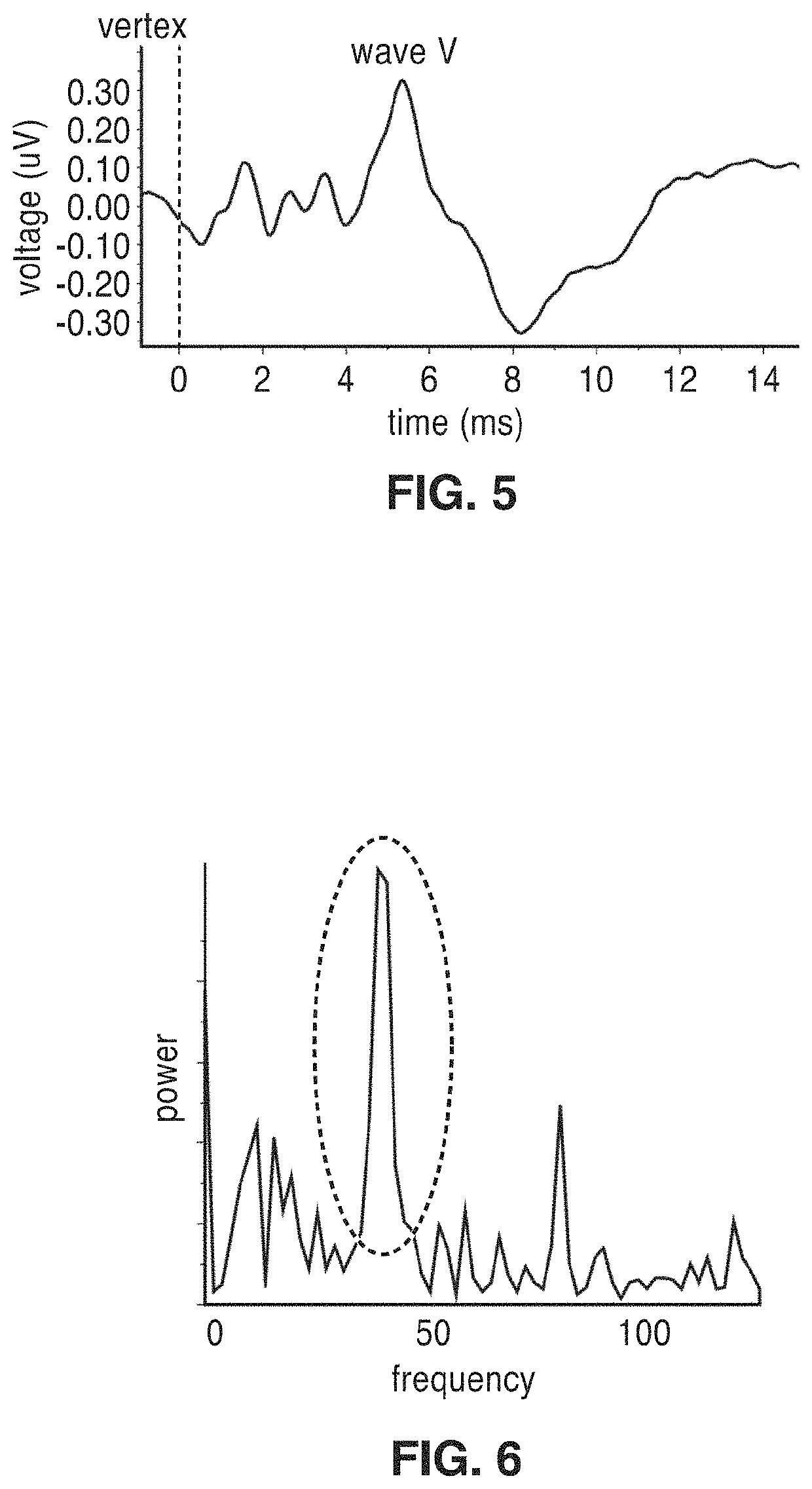
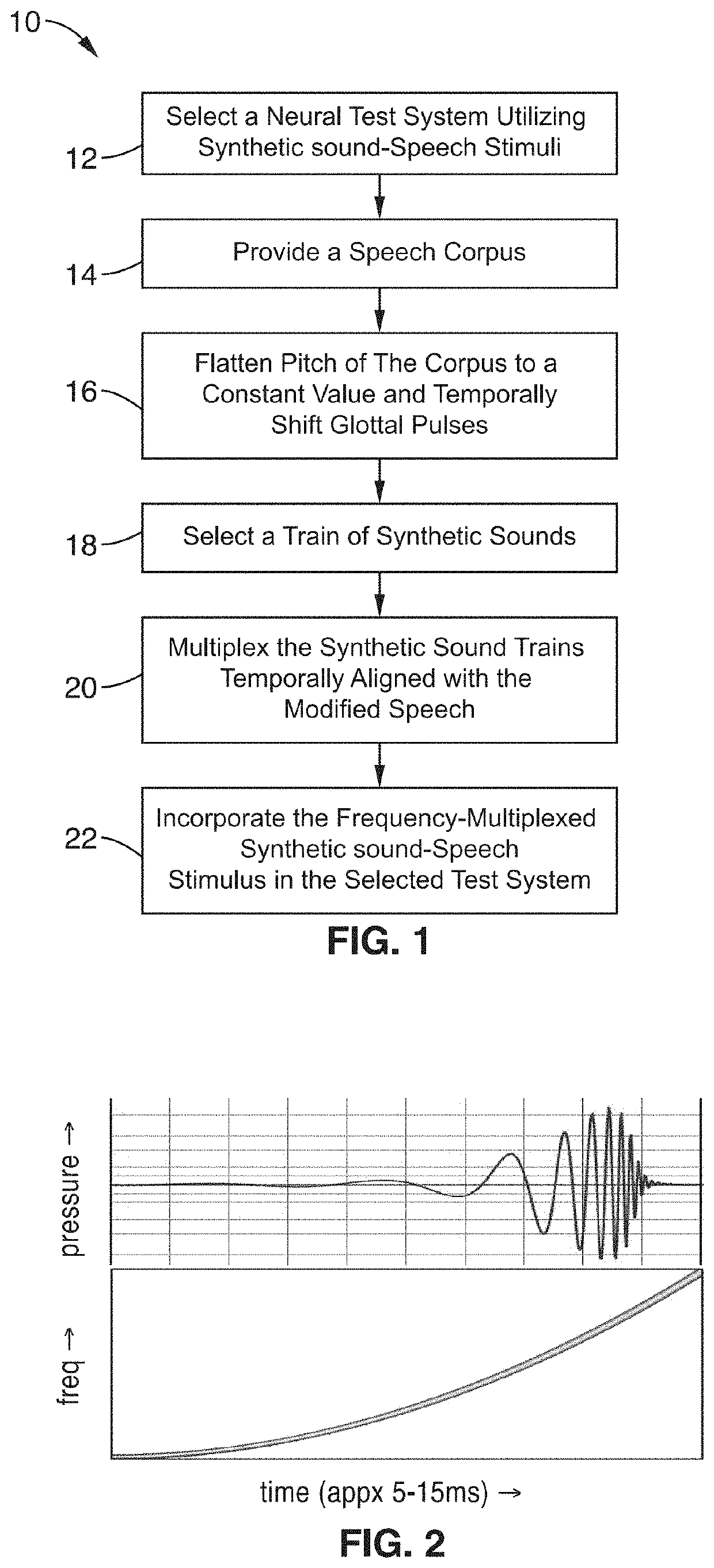
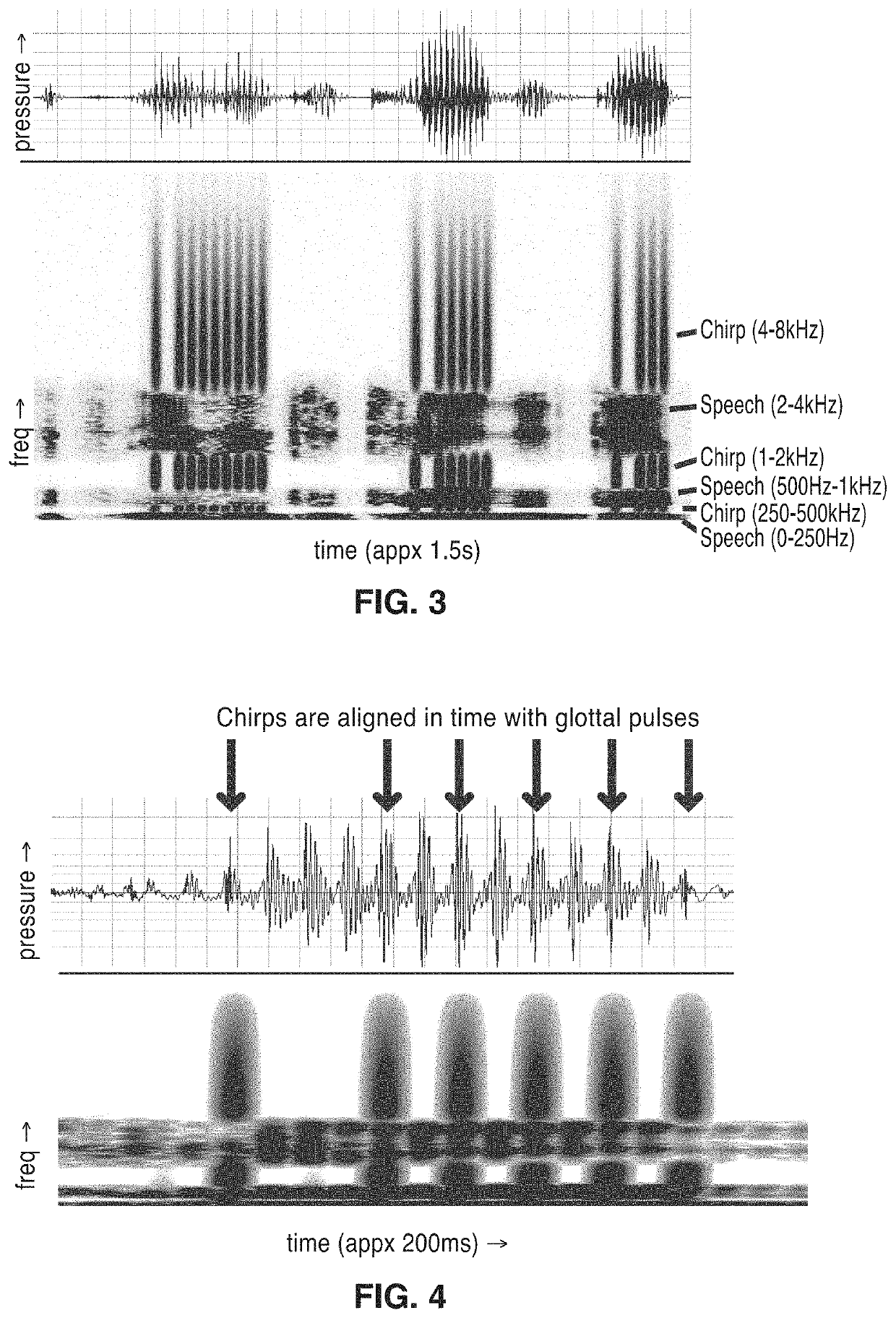
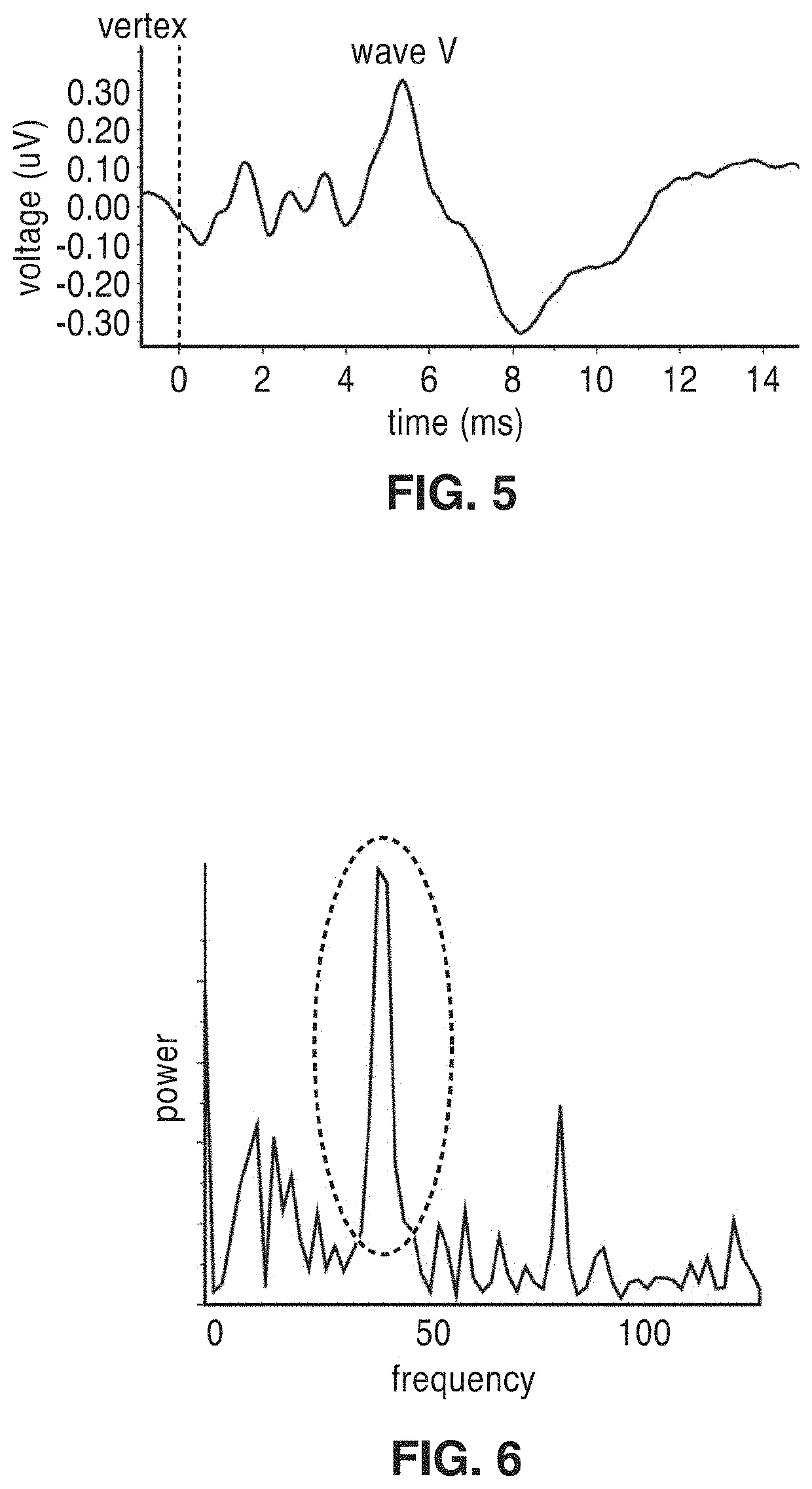
Frequency-multiplexed speech-sound stimuli for hierarchical neural characterization of speech processing
ActiveUS20170196519A1Accelerated programMaximize responseElectroencephalographySensorsMultiplexingAuditory system
A system and method for generating frequency-multiplexed synthetic sound-speech stimuli and for detecting and analyzing electrical brain activity of a subject in response to the stimuli. Frequency-multiplexing of speech copora and synthetic sounds helps the composite sound to blend into a single auditory object. The synthetic sounds are temporally aligned with the utterances of the speech corpus. Frequency multiplexing may include splitting the frequency axis into alternating bands of speech and synthetic sound to minimize the disruptive interaction between the speech and synthetic sounds along the basilar membrane and in their neural representations. The generated stimuli can be used with both traditional and advanced techniques to analyze electrical brain activity and provides a rapid, synoptic view into the functional health of the early auditory system, including how speech is processed at different levels and how these levels interact.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multitone Harmonic Radar and Method of Use
ActiveUS20150253415A1Minimize or eliminate system-generated nonlinear productsRaise the ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHarmonic radarRadar systems
A multitone nonlinear radar system (and a method of operating such a system) comprising a transmitter that transmits a signal comprising at least two predetermined frequency components; a receiver operating to receive return signals comprising harmonics of at least two predetermined frequencies, combinations of the at least two predetermined frequency components, and combinations of the harmonics of the at least two predetermined frequency components that are within a predetermined selected frequency range that has been predetermined to enable detection and / or classification of an electronic device; at least one antenna operating to transmit and receive electromagnetic radiation operatively connected to the transmitter and receiver; the receiver comprising at least one high pass filter for attenuating linear reflections at the two predetermined frequencies, and an analyzer;whereby electronic devices may be detected and identified by analyzing return signals within a predetermined frequency range.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Visual Prosthesis with an Improved Electrode Array Adapted for Foveal Stimulation
ActiveUS20120123501A1Limited perceptionMaximize retinal responseHead electrodesEye treatmentElectricityHigh density
The present invention is an improved method of electrically stimulating percepts in a patient with a visual prosthesis, to induce a more controlled perception of light. In particular, the present invention is an improved electrode array to maximize retinal response. The array of the present invention is an array with a center section with no electrode, surrounded by a ring of small high density electrodes. Electrodes beyond to ring are gradually larger and more widely spaced.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Acellular bioabsorbable tissue regeneration matrices
ActiveUS8268361B2Lightweight productionPromote regenerationBiocideNervous disorderNerves tissuePathology
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
High-speed actuator for valves
ActiveUS20100090144A1Improve dispensing accuracyPrecise positioningOperating means/releasing devices for valvesClosuresLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
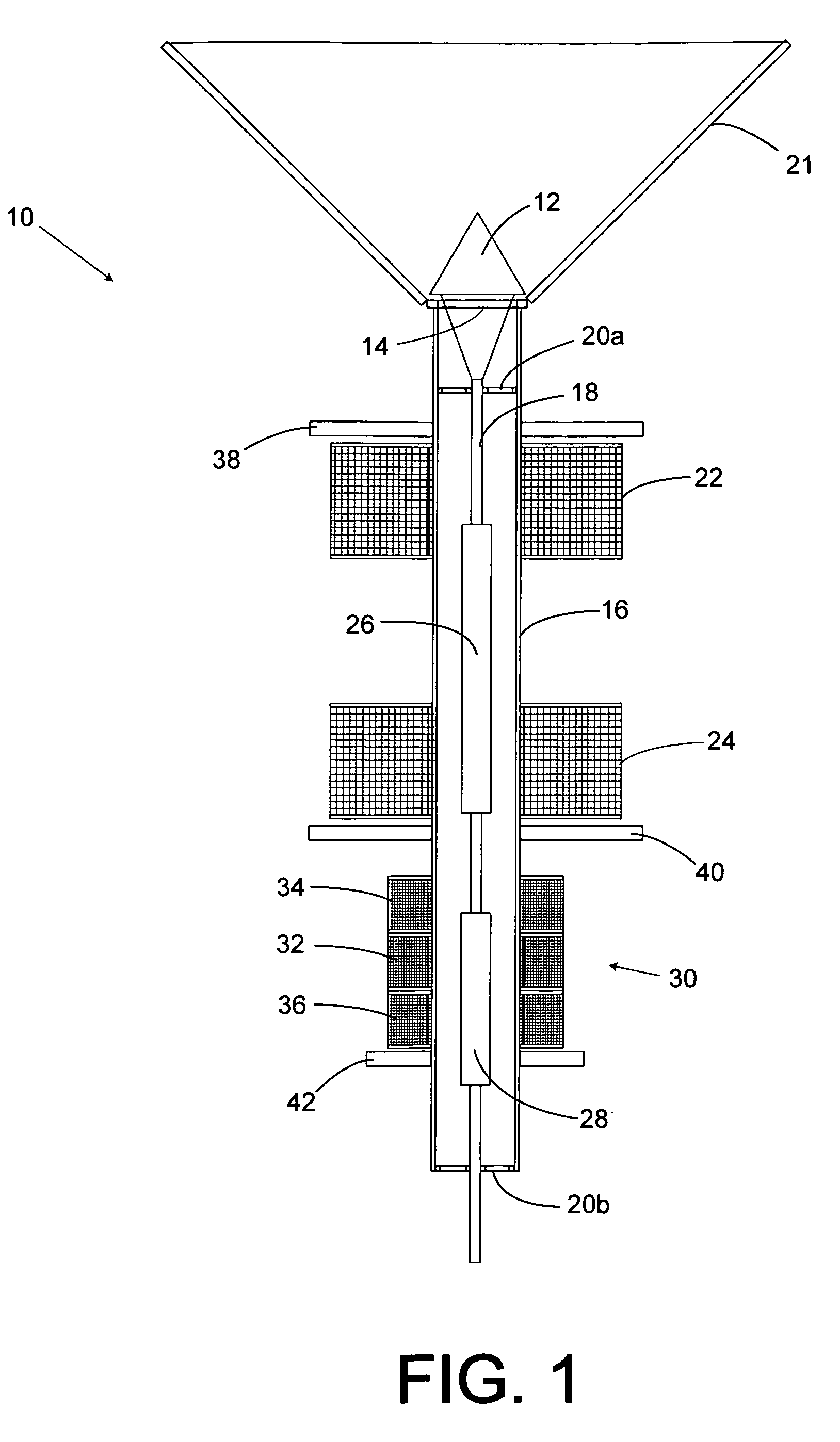
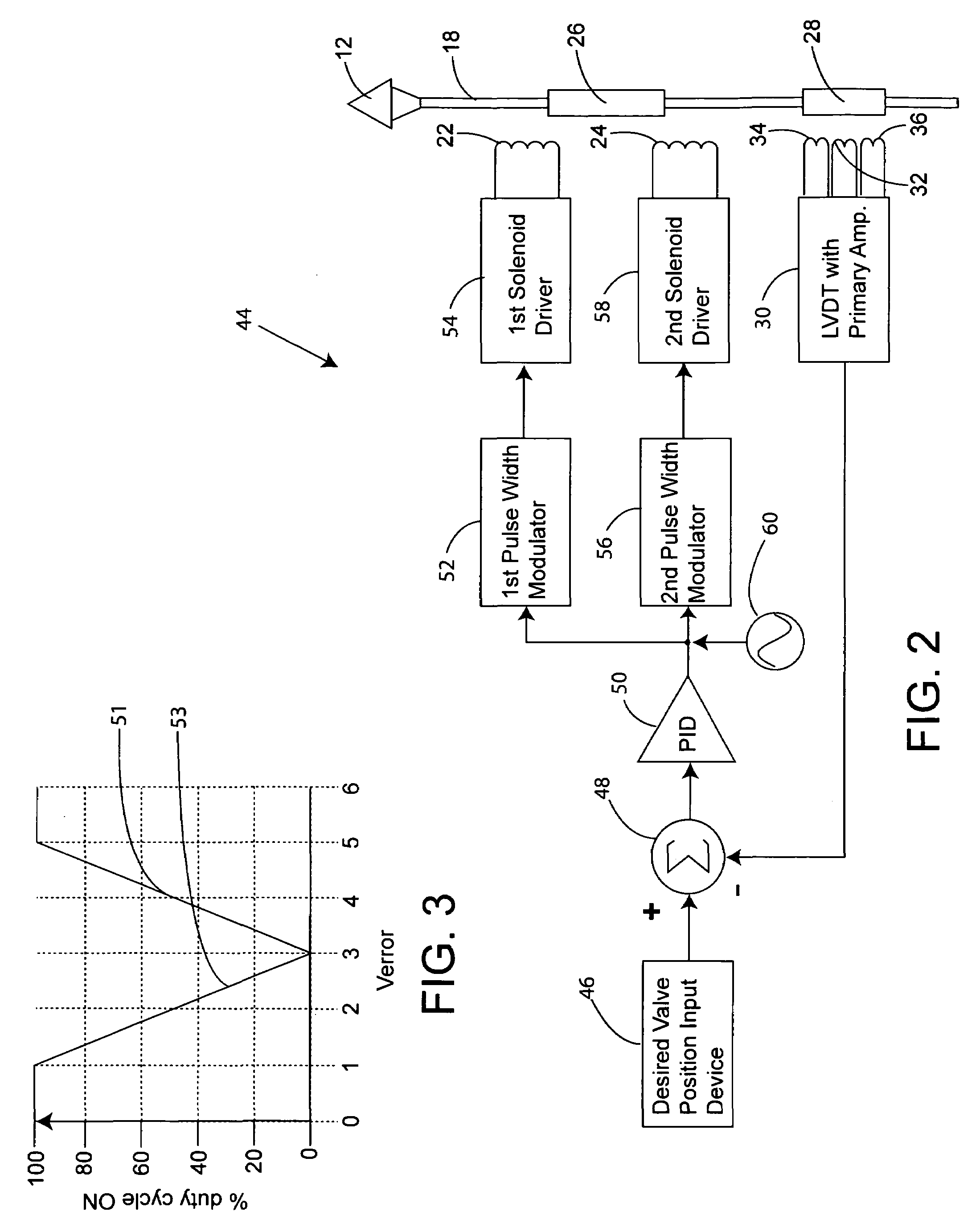
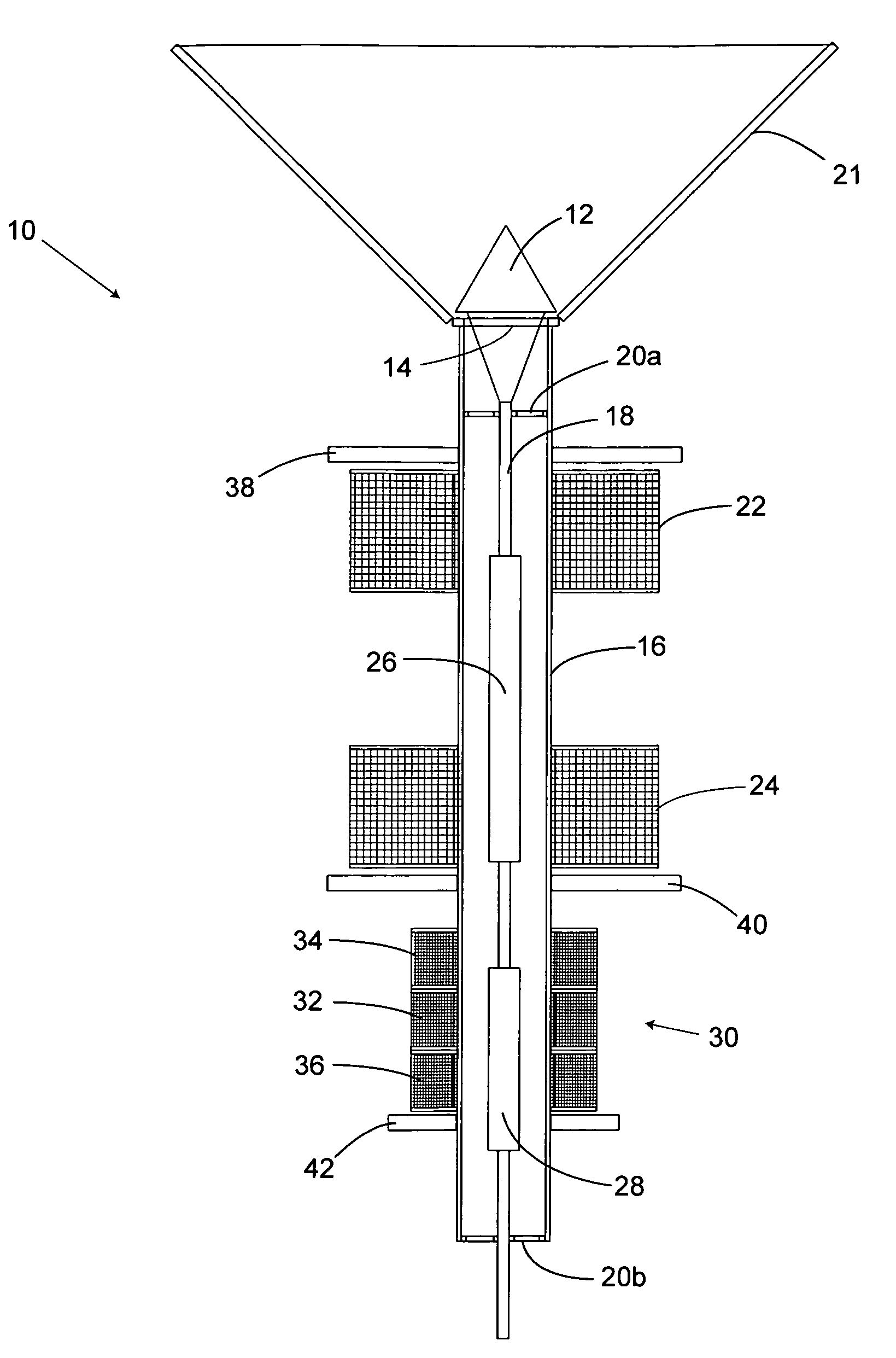
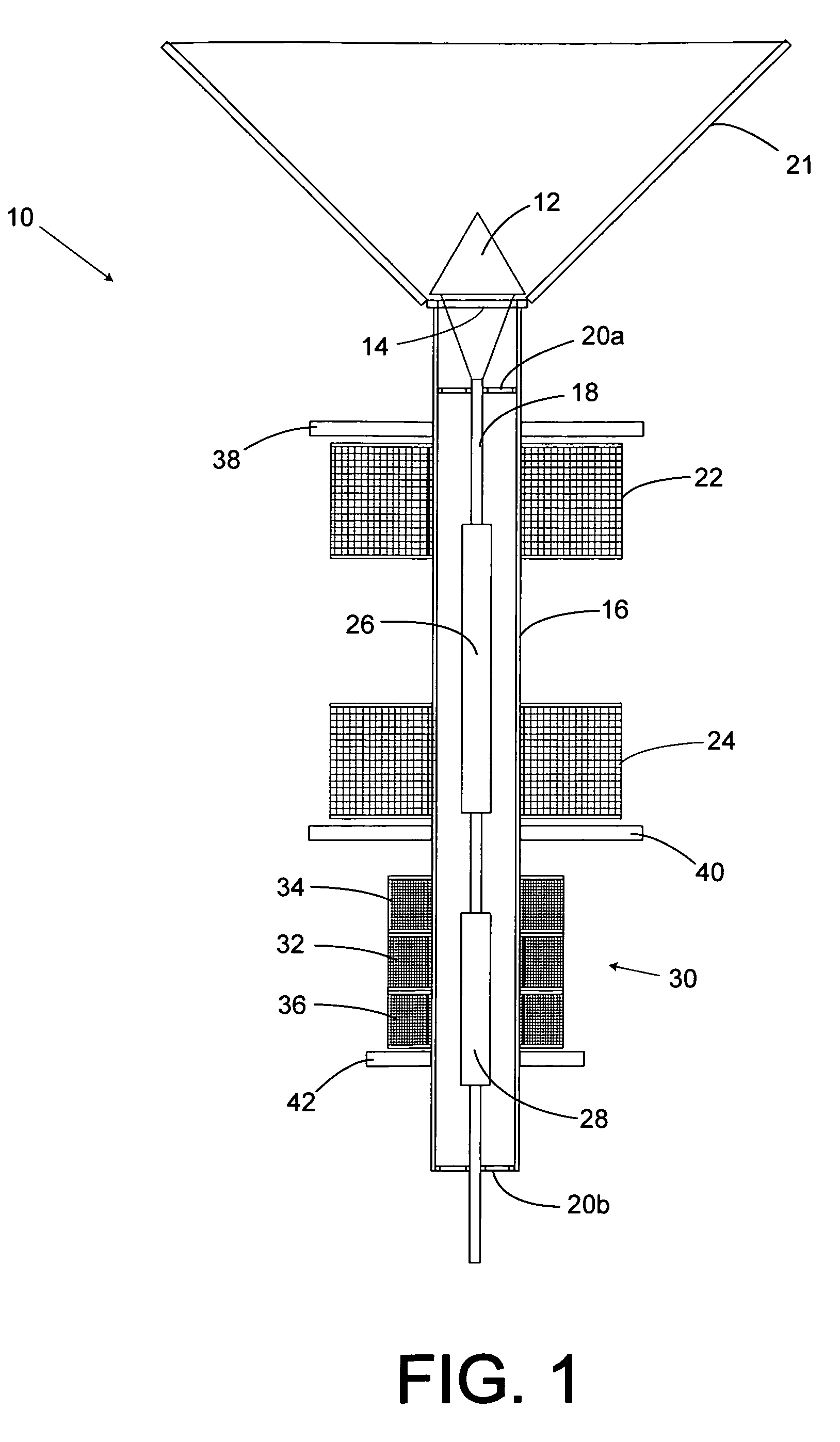
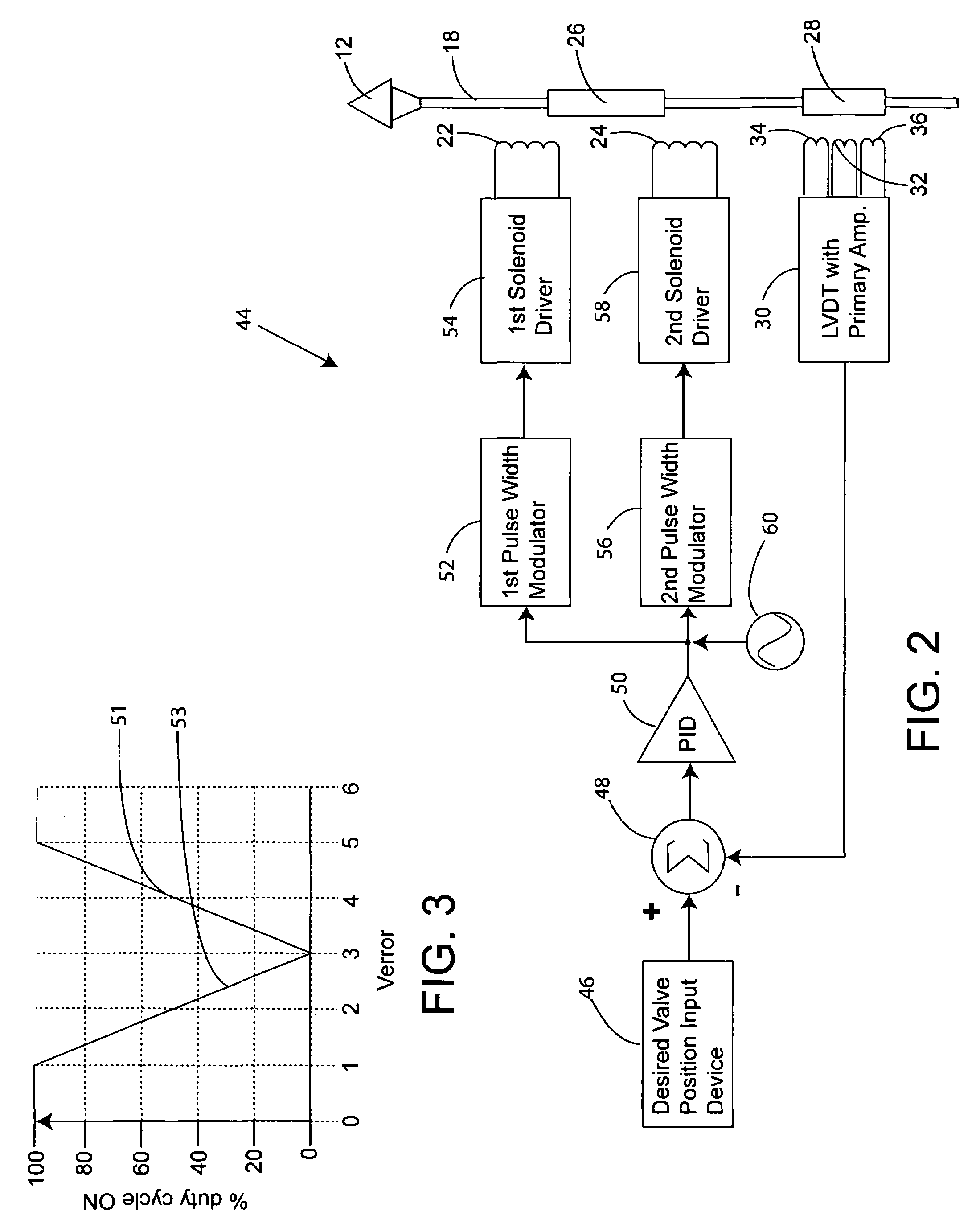
A high-speed actuator to move a valve stopper to a closed position against a valve seat and an open position away from the valve seat is disclosed. The actuator includes a rod carrying first and second axially spaced solenoid armatures. The rod also has a valve stopper connector end. A first solenoid coil surrounds and is spaced from the rod to bias the first solenoid armature along with the rod and valve stopper toward the valve's open position. A second solenoid surrounds and is spaced from the rod. The second solenoid is axially spaced from the first solenoid to bias the first armature towards the valve's closed position. A linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) magnetically coupled to the second solenoid armature is included to determine the instantaneous position of the valve stopper relative to the valve's seat. The LVDT is responsive to the position of the second armature. The LVDT generates an instantaneous valve position signal in concert with the movements of the rod. A valve position control circuit is adapted to receive a valve position set point from a user's input, and a valve position feedback signal from the LVDT. The valve position control circuit includes first and second solenoid coil drive signals that urge the first armature, and hence the valve stopper to the valve position set point inputted by a user. A signal generator circuit is provided to vibrate the valve about a position set point in order to enhance material discharge down the discharge tube.
Owner:BRANDT JR ROBERT O
Methods and compositions for immunization against virus
ActiveUS8741311B2Improving immunogenicityGood antigenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseHemagglutininViral glycoprotein
Immunogenic compositions comprising partially glycosylated viral glycoproteins for use as vaccines against viruses are provided. Vaccines formulated using mono-, di-, or tri-glycosylated viral surface glycoproteins and polypeptides provide potent and broad protection against viruses, even across strains. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising monoglycosylated hemagglutinin polypeptides and vaccines generated therefrom and methods of their use for prophylaxis or treatment of viral infections are disclosed. Methods and compositions are disclosed for influenza virus HA, NA and M2, RSV proteins F, G and SH, Dengue virus glycoproteins M or E, hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E1 or E2 and HIV glycoproteins gp120 and gp41.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
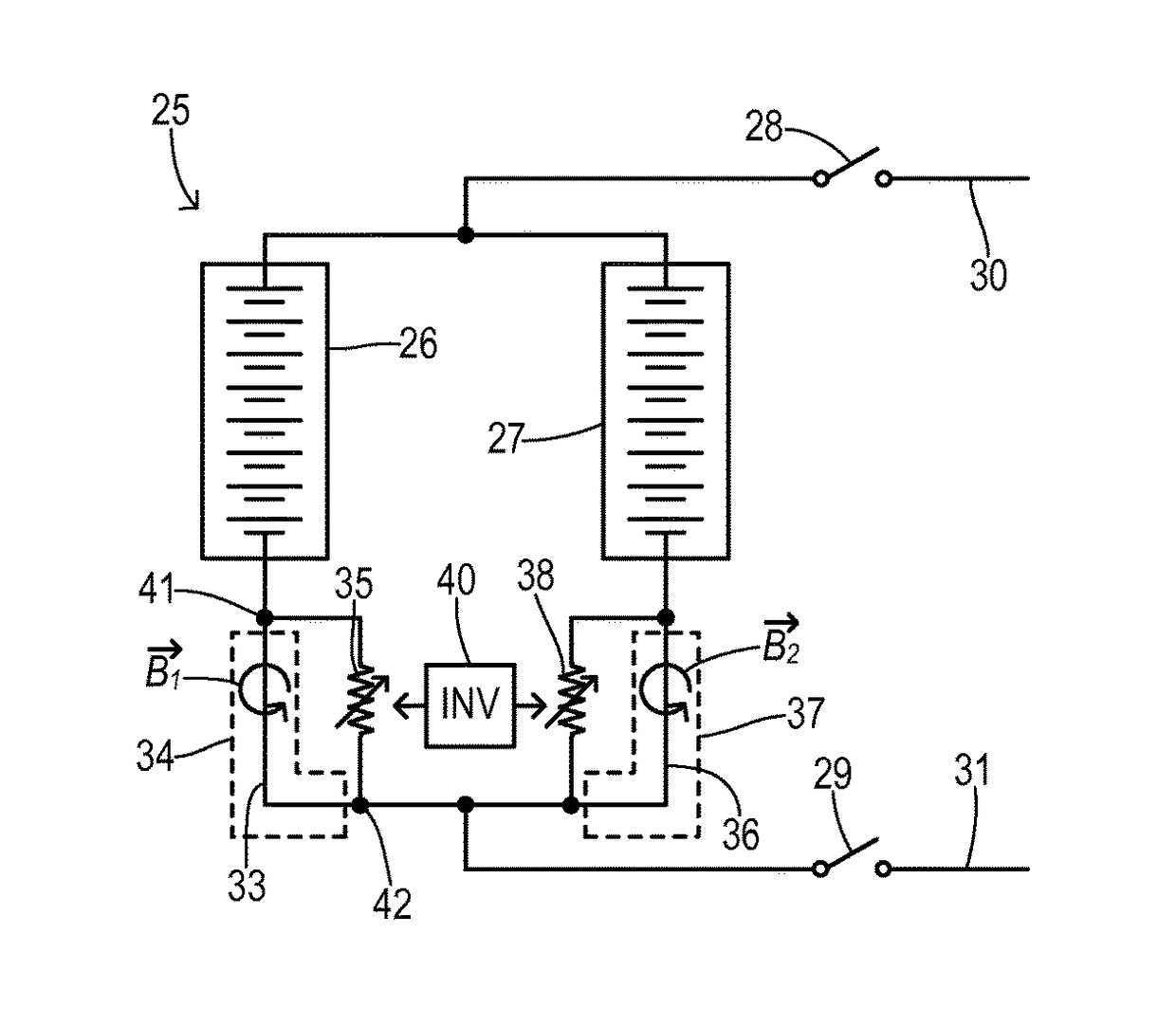
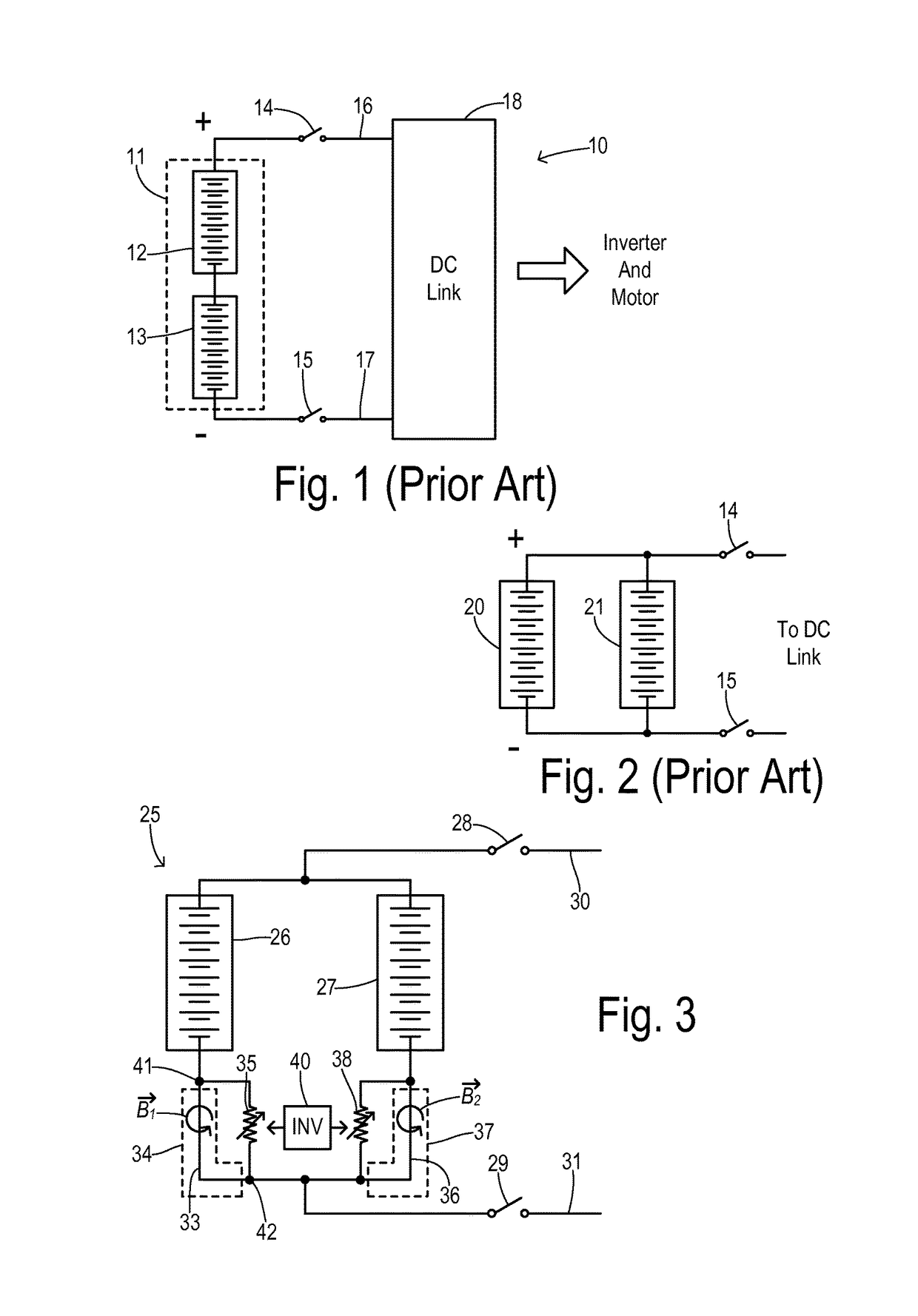
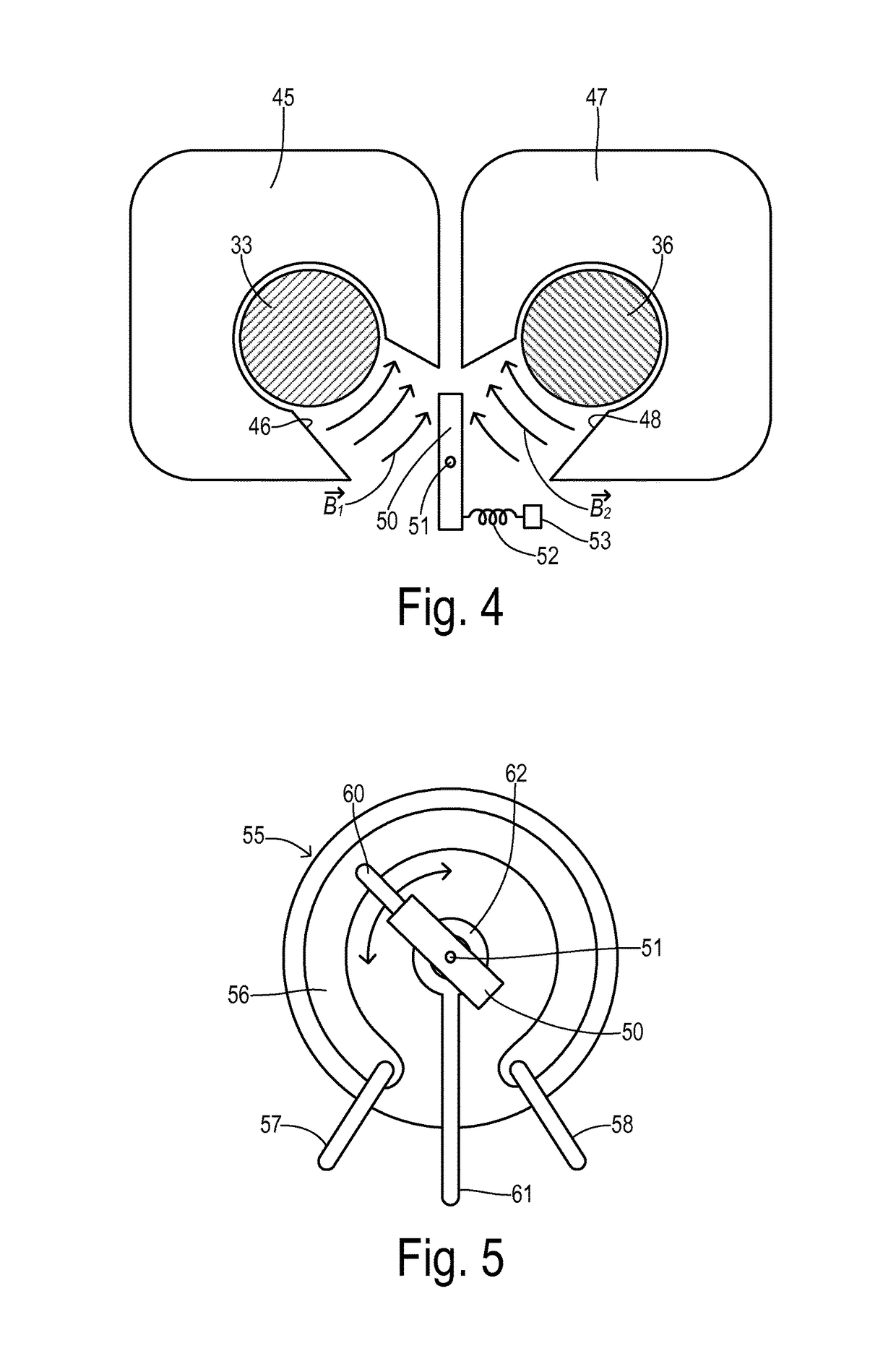
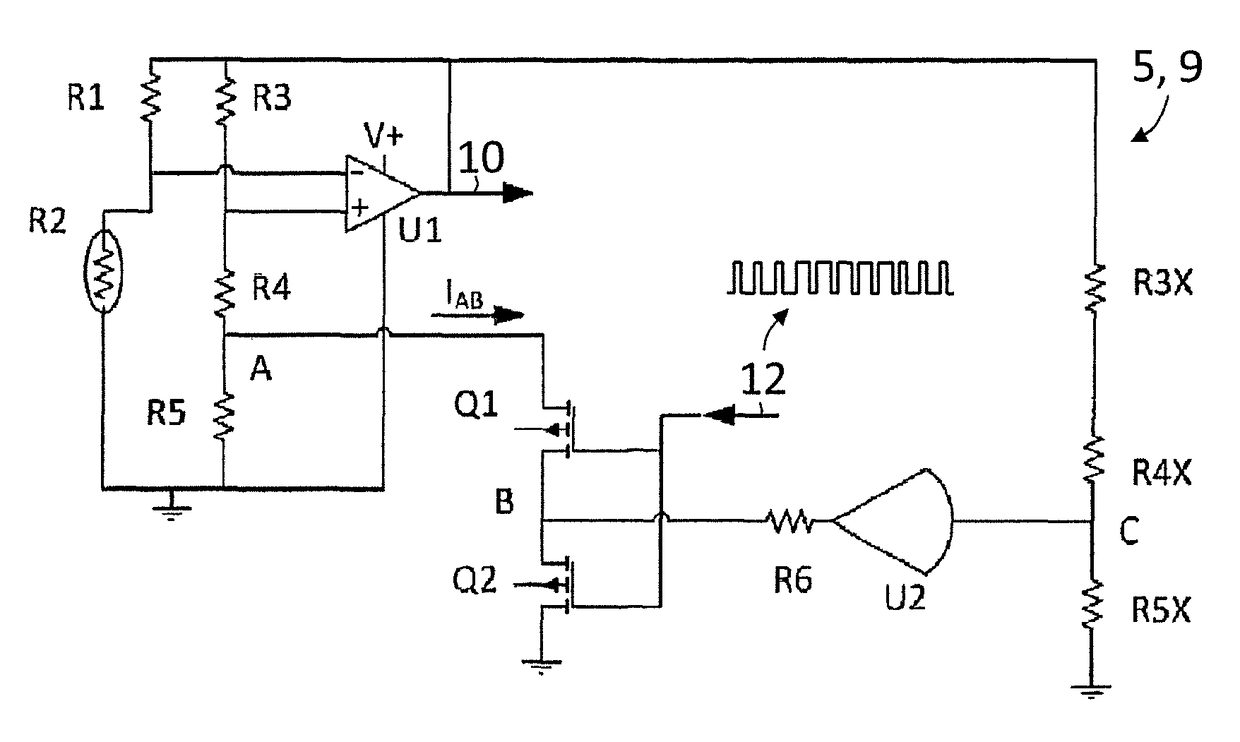
Current balancing device for parallel battery cells in an electrified vehicle
InactiveUS9685796B2Improve responseImprove permeabilityCharge equalisation circuitSecondary cellsRelative magnitudeTotal current
A current equalizer is provided for first and second battery elements connected in parallel to supply a DC link. A first constant resistance carries a first current from the first battery element to the DC link. A first variable resistance is connected in parallel with the first constant resistance. A second constant resistance carries a second current from the second battery element to the DC link. A second variable resistance is connected in parallel with the second constant resistance. A balancer inversely adjusts the first and second variable resistances in response to relative magnitudes of the first and second currents. As a result, the total currents supplied from each battery element to the DC link are equalized because the effective total resistance in series with each battery element compensates for the difference in the internal battery resistances.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and thermal conductivity detector
ActiveUS10126277B2Uncertainty in operating temperatureAccurate compensationMaterial thermal conductivityComponent separationManufacturing variationChromatography column
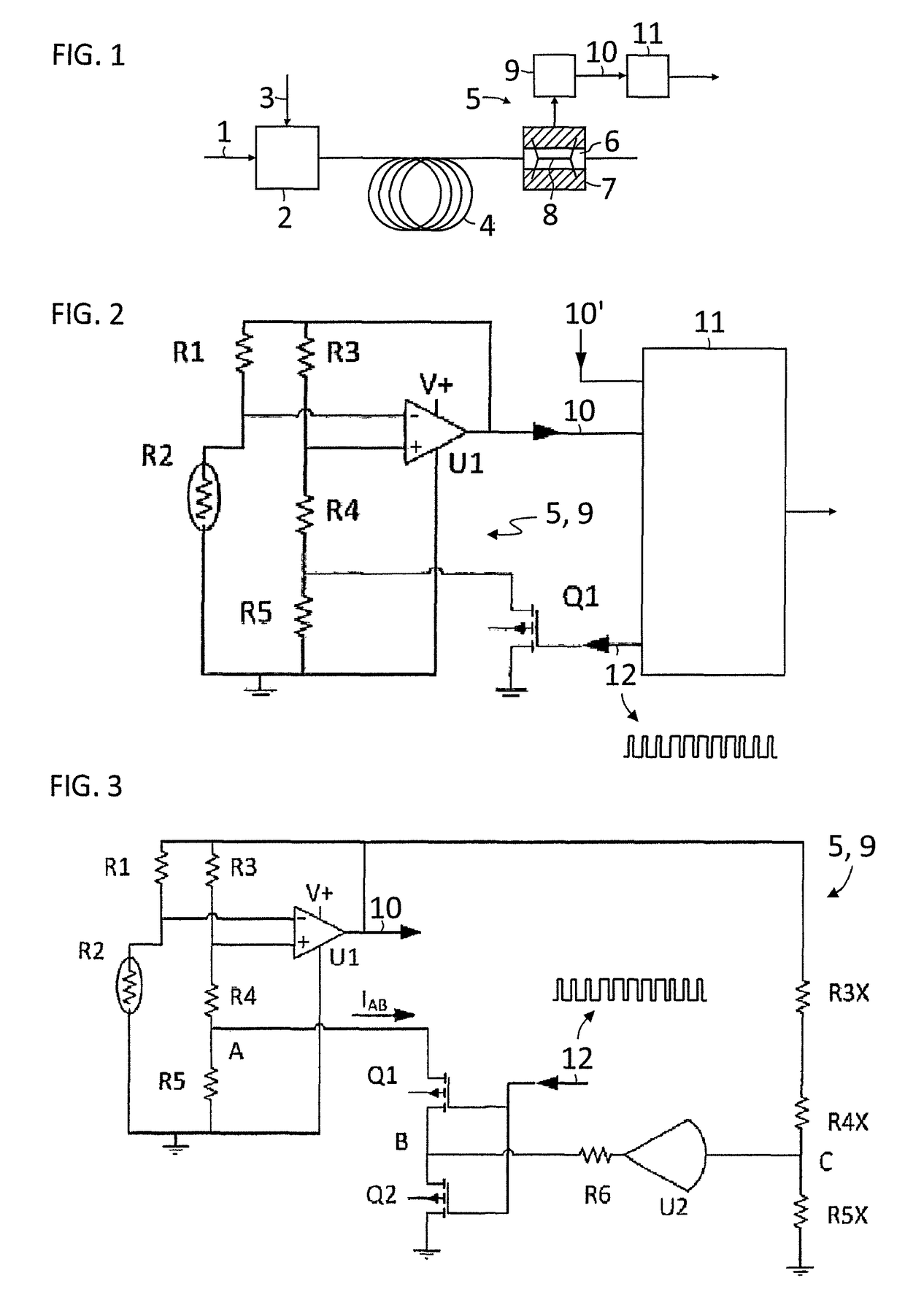
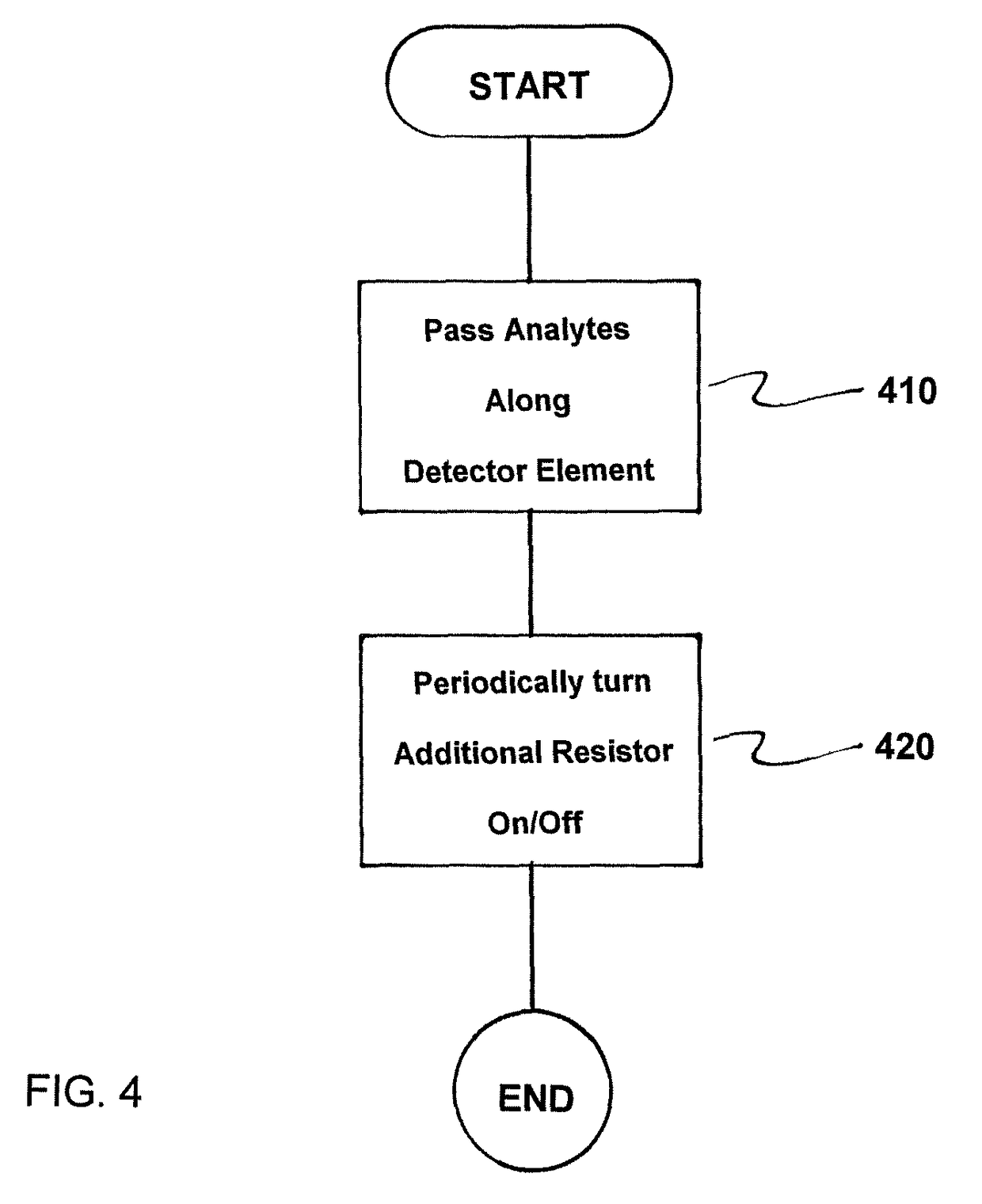
A thermal conductivity detector includes a heatable resistive detector configured to be physically arranged in an analytes flow eluting from a chromatography column and electrically arranged with resistors in separate arms of a measuring bridge, an amplifier which detects differential voltage between two opposite nodes of the bridge and applies an output voltage to other opposite nodes of the measuring bridge to maintain the detector at a constant operating temperature, and an additional resistor with a controllable switch in parallel connected in series with the detector or resistor arranged in one arm of the bridge, where the switch is periodically turned on and off at a predetermined duty cycle and / or controlled by information on characteristic times-of-arrival of analytes at the detector to compensate for operating temperature uncertainties due to manufacturing variations of the resistors and / or to allow for processing small and large peaks of a chromatogram with highest available resolution.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
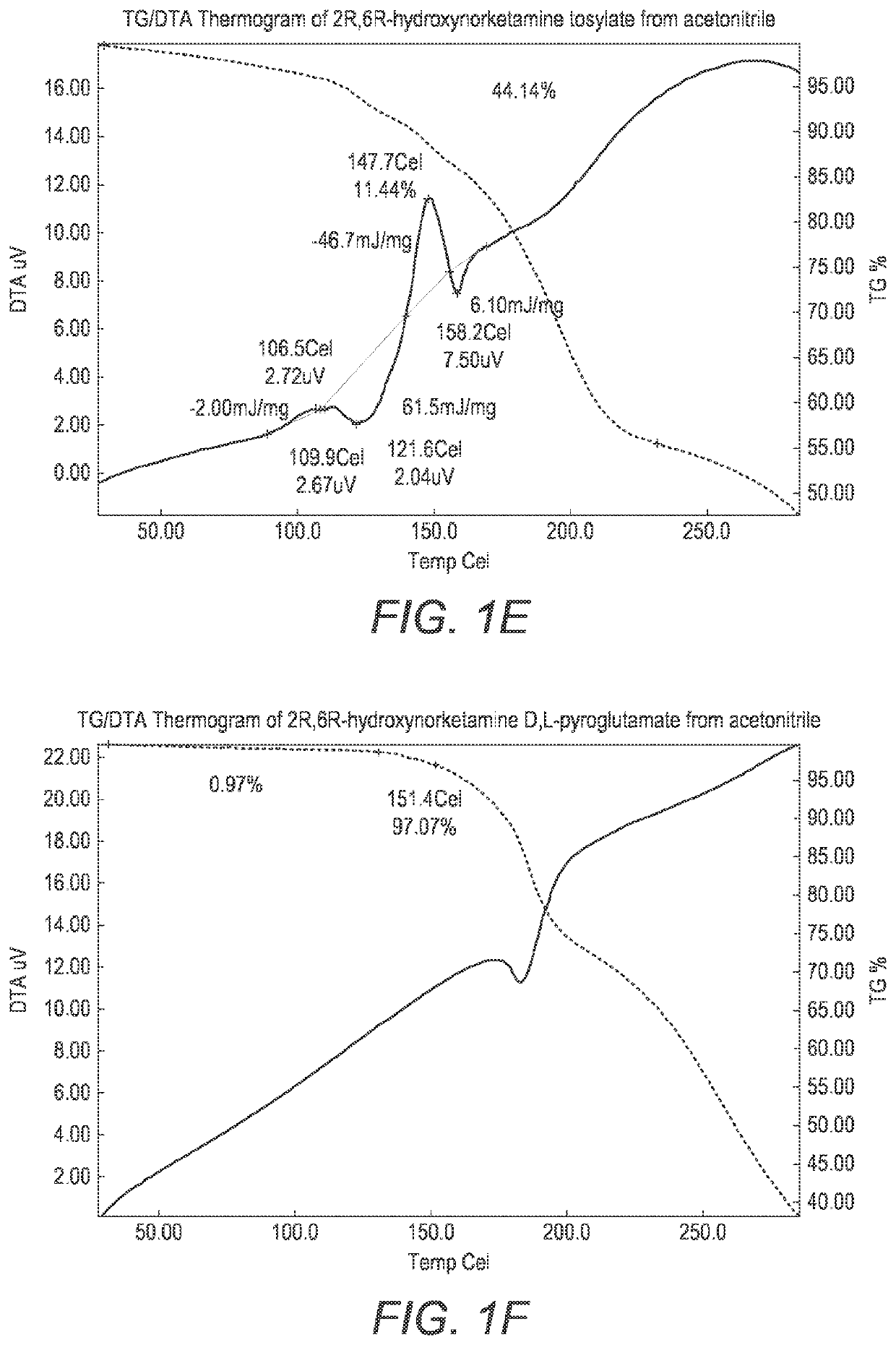
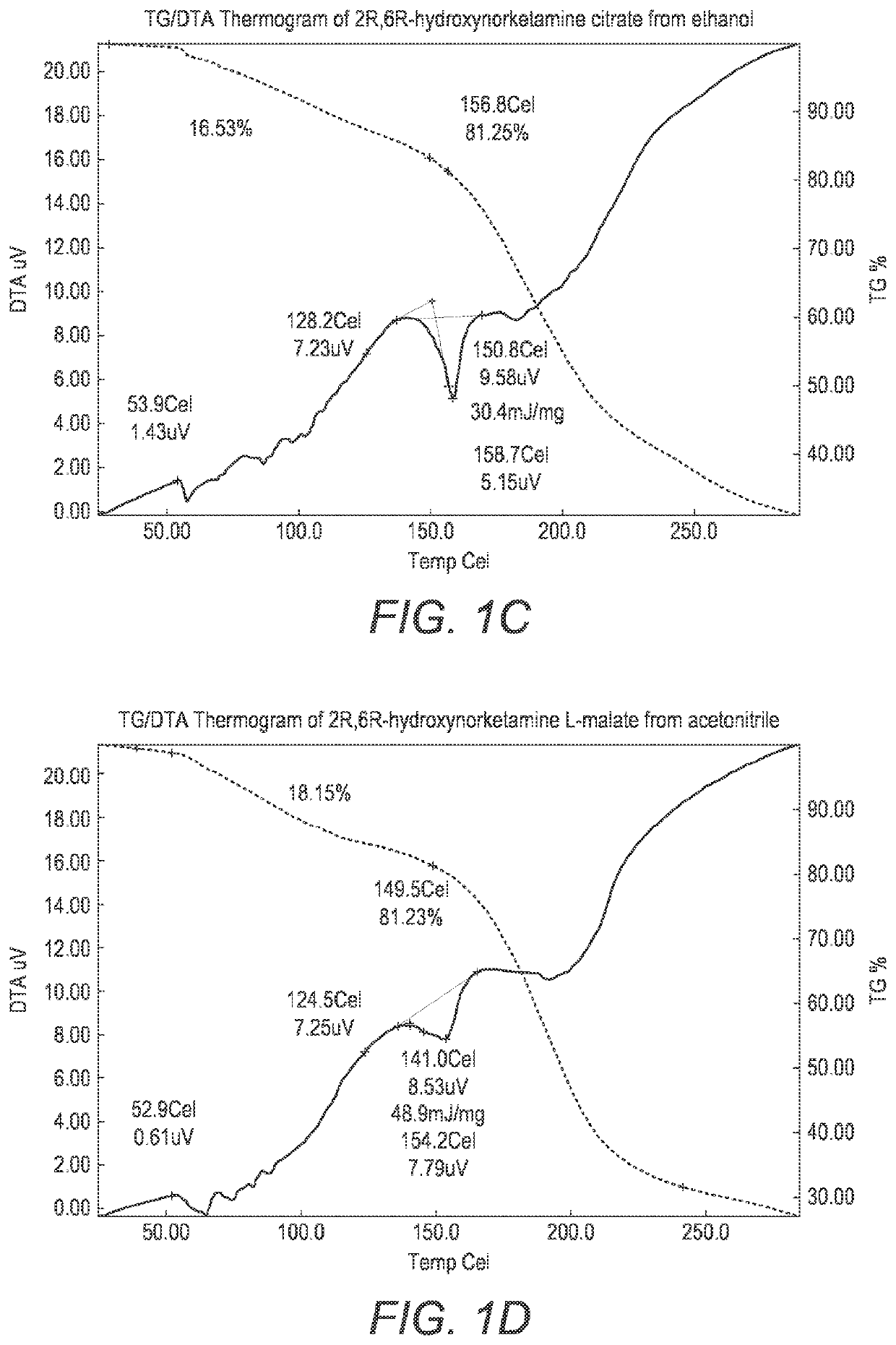
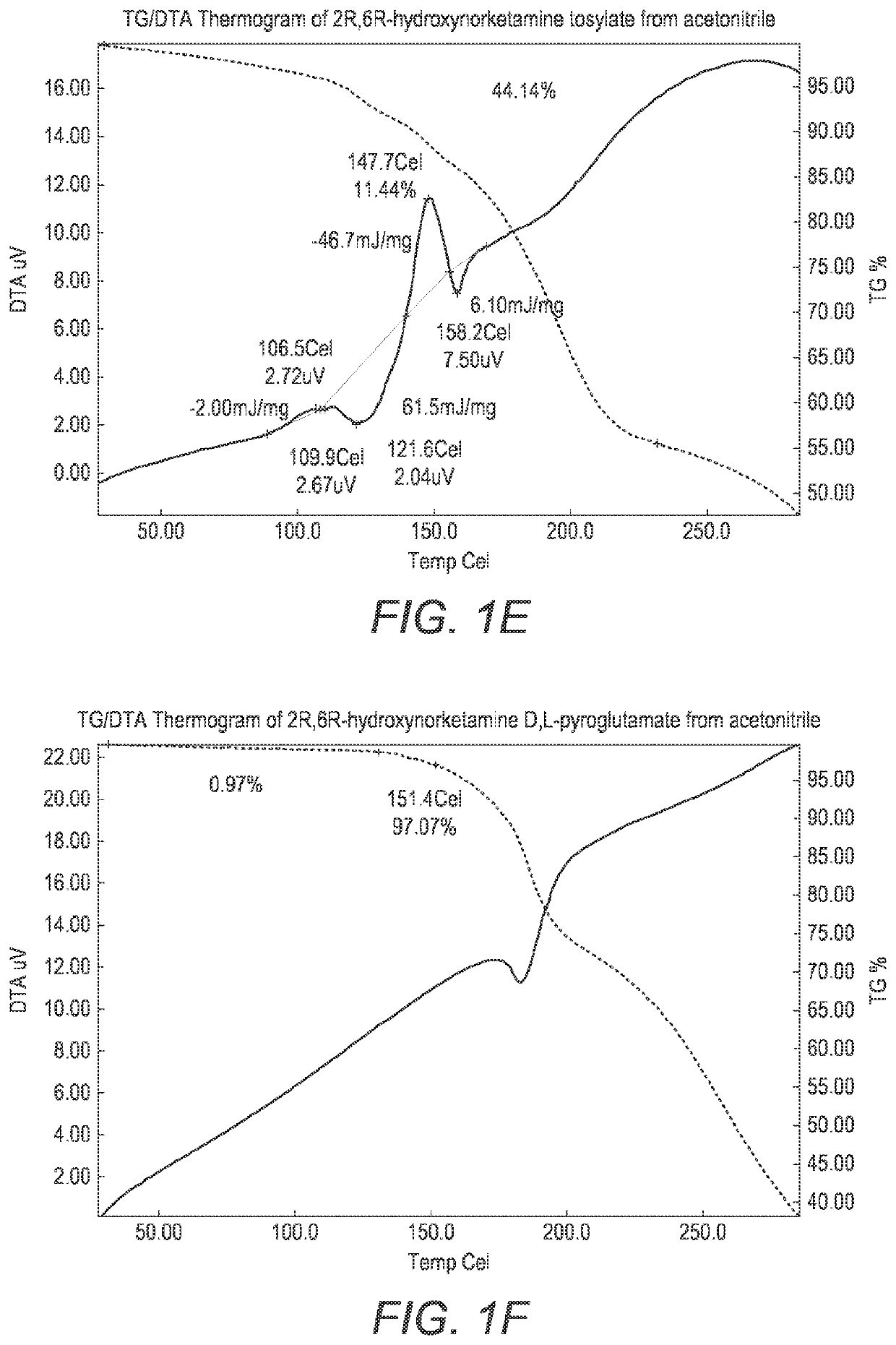
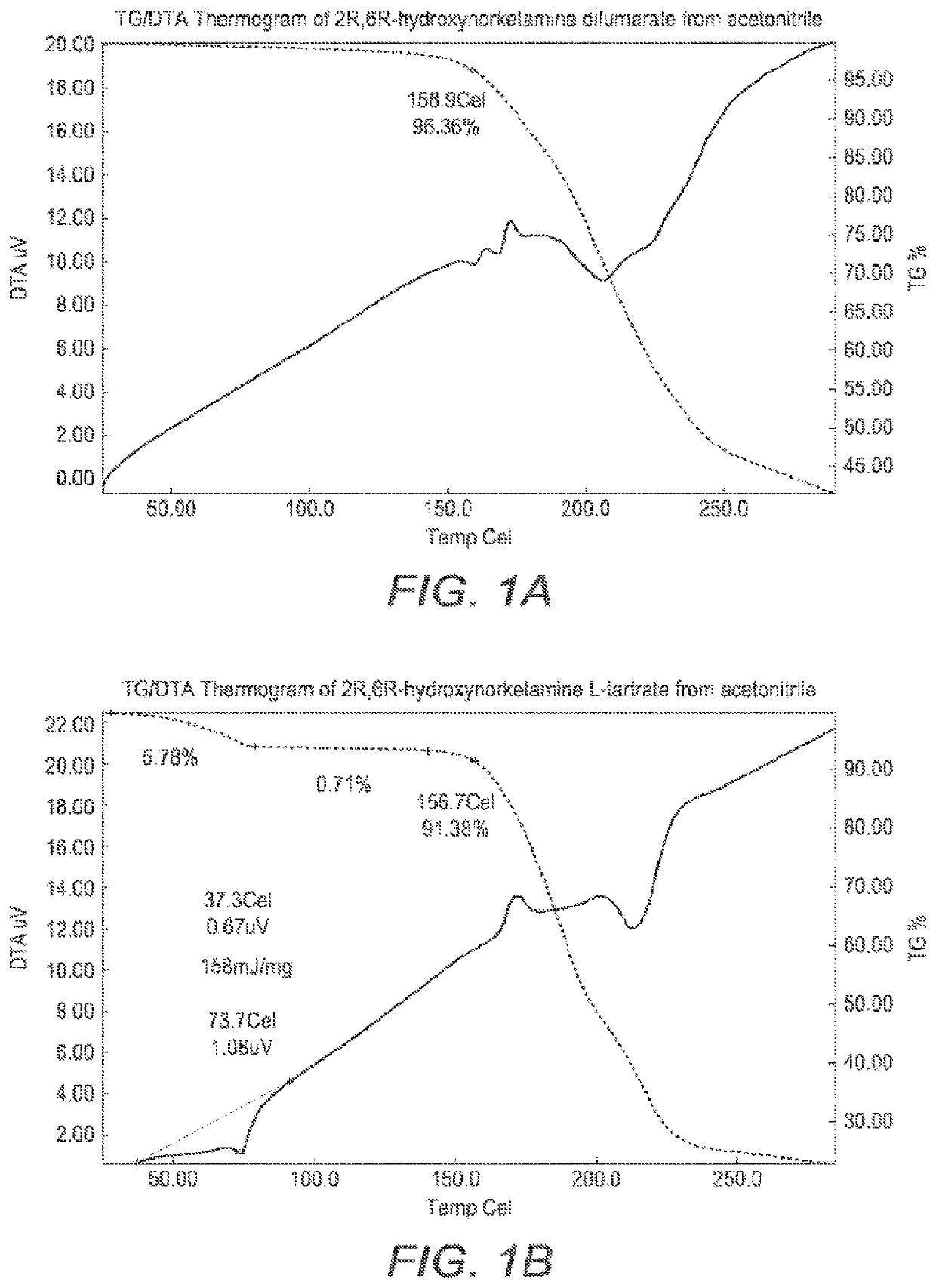
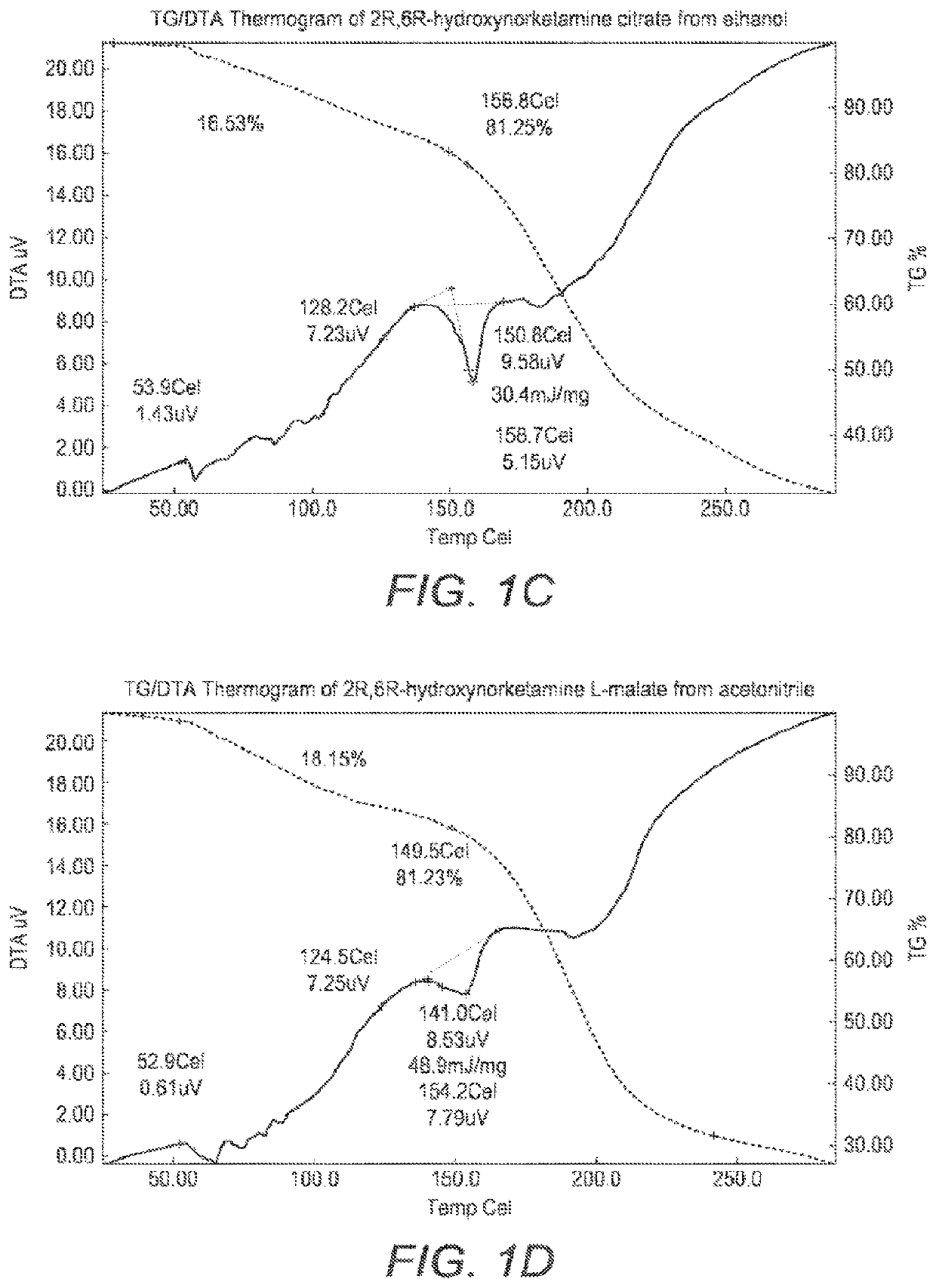
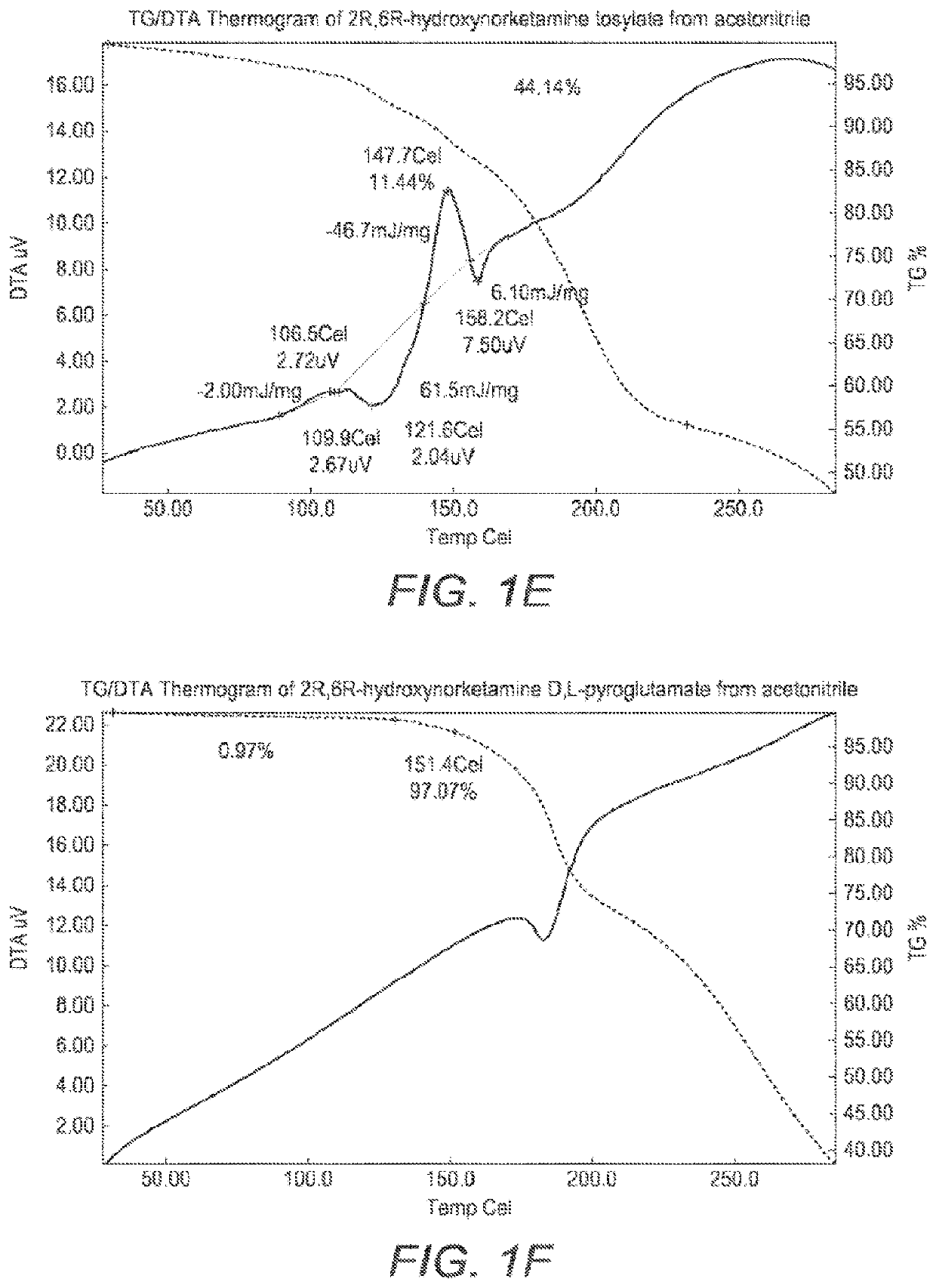
Crystalline forms of hydroxynorketamine
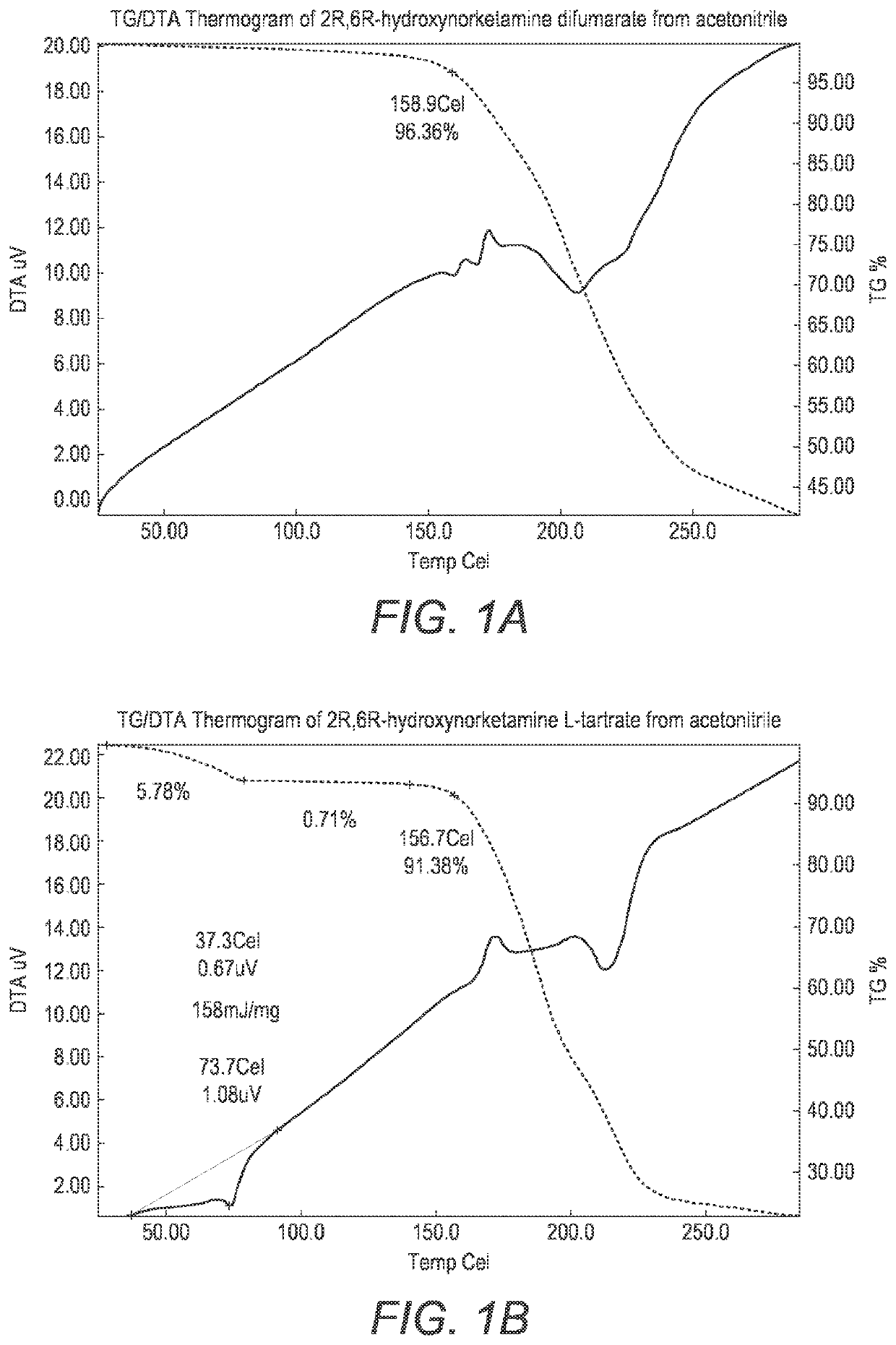
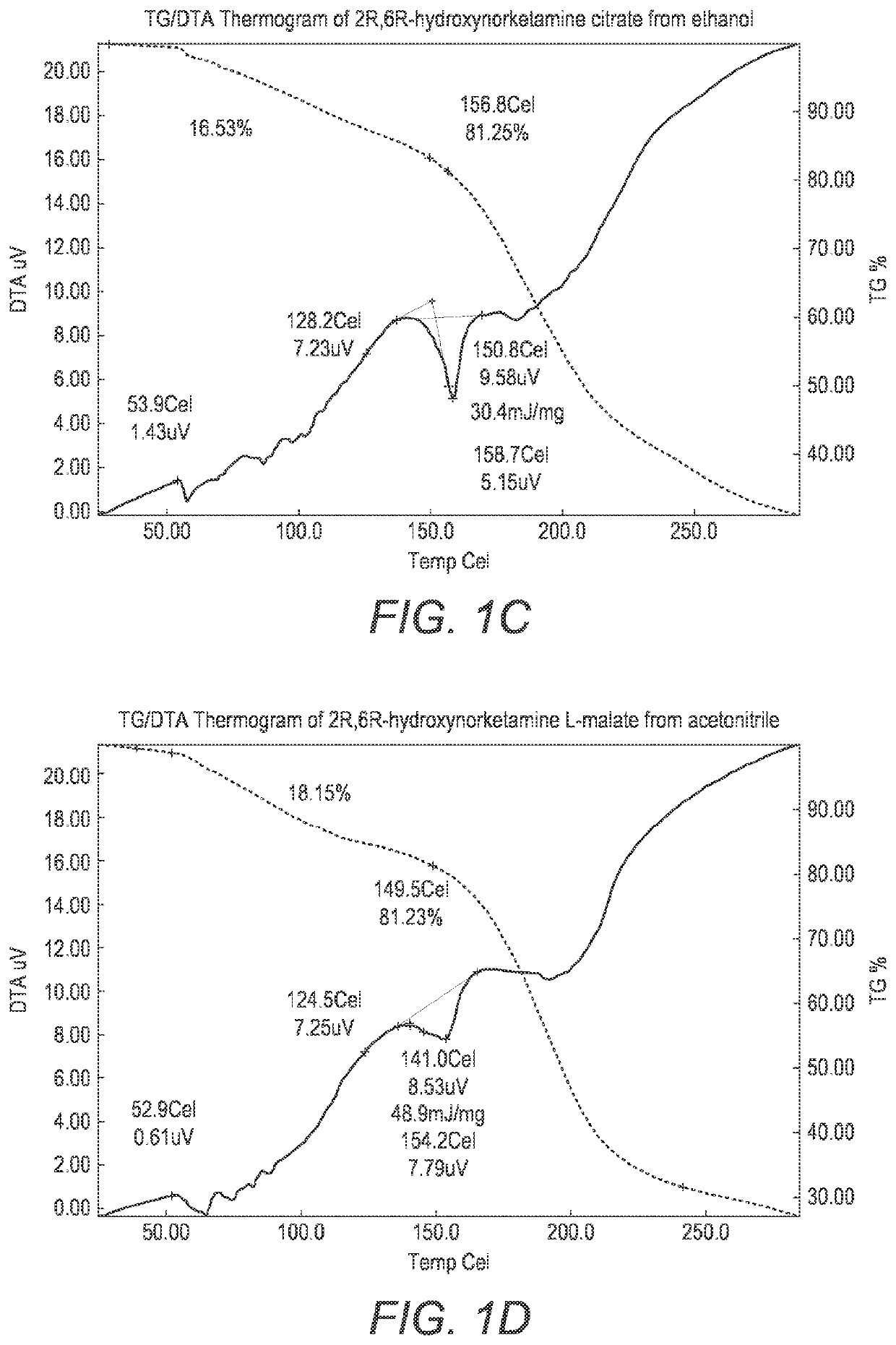
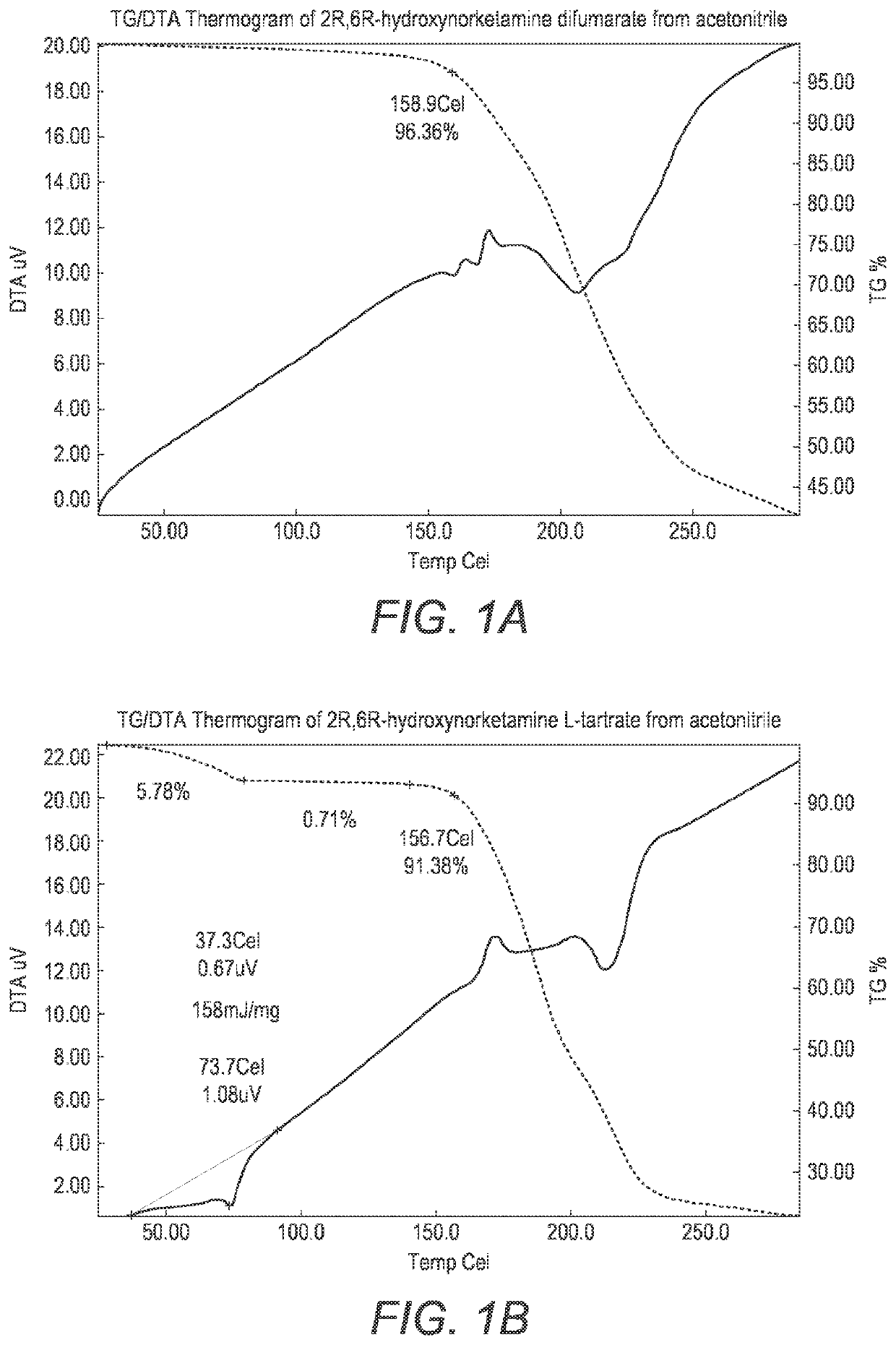
ActiveUS20200157040A1Good water solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsMedicineAqueous solubility
The present invention provides novel, stable, processable and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms of 2R,6R-hydroxynorketamine or 2S,6S-hydroxynorketamine with high aqueous solubility.
Owner:SMALL PHARMA LTD
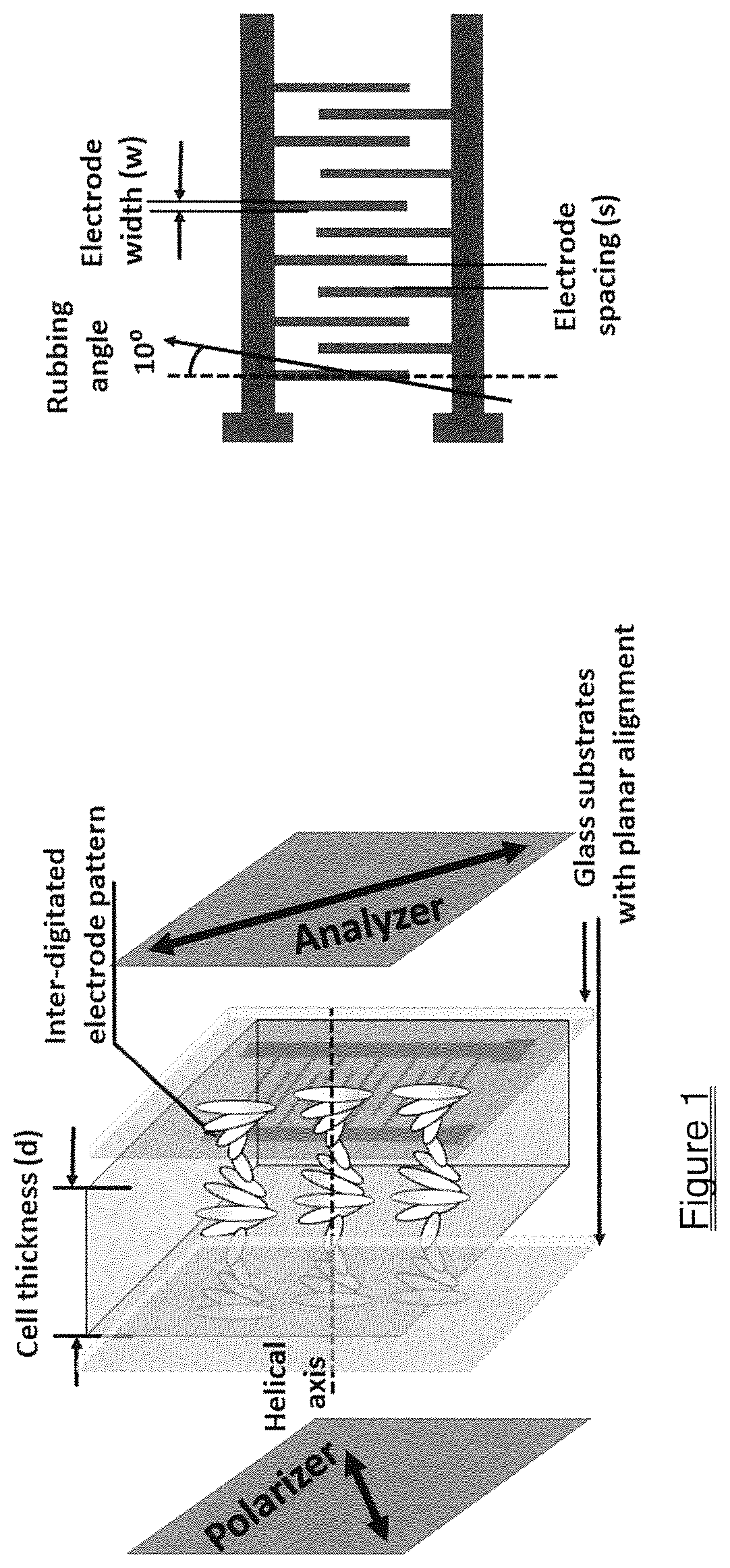
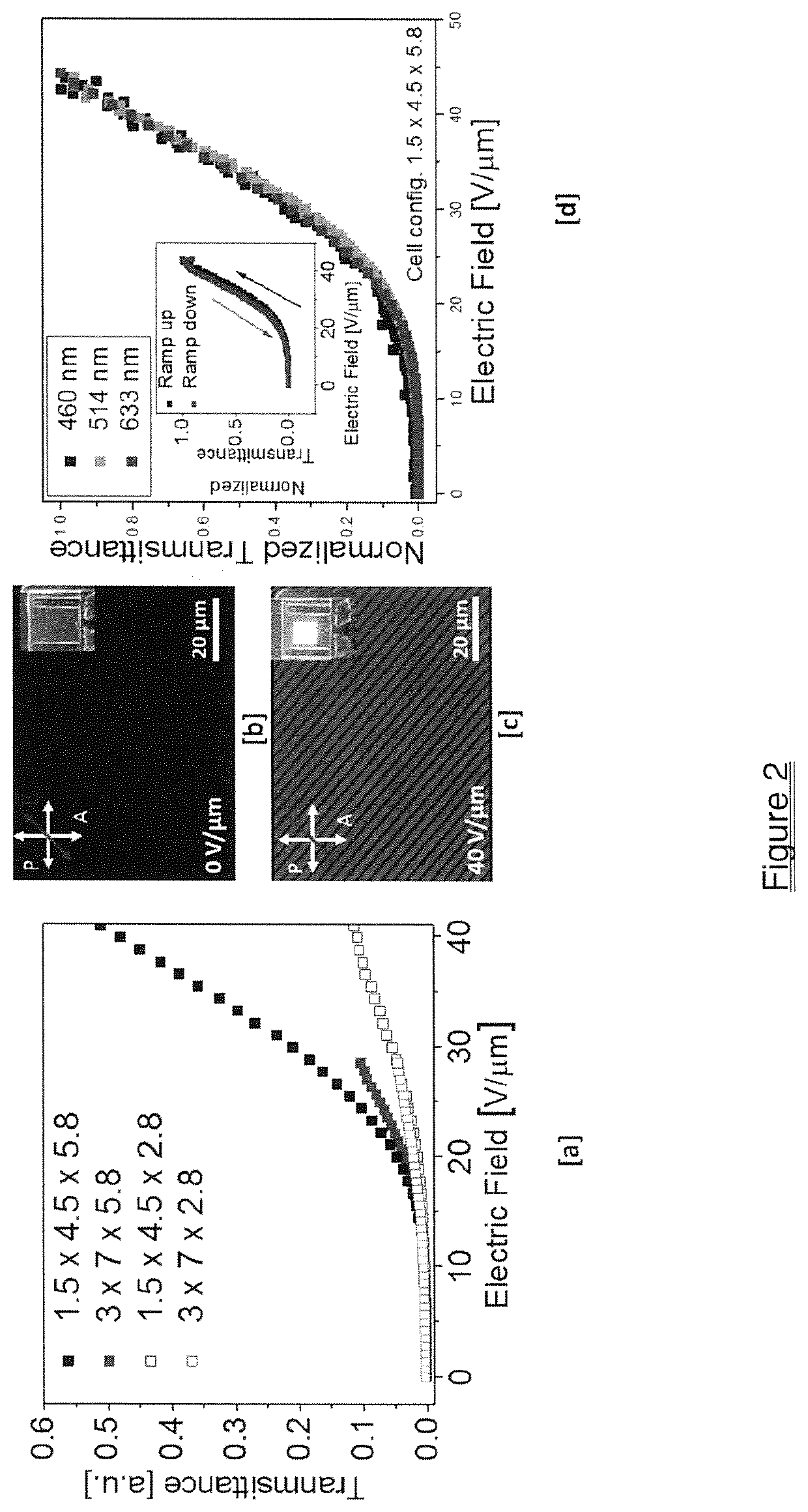
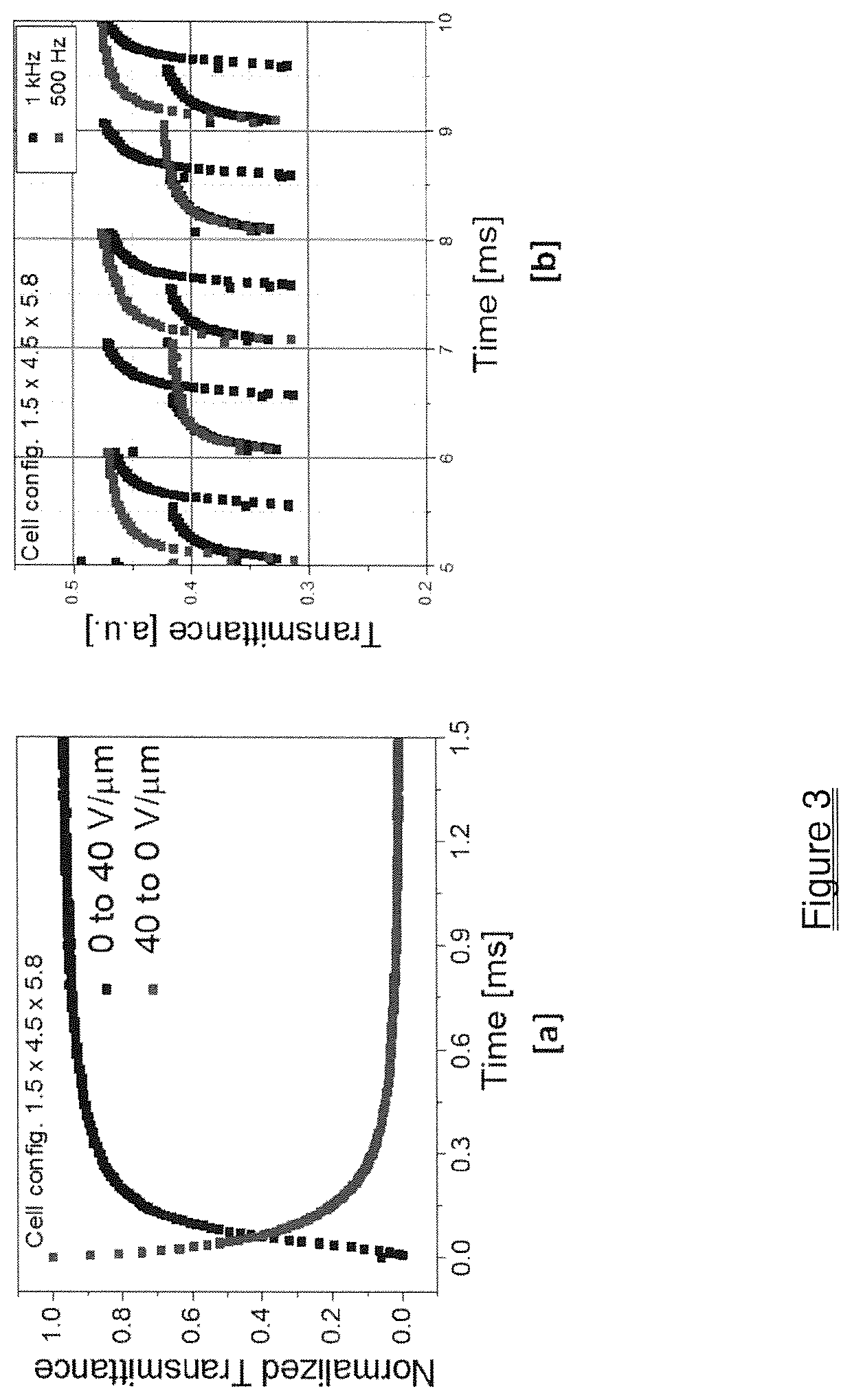
Fast Flexoelectro-Optic Switching Based on Bimesogen-Doped and Polymer-Stabilized Vertical Standing Helix Mode
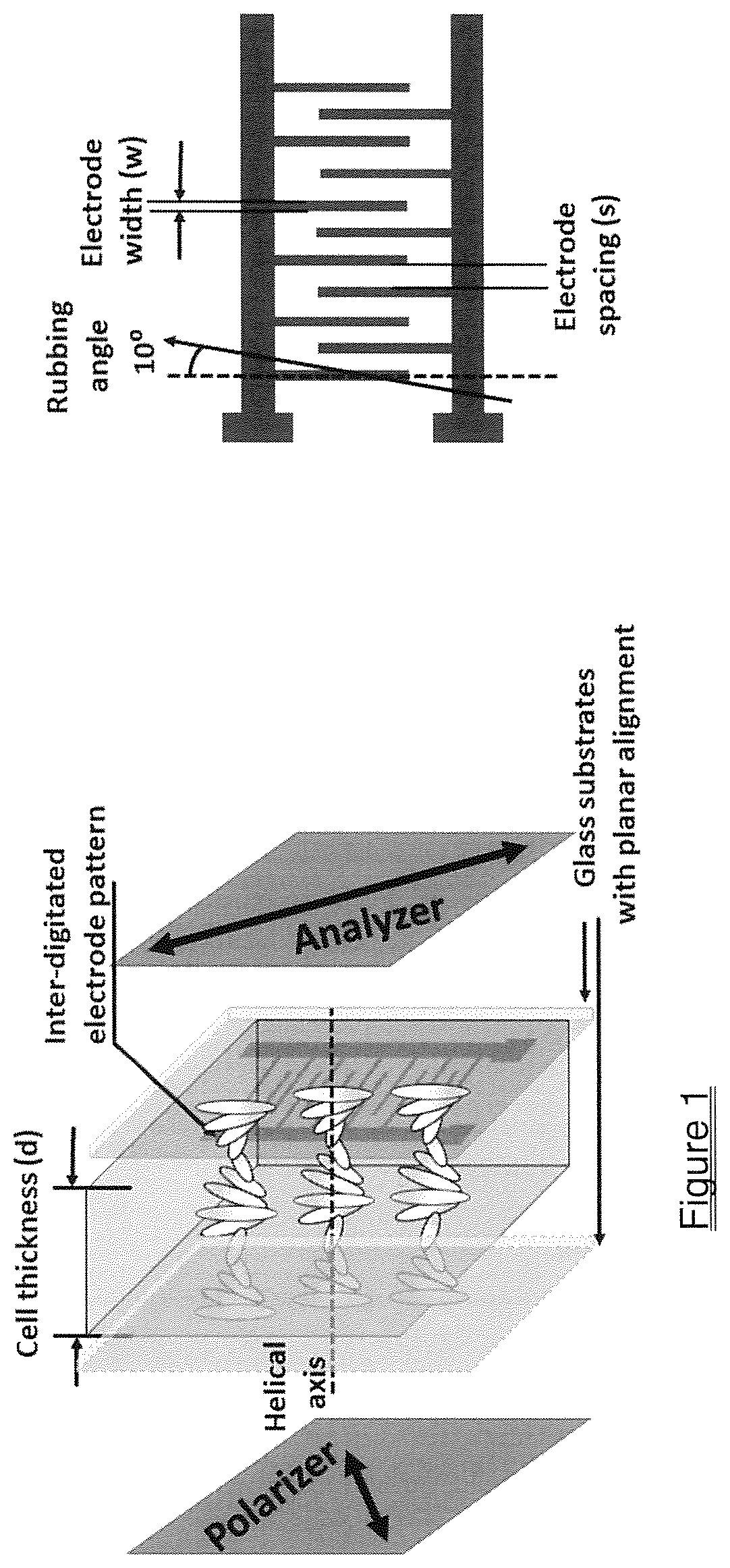
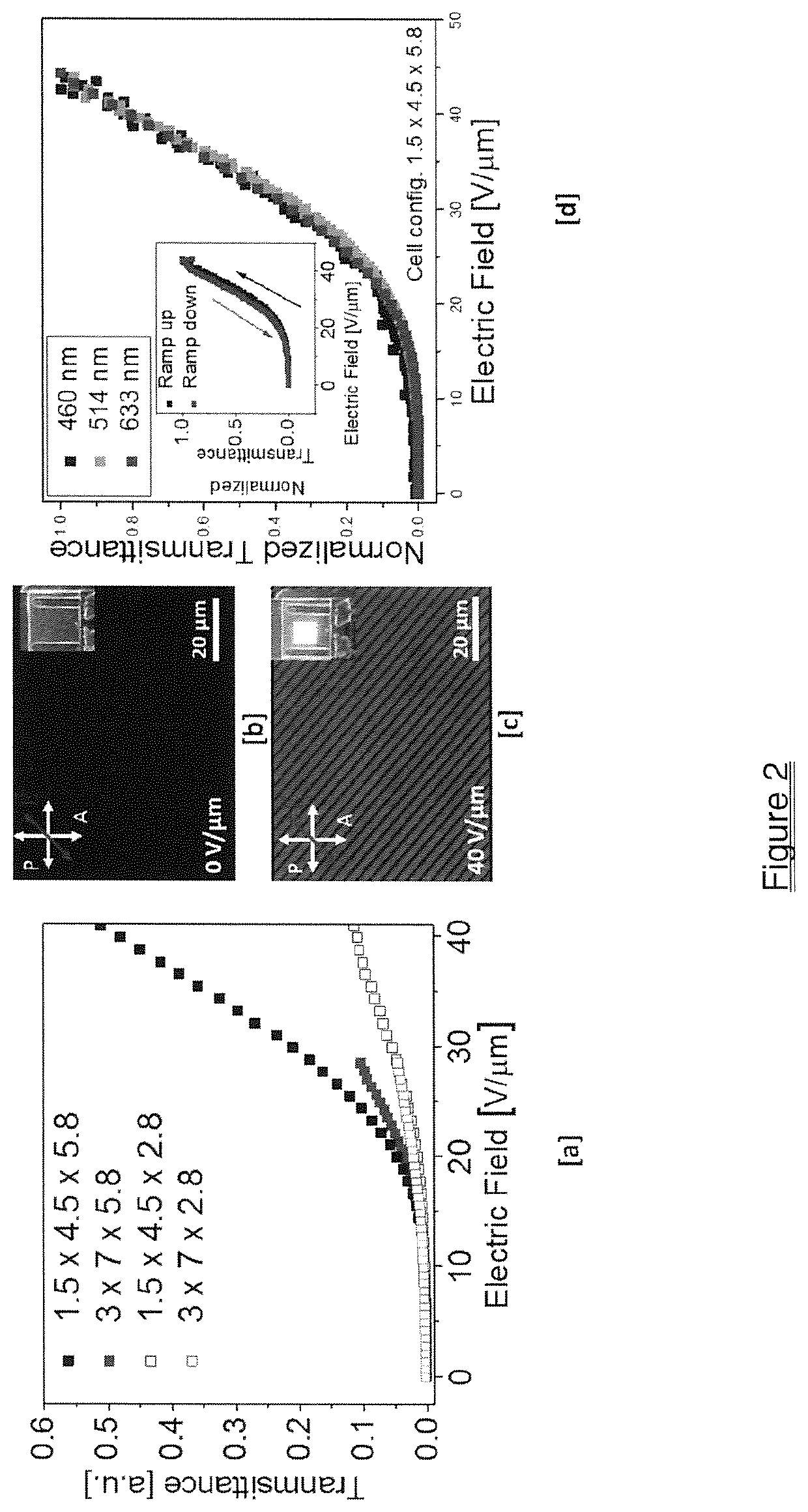
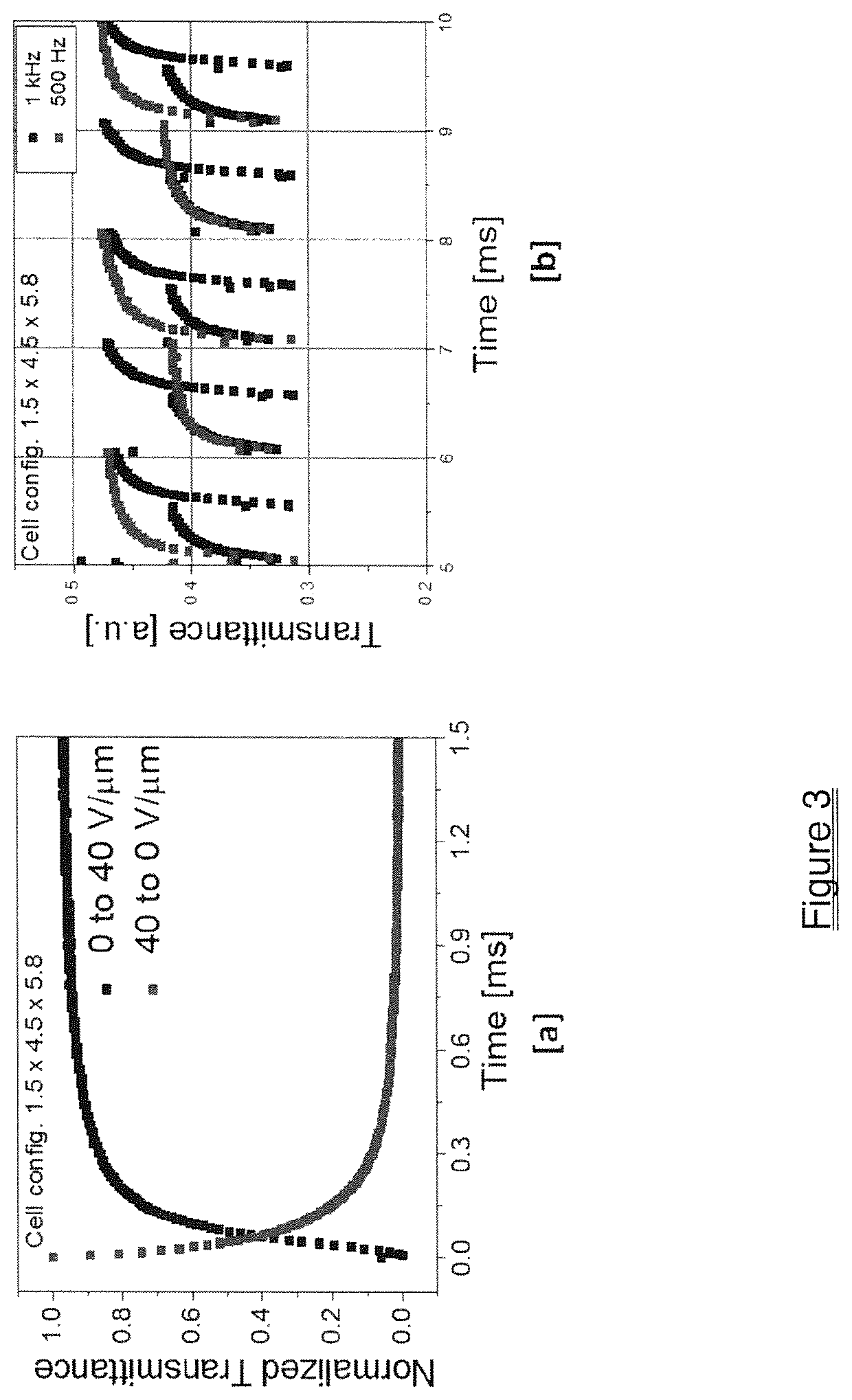
ActiveUS20200385634A1Fast mechanismHigh viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceOptical switch
A fast flexoelectro-optic switching device containing bimesogen-doped and polymer-stabilized vertical standing helix (PSVSH) in a cholesteric liquid crystal. The PSVSH device exhibits a response time of less than 0.7 millisecond, high contrast and negligible hysteresis which is suitable for applications including blur-free displays, field-sequential color displays and active optical elements.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
High-speed actuator for valves
ActiveUS8235252B2Improve dispensing accuracyPrecise positioningOperating means/releasing devices for valvesClosuresLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
A high-speed actuator moves a valve stopper to a selected position to control material flow. The actuator includes a rod carrying first and second axially spaced solenoid armatures attached to the stopper. First and second solenoid coil surround and are spaced from the rod to bias the first solenoid armature along with the rod and valve stopper. A linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) responsive to the position of the second armature determines the instantaneous position of the valve stopper. A valve position control circuit receives a valve position set point from a user's input, and a valve position feedback signal from the LVDT. The valve position control circuit includes first and second solenoid coil drive signals that urge the first armature and stopper to the valve position set point. A signal generator circuit vibrates the valve about a set point to enhance material discharge.
Owner:BRANDT JR ROBERT O
Crystalline forms of hydroxynorketamine
ActiveUS11377416B2Good water solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsAqueous solubilityOrganic chemistry
Owner:SMALL PHARMA LTD
Frequency-multiplexed speech-sound stimuli for hierarchical neural characterization of speech processing
ActiveUS10729387B2Maximize responseImprove synchronicityElectroencephalographySensorsAuditory systemSpeech corpus
A system and method for generating frequency-multiplexed synthetic sound-speech stimuli and for detecting and analyzing electrical brain activity of a subject in response to the stimuli. Frequency-multiplexing of speech copora and synthetic sounds helps the composite sound to blend into a single auditory object. The synthetic sounds are temporally aligned with the utterances of the speech corpus. Frequency multiplexing may include splitting the frequency axis into alternating bands of speech and synthetic sound to minimize the disruptive interaction between the speech and synthetic sounds along the basilar membrane and in their neural representations. The generated stimuli can be used with both traditional and advanced techniques to analyze electrical brain activity and provides a rapid, synoptic view into the functional health of the early auditory system, including how speech is processed at different levels and how these levels interact.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Frequency-multiplexed speech-sound stimuli for hierarchical neural characterization of speech processing
InactiveUS20200323495A1Maximize responseImprove synchronicityElectroencephalographySensorsAuditory systemSpeech corpus
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Crystalline forms of hydroxynorketamine
PendingUS20220306569A1Good water solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsAqueous solubilityOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides novel, stable, processable and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms of 2R,6R-hydrox-ynorketamineor 2S,6S-hydroxynorketamine with high aqueous solubility.
Owner:CYBIN UK LTD
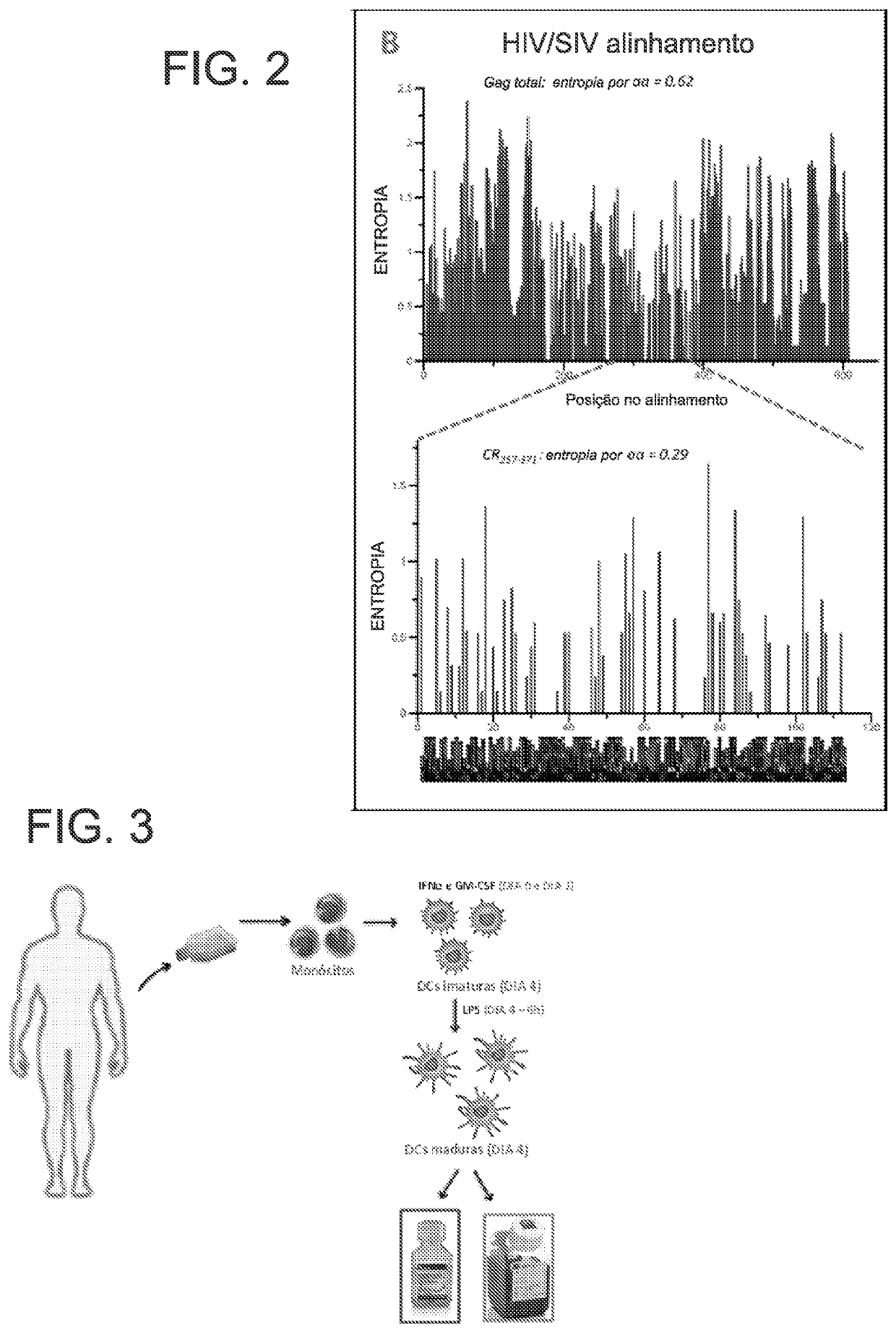
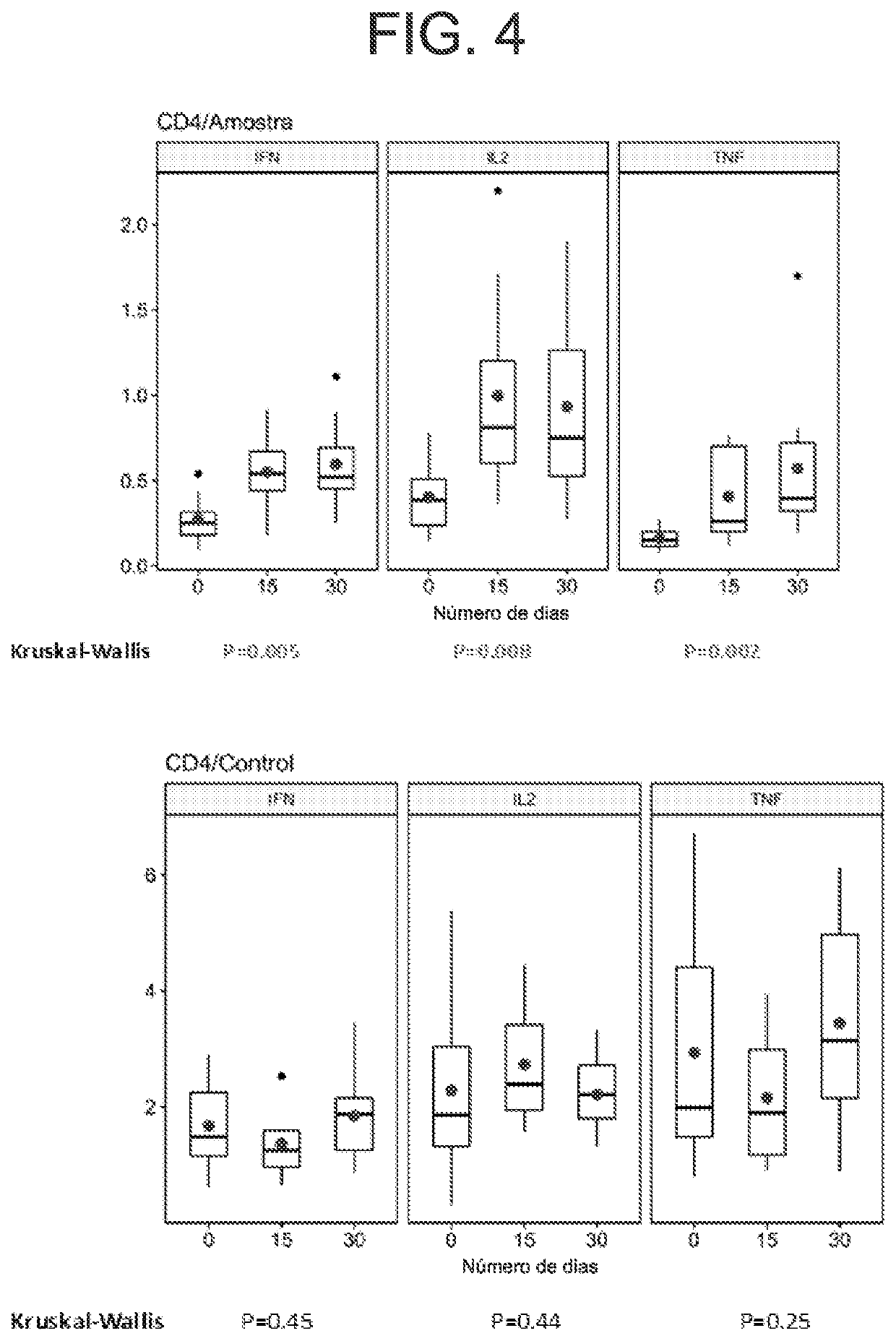
Method for defining a personalized vaccine against hiv/aids
PendingUS20220111036A1Improve bindingMaximize immune responseOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsProteinAllelic gene
A novel approach to the development of a personalized vaccine. This approach is based on: A) sequencing of the gag gene from an HIV-infected individual treated with antiretroviral therapy; B) sequencing of the HLA alleles of the same individual; C) selecting the epitopes recognized by the individual's own HLA Class I within the highly-conserved Gag256-377, Gag147-169 and / or Gag225-251 amino acid sequences. An original algorithm that designs the target peptide for the vaccine starting from viral and HLA sequences of an individual with HIV / AIDS, forms the core of the present invention. The original algorithm makes extensive use of existing open- source software for protein design. The peptides designed in this manner and accordingly synthesized may be exploited as a therapeutic vaccine against HIV / AIDS. Vehicles for such peptides may be an individual's own dendritic cells pulsed with the peptide combination or a specific viral or DNA vector leading to intracellular expression of the viral peptides. The present vaccine approach may contribute to control of viremia once antiretroviral therapies are suspended.
Owner:CUNHA DANIELE
Visual Prosthesis with an Improved Electrode Array Adapted for Foveal Stimulation
ActiveUS20140309710A1Limited perceptionMaximize responseHead electrodesExternal electrodesElectricityHigh density
The present invention is an improved method of electrically stimulating percepts in a patient with a visual prosthesis, to induce a more controlled perception of light. In particular, the present invention is an improved electrode array to maximize retinal response. The array of the present invention is an array with a center section with no electrode, surrounded by a ring of small high density electrodes. Electrodes beyond to ring are gradually larger and more widely spaced.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Visual prosthesis with an improved electrode array adapted for foveal stimulation
ActiveUS8588921B2Limited perceptionMaximize responseHead electrodesExternal electrodesElectricityHigh density
The present invention is an improved method of electrically stimulating percepts in a patient with a visual prosthesis, to induce a more controlled perception of light. In particular, the present invention is an improved electrode array to maximize retinal response. The array of the present invention is an array with a center section with no electrode, surrounded by a ring of small high density electrodes. Electrodes beyond to ring are gradually larger and more widely spaced.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Fast flexoelectro-optic switching based on bimesogen-doped and polymer-stabilized vertical standing helix mode
ActiveUS11434426B2Fast mechanismHigh viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceMaterials science
A fast flexoelectro-optic switching device containing bimesogen-doped and polymer-stabilized vertical standing helix (PSVSH) in a cholesteric liquid crystal. The PSVSH device exhibits a response time of less than 0.7 millisecond, high contrast and negligible hysteresis which is suitable for applications including blur-free displays, field-sequential color displays and active optical elements.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com