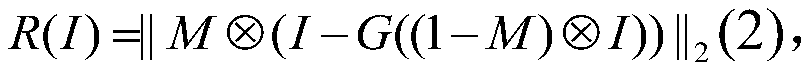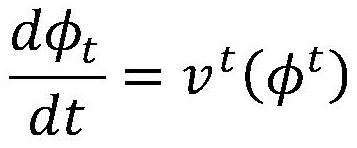Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Reduce X-ray radiation dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
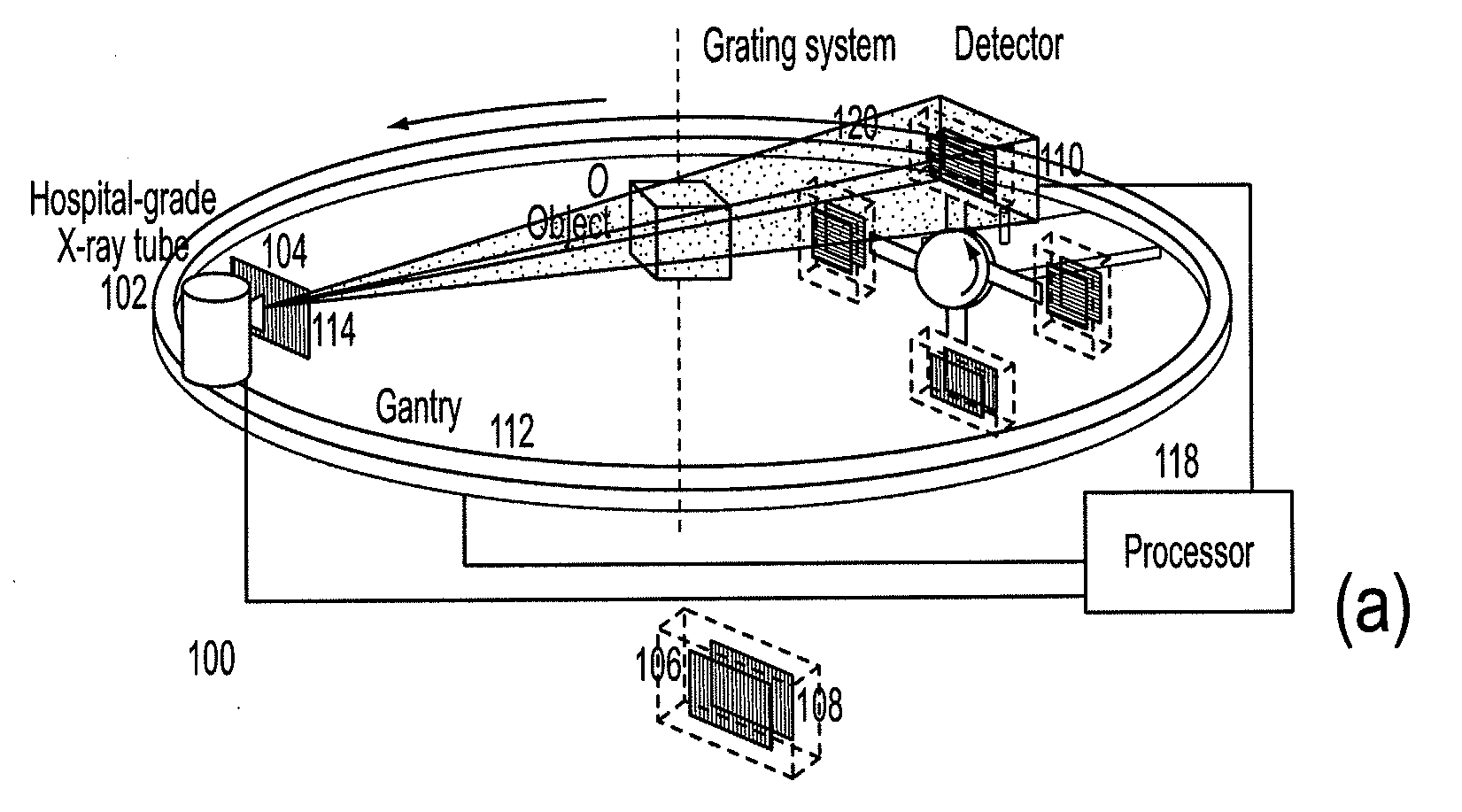
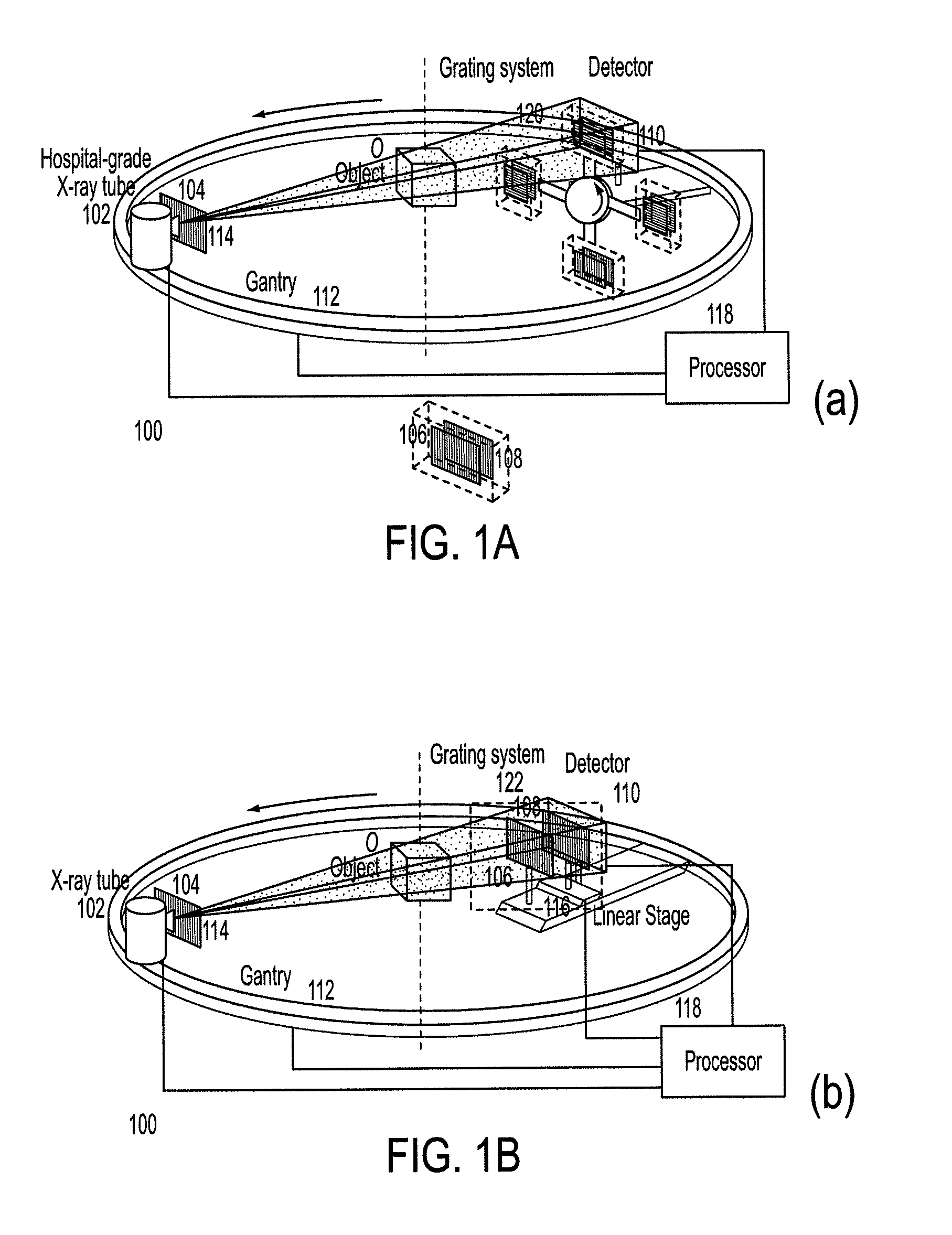
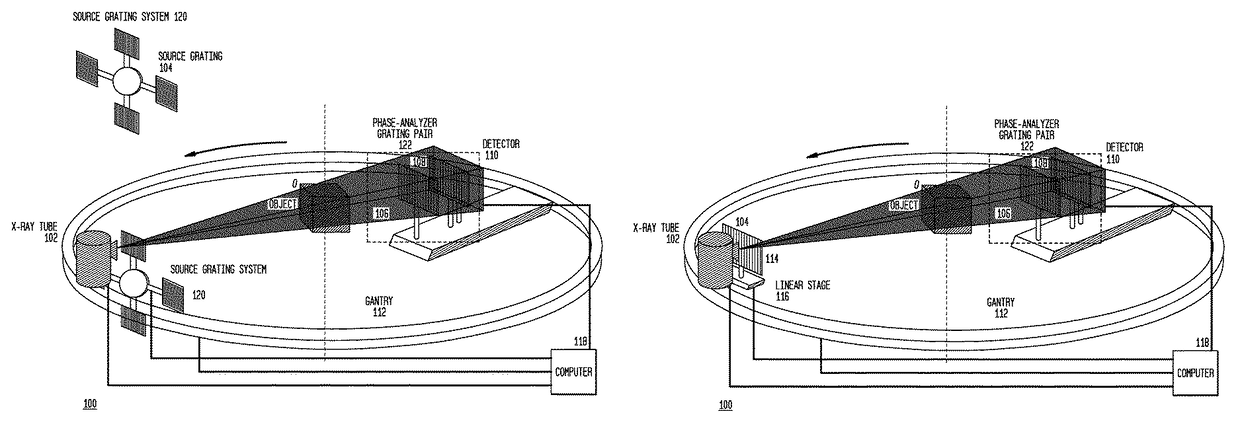
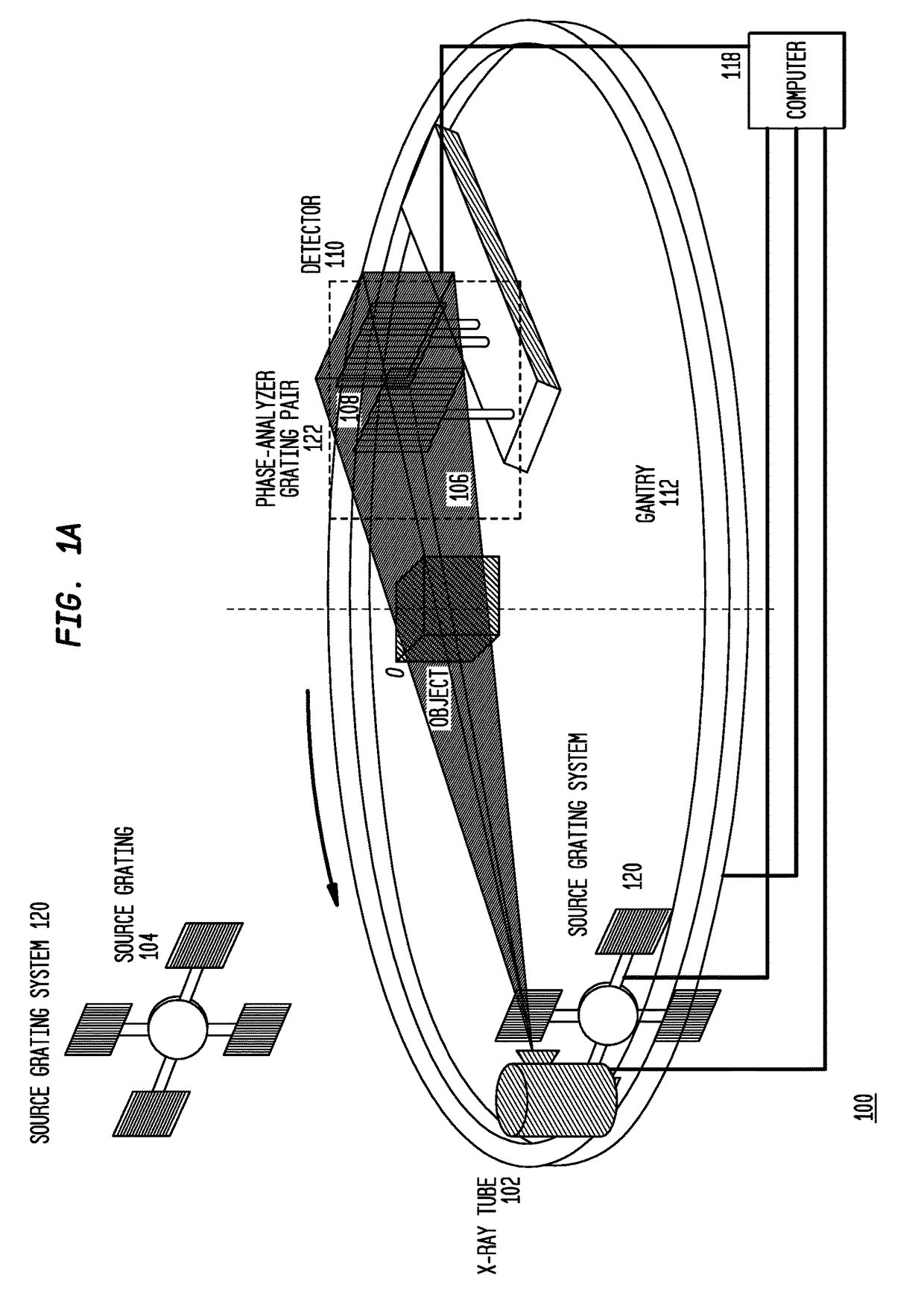
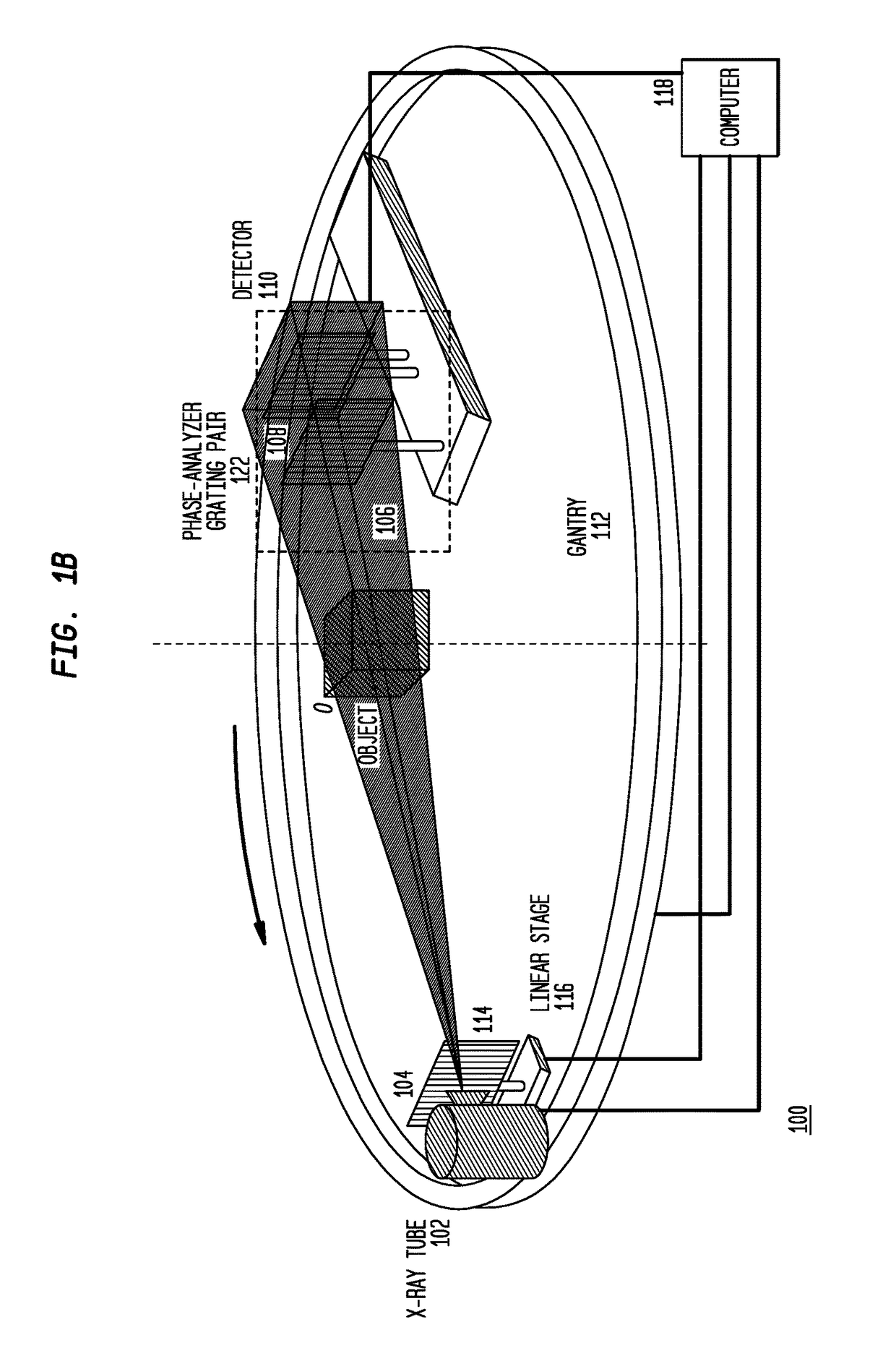
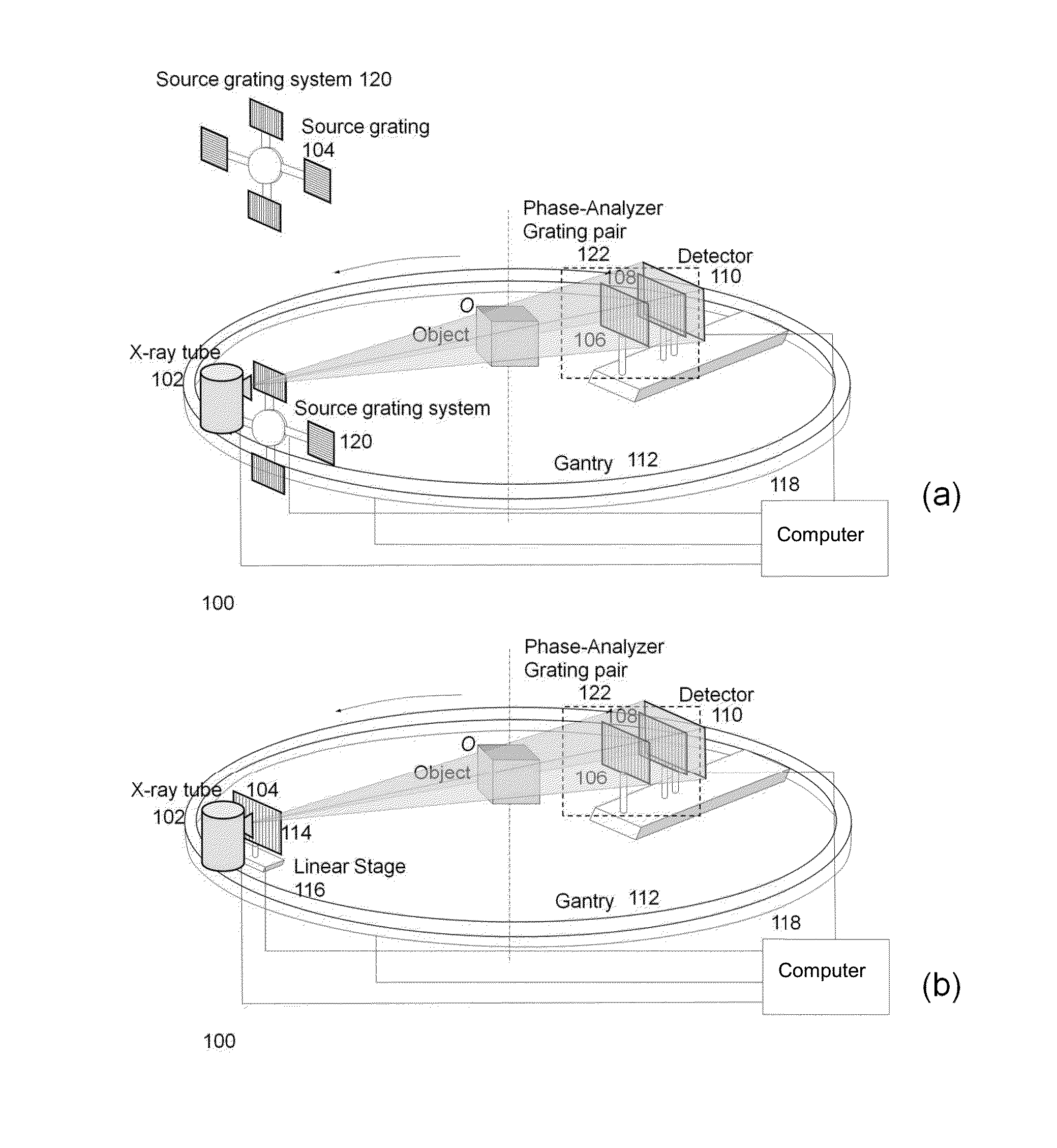
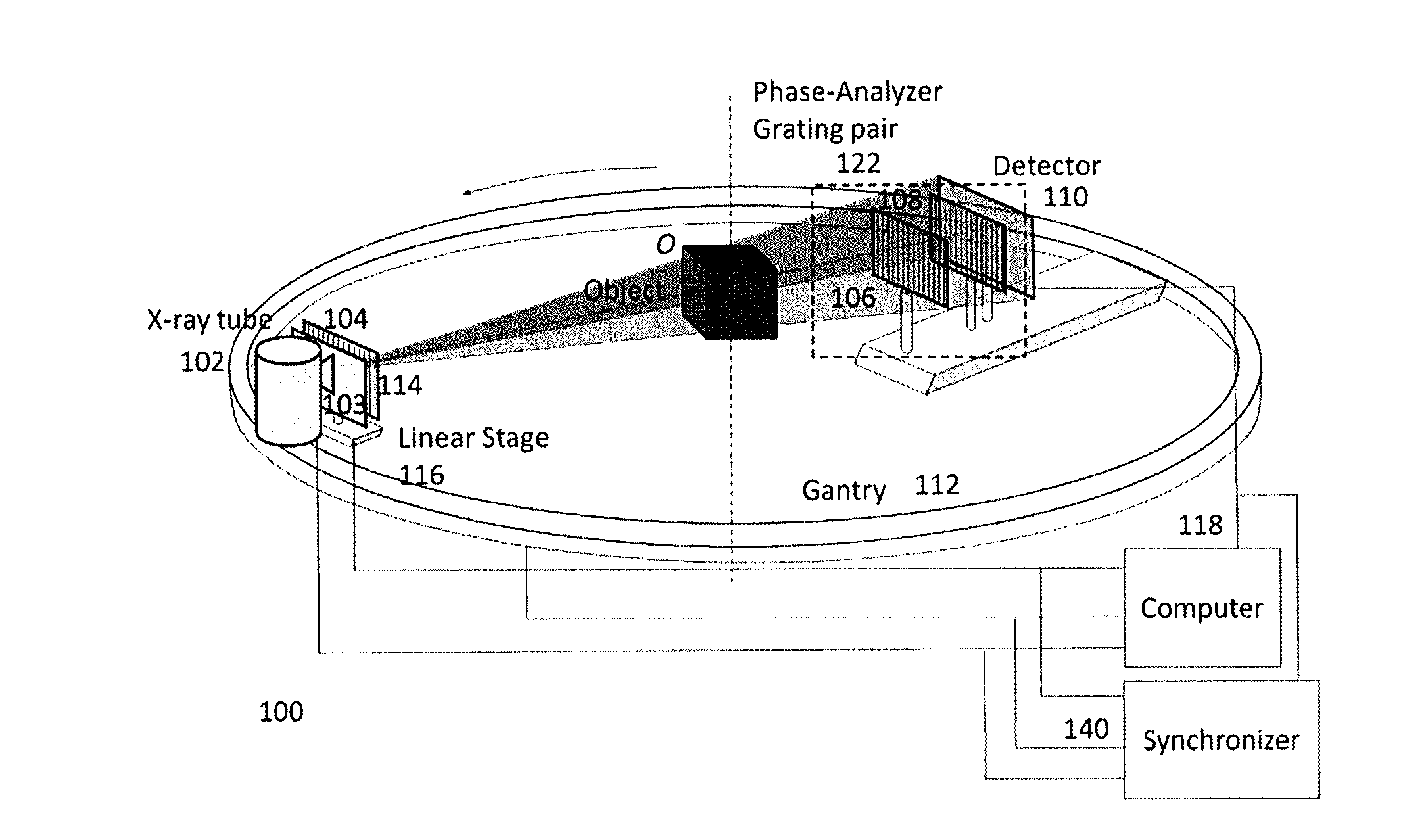
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
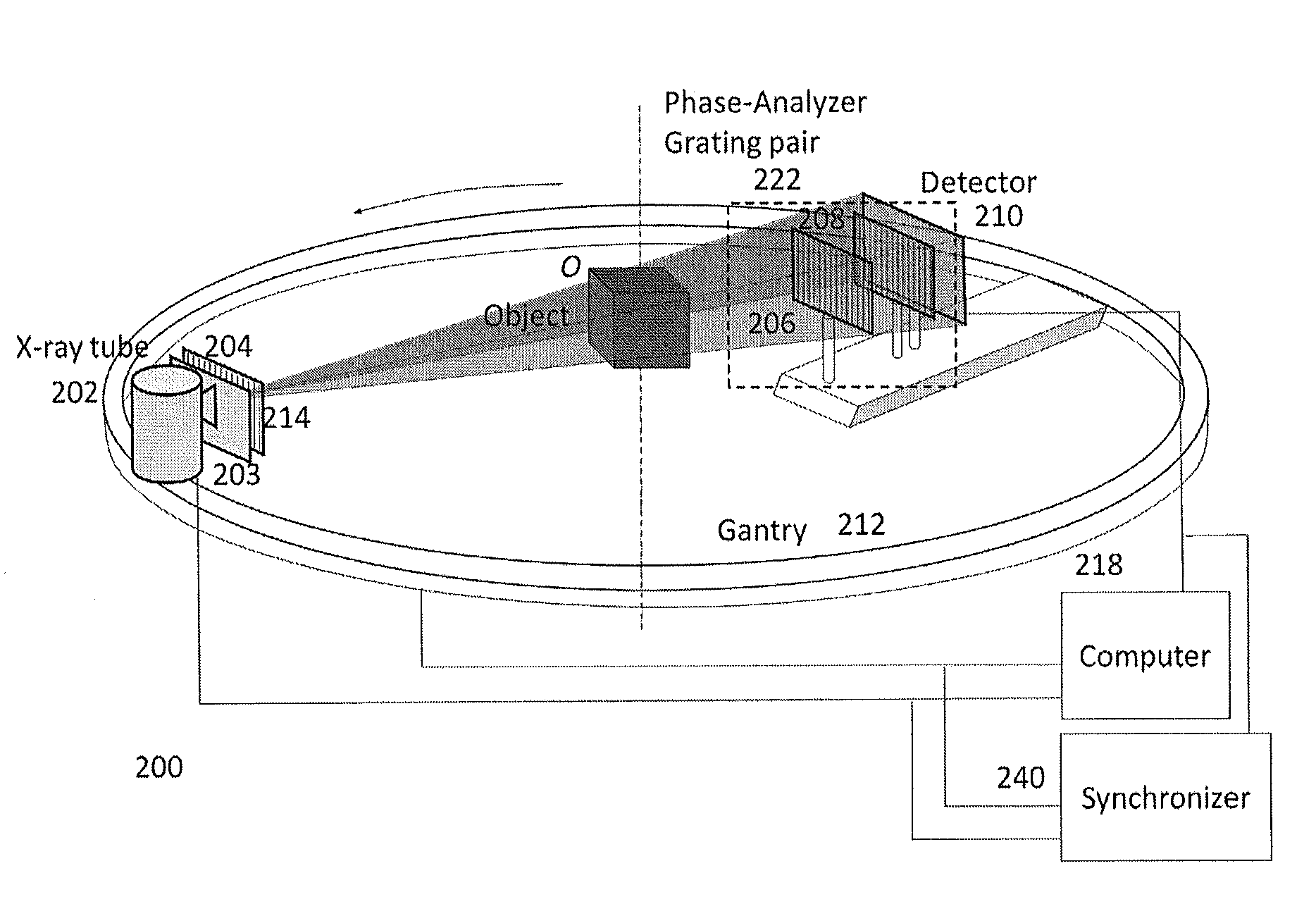
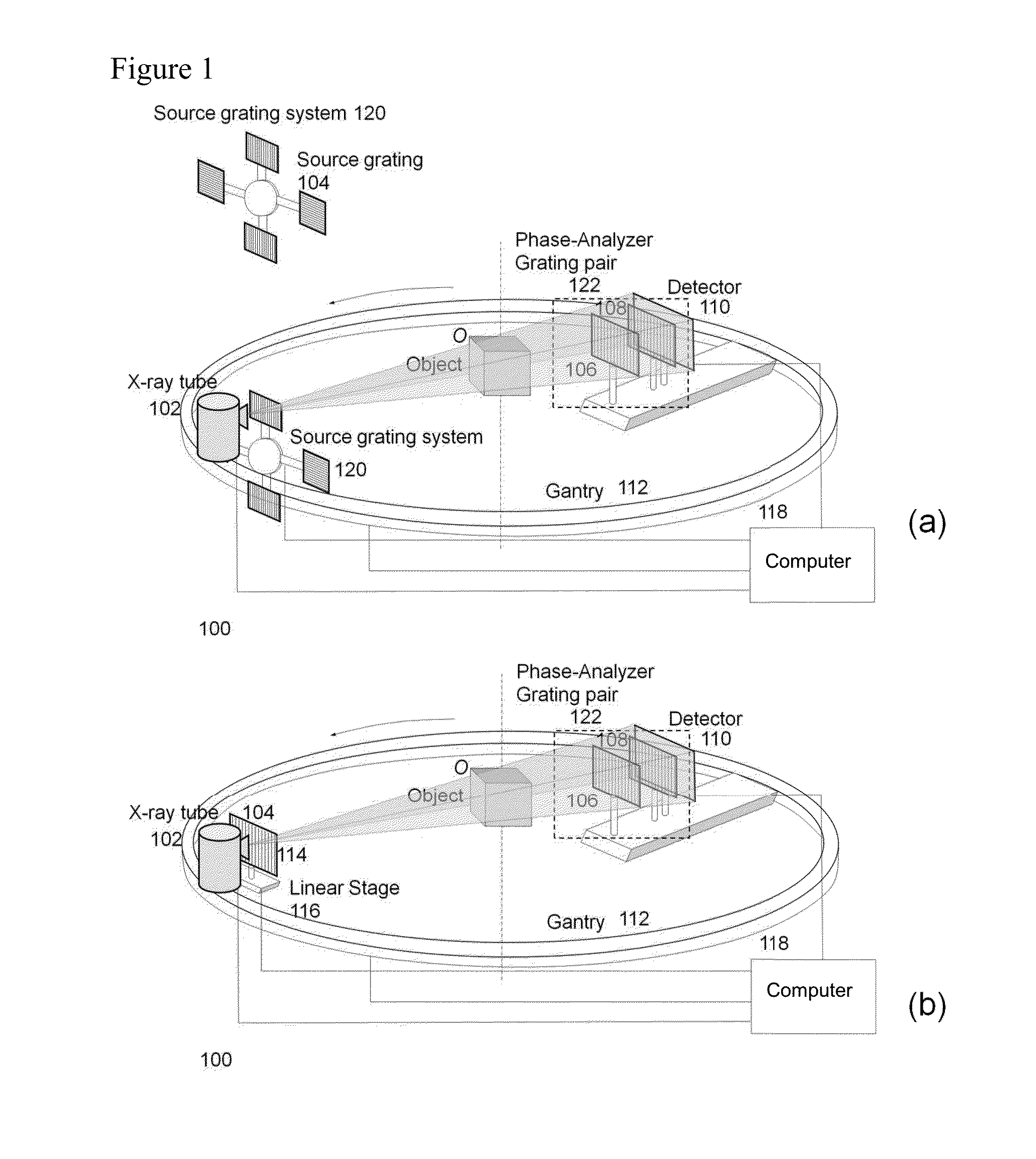
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
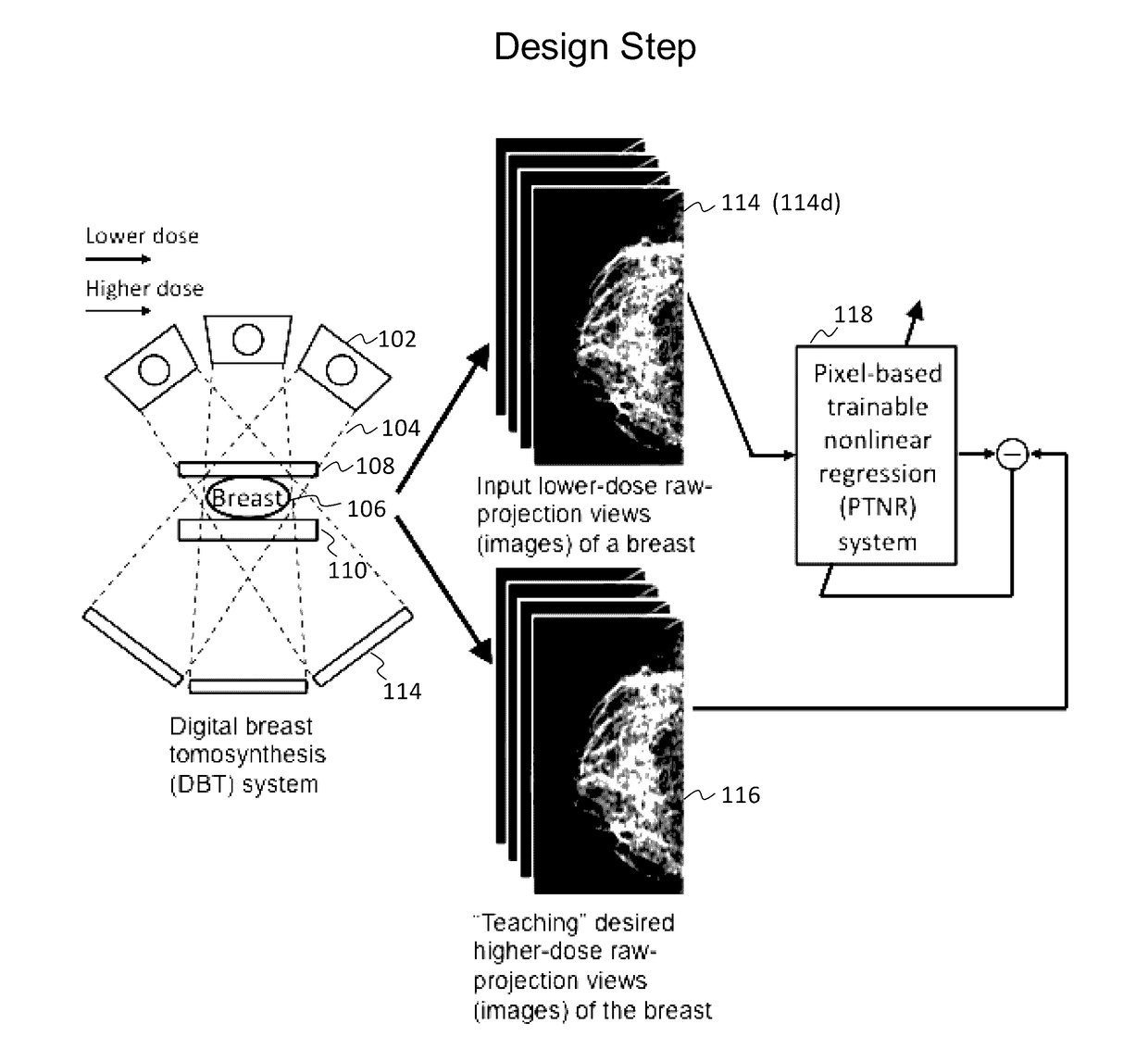
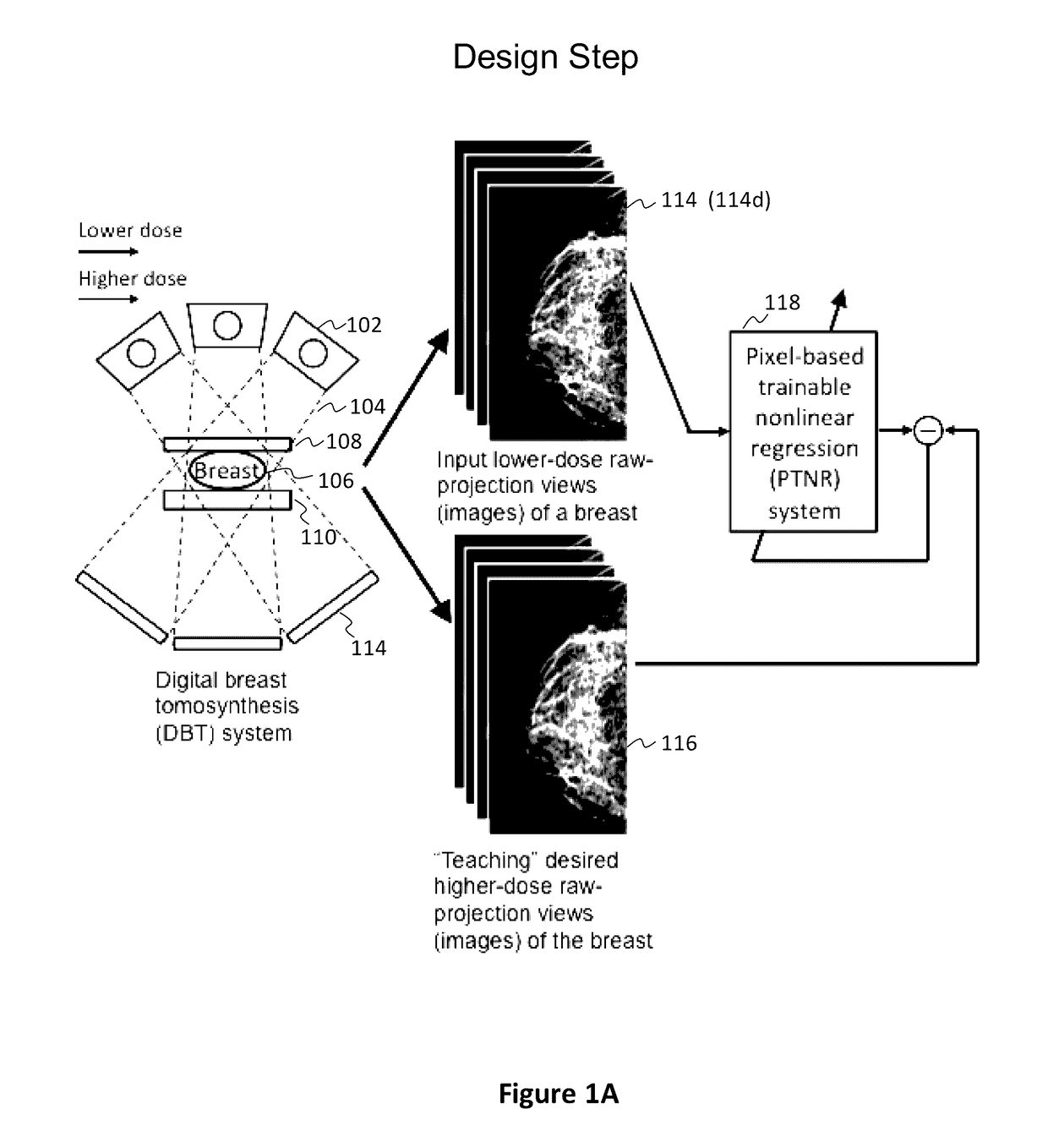
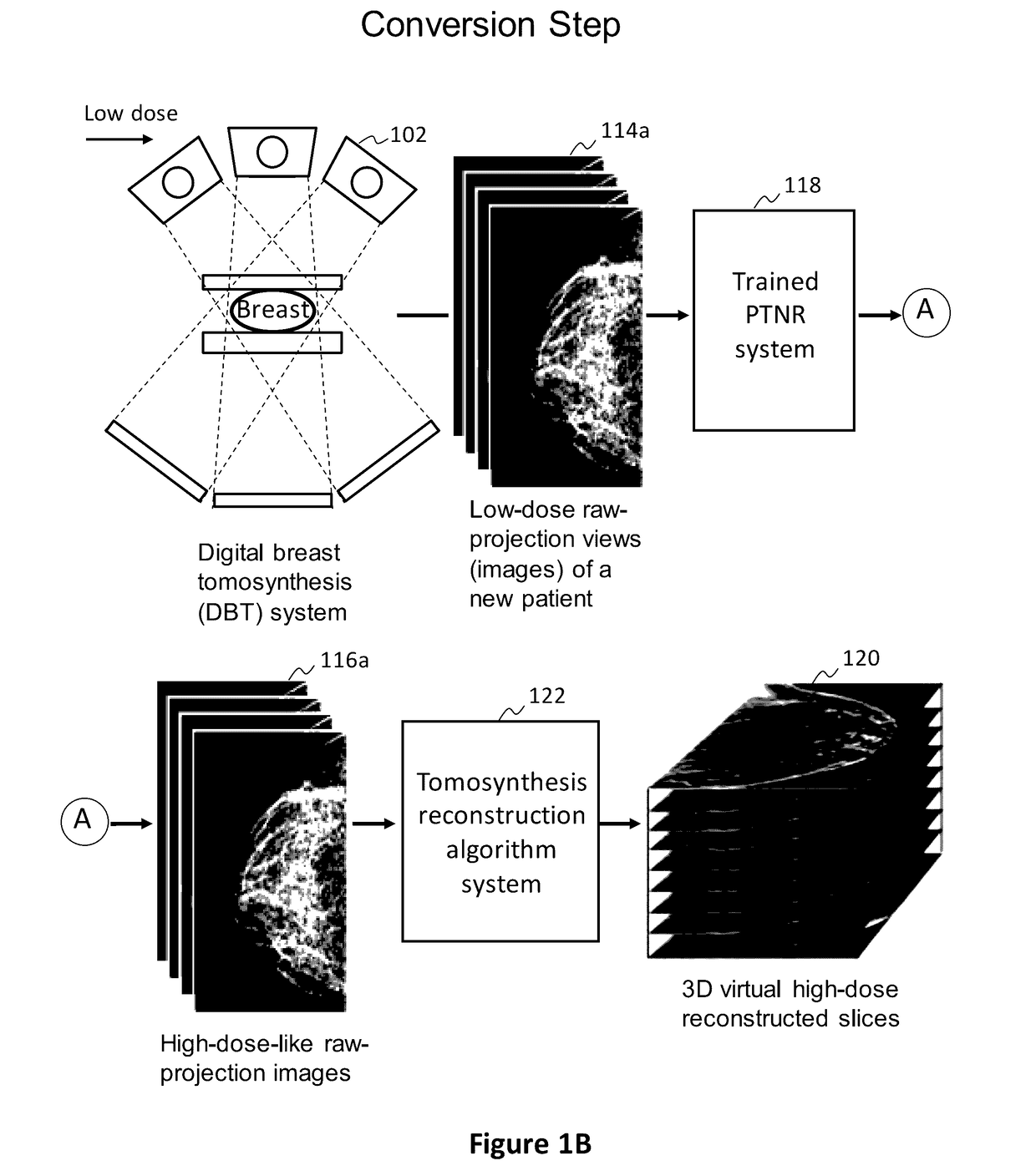
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20170071562A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisImaging quality
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method and apparatus of spectral differential phase-contrast cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
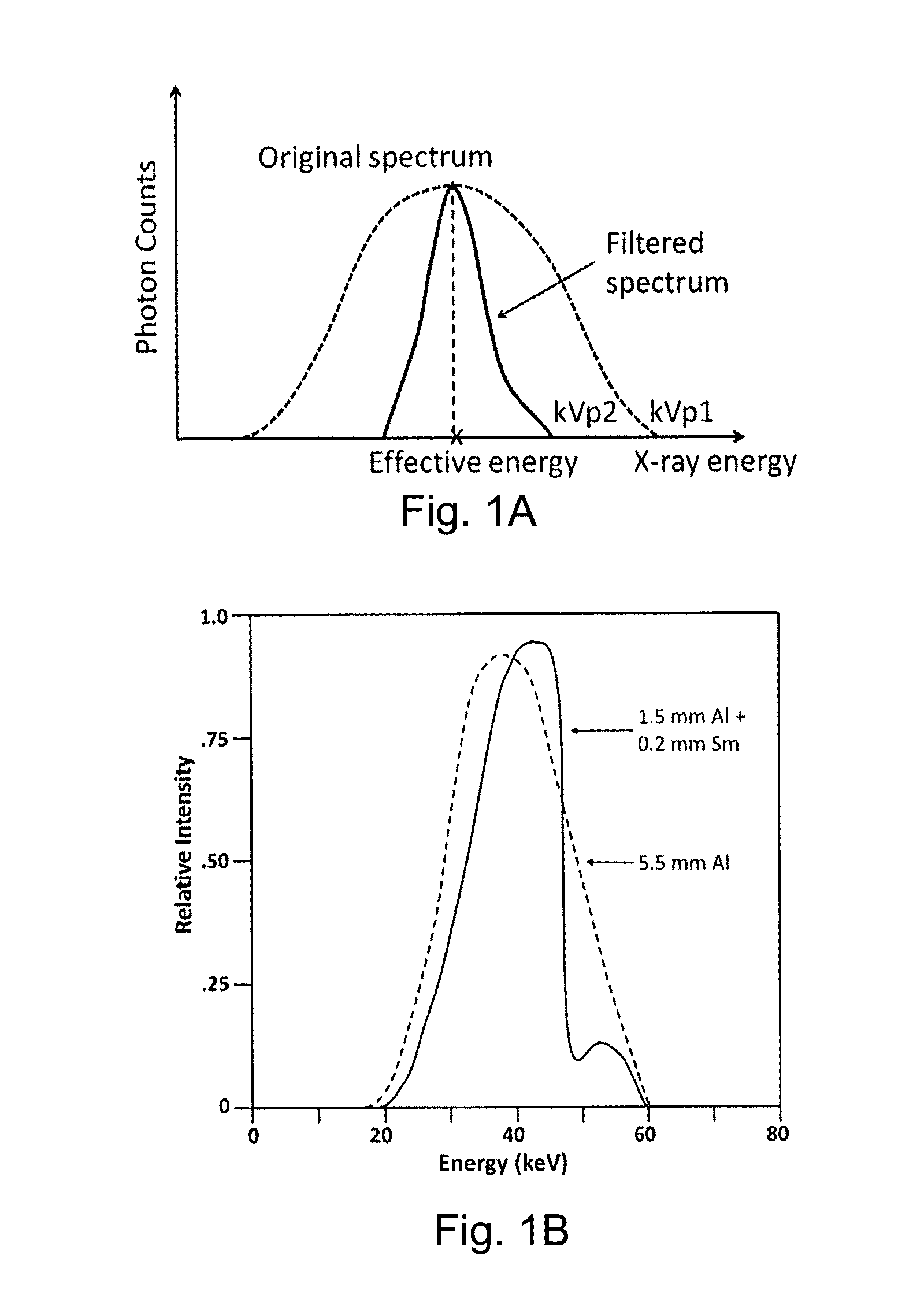
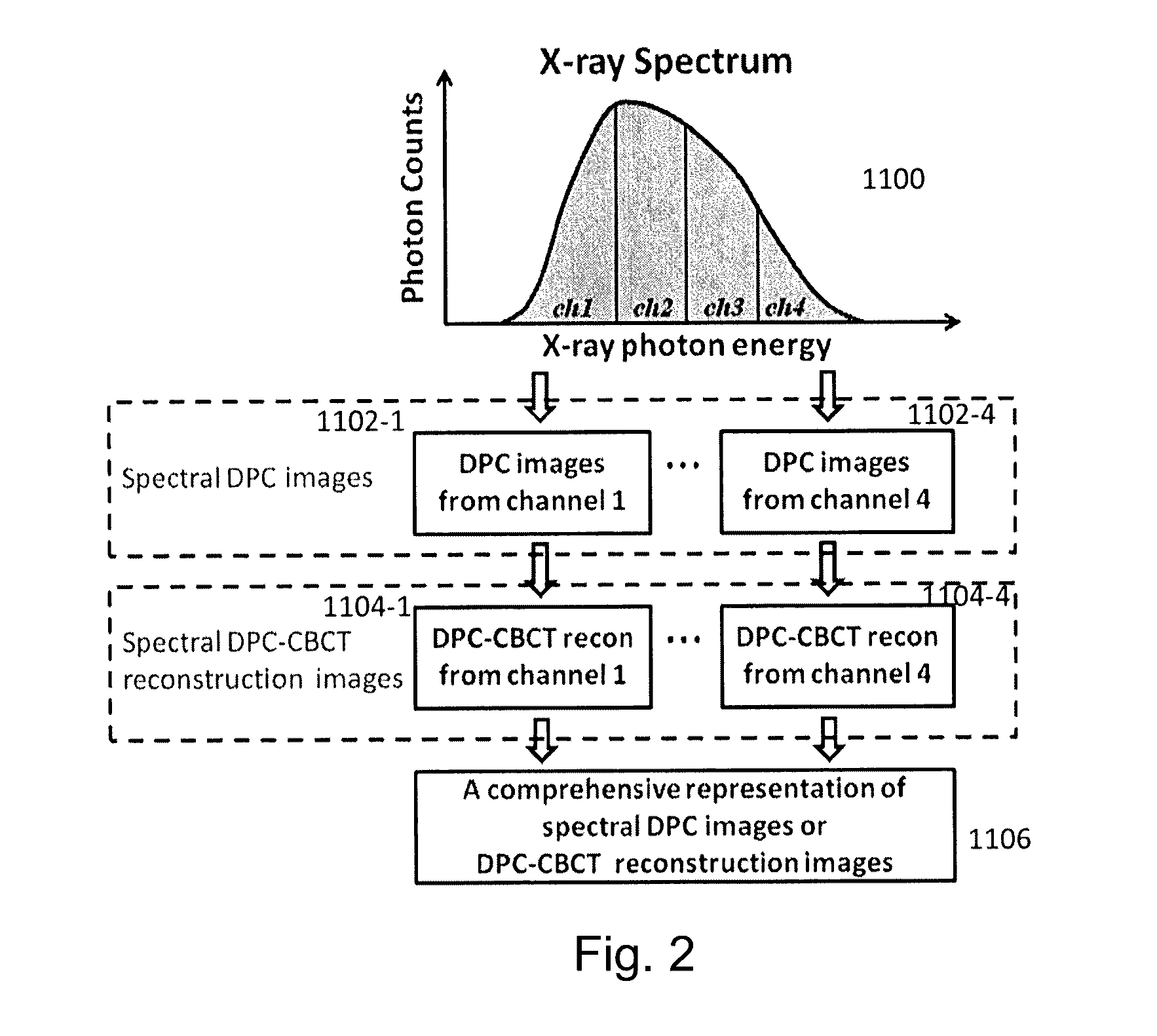
ActiveUS20140226783A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce X-ray radiationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPhysicsPhoton energy
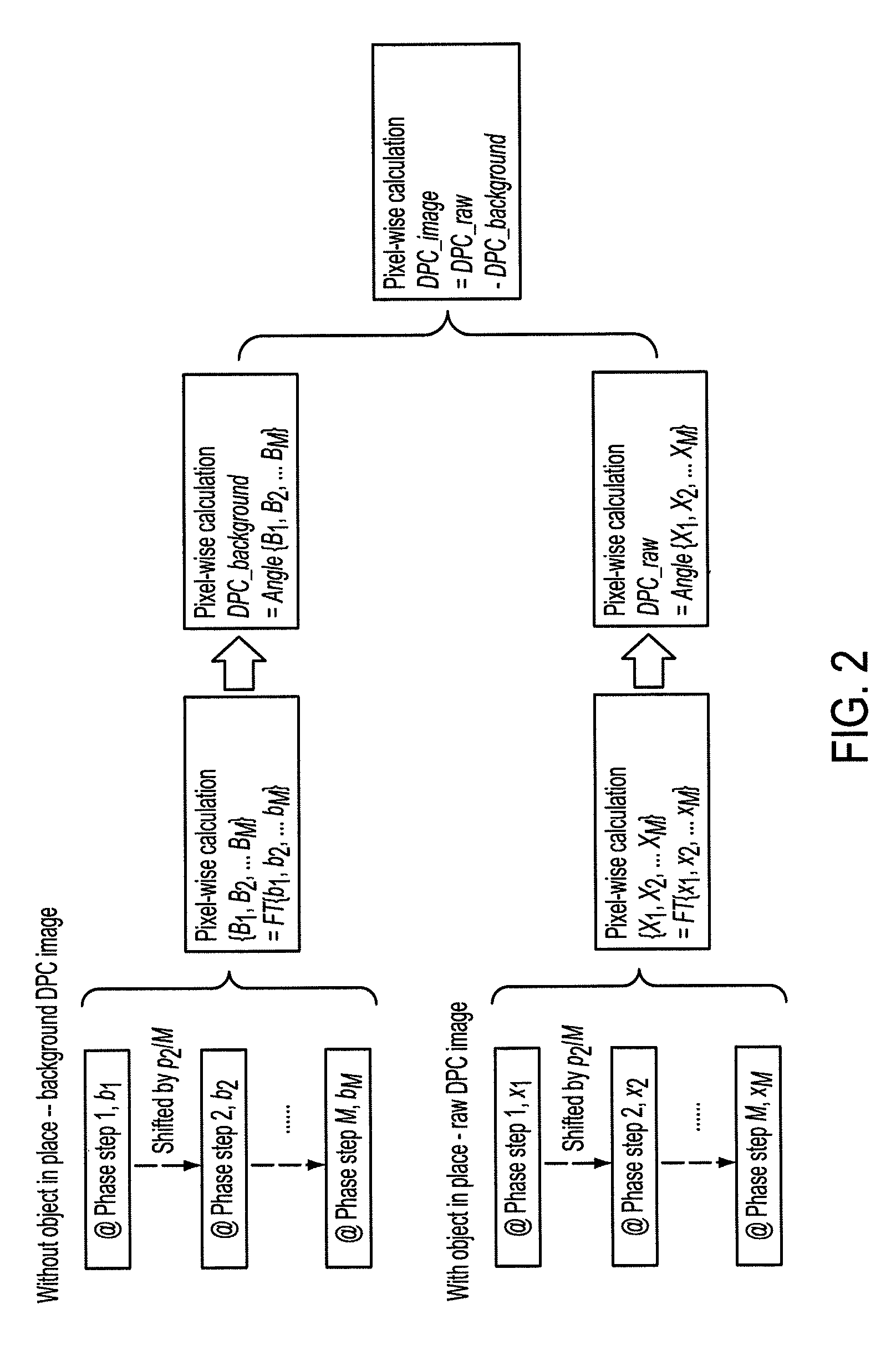
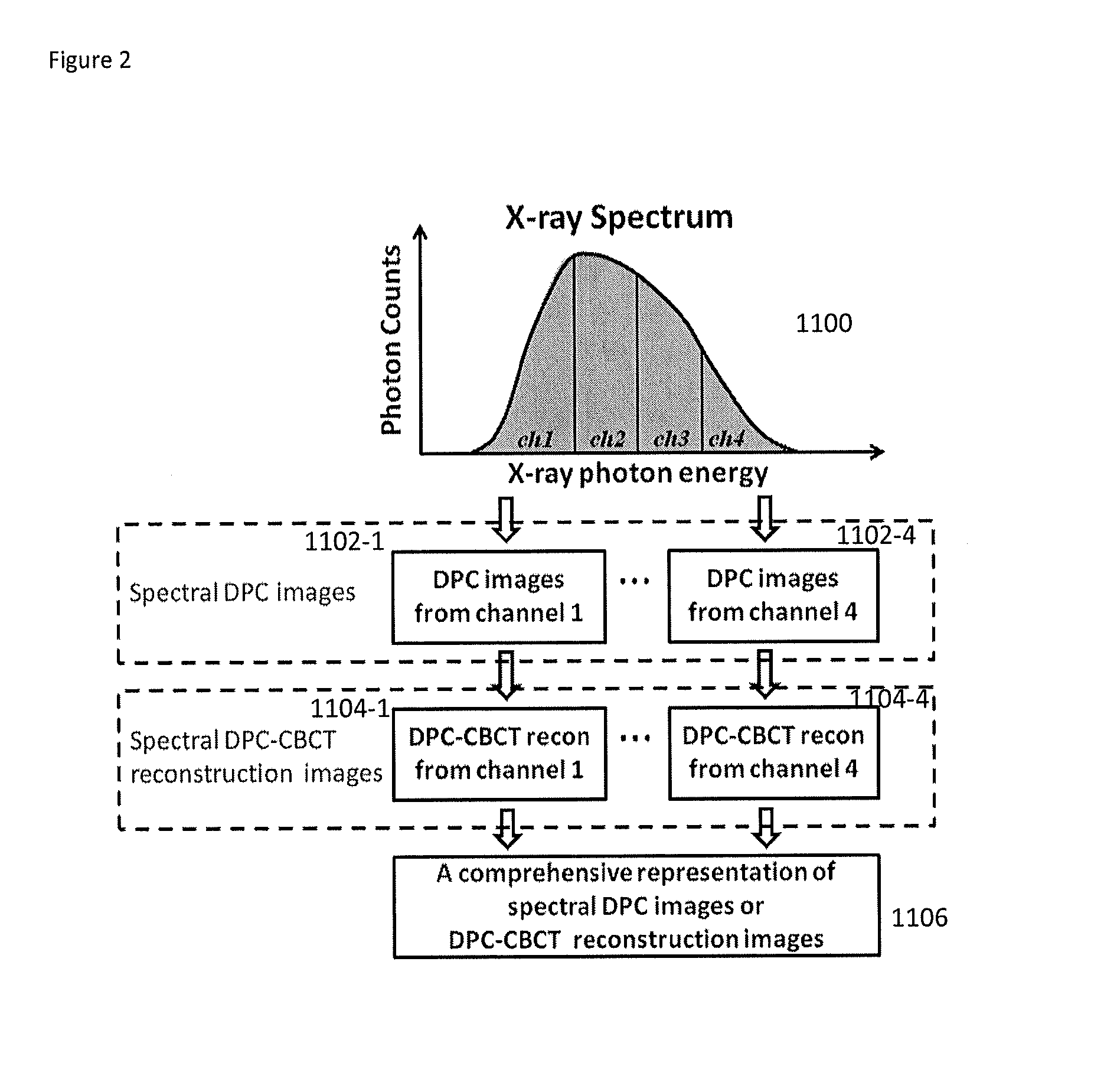
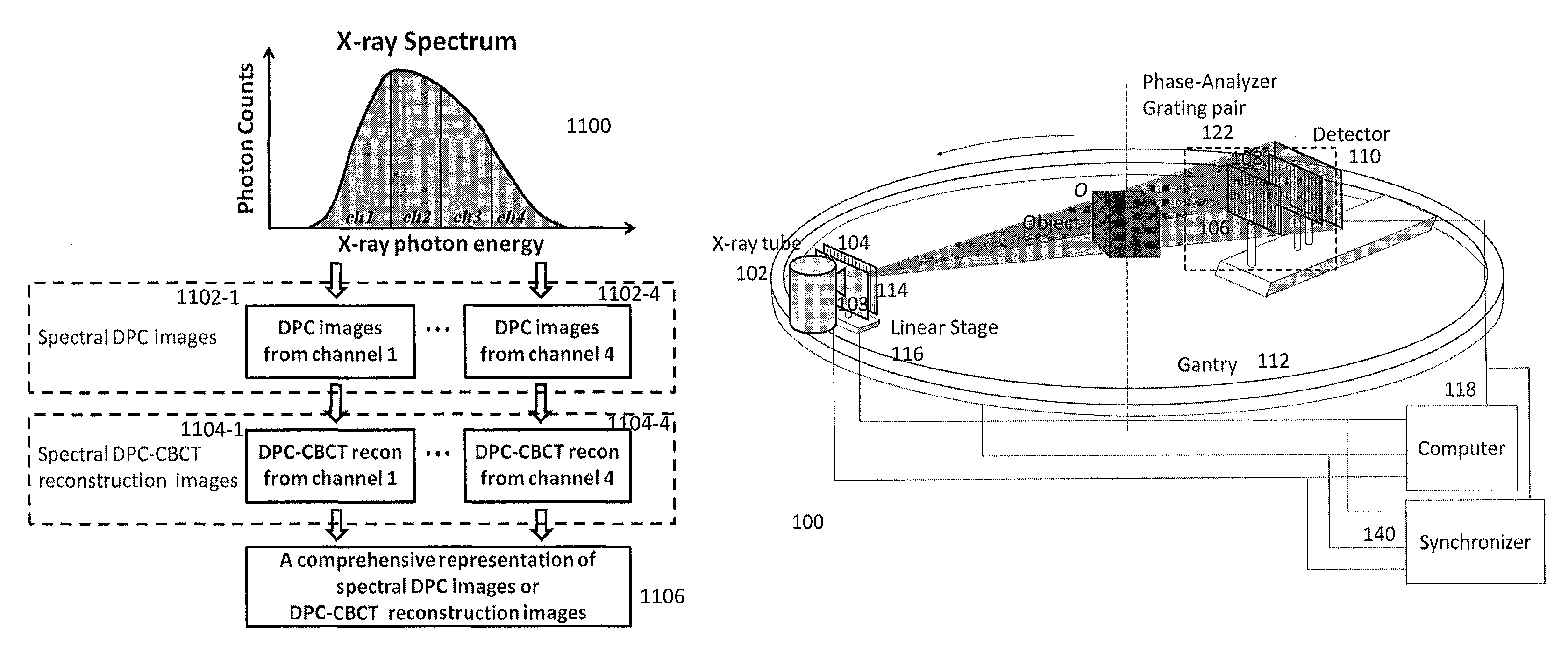
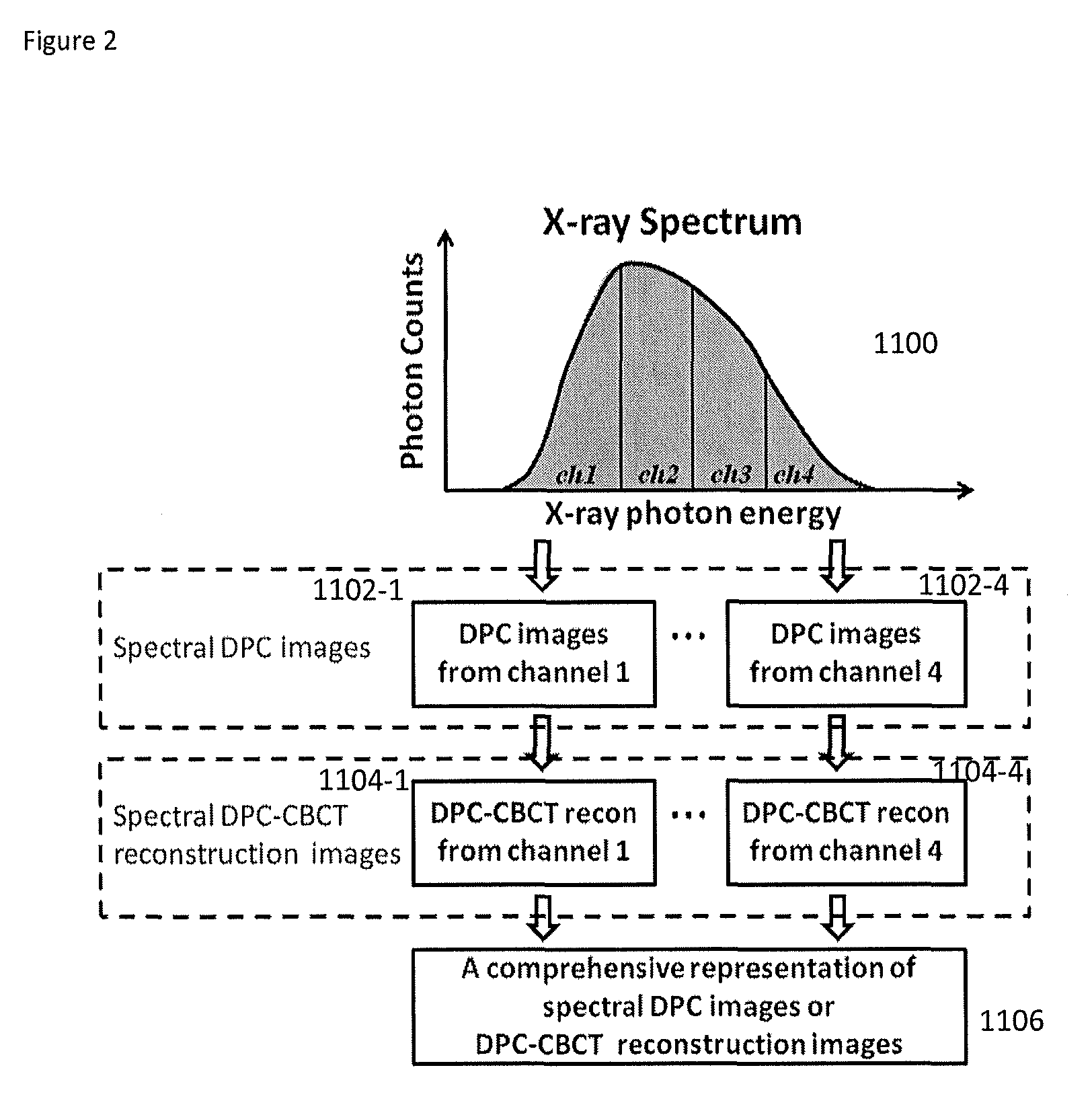
DPC (differential phase contrast) images are acquired for each photon energy channel, which are called spectral DPC images. The final DPC image can be computed by summing up these spectral DPC images or just computed using certain ‘color’ representation algorithms to enhance desired features. In addition, with quasi-monochromatic x-ray source, the required radiation dose is substantially reduced, while the image quality of DPC images remains acceptable.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
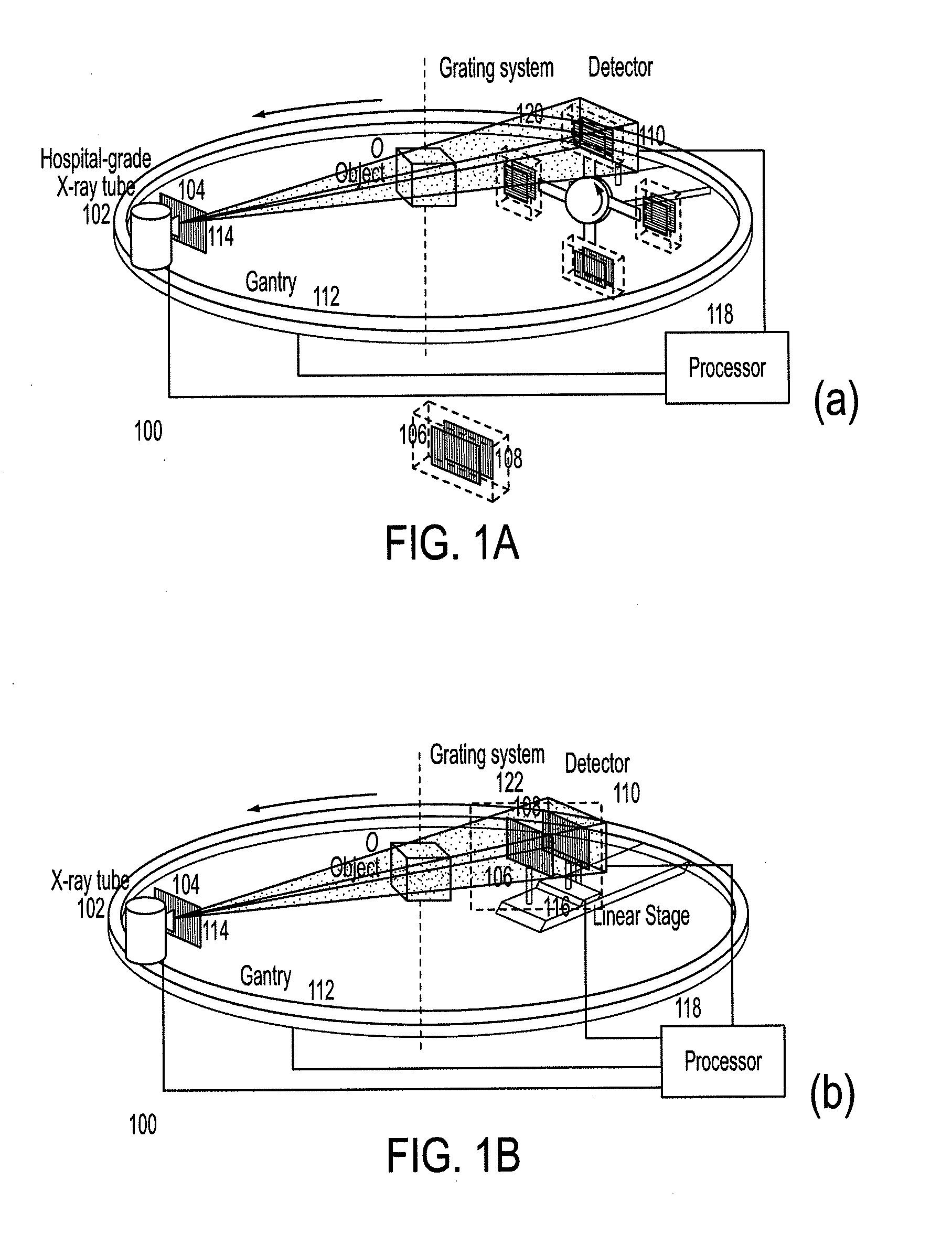
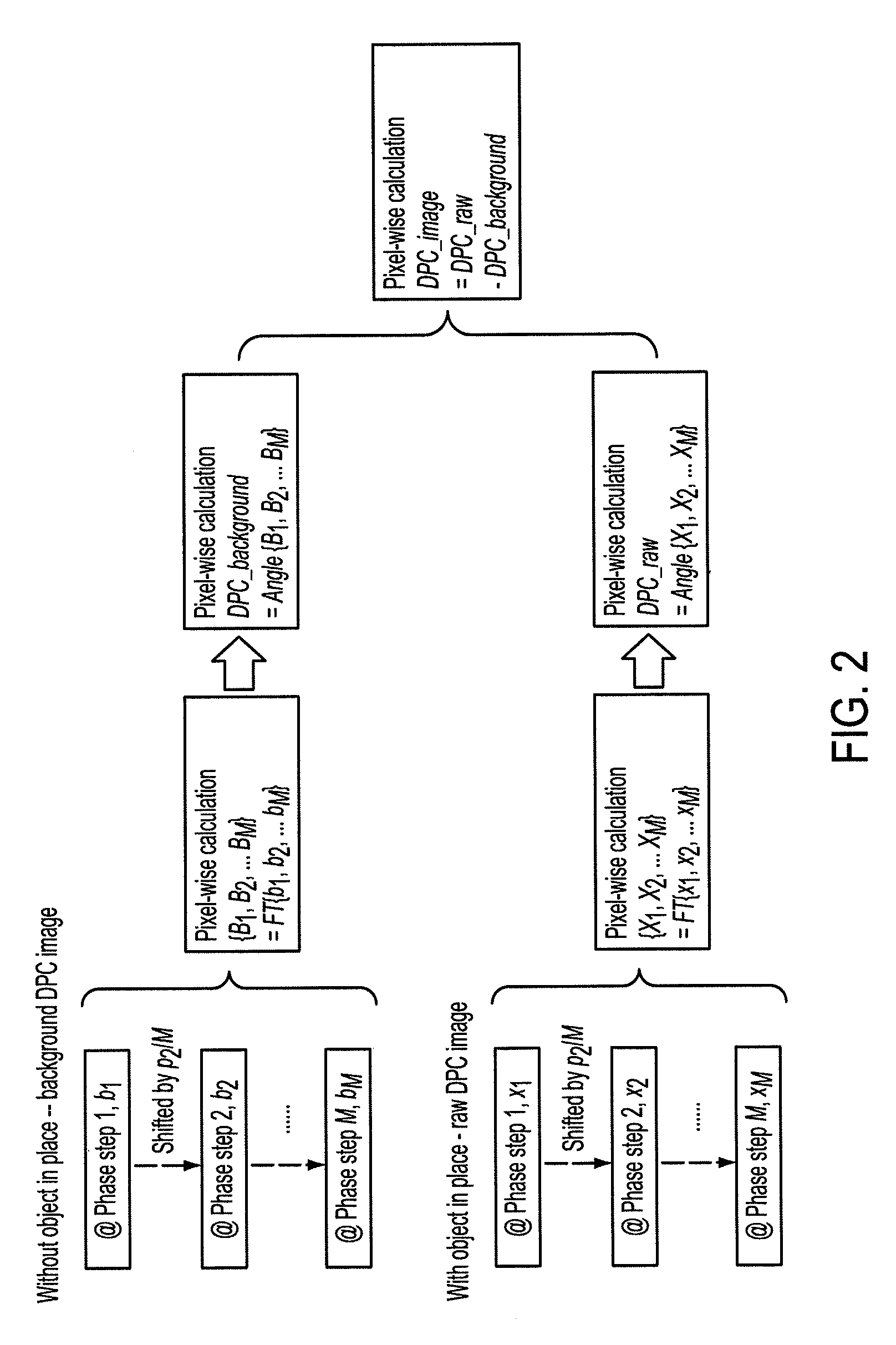
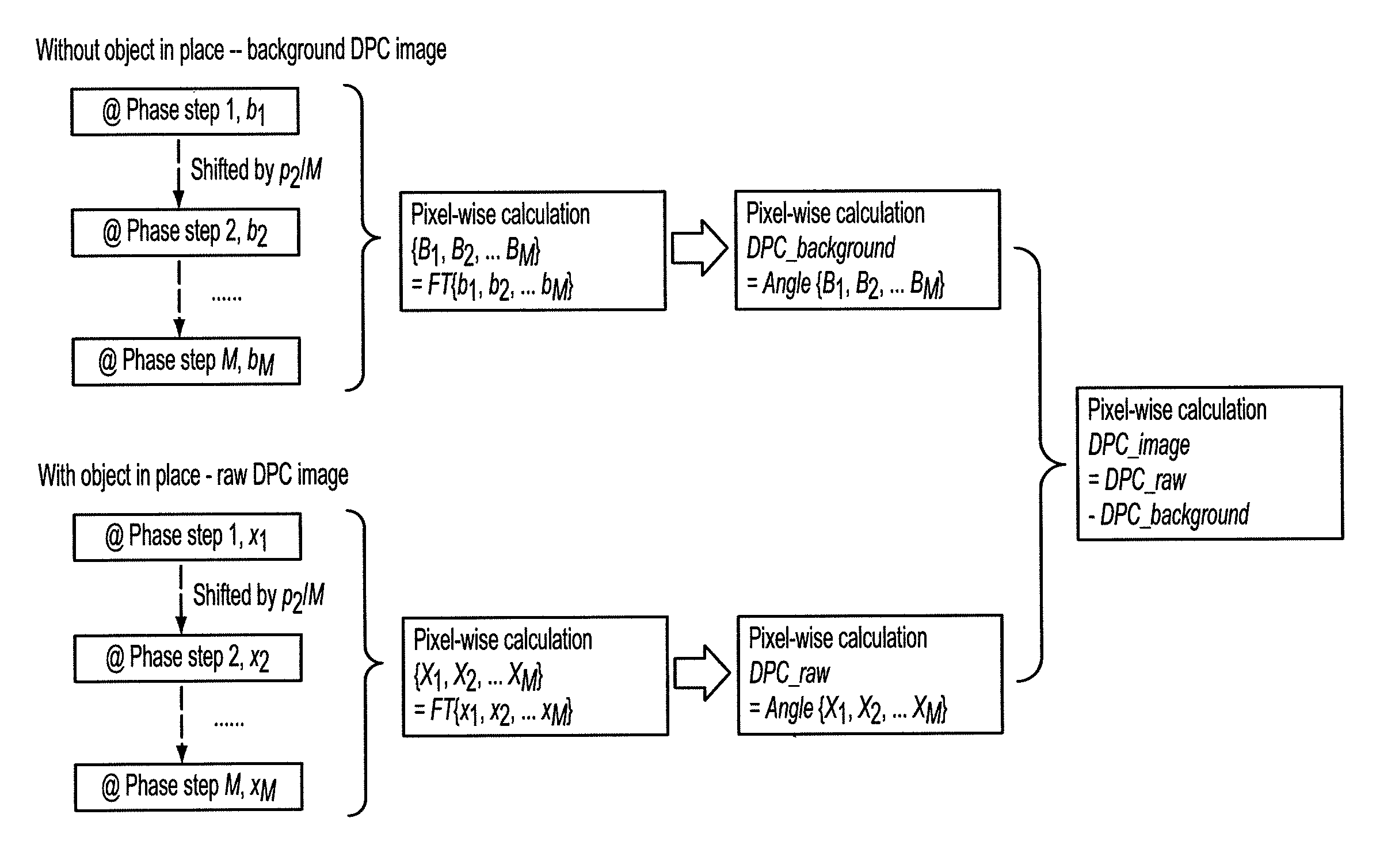
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS9826949B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsComputer visionDifferential phase contrast
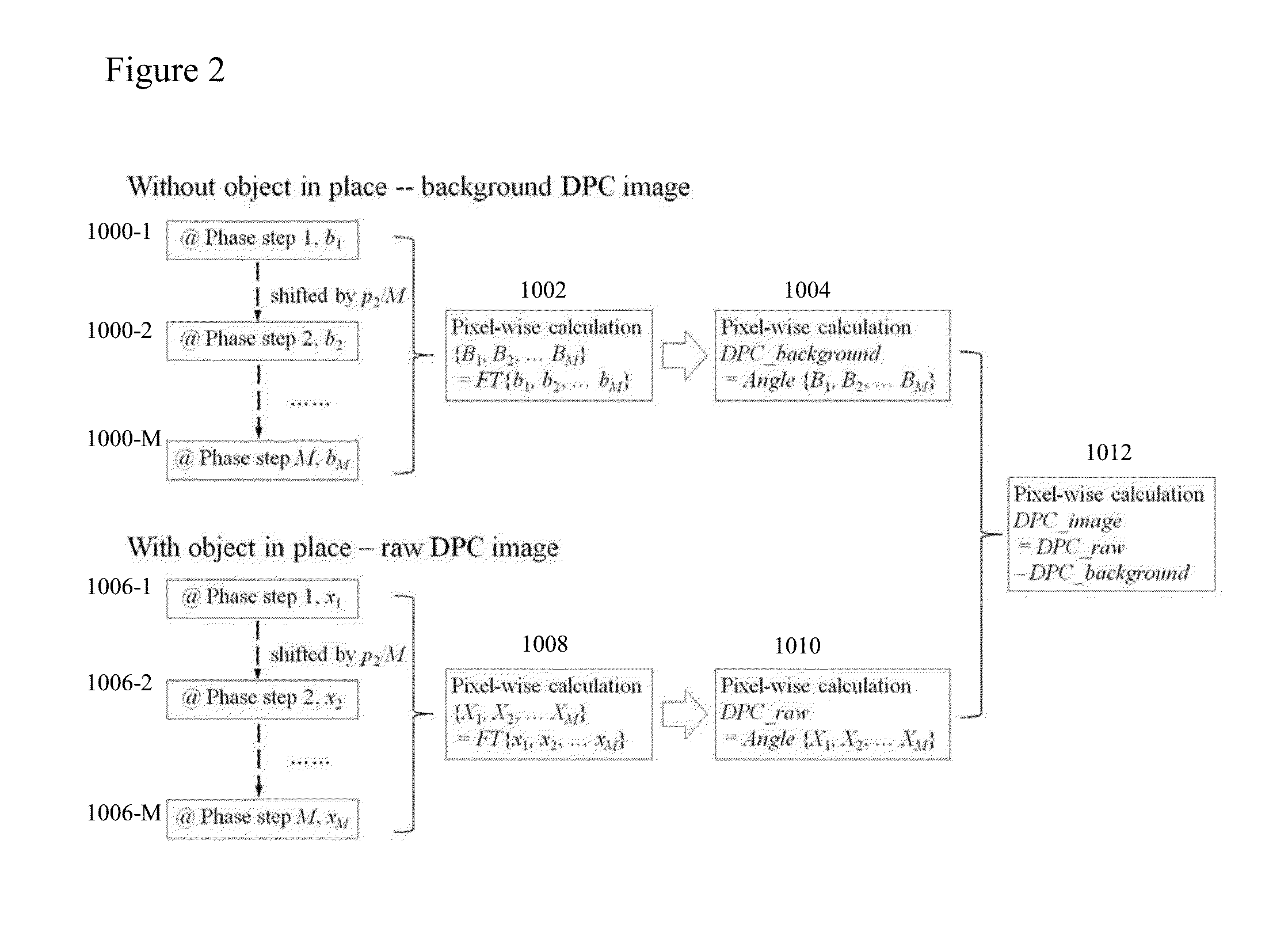
A raw DPC (differential phase contrast) image of an object is acquired. The background phase distribution due to the non-uniformity of the grating system is acquired by the same process without an object in place, and the true DPC image of the object is acquired by subtracting the background phase distribution from the raw DPC image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20160022235A1Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDifferential phaseRadiology
A raw DPC (differential phase contrast) image of an object is acquired. The background phase distribution due to the non-uniformity of the grating system is acquired by the same process without an object in place, and the true DPC image of the object is acquired by subtracting the background phase distribution from the raw DPC image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
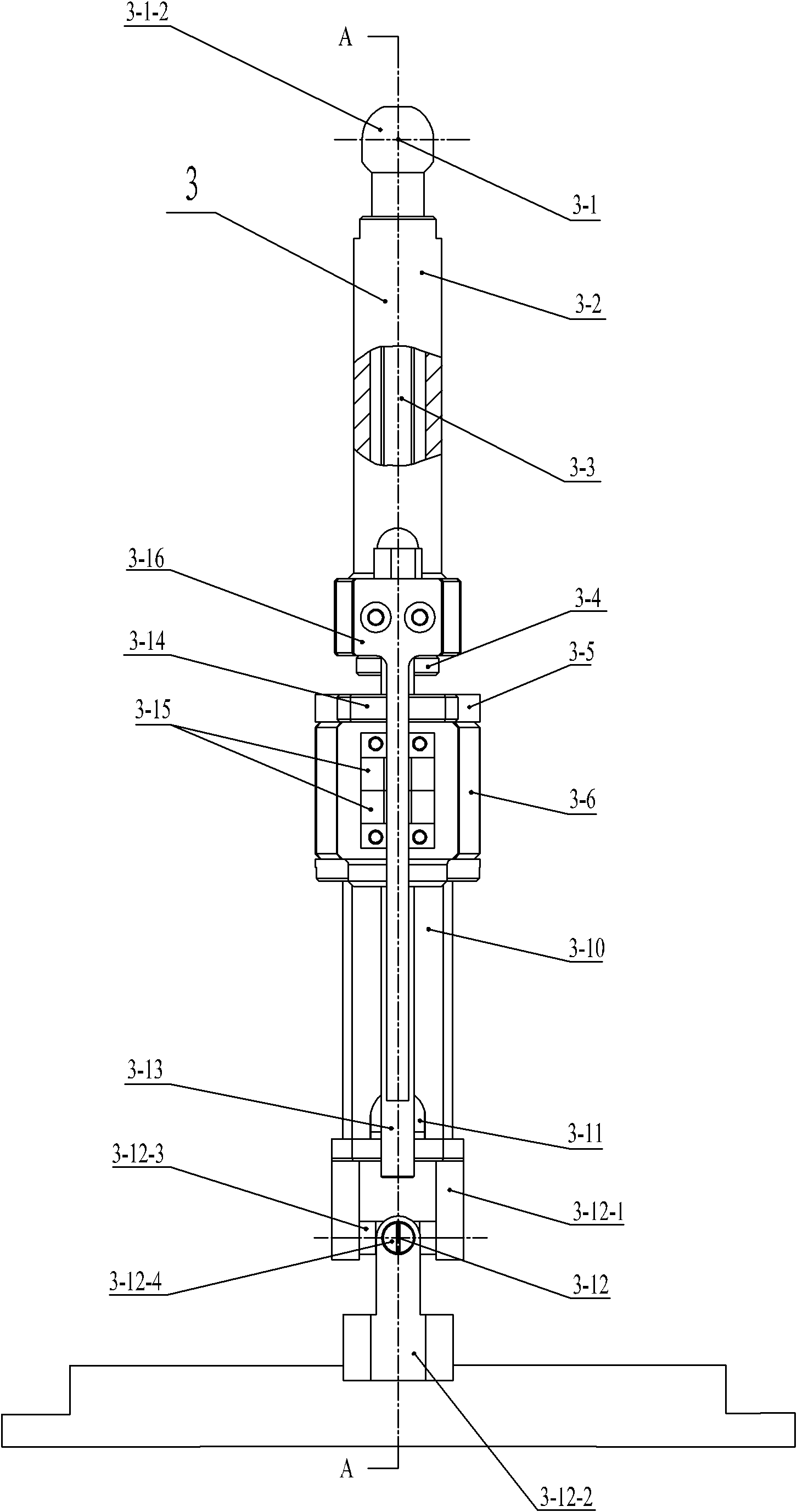
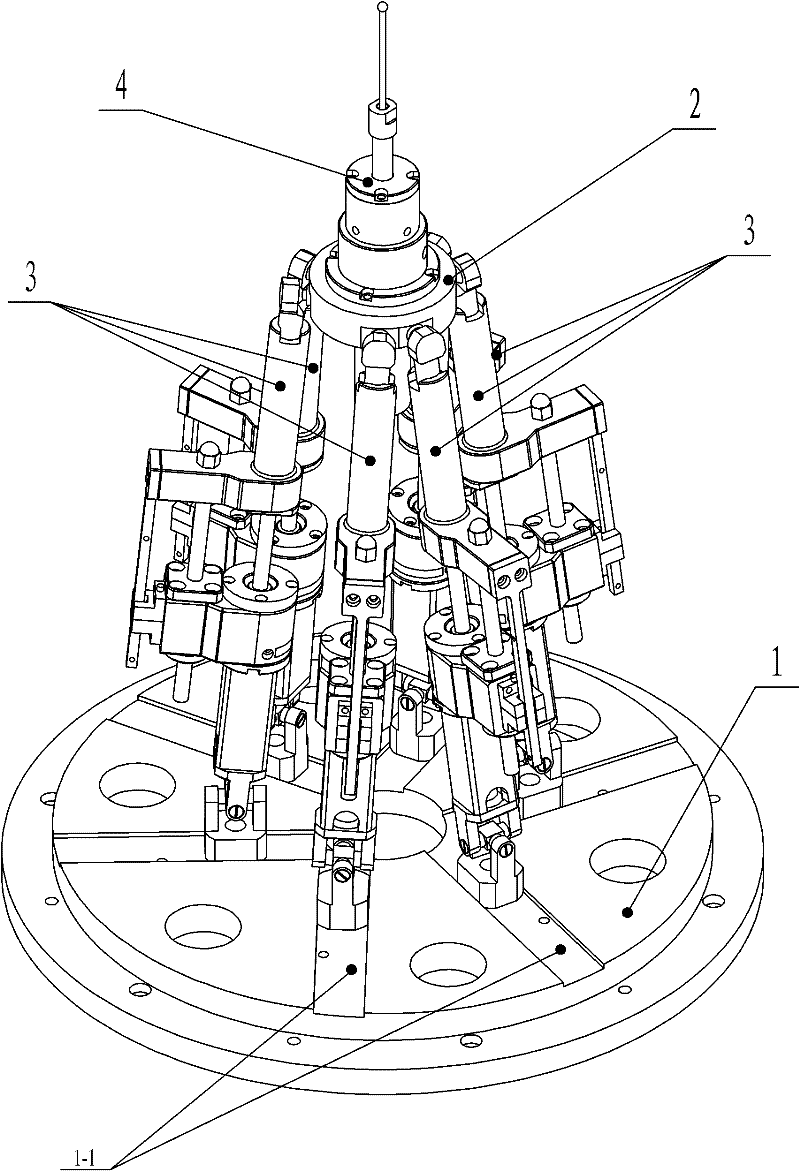
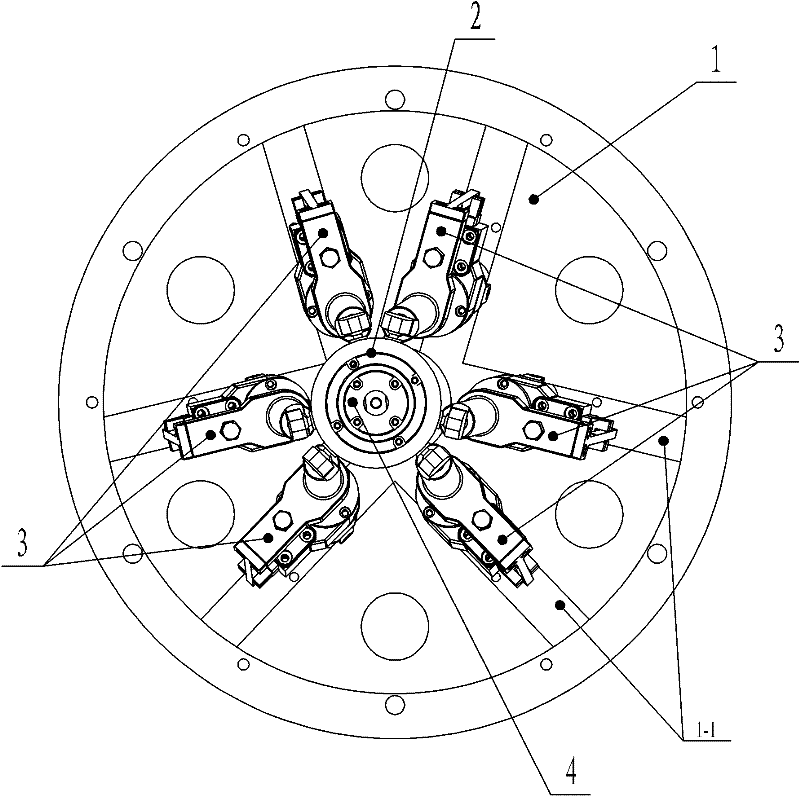
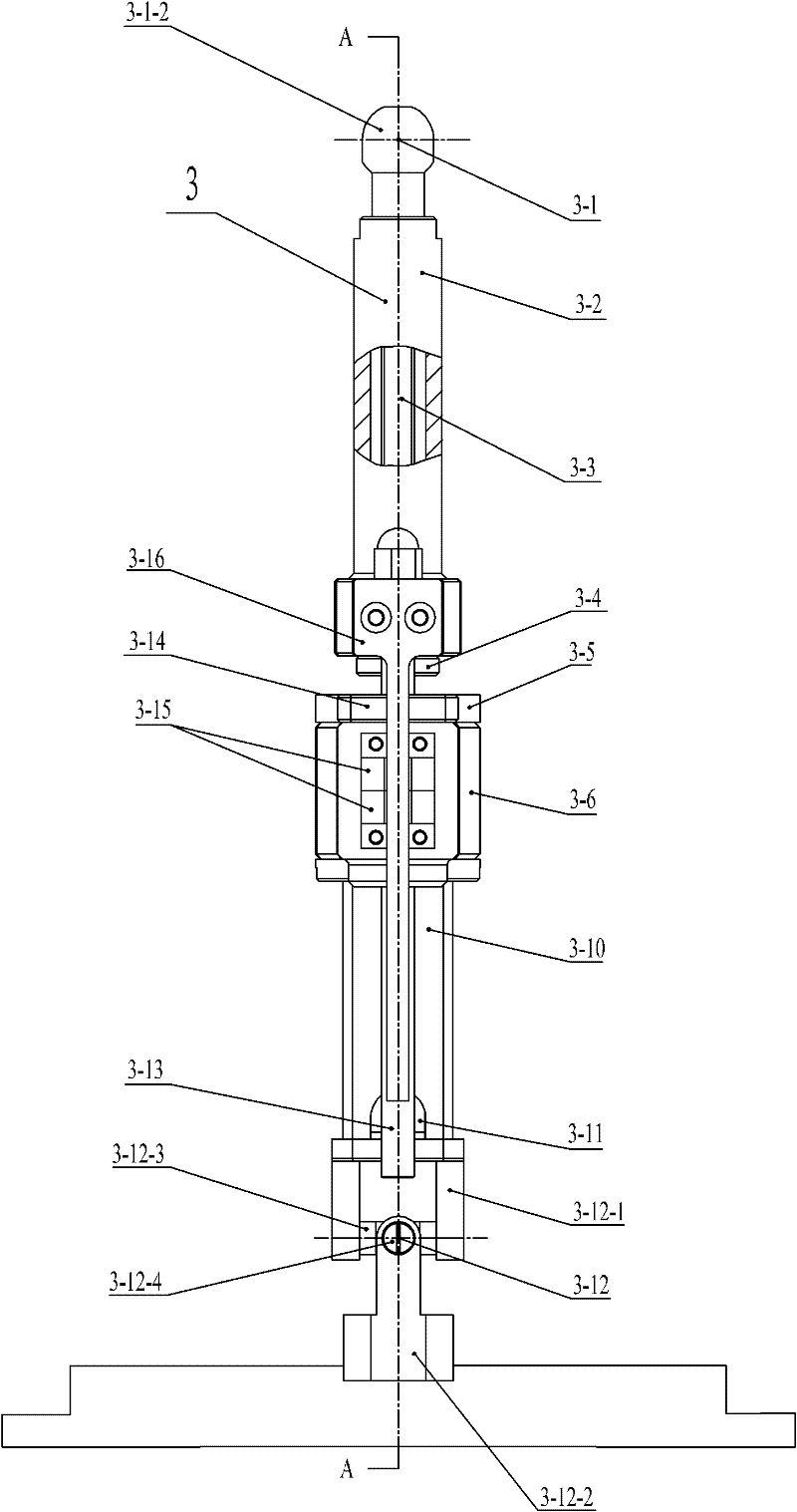
Six-degree-of-freedom cervical-vertebra grinding parallel robot
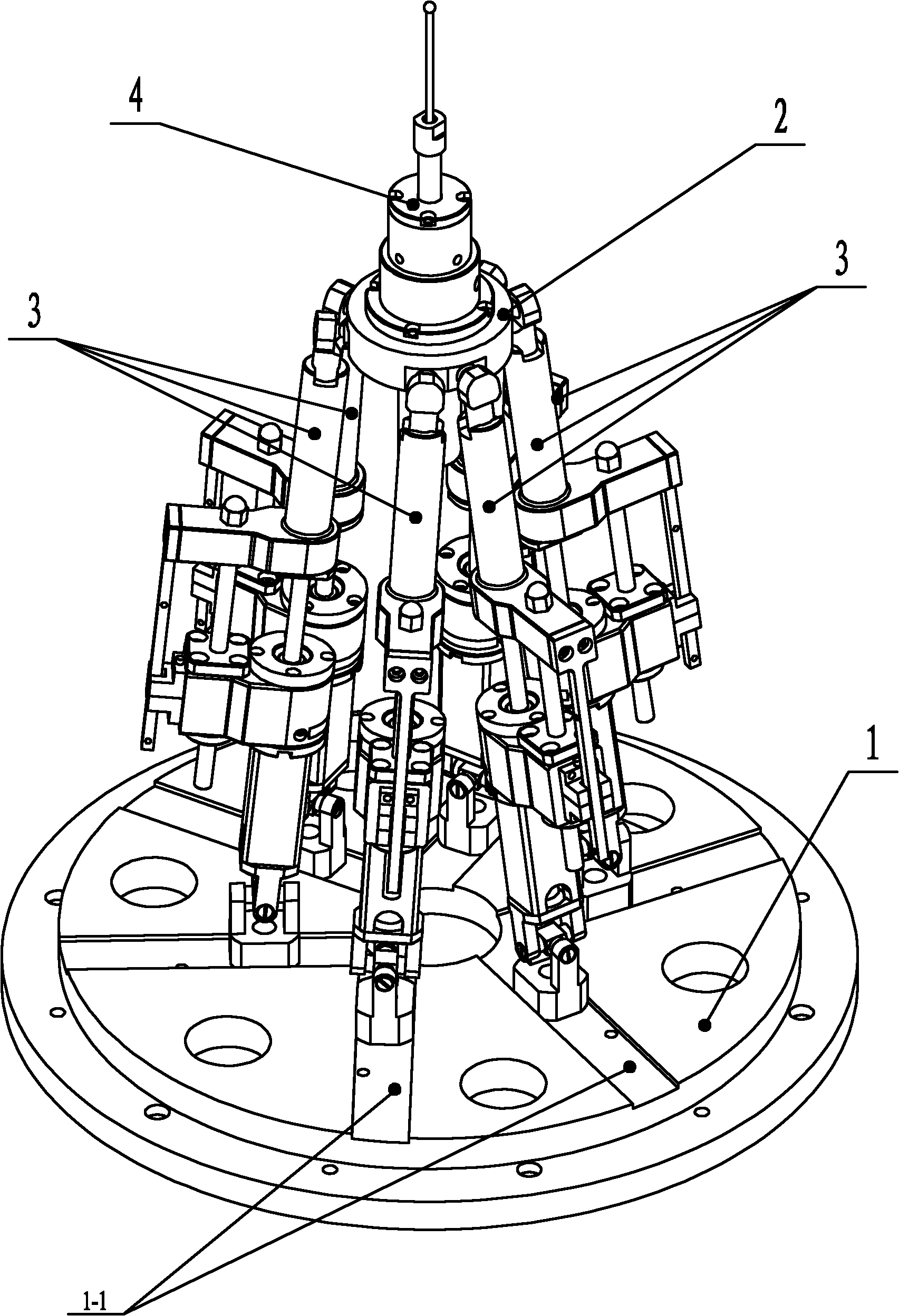
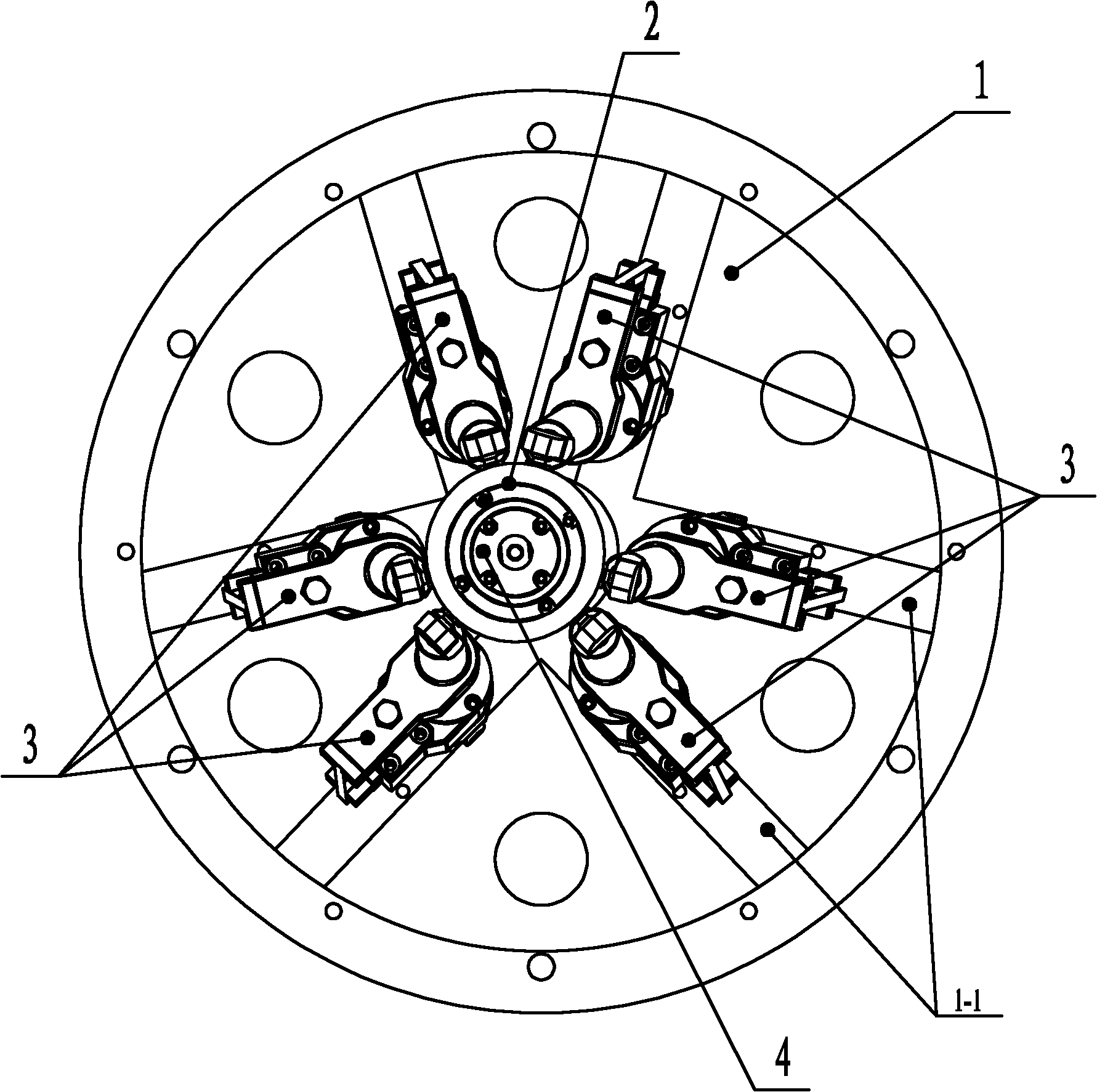
The invention relates to a six-degree-of-freedom cervical-vertebra grinding parallel robot which relates to a grinding parallel robot. The invention aims to solve the problems of insufficient precision, overmuch radiation and large doctor working strength of a traditional manual cervical intervertebral-disc replacement operation. A fixed platform and a movable platform are connected through three pairs of branched chains, a spherical hinge mechanism is arranged at the upper end of a ball-screw linear driving mechanism, a hooker hinge mechanism is arranged at the lower end of the ball-screw linear driving mechanism, the spherical hinge mechanism is connected with the movable platform, the hooker hinge mechanism is connected with the fixed platform, an abrasive-drilling motor penetrates the movable platform, the abrasive-drilling motor is fixedly connected with an abrasive-drilling motor connecting body, the abrasive-drilling motor connecting body is fixedly connected with the movable platform, an abrasive-drilling body is fixedly installed on the abrasive-drilling motor connecting body, an abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole is arranged on the abrasive-drilling body, an abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole cover is installed on the abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole, an abrasive-drilling shaft is connected with the abrasive-drilling motor through a shaft coupler, and a cutting head is connected with the abrasive-drilling shaft through a tightening nut. The invention is applicable to the grinding of cervical vertebra.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus of spectral differential phase-contrast cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
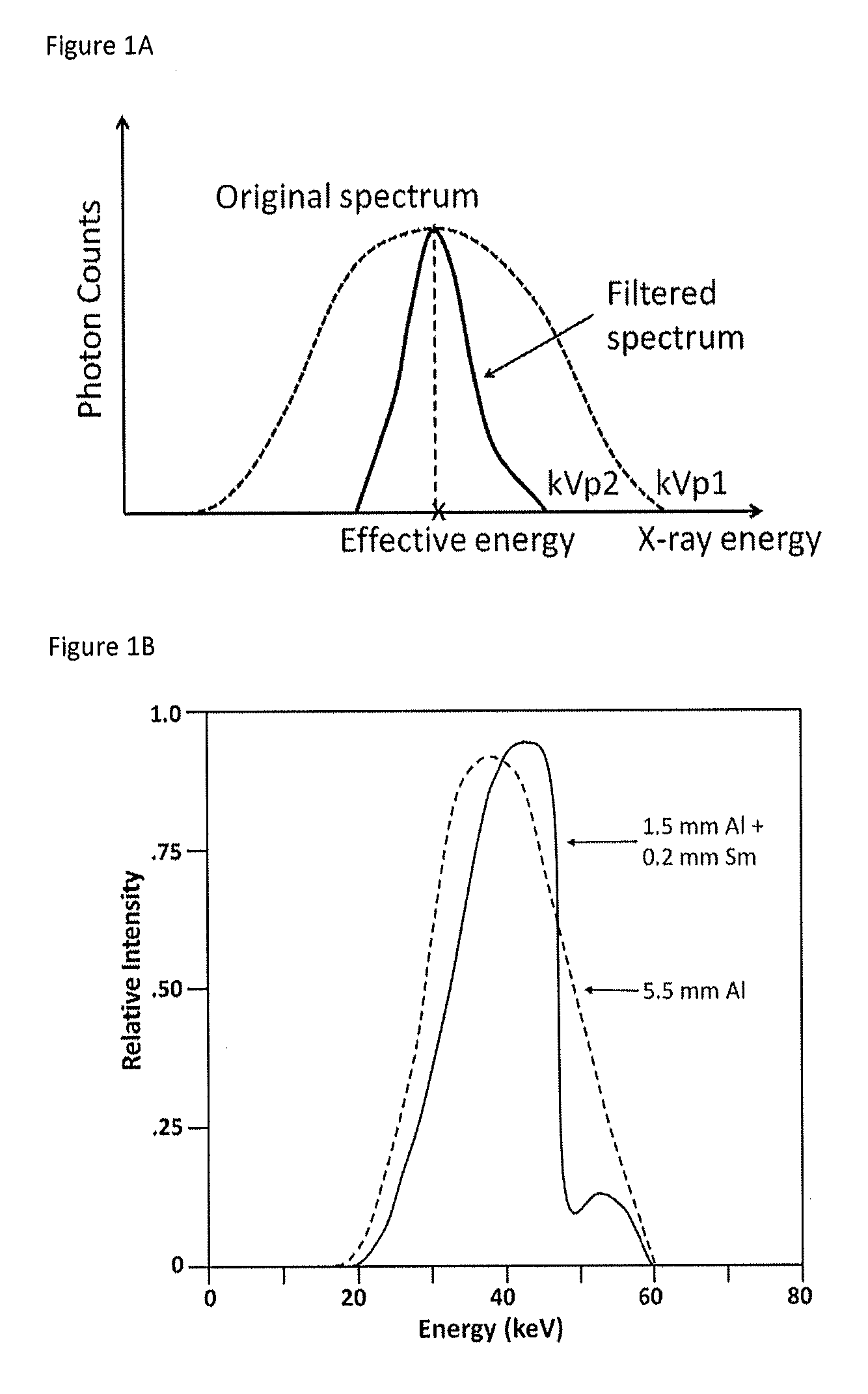
ActiveUS9364191B2Reduce X-ray radiationReduce spacingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionFrequency spectrumImaging quality
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
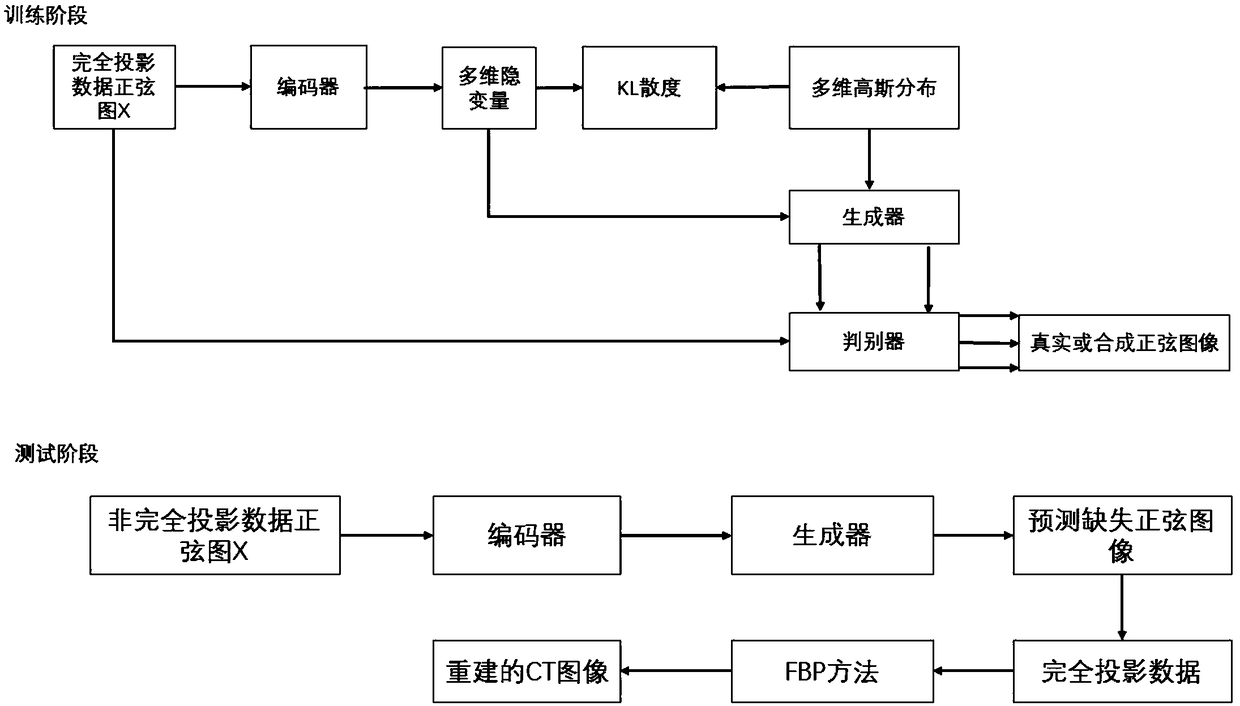
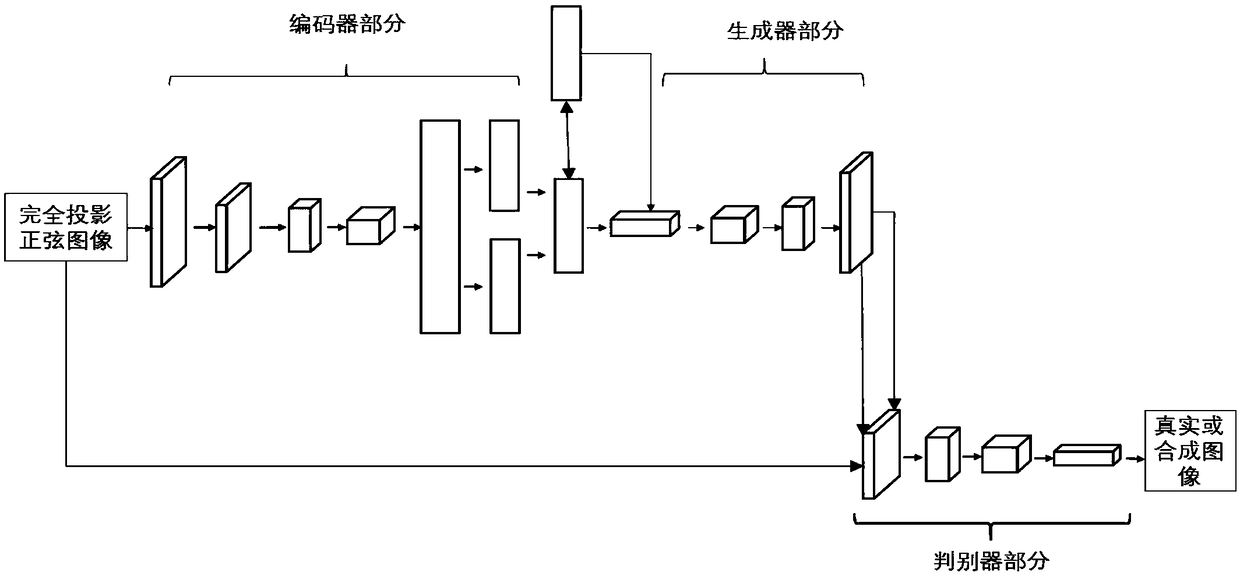
VAEGAN-based incomplete projection CT image reconstruction method
ActiveCN109146988AQuality improvementReduce X-ray radiation doseReconstruction from projectionImage generationConvolution filterBack projection
The invention discloses an incomplete projection CT image reconstruction method based on VAEGAN. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a sinusoidal image of complete projection data is used for training a VAEGAN model to obtain a VAEGAN model capable of generating a high-quality sinusoidal image; secondly, using the trained model to predict the missing part of sinusoidal graph of incomplete projection data, the completed projection data can be obtained. Finally, the CT image is reconstructed from the completed projection data using the convolution filtered back projection (FBP) method. The invention can predict the missing projection data and further reconstruct the CT image with high quality in accordance with clinical diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
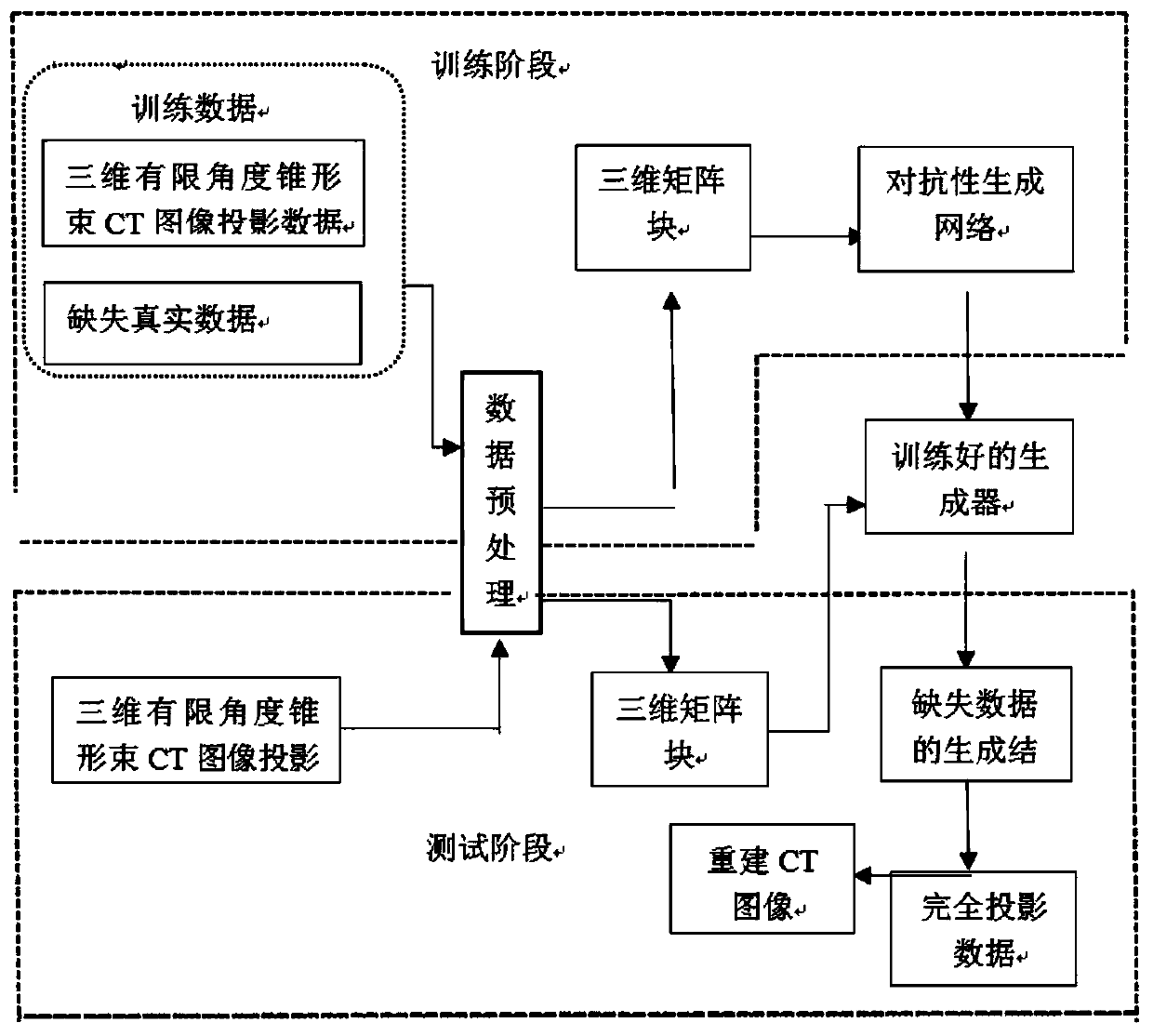
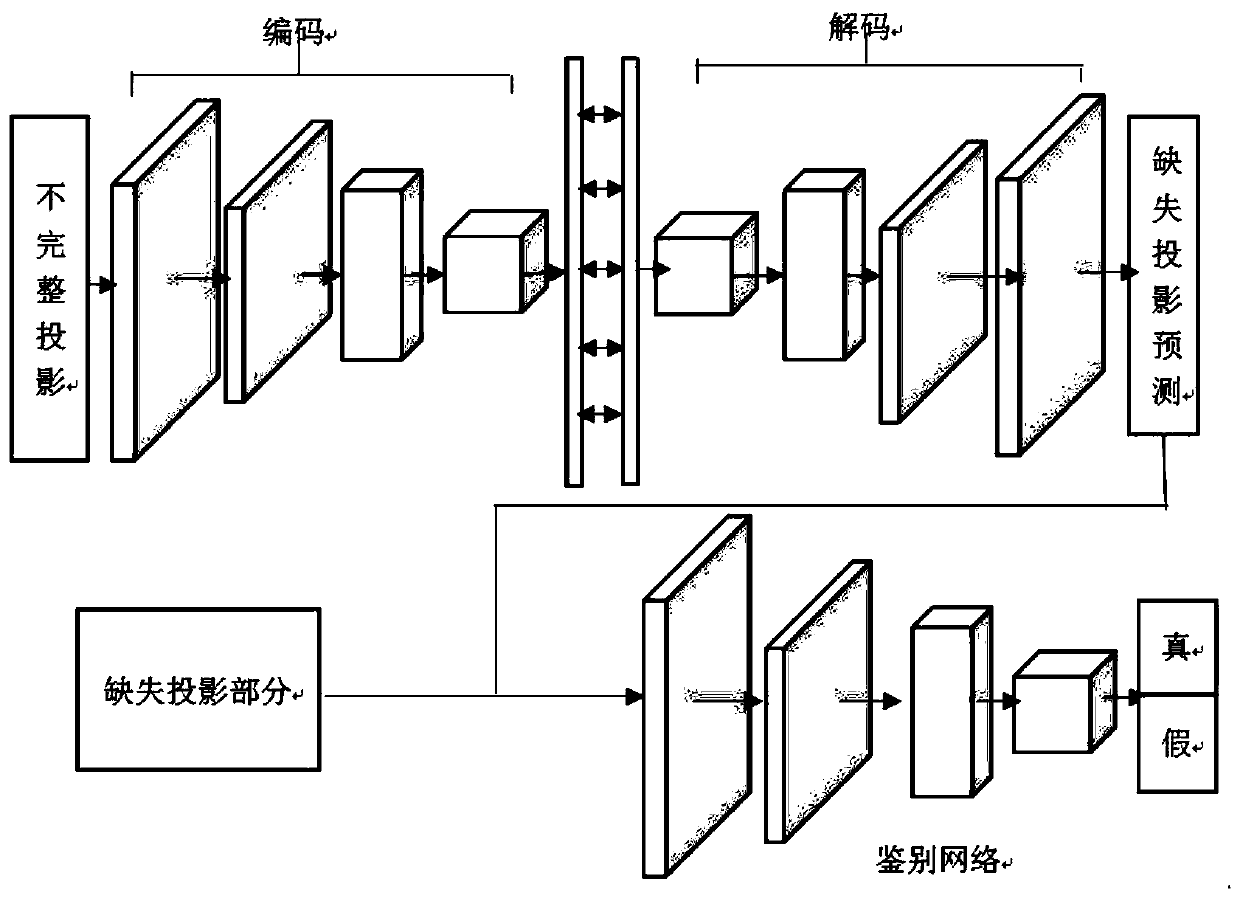
Low-dose CBCT image reconstruction method based on three-dimensional adversarial generation network
InactiveCN110288671AQuality improvementReduce X-ray radiation doseReconstruction from projectionImaging processingAcquisition time
The invention discloses a low-dose CBCT image reconstruction method based on a three-dimensional adversarial generation network, and belongs to the technical field of medical image processing. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a three-dimensional adversarial resistance generation network model; training a three-dimensional adversarial resistance generation network model through the sine image and the corresponding projection data; inputting the test image into the trained adversarial resistance generation network model, and predicting the missing part of the sine image of the incomplete projection data to obtain a sine image of complete projection; and reconstructing a CT image according to the sine image of the complete projection data. The method effectively shortens the acquisition time of the cone beam projection data, and improves the clinical diagnosis efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
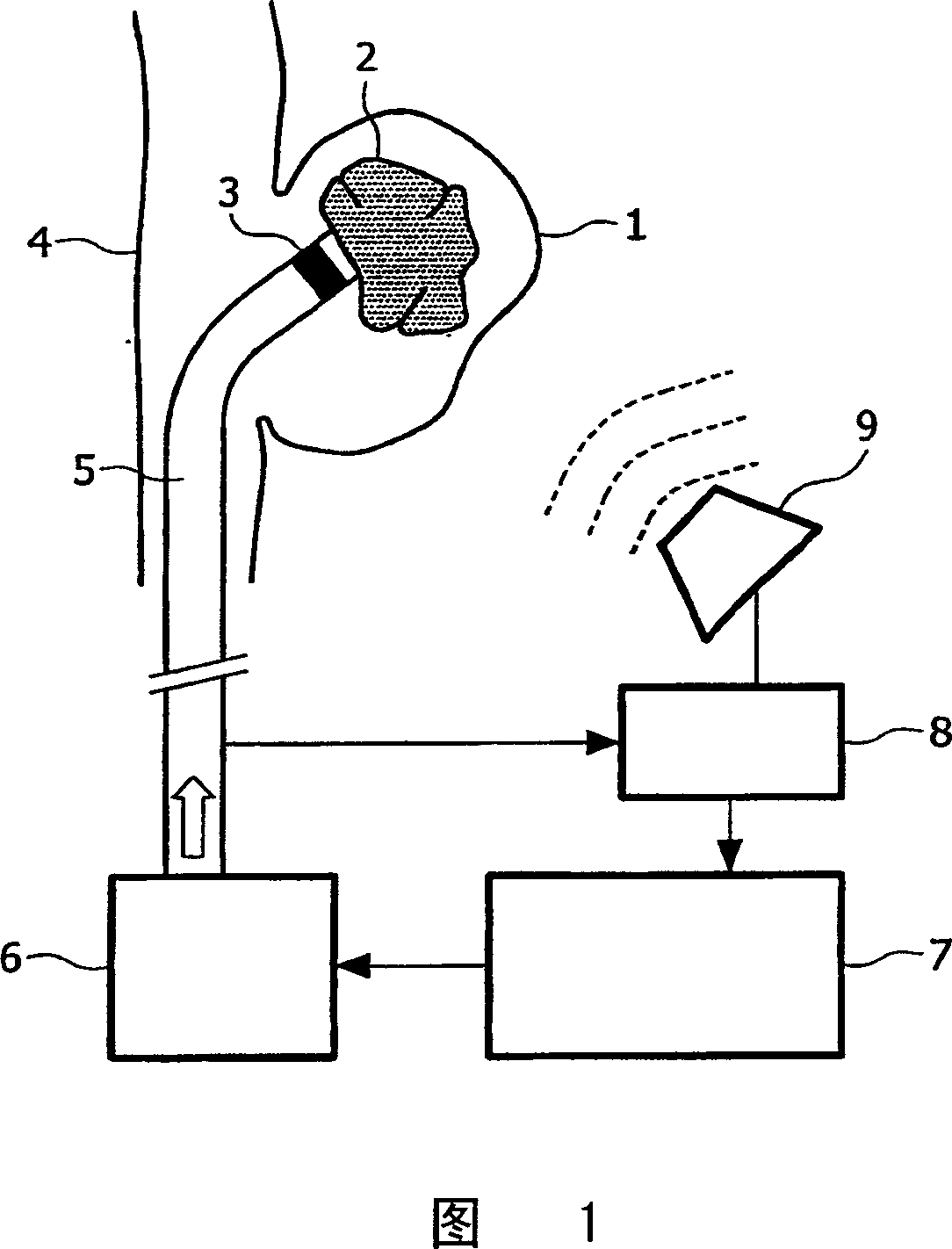
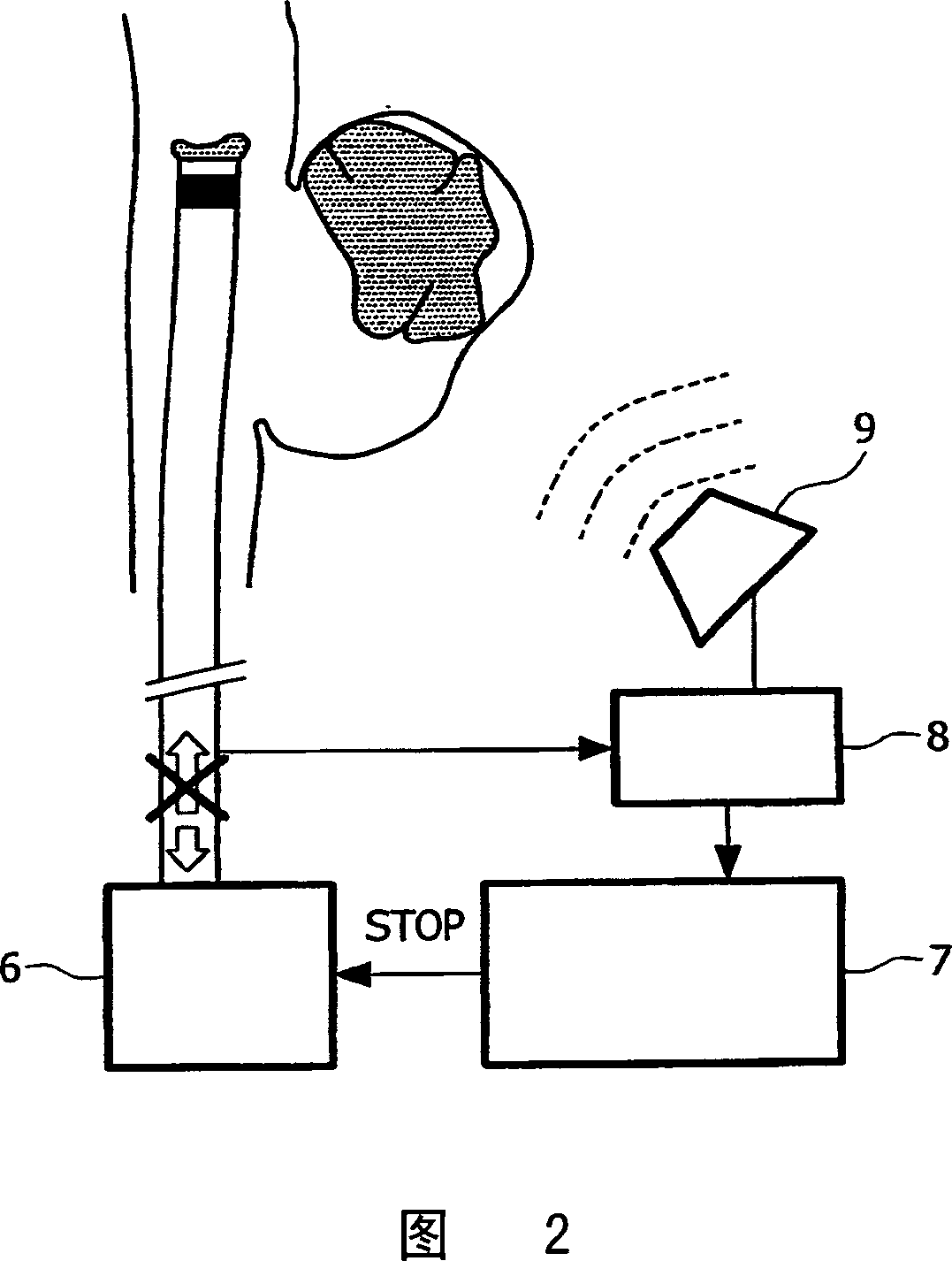
Catheter, apparatus and method for therapeutic embolization
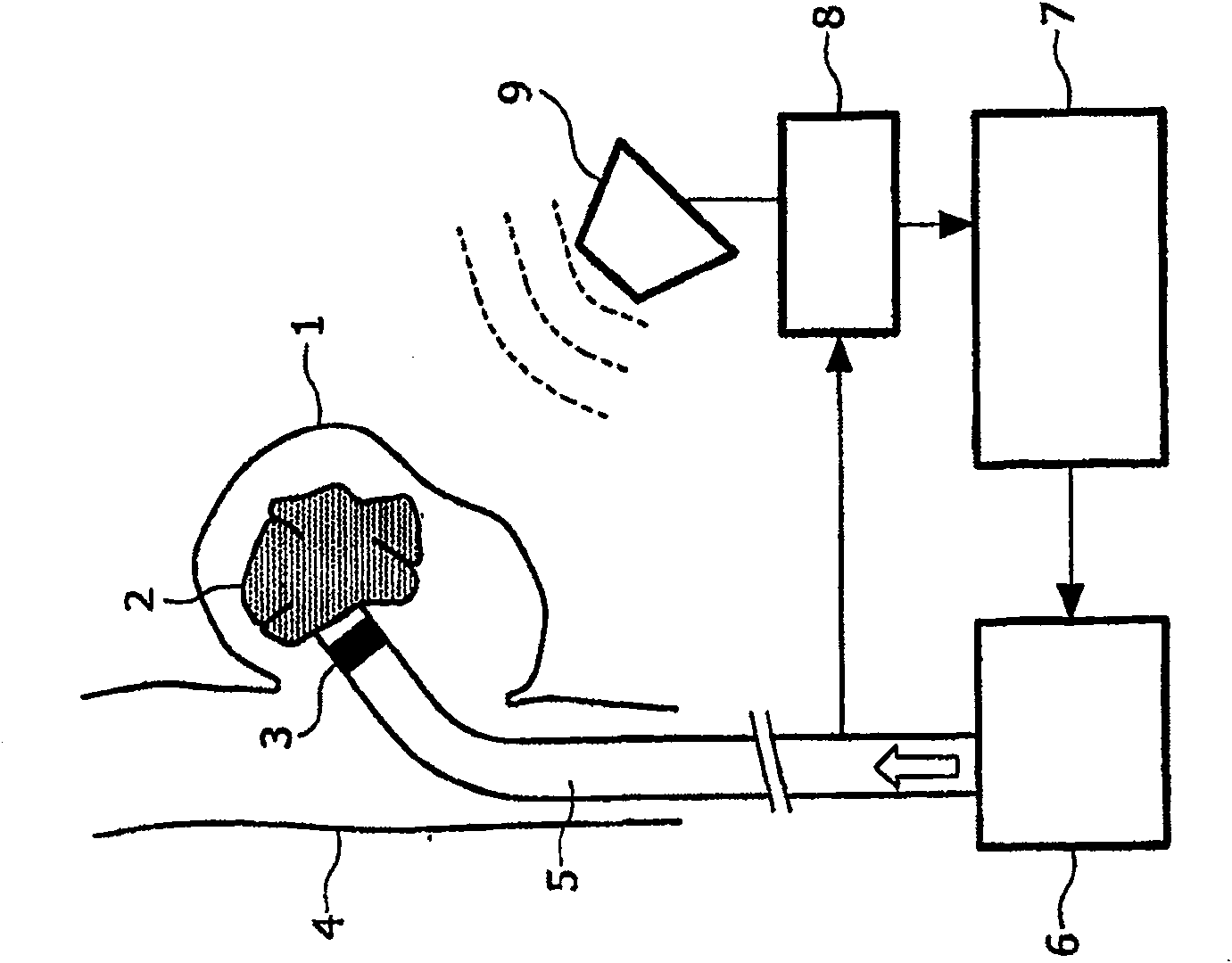
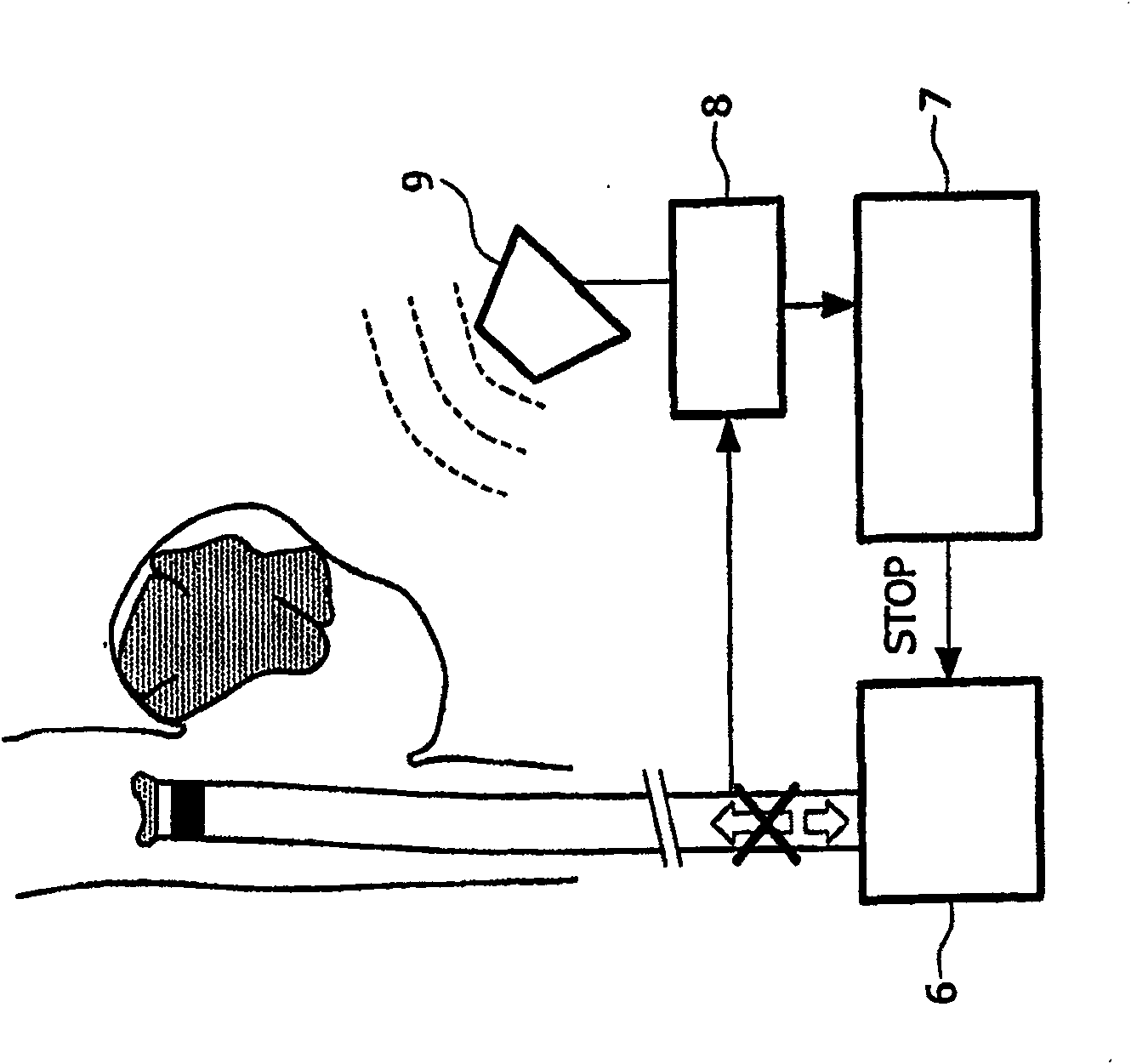
InactiveCN1929788AEnsure safetyReduce radiation doseDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTherapeutic embolizationBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for the therapeutic embolization of an aneurysm ( 1 ) as well as to a catheter. A plugging material ( 2 ) is injected via a catheter ( 5 ) inserted into the aneurysm ( 1 ). During the injection, the spatial position of an active locator ( 3 ), such as a magnetic field sensor for example, which is fitted to the tip of the catheter ( 5 ) is observed by a locating device ( 8, 9 ). If emergence of the catheter tip from the aneurysm ( 1 ) is detected by a monitoring unit ( 7 ), said monitoring unit stops the further supply of plugging material to the catheter ( 5 ).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus of spectral differential phase-contrast cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20160374635A1Reduce X-ray radiationReduce spacingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging qualityImage quality
DPC (differential phase contrast) images are acquired for each photon energy channel, which are called spectral DPC images. The final DPC image can be computed by summing up these spectral DPC images or just computed using certain ‘color’ representation algorithms to enhance desired features. In addition, with quasi-monochromatic x-ray source, the required radiation dose is substantially reduced, while the image quality of DPC images remains acceptable.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
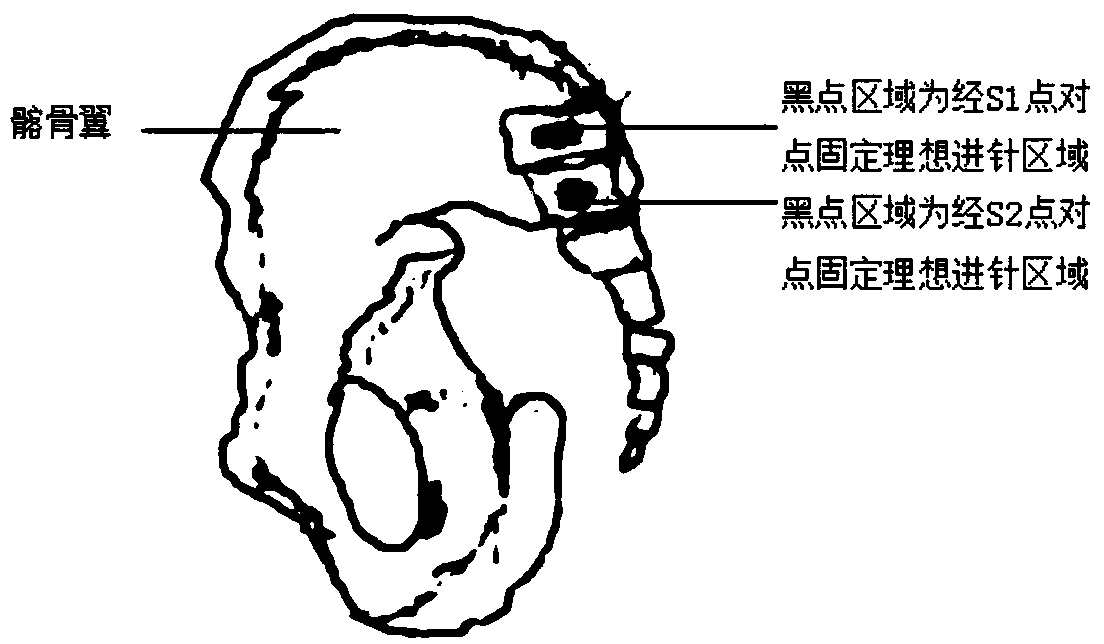
Sacroiliac joint through-screw positioning coaxial guide and assembly thereof
PendingCN109674523AEasy to operateReduce radiation exposureDiagnosticsOsteosynthesis devicesAxis of symmetryEngineering
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a sacroiliac joint through-screw positioning coaxial guide and an assembly thereof. The sacroiliac joint through-screw positioning coaxial guide comprises a first positioning rod for fixing a first puncture sleeve, a second positioning rod for fixing a second puncture sleeve, an adjusting device for adjusting a relative distance between the first positioning rod and the second positioning rod, and a fixing device for fixing the positions of the first positioning rod and the second positioning rod. The first positioningrod and the second positioning rod are respectively connected with the adjusting device, and the first positioning rod and the second positioning rod are axially symmetric by taking a vertical centerline of the adjusting device as an axis of symmetry, such that a horizontal centerline of the first puncture sleeve and a horizontal centerline of the second puncture sleeve are in the same line. Thefixing device is connected with the adjusting device. A sacroiliac joint screw can penetrate through a sacroiliac joint and can be accurately placed into the patient body, so that the surgical positioning is accurate, the stability is high, the safety is high, and complications such as vascular nerve injury are avoided.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
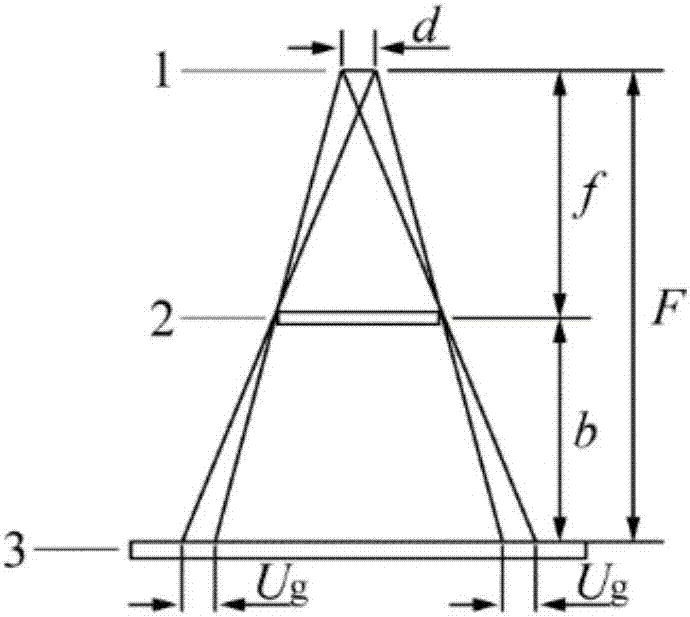
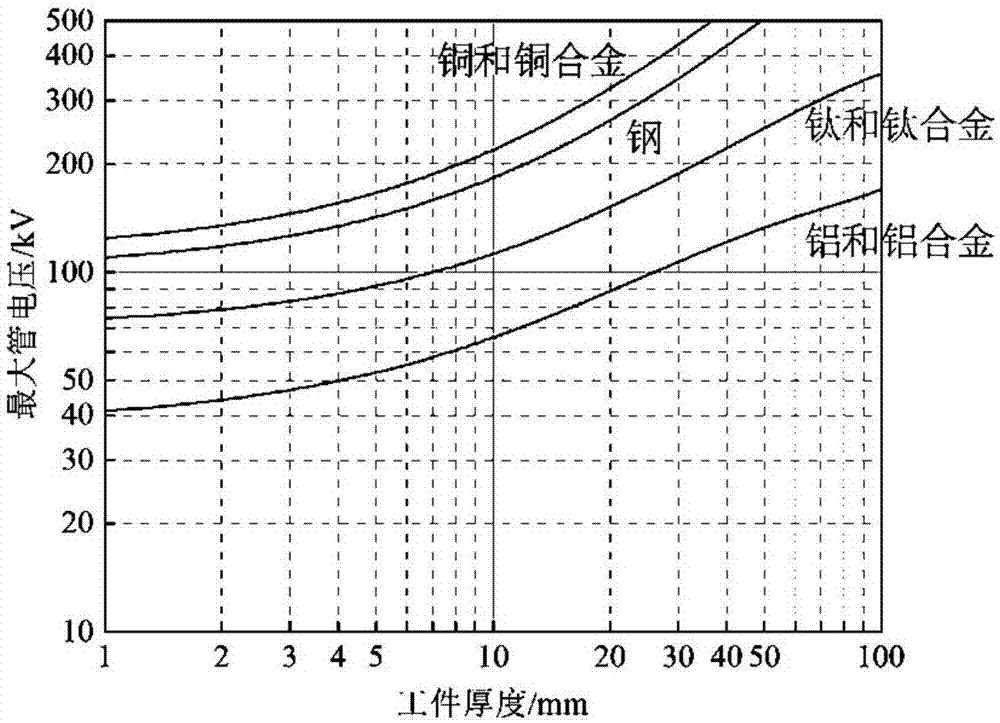
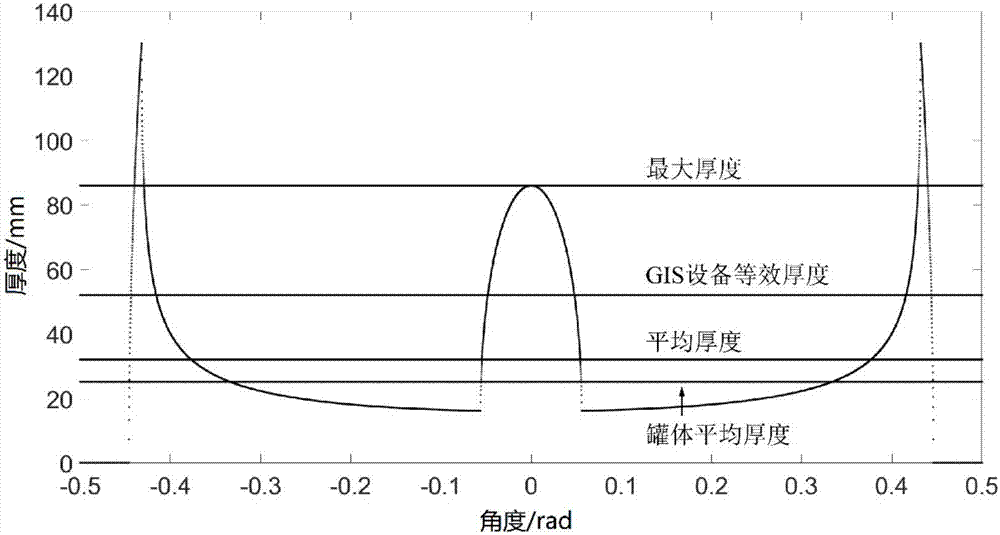
Method for selecting X-ray detection parameters of GIS device
InactiveCN107290357AReduce the problem of selection biasReduce X-ray radiation doseTesting using optic methodsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-ray generatorEngineering
The invention discloses a method for confirming X-ray detection parameters of a GIS device. The method comprises the following steps: 1) confirming focal length: collecting a focus size d of an X-ray machine and an outer wall with outer wall radius R of the GIS device and confirming the focal length F according to the focus size d of the X-ray machine and the outer wall with outer wall radius R of the GIS device; 2) confirming tube voltage: confirming the tube voltage used by the X-ray machine according to the structure and size of the GIS device; 3) confirming tube current: selecting the tube current corresponding to the tube voltage confirmed in the step 2) according to a characteristic curve of the tube voltage and the tube current of the X-ray machine; and 4) confirming exposure time: confirming the exposure time according to an exposure curve or the selected blackness and the tube voltage. According to the invention, the parameters required by the X-ray detection of the GIS device can be quickly selected, the problem of parameter selection deviation caused by experience-based judgment can be reduced and the detection efficiency and stability can be effectively increased.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Medical system control method, device and equipment and medium
InactiveCN110197496AReduce radiation doseReduce X-ray radiation doseReconstruction from projectionImage analysisX-rayBiomedical engineering
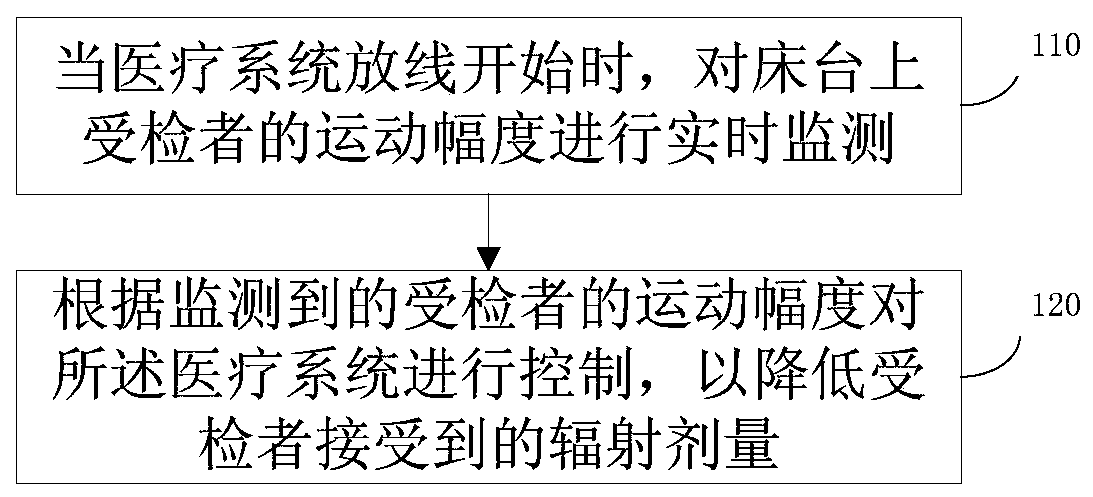
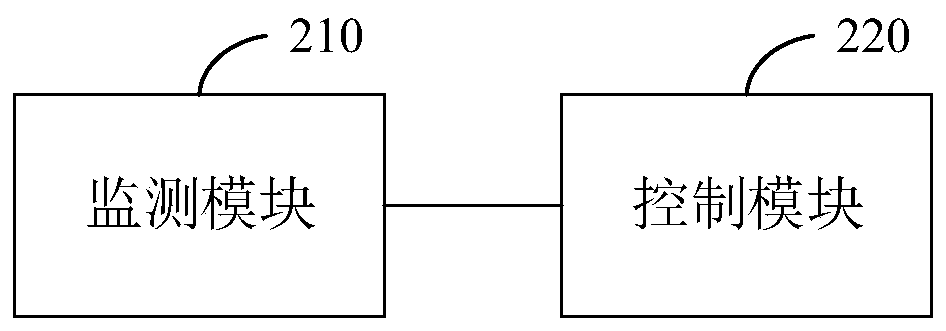
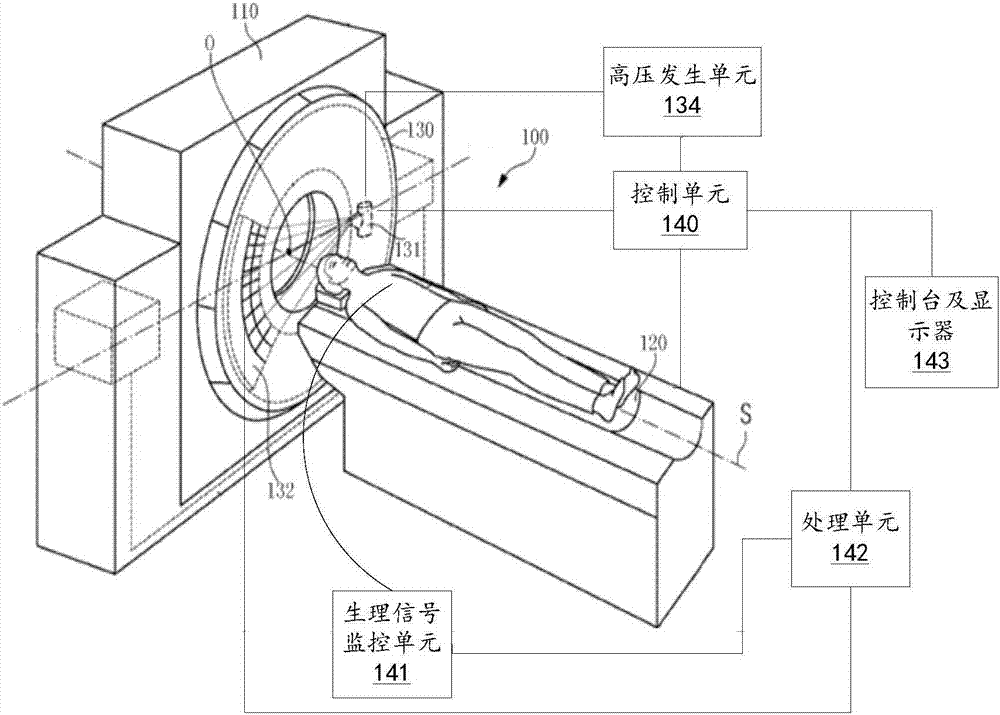
The embodiment of the invention discloses a medical system control method and device, equipment and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the real-time monitoring of the movementamplitude of a subject on a bed when the medical system starts to pay off; and controlling the medical system according to the monitored movement amplitude of the subject so as to reduce the radiationdosage received by the subject. Through the technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention, the purpose of reducing the X-ray radiation dose received by the subject is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
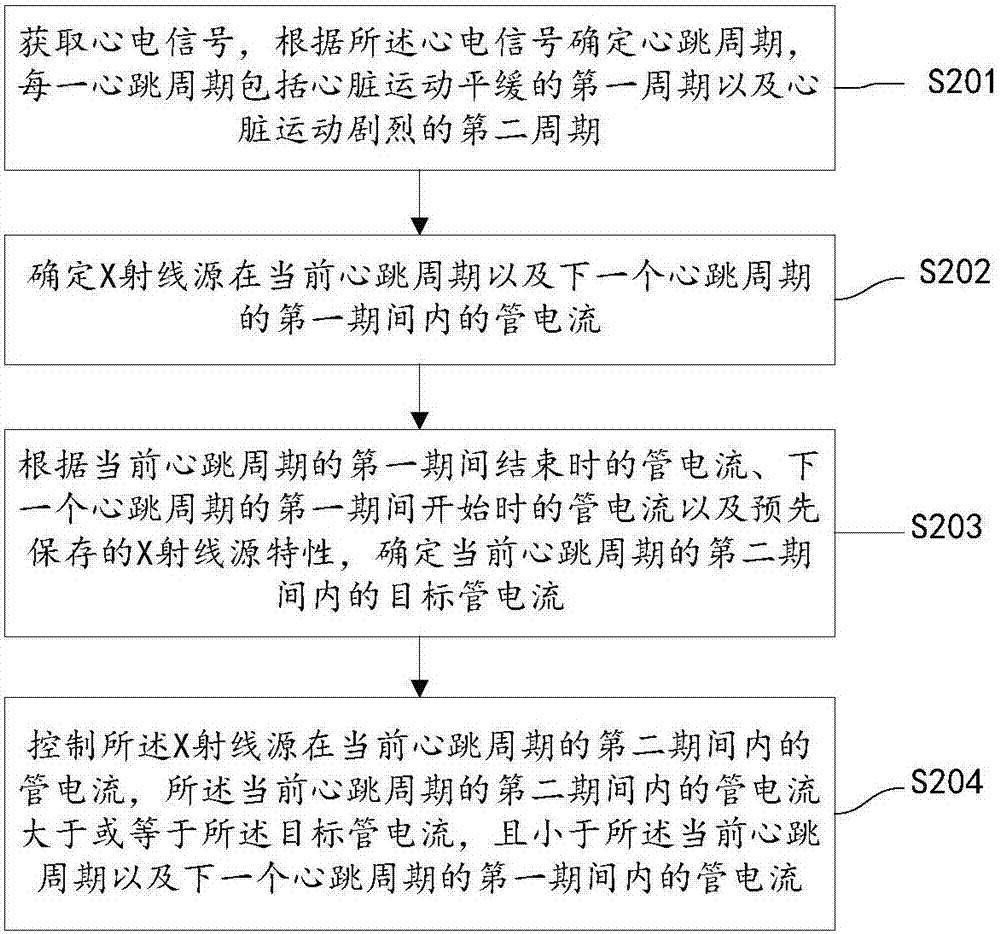
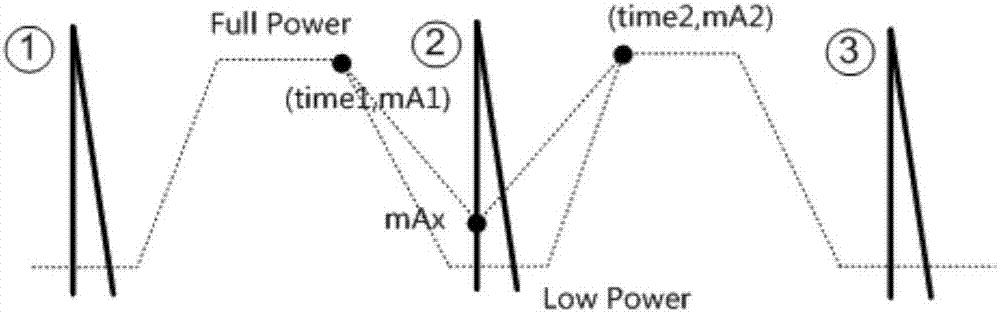
CT scanning X-ray source tube current modulating method and computed tomography device
ActiveCN107303184AReduce X-ray radiation doseReduce radiation doseComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalComputing tomography
The invention provides a CT scanning X-ray source tube current modulating method and a computed tomography device. The method comprises the following steps: determining a heartbeat cycle in accordance with electrocardiogram signals, wherein each heartbeat cycle comprises a first period that cardiac motion is gentle and a second period that the cardiac motion is vigorous; determining target tube current within the second period of the current heartbeat cycle in accordance with tube current at the end of the period of the current heartbeat cycle which is determined in advance, tube current at the beginning of the first period of a next heartbeat cycle and pre-saved X-ray source characteristics; and controlling tube current of the X-ray source within the second period of the current heartbeat cycle, wherein the tube current within the second period of the current heartbeat cycle is greater than or equal to the target tube current and is less than tube current within the first periods of the current heartbeat cycle and the next heartbeat cycle. With the application of the method provided by the invention, an X-ray radiation dose on an examined object in CT scanning can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
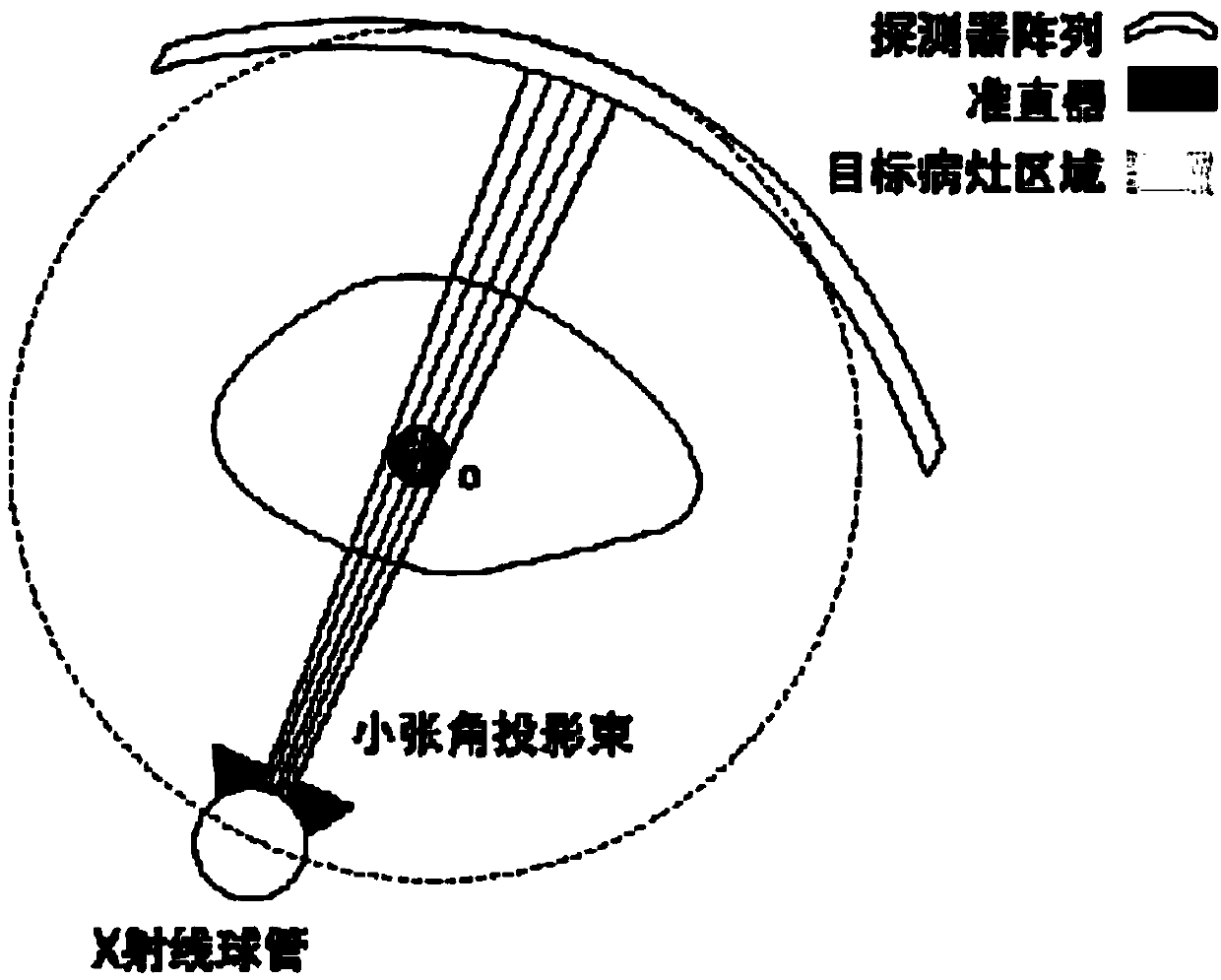
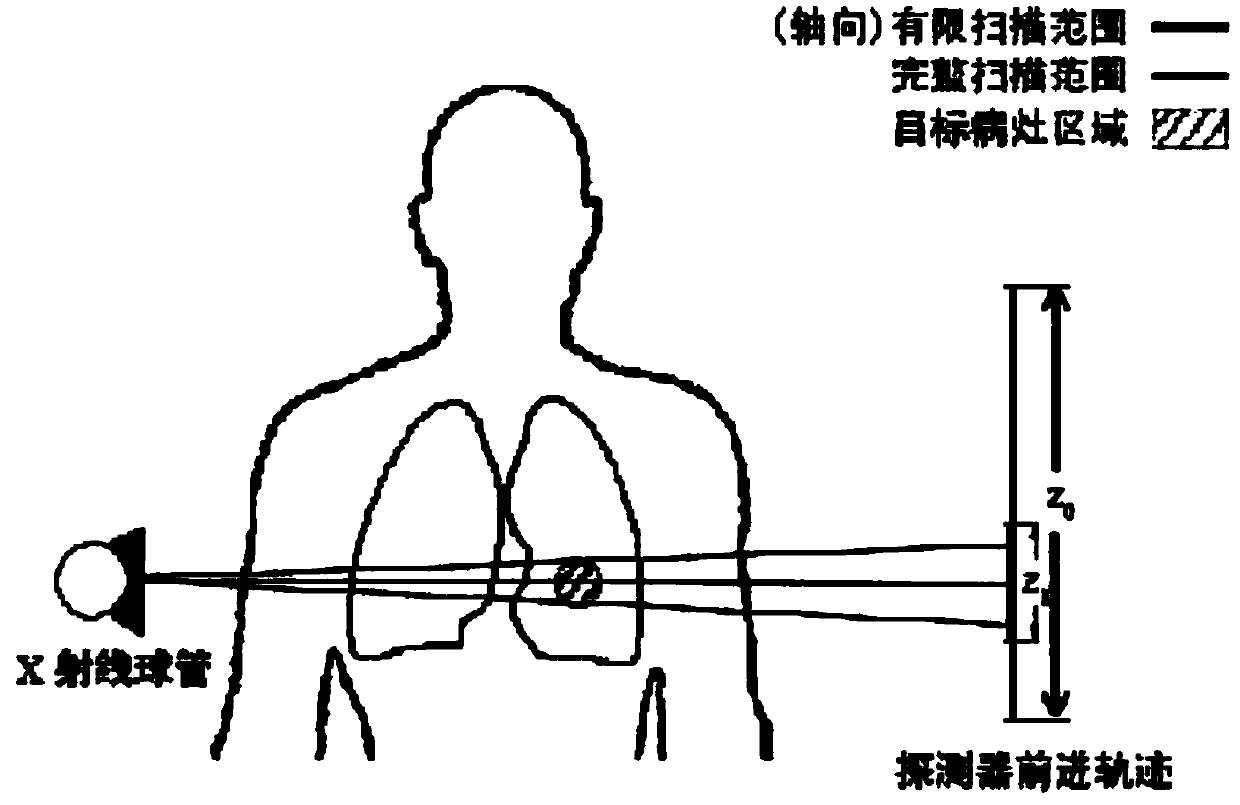
CT scanning method of low radiation dosage
PendingCN109717886AQuality improvementReduce X-ray radiation doseComputerised tomographsTomographyCT.scanogramCancer
The invention discloses a CT scanning method of low radiation dosage. A CT scanning manner of a limited X-ray projection beam is designed through the priori knowledge of the CT scanning of the previous focus of a patient, and through combination with the priori image of the CT scanning of the previous focus, the reconstruction of a CT image of an object region is performed. The CT scanning methodspecifically comprises the following steps of step 1, extracting a focus region in the priori CT scanning image in advance, positioning the object focus, and estimating the range required by CT scanning; step 2, according to different scanning requirements, designing the CT scanning manner and the scanning parameters of the limited X-ray projection beam so as to obtain the limited X-ray projectionbeam; and step 3, extracting the priori knowledge in the priori CT scanning image, performing adjustment so as to enable the priori CT scanning image to use the focus region as a center, and fusing the priori CT scanning image and the limited X-ray projection beam to reconstruct the CT image. Through the adoption of the CT scanning method disclosed by the invention, the X-ray radiation dosage received by human bodies in single-time CT scanning can be greatly reduced, the risk of inducing cancer can be reduced, and the requirements for reconstructing and detecting the focus region can be met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Limited angle cone-beam CT image reconstruction method based on geometric image moment
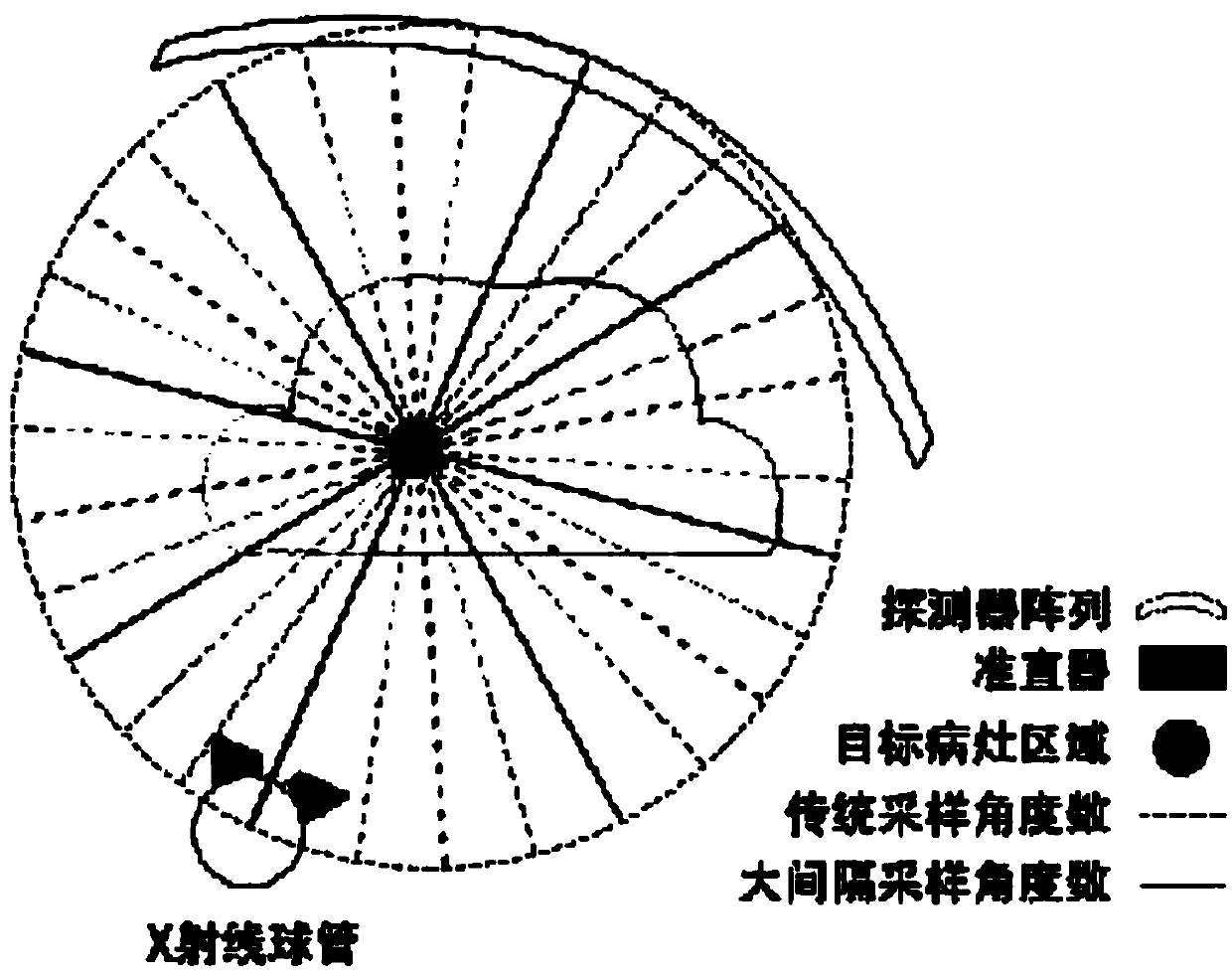
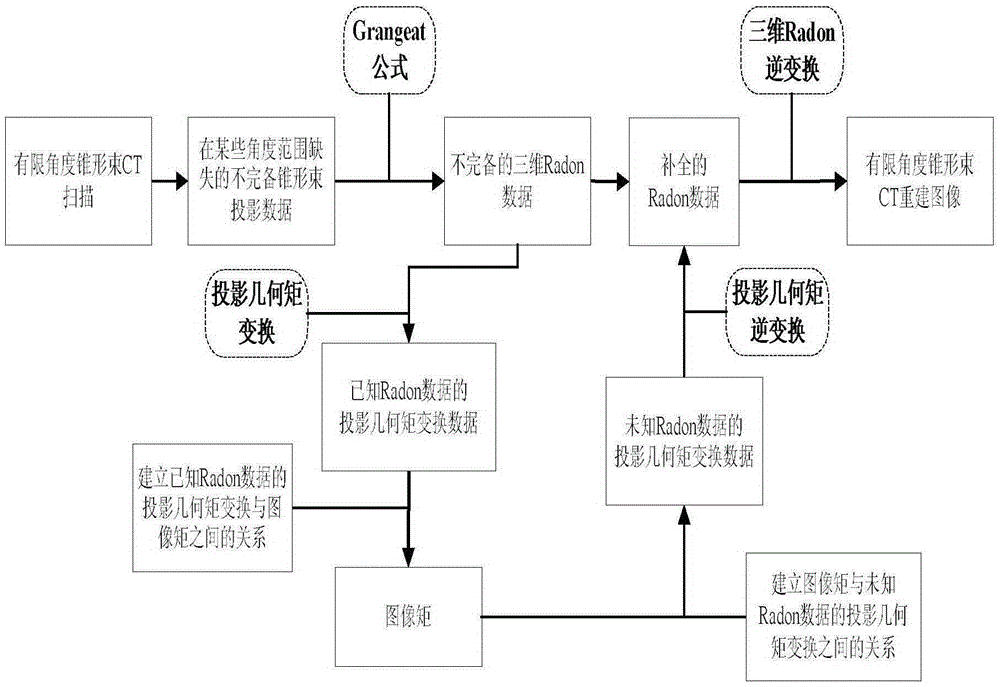
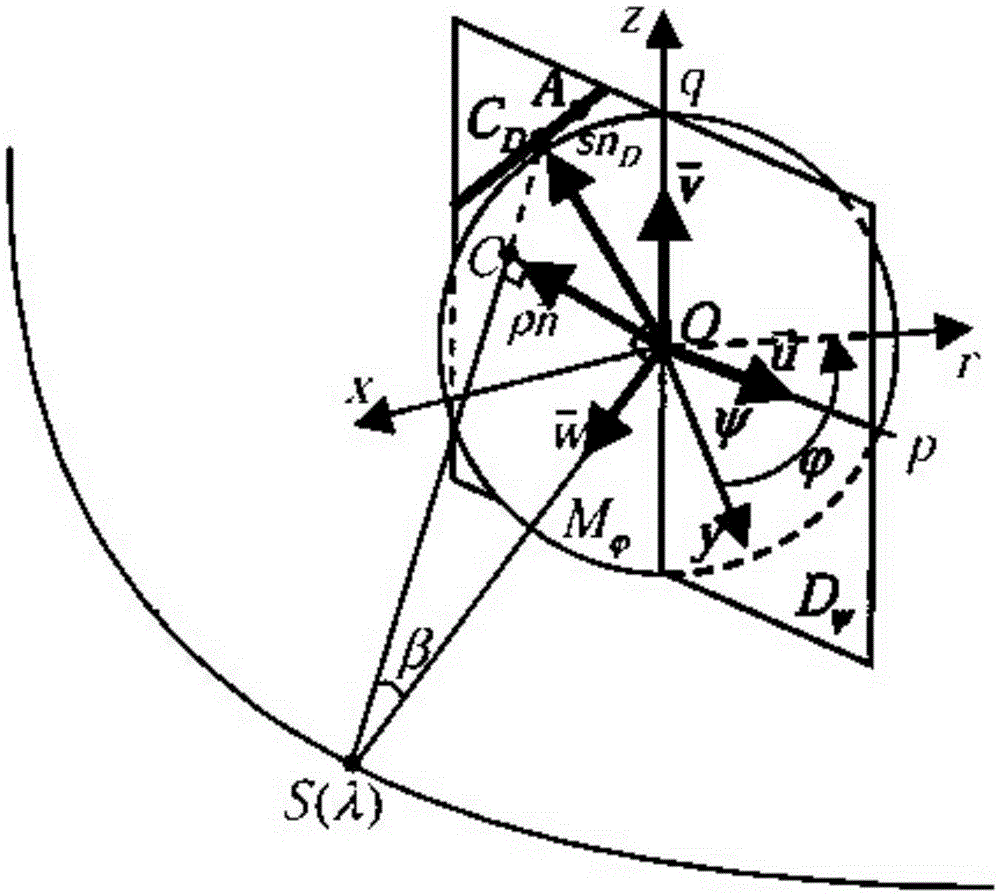
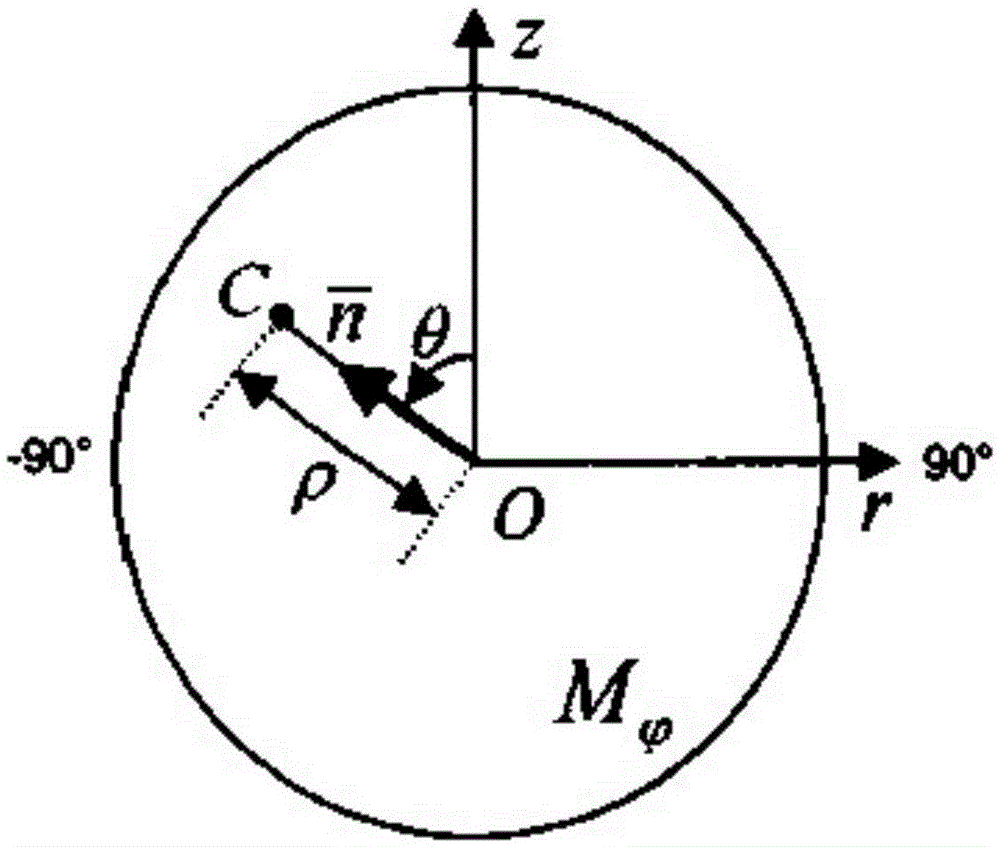
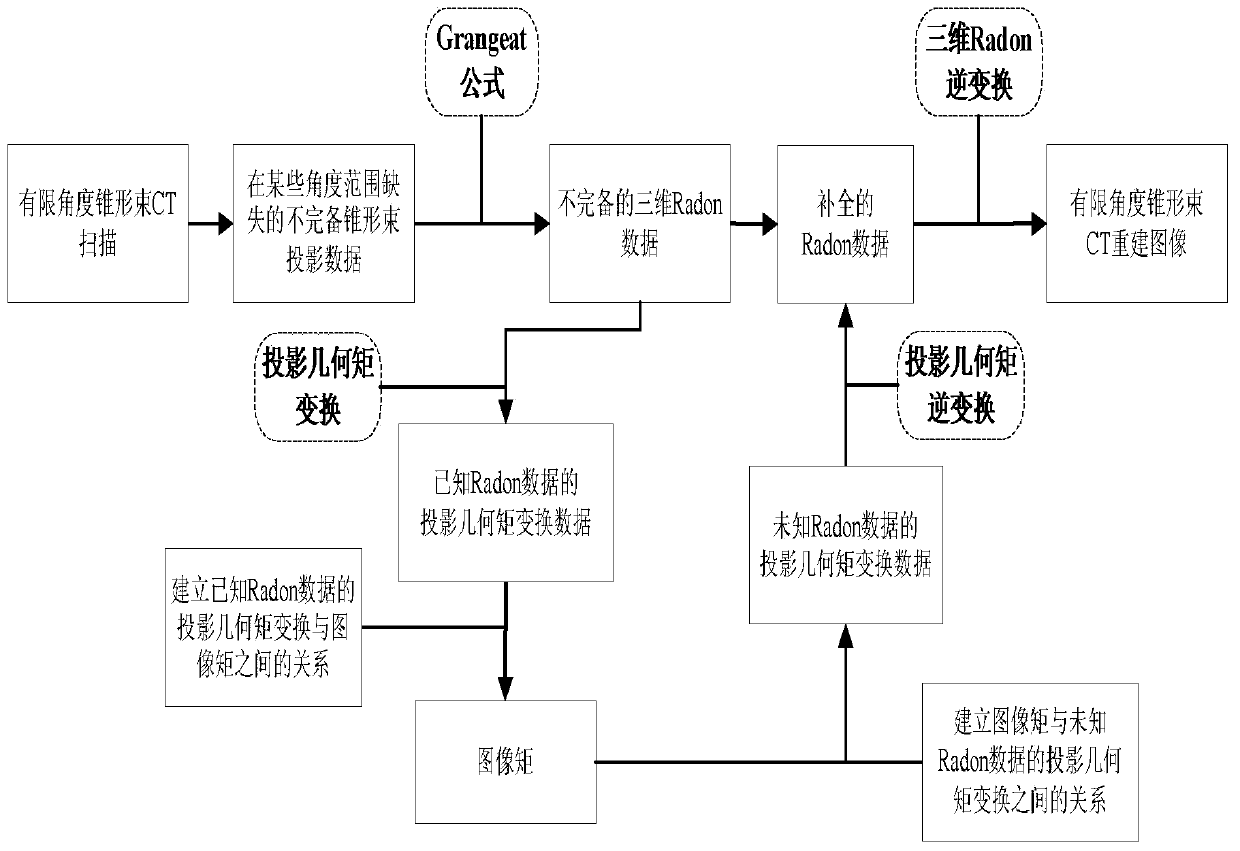
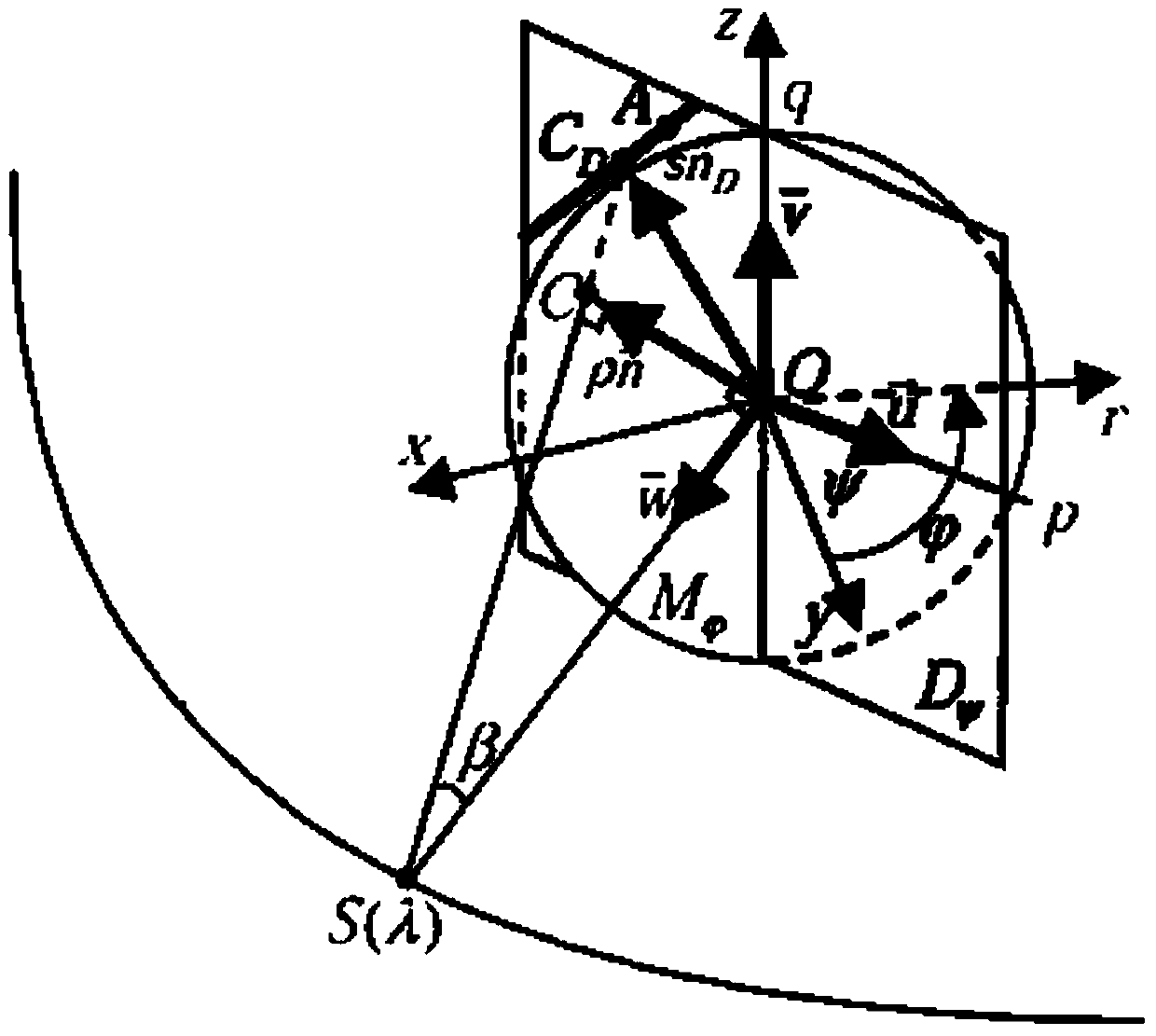
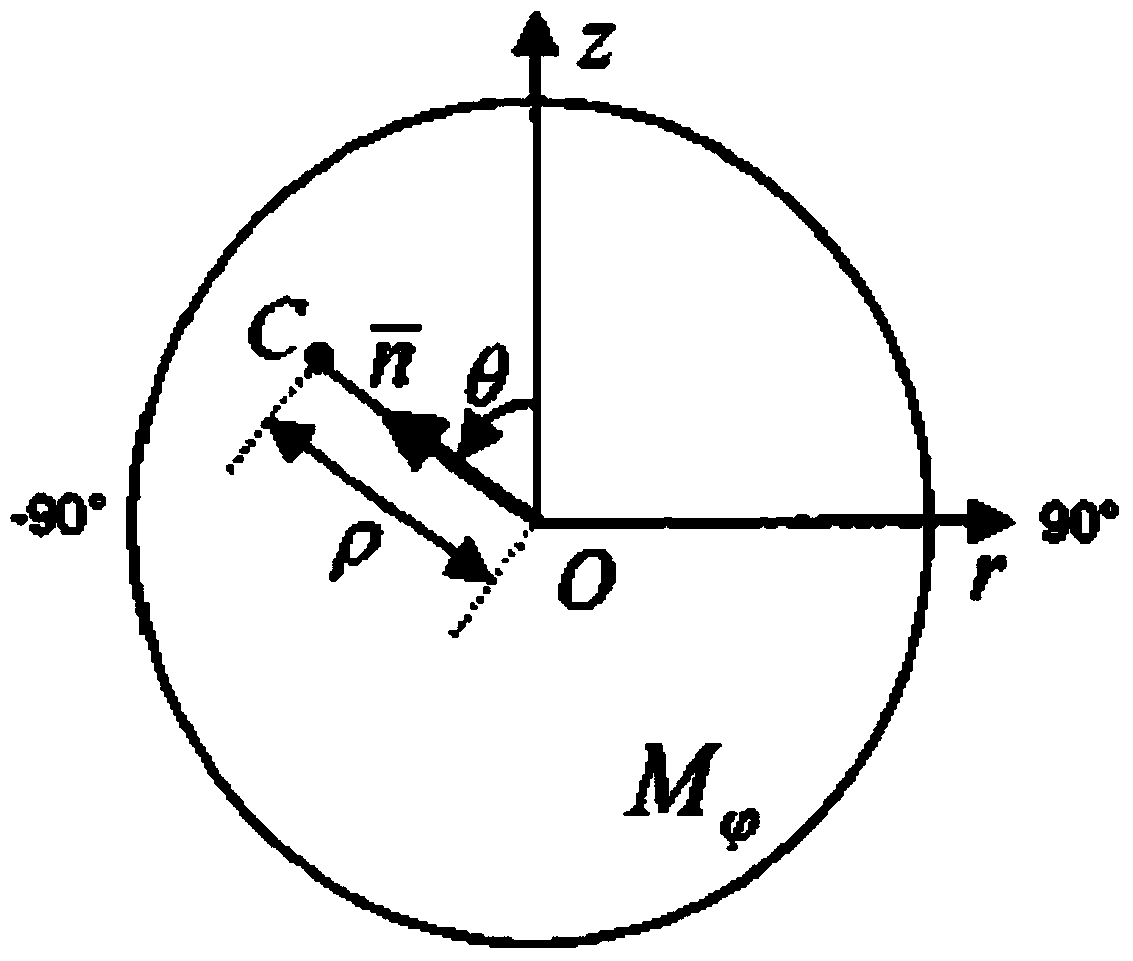
ActiveCN105354868AMeet clinical diagnostic requirementsQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionReconstruction methodRadon
The present invention discloses a limited angle cone-beam CT image reconstruction method based on a geometric image moment. The method comprises the steps of: converting obtained cone-beam projection data into known Radon data; obtaining projection-geometric moment transformation of the known Radon data; according to the projection-geometric moment transformation of the known Radon data, calculating the geometric image moment; according to the geometric image moment, estimating projection-geometric moment transformation of unknown Radon data; determining the unknown Radon data through inverse transformation; performing data combination on the known Radon data and the unknown Radon data; obtaining complemented three-dimensional data; and reconstructing a CT image. According to the method of the present invention, a cone-beam CT image that meets the requirements of clinical diagnosis and has high quality can be reconstructed under the conditions of reducing a scanning range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
X-ray imaging system and method with a real-time controllable 3D X-ray attenuator
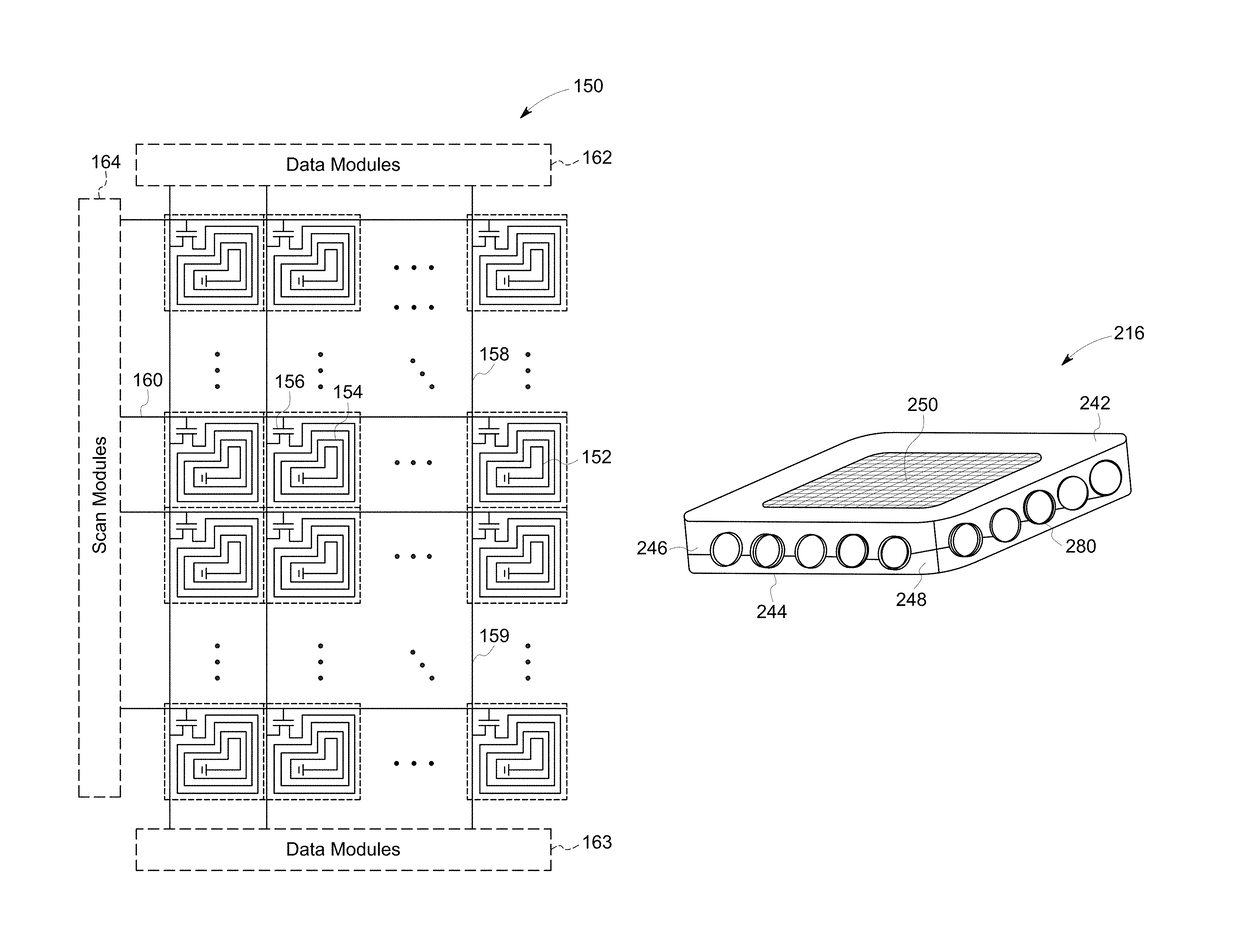
ActiveUS10068677B2Reduce X-ray radiation doseImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImaging qualityX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Six-degree-of-freedom cervical-vertebra grinding parallel robot
The invention relates to a six-degree-of-freedom cervical-vertebra grinding parallel robot which relates to a grinding parallel robot. The invention aims to solve the problems of insufficient precision, overmuch radiation and large doctor working strength of a traditional manual cervical intervertebral-disc replacement operation. A fixed platform and a movable platform are connected through threepairs of branched chains, a spherical hinge mechanism is arranged at the upper end of a ball-screw linear driving mechanism, a hooker hinge mechanism is arranged at the lower end of the ball-screw linear driving mechanism, the spherical hinge mechanism is connected with the movable platform, the hooker hinge mechanism is connected with the fixed platform, an abrasive-drilling motor penetrates themovable platform, the abrasive-drilling motor is fixedly connected with an abrasive-drilling motor connecting body, the abrasive-drilling motor connecting body is fixedly connected with the movable platform, an abrasive-drilling body is fixedly installed on the abrasive-drilling motor connecting body, an abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole is arranged on the abrasive-drilling body, an abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole cover is installed on the abrasive-drilling jackscrew hole, an abrasive-drilling shaft is connected with the abrasive-drilling motor through a shaft coupler, and a cutting head is connected with the abrasive-drilling shaft through a tightening nut. The invention is applicable to the grinding of cervical vertebra.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Catheter, apparatus and method for therapeutic embolization
InactiveCN100591291CEnsure safetyReduce radiation doseDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTherapeutic embolizationAnterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for the therapeutic embolization of an aneurysm (1) as well as to a catheter. A plugging material (2) is injected via a catheter (5) inserted into the aneurysm (1). During the injection, the spatial position of an active locator (3), such as a magnetic field sensor for example, which is fitted to the tip of the catheter (5) is observed by a locating device (8, 9). If emergence of the catheter tip from the aneurysm (1) is detected by a monitoring unit (7), said monitoring unit stops the further supply of plugging material to the catheter (5).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Anti-scattering X-ray grid plate device for medical diagnosis x-ray imaging device and method for producing grid plate
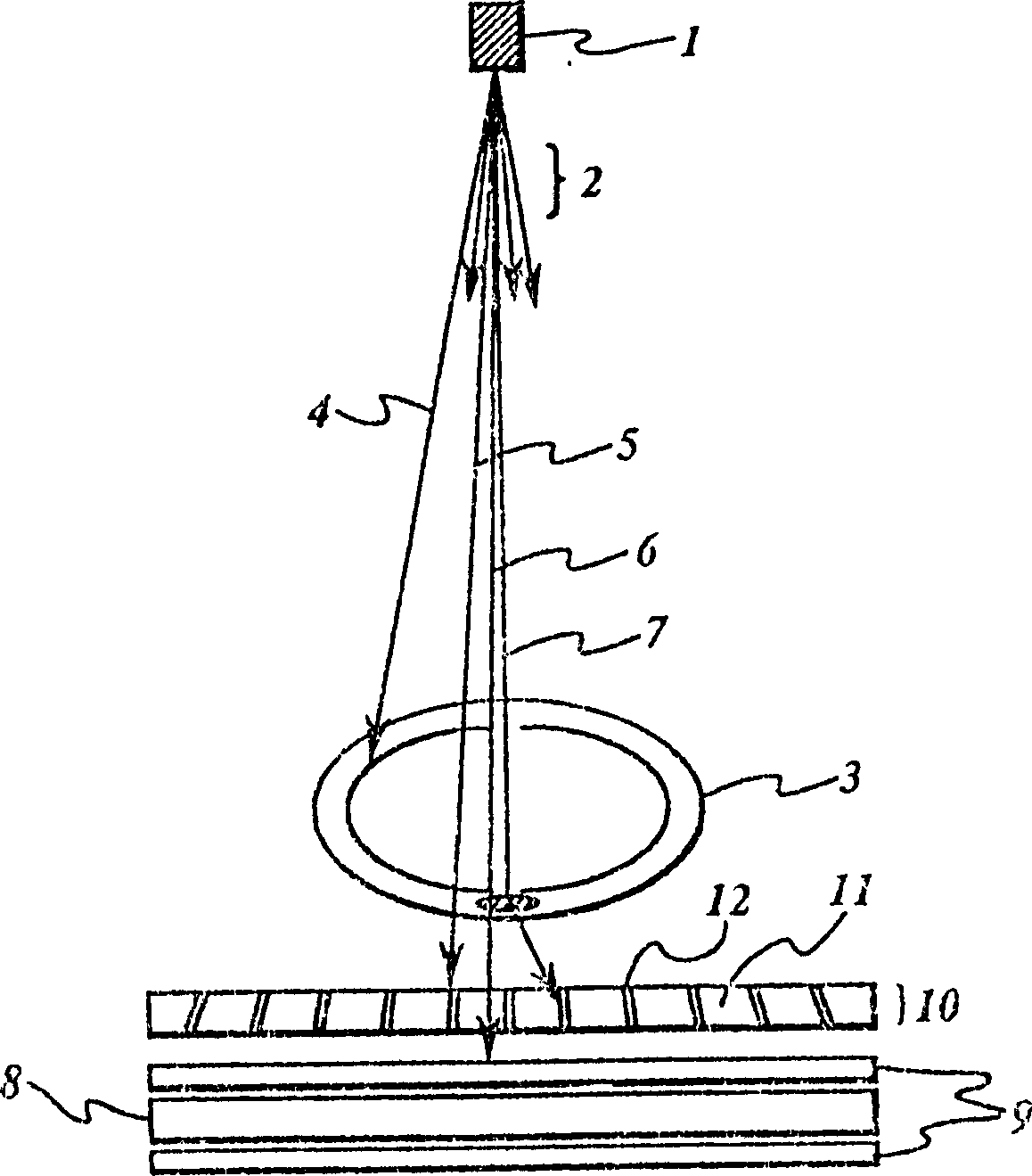
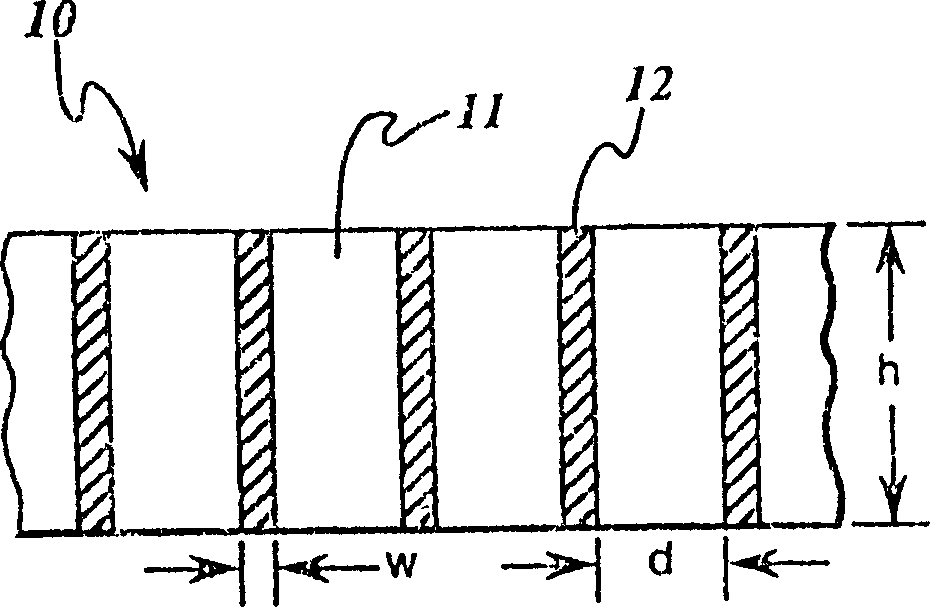
InactiveCN1230122CReduce absorptionReduce X-ray radiation doseHandling using diaphragms/collimetersTomographyX-rayAbsorbent material
An anti-scatter x-ray grid for medical diagnostic radiography and a method for fabricating includes a substrate having channels therein of material that is substantially non-absorbent of x-radiation and absorbing material in the channels including material that is substantially absorbent of x-radiation. The substrate preferably comprises material capable of remaining stable at the melting temperature of the absorbing material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Scanning imaging method and system for computed tomography (CT) machine and CT machine
ActiveCN103356216AReduce X-ray radiation doseReduce radiation doseComputerised tomographsTomographyPhysicsComputed tomography scanner
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Method and device for optimizing scanning flow
ActiveCN102805635AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityComputerised tomographsTomographyMedical equipmentX-ray
The invention relates to the field of medical equipment, in particular to a method for optimizing a scanning flow. The method comprises the following steps of: judging a position where an object to be inspected moves according to an original projection data group; and scanning the position once again. The invention further provides a device for optimizing a scanning flow. According to the method and the device, a specific position where the object to be inspected moves during scanning can be judged automatically, and only the specific position is scanned once again, so that higher accuracy is achieved, and the dose of X-ray radiation received by the object to be inspected is reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS SHANGHAI MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Intravascular foresight detection device
PendingCN113081045AHigh resolutionLarge scanning angleOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryContrast mediumMedical physics
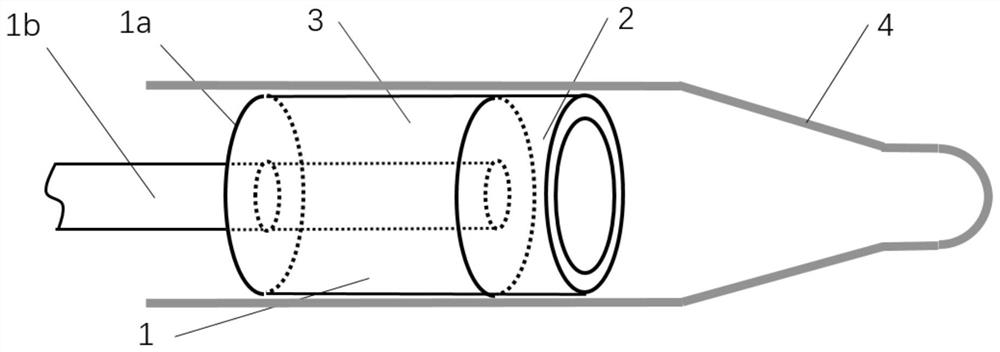
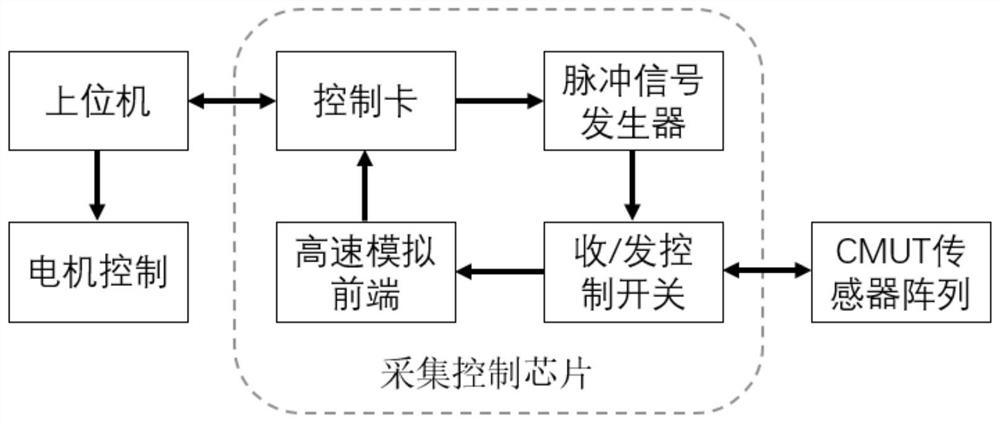
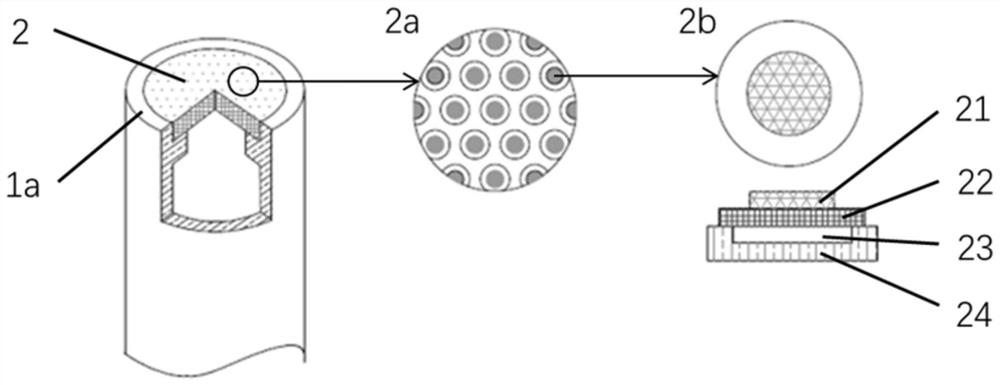
The invention provides an intravascular foresight detection device which comprises an intravascular foresight probe; the intravascular foresight probe comprises a shell, a CMUT ultrasonic sensor array, an acquisition control chip and a flexible shaft with a cable; the shell is of a hollow cylindrical structure; the CMUT ultrasonic sensor array and the acquisition control chip are embedded in the shell, the whole body is fixedly connected with the flexible shaft with the cable and moves back and forth along with the flexible shaft with the cable; the intravascular foresight detection device can perform forward imaging at the far end of a catheter head end, determine the deformation direction of a blood vessel cavity and the morphological structure of a lesion, improve the success rate of a CTO lesion operation, reduce occurrence of blood vessel perforation, interlayers and the like in the operation, shorten the operation time, reduce the X-ray radiation quantity, remarkably reduce the dosage of a contrast agent in the operation, and reduce the occurrence of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Owner:TIANJIN CHEST HOSPITAL
Detecting device of early-stage breast cancer
ActiveCN104873214AEfficient and accurate detectionReduce Radiation DamageRadiation diagnosticsX-rayEarly breast cancer
The invention discloses a detecting device of early-stage breast cancer. The detecting device of the early-stage breast cancer comprises an X-ray light source, a capillary X-ray convergent lens, a capillary X-ray collimating lens and an X-ray detector. The capillary X-ray convergent lens is used for collecting and gathering X-rays emitted out of the X-ray light source, and micro focal spots used for irradiating mammary tissue to be detected are formed at the outlet end. Inlet focal spots of the capillary X-ray collimating lens coincide with the output focal spots of the capillary X-ray convergent lens to form confocal X-ray small angle scattering, and a confocal micro unit for irradiating a sample is obtained. The capillary X-ray collimating lens is used for collecting X-ray small angle scattering signals of the mammary tissue in the confocal micro unit. The X-ray detector is arranged at the outlet end of the capillary X-ray collimating lens, and used for detecting and collecting the X-ray small angle scattering signals corresponding to the mammary tissue to be detected. Therefore, the early-stage breast cancer can be detected efficiently and accurately by means of the detecting device, and meanwhile the X-ray radiant quantity borne by an examinee can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
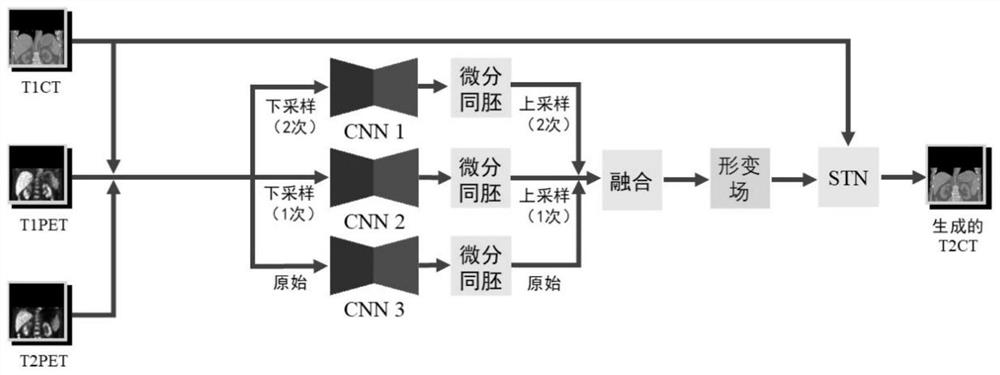
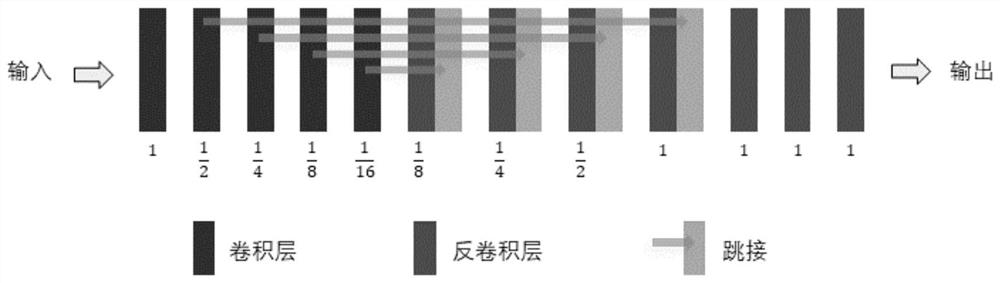
Delayed CT image generation method based on deep learning algorithm
ActiveCN113436708AReduce X-ray radiation doseSpeed up the build processImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionMulti resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical images, and particularly relates to a delayed CT (T2CT) image generation method based on the deep learning algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting T2PET, T1PET and T1CT images of a patient; s2, inputting the acquired T2PET, T1PET and T1CT images into the proposed multi-resolution registration convolutional neural network, and then outputting three deformation fields including large, medium and small deformation quantities; s3, fusing the three deformation fields including the large deformation quantity, the medium deformation quantity and the small deformation quantity output in the step S2 into one deformation field; and S4, inputting the deformation field and the input T1CT image into a space conversion network to generate a T2CT image. The method has the advantages that attenuation correction can be performed in delayed PET scanning, and meanwhile, the T2CT image is generated to avoid additional CT scanning of the patient, so that the X-ray radiation dose suffered by the patient is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
A method for outputting blood flow parameter images under low radiation dose
InactiveCN104899904BImprove securityReduce X-ray radiation doseImage enhancement2D-image generationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputed tomography
An output method for blood flow parameter images under a low radiation dose comprises the following steps: acquiring CT (Computed Tomography) cerebral apoplexy image data under the low radiation dose; pre-processing the CT cerebral apoplexy image data; acquiring image characteristics of the pre-processed CT cerebral apoplexy image data; matching the image characteristics in a large medical database to obtain matching results; and outputting the blood flow parameter images according to the matching results. According to the output method provided by the invention, complementary multi-modal medical data is effectively utilized. The radiation dose of X rays accepted by patients in CT perfusion medicinal images is reduced to a great extent, the medical safety is improved and the use value of CT for acute cerebral apoplexy is improved.
Owner:方若谷
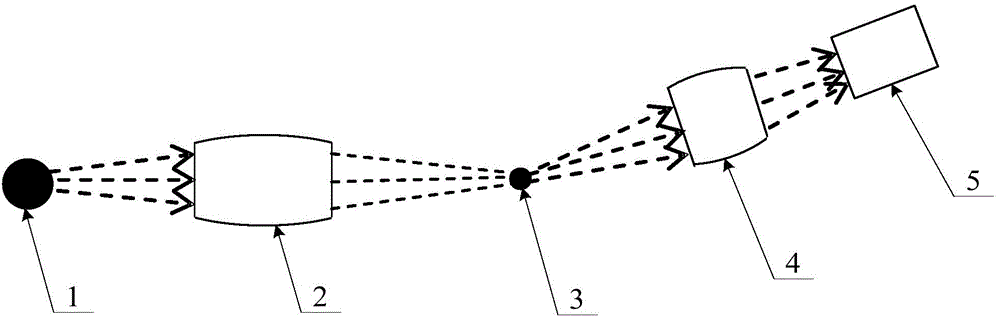
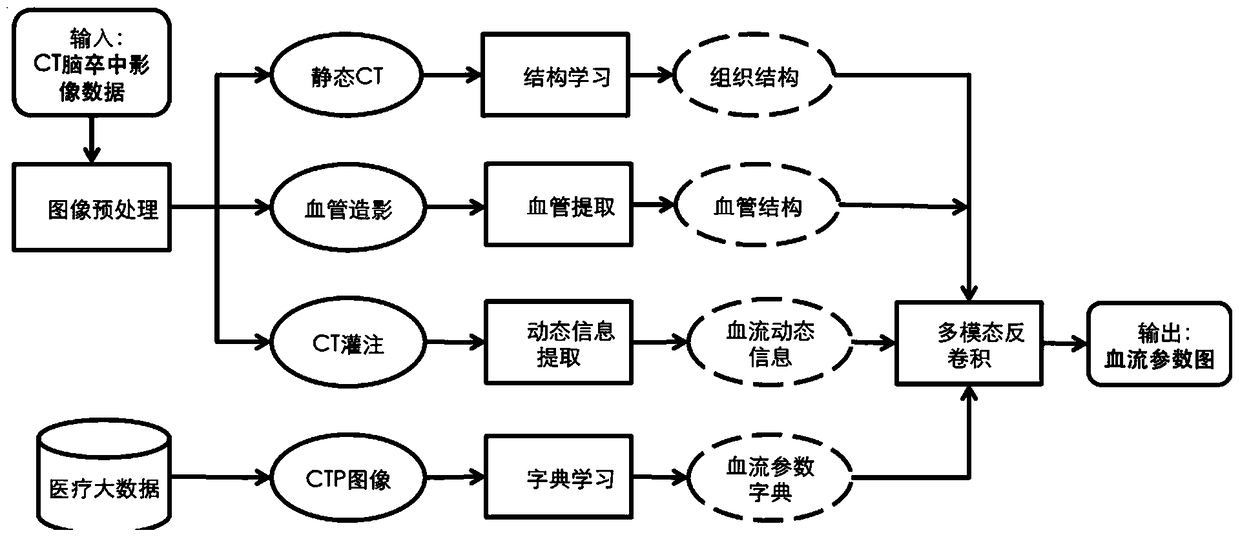
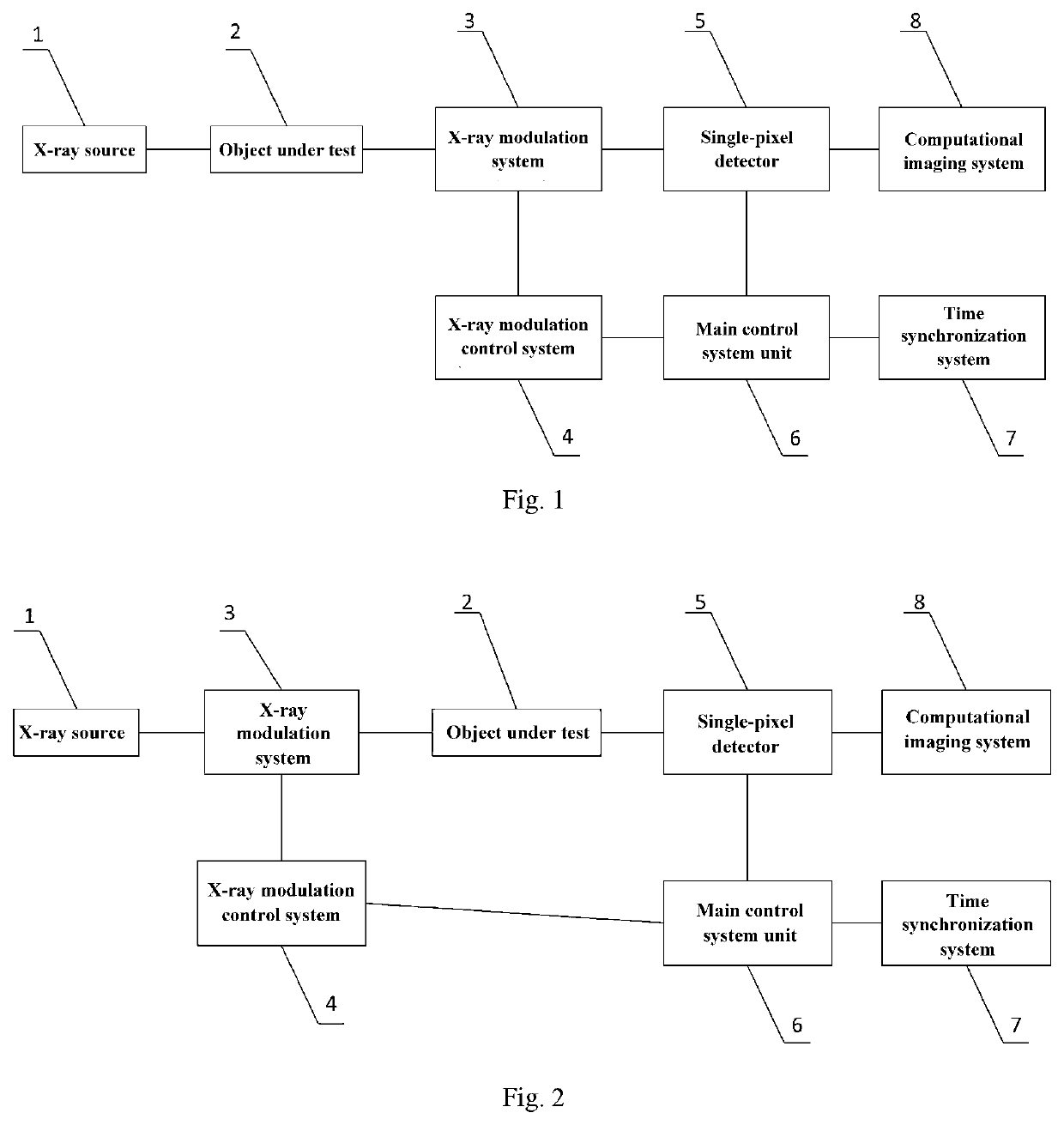
X-ray single-pixel camera based on x-ray computational correlated imaging
ActiveUS20220042928A1Low costImage degradationUsing optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImaging qualityDose imaging
An X-ray single-pixel camera based on X-ray computational correlated imaging, which belongs to the technical research fields of X-ray computational correlated imaging and X-ray single-pixel imaging. The X-ray single-pixel camera includes: an X-ray modulation system (3), an X-ray modulation control system (4), an X-ray single-pixel detector (5), a main control system unit (6), a time synchronization system (7) and a computational imaging system (8). The main control system unit (6) controls each module through software; the time synchronization system (7) controls synchronization of each module for automatic collection; and the computational imaging system (8) is configured to perform a second-order correlated computation or a compressed sensing computation or a deep learning computation on the signals collected by the X-ray single-pixel detector (5) and a preset modulation matrix, so as to obtain an image of an object under test. The X-ray single-pixel camera based on X-ray computational correlated imaging, provided by the present invention, realizes single-pixel imaging, greatly reduces the sampling number while ensuring the imaging quality, and reduces the X-ray radiation dose in an imaging process.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reconstruction Method of Cone Beam CT Image with Limited Angle Based on Geometric Image Moments
ActiveCN105354868BMeet clinical diagnostic requirementsQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionReconstruction methodComputer science
The present invention discloses a limited angle cone-beam CT image reconstruction method based on a geometric image moment. The method comprises the steps of: converting obtained cone-beam projection data into known Radon data; obtaining projection-geometric moment transformation of the known Radon data; according to the projection-geometric moment transformation of the known Radon data, calculating the geometric image moment; according to the geometric image moment, estimating projection-geometric moment transformation of unknown Radon data; determining the unknown Radon data through inverse transformation; performing data combination on the known Radon data and the unknown Radon data; obtaining complemented three-dimensional data; and reconstructing a CT image. According to the method of the present invention, a cone-beam CT image that meets the requirements of clinical diagnosis and has high quality can be reconstructed under the conditions of reducing a scanning range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com