Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Variation in sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
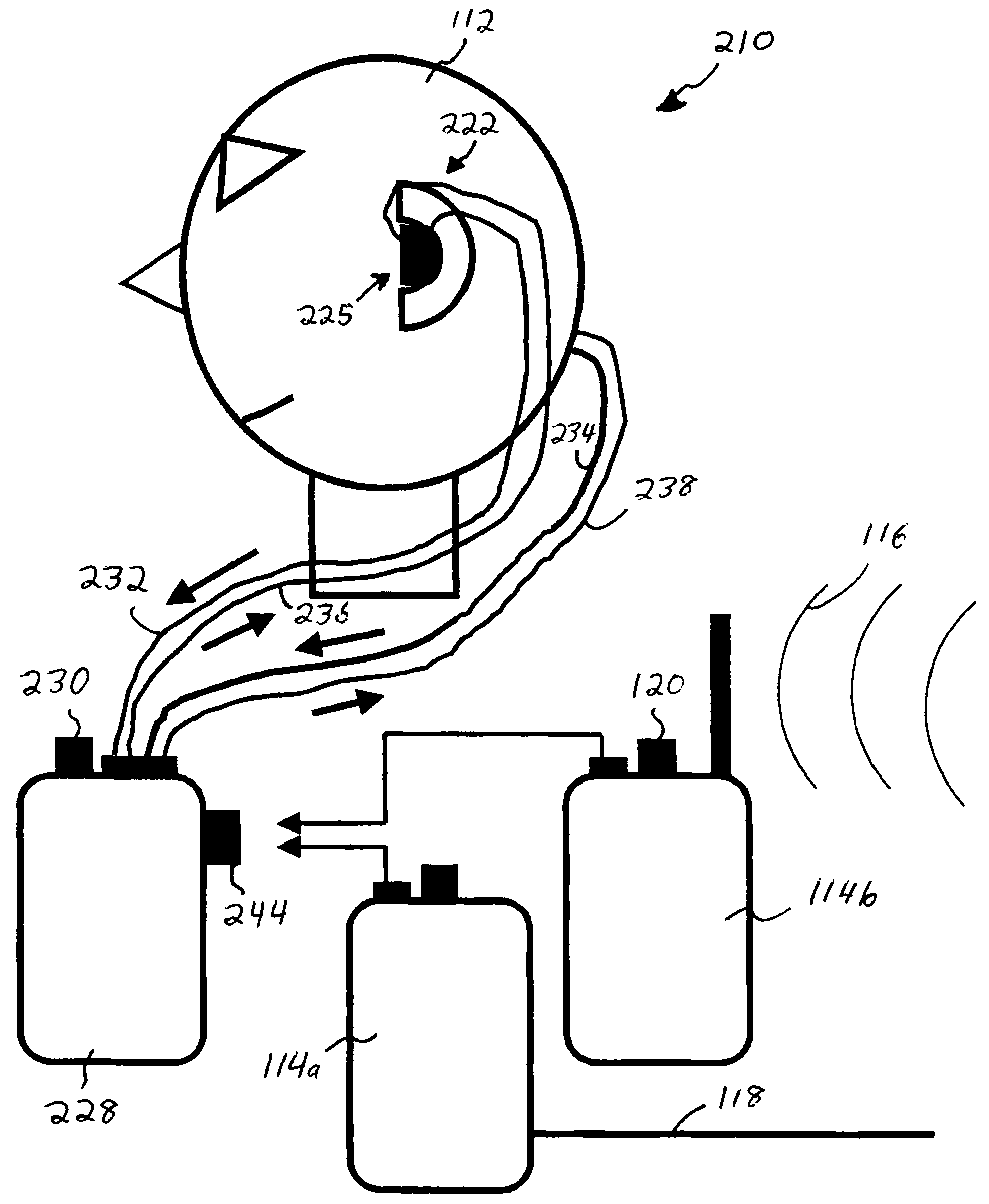
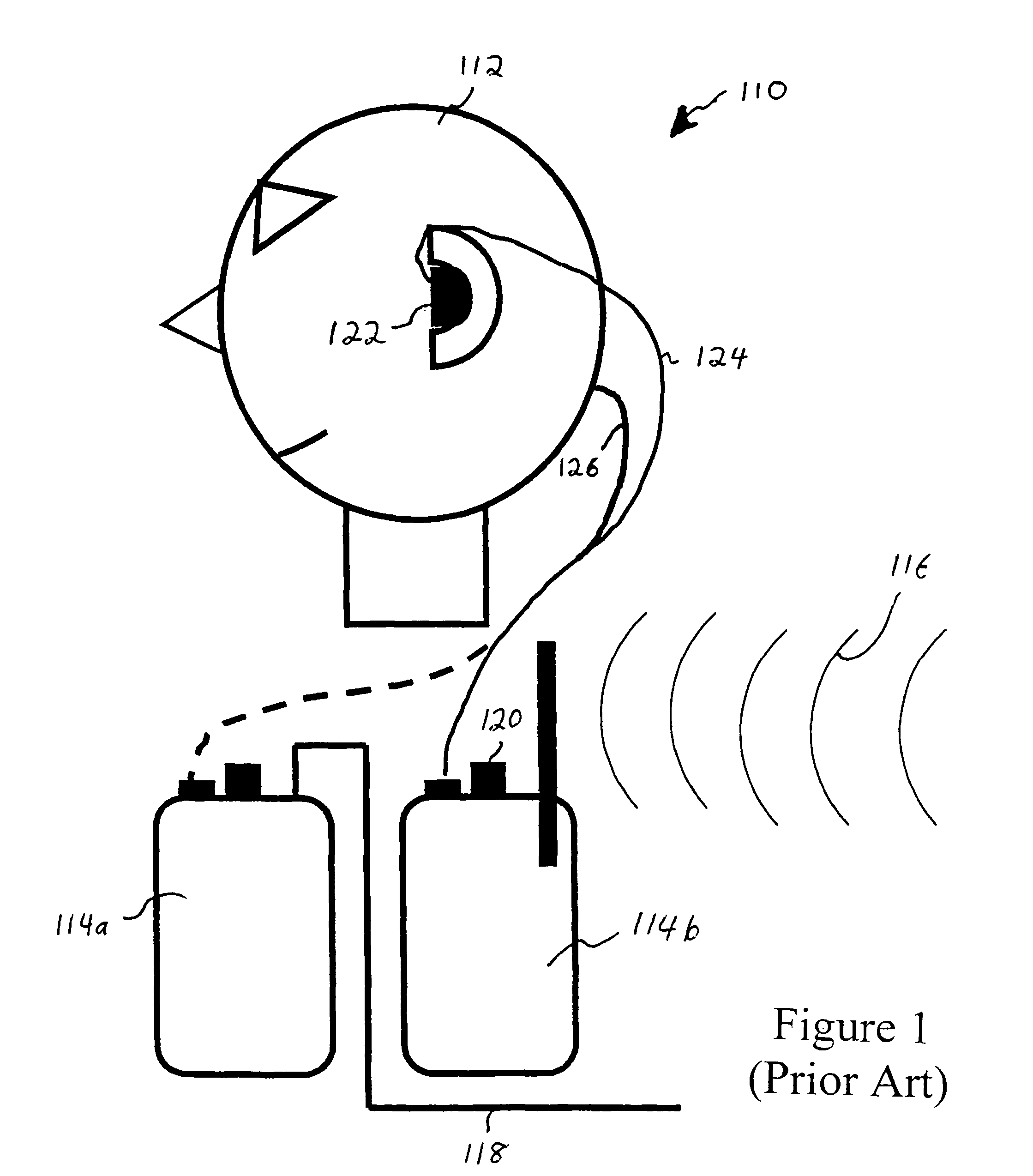
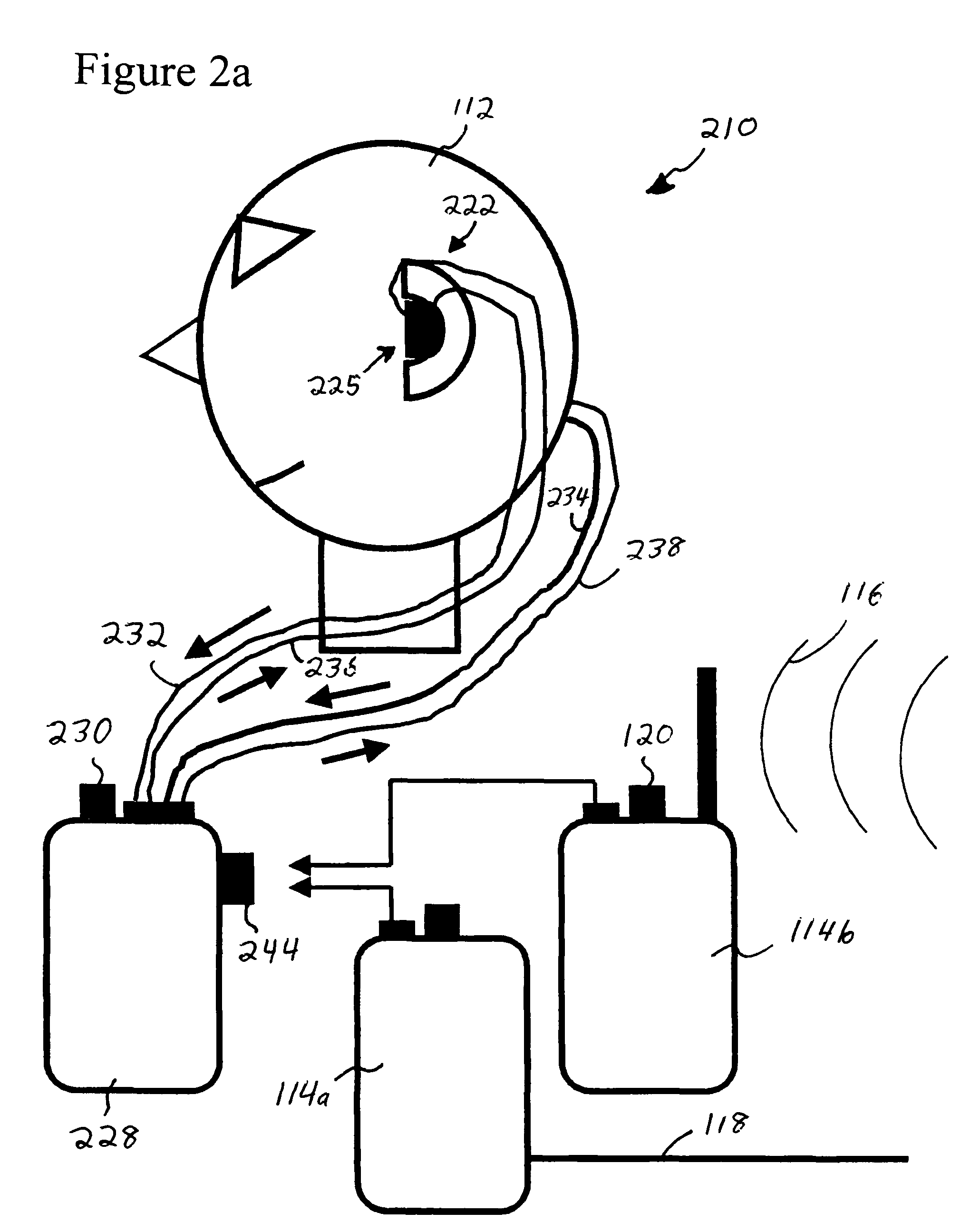
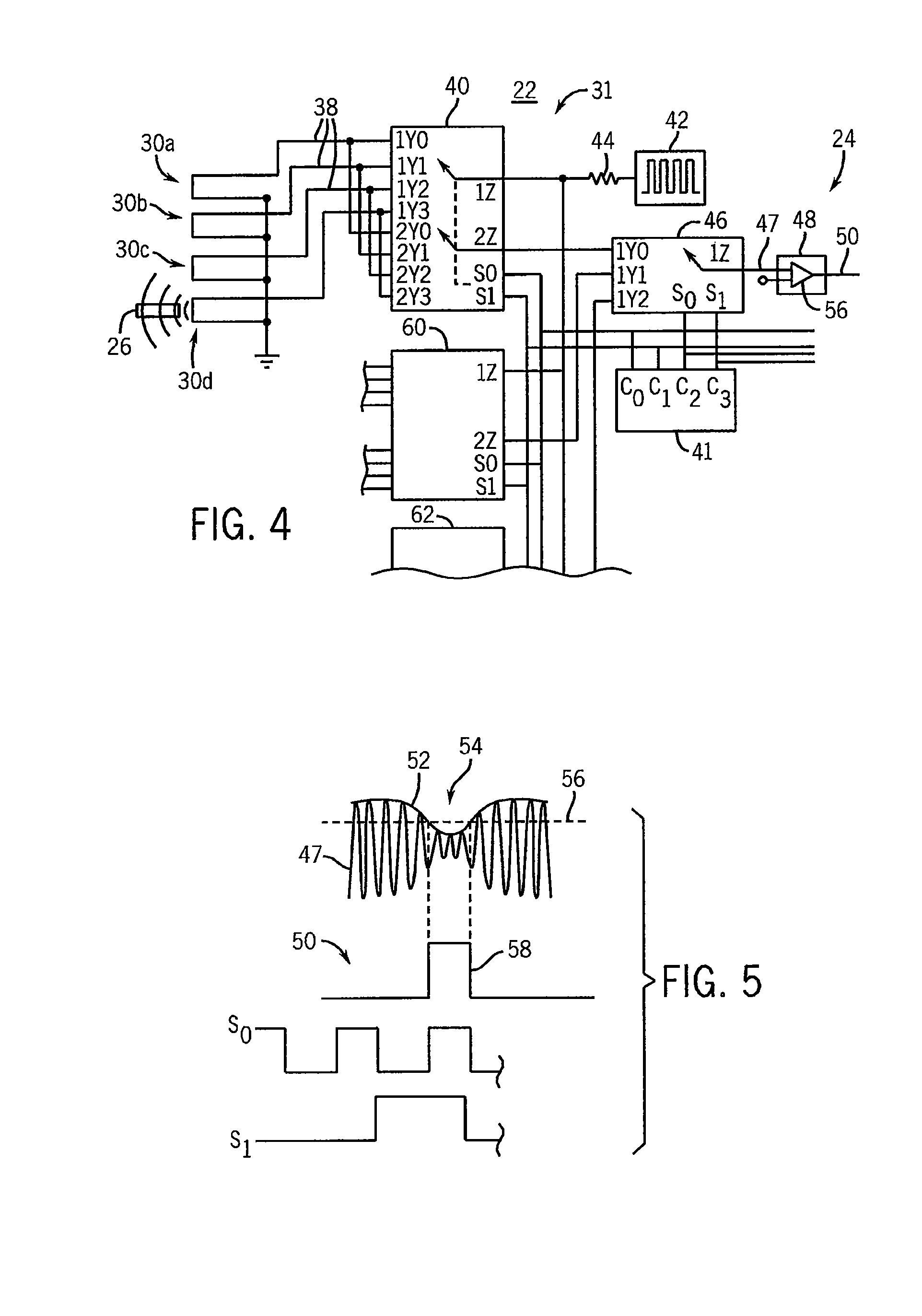
Audio monitoring system
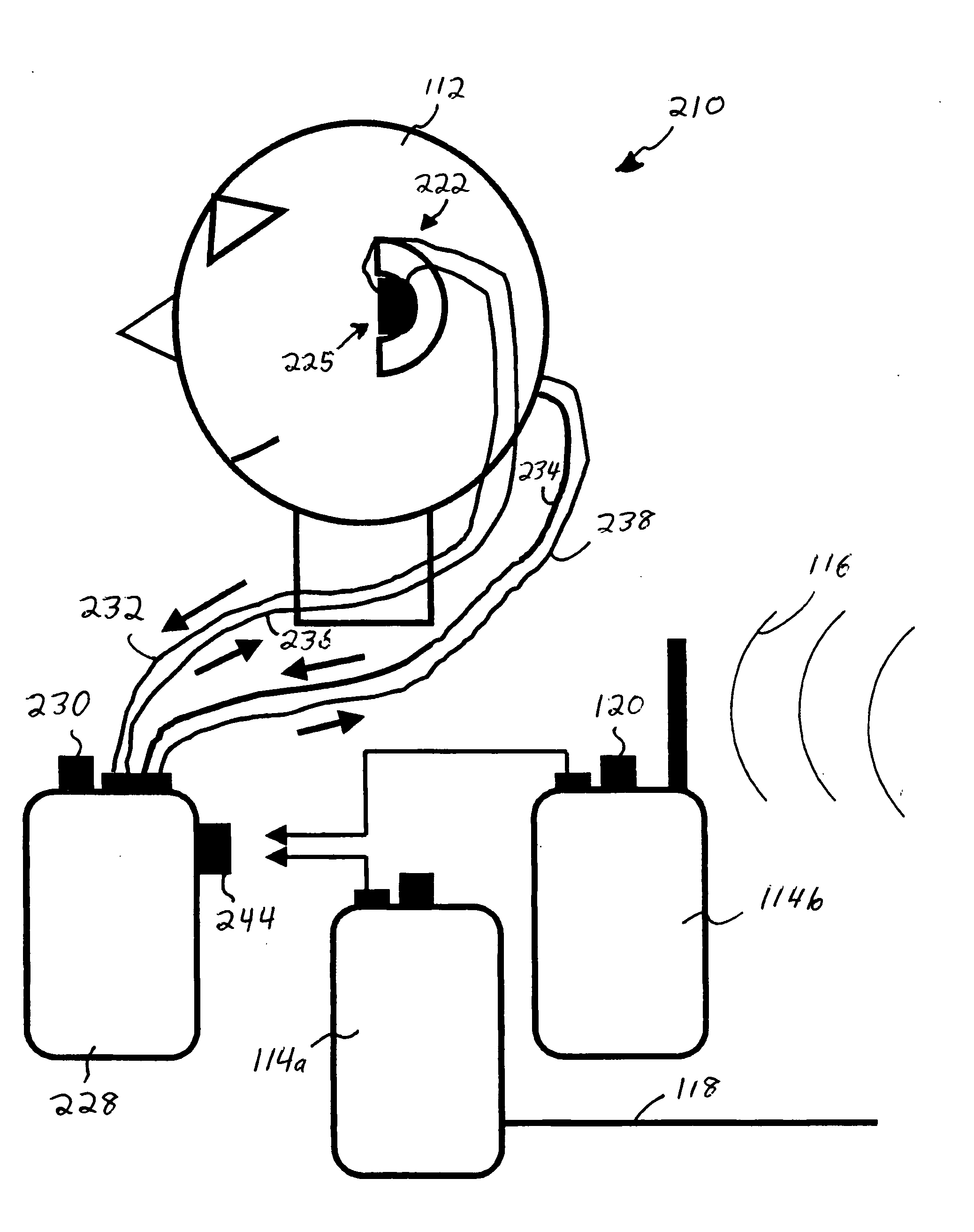
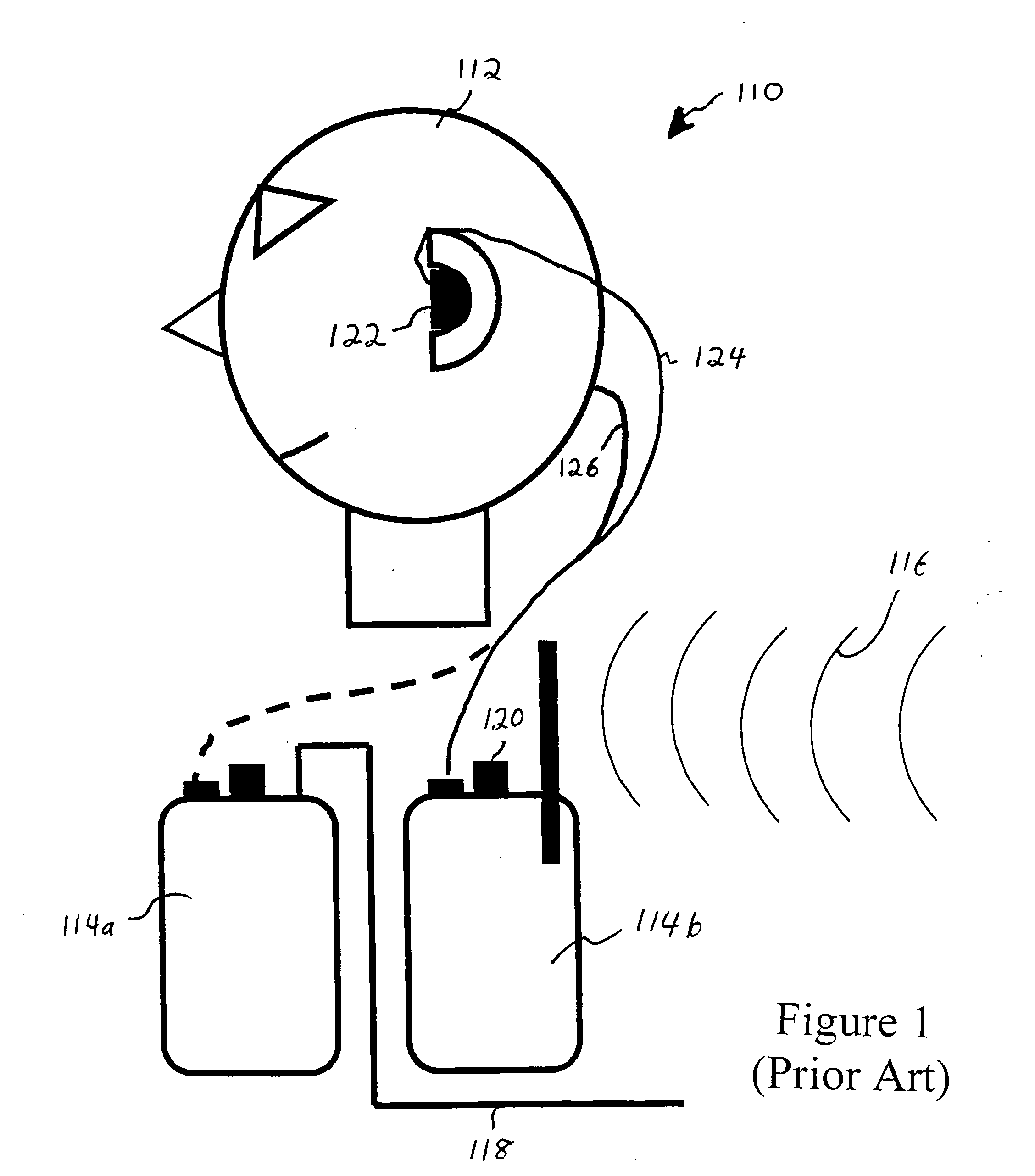
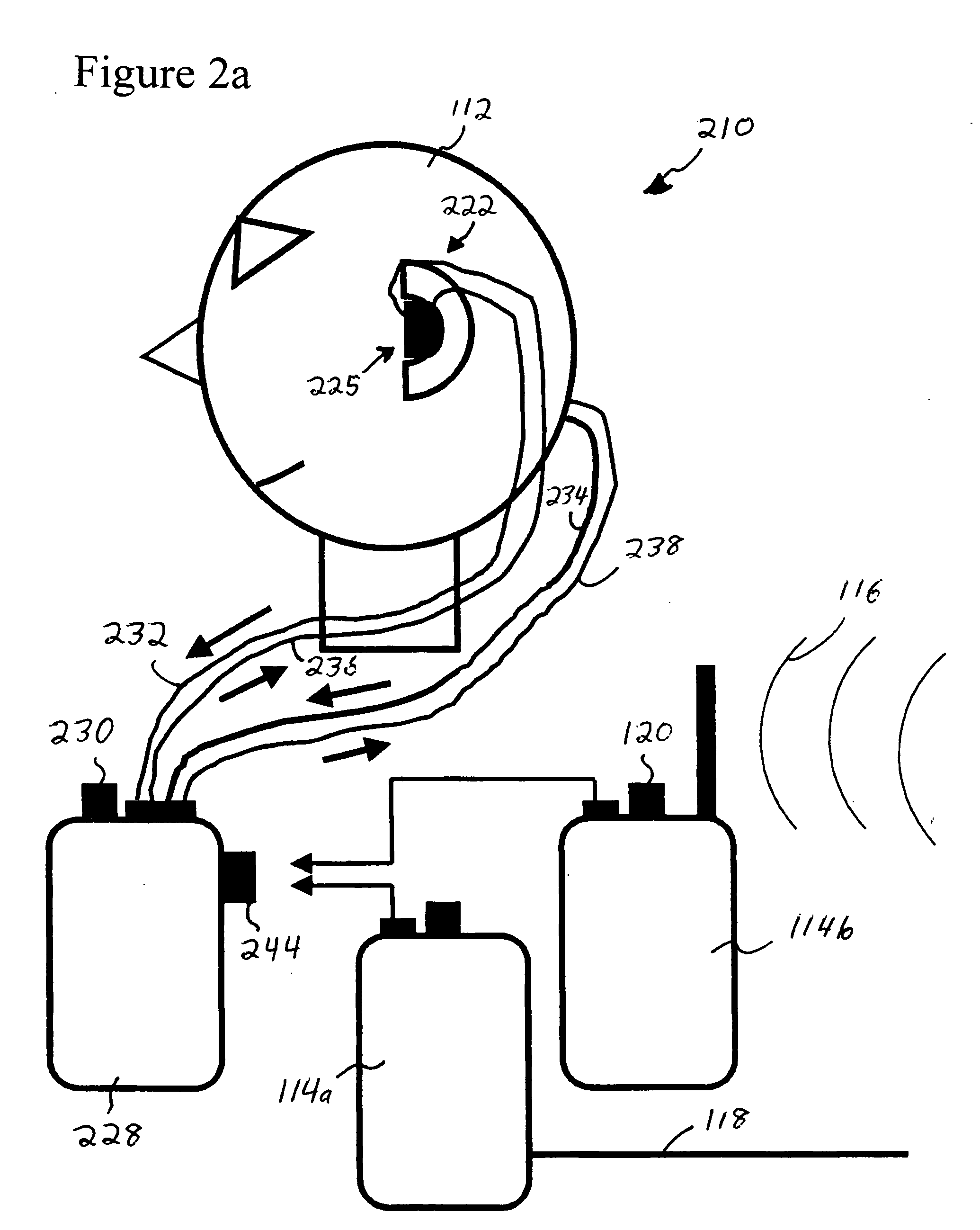
ActiveUS20060182287A1Variation in sensitivityReduce gainGain controlIntra aural earpiecesMonitoring systemHeadphones
An earphone monitoring system is disclosed that provides for user information and control regarding ambient and monitored sound levels.
Owner:SENSAPHONICS
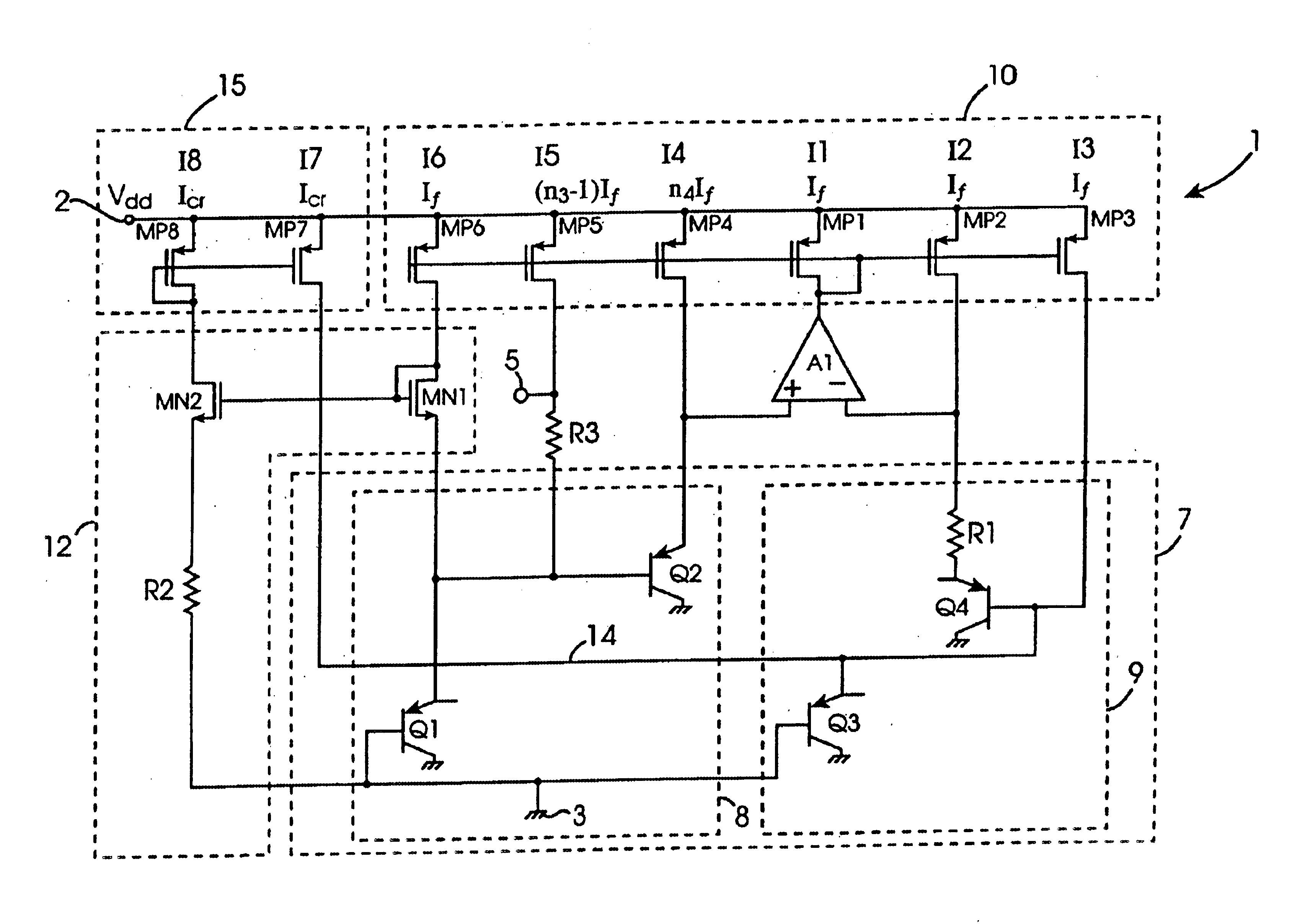
Bandgap voltage reference circuit and method for producing a temperature curvature corrected voltage reference
InactiveUS6828847B1Easy to implementLower requirementElectronic switchingPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
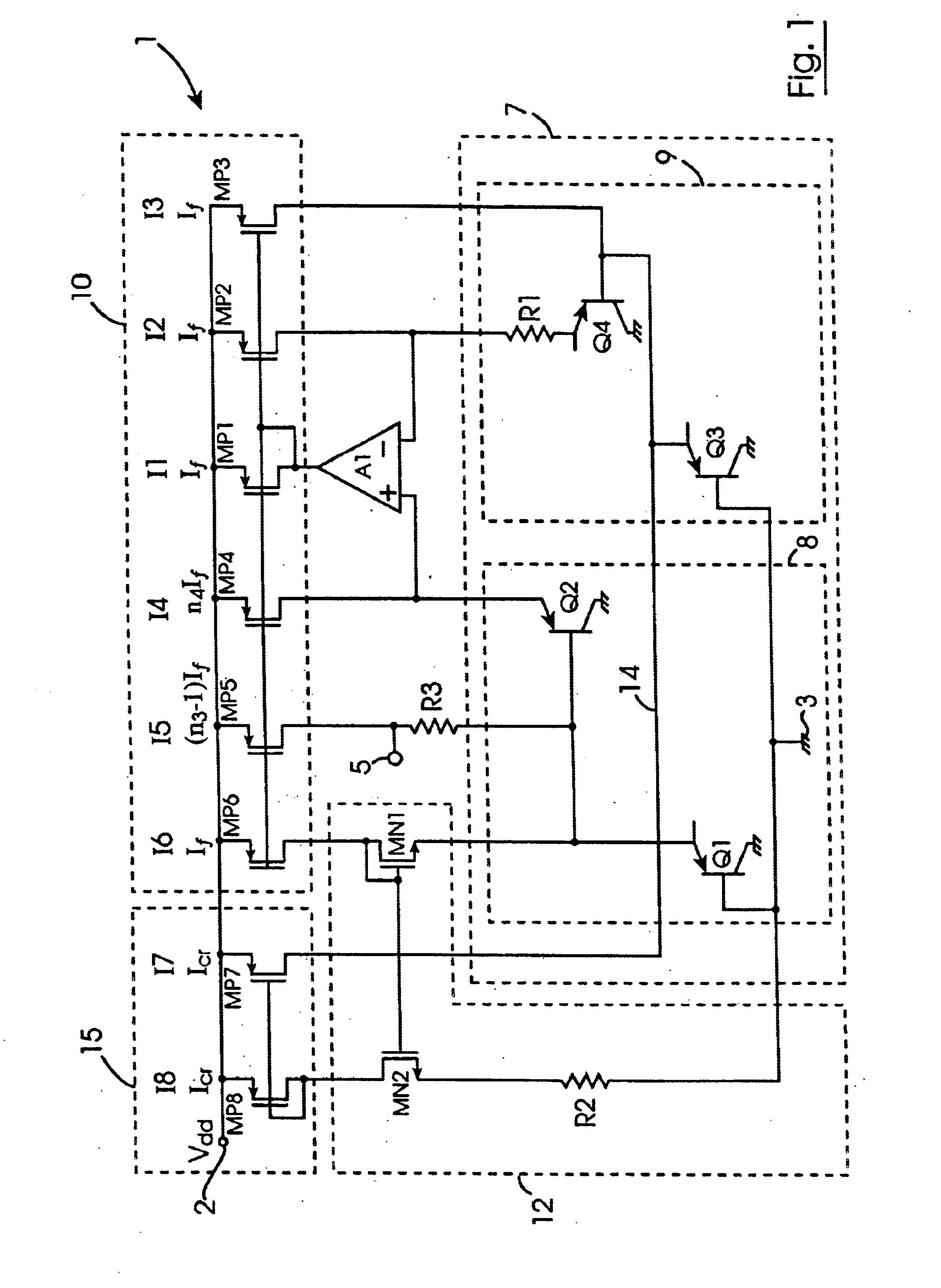
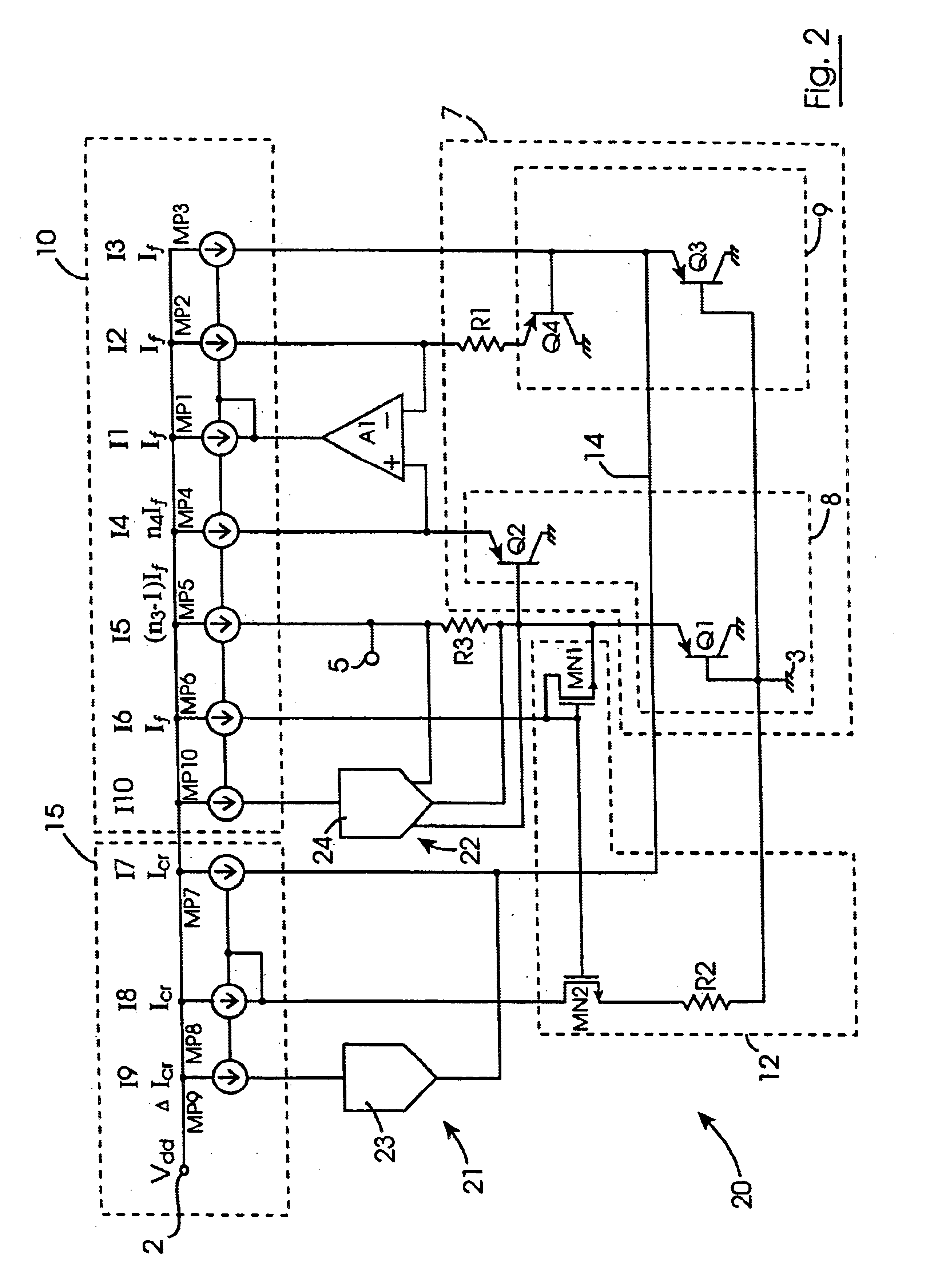
A bandgap voltage reference circuit (1) comprises a bandgap cell (7) comprising first and second transistor stacks (8,9) of first transistors (Q1,Q2) and second transistors (Q3,Q4), respectively, arranged for developing a correcting PTAT voltage (DeltaVbe) across a primary resistor (R1) proportional to the difference in the base-emitter voltages of the first and second transistor stacks (8,9). A first current mirror circuit (10) provides PTAT currents (12 to 15) to the emitters of the first and second transistors (Q1 to Q4), and an operational amplifier (A1) maintains the voltage on the emitter of the first transistor (Q2) of the first transistor stack (8) at the same level as the resistor (R1) and sinks a PTAT current from the first current mirror circuit (10) from which the other PTAT currents are mirrored. The correcting PTAT voltage (DeltaVbe) developed across the primary resistor (R1) is scaled onto a secondary resistor (R3) and summed with the uncorrected base-emitter CTAT voltage of the first transistor (Q1) of the first transistor stack (8) for providing the voltage reference between an output terminal (5) and ground (3). A CTAT correcting current (Icr) is summed with the PTAT current (13) and applied to the emitter of the second transistor (Q3) of the second transistor stack (9) so that the correcting PTAT voltage (DeltaVbe) developed across the primary resistor (R1) has a TlnT curvature complementary to the TlnT temperature curvature of the uncorrected base-emitter CTAT voltage of the first transistor (Q1). Thus the reference voltage developed between the output terminal (5) and the ground (3) is temperature stable and TlnT temperature curvature corrected. The CTAT correcting current is derived from the base-emitter CTAT voltage of the first transistor (Q1) in a CTAT current generating circuit (12) through a second current mirror circuit (15).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
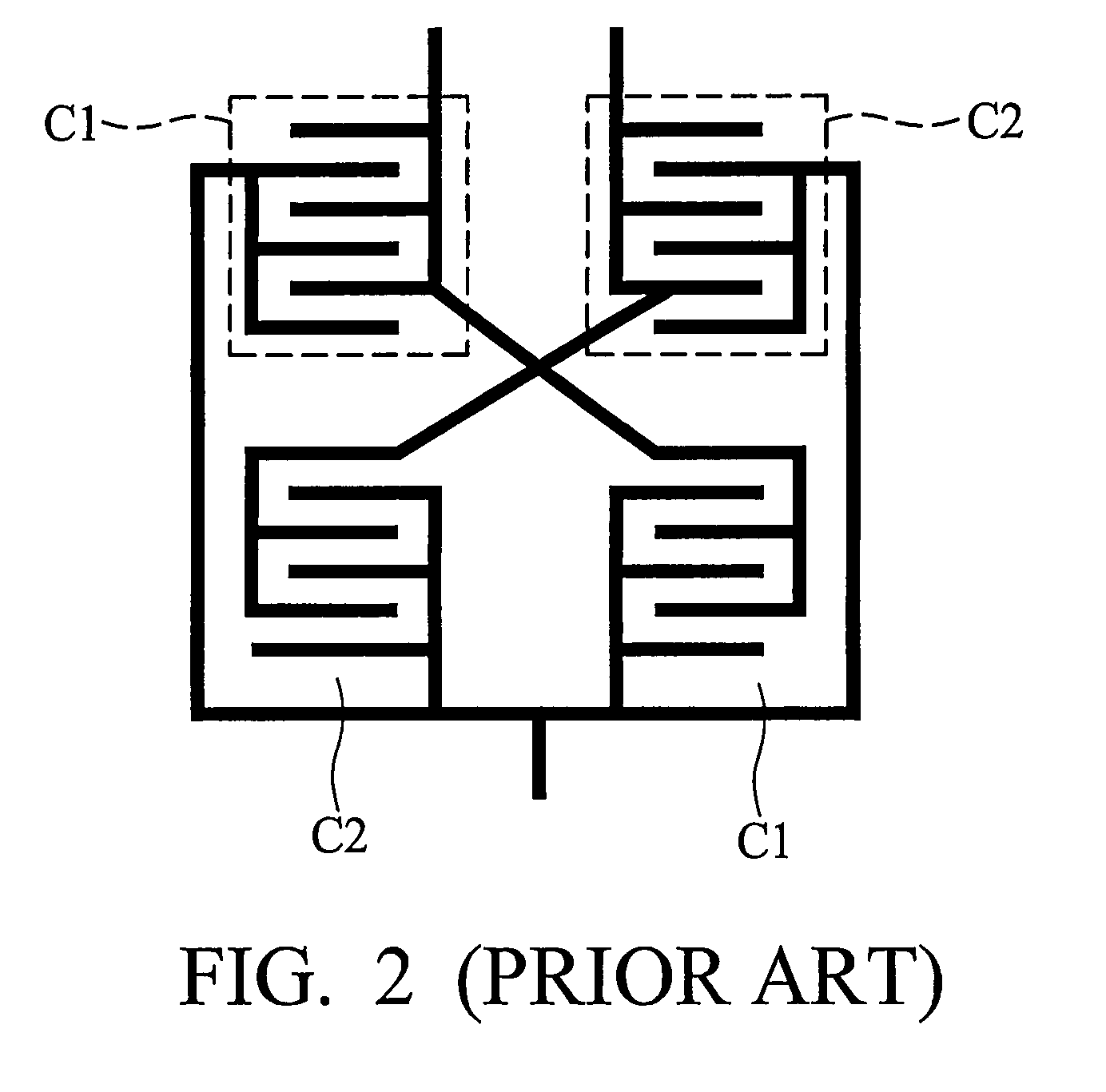
Solid state image pickup device, method for producing the same, and image pickup system comprising the solid state image pickup device
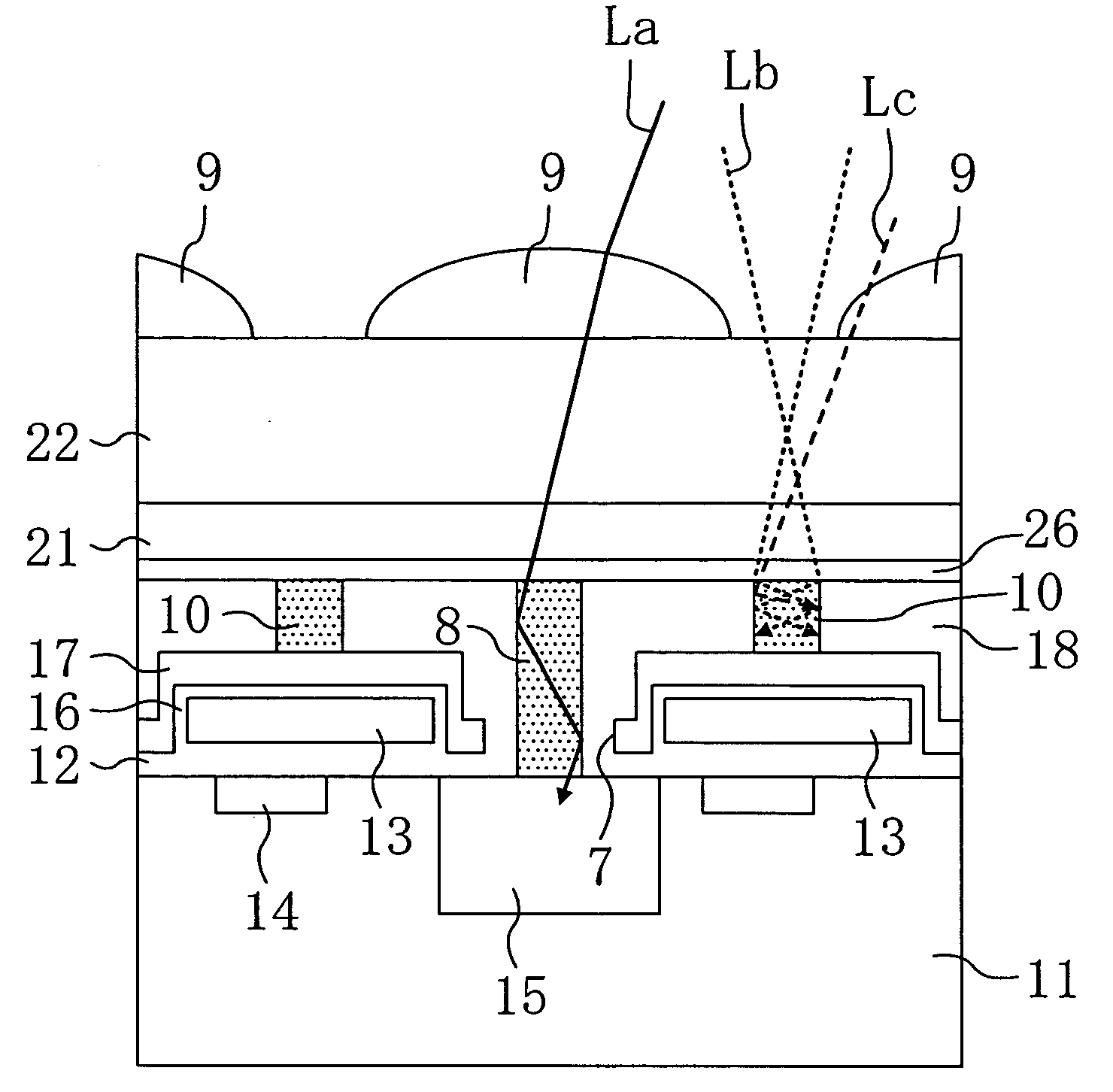
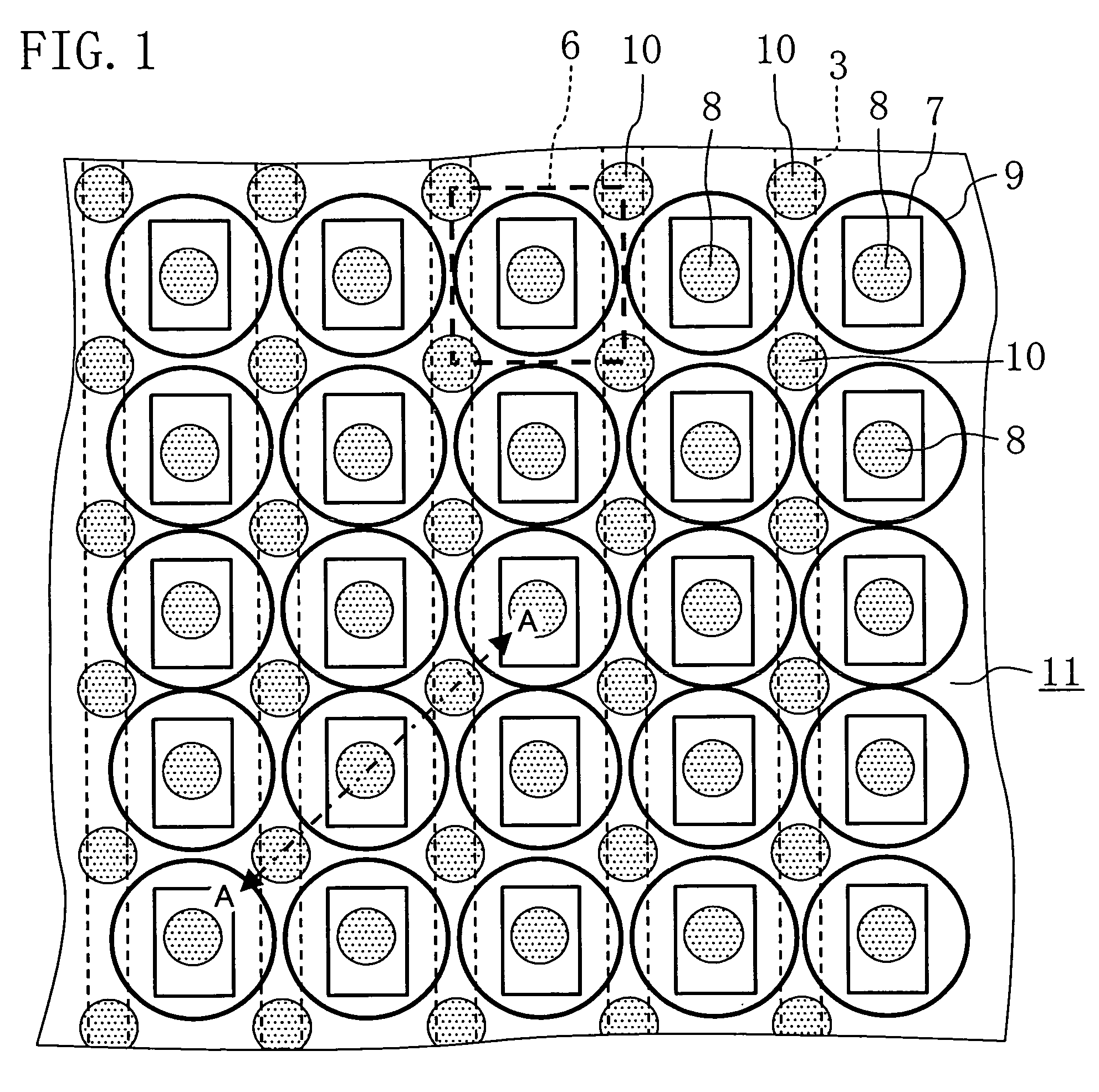
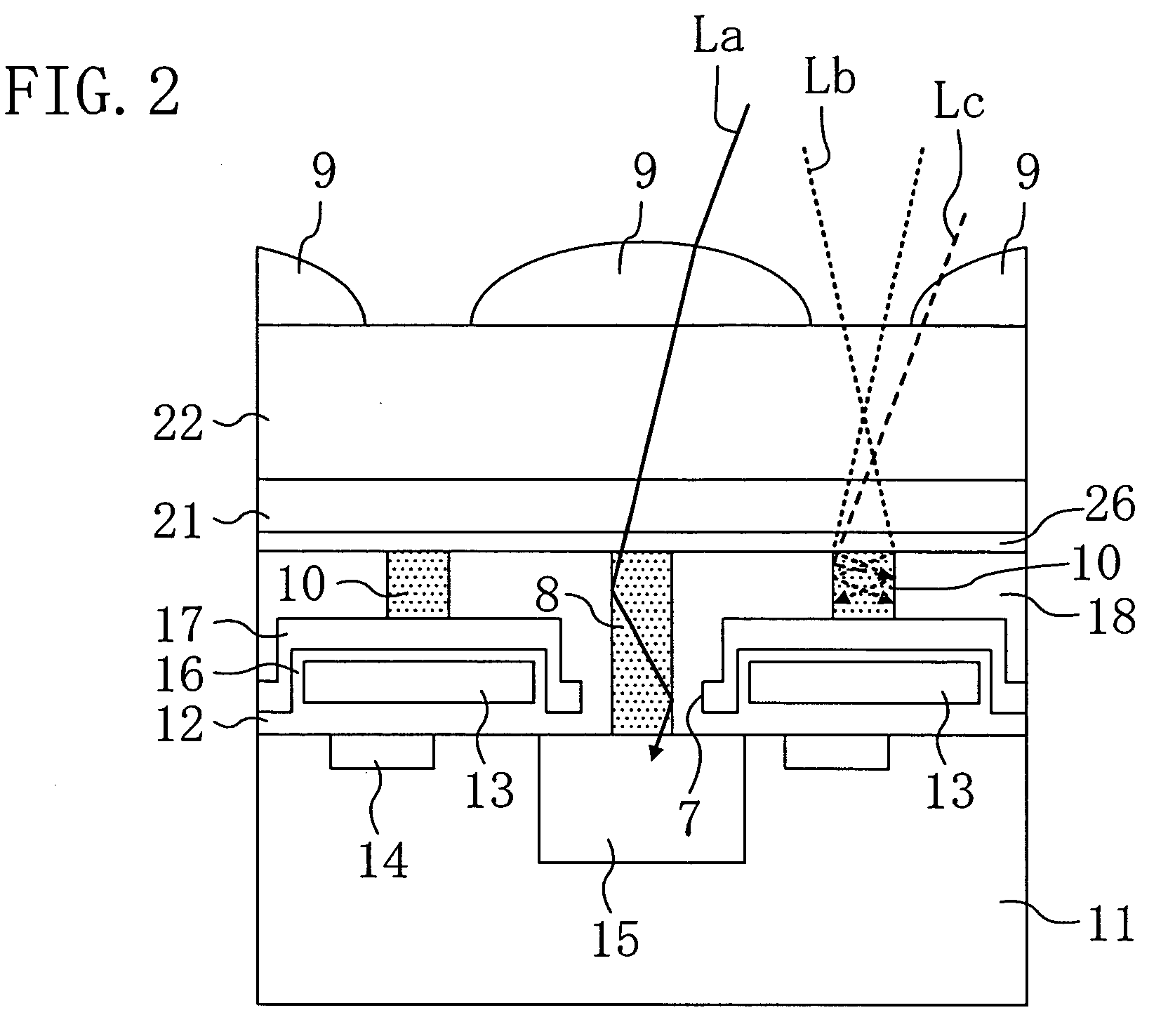
InactiveUS7283305B2Reduce variationOptimize dataTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerOptical axis
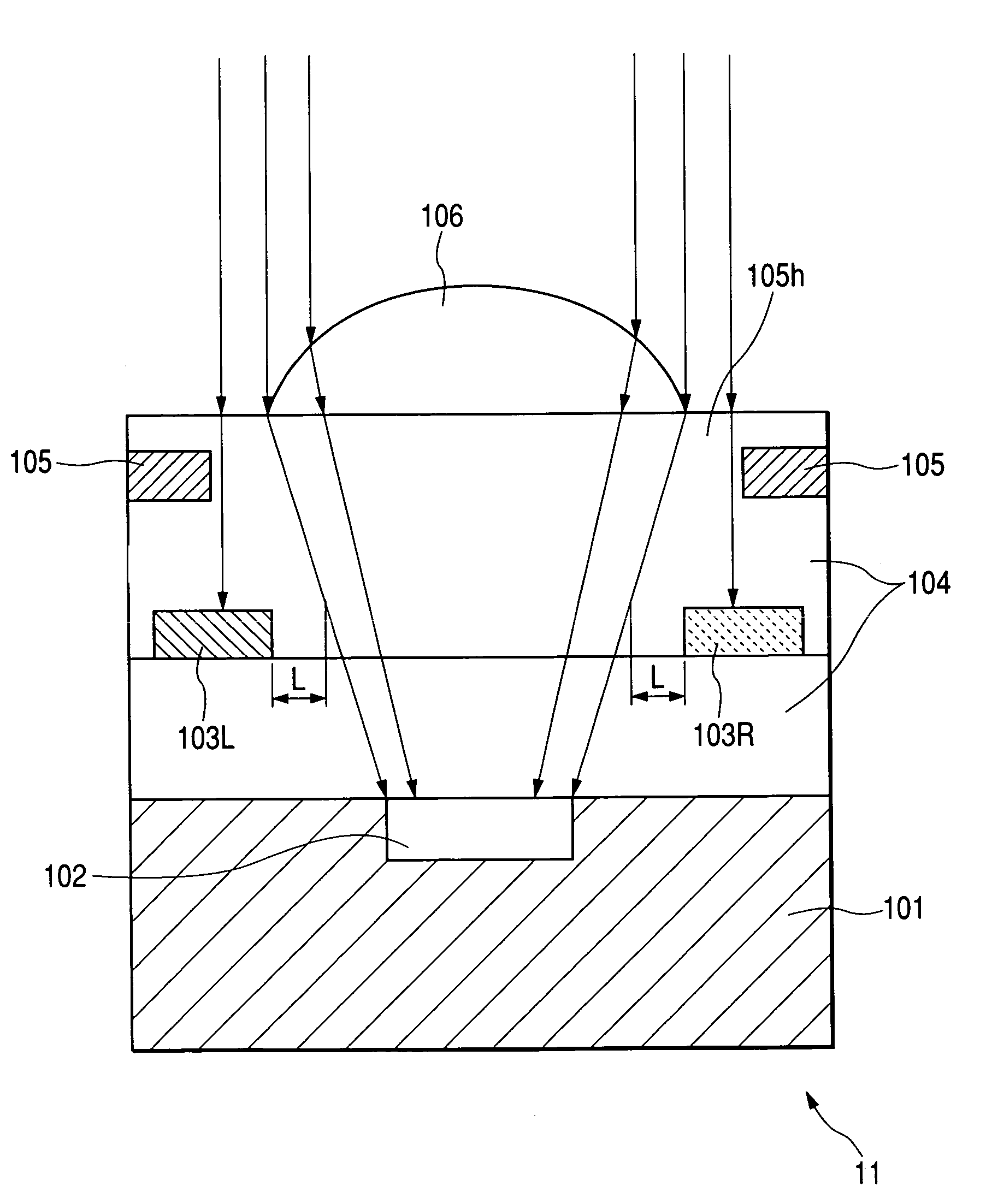
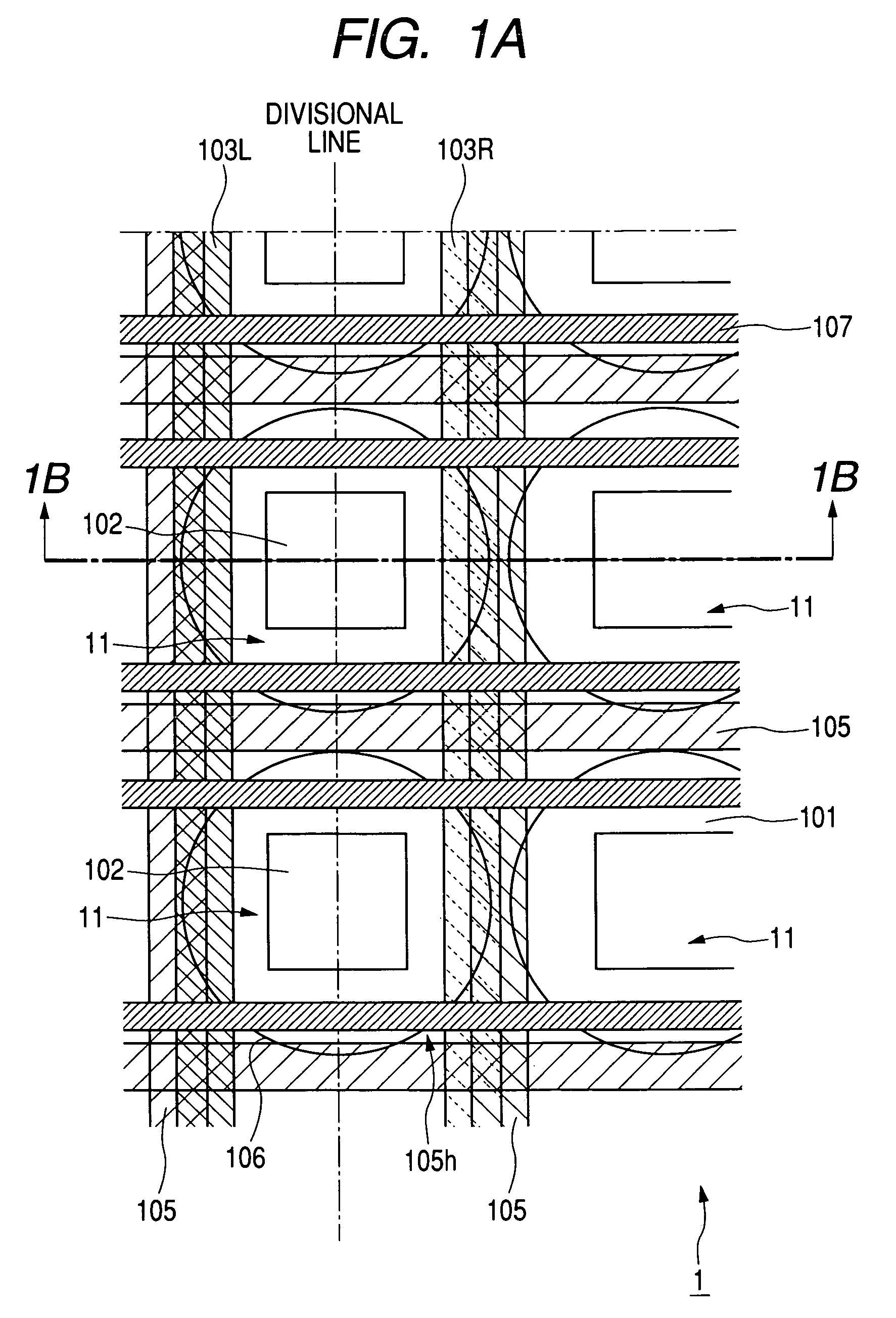
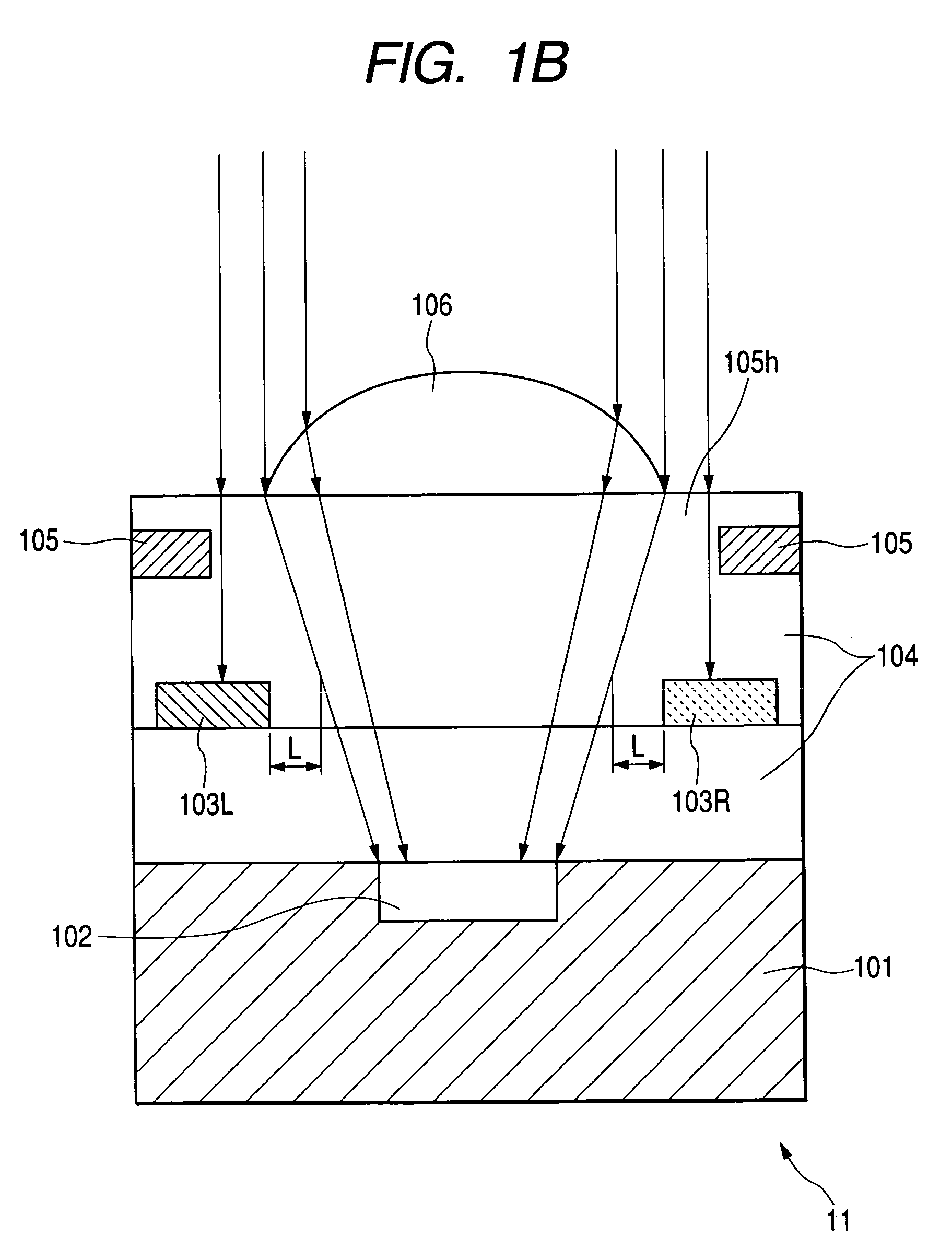
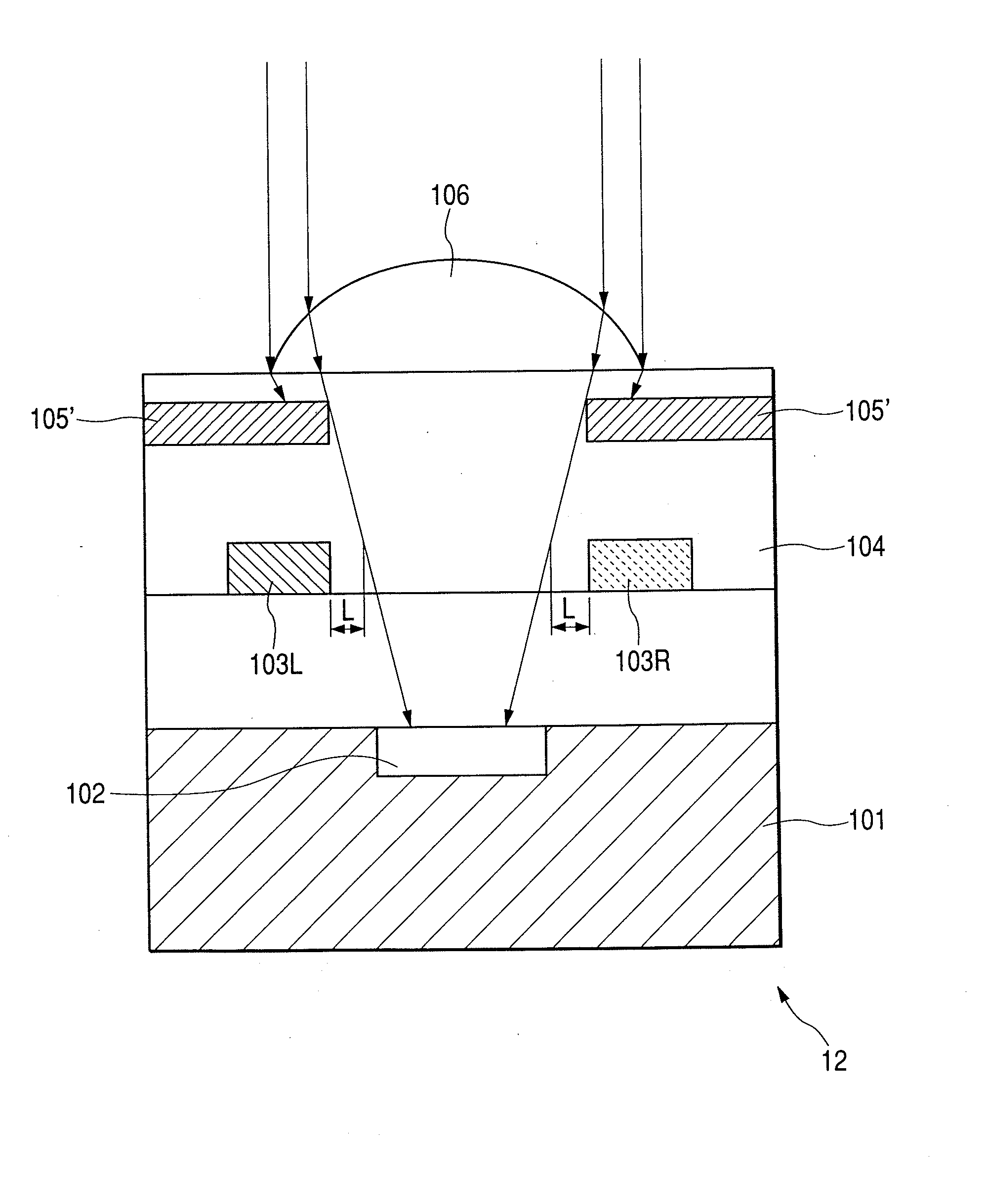
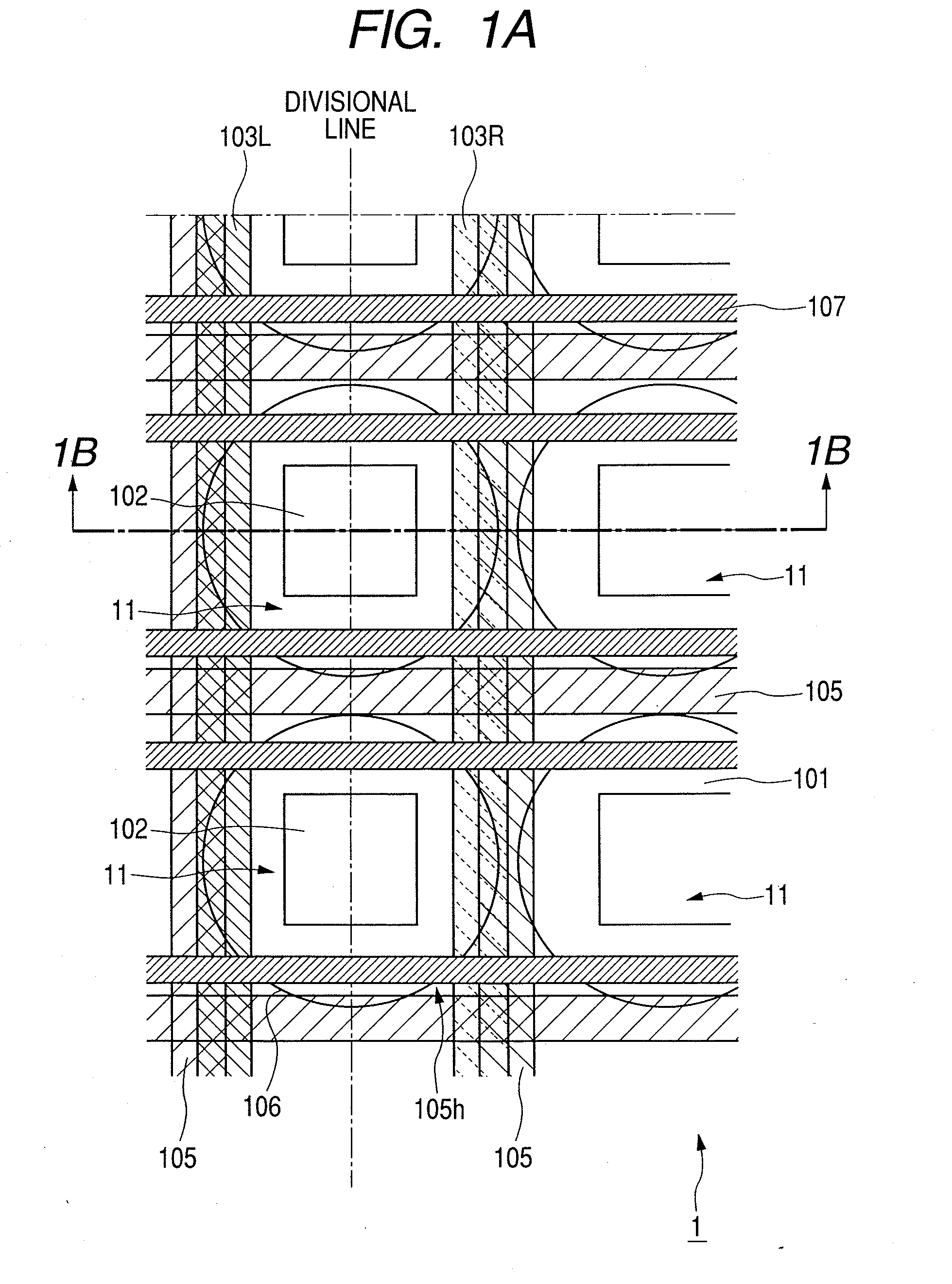
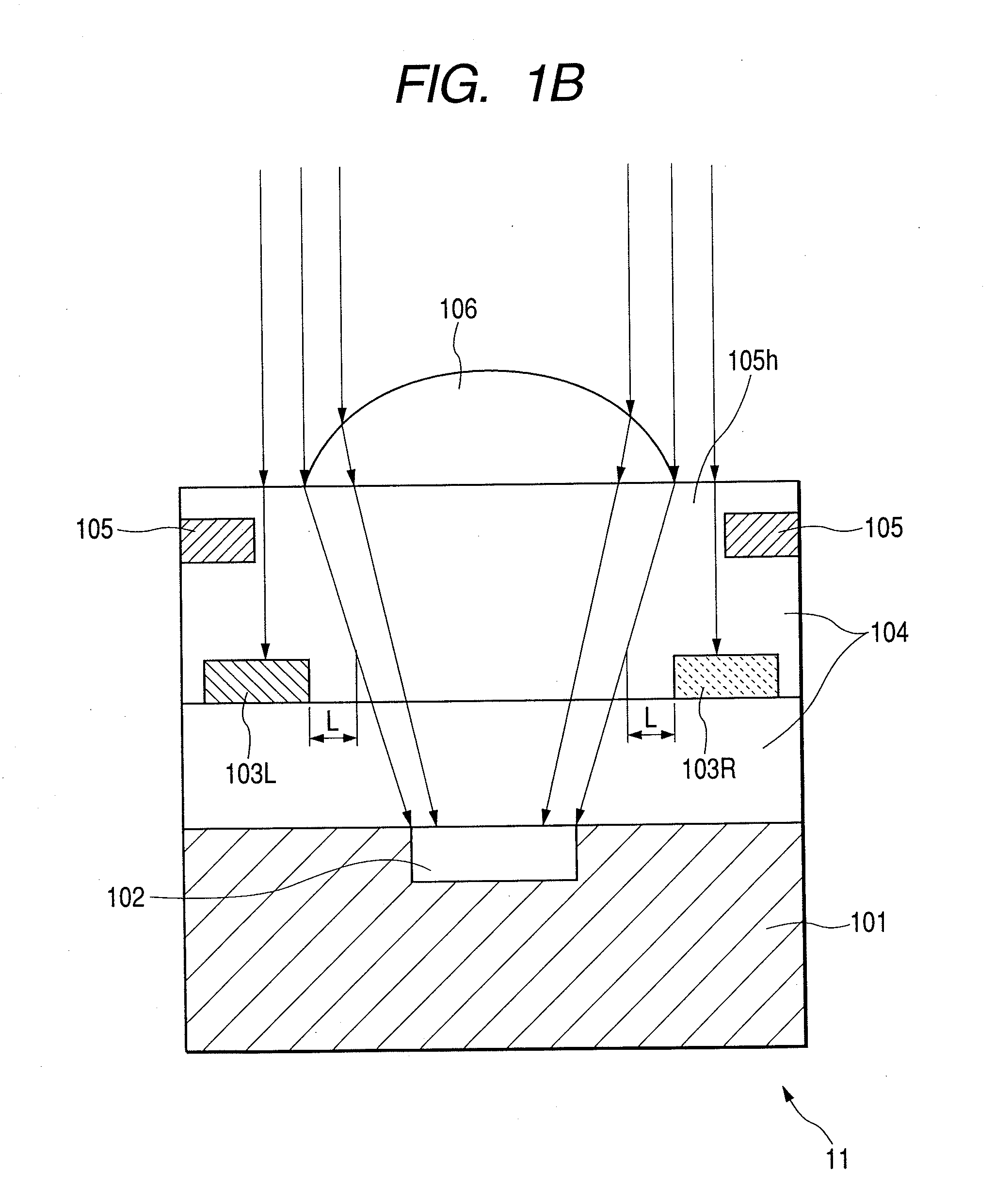
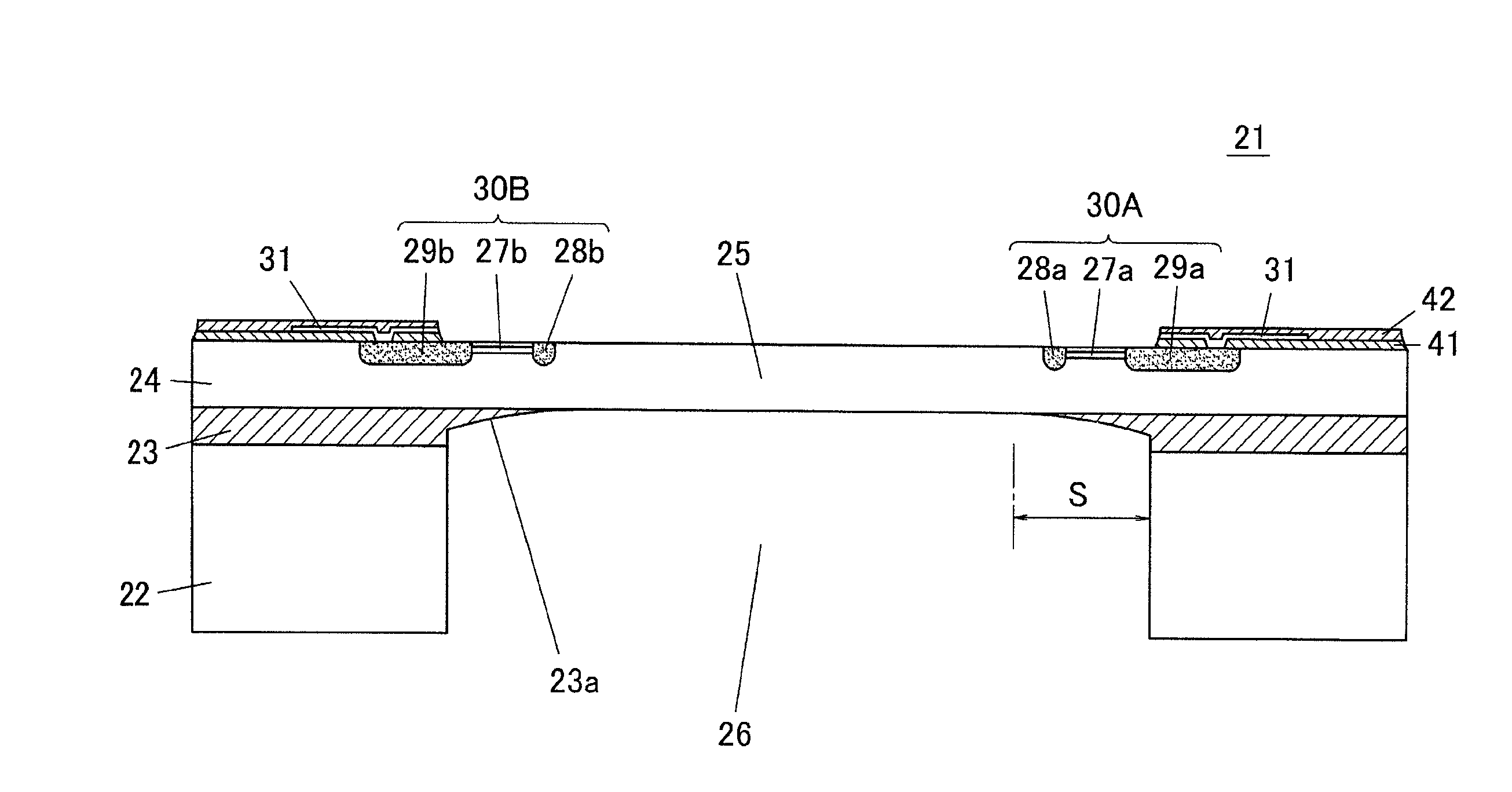
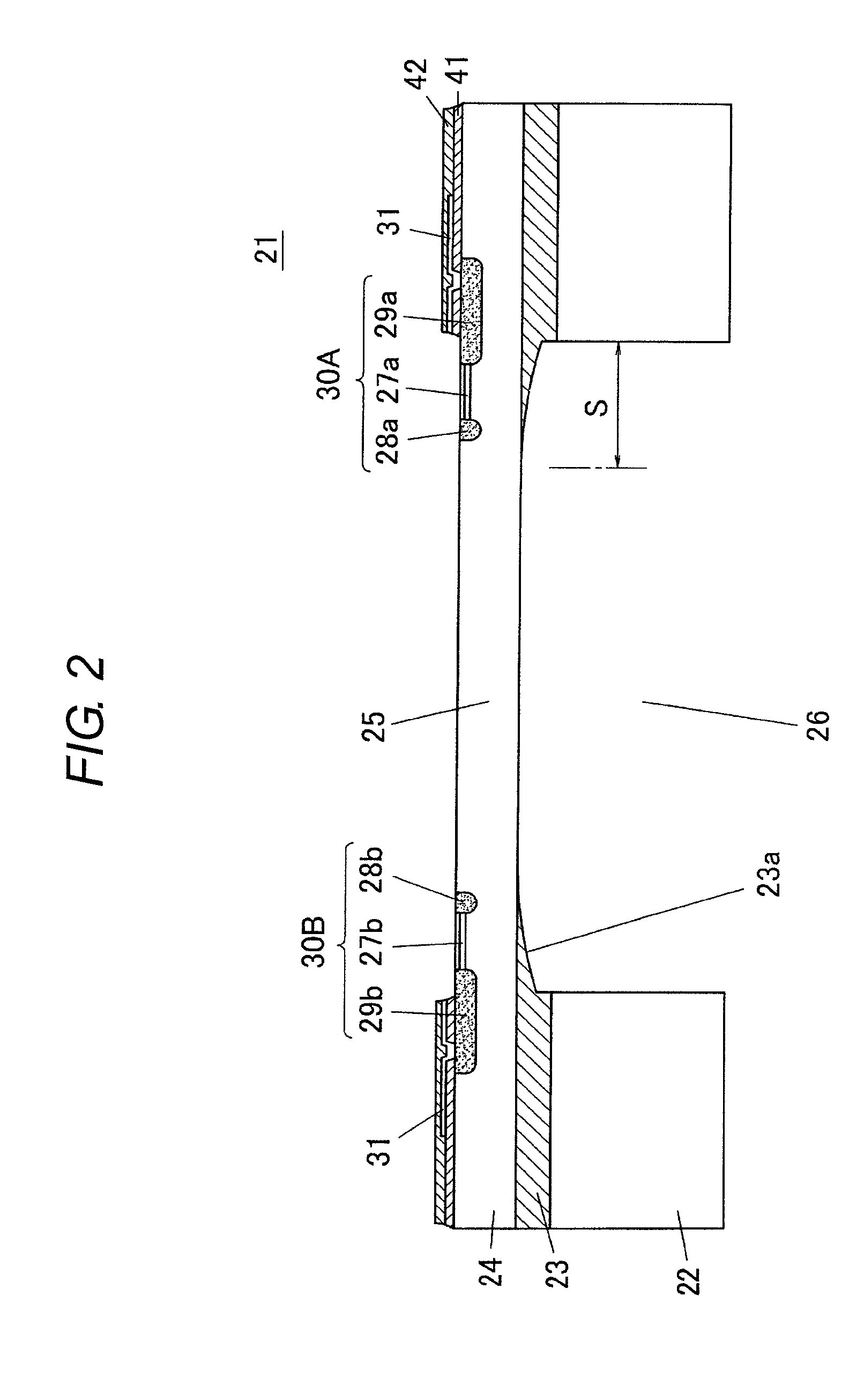
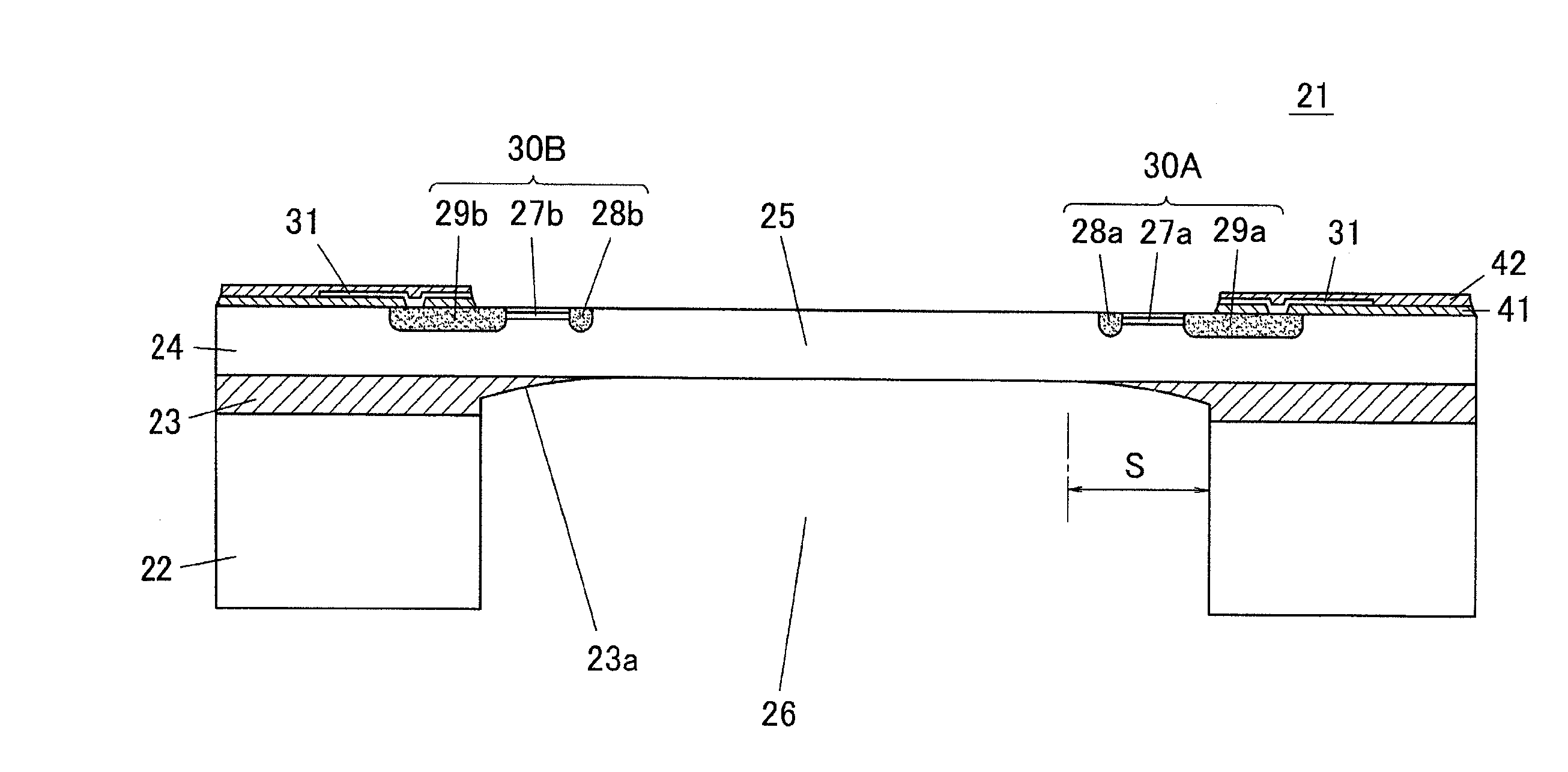
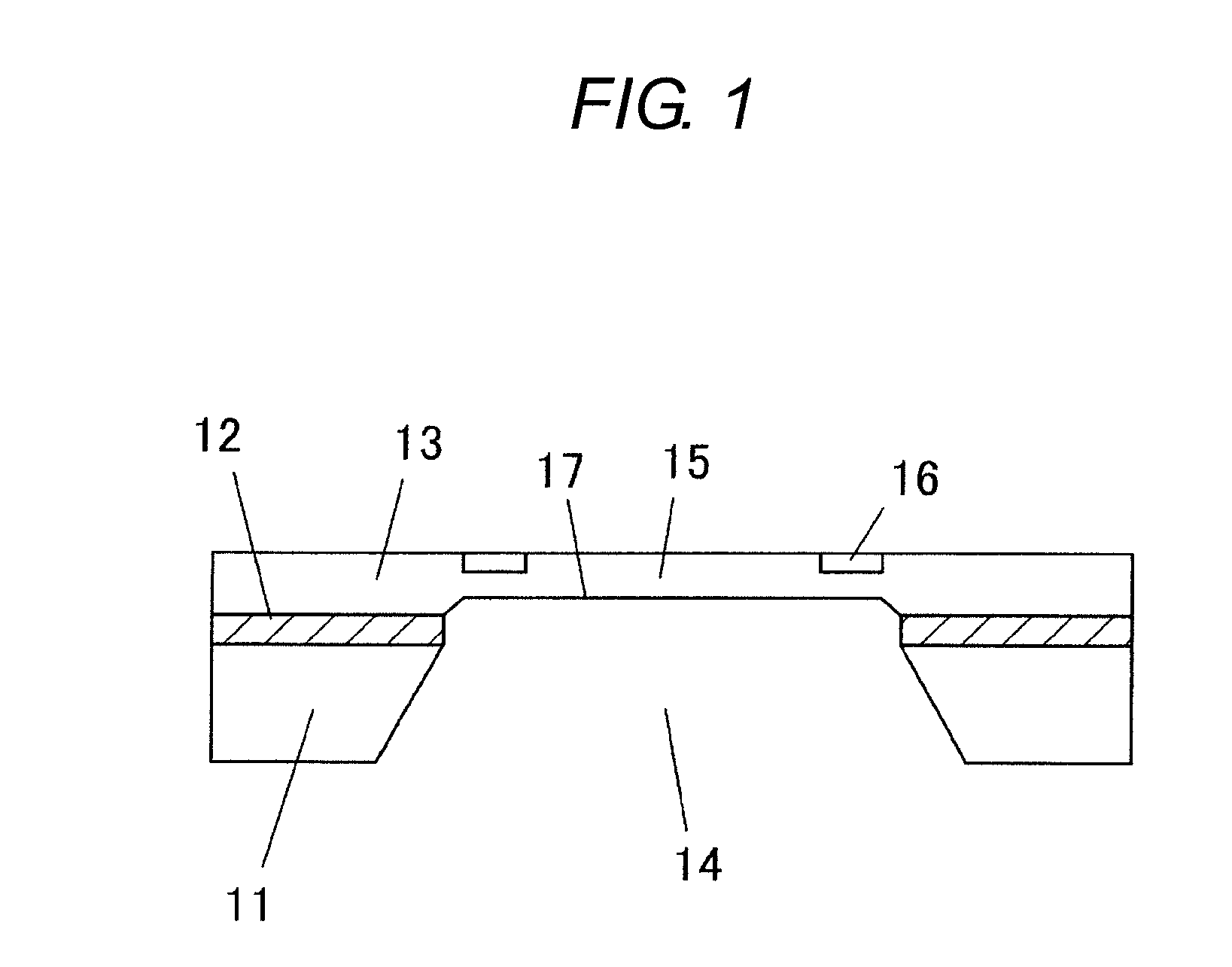
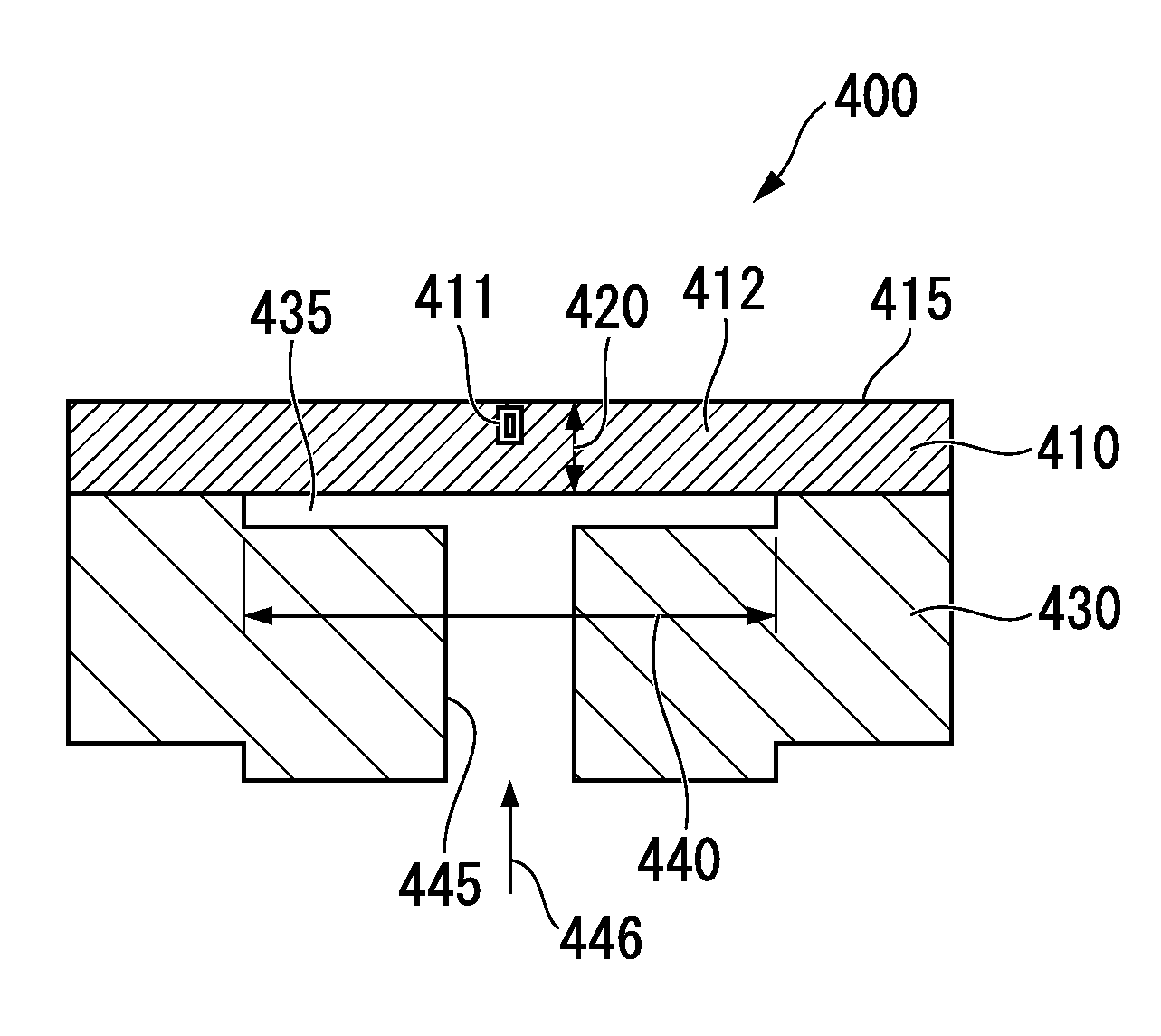
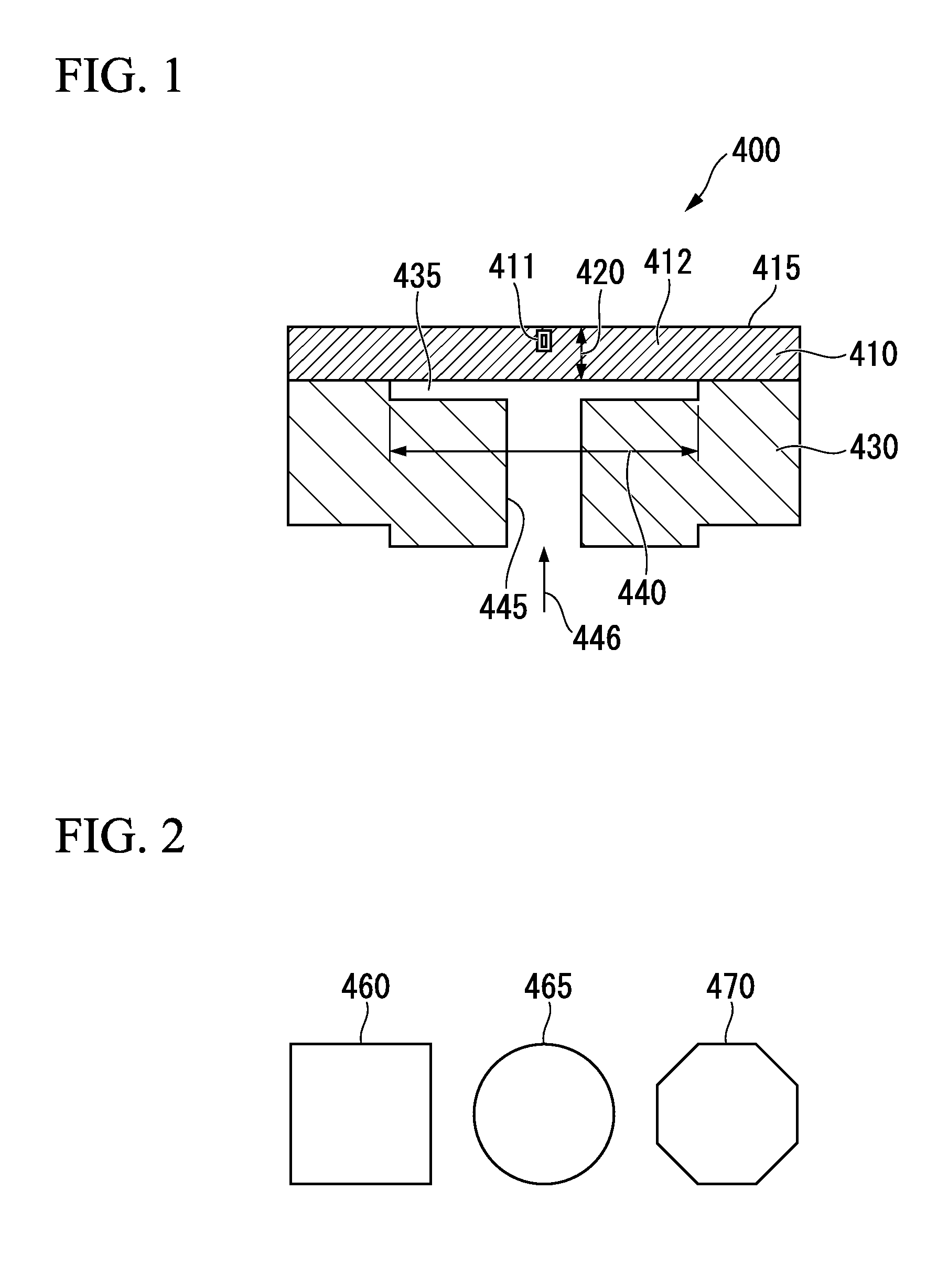
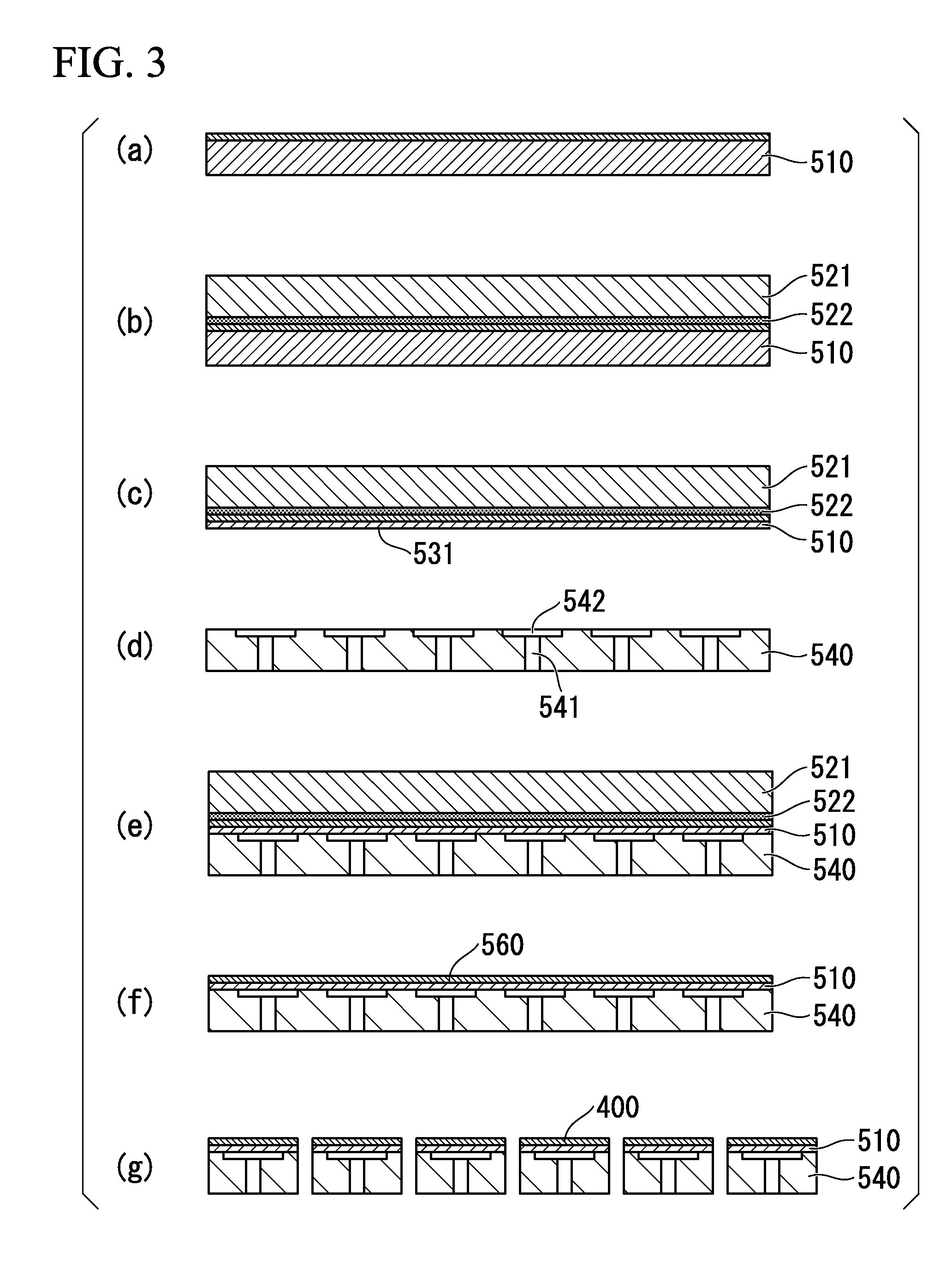
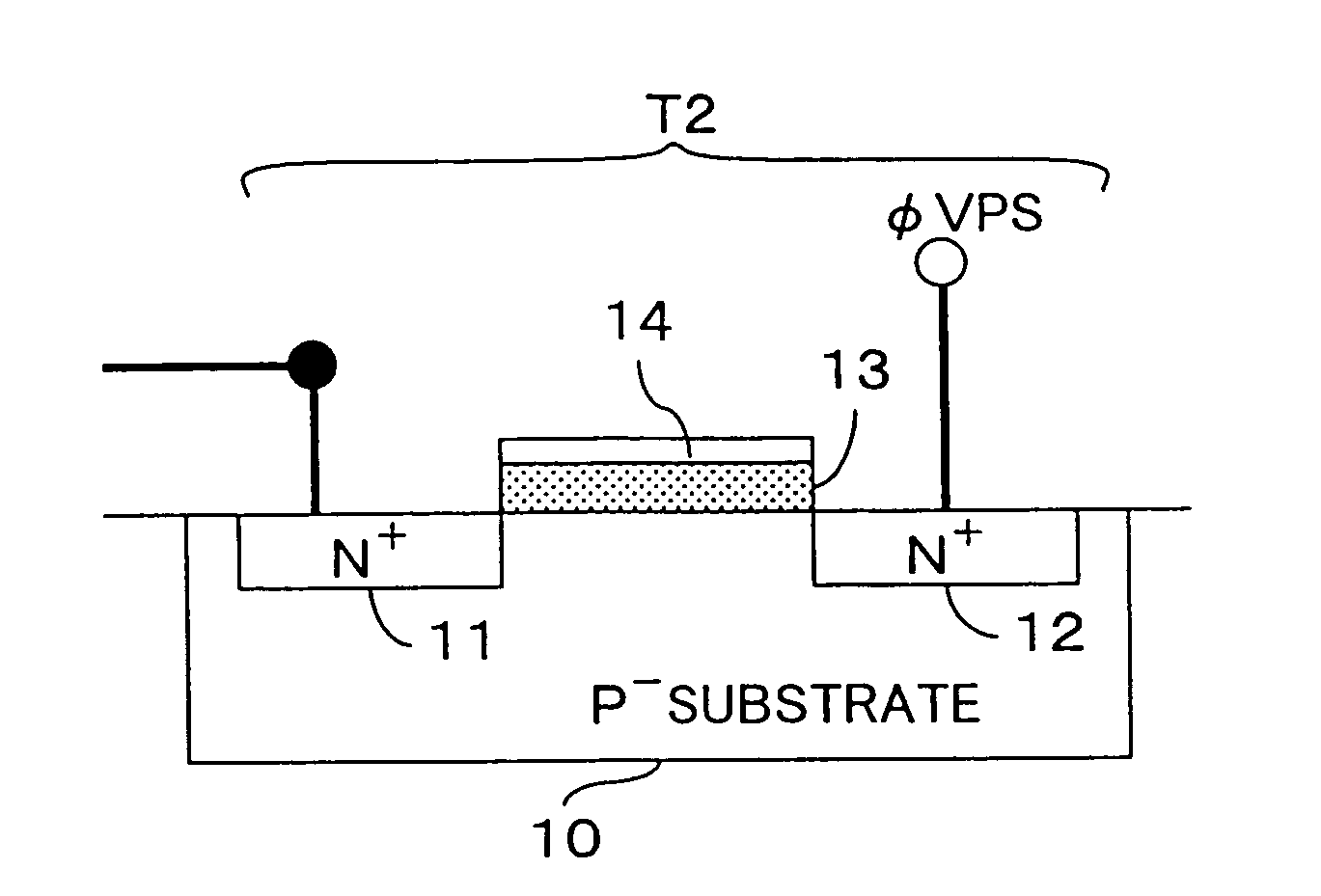
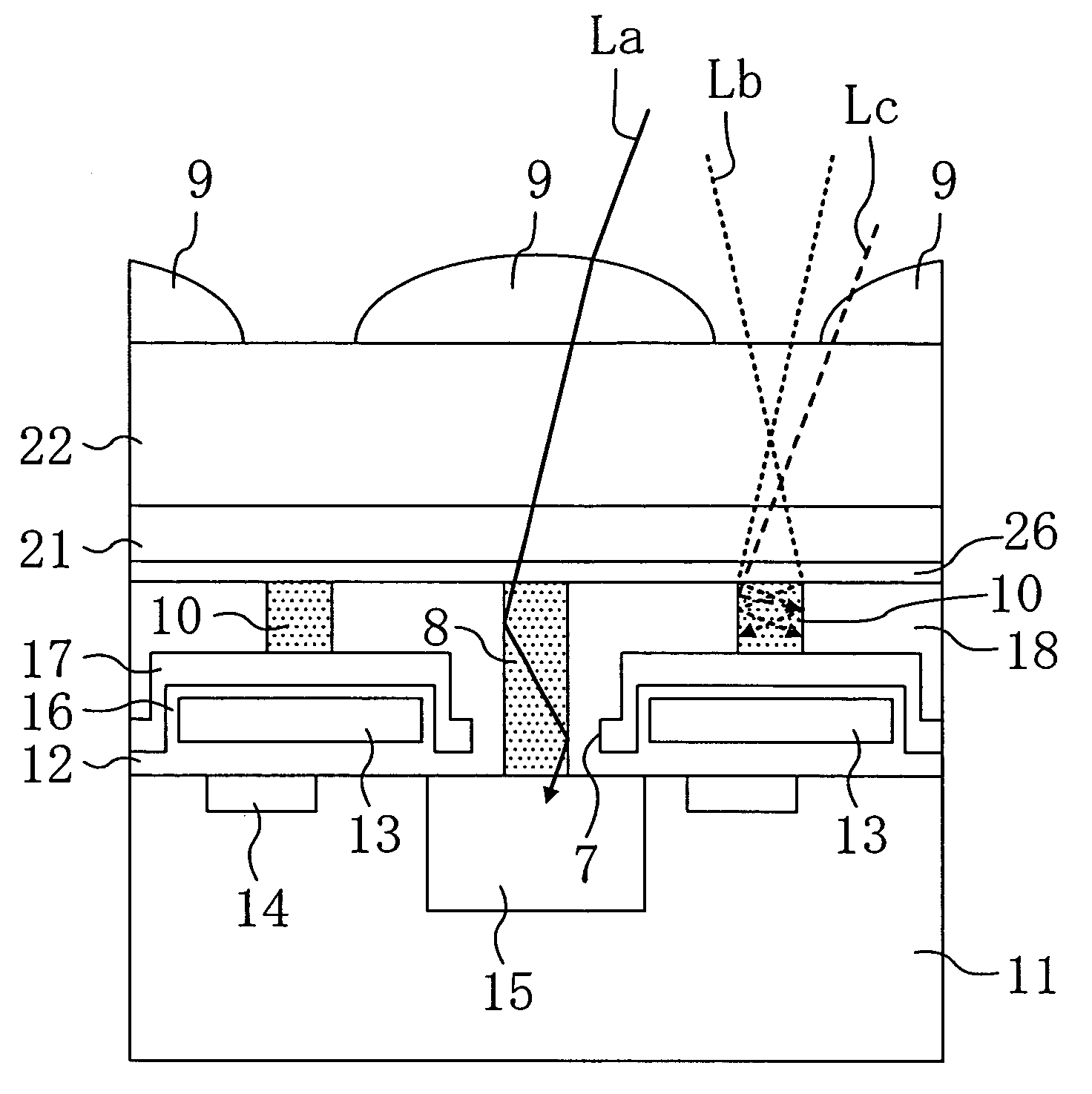
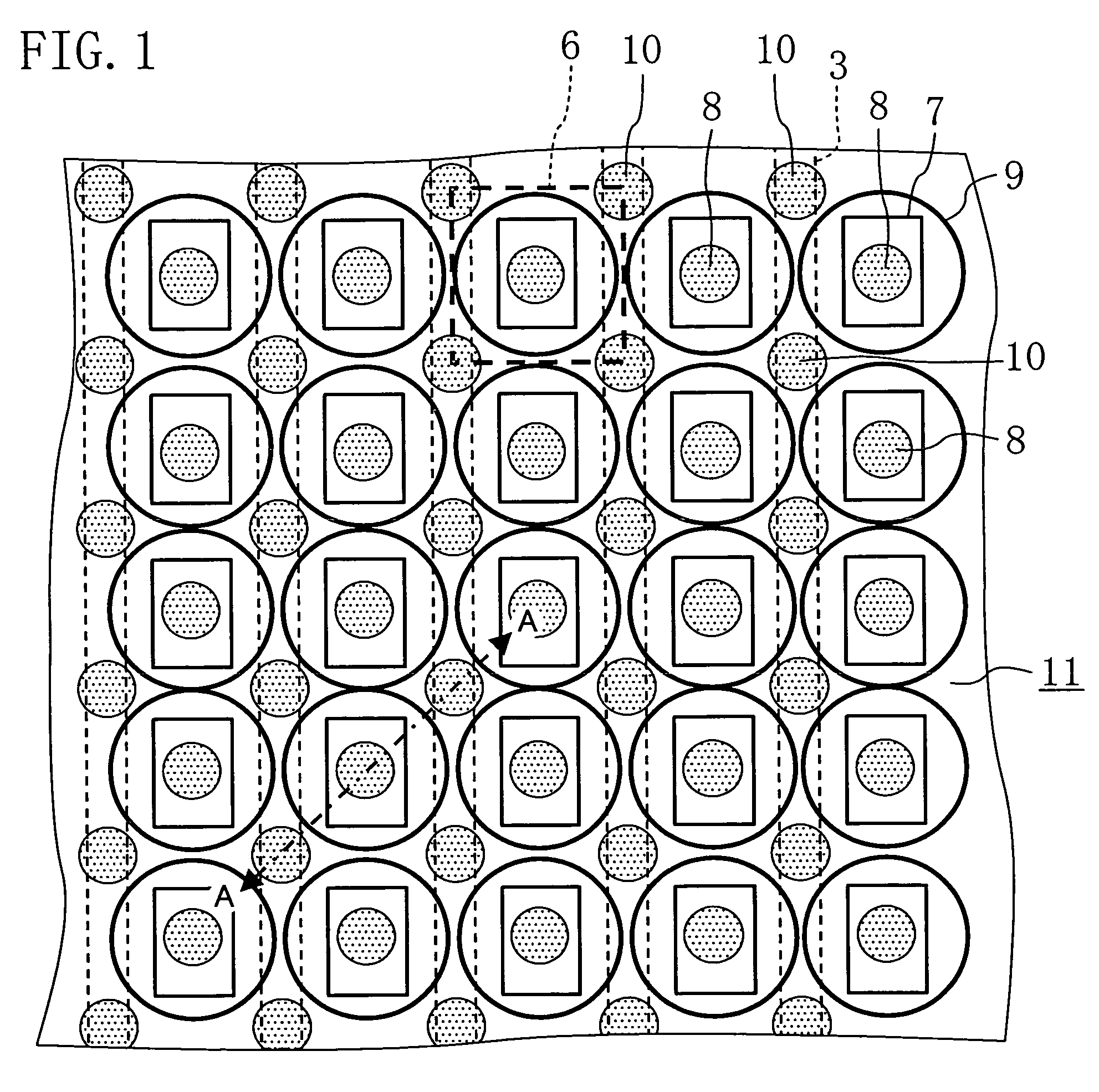
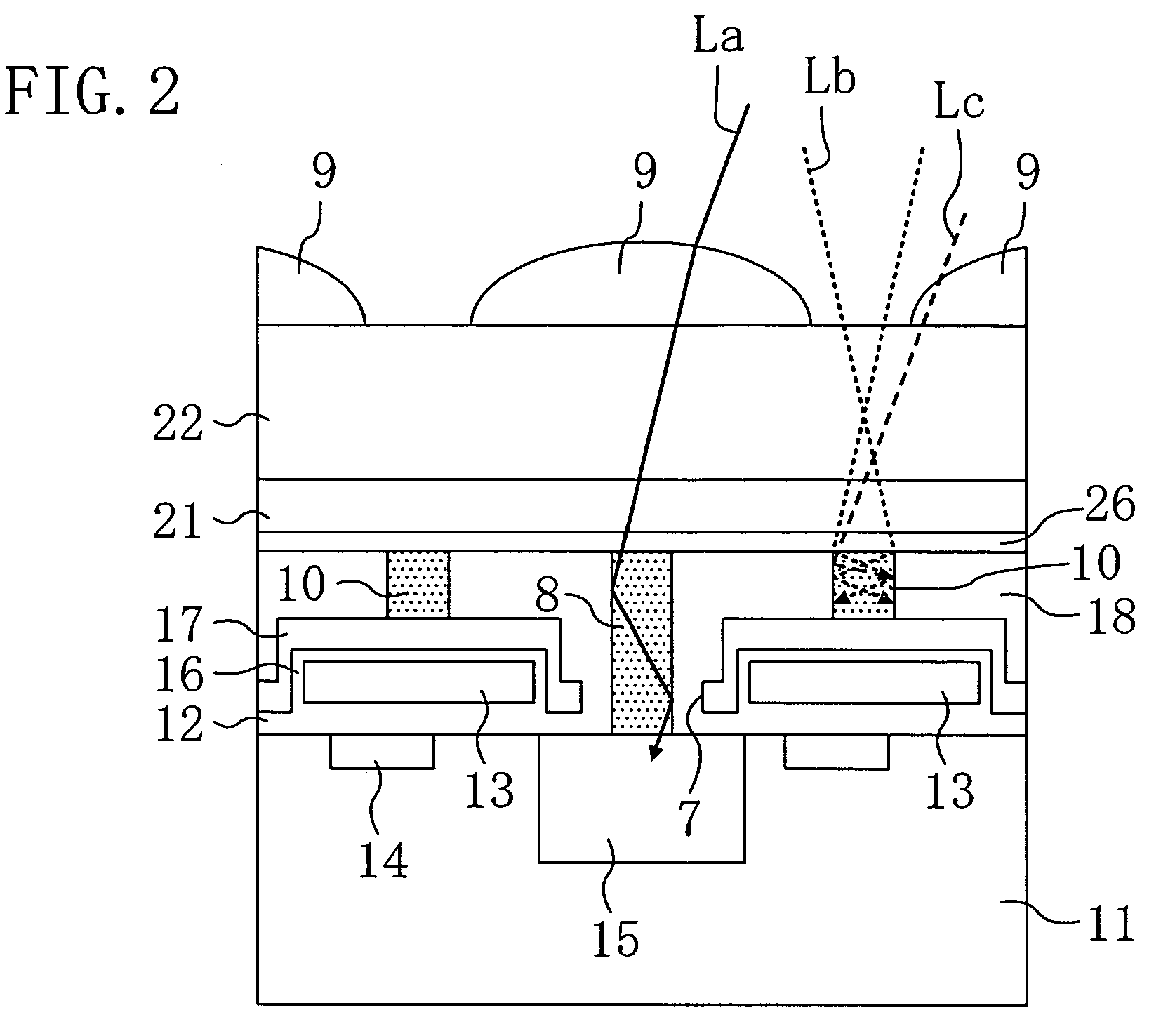
The present invention inhibits variations in sensitivity of an image pickup element formed in a jointed area in the image pickup element produced using exposure in a joined fashion.The image pickup element 11 has a light receiving area 102 formed on a substrate 101, an insulation layer 104 deposited on a light receiving area 102, and a microlens 106 formed on the insulation layer 104 and collecting incident light onto the light receiving area 102. A pattern 103L and a pattern 103R with an optical axis of the microlens 106 as a divisional line by exposure in a joined fashion in different exposure steps are arranged with an optical path for incident light collected by the microlens 106 held therebetween, and are provided so that a clearance from the optical path equals a distance L. The distance L is set to be larger than the alignment accuracy of an exposure device exposing the patterns 103L and 103R.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiometer measurement linearization system and method
ActiveUS7250747B1Variation in sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeRadiation pyrometryDirection finders using radio wavesAudio power amplifierDetector circuits
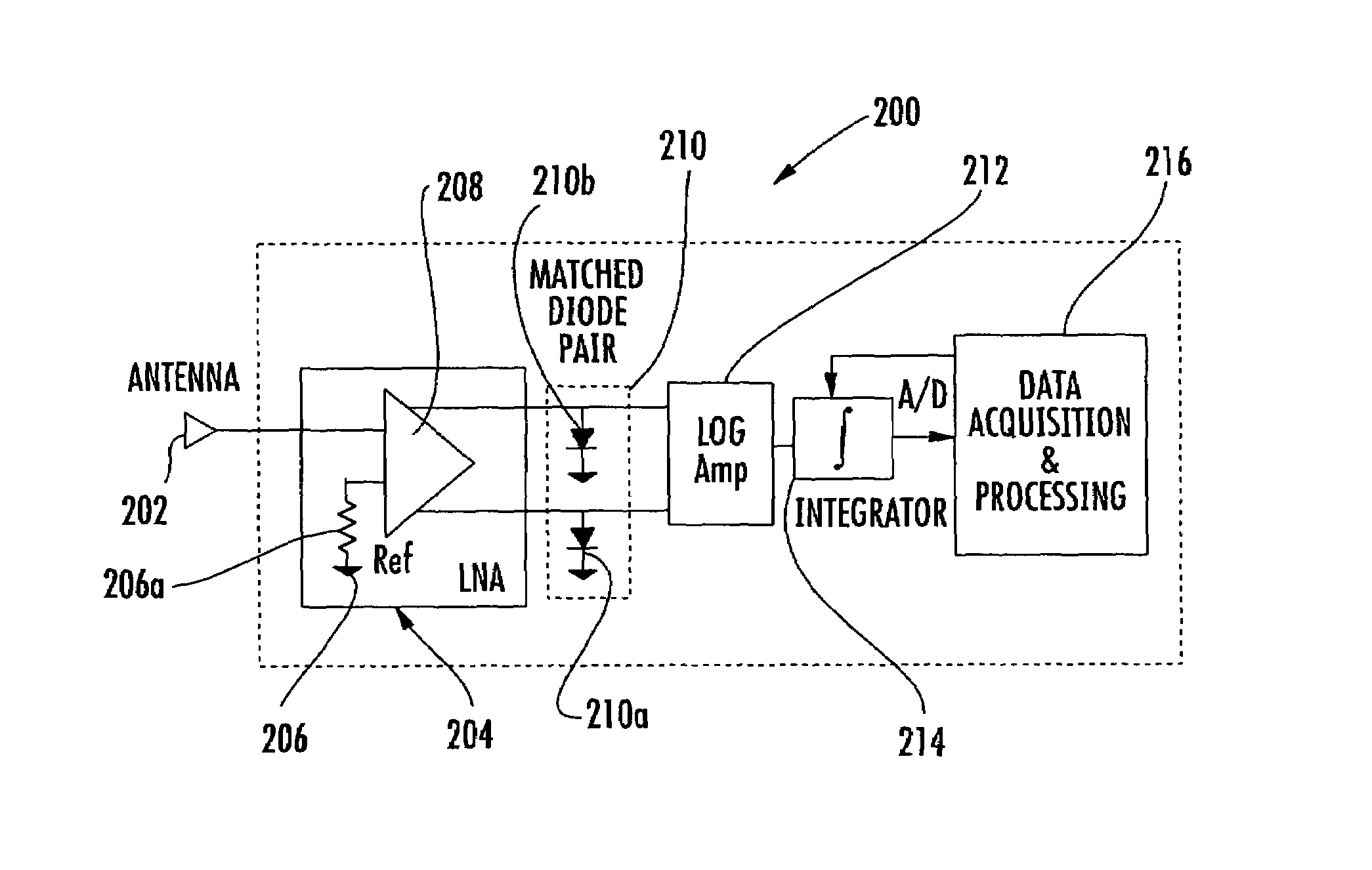
A radiometer system includes a dual channel, quadrature hybrid amplifier circuit that receives an antenna signal and a known reference signal to equalize gain in two parallel gain stages. A detector circuit receives a signal from the quadrature hybrid amplifier circuit and detects the signals to form a detected output for eliminating sensitivity to gain variations, improving dynamic range of the input signal, and reducing calibration requirements. A log ratio amplifier receives and linearizes the detected output. An integrator circuit receives a signal from the log ratio amplifier and sums the signal over an observation.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
Audio monitoring system
ActiveUS8160261B2Variation in sensitivityReduce gainGain controlIntra aural earpiecesMonitoring systemComputer science
An earphone monitoring system is disclosed that provides for user information and control regarding ambient and monitored sound levels.
Owner:SENSAPHONICS
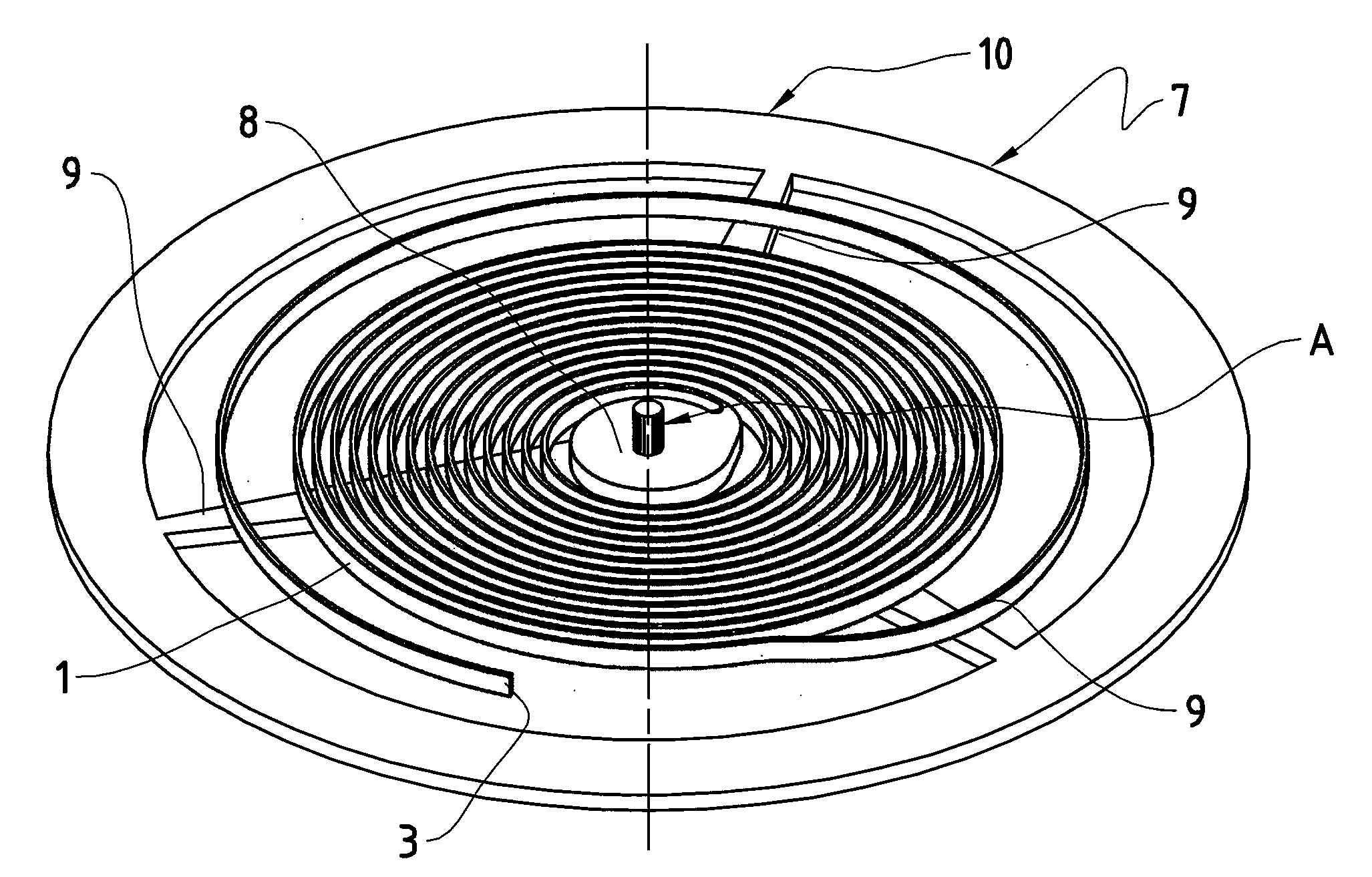
Mechanical oscillator having an optimized thermoelastic coefficient
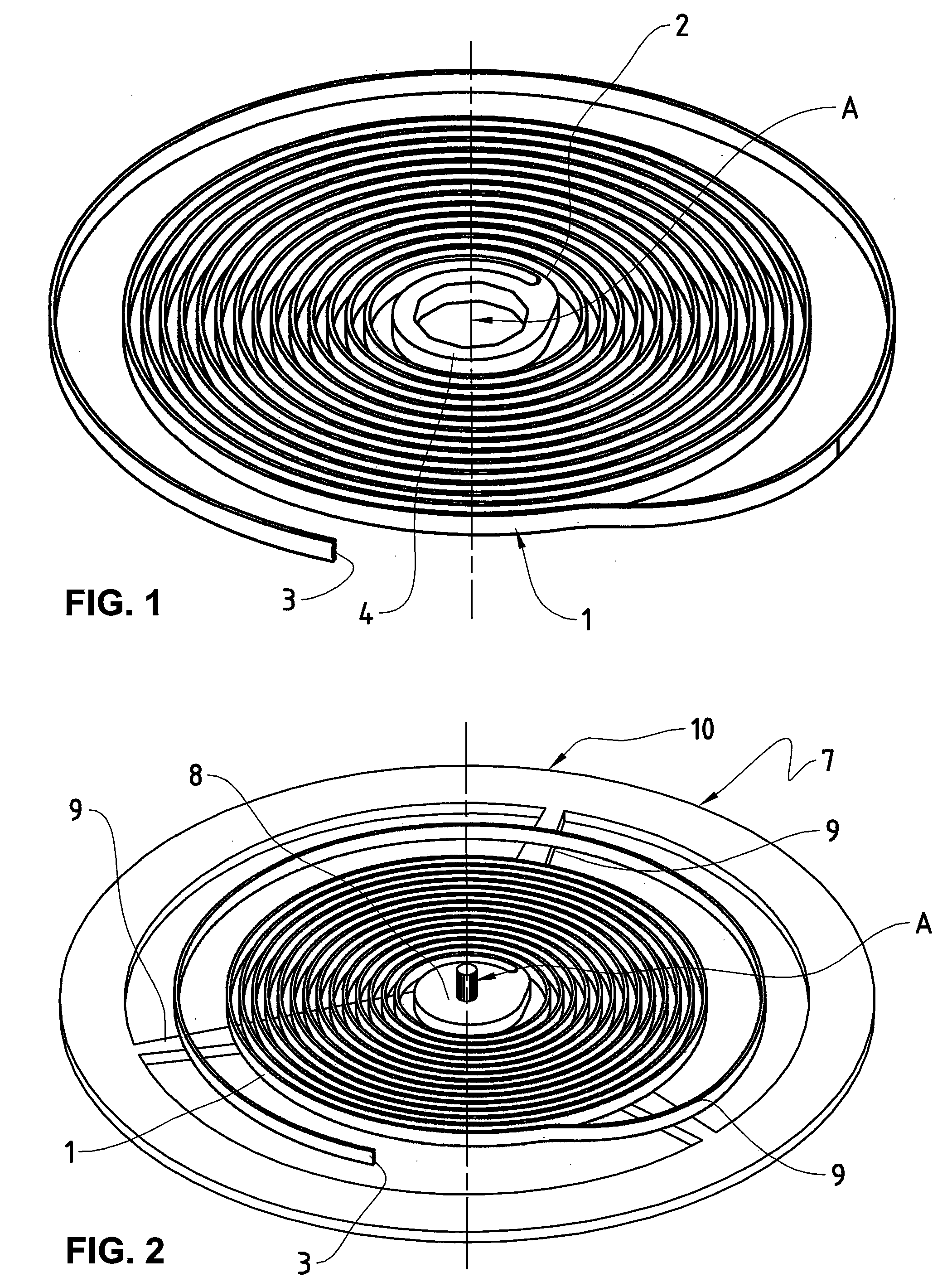
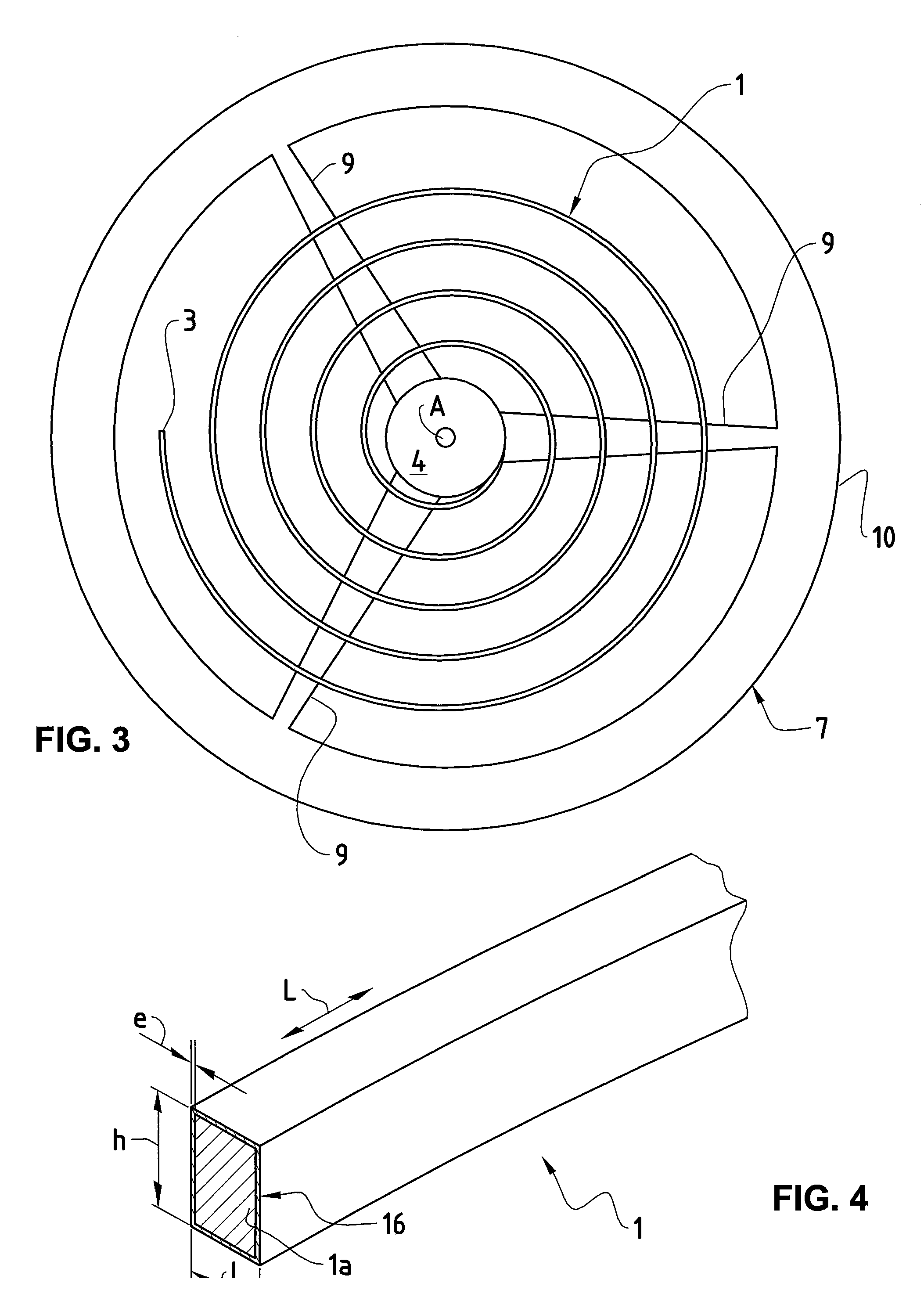
ActiveUS20100290320A1Variation in sensitivityReliable and precise mechanical oscillatorsImpedence networksFrequency stabilisation mechanismCoil springEngineering
The invention relates to a mechanical oscillator, in particular for watchmaking, comprising a spiral spring (1) having a number N of turns, a central end (2), an eccentric end (3) and a rotary collet (4), connected to the central end (2), comprising an orifice intended to receive an arbor for rotation about an axis (A), and a balance (7), the axis of rotation of which coincides with the rotation arbor (A), the eccentric end (3) being intended to be integral with a stationary element of the “balance-cock” type, said spiral spring (1) being made up of a single-crystal silicon (Si) core (1a) and at least one peripheral coating (1b) based on a material having a thermoelastic coefficient different from that of silicon, the single-crystal silicon (Si) being oriented along the crystallographic axis {1,1,1} to optimize the temperature coefficient of the mechanical oscillator as a whole. In addition, this invention likewise relates to a method of designing said mechanical oscillator, consisting in optimizing the temperature coefficient of the complete oscillator in order to limit its thermal drift.
Owner:MFG & FAB DE MONTRES & DE CHRONOMETRES ULYSSE NARDIN LE LOCLE SA
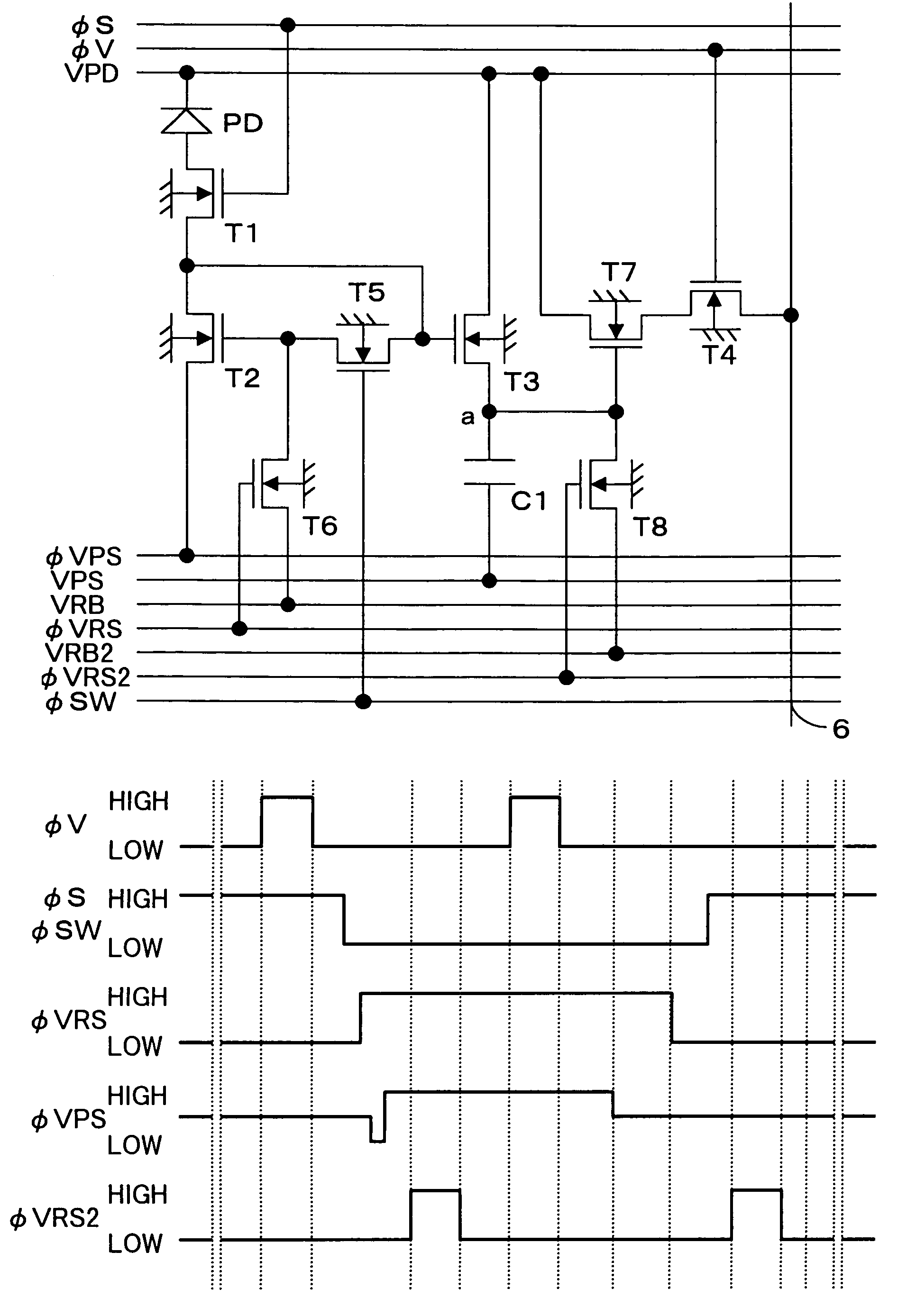
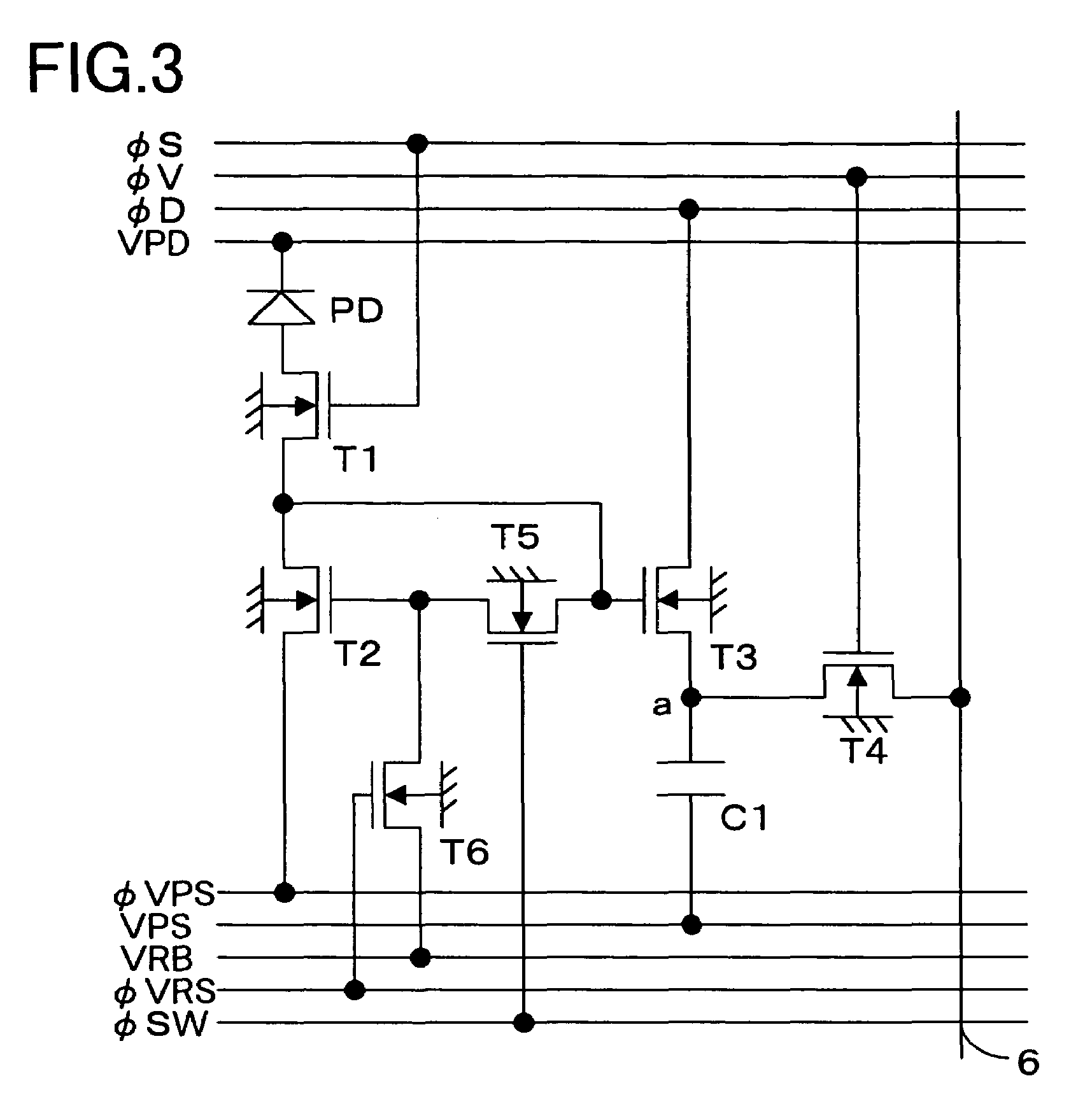
Solid-state image-sensing device
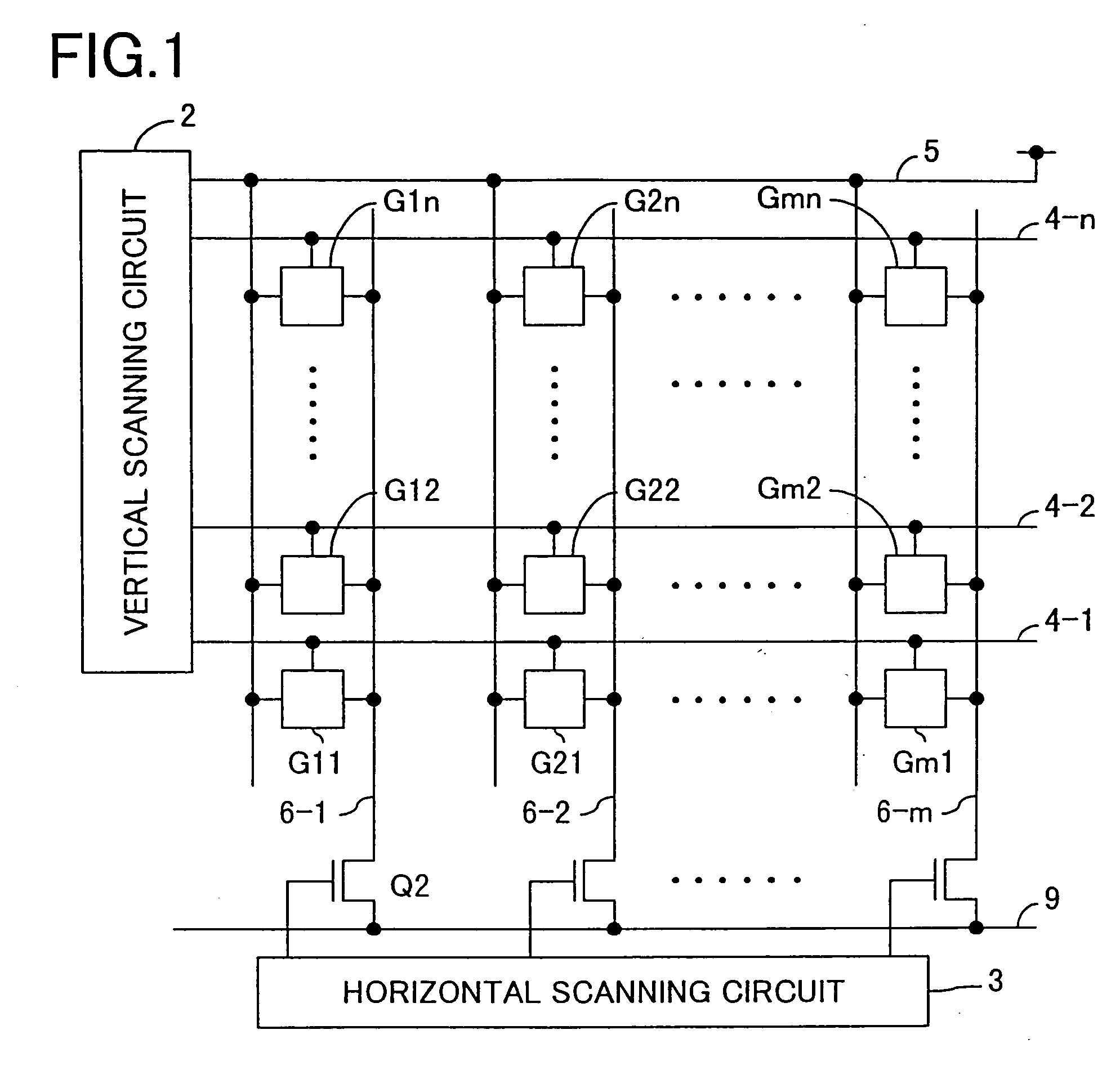
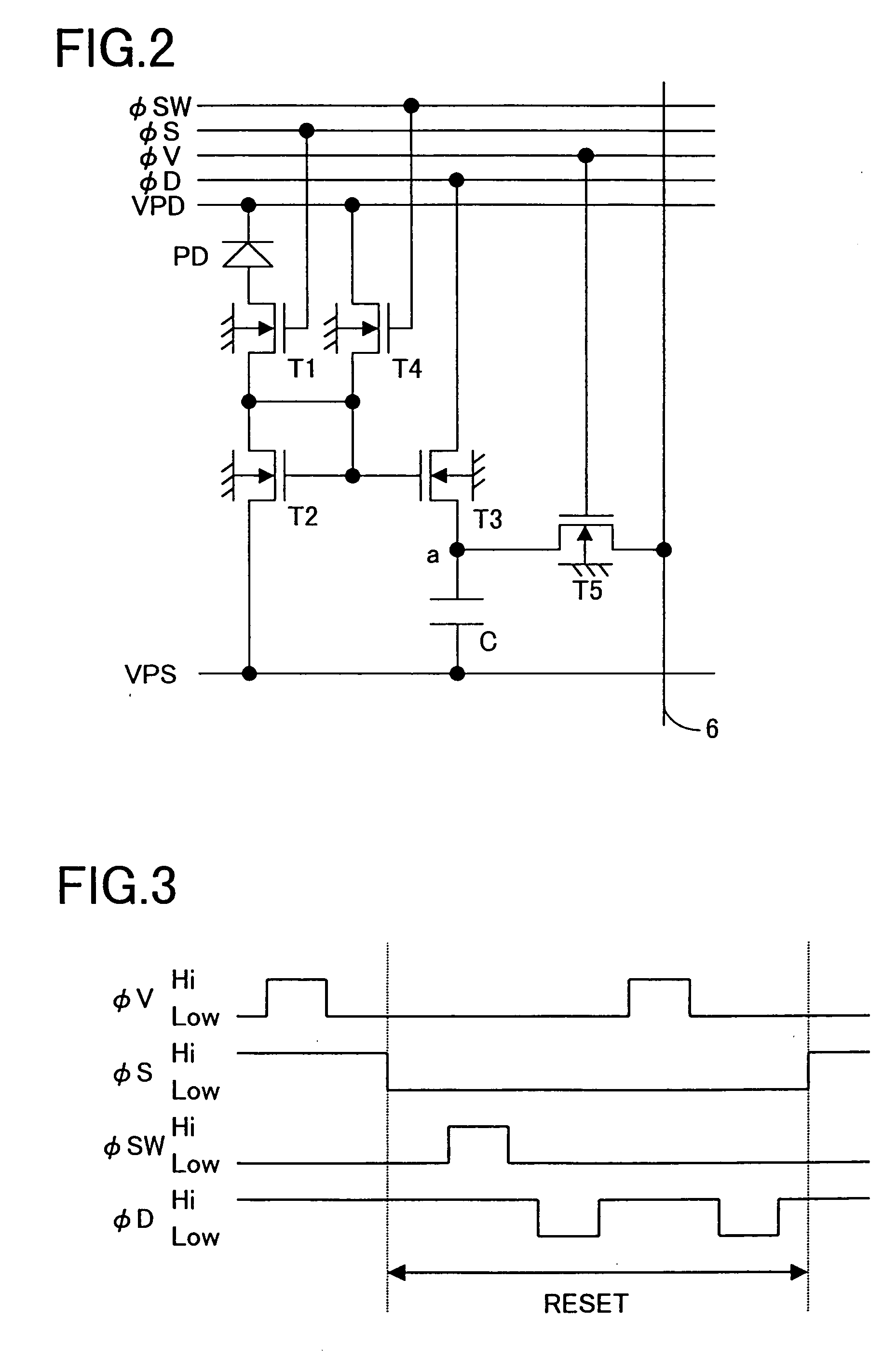
InactiveUS7030921B2Accurate collectionMinimize changesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage sensingTransistor
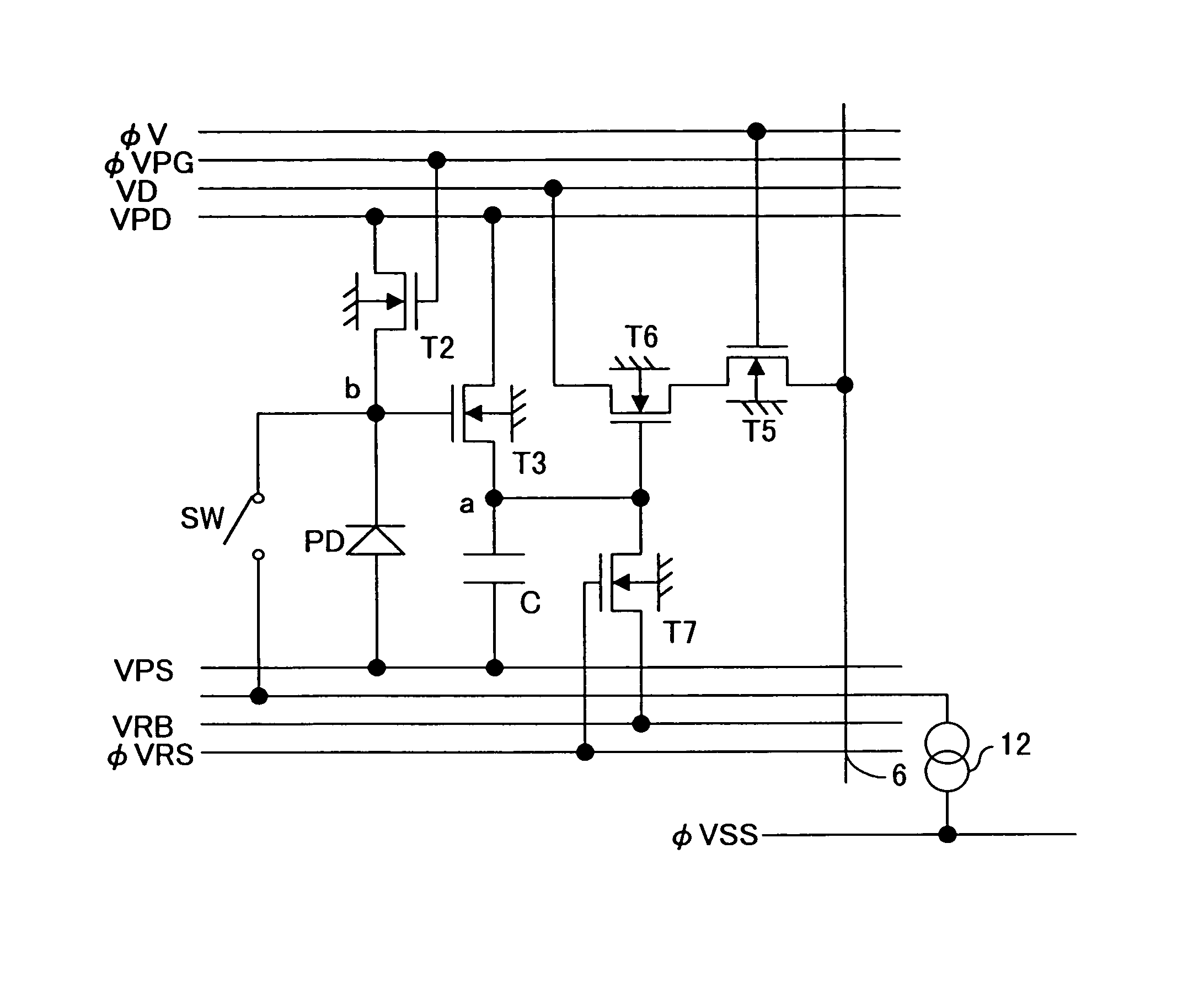
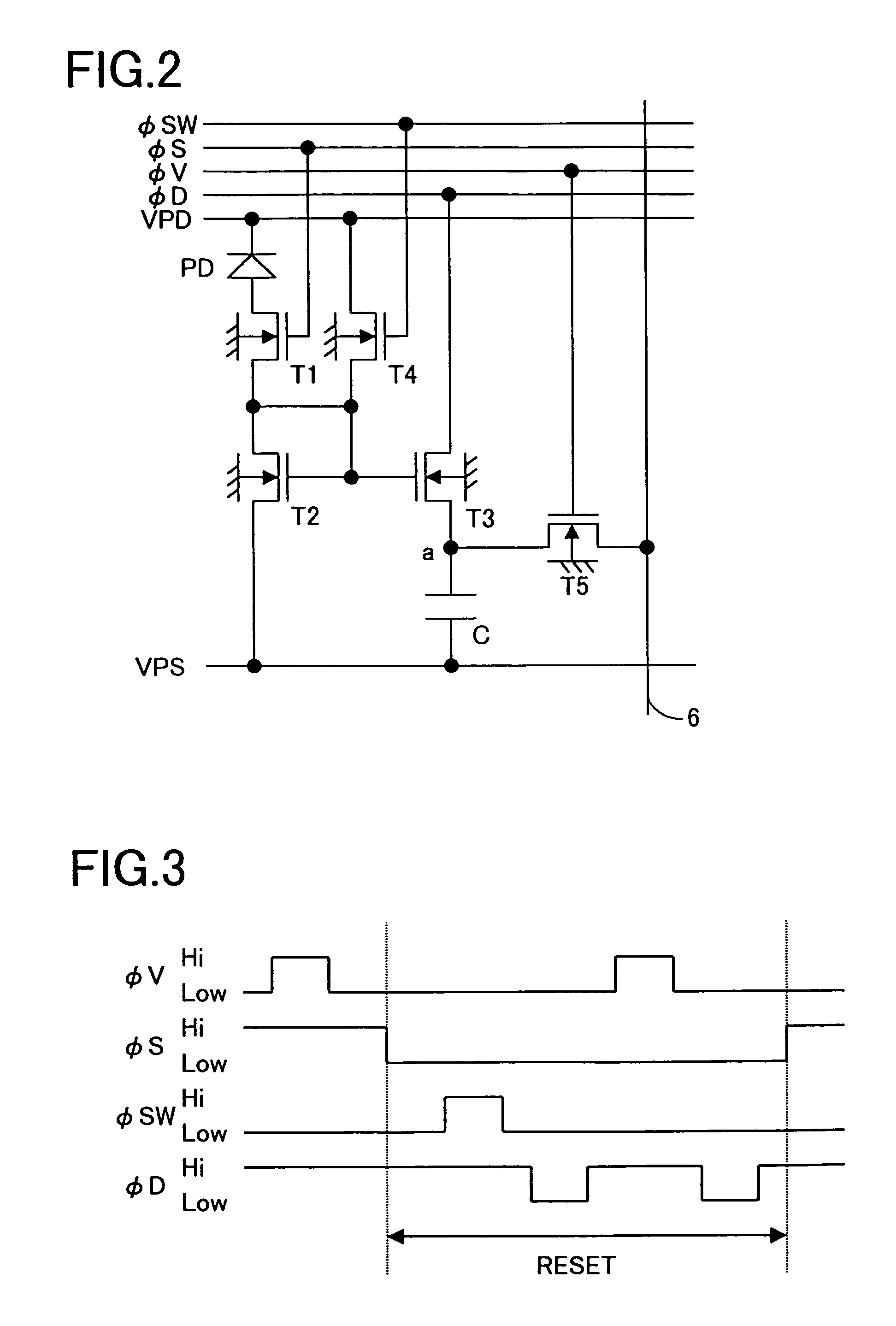
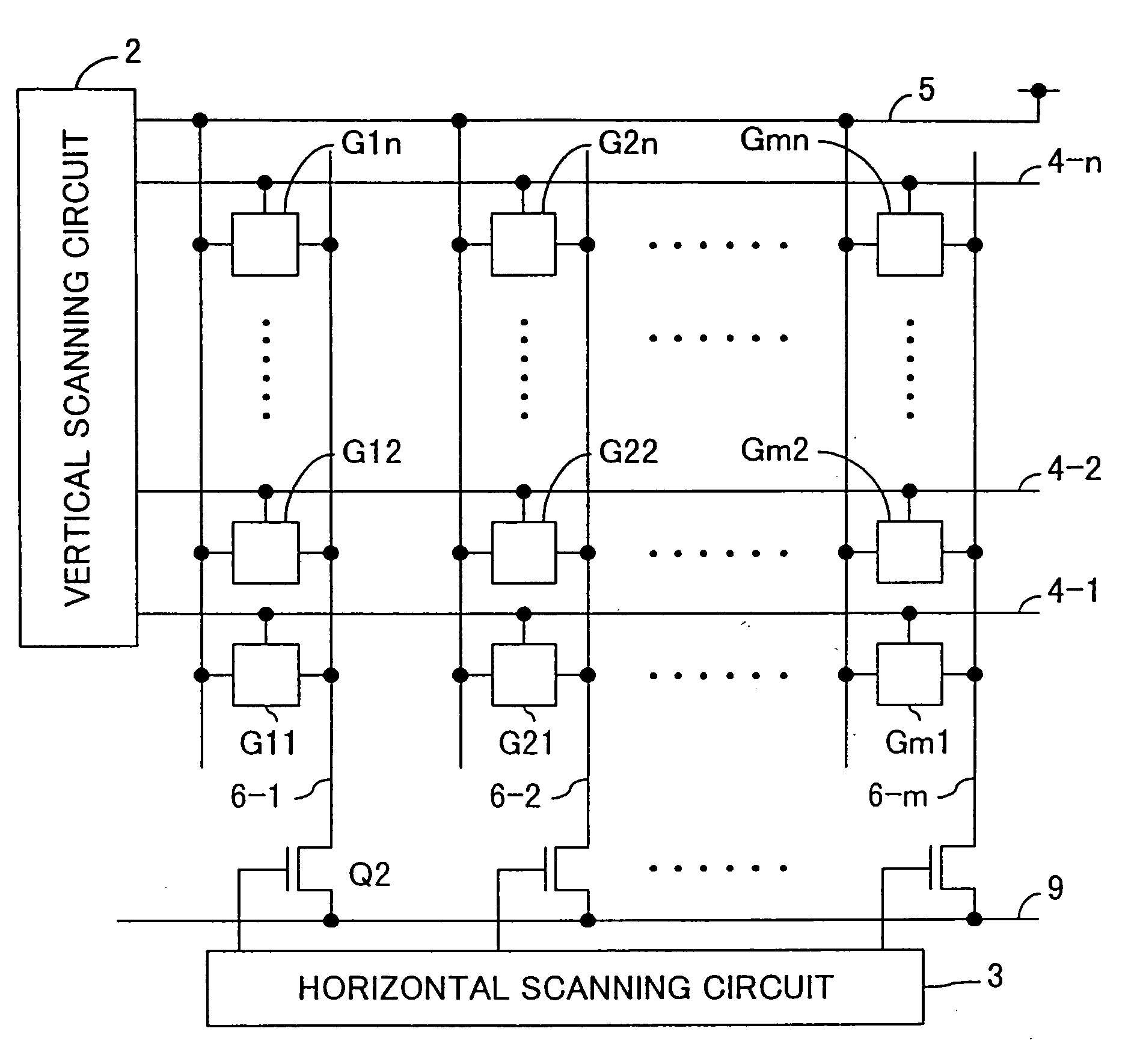
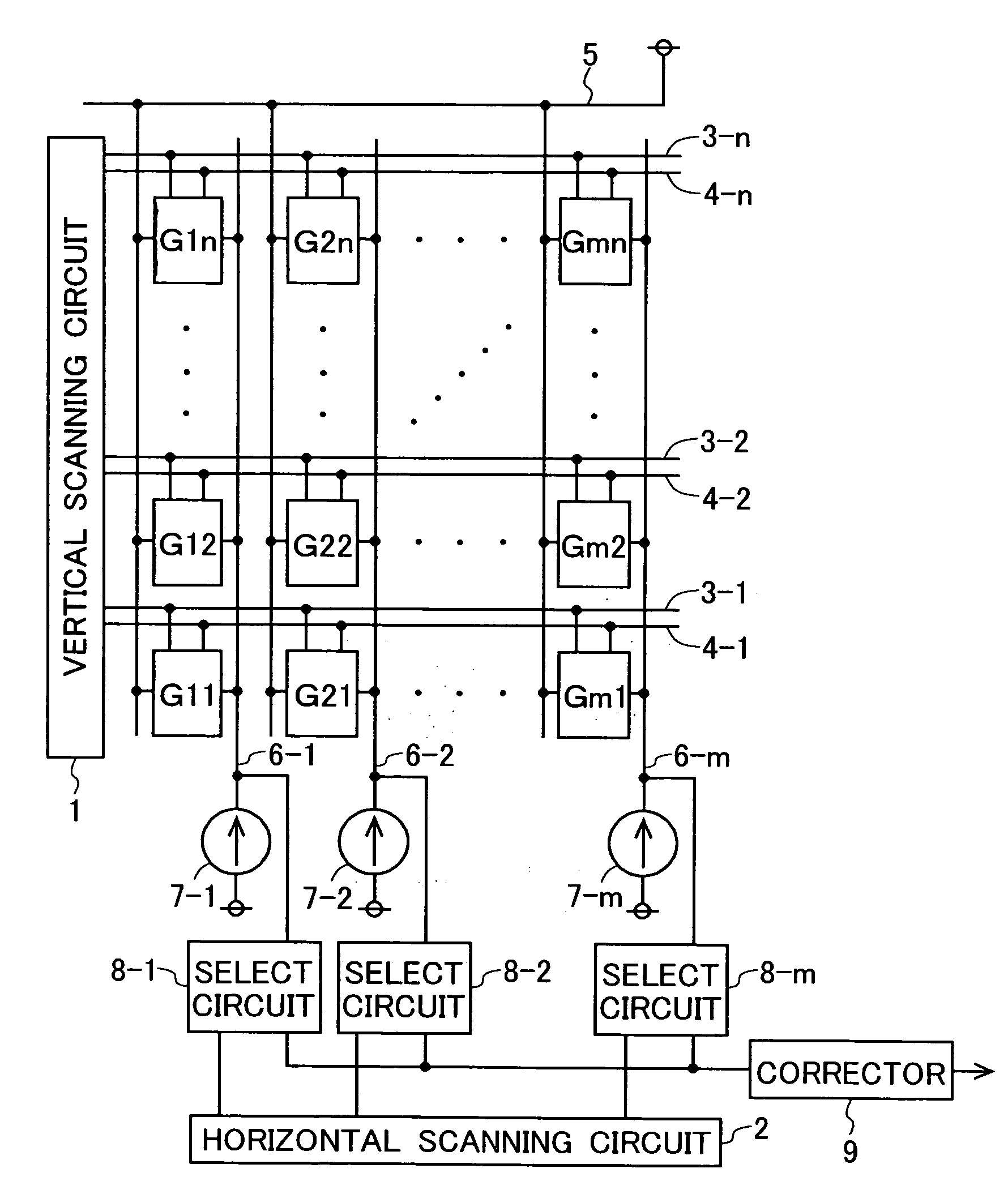
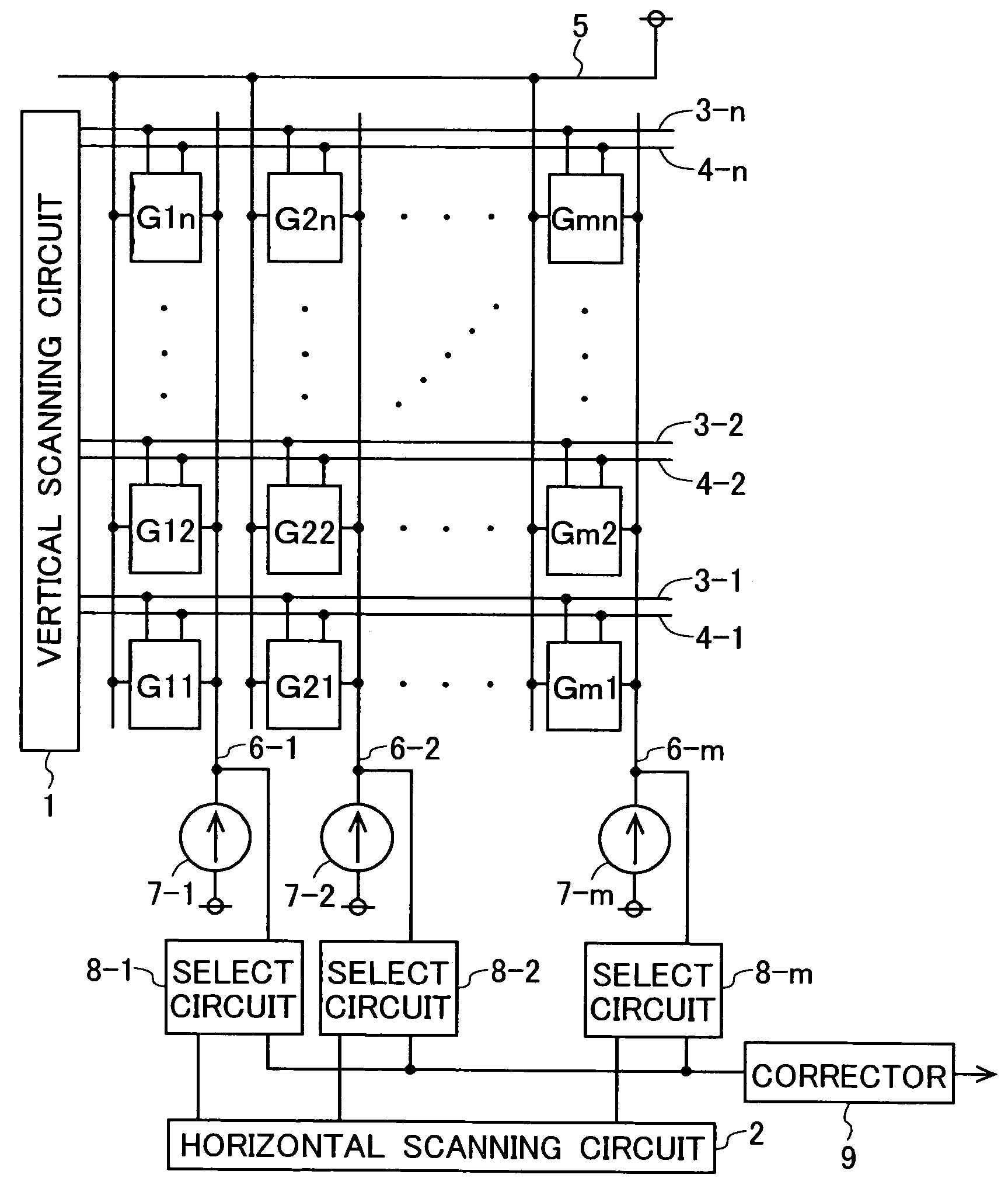
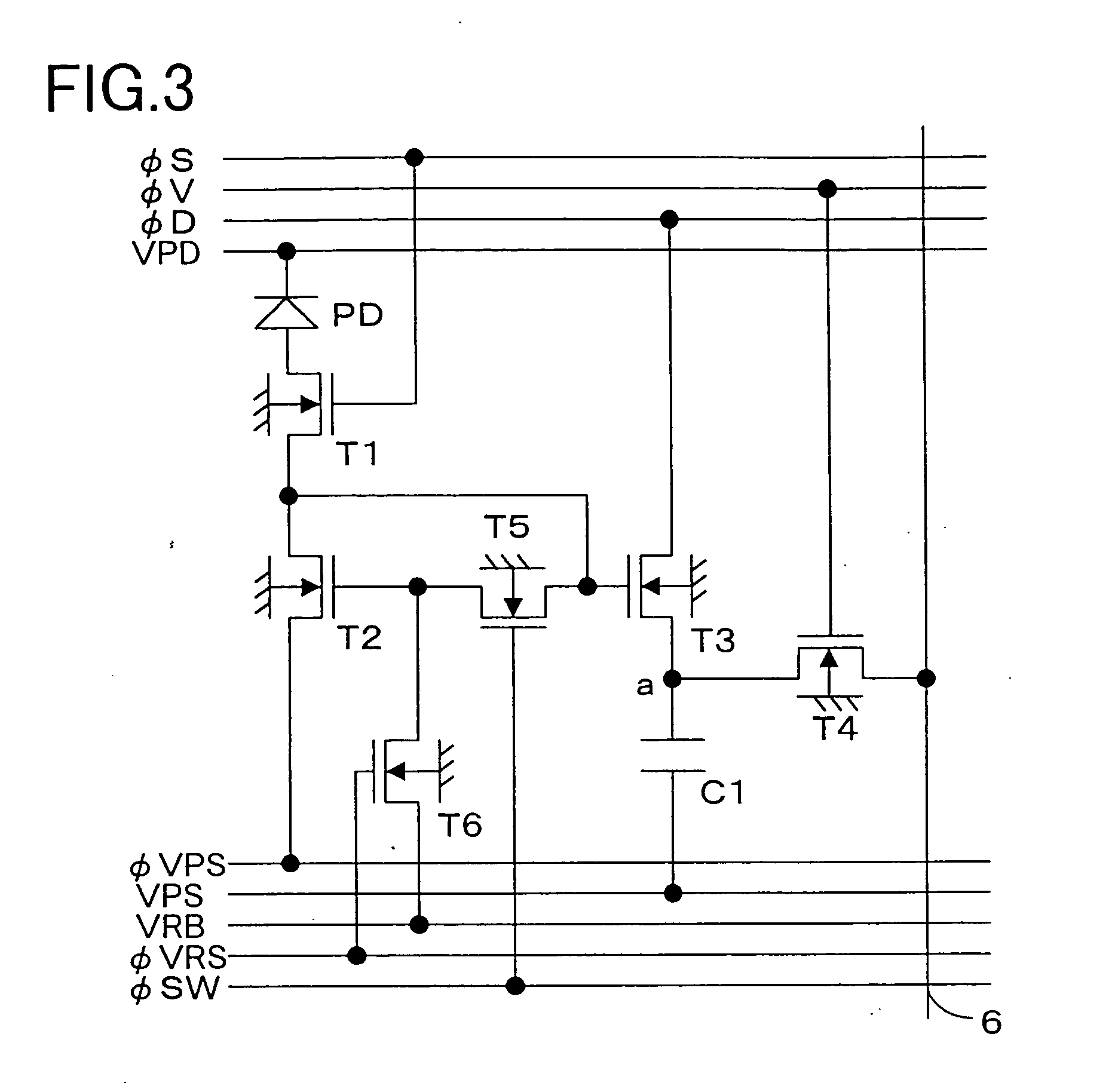
In a solid-state image-sensing device, when an image sensing operation is performed in each pixel, a MOS transistor T1 is turned on and a MOS transistor T4 is turned off to make a MOS transistor T2 operate in a subthreshold region. When a reset operation is performed in each pixel, the MOS transistor T1 is turned off and the MOS transistor T4 is turned on to feed a constant voltage to the gate and drain of the MOS transistor T2. Then, the MOS transistor T4 is turned off, then the voltage at the node “a” is reset, and then a pulse signal φV is fed to a MOS transistor T5 to obtain an output. By using the thus obtained output as compensation data, variations in sensitivity among individual pixels are reduced.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Solid state image pickup device, method for producing the same, and image pickup system comprising the solid state image pickup device
InactiveUS20080174688A1Reduce variationOptimize dataTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerOptical axis
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor sensor and method of manufacturing the same
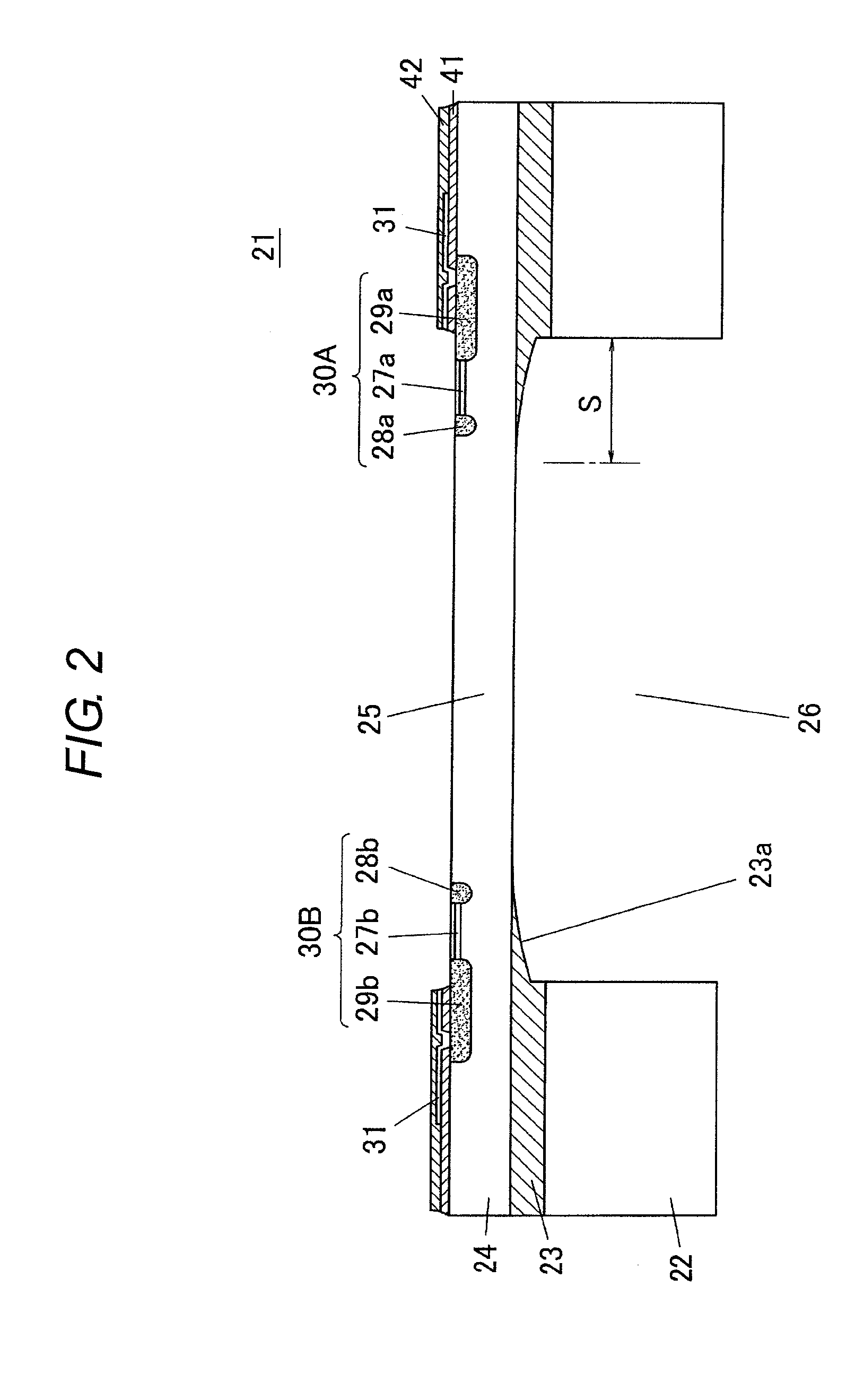
ActiveUS8188556B2Reduce the temperatureResistant to breakageAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTransducer detailsElectrical conductorSemiconductor sensor
A semiconductor sensor has a first semiconductor layer as a base, an insulating layer formed on the first semiconductor layer, and a second semiconductor layer formed on the insulating layer. A recess is formed from a bottom surface of the first semiconductor layer up to a top surface of the insulating layer. The second semiconductor layer is covered with the insulating layer in an outer circumference of a top surface of the recess. A sensitive region of the second semiconductor layer is exposed in a region except the outer circumference of the top surface of the recess.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Semiconductor sensor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100219490A1Reduce the temperatureResistant to breakageAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTransducer detailsElectrical conductorSemiconductor sensor
A semiconductor sensor has a first semiconductor layer as a base, an insulating layer formed on the first semiconductor layer, and a second semiconductor layer formed on the insulating layer. A recess is formed from a bottom surface of the first semiconductor layer up to a top surface of the insulating layer. The second semiconductor layer is covered with the insulating layer in an outer circumference of a top surface of the recess. A sensitive region of the second semiconductor layer is exposed in a region except the outer circumference of the top surface of the recess.
Owner:ORMON CORP
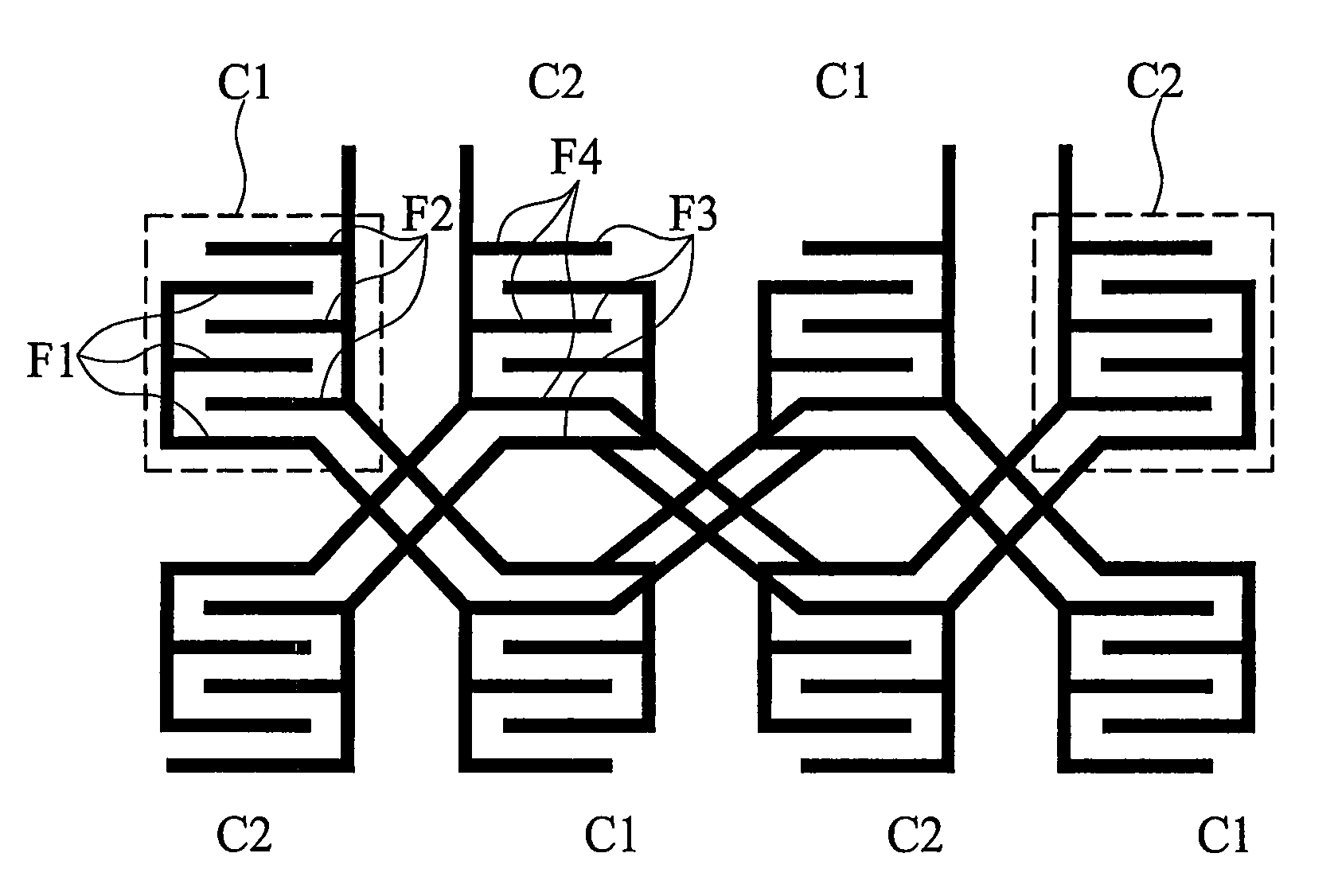
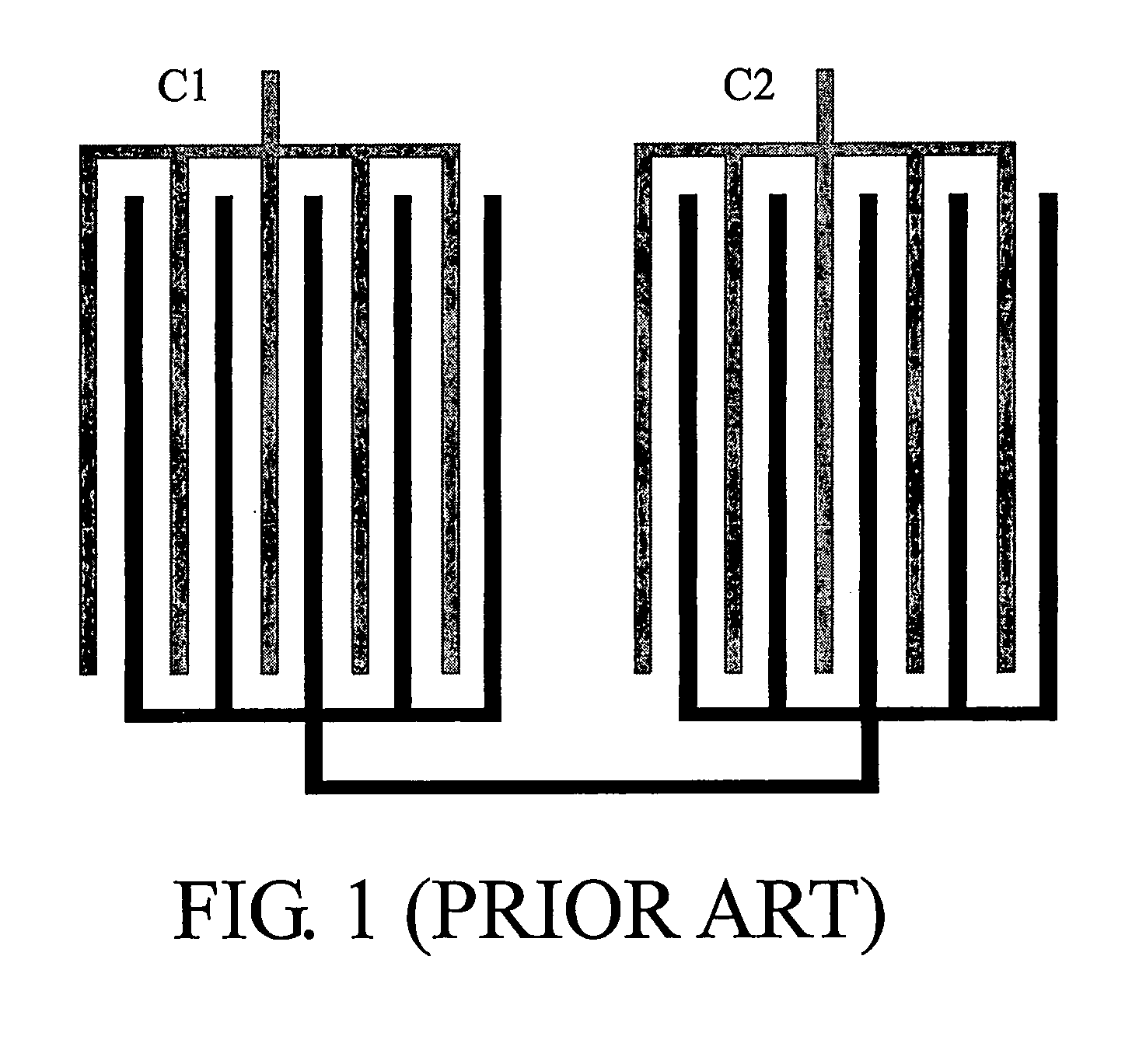
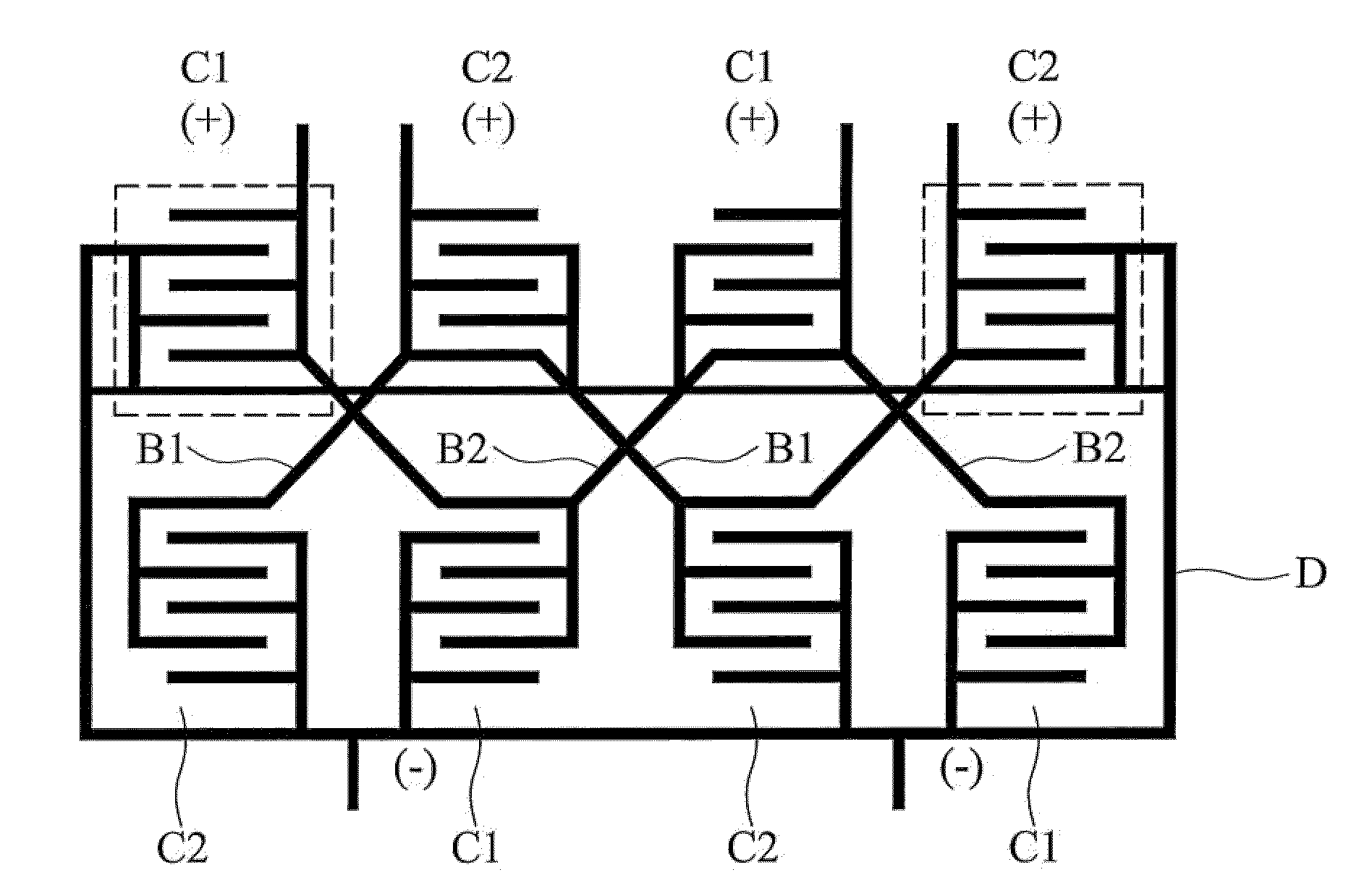
Capacitor pairs with improved mismatch performance
ActiveUS7545022B2Increasing relative capacitance mismatchVariation in sensitivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a first capacitor comprising a plurality of first unit capacitors interconnected to each other, each having a first unit capacitance; and a second capacitor comprising a plurality of second unit capacitors interconnected to each other, each having a second unit capacitance, wherein the first unit capacitors and the second unit capacitors have equal numbers of unit capacitors. The first unit capacitors and the second unit capacitors are arranged in an array with rows and columns and placed in an alternating pattern in each row and each column. The first and the second unit capacitors each have a total number greater than two.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Image-sensing apparatus
InactiveUS6950136B1Accurate collectionMinimize changesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsGate voltageImage sensing
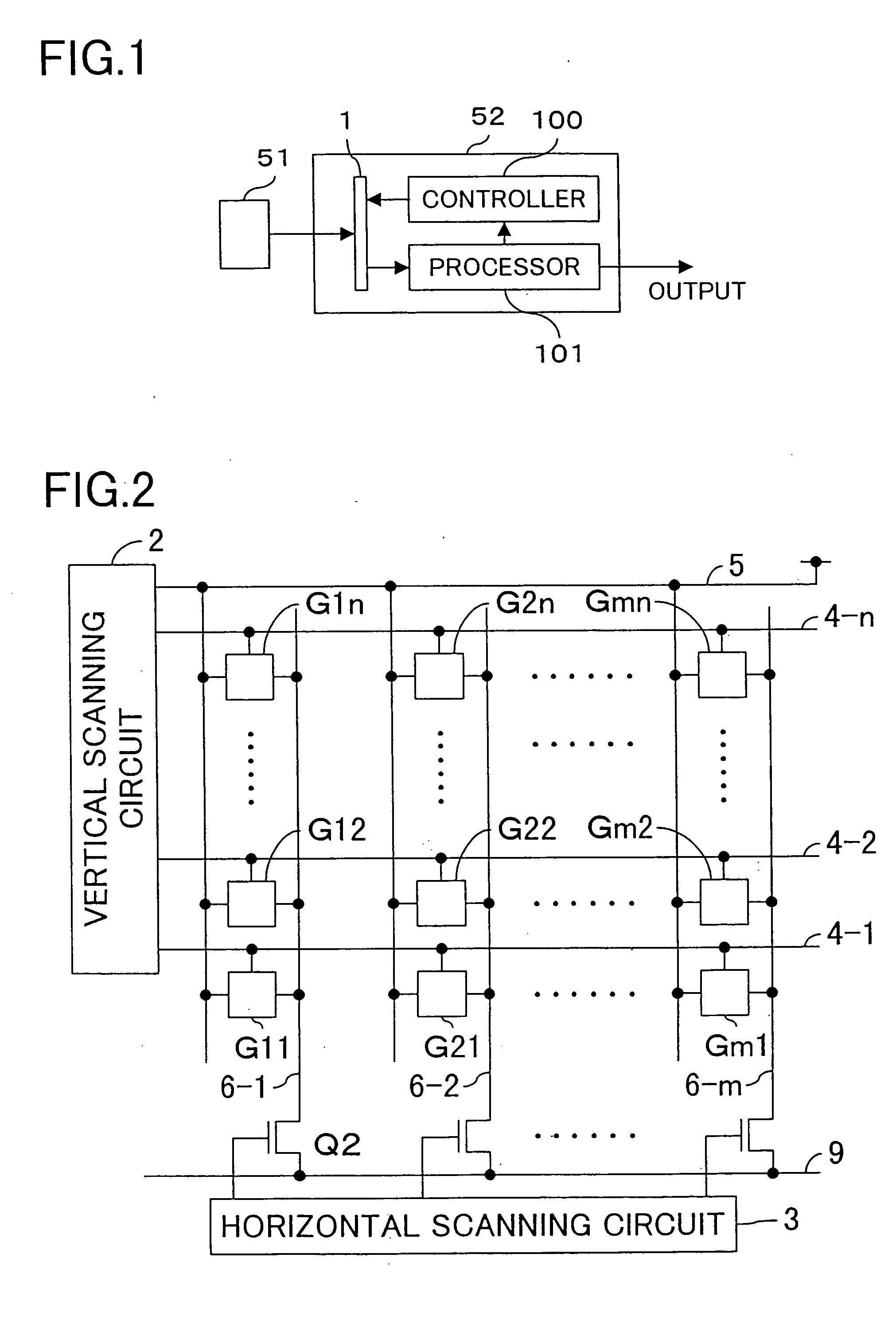
In a solid-state image-sensing device, when image sensing is performed, in each pixel, MOS transistors T1 and T5 are turned on and a MOS transistor T6 is turned off so that a MOS transistor T2 operates in a subthreshold region. When resetting is preformed, in each pixel, the MOS transistors T1 and T5 are turned off and the MOS transistor T6 is turned on so that the gate voltage of the MOS transistor T2 is kept constant. In this state, the MOS transistor T2 is brought first into a conducting state and then, by turning a signal φVPS to a high level, into a cut-off state. This permits a signal proportional to the threshold value of the MOS transistor T2 to be output as compensation data.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Solid state imaging device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070170477A1Convenient lightingReduce variationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaveguideSemiconductor
A plurality of light receiving elements are arranged in a matrix with uniform space therebetween in a light receiving region defined on a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of read-out electrodes are formed on the semiconductor substrate in an arrangement corresponding to the light receiving elements to read charges generated by the light receiving elements, a light shield film having openings positioned above the light receiving elements is formed to cover the read-out electrodes, first optical waveguides are formed in the openings above the light receiving elements and second optical waveguides are formed on the light shield film. The second optical waveguides are in the form of dots, stripes or a grid when viewed in plan.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Solid-state image-sensing device
InactiveUS20060119723A1Accurate collectionMinimize changesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringImage sensing
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Condenser microphone
InactiveUS8848950B2Variation in sensitivityEasy to adjustPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrets selectrostatic transducerCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
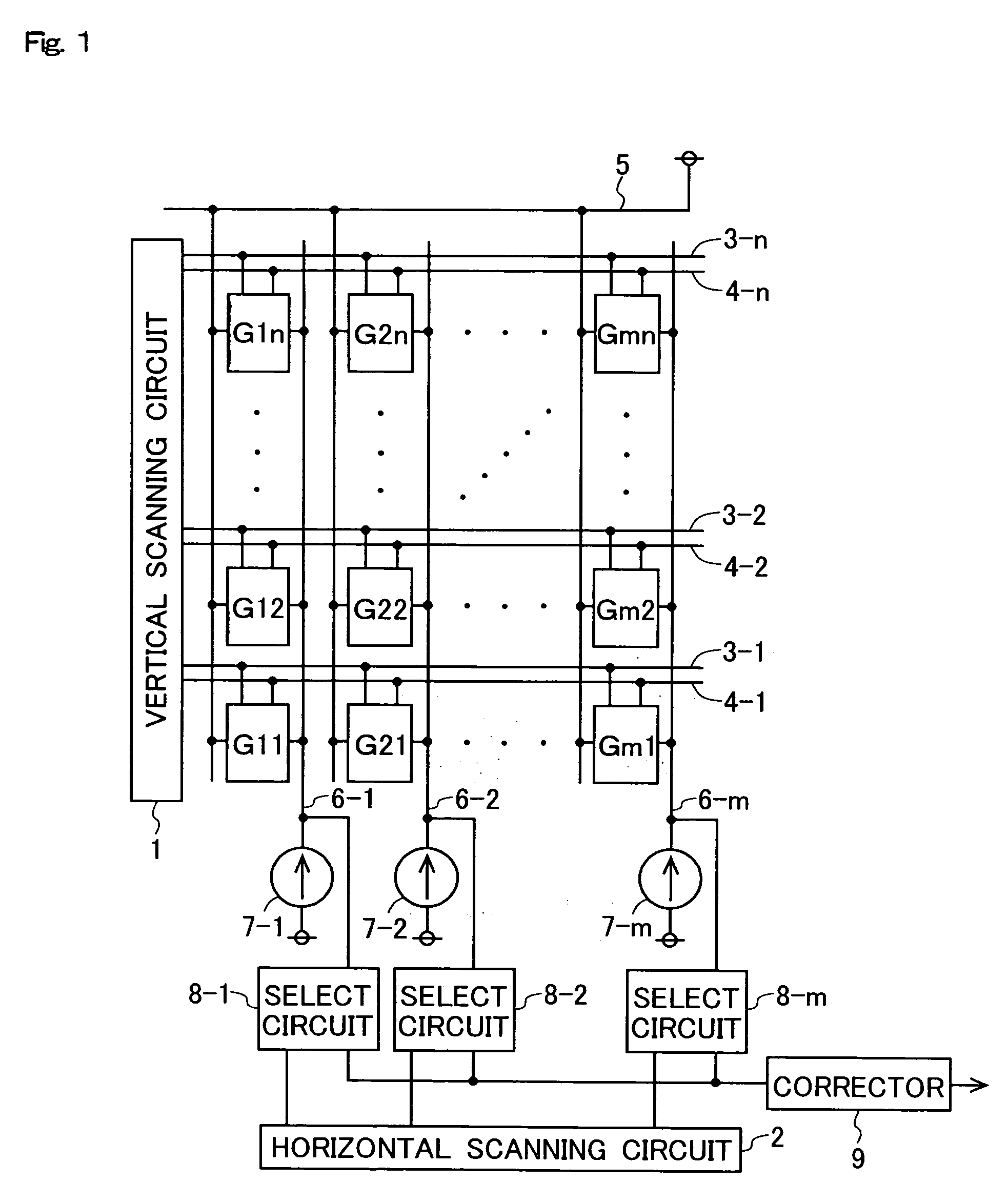
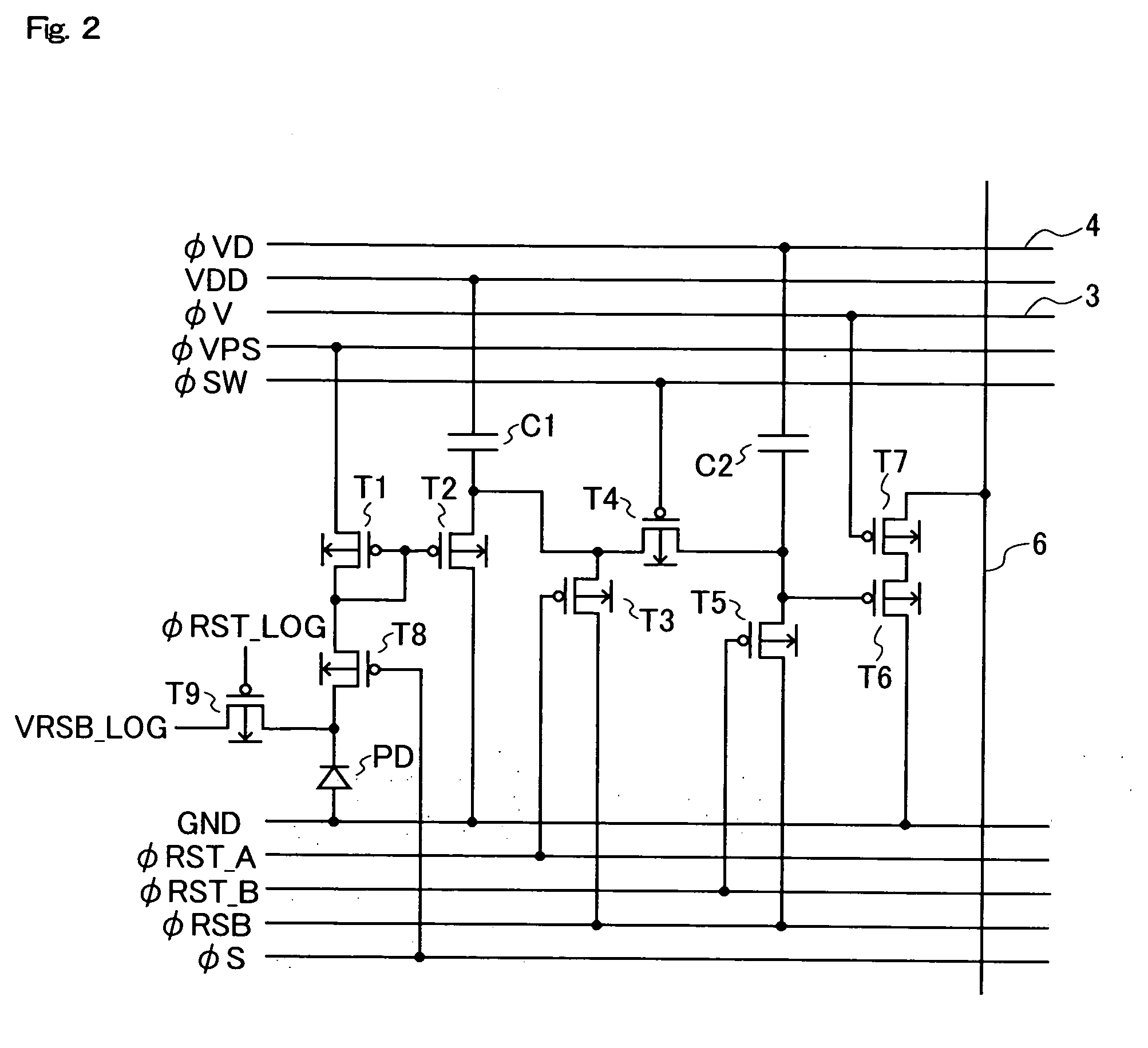
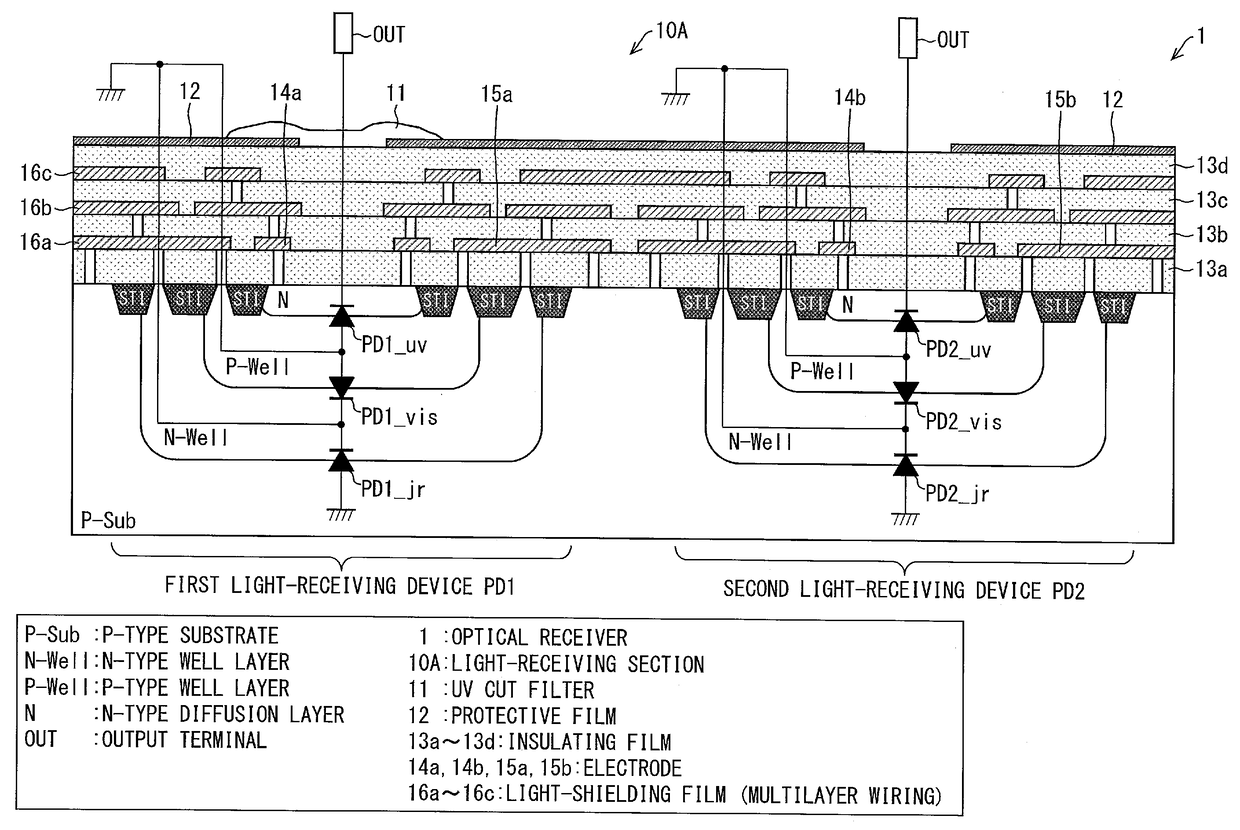
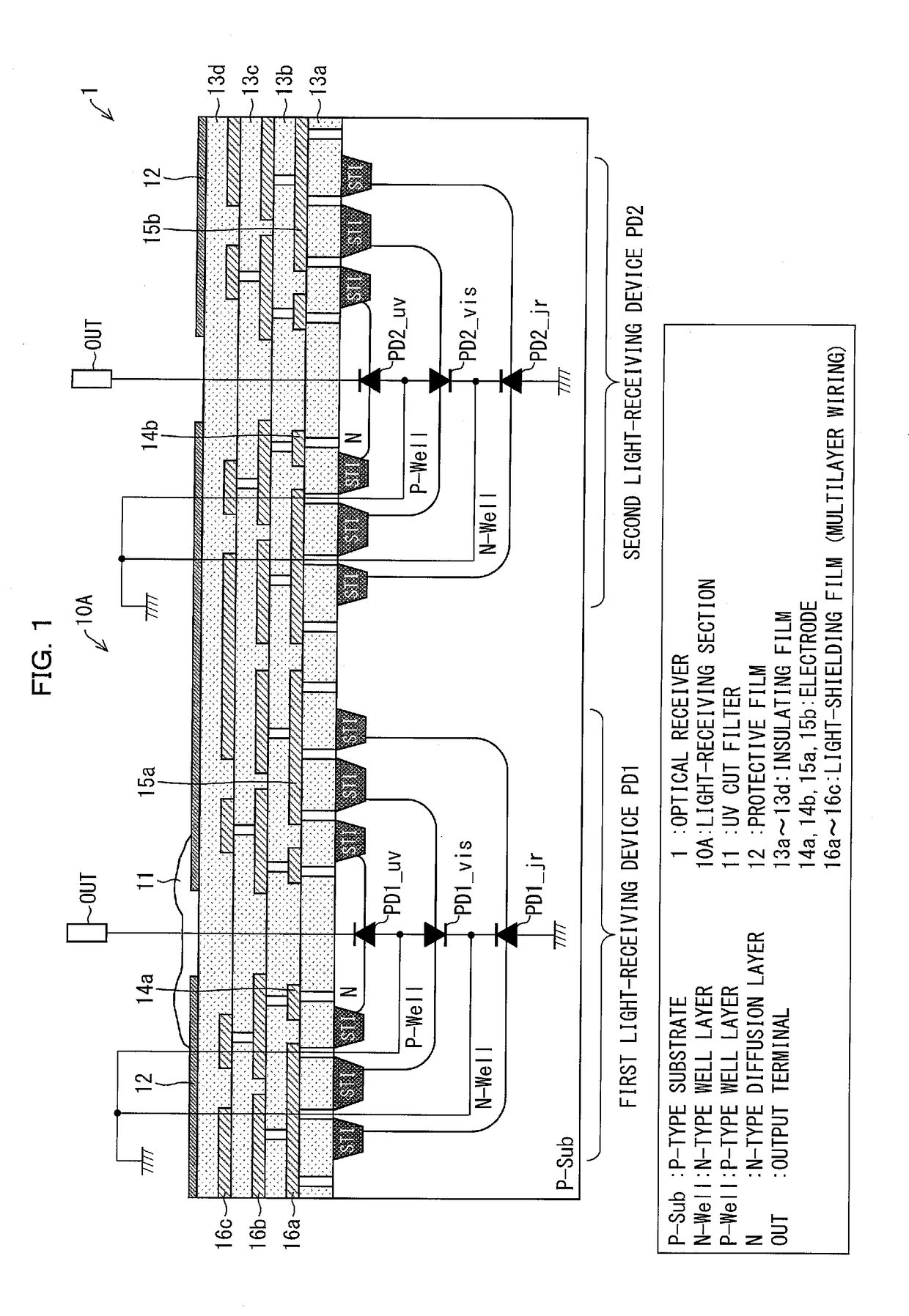
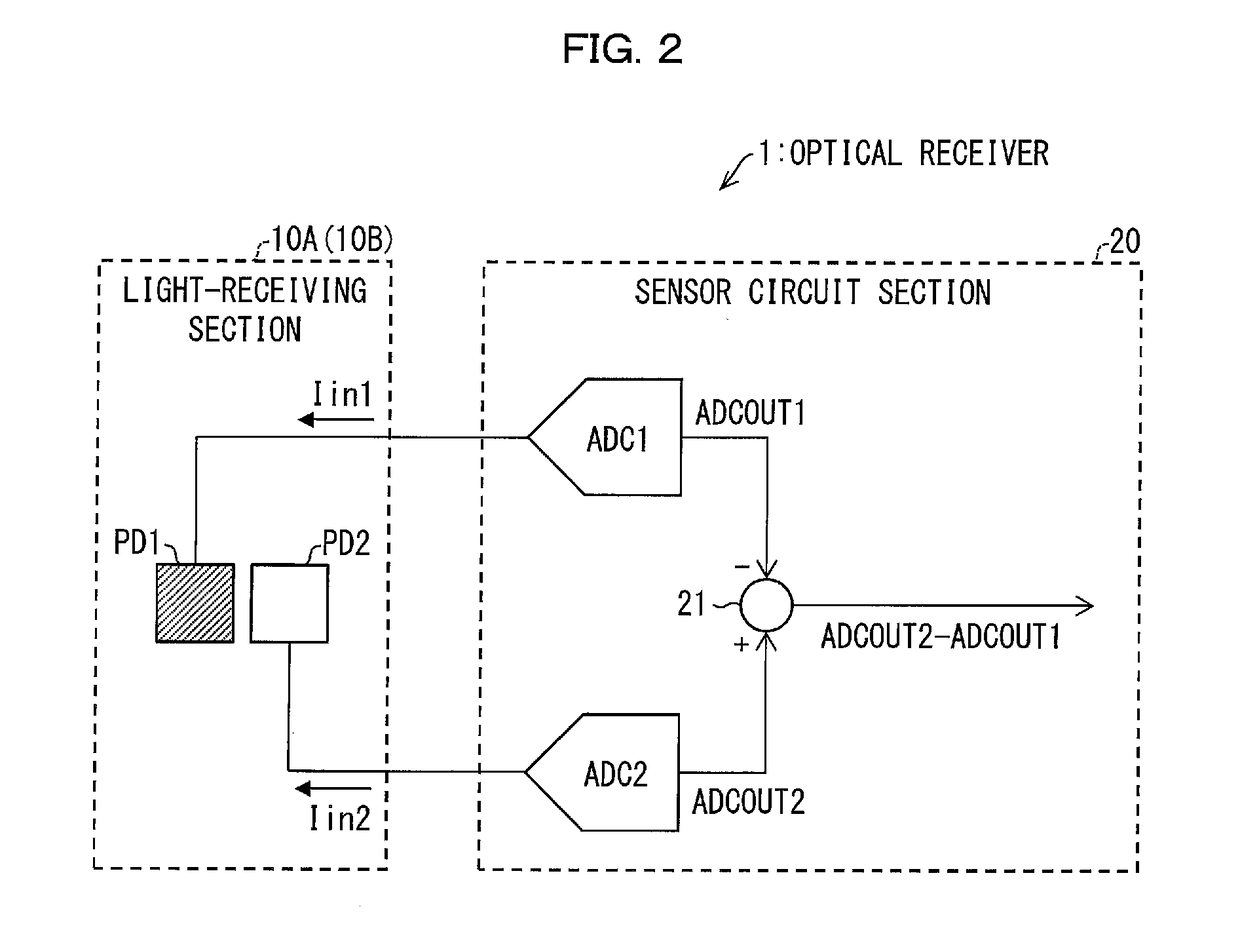
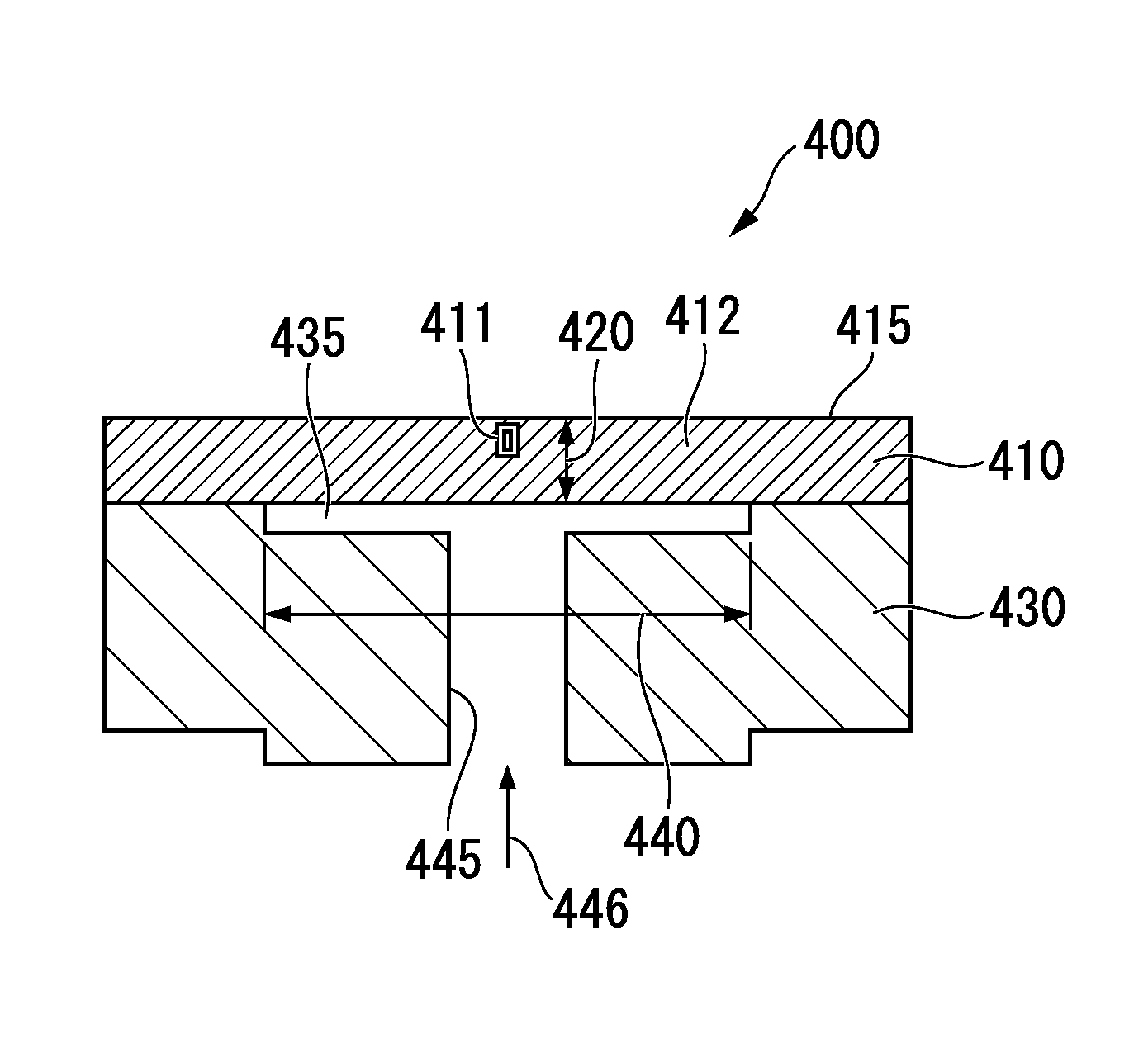
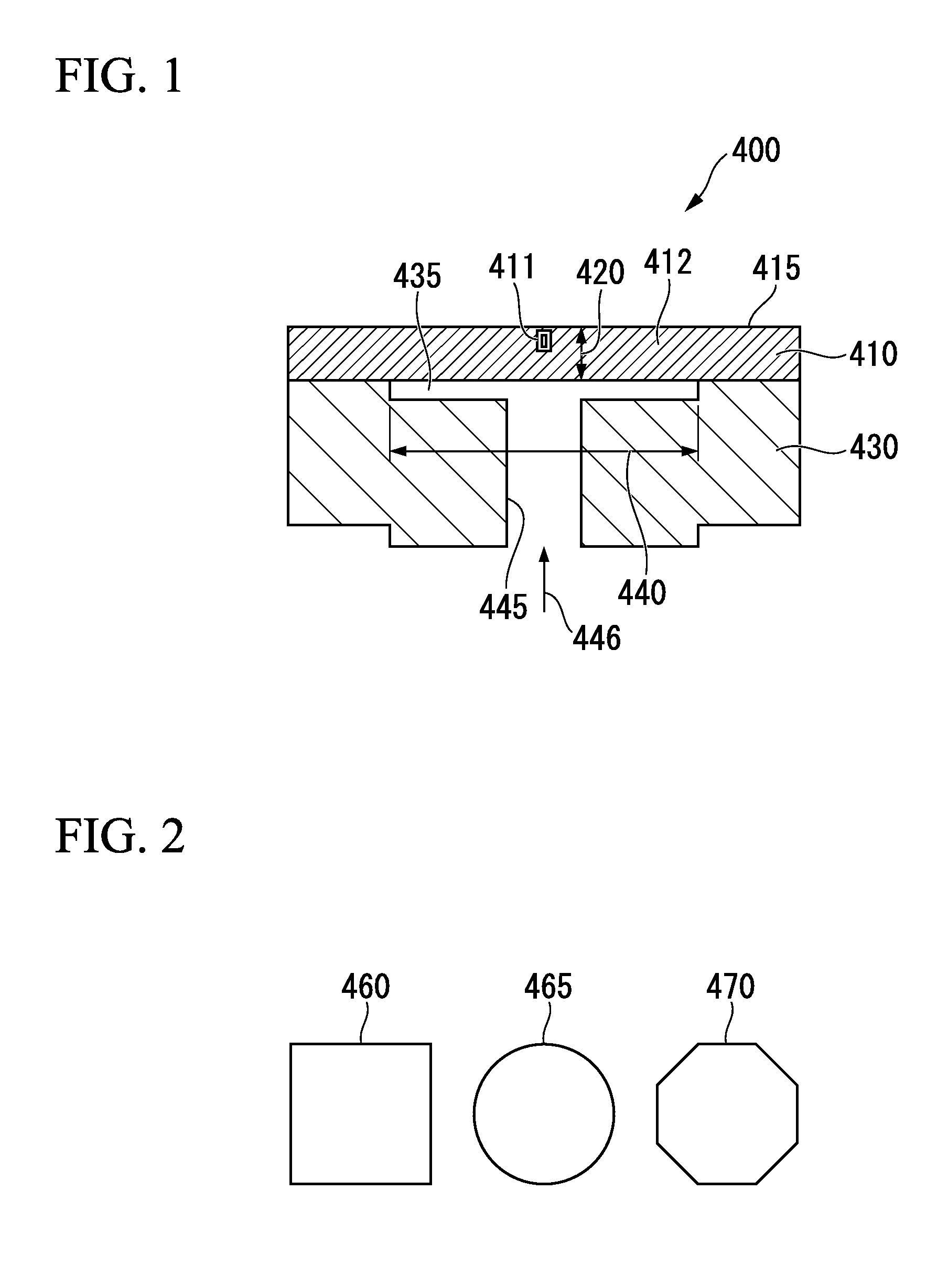
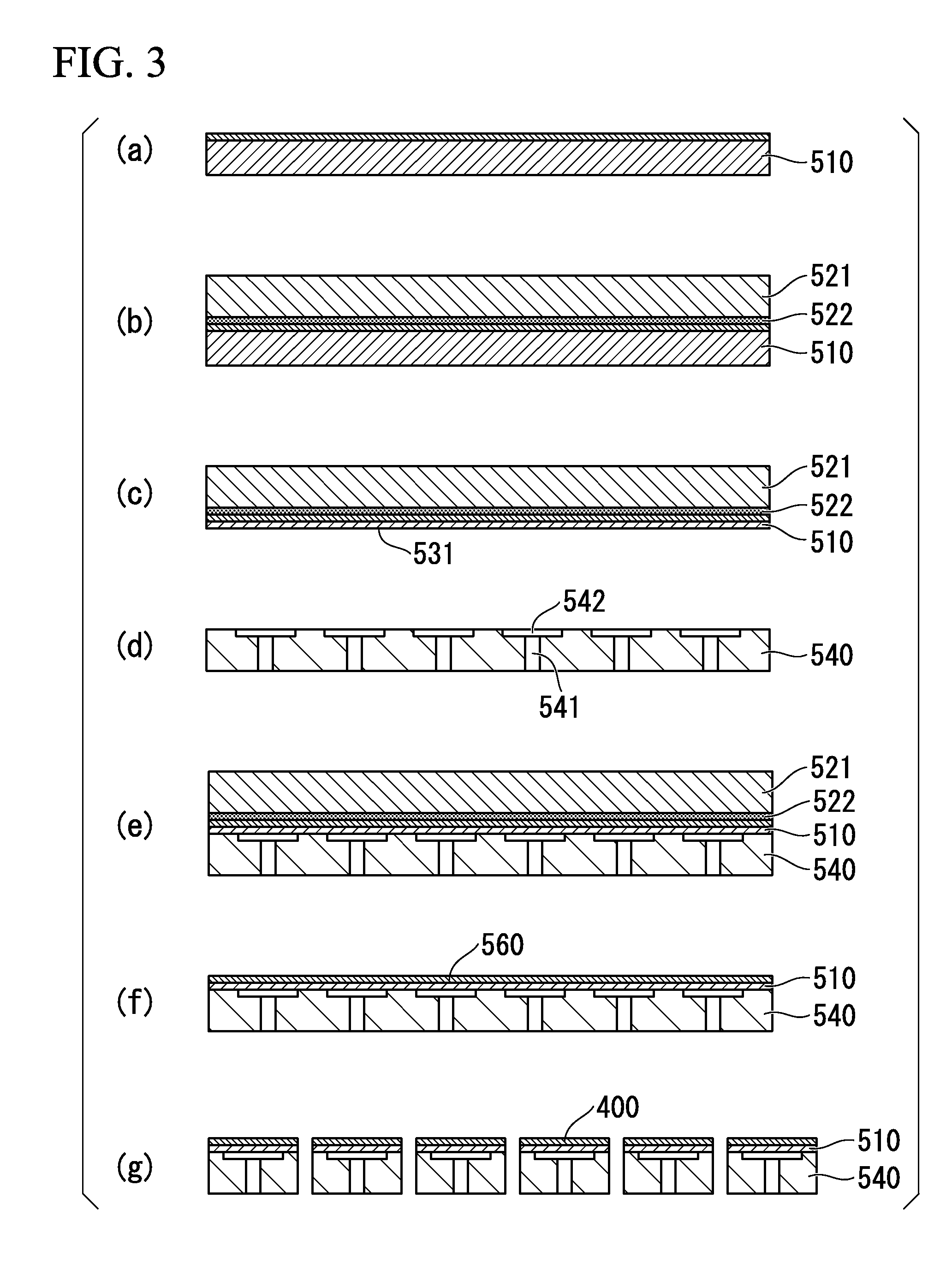
Optical receiver, portable electronic device, and method of producing optical receiver
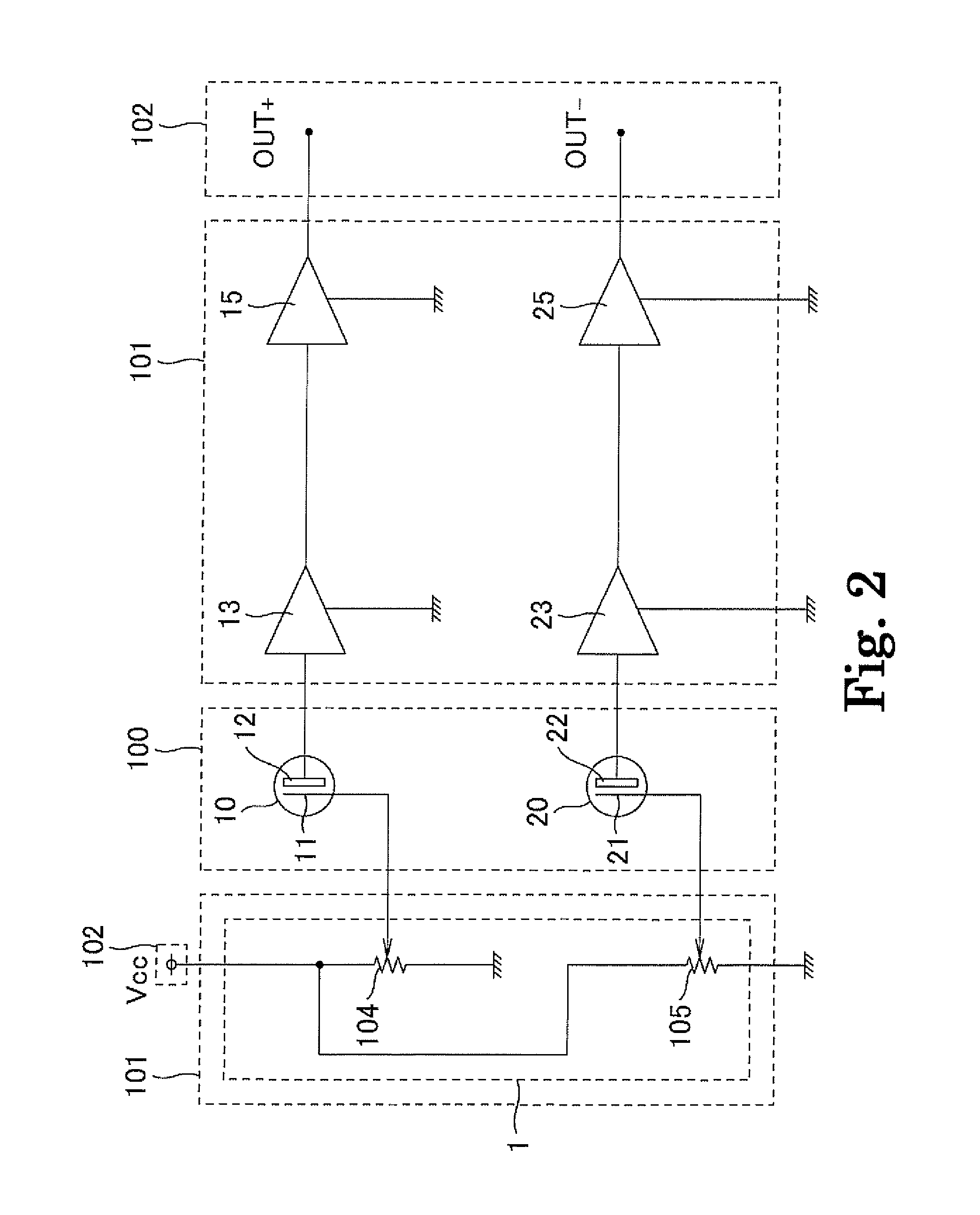
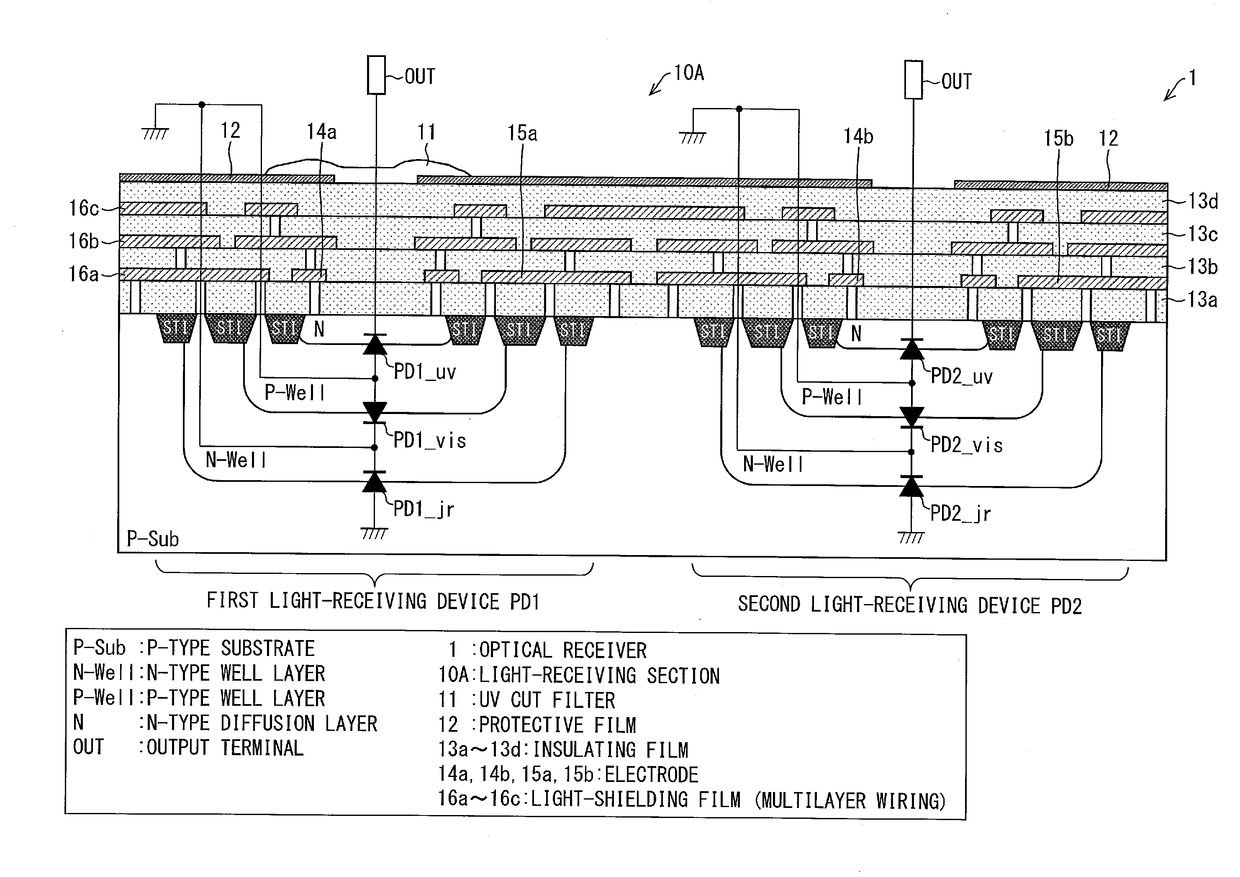
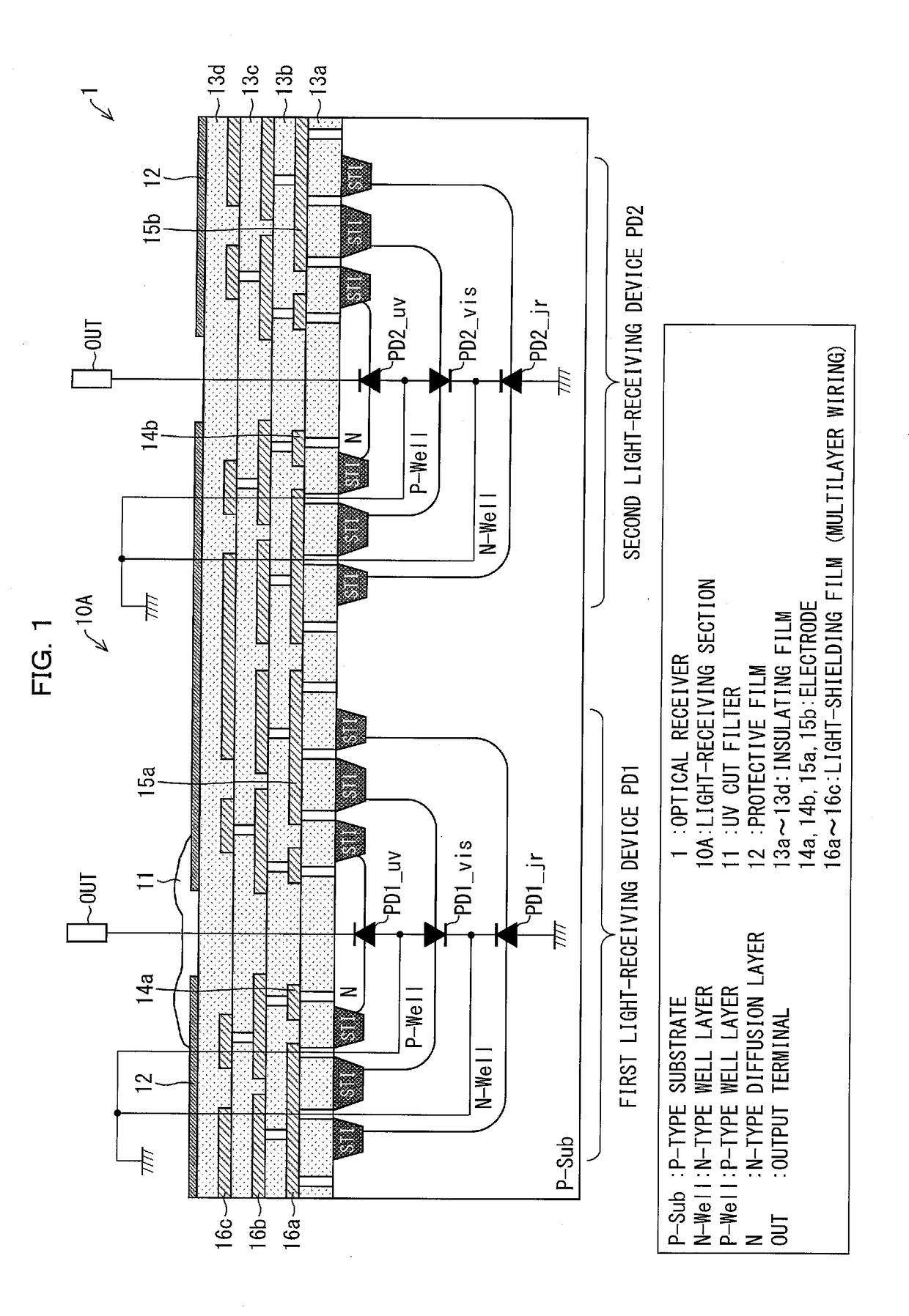
ActiveUS20170294474A1Variation in sensitivityReduce noiseSolid-state devicesDiodeOptical receiversDiffusion layer
Provided are an optical receiver that can realize a reduction in the variation of sensitivity in the ultraviolet light region and a reduction in noise in the visible light region and the infrared light region, a portable electronic device, and a method of producing an optical receiver. The first light-receiving device (PD1) and the second light-receiving device (PD2) of the optical receiver (1) are each constituted by forming a second conductivity-type N-type well layer (N_well) on a first conductivity-type P-type substrate (P_sub), forming a first conductivity-type P-type well layer (P_well) in the N-type well layer (N_well), and forming a second conductivity-type N-type diffusion layer (N) in the P-type well layer (P_well). The P-type substrate P_sub, the N-type well layer (N_well), and the P-type well layer (P_well) are electrically at the same potential or are short-circuited.
Owner:SHARP KK
Resonant pressure sensor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130047734A1Variation can be suppressedGood thickness controllabilityLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsForeign matterEngineering
A resonant pressure sensor including one or more resonant-type strain gauges arranged on a diaphragm may include a sensor substrate made of silicon and including one surface on which one or more resonant-type strain gauge elements are arranged and the other surface which is polished to have a thickness corresponding to the diaphragm, a base substrate made of silicon and including one surface directly bonded with the other surface of the sensor substrate, a concave portion formed in a portion of the base substrate bonding with the sensor substrate, substantially forming the diaphragm in the sensor substrate, and including a predetermined gap that does not restrict a movable range of the diaphragm due to foreign substances and suppresses vibration of the diaphragm excited by vibration of the resonant-type strain gauge elements, one or more conducting holes, and a fluid.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Micro-electromechanical resonator geometry
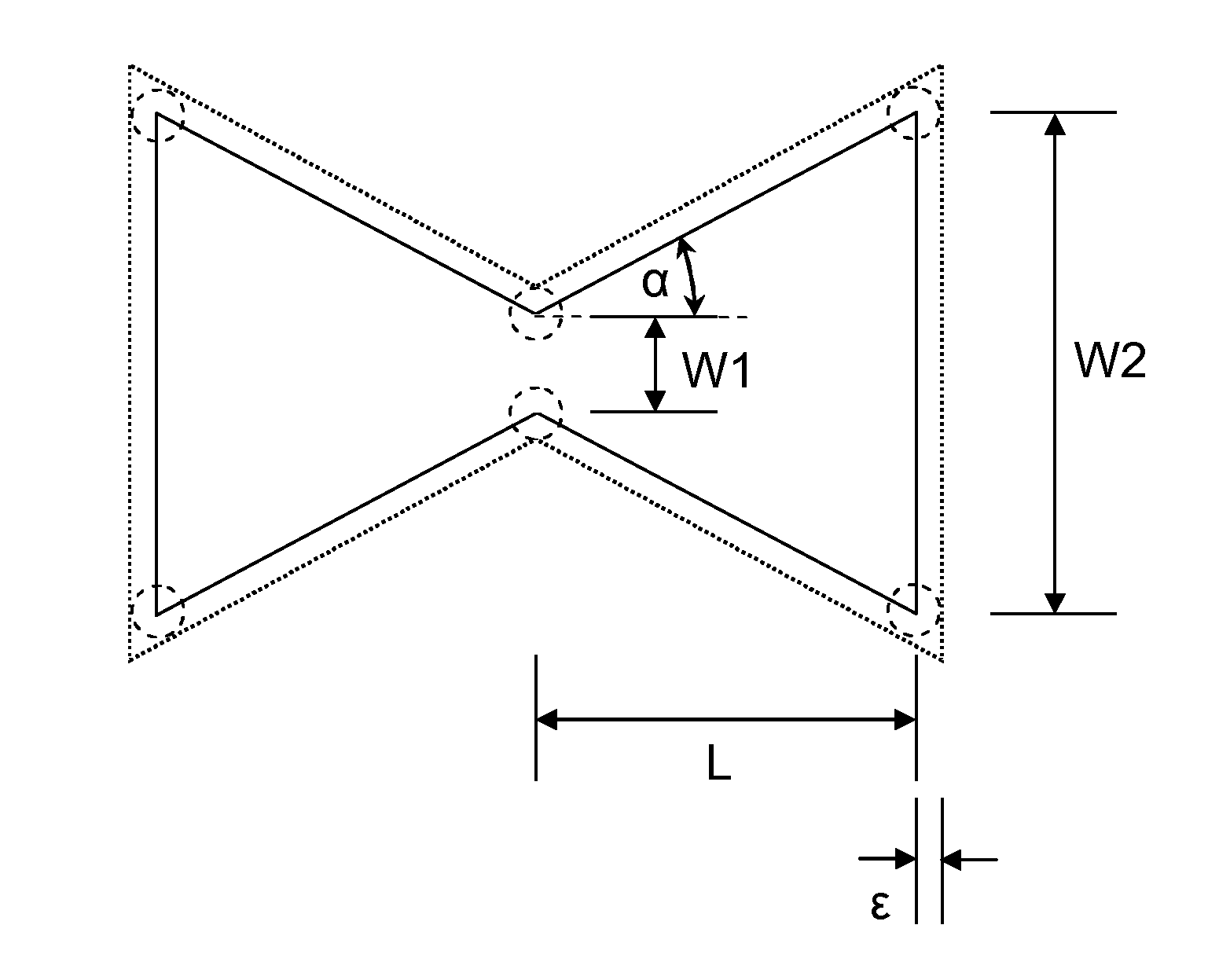
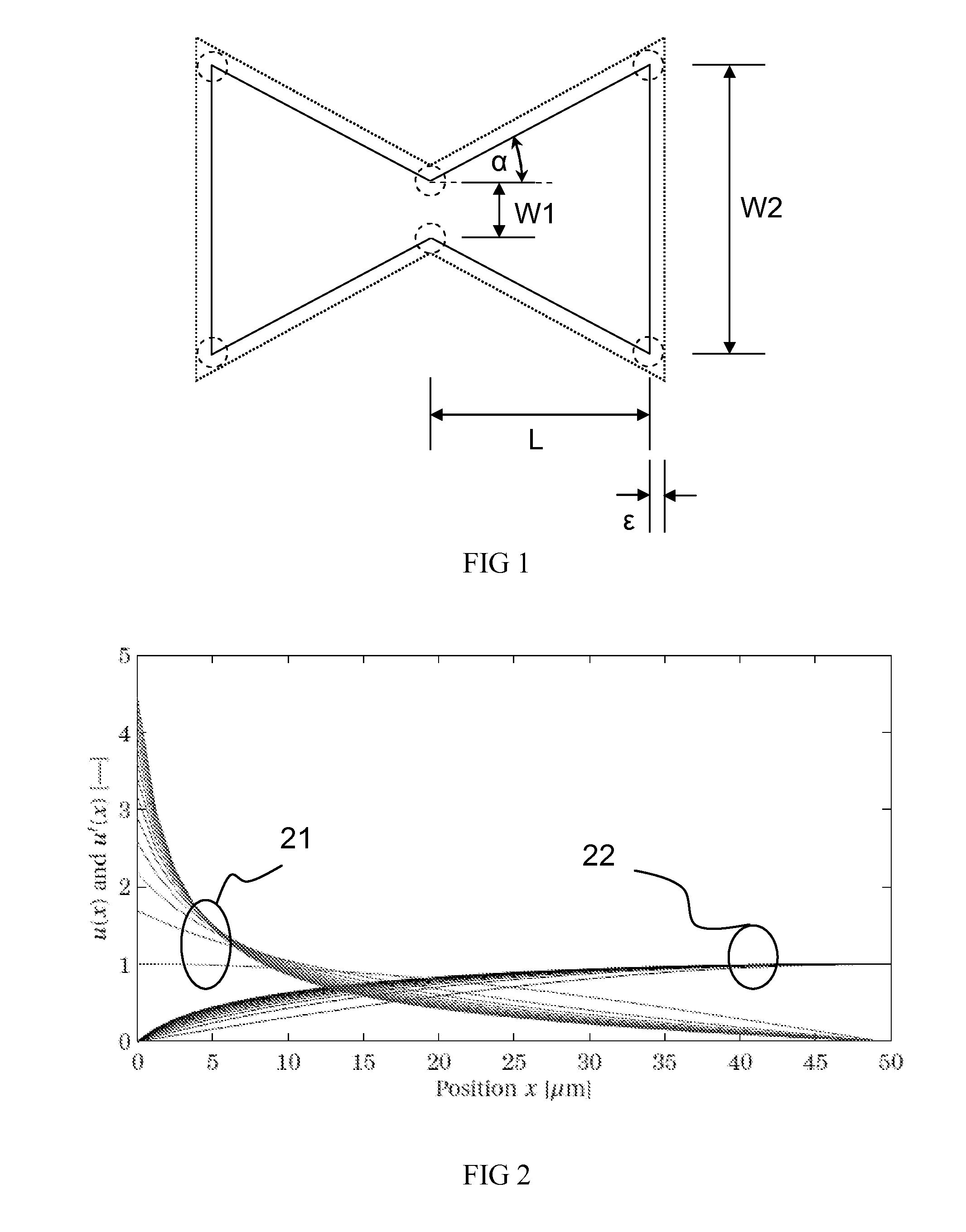
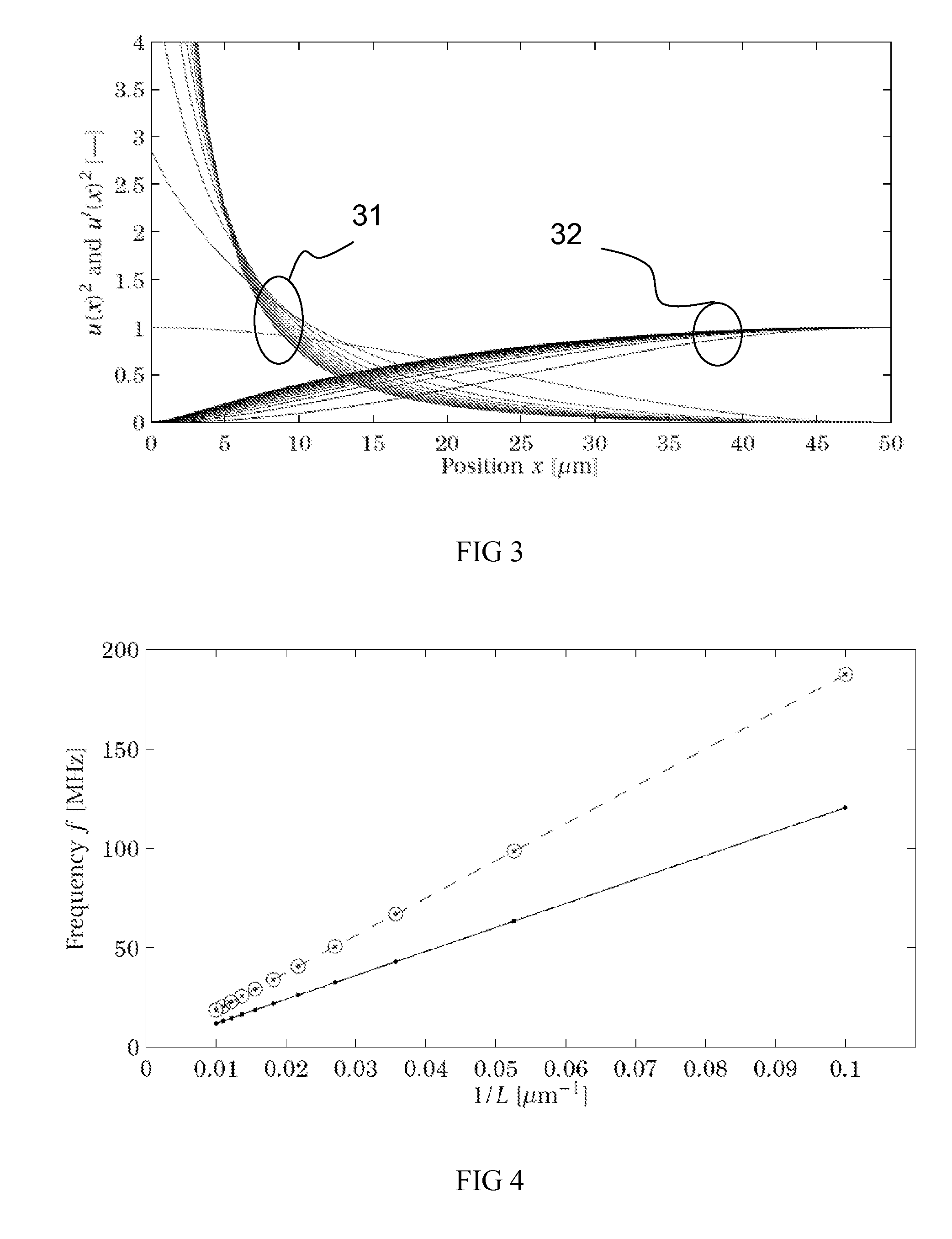
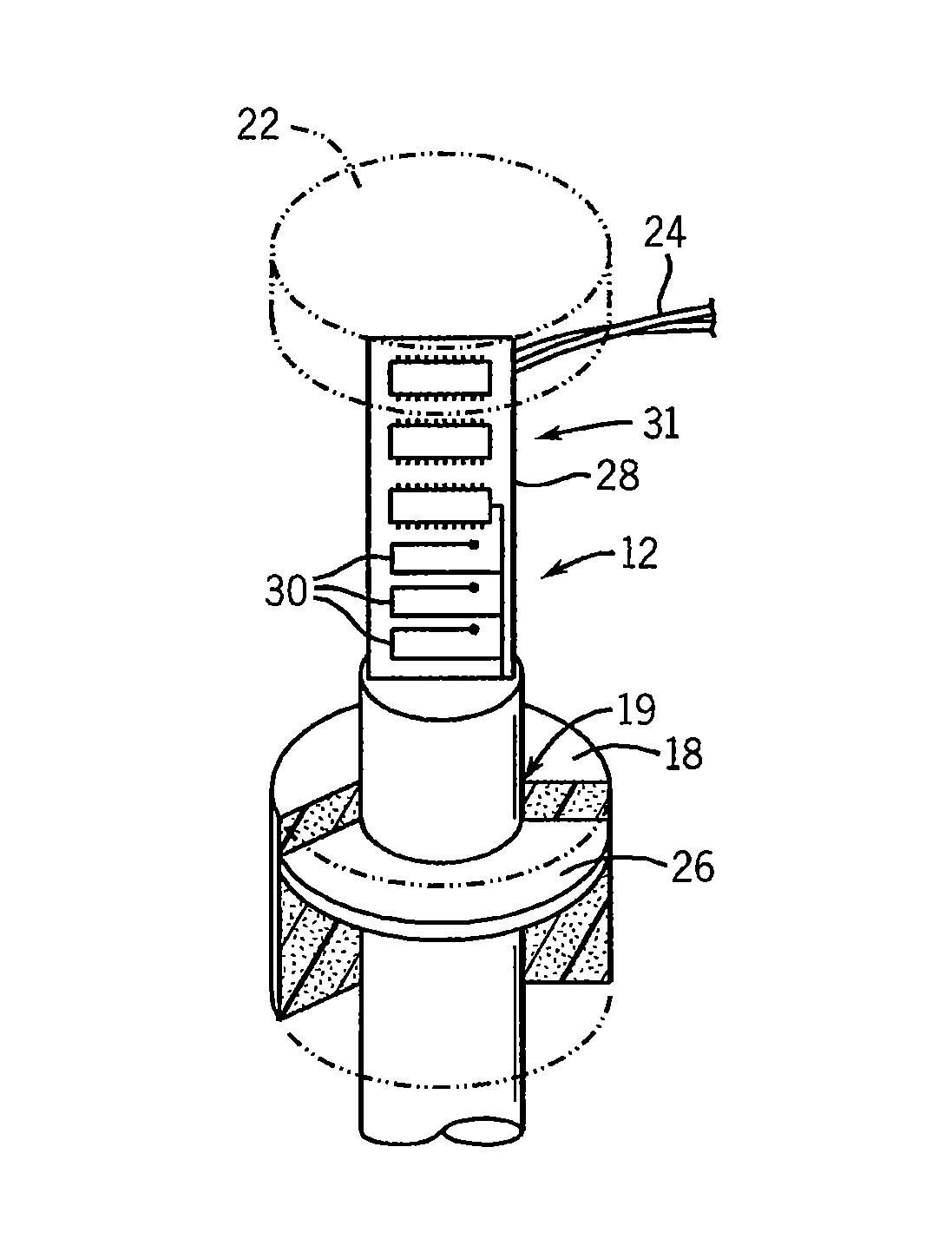
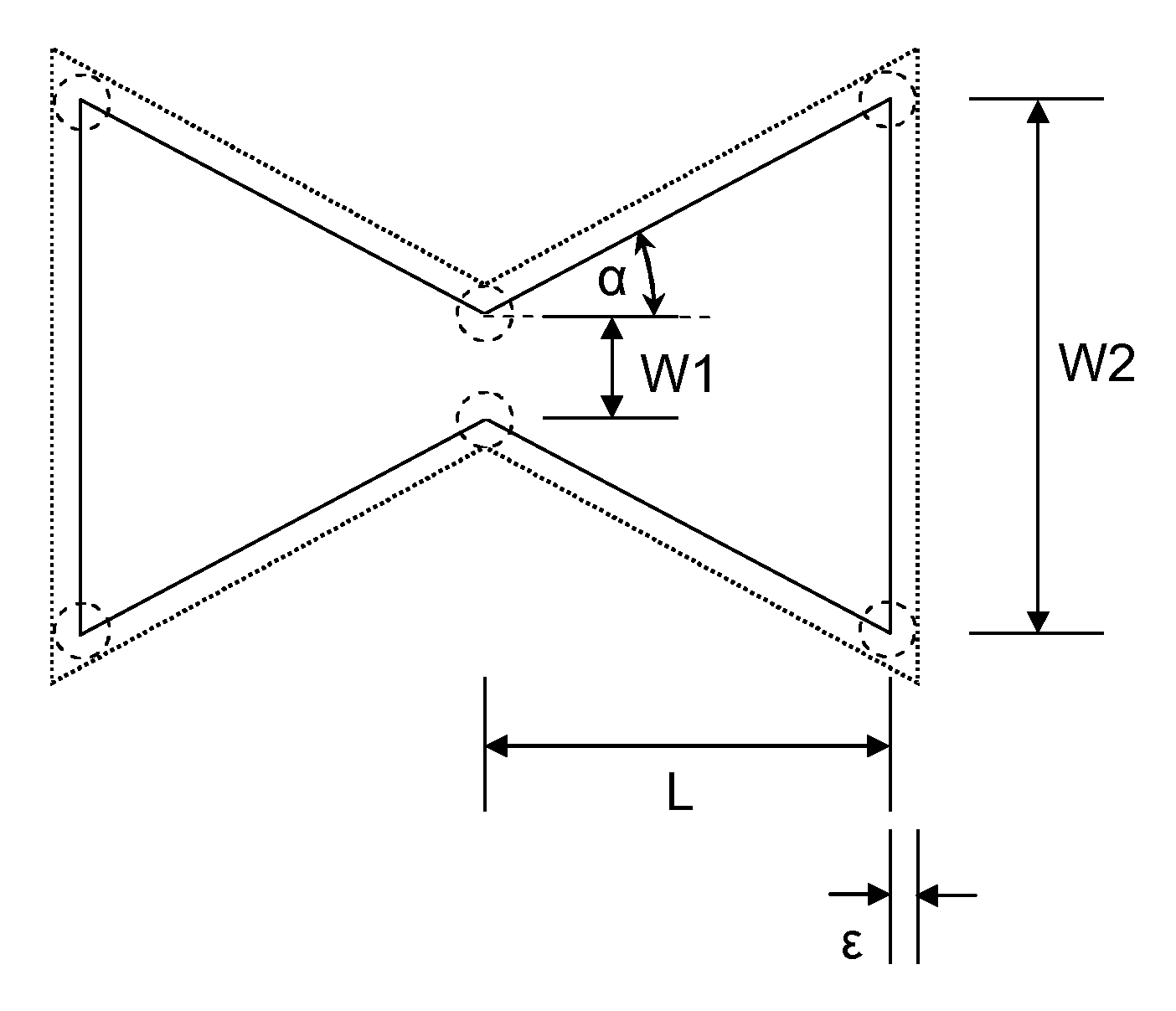
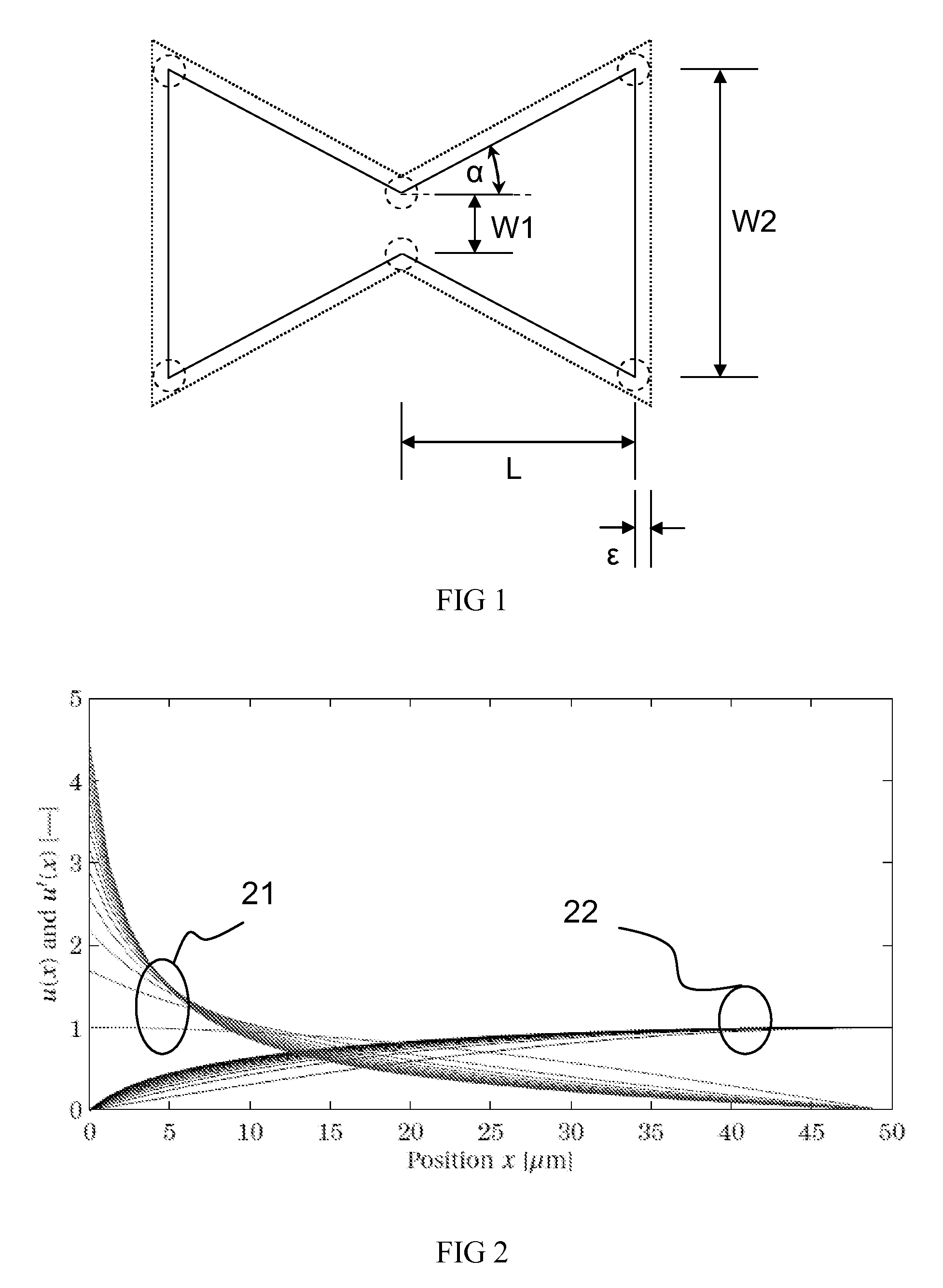
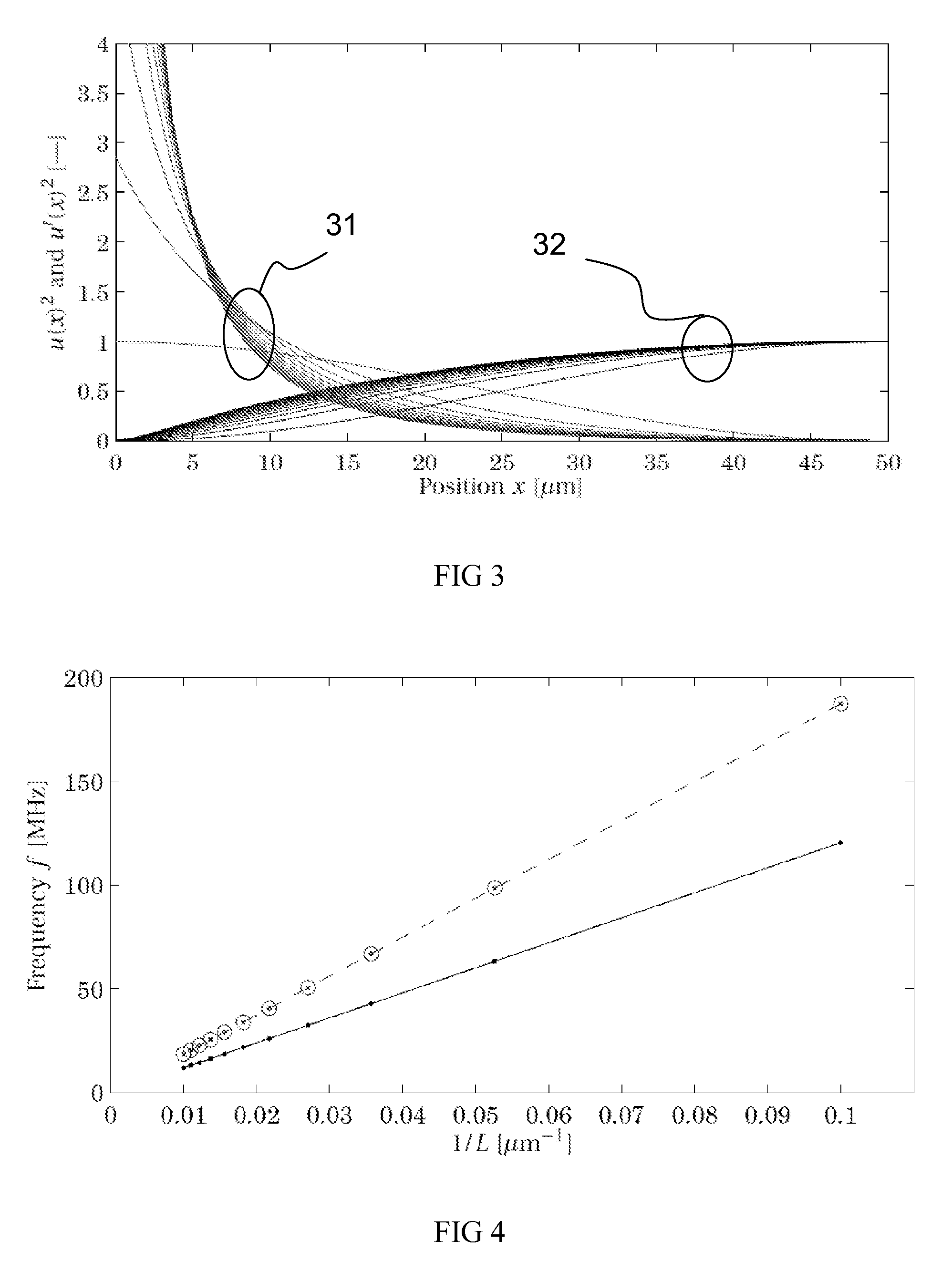
ActiveUS20110309891A1Minimise sensitivityMinimise variationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksPhysicsResonator
A micro-electromechanical resonator suspended from an anchor. The resonator has: a length; a first width at a first distance from the anchor; and a second width at a second, greater distance from the anchor. The second width is greater than the first width, and the width of the resonator tapers gradually along at least part of its length from the second width to the first width.
Owner:NXP BV
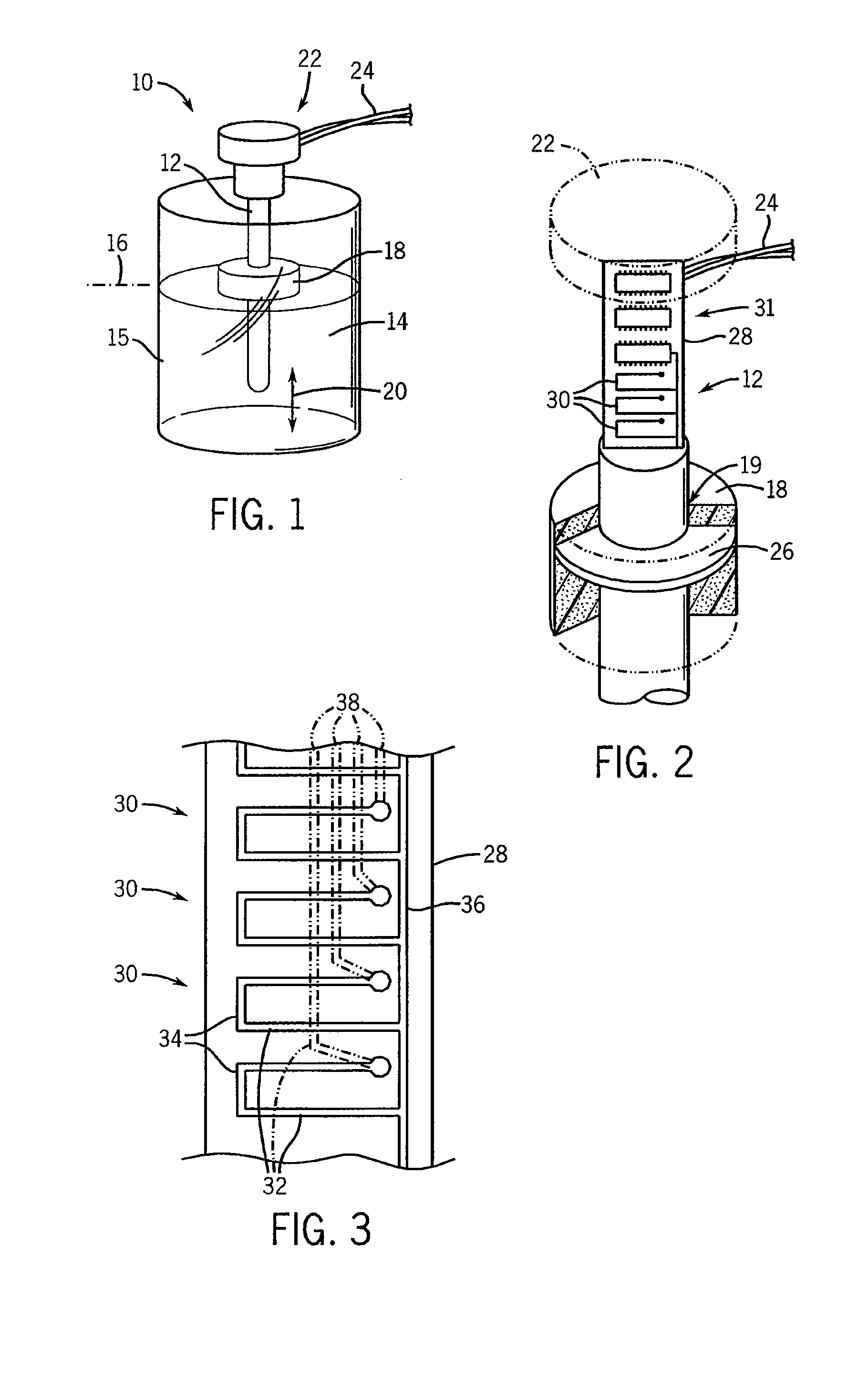
Inductive liquid-level sensor
ActiveUS8082785B2Sure easyVariation in sensitivityMachines/enginesAlarmsLiquid heightLiquid level sensor
An inductive liquid-level sensor employs a central shaft supporting multiple independent electrical loops that may be interrogated to detect the proximity of the conductive element in the float rising and falling with changes in liquid height outside of the shaft.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Capacitor Pairs with Improved Mismatch Performance
InactiveUS20090212392A1Increasing relative capacitance mismatchVariation in sensitivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and system for transforming spectral images
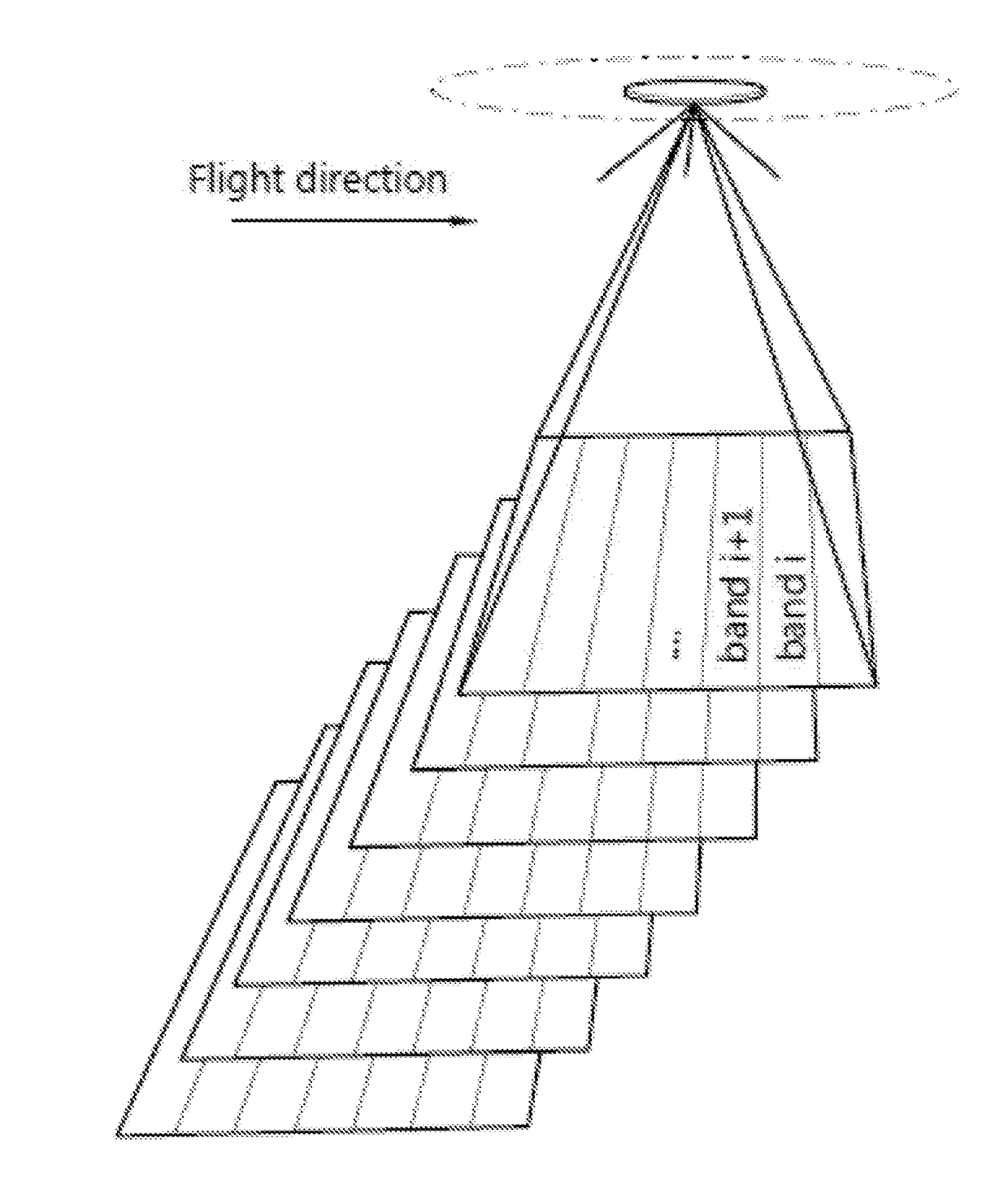
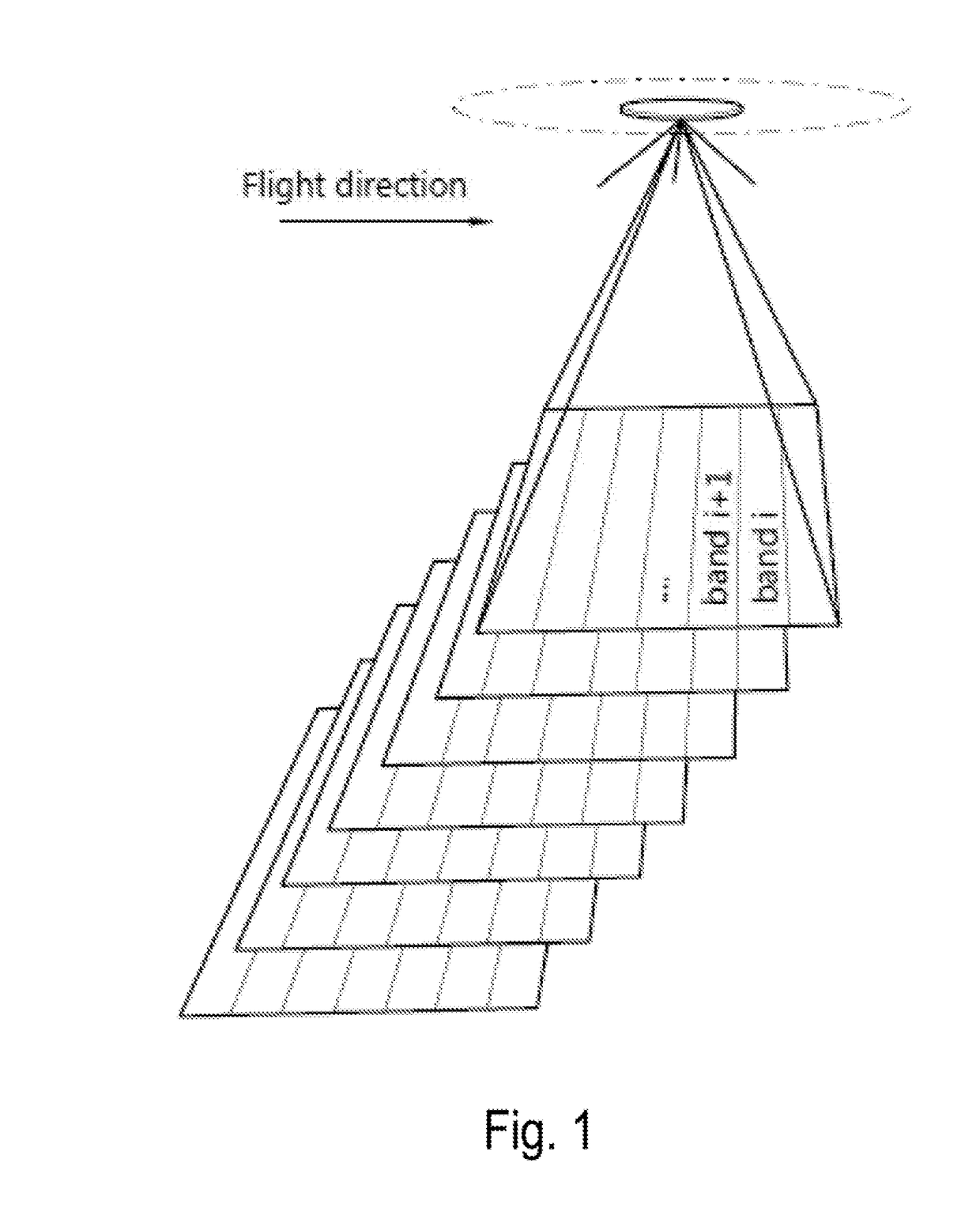
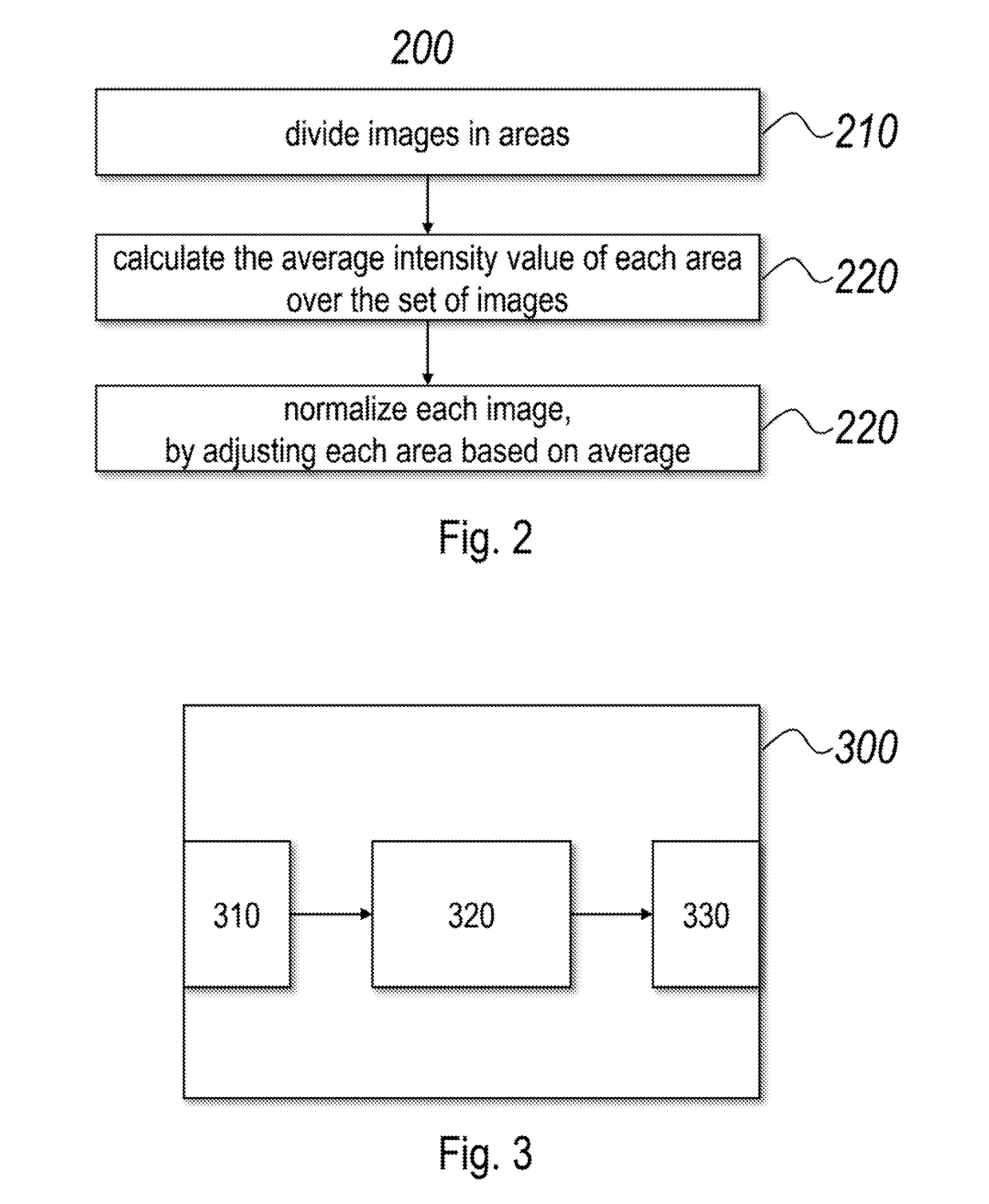
InactiveUS20180172515A1Simple methodImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
A method for transforming a set of spectral images, the method including: dividing the images in the set in identically arranged areas; for each of the areas, calculating a predetermined characteristic across the set of images; and, for each of the images, normalizing intensity values in each of the areas in function of the predetermined characteristic of the area. Additionally, a corresponding computer program product and a corresponding image processing system.
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
Solid-state image-sensing device
InactiveUS20060233008A1VariationVariation in sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIrradiationVoltage control
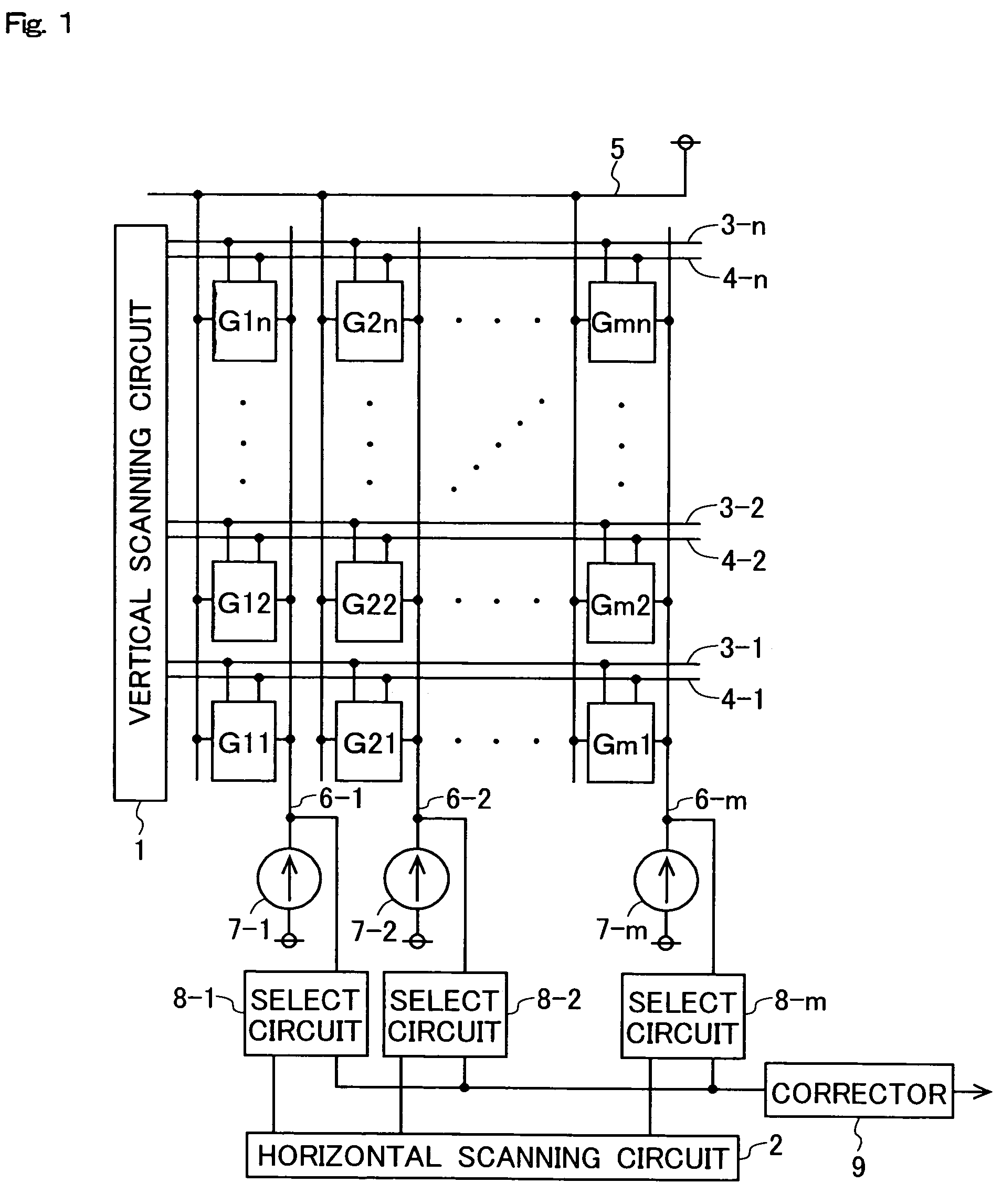
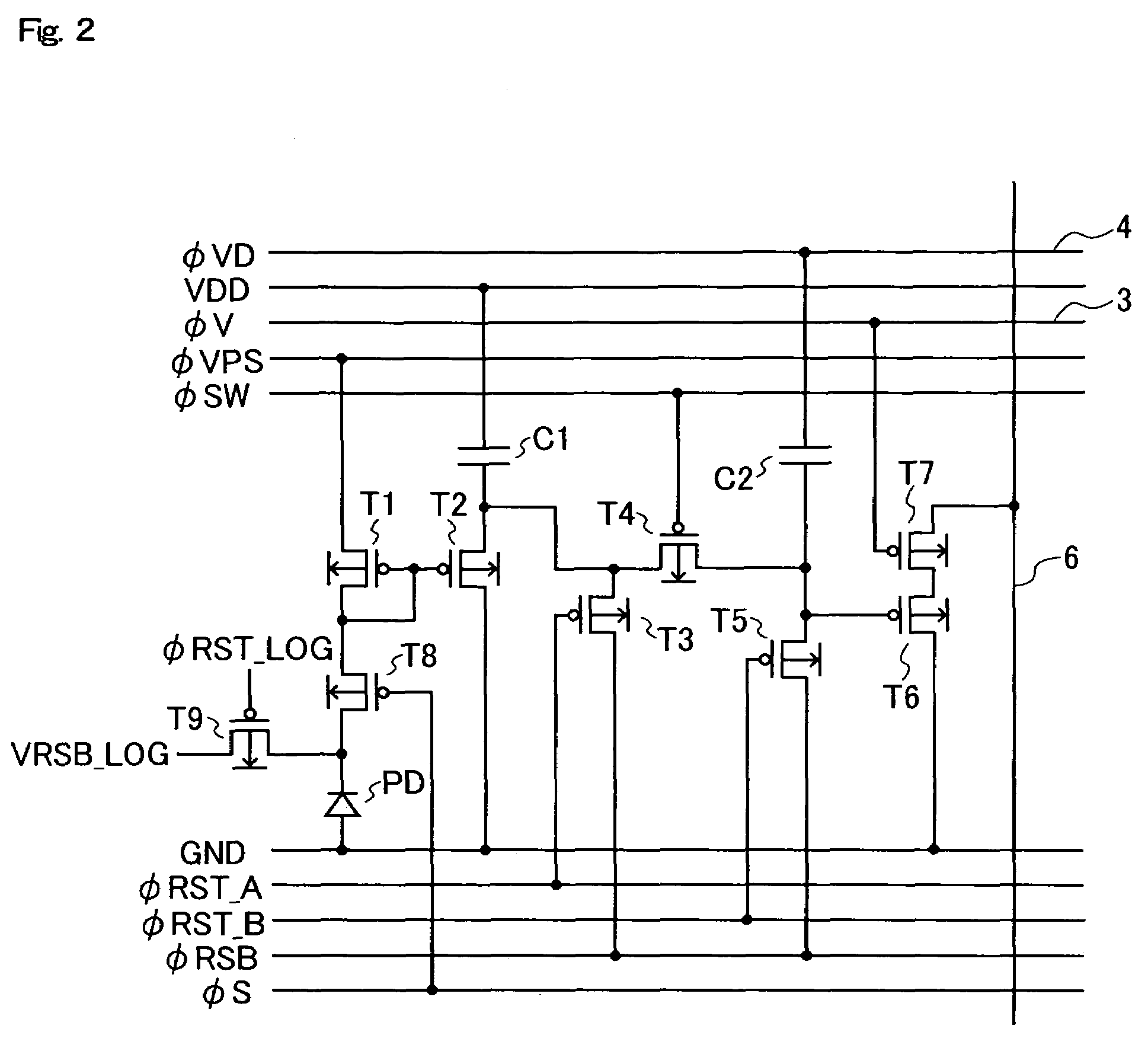
In a solid-state image-sensing device of the invention, for acquisition of sensed-image data, a photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is turned on to make a forcible reset switch perform resetting, then the voltage at the end of a logarithmic conversion MOS transistor that is not connected to the photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is so controlled that the logarithmic conversion MOS transistor is reset according to the threshold voltage thereof, and then an output commensurate with the amount of light incident on the photoelectric converter is delivered; for acquisition of noise data, the photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is turned on to make the forcible reset switch perform resetting, then the photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is turned off, then the voltage at the end of the logarithmic conversion MOS transistor that is not connected to the photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is so controlled that the logarithmic conversion MOS transistor is reset according to the threshold voltage thereof, and then an output unrelated to the amount of light incident on the photoelectric converter is delivered. With this sequence of operations, variations in sensitivity among individual pixels can be corrected for without irradiation with uniform light.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC +1
Optical receiver, portable electronic device, and method of producing optical receiver
ActiveUS10084006B2Variation in sensitivityReduce noiseSolid-state devicesDiodeUltraviolet lightsDiffusion layer
Owner:SHARP KK
Resonant pressure sensor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9003889B2Variation can be suppressedGood thickness controllabilityLamination ancillary operationsDecorative surface effectsEngineeringStrain gauge
A resonant pressure sensor including one or more resonant-type strain gauges arranged on a diaphragm may include a sensor substrate made of silicon and including one surface on which one or more resonant-type strain gauge elements are arranged and the other surface which is polished to have a thickness corresponding to the diaphragm, a base substrate made of silicon and including one surface directly bonded with the other surface of the sensor substrate, a concave portion formed in a portion of the base substrate bonding with the sensor substrate, substantially forming the diaphragm in the sensor substrate, and including a predetermined gap that does not restrict a movable range of the diaphragm due to foreign substances and suppresses vibration of the diaphragm excited by vibration of the resonant-type strain gauge elements, one or more conducting holes, and a fluid.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Capacitive touch panel
InactiveUS20120146937A1Variation in sensitivityImprove scalabilityInput/output processes for data processingInternal resistanceTouch panel
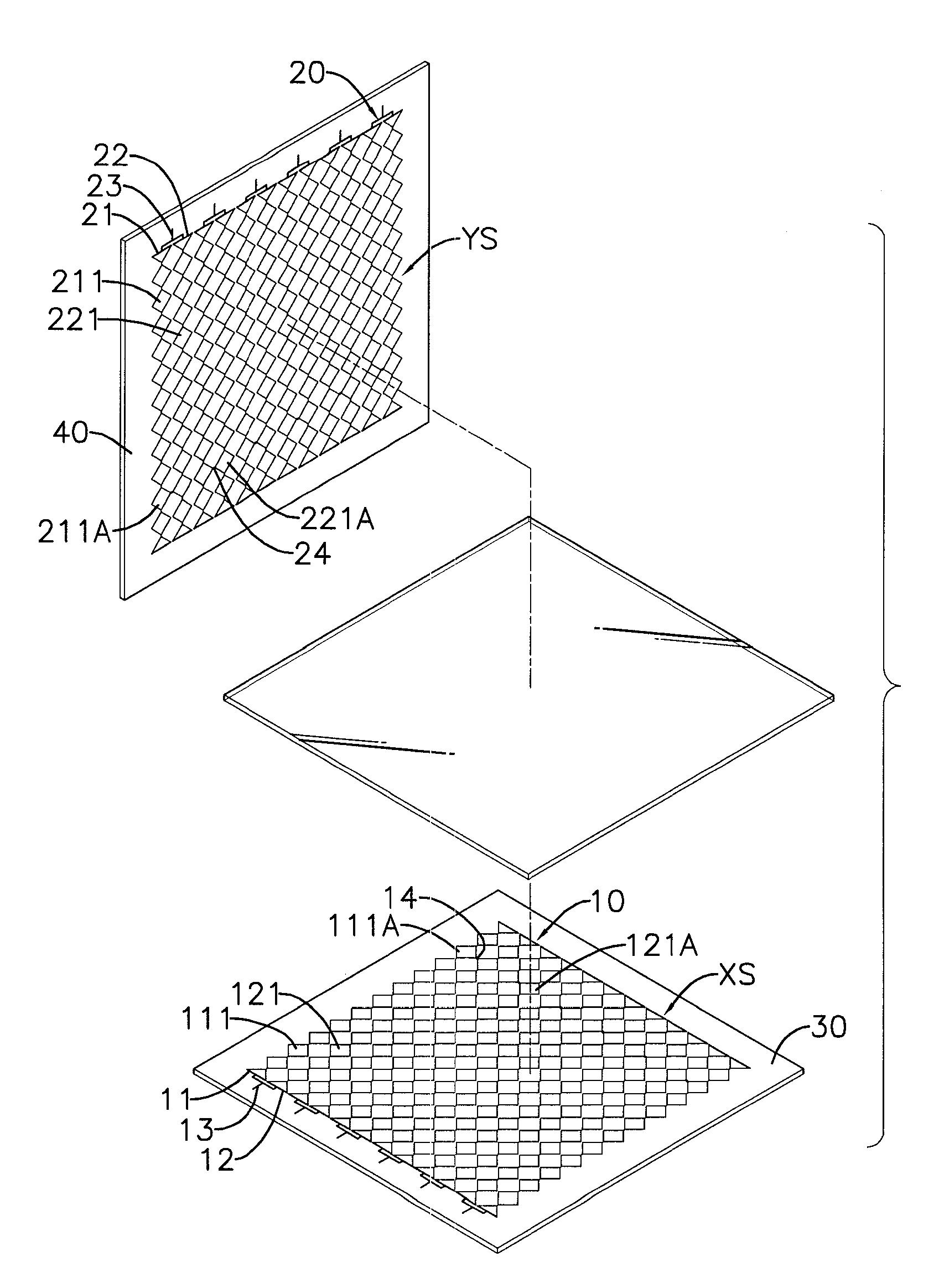
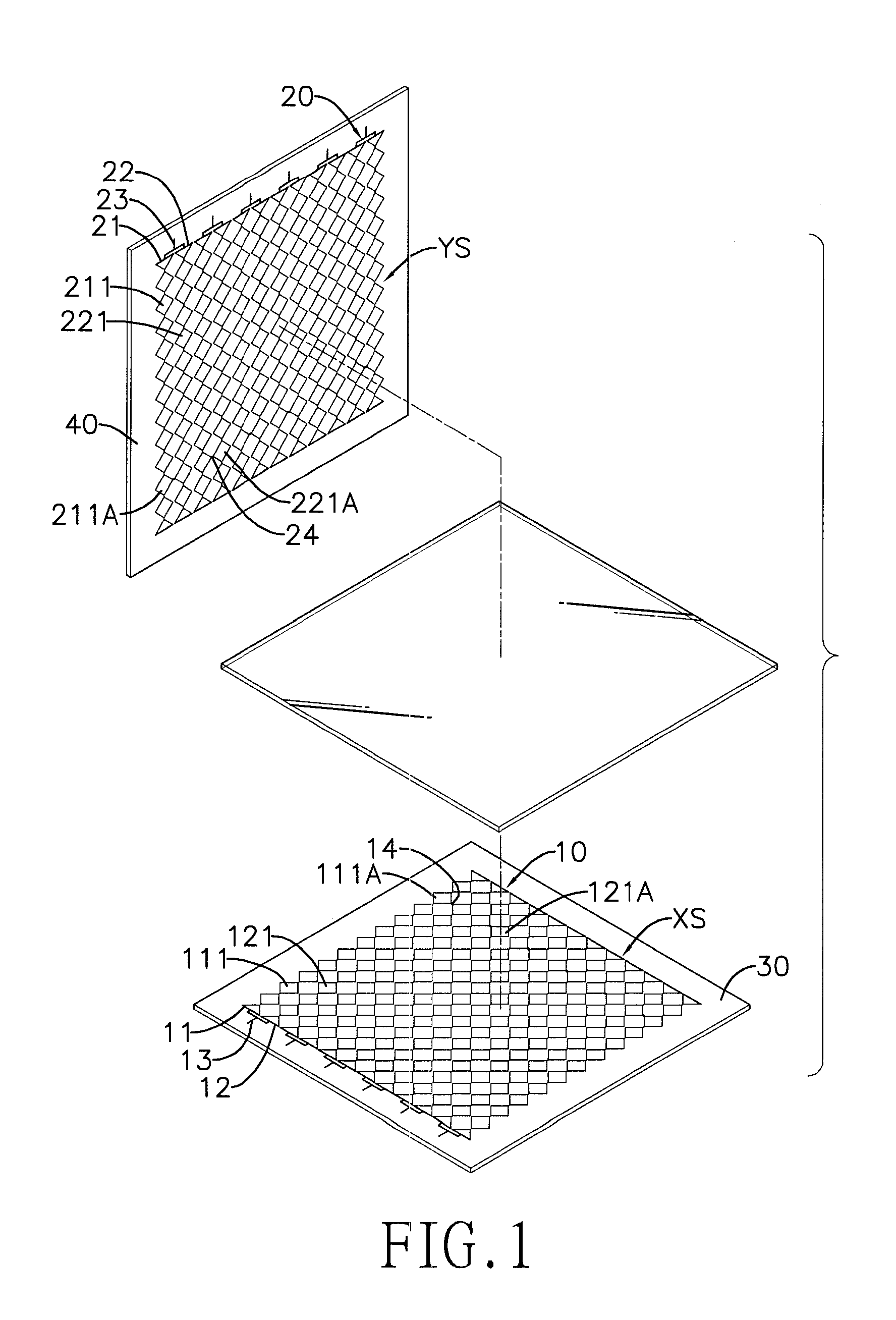
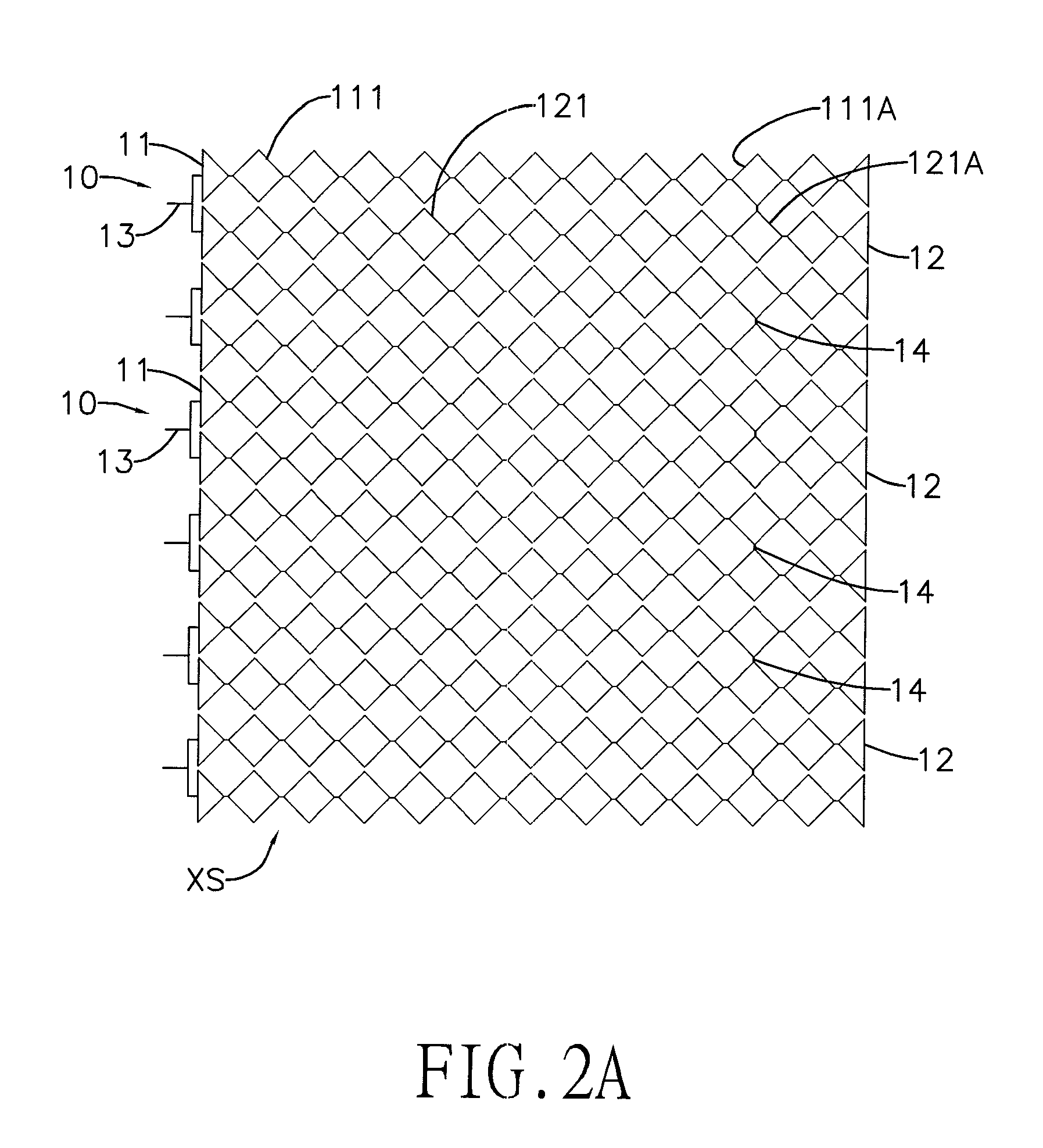
A capacitive touch panel has an. X-axis sensing layer and a Y-axis sensing layer. The X-axis and Y-axis sensing layers respectively have multiple sensing rows and sensing columns. Each sensing row or sensing column has multiple X-axis or Y-axis electrode strings. Each X-axis or Y-axis electrode string has multiple X-axis electrodes or Y-axis electrodes serially connected. The X-axis electrode strings or Y-axis electrode strings are connected in parallel with each other. The Y-axis electrodes are alternately or directly aligned with the X-axis electrodes. With the foregoing design, the resistance of each row and column can be effectively reduced so as to raise the reading sensitivity of a controller and maintain uniform internal resistance for each sensing row and column to facilitate enlargement of the capacitive touch panel.
Owner:MINLEAD
Solid-state image-sensing device
InactiveUS7417212B2Variation in sensitivityEliminate needTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringIrradiation
Solid-state image-sensing device for acquisition of sensed-image data is described. A photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is turned on to make a forcible reset switch perform resetting. Then, the logarithmic conversion MOS transistor is reset according to the threshold voltage thereof. Then, an output commensurate with the amount of light incident on the photoelectric converter is delivered. The photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is turned on to perform resetting and then turned off. Then, the voltage at the end of the logarithmic conversion MOS transistor that is not connected to the photoelectric converter disconnecting switch is reset according to its threshold voltage. This provides an output unrelated to the incident light. With this sequence of operations, variations in sensitivity among individual pixels can be corrected for without irradiation with uniform light.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC +1
Image-sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20050280056A1Accurate collectionMinimize changesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsGate voltageImage sensing
In a solid-state image-sensing device, when image sensing is performed, in each pixel, MOS transistors T1 and T5 are turned on and a MOS transistor T6 is turned off so that a MOS transistor T2 operates in a subthreshold region. When resetting is preformed, in each pixel, the MOS transistors T1 and T5 are turned off and the MOS transistor T6 is turned on so that the gate voltage of the MOS transistor T2 is kept constant. In this state, the MOS transistor T2 is brought first into a conducting state and then, by turning a signal φVPS to a high level, into a cut-off state. This permits a signal proportional to the threshold value of the MOS transistor T2 to be output as compensation data.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Inductive position sensor with secondary turns extending through a printed circuit board
ActiveUS10816364B2Variation in sensitivityReduce sensitivityUsing electrical meansConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
Solid state imaging device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7548666B2Convenient lightingReduce variationSolid-state devicesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideSemiconductor
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Micro-electromechanical resonator geometry
ActiveUS8432233B2Good control over strainImprove piezo-resistive gainPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResonatorPhysics
A micro-electromechanical resonator suspended from an anchor. The resonator has: a length; a first width at a first distance from the anchor; and a second width at a second, greater distance from the anchor. The second width is greater than the first width, and the width of the resonator tapers gradually along at least part of its length from the second width to the first width.
Owner:NXP BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com