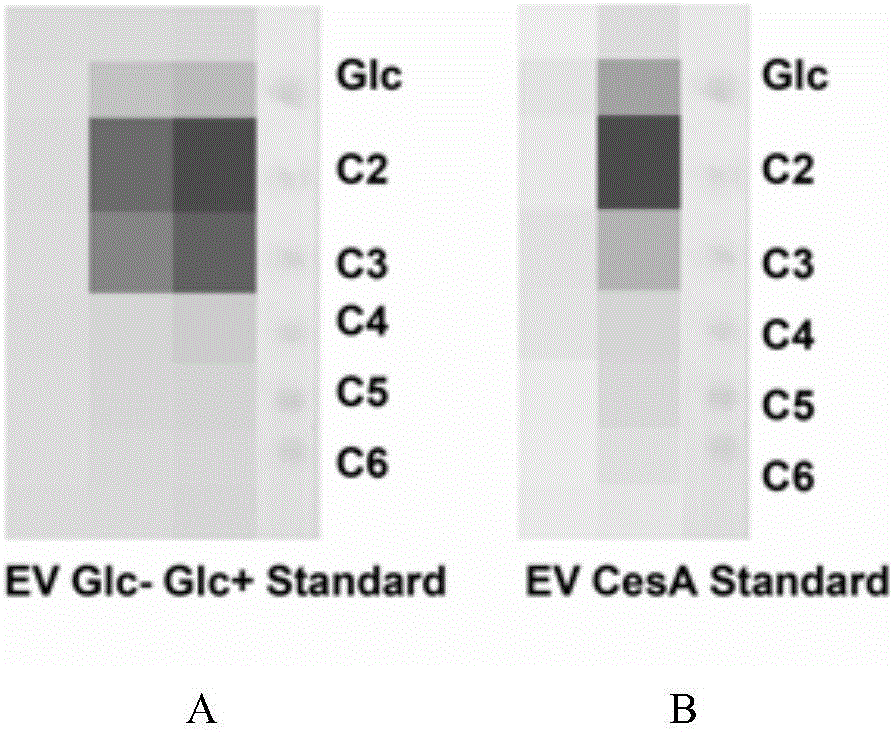
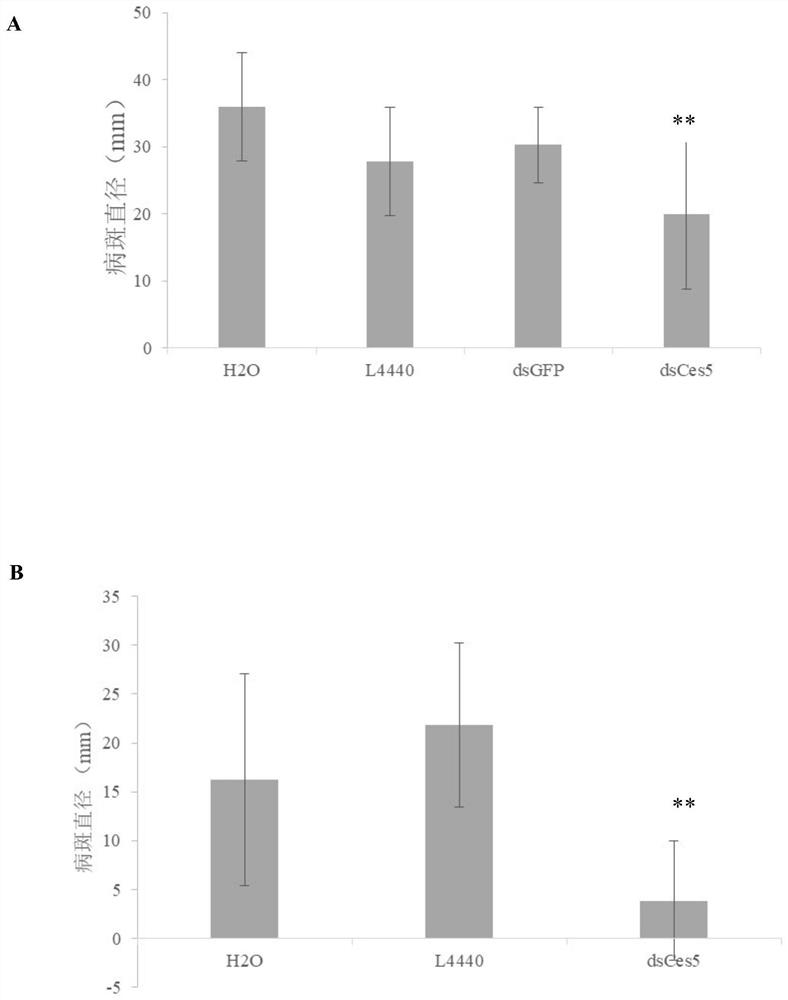
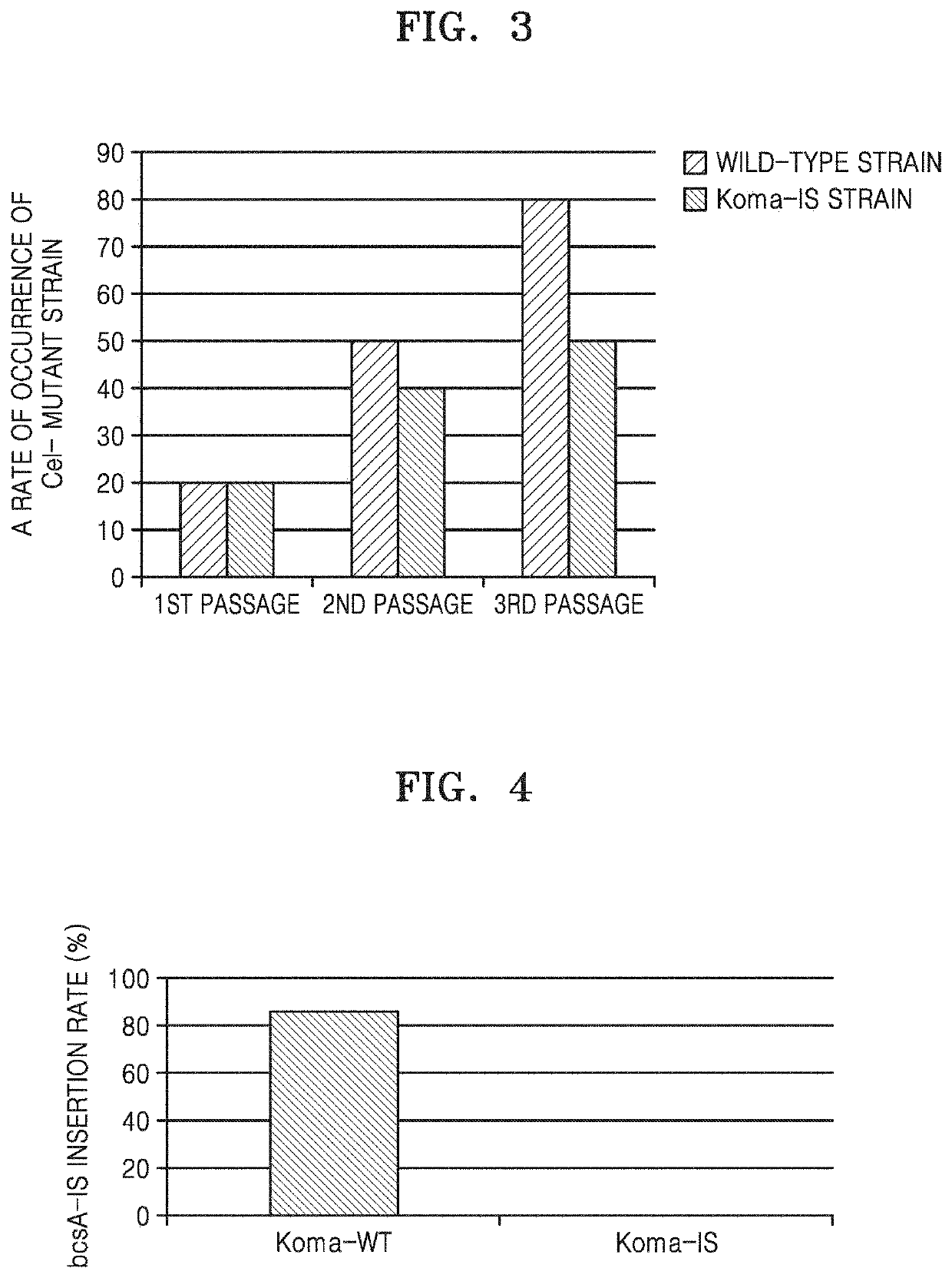
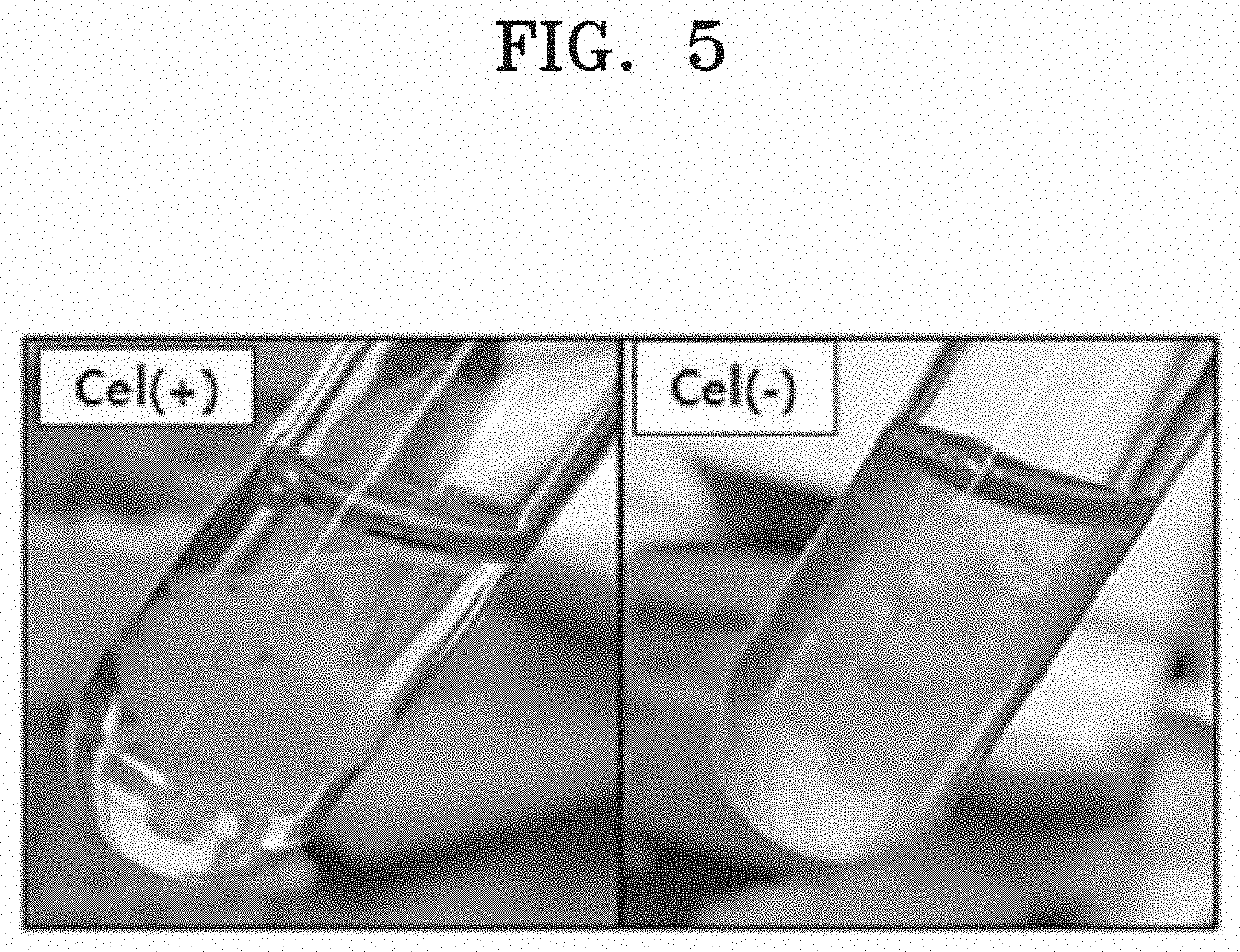
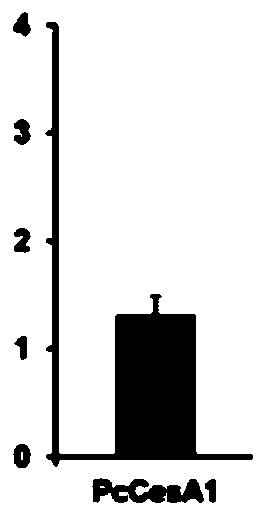
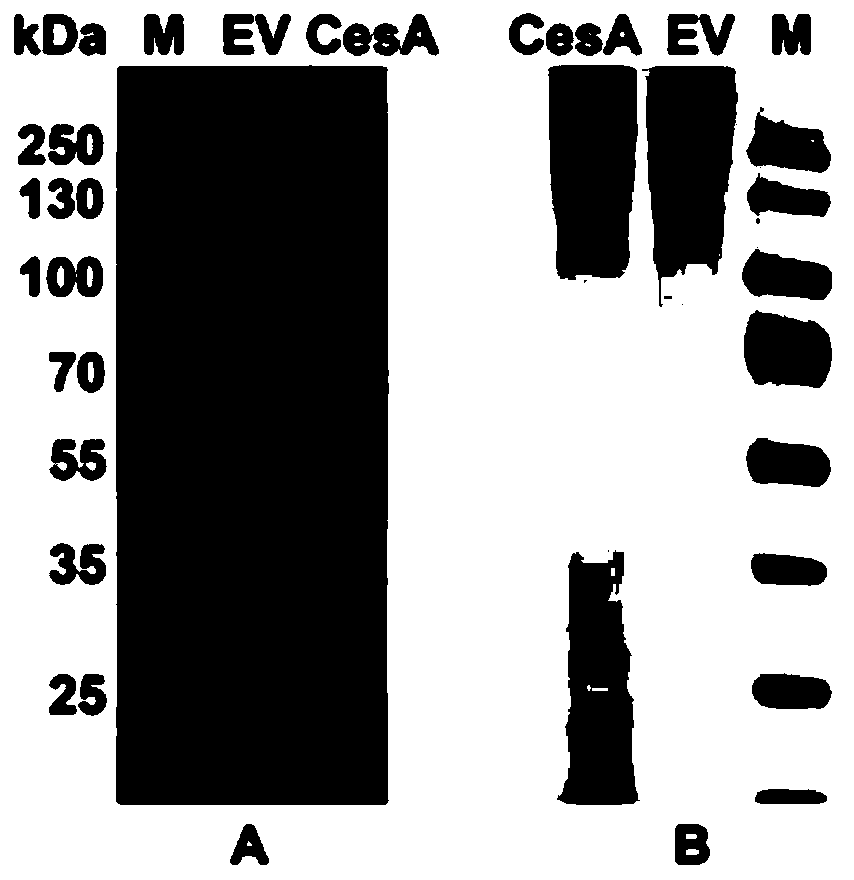
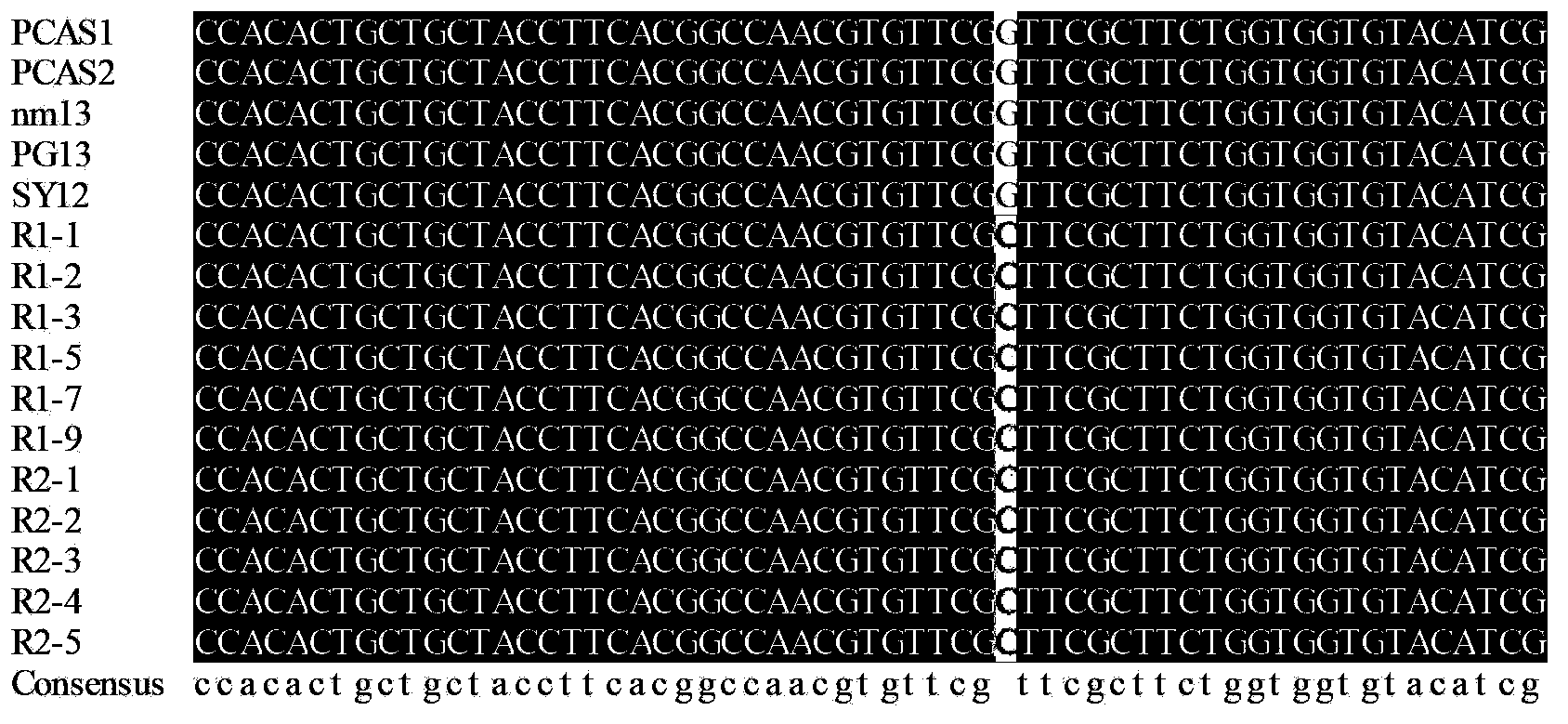Patents
Literature
30 results about "Cellulose synthetase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
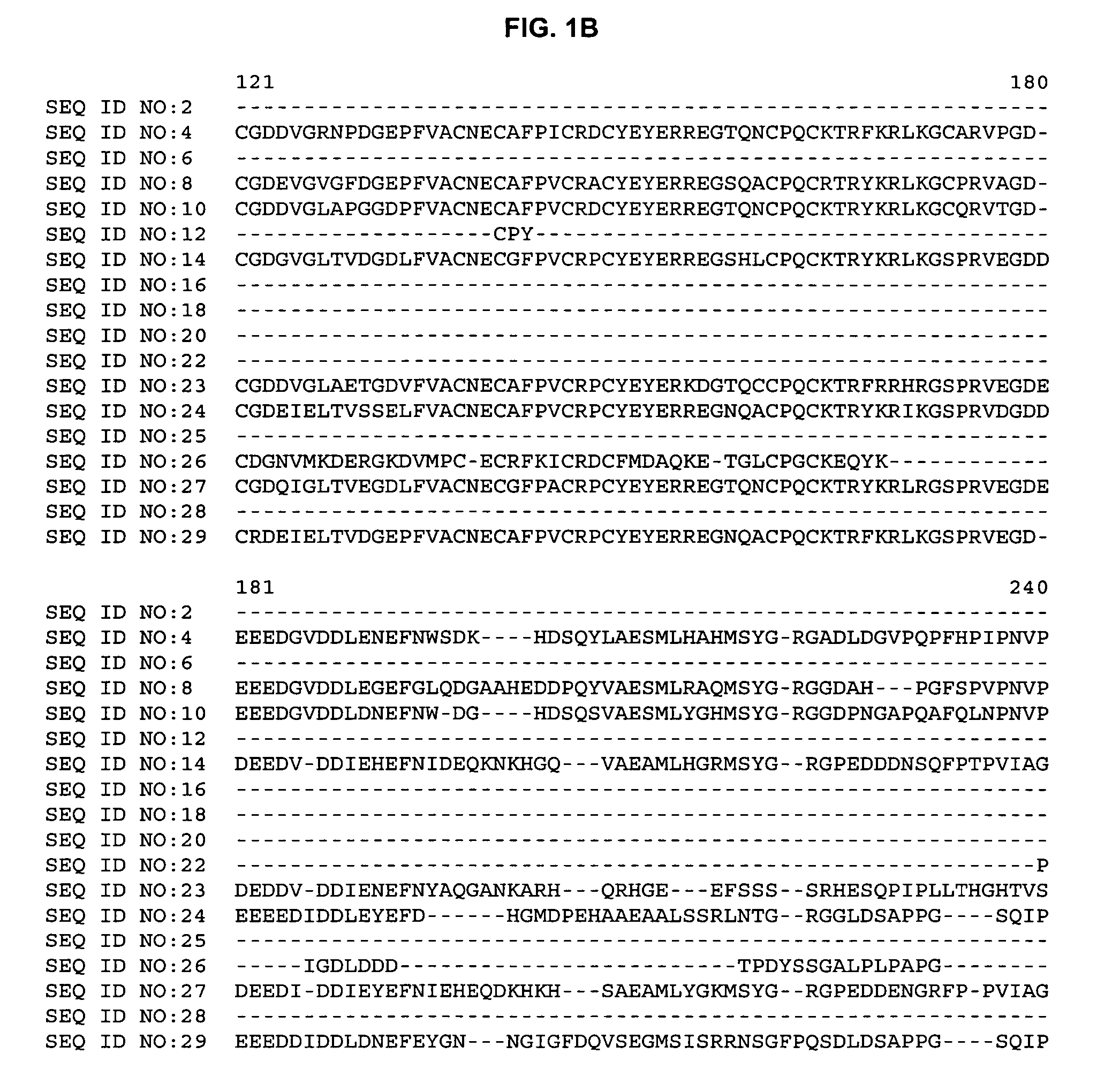
Maize cellulose synthases and uses thereof
The invention provides isolated cellulose synthase nucleic acids and their encoded proteins. The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering cellulose synthase levels in plants. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising said nucleic acids.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Fresh bamboo shoot coating preservative prepared by edible material
InactiveCN101744045AAbsolute securityNo harmFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingPreservativeAtmospheric temperature
The invention relates to fresh bamboo shoot coating preservative prepared by edible materials, belonging to the technical field of fruit and vegetable freshness preservation. The preservative mainly comprises one kind or more of substances such as natural plant gum, polysaccharose, natural macromolecular substances, stabilizing agent, bacteriostatic agent and the like. In the process of preparation, components are dissolved in certain proportion, the obtain solution is agitated and heated to accelerate dissolution, and the obtained solution is prepared into water solution or colloidal solution after being cooled. The preservative can be used under atmospheric temperature. The coating preservative prepared through the invention belongs to natural preservative and has the advantages that the cost is low, the effectiveness is high, the environment is protected, the activity of the cellulose synthase and other enzymes is effectively inhibited, the weight loss of bamboo shoots is reduced, the low-temperature damage is avoided and the quality guarantee period of the fresh bamboo shoots is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cellulose synthase encoding polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7049481B1Quality improvementLow lignin contentBryophytesSugar derivativesNucleotidePlant cell
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding functional cellulose synthases and UDP-glucose binding domain thereof, transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with the polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods of transforming plants and plant cells with cellulose synthase or UDP-encoding polynucleotides.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Liriodendron chinensis cellulose synthase gene LcCESA1 as well as expression protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a liriodendron chinensis cellulose synthase gene LcCESA1 and as well as expression protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of LcCESA1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the amino acid sequence of the expression protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. By taking a model plant arabidopsis as a research object, a Chinese liriodendron chinensis cellulose synthase gene LcCESA1 obtained by cloning is mediated and transformed into arabidopsis, and a T3 generation homozygosous gene plant is finally obtained by means of screening and cultivation; by observing microstructures of the wild arabidopsis and transgenetic arabidopsis, and the condition that cell walls of histocytes of vascular bundles of stem sections and the blade histocytes of the transgenetic arabidopsis are different from those of the wild arabidopsis is found, so that the LcCESA1 gene affects the cell walls of histocytes of vascular bundles of stem sections and the blade histocytes of the transgeneticarabidopsis, can promote accumulation of cellulose and has wide application.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Isolated cellulose synthase promoter regions
InactiveUS7674951B1Quality improvementLow lignin contentBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesBiologyGene
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention is the protein as shown in a sequence 2; the encoding gene of the protein is as shown in a sequence 1. An experiment proves that the protein PCCESA1 provided by the invention can catalyze substrate uridine diphosphate D glucose (UDPG) to generate cellobiose, and has significance on biosynthesis of main component cellulose of a cell wall of the phytophthora capsici; as an oomycetes cell wall plays an important role in maintaining oomycetes vital movement, including maintaining cell shapes, participating in host interaction and the like. Therefore, the cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention provides technical support for the oomycetes cell wall, and provides a new molecular target for future bactericide research and development.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for synthesizing cellulose in vitro
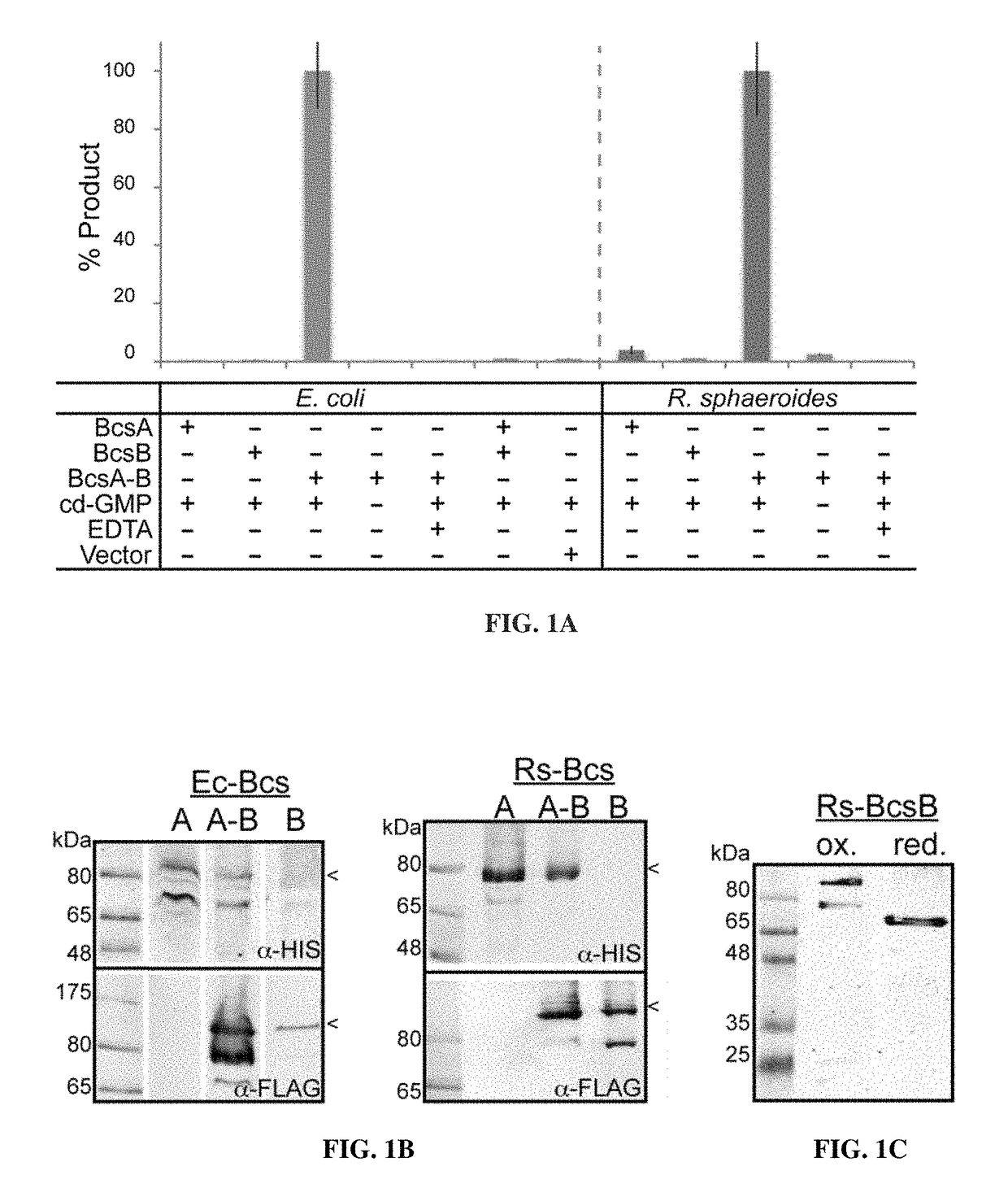
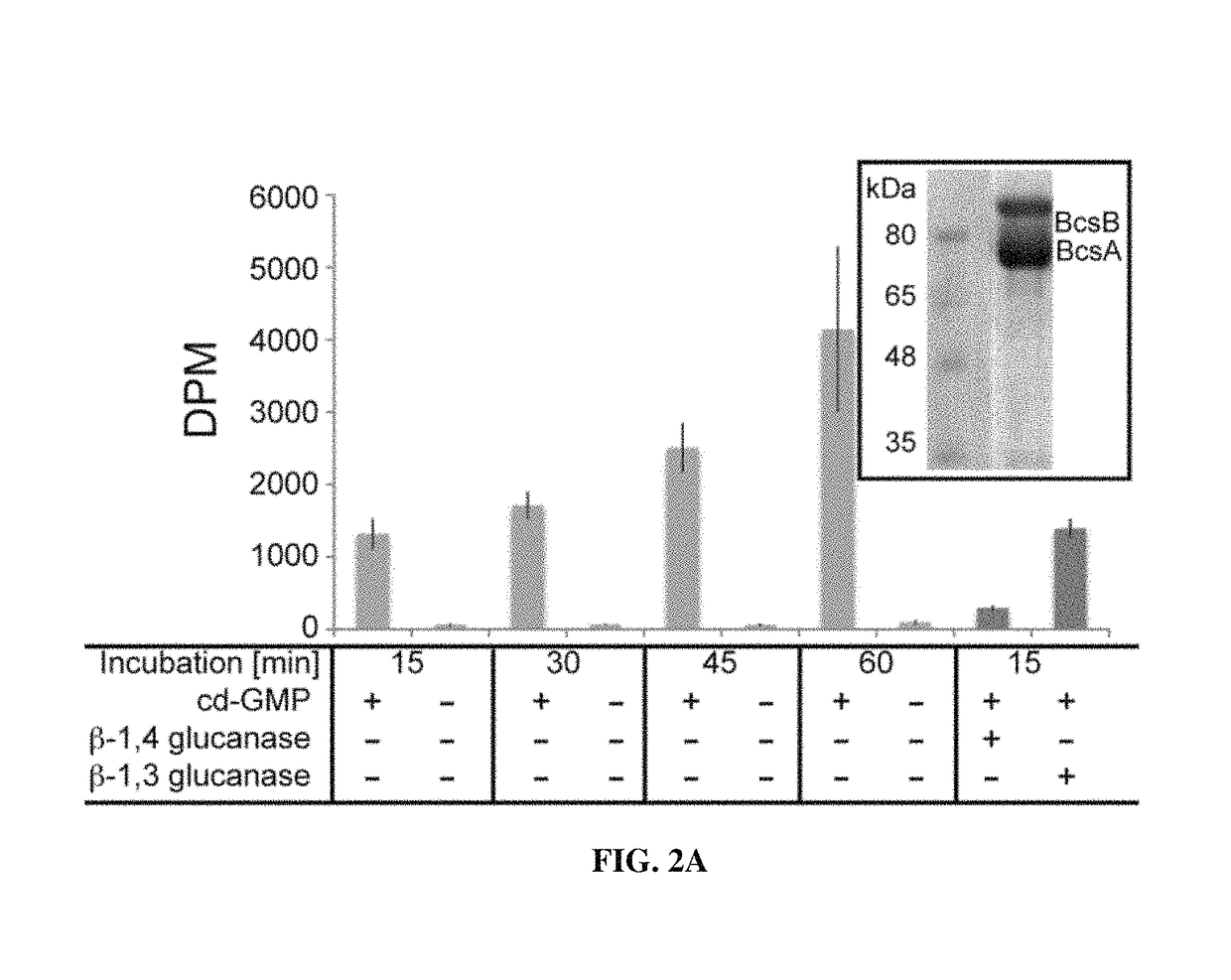
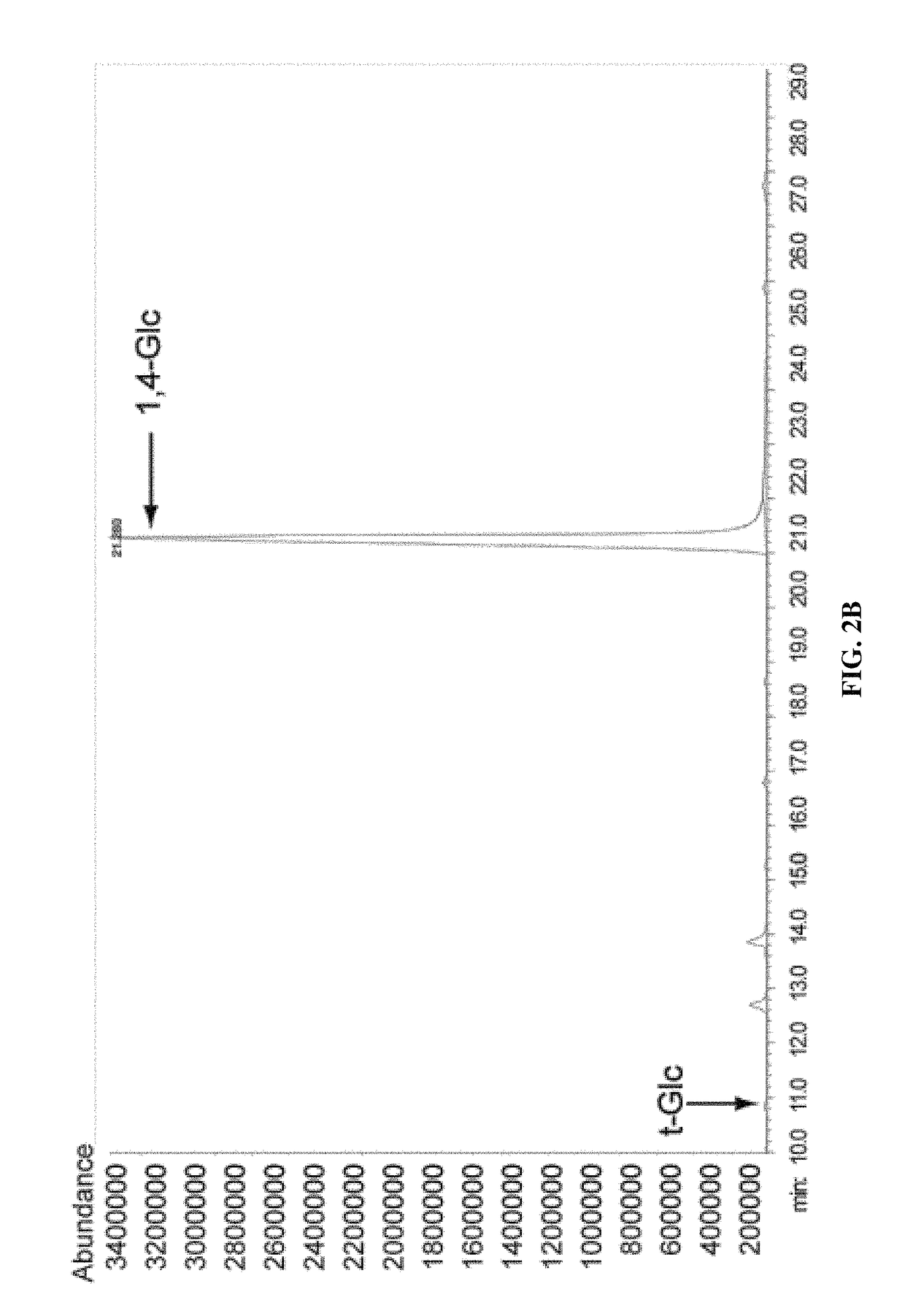
Disclosed herein is in vitro cellulose synthesis reconstituted from purified BcsA and BcsB proteins from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Further disclosed is that BcsB is essential for catalysis by BcsA. The purified BcsA-B complex produces cellulose chains of a degree of polymerization in the range 200-300. Catalytic activity of native proteins depends on the presence of cyclic-di-GMP, but is independent of lipid-linked reactants. Further disclosed is strict substrate specificity of cellulose synthase for UDP-glucose. Truncation analysis of BcsB localized the region required for activity of BcsA within its C-terminal membrane-associated domain. Further disclosed are crystal structures of the cyclic-di-GMP-activated BcsA-B complex revealing that cyclic-di-GMP releases an auto-inhibited state of the enzyme by breaking a salt bridge which otherwise tethers a conserved gating loop that controls access to and substrate coordination at the active site. Unexpectedly, disrupting the salt bridge by mutagenesis generates a constitutively and fully active cellulose synthase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
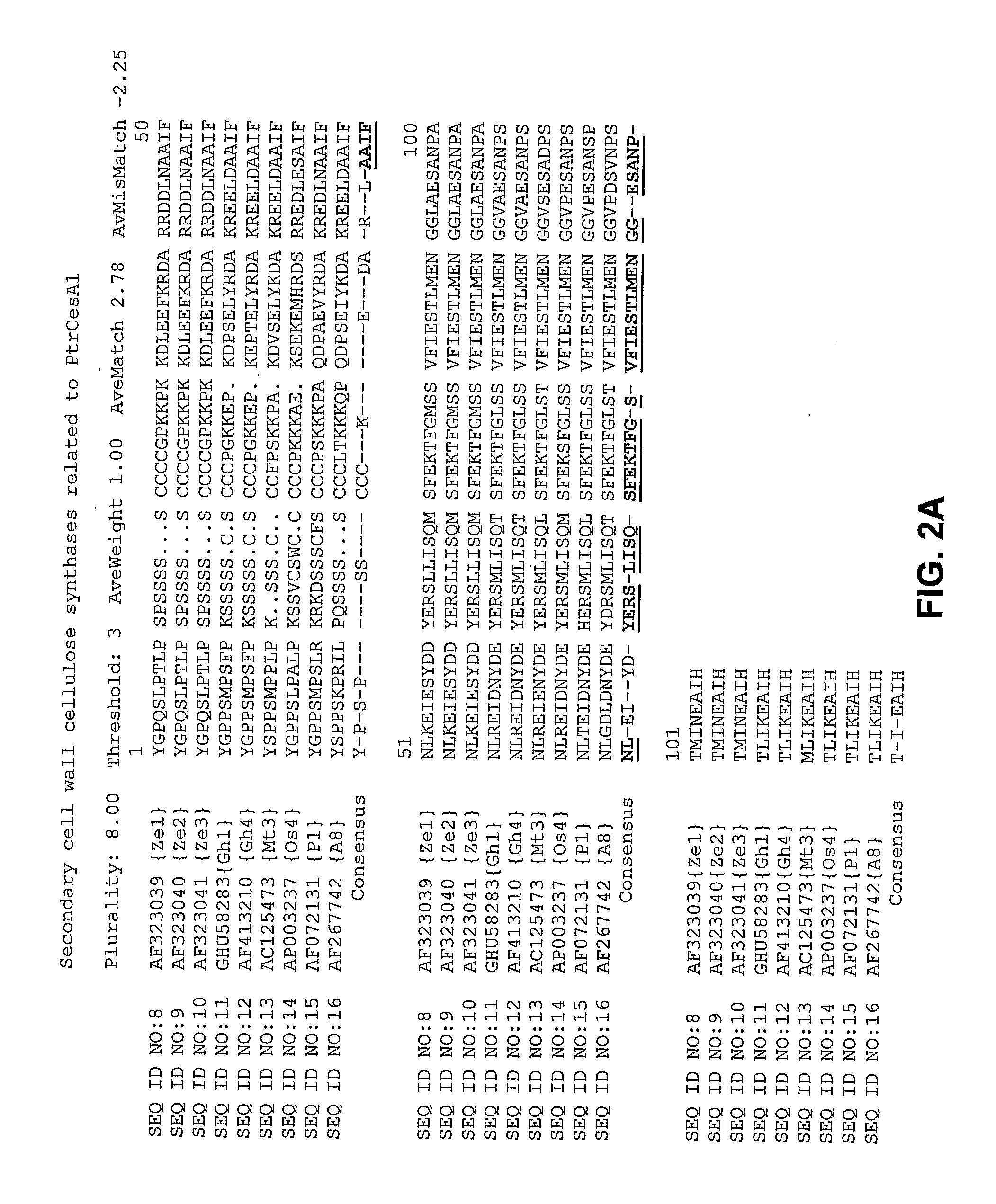
Methods for Enhancing Expression of Secondary Cell Wall Cellulose Synthases in Plants
Described are methods for making transgenic plants capable of expressing secondary cell wall cellulose synthases and methods of enhancing expression of secondary cell wall cellulose synthases in plants. Also described are plants produced by the methods. Plants comprising at least three exogenous polynucleotides encoding secondary cell wall cellulose synthases are also provided.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
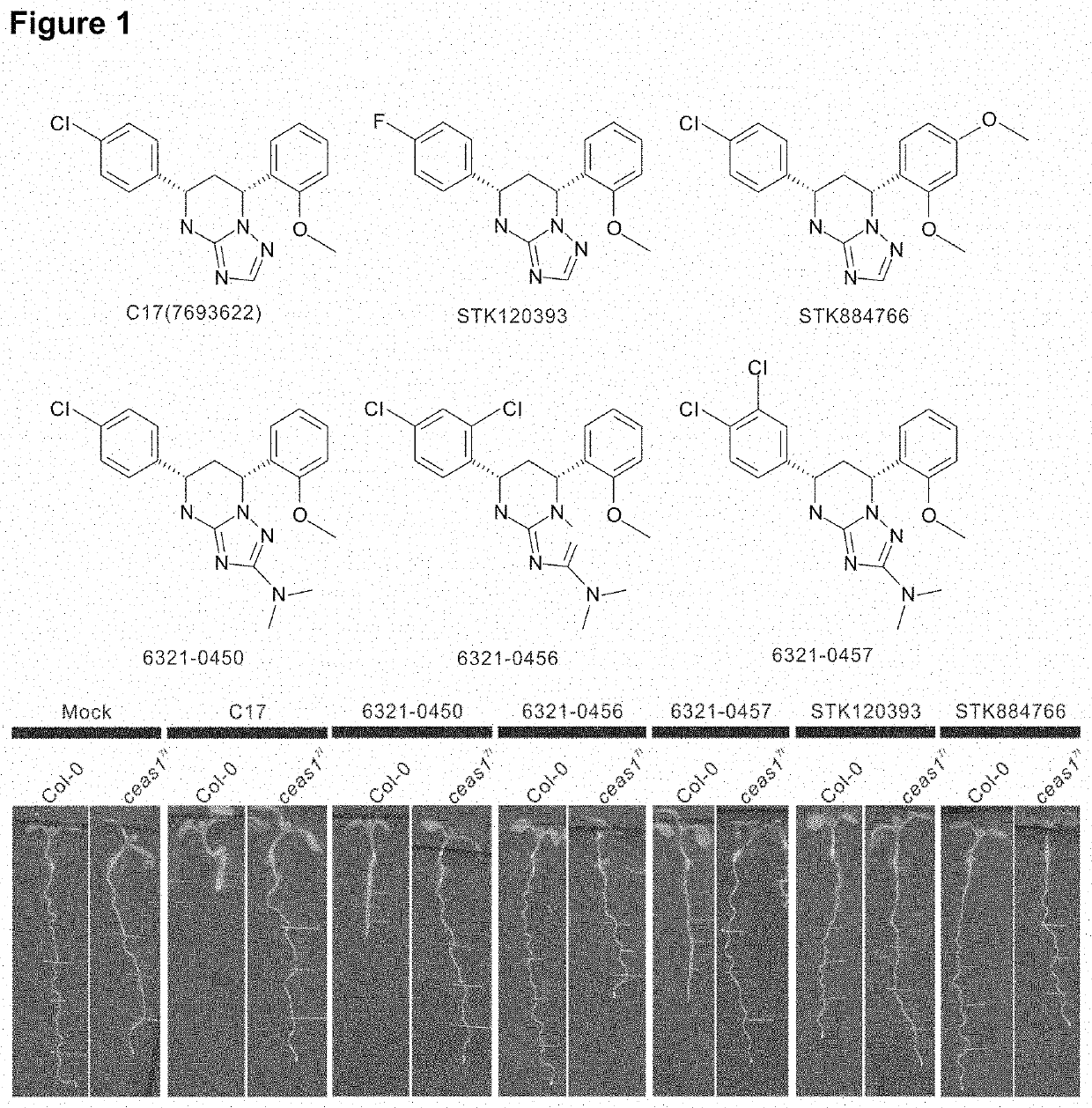
Cellulose synthase inhibitors as a new class of herbicide and non-gmo crops that are resistant to the herbicide
PendingUS20200290959A1Easy to understandEasy to operateBiocideOrganic chemistryGenetically modified cropsPlant growth
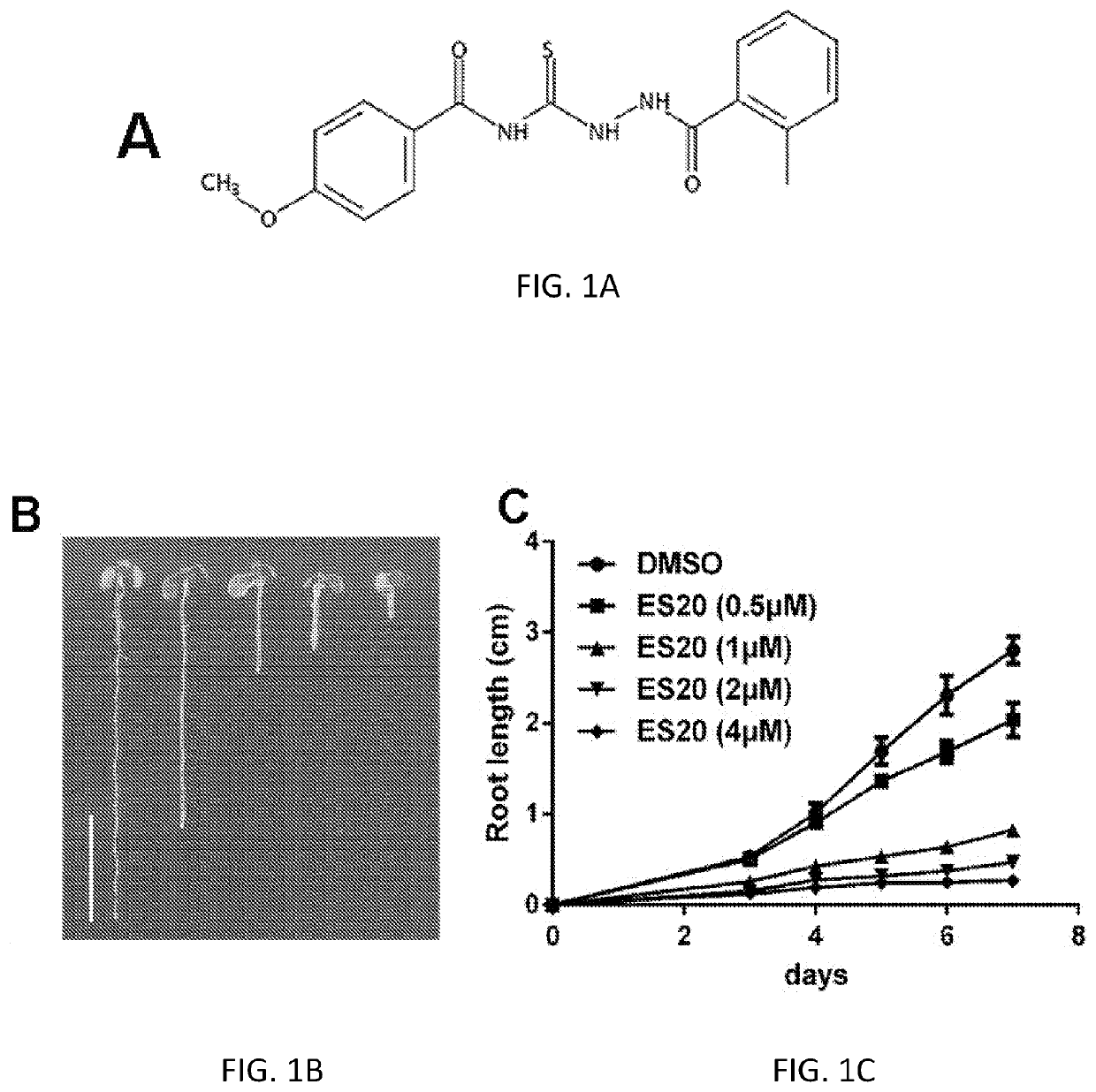
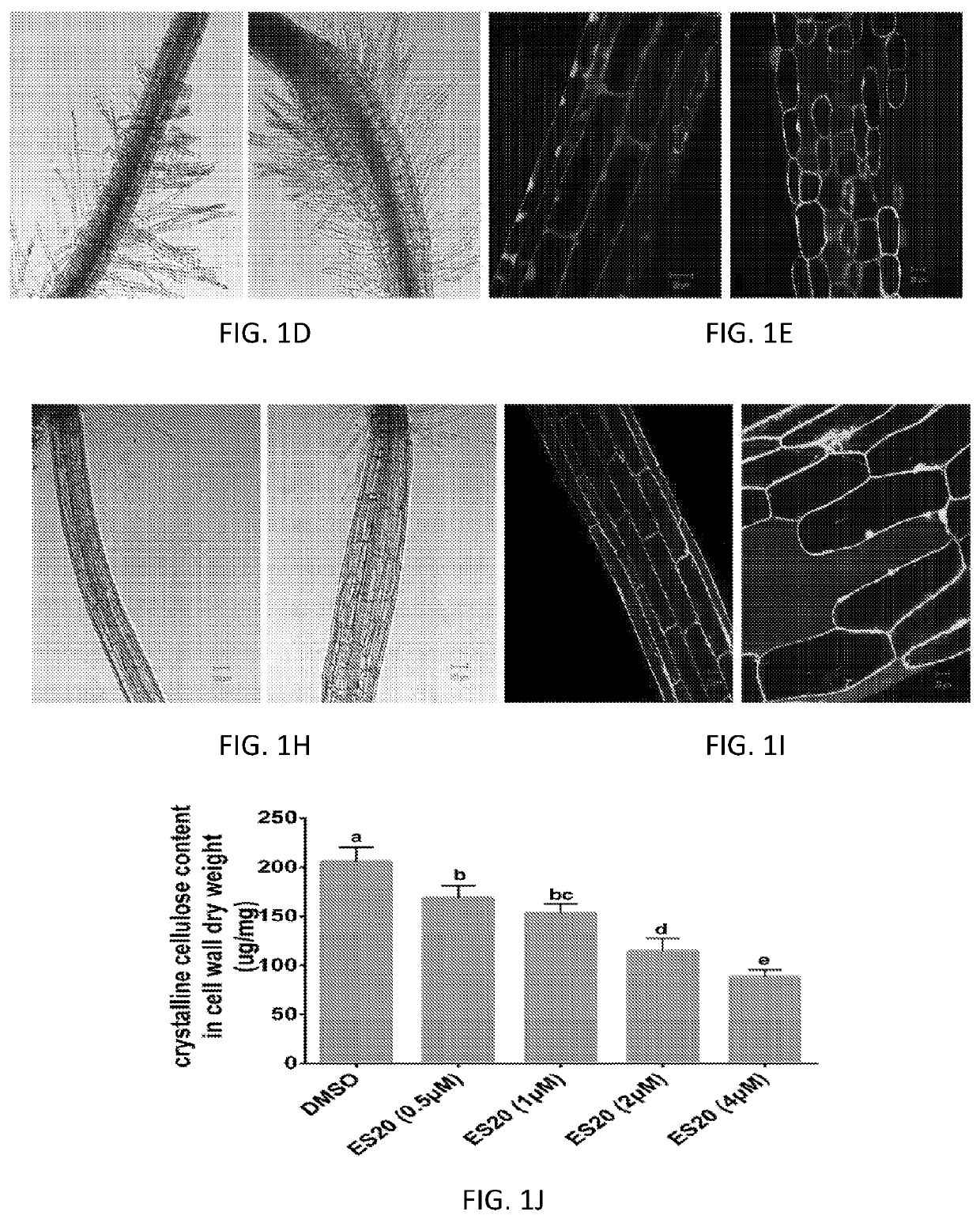
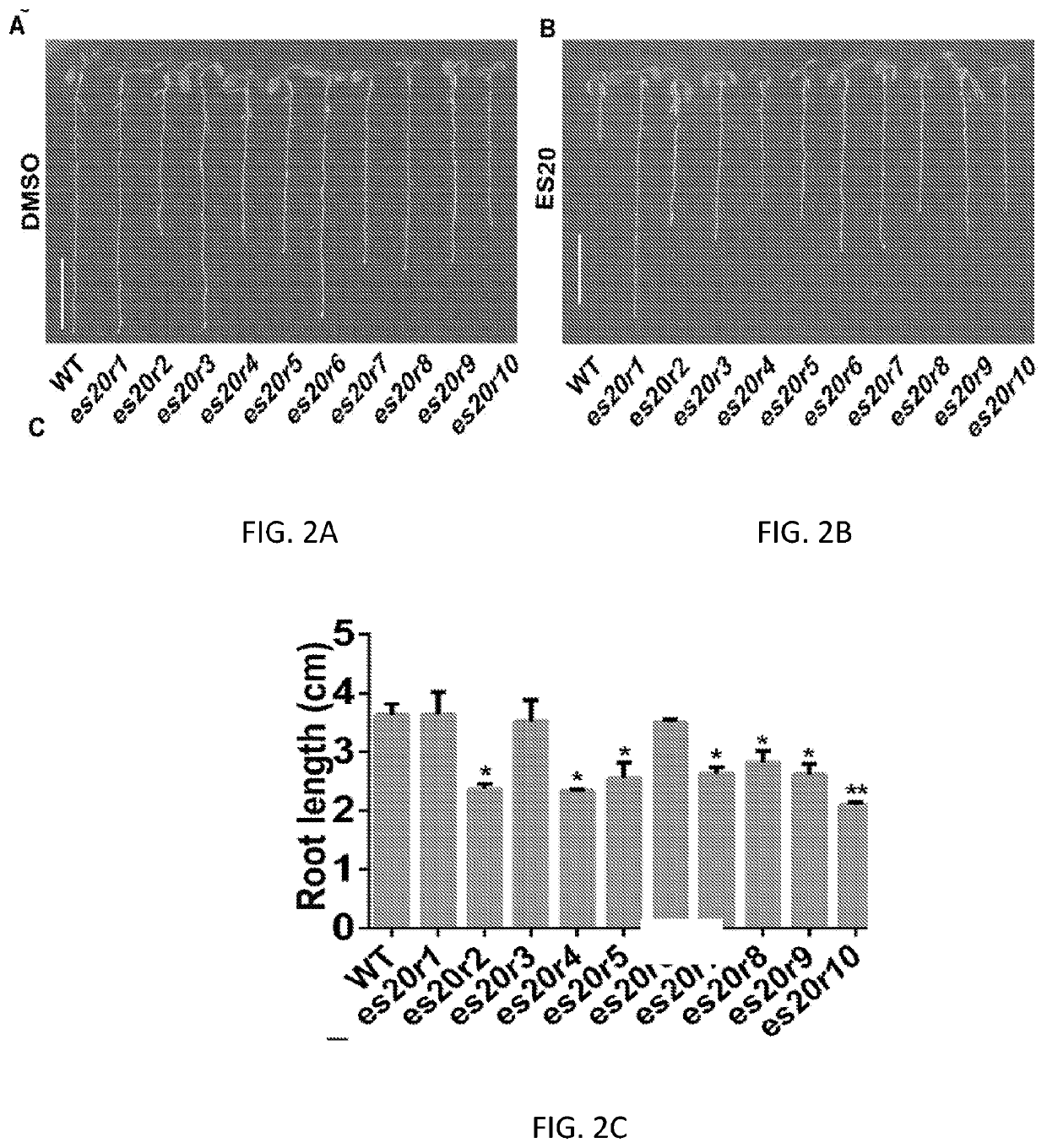
Using chemical genetic screening, we discovered a small molecule Cellulosin (aka endosidin20 or ES20) that causes cell swollen and inhibits plant growth, but does not disrupt global vesicle trafficking. By doing mutant screening, we obtained multiple alleles of Arabidopsis thaliana that are resistant to Cellulosin inhibition in growth. Those mutated amino acid residues are conserved across plant species. Cellulosin targets a group of cellulose synthases (CesAs) of Arabidopsis thaliana by binding to a conserved domain essential for the catalytic activity of CesA. Cellulosin may target and inhibit all subtypes of CesAs in plants. The present invention relates to Cellulosin, a cellulose synthase inhibitor, its analogs or derivatives as abroad-spectrum herbicide. The mutated genes, their protein products and a cell or a plant having those mutated genes or expressing those protein products are within the scope of this disclosure.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Plant cellulose synthases
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a cellulose synthase. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the cellulose synthase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the cellulose synthase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:ALLEN STEPHEN +2
Cellulose synthase from pine and methods of use
The present invention concerns isolated polynucleotides that encode a polypeptide with cellulose synthase activity and methods of producing a plant that expresses the cellulose synthase-encoding polynucleotides and thereby has a different phenotype compared to a non-transformed plant of the same species.
Owner:ARBORGEN
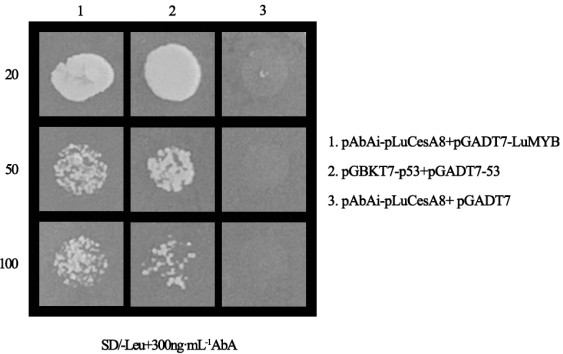
LuMyb gene for regulating and controlling flax cellulose synthesis and application of LuMyb gene
Owner:黑龙江省农业科学院经济作物研究所 +1
Cellulose synthase inhibitors and mutant plants
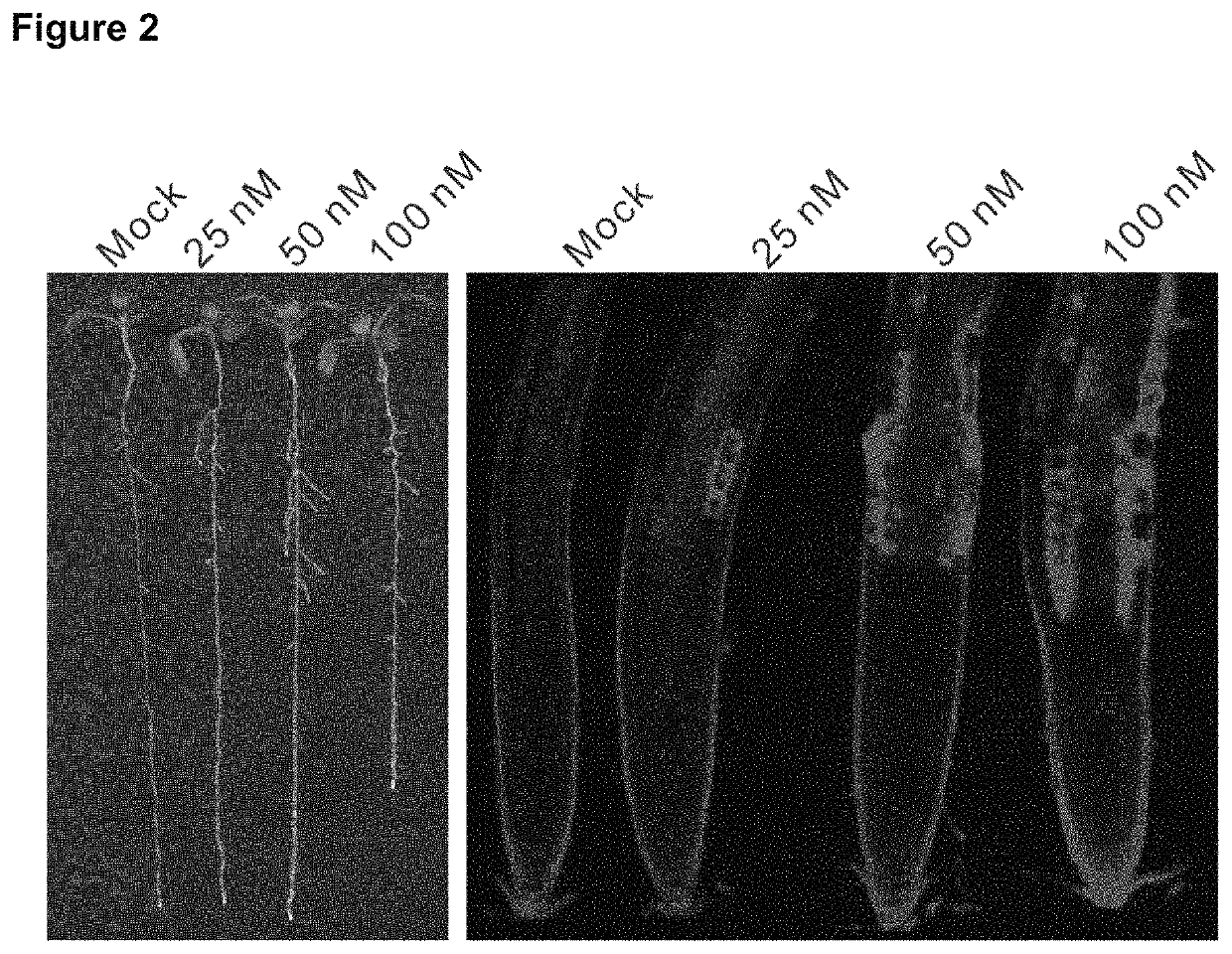
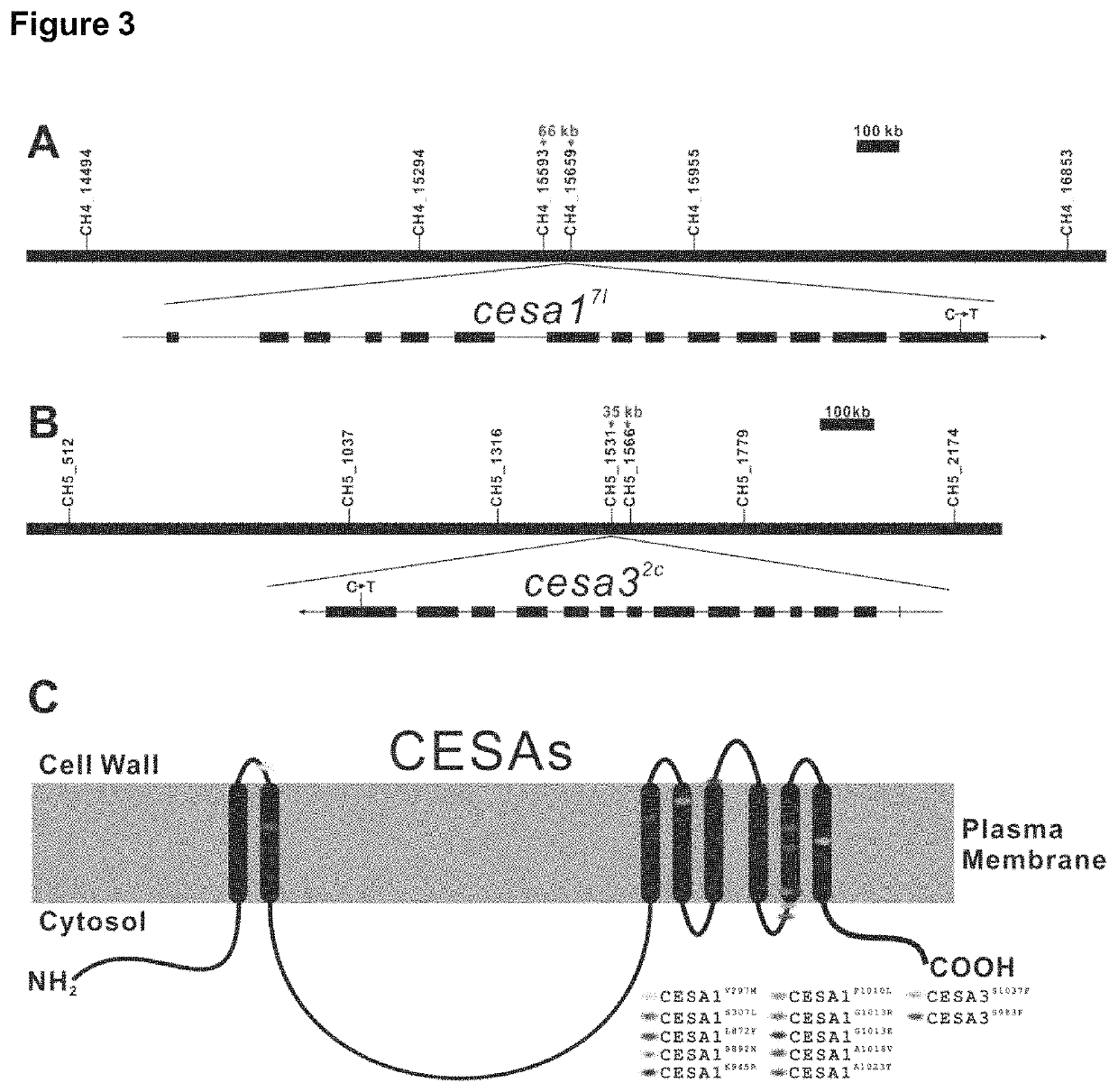
The present invention relates to specific inhibitors of the cellulose synthase subunits 1 and 3 activity in plants, useful as a herbicide. In addition, the invention relates to mutant plants which are tolerant to the identified inhibitors. Specific mutant alleles of CESA1 and CESA3 genes can be used to obtain resistance in a plant when the inhibitors are used as herbicide.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Maize cellulose synthase and uses thereof
The invention provides isolated cellulose synthase nucleic acids and their encoded proteins. The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering cellulose synthase concentration and / or composition of plants. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, and transgenic plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Maize cellulose synthases and uses thereof
The invention provides isolated cellulose synthase nucleic acids and their encoded proteins. The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering cellulose synthase concentration and / or composition of plants. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, and transgenic plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Liriodendron cellulose synthase gene lccesa1 and its expression protein and application
The invention discloses a Liriodendron cellulose synthase gene LcCESA1 and its expression protein and application, LcCESA1 The nucleotide sequence of the protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the amino acid sequence of the expressed protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The present invention takes the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana as the research object, and clones the cellulose synthase gene of Liriodendron chinensis LcCESA1 Using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation into Arabidopsis thaliana, through screening and cultivation, the homozygous transgenic plants of the T3 generation were finally obtained; by observing the microstructure of wild-type Arabidopsis and transgenic Arabidopsis, it was found that the stem of transgenic Arabidopsis The thickness of the cell wall of segmental vascular bundle tissue cells and leaf tissue cells is different from that of wild type Arabidopsis. It can be seen that LcCESA1 The gene affects both the cell wall of Arabidopsis stem vascular bundle tissue cells and leaf tissue cells, can promote the accumulation of cellulose, and will have a wide range of applications.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Plant expression vector for targeting silence phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 and application thereof
InactiveCN113151281ANo pollution problemReduce usageEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGene silencing
The invention discloses a plant expression vector capable of effectively interfering a phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 gene through host-induced gene silencing and application thereof. The plant expression vector disclosed by the invention can be transcribed to form a double-stranded RNA with a reverse complementary structure, and the double-stranded RNA is formed by respectively inserting a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 or SEQ ID No.2 into the vector twice in the forward direction and the reverse direction. The invention also discloses application of the expression vectors in preventing and treating plant diseases caused by phytophthora capsici. The plant expressing the vector provided by the invention has obviously enhanced disease resistance to phytophthora capsici, the expression of the cellulose synthase 3 gene of the phytophthora capsici infecting the plants is significantly inhibited, and the cellulose synthase 3 gene is necessary for the development and pathopoiesis of the phytophthora capsici, therefore, the plant expression vector disclosed by the invention can effectively inhibit plant infection caused by phytophthora capsici, and an effective way is provided for preventing and treating related diseases caused by phytophthora capsici.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
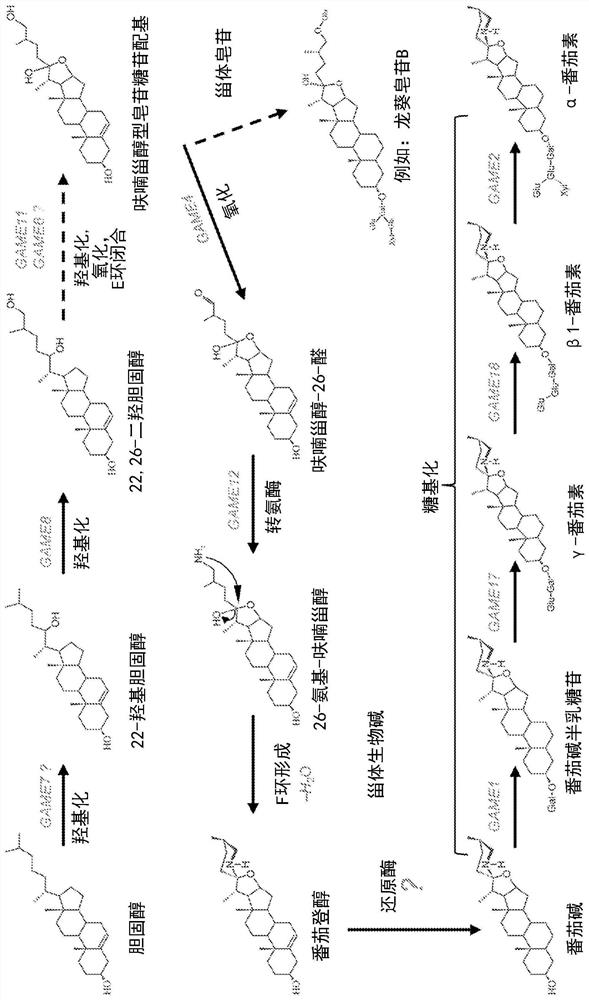
Cellulose-synthase-like enzymes and uses thereof
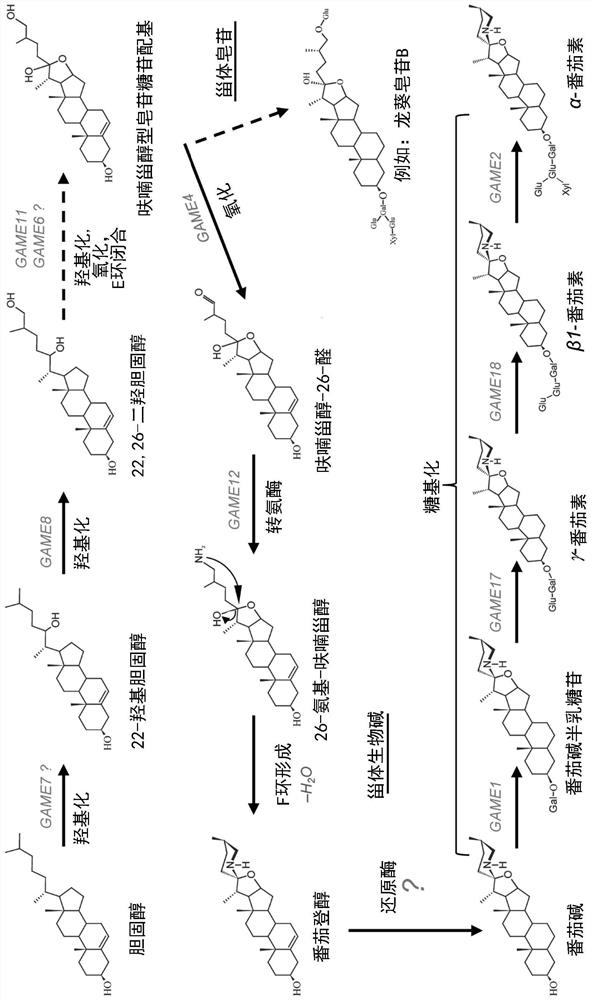
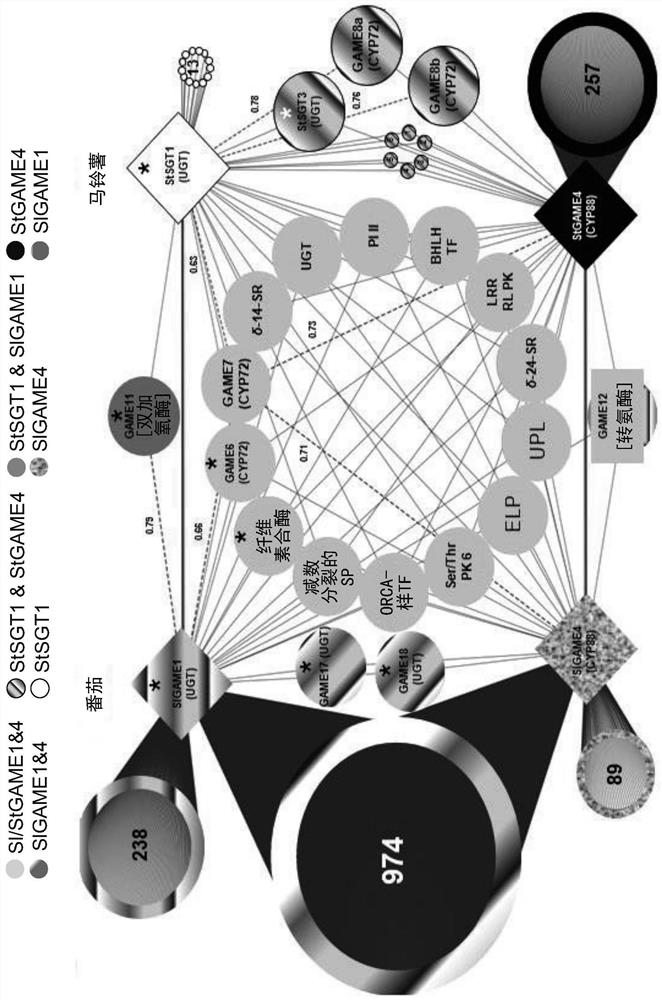
Provided herein are genetically modified cells and genetically modified plants having increased or decreased expression of a cellulose synthase like G (CSLG) enzyme. These cells and plants may have an increased or decreased content a steroidal alkaloid, a steroidal saponin, or a triterpenoid saponin, compared to a corresponding unmodified cell or plant. Also provided herein are methods of producing a steroidal alkaloid, a steroidal saponin, or a triterpenoid saponin in a genetically modified cell, as well as methods of reducing the content of a steroidal alkaloid, a steroidal saponin, or a triterpenoid saponin in a cell of a plant or a plant part, and methods of increasing the content of a steroidal alkaloid, a steroidal saponin, or a triterpenoid saponin in a cell of a plant or a plant part.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Double-stranded RNA molecule for targeted silence of phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 and application of double-stranded RNA molecule
PendingCN114854752AAvoid infectionNo pollution problemEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionDouble strandPlant disease
The invention discloses a double-stranded RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) molecule capable of efficiently inhibiting the expression of a phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 gene, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology. The double-stranded RNA molecule disclosed by the invention consists of nucleic acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2. The invention also discloses application of the double-stranded RNA molecule in preventing and treating plant diseases caused by phytophthora capsici. The double-stranded RNA molecule disclosed by the invention can be used for inhibiting infection of phytophthora capsici by directly treating the phytophthora capsici or spraying the phytophthora capsici on plants. Meanwhile, the double-stranded RNA provided by the invention has strong specificity on essential genes for growth and development of the phytophthora capsici, does not have the problem of drug resistance, and can provide an effective way for preventing and treating related diseases caused by the phytophthora capsici when being used for preparing biopesticides.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting mutation site of phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase Q1077H
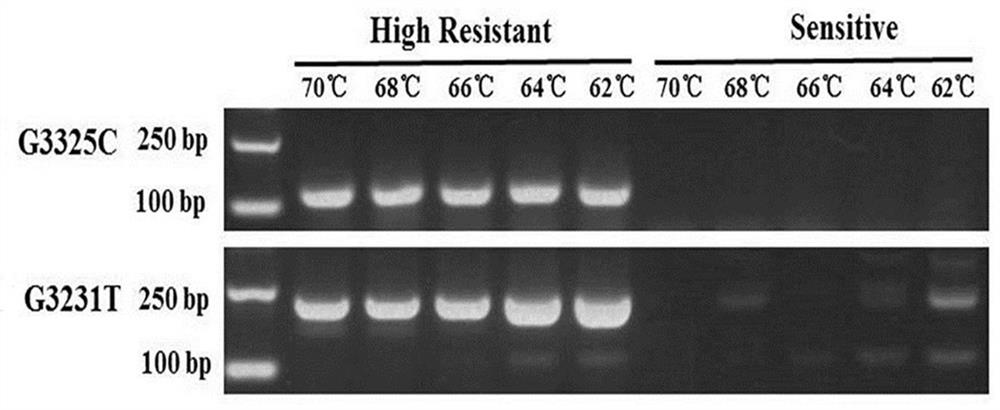
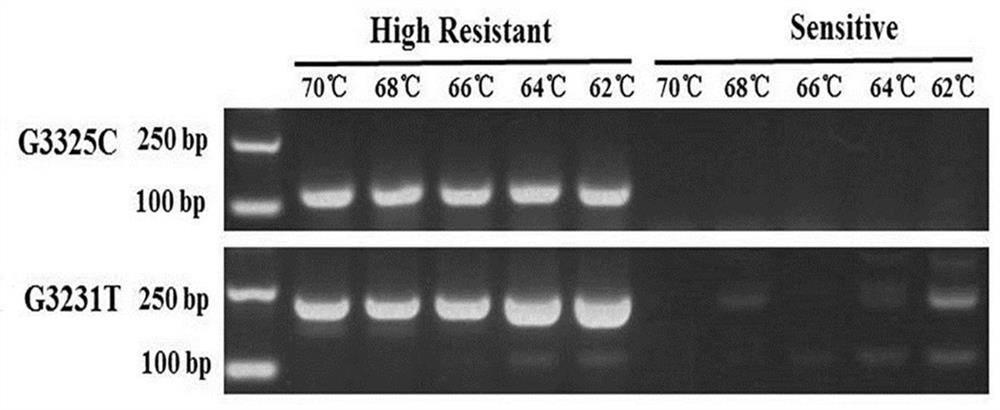
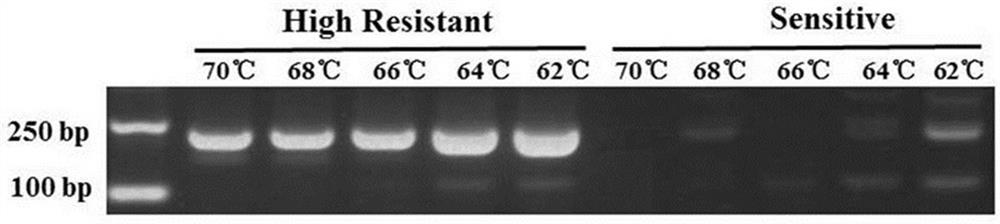
ActiveCN112322776AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco gene engineering, and particularly relates to a method for detecting Q1077H mutation sites in phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3.Compared with a wild type, after the 3231th nucleotide of the cDNA sequence of the phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 gene mutates from G to T from the 5'end, the resistance of phytophthora nicotianae to dimethomorph can be mutated from a sensitive type to a high-resistance type; correspondingly, the 1077th amino acid of the phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 from the Nterminal is mutated into histidine from wild glutamine. The inventor designs related primers on the basis of an ASPCR technical principle, so that the mutated phytophthora nicotianae with dimethomorph resistance can be quickly detected and identified, and a certain technical foundation can be laid for regulation of a tobacco black shank prevention and treatment strategy, delaying and control of further development of drug resistance and research and development of related new chemical drugs.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC +1
Plant expression vector for targeted silence of phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 and application of plant expression vector
The invention discloses a plant expression vector capable of effectively interfering a phytophthora capsici cellulose synthase 3 gene through host-induced gene silencing and application of the plant expression vector. The plant expression vector disclosed by the invention can be transcribed to form double-stranded RNA with a reverse complementary structure, and the double-stranded RNA is formed by respectively inserting a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 or SEQ ID No.2 into the vector twice in the forward direction and the reverse direction. The invention also discloses application of the expression vectors in preventing and treating plant diseases caused by phytophthora capsici. The plant expressing the vector provided by the invention has obviously enhanced disease resistance to phytophthora capsici, the expression of the cellulose synthase 3 gene of the phytophthora capsici infecting the plants is significantly inhibited, and the cellulose synthase 3 gene is necessary for the development and pathopoiesis of the phytophthora capsici. Therefore, the plant expression vector can effectively inhibit plant infection caused by phytophthora capsici, and an effective way is provided for preventing and treating related diseases caused by phytophthora capsici.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
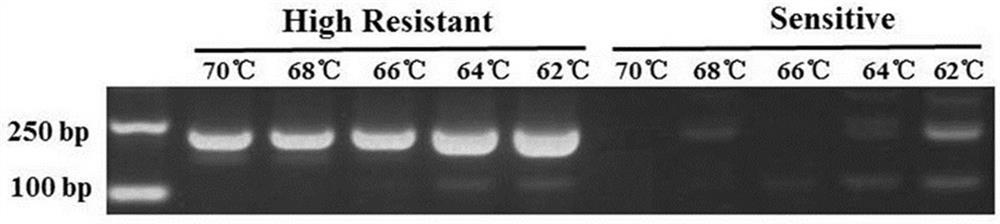
Method for detecting V1109L mutation site in phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae cellulose synthase
PendingCN112391454AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco gene engineering and particularly relates to a method for detecting a V1109L mutation site in a phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3. Compared with a wild type, after a 3325th nucleotide of a cDNA sequence of a phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 gene mutates from G to C from a 5'end, aresistance of a phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae to dimethomorph can be mutated from a sensitive type to a high-resistance type. Correspondingly, a 1109th amino acid of the phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 is mutates from a wild-type valine into leucine from an N end. Related primers are designed on the basis of an AS-PCR technical principle, so that the mutated phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with the dimethomorph resistance can be quickly detected and identified, and a certain technical foundation can be laid for regulating a prevention and treatment strategyfor tobacco black shank, delaying and controlling a further development of drug resistance, and promoting research and development of related new chemical drugs.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC +1
Plant cellulose synthases
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Microorganism having enhanced cellulose synthase gene stability and method of producing cellulose by using the same
Provided is a recombinant microorganism having enhanced cellulose synthase gene stability, a method of producing cellulose by using the recombinant microorganism, and a method of preparing the recombinant microorganism.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Detection method of Phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase q1077h mutation site
ActiveCN112322776BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The present application belongs to the technical field of tobacco genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a patent application for a method for detecting the Q1077H mutation site in Phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3. Compared with the wild type, after the cDNA sequence of Phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 gene was mutated from G to T at the 3231st nucleotide from the 5' end, the resistance of Phytophthora nicotianae to dimethomorph can be determined by the sensitive mutation. Correspondingly, amino acid 1077 from the N-terminus of Phytophthora nicotianae cellulose synthase CesA3 was mutated from wild-type glutamine to histidine. Based on the principle of AS-PCR technology, the inventors designed relevant primers for rapid detection and identification of Phytophthora nicotianae with resistance to dimorpholine after mutation, which can be used to adjust the prevention and control strategies of tobacco black shank, as well as delay and control The further development of drug resistance and the research and development of related new chemical drugs lay a certain technical foundation.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC +1
Microorganism having enhanced cellulose synthase gene stability and method of producing cellulose by using the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
A kind of cellulose synthase pccesa1 protein from Phytophthora capsici and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN106754804BMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisUridine diphosphateCellobiose
The invention discloses a cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention is the protein as shown in a sequence 2; the encoding gene of the protein is as shown in a sequence 1. An experiment proves that the protein PCCESA1 provided by the invention can catalyze substrate uridine diphosphate D glucose (UDPG) to generate cellobiose, and has significance on biosynthesis of main component cellulose of a cell wall of the phytophthora capsici; as an oomycetes cell wall plays an important role in maintaining oomycetes vital movement, including maintaining cell shapes, participating in host interaction and the like. Therefore, the cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention provides technical support for the oomycetes cell wall, and provides a new molecular target for future bactericide research and development.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
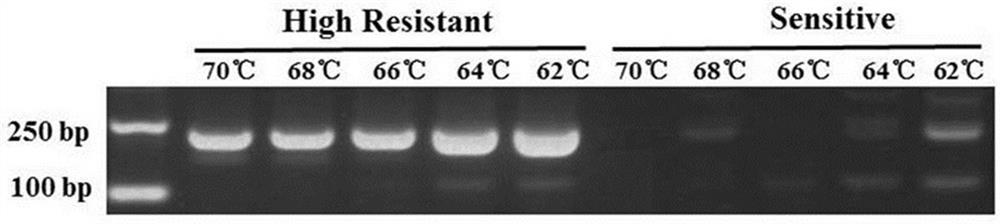
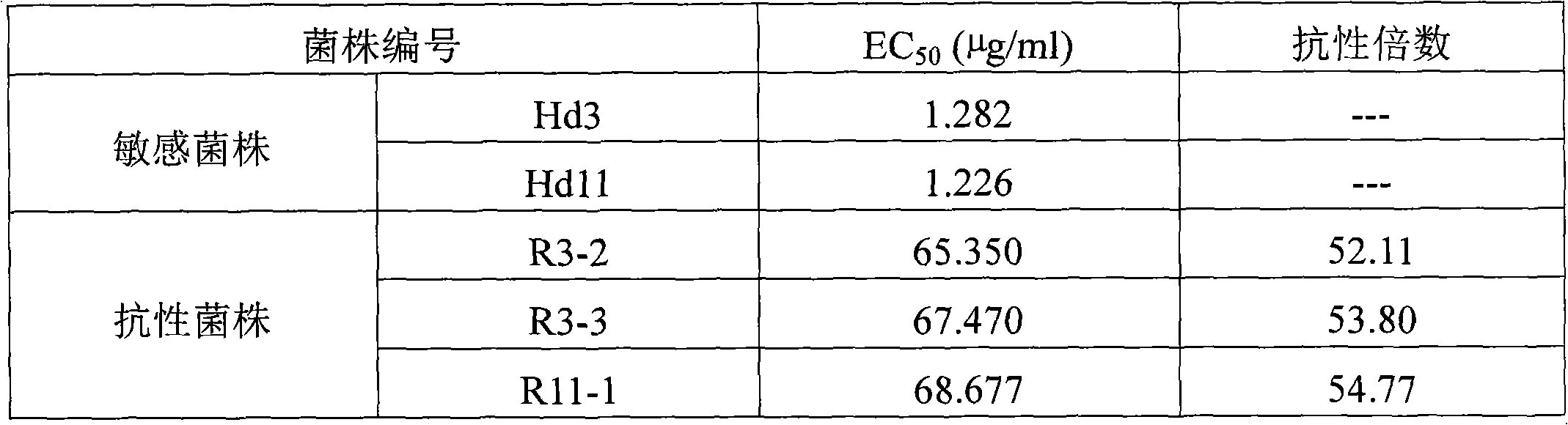
Method for detecting phytophora capsic CesA3 gene nucleotide point mutation and drug resistance of same to CAA bactericides
ActiveCN102776290BResistance delay and controlTimely adjustment of disease control strategiesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to clone of phytophora capsic cellulose synthase related genes CesA3 and application of the clone in resistance detection of CAA bactericides, in particular to a method for detecting drug resistance molecules of phytophora capsic to the CAA bactericides and a special primer and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The primer consists of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules represented by SEG ID NO:1 and SEG ID NO:2. The method for detecting drug resistance produced phytophora capsic point mutation to the CAA bactericides has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, simple, quick and stable in stality, can be used for quickly and sensitively detecting occurrence and development trends of resistance of the phytophora capsic in fields to the CAA bactericides and early warning resistance diseases, guiding and timely adjusting disease control strategies, and has great significance on effective control of development of the resistance diseases.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fresh bamboo shoot antistaling method
An antistaling method for fresh bamboo shoot includes such steps as preparing antistaling agent from aloe and water, coating it on the pretreated fresh bamboo shoot, drying in air, filming on its surface, microwave irradiating 5-20S and storage at 2-8 deg.C.
Owner:浙江教育学院
Method and special primers for fast identifying phytophthora capsici leonian resistance to pyrimorph
ActiveCN102851363BQuick checkSensitive detectionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to identification of nucleotide point mutation of a phytophthora capsici leonian-cellulose synthase-related gene CesA3 and a use of the phytophthora capsici leonian-cellulose synthase-related gene CesA3 in detection of resistance to pyrimorph as a fungicide, and discloses a molecular detection method and special primers for identifying phytophthora capsici leonian gene CesA3 3365-site nucleotide mutation-caused resistance to pyrimorph. The pair of special primers is composed of DNA molecules shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3. The molecular diagnosis method for detecting phytophthora capsici leonian resistance to pyrimorph as a fungicide has high sensitivity, good stability and a short detection period, can be used for high-flux detection of generation and development of field phytophthora capsici leonian resistance to pyrimorph as a fungicide, realizes early warning of diseases with resistance and has an important meaning for timely and effective control of development of diseases with resistance.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com