Patents
Literature
32 results about "Dinitrogen monoxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The chemical formula for dinitrogen monoxide also known as nitrous oxide (laughing gas) is N2O. According to the IUPAC N2O follows the Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds, both nitrogen and oxygen are nonmetals therefore they form an molecular compound.
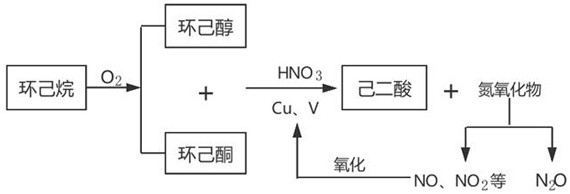
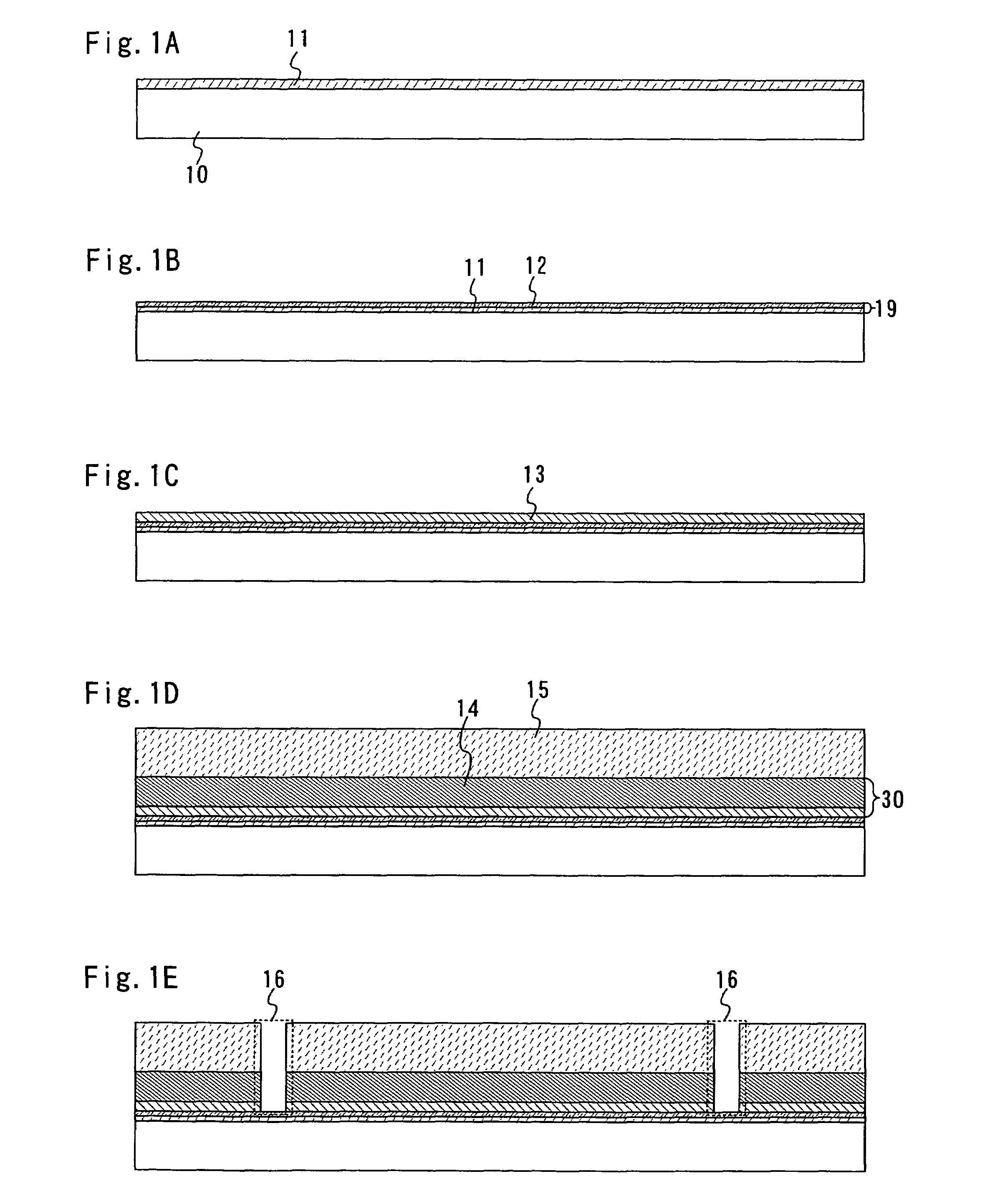
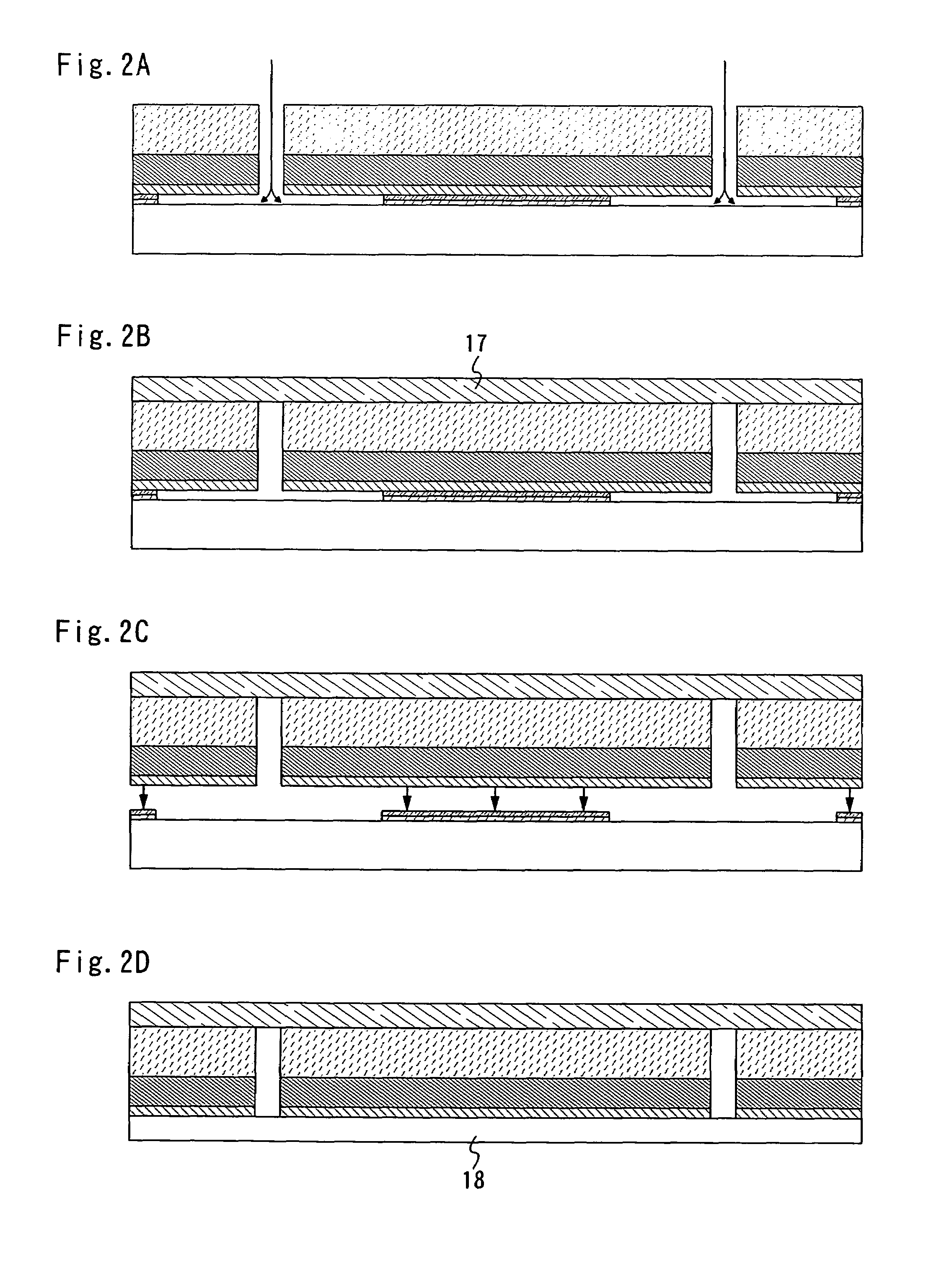
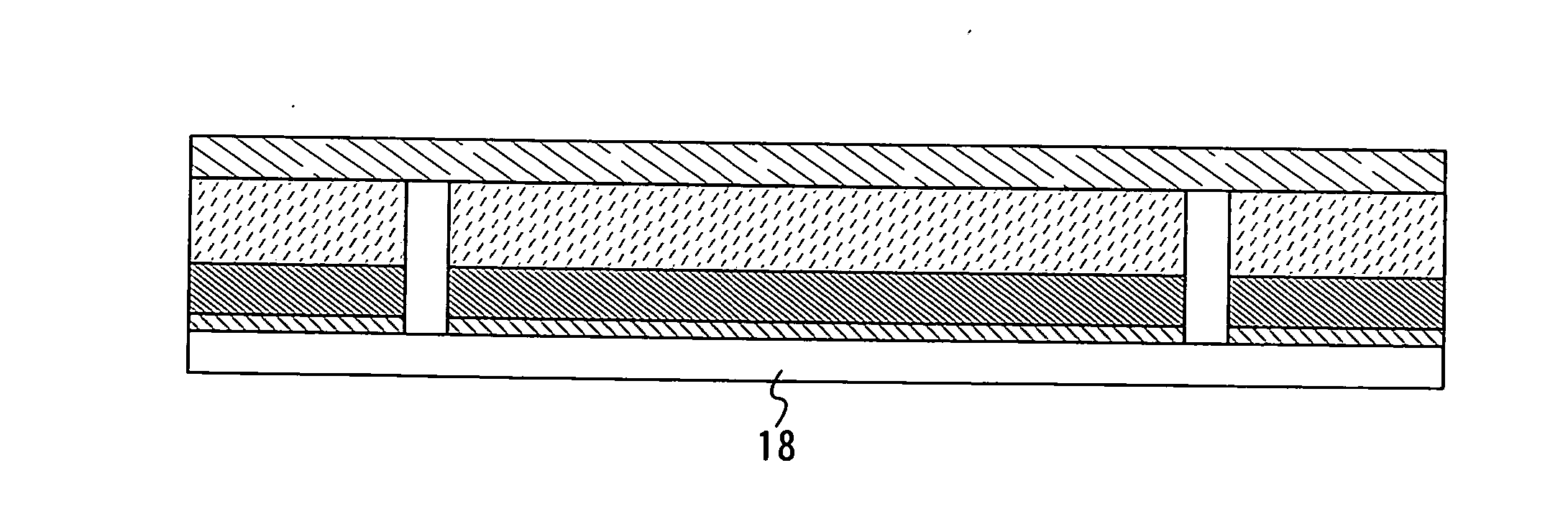
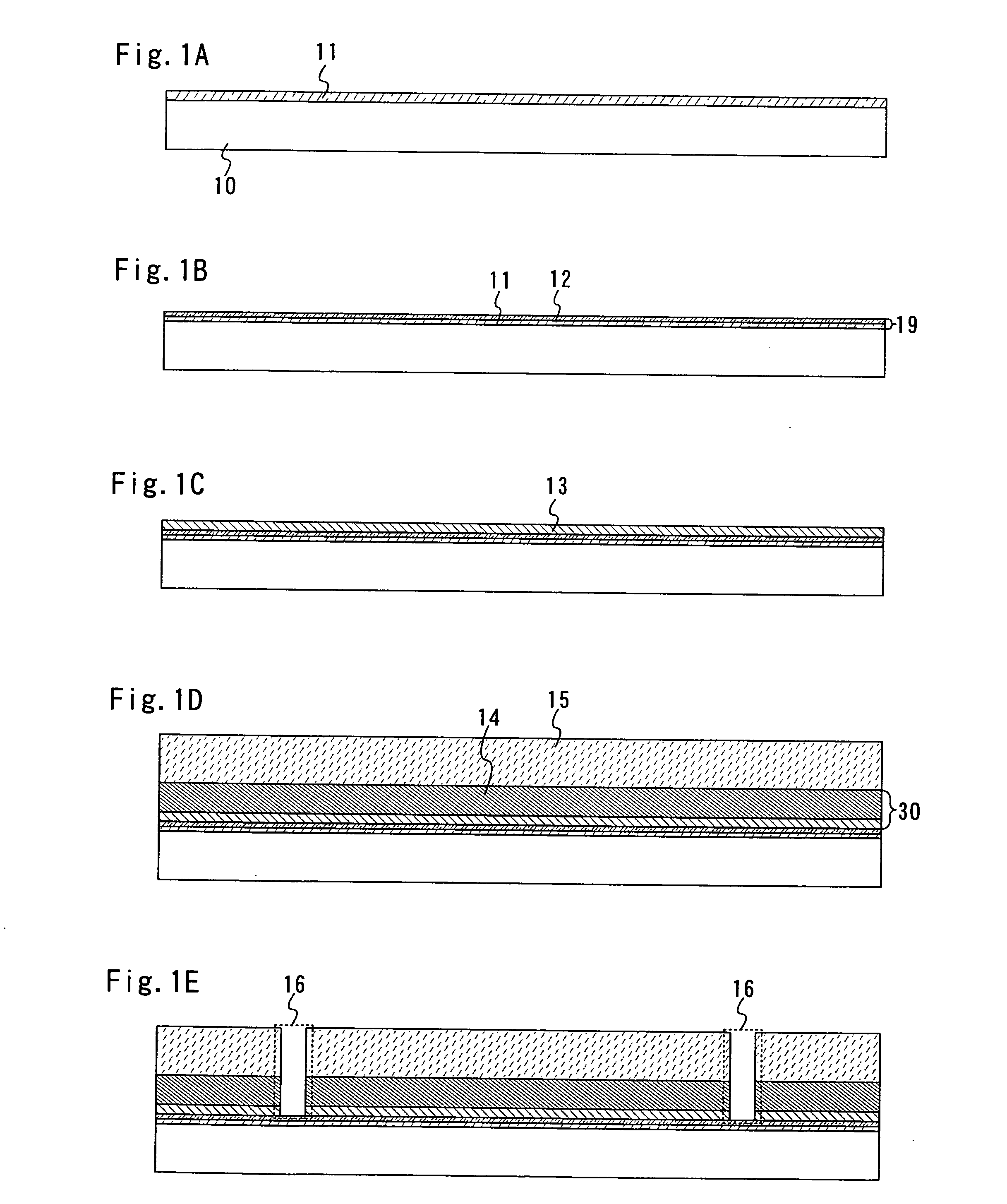
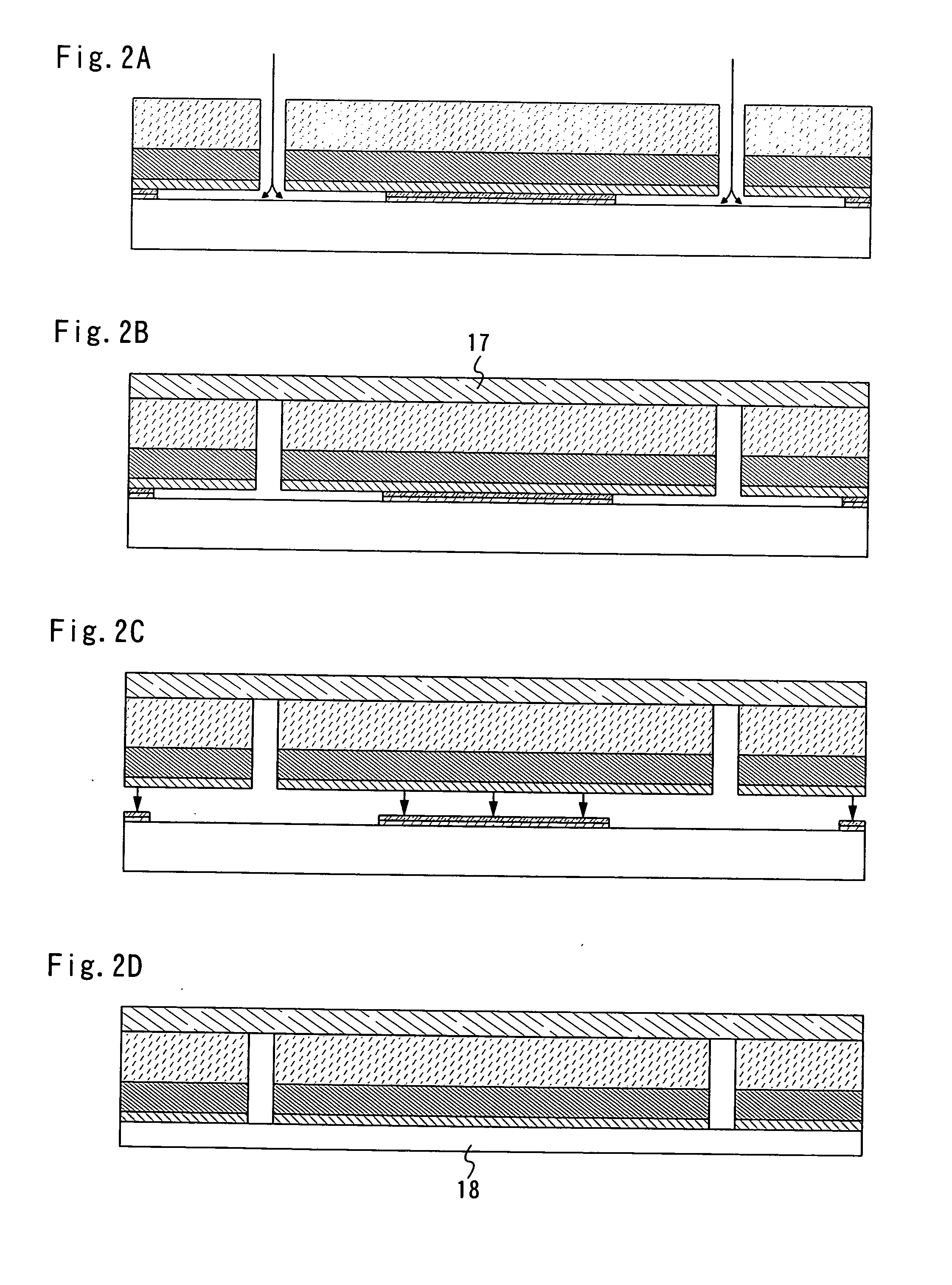
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7465674B2Low costImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialMetal membrane
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with high reliability, at low cost, in which an element forming layer having a thin film transistor and the like provided over a substrate is peeled from the substrate, so that a semiconductor device is manufactured. According to the invention, a metal film is formed over a substrate, a plasma treatment is performed to the metal film in a dinitrogen monoxide atmosphere to form a metal oxide film over the metal film, a first insulating film is formed continuously without being exposed to the air, an element forming layer is formed over the first insulating film, and the element forming layer is peeled from the substrate, so that a semiconductor device is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060270191A1Low costImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialDinitrogen monoxide
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with high reliability, at low cost, in which an element forming layer having a thin film transistor and the like provided over a substrate is peeled from the substrate, so that a semiconductor device is manufactured. According to the invention, a metal film is formed over a substrate, a plasma treatment is performed to the metal film in a dinitrogen monoxide atmosphere to form a metal oxide film over the metal film, a first insulating film is formed continuously without being exposed to the air, an element forming layer is formed over the first insulating film, and the element forming layer is peeled from the substrate, so that a semiconductor device is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Process for producing polyolefins
A novel process for producing homopolymers and interpolymers of olefins which involves contacting an olefin and / or an olefin and at least one or more other olefin(s) under polymerization conditions with a metallocene catalyst and dinitrogen monoxide in amounts sufficient to reduce the electrostatic charge in the polymerization medium. Also provided is a process for reducing electrostatic charge in the production of polyolefins by introducing dinitrogen monoxide into the polymerization medium.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
Process for producing polyolefins
A novel process for producing homopolymers and interpolymers of olefins which involves contacting an olefin and / or an olefin and at least one or more other olefin(s) under polymerization conditions with a metallocene catalyst and dinitrogen monoxide in amounts sufficient to reduce the electrostatic charge in the polymerization medium. Also provided is a process for reducing electrostatic charge in the production of polyolefins by introducing dinitrogen monoxide into the polymerization medium.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
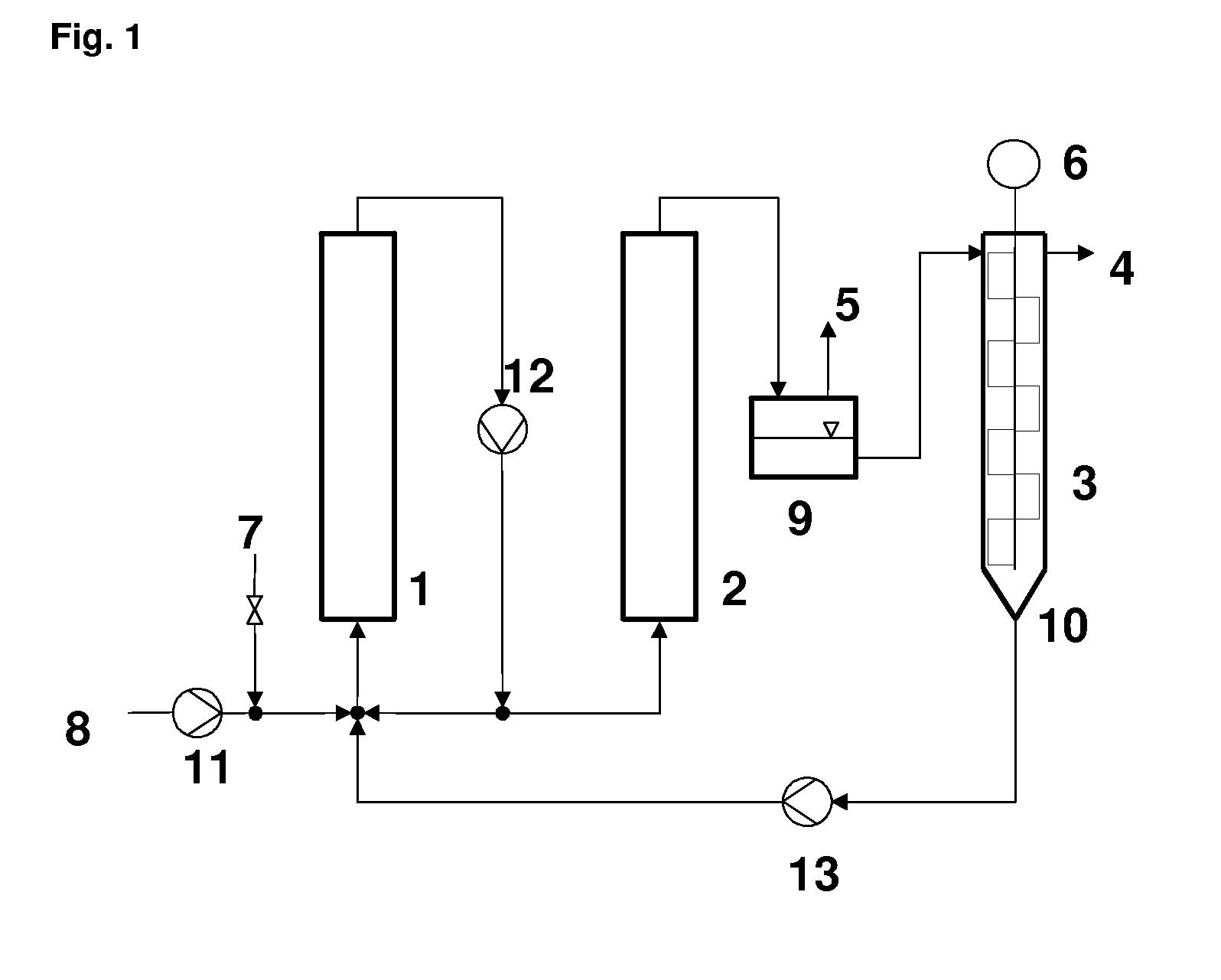
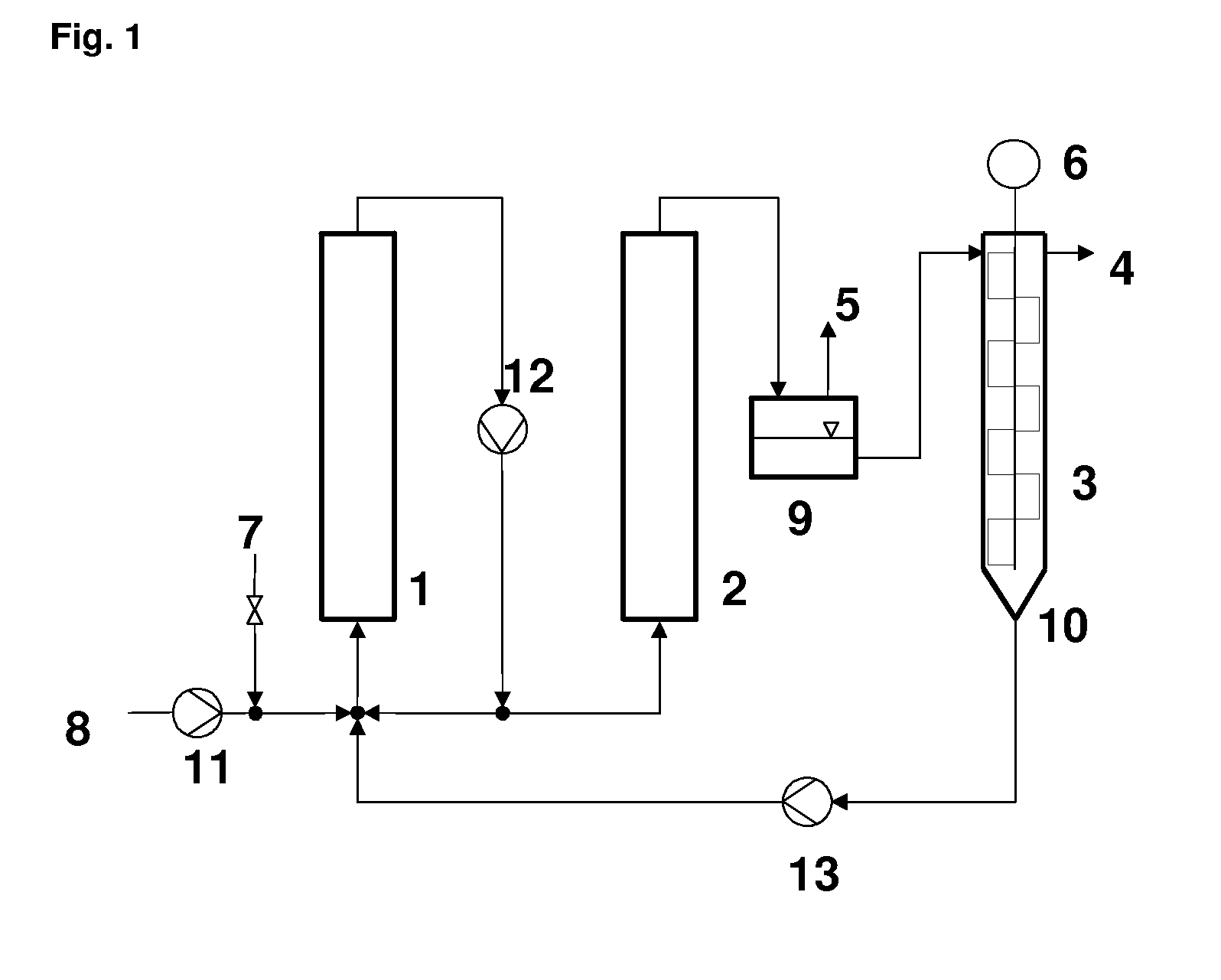
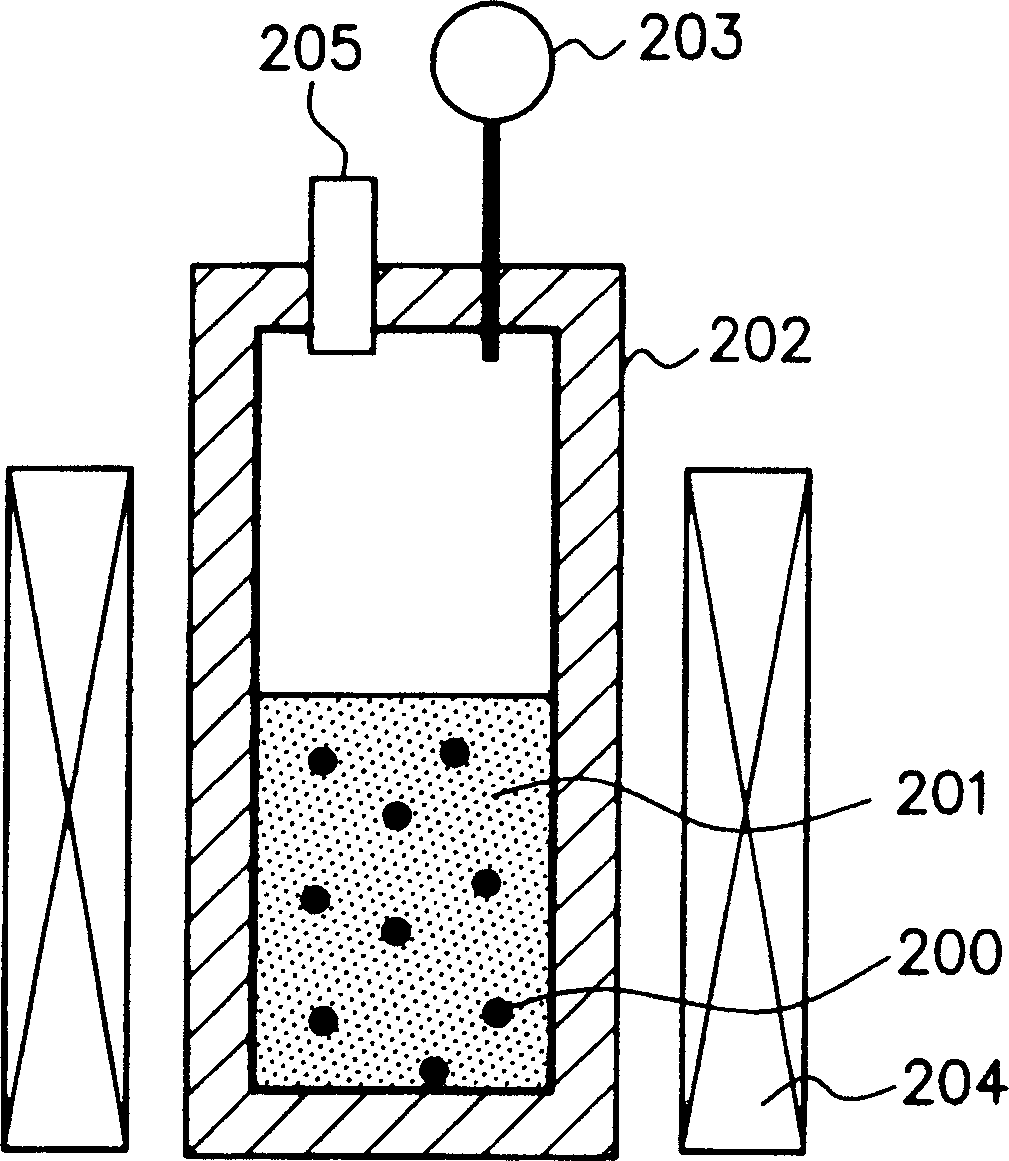
Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes
ActiveUS20130109827A1Increase in costLimited utilityOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionReaction intermediateReactive intermediate
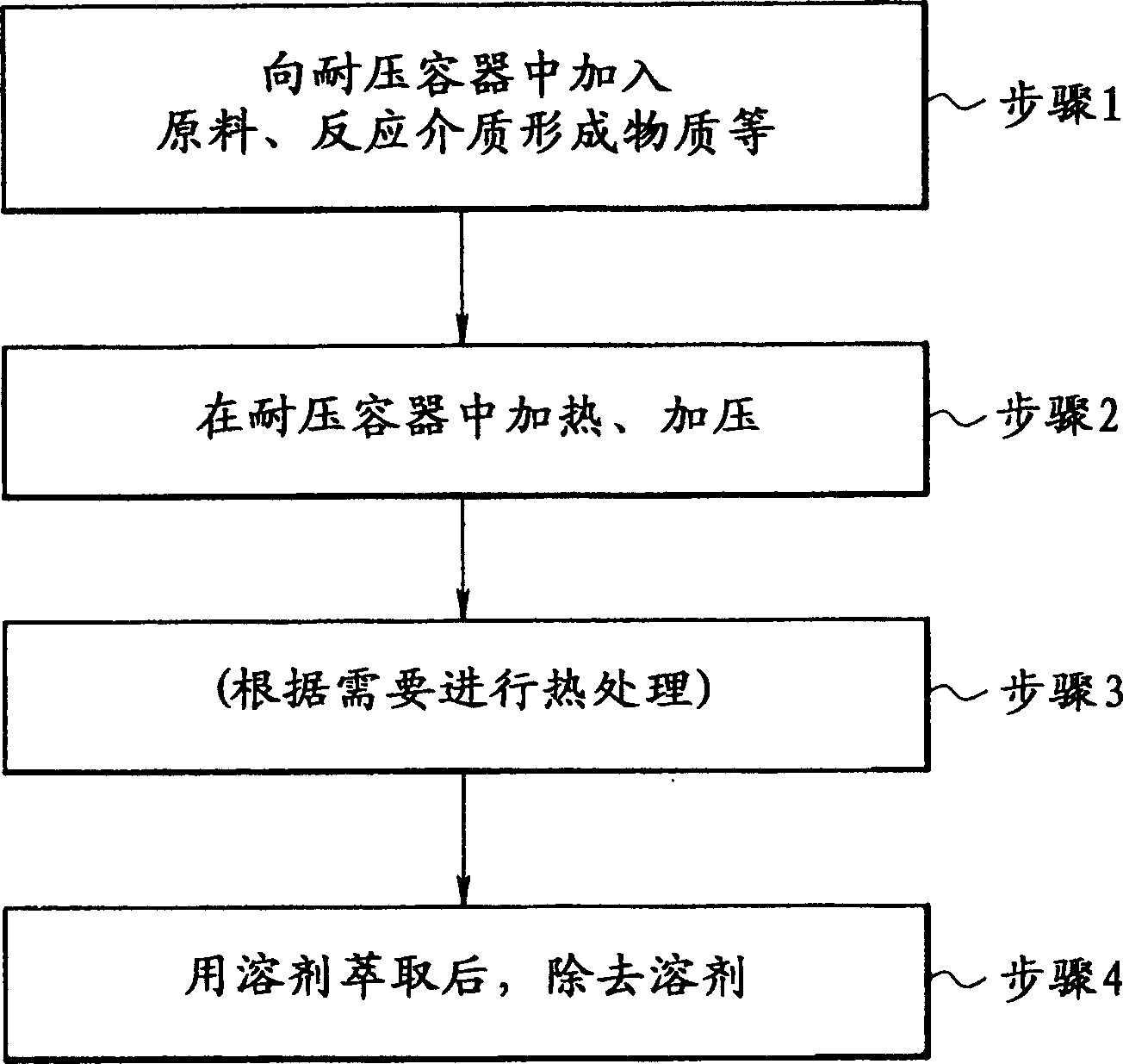
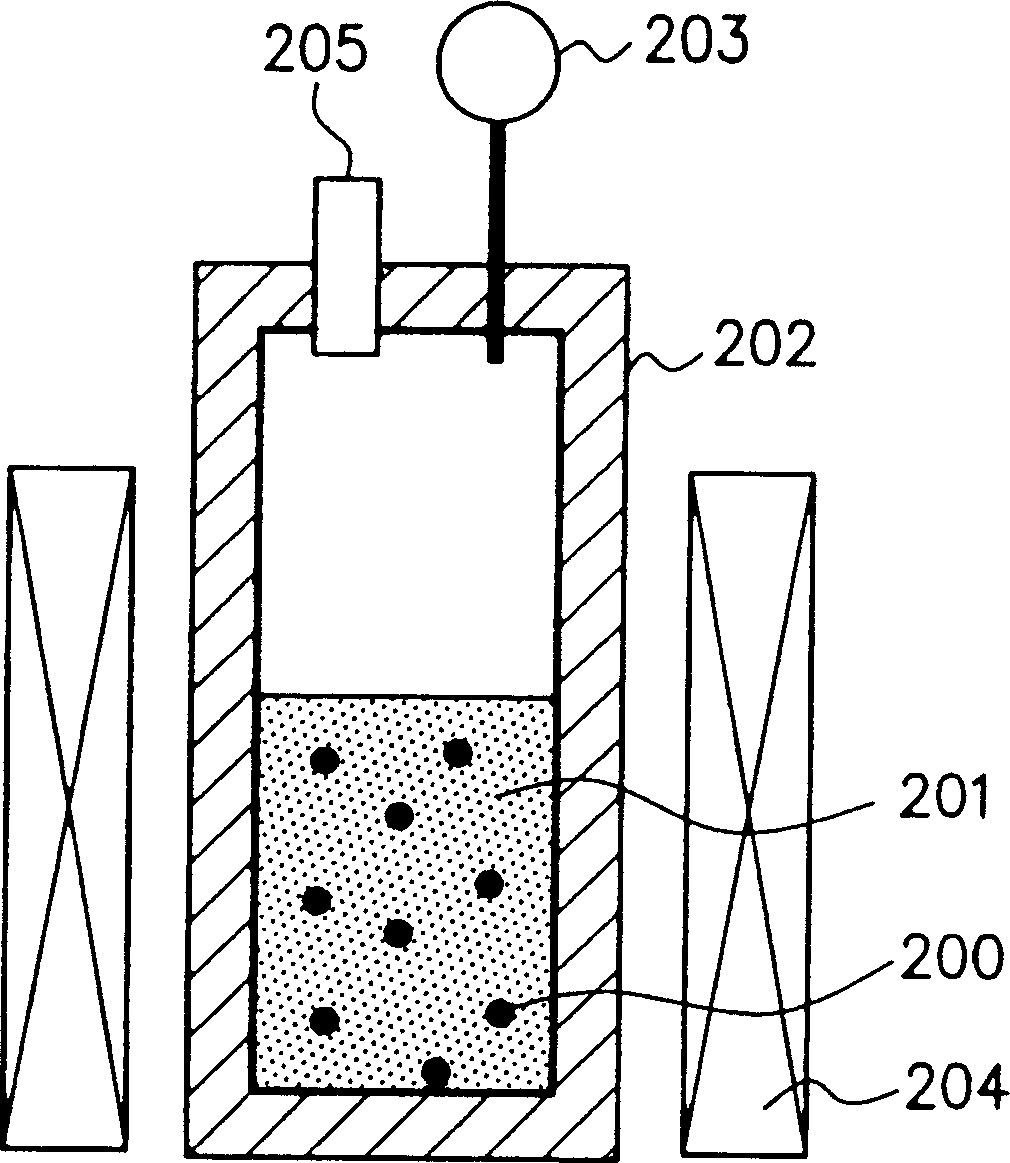
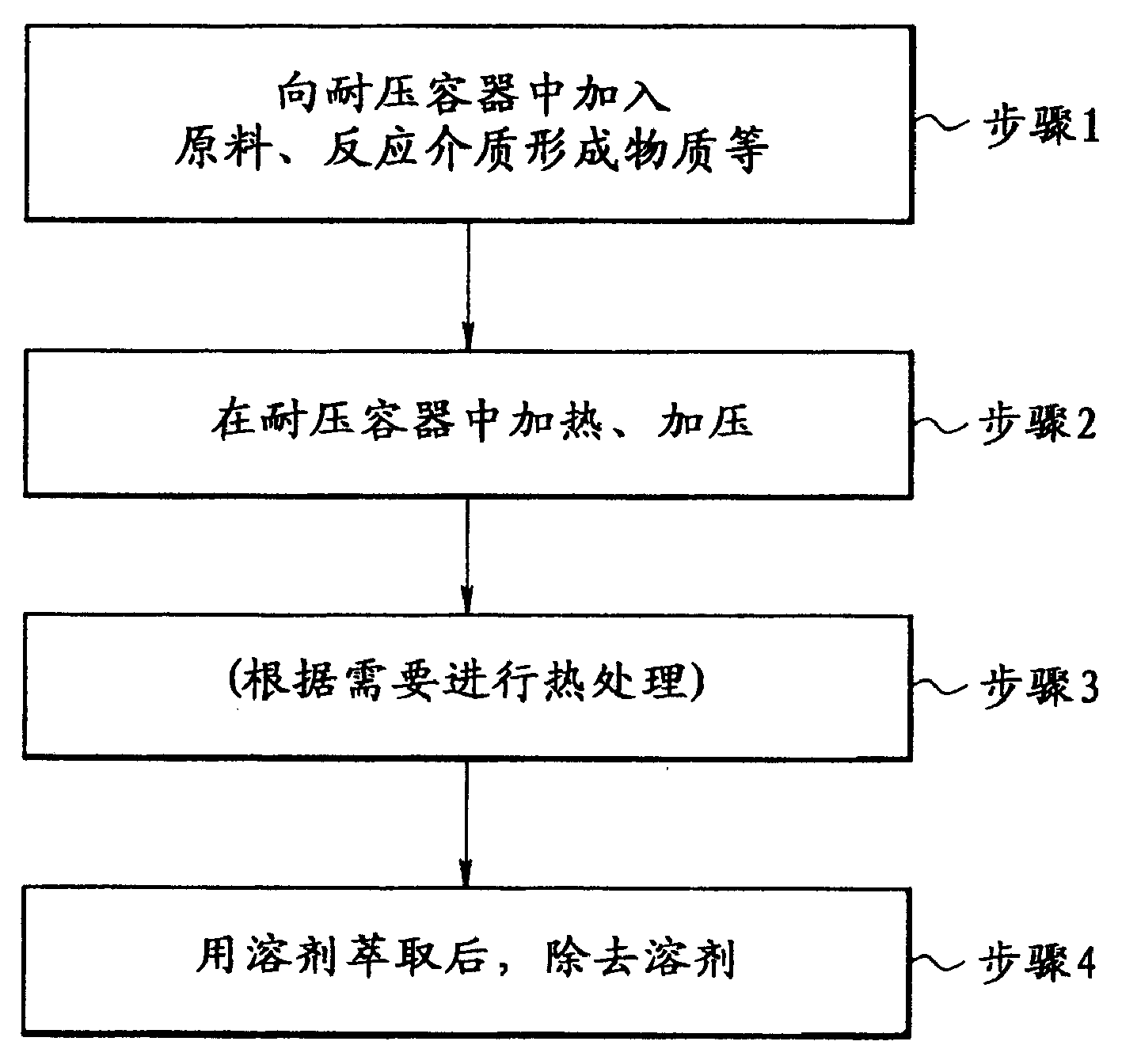
An improved process and method for the formation of stable intermediate cyclophanes. Embodiments describe a general method for the production of substituted and unsubstituted cyclophanes. The components include a pyrolysis reaction tube that may be electrically heated into which a flowing stream of nitrous oxide with xylene vapor in an optional inert carrier gas at atmospheric pressure. The exit gas is condensed resulting in the deposition of [2,2′]paracyclophane. Additionally a process and method whereby the reactive intermediates of the reaction described above can be directly deposited and polymerized at atmospheric pressures or thereabout is disclosed.
Owner:CARVER SCI INC
Process for the preparation of cyclododecanone
InactiveUS7838705B2Organic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationCyclododecanoneCyclododecatriene
A process for preparing cyclododecanone by reacting cyclododecene with dinitrogen monoxide, comprising in particular steps (I) and (II):(I) preparing cyclododecene by partially hydrogenating cyclododecatriene;(II) reacting cyclododecene obtained in (I) with dinitrogen monoxide to obtain cyclododecanone.
Owner:BASF SE
Process for the preparation of cyclododecanone
InactiveUS20090227815A1Organic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationCyclododecanoneCyclododecatriene
A process for preparing cyclododecanone by reacting cyclododecene with dinitrogen monoxide, comprising in particular steps (I) and (II):(I) preparing cyclododecene by partially hydrogenating cyclododecatriene;(II) reacting cyclododecene obtained in (I) with dinitrogen monoxide to obtain cyclododecanone.
Owner:BASF AG
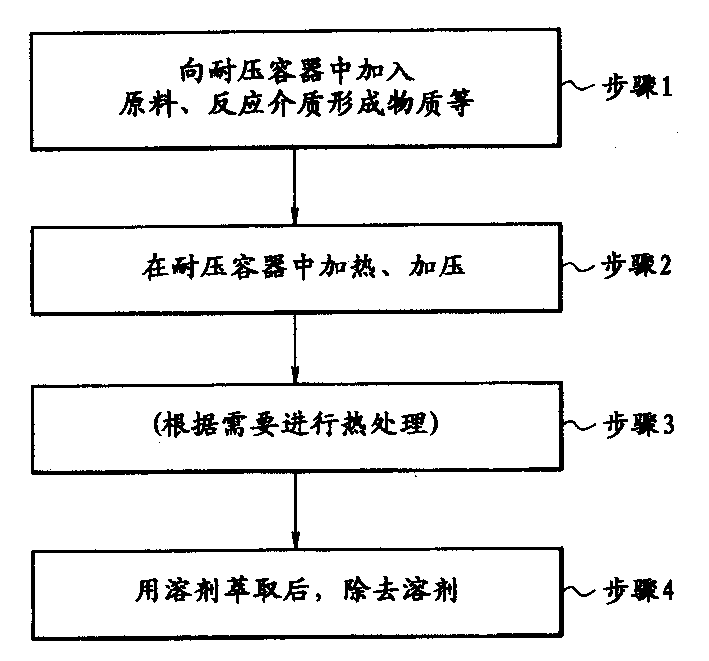
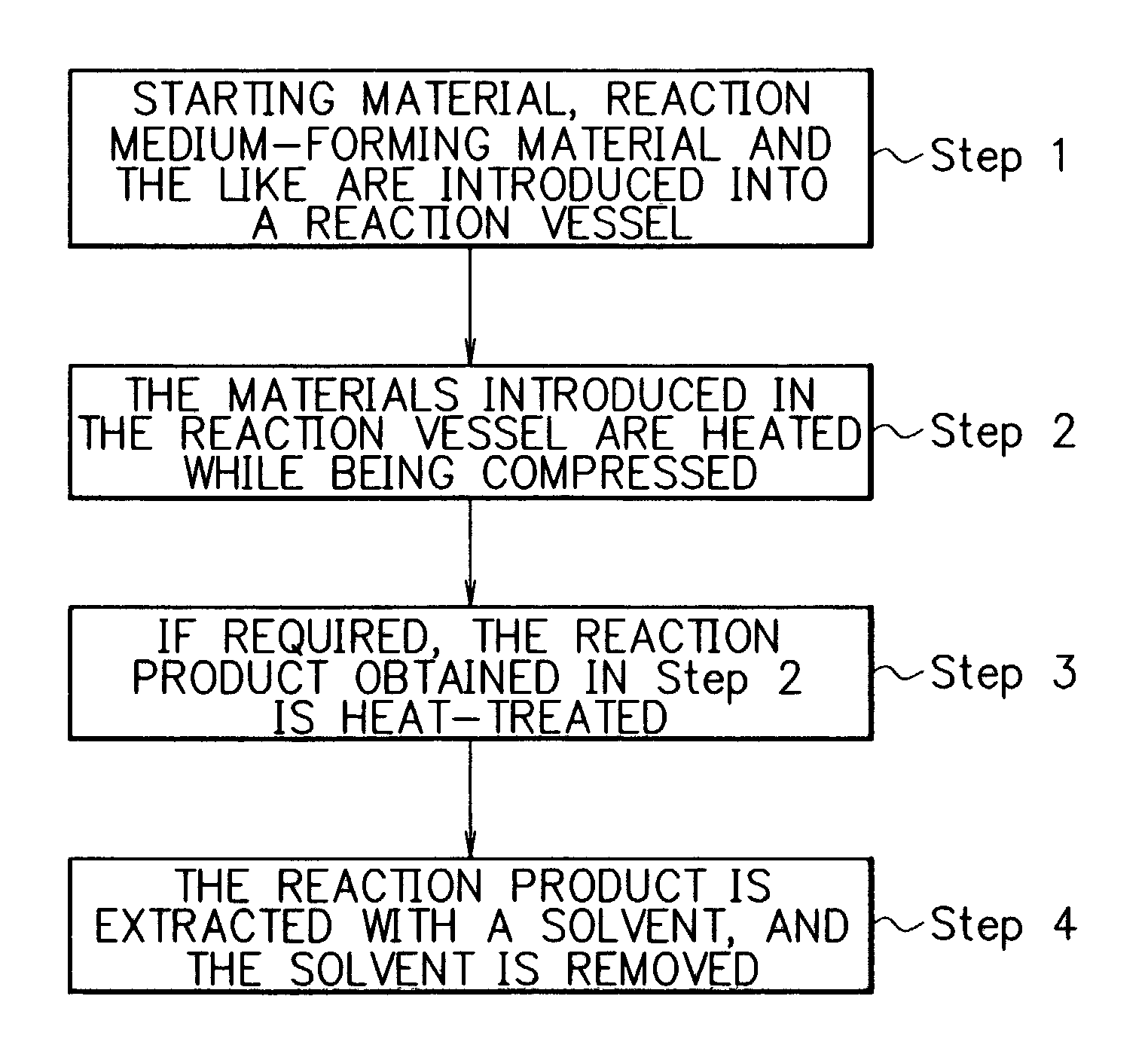
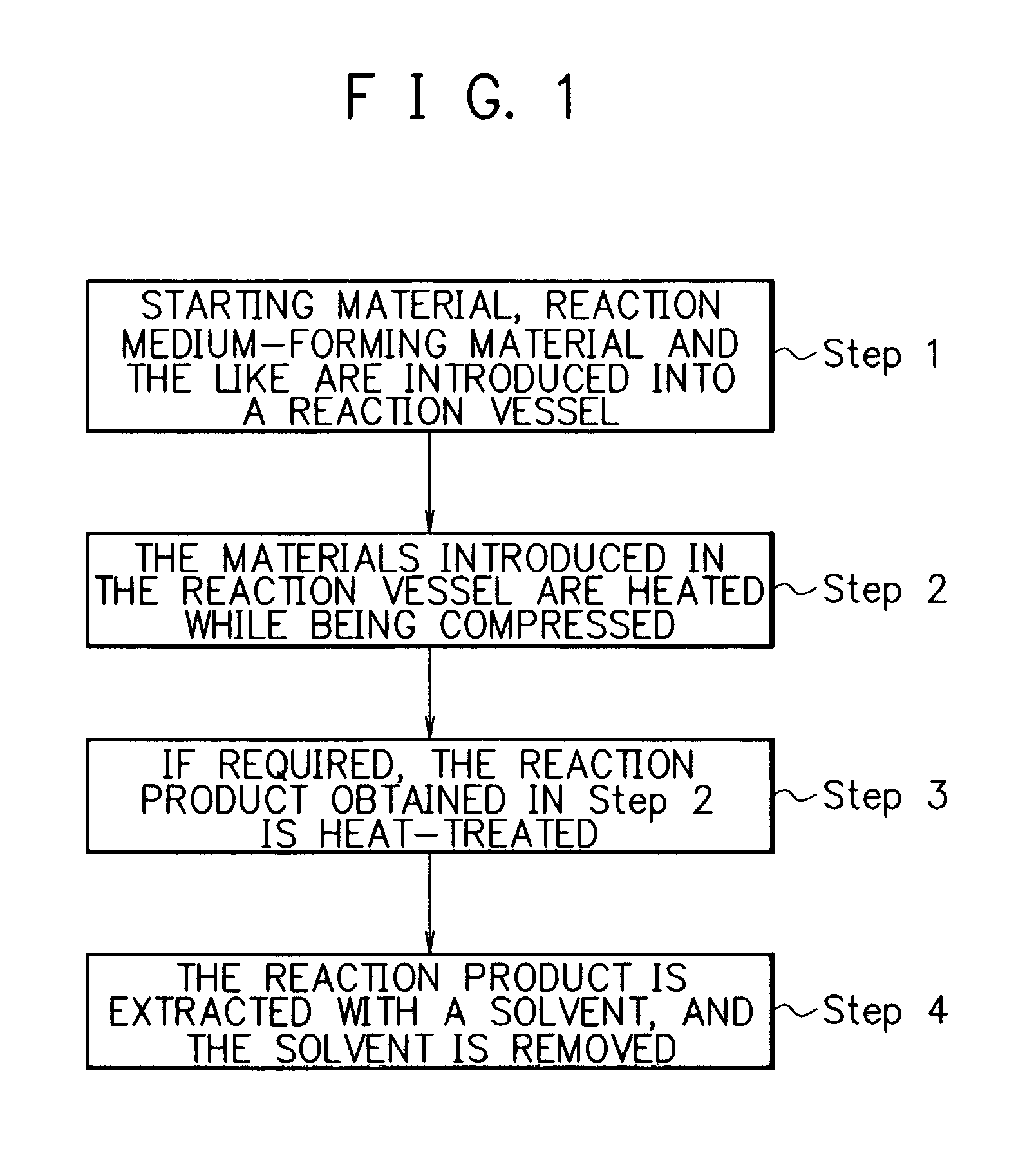
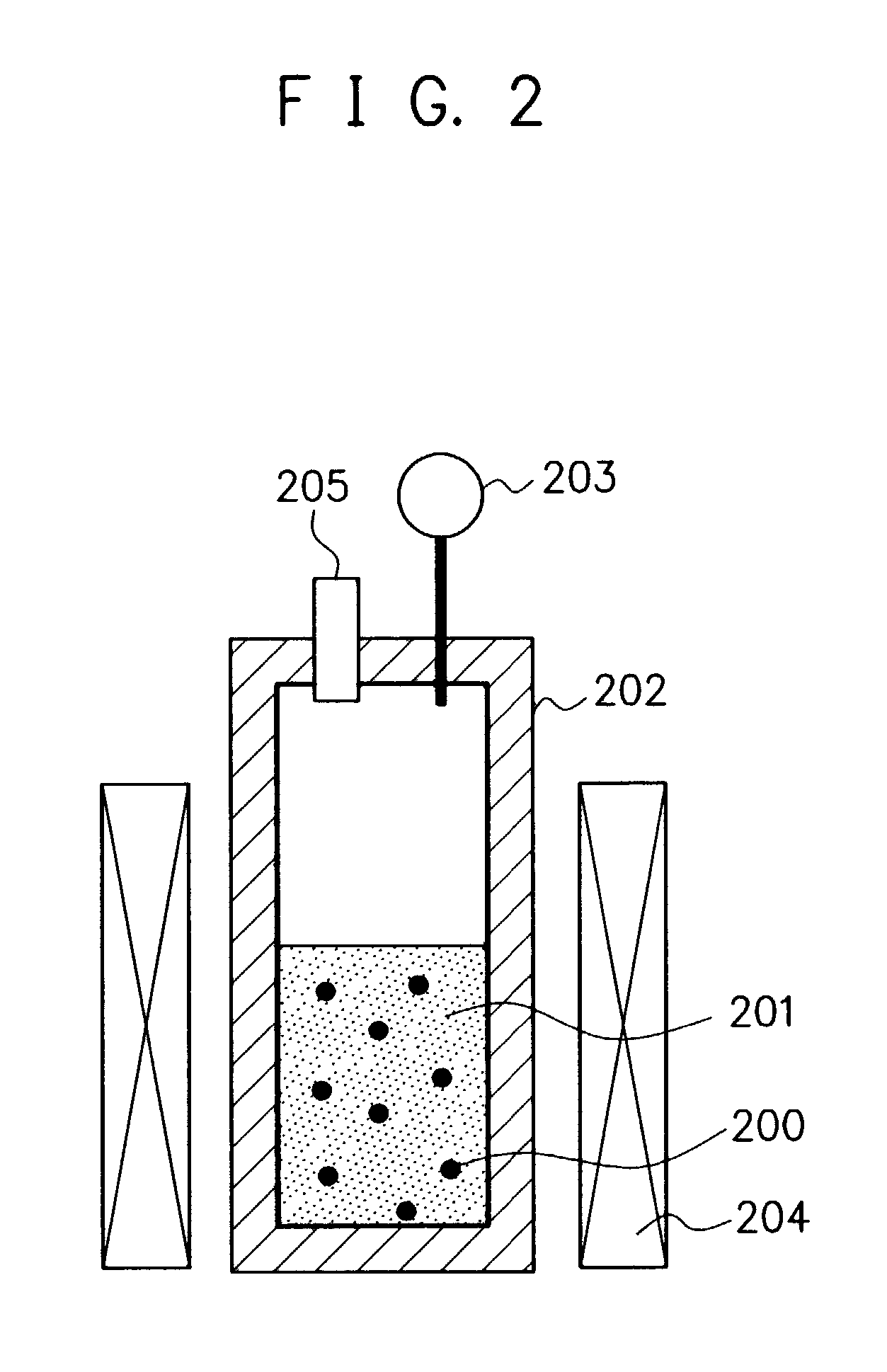
Process for preparing Fuller-ene
A method for producing fullerenes, characterized in that said method includes a step (a) of contacting an aromatic compound-containing starting material with a supercritical fluid or a subcritical fluid at a temperature in a range of from 31 DEG C to 500 DEG C and at a pressure in a range of from 3.8 MPa to 60 MPa. Said supercritical fluid or said subcritical fluid is formed from one or more kinds of materials selected from the group consisting of an aromatic compound as said starting material, a solvent capable of dissolving said aromatic compound, water, dinitrogen monoxide, and ammonia.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for producing fullerenes
InactiveUS6953564B2InexpensiveSimple wayMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesMulti materialDinitrogen monoxide
A method for producing fullerenes, characterized in that said method includes a step (a) of contacting an aromatic compound-containing starting material with a supercritical fluid or a subcritical fluid at a temperature in a range of from 31° C. to 500° C. and at a pressure in a range of from 3.8 MPa to 60 MPa. Said supercritical fluid or said subcritical fluid is formed from one or more kinds of materials selected from the group consisting of an aromatic compound as said starting material, a solvent capable of dissolving said aromatic compound, water, dinitrogen monoxide, and ammonia.
Owner:CANON KK
Process for the polymerization of olefins
A novel process for the polymerization of olefins is provided. The process involves contacting at least one olefin with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst in the presence of dinitrogen monoxide in the production of polymeric products having a narrower molecular weight distribution. A process for narrowing molecular weight distribution of polyolefins utilizing dinitrogen monoxide is also provided.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
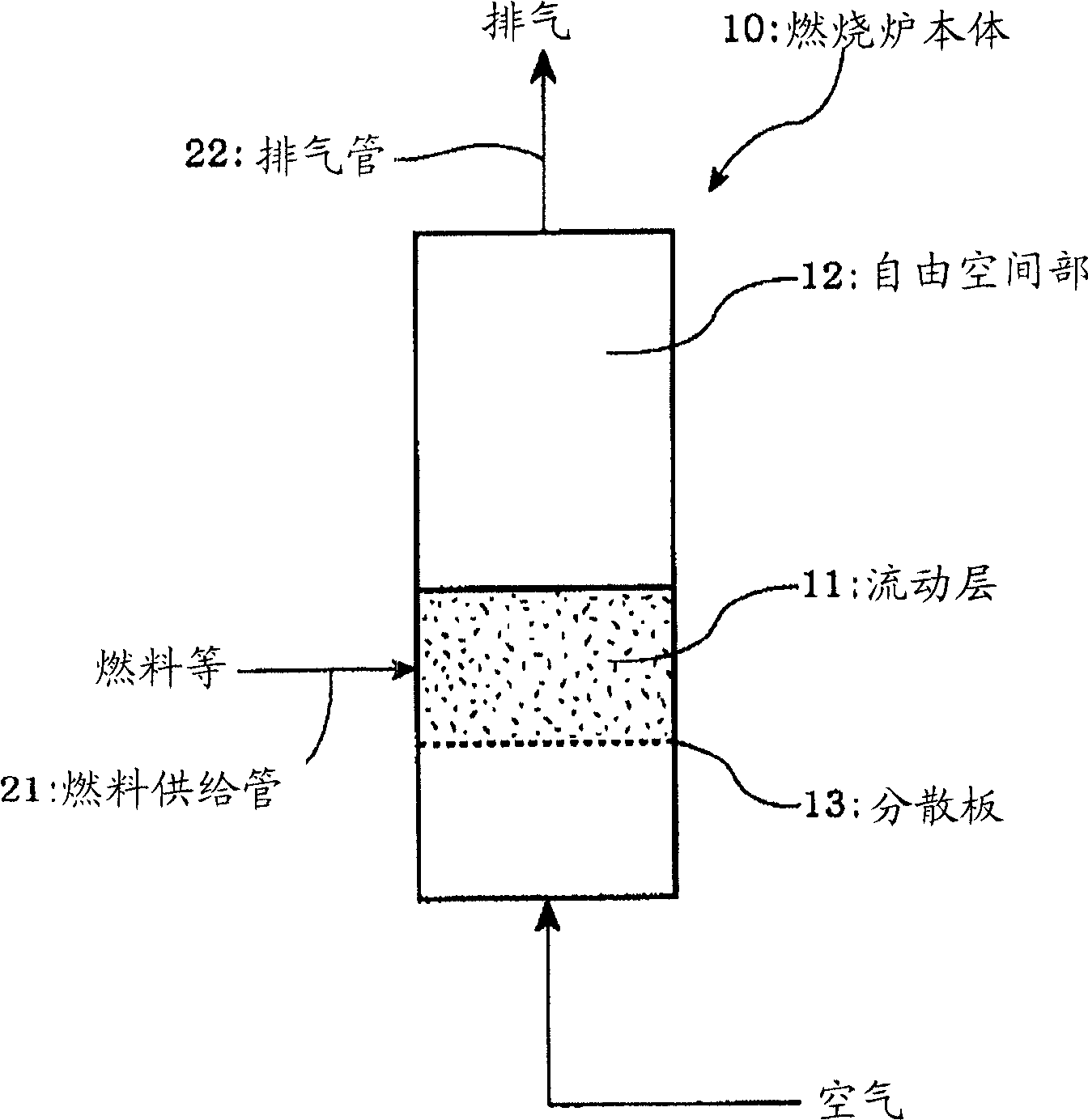
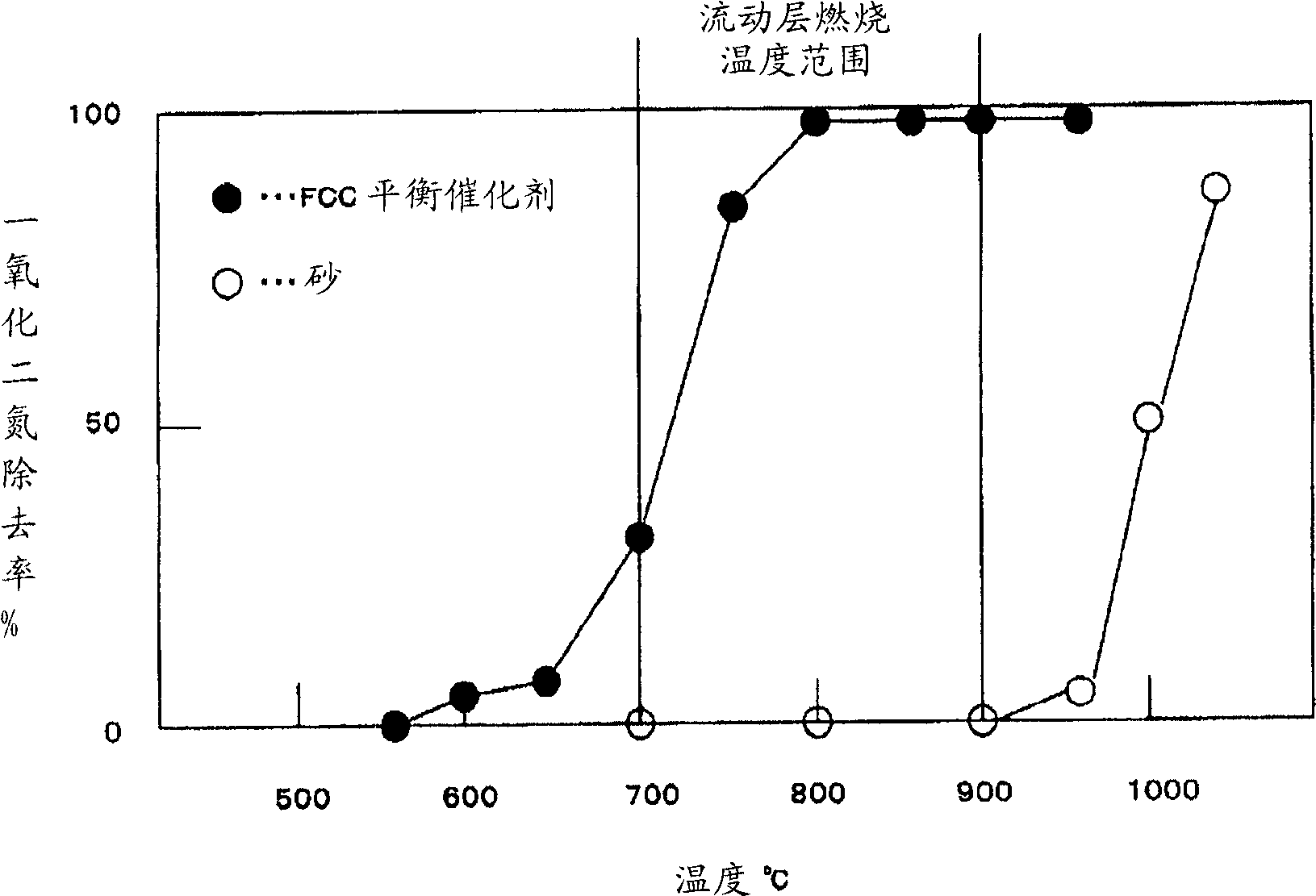
Method for decomposing dinitrogen monoxide
InactiveCN101500693AAvoid remodelingLow costNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentDinitrogen monoxideFluid catalytic cracking
A method for decomposing dinitrogen monoxide including bringing a gas containing dinitrogen monoxide into contact with a fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) equilibrium catalyst.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
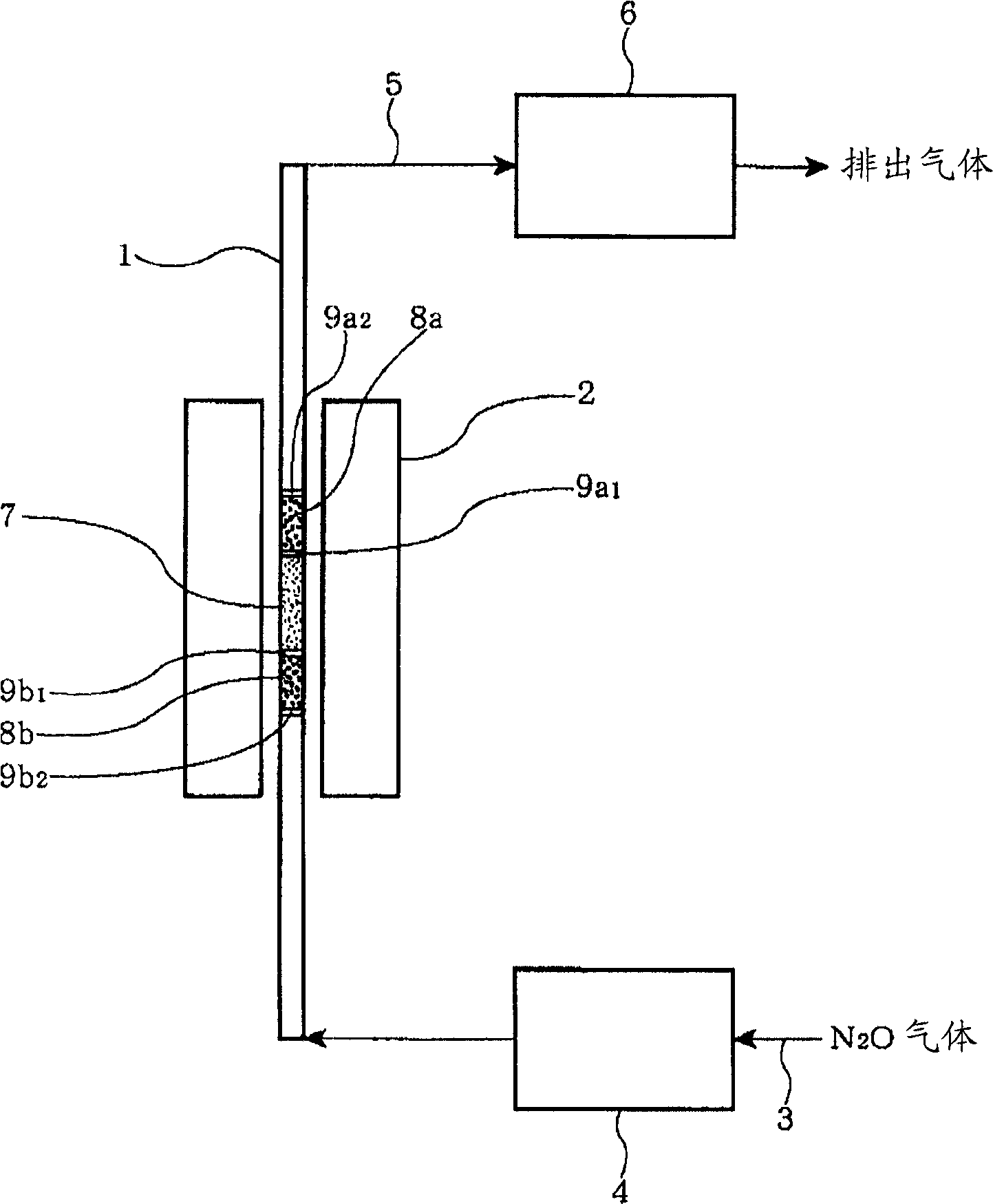
Process for obtaining dinitrogen monoxide (N20)
InactiveUS20130171711A1Improve energy balanceHighly climate-damagingWater treatment parameter controlTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesMicroorganismCell Fraction
In a method for obtaining dinitrogen monoxide by microbiological or enzymatic processes from nitrogen-containing substances, the microorganisms, bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes, fungi, parasites, phages, cells, cell fractions or membrane fractions, and / or enzymes, and / or a combination thereof to be used in this context are selected, or manipulated or partly or entirely reversibly and / or irreversibly inhibited by suitable actions, or the corresponding microbiological or enzymatic processes are controlled, for example, by way of suitable process conditions, so that, in part or entirely, dinitrogen monoxide (N2O) is formed from the nitrogen-containing compounds of the nitrogen-containing substances.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for the production of cyclic ketones
InactiveUS7649119B2High puritySimple wayOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationDinitrogen monoxideDouble bond
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a cyclic ketone having from 7 to 16 carbon atoms, which comprises at least the steps(a) oxidation of a composition (I) comprising at least one cyclic olefin which has from 7 to 16 carbon atoms and at least one C—C double bond by means of dinitrogen monoxide to give a composition (A),(b) treatment of the composition (A) with at least one base to give a composition (B).
Owner:BASF AG
Process for producing polyolefins
A novel process for producing homopolymers and interpolymers of olefins which involves contacting an olefin and / or an olefin and at least one or more other olefin(s) under polymerization conditions with an olefin polymerization catalyst and dinitrogen monoxide in an amount sufficient to reduce the electrostatic charge in the polymerization medium. Also provided is a process for reducing electrostatic charge in the polymerization of an olefin by adding dinitrogen monoxide.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
Process for preparing 4-pentenoic acid
InactiveUS20110046413A1Improve the level ofOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationCyclopentene4-pentenoic acid
The present invention relates to a process for preparing 4-pentenoic acid, at least comprising the oxidation of a mixture (G) comprising 4-pentenal, 3-methyl-2-butanone and cyclopentene oxide, and to the use of a mixture (G) comprising 4-pentenal, 3-methyl-2-butanone and cyclopentene oxide for preparing 4-pentenoic acid. In the context of the present invention, the mixture (G) is preferably obtained as a by-product of the oxidation of cyclopentene to cyclopentanone by means of dinitrogen monoxide.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for producing polyolefins
A novel process for producing homopolymers and interpolymers of olefins which involves contacting an olefin and / or an olefin and at least one or more other olefin(s) under polymerization conditions with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst and dinitrogen monoxide in an amount sufficient to reduce the electrostatic charge in the polymerization medium. Also provided is a process for reducing electrostatic charge in the polymerization of an olefin by adding dinitrogen monoxide.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
Process for preparing cyclic ketones
ActiveUS8461392B2High yieldMaximum purityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationPolymer scienceDinitrogen monoxide
The present invention relates to a process for preparing at least one monocyclic ketone having from 4 to 20 carbon atoms by reacting a mixture G1 comprising at least one monocyclic olefin having from 4 to 20 carbon atoms with a mixture G2 comprising at least dinitrogen monoxide, wherein said reaction is performed adiabatically.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for the production of cyclic ketones
InactiveUS7714172B2High purityLow costOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationDistillationDouble bond
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a cyclic ketone having from 7 to 16 carbon atoms, which comprises at least the steps(a) oxidation of a composition (I) comprising at least one cyclic alkene which has from 7 to 16 carbon atoms and at least one C—C double bond by means of dinitrogen monoxide to give a composition (A),(b) treatment of the composition (A) with at least one base to give a composition (B),(c) hydrogenation of the composition (B) in the presence of at least one catalyst to give a composition (C),(d) purification of the composition (C), comprising at least the steps(di) thermal treatment of the composition (C) with at least one acid or at least one catalyst comprising at least one transition metal,(dii) further purification by a method selected from the group consisting of distillation, extraction and crystallization.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for preparing ketones, in particular macrocyclic ketones
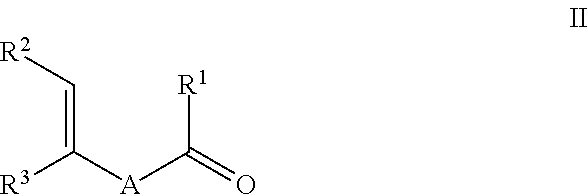
ActiveUS8563781B2Organic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationHydrogenDinitrogen monoxide
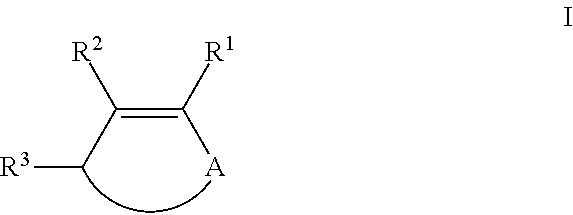
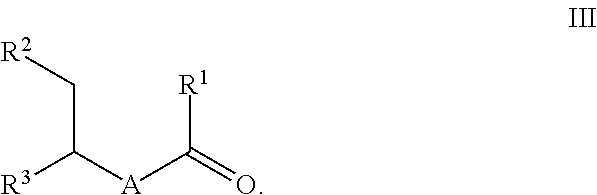
Ketones of the formula IIwhere A is optionally alkyl-substituted C2-C12-alkanediyl, R1 and R2 are each, independently of one another, C1-C6-alkyl, or R1 and R2 together form optionally alkyl-substituted C3-C10-alkanediyl, and R3 is hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl, are prepared by reacting a cyclic olefin of the formula Iwith dinitrogen monoxide to form the ketone of the formula II. The ketone of the formula II can be further hydrogenated to form the saturated ketone of the formula III.Macrocyclic ketones of the formula III, e.g. muscone, are sought after as fragrances.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for purifying dinitrogen monoxide
The present invention relates to a process for purifying a gas mixture comprising dinitrogen monoxide, at least comprising the at least partial condensation of a gas mixture G-I comprising dinitrogen monoxide to obtain a liquid composition C-1 comprising dinitrogen monoxide, and the contacting of the composition C-1 with a gas mixture M-1 to obtain a composition C-2 and a gas mixture M-2.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for producing polyolefins
A novel process for producing homopolymers and interpolymers of olefins which involves contacting an olefin and / or an olefin and at least one or more other olefin(s) under polymerization conditions with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst and dinitrogen monoxide in an amount sufficient to reduce the electrostatic charge in the polymerization medium. Also provided is a process for reducing electrostatic charge in the polymerization of an olefin by adding dinitrogen monoxide.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
Process for the polymerization of olefins
A novel process for the polymerization of olefins is provided. The process involves contacting at least one olefin with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst in the presence of dinitrogen monoxide in the production of polymeric products having a narrower molecular weight distribution. A process for narrowing molecular weight distribution of polyolefins utilizing dinitrogen monoxide is also provided.
Owner:WESTLAKE LONGVIEW
Process for preparing 4-pentenoic acid
InactiveUS8362296B2Improve the level ofOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparation4-pentenoic acidCyclopentene
Owner:BASF SE
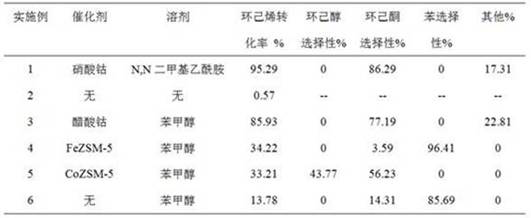
A kind of magnesium cobaltate catalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107335437BSimple preparation processPreparation process parameters are easy to controlNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentPtru catalystCatalytic decomposition
The invention relates to a magnesium cobaltate catalyst and its preparation method and use. The carbon spheres are first hydrothermally synthesized, and then the surface of the carbon spheres is impregnated with a mixed aqueous solution of cobalt nitrate, magnesium nitrate and urea. Then, it was rotated and crystallized for 4 hours in an autoclave equipped with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and cobalt-magnesium composite hydroxide was hydrothermally synthesized on the surface of the carbon sphere. Then, the carbon balls are calcined in air to obtain the magnesium cobaltate catalyst. The catalyst prepared by the invention has a cavity morphology formed by porous worm-shaped nanoparticles, that is, the porous worm-shaped nanoparticles surround each cavity. This catalyst is used to catalyze the decomposition of high concentrations of nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Exhaust gas, which significantly increases the internal and external diffusion rate of reactants, thus improving the catalyst activity.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
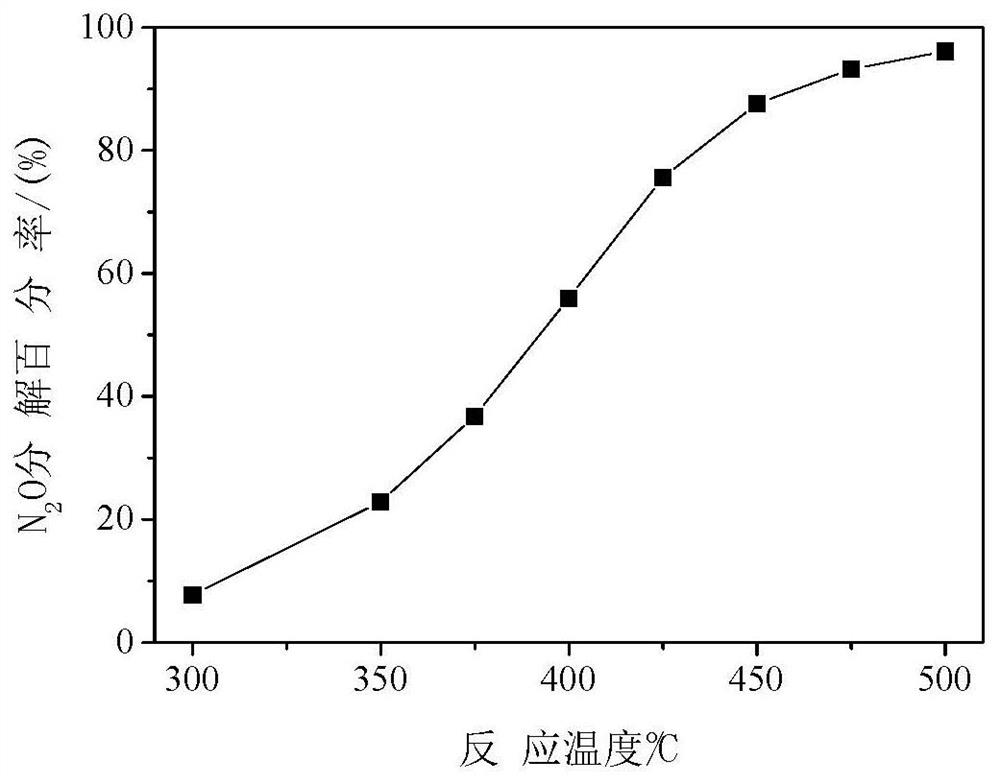
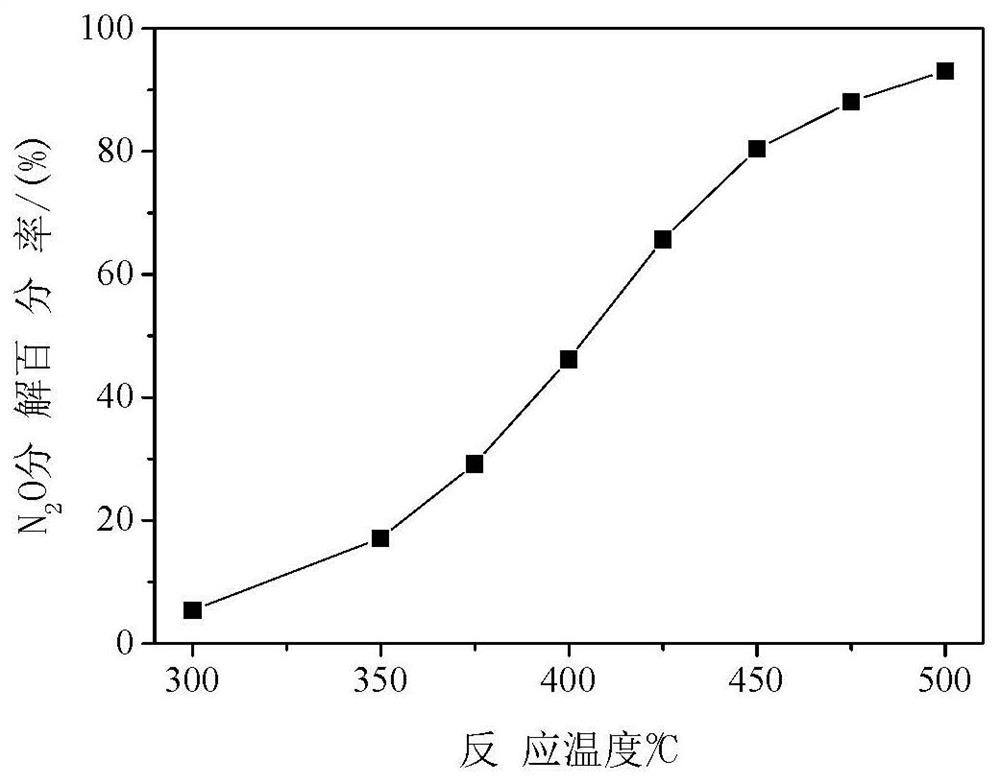
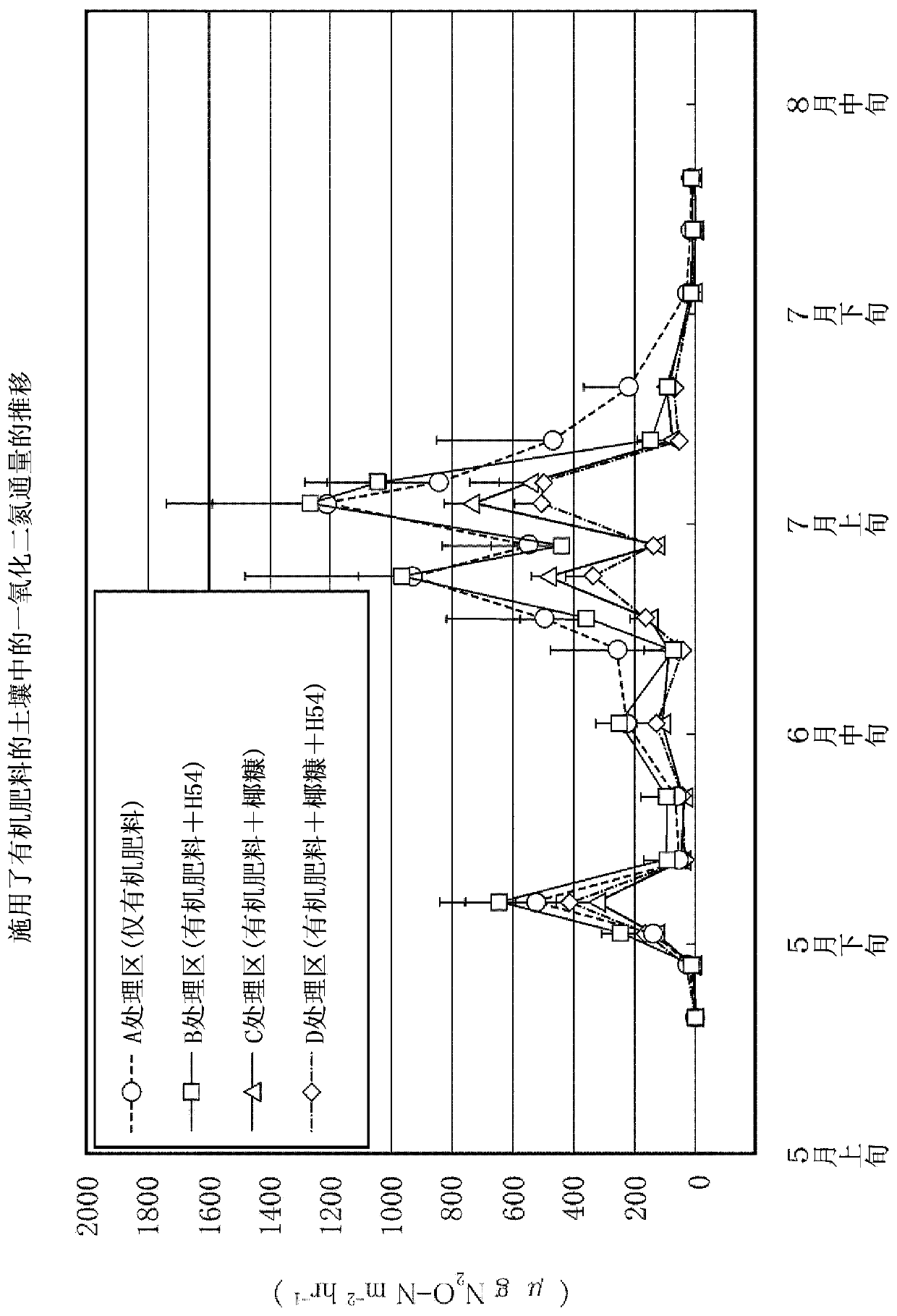
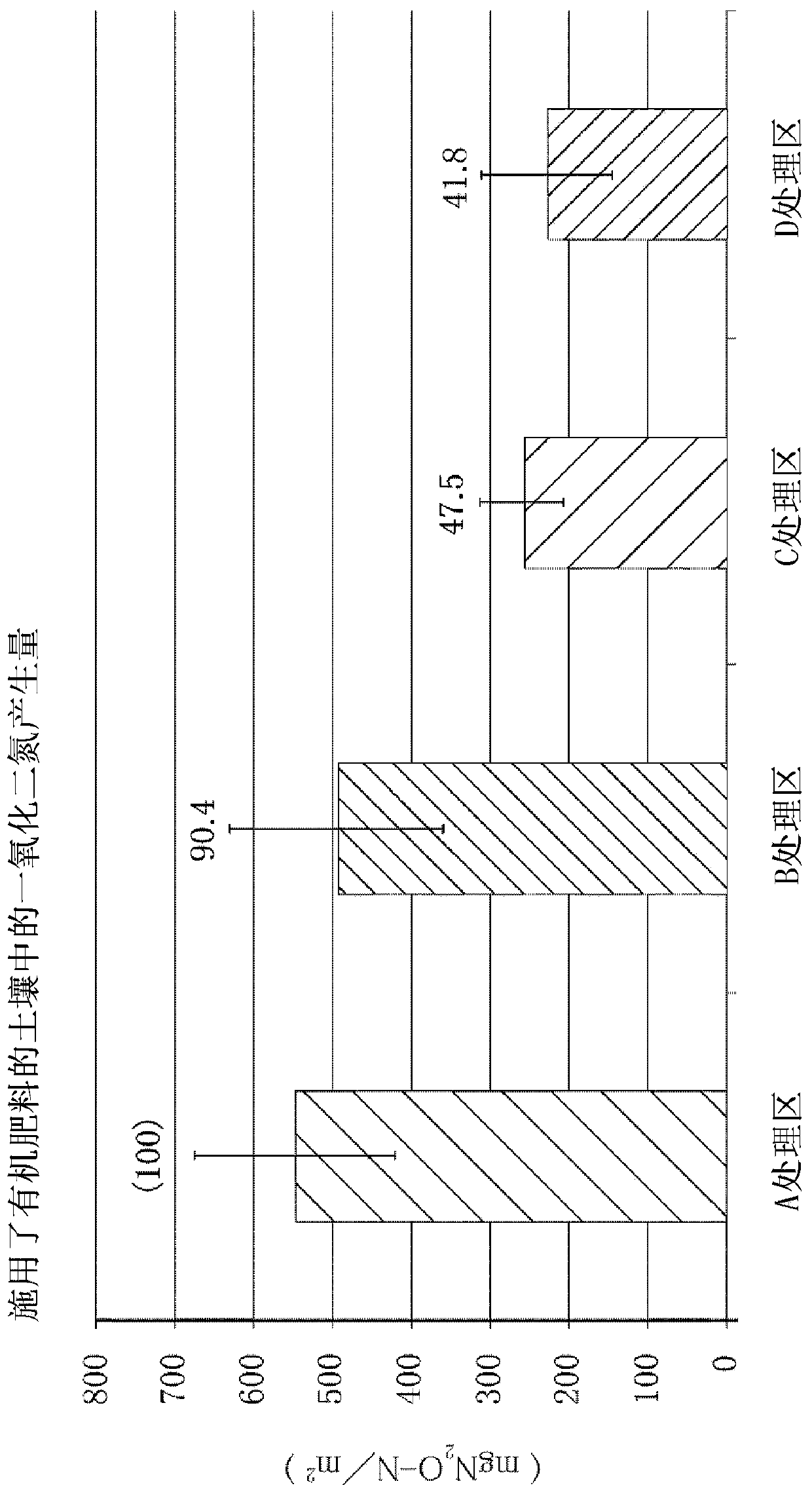
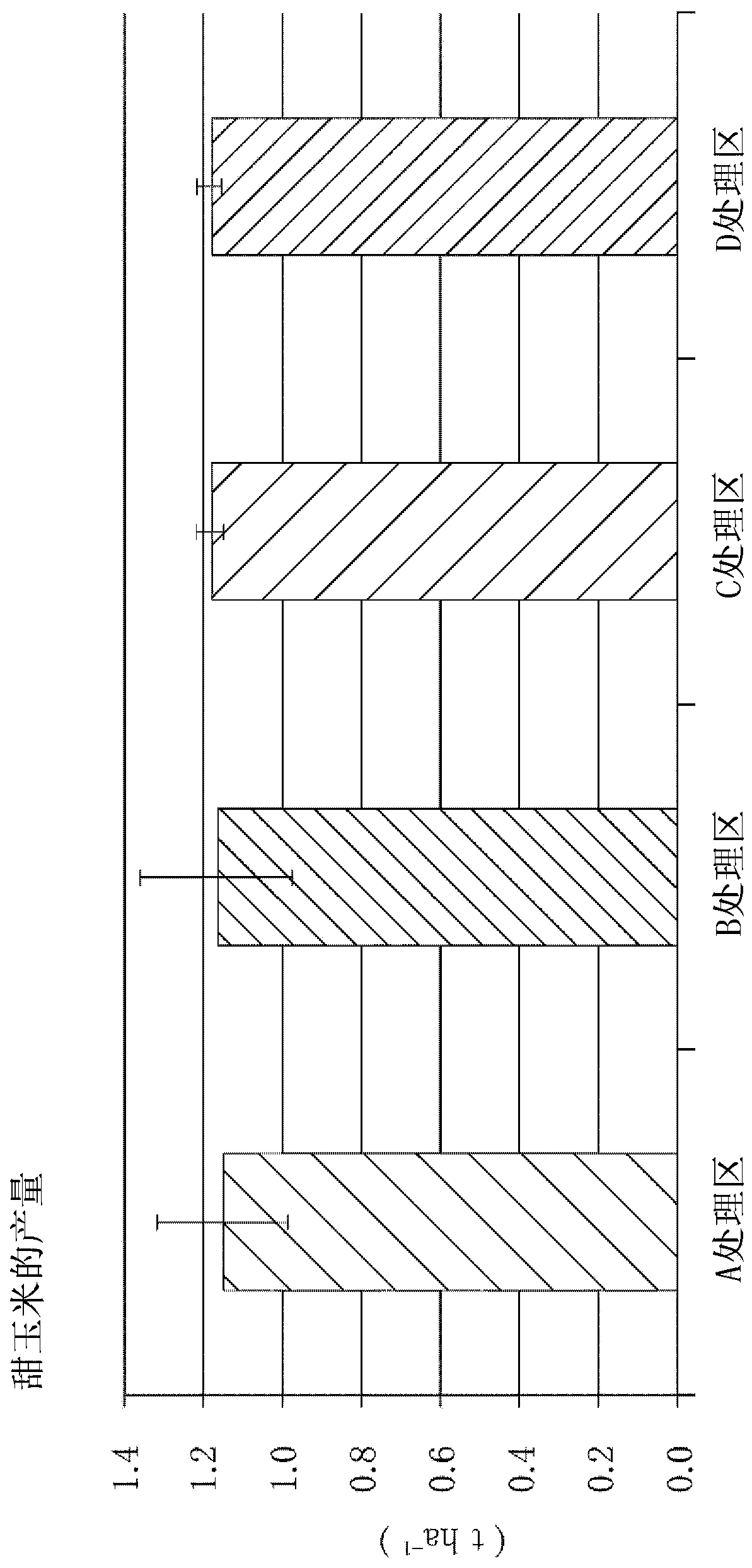
Dinitrogen monoxide reducing material for farmland
Provided is a dinitrogen monoxide reducing material for a farmland, wherein the amount of dinitrogen monoxide generated due to nitrogen inclusion applied to this farmland is reduced regardless of thesoil quality or the use form of the farmland. The dinitrogen monoxide reducing material for a farmland is to reduce dinitrogen monoxide generated due to nitrogen inclusion, such as a fertilizer, a compost, and a harvest residue used in a farmland, and then released into the air, and contains, as a main component, a fungivorous soil animal activation material which proliferates a fungivorous soil animal intaking fungi inhabiting in said farmland, occurring in the nitrogen inclusion used in the farmland, and generating dinitrogen monoxide, or which activates the activity of the fungivorous soilanimal.
Owner:NIIGATA PREFECTURE +2
Process for preparing Fuller-ene
A method for producing fullerenes, characterized in that said method includes a step (a) of contacting an aromatic compound-containing starting material with a supercritical fluid or a subcritical fluid at a temperature in a range of from 31 DEG C to 500 DEG C and at a pressure in a range of from 3.8 MPa to 60 MPa. Said supercritical fluid or said subcritical fluid is formed from one or more kinds of materials selected from the group consisting of an aromatic compound as said starting material, a solvent capable of dissolving said aromatic compound, water, dinitrogen monoxide, and ammonia.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for preparing nitro compound from low-valent nitric oxide
ActiveCN102276471BIncrease profitAtom economy is highNitro compound preparationNitro compoundPhosphomolybdic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitro compounds using nitrogen subvalent oxides. Nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, dinitrogen monoxide, dinitrogen trioxide, dinitrogen tetroxide and other low-valent oxides of nitrogen are used, under the promotion of molecular oxygen, through aluminosilicate, silicon aluminum phosphate, phosphorus molybdenum Sodium acid and other heteropoly acid salts, transition metal oxides, triphenylphosphine metal-organic complexes, transition metal ion clay catalysts, and react with alicyclic compounds, aromatic compounds, and heterocyclic compounds to prepare nitro compounds. The method is used to replace the traditional industrial preparation method of nitrogen (V) compounds such as dinitrogen pentoxide, nitric acid, nitrate, and nitrate to prepare nitro compounds, and improves the atomic utilization rate of industrial nitration to prepare nitro compounds. Atom economic properties of nitro compounds.
Owner:彭新华
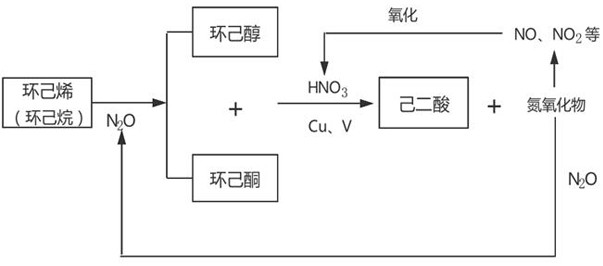
Production process for preparing cyclohexanone by oxidizing cyclohexene and laughing gas by using cobalt-based catalyst
ActiveCN112794795AReduce consumptionSolve processing problemsNitrous oxide captureOrganic compound preparationChemical industryPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a production process for preparing cyclohexanone by oxidizing cyclohexene and laughing gas by using a cobalt-based catalyst. The process is mainly applied to a synthesis section of adipic acid in a nylon industry chain. The cobalt-based catalyst is a cobalt-containing salt, cobalt-containing oxide, cobalt simple substance or a cobalt-containing solid catalyst. According to the invention, nitrous oxide (laughing gas) and cyclohexene in the nitric oxide waste gas generated in the adipic acid working section directly react under the action of the catalyst to produce cyclohexanone, so that the process not only solves the problem of treating the waste gas laughing gas, but also reduces the consumption of oxygen in the adipic acid working section; and meanwhile, the energy consumption and three-waste treatment in the cyclohexanol oxidation process are also reduced. Therefore, the catalyst and the technical process have good application prospects, have the advantages of optimizing reaction products, reducing separation cost and the like, and accord with the development trend of green chemical industry.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method for obtaining dinitrogen oxide
Owner:FINKE THOMAS
Process for the removal of dinitrogen oxide in process off-gas
ActiveUS11179674B2Lower overall pressure dropLess stringent requirementNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentPtru catalystExhaust fumes
A process for the removal of nitrous oxide (N2O) contained in a process off-gas in an axial flow reactor. The process includes the steps of (a) adding an amount of reducing agent into the process off-gas; (b) in a first stage passing in axial flow direction the process off-gas admixed with the reducing agent through a first monolithic shaped catalyst active in decomposing nitrous oxide by reaction with the reducing agent to provide a gas with a reduced amount of nitrous oxide and residual amounts of reducing agent; and (c) in a second stage passing the gas with a reduced amount of nitrous oxide and residual amounts of the reducing agent in axial flow direction through a second monolithic shaped catalyst active in oxidation of the residual amounts of the reducing agent.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-D00001.png)
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-D00002.png)
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-C00001.png)