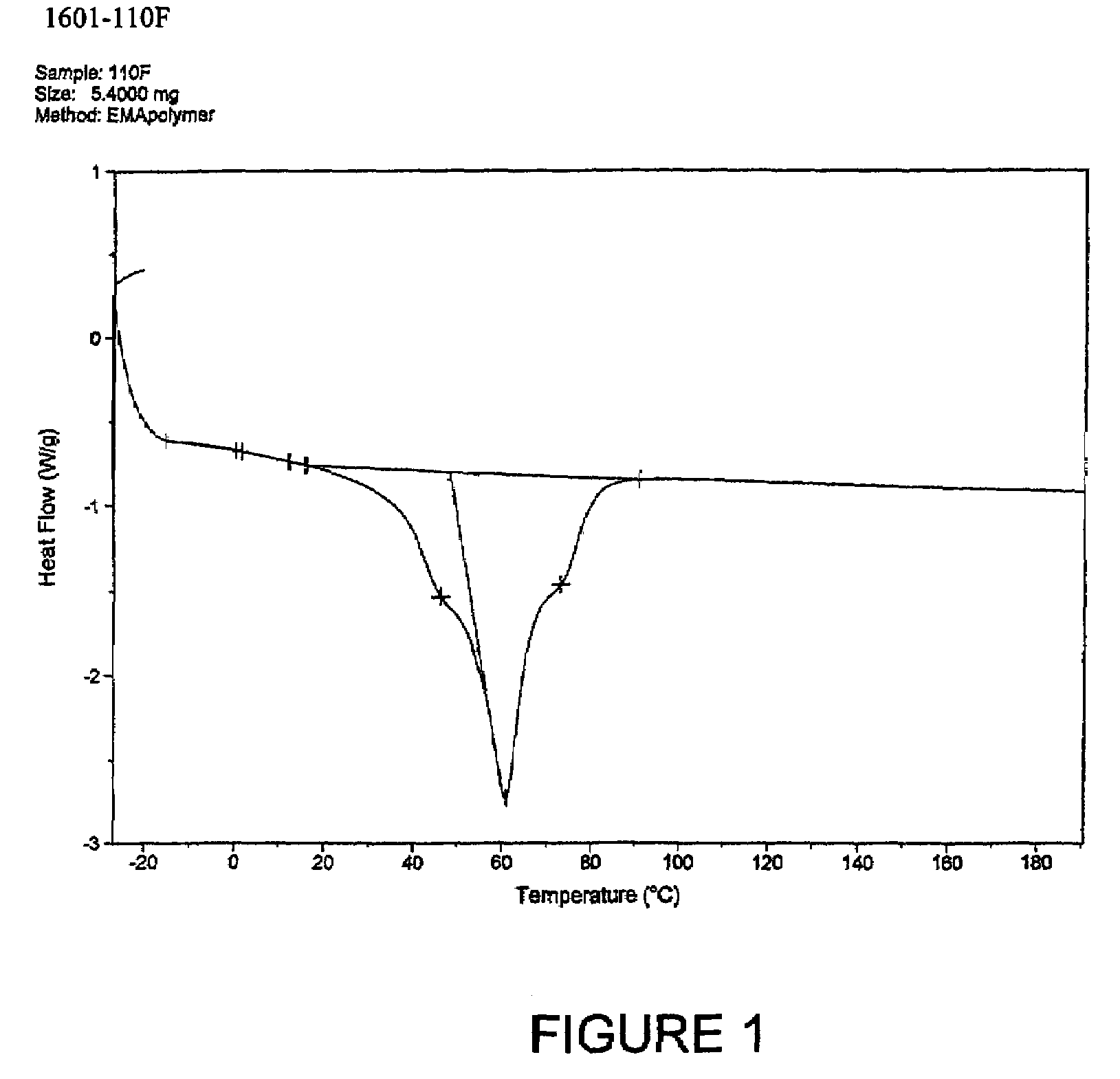
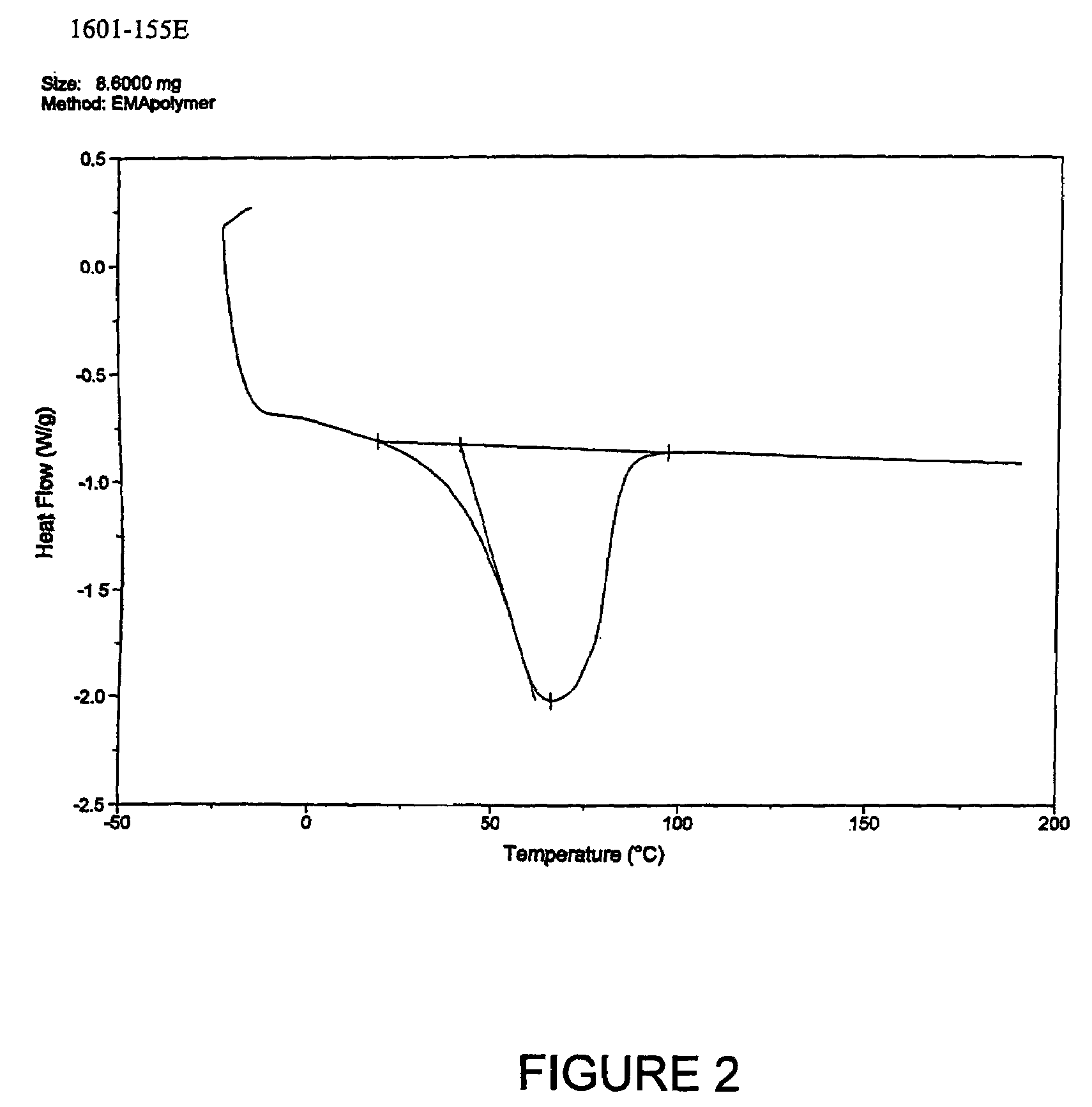
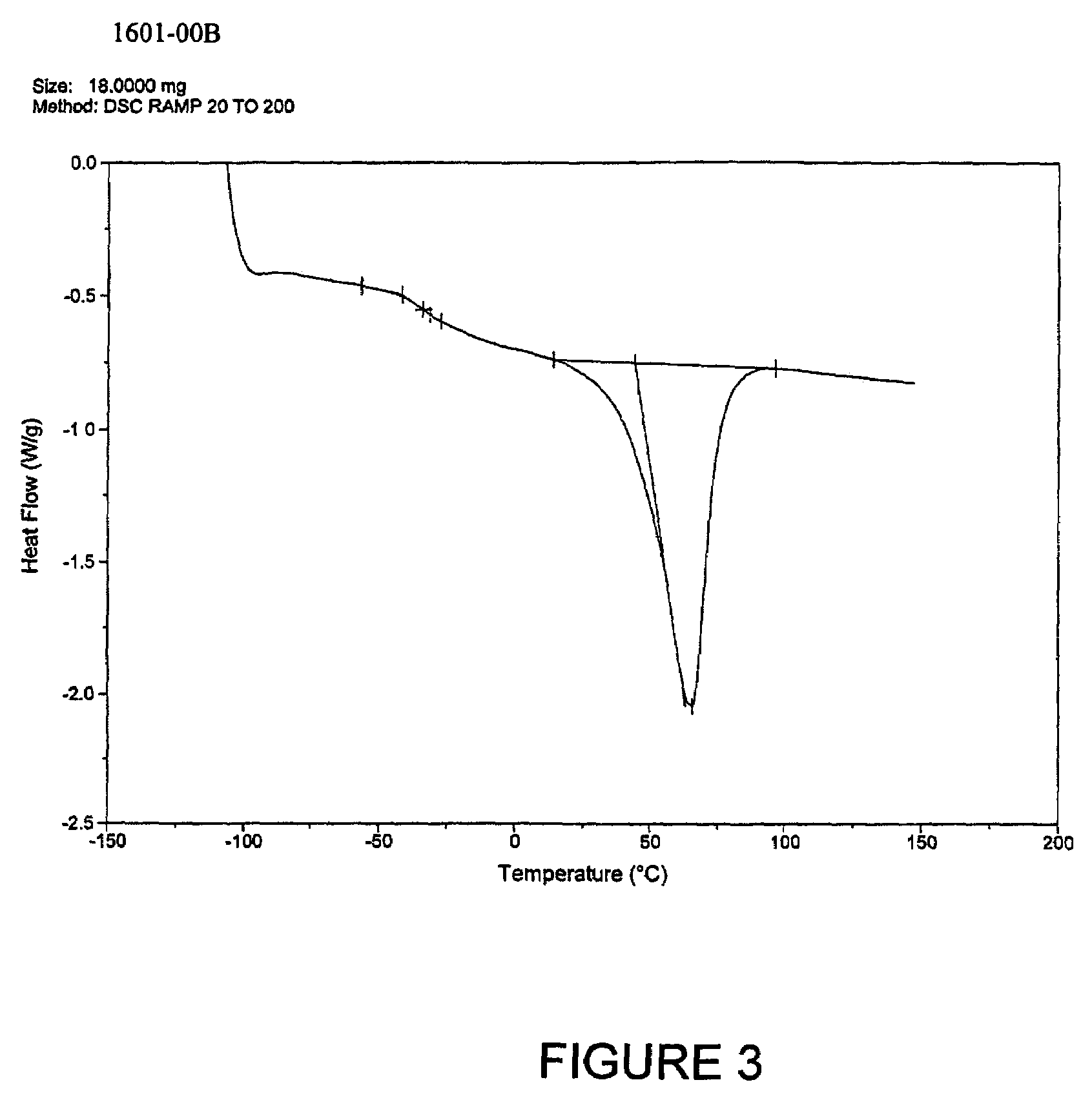
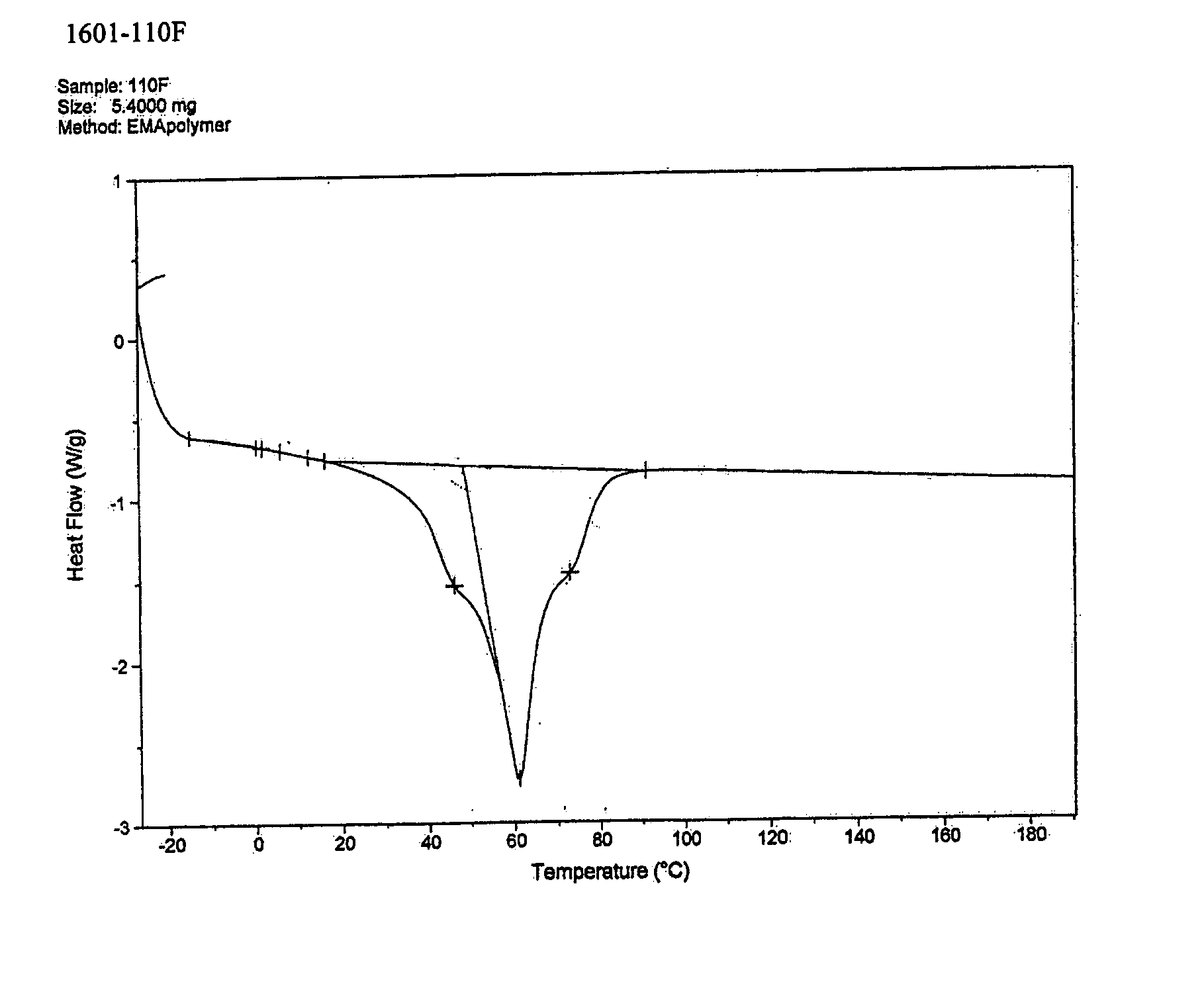
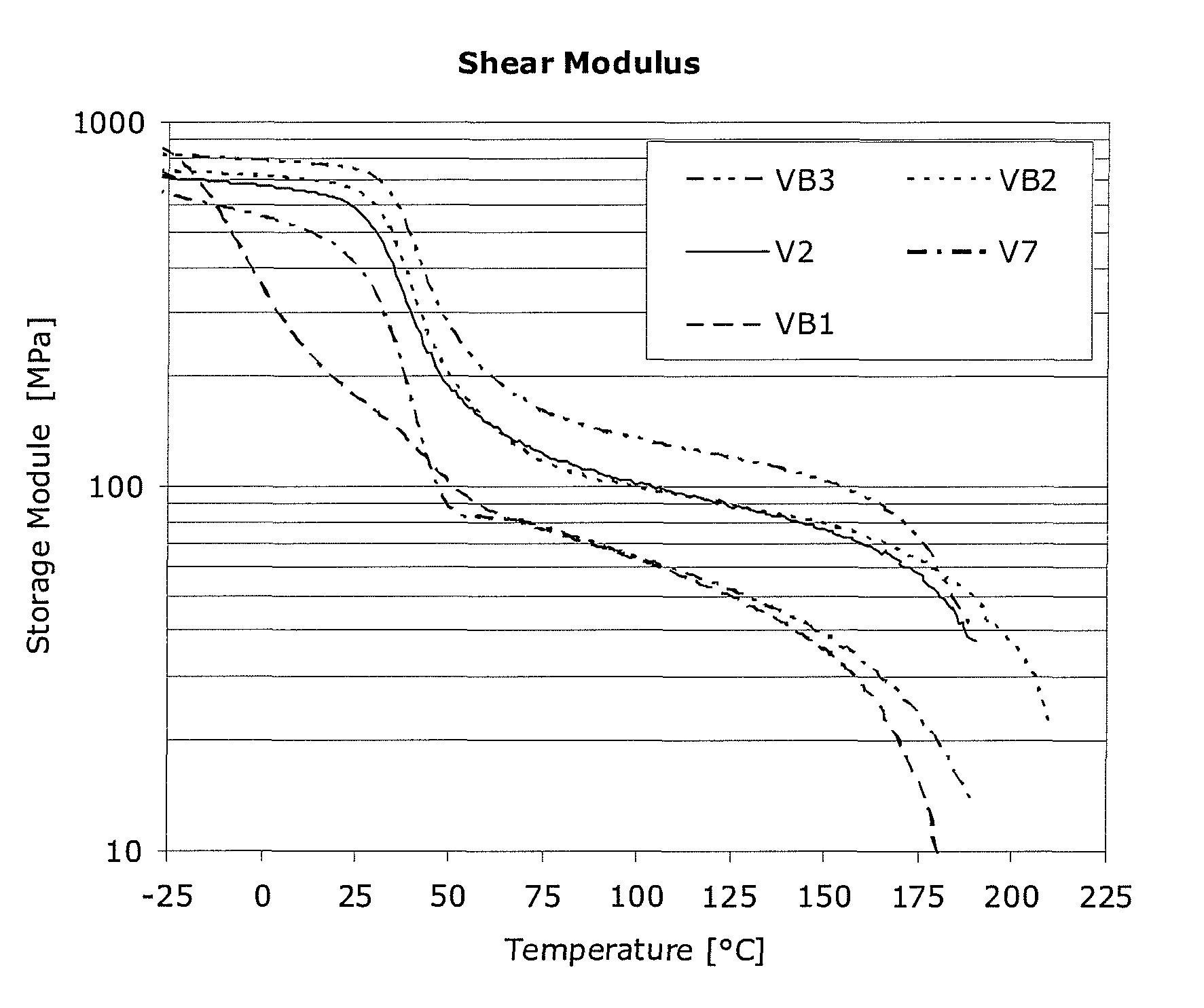
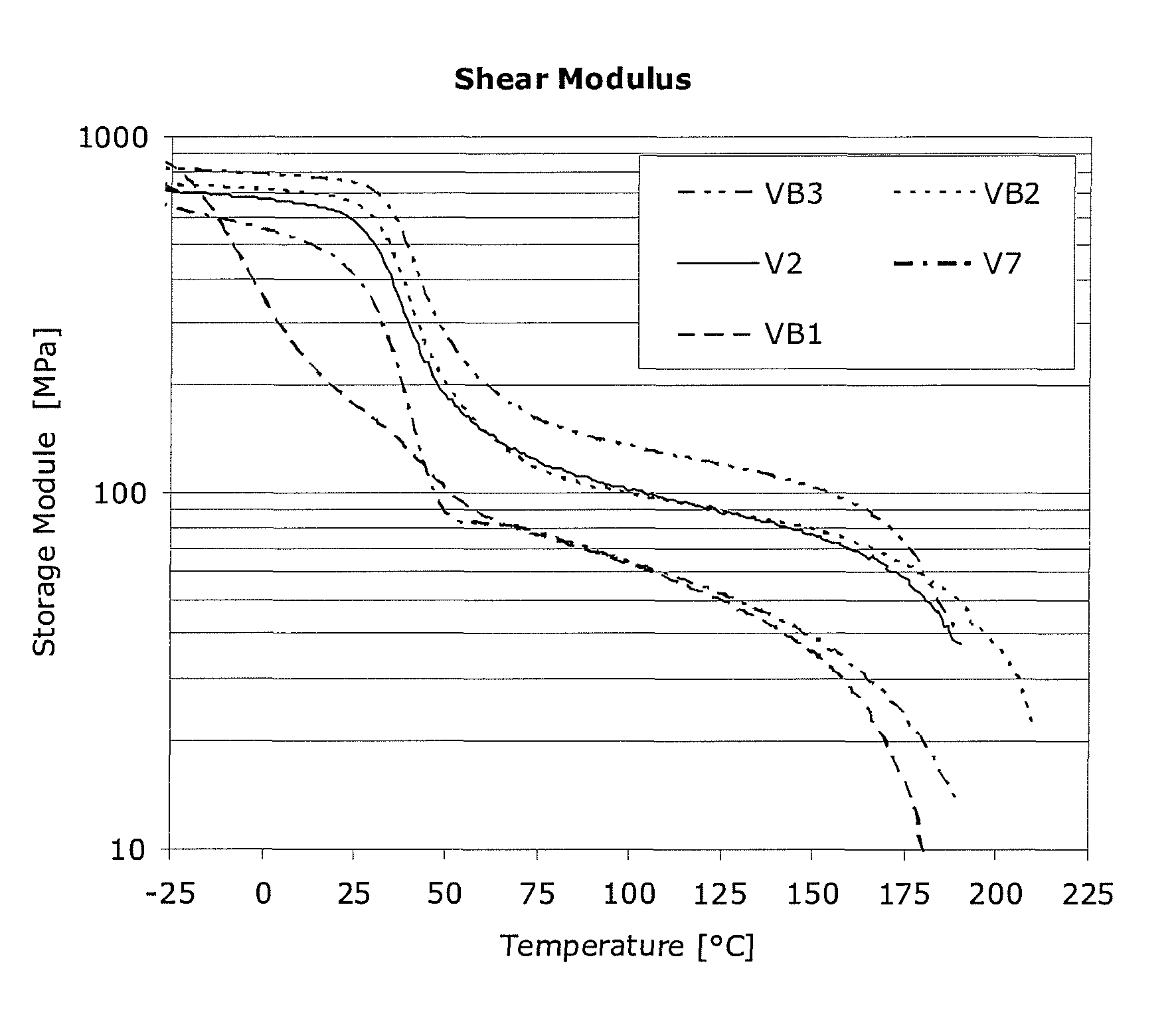
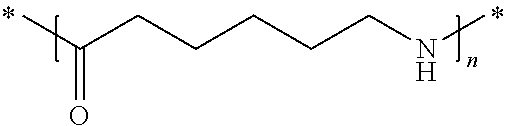
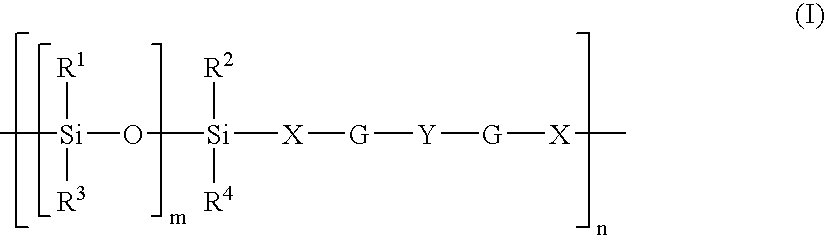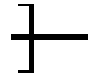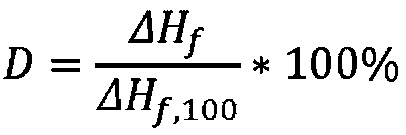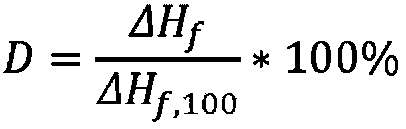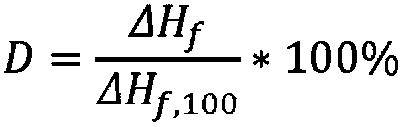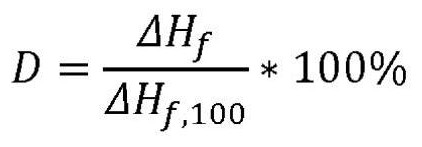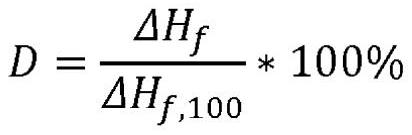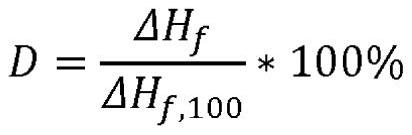Patents
Literature
33 results about "Enthalpy of fusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid, at constant pressure. For example, when melting 1 kg of ice (at 0 °C under a wide range of pressures), 333.55 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature change. The heat of solidification (when a substance changes from liquid to solid) is equal and opposite.
Process for packaging plastic materials like hot melt adhesives
A method for packaging plastic material using a film to surround the material, and more particularly to a method for packaging hot melt adhesives, the resulting package formed thereby, and the film composition used therein. The method is preferably a coextrusion process for packaging a pressure sensitive hot melt adhesive by extruding a hot melt adhesive through a die orifice, and coextruding a wax-based polymeric film to surround the hot melt adhesive. The coated adhesive may then be formed into individual packaged units having a finite size and shape. The polymeric film comprises a composition having at least 25% by weight of a wax material, an enthalpy of fusion of at least about 100 J / g, and an elongation value at break of at least about 100%. Any type of hot melt adhesive formulation can be packaged or surrounded by the polymeric film in the process. Also, the specific enthalpy of fusion desired and / or elongation value at break desired for the polymeric film can be obtained by blending an appropriate amount of partially crystalline ethylene-based polymer together with a thermoplastic elastomeric block copolymer and / or an ethylene based or propylene-based elastomer.
Owner:BOSTIK INC
Encapsulated phase change materials in seed coatings
InactiveUS20090227451A1Good flexibilityIncrease productionBiocideFertilising methodsSeed dormancyPhase change
The present invention is directed to improved seed coatings which facilitate fall or early spring planting while maintaining seed dormancy until soil temperatures are appropriate for successful germination. The improved seed coatings contain encapsulated phase change materials within a polymeric shell which preserve the dormancy of the seed during early planting by slowing the rate at which the seed temperature rises in the event of a temperature spike thus preventing premature germination. The encapsulated phase change material is a material characterized by a solid / liquid or liquid / solid phase change which occurs at a temperature which ranges from about −5 to about 20° C., preferably between about 0 to about 19° C., most preferably between about 5 to about 15° C. The solid / liquid or liquid / solid phase change is further characterized by an effective enthalpy of fusion / crystallization for the solid-liquid / liquid-solid phase change equal to or greater than 20 J / g when determined by Differential Scanning Calorimetry.
Owner:CIBA CORP
Process for packaging plastic materials like hot melt adhesives
ActiveUS20060093764A1Eliminate wasteDesired performancePackage sterilisationPaper coatingElastomerWax
A method for packaging plastic material using a film to surround the material, and more particularly to a method for packaging hot melt adhesives, the resulting package formed thereby, and the film composition used therein. The method is preferably a coextrusion process for packaging a pressure sensitive hot melt adhesive by extruding a hot melt adhesive through a die orifice, and coextruding a wax-based polymeric film to surround the hot melt adhesive. The coated adhesive may then be formed into individual packaged units having a finite size and shape. The polymeric film comprises a composition having at least 25% by weight of a wax material, an enthalpy of fusion of at least about 100 J / g, and an elongation value at break of at least about 100%. Any type of hot melt adhesive formulation can be packaged or surrounded by the polymeric film in the process. Also, the specific enthalpy of fusion desired and / or elongation value at break desired for the polymeric film can be obtained by blending an appropriate amount of partially crystalline ethylene-based polymer together with a thermoplastic elastomeric block copolymer and / or an ethylene based or propylene-based elastomer.
Owner:BOSTIK INC
Polyamide blend molding compound
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
Aromatic polycarbonate resin composition
InactiveUS20100222486A1Improve heat resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesPhosphoric Acid EstersPolycarbonate
The object of this invention is to provide a resin composition that contains a polymer obtained from biomass resources and constitutes molded articles excellent in heat resistance, mechanical properties and durable stability, this invention including a resin composition comprising(i) a resin component containing 95 to 5% by weight of an aromatic polycarbonate (component A) and 5 to 95% by weight of polylactic acid (component B),(ii) 0.001 to 10 parts by weight, per 100 parts by weight of the resin component, of a phosphoric ester metal salt (component C), and(iii) 0.01 to 5 parts by weight, per 100 parts by weight of the polylactic acid (component B), of a terminal blocker (component F),the stereo-complex crystal content (X) of the following expression (I) being 80% or more,X (%)={ΔHb / (ΔHa+ΔHb)}×100 (I)wherein ΔHa and ΔHb are a melting enthalpy (ΔHa) of a crystal melting point that appears at lower than 190° C. and a melting enthalpy (ΔHb) of a crystal melting point that appears at 190° C. or higher but less than 250° C., respectively, in a temperature-elevation process by a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), and molded articles thereof.
Owner:TEIJIN KASEK KK
Hot Melt Adhesive Based On Low Melting Point Polypropylene Homopolymers
ActiveUS20140350155A1Increase setting speedHigh bond strength levelMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesPersonal carePorous substrateWax
A hot melt adhesive for use on porous substrates, wherein the hot melt adhesive hasa) about 10% to about 70% by weight of a polypropylene homopolymer having a DSC melting point of less than 100° C.;b) about 10% to about 60% of a first tackifying resin having a Ring & Ball Softening Point of about 95° C. to about 140° C.;c) about 0% to about 65% of a second tackifying resin that is different than the first tackifying resin;d) about 5% to about 50% of a plasticizer;e) about 1% to about 40% by weight of a secondary polymer which is either a semi-crystalline polymer or wax with an enthalpy of fusion of greater than 30 Joules / gram;f) about 0.1% to about 5% of a stabilizer or antioxidant;wherein the components total 100% by weight of the composition, and the viscosity of the composition is equal to or less than about 20,000 centipoise (cP) at 163° C. (325° F.).
Owner:BOSTIK INC
Care and/or make-up cosmetic composition structured with silicone polymers
InactiveUS7887786B2Efficient use ofFew or no effectsCosmetic preparationsMake-upThiocarbamateCarbamate
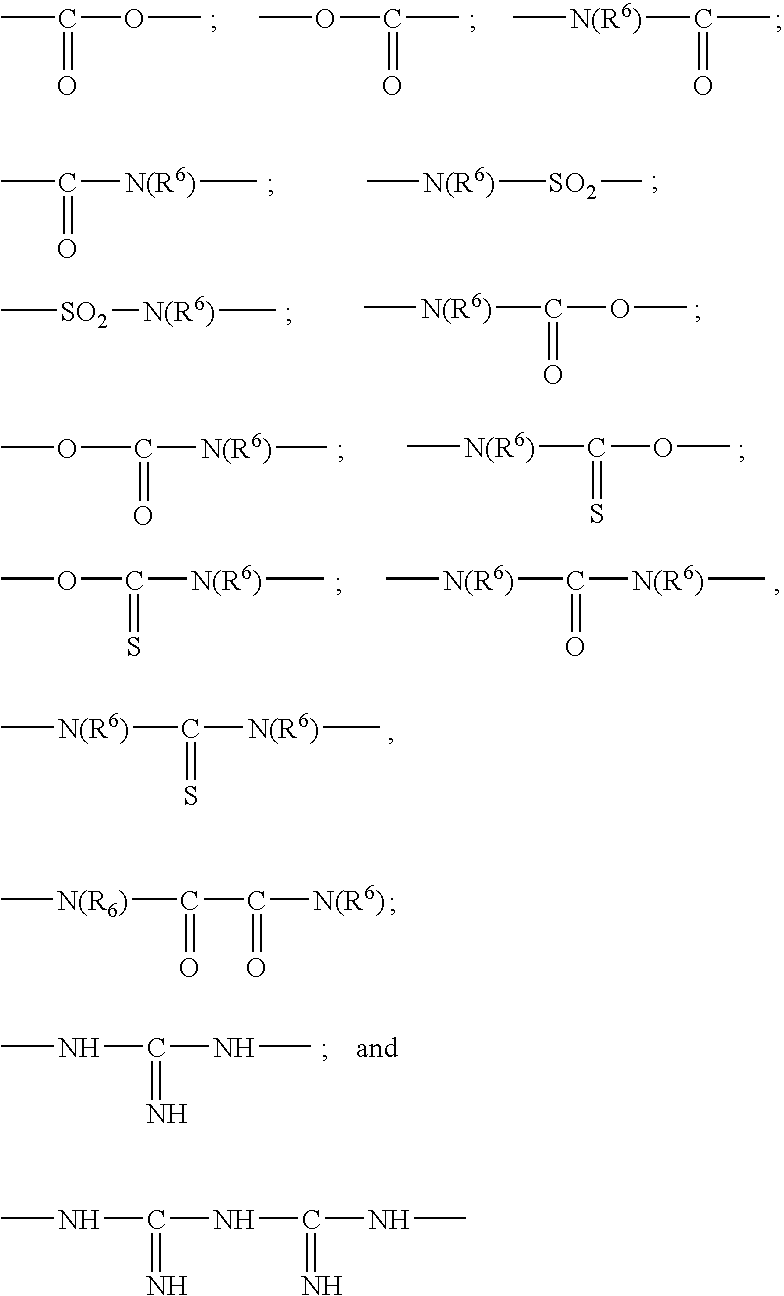
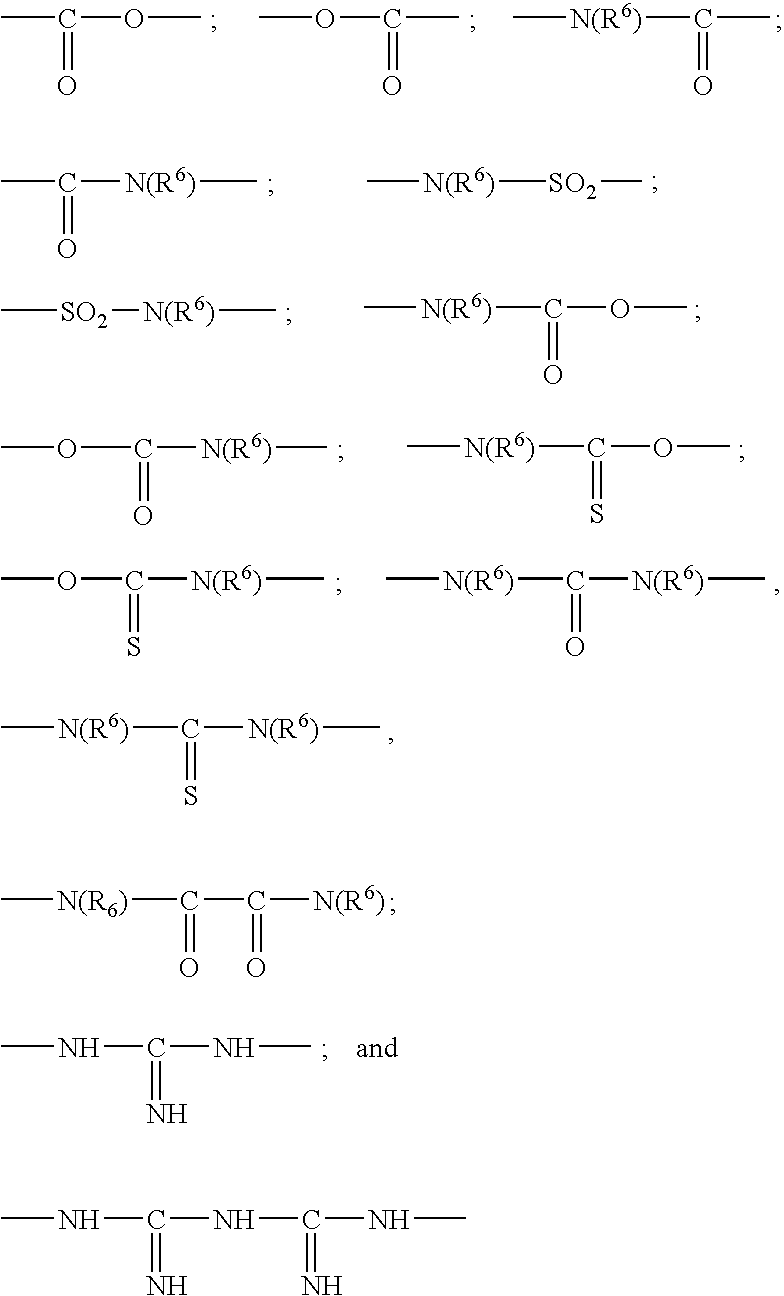
Care and / or make-up cosmetic composition comprising: a liquid continuous fatty Phase structured with at least one structuring polymer (homopolymer or copolymer) having a weight-average molecular mass ranging from 500 to 500 000, containing at least one moiety comprising: at least one polyorganosiloxane group consisting of 1 to 1 000 organosiloxane units in the chain of the moiety or in the form of a graft, and at least two groups capable of establishing hydrogen interactions, Chosen from ester, amide, sulphonamide, carbamate, thiocarbamate, urea, urethane, thiourea, oxamido, guanidino and biguanidino groups, and combinations thereof, the polymer being solid at room temperature and soluble in the liquid fatty Phase at a temperature of 25 to 250° C., the Said liquid fatty Phase comprising at least one compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer, and then the liquid fatty Phase, the structuring polymer and the compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer forming a physiologically acceptable medium.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Care and /or Make-Up Cosmetic Composition Structured with Silicone Polymers
ActiveUS20060204470A1Efficient use ofGood disintegrationCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsThiocarbamateCarbamate
Care and / or make-up cosmetic composition comprising: a liquid continuous fatty Phase structured with at least one structuring polymer (homopolymer or copolymer) having a weight-average molecular mass ranging from 500 to 500 000, containing at least one moiety comprising: at least one polyorganosiloxane group consisting of I to 1 000 organosiloxane units in the chain of the moiety or in the form of a graft, and at least two groups capable of establishing hydrogen interactions, Chosen from ester, amide, sulphonamide, carbamate, thiocarbamate, urea, urethane, thiourea, oxamido, guanidino and biguanidino groups, and combinations thereof, the polymer being solid at room temperature and soluble in the liquid fatty Phase at a temperature of 25 to 250° C., the Said liquid fatty Phase comprising at least one compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer, and then the liquid fatty Phase, the structuring polymer and the compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer forming a physiologically acceptable medium.
Owner:LOREAL SA
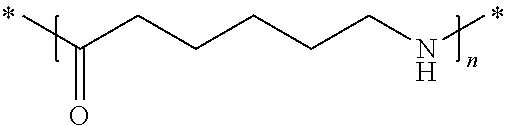
Copolymers having amide units and ether units with improved optical properties
The present invention is a copolymer based on amide units and ether units, wherein the amide units being comprise a major portion of an equimolar combination of at least one diamine and at least one dicarboxylic acid, the diamine(s) is / are mainly cycloaliphatic and the dicarboxylic acid(s) is / are mainly linear and aliphatic, the amide units optionally comprise, but in a minor proportion, at least one other polyamide comonomer, the respective proportions of ether and amide unit monomers are selected in such a way that said copolymer is highly transparent to such an extent that the transmittance at 560 nm on a plate 2 mm thick is greater than 75%; the crystallinity of said copolymer is such that the enthalpy of fusion during the first heating of a ISO DSC (delta Hm(2)) is at least 30 J / g, where the mass is related to the number of amide units contained or of polyamide contained, which fusion corresponds to that of the amide units; and said copolymer has a glass transition temperature of at least 75° C.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Liquid-crystal polymer and molded articles
InactiveUS20120190813A1Improve thermal conductivityHigh mechanical strengthLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineN-Acetyl-p-aminophenol
To provide an easily-manufactured liquid-crystalline polymer having high thermal conductivity, as well as a molded article that is formed of the liquid crystalline polymer and has a property of being highly mechanical. A liquid-crystalline polymer is used that is formed by polymerizing monomers having an asymmetrical molecular structure, in which the enthalpy of fusion ΔH measured by way of DSC (Differential Scanning calorimetry) is greater than or equal to 2.5 J / g (joules per gram) and less than or equal to 10 J / g, and the inherent viscosity (I.V.) is greater than or equal to 5 dl / g and less than or equal to 7 dl / g. It is preferable for the monomer having asymmetrical molecular structure to be at least one selected from a group consisting of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (HBA), 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (HNA), N-acetyl-p-aminophenol (APAP), and 4-hydroxy-4′-biphenylcarboxylic acid (HBCA).
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
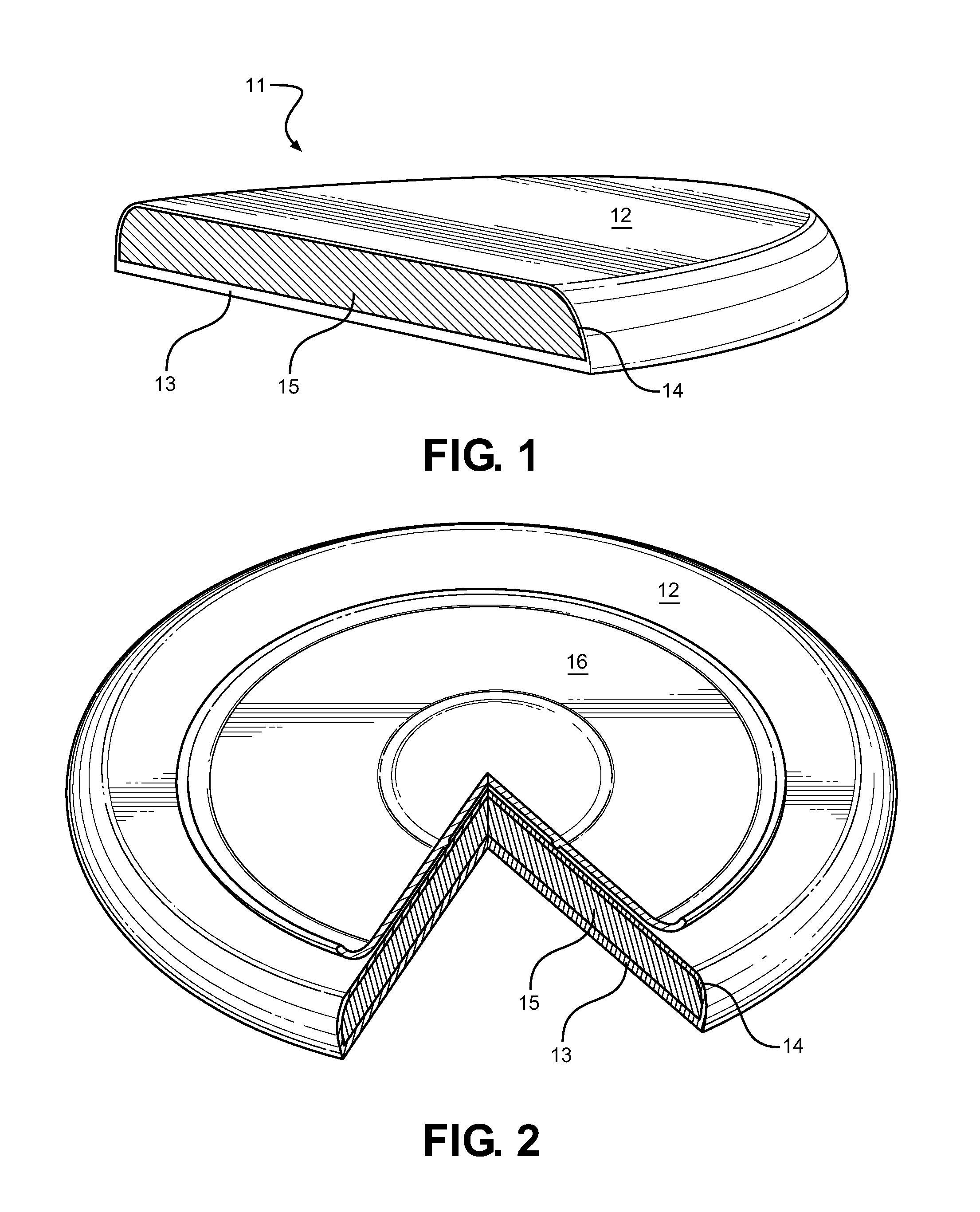
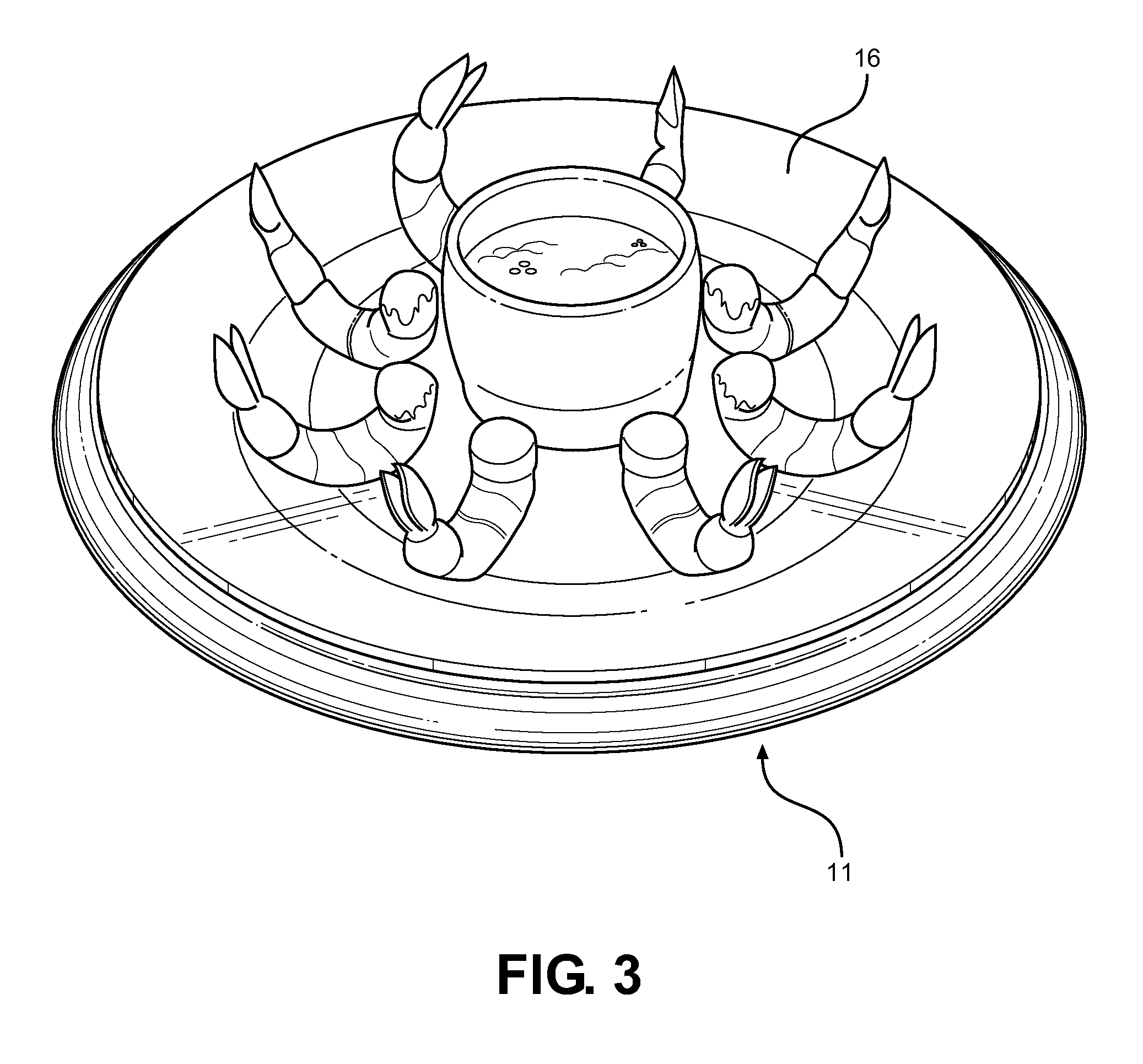
Serving Mat having a Heated or Freezable Internal Medium
InactiveUS20140042172A1Readily frozenReadily heatableUnderlaysCooking vesselsLiquid stateEngineering
Disclosed is a serving dish mat adapted to maintain the serving temperature of a supported article and further prevent damage to an underlying support surface. The mat comprises a geometric shape having a thermally insulating base surface, a thermally conductive upper surface and an internal gel-like material therebetween that is readily freezable or heated. The gel material is one of high specific heat capacity and high enthalpy of fusion that is pre-heated or frozen, after which it releases heat or draws heat through the thermally conductive upper surface for maintaining a serving dish temperature resting thereupon. The gel slowly dissipates heat when heated and absorbs considerable heat when frozen prior to returning to a liquid state. The base surface insulates the support surface from the temperature of the internal material, while a serving dish temperature is maintained over a period without active heating or cooling sources.
Owner:MCNAUL ALAN
Hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes
The hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes according to the present invention have degrees of hydrogenation of from 20 to 100%, Mooney viscosities in the range of from 10 to 150 Mooney units (ML 1+4 / 100° C.), glass transition temperatures (Tg) of ≦−57° C. and enthalpies of fusion (ΔH) of ≦30 J / g and having a microstructure witha) from 0 to 44 wt. % 1,2-vinyl-butadiene units of the formulab) from 20 to 64 wt. % 1,2-butylene units of the formulac) from 0 to 60 wt. % 1,4-butenylene units of the formulaCH2—CH═CH—CH2andd) from 0 to 60 wt. % 1,4-butylene units of the formulaCH2—CH2—CH2—CH2are outstandingly suitable for the production of rubber molded bodies of any kind, especially for the production of industrial rubber articles and of tires and tire components. The rubber molded bodies produced from the hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes according to the present invention have good resistance to ageing and good elasticity at low temperatures.
Owner:ARLANXEO DEUT GMBH
Expandable pelletized materials based on polyester
An expandable pelletized material comprisingA) a polymer matrix composed ofA1) at least 55% by weight of polyester (based on the entirety of components A1) and A2)) with a total enthalpy of fusion of up to 60 J / g, optionally of one or more melting points in the range from 100 to 300° C. and of one or more glass transition temperatures in the range from 0 to 250° C., andA2) from 0 to 45% by weight (based on the entirety of components A1) and A2)) of one or more thermoplastic polymers different from component A1);B) a physical blowing agent component, andC) optionally further additivesis suitable for producing moldable foams for use in the automobile industry, airline industry, construction industry, packaging industry, sports and leisure industry, in transport, in engineering, in lightweight construction, and / or in composite construction.
Owner:BASF AG
Composite part consisting of a film and a substrate based on an amorphous polyamide
InactiveUS20100055425A1Sufficiently abrasion-resistantSufficiently scratch-resistantSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPolyamideMaterials science
A film which comprises a layer composed of a moulding composition composed of a semicrystalline polyamide whose enthalpy of fusion is at least 8 J / g is used for production of a composite part with a substrate composed of a moulding composition composed of a substantially amorphous polyamide whose enthalpy of fusion is less than 8 J / g.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polyamide blend molding compound
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
Hot melt adhesive based on low melting point polypropylene homopolymers and methods for making and using the adhesive
ActiveUS20160230055A1Increase speedGood viscosity stabilityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesPersonal carePorous substrateEthylene Homopolymers
A hot melt adhesive for use on porous substrates, wherein the hot melt adhesive hasabout 10% to about 70% by weight of a polypropylene homopolymer having a DSC melting point of less than 100° C.;about 10% to about 60% of a first tackifying resin having a Ring & Ball Softening Point ofabout 95° C. to about 140° C.;about 0% to about 65% of a second tackifying resin that is different than the first tackifying resin;about 5% to about 50% of a plasticizer;about 1% to about 40% by weight of a secondary polymer which is either a semi crystalline polymer or wax with an enthalpy of fusion of greater than 30 Joules / gram;about 0.1% to about 5% of a stabilizer or antioxidant; wherein the components total 100% by weight of the composition, and the viscosity of the composition is equal to or less than about 20,000 centipoise (cP) at 163° C. (325° F.).
Owner:BOSTIK INC
Polymer composition for selective sintering
ActiveCN109563246AAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresSelective laser sinteringContinuous use
The present invention relates to a polymer composition for production of shaped objects via selective laser sintering wherein the polymer composition comprises a thermoplastic material having: a crystallisation half time of >= 30 s and <= 12 min at a supercooling of 50 DEG C below the peak melt temperature, wherein the crystallisation half time t1 / 2,c as determined via differential scanning calorimetry in accordance with ISO 11357-1 (2009); a glass transition temperature Tg of >= 50 DEG C as determined in accordance with ISO 11357-2 (2013); a peak melt temperature Tp,m of >= 200 DEG C as determined in accordance with ISO 11357-3 (2011), first heating run; an extrapolated first heating run melt onset temperature Tei,m of >= 5 DEG C above the extrapolated first cooling run crystallisation end temperature Tef,c as determined in accordance with ISO 11357-1 (2009), first heating and cooling run; and a degree of crystallinity of >= 10.0 % as determined according to the formula (I), wherein:D = degree of crystallinity of the thermoplastic material (%); deltaHf = enthalpy of fusion of the thermoplastic material as determined in accordance with ISO 11357-3 (2011); deltaHf,100 = enthalpy offusion of the thermoplastic material in a 100% crystalline state. Such polymer composition has a continuous use temperature of >= 100 DEG C, and a low change of molecular weight during exposure to selective laser sintering processing temperatures.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
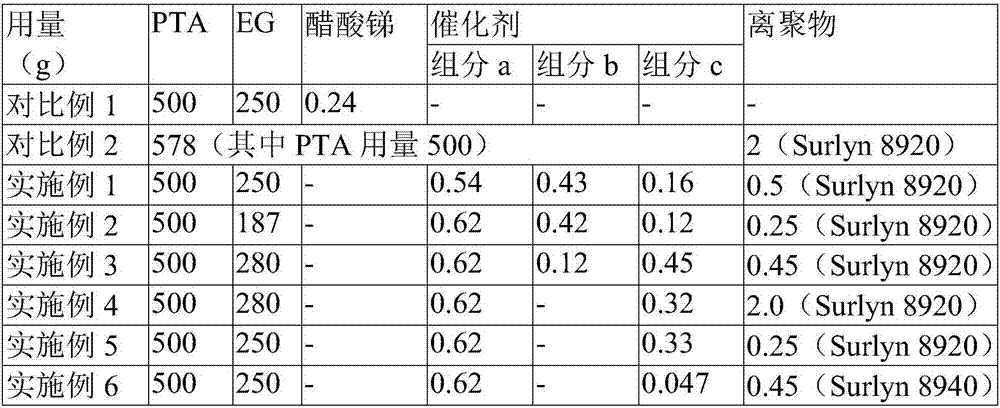
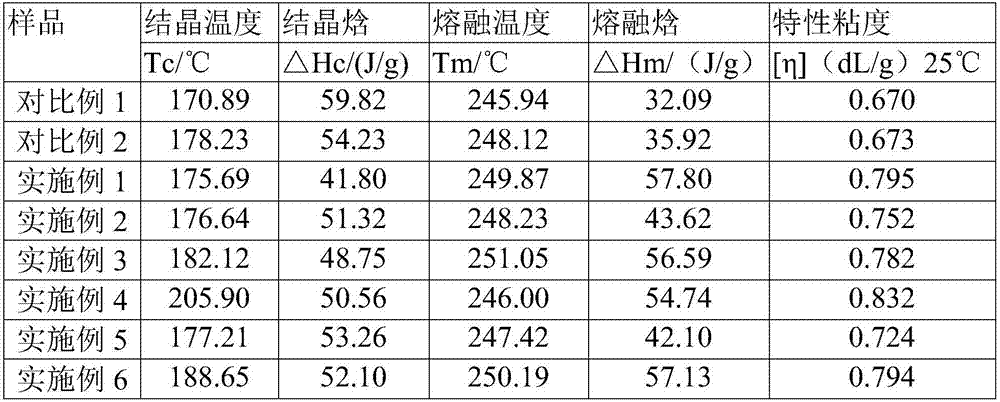
Modified polyethylene terephthalate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107987259AHigh crystallinityRaise the crystallization temperatureCrystallinityIntrinsic viscosity
The invention discloses modified polyethylene terephthalate and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) ethylene glycol, terephthalic acid and a crystallization promoter are subjected to a reaction in the presence of a catalyst, and a reaction product is obtained; (2) excess unreacted ethylene glycol is removed from the reaction product, polycondensation is performed under the polycondensation reaction condition, and modified polyethylene terephthalate is obtained, wherein the crystallization promoter is selected from an ionomer, and the non-ionic skeleton chain of the ionomer is an ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer. According to the method, the crystallization rate (crystallization temperature) and crystallinity (enthalpy of fusion) of polyethylene terephthalate can be comprehensively improved without decreasing the intrinsic viscosity (molecular weight) of the polymer.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Thermally adhesive flexible polylactic acid resin composition
ActiveUS10087282B2Lower melting temperatureExcellent film processabilityHeat-activated film/foil adhesivesPolyolGlass transition
The present invention relates to a polylactic acid resin composition which has a low glass transition temperature, fusion temperature, and enthalpy of fusion, can be crystallized under commercially meaningful processing conditions, has good film processability such as extrusion properties, has excellent storage stability, and is highly biodegradable. The polylactic acid resin composition comprises a block copolymer comprising a hard segment and a soft segment, the hard segment comprising polylactic acid repeat units, and the soft segment comprising polyurethane polyol repeat units which have polyether-based polyol repeat units linearly connected via a urethane bond, wherein the soft segment is contained by 5% to 35% by weight based on the weight of the block copolymer, and the polylactic acid repeat units include poly(L-lactic acid) repeat units and poly(D-lactic acid) repeat units by a molar ratio of 94:6 to 88:12.
Owner:SK CHEM CO LTD
Process for producing plastic rods
InactiveUS20120232531A1Lower levelEasy to processLayered productsFilament/thread formingThermoplasticCrystallization temperature
A process for producing a plastic rod, in particular round rods, suitable for machining is provided. The process includes extruding a plastic profile of a first plastic molding composition which forms the outermost layer of the plastic rod, and inserting a second plastic molding composition as a rod core into the profile within a calibrator downstream of the extruder. The first plastic molding composition contains at least 50% by weight of a semicrystalline thermoplastic and the first plastics moulding composition has the following properties: a) crystallite melting point Tm in accordance with ISO 11357 of at least 170° C., b) crystallization temperature Tk in accordance with ISO 11357 of at most 70 K below T. and c) enthalpy of fusion AH in accordance with ISO 11357 of at least 20 J / g.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Hydrogenated copolymers from non-substituted and substituted conjugated dienes
The random, hydrogenated copolymers according to the present invention of unsubstituted conjugated dienes and substituted conjugated dienes, having a glass transition temperature of <=-60 DEG C, an enthalpy of fusion of <=100 J / g and a content of residual double bonds in the range from 0 to 80%, are suitable for the production of rubber moldings of all kinds which have good resistance to ageing and high resilience at low temperatures. In particular, various tire components and industrial rubber articles may be mentioned as rubber moldings. The copolymers are also suitable for the rubber modification of brittle thermoplastics.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
Resin composition and use thereof
ActiveUS11098229B2Increase heat storageGood molding effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat-exchange elementsPolymer scienceChemical compound
A resin composition contains a polymer whose enthalpy of fusion (ΔH) observed within a temperature range of 10° C. or higher and lower than 60° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more; and a low-molecular-weight compound whose enthalpy of fusion (ΔH) observed within a temperature range of 0° C. or higher and lower than 100° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more and whose molecular weight is 2000 or lower. A content of the low-molecular-weight compound is 3 parts by weight to 1000 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the total amount of polymer components contained in the resin composition except the low-molecular-weight compound.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes
The hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes according to the present invention have degrees of hydrogenation of from 20 to 100%, Mooney viscosities in the range of from 10 to 150 Mooney units (ML 1+4 / 100° C.), glass transition temperatures (Tg) of ≦−57° C. and enthalpies of fusion (ΔH) of ≦30 J / g and having a microstructure with a) from 0 to 44 wt. % 1,2-vinyl-butadiene units of the formula b) from 20 to 64 wt. % 1,2-butylene units of the formula c) from 0 to 60 wt. % 1,4-butenylene units of the formula and d) from 0 to 60 wt. % 1,4-butylene units of the formula are outstandingly suitable for the production of rubber molded bodies of any kind, especially for the production of industrial rubber articles and of tires and tire components. The rubber molded bodies produced from the hydrogenated vinyl-polybutadienes according to the present invention have good resistance to ageing and good elasticity at low temperatures.
Owner:ARLANXEO DEUT GMBH
Resin composition and use thereof
ActiveUS20190270923A1Increase heat storageGood molding effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat-exchange elementsPolymerEnthalpy of fusion
A resin composition contains a polymer whose enthalpy of fusion (ΔH) observed within a temperature range of 10° C. or higher and lower than 60° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more; and a low-molecular-weight compound whose enthalpy of fusion (ΔH) observed within a temperature range of 0° C. or higher and lower than 100° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more and whose molecular weight is 2000 or lower. A content of the low-molecular-weight compound is 3 parts by weight to 1000 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the total amount of polymer components contained in the resin composition except the low-molecular-weight compound.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Nursing and / or make-up cosmetic composition structured with silicone polymer
The invention refers to a nursing and / or make-up cosmetic composition structured with a silicone polymer, comprising a liquid continuous fatty phase structured with at least one structuring polymer having a weight average molecular weight of 500-500000 containing at least one moiety comprising at least one polyorganosiloxane group consisting of 1-1000 organosiloxane units in the chain of the moiety or in the form of a graft, and at least two groups capable of establishing hydrogen interactions consisting of ester, amide, sulfonamide, carbamate, thiocarbamate, urea, urethane, thiourea, oxamido, guanidino and / or biguanidino groups. The polymer is solid at room temperature and soluble in the liquid fatty phase at 25-250 degrees C. The liquid fatty phase comprises at least one compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer. The composition contains at least one pigment. The liquid fatty phase, the structuring polymer and the compound capable of reducing the enthalpy of fusion of the structuring polymer form a medium.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Polymer composition for selective sintering
ActiveCN109563246BAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer scienceSelective laser sintering
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Modified polyethylene terephthalate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107987258AHigh crystallinityRaise the crystallization temperaturePolyethylene terephthalate glycolCrystallinity
The invention discloses modified polyethylene terephthalate and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) ethylene glycol, terephthalic acid and a crystallization promoter are subjected to a reaction in the presence of a catalyst, and a reaction product is obtained; (2) excess unreacted ethylene glycol is removed from the reaction product, polycondensation is performed under the polycondensation reaction condition, and modified polyethylene terephthalate is obtained, wherein the crystallization promoter is selected from polyvinyl acetal. According to the method, the crystallization rate (crystallization temperature) and crystallinity (enthalpy of fusion) of polyethylene terephthalate can be comprehensively improved without decreasing the intrinsic viscosity (molecular weight) of the polymer.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Polypropylene-based composite material
ActiveCN113795524AHigh mechanical strengthImproved impact strength propertiesPolymer sciencePolypropylene
The present invention relates to a polypropylene-based composite material comprising: (A) polypropylene; and (B) an olefin-based polymer satisfying the requirements of: (1) a melt index (MI, 190 DEG C and 2.16 kg load conditions) of 0.1-10.0 g / 10 min; (2) a melting temperature of 20-70 DEG C as measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC); and (3) high-temperature melting peaks being confirmed at 75-150 DEG C, as measured by a differential scanning calorimetry precision measurement method (SSA), in which the sum of melting enthalpies, DeltaH (75), in the corresponding region is 1.0 J / g or more. The polypropylene-based composite material of the present invention can exhibit excellent impact strength.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Resin composition and use thereof
ActiveUS20190211178A1Suppress temperature elevationAvoid temperature riseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialsHeat sink
Provided is a resin composition from which a heat dissipation sheet having high effect to suppress temperature elevation due to heat generated by electronic parts (elements) can be obtained. Specifically provided is a resin composition containing: a polymer (1) whose enthalpy of fusion observed within a temperature range of 10° C. or higher and lower than 60° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more; and a thermally conductive material (3) whose thermal conductivity is 1 W / (m·K) or higher, wherein the content of the thermally conductive material (3) is 1 part by weight or more and 80 parts by weight or less, with respect to 100 parts by weight of the total amount of polymer components contained in the resin composition.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Resin composition and use thereof
ActiveUS10920034B2Avoid temperature riseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceConductive materials
Provided is a resin composition from which a heat dissipation sheet having high effect to suppress temperature elevation due to heat generated by electronic parts (elements) can be obtained. Specifically provided is a resin composition containing: a polymer (1) whose enthalpy of fusion observed within a temperature range of 10° C. or higher and lower than 60° C. in differential scanning calorimetry is 30 J / g or more; and a thermally conductive material (3) whose thermal conductivity is 1 W / (m·K) or higher, wherein the content of the thermally conductive material (3) is 1 part by weight or more and 80 parts by weight or less, with respect to 100 parts by weight of the total amount of polymer components contained in the resin composition.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com