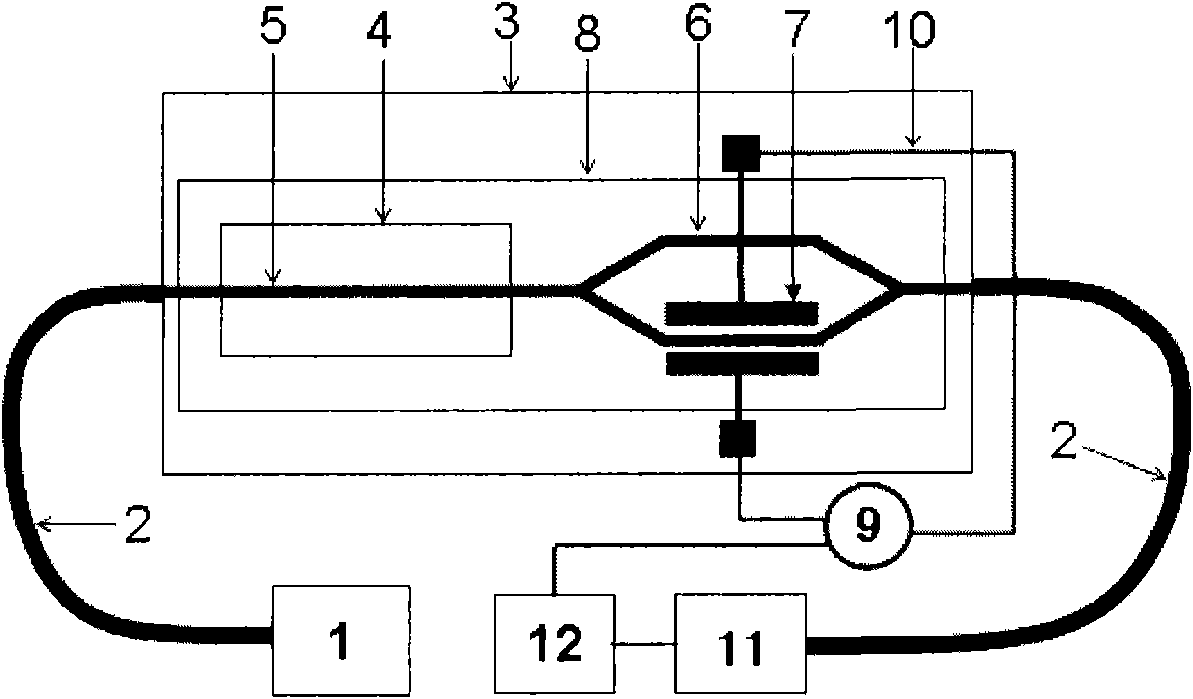
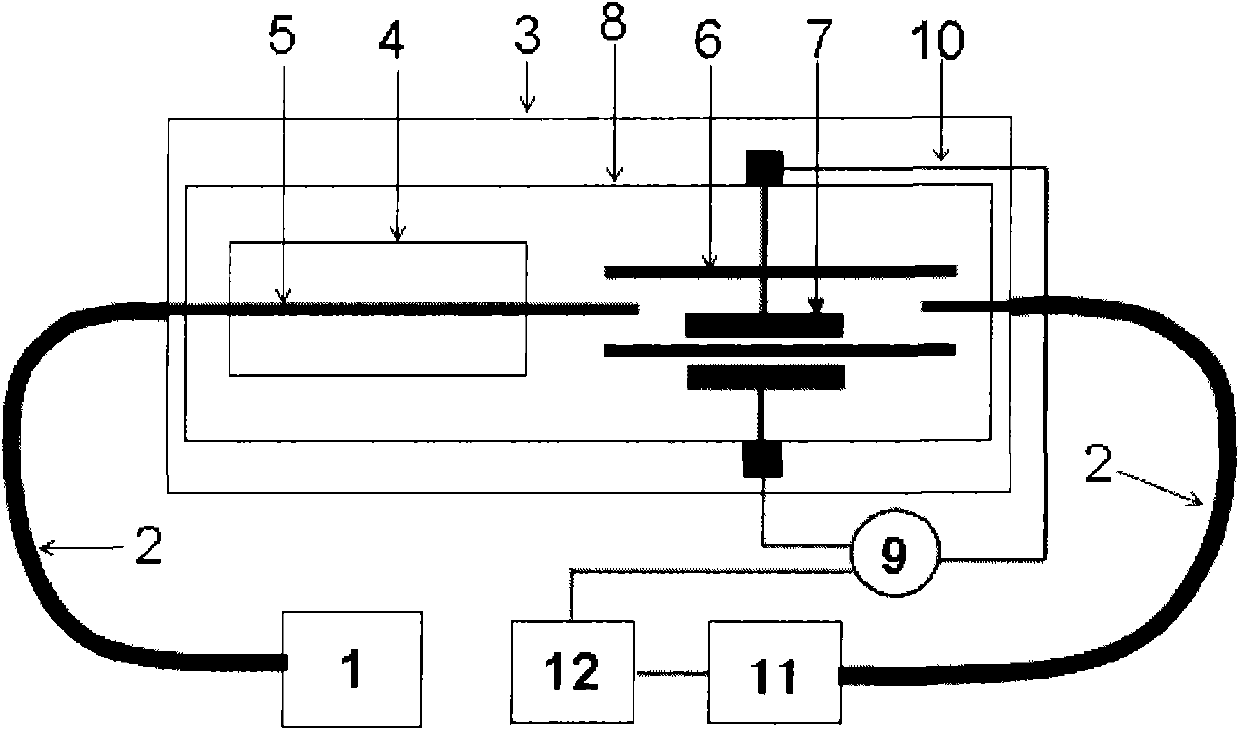
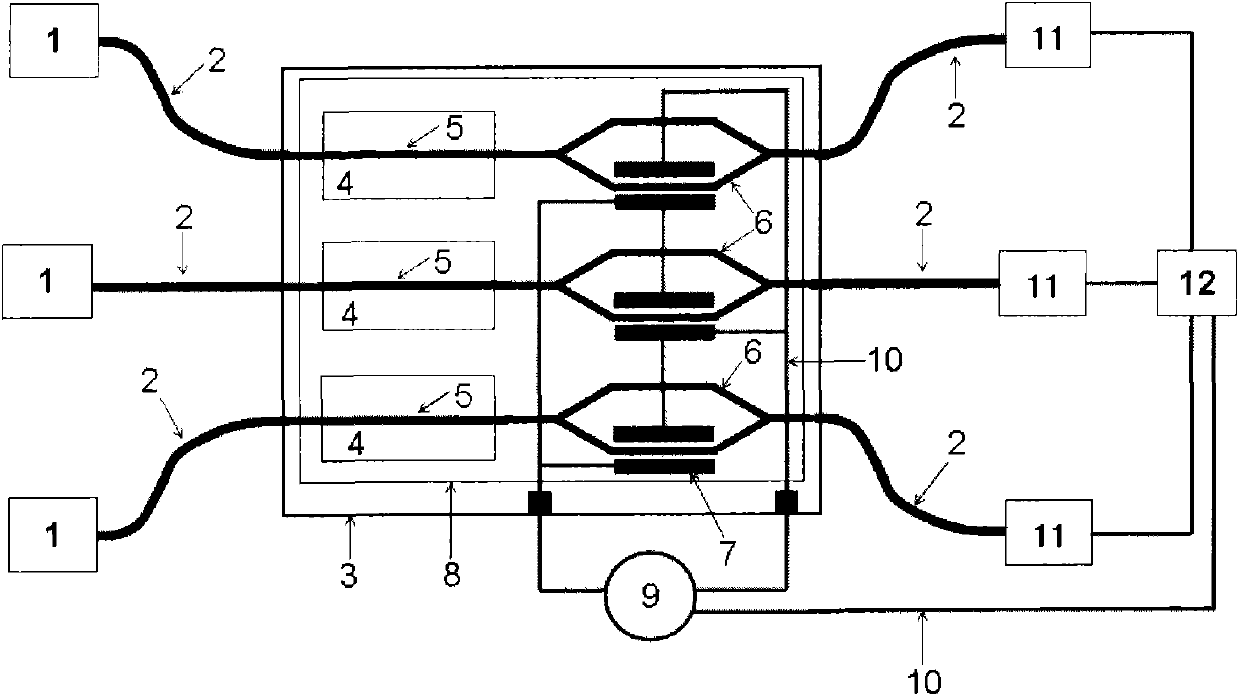
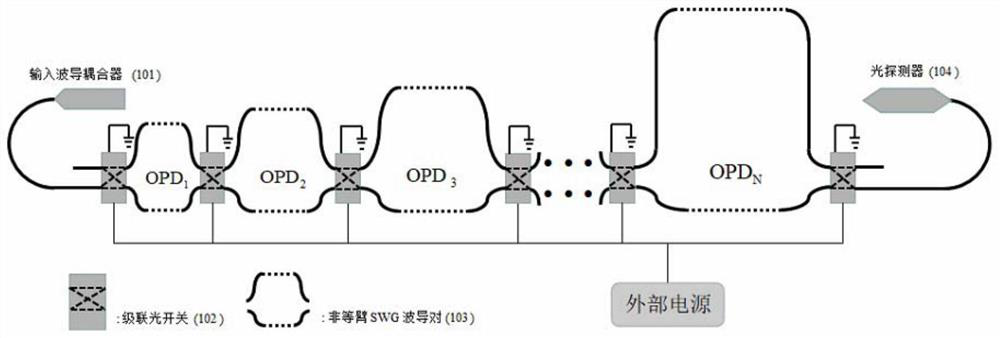
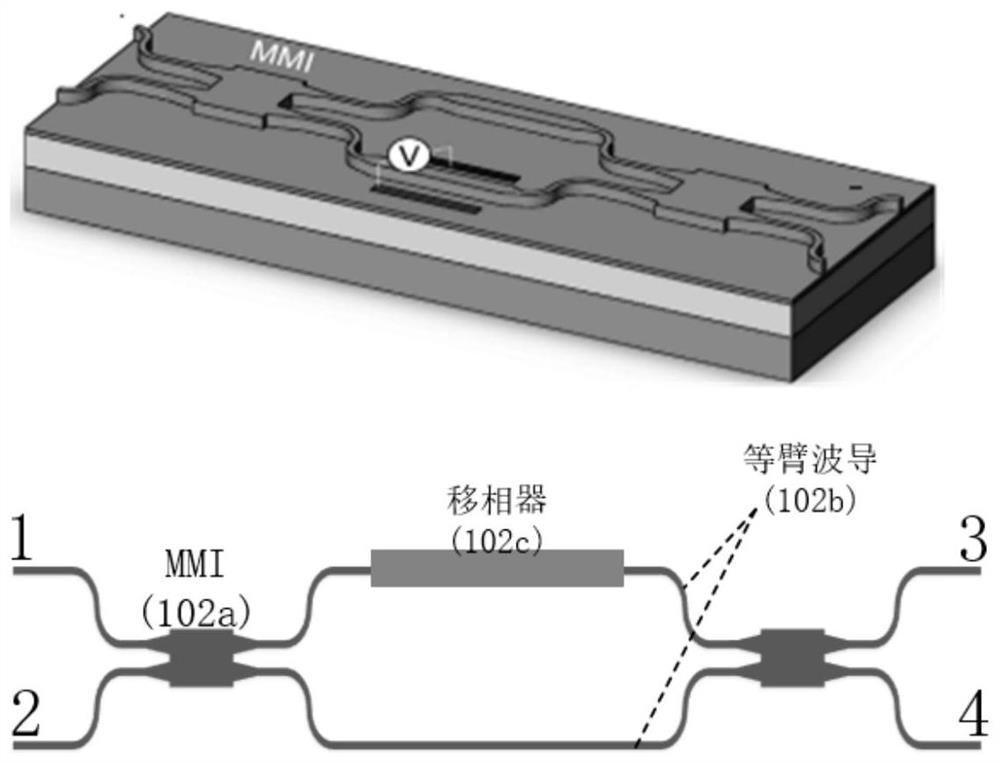
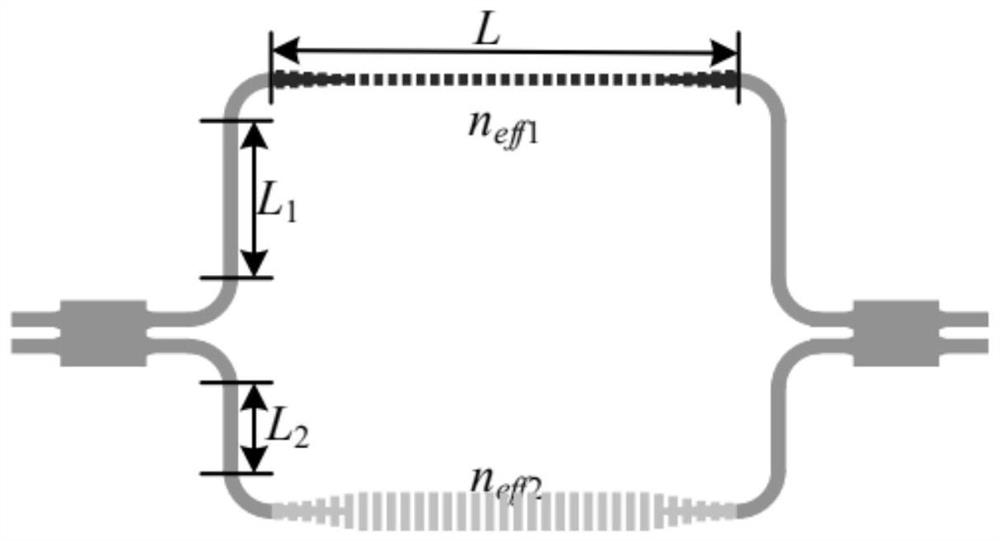
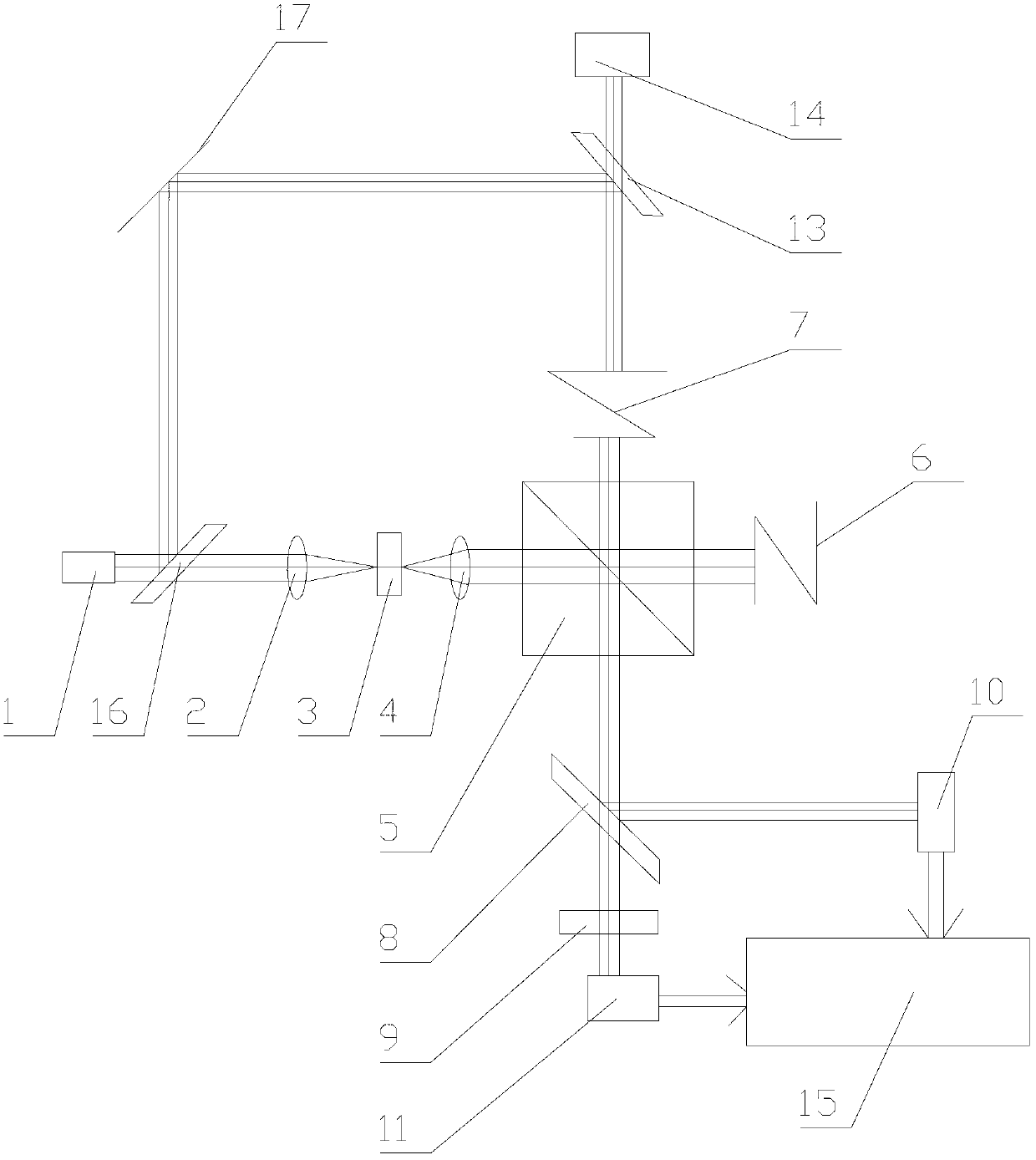
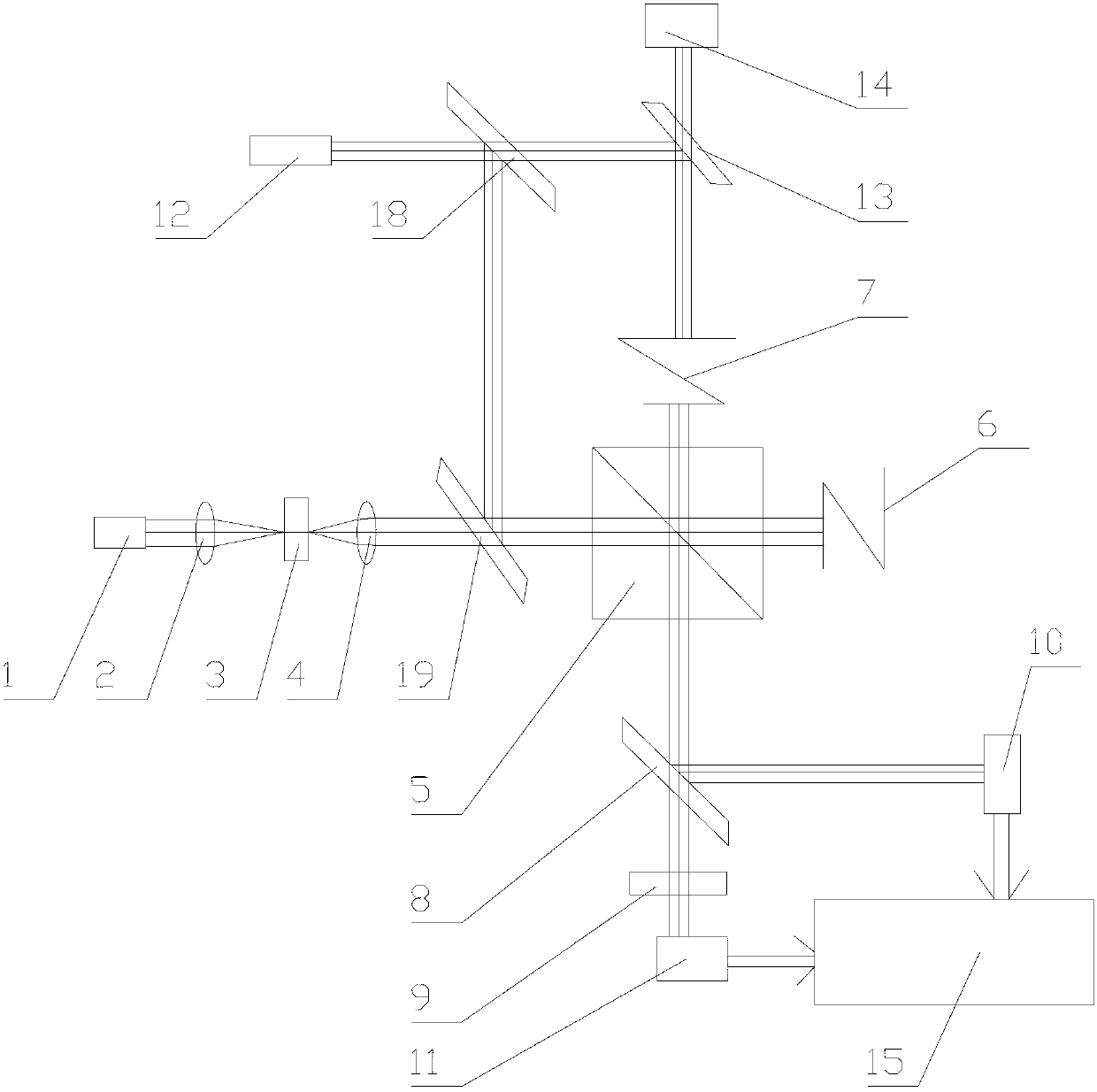
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Fourier transform spectrometers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
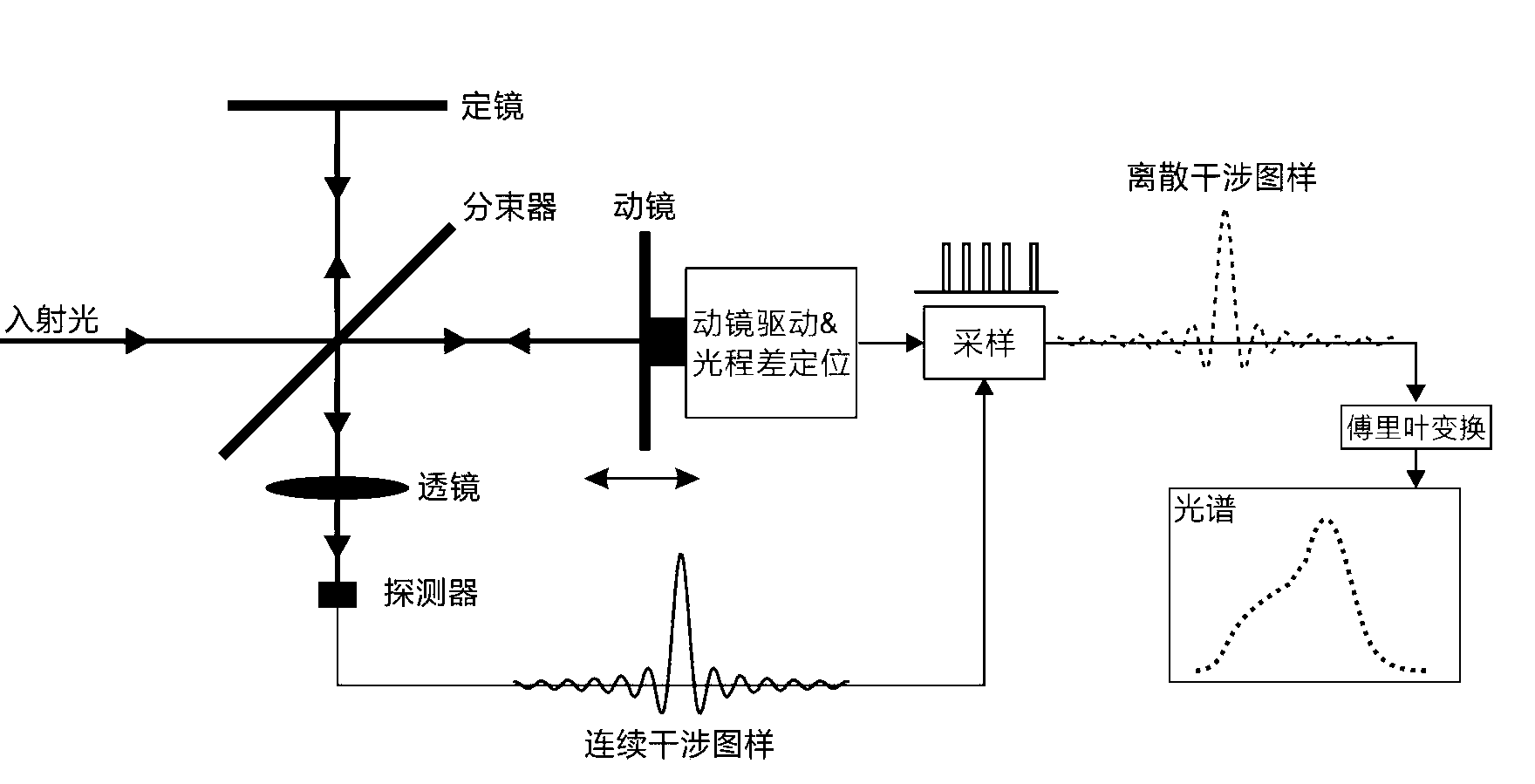
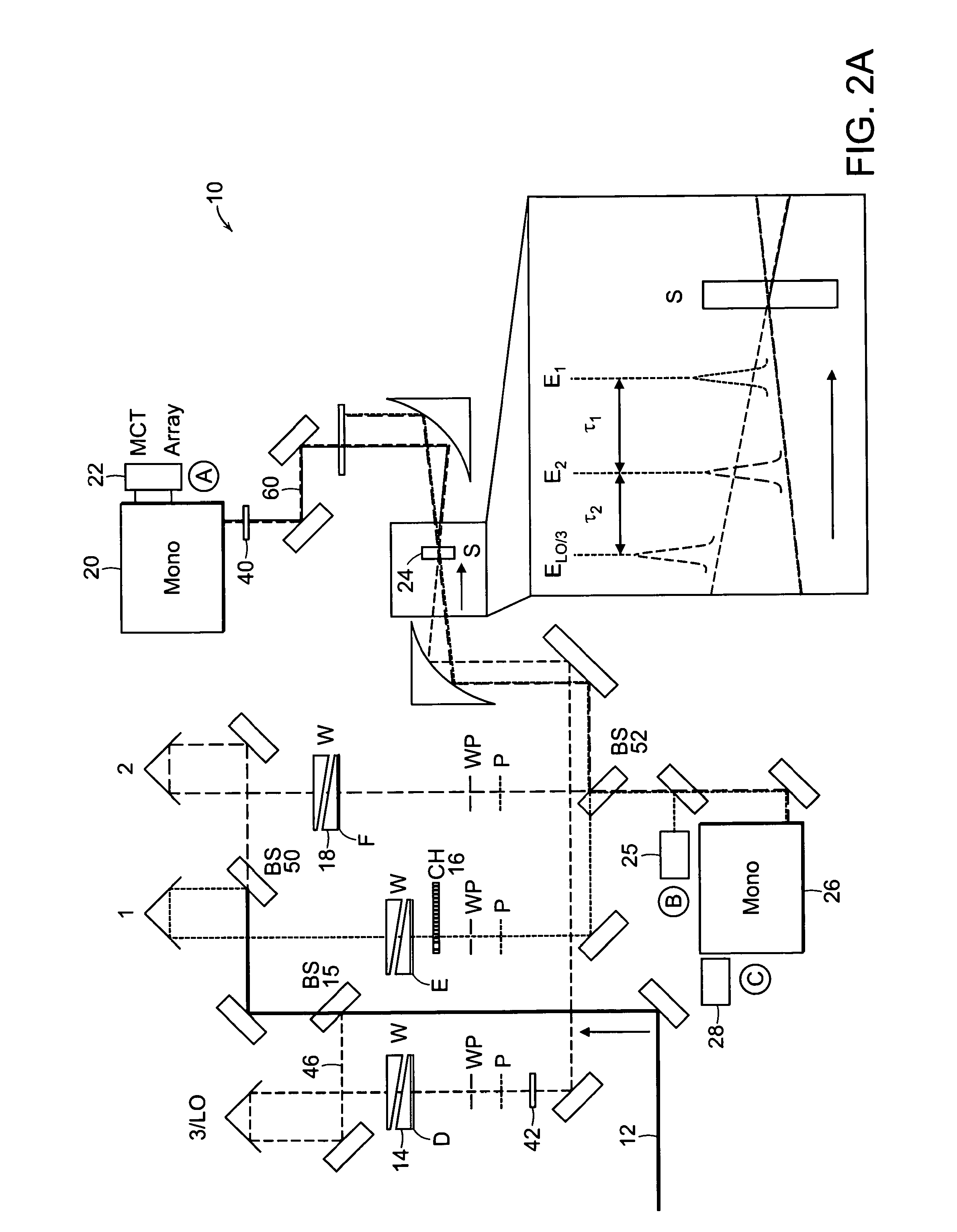
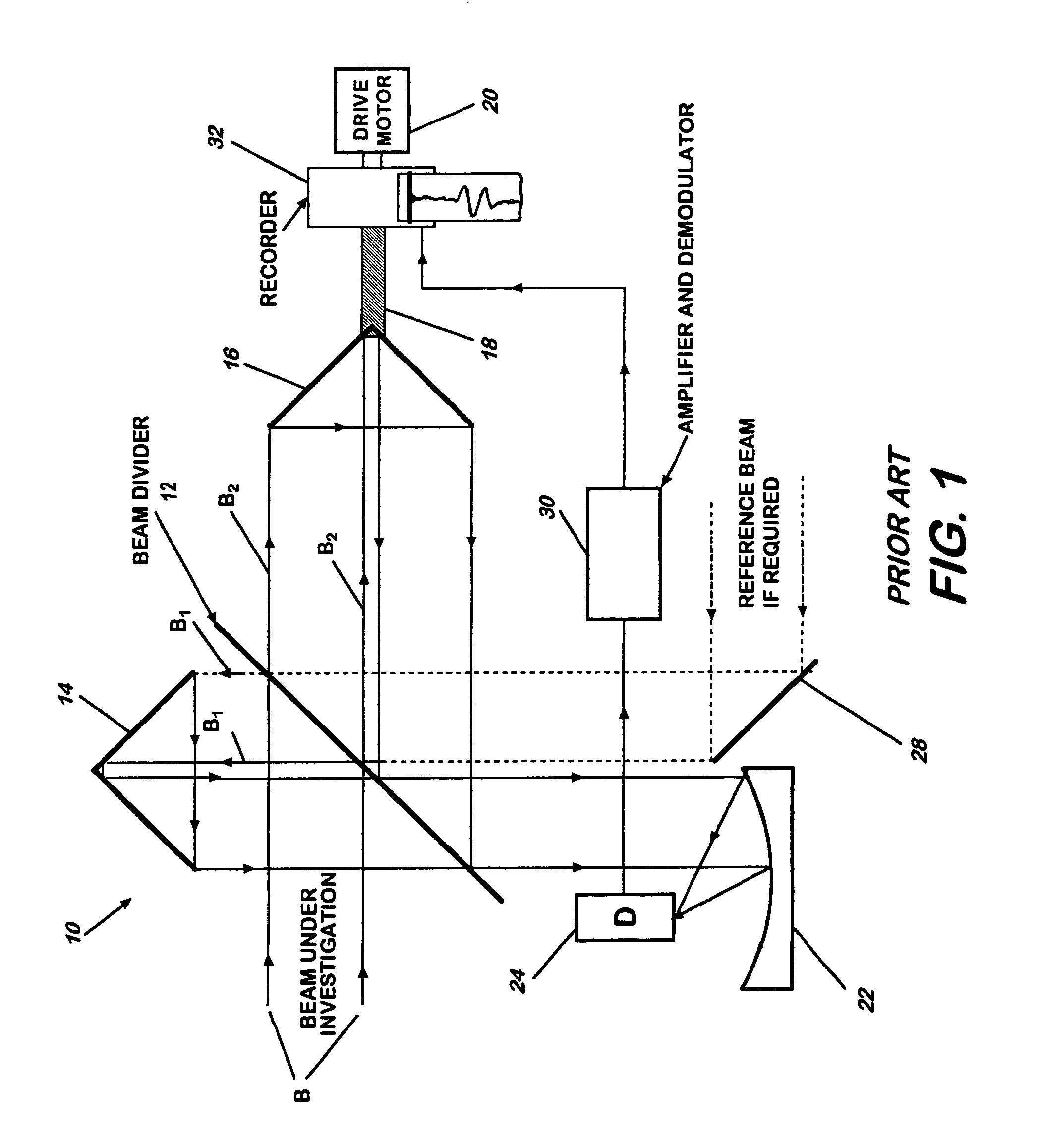
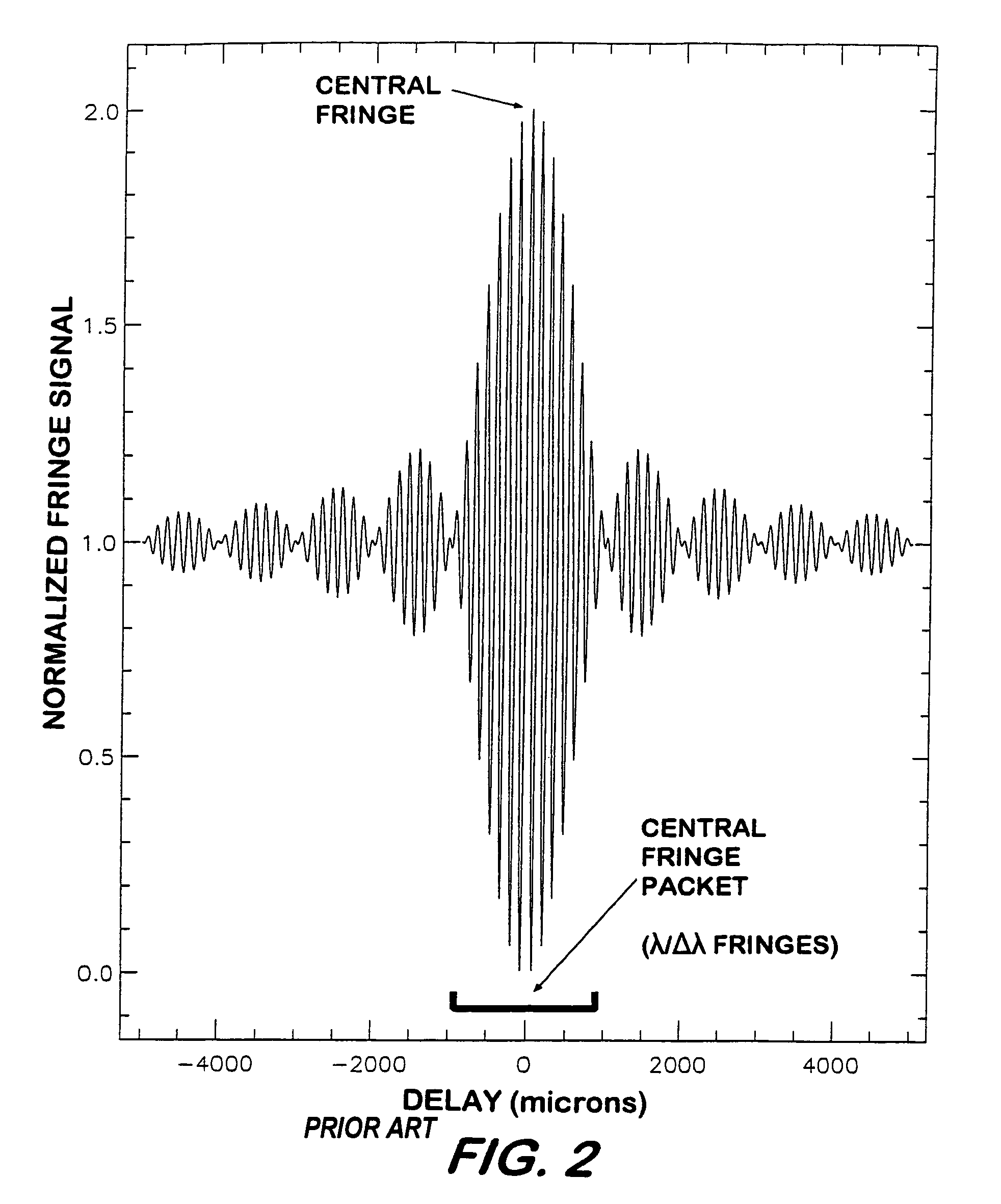
Fourier Transform Spectrometer. A Fourier transform spectrometer (abbreviated FTS) is a Michelson interferometer with a movable mirror. By scanning the movable mirror over some distance, an interference pattern is produced that encodes the spectrum of the source (in fact, it turns out to be its Fourier transform ).
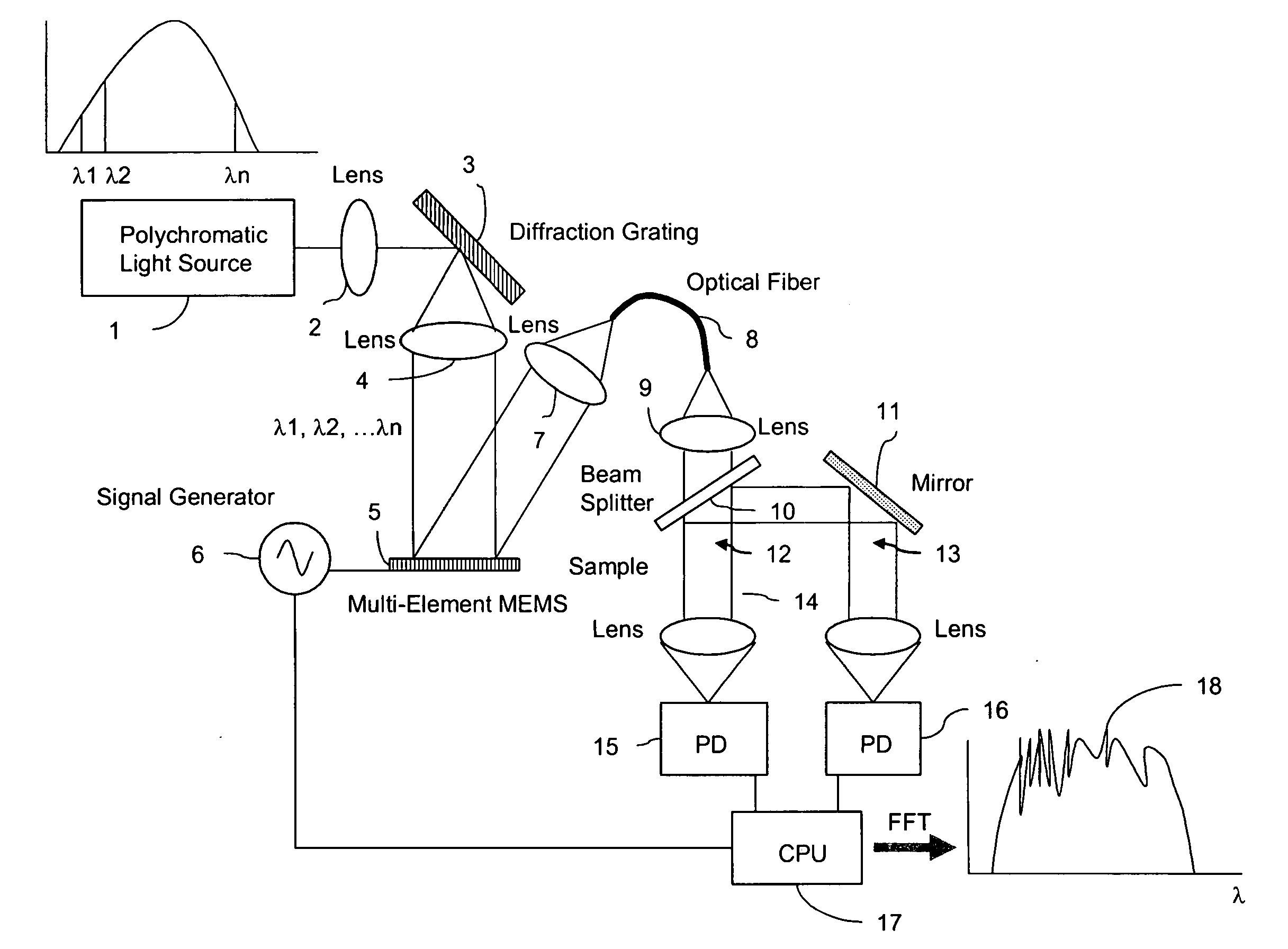
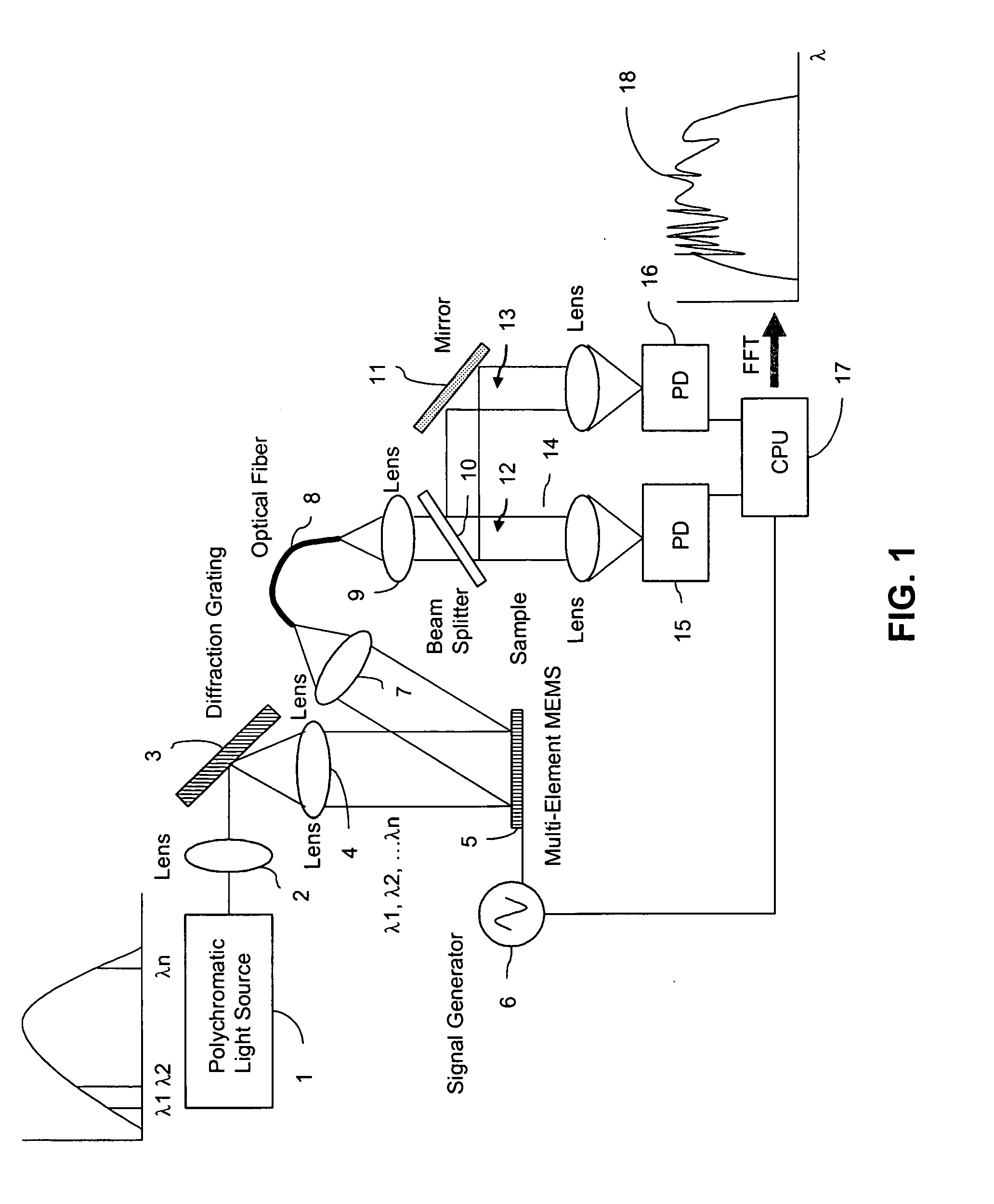
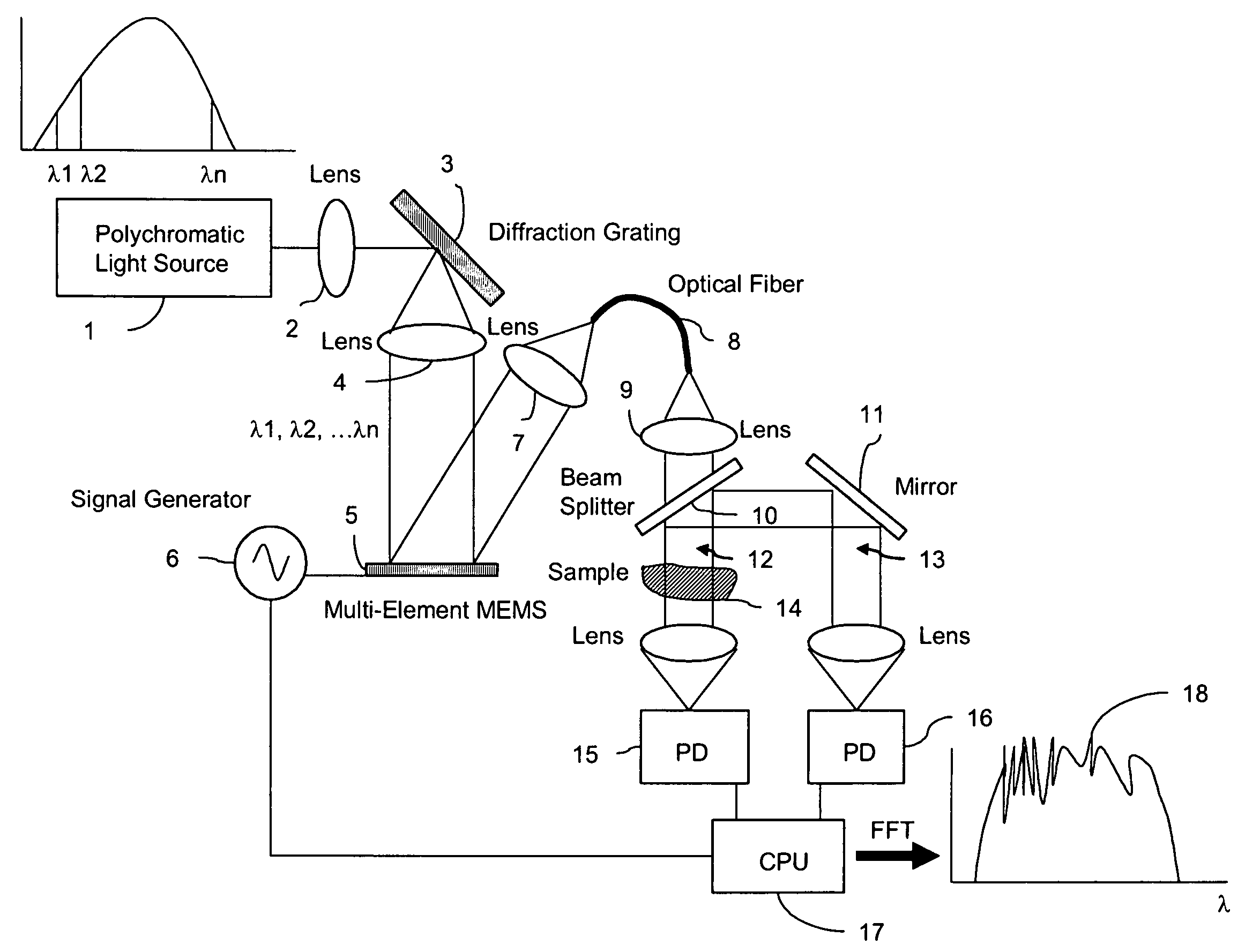
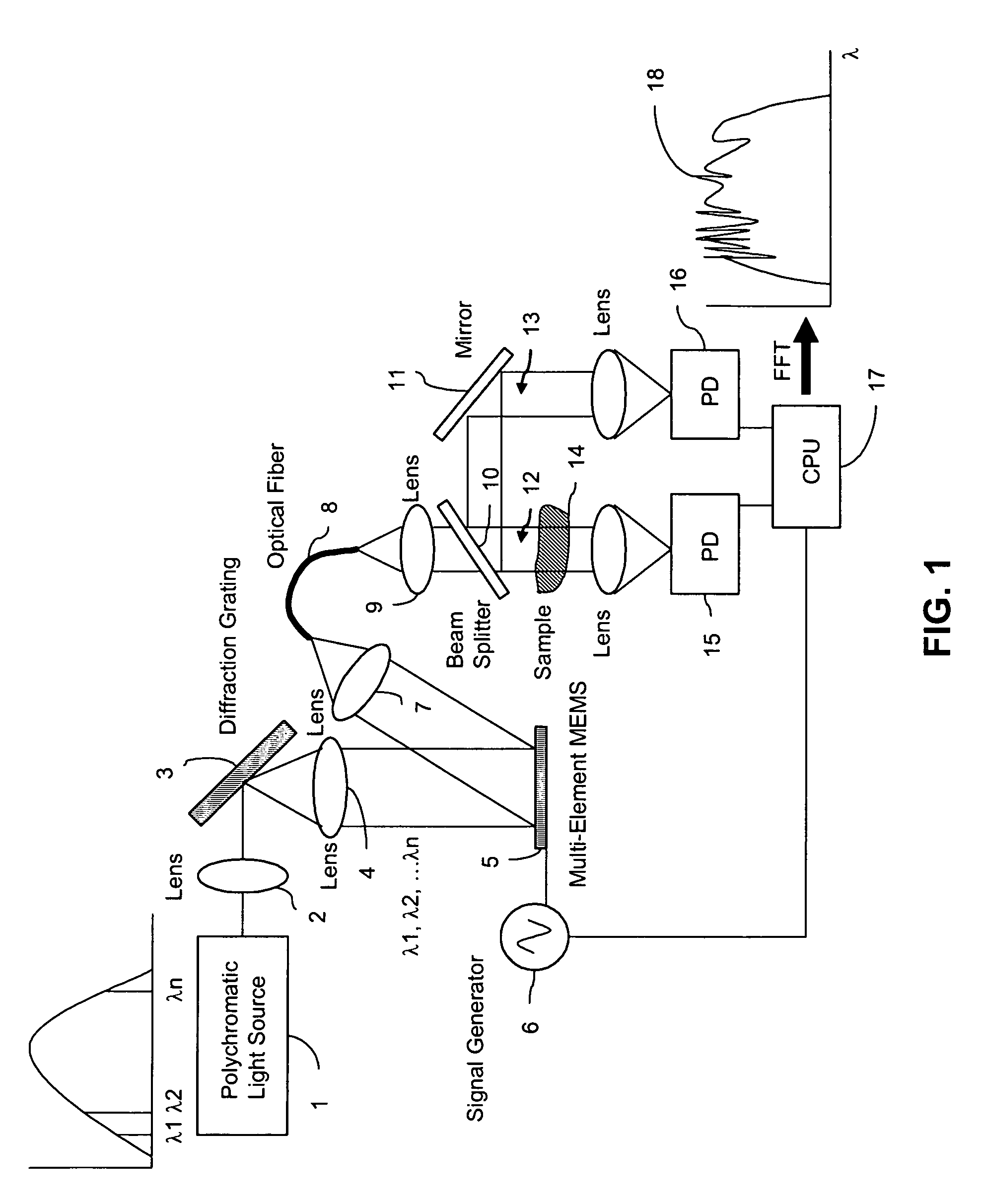
Fourier transform spectrometer apparatus using multi-element mems
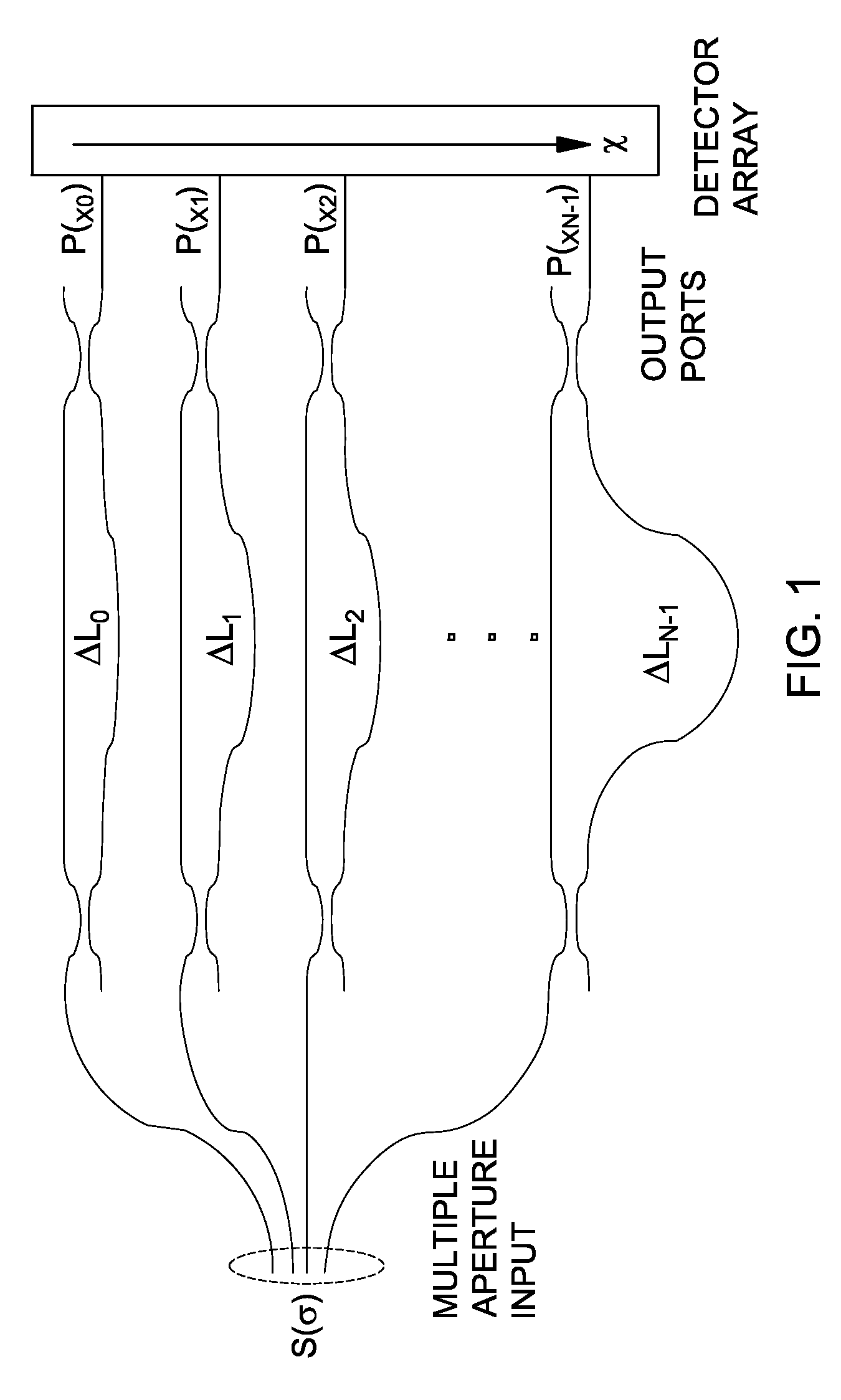
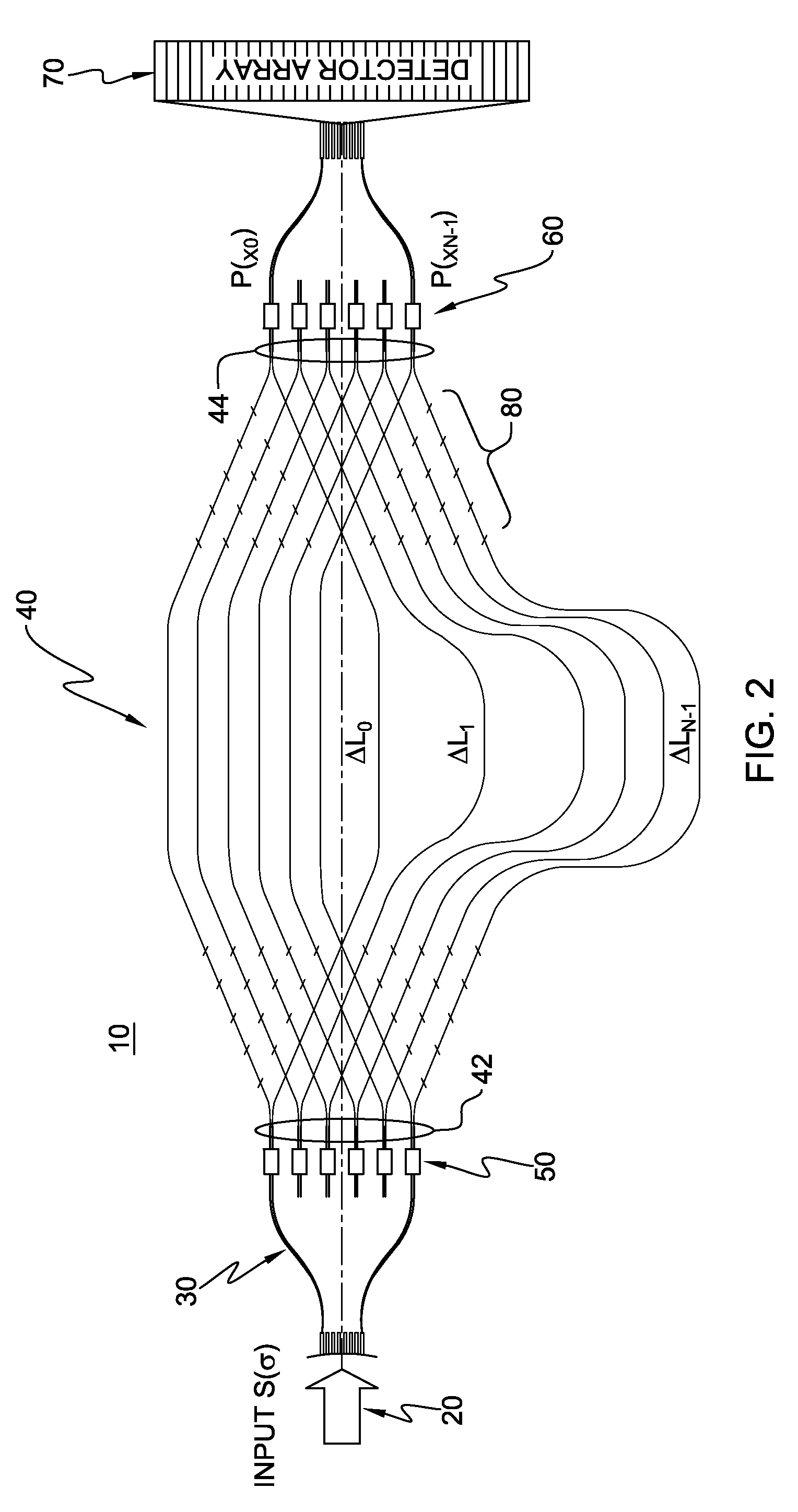
InactiveUS20050185179A1Low costHigh enough speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A Fourier Transform (FT) spectrometer apparatus uses multi-element MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) or D-MEMS (Diffractive Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) devices. A polychromatic light source is first diffracted or refracted by a dispersive component such as a grating or prism. The dispersed beam is intersected by a multi-element MEMS apparatus. The MEMS apparatus encodes each spectral component thereof with different time varying modulation through corresponding MEMS element. The light radiation is then spectrally recombined as a single beam. The beam is further split into to a reference beam and a probe beam. The probe light is directed to a sample and then the transmitted or reflected light is collected. Both the reference beam and probe beam are detected by a photo-detector. The detected time varying signal is analyzed by Fourier transformation to resolve the spectral components of the sample under measurement.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
Fourier Transform spectrometer apparatus using multi-element MEMS
InactiveUS7265830B2Simple wayNo noiseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingFourier transform on finite groups
A Fourier Transform (FT) spectrometer apparatus uses multi-element MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) or D-MEMS (Diffractive Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) devices. A polychromatic light source is first diffracted or refracted by a dispersive component such as a grating or prism. The dispersed beam is intersected by a multi-element MEMS apparatus. The MEMS apparatus encodes each spectral component thereof with different time varying modulation through corresponding MEMS element. The light radiation is then spectrally recombined as a single beam. The beam is further split into to a reference beam and a probe beam. The probe light is directed to a sample and then the transmitted or reflected light is collected. Both the reference beam and probe beam are detected by a photo-detector. The detected time varying signal is analyzed by Fourier transformation to resolve the spectral components of the sample under measurement.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
Miniature fourier transform spectrometer based on modulation
ActiveCN101251484ARealize spatial modulationIncrease luminous fluxPhase-affecting property measurementsBeam splitterLight beam
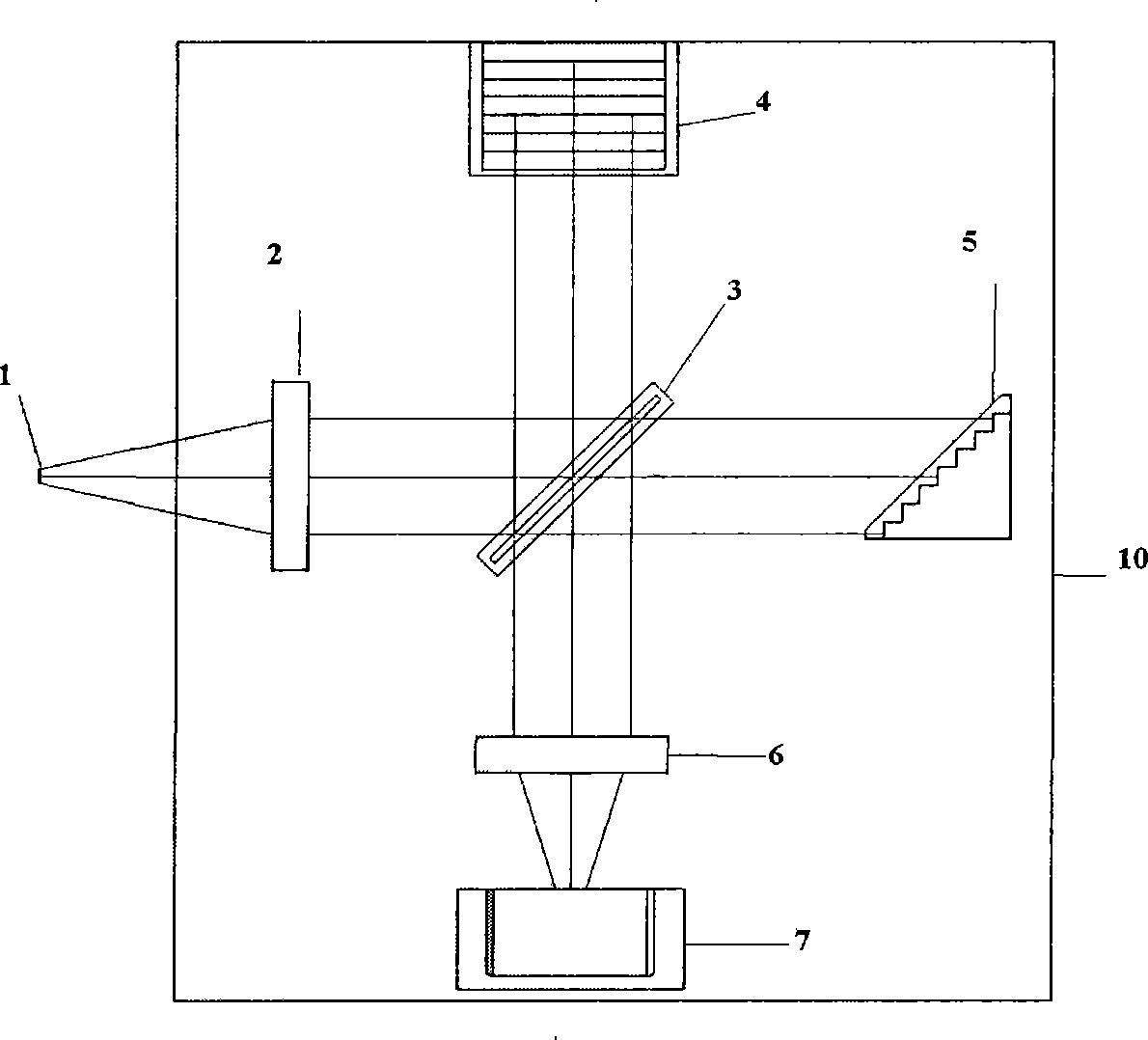
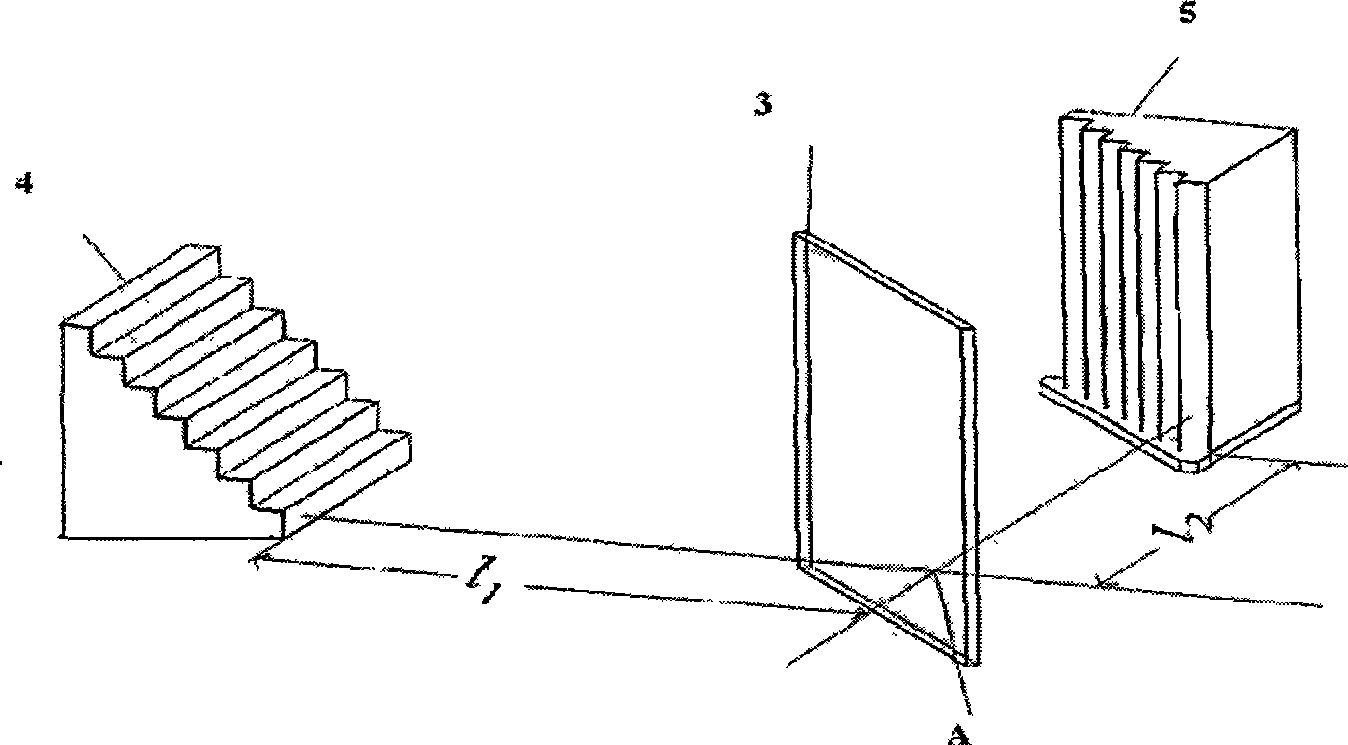
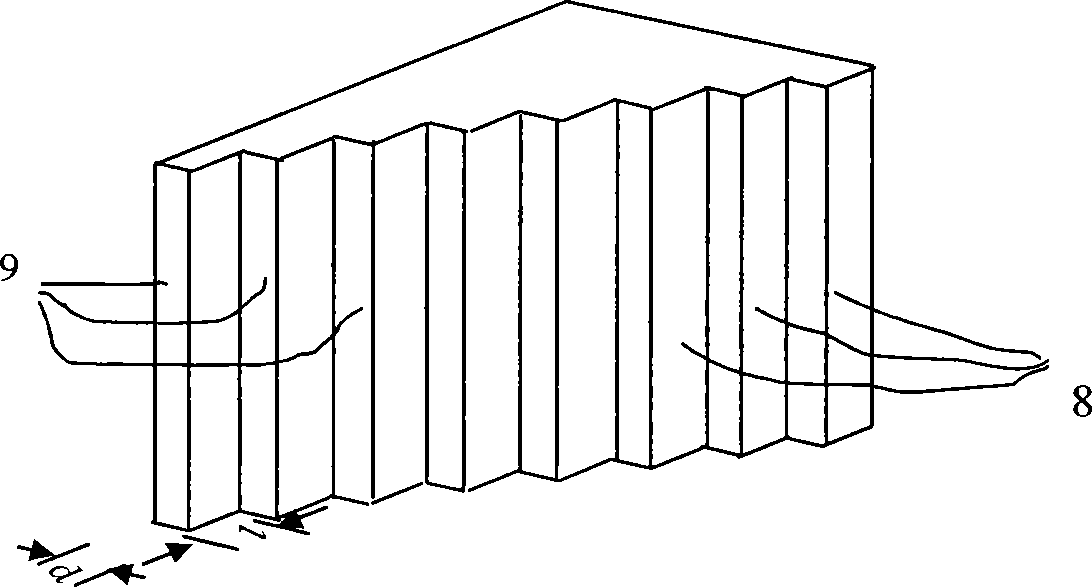
The invention belongs to the spectrometer technical field, in particular relating to a miniature Fourier transform spectrometer based on modulation, mainly comprising a collimation system, a beam splitting system and a detection receiving system, wherein, light beams which are transmitted by a light source to be detected are collimated by the collimation system and then incident upon a beam splitter which divides incident light into two bundles of coherent light with equal intensity; one bundle of the coherent light is reflected by the beam splitter, incident upon a second reflector and then returns back to the beam splitter after reflection; the other bundle of the coherent light is incident upon a first step mirror and returns back to the beam splitter after reflection; a plurality of localization interference fringes are formed by interference of light which are reflected on different positions of the second reflector and the first step mirror on different positions of the space of the detection receiving system. The miniature Fourier transform spectrometer has the advantages of high luminous flux, high resolution, good repeatability, reliable operation, good measuring real-time performance and so on, realizes simultaneous sampling of all levels on the basis of removing a laser reference interferometer and can be widely applied to various spectrum measurements like light sources and so on.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fourier transform spectrometer and fourier transform spectroscopic method
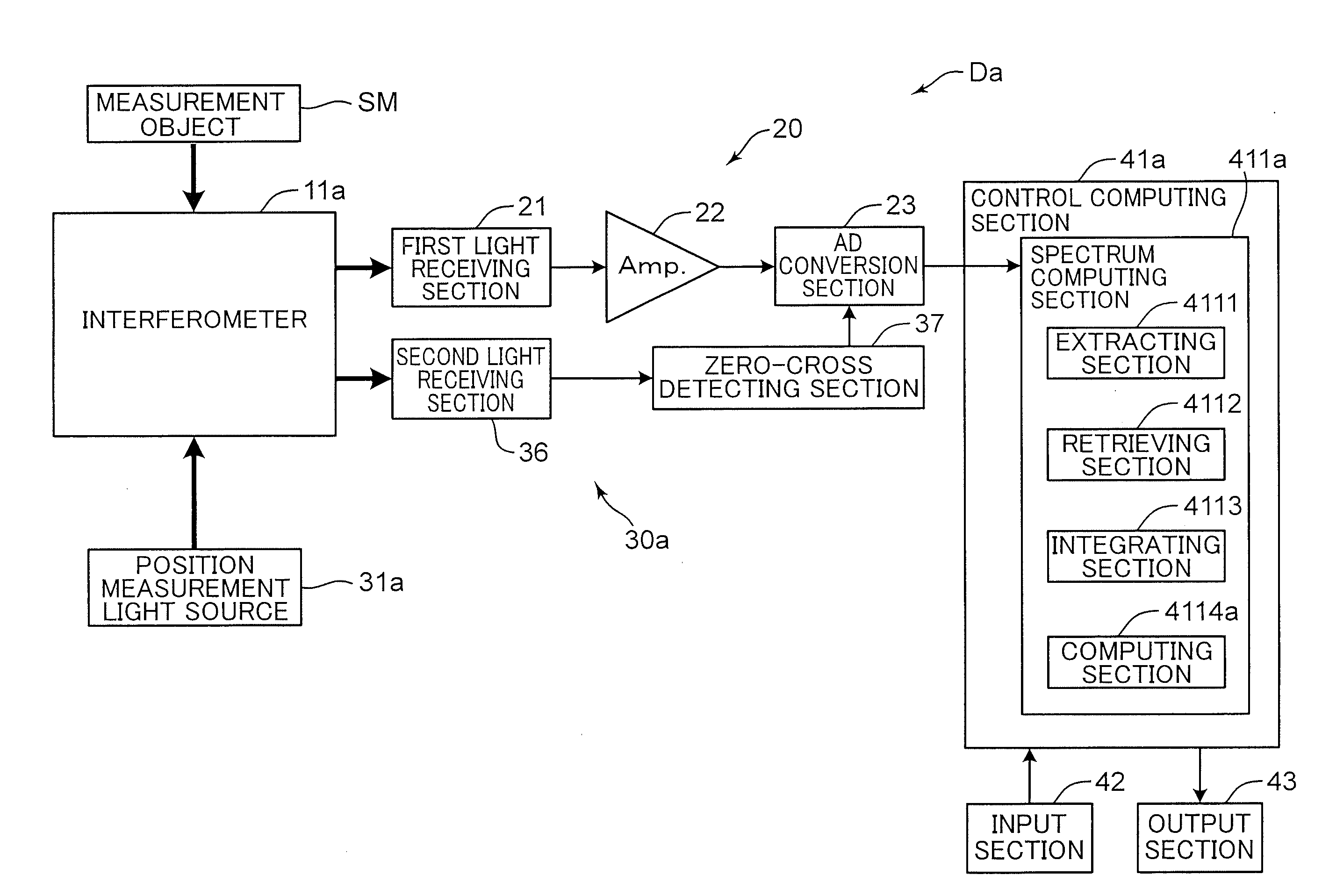
InactiveUS20140022546A1Appropriately extractedAppropriately integrating the interferogramsRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFourier transform spectrometersPhysics
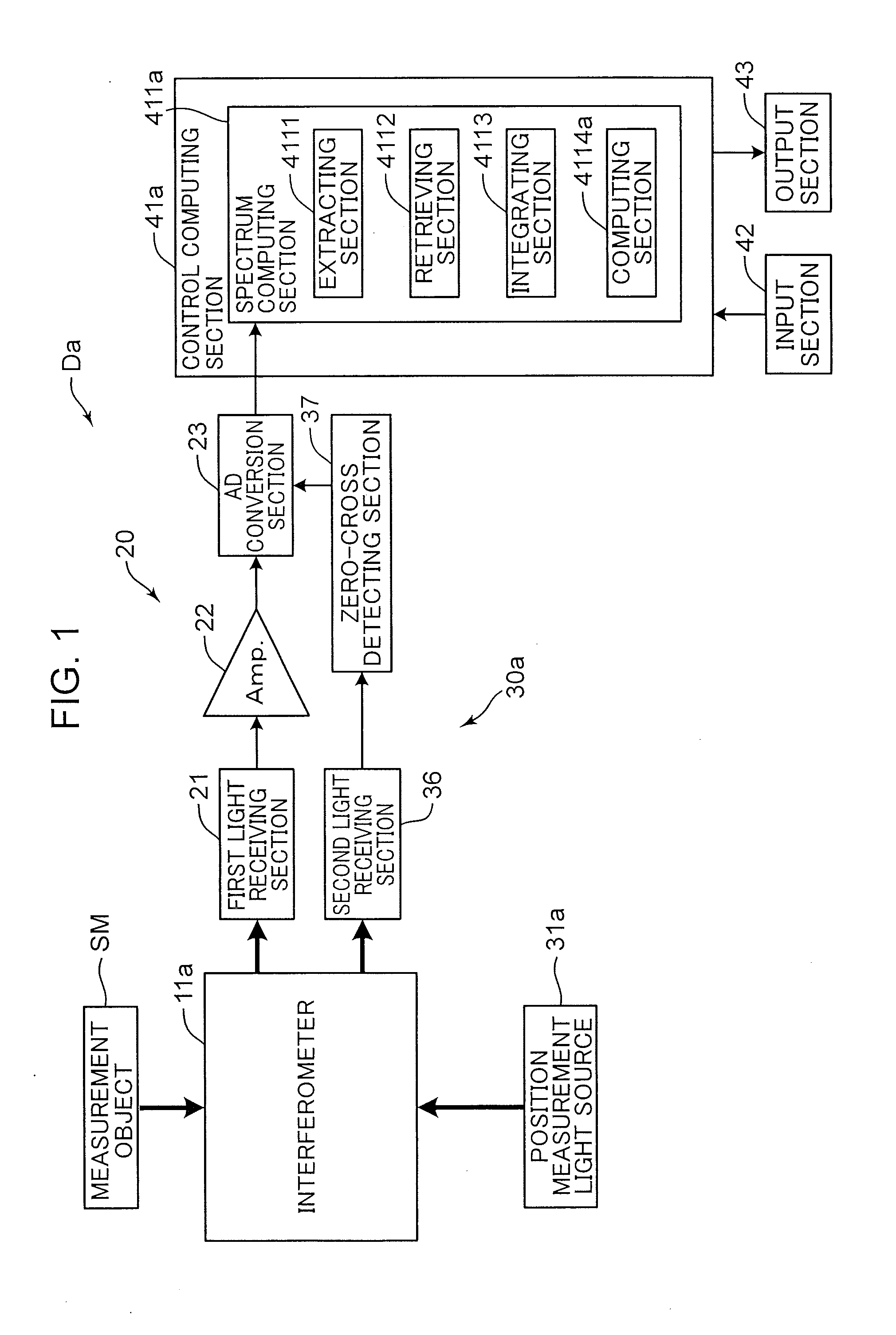
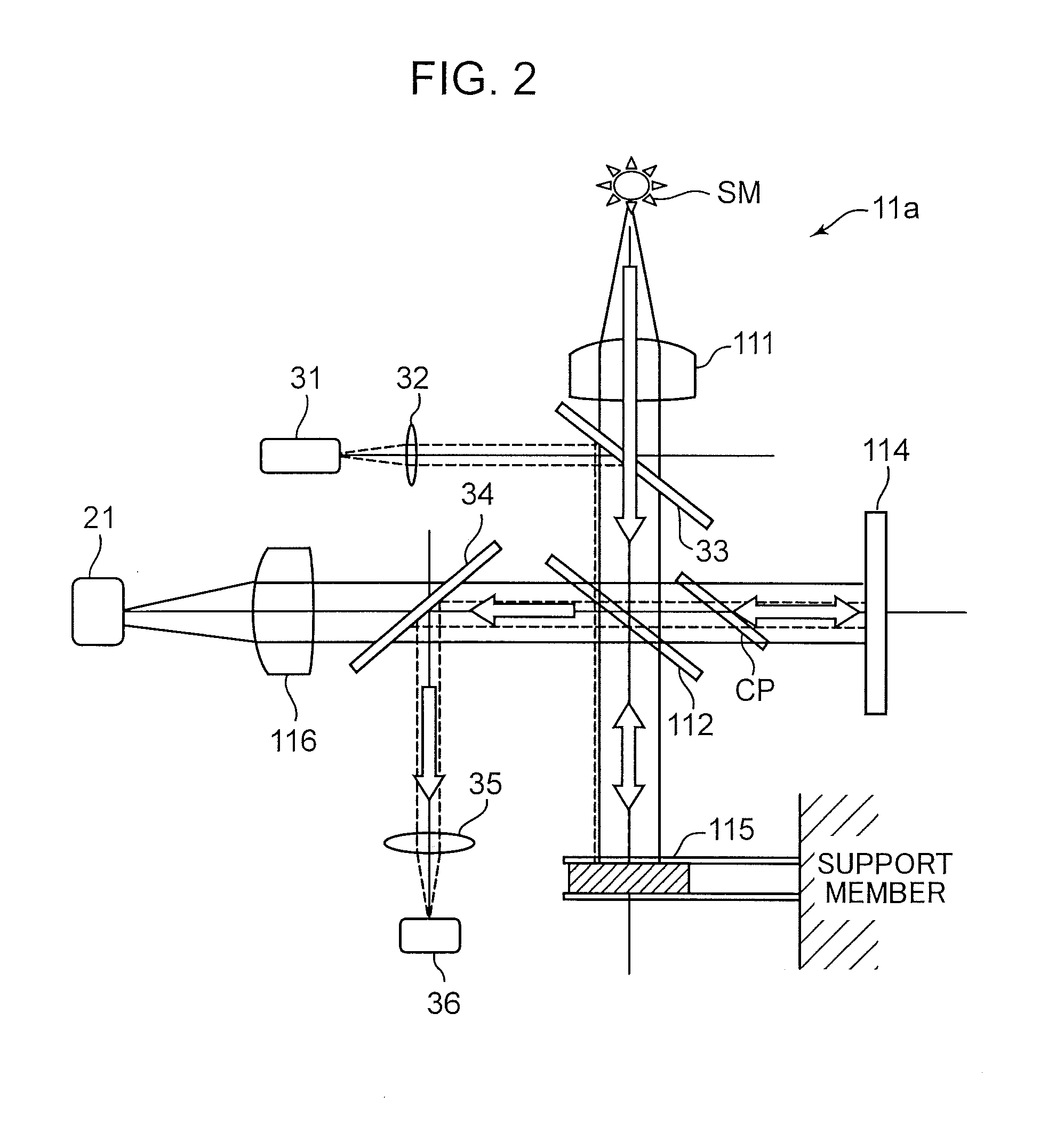
A Fourier transform spectrometer (Da) of the invention extracts, in generating an integrated interferogram obtained by integrating a plurality of interferograms, an output of an interferometer (11a) within a predetermined range according to positioning information of a center burst in an interferogram measured at a time before measurement of an interferogram at the present time.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
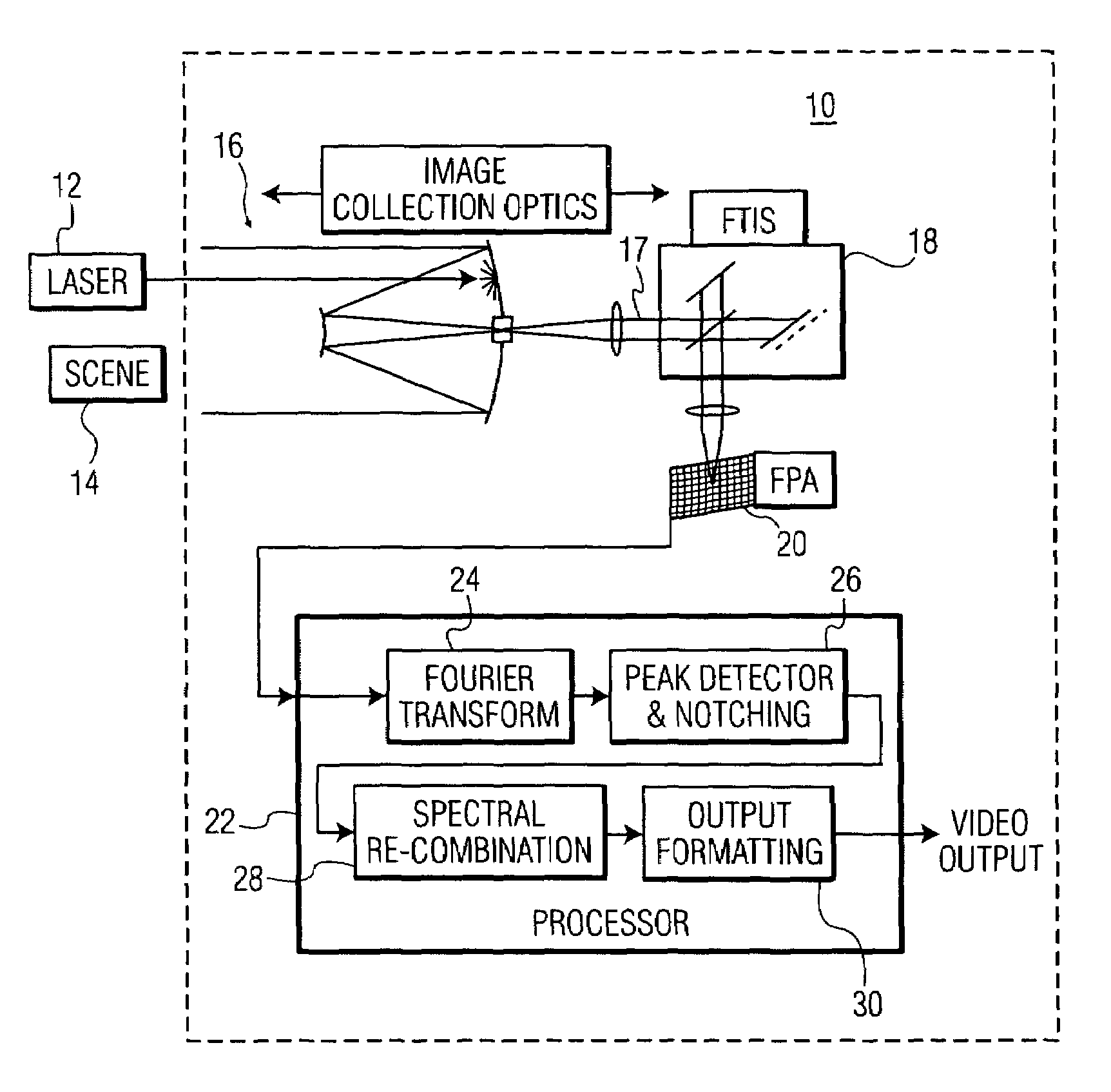
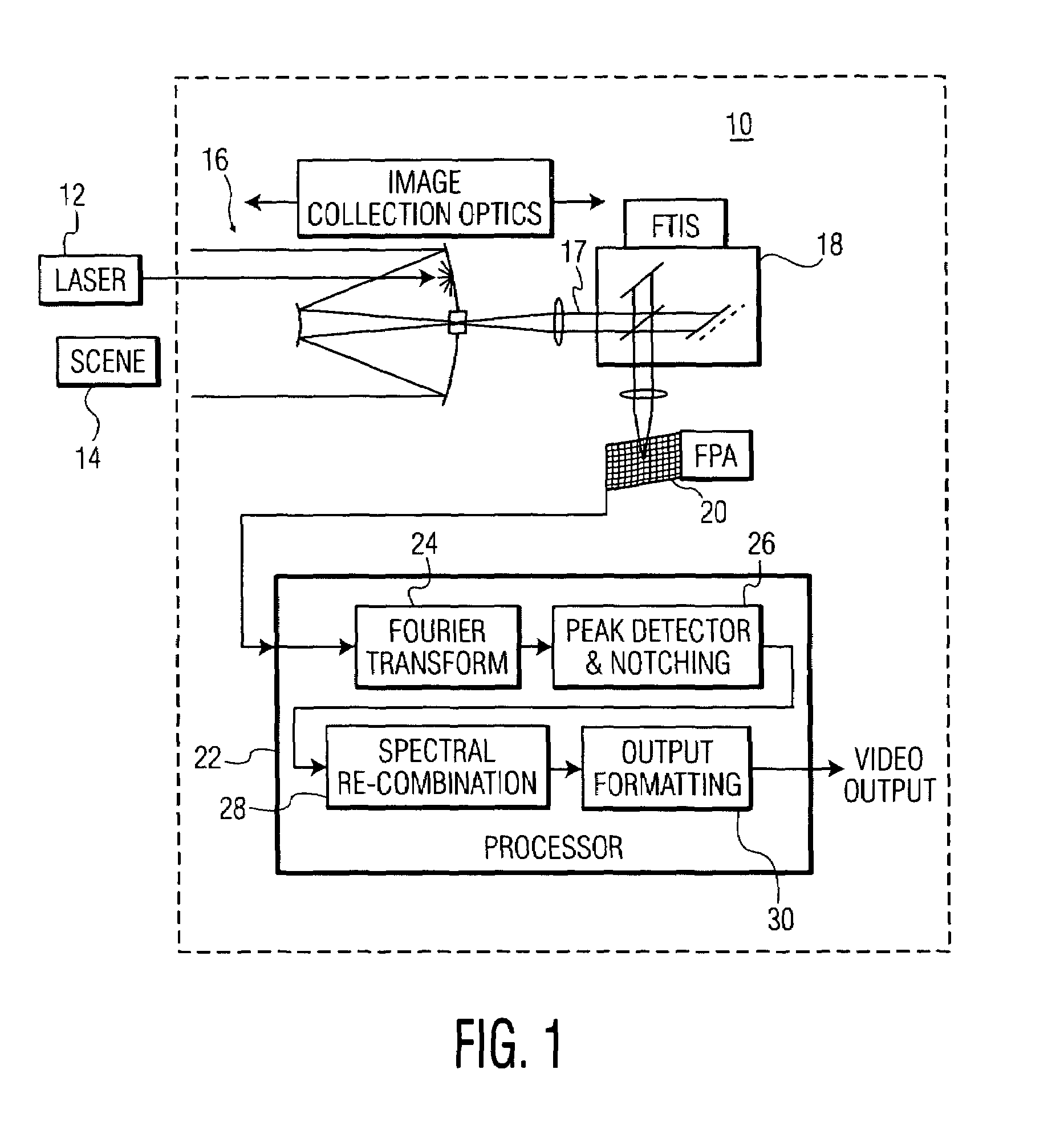
Laser counter-measure using fourier transform imaging spectrometers
ActiveUS6963405B1Lower Level RequirementsRadiation pyrometryWave based measurement systemsSpectral bandsOptical energy
In an imaging system providing an image of a target of interest, a method of reducing interference from a laser beam includes the steps of: (a) receiving optical energy from the target of interest and the laser beam; (b) forming an interferogram of spectral energy, at each spatial position of an image, based on the optical energy received in step (a); (c) detecting the interferogram of spectral energy, at each of the spatial positions, to provide a corresponding spectral band of intensity values; (d) selecting an intensity level in the spectral band, detected in step (c), that is greater than a predetermined value, and reducing the selected intensity level; and (e) forming an image of the target of interest, after reducing the selected intensity level of step (d).
Owner:HARRIS CORP
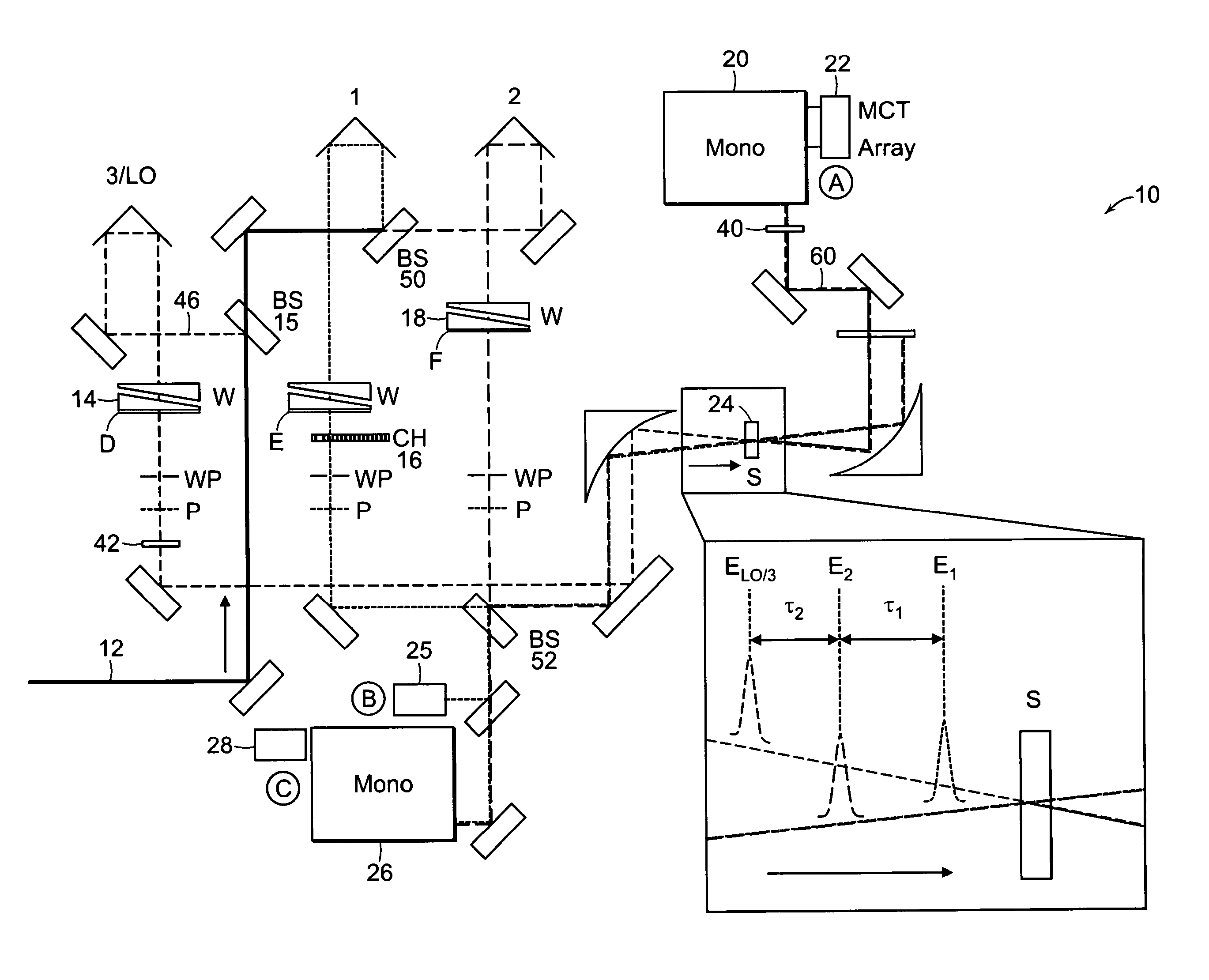
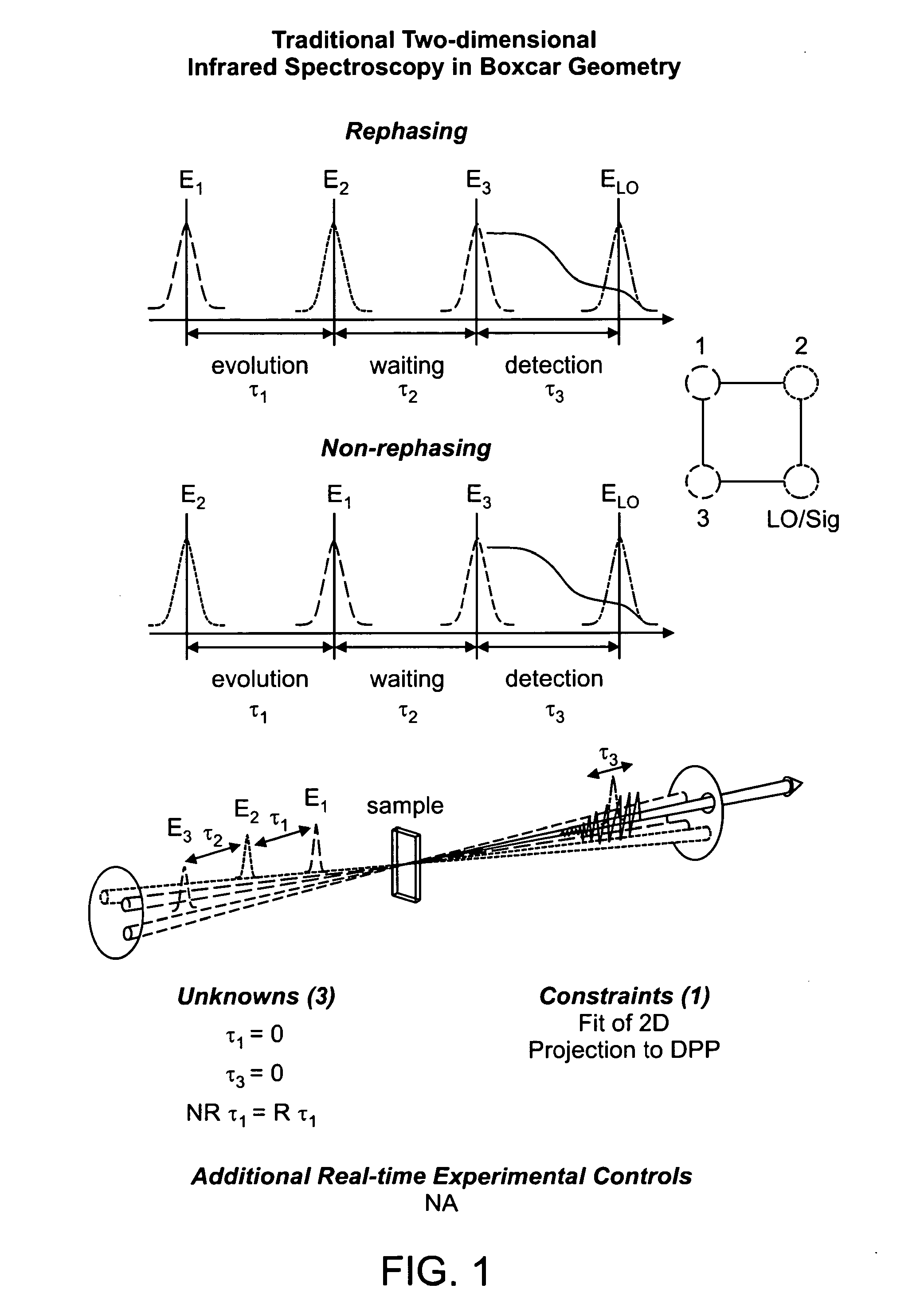
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS8526002B2Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumCoupling
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fourier transform chip spectrometer based on integrated light technique
ActiveCN102207459ASensitive assayFast and Sensitive Absorption SpectroscopyPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsModulation functionLighting spectrum
The invention discloses a Fourier transform chip spectrometer based on integrated light technique, comprising an integrated optical waveguide chip having electro-optic modulation function. Light from a light source enters the integrated optical waveguide chip through a fiber transmission coupler, and waveguide light from the chip enters an optical waveguide interferometer through a sensitive window interval. The interferometer outputs signals to a photoelectric detector. A voltage function generator is used for applying voltages varying with time between two modulated electrodes of the optical waveguide interferometer, the photoelectric detector is used for real-time measuring the change of the signal strength of the interferometer varying with the modulated voltage, and a signal processing chip connected with the photoelectric detector and the voltage function generator at same time is used for rapidly processing Fourier transform on the signals of the interferometer to obtain an incident light spectrum. The Fourier transform chip spectrometer provided by the invention can determine visible-infrared light absorbing spectra of solids, liquid, even monomolecular adsorption layers in the sensitive window, and determine fluorescence spectra of fluorescent substances in the sensitive window, with the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, and is suitable for rapid on-site quantitative determination.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Living body fluorescent endoscopic spectrum imaging device
ActiveCN101904737AHigh spectral resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBand-pass filterMolecular level
The invention relates to a live body fluorescent endoscopic spectrum imaging device, comprising a light source unit, a light split unit, a scanning light guide unit, a fiber bundle endoscopic unit, an electrooptical signal detection and acquisition unit and a computer, wherein the light source unit consists of a collimating unit and a band filter. The imaging device is characterized in that the light of the collimating unit passes through the band filter and then enters the light split unit, the light split unit is provided with two paths of interfaces, one path of the interfaces of the light split unit is connected with the scanning light guide unit, the scanning light guide unit is connected with the fiber bundle endoscopic unit, and the other path of the interfaces of the light split unit is connected with the electrooptical signal detection and acquisition unit which is connected with the computer. The imaging device has the characteristics that: 1, a Fourier transform spectrometer is used to detect a sample excitation spectrum, and has the advantages of high spectral resolution (1nm), adjustable spectral resolution and the like; and 2, the fluorescent live body endoscopic spectrum imaging system can provide not only imaging diagnosis at tissue level but also spectrum diagnosis at molecular level.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
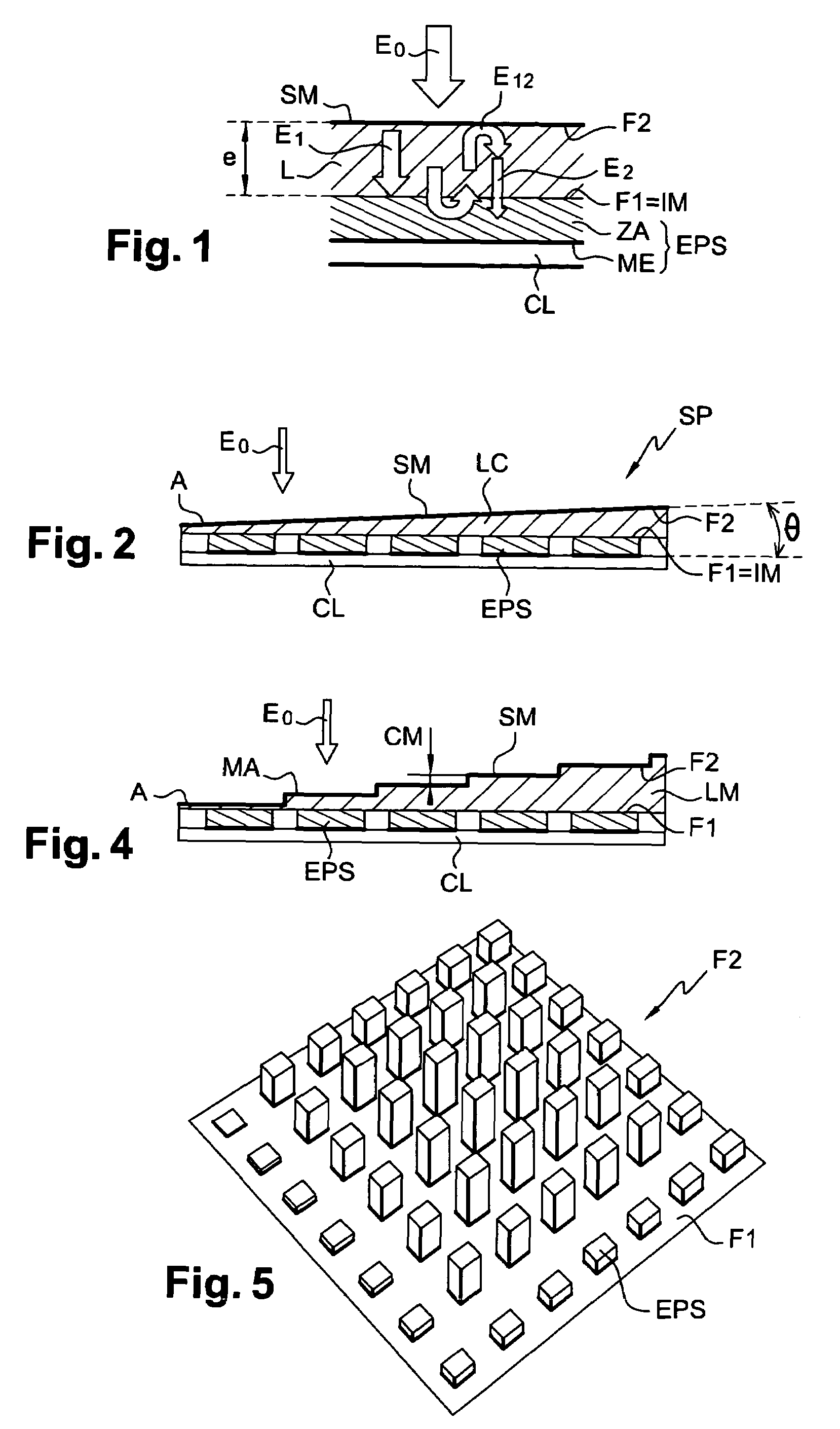
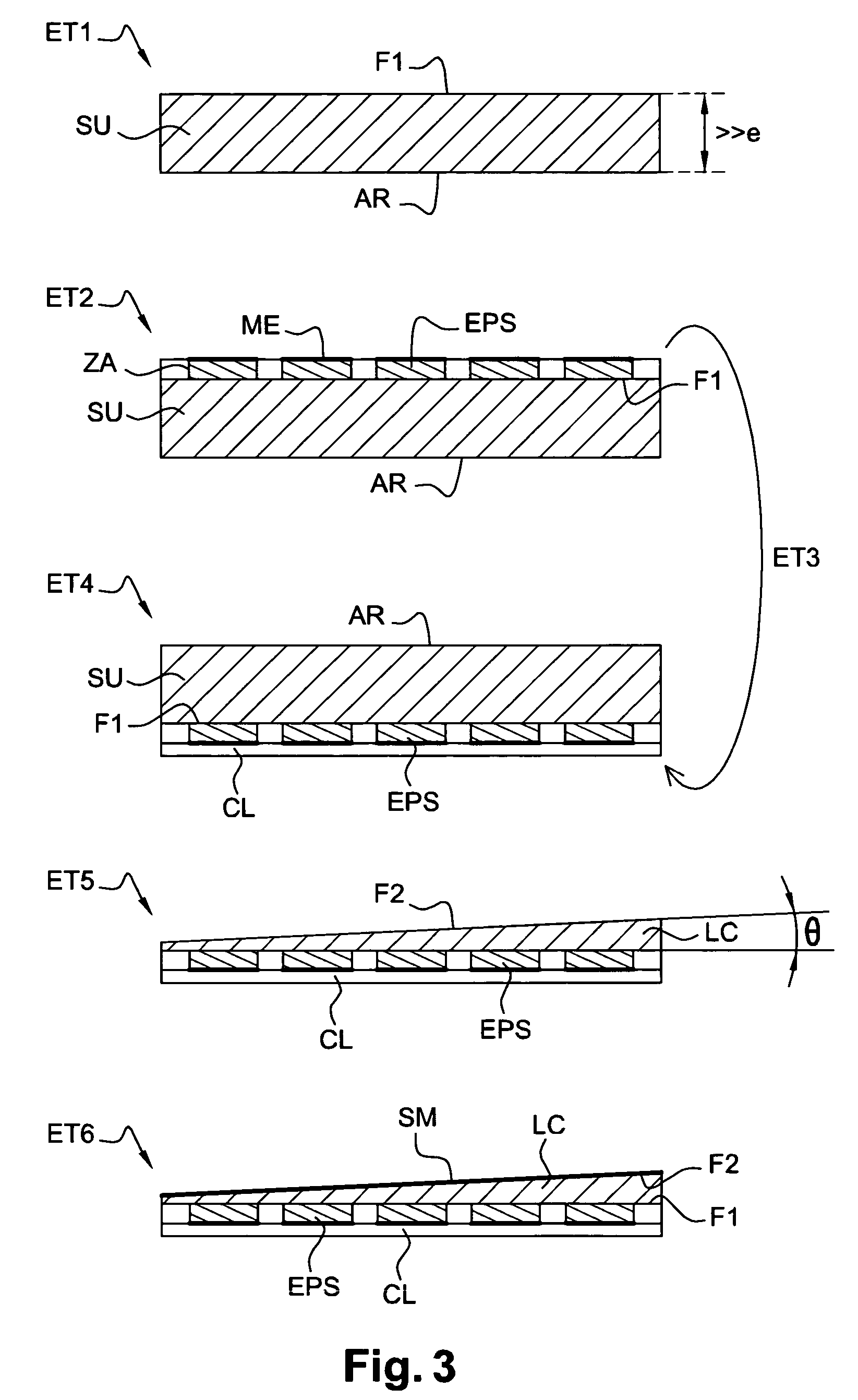
Spatial modulation Fourier transform infrared spectrometer based on MOEMS technology
ActiveCN103913235AMeet lightweightMeet needsRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterMichelson interferometer
The invention discloses a spatial modulation Fourier transform infrared spectrometer based on the MOEMS technology and relates to the field of spectrum analysis instruments. The spatial modulation Fourier transform infrared spectrometer solves the problems that the FTIR is adopted in the prior art, the size is large, the weight is high, and online reliability is limited. The infrared spectrometer is based on the Michelson interferometer principle, two multistage step reflectors which are arranged in an orthogonal mode are used for replacing a movable mirror system and a fixed mirror in a system, staticizing of the system is achieved, and meanwhile the reliability, the repeatability and the real-time performance of the system are greatly improved. Real-time and online measurement on unknown objects is conveniently achieved. A grid type beam splitter is used for replacing a beam splitter and a compensating plate in a traditional Fourier transform spectrometer, the light weight of the system is achieved, a micro-reflector array is used for replacing a beam contracting system in the traditional Fourier transform spectrometer, and the requirement for the light weight and the microminiaturization of the spectrometer can be better met.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Planar lightwave fourier-transform spectrometer
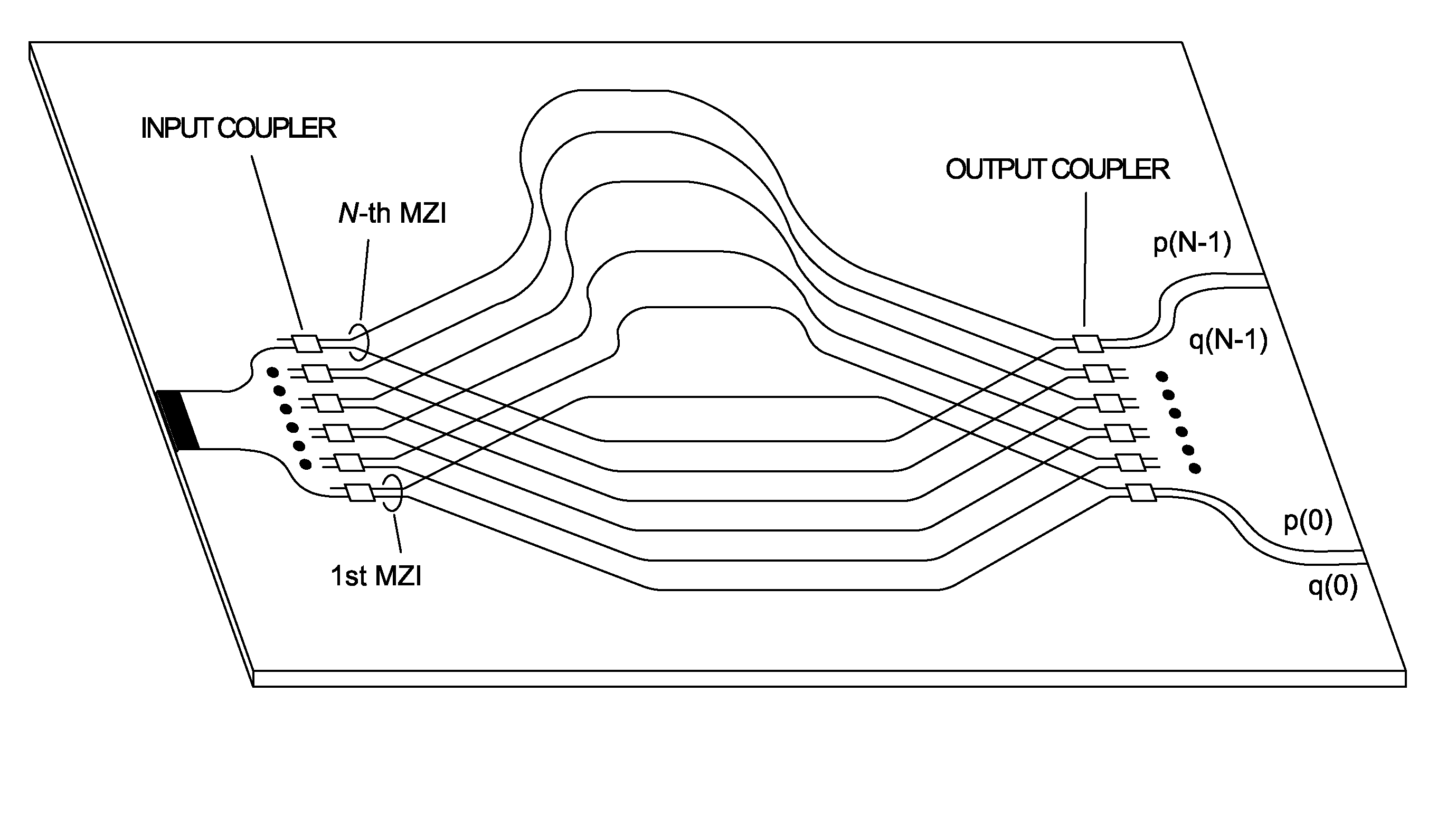
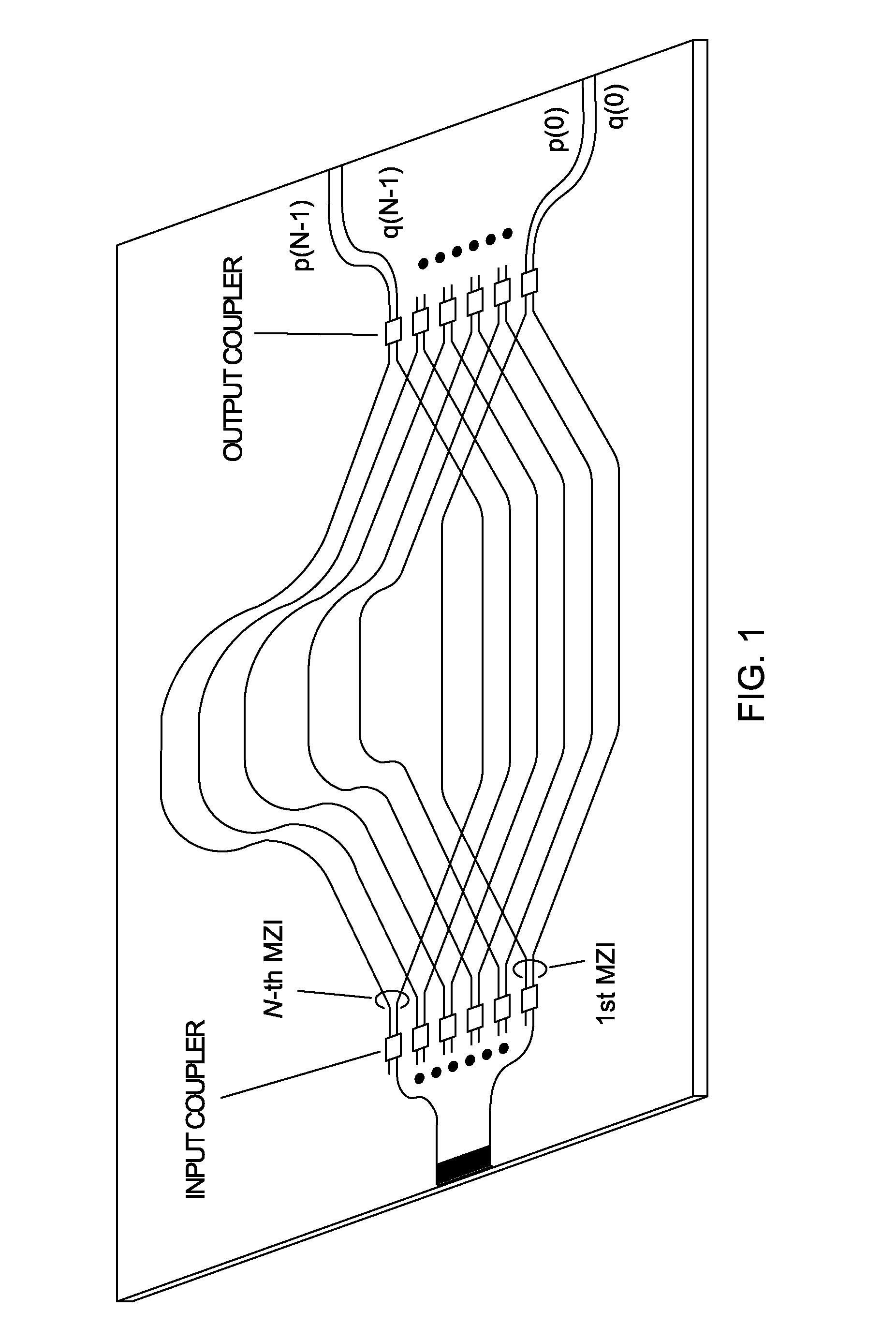
InactiveUS20100245831A1Increase luminous fluxSmall sizeRadiation pyrometryWave amplification devicesUltrasound attenuationWaveguide
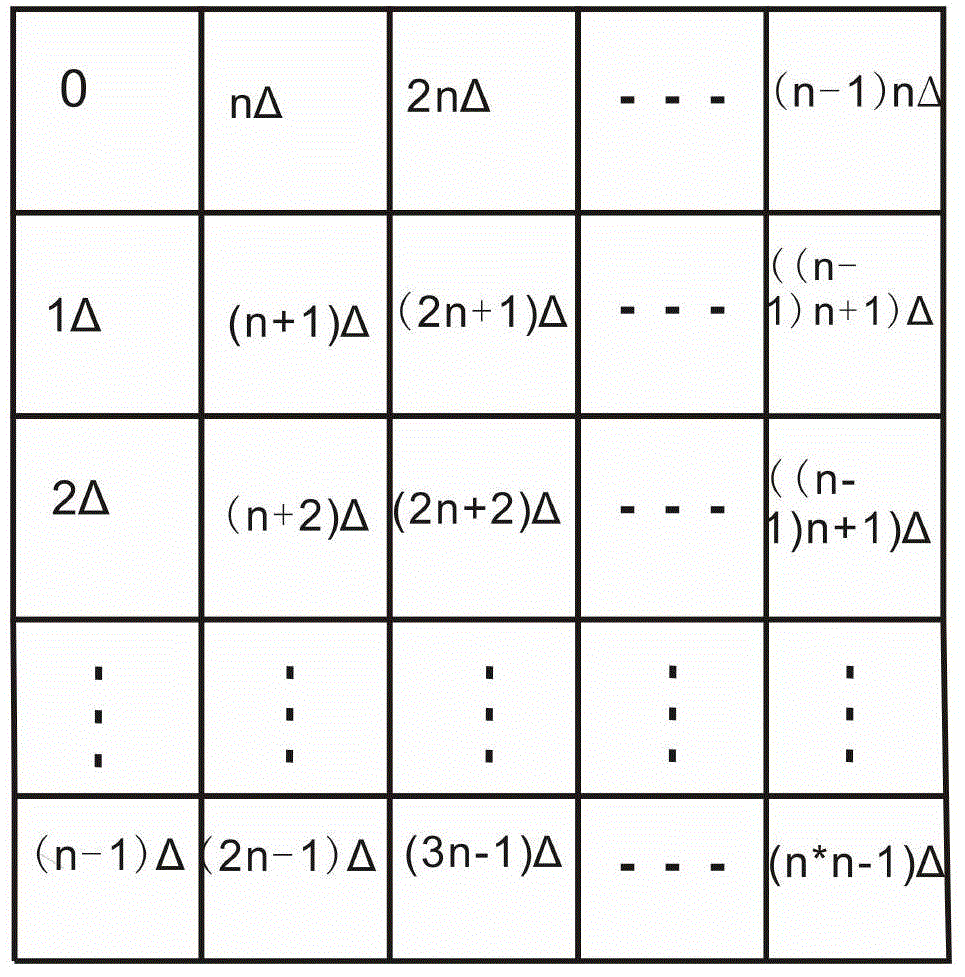
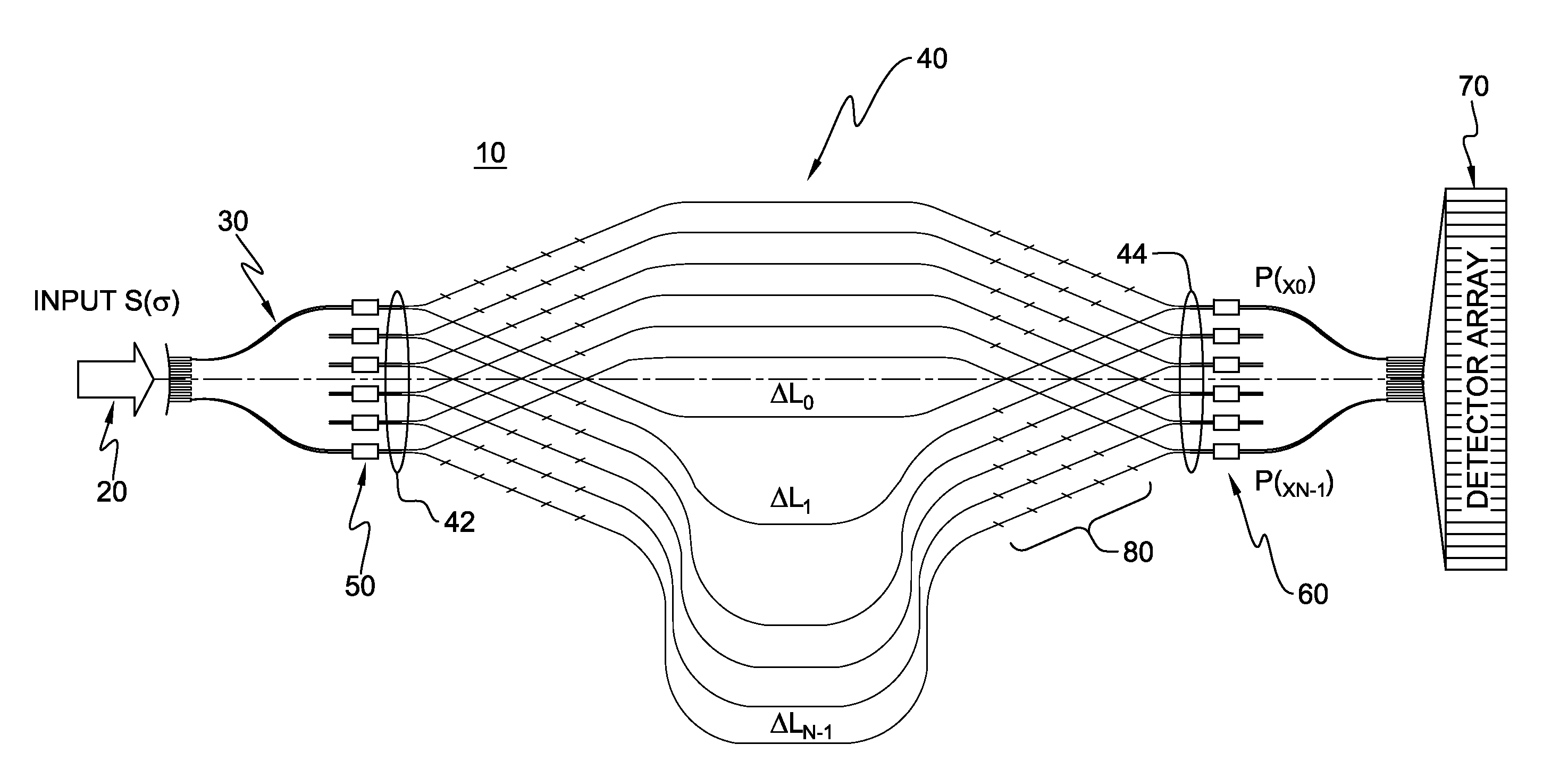
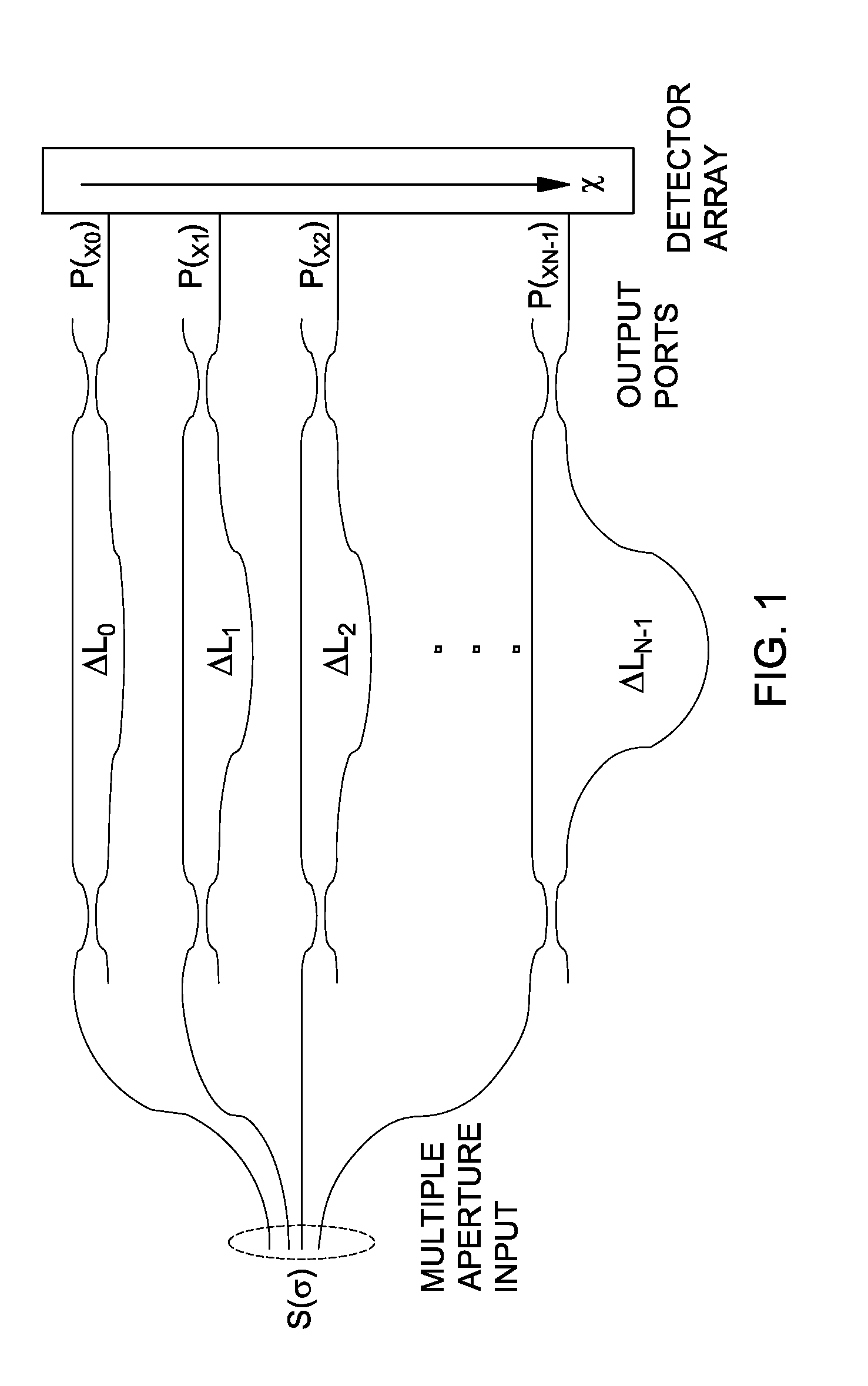
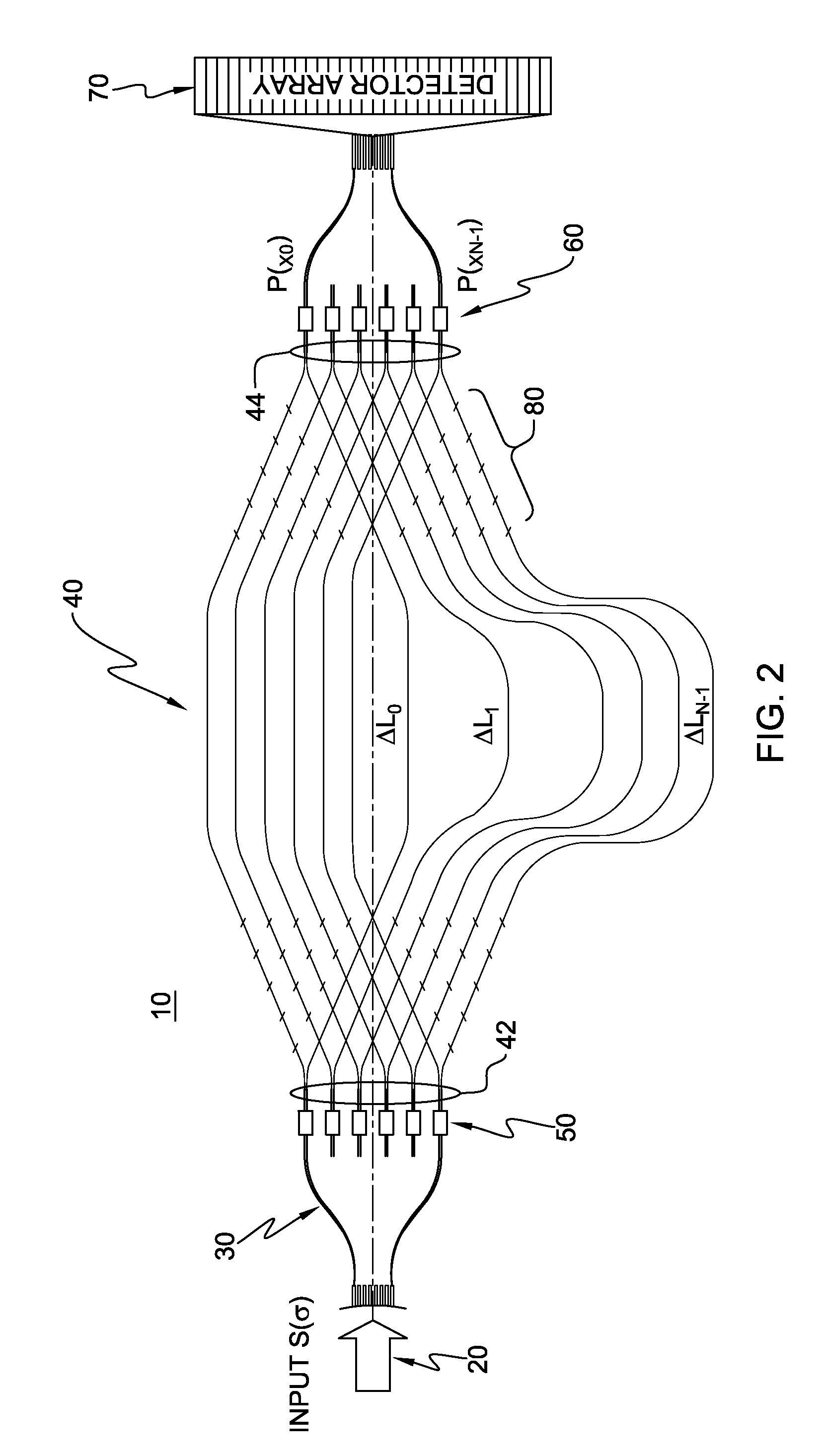
A transform spectrometer implemented on a planar waveguide circuit (PLC), having an input optical signal waveguide carrying an input optical signal to be analyzed; a plurality of couplers, each connected to the input optical signal waveguide, and each including a coupler output for carrying a coupled optical signal related to the input optical signal. An array of interleaved, asymmetrical waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometers (MZI) is formed on the PLC, each having at least one input MZI waveguide, each MZI input waveguide receiving a coupled optical signal from a respective coupler output; wherein at least some of the input MZI waveguides intersect in a common layer of the PLC, at an angle which allows their respective coupled optical signals to transmit without unacceptable attenuation. This arrangement improves spatial efficiency of the PLC, allowing more MZIs to be implemented, resulting in increased spectral resolution.
Owner:SIPHX
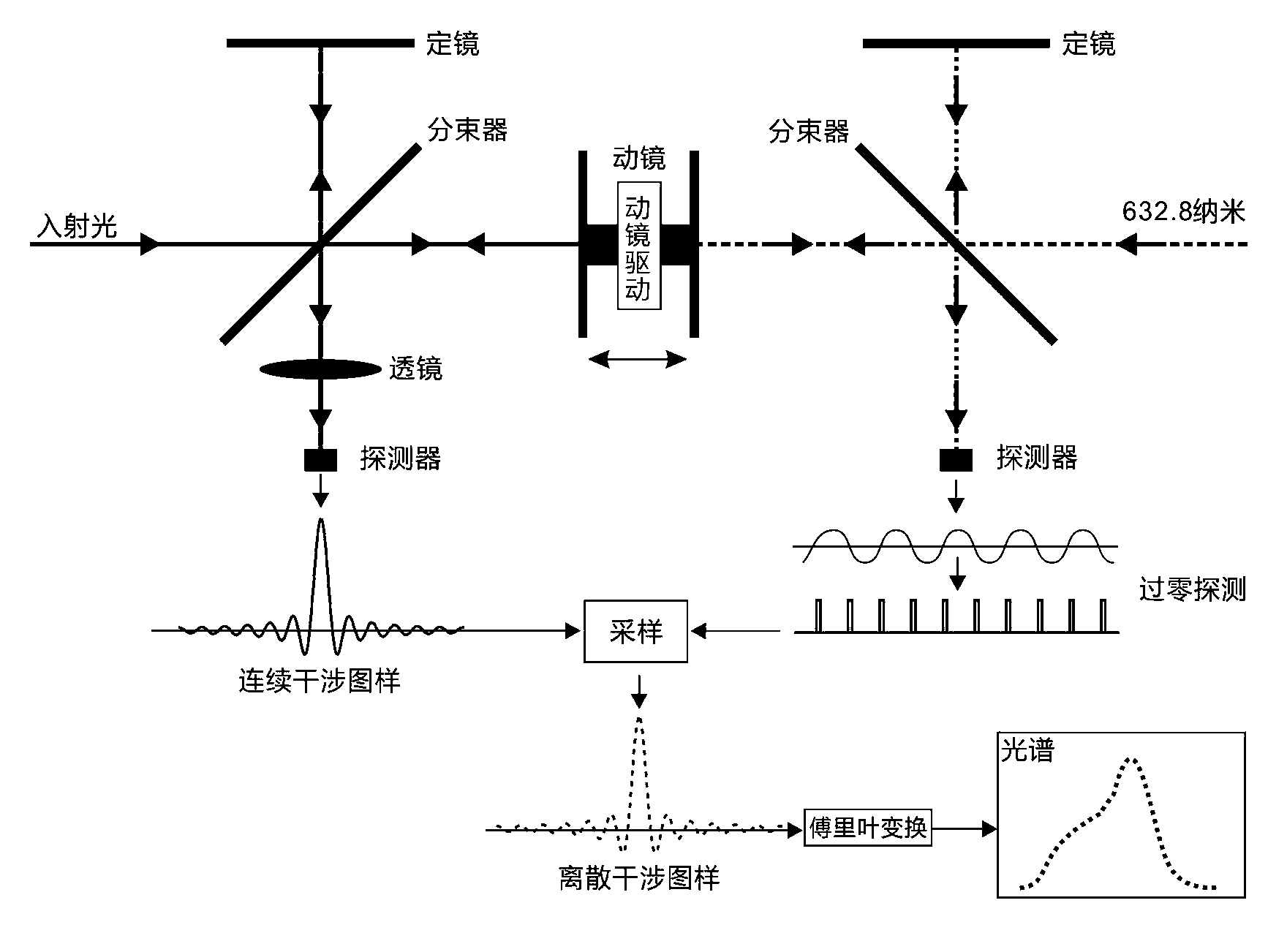
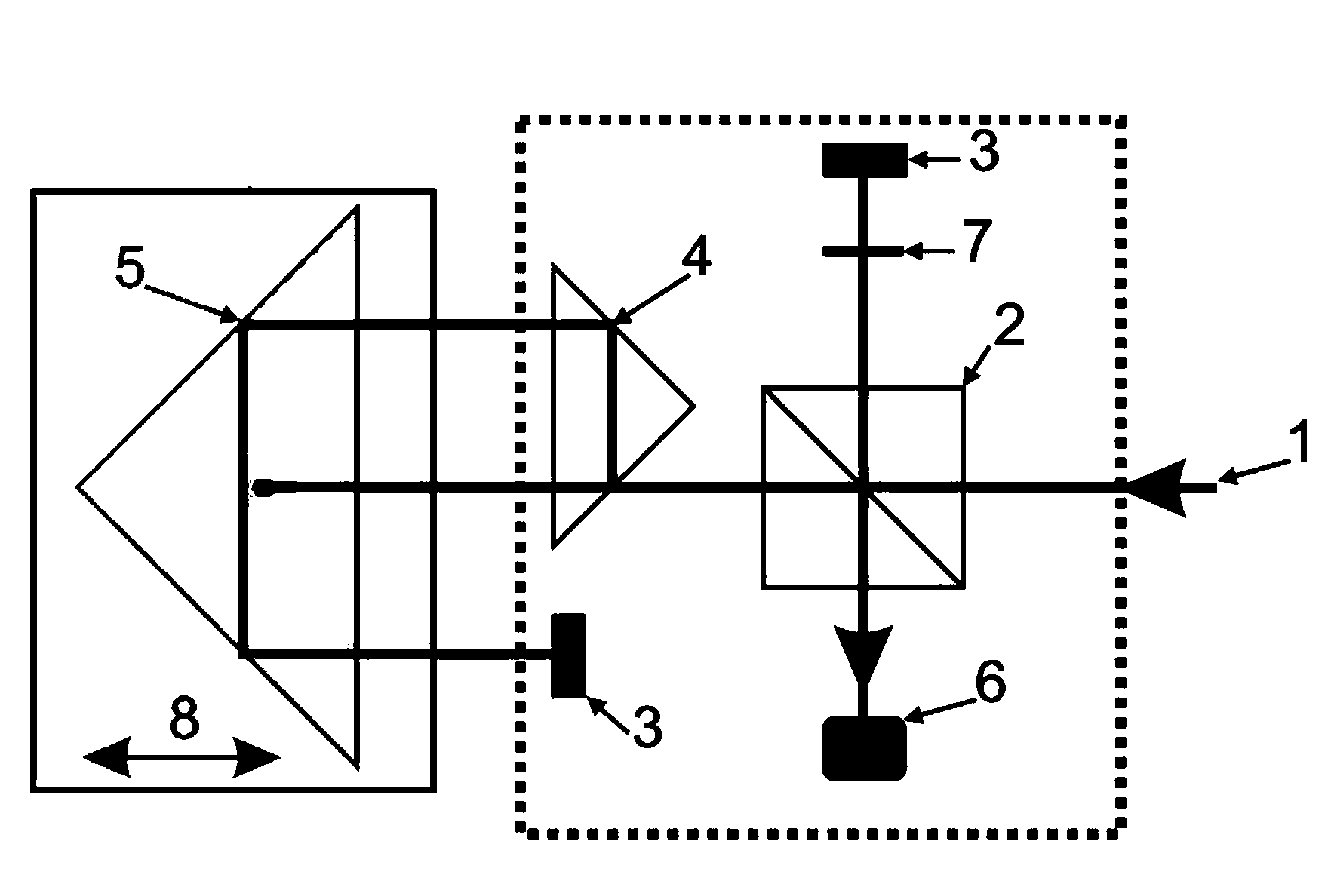
Laser interferometer optical path difference location method and system
ActiveCN103076090AHigh measurement accuracyMiniaturizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsSpectrographOptical pathlength
The invention discloses an optical path folding laser interferometer system which is simple and compact in structure and used for precisely locating the difference of two optical paths of a movable mirror and a stationary mirror of a Fourier transform spectrometer. By combining a pyramidal retroreflector and a reflecting mirror, which are compact in spatial layout, the optical path of a movable arm of the laser interferometer are folded for four times, and the period of an interference pattern generated by the interferometer is reduced by four times. Through the photoelectric transformation of a zero-passage detection circuit, a pulse signal with identical optical path difference interval being less than 100 nanometers, and a detector for triggering the Fourier transform spectrometer is used for sampling the interference pattern of a signal to be detected. Due to the adoption of the laser interferometer system, not only can the working spectrum of the Fourier transform spectrometer be expanded to near ultraviolet (to 350 nanometers) of a shortwave band, but also the high measurement precision advantage of the Fourier transform spectrometer can be maintained. Therefore, an ultraviolet-visible light Fourier transform spectrometer which is realized through the method and the system can be widely applied in multiple fields such as chemistry, biology, medicine, materials and optics.
Owner:深圳市趣方科技有限公司
Compact spectrometer
ActiveUS9316539B1Small sizeEasy to carryRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesFourier transform spectrometersMobile device
A spectrometer for measuring a spectral signature of an object comprises fringe generating optics for use with a camera and a processor. The fringe generating optics are formed of front optics and birefringent optics. The front optics comprises a diffuser adapted to receive light from the object. The birefringent optics is adapted to receive light from the diffuser and to generate interference fringes. The camera is adapted to receive the interference fringes and the processor generates the spectral signature of the object. This spectrometer is an improved Fourier transform spectrometer suitable for use with digital cameras, such as cameras found in mobile devices.
Owner:LIGHTHAUS PHOTONICS
Electro-Optic Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer
InactiveUS20070070354A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPolarizerFourier transform spectrometers
An Electro-Optic Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer (EOIFTS) for Hyperspectral Imaging is described. The EOIFTS includes an input polarizer, an output polarizer, and a plurality of birefringent phase elements. The relative orientations of the polarizers and birefringent phase elements can be changed mechanically or via a controller, using ferroelectric liquid crystals, to substantially measure the spectral Fourier components of light propagating through the EIOFTS. When achromatic switches are used as an integral part of the birefringent phase elements, the EIOFTS becomes suitable for broadband applications, with over 1 micron infrared bandwidth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
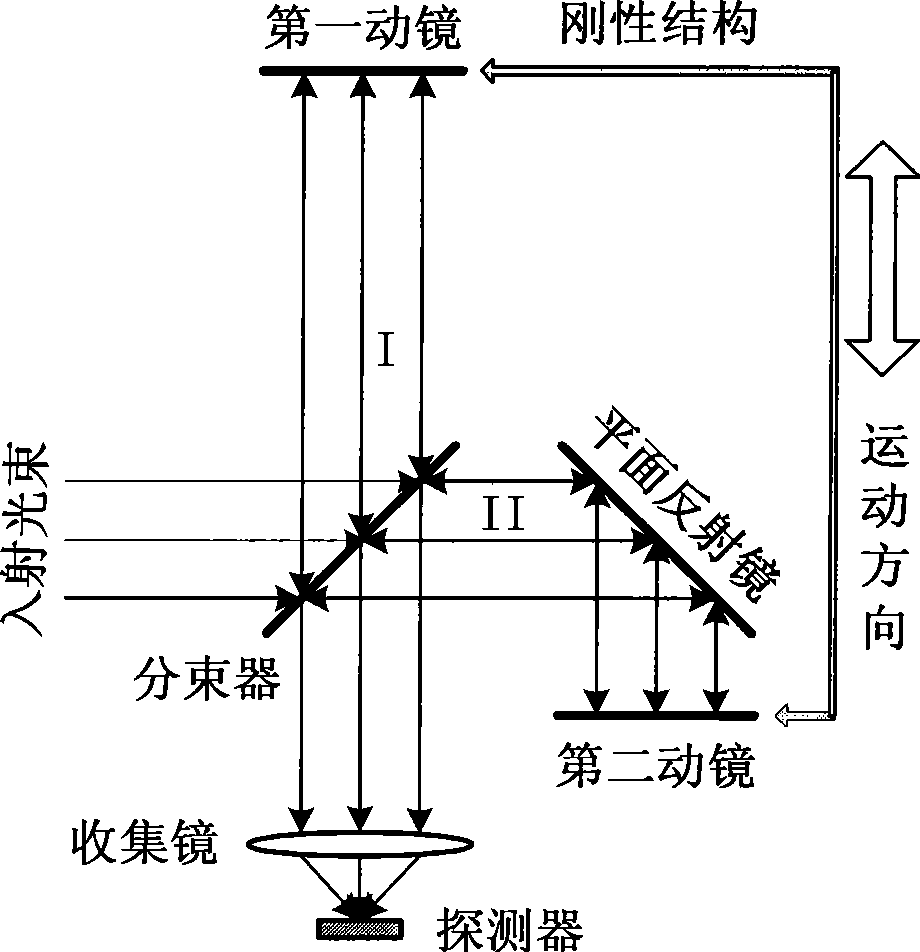
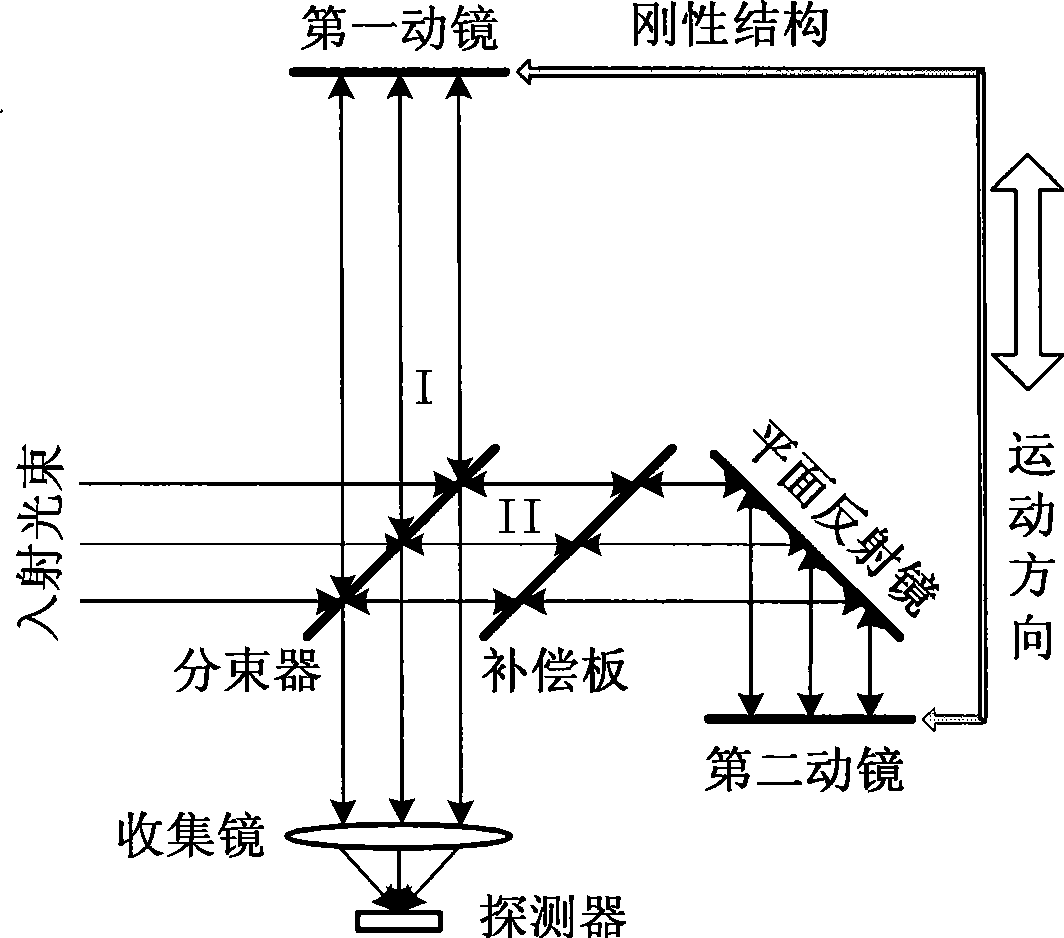
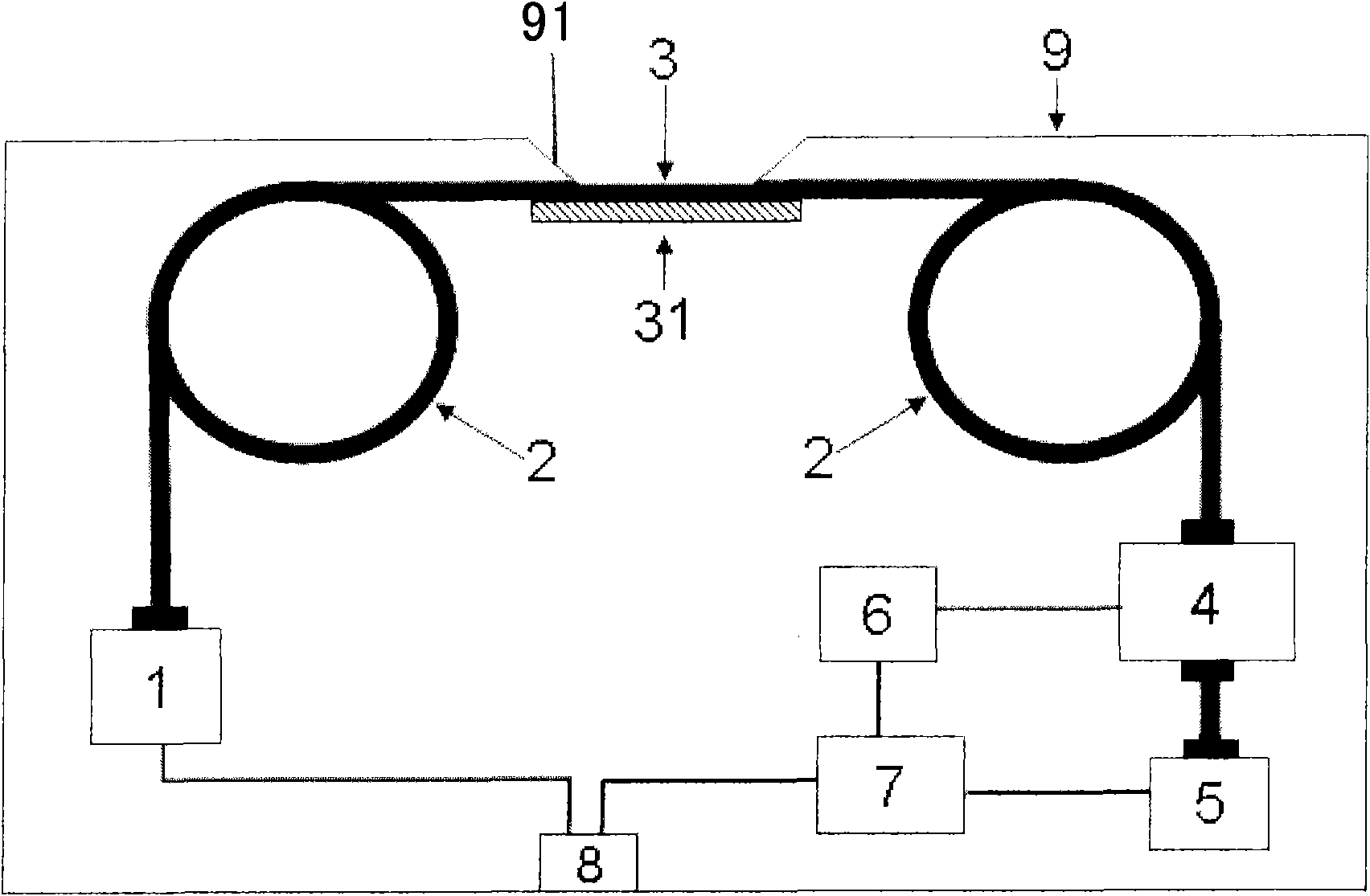
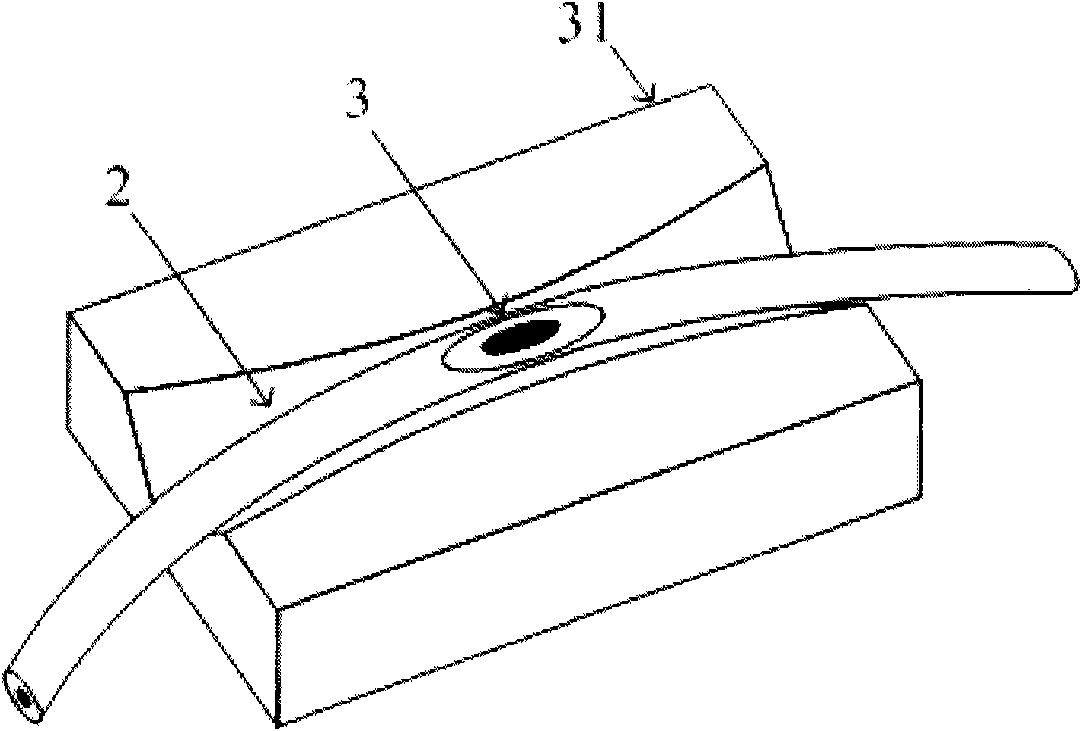
Double movable mirror interferometer
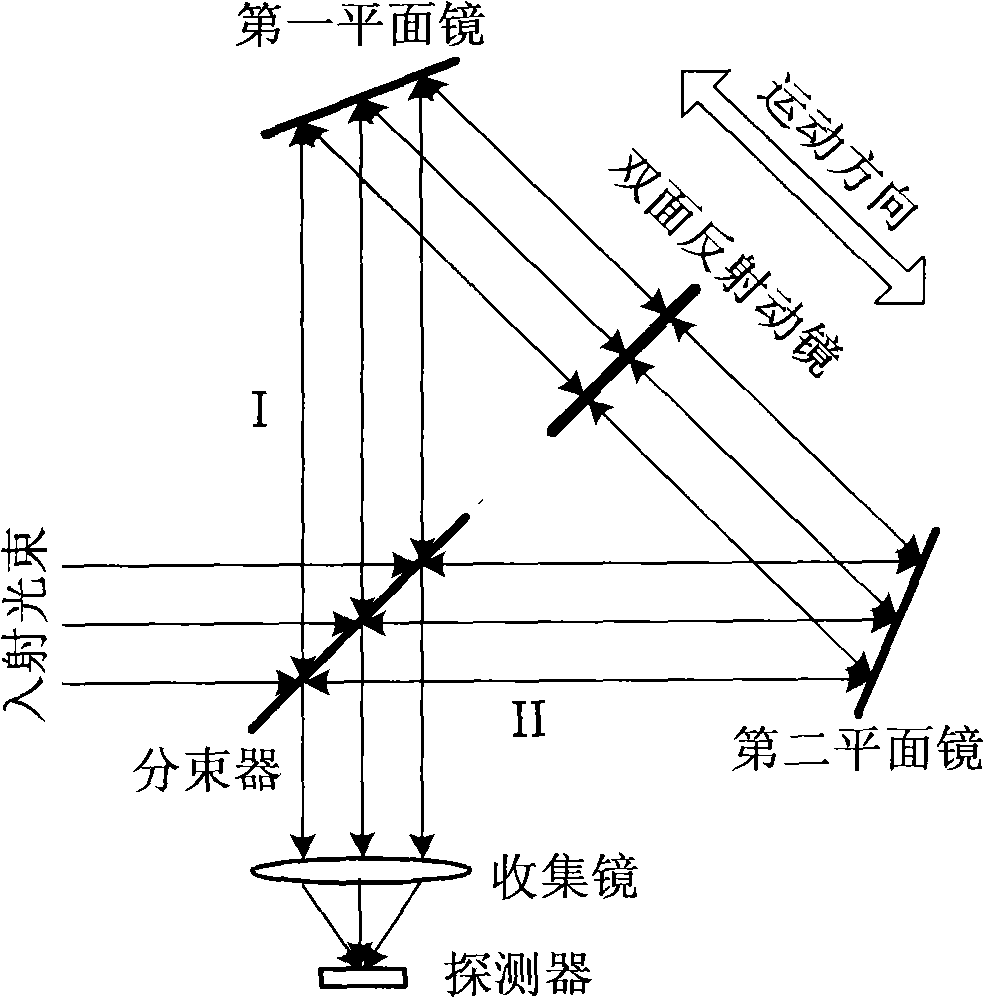
InactiveCN101532880ASmall modulationPhase influence is smallInterferometric spectrometryOptical elementsBeam splitterPlane mirror
The invention relates to a double movable mirror interferometer which comprises a beam splitter, a fixed plane mirror and a first movable mirror and a second movable mirror which are arranged parallelly on a common sliding component which can be moved linearly; the first movable mirror and the second movable mirror are parallelly fixed together by a rigid structure as an independent moving component; the beam splitter and the plane mirror are mutually vertical and has an inclined angle of 45 degrees with the first movable mirror and the second movable mirror; optical path difference is generated by straight reciprocating motion of the two parallel plane movable mirrors and is four times of displacement (relative to zero optical path difference position) of the two movable mirrors. The interferometer has simple structure and low cost and is applicable to various high-resolution Fourier transform spectrometers in spectrum working areas.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stationary fourier transform spectrometer
ActiveUS7330266B2Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhase difference
The invention aims to integrate a two-wave stationary interferometer on a photodetector during fabrication in order to constitute a miniature stationary Fourier transform spectrometer. The interferometer essentially comprises a plate having a first plane face coinciding with an image plane on semiconductor photosensitive elements and a second face that is not parallel to the first face. The second face reflects a wave that has a phase difference relative to the incident wave interfering with it that is a function of the local thickness of the plate.
Owner:OFFICE NAT DETUD & DE RECH AEROSPATIALES
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS20100171952A1Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Attenuated total reflection (ATR) spectrum measurement type Fourier transform spectrometer based on integrated optical waveguide
ActiveCN102374974ANovel structureEasy to manufactureAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberWaveguide
The invention provides an ATR spectrum measurement type Fourier transform spectrometer based on integrated optical waveguide. The spectrometer comprises an integrated optical waveguide electro-optical modulator, a voltage function generator, a broadband light source, a photoelectric detector, a signal processing chip and a fiber having an ATR sensitive window. According to the invention, light from the light source is coupled into the fiber, passes through an ATR sensitive window zone along the fiber and coupled into the integrated optical waveguide electro-optical modulator; voltage varying with time is applied on the integrated optical waveguide electro-optical modulator by using the voltage function generator, the intensity of output light of the integrated optical waveguide electro-optical modulator is measured by using the photoelectric detector simultaneously, and the signal processing chip connected with the photoelectric detector and the voltage function generator carries out Fourier transform processing on measured optical signals so as to obtain the spectrum of incident light. The spectrometer provided in the invention can determine visible-infrared absorption spectrum of solid, liquid and monomolecular layers adsorbed on the surface of the ATR sensitive window, has strong anti-interference capability and is applicable to on-site rapid quantitative detection.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Planar lightwave fourier-transform spectrometer measurement including phase shifting for error correction
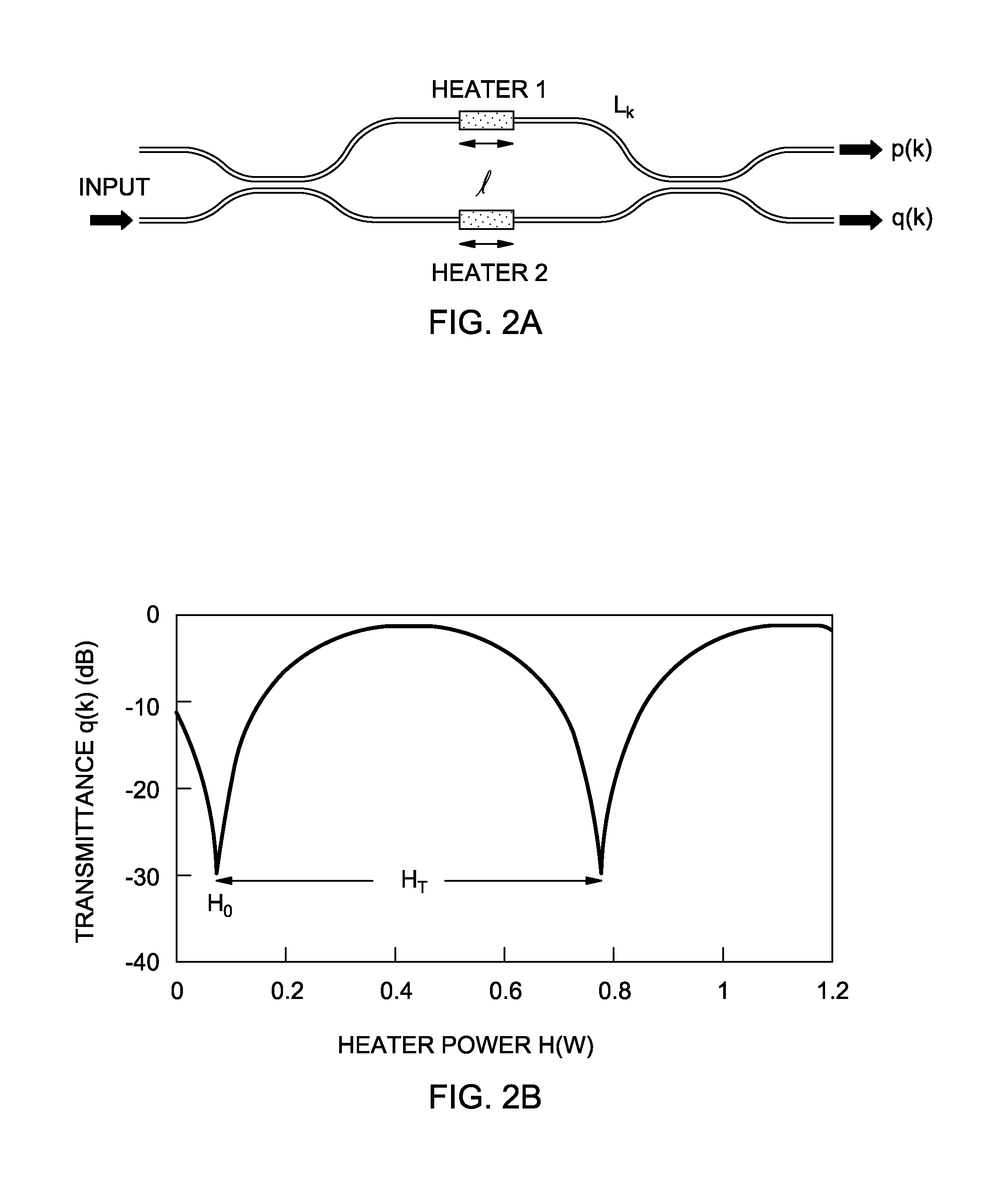
A transform spectrometer measurement apparatus and method for a planar waveguide circuit (PLC). The spectrometer typically includes an input optical signal waveguide carrying an input optical signal; a plurality of couplers, each connected to the input optical signal waveguide, and each including a coupler output for carrying a coupled optical signal related to the input optical signal; and an array of interleaved, waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometers (MZI), each having at least one input MZI waveguide, each MZI input waveguide receiving a coupled optical signal from a respective coupler output. A phase shifting circuit is applied to at least one arm of the MZIs to induce an active phase shift on the arm to thereby measure phase error in the MZIs. Light output from the MZIs is measured under intrinsic phase error conditions and after an active phase shift by the phase shifting circuit.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY +1
Planar lightwave fourier-transform spectrometer
InactiveUS8098379B2Increase luminous fluxSmall sizeRadiation pyrometryWave amplification devicesUltrasound attenuationFourier transform spectrometers
A transform spectrometer implemented on a planar waveguide circuit (PLC), having an input optical signal waveguide carrying an input optical signal to be analyzed; a plurality of couplers, each connected to the input optical signal waveguide, and each including a coupler output for carrying a coupled optical signal related to the input optical signal. An array of interleaved, asymmetrical waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometers (MZI) is formed on the PLC, each having at least one input MZI waveguide, each MZI input waveguide receiving a coupled optical signal from a respective coupler output; wherein at least some of the input MZI waveguides intersect in a common layer of the PLC, at an angle which allows their respective coupled optical signals to transmit without unacceptable attenuation. This arrangement improves spatial efficiency of the PLC, allowing more MZIs to be implemented, resulting in increased spectral resolution.
Owner:SIPHX
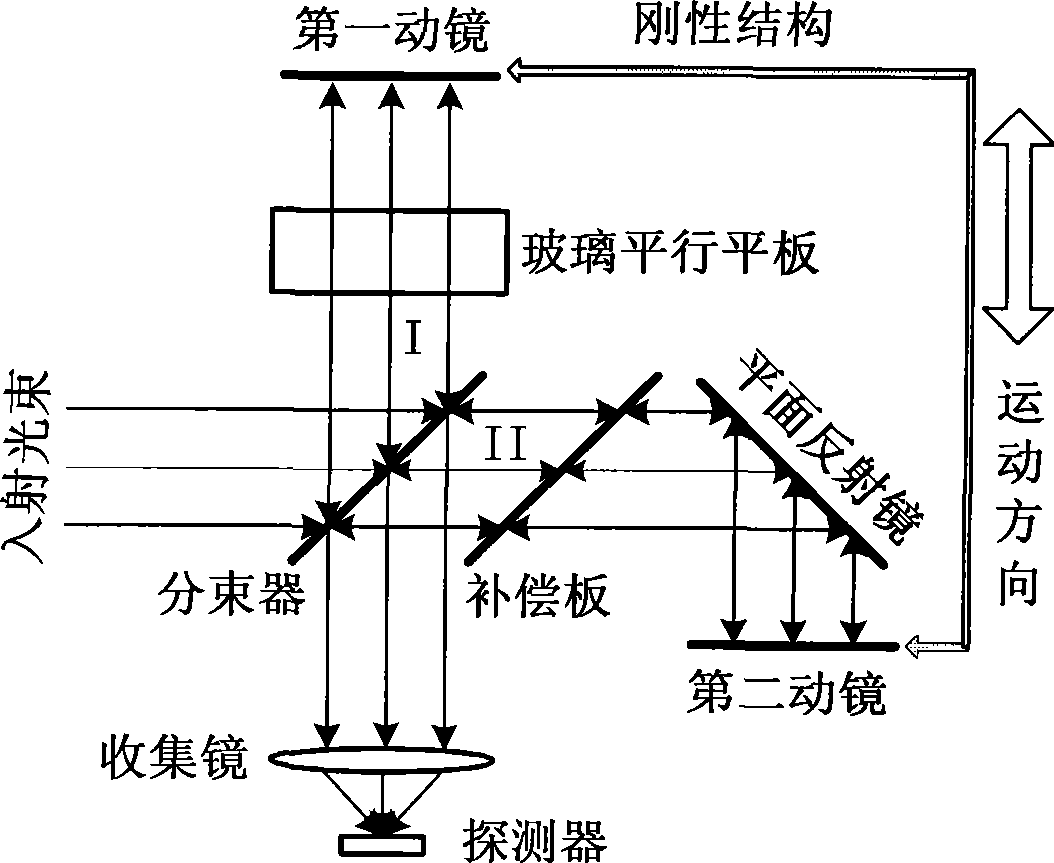
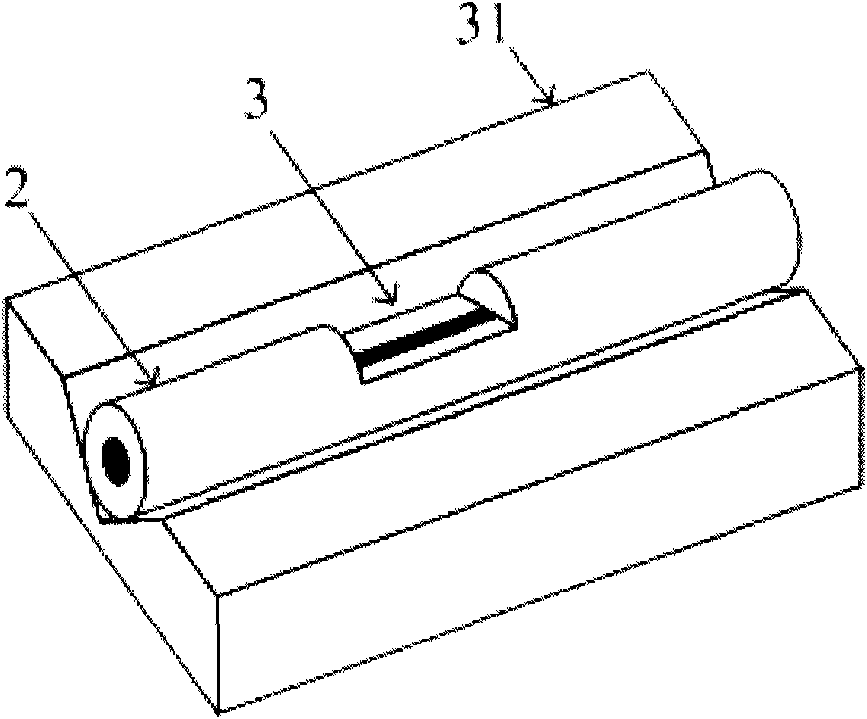
Two-sided reflection movable mirror interferometer
InactiveCN101320126ACompact structureReduce volumeSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptical elementsBeam splitterPlane mirror
A double-sided movable reflecting mirror interferometer comprises a beam splitter, two fixed plane mirrors and a double-sided movable reflecting mirror which is a plane parallel glass sheet, and both sides of the glass sheet are plated with reflecting film; the double-sided movable reflecting mirror is parallel to the half-reflection surface of the beam splitter; a first plane mirror and a second plane mirror are symmetrical to the half-reflection surface of the beam splitter; the double-sided movable reflecting mirror makes straight reciprocating motion along the normal direction of the half-reflection surface of the beam splitter; the optical path difference is four times longer than the displacement (relative to the position of zero optical path difference) of the double-sided movable reflecting mirror. The interferometer has compact structure, small volume and low cost, and is suitable for high resolution Fourier transform spectrometers of various spectral regions.
Owner:杨庆华
Fourier transform spectrometer on silicon substrate and method for obtaining reconstructed spectrum of light source
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
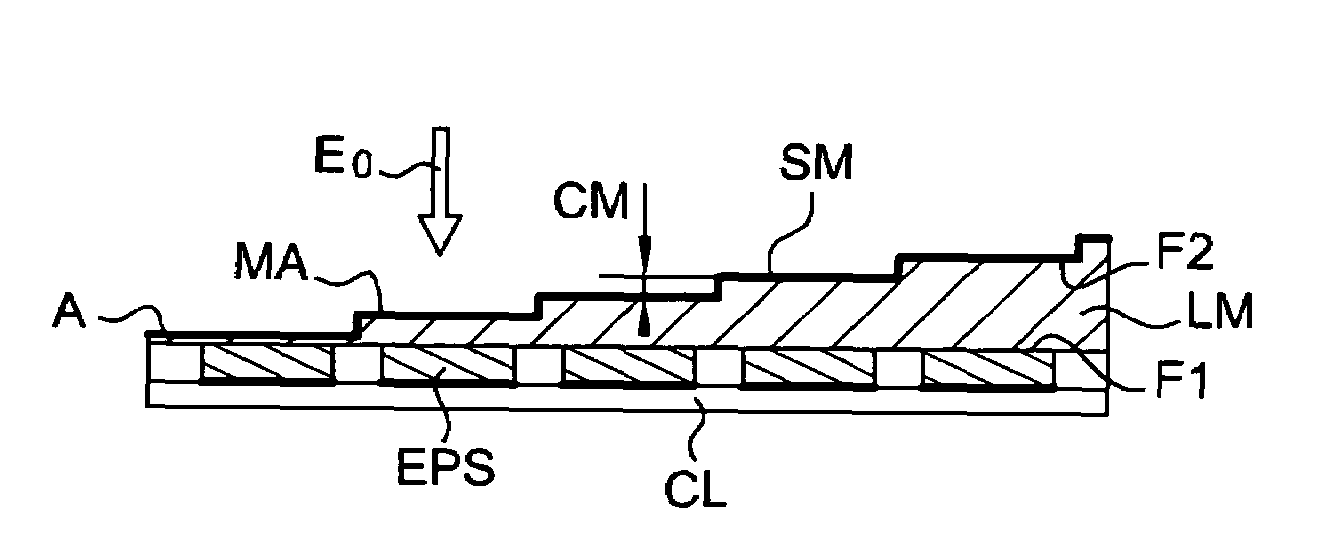
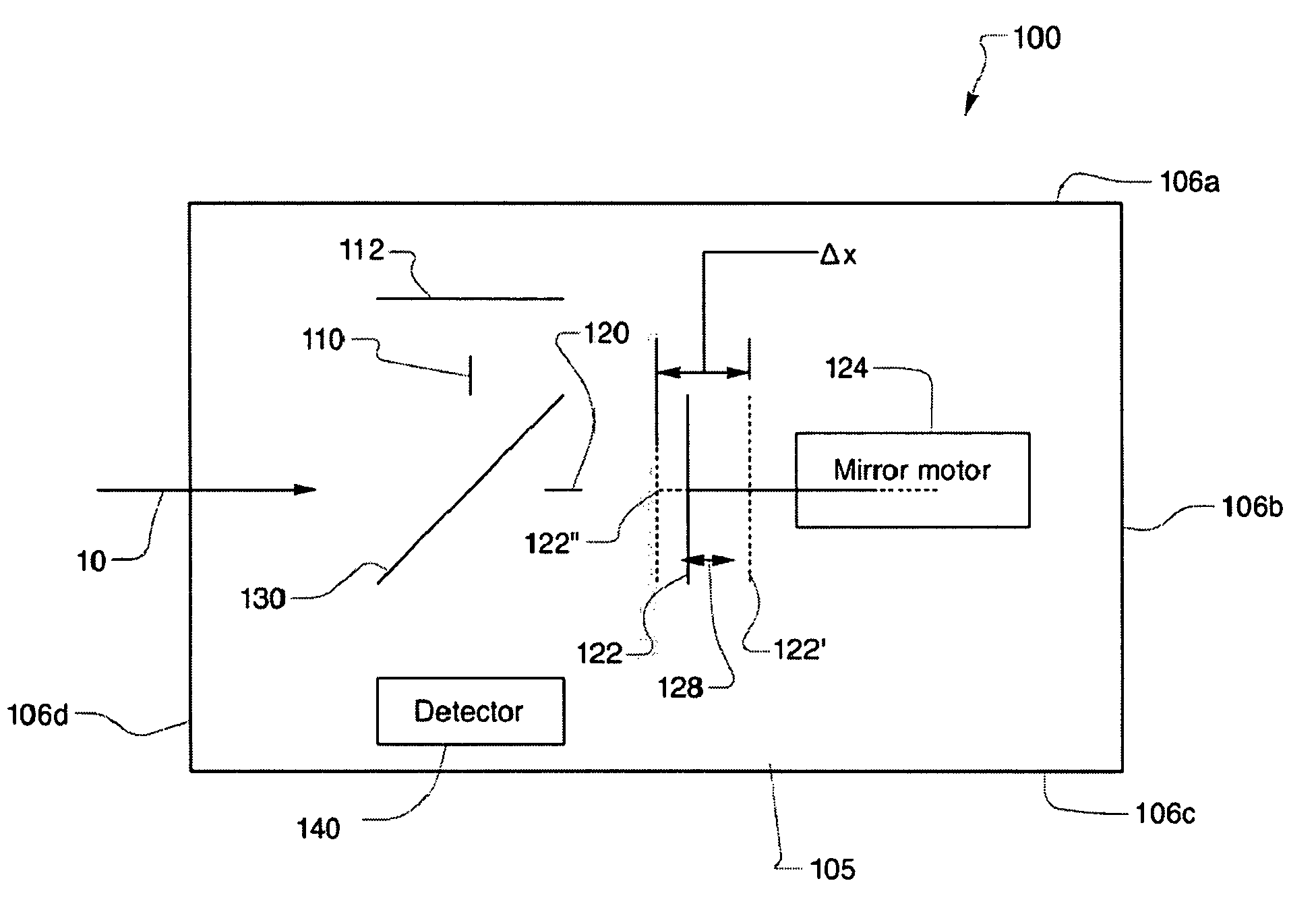
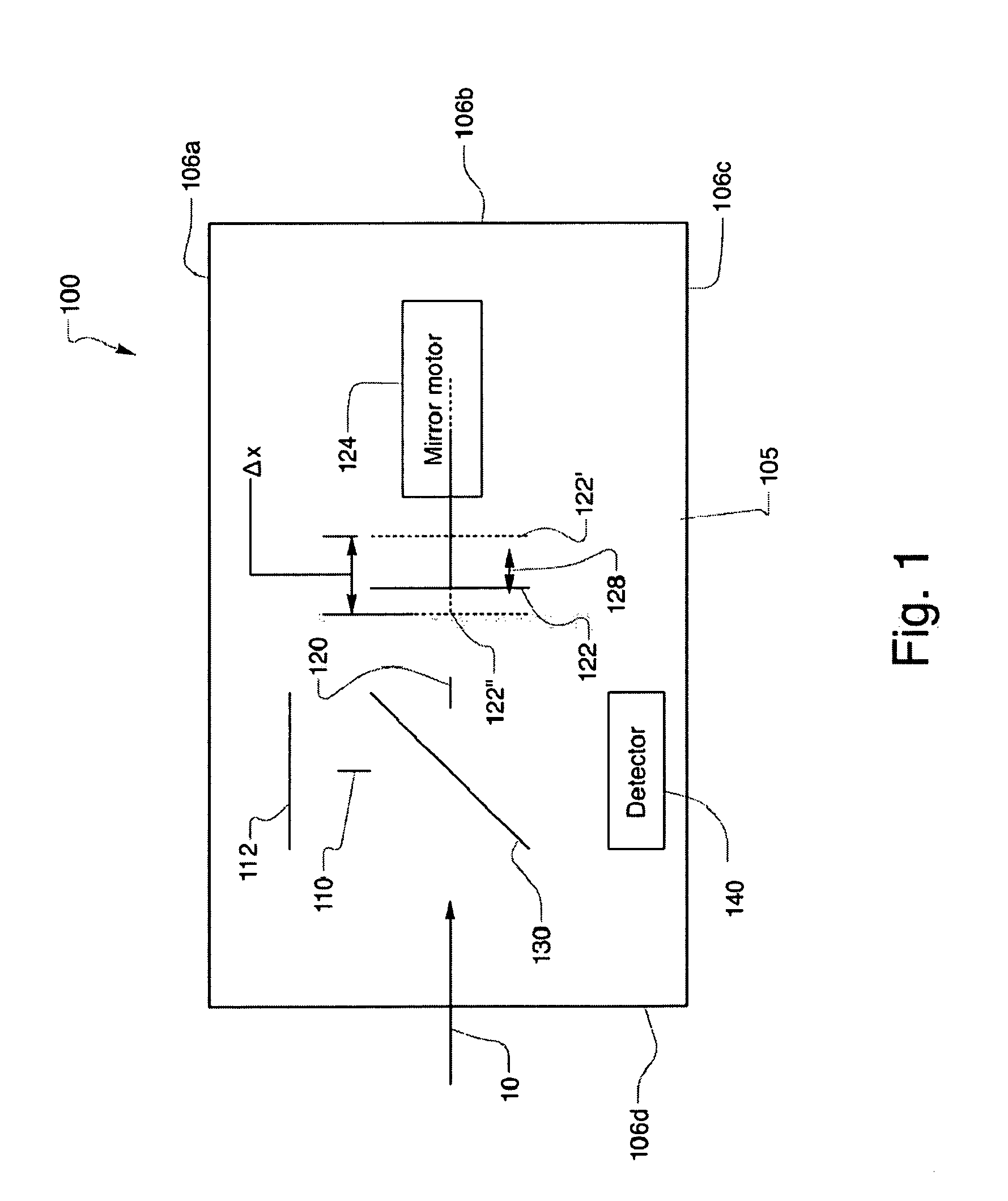
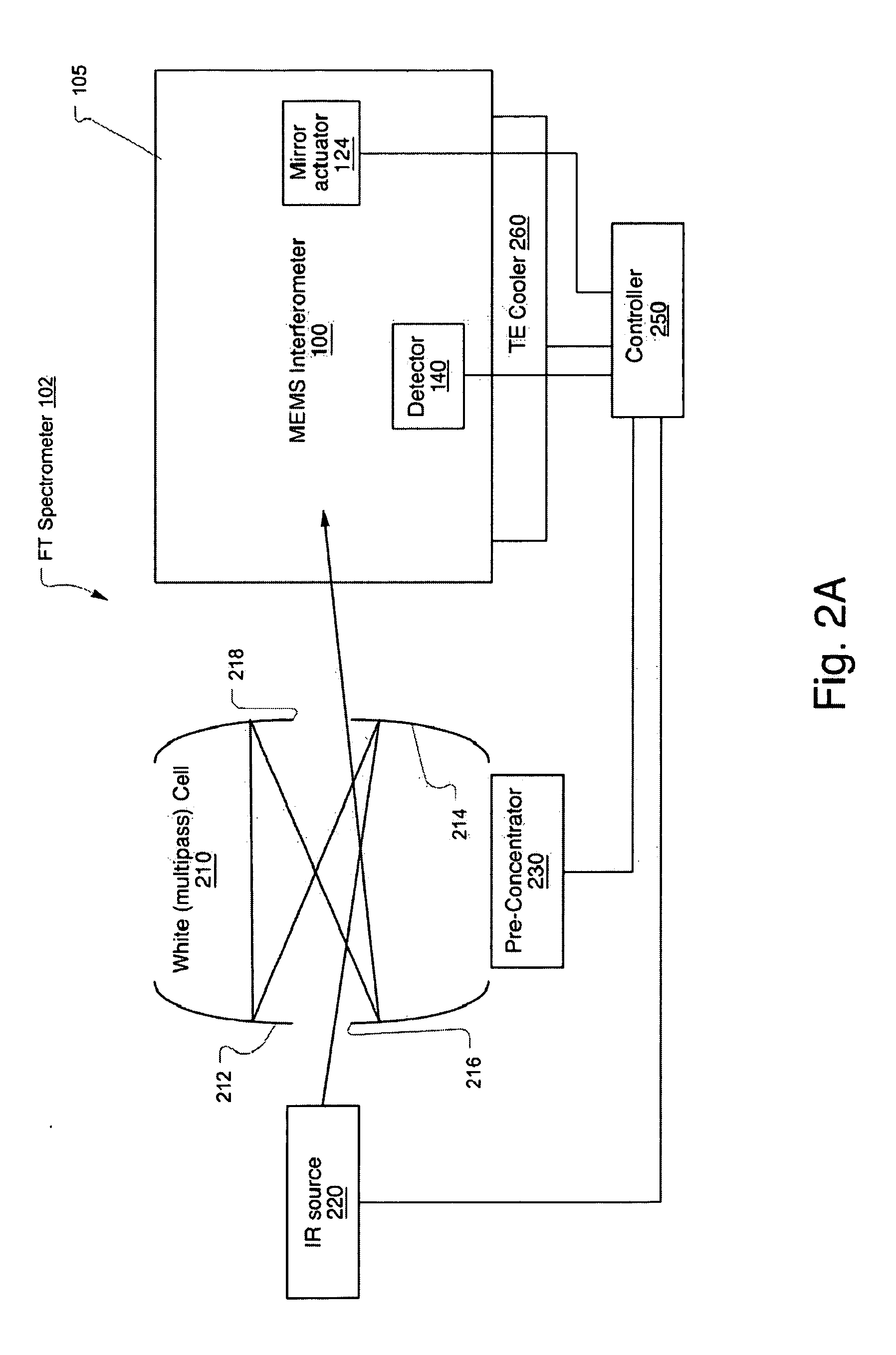
Miniature Fourier Transform Spectrometer and Method of Operation
InactiveUS20100284017A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical tableFourier transform spectrometers
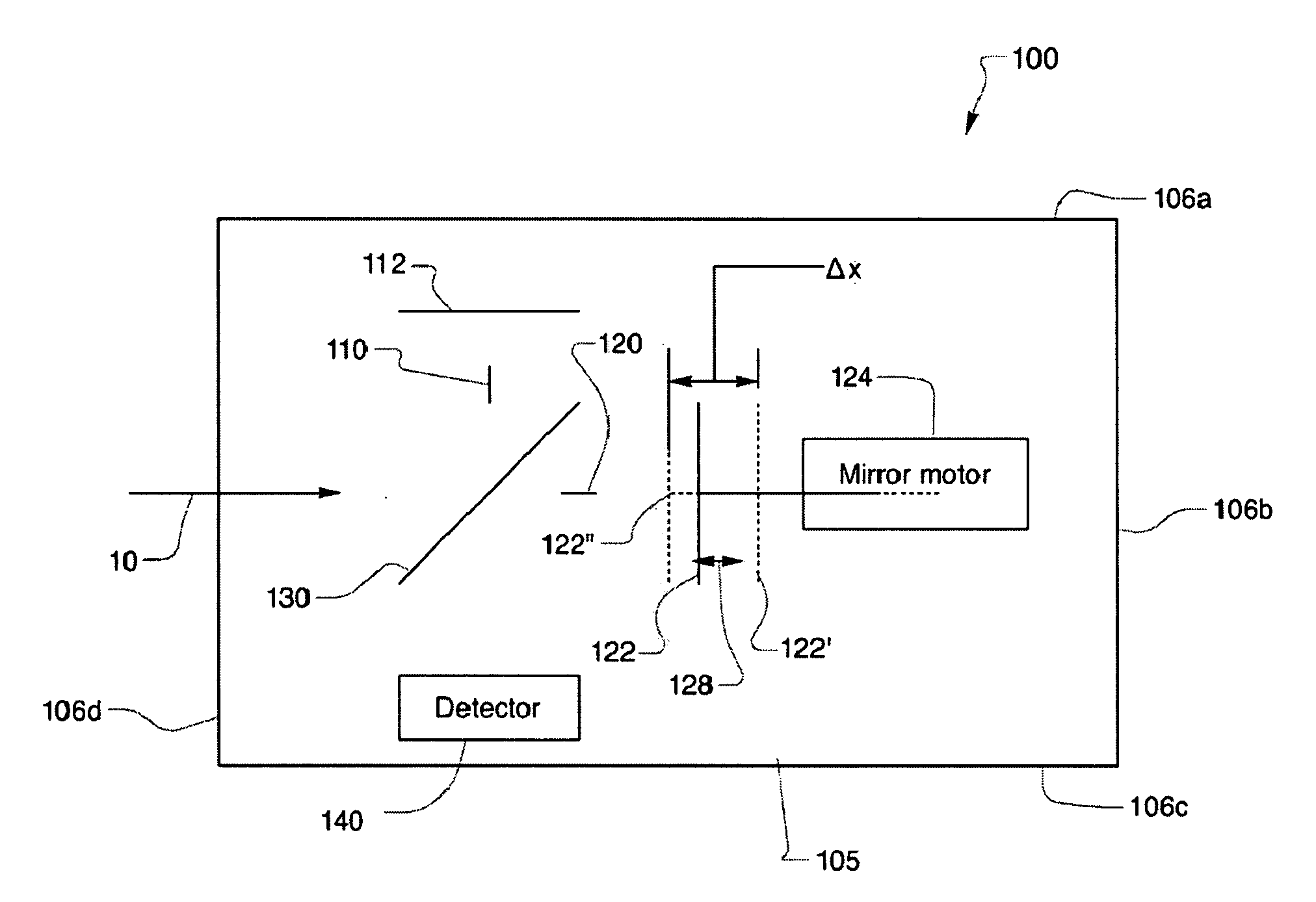
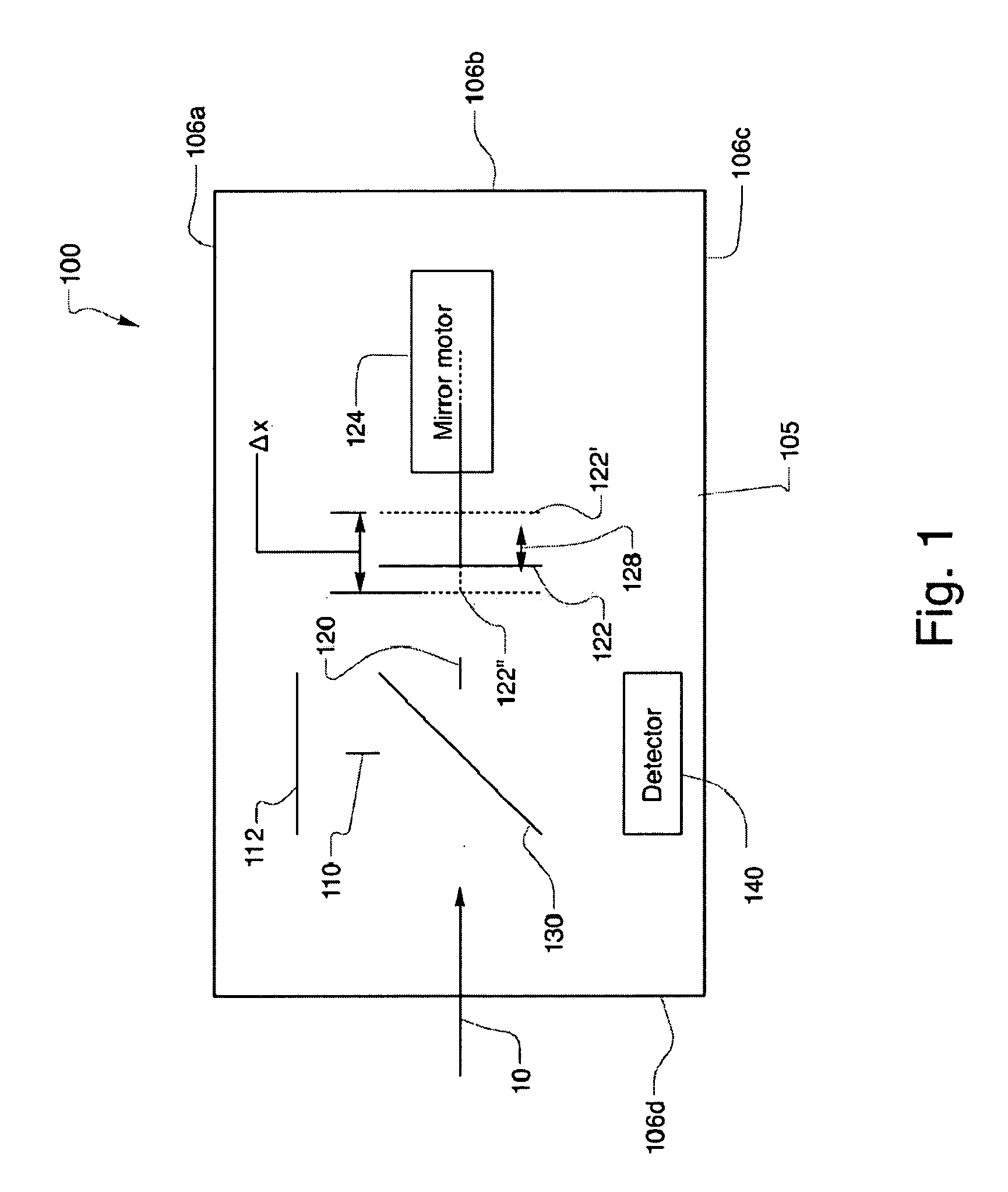
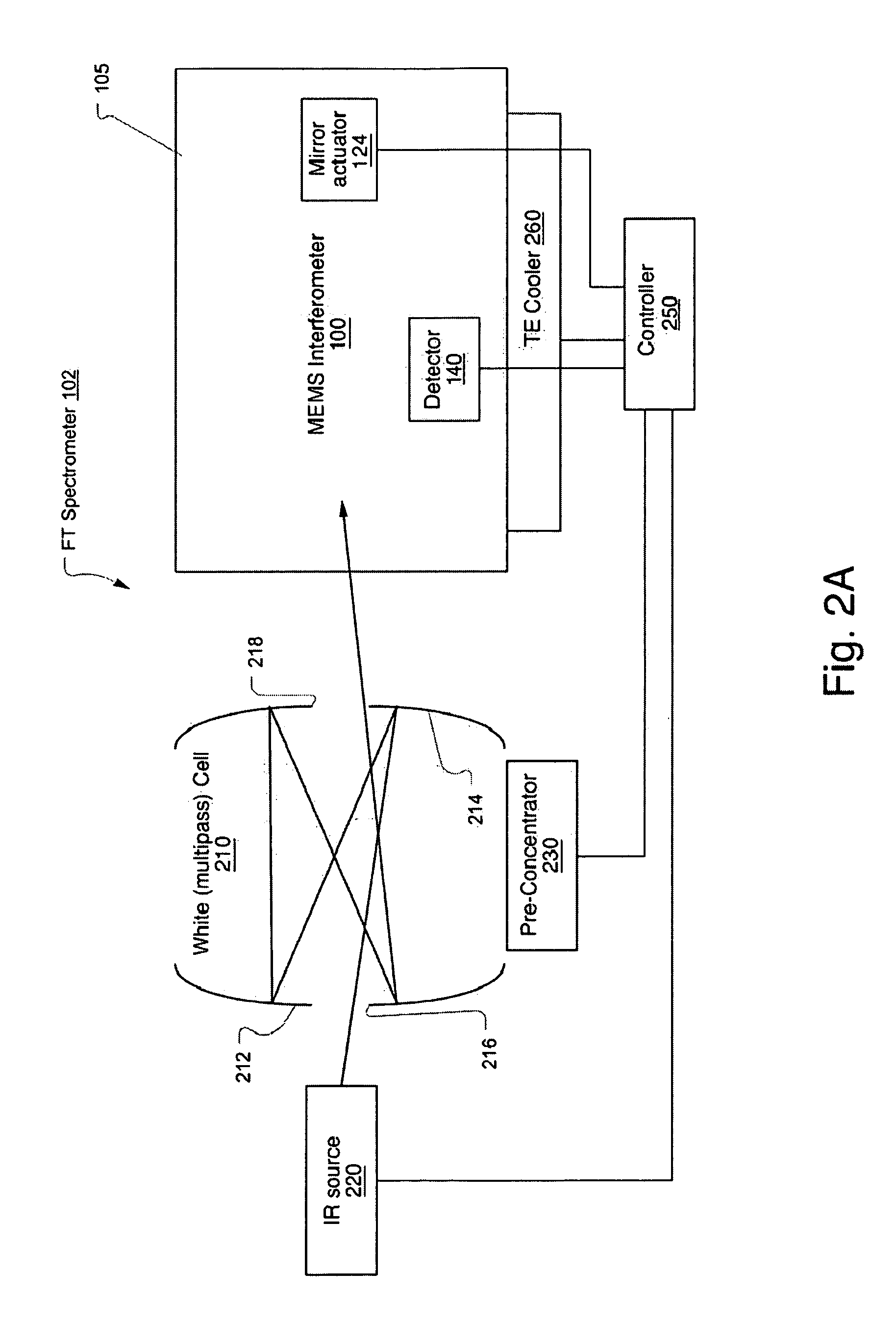
A Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) interferometer is implemented in a Fourier transform spectrometer, which includes a common housing containing the interferometer and a gas cell, possibly including a preconcentrator. The interferometer system includes an optical bench and at least two mirror structures, being patterned from one or more layers on the optical bench and erected to extend substantially perpendicularly to the bench to define two interferometer arms to provide a MEMS interferometer.
Owner:BLOCK ENG
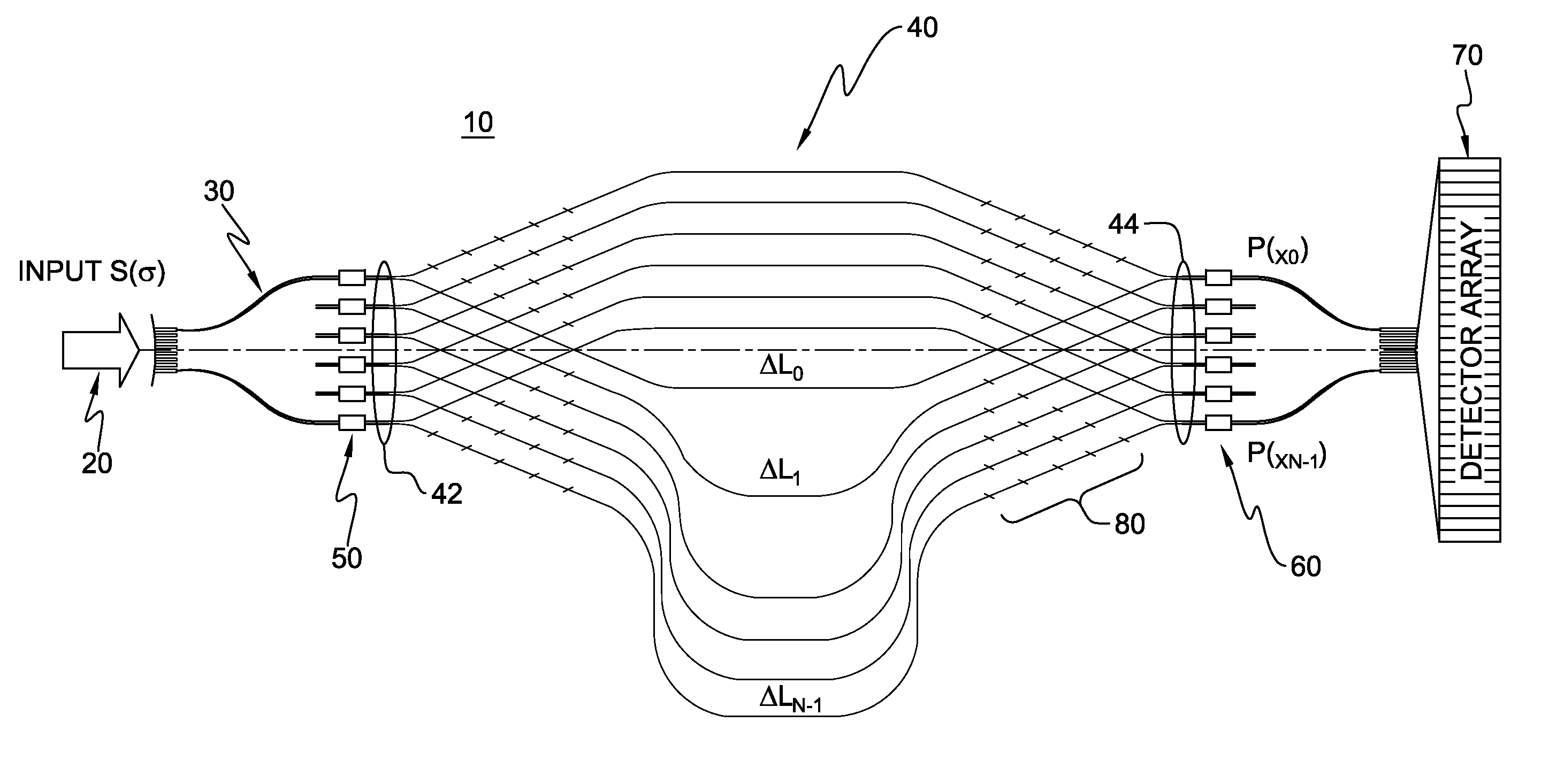
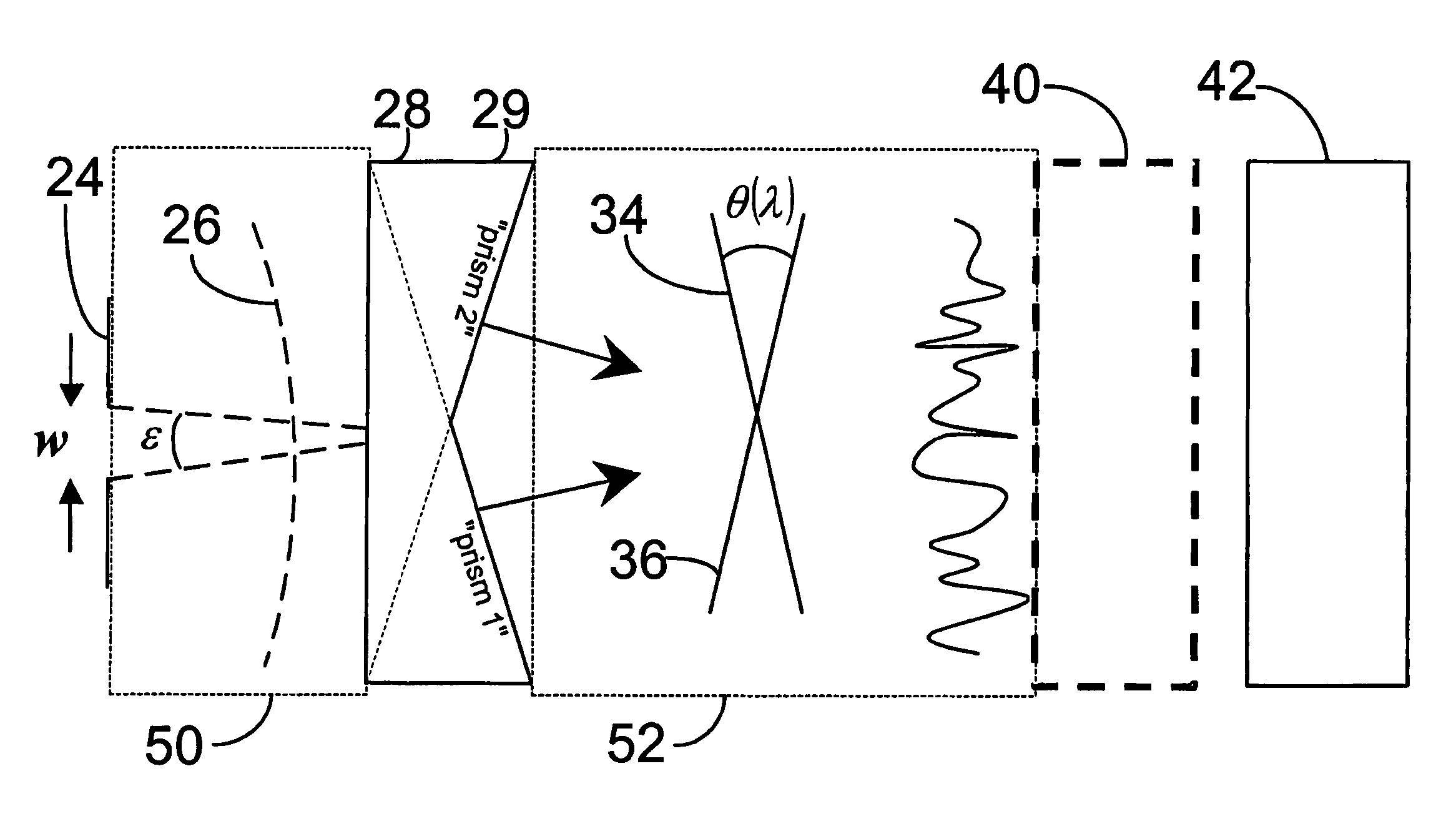
Wavelength dispersive fourier transform spectrometer
A spectroscopic method and system for the spectral analysis of an optical signal directed to a wavelength dispersive component having two interleaved dispersive devices. For a single wavelength, the optical signal exiting the interleaved dispersive devices includes two wavefronts generally disposed at an angle to one another and producing an interference pattern. The interference pattern is detected and subsequently analyzed via a Fourier transform to produce the optical spectrum of the input beam. The method and system are applicable in a planar waveguide environment, in reflection and transmission geometries.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
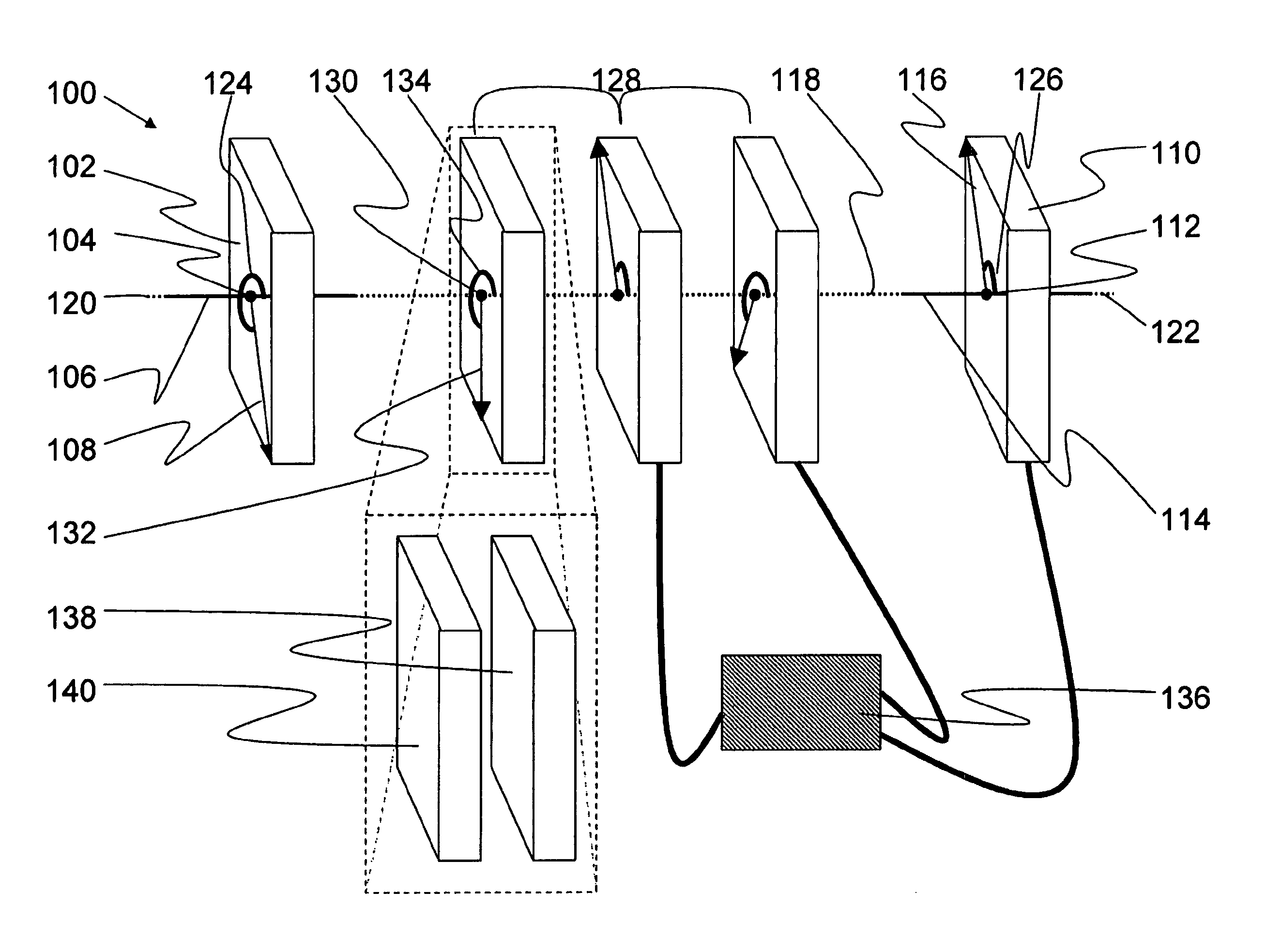
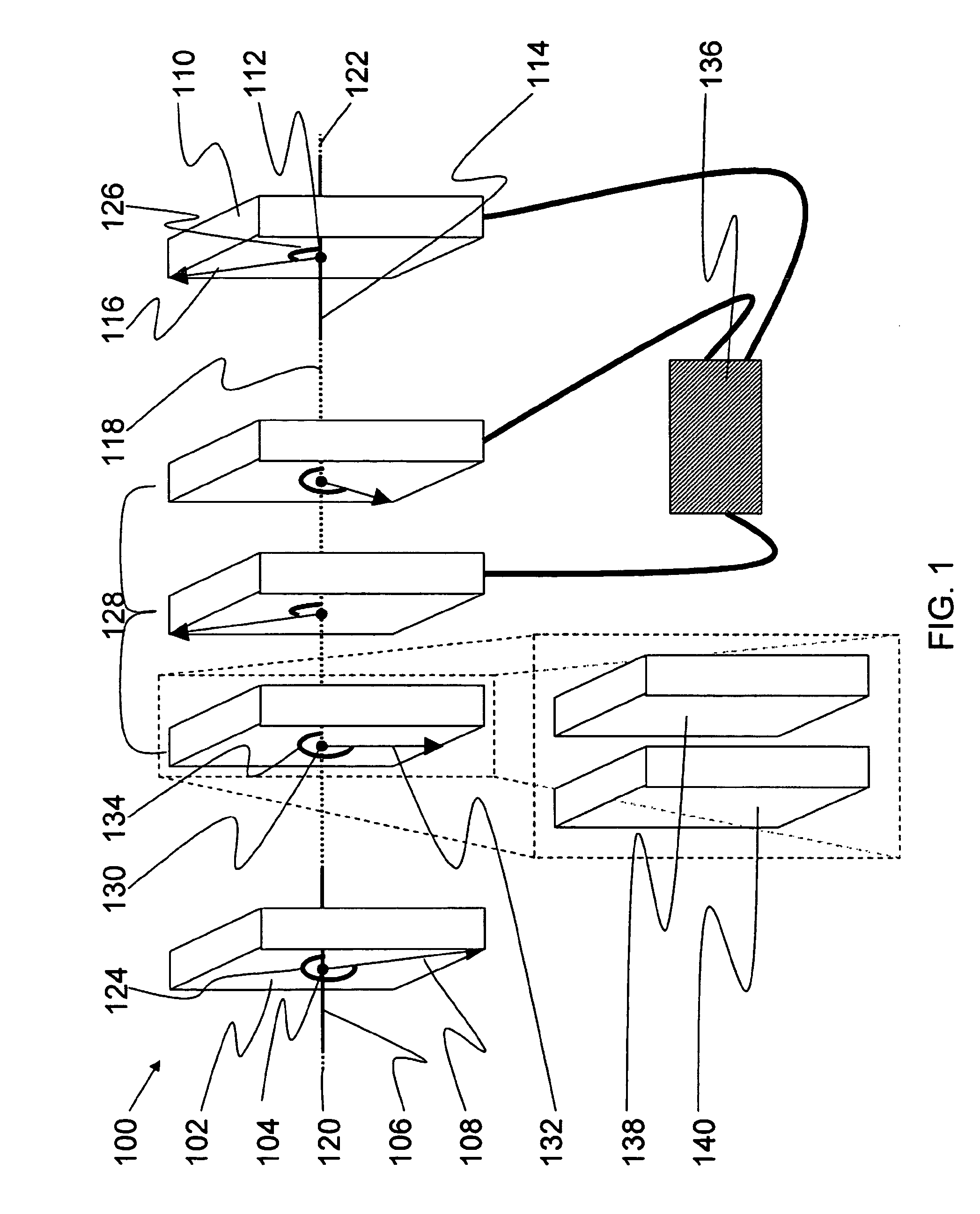
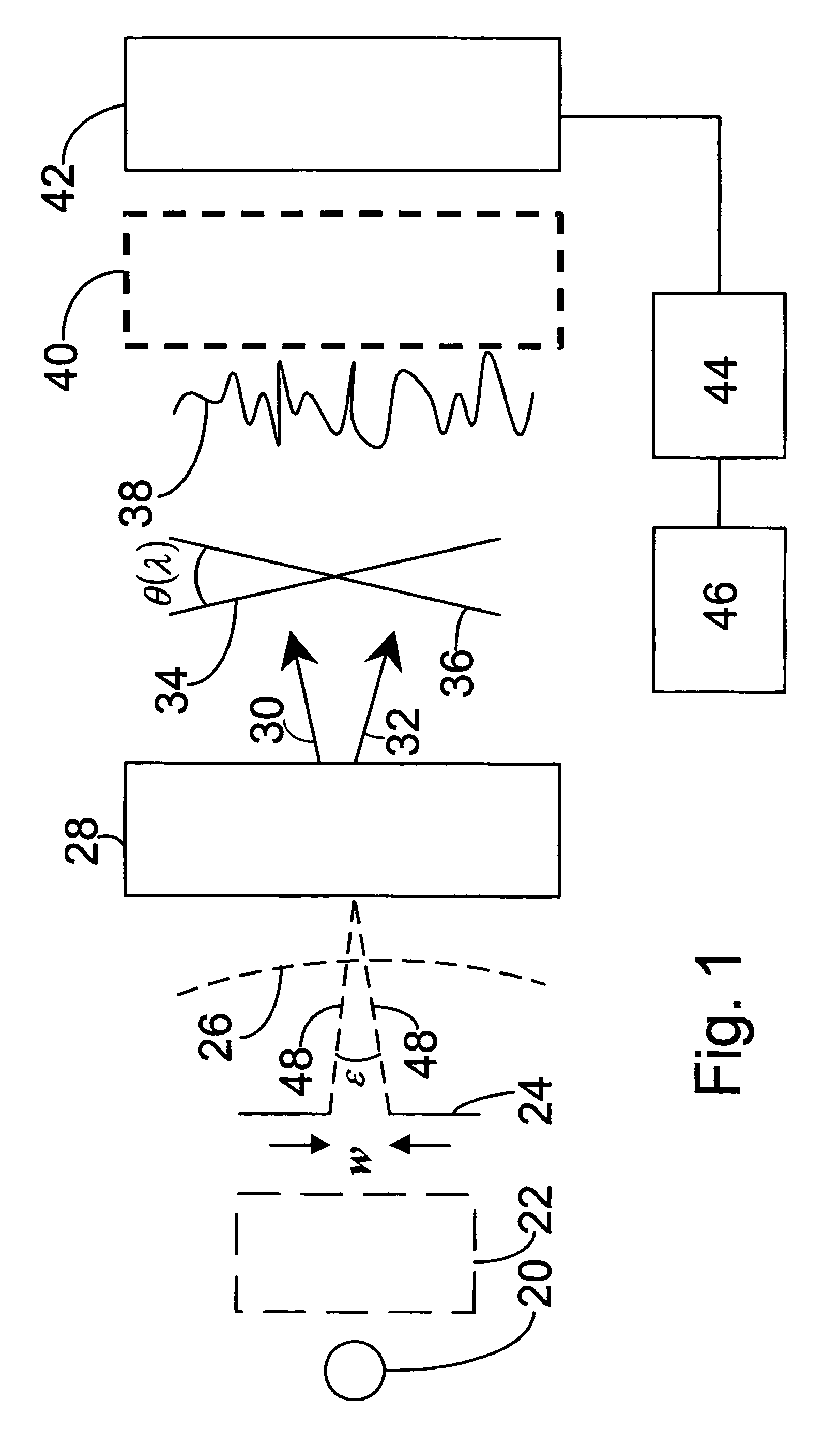
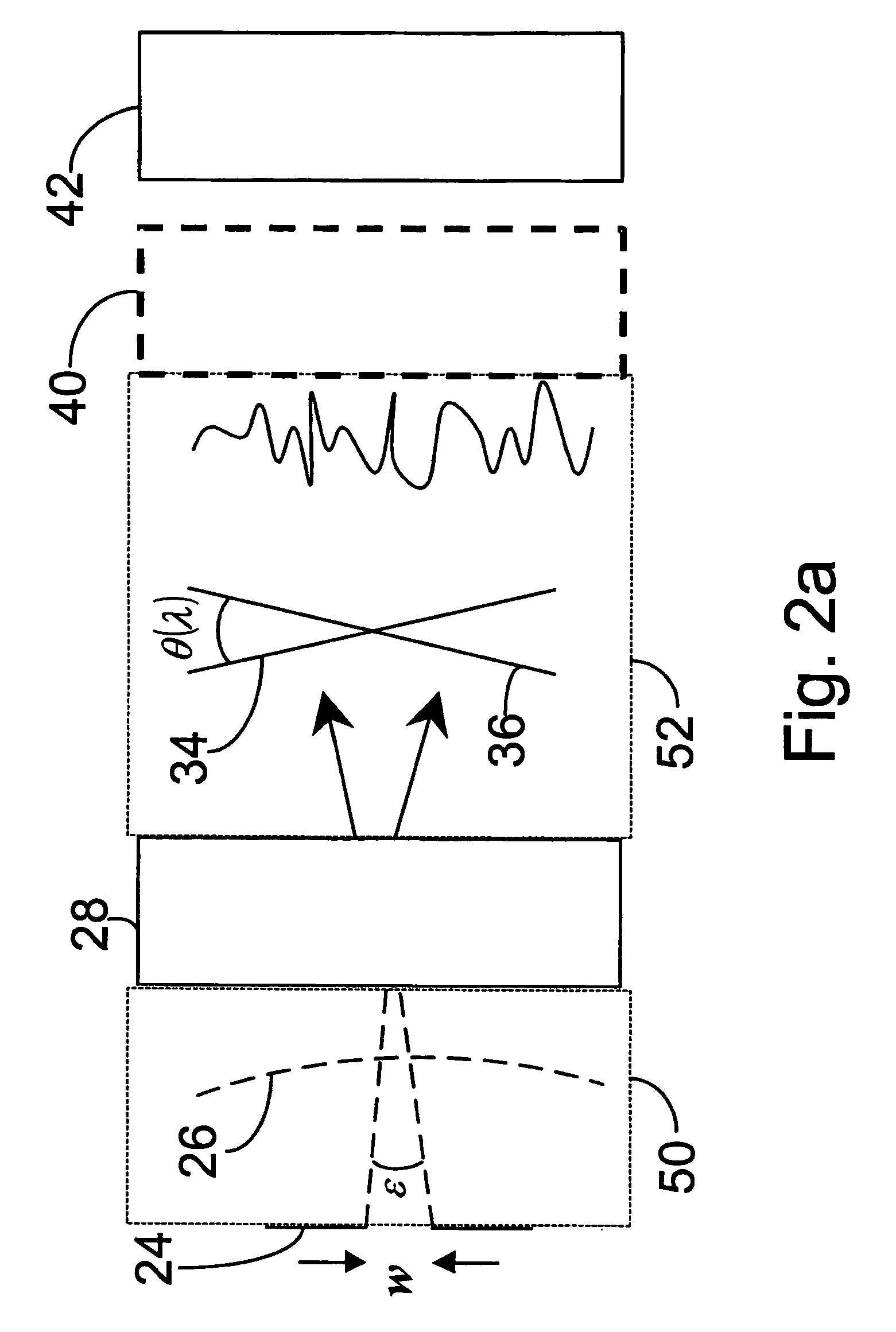
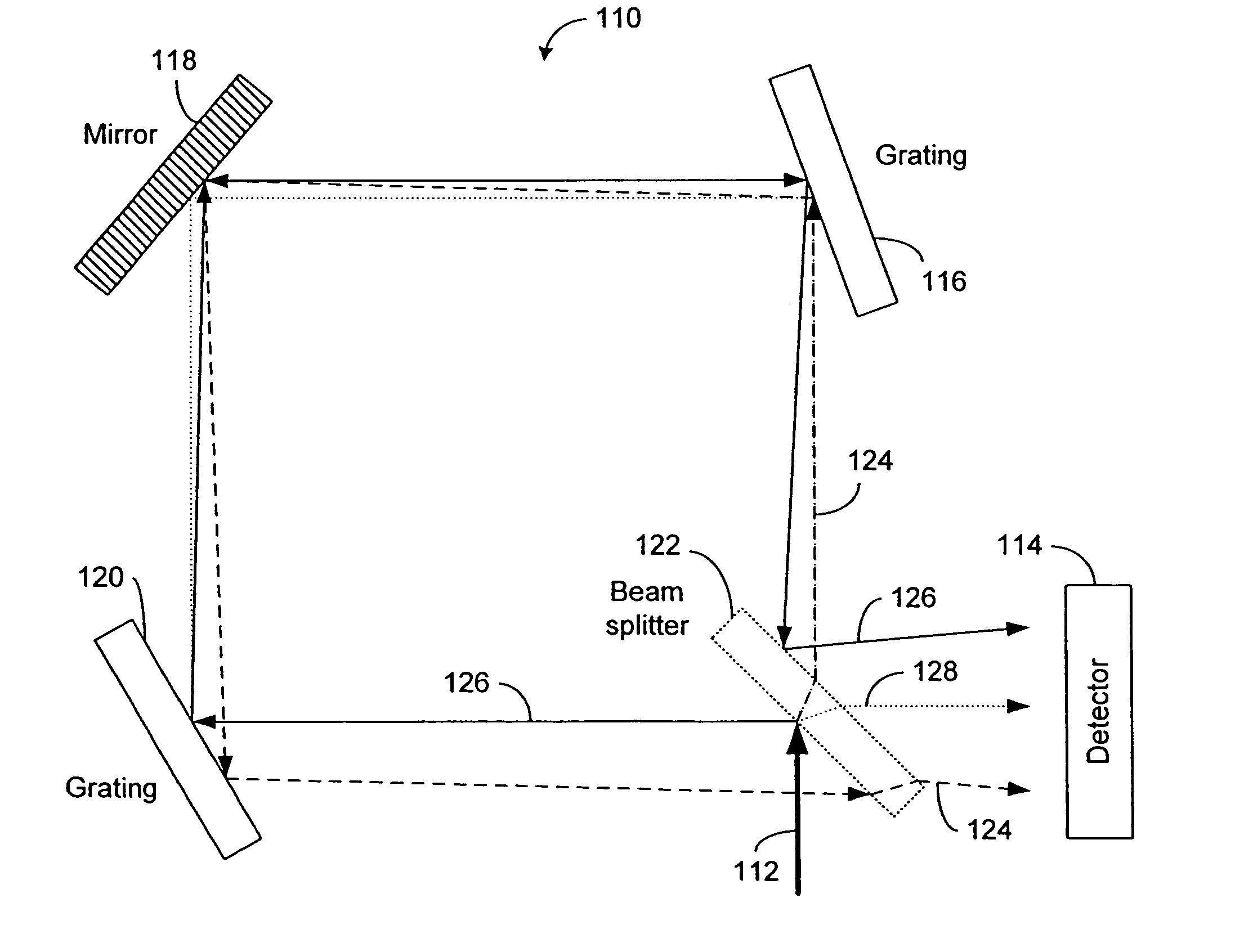
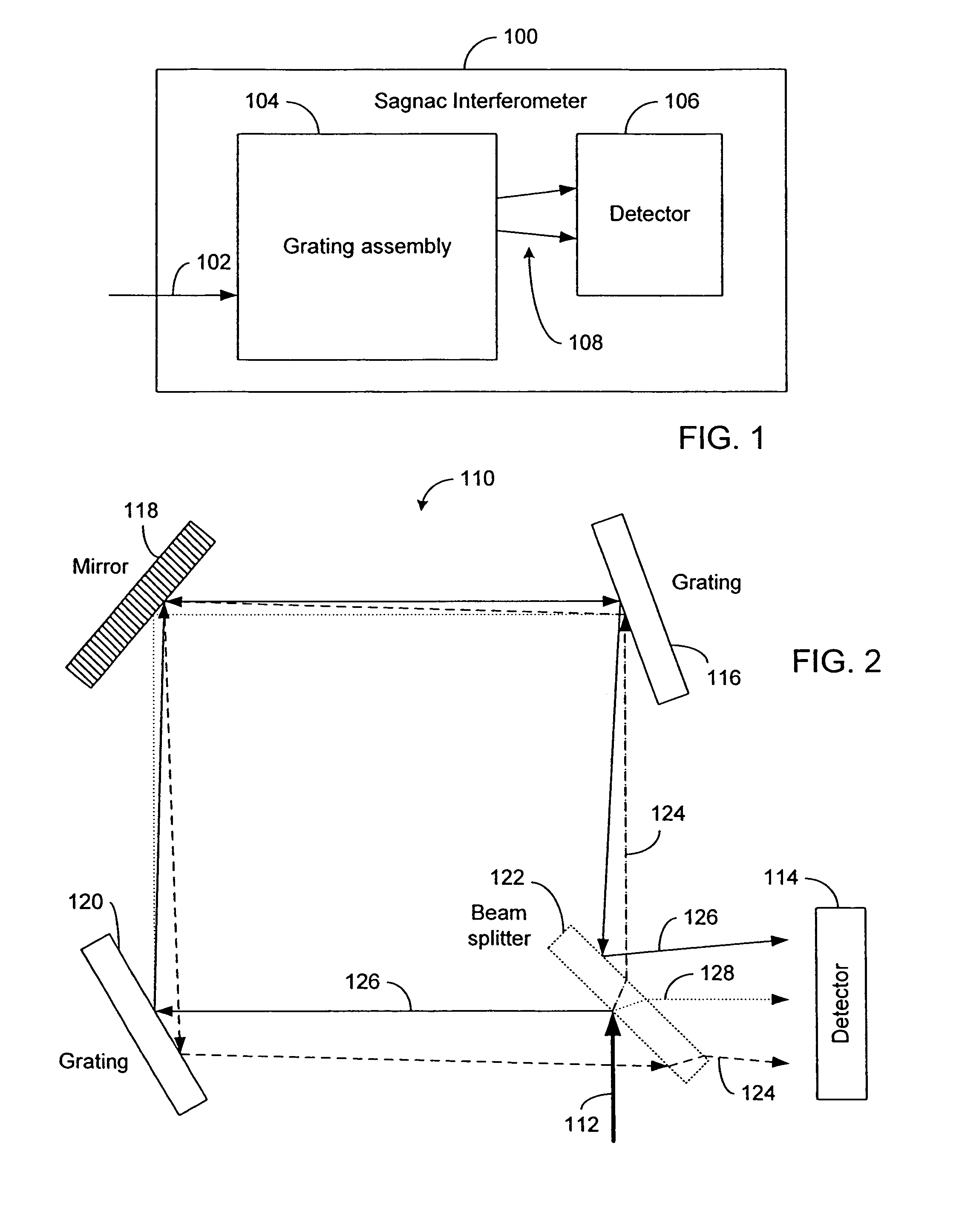
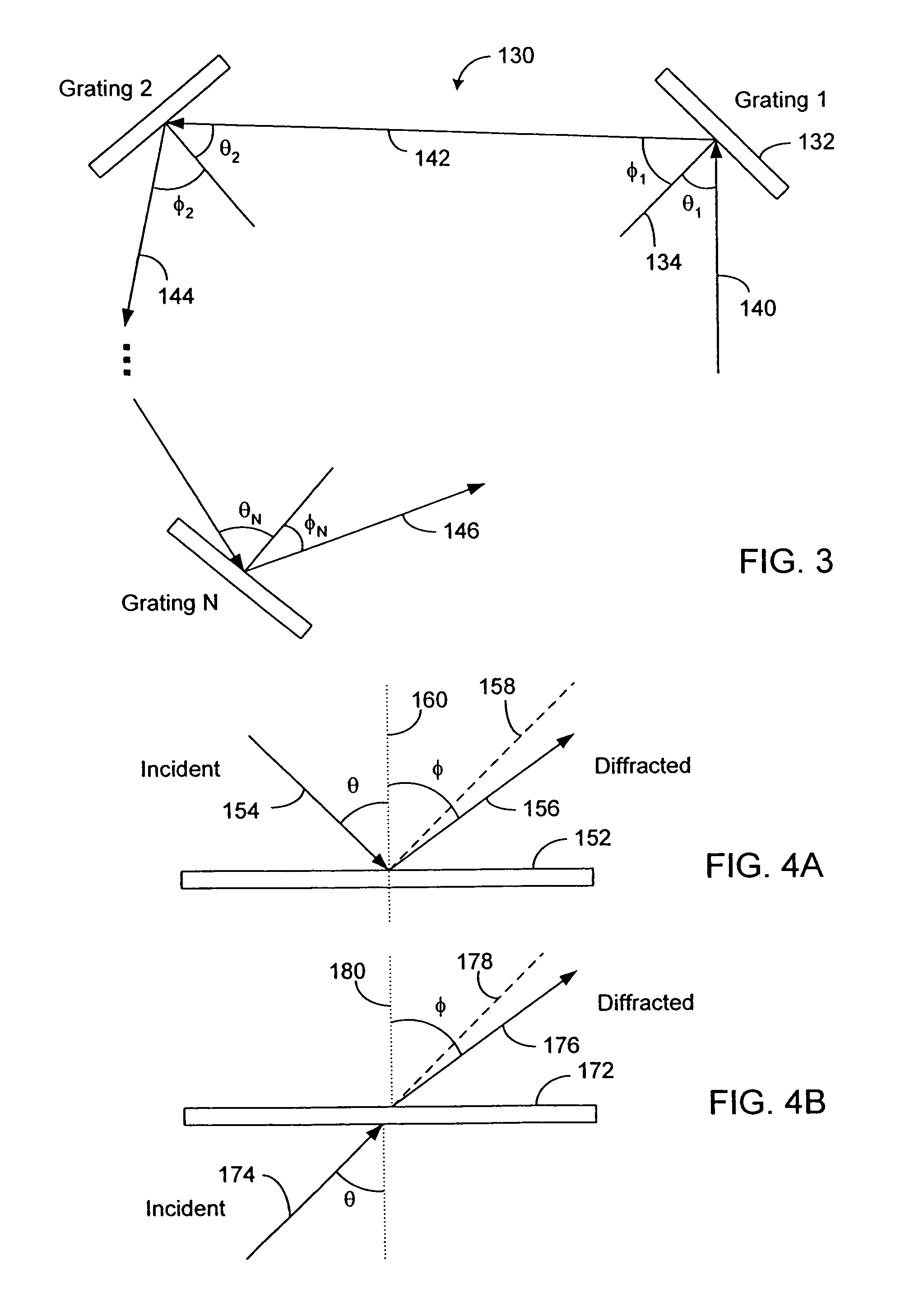
Sagnac fourier transform spectrometer having improved resolution
Systems and methods are disclosed for a modified Sagnac interferometer having a plurality of gratings that can be reflective or transmissive. The gratings allow measurement of wavelength spectra in counter-circulating beams of the interferometer. In one embodiment, diffraction geometries at each pair of neighboring gratings are configured so that diffractive and angular contributions reinforce each other at the second of the pair of gratings. In one embodiment, diffraction geometries at the gratings are configured so that the exiting beams of the interferometer satisfy the crossing condition wherein the exiting beams are on the opposite sides of a reference beam axis for a design wavelength input beam. Also disclosed are techniques for restoring the reinforcement and / or crossing conditions when these conditions are not otherwise met.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
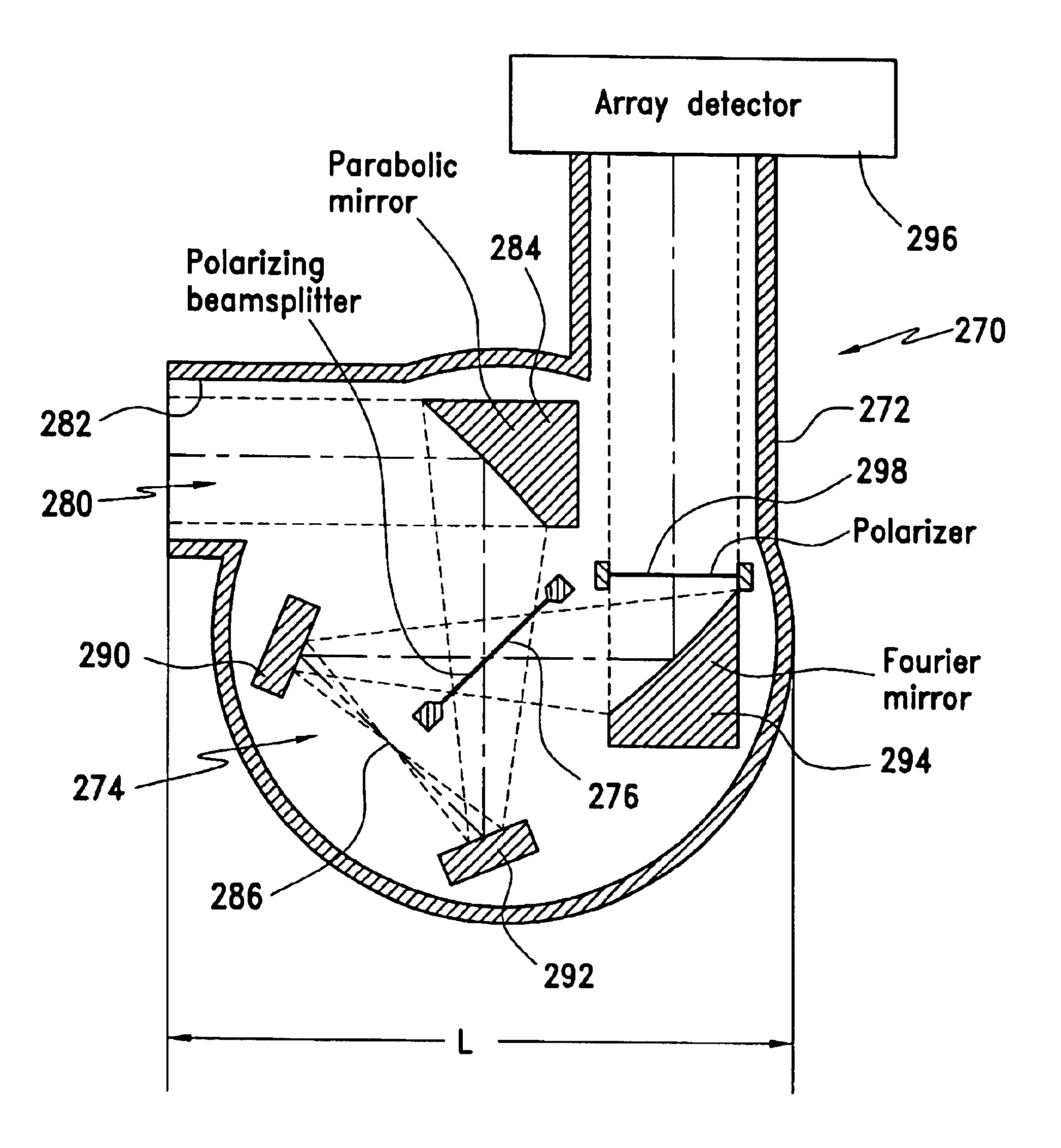
Miniaturized holographic fourier transform spectrometer with digital aberration correction
ActiveUS6930781B2Aberration correctionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometry2d arrayMiniaturization
A digitally aberration corrected miniaturized holographic Fourier transform spectrometer (HFTS) made from simple optical components and with no moving parts is provided. The disclosed digitally aberration corrected HFTS is comprised of a two beam interferometer, which provides two interfering beams; a 2D array detector to detect the interference pattern created by the beams; a computer for correcting effects of aberrations in the pattern and calculating the spectrum from thus corrected interferogram.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
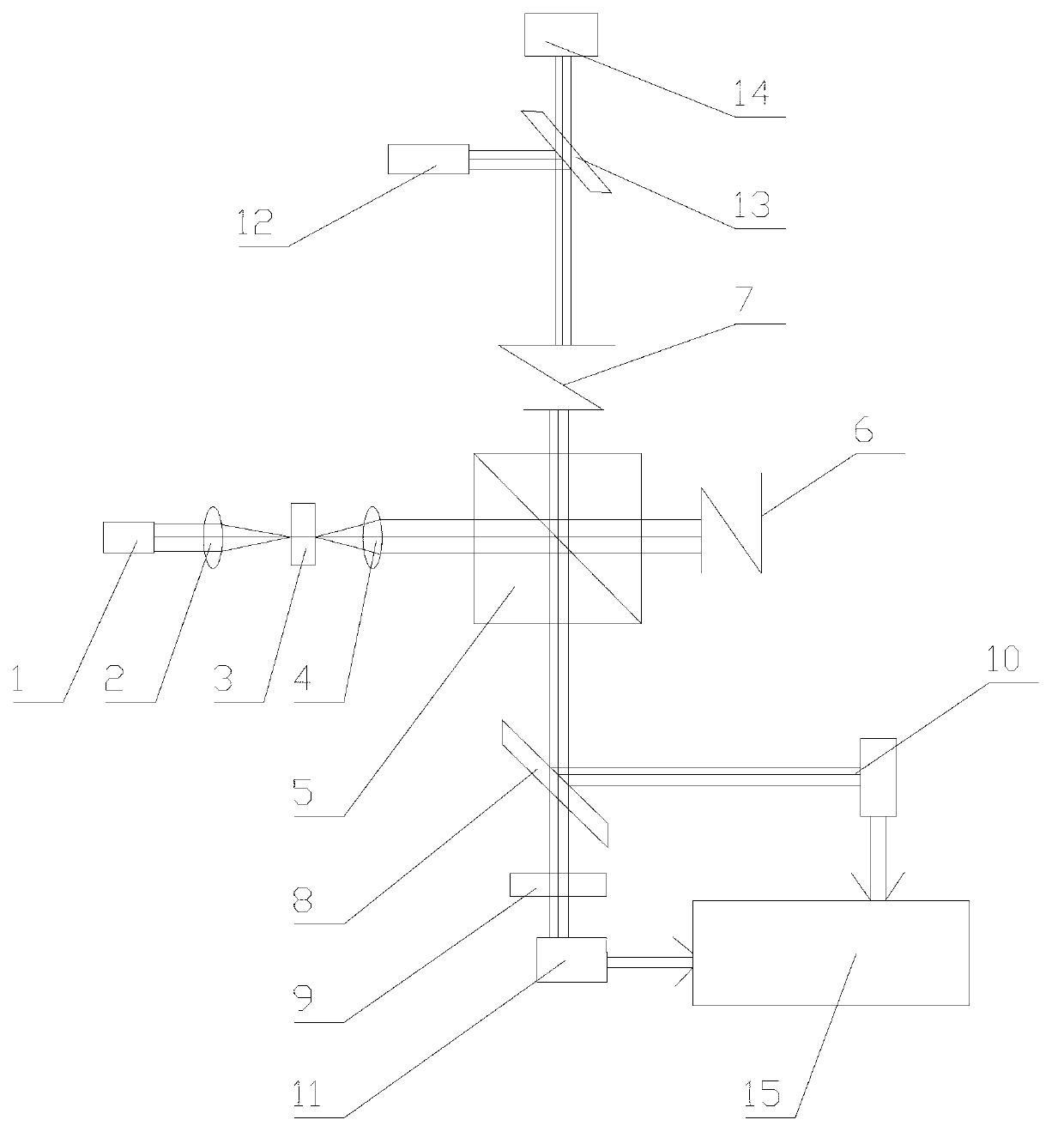
Terahertz wave band nanosecond time-resolved Fourier transform spectrometer
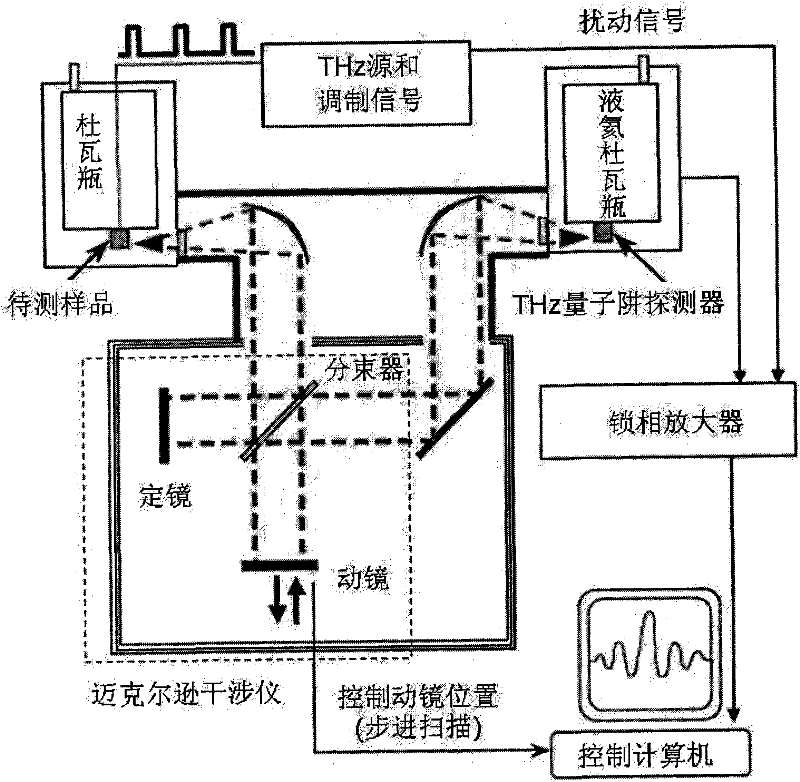
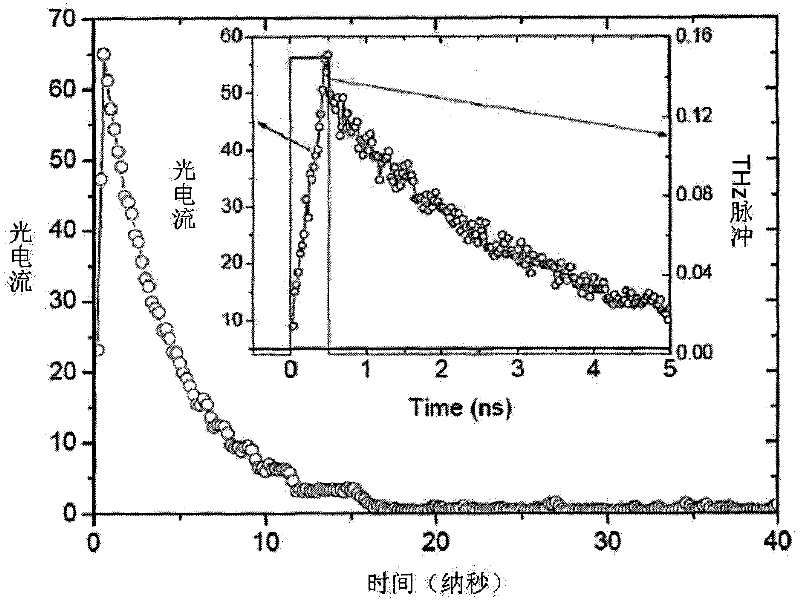
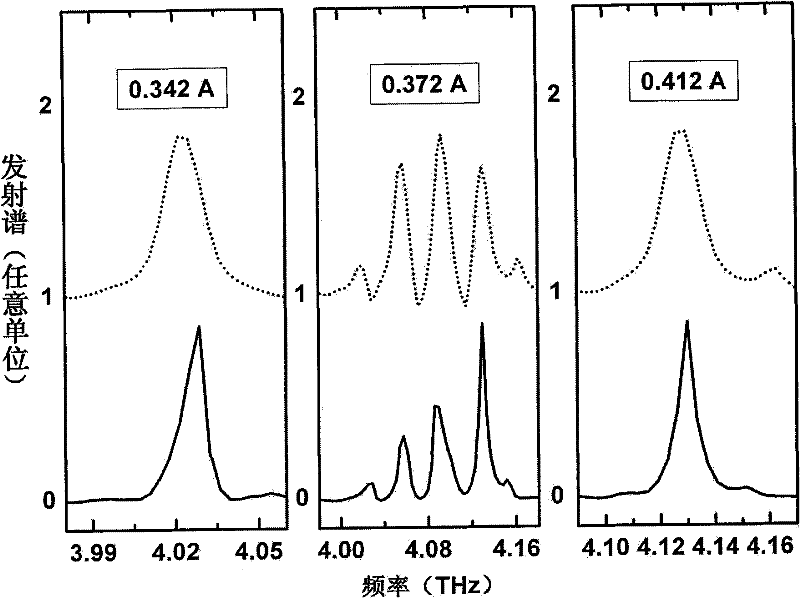
InactiveCN102346071AImprove time resolutionInterferometric spectrometryPyroelectric detectorsNanosecond
The invention discloses a terahertz wave band nanosecond time-resolved Fourier transform spectrometer, comprising a michelson interferometer, a sample room arranged at an input end of the michelson interferometer, a THz quantum well detector arranged at an output end of the michelson interferometer, a THz source, a modulating signal module, a phase-locked amplifier and a control computer. The phase-locked amplifier is connected with the THz quantum well detector; the control computer is connected with the phase-locked amplifier and is further connected with a movable mirror of the michelson interferometer to control the position of the movable mirror so as to move the fixed step length of the movable mirror; and the THz source and the modulating signal module emit a THz laser with a disturbing signal to the sample room, transmit the disturbing signal to the phase-locked amplifier, and transmit the disturbing signal which is amplified by the phase-locked amplifier to the control computer. The existing DTGS-PE and Si pyroelectric detector is replaced by the THz quantum well detector, so that the time resolution of the Fourier transform spectrometer within the THz wave band is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispersed fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS7206073B2Precise spectral measurementGood informationRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryImage resolutionLength wave
A dispersing Fourier Transform interferometer (DFTS) includes a Fourier Transform Spectrometer having an input for receiving a source light and an output, and a dispersive element having an input coupled to the Fourier Transform Spectrometer output and an output for providing the resulting multiple narrowband interferogram outputs of different wavelengths representative of the source light input. A processor applies a sparse sampling algorithm for determining the best fit between a set of model interferograms and the set of data interferograms. The model interferogram is inferred as specified at a discrete set of lags, a difference is determined between the model interferogram and the data interferogram, and an optimization method determines the model interferogram best matched to the data interferogram. The DFTS interferometer improves the sensitivity of a standard FTS by including a dispersive element, increasing the SNR by a factor of (Rg)1 / 2 as compared to the FTS, where Rg is the resolving power of the conventional dispersing spectrometer (i.e. Rg=λ / Δλ).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
MEMS Michelson Interferometer and Method of Fabrication
An interferometer system includes an optical bench and at least two mirror structures, being patterned from one or more layers on the optical bench and erected to extend substantially perpendicularly to the bench to define two interferometer arms to provide a Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) interferometer. The MEMS interferometer is further implemented in a Fourier transform spectrometer, which includes a common housing containing the interferometer and a gas cell, possibly including a preconcentrator.
Owner:BLOCK ENG
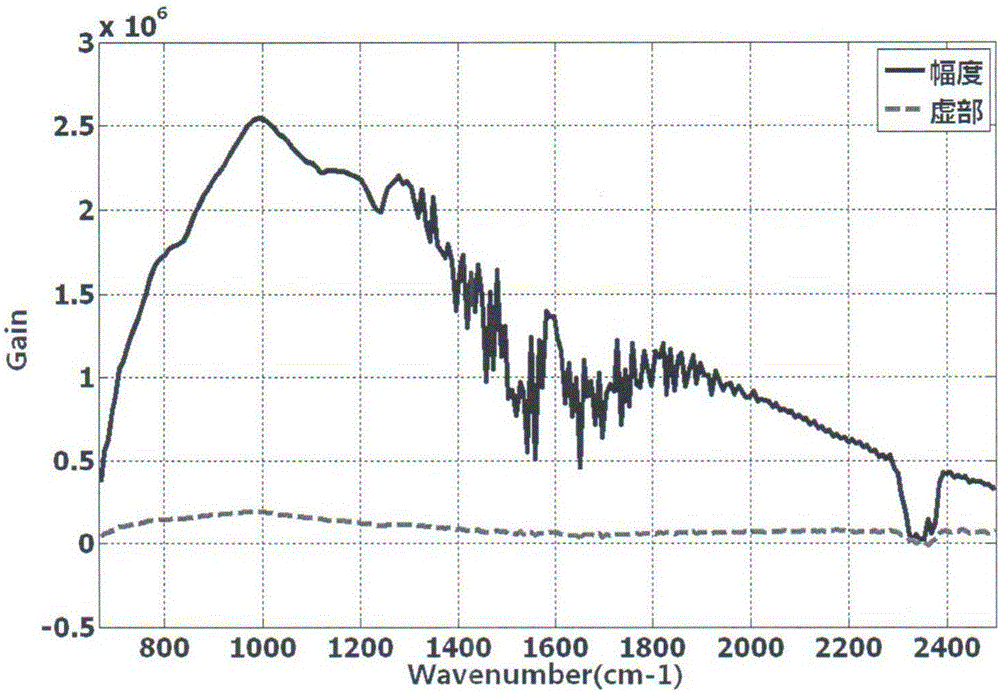
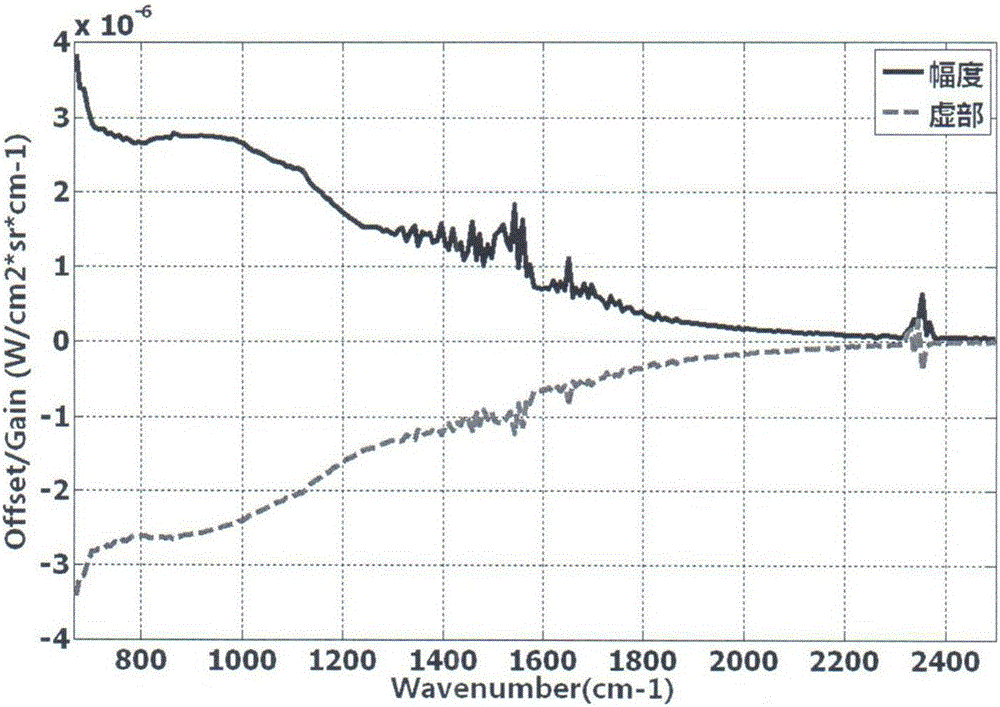
Complex spectrum multi-spot radiation scaling method for Fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveCN105043548AImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing precisionInterferometric spectrometryRadianceFourier transform spectrometers
The invention discloses a complex spectrum multi-spot radiation scaling method for a Fourier transform spectrometer. The complex spectrum multi-spot radiation scaling method for a Fourier transform spectrometer comprises: respectively acquiring measuring voltage values (shown in the description) corresponding to n temperature spots of a Fourier transform spectrometer, wherein n>=2; calculating the spectral radiance (shown in the description) of each temperature spot; calculating the practical linear gain (shown in the description) for the Fourier transform spectrometer under each wave number v and the practical offset (shown in the description) for the Fourier transform spectrometer under each wave number v; and acquiring the target spectral radiance (shown in the description) input by the Fourier transform spectrometer through the following formula (shown in the description).
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Micro Fourier transform spectrometer
ActiveCN103344609AHigh control precisionAccurate motion precisionPhase-affecting property measurementsBeam splitterPlane mirror
The invention discloses a micro Fourier transform spectrometer comprising a light source and an interference system, wherein the interference system comprises a first beam splitter mirror, a movable mirror and a fixed mirror, a light beam emitted by the light source irradiates onto the first beam splitter mirror, the first beam splitter mirror divides a light beam into two paths, one path of the light beam irradiates the movable mirror, the other path of the light beam irradiates the fixed mirror, two light beams reflected by the movable mirror and the fixed mirror are reflected onto the first beam splitter mirror to form interference light paths and generate interference fringes, the movable mirror is an MEMS (Micro-electromechanical Systems) micro-mirror, the fixed mirror is an MEMS micro-mirror or a plane mirror, and if the fixed mirror is the MEMS micro-mirror, the fixed mirror generates displacement so as to perform phase modulation. The micro Fourier transform spectrometer disclosed by the invention is accurate in precision and small in volume.
Owner:无锡微文半导体科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com