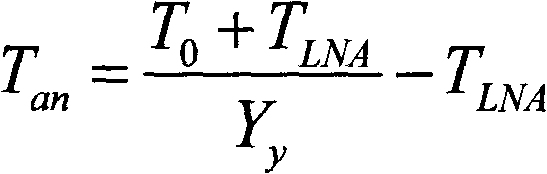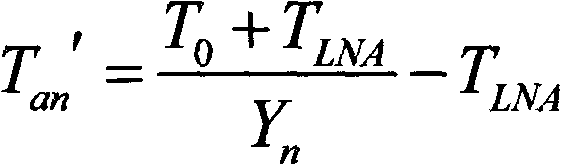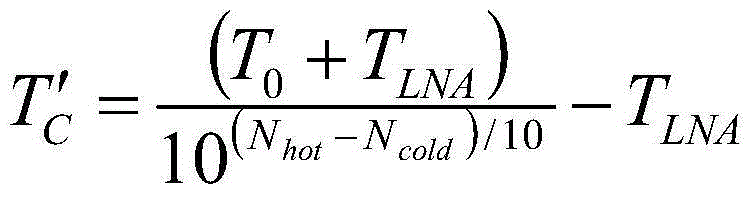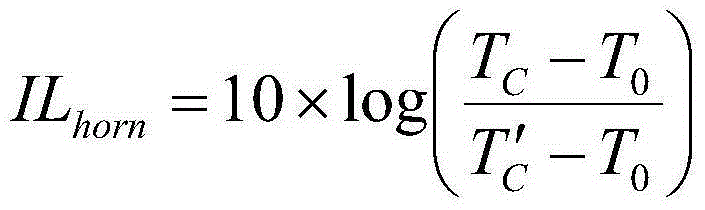Patents
Literature
91 results about "Noise temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
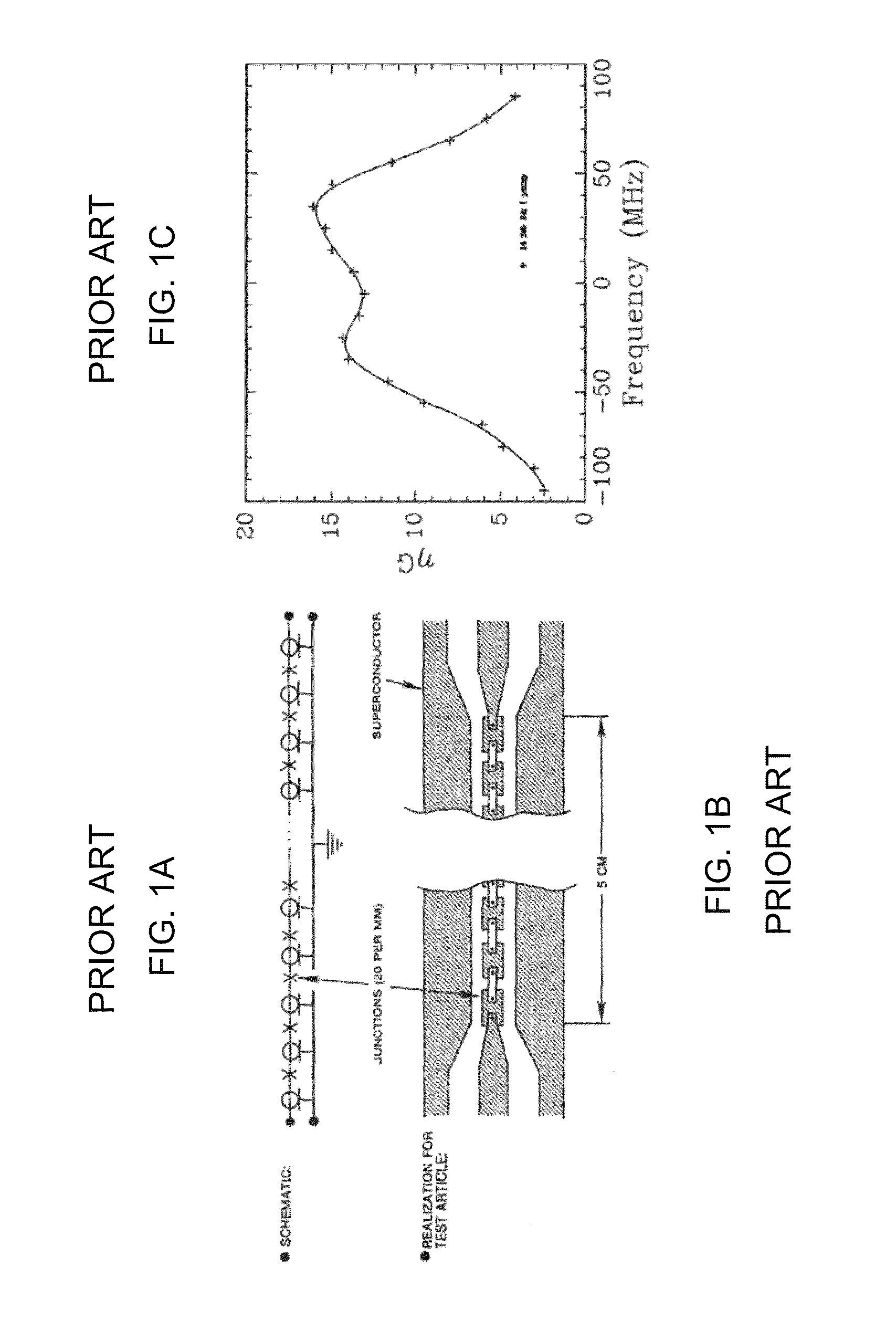
In electronics, noise temperature is one way of expressing the level of available noise power introduced by a component or source. The power spectral density of the noise is expressed in terms of the temperature (in kelvins) that would produce that level of Johnson–Nyquist noise, thus: PN/B=kBT where: PN is the noise power (in W, watts) B is the total bandwidth (Hz, hertz) over which that noise power is measured kB is the Boltzmann constant (1.381×10⁻²³ J/K, joules per kelvin) T is the noise temperature (K, kelvin) Thus the noise temperature is proportional to the power spectral density of the noise, PN/B.
Nonlinear calibrating method and device for foundation microwave radiometer
InactiveCN102243294AWave based measurement systemsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsBrightness temperatureMicrowave radiometer
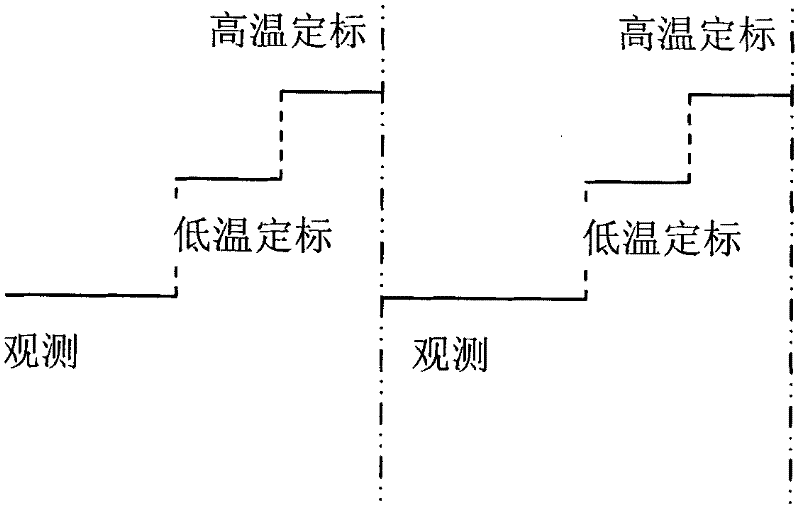
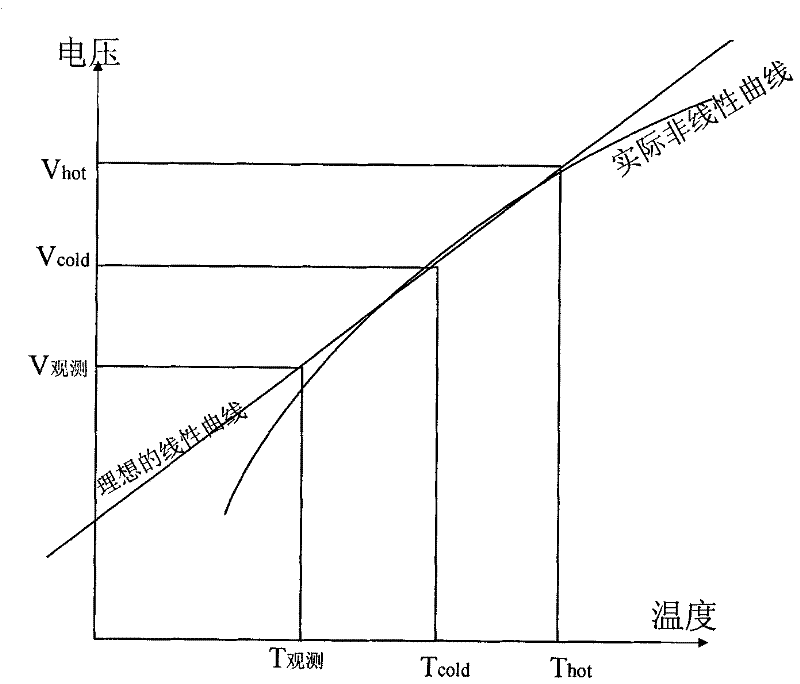
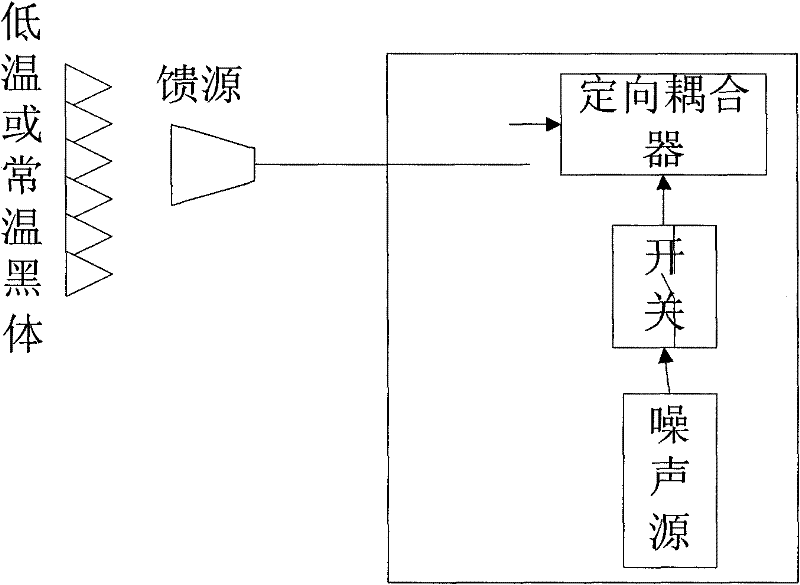
The invention provides a nonlinear calibrating method for a foundation microwave radiometer, and the nonlinear calibrating method can be used for realizing noise injected multi-point brightness temperature on the basis of foundation microwave radiometer noise injected two-point calibration. In the method, periodical calibration is performed on drifting of noise temperature and gain of a receiver by utilizing multi-point brightness temperature values which are acquired by two known reference targets and the other two known noise injected reference targets, and a calibration equation acquired by nonlinear factors of a foundation microwave radiometer system can be determined for real-time measurement of the target brightness temperature. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a nonlinear calibrating device for the foundation microwave radiometer, and the nonlinear calibrating device comprises a noise injection module and a system built-in calibration blackbody, wherein the noise injection module comprises a noise source, a switch and a directional coupler; and the system built-in calibration blackbody provides standard brightness temperature equivalent to the environment temperature. By utilizing the method, nonlinear errors caused by the nonlinear power characters of a detector diode can be reduced, so that the detection accuracy can be improved.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
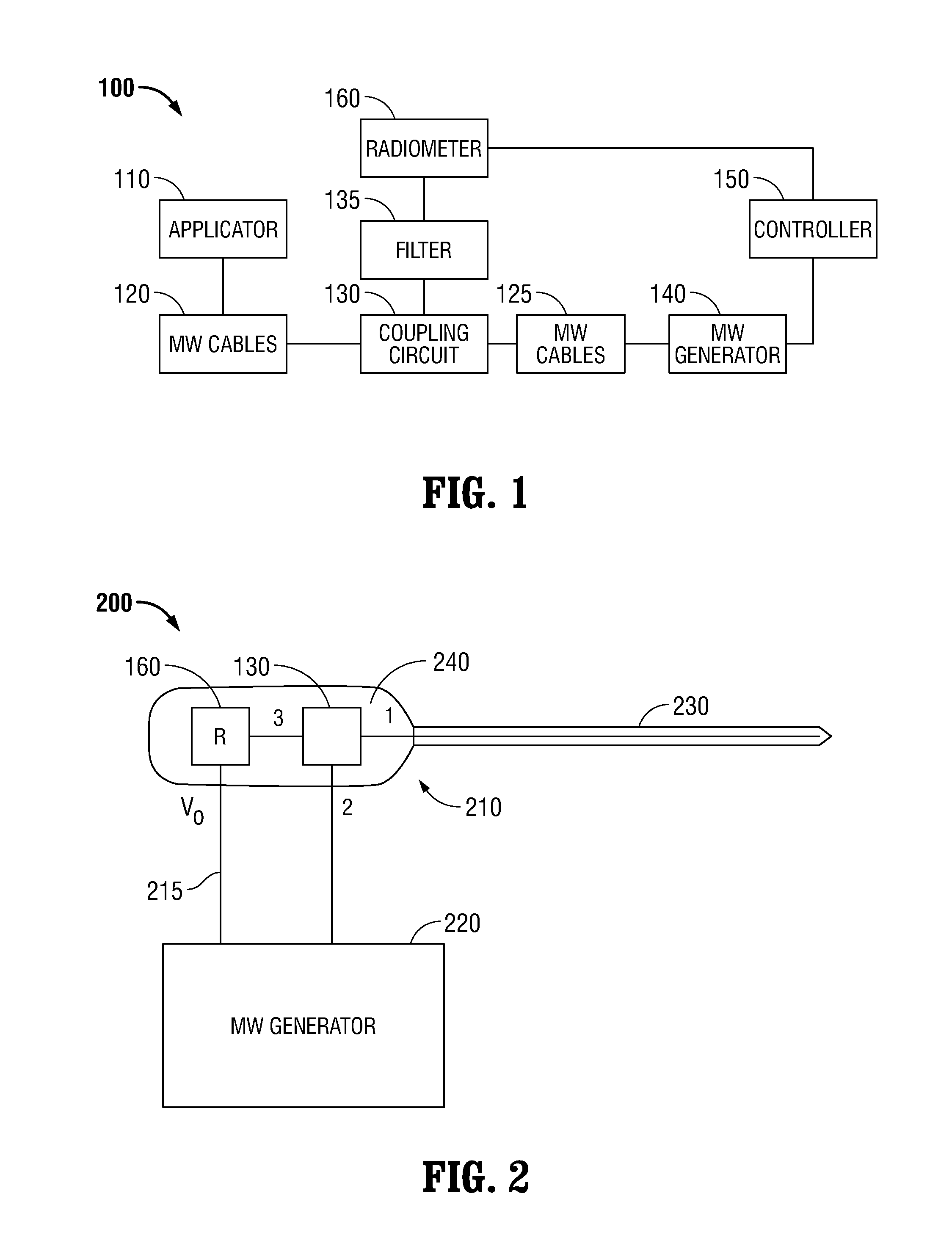
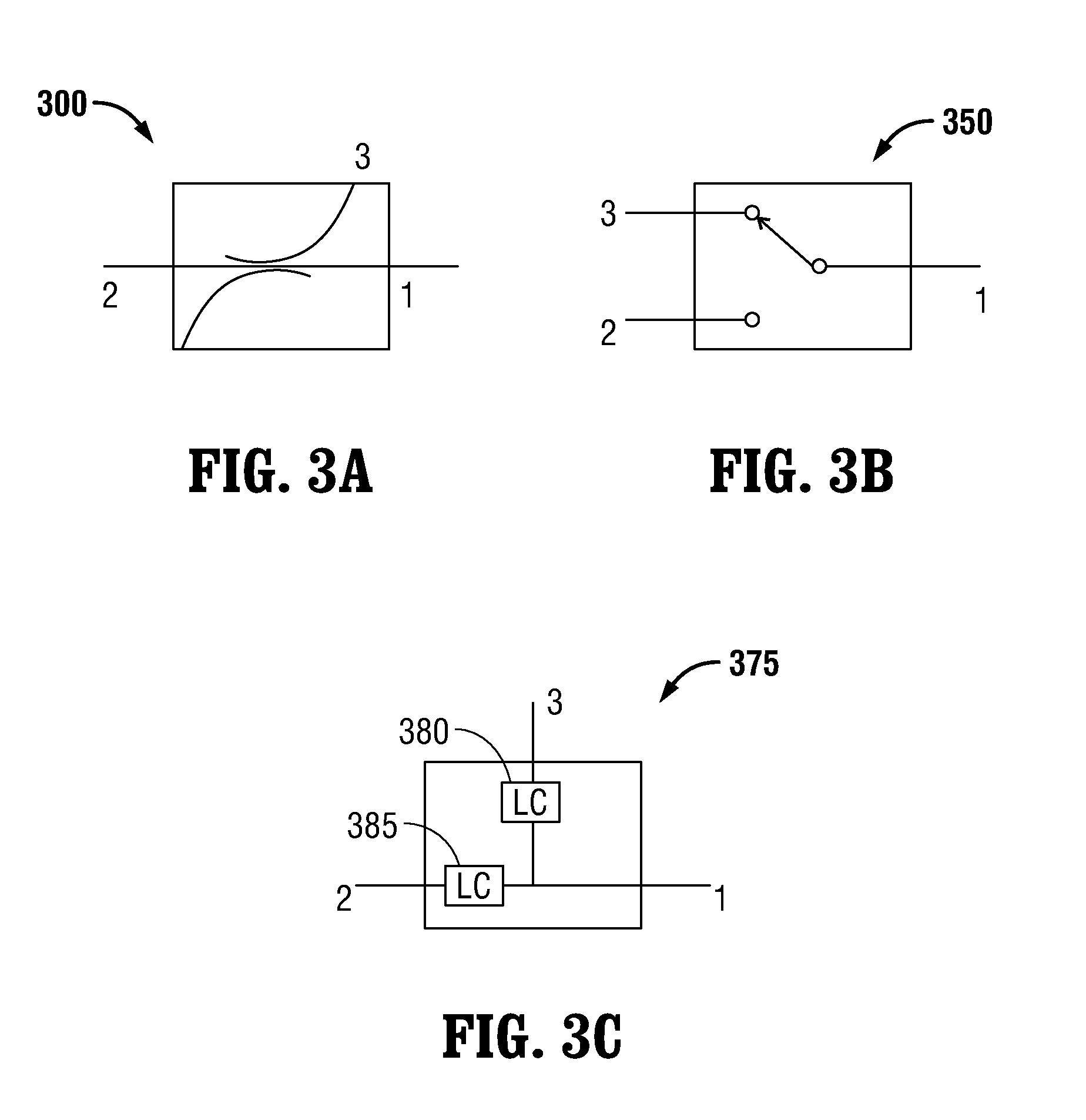
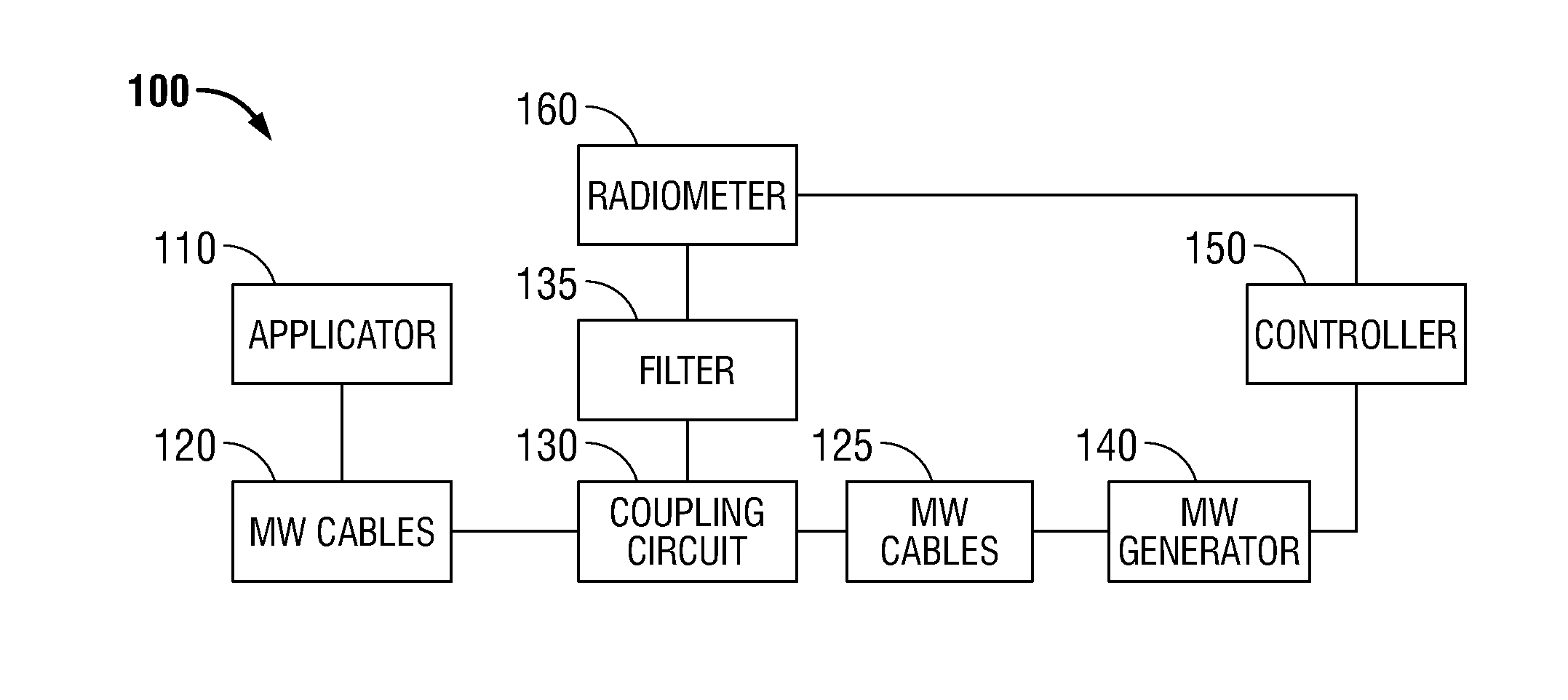
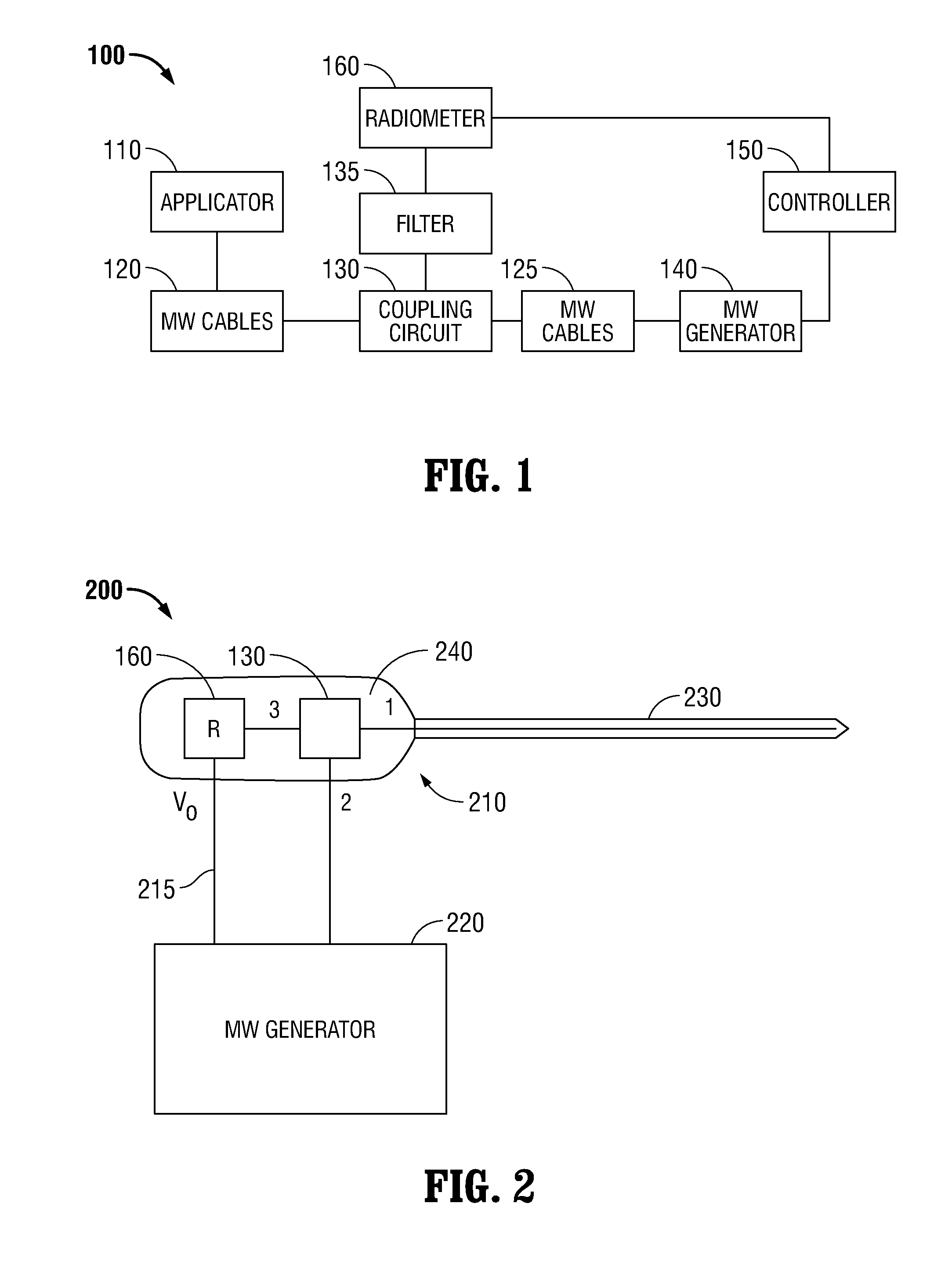
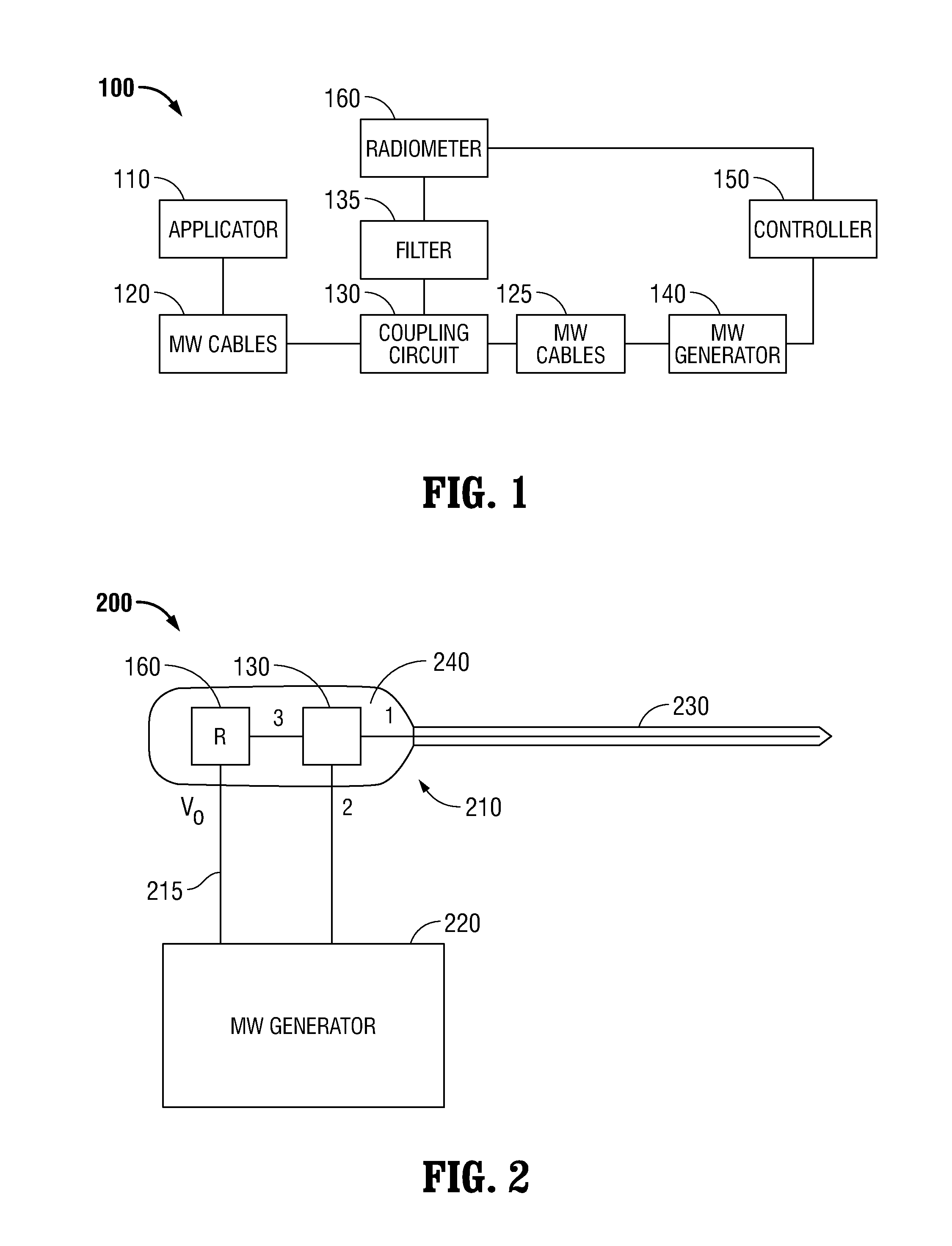
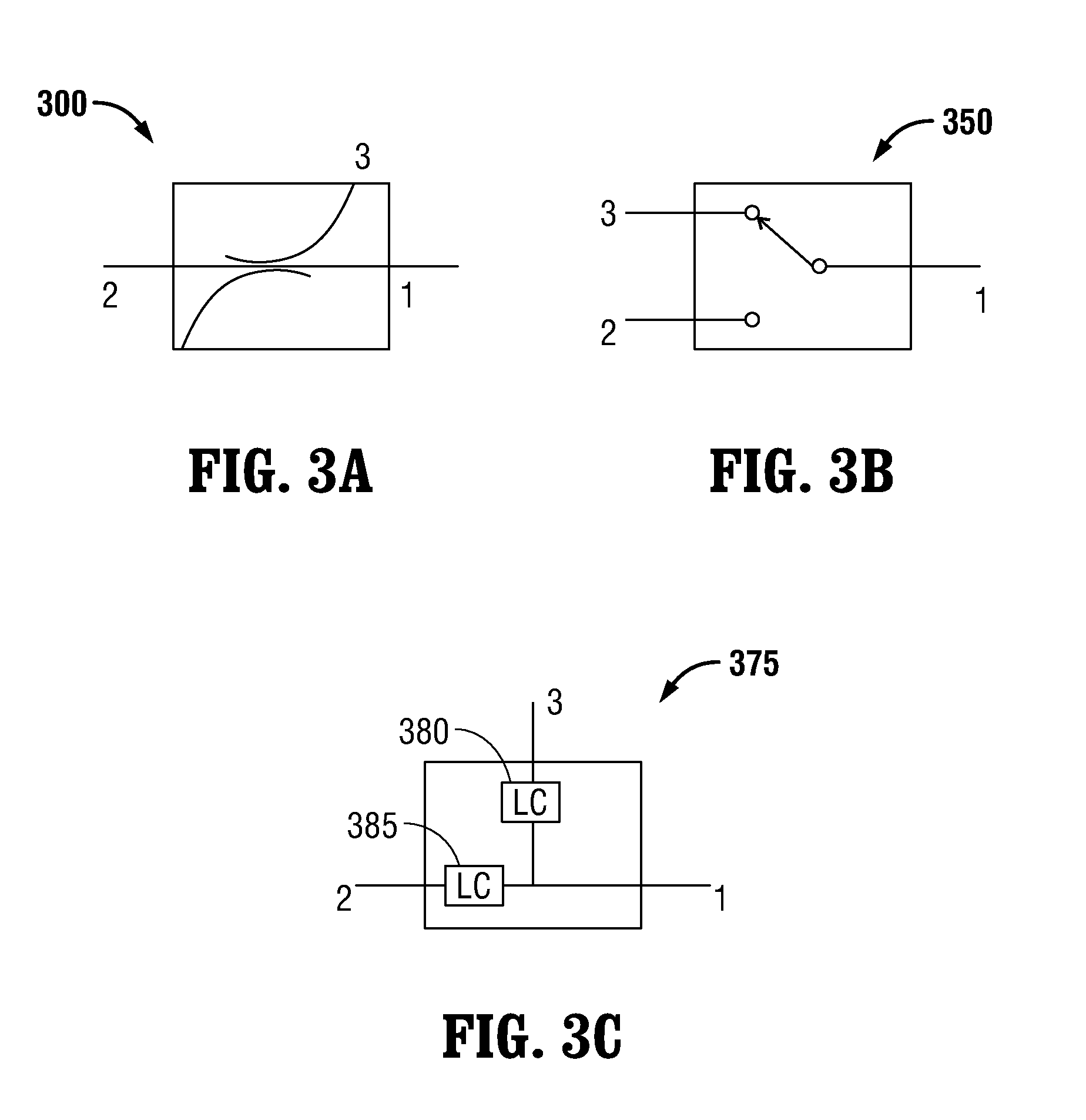
Microwave thermometry for microwave ablation systems
ActiveUS20130345692A1Reducing duty cycleThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsCoupling device detailsRadiometerEngineering
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Microwave thermometry for microwave ablation systems
ActiveUS20130345693A1Radiation pyrometryThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsRadiometerEngineering
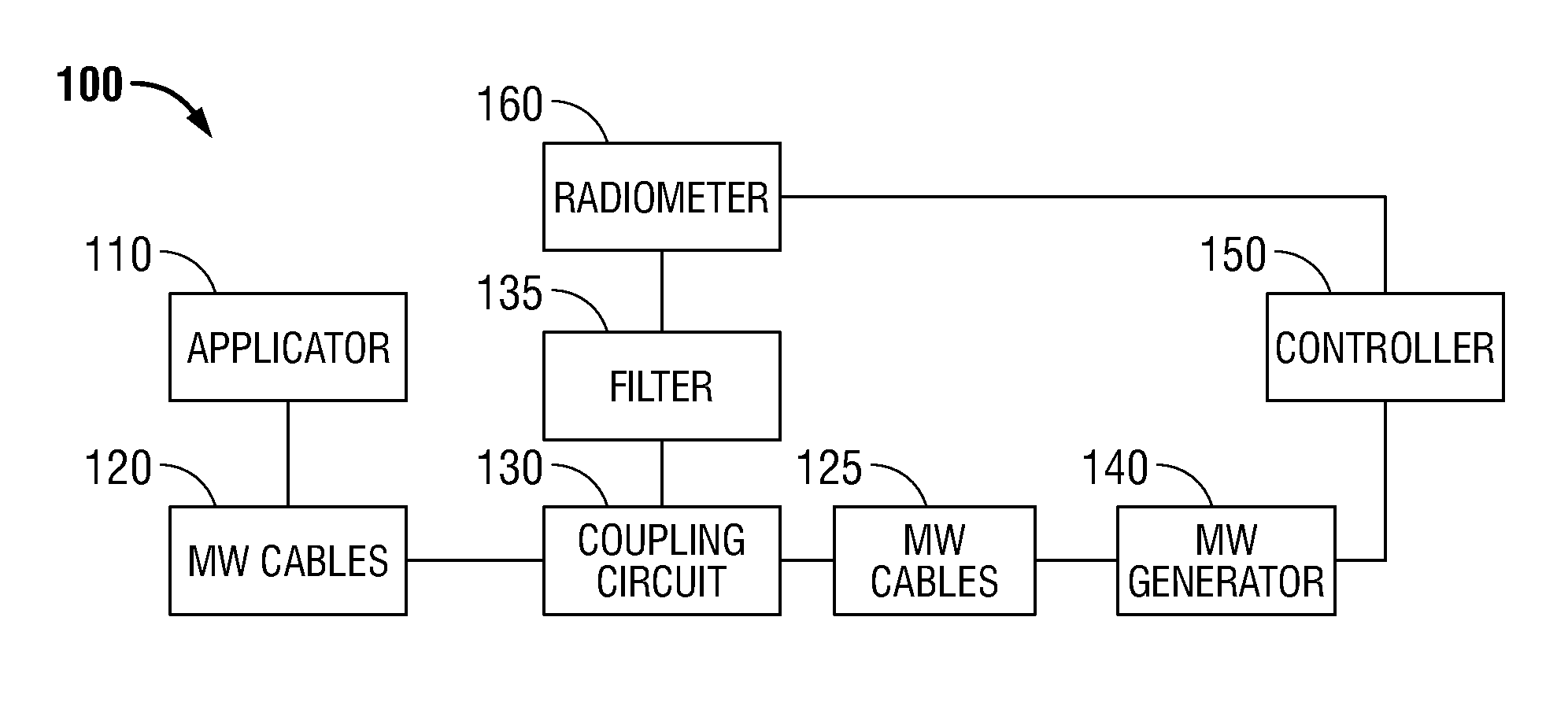
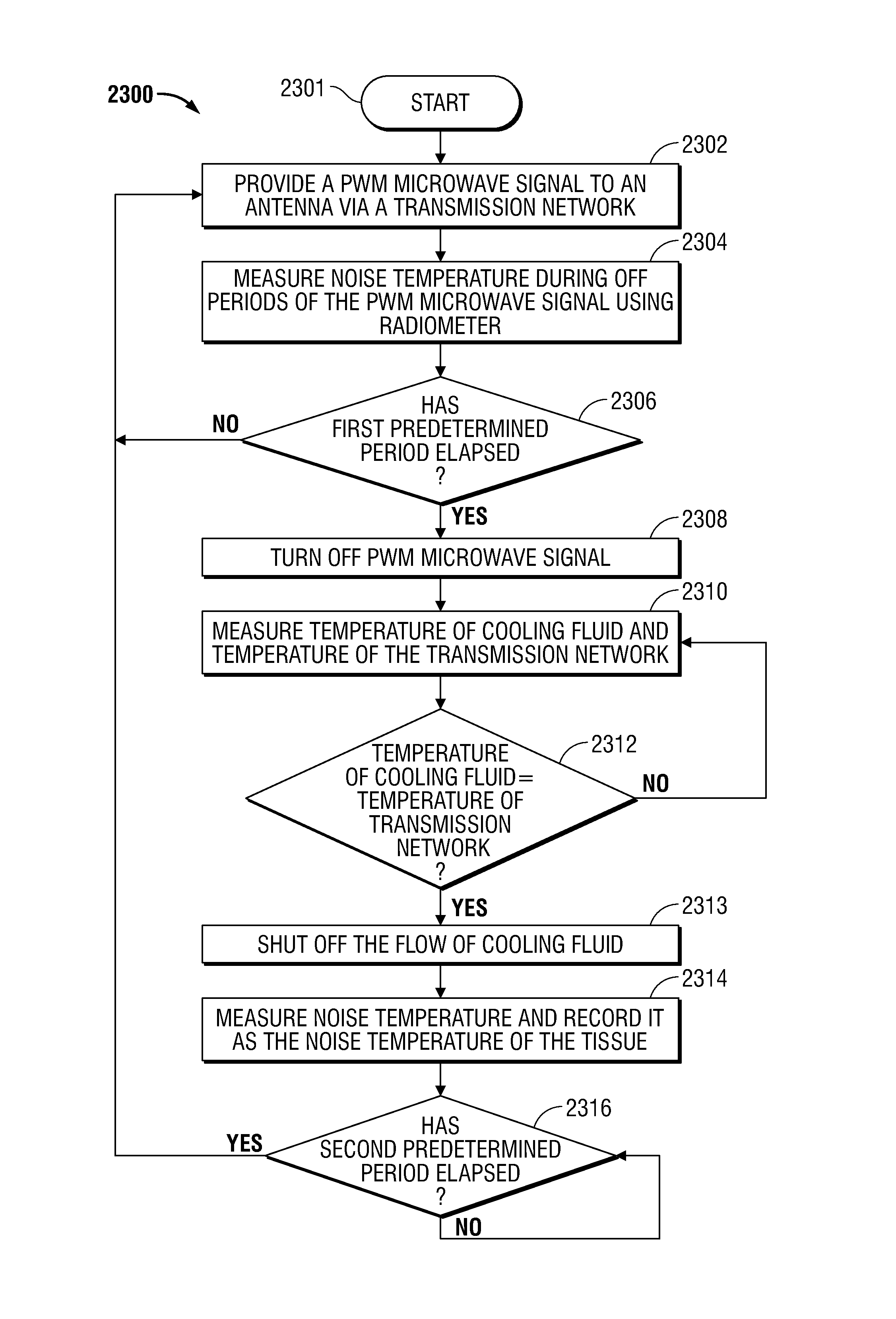
A microwave ablation system incorporates a microwave thermometer that couples to a microwave transmission network connecting a microwave generator to a microwave applicator to measure noise temperature. The noise temperature is processed to separate out components the noise temperature including the noise temperature of the tissue being treated and the noise temperature of the microwave transmission network. The noise temperature may be measured by a radiometer while the microwave generator is generating the microwave signal or during a period when the microwave signal is turned off. The microwave ablation system may be configured as a modular system having one or more thermometry network modules that are connectable between a microwave applicator and a microwave generator. Alternatively, the modular system includes a microwave generator, a microwave applicator, and a microwave cable that incorporate a microwave thermometry network module.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Scaling method of foundation microwave radiometer
InactiveCN104181511AImprove inversion accuracyReduce calibration errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationCold airData matching
The invention relates to a scaling method of a foundation microwave radiometer. The scaling method comprises: obtaining voltage values output through each channel in different attenuation values, calculating corresponding equivalent brightness temperature values through attenuation values, calculating system non-linear factors and noise source injection noises according to corresponding relation between each equivalent brightness temperature value and the output voltage of each channel, and completing preliminary scaling; according to sounding profile data matching with time and place, establishing a corresponding relation of atmosphere optics thickness and atmosphere quality, substituting scaling parameters, obtaining a scaling relation curve, determining the scaling parameters according to the scaling relation curve; observing cold air and cold air coupling noises at each attenuation value, obtaining voltage values output through each channel at different attenuation values and fitting the attenuation values and the voltage values; calculating the equivalent noise temperature when an antenna aligns with the cold air through the relation of the attenuation values and the output voltage values of the attenuator, and determining the brightness temperature values corresponding to the cold air observed by the foundation microwave radiometer in different time and places.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
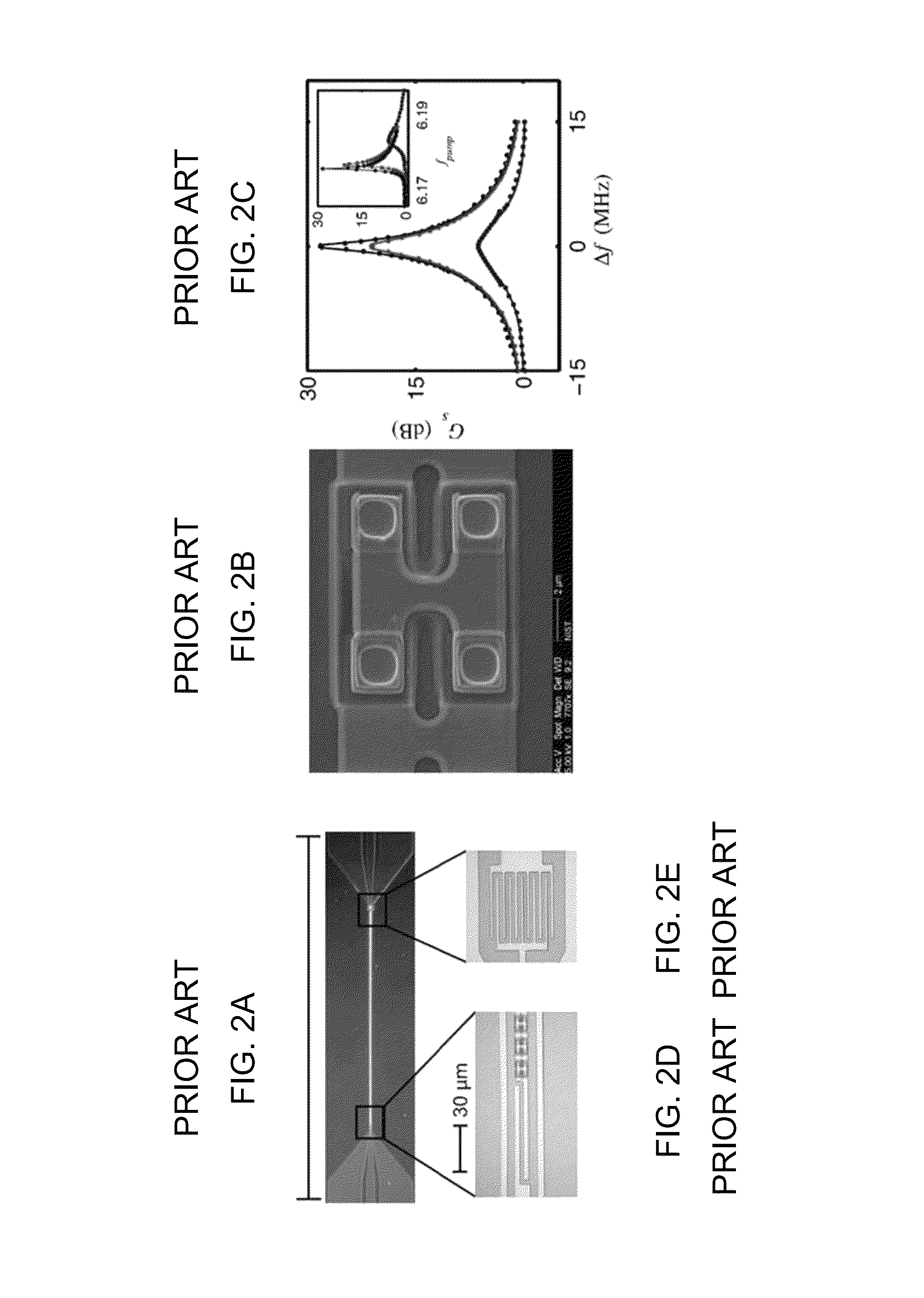
Dispersion-engineered traveling wave kinetic inductance parametric amplifier
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Microwave thermometry for microwave ablation systems
ActiveUS20130345691A1Radiation pyrometryThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsRadiometerEngineering
A microwave ablation system incorporates a microwave thermometer that couples to a microwave transmission network connecting a microwave generator to a microwave applicator to measure noise temperature. The noise temperature is processed to separate out components the noise temperature including the noise temperature of the tissue being treated and the noise temperature of the microwave transmission network. The noise temperature may be measured by a radiometer while the microwave generator is generating the microwave signal or during a period when the microwave signal is turned off. The microwave ablation system may be configured as a modular system having one or more thermometry network modules that are connectable between a microwave applicator and a microwave generator. Alternatively, the modular system includes a microwave generator, a microwave applicator, and a microwave cable that incorporate a microwave thermometry network module.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
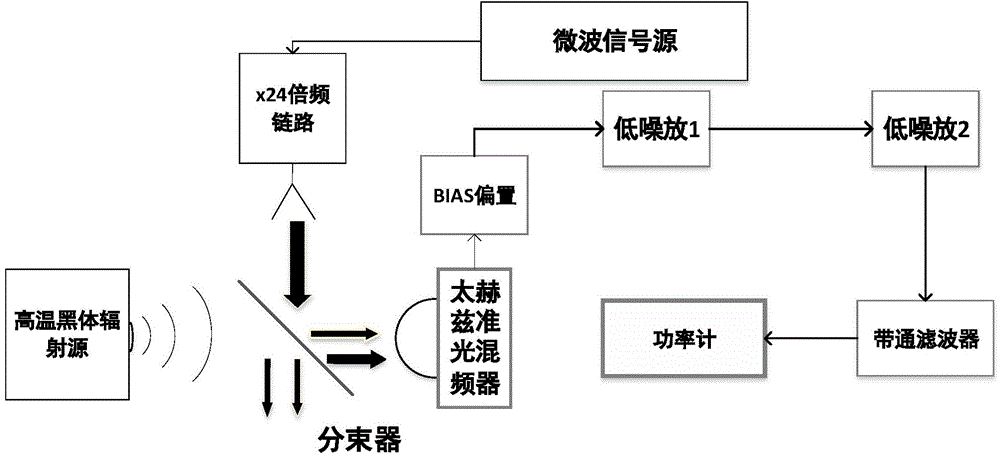
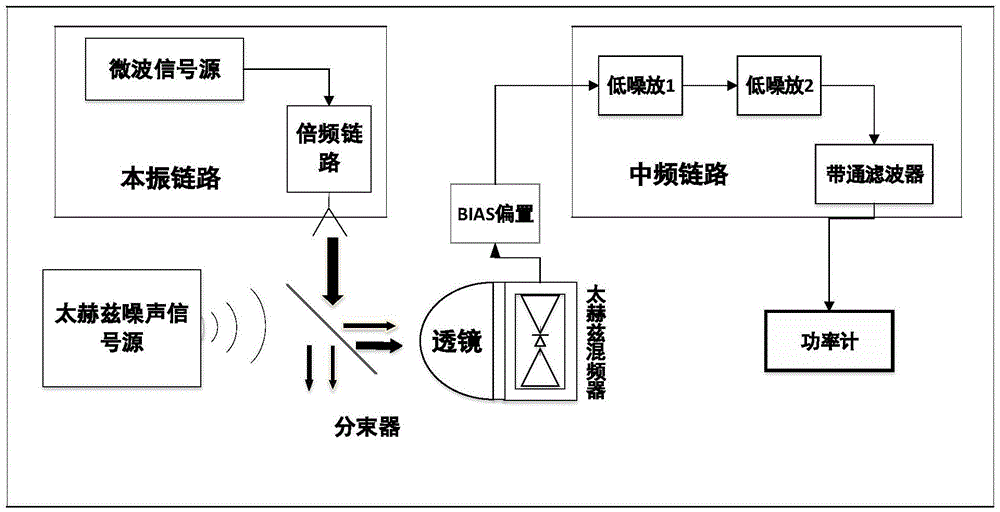
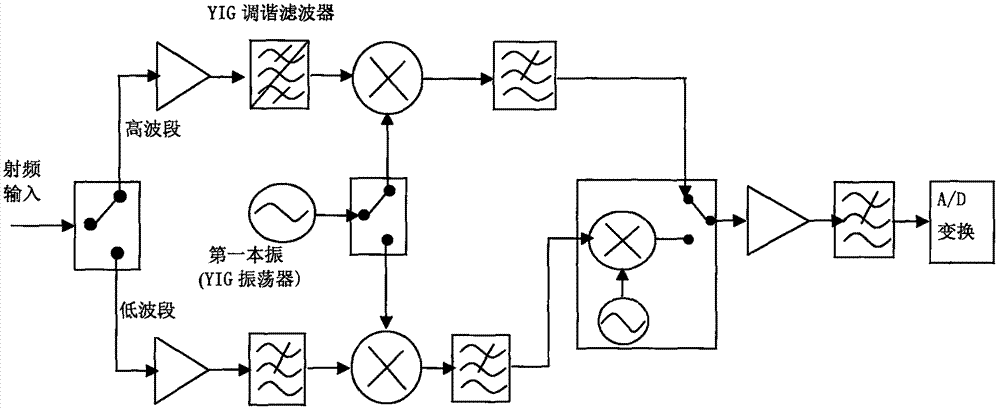
Testing system and testing method for front end of heterodyne terahertz quasi-optical receiver
InactiveCN104634540AHigh magnificationHigh gainTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterFrequency mixer
The invention relates to the technical field of terahertz detection and testing and relates to a testing system and a testing method for testing a noise temperature of the front end of a heterodyne terahertz quasi-optical receiver. The system comprises a high-temperature blackbody radiation source, a frequency doubling link, a microwave signal source, a beam splitter, a terahertz quasi-optical frequency mixer, a BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprogram) bias, a first-stage low noise amplifier, a second-stage low noise amplifier, a band-pass filter and a power meter. According to the testing system and the testing method, the high-temperature blackbody source is used as a terahertz noise signal source, so that a temperature variation range of the terahertz noise signal source is enlarged and a noise temperature testing range of the testing system is effectively enlarged; a terahertz quasi-optical lens is used as a beam bunching device of the terahertz frequency mixer, so that detection sensitivity of a front end system of the heterodyne terahertz quasi-optical receiver is improved and the problems of weak terahertz noise signal and difficulty in detection on the terahertz noise signal are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
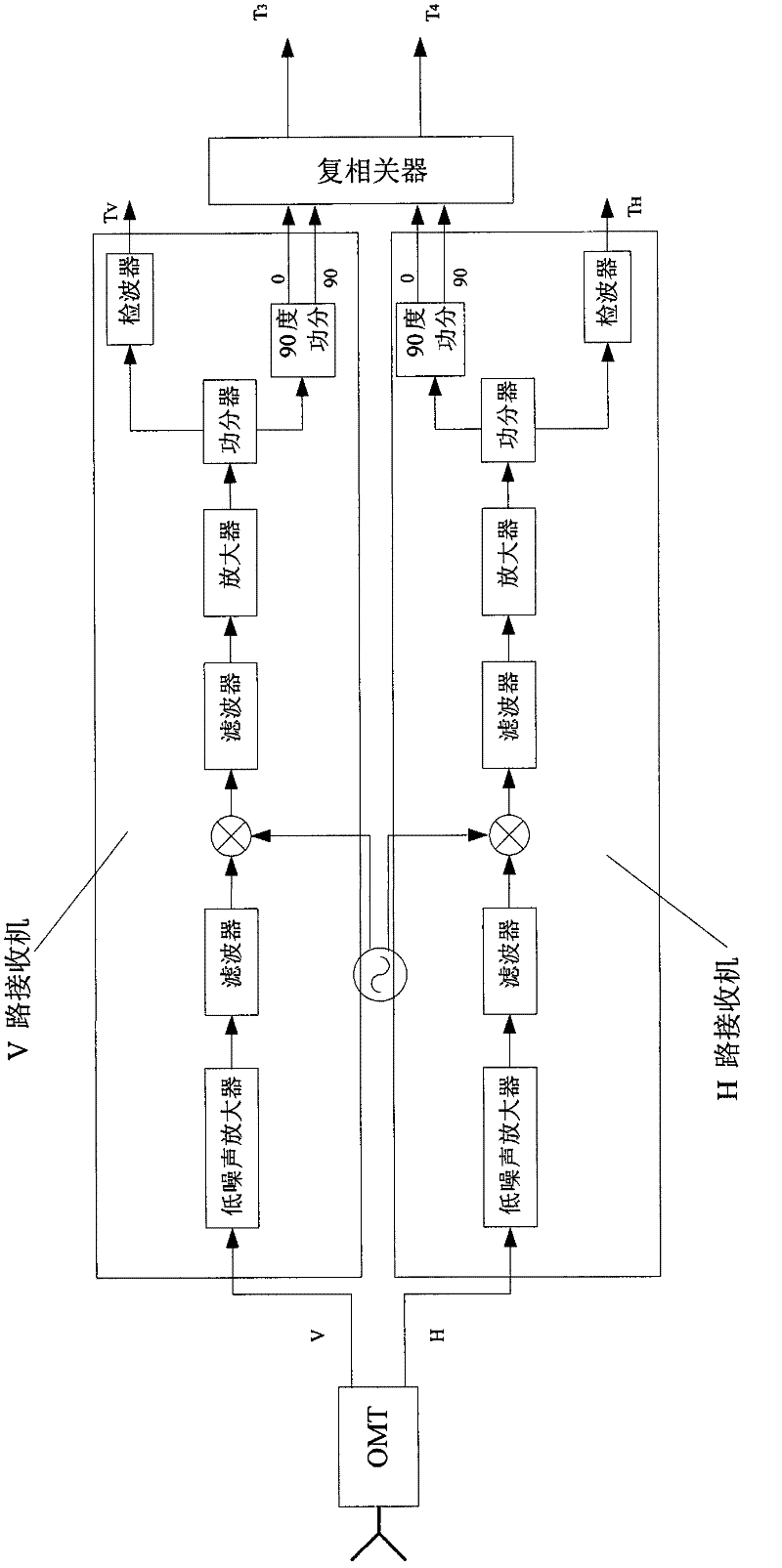
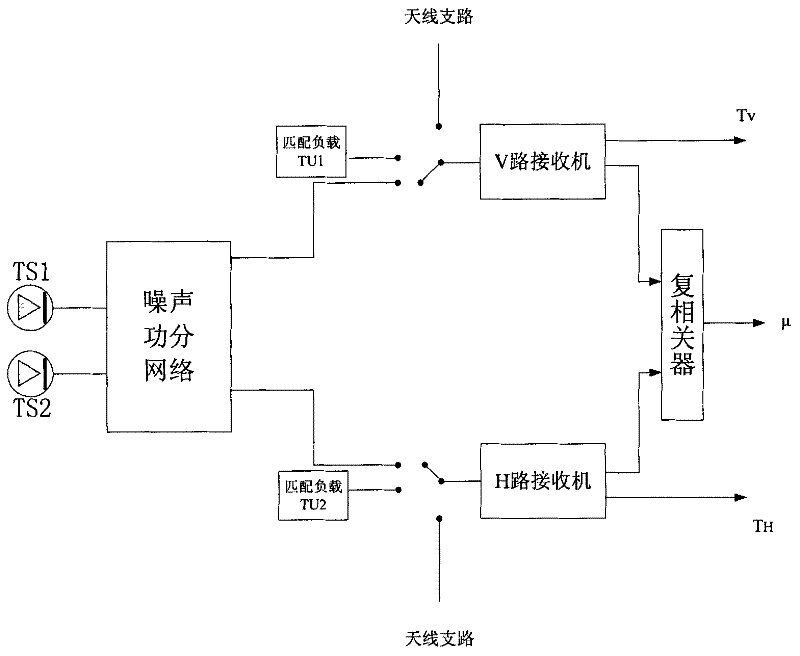
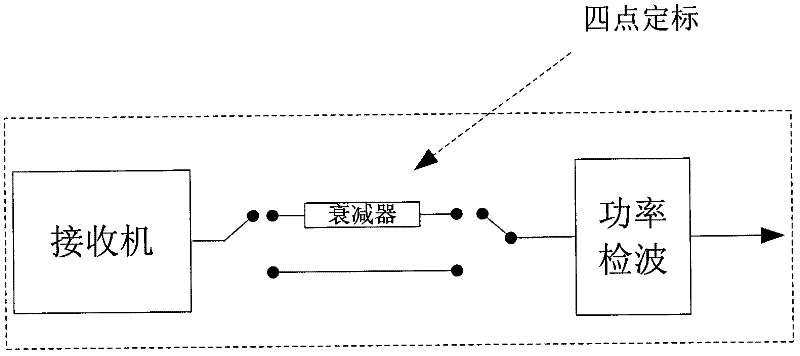
Direct correlation-type complete polarization microwave radiometer receiver scaling method
ActiveCN102353944AImprove calibration accuracyImprove stabilityWave based measurement systemsBrightness temperatureCorrelation function
The invention provides a direct correlation-type complete polarization microwave radiometer receiver scaling method. According to a step scaling method, scaling a receiver is completed. The method comprises the following steps: employing signals generated by correlated noise sources of different output temperatures (high temperature source, low temperature source) to fill into a V (vertical polarization) receiver and a H (horizontal polarization) receiver in order through a noise power division network, through four-point scaling, obtaining receiver voltage bias; by utilizing input high temperature source and low temperature source results, obtaining a value of a receiver strip elimination function at a zero point, obtaining reception noise temperatures of the V receiver and the H receiver, and completing normalization processing; through non-relevant noise filling, completing correction of a reception channel residual error, obtaining a multiple association function after final correction, thus obtaining a complete brightness temperature. The method has the characteristics of high scaling precision, simple realization and high reliability, is suitable to spaceborne application, and has wide market application prospect.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
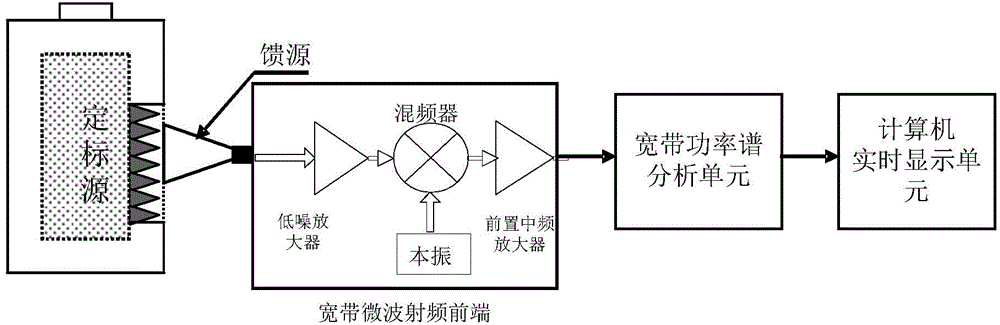
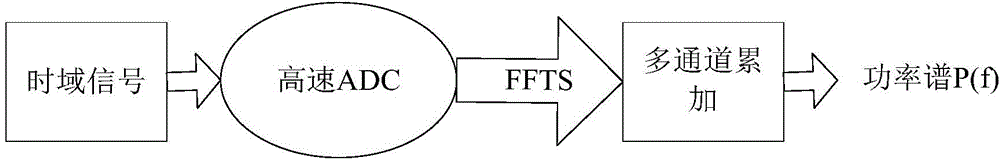
Microwave radio-frequency front end noise measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN105842551ANo noise figure increaseNoise measurement errors do not accumulateNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow noiseFrequency spectrum
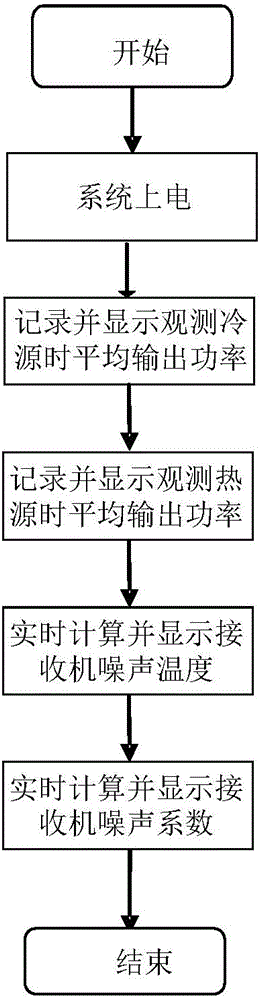
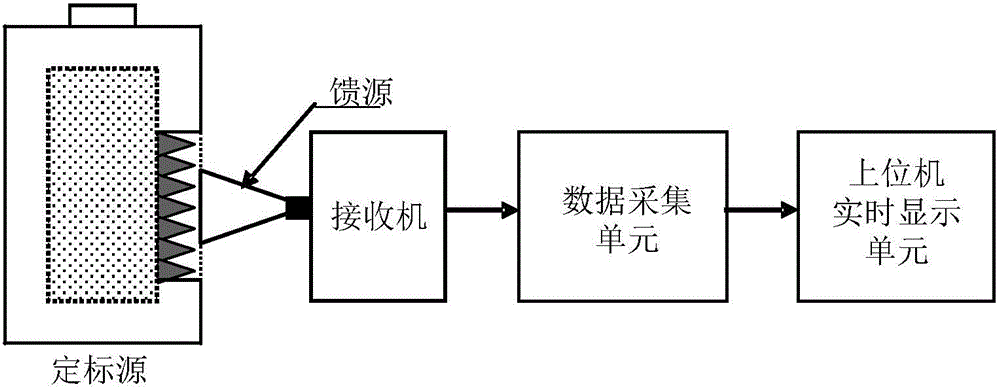
The invention relates to a microwave radio-frequency front end noise measuring device comprising a feed source, a calibration source, a broadband power spectrum analysis unit, and a computer real-time display unit. The feed source is used for receiving microwave radiation signals from atmosphere and the calibration source, the received microwave radiation signals are input to a measured microwave radio-frequency front end, and the microwave radio-frequency front end carries out low-noise amplification and down-conversion of the microwave radiation signals to generate intermediate-frequency signals; the intermediate-frequency signals are input to the broadband power spectrum analysis unit, and the broadband power spectrum analysis unit carries out data acquisition and spectrum analysis on the intermediate-frequency signals to get the power spectrum, noise temperature and noise coefficient of the measured microwave radio-frequency front end; and the results are displayed in real time by the computer real-time display unit.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Microwave receiver noise measuring device and measuring method
InactiveCN105842552AImprove noise figureNoise measurement errors do not accumulateNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMicrowave irradiationNoise temperature
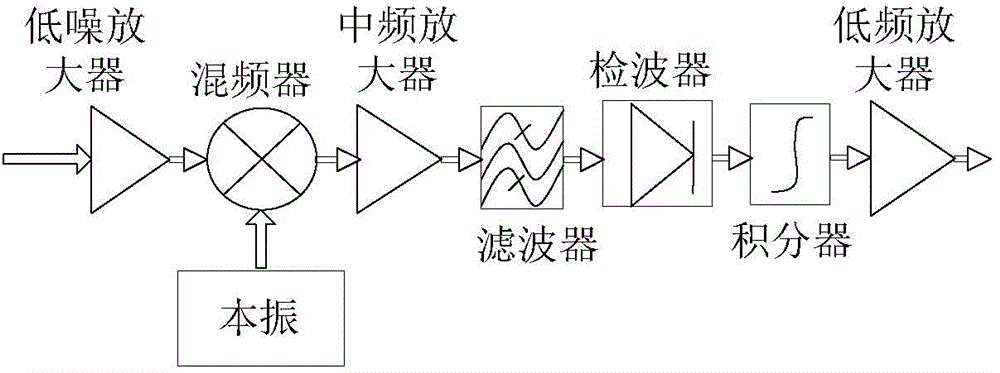
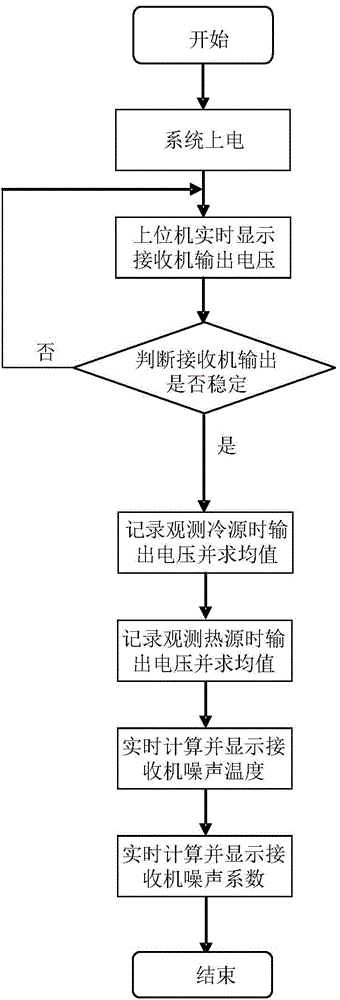
The invention relates to a microwave receiver noise measuring device comprising a calibration source, a feed source, a data acquisition unit, and a principal computer real-time display unit. The feed source is used for receiving microwave radiation signals from atmosphere and the calibration source and inputting the microwave radiation signals to a microwave receiver to be measured; the microwave receiver to be measured carries out down-conversion, amplification, filtering, detection, integration and low-frequency amplification of the microwave radiation signals in sequence, and outputs voltage signals; the data acquisition unit acquires and stores the voltage signals output by the receiver, and transmits the voltage signals to the principal computer real-time display unit; and the principal computer real-time display unit processes the voltage signals according to the observed calibration source to get the receiver noise temperature and the noise coefficient of the receiver, and displays the voltage signals, the receiver noise temperature and the noise coefficient in real time.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
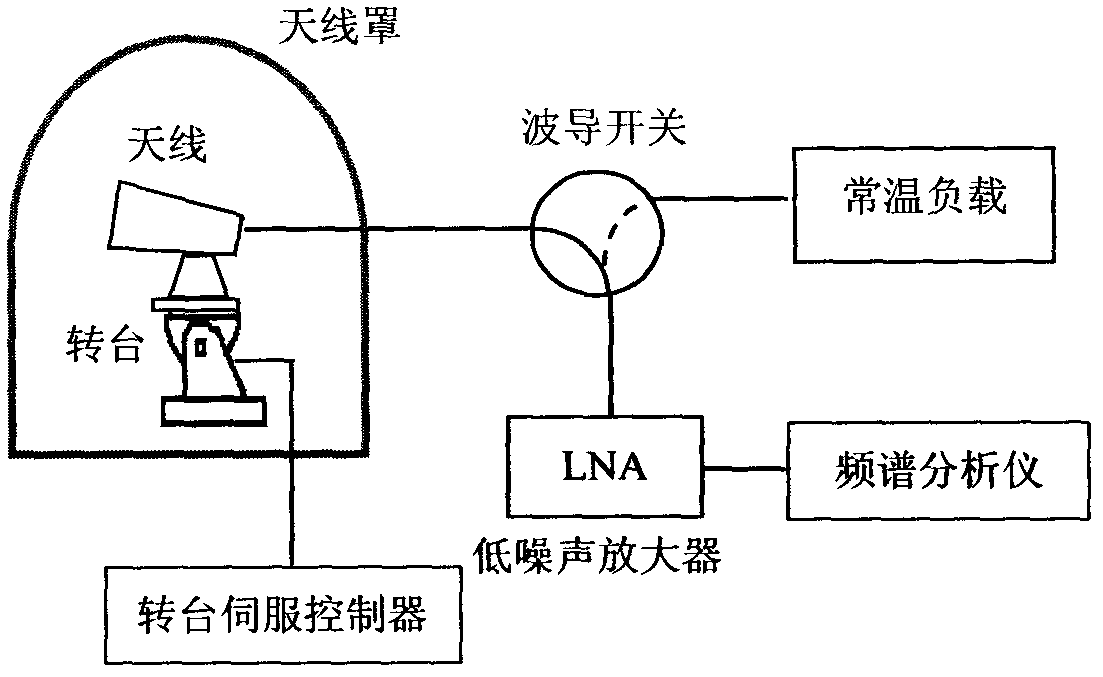
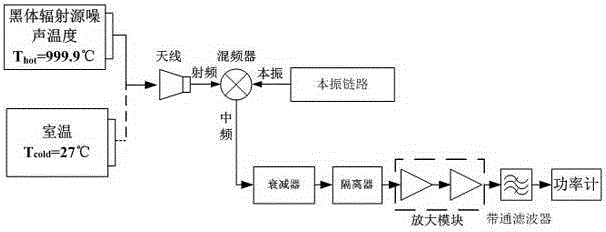
Method for measuring insertion loss of any position of antenna housing
InactiveCN102590616ADetermining Insertion LossAvoid influenceSpectral/fourier analysisAntenna noise temperatureY-factor
The invention discloses a method for measuring insertion loss of any position of an antenna housing. When an antenna housing is at any position, the noise temperature of the antenna with or without the housing is measured by an Y-factor method, the residual antenna noise temperature which is caused by the antenna housing is obtained by calculating the difference of the noise temperature of the antenna with or without the housing, and thus, the insertion loss of the antenna housing is determined. The method is simple and practicable and has popularization and application value.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Microwave thermometry for microwave ablation systems
ActiveUS9121774B2Reduce signalingReducing duty cycleThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsCoupling device detailsRadiometerComputer module
A microwave ablation system incorporates a microwave thermometer that couples to a microwave transmission network connecting a microwave generator to a microwave applicator to measure noise temperature. The noise temperature is processed to separate out components the noise temperature including the noise temperature of the tissue being treated and the noise temperature of the microwave transmission network. The noise temperature may be measured by a radiometer while the microwave generator is generating the microwave signal or during a period when the microwave signal is turned off. The microwave ablation system may be configured as a modular system having one or more thermometry network modules that are connectable between a microwave applicator and a microwave generator. Alternatively, the modular system includes a microwave generator, a microwave applicator, and a microwave cable that incorporate a microwave thermometry network module.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
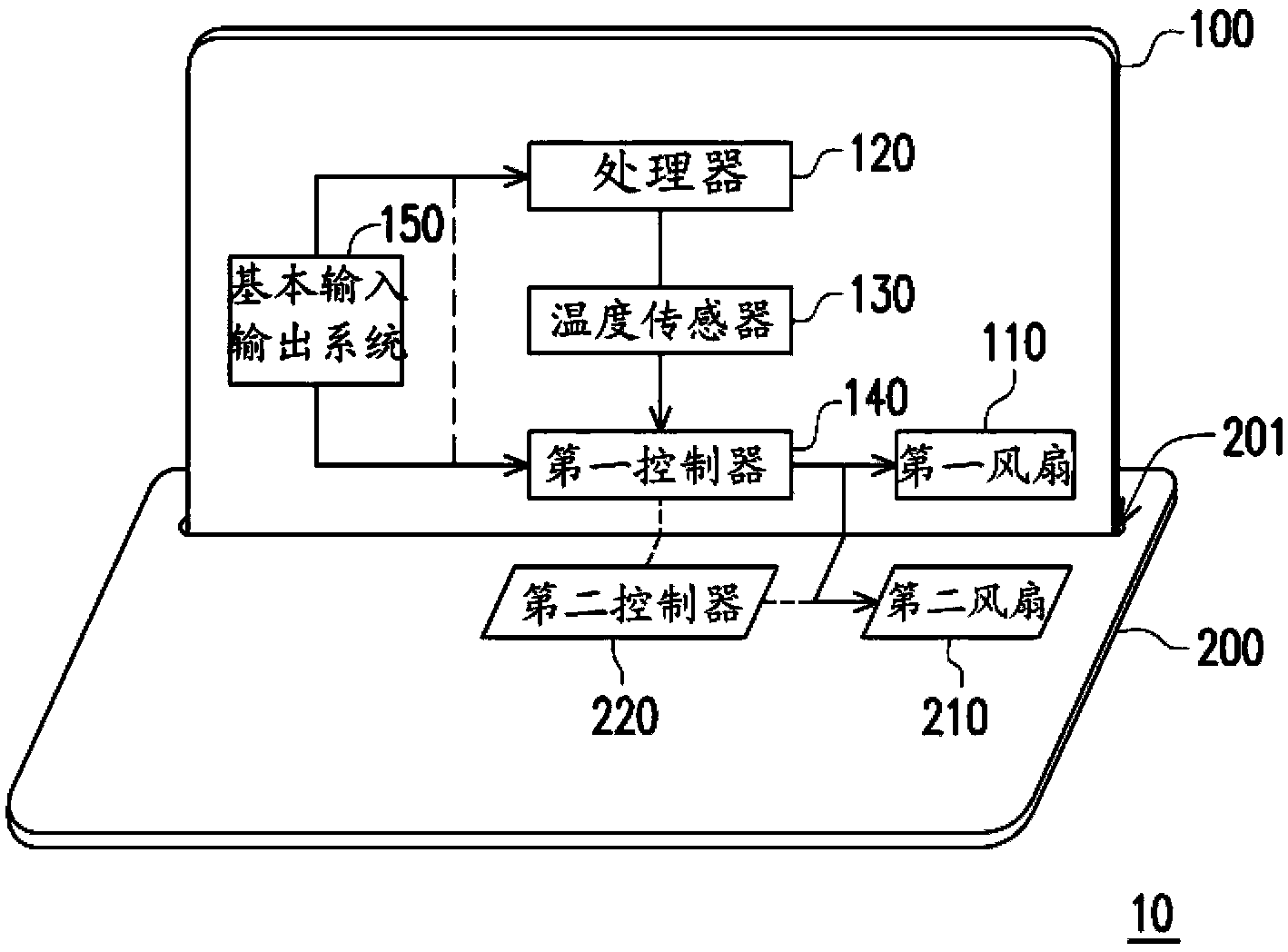
Electronic device and fan control method thereof
The invention relates to a fan control method suitable for an electronic device comprising a portable device and an expansion pedestal. The portable device comprises a first fan. The expansion pedestal comprises a second fan. The fan control method comprises the following steps of determining whether sensing signals from the expansion pedestal are received or not, so as to switch a portable device to a laptop mode or a tablet mode; and dynamically adjusting the rotation speed of the first fan and the second fan according to a first noise temperature comparison table and an internal temperature value of the portable device under the laptop mode.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
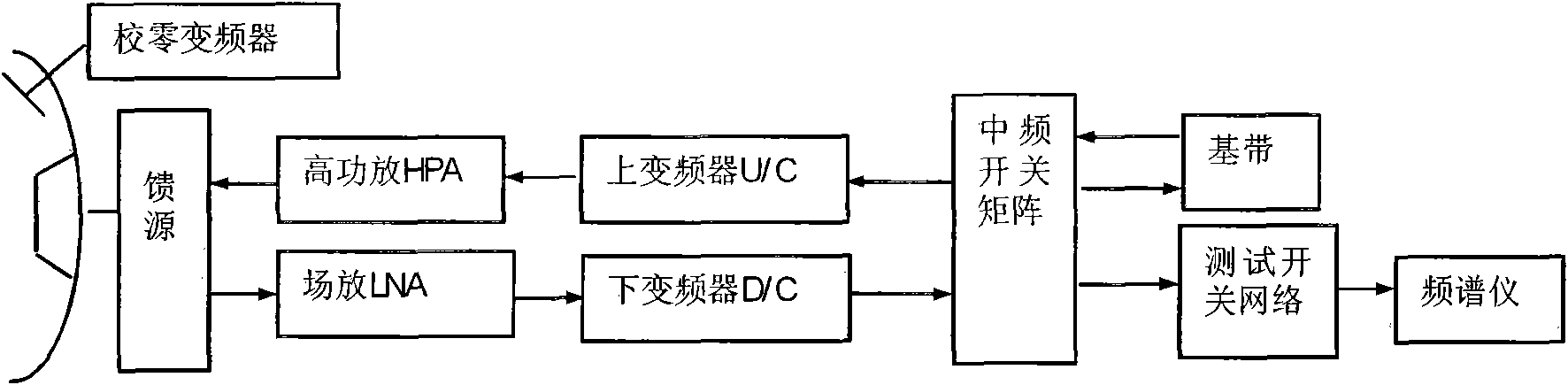
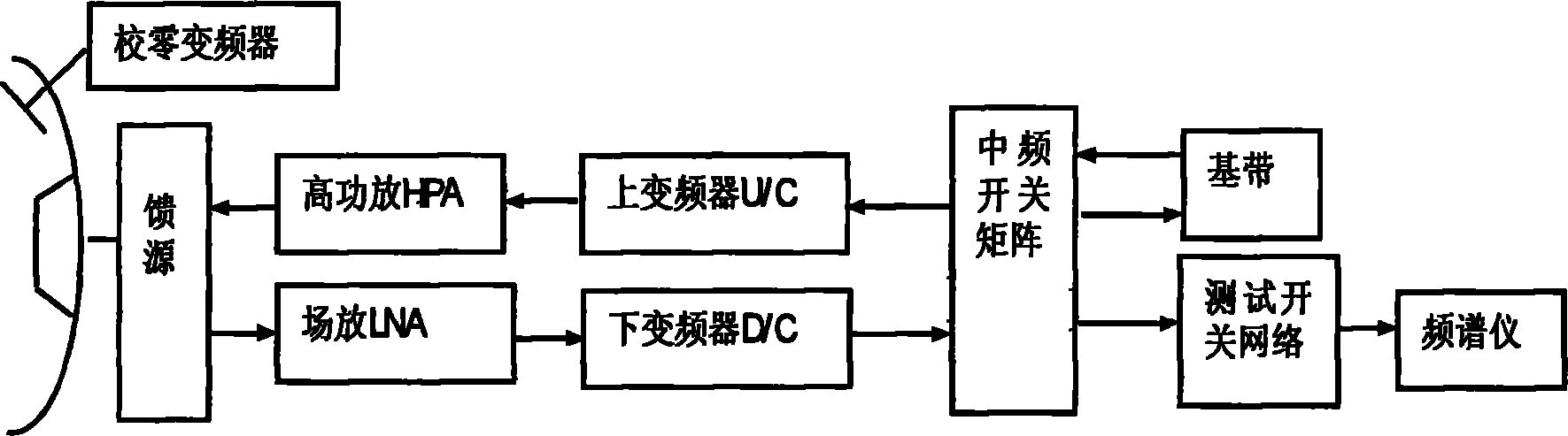
Method for detecting G/T value of ground monitoring station by towery and towerless comparison
InactiveCN101848039AAvoid dependencyEasy to operateTransmission monitoringUltrasound attenuationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method for detecting a G / T value of a ground monitoring station by towery and towerless comparison, comprising the following steps of: testing and recording a G / T tower value and a corresponding signal-noise spectrum density specific value (S / Phi tower by using a towery test; testing the output power PO of a HPA (High-Power Amplifier) corresponding to the same S / Phi and the attenuation value ATT0 of a zero-calibration frequency converter by using an offset feed wireless closed loop and recording the PO; during detection by using a comparison method, setting the high-power amplifier output power as the PO and the attenuation value of the zero-calibration frequency converter as the ATT0; and testing the current S / Phi value and comparing the current S / Phi value with the obtained S / Phi tower to obtain the change condition of the G / T value and obtaining G / T=G / T tower+ S / Phi - S / Phi tower of the current system. In the invention, the downlink signal-noise ratio can be conveniently obtained by using an offset feed wireless closed loop and has the convenience of a towerless test and the precision of the towery test in comparison with an initial state offset feed wireless closed loop; and the grain noise-temperature specific value (G / T) of the ground monitoring station can be obtained conveniently and more accurately.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
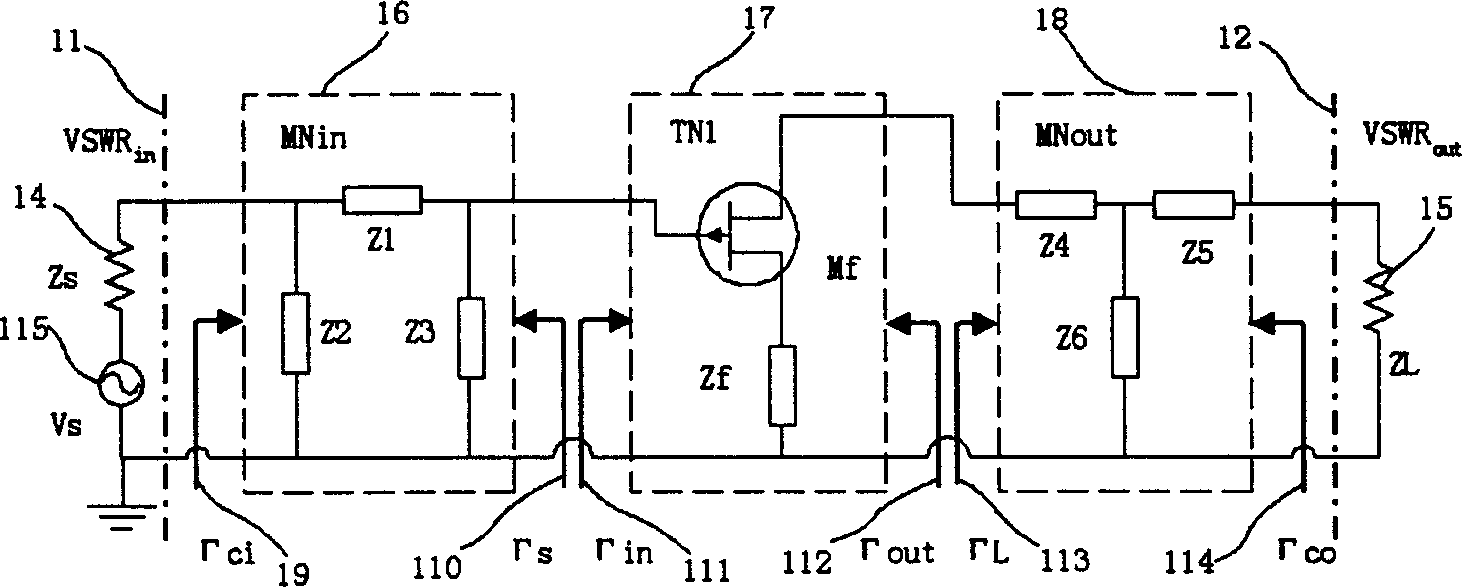
Optimized design method of microwave amplifying circuit
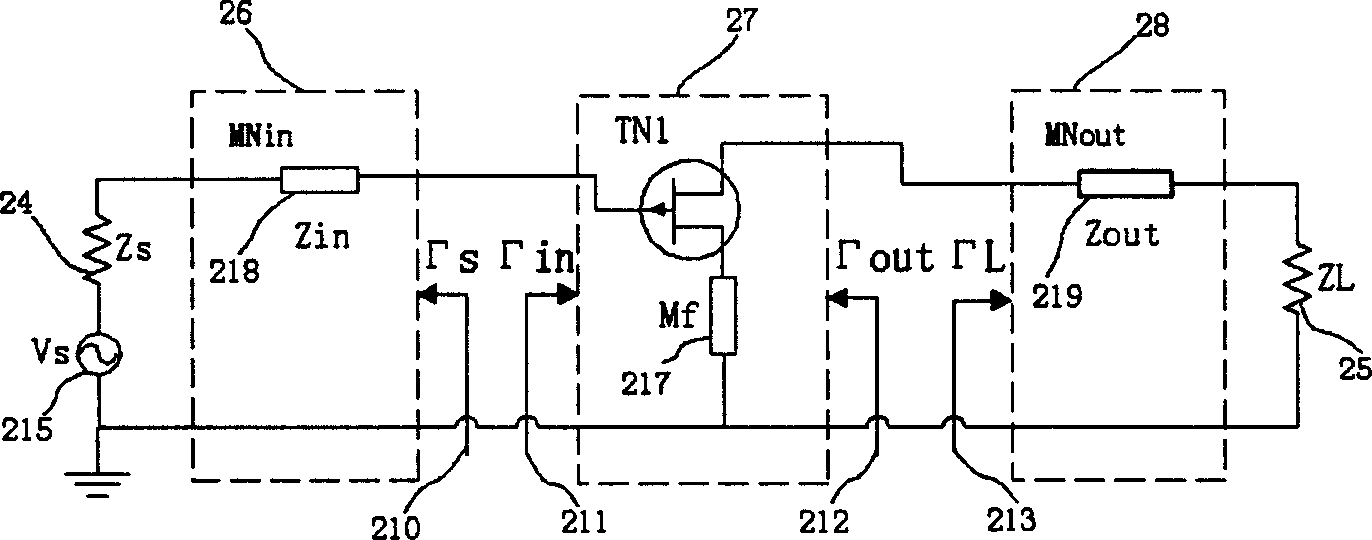
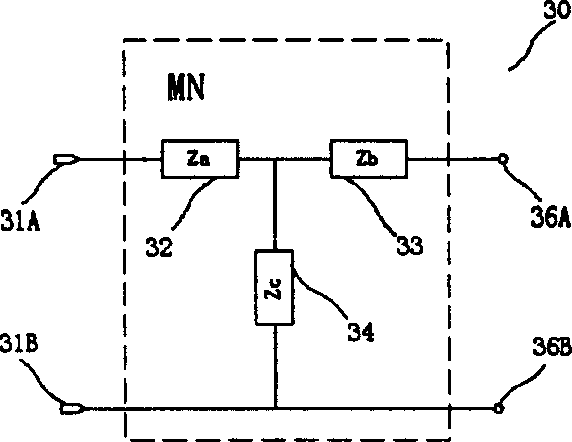
Improving efficiency of designing circuits and reducing complexity for match between input and output networks is realized through Pi type or T type network or degraded Pi type or T type network. Transition matrix is utilized to describe and calculate optimal input and output networks of amplification circuit. Active circuit unit containing transistor in negative feedback is described and calculated through scattering matrix, which then transformed to transition matrix and scattering matrix for integral amplification circuit. Standing wave ratio of input and output, gain, noise temperature and stability coefficient are calculated and optimized through scattering matrix for integral amplification circuit. Advantages of precision, high efficiency and convenience of the method is proved by execution of computer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
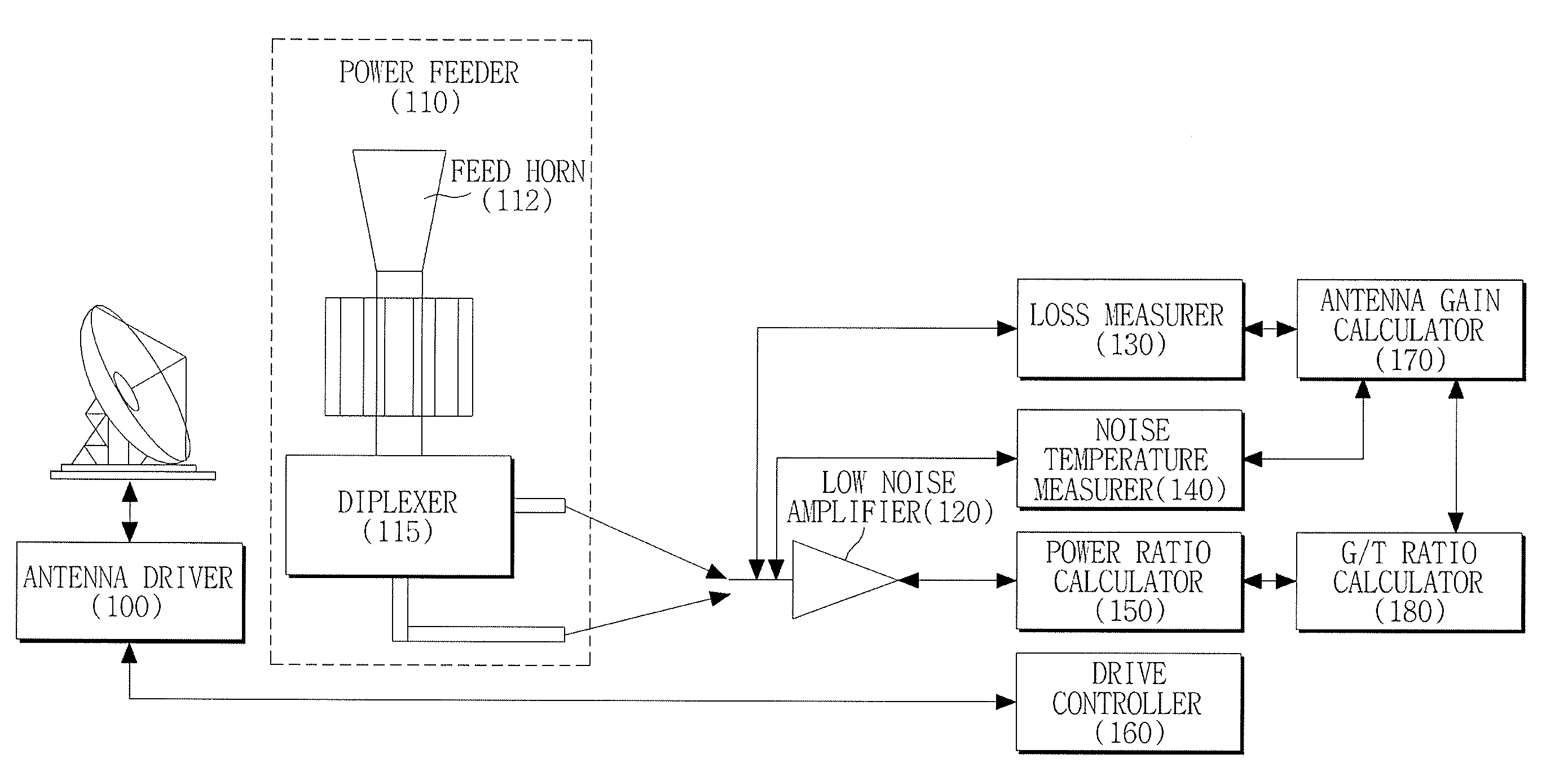
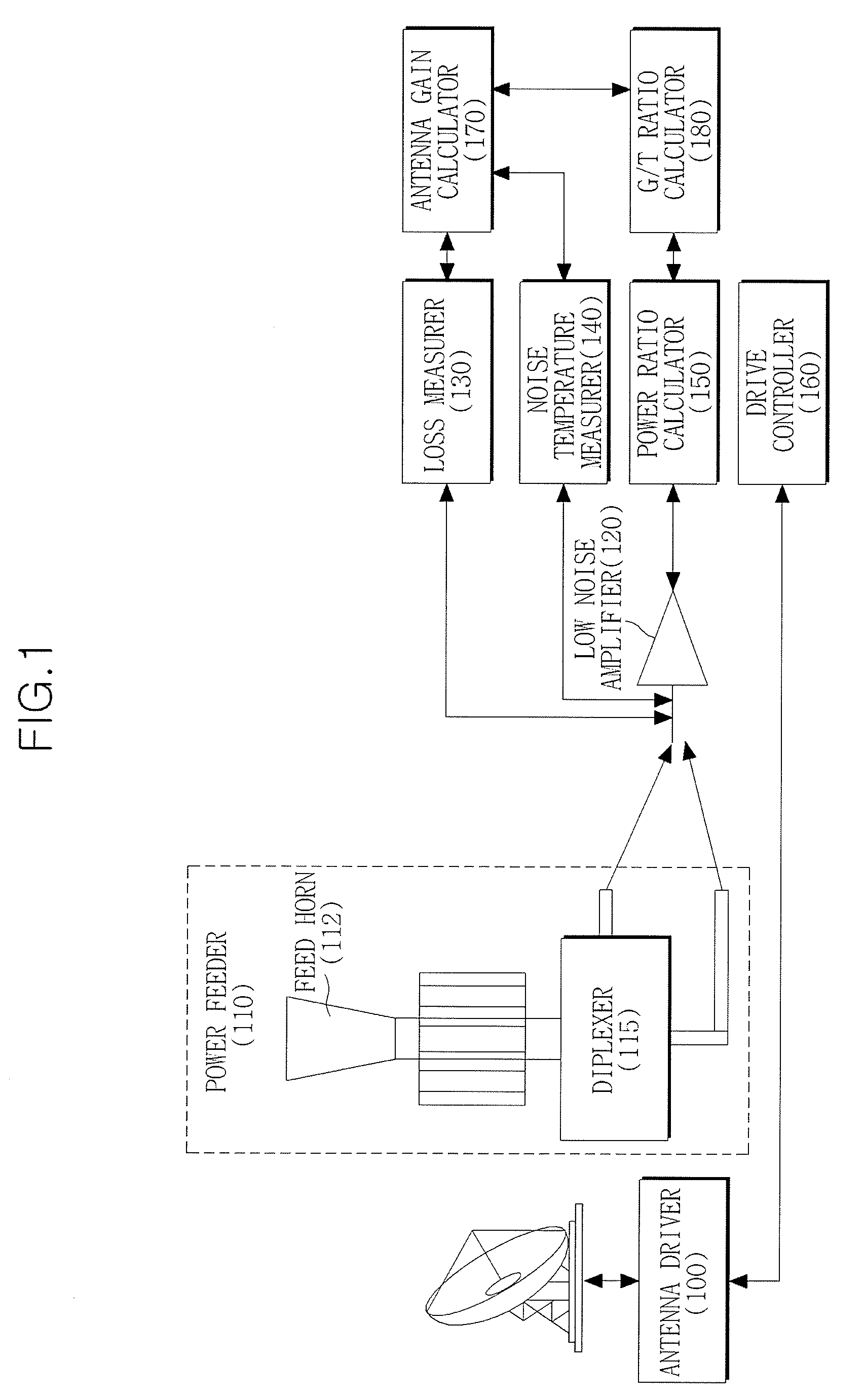
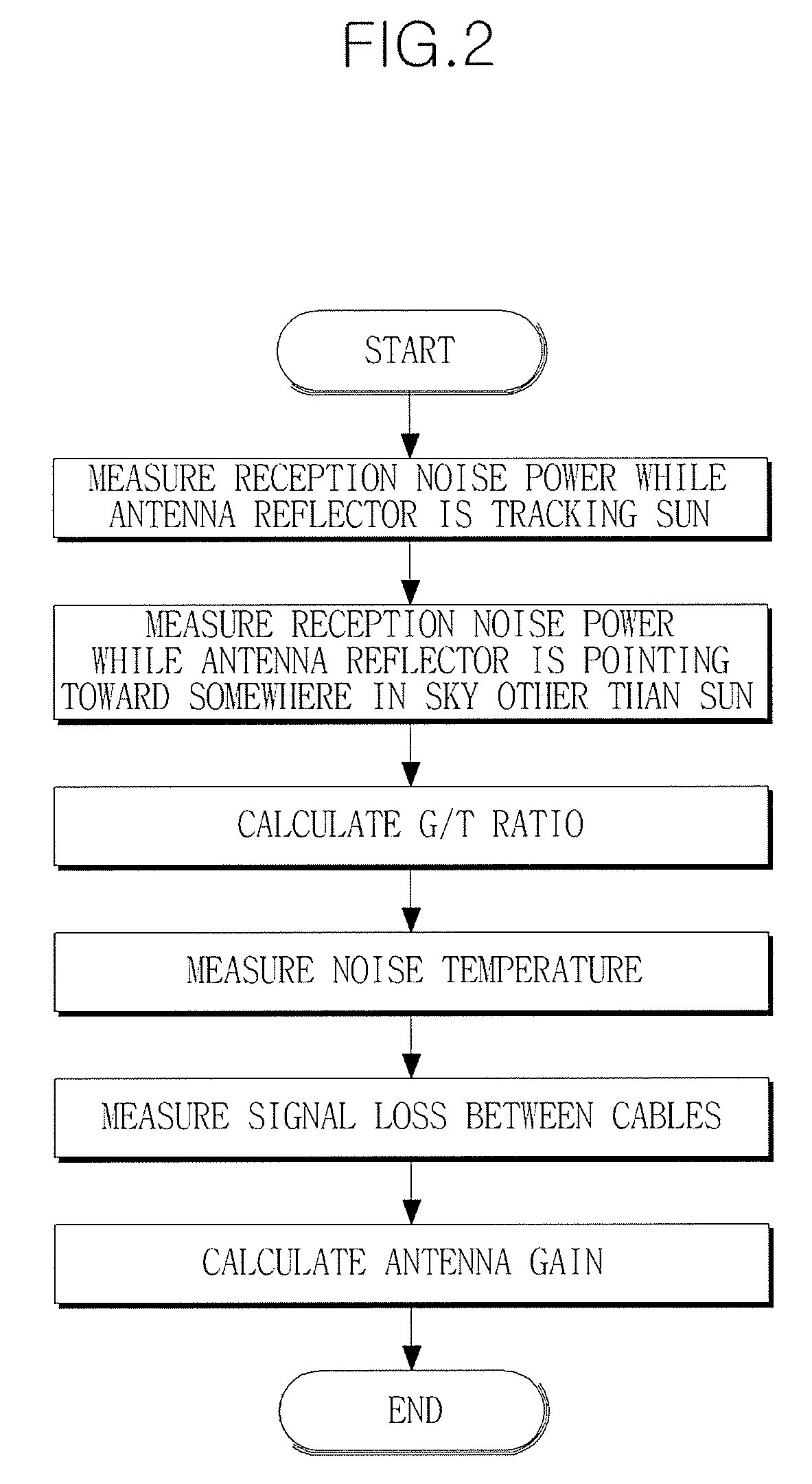
Apparatus and method for measuring antenna gain using sun
InactiveUS20100039335A1Transmission monitoringElectromagentic field characteristicsReference antennaAntenna gain
Provided are an apparatus and method for measuring an antenna gain. The apparatus includes an antenna gain-to-noise-temperature (G / T) ratio calculator for calculating a G / T ratio using a reception noise power measured while an antenna is tracking the sun, a noise temperature measurer for measuring a noise temperature when a signal is transmitted or received through the antenna, and an antenna gain calculator for calculating an antenna gain using the calculated G / T ratio and the measured noise temperature. Thus, it is possible to easily measure the antenna gain of a ground station without a reference antenna or a satellite-mounted device capable of functioning as a reference antenna.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Quasi-optical testing system and method for terahertz frequency mixer
InactiveCN104634541AHigh detection sensitivityWide temperature rangeTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to the field of terahertz testing, in particular to a quasi-optical testing system and method for the noise temperature and frequency conversion loss of a terahertz frequency mixer. The system comprises a terahertz noise signal source, a local oscillation link, a beam splitter, a terahertz collimation lens, a BLAS (Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms) bias, a medium-frequency link and a power meter. The terahertz collimation lens is taken as a beam gathering device of the terahertz frequency mixer, so that the detection sensitivity of the terahertz frequency mixer is increased, and the problem of difficulty in detecting weak terahertz noise signals is effectively solved; a high-temperature blackbody source is taken as the terahertz noise signal source, so that the temperature change range of the terahertz noise signal source is expanded, and the testing range of the noise temperature of the testing system is effectively expanded; a two-stage low noise amplifier is adopted, so that the magnification times of medium-frequency signals are increased, the overall gain of a force testing system is effectively increased, and the problem that weak medium-frequency signals are easily submerged into noise is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
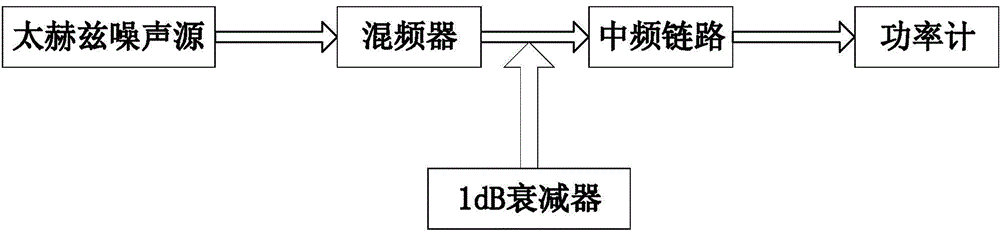
Terahertz receiver noise temperature test system and method
InactiveCN105187136AAvoid the problem of out-of-sync testing frequencyAvoid test errorReceivers monitoringFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a terahertz receiver noise temperature test system and method. The system comprises an intermediate frequency link and a power meter. The output end of the intermediate frequency link is connected with the detection port of the power meter. The intermediate frequency link comprises an attenuator, an isolator, an amplifier module and a band-pass filter. The input end of the attenuator is connected with the intermediate frequency signal port of a terahertz receiver to be detected. The output end of the attenuator is connected with the input end of the isolator. The output end of the isolator is connected with the input end of the amplifier module. The output end of the amplifier module is connected with the input end of the band-pass filter through a cable. The output end of the band-pass filter is connected with the power meter. According to a test result, the double-sideband conversion loss and the double-sideband equivalent noise temperature of a mixer are calculated. According to the invention, local frequency is adjusted through a fixed intermediate frequency; the problems of unsynchronized test frequency and test errors can be avoided; and physical characteristic changes caused by the fact that the entire system cannot continuously work under a traditional test method are avoided.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Digital automatic compensation microwave radiometer
InactiveCN102169142AReduce power consumptionReduce weightBeacon systems using radio wavesElectromagentic field characteristicsPlatinumElectrical resistance and conductance
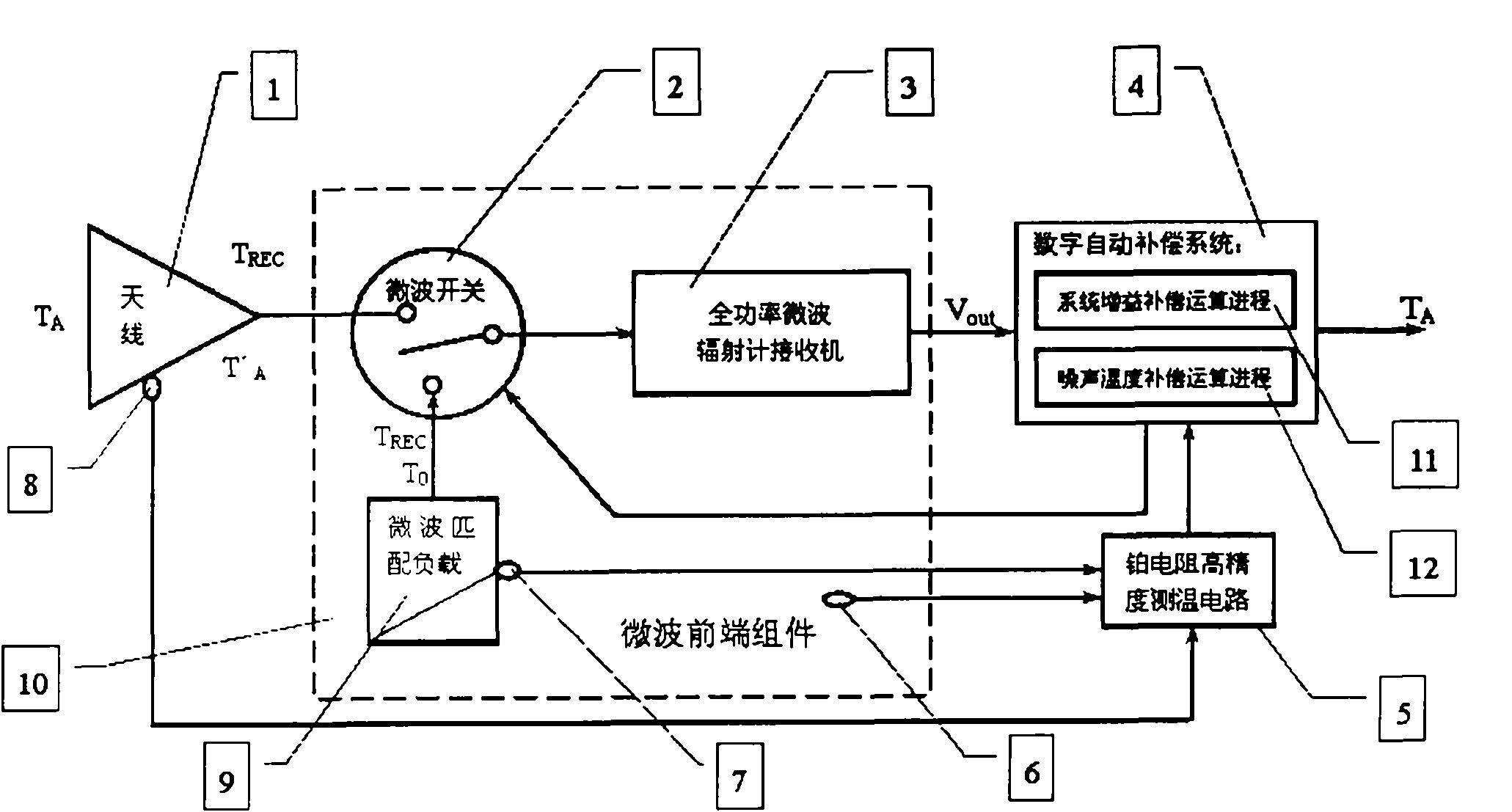
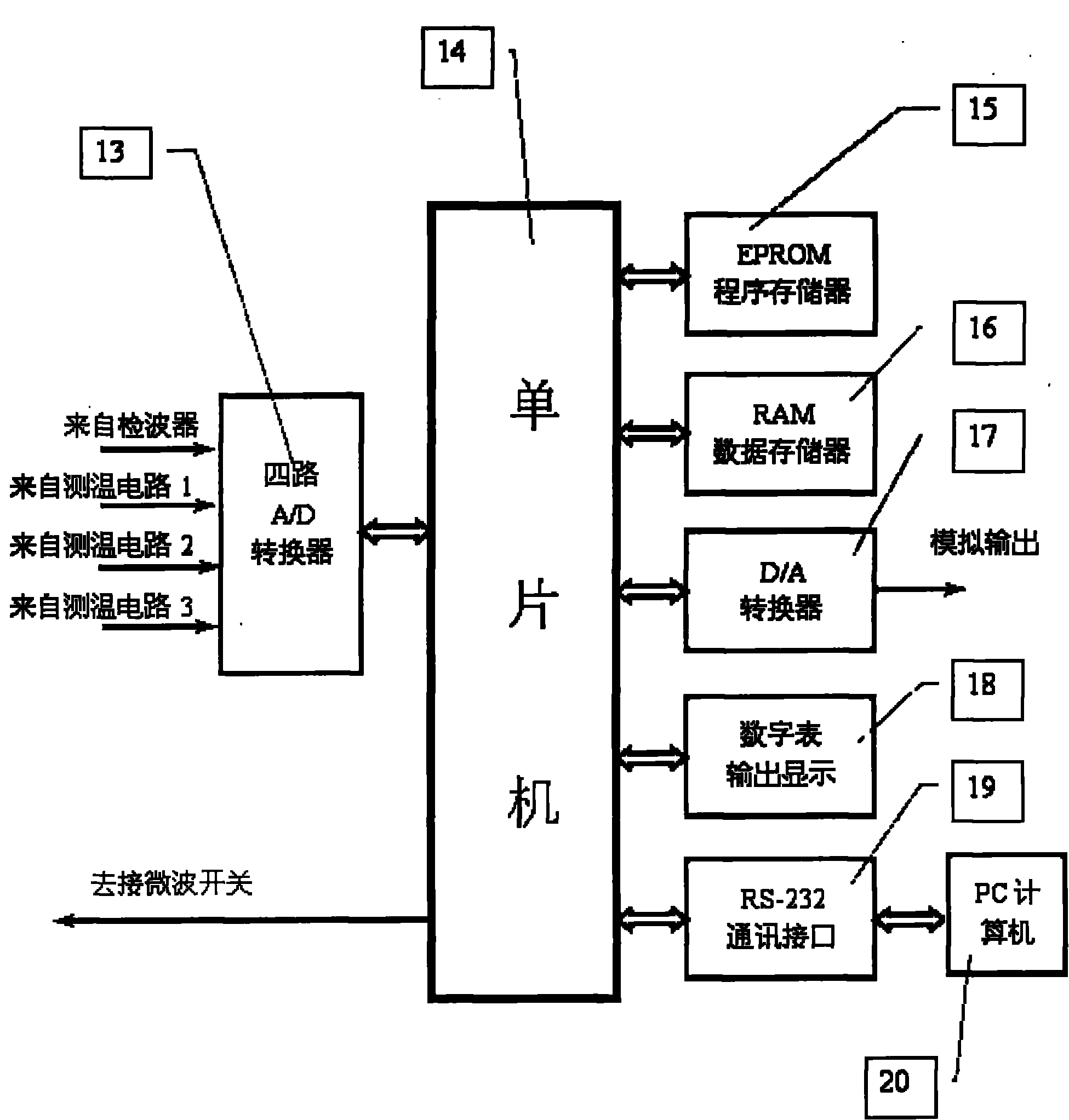
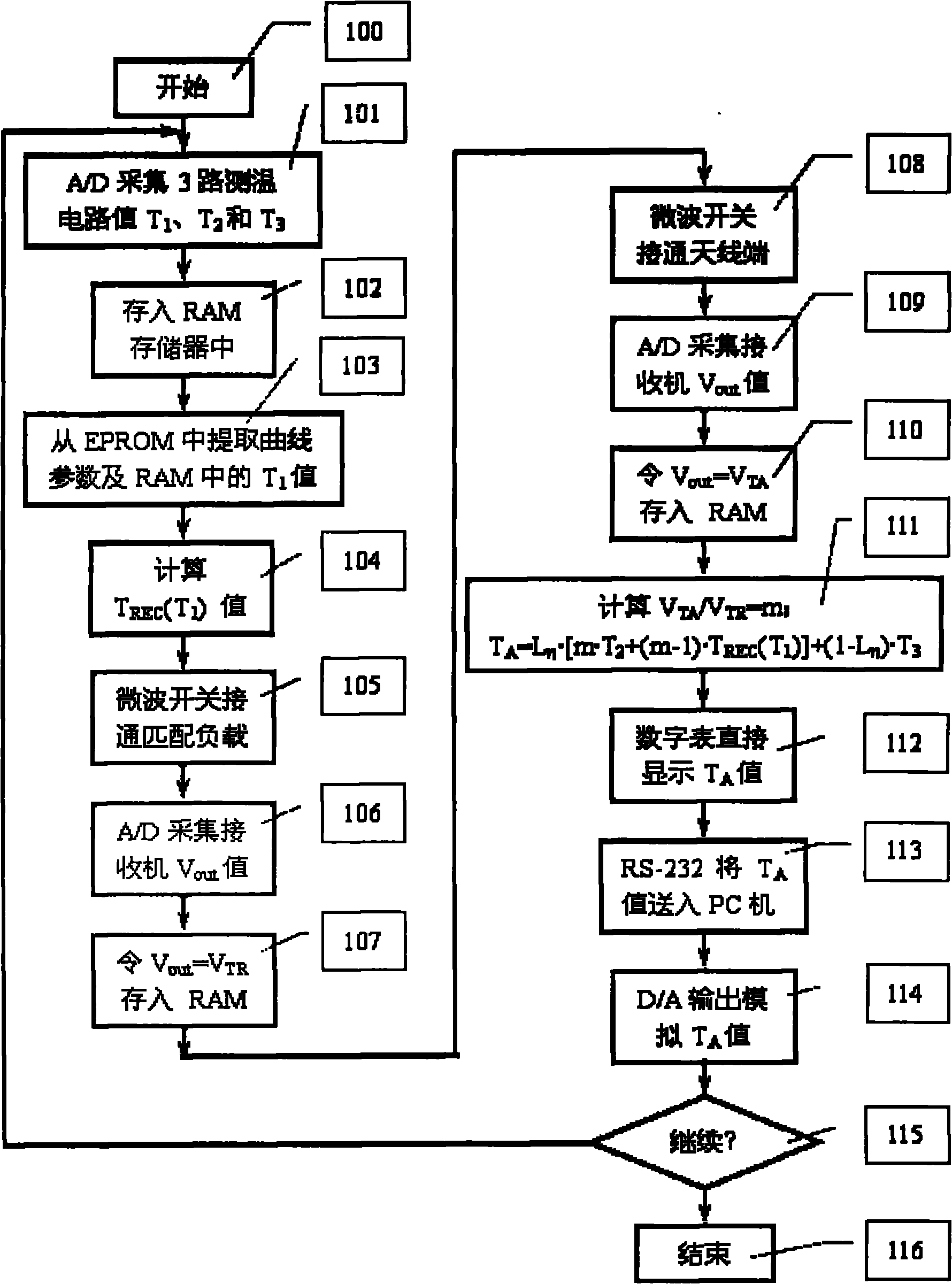
The invention provides a digital automatic compensation microwave radiometer which comprises an antenna, a microwave switch, a total power microwave radiometer receiver, a digital automatic compensation system, a high-precision platinum resistor temperature detecting circuit, a temperature detecting platinum resistor of a microwave front-end component, a matching load and a temperature-detecting platinum resistor of the matching load, and a physical temperature detecting platinum resistor of the antenna, wherein a high-precision platinum resistor temperature detecting sensor is used for measuring the physical temperatures of the microwave front-end component, the microwave antenna and the microwave matching load in real time; and a computer is used for realizing two operation processes of system gain compensation and noise temperature compensation. By the digital automatic compensation microwave radiometer, the influence of gain fluctuation on the measuring precision and the influence of the uncertainty of the noise caused by the system noise temperature TREC, antenna and feeder loss L Eta on the measuring precision are eliminated, and an accurate luminance temperature value which directly reflects that the antenna of microwave radiometer receives a target noise signal TA can be provided. The microwave radiometer has the advantages of small volume, light weight and low power consumption, is capable of shortening the waiting time for starting up and is greatly convenient for user to use outdoors and transport.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Calibration device and method for fully polarized microwave radiometer
ActiveCN108957377ASimplify complexityGood calibration accuracyElectrical measurementsGeological measurementsCorrelation coefficientGrating
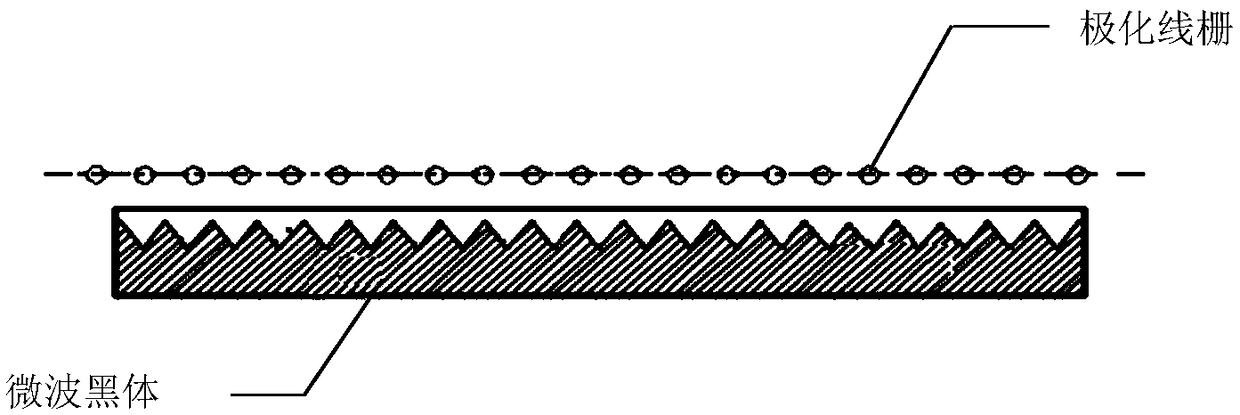
The invention discloses a calibration device for a fully polarized microwave radiometer, which is used for calibrating a fully polarized microwave radiometer. The calibration device comprises a non-polarized calibration heat source and a non-polarized calibration cold source. The calibration device further comprises a polarized calibration source, wherein the polarized calibration source includesa polarized wire grating and a microwave blackbody, and the polarized line grating covers the microwave blackbody. The invention further provides a calibration method for the fully polarized microwaveradiometer. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a set of calibration reference brightness temperatures by using the calibration device; determining the gain and offset of horizontal and vertical channels by adopting two-point calibration, and obtaining a brightness temperature TV of the horizontal channel and a brightness temperature TH of the vertical channel; and realizing the calibration for brightness temperatures T3 and T4 of another two channels of full polarization by using the system noise temperature of correlation coefficient of the radiometer by adopting a Y- factor method.The device and method disclosed by the invention can enable the polarization measurement accuracy to reach high requirements and be better than 0.25K so as to solve the problems of coupling and amplitude and phase imbalance between different receiving channels.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
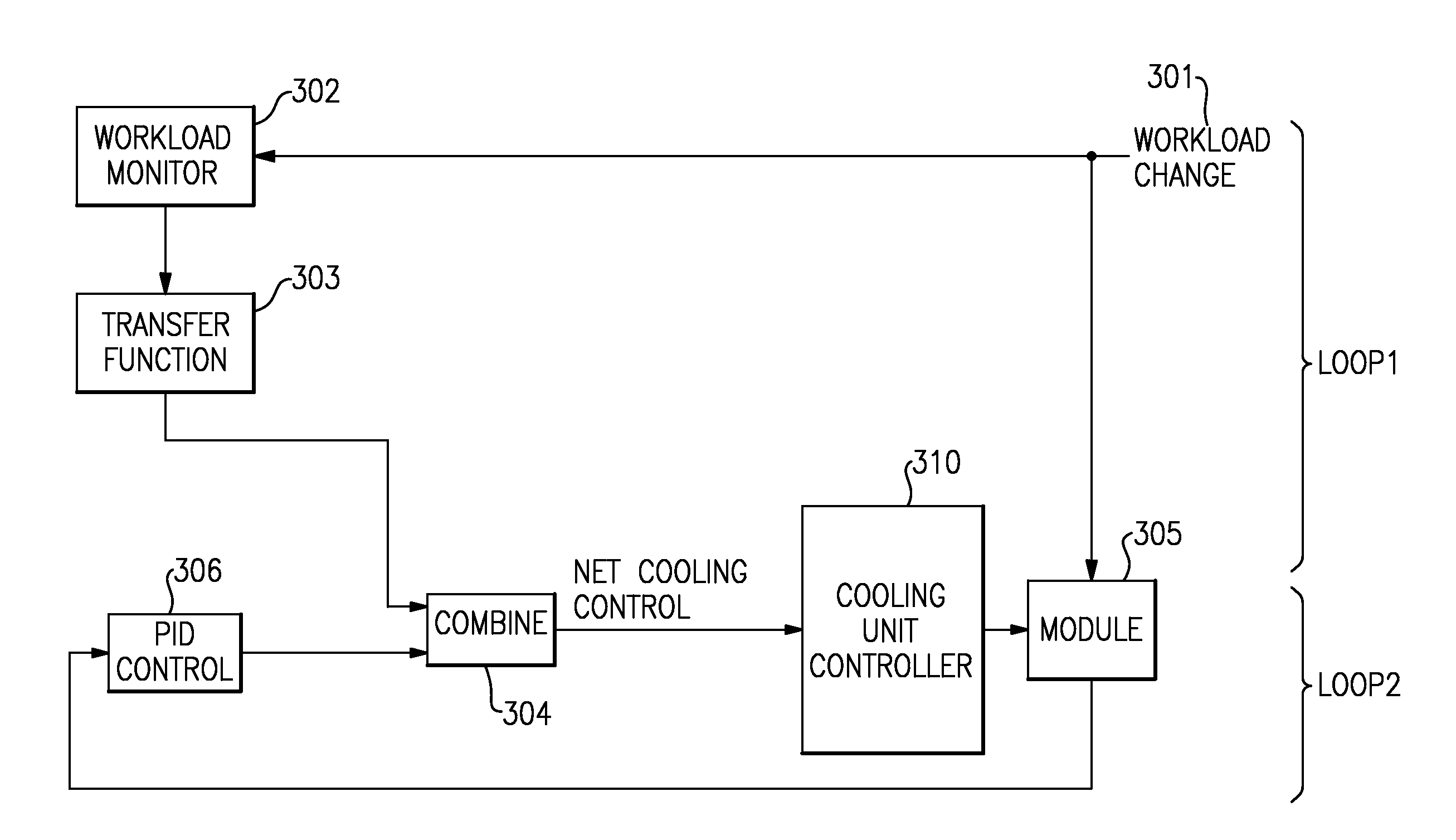
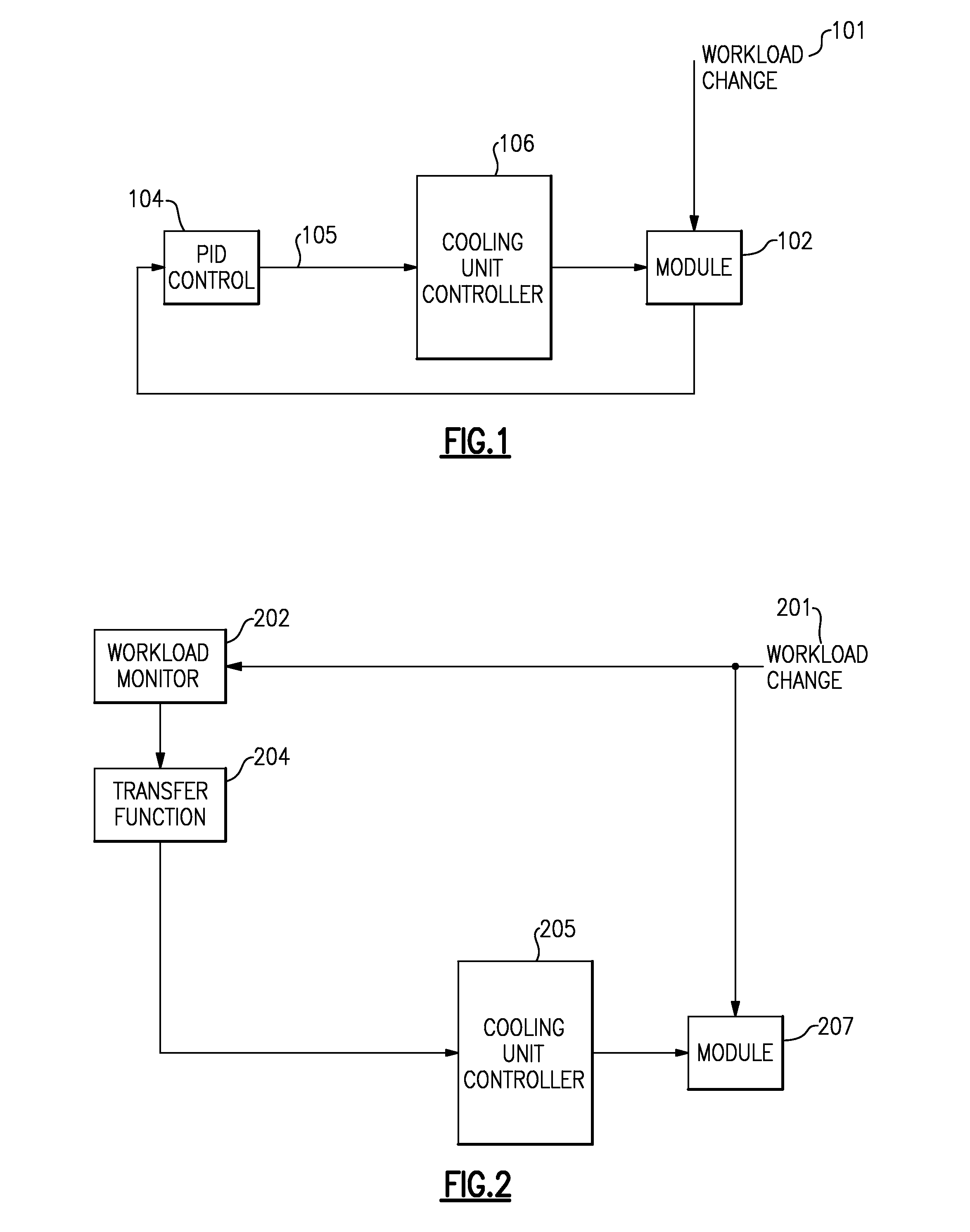
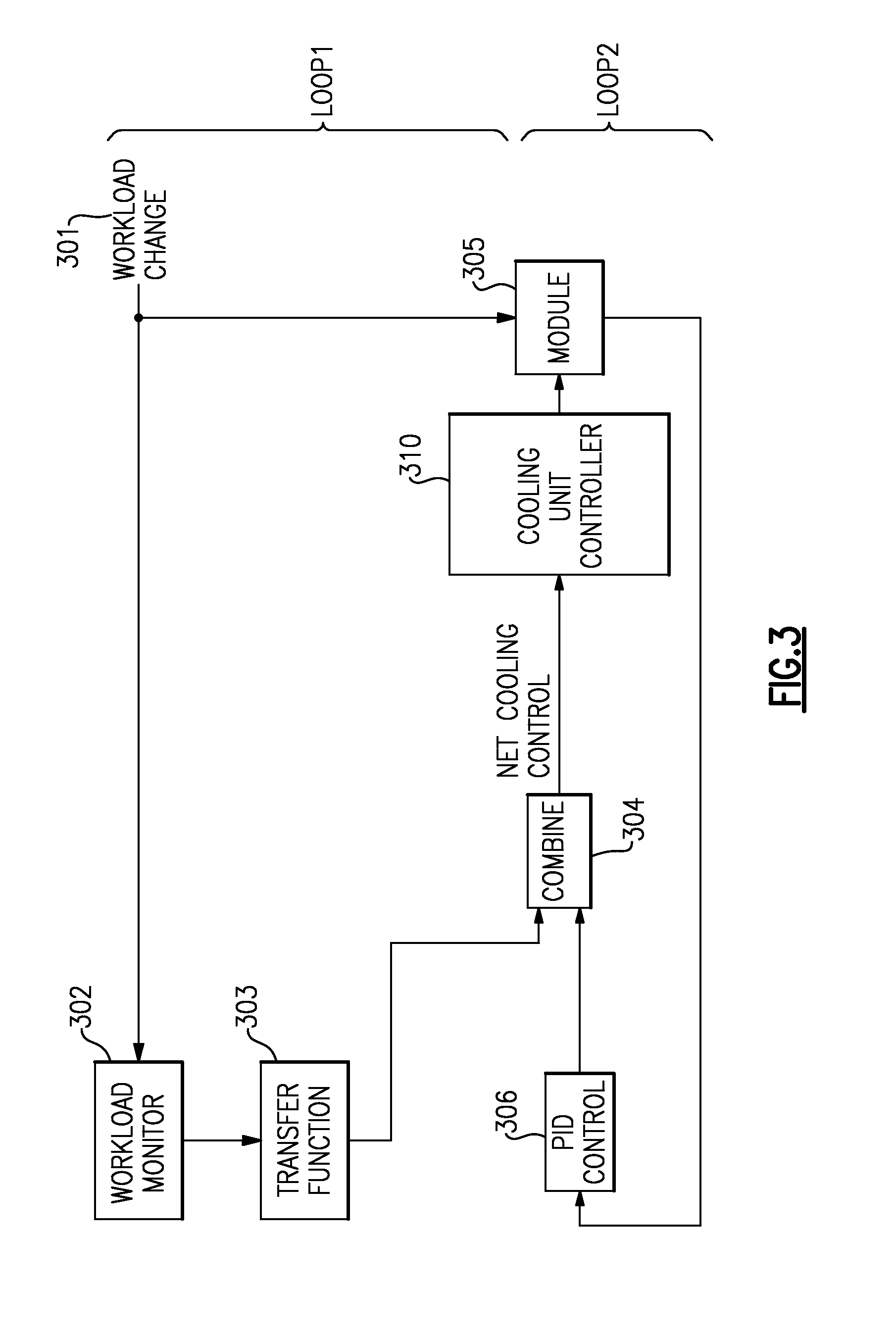
Proactive cooling of chips using workload information and controls
ActiveUS8909383B2Accurately and predicatively adjustEnergy efficient ICTTemperatue controlActive coolingEngineering
A method to reduce large temperature over / undershoot in a computer system. Using workload data, the method proactively modifies controls of mechanical cooling system to anticipate power and take appropriate actions to maintain temperature. Workload control modifies workload and scheduling to reduce power transients and subsequent temperature deviations. In addition, workload control allows more even distribution of temp across chips, allowing for even wear and reduction of small / ripple / noise temp oscillations. A system and program product for carrying out the method are also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for measuring corrugated horn loss
ActiveCN105116261AHigh measurement accuracyReduce the impactElectrical testingEngineeringNoise power
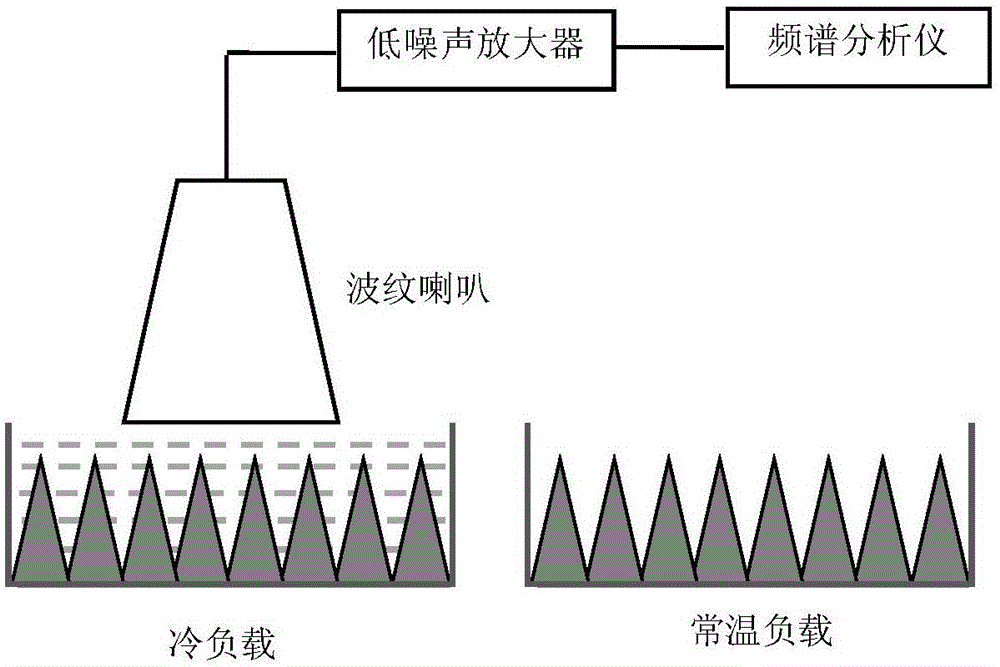
The invention discloses a method for measuring corrugated horn loss. According to the method, the noise power of a directional normal temperature load and cold load of a corrugated horn are measured respectively, and the noise temperature of the corrugated horn is determined, and therefore, the loss of the corrugated horn can be calculated. The method is simple and feasible, and has popularization and application values.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
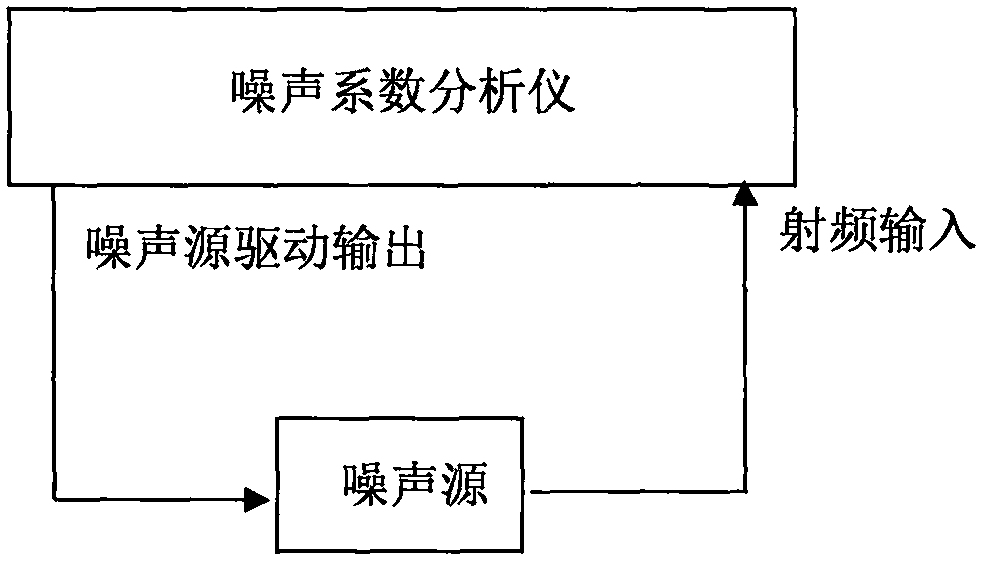
Noise coefficient scanning measurement method
ActiveCN107276695ARealize continuous scanning measurementFast measurementReceivers monitoringContinuous scanningEngineering
The invention provides a noise coefficient scanning measurement method. The method comprises the steps that a noise coefficient analyzer controls a noise source to be powered off and finishes single scanning measurement, thereby obtaining a group of cold noise power values P <cold > corresponding to scanning frequency points; the noise coefficient analyzer controls the noise source to be powered on and finishes the single scanning measurement, thereby obtaining a group of hot noise power values P <hot > corresponding to the scanning frequency points; and operating and displaying Y factors, equivalent noise temperature and noise coefficients according to the cold and hot noise power values of the corresponding scanning frequency points. According to the noise coefficient scanning measurement method provided by the invention, the continuous scanning measurement of the noise coefficients can be realized, the measurement speed of the noise coefficients is clearly improved, the noise coefficients of tested pieces can be measured precisely in real time, the operation of carrying out noise source power-on and power-off, channel presetting and response waiting needs to be carried out repeatedly at each measurement frequency point in the existing Y factor method is avoided, and the measurement efficiency of the noise coefficients is improved.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Normal-temperature output port microwave variable-temperature noise source
ActiveCN103812451ASolve the difficulty of accurate measurementSolve the problem that the noise figure parameter is difficult to measure accuratelyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierMicrowave
The invention provides a normal-temperature output port microwave variable-temperature noise source, and aims to provide a microwave noise source, wherein the physical temperature of an output port of the noise source is at normal temperature, the equivalent output noise temperature can vary from 50K to 200K, and the noise source can be used for measuring ultralow noise factors of a microwave ultralow noise amplifier provided with a normal-temperature input port. According to the technical scheme, the normal-temperature output port microwave variable-temperature noise source is formed through the following steps: a microwave load (5) of the noise source, a microwave thermal insulation transmission line (6) and a microwave coaxial output port (8) are respectively provided with temperature sensors (7), wherein the temperature sensors (7) are distributed for monitoring the physical temperature of a microwave closed circuit; a cold head fixedly connected to a mains haft of a refrigerator (1) and the temperature sensors arranged on the microwave thermal insulation transmission line (6) in an array are sealed inside a low-temperature dewar (4), the cold head (2) in the dewar (4) is connected with a monitoring control circuit (3) through a temperature monitoring control line, and the microwave thermal insulation transmission line (6) passes through the normal-temperature microwave coaxial output port (8) outside a vacuum cavity wall in the radial direction.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
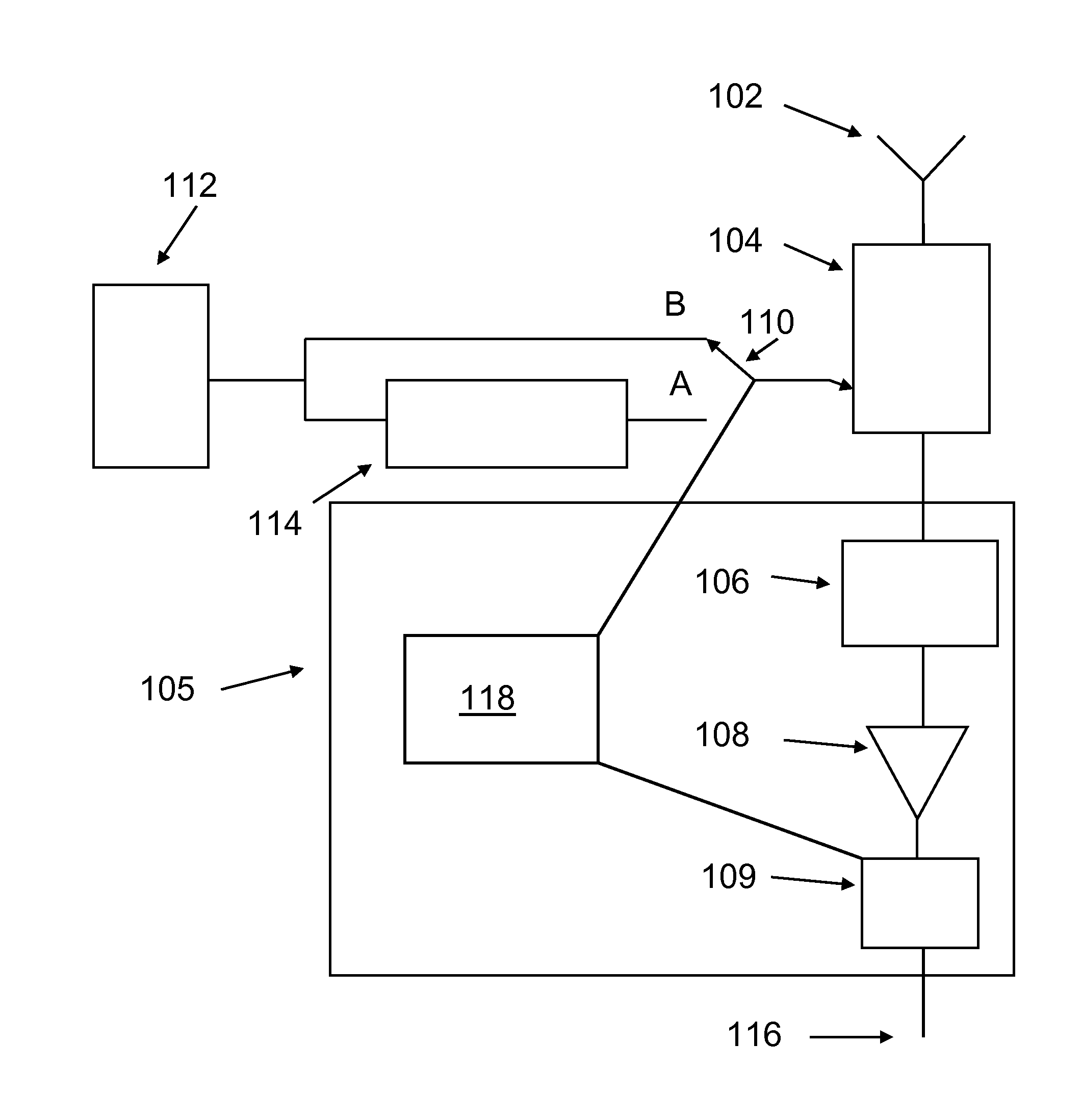
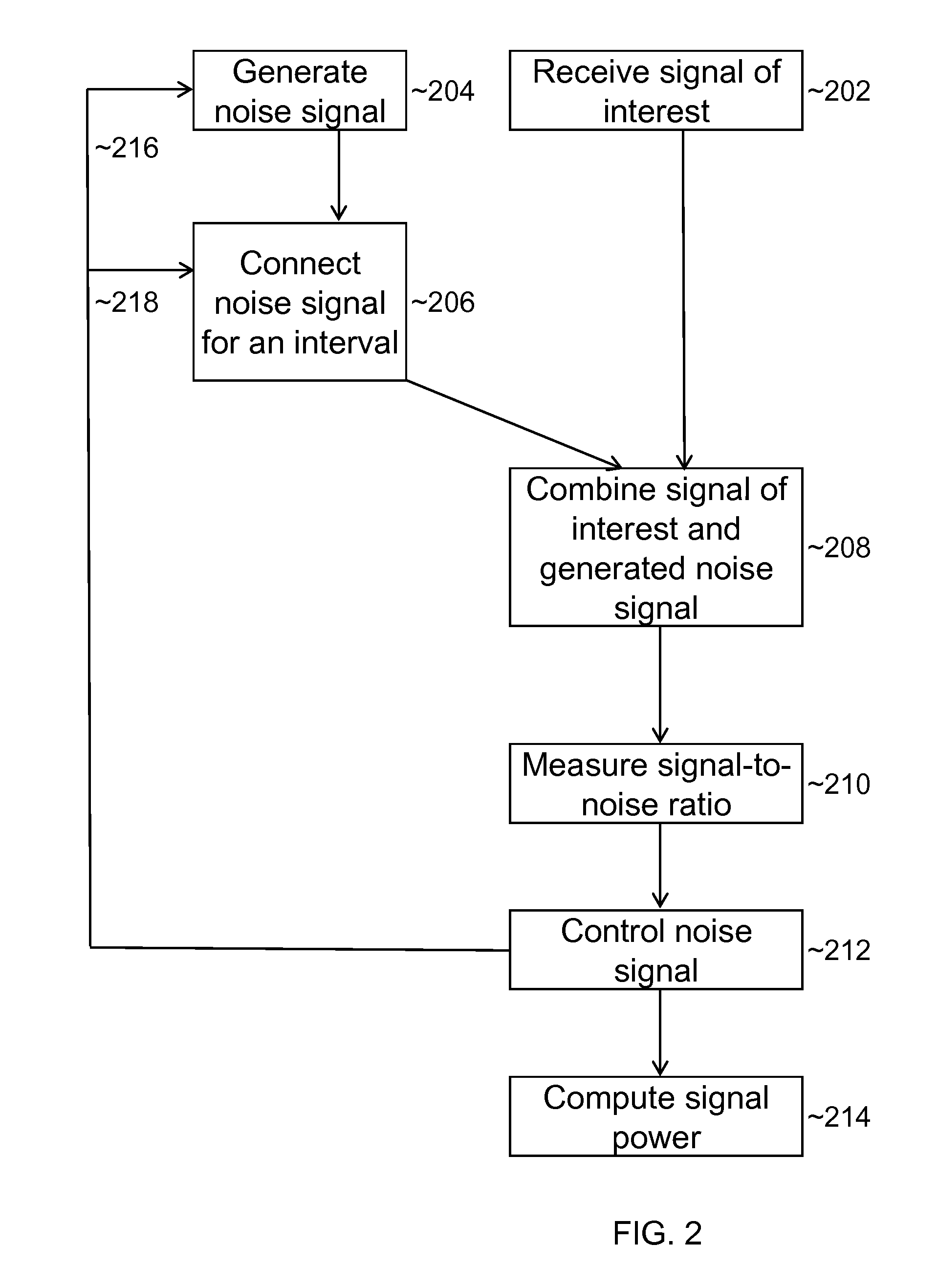
Method to measure total noise temperature of a wireless receiver during operation
ActiveUS20140065994A1Transmission monitoringWireless communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise level
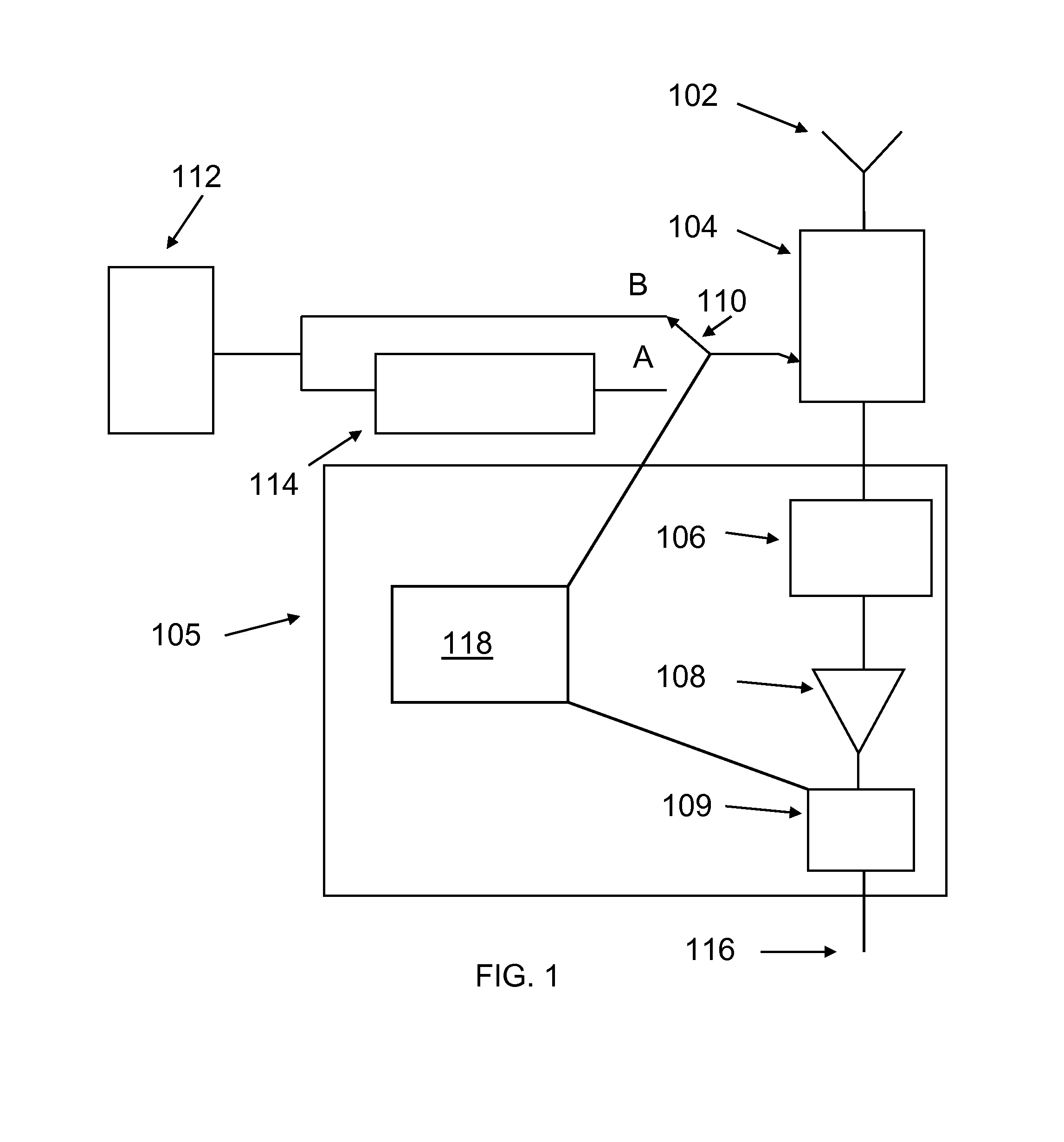
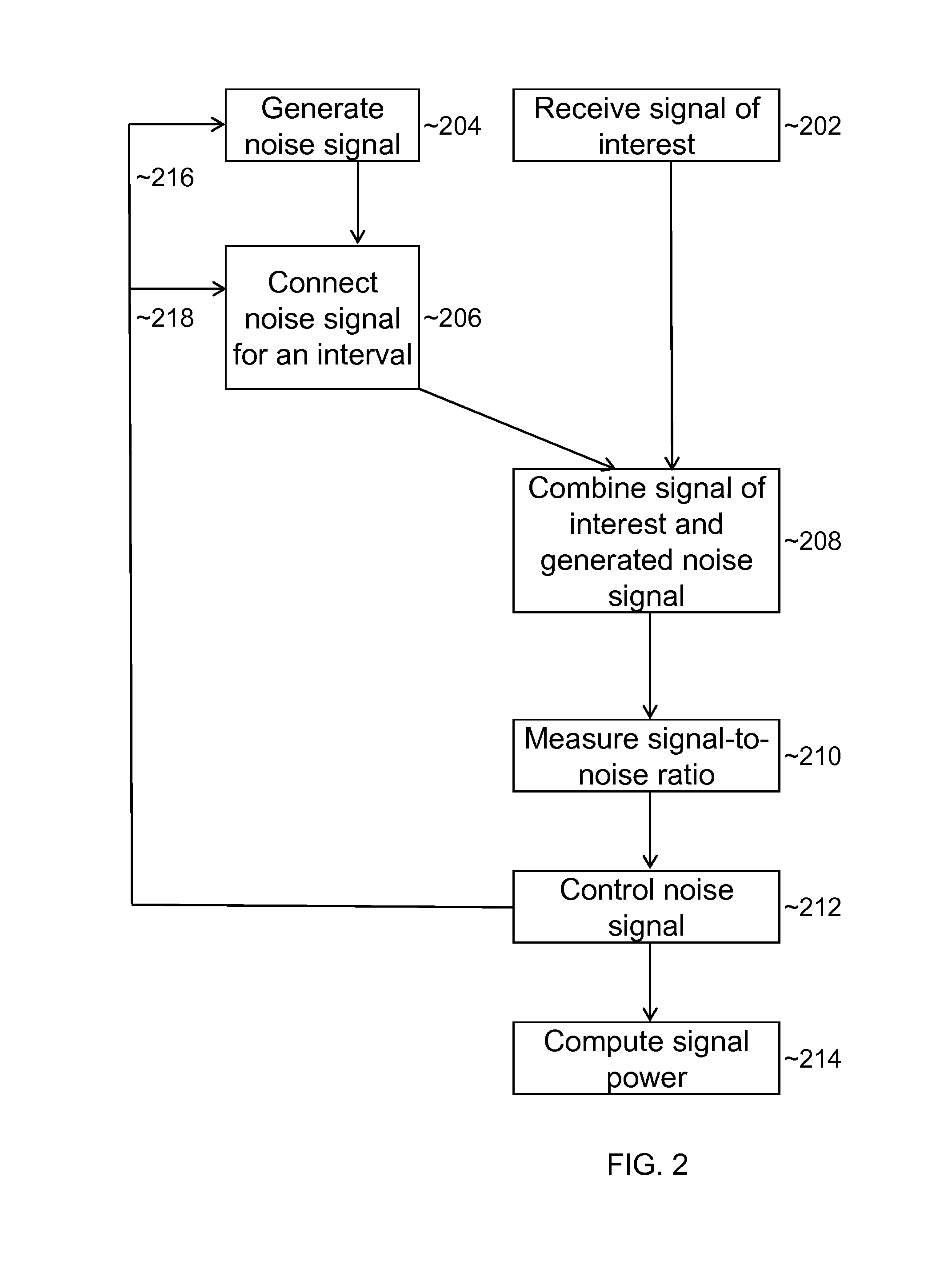
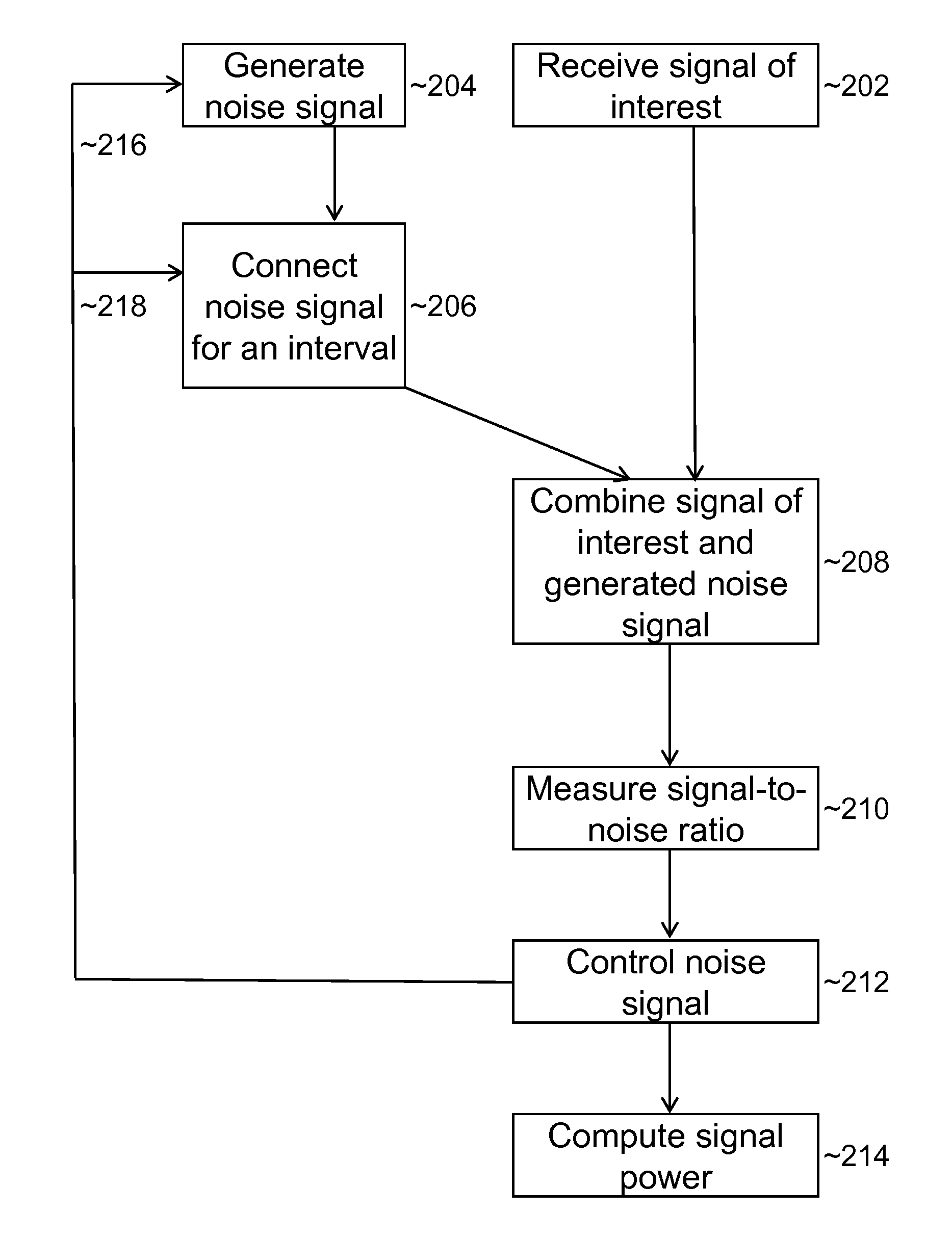
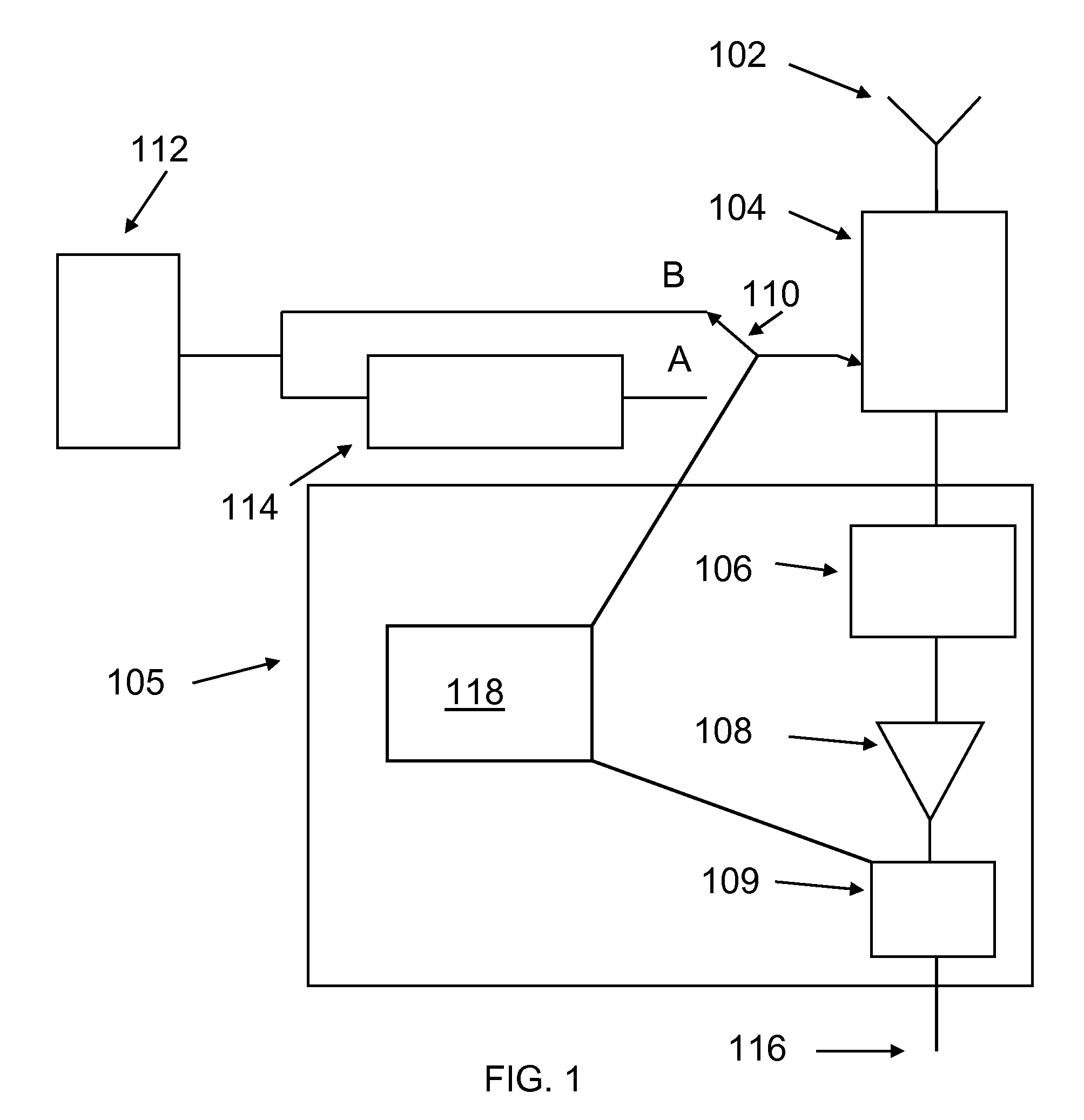
An electromagnetic signal receiver and methods for determining the noise level and signal power in a signal of interest while the receiver is operating. In some embodiments, the signal of interest is a GPS signal. The receiver includes a noise source that provides a noise signal of known power during intervals while the signal of interest is observed. By measuring a signal-to-noise ratio for the signal of interest and the noise power in the signal of interest, the noise level and signal power of the signal of interest can be computed. Various methods of making the measurements and computing the power of the signal of interest are described. Applications of the system and method are described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method to measure total noise temperature of a wireless receiver during operation
ActiveUS8688065B2Transmission monitoringWireless communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise level
An electromagnetic signal receiver and methods for determining the noise level and signal power in a signal of interest while the receiver is operating. In some embodiments, the signal of interest is a GPS signal. The receiver includes a noise source that provides a noise signal of known power during intervals while the signal of interest is observed. By measuring a signal-to-noise ratio for the signal of interest and the noise power in the signal of interest, the noise level and signal power of the signal of interest can be computed. Various methods of making the measurements and computing the power of the signal of interest are described. Applications of the system and method are described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
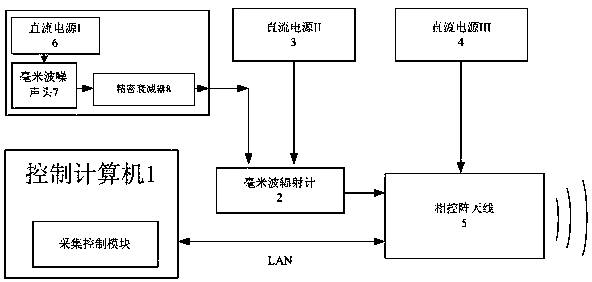
Radiometer imaging method based on phased array scanning system
ActiveCN108088570AThe testing process is simpleImprove test efficiencyPyrometry using electric radation detectorsRadiometerMillimetre wave
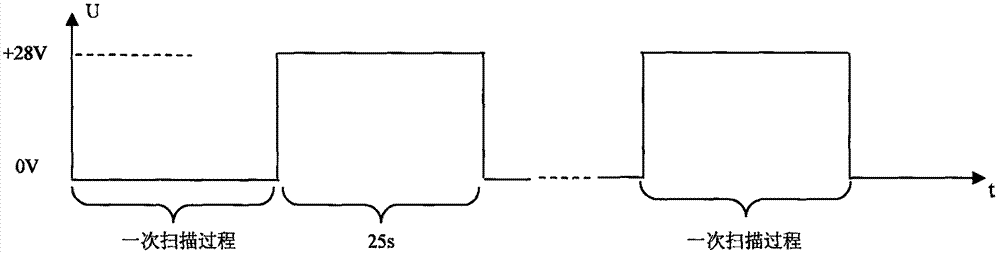
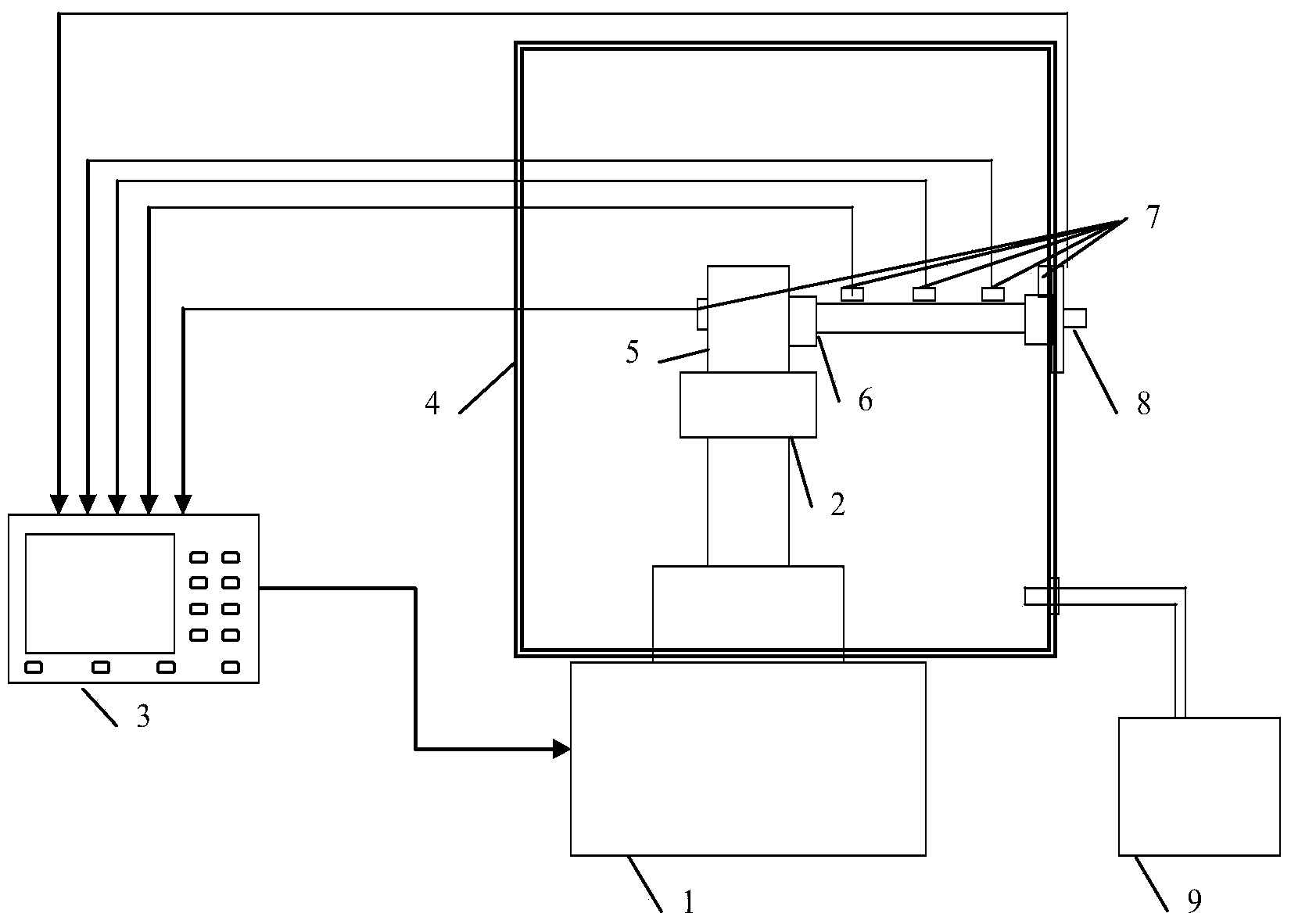
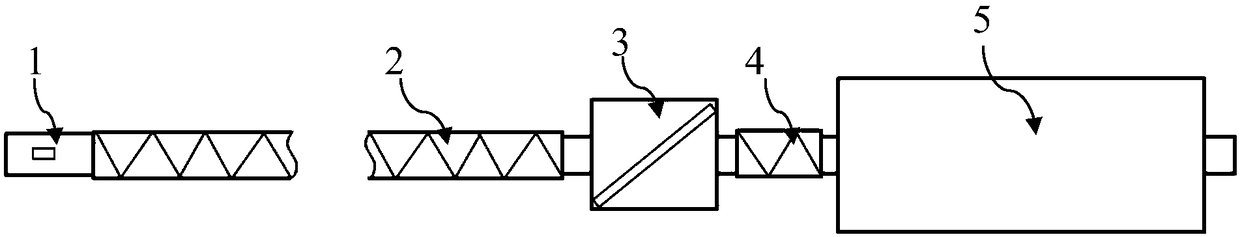
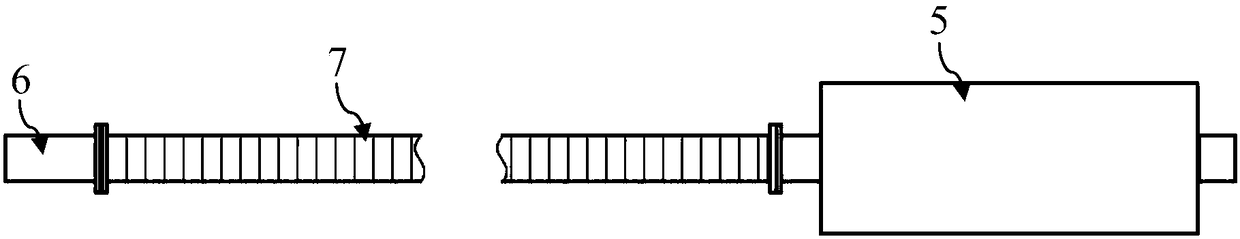
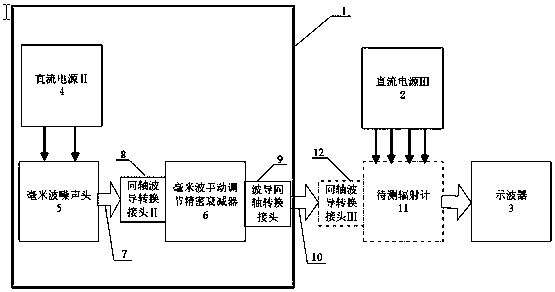
The invention discloses a radiometer imaging method based on a phased array scanning system. The system according to the radiometer imaging method comprises a control computer (1), a millimeter wave radiometer (2), a DC power supply II (3), a DC power supply III (4), a phased array antenna (5), a DC power supply I (6), a millimeter wave noise head (7) and a precision attenuator (8). The millimeterwave noise head generates the accurately calibrated noise temperature output in the required millimeter wave band under the +28V DC voltage excitation of the DC power supply I and the required noisetemperature is outputted through millimeter wave manual adjusting precision attenuator. The control computer (1) controls switching of the phased array antenna beams to perform two-dimensional image acquisition and storage. Compared with the conventional radiometer imaging method, only one radiometer is required without servo mechanism so as to have the advantages of simple equipment, easy and convenient operation and adjustable equivalent noise temperature test.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF REMOTE SENSING EQUIP
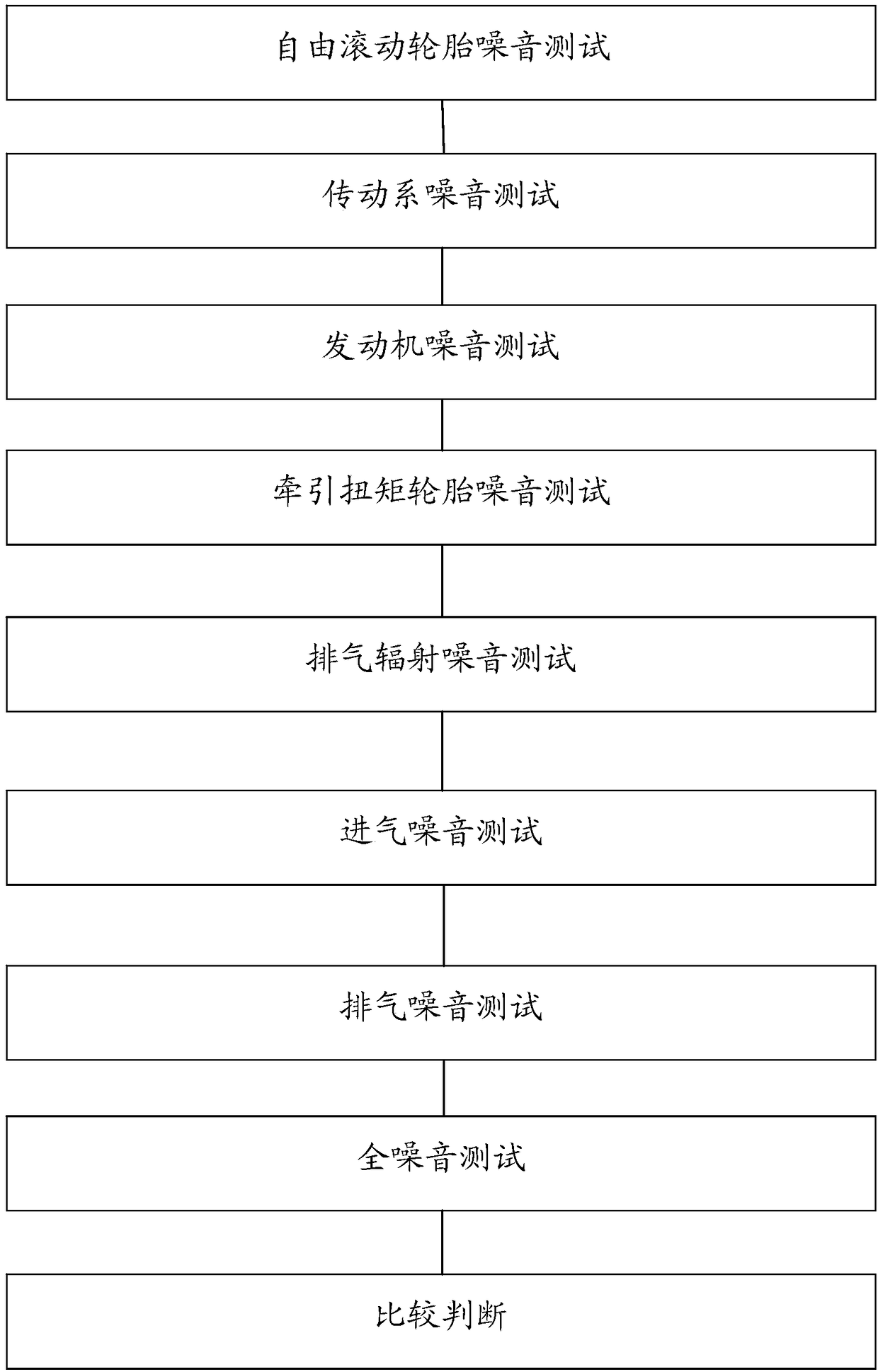
Test method for noise outside automobile
ActiveCN109443793AEliminate the effects ofImprove accuracyVehicle testingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesCar noise
The invention discloses a test method for noise outside an automobile. The method comprises free rolling tire test steps that A, air intake and exhaust ports of the automobile are silenced by mufflers, a casing of an exhaust system is sealed, original automobile tires are utilized by the automobile, the automobile is turned off, neutral taxiing operation is performed, through testing, the noise outside the automobile is Sa, the road surface temperature is Ta, free rolling tire noise S tire rolling=Sa+K(T0-Ta), wherein T0 is the reference temperature, and K is a tire noise temperature conversion coefficient. The method is advantaged in that influence of the road surface temperature on the calculation result can be eliminated, free rolling tire noise can be distinguished from traction torquetire noise, each main sound source of the noise outside the automobile can be identified to the greatest extent, and accuracy of the experimental result is improved.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CO LTD
Focal plane imaging type radiometer temperature sensitivity testing system
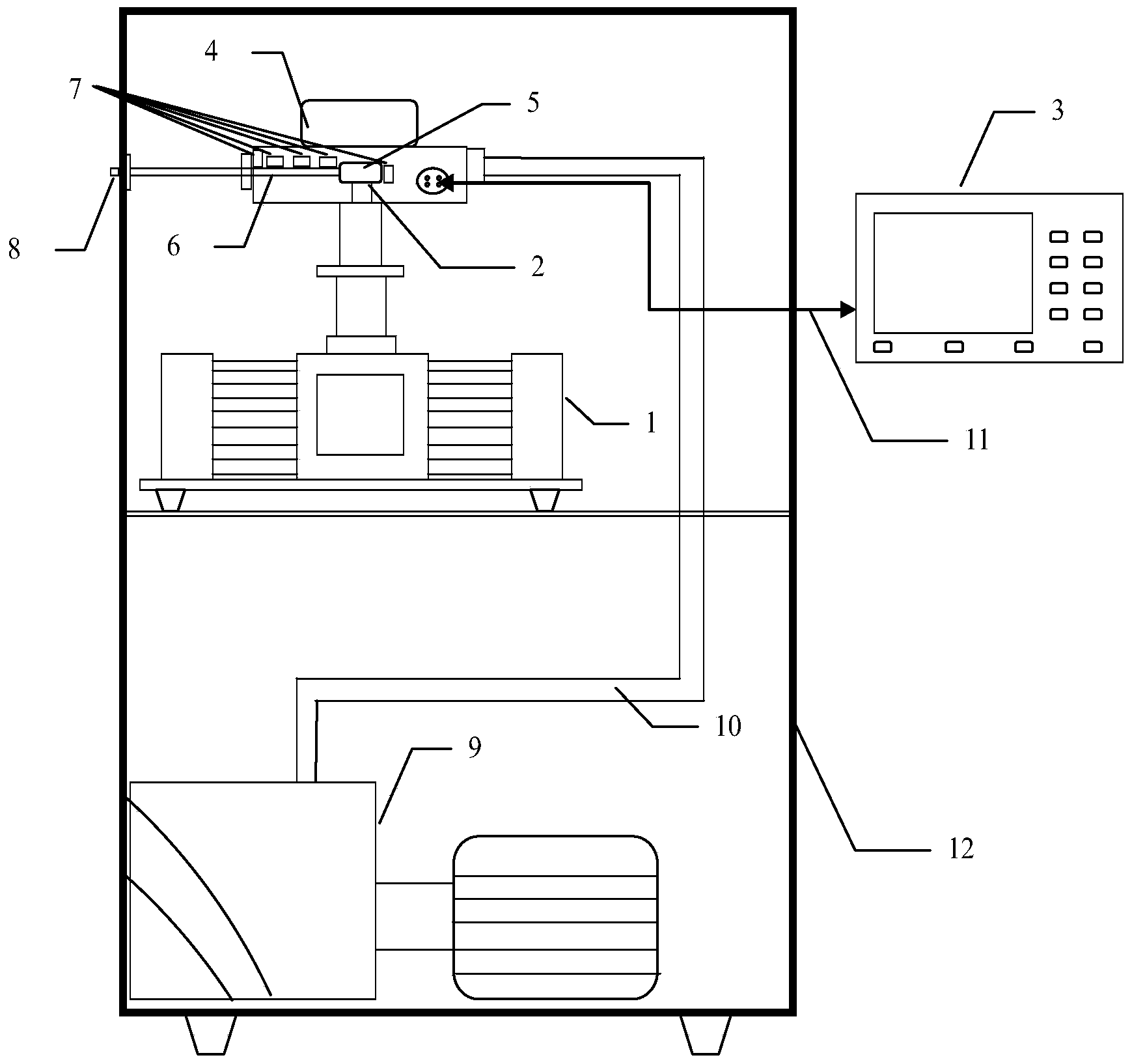
InactiveCN107764411AThe testing process is simpleImprove test efficiencyPyrometry using electric radation detectorsUltrasound attenuationRadiometer
The invention discloses a focal plane imaging type radiometer temperature sensitivity testing system comprising a millimeter-wave test case, a direct-current power supply III, an oscilloscope and a to-be-tested radiometer. The millimeter-wave test case consists of a direct-current power supply II, a millimeter-wave noise head, a millimeter-wave hand-operated adjustment precision attenuator, a coaxial line II, a coaxial waveguide conversion joint II, a waveguide coaxial conversion joint, and a coaxial line III. The direct-current power supply II and the direct-current power supply III provide excitation and bias voltages for the millimeter-wave noise head and the to-be-tested radiometer. The millimeter-wave noise head is used for generating a calibrated noise temperature output. The millimeter-wave hand-operated adjustment precision attenuator is used for carrying out attenuation value adjustment and outputting a corresponding noise temperature as a reference of temperature sensitivitymeasurement of the to-be-tested radiometer. The oscilloscope completes collection of output data of the to-be-tested radiometer. Compared with the traditional radiometer temperature sensitivity testing system, the focal plane imaging type radiometer temperature sensitivity testing system disclosed by the invention has advantages of simple equipment, simple operation, and high adjustability and flexibility for equivalent noise temperature testing and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF REMOTE SENSING EQUIP
K wave band receiver noise temperature test method
ActiveCN109302246AThe noise temperature can then be calculatedNoise temperature can be calculatedReceivers monitoringThermometer applicationsSky brightnessBlocked Connection
The invention relates to a K wave band receiver noise temperature test method. A device related in the method is composed of a K wave band receiver, a pedestal, a fixed frame, a rotary shaft, a turn table, a normal temperature black body, a rotating shaft, a U-shaped bolt, a first rotating shaft fixing board, a second rotating shaft fixing board, a first fixing pin, a second fixing pin, a slidingblock, a sliding block connection rod, a sliding guide rail, an angle fixing threaded rod, an angle fixing nut and angle fixing sliding chute. In the method, a cold load which is difficult to operateis replaced by cold air; a test device can introduce or remove a normal temperature black body load at a feed source port surface, also can discretionarily adjust the K wave band receiver and a beam direction thereof in elevation of 0-90 degrees, and can complete measurement and calculation of noise temperature of the receiver in combination with sky brightness temperature corresponding to the K wave band under the current elevation. The method simulates performing quick noise temperature test for the K wave band receiver in an observation process, avoids potential safety hazards caused by that an antenna elevation must be kept at 90 degrees for test and low-temperature liquid nitrogen is used in the conventional cold and hot load method, and promotes test efficiency and safety remarkably.
Owner:XINJIANG ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com